User login
Choice of infant sleep location is multifactorial
according to a recent nationally representative study.
Of 3,260 mothers surveyed, 59% of mothers said that they intended to room-share without bed-sharing, but only 45% practiced – and also had the intent to practice – room-sharing without bed-sharing. Of the 41% who said that they did not intend to bed-share, 24% actually did intend to practice at least some bed-sharing with their infants, who were all aged 2-6 months at the time of survey administration.
Mothers who were African American and those who were breastfeeding exclusively were most likely to report that they intended to bed-share, reported Ann Kellams, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the University of Virginia,Charlottesville, and coauthors. Mothers who were exclusively breastfeeding had a nearly threefold higher rate of intending to bed-share than mothers whose infants were fed formula.
How mothers perceived social norms about bed- and room-sharing practices also plays a role. Women who considered that social norms supported bed-sharing and discouraged room-sharing had almost 200 times the odds of intending to bed-share, compared with those who perceived that social norms supported room-sharing without bed-sharing.
Conversely, being advised by a doctor to follow the American Academy of Pediatrics–recommended practice of room-sharing without bed-sharing made it less likely that mothers would plan to share a bed with their infant (adjusted odds ratio, 0.56). Yet women who intended to room-share without bed-sharing but who actually did bed-share some of the time, their doctor’s advice to room-share only had no impact (aOR, 1.01).
The investigators noted that, “although other studies have investigated factors influencing maternal decisions, no studies to date have examined maternal intention regarding sleep location and what factors influence intention.”
The Study of Attitudes and Factors Effecting Infant Care drew from 32 U.S. hospitals, and asked mothers about feeding and care practices, including the infant’s usual sleep locations and all sleep locations over the 2 weeks preceding the survey. Additionally, the survey asked about future intent for sleeping practices, looking ahead to the next 2 weeks.
The survey design and the analysis performed in the study were based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB), “which hypothesizes that attitudes, subjective social norms, and perceptions about control over behavior impact one’s intention, which leads to actual behavior,” explained Dr. Kellams and coinvestigators. They reported that they had previously used TPB to analyze mothers’ intentions and actions regarding supine sleep position for infants, finding that a variety of behavioral and social facets accounted for by TPB affected maternal intention and decision making.
Additionally, the study’s design captured partial-night bed-sharing, where an infant may start the night in a separate bed but be brought to bed for feeding or comforting, then share a bed with the mother for the remainder of the night. “Unintended bed-sharing may explain our finding that there is frequent inconsistency between those whose near-future intention is to room-share without bed-sharing but whose actual practice includes bed-sharing,” the authors wrote.
“Attitudes, social norms, and doctor advice are associated with infant sleep location and may be potential targets for educational interventions,” concluded Dr. Kellams and coinvestigators.
Dr. Kellams and associates reported no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Kellams A et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 7;145(3):e20191523.
according to a recent nationally representative study.
Of 3,260 mothers surveyed, 59% of mothers said that they intended to room-share without bed-sharing, but only 45% practiced – and also had the intent to practice – room-sharing without bed-sharing. Of the 41% who said that they did not intend to bed-share, 24% actually did intend to practice at least some bed-sharing with their infants, who were all aged 2-6 months at the time of survey administration.
Mothers who were African American and those who were breastfeeding exclusively were most likely to report that they intended to bed-share, reported Ann Kellams, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the University of Virginia,Charlottesville, and coauthors. Mothers who were exclusively breastfeeding had a nearly threefold higher rate of intending to bed-share than mothers whose infants were fed formula.
How mothers perceived social norms about bed- and room-sharing practices also plays a role. Women who considered that social norms supported bed-sharing and discouraged room-sharing had almost 200 times the odds of intending to bed-share, compared with those who perceived that social norms supported room-sharing without bed-sharing.
Conversely, being advised by a doctor to follow the American Academy of Pediatrics–recommended practice of room-sharing without bed-sharing made it less likely that mothers would plan to share a bed with their infant (adjusted odds ratio, 0.56). Yet women who intended to room-share without bed-sharing but who actually did bed-share some of the time, their doctor’s advice to room-share only had no impact (aOR, 1.01).
The investigators noted that, “although other studies have investigated factors influencing maternal decisions, no studies to date have examined maternal intention regarding sleep location and what factors influence intention.”
The Study of Attitudes and Factors Effecting Infant Care drew from 32 U.S. hospitals, and asked mothers about feeding and care practices, including the infant’s usual sleep locations and all sleep locations over the 2 weeks preceding the survey. Additionally, the survey asked about future intent for sleeping practices, looking ahead to the next 2 weeks.
The survey design and the analysis performed in the study were based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB), “which hypothesizes that attitudes, subjective social norms, and perceptions about control over behavior impact one’s intention, which leads to actual behavior,” explained Dr. Kellams and coinvestigators. They reported that they had previously used TPB to analyze mothers’ intentions and actions regarding supine sleep position for infants, finding that a variety of behavioral and social facets accounted for by TPB affected maternal intention and decision making.
Additionally, the study’s design captured partial-night bed-sharing, where an infant may start the night in a separate bed but be brought to bed for feeding or comforting, then share a bed with the mother for the remainder of the night. “Unintended bed-sharing may explain our finding that there is frequent inconsistency between those whose near-future intention is to room-share without bed-sharing but whose actual practice includes bed-sharing,” the authors wrote.
“Attitudes, social norms, and doctor advice are associated with infant sleep location and may be potential targets for educational interventions,” concluded Dr. Kellams and coinvestigators.
Dr. Kellams and associates reported no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Kellams A et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 7;145(3):e20191523.
according to a recent nationally representative study.
Of 3,260 mothers surveyed, 59% of mothers said that they intended to room-share without bed-sharing, but only 45% practiced – and also had the intent to practice – room-sharing without bed-sharing. Of the 41% who said that they did not intend to bed-share, 24% actually did intend to practice at least some bed-sharing with their infants, who were all aged 2-6 months at the time of survey administration.
Mothers who were African American and those who were breastfeeding exclusively were most likely to report that they intended to bed-share, reported Ann Kellams, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the University of Virginia,Charlottesville, and coauthors. Mothers who were exclusively breastfeeding had a nearly threefold higher rate of intending to bed-share than mothers whose infants were fed formula.
How mothers perceived social norms about bed- and room-sharing practices also plays a role. Women who considered that social norms supported bed-sharing and discouraged room-sharing had almost 200 times the odds of intending to bed-share, compared with those who perceived that social norms supported room-sharing without bed-sharing.
Conversely, being advised by a doctor to follow the American Academy of Pediatrics–recommended practice of room-sharing without bed-sharing made it less likely that mothers would plan to share a bed with their infant (adjusted odds ratio, 0.56). Yet women who intended to room-share without bed-sharing but who actually did bed-share some of the time, their doctor’s advice to room-share only had no impact (aOR, 1.01).
The investigators noted that, “although other studies have investigated factors influencing maternal decisions, no studies to date have examined maternal intention regarding sleep location and what factors influence intention.”
The Study of Attitudes and Factors Effecting Infant Care drew from 32 U.S. hospitals, and asked mothers about feeding and care practices, including the infant’s usual sleep locations and all sleep locations over the 2 weeks preceding the survey. Additionally, the survey asked about future intent for sleeping practices, looking ahead to the next 2 weeks.
The survey design and the analysis performed in the study were based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB), “which hypothesizes that attitudes, subjective social norms, and perceptions about control over behavior impact one’s intention, which leads to actual behavior,” explained Dr. Kellams and coinvestigators. They reported that they had previously used TPB to analyze mothers’ intentions and actions regarding supine sleep position for infants, finding that a variety of behavioral and social facets accounted for by TPB affected maternal intention and decision making.
Additionally, the study’s design captured partial-night bed-sharing, where an infant may start the night in a separate bed but be brought to bed for feeding or comforting, then share a bed with the mother for the remainder of the night. “Unintended bed-sharing may explain our finding that there is frequent inconsistency between those whose near-future intention is to room-share without bed-sharing but whose actual practice includes bed-sharing,” the authors wrote.
“Attitudes, social norms, and doctor advice are associated with infant sleep location and may be potential targets for educational interventions,” concluded Dr. Kellams and coinvestigators.
Dr. Kellams and associates reported no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Kellams A et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 7;145(3):e20191523.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Posttraumatic stress may persist up to 9 months after pregnancy loss
new research suggests.
The outcomes of a prospective cohort study involving 737 women who had experienced miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy and 171 controls with healthy pregnancies were presented in a report in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
One month after their pregnancy loss, 29% of these women met the criteria for posttraumatic stress, 24% reported moderate to severe anxiety, and 11% reported moderate to severe depression. In comparison, just 13% of women in the control group met the criteria for anxiety, and 2% met the criteria for depression, which meant women who had experienced early pregnancy loss had a greater than twofold odds of anxiety and nearly fourfold (odds ratio, 3.88) greater odds of depression, reported Jessica Farren, PhD, of the Queen Charlotte’s and Chelsea Hospital, London, and coauthors.
The most common posttraumatic symptom, experienced by 91% of respondents with posttraumatic stress at 1 month after the pregnancy, was reexperiencing symptoms, while 60% experienced avoidance and hyperarousal symptoms. At 3 months after the loss, 50% of those with posttraumatic stress reported an interruption of their general satisfaction with life.
While the incidence of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression decreased over time in the women who had early pregnancy loss, by the third month 21% still met the criteria for posttraumatic stress, and by 9 months, 18% still were experiencing posttraumatic stress. Similarly, moderate to severe anxiety was still present in 23% of women at 3 months and 17% at 9 months, and moderate to severe depression was still experienced by 8% of women at 3 months and 6% of women at 9 months.
Dr. Farren and coauthors wrote that, given the incidence of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy in the population, the high proportion of women still experiencing posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression at 9 months pointed to a significant public health issue. “It is recognized that PTSD in other contexts can have a significant impact on work, social interaction, health care utilization, and risks in future pregnancies,” they wrote. “Work is needed to evaluate strategies to effectively identify and treat affected women with these specific psychopathologies.”
The investigators also looked at the differences in outcomes in women who experienced miscarriage, compared with those who experienced ectopic pregnancy.
Of the 363 women who had a miscarriage, 30% met criteria for posttraumatic stress at 1 month, 20% at 3 months, and 17% at 9 months. Moderate to severe anxiety was reported by 25% women at 1 month, 22% at 3 months, and 17% at 9 months. Moderate to severe depression was reported by 12% at 1 month, 7% at 3 months, and 5% at 9 months.
Of the 74 women who had an ectopic pregnancy, 23% met criteria for posttraumatic stress at 1 month, 28% at 3 months, and 21% at 9 months. Moderate to severe anxiety was reported by 21% at 1 month, 30% at 3 months, and 23% at 9 months. Moderate to severe depression was reported by 7% at 1 month, 12% at 3 months, and 11% at 9 months.
The authors noted that the incidence of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression decreased more strongly over time in women who had experienced miscarriage, compared with those who experienced ectopic pregnancy, although they commented that the confidence intervals were wide.
One coauthor was supported by an Imperial Health Charity grant and another by the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Farren J et al. Amer J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec 13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.10.102.
new research suggests.
The outcomes of a prospective cohort study involving 737 women who had experienced miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy and 171 controls with healthy pregnancies were presented in a report in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
One month after their pregnancy loss, 29% of these women met the criteria for posttraumatic stress, 24% reported moderate to severe anxiety, and 11% reported moderate to severe depression. In comparison, just 13% of women in the control group met the criteria for anxiety, and 2% met the criteria for depression, which meant women who had experienced early pregnancy loss had a greater than twofold odds of anxiety and nearly fourfold (odds ratio, 3.88) greater odds of depression, reported Jessica Farren, PhD, of the Queen Charlotte’s and Chelsea Hospital, London, and coauthors.
The most common posttraumatic symptom, experienced by 91% of respondents with posttraumatic stress at 1 month after the pregnancy, was reexperiencing symptoms, while 60% experienced avoidance and hyperarousal symptoms. At 3 months after the loss, 50% of those with posttraumatic stress reported an interruption of their general satisfaction with life.
While the incidence of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression decreased over time in the women who had early pregnancy loss, by the third month 21% still met the criteria for posttraumatic stress, and by 9 months, 18% still were experiencing posttraumatic stress. Similarly, moderate to severe anxiety was still present in 23% of women at 3 months and 17% at 9 months, and moderate to severe depression was still experienced by 8% of women at 3 months and 6% of women at 9 months.
Dr. Farren and coauthors wrote that, given the incidence of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy in the population, the high proportion of women still experiencing posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression at 9 months pointed to a significant public health issue. “It is recognized that PTSD in other contexts can have a significant impact on work, social interaction, health care utilization, and risks in future pregnancies,” they wrote. “Work is needed to evaluate strategies to effectively identify and treat affected women with these specific psychopathologies.”
The investigators also looked at the differences in outcomes in women who experienced miscarriage, compared with those who experienced ectopic pregnancy.
Of the 363 women who had a miscarriage, 30% met criteria for posttraumatic stress at 1 month, 20% at 3 months, and 17% at 9 months. Moderate to severe anxiety was reported by 25% women at 1 month, 22% at 3 months, and 17% at 9 months. Moderate to severe depression was reported by 12% at 1 month, 7% at 3 months, and 5% at 9 months.
Of the 74 women who had an ectopic pregnancy, 23% met criteria for posttraumatic stress at 1 month, 28% at 3 months, and 21% at 9 months. Moderate to severe anxiety was reported by 21% at 1 month, 30% at 3 months, and 23% at 9 months. Moderate to severe depression was reported by 7% at 1 month, 12% at 3 months, and 11% at 9 months.
The authors noted that the incidence of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression decreased more strongly over time in women who had experienced miscarriage, compared with those who experienced ectopic pregnancy, although they commented that the confidence intervals were wide.
One coauthor was supported by an Imperial Health Charity grant and another by the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Farren J et al. Amer J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec 13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.10.102.
new research suggests.
The outcomes of a prospective cohort study involving 737 women who had experienced miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy and 171 controls with healthy pregnancies were presented in a report in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
One month after their pregnancy loss, 29% of these women met the criteria for posttraumatic stress, 24% reported moderate to severe anxiety, and 11% reported moderate to severe depression. In comparison, just 13% of women in the control group met the criteria for anxiety, and 2% met the criteria for depression, which meant women who had experienced early pregnancy loss had a greater than twofold odds of anxiety and nearly fourfold (odds ratio, 3.88) greater odds of depression, reported Jessica Farren, PhD, of the Queen Charlotte’s and Chelsea Hospital, London, and coauthors.
The most common posttraumatic symptom, experienced by 91% of respondents with posttraumatic stress at 1 month after the pregnancy, was reexperiencing symptoms, while 60% experienced avoidance and hyperarousal symptoms. At 3 months after the loss, 50% of those with posttraumatic stress reported an interruption of their general satisfaction with life.
While the incidence of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression decreased over time in the women who had early pregnancy loss, by the third month 21% still met the criteria for posttraumatic stress, and by 9 months, 18% still were experiencing posttraumatic stress. Similarly, moderate to severe anxiety was still present in 23% of women at 3 months and 17% at 9 months, and moderate to severe depression was still experienced by 8% of women at 3 months and 6% of women at 9 months.
Dr. Farren and coauthors wrote that, given the incidence of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy in the population, the high proportion of women still experiencing posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression at 9 months pointed to a significant public health issue. “It is recognized that PTSD in other contexts can have a significant impact on work, social interaction, health care utilization, and risks in future pregnancies,” they wrote. “Work is needed to evaluate strategies to effectively identify and treat affected women with these specific psychopathologies.”
The investigators also looked at the differences in outcomes in women who experienced miscarriage, compared with those who experienced ectopic pregnancy.
Of the 363 women who had a miscarriage, 30% met criteria for posttraumatic stress at 1 month, 20% at 3 months, and 17% at 9 months. Moderate to severe anxiety was reported by 25% women at 1 month, 22% at 3 months, and 17% at 9 months. Moderate to severe depression was reported by 12% at 1 month, 7% at 3 months, and 5% at 9 months.
Of the 74 women who had an ectopic pregnancy, 23% met criteria for posttraumatic stress at 1 month, 28% at 3 months, and 21% at 9 months. Moderate to severe anxiety was reported by 21% at 1 month, 30% at 3 months, and 23% at 9 months. Moderate to severe depression was reported by 7% at 1 month, 12% at 3 months, and 11% at 9 months.
The authors noted that the incidence of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, and depression decreased more strongly over time in women who had experienced miscarriage, compared with those who experienced ectopic pregnancy, although they commented that the confidence intervals were wide.
One coauthor was supported by an Imperial Health Charity grant and another by the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Farren J et al. Amer J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec 13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.10.102.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Mailed fecal testing may catch more cancer than endoscopic screening
On a population level, mailed fecal immunohistochemical tests (FITs) may catch more cases of advanced neoplasia than endoscopic methods, based on a Dutch screening study that invited more than 30,000 people to participate.
, reported lead author Esmée J. Grobbee, MD, of Erasmus University Medical Centre in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
In addition to high participation, previous research has shown that successful FIT screening depends upon continued adherence to the screening program, the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. They noted that, in the present study, just two rounds of FIT were needed to outperform endoscopic methods, and that these comparative findings are a first for the field.
“No literature is available on the comparison between endoscopic screening strategies and multiple rounds of FIT screening,” the investigators wrote. “It is of key importance for policy makers to know the impact of different screening programs over multiple rounds with long-term follow-up.”
To this end, the investigators invited 30,052 screening-naive people in the Netherlands to participate in the present study. Each invitation was for one of three groups: once-only colonoscopy, once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy, or four rounds of FIT. All individuals received an advanced notification by mail followed 2 weeks later by a more substantial information kit (and first FIT test when applicable). If these steps received no response, a reminder was sent 6 weeks later.
Participants in the FIT group received one test every 2 years. Patients who had a positive FIT (hemoglobin concentration of at least 10 mcg Hb/g feces) were scheduled for a colonoscopy. Similarly, colonoscopies were performed in patients who had concerning findings on flexible sigmoidoscopy (e.g., sessile serrated adenoma. This sequential system reduced the relative number of colonoscopies in these two groups; colonoscopy rates in the FIT group and flexible sigmoidoscopy group were 13% and 3%, respectively, compared with the 24% participation rate in the colonoscopy group.
At a population level, FIT screening had the highest advanced neoplasia detection rate, at 4.5%, compared with 2.3% and 2.2% for screening by sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, respectively.
“In the intention-to-screen analysis, FIT already detected significantly more advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer (CRC) after only 2 rounds of FIT, and this difference increased over rounds,” the investigators noted.
Again in the intention-to-screen population, mailed FIT detected three times as many cases of CRC than either of the other two groups (0.6% vs. 0.2% for both). In contrast, colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy had higher detection rates for nonadvanced adenomas, at 5.6% and 3.7%, respectively, compared with 3.2% for FIT, although the investigators noted that nonadvanced adenomas are “of uncertain clinical importance.” Sessile adenoma detection rates were similar across all three groups.
The as-screened analysis revealed higher detection rates of advanced neoplasia for colonoscopy (9.1%), compared with sigmoidoscopy (7.4%) and FIT (6.1%). In the same analysis, detection rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) were comparable across all three groups.
According to the investigators, the CRC-related findings require careful interpretation.
“Comparing CRC detection rates of FIT and endoscopic screening is complex … because CRCs detected in FIT screening could in theory have been prevented in a once-only colonoscopy by the removal of adenomas,” they wrote.
Still, the key takeaway of the study – that FIT screening was the most effective strategy – may have practical implications on a global scale, according to the investigators.
“Because many countries are considering implementing screening programs, the findings of this study aid in deciding on choice of screening strategies worldwide, which is based on expected participation rates and available colonoscopy resources,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Grobbee EJ et al. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2019 Aug 13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.015.
On a population level, mailed fecal immunohistochemical tests (FITs) may catch more cases of advanced neoplasia than endoscopic methods, based on a Dutch screening study that invited more than 30,000 people to participate.
, reported lead author Esmée J. Grobbee, MD, of Erasmus University Medical Centre in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
In addition to high participation, previous research has shown that successful FIT screening depends upon continued adherence to the screening program, the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. They noted that, in the present study, just two rounds of FIT were needed to outperform endoscopic methods, and that these comparative findings are a first for the field.
“No literature is available on the comparison between endoscopic screening strategies and multiple rounds of FIT screening,” the investigators wrote. “It is of key importance for policy makers to know the impact of different screening programs over multiple rounds with long-term follow-up.”
To this end, the investigators invited 30,052 screening-naive people in the Netherlands to participate in the present study. Each invitation was for one of three groups: once-only colonoscopy, once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy, or four rounds of FIT. All individuals received an advanced notification by mail followed 2 weeks later by a more substantial information kit (and first FIT test when applicable). If these steps received no response, a reminder was sent 6 weeks later.
Participants in the FIT group received one test every 2 years. Patients who had a positive FIT (hemoglobin concentration of at least 10 mcg Hb/g feces) were scheduled for a colonoscopy. Similarly, colonoscopies were performed in patients who had concerning findings on flexible sigmoidoscopy (e.g., sessile serrated adenoma. This sequential system reduced the relative number of colonoscopies in these two groups; colonoscopy rates in the FIT group and flexible sigmoidoscopy group were 13% and 3%, respectively, compared with the 24% participation rate in the colonoscopy group.
At a population level, FIT screening had the highest advanced neoplasia detection rate, at 4.5%, compared with 2.3% and 2.2% for screening by sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, respectively.
“In the intention-to-screen analysis, FIT already detected significantly more advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer (CRC) after only 2 rounds of FIT, and this difference increased over rounds,” the investigators noted.
Again in the intention-to-screen population, mailed FIT detected three times as many cases of CRC than either of the other two groups (0.6% vs. 0.2% for both). In contrast, colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy had higher detection rates for nonadvanced adenomas, at 5.6% and 3.7%, respectively, compared with 3.2% for FIT, although the investigators noted that nonadvanced adenomas are “of uncertain clinical importance.” Sessile adenoma detection rates were similar across all three groups.
The as-screened analysis revealed higher detection rates of advanced neoplasia for colonoscopy (9.1%), compared with sigmoidoscopy (7.4%) and FIT (6.1%). In the same analysis, detection rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) were comparable across all three groups.
According to the investigators, the CRC-related findings require careful interpretation.
“Comparing CRC detection rates of FIT and endoscopic screening is complex … because CRCs detected in FIT screening could in theory have been prevented in a once-only colonoscopy by the removal of adenomas,” they wrote.
Still, the key takeaway of the study – that FIT screening was the most effective strategy – may have practical implications on a global scale, according to the investigators.
“Because many countries are considering implementing screening programs, the findings of this study aid in deciding on choice of screening strategies worldwide, which is based on expected participation rates and available colonoscopy resources,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Grobbee EJ et al. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2019 Aug 13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.015.
On a population level, mailed fecal immunohistochemical tests (FITs) may catch more cases of advanced neoplasia than endoscopic methods, based on a Dutch screening study that invited more than 30,000 people to participate.
, reported lead author Esmée J. Grobbee, MD, of Erasmus University Medical Centre in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
In addition to high participation, previous research has shown that successful FIT screening depends upon continued adherence to the screening program, the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. They noted that, in the present study, just two rounds of FIT were needed to outperform endoscopic methods, and that these comparative findings are a first for the field.
“No literature is available on the comparison between endoscopic screening strategies and multiple rounds of FIT screening,” the investigators wrote. “It is of key importance for policy makers to know the impact of different screening programs over multiple rounds with long-term follow-up.”
To this end, the investigators invited 30,052 screening-naive people in the Netherlands to participate in the present study. Each invitation was for one of three groups: once-only colonoscopy, once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy, or four rounds of FIT. All individuals received an advanced notification by mail followed 2 weeks later by a more substantial information kit (and first FIT test when applicable). If these steps received no response, a reminder was sent 6 weeks later.
Participants in the FIT group received one test every 2 years. Patients who had a positive FIT (hemoglobin concentration of at least 10 mcg Hb/g feces) were scheduled for a colonoscopy. Similarly, colonoscopies were performed in patients who had concerning findings on flexible sigmoidoscopy (e.g., sessile serrated adenoma. This sequential system reduced the relative number of colonoscopies in these two groups; colonoscopy rates in the FIT group and flexible sigmoidoscopy group were 13% and 3%, respectively, compared with the 24% participation rate in the colonoscopy group.
At a population level, FIT screening had the highest advanced neoplasia detection rate, at 4.5%, compared with 2.3% and 2.2% for screening by sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, respectively.
“In the intention-to-screen analysis, FIT already detected significantly more advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer (CRC) after only 2 rounds of FIT, and this difference increased over rounds,” the investigators noted.
Again in the intention-to-screen population, mailed FIT detected three times as many cases of CRC than either of the other two groups (0.6% vs. 0.2% for both). In contrast, colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy had higher detection rates for nonadvanced adenomas, at 5.6% and 3.7%, respectively, compared with 3.2% for FIT, although the investigators noted that nonadvanced adenomas are “of uncertain clinical importance.” Sessile adenoma detection rates were similar across all three groups.
The as-screened analysis revealed higher detection rates of advanced neoplasia for colonoscopy (9.1%), compared with sigmoidoscopy (7.4%) and FIT (6.1%). In the same analysis, detection rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) were comparable across all three groups.
According to the investigators, the CRC-related findings require careful interpretation.
“Comparing CRC detection rates of FIT and endoscopic screening is complex … because CRCs detected in FIT screening could in theory have been prevented in a once-only colonoscopy by the removal of adenomas,” they wrote.
Still, the key takeaway of the study – that FIT screening was the most effective strategy – may have practical implications on a global scale, according to the investigators.
“Because many countries are considering implementing screening programs, the findings of this study aid in deciding on choice of screening strategies worldwide, which is based on expected participation rates and available colonoscopy resources,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Grobbee EJ et al. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2019 Aug 13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.015.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
GALAD score predicts NASH-HCC more than a year in advance
For patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the GALAD score may accurately predict hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as early as 560 days before diagnosis, according to investigators.
The GALAD score, which combines sex, age, alpha-fetoprotein-L3 (AFP-L3), alpha-fetoprotein, and des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (DCP), could improve cancer surveillance among NASH patients whose obesity limits sensitivity of ultrasound, reported lead author Jan Best, MD, of the University Hospital Magdeburg in Germany, and colleagues.
“The limitations of ultrasound surveillance alone for early detection of HCC are particularly evident in patients with NASH,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Serum-based biomarkers might be more effective, with or without ultrasound surveillance, for HCC surveillance in NASH patients, although data in this patient population are currently lacking. The current study assessed the performance of the GALAD score for early HCC detection in patients with NASH-related liver disease.”
The study consisted of two parts: first, a retrospective case-control analysis, and second, a phase 3 prospective trial that implemented the GALAD score in a real-world population.
The retrospective component of the study involved 126 NASH patients with HCC (cases) and 231 NASH patients without HCC (controls), all of whom were treated at eight centers in Germany. The median GALAD score was significantly higher among NASH patients with HCC than in those without (2.93 vs. –3.96; P less than .001). At an optimal cutoff of –1.334, the GALAD score predicted HCC with a sensitivity of 91.2% and a specificity of 95.2%. Each component of the GALAD score aligned with previously published findings, as patients with HCC were predominantly older men with elevated serum AFP-L3, AFP, and DCP. But a closer look at the data showed that the GALAD score more accurately predicted HCC than any of its constituent serum measurements in isolation. For any stage of HCC, GALAD had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96, compared with significantly lower values for AFP (0.88), AFP-L3 (0.86), and DCP (0.87). Similarly, for early-stage HCC, GALAD score AUC was 0.92, compared with significantly lower values for AFP (0.77), AFP-L3 (0.74), and DCP (0.87).
The accuracy of the GALAD score – for detection of both any-stage and early-stage HCC — remained high regardless of cirrhosis status. Among patients with cirrhosis, the AUC for any-stage HCC was 0.93, and 0.85 for early-stage HCC. For patients without cirrhosis, GALAD was slightly more predictive, based on AUC’s of 0.98 and 0.94 for detection of any-stage and early-stage HCC, respectively. Again, these accuracy values significantly outmatched each serum measurement in isolation.
“These data on NASH-HCC patients demonstrate that GALAD can detect HCC independent of cirrhosis or stage of HCC,” the investigators wrote. “Indeed, even early noncirrhotic NASH-HCC seems clearly separable from NASH controls, as even small groups resulted in robust performance.”
The prospective component of the study involved screening 392 patients with NASH at a single treatment center in Japan. From this cohort, 28 patients developed HCC after a median of 10.1 years. Many patients in this group had significantly higher GALAD scores for 5 or more years before being diagnosed with HCC, and scores rose sharply in the months preceding diagnosis. Depending on selected cutoff value, the GALAD score predicted HCC from 200 to 560 days prior to diagnosis.
“While this specific result has to be confirmed in further prospective studies, it is a promising observation for potential use of GALAD as a screening tool in NASH patients,” the investigators wrote.
“In conclusion, our data confirm that the GALAD score is superior to individual serum markers for detection of HCC in NASH, independent of tumor stage or cirrhosis,” the investigators wrote. “The findings suggest that GALAD should be investigated as a potential tool for screening of NASH individuals to detect HCC at a resectable stage in a sufficiently large prospective study to identify a cutoff.”
The study was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Wilhelm-Laupitz Foundation, and the Werner Jackstaedt Foundation. The investigators declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Best J et al. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.012.
There has been increasing recognition that ultrasound-based HCC surveillance in patients with cirrhosis has suboptimal sensitivity and specificity for early HCC detection, particularly when applied to those with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). These data highlight the critical need for novel biomarkers to improve early HCC detection and reduce mortality. The study by Dr. Best and colleagues evaluated a blood-based biomarker panel, GALAD, in patients with NASH and found that it was able to detect HCC at an early stage with a sensitivity of 68% and specificity of 95% - performance comparable, if not superior, to that of abdominal ultrasound. In an accompanying pilot prospective cohort study, the authors also found GALAD may detect HCC more than 1 year prior to diagnosis. Although earlier studies had similarly demonstrated high performance of GALAD for early HCC detection, this study specifically examined patients with NASH - a cohort that increasingly accounts for HCC cases in the Western world but has been underrepresented in prior studies. Therefore, it is reassuring to know that GALAD appears to have high sensitivity and specificity in this patient group. However, while the data by Best et al. are promising, validation of these results in larger cohort studies is needed before routine adoption in clinical practice. Fortunately, maturation of phase 3 biomarker cohorts, including the Early Detection Research Network Hepatocellular Early Detection Strategy (EDRN HEDS) and Texas HCC Consortium, will facilitate this evaluation in the near future and will hopefully translate promising biomarkers into clinical practice.
Amit G. Singal, MD, is an associate professor of medicine, medical director of the liver tumor program, and chief of hepatology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. He has served as a consultant for Wako Diagnostics, Glycotest, Exact Sciences, Roche Diagnostics, and TARGET Pharmasolutions.
There has been increasing recognition that ultrasound-based HCC surveillance in patients with cirrhosis has suboptimal sensitivity and specificity for early HCC detection, particularly when applied to those with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). These data highlight the critical need for novel biomarkers to improve early HCC detection and reduce mortality. The study by Dr. Best and colleagues evaluated a blood-based biomarker panel, GALAD, in patients with NASH and found that it was able to detect HCC at an early stage with a sensitivity of 68% and specificity of 95% - performance comparable, if not superior, to that of abdominal ultrasound. In an accompanying pilot prospective cohort study, the authors also found GALAD may detect HCC more than 1 year prior to diagnosis. Although earlier studies had similarly demonstrated high performance of GALAD for early HCC detection, this study specifically examined patients with NASH - a cohort that increasingly accounts for HCC cases in the Western world but has been underrepresented in prior studies. Therefore, it is reassuring to know that GALAD appears to have high sensitivity and specificity in this patient group. However, while the data by Best et al. are promising, validation of these results in larger cohort studies is needed before routine adoption in clinical practice. Fortunately, maturation of phase 3 biomarker cohorts, including the Early Detection Research Network Hepatocellular Early Detection Strategy (EDRN HEDS) and Texas HCC Consortium, will facilitate this evaluation in the near future and will hopefully translate promising biomarkers into clinical practice.
Amit G. Singal, MD, is an associate professor of medicine, medical director of the liver tumor program, and chief of hepatology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. He has served as a consultant for Wako Diagnostics, Glycotest, Exact Sciences, Roche Diagnostics, and TARGET Pharmasolutions.
There has been increasing recognition that ultrasound-based HCC surveillance in patients with cirrhosis has suboptimal sensitivity and specificity for early HCC detection, particularly when applied to those with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). These data highlight the critical need for novel biomarkers to improve early HCC detection and reduce mortality. The study by Dr. Best and colleagues evaluated a blood-based biomarker panel, GALAD, in patients with NASH and found that it was able to detect HCC at an early stage with a sensitivity of 68% and specificity of 95% - performance comparable, if not superior, to that of abdominal ultrasound. In an accompanying pilot prospective cohort study, the authors also found GALAD may detect HCC more than 1 year prior to diagnosis. Although earlier studies had similarly demonstrated high performance of GALAD for early HCC detection, this study specifically examined patients with NASH - a cohort that increasingly accounts for HCC cases in the Western world but has been underrepresented in prior studies. Therefore, it is reassuring to know that GALAD appears to have high sensitivity and specificity in this patient group. However, while the data by Best et al. are promising, validation of these results in larger cohort studies is needed before routine adoption in clinical practice. Fortunately, maturation of phase 3 biomarker cohorts, including the Early Detection Research Network Hepatocellular Early Detection Strategy (EDRN HEDS) and Texas HCC Consortium, will facilitate this evaluation in the near future and will hopefully translate promising biomarkers into clinical practice.
Amit G. Singal, MD, is an associate professor of medicine, medical director of the liver tumor program, and chief of hepatology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. He has served as a consultant for Wako Diagnostics, Glycotest, Exact Sciences, Roche Diagnostics, and TARGET Pharmasolutions.
For patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the GALAD score may accurately predict hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as early as 560 days before diagnosis, according to investigators.
The GALAD score, which combines sex, age, alpha-fetoprotein-L3 (AFP-L3), alpha-fetoprotein, and des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (DCP), could improve cancer surveillance among NASH patients whose obesity limits sensitivity of ultrasound, reported lead author Jan Best, MD, of the University Hospital Magdeburg in Germany, and colleagues.
“The limitations of ultrasound surveillance alone for early detection of HCC are particularly evident in patients with NASH,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Serum-based biomarkers might be more effective, with or without ultrasound surveillance, for HCC surveillance in NASH patients, although data in this patient population are currently lacking. The current study assessed the performance of the GALAD score for early HCC detection in patients with NASH-related liver disease.”
The study consisted of two parts: first, a retrospective case-control analysis, and second, a phase 3 prospective trial that implemented the GALAD score in a real-world population.
The retrospective component of the study involved 126 NASH patients with HCC (cases) and 231 NASH patients without HCC (controls), all of whom were treated at eight centers in Germany. The median GALAD score was significantly higher among NASH patients with HCC than in those without (2.93 vs. –3.96; P less than .001). At an optimal cutoff of –1.334, the GALAD score predicted HCC with a sensitivity of 91.2% and a specificity of 95.2%. Each component of the GALAD score aligned with previously published findings, as patients with HCC were predominantly older men with elevated serum AFP-L3, AFP, and DCP. But a closer look at the data showed that the GALAD score more accurately predicted HCC than any of its constituent serum measurements in isolation. For any stage of HCC, GALAD had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96, compared with significantly lower values for AFP (0.88), AFP-L3 (0.86), and DCP (0.87). Similarly, for early-stage HCC, GALAD score AUC was 0.92, compared with significantly lower values for AFP (0.77), AFP-L3 (0.74), and DCP (0.87).
The accuracy of the GALAD score – for detection of both any-stage and early-stage HCC — remained high regardless of cirrhosis status. Among patients with cirrhosis, the AUC for any-stage HCC was 0.93, and 0.85 for early-stage HCC. For patients without cirrhosis, GALAD was slightly more predictive, based on AUC’s of 0.98 and 0.94 for detection of any-stage and early-stage HCC, respectively. Again, these accuracy values significantly outmatched each serum measurement in isolation.
“These data on NASH-HCC patients demonstrate that GALAD can detect HCC independent of cirrhosis or stage of HCC,” the investigators wrote. “Indeed, even early noncirrhotic NASH-HCC seems clearly separable from NASH controls, as even small groups resulted in robust performance.”
The prospective component of the study involved screening 392 patients with NASH at a single treatment center in Japan. From this cohort, 28 patients developed HCC after a median of 10.1 years. Many patients in this group had significantly higher GALAD scores for 5 or more years before being diagnosed with HCC, and scores rose sharply in the months preceding diagnosis. Depending on selected cutoff value, the GALAD score predicted HCC from 200 to 560 days prior to diagnosis.
“While this specific result has to be confirmed in further prospective studies, it is a promising observation for potential use of GALAD as a screening tool in NASH patients,” the investigators wrote.
“In conclusion, our data confirm that the GALAD score is superior to individual serum markers for detection of HCC in NASH, independent of tumor stage or cirrhosis,” the investigators wrote. “The findings suggest that GALAD should be investigated as a potential tool for screening of NASH individuals to detect HCC at a resectable stage in a sufficiently large prospective study to identify a cutoff.”
The study was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Wilhelm-Laupitz Foundation, and the Werner Jackstaedt Foundation. The investigators declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Best J et al. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.012.
For patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the GALAD score may accurately predict hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as early as 560 days before diagnosis, according to investigators.
The GALAD score, which combines sex, age, alpha-fetoprotein-L3 (AFP-L3), alpha-fetoprotein, and des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (DCP), could improve cancer surveillance among NASH patients whose obesity limits sensitivity of ultrasound, reported lead author Jan Best, MD, of the University Hospital Magdeburg in Germany, and colleagues.
“The limitations of ultrasound surveillance alone for early detection of HCC are particularly evident in patients with NASH,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Serum-based biomarkers might be more effective, with or without ultrasound surveillance, for HCC surveillance in NASH patients, although data in this patient population are currently lacking. The current study assessed the performance of the GALAD score for early HCC detection in patients with NASH-related liver disease.”
The study consisted of two parts: first, a retrospective case-control analysis, and second, a phase 3 prospective trial that implemented the GALAD score in a real-world population.
The retrospective component of the study involved 126 NASH patients with HCC (cases) and 231 NASH patients without HCC (controls), all of whom were treated at eight centers in Germany. The median GALAD score was significantly higher among NASH patients with HCC than in those without (2.93 vs. –3.96; P less than .001). At an optimal cutoff of –1.334, the GALAD score predicted HCC with a sensitivity of 91.2% and a specificity of 95.2%. Each component of the GALAD score aligned with previously published findings, as patients with HCC were predominantly older men with elevated serum AFP-L3, AFP, and DCP. But a closer look at the data showed that the GALAD score more accurately predicted HCC than any of its constituent serum measurements in isolation. For any stage of HCC, GALAD had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96, compared with significantly lower values for AFP (0.88), AFP-L3 (0.86), and DCP (0.87). Similarly, for early-stage HCC, GALAD score AUC was 0.92, compared with significantly lower values for AFP (0.77), AFP-L3 (0.74), and DCP (0.87).
The accuracy of the GALAD score – for detection of both any-stage and early-stage HCC — remained high regardless of cirrhosis status. Among patients with cirrhosis, the AUC for any-stage HCC was 0.93, and 0.85 for early-stage HCC. For patients without cirrhosis, GALAD was slightly more predictive, based on AUC’s of 0.98 and 0.94 for detection of any-stage and early-stage HCC, respectively. Again, these accuracy values significantly outmatched each serum measurement in isolation.
“These data on NASH-HCC patients demonstrate that GALAD can detect HCC independent of cirrhosis or stage of HCC,” the investigators wrote. “Indeed, even early noncirrhotic NASH-HCC seems clearly separable from NASH controls, as even small groups resulted in robust performance.”
The prospective component of the study involved screening 392 patients with NASH at a single treatment center in Japan. From this cohort, 28 patients developed HCC after a median of 10.1 years. Many patients in this group had significantly higher GALAD scores for 5 or more years before being diagnosed with HCC, and scores rose sharply in the months preceding diagnosis. Depending on selected cutoff value, the GALAD score predicted HCC from 200 to 560 days prior to diagnosis.
“While this specific result has to be confirmed in further prospective studies, it is a promising observation for potential use of GALAD as a screening tool in NASH patients,” the investigators wrote.
“In conclusion, our data confirm that the GALAD score is superior to individual serum markers for detection of HCC in NASH, independent of tumor stage or cirrhosis,” the investigators wrote. “The findings suggest that GALAD should be investigated as a potential tool for screening of NASH individuals to detect HCC at a resectable stage in a sufficiently large prospective study to identify a cutoff.”
The study was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Wilhelm-Laupitz Foundation, and the Werner Jackstaedt Foundation. The investigators declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Best J et al. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.012.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Fewer complications, better outcomes with outpatient UKA
according to a review from the University of Tennessee Campbell Clinic, Memphis.
“In carefully selected patients, the ASC [ambulatory surgery center] seems to be a safe alternative to the inpatient hospital setting,” concluded investigators led by led by Marcus Ford, MD, a Campbell Clinic orthopedic surgeon.
He and his colleagues have been doing outpatient unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) since 2009, and “based on the subjective success,” recently increased the number of total knee, hip, and shoulder arthroplasties performed in their ASC.
They wanted to make sure, however, that their impression of good outpatient UKA results was supported by the data, so they compared outcomes in 48 UKA patients treated at their ASC with 48 treated in the hospital. The operations were done by two surgeons using the same technique and same medial UKA implant.
“Naturally, surgeons select those patients who are deemed physically and mentally capable of succeeding with an accelerated discharge plan” for outpatient service, the investigators wrote. To address that potential selection bias, the team matched their subjects by age and comorbidities.
There was only one minor complication in the outpatient group, a superficial stitch abscess. No patient needed a second operation, and all went home the same day.
It was different on the inpatient side. The average length of stay was 2.9 days, and there were four major complications: a deep venous thrombosis, a pulmonary embolus, an acute postoperative infection, and a periprosthetic fracture. All four required hospital readmission, and two patients needed a second operation.
The report didn’t directly address the reasons for the differences, but Dr. Ford and colleagues did note that they “believe that the ASC allows the surgeon greater direct control of perioperative variables that can impact patient outcome.”
Patients were in their late 50s, on average, and there were more women than men in both groups. The mean American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classification score was 1.94 and mean body mass index was 34.3 kg/m2 in the outpatient group, compared with a mean physical status classification score of 2.08 and mean body mass index of 32.9 kg/m2 in the inpatient group. The differences were not statistically significant.
No funding source was reported. The investigators did not report any disclosures.
SOURCE: Ford M et al. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020 Jan;51[1]:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2019.08.001
according to a review from the University of Tennessee Campbell Clinic, Memphis.
“In carefully selected patients, the ASC [ambulatory surgery center] seems to be a safe alternative to the inpatient hospital setting,” concluded investigators led by led by Marcus Ford, MD, a Campbell Clinic orthopedic surgeon.
He and his colleagues have been doing outpatient unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) since 2009, and “based on the subjective success,” recently increased the number of total knee, hip, and shoulder arthroplasties performed in their ASC.
They wanted to make sure, however, that their impression of good outpatient UKA results was supported by the data, so they compared outcomes in 48 UKA patients treated at their ASC with 48 treated in the hospital. The operations were done by two surgeons using the same technique and same medial UKA implant.
“Naturally, surgeons select those patients who are deemed physically and mentally capable of succeeding with an accelerated discharge plan” for outpatient service, the investigators wrote. To address that potential selection bias, the team matched their subjects by age and comorbidities.
There was only one minor complication in the outpatient group, a superficial stitch abscess. No patient needed a second operation, and all went home the same day.
It was different on the inpatient side. The average length of stay was 2.9 days, and there were four major complications: a deep venous thrombosis, a pulmonary embolus, an acute postoperative infection, and a periprosthetic fracture. All four required hospital readmission, and two patients needed a second operation.
The report didn’t directly address the reasons for the differences, but Dr. Ford and colleagues did note that they “believe that the ASC allows the surgeon greater direct control of perioperative variables that can impact patient outcome.”
Patients were in their late 50s, on average, and there were more women than men in both groups. The mean American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classification score was 1.94 and mean body mass index was 34.3 kg/m2 in the outpatient group, compared with a mean physical status classification score of 2.08 and mean body mass index of 32.9 kg/m2 in the inpatient group. The differences were not statistically significant.
No funding source was reported. The investigators did not report any disclosures.
SOURCE: Ford M et al. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020 Jan;51[1]:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2019.08.001
according to a review from the University of Tennessee Campbell Clinic, Memphis.
“In carefully selected patients, the ASC [ambulatory surgery center] seems to be a safe alternative to the inpatient hospital setting,” concluded investigators led by led by Marcus Ford, MD, a Campbell Clinic orthopedic surgeon.
He and his colleagues have been doing outpatient unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) since 2009, and “based on the subjective success,” recently increased the number of total knee, hip, and shoulder arthroplasties performed in their ASC.
They wanted to make sure, however, that their impression of good outpatient UKA results was supported by the data, so they compared outcomes in 48 UKA patients treated at their ASC with 48 treated in the hospital. The operations were done by two surgeons using the same technique and same medial UKA implant.
“Naturally, surgeons select those patients who are deemed physically and mentally capable of succeeding with an accelerated discharge plan” for outpatient service, the investigators wrote. To address that potential selection bias, the team matched their subjects by age and comorbidities.
There was only one minor complication in the outpatient group, a superficial stitch abscess. No patient needed a second operation, and all went home the same day.
It was different on the inpatient side. The average length of stay was 2.9 days, and there were four major complications: a deep venous thrombosis, a pulmonary embolus, an acute postoperative infection, and a periprosthetic fracture. All four required hospital readmission, and two patients needed a second operation.
The report didn’t directly address the reasons for the differences, but Dr. Ford and colleagues did note that they “believe that the ASC allows the surgeon greater direct control of perioperative variables that can impact patient outcome.”
Patients were in their late 50s, on average, and there were more women than men in both groups. The mean American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classification score was 1.94 and mean body mass index was 34.3 kg/m2 in the outpatient group, compared with a mean physical status classification score of 2.08 and mean body mass index of 32.9 kg/m2 in the inpatient group. The differences were not statistically significant.
No funding source was reported. The investigators did not report any disclosures.
SOURCE: Ford M et al. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020 Jan;51[1]:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2019.08.001
FROM ORTHOPEDIC CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA
Effect of In-Office Samples on Dermatologists’ Prescribing Habits: A Retrospective Review
Over the years, there has been growing concern about the relationship between physicians and pharmaceutical companies. Many studies have demonstrated that pharmaceutical interactions and incentives can influence physicians’ prescribing habits.1-3 As a result, many academic centers have adopted policies that attempt to limit the pharmaceutical industry’s influence on faculty and in-training physicians. Although these policies can vary greatly, they generally limit access of pharmaceutical representatives to providers and restrict pharmaceutical samples.4,5 This policy shift has even been reported in private practice.6
At the heart of the matter is the question: What really influences physicians to write a prescription for a particular medication? Is it cost, efficacy, or representatives pushing a product? Prior studies illustrate that generic medications are equivalent to their brand-name counterparts. In fact, current regulations require no more than 5% to 7% difference in bioequivalence.7-9 Although most generic medications are bioequivalent, it may not be universal.10
Garrison and Levin11 distributed a survey to US-based prescribers in family practice, psychiatry, and internal medicine and found that prescribers deemed patient response and success as the highest priority when determining which drugs to prescribe. In contrast, drug representatives and free samples only slightly contributed.11 Considering the minimum duration for efficacy of a medication such as an antidepressant vs a topical steroid, this pattern may differ with samples in dermatologic settings. Interestingly, another survey concluded that samples were associated with “sticky” prescribing habits, noting that physicians would prescribe a brand-name medication after using a sample, despite increased cost to the patient.12 Further, it has been suggested that recipients of free samples may experience increased costs in the long run, which contrasts a stated goal of affordability to patients.12,13
Physician interaction with pharmaceutical companies begins as early as medical school,14 with physicians reporting interactions as often as 4 times each month.14-18 Interactions can include meetings with pharmaceutical representatives, sponsored meals, gifts, continuing medical education sponsorship, funding for travel, pharmaceutical representative speakers, research funding, and drug samples.3
A 2014 study reported that prescribing habits are influenced by the free drug samples provided by nongeneric pharmaceutical companies.19 Nationally, the number of brand-name and branded generic medications constitute 79% of prescriptions, yet together they only comprise 17% of medications prescribed at an academic medical clinic that does not provide samples. The number of medications with samples being prescribed by dermatologists increased by 15% over 9 years, which may correlate with the wider availability of medication samples, more specifically an increase in branded generic samples.19 This potential interaction is the reason why institutions question the current influence of pharmaceutical companies. Samples may appear convenient, allowing a patient to test the medication prior to committing; however, with brand-name samples being provided to the physician, he/she may become more inclined to prescribe the branded medication.12,15,19-22 Because brand-name medications are more expensive than generic medications, this practice can increase the cost of health care.13 One study found that over 1 year, the overuse of nongeneric medications led to a loss of potential savings throughout 49 states, equating to $229 million just through Medicaid; interestingly, it was noted that in some states, a maximum reimbursement is set by Medicaid, regardless of whether the generic or branded medication is dispensed. The authors also noted variability in the potential savings by state, which may be a function of the state-by-state maximum reimbursements for certain medications.23 Another study on oral combination medications estimated Medicare spending on branded drugs relative to the cost if generic combinations had been purchased instead. This study examined branded medications for which the active components were available as over-the-counter (OTC), generic, or same-class generic, and the authors estimated that $925 million could have been saved in 2016 by purchasing a generic substitute.24 The overuse of nongeneric medications when generic alternatives are available becomes an issue that not only financially impacts patients but all taxpayers. However, this pattern may differ if limited only to dermatologic medications, which was not the focus of the prior studies.
To limit conflicts of interest in interactions with the pharmaceutical, medical device, and biotechnology industries, the University of South Florida (USF) Morsani College of Medicine (COM)(Tampa, Florida) implemented its own set of regulations that eliminated in-office pharmaceutical samples, in addition to other restrictions. This study aimed to investigate if there was a change in the prescribing habits of academic dermatologists after their medical school implemented these new policies.
We hypothesized that the number of brand-name drugs prescribed by physicians in the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery would change following USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes. We sought to determine how physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery changed following USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes.
Methods
Data Collection
A retrospective review of medical records was conducted to investigate the effect of the USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes on physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery. Medical records of patients seen for common dermatology diagnoses before (January 1, 2010, to May 30, 2010) and after (August 1, 2011, to December 31, 2011) the pharmaceutical policy changes were reviewed, and all medications prescribed were recorded. Data were collected from medical records within the USF Health electronic medical record system and included visits with each of the department’s 3 attending dermatologists. The diagnoses included in the study—acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, and rosacea—were chosen because in-office samples were available. Prescribing data from the first 100 consecutive medical records were collected from each time period, and a medical record was included only if it contained at least 1 of the following diagnoses: acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, or rosacea. The assessment and plan of each progress note were reviewed, and the exact medication name and associated diagnosis were recorded for each prescription. Subsequently, each medication was reviewed and placed in 1 of 3 categories: brand name, generic, and OTC. The total number of prescriptions for each diagnosis (per visit/note); the specific number of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note); and the percentage of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note and per diagnosis in total) were calculated. To ensure only intended medications were included, each medication recorded in the medical record note was cross-referenced with the prescribed medication in the electronic medical record. The primary objective of this study was to capture the prescribing physician’s intent as proxied by the pattern of prescription. Thus, changes made in prescriptions after the initial plan—whether insurance related or otherwise—were not relevant to this investigation.
The data were collected to compare the percentage of brand vs generic or OTC prescriptions per diagnosis to see if there was a difference in the prescribing habits before and after the pharmaceutical policy changes. Of note, several other pieces of data were collected from each medical record, including age, race, class of insurance (ie, Medicare, Medicaid, private health maintenance organization, private preferred provider organization), subtype diagnoses, and whether the prescription was new or a refill. The information gathered from the written record on the assessment and plan was verified using prescriptions ordered in the Allscripts electronic record, and any difference was noted. No identifying information that could be used to easily identify study participants was recorded.
Differences in prescribing habits across diagnoses before and after the policy changes were ascertained using a Fisher exact test and were further assessed using a mixed effects ordinal logistic regression model that accounted for within-provider clustering and baseline patient characteristics. An ordinal model was chosen to recognize differences in average cost among brand-name, generic, and OTC medications.
Results
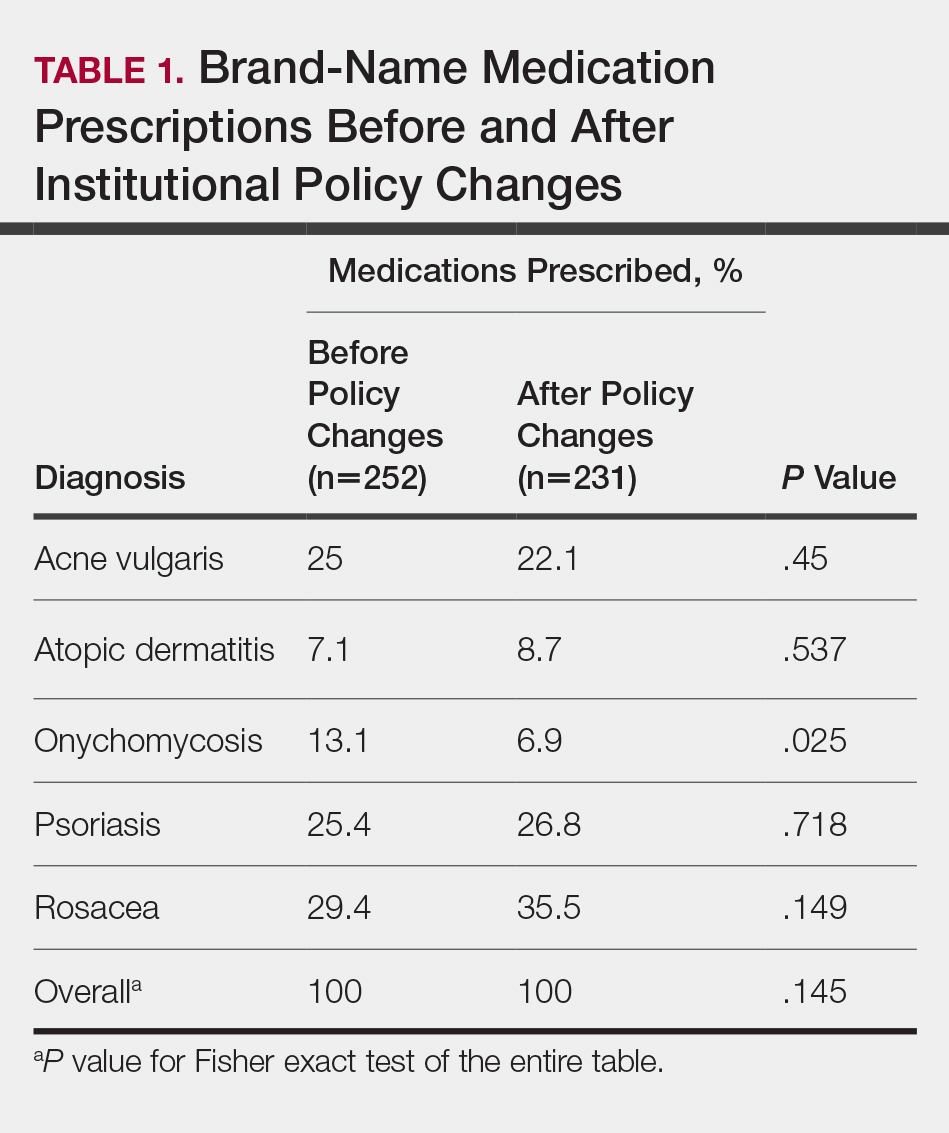
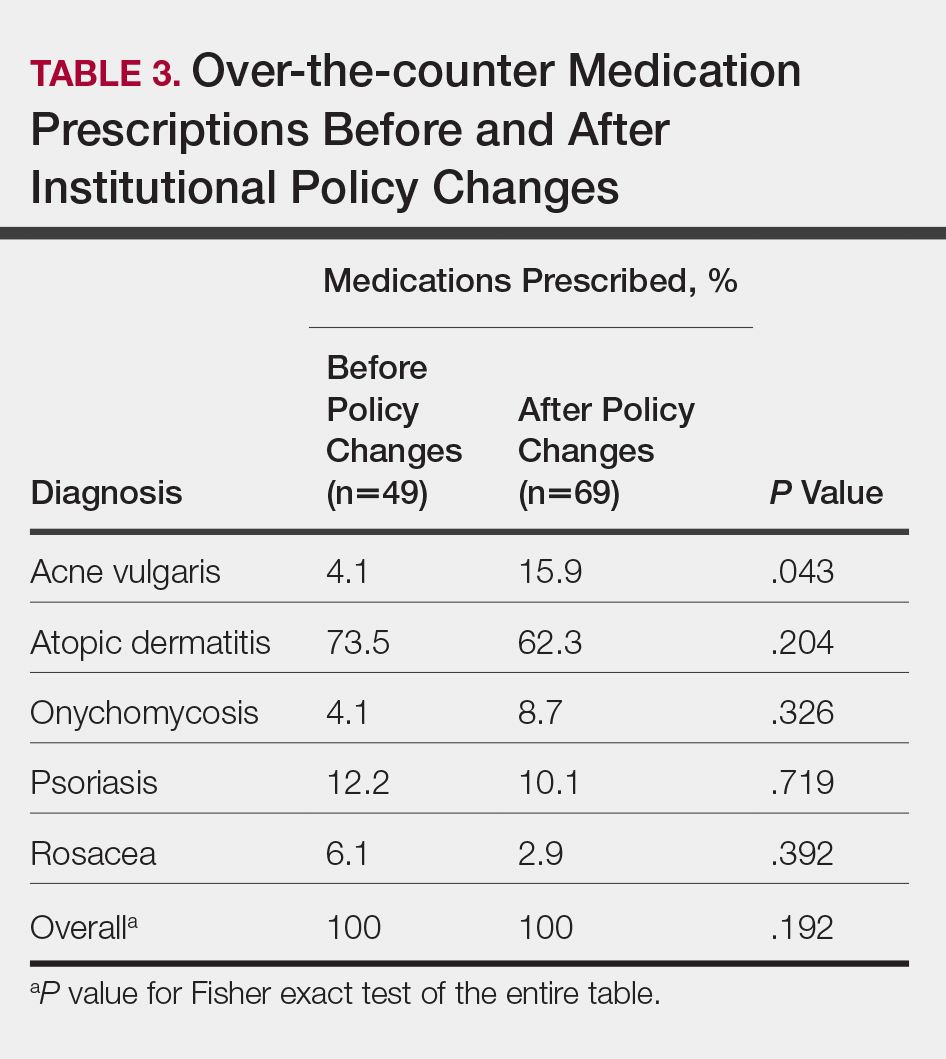
In total, 200 medical records were collected. For the period analyzed before the policy change, 252 brand-name medications were prescribed compared to 231 prescribed for the period analyzed after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in brand-name medications prescribed before and after the policy changes (P=.145; Fisher exact test)(Table 1). There also was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in generic prescriptions, which totaled 153 before and 134 after the policy changes (P=.872; Fisher exact test)(Table 2). Over-the-counter prescriptions totaled 49 before and 69 after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference before and after the policy changes for OTC medications (P=.192; Fisher exact test)(Table 3).

Comment
Although some medical institutions are diligently working to limit the potential influence pharmaceutical companies have on physician prescribing habits,4,5,25 the effect on physician prescribing habits is only now being established.15 Prior studies12,19,21 have found evidence that medication samples may lead to overuse of brand-name medications, but these findings do not hold true for the USF dermatologists included in this study, perhaps due to the difference in pharmaceutical company interactions or physicians maintaining prior prescription habits that were unrelated to the policy. Although this study focused on policy changes for in-office samples, prior studies either included other forms of interaction21 or did not include samples.22
Pharmaceutical samples allow patients to try a medication before committing to a long-term course of treatment with a particular medication, which has utility for physicians and patients. Although brand-name prescriptions may cost more, a trial period may assist the patient in deciding whether the medication is worth purchasing. Furthermore, physicians may feel more comfortable prescribing a medication once the individual patient has demonstrated a benefit from the sample, which may be particularly true in a specialty such as dermatology in which many branded topical medications contain a different vehicle than generic formulations, resulting in notable variations in active medication delivery and efficacy. Given the higher cost of branded topical medications, proving efficacy in patients through samples can provide a useful tool to the physician to determine the need for a branded formulation.
The benefits described are subjective but should not be disregarded. Although Hurley et al19 found that the number of brand-name medications prescribed increases as more samples are given out, our study demonstrated that after eliminating medication samples, there was no significant difference in the percentage of brand-name medications prescribed compared to generic and OTC medications.
Physician education concerning the price of each brand-name medication prescribed in office may be one method of reducing the amount of such prescriptions. Physicians generally are uninformed of the cost of the medications being prescribed26 and may not recognize the financial burden one medication may have compared to its alternative. However, educating physicians will empower them to make the conscious decision to prefer or not prefer a brand-name medication. With some generic medications shown to have a difference in bioequivalence compared to their brand-name counterparts, a physician may find more success prescribing the brand-name medications, regardless of pharmaceutical company influence, which is an alternative solution to policy changes that eliminate samples entirely. Although this study found insufficient evidence that removing samples decreases brand-name medication prescriptions, it is imperative that solutions are established to reduce the country’s increasing burden of medical costs.
Possible shortfalls of this study include the short period of time between which prepolicy data and postpolicy data were collected. It is possible that providers did not have enough time to adjust their prescribing habits or that providers would not have changed a prescribing pattern or preference simply because of a policy change. Future studies could allow a time period greater than 2 years to compare prepolicy and postpolicy prescribing habits, or a future study might make comparisons of prescriber patterns at different institutions that have different policies. Another possible shortfall is that providers and patients were limited to those at the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery at the USF Morsani COM. Although this study has found insufficient evidence of a difference in prescribing habits, it may be beneficial to conduct a larger study that encompasses multiple academic institutions with similar policy changes. Most importantly, this study only investigated the influence of in-office pharmaceutical samples on prescribing patterns. This study did not look at the many other ways in which providers may be influenced by pharmaceutical companies, which likely is a significant confounding variable in this study. Continued additional studies that specifically examine other methods through which providers may be influenced would be helpful in further examining the many ways in which physician prescription habits are influenced.
Conclusion
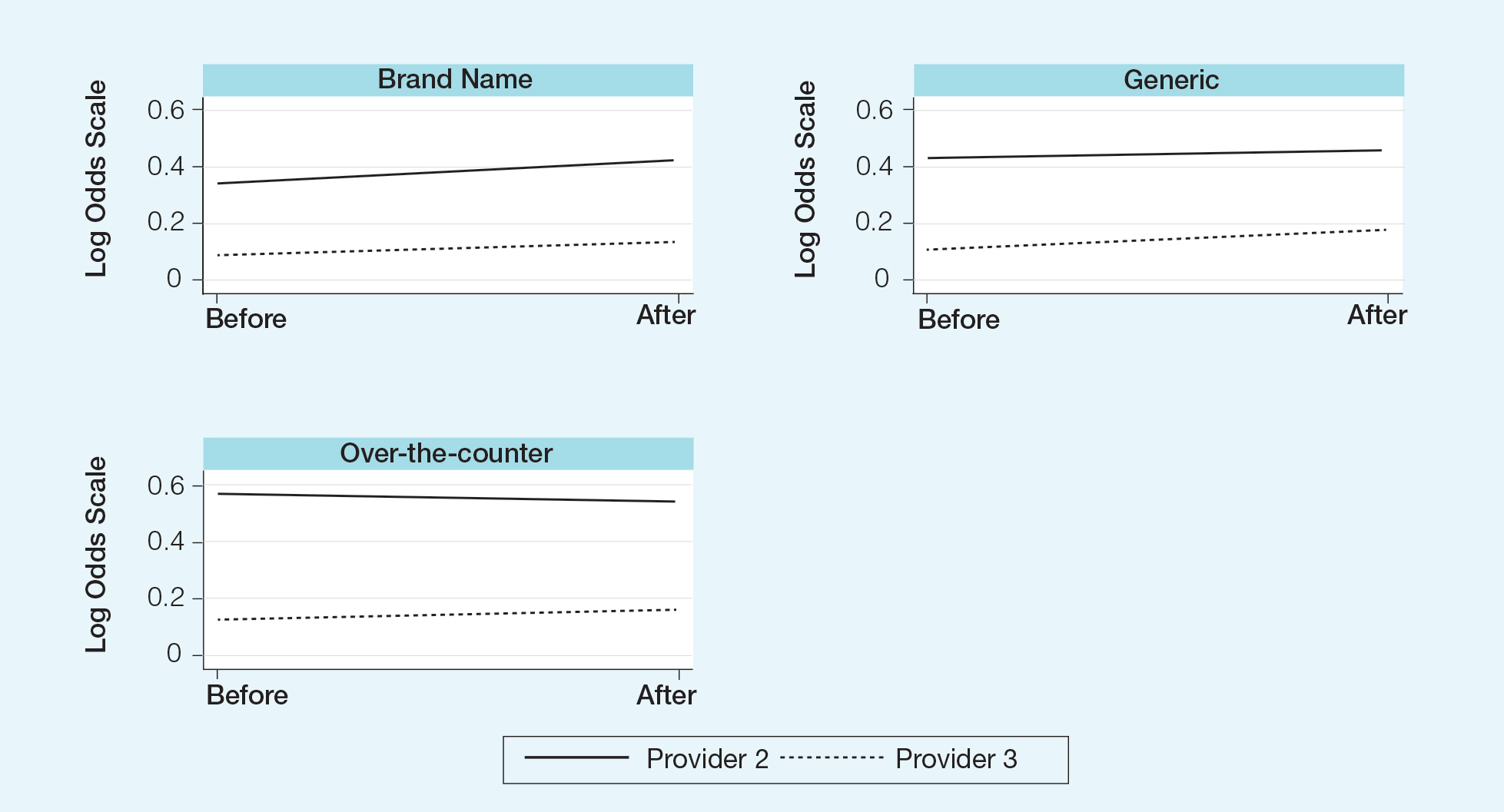
Changes in pharmaceutical policy in 2011 at USF Morsani COM specifically banned in-office samples. The totality of evidence in this study shows modest observational evidence of a change in the postpolicy odds relative to prepolicy odds, but the data also are compatible with no change between prescribing habits before and after the policy changes. Further study is needed to fully understand this relationship.
- Sondergaard J, Vach K, Kragstrup J, et al. Impact of pharmaceutical representative visits on GPs’ drug preferences. Fam Pract. 2009;26:204-209.
- Jelinek GA, Neate SL. The influence of the pharmaceutical industry in medicine. J Law Med. 2009;17:216-223.
- Wazana A. Physicians and the pharmaceutical industry: is a gift ever just a gift? JAMA. 2000;283:373-380.
- Coleman DL. Establishing policies for the relationship between industry and clinicians: lessons learned from two academic health centers. Acad Med. 2008;83:882-887.
- Coleman DL, Kazdin AE, Miller LA, et al. Guidelines for interactions between clinical faculty and the pharmaceutical industry: one medical school’s approach. Acad Med. 2006;81:154-160.
- Evans D, Hartung DM, Beasley D, et al. Breaking up is hard to do: lessons learned from a pharma-free practice transformation. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:332-338.
- Davit BM, Nwakama PE, Buehler GJ, et al. Comparing generic and innovator drugs: a review of 12 years of bioequivalence data from the United States Food and Drug Administration. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43:1583-1597.
- Kesselheim AS, Misono AS, Lee JL, et al. Clinical equivalence of generic and brand-name drugs used in cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300:2514-2526.
- McCormack J, Chmelicek JT. Generic versus brand name: the other drug war. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60:911.
- Borgheini G. The bioequivalence and therapeutic efficacy of generic versus brand-name psychoactive drugs. Clin Ther. 2003;25:1578-1592.
- Garrison GD, Levin GM. Factors affecting prescribing of the newer antidepressants. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34:10-14.
- Rafique S, Sarwar W, Rashid A, et al. Influence of free drug samples on prescribing by physicians: a cross sectional survey. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017;67:465-467.
- Alexander GC, Zhang J, Basu A. Characteristics of patients receiving pharmaceutical samples and association between sample receipt and out-of-pocket prescription costs. Med Care. 2008;46:394-402.
- Hodges B. Interactions with the pharmaceutical industry: experiences and attitudes of psychiatry residents, interns and clerks. CMAJ. 1995;153:553-559.
- Brotzman GL, Mark DH. The effect on resident attitudes of regulatory policies regarding pharmaceutical representative activities. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8:130-134.
- Keim SM, Sanders AB, Witzke DB, et al. Beliefs and practices of emergency medicine faculty and residents regarding professional interactions with the biomedical industry. Ann Emerg Med. 1993;22:1576-1581.
- Thomson AN, Craig BJ, Barham PM. Attitudes of general practitioners in New Zealand to pharmaceutical representatives. Br J Gen Pract. 1994;44:220-223.
- Ziegler MG, Lew P, Singer BC. The accuracy of drug information from pharmaceutical sales representatives. JAMA. 1995;273:1296-1298.
- Hurley MP, Stafford RS, Lane AT. Characterizing the relationship between free drug samples and prescription patterns for acne vulgaris and rosacea. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:487-493.
- Lexchin J. Interactions between physicians and the pharmaceutical industry: what does the literature say? CMAJ. 1993;149:1401-1407.
- Lieb K, Scheurich A. Contact between doctors and the pharmaceutical industry, their perceptions, and the effects on prescribing habits. PLoS One. 2014;9:e110130.
- Spurling GK, Mansfield PR, Montgomery BD, et al. Information from pharmaceutical companies and the quality, quantity, and cost of physicians’ prescribing: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000352.
- Fischer MA, Avorn J. Economic consequences of underuse of generic drugs: evidence from Medicaid and implications for prescription drug benefit plans. Health Serv Res. 2003;38:1051-1064.
- Sacks CA, Lee CC, Kesselheim AS, et al. Medicare spending on brand-name combination medications vs their generic constituents. JAMA. 2018;320:650-656.
- Brennan TA, Rothman DJ, Blank L, et al. Health industry practices that create conflicts of interest: a policy proposal for academic medical centers. JAMA. 2006;295:429-433.
- Allan GM, Lexchin J, Wiebe N. Physician awareness of drug cost: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e283.
Over the years, there has been growing concern about the relationship between physicians and pharmaceutical companies. Many studies have demonstrated that pharmaceutical interactions and incentives can influence physicians’ prescribing habits.1-3 As a result, many academic centers have adopted policies that attempt to limit the pharmaceutical industry’s influence on faculty and in-training physicians. Although these policies can vary greatly, they generally limit access of pharmaceutical representatives to providers and restrict pharmaceutical samples.4,5 This policy shift has even been reported in private practice.6
At the heart of the matter is the question: What really influences physicians to write a prescription for a particular medication? Is it cost, efficacy, or representatives pushing a product? Prior studies illustrate that generic medications are equivalent to their brand-name counterparts. In fact, current regulations require no more than 5% to 7% difference in bioequivalence.7-9 Although most generic medications are bioequivalent, it may not be universal.10
Garrison and Levin11 distributed a survey to US-based prescribers in family practice, psychiatry, and internal medicine and found that prescribers deemed patient response and success as the highest priority when determining which drugs to prescribe. In contrast, drug representatives and free samples only slightly contributed.11 Considering the minimum duration for efficacy of a medication such as an antidepressant vs a topical steroid, this pattern may differ with samples in dermatologic settings. Interestingly, another survey concluded that samples were associated with “sticky” prescribing habits, noting that physicians would prescribe a brand-name medication after using a sample, despite increased cost to the patient.12 Further, it has been suggested that recipients of free samples may experience increased costs in the long run, which contrasts a stated goal of affordability to patients.12,13
Physician interaction with pharmaceutical companies begins as early as medical school,14 with physicians reporting interactions as often as 4 times each month.14-18 Interactions can include meetings with pharmaceutical representatives, sponsored meals, gifts, continuing medical education sponsorship, funding for travel, pharmaceutical representative speakers, research funding, and drug samples.3
A 2014 study reported that prescribing habits are influenced by the free drug samples provided by nongeneric pharmaceutical companies.19 Nationally, the number of brand-name and branded generic medications constitute 79% of prescriptions, yet together they only comprise 17% of medications prescribed at an academic medical clinic that does not provide samples. The number of medications with samples being prescribed by dermatologists increased by 15% over 9 years, which may correlate with the wider availability of medication samples, more specifically an increase in branded generic samples.19 This potential interaction is the reason why institutions question the current influence of pharmaceutical companies. Samples may appear convenient, allowing a patient to test the medication prior to committing; however, with brand-name samples being provided to the physician, he/she may become more inclined to prescribe the branded medication.12,15,19-22 Because brand-name medications are more expensive than generic medications, this practice can increase the cost of health care.13 One study found that over 1 year, the overuse of nongeneric medications led to a loss of potential savings throughout 49 states, equating to $229 million just through Medicaid; interestingly, it was noted that in some states, a maximum reimbursement is set by Medicaid, regardless of whether the generic or branded medication is dispensed. The authors also noted variability in the potential savings by state, which may be a function of the state-by-state maximum reimbursements for certain medications.23 Another study on oral combination medications estimated Medicare spending on branded drugs relative to the cost if generic combinations had been purchased instead. This study examined branded medications for which the active components were available as over-the-counter (OTC), generic, or same-class generic, and the authors estimated that $925 million could have been saved in 2016 by purchasing a generic substitute.24 The overuse of nongeneric medications when generic alternatives are available becomes an issue that not only financially impacts patients but all taxpayers. However, this pattern may differ if limited only to dermatologic medications, which was not the focus of the prior studies.
To limit conflicts of interest in interactions with the pharmaceutical, medical device, and biotechnology industries, the University of South Florida (USF) Morsani College of Medicine (COM)(Tampa, Florida) implemented its own set of regulations that eliminated in-office pharmaceutical samples, in addition to other restrictions. This study aimed to investigate if there was a change in the prescribing habits of academic dermatologists after their medical school implemented these new policies.
We hypothesized that the number of brand-name drugs prescribed by physicians in the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery would change following USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes. We sought to determine how physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery changed following USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes.
Methods
Data Collection
A retrospective review of medical records was conducted to investigate the effect of the USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes on physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery. Medical records of patients seen for common dermatology diagnoses before (January 1, 2010, to May 30, 2010) and after (August 1, 2011, to December 31, 2011) the pharmaceutical policy changes were reviewed, and all medications prescribed were recorded. Data were collected from medical records within the USF Health electronic medical record system and included visits with each of the department’s 3 attending dermatologists. The diagnoses included in the study—acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, and rosacea—were chosen because in-office samples were available. Prescribing data from the first 100 consecutive medical records were collected from each time period, and a medical record was included only if it contained at least 1 of the following diagnoses: acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, or rosacea. The assessment and plan of each progress note were reviewed, and the exact medication name and associated diagnosis were recorded for each prescription. Subsequently, each medication was reviewed and placed in 1 of 3 categories: brand name, generic, and OTC. The total number of prescriptions for each diagnosis (per visit/note); the specific number of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note); and the percentage of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note and per diagnosis in total) were calculated. To ensure only intended medications were included, each medication recorded in the medical record note was cross-referenced with the prescribed medication in the electronic medical record. The primary objective of this study was to capture the prescribing physician’s intent as proxied by the pattern of prescription. Thus, changes made in prescriptions after the initial plan—whether insurance related or otherwise—were not relevant to this investigation.
The data were collected to compare the percentage of brand vs generic or OTC prescriptions per diagnosis to see if there was a difference in the prescribing habits before and after the pharmaceutical policy changes. Of note, several other pieces of data were collected from each medical record, including age, race, class of insurance (ie, Medicare, Medicaid, private health maintenance organization, private preferred provider organization), subtype diagnoses, and whether the prescription was new or a refill. The information gathered from the written record on the assessment and plan was verified using prescriptions ordered in the Allscripts electronic record, and any difference was noted. No identifying information that could be used to easily identify study participants was recorded.
Differences in prescribing habits across diagnoses before and after the policy changes were ascertained using a Fisher exact test and were further assessed using a mixed effects ordinal logistic regression model that accounted for within-provider clustering and baseline patient characteristics. An ordinal model was chosen to recognize differences in average cost among brand-name, generic, and OTC medications.
Results
In total, 200 medical records were collected. For the period analyzed before the policy change, 252 brand-name medications were prescribed compared to 231 prescribed for the period analyzed after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in brand-name medications prescribed before and after the policy changes (P=.145; Fisher exact test)(Table 1). There also was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in generic prescriptions, which totaled 153 before and 134 after the policy changes (P=.872; Fisher exact test)(Table 2). Over-the-counter prescriptions totaled 49 before and 69 after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference before and after the policy changes for OTC medications (P=.192; Fisher exact test)(Table 3).




Comment
Although some medical institutions are diligently working to limit the potential influence pharmaceutical companies have on physician prescribing habits,4,5,25 the effect on physician prescribing habits is only now being established.15 Prior studies12,19,21 have found evidence that medication samples may lead to overuse of brand-name medications, but these findings do not hold true for the USF dermatologists included in this study, perhaps due to the difference in pharmaceutical company interactions or physicians maintaining prior prescription habits that were unrelated to the policy. Although this study focused on policy changes for in-office samples, prior studies either included other forms of interaction21 or did not include samples.22
Pharmaceutical samples allow patients to try a medication before committing to a long-term course of treatment with a particular medication, which has utility for physicians and patients. Although brand-name prescriptions may cost more, a trial period may assist the patient in deciding whether the medication is worth purchasing. Furthermore, physicians may feel more comfortable prescribing a medication once the individual patient has demonstrated a benefit from the sample, which may be particularly true in a specialty such as dermatology in which many branded topical medications contain a different vehicle than generic formulations, resulting in notable variations in active medication delivery and efficacy. Given the higher cost of branded topical medications, proving efficacy in patients through samples can provide a useful tool to the physician to determine the need for a branded formulation.
The benefits described are subjective but should not be disregarded. Although Hurley et al19 found that the number of brand-name medications prescribed increases as more samples are given out, our study demonstrated that after eliminating medication samples, there was no significant difference in the percentage of brand-name medications prescribed compared to generic and OTC medications.
Physician education concerning the price of each brand-name medication prescribed in office may be one method of reducing the amount of such prescriptions. Physicians generally are uninformed of the cost of the medications being prescribed26 and may not recognize the financial burden one medication may have compared to its alternative. However, educating physicians will empower them to make the conscious decision to prefer or not prefer a brand-name medication. With some generic medications shown to have a difference in bioequivalence compared to their brand-name counterparts, a physician may find more success prescribing the brand-name medications, regardless of pharmaceutical company influence, which is an alternative solution to policy changes that eliminate samples entirely. Although this study found insufficient evidence that removing samples decreases brand-name medication prescriptions, it is imperative that solutions are established to reduce the country’s increasing burden of medical costs.
Possible shortfalls of this study include the short period of time between which prepolicy data and postpolicy data were collected. It is possible that providers did not have enough time to adjust their prescribing habits or that providers would not have changed a prescribing pattern or preference simply because of a policy change. Future studies could allow a time period greater than 2 years to compare prepolicy and postpolicy prescribing habits, or a future study might make comparisons of prescriber patterns at different institutions that have different policies. Another possible shortfall is that providers and patients were limited to those at the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery at the USF Morsani COM. Although this study has found insufficient evidence of a difference in prescribing habits, it may be beneficial to conduct a larger study that encompasses multiple academic institutions with similar policy changes. Most importantly, this study only investigated the influence of in-office pharmaceutical samples on prescribing patterns. This study did not look at the many other ways in which providers may be influenced by pharmaceutical companies, which likely is a significant confounding variable in this study. Continued additional studies that specifically examine other methods through which providers may be influenced would be helpful in further examining the many ways in which physician prescription habits are influenced.
Conclusion
Changes in pharmaceutical policy in 2011 at USF Morsani COM specifically banned in-office samples. The totality of evidence in this study shows modest observational evidence of a change in the postpolicy odds relative to prepolicy odds, but the data also are compatible with no change between prescribing habits before and after the policy changes. Further study is needed to fully understand this relationship.
Over the years, there has been growing concern about the relationship between physicians and pharmaceutical companies. Many studies have demonstrated that pharmaceutical interactions and incentives can influence physicians’ prescribing habits.1-3 As a result, many academic centers have adopted policies that attempt to limit the pharmaceutical industry’s influence on faculty and in-training physicians. Although these policies can vary greatly, they generally limit access of pharmaceutical representatives to providers and restrict pharmaceutical samples.4,5 This policy shift has even been reported in private practice.6
At the heart of the matter is the question: What really influences physicians to write a prescription for a particular medication? Is it cost, efficacy, or representatives pushing a product? Prior studies illustrate that generic medications are equivalent to their brand-name counterparts. In fact, current regulations require no more than 5% to 7% difference in bioequivalence.7-9 Although most generic medications are bioequivalent, it may not be universal.10
Garrison and Levin11 distributed a survey to US-based prescribers in family practice, psychiatry, and internal medicine and found that prescribers deemed patient response and success as the highest priority when determining which drugs to prescribe. In contrast, drug representatives and free samples only slightly contributed.11 Considering the minimum duration for efficacy of a medication such as an antidepressant vs a topical steroid, this pattern may differ with samples in dermatologic settings. Interestingly, another survey concluded that samples were associated with “sticky” prescribing habits, noting that physicians would prescribe a brand-name medication after using a sample, despite increased cost to the patient.12 Further, it has been suggested that recipients of free samples may experience increased costs in the long run, which contrasts a stated goal of affordability to patients.12,13
Physician interaction with pharmaceutical companies begins as early as medical school,14 with physicians reporting interactions as often as 4 times each month.14-18 Interactions can include meetings with pharmaceutical representatives, sponsored meals, gifts, continuing medical education sponsorship, funding for travel, pharmaceutical representative speakers, research funding, and drug samples.3
A 2014 study reported that prescribing habits are influenced by the free drug samples provided by nongeneric pharmaceutical companies.19 Nationally, the number of brand-name and branded generic medications constitute 79% of prescriptions, yet together they only comprise 17% of medications prescribed at an academic medical clinic that does not provide samples. The number of medications with samples being prescribed by dermatologists increased by 15% over 9 years, which may correlate with the wider availability of medication samples, more specifically an increase in branded generic samples.19 This potential interaction is the reason why institutions question the current influence of pharmaceutical companies. Samples may appear convenient, allowing a patient to test the medication prior to committing; however, with brand-name samples being provided to the physician, he/she may become more inclined to prescribe the branded medication.12,15,19-22 Because brand-name medications are more expensive than generic medications, this practice can increase the cost of health care.13 One study found that over 1 year, the overuse of nongeneric medications led to a loss of potential savings throughout 49 states, equating to $229 million just through Medicaid; interestingly, it was noted that in some states, a maximum reimbursement is set by Medicaid, regardless of whether the generic or branded medication is dispensed. The authors also noted variability in the potential savings by state, which may be a function of the state-by-state maximum reimbursements for certain medications.23 Another study on oral combination medications estimated Medicare spending on branded drugs relative to the cost if generic combinations had been purchased instead. This study examined branded medications for which the active components were available as over-the-counter (OTC), generic, or same-class generic, and the authors estimated that $925 million could have been saved in 2016 by purchasing a generic substitute.24 The overuse of nongeneric medications when generic alternatives are available becomes an issue that not only financially impacts patients but all taxpayers. However, this pattern may differ if limited only to dermatologic medications, which was not the focus of the prior studies.
To limit conflicts of interest in interactions with the pharmaceutical, medical device, and biotechnology industries, the University of South Florida (USF) Morsani College of Medicine (COM)(Tampa, Florida) implemented its own set of regulations that eliminated in-office pharmaceutical samples, in addition to other restrictions. This study aimed to investigate if there was a change in the prescribing habits of academic dermatologists after their medical school implemented these new policies.
We hypothesized that the number of brand-name drugs prescribed by physicians in the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery would change following USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes. We sought to determine how physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery changed following USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes.
Methods
Data Collection
A retrospective review of medical records was conducted to investigate the effect of the USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes on physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery. Medical records of patients seen for common dermatology diagnoses before (January 1, 2010, to May 30, 2010) and after (August 1, 2011, to December 31, 2011) the pharmaceutical policy changes were reviewed, and all medications prescribed were recorded. Data were collected from medical records within the USF Health electronic medical record system and included visits with each of the department’s 3 attending dermatologists. The diagnoses included in the study—acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, and rosacea—were chosen because in-office samples were available. Prescribing data from the first 100 consecutive medical records were collected from each time period, and a medical record was included only if it contained at least 1 of the following diagnoses: acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, or rosacea. The assessment and plan of each progress note were reviewed, and the exact medication name and associated diagnosis were recorded for each prescription. Subsequently, each medication was reviewed and placed in 1 of 3 categories: brand name, generic, and OTC. The total number of prescriptions for each diagnosis (per visit/note); the specific number of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note); and the percentage of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note and per diagnosis in total) were calculated. To ensure only intended medications were included, each medication recorded in the medical record note was cross-referenced with the prescribed medication in the electronic medical record. The primary objective of this study was to capture the prescribing physician’s intent as proxied by the pattern of prescription. Thus, changes made in prescriptions after the initial plan—whether insurance related or otherwise—were not relevant to this investigation.
The data were collected to compare the percentage of brand vs generic or OTC prescriptions per diagnosis to see if there was a difference in the prescribing habits before and after the pharmaceutical policy changes. Of note, several other pieces of data were collected from each medical record, including age, race, class of insurance (ie, Medicare, Medicaid, private health maintenance organization, private preferred provider organization), subtype diagnoses, and whether the prescription was new or a refill. The information gathered from the written record on the assessment and plan was verified using prescriptions ordered in the Allscripts electronic record, and any difference was noted. No identifying information that could be used to easily identify study participants was recorded.
Differences in prescribing habits across diagnoses before and after the policy changes were ascertained using a Fisher exact test and were further assessed using a mixed effects ordinal logistic regression model that accounted for within-provider clustering and baseline patient characteristics. An ordinal model was chosen to recognize differences in average cost among brand-name, generic, and OTC medications.
Results
In total, 200 medical records were collected. For the period analyzed before the policy change, 252 brand-name medications were prescribed compared to 231 prescribed for the period analyzed after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in brand-name medications prescribed before and after the policy changes (P=.145; Fisher exact test)(Table 1). There also was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in generic prescriptions, which totaled 153 before and 134 after the policy changes (P=.872; Fisher exact test)(Table 2). Over-the-counter prescriptions totaled 49 before and 69 after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference before and after the policy changes for OTC medications (P=.192; Fisher exact test)(Table 3).




Comment
Although some medical institutions are diligently working to limit the potential influence pharmaceutical companies have on physician prescribing habits,4,5,25 the effect on physician prescribing habits is only now being established.15 Prior studies12,19,21 have found evidence that medication samples may lead to overuse of brand-name medications, but these findings do not hold true for the USF dermatologists included in this study, perhaps due to the difference in pharmaceutical company interactions or physicians maintaining prior prescription habits that were unrelated to the policy. Although this study focused on policy changes for in-office samples, prior studies either included other forms of interaction21 or did not include samples.22
Pharmaceutical samples allow patients to try a medication before committing to a long-term course of treatment with a particular medication, which has utility for physicians and patients. Although brand-name prescriptions may cost more, a trial period may assist the patient in deciding whether the medication is worth purchasing. Furthermore, physicians may feel more comfortable prescribing a medication once the individual patient has demonstrated a benefit from the sample, which may be particularly true in a specialty such as dermatology in which many branded topical medications contain a different vehicle than generic formulations, resulting in notable variations in active medication delivery and efficacy. Given the higher cost of branded topical medications, proving efficacy in patients through samples can provide a useful tool to the physician to determine the need for a branded formulation.
The benefits described are subjective but should not be disregarded. Although Hurley et al19 found that the number of brand-name medications prescribed increases as more samples are given out, our study demonstrated that after eliminating medication samples, there was no significant difference in the percentage of brand-name medications prescribed compared to generic and OTC medications.
Physician education concerning the price of each brand-name medication prescribed in office may be one method of reducing the amount of such prescriptions. Physicians generally are uninformed of the cost of the medications being prescribed26 and may not recognize the financial burden one medication may have compared to its alternative. However, educating physicians will empower them to make the conscious decision to prefer or not prefer a brand-name medication. With some generic medications shown to have a difference in bioequivalence compared to their brand-name counterparts, a physician may find more success prescribing the brand-name medications, regardless of pharmaceutical company influence, which is an alternative solution to policy changes that eliminate samples entirely. Although this study found insufficient evidence that removing samples decreases brand-name medication prescriptions, it is imperative that solutions are established to reduce the country’s increasing burden of medical costs.
Possible shortfalls of this study include the short period of time between which prepolicy data and postpolicy data were collected. It is possible that providers did not have enough time to adjust their prescribing habits or that providers would not have changed a prescribing pattern or preference simply because of a policy change. Future studies could allow a time period greater than 2 years to compare prepolicy and postpolicy prescribing habits, or a future study might make comparisons of prescriber patterns at different institutions that have different policies. Another possible shortfall is that providers and patients were limited to those at the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery at the USF Morsani COM. Although this study has found insufficient evidence of a difference in prescribing habits, it may be beneficial to conduct a larger study that encompasses multiple academic institutions with similar policy changes. Most importantly, this study only investigated the influence of in-office pharmaceutical samples on prescribing patterns. This study did not look at the many other ways in which providers may be influenced by pharmaceutical companies, which likely is a significant confounding variable in this study. Continued additional studies that specifically examine other methods through which providers may be influenced would be helpful in further examining the many ways in which physician prescription habits are influenced.
Conclusion
Changes in pharmaceutical policy in 2011 at USF Morsani COM specifically banned in-office samples. The totality of evidence in this study shows modest observational evidence of a change in the postpolicy odds relative to prepolicy odds, but the data also are compatible with no change between prescribing habits before and after the policy changes. Further study is needed to fully understand this relationship.
- Sondergaard J, Vach K, Kragstrup J, et al. Impact of pharmaceutical representative visits on GPs’ drug preferences. Fam Pract. 2009;26:204-209.
- Jelinek GA, Neate SL. The influence of the pharmaceutical industry in medicine. J Law Med. 2009;17:216-223.
- Wazana A. Physicians and the pharmaceutical industry: is a gift ever just a gift? JAMA. 2000;283:373-380.
- Coleman DL. Establishing policies for the relationship between industry and clinicians: lessons learned from two academic health centers. Acad Med. 2008;83:882-887.
- Coleman DL, Kazdin AE, Miller LA, et al. Guidelines for interactions between clinical faculty and the pharmaceutical industry: one medical school’s approach. Acad Med. 2006;81:154-160.
- Evans D, Hartung DM, Beasley D, et al. Breaking up is hard to do: lessons learned from a pharma-free practice transformation. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:332-338.
- Davit BM, Nwakama PE, Buehler GJ, et al. Comparing generic and innovator drugs: a review of 12 years of bioequivalence data from the United States Food and Drug Administration. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43:1583-1597.
- Kesselheim AS, Misono AS, Lee JL, et al. Clinical equivalence of generic and brand-name drugs used in cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300:2514-2526.
- McCormack J, Chmelicek JT. Generic versus brand name: the other drug war. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60:911.
- Borgheini G. The bioequivalence and therapeutic efficacy of generic versus brand-name psychoactive drugs. Clin Ther. 2003;25:1578-1592.
- Garrison GD, Levin GM. Factors affecting prescribing of the newer antidepressants. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34:10-14.
- Rafique S, Sarwar W, Rashid A, et al. Influence of free drug samples on prescribing by physicians: a cross sectional survey. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017;67:465-467.
- Alexander GC, Zhang J, Basu A. Characteristics of patients receiving pharmaceutical samples and association between sample receipt and out-of-pocket prescription costs. Med Care. 2008;46:394-402.
- Hodges B. Interactions with the pharmaceutical industry: experiences and attitudes of psychiatry residents, interns and clerks. CMAJ. 1995;153:553-559.
- Brotzman GL, Mark DH. The effect on resident attitudes of regulatory policies regarding pharmaceutical representative activities. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8:130-134.
- Keim SM, Sanders AB, Witzke DB, et al. Beliefs and practices of emergency medicine faculty and residents regarding professional interactions with the biomedical industry. Ann Emerg Med. 1993;22:1576-1581.
- Thomson AN, Craig BJ, Barham PM. Attitudes of general practitioners in New Zealand to pharmaceutical representatives. Br J Gen Pract. 1994;44:220-223.
- Ziegler MG, Lew P, Singer BC. The accuracy of drug information from pharmaceutical sales representatives. JAMA. 1995;273:1296-1298.
- Hurley MP, Stafford RS, Lane AT. Characterizing the relationship between free drug samples and prescription patterns for acne vulgaris and rosacea. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:487-493.
- Lexchin J. Interactions between physicians and the pharmaceutical industry: what does the literature say? CMAJ. 1993;149:1401-1407.
- Lieb K, Scheurich A. Contact between doctors and the pharmaceutical industry, their perceptions, and the effects on prescribing habits. PLoS One. 2014;9:e110130.
- Spurling GK, Mansfield PR, Montgomery BD, et al. Information from pharmaceutical companies and the quality, quantity, and cost of physicians’ prescribing: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000352.
- Fischer MA, Avorn J. Economic consequences of underuse of generic drugs: evidence from Medicaid and implications for prescription drug benefit plans. Health Serv Res. 2003;38:1051-1064.
- Sacks CA, Lee CC, Kesselheim AS, et al. Medicare spending on brand-name combination medications vs their generic constituents. JAMA. 2018;320:650-656.
- Brennan TA, Rothman DJ, Blank L, et al. Health industry practices that create conflicts of interest: a policy proposal for academic medical centers. JAMA. 2006;295:429-433.
- Allan GM, Lexchin J, Wiebe N. Physician awareness of drug cost: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e283.
- Sondergaard J, Vach K, Kragstrup J, et al. Impact of pharmaceutical representative visits on GPs’ drug preferences. Fam Pract. 2009;26:204-209.
- Jelinek GA, Neate SL. The influence of the pharmaceutical industry in medicine. J Law Med. 2009;17:216-223.
- Wazana A. Physicians and the pharmaceutical industry: is a gift ever just a gift? JAMA. 2000;283:373-380.
- Coleman DL. Establishing policies for the relationship between industry and clinicians: lessons learned from two academic health centers. Acad Med. 2008;83:882-887.
- Coleman DL, Kazdin AE, Miller LA, et al. Guidelines for interactions between clinical faculty and the pharmaceutical industry: one medical school’s approach. Acad Med. 2006;81:154-160.
- Evans D, Hartung DM, Beasley D, et al. Breaking up is hard to do: lessons learned from a pharma-free practice transformation. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:332-338.
- Davit BM, Nwakama PE, Buehler GJ, et al. Comparing generic and innovator drugs: a review of 12 years of bioequivalence data from the United States Food and Drug Administration. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43:1583-1597.
- Kesselheim AS, Misono AS, Lee JL, et al. Clinical equivalence of generic and brand-name drugs used in cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300:2514-2526.
- McCormack J, Chmelicek JT. Generic versus brand name: the other drug war. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60:911.
- Borgheini G. The bioequivalence and therapeutic efficacy of generic versus brand-name psychoactive drugs. Clin Ther. 2003;25:1578-1592.
- Garrison GD, Levin GM. Factors affecting prescribing of the newer antidepressants. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34:10-14.
- Rafique S, Sarwar W, Rashid A, et al. Influence of free drug samples on prescribing by physicians: a cross sectional survey. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017;67:465-467.
- Alexander GC, Zhang J, Basu A. Characteristics of patients receiving pharmaceutical samples and association between sample receipt and out-of-pocket prescription costs. Med Care. 2008;46:394-402.
- Hodges B. Interactions with the pharmaceutical industry: experiences and attitudes of psychiatry residents, interns and clerks. CMAJ. 1995;153:553-559.
- Brotzman GL, Mark DH. The effect on resident attitudes of regulatory policies regarding pharmaceutical representative activities. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8:130-134.
- Keim SM, Sanders AB, Witzke DB, et al. Beliefs and practices of emergency medicine faculty and residents regarding professional interactions with the biomedical industry. Ann Emerg Med. 1993;22:1576-1581.
- Thomson AN, Craig BJ, Barham PM. Attitudes of general practitioners in New Zealand to pharmaceutical representatives. Br J Gen Pract. 1994;44:220-223.
- Ziegler MG, Lew P, Singer BC. The accuracy of drug information from pharmaceutical sales representatives. JAMA. 1995;273:1296-1298.
- Hurley MP, Stafford RS, Lane AT. Characterizing the relationship between free drug samples and prescription patterns for acne vulgaris and rosacea. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:487-493.
- Lexchin J. Interactions between physicians and the pharmaceutical industry: what does the literature say? CMAJ. 1993;149:1401-1407.
- Lieb K, Scheurich A. Contact between doctors and the pharmaceutical industry, their perceptions, and the effects on prescribing habits. PLoS One. 2014;9:e110130.
- Spurling GK, Mansfield PR, Montgomery BD, et al. Information from pharmaceutical companies and the quality, quantity, and cost of physicians’ prescribing: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000352.
- Fischer MA, Avorn J. Economic consequences of underuse of generic drugs: evidence from Medicaid and implications for prescription drug benefit plans. Health Serv Res. 2003;38:1051-1064.
- Sacks CA, Lee CC, Kesselheim AS, et al. Medicare spending on brand-name combination medications vs their generic constituents. JAMA. 2018;320:650-656.
- Brennan TA, Rothman DJ, Blank L, et al. Health industry practices that create conflicts of interest: a policy proposal for academic medical centers. JAMA. 2006;295:429-433.
- Allan GM, Lexchin J, Wiebe N. Physician awareness of drug cost: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e283.
Practice Points
- There has been growing concern that pharmaceutical interactions and incentives can influence physicians’ prescribing habits.
- Many academic centers have adopted policies that attempt to limit the pharmaceutical industry’s influence on faculty and in-training physicians.
- This study aimed to investigate if there was a change in the prescribing habits of academic dermatologists after the medical school implemented new policies that banned in-office samples.
‘Antibacterial’ soap labels still list banned ingredients
The website of retail pharmacy giant Walgreens, for example, lists Dial Complete antibacterial soap with the active ingredient triclosan, a chemical the Food and Drug Administration banned along with others in 2017. The agency cited a lack of evidence that the ingredients were more effective than plain soap and water and that they were safe for long-term daily use.
A Dial Complete soap product page on Walgreens’ website lists, as of Feb. 4, 2020, an ingredient that was banned by the FDA.
Yet banned substances such as the triclosan in this Dial soap still commonly appear on online product descriptions, researchers found after searching the National Drug Code Directory and the websites of major online retailers, including Amazon, Walmart, and Target. The health effects of antibacterial ingredients “are very poorly defined,” said Chandler Rundle, MD, first author of the study, which was published in Dermatitis. Dr. Rundle is with the department of dermatology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
The label on the back of the Dial soap bottle sold on Walgreens.com states that it “[k]ills more bacteria than ordinary liquid hand soap.” The website displays a close-up graphic of a hand that has been washed with Dial soap and that has fewer bacteria than a hand washed with “Others.” The graphic includes a dramatization disclaimer.
When asked about the product, a Walgreens corporate relations spokesperson checked the soap’s ingredients list they had on file from Dial’s parent company, Henkel North American Consumer Goods.
“I did not see that particular ingredient,” the representative said. Their ingredients list reflected a version of the soap that was updated after the ban. That label differs from Walgreens.com’s product information. The updated, ban-compliant version of the soap contains an alternative antibacterial compound, benzalkonium chloride. The spokesperson wasn’t sure of the source of the incorrect information on the website. Dial did not respond to a request for comment.
The ingredients list for Dial Complete soap on Walgreens.com shows FDA-banned triclosan as the active ingredient.
The 2017 FDA ban restricted the marketing of triclosan and triclocarban along with 17 other ingredients in consumer antibacterial soaps because manufacturers did not provide sufficient data to demonstrate that the ingredients were safe and effective, according to the FDA’s announcement. Independent research also showed that some ingredients worked no better than traditional soap and could create antibacterial-resistant microbes. Regular hand soap “still kills bacteria,” Dr. Rundle said. “The inclusion of an antibacterial substance does not make it better.”
Retailers (such as Walgreens) aren’t required to update their products’ online ingredient lists, which can pose a challenge for people who suffer from skin allergies, said Dr. Rundle. People at risk of having a reaction must read labels to verify the ingredients that are included.
Consumer antibacterial soap products that contain the banned compounds have largely been replaced with stand-ins, such as benzalkonium chloride and chloroxylenol, according to Dr. Rundle’s study. He and other researchers are trying to determine whether those compounds have the same shortcomings. “We’re talking 10-20 years down the line, and we’re worried about things like antibacterial resistance and systemic effects,” Dr. Rundle said.
The FDA has considered a ban on benzalkonium chloride and additional antibacterial ingredients, but in 2016, it granted ban deferrals, pending more research. The agency exchanged letters with the American Cleaning Institute (ACI), a trade association that represents companies, including Henkel. The FDA required that its companies fund research to show that the new antibacterial ingredients are safe and effective. The FDA granted subsequent annual extensions in 2017, 2018, and, most recently, in August 2019 to allow continued research into whether several ingredients are effective in soaps. In its most recent letter to the ACI, the FDA gave a checklist of research tasks to be submitted by July 2020.
The letter from August 2019 stated that the ACI, in its March 2019 progress report, failed to address milestones in studies of health care personnel handwashing for two of the substances. It also referenced the ACI’s lack of funding for the studies and reminded the organization that further deferrals would not be granted unless the ACI can show ongoing progress.
The ACI plans to meet with the FDA to have an in-depth discussion, Brian Sansoni, a spokesperson for the ACI, told Medscape Medical News. The ACI plans to give the FDA data that show the effectiveness of these ingredients over the course of several years, “due to the complexity of what FDA is asking for,” Mr. Sansoni said. “We’re working as diligently as possible to meet FDA requests.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The website of retail pharmacy giant Walgreens, for example, lists Dial Complete antibacterial soap with the active ingredient triclosan, a chemical the Food and Drug Administration banned along with others in 2017. The agency cited a lack of evidence that the ingredients were more effective than plain soap and water and that they were safe for long-term daily use.
A Dial Complete soap product page on Walgreens’ website lists, as of Feb. 4, 2020, an ingredient that was banned by the FDA.
Yet banned substances such as the triclosan in this Dial soap still commonly appear on online product descriptions, researchers found after searching the National Drug Code Directory and the websites of major online retailers, including Amazon, Walmart, and Target. The health effects of antibacterial ingredients “are very poorly defined,” said Chandler Rundle, MD, first author of the study, which was published in Dermatitis. Dr. Rundle is with the department of dermatology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
The label on the back of the Dial soap bottle sold on Walgreens.com states that it “[k]ills more bacteria than ordinary liquid hand soap.” The website displays a close-up graphic of a hand that has been washed with Dial soap and that has fewer bacteria than a hand washed with “Others.” The graphic includes a dramatization disclaimer.
When asked about the product, a Walgreens corporate relations spokesperson checked the soap’s ingredients list they had on file from Dial’s parent company, Henkel North American Consumer Goods.
“I did not see that particular ingredient,” the representative said. Their ingredients list reflected a version of the soap that was updated after the ban. That label differs from Walgreens.com’s product information. The updated, ban-compliant version of the soap contains an alternative antibacterial compound, benzalkonium chloride. The spokesperson wasn’t sure of the source of the incorrect information on the website. Dial did not respond to a request for comment.
The ingredients list for Dial Complete soap on Walgreens.com shows FDA-banned triclosan as the active ingredient.
The 2017 FDA ban restricted the marketing of triclosan and triclocarban along with 17 other ingredients in consumer antibacterial soaps because manufacturers did not provide sufficient data to demonstrate that the ingredients were safe and effective, according to the FDA’s announcement. Independent research also showed that some ingredients worked no better than traditional soap and could create antibacterial-resistant microbes. Regular hand soap “still kills bacteria,” Dr. Rundle said. “The inclusion of an antibacterial substance does not make it better.”
Retailers (such as Walgreens) aren’t required to update their products’ online ingredient lists, which can pose a challenge for people who suffer from skin allergies, said Dr. Rundle. People at risk of having a reaction must read labels to verify the ingredients that are included.
Consumer antibacterial soap products that contain the banned compounds have largely been replaced with stand-ins, such as benzalkonium chloride and chloroxylenol, according to Dr. Rundle’s study. He and other researchers are trying to determine whether those compounds have the same shortcomings. “We’re talking 10-20 years down the line, and we’re worried about things like antibacterial resistance and systemic effects,” Dr. Rundle said.
The FDA has considered a ban on benzalkonium chloride and additional antibacterial ingredients, but in 2016, it granted ban deferrals, pending more research. The agency exchanged letters with the American Cleaning Institute (ACI), a trade association that represents companies, including Henkel. The FDA required that its companies fund research to show that the new antibacterial ingredients are safe and effective. The FDA granted subsequent annual extensions in 2017, 2018, and, most recently, in August 2019 to allow continued research into whether several ingredients are effective in soaps. In its most recent letter to the ACI, the FDA gave a checklist of research tasks to be submitted by July 2020.
The letter from August 2019 stated that the ACI, in its March 2019 progress report, failed to address milestones in studies of health care personnel handwashing for two of the substances. It also referenced the ACI’s lack of funding for the studies and reminded the organization that further deferrals would not be granted unless the ACI can show ongoing progress.
The ACI plans to meet with the FDA to have an in-depth discussion, Brian Sansoni, a spokesperson for the ACI, told Medscape Medical News. The ACI plans to give the FDA data that show the effectiveness of these ingredients over the course of several years, “due to the complexity of what FDA is asking for,” Mr. Sansoni said. “We’re working as diligently as possible to meet FDA requests.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The website of retail pharmacy giant Walgreens, for example, lists Dial Complete antibacterial soap with the active ingredient triclosan, a chemical the Food and Drug Administration banned along with others in 2017. The agency cited a lack of evidence that the ingredients were more effective than plain soap and water and that they were safe for long-term daily use.
A Dial Complete soap product page on Walgreens’ website lists, as of Feb. 4, 2020, an ingredient that was banned by the FDA.
Yet banned substances such as the triclosan in this Dial soap still commonly appear on online product descriptions, researchers found after searching the National Drug Code Directory and the websites of major online retailers, including Amazon, Walmart, and Target. The health effects of antibacterial ingredients “are very poorly defined,” said Chandler Rundle, MD, first author of the study, which was published in Dermatitis. Dr. Rundle is with the department of dermatology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
The label on the back of the Dial soap bottle sold on Walgreens.com states that it “[k]ills more bacteria than ordinary liquid hand soap.” The website displays a close-up graphic of a hand that has been washed with Dial soap and that has fewer bacteria than a hand washed with “Others.” The graphic includes a dramatization disclaimer.
When asked about the product, a Walgreens corporate relations spokesperson checked the soap’s ingredients list they had on file from Dial’s parent company, Henkel North American Consumer Goods.
“I did not see that particular ingredient,” the representative said. Their ingredients list reflected a version of the soap that was updated after the ban. That label differs from Walgreens.com’s product information. The updated, ban-compliant version of the soap contains an alternative antibacterial compound, benzalkonium chloride. The spokesperson wasn’t sure of the source of the incorrect information on the website. Dial did not respond to a request for comment.
The ingredients list for Dial Complete soap on Walgreens.com shows FDA-banned triclosan as the active ingredient.
The 2017 FDA ban restricted the marketing of triclosan and triclocarban along with 17 other ingredients in consumer antibacterial soaps because manufacturers did not provide sufficient data to demonstrate that the ingredients were safe and effective, according to the FDA’s announcement. Independent research also showed that some ingredients worked no better than traditional soap and could create antibacterial-resistant microbes. Regular hand soap “still kills bacteria,” Dr. Rundle said. “The inclusion of an antibacterial substance does not make it better.”
Retailers (such as Walgreens) aren’t required to update their products’ online ingredient lists, which can pose a challenge for people who suffer from skin allergies, said Dr. Rundle. People at risk of having a reaction must read labels to verify the ingredients that are included.
Consumer antibacterial soap products that contain the banned compounds have largely been replaced with stand-ins, such as benzalkonium chloride and chloroxylenol, according to Dr. Rundle’s study. He and other researchers are trying to determine whether those compounds have the same shortcomings. “We’re talking 10-20 years down the line, and we’re worried about things like antibacterial resistance and systemic effects,” Dr. Rundle said.
The FDA has considered a ban on benzalkonium chloride and additional antibacterial ingredients, but in 2016, it granted ban deferrals, pending more research. The agency exchanged letters with the American Cleaning Institute (ACI), a trade association that represents companies, including Henkel. The FDA required that its companies fund research to show that the new antibacterial ingredients are safe and effective. The FDA granted subsequent annual extensions in 2017, 2018, and, most recently, in August 2019 to allow continued research into whether several ingredients are effective in soaps. In its most recent letter to the ACI, the FDA gave a checklist of research tasks to be submitted by July 2020.
The letter from August 2019 stated that the ACI, in its March 2019 progress report, failed to address milestones in studies of health care personnel handwashing for two of the substances. It also referenced the ACI’s lack of funding for the studies and reminded the organization that further deferrals would not be granted unless the ACI can show ongoing progress.
The ACI plans to meet with the FDA to have an in-depth discussion, Brian Sansoni, a spokesperson for the ACI, told Medscape Medical News. The ACI plans to give the FDA data that show the effectiveness of these ingredients over the course of several years, “due to the complexity of what FDA is asking for,” Mr. Sansoni said. “We’re working as diligently as possible to meet FDA requests.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Serum levels of neurofilament light are increased before clinical onset of MS
(MS), according to research published in the January issue of JAMA Neurology. These results lend weight to the idea that MS has a prodromal phase, and this phase appears to be associated with neurodegeneration, according to the authors.
Patients often have CNS lesions of various stages of development at the time of their first demyelinating event, and this finding was one basis for neurologists’ hypothesis of a prodromal phase of MS. The finding that one-third of patients with radiologically isolated syndrome develop MS within 5 years also lends credence to this idea. Diagnosing MS early would enable early treatment that could prevent demyelination and the progression of neurodegeneration.
Researchers compared presymptomatic and symptomatic samples
With this idea in mind, Kjetil Bjornevik, MD, PhD, a member of the neuroepidemiology research group at Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health in Boston, and colleagues evaluated whether serum levels of NfL, a marker of ongoing neuroaxonal degeneration, were increased in the years before and around the time of clinical onset of MS. For their study population, the investigators chose active-duty U.S. military personnel who have at least one serum sample stored in the U.S. Department of Defense Serum Repository. Samples are collected after routine HIV type 1 antibody testing.
Within this population, Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues identified patients with MS who had at least one presymptomatic serum sample. The date of clinical MS onset was defined as the date of the first neurologic symptoms attributable to MS documented in the medical record. The investigators randomly selected two control individuals from the population and matched them to each case by age, sex, race or ethnicity, and dates of sample collection. Eligible controls were on active duty on the date of onset of the matched case.
Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues identified 245 patients with MS. Among this sample, the researchers selected two groups that each included 30 cases and 30 controls. The first group included patients who had provided at least one serum sample before MS onset and one sample within 2 years after MS onset. The second group included cases with at least two presymptomatic serum samples, one of which was collected more than 5 years before MS diagnosis, and the other of which was collected between 2 and 5 years before diagnosis. The investigators handled pairs of serum samples in the same way and assayed them in the same batch. The order of the samples in each pair was arranged at random.
Levels were higher in cases than in controls
About 77% of the population was male. Sixty percent of participants were white, 28% were black, and 6.7% were Hispanic. The population’s mean age at first sample collection was approximately 27 years. Mean age at MS onset was approximately 31 years.
For patients who provided samples before and after the clinical onset of MS, serum NfL levels were higher than in matched controls at both points. Most patients who passed from the presymptomatic stage to the symptomatic stage had a significant increase in serum NfL level (i.e., from a median of 25.0 pg/mL to a median of 45.1 pg/mL). Serum NfL levels at the two time points in controls did not differ significantly. For any given patient, an increase in serum NfL level from the presymptomatic measurement to the symptomatic measurement was associated with an increased risk of MS.
In patients with two presymptomatic samples, serum NfL levels were significantly higher in both samples than in the corresponding samples from matched controls. In cases, the earlier sample was collected at a median of 6 years before clinical onset of MS, and the later sample was collected at a median of 1 year before clinical onset. The serum NfL levels increased significantly between the two points for cases (i.e., a median increase of 1.3 pg/mL per year), but there was no significant difference in serum NfL level between the two samples in controls. A within-patient increase in presymptomatic serum NfL level was associated with an increased risk of MS.
Population included few women
“Our study differs from previous studies on the prodromal phase of MS because these have used indirect markers of this phase, which included unspecific symptoms or disturbances occurring before the clinical onset, compared with a marker of neurodegeneration,” wrote Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues. Initiation of treatment with disease-modifying therapy is associated with reductions in serum NfL levels, and this association could explain why some patients in the current study had higher NfL levels before MS onset than afterward. Furthermore, serum NfL levels are highly associated with levels of NfL in cerebrospinal fluid. “Thus, our findings of a presymptomatic increase in serum NfL not only suggest the presence of a prodromal phase in MS, but also that this phase is associated with neurodegeneration,” wrote the investigators.
The study’s well-defined population helped to minimize selection bias, and the blinded, randomized method of analyzing the serum samples eliminated artifactual differences in serum NfL concentrations. But the small sample size precluded analyses that could have influenced clinical practice, wrote Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues. For example, the researchers could not evaluate distinct cutoffs in serum NfL level that could mark the beginning of the prodromal phase of MS. Nor could they determine whether presymptomatic serum NfL levels varied with age at clinical onset, sex, or race. The small number of women in the sample was another limitation of the study.
The Swiss National Research Foundation and the National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke funded the study. Several of the investigators received fees from various drug companies that were unrelated to the study, and one researcher received grants from the National Institutes of Health during the study.
SOURCE: Bjornevik K et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(1):58-64.
(MS), according to research published in the January issue of JAMA Neurology. These results lend weight to the idea that MS has a prodromal phase, and this phase appears to be associated with neurodegeneration, according to the authors.
Patients often have CNS lesions of various stages of development at the time of their first demyelinating event, and this finding was one basis for neurologists’ hypothesis of a prodromal phase of MS. The finding that one-third of patients with radiologically isolated syndrome develop MS within 5 years also lends credence to this idea. Diagnosing MS early would enable early treatment that could prevent demyelination and the progression of neurodegeneration.
Researchers compared presymptomatic and symptomatic samples
With this idea in mind, Kjetil Bjornevik, MD, PhD, a member of the neuroepidemiology research group at Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health in Boston, and colleagues evaluated whether serum levels of NfL, a marker of ongoing neuroaxonal degeneration, were increased in the years before and around the time of clinical onset of MS. For their study population, the investigators chose active-duty U.S. military personnel who have at least one serum sample stored in the U.S. Department of Defense Serum Repository. Samples are collected after routine HIV type 1 antibody testing.
Within this population, Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues identified patients with MS who had at least one presymptomatic serum sample. The date of clinical MS onset was defined as the date of the first neurologic symptoms attributable to MS documented in the medical record. The investigators randomly selected two control individuals from the population and matched them to each case by age, sex, race or ethnicity, and dates of sample collection. Eligible controls were on active duty on the date of onset of the matched case.
Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues identified 245 patients with MS. Among this sample, the researchers selected two groups that each included 30 cases and 30 controls. The first group included patients who had provided at least one serum sample before MS onset and one sample within 2 years after MS onset. The second group included cases with at least two presymptomatic serum samples, one of which was collected more than 5 years before MS diagnosis, and the other of which was collected between 2 and 5 years before diagnosis. The investigators handled pairs of serum samples in the same way and assayed them in the same batch. The order of the samples in each pair was arranged at random.
Levels were higher in cases than in controls
About 77% of the population was male. Sixty percent of participants were white, 28% were black, and 6.7% were Hispanic. The population’s mean age at first sample collection was approximately 27 years. Mean age at MS onset was approximately 31 years.
For patients who provided samples before and after the clinical onset of MS, serum NfL levels were higher than in matched controls at both points. Most patients who passed from the presymptomatic stage to the symptomatic stage had a significant increase in serum NfL level (i.e., from a median of 25.0 pg/mL to a median of 45.1 pg/mL). Serum NfL levels at the two time points in controls did not differ significantly. For any given patient, an increase in serum NfL level from the presymptomatic measurement to the symptomatic measurement was associated with an increased risk of MS.
In patients with two presymptomatic samples, serum NfL levels were significantly higher in both samples than in the corresponding samples from matched controls. In cases, the earlier sample was collected at a median of 6 years before clinical onset of MS, and the later sample was collected at a median of 1 year before clinical onset. The serum NfL levels increased significantly between the two points for cases (i.e., a median increase of 1.3 pg/mL per year), but there was no significant difference in serum NfL level between the two samples in controls. A within-patient increase in presymptomatic serum NfL level was associated with an increased risk of MS.
Population included few women
“Our study differs from previous studies on the prodromal phase of MS because these have used indirect markers of this phase, which included unspecific symptoms or disturbances occurring before the clinical onset, compared with a marker of neurodegeneration,” wrote Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues. Initiation of treatment with disease-modifying therapy is associated with reductions in serum NfL levels, and this association could explain why some patients in the current study had higher NfL levels before MS onset than afterward. Furthermore, serum NfL levels are highly associated with levels of NfL in cerebrospinal fluid. “Thus, our findings of a presymptomatic increase in serum NfL not only suggest the presence of a prodromal phase in MS, but also that this phase is associated with neurodegeneration,” wrote the investigators.
The study’s well-defined population helped to minimize selection bias, and the blinded, randomized method of analyzing the serum samples eliminated artifactual differences in serum NfL concentrations. But the small sample size precluded analyses that could have influenced clinical practice, wrote Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues. For example, the researchers could not evaluate distinct cutoffs in serum NfL level that could mark the beginning of the prodromal phase of MS. Nor could they determine whether presymptomatic serum NfL levels varied with age at clinical onset, sex, or race. The small number of women in the sample was another limitation of the study.
The Swiss National Research Foundation and the National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke funded the study. Several of the investigators received fees from various drug companies that were unrelated to the study, and one researcher received grants from the National Institutes of Health during the study.
SOURCE: Bjornevik K et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(1):58-64.
(MS), according to research published in the January issue of JAMA Neurology. These results lend weight to the idea that MS has a prodromal phase, and this phase appears to be associated with neurodegeneration, according to the authors.
Patients often have CNS lesions of various stages of development at the time of their first demyelinating event, and this finding was one basis for neurologists’ hypothesis of a prodromal phase of MS. The finding that one-third of patients with radiologically isolated syndrome develop MS within 5 years also lends credence to this idea. Diagnosing MS early would enable early treatment that could prevent demyelination and the progression of neurodegeneration.
Researchers compared presymptomatic and symptomatic samples
With this idea in mind, Kjetil Bjornevik, MD, PhD, a member of the neuroepidemiology research group at Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health in Boston, and colleagues evaluated whether serum levels of NfL, a marker of ongoing neuroaxonal degeneration, were increased in the years before and around the time of clinical onset of MS. For their study population, the investigators chose active-duty U.S. military personnel who have at least one serum sample stored in the U.S. Department of Defense Serum Repository. Samples are collected after routine HIV type 1 antibody testing.
Within this population, Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues identified patients with MS who had at least one presymptomatic serum sample. The date of clinical MS onset was defined as the date of the first neurologic symptoms attributable to MS documented in the medical record. The investigators randomly selected two control individuals from the population and matched them to each case by age, sex, race or ethnicity, and dates of sample collection. Eligible controls were on active duty on the date of onset of the matched case.
Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues identified 245 patients with MS. Among this sample, the researchers selected two groups that each included 30 cases and 30 controls. The first group included patients who had provided at least one serum sample before MS onset and one sample within 2 years after MS onset. The second group included cases with at least two presymptomatic serum samples, one of which was collected more than 5 years before MS diagnosis, and the other of which was collected between 2 and 5 years before diagnosis. The investigators handled pairs of serum samples in the same way and assayed them in the same batch. The order of the samples in each pair was arranged at random.
Levels were higher in cases than in controls
About 77% of the population was male. Sixty percent of participants were white, 28% were black, and 6.7% were Hispanic. The population’s mean age at first sample collection was approximately 27 years. Mean age at MS onset was approximately 31 years.
For patients who provided samples before and after the clinical onset of MS, serum NfL levels were higher than in matched controls at both points. Most patients who passed from the presymptomatic stage to the symptomatic stage had a significant increase in serum NfL level (i.e., from a median of 25.0 pg/mL to a median of 45.1 pg/mL). Serum NfL levels at the two time points in controls did not differ significantly. For any given patient, an increase in serum NfL level from the presymptomatic measurement to the symptomatic measurement was associated with an increased risk of MS.
In patients with two presymptomatic samples, serum NfL levels were significantly higher in both samples than in the corresponding samples from matched controls. In cases, the earlier sample was collected at a median of 6 years before clinical onset of MS, and the later sample was collected at a median of 1 year before clinical onset. The serum NfL levels increased significantly between the two points for cases (i.e., a median increase of 1.3 pg/mL per year), but there was no significant difference in serum NfL level between the two samples in controls. A within-patient increase in presymptomatic serum NfL level was associated with an increased risk of MS.
Population included few women
“Our study differs from previous studies on the prodromal phase of MS because these have used indirect markers of this phase, which included unspecific symptoms or disturbances occurring before the clinical onset, compared with a marker of neurodegeneration,” wrote Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues. Initiation of treatment with disease-modifying therapy is associated with reductions in serum NfL levels, and this association could explain why some patients in the current study had higher NfL levels before MS onset than afterward. Furthermore, serum NfL levels are highly associated with levels of NfL in cerebrospinal fluid. “Thus, our findings of a presymptomatic increase in serum NfL not only suggest the presence of a prodromal phase in MS, but also that this phase is associated with neurodegeneration,” wrote the investigators.
The study’s well-defined population helped to minimize selection bias, and the blinded, randomized method of analyzing the serum samples eliminated artifactual differences in serum NfL concentrations. But the small sample size precluded analyses that could have influenced clinical practice, wrote Dr. Bjornevik and colleagues. For example, the researchers could not evaluate distinct cutoffs in serum NfL level that could mark the beginning of the prodromal phase of MS. Nor could they determine whether presymptomatic serum NfL levels varied with age at clinical onset, sex, or race. The small number of women in the sample was another limitation of the study.
The Swiss National Research Foundation and the National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke funded the study. Several of the investigators received fees from various drug companies that were unrelated to the study, and one researcher received grants from the National Institutes of Health during the study.
SOURCE: Bjornevik K et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(1):58-64.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
CRISPR-engineered T cells may be safe for cancer, but do they work?
according to a report in Science.
The results of no harm support this “promising” area of cancer immunotherapy, according to study investigator Edward A. Stadtmauer, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia and colleagues.
However, there was no evidence of benefit in this trial. One patient transfused with CRISPR-engineered T cells has since died, and the other two have moved on to other treatments.
“The big question that remains unanswered by this study is whether gene-edited, engineered T cells are effective against advanced cancer,” Jennifer Hamilton, PhD, and Jennifer Doudna, PhD, both of the University of California, Berkeley, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The study enrolled six patients with refractory cancer, and three of them received CRISPR-engineered T cells. Two patients had multiple myeloma, and one had metastatic sarcoma.
Dr. Stadtmauer and colleagues drew blood from the patients, isolated the T cells, and used CRISPR-Cas9 to modify the cells. The T cells were transfected with Cas9 protein complexed with single guide RNAs against TRAC and TRBC (genes encoding the T-cell receptor chains TCR-alpha and TCR-beta) as well as PDCD1 (a gene encoding programmed cell death protein 1). The T cells were then transduced with a lentiviral vector to express a transgenic NY-ESO-1 cancer-specific T-cell receptor.
The investigators expanded the cell lines and infused them back into the patients after administering lymphodepleting chemotherapy. The sarcoma patient initially had a 50% decrease in a large abdominal mass, but all three patients ultimately progressed.
The editorialists noted that gene disruption efficiencies in this study were “modest,” ranging from 15% to 45%, but the investigators used a protocol from 2016, when the study was given the go-ahead by the National Institutes of Health and the Food and Drug Administration. With current protocols, gene disruption efficiencies can exceed 90%, which means patients might do better in subsequent trials.
There was no more than mild toxicity in this trial, and most adverse events were attributed to the lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
There was concern about potential rejection of infused cells because of preexisting immune responses to Cas9, but it doesn’t seem “to be a barrier to the application of this promising technology,” the investigators said.
They noted that “the stable engraftment of our engineered T cells is remarkably different from previously reported trials ... where the half-life of the cells in blood was [about] 1 week. Biopsy specimens of bone marrow in the myeloma patients and tumor in the sarcoma patient demonstrated trafficking of the engineered T cells to the tumor in all three patients” beyond that point. The decay half-life of the transduced cells was 20.3 days, 121.8 days, and 293.5 days in these patients.
The editorialists said the details in the report are a model for other researchers to follow, but “as more gene-based therapies are demonstrated to be safe and effective, the barrier to clinical translation will become cell manufacturing and administration.”
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health and others. Dr. Stadtmauer didn’t report any disclosures, but other investigators disclosed patent applications and commercialization efforts. Dr. Doudna disclosed that she is a cofounder or adviser for several companies developing gene-editing therapeutics.
SOURCE: Stadtmauer EA et al. Science. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1126/science.aba7365.
according to a report in Science.
The results of no harm support this “promising” area of cancer immunotherapy, according to study investigator Edward A. Stadtmauer, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia and colleagues.
However, there was no evidence of benefit in this trial. One patient transfused with CRISPR-engineered T cells has since died, and the other two have moved on to other treatments.
“The big question that remains unanswered by this study is whether gene-edited, engineered T cells are effective against advanced cancer,” Jennifer Hamilton, PhD, and Jennifer Doudna, PhD, both of the University of California, Berkeley, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The study enrolled six patients with refractory cancer, and three of them received CRISPR-engineered T cells. Two patients had multiple myeloma, and one had metastatic sarcoma.
Dr. Stadtmauer and colleagues drew blood from the patients, isolated the T cells, and used CRISPR-Cas9 to modify the cells. The T cells were transfected with Cas9 protein complexed with single guide RNAs against TRAC and TRBC (genes encoding the T-cell receptor chains TCR-alpha and TCR-beta) as well as PDCD1 (a gene encoding programmed cell death protein 1). The T cells were then transduced with a lentiviral vector to express a transgenic NY-ESO-1 cancer-specific T-cell receptor.
The investigators expanded the cell lines and infused them back into the patients after administering lymphodepleting chemotherapy. The sarcoma patient initially had a 50% decrease in a large abdominal mass, but all three patients ultimately progressed.
The editorialists noted that gene disruption efficiencies in this study were “modest,” ranging from 15% to 45%, but the investigators used a protocol from 2016, when the study was given the go-ahead by the National Institutes of Health and the Food and Drug Administration. With current protocols, gene disruption efficiencies can exceed 90%, which means patients might do better in subsequent trials.
There was no more than mild toxicity in this trial, and most adverse events were attributed to the lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
There was concern about potential rejection of infused cells because of preexisting immune responses to Cas9, but it doesn’t seem “to be a barrier to the application of this promising technology,” the investigators said.
They noted that “the stable engraftment of our engineered T cells is remarkably different from previously reported trials ... where the half-life of the cells in blood was [about] 1 week. Biopsy specimens of bone marrow in the myeloma patients and tumor in the sarcoma patient demonstrated trafficking of the engineered T cells to the tumor in all three patients” beyond that point. The decay half-life of the transduced cells was 20.3 days, 121.8 days, and 293.5 days in these patients.
The editorialists said the details in the report are a model for other researchers to follow, but “as more gene-based therapies are demonstrated to be safe and effective, the barrier to clinical translation will become cell manufacturing and administration.”
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health and others. Dr. Stadtmauer didn’t report any disclosures, but other investigators disclosed patent applications and commercialization efforts. Dr. Doudna disclosed that she is a cofounder or adviser for several companies developing gene-editing therapeutics.
SOURCE: Stadtmauer EA et al. Science. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1126/science.aba7365.
according to a report in Science.
The results of no harm support this “promising” area of cancer immunotherapy, according to study investigator Edward A. Stadtmauer, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia and colleagues.
However, there was no evidence of benefit in this trial. One patient transfused with CRISPR-engineered T cells has since died, and the other two have moved on to other treatments.
“The big question that remains unanswered by this study is whether gene-edited, engineered T cells are effective against advanced cancer,” Jennifer Hamilton, PhD, and Jennifer Doudna, PhD, both of the University of California, Berkeley, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The study enrolled six patients with refractory cancer, and three of them received CRISPR-engineered T cells. Two patients had multiple myeloma, and one had metastatic sarcoma.
Dr. Stadtmauer and colleagues drew blood from the patients, isolated the T cells, and used CRISPR-Cas9 to modify the cells. The T cells were transfected with Cas9 protein complexed with single guide RNAs against TRAC and TRBC (genes encoding the T-cell receptor chains TCR-alpha and TCR-beta) as well as PDCD1 (a gene encoding programmed cell death protein 1). The T cells were then transduced with a lentiviral vector to express a transgenic NY-ESO-1 cancer-specific T-cell receptor.
The investigators expanded the cell lines and infused them back into the patients after administering lymphodepleting chemotherapy. The sarcoma patient initially had a 50% decrease in a large abdominal mass, but all three patients ultimately progressed.
The editorialists noted that gene disruption efficiencies in this study were “modest,” ranging from 15% to 45%, but the investigators used a protocol from 2016, when the study was given the go-ahead by the National Institutes of Health and the Food and Drug Administration. With current protocols, gene disruption efficiencies can exceed 90%, which means patients might do better in subsequent trials.
There was no more than mild toxicity in this trial, and most adverse events were attributed to the lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
There was concern about potential rejection of infused cells because of preexisting immune responses to Cas9, but it doesn’t seem “to be a barrier to the application of this promising technology,” the investigators said.
They noted that “the stable engraftment of our engineered T cells is remarkably different from previously reported trials ... where the half-life of the cells in blood was [about] 1 week. Biopsy specimens of bone marrow in the myeloma patients and tumor in the sarcoma patient demonstrated trafficking of the engineered T cells to the tumor in all three patients” beyond that point. The decay half-life of the transduced cells was 20.3 days, 121.8 days, and 293.5 days in these patients.
The editorialists said the details in the report are a model for other researchers to follow, but “as more gene-based therapies are demonstrated to be safe and effective, the barrier to clinical translation will become cell manufacturing and administration.”
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health and others. Dr. Stadtmauer didn’t report any disclosures, but other investigators disclosed patent applications and commercialization efforts. Dr. Doudna disclosed that she is a cofounder or adviser for several companies developing gene-editing therapeutics.
SOURCE: Stadtmauer EA et al. Science. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1126/science.aba7365.
FROM SCIENCE
Uptick in lung cancer in younger women, not related to smoking
A study of lung cancer in younger adults (less than 50 years) has found a recent trend of higher lung cancer rates in women, compared with men. The increase is driven by cases of adenocarcinoma of the lung.
The “emerging pattern of higher lung cancer incidence in young females” is not confined to geographic areas and income levels and “is not fully explained by sex-differences in smoking prevalence,” the authors comment.
Miranda M. Fidler-Benaoudia, PhD, Cancer Control Alberta, Alberta Health Services, Calgary, and colleagues examined lung cancer cases in 40 countries from 1993 to 2012.
They found that the female-to-male incidence rate ratio (IRR) had significantly crossed over from men to women in six countries, including the United States and Canada, and had nonsignificantly crossed over in a further 23 countries.
The research was published online Feb. 5 in the International Journal of Cancer.
These findings “forewarn of a higher lung cancer burden in women than men at older ages in the decades to follow, especially in higher-income settings,” write the authors. They highlight “the need for etiologic studies.”
Historically, lung cancer higher in men
Historically, lung cancer rates have been higher among men than women, owing to the fact that men start smoking in large numbers earlier and smoke at higher rates, the researchers comment.
However, there has been a convergence in lung cancer incidence between men and women. A recent study suggests that, in the United States, the incidence in young women is higher than that in their male counterparts.
To determine the degree to which this phenomenon is occurring globally, the team used national or subnational registry data from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, volumes VIII–XI.
These included lung and bronchial cancer cases in 40 countries from 1993 to 2012, divided into 5-year periods. Individuals were categorized into 5-year age bands.
In addition, the team used the Global Health Data Exchange to extract data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 and derive country- and sex-specific daily smoking prevalence rates.
The researchers found that among young men and women, there were three patterns in the occurrence of lung cancer between the periods 1993-1997 and 2008-2012:
- A significant crossover from male to female dominance, seen in six countries.
- An insignificant crossover from male to female dominance, found in 23 countries.
- A continued male dominance, observed in 11 countries.
Higher incidence in women in six countries
The six countries with significant crossover from male to female dominance were Canada, Denmark, Germany, New Zealand, the Netherlands, and the United States.
Further analysis showed that, in general, age-specific lung cancer incidence rates decreased in successive male birth cohorts in these six countries. There was more variation across female birth cohorts.
Calculating female-to-male incidence rate ratios, the team found, for example, the IRR increased in New Zealand from 1.0 in the 1953 birth cohort to 1.6 in the 1968 birth cohort for people aged 40-44 years.
In addition, among adults aged 45-49 years in the Netherlands, the IRR rose from 0.7 in those born in the circa 1948 cohort to 1.4 in those from the circa 1958 cohort.
Overall, female-to-male IRRs increased notably among the following groups:
- Individuals aged 30-34 years in Canada, Denmark, and Germany.
- Those aged 40-44 years in Germany, the Netherlands, and the United States.
- Those aged 44-50 years in the Netherlands and the United States.
- Those aged 50-54 years in Canada, Denmark, and New Zealand.
Countries with an insignificant crossover from male to female dominance of lung cancer were located across Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.
Again, incidence rates were typically characterized by falling rates of lung cancer among men in more recent birth cohorts, and lung cancer incidence trends were more variable in women.
The team writes: “Of note, the six countries demonstrating a significant crossover are among those considered to be more advanced in the tobacco epidemic.
“Many of the countries where the crossover was insignificant or when there was no crossover are considered to be late adopters of the tobacco epidemic, with the effects of the epidemic on the burden of lung cancer and other smoking-related diseases beginning to manifest more recently, or perhaps yet to come.”
They suggest that low- and middle-resource countries may not follow the tobacco epidemic pattern of high-income countries, and so “we may not see higher lung cancer incidence rates in women than men for the foreseeable future in these countries.”
No funding for the study has been disclosed. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study of lung cancer in younger adults (less than 50 years) has found a recent trend of higher lung cancer rates in women, compared with men. The increase is driven by cases of adenocarcinoma of the lung.
The “emerging pattern of higher lung cancer incidence in young females” is not confined to geographic areas and income levels and “is not fully explained by sex-differences in smoking prevalence,” the authors comment.
Miranda M. Fidler-Benaoudia, PhD, Cancer Control Alberta, Alberta Health Services, Calgary, and colleagues examined lung cancer cases in 40 countries from 1993 to 2012.
They found that the female-to-male incidence rate ratio (IRR) had significantly crossed over from men to women in six countries, including the United States and Canada, and had nonsignificantly crossed over in a further 23 countries.
The research was published online Feb. 5 in the International Journal of Cancer.
These findings “forewarn of a higher lung cancer burden in women than men at older ages in the decades to follow, especially in higher-income settings,” write the authors. They highlight “the need for etiologic studies.”
Historically, lung cancer higher in men
Historically, lung cancer rates have been higher among men than women, owing to the fact that men start smoking in large numbers earlier and smoke at higher rates, the researchers comment.
However, there has been a convergence in lung cancer incidence between men and women. A recent study suggests that, in the United States, the incidence in young women is higher than that in their male counterparts.
To determine the degree to which this phenomenon is occurring globally, the team used national or subnational registry data from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, volumes VIII–XI.
These included lung and bronchial cancer cases in 40 countries from 1993 to 2012, divided into 5-year periods. Individuals were categorized into 5-year age bands.
In addition, the team used the Global Health Data Exchange to extract data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 and derive country- and sex-specific daily smoking prevalence rates.
The researchers found that among young men and women, there were three patterns in the occurrence of lung cancer between the periods 1993-1997 and 2008-2012:
- A significant crossover from male to female dominance, seen in six countries.
- An insignificant crossover from male to female dominance, found in 23 countries.
- A continued male dominance, observed in 11 countries.
Higher incidence in women in six countries
The six countries with significant crossover from male to female dominance were Canada, Denmark, Germany, New Zealand, the Netherlands, and the United States.
Further analysis showed that, in general, age-specific lung cancer incidence rates decreased in successive male birth cohorts in these six countries. There was more variation across female birth cohorts.
Calculating female-to-male incidence rate ratios, the team found, for example, the IRR increased in New Zealand from 1.0 in the 1953 birth cohort to 1.6 in the 1968 birth cohort for people aged 40-44 years.
In addition, among adults aged 45-49 years in the Netherlands, the IRR rose from 0.7 in those born in the circa 1948 cohort to 1.4 in those from the circa 1958 cohort.
Overall, female-to-male IRRs increased notably among the following groups:
- Individuals aged 30-34 years in Canada, Denmark, and Germany.
- Those aged 40-44 years in Germany, the Netherlands, and the United States.
- Those aged 44-50 years in the Netherlands and the United States.
- Those aged 50-54 years in Canada, Denmark, and New Zealand.
Countries with an insignificant crossover from male to female dominance of lung cancer were located across Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.
Again, incidence rates were typically characterized by falling rates of lung cancer among men in more recent birth cohorts, and lung cancer incidence trends were more variable in women.
The team writes: “Of note, the six countries demonstrating a significant crossover are among those considered to be more advanced in the tobacco epidemic.
“Many of the countries where the crossover was insignificant or when there was no crossover are considered to be late adopters of the tobacco epidemic, with the effects of the epidemic on the burden of lung cancer and other smoking-related diseases beginning to manifest more recently, or perhaps yet to come.”
They suggest that low- and middle-resource countries may not follow the tobacco epidemic pattern of high-income countries, and so “we may not see higher lung cancer incidence rates in women than men for the foreseeable future in these countries.”
No funding for the study has been disclosed. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study of lung cancer in younger adults (less than 50 years) has found a recent trend of higher lung cancer rates in women, compared with men. The increase is driven by cases of adenocarcinoma of the lung.
The “emerging pattern of higher lung cancer incidence in young females” is not confined to geographic areas and income levels and “is not fully explained by sex-differences in smoking prevalence,” the authors comment.
Miranda M. Fidler-Benaoudia, PhD, Cancer Control Alberta, Alberta Health Services, Calgary, and colleagues examined lung cancer cases in 40 countries from 1993 to 2012.
They found that the female-to-male incidence rate ratio (IRR) had significantly crossed over from men to women in six countries, including the United States and Canada, and had nonsignificantly crossed over in a further 23 countries.
The research was published online Feb. 5 in the International Journal of Cancer.
These findings “forewarn of a higher lung cancer burden in women than men at older ages in the decades to follow, especially in higher-income settings,” write the authors. They highlight “the need for etiologic studies.”
Historically, lung cancer higher in men
Historically, lung cancer rates have been higher among men than women, owing to the fact that men start smoking in large numbers earlier and smoke at higher rates, the researchers comment.
However, there has been a convergence in lung cancer incidence between men and women. A recent study suggests that, in the United States, the incidence in young women is higher than that in their male counterparts.
To determine the degree to which this phenomenon is occurring globally, the team used national or subnational registry data from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, volumes VIII–XI.
These included lung and bronchial cancer cases in 40 countries from 1993 to 2012, divided into 5-year periods. Individuals were categorized into 5-year age bands.
In addition, the team used the Global Health Data Exchange to extract data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 and derive country- and sex-specific daily smoking prevalence rates.
The researchers found that among young men and women, there were three patterns in the occurrence of lung cancer between the periods 1993-1997 and 2008-2012:
- A significant crossover from male to female dominance, seen in six countries.
- An insignificant crossover from male to female dominance, found in 23 countries.
- A continued male dominance, observed in 11 countries.
Higher incidence in women in six countries
The six countries with significant crossover from male to female dominance were Canada, Denmark, Germany, New Zealand, the Netherlands, and the United States.
Further analysis showed that, in general, age-specific lung cancer incidence rates decreased in successive male birth cohorts in these six countries. There was more variation across female birth cohorts.
Calculating female-to-male incidence rate ratios, the team found, for example, the IRR increased in New Zealand from 1.0 in the 1953 birth cohort to 1.6 in the 1968 birth cohort for people aged 40-44 years.
In addition, among adults aged 45-49 years in the Netherlands, the IRR rose from 0.7 in those born in the circa 1948 cohort to 1.4 in those from the circa 1958 cohort.
Overall, female-to-male IRRs increased notably among the following groups:
- Individuals aged 30-34 years in Canada, Denmark, and Germany.
- Those aged 40-44 years in Germany, the Netherlands, and the United States.
- Those aged 44-50 years in the Netherlands and the United States.
- Those aged 50-54 years in Canada, Denmark, and New Zealand.
Countries with an insignificant crossover from male to female dominance of lung cancer were located across Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.
Again, incidence rates were typically characterized by falling rates of lung cancer among men in more recent birth cohorts, and lung cancer incidence trends were more variable in women.
The team writes: “Of note, the six countries demonstrating a significant crossover are among those considered to be more advanced in the tobacco epidemic.
“Many of the countries where the crossover was insignificant or when there was no crossover are considered to be late adopters of the tobacco epidemic, with the effects of the epidemic on the burden of lung cancer and other smoking-related diseases beginning to manifest more recently, or perhaps yet to come.”
They suggest that low- and middle-resource countries may not follow the tobacco epidemic pattern of high-income countries, and so “we may not see higher lung cancer incidence rates in women than men for the foreseeable future in these countries.”
No funding for the study has been disclosed. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.