User login
Cardiac arrest: Targeted temperature management a game changer
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Targeted temperature management maintained at 32-36 degrees Celsius is now a strong class I recommendation for all comatose patients who experience return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, including those with nonshockable rhythms, Erin A. Bohula, MD, PhD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“Our practice is that ,” said Dr. Bohula, a cardiologist and critical care specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The current ACC/AHA guidelines declare: “There are essentially no patients for whom temperature control somewhere in the range between 32 degrees C [89.6 F) and 36 degrees C [96.8 F] is contraindicated.” The writing committee cited “recent clinical trial data enrolling patients with all rhythms, the rarity of adverse effects in trials, the high neurologic morbidity and mortality without any specific interventions, and the preponderance of data suggesting that temperature is an important variable for neurologic recovery” (Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132[18 Suppl 2]:S465-82).
“That’s a pretty strong statement,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The current guidelines, which date back to 2015, give a class I, level of evidence B recommendation for targeted temperature management (TTM) in patients who are comatose with return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest involving ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular fibrillation. The bedside definition of comatose is lack of meaningful response to verbal commands to squeeze hands, blink, or move toes.
The current recommendation for TTM in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm is class I, level of evidence C, meaning it’s based on expert consensus. However, that recommendation is now out of date and due for a level-of-evidence upgrade in light of the recent results of the French HYPERION trial, an open-label randomized trial of 584 patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm. Although 90-day mortality was similarly high in the TTM and targeted normothermia groups, the rate of favorable neurologic outcome as assessed by a Cerebral Performance Category scale score of 1 or 2 was 10.2% in the TTM group, significantly better than the 5.7% rate in controls (N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381[24]:2327-37).
The 2010, ACC/AHA guidelines recommended a TTM range of 32-34 degrees C, but on the basis of subsequent persuasive randomized trial data, that range was broadened to 32-36 degrees C in the 2015 guidelines, with a class IB recommendation. Maintenance of TTM for at least 24 hours has a IIa, level of evidence C recommendation in the current guidelines.
The guidelines emphasize that specific features may favor selection of one temperature for TTM over another. For example, patients with seizures or cerebral edema might be better off with TTM at a lower temperature, while a higher temperature may be best for those with bleeding or severe bradycardia. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, the default temperature is 33 degrees C. However, TTM with a goal of 36 degrees C is seriously considered in patients with recent head trauma, major surgery within the past 2 weeks, refractory hypotension, severe sepsis, pregnancy, or high bleeding risk. Rewarming is done at a rate of 0.25 degrees C per hour, with sedation maintained until the patient has been returned to 98.6 degrees F, according to Dr. Bohula.
Based on several negative studies of TTM using rapid infusion of chilled fluids in the ambulance en route to the hospital, the guidelines rate that practice class IIIA, meaning don’t do it. Avoidance of a systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg and a mean arterial pressure of less than 65 mm Hg gets a class IIb level of evidence C recommendation to lessen the risk of cerebral hypoxia.
TTM a major breakthrough
Prior to the introduction of TTM, comatose patients with ROSC after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had a dreadful prognosis, with survival rates of 1%-10% in registry studies. In contrast, the survival rate in the landmark TTM clinical trials was 50%-60%. And while that’s a dramatic improvement, ROSC after cardiac arrest remains a high-mortality condition. Dr. Bohula was first author of a report by the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network, composed of 16 tertiary cardiac intensive care units in the United States and Canada. Cardiac arrest was the primary indication for 8.7% of 3,049 consecutive admissions, and its 38% mortality rate was the highest of all cardiac critical care indications (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 24;4[9]:928-35).
TTM was developed in response to a recognition that two-thirds of deaths in patients who make it to the hospital after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are neurologic – the result of brain anoxia – rather than being due to the myocardial ischemia that may have initially brought them to medical attention.
“Time is brain cells, the same way we think of time as cardiac muscle,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The main idea behind therapeutic hypothermia is that it lowers the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen to reduce the consequences of ongoing anoxia. The brain doesn’t require as much perfusion when cooled.
TTM has other beneficial neurologic effects as well: It reduces cerebral blood volume via autoregulation, decreases intracranial pressure, and blunts the inflammatory response involved in the postcardiac arrest syndrome. In addition, TTM has anticonvulsant properties, an important effect because seizures and/or myoclonus occur in up to 15% of adults who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest – and in even more of those who are comatose after doing so. And seizures increase the brain’s metabolic rate threefold, resulting in more cerebral ischemic injury, she explained.
Seizure activity can be difficult to distinguish from shivering in a patient on TTM. For this reason Dr. Bohula recommends putting patients on continuous EEG monitoring from the time of admission, as is the routine practice at the Brigham.
She reported serving as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Servier, Lexicon, Kowa, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and the National Institutes of Health. In addition, she generates institutional research grants provided by a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Targeted temperature management maintained at 32-36 degrees Celsius is now a strong class I recommendation for all comatose patients who experience return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, including those with nonshockable rhythms, Erin A. Bohula, MD, PhD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“Our practice is that ,” said Dr. Bohula, a cardiologist and critical care specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The current ACC/AHA guidelines declare: “There are essentially no patients for whom temperature control somewhere in the range between 32 degrees C [89.6 F) and 36 degrees C [96.8 F] is contraindicated.” The writing committee cited “recent clinical trial data enrolling patients with all rhythms, the rarity of adverse effects in trials, the high neurologic morbidity and mortality without any specific interventions, and the preponderance of data suggesting that temperature is an important variable for neurologic recovery” (Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132[18 Suppl 2]:S465-82).
“That’s a pretty strong statement,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The current guidelines, which date back to 2015, give a class I, level of evidence B recommendation for targeted temperature management (TTM) in patients who are comatose with return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest involving ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular fibrillation. The bedside definition of comatose is lack of meaningful response to verbal commands to squeeze hands, blink, or move toes.
The current recommendation for TTM in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm is class I, level of evidence C, meaning it’s based on expert consensus. However, that recommendation is now out of date and due for a level-of-evidence upgrade in light of the recent results of the French HYPERION trial, an open-label randomized trial of 584 patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm. Although 90-day mortality was similarly high in the TTM and targeted normothermia groups, the rate of favorable neurologic outcome as assessed by a Cerebral Performance Category scale score of 1 or 2 was 10.2% in the TTM group, significantly better than the 5.7% rate in controls (N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381[24]:2327-37).
The 2010, ACC/AHA guidelines recommended a TTM range of 32-34 degrees C, but on the basis of subsequent persuasive randomized trial data, that range was broadened to 32-36 degrees C in the 2015 guidelines, with a class IB recommendation. Maintenance of TTM for at least 24 hours has a IIa, level of evidence C recommendation in the current guidelines.
The guidelines emphasize that specific features may favor selection of one temperature for TTM over another. For example, patients with seizures or cerebral edema might be better off with TTM at a lower temperature, while a higher temperature may be best for those with bleeding or severe bradycardia. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, the default temperature is 33 degrees C. However, TTM with a goal of 36 degrees C is seriously considered in patients with recent head trauma, major surgery within the past 2 weeks, refractory hypotension, severe sepsis, pregnancy, or high bleeding risk. Rewarming is done at a rate of 0.25 degrees C per hour, with sedation maintained until the patient has been returned to 98.6 degrees F, according to Dr. Bohula.
Based on several negative studies of TTM using rapid infusion of chilled fluids in the ambulance en route to the hospital, the guidelines rate that practice class IIIA, meaning don’t do it. Avoidance of a systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg and a mean arterial pressure of less than 65 mm Hg gets a class IIb level of evidence C recommendation to lessen the risk of cerebral hypoxia.
TTM a major breakthrough
Prior to the introduction of TTM, comatose patients with ROSC after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had a dreadful prognosis, with survival rates of 1%-10% in registry studies. In contrast, the survival rate in the landmark TTM clinical trials was 50%-60%. And while that’s a dramatic improvement, ROSC after cardiac arrest remains a high-mortality condition. Dr. Bohula was first author of a report by the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network, composed of 16 tertiary cardiac intensive care units in the United States and Canada. Cardiac arrest was the primary indication for 8.7% of 3,049 consecutive admissions, and its 38% mortality rate was the highest of all cardiac critical care indications (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 24;4[9]:928-35).
TTM was developed in response to a recognition that two-thirds of deaths in patients who make it to the hospital after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are neurologic – the result of brain anoxia – rather than being due to the myocardial ischemia that may have initially brought them to medical attention.
“Time is brain cells, the same way we think of time as cardiac muscle,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The main idea behind therapeutic hypothermia is that it lowers the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen to reduce the consequences of ongoing anoxia. The brain doesn’t require as much perfusion when cooled.
TTM has other beneficial neurologic effects as well: It reduces cerebral blood volume via autoregulation, decreases intracranial pressure, and blunts the inflammatory response involved in the postcardiac arrest syndrome. In addition, TTM has anticonvulsant properties, an important effect because seizures and/or myoclonus occur in up to 15% of adults who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest – and in even more of those who are comatose after doing so. And seizures increase the brain’s metabolic rate threefold, resulting in more cerebral ischemic injury, she explained.
Seizure activity can be difficult to distinguish from shivering in a patient on TTM. For this reason Dr. Bohula recommends putting patients on continuous EEG monitoring from the time of admission, as is the routine practice at the Brigham.
She reported serving as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Servier, Lexicon, Kowa, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and the National Institutes of Health. In addition, she generates institutional research grants provided by a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Targeted temperature management maintained at 32-36 degrees Celsius is now a strong class I recommendation for all comatose patients who experience return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, including those with nonshockable rhythms, Erin A. Bohula, MD, PhD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“Our practice is that ,” said Dr. Bohula, a cardiologist and critical care specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The current ACC/AHA guidelines declare: “There are essentially no patients for whom temperature control somewhere in the range between 32 degrees C [89.6 F) and 36 degrees C [96.8 F] is contraindicated.” The writing committee cited “recent clinical trial data enrolling patients with all rhythms, the rarity of adverse effects in trials, the high neurologic morbidity and mortality without any specific interventions, and the preponderance of data suggesting that temperature is an important variable for neurologic recovery” (Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132[18 Suppl 2]:S465-82).
“That’s a pretty strong statement,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The current guidelines, which date back to 2015, give a class I, level of evidence B recommendation for targeted temperature management (TTM) in patients who are comatose with return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest involving ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular fibrillation. The bedside definition of comatose is lack of meaningful response to verbal commands to squeeze hands, blink, or move toes.
The current recommendation for TTM in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm is class I, level of evidence C, meaning it’s based on expert consensus. However, that recommendation is now out of date and due for a level-of-evidence upgrade in light of the recent results of the French HYPERION trial, an open-label randomized trial of 584 patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm. Although 90-day mortality was similarly high in the TTM and targeted normothermia groups, the rate of favorable neurologic outcome as assessed by a Cerebral Performance Category scale score of 1 or 2 was 10.2% in the TTM group, significantly better than the 5.7% rate in controls (N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381[24]:2327-37).
The 2010, ACC/AHA guidelines recommended a TTM range of 32-34 degrees C, but on the basis of subsequent persuasive randomized trial data, that range was broadened to 32-36 degrees C in the 2015 guidelines, with a class IB recommendation. Maintenance of TTM for at least 24 hours has a IIa, level of evidence C recommendation in the current guidelines.
The guidelines emphasize that specific features may favor selection of one temperature for TTM over another. For example, patients with seizures or cerebral edema might be better off with TTM at a lower temperature, while a higher temperature may be best for those with bleeding or severe bradycardia. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, the default temperature is 33 degrees C. However, TTM with a goal of 36 degrees C is seriously considered in patients with recent head trauma, major surgery within the past 2 weeks, refractory hypotension, severe sepsis, pregnancy, or high bleeding risk. Rewarming is done at a rate of 0.25 degrees C per hour, with sedation maintained until the patient has been returned to 98.6 degrees F, according to Dr. Bohula.
Based on several negative studies of TTM using rapid infusion of chilled fluids in the ambulance en route to the hospital, the guidelines rate that practice class IIIA, meaning don’t do it. Avoidance of a systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg and a mean arterial pressure of less than 65 mm Hg gets a class IIb level of evidence C recommendation to lessen the risk of cerebral hypoxia.
TTM a major breakthrough
Prior to the introduction of TTM, comatose patients with ROSC after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had a dreadful prognosis, with survival rates of 1%-10% in registry studies. In contrast, the survival rate in the landmark TTM clinical trials was 50%-60%. And while that’s a dramatic improvement, ROSC after cardiac arrest remains a high-mortality condition. Dr. Bohula was first author of a report by the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network, composed of 16 tertiary cardiac intensive care units in the United States and Canada. Cardiac arrest was the primary indication for 8.7% of 3,049 consecutive admissions, and its 38% mortality rate was the highest of all cardiac critical care indications (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 24;4[9]:928-35).
TTM was developed in response to a recognition that two-thirds of deaths in patients who make it to the hospital after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are neurologic – the result of brain anoxia – rather than being due to the myocardial ischemia that may have initially brought them to medical attention.
“Time is brain cells, the same way we think of time as cardiac muscle,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The main idea behind therapeutic hypothermia is that it lowers the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen to reduce the consequences of ongoing anoxia. The brain doesn’t require as much perfusion when cooled.
TTM has other beneficial neurologic effects as well: It reduces cerebral blood volume via autoregulation, decreases intracranial pressure, and blunts the inflammatory response involved in the postcardiac arrest syndrome. In addition, TTM has anticonvulsant properties, an important effect because seizures and/or myoclonus occur in up to 15% of adults who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest – and in even more of those who are comatose after doing so. And seizures increase the brain’s metabolic rate threefold, resulting in more cerebral ischemic injury, she explained.
Seizure activity can be difficult to distinguish from shivering in a patient on TTM. For this reason Dr. Bohula recommends putting patients on continuous EEG monitoring from the time of admission, as is the routine practice at the Brigham.
She reported serving as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Servier, Lexicon, Kowa, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and the National Institutes of Health. In addition, she generates institutional research grants provided by a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC SNOWMASS 2020
CDC begins coronavirus diagnostic test kit distribution; new case confirmed in Wisconsin
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
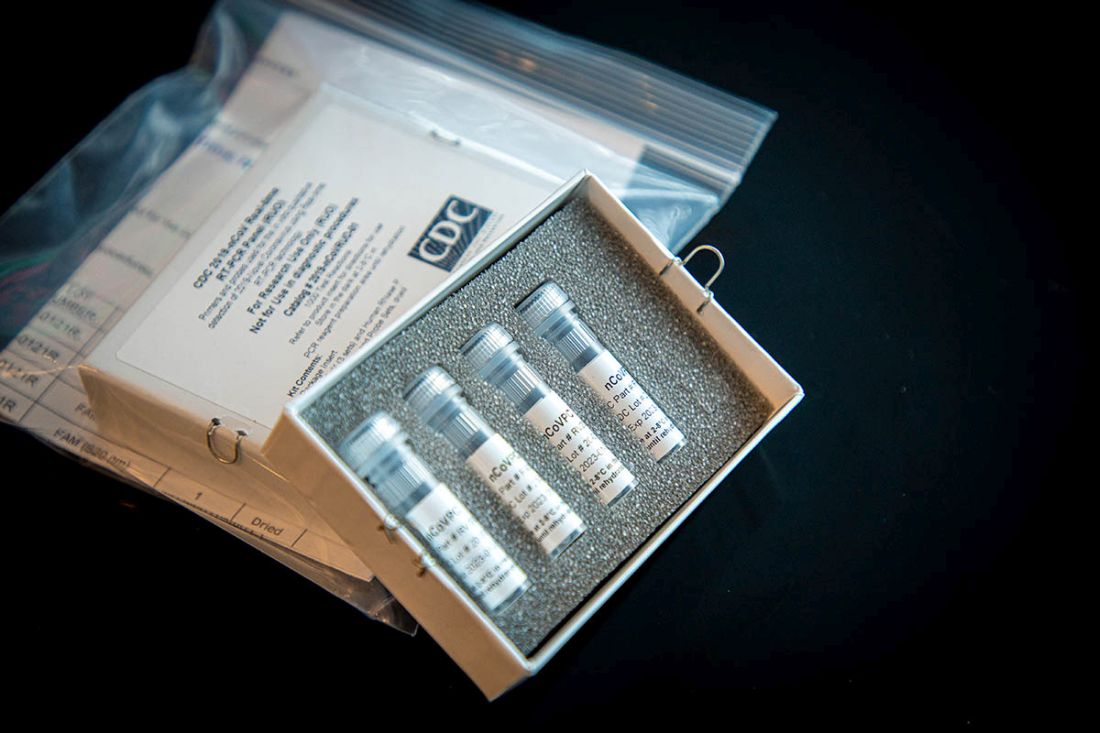
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
Global project reveals cancer’s genomic playbook
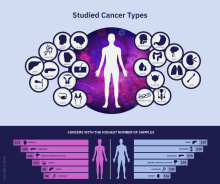
A massive collaborative project spanning four continents and 744 research centers has revealed driver mutations in both protein-coding and noncoding regions of 38 cancer types.
The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) is an integrative analysis of the whole-genome sequences from 2,658 donors across 38 common tumor types. The findings are expected to add exponentially to what’s currently known about the complex genetics of cancer, and they point to possible strategies for improving cancer prevention, diagnosis, and care.
Six articles summarizing the findings are presented in a series of papers in Nature, and 16 more appear in affiliated publications.
“It’s humbling that it was only 14 years ago that the genomics community sequenced its very first cancer exome, and it was able to identify mutations within the roughly 20,000 protein-coding genes in the human cell,” investigator Lincoln Stein, MD, PhD, of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research in Toronto, said in a telephone briefing.
Exome sequencing, however, covers only protein-coding genomic regions, which constitute only about 1% of the entire genome, “so assembling an accurate portrait of the cancer genome using just the exome data is like trying to put together a 100,000-piece jigsaw puzzle when you’re missing 99% of the pieces and there’s no puzzle box with a completed picture to guide you,” Dr. Stein said.
Members of the PCAWG from centers in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia screened 2,658 whole-cancer genomes and matched samples of noncancerous tissues from the same individuals, along with 1,188 transcriptomes cataloging the sequences and expression of RNA transcripts in a given tumor. The 6-year project netted more than 800 terabytes of genomic data, roughly equivalent to the digital holdings of the U.S. Library of Congress multiplied by 11.
The findings are summarized in papers focusing on cancer drivers, noncoding changes, mutational signatures, structural variants, cancer evolution over time, and RNA alterations.
Driver mutations
Investigators found that the average cancer genome contains four or five driver mutations located in both coding and noncoding regions. They also found, however, that in approximately 5% of cases no driver mutations could be identified.
A substantial proportion of tumors displayed “hallmarks of genomic catastrophes.” About 22% of tumors exhibited chromothripsis, a mutational process marked by hundreds or even thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements. About 18% showed chromoplexy, which is characterized by scattering and rearrangement of multiple strands of DNA from one or more chromosomes.
Analyzing driver point mutations and structural variants in noncoding regions, the investigators found the usual suspects – previously reported culprits – as well as novel candidates.
For example, they identified point mutations in the five prime region of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and the three prime untranslated regions of NFKBIZ (a nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor) and TOB1 (an antiproliferative protein), focal deletion in BRD4 (a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator), and rearrangements in chromosomal loci in members of the AKR1C family of enzymes thought to play a role in disease progression.
In addition, investigators identified mutations in noncoding regions of TERT, a telomerase gene. These mutations result in ramped-up expression of telomerase, which in turn promotes uncontrollable division of tumor cells.
Mutational signatures
In a related line of research, PCAWG investigators identified new DNA mutational signatures ranging from single nucleotide polymorphisms to insertions and deletions, as well as to structural variants – rearrangements of large sections of the genome.
“The substantial size of our dataset, compared with previous analyses, enabled the discovery of new signatures, the separation of overlapping signatures, and the decomposition of signatures into components that may represent associated – but distinct – DNA damage, repair, and/or replication mechanisms. By estimating the contribution of each signature to the mutational catalogs of individual cancer genomes, we revealed associations of signatures to exogenous or endogenous exposures, as well as to defective DNA maintenance processes,” the investigators wrote.
They also acknowledged, however, that “many signatures are of unknown cause.”
Cancer evolution
One of the six main studies focused on the evolution of cancer over time. Instead of providing a “snapshot” of the genome as captured by sequencing tissue from a single biopsy, consortium investigators created full-length features of the “life history and evolution of mutational processes and driver mutation sequences.”
They found that early cancer development was marked by relatively few mutations in driver genes and by identifiable copy-number gains, including trisomy 7 in glioblastoma, and an abnormal mirroring of the arms (isochromosome) of chromosome 17 in medulloblastoma.
In 40% of the samples, however, there were significant changes in the mutational spectrum as the cancers grew, leading to a near quadrupling of driver genes and increased genomic instability in later-stage tumors.
“Copy-number alterations often occur in mitotic crises and lead to simultaneous gains of chromosomal segments,” the investigators wrote. “Timing analyses suggest that driver mutations often precede diagnosis by many years, if not decades. Together, these results determine the evolutionary trajectories of cancer and highlight opportunities for early cancer detection.”
Implications for cancer care
“When I used to treat patients with cancer, I was always completely amazed and puzzled by how two patients could have what looked like the same tumor. It would look the same under the microscope, have the same size, and the two patients would receive exactly the same treatment, but the two patients would have completely opposite outcomes; one would survive, and one would die. What this analysis … has done is really laid bare the reasons for that unpredictability in clinical outcomes,” Peter Campbell, MD, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Hinxton, England, said during the telebriefing.
“The most striking finding out of all of the suite of papers is just how different one person’s cancer genome is from another person’s. We see thousands of different combinations of mutations that can cause the cancer, and more than 80 different underlying processes generating the mutations in a cancer, and that leads to very different shapes and patterns in the genome that result,” he added.
On a positive note, the research shows that one or more driver mutations can be identified in about 95% of all cancer patients, and it elucidates the sequence of events leading to oncogenesis and tumor evolution, providing opportunities for earlier identification and potential interventions to prevent cancer, Dr. Campbell said.
The PCAWG was a collaborative multinational effort with multiple funding sources and many investigators.
SOURCE: Nature. 2020 Feb 5. https://www.nature.com/collections/pcawg/
A massive collaborative project spanning four continents and 744 research centers has revealed driver mutations in both protein-coding and noncoding regions of 38 cancer types.
The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) is an integrative analysis of the whole-genome sequences from 2,658 donors across 38 common tumor types. The findings are expected to add exponentially to what’s currently known about the complex genetics of cancer, and they point to possible strategies for improving cancer prevention, diagnosis, and care.
Six articles summarizing the findings are presented in a series of papers in Nature, and 16 more appear in affiliated publications.
“It’s humbling that it was only 14 years ago that the genomics community sequenced its very first cancer exome, and it was able to identify mutations within the roughly 20,000 protein-coding genes in the human cell,” investigator Lincoln Stein, MD, PhD, of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research in Toronto, said in a telephone briefing.
Exome sequencing, however, covers only protein-coding genomic regions, which constitute only about 1% of the entire genome, “so assembling an accurate portrait of the cancer genome using just the exome data is like trying to put together a 100,000-piece jigsaw puzzle when you’re missing 99% of the pieces and there’s no puzzle box with a completed picture to guide you,” Dr. Stein said.
Members of the PCAWG from centers in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia screened 2,658 whole-cancer genomes and matched samples of noncancerous tissues from the same individuals, along with 1,188 transcriptomes cataloging the sequences and expression of RNA transcripts in a given tumor. The 6-year project netted more than 800 terabytes of genomic data, roughly equivalent to the digital holdings of the U.S. Library of Congress multiplied by 11.
The findings are summarized in papers focusing on cancer drivers, noncoding changes, mutational signatures, structural variants, cancer evolution over time, and RNA alterations.
Driver mutations
Investigators found that the average cancer genome contains four or five driver mutations located in both coding and noncoding regions. They also found, however, that in approximately 5% of cases no driver mutations could be identified.
A substantial proportion of tumors displayed “hallmarks of genomic catastrophes.” About 22% of tumors exhibited chromothripsis, a mutational process marked by hundreds or even thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements. About 18% showed chromoplexy, which is characterized by scattering and rearrangement of multiple strands of DNA from one or more chromosomes.
Analyzing driver point mutations and structural variants in noncoding regions, the investigators found the usual suspects – previously reported culprits – as well as novel candidates.
For example, they identified point mutations in the five prime region of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and the three prime untranslated regions of NFKBIZ (a nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor) and TOB1 (an antiproliferative protein), focal deletion in BRD4 (a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator), and rearrangements in chromosomal loci in members of the AKR1C family of enzymes thought to play a role in disease progression.
In addition, investigators identified mutations in noncoding regions of TERT, a telomerase gene. These mutations result in ramped-up expression of telomerase, which in turn promotes uncontrollable division of tumor cells.
Mutational signatures
In a related line of research, PCAWG investigators identified new DNA mutational signatures ranging from single nucleotide polymorphisms to insertions and deletions, as well as to structural variants – rearrangements of large sections of the genome.
“The substantial size of our dataset, compared with previous analyses, enabled the discovery of new signatures, the separation of overlapping signatures, and the decomposition of signatures into components that may represent associated – but distinct – DNA damage, repair, and/or replication mechanisms. By estimating the contribution of each signature to the mutational catalogs of individual cancer genomes, we revealed associations of signatures to exogenous or endogenous exposures, as well as to defective DNA maintenance processes,” the investigators wrote.
They also acknowledged, however, that “many signatures are of unknown cause.”
Cancer evolution
One of the six main studies focused on the evolution of cancer over time. Instead of providing a “snapshot” of the genome as captured by sequencing tissue from a single biopsy, consortium investigators created full-length features of the “life history and evolution of mutational processes and driver mutation sequences.”
They found that early cancer development was marked by relatively few mutations in driver genes and by identifiable copy-number gains, including trisomy 7 in glioblastoma, and an abnormal mirroring of the arms (isochromosome) of chromosome 17 in medulloblastoma.
In 40% of the samples, however, there were significant changes in the mutational spectrum as the cancers grew, leading to a near quadrupling of driver genes and increased genomic instability in later-stage tumors.
“Copy-number alterations often occur in mitotic crises and lead to simultaneous gains of chromosomal segments,” the investigators wrote. “Timing analyses suggest that driver mutations often precede diagnosis by many years, if not decades. Together, these results determine the evolutionary trajectories of cancer and highlight opportunities for early cancer detection.”
Implications for cancer care
“When I used to treat patients with cancer, I was always completely amazed and puzzled by how two patients could have what looked like the same tumor. It would look the same under the microscope, have the same size, and the two patients would receive exactly the same treatment, but the two patients would have completely opposite outcomes; one would survive, and one would die. What this analysis … has done is really laid bare the reasons for that unpredictability in clinical outcomes,” Peter Campbell, MD, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Hinxton, England, said during the telebriefing.
“The most striking finding out of all of the suite of papers is just how different one person’s cancer genome is from another person’s. We see thousands of different combinations of mutations that can cause the cancer, and more than 80 different underlying processes generating the mutations in a cancer, and that leads to very different shapes and patterns in the genome that result,” he added.
On a positive note, the research shows that one or more driver mutations can be identified in about 95% of all cancer patients, and it elucidates the sequence of events leading to oncogenesis and tumor evolution, providing opportunities for earlier identification and potential interventions to prevent cancer, Dr. Campbell said.
The PCAWG was a collaborative multinational effort with multiple funding sources and many investigators.
SOURCE: Nature. 2020 Feb 5. https://www.nature.com/collections/pcawg/
A massive collaborative project spanning four continents and 744 research centers has revealed driver mutations in both protein-coding and noncoding regions of 38 cancer types.
The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) is an integrative analysis of the whole-genome sequences from 2,658 donors across 38 common tumor types. The findings are expected to add exponentially to what’s currently known about the complex genetics of cancer, and they point to possible strategies for improving cancer prevention, diagnosis, and care.
Six articles summarizing the findings are presented in a series of papers in Nature, and 16 more appear in affiliated publications.
“It’s humbling that it was only 14 years ago that the genomics community sequenced its very first cancer exome, and it was able to identify mutations within the roughly 20,000 protein-coding genes in the human cell,” investigator Lincoln Stein, MD, PhD, of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research in Toronto, said in a telephone briefing.
Exome sequencing, however, covers only protein-coding genomic regions, which constitute only about 1% of the entire genome, “so assembling an accurate portrait of the cancer genome using just the exome data is like trying to put together a 100,000-piece jigsaw puzzle when you’re missing 99% of the pieces and there’s no puzzle box with a completed picture to guide you,” Dr. Stein said.
Members of the PCAWG from centers in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia screened 2,658 whole-cancer genomes and matched samples of noncancerous tissues from the same individuals, along with 1,188 transcriptomes cataloging the sequences and expression of RNA transcripts in a given tumor. The 6-year project netted more than 800 terabytes of genomic data, roughly equivalent to the digital holdings of the U.S. Library of Congress multiplied by 11.
The findings are summarized in papers focusing on cancer drivers, noncoding changes, mutational signatures, structural variants, cancer evolution over time, and RNA alterations.
Driver mutations
Investigators found that the average cancer genome contains four or five driver mutations located in both coding and noncoding regions. They also found, however, that in approximately 5% of cases no driver mutations could be identified.
A substantial proportion of tumors displayed “hallmarks of genomic catastrophes.” About 22% of tumors exhibited chromothripsis, a mutational process marked by hundreds or even thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements. About 18% showed chromoplexy, which is characterized by scattering and rearrangement of multiple strands of DNA from one or more chromosomes.
Analyzing driver point mutations and structural variants in noncoding regions, the investigators found the usual suspects – previously reported culprits – as well as novel candidates.
For example, they identified point mutations in the five prime region of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and the three prime untranslated regions of NFKBIZ (a nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor) and TOB1 (an antiproliferative protein), focal deletion in BRD4 (a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator), and rearrangements in chromosomal loci in members of the AKR1C family of enzymes thought to play a role in disease progression.
In addition, investigators identified mutations in noncoding regions of TERT, a telomerase gene. These mutations result in ramped-up expression of telomerase, which in turn promotes uncontrollable division of tumor cells.
Mutational signatures
In a related line of research, PCAWG investigators identified new DNA mutational signatures ranging from single nucleotide polymorphisms to insertions and deletions, as well as to structural variants – rearrangements of large sections of the genome.
“The substantial size of our dataset, compared with previous analyses, enabled the discovery of new signatures, the separation of overlapping signatures, and the decomposition of signatures into components that may represent associated – but distinct – DNA damage, repair, and/or replication mechanisms. By estimating the contribution of each signature to the mutational catalogs of individual cancer genomes, we revealed associations of signatures to exogenous or endogenous exposures, as well as to defective DNA maintenance processes,” the investigators wrote.
They also acknowledged, however, that “many signatures are of unknown cause.”
Cancer evolution
One of the six main studies focused on the evolution of cancer over time. Instead of providing a “snapshot” of the genome as captured by sequencing tissue from a single biopsy, consortium investigators created full-length features of the “life history and evolution of mutational processes and driver mutation sequences.”
They found that early cancer development was marked by relatively few mutations in driver genes and by identifiable copy-number gains, including trisomy 7 in glioblastoma, and an abnormal mirroring of the arms (isochromosome) of chromosome 17 in medulloblastoma.
In 40% of the samples, however, there were significant changes in the mutational spectrum as the cancers grew, leading to a near quadrupling of driver genes and increased genomic instability in later-stage tumors.
“Copy-number alterations often occur in mitotic crises and lead to simultaneous gains of chromosomal segments,” the investigators wrote. “Timing analyses suggest that driver mutations often precede diagnosis by many years, if not decades. Together, these results determine the evolutionary trajectories of cancer and highlight opportunities for early cancer detection.”
Implications for cancer care
“When I used to treat patients with cancer, I was always completely amazed and puzzled by how two patients could have what looked like the same tumor. It would look the same under the microscope, have the same size, and the two patients would receive exactly the same treatment, but the two patients would have completely opposite outcomes; one would survive, and one would die. What this analysis … has done is really laid bare the reasons for that unpredictability in clinical outcomes,” Peter Campbell, MD, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Hinxton, England, said during the telebriefing.
“The most striking finding out of all of the suite of papers is just how different one person’s cancer genome is from another person’s. We see thousands of different combinations of mutations that can cause the cancer, and more than 80 different underlying processes generating the mutations in a cancer, and that leads to very different shapes and patterns in the genome that result,” he added.
On a positive note, the research shows that one or more driver mutations can be identified in about 95% of all cancer patients, and it elucidates the sequence of events leading to oncogenesis and tumor evolution, providing opportunities for earlier identification and potential interventions to prevent cancer, Dr. Campbell said.
The PCAWG was a collaborative multinational effort with multiple funding sources and many investigators.
SOURCE: Nature. 2020 Feb 5. https://www.nature.com/collections/pcawg/
FROM NATURE
FDA issues public health warning recommending against cesium salt usage
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a public health alert warning consumers to avoid the use of dietary supplements that contain cesium chloride or any other cesium salt because of significant safety risks.
Cesium salts are sometimes advertised as an alternative treatment for cancer, the FDA said in the announcement, but these salts have never proved to be safe or effective at treating cancer or any other disease. Clinical case reports and nonclinical trials have shown that cesium salts are associated with a variety of adverse events, including cardiac arrhythmias, hypokalemia, seizures, syncope, and death.
The FDA warned health care providers that cesium salts presented a significant safety risk in compounding drugs in July 2018.
Health care providers should not recommend dietary supplements containing cesium salts to their patients, the FDA said, and if a patient experiences an adverse event while taking a supplement containing cesium salt, the event should be reported to the agency.
While there are few dietary supplements on the market that contain cesium salt, consumers should be aware of the risks and avoid these products. The FDA noted that “if claims sound too good to be true, they probably are.”
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a public health alert warning consumers to avoid the use of dietary supplements that contain cesium chloride or any other cesium salt because of significant safety risks.
Cesium salts are sometimes advertised as an alternative treatment for cancer, the FDA said in the announcement, but these salts have never proved to be safe or effective at treating cancer or any other disease. Clinical case reports and nonclinical trials have shown that cesium salts are associated with a variety of adverse events, including cardiac arrhythmias, hypokalemia, seizures, syncope, and death.
The FDA warned health care providers that cesium salts presented a significant safety risk in compounding drugs in July 2018.
Health care providers should not recommend dietary supplements containing cesium salts to their patients, the FDA said, and if a patient experiences an adverse event while taking a supplement containing cesium salt, the event should be reported to the agency.
While there are few dietary supplements on the market that contain cesium salt, consumers should be aware of the risks and avoid these products. The FDA noted that “if claims sound too good to be true, they probably are.”
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a public health alert warning consumers to avoid the use of dietary supplements that contain cesium chloride or any other cesium salt because of significant safety risks.
Cesium salts are sometimes advertised as an alternative treatment for cancer, the FDA said in the announcement, but these salts have never proved to be safe or effective at treating cancer or any other disease. Clinical case reports and nonclinical trials have shown that cesium salts are associated with a variety of adverse events, including cardiac arrhythmias, hypokalemia, seizures, syncope, and death.
The FDA warned health care providers that cesium salts presented a significant safety risk in compounding drugs in July 2018.
Health care providers should not recommend dietary supplements containing cesium salts to their patients, the FDA said, and if a patient experiences an adverse event while taking a supplement containing cesium salt, the event should be reported to the agency.
While there are few dietary supplements on the market that contain cesium salt, consumers should be aware of the risks and avoid these products. The FDA noted that “if claims sound too good to be true, they probably are.”
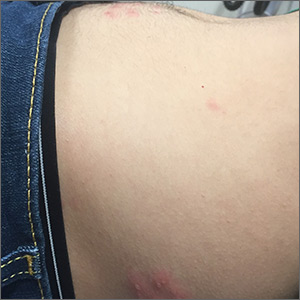
Abdominal rash
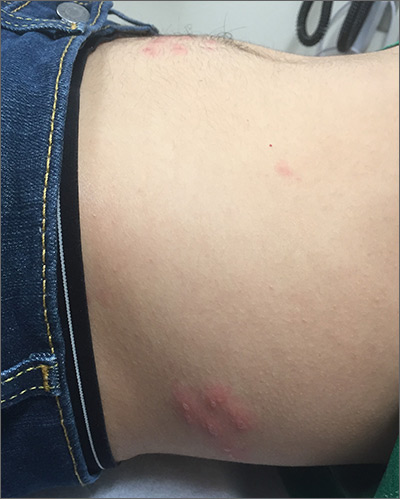
The pruritic prodrome, which evolved into painful vesicles, on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution was a classic presentation of herpes zoster.
Although herpes zoster is usually thought of as a disease that strikes older individuals, a study by Kawai et al found that of 8000 patients experiencing an outbreak, 43% were < 50 years of age. Additionally, this study found that the rate of herpes zoster infection had increased 4-fold in the past 60 years, and the rise had not been affected by the introduction of varicella vaccination. In Kawai’s series, 6.6% of the cases were in immunocompromised individuals.
In this case, the patient began antiviral therapy (Valacyclovir 1g tid for 7 days) to treat the active lesions. In further discussion with the patient, he indicated that he was concerned he might have an underlying undiagnosed autoimmune condition or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. His provider completed routine health care maintenance recommendations including an HIV screen, which was negative. Since he was otherwise asymptomatic, with no history of recurrent infections, no additional testing was warranted. However, since the patient worked with immunocompromised patients at a local hospital, he was placed on medical leave (per the facility’s protocol) until the lesions had crusted over. By Day 10, his lesions had crusted over and he returned to work.
Text courtesy of Brent Gillespie, PAC, University of New Mexico. Photo and editing courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Kawai K, Yawn BP, Wollan P, et al. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster over a 60-year period from a population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:221-226.

The pruritic prodrome, which evolved into painful vesicles, on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution was a classic presentation of herpes zoster.
Although herpes zoster is usually thought of as a disease that strikes older individuals, a study by Kawai et al found that of 8000 patients experiencing an outbreak, 43% were < 50 years of age. Additionally, this study found that the rate of herpes zoster infection had increased 4-fold in the past 60 years, and the rise had not been affected by the introduction of varicella vaccination. In Kawai’s series, 6.6% of the cases were in immunocompromised individuals.
In this case, the patient began antiviral therapy (Valacyclovir 1g tid for 7 days) to treat the active lesions. In further discussion with the patient, he indicated that he was concerned he might have an underlying undiagnosed autoimmune condition or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. His provider completed routine health care maintenance recommendations including an HIV screen, which was negative. Since he was otherwise asymptomatic, with no history of recurrent infections, no additional testing was warranted. However, since the patient worked with immunocompromised patients at a local hospital, he was placed on medical leave (per the facility’s protocol) until the lesions had crusted over. By Day 10, his lesions had crusted over and he returned to work.
Text courtesy of Brent Gillespie, PAC, University of New Mexico. Photo and editing courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The pruritic prodrome, which evolved into painful vesicles, on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution was a classic presentation of herpes zoster.
Although herpes zoster is usually thought of as a disease that strikes older individuals, a study by Kawai et al found that of 8000 patients experiencing an outbreak, 43% were < 50 years of age. Additionally, this study found that the rate of herpes zoster infection had increased 4-fold in the past 60 years, and the rise had not been affected by the introduction of varicella vaccination. In Kawai’s series, 6.6% of the cases were in immunocompromised individuals.
In this case, the patient began antiviral therapy (Valacyclovir 1g tid for 7 days) to treat the active lesions. In further discussion with the patient, he indicated that he was concerned he might have an underlying undiagnosed autoimmune condition or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. His provider completed routine health care maintenance recommendations including an HIV screen, which was negative. Since he was otherwise asymptomatic, with no history of recurrent infections, no additional testing was warranted. However, since the patient worked with immunocompromised patients at a local hospital, he was placed on medical leave (per the facility’s protocol) until the lesions had crusted over. By Day 10, his lesions had crusted over and he returned to work.
Text courtesy of Brent Gillespie, PAC, University of New Mexico. Photo and editing courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Kawai K, Yawn BP, Wollan P, et al. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster over a 60-year period from a population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:221-226.
Kawai K, Yawn BP, Wollan P, et al. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster over a 60-year period from a population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:221-226.
Circulating tumor cells at baseline predict recurrence in stage III melanoma
Patients with stage III melanoma who have circulating tumor cells (CTCs) at baseline may benefit from adjuvant therapy, according to investigators.
A prospective study showed that patients with at least one CTC upon first presentation had increased risks of both short-term and long-term recurrence, reported lead author Anthony Lucci, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues.
While previous studies have suggested that CTCs hold prognostic value for melanoma patients, no trials had evaluated the CellSearch CTC Test – a standardized technique approved by the Food and Drug Administration – in patients with stage III disease, the investigators wrote. Their report is in Clinical Cancer Research.
In the present study, the investigators tested the CellSearch system in 243 patients with stage III cutaneous melanoma who were treated at MD Anderson Cancer Center. Patients with uveal or mucosal melanoma, or distant metastatic disease, were excluded.
Baseline blood samples were drawn within 3 months of regional lymph node metastasis, determined by either lymphadenectomy or sentinel lymph node biopsy. CTC assay positivity required that at least one CTC was detected within a single 7.5 mL tube of blood.
Out of 243 patients, 90 (37%) had a positive test. Of these 90 patients, almost one-quarter (23%) relapsed within 6 months, compared with 8% of patients who had a negative CTC assay. Within the full follow-up period, which was as long as 64 months, 48% of patients with CTCs at baseline relapsed, compared with 37% of patients without CTCs.
Multivariable regression analysis, which was adjusted for age, sex, pathological nodal stage, Breslow thickness, ulceration, and lymphovascular invasion, showed that baseline CTC positivity was an independent risk factor for melanoma recurrence, both in the short term and the long term. Compared with patients who lacked CTCs, those who tested positive were three times as likely to have disease recurrence within 6 months (hazard ratio, 3.13; P = .018). For relapse-free survival within 54 months, this hazard ratio decreased to 2.25 (P = .006).
Although a Cochran-Armitage test suggested that recurrence risks increased with CTC count, the investigators noted that a minority of patients (17%) had two or more CTCs, and just 5% had three or more CTCs.
According to the investigators, CTCs at baseline could become the first reliable blood-based biomarker for this patient population.
“[CTCs] clearly identified a group of stage III patients at high risk for relapse,” the investigators wrote. “This would be clinically very significant as an independent risk factor to help identify the stage III patients who would benefit most from adjuvant systemic therapy.”
This study was funded by the Kiefer family, Sheila Prenowitz, the Simon and Linda Eyles Foundation, the Sam and Janna Moore family, and the Wintermann Foundation. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lucci et al. Clin Cancer Res. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2670.
Patients with stage III melanoma who have circulating tumor cells (CTCs) at baseline may benefit from adjuvant therapy, according to investigators.
A prospective study showed that patients with at least one CTC upon first presentation had increased risks of both short-term and long-term recurrence, reported lead author Anthony Lucci, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues.
While previous studies have suggested that CTCs hold prognostic value for melanoma patients, no trials had evaluated the CellSearch CTC Test – a standardized technique approved by the Food and Drug Administration – in patients with stage III disease, the investigators wrote. Their report is in Clinical Cancer Research.
In the present study, the investigators tested the CellSearch system in 243 patients with stage III cutaneous melanoma who were treated at MD Anderson Cancer Center. Patients with uveal or mucosal melanoma, or distant metastatic disease, were excluded.
Baseline blood samples were drawn within 3 months of regional lymph node metastasis, determined by either lymphadenectomy or sentinel lymph node biopsy. CTC assay positivity required that at least one CTC was detected within a single 7.5 mL tube of blood.
Out of 243 patients, 90 (37%) had a positive test. Of these 90 patients, almost one-quarter (23%) relapsed within 6 months, compared with 8% of patients who had a negative CTC assay. Within the full follow-up period, which was as long as 64 months, 48% of patients with CTCs at baseline relapsed, compared with 37% of patients without CTCs.
Multivariable regression analysis, which was adjusted for age, sex, pathological nodal stage, Breslow thickness, ulceration, and lymphovascular invasion, showed that baseline CTC positivity was an independent risk factor for melanoma recurrence, both in the short term and the long term. Compared with patients who lacked CTCs, those who tested positive were three times as likely to have disease recurrence within 6 months (hazard ratio, 3.13; P = .018). For relapse-free survival within 54 months, this hazard ratio decreased to 2.25 (P = .006).
Although a Cochran-Armitage test suggested that recurrence risks increased with CTC count, the investigators noted that a minority of patients (17%) had two or more CTCs, and just 5% had three or more CTCs.
According to the investigators, CTCs at baseline could become the first reliable blood-based biomarker for this patient population.
“[CTCs] clearly identified a group of stage III patients at high risk for relapse,” the investigators wrote. “This would be clinically very significant as an independent risk factor to help identify the stage III patients who would benefit most from adjuvant systemic therapy.”
This study was funded by the Kiefer family, Sheila Prenowitz, the Simon and Linda Eyles Foundation, the Sam and Janna Moore family, and the Wintermann Foundation. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lucci et al. Clin Cancer Res. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2670.
Patients with stage III melanoma who have circulating tumor cells (CTCs) at baseline may benefit from adjuvant therapy, according to investigators.
A prospective study showed that patients with at least one CTC upon first presentation had increased risks of both short-term and long-term recurrence, reported lead author Anthony Lucci, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues.
While previous studies have suggested that CTCs hold prognostic value for melanoma patients, no trials had evaluated the CellSearch CTC Test – a standardized technique approved by the Food and Drug Administration – in patients with stage III disease, the investigators wrote. Their report is in Clinical Cancer Research.
In the present study, the investigators tested the CellSearch system in 243 patients with stage III cutaneous melanoma who were treated at MD Anderson Cancer Center. Patients with uveal or mucosal melanoma, or distant metastatic disease, were excluded.
Baseline blood samples were drawn within 3 months of regional lymph node metastasis, determined by either lymphadenectomy or sentinel lymph node biopsy. CTC assay positivity required that at least one CTC was detected within a single 7.5 mL tube of blood.
Out of 243 patients, 90 (37%) had a positive test. Of these 90 patients, almost one-quarter (23%) relapsed within 6 months, compared with 8% of patients who had a negative CTC assay. Within the full follow-up period, which was as long as 64 months, 48% of patients with CTCs at baseline relapsed, compared with 37% of patients without CTCs.
Multivariable regression analysis, which was adjusted for age, sex, pathological nodal stage, Breslow thickness, ulceration, and lymphovascular invasion, showed that baseline CTC positivity was an independent risk factor for melanoma recurrence, both in the short term and the long term. Compared with patients who lacked CTCs, those who tested positive were three times as likely to have disease recurrence within 6 months (hazard ratio, 3.13; P = .018). For relapse-free survival within 54 months, this hazard ratio decreased to 2.25 (P = .006).
Although a Cochran-Armitage test suggested that recurrence risks increased with CTC count, the investigators noted that a minority of patients (17%) had two or more CTCs, and just 5% had three or more CTCs.
According to the investigators, CTCs at baseline could become the first reliable blood-based biomarker for this patient population.
“[CTCs] clearly identified a group of stage III patients at high risk for relapse,” the investigators wrote. “This would be clinically very significant as an independent risk factor to help identify the stage III patients who would benefit most from adjuvant systemic therapy.”
This study was funded by the Kiefer family, Sheila Prenowitz, the Simon and Linda Eyles Foundation, the Sam and Janna Moore family, and the Wintermann Foundation. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lucci et al. Clin Cancer Res. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2670.
FROM CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
Is primary care relevant?
You probably still remember your pediatrician. Your relationship with her may have influenced your decision to become a physician. She was your parents’ go-to source for pretty much anything to do with your health. You had a primary care physician in large part because your parents felt that children were particularly vulnerable to disease and wanted to avoid any missteps on your road to maturity. On the other hand, while you were growing up your parents probably were much less concerned about their own health. Their peers and friends seemed healthy enough; why would they need annual checkups? Your folks made sure they had life insurance because accidental death and injury felt like more pressing concerns. If they had a primary physician, they may have visited him infrequently. They may have been more likely to visit their dentist, in part because the office put a strong emphasis on the value of preventive care.
A recent survey from Harvard Medical School, Boston, determined that, in 2015, 75% of adult Americans had an established source of primary care. (“Fewer Americans are getting primary care,” Jake Miller, the Harvard Gazette, Dec. 16, 2019). This number sounds pretty good and not unexpected until you learn that in 2002 that number was 77%. While 2% seems like a drop in the bucket, remember we live in a very populous bucket, and that 2% translates to millions fewer Americans who are not receiving primary care than did more than a decade ago.
While the researchers don’t have data to explain the decline in primary care, they suggest raising the pay of primary care physicians, incentivizing rural practice, and making health insurance more available and affordable as solutions. Of course these recommendations are not surprising. We’ve heard them before. More supply might translate into more usage. But could some of the decline in primary care be because it no longer feels relevant to a population that has become accustomed to instant gratification? One click and the thing you didn’t feel like waiting for in line today is on your doorstep tomorrow, or even sooner.
If we want to create meaningful change, we need to learn a thing or two about marketing from the competition and from the successful businesses who are shaping consumer behavior. It’s not surprising that, when people feel healthy (whether they are or not), they will devalue primary care. But if they sprain an ankle or have a cough that is keeping them up at night, they would like some medical attention ... now. And that will drive them away from primary care toward sources of fragmented care – the doc-in-the-box, the walk-in clinic, or even more unfortunately to the local emergency department.
If we want more people to establish relationships with primary care providers, we need to welcome them in the door ... when they feel a need. Once in the door we can establish rapport and show them there is a value to primary care while they are feeling grateful for the prompt attention we gave them. But too many primary care practices are shunting potential patients into fragmented care by appearing unwelcome to minor emergencies and by creating customer-unfriendly communication networks. Most people I know would be happy to go back to the old days of “take two aspirin and call me in the morning” primary care. At least you had talked to a doctor in real time, and you knew that he or she would see you the next day if you still had a problem.
You may think I’ve suddenly gone utopian. But there are ways to run a practice that welcomes patients with minor complaints on short notice. It requires some flexibility, some willingness to work longer on some days, and being more efficient.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
You probably still remember your pediatrician. Your relationship with her may have influenced your decision to become a physician. She was your parents’ go-to source for pretty much anything to do with your health. You had a primary care physician in large part because your parents felt that children were particularly vulnerable to disease and wanted to avoid any missteps on your road to maturity. On the other hand, while you were growing up your parents probably were much less concerned about their own health. Their peers and friends seemed healthy enough; why would they need annual checkups? Your folks made sure they had life insurance because accidental death and injury felt like more pressing concerns. If they had a primary physician, they may have visited him infrequently. They may have been more likely to visit their dentist, in part because the office put a strong emphasis on the value of preventive care.
A recent survey from Harvard Medical School, Boston, determined that, in 2015, 75% of adult Americans had an established source of primary care. (“Fewer Americans are getting primary care,” Jake Miller, the Harvard Gazette, Dec. 16, 2019). This number sounds pretty good and not unexpected until you learn that in 2002 that number was 77%. While 2% seems like a drop in the bucket, remember we live in a very populous bucket, and that 2% translates to millions fewer Americans who are not receiving primary care than did more than a decade ago.
While the researchers don’t have data to explain the decline in primary care, they suggest raising the pay of primary care physicians, incentivizing rural practice, and making health insurance more available and affordable as solutions. Of course these recommendations are not surprising. We’ve heard them before. More supply might translate into more usage. But could some of the decline in primary care be because it no longer feels relevant to a population that has become accustomed to instant gratification? One click and the thing you didn’t feel like waiting for in line today is on your doorstep tomorrow, or even sooner.
If we want to create meaningful change, we need to learn a thing or two about marketing from the competition and from the successful businesses who are shaping consumer behavior. It’s not surprising that, when people feel healthy (whether they are or not), they will devalue primary care. But if they sprain an ankle or have a cough that is keeping them up at night, they would like some medical attention ... now. And that will drive them away from primary care toward sources of fragmented care – the doc-in-the-box, the walk-in clinic, or even more unfortunately to the local emergency department.
If we want more people to establish relationships with primary care providers, we need to welcome them in the door ... when they feel a need. Once in the door we can establish rapport and show them there is a value to primary care while they are feeling grateful for the prompt attention we gave them. But too many primary care practices are shunting potential patients into fragmented care by appearing unwelcome to minor emergencies and by creating customer-unfriendly communication networks. Most people I know would be happy to go back to the old days of “take two aspirin and call me in the morning” primary care. At least you had talked to a doctor in real time, and you knew that he or she would see you the next day if you still had a problem.
You may think I’ve suddenly gone utopian. But there are ways to run a practice that welcomes patients with minor complaints on short notice. It requires some flexibility, some willingness to work longer on some days, and being more efficient.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
You probably still remember your pediatrician. Your relationship with her may have influenced your decision to become a physician. She was your parents’ go-to source for pretty much anything to do with your health. You had a primary care physician in large part because your parents felt that children were particularly vulnerable to disease and wanted to avoid any missteps on your road to maturity. On the other hand, while you were growing up your parents probably were much less concerned about their own health. Their peers and friends seemed healthy enough; why would they need annual checkups? Your folks made sure they had life insurance because accidental death and injury felt like more pressing concerns. If they had a primary physician, they may have visited him infrequently. They may have been more likely to visit their dentist, in part because the office put a strong emphasis on the value of preventive care.
A recent survey from Harvard Medical School, Boston, determined that, in 2015, 75% of adult Americans had an established source of primary care. (“Fewer Americans are getting primary care,” Jake Miller, the Harvard Gazette, Dec. 16, 2019). This number sounds pretty good and not unexpected until you learn that in 2002 that number was 77%. While 2% seems like a drop in the bucket, remember we live in a very populous bucket, and that 2% translates to millions fewer Americans who are not receiving primary care than did more than a decade ago.
While the researchers don’t have data to explain the decline in primary care, they suggest raising the pay of primary care physicians, incentivizing rural practice, and making health insurance more available and affordable as solutions. Of course these recommendations are not surprising. We’ve heard them before. More supply might translate into more usage. But could some of the decline in primary care be because it no longer feels relevant to a population that has become accustomed to instant gratification? One click and the thing you didn’t feel like waiting for in line today is on your doorstep tomorrow, or even sooner.
If we want to create meaningful change, we need to learn a thing or two about marketing from the competition and from the successful businesses who are shaping consumer behavior. It’s not surprising that, when people feel healthy (whether they are or not), they will devalue primary care. But if they sprain an ankle or have a cough that is keeping them up at night, they would like some medical attention ... now. And that will drive them away from primary care toward sources of fragmented care – the doc-in-the-box, the walk-in clinic, or even more unfortunately to the local emergency department.
If we want more people to establish relationships with primary care providers, we need to welcome them in the door ... when they feel a need. Once in the door we can establish rapport and show them there is a value to primary care while they are feeling grateful for the prompt attention we gave them. But too many primary care practices are shunting potential patients into fragmented care by appearing unwelcome to minor emergencies and by creating customer-unfriendly communication networks. Most people I know would be happy to go back to the old days of “take two aspirin and call me in the morning” primary care. At least you had talked to a doctor in real time, and you knew that he or she would see you the next day if you still had a problem.
You may think I’ve suddenly gone utopian. But there are ways to run a practice that welcomes patients with minor complaints on short notice. It requires some flexibility, some willingness to work longer on some days, and being more efficient.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
The 2019 novel coronavirus: Case review IDs clinical characteristics
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
FROM THE LANCET
World Cancer Day survey exposes ‘glaring inequities’
The first international public survey on cancer perceptions and attitudes in a decade shows that, in spite of progress, low socioeconomic status and lack of education continue to jeopardize the health of the world’s most vulnerable populations.
The survey was commissioned by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) to mark the 20th anniversary of World Cancer Day on Feb. 4, 2020.
The survey, which was conducted by Ipsos, was taken by more than 15,000 people in 20 countries. It shows that people of lower socioeconomic status are less likely than those in higher-income households to recognize the risk factors for cancer or to make lifestyle changes. With the exception of tobacco use, people with low educational attainment also showed less cancer awareness and were less likely to engage in preventive behaviors than those with a university degree.
It is “unacceptable that millions of people have a greater chance of developing cancer in their lifetime because they are simply not aware of the cancer risks to avoid and the healthy behaviors to adopt – information that many of us take for granted. And this is true around the world,” Cary Adams, MBA, CEO of the UICC, commented in a statement.
The survey was conducted from Oct. 25 to Nov., 2019, and included 15,427 participants from Australia, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Great Britain, India, Israel, Japan, Kenya, Mexico, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, and the United States.
The vast majority of those surveyed – 87% – said they were aware of the major risk factors for cancer, while only 6% said they were not.
The cancer risk factors that were most recognized were tobacco use (63%), ultraviolet light exposure (54%), and exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke (50%).
The cancer risks that were least recognized included being overweight (29%), a lack of exercise (28%), and exposure to certain viruses or bacteria (28%).
The difference in awareness across the social spectrum was striking. “Emerging from the survey are the apparent and glaring inequities faced by socioeconomically disadvantaged groups,” the authors said.
“Much more must be done to ensure that everyone has an equal chance to reduce their risk of preventable cancer,” commented Sonali Johnson, PhD, head of knowledge, advocacy, and policy at the UICC in Geneva, Switzerland.
“We’ve seen in the results that those surveyed with a lower education and those on lower incomes appear less aware of the main risk factors associated with cancer and thus are less likely to proactively take the steps needed to reduce their cancer risk as compared to those from a high income household or those with a university education,” Dr. Johnson said in an interview.
Does increased cancer awareness translate into behavioral change for the better? This question can only be answered by more research, the survey authors said. They reported that 7 of 10 survey respondents (69%) said they had made a behavioral change to reduce their cancer risk within the past 12 months. Most said they were eating more healthfully.
Slightly fewer than one-quarter reported that they had not taken any preventive measures in the past year.
When it comes to raising cancer awareness, World Cancer Day is “a powerful tool to remind every person that they can play a crucial role in reducing the impact of cancer,” said Dr. Johnson.
Health care providers are “crucial”
Reacting to the findings of the survey, the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) emphasized the key role that physicians play in cancer prevention.
“Research speaks very clearly for prevention,” said ESMO President Solange Peters, MD, PhD. “With the number of cancer cases expected to rise to 29.5 million by 2040, we must act now. ESMO is committed to educating doctors on all aspects of cancer control, which should begin well before a cancer diagnosis.
“In the face of this emergency, which is rendered even more salient by the results of the report, we must work to enlarge the basis of doctors who are properly educated and trained in key prevention measures,” Dr. Peters added. “General practitioners and organ specialists are in the front line to guide and support patients on their quest for healthy lifestyles and reliable ways to detect cancer early.”
In a comment, Dr. Johnson acknowledged the role physicians play in health promotion and informing patients about noncommunicable disease risks, including those related to cancer. However, she emphasized that nurses, pharmacists, community health workers, midwives, and other health care providers who deliver primary care “are crucial around the world to imparting health information and offering services.”
Frontline health care workers can assess patients’ cancer knowledge and health literacy, determine the barriers to health care, and assess “how best to engage with people across the life course,” Dr. Johnson explained. “Rather than just focusing on physicians, we must work with all those involved in primary care, especially as primary care services are scaled up to achieve universal health coverage.”
Call on governments to do more
The authors noted that, although there is wide awareness of the cancer risks from tobacco use, adults younger than 35 years were less likely than those older than 50 to identify tobacco as a cancer risk factor. They described this finding as “most concerning” and said it “underscores the ongoing need to raise awareness about cancer risk factors in every new generation.”
Almost 60% of survey respondents, regardless of age, education, or income, expressed concern about being diagnosed with cancer in the future or having cancer recur.
In Kenya, where the death toll from cancer rose 30% from 2014 to 2018, people appeared to be the most worried about cancer, with four of five survey respondents (82%) expressing concern.
Survey respondents from Saudi Arabia appeared the least concerned, with one of three people saying they were worried.
Notably, 84% of survey respondents said that governments should be doing more to increase cancer prevention and awareness; 33% demanded that governments improve the affordability of cancer care.
“It is understandable that people turn to their governments for support,” Dr. Johnson commented. “Affordability is a big challenge for low-income settings.”
Data from the World Health Organization show that, for every U.S. $1 invested in low- and middle-income countries, the return is U.S. $3.20, Johnson pointed out. “We really need to convince decision makers ... and see the right investments being made. It is important to ensure that the health system strengthening takes place in tandem with prevention services.”
Governments have begun making commitments to tackle noncommunicable diseases and cancer, Dr. Johnson commented. He highlighted the WHO’s Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All and the updated cancer resolution adopted at the 2017 World Health Assembly.
“Education, training, and awareness-raising efforts need to be backed by strong and progressive health policies that prioritize prevention and help reduce the consumption of known cancer-causing products such as tobacco, sugary food, and beverages,” she said. “Countries should also invest proactively in national cancer control planning and the establishment of population-based registries to ensure the most effective resource allocation that benefits all groups.”
Up-to-date information on cancer risks and cancer prevention must be delivered to the public in ways that are accessible to those in lower socioeconomic groups, Dr. Johnson added. “Awareness needs to be raised continuously with each new generation,” she noted.
The UICC has relationships with Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Diaceutics, MSD Inventing for Life, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CUBEBIO, the Icon Group, Roche, and Sanofi.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first international public survey on cancer perceptions and attitudes in a decade shows that, in spite of progress, low socioeconomic status and lack of education continue to jeopardize the health of the world’s most vulnerable populations.
The survey was commissioned by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) to mark the 20th anniversary of World Cancer Day on Feb. 4, 2020.
The survey, which was conducted by Ipsos, was taken by more than 15,000 people in 20 countries. It shows that people of lower socioeconomic status are less likely than those in higher-income households to recognize the risk factors for cancer or to make lifestyle changes. With the exception of tobacco use, people with low educational attainment also showed less cancer awareness and were less likely to engage in preventive behaviors than those with a university degree.
It is “unacceptable that millions of people have a greater chance of developing cancer in their lifetime because they are simply not aware of the cancer risks to avoid and the healthy behaviors to adopt – information that many of us take for granted. And this is true around the world,” Cary Adams, MBA, CEO of the UICC, commented in a statement.
The survey was conducted from Oct. 25 to Nov., 2019, and included 15,427 participants from Australia, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Great Britain, India, Israel, Japan, Kenya, Mexico, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, and the United States.
The vast majority of those surveyed – 87% – said they were aware of the major risk factors for cancer, while only 6% said they were not.
The cancer risk factors that were most recognized were tobacco use (63%), ultraviolet light exposure (54%), and exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke (50%).
The cancer risks that were least recognized included being overweight (29%), a lack of exercise (28%), and exposure to certain viruses or bacteria (28%).
The difference in awareness across the social spectrum was striking. “Emerging from the survey are the apparent and glaring inequities faced by socioeconomically disadvantaged groups,” the authors said.
“Much more must be done to ensure that everyone has an equal chance to reduce their risk of preventable cancer,” commented Sonali Johnson, PhD, head of knowledge, advocacy, and policy at the UICC in Geneva, Switzerland.
“We’ve seen in the results that those surveyed with a lower education and those on lower incomes appear less aware of the main risk factors associated with cancer and thus are less likely to proactively take the steps needed to reduce their cancer risk as compared to those from a high income household or those with a university education,” Dr. Johnson said in an interview.
Does increased cancer awareness translate into behavioral change for the better? This question can only be answered by more research, the survey authors said. They reported that 7 of 10 survey respondents (69%) said they had made a behavioral change to reduce their cancer risk within the past 12 months. Most said they were eating more healthfully.
Slightly fewer than one-quarter reported that they had not taken any preventive measures in the past year.
When it comes to raising cancer awareness, World Cancer Day is “a powerful tool to remind every person that they can play a crucial role in reducing the impact of cancer,” said Dr. Johnson.
Health care providers are “crucial”
Reacting to the findings of the survey, the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) emphasized the key role that physicians play in cancer prevention.
“Research speaks very clearly for prevention,” said ESMO President Solange Peters, MD, PhD. “With the number of cancer cases expected to rise to 29.5 million by 2040, we must act now. ESMO is committed to educating doctors on all aspects of cancer control, which should begin well before a cancer diagnosis.
“In the face of this emergency, which is rendered even more salient by the results of the report, we must work to enlarge the basis of doctors who are properly educated and trained in key prevention measures,” Dr. Peters added. “General practitioners and organ specialists are in the front line to guide and support patients on their quest for healthy lifestyles and reliable ways to detect cancer early.”
In a comment, Dr. Johnson acknowledged the role physicians play in health promotion and informing patients about noncommunicable disease risks, including those related to cancer. However, she emphasized that nurses, pharmacists, community health workers, midwives, and other health care providers who deliver primary care “are crucial around the world to imparting health information and offering services.”
Frontline health care workers can assess patients’ cancer knowledge and health literacy, determine the barriers to health care, and assess “how best to engage with people across the life course,” Dr. Johnson explained. “Rather than just focusing on physicians, we must work with all those involved in primary care, especially as primary care services are scaled up to achieve universal health coverage.”
Call on governments to do more
The authors noted that, although there is wide awareness of the cancer risks from tobacco use, adults younger than 35 years were less likely than those older than 50 to identify tobacco as a cancer risk factor. They described this finding as “most concerning” and said it “underscores the ongoing need to raise awareness about cancer risk factors in every new generation.”
Almost 60% of survey respondents, regardless of age, education, or income, expressed concern about being diagnosed with cancer in the future or having cancer recur.
In Kenya, where the death toll from cancer rose 30% from 2014 to 2018, people appeared to be the most worried about cancer, with four of five survey respondents (82%) expressing concern.
Survey respondents from Saudi Arabia appeared the least concerned, with one of three people saying they were worried.
Notably, 84% of survey respondents said that governments should be doing more to increase cancer prevention and awareness; 33% demanded that governments improve the affordability of cancer care.
“It is understandable that people turn to their governments for support,” Dr. Johnson commented. “Affordability is a big challenge for low-income settings.”
Data from the World Health Organization show that, for every U.S. $1 invested in low- and middle-income countries, the return is U.S. $3.20, Johnson pointed out. “We really need to convince decision makers ... and see the right investments being made. It is important to ensure that the health system strengthening takes place in tandem with prevention services.”
Governments have begun making commitments to tackle noncommunicable diseases and cancer, Dr. Johnson commented. He highlighted the WHO’s Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All and the updated cancer resolution adopted at the 2017 World Health Assembly.
“Education, training, and awareness-raising efforts need to be backed by strong and progressive health policies that prioritize prevention and help reduce the consumption of known cancer-causing products such as tobacco, sugary food, and beverages,” she said. “Countries should also invest proactively in national cancer control planning and the establishment of population-based registries to ensure the most effective resource allocation that benefits all groups.”
Up-to-date information on cancer risks and cancer prevention must be delivered to the public in ways that are accessible to those in lower socioeconomic groups, Dr. Johnson added. “Awareness needs to be raised continuously with each new generation,” she noted.
The UICC has relationships with Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Diaceutics, MSD Inventing for Life, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CUBEBIO, the Icon Group, Roche, and Sanofi.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first international public survey on cancer perceptions and attitudes in a decade shows that, in spite of progress, low socioeconomic status and lack of education continue to jeopardize the health of the world’s most vulnerable populations.
The survey was commissioned by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) to mark the 20th anniversary of World Cancer Day on Feb. 4, 2020.
The survey, which was conducted by Ipsos, was taken by more than 15,000 people in 20 countries. It shows that people of lower socioeconomic status are less likely than those in higher-income households to recognize the risk factors for cancer or to make lifestyle changes. With the exception of tobacco use, people with low educational attainment also showed less cancer awareness and were less likely to engage in preventive behaviors than those with a university degree.
It is “unacceptable that millions of people have a greater chance of developing cancer in their lifetime because they are simply not aware of the cancer risks to avoid and the healthy behaviors to adopt – information that many of us take for granted. And this is true around the world,” Cary Adams, MBA, CEO of the UICC, commented in a statement.
The survey was conducted from Oct. 25 to Nov., 2019, and included 15,427 participants from Australia, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Great Britain, India, Israel, Japan, Kenya, Mexico, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, and the United States.
The vast majority of those surveyed – 87% – said they were aware of the major risk factors for cancer, while only 6% said they were not.
The cancer risk factors that were most recognized were tobacco use (63%), ultraviolet light exposure (54%), and exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke (50%).
The cancer risks that were least recognized included being overweight (29%), a lack of exercise (28%), and exposure to certain viruses or bacteria (28%).
The difference in awareness across the social spectrum was striking. “Emerging from the survey are the apparent and glaring inequities faced by socioeconomically disadvantaged groups,” the authors said.
“Much more must be done to ensure that everyone has an equal chance to reduce their risk of preventable cancer,” commented Sonali Johnson, PhD, head of knowledge, advocacy, and policy at the UICC in Geneva, Switzerland.
“We’ve seen in the results that those surveyed with a lower education and those on lower incomes appear less aware of the main risk factors associated with cancer and thus are less likely to proactively take the steps needed to reduce their cancer risk as compared to those from a high income household or those with a university education,” Dr. Johnson said in an interview.
Does increased cancer awareness translate into behavioral change for the better? This question can only be answered by more research, the survey authors said. They reported that 7 of 10 survey respondents (69%) said they had made a behavioral change to reduce their cancer risk within the past 12 months. Most said they were eating more healthfully.
Slightly fewer than one-quarter reported that they had not taken any preventive measures in the past year.
When it comes to raising cancer awareness, World Cancer Day is “a powerful tool to remind every person that they can play a crucial role in reducing the impact of cancer,” said Dr. Johnson.
Health care providers are “crucial”
Reacting to the findings of the survey, the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) emphasized the key role that physicians play in cancer prevention.
“Research speaks very clearly for prevention,” said ESMO President Solange Peters, MD, PhD. “With the number of cancer cases expected to rise to 29.5 million by 2040, we must act now. ESMO is committed to educating doctors on all aspects of cancer control, which should begin well before a cancer diagnosis.
“In the face of this emergency, which is rendered even more salient by the results of the report, we must work to enlarge the basis of doctors who are properly educated and trained in key prevention measures,” Dr. Peters added. “General practitioners and organ specialists are in the front line to guide and support patients on their quest for healthy lifestyles and reliable ways to detect cancer early.”
In a comment, Dr. Johnson acknowledged the role physicians play in health promotion and informing patients about noncommunicable disease risks, including those related to cancer. However, she emphasized that nurses, pharmacists, community health workers, midwives, and other health care providers who deliver primary care “are crucial around the world to imparting health information and offering services.”
Frontline health care workers can assess patients’ cancer knowledge and health literacy, determine the barriers to health care, and assess “how best to engage with people across the life course,” Dr. Johnson explained. “Rather than just focusing on physicians, we must work with all those involved in primary care, especially as primary care services are scaled up to achieve universal health coverage.”
Call on governments to do more
The authors noted that, although there is wide awareness of the cancer risks from tobacco use, adults younger than 35 years were less likely than those older than 50 to identify tobacco as a cancer risk factor. They described this finding as “most concerning” and said it “underscores the ongoing need to raise awareness about cancer risk factors in every new generation.”
Almost 60% of survey respondents, regardless of age, education, or income, expressed concern about being diagnosed with cancer in the future or having cancer recur.
In Kenya, where the death toll from cancer rose 30% from 2014 to 2018, people appeared to be the most worried about cancer, with four of five survey respondents (82%) expressing concern.
Survey respondents from Saudi Arabia appeared the least concerned, with one of three people saying they were worried.
Notably, 84% of survey respondents said that governments should be doing more to increase cancer prevention and awareness; 33% demanded that governments improve the affordability of cancer care.
“It is understandable that people turn to their governments for support,” Dr. Johnson commented. “Affordability is a big challenge for low-income settings.”
Data from the World Health Organization show that, for every U.S. $1 invested in low- and middle-income countries, the return is U.S. $3.20, Johnson pointed out. “We really need to convince decision makers ... and see the right investments being made. It is important to ensure that the health system strengthening takes place in tandem with prevention services.”
Governments have begun making commitments to tackle noncommunicable diseases and cancer, Dr. Johnson commented. He highlighted the WHO’s Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All and the updated cancer resolution adopted at the 2017 World Health Assembly.
“Education, training, and awareness-raising efforts need to be backed by strong and progressive health policies that prioritize prevention and help reduce the consumption of known cancer-causing products such as tobacco, sugary food, and beverages,” she said. “Countries should also invest proactively in national cancer control planning and the establishment of population-based registries to ensure the most effective resource allocation that benefits all groups.”
Up-to-date information on cancer risks and cancer prevention must be delivered to the public in ways that are accessible to those in lower socioeconomic groups, Dr. Johnson added. “Awareness needs to be raised continuously with each new generation,” she noted.
The UICC has relationships with Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Diaceutics, MSD Inventing for Life, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CUBEBIO, the Icon Group, Roche, and Sanofi.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How much exercise is needed for maximum heart benefit?
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Physical activity is potent medicine, and it doesn’t take all that much of it to derive the maximum cardiovascular benefit: namely, the equivalent of a brisk hour-long walk 5 days/week or jogging at a 10-minute-per-mile pace for half an hour twice weekly, Robert A. Vogel, MD, asserted at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“I’m not telling you to run marathons. said Dr. Vogel, a cardiologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, with a longstanding interest in preventive cardiology.
He presented selected highlights from the massive evidence base underlying the recommendations put forth in the current comprehensive U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
One particularly compelling chunk of evidence comes from a Taiwanese government–funded prospective cohort study of more than 416,000 individuals followed for an average of 8 years. A key finding: 15 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity daily was associated with a 14% reduction in the relative risk of all-cause mortality and a 19% reduction in death caused by cardiovascular disease, compared with that of inactive individuals. Moreover, each additional 15 minutes of daily moderate exercise further reduced mortality by 4%. These benefits extended across the full age spectrum of both sexes and applied to patients with cardiovascular disease (Lancet. 2011 Oct 1;378[9798]:1244-53).
“That’s a very impressive result for modest physical activity,” the cardiologist commented.
Data on more than 50,000 adult participants in the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study based at the Cooper Clinic in Dallas show that vigorous exercise in the form of running at 6 mph for half an hour twice weekly, or a total of 10 metabolic equivalent of task hours (MET-HR) per week, was associated with a roughly 40% reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality. Importantly, 20, 40, or 50 MET-HR/week of vigorous exercise conferred no further survival benefit (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 5;64[5]:472-81). The same group showed that the sweet spot for moderate physical activity in terms of reduced cardiovascular mortality was brisk walking for an hour daily 5 days/week, for a total of 20 MET-HR, which was also associated with roughly a 40% risk reduction compared to inactivity. At that point the benefit plateaued, with no further mortality reduction noted with additional MET-HR of moderate exercise.
“For more than that, we have no evidence of additional cardiovascular benefit. It’s not going to get you to the Tokyo Olympics, but that’s what we need to be doing,” Dr. Vogel observed.
In another report from the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study, investigators found that moderate-level cardiorespiratory fitness as defined by METs was associated with a 44% reduction in the risk of sudden cardiac death in men and women after adjustment for potential confounders, while high-level cardiorespiratory fitness was associated with a closely similar 48% reduction in risk. This applied to individuals who were hypertensive, overweight, and/or had poor health status, as well as to others (Mayo Clin Proc. 2016 Jul;91[7]:849-57).
All activity counts
Exercise physiologists speak of NEPA – nonexercise physical activity – such as taking out the garbage. Swedish investigators followed more than 4,200 individuals for an average of 12.5 years and found that high NEPA activity was independently associated with a 30% reduction in all-cause mortality and a 27% lower risk of a first cardiovascular disease event, compared with low NEPA. High NEPA in regular exercisers was associated with a lower rate of metabolic syndrome than in low-NEPA regular exercisers (Br J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;48[3]:233-8).
Don’t just sit there – stand!
The current federal physical activity guidelines place a new emphasis on the detrimental effects of sitting. A report on more than 221,000 participants in the Australian 45 and Up Study, with close to 1 million person-years of follow-up, demonstrated a linear inverse relationship between standing time per day and all-cause mortality. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for potential confounders, individuals who stood for 2-5 hours per day had a 10% lower risk of all-cause mortality than did those who stood for less than 2 hours. Standing for 5-8 hours was associated with a 15% relative risk reduction. And standing for more than 8 hours daily was linked to a 24% reduction in risk (Prev Med. 2014 Dec;69:187-91).
And it’s not just total daily sitting time that’s a risk factor. Prolonged, uninterrupted sedentary time was also associated with a dose-dependent increase in all-cause mortality in a prospective cohort study of nearly 8,000 U.S. adults (Ann Intern Med. 2017 Oct 3;167[7]:465-75).
“If you can’t walk around, talk to your patients standing up. That activity of getting out of your chair is lifesaving,” the cardiologist advised.
Get strong
Muscle-strengthening activity on at least 2 days/week is recommended in the federal guidelines because it’s independently associated with decreased all-cause mortality, even in individuals getting sufficient aerobic exercise, as shown in a large national study with 15-years’ follow-up (Prev Med. 2016 Jun;87:121-127).
“As we get older, we tend to forget about muscle. I work with the National Football League. These folks are pretty strong, but we never see diabetes in these very big players, who are often well over 300 lb. They’ve got a lot of muscle. If you want to prevent diabetes, be strong. It’s a very important factor,” Dr. Vogel said.
For the time constrained
Jogging is more time-efficient than brisk walking as a way to attain the maximum cardiovascular benefit of exercise. And the so-called “Weekend Warrior” study of nearly 64,000 U.K. adults showed that it’s okay to cram the full week’s worth of exercise into one or two sessions and be done with it. Compared with the inactive study participants, the weekend warriors had a 40% reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality, while individuals who split their physical activity up into three or more sessions per week had a nearly identical 41% relative risk reduction (JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Mar 1;177[3]:335-42).
Interval training is a standard way for athletes in training to improve their endurance by alternating short, intense exercise with brief recovery periods. It’s also a time saver: In one classic bicycling study, physically active men were randomized to standardized 2-week programs of sprint interval training or high-volume endurance training on the bike. The training time required to pass a rigorous cycling time trial test was 90% lower in the interval training group (J Physiol. 2006 Sep 15;575(Pt 3):901-11).
The same principle is applicable to the nonathlete interested in physical activity for heart health.
“When I run a couple of miles, I walk for 5 minutes, then maybe run for three-quarters of a mile, then walk again, then run. In interval training you get your heart rate up, and you drop it down. It’s a very good form of exercise. As a vascular biologist I know that if you put endothelial cells in a Petri dish and spin them real fast continuously, you will not get as good an improvement in endothelial function as if you spin the dish, stop it, spin it, stop it,” Dr. Vogel said.
High-volume exercise is safe, even with high coronary calcium
A clinically significant coronary artery calcification score of 100 Agatston units or more is no reason not to exercise. A Cooper Clinic report on nearly 22,000 middle-aged men without baseline cardiovascular disease who were followed for a mean of 10.4 years concluded that those in the highest-volume exercise group, many of whom were marathon runners and engaged in the equivalent of running for at least 5-6 hours/week at a pace of 10 minutes per mile, were 11% more likely to have an elevated baseline coronary artery calcification score than those who exercised less. But these highest-volume exercisers with elevated coronary calcium – their mean level was 807 Agatston units – had risks of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality that weren’t significantly different from those of men with elevated coronary calcium who exercised more moderately (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Feb 1;4[2]:174-81).
Cardiac rehab
Dr. Vogel had harsh words for his physician colleagues with respect to the widespread underprescribing of cardiac rehabilitation programs.
“You guys are doing a crappy job with exercise in our most vulnerable patients: those who’ve had cardiovascular events,” he charged. “Cardiac rehabilitation is a Class I recommendation in our guidelines. And yet utilization in the United States is just 10%-20%. No other Class I recommendation is in that ballpark.”
A meta-analysis of 34 randomized trials totaling more than 6,000 post-MI patients concluded that those randomized to exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation had a 47% reduction in the risk of reinfarction, 36% lower cardiac mortality, and a 26% reduction in all-cause mortality (Am Heart J. 2011 Oct;162[4]:571-584.e2).
“The data show that cardiac rehabilitation is as effective as anything else we do in cardiovascular medicine. I understand that patients live far away, they don’t like to exercise – I’ve heard every excuse. But I am charging you with the responsibility of meeting a Class I recommendation that gets patients to live longer,” he declared.
Medicare now covers an enhanced, 72-session program called Intensive Cardiac Rehabilitation that teaches comprehensive lifestyle change and provides reasonable reimbursement. “It’s a good thing for our patients,” Dr. Vogel commented.
Yoga
For patients who are reluctant to pound the pavement, yoga may provide an alternative form of physical activity with tangible cardiovascular benefits. Dr. Vogel pointed to the Yoga-CaRe trial presented at the 2018 scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Yoga-CaRe randomized 3,959 post-MI patients at 29 centers in India to a program of 13 supervised in-hospital yoga classes followed by yoga at home, or to a control group with three educational sessions. The rate of major adverse cardiovascular events over 42 months of follow-up was cut in half, compared with controls, in the 27% of participants who attended at least 10 of the 13 yoga classes. Their quality of life scores were higher, too.
Dr. Vogel reported serving as a paid consultant to the National Football League and the Pritikin Longevity Center. He is on the speaker’s bureau for Sanofi and Regeneron.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Physical activity is potent medicine, and it doesn’t take all that much of it to derive the maximum cardiovascular benefit: namely, the equivalent of a brisk hour-long walk 5 days/week or jogging at a 10-minute-per-mile pace for half an hour twice weekly, Robert A. Vogel, MD, asserted at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“I’m not telling you to run marathons. said Dr. Vogel, a cardiologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, with a longstanding interest in preventive cardiology.
He presented selected highlights from the massive evidence base underlying the recommendations put forth in the current comprehensive U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
One particularly compelling chunk of evidence comes from a Taiwanese government–funded prospective cohort study of more than 416,000 individuals followed for an average of 8 years. A key finding: 15 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity daily was associated with a 14% reduction in the relative risk of all-cause mortality and a 19% reduction in death caused by cardiovascular disease, compared with that of inactive individuals. Moreover, each additional 15 minutes of daily moderate exercise further reduced mortality by 4%. These benefits extended across the full age spectrum of both sexes and applied to patients with cardiovascular disease (Lancet. 2011 Oct 1;378[9798]:1244-53).
“That’s a very impressive result for modest physical activity,” the cardiologist commented.
Data on more than 50,000 adult participants in the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study based at the Cooper Clinic in Dallas show that vigorous exercise in the form of running at 6 mph for half an hour twice weekly, or a total of 10 metabolic equivalent of task hours (MET-HR) per week, was associated with a roughly 40% reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality. Importantly, 20, 40, or 50 MET-HR/week of vigorous exercise conferred no further survival benefit (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 5;64[5]:472-81). The same group showed that the sweet spot for moderate physical activity in terms of reduced cardiovascular mortality was brisk walking for an hour daily 5 days/week, for a total of 20 MET-HR, which was also associated with roughly a 40% risk reduction compared to inactivity. At that point the benefit plateaued, with no further mortality reduction noted with additional MET-HR of moderate exercise.
“For more than that, we have no evidence of additional cardiovascular benefit. It’s not going to get you to the Tokyo Olympics, but that’s what we need to be doing,” Dr. Vogel observed.
In another report from the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study, investigators found that moderate-level cardiorespiratory fitness as defined by METs was associated with a 44% reduction in the risk of sudden cardiac death in men and women after adjustment for potential confounders, while high-level cardiorespiratory fitness was associated with a closely similar 48% reduction in risk. This applied to individuals who were hypertensive, overweight, and/or had poor health status, as well as to others (Mayo Clin Proc. 2016 Jul;91[7]:849-57).
All activity counts
Exercise physiologists speak of NEPA – nonexercise physical activity – such as taking out the garbage. Swedish investigators followed more than 4,200 individuals for an average of 12.5 years and found that high NEPA activity was independently associated with a 30% reduction in all-cause mortality and a 27% lower risk of a first cardiovascular disease event, compared with low NEPA. High NEPA in regular exercisers was associated with a lower rate of metabolic syndrome than in low-NEPA regular exercisers (Br J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;48[3]:233-8).
Don’t just sit there – stand!
The current federal physical activity guidelines place a new emphasis on the detrimental effects of sitting. A report on more than 221,000 participants in the Australian 45 and Up Study, with close to 1 million person-years of follow-up, demonstrated a linear inverse relationship between standing time per day and all-cause mortality. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for potential confounders, individuals who stood for 2-5 hours per day had a 10% lower risk of all-cause mortality than did those who stood for less than 2 hours. Standing for 5-8 hours was associated with a 15% relative risk reduction. And standing for more than 8 hours daily was linked to a 24% reduction in risk (Prev Med. 2014 Dec;69:187-91).
And it’s not just total daily sitting time that’s a risk factor. Prolonged, uninterrupted sedentary time was also associated with a dose-dependent increase in all-cause mortality in a prospective cohort study of nearly 8,000 U.S. adults (Ann Intern Med. 2017 Oct 3;167[7]:465-75).
“If you can’t walk around, talk to your patients standing up. That activity of getting out of your chair is lifesaving,” the cardiologist advised.
Get strong
Muscle-strengthening activity on at least 2 days/week is recommended in the federal guidelines because it’s independently associated with decreased all-cause mortality, even in individuals getting sufficient aerobic exercise, as shown in a large national study with 15-years’ follow-up (Prev Med. 2016 Jun;87:121-127).
“As we get older, we tend to forget about muscle. I work with the National Football League. These folks are pretty strong, but we never see diabetes in these very big players, who are often well over 300 lb. They’ve got a lot of muscle. If you want to prevent diabetes, be strong. It’s a very important factor,” Dr. Vogel said.
For the time constrained
Jogging is more time-efficient than brisk walking as a way to attain the maximum cardiovascular benefit of exercise. And the so-called “Weekend Warrior” study of nearly 64,000 U.K. adults showed that it’s okay to cram the full week’s worth of exercise into one or two sessions and be done with it. Compared with the inactive study participants, the weekend warriors had a 40% reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality, while individuals who split their physical activity up into three or more sessions per week had a nearly identical 41% relative risk reduction (JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Mar 1;177[3]:335-42).
Interval training is a standard way for athletes in training to improve their endurance by alternating short, intense exercise with brief recovery periods. It’s also a time saver: In one classic bicycling study, physically active men were randomized to standardized 2-week programs of sprint interval training or high-volume endurance training on the bike. The training time required to pass a rigorous cycling time trial test was 90% lower in the interval training group (J Physiol. 2006 Sep 15;575(Pt 3):901-11).
The same principle is applicable to the nonathlete interested in physical activity for heart health.
“When I run a couple of miles, I walk for 5 minutes, then maybe run for three-quarters of a mile, then walk again, then run. In interval training you get your heart rate up, and you drop it down. It’s a very good form of exercise. As a vascular biologist I know that if you put endothelial cells in a Petri dish and spin them real fast continuously, you will not get as good an improvement in endothelial function as if you spin the dish, stop it, spin it, stop it,” Dr. Vogel said.
High-volume exercise is safe, even with high coronary calcium
A clinically significant coronary artery calcification score of 100 Agatston units or more is no reason not to exercise. A Cooper Clinic report on nearly 22,000 middle-aged men without baseline cardiovascular disease who were followed for a mean of 10.4 years concluded that those in the highest-volume exercise group, many of whom were marathon runners and engaged in the equivalent of running for at least 5-6 hours/week at a pace of 10 minutes per mile, were 11% more likely to have an elevated baseline coronary artery calcification score than those who exercised less. But these highest-volume exercisers with elevated coronary calcium – their mean level was 807 Agatston units – had risks of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality that weren’t significantly different from those of men with elevated coronary calcium who exercised more moderately (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Feb 1;4[2]:174-81).
Cardiac rehab
Dr. Vogel had harsh words for his physician colleagues with respect to the widespread underprescribing of cardiac rehabilitation programs.
“You guys are doing a crappy job with exercise in our most vulnerable patients: those who’ve had cardiovascular events,” he charged. “Cardiac rehabilitation is a Class I recommendation in our guidelines. And yet utilization in the United States is just 10%-20%. No other Class I recommendation is in that ballpark.”
A meta-analysis of 34 randomized trials totaling more than 6,000 post-MI patients concluded that those randomized to exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation had a 47% reduction in the risk of reinfarction, 36% lower cardiac mortality, and a 26% reduction in all-cause mortality (Am Heart J. 2011 Oct;162[4]:571-584.e2).
“The data show that cardiac rehabilitation is as effective as anything else we do in cardiovascular medicine. I understand that patients live far away, they don’t like to exercise – I’ve heard every excuse. But I am charging you with the responsibility of meeting a Class I recommendation that gets patients to live longer,” he declared.
Medicare now covers an enhanced, 72-session program called Intensive Cardiac Rehabilitation that teaches comprehensive lifestyle change and provides reasonable reimbursement. “It’s a good thing for our patients,” Dr. Vogel commented.
Yoga
For patients who are reluctant to pound the pavement, yoga may provide an alternative form of physical activity with tangible cardiovascular benefits. Dr. Vogel pointed to the Yoga-CaRe trial presented at the 2018 scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Yoga-CaRe randomized 3,959 post-MI patients at 29 centers in India to a program of 13 supervised in-hospital yoga classes followed by yoga at home, or to a control group with three educational sessions. The rate of major adverse cardiovascular events over 42 months of follow-up was cut in half, compared with controls, in the 27% of participants who attended at least 10 of the 13 yoga classes. Their quality of life scores were higher, too.
Dr. Vogel reported serving as a paid consultant to the National Football League and the Pritikin Longevity Center. He is on the speaker’s bureau for Sanofi and Regeneron.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Physical activity is potent medicine, and it doesn’t take all that much of it to derive the maximum cardiovascular benefit: namely, the equivalent of a brisk hour-long walk 5 days/week or jogging at a 10-minute-per-mile pace for half an hour twice weekly, Robert A. Vogel, MD, asserted at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“I’m not telling you to run marathons. said Dr. Vogel, a cardiologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, with a longstanding interest in preventive cardiology.
He presented selected highlights from the massive evidence base underlying the recommendations put forth in the current comprehensive U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
One particularly compelling chunk of evidence comes from a Taiwanese government–funded prospective cohort study of more than 416,000 individuals followed for an average of 8 years. A key finding: 15 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity daily was associated with a 14% reduction in the relative risk of all-cause mortality and a 19% reduction in death caused by cardiovascular disease, compared with that of inactive individuals. Moreover, each additional 15 minutes of daily moderate exercise further reduced mortality by 4%. These benefits extended across the full age spectrum of both sexes and applied to patients with cardiovascular disease (Lancet. 2011 Oct 1;378[9798]:1244-53).
“That’s a very impressive result for modest physical activity,” the cardiologist commented.
Data on more than 50,000 adult participants in the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study based at the Cooper Clinic in Dallas show that vigorous exercise in the form of running at 6 mph for half an hour twice weekly, or a total of 10 metabolic equivalent of task hours (MET-HR) per week, was associated with a roughly 40% reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality. Importantly, 20, 40, or 50 MET-HR/week of vigorous exercise conferred no further survival benefit (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 5;64[5]:472-81). The same group showed that the sweet spot for moderate physical activity in terms of reduced cardiovascular mortality was brisk walking for an hour daily 5 days/week, for a total of 20 MET-HR, which was also associated with roughly a 40% risk reduction compared to inactivity. At that point the benefit plateaued, with no further mortality reduction noted with additional MET-HR of moderate exercise.
“For more than that, we have no evidence of additional cardiovascular benefit. It’s not going to get you to the Tokyo Olympics, but that’s what we need to be doing,” Dr. Vogel observed.
In another report from the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study, investigators found that moderate-level cardiorespiratory fitness as defined by METs was associated with a 44% reduction in the risk of sudden cardiac death in men and women after adjustment for potential confounders, while high-level cardiorespiratory fitness was associated with a closely similar 48% reduction in risk. This applied to individuals who were hypertensive, overweight, and/or had poor health status, as well as to others (Mayo Clin Proc. 2016 Jul;91[7]:849-57).
All activity counts
Exercise physiologists speak of NEPA – nonexercise physical activity – such as taking out the garbage. Swedish investigators followed more than 4,200 individuals for an average of 12.5 years and found that high NEPA activity was independently associated with a 30% reduction in all-cause mortality and a 27% lower risk of a first cardiovascular disease event, compared with low NEPA. High NEPA in regular exercisers was associated with a lower rate of metabolic syndrome than in low-NEPA regular exercisers (Br J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;48[3]:233-8).
Don’t just sit there – stand!
The current federal physical activity guidelines place a new emphasis on the detrimental effects of sitting. A report on more than 221,000 participants in the Australian 45 and Up Study, with close to 1 million person-years of follow-up, demonstrated a linear inverse relationship between standing time per day and all-cause mortality. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for potential confounders, individuals who stood for 2-5 hours per day had a 10% lower risk of all-cause mortality than did those who stood for less than 2 hours. Standing for 5-8 hours was associated with a 15% relative risk reduction. And standing for more than 8 hours daily was linked to a 24% reduction in risk (Prev Med. 2014 Dec;69:187-91).
And it’s not just total daily sitting time that’s a risk factor. Prolonged, uninterrupted sedentary time was also associated with a dose-dependent increase in all-cause mortality in a prospective cohort study of nearly 8,000 U.S. adults (Ann Intern Med. 2017 Oct 3;167[7]:465-75).
“If you can’t walk around, talk to your patients standing up. That activity of getting out of your chair is lifesaving,” the cardiologist advised.
Get strong
Muscle-strengthening activity on at least 2 days/week is recommended in the federal guidelines because it’s independently associated with decreased all-cause mortality, even in individuals getting sufficient aerobic exercise, as shown in a large national study with 15-years’ follow-up (Prev Med. 2016 Jun;87:121-127).
“As we get older, we tend to forget about muscle. I work with the National Football League. These folks are pretty strong, but we never see diabetes in these very big players, who are often well over 300 lb. They’ve got a lot of muscle. If you want to prevent diabetes, be strong. It’s a very important factor,” Dr. Vogel said.
For the time constrained
Jogging is more time-efficient than brisk walking as a way to attain the maximum cardiovascular benefit of exercise. And the so-called “Weekend Warrior” study of nearly 64,000 U.K. adults showed that it’s okay to cram the full week’s worth of exercise into one or two sessions and be done with it. Compared with the inactive study participants, the weekend warriors had a 40% reduction in cardiovascular disease mortality, while individuals who split their physical activity up into three or more sessions per week had a nearly identical 41% relative risk reduction (JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Mar 1;177[3]:335-42).
Interval training is a standard way for athletes in training to improve their endurance by alternating short, intense exercise with brief recovery periods. It’s also a time saver: In one classic bicycling study, physically active men were randomized to standardized 2-week programs of sprint interval training or high-volume endurance training on the bike. The training time required to pass a rigorous cycling time trial test was 90% lower in the interval training group (J Physiol. 2006 Sep 15;575(Pt 3):901-11).
The same principle is applicable to the nonathlete interested in physical activity for heart health.
“When I run a couple of miles, I walk for 5 minutes, then maybe run for three-quarters of a mile, then walk again, then run. In interval training you get your heart rate up, and you drop it down. It’s a very good form of exercise. As a vascular biologist I know that if you put endothelial cells in a Petri dish and spin them real fast continuously, you will not get as good an improvement in endothelial function as if you spin the dish, stop it, spin it, stop it,” Dr. Vogel said.
High-volume exercise is safe, even with high coronary calcium
A clinically significant coronary artery calcification score of 100 Agatston units or more is no reason not to exercise. A Cooper Clinic report on nearly 22,000 middle-aged men without baseline cardiovascular disease who were followed for a mean of 10.4 years concluded that those in the highest-volume exercise group, many of whom were marathon runners and engaged in the equivalent of running for at least 5-6 hours/week at a pace of 10 minutes per mile, were 11% more likely to have an elevated baseline coronary artery calcification score than those who exercised less. But these highest-volume exercisers with elevated coronary calcium – their mean level was 807 Agatston units – had risks of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality that weren’t significantly different from those of men with elevated coronary calcium who exercised more moderately (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Feb 1;4[2]:174-81).
Cardiac rehab
Dr. Vogel had harsh words for his physician colleagues with respect to the widespread underprescribing of cardiac rehabilitation programs.
“You guys are doing a crappy job with exercise in our most vulnerable patients: those who’ve had cardiovascular events,” he charged. “Cardiac rehabilitation is a Class I recommendation in our guidelines. And yet utilization in the United States is just 10%-20%. No other Class I recommendation is in that ballpark.”
A meta-analysis of 34 randomized trials totaling more than 6,000 post-MI patients concluded that those randomized to exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation had a 47% reduction in the risk of reinfarction, 36% lower cardiac mortality, and a 26% reduction in all-cause mortality (Am Heart J. 2011 Oct;162[4]:571-584.e2).
“The data show that cardiac rehabilitation is as effective as anything else we do in cardiovascular medicine. I understand that patients live far away, they don’t like to exercise – I’ve heard every excuse. But I am charging you with the responsibility of meeting a Class I recommendation that gets patients to live longer,” he declared.
Medicare now covers an enhanced, 72-session program called Intensive Cardiac Rehabilitation that teaches comprehensive lifestyle change and provides reasonable reimbursement. “It’s a good thing for our patients,” Dr. Vogel commented.
Yoga
For patients who are reluctant to pound the pavement, yoga may provide an alternative form of physical activity with tangible cardiovascular benefits. Dr. Vogel pointed to the Yoga-CaRe trial presented at the 2018 scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Yoga-CaRe randomized 3,959 post-MI patients at 29 centers in India to a program of 13 supervised in-hospital yoga classes followed by yoga at home, or to a control group with three educational sessions. The rate of major adverse cardiovascular events over 42 months of follow-up was cut in half, compared with controls, in the 27% of participants who attended at least 10 of the 13 yoga classes. Their quality of life scores were higher, too.
Dr. Vogel reported serving as a paid consultant to the National Football League and the Pritikin Longevity Center. He is on the speaker’s bureau for Sanofi and Regeneron.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC SNOWMASS 2020