User login
ACIP updates recommendations for adult vaccines
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released an updated schedule for adult vaccines. The update includes changes regarding the administration of several vaccines, including those for influenza, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis A and B, and meningitis B, as well as the pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13) vaccine.
The schedule, revised annually by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC, was simultaneously published online February 3, 2020, in the Annals of Internal Medicine and on the CDC website.
Perhaps the change most likely to raise questions is that concerning the PCV13 vaccine. “Owing to a decline in prevalence of the types covered by the PCV13 vaccine, this is no longer routinely recommended for all persons age 65 and older,” senior author Mark Freedman, DVM, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Disease, said in an interview.
For purposes of shared clinical decision, however, it should be discussed with previously unvaccinated seniors who do not have risk factors, such as an immunocompromising condition, a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or a cochlear implant.
“But the circumstances for use of the vaccine are not always clear even based on the detailed list of considerations provided, because it’s impossible to think of every conceivable combination of risk factors,” Mr. Freedman added.
Possible beneficiaries of this vaccine are vulnerable elderly people living in nursing homes and long-term care facilities and those living in or traveling to settings in which the rate of pediatric PCV13 uptake is low or zero.
All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine.*
HPV
The advisory committee now recommends catch-up immunization for women and men through age 26 years (the previous cutoff for men was 21). And in another new recommendation, the ACIP advises considering vaccination for some patients aged 27-45 years who have not been adequately vaccinated.
“Most people ages 27-45 do not need vaccination, but some may benefit,” Mr. Freedman said. “For example, somebody who’s been in a prior long-term monogamous relationship and suddenly finds himself with a new sexual partner.”
“That makes very good sense for older people who haven’t been vaccinated and might continue to be exposed to HPV,” Daniel M. Musher, MD, a professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and an infectious diseases physician at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Houston, said in an interview.
Here again, the ACIP advises taking a shared decision-making approach, with clinicians discussing the merits of vaccination in this and other scenarios with patients according to the talking points outlined in the HPV section.
Influenza, hepatitis A and B
For the 2019-2020 influenza season, routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 6 months or older who have no contraindications. Where more than one appropriate option is available, the ACIP does not recommend any product over another.
Routine hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 1 year or older who have HIV infection regardless of their level of immune suppression.
For hepatitis B, a new addition to the list of vulnerable patients who may possibly benefit from vaccination is pregnant women at risk for infection or an adverse infection-related pregnancy outcome. Whereas older formulations are safe, the ACIP does not recommend the HepB-CpG (Heplisav-B) vaccine during pregnancy, owing to the fact that safety data are lacking.
Meningitis B
Individuals aged 10 years or older who have complement deficiency, who use a complement inhibitor, who have asplenia, or who are microbiologists should receive a meningitis B booster dose 1 year following completion of a primary series. After that, they should receive booster doses every 2-3 years for as long they are at elevated risk.
Vaccination should be discussed with individuals aged 16-23 years even if they are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease. Persons aged 10 years or older whom public health authorities deem to be at increased risk during an outbreak should have a one-time booster dose if at least 1 year has elapsed since completion of a meningitis B primary series.
Td/Tdap, varicella
The ACIP now recommends that either the Td or Tdap vaccine be given in cases in which currently just the Td vaccine is recommended; that is, for the 10-year booster shot as well as for tetanus prophylaxis in wound management and the catch-up immunization schedule, including that for pregnant women.
Vaccination against varicella should be considered for HIV-infected individuals who are without evidence of varicella immunity and whose CD4 counts are at least 200 cells/mL.
Dr. Musher, who was not involved in drafting the recommendations, takes issue generally with the addition of shared clinical decision making on vaccination. “Shared decision making is a problem for anyone practicing medicine. It places a terrible burden [on] the doctors to discuss these options with patients at great length. Most patients want the doctor to make the decision.”
In his view, this approach makes little sense in the case of the PCV13 vaccine because the strains it covers have disappeared from the population through the widespread vaccination of children. “But discussions are important for some vaccines, such as the herpes zoster vaccine, since patients can have a terrible reaction to the first dose and refuse to have the second,” he said.
Some of these new recommendations were released in 2019 after ACIP members met to vote on them in February, June, and October.
As in previous years, the schedule has been streamlined for easier reference. Physicians are reminded to closely read the details in the vaccine notes, as these specify who needs what vaccine, when, and at what dose.
The ACIP develops its recommendations after reviewing vaccine-related data, including the data regarding the epidemiology and burden of the vaccine-preventable disease, vaccine effectiveness and safety, the quality of evidence, implementability, and the economics of immunization policy.
The authors have received grants and expense payments from public and not-for-profit institutions. One coauthor has received fees from ACI Clinical for data and safety monitoring in an immunization trial. Dr. Musher has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 3/31/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the recommendation for administration of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine. All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of this vaccine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released an updated schedule for adult vaccines. The update includes changes regarding the administration of several vaccines, including those for influenza, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis A and B, and meningitis B, as well as the pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13) vaccine.
The schedule, revised annually by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC, was simultaneously published online February 3, 2020, in the Annals of Internal Medicine and on the CDC website.
Perhaps the change most likely to raise questions is that concerning the PCV13 vaccine. “Owing to a decline in prevalence of the types covered by the PCV13 vaccine, this is no longer routinely recommended for all persons age 65 and older,” senior author Mark Freedman, DVM, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Disease, said in an interview.
For purposes of shared clinical decision, however, it should be discussed with previously unvaccinated seniors who do not have risk factors, such as an immunocompromising condition, a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or a cochlear implant.
“But the circumstances for use of the vaccine are not always clear even based on the detailed list of considerations provided, because it’s impossible to think of every conceivable combination of risk factors,” Mr. Freedman added.
Possible beneficiaries of this vaccine are vulnerable elderly people living in nursing homes and long-term care facilities and those living in or traveling to settings in which the rate of pediatric PCV13 uptake is low or zero.
All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine.*
HPV
The advisory committee now recommends catch-up immunization for women and men through age 26 years (the previous cutoff for men was 21). And in another new recommendation, the ACIP advises considering vaccination for some patients aged 27-45 years who have not been adequately vaccinated.
“Most people ages 27-45 do not need vaccination, but some may benefit,” Mr. Freedman said. “For example, somebody who’s been in a prior long-term monogamous relationship and suddenly finds himself with a new sexual partner.”
“That makes very good sense for older people who haven’t been vaccinated and might continue to be exposed to HPV,” Daniel M. Musher, MD, a professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and an infectious diseases physician at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Houston, said in an interview.
Here again, the ACIP advises taking a shared decision-making approach, with clinicians discussing the merits of vaccination in this and other scenarios with patients according to the talking points outlined in the HPV section.
Influenza, hepatitis A and B
For the 2019-2020 influenza season, routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 6 months or older who have no contraindications. Where more than one appropriate option is available, the ACIP does not recommend any product over another.
Routine hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 1 year or older who have HIV infection regardless of their level of immune suppression.
For hepatitis B, a new addition to the list of vulnerable patients who may possibly benefit from vaccination is pregnant women at risk for infection or an adverse infection-related pregnancy outcome. Whereas older formulations are safe, the ACIP does not recommend the HepB-CpG (Heplisav-B) vaccine during pregnancy, owing to the fact that safety data are lacking.
Meningitis B
Individuals aged 10 years or older who have complement deficiency, who use a complement inhibitor, who have asplenia, or who are microbiologists should receive a meningitis B booster dose 1 year following completion of a primary series. After that, they should receive booster doses every 2-3 years for as long they are at elevated risk.
Vaccination should be discussed with individuals aged 16-23 years even if they are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease. Persons aged 10 years or older whom public health authorities deem to be at increased risk during an outbreak should have a one-time booster dose if at least 1 year has elapsed since completion of a meningitis B primary series.
Td/Tdap, varicella
The ACIP now recommends that either the Td or Tdap vaccine be given in cases in which currently just the Td vaccine is recommended; that is, for the 10-year booster shot as well as for tetanus prophylaxis in wound management and the catch-up immunization schedule, including that for pregnant women.
Vaccination against varicella should be considered for HIV-infected individuals who are without evidence of varicella immunity and whose CD4 counts are at least 200 cells/mL.
Dr. Musher, who was not involved in drafting the recommendations, takes issue generally with the addition of shared clinical decision making on vaccination. “Shared decision making is a problem for anyone practicing medicine. It places a terrible burden [on] the doctors to discuss these options with patients at great length. Most patients want the doctor to make the decision.”
In his view, this approach makes little sense in the case of the PCV13 vaccine because the strains it covers have disappeared from the population through the widespread vaccination of children. “But discussions are important for some vaccines, such as the herpes zoster vaccine, since patients can have a terrible reaction to the first dose and refuse to have the second,” he said.
Some of these new recommendations were released in 2019 after ACIP members met to vote on them in February, June, and October.
As in previous years, the schedule has been streamlined for easier reference. Physicians are reminded to closely read the details in the vaccine notes, as these specify who needs what vaccine, when, and at what dose.
The ACIP develops its recommendations after reviewing vaccine-related data, including the data regarding the epidemiology and burden of the vaccine-preventable disease, vaccine effectiveness and safety, the quality of evidence, implementability, and the economics of immunization policy.
The authors have received grants and expense payments from public and not-for-profit institutions. One coauthor has received fees from ACI Clinical for data and safety monitoring in an immunization trial. Dr. Musher has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 3/31/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the recommendation for administration of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine. All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of this vaccine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released an updated schedule for adult vaccines. The update includes changes regarding the administration of several vaccines, including those for influenza, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis A and B, and meningitis B, as well as the pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13) vaccine.
The schedule, revised annually by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC, was simultaneously published online February 3, 2020, in the Annals of Internal Medicine and on the CDC website.
Perhaps the change most likely to raise questions is that concerning the PCV13 vaccine. “Owing to a decline in prevalence of the types covered by the PCV13 vaccine, this is no longer routinely recommended for all persons age 65 and older,” senior author Mark Freedman, DVM, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Disease, said in an interview.
For purposes of shared clinical decision, however, it should be discussed with previously unvaccinated seniors who do not have risk factors, such as an immunocompromising condition, a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or a cochlear implant.
“But the circumstances for use of the vaccine are not always clear even based on the detailed list of considerations provided, because it’s impossible to think of every conceivable combination of risk factors,” Mr. Freedman added.
Possible beneficiaries of this vaccine are vulnerable elderly people living in nursing homes and long-term care facilities and those living in or traveling to settings in which the rate of pediatric PCV13 uptake is low or zero.
All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine.*
HPV
The advisory committee now recommends catch-up immunization for women and men through age 26 years (the previous cutoff for men was 21). And in another new recommendation, the ACIP advises considering vaccination for some patients aged 27-45 years who have not been adequately vaccinated.
“Most people ages 27-45 do not need vaccination, but some may benefit,” Mr. Freedman said. “For example, somebody who’s been in a prior long-term monogamous relationship and suddenly finds himself with a new sexual partner.”
“That makes very good sense for older people who haven’t been vaccinated and might continue to be exposed to HPV,” Daniel M. Musher, MD, a professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and an infectious diseases physician at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Houston, said in an interview.
Here again, the ACIP advises taking a shared decision-making approach, with clinicians discussing the merits of vaccination in this and other scenarios with patients according to the talking points outlined in the HPV section.
Influenza, hepatitis A and B
For the 2019-2020 influenza season, routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 6 months or older who have no contraindications. Where more than one appropriate option is available, the ACIP does not recommend any product over another.
Routine hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 1 year or older who have HIV infection regardless of their level of immune suppression.
For hepatitis B, a new addition to the list of vulnerable patients who may possibly benefit from vaccination is pregnant women at risk for infection or an adverse infection-related pregnancy outcome. Whereas older formulations are safe, the ACIP does not recommend the HepB-CpG (Heplisav-B) vaccine during pregnancy, owing to the fact that safety data are lacking.
Meningitis B
Individuals aged 10 years or older who have complement deficiency, who use a complement inhibitor, who have asplenia, or who are microbiologists should receive a meningitis B booster dose 1 year following completion of a primary series. After that, they should receive booster doses every 2-3 years for as long they are at elevated risk.
Vaccination should be discussed with individuals aged 16-23 years even if they are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease. Persons aged 10 years or older whom public health authorities deem to be at increased risk during an outbreak should have a one-time booster dose if at least 1 year has elapsed since completion of a meningitis B primary series.
Td/Tdap, varicella
The ACIP now recommends that either the Td or Tdap vaccine be given in cases in which currently just the Td vaccine is recommended; that is, for the 10-year booster shot as well as for tetanus prophylaxis in wound management and the catch-up immunization schedule, including that for pregnant women.
Vaccination against varicella should be considered for HIV-infected individuals who are without evidence of varicella immunity and whose CD4 counts are at least 200 cells/mL.
Dr. Musher, who was not involved in drafting the recommendations, takes issue generally with the addition of shared clinical decision making on vaccination. “Shared decision making is a problem for anyone practicing medicine. It places a terrible burden [on] the doctors to discuss these options with patients at great length. Most patients want the doctor to make the decision.”
In his view, this approach makes little sense in the case of the PCV13 vaccine because the strains it covers have disappeared from the population through the widespread vaccination of children. “But discussions are important for some vaccines, such as the herpes zoster vaccine, since patients can have a terrible reaction to the first dose and refuse to have the second,” he said.
Some of these new recommendations were released in 2019 after ACIP members met to vote on them in February, June, and October.
As in previous years, the schedule has been streamlined for easier reference. Physicians are reminded to closely read the details in the vaccine notes, as these specify who needs what vaccine, when, and at what dose.
The ACIP develops its recommendations after reviewing vaccine-related data, including the data regarding the epidemiology and burden of the vaccine-preventable disease, vaccine effectiveness and safety, the quality of evidence, implementability, and the economics of immunization policy.
The authors have received grants and expense payments from public and not-for-profit institutions. One coauthor has received fees from ACI Clinical for data and safety monitoring in an immunization trial. Dr. Musher has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 3/31/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the recommendation for administration of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine. All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of this vaccine.
NASH ‘an epidemic of the 21st century’
LOS ANGELES – The way Christos S. Mantzoros, MD, DSc, PhD, sees it, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an epidemic of the 21st century that can trigger a cascade of reactions.
“If more than 5.8% of fat is in the liver, we call it nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD],” Dr. Mantzoros, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Boston University, explained at the World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease. “If inflammation develops to remove the fat, we call it NASH. If this progresses to decompensated reaction and fibrosis and cirrhosis, then we call it nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis. That can lead to liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure.”
The underlying problem stems from the rise in obesity prevalence, according to Dr. Mantzoros, who is also chief of endocrinology at the Boston Veterans Affairs Healthcare System. For 75%-80% of individuals with metabolically unhealthy obesity, the storage space in their adipose tissue is exceeded. “Fat is deposited into muscle, causing insulin resistance, and into the liver,” he explained. “If it’s more than 5.8%, it causes NAFLD. Most of us don’t realize that most of the patients with diabetes we have in our clinics also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. That’s because we don’t have an easy diagnostic tool or an easy treatment. It’s an unmet clinical need.” (There are currently no drugs approved for the treatment of NASH or NAFLD. Current recommended first-line treatment is weight loss through diet and exercise and control of diabetes, if it is present.)
“Assuming the rate of increase in cost due to NAFLD parallels the growth in obesity, the 10-year projection for direct cost is $1.005 trillion,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is also editor in chief of the journal Metabolism. “Obesity, NAFLD, and insulin resistance are each independently associated with a twofold risk for diabetes. If all three are present, there is a 14-fold risk for diabetes. Insulin resistance promotes an increase in free fatty acid traffic to the liver, which can trigger hepatic lipotoxicity. Hyperinsulinemia enhances free fatty acid uptake and activates de novo lipogenesis. Hyperglycemia can also activate de novo lipogenesis.”
About 85 million Americans have NAFLD, he continued. Most (80%) are cases of steatosis, but 20% have NASH. Of those, 20% develop advanced fibrosis, which leads to liver failure and transplantation or death. A study of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that (odds ratio, 18.20), followed by a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater (OR, 9.10), hypertension (OR, 1.20), and age (OR, 1.08; Ailment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:974-80). “Most of the patients who come to our clinics with diabetes have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – 75%-80% in our clinics, and about 10% have advanced fibrosis,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “Most of them go undiagnosed.”
Patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD progress faster to fibrosis and end-stage liver disease, compared with those who do not have diabetes. One study of 108 patients with biopsy-proven NALFD showed that 84% of those with fibrosis progression had type 2 diabetes (J Hepatol. 2015;62:1148-55). Other findings have shown that patients with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of chronic NAFLD and hepatocellular carcinoma (Gastroenterol. 2001;126:460-8). “We are doing more liver transplantations because of NAFLD and NASH than because of hepatitis C,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “What we need to keep in mind is that, although liver morbidity and mortality is important, this is a component of the cardiometabolic syndrome. So, people have all the risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Because CVD is much more common, people with NAFLD suffer from and die from CVD. The more advanced the NAFLD, the higher the risk of death from cardiovascular disease.”
Multiple risk factors can help identify patients with advanced fibrosis because of NASH, he continued, including having features of the metabolic syndrome, being over 50 years of age, being Hispanic, having high levels of ALT/AST, low platelets, and having low albumin. “These are frequent tests that we can find in the EMR,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “The problem with ALT is that, in many stages of the disease, ALT goes up. But after a certain stage of the disease, when most of the liver is controlled by fibrosis and cirrhosis, most of the hepatocytes are dead and don’t secrete ALT, so ALT in end-stage renal disease goes up.”
Recent guidelines recognize the association between diabetes, NAFLD, and NASH, and call for increased vigilance and screening tests. According to guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Fibrosis-4 Index or the NAFLD Fibrosis Score are clinically useful tools for identifying NAFLD in patients with higher likelihood of having bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis (Hepatology. 2018;67[1]:328-57). Vibration-controlled transient elastography or MRI are clinically useful tools for identifying advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD, whereas clinical decision aids, such as Fibrosis-4, NAFLD Fibrosis Score, or vibration-controlled transient elastography, can be used to identify patients at low or high risk for advanced fibrosis.
“If we have a patient with suspected NAFLD, we need to rule out alcohol use, we need to confirm NAFLD, and we need to risk stratify, and classify as low, intermediate, or high risk,” Dr. Mantzoros said. Most of his patients who meet criteria for high-risk NASH do not elect to undergo a liver biopsy. “I don’t blame them for that,” he said. “There is a 0.1 per 1,000 mortality risk, even in the best hands. If 80 million people who have fatty liver were to undergo a liver biopsy, we would have 16,000 deaths every year just because of that. We would not tolerate that.”
Recently, Dr. Mantzoros and colleagues published a proof-of-concept study that proposes novel models using lipids, hormones, and glycans that can diagnose the presence of NASH, NAFLD, or healthy status with high accuracy (Metabolism. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154005). “We are now working with companies to validate it and expand it, not only as a diagnostic marker, but as a prognostic marker, and to try to commercialize it in the future,” he said.
Current pharmacotherapies are limited to patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH and fibrosis. Pioglitazone is a first-line, off-label pharmacologic treatment, while vitamin E may be used in patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH without diabetes. Metformin, glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists, and sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors are either not recommended or have insufficient evidence to recommend their use. More than 60 phase 2 trials are planned or ongoing, Dr. Mantzoros added, with phase trials underway for cenicriviroc, elafibranor, obeticholic acid, and selonsertib.
The role of lifestyle management is also important. “The Mediterranean diet has the best evidence, along with exercise, to improve early stages of NAFLD,” he said. “Weight loss is very important. If the patient loses 10% of their weight or more, there is NASH resolution 90% of the time. With less weight loss, we have less resolution. The problem is that only 10% of patients or less can sustain a more than 90% weight loss over a year.”
Dr. Mantzoros reported being a shareholder of Coherus BioSciences and Pangea Therapeutics, having served as an adviser to Coherus, Novo Nordisk, and Genfit and having received research grants through his institution from Coherus, Eisai, and Novo Nordisk.
LOS ANGELES – The way Christos S. Mantzoros, MD, DSc, PhD, sees it, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an epidemic of the 21st century that can trigger a cascade of reactions.
“If more than 5.8% of fat is in the liver, we call it nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD],” Dr. Mantzoros, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Boston University, explained at the World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease. “If inflammation develops to remove the fat, we call it NASH. If this progresses to decompensated reaction and fibrosis and cirrhosis, then we call it nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis. That can lead to liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure.”
The underlying problem stems from the rise in obesity prevalence, according to Dr. Mantzoros, who is also chief of endocrinology at the Boston Veterans Affairs Healthcare System. For 75%-80% of individuals with metabolically unhealthy obesity, the storage space in their adipose tissue is exceeded. “Fat is deposited into muscle, causing insulin resistance, and into the liver,” he explained. “If it’s more than 5.8%, it causes NAFLD. Most of us don’t realize that most of the patients with diabetes we have in our clinics also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. That’s because we don’t have an easy diagnostic tool or an easy treatment. It’s an unmet clinical need.” (There are currently no drugs approved for the treatment of NASH or NAFLD. Current recommended first-line treatment is weight loss through diet and exercise and control of diabetes, if it is present.)
“Assuming the rate of increase in cost due to NAFLD parallels the growth in obesity, the 10-year projection for direct cost is $1.005 trillion,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is also editor in chief of the journal Metabolism. “Obesity, NAFLD, and insulin resistance are each independently associated with a twofold risk for diabetes. If all three are present, there is a 14-fold risk for diabetes. Insulin resistance promotes an increase in free fatty acid traffic to the liver, which can trigger hepatic lipotoxicity. Hyperinsulinemia enhances free fatty acid uptake and activates de novo lipogenesis. Hyperglycemia can also activate de novo lipogenesis.”
About 85 million Americans have NAFLD, he continued. Most (80%) are cases of steatosis, but 20% have NASH. Of those, 20% develop advanced fibrosis, which leads to liver failure and transplantation or death. A study of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that (odds ratio, 18.20), followed by a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater (OR, 9.10), hypertension (OR, 1.20), and age (OR, 1.08; Ailment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:974-80). “Most of the patients who come to our clinics with diabetes have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – 75%-80% in our clinics, and about 10% have advanced fibrosis,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “Most of them go undiagnosed.”
Patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD progress faster to fibrosis and end-stage liver disease, compared with those who do not have diabetes. One study of 108 patients with biopsy-proven NALFD showed that 84% of those with fibrosis progression had type 2 diabetes (J Hepatol. 2015;62:1148-55). Other findings have shown that patients with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of chronic NAFLD and hepatocellular carcinoma (Gastroenterol. 2001;126:460-8). “We are doing more liver transplantations because of NAFLD and NASH than because of hepatitis C,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “What we need to keep in mind is that, although liver morbidity and mortality is important, this is a component of the cardiometabolic syndrome. So, people have all the risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Because CVD is much more common, people with NAFLD suffer from and die from CVD. The more advanced the NAFLD, the higher the risk of death from cardiovascular disease.”
Multiple risk factors can help identify patients with advanced fibrosis because of NASH, he continued, including having features of the metabolic syndrome, being over 50 years of age, being Hispanic, having high levels of ALT/AST, low platelets, and having low albumin. “These are frequent tests that we can find in the EMR,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “The problem with ALT is that, in many stages of the disease, ALT goes up. But after a certain stage of the disease, when most of the liver is controlled by fibrosis and cirrhosis, most of the hepatocytes are dead and don’t secrete ALT, so ALT in end-stage renal disease goes up.”
Recent guidelines recognize the association between diabetes, NAFLD, and NASH, and call for increased vigilance and screening tests. According to guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Fibrosis-4 Index or the NAFLD Fibrosis Score are clinically useful tools for identifying NAFLD in patients with higher likelihood of having bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis (Hepatology. 2018;67[1]:328-57). Vibration-controlled transient elastography or MRI are clinically useful tools for identifying advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD, whereas clinical decision aids, such as Fibrosis-4, NAFLD Fibrosis Score, or vibration-controlled transient elastography, can be used to identify patients at low or high risk for advanced fibrosis.
“If we have a patient with suspected NAFLD, we need to rule out alcohol use, we need to confirm NAFLD, and we need to risk stratify, and classify as low, intermediate, or high risk,” Dr. Mantzoros said. Most of his patients who meet criteria for high-risk NASH do not elect to undergo a liver biopsy. “I don’t blame them for that,” he said. “There is a 0.1 per 1,000 mortality risk, even in the best hands. If 80 million people who have fatty liver were to undergo a liver biopsy, we would have 16,000 deaths every year just because of that. We would not tolerate that.”
Recently, Dr. Mantzoros and colleagues published a proof-of-concept study that proposes novel models using lipids, hormones, and glycans that can diagnose the presence of NASH, NAFLD, or healthy status with high accuracy (Metabolism. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154005). “We are now working with companies to validate it and expand it, not only as a diagnostic marker, but as a prognostic marker, and to try to commercialize it in the future,” he said.
Current pharmacotherapies are limited to patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH and fibrosis. Pioglitazone is a first-line, off-label pharmacologic treatment, while vitamin E may be used in patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH without diabetes. Metformin, glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists, and sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors are either not recommended or have insufficient evidence to recommend their use. More than 60 phase 2 trials are planned or ongoing, Dr. Mantzoros added, with phase trials underway for cenicriviroc, elafibranor, obeticholic acid, and selonsertib.
The role of lifestyle management is also important. “The Mediterranean diet has the best evidence, along with exercise, to improve early stages of NAFLD,” he said. “Weight loss is very important. If the patient loses 10% of their weight or more, there is NASH resolution 90% of the time. With less weight loss, we have less resolution. The problem is that only 10% of patients or less can sustain a more than 90% weight loss over a year.”
Dr. Mantzoros reported being a shareholder of Coherus BioSciences and Pangea Therapeutics, having served as an adviser to Coherus, Novo Nordisk, and Genfit and having received research grants through his institution from Coherus, Eisai, and Novo Nordisk.
LOS ANGELES – The way Christos S. Mantzoros, MD, DSc, PhD, sees it, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an epidemic of the 21st century that can trigger a cascade of reactions.
“If more than 5.8% of fat is in the liver, we call it nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD],” Dr. Mantzoros, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Boston University, explained at the World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease. “If inflammation develops to remove the fat, we call it NASH. If this progresses to decompensated reaction and fibrosis and cirrhosis, then we call it nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis. That can lead to liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure.”
The underlying problem stems from the rise in obesity prevalence, according to Dr. Mantzoros, who is also chief of endocrinology at the Boston Veterans Affairs Healthcare System. For 75%-80% of individuals with metabolically unhealthy obesity, the storage space in their adipose tissue is exceeded. “Fat is deposited into muscle, causing insulin resistance, and into the liver,” he explained. “If it’s more than 5.8%, it causes NAFLD. Most of us don’t realize that most of the patients with diabetes we have in our clinics also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. That’s because we don’t have an easy diagnostic tool or an easy treatment. It’s an unmet clinical need.” (There are currently no drugs approved for the treatment of NASH or NAFLD. Current recommended first-line treatment is weight loss through diet and exercise and control of diabetes, if it is present.)
“Assuming the rate of increase in cost due to NAFLD parallels the growth in obesity, the 10-year projection for direct cost is $1.005 trillion,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is also editor in chief of the journal Metabolism. “Obesity, NAFLD, and insulin resistance are each independently associated with a twofold risk for diabetes. If all three are present, there is a 14-fold risk for diabetes. Insulin resistance promotes an increase in free fatty acid traffic to the liver, which can trigger hepatic lipotoxicity. Hyperinsulinemia enhances free fatty acid uptake and activates de novo lipogenesis. Hyperglycemia can also activate de novo lipogenesis.”
About 85 million Americans have NAFLD, he continued. Most (80%) are cases of steatosis, but 20% have NASH. Of those, 20% develop advanced fibrosis, which leads to liver failure and transplantation or death. A study of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that (odds ratio, 18.20), followed by a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater (OR, 9.10), hypertension (OR, 1.20), and age (OR, 1.08; Ailment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:974-80). “Most of the patients who come to our clinics with diabetes have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – 75%-80% in our clinics, and about 10% have advanced fibrosis,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “Most of them go undiagnosed.”
Patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD progress faster to fibrosis and end-stage liver disease, compared with those who do not have diabetes. One study of 108 patients with biopsy-proven NALFD showed that 84% of those with fibrosis progression had type 2 diabetes (J Hepatol. 2015;62:1148-55). Other findings have shown that patients with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of chronic NAFLD and hepatocellular carcinoma (Gastroenterol. 2001;126:460-8). “We are doing more liver transplantations because of NAFLD and NASH than because of hepatitis C,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “What we need to keep in mind is that, although liver morbidity and mortality is important, this is a component of the cardiometabolic syndrome. So, people have all the risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Because CVD is much more common, people with NAFLD suffer from and die from CVD. The more advanced the NAFLD, the higher the risk of death from cardiovascular disease.”
Multiple risk factors can help identify patients with advanced fibrosis because of NASH, he continued, including having features of the metabolic syndrome, being over 50 years of age, being Hispanic, having high levels of ALT/AST, low platelets, and having low albumin. “These are frequent tests that we can find in the EMR,” Dr. Mantzoros said. “The problem with ALT is that, in many stages of the disease, ALT goes up. But after a certain stage of the disease, when most of the liver is controlled by fibrosis and cirrhosis, most of the hepatocytes are dead and don’t secrete ALT, so ALT in end-stage renal disease goes up.”
Recent guidelines recognize the association between diabetes, NAFLD, and NASH, and call for increased vigilance and screening tests. According to guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Fibrosis-4 Index or the NAFLD Fibrosis Score are clinically useful tools for identifying NAFLD in patients with higher likelihood of having bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis (Hepatology. 2018;67[1]:328-57). Vibration-controlled transient elastography or MRI are clinically useful tools for identifying advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD, whereas clinical decision aids, such as Fibrosis-4, NAFLD Fibrosis Score, or vibration-controlled transient elastography, can be used to identify patients at low or high risk for advanced fibrosis.
“If we have a patient with suspected NAFLD, we need to rule out alcohol use, we need to confirm NAFLD, and we need to risk stratify, and classify as low, intermediate, or high risk,” Dr. Mantzoros said. Most of his patients who meet criteria for high-risk NASH do not elect to undergo a liver biopsy. “I don’t blame them for that,” he said. “There is a 0.1 per 1,000 mortality risk, even in the best hands. If 80 million people who have fatty liver were to undergo a liver biopsy, we would have 16,000 deaths every year just because of that. We would not tolerate that.”
Recently, Dr. Mantzoros and colleagues published a proof-of-concept study that proposes novel models using lipids, hormones, and glycans that can diagnose the presence of NASH, NAFLD, or healthy status with high accuracy (Metabolism. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154005). “We are now working with companies to validate it and expand it, not only as a diagnostic marker, but as a prognostic marker, and to try to commercialize it in the future,” he said.
Current pharmacotherapies are limited to patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH and fibrosis. Pioglitazone is a first-line, off-label pharmacologic treatment, while vitamin E may be used in patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH without diabetes. Metformin, glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists, and sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors are either not recommended or have insufficient evidence to recommend their use. More than 60 phase 2 trials are planned or ongoing, Dr. Mantzoros added, with phase trials underway for cenicriviroc, elafibranor, obeticholic acid, and selonsertib.
The role of lifestyle management is also important. “The Mediterranean diet has the best evidence, along with exercise, to improve early stages of NAFLD,” he said. “Weight loss is very important. If the patient loses 10% of their weight or more, there is NASH resolution 90% of the time. With less weight loss, we have less resolution. The problem is that only 10% of patients or less can sustain a more than 90% weight loss over a year.”
Dr. Mantzoros reported being a shareholder of Coherus BioSciences and Pangea Therapeutics, having served as an adviser to Coherus, Novo Nordisk, and Genfit and having received research grants through his institution from Coherus, Eisai, and Novo Nordisk.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM WCIRDC 2019
The removal of the multiple-kilogram uterus using MIGSs
It has now been 30 years since the first total laparoscopic hysterectomy was performed. The benefits of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS) – and of minimally invasive hysterectomy specifically – are now well documented. Since this milestone procedure, both instrumentation and technique have improved significantly.
This includes traditional laparoscopy, as well as the robotically assisted laparoscopic approach. However, certain patient characteristics also may influence the choice. A uterus that is undescended, combined with a narrow introitus, for instance, can be a contributory factor in choosing to perform laparoscopic hysterectomy. Additionally, so can an extremely large uterus and an extremely high body mass index (BMI).
These latter two factors – a very large uterus (which we define as more than 15-16 weeks’ gestational size) and a BMI over 60 kg/m2 – historically were considered to be contraindications to laparoscopic hysterectomy. But as the proficiency, comfort, and skill of a new generation of laparoscopic surgeons increases, the tide is shifting with respect to both morbid obesity and the very large uterus.
With growing experience and improved instrumentation, the majority of gynecologists who are fellowship-trained in MIGS are able to routinely and safely perform laparoscopic hysterectomy for uteri weighing 1-2 kg and in patients who have extreme morbid obesity. The literature, moreover, increasingly features case reports of laparoscopic removal of very large uteri and reviews/discussions of total laparoscopic hysterectomy being feasible.
In our own experience, total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) of the very large uterus can be safely and advantageously performed using key instruments and refinements in technique, as well as thorough patient counseling regarding the risk of unexpected sarcomas. Recently, we safely performed total laparoscopic hysterectomy for a patient with a uterus that – somewhat unexpectedly – weighed 7.4 kg.
Surgical pearls
Performing safe and effective total laparoscopic hysterectomy for large uteri – and for morbidly obese patients – hinges largely on modifications in entry and port placement, patient positioning, and choice of instrumentation. With these modifications, we can achieve adequate visualization of critical anatomy and can minimize bleeding. Otherwise, the surgery itself is largely the same. Here are the principles we find most helpful.
Entry and port placement
Traditionally, for TLHs, a camera port is placed at the umbilicus to provide a full view of the pelvis. For the larger uterus – and in women who are extremely obese – we aim to introduce the laparoscope higher. A reliable landmark is the Palmer’s point in the left upper quadrant. From here, we can identify areas for the placement of additional trocars.
In general, we place ancillary 5-mm ports more cephalad and lateral to the uterus than we otherwise would. Such placement facilitates effective visualization while accommodating manipulation of the uterus and allows us to avoid bleeding around the vascular upper pedicles. Overall, we have much better control through all parts of the surgery when we operate lateral to the uterus.
Patient positioning
In addition to the Trendelenburg position, we have adopted an “airplaning” technique for patients with a very large uterus in which the bed is tilted from side to side so that the left and right sides of the body are rotated upward as needed. This allows for gravitational-assisted retraction when it otherwise is not possible.
Instrumentation
For morbidly obese patients, we use Kii Fios advanced fixation trocars. These come in 5- and 10-mm sizes and are equipped with an intraperitoneal balloon that can be inflated to prevent sliding of the trocar out of the abdominal wall.
By far the most valuable instrument for the morbidly obese and the very large uterus is a 30-degree laparoscope. With our higher port placement as described, the 30-degree scope provides visualization of critical structures that wouldn’t be possible with a 0-degree scope.
The Rumi uterine manipulator comes with cups that come in different sizes and can fit around the cervix and help delineate the cervicouterine junction. We use this manipulator for all laparoscopic hysterectomies, but it is a must for the very large uterus.
Extensive desiccation of the utero-ovarian pedicles and uterine arteries is critical, and for this we advise using the rotating bipolar RoBi instrument. Use of the conventional bipolar instrument allows us to use targeted and anatomically guided application of energy. This ensures certainty that vessels whose limits exceed the diameter for advanced bipolar devices (typically 7 mm) are completely sealed. In-depth knowledge of pelvic anatomy and advanced laparoscopic dissection is paramount during these steps to ensure that vital structures are not damaged by the wider thermal spread of the traditional bipolar device. For cutting, the use of ultrasonic energy is important to prevent energy from spreading laterally.
Lastly, we recommend a good suction irrigator because, if bleeding occurs, it tends to be heavy because of the enlarged nature of feeding vasculature. When placed through an umbilical or suprapubic port, the suction irrigator also may be used to help with the rotational vectors and traction for further uterine manipulation.
Technique
We usually operate from top to bottom, transecting the upper pedicles such as the infundibulopelvic (IP) ligaments or utero-ovarian ligaments first, rather than the round ligaments. This helps us achieve additional mobility of the uterus. Some surgeons believe that retroperitoneal dissection and ligation of the uterine arteries at their origin is essential, but we find that, with good uterine manipulation and the use of a 30-degree scope, we achieve adequate visualization for identifying the ureter and uterine artery on the sidewall and consequently do not need to dissect retroperitoneally.
When using the uterine manipulator with the colpotomy cup, the uterus is pushed upward, increasing the distance between the vaginal fornix and the ureters. Uterine arteries can easily be identified and desiccated using conventional bipolar energy. When the colpotomy cup is pushed cephalad, the application of the bipolar energy within the limits of the cup is safe. The thermal spread does not pose a threat to the ureters, which are displaced 1.5-2 cm laterally. Large fibroids often contribute to distorted anatomical planes, and a colpotomy cup provides a firm palpable surface between the cervix and vagina during dissection.
When dealing with large uteri, one must sometimes think outside the box and deviate from standard technique. For instance, in patients with distorted anatomy because of large fibroids, it helps to first control the pedicles that are most easily accessible. Sometimes it is acceptable to perform oophorectomy if the IP ligament is more accessible and the utero-ovarian pedicle is distorted by dilated veins and adherent to the uterus. After transection of each pedicle, we gain more mobility of the uterus and better visualization for the next step.
Inserting the camera through ancillary ports – a technique known as “port hopping” – helps to visualize and take down adhesions much better and more safely than using the camera from the umbilical port only. Port hopping with a 30-degree laparoscope helps to obtain a 360-degree view of adhesions and anatomy, which is exceedingly helpful in cases in which crucial anatomical structures are within close proximity of one another.
In general it is more challenging to perform TLH on a patient with a broad uterus or a patient with low posterior fibroids that are occupying the pelvis than on a patient with fibroids in the upper abdomen. The main challenge for the surgeon is to safely secure the uterine arteries and control the blood supply to the uterus.
Access to the pelvic sidewall is obtained with the combination of 30-degree scope, uterine manipulator, and the suction irrigator introduced through the midline port; the cervix and uterus are deviated upward. Instead of the suction irrigator or blunt dissector used for internal uterine manipulation, some surgeons use myoma screws or a 5-mm single-tooth tenaculum to manipulate a large uterus. Both of those instruments are valuable and work well, but often a large uterus requires extensive manipulation. Repositioning of any sharp instruments that pierce the serosa can often lead to additional blood loss. It is preferable to avoid this blood loss on a large uterus at all costs because it can be brisk and stains the surgical pedicles, making the remainder of the procedure unnecessarily difficult.
Once the uterine arteries are desiccated, if fibroids are obscuring the view, the corpus of the uterus can be detached from the cervix as in supracervical hysterectomy fashion. From there, the uterus can be placed in the upper abdomen while colpotomy can be performed.
In patients with multiple fibroids, we do not recommend performing myomectomy first, unless the fibroid is pedunculated and on a very small stalk. Improved uterine manipulation and retroperitoneal dissection are preferred over myomectomy to safely complete hysterectomy for the broad uterus. In our opinion, any attempt at myomectomy would lead to unnecessary blood loss and additional operative time with minimal benefit.
In patients with fibroids that grow into the broad ligament and pelvic sidewall, the natural course of the ureter becomes displaced laterally. This is contrary to the popular misconception that the ureter is more medially located in the setting of broad-ligament fibroids. To ensure safe access to the uterine arteries, the vesicouterine peritoneum can be incised and extended cephalad along the broad ligament and, then, using the above-mentioned technique, by pushing the uterus and the fibroid to the contralateral side via the suction irrigator, the uterine arteries can be easily accessed.
Another useful technique is to use diluted vasopressin injected into the lower pole of the uterus to cause vasoconstriction and minimize the bleeding. The concentration is 1 cc of 20 units of vasopressin in 100-400 cc of saline. This technique is very useful for myomectomies, and some surgeons find it also helpful for hysterectomy. The plasma half-life of vasopressin is 10-20 minutes, and a large quantity is needed to help with vasoconstriction in a big uterus. The safe upper limits of vasopressin dosing are not firmly established. A fibroid uterus with aberrant vasculature may require a greater-than-acceptable dose to control bleeding.
It is important to ensure that patients have an optimized hemoglobin level preoperatively. We use a hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL as a lowest cutoff value for performing TLH without preoperative transfusion. Regarding bowel preparation, neither the literature nor our own experience support its value, so we typically do not use it.
Morcellation and patient counseling
Uteri up to 12 weeks’ gestational size usually can be extracted transvaginally, and most uteri regardless of size can be morcellated and extracted through the vagina, providing that the vaginal fornix is accessible from below. In some cases, such as when the apex is too high, a minilaparotomic incision is needed to extract the uterus, or when available, power morcellation can be performed.
A major challenge, given our growing ability to laparoscopically remove very larger uteri, is that uteri heavier than about 2.5 kg in weight cannot be morcellated inside a morcellation bag. The risk of upstaging a known or suspected uterine malignancy, or of spreading an unknown malignant sarcoma (presumed benign myoma), should be incorporated in each patient’s decision making.
Thorough counseling about surgical options and on the risks of morcellating a very large uterus without containment in a bag is essential. Each patient must understand the risks and decide whether the benefits of minimally invasive surgery outweigh these risks. While MRI can sometimes provide increased suspicion of a leiomyosarcoma, malignancy can never be completed excluded preoperatively.
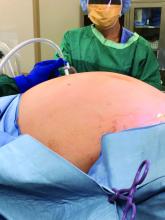
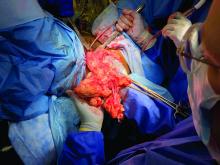
Removal of a 7.4-kg uterus
Our patient was a 44-year-old with a markedly enlarged fibroid uterus. Having been told by other providers that she was not a candidate for minimally invasive hysterectomy, she had delayed surgical management for a number of years, allowing for such a generous uterine size to develop.
The patient was knowledgeable about her condition and, given her comorbid obesity, she requested a minimally invasive approach. Preoperative imaging included an ultrasound, which had to be completed abdominally because of the size of her uterus, and an additional MRI was needed to further characterize the extent and nature of her uterus. A very detailed discussion regarding risk of leiomyosarcoma, operative complications, and conversion to laparotomy ensued.
Intraoperatively, we placed the first 5 mm port in the left upper quadrant initially to survey the anatomy for feasibility of laparoscopic hysterectomy. The left utero-ovarian pedicle was easily viewed by airplaning the bed alone. While the right utero-ovarian pedicle was much more skewed and enlarged, the right IP was easily accessible and the ureter well visualized.
The decision was made to place additional ports and proceed with laparoscopic hysterectomy. The 5-mm assistant ports were placed lateral and directly above the upper vascular pedicles. Operative time was 4 hours and 12 minutes, and blood loss was only 700 cc. Her preoperative hemoglobin was optimized at 13.3 g/dL and dropped to 11.3 g/dL postoperatively. The patient was discharged home the next morning and had a normal recovery with no complications.
Dr. Pasic is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director of the section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy; and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as well as an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Louisville. Dr. Pasic disclosed he is a consultant for Ethicon Endo, Medtronic, and Olympus and is a speaker for Cooper Surgical, which manufactures some of the instruments mentioned in this article. Dr. Cesta had no relevant financial disclosures.
It has now been 30 years since the first total laparoscopic hysterectomy was performed. The benefits of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS) – and of minimally invasive hysterectomy specifically – are now well documented. Since this milestone procedure, both instrumentation and technique have improved significantly.
This includes traditional laparoscopy, as well as the robotically assisted laparoscopic approach. However, certain patient characteristics also may influence the choice. A uterus that is undescended, combined with a narrow introitus, for instance, can be a contributory factor in choosing to perform laparoscopic hysterectomy. Additionally, so can an extremely large uterus and an extremely high body mass index (BMI).
These latter two factors – a very large uterus (which we define as more than 15-16 weeks’ gestational size) and a BMI over 60 kg/m2 – historically were considered to be contraindications to laparoscopic hysterectomy. But as the proficiency, comfort, and skill of a new generation of laparoscopic surgeons increases, the tide is shifting with respect to both morbid obesity and the very large uterus.
With growing experience and improved instrumentation, the majority of gynecologists who are fellowship-trained in MIGS are able to routinely and safely perform laparoscopic hysterectomy for uteri weighing 1-2 kg and in patients who have extreme morbid obesity. The literature, moreover, increasingly features case reports of laparoscopic removal of very large uteri and reviews/discussions of total laparoscopic hysterectomy being feasible.
In our own experience, total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) of the very large uterus can be safely and advantageously performed using key instruments and refinements in technique, as well as thorough patient counseling regarding the risk of unexpected sarcomas. Recently, we safely performed total laparoscopic hysterectomy for a patient with a uterus that – somewhat unexpectedly – weighed 7.4 kg.
Surgical pearls
Performing safe and effective total laparoscopic hysterectomy for large uteri – and for morbidly obese patients – hinges largely on modifications in entry and port placement, patient positioning, and choice of instrumentation. With these modifications, we can achieve adequate visualization of critical anatomy and can minimize bleeding. Otherwise, the surgery itself is largely the same. Here are the principles we find most helpful.
Entry and port placement
Traditionally, for TLHs, a camera port is placed at the umbilicus to provide a full view of the pelvis. For the larger uterus – and in women who are extremely obese – we aim to introduce the laparoscope higher. A reliable landmark is the Palmer’s point in the left upper quadrant. From here, we can identify areas for the placement of additional trocars.
In general, we place ancillary 5-mm ports more cephalad and lateral to the uterus than we otherwise would. Such placement facilitates effective visualization while accommodating manipulation of the uterus and allows us to avoid bleeding around the vascular upper pedicles. Overall, we have much better control through all parts of the surgery when we operate lateral to the uterus.
Patient positioning
In addition to the Trendelenburg position, we have adopted an “airplaning” technique for patients with a very large uterus in which the bed is tilted from side to side so that the left and right sides of the body are rotated upward as needed. This allows for gravitational-assisted retraction when it otherwise is not possible.
Instrumentation
For morbidly obese patients, we use Kii Fios advanced fixation trocars. These come in 5- and 10-mm sizes and are equipped with an intraperitoneal balloon that can be inflated to prevent sliding of the trocar out of the abdominal wall.
By far the most valuable instrument for the morbidly obese and the very large uterus is a 30-degree laparoscope. With our higher port placement as described, the 30-degree scope provides visualization of critical structures that wouldn’t be possible with a 0-degree scope.
The Rumi uterine manipulator comes with cups that come in different sizes and can fit around the cervix and help delineate the cervicouterine junction. We use this manipulator for all laparoscopic hysterectomies, but it is a must for the very large uterus.
Extensive desiccation of the utero-ovarian pedicles and uterine arteries is critical, and for this we advise using the rotating bipolar RoBi instrument. Use of the conventional bipolar instrument allows us to use targeted and anatomically guided application of energy. This ensures certainty that vessels whose limits exceed the diameter for advanced bipolar devices (typically 7 mm) are completely sealed. In-depth knowledge of pelvic anatomy and advanced laparoscopic dissection is paramount during these steps to ensure that vital structures are not damaged by the wider thermal spread of the traditional bipolar device. For cutting, the use of ultrasonic energy is important to prevent energy from spreading laterally.
Lastly, we recommend a good suction irrigator because, if bleeding occurs, it tends to be heavy because of the enlarged nature of feeding vasculature. When placed through an umbilical or suprapubic port, the suction irrigator also may be used to help with the rotational vectors and traction for further uterine manipulation.
Technique
We usually operate from top to bottom, transecting the upper pedicles such as the infundibulopelvic (IP) ligaments or utero-ovarian ligaments first, rather than the round ligaments. This helps us achieve additional mobility of the uterus. Some surgeons believe that retroperitoneal dissection and ligation of the uterine arteries at their origin is essential, but we find that, with good uterine manipulation and the use of a 30-degree scope, we achieve adequate visualization for identifying the ureter and uterine artery on the sidewall and consequently do not need to dissect retroperitoneally.
When using the uterine manipulator with the colpotomy cup, the uterus is pushed upward, increasing the distance between the vaginal fornix and the ureters. Uterine arteries can easily be identified and desiccated using conventional bipolar energy. When the colpotomy cup is pushed cephalad, the application of the bipolar energy within the limits of the cup is safe. The thermal spread does not pose a threat to the ureters, which are displaced 1.5-2 cm laterally. Large fibroids often contribute to distorted anatomical planes, and a colpotomy cup provides a firm palpable surface between the cervix and vagina during dissection.
When dealing with large uteri, one must sometimes think outside the box and deviate from standard technique. For instance, in patients with distorted anatomy because of large fibroids, it helps to first control the pedicles that are most easily accessible. Sometimes it is acceptable to perform oophorectomy if the IP ligament is more accessible and the utero-ovarian pedicle is distorted by dilated veins and adherent to the uterus. After transection of each pedicle, we gain more mobility of the uterus and better visualization for the next step.
Inserting the camera through ancillary ports – a technique known as “port hopping” – helps to visualize and take down adhesions much better and more safely than using the camera from the umbilical port only. Port hopping with a 30-degree laparoscope helps to obtain a 360-degree view of adhesions and anatomy, which is exceedingly helpful in cases in which crucial anatomical structures are within close proximity of one another.
In general it is more challenging to perform TLH on a patient with a broad uterus or a patient with low posterior fibroids that are occupying the pelvis than on a patient with fibroids in the upper abdomen. The main challenge for the surgeon is to safely secure the uterine arteries and control the blood supply to the uterus.
Access to the pelvic sidewall is obtained with the combination of 30-degree scope, uterine manipulator, and the suction irrigator introduced through the midline port; the cervix and uterus are deviated upward. Instead of the suction irrigator or blunt dissector used for internal uterine manipulation, some surgeons use myoma screws or a 5-mm single-tooth tenaculum to manipulate a large uterus. Both of those instruments are valuable and work well, but often a large uterus requires extensive manipulation. Repositioning of any sharp instruments that pierce the serosa can often lead to additional blood loss. It is preferable to avoid this blood loss on a large uterus at all costs because it can be brisk and stains the surgical pedicles, making the remainder of the procedure unnecessarily difficult.
Once the uterine arteries are desiccated, if fibroids are obscuring the view, the corpus of the uterus can be detached from the cervix as in supracervical hysterectomy fashion. From there, the uterus can be placed in the upper abdomen while colpotomy can be performed.
In patients with multiple fibroids, we do not recommend performing myomectomy first, unless the fibroid is pedunculated and on a very small stalk. Improved uterine manipulation and retroperitoneal dissection are preferred over myomectomy to safely complete hysterectomy for the broad uterus. In our opinion, any attempt at myomectomy would lead to unnecessary blood loss and additional operative time with minimal benefit.
In patients with fibroids that grow into the broad ligament and pelvic sidewall, the natural course of the ureter becomes displaced laterally. This is contrary to the popular misconception that the ureter is more medially located in the setting of broad-ligament fibroids. To ensure safe access to the uterine arteries, the vesicouterine peritoneum can be incised and extended cephalad along the broad ligament and, then, using the above-mentioned technique, by pushing the uterus and the fibroid to the contralateral side via the suction irrigator, the uterine arteries can be easily accessed.
Another useful technique is to use diluted vasopressin injected into the lower pole of the uterus to cause vasoconstriction and minimize the bleeding. The concentration is 1 cc of 20 units of vasopressin in 100-400 cc of saline. This technique is very useful for myomectomies, and some surgeons find it also helpful for hysterectomy. The plasma half-life of vasopressin is 10-20 minutes, and a large quantity is needed to help with vasoconstriction in a big uterus. The safe upper limits of vasopressin dosing are not firmly established. A fibroid uterus with aberrant vasculature may require a greater-than-acceptable dose to control bleeding.
It is important to ensure that patients have an optimized hemoglobin level preoperatively. We use a hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL as a lowest cutoff value for performing TLH without preoperative transfusion. Regarding bowel preparation, neither the literature nor our own experience support its value, so we typically do not use it.
Morcellation and patient counseling
Uteri up to 12 weeks’ gestational size usually can be extracted transvaginally, and most uteri regardless of size can be morcellated and extracted through the vagina, providing that the vaginal fornix is accessible from below. In some cases, such as when the apex is too high, a minilaparotomic incision is needed to extract the uterus, or when available, power morcellation can be performed.
A major challenge, given our growing ability to laparoscopically remove very larger uteri, is that uteri heavier than about 2.5 kg in weight cannot be morcellated inside a morcellation bag. The risk of upstaging a known or suspected uterine malignancy, or of spreading an unknown malignant sarcoma (presumed benign myoma), should be incorporated in each patient’s decision making.
Thorough counseling about surgical options and on the risks of morcellating a very large uterus without containment in a bag is essential. Each patient must understand the risks and decide whether the benefits of minimally invasive surgery outweigh these risks. While MRI can sometimes provide increased suspicion of a leiomyosarcoma, malignancy can never be completed excluded preoperatively.
Removal of a 7.4-kg uterus
Our patient was a 44-year-old with a markedly enlarged fibroid uterus. Having been told by other providers that she was not a candidate for minimally invasive hysterectomy, she had delayed surgical management for a number of years, allowing for such a generous uterine size to develop.
The patient was knowledgeable about her condition and, given her comorbid obesity, she requested a minimally invasive approach. Preoperative imaging included an ultrasound, which had to be completed abdominally because of the size of her uterus, and an additional MRI was needed to further characterize the extent and nature of her uterus. A very detailed discussion regarding risk of leiomyosarcoma, operative complications, and conversion to laparotomy ensued.
Intraoperatively, we placed the first 5 mm port in the left upper quadrant initially to survey the anatomy for feasibility of laparoscopic hysterectomy. The left utero-ovarian pedicle was easily viewed by airplaning the bed alone. While the right utero-ovarian pedicle was much more skewed and enlarged, the right IP was easily accessible and the ureter well visualized.
The decision was made to place additional ports and proceed with laparoscopic hysterectomy. The 5-mm assistant ports were placed lateral and directly above the upper vascular pedicles. Operative time was 4 hours and 12 minutes, and blood loss was only 700 cc. Her preoperative hemoglobin was optimized at 13.3 g/dL and dropped to 11.3 g/dL postoperatively. The patient was discharged home the next morning and had a normal recovery with no complications.
Dr. Pasic is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director of the section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy; and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as well as an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Louisville. Dr. Pasic disclosed he is a consultant for Ethicon Endo, Medtronic, and Olympus and is a speaker for Cooper Surgical, which manufactures some of the instruments mentioned in this article. Dr. Cesta had no relevant financial disclosures.
It has now been 30 years since the first total laparoscopic hysterectomy was performed. The benefits of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS) – and of minimally invasive hysterectomy specifically – are now well documented. Since this milestone procedure, both instrumentation and technique have improved significantly.
This includes traditional laparoscopy, as well as the robotically assisted laparoscopic approach. However, certain patient characteristics also may influence the choice. A uterus that is undescended, combined with a narrow introitus, for instance, can be a contributory factor in choosing to perform laparoscopic hysterectomy. Additionally, so can an extremely large uterus and an extremely high body mass index (BMI).
These latter two factors – a very large uterus (which we define as more than 15-16 weeks’ gestational size) and a BMI over 60 kg/m2 – historically were considered to be contraindications to laparoscopic hysterectomy. But as the proficiency, comfort, and skill of a new generation of laparoscopic surgeons increases, the tide is shifting with respect to both morbid obesity and the very large uterus.
With growing experience and improved instrumentation, the majority of gynecologists who are fellowship-trained in MIGS are able to routinely and safely perform laparoscopic hysterectomy for uteri weighing 1-2 kg and in patients who have extreme morbid obesity. The literature, moreover, increasingly features case reports of laparoscopic removal of very large uteri and reviews/discussions of total laparoscopic hysterectomy being feasible.
In our own experience, total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) of the very large uterus can be safely and advantageously performed using key instruments and refinements in technique, as well as thorough patient counseling regarding the risk of unexpected sarcomas. Recently, we safely performed total laparoscopic hysterectomy for a patient with a uterus that – somewhat unexpectedly – weighed 7.4 kg.
Surgical pearls
Performing safe and effective total laparoscopic hysterectomy for large uteri – and for morbidly obese patients – hinges largely on modifications in entry and port placement, patient positioning, and choice of instrumentation. With these modifications, we can achieve adequate visualization of critical anatomy and can minimize bleeding. Otherwise, the surgery itself is largely the same. Here are the principles we find most helpful.
Entry and port placement
Traditionally, for TLHs, a camera port is placed at the umbilicus to provide a full view of the pelvis. For the larger uterus – and in women who are extremely obese – we aim to introduce the laparoscope higher. A reliable landmark is the Palmer’s point in the left upper quadrant. From here, we can identify areas for the placement of additional trocars.
In general, we place ancillary 5-mm ports more cephalad and lateral to the uterus than we otherwise would. Such placement facilitates effective visualization while accommodating manipulation of the uterus and allows us to avoid bleeding around the vascular upper pedicles. Overall, we have much better control through all parts of the surgery when we operate lateral to the uterus.
Patient positioning
In addition to the Trendelenburg position, we have adopted an “airplaning” technique for patients with a very large uterus in which the bed is tilted from side to side so that the left and right sides of the body are rotated upward as needed. This allows for gravitational-assisted retraction when it otherwise is not possible.
Instrumentation
For morbidly obese patients, we use Kii Fios advanced fixation trocars. These come in 5- and 10-mm sizes and are equipped with an intraperitoneal balloon that can be inflated to prevent sliding of the trocar out of the abdominal wall.
By far the most valuable instrument for the morbidly obese and the very large uterus is a 30-degree laparoscope. With our higher port placement as described, the 30-degree scope provides visualization of critical structures that wouldn’t be possible with a 0-degree scope.
The Rumi uterine manipulator comes with cups that come in different sizes and can fit around the cervix and help delineate the cervicouterine junction. We use this manipulator for all laparoscopic hysterectomies, but it is a must for the very large uterus.
Extensive desiccation of the utero-ovarian pedicles and uterine arteries is critical, and for this we advise using the rotating bipolar RoBi instrument. Use of the conventional bipolar instrument allows us to use targeted and anatomically guided application of energy. This ensures certainty that vessels whose limits exceed the diameter for advanced bipolar devices (typically 7 mm) are completely sealed. In-depth knowledge of pelvic anatomy and advanced laparoscopic dissection is paramount during these steps to ensure that vital structures are not damaged by the wider thermal spread of the traditional bipolar device. For cutting, the use of ultrasonic energy is important to prevent energy from spreading laterally.
Lastly, we recommend a good suction irrigator because, if bleeding occurs, it tends to be heavy because of the enlarged nature of feeding vasculature. When placed through an umbilical or suprapubic port, the suction irrigator also may be used to help with the rotational vectors and traction for further uterine manipulation.
Technique
We usually operate from top to bottom, transecting the upper pedicles such as the infundibulopelvic (IP) ligaments or utero-ovarian ligaments first, rather than the round ligaments. This helps us achieve additional mobility of the uterus. Some surgeons believe that retroperitoneal dissection and ligation of the uterine arteries at their origin is essential, but we find that, with good uterine manipulation and the use of a 30-degree scope, we achieve adequate visualization for identifying the ureter and uterine artery on the sidewall and consequently do not need to dissect retroperitoneally.
When using the uterine manipulator with the colpotomy cup, the uterus is pushed upward, increasing the distance between the vaginal fornix and the ureters. Uterine arteries can easily be identified and desiccated using conventional bipolar energy. When the colpotomy cup is pushed cephalad, the application of the bipolar energy within the limits of the cup is safe. The thermal spread does not pose a threat to the ureters, which are displaced 1.5-2 cm laterally. Large fibroids often contribute to distorted anatomical planes, and a colpotomy cup provides a firm palpable surface between the cervix and vagina during dissection.
When dealing with large uteri, one must sometimes think outside the box and deviate from standard technique. For instance, in patients with distorted anatomy because of large fibroids, it helps to first control the pedicles that are most easily accessible. Sometimes it is acceptable to perform oophorectomy if the IP ligament is more accessible and the utero-ovarian pedicle is distorted by dilated veins and adherent to the uterus. After transection of each pedicle, we gain more mobility of the uterus and better visualization for the next step.
Inserting the camera through ancillary ports – a technique known as “port hopping” – helps to visualize and take down adhesions much better and more safely than using the camera from the umbilical port only. Port hopping with a 30-degree laparoscope helps to obtain a 360-degree view of adhesions and anatomy, which is exceedingly helpful in cases in which crucial anatomical structures are within close proximity of one another.
In general it is more challenging to perform TLH on a patient with a broad uterus or a patient with low posterior fibroids that are occupying the pelvis than on a patient with fibroids in the upper abdomen. The main challenge for the surgeon is to safely secure the uterine arteries and control the blood supply to the uterus.
Access to the pelvic sidewall is obtained with the combination of 30-degree scope, uterine manipulator, and the suction irrigator introduced through the midline port; the cervix and uterus are deviated upward. Instead of the suction irrigator or blunt dissector used for internal uterine manipulation, some surgeons use myoma screws or a 5-mm single-tooth tenaculum to manipulate a large uterus. Both of those instruments are valuable and work well, but often a large uterus requires extensive manipulation. Repositioning of any sharp instruments that pierce the serosa can often lead to additional blood loss. It is preferable to avoid this blood loss on a large uterus at all costs because it can be brisk and stains the surgical pedicles, making the remainder of the procedure unnecessarily difficult.
Once the uterine arteries are desiccated, if fibroids are obscuring the view, the corpus of the uterus can be detached from the cervix as in supracervical hysterectomy fashion. From there, the uterus can be placed in the upper abdomen while colpotomy can be performed.
In patients with multiple fibroids, we do not recommend performing myomectomy first, unless the fibroid is pedunculated and on a very small stalk. Improved uterine manipulation and retroperitoneal dissection are preferred over myomectomy to safely complete hysterectomy for the broad uterus. In our opinion, any attempt at myomectomy would lead to unnecessary blood loss and additional operative time with minimal benefit.
In patients with fibroids that grow into the broad ligament and pelvic sidewall, the natural course of the ureter becomes displaced laterally. This is contrary to the popular misconception that the ureter is more medially located in the setting of broad-ligament fibroids. To ensure safe access to the uterine arteries, the vesicouterine peritoneum can be incised and extended cephalad along the broad ligament and, then, using the above-mentioned technique, by pushing the uterus and the fibroid to the contralateral side via the suction irrigator, the uterine arteries can be easily accessed.
Another useful technique is to use diluted vasopressin injected into the lower pole of the uterus to cause vasoconstriction and minimize the bleeding. The concentration is 1 cc of 20 units of vasopressin in 100-400 cc of saline. This technique is very useful for myomectomies, and some surgeons find it also helpful for hysterectomy. The plasma half-life of vasopressin is 10-20 minutes, and a large quantity is needed to help with vasoconstriction in a big uterus. The safe upper limits of vasopressin dosing are not firmly established. A fibroid uterus with aberrant vasculature may require a greater-than-acceptable dose to control bleeding.
It is important to ensure that patients have an optimized hemoglobin level preoperatively. We use a hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL as a lowest cutoff value for performing TLH without preoperative transfusion. Regarding bowel preparation, neither the literature nor our own experience support its value, so we typically do not use it.
Morcellation and patient counseling
Uteri up to 12 weeks’ gestational size usually can be extracted transvaginally, and most uteri regardless of size can be morcellated and extracted through the vagina, providing that the vaginal fornix is accessible from below. In some cases, such as when the apex is too high, a minilaparotomic incision is needed to extract the uterus, or when available, power morcellation can be performed.
A major challenge, given our growing ability to laparoscopically remove very larger uteri, is that uteri heavier than about 2.5 kg in weight cannot be morcellated inside a morcellation bag. The risk of upstaging a known or suspected uterine malignancy, or of spreading an unknown malignant sarcoma (presumed benign myoma), should be incorporated in each patient’s decision making.
Thorough counseling about surgical options and on the risks of morcellating a very large uterus without containment in a bag is essential. Each patient must understand the risks and decide whether the benefits of minimally invasive surgery outweigh these risks. While MRI can sometimes provide increased suspicion of a leiomyosarcoma, malignancy can never be completed excluded preoperatively.
Removal of a 7.4-kg uterus
Our patient was a 44-year-old with a markedly enlarged fibroid uterus. Having been told by other providers that she was not a candidate for minimally invasive hysterectomy, she had delayed surgical management for a number of years, allowing for such a generous uterine size to develop.
The patient was knowledgeable about her condition and, given her comorbid obesity, she requested a minimally invasive approach. Preoperative imaging included an ultrasound, which had to be completed abdominally because of the size of her uterus, and an additional MRI was needed to further characterize the extent and nature of her uterus. A very detailed discussion regarding risk of leiomyosarcoma, operative complications, and conversion to laparotomy ensued.
Intraoperatively, we placed the first 5 mm port in the left upper quadrant initially to survey the anatomy for feasibility of laparoscopic hysterectomy. The left utero-ovarian pedicle was easily viewed by airplaning the bed alone. While the right utero-ovarian pedicle was much more skewed and enlarged, the right IP was easily accessible and the ureter well visualized.
The decision was made to place additional ports and proceed with laparoscopic hysterectomy. The 5-mm assistant ports were placed lateral and directly above the upper vascular pedicles. Operative time was 4 hours and 12 minutes, and blood loss was only 700 cc. Her preoperative hemoglobin was optimized at 13.3 g/dL and dropped to 11.3 g/dL postoperatively. The patient was discharged home the next morning and had a normal recovery with no complications.
Dr. Pasic is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director of the section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy; and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as well as an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Louisville. Dr. Pasic disclosed he is a consultant for Ethicon Endo, Medtronic, and Olympus and is a speaker for Cooper Surgical, which manufactures some of the instruments mentioned in this article. Dr. Cesta had no relevant financial disclosures.
Safely pushing the limits of MIGS surgery
In his excellent treatise on the history of hysterectomy, Chris Sutton, MBBch, noted that, while Themison of Athens in 50 bc and Soranus of Ephesus in 120 ad were reported to have performed vaginal hysterectomy, these cases essentially were emergency amputation of severely prolapsed uteri, which usually involved cutting both ureters and the bladder (J Minim Invas Gynecol. 2010 Jul;17[4]:421–35). It was not until 1801 that the first planned elective vaginal hysterectomy was performed, and it was not until the mid 19th century, in 1853, that Walter Burnham, MD, in Lowell, Mass., performed the first abdominal hysterectomy resulting in patient survival.
Seemingly incredible, it was only 125 years later, in autumn of 1988 at William Nesbitt Memorial Hospital in Kingston, Pa., that Harry Reich, MD, performed the first total laparoscopically assisted hysterectomy.
Since Dr. Reich’s groundbreaking procedure, the performance of laparoscopic hysterectomy has advanced at a feverish pace. In my own practice, I have not performed an abdominal hysterectomy since 1998. My two partners, who are both fellowship-trained in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS), Aarathi Cholkeri-Singh, MD, who joined my practice in 2007, and Kristen Sasaki, MD, who joined my practice in 2014, have never performed an open hysterectomy since starting practice. Despite these advances, One of the most difficult situations is the truly large uterus – greater than 2,500 grams.
For this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted the assistance of Paya Pasic, MD, and Megan Cesta, MD, to discuss the next frontier: the removal of the multiple kilogram uterus.
Dr. Pasic is an internationally recognized leader in laparoscopic MIGS. He is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director, section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy, and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in MIGS at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Pasic is published in the field of MIGS, having authored many publications, book chapters, monographs, and textbooks.
Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in MIGS and an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the university.
It is truly a pleasure to welcome Dr. Pasic and Dr. Cesta to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is a clinical associate professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago and past president of the AAGL. He is a reproductive endocrinologist and minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in metropolitan Chicago and the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. He has no disclosures relevant to this Master Class. Email him at [email protected].
In his excellent treatise on the history of hysterectomy, Chris Sutton, MBBch, noted that, while Themison of Athens in 50 bc and Soranus of Ephesus in 120 ad were reported to have performed vaginal hysterectomy, these cases essentially were emergency amputation of severely prolapsed uteri, which usually involved cutting both ureters and the bladder (J Minim Invas Gynecol. 2010 Jul;17[4]:421–35). It was not until 1801 that the first planned elective vaginal hysterectomy was performed, and it was not until the mid 19th century, in 1853, that Walter Burnham, MD, in Lowell, Mass., performed the first abdominal hysterectomy resulting in patient survival.
Seemingly incredible, it was only 125 years later, in autumn of 1988 at William Nesbitt Memorial Hospital in Kingston, Pa., that Harry Reich, MD, performed the first total laparoscopically assisted hysterectomy.
Since Dr. Reich’s groundbreaking procedure, the performance of laparoscopic hysterectomy has advanced at a feverish pace. In my own practice, I have not performed an abdominal hysterectomy since 1998. My two partners, who are both fellowship-trained in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS), Aarathi Cholkeri-Singh, MD, who joined my practice in 2007, and Kristen Sasaki, MD, who joined my practice in 2014, have never performed an open hysterectomy since starting practice. Despite these advances, One of the most difficult situations is the truly large uterus – greater than 2,500 grams.
For this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted the assistance of Paya Pasic, MD, and Megan Cesta, MD, to discuss the next frontier: the removal of the multiple kilogram uterus.
Dr. Pasic is an internationally recognized leader in laparoscopic MIGS. He is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director, section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy, and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in MIGS at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Pasic is published in the field of MIGS, having authored many publications, book chapters, monographs, and textbooks.
Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in MIGS and an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the university.
It is truly a pleasure to welcome Dr. Pasic and Dr. Cesta to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is a clinical associate professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago and past president of the AAGL. He is a reproductive endocrinologist and minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in metropolitan Chicago and the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. He has no disclosures relevant to this Master Class. Email him at [email protected].
In his excellent treatise on the history of hysterectomy, Chris Sutton, MBBch, noted that, while Themison of Athens in 50 bc and Soranus of Ephesus in 120 ad were reported to have performed vaginal hysterectomy, these cases essentially were emergency amputation of severely prolapsed uteri, which usually involved cutting both ureters and the bladder (J Minim Invas Gynecol. 2010 Jul;17[4]:421–35). It was not until 1801 that the first planned elective vaginal hysterectomy was performed, and it was not until the mid 19th century, in 1853, that Walter Burnham, MD, in Lowell, Mass., performed the first abdominal hysterectomy resulting in patient survival.
Seemingly incredible, it was only 125 years later, in autumn of 1988 at William Nesbitt Memorial Hospital in Kingston, Pa., that Harry Reich, MD, performed the first total laparoscopically assisted hysterectomy.
Since Dr. Reich’s groundbreaking procedure, the performance of laparoscopic hysterectomy has advanced at a feverish pace. In my own practice, I have not performed an abdominal hysterectomy since 1998. My two partners, who are both fellowship-trained in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS), Aarathi Cholkeri-Singh, MD, who joined my practice in 2007, and Kristen Sasaki, MD, who joined my practice in 2014, have never performed an open hysterectomy since starting practice. Despite these advances, One of the most difficult situations is the truly large uterus – greater than 2,500 grams.
For this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted the assistance of Paya Pasic, MD, and Megan Cesta, MD, to discuss the next frontier: the removal of the multiple kilogram uterus.
Dr. Pasic is an internationally recognized leader in laparoscopic MIGS. He is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director, section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy, and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in MIGS at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Pasic is published in the field of MIGS, having authored many publications, book chapters, monographs, and textbooks.
Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in MIGS and an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the university.
It is truly a pleasure to welcome Dr. Pasic and Dr. Cesta to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is a clinical associate professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago and past president of the AAGL. He is a reproductive endocrinologist and minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in metropolitan Chicago and the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. He has no disclosures relevant to this Master Class. Email him at [email protected].
Avelumab maintenance in gastric cancer is down but maybe not out
SAN FRANCISCO – Maintenance therapy with avelumab does not prolong survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer relative to continued chemotherapy, results of the JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial suggest.
However, it may not be end of the line for avelumab in this setting, as the checkpoint inhibitor may benefit certain subgroups of patients, according to Markus H. Moehler, MD, PhD, of the Johannes Gutenberg-University Clinic in Mainz, Germany, who presented results from the trial at the symposium.
In the phase 3 trial, investigators enrolled 805 patients with untreated locally advanced or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer. All patients received first-line chemotherapy.
The 499 patients (62%) who did not experience progression were randomized to receive the anti– programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody avelumab (n = 249) or continued chemotherapy (n = 250). There were 6 patients in the avelumab arm and 12 in the chemotherapy arm who did not receive maintenance treatment, and 7 patients in the chemotherapy arm received best supportive care as maintenance.
Efficacy and safety
The minimum follow-up was 18 months. The median overall survival in the entire population was about the same for both treatment groups, 10.4 months with avelumab and 10.9 months with chemotherapy (P = .1779).
Findings were similar among the 12.3% of patients whose tumors were PD-L1 positive as defined by staining of at least 1% of tumor cells. The median overall survival in this group was 16.2 months with avelumab and 17.7 months with chemotherapy (P = .6352).
On exploratory analysis, results with avelumab were more favorable among the 64.3% of patients whose tumors were PD-L1 positive as defined by a combined positive score (CPS) of 1 or greater. The median overall survival in this group was 14.9 months with avelumab and 11.6 months with chemotherapy.
In subgroup analyses by other characteristics, avelumab appeared to have the edge among patients free of metastases at baseline. In this group, the median overall survival was 16.3 months with avelumab, compared with 10.7 months with chemotherapy (hazard ratio for death, 0.52).
Among all patients, the pattern comparing avelumab with chemotherapy was similar for median progression-free survival (3.2 months vs. 4.4 months) and objective response rate (13.3% vs. 14.4%). The median duration of response was not reached.
“JAVELIN Gastric 100 did not meet its primary objective of demonstrating superior overall survival with avelumab maintenance versus chemotherapy or best supportive care in gastric cancer, either in all randomized patients or in the PD-L1–positive population,” Dr. Moehler said. “However, avelumab maintenance showed clear clinical activity. Further studies are needed to identify patients who can derive benefit from checkpoint inhibitor therapy across the continuum of care with gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer.”
The avelumab and chemotherapy groups had similar rates of any grade 3 or higher adverse events (54.3% vs. 53.8%), but the avelumab group had a lower rate of treatment-related grade 3 or higher adverse events (12.8% vs. 32.8%).
A ‘yin-yang’ pattern of survival
“Monotherapy checkpoint blockade with anti–programmed death-1 (PD-1) and anti–PD-L1 inhibitors has had relatively unimpressive results in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma as a whole,” said invited discussant Daniel V. T. Catenacci, MD, of University of Chicago Medicine.
He added that the JAVELIN Gastric 100 survival analysis was noteworthy for the presence of a “yin-yang” pattern, whereby the avelumab curve during follow-up was lower than the chemotherapy curve initially but came out on top eventually.
The 12-month overall survival rate was 43.6% with avelumab and 45.3% with chemotherapy. The 24-month overall survival rates were 22.1% and 15.5%, respectively.
This type of pattern is seen in many similar gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma trials of checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy, even among patients selected for higher CPS, Dr. Catenacci noted.
“This tells us that standard chemotherapy is better in a large subgroup of patients and worse in a separate subgroup: those with MSI-high [microsatellite instability–high], and then MSS [microsatellite stable] with even higher PD-L1 scores like CPS greater than 50, low burden of disease (few metastatic sites), preserved performance status, EBV [Epstein-Barr virus] positivity, Asians within global studies compared with non-Asians, and other unknown factors,” Dr. Catenacci explained.
He commended the design of the JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial, whereby the 38% of patients having rapidly progressive disease were excluded, as this subset is known to fare poorly on checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy.
“This could be potentially a great way to select for those patients most likely to benefit,” Dr. Catenacci said. “Unfortunately, even despite that large fallout, the yin-yang curve was still observed in the intention-to-treat population (unselected by any biomarker). This tells us that, even among the most stable and best prognostic patients, checkpoint blockade is still inferior to standard chemotherapy in a large subgroup of patients.”
However, among patients with a CPS of at least 1, the overall survival curve was consistently higher with avelumab.
“So perhaps by excluding patients with rapid disease progression (about 40% of patients) and then those that are CPS 0 (about 33% more of the total), you can then safely switch to monotherapy checkpoint blockade to first do no harm, and also to do better than standard chemotherapy,” Dr. Catenacci proposed.
“However, we have to be careful, as this was an unplanned retrospective analysis and so should be confirmed prospectively. We might also argue that a higher CPS cut off of greater than or equal to 10 could enrich for the benefit observed. Future ongoing phase 3 studies may help to further increase our understanding of where and where not to implement checkpoint monotherapy or combination therapy with standard chemotherapy.”
The JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial was sponsored by EMD Serono and Merck KGaA, which market avelumab in collaboration with Pfizer. Dr. Moehler disclosed relationships with these companies and many others. Dr. Catenacci disclosed relationships with Merck and other companies.
The 2020 GI Cancers Symposium is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the American Society for Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Surgical Oncology.
SOURCE: Moehler MH et al. 2020 GI Cancers Symposium, Abstract 278.
SAN FRANCISCO – Maintenance therapy with avelumab does not prolong survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer relative to continued chemotherapy, results of the JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial suggest.
However, it may not be end of the line for avelumab in this setting, as the checkpoint inhibitor may benefit certain subgroups of patients, according to Markus H. Moehler, MD, PhD, of the Johannes Gutenberg-University Clinic in Mainz, Germany, who presented results from the trial at the symposium.
In the phase 3 trial, investigators enrolled 805 patients with untreated locally advanced or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer. All patients received first-line chemotherapy.
The 499 patients (62%) who did not experience progression were randomized to receive the anti– programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody avelumab (n = 249) or continued chemotherapy (n = 250). There were 6 patients in the avelumab arm and 12 in the chemotherapy arm who did not receive maintenance treatment, and 7 patients in the chemotherapy arm received best supportive care as maintenance.
Efficacy and safety
The minimum follow-up was 18 months. The median overall survival in the entire population was about the same for both treatment groups, 10.4 months with avelumab and 10.9 months with chemotherapy (P = .1779).
Findings were similar among the 12.3% of patients whose tumors were PD-L1 positive as defined by staining of at least 1% of tumor cells. The median overall survival in this group was 16.2 months with avelumab and 17.7 months with chemotherapy (P = .6352).
On exploratory analysis, results with avelumab were more favorable among the 64.3% of patients whose tumors were PD-L1 positive as defined by a combined positive score (CPS) of 1 or greater. The median overall survival in this group was 14.9 months with avelumab and 11.6 months with chemotherapy.
In subgroup analyses by other characteristics, avelumab appeared to have the edge among patients free of metastases at baseline. In this group, the median overall survival was 16.3 months with avelumab, compared with 10.7 months with chemotherapy (hazard ratio for death, 0.52).
Among all patients, the pattern comparing avelumab with chemotherapy was similar for median progression-free survival (3.2 months vs. 4.4 months) and objective response rate (13.3% vs. 14.4%). The median duration of response was not reached.
“JAVELIN Gastric 100 did not meet its primary objective of demonstrating superior overall survival with avelumab maintenance versus chemotherapy or best supportive care in gastric cancer, either in all randomized patients or in the PD-L1–positive population,” Dr. Moehler said. “However, avelumab maintenance showed clear clinical activity. Further studies are needed to identify patients who can derive benefit from checkpoint inhibitor therapy across the continuum of care with gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer.”
The avelumab and chemotherapy groups had similar rates of any grade 3 or higher adverse events (54.3% vs. 53.8%), but the avelumab group had a lower rate of treatment-related grade 3 or higher adverse events (12.8% vs. 32.8%).
A ‘yin-yang’ pattern of survival
“Monotherapy checkpoint blockade with anti–programmed death-1 (PD-1) and anti–PD-L1 inhibitors has had relatively unimpressive results in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma as a whole,” said invited discussant Daniel V. T. Catenacci, MD, of University of Chicago Medicine.
He added that the JAVELIN Gastric 100 survival analysis was noteworthy for the presence of a “yin-yang” pattern, whereby the avelumab curve during follow-up was lower than the chemotherapy curve initially but came out on top eventually.
The 12-month overall survival rate was 43.6% with avelumab and 45.3% with chemotherapy. The 24-month overall survival rates were 22.1% and 15.5%, respectively.
This type of pattern is seen in many similar gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma trials of checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy, even among patients selected for higher CPS, Dr. Catenacci noted.
“This tells us that standard chemotherapy is better in a large subgroup of patients and worse in a separate subgroup: those with MSI-high [microsatellite instability–high], and then MSS [microsatellite stable] with even higher PD-L1 scores like CPS greater than 50, low burden of disease (few metastatic sites), preserved performance status, EBV [Epstein-Barr virus] positivity, Asians within global studies compared with non-Asians, and other unknown factors,” Dr. Catenacci explained.
He commended the design of the JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial, whereby the 38% of patients having rapidly progressive disease were excluded, as this subset is known to fare poorly on checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy.
“This could be potentially a great way to select for those patients most likely to benefit,” Dr. Catenacci said. “Unfortunately, even despite that large fallout, the yin-yang curve was still observed in the intention-to-treat population (unselected by any biomarker). This tells us that, even among the most stable and best prognostic patients, checkpoint blockade is still inferior to standard chemotherapy in a large subgroup of patients.”
However, among patients with a CPS of at least 1, the overall survival curve was consistently higher with avelumab.
“So perhaps by excluding patients with rapid disease progression (about 40% of patients) and then those that are CPS 0 (about 33% more of the total), you can then safely switch to monotherapy checkpoint blockade to first do no harm, and also to do better than standard chemotherapy,” Dr. Catenacci proposed.
“However, we have to be careful, as this was an unplanned retrospective analysis and so should be confirmed prospectively. We might also argue that a higher CPS cut off of greater than or equal to 10 could enrich for the benefit observed. Future ongoing phase 3 studies may help to further increase our understanding of where and where not to implement checkpoint monotherapy or combination therapy with standard chemotherapy.”
The JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial was sponsored by EMD Serono and Merck KGaA, which market avelumab in collaboration with Pfizer. Dr. Moehler disclosed relationships with these companies and many others. Dr. Catenacci disclosed relationships with Merck and other companies.
The 2020 GI Cancers Symposium is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the American Society for Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Surgical Oncology.
SOURCE: Moehler MH et al. 2020 GI Cancers Symposium, Abstract 278.
SAN FRANCISCO – Maintenance therapy with avelumab does not prolong survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer relative to continued chemotherapy, results of the JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial suggest.
However, it may not be end of the line for avelumab in this setting, as the checkpoint inhibitor may benefit certain subgroups of patients, according to Markus H. Moehler, MD, PhD, of the Johannes Gutenberg-University Clinic in Mainz, Germany, who presented results from the trial at the symposium.
In the phase 3 trial, investigators enrolled 805 patients with untreated locally advanced or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer. All patients received first-line chemotherapy.
The 499 patients (62%) who did not experience progression were randomized to receive the anti– programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody avelumab (n = 249) or continued chemotherapy (n = 250). There were 6 patients in the avelumab arm and 12 in the chemotherapy arm who did not receive maintenance treatment, and 7 patients in the chemotherapy arm received best supportive care as maintenance.
Efficacy and safety
The minimum follow-up was 18 months. The median overall survival in the entire population was about the same for both treatment groups, 10.4 months with avelumab and 10.9 months with chemotherapy (P = .1779).
Findings were similar among the 12.3% of patients whose tumors were PD-L1 positive as defined by staining of at least 1% of tumor cells. The median overall survival in this group was 16.2 months with avelumab and 17.7 months with chemotherapy (P = .6352).
On exploratory analysis, results with avelumab were more favorable among the 64.3% of patients whose tumors were PD-L1 positive as defined by a combined positive score (CPS) of 1 or greater. The median overall survival in this group was 14.9 months with avelumab and 11.6 months with chemotherapy.
In subgroup analyses by other characteristics, avelumab appeared to have the edge among patients free of metastases at baseline. In this group, the median overall survival was 16.3 months with avelumab, compared with 10.7 months with chemotherapy (hazard ratio for death, 0.52).
Among all patients, the pattern comparing avelumab with chemotherapy was similar for median progression-free survival (3.2 months vs. 4.4 months) and objective response rate (13.3% vs. 14.4%). The median duration of response was not reached.
“JAVELIN Gastric 100 did not meet its primary objective of demonstrating superior overall survival with avelumab maintenance versus chemotherapy or best supportive care in gastric cancer, either in all randomized patients or in the PD-L1–positive population,” Dr. Moehler said. “However, avelumab maintenance showed clear clinical activity. Further studies are needed to identify patients who can derive benefit from checkpoint inhibitor therapy across the continuum of care with gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer.”
The avelumab and chemotherapy groups had similar rates of any grade 3 or higher adverse events (54.3% vs. 53.8%), but the avelumab group had a lower rate of treatment-related grade 3 or higher adverse events (12.8% vs. 32.8%).
A ‘yin-yang’ pattern of survival
“Monotherapy checkpoint blockade with anti–programmed death-1 (PD-1) and anti–PD-L1 inhibitors has had relatively unimpressive results in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma as a whole,” said invited discussant Daniel V. T. Catenacci, MD, of University of Chicago Medicine.
He added that the JAVELIN Gastric 100 survival analysis was noteworthy for the presence of a “yin-yang” pattern, whereby the avelumab curve during follow-up was lower than the chemotherapy curve initially but came out on top eventually.
The 12-month overall survival rate was 43.6% with avelumab and 45.3% with chemotherapy. The 24-month overall survival rates were 22.1% and 15.5%, respectively.
This type of pattern is seen in many similar gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma trials of checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy, even among patients selected for higher CPS, Dr. Catenacci noted.
“This tells us that standard chemotherapy is better in a large subgroup of patients and worse in a separate subgroup: those with MSI-high [microsatellite instability–high], and then MSS [microsatellite stable] with even higher PD-L1 scores like CPS greater than 50, low burden of disease (few metastatic sites), preserved performance status, EBV [Epstein-Barr virus] positivity, Asians within global studies compared with non-Asians, and other unknown factors,” Dr. Catenacci explained.
He commended the design of the JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial, whereby the 38% of patients having rapidly progressive disease were excluded, as this subset is known to fare poorly on checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy.
“This could be potentially a great way to select for those patients most likely to benefit,” Dr. Catenacci said. “Unfortunately, even despite that large fallout, the yin-yang curve was still observed in the intention-to-treat population (unselected by any biomarker). This tells us that, even among the most stable and best prognostic patients, checkpoint blockade is still inferior to standard chemotherapy in a large subgroup of patients.”
However, among patients with a CPS of at least 1, the overall survival curve was consistently higher with avelumab.
“So perhaps by excluding patients with rapid disease progression (about 40% of patients) and then those that are CPS 0 (about 33% more of the total), you can then safely switch to monotherapy checkpoint blockade to first do no harm, and also to do better than standard chemotherapy,” Dr. Catenacci proposed.
“However, we have to be careful, as this was an unplanned retrospective analysis and so should be confirmed prospectively. We might also argue that a higher CPS cut off of greater than or equal to 10 could enrich for the benefit observed. Future ongoing phase 3 studies may help to further increase our understanding of where and where not to implement checkpoint monotherapy or combination therapy with standard chemotherapy.”
The JAVELIN Gastric 100 trial was sponsored by EMD Serono and Merck KGaA, which market avelumab in collaboration with Pfizer. Dr. Moehler disclosed relationships with these companies and many others. Dr. Catenacci disclosed relationships with Merck and other companies.
The 2020 GI Cancers Symposium is sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the American Society for Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Surgical Oncology.
SOURCE: Moehler MH et al. 2020 GI Cancers Symposium, Abstract 278.
REPORTING FROM THE 2020 GI CANCERS SYMPOSIUM
New Barbie lineup includes a doll with vitiligo
A new line of Barbie dolls unveiled by Mattel earlier this month includes one with vitiligo, much to the delight of clinicians who treat children and adolescents with the condition.
“When I see young children and adolescents with vitiligo, it is very common for me to feel their emotional suffering from their skin condition,” Seemal R. Desai, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas said in an interview. “Kids can be cruel. Name calling, social ostracizing, [and] effects on self-esteem are all things I have seen amongst my patients and their families in their own struggles with vitiligo.”
According to a brand communications representative from toymaker Mattel, which began manufacturing Barbie dolls in 1959, the company worked with a board-certified dermatologist to include a doll with vitiligo in its 2020 “Fashionistas” line. “As we continue to redefine what it means to be a ‘Barbie’ or look like Barbie, offering a doll with vitiligo in our main doll line allows kids to play out even more stories they see in the world around them,” the representative wrote in an email message. Other dolls debuting as part of the lineup include one with no hair, one with a darker skin tone that uses a gold prosthetic limb, and a Ken doll with long rooted hair (think Jeff Spicoli in “Fast Times at Ridgemont High,” but about six inches longer).
Such efforts to celebrate diversity and inclusiveness go far in helping children and young adults to embrace their skin and their own identities, said Dr. Desai, the immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology board of directors. “One nuance, perhaps even more important, is that the Barbie can help to break down barriers, create awareness, and potentially even reduce bullying, stigma, and lack of knowledge about vitiligo amongst the general public who don’t understand vitiligo,” he said. “I hope the public and social media will embrace this new Barbie. Who knows? Pretty soon, vitiligo may no longer be a ‘thing’ that causes ‘stares’ and ‘glares.’ ”
Referring to the Barbie with no hair in the new line of dolls, the Mattel statement said, “ if a girl is experiencing hair loss for any reason, she can see herself reflected in the line.”
In 2019, Mattel introduced a lineup of Barbie dolls reflecting permanent disabilities, including one with a prosthetic limb. For that effort, the company collaborated with then-12-year-old Jordan Reeves, the “Born Just Right” coauthor “who is on a mission to build creative solutions that help kids with disabilities, to create a play experience that is as representative as possible,” the Mattel representative wrote.
A new line of Barbie dolls unveiled by Mattel earlier this month includes one with vitiligo, much to the delight of clinicians who treat children and adolescents with the condition.
“When I see young children and adolescents with vitiligo, it is very common for me to feel their emotional suffering from their skin condition,” Seemal R. Desai, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas said in an interview. “Kids can be cruel. Name calling, social ostracizing, [and] effects on self-esteem are all things I have seen amongst my patients and their families in their own struggles with vitiligo.”
According to a brand communications representative from toymaker Mattel, which began manufacturing Barbie dolls in 1959, the company worked with a board-certified dermatologist to include a doll with vitiligo in its 2020 “Fashionistas” line. “As we continue to redefine what it means to be a ‘Barbie’ or look like Barbie, offering a doll with vitiligo in our main doll line allows kids to play out even more stories they see in the world around them,” the representative wrote in an email message. Other dolls debuting as part of the lineup include one with no hair, one with a darker skin tone that uses a gold prosthetic limb, and a Ken doll with long rooted hair (think Jeff Spicoli in “Fast Times at Ridgemont High,” but about six inches longer).
Such efforts to celebrate diversity and inclusiveness go far in helping children and young adults to embrace their skin and their own identities, said Dr. Desai, the immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology board of directors. “One nuance, perhaps even more important, is that the Barbie can help to break down barriers, create awareness, and potentially even reduce bullying, stigma, and lack of knowledge about vitiligo amongst the general public who don’t understand vitiligo,” he said. “I hope the public and social media will embrace this new Barbie. Who knows? Pretty soon, vitiligo may no longer be a ‘thing’ that causes ‘stares’ and ‘glares.’ ”
Referring to the Barbie with no hair in the new line of dolls, the Mattel statement said, “ if a girl is experiencing hair loss for any reason, she can see herself reflected in the line.”
In 2019, Mattel introduced a lineup of Barbie dolls reflecting permanent disabilities, including one with a prosthetic limb. For that effort, the company collaborated with then-12-year-old Jordan Reeves, the “Born Just Right” coauthor “who is on a mission to build creative solutions that help kids with disabilities, to create a play experience that is as representative as possible,” the Mattel representative wrote.
A new line of Barbie dolls unveiled by Mattel earlier this month includes one with vitiligo, much to the delight of clinicians who treat children and adolescents with the condition.
“When I see young children and adolescents with vitiligo, it is very common for me to feel their emotional suffering from their skin condition,” Seemal R. Desai, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas said in an interview. “Kids can be cruel. Name calling, social ostracizing, [and] effects on self-esteem are all things I have seen amongst my patients and their families in their own struggles with vitiligo.”
According to a brand communications representative from toymaker Mattel, which began manufacturing Barbie dolls in 1959, the company worked with a board-certified dermatologist to include a doll with vitiligo in its 2020 “Fashionistas” line. “As we continue to redefine what it means to be a ‘Barbie’ or look like Barbie, offering a doll with vitiligo in our main doll line allows kids to play out even more stories they see in the world around them,” the representative wrote in an email message. Other dolls debuting as part of the lineup include one with no hair, one with a darker skin tone that uses a gold prosthetic limb, and a Ken doll with long rooted hair (think Jeff Spicoli in “Fast Times at Ridgemont High,” but about six inches longer).
Such efforts to celebrate diversity and inclusiveness go far in helping children and young adults to embrace their skin and their own identities, said Dr. Desai, the immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology board of directors. “One nuance, perhaps even more important, is that the Barbie can help to break down barriers, create awareness, and potentially even reduce bullying, stigma, and lack of knowledge about vitiligo amongst the general public who don’t understand vitiligo,” he said. “I hope the public and social media will embrace this new Barbie. Who knows? Pretty soon, vitiligo may no longer be a ‘thing’ that causes ‘stares’ and ‘glares.’ ”
Referring to the Barbie with no hair in the new line of dolls, the Mattel statement said, “ if a girl is experiencing hair loss for any reason, she can see herself reflected in the line.”
In 2019, Mattel introduced a lineup of Barbie dolls reflecting permanent disabilities, including one with a prosthetic limb. For that effort, the company collaborated with then-12-year-old Jordan Reeves, the “Born Just Right” coauthor “who is on a mission to build creative solutions that help kids with disabilities, to create a play experience that is as representative as possible,” the Mattel representative wrote.
Novel coronavirus cases now at 11; entry ban and quarantine measures begin
, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention press briefing.
Four of the new cases are in California, and one in Massachusetts. Although four of the new cases have recent travel history to Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the 2019-nCoV outbreak, the fifth is a close household contact of one of the other California patients, said Dr. Messonnier. This last case is the second instance of person-to-person spread of 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“We expect to find additional cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States,” she said. “We expect to see more cases of person-to-person spread among close contacts. And we continue to expect this will happen given the explosive nature of this outbreak in China.”
As of the morning of Feb. 3, 167 persons under investigation, or PUIs, for possible 2019-nCoV have tested negative for the virus, and an additional 82 PUIs have testing pending – this latter figure includes some tests that are still in transit to the CDC, said Dr. Messonnier.
During the briefing, Dr. Messonnier emphasized both the aggressive nature of the U.S. public health response and the rationale for quick and assertive action. “The goal of our public health response is to protect and contain,” she said. “Strong measures now may blunt the impact of this virus on the United States.”
She cited the intensity of transmission in Hubei Province, the expansion of transmission to other provinces in China, the expansion of cases outside of China, and sporadic ongoing deaths from 2019-nCoV as drivers of the aggressive U.S. public health response.
A presidential proclamation is currently in place that bars U.S. entry to foreign nationals who have visited mainland China within the past 14 days; the ban does not apply to travelers from Hong Kong and Macao. Immediate family members of U.S. citizens and individuals who have U.S. permanent resident status are exempted from the entry ban and will be allowed entry into the United States.
However, explained Dr. Messonnier, those who have traveled to China recently and are permitted entry will be subject to screening. All passengers with such recent travel will be directed to one of 11 U.S. airports set up to perform additional screening.
As of Feb 3, the list of airports includes:
- San Francisco International Airport in California.
- Los Angeles International Airport in California.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Georgia.
- Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Hawaii.
- O’Hare International Airport in Illinois.
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport in Michigan.
- Newark Liberty International Airport in New Jersey.
- John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York.
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport in Texas.
- Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia.
- Seattle-Tacoma International Airport in Washington.
Travelers who have been to Hubei Province in the previous 14 days will have an additional health assessment at which they will be screened for fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Any American citizens or exempt individuals who are symptomatic would then be transferred for further medical evaluation. Asymptomatic travelers in this category will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine near their point of entry, rather than continuing on to their final destinations.
Dr. Messonnier emphasized that the mandatory 14-day quarantine is specifically for Americans or exempt individuals returning from Hubei Province, adding that the CDC is presently working with individual states to determine the exact venues for quarantine.
American citizens and exempt individuals returning from other parts of mainland China will be routed to one of the 11 airports and will also receive additional health screening. Symptomatic individuals in this travel category would be referred for further evaluation before being able to complete their itinerary.
Asymptomatic American citizens and exempt individuals who are returning from mainland China – but not Hubei Province – will be allowed to travel on to their final destinations, but will be asked to stay home as much as possible and to monitor their health during the 14 days after their return.
The U.S. Department of State is bringing back more Americans from Wuhan province this week, and these individuals will also be kept under federal quarantine for 14 days.
“There are likely to be confirmed infections among returning travelers,” said Dr. Messonnier. “It is important to note that this strategy is not meant to catch every single traveler returning from China with novel coronavirus; given the nature of this virus and how it’s spreading, that would be impossible, but working together we can catch the majority of them.
“The goal here is to slow the entry of this virus into the United States,” she said, adding that the nation’s health care and public health systems stand on high alert to detect the virus in community settings. In response to questioning from the press, Dr. Messonnier defended the stringent quarantine measures, noting that they are in line with those taken by some other nations, and with the aggressive action being taken by the Chinese government itself. “These actions are science based and aimed at protecting the health of all Americans,” she said.
The real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay that the CDC has developed detects 2019-nCoV in both respiratory and serum specimens. Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is today filing an emergency use authorization (EUA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to expedite access to the assay for public health laboratories across the country. “This will greatly enhance our capacity to test for this virus,” she said, noting that EUA approval may come as soon as the end of this week.
Although the CDC is poised to send an expert team to China, it’s still awaiting favorable results from the international negotiations currently underway. “This is a horrible situation in China,” said Dr. Messonnier. “Our presence on the ground in China would be a help to China. ... Science should trump everything else; that’s what we’re hoping – that the scientific expertise of the global community can be brought to bear on the incredibly complicated, difficult situation that our colleagues in China are dealing with.”
, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention press briefing.
Four of the new cases are in California, and one in Massachusetts. Although four of the new cases have recent travel history to Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the 2019-nCoV outbreak, the fifth is a close household contact of one of the other California patients, said Dr. Messonnier. This last case is the second instance of person-to-person spread of 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“We expect to find additional cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States,” she said. “We expect to see more cases of person-to-person spread among close contacts. And we continue to expect this will happen given the explosive nature of this outbreak in China.”
As of the morning of Feb. 3, 167 persons under investigation, or PUIs, for possible 2019-nCoV have tested negative for the virus, and an additional 82 PUIs have testing pending – this latter figure includes some tests that are still in transit to the CDC, said Dr. Messonnier.
During the briefing, Dr. Messonnier emphasized both the aggressive nature of the U.S. public health response and the rationale for quick and assertive action. “The goal of our public health response is to protect and contain,” she said. “Strong measures now may blunt the impact of this virus on the United States.”
She cited the intensity of transmission in Hubei Province, the expansion of transmission to other provinces in China, the expansion of cases outside of China, and sporadic ongoing deaths from 2019-nCoV as drivers of the aggressive U.S. public health response.
A presidential proclamation is currently in place that bars U.S. entry to foreign nationals who have visited mainland China within the past 14 days; the ban does not apply to travelers from Hong Kong and Macao. Immediate family members of U.S. citizens and individuals who have U.S. permanent resident status are exempted from the entry ban and will be allowed entry into the United States.
However, explained Dr. Messonnier, those who have traveled to China recently and are permitted entry will be subject to screening. All passengers with such recent travel will be directed to one of 11 U.S. airports set up to perform additional screening.
As of Feb 3, the list of airports includes:
- San Francisco International Airport in California.
- Los Angeles International Airport in California.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Georgia.
- Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Hawaii.
- O’Hare International Airport in Illinois.
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport in Michigan.
- Newark Liberty International Airport in New Jersey.
- John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York.
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport in Texas.
- Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia.
- Seattle-Tacoma International Airport in Washington.
Travelers who have been to Hubei Province in the previous 14 days will have an additional health assessment at which they will be screened for fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Any American citizens or exempt individuals who are symptomatic would then be transferred for further medical evaluation. Asymptomatic travelers in this category will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine near their point of entry, rather than continuing on to their final destinations.
Dr. Messonnier emphasized that the mandatory 14-day quarantine is specifically for Americans or exempt individuals returning from Hubei Province, adding that the CDC is presently working with individual states to determine the exact venues for quarantine.
American citizens and exempt individuals returning from other parts of mainland China will be routed to one of the 11 airports and will also receive additional health screening. Symptomatic individuals in this travel category would be referred for further evaluation before being able to complete their itinerary.
Asymptomatic American citizens and exempt individuals who are returning from mainland China – but not Hubei Province – will be allowed to travel on to their final destinations, but will be asked to stay home as much as possible and to monitor their health during the 14 days after their return.
The U.S. Department of State is bringing back more Americans from Wuhan province this week, and these individuals will also be kept under federal quarantine for 14 days.
“There are likely to be confirmed infections among returning travelers,” said Dr. Messonnier. “It is important to note that this strategy is not meant to catch every single traveler returning from China with novel coronavirus; given the nature of this virus and how it’s spreading, that would be impossible, but working together we can catch the majority of them.
“The goal here is to slow the entry of this virus into the United States,” she said, adding that the nation’s health care and public health systems stand on high alert to detect the virus in community settings. In response to questioning from the press, Dr. Messonnier defended the stringent quarantine measures, noting that they are in line with those taken by some other nations, and with the aggressive action being taken by the Chinese government itself. “These actions are science based and aimed at protecting the health of all Americans,” she said.
The real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay that the CDC has developed detects 2019-nCoV in both respiratory and serum specimens. Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is today filing an emergency use authorization (EUA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to expedite access to the assay for public health laboratories across the country. “This will greatly enhance our capacity to test for this virus,” she said, noting that EUA approval may come as soon as the end of this week.
Although the CDC is poised to send an expert team to China, it’s still awaiting favorable results from the international negotiations currently underway. “This is a horrible situation in China,” said Dr. Messonnier. “Our presence on the ground in China would be a help to China. ... Science should trump everything else; that’s what we’re hoping – that the scientific expertise of the global community can be brought to bear on the incredibly complicated, difficult situation that our colleagues in China are dealing with.”
, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention press briefing.
Four of the new cases are in California, and one in Massachusetts. Although four of the new cases have recent travel history to Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the 2019-nCoV outbreak, the fifth is a close household contact of one of the other California patients, said Dr. Messonnier. This last case is the second instance of person-to-person spread of 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“We expect to find additional cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States,” she said. “We expect to see more cases of person-to-person spread among close contacts. And we continue to expect this will happen given the explosive nature of this outbreak in China.”
As of the morning of Feb. 3, 167 persons under investigation, or PUIs, for possible 2019-nCoV have tested negative for the virus, and an additional 82 PUIs have testing pending – this latter figure includes some tests that are still in transit to the CDC, said Dr. Messonnier.
During the briefing, Dr. Messonnier emphasized both the aggressive nature of the U.S. public health response and the rationale for quick and assertive action. “The goal of our public health response is to protect and contain,” she said. “Strong measures now may blunt the impact of this virus on the United States.”
She cited the intensity of transmission in Hubei Province, the expansion of transmission to other provinces in China, the expansion of cases outside of China, and sporadic ongoing deaths from 2019-nCoV as drivers of the aggressive U.S. public health response.
A presidential proclamation is currently in place that bars U.S. entry to foreign nationals who have visited mainland China within the past 14 days; the ban does not apply to travelers from Hong Kong and Macao. Immediate family members of U.S. citizens and individuals who have U.S. permanent resident status are exempted from the entry ban and will be allowed entry into the United States.
However, explained Dr. Messonnier, those who have traveled to China recently and are permitted entry will be subject to screening. All passengers with such recent travel will be directed to one of 11 U.S. airports set up to perform additional screening.
As of Feb 3, the list of airports includes:
- San Francisco International Airport in California.
- Los Angeles International Airport in California.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Georgia.
- Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Hawaii.
- O’Hare International Airport in Illinois.
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport in Michigan.
- Newark Liberty International Airport in New Jersey.
- John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York.
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport in Texas.
- Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia.
- Seattle-Tacoma International Airport in Washington.
Travelers who have been to Hubei Province in the previous 14 days will have an additional health assessment at which they will be screened for fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Any American citizens or exempt individuals who are symptomatic would then be transferred for further medical evaluation. Asymptomatic travelers in this category will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine near their point of entry, rather than continuing on to their final destinations.
Dr. Messonnier emphasized that the mandatory 14-day quarantine is specifically for Americans or exempt individuals returning from Hubei Province, adding that the CDC is presently working with individual states to determine the exact venues for quarantine.
American citizens and exempt individuals returning from other parts of mainland China will be routed to one of the 11 airports and will also receive additional health screening. Symptomatic individuals in this travel category would be referred for further evaluation before being able to complete their itinerary.
Asymptomatic American citizens and exempt individuals who are returning from mainland China – but not Hubei Province – will be allowed to travel on to their final destinations, but will be asked to stay home as much as possible and to monitor their health during the 14 days after their return.
The U.S. Department of State is bringing back more Americans from Wuhan province this week, and these individuals will also be kept under federal quarantine for 14 days.
“There are likely to be confirmed infections among returning travelers,” said Dr. Messonnier. “It is important to note that this strategy is not meant to catch every single traveler returning from China with novel coronavirus; given the nature of this virus and how it’s spreading, that would be impossible, but working together we can catch the majority of them.
“The goal here is to slow the entry of this virus into the United States,” she said, adding that the nation’s health care and public health systems stand on high alert to detect the virus in community settings. In response to questioning from the press, Dr. Messonnier defended the stringent quarantine measures, noting that they are in line with those taken by some other nations, and with the aggressive action being taken by the Chinese government itself. “These actions are science based and aimed at protecting the health of all Americans,” she said.
The real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay that the CDC has developed detects 2019-nCoV in both respiratory and serum specimens. Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is today filing an emergency use authorization (EUA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to expedite access to the assay for public health laboratories across the country. “This will greatly enhance our capacity to test for this virus,” she said, noting that EUA approval may come as soon as the end of this week.
Although the CDC is poised to send an expert team to China, it’s still awaiting favorable results from the international negotiations currently underway. “This is a horrible situation in China,” said Dr. Messonnier. “Our presence on the ground in China would be a help to China. ... Science should trump everything else; that’s what we’re hoping – that the scientific expertise of the global community can be brought to bear on the incredibly complicated, difficult situation that our colleagues in China are dealing with.”
FROM A CDC PRESS BRIEFING
Who’ll get SAVR in 2020?
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The number of transcatheter aortic valve replacements (TAVRs) performed annually in the United States is forecast to rocket up from 75,000 in 2019 to 100,000 in 2020 in response to the procedure’s recent approval in low-surgical-risk patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, Michael J. Mack, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“In 2020, TAVR seems like a tsunami that’s totally overwhelming SAVR [surgical aortic valve replacement]. And the question is, after the wave hits shore, is there going to be anything left in the surgical arena?” asked Dr. Mack, who is medical director of cardiothoracic surgery and chairman of the Baylor Scott & White The Heart Hospital – Plano (Tex.) Research Center.
He answered his own question with a quote from Mark Twain: “Reports of my death are greatly exaggerated.”
The trend is clear: TAVR will take over the market for isolated aortic valve replacement in much the same way that endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) has come to dominate open surgical repair by an 80:20 margin. And By one estimate, it could include some 270,000 individuals per year in North America and the European Union (Eur Heart J. 2018 Jul 21;39[28]:2635-42).
But there’s no need to shed a tear at the prospect of SAVR surgeons standing in unemployment lines. They will continue to have their hands full performing combined SAVR plus coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) procedures, SAVR plus mitral or tricuspid valve operations, and Bentall procedures, Dr. Mack predicted.
Who should get SAVR for aortic stenosis in 2020? For starters, he said, the sorts of patients who were excluded from the major TAVR-versus-SAVR randomized trials. The low-surgical-risk trials were restricted to patients who had symptomatic aortic stenosis involving a tricuspid valve, no left ventricular outflow tract calcium, no or minimal coronary artery disease (CAD), a relatively normal left ventricular ejection fraction, and an aortic valve anatomy suitable for TAVR. And, 92% of study participants were over age 65 years.
Dr. Mack called the evidence for the safety and effectiveness of TAVR “the most robust evidence base in the history of medical devices,” backed by nine U.S. trials and 8,000 randomized patients during the last dozen years. He has played a major role in developing that evidence base, having served most recently as cochair of the landmark PARTNER 3 trial, which demonstrated superiority for TAVR over SAVR in low-surgical-risk patients. But the evidence base doesn’t apply to patients not enrolled in the trials. So for the foreseeable future, patients younger than age 65 years should probably stick with SAVR, mainly because of the still-open question of tissue valve durability and TAVR’s high rate of associated conduction system impairment and need for new pacemaker implantation. Younger patients find permanent pacemakers particularly problematic, he noted.
Others who should stick with surgery include patients with bicuspid valves, especially when aortopathy is present, individuals with low-lying coronary arteries, patients with heavy calcium deposits at the left ventricular outflow tract, those with infective endocarditis or rheumatic valve disease, and patients with structural valve deterioration after a valve-in-valve TAVR.
“Once you get beyond the first valve-in-valve, the outcomes are not going to be good. Those patients should preferentially be considered for surgery. The results for valve-in-valve have been very disappointing, with a 33% all-cause mortality at 3 years in the PARTNER Aortic Valve-in-Valve Registry,” according to the surgeon.
In patients with aortic stenosis and CAD, the clinical decision making should be based on the coronary disease. In a patient with triple-vessel disease, diabetes, and/or a high Syntax score for whom the collaborative multidisciplinary heart team would recommend surgical revascularization if aortic stenosis wasn’t present, the most appropriate option is SAVR plus CABG. On the other hand, if the CAD is amenable to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and the Syntax score is low, TAVR plus PCI is a safe and solid strategy, he continued.
In addition to the unresolved issue of tissue valve durability, another unanswered question pushing against universal adoption of TAVR involves the clinical implications of bioprosthetic valve leaflet thrombosis and the optimal antithrombotic therapy, both early and late. Leaflet thrombosis post-TAVR is common – as well as post-SAVR with bioprosthetic valves, albeit less so – but the lesions often come and go. Although there is a theoretical concern that they might be a precursor to leaflet destruction, at this point, their clinical significance remains unclear. In the recent GALILEO trial, TAVR patients randomized to low-dose rivaroxaban (Xarelto) plus aspirin showed fewer leaflet motion abnormalities and less leaflet thickening than did those on dual-antiplatelet therapy, but a significantly higher all-cause mortality (N Engl J Med 2020 Jan 9;382:120-9).
“I know that nowhere else in the body is thrombus a good thing, so thrombus in the valve can’t be a good thing. The only question is, how bad is it? And right now all we know is, some of our treatments for it are worse than the disease,” the surgeon commented.
Dr. Mack indicated that, at this time, clinical decision making in aortic stenosis should begin on the basis of patient age, which influences the key decision of whether to opt for a mechanical versus tissue replacement valve. For patients aged 50-70 years, shared decision making between the heart team and patient is appropriate. The evidence suggests SAVR with a mechanical valve is the better option, but many patients in this intermediate age group loathe the ideal of lifelong oral anticoagulation and favor a tissue valve.
For patients under age 50 years, the best evidence indicates that SAVR with a mechanical valve is clearly the best option; however, most young patients are instead opting for a tissue valve, even after being cautioned about the lingering uncertainty surrounding tissue valve durability, be it SAVR or TAVR. For patients over age 70 years, a tissue valve is the best choice based on the outcomes in PARTNER 3 and other low-surgical-risk trials. If the patient is younger than 65 years and wants a tissue valve, Dr. Mack thinks the best evidence-based option is SAVR. Above age 80 years, TAVR is the clear choice. Age 65-80 years is shared–decision making territory regarding TAVR versus SAVR.
Dr. Mack reported serving as a consultant to Gore and receiving research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The number of transcatheter aortic valve replacements (TAVRs) performed annually in the United States is forecast to rocket up from 75,000 in 2019 to 100,000 in 2020 in response to the procedure’s recent approval in low-surgical-risk patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, Michael J. Mack, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“In 2020, TAVR seems like a tsunami that’s totally overwhelming SAVR [surgical aortic valve replacement]. And the question is, after the wave hits shore, is there going to be anything left in the surgical arena?” asked Dr. Mack, who is medical director of cardiothoracic surgery and chairman of the Baylor Scott & White The Heart Hospital – Plano (Tex.) Research Center.
He answered his own question with a quote from Mark Twain: “Reports of my death are greatly exaggerated.”
The trend is clear: TAVR will take over the market for isolated aortic valve replacement in much the same way that endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) has come to dominate open surgical repair by an 80:20 margin. And By one estimate, it could include some 270,000 individuals per year in North America and the European Union (Eur Heart J. 2018 Jul 21;39[28]:2635-42).
But there’s no need to shed a tear at the prospect of SAVR surgeons standing in unemployment lines. They will continue to have their hands full performing combined SAVR plus coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) procedures, SAVR plus mitral or tricuspid valve operations, and Bentall procedures, Dr. Mack predicted.
Who should get SAVR for aortic stenosis in 2020? For starters, he said, the sorts of patients who were excluded from the major TAVR-versus-SAVR randomized trials. The low-surgical-risk trials were restricted to patients who had symptomatic aortic stenosis involving a tricuspid valve, no left ventricular outflow tract calcium, no or minimal coronary artery disease (CAD), a relatively normal left ventricular ejection fraction, and an aortic valve anatomy suitable for TAVR. And, 92% of study participants were over age 65 years.
Dr. Mack called the evidence for the safety and effectiveness of TAVR “the most robust evidence base in the history of medical devices,” backed by nine U.S. trials and 8,000 randomized patients during the last dozen years. He has played a major role in developing that evidence base, having served most recently as cochair of the landmark PARTNER 3 trial, which demonstrated superiority for TAVR over SAVR in low-surgical-risk patients. But the evidence base doesn’t apply to patients not enrolled in the trials. So for the foreseeable future, patients younger than age 65 years should probably stick with SAVR, mainly because of the still-open question of tissue valve durability and TAVR’s high rate of associated conduction system impairment and need for new pacemaker implantation. Younger patients find permanent pacemakers particularly problematic, he noted.
Others who should stick with surgery include patients with bicuspid valves, especially when aortopathy is present, individuals with low-lying coronary arteries, patients with heavy calcium deposits at the left ventricular outflow tract, those with infective endocarditis or rheumatic valve disease, and patients with structural valve deterioration after a valve-in-valve TAVR.
“Once you get beyond the first valve-in-valve, the outcomes are not going to be good. Those patients should preferentially be considered for surgery. The results for valve-in-valve have been very disappointing, with a 33% all-cause mortality at 3 years in the PARTNER Aortic Valve-in-Valve Registry,” according to the surgeon.
In patients with aortic stenosis and CAD, the clinical decision making should be based on the coronary disease. In a patient with triple-vessel disease, diabetes, and/or a high Syntax score for whom the collaborative multidisciplinary heart team would recommend surgical revascularization if aortic stenosis wasn’t present, the most appropriate option is SAVR plus CABG. On the other hand, if the CAD is amenable to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and the Syntax score is low, TAVR plus PCI is a safe and solid strategy, he continued.
In addition to the unresolved issue of tissue valve durability, another unanswered question pushing against universal adoption of TAVR involves the clinical implications of bioprosthetic valve leaflet thrombosis and the optimal antithrombotic therapy, both early and late. Leaflet thrombosis post-TAVR is common – as well as post-SAVR with bioprosthetic valves, albeit less so – but the lesions often come and go. Although there is a theoretical concern that they might be a precursor to leaflet destruction, at this point, their clinical significance remains unclear. In the recent GALILEO trial, TAVR patients randomized to low-dose rivaroxaban (Xarelto) plus aspirin showed fewer leaflet motion abnormalities and less leaflet thickening than did those on dual-antiplatelet therapy, but a significantly higher all-cause mortality (N Engl J Med 2020 Jan 9;382:120-9).
“I know that nowhere else in the body is thrombus a good thing, so thrombus in the valve can’t be a good thing. The only question is, how bad is it? And right now all we know is, some of our treatments for it are worse than the disease,” the surgeon commented.
Dr. Mack indicated that, at this time, clinical decision making in aortic stenosis should begin on the basis of patient age, which influences the key decision of whether to opt for a mechanical versus tissue replacement valve. For patients aged 50-70 years, shared decision making between the heart team and patient is appropriate. The evidence suggests SAVR with a mechanical valve is the better option, but many patients in this intermediate age group loathe the ideal of lifelong oral anticoagulation and favor a tissue valve.
For patients under age 50 years, the best evidence indicates that SAVR with a mechanical valve is clearly the best option; however, most young patients are instead opting for a tissue valve, even after being cautioned about the lingering uncertainty surrounding tissue valve durability, be it SAVR or TAVR. For patients over age 70 years, a tissue valve is the best choice based on the outcomes in PARTNER 3 and other low-surgical-risk trials. If the patient is younger than 65 years and wants a tissue valve, Dr. Mack thinks the best evidence-based option is SAVR. Above age 80 years, TAVR is the clear choice. Age 65-80 years is shared–decision making territory regarding TAVR versus SAVR.
Dr. Mack reported serving as a consultant to Gore and receiving research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The number of transcatheter aortic valve replacements (TAVRs) performed annually in the United States is forecast to rocket up from 75,000 in 2019 to 100,000 in 2020 in response to the procedure’s recent approval in low-surgical-risk patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, Michael J. Mack, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“In 2020, TAVR seems like a tsunami that’s totally overwhelming SAVR [surgical aortic valve replacement]. And the question is, after the wave hits shore, is there going to be anything left in the surgical arena?” asked Dr. Mack, who is medical director of cardiothoracic surgery and chairman of the Baylor Scott & White The Heart Hospital – Plano (Tex.) Research Center.
He answered his own question with a quote from Mark Twain: “Reports of my death are greatly exaggerated.”
The trend is clear: TAVR will take over the market for isolated aortic valve replacement in much the same way that endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) has come to dominate open surgical repair by an 80:20 margin. And By one estimate, it could include some 270,000 individuals per year in North America and the European Union (Eur Heart J. 2018 Jul 21;39[28]:2635-42).
But there’s no need to shed a tear at the prospect of SAVR surgeons standing in unemployment lines. They will continue to have their hands full performing combined SAVR plus coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) procedures, SAVR plus mitral or tricuspid valve operations, and Bentall procedures, Dr. Mack predicted.
Who should get SAVR for aortic stenosis in 2020? For starters, he said, the sorts of patients who were excluded from the major TAVR-versus-SAVR randomized trials. The low-surgical-risk trials were restricted to patients who had symptomatic aortic stenosis involving a tricuspid valve, no left ventricular outflow tract calcium, no or minimal coronary artery disease (CAD), a relatively normal left ventricular ejection fraction, and an aortic valve anatomy suitable for TAVR. And, 92% of study participants were over age 65 years.
Dr. Mack called the evidence for the safety and effectiveness of TAVR “the most robust evidence base in the history of medical devices,” backed by nine U.S. trials and 8,000 randomized patients during the last dozen years. He has played a major role in developing that evidence base, having served most recently as cochair of the landmark PARTNER 3 trial, which demonstrated superiority for TAVR over SAVR in low-surgical-risk patients. But the evidence base doesn’t apply to patients not enrolled in the trials. So for the foreseeable future, patients younger than age 65 years should probably stick with SAVR, mainly because of the still-open question of tissue valve durability and TAVR’s high rate of associated conduction system impairment and need for new pacemaker implantation. Younger patients find permanent pacemakers particularly problematic, he noted.
Others who should stick with surgery include patients with bicuspid valves, especially when aortopathy is present, individuals with low-lying coronary arteries, patients with heavy calcium deposits at the left ventricular outflow tract, those with infective endocarditis or rheumatic valve disease, and patients with structural valve deterioration after a valve-in-valve TAVR.
“Once you get beyond the first valve-in-valve, the outcomes are not going to be good. Those patients should preferentially be considered for surgery. The results for valve-in-valve have been very disappointing, with a 33% all-cause mortality at 3 years in the PARTNER Aortic Valve-in-Valve Registry,” according to the surgeon.
In patients with aortic stenosis and CAD, the clinical decision making should be based on the coronary disease. In a patient with triple-vessel disease, diabetes, and/or a high Syntax score for whom the collaborative multidisciplinary heart team would recommend surgical revascularization if aortic stenosis wasn’t present, the most appropriate option is SAVR plus CABG. On the other hand, if the CAD is amenable to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and the Syntax score is low, TAVR plus PCI is a safe and solid strategy, he continued.
In addition to the unresolved issue of tissue valve durability, another unanswered question pushing against universal adoption of TAVR involves the clinical implications of bioprosthetic valve leaflet thrombosis and the optimal antithrombotic therapy, both early and late. Leaflet thrombosis post-TAVR is common – as well as post-SAVR with bioprosthetic valves, albeit less so – but the lesions often come and go. Although there is a theoretical concern that they might be a precursor to leaflet destruction, at this point, their clinical significance remains unclear. In the recent GALILEO trial, TAVR patients randomized to low-dose rivaroxaban (Xarelto) plus aspirin showed fewer leaflet motion abnormalities and less leaflet thickening than did those on dual-antiplatelet therapy, but a significantly higher all-cause mortality (N Engl J Med 2020 Jan 9;382:120-9).
“I know that nowhere else in the body is thrombus a good thing, so thrombus in the valve can’t be a good thing. The only question is, how bad is it? And right now all we know is, some of our treatments for it are worse than the disease,” the surgeon commented.
Dr. Mack indicated that, at this time, clinical decision making in aortic stenosis should begin on the basis of patient age, which influences the key decision of whether to opt for a mechanical versus tissue replacement valve. For patients aged 50-70 years, shared decision making between the heart team and patient is appropriate. The evidence suggests SAVR with a mechanical valve is the better option, but many patients in this intermediate age group loathe the ideal of lifelong oral anticoagulation and favor a tissue valve.
For patients under age 50 years, the best evidence indicates that SAVR with a mechanical valve is clearly the best option; however, most young patients are instead opting for a tissue valve, even after being cautioned about the lingering uncertainty surrounding tissue valve durability, be it SAVR or TAVR. For patients over age 70 years, a tissue valve is the best choice based on the outcomes in PARTNER 3 and other low-surgical-risk trials. If the patient is younger than 65 years and wants a tissue valve, Dr. Mack thinks the best evidence-based option is SAVR. Above age 80 years, TAVR is the clear choice. Age 65-80 years is shared–decision making territory regarding TAVR versus SAVR.
Dr. Mack reported serving as a consultant to Gore and receiving research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC SNOWMASS 2020
Heart rhythm data from wearables confounds EP practice
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – or other warnings that flagged a possible cardiac arrhythmia.
While the clinical community has yet to reach an evidence-based consensus on how to deal with this information, or even asymptomatic arrhythmias identified by more standard means, the American public is voting with their wrists. People seem to like collecting and reviewing readouts on their heart rhythm and other vital data, and then they often take their numbers to a physician, especially when their device suggests a possible problem.
“The whole paradigm of ordering a test only if you intend to act on the result has been flipped. People now get what they want directly, and our job is to guide them” after the fact. “You need to teach people what’s actionable and what’s not,” Mintu P. Turakhia, MD, said at the annual International AF Symposium.
“We’re in a situation where the ability of a sensor to detect things is separate from access to the health care system. They are no longer coupled; they are disjointed. People can create their own ICU in their house just by shopping online, but what do we do with this information, whether it’s an irregular heart rhythm or their whole genome?” asked Dr. Turakhia, executive director of the Center for Digital Health at Stanford (Calif.) University and director of cardiac electrophysiology at the VA Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System.
“The main challenge is people without a diagnosis who get a notification. How much monitoring should you do until you can say it was a false positive? We don’t know what to do, so we monitor them. People are trying to figure this out.” Dr. Turakhia said. Some people who seek out electrophysiologists this way “may not even have a primary care physician,” he noted.
The potential implications of widespread monitoring for heartbeat irregularities in the general public began to surface in a study that Dr. Turakhia helped run that collected wearable data from nearly 420,000 Americans. Results from the Apple Heart Study showed that, during a median 117 days of monitoring with a smart watch, 2,161 people (0.5%) received a report of an irregular pulse, which led to further investigations that eventually diagnosed atrial fibrillation (AFib) in 153 people of the 450 who underwent follow-up assessment (N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 14;381[20]:1909-17). These results “raise questions” about the large number of people who underwent follow-up testing who did not have arrhythmia, Dr. Turakhia noted.
“The dissemination of wearables has been quite dramatic, and electrophysiologists end up owning this,” commented Jeremy N. Ruskin, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director emeritus of the cardiac arrhythmia service at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston. “I get a ton of calls from people whom I wish never bought a smart watch, and they say ‘I have atrial fibrillation. What do I do?’ ”
To document the growth of this trend, Dr. Turakhia cited results from a survey he collaborated on, run by Stanford and Rock Health, that found a 33% ownership rate among American adults of a wearable device capable of collecting health data, and a 42% rate of people who tracked their health data with a device, app, journal, or log. Both of these rates more than doubled what a similar survey found in 2015.
The cardiac electrophysiology community took a first step toward addressing one aspect of this evolving situation. In early 2020, the Heart Rhythm Society and the Consumer Technology Association jointly issued a guidance document targeted at consumers that walks them through the kinds of information their wearable devices might collect and how to approach this information. The main message: If you have questions or concerns about your data, consult a clinician. What remains in short supply is guidance to clinicians on what to do when they see these patients.
“Until recently, device-detected AFib was the sole purview of electrophysiologists using implanted rhythm-monitoring devices. Now mobile and other devices raise issues [of asymptomatic AFib] for a much broader population,” noted Daniel E. Singer, MD, professor of medicine and epidemiology at Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital. “The world of device-detected AFib now includes watches.”
Researchers have tried for years to better understand the stroke risk faced by patients with asymptomatic or subclinical AFib that’s detected by an implanted device, as in the ASSERT study of nearly 2,600 patients followed for a median of 2.5 years that found an increased stroke risk when the duration of individual, subclinical AFib episodes surpassed 24 hours (Eur Heart J. 2017 May 1;38[17]:1339-44). More recently, a study of AFib duration collected by implanted cardiac devices in nearly 22,000 Americans showed a relationship between stroke risk and both the duration of AFib episodes and the underlying risk of a person for stroke as measured by their CHA2DS2-VAScscore (Circulation. 2019 Nov 12;140[20]:1639-46). Just under 30% of patients in the study were diagnosed with AFib at entry.
The implications of asymptomatic episodes of AFib have so far been largely studied in people with an implanted cardiac device, which may have limited applicability to wearable users. In addition, the field has not yet fully sorted out the relationships between the duration of individual AFib episodes and overall AFib burden, and a person’s stroke risk and the window of time when the potential stroke-preventing benefits of anticoagulation outweigh its bleeding risk.
The results of trials now in progress that are examining the safety and efficacy of medical interventions designed to avert strokes in patients with asymptomatic AFib “will bear on the use of anticoagulants in a large group of patients,” including people with AFib detected by a wearable, Dr. Singer predicted.
The Apple Heart Study was sponsored Apple. Dr. Turakhia has received funding from Apple, and he has received honoraria or research funding from several other companies. Dr. Ruskin has been a consultant or adviser to several companies, is a steering committee member for Pfizer, and holds equity or options in Portola, Element Science, NewPace, Gilead, and InfoBionic. Dr. Singer has been a consultant and adviser to Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer, and he has received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – or other warnings that flagged a possible cardiac arrhythmia.
While the clinical community has yet to reach an evidence-based consensus on how to deal with this information, or even asymptomatic arrhythmias identified by more standard means, the American public is voting with their wrists. People seem to like collecting and reviewing readouts on their heart rhythm and other vital data, and then they often take their numbers to a physician, especially when their device suggests a possible problem.
“The whole paradigm of ordering a test only if you intend to act on the result has been flipped. People now get what they want directly, and our job is to guide them” after the fact. “You need to teach people what’s actionable and what’s not,” Mintu P. Turakhia, MD, said at the annual International AF Symposium.
“We’re in a situation where the ability of a sensor to detect things is separate from access to the health care system. They are no longer coupled; they are disjointed. People can create their own ICU in their house just by shopping online, but what do we do with this information, whether it’s an irregular heart rhythm or their whole genome?” asked Dr. Turakhia, executive director of the Center for Digital Health at Stanford (Calif.) University and director of cardiac electrophysiology at the VA Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System.
“The main challenge is people without a diagnosis who get a notification. How much monitoring should you do until you can say it was a false positive? We don’t know what to do, so we monitor them. People are trying to figure this out.” Dr. Turakhia said. Some people who seek out electrophysiologists this way “may not even have a primary care physician,” he noted.
The potential implications of widespread monitoring for heartbeat irregularities in the general public began to surface in a study that Dr. Turakhia helped run that collected wearable data from nearly 420,000 Americans. Results from the Apple Heart Study showed that, during a median 117 days of monitoring with a smart watch, 2,161 people (0.5%) received a report of an irregular pulse, which led to further investigations that eventually diagnosed atrial fibrillation (AFib) in 153 people of the 450 who underwent follow-up assessment (N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 14;381[20]:1909-17). These results “raise questions” about the large number of people who underwent follow-up testing who did not have arrhythmia, Dr. Turakhia noted.
“The dissemination of wearables has been quite dramatic, and electrophysiologists end up owning this,” commented Jeremy N. Ruskin, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director emeritus of the cardiac arrhythmia service at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston. “I get a ton of calls from people whom I wish never bought a smart watch, and they say ‘I have atrial fibrillation. What do I do?’ ”
To document the growth of this trend, Dr. Turakhia cited results from a survey he collaborated on, run by Stanford and Rock Health, that found a 33% ownership rate among American adults of a wearable device capable of collecting health data, and a 42% rate of people who tracked their health data with a device, app, journal, or log. Both of these rates more than doubled what a similar survey found in 2015.
The cardiac electrophysiology community took a first step toward addressing one aspect of this evolving situation. In early 2020, the Heart Rhythm Society and the Consumer Technology Association jointly issued a guidance document targeted at consumers that walks them through the kinds of information their wearable devices might collect and how to approach this information. The main message: If you have questions or concerns about your data, consult a clinician. What remains in short supply is guidance to clinicians on what to do when they see these patients.
“Until recently, device-detected AFib was the sole purview of electrophysiologists using implanted rhythm-monitoring devices. Now mobile and other devices raise issues [of asymptomatic AFib] for a much broader population,” noted Daniel E. Singer, MD, professor of medicine and epidemiology at Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital. “The world of device-detected AFib now includes watches.”
Researchers have tried for years to better understand the stroke risk faced by patients with asymptomatic or subclinical AFib that’s detected by an implanted device, as in the ASSERT study of nearly 2,600 patients followed for a median of 2.5 years that found an increased stroke risk when the duration of individual, subclinical AFib episodes surpassed 24 hours (Eur Heart J. 2017 May 1;38[17]:1339-44). More recently, a study of AFib duration collected by implanted cardiac devices in nearly 22,000 Americans showed a relationship between stroke risk and both the duration of AFib episodes and the underlying risk of a person for stroke as measured by their CHA2DS2-VAScscore (Circulation. 2019 Nov 12;140[20]:1639-46). Just under 30% of patients in the study were diagnosed with AFib at entry.
The implications of asymptomatic episodes of AFib have so far been largely studied in people with an implanted cardiac device, which may have limited applicability to wearable users. In addition, the field has not yet fully sorted out the relationships between the duration of individual AFib episodes and overall AFib burden, and a person’s stroke risk and the window of time when the potential stroke-preventing benefits of anticoagulation outweigh its bleeding risk.
The results of trials now in progress that are examining the safety and efficacy of medical interventions designed to avert strokes in patients with asymptomatic AFib “will bear on the use of anticoagulants in a large group of patients,” including people with AFib detected by a wearable, Dr. Singer predicted.
The Apple Heart Study was sponsored Apple. Dr. Turakhia has received funding from Apple, and he has received honoraria or research funding from several other companies. Dr. Ruskin has been a consultant or adviser to several companies, is a steering committee member for Pfizer, and holds equity or options in Portola, Element Science, NewPace, Gilead, and InfoBionic. Dr. Singer has been a consultant and adviser to Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer, and he has received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – or other warnings that flagged a possible cardiac arrhythmia.
While the clinical community has yet to reach an evidence-based consensus on how to deal with this information, or even asymptomatic arrhythmias identified by more standard means, the American public is voting with their wrists. People seem to like collecting and reviewing readouts on their heart rhythm and other vital data, and then they often take their numbers to a physician, especially when their device suggests a possible problem.
“The whole paradigm of ordering a test only if you intend to act on the result has been flipped. People now get what they want directly, and our job is to guide them” after the fact. “You need to teach people what’s actionable and what’s not,” Mintu P. Turakhia, MD, said at the annual International AF Symposium.
“We’re in a situation where the ability of a sensor to detect things is separate from access to the health care system. They are no longer coupled; they are disjointed. People can create their own ICU in their house just by shopping online, but what do we do with this information, whether it’s an irregular heart rhythm or their whole genome?” asked Dr. Turakhia, executive director of the Center for Digital Health at Stanford (Calif.) University and director of cardiac electrophysiology at the VA Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System.
“The main challenge is people without a diagnosis who get a notification. How much monitoring should you do until you can say it was a false positive? We don’t know what to do, so we monitor them. People are trying to figure this out.” Dr. Turakhia said. Some people who seek out electrophysiologists this way “may not even have a primary care physician,” he noted.
The potential implications of widespread monitoring for heartbeat irregularities in the general public began to surface in a study that Dr. Turakhia helped run that collected wearable data from nearly 420,000 Americans. Results from the Apple Heart Study showed that, during a median 117 days of monitoring with a smart watch, 2,161 people (0.5%) received a report of an irregular pulse, which led to further investigations that eventually diagnosed atrial fibrillation (AFib) in 153 people of the 450 who underwent follow-up assessment (N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 14;381[20]:1909-17). These results “raise questions” about the large number of people who underwent follow-up testing who did not have arrhythmia, Dr. Turakhia noted.
“The dissemination of wearables has been quite dramatic, and electrophysiologists end up owning this,” commented Jeremy N. Ruskin, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director emeritus of the cardiac arrhythmia service at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston. “I get a ton of calls from people whom I wish never bought a smart watch, and they say ‘I have atrial fibrillation. What do I do?’ ”
To document the growth of this trend, Dr. Turakhia cited results from a survey he collaborated on, run by Stanford and Rock Health, that found a 33% ownership rate among American adults of a wearable device capable of collecting health data, and a 42% rate of people who tracked their health data with a device, app, journal, or log. Both of these rates more than doubled what a similar survey found in 2015.
The cardiac electrophysiology community took a first step toward addressing one aspect of this evolving situation. In early 2020, the Heart Rhythm Society and the Consumer Technology Association jointly issued a guidance document targeted at consumers that walks them through the kinds of information their wearable devices might collect and how to approach this information. The main message: If you have questions or concerns about your data, consult a clinician. What remains in short supply is guidance to clinicians on what to do when they see these patients.
“Until recently, device-detected AFib was the sole purview of electrophysiologists using implanted rhythm-monitoring devices. Now mobile and other devices raise issues [of asymptomatic AFib] for a much broader population,” noted Daniel E. Singer, MD, professor of medicine and epidemiology at Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital. “The world of device-detected AFib now includes watches.”
Researchers have tried for years to better understand the stroke risk faced by patients with asymptomatic or subclinical AFib that’s detected by an implanted device, as in the ASSERT study of nearly 2,600 patients followed for a median of 2.5 years that found an increased stroke risk when the duration of individual, subclinical AFib episodes surpassed 24 hours (Eur Heart J. 2017 May 1;38[17]:1339-44). More recently, a study of AFib duration collected by implanted cardiac devices in nearly 22,000 Americans showed a relationship between stroke risk and both the duration of AFib episodes and the underlying risk of a person for stroke as measured by their CHA2DS2-VAScscore (Circulation. 2019 Nov 12;140[20]:1639-46). Just under 30% of patients in the study were diagnosed with AFib at entry.
The implications of asymptomatic episodes of AFib have so far been largely studied in people with an implanted cardiac device, which may have limited applicability to wearable users. In addition, the field has not yet fully sorted out the relationships between the duration of individual AFib episodes and overall AFib burden, and a person’s stroke risk and the window of time when the potential stroke-preventing benefits of anticoagulation outweigh its bleeding risk.
The results of trials now in progress that are examining the safety and efficacy of medical interventions designed to avert strokes in patients with asymptomatic AFib “will bear on the use of anticoagulants in a large group of patients,” including people with AFib detected by a wearable, Dr. Singer predicted.
The Apple Heart Study was sponsored Apple. Dr. Turakhia has received funding from Apple, and he has received honoraria or research funding from several other companies. Dr. Ruskin has been a consultant or adviser to several companies, is a steering committee member for Pfizer, and holds equity or options in Portola, Element Science, NewPace, Gilead, and InfoBionic. Dr. Singer has been a consultant and adviser to Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer, and he has received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
REPORTING FROM THE AF SYMPOSIUM 2020
Endobronchial ultrasound with aspiration yields most lung lesions
, according to a multisite study of current and former smokers with suspected lung cancer.
Bronchoscopy has long played a role in the identification of lung lesions, but the yield varies according to many factors associated with the lesion and the type of bronchoscopy, and recent studies suggest that the yield may be lower than previously thought, wrote Gerard A. Silvestri, MD, of Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers sought to assess the yield of bronchoscopy based on procedure and characteristics, as well as the physician-calculated pretest probability of cancer.
They conducted a secondary analysis of 687 patients from the AEGIS trial, a prospective 28-site study of current and former smokers who underwent bronchoscopy for suspected lung cancer. Patients under 21, those without a history of smoking, and those with a concurrent cancer or history of lung cancer were excluded. The average age of the participants was 63 years, and two-thirds were male. Of these, 474 had diagnostic bronchoscopies and 213 had nondiagnostic bronchoscopies.
The overall diagnostic yield was 69%. However, the diagnostic yield significantly higher (80%) with the use of EBUS-TBNA, compared with 55% for standard bronchoscopy with biopsy +/– fluoroscopy, 57% for electromagnetic navigation, and 74% for combination procedures.
Patients with diagnostic bronchoscopies were significantly more likely than were those who had nondiagnostic bronchoscopies to have lesions greater than 3 cm (67% vs. 45%), to have central locations (75% vs. 50%), and to have lymphadenopathy (57% vs. 55%).
In addition, yields were significantly higher (77%) for patients whose preprocedure physician-assessed probability of cancer was at least 60%, compared with yields in those whose preprocedure physician-assessed probability of cancer was less than 10% or 10%-60% (44% and 42%, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the high prevalence of cancer in the study population, a 1-year follow-up that may have missed slow-growing cancers, and lack of data on the presence or absence of a bronchus sign, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large size, mixture of sites, and use of multiple technologies and presentations, they said.
The study is the largest to assess diagnostic yields and various bronchoscopy techniques and supports EBUS-TBNA as the most reliable, but patient selection and improved procedural training can help improve diagnostic yields, the researchers emphasized.
“While the overall yield of bronchoscopy is reasonable, EBUS-TBNA is the only technique that reliably provides a diagnosis in those suspected of having lung cancer, likely because the biopsy is targeting a central lymph node and there is direct visualization of the needle passing into the target,” they said. However,“better bronchoscopic technology is needed and there are devices in the development pipeline that promise improved diagnostic yield, though these products will require evaluation through prospective comparative effectiveness trials prior to widespread adoption,” they noted. Clinicians should be prepared to pursue alternatives to bronchoscopy if a diagnosis is unlikely, they concluded.
Dr. Silvestri disclosed research grant awards to his university from Olympus America, Auris robotics, Veracyte, and Veran Medical, as well as consulting fees from Olympus and Auris robotics.
SOURCE: Silvestri GA et al. CHEST. 2020 Jan 21. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.12.024.
, according to a multisite study of current and former smokers with suspected lung cancer.
Bronchoscopy has long played a role in the identification of lung lesions, but the yield varies according to many factors associated with the lesion and the type of bronchoscopy, and recent studies suggest that the yield may be lower than previously thought, wrote Gerard A. Silvestri, MD, of Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers sought to assess the yield of bronchoscopy based on procedure and characteristics, as well as the physician-calculated pretest probability of cancer.
They conducted a secondary analysis of 687 patients from the AEGIS trial, a prospective 28-site study of current and former smokers who underwent bronchoscopy for suspected lung cancer. Patients under 21, those without a history of smoking, and those with a concurrent cancer or history of lung cancer were excluded. The average age of the participants was 63 years, and two-thirds were male. Of these, 474 had diagnostic bronchoscopies and 213 had nondiagnostic bronchoscopies.
The overall diagnostic yield was 69%. However, the diagnostic yield significantly higher (80%) with the use of EBUS-TBNA, compared with 55% for standard bronchoscopy with biopsy +/– fluoroscopy, 57% for electromagnetic navigation, and 74% for combination procedures.
Patients with diagnostic bronchoscopies were significantly more likely than were those who had nondiagnostic bronchoscopies to have lesions greater than 3 cm (67% vs. 45%), to have central locations (75% vs. 50%), and to have lymphadenopathy (57% vs. 55%).
In addition, yields were significantly higher (77%) for patients whose preprocedure physician-assessed probability of cancer was at least 60%, compared with yields in those whose preprocedure physician-assessed probability of cancer was less than 10% or 10%-60% (44% and 42%, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the high prevalence of cancer in the study population, a 1-year follow-up that may have missed slow-growing cancers, and lack of data on the presence or absence of a bronchus sign, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large size, mixture of sites, and use of multiple technologies and presentations, they said.
The study is the largest to assess diagnostic yields and various bronchoscopy techniques and supports EBUS-TBNA as the most reliable, but patient selection and improved procedural training can help improve diagnostic yields, the researchers emphasized.
“While the overall yield of bronchoscopy is reasonable, EBUS-TBNA is the only technique that reliably provides a diagnosis in those suspected of having lung cancer, likely because the biopsy is targeting a central lymph node and there is direct visualization of the needle passing into the target,” they said. However,“better bronchoscopic technology is needed and there are devices in the development pipeline that promise improved diagnostic yield, though these products will require evaluation through prospective comparative effectiveness trials prior to widespread adoption,” they noted. Clinicians should be prepared to pursue alternatives to bronchoscopy if a diagnosis is unlikely, they concluded.
Dr. Silvestri disclosed research grant awards to his university from Olympus America, Auris robotics, Veracyte, and Veran Medical, as well as consulting fees from Olympus and Auris robotics.
SOURCE: Silvestri GA et al. CHEST. 2020 Jan 21. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.12.024.
, according to a multisite study of current and former smokers with suspected lung cancer.
Bronchoscopy has long played a role in the identification of lung lesions, but the yield varies according to many factors associated with the lesion and the type of bronchoscopy, and recent studies suggest that the yield may be lower than previously thought, wrote Gerard A. Silvestri, MD, of Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers sought to assess the yield of bronchoscopy based on procedure and characteristics, as well as the physician-calculated pretest probability of cancer.
They conducted a secondary analysis of 687 patients from the AEGIS trial, a prospective 28-site study of current and former smokers who underwent bronchoscopy for suspected lung cancer. Patients under 21, those without a history of smoking, and those with a concurrent cancer or history of lung cancer were excluded. The average age of the participants was 63 years, and two-thirds were male. Of these, 474 had diagnostic bronchoscopies and 213 had nondiagnostic bronchoscopies.
The overall diagnostic yield was 69%. However, the diagnostic yield significantly higher (80%) with the use of EBUS-TBNA, compared with 55% for standard bronchoscopy with biopsy +/– fluoroscopy, 57% for electromagnetic navigation, and 74% for combination procedures.
Patients with diagnostic bronchoscopies were significantly more likely than were those who had nondiagnostic bronchoscopies to have lesions greater than 3 cm (67% vs. 45%), to have central locations (75% vs. 50%), and to have lymphadenopathy (57% vs. 55%).
In addition, yields were significantly higher (77%) for patients whose preprocedure physician-assessed probability of cancer was at least 60%, compared with yields in those whose preprocedure physician-assessed probability of cancer was less than 10% or 10%-60% (44% and 42%, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the high prevalence of cancer in the study population, a 1-year follow-up that may have missed slow-growing cancers, and lack of data on the presence or absence of a bronchus sign, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large size, mixture of sites, and use of multiple technologies and presentations, they said.
The study is the largest to assess diagnostic yields and various bronchoscopy techniques and supports EBUS-TBNA as the most reliable, but patient selection and improved procedural training can help improve diagnostic yields, the researchers emphasized.
“While the overall yield of bronchoscopy is reasonable, EBUS-TBNA is the only technique that reliably provides a diagnosis in those suspected of having lung cancer, likely because the biopsy is targeting a central lymph node and there is direct visualization of the needle passing into the target,” they said. However,“better bronchoscopic technology is needed and there are devices in the development pipeline that promise improved diagnostic yield, though these products will require evaluation through prospective comparative effectiveness trials prior to widespread adoption,” they noted. Clinicians should be prepared to pursue alternatives to bronchoscopy if a diagnosis is unlikely, they concluded.
Dr. Silvestri disclosed research grant awards to his university from Olympus America, Auris robotics, Veracyte, and Veran Medical, as well as consulting fees from Olympus and Auris robotics.
SOURCE: Silvestri GA et al. CHEST. 2020 Jan 21. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.12.024.
FROM CHEST