User login
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
TOPLINE:
Energy insecurity, the inability to meet household energy needs, was associated with more than twice the odds of having depression and anxiety symptoms than energy security in US adults, a new cross-sectional study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Using data from the US Census Bureau's online Household Pulse Survey, administered between 2022 and 2024, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study with a weighted population of > 187 million US adults (51% women; 64% White, 16% Hispanic, 10% Black, and 5% Asian). About a quarter of the population was in each of 4 age groups: 18-34 years, 35-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
- Three indicators of energy insecurity—inability to pay energy bills, maintaining unsafe/unhealthy home temperatures, and forgoing expenses on basic necessities to pay energy bills—were assessed individually and as a composite measure.
- Mental health was assessed using modified versions of the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire for depression and the 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale for anxiety.
- The analysis was adjusted for other social determinants of health, including unemployment, housing instability, and food insecurity. Covariates included a wide range of factors, such as age, educational level, sex, and annual household income.
TAKEAWAY:
- In all, > 43% of the population reported having ≥ 1 form of energy security; around 22% reported being unable to pay energy bills, 22% maintained unsafe home temperatures, and nearly 34% forewent spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills.
- Individuals who gave up spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills had higher odds of anxiety (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79) and depression (aOR, 1.74) than those who did not.
- Adults with energy insecurity on the composite measure had higher odds for anxiety (aOR, 2.29) and depression (aOR, 2.31) than those with energy security.
- Food insecurity was also associated with poorer mental health, with higher odds for symptoms of depression (aOR, 2.05) and anxiety (aOR, 2.07).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite its high prevalence, energy insecurity remains underrecognized in public health and policy intervention strategies," the investigators wrote.
"These findings suggest that energy insecurity is a widespread and important factor associated with mental health symptoms and may warrant consideration in efforts to reduce adverse mental health outcomes," they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Michelle Graf, PhD, Carter School of Public Policy, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta. It was published online on October 27 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the data limited causal interference and increased the possibility of reverse causality. The questionnaire captured subjective interpretations of unsafe and unhealthy indoor temperatures, which may have varied among respondents. Additionally, the recall periods for energy insecurity and mental health outcomes were different.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Energy insecurity, the inability to meet household energy needs, was associated with more than twice the odds of having depression and anxiety symptoms than energy security in US adults, a new cross-sectional study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Using data from the US Census Bureau's online Household Pulse Survey, administered between 2022 and 2024, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study with a weighted population of > 187 million US adults (51% women; 64% White, 16% Hispanic, 10% Black, and 5% Asian). About a quarter of the population was in each of 4 age groups: 18-34 years, 35-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
- Three indicators of energy insecurity—inability to pay energy bills, maintaining unsafe/unhealthy home temperatures, and forgoing expenses on basic necessities to pay energy bills—were assessed individually and as a composite measure.
- Mental health was assessed using modified versions of the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire for depression and the 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale for anxiety.
- The analysis was adjusted for other social determinants of health, including unemployment, housing instability, and food insecurity. Covariates included a wide range of factors, such as age, educational level, sex, and annual household income.
TAKEAWAY:
- In all, > 43% of the population reported having ≥ 1 form of energy security; around 22% reported being unable to pay energy bills, 22% maintained unsafe home temperatures, and nearly 34% forewent spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills.
- Individuals who gave up spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills had higher odds of anxiety (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79) and depression (aOR, 1.74) than those who did not.
- Adults with energy insecurity on the composite measure had higher odds for anxiety (aOR, 2.29) and depression (aOR, 2.31) than those with energy security.
- Food insecurity was also associated with poorer mental health, with higher odds for symptoms of depression (aOR, 2.05) and anxiety (aOR, 2.07).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite its high prevalence, energy insecurity remains underrecognized in public health and policy intervention strategies," the investigators wrote.
"These findings suggest that energy insecurity is a widespread and important factor associated with mental health symptoms and may warrant consideration in efforts to reduce adverse mental health outcomes," they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Michelle Graf, PhD, Carter School of Public Policy, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta. It was published online on October 27 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the data limited causal interference and increased the possibility of reverse causality. The questionnaire captured subjective interpretations of unsafe and unhealthy indoor temperatures, which may have varied among respondents. Additionally, the recall periods for energy insecurity and mental health outcomes were different.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Energy insecurity, the inability to meet household energy needs, was associated with more than twice the odds of having depression and anxiety symptoms than energy security in US adults, a new cross-sectional study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Using data from the US Census Bureau's online Household Pulse Survey, administered between 2022 and 2024, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study with a weighted population of > 187 million US adults (51% women; 64% White, 16% Hispanic, 10% Black, and 5% Asian). About a quarter of the population was in each of 4 age groups: 18-34 years, 35-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
- Three indicators of energy insecurity—inability to pay energy bills, maintaining unsafe/unhealthy home temperatures, and forgoing expenses on basic necessities to pay energy bills—were assessed individually and as a composite measure.
- Mental health was assessed using modified versions of the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire for depression and the 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale for anxiety.
- The analysis was adjusted for other social determinants of health, including unemployment, housing instability, and food insecurity. Covariates included a wide range of factors, such as age, educational level, sex, and annual household income.
TAKEAWAY:
- In all, > 43% of the population reported having ≥ 1 form of energy security; around 22% reported being unable to pay energy bills, 22% maintained unsafe home temperatures, and nearly 34% forewent spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills.
- Individuals who gave up spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills had higher odds of anxiety (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79) and depression (aOR, 1.74) than those who did not.
- Adults with energy insecurity on the composite measure had higher odds for anxiety (aOR, 2.29) and depression (aOR, 2.31) than those with energy security.
- Food insecurity was also associated with poorer mental health, with higher odds for symptoms of depression (aOR, 2.05) and anxiety (aOR, 2.07).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite its high prevalence, energy insecurity remains underrecognized in public health and policy intervention strategies," the investigators wrote.
"These findings suggest that energy insecurity is a widespread and important factor associated with mental health symptoms and may warrant consideration in efforts to reduce adverse mental health outcomes," they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Michelle Graf, PhD, Carter School of Public Policy, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta. It was published online on October 27 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the data limited causal interference and increased the possibility of reverse causality. The questionnaire captured subjective interpretations of unsafe and unhealthy indoor temperatures, which may have varied among respondents. Additionally, the recall periods for energy insecurity and mental health outcomes were different.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
Veterans and Loneliness: More Than Just Isolation
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, > 1 in 10 veterans have been diagnosed with substance use disorder (SUD). Additionally, 7 out of every 100 veterans will have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) at some point in their life, per research from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). However, a common and perhaps unsuspected parallel is found in those statistics: loneliness.
Of the 4069 veterans who participated in the 2019-2020 National Health and Resilience in Veterans Survey, 56.9% reported they felt lonely sometimes or often, while 1 in 5 reported feeling lonely often.
An Epidemic
In his 2023 advisory, Former US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called it an epidemic noting that when he spoke with veterans during a cross-country listening tour, he heard how they felt “isolated, invisible, and insignificant.” About 1 in 2 adults in America experience loneliness, even before the COVID-19 pandemic isolation.
Loneliness can have individual and synergistic ill effects, including a greater risk of cardiovascular disease, dementia, stroke, depression, anxiety, and premature death. It also can both trigger and exacerbate substance use and PTSD.
A study using data from the RAND Health and Retirement Study Longitudinal File 2020 (N = 5259) found significant associations between loneliness and being unmarried/unpartnered, and greater depressive symptoms for both veterans and civilians, as well as significant negative associations between loneliness and greater life satisfaction and positive affect. Health conditions that limited an individual's ability to work was a “unique risk factor for loneliness among veterans.”
The National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study found that those aged ≤ 50 years were 3 times more likely to screen positive for PTSD compared to older veterans. In a survey of 409 veterans, many who engaged in problematic substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic reported that despite having social supports they still felt lonely. In regression analyses, higher levels of loneliness were associated with more negative impacts of the pandemic, greater substance use, and poorer physical and mental health functioning.
Addressing Loneliness
Researchers believe an answer to some mental health and substance abuse problems may lie in addressing loneliness. Positive psychology is providing promising results in the treatment of SUD. Bryant Stone, from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, emphasizes focusing on well-being and quality of life rather than solely on abstinence with “positive psychological interventions,” or activities and behavioral interventions that target positive variables to promote adaptive functioning.
Veterans can face tough challenges as they rejoin civilian life. How successfully they meet and conquer those challenges, especially if they include drug problems, may directly relate to their general feeling of well-being.
The PERMA model outlines 5 core elements to assess well-being: Positive emotions, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment. A study based on that model found loneliness to be a “particularly significant factor” among key variables influencing the prevention and treatment of SUDs. The study of 156 veterans with self-reported mental health conditions found the ability to engage in social roles and activities was positively correlated with overall well-being and negatively correlated with degree of problems related to drug abuse.
Rural Veterans
The estimated 4.4 million veterans living in rural communities may benefit most from interventions that tackle isolation. Compared with urban counterparts, they’re more likely to be older, have more complex medical issues, have a service-connected disability, and be unemployed. Those factors, compounded by geographical and social isolation, can have a substantial impact on well-being.
A study centered on the initial validation of a short (5-item) version of PERMA found that individuals who scored higher on the short form tended to report higher levels of optimism, resilience, and happiness. Thus, the short form may be particularly useful for rural veterans who do not always have easy access to health care.
VA has instituted a variety of programs to encourage and support social connection. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth interventions targeted social support and loneliness among veterans—albeit with mixed results. VA CONNECT, a 10-session group telehealth intervention that integrated peer support, did not show significant changes in loneliness, but did significantly reduce perceived stress.
Another initiative, Compassionate Contact Corps, trained volunteers made weekly phone calls aimed at reducing loneliness and fostering social connection. Started in Columbus, Ohio, in 2020, > 80 sites had adopted the initiative by 2021, with 310 volunteers, 5320 visits, and 4757 hours spent with veterans.
In 2014, VA peer specialists developed and co-hosted Veterans Socials through community partnerships between VA, veteran-serving organizations, and veteran community leaders. As of 2025, 178 known Veterans Socials were spread across 26 states and territories.
The researchers say their case examples collectively demonstrate that Veterans Socials have the potential to serve as a vital platform for peer support, resource sharing, and health service use among veterans. Virtual Veterans Socials also provided hosts with a channel to reach potentially isolated veterans who might not otherwise access services while simultaneously offering veterans an opportunity for social connection.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, > 1 in 10 veterans have been diagnosed with substance use disorder (SUD). Additionally, 7 out of every 100 veterans will have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) at some point in their life, per research from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). However, a common and perhaps unsuspected parallel is found in those statistics: loneliness.
Of the 4069 veterans who participated in the 2019-2020 National Health and Resilience in Veterans Survey, 56.9% reported they felt lonely sometimes or often, while 1 in 5 reported feeling lonely often.
An Epidemic
In his 2023 advisory, Former US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called it an epidemic noting that when he spoke with veterans during a cross-country listening tour, he heard how they felt “isolated, invisible, and insignificant.” About 1 in 2 adults in America experience loneliness, even before the COVID-19 pandemic isolation.
Loneliness can have individual and synergistic ill effects, including a greater risk of cardiovascular disease, dementia, stroke, depression, anxiety, and premature death. It also can both trigger and exacerbate substance use and PTSD.
A study using data from the RAND Health and Retirement Study Longitudinal File 2020 (N = 5259) found significant associations between loneliness and being unmarried/unpartnered, and greater depressive symptoms for both veterans and civilians, as well as significant negative associations between loneliness and greater life satisfaction and positive affect. Health conditions that limited an individual's ability to work was a “unique risk factor for loneliness among veterans.”
The National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study found that those aged ≤ 50 years were 3 times more likely to screen positive for PTSD compared to older veterans. In a survey of 409 veterans, many who engaged in problematic substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic reported that despite having social supports they still felt lonely. In regression analyses, higher levels of loneliness were associated with more negative impacts of the pandemic, greater substance use, and poorer physical and mental health functioning.
Addressing Loneliness
Researchers believe an answer to some mental health and substance abuse problems may lie in addressing loneliness. Positive psychology is providing promising results in the treatment of SUD. Bryant Stone, from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, emphasizes focusing on well-being and quality of life rather than solely on abstinence with “positive psychological interventions,” or activities and behavioral interventions that target positive variables to promote adaptive functioning.
Veterans can face tough challenges as they rejoin civilian life. How successfully they meet and conquer those challenges, especially if they include drug problems, may directly relate to their general feeling of well-being.
The PERMA model outlines 5 core elements to assess well-being: Positive emotions, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment. A study based on that model found loneliness to be a “particularly significant factor” among key variables influencing the prevention and treatment of SUDs. The study of 156 veterans with self-reported mental health conditions found the ability to engage in social roles and activities was positively correlated with overall well-being and negatively correlated with degree of problems related to drug abuse.
Rural Veterans
The estimated 4.4 million veterans living in rural communities may benefit most from interventions that tackle isolation. Compared with urban counterparts, they’re more likely to be older, have more complex medical issues, have a service-connected disability, and be unemployed. Those factors, compounded by geographical and social isolation, can have a substantial impact on well-being.
A study centered on the initial validation of a short (5-item) version of PERMA found that individuals who scored higher on the short form tended to report higher levels of optimism, resilience, and happiness. Thus, the short form may be particularly useful for rural veterans who do not always have easy access to health care.
VA has instituted a variety of programs to encourage and support social connection. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth interventions targeted social support and loneliness among veterans—albeit with mixed results. VA CONNECT, a 10-session group telehealth intervention that integrated peer support, did not show significant changes in loneliness, but did significantly reduce perceived stress.
Another initiative, Compassionate Contact Corps, trained volunteers made weekly phone calls aimed at reducing loneliness and fostering social connection. Started in Columbus, Ohio, in 2020, > 80 sites had adopted the initiative by 2021, with 310 volunteers, 5320 visits, and 4757 hours spent with veterans.
In 2014, VA peer specialists developed and co-hosted Veterans Socials through community partnerships between VA, veteran-serving organizations, and veteran community leaders. As of 2025, 178 known Veterans Socials were spread across 26 states and territories.
The researchers say their case examples collectively demonstrate that Veterans Socials have the potential to serve as a vital platform for peer support, resource sharing, and health service use among veterans. Virtual Veterans Socials also provided hosts with a channel to reach potentially isolated veterans who might not otherwise access services while simultaneously offering veterans an opportunity for social connection.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, > 1 in 10 veterans have been diagnosed with substance use disorder (SUD). Additionally, 7 out of every 100 veterans will have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) at some point in their life, per research from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). However, a common and perhaps unsuspected parallel is found in those statistics: loneliness.
Of the 4069 veterans who participated in the 2019-2020 National Health and Resilience in Veterans Survey, 56.9% reported they felt lonely sometimes or often, while 1 in 5 reported feeling lonely often.
An Epidemic
In his 2023 advisory, Former US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called it an epidemic noting that when he spoke with veterans during a cross-country listening tour, he heard how they felt “isolated, invisible, and insignificant.” About 1 in 2 adults in America experience loneliness, even before the COVID-19 pandemic isolation.
Loneliness can have individual and synergistic ill effects, including a greater risk of cardiovascular disease, dementia, stroke, depression, anxiety, and premature death. It also can both trigger and exacerbate substance use and PTSD.
A study using data from the RAND Health and Retirement Study Longitudinal File 2020 (N = 5259) found significant associations between loneliness and being unmarried/unpartnered, and greater depressive symptoms for both veterans and civilians, as well as significant negative associations between loneliness and greater life satisfaction and positive affect. Health conditions that limited an individual's ability to work was a “unique risk factor for loneliness among veterans.”
The National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study found that those aged ≤ 50 years were 3 times more likely to screen positive for PTSD compared to older veterans. In a survey of 409 veterans, many who engaged in problematic substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic reported that despite having social supports they still felt lonely. In regression analyses, higher levels of loneliness were associated with more negative impacts of the pandemic, greater substance use, and poorer physical and mental health functioning.
Addressing Loneliness
Researchers believe an answer to some mental health and substance abuse problems may lie in addressing loneliness. Positive psychology is providing promising results in the treatment of SUD. Bryant Stone, from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, emphasizes focusing on well-being and quality of life rather than solely on abstinence with “positive psychological interventions,” or activities and behavioral interventions that target positive variables to promote adaptive functioning.
Veterans can face tough challenges as they rejoin civilian life. How successfully they meet and conquer those challenges, especially if they include drug problems, may directly relate to their general feeling of well-being.
The PERMA model outlines 5 core elements to assess well-being: Positive emotions, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment. A study based on that model found loneliness to be a “particularly significant factor” among key variables influencing the prevention and treatment of SUDs. The study of 156 veterans with self-reported mental health conditions found the ability to engage in social roles and activities was positively correlated with overall well-being and negatively correlated with degree of problems related to drug abuse.
Rural Veterans
The estimated 4.4 million veterans living in rural communities may benefit most from interventions that tackle isolation. Compared with urban counterparts, they’re more likely to be older, have more complex medical issues, have a service-connected disability, and be unemployed. Those factors, compounded by geographical and social isolation, can have a substantial impact on well-being.
A study centered on the initial validation of a short (5-item) version of PERMA found that individuals who scored higher on the short form tended to report higher levels of optimism, resilience, and happiness. Thus, the short form may be particularly useful for rural veterans who do not always have easy access to health care.
VA has instituted a variety of programs to encourage and support social connection. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth interventions targeted social support and loneliness among veterans—albeit with mixed results. VA CONNECT, a 10-session group telehealth intervention that integrated peer support, did not show significant changes in loneliness, but did significantly reduce perceived stress.
Another initiative, Compassionate Contact Corps, trained volunteers made weekly phone calls aimed at reducing loneliness and fostering social connection. Started in Columbus, Ohio, in 2020, > 80 sites had adopted the initiative by 2021, with 310 volunteers, 5320 visits, and 4757 hours spent with veterans.
In 2014, VA peer specialists developed and co-hosted Veterans Socials through community partnerships between VA, veteran-serving organizations, and veteran community leaders. As of 2025, 178 known Veterans Socials were spread across 26 states and territories.
The researchers say their case examples collectively demonstrate that Veterans Socials have the potential to serve as a vital platform for peer support, resource sharing, and health service use among veterans. Virtual Veterans Socials also provided hosts with a channel to reach potentially isolated veterans who might not otherwise access services while simultaneously offering veterans an opportunity for social connection.
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Cancer patients experience depression at rates > 5 times that of the general population.1-11 Despite an increase in palliative care use, depression rates continued to rise.2-4 Between 5% to 16% of outpatients, 4% to 14% of inpatients, and up to 49% of patients receiving palliative care experience depression.5 This issue also impacts families and caregivers.1 A 2021 meta-analysis found that 23% of active military personnel and 20% of veterans experience depression.11
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) target the serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine systems and include boxed warnings about an increased risk of suicidal thoughts in adults aged 18 to 24 years.12,13 These medications are categorized into several classes: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), serotonin receptor modulators (SRMs), serotonin-melatonin receptor antagonists (SMRAs), and N—methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (NMDARAs).14,15 The first FDA-approved antidepressants, iproniazid (an MAOI) and imipramine (a TCA) laid the foundation for the development of newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs.15-17
Older antidepressants such as MAOIs and TCAs are used less due to their adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions. MAOIs, such as iproniazid, selegiline, moclobemide, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, and phenelzine, have numerous AEs and drug interactions, making them unsuitable for first- or second-line treatment of depression.14,18-21 TCAs such as doxepin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, clomipramine, trimipramine, protriptyline, maprotiline, and amoxapine have a narrow therapeutic index requiring careful monitoring for signs of toxicity such as QRS widening, tremors, or confusion. Despite the issues, TCAs are generally classified as second-line agents for major depressive disorder (MDD). TCAs have off-label uses for migraine prophylaxis, treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), insomnia, and chronic pain management first-line.14,22-29
Newer antidepressants, including TeCAs and NDRIs, are typically more effective, but also come with safety concerns. TeCAs like mirtazapine interact with several medications, including MAOIs, serotonin-increasing drugs, alcohol, cannabidiol, and marijuana. Mirtazapine is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe depression in adults. It is also used off-label to treat insomnia, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), headaches, and migraines. Compared to other antidepressants, mirtazapine is effective for all stages of depression and addresses a broad range of related symptoms.14,30-34 NDRIs, such as bupropion, also interact with various medications, including MAOIs, other antidepressants, stimulants, and alcohol. Bupropion is FDA-approved for smoking cessation and to treat depression and SAD. It is also used off-label for depression- related bipolar disorder or sexual dysfunction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity.14,35-42
SSRIs, SNRIs, and SRMs should be used with caution. SSRIs such as sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine are first-line treatments for depression and various psychiatric disorders due to their safety and efficacy. Common AEs of SSRIs include sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, weight changes, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues. SSRIs can prolong the QT interval, posing a risk of life-threatening arrhythmia, and may interact with other medications, necessitating treatment adjustments. The FDA approved SSRIs for MDD, GAD, bulimia nervosa, bipolar depression, OCD, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and SAD. Off-label uses include binge eating disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, fibromyalgia, premature ejaculation, paraphilias, autism, Raynaud phenomenon, and vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Among SSRIs, sertraline and escitalopram are noted for their effectiveness and tolerability.14,43-53
SNRIs, including duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran, may increase bleeding risk, especially when taken with blood thinners. They can also elevate blood pressure, which may worsen if combined with stimulants. SNRIs may interact with other medications that affect serotonin levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with triptans, pain medications, or other antidepressants.14 Desvenlafaxine has been approved by the FDA (but not by the European Medicines Agency).54-56 Duloxetine is FDA-approved for the treatment of depression, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal disorders. It is used off-label to treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence.57-61 Venlafaxine is FDA-approved for depression, SAD, and panic disorder, and is prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, neuropathy, fibromyalgia, cataplexy, and PTSD, either alone or in combination with other medications.62,63 Milnacipran is not approved for MDD; levomilnacipran received approval in 2013.64
SRMs such as trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, and vortioxetine also function as serotonin reuptake inhibitors.14,15 Trazodone is FDA-approved for MDD. It has been used off-label to treat anxiety, Alzheimer disease, substance misuse, bulimia nervosa, insomnia, fibromyalgia, and PTSD when first-line SSRIs are ineffective. A notable AE of trazodone is orthostatic hypotension, which can lead to dizziness and increase the risk of falls, especially in geriatric patients.65-70 Nefazodone was discontinued in Europe in 2003 due to rare cases of liver toxicity but remains available in the US.71-74 Vilazodone and vortioxetine are FDA-approved.
The latest classes of antidepressants include SMRAs and NMDARAs.14 Agomelatine, an SMRA, was approved in Europe in 2009 but rejected by the FDA in 2011 due to liver toxicity.75 NMDARAs like esketamine and a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion received FDA approval in 2019 and 2022, respectively.76,77
This retrospective study analyzes noncancer drugs used during systemic chemotherapy based on a dataset of 14 antineoplastic agents. It sought to identify the most dispensed noncancer drug groups, discuss findings, compare patients with and without antidepressant prescriptions, and examine trends in antidepressant use from 2002 to 2023. This analysis expands on prior research.78-81
Methods
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and Military Health System (MHS) data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
Data Sources
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry Program contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in CAPER represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER records are available from 2003 to 2024. PDTS records are available from 2002 to 2004. Each observation in PDTS represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary, excluding those filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions.
This cross-sectional analysis requested data extraction for specific cancer drugs from the DoD Cancer Registry, focusing on treatment details, diagnosis dates, patient demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. After identifying patients, CAPER was used to identify additional health conditions. PDTS was used to compile a list of prescription medications filled during systemic cancer treatment or < 2 years postdiagnosis.
The 2016 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.82,83 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients or data variables. To compare the mean number of dispensed antidepressants to those without antidepressants, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to calculate the P value and determine statistical significance (P < .05) using socscistatistics.com.
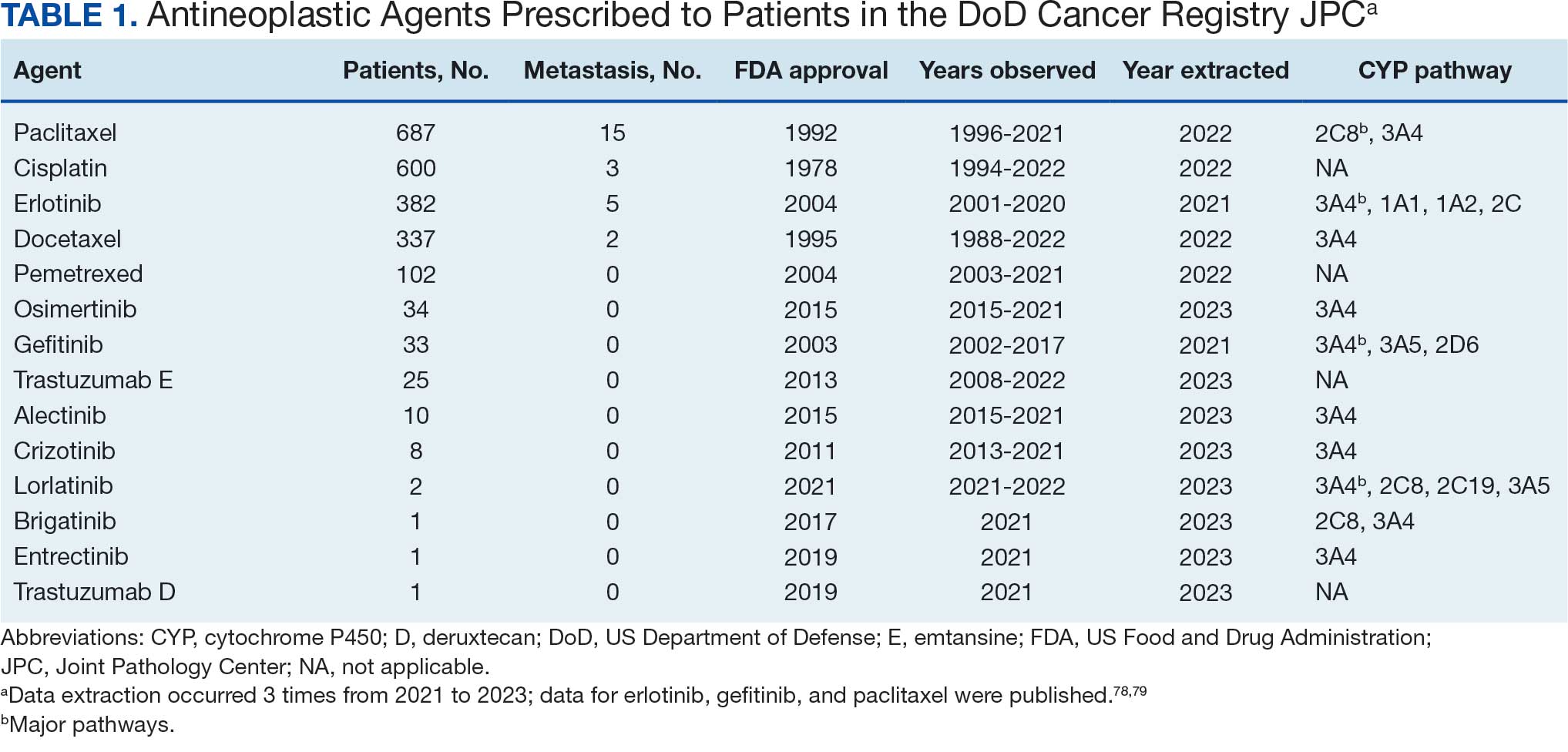
Data were extracted 3 times between 2021 and 2023. The initial 2021 protocol focused on erlotinib and gefitinib. A modified protocol in 2022 added paclitaxel, cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, and crizotinib; further modification in 2023 included 8 new antineoplastic agents and 2 anticoagulants. Sotorasib has not been prescribed in the MHS, and JPC lacks records for noncancer drugs. The 2023 dataset comprised 2210 patients with cancer treated with 14 antineoplastic agents; 2104 had documented diagnoses and 2113 had recorded prescriptions. Data for erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel have been published previously.78,79
Results
Of 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 1297 patients (61.4%) received 109 cancer drugs, including 96 antineoplastics, 7 disease-modifying antirheumatic agents, 4 biologic response modifiers, and 2 calcitonin gene-related peptides. Fourteen antineoplastic agents had complete data from JPC, while others were noted for combination therapies or treatment switches from the PDTS (Table 1). Seventy-six cancer drugs were prescribed with antidepressants in 489 patients (eAppendix).
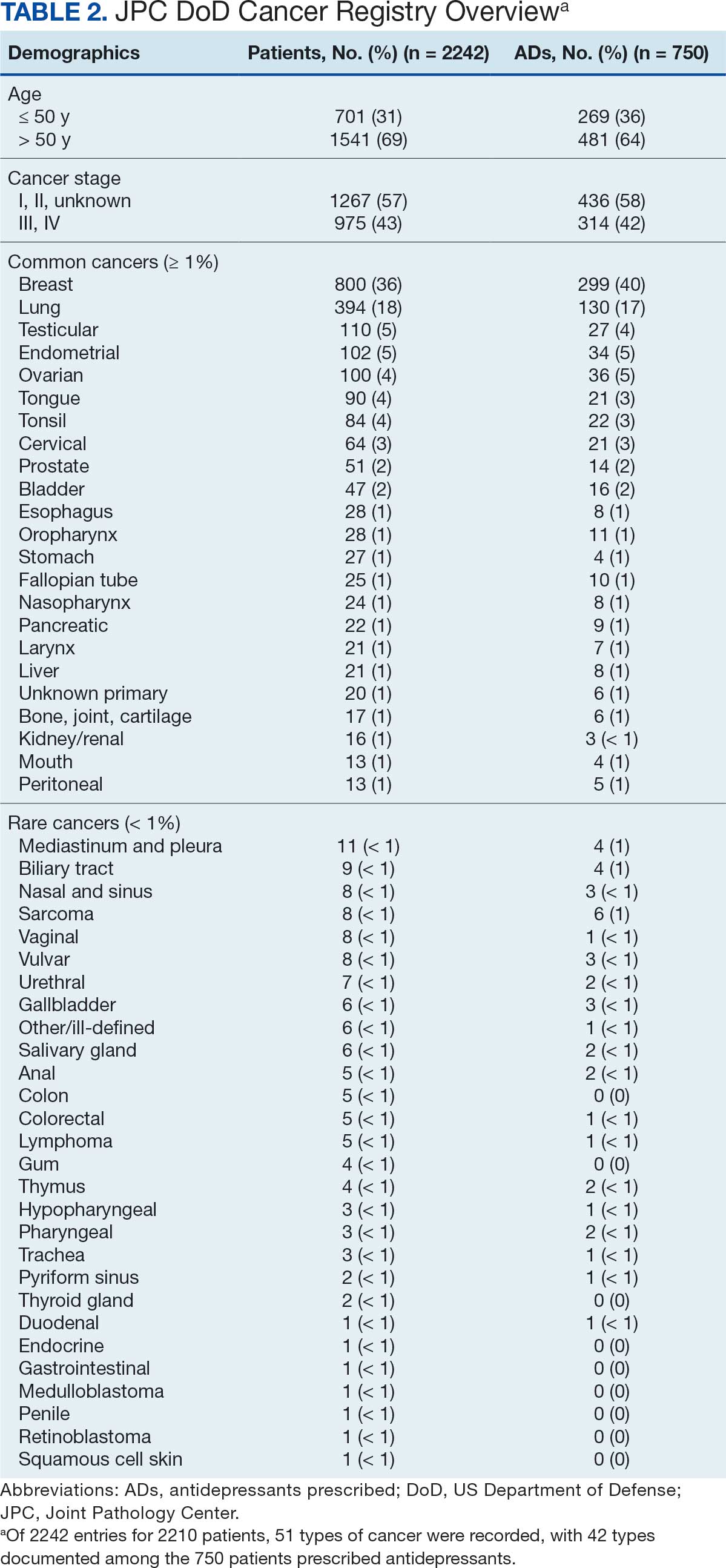
The JPC provided 2242 entries for 2210 patients, ranging in age from 2 months to 88 years (mean, 56 years), documenting treatment from September 1988 to January 2023. Thirty-two patients had duplicate entries due to multiple cancer locations or occurrences. Of the 2242 patients, 1541 (68.7%) were aged > 50 years, 975 patients (43.5%) had cancers that were stage III or IV, and 1267 (56.5%) had cancers that were stage 0, I, II, or not applicable/unknown. There were 51 different types of cancer: breast, lung, testicular, endometrial, and ovarian were most common (n ≥ 100 patients). Forty-two cancer types were documented among 750 patients prescribed antidepressants (Table 2).
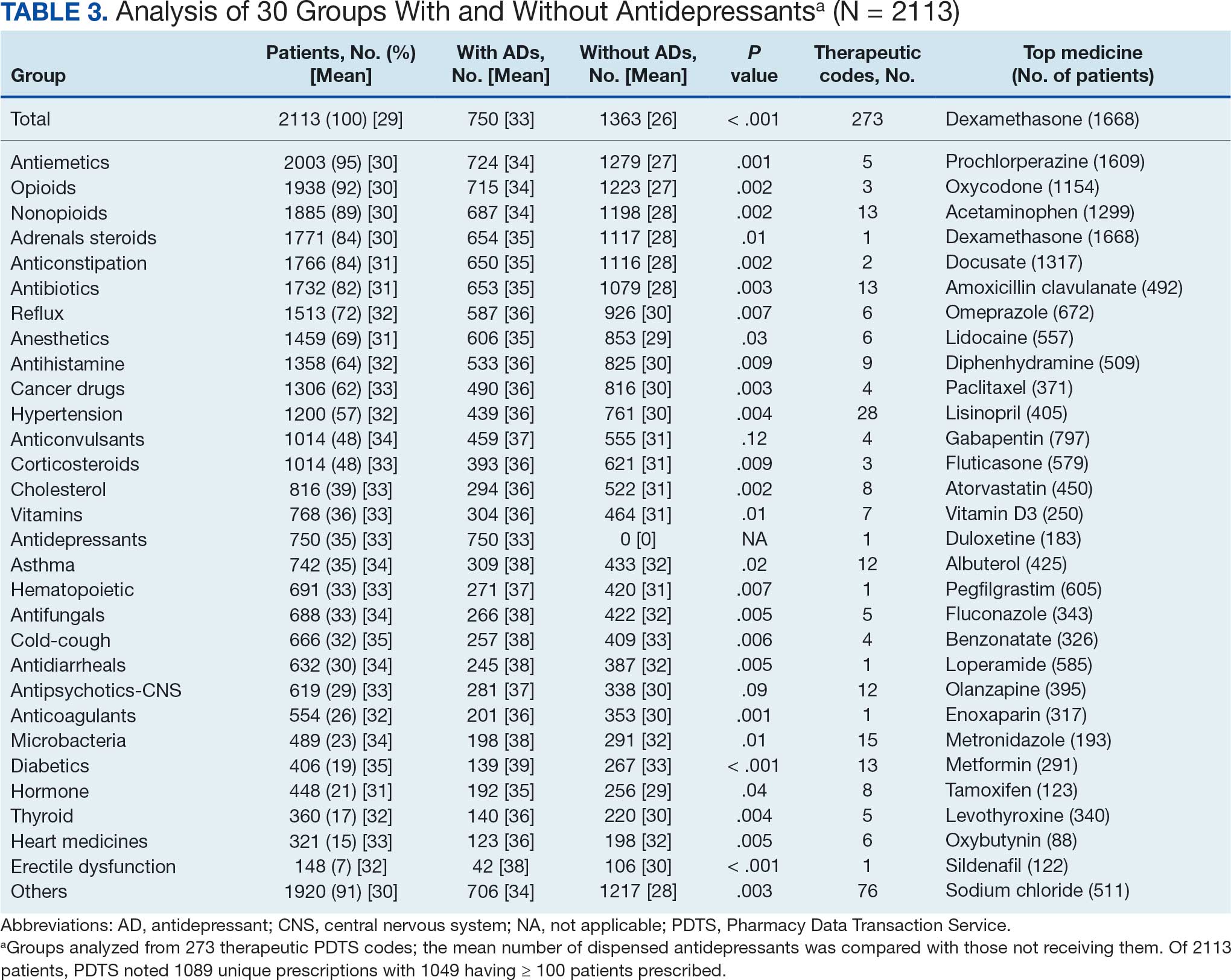
The CAPER database recorded 8882 unique diagnoses for 2104 patients, while PDTS noted 1089 unique prescriptions within 273 therapeutic codes for 2113 patients. Nine therapeutic codes (opiate agonists, adrenals, cathartics-laxatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihistamines for GI conditions, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, analgesics and antipyretic miscellanea, antineoplastic agents, and proton-pump inhibitors) and 8 drugs (dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, ondansetron, docusate, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, oxycodone, and polyethylene glycol 3350) were associated with > 1000 patients (≥ 50%). Patients had between 1 and 275 unique health conditions and filled 1 to 108 prescriptions. The mean (SD) number of diagnoses and prescriptions was 50 (28) and 29 (12), respectively. Of the 273 therapeutic codes, 30 groups were analyzed, with others categorized into miscellaneous groups such as lotions, vaccines, and devices. Significant differences in mean number of prescriptions were found for patients taking antidepressants compared to those not (P < .05), except for anticonvulsants and antipsychotics (P = .12 and .09, respectively) (Table 3).
Antidepressants
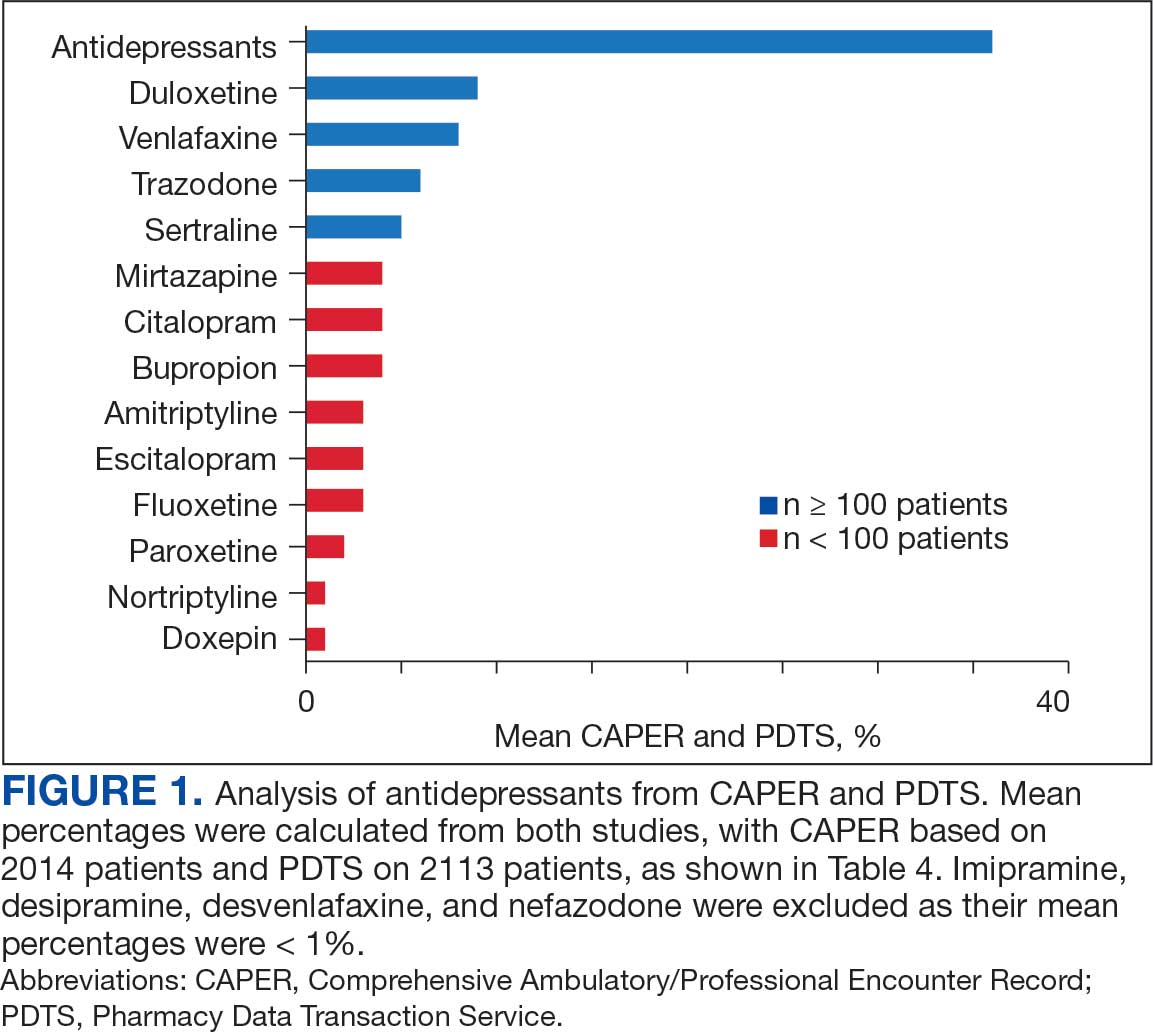
Of the 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 750 (35.5%) were dispensed 17 different antidepressants. Among these 17 antidepressants, 183 (8.7%) patients received duloxetine, 158 (7.5%) received venlafaxine, 118 (5.6%) received trazodone, and 107 (5.1%) received sertraline (Figure 1, Table 4). Of the 750 patients, 509 (67.9%) received 1 antidepressant, 168 (22.4%) received 2, 60 (8.0%) received 3, and 13 (1.7%) received > 3. Combinations varied, but only duloxetine and trazodone were prescribed to > 10 patients.
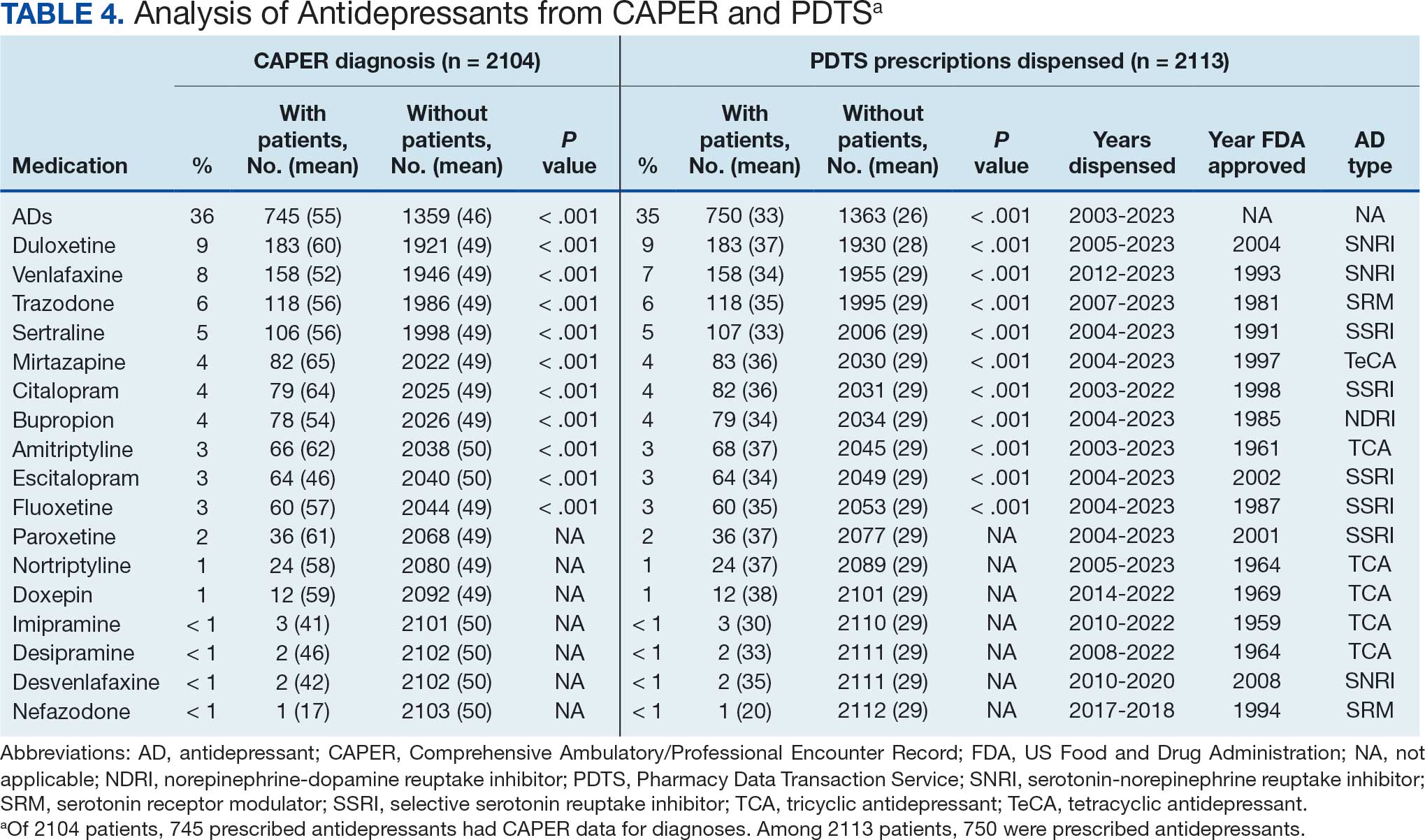
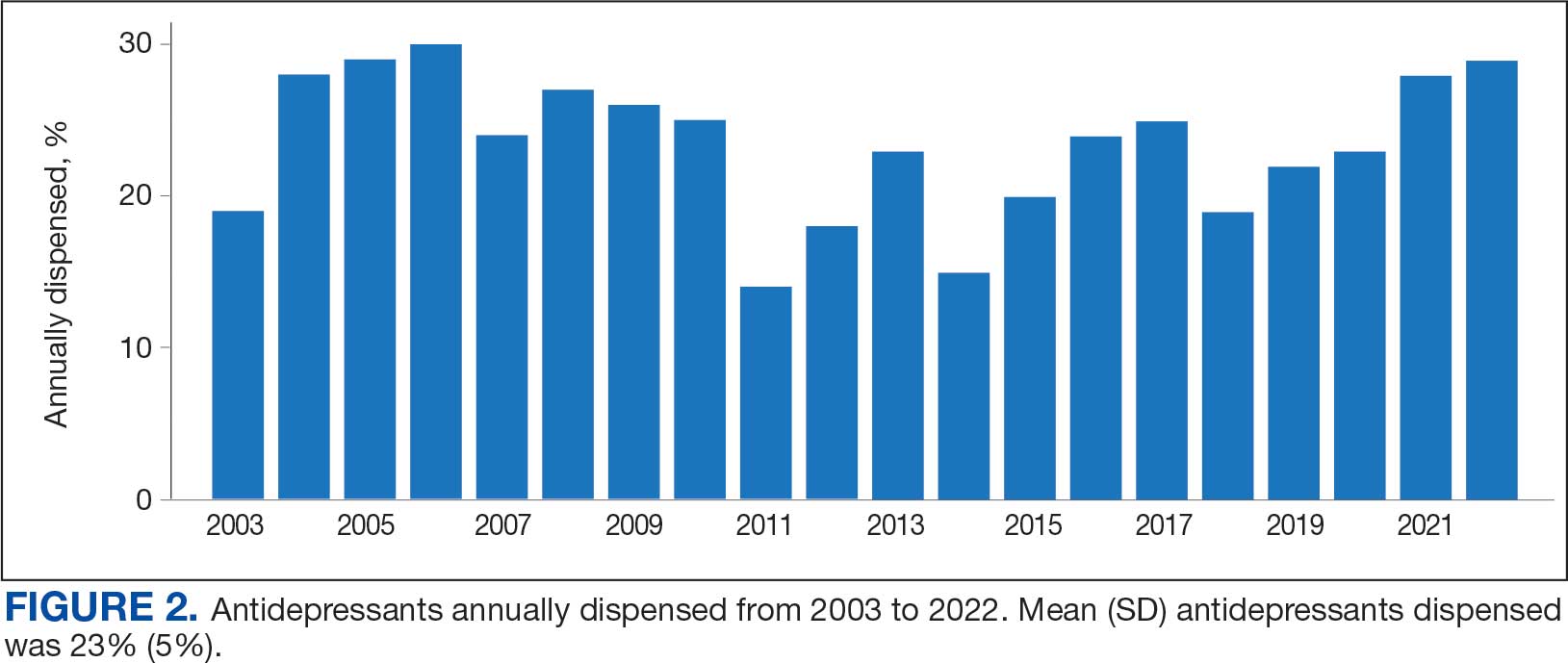
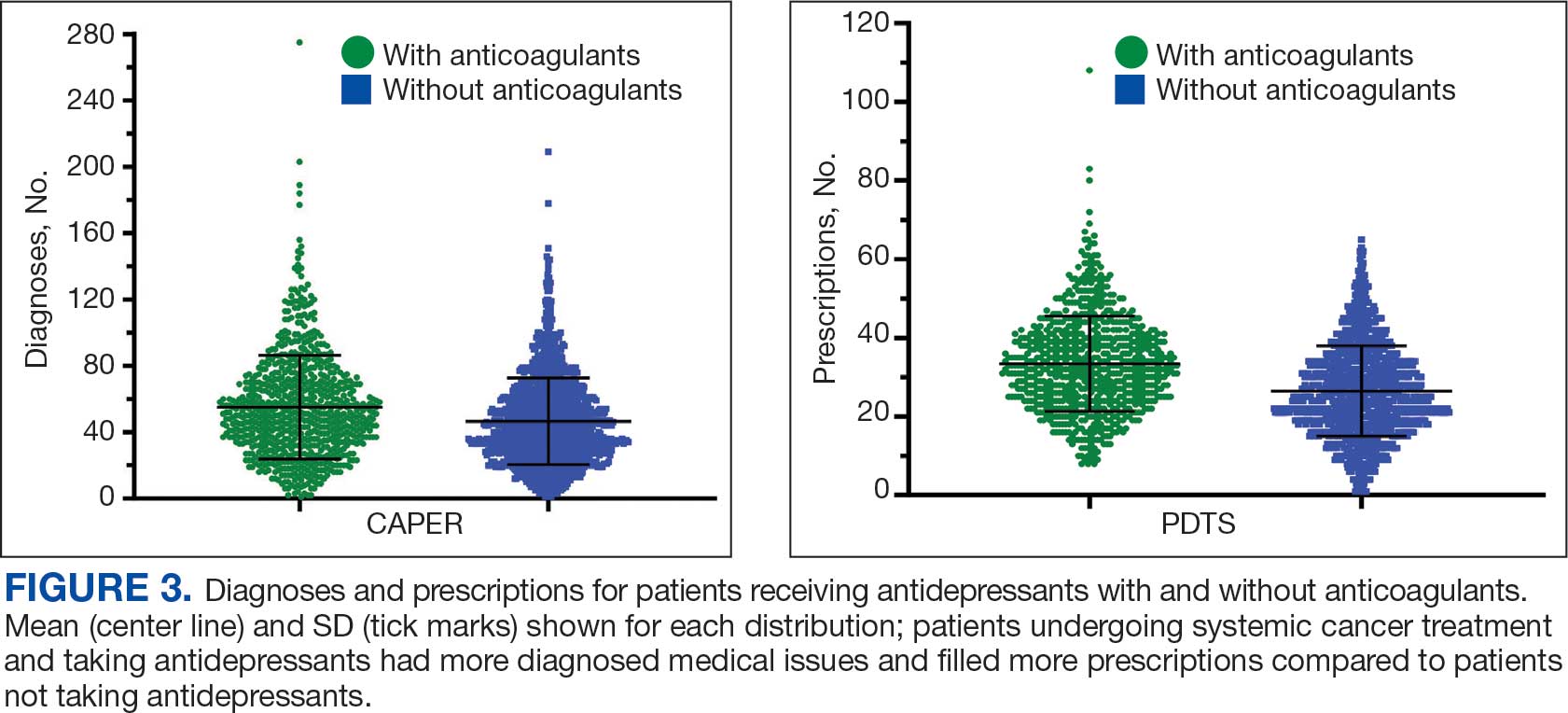
Antidepressants were prescribed annually at an overall mean (SD) rate of 23% (5%) from 2003 to 2022 (Figure 2). Patients on antidepressants during systemic therapy had a greater number of diagnosed medical conditions and received more prescription medications compared to those not taking antidepressants (P < .001) (Figure 3). The 745 patients taking antidepressants in CAPER data had between 1 and 275 diagnosed medical issues, with a mean (SD) of 55 (31) vs a range of 1 to 209 and a mean (SD) of 46 (26) for the 1359 patients not taking antidepressants. The 750 patients on antidepressants in PDTS data had between 8 and 108 prescriptions dispensed, with a mean (SD) of 32 (12), vs a range of 1 to 65 prescriptions and a mean (SD) of 29 (12) for 1363 patients not taking antidepressants.
Discussion
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry includes information on cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes, while noncancer drugs are sourced from the PDTS database. The pharmacy uses a different documentation system, leading to varied classifications.
Database reliance has its drawbacks. For example, megestrol is coded as a cancer drug, although it’s primarily used for endometrial or gynecologic cancers. Many drugs have multiple therapeutic codes assigned to them, including 10 antineoplastic agents: diclofenac, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), megestrol acetate, tamoxifen, anastrozole, letrozole, leuprolide, goserelin, degarelix, and fluorouracil. Diclofenac, BCG, and mitomycin have been repurposed for cancer treatment.84-87 From 2003 to 2023, diclofenac was prescribed to 350 patients for mild-to-moderate pain, with only 2 patients receiving it for cancer in 2018. FDA-approved for bladder cancer in 1990, BCG was prescribed for cancer treatment for 1 patient in 2021 after being used for vaccines between 2003 and 2018. Tamoxifen, used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer from 2004 to 2017 with 53 patients, switched to estrogen agonist-antagonists from 2017 to 2023 with 123 patients. Only a few of the 168 patients were prescribed tamoxifen using both codes.88-91 Anastrozole and letrozole were coded as antiestrogens for 7 and 18 patients, respectively, while leuprolide and goserelin were coded as gonadotropins for 59 and 18 patients. Degarelix was coded as antigonadotropins, fluorouracil as skin and mucous membrane agents miscellaneous, and megestrol acetate as progestins for 7, 6, and 3 patients, respectively. Duloxetine was given to 186 patients, primarily for depression from 2005 to 2023, with 7 patients treated for fibromyalgia from 2022 to 2023.
Antidepressants Observed
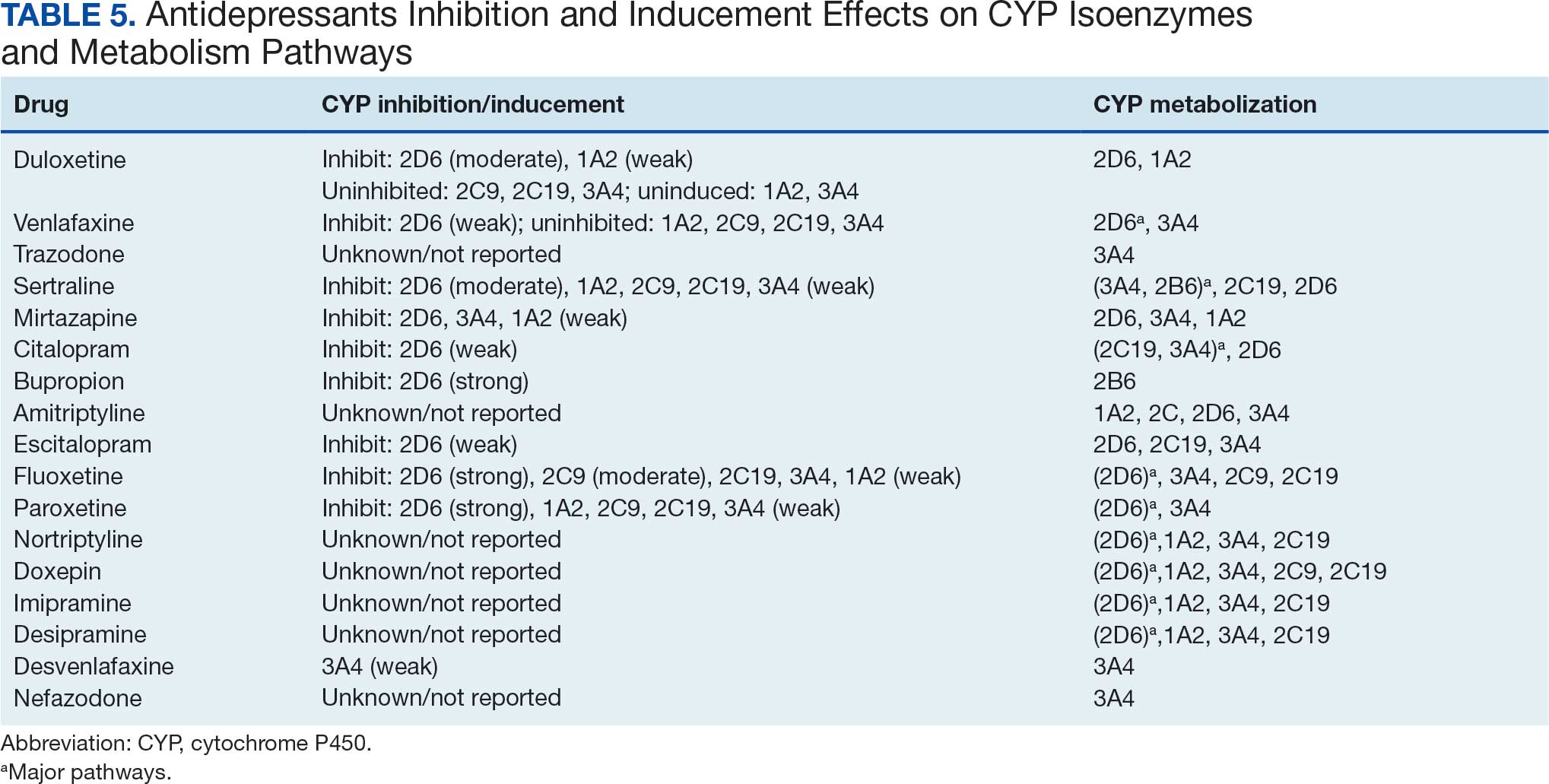
Tables 1 and 5 provide insight into the FDA approval of 14 antineoplastics and antidepressants and their CYP metabolic pathways.92-122 In Table 4, the most prescribed antidepressant classes are SNRIs, SRMs, SSRIs, TeCAs, NDRIs, and TCAs. This trend highlights a preference for newer medications with weak CYP inhibition. A total of 349 patients were prescribed SSRIs, 343 SNRIs, 119 SRMs, 109 TCAs, 83 TeCAs, and 79 NDRIs. MAOIs, SMRAs, and NMDARAs were not observed in this dataset. While there are instances of dextromethorphan-bupropion and sertraline-escitalopram being dispensed together, it remains unclear whether these were NMDARA combinations.
Among the 14 specific antineoplastic agents, 10 are metabolized by CYP isoenzymes, primarily CYP3A4. Duloxetine neither inhibits nor is metabolized by CYP3A4, a reason it is often recommended, following venlafaxine.
Both duloxetine and venlafaxine are used off-label for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy related to paclitaxel and docetaxel. According to the CYP metabolized pathway, duloxetine tends to have more favorable DDIs than venlafaxine. In PDTS data, 371 patients were treated with paclitaxel and 180 with docetaxel, with respective antidepressant prescriptions of 156 and 70. Of the 156 patients dispensed paclitaxel, 62 (40%) were dispensed with duloxetine compared to 43 (28%) with venlafaxine. Of the 70 patients dispensed docetaxel, 23 (33%) received duloxetine vs 24 (34%) with venlafaxine.
Of 85 patients prescribed duloxetine, 75 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel (5 received both). Five patients had documented AEs (1 neuropathy related). Of 67 patients prescribed venlafaxine, 66 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel. Two patients had documented AEs (1 was neuropathy related, the same patient who received duloxetine). Of the 687 patients treated with paclitaxel and 337 with docetaxel in all databases, 4 experienced neuropathic AEs from both medications.79
Antidepressants can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners, and may elevate blood pressure, particularly alongside stimulants. Of the 554 patients prescribed 9 different anticoagulants, enoxaparin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban were the most common (each > 100 patients). Among these, 201 patients (36%) received both anticoagulants and antidepressants: duloxetine for 64 patients, venlafaxine for 30, trazodone for 35, and sertraline for 26. There were no data available to assess bleeding rates related to the evaluation of DDIs between these medication classes.
Antidepressants can be prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Of the 148 patients prescribed an antidepressant for erectile dysfunction, duloxetine, trazodone, and mirtazapine were the most common. Antidepressant preferences varied by cancer type. Duloxetine was the only antidepressant used for all types of cancer. Venlafaxine, duloxetine, trazodone, sertraline, and escitalopram were the most prescribed antidepressants for breast cancer, while duloxetine, mirtazapine, citalopram, sertraline, and trazodone were the most prescribed for lung cancer. Sertraline, duloxetine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and escitalopram were most common for testicular cancer. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and sertraline were the most prescribed for endometrial cancer, while duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, citalopram, and sertraline were most prescribed for ovarian cancer.
The broadness of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes made it challenging to identify nondepression diagnoses in the analyzed population. However, if all antidepressants were prescribed to treat depression, service members with cancer exhibited a higher depression rate (35%) than the general population (25%). Of 2104 patients, 191 (9.1%) had mood disorders, and 706 (33.6%) had mental disorders: 346 (49.0%) had 1 diagnosis, and 360 (51.0%) had multiple diagnoses. The percentage of diagnoses varied yearly, with notable drops in 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, and peaks in 2006, 2008, 2013, 2017, and 2022. This fluctuation was influenced by events like the establishment of PDTS in 2002, the 2008 economic recession, a hospital relocation in 2011, the 2014 Ebola outbreak, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the number of patients receiving antidepressants increased from 2019 to 2022, the overall percentage of patients receiving them did not significantly change from 2003 to 2022, aligning with previous research.5,125
Many medications have potential uses beyond what is detailed in the prescribing information. Antidepressants can relieve pain, while pain medications may help with depression. Opioids were once thought to effectively treat depression, but this perspective has changed with a greater understanding of their risks, including misuse.126-131 Pain is a severe and often unbearable AE of cancer. Of 2113 patients, 92% received opioids; 34% received both opioids and antidepressants; 2% received only antidepressants; and 7% received neither. This study didn’t clarify whether those on opioids alone recognized their depression or if those on both were aware of their dependence. While SSRIs are generally not addictive, they can lead to physical dependence, and any medication can be abused if not managed properly.132-134
Conclusions
This retrospective study analyzes data from antineoplastic agents used in systemic cancer treatment between 1988 and 2023, with a particular focus on the use of antidepressants. Data on antidepressant prescriptions are incomplete and specific to these agents, which means the findings cannot be generalized to all antidepressants. Hence, the results indicate that patients taking antidepressants had more diagnosed health issues and received more medications compared to patients who were not on these drugs.
This study underscores the need for further research into the effects of antidepressants on cancer treatment, utilizing all data from the DoD Cancer Registry. Future research should explore DDIs between antidepressants and other cancer and noncancer medications, as this study did not assess AE documentation, unlike in studies involving erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel.78,79 Further investigation is needed to evaluate the impact of discontinuing antidepressant use during cancer treatment. This comprehensive overview provides insights for clinicians to help them make informed decisions regarding the prescription of antidepressants in the context of cancer treatment.
- National Cancer Institute. Depression (PDQ)-Health Professional Version. Updated July 25, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/feelings/depression-hp-pdq
- Krebber AM, Buffart LM, Kleijn G, et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology. 2014;23(2):121-130. doi:10.1002/pon.3409
- Xiang X, An R, Gehlert S. Trends in antidepressant use among U.S. cancer survivors, 1999-2012. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):564. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201500007
- Hartung TJ, Brähler E, Faller H, et al. The risk of being depressed is significantly higher in cancer patients than in the general population: Prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms across major cancer types. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:46-53. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.017
- Walker J, Holm Hansen C, Martin P, et al. Prevalence of depression in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):895-900. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds575
- Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. doi:10.1136/bmj.k1415
- Kisely S, Alotiby MKN, Protani MM, Soole R, Arnautovska U, Siskind D. Breast cancer treatment disparities in patients with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2023;32(5):651-662. doi:10.1002/pon.6120
- Massie MJ. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;(32):57-71. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh014
- Rodin G, Katz M, Lloyd N, Green E, Mackay JA, Wong RK. Treatment of depression in cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2007;14(5):180-188. doi:10.3747/co.2007.146
- Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG, et al. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(2):118-129. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016
- Moradi Y, Dowran B, Sepandi M. The global prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, and attempts in the military forces: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross sectional studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
- Lu CY, Zhang F, Lakoma MD, et al. Changes in antidepressant use by young people and suicidal behavior after FDA warnings and media coverage: quasi-experimental study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3596. doi:10.1136/bmj.g3596
- Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning--10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(18):1666-1668. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408480
- Sheffler ZM, Patel P, Abdijadid S. Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 26, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
- Miller JJ. Antidepressants, Part 1: 100 Years and Counting. Accessed April 4, 2025. Psychiatric Times. https:// www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/antidepressants-part-1-100-years-and-counting
- Hillhouse TM, Porter JH. A brief history of the development of antidepressant drugs: from monoamines to glutamate. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(1):1-21. doi:10.1037/a0038550
- Mitchell PB, Mitchell MS. The management of depression. Part 2. The place of the new antidepressants. Aust Fam Physician. 1994;23(9):1771-1781.
- Sabri MA, Saber-Ayad MM. MAO Inhibitors. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557395/
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/
- Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248. doi:10.1097/00131746-200407000-00005
- Flockhart DA. Dietary restrictions and drug interactions with monoamine oxidase inhibitors: an update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:17-24. doi:10.4088/JCP.11096su1c.03
- Moraczewski J, Awosika AO, Aedma KK. Tricyclic Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557791/
- Almasi A, Patel P, Meza CE. Doxepin. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 14, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/
- Thour A, Marwaha R. Amitriptyline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/
- Radley DC, Finkelstein SN, Stafford RS. Off-label prescribing among office-based physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):1021-1026. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.9.1021
- Tesfaye S, Sloan G, Petrie J, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10353):680- 690. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01472-6
- Farag HM, Yunusa I, Goswami H, Sultan I, Doucette JA, Eguale T. Comparison of amitriptyline and US Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and network metaanalysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212939. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12939
- Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, Saadabadi A. Nortriptyline. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
- Fayez R, Gupta V. Imipramine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 22, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/
- Jilani TN, Gibbons JR, Faizy RM, Saadabadi A. Mirtazapine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519059/
- Nutt DJ. Tolerability and safety aspects of mirtazapine. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17 Suppl 1:S37-S41. doi:10.1002/hup.388
- Gandotra K, Chen P, Jaskiw GE, Konicki PE, Strohl KP. Effective treatment of insomnia with mirtazapine attenuates concomitant suicidal ideation. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(5):901-902. doi:10.5664/jcsm.7142
- Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00198.x
- Wang SM, Han C, Bahk WM, et al. Addressing the side effects of contemporary antidepressant drugs: a comprehensive review. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(2):101-112. doi:10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.101
- Huecker MR, Smiley A, Saadabadi A. Bupropion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated April 9, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/
- Hsieh MT, Tseng PT, Wu YC, et al. Effects of different pharmacologic smoking cessation treatments on body weight changes and success rates in patients with nicotine dependence: a network meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):895- 905. doi:10.1111/obr.12835
- Hankosky ER, Bush HM, Dwoskin LP, et al. Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1292-1299.
- Livingstone-Banks J, Norris E, Hartmann-Boyce J, West R, Jarvis M, Hajek P. Relapse prevention interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2(2):CD003999. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003999.pub5
- Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Sex Med. 2018;6(2):59-74. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
- Verbeeck W, Bekkering GE, Van den Noortgate W, Kramers C. Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD009504. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
- Ng QX. A systematic review of the use of bupropion for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):112-116. doi:10.1089/cap.2016.0124
- Fava M, Rush AJ, Thase ME, et al. 15 years of clinical experience with bupropion HCl: from bupropion to bupropion SR to bupropion XL. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;7(3):106-113. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0305
- Chu A, Wadhwa R. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 1, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
- Singh HK, Saadabadi A. Sertraline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated February 13, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- MacQueen G, Born L, Steiner M. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline: its profile and use in psychiatric disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(1):1-24. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00188.x
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):746-758. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- Nelson JC. The STAR*D study: a four-course meal that leaves us wanting more. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1864-1866. doi:10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1864
- Sharbaf Shoar N, Fariba KA, Padhy RK. Citalopram. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 7, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482222/
- Landy K, Rosani A, Estevez R. Escitalopram. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/
- Cavanah LR, Ray P, Goldhirsh JL, Huey LY, Piper BJ. Rise of escitalopram and the fall of citalopram. medRxiv. Preprint published online May 8, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.05.07.23289632
- Sohel AJ, Shutter MC, Patel P, Molla M. Fluoxetine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459223/
- Wong DT, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Case history: the discovery of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):764-774. doi:10.1038/nrd1821
- Shrestha P, Fariba KA, Abdijadid S. Paroxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526022/
- Naseeruddin R, Rosani A, Marwaha R. Desvenlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534829
- Lieberman DZ, Massey SH. Desvenlafaxine in major depressive disorder: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid. 2010;4:67-82. doi:10.2147/ce.s5998
- Withdrawal assessment report for Ellefore (desvenlafaxine). European Medicine Agency. 2009. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/withdrawal-report/withdrawal-assessment-report-ellefore_en.pdf
- Dhaliwal JS, Spurling BC, Molla M. Duloxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. Statpearls Publishing. Updated May 29, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/
- Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(18):1941-1967. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, et al. Medikamentöse Therapie des Fibromyalgiesyndroms. Systematische Übersicht und Metaanalyse [Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline]. Schmerz. 2012;26(3):297-310. doi:10.1007/s00482-012-1172-2
- Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758-1765. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1113-e88. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
- Singh D, Saadabadi A. Venlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatePearls Publishing. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/
- Sertraline and venlafaxine: new indication. Prevention of recurrent depression: no advance. Prescrire Int. 2005;14(75):19-20.
- Bruno A, Morabito P, S p i n a E , M u s c a t ello MRl. The role of levomilnacipran in the management of major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Curr Neuro pharmacol. 2016;14(2):191-199. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666151117122458
- Shin JJ, Saadabadi A. Trazodone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/
- Khouzam HR. A review of trazodone use in psychiatric and medical conditions. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(1):140-148. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1249265
- Smales ET, Edwards BA, Deyoung PN, et al. Trazodone effects on obstructive sleep apnea and non-REM arousal threshold. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(5):758-764. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-399OC
- Eckert DJ, Malhotra A, Wellman A, White DP. Trazodone increases the respiratory arousal threshold in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and a low arousal threshold. Sleep. 2014;37(4):811-819. doi:10.5665/sleep.3596
- Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB, eds. The American Psychiat ric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2009.
- Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and allcause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209-220. doi:10.1111/bcp.12617
- Nefazodone. In: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Updated March 6, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548179/
- Drugs of Current Interest: Nefazodone. WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter:(1). 2003(1):7. https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165029/http:/apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4944e/3.html
- Choi S. Nefazodone (serzone) withdrawn because of hepatotoxicity. CMAJ. 2003;169(11):1187.
- Teva Nefazodone Statement. News release. Teva USA. December 20, 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.tevausa.com/news-and-media/press-releases/teva-nefazodone-statement/
- Levitan MN, Papelbaum M, Nardi AE. Profile of agomelatine and its potential in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1149- 1155. doi:10.2147/NDT.S67470
- Fu DJ, Ionescu DF, Li X, et al. Esketamine nasal spray for rapid reduction of major depressive disorder symptoms in patients who have active suicidal ideation with intent: double-blind, randomized study (ASPIRE I). J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(3):19m13191. doi:10.4088/JCP.19m13191
- Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4): 21m14345. doi:10.4088/JCP.21m14345
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2023;40(Suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
- Luong TT, Shou KJ, Reinhard BJ, Kigelman OF, Greenfield KM. Paclitaxel drug-drug interactions in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2024;41(Suppl 3):S70-S82. doi:10.12788/fp.0499
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Preclinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
- Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217- 224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006,
- Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
- World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
- Simon S. FDA approves Jelmyto (mitomycin gel) for urothelial cancer. American Cancer Society. April 20, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/latest-news/fda-approves-jelmyto-mitomycin-gel-for-urothelial-cancer.html
- Pantziarka P, Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme VP. Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)- diclofenac as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10:610. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2016.610
- Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D. Diclofenac: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):1009. doi:10.3390/antiox11051009
- Tontonoz M. The ABCs of BCG: oldest approved immunotherapy gets new explanation. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. July 17, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.mskcc.org/news/oldest-approved-immunotherapy-gets-new-explanation
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen as the first targeted long-term adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R235-R246. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0092
- Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br J Cancer. 1971;25(2):270-275. doi:10.1038/bjc.1971.33
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205-213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
- Maximov PY, McDaniel RE, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Basel; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-0348-0664-0
- Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2011. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
- Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
- Tarceva (erlotinib). Prescribing information. OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021743s025lbl.pdf
- Docetaxel. Prescribing information. Sichuan Hyiyu Pharmaceutical Co.; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215813s000lbl.pdf
- Alimta (pemetrexed). Prescribing information. Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208419s004lbl.pdf
- Tagrisso (osimertinib). Prescribing information. Astra- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208065s021lbl.pdf
- Iressa (gefitinib). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206995s003lbl.pdf
- Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125427lbl.pdf
- Alecensa (alectinib). Prescribing information. Genetech, Inc.; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdf
- Xalkori (crizotinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/202570s033lbl.pdf
- Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2018. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdf
- Alunbrig (brigatinib). Prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208772s008lbl.pdf
- Rozlytrek (entrectinib). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf
- Herceptin (trastuzumab). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2010. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103792s5250lbl.pdf
- Cybalta (duloxetine). Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021427s049lbl.pdf
- Effexor XR (venlafaxine). Prescribing information. Pfizer Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020699s112lbl.pdf
- Desyrel (trazodone hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Pragma Pharmaceuticals; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018207s032lbl.pdf
- Sertraline hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Almatica Pharma LLC; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215133s000lbl.pdf
- Remeron (mirtazapine). Prescribing information. Merck & Co. Inc; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020415s029,%20021208s019lbl.pdf
- Celexa (citalopram). Prescribing information. Allergan USA Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020822s041lbl.pdf
- information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020358s066lbl.pdf
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride tablet. Prescribing information. Quality Care Products LLC; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f.xml
- Lexapro (escitalopram). Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/021323s055,021365s039lbl.pdf
- Fluoxetine. Prescribing information. Edgemont Pharmaceutical, LLC; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/202133s004s005lbl.pdf
- Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing Information. Apotex Inc; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
- Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
- Silenor (doxepin). Prescribing information. Currax Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/022036s006lbl.pdf
- Tofranil-PM (imipramine pamote). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/017090s078lbl.pdf
- Norpramin (desipramine hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/014399s069lbl.pdf
- Khedezla (desvenlafaxine). Prescribing information. Osmotical Pharmaceutical US LLC; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/204683s006lbl.pdf
- Nefazodone hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5.xml
- Grassi L, Nanni MG, Rodin G, Li M, Caruso R. The use of antidepressants in oncology: a review and practical tips for oncologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):101-111. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx526
- Lee E, Park Y, Li D, Rodriguez-Fuguet A, Wang X, Zhang WC. Antidepressant use and lung cancer risk and survival: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Res Commun. 2023;3(6):1013-1025. doi:10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0003
- Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848 -856. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81
- Grattan A, Sullivan MD, Saunders KW, Campbell CI, Von Korff MR. Depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic opioid therapy recipients with no history of substance abuse. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10(4):304-311. doi:10.1370/afm.1371
- Cowan DT, Wilson-Barnett J, Griffiths P, Allan LG. A survey of chronic noncancer pain patients prescribed opioid analgesics. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):340-351. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03038.x
- Breckenridge J, Clark JD. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. J Pain. 2003;4(6):344-350. doi:10.1016/s1526-5900(03)00638-2
- Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b99f35
- Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Fan MY, DeVries A, Braden JB, Martin BC. Risks for possible and probable opioid misuse among recipients of chronic opioid therapy in commercial and medicaid insurance plans: the TROUP study. Pain. 2010;150(2):332-339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.020
- Dunn KM, Saunders KW, Rutter CM, et al. Opioid prescriptions for chronic pain and overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(2):85-92. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-2-201001190-00006
- Haddad P. Do antidepressants have any potential to cause addiction? J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(3):300- 307. doi:10.1177/026988119901300321
- Lakeview Health Staff. America’s most abused antidepressants. Lakeview Health. January 24, 2004. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.lakeviewhealth.com/blog/us-most-abused-antidepressants/
- Greenhouse Treatment Center Editorial Staff. Addiction to antidepressants: is it possible? America Addiction Centers: Greenhouse Treatment Center. Updated April 23, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://greenhousetreatment.com/prescription-medication/antidepressants/
Cancer patients experience depression at rates > 5 times that of the general population.1-11 Despite an increase in palliative care use, depression rates continued to rise.2-4 Between 5% to 16% of outpatients, 4% to 14% of inpatients, and up to 49% of patients receiving palliative care experience depression.5 This issue also impacts families and caregivers.1 A 2021 meta-analysis found that 23% of active military personnel and 20% of veterans experience depression.11
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) target the serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine systems and include boxed warnings about an increased risk of suicidal thoughts in adults aged 18 to 24 years.12,13 These medications are categorized into several classes: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), serotonin receptor modulators (SRMs), serotonin-melatonin receptor antagonists (SMRAs), and N—methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (NMDARAs).14,15 The first FDA-approved antidepressants, iproniazid (an MAOI) and imipramine (a TCA) laid the foundation for the development of newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs.15-17
Older antidepressants such as MAOIs and TCAs are used less due to their adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions. MAOIs, such as iproniazid, selegiline, moclobemide, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, and phenelzine, have numerous AEs and drug interactions, making them unsuitable for first- or second-line treatment of depression.14,18-21 TCAs such as doxepin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, clomipramine, trimipramine, protriptyline, maprotiline, and amoxapine have a narrow therapeutic index requiring careful monitoring for signs of toxicity such as QRS widening, tremors, or confusion. Despite the issues, TCAs are generally classified as second-line agents for major depressive disorder (MDD). TCAs have off-label uses for migraine prophylaxis, treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), insomnia, and chronic pain management first-line.14,22-29
Newer antidepressants, including TeCAs and NDRIs, are typically more effective, but also come with safety concerns. TeCAs like mirtazapine interact with several medications, including MAOIs, serotonin-increasing drugs, alcohol, cannabidiol, and marijuana. Mirtazapine is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe depression in adults. It is also used off-label to treat insomnia, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), headaches, and migraines. Compared to other antidepressants, mirtazapine is effective for all stages of depression and addresses a broad range of related symptoms.14,30-34 NDRIs, such as bupropion, also interact with various medications, including MAOIs, other antidepressants, stimulants, and alcohol. Bupropion is FDA-approved for smoking cessation and to treat depression and SAD. It is also used off-label for depression- related bipolar disorder or sexual dysfunction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity.14,35-42
SSRIs, SNRIs, and SRMs should be used with caution. SSRIs such as sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine are first-line treatments for depression and various psychiatric disorders due to their safety and efficacy. Common AEs of SSRIs include sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, weight changes, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues. SSRIs can prolong the QT interval, posing a risk of life-threatening arrhythmia, and may interact with other medications, necessitating treatment adjustments. The FDA approved SSRIs for MDD, GAD, bulimia nervosa, bipolar depression, OCD, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and SAD. Off-label uses include binge eating disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, fibromyalgia, premature ejaculation, paraphilias, autism, Raynaud phenomenon, and vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Among SSRIs, sertraline and escitalopram are noted for their effectiveness and tolerability.14,43-53
SNRIs, including duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran, may increase bleeding risk, especially when taken with blood thinners. They can also elevate blood pressure, which may worsen if combined with stimulants. SNRIs may interact with other medications that affect serotonin levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with triptans, pain medications, or other antidepressants.14 Desvenlafaxine has been approved by the FDA (but not by the European Medicines Agency).54-56 Duloxetine is FDA-approved for the treatment of depression, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal disorders. It is used off-label to treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence.57-61 Venlafaxine is FDA-approved for depression, SAD, and panic disorder, and is prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, neuropathy, fibromyalgia, cataplexy, and PTSD, either alone or in combination with other medications.62,63 Milnacipran is not approved for MDD; levomilnacipran received approval in 2013.64
SRMs such as trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, and vortioxetine also function as serotonin reuptake inhibitors.14,15 Trazodone is FDA-approved for MDD. It has been used off-label to treat anxiety, Alzheimer disease, substance misuse, bulimia nervosa, insomnia, fibromyalgia, and PTSD when first-line SSRIs are ineffective. A notable AE of trazodone is orthostatic hypotension, which can lead to dizziness and increase the risk of falls, especially in geriatric patients.65-70 Nefazodone was discontinued in Europe in 2003 due to rare cases of liver toxicity but remains available in the US.71-74 Vilazodone and vortioxetine are FDA-approved.
The latest classes of antidepressants include SMRAs and NMDARAs.14 Agomelatine, an SMRA, was approved in Europe in 2009 but rejected by the FDA in 2011 due to liver toxicity.75 NMDARAs like esketamine and a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion received FDA approval in 2019 and 2022, respectively.76,77
This retrospective study analyzes noncancer drugs used during systemic chemotherapy based on a dataset of 14 antineoplastic agents. It sought to identify the most dispensed noncancer drug groups, discuss findings, compare patients with and without antidepressant prescriptions, and examine trends in antidepressant use from 2002 to 2023. This analysis expands on prior research.78-81
Methods
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and Military Health System (MHS) data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
Data Sources
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry Program contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in CAPER represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER records are available from 2003 to 2024. PDTS records are available from 2002 to 2004. Each observation in PDTS represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary, excluding those filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions.
This cross-sectional analysis requested data extraction for specific cancer drugs from the DoD Cancer Registry, focusing on treatment details, diagnosis dates, patient demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. After identifying patients, CAPER was used to identify additional health conditions. PDTS was used to compile a list of prescription medications filled during systemic cancer treatment or < 2 years postdiagnosis.
The 2016 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.82,83 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients or data variables. To compare the mean number of dispensed antidepressants to those without antidepressants, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to calculate the P value and determine statistical significance (P < .05) using socscistatistics.com.
Data were extracted 3 times between 2021 and 2023. The initial 2021 protocol focused on erlotinib and gefitinib. A modified protocol in 2022 added paclitaxel, cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, and crizotinib; further modification in 2023 included 8 new antineoplastic agents and 2 anticoagulants. Sotorasib has not been prescribed in the MHS, and JPC lacks records for noncancer drugs. The 2023 dataset comprised 2210 patients with cancer treated with 14 antineoplastic agents; 2104 had documented diagnoses and 2113 had recorded prescriptions. Data for erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel have been published previously.78,79
Results
Of 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 1297 patients (61.4%) received 109 cancer drugs, including 96 antineoplastics, 7 disease-modifying antirheumatic agents, 4 biologic response modifiers, and 2 calcitonin gene-related peptides. Fourteen antineoplastic agents had complete data from JPC, while others were noted for combination therapies or treatment switches from the PDTS (Table 1). Seventy-six cancer drugs were prescribed with antidepressants in 489 patients (eAppendix).

The JPC provided 2242 entries for 2210 patients, ranging in age from 2 months to 88 years (mean, 56 years), documenting treatment from September 1988 to January 2023. Thirty-two patients had duplicate entries due to multiple cancer locations or occurrences. Of the 2242 patients, 1541 (68.7%) were aged > 50 years, 975 patients (43.5%) had cancers that were stage III or IV, and 1267 (56.5%) had cancers that were stage 0, I, II, or not applicable/unknown. There were 51 different types of cancer: breast, lung, testicular, endometrial, and ovarian were most common (n ≥ 100 patients). Forty-two cancer types were documented among 750 patients prescribed antidepressants (Table 2).

The CAPER database recorded 8882 unique diagnoses for 2104 patients, while PDTS noted 1089 unique prescriptions within 273 therapeutic codes for 2113 patients. Nine therapeutic codes (opiate agonists, adrenals, cathartics-laxatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihistamines for GI conditions, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, analgesics and antipyretic miscellanea, antineoplastic agents, and proton-pump inhibitors) and 8 drugs (dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, ondansetron, docusate, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, oxycodone, and polyethylene glycol 3350) were associated with > 1000 patients (≥ 50%). Patients had between 1 and 275 unique health conditions and filled 1 to 108 prescriptions. The mean (SD) number of diagnoses and prescriptions was 50 (28) and 29 (12), respectively. Of the 273 therapeutic codes, 30 groups were analyzed, with others categorized into miscellaneous groups such as lotions, vaccines, and devices. Significant differences in mean number of prescriptions were found for patients taking antidepressants compared to those not (P < .05), except for anticonvulsants and antipsychotics (P = .12 and .09, respectively) (Table 3).

Antidepressants
Of the 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 750 (35.5%) were dispensed 17 different antidepressants. Among these 17 antidepressants, 183 (8.7%) patients received duloxetine, 158 (7.5%) received venlafaxine, 118 (5.6%) received trazodone, and 107 (5.1%) received sertraline (Figure 1, Table 4). Of the 750 patients, 509 (67.9%) received 1 antidepressant, 168 (22.4%) received 2, 60 (8.0%) received 3, and 13 (1.7%) received > 3. Combinations varied, but only duloxetine and trazodone were prescribed to > 10 patients.



Antidepressants were prescribed annually at an overall mean (SD) rate of 23% (5%) from 2003 to 2022 (Figure 2). Patients on antidepressants during systemic therapy had a greater number of diagnosed medical conditions and received more prescription medications compared to those not taking antidepressants (P < .001) (Figure 3). The 745 patients taking antidepressants in CAPER data had between 1 and 275 diagnosed medical issues, with a mean (SD) of 55 (31) vs a range of 1 to 209 and a mean (SD) of 46 (26) for the 1359 patients not taking antidepressants. The 750 patients on antidepressants in PDTS data had between 8 and 108 prescriptions dispensed, with a mean (SD) of 32 (12), vs a range of 1 to 65 prescriptions and a mean (SD) of 29 (12) for 1363 patients not taking antidepressants.


Discussion
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry includes information on cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes, while noncancer drugs are sourced from the PDTS database. The pharmacy uses a different documentation system, leading to varied classifications.
Database reliance has its drawbacks. For example, megestrol is coded as a cancer drug, although it’s primarily used for endometrial or gynecologic cancers. Many drugs have multiple therapeutic codes assigned to them, including 10 antineoplastic agents: diclofenac, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), megestrol acetate, tamoxifen, anastrozole, letrozole, leuprolide, goserelin, degarelix, and fluorouracil. Diclofenac, BCG, and mitomycin have been repurposed for cancer treatment.84-87 From 2003 to 2023, diclofenac was prescribed to 350 patients for mild-to-moderate pain, with only 2 patients receiving it for cancer in 2018. FDA-approved for bladder cancer in 1990, BCG was prescribed for cancer treatment for 1 patient in 2021 after being used for vaccines between 2003 and 2018. Tamoxifen, used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer from 2004 to 2017 with 53 patients, switched to estrogen agonist-antagonists from 2017 to 2023 with 123 patients. Only a few of the 168 patients were prescribed tamoxifen using both codes.88-91 Anastrozole and letrozole were coded as antiestrogens for 7 and 18 patients, respectively, while leuprolide and goserelin were coded as gonadotropins for 59 and 18 patients. Degarelix was coded as antigonadotropins, fluorouracil as skin and mucous membrane agents miscellaneous, and megestrol acetate as progestins for 7, 6, and 3 patients, respectively. Duloxetine was given to 186 patients, primarily for depression from 2005 to 2023, with 7 patients treated for fibromyalgia from 2022 to 2023.
Antidepressants Observed
Tables 1 and 5 provide insight into the FDA approval of 14 antineoplastics and antidepressants and their CYP metabolic pathways.92-122 In Table 4, the most prescribed antidepressant classes are SNRIs, SRMs, SSRIs, TeCAs, NDRIs, and TCAs. This trend highlights a preference for newer medications with weak CYP inhibition. A total of 349 patients were prescribed SSRIs, 343 SNRIs, 119 SRMs, 109 TCAs, 83 TeCAs, and 79 NDRIs. MAOIs, SMRAs, and NMDARAs were not observed in this dataset. While there are instances of dextromethorphan-bupropion and sertraline-escitalopram being dispensed together, it remains unclear whether these were NMDARA combinations.
Among the 14 specific antineoplastic agents, 10 are metabolized by CYP isoenzymes, primarily CYP3A4. Duloxetine neither inhibits nor is metabolized by CYP3A4, a reason it is often recommended, following venlafaxine.
Both duloxetine and venlafaxine are used off-label for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy related to paclitaxel and docetaxel. According to the CYP metabolized pathway, duloxetine tends to have more favorable DDIs than venlafaxine. In PDTS data, 371 patients were treated with paclitaxel and 180 with docetaxel, with respective antidepressant prescriptions of 156 and 70. Of the 156 patients dispensed paclitaxel, 62 (40%) were dispensed with duloxetine compared to 43 (28%) with venlafaxine. Of the 70 patients dispensed docetaxel, 23 (33%) received duloxetine vs 24 (34%) with venlafaxine.
Of 85 patients prescribed duloxetine, 75 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel (5 received both). Five patients had documented AEs (1 neuropathy related). Of 67 patients prescribed venlafaxine, 66 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel. Two patients had documented AEs (1 was neuropathy related, the same patient who received duloxetine). Of the 687 patients treated with paclitaxel and 337 with docetaxel in all databases, 4 experienced neuropathic AEs from both medications.79
Antidepressants can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners, and may elevate blood pressure, particularly alongside stimulants. Of the 554 patients prescribed 9 different anticoagulants, enoxaparin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban were the most common (each > 100 patients). Among these, 201 patients (36%) received both anticoagulants and antidepressants: duloxetine for 64 patients, venlafaxine for 30, trazodone for 35, and sertraline for 26. There were no data available to assess bleeding rates related to the evaluation of DDIs between these medication classes.
Antidepressants can be prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Of the 148 patients prescribed an antidepressant for erectile dysfunction, duloxetine, trazodone, and mirtazapine were the most common. Antidepressant preferences varied by cancer type. Duloxetine was the only antidepressant used for all types of cancer. Venlafaxine, duloxetine, trazodone, sertraline, and escitalopram were the most prescribed antidepressants for breast cancer, while duloxetine, mirtazapine, citalopram, sertraline, and trazodone were the most prescribed for lung cancer. Sertraline, duloxetine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and escitalopram were most common for testicular cancer. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and sertraline were the most prescribed for endometrial cancer, while duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, citalopram, and sertraline were most prescribed for ovarian cancer.
The broadness of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes made it challenging to identify nondepression diagnoses in the analyzed population. However, if all antidepressants were prescribed to treat depression, service members with cancer exhibited a higher depression rate (35%) than the general population (25%). Of 2104 patients, 191 (9.1%) had mood disorders, and 706 (33.6%) had mental disorders: 346 (49.0%) had 1 diagnosis, and 360 (51.0%) had multiple diagnoses. The percentage of diagnoses varied yearly, with notable drops in 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, and peaks in 2006, 2008, 2013, 2017, and 2022. This fluctuation was influenced by events like the establishment of PDTS in 2002, the 2008 economic recession, a hospital relocation in 2011, the 2014 Ebola outbreak, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the number of patients receiving antidepressants increased from 2019 to 2022, the overall percentage of patients receiving them did not significantly change from 2003 to 2022, aligning with previous research.5,125
Many medications have potential uses beyond what is detailed in the prescribing information. Antidepressants can relieve pain, while pain medications may help with depression. Opioids were once thought to effectively treat depression, but this perspective has changed with a greater understanding of their risks, including misuse.126-131 Pain is a severe and often unbearable AE of cancer. Of 2113 patients, 92% received opioids; 34% received both opioids and antidepressants; 2% received only antidepressants; and 7% received neither. This study didn’t clarify whether those on opioids alone recognized their depression or if those on both were aware of their dependence. While SSRIs are generally not addictive, they can lead to physical dependence, and any medication can be abused if not managed properly.132-134
Conclusions
This retrospective study analyzes data from antineoplastic agents used in systemic cancer treatment between 1988 and 2023, with a particular focus on the use of antidepressants. Data on antidepressant prescriptions are incomplete and specific to these agents, which means the findings cannot be generalized to all antidepressants. Hence, the results indicate that patients taking antidepressants had more diagnosed health issues and received more medications compared to patients who were not on these drugs.
This study underscores the need for further research into the effects of antidepressants on cancer treatment, utilizing all data from the DoD Cancer Registry. Future research should explore DDIs between antidepressants and other cancer and noncancer medications, as this study did not assess AE documentation, unlike in studies involving erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel.78,79 Further investigation is needed to evaluate the impact of discontinuing antidepressant use during cancer treatment. This comprehensive overview provides insights for clinicians to help them make informed decisions regarding the prescription of antidepressants in the context of cancer treatment.
Cancer patients experience depression at rates > 5 times that of the general population.1-11 Despite an increase in palliative care use, depression rates continued to rise.2-4 Between 5% to 16% of outpatients, 4% to 14% of inpatients, and up to 49% of patients receiving palliative care experience depression.5 This issue also impacts families and caregivers.1 A 2021 meta-analysis found that 23% of active military personnel and 20% of veterans experience depression.11
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) target the serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine systems and include boxed warnings about an increased risk of suicidal thoughts in adults aged 18 to 24 years.12,13 These medications are categorized into several classes: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), serotonin receptor modulators (SRMs), serotonin-melatonin receptor antagonists (SMRAs), and N—methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (NMDARAs).14,15 The first FDA-approved antidepressants, iproniazid (an MAOI) and imipramine (a TCA) laid the foundation for the development of newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs.15-17
Older antidepressants such as MAOIs and TCAs are used less due to their adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions. MAOIs, such as iproniazid, selegiline, moclobemide, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, and phenelzine, have numerous AEs and drug interactions, making them unsuitable for first- or second-line treatment of depression.14,18-21 TCAs such as doxepin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, clomipramine, trimipramine, protriptyline, maprotiline, and amoxapine have a narrow therapeutic index requiring careful monitoring for signs of toxicity such as QRS widening, tremors, or confusion. Despite the issues, TCAs are generally classified as second-line agents for major depressive disorder (MDD). TCAs have off-label uses for migraine prophylaxis, treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), insomnia, and chronic pain management first-line.14,22-29
Newer antidepressants, including TeCAs and NDRIs, are typically more effective, but also come with safety concerns. TeCAs like mirtazapine interact with several medications, including MAOIs, serotonin-increasing drugs, alcohol, cannabidiol, and marijuana. Mirtazapine is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe depression in adults. It is also used off-label to treat insomnia, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), headaches, and migraines. Compared to other antidepressants, mirtazapine is effective for all stages of depression and addresses a broad range of related symptoms.14,30-34 NDRIs, such as bupropion, also interact with various medications, including MAOIs, other antidepressants, stimulants, and alcohol. Bupropion is FDA-approved for smoking cessation and to treat depression and SAD. It is also used off-label for depression- related bipolar disorder or sexual dysfunction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity.14,35-42
SSRIs, SNRIs, and SRMs should be used with caution. SSRIs such as sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine are first-line treatments for depression and various psychiatric disorders due to their safety and efficacy. Common AEs of SSRIs include sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, weight changes, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues. SSRIs can prolong the QT interval, posing a risk of life-threatening arrhythmia, and may interact with other medications, necessitating treatment adjustments. The FDA approved SSRIs for MDD, GAD, bulimia nervosa, bipolar depression, OCD, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and SAD. Off-label uses include binge eating disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, fibromyalgia, premature ejaculation, paraphilias, autism, Raynaud phenomenon, and vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Among SSRIs, sertraline and escitalopram are noted for their effectiveness and tolerability.14,43-53
SNRIs, including duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran, may increase bleeding risk, especially when taken with blood thinners. They can also elevate blood pressure, which may worsen if combined with stimulants. SNRIs may interact with other medications that affect serotonin levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with triptans, pain medications, or other antidepressants.14 Desvenlafaxine has been approved by the FDA (but not by the European Medicines Agency).54-56 Duloxetine is FDA-approved for the treatment of depression, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal disorders. It is used off-label to treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence.57-61 Venlafaxine is FDA-approved for depression, SAD, and panic disorder, and is prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, neuropathy, fibromyalgia, cataplexy, and PTSD, either alone or in combination with other medications.62,63 Milnacipran is not approved for MDD; levomilnacipran received approval in 2013.64
SRMs such as trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, and vortioxetine also function as serotonin reuptake inhibitors.14,15 Trazodone is FDA-approved for MDD. It has been used off-label to treat anxiety, Alzheimer disease, substance misuse, bulimia nervosa, insomnia, fibromyalgia, and PTSD when first-line SSRIs are ineffective. A notable AE of trazodone is orthostatic hypotension, which can lead to dizziness and increase the risk of falls, especially in geriatric patients.65-70 Nefazodone was discontinued in Europe in 2003 due to rare cases of liver toxicity but remains available in the US.71-74 Vilazodone and vortioxetine are FDA-approved.
The latest classes of antidepressants include SMRAs and NMDARAs.14 Agomelatine, an SMRA, was approved in Europe in 2009 but rejected by the FDA in 2011 due to liver toxicity.75 NMDARAs like esketamine and a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion received FDA approval in 2019 and 2022, respectively.76,77
This retrospective study analyzes noncancer drugs used during systemic chemotherapy based on a dataset of 14 antineoplastic agents. It sought to identify the most dispensed noncancer drug groups, discuss findings, compare patients with and without antidepressant prescriptions, and examine trends in antidepressant use from 2002 to 2023. This analysis expands on prior research.78-81
Methods
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and Military Health System (MHS) data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
Data Sources
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry Program contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in CAPER represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER records are available from 2003 to 2024. PDTS records are available from 2002 to 2004. Each observation in PDTS represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary, excluding those filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions.
This cross-sectional analysis requested data extraction for specific cancer drugs from the DoD Cancer Registry, focusing on treatment details, diagnosis dates, patient demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. After identifying patients, CAPER was used to identify additional health conditions. PDTS was used to compile a list of prescription medications filled during systemic cancer treatment or < 2 years postdiagnosis.
The 2016 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.82,83 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients or data variables. To compare the mean number of dispensed antidepressants to those without antidepressants, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to calculate the P value and determine statistical significance (P < .05) using socscistatistics.com.
Data were extracted 3 times between 2021 and 2023. The initial 2021 protocol focused on erlotinib and gefitinib. A modified protocol in 2022 added paclitaxel, cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, and crizotinib; further modification in 2023 included 8 new antineoplastic agents and 2 anticoagulants. Sotorasib has not been prescribed in the MHS, and JPC lacks records for noncancer drugs. The 2023 dataset comprised 2210 patients with cancer treated with 14 antineoplastic agents; 2104 had documented diagnoses and 2113 had recorded prescriptions. Data for erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel have been published previously.78,79
Results
Of 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 1297 patients (61.4%) received 109 cancer drugs, including 96 antineoplastics, 7 disease-modifying antirheumatic agents, 4 biologic response modifiers, and 2 calcitonin gene-related peptides. Fourteen antineoplastic agents had complete data from JPC, while others were noted for combination therapies or treatment switches from the PDTS (Table 1). Seventy-six cancer drugs were prescribed with antidepressants in 489 patients (eAppendix).

The JPC provided 2242 entries for 2210 patients, ranging in age from 2 months to 88 years (mean, 56 years), documenting treatment from September 1988 to January 2023. Thirty-two patients had duplicate entries due to multiple cancer locations or occurrences. Of the 2242 patients, 1541 (68.7%) were aged > 50 years, 975 patients (43.5%) had cancers that were stage III or IV, and 1267 (56.5%) had cancers that were stage 0, I, II, or not applicable/unknown. There were 51 different types of cancer: breast, lung, testicular, endometrial, and ovarian were most common (n ≥ 100 patients). Forty-two cancer types were documented among 750 patients prescribed antidepressants (Table 2).

The CAPER database recorded 8882 unique diagnoses for 2104 patients, while PDTS noted 1089 unique prescriptions within 273 therapeutic codes for 2113 patients. Nine therapeutic codes (opiate agonists, adrenals, cathartics-laxatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihistamines for GI conditions, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, analgesics and antipyretic miscellanea, antineoplastic agents, and proton-pump inhibitors) and 8 drugs (dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, ondansetron, docusate, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, oxycodone, and polyethylene glycol 3350) were associated with > 1000 patients (≥ 50%). Patients had between 1 and 275 unique health conditions and filled 1 to 108 prescriptions. The mean (SD) number of diagnoses and prescriptions was 50 (28) and 29 (12), respectively. Of the 273 therapeutic codes, 30 groups were analyzed, with others categorized into miscellaneous groups such as lotions, vaccines, and devices. Significant differences in mean number of prescriptions were found for patients taking antidepressants compared to those not (P < .05), except for anticonvulsants and antipsychotics (P = .12 and .09, respectively) (Table 3).

Antidepressants
Of the 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 750 (35.5%) were dispensed 17 different antidepressants. Among these 17 antidepressants, 183 (8.7%) patients received duloxetine, 158 (7.5%) received venlafaxine, 118 (5.6%) received trazodone, and 107 (5.1%) received sertraline (Figure 1, Table 4). Of the 750 patients, 509 (67.9%) received 1 antidepressant, 168 (22.4%) received 2, 60 (8.0%) received 3, and 13 (1.7%) received > 3. Combinations varied, but only duloxetine and trazodone were prescribed to > 10 patients.



Antidepressants were prescribed annually at an overall mean (SD) rate of 23% (5%) from 2003 to 2022 (Figure 2). Patients on antidepressants during systemic therapy had a greater number of diagnosed medical conditions and received more prescription medications compared to those not taking antidepressants (P < .001) (Figure 3). The 745 patients taking antidepressants in CAPER data had between 1 and 275 diagnosed medical issues, with a mean (SD) of 55 (31) vs a range of 1 to 209 and a mean (SD) of 46 (26) for the 1359 patients not taking antidepressants. The 750 patients on antidepressants in PDTS data had between 8 and 108 prescriptions dispensed, with a mean (SD) of 32 (12), vs a range of 1 to 65 prescriptions and a mean (SD) of 29 (12) for 1363 patients not taking antidepressants.


Discussion
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry includes information on cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes, while noncancer drugs are sourced from the PDTS database. The pharmacy uses a different documentation system, leading to varied classifications.
Database reliance has its drawbacks. For example, megestrol is coded as a cancer drug, although it’s primarily used for endometrial or gynecologic cancers. Many drugs have multiple therapeutic codes assigned to them, including 10 antineoplastic agents: diclofenac, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), megestrol acetate, tamoxifen, anastrozole, letrozole, leuprolide, goserelin, degarelix, and fluorouracil. Diclofenac, BCG, and mitomycin have been repurposed for cancer treatment.84-87 From 2003 to 2023, diclofenac was prescribed to 350 patients for mild-to-moderate pain, with only 2 patients receiving it for cancer in 2018. FDA-approved for bladder cancer in 1990, BCG was prescribed for cancer treatment for 1 patient in 2021 after being used for vaccines between 2003 and 2018. Tamoxifen, used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer from 2004 to 2017 with 53 patients, switched to estrogen agonist-antagonists from 2017 to 2023 with 123 patients. Only a few of the 168 patients were prescribed tamoxifen using both codes.88-91 Anastrozole and letrozole were coded as antiestrogens for 7 and 18 patients, respectively, while leuprolide and goserelin were coded as gonadotropins for 59 and 18 patients. Degarelix was coded as antigonadotropins, fluorouracil as skin and mucous membrane agents miscellaneous, and megestrol acetate as progestins for 7, 6, and 3 patients, respectively. Duloxetine was given to 186 patients, primarily for depression from 2005 to 2023, with 7 patients treated for fibromyalgia from 2022 to 2023.
Antidepressants Observed
Tables 1 and 5 provide insight into the FDA approval of 14 antineoplastics and antidepressants and their CYP metabolic pathways.92-122 In Table 4, the most prescribed antidepressant classes are SNRIs, SRMs, SSRIs, TeCAs, NDRIs, and TCAs. This trend highlights a preference for newer medications with weak CYP inhibition. A total of 349 patients were prescribed SSRIs, 343 SNRIs, 119 SRMs, 109 TCAs, 83 TeCAs, and 79 NDRIs. MAOIs, SMRAs, and NMDARAs were not observed in this dataset. While there are instances of dextromethorphan-bupropion and sertraline-escitalopram being dispensed together, it remains unclear whether these were NMDARA combinations.
Among the 14 specific antineoplastic agents, 10 are metabolized by CYP isoenzymes, primarily CYP3A4. Duloxetine neither inhibits nor is metabolized by CYP3A4, a reason it is often recommended, following venlafaxine.
Both duloxetine and venlafaxine are used off-label for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy related to paclitaxel and docetaxel. According to the CYP metabolized pathway, duloxetine tends to have more favorable DDIs than venlafaxine. In PDTS data, 371 patients were treated with paclitaxel and 180 with docetaxel, with respective antidepressant prescriptions of 156 and 70. Of the 156 patients dispensed paclitaxel, 62 (40%) were dispensed with duloxetine compared to 43 (28%) with venlafaxine. Of the 70 patients dispensed docetaxel, 23 (33%) received duloxetine vs 24 (34%) with venlafaxine.
Of 85 patients prescribed duloxetine, 75 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel (5 received both). Five patients had documented AEs (1 neuropathy related). Of 67 patients prescribed venlafaxine, 66 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel. Two patients had documented AEs (1 was neuropathy related, the same patient who received duloxetine). Of the 687 patients treated with paclitaxel and 337 with docetaxel in all databases, 4 experienced neuropathic AEs from both medications.79
Antidepressants can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners, and may elevate blood pressure, particularly alongside stimulants. Of the 554 patients prescribed 9 different anticoagulants, enoxaparin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban were the most common (each > 100 patients). Among these, 201 patients (36%) received both anticoagulants and antidepressants: duloxetine for 64 patients, venlafaxine for 30, trazodone for 35, and sertraline for 26. There were no data available to assess bleeding rates related to the evaluation of DDIs between these medication classes.
Antidepressants can be prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Of the 148 patients prescribed an antidepressant for erectile dysfunction, duloxetine, trazodone, and mirtazapine were the most common. Antidepressant preferences varied by cancer type. Duloxetine was the only antidepressant used for all types of cancer. Venlafaxine, duloxetine, trazodone, sertraline, and escitalopram were the most prescribed antidepressants for breast cancer, while duloxetine, mirtazapine, citalopram, sertraline, and trazodone were the most prescribed for lung cancer. Sertraline, duloxetine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and escitalopram were most common for testicular cancer. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and sertraline were the most prescribed for endometrial cancer, while duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, citalopram, and sertraline were most prescribed for ovarian cancer.
The broadness of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes made it challenging to identify nondepression diagnoses in the analyzed population. However, if all antidepressants were prescribed to treat depression, service members with cancer exhibited a higher depression rate (35%) than the general population (25%). Of 2104 patients, 191 (9.1%) had mood disorders, and 706 (33.6%) had mental disorders: 346 (49.0%) had 1 diagnosis, and 360 (51.0%) had multiple diagnoses. The percentage of diagnoses varied yearly, with notable drops in 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, and peaks in 2006, 2008, 2013, 2017, and 2022. This fluctuation was influenced by events like the establishment of PDTS in 2002, the 2008 economic recession, a hospital relocation in 2011, the 2014 Ebola outbreak, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the number of patients receiving antidepressants increased from 2019 to 2022, the overall percentage of patients receiving them did not significantly change from 2003 to 2022, aligning with previous research.5,125
Many medications have potential uses beyond what is detailed in the prescribing information. Antidepressants can relieve pain, while pain medications may help with depression. Opioids were once thought to effectively treat depression, but this perspective has changed with a greater understanding of their risks, including misuse.126-131 Pain is a severe and often unbearable AE of cancer. Of 2113 patients, 92% received opioids; 34% received both opioids and antidepressants; 2% received only antidepressants; and 7% received neither. This study didn’t clarify whether those on opioids alone recognized their depression or if those on both were aware of their dependence. While SSRIs are generally not addictive, they can lead to physical dependence, and any medication can be abused if not managed properly.132-134
Conclusions
This retrospective study analyzes data from antineoplastic agents used in systemic cancer treatment between 1988 and 2023, with a particular focus on the use of antidepressants. Data on antidepressant prescriptions are incomplete and specific to these agents, which means the findings cannot be generalized to all antidepressants. Hence, the results indicate that patients taking antidepressants had more diagnosed health issues and received more medications compared to patients who were not on these drugs.
This study underscores the need for further research into the effects of antidepressants on cancer treatment, utilizing all data from the DoD Cancer Registry. Future research should explore DDIs between antidepressants and other cancer and noncancer medications, as this study did not assess AE documentation, unlike in studies involving erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel.78,79 Further investigation is needed to evaluate the impact of discontinuing antidepressant use during cancer treatment. This comprehensive overview provides insights for clinicians to help them make informed decisions regarding the prescription of antidepressants in the context of cancer treatment.
- National Cancer Institute. Depression (PDQ)-Health Professional Version. Updated July 25, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/feelings/depression-hp-pdq
- Krebber AM, Buffart LM, Kleijn G, et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology. 2014;23(2):121-130. doi:10.1002/pon.3409
- Xiang X, An R, Gehlert S. Trends in antidepressant use among U.S. cancer survivors, 1999-2012. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):564. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201500007
- Hartung TJ, Brähler E, Faller H, et al. The risk of being depressed is significantly higher in cancer patients than in the general population: Prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms across major cancer types. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:46-53. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.017
- Walker J, Holm Hansen C, Martin P, et al. Prevalence of depression in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):895-900. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds575
- Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. doi:10.1136/bmj.k1415
- Kisely S, Alotiby MKN, Protani MM, Soole R, Arnautovska U, Siskind D. Breast cancer treatment disparities in patients with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2023;32(5):651-662. doi:10.1002/pon.6120
- Massie MJ. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;(32):57-71. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh014
- Rodin G, Katz M, Lloyd N, Green E, Mackay JA, Wong RK. Treatment of depression in cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2007;14(5):180-188. doi:10.3747/co.2007.146
- Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG, et al. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(2):118-129. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016
- Moradi Y, Dowran B, Sepandi M. The global prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, and attempts in the military forces: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross sectional studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
- Lu CY, Zhang F, Lakoma MD, et al. Changes in antidepressant use by young people and suicidal behavior after FDA warnings and media coverage: quasi-experimental study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3596. doi:10.1136/bmj.g3596
- Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning--10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(18):1666-1668. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408480
- Sheffler ZM, Patel P, Abdijadid S. Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 26, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
- Miller JJ. Antidepressants, Part 1: 100 Years and Counting. Accessed April 4, 2025. Psychiatric Times. https:// www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/antidepressants-part-1-100-years-and-counting
- Hillhouse TM, Porter JH. A brief history of the development of antidepressant drugs: from monoamines to glutamate. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(1):1-21. doi:10.1037/a0038550
- Mitchell PB, Mitchell MS. The management of depression. Part 2. The place of the new antidepressants. Aust Fam Physician. 1994;23(9):1771-1781.
- Sabri MA, Saber-Ayad MM. MAO Inhibitors. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557395/
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/
- Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248. doi:10.1097/00131746-200407000-00005
- Flockhart DA. Dietary restrictions and drug interactions with monoamine oxidase inhibitors: an update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:17-24. doi:10.4088/JCP.11096su1c.03
- Moraczewski J, Awosika AO, Aedma KK. Tricyclic Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557791/
- Almasi A, Patel P, Meza CE. Doxepin. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 14, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/
- Thour A, Marwaha R. Amitriptyline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/
- Radley DC, Finkelstein SN, Stafford RS. Off-label prescribing among office-based physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):1021-1026. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.9.1021
- Tesfaye S, Sloan G, Petrie J, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10353):680- 690. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01472-6
- Farag HM, Yunusa I, Goswami H, Sultan I, Doucette JA, Eguale T. Comparison of amitriptyline and US Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and network metaanalysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212939. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12939
- Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, Saadabadi A. Nortriptyline. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
- Fayez R, Gupta V. Imipramine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 22, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/
- Jilani TN, Gibbons JR, Faizy RM, Saadabadi A. Mirtazapine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519059/
- Nutt DJ. Tolerability and safety aspects of mirtazapine. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17 Suppl 1:S37-S41. doi:10.1002/hup.388
- Gandotra K, Chen P, Jaskiw GE, Konicki PE, Strohl KP. Effective treatment of insomnia with mirtazapine attenuates concomitant suicidal ideation. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(5):901-902. doi:10.5664/jcsm.7142
- Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00198.x
- Wang SM, Han C, Bahk WM, et al. Addressing the side effects of contemporary antidepressant drugs: a comprehensive review. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(2):101-112. doi:10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.101
- Huecker MR, Smiley A, Saadabadi A. Bupropion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated April 9, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/
- Hsieh MT, Tseng PT, Wu YC, et al. Effects of different pharmacologic smoking cessation treatments on body weight changes and success rates in patients with nicotine dependence: a network meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):895- 905. doi:10.1111/obr.12835
- Hankosky ER, Bush HM, Dwoskin LP, et al. Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1292-1299.
- Livingstone-Banks J, Norris E, Hartmann-Boyce J, West R, Jarvis M, Hajek P. Relapse prevention interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2(2):CD003999. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003999.pub5
- Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Sex Med. 2018;6(2):59-74. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
- Verbeeck W, Bekkering GE, Van den Noortgate W, Kramers C. Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD009504. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
- Ng QX. A systematic review of the use of bupropion for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):112-116. doi:10.1089/cap.2016.0124
- Fava M, Rush AJ, Thase ME, et al. 15 years of clinical experience with bupropion HCl: from bupropion to bupropion SR to bupropion XL. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;7(3):106-113. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0305
- Chu A, Wadhwa R. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 1, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
- Singh HK, Saadabadi A. Sertraline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated February 13, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- MacQueen G, Born L, Steiner M. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline: its profile and use in psychiatric disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(1):1-24. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00188.x
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):746-758. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- Nelson JC. The STAR*D study: a four-course meal that leaves us wanting more. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1864-1866. doi:10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1864
- Sharbaf Shoar N, Fariba KA, Padhy RK. Citalopram. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 7, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482222/
- Landy K, Rosani A, Estevez R. Escitalopram. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/
- Cavanah LR, Ray P, Goldhirsh JL, Huey LY, Piper BJ. Rise of escitalopram and the fall of citalopram. medRxiv. Preprint published online May 8, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.05.07.23289632
- Sohel AJ, Shutter MC, Patel P, Molla M. Fluoxetine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459223/
- Wong DT, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Case history: the discovery of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):764-774. doi:10.1038/nrd1821
- Shrestha P, Fariba KA, Abdijadid S. Paroxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526022/
- Naseeruddin R, Rosani A, Marwaha R. Desvenlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534829
- Lieberman DZ, Massey SH. Desvenlafaxine in major depressive disorder: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid. 2010;4:67-82. doi:10.2147/ce.s5998
- Withdrawal assessment report for Ellefore (desvenlafaxine). European Medicine Agency. 2009. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/withdrawal-report/withdrawal-assessment-report-ellefore_en.pdf
- Dhaliwal JS, Spurling BC, Molla M. Duloxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. Statpearls Publishing. Updated May 29, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/
- Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(18):1941-1967. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, et al. Medikamentöse Therapie des Fibromyalgiesyndroms. Systematische Übersicht und Metaanalyse [Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline]. Schmerz. 2012;26(3):297-310. doi:10.1007/s00482-012-1172-2
- Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758-1765. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1113-e88. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
- Singh D, Saadabadi A. Venlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatePearls Publishing. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/
- Sertraline and venlafaxine: new indication. Prevention of recurrent depression: no advance. Prescrire Int. 2005;14(75):19-20.
- Bruno A, Morabito P, S p i n a E , M u s c a t ello MRl. The role of levomilnacipran in the management of major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Curr Neuro pharmacol. 2016;14(2):191-199. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666151117122458
- Shin JJ, Saadabadi A. Trazodone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/
- Khouzam HR. A review of trazodone use in psychiatric and medical conditions. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(1):140-148. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1249265
- Smales ET, Edwards BA, Deyoung PN, et al. Trazodone effects on obstructive sleep apnea and non-REM arousal threshold. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(5):758-764. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-399OC
- Eckert DJ, Malhotra A, Wellman A, White DP. Trazodone increases the respiratory arousal threshold in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and a low arousal threshold. Sleep. 2014;37(4):811-819. doi:10.5665/sleep.3596
- Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB, eds. The American Psychiat ric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2009.
- Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and allcause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209-220. doi:10.1111/bcp.12617
- Nefazodone. In: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Updated March 6, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548179/
- Drugs of Current Interest: Nefazodone. WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter:(1). 2003(1):7. https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165029/http:/apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4944e/3.html
- Choi S. Nefazodone (serzone) withdrawn because of hepatotoxicity. CMAJ. 2003;169(11):1187.
- Teva Nefazodone Statement. News release. Teva USA. December 20, 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.tevausa.com/news-and-media/press-releases/teva-nefazodone-statement/
- Levitan MN, Papelbaum M, Nardi AE. Profile of agomelatine and its potential in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1149- 1155. doi:10.2147/NDT.S67470
- Fu DJ, Ionescu DF, Li X, et al. Esketamine nasal spray for rapid reduction of major depressive disorder symptoms in patients who have active suicidal ideation with intent: double-blind, randomized study (ASPIRE I). J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(3):19m13191. doi:10.4088/JCP.19m13191
- Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4): 21m14345. doi:10.4088/JCP.21m14345
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2023;40(Suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
- Luong TT, Shou KJ, Reinhard BJ, Kigelman OF, Greenfield KM. Paclitaxel drug-drug interactions in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2024;41(Suppl 3):S70-S82. doi:10.12788/fp.0499
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Preclinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
- Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217- 224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006,
- Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
- World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
- Simon S. FDA approves Jelmyto (mitomycin gel) for urothelial cancer. American Cancer Society. April 20, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/latest-news/fda-approves-jelmyto-mitomycin-gel-for-urothelial-cancer.html
- Pantziarka P, Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme VP. Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)- diclofenac as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10:610. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2016.610
- Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D. Diclofenac: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):1009. doi:10.3390/antiox11051009
- Tontonoz M. The ABCs of BCG: oldest approved immunotherapy gets new explanation. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. July 17, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.mskcc.org/news/oldest-approved-immunotherapy-gets-new-explanation
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen as the first targeted long-term adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R235-R246. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0092
- Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br J Cancer. 1971;25(2):270-275. doi:10.1038/bjc.1971.33
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205-213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
- Maximov PY, McDaniel RE, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Basel; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-0348-0664-0
- Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2011. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
- Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
- Tarceva (erlotinib). Prescribing information. OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021743s025lbl.pdf
- Docetaxel. Prescribing information. Sichuan Hyiyu Pharmaceutical Co.; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215813s000lbl.pdf
- Alimta (pemetrexed). Prescribing information. Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208419s004lbl.pdf
- Tagrisso (osimertinib). Prescribing information. Astra- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208065s021lbl.pdf
- Iressa (gefitinib). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206995s003lbl.pdf
- Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125427lbl.pdf
- Alecensa (alectinib). Prescribing information. Genetech, Inc.; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdf
- Xalkori (crizotinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/202570s033lbl.pdf
- Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2018. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdf
- Alunbrig (brigatinib). Prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208772s008lbl.pdf
- Rozlytrek (entrectinib). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf
- Herceptin (trastuzumab). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2010. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103792s5250lbl.pdf
- Cybalta (duloxetine). Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021427s049lbl.pdf
- Effexor XR (venlafaxine). Prescribing information. Pfizer Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020699s112lbl.pdf
- Desyrel (trazodone hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Pragma Pharmaceuticals; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018207s032lbl.pdf
- Sertraline hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Almatica Pharma LLC; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215133s000lbl.pdf
- Remeron (mirtazapine). Prescribing information. Merck & Co. Inc; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020415s029,%20021208s019lbl.pdf
- Celexa (citalopram). Prescribing information. Allergan USA Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020822s041lbl.pdf
- information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020358s066lbl.pdf
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride tablet. Prescribing information. Quality Care Products LLC; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f.xml
- Lexapro (escitalopram). Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/021323s055,021365s039lbl.pdf
- Fluoxetine. Prescribing information. Edgemont Pharmaceutical, LLC; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/202133s004s005lbl.pdf
- Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing Information. Apotex Inc; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
- Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
- Silenor (doxepin). Prescribing information. Currax Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/022036s006lbl.pdf
- Tofranil-PM (imipramine pamote). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/017090s078lbl.pdf
- Norpramin (desipramine hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/014399s069lbl.pdf
- Khedezla (desvenlafaxine). Prescribing information. Osmotical Pharmaceutical US LLC; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/204683s006lbl.pdf
- Nefazodone hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5.xml
- Grassi L, Nanni MG, Rodin G, Li M, Caruso R. The use of antidepressants in oncology: a review and practical tips for oncologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):101-111. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx526
- Lee E, Park Y, Li D, Rodriguez-Fuguet A, Wang X, Zhang WC. Antidepressant use and lung cancer risk and survival: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Res Commun. 2023;3(6):1013-1025. doi:10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0003
- Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848 -856. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81
- Grattan A, Sullivan MD, Saunders KW, Campbell CI, Von Korff MR. Depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic opioid therapy recipients with no history of substance abuse. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10(4):304-311. doi:10.1370/afm.1371
- Cowan DT, Wilson-Barnett J, Griffiths P, Allan LG. A survey of chronic noncancer pain patients prescribed opioid analgesics. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):340-351. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03038.x
- Breckenridge J, Clark JD. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. J Pain. 2003;4(6):344-350. doi:10.1016/s1526-5900(03)00638-2
- Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b99f35
- Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Fan MY, DeVries A, Braden JB, Martin BC. Risks for possible and probable opioid misuse among recipients of chronic opioid therapy in commercial and medicaid insurance plans: the TROUP study. Pain. 2010;150(2):332-339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.020
- Dunn KM, Saunders KW, Rutter CM, et al. Opioid prescriptions for chronic pain and overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(2):85-92. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-2-201001190-00006
- Haddad P. Do antidepressants have any potential to cause addiction? J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(3):300- 307. doi:10.1177/026988119901300321
- Lakeview Health Staff. America’s most abused antidepressants. Lakeview Health. January 24, 2004. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.lakeviewhealth.com/blog/us-most-abused-antidepressants/
- Greenhouse Treatment Center Editorial Staff. Addiction to antidepressants: is it possible? America Addiction Centers: Greenhouse Treatment Center. Updated April 23, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://greenhousetreatment.com/prescription-medication/antidepressants/
- National Cancer Institute. Depression (PDQ)-Health Professional Version. Updated July 25, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/feelings/depression-hp-pdq
- Krebber AM, Buffart LM, Kleijn G, et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology. 2014;23(2):121-130. doi:10.1002/pon.3409
- Xiang X, An R, Gehlert S. Trends in antidepressant use among U.S. cancer survivors, 1999-2012. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):564. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201500007
- Hartung TJ, Brähler E, Faller H, et al. The risk of being depressed is significantly higher in cancer patients than in the general population: Prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms across major cancer types. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:46-53. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.017
- Walker J, Holm Hansen C, Martin P, et al. Prevalence of depression in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):895-900. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds575
- Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. doi:10.1136/bmj.k1415
- Kisely S, Alotiby MKN, Protani MM, Soole R, Arnautovska U, Siskind D. Breast cancer treatment disparities in patients with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2023;32(5):651-662. doi:10.1002/pon.6120
- Massie MJ. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;(32):57-71. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh014
- Rodin G, Katz M, Lloyd N, Green E, Mackay JA, Wong RK. Treatment of depression in cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2007;14(5):180-188. doi:10.3747/co.2007.146
- Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG, et al. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(2):118-129. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016
- Moradi Y, Dowran B, Sepandi M. The global prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, and attempts in the military forces: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross sectional studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
- Lu CY, Zhang F, Lakoma MD, et al. Changes in antidepressant use by young people and suicidal behavior after FDA warnings and media coverage: quasi-experimental study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3596. doi:10.1136/bmj.g3596
- Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning--10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(18):1666-1668. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408480
- Sheffler ZM, Patel P, Abdijadid S. Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 26, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
- Miller JJ. Antidepressants, Part 1: 100 Years and Counting. Accessed April 4, 2025. Psychiatric Times. https:// www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/antidepressants-part-1-100-years-and-counting
- Hillhouse TM, Porter JH. A brief history of the development of antidepressant drugs: from monoamines to glutamate. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(1):1-21. doi:10.1037/a0038550
- Mitchell PB, Mitchell MS. The management of depression. Part 2. The place of the new antidepressants. Aust Fam Physician. 1994;23(9):1771-1781.
- Sabri MA, Saber-Ayad MM. MAO Inhibitors. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557395/
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/
- Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248. doi:10.1097/00131746-200407000-00005
- Flockhart DA. Dietary restrictions and drug interactions with monoamine oxidase inhibitors: an update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:17-24. doi:10.4088/JCP.11096su1c.03
- Moraczewski J, Awosika AO, Aedma KK. Tricyclic Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557791/
- Almasi A, Patel P, Meza CE. Doxepin. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 14, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/
- Thour A, Marwaha R. Amitriptyline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/
- Radley DC, Finkelstein SN, Stafford RS. Off-label prescribing among office-based physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):1021-1026. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.9.1021
- Tesfaye S, Sloan G, Petrie J, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10353):680- 690. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01472-6
- Farag HM, Yunusa I, Goswami H, Sultan I, Doucette JA, Eguale T. Comparison of amitriptyline and US Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and network metaanalysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212939. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12939
- Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, Saadabadi A. Nortriptyline. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
- Fayez R, Gupta V. Imipramine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 22, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/
- Jilani TN, Gibbons JR, Faizy RM, Saadabadi A. Mirtazapine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519059/
- Nutt DJ. Tolerability and safety aspects of mirtazapine. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17 Suppl 1:S37-S41. doi:10.1002/hup.388
- Gandotra K, Chen P, Jaskiw GE, Konicki PE, Strohl KP. Effective treatment of insomnia with mirtazapine attenuates concomitant suicidal ideation. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(5):901-902. doi:10.5664/jcsm.7142
- Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00198.x
- Wang SM, Han C, Bahk WM, et al. Addressing the side effects of contemporary antidepressant drugs: a comprehensive review. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(2):101-112. doi:10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.101
- Huecker MR, Smiley A, Saadabadi A. Bupropion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated April 9, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/
- Hsieh MT, Tseng PT, Wu YC, et al. Effects of different pharmacologic smoking cessation treatments on body weight changes and success rates in patients with nicotine dependence: a network meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):895- 905. doi:10.1111/obr.12835
- Hankosky ER, Bush HM, Dwoskin LP, et al. Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1292-1299.
- Livingstone-Banks J, Norris E, Hartmann-Boyce J, West R, Jarvis M, Hajek P. Relapse prevention interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2(2):CD003999. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003999.pub5
- Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Sex Med. 2018;6(2):59-74. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
- Verbeeck W, Bekkering GE, Van den Noortgate W, Kramers C. Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD009504. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
- Ng QX. A systematic review of the use of bupropion for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):112-116. doi:10.1089/cap.2016.0124
- Fava M, Rush AJ, Thase ME, et al. 15 years of clinical experience with bupropion HCl: from bupropion to bupropion SR to bupropion XL. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;7(3):106-113. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0305
- Chu A, Wadhwa R. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 1, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
- Singh HK, Saadabadi A. Sertraline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated February 13, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- MacQueen G, Born L, Steiner M. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline: its profile and use in psychiatric disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(1):1-24. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00188.x
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):746-758. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- Nelson JC. The STAR*D study: a four-course meal that leaves us wanting more. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1864-1866. doi:10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1864
- Sharbaf Shoar N, Fariba KA, Padhy RK. Citalopram. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 7, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482222/
- Landy K, Rosani A, Estevez R. Escitalopram. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/
- Cavanah LR, Ray P, Goldhirsh JL, Huey LY, Piper BJ. Rise of escitalopram and the fall of citalopram. medRxiv. Preprint published online May 8, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.05.07.23289632
- Sohel AJ, Shutter MC, Patel P, Molla M. Fluoxetine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459223/
- Wong DT, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Case history: the discovery of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):764-774. doi:10.1038/nrd1821
- Shrestha P, Fariba KA, Abdijadid S. Paroxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526022/
- Naseeruddin R, Rosani A, Marwaha R. Desvenlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534829
- Lieberman DZ, Massey SH. Desvenlafaxine in major depressive disorder: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid. 2010;4:67-82. doi:10.2147/ce.s5998
- Withdrawal assessment report for Ellefore (desvenlafaxine). European Medicine Agency. 2009. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/withdrawal-report/withdrawal-assessment-report-ellefore_en.pdf
- Dhaliwal JS, Spurling BC, Molla M. Duloxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. Statpearls Publishing. Updated May 29, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/
- Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(18):1941-1967. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, et al. Medikamentöse Therapie des Fibromyalgiesyndroms. Systematische Übersicht und Metaanalyse [Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline]. Schmerz. 2012;26(3):297-310. doi:10.1007/s00482-012-1172-2
- Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758-1765. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1113-e88. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
- Singh D, Saadabadi A. Venlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatePearls Publishing. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/
- Sertraline and venlafaxine: new indication. Prevention of recurrent depression: no advance. Prescrire Int. 2005;14(75):19-20.
- Bruno A, Morabito P, S p i n a E , M u s c a t ello MRl. The role of levomilnacipran in the management of major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Curr Neuro pharmacol. 2016;14(2):191-199. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666151117122458
- Shin JJ, Saadabadi A. Trazodone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/
- Khouzam HR. A review of trazodone use in psychiatric and medical conditions. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(1):140-148. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1249265
- Smales ET, Edwards BA, Deyoung PN, et al. Trazodone effects on obstructive sleep apnea and non-REM arousal threshold. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(5):758-764. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-399OC
- Eckert DJ, Malhotra A, Wellman A, White DP. Trazodone increases the respiratory arousal threshold in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and a low arousal threshold. Sleep. 2014;37(4):811-819. doi:10.5665/sleep.3596
- Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB, eds. The American Psychiat ric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2009.
- Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and allcause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209-220. doi:10.1111/bcp.12617
- Nefazodone. In: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Updated March 6, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548179/
- Drugs of Current Interest: Nefazodone. WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter:(1). 2003(1):7. https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165029/http:/apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4944e/3.html
- Choi S. Nefazodone (serzone) withdrawn because of hepatotoxicity. CMAJ. 2003;169(11):1187.
- Teva Nefazodone Statement. News release. Teva USA. December 20, 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.tevausa.com/news-and-media/press-releases/teva-nefazodone-statement/
- Levitan MN, Papelbaum M, Nardi AE. Profile of agomelatine and its potential in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1149- 1155. doi:10.2147/NDT.S67470
- Fu DJ, Ionescu DF, Li X, et al. Esketamine nasal spray for rapid reduction of major depressive disorder symptoms in patients who have active suicidal ideation with intent: double-blind, randomized study (ASPIRE I). J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(3):19m13191. doi:10.4088/JCP.19m13191
- Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4): 21m14345. doi:10.4088/JCP.21m14345
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2023;40(Suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
- Luong TT, Shou KJ, Reinhard BJ, Kigelman OF, Greenfield KM. Paclitaxel drug-drug interactions in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2024;41(Suppl 3):S70-S82. doi:10.12788/fp.0499
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Preclinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
- Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217- 224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006,
- Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
- World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
- Simon S. FDA approves Jelmyto (mitomycin gel) for urothelial cancer. American Cancer Society. April 20, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/latest-news/fda-approves-jelmyto-mitomycin-gel-for-urothelial-cancer.html
- Pantziarka P, Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme VP. Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)- diclofenac as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10:610. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2016.610
- Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D. Diclofenac: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):1009. doi:10.3390/antiox11051009
- Tontonoz M. The ABCs of BCG: oldest approved immunotherapy gets new explanation. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. July 17, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.mskcc.org/news/oldest-approved-immunotherapy-gets-new-explanation
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen as the first targeted long-term adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R235-R246. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0092
- Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br J Cancer. 1971;25(2):270-275. doi:10.1038/bjc.1971.33
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205-213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
- Maximov PY, McDaniel RE, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Basel; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-0348-0664-0
- Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2011. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
- Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
- Tarceva (erlotinib). Prescribing information. OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021743s025lbl.pdf
- Docetaxel. Prescribing information. Sichuan Hyiyu Pharmaceutical Co.; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215813s000lbl.pdf
- Alimta (pemetrexed). Prescribing information. Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208419s004lbl.pdf
- Tagrisso (osimertinib). Prescribing information. Astra- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208065s021lbl.pdf
- Iressa (gefitinib). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206995s003lbl.pdf
- Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125427lbl.pdf
- Alecensa (alectinib). Prescribing information. Genetech, Inc.; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdf
- Xalkori (crizotinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/202570s033lbl.pdf
- Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2018. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdf
- Alunbrig (brigatinib). Prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208772s008lbl.pdf
- Rozlytrek (entrectinib). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf
- Herceptin (trastuzumab). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2010. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103792s5250lbl.pdf
- Cybalta (duloxetine). Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021427s049lbl.pdf
- Effexor XR (venlafaxine). Prescribing information. Pfizer Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020699s112lbl.pdf
- Desyrel (trazodone hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Pragma Pharmaceuticals; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018207s032lbl.pdf
- Sertraline hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Almatica Pharma LLC; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215133s000lbl.pdf
- Remeron (mirtazapine). Prescribing information. Merck & Co. Inc; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020415s029,%20021208s019lbl.pdf
- Celexa (citalopram). Prescribing information. Allergan USA Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020822s041lbl.pdf
- information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020358s066lbl.pdf
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride tablet. Prescribing information. Quality Care Products LLC; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f.xml
- Lexapro (escitalopram). Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/021323s055,021365s039lbl.pdf
- Fluoxetine. Prescribing information. Edgemont Pharmaceutical, LLC; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/202133s004s005lbl.pdf
- Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing Information. Apotex Inc; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
- Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
- Silenor (doxepin). Prescribing information. Currax Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/022036s006lbl.pdf
- Tofranil-PM (imipramine pamote). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/017090s078lbl.pdf
- Norpramin (desipramine hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/014399s069lbl.pdf
- Khedezla (desvenlafaxine). Prescribing information. Osmotical Pharmaceutical US LLC; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/204683s006lbl.pdf
- Nefazodone hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5.xml
- Grassi L, Nanni MG, Rodin G, Li M, Caruso R. The use of antidepressants in oncology: a review and practical tips for oncologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):101-111. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx526
- Lee E, Park Y, Li D, Rodriguez-Fuguet A, Wang X, Zhang WC. Antidepressant use and lung cancer risk and survival: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Res Commun. 2023;3(6):1013-1025. doi:10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0003
- Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848 -856. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81
- Grattan A, Sullivan MD, Saunders KW, Campbell CI, Von Korff MR. Depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic opioid therapy recipients with no history of substance abuse. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10(4):304-311. doi:10.1370/afm.1371
- Cowan DT, Wilson-Barnett J, Griffiths P, Allan LG. A survey of chronic noncancer pain patients prescribed opioid analgesics. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):340-351. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03038.x
- Breckenridge J, Clark JD. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. J Pain. 2003;4(6):344-350. doi:10.1016/s1526-5900(03)00638-2
- Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b99f35
- Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Fan MY, DeVries A, Braden JB, Martin BC. Risks for possible and probable opioid misuse among recipients of chronic opioid therapy in commercial and medicaid insurance plans: the TROUP study. Pain. 2010;150(2):332-339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.020
- Dunn KM, Saunders KW, Rutter CM, et al. Opioid prescriptions for chronic pain and overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(2):85-92. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-2-201001190-00006
- Haddad P. Do antidepressants have any potential to cause addiction? J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(3):300- 307. doi:10.1177/026988119901300321
- Lakeview Health Staff. America’s most abused antidepressants. Lakeview Health. January 24, 2004. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.lakeviewhealth.com/blog/us-most-abused-antidepressants/
- Greenhouse Treatment Center Editorial Staff. Addiction to antidepressants: is it possible? America Addiction Centers: Greenhouse Treatment Center. Updated April 23, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://greenhousetreatment.com/prescription-medication/antidepressants/
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Loneliness, Isolation Affect One Third of US Adults Over 50
TOPLINE:
About one third of US adults aged 50-80 years report feeling lonely and socially isolated, a new study of data from 2018-2024 shows. While the levels have returned to the prepandemic range, investigators say the findings suggest clinicians should screen for loneliness and isolation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nationally representative survey of US adults aged 50-80 years through the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging at six timepoints between 2018 and 2024.
- Data collection involved online surveys conducted using the Ipsos KnowledgePanel from 2018 to 2021, transitioning to online and phone surveys conducted using the National Opinion Research Center AmeriSpeak panel from 2022 to 2024.
- Sample sizes ranged between 2051 and 2576 respondents, with completion rates ranging from 61% to 78% across the survey periods.
TAKEAWAY:
- Loneliness rates among adults aged 50-80 years showed notable fluctuation, starting at 34% (95% CI, 31.7%-36.2%) in 2018, rising to 41% (95% CI, 39.1%-43.7%) in 2020, and returning to 33% (95% CI, 31.7%-35.1%) by 2024.
- Social isolation showed a similar pattern in the study group, starting at 27% (95% CI, 24.5%-28.8%) in 2018, peaking at 56% (95% CI, 53.4%-58.1%) in 2020, and declining to 29% (95% CI, 27.5%-30.9%) by 2024.
- Higher loneliness and social isolation rates were frequently reported among individuals who did not work, lived alone, had lower household incomes, and had self-reported fair and poor physical and mental health than those who reported excellent, very good, or good health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest that “much like routinely asking about diet and exercise, clinicians should consider screening older adults for loneliness and social isolation and connect them with appropriate resources,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor. It was published online on December 9 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by possible recall bias, reliance on self-reported data, lack of longitudinal results, and differences in survey timing, panels, and question framing across years. The findings may not have been applicable to excluded groups such as nursing home residents or individuals aged > 80 years, which limited their generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine and the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, and Health Systems Research. One author reported receiving consulting fees and honoraria from various organizations. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
About one third of US adults aged 50-80 years report feeling lonely and socially isolated, a new study of data from 2018-2024 shows. While the levels have returned to the prepandemic range, investigators say the findings suggest clinicians should screen for loneliness and isolation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nationally representative survey of US adults aged 50-80 years through the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging at six timepoints between 2018 and 2024.
- Data collection involved online surveys conducted using the Ipsos KnowledgePanel from 2018 to 2021, transitioning to online and phone surveys conducted using the National Opinion Research Center AmeriSpeak panel from 2022 to 2024.
- Sample sizes ranged between 2051 and 2576 respondents, with completion rates ranging from 61% to 78% across the survey periods.
TAKEAWAY:
- Loneliness rates among adults aged 50-80 years showed notable fluctuation, starting at 34% (95% CI, 31.7%-36.2%) in 2018, rising to 41% (95% CI, 39.1%-43.7%) in 2020, and returning to 33% (95% CI, 31.7%-35.1%) by 2024.
- Social isolation showed a similar pattern in the study group, starting at 27% (95% CI, 24.5%-28.8%) in 2018, peaking at 56% (95% CI, 53.4%-58.1%) in 2020, and declining to 29% (95% CI, 27.5%-30.9%) by 2024.
- Higher loneliness and social isolation rates were frequently reported among individuals who did not work, lived alone, had lower household incomes, and had self-reported fair and poor physical and mental health than those who reported excellent, very good, or good health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest that “much like routinely asking about diet and exercise, clinicians should consider screening older adults for loneliness and social isolation and connect them with appropriate resources,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor. It was published online on December 9 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by possible recall bias, reliance on self-reported data, lack of longitudinal results, and differences in survey timing, panels, and question framing across years. The findings may not have been applicable to excluded groups such as nursing home residents or individuals aged > 80 years, which limited their generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine and the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, and Health Systems Research. One author reported receiving consulting fees and honoraria from various organizations. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
About one third of US adults aged 50-80 years report feeling lonely and socially isolated, a new study of data from 2018-2024 shows. While the levels have returned to the prepandemic range, investigators say the findings suggest clinicians should screen for loneliness and isolation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nationally representative survey of US adults aged 50-80 years through the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging at six timepoints between 2018 and 2024.
- Data collection involved online surveys conducted using the Ipsos KnowledgePanel from 2018 to 2021, transitioning to online and phone surveys conducted using the National Opinion Research Center AmeriSpeak panel from 2022 to 2024.
- Sample sizes ranged between 2051 and 2576 respondents, with completion rates ranging from 61% to 78% across the survey periods.
TAKEAWAY:
- Loneliness rates among adults aged 50-80 years showed notable fluctuation, starting at 34% (95% CI, 31.7%-36.2%) in 2018, rising to 41% (95% CI, 39.1%-43.7%) in 2020, and returning to 33% (95% CI, 31.7%-35.1%) by 2024.
- Social isolation showed a similar pattern in the study group, starting at 27% (95% CI, 24.5%-28.8%) in 2018, peaking at 56% (95% CI, 53.4%-58.1%) in 2020, and declining to 29% (95% CI, 27.5%-30.9%) by 2024.
- Higher loneliness and social isolation rates were frequently reported among individuals who did not work, lived alone, had lower household incomes, and had self-reported fair and poor physical and mental health than those who reported excellent, very good, or good health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest that “much like routinely asking about diet and exercise, clinicians should consider screening older adults for loneliness and social isolation and connect them with appropriate resources,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor. It was published online on December 9 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by possible recall bias, reliance on self-reported data, lack of longitudinal results, and differences in survey timing, panels, and question framing across years. The findings may not have been applicable to excluded groups such as nursing home residents or individuals aged > 80 years, which limited their generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine and the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, and Health Systems Research. One author reported receiving consulting fees and honoraria from various organizations. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Major Depression in Older Adults Tied to Risky Driving Behaviors
Older adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) exhibit riskier driving behaviors, compared with their nondepressed peers, including hard braking, cornering, and unpredictable driving patterns, new research showed.
Data for the study came from commercial vehicle data trackers installed in participants’ vehicles. After about a year of follow-up, the investigators found that MDD was associated with an increase in the amount and severity of risking driving, even after they controlled for antidepressant use.
Late-life depression often goes undiagnosed, and the new findings highlight the importance of routine depression screening and targeted interventions to ensure driving safety among older adults, the study team said.
“By using longitudinal, real-world driving data rather than controlled settings or self-reports, the study provides robust evidence of how MDD influences driving behaviors in day-to-day contexts,” first author Ganesh M. Babulal, PhD, OTD, with the Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, said in an interview.
“By analyzing the influence of antidepressant use and overall medication load, the study disentangles the effects of MDD from those of driver-impairing medications, further clarifying the unique contributions of depression to driving behaviors,” Babulal noted.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Road Risks
As the number of older adults grows, safe driving practices in this age group become increasingly crucial. By 2050, one quarter of drivers in the United States will be older than 65 years. MDD affects about 8% of US adults and is linked to cognitive impairments that may compromise driving safety.
Prior studies revealed a link between depression and increased car crash risk, regardless of age. And earlier research by Babulal and colleagues showed that older adults with depression were three times more likely to receive a marginal or failing score on a standardized road test.
To further study the issue, Babulal and colleagues examined the impact of MDD on naturalistic driving behaviors among older adults using longitudinal data.
Participants were recruited from the Driving Real-World In-Vehicle Evaluation System Project, where their daily driving behaviors were recorded using commercial vehicle data loggers installed in their personal vehicles.
The cohort included 85 adults with MDD (mean age, 69 years; 71% women) and 310 adults without MDD (mean age, 70 years; 49% women). The majority of participants in both groups were non-Hispanic White individuals.
Based on intercepts, adults with MDD had a propensity toward riskier driving habits with a higher frequency of speeding events and spending more time on the road than those without MDD, they found.
During a mean of 1.1 years of follow-up, compared with older adults without MDD, those with MDD exhibited significantly more hard braking (P < .001) and hard cornering events per trip (P = .04) over time. They also traveled farther from home and visited more unique destinations (P < .001 for both).
Over time, older adults also displayed increased entropy in driving patterns (P < .001), indicated less predictable driving routes.
“Driving unpredictability, as evidenced by increased random entropy, highlights the unique challenges posed by MDD in maintaining safe driving practices,” the researchers wrote.
Adjustment for antidepressant use, which could impair driving, or total medication burden did not change the findings, suggesting MDD independently affects driving.
“Most importantly, our findings demonstrate that MDD — a common and treatable illness in older adults — was associated with an increase in both the amount and magnitude of risky driving behaviors over time,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers noted that the study did not account for changes in depression severity over time and other psychiatric conditions co-occurring with MDD were not adjusted for. Also, situational factors like weather or traffic conditions were not assessed.
Clear Clinical Implications
There is a “pressing need” for targeted interventions to manage and mitigate the driving risks associated with late-life depression, the researchers wrote.
“The study emphasizes the need for interventions tailored to the mental health and driving behaviors of older adults. These could include cognitive retraining, driver rehabilitation programs, and routine depression screening to enhance road safety and preserve independence,” Babulal said.
“Encouraging older adults with MDD to self-regulate their driving habits (eg, avoiding night driving or high-traffic situations) and educating them about potential driving challenges related to their condition can enhance safety,” he added.
Commenting on this study, Ipsit Vahia, MD, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Massachusetts, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, said it “adds nuance to our understanding of how depression can impact driving among older adults.
“While the connection between depression and a higher incident of crashes is known, this study demonstrates an association with riskier driving behaviors such as speeding,” Vahia said. “It highlights the importance of clinicians proactively initiating discussion of driving and safety when working with older adults with depressive symptoms.”
This work was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and National Institute on Aging. Babulal had no relevant disclosures. Vahia had served as a consultant for Otsuka.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) exhibit riskier driving behaviors, compared with their nondepressed peers, including hard braking, cornering, and unpredictable driving patterns, new research showed.
Data for the study came from commercial vehicle data trackers installed in participants’ vehicles. After about a year of follow-up, the investigators found that MDD was associated with an increase in the amount and severity of risking driving, even after they controlled for antidepressant use.
Late-life depression often goes undiagnosed, and the new findings highlight the importance of routine depression screening and targeted interventions to ensure driving safety among older adults, the study team said.
“By using longitudinal, real-world driving data rather than controlled settings or self-reports, the study provides robust evidence of how MDD influences driving behaviors in day-to-day contexts,” first author Ganesh M. Babulal, PhD, OTD, with the Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, said in an interview.
“By analyzing the influence of antidepressant use and overall medication load, the study disentangles the effects of MDD from those of driver-impairing medications, further clarifying the unique contributions of depression to driving behaviors,” Babulal noted.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Road Risks
As the number of older adults grows, safe driving practices in this age group become increasingly crucial. By 2050, one quarter of drivers in the United States will be older than 65 years. MDD affects about 8% of US adults and is linked to cognitive impairments that may compromise driving safety.
Prior studies revealed a link between depression and increased car crash risk, regardless of age. And earlier research by Babulal and colleagues showed that older adults with depression were three times more likely to receive a marginal or failing score on a standardized road test.
To further study the issue, Babulal and colleagues examined the impact of MDD on naturalistic driving behaviors among older adults using longitudinal data.
Participants were recruited from the Driving Real-World In-Vehicle Evaluation System Project, where their daily driving behaviors were recorded using commercial vehicle data loggers installed in their personal vehicles.
The cohort included 85 adults with MDD (mean age, 69 years; 71% women) and 310 adults without MDD (mean age, 70 years; 49% women). The majority of participants in both groups were non-Hispanic White individuals.
Based on intercepts, adults with MDD had a propensity toward riskier driving habits with a higher frequency of speeding events and spending more time on the road than those without MDD, they found.
During a mean of 1.1 years of follow-up, compared with older adults without MDD, those with MDD exhibited significantly more hard braking (P < .001) and hard cornering events per trip (P = .04) over time. They also traveled farther from home and visited more unique destinations (P < .001 for both).
Over time, older adults also displayed increased entropy in driving patterns (P < .001), indicated less predictable driving routes.
“Driving unpredictability, as evidenced by increased random entropy, highlights the unique challenges posed by MDD in maintaining safe driving practices,” the researchers wrote.
Adjustment for antidepressant use, which could impair driving, or total medication burden did not change the findings, suggesting MDD independently affects driving.
“Most importantly, our findings demonstrate that MDD — a common and treatable illness in older adults — was associated with an increase in both the amount and magnitude of risky driving behaviors over time,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers noted that the study did not account for changes in depression severity over time and other psychiatric conditions co-occurring with MDD were not adjusted for. Also, situational factors like weather or traffic conditions were not assessed.
Clear Clinical Implications
There is a “pressing need” for targeted interventions to manage and mitigate the driving risks associated with late-life depression, the researchers wrote.
“The study emphasizes the need for interventions tailored to the mental health and driving behaviors of older adults. These could include cognitive retraining, driver rehabilitation programs, and routine depression screening to enhance road safety and preserve independence,” Babulal said.
“Encouraging older adults with MDD to self-regulate their driving habits (eg, avoiding night driving or high-traffic situations) and educating them about potential driving challenges related to their condition can enhance safety,” he added.
Commenting on this study, Ipsit Vahia, MD, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Massachusetts, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, said it “adds nuance to our understanding of how depression can impact driving among older adults.
“While the connection between depression and a higher incident of crashes is known, this study demonstrates an association with riskier driving behaviors such as speeding,” Vahia said. “It highlights the importance of clinicians proactively initiating discussion of driving and safety when working with older adults with depressive symptoms.”
This work was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and National Institute on Aging. Babulal had no relevant disclosures. Vahia had served as a consultant for Otsuka.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) exhibit riskier driving behaviors, compared with their nondepressed peers, including hard braking, cornering, and unpredictable driving patterns, new research showed.
Data for the study came from commercial vehicle data trackers installed in participants’ vehicles. After about a year of follow-up, the investigators found that MDD was associated with an increase in the amount and severity of risking driving, even after they controlled for antidepressant use.
Late-life depression often goes undiagnosed, and the new findings highlight the importance of routine depression screening and targeted interventions to ensure driving safety among older adults, the study team said.
“By using longitudinal, real-world driving data rather than controlled settings or self-reports, the study provides robust evidence of how MDD influences driving behaviors in day-to-day contexts,” first author Ganesh M. Babulal, PhD, OTD, with the Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, said in an interview.
“By analyzing the influence of antidepressant use and overall medication load, the study disentangles the effects of MDD from those of driver-impairing medications, further clarifying the unique contributions of depression to driving behaviors,” Babulal noted.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Road Risks
As the number of older adults grows, safe driving practices in this age group become increasingly crucial. By 2050, one quarter of drivers in the United States will be older than 65 years. MDD affects about 8% of US adults and is linked to cognitive impairments that may compromise driving safety.
Prior studies revealed a link between depression and increased car crash risk, regardless of age. And earlier research by Babulal and colleagues showed that older adults with depression were three times more likely to receive a marginal or failing score on a standardized road test.
To further study the issue, Babulal and colleagues examined the impact of MDD on naturalistic driving behaviors among older adults using longitudinal data.
Participants were recruited from the Driving Real-World In-Vehicle Evaluation System Project, where their daily driving behaviors were recorded using commercial vehicle data loggers installed in their personal vehicles.
The cohort included 85 adults with MDD (mean age, 69 years; 71% women) and 310 adults without MDD (mean age, 70 years; 49% women). The majority of participants in both groups were non-Hispanic White individuals.
Based on intercepts, adults with MDD had a propensity toward riskier driving habits with a higher frequency of speeding events and spending more time on the road than those without MDD, they found.
During a mean of 1.1 years of follow-up, compared with older adults without MDD, those with MDD exhibited significantly more hard braking (P < .001) and hard cornering events per trip (P = .04) over time. They also traveled farther from home and visited more unique destinations (P < .001 for both).
Over time, older adults also displayed increased entropy in driving patterns (P < .001), indicated less predictable driving routes.
“Driving unpredictability, as evidenced by increased random entropy, highlights the unique challenges posed by MDD in maintaining safe driving practices,” the researchers wrote.
Adjustment for antidepressant use, which could impair driving, or total medication burden did not change the findings, suggesting MDD independently affects driving.
“Most importantly, our findings demonstrate that MDD — a common and treatable illness in older adults — was associated with an increase in both the amount and magnitude of risky driving behaviors over time,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers noted that the study did not account for changes in depression severity over time and other psychiatric conditions co-occurring with MDD were not adjusted for. Also, situational factors like weather or traffic conditions were not assessed.
Clear Clinical Implications
There is a “pressing need” for targeted interventions to manage and mitigate the driving risks associated with late-life depression, the researchers wrote.
“The study emphasizes the need for interventions tailored to the mental health and driving behaviors of older adults. These could include cognitive retraining, driver rehabilitation programs, and routine depression screening to enhance road safety and preserve independence,” Babulal said.
“Encouraging older adults with MDD to self-regulate their driving habits (eg, avoiding night driving or high-traffic situations) and educating them about potential driving challenges related to their condition can enhance safety,” he added.
Commenting on this study, Ipsit Vahia, MD, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Massachusetts, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, said it “adds nuance to our understanding of how depression can impact driving among older adults.
“While the connection between depression and a higher incident of crashes is known, this study demonstrates an association with riskier driving behaviors such as speeding,” Vahia said. “It highlights the importance of clinicians proactively initiating discussion of driving and safety when working with older adults with depressive symptoms.”
This work was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and National Institute on Aging. Babulal had no relevant disclosures. Vahia had served as a consultant for Otsuka.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Should the FDA Reconsider Boxed Warnings for Antidepressants?
Paradoxically, and for almost as long, evidence suggests these warnings may have led to fewer depression diagnoses, reduced prescriptions, and, ultimately, higher suicide rates.
With mounting evidence of these negative unintended consequences, some clinicians and researchers are urging the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider revising — or even eliminating — boxed warnings on these medications.
The latest report challenging the utility of the 2005 warnings was particularly sobering. Published in October in Health Affairs, the systematic review of studies from 2003 to 2022 showed a 20%-40% decline in physician visits for depression, a 20%-50% decline in antidepressant use, and an abrupt increase in psychotropic drug poisonings and suicides — all after the warnings were added.
“FDA officials should review the totality of evidence and err on the side of caution in acknowledging possible harms of the antidepressant warnings,” lead author Stephen Soumerai, ScD, professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts and colleagues wrote. They called on the FDA to replace the boxed warnings with a routine warning in labeling.
While good prospective data on the risks and benefits of antidepressants in youth were limited when the boxed warnings were instituted, there is more information now, said Jeffrey Strawn, MD, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Ohio. Strawn, whose research on the topic has been cited frequently over the years, said the new evidence suggests it is time for the FDA to reevaluate the warnings.
“I don’t think that they’ve been useful. They’ve actually been harmful,” Strawn told this news organization. “These boxed warnings have decreased physicians’ and other clinicians’ comfort and tendency to prescribe.”
Decline in Diagnoses
The FDA issued its first warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior in children in 2003. After an advisory panel weighed the evidence, the agency added a boxed warning in 2005 to all antidepressants for children younger than 18 years. The warning was expanded in 2007 to include young adults through age 24.
Data suggesting that the warnings have had unintended effects can be found going back to just after they were issued. For instance, in 2009, after rising for years, the rate of new pediatric depression diagnoses fell precipitously after the warning was added, with primary care physicians diagnosing 44% fewer cases.
In 2014, citing evidence of fewer diagnoses and rising psychotropic drug poisonings, Weill Cornell Medicine Professor Richard A. Friedman, MD, called on the FDA in a perspective to remove the boxed warnings.
Strawn and colleagues reported in an often-cited 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that, in nine trials involving 1673 patients and six medications, antidepressants were superior to placebo, with no increased risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior.
He has also studied adverse effects of the medications, reporting in Pharmacotherapy that suicidality risk might be more likely with some medications, such as paroxetine and venlafaxine, and that it could be influenced by baseline suicidality, among many other factors. A Swedish register study found that risk was highest the month before starting a medication, Strawn and colleagues wrote.
Dara Sakolsky, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and associate medical director, Services for Teens at Risk at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, told this news organization that, because of “these negative unintended consequences,” the FDA should lower the temperature by putting the warnings in labeling.
“It makes sense based on the data that we have at hand now,” said Sakolsky.
The Dangers of Untreated Depression
Even with this new information, lingering concerns about earlier studies that pointed to increased suicidality risk may discourage prescribing by primary care physicians and pediatricians, and that worries researchers and psychiatrists.
“My concern is that the risk for suicide and suicidal behavior may be higher in untreated depression than the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors from antidepressants,” Jeffrey Bridge, PhD, director of the Center for Suicide Prevention and Research at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, told this news organization.
Bridge is the lead author of a much-cited 2007 meta-analysis in JAMA that showed that the benefits of antidepressants in children and adolescents appeared to be greater than the risks for suicidality. “The concern about antidepressants must be considered in the context of possible benefit,” wrote Bridge, who also is professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and behavioral health at Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Depression and suicide are a scourge for those younger than 25 years. A 2021 literature review noted that the prevalence of depression — which has been increasing for all Americans — has risen more among adolescents than adults. Depression is “strongly associated with suicide,” the authors wrote.
In 2021, the National Institute of Mental Health reported suicide was the second leading cause of death among 10- to 14-year-olds and the third leading cause of death among those aged 15-24 years.
Suicide kills more kids aged between 10 and 24 years than cancer and all other illnesses combined, John Campo, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and vice president of psychiatric services at Kennedy Krieger Institute, told this news organization.
Meanwhile, he added, the medications work and clinicians balance risk and benefit in prescribing.
The landmark 2007 Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study showed that fluoxetine, especially in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), was significantly better than placebo. Since that time, legions of trials have shown the drugs’ effectiveness.
The most effective treatment for teen depression is a combination of CBT and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, said Sakolsky.
“We know that the evidence for that is pretty good,” she said. “On the flip side, we know the risk of having an adverse outcome is pretty low.”
Sakolsky tells patients and families that perhaps 1 in 146 will have a suicidal thought or behavior. “That’s pretty rare when we know how effective these medicines are.”
Strawn said he always notes that no suicides took place in the trials that led to the warning and stresses that he closely monitors patients. “While the more recent prospective data are reassuring,” the suicidality risk “is something that we still talk about,” he said. He also discusses how some antidepressants seem to increase risk more than others.
For Campo, the discussion is based on his reading of the evidence, not the presence of the FDA warning.
“Based on what we know, I still think it’s fair to proceed with the idea that there is a small, but real risk,” he said. However, “at the same time, the medications might be exceptionally helpful for some kids.”
‘What Do We Do Now?’
When the FDA issued its warning in 2005, the agency said it identified the risk for suicidality in a combined analysis of short-term placebo-controlled trials of nine antidepressants. It ultimately included 24 trials involving more than 4400 patients. The risk was highest in the first few months. The average risk for those taking antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There were no suicides in these trials, however.
The trials relied on spontaneous reports of adverse events, not predetermined measures, Campo said. Even so, that 2% difference is “nothing to sneeze at,” he noted.
Bridge’s meta-analysis showed a smaller difference — closer to 0.7%. “But it was still statistically significant,” Campo said. “I have trouble ignoring that.”
The unintended consequences of the warning can’t be studied in a randomized controlled trial. Studies have shown an association but not a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the warning and a decline in treatment and rise in suicides.
But the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressants has been studied prospectively. Some older studies found a significant risk, while more recent trials have not.
While the Health Affairs analysis “certainly makes a strong case,” it is observational data, Campo said.
“The question is, what do we do now in retrospect? Do you say, ‘Never mind. We don’t need the black box warning anymore?’ ” he said. “That would require a pretty careful look.”
The Health Affairs paper “makes me think that there are other areas of research that that need to be completed and done and updated, and then there should be an assessment, a reevaluation from the FDA,” said Bridge. A new meta-analysis “would be very informative,” he said.
What’s Next?
When asked about the Health Affairs paper and whether the agency would review the warnings, an FDA spokesperson told this news organization that the agency “does not comment on specific studies but evaluates them as part of the body of evidence to further our understanding about a particular issue and assist in our mission to protect public health.”
Sakolsky said the data clearly point to the damage that the warning has done over the past 2 decades, but that things might be improving. Studies conducted more recently might not have captured some changes in practice.
For instance, she noted, in 2022, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for major depressive disorder in adolescents aged 12-18 years. In turn, she has seen more patients in her office who were referred by pediatricians who had conducted the screening, said Sakolsky.
Strawn said the time for pontificating is long past due. “We’re withholding medications and other treatments that could potentially be effective for disorders that, in and of themselves, are associated with a significant increase in the risk of suicide.”
After the FDA instituted the warning, “we were all very nervous,” about the potential fallout, said Campo, adding that a part of him wishes that the warnings had been “more mundane and less dramatic.”
Despite the unintended consequences, “it’s going to be hard to put the genie back in the bottle,” he said.
Campo and Sakolsky reported no relevant financial relationships. Strawn disclosed that his institution has received research funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and AbbVie. Bridge reported that he received grant support from the National Institute of Mental Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and PCORI; is a scientific adviser to Clarigent Health; and is on the Scientific Council of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paradoxically, and for almost as long, evidence suggests these warnings may have led to fewer depression diagnoses, reduced prescriptions, and, ultimately, higher suicide rates.
With mounting evidence of these negative unintended consequences, some clinicians and researchers are urging the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider revising — or even eliminating — boxed warnings on these medications.
The latest report challenging the utility of the 2005 warnings was particularly sobering. Published in October in Health Affairs, the systematic review of studies from 2003 to 2022 showed a 20%-40% decline in physician visits for depression, a 20%-50% decline in antidepressant use, and an abrupt increase in psychotropic drug poisonings and suicides — all after the warnings were added.
“FDA officials should review the totality of evidence and err on the side of caution in acknowledging possible harms of the antidepressant warnings,” lead author Stephen Soumerai, ScD, professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts and colleagues wrote. They called on the FDA to replace the boxed warnings with a routine warning in labeling.
While good prospective data on the risks and benefits of antidepressants in youth were limited when the boxed warnings were instituted, there is more information now, said Jeffrey Strawn, MD, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Ohio. Strawn, whose research on the topic has been cited frequently over the years, said the new evidence suggests it is time for the FDA to reevaluate the warnings.
“I don’t think that they’ve been useful. They’ve actually been harmful,” Strawn told this news organization. “These boxed warnings have decreased physicians’ and other clinicians’ comfort and tendency to prescribe.”
Decline in Diagnoses
The FDA issued its first warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior in children in 2003. After an advisory panel weighed the evidence, the agency added a boxed warning in 2005 to all antidepressants for children younger than 18 years. The warning was expanded in 2007 to include young adults through age 24.
Data suggesting that the warnings have had unintended effects can be found going back to just after they were issued. For instance, in 2009, after rising for years, the rate of new pediatric depression diagnoses fell precipitously after the warning was added, with primary care physicians diagnosing 44% fewer cases.
In 2014, citing evidence of fewer diagnoses and rising psychotropic drug poisonings, Weill Cornell Medicine Professor Richard A. Friedman, MD, called on the FDA in a perspective to remove the boxed warnings.
Strawn and colleagues reported in an often-cited 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that, in nine trials involving 1673 patients and six medications, antidepressants were superior to placebo, with no increased risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior.
He has also studied adverse effects of the medications, reporting in Pharmacotherapy that suicidality risk might be more likely with some medications, such as paroxetine and venlafaxine, and that it could be influenced by baseline suicidality, among many other factors. A Swedish register study found that risk was highest the month before starting a medication, Strawn and colleagues wrote.
Dara Sakolsky, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and associate medical director, Services for Teens at Risk at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, told this news organization that, because of “these negative unintended consequences,” the FDA should lower the temperature by putting the warnings in labeling.
“It makes sense based on the data that we have at hand now,” said Sakolsky.
The Dangers of Untreated Depression
Even with this new information, lingering concerns about earlier studies that pointed to increased suicidality risk may discourage prescribing by primary care physicians and pediatricians, and that worries researchers and psychiatrists.
“My concern is that the risk for suicide and suicidal behavior may be higher in untreated depression than the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors from antidepressants,” Jeffrey Bridge, PhD, director of the Center for Suicide Prevention and Research at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, told this news organization.
Bridge is the lead author of a much-cited 2007 meta-analysis in JAMA that showed that the benefits of antidepressants in children and adolescents appeared to be greater than the risks for suicidality. “The concern about antidepressants must be considered in the context of possible benefit,” wrote Bridge, who also is professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and behavioral health at Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Depression and suicide are a scourge for those younger than 25 years. A 2021 literature review noted that the prevalence of depression — which has been increasing for all Americans — has risen more among adolescents than adults. Depression is “strongly associated with suicide,” the authors wrote.
In 2021, the National Institute of Mental Health reported suicide was the second leading cause of death among 10- to 14-year-olds and the third leading cause of death among those aged 15-24 years.
Suicide kills more kids aged between 10 and 24 years than cancer and all other illnesses combined, John Campo, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and vice president of psychiatric services at Kennedy Krieger Institute, told this news organization.
Meanwhile, he added, the medications work and clinicians balance risk and benefit in prescribing.
The landmark 2007 Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study showed that fluoxetine, especially in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), was significantly better than placebo. Since that time, legions of trials have shown the drugs’ effectiveness.
The most effective treatment for teen depression is a combination of CBT and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, said Sakolsky.
“We know that the evidence for that is pretty good,” she said. “On the flip side, we know the risk of having an adverse outcome is pretty low.”
Sakolsky tells patients and families that perhaps 1 in 146 will have a suicidal thought or behavior. “That’s pretty rare when we know how effective these medicines are.”
Strawn said he always notes that no suicides took place in the trials that led to the warning and stresses that he closely monitors patients. “While the more recent prospective data are reassuring,” the suicidality risk “is something that we still talk about,” he said. He also discusses how some antidepressants seem to increase risk more than others.
For Campo, the discussion is based on his reading of the evidence, not the presence of the FDA warning.
“Based on what we know, I still think it’s fair to proceed with the idea that there is a small, but real risk,” he said. However, “at the same time, the medications might be exceptionally helpful for some kids.”
‘What Do We Do Now?’
When the FDA issued its warning in 2005, the agency said it identified the risk for suicidality in a combined analysis of short-term placebo-controlled trials of nine antidepressants. It ultimately included 24 trials involving more than 4400 patients. The risk was highest in the first few months. The average risk for those taking antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There were no suicides in these trials, however.
The trials relied on spontaneous reports of adverse events, not predetermined measures, Campo said. Even so, that 2% difference is “nothing to sneeze at,” he noted.
Bridge’s meta-analysis showed a smaller difference — closer to 0.7%. “But it was still statistically significant,” Campo said. “I have trouble ignoring that.”
The unintended consequences of the warning can’t be studied in a randomized controlled trial. Studies have shown an association but not a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the warning and a decline in treatment and rise in suicides.
But the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressants has been studied prospectively. Some older studies found a significant risk, while more recent trials have not.
While the Health Affairs analysis “certainly makes a strong case,” it is observational data, Campo said.
“The question is, what do we do now in retrospect? Do you say, ‘Never mind. We don’t need the black box warning anymore?’ ” he said. “That would require a pretty careful look.”
The Health Affairs paper “makes me think that there are other areas of research that that need to be completed and done and updated, and then there should be an assessment, a reevaluation from the FDA,” said Bridge. A new meta-analysis “would be very informative,” he said.
What’s Next?
When asked about the Health Affairs paper and whether the agency would review the warnings, an FDA spokesperson told this news organization that the agency “does not comment on specific studies but evaluates them as part of the body of evidence to further our understanding about a particular issue and assist in our mission to protect public health.”
Sakolsky said the data clearly point to the damage that the warning has done over the past 2 decades, but that things might be improving. Studies conducted more recently might not have captured some changes in practice.
For instance, she noted, in 2022, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for major depressive disorder in adolescents aged 12-18 years. In turn, she has seen more patients in her office who were referred by pediatricians who had conducted the screening, said Sakolsky.
Strawn said the time for pontificating is long past due. “We’re withholding medications and other treatments that could potentially be effective for disorders that, in and of themselves, are associated with a significant increase in the risk of suicide.”
After the FDA instituted the warning, “we were all very nervous,” about the potential fallout, said Campo, adding that a part of him wishes that the warnings had been “more mundane and less dramatic.”
Despite the unintended consequences, “it’s going to be hard to put the genie back in the bottle,” he said.
Campo and Sakolsky reported no relevant financial relationships. Strawn disclosed that his institution has received research funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and AbbVie. Bridge reported that he received grant support from the National Institute of Mental Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and PCORI; is a scientific adviser to Clarigent Health; and is on the Scientific Council of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paradoxically, and for almost as long, evidence suggests these warnings may have led to fewer depression diagnoses, reduced prescriptions, and, ultimately, higher suicide rates.
With mounting evidence of these negative unintended consequences, some clinicians and researchers are urging the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider revising — or even eliminating — boxed warnings on these medications.
The latest report challenging the utility of the 2005 warnings was particularly sobering. Published in October in Health Affairs, the systematic review of studies from 2003 to 2022 showed a 20%-40% decline in physician visits for depression, a 20%-50% decline in antidepressant use, and an abrupt increase in psychotropic drug poisonings and suicides — all after the warnings were added.
“FDA officials should review the totality of evidence and err on the side of caution in acknowledging possible harms of the antidepressant warnings,” lead author Stephen Soumerai, ScD, professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts and colleagues wrote. They called on the FDA to replace the boxed warnings with a routine warning in labeling.
While good prospective data on the risks and benefits of antidepressants in youth were limited when the boxed warnings were instituted, there is more information now, said Jeffrey Strawn, MD, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Ohio. Strawn, whose research on the topic has been cited frequently over the years, said the new evidence suggests it is time for the FDA to reevaluate the warnings.
“I don’t think that they’ve been useful. They’ve actually been harmful,” Strawn told this news organization. “These boxed warnings have decreased physicians’ and other clinicians’ comfort and tendency to prescribe.”
Decline in Diagnoses
The FDA issued its first warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior in children in 2003. After an advisory panel weighed the evidence, the agency added a boxed warning in 2005 to all antidepressants for children younger than 18 years. The warning was expanded in 2007 to include young adults through age 24.
Data suggesting that the warnings have had unintended effects can be found going back to just after they were issued. For instance, in 2009, after rising for years, the rate of new pediatric depression diagnoses fell precipitously after the warning was added, with primary care physicians diagnosing 44% fewer cases.
In 2014, citing evidence of fewer diagnoses and rising psychotropic drug poisonings, Weill Cornell Medicine Professor Richard A. Friedman, MD, called on the FDA in a perspective to remove the boxed warnings.
Strawn and colleagues reported in an often-cited 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that, in nine trials involving 1673 patients and six medications, antidepressants were superior to placebo, with no increased risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior.
He has also studied adverse effects of the medications, reporting in Pharmacotherapy that suicidality risk might be more likely with some medications, such as paroxetine and venlafaxine, and that it could be influenced by baseline suicidality, among many other factors. A Swedish register study found that risk was highest the month before starting a medication, Strawn and colleagues wrote.
Dara Sakolsky, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and associate medical director, Services for Teens at Risk at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, told this news organization that, because of “these negative unintended consequences,” the FDA should lower the temperature by putting the warnings in labeling.
“It makes sense based on the data that we have at hand now,” said Sakolsky.
The Dangers of Untreated Depression
Even with this new information, lingering concerns about earlier studies that pointed to increased suicidality risk may discourage prescribing by primary care physicians and pediatricians, and that worries researchers and psychiatrists.
“My concern is that the risk for suicide and suicidal behavior may be higher in untreated depression than the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors from antidepressants,” Jeffrey Bridge, PhD, director of the Center for Suicide Prevention and Research at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, told this news organization.
Bridge is the lead author of a much-cited 2007 meta-analysis in JAMA that showed that the benefits of antidepressants in children and adolescents appeared to be greater than the risks for suicidality. “The concern about antidepressants must be considered in the context of possible benefit,” wrote Bridge, who also is professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and behavioral health at Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Depression and suicide are a scourge for those younger than 25 years. A 2021 literature review noted that the prevalence of depression — which has been increasing for all Americans — has risen more among adolescents than adults. Depression is “strongly associated with suicide,” the authors wrote.
In 2021, the National Institute of Mental Health reported suicide was the second leading cause of death among 10- to 14-year-olds and the third leading cause of death among those aged 15-24 years.
Suicide kills more kids aged between 10 and 24 years than cancer and all other illnesses combined, John Campo, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and vice president of psychiatric services at Kennedy Krieger Institute, told this news organization.
Meanwhile, he added, the medications work and clinicians balance risk and benefit in prescribing.
The landmark 2007 Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study showed that fluoxetine, especially in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), was significantly better than placebo. Since that time, legions of trials have shown the drugs’ effectiveness.
The most effective treatment for teen depression is a combination of CBT and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, said Sakolsky.
“We know that the evidence for that is pretty good,” she said. “On the flip side, we know the risk of having an adverse outcome is pretty low.”
Sakolsky tells patients and families that perhaps 1 in 146 will have a suicidal thought or behavior. “That’s pretty rare when we know how effective these medicines are.”
Strawn said he always notes that no suicides took place in the trials that led to the warning and stresses that he closely monitors patients. “While the more recent prospective data are reassuring,” the suicidality risk “is something that we still talk about,” he said. He also discusses how some antidepressants seem to increase risk more than others.
For Campo, the discussion is based on his reading of the evidence, not the presence of the FDA warning.
“Based on what we know, I still think it’s fair to proceed with the idea that there is a small, but real risk,” he said. However, “at the same time, the medications might be exceptionally helpful for some kids.”
‘What Do We Do Now?’
When the FDA issued its warning in 2005, the agency said it identified the risk for suicidality in a combined analysis of short-term placebo-controlled trials of nine antidepressants. It ultimately included 24 trials involving more than 4400 patients. The risk was highest in the first few months. The average risk for those taking antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There were no suicides in these trials, however.
The trials relied on spontaneous reports of adverse events, not predetermined measures, Campo said. Even so, that 2% difference is “nothing to sneeze at,” he noted.
Bridge’s meta-analysis showed a smaller difference — closer to 0.7%. “But it was still statistically significant,” Campo said. “I have trouble ignoring that.”
The unintended consequences of the warning can’t be studied in a randomized controlled trial. Studies have shown an association but not a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the warning and a decline in treatment and rise in suicides.
But the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressants has been studied prospectively. Some older studies found a significant risk, while more recent trials have not.
While the Health Affairs analysis “certainly makes a strong case,” it is observational data, Campo said.
“The question is, what do we do now in retrospect? Do you say, ‘Never mind. We don’t need the black box warning anymore?’ ” he said. “That would require a pretty careful look.”
The Health Affairs paper “makes me think that there are other areas of research that that need to be completed and done and updated, and then there should be an assessment, a reevaluation from the FDA,” said Bridge. A new meta-analysis “would be very informative,” he said.
What’s Next?
When asked about the Health Affairs paper and whether the agency would review the warnings, an FDA spokesperson told this news organization that the agency “does not comment on specific studies but evaluates them as part of the body of evidence to further our understanding about a particular issue and assist in our mission to protect public health.”
Sakolsky said the data clearly point to the damage that the warning has done over the past 2 decades, but that things might be improving. Studies conducted more recently might not have captured some changes in practice.
For instance, she noted, in 2022, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for major depressive disorder in adolescents aged 12-18 years. In turn, she has seen more patients in her office who were referred by pediatricians who had conducted the screening, said Sakolsky.
Strawn said the time for pontificating is long past due. “We’re withholding medications and other treatments that could potentially be effective for disorders that, in and of themselves, are associated with a significant increase in the risk of suicide.”
After the FDA instituted the warning, “we were all very nervous,” about the potential fallout, said Campo, adding that a part of him wishes that the warnings had been “more mundane and less dramatic.”
Despite the unintended consequences, “it’s going to be hard to put the genie back in the bottle,” he said.
Campo and Sakolsky reported no relevant financial relationships. Strawn disclosed that his institution has received research funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and AbbVie. Bridge reported that he received grant support from the National Institute of Mental Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and PCORI; is a scientific adviser to Clarigent Health; and is on the Scientific Council of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
California Seeks Mental Health Warning Labels on Social Media
In the latest effort to address the mental health crisis among adolescents, legislation in California would require social media platforms to come with a “black box” mental health warning label.
Despite growing evidence linking young people’s use of social media to significant health risks including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts, social media companies have failed to be transparent about the risks, said Assembly member Rebecca Bauer-Kahan (D-Orinda), who introduced Assembly Bill (AB) 56.
“AB 56 ensures that families are armed with clear, actionable information to understand these dangers and make decisions that prioritizes their children’s well-being,” she said in a press release.
Bauer-Kahan noted that 95% of teens report using at least one social media platform and that more than one third say they use social media almost constantly.
“There is a powerful profit motive to keep our young people hooked online and engaged and it is exploiting the human psychology with notifications, likes, endless scrolling, and algorithmic amplification that is harming our children every day,” she said at a press conference on December 9 announcing the bill.
, a sponsor of AB 56, said in a press release.
Speaking at the press conference, Bonta said social media has many “incredible benefits” from giving people an outlet of expression to providing access to critical information but “there is no disputing the fact, it can have an enormously detrimental and dangerous impact on our young people. You cannot debate that. Our children are suffering.”
If AB 56 is successful, he said social media platforms would be required to display a “black box warning” for all users that would appear upon the first use of a platform and weekly thereafter.
The proposed language for the warning label is: “The Surgeon General has advised that there are ample indicators that social media can have a profound risk of harm to the mental health and well-being of children and adolescents.”
“This warning label isn’t a panacea, we know that, but it is another tool in our toolbox. It’s one prong in what has to be a multi-pronged continued, coordinated effort to address this public health crisis,” Bonta said.
Reached for comment, Bonta’s office said sponsorship of the bill was informed by their ongoing work to create a safer online space for children and teens and by the US Surgeon General’s call to Congress to add warning labels to social media.
In June, US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, said a Surgeon General’s warning label is needed to address the mental health emergency among adolescents and noted that evidence from tobacco studies shows warning labels can increase awareness and change behavior. In September, the attorneys general of 42 states announced their support of the proposal.
Also in September, US Senators John Fetterman (D-PA) and Katie Britt (R-AL) introduced the Stop the Scroll Act to create a mental health warning label requirement for social media platforms.
In a controversial move in November, Australia passed the world’s first law banning social media for children younger than 16 years. The law gives platforms such as TikTok, Facebook, X, Snapchat, and Instagram 1 year to figure out how to implement the ban before facing fines of up 50 million Australian dollars ($33 million) for systemic failures to prevent children younger than 16 years from holding accounts.
‘A Broken Fire Alarm’
“Slapping a warning label on social media is like a broken fire alarm going off with no evidence of smoke. It ignores the reality that most teens view social media as an important outlet for social connection,” Todd O’Boyle, with the tech industry policy group Chamber of Progress, said in a statement on AB 56.
He highlighted a 2022 Pew Research Center survey reporting that most teens credit social media with deepening connections and providing a support network and a 2020 study reporting that social media is not a strong or consistent risk factor for depressive symptoms in US adolescents.
O’Boyle predicted that, without strong evidence, AB 56 will run into the same “First Amendment buzzsaw” that has doomed other California kids’ bills.
Pediatrician Jason Nagata, MD, University of California San Francisco, points out in Bonta’s press release that social media can displace time for other healthful activities including sleep, exercise, and in-person socialization.
“While social media can provide educational content, it can also provide misinformation about health and expose children to content that damages their mental well-being. These are risks that adolescents and their parents should be aware of,” Nagata said.
Indeed, a tearful Victoria Hinks of Larkspur, California, spoke at the press conference of her 16-year-old daughter, Alexandra, who committed suicide 4 months ago after being sucked into social media and served content on self-harm, eating disorders, suicidal ideation, and glamorization of suicide.
“She was led down dark rabbit holes she had no hope of escaping,” Hinks said. “There is not a bone in my body that doubts social media played a role leading her to that final irreversible decision.”
Jim Steyer, CEO and founder of Common Sense Media, applauded California for being the first state to introduce social media warning label legislation. The group plans to lobby for similar proposals in other states he said at the press conference, noting that there are “tens of thousands of Alexandras out there.”
“We have seat belt laws, we have warning labels on cigarettes and alcohol, and that’s what we’re doing here,” Steyer said. “It’s a straightforward simple proposition, which is put your kids and teenagers first, put their self-interest first and hold the largest, most powerful, and wealthy companies in all of our lifetimes accountable for the harms that have happened on their platforms.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the latest effort to address the mental health crisis among adolescents, legislation in California would require social media platforms to come with a “black box” mental health warning label.
Despite growing evidence linking young people’s use of social media to significant health risks including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts, social media companies have failed to be transparent about the risks, said Assembly member Rebecca Bauer-Kahan (D-Orinda), who introduced Assembly Bill (AB) 56.
“AB 56 ensures that families are armed with clear, actionable information to understand these dangers and make decisions that prioritizes their children’s well-being,” she said in a press release.
Bauer-Kahan noted that 95% of teens report using at least one social media platform and that more than one third say they use social media almost constantly.
“There is a powerful profit motive to keep our young people hooked online and engaged and it is exploiting the human psychology with notifications, likes, endless scrolling, and algorithmic amplification that is harming our children every day,” she said at a press conference on December 9 announcing the bill.
, a sponsor of AB 56, said in a press release.
Speaking at the press conference, Bonta said social media has many “incredible benefits” from giving people an outlet of expression to providing access to critical information but “there is no disputing the fact, it can have an enormously detrimental and dangerous impact on our young people. You cannot debate that. Our children are suffering.”
If AB 56 is successful, he said social media platforms would be required to display a “black box warning” for all users that would appear upon the first use of a platform and weekly thereafter.
The proposed language for the warning label is: “The Surgeon General has advised that there are ample indicators that social media can have a profound risk of harm to the mental health and well-being of children and adolescents.”
“This warning label isn’t a panacea, we know that, but it is another tool in our toolbox. It’s one prong in what has to be a multi-pronged continued, coordinated effort to address this public health crisis,” Bonta said.
Reached for comment, Bonta’s office said sponsorship of the bill was informed by their ongoing work to create a safer online space for children and teens and by the US Surgeon General’s call to Congress to add warning labels to social media.
In June, US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, said a Surgeon General’s warning label is needed to address the mental health emergency among adolescents and noted that evidence from tobacco studies shows warning labels can increase awareness and change behavior. In September, the attorneys general of 42 states announced their support of the proposal.
Also in September, US Senators John Fetterman (D-PA) and Katie Britt (R-AL) introduced the Stop the Scroll Act to create a mental health warning label requirement for social media platforms.
In a controversial move in November, Australia passed the world’s first law banning social media for children younger than 16 years. The law gives platforms such as TikTok, Facebook, X, Snapchat, and Instagram 1 year to figure out how to implement the ban before facing fines of up 50 million Australian dollars ($33 million) for systemic failures to prevent children younger than 16 years from holding accounts.
‘A Broken Fire Alarm’
“Slapping a warning label on social media is like a broken fire alarm going off with no evidence of smoke. It ignores the reality that most teens view social media as an important outlet for social connection,” Todd O’Boyle, with the tech industry policy group Chamber of Progress, said in a statement on AB 56.
He highlighted a 2022 Pew Research Center survey reporting that most teens credit social media with deepening connections and providing a support network and a 2020 study reporting that social media is not a strong or consistent risk factor for depressive symptoms in US adolescents.
O’Boyle predicted that, without strong evidence, AB 56 will run into the same “First Amendment buzzsaw” that has doomed other California kids’ bills.
Pediatrician Jason Nagata, MD, University of California San Francisco, points out in Bonta’s press release that social media can displace time for other healthful activities including sleep, exercise, and in-person socialization.
“While social media can provide educational content, it can also provide misinformation about health and expose children to content that damages their mental well-being. These are risks that adolescents and their parents should be aware of,” Nagata said.
Indeed, a tearful Victoria Hinks of Larkspur, California, spoke at the press conference of her 16-year-old daughter, Alexandra, who committed suicide 4 months ago after being sucked into social media and served content on self-harm, eating disorders, suicidal ideation, and glamorization of suicide.
“She was led down dark rabbit holes she had no hope of escaping,” Hinks said. “There is not a bone in my body that doubts social media played a role leading her to that final irreversible decision.”
Jim Steyer, CEO and founder of Common Sense Media, applauded California for being the first state to introduce social media warning label legislation. The group plans to lobby for similar proposals in other states he said at the press conference, noting that there are “tens of thousands of Alexandras out there.”
“We have seat belt laws, we have warning labels on cigarettes and alcohol, and that’s what we’re doing here,” Steyer said. “It’s a straightforward simple proposition, which is put your kids and teenagers first, put their self-interest first and hold the largest, most powerful, and wealthy companies in all of our lifetimes accountable for the harms that have happened on their platforms.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the latest effort to address the mental health crisis among adolescents, legislation in California would require social media platforms to come with a “black box” mental health warning label.
Despite growing evidence linking young people’s use of social media to significant health risks including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts, social media companies have failed to be transparent about the risks, said Assembly member Rebecca Bauer-Kahan (D-Orinda), who introduced Assembly Bill (AB) 56.
“AB 56 ensures that families are armed with clear, actionable information to understand these dangers and make decisions that prioritizes their children’s well-being,” she said in a press release.
Bauer-Kahan noted that 95% of teens report using at least one social media platform and that more than one third say they use social media almost constantly.
“There is a powerful profit motive to keep our young people hooked online and engaged and it is exploiting the human psychology with notifications, likes, endless scrolling, and algorithmic amplification that is harming our children every day,” she said at a press conference on December 9 announcing the bill.
, a sponsor of AB 56, said in a press release.
Speaking at the press conference, Bonta said social media has many “incredible benefits” from giving people an outlet of expression to providing access to critical information but “there is no disputing the fact, it can have an enormously detrimental and dangerous impact on our young people. You cannot debate that. Our children are suffering.”
If AB 56 is successful, he said social media platforms would be required to display a “black box warning” for all users that would appear upon the first use of a platform and weekly thereafter.
The proposed language for the warning label is: “The Surgeon General has advised that there are ample indicators that social media can have a profound risk of harm to the mental health and well-being of children and adolescents.”
“This warning label isn’t a panacea, we know that, but it is another tool in our toolbox. It’s one prong in what has to be a multi-pronged continued, coordinated effort to address this public health crisis,” Bonta said.
Reached for comment, Bonta’s office said sponsorship of the bill was informed by their ongoing work to create a safer online space for children and teens and by the US Surgeon General’s call to Congress to add warning labels to social media.
In June, US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, said a Surgeon General’s warning label is needed to address the mental health emergency among adolescents and noted that evidence from tobacco studies shows warning labels can increase awareness and change behavior. In September, the attorneys general of 42 states announced their support of the proposal.
Also in September, US Senators John Fetterman (D-PA) and Katie Britt (R-AL) introduced the Stop the Scroll Act to create a mental health warning label requirement for social media platforms.
In a controversial move in November, Australia passed the world’s first law banning social media for children younger than 16 years. The law gives platforms such as TikTok, Facebook, X, Snapchat, and Instagram 1 year to figure out how to implement the ban before facing fines of up 50 million Australian dollars ($33 million) for systemic failures to prevent children younger than 16 years from holding accounts.
‘A Broken Fire Alarm’
“Slapping a warning label on social media is like a broken fire alarm going off with no evidence of smoke. It ignores the reality that most teens view social media as an important outlet for social connection,” Todd O’Boyle, with the tech industry policy group Chamber of Progress, said in a statement on AB 56.
He highlighted a 2022 Pew Research Center survey reporting that most teens credit social media with deepening connections and providing a support network and a 2020 study reporting that social media is not a strong or consistent risk factor for depressive symptoms in US adolescents.
O’Boyle predicted that, without strong evidence, AB 56 will run into the same “First Amendment buzzsaw” that has doomed other California kids’ bills.
Pediatrician Jason Nagata, MD, University of California San Francisco, points out in Bonta’s press release that social media can displace time for other healthful activities including sleep, exercise, and in-person socialization.
“While social media can provide educational content, it can also provide misinformation about health and expose children to content that damages their mental well-being. These are risks that adolescents and their parents should be aware of,” Nagata said.
Indeed, a tearful Victoria Hinks of Larkspur, California, spoke at the press conference of her 16-year-old daughter, Alexandra, who committed suicide 4 months ago after being sucked into social media and served content on self-harm, eating disorders, suicidal ideation, and glamorization of suicide.
“She was led down dark rabbit holes she had no hope of escaping,” Hinks said. “There is not a bone in my body that doubts social media played a role leading her to that final irreversible decision.”
Jim Steyer, CEO and founder of Common Sense Media, applauded California for being the first state to introduce social media warning label legislation. The group plans to lobby for similar proposals in other states he said at the press conference, noting that there are “tens of thousands of Alexandras out there.”
“We have seat belt laws, we have warning labels on cigarettes and alcohol, and that’s what we’re doing here,” Steyer said. “It’s a straightforward simple proposition, which is put your kids and teenagers first, put their self-interest first and hold the largest, most powerful, and wealthy companies in all of our lifetimes accountable for the harms that have happened on their platforms.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Managing Return-to-Work Barriers for People With Long COVID
Although some patients experience symptoms so severe that they cannot work under any conditions, medical providers and employers can help ensure many patients with long COVID can stay in the workforce.
Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems. By the end of 2023, at least 400 million people worldwide were estimated to have long COVID.
As members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers and health advocates living with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions, we have published one of the first research studies of people with long COVID and their desire to work, the specific needs they have, and what doctors and employers can do to create a path for returning to the workforce.
In our recent paper, we document the barriers and facilitators that individuals living with long COVID experience when attempting to return to work. Our recommendations are based on these findings and include recommendations for both medical providers and employers.
If you are a medical provider:
- Ensure you adequately document your patients’ COVID cases, any long COVID diagnoses, and the functional impairment that long COVID causes. Remember that you can diagnose a patient with long COVID on the basis of their symptoms, and clinical guidelines do not require a record of a positive COVID-19 test, which many patients lack owing to testing barriers.
- Keep up to date on research on long COVID and related infection-associated chronic conditions — for example, through the Project ECHO Long COVID and Fatiguing Illness Recovery Program — and learn about pacing and other treatment options.
If you are an employer:
- Utilize a return-to-work model in which any worker with suspected or confirmed COVID discusses support they may need with their employer when they return to work, with additional check-in dates scheduled to reevaluate supports as needed. Planning for this collaborative and iterative evaluation of return-to-work supports for all workers with COVID-19 is important because it may not be immediately clear to a worker whether they have developed long COVID or are generally recuperating from the illness.
- Do not require medical documentation of a SARS-CoV-2 infection or a Long COVID diagnosis to access accommodations — this is owing to disparities in accessing documentation.
- Tailor job responsibilities, provide remote options, allow flexible hours, and provide longer-range deadlines to account for symptoms for people with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions.
- Provide accommodations to any caregivers of people with long COVID in your workplace.
- If requiring in-person work, make the workplace as safe as possible through ventilation and masking requirements, which will help ensure fewer of your workers develop long COVID, and those already with infection-associated chronic conditions will not get worse.
Our findings and recommendations are specific to long COVID, but they can and should apply to other disabilities. Given that our study’s sample was predominately White and working in jobs that did not require substantial physical labor, additional recommendations may be needed for other populations and workers who have labor-intensive jobs.
510 Study Participants
Long COVID is characterized as a relapsing-remitting illness, often described as episodic, in which an individual’s symptoms may fluctuate. Symptoms can become more or less severe depending on tasks, exertion, and social support in addition to physiologic processes and medical intervention. In our paper, we illustrate how the long COVID return-to-work experience and individuals’ symptoms can be shaped by workplace, home, and medical environments.
We randomly selected 510 participants from a global survey of people living with long COVID and systematically analyzed their open-ended responses using established qualitative analysis methods. In this study, we specifically analyzed what patients wrote about their return-to-work experiences, considering how work experiences and relapsing and remitting long COVID symptoms intersected with personal lives and medical care.
Most of the study participants identified as White, were 30-60 years old (ie, in their key earning years), and had at least a baccalaureate degree. Participants lived in the United States (38%), United Kingdom (25%), continental Europe (8%), Canada (4%), or other countries (25%). Most participants worked in professions that did not require substantial physical labor, and individuals in those fields may experience even greater return-to-work barriers than are reported in this study.
Key Findings
Through our qualitative analysis, we identified four primary return-to-work themes:
1. People living with long COVID have a strong desire and financial need to return to work.
The participants in our study described how they had experienced financial hardship because they could not successfully return to work and may have incurred new expenses with long COVID. They also often wrote how they wanted to return to work because their jobs provided meaning and structure for their lives. Some people in this study shared how they had tried to return to their jobs but relapsed. As a result, they considered leaving the workforce.
2. Workers’ long COVID symptoms intersect with organization of work and home life.
Most of the people in our study were employed in positions that did not require substantial physical labor. Even so, workers described how their long COVID symptoms were exacerbated by some job tasks. Computer screen time; reading dense material or writing (including emails); and conversations and meetings, regardless of whether they were in-person or via phone or video conferencing, could trigger or make symptoms worse. Workers who needed to stand for long periods of time, such as teachers and healthcare workers, and workers who needed to do lifting as part of their jobs described how these requirements were too taxing and could lead to relapses.
Because of the relapsing and remitting nature of many long COVID symptoms, people reported how it could be difficult to predict how job tasks, long hours, or pressing deadlines may exacerbate symptoms, which would require them to take time off work. For these participants, “pushing through” symptoms only made the symptoms worse. However, people in the study who were allowed to work from home reported how pacing, elevating their legs, and conserving energy (especially by not commuting) was key to doing their jobs well.
Some people in the study described how they were only able to return to work because they had substantial support from family or partners at home. These individuals shared how the people they lived with did most of the cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks so that the person living with long COVID could conserve their energy for work. This reorganization of home life notably shifted household tasks and caregiving to other people in the household, but without this shift, the individual’s long COVID symptoms may be too severe to work.
3. People with long COVID experience disbelief and stigma at work and healthcare settings.
Some people in our study described how their colleagues, supervisors, and human resource managers insinuated that they were fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. This made it hard for workers to communicate what support they needed and could limit access to necessary work accommodations.
Many people in our study also described how medical providers did not believe that they had long COVID despite experiencing debilitating symptoms, often because they did not have a positive COVID-19 test to prove they had had an acute infection. Many people with long COVID may not have a positive COVID-19 test because:
- They could not access a test because testing access was limited at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are transportation and cost barriers to tests, many health insurance providers no longer cover tests; and there are fewer public testing sites since the World Health Organization declared an end to the public health emergency;
- There is a high probability of false-negative results for viral and antibody tests (especially during the first wave of the pandemic and for individuals with limited immune response); and
- People can develop long COVID after asymptomatic acute infection.
Although healthcare providers can provide a long COVID diagnosis without a positive COVID-19 test on the basis of a patient’s presentation of symptoms and clinical history, many people in our study said that their providers would not provide this diagnosis, which restricted access to worker’s compensation, paid time off, and job accommodations.
Many people in the study also reported that their medical providers misdiagnosed them with a mental health disorder, such as anxiety, instead of long COVID. Although some people with long COVID may experience poor mental health as a natural consequence of dealing with a debilitating medical condition or may have neuropsychiatric symptoms as part of their long COVID, long COVID is not caused by an underlying psychiatric illness.
4. Support of medical providers is key to successful return to work for people living with long COVID.
Some people in our study described how they were able to get workplace accommodations or access workers’ compensation or sick leave because their medical providers recognized they had long COVID and provided them with this documentation. Some of these participants did not have a positive COVID-19 test, but their medical providers were able to diagnose them with long COVID on the basis of symptom presentation and clinical history. This documentation was critical for helping workers remain financially stable and able to return to work.
Conclusion
While we continue to search for treatment and cures for long COVID and work to provide a robust social safety net, it is crucial to address the stigma, inaccessibility, and lack of support often experienced by patients in their workplaces. Disabled people have long faced these issues; long COVID may be an opportunity to revolutionize the workplace to ensure an inclusive and accessible environment that can improve the lives of all workers.
For more on how to best be inclusive of employees with long COVID, read Harvard Business Review’s “Long Covid at Work: A Manager’s Guide” and visit the Job Accommodation Network webpage dedicated to long COVID.
Additional discussion about our study and applying the findings to improve work and medical care can be found by listening to the Healthy Work podcast episode titled “Supporting Long COVID at Work.”
Elisabeth Stelson, Gina Assaf, and Lisa McCorkell are members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers. Dr Stelson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Gina Assaf is Research Lead, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC. Lisa McCorkell is a long COVID patient; Cofounder, Team Lead, Researcher, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Although some patients experience symptoms so severe that they cannot work under any conditions, medical providers and employers can help ensure many patients with long COVID can stay in the workforce.
Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems. By the end of 2023, at least 400 million people worldwide were estimated to have long COVID.
As members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers and health advocates living with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions, we have published one of the first research studies of people with long COVID and their desire to work, the specific needs they have, and what doctors and employers can do to create a path for returning to the workforce.
In our recent paper, we document the barriers and facilitators that individuals living with long COVID experience when attempting to return to work. Our recommendations are based on these findings and include recommendations for both medical providers and employers.
If you are a medical provider:
- Ensure you adequately document your patients’ COVID cases, any long COVID diagnoses, and the functional impairment that long COVID causes. Remember that you can diagnose a patient with long COVID on the basis of their symptoms, and clinical guidelines do not require a record of a positive COVID-19 test, which many patients lack owing to testing barriers.
- Keep up to date on research on long COVID and related infection-associated chronic conditions — for example, through the Project ECHO Long COVID and Fatiguing Illness Recovery Program — and learn about pacing and other treatment options.
If you are an employer:
- Utilize a return-to-work model in which any worker with suspected or confirmed COVID discusses support they may need with their employer when they return to work, with additional check-in dates scheduled to reevaluate supports as needed. Planning for this collaborative and iterative evaluation of return-to-work supports for all workers with COVID-19 is important because it may not be immediately clear to a worker whether they have developed long COVID or are generally recuperating from the illness.
- Do not require medical documentation of a SARS-CoV-2 infection or a Long COVID diagnosis to access accommodations — this is owing to disparities in accessing documentation.
- Tailor job responsibilities, provide remote options, allow flexible hours, and provide longer-range deadlines to account for symptoms for people with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions.
- Provide accommodations to any caregivers of people with long COVID in your workplace.
- If requiring in-person work, make the workplace as safe as possible through ventilation and masking requirements, which will help ensure fewer of your workers develop long COVID, and those already with infection-associated chronic conditions will not get worse.
Our findings and recommendations are specific to long COVID, but they can and should apply to other disabilities. Given that our study’s sample was predominately White and working in jobs that did not require substantial physical labor, additional recommendations may be needed for other populations and workers who have labor-intensive jobs.
510 Study Participants
Long COVID is characterized as a relapsing-remitting illness, often described as episodic, in which an individual’s symptoms may fluctuate. Symptoms can become more or less severe depending on tasks, exertion, and social support in addition to physiologic processes and medical intervention. In our paper, we illustrate how the long COVID return-to-work experience and individuals’ symptoms can be shaped by workplace, home, and medical environments.
We randomly selected 510 participants from a global survey of people living with long COVID and systematically analyzed their open-ended responses using established qualitative analysis methods. In this study, we specifically analyzed what patients wrote about their return-to-work experiences, considering how work experiences and relapsing and remitting long COVID symptoms intersected with personal lives and medical care.
Most of the study participants identified as White, were 30-60 years old (ie, in their key earning years), and had at least a baccalaureate degree. Participants lived in the United States (38%), United Kingdom (25%), continental Europe (8%), Canada (4%), or other countries (25%). Most participants worked in professions that did not require substantial physical labor, and individuals in those fields may experience even greater return-to-work barriers than are reported in this study.
Key Findings
Through our qualitative analysis, we identified four primary return-to-work themes:
1. People living with long COVID have a strong desire and financial need to return to work.
The participants in our study described how they had experienced financial hardship because they could not successfully return to work and may have incurred new expenses with long COVID. They also often wrote how they wanted to return to work because their jobs provided meaning and structure for their lives. Some people in this study shared how they had tried to return to their jobs but relapsed. As a result, they considered leaving the workforce.
2. Workers’ long COVID symptoms intersect with organization of work and home life.
Most of the people in our study were employed in positions that did not require substantial physical labor. Even so, workers described how their long COVID symptoms were exacerbated by some job tasks. Computer screen time; reading dense material or writing (including emails); and conversations and meetings, regardless of whether they were in-person or via phone or video conferencing, could trigger or make symptoms worse. Workers who needed to stand for long periods of time, such as teachers and healthcare workers, and workers who needed to do lifting as part of their jobs described how these requirements were too taxing and could lead to relapses.
Because of the relapsing and remitting nature of many long COVID symptoms, people reported how it could be difficult to predict how job tasks, long hours, or pressing deadlines may exacerbate symptoms, which would require them to take time off work. For these participants, “pushing through” symptoms only made the symptoms worse. However, people in the study who were allowed to work from home reported how pacing, elevating their legs, and conserving energy (especially by not commuting) was key to doing their jobs well.
Some people in the study described how they were only able to return to work because they had substantial support from family or partners at home. These individuals shared how the people they lived with did most of the cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks so that the person living with long COVID could conserve their energy for work. This reorganization of home life notably shifted household tasks and caregiving to other people in the household, but without this shift, the individual’s long COVID symptoms may be too severe to work.
3. People with long COVID experience disbelief and stigma at work and healthcare settings.
Some people in our study described how their colleagues, supervisors, and human resource managers insinuated that they were fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. This made it hard for workers to communicate what support they needed and could limit access to necessary work accommodations.
Many people in our study also described how medical providers did not believe that they had long COVID despite experiencing debilitating symptoms, often because they did not have a positive COVID-19 test to prove they had had an acute infection. Many people with long COVID may not have a positive COVID-19 test because:
- They could not access a test because testing access was limited at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are transportation and cost barriers to tests, many health insurance providers no longer cover tests; and there are fewer public testing sites since the World Health Organization declared an end to the public health emergency;
- There is a high probability of false-negative results for viral and antibody tests (especially during the first wave of the pandemic and for individuals with limited immune response); and
- People can develop long COVID after asymptomatic acute infection.
Although healthcare providers can provide a long COVID diagnosis without a positive COVID-19 test on the basis of a patient’s presentation of symptoms and clinical history, many people in our study said that their providers would not provide this diagnosis, which restricted access to worker’s compensation, paid time off, and job accommodations.
Many people in the study also reported that their medical providers misdiagnosed them with a mental health disorder, such as anxiety, instead of long COVID. Although some people with long COVID may experience poor mental health as a natural consequence of dealing with a debilitating medical condition or may have neuropsychiatric symptoms as part of their long COVID, long COVID is not caused by an underlying psychiatric illness.
4. Support of medical providers is key to successful return to work for people living with long COVID.
Some people in our study described how they were able to get workplace accommodations or access workers’ compensation or sick leave because their medical providers recognized they had long COVID and provided them with this documentation. Some of these participants did not have a positive COVID-19 test, but their medical providers were able to diagnose them with long COVID on the basis of symptom presentation and clinical history. This documentation was critical for helping workers remain financially stable and able to return to work.
Conclusion
While we continue to search for treatment and cures for long COVID and work to provide a robust social safety net, it is crucial to address the stigma, inaccessibility, and lack of support often experienced by patients in their workplaces. Disabled people have long faced these issues; long COVID may be an opportunity to revolutionize the workplace to ensure an inclusive and accessible environment that can improve the lives of all workers.
For more on how to best be inclusive of employees with long COVID, read Harvard Business Review’s “Long Covid at Work: A Manager’s Guide” and visit the Job Accommodation Network webpage dedicated to long COVID.
Additional discussion about our study and applying the findings to improve work and medical care can be found by listening to the Healthy Work podcast episode titled “Supporting Long COVID at Work.”
Elisabeth Stelson, Gina Assaf, and Lisa McCorkell are members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers. Dr Stelson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Gina Assaf is Research Lead, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC. Lisa McCorkell is a long COVID patient; Cofounder, Team Lead, Researcher, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Although some patients experience symptoms so severe that they cannot work under any conditions, medical providers and employers can help ensure many patients with long COVID can stay in the workforce.
Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems. By the end of 2023, at least 400 million people worldwide were estimated to have long COVID.
As members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers and health advocates living with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions, we have published one of the first research studies of people with long COVID and their desire to work, the specific needs they have, and what doctors and employers can do to create a path for returning to the workforce.
In our recent paper, we document the barriers and facilitators that individuals living with long COVID experience when attempting to return to work. Our recommendations are based on these findings and include recommendations for both medical providers and employers.
If you are a medical provider:
- Ensure you adequately document your patients’ COVID cases, any long COVID diagnoses, and the functional impairment that long COVID causes. Remember that you can diagnose a patient with long COVID on the basis of their symptoms, and clinical guidelines do not require a record of a positive COVID-19 test, which many patients lack owing to testing barriers.
- Keep up to date on research on long COVID and related infection-associated chronic conditions — for example, through the Project ECHO Long COVID and Fatiguing Illness Recovery Program — and learn about pacing and other treatment options.
If you are an employer:
- Utilize a return-to-work model in which any worker with suspected or confirmed COVID discusses support they may need with their employer when they return to work, with additional check-in dates scheduled to reevaluate supports as needed. Planning for this collaborative and iterative evaluation of return-to-work supports for all workers with COVID-19 is important because it may not be immediately clear to a worker whether they have developed long COVID or are generally recuperating from the illness.
- Do not require medical documentation of a SARS-CoV-2 infection or a Long COVID diagnosis to access accommodations — this is owing to disparities in accessing documentation.
- Tailor job responsibilities, provide remote options, allow flexible hours, and provide longer-range deadlines to account for symptoms for people with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions.
- Provide accommodations to any caregivers of people with long COVID in your workplace.
- If requiring in-person work, make the workplace as safe as possible through ventilation and masking requirements, which will help ensure fewer of your workers develop long COVID, and those already with infection-associated chronic conditions will not get worse.
Our findings and recommendations are specific to long COVID, but they can and should apply to other disabilities. Given that our study’s sample was predominately White and working in jobs that did not require substantial physical labor, additional recommendations may be needed for other populations and workers who have labor-intensive jobs.
510 Study Participants
Long COVID is characterized as a relapsing-remitting illness, often described as episodic, in which an individual’s symptoms may fluctuate. Symptoms can become more or less severe depending on tasks, exertion, and social support in addition to physiologic processes and medical intervention. In our paper, we illustrate how the long COVID return-to-work experience and individuals’ symptoms can be shaped by workplace, home, and medical environments.
We randomly selected 510 participants from a global survey of people living with long COVID and systematically analyzed their open-ended responses using established qualitative analysis methods. In this study, we specifically analyzed what patients wrote about their return-to-work experiences, considering how work experiences and relapsing and remitting long COVID symptoms intersected with personal lives and medical care.
Most of the study participants identified as White, were 30-60 years old (ie, in their key earning years), and had at least a baccalaureate degree. Participants lived in the United States (38%), United Kingdom (25%), continental Europe (8%), Canada (4%), or other countries (25%). Most participants worked in professions that did not require substantial physical labor, and individuals in those fields may experience even greater return-to-work barriers than are reported in this study.
Key Findings
Through our qualitative analysis, we identified four primary return-to-work themes:
1. People living with long COVID have a strong desire and financial need to return to work.
The participants in our study described how they had experienced financial hardship because they could not successfully return to work and may have incurred new expenses with long COVID. They also often wrote how they wanted to return to work because their jobs provided meaning and structure for their lives. Some people in this study shared how they had tried to return to their jobs but relapsed. As a result, they considered leaving the workforce.
2. Workers’ long COVID symptoms intersect with organization of work and home life.
Most of the people in our study were employed in positions that did not require substantial physical labor. Even so, workers described how their long COVID symptoms were exacerbated by some job tasks. Computer screen time; reading dense material or writing (including emails); and conversations and meetings, regardless of whether they were in-person or via phone or video conferencing, could trigger or make symptoms worse. Workers who needed to stand for long periods of time, such as teachers and healthcare workers, and workers who needed to do lifting as part of their jobs described how these requirements were too taxing and could lead to relapses.
Because of the relapsing and remitting nature of many long COVID symptoms, people reported how it could be difficult to predict how job tasks, long hours, or pressing deadlines may exacerbate symptoms, which would require them to take time off work. For these participants, “pushing through” symptoms only made the symptoms worse. However, people in the study who were allowed to work from home reported how pacing, elevating their legs, and conserving energy (especially by not commuting) was key to doing their jobs well.
Some people in the study described how they were only able to return to work because they had substantial support from family or partners at home. These individuals shared how the people they lived with did most of the cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks so that the person living with long COVID could conserve their energy for work. This reorganization of home life notably shifted household tasks and caregiving to other people in the household, but without this shift, the individual’s long COVID symptoms may be too severe to work.
3. People with long COVID experience disbelief and stigma at work and healthcare settings.
Some people in our study described how their colleagues, supervisors, and human resource managers insinuated that they were fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. This made it hard for workers to communicate what support they needed and could limit access to necessary work accommodations.
Many people in our study also described how medical providers did not believe that they had long COVID despite experiencing debilitating symptoms, often because they did not have a positive COVID-19 test to prove they had had an acute infection. Many people with long COVID may not have a positive COVID-19 test because:
- They could not access a test because testing access was limited at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are transportation and cost barriers to tests, many health insurance providers no longer cover tests; and there are fewer public testing sites since the World Health Organization declared an end to the public health emergency;
- There is a high probability of false-negative results for viral and antibody tests (especially during the first wave of the pandemic and for individuals with limited immune response); and
- People can develop long COVID after asymptomatic acute infection.
Although healthcare providers can provide a long COVID diagnosis without a positive COVID-19 test on the basis of a patient’s presentation of symptoms and clinical history, many people in our study said that their providers would not provide this diagnosis, which restricted access to worker’s compensation, paid time off, and job accommodations.
Many people in the study also reported that their medical providers misdiagnosed them with a mental health disorder, such as anxiety, instead of long COVID. Although some people with long COVID may experience poor mental health as a natural consequence of dealing with a debilitating medical condition or may have neuropsychiatric symptoms as part of their long COVID, long COVID is not caused by an underlying psychiatric illness.
4. Support of medical providers is key to successful return to work for people living with long COVID.
Some people in our study described how they were able to get workplace accommodations or access workers’ compensation or sick leave because their medical providers recognized they had long COVID and provided them with this documentation. Some of these participants did not have a positive COVID-19 test, but their medical providers were able to diagnose them with long COVID on the basis of symptom presentation and clinical history. This documentation was critical for helping workers remain financially stable and able to return to work.
Conclusion
While we continue to search for treatment and cures for long COVID and work to provide a robust social safety net, it is crucial to address the stigma, inaccessibility, and lack of support often experienced by patients in their workplaces. Disabled people have long faced these issues; long COVID may be an opportunity to revolutionize the workplace to ensure an inclusive and accessible environment that can improve the lives of all workers.
For more on how to best be inclusive of employees with long COVID, read Harvard Business Review’s “Long Covid at Work: A Manager’s Guide” and visit the Job Accommodation Network webpage dedicated to long COVID.
Additional discussion about our study and applying the findings to improve work and medical care can be found by listening to the Healthy Work podcast episode titled “Supporting Long COVID at Work.”
Elisabeth Stelson, Gina Assaf, and Lisa McCorkell are members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers. Dr Stelson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Gina Assaf is Research Lead, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC. Lisa McCorkell is a long COVID patient; Cofounder, Team Lead, Researcher, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel Digital Intervention Shows Promise for Depression
TOPLINE:
InterRhythmic care (IRC), a novel digital intervention, was linked to greater improvements in depressive symptoms, anxiety, interpersonal relationships, and social functioning in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), compared with internet general psychoeducation in new research.
METHODOLOGY:
- The randomized, single-blind trial included 120 outpatients from the Shanghai Mental Health Center between March and November 2021 with MDD (mean age, 28.2 years; 99% Han Chinese; 83% women) who were randomly assigned to receive either IRC or internet general psychoeducation (control group).
- IRC included computer-based psychoeducation on stabilizing social rhythm regularity and resolution of interpersonal problems plus brief online interactions with clinicians. Patients received 10 minutes of IRC daily, Monday through Friday, for 8 weeks.
- The researchers assessed participants’ depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, interpersonal relationships, social function, and biological rhythms using the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Scale, Interpersonal Comprehensive Diagnostic Scale, Sheehan Disability Scale, and Morning and Evening Questionnaire at baseline and at 8 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The participants who received IRC had significantly lower Hamilton Depression Rating total scores than those who received internet general psychoeducation (P < .001).
- The IRC group demonstrated improved anxiety symptoms, as evidenced by lower Hamilton Anxiety Scale total scores, than those observed for the control group (P < .001).
- The IRC group also showed improved outcomes in interpersonal relationships, as indicated by lower Interpersonal Comprehensive Diagnostic Scale total scores (P < .001).
- Social functioning improved significantly in the IRC group, as measured by the Sheehan Disability Scale subscores for work/school (P = .03), social life (P < .001), and family life (P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study demonstrated that IRC can improve clinical symptoms such as depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, interpersonal problems, and social function in patients with MDD. Our study suggested that the IRC can be used in clinical practice,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Chuchen Xu, Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China. It was published online on November 20, 2024, in The Journal of Psychiatric Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The 8-week follow-up period was considered too short to comprehensively evaluate the intervention’s long-term impact. Additionally, the researchers had to check and supervise assignment completion, which increased research costs and may, therefore, potentially limit broader implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
InterRhythmic care (IRC), a novel digital intervention, was linked to greater improvements in depressive symptoms, anxiety, interpersonal relationships, and social functioning in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), compared with internet general psychoeducation in new research.
METHODOLOGY:
- The randomized, single-blind trial included 120 outpatients from the Shanghai Mental Health Center between March and November 2021 with MDD (mean age, 28.2 years; 99% Han Chinese; 83% women) who were randomly assigned to receive either IRC or internet general psychoeducation (control group).
- IRC included computer-based psychoeducation on stabilizing social rhythm regularity and resolution of interpersonal problems plus brief online interactions with clinicians. Patients received 10 minutes of IRC daily, Monday through Friday, for 8 weeks.
- The researchers assessed participants’ depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, interpersonal relationships, social function, and biological rhythms using the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Scale, Interpersonal Comprehensive Diagnostic Scale, Sheehan Disability Scale, and Morning and Evening Questionnaire at baseline and at 8 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The participants who received IRC had significantly lower Hamilton Depression Rating total scores than those who received internet general psychoeducation (P < .001).
- The IRC group demonstrated improved anxiety symptoms, as evidenced by lower Hamilton Anxiety Scale total scores, than those observed for the control group (P < .001).
- The IRC group also showed improved outcomes in interpersonal relationships, as indicated by lower Interpersonal Comprehensive Diagnostic Scale total scores (P < .001).
- Social functioning improved significantly in the IRC group, as measured by the Sheehan Disability Scale subscores for work/school (P = .03), social life (P < .001), and family life (P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study demonstrated that IRC can improve clinical symptoms such as depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, interpersonal problems, and social function in patients with MDD. Our study suggested that the IRC can be used in clinical practice,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Chuchen Xu, Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China. It was published online on November 20, 2024, in The Journal of Psychiatric Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The 8-week follow-up period was considered too short to comprehensively evaluate the intervention’s long-term impact. Additionally, the researchers had to check and supervise assignment completion, which increased research costs and may, therefore, potentially limit broader implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
InterRhythmic care (IRC), a novel digital intervention, was linked to greater improvements in depressive symptoms, anxiety, interpersonal relationships, and social functioning in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), compared with internet general psychoeducation in new research.
METHODOLOGY:
- The randomized, single-blind trial included 120 outpatients from the Shanghai Mental Health Center between March and November 2021 with MDD (mean age, 28.2 years; 99% Han Chinese; 83% women) who were randomly assigned to receive either IRC or internet general psychoeducation (control group).
- IRC included computer-based psychoeducation on stabilizing social rhythm regularity and resolution of interpersonal problems plus brief online interactions with clinicians. Patients received 10 minutes of IRC daily, Monday through Friday, for 8 weeks.
- The researchers assessed participants’ depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, interpersonal relationships, social function, and biological rhythms using the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Scale, Interpersonal Comprehensive Diagnostic Scale, Sheehan Disability Scale, and Morning and Evening Questionnaire at baseline and at 8 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The participants who received IRC had significantly lower Hamilton Depression Rating total scores than those who received internet general psychoeducation (P < .001).
- The IRC group demonstrated improved anxiety symptoms, as evidenced by lower Hamilton Anxiety Scale total scores, than those observed for the control group (P < .001).
- The IRC group also showed improved outcomes in interpersonal relationships, as indicated by lower Interpersonal Comprehensive Diagnostic Scale total scores (P < .001).
- Social functioning improved significantly in the IRC group, as measured by the Sheehan Disability Scale subscores for work/school (P = .03), social life (P < .001), and family life (P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study demonstrated that IRC can improve clinical symptoms such as depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, interpersonal problems, and social function in patients with MDD. Our study suggested that the IRC can be used in clinical practice,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Chuchen Xu, Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China. It was published online on November 20, 2024, in The Journal of Psychiatric Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The 8-week follow-up period was considered too short to comprehensively evaluate the intervention’s long-term impact. Additionally, the researchers had to check and supervise assignment completion, which increased research costs and may, therefore, potentially limit broader implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychologists and Psychotropic Prescribing: An Old Debate Heats Up
Earlier in 2024, Utah became the seventh state to allow psychologists with the proper training to prescribe psychotropic medications, giving supporters reason to hope that more states might support expanding this scope of practice.
However, the American Psychiatric Association — and some psychologists — oppose granting psychologists this privilege, arguing that the training offered is insufficient and could jeopardize patient safety.
The controversy over whether psychologists should be allowed to prescribe is as old as the so-called RxP movement itself, which began in the early 1990s.
Psychologists have not rushed to become licensed prescribers. After three decades, an estimated 226 psychologists — representing just 0.14% of all those licensed in the United States — have been authorized to prescribe in the six states and one territory where it has been legalized, according to a just-published study in Clinical Psychology.
These are Colorado, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Louisiana, New Mexico, and Guam. Data from the study show that only 73 psychologists are prescribing in New Mexico, which authorized it in 2002.
Less is known about the number of psychologists who are prescribing under allowances in the Department of Defense, Indian Health Service and US Public Health Service.
Some psychologists — and the American Psychological Association (APA) — believe that the persistence of the opioid epidemic coupled with a continued lack of access to mental health care for millions of Americans will bring more legislators on-side.
“I feel like we’re on an upswing again,” Deborah Baker, director of legal and regulatory policy for the APA, told Medscape Medical News. “The access issue continues to be a perennial kind of driver.” She noted that at least six states pursued expanding privileges this year.
Robert L. Trestman, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing, said he doesn’t see new momentum. The interest in having psychologists prescribe “continues to trickle based on just the frustration that people have about not getting adequate access to psychiatry,” he told Medscape Medical News.
While states may be trying to increase access to care, granting psychologists privileges is “not a very effective way of doing it,” said Trestman, Chair of Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine at Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine in Roanoke. Psychologists are needed to deliver psychotherapy, he said. “It makes almost no sense to try to make them into pseudo medical professionals,” said Trestman. “It just exposes people to risks.”
William Robiner, PhD — author of Clinical Psychology study — is a long-time opponent of RxP. The psychologist told Medscape Medical News he’s concerned about patient safety and “about some of the disingenuous reasons” that psychologists want to prescribe. Among these are the ability to increase status and income, said Robiner, a professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, and a board member of Psychologists Opposed to Prescription Privileges for Psychologists.
Adequate Training?
Only PhD and PsyD psychologists are eligible for RxP training, which entails a master’s in clinical psychopharmacology. After receiving the master’s, they must pass the Psychopharmacology Examination for Psychologists and then are only permitted to prescribe medications for mental health disorders.
They must also obtain a Drug Enforcement Administration license but can’t write prescriptions for schedule 2 medications. In some states, psychologists can prescribe buprenorphine and other opioid use disorder medications.
The APA has developed guidance for master’s programs, which currently number just over a handful in the United States.
At Fairleigh Dickinson University in New Jersey, students enrolled in the master’s program — a distance-learning format — complete 10 courses over five 15-week semesters. The curriculum spans a range of topics, from foundational sciences and legal and ethical considerations to strategies for treating specific disorders.
Derek Phillips, PhD, the program’s executive director, said that when he took the position in 2020, enrollment was capped at 45 students, but “we were not routinely enrolling the maximum.” Now, even with class size increased to 60 “we are consistently full and have a waitlist,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Interest is being driven in part by new laws in Colorado (2023) and Utah, said Phillips. But many are enrolling without intending to write a prescription, he said. The degree gives graduates the ability to better collaborate with other clinicians, teach clinical psychopharmacology, and be expert witnesses in medico-legal cases, he said.
In addition, the training gives students “a balanced and thorough biopsychosocial understanding of our patients,” he said. Students also see the “potential of being able to be a ‘one-stop-stop’ of mental health services,” said Phillips.
The American Board of Professional Psychology is developing a board certification in clinical psychopharmacology.
The APA states on its website that prescribing psychologists have “more training in diagnosing and treating (including prescribing) mental health disorders than primary care physicians.”
However, critics argue that the training falls short. Most psychologists, said Robiner, have not completed the undergraduate prerequisites — such as anatomy, physiology, and chemistry — that are required for other prescribing professionals.
In a 2019 article comparing the training of prescribing professionals, Robiner and colleagues reported that psychiatrists undergo 4- to 6-week rotations during medical school and accumulate 8000 clinical hours focused on psychiatric conditions over the course of their 4-year residencies.
States set requirements for clinical hours for prescribing psychologists, but they are generally elective and completed after individuals receive a master’s degree.
Robiner said psychologists aren’t trained in evaluating drug-related adverse events. “If you show a psychologist a rash, they have no idea whether that rash might be a medication adverse effect or poison ivy,” he said.
Trestman pointed out that many psychotropic medications have black box warnings. “The risk of toxicity is by no means trivial, and the majority of people who are seeking care in psychiatry have multiple comorbidities,” he said. “Giving people the equivalent of more or less 10 weeks of training is just woefully inappropriate,” Trestman said.
Increase in Access?
Psychology’s main argument for expanding its scope of practice is that it will increase the number of clinicians available to provide behavioral and mental health care.
Critics said that is a failed experiment, in part because so few psychologists have become prescribers, but also because most psychologists practice in the same areas as psychiatrists. Both specialists tend to cluster in urban regions, which already have high clinician density, said Trestman.
Psychologists are not practicing in underserved rural areas, as even APA data show. A 2018 APA snapshot of the workforce found that the highest density of psychologists was in Washington, DC, Massachusetts, and New York. South Carolina, West Virginia and Mississippi had the fewest number of psychologists per 100,000 people.
The University of Washington Rural Health Research Center reported in 2022 that in 2021, almost half of rural counties did not have a psychologist compared with 15.7% of urban counties.
Psychiatrists also are concentrated on the coasts and New England, according to a study by Ohio State researchers. The highest densities were in Washington, DC (79 per 100,000), Massachusetts (45.3), Rhode Island (42.6), Connecticut (38.6) and Vermont (37.7), whereas the lowest densities were in Idaho (11.8), Mississippi (11.8), Wyoming (12.4), Alabama (13.1), and Indiana (13.5). The study estimated that there were 57,163 psychiatrists responsible for the care of 333,287,557 Americans. “Clinical psychologists, psychotherapists, and counselors can provide alternative forms of intervention, though access to such services is also poor in rural areas,” wrote the authors.
The APA counters with data it says shows that RxP may have increased access. Using the number of psychology practices as a proxy for supply, the authors reported that practices grew in New Mexico, Illinois, Iowa, and Idaho — states that have implemented prescription privileges. Overall, there was an increase of 0.8047 practices per 100,000 residents per county.
However, the access argument “is seriously challenged by the reality of the limited number of psychologists who complete the pathway to prescribing,” Robiner and his colleague Tanya Tompkins countered in Clinical Psychology. They note that in Idaho — a state with shortages of psychologists and psychiatrists — just 10 of the state’s 615 psychologists had prescriptive authority. An estimated 5131 nonpsychologists are prescribers.
Robiner and Tompkins noted that it’s not clear why so few psychologists are pursuing RxP but that many seem to be unaware of the possibility.
Do Benefits Outweigh the Harms?
There is not a large body of literature assessing the harms or benefits of prescribing privileges for psychologists.
Baker shared several studies by Phillip Hughes, PhD, an outcomes researcher at the University of North Carolina Eshelman School of Pharmacy, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. In one study, Hughes found that patients of prescribing psychologists had a 24% lower rate of adverse drug events than patients of psychiatrists. Psychologists’ patients had lower rates of psychotropic polypharmacy but similar rates of emergency room use.
In another paper Hughes suggested that deaths attributable to mental illness had declined in New Mexico after it passed its law. There was no change in Louisiana.
With little evidence of harm — and ongoing provider shortages — making use of nonphysician prescribers is gaining traction with policymakers, claims the psychology association’s Baker, adding that in Utah, the Republican governor was the biggest supporter.
But psychiatrists argue that it’s more important to increase their numbers. Congress agreed in 2021 and 2023 to add 1200 new residency slots — in every specialty — to ease physician shortages. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services recently announced that 70% of the new slots for July 2025 will go to primary care and psychiatry.
“Once those positions are in place, it will be four more years before the first crop of new psychiatrists come out,” noted Trestman. “None of these fixes are quick,” he said.
Baker, Robiner, and Trestman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier in 2024, Utah became the seventh state to allow psychologists with the proper training to prescribe psychotropic medications, giving supporters reason to hope that more states might support expanding this scope of practice.
However, the American Psychiatric Association — and some psychologists — oppose granting psychologists this privilege, arguing that the training offered is insufficient and could jeopardize patient safety.
The controversy over whether psychologists should be allowed to prescribe is as old as the so-called RxP movement itself, which began in the early 1990s.
Psychologists have not rushed to become licensed prescribers. After three decades, an estimated 226 psychologists — representing just 0.14% of all those licensed in the United States — have been authorized to prescribe in the six states and one territory where it has been legalized, according to a just-published study in Clinical Psychology.
These are Colorado, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Louisiana, New Mexico, and Guam. Data from the study show that only 73 psychologists are prescribing in New Mexico, which authorized it in 2002.
Less is known about the number of psychologists who are prescribing under allowances in the Department of Defense, Indian Health Service and US Public Health Service.
Some psychologists — and the American Psychological Association (APA) — believe that the persistence of the opioid epidemic coupled with a continued lack of access to mental health care for millions of Americans will bring more legislators on-side.
“I feel like we’re on an upswing again,” Deborah Baker, director of legal and regulatory policy for the APA, told Medscape Medical News. “The access issue continues to be a perennial kind of driver.” She noted that at least six states pursued expanding privileges this year.
Robert L. Trestman, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing, said he doesn’t see new momentum. The interest in having psychologists prescribe “continues to trickle based on just the frustration that people have about not getting adequate access to psychiatry,” he told Medscape Medical News.
While states may be trying to increase access to care, granting psychologists privileges is “not a very effective way of doing it,” said Trestman, Chair of Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine at Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine in Roanoke. Psychologists are needed to deliver psychotherapy, he said. “It makes almost no sense to try to make them into pseudo medical professionals,” said Trestman. “It just exposes people to risks.”
William Robiner, PhD — author of Clinical Psychology study — is a long-time opponent of RxP. The psychologist told Medscape Medical News he’s concerned about patient safety and “about some of the disingenuous reasons” that psychologists want to prescribe. Among these are the ability to increase status and income, said Robiner, a professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, and a board member of Psychologists Opposed to Prescription Privileges for Psychologists.
Adequate Training?
Only PhD and PsyD psychologists are eligible for RxP training, which entails a master’s in clinical psychopharmacology. After receiving the master’s, they must pass the Psychopharmacology Examination for Psychologists and then are only permitted to prescribe medications for mental health disorders.
They must also obtain a Drug Enforcement Administration license but can’t write prescriptions for schedule 2 medications. In some states, psychologists can prescribe buprenorphine and other opioid use disorder medications.
The APA has developed guidance for master’s programs, which currently number just over a handful in the United States.
At Fairleigh Dickinson University in New Jersey, students enrolled in the master’s program — a distance-learning format — complete 10 courses over five 15-week semesters. The curriculum spans a range of topics, from foundational sciences and legal and ethical considerations to strategies for treating specific disorders.
Derek Phillips, PhD, the program’s executive director, said that when he took the position in 2020, enrollment was capped at 45 students, but “we were not routinely enrolling the maximum.” Now, even with class size increased to 60 “we are consistently full and have a waitlist,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Interest is being driven in part by new laws in Colorado (2023) and Utah, said Phillips. But many are enrolling without intending to write a prescription, he said. The degree gives graduates the ability to better collaborate with other clinicians, teach clinical psychopharmacology, and be expert witnesses in medico-legal cases, he said.
In addition, the training gives students “a balanced and thorough biopsychosocial understanding of our patients,” he said. Students also see the “potential of being able to be a ‘one-stop-stop’ of mental health services,” said Phillips.
The American Board of Professional Psychology is developing a board certification in clinical psychopharmacology.
The APA states on its website that prescribing psychologists have “more training in diagnosing and treating (including prescribing) mental health disorders than primary care physicians.”
However, critics argue that the training falls short. Most psychologists, said Robiner, have not completed the undergraduate prerequisites — such as anatomy, physiology, and chemistry — that are required for other prescribing professionals.
In a 2019 article comparing the training of prescribing professionals, Robiner and colleagues reported that psychiatrists undergo 4- to 6-week rotations during medical school and accumulate 8000 clinical hours focused on psychiatric conditions over the course of their 4-year residencies.
States set requirements for clinical hours for prescribing psychologists, but they are generally elective and completed after individuals receive a master’s degree.
Robiner said psychologists aren’t trained in evaluating drug-related adverse events. “If you show a psychologist a rash, they have no idea whether that rash might be a medication adverse effect or poison ivy,” he said.
Trestman pointed out that many psychotropic medications have black box warnings. “The risk of toxicity is by no means trivial, and the majority of people who are seeking care in psychiatry have multiple comorbidities,” he said. “Giving people the equivalent of more or less 10 weeks of training is just woefully inappropriate,” Trestman said.
Increase in Access?
Psychology’s main argument for expanding its scope of practice is that it will increase the number of clinicians available to provide behavioral and mental health care.
Critics said that is a failed experiment, in part because so few psychologists have become prescribers, but also because most psychologists practice in the same areas as psychiatrists. Both specialists tend to cluster in urban regions, which already have high clinician density, said Trestman.
Psychologists are not practicing in underserved rural areas, as even APA data show. A 2018 APA snapshot of the workforce found that the highest density of psychologists was in Washington, DC, Massachusetts, and New York. South Carolina, West Virginia and Mississippi had the fewest number of psychologists per 100,000 people.
The University of Washington Rural Health Research Center reported in 2022 that in 2021, almost half of rural counties did not have a psychologist compared with 15.7% of urban counties.
Psychiatrists also are concentrated on the coasts and New England, according to a study by Ohio State researchers. The highest densities were in Washington, DC (79 per 100,000), Massachusetts (45.3), Rhode Island (42.6), Connecticut (38.6) and Vermont (37.7), whereas the lowest densities were in Idaho (11.8), Mississippi (11.8), Wyoming (12.4), Alabama (13.1), and Indiana (13.5). The study estimated that there were 57,163 psychiatrists responsible for the care of 333,287,557 Americans. “Clinical psychologists, psychotherapists, and counselors can provide alternative forms of intervention, though access to such services is also poor in rural areas,” wrote the authors.
The APA counters with data it says shows that RxP may have increased access. Using the number of psychology practices as a proxy for supply, the authors reported that practices grew in New Mexico, Illinois, Iowa, and Idaho — states that have implemented prescription privileges. Overall, there was an increase of 0.8047 practices per 100,000 residents per county.
However, the access argument “is seriously challenged by the reality of the limited number of psychologists who complete the pathway to prescribing,” Robiner and his colleague Tanya Tompkins countered in Clinical Psychology. They note that in Idaho — a state with shortages of psychologists and psychiatrists — just 10 of the state’s 615 psychologists had prescriptive authority. An estimated 5131 nonpsychologists are prescribers.
Robiner and Tompkins noted that it’s not clear why so few psychologists are pursuing RxP but that many seem to be unaware of the possibility.
Do Benefits Outweigh the Harms?
There is not a large body of literature assessing the harms or benefits of prescribing privileges for psychologists.
Baker shared several studies by Phillip Hughes, PhD, an outcomes researcher at the University of North Carolina Eshelman School of Pharmacy, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. In one study, Hughes found that patients of prescribing psychologists had a 24% lower rate of adverse drug events than patients of psychiatrists. Psychologists’ patients had lower rates of psychotropic polypharmacy but similar rates of emergency room use.
In another paper Hughes suggested that deaths attributable to mental illness had declined in New Mexico after it passed its law. There was no change in Louisiana.
With little evidence of harm — and ongoing provider shortages — making use of nonphysician prescribers is gaining traction with policymakers, claims the psychology association’s Baker, adding that in Utah, the Republican governor was the biggest supporter.
But psychiatrists argue that it’s more important to increase their numbers. Congress agreed in 2021 and 2023 to add 1200 new residency slots — in every specialty — to ease physician shortages. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services recently announced that 70% of the new slots for July 2025 will go to primary care and psychiatry.
“Once those positions are in place, it will be four more years before the first crop of new psychiatrists come out,” noted Trestman. “None of these fixes are quick,” he said.
Baker, Robiner, and Trestman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier in 2024, Utah became the seventh state to allow psychologists with the proper training to prescribe psychotropic medications, giving supporters reason to hope that more states might support expanding this scope of practice.
However, the American Psychiatric Association — and some psychologists — oppose granting psychologists this privilege, arguing that the training offered is insufficient and could jeopardize patient safety.
The controversy over whether psychologists should be allowed to prescribe is as old as the so-called RxP movement itself, which began in the early 1990s.
Psychologists have not rushed to become licensed prescribers. After three decades, an estimated 226 psychologists — representing just 0.14% of all those licensed in the United States — have been authorized to prescribe in the six states and one territory where it has been legalized, according to a just-published study in Clinical Psychology.
These are Colorado, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Louisiana, New Mexico, and Guam. Data from the study show that only 73 psychologists are prescribing in New Mexico, which authorized it in 2002.
Less is known about the number of psychologists who are prescribing under allowances in the Department of Defense, Indian Health Service and US Public Health Service.
Some psychologists — and the American Psychological Association (APA) — believe that the persistence of the opioid epidemic coupled with a continued lack of access to mental health care for millions of Americans will bring more legislators on-side.
“I feel like we’re on an upswing again,” Deborah Baker, director of legal and regulatory policy for the APA, told Medscape Medical News. “The access issue continues to be a perennial kind of driver.” She noted that at least six states pursued expanding privileges this year.
Robert L. Trestman, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing, said he doesn’t see new momentum. The interest in having psychologists prescribe “continues to trickle based on just the frustration that people have about not getting adequate access to psychiatry,” he told Medscape Medical News.
While states may be trying to increase access to care, granting psychologists privileges is “not a very effective way of doing it,” said Trestman, Chair of Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine at Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine in Roanoke. Psychologists are needed to deliver psychotherapy, he said. “It makes almost no sense to try to make them into pseudo medical professionals,” said Trestman. “It just exposes people to risks.”
William Robiner, PhD — author of Clinical Psychology study — is a long-time opponent of RxP. The psychologist told Medscape Medical News he’s concerned about patient safety and “about some of the disingenuous reasons” that psychologists want to prescribe. Among these are the ability to increase status and income, said Robiner, a professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, and a board member of Psychologists Opposed to Prescription Privileges for Psychologists.
Adequate Training?
Only PhD and PsyD psychologists are eligible for RxP training, which entails a master’s in clinical psychopharmacology. After receiving the master’s, they must pass the Psychopharmacology Examination for Psychologists and then are only permitted to prescribe medications for mental health disorders.
They must also obtain a Drug Enforcement Administration license but can’t write prescriptions for schedule 2 medications. In some states, psychologists can prescribe buprenorphine and other opioid use disorder medications.
The APA has developed guidance for master’s programs, which currently number just over a handful in the United States.
At Fairleigh Dickinson University in New Jersey, students enrolled in the master’s program — a distance-learning format — complete 10 courses over five 15-week semesters. The curriculum spans a range of topics, from foundational sciences and legal and ethical considerations to strategies for treating specific disorders.
Derek Phillips, PhD, the program’s executive director, said that when he took the position in 2020, enrollment was capped at 45 students, but “we were not routinely enrolling the maximum.” Now, even with class size increased to 60 “we are consistently full and have a waitlist,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Interest is being driven in part by new laws in Colorado (2023) and Utah, said Phillips. But many are enrolling without intending to write a prescription, he said. The degree gives graduates the ability to better collaborate with other clinicians, teach clinical psychopharmacology, and be expert witnesses in medico-legal cases, he said.
In addition, the training gives students “a balanced and thorough biopsychosocial understanding of our patients,” he said. Students also see the “potential of being able to be a ‘one-stop-stop’ of mental health services,” said Phillips.
The American Board of Professional Psychology is developing a board certification in clinical psychopharmacology.
The APA states on its website that prescribing psychologists have “more training in diagnosing and treating (including prescribing) mental health disorders than primary care physicians.”
However, critics argue that the training falls short. Most psychologists, said Robiner, have not completed the undergraduate prerequisites — such as anatomy, physiology, and chemistry — that are required for other prescribing professionals.
In a 2019 article comparing the training of prescribing professionals, Robiner and colleagues reported that psychiatrists undergo 4- to 6-week rotations during medical school and accumulate 8000 clinical hours focused on psychiatric conditions over the course of their 4-year residencies.
States set requirements for clinical hours for prescribing psychologists, but they are generally elective and completed after individuals receive a master’s degree.
Robiner said psychologists aren’t trained in evaluating drug-related adverse events. “If you show a psychologist a rash, they have no idea whether that rash might be a medication adverse effect or poison ivy,” he said.
Trestman pointed out that many psychotropic medications have black box warnings. “The risk of toxicity is by no means trivial, and the majority of people who are seeking care in psychiatry have multiple comorbidities,” he said. “Giving people the equivalent of more or less 10 weeks of training is just woefully inappropriate,” Trestman said.
Increase in Access?
Psychology’s main argument for expanding its scope of practice is that it will increase the number of clinicians available to provide behavioral and mental health care.
Critics said that is a failed experiment, in part because so few psychologists have become prescribers, but also because most psychologists practice in the same areas as psychiatrists. Both specialists tend to cluster in urban regions, which already have high clinician density, said Trestman.
Psychologists are not practicing in underserved rural areas, as even APA data show. A 2018 APA snapshot of the workforce found that the highest density of psychologists was in Washington, DC, Massachusetts, and New York. South Carolina, West Virginia and Mississippi had the fewest number of psychologists per 100,000 people.
The University of Washington Rural Health Research Center reported in 2022 that in 2021, almost half of rural counties did not have a psychologist compared with 15.7% of urban counties.
Psychiatrists also are concentrated on the coasts and New England, according to a study by Ohio State researchers. The highest densities were in Washington, DC (79 per 100,000), Massachusetts (45.3), Rhode Island (42.6), Connecticut (38.6) and Vermont (37.7), whereas the lowest densities were in Idaho (11.8), Mississippi (11.8), Wyoming (12.4), Alabama (13.1), and Indiana (13.5). The study estimated that there were 57,163 psychiatrists responsible for the care of 333,287,557 Americans. “Clinical psychologists, psychotherapists, and counselors can provide alternative forms of intervention, though access to such services is also poor in rural areas,” wrote the authors.
The APA counters with data it says shows that RxP may have increased access. Using the number of psychology practices as a proxy for supply, the authors reported that practices grew in New Mexico, Illinois, Iowa, and Idaho — states that have implemented prescription privileges. Overall, there was an increase of 0.8047 practices per 100,000 residents per county.
However, the access argument “is seriously challenged by the reality of the limited number of psychologists who complete the pathway to prescribing,” Robiner and his colleague Tanya Tompkins countered in Clinical Psychology. They note that in Idaho — a state with shortages of psychologists and psychiatrists — just 10 of the state’s 615 psychologists had prescriptive authority. An estimated 5131 nonpsychologists are prescribers.
Robiner and Tompkins noted that it’s not clear why so few psychologists are pursuing RxP but that many seem to be unaware of the possibility.
Do Benefits Outweigh the Harms?
There is not a large body of literature assessing the harms or benefits of prescribing privileges for psychologists.
Baker shared several studies by Phillip Hughes, PhD, an outcomes researcher at the University of North Carolina Eshelman School of Pharmacy, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. In one study, Hughes found that patients of prescribing psychologists had a 24% lower rate of adverse drug events than patients of psychiatrists. Psychologists’ patients had lower rates of psychotropic polypharmacy but similar rates of emergency room use.
In another paper Hughes suggested that deaths attributable to mental illness had declined in New Mexico after it passed its law. There was no change in Louisiana.
With little evidence of harm — and ongoing provider shortages — making use of nonphysician prescribers is gaining traction with policymakers, claims the psychology association’s Baker, adding that in Utah, the Republican governor was the biggest supporter.
But psychiatrists argue that it’s more important to increase their numbers. Congress agreed in 2021 and 2023 to add 1200 new residency slots — in every specialty — to ease physician shortages. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services recently announced that 70% of the new slots for July 2025 will go to primary care and psychiatry.
“Once those positions are in place, it will be four more years before the first crop of new psychiatrists come out,” noted Trestman. “None of these fixes are quick,” he said.
Baker, Robiner, and Trestman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
