User login
Antibiotic and glucocorticoid use before cancer therapy could have detrimental effect on outcomes
“Our results confirm the detrimental impact on oncological outcomes of antibiotics and glucocorticoids at a dosage ≥10 mg/day when given within 1 month before or after ICI onset,” Marie Kostine, MD, of Bordeaux (France) University Hospital, and colleagues wrote in the European Journal of Cancer. “Moreover, we show that other comedications may significantly alter the antitumoral response of ICI, such as proton pump inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, morphine, aspirin, and insulin, whereas others seem to have no impact.”
While immune checkpoint inhibitors are transforming the treatment of advanced cancers, gut microbiota composition is an important determinant of response to ICIs. Antibiotic treatments are known to alter the gut microbiota. Other drugs, such as proton pump inhibitors, antidiabetic agents, aspirin, NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, immunomodulators, psychotropic drugs, and analgesics, have been associated with changes in microbiome composition. Since many patients with advanced cancer are exposed to such drugs, this study looked at the possible influence of these comedications on the antitumor effect and safety of ICIs.
The observational study included 635 patients with advanced cancer treated with ICIs between May 2015 and September 2017. Comedications given within 1 month before or 1 month after the first administration of an ICI were reviewed from medical records. Psychotropic drugs, proton pump inhibitors, ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), glucocorticoids, antibiotics, statins, and morphine were the most prescribed comedications.
Baseline use of antibiotics, glucocorticoids greater than 10 mg/day, proton pump inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, morphine, and insulin was associated with decreased overall survival and tumor response. However, the coadministration of statins, ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs, NSAIDs, aspirin, and oral diabetes drugs did not impact patient outcomes. Additionally, treatments that altered the response to ICIs were associated with a decreased incidence of immune-related adverse events.
“These results suggest some practical advice in a patient candidate to ICIs,” the authors wrote. “First, antibiotic treatment should be limited to documented infections,” and “withdrawal of proton pump inhibitors and psychotropic drugs should be considered.
“Regarding baseline glucocorticoids use, the cutoff of 10 mg/day should be respected, considering the deleterious effect of higher dosage. Moreover, because of the lack of impact of inhaled or topical glucocorticoids, local routes should be preferred,” the authors wrote. “Conversely, our study brings reassuring data regarding the use of glucocorticoids for the management of immune-related adverse events, which did not alter ICI efficacy, confirming previous reports.”
The authors noted that the observational nature of the study does not allow any causal conclusion, adding that it remains unknown whether the effect of comedications “on cancer outcomes is thoroughly mediated by changes in microbiota or other immunomodulatory properties.”
Along with the retrospective design, study limitations included reporting bias and missing data on baseline comedications, specific prognostic factors and cancer outcomes.
The authors noted no conflicts of interest.
“Our results confirm the detrimental impact on oncological outcomes of antibiotics and glucocorticoids at a dosage ≥10 mg/day when given within 1 month before or after ICI onset,” Marie Kostine, MD, of Bordeaux (France) University Hospital, and colleagues wrote in the European Journal of Cancer. “Moreover, we show that other comedications may significantly alter the antitumoral response of ICI, such as proton pump inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, morphine, aspirin, and insulin, whereas others seem to have no impact.”
While immune checkpoint inhibitors are transforming the treatment of advanced cancers, gut microbiota composition is an important determinant of response to ICIs. Antibiotic treatments are known to alter the gut microbiota. Other drugs, such as proton pump inhibitors, antidiabetic agents, aspirin, NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, immunomodulators, psychotropic drugs, and analgesics, have been associated with changes in microbiome composition. Since many patients with advanced cancer are exposed to such drugs, this study looked at the possible influence of these comedications on the antitumor effect and safety of ICIs.
The observational study included 635 patients with advanced cancer treated with ICIs between May 2015 and September 2017. Comedications given within 1 month before or 1 month after the first administration of an ICI were reviewed from medical records. Psychotropic drugs, proton pump inhibitors, ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), glucocorticoids, antibiotics, statins, and morphine were the most prescribed comedications.
Baseline use of antibiotics, glucocorticoids greater than 10 mg/day, proton pump inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, morphine, and insulin was associated with decreased overall survival and tumor response. However, the coadministration of statins, ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs, NSAIDs, aspirin, and oral diabetes drugs did not impact patient outcomes. Additionally, treatments that altered the response to ICIs were associated with a decreased incidence of immune-related adverse events.
“These results suggest some practical advice in a patient candidate to ICIs,” the authors wrote. “First, antibiotic treatment should be limited to documented infections,” and “withdrawal of proton pump inhibitors and psychotropic drugs should be considered.
“Regarding baseline glucocorticoids use, the cutoff of 10 mg/day should be respected, considering the deleterious effect of higher dosage. Moreover, because of the lack of impact of inhaled or topical glucocorticoids, local routes should be preferred,” the authors wrote. “Conversely, our study brings reassuring data regarding the use of glucocorticoids for the management of immune-related adverse events, which did not alter ICI efficacy, confirming previous reports.”
The authors noted that the observational nature of the study does not allow any causal conclusion, adding that it remains unknown whether the effect of comedications “on cancer outcomes is thoroughly mediated by changes in microbiota or other immunomodulatory properties.”
Along with the retrospective design, study limitations included reporting bias and missing data on baseline comedications, specific prognostic factors and cancer outcomes.
The authors noted no conflicts of interest.
“Our results confirm the detrimental impact on oncological outcomes of antibiotics and glucocorticoids at a dosage ≥10 mg/day when given within 1 month before or after ICI onset,” Marie Kostine, MD, of Bordeaux (France) University Hospital, and colleagues wrote in the European Journal of Cancer. “Moreover, we show that other comedications may significantly alter the antitumoral response of ICI, such as proton pump inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, morphine, aspirin, and insulin, whereas others seem to have no impact.”
While immune checkpoint inhibitors are transforming the treatment of advanced cancers, gut microbiota composition is an important determinant of response to ICIs. Antibiotic treatments are known to alter the gut microbiota. Other drugs, such as proton pump inhibitors, antidiabetic agents, aspirin, NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, immunomodulators, psychotropic drugs, and analgesics, have been associated with changes in microbiome composition. Since many patients with advanced cancer are exposed to such drugs, this study looked at the possible influence of these comedications on the antitumor effect and safety of ICIs.
The observational study included 635 patients with advanced cancer treated with ICIs between May 2015 and September 2017. Comedications given within 1 month before or 1 month after the first administration of an ICI were reviewed from medical records. Psychotropic drugs, proton pump inhibitors, ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), glucocorticoids, antibiotics, statins, and morphine were the most prescribed comedications.
Baseline use of antibiotics, glucocorticoids greater than 10 mg/day, proton pump inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, morphine, and insulin was associated with decreased overall survival and tumor response. However, the coadministration of statins, ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs, NSAIDs, aspirin, and oral diabetes drugs did not impact patient outcomes. Additionally, treatments that altered the response to ICIs were associated with a decreased incidence of immune-related adverse events.
“These results suggest some practical advice in a patient candidate to ICIs,” the authors wrote. “First, antibiotic treatment should be limited to documented infections,” and “withdrawal of proton pump inhibitors and psychotropic drugs should be considered.
“Regarding baseline glucocorticoids use, the cutoff of 10 mg/day should be respected, considering the deleterious effect of higher dosage. Moreover, because of the lack of impact of inhaled or topical glucocorticoids, local routes should be preferred,” the authors wrote. “Conversely, our study brings reassuring data regarding the use of glucocorticoids for the management of immune-related adverse events, which did not alter ICI efficacy, confirming previous reports.”
The authors noted that the observational nature of the study does not allow any causal conclusion, adding that it remains unknown whether the effect of comedications “on cancer outcomes is thoroughly mediated by changes in microbiota or other immunomodulatory properties.”
Along with the retrospective design, study limitations included reporting bias and missing data on baseline comedications, specific prognostic factors and cancer outcomes.
The authors noted no conflicts of interest.
FROM THE EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF CANCER
ANCHOR study findings may usher in new care standards for anal cancer in HIV-infected patients
Can treatment or removal of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) reduce the likelihood of developing anal cancer in people living with HIV (PLHIV)?
“In theory, looking for and treating high-grade disease (like we know works in the cervix) is a potential way to prevent anal cancer in high-risk individuals,” Joel Palefsky, MD, lead investigator of the Anal Cancer/HSIL Outcomes Research (ANCHOR) study and founder/director of the University of California, San Francisco’s Anal Neoplasia Clinic, told this news organization. “But we’ve never had any direct evidence that it worked,” he said.
Initial findings from ANCHOR – the first randomized trial to demonstrate that anal cancer can be prevented in high-risk, HIV-infected patients – promise to change that paradigm and may even portend a new standard of care.
Undoubtedly, this is welcome news for the HIV community, who are not only at increased risk for anal HSIL overall, but among whom anal cancer cases have been rising over the past decade. This is especially true for women who are expected to bear a large portion of overall burden of human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated anal squamous cell carcinoma over the next 10 to 20 years.
In the study, 4,446 PLHIV ages 35 and older with precursor anal HSIL were randomly assigned to topical (imiquimod intra-anally, perianally, or both, or fluorouracil) or ablative (infrared coagulation, hyfrecation/electrocautery) treatment, or active surveillance, and followed every 6 months for 5 years. The study population was broadly representative, including men who have sex with men (MSM), women, transgender people, and historically underrepresented minorities, a factor that reinforces the study’s importance in this specific population.
Because the primary endpoint was reached (that is, to determine if HSIL treatment and removal effectively reduces anal cancer incidence in HIV-infected men and women), the Data Safety Board halted accrual and recommended that participants in the surveillance group be offered treatment moving forward. While the investigators are currently working on publication of the results, the study is ongoing.
Still, the ANCHOR study, which is one of the largest malignancy screening studies conducted in PLHIV, has also highlighted significant challenges in how anal cancer is approached in general.
“Anal cancer has many similarities to cervical cancer, where screening for precancerous lesions and treatment have been shown to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality,” said Joseph Sparano, MD, a medical oncologist specializing in HIV and breast cancer at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Sparano is chair and principal investigator of the AIDS Malignancy Consortium but was not involved in the ANCHOR study.
But, he explained in an interview, “it’s much more difficult and technically challenging to screen for and evaluate the anal canal histology,” noting that
Availability and access to high-resolution anoscopy is limited, said Robert Yarchoan, MD, chief of the HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch at the National Cancer Institute’s Clinical Cancer Research Division and director of the Office of HIV and AIDS Malignancy (which, incidentally, cosponsored ANCHOR).
“There are relatively few people that do this at this time,” he added in an interview, pointing out that among those who do, most are obstetricians/gynecologists.
A bit of digging into ANCHOR’s backstory revealed that this was a point of contention at the study’s onset. While physicians participating in the study received extensive training in high-resolution anoscopy, ob/gyns were the fastest to achieve competency and/or had the most prior experience, namely because of their experience in cervical cancer screening in women.
But initial objections by the American Board of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (which at the time, insisted that its members only treat women and threatened to remove their certification if they participated in the research), almost threw a wrench into the study’s start, according to a report in The New York Times. While rational minds prevailed and the board reversed its earlier statements, lack of ample training in the procedure may signal future barriers to treatment.
Another challenge lies in how study findings might be applicable to other groups outside of the HIV/AIDS population, such as people with other forms of immunosuppression who have HSIL, or even healthy women or men who are at risk as a result of penetrative/nonpenetrative sexual or nonsexual (for example, vaginal discharge to the anus) contact.
Although he was unable to share specifics at this time, Dr. Palefsky said that when they designed the ANCHOR study, they were aware that “merely showing efficacy wouldn’t necessarily be sufficient for establishing a standard of care, where[as] other pieces of information undoubtedly would be considered by entities that make guidelines” (for example, an examination of adverse events, risks/benefits, and factors that influence quality of life).
“With that in mind, we are doing a quality-of-life study and, in fact, have [collaborated on], developed, and validated what I think is the first anal disease-specific, quality of life instrument,” Dr. Palefsky said. “The work is still ongoing because we did not complete enrollment in the study, but we are continuing it as part of the follow up.”
Study investigators have also collected samples for a biorepository of specimens that will hopefully facilitate a better understanding of the molecular events driving progression from precancer to cancer. “A lot of people with HIV have these high-grade lesions,” Dr. Palefsky said. “If we were able to identify who’s at highest risk of all of them, that would be very important, because we prefer not to treat everybody with high-grade disease,” he noted, adding that the “underlying hope is that the biomarkers we find in the setting will also be relevant for other HPV-related cancers,” especially in women.
Dr. Yarchoan concurred. “One of the challenges is going to be to digest this information and see how to use it to potentially address the growing problem of females with HIV,” he said.
Dr. Palefsky, Dr. Sparano, and Dr. Yarchoan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can treatment or removal of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) reduce the likelihood of developing anal cancer in people living with HIV (PLHIV)?
“In theory, looking for and treating high-grade disease (like we know works in the cervix) is a potential way to prevent anal cancer in high-risk individuals,” Joel Palefsky, MD, lead investigator of the Anal Cancer/HSIL Outcomes Research (ANCHOR) study and founder/director of the University of California, San Francisco’s Anal Neoplasia Clinic, told this news organization. “But we’ve never had any direct evidence that it worked,” he said.
Initial findings from ANCHOR – the first randomized trial to demonstrate that anal cancer can be prevented in high-risk, HIV-infected patients – promise to change that paradigm and may even portend a new standard of care.
Undoubtedly, this is welcome news for the HIV community, who are not only at increased risk for anal HSIL overall, but among whom anal cancer cases have been rising over the past decade. This is especially true for women who are expected to bear a large portion of overall burden of human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated anal squamous cell carcinoma over the next 10 to 20 years.
In the study, 4,446 PLHIV ages 35 and older with precursor anal HSIL were randomly assigned to topical (imiquimod intra-anally, perianally, or both, or fluorouracil) or ablative (infrared coagulation, hyfrecation/electrocautery) treatment, or active surveillance, and followed every 6 months for 5 years. The study population was broadly representative, including men who have sex with men (MSM), women, transgender people, and historically underrepresented minorities, a factor that reinforces the study’s importance in this specific population.
Because the primary endpoint was reached (that is, to determine if HSIL treatment and removal effectively reduces anal cancer incidence in HIV-infected men and women), the Data Safety Board halted accrual and recommended that participants in the surveillance group be offered treatment moving forward. While the investigators are currently working on publication of the results, the study is ongoing.
Still, the ANCHOR study, which is one of the largest malignancy screening studies conducted in PLHIV, has also highlighted significant challenges in how anal cancer is approached in general.
“Anal cancer has many similarities to cervical cancer, where screening for precancerous lesions and treatment have been shown to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality,” said Joseph Sparano, MD, a medical oncologist specializing in HIV and breast cancer at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Sparano is chair and principal investigator of the AIDS Malignancy Consortium but was not involved in the ANCHOR study.
But, he explained in an interview, “it’s much more difficult and technically challenging to screen for and evaluate the anal canal histology,” noting that
Availability and access to high-resolution anoscopy is limited, said Robert Yarchoan, MD, chief of the HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch at the National Cancer Institute’s Clinical Cancer Research Division and director of the Office of HIV and AIDS Malignancy (which, incidentally, cosponsored ANCHOR).
“There are relatively few people that do this at this time,” he added in an interview, pointing out that among those who do, most are obstetricians/gynecologists.
A bit of digging into ANCHOR’s backstory revealed that this was a point of contention at the study’s onset. While physicians participating in the study received extensive training in high-resolution anoscopy, ob/gyns were the fastest to achieve competency and/or had the most prior experience, namely because of their experience in cervical cancer screening in women.
But initial objections by the American Board of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (which at the time, insisted that its members only treat women and threatened to remove their certification if they participated in the research), almost threw a wrench into the study’s start, according to a report in The New York Times. While rational minds prevailed and the board reversed its earlier statements, lack of ample training in the procedure may signal future barriers to treatment.
Another challenge lies in how study findings might be applicable to other groups outside of the HIV/AIDS population, such as people with other forms of immunosuppression who have HSIL, or even healthy women or men who are at risk as a result of penetrative/nonpenetrative sexual or nonsexual (for example, vaginal discharge to the anus) contact.
Although he was unable to share specifics at this time, Dr. Palefsky said that when they designed the ANCHOR study, they were aware that “merely showing efficacy wouldn’t necessarily be sufficient for establishing a standard of care, where[as] other pieces of information undoubtedly would be considered by entities that make guidelines” (for example, an examination of adverse events, risks/benefits, and factors that influence quality of life).
“With that in mind, we are doing a quality-of-life study and, in fact, have [collaborated on], developed, and validated what I think is the first anal disease-specific, quality of life instrument,” Dr. Palefsky said. “The work is still ongoing because we did not complete enrollment in the study, but we are continuing it as part of the follow up.”
Study investigators have also collected samples for a biorepository of specimens that will hopefully facilitate a better understanding of the molecular events driving progression from precancer to cancer. “A lot of people with HIV have these high-grade lesions,” Dr. Palefsky said. “If we were able to identify who’s at highest risk of all of them, that would be very important, because we prefer not to treat everybody with high-grade disease,” he noted, adding that the “underlying hope is that the biomarkers we find in the setting will also be relevant for other HPV-related cancers,” especially in women.
Dr. Yarchoan concurred. “One of the challenges is going to be to digest this information and see how to use it to potentially address the growing problem of females with HIV,” he said.
Dr. Palefsky, Dr. Sparano, and Dr. Yarchoan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can treatment or removal of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) reduce the likelihood of developing anal cancer in people living with HIV (PLHIV)?
“In theory, looking for and treating high-grade disease (like we know works in the cervix) is a potential way to prevent anal cancer in high-risk individuals,” Joel Palefsky, MD, lead investigator of the Anal Cancer/HSIL Outcomes Research (ANCHOR) study and founder/director of the University of California, San Francisco’s Anal Neoplasia Clinic, told this news organization. “But we’ve never had any direct evidence that it worked,” he said.
Initial findings from ANCHOR – the first randomized trial to demonstrate that anal cancer can be prevented in high-risk, HIV-infected patients – promise to change that paradigm and may even portend a new standard of care.
Undoubtedly, this is welcome news for the HIV community, who are not only at increased risk for anal HSIL overall, but among whom anal cancer cases have been rising over the past decade. This is especially true for women who are expected to bear a large portion of overall burden of human papillomavirus (HPV)–associated anal squamous cell carcinoma over the next 10 to 20 years.
In the study, 4,446 PLHIV ages 35 and older with precursor anal HSIL were randomly assigned to topical (imiquimod intra-anally, perianally, or both, or fluorouracil) or ablative (infrared coagulation, hyfrecation/electrocautery) treatment, or active surveillance, and followed every 6 months for 5 years. The study population was broadly representative, including men who have sex with men (MSM), women, transgender people, and historically underrepresented minorities, a factor that reinforces the study’s importance in this specific population.
Because the primary endpoint was reached (that is, to determine if HSIL treatment and removal effectively reduces anal cancer incidence in HIV-infected men and women), the Data Safety Board halted accrual and recommended that participants in the surveillance group be offered treatment moving forward. While the investigators are currently working on publication of the results, the study is ongoing.
Still, the ANCHOR study, which is one of the largest malignancy screening studies conducted in PLHIV, has also highlighted significant challenges in how anal cancer is approached in general.
“Anal cancer has many similarities to cervical cancer, where screening for precancerous lesions and treatment have been shown to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality,” said Joseph Sparano, MD, a medical oncologist specializing in HIV and breast cancer at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Sparano is chair and principal investigator of the AIDS Malignancy Consortium but was not involved in the ANCHOR study.
But, he explained in an interview, “it’s much more difficult and technically challenging to screen for and evaluate the anal canal histology,” noting that
Availability and access to high-resolution anoscopy is limited, said Robert Yarchoan, MD, chief of the HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch at the National Cancer Institute’s Clinical Cancer Research Division and director of the Office of HIV and AIDS Malignancy (which, incidentally, cosponsored ANCHOR).
“There are relatively few people that do this at this time,” he added in an interview, pointing out that among those who do, most are obstetricians/gynecologists.
A bit of digging into ANCHOR’s backstory revealed that this was a point of contention at the study’s onset. While physicians participating in the study received extensive training in high-resolution anoscopy, ob/gyns were the fastest to achieve competency and/or had the most prior experience, namely because of their experience in cervical cancer screening in women.
But initial objections by the American Board of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (which at the time, insisted that its members only treat women and threatened to remove their certification if they participated in the research), almost threw a wrench into the study’s start, according to a report in The New York Times. While rational minds prevailed and the board reversed its earlier statements, lack of ample training in the procedure may signal future barriers to treatment.
Another challenge lies in how study findings might be applicable to other groups outside of the HIV/AIDS population, such as people with other forms of immunosuppression who have HSIL, or even healthy women or men who are at risk as a result of penetrative/nonpenetrative sexual or nonsexual (for example, vaginal discharge to the anus) contact.
Although he was unable to share specifics at this time, Dr. Palefsky said that when they designed the ANCHOR study, they were aware that “merely showing efficacy wouldn’t necessarily be sufficient for establishing a standard of care, where[as] other pieces of information undoubtedly would be considered by entities that make guidelines” (for example, an examination of adverse events, risks/benefits, and factors that influence quality of life).
“With that in mind, we are doing a quality-of-life study and, in fact, have [collaborated on], developed, and validated what I think is the first anal disease-specific, quality of life instrument,” Dr. Palefsky said. “The work is still ongoing because we did not complete enrollment in the study, but we are continuing it as part of the follow up.”
Study investigators have also collected samples for a biorepository of specimens that will hopefully facilitate a better understanding of the molecular events driving progression from precancer to cancer. “A lot of people with HIV have these high-grade lesions,” Dr. Palefsky said. “If we were able to identify who’s at highest risk of all of them, that would be very important, because we prefer not to treat everybody with high-grade disease,” he noted, adding that the “underlying hope is that the biomarkers we find in the setting will also be relevant for other HPV-related cancers,” especially in women.
Dr. Yarchoan concurred. “One of the challenges is going to be to digest this information and see how to use it to potentially address the growing problem of females with HIV,” he said.
Dr. Palefsky, Dr. Sparano, and Dr. Yarchoan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rash in an immunocompromised patient
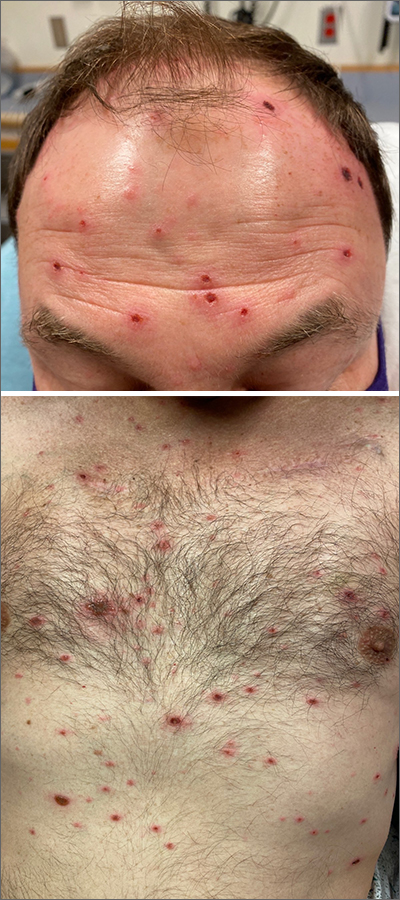
The patient’s history and presentation, as well as a positive varicella zoster virus (VZV) culture of vesicular fluid, led to a diagnosis of disseminated herpes zoster (DHZ). The patient’s laboratory studies were remarkable for mild lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated liver function tests. Shave and punch biopsies of the lesion showed ballooning epithelial necrosis with multinucleated giant cells.
DHZ is characterized by more than 20 vesicles outside of a primary or adjacent dermatome and is caused by extensive reactivation of VZV. DHZ is most often encountered in immunocompromised patients.1 Untreated DHZ can lead to encephalitis, myelitis, nerve palsies, pneumonitis, hepatitis, and ocular complications.
Diagnosis is usually made clinically and confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction test, direct fluorescent antibody testing, or viral culture.2 In immunocompetent patients, uncomplicated DHZ is treated with oral acyclovir 800 mg 5 times daily, valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily, or famciclovir 500 mg 3 times daily for 7 days. Hospital admission for intravenous acyclovir is recommended for immunocompromised patients, especially those with internal organ involvement, such as hepatitis or encephalitis.3
Early treatment is imperative to avoid life-threatening complications. Active herpes zoster lesions are infectious by contact with vesicular fluid until they dry and crust over. Patients should be instructed to avoid contact with susceptible people, including those who are immunocompromised, babies who have not received their varicella vaccine, and pregnant women. It is important to keep DHZ on the differential—especially in an immunosuppressed patient with a diffuse vesicular rash—as it can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
Our patient was treated with oral valacyclovir 1 g tid for 10 days and he improved without developing systemic symptoms.
Image courtesy of Christen B. Samaan, MD. Text courtesy of Christen B. Samaan, MD, and Matthew F. Helm, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Nanjiba Nawaz, BA, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey.
1. Bollea-Garlatti ML, Bollea-Garlatti LA, Vacas AS, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in a population with disseminated herpes zoster: a retrospective cohort study. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2016.10.009
2. Chiriac A, Chiriac AE, Podoleanu C, et al. Disseminated cutaneous herpes zoster—a frequently misdiagnosed entity. Int Wound J. 2020;17:1089-1091. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13370
3. Lewis DJ, Schlichte MJ, Dao H Jr. Atypical disseminated herpes zoster: management guidelines in immunocompromised patients. Cutis. 2017;100:321;324;330.

The patient’s history and presentation, as well as a positive varicella zoster virus (VZV) culture of vesicular fluid, led to a diagnosis of disseminated herpes zoster (DHZ). The patient’s laboratory studies were remarkable for mild lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated liver function tests. Shave and punch biopsies of the lesion showed ballooning epithelial necrosis with multinucleated giant cells.
DHZ is characterized by more than 20 vesicles outside of a primary or adjacent dermatome and is caused by extensive reactivation of VZV. DHZ is most often encountered in immunocompromised patients.1 Untreated DHZ can lead to encephalitis, myelitis, nerve palsies, pneumonitis, hepatitis, and ocular complications.
Diagnosis is usually made clinically and confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction test, direct fluorescent antibody testing, or viral culture.2 In immunocompetent patients, uncomplicated DHZ is treated with oral acyclovir 800 mg 5 times daily, valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily, or famciclovir 500 mg 3 times daily for 7 days. Hospital admission for intravenous acyclovir is recommended for immunocompromised patients, especially those with internal organ involvement, such as hepatitis or encephalitis.3
Early treatment is imperative to avoid life-threatening complications. Active herpes zoster lesions are infectious by contact with vesicular fluid until they dry and crust over. Patients should be instructed to avoid contact with susceptible people, including those who are immunocompromised, babies who have not received their varicella vaccine, and pregnant women. It is important to keep DHZ on the differential—especially in an immunosuppressed patient with a diffuse vesicular rash—as it can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
Our patient was treated with oral valacyclovir 1 g tid for 10 days and he improved without developing systemic symptoms.
Image courtesy of Christen B. Samaan, MD. Text courtesy of Christen B. Samaan, MD, and Matthew F. Helm, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Nanjiba Nawaz, BA, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey.

The patient’s history and presentation, as well as a positive varicella zoster virus (VZV) culture of vesicular fluid, led to a diagnosis of disseminated herpes zoster (DHZ). The patient’s laboratory studies were remarkable for mild lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated liver function tests. Shave and punch biopsies of the lesion showed ballooning epithelial necrosis with multinucleated giant cells.
DHZ is characterized by more than 20 vesicles outside of a primary or adjacent dermatome and is caused by extensive reactivation of VZV. DHZ is most often encountered in immunocompromised patients.1 Untreated DHZ can lead to encephalitis, myelitis, nerve palsies, pneumonitis, hepatitis, and ocular complications.
Diagnosis is usually made clinically and confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction test, direct fluorescent antibody testing, or viral culture.2 In immunocompetent patients, uncomplicated DHZ is treated with oral acyclovir 800 mg 5 times daily, valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily, or famciclovir 500 mg 3 times daily for 7 days. Hospital admission for intravenous acyclovir is recommended for immunocompromised patients, especially those with internal organ involvement, such as hepatitis or encephalitis.3
Early treatment is imperative to avoid life-threatening complications. Active herpes zoster lesions are infectious by contact with vesicular fluid until they dry and crust over. Patients should be instructed to avoid contact with susceptible people, including those who are immunocompromised, babies who have not received their varicella vaccine, and pregnant women. It is important to keep DHZ on the differential—especially in an immunosuppressed patient with a diffuse vesicular rash—as it can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
Our patient was treated with oral valacyclovir 1 g tid for 10 days and he improved without developing systemic symptoms.
Image courtesy of Christen B. Samaan, MD. Text courtesy of Christen B. Samaan, MD, and Matthew F. Helm, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Nanjiba Nawaz, BA, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey.
1. Bollea-Garlatti ML, Bollea-Garlatti LA, Vacas AS, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in a population with disseminated herpes zoster: a retrospective cohort study. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2016.10.009
2. Chiriac A, Chiriac AE, Podoleanu C, et al. Disseminated cutaneous herpes zoster—a frequently misdiagnosed entity. Int Wound J. 2020;17:1089-1091. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13370
3. Lewis DJ, Schlichte MJ, Dao H Jr. Atypical disseminated herpes zoster: management guidelines in immunocompromised patients. Cutis. 2017;100:321;324;330.
1. Bollea-Garlatti ML, Bollea-Garlatti LA, Vacas AS, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in a population with disseminated herpes zoster: a retrospective cohort study. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2016.10.009
2. Chiriac A, Chiriac AE, Podoleanu C, et al. Disseminated cutaneous herpes zoster—a frequently misdiagnosed entity. Int Wound J. 2020;17:1089-1091. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13370
3. Lewis DJ, Schlichte MJ, Dao H Jr. Atypical disseminated herpes zoster: management guidelines in immunocompromised patients. Cutis. 2017;100:321;324;330.
Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency for the hospitalist
Consider OIAI, even among patients with common infections
Case
A 60-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer using morphine extended release 30 mg twice daily and as-needed oxycodone for cancer-related pain presents with fever, dyspnea, and productive cough for 2 days. She also notes several weeks of fatigue, nausea, weight loss, and orthostatic lightheadedness. She is found to have pneumonia and is admitted for intravenous antibiotics. She remains borderline hypotensive after intravenous fluids and the hospitalist suspects opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency (OIAI).
How is OIAI diagnosed and managed?
Brief overview of issue
In the United States, 5.4% of the population is currently using long-term opioids.1 Patients using high doses of opioids for greater than 3 months are 40%-50% more likely to be hospitalized than those on a lower dose or no opioids.2 Hospitalists frequently encounter common opioid side effects such as constipation, nausea, and drowsiness, but may be less familiar with their effects on the endocrine system. Chronic, high-dose opioids can suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and cause secondary, or central, adrenal insufficiency (AI).1
Recognition of OIAI is critical given the current opioid epidemic and life-threatening consequences of AI in systemically ill patients. While high-dose opioids may acutely suppress the HPA axis,3 OIAI is more commonly associated with long-term opioid use.4 The prevalence of OIAI among patients receiving long-term opioids ranges from 8.3% to 29%. This range reflects variations in opioid dose, duration of use, and different methods of assessing the HPA axis.1,4 When screening for HPA axis suppression in subjects taking chronic opioids, Lamprecht and colleagues found a prevalence of 22.5%.5 In comparison, Gibb and colleagues found the prevalence of secondary AI to be 8.3% in patients enrolled in a chronic pain clinic.6 Despite the high prevalence on biochemical screening, the clinical significance of OIAI is less clear. Clinical AI and adrenal crisis among patients on opioids are less frequent and mostly limited to case reports.7,8 In one retrospective cohort, one in 40 patients with OIAI presented with adrenal crisis during a hospitalization for viral gastroenteritis.9
With this prevalence, one would expect to diagnose OIAI more commonly in hospitalized patients. A concerning possibility is that this diagnosis is underrecognized because of either a lack of knowledge of the disease or the clinical overlap between the nonspecific symptoms of AI and other diagnoses. In patients reporting symptoms suggestive of OIAI, the diagnosis was delayed by a median of 12 months.9 The challenge for the hospitalist is to consider OIAI, even among patients with common infections such as pneumonia, viral gastroenteritis, or endocarditis who present with these nonspecific symptoms, while also avoiding unnecessary testing and treatment with glucocorticoids.
Overview of the data
Opiates and opioids exert their physiologic effect through activation of the mu, kappa, and delta receptors. These receptors are located throughout the body, including the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.4 Activation of these receptors results in tonic inhibition of the HPA axis and results in central AI.4 Central AI is characterized by a low a.m. cortisol, low adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and low dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) levels.1,4 The low ACTH is indicative of central etiology. This effect of opioids is likely dose dependent with patients using more than 60 morphine-equivalent daily dose at greater risk.1,5
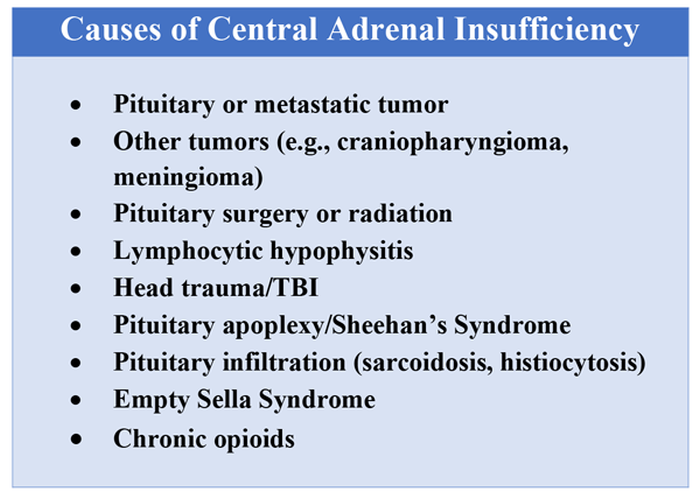
Unexplained or unresolved fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain, and orthostatic hypotension in a patient on chronic opioids should prompt consideration of OIAI.9 Once suspected, an 8 a.m. cortisol, ACTH level, and DHEAS level should be ordered. Because of the diurnal variation of cortisol levels, 8 a.m. values are best validated for diagnosis.10 While cutoffs differ, an 8 a.m. cortisol less than 5 mcg/dL combined with ACTH less than 10 pmol/L, and DHEAS less than 50 mcg/dL are highly suggestive of OIAI. Low or indeterminate baseline a.m. cortisol levels warrant confirmatory testing.4,10 While the insulin tolerance test is considered the gold standard, the high dose (250 mcg) cosyntropin stimulation test (CST) is the more commonly used test to diagnose and confirm AI. A CST peak response greater than 18-20 mcg/dL suggests an intact HPA axis (see Figure 1).10 This testing will diagnose central AI, but is not specific for OIAI. Other causes of central AI such as exogenous steroid use, pituitary pathology, and head trauma should be considered before attributing AI to opioids (see Table 1).4
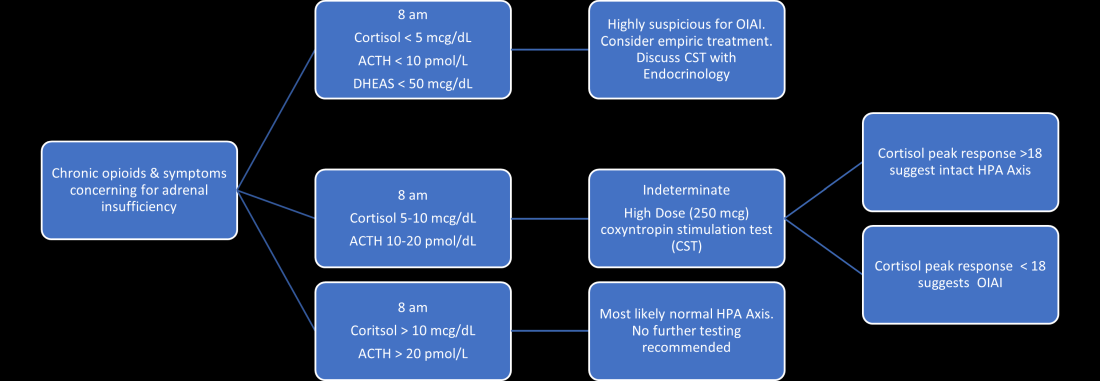
The abnormal CST in central AI is from chronic ACTH deficiency and lack of adrenal stimulation resulting in adrenal atrophy. Adrenal atrophy leaves the adrenal glands incapable of responding to exogenous ACTH. This process takes several weeks; therefore, those with ACTH suppression caused by recent high-dose opioid use or subacute pituitary injury may have an indeterminate or normal cortisol response to high-dose exogenous ACTH.4 Even in the setting of a normal CST, there may remain uncertainty in the diagnosis of OIAI. When evaluating for central AI, the sensitivity and negative likelihood ratio of the CST are only 0.64 and 0.39, respectively.4 In the same cohort of 40 patients with OIAI, 11 patients had a normal CST.9 The low-dose (1 mcg) CST may increase the sensitivity, but the use of this test is limited because of technical challenges.1 Endocrinology consultation can assist when the initial diagnostic and clinical presentation is unclear.
To manage a patient on opioid therapy who has laboratory data consistent with central AI, the clinician must weigh the severity of symptoms, probability of opioid weaning, and risks associated with glucocorticoid treatment. Patients presenting with acute adrenal crisis, hypotension, or critical illness should be managed with intravenous steroid replacement per existing guideline recommendations.10,11
Patients with mild symptoms of nausea, vomiting, or orthostatic symptoms that resolve with treatment of their admitting diagnosis but who have evidence of an abnormal HPA axis should be considered for weaning opioid therapy. Evidence suggests that OIAI is reversible with reduction and cessation of chronic opioid use.4,9 These patients may not need chronic steroid replacement; however, they should receive education on the symptoms of AI and potentially rescue steroids for home use in the setting of severe illness. Patients with OIAI admitted for surgical procedures should be managed in accordance with existing guidelines for perioperative stress dosing of glucocorticoids for AI.
Those with persisting symptoms of OIAI and an abnormal HPA axis require endocrinology consultation and glucocorticoid replacement. There is limited evidence that suggests low dose steroid replacement in patients with OIAI can improve subjective perception of bodily pain, activity level, and mood in chronic opioid users.9 Li and colleagues found that 16 of 23 patients experienced improvement of symptoms on glucocorticoids, and 15 were able to discontinue opioids completely.9 The authors speculated that the improvement in fatigue and musculoskeletal pain after steroid replacement is what allowed for successful opioid weaning. Seven of 10 of these patients with available follow-up had recovery of the HPA axis during the follow-up period.9 In central AI, doses as low as 10-20 mg/day of hydrocortisone have been used.10,11 Hospitalists should educate patients on recognizing symptoms of AI, as this low dose may not be sufficient to prevent adrenal crisis.
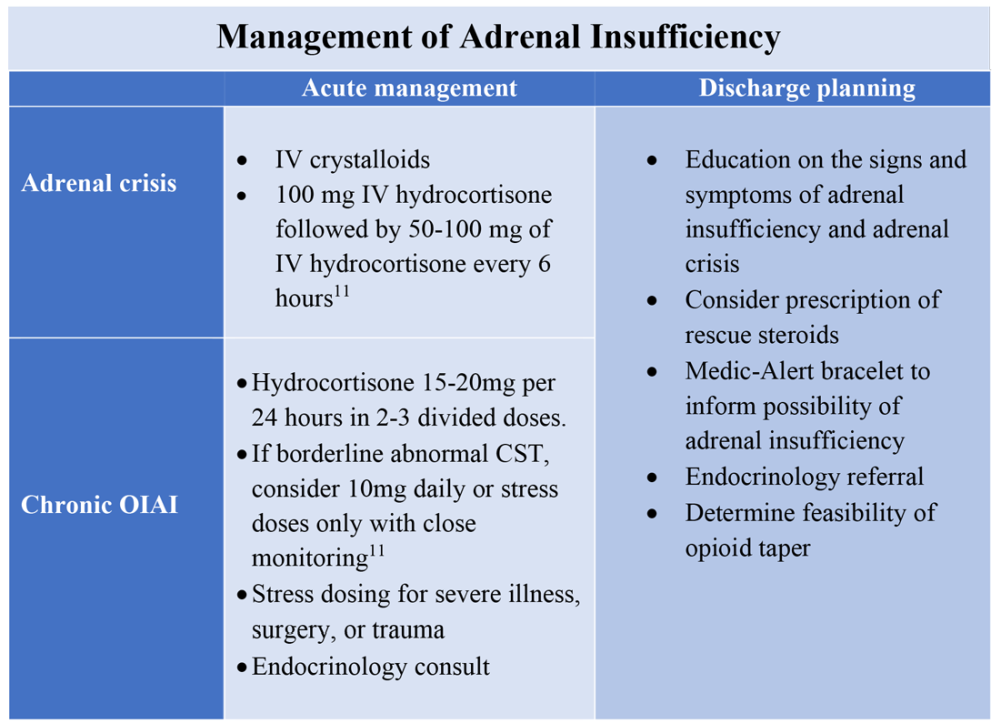
All patients with evidence of abnormalities in the HPA axis should receive a Medic-Alert bracelet to inform other providers of the possibility of adrenal crisis should a major trauma or critical illness render them unconscious.4,10 Since OIAI is a form of central AI, mineralocorticoid replacement is not generally necessary.11 Endocrinology follow-up can help wean steroids as the HPA axis recovers after weaning opioid therapy. Recognizing and diagnosing OIAI can identify patients with untreated symptoms who are at risk for adrenal crisis, improve communication with patients on benefits of weaning opioids, and provide valuable patient education and safe transition of care.
Application of the data to the original case
To make the diagnosis of OIAI, 8 a.m. cortisol, ACTH, and DHEAS should be obtained. Her cortisol was less than 5 mcg/dL, ACTH was 6 pmol/L and DHEAS was 30 mcg/dL. A high dose CST was performed with 30-minute and 60-minute cortisol values of 6 mcg/dL and 9 mcg/dL, respectively. The abnormal CST and low ACTH indicate central AI. She should undergo testing for other etiologies of central AI, such as a brain MRI and pituitary hormone testing, before confirming the diagnosis of OIAI.
The insufficient adrenal response to ACTH in the setting of infection and hypotension should prompt glucocorticoid replacement. Tapering opioids could result in recovery of the HPA axis, though may not be realistic in this patient with chronic cancer-related pain. If the patient is at high risk for adverse effects of glucocorticoids, repeat testing of the HPA axis in the outpatient setting can assess if the patient truly needs steroid replacement daily rather than only during physiologic stress. The patient should be given a Medic-Alert bracelet and instructions on symptoms of AI and stress dosing upon discharge.
Bottom line
OIAI is underrecognized because of central adrenal insufficiency. Knowing its clinical characteristics, diagnostic pathways, and treatment options aids in recognition and management.
Dr. Cunningham, Dr. Munoa, and Dr. Indovina are based in the division of hospital medicine at Denver Health and Hospital Authority.
References
1. Donegan D. Opioid induced adrenal insufficiency: What is new? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2019 Jun;26(3):133-8. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000474.
2. Liang Y and Turner BJ. Opioid risk measure for hospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2015 July;10(7):425-31. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2350.
3. Policola C et al. Adrenal insufficiency in acute oral opiate therapy. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2014;2014:130071. doi: 10.1530/EDM-13-0071.
4. Donegan D and Bancos I. Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 July;93(7):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.010.
5. Lamprecht A et al. Secondary adrenal insufficiency and pituitary dysfunction in oral/transdermal opioid users with non-cancer pain. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018 Dec 1;179(6):353-62. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0530.
6. Gibb FW et al. Adrenal insufficiency in patients on long-term opioid analgesia. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016 June;85(6):831-5. doi:10.1111/cen.13125.
7. Abs R et al. Endocrine consequences of long-term intrathecal administration of opioids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000 June;85(6):2215-22. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.6.6615.
8. Tabet EJ et al. Opioid-induced hypoadrenalism resulting in fasting hypoglycaemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Dec 11;12(12):e230551. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-230551.
9. Li T et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of opioid induced adrenal insufficiency. Endocr Pract. 2020 Nov;26(11):1291-1297. doi: 10.4158/EP-2020-0297.
10. Grossman AB. Clinical Review: The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;95(11):4855-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0982.
11. Charmandari E et al. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet. 2014 June 21;383(9935):2152-67. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61684-0.
Key points
- Opioids can cause central adrenal insufficiency because of tonic suppression of the HPA axis. This effect is likely dose dependent, and reversible upon tapering or withdrawal of opioids.
- The prevalence of biochemical OIAI in chronic opioid users of 8%-29% clinical AI is less frequent but may be underrecognized in hospitalized patients leading to delayed diagnosis.
- Diagnosis of central adrenal insufficiency is based upon low 8 a.m. cortisol and ACTH levels and/or an abnormal CST. OIAI is the likely etiology in patients on chronic opioids for whom other causes of central adrenal insufficiency have been ruled out.
- Management with glucocorticoid replacement is variable depending on clinical presentation, severity of HPA axis suppression, and ability to wean opioid therapy. Patient education regarding symptoms of AI and stress dosing is essential.
Additional reading
Grossman AB. Clinical Review: The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;95(11):4855-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0982.
Donegan D and Bancos I. Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 July;93(7):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.010.
Li T et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of opioid induced adrenal insufficiency. Endocr Pract. 2020 Nov;26(11):1291-7. doi: 10.4158/EP-2020-0297.
Quiz
A 55-year-old man with chronic back pain, for which he takes a total of 90 mg of oral morphine daily, is admitted for pyelonephritis with fever, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and abdominal pain. He is febrile and tachycardic on presentation, but his vitals quickly normalize after hydration and antibiotics. About 48 hours into his hospitalization his fevers, dysuria, and abdominal pain have resolved, but he has persistent nausea and headaches. On further questioning, he also reports weight loss and fatigue over the past 3 weeks. He is found to have a morning cortisol level less than 5 mcg/dL, as well as low levels of ACTH and DHEAS. OIAI is suspected.
Which of the following is true about management?
A. Glucocorticoid replacement therapy with oral hydrocortisone should be considered to improve his symptoms.
B. Tapering off opioids is unlikely to resolve his adrenal insufficiency.
C. Stress dose steroids should be started immediately with high-dose intravenous hydrocortisone.
D. Given high clinical suspicion for OIAI, further testing for other etiologies of central adrenal insufficiency is not recommended.
Explanation of correct answer
The correct answer is A. This patient’s ongoing nonspecific symptoms that have persisted despite treatment of his acute pyelonephritis are likely caused by adrenal insufficiency. In a symptomatic patient with OIAI, treatment with oral hydrocortisone should be considered to control symptoms and facilitate tapering opioids. Tapering and stopping opioids often leads to recovery of the HPA axis and resolution of the OIAI. Tapering opioids should be considered a mainstay of therapy for OIAI when clinically appropriate, as in this patient with chronic benign pain. Stress dose steroids are not indicated in the absence of critical illness, adrenal crisis, or major surgery. OIAI is a diagnosis of exclusion, and patients should undergo workup for other causes of secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Consider OIAI, even among patients with common infections
Consider OIAI, even among patients with common infections
Case
A 60-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer using morphine extended release 30 mg twice daily and as-needed oxycodone for cancer-related pain presents with fever, dyspnea, and productive cough for 2 days. She also notes several weeks of fatigue, nausea, weight loss, and orthostatic lightheadedness. She is found to have pneumonia and is admitted for intravenous antibiotics. She remains borderline hypotensive after intravenous fluids and the hospitalist suspects opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency (OIAI).
How is OIAI diagnosed and managed?
Brief overview of issue
In the United States, 5.4% of the population is currently using long-term opioids.1 Patients using high doses of opioids for greater than 3 months are 40%-50% more likely to be hospitalized than those on a lower dose or no opioids.2 Hospitalists frequently encounter common opioid side effects such as constipation, nausea, and drowsiness, but may be less familiar with their effects on the endocrine system. Chronic, high-dose opioids can suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and cause secondary, or central, adrenal insufficiency (AI).1
Recognition of OIAI is critical given the current opioid epidemic and life-threatening consequences of AI in systemically ill patients. While high-dose opioids may acutely suppress the HPA axis,3 OIAI is more commonly associated with long-term opioid use.4 The prevalence of OIAI among patients receiving long-term opioids ranges from 8.3% to 29%. This range reflects variations in opioid dose, duration of use, and different methods of assessing the HPA axis.1,4 When screening for HPA axis suppression in subjects taking chronic opioids, Lamprecht and colleagues found a prevalence of 22.5%.5 In comparison, Gibb and colleagues found the prevalence of secondary AI to be 8.3% in patients enrolled in a chronic pain clinic.6 Despite the high prevalence on biochemical screening, the clinical significance of OIAI is less clear. Clinical AI and adrenal crisis among patients on opioids are less frequent and mostly limited to case reports.7,8 In one retrospective cohort, one in 40 patients with OIAI presented with adrenal crisis during a hospitalization for viral gastroenteritis.9
With this prevalence, one would expect to diagnose OIAI more commonly in hospitalized patients. A concerning possibility is that this diagnosis is underrecognized because of either a lack of knowledge of the disease or the clinical overlap between the nonspecific symptoms of AI and other diagnoses. In patients reporting symptoms suggestive of OIAI, the diagnosis was delayed by a median of 12 months.9 The challenge for the hospitalist is to consider OIAI, even among patients with common infections such as pneumonia, viral gastroenteritis, or endocarditis who present with these nonspecific symptoms, while also avoiding unnecessary testing and treatment with glucocorticoids.
Overview of the data
Opiates and opioids exert their physiologic effect through activation of the mu, kappa, and delta receptors. These receptors are located throughout the body, including the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.4 Activation of these receptors results in tonic inhibition of the HPA axis and results in central AI.4 Central AI is characterized by a low a.m. cortisol, low adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and low dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) levels.1,4 The low ACTH is indicative of central etiology. This effect of opioids is likely dose dependent with patients using more than 60 morphine-equivalent daily dose at greater risk.1,5
Unexplained or unresolved fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain, and orthostatic hypotension in a patient on chronic opioids should prompt consideration of OIAI.9 Once suspected, an 8 a.m. cortisol, ACTH level, and DHEAS level should be ordered. Because of the diurnal variation of cortisol levels, 8 a.m. values are best validated for diagnosis.10 While cutoffs differ, an 8 a.m. cortisol less than 5 mcg/dL combined with ACTH less than 10 pmol/L, and DHEAS less than 50 mcg/dL are highly suggestive of OIAI. Low or indeterminate baseline a.m. cortisol levels warrant confirmatory testing.4,10 While the insulin tolerance test is considered the gold standard, the high dose (250 mcg) cosyntropin stimulation test (CST) is the more commonly used test to diagnose and confirm AI. A CST peak response greater than 18-20 mcg/dL suggests an intact HPA axis (see Figure 1).10 This testing will diagnose central AI, but is not specific for OIAI. Other causes of central AI such as exogenous steroid use, pituitary pathology, and head trauma should be considered before attributing AI to opioids (see Table 1).4

The abnormal CST in central AI is from chronic ACTH deficiency and lack of adrenal stimulation resulting in adrenal atrophy. Adrenal atrophy leaves the adrenal glands incapable of responding to exogenous ACTH. This process takes several weeks; therefore, those with ACTH suppression caused by recent high-dose opioid use or subacute pituitary injury may have an indeterminate or normal cortisol response to high-dose exogenous ACTH.4 Even in the setting of a normal CST, there may remain uncertainty in the diagnosis of OIAI. When evaluating for central AI, the sensitivity and negative likelihood ratio of the CST are only 0.64 and 0.39, respectively.4 In the same cohort of 40 patients with OIAI, 11 patients had a normal CST.9 The low-dose (1 mcg) CST may increase the sensitivity, but the use of this test is limited because of technical challenges.1 Endocrinology consultation can assist when the initial diagnostic and clinical presentation is unclear.

To manage a patient on opioid therapy who has laboratory data consistent with central AI, the clinician must weigh the severity of symptoms, probability of opioid weaning, and risks associated with glucocorticoid treatment. Patients presenting with acute adrenal crisis, hypotension, or critical illness should be managed with intravenous steroid replacement per existing guideline recommendations.10,11
Patients with mild symptoms of nausea, vomiting, or orthostatic symptoms that resolve with treatment of their admitting diagnosis but who have evidence of an abnormal HPA axis should be considered for weaning opioid therapy. Evidence suggests that OIAI is reversible with reduction and cessation of chronic opioid use.4,9 These patients may not need chronic steroid replacement; however, they should receive education on the symptoms of AI and potentially rescue steroids for home use in the setting of severe illness. Patients with OIAI admitted for surgical procedures should be managed in accordance with existing guidelines for perioperative stress dosing of glucocorticoids for AI.
Those with persisting symptoms of OIAI and an abnormal HPA axis require endocrinology consultation and glucocorticoid replacement. There is limited evidence that suggests low dose steroid replacement in patients with OIAI can improve subjective perception of bodily pain, activity level, and mood in chronic opioid users.9 Li and colleagues found that 16 of 23 patients experienced improvement of symptoms on glucocorticoids, and 15 were able to discontinue opioids completely.9 The authors speculated that the improvement in fatigue and musculoskeletal pain after steroid replacement is what allowed for successful opioid weaning. Seven of 10 of these patients with available follow-up had recovery of the HPA axis during the follow-up period.9 In central AI, doses as low as 10-20 mg/day of hydrocortisone have been used.10,11 Hospitalists should educate patients on recognizing symptoms of AI, as this low dose may not be sufficient to prevent adrenal crisis.

All patients with evidence of abnormalities in the HPA axis should receive a Medic-Alert bracelet to inform other providers of the possibility of adrenal crisis should a major trauma or critical illness render them unconscious.4,10 Since OIAI is a form of central AI, mineralocorticoid replacement is not generally necessary.11 Endocrinology follow-up can help wean steroids as the HPA axis recovers after weaning opioid therapy. Recognizing and diagnosing OIAI can identify patients with untreated symptoms who are at risk for adrenal crisis, improve communication with patients on benefits of weaning opioids, and provide valuable patient education and safe transition of care.
Application of the data to the original case
To make the diagnosis of OIAI, 8 a.m. cortisol, ACTH, and DHEAS should be obtained. Her cortisol was less than 5 mcg/dL, ACTH was 6 pmol/L and DHEAS was 30 mcg/dL. A high dose CST was performed with 30-minute and 60-minute cortisol values of 6 mcg/dL and 9 mcg/dL, respectively. The abnormal CST and low ACTH indicate central AI. She should undergo testing for other etiologies of central AI, such as a brain MRI and pituitary hormone testing, before confirming the diagnosis of OIAI.
The insufficient adrenal response to ACTH in the setting of infection and hypotension should prompt glucocorticoid replacement. Tapering opioids could result in recovery of the HPA axis, though may not be realistic in this patient with chronic cancer-related pain. If the patient is at high risk for adverse effects of glucocorticoids, repeat testing of the HPA axis in the outpatient setting can assess if the patient truly needs steroid replacement daily rather than only during physiologic stress. The patient should be given a Medic-Alert bracelet and instructions on symptoms of AI and stress dosing upon discharge.
Bottom line
OIAI is underrecognized because of central adrenal insufficiency. Knowing its clinical characteristics, diagnostic pathways, and treatment options aids in recognition and management.
Dr. Cunningham, Dr. Munoa, and Dr. Indovina are based in the division of hospital medicine at Denver Health and Hospital Authority.
References
1. Donegan D. Opioid induced adrenal insufficiency: What is new? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2019 Jun;26(3):133-8. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000474.
2. Liang Y and Turner BJ. Opioid risk measure for hospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2015 July;10(7):425-31. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2350.
3. Policola C et al. Adrenal insufficiency in acute oral opiate therapy. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2014;2014:130071. doi: 10.1530/EDM-13-0071.
4. Donegan D and Bancos I. Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 July;93(7):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.010.
5. Lamprecht A et al. Secondary adrenal insufficiency and pituitary dysfunction in oral/transdermal opioid users with non-cancer pain. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018 Dec 1;179(6):353-62. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0530.
6. Gibb FW et al. Adrenal insufficiency in patients on long-term opioid analgesia. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016 June;85(6):831-5. doi:10.1111/cen.13125.
7. Abs R et al. Endocrine consequences of long-term intrathecal administration of opioids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000 June;85(6):2215-22. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.6.6615.
8. Tabet EJ et al. Opioid-induced hypoadrenalism resulting in fasting hypoglycaemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Dec 11;12(12):e230551. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-230551.
9. Li T et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of opioid induced adrenal insufficiency. Endocr Pract. 2020 Nov;26(11):1291-1297. doi: 10.4158/EP-2020-0297.
10. Grossman AB. Clinical Review: The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;95(11):4855-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0982.
11. Charmandari E et al. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet. 2014 June 21;383(9935):2152-67. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61684-0.
Key points
- Opioids can cause central adrenal insufficiency because of tonic suppression of the HPA axis. This effect is likely dose dependent, and reversible upon tapering or withdrawal of opioids.
- The prevalence of biochemical OIAI in chronic opioid users of 8%-29% clinical AI is less frequent but may be underrecognized in hospitalized patients leading to delayed diagnosis.
- Diagnosis of central adrenal insufficiency is based upon low 8 a.m. cortisol and ACTH levels and/or an abnormal CST. OIAI is the likely etiology in patients on chronic opioids for whom other causes of central adrenal insufficiency have been ruled out.
- Management with glucocorticoid replacement is variable depending on clinical presentation, severity of HPA axis suppression, and ability to wean opioid therapy. Patient education regarding symptoms of AI and stress dosing is essential.
Additional reading
Grossman AB. Clinical Review: The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;95(11):4855-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0982.
Donegan D and Bancos I. Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 July;93(7):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.010.
Li T et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of opioid induced adrenal insufficiency. Endocr Pract. 2020 Nov;26(11):1291-7. doi: 10.4158/EP-2020-0297.
Quiz
A 55-year-old man with chronic back pain, for which he takes a total of 90 mg of oral morphine daily, is admitted for pyelonephritis with fever, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and abdominal pain. He is febrile and tachycardic on presentation, but his vitals quickly normalize after hydration and antibiotics. About 48 hours into his hospitalization his fevers, dysuria, and abdominal pain have resolved, but he has persistent nausea and headaches. On further questioning, he also reports weight loss and fatigue over the past 3 weeks. He is found to have a morning cortisol level less than 5 mcg/dL, as well as low levels of ACTH and DHEAS. OIAI is suspected.
Which of the following is true about management?
A. Glucocorticoid replacement therapy with oral hydrocortisone should be considered to improve his symptoms.
B. Tapering off opioids is unlikely to resolve his adrenal insufficiency.
C. Stress dose steroids should be started immediately with high-dose intravenous hydrocortisone.
D. Given high clinical suspicion for OIAI, further testing for other etiologies of central adrenal insufficiency is not recommended.
Explanation of correct answer
The correct answer is A. This patient’s ongoing nonspecific symptoms that have persisted despite treatment of his acute pyelonephritis are likely caused by adrenal insufficiency. In a symptomatic patient with OIAI, treatment with oral hydrocortisone should be considered to control symptoms and facilitate tapering opioids. Tapering and stopping opioids often leads to recovery of the HPA axis and resolution of the OIAI. Tapering opioids should be considered a mainstay of therapy for OIAI when clinically appropriate, as in this patient with chronic benign pain. Stress dose steroids are not indicated in the absence of critical illness, adrenal crisis, or major surgery. OIAI is a diagnosis of exclusion, and patients should undergo workup for other causes of secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Case
A 60-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer using morphine extended release 30 mg twice daily and as-needed oxycodone for cancer-related pain presents with fever, dyspnea, and productive cough for 2 days. She also notes several weeks of fatigue, nausea, weight loss, and orthostatic lightheadedness. She is found to have pneumonia and is admitted for intravenous antibiotics. She remains borderline hypotensive after intravenous fluids and the hospitalist suspects opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency (OIAI).
How is OIAI diagnosed and managed?
Brief overview of issue
In the United States, 5.4% of the population is currently using long-term opioids.1 Patients using high doses of opioids for greater than 3 months are 40%-50% more likely to be hospitalized than those on a lower dose or no opioids.2 Hospitalists frequently encounter common opioid side effects such as constipation, nausea, and drowsiness, but may be less familiar with their effects on the endocrine system. Chronic, high-dose opioids can suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and cause secondary, or central, adrenal insufficiency (AI).1
Recognition of OIAI is critical given the current opioid epidemic and life-threatening consequences of AI in systemically ill patients. While high-dose opioids may acutely suppress the HPA axis,3 OIAI is more commonly associated with long-term opioid use.4 The prevalence of OIAI among patients receiving long-term opioids ranges from 8.3% to 29%. This range reflects variations in opioid dose, duration of use, and different methods of assessing the HPA axis.1,4 When screening for HPA axis suppression in subjects taking chronic opioids, Lamprecht and colleagues found a prevalence of 22.5%.5 In comparison, Gibb and colleagues found the prevalence of secondary AI to be 8.3% in patients enrolled in a chronic pain clinic.6 Despite the high prevalence on biochemical screening, the clinical significance of OIAI is less clear. Clinical AI and adrenal crisis among patients on opioids are less frequent and mostly limited to case reports.7,8 In one retrospective cohort, one in 40 patients with OIAI presented with adrenal crisis during a hospitalization for viral gastroenteritis.9
With this prevalence, one would expect to diagnose OIAI more commonly in hospitalized patients. A concerning possibility is that this diagnosis is underrecognized because of either a lack of knowledge of the disease or the clinical overlap between the nonspecific symptoms of AI and other diagnoses. In patients reporting symptoms suggestive of OIAI, the diagnosis was delayed by a median of 12 months.9 The challenge for the hospitalist is to consider OIAI, even among patients with common infections such as pneumonia, viral gastroenteritis, or endocarditis who present with these nonspecific symptoms, while also avoiding unnecessary testing and treatment with glucocorticoids.
Overview of the data
Opiates and opioids exert their physiologic effect through activation of the mu, kappa, and delta receptors. These receptors are located throughout the body, including the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.4 Activation of these receptors results in tonic inhibition of the HPA axis and results in central AI.4 Central AI is characterized by a low a.m. cortisol, low adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and low dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) levels.1,4 The low ACTH is indicative of central etiology. This effect of opioids is likely dose dependent with patients using more than 60 morphine-equivalent daily dose at greater risk.1,5
Unexplained or unresolved fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain, and orthostatic hypotension in a patient on chronic opioids should prompt consideration of OIAI.9 Once suspected, an 8 a.m. cortisol, ACTH level, and DHEAS level should be ordered. Because of the diurnal variation of cortisol levels, 8 a.m. values are best validated for diagnosis.10 While cutoffs differ, an 8 a.m. cortisol less than 5 mcg/dL combined with ACTH less than 10 pmol/L, and DHEAS less than 50 mcg/dL are highly suggestive of OIAI. Low or indeterminate baseline a.m. cortisol levels warrant confirmatory testing.4,10 While the insulin tolerance test is considered the gold standard, the high dose (250 mcg) cosyntropin stimulation test (CST) is the more commonly used test to diagnose and confirm AI. A CST peak response greater than 18-20 mcg/dL suggests an intact HPA axis (see Figure 1).10 This testing will diagnose central AI, but is not specific for OIAI. Other causes of central AI such as exogenous steroid use, pituitary pathology, and head trauma should be considered before attributing AI to opioids (see Table 1).4

The abnormal CST in central AI is from chronic ACTH deficiency and lack of adrenal stimulation resulting in adrenal atrophy. Adrenal atrophy leaves the adrenal glands incapable of responding to exogenous ACTH. This process takes several weeks; therefore, those with ACTH suppression caused by recent high-dose opioid use or subacute pituitary injury may have an indeterminate or normal cortisol response to high-dose exogenous ACTH.4 Even in the setting of a normal CST, there may remain uncertainty in the diagnosis of OIAI. When evaluating for central AI, the sensitivity and negative likelihood ratio of the CST are only 0.64 and 0.39, respectively.4 In the same cohort of 40 patients with OIAI, 11 patients had a normal CST.9 The low-dose (1 mcg) CST may increase the sensitivity, but the use of this test is limited because of technical challenges.1 Endocrinology consultation can assist when the initial diagnostic and clinical presentation is unclear.

To manage a patient on opioid therapy who has laboratory data consistent with central AI, the clinician must weigh the severity of symptoms, probability of opioid weaning, and risks associated with glucocorticoid treatment. Patients presenting with acute adrenal crisis, hypotension, or critical illness should be managed with intravenous steroid replacement per existing guideline recommendations.10,11
Patients with mild symptoms of nausea, vomiting, or orthostatic symptoms that resolve with treatment of their admitting diagnosis but who have evidence of an abnormal HPA axis should be considered for weaning opioid therapy. Evidence suggests that OIAI is reversible with reduction and cessation of chronic opioid use.4,9 These patients may not need chronic steroid replacement; however, they should receive education on the symptoms of AI and potentially rescue steroids for home use in the setting of severe illness. Patients with OIAI admitted for surgical procedures should be managed in accordance with existing guidelines for perioperative stress dosing of glucocorticoids for AI.
Those with persisting symptoms of OIAI and an abnormal HPA axis require endocrinology consultation and glucocorticoid replacement. There is limited evidence that suggests low dose steroid replacement in patients with OIAI can improve subjective perception of bodily pain, activity level, and mood in chronic opioid users.9 Li and colleagues found that 16 of 23 patients experienced improvement of symptoms on glucocorticoids, and 15 were able to discontinue opioids completely.9 The authors speculated that the improvement in fatigue and musculoskeletal pain after steroid replacement is what allowed for successful opioid weaning. Seven of 10 of these patients with available follow-up had recovery of the HPA axis during the follow-up period.9 In central AI, doses as low as 10-20 mg/day of hydrocortisone have been used.10,11 Hospitalists should educate patients on recognizing symptoms of AI, as this low dose may not be sufficient to prevent adrenal crisis.

All patients with evidence of abnormalities in the HPA axis should receive a Medic-Alert bracelet to inform other providers of the possibility of adrenal crisis should a major trauma or critical illness render them unconscious.4,10 Since OIAI is a form of central AI, mineralocorticoid replacement is not generally necessary.11 Endocrinology follow-up can help wean steroids as the HPA axis recovers after weaning opioid therapy. Recognizing and diagnosing OIAI can identify patients with untreated symptoms who are at risk for adrenal crisis, improve communication with patients on benefits of weaning opioids, and provide valuable patient education and safe transition of care.
Application of the data to the original case
To make the diagnosis of OIAI, 8 a.m. cortisol, ACTH, and DHEAS should be obtained. Her cortisol was less than 5 mcg/dL, ACTH was 6 pmol/L and DHEAS was 30 mcg/dL. A high dose CST was performed with 30-minute and 60-minute cortisol values of 6 mcg/dL and 9 mcg/dL, respectively. The abnormal CST and low ACTH indicate central AI. She should undergo testing for other etiologies of central AI, such as a brain MRI and pituitary hormone testing, before confirming the diagnosis of OIAI.
The insufficient adrenal response to ACTH in the setting of infection and hypotension should prompt glucocorticoid replacement. Tapering opioids could result in recovery of the HPA axis, though may not be realistic in this patient with chronic cancer-related pain. If the patient is at high risk for adverse effects of glucocorticoids, repeat testing of the HPA axis in the outpatient setting can assess if the patient truly needs steroid replacement daily rather than only during physiologic stress. The patient should be given a Medic-Alert bracelet and instructions on symptoms of AI and stress dosing upon discharge.
Bottom line
OIAI is underrecognized because of central adrenal insufficiency. Knowing its clinical characteristics, diagnostic pathways, and treatment options aids in recognition and management.
Dr. Cunningham, Dr. Munoa, and Dr. Indovina are based in the division of hospital medicine at Denver Health and Hospital Authority.
References
1. Donegan D. Opioid induced adrenal insufficiency: What is new? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2019 Jun;26(3):133-8. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000474.
2. Liang Y and Turner BJ. Opioid risk measure for hospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2015 July;10(7):425-31. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2350.
3. Policola C et al. Adrenal insufficiency in acute oral opiate therapy. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2014;2014:130071. doi: 10.1530/EDM-13-0071.
4. Donegan D and Bancos I. Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 July;93(7):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.010.
5. Lamprecht A et al. Secondary adrenal insufficiency and pituitary dysfunction in oral/transdermal opioid users with non-cancer pain. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018 Dec 1;179(6):353-62. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0530.
6. Gibb FW et al. Adrenal insufficiency in patients on long-term opioid analgesia. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016 June;85(6):831-5. doi:10.1111/cen.13125.
7. Abs R et al. Endocrine consequences of long-term intrathecal administration of opioids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000 June;85(6):2215-22. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.6.6615.
8. Tabet EJ et al. Opioid-induced hypoadrenalism resulting in fasting hypoglycaemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Dec 11;12(12):e230551. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-230551.
9. Li T et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of opioid induced adrenal insufficiency. Endocr Pract. 2020 Nov;26(11):1291-1297. doi: 10.4158/EP-2020-0297.
10. Grossman AB. Clinical Review: The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;95(11):4855-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0982.
11. Charmandari E et al. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet. 2014 June 21;383(9935):2152-67. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61684-0.
Key points
- Opioids can cause central adrenal insufficiency because of tonic suppression of the HPA axis. This effect is likely dose dependent, and reversible upon tapering or withdrawal of opioids.
- The prevalence of biochemical OIAI in chronic opioid users of 8%-29% clinical AI is less frequent but may be underrecognized in hospitalized patients leading to delayed diagnosis.
- Diagnosis of central adrenal insufficiency is based upon low 8 a.m. cortisol and ACTH levels and/or an abnormal CST. OIAI is the likely etiology in patients on chronic opioids for whom other causes of central adrenal insufficiency have been ruled out.
- Management with glucocorticoid replacement is variable depending on clinical presentation, severity of HPA axis suppression, and ability to wean opioid therapy. Patient education regarding symptoms of AI and stress dosing is essential.
Additional reading
Grossman AB. Clinical Review: The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;95(11):4855-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0982.
Donegan D and Bancos I. Opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 July;93(7):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.010.
Li T et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of opioid induced adrenal insufficiency. Endocr Pract. 2020 Nov;26(11):1291-7. doi: 10.4158/EP-2020-0297.
Quiz
A 55-year-old man with chronic back pain, for which he takes a total of 90 mg of oral morphine daily, is admitted for pyelonephritis with fever, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and abdominal pain. He is febrile and tachycardic on presentation, but his vitals quickly normalize after hydration and antibiotics. About 48 hours into his hospitalization his fevers, dysuria, and abdominal pain have resolved, but he has persistent nausea and headaches. On further questioning, he also reports weight loss and fatigue over the past 3 weeks. He is found to have a morning cortisol level less than 5 mcg/dL, as well as low levels of ACTH and DHEAS. OIAI is suspected.
Which of the following is true about management?
A. Glucocorticoid replacement therapy with oral hydrocortisone should be considered to improve his symptoms.
B. Tapering off opioids is unlikely to resolve his adrenal insufficiency.
C. Stress dose steroids should be started immediately with high-dose intravenous hydrocortisone.
D. Given high clinical suspicion for OIAI, further testing for other etiologies of central adrenal insufficiency is not recommended.
Explanation of correct answer
The correct answer is A. This patient’s ongoing nonspecific symptoms that have persisted despite treatment of his acute pyelonephritis are likely caused by adrenal insufficiency. In a symptomatic patient with OIAI, treatment with oral hydrocortisone should be considered to control symptoms and facilitate tapering opioids. Tapering and stopping opioids often leads to recovery of the HPA axis and resolution of the OIAI. Tapering opioids should be considered a mainstay of therapy for OIAI when clinically appropriate, as in this patient with chronic benign pain. Stress dose steroids are not indicated in the absence of critical illness, adrenal crisis, or major surgery. OIAI is a diagnosis of exclusion, and patients should undergo workup for other causes of secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Judge dismisses Lyme disease lawsuit against IDSA, doctors, but the ordeal has left its scars
Years ago, when rheumatologist Leonard Sigal, MD, was undertaking research on Lyme disease and treating patients with the condition at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., a regular stream of abuse and threats became the usual background noise of his work. He didn’t get used to it, but it never stopped.
“I was accused of incredibly heinous crimes,” Dr. Sigal said in an interview. “I was accused of lying, cheating, of doing things to make money that were against the public interest and against the interest of patients in general.”
It’s an experience many doctors who treat Lyme disease have endured, so much so that some infectious disease doctors aren’t comfortable treating patients with Lyme disease, according to Timothy Flanigan, MD, a professor of infectious disease at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
But it wasn’t until Dr. Sigal left academia in 2003 that he realized the toll all that background abuse had been taking on him.
“It was a breath of fresh air,” he said. “I didn’t have to go into clinic and argue with people. I didn’t have to read articles in the newspaper that made no sense whatsoever. I didn’t have to hear through second and third parties how such and such was saying horrible things about me. I didn’t have to fight anymore. When I was in industry and working on stuff that had nothing to do with Lyme disease, I realized what a relief it was not to have that burden.”
So the last thing Dr. Sigal expected after all these years was to find himself named in a lawsuit alleging that he was part of a conspiracy to deny patients of what they claimed was appropriate treatment for Lyme disease. Yet, that’s exactly what happened in November 2017, when a group of 24 patients with Lyme disease, led by Texas resident Lisa Torrey, filed a lawsuit against the Infectious Diseases Society of America, eight insurance companies, and 7 of the doctors involved in producing the IDSA guidelines on Lyme disease diagnosis and management. Dr. Sigal himself had not even participated in writing the guidelines. He simply reviewed them, made a few grammatical suggestions, and said they looked good. Over the next 4 years, however, he and his fellow defendants rode an emotional roller coaster of seemingly endless motions, amendments, and other legal developments, waiting to find out whether they would owe millions of dollars for simply summarizing – or just reviewing – the available medical literature on Lyme disease.
“There were times I was on the verge of real anger. I was frustrated. There were times I was frightened, and, occasionally, I would just think of it as being silly. But when I thought of it as being silly, I had to remember I was being sued in Texas, because who knows what’s going to happen,” Dr. Sigal said. “It’s not as though I was being sued in a jurisdiction where anybody knew about Lyme disease. There are examples of physicians who are convicted of doing things they didn’t do because they were sued in the wrong jurisdiction.”
Several individuals who spoke with this news organization on condition of anonymity said that the district court where the suit was filed is notorious for being especially friendly to plaintiffs. But in legal rulings issued on Sept. 1 and Sept. 20, 2021, a federal judge in Texas dismissed all the patient group’s claims. The plaintiffs filed an appeal on Oct. 19. It’s unclear whether that has any reasonable chance of success.
“One of the things this court case does is validate the fact that our [guidelines] process is a legitimate process and there isn’t outside influence from insurance companies or pharma firms,” Daniel McQuillen, MD, president of IDSA, said in an interview. “We don’t really want anything other than to be vindicated, which we were, 100%.”
But that vindication came with a cost, both emotional and financial. Although IDSA’s insurance covered many of its legal costs, “it’s not a trivial expense,” Dr. McQuillen said. “We’re left with a baseless lawsuit with no facts that went on for 4 years, and our [medical] society basically bore all that expense, which isn’t really particularly fair.”
‘Preposterous’ accusations
The lawsuit alleged that the IDSA, the seven named physicians, and the insurance companies had “engaged in a decades-long conspiracy to deny the existence and prevent treatment of chronic Lyme disease.” The patient group claimed that the doctors knew that many patients with Lyme disease do not respond to short-term antibiotic treatment and instead need “long-term antibiotic treatment until the symptoms are resolved,” an assertion not supported by the scientific evidence.
What many patients call “chronic Lyme disease” is termed posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTDLS), a constellation of symptoms that include pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties that some people experience after a 2- to 4-week course of antibiotics for Lyme disease. It took years of patient advocacy before the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recognized PTLDS as a condition, but awareness of it has been increasing, said Dr. Flanigan, who was not involved in the lawsuit but treats patients with Lyme disease and PTLDS.
“Long haulers and sequelae of COVID have really opened the eyes of many practitioners that these long-term inflammatory conditions are real and very challenging to treat, and we need to work with patients to help them improve their health,” Dr. Flanigan said. “It’s a sad commentary on our society that the difficulty in treating patients with posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome, or what is commonly referred to by patients as chronic Lyme, ends up in a lawsuit in court.” He said he’s glad the lawsuit was dismissed but added that “there’s a crying need for additional high-quality, evidence-based research to help patients who are suffering from posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome.”
Patients fought for broader recognition of their condition, and some of them organized. They came up with their own ideas of what was causing their symptoms to persist. One that especially took hold was that infection from Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, persists after initial antibiotic treatment, causing so-called chronic Lyme disease. The cause of PTLDS is still under investigation, and the evidence does not support the idea of a persistent bacterial infection. Multiple studies from the National Institutes of Health have shown that long-term use of antibiotics does not benefit patients who continue to experience symptoms after initial treatment. Several studies have shown that severe adverse effects can result from extended intravenous antibiotic treatment, including death.
Nevertheless, the plaintiffs in the lawsuit argued that the insurance companies “enlisted the help of doctors who were researching Lyme disease – the IDSA panelists – and paid them large fees to develop arbitrary guidelines for testing Lyme disease,” thereby enabling the insurance companies to deny coverage for long-term antibiotic treatment to patients.
“The assertions were just preposterous,” Dr. McQuillen said.
In addition to the conspiracy charge, the plaintiffs brought additional accusations to the lawsuit over the years, including racketeering and claims that the guidelines contain false representations regarding Lyme disease testing and treatment. The plaintiffs claimed that the guidelines didn’t acknowledge that treatment can fail and included false information about how to test for Lyme disease. In reality, however, the guidelines do acknowledge that not all patients respond to the recommended 2- to 4-week course of antibiotics and that some diagnoses should be made clinically rather than on the basis of testing.
Regardless, guidelines are not stipulations. They’re a summation of the medical and scientific findings on Lyme disease based on careful review of hundreds of studies.
“They make really clear that adherence to the guidelines [is] voluntary. They aren’t a standard of care from which deviation of care is a problem,” Dr. McQuillen said. “You take those guidelines and apply it to the patient in front of you, and you see what fits best for that patient, because not every patient is going to fit into guidelines.”
Further, the authors said that IDSA vets their recommendations for any potential conflicts of interest in accordance with the organization’s guidelines practices.
“The point of the guidelines is to have people on the committee who don’t care what the guidelines are as long as we have good patient care,” Dr. McQuillen said.
Choosing to fight
Malpractice insurance does not cover this kind of lawsuit, because the doctors named in it did not personally treat any of the patients who filed it. Thus, the doctors were at risk of losing thousands, or millions, of dollars in legal fees, even if they ultimately prevail. Several of the physicians’ academic and health care institutions stepped in to cover some fees, and IDSA covered the rest in a joint defense.
“The IDSA provided me a lawyer at no cost to me, and I felt protected by them,” Dr. Sigal said. “They took care of me and made sure I was safe, and I am grateful to them for that.”
Dr. McQuillen said the expenses exceeded what the organization’s umbrella insurance covered. The physicians had invested their time and effort into the guidelines without any financial compensation.
“They’ve basically put a lot of sweat equity into producing guidelines” that follow the organization’s practices and ethics, Dr. McQuillen said. “To leave them out on an island by themselves is just not the right thing to do. We wouldn’t do that for any of our members who did something on behalf of our society.”
IDSA could have chosen to settle the lawsuit, as the insurance companies did.
“None of us on the board felt that was the right thing to do, because we believe in the process, and the science is right, and you shouldn’t be able to try to change that by having a lawsuit that’s baseless,” Dr. McQuillen said.
Several of the doctors named in the suit spoke with this news organization off the record about the exhaustion, frustration, and general suffering the suit has caused them over the past several years, including ongoing harassment that targeted their families and often became quite personal. But none expressed any wish that IDSA had chosen the faster, cheaper, easier route of settling.
“I love the organization for having done this rather than caving and paying,” Dr. Sigal said. “They showed real moral character, real integrity in fighting this suit, because they had done nothing wrong.”
Fighting the suit was about more than standing by the science, though. It’s essential to ensure physicians continue to conduct research and write clinical guidelines, even about ambiguous or controversial topics, said Raymond J. Dattwyler, MD, a professor of microbiology, immunology, and medicine at New York Medical College, Valhalla, who wrote the treatment part of the guidelines and was named in the suit.
“I was really surprised that someone would sue for scientific guidelines, because guidelines are common across medicine, and they’re just a roadmap to help practicing physicians understand how to handle evaluation or treatment of any number of particular problems,” Dr. Dattwyler said in an interview. But he wasn’t surprised that IDSA chose to fight the accusations, “because the principle involved is so compelling. It’s really standing up for all medical societies, and it’s very important to have guidelines. For the health and welfare of the American public, you need to have good information readily available to the practicing physicians.”
If the patient group had won in a settlement, it could potentially have led to less rigorous guidelines from other medical organizations, which would have had an adverse effect on public health, Dr. Dattwyler said. Such a chilling effect could reverberate far beyond the management of Lyme disease.
“One of the problems with our legal system is anybody can sue anybody, but it costs so much to defend yourself,” Dr. Dattwyler said. “This lawsuit costs millions, so that’s chilling. That’s going to inhibit guidelines, and it’s not only guidelines for infectious disease but it’s guidelines for cancer, guidelines for allergic diseases, guidelines for any number of things.”
To an extent, the threats and harassment that patient groups have directed toward different doctors have already had a chilling effect.
“For the people who gave of their time in good faith to generate these guidelines to get harassed everywhere, all the time, sometimes at home, sometimes at their place of work, it’s just unfair,” Dr. McQuillen said. “It also might discourage people from working in research to try to figure out better diagnostics or get a vaccine that actually works. Even if you really find it incredibly interesting, if laying over you is the threat that someone is going to sue you baselessly, and you’re going to have to put the time and effort into defending that, not to mention the money, I can’t see how that would be considered a positive that would encourage you to do it. In some ways, attacking people that are trying to help may drive them away from trying to help.
“At the same time, professional disagreements among practitioners – including a small minority who do treat patients with lengthy courses of antibiotics – can ultimately harm patient care, Dr. Flanigan said.
“There’s a lot of energy being expended fighting among different care providers, and often the individual needs of the patients seem to be not addressed,” Dr. Flanigan said. “The discord between different approaches often seems more important than spending time with the individual patient and trying to find a tailored approach to treatment which can benefit the patient best.”
At the same time, Dr. Sigal said he believes most of the clinicians who use non–evidence-based treatments for their patients do so because they genuinely believe it’s the right thing to do.
“I think they’re motivated by the same concerns that I have, and that is, I need to do what’s best for my patient,” Dr. Sigal said. Ultimately, the evidence should lead the way. “The only arbiter we possibly have in deciding these things is the medical scientific literature,” he added, “and if you can’t subscribe to that, then this way lies madness.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Years ago, when rheumatologist Leonard Sigal, MD, was undertaking research on Lyme disease and treating patients with the condition at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., a regular stream of abuse and threats became the usual background noise of his work. He didn’t get used to it, but it never stopped.
“I was accused of incredibly heinous crimes,” Dr. Sigal said in an interview. “I was accused of lying, cheating, of doing things to make money that were against the public interest and against the interest of patients in general.”
It’s an experience many doctors who treat Lyme disease have endured, so much so that some infectious disease doctors aren’t comfortable treating patients with Lyme disease, according to Timothy Flanigan, MD, a professor of infectious disease at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
But it wasn’t until Dr. Sigal left academia in 2003 that he realized the toll all that background abuse had been taking on him.
“It was a breath of fresh air,” he said. “I didn’t have to go into clinic and argue with people. I didn’t have to read articles in the newspaper that made no sense whatsoever. I didn’t have to hear through second and third parties how such and such was saying horrible things about me. I didn’t have to fight anymore. When I was in industry and working on stuff that had nothing to do with Lyme disease, I realized what a relief it was not to have that burden.”
So the last thing Dr. Sigal expected after all these years was to find himself named in a lawsuit alleging that he was part of a conspiracy to deny patients of what they claimed was appropriate treatment for Lyme disease. Yet, that’s exactly what happened in November 2017, when a group of 24 patients with Lyme disease, led by Texas resident Lisa Torrey, filed a lawsuit against the Infectious Diseases Society of America, eight insurance companies, and 7 of the doctors involved in producing the IDSA guidelines on Lyme disease diagnosis and management. Dr. Sigal himself had not even participated in writing the guidelines. He simply reviewed them, made a few grammatical suggestions, and said they looked good. Over the next 4 years, however, he and his fellow defendants rode an emotional roller coaster of seemingly endless motions, amendments, and other legal developments, waiting to find out whether they would owe millions of dollars for simply summarizing – or just reviewing – the available medical literature on Lyme disease.
“There were times I was on the verge of real anger. I was frustrated. There were times I was frightened, and, occasionally, I would just think of it as being silly. But when I thought of it as being silly, I had to remember I was being sued in Texas, because who knows what’s going to happen,” Dr. Sigal said. “It’s not as though I was being sued in a jurisdiction where anybody knew about Lyme disease. There are examples of physicians who are convicted of doing things they didn’t do because they were sued in the wrong jurisdiction.”
Several individuals who spoke with this news organization on condition of anonymity said that the district court where the suit was filed is notorious for being especially friendly to plaintiffs. But in legal rulings issued on Sept. 1 and Sept. 20, 2021, a federal judge in Texas dismissed all the patient group’s claims. The plaintiffs filed an appeal on Oct. 19. It’s unclear whether that has any reasonable chance of success.
“One of the things this court case does is validate the fact that our [guidelines] process is a legitimate process and there isn’t outside influence from insurance companies or pharma firms,” Daniel McQuillen, MD, president of IDSA, said in an interview. “We don’t really want anything other than to be vindicated, which we were, 100%.”
But that vindication came with a cost, both emotional and financial. Although IDSA’s insurance covered many of its legal costs, “it’s not a trivial expense,” Dr. McQuillen said. “We’re left with a baseless lawsuit with no facts that went on for 4 years, and our [medical] society basically bore all that expense, which isn’t really particularly fair.”
‘Preposterous’ accusations
The lawsuit alleged that the IDSA, the seven named physicians, and the insurance companies had “engaged in a decades-long conspiracy to deny the existence and prevent treatment of chronic Lyme disease.” The patient group claimed that the doctors knew that many patients with Lyme disease do not respond to short-term antibiotic treatment and instead need “long-term antibiotic treatment until the symptoms are resolved,” an assertion not supported by the scientific evidence.
What many patients call “chronic Lyme disease” is termed posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTDLS), a constellation of symptoms that include pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties that some people experience after a 2- to 4-week course of antibiotics for Lyme disease. It took years of patient advocacy before the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recognized PTLDS as a condition, but awareness of it has been increasing, said Dr. Flanigan, who was not involved in the lawsuit but treats patients with Lyme disease and PTLDS.
“Long haulers and sequelae of COVID have really opened the eyes of many practitioners that these long-term inflammatory conditions are real and very challenging to treat, and we need to work with patients to help them improve their health,” Dr. Flanigan said. “It’s a sad commentary on our society that the difficulty in treating patients with posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome, or what is commonly referred to by patients as chronic Lyme, ends up in a lawsuit in court.” He said he’s glad the lawsuit was dismissed but added that “there’s a crying need for additional high-quality, evidence-based research to help patients who are suffering from posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome.”
Patients fought for broader recognition of their condition, and some of them organized. They came up with their own ideas of what was causing their symptoms to persist. One that especially took hold was that infection from Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, persists after initial antibiotic treatment, causing so-called chronic Lyme disease. The cause of PTLDS is still under investigation, and the evidence does not support the idea of a persistent bacterial infection. Multiple studies from the National Institutes of Health have shown that long-term use of antibiotics does not benefit patients who continue to experience symptoms after initial treatment. Several studies have shown that severe adverse effects can result from extended intravenous antibiotic treatment, including death.
Nevertheless, the plaintiffs in the lawsuit argued that the insurance companies “enlisted the help of doctors who were researching Lyme disease – the IDSA panelists – and paid them large fees to develop arbitrary guidelines for testing Lyme disease,” thereby enabling the insurance companies to deny coverage for long-term antibiotic treatment to patients.
“The assertions were just preposterous,” Dr. McQuillen said.
In addition to the conspiracy charge, the plaintiffs brought additional accusations to the lawsuit over the years, including racketeering and claims that the guidelines contain false representations regarding Lyme disease testing and treatment. The plaintiffs claimed that the guidelines didn’t acknowledge that treatment can fail and included false information about how to test for Lyme disease. In reality, however, the guidelines do acknowledge that not all patients respond to the recommended 2- to 4-week course of antibiotics and that some diagnoses should be made clinically rather than on the basis of testing.
Regardless, guidelines are not stipulations. They’re a summation of the medical and scientific findings on Lyme disease based on careful review of hundreds of studies.
“They make really clear that adherence to the guidelines [is] voluntary. They aren’t a standard of care from which deviation of care is a problem,” Dr. McQuillen said. “You take those guidelines and apply it to the patient in front of you, and you see what fits best for that patient, because not every patient is going to fit into guidelines.”
Further, the authors said that IDSA vets their recommendations for any potential conflicts of interest in accordance with the organization’s guidelines practices.
“The point of the guidelines is to have people on the committee who don’t care what the guidelines are as long as we have good patient care,” Dr. McQuillen said.
Choosing to fight
Malpractice insurance does not cover this kind of lawsuit, because the doctors named in it did not personally treat any of the patients who filed it. Thus, the doctors were at risk of losing thousands, or millions, of dollars in legal fees, even if they ultimately prevail. Several of the physicians’ academic and health care institutions stepped in to cover some fees, and IDSA covered the rest in a joint defense.
“The IDSA provided me a lawyer at no cost to me, and I felt protected by them,” Dr. Sigal said. “They took care of me and made sure I was safe, and I am grateful to them for that.”
Dr. McQuillen said the expenses exceeded what the organization’s umbrella insurance covered. The physicians had invested their time and effort into the guidelines without any financial compensation.
“They’ve basically put a lot of sweat equity into producing guidelines” that follow the organization’s practices and ethics, Dr. McQuillen said. “To leave them out on an island by themselves is just not the right thing to do. We wouldn’t do that for any of our members who did something on behalf of our society.”
IDSA could have chosen to settle the lawsuit, as the insurance companies did.
“None of us on the board felt that was the right thing to do, because we believe in the process, and the science is right, and you shouldn’t be able to try to change that by having a lawsuit that’s baseless,” Dr. McQuillen said.
Several of the doctors named in the suit spoke with this news organization off the record about the exhaustion, frustration, and general suffering the suit has caused them over the past several years, including ongoing harassment that targeted their families and often became quite personal. But none expressed any wish that IDSA had chosen the faster, cheaper, easier route of settling.
“I love the organization for having done this rather than caving and paying,” Dr. Sigal said. “They showed real moral character, real integrity in fighting this suit, because they had done nothing wrong.”
Fighting the suit was about more than standing by the science, though. It’s essential to ensure physicians continue to conduct research and write clinical guidelines, even about ambiguous or controversial topics, said Raymond J. Dattwyler, MD, a professor of microbiology, immunology, and medicine at New York Medical College, Valhalla, who wrote the treatment part of the guidelines and was named in the suit.
“I was really surprised that someone would sue for scientific guidelines, because guidelines are common across medicine, and they’re just a roadmap to help practicing physicians understand how to handle evaluation or treatment of any number of particular problems,” Dr. Dattwyler said in an interview. But he wasn’t surprised that IDSA chose to fight the accusations, “because the principle involved is so compelling. It’s really standing up for all medical societies, and it’s very important to have guidelines. For the health and welfare of the American public, you need to have good information readily available to the practicing physicians.”
If the patient group had won in a settlement, it could potentially have led to less rigorous guidelines from other medical organizations, which would have had an adverse effect on public health, Dr. Dattwyler said. Such a chilling effect could reverberate far beyond the management of Lyme disease.
“One of the problems with our legal system is anybody can sue anybody, but it costs so much to defend yourself,” Dr. Dattwyler said. “This lawsuit costs millions, so that’s chilling. That’s going to inhibit guidelines, and it’s not only guidelines for infectious disease but it’s guidelines for cancer, guidelines for allergic diseases, guidelines for any number of things.”
To an extent, the threats and harassment that patient groups have directed toward different doctors have already had a chilling effect.
“For the people who gave of their time in good faith to generate these guidelines to get harassed everywhere, all the time, sometimes at home, sometimes at their place of work, it’s just unfair,” Dr. McQuillen said. “It also might discourage people from working in research to try to figure out better diagnostics or get a vaccine that actually works. Even if you really find it incredibly interesting, if laying over you is the threat that someone is going to sue you baselessly, and you’re going to have to put the time and effort into defending that, not to mention the money, I can’t see how that would be considered a positive that would encourage you to do it. In some ways, attacking people that are trying to help may drive them away from trying to help.
“At the same time, professional disagreements among practitioners – including a small minority who do treat patients with lengthy courses of antibiotics – can ultimately harm patient care, Dr. Flanigan said.
“There’s a lot of energy being expended fighting among different care providers, and often the individual needs of the patients seem to be not addressed,” Dr. Flanigan said. “The discord between different approaches often seems more important than spending time with the individual patient and trying to find a tailored approach to treatment which can benefit the patient best.”
At the same time, Dr. Sigal said he believes most of the clinicians who use non–evidence-based treatments for their patients do so because they genuinely believe it’s the right thing to do.
“I think they’re motivated by the same concerns that I have, and that is, I need to do what’s best for my patient,” Dr. Sigal said. Ultimately, the evidence should lead the way. “The only arbiter we possibly have in deciding these things is the medical scientific literature,” he added, “and if you can’t subscribe to that, then this way lies madness.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Years ago, when rheumatologist Leonard Sigal, MD, was undertaking research on Lyme disease and treating patients with the condition at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., a regular stream of abuse and threats became the usual background noise of his work. He didn’t get used to it, but it never stopped.
“I was accused of incredibly heinous crimes,” Dr. Sigal said in an interview. “I was accused of lying, cheating, of doing things to make money that were against the public interest and against the interest of patients in general.”
It’s an experience many doctors who treat Lyme disease have endured, so much so that some infectious disease doctors aren’t comfortable treating patients with Lyme disease, according to Timothy Flanigan, MD, a professor of infectious disease at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
But it wasn’t until Dr. Sigal left academia in 2003 that he realized the toll all that background abuse had been taking on him.
“It was a breath of fresh air,” he said. “I didn’t have to go into clinic and argue with people. I didn’t have to read articles in the newspaper that made no sense whatsoever. I didn’t have to hear through second and third parties how such and such was saying horrible things about me. I didn’t have to fight anymore. When I was in industry and working on stuff that had nothing to do with Lyme disease, I realized what a relief it was not to have that burden.”
So the last thing Dr. Sigal expected after all these years was to find himself named in a lawsuit alleging that he was part of a conspiracy to deny patients of what they claimed was appropriate treatment for Lyme disease. Yet, that’s exactly what happened in November 2017, when a group of 24 patients with Lyme disease, led by Texas resident Lisa Torrey, filed a lawsuit against the Infectious Diseases Society of America, eight insurance companies, and 7 of the doctors involved in producing the IDSA guidelines on Lyme disease diagnosis and management. Dr. Sigal himself had not even participated in writing the guidelines. He simply reviewed them, made a few grammatical suggestions, and said they looked good. Over the next 4 years, however, he and his fellow defendants rode an emotional roller coaster of seemingly endless motions, amendments, and other legal developments, waiting to find out whether they would owe millions of dollars for simply summarizing – or just reviewing – the available medical literature on Lyme disease.
“There were times I was on the verge of real anger. I was frustrated. There were times I was frightened, and, occasionally, I would just think of it as being silly. But when I thought of it as being silly, I had to remember I was being sued in Texas, because who knows what’s going to happen,” Dr. Sigal said. “It’s not as though I was being sued in a jurisdiction where anybody knew about Lyme disease. There are examples of physicians who are convicted of doing things they didn’t do because they were sued in the wrong jurisdiction.”
Several individuals who spoke with this news organization on condition of anonymity said that the district court where the suit was filed is notorious for being especially friendly to plaintiffs. But in legal rulings issued on Sept. 1 and Sept. 20, 2021, a federal judge in Texas dismissed all the patient group’s claims. The plaintiffs filed an appeal on Oct. 19. It’s unclear whether that has any reasonable chance of success.
“One of the things this court case does is validate the fact that our [guidelines] process is a legitimate process and there isn’t outside influence from insurance companies or pharma firms,” Daniel McQuillen, MD, president of IDSA, said in an interview. “We don’t really want anything other than to be vindicated, which we were, 100%.”
But that vindication came with a cost, both emotional and financial. Although IDSA’s insurance covered many of its legal costs, “it’s not a trivial expense,” Dr. McQuillen said. “We’re left with a baseless lawsuit with no facts that went on for 4 years, and our [medical] society basically bore all that expense, which isn’t really particularly fair.”
‘Preposterous’ accusations
The lawsuit alleged that the IDSA, the seven named physicians, and the insurance companies had “engaged in a decades-long conspiracy to deny the existence and prevent treatment of chronic Lyme disease.” The patient group claimed that the doctors knew that many patients with Lyme disease do not respond to short-term antibiotic treatment and instead need “long-term antibiotic treatment until the symptoms are resolved,” an assertion not supported by the scientific evidence.
What many patients call “chronic Lyme disease” is termed posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTDLS), a constellation of symptoms that include pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties that some people experience after a 2- to 4-week course of antibiotics for Lyme disease. It took years of patient advocacy before the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recognized PTLDS as a condition, but awareness of it has been increasing, said Dr. Flanigan, who was not involved in the lawsuit but treats patients with Lyme disease and PTLDS.
“Long haulers and sequelae of COVID have really opened the eyes of many practitioners that these long-term inflammatory conditions are real and very challenging to treat, and we need to work with patients to help them improve their health,” Dr. Flanigan said. “It’s a sad commentary on our society that the difficulty in treating patients with posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome, or what is commonly referred to by patients as chronic Lyme, ends up in a lawsuit in court.” He said he’s glad the lawsuit was dismissed but added that “there’s a crying need for additional high-quality, evidence-based research to help patients who are suffering from posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome.”
Patients fought for broader recognition of their condition, and some of them organized. They came up with their own ideas of what was causing their symptoms to persist. One that especially took hold was that infection from Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, persists after initial antibiotic treatment, causing so-called chronic Lyme disease. The cause of PTLDS is still under investigation, and the evidence does not support the idea of a persistent bacterial infection. Multiple studies from the National Institutes of Health have shown that long-term use of antibiotics does not benefit patients who continue to experience symptoms after initial treatment. Several studies have shown that severe adverse effects can result from extended intravenous antibiotic treatment, including death.
Nevertheless, the plaintiffs in the lawsuit argued that the insurance companies “enlisted the help of doctors who were researching Lyme disease – the IDSA panelists – and paid them large fees to develop arbitrary guidelines for testing Lyme disease,” thereby enabling the insurance companies to deny coverage for long-term antibiotic treatment to patients.
“The assertions were just preposterous,” Dr. McQuillen said.
In addition to the conspiracy charge, the plaintiffs brought additional accusations to the lawsuit over the years, including racketeering and claims that the guidelines contain false representations regarding Lyme disease testing and treatment. The plaintiffs claimed that the guidelines didn’t acknowledge that treatment can fail and included false information about how to test for Lyme disease. In reality, however, the guidelines do acknowledge that not all patients respond to the recommended 2- to 4-week course of antibiotics and that some diagnoses should be made clinically rather than on the basis of testing.
Regardless, guidelines are not stipulations. They’re a summation of the medical and scientific findings on Lyme disease based on careful review of hundreds of studies.
“They make really clear that adherence to the guidelines [is] voluntary. They aren’t a standard of care from which deviation of care is a problem,” Dr. McQuillen said. “You take those guidelines and apply it to the patient in front of you, and you see what fits best for that patient, because not every patient is going to fit into guidelines.”
Further, the authors said that IDSA vets their recommendations for any potential conflicts of interest in accordance with the organization’s guidelines practices.
“The point of the guidelines is to have people on the committee who don’t care what the guidelines are as long as we have good patient care,” Dr. McQuillen said.
Choosing to fight
Malpractice insurance does not cover this kind of lawsuit, because the doctors named in it did not personally treat any of the patients who filed it. Thus, the doctors were at risk of losing thousands, or millions, of dollars in legal fees, even if they ultimately prevail. Several of the physicians’ academic and health care institutions stepped in to cover some fees, and IDSA covered the rest in a joint defense.
“The IDSA provided me a lawyer at no cost to me, and I felt protected by them,” Dr. Sigal said. “They took care of me and made sure I was safe, and I am grateful to them for that.”
Dr. McQuillen said the expenses exceeded what the organization’s umbrella insurance covered. The physicians had invested their time and effort into the guidelines without any financial compensation.
“They’ve basically put a lot of sweat equity into producing guidelines” that follow the organization’s practices and ethics, Dr. McQuillen said. “To leave them out on an island by themselves is just not the right thing to do. We wouldn’t do that for any of our members who did something on behalf of our society.”
IDSA could have chosen to settle the lawsuit, as the insurance companies did.
“None of us on the board felt that was the right thing to do, because we believe in the process, and the science is right, and you shouldn’t be able to try to change that by having a lawsuit that’s baseless,” Dr. McQuillen said.
Several of the doctors named in the suit spoke with this news organization off the record about the exhaustion, frustration, and general suffering the suit has caused them over the past several years, including ongoing harassment that targeted their families and often became quite personal. But none expressed any wish that IDSA had chosen the faster, cheaper, easier route of settling.
“I love the organization for having done this rather than caving and paying,” Dr. Sigal said. “They showed real moral character, real integrity in fighting this suit, because they had done nothing wrong.”
Fighting the suit was about more than standing by the science, though. It’s essential to ensure physicians continue to conduct research and write clinical guidelines, even about ambiguous or controversial topics, said Raymond J. Dattwyler, MD, a professor of microbiology, immunology, and medicine at New York Medical College, Valhalla, who wrote the treatment part of the guidelines and was named in the suit.
“I was really surprised that someone would sue for scientific guidelines, because guidelines are common across medicine, and they’re just a roadmap to help practicing physicians understand how to handle evaluation or treatment of any number of particular problems,” Dr. Dattwyler said in an interview. But he wasn’t surprised that IDSA chose to fight the accusations, “because the principle involved is so compelling. It’s really standing up for all medical societies, and it’s very important to have guidelines. For the health and welfare of the American public, you need to have good information readily available to the practicing physicians.”
If the patient group had won in a settlement, it could potentially have led to less rigorous guidelines from other medical organizations, which would have had an adverse effect on public health, Dr. Dattwyler said. Such a chilling effect could reverberate far beyond the management of Lyme disease.
“One of the problems with our legal system is anybody can sue anybody, but it costs so much to defend yourself,” Dr. Dattwyler said. “This lawsuit costs millions, so that’s chilling. That’s going to inhibit guidelines, and it’s not only guidelines for infectious disease but it’s guidelines for cancer, guidelines for allergic diseases, guidelines for any number of things.”
To an extent, the threats and harassment that patient groups have directed toward different doctors have already had a chilling effect.
“For the people who gave of their time in good faith to generate these guidelines to get harassed everywhere, all the time, sometimes at home, sometimes at their place of work, it’s just unfair,” Dr. McQuillen said. “It also might discourage people from working in research to try to figure out better diagnostics or get a vaccine that actually works. Even if you really find it incredibly interesting, if laying over you is the threat that someone is going to sue you baselessly, and you’re going to have to put the time and effort into defending that, not to mention the money, I can’t see how that would be considered a positive that would encourage you to do it. In some ways, attacking people that are trying to help may drive them away from trying to help.
“At the same time, professional disagreements among practitioners – including a small minority who do treat patients with lengthy courses of antibiotics – can ultimately harm patient care, Dr. Flanigan said.
“There’s a lot of energy being expended fighting among different care providers, and often the individual needs of the patients seem to be not addressed,” Dr. Flanigan said. “The discord between different approaches often seems more important than spending time with the individual patient and trying to find a tailored approach to treatment which can benefit the patient best.”
At the same time, Dr. Sigal said he believes most of the clinicians who use non–evidence-based treatments for their patients do so because they genuinely believe it’s the right thing to do.
“I think they’re motivated by the same concerns that I have, and that is, I need to do what’s best for my patient,” Dr. Sigal said. Ultimately, the evidence should lead the way. “The only arbiter we possibly have in deciding these things is the medical scientific literature,” he added, “and if you can’t subscribe to that, then this way lies madness.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fluoroquinolones linked to sudden death risk for those on hemodialysis
, a large observational study suggests.
However, in many cases, the absolute risk is relatively small, and the antimicrobial benefits of a fluoroquinolone may outweigh the potential cardiac risks, the researchers say.
“Pathogen-directed treatment of respiratory infections is of the utmost importance. Respiratory fluoroquinolones should be prescribed whenever an amoxicillin-based antibiotic offers suboptimal antimicrobial coverage and clinicians should consider electrocardiographic monitoring,” first author Magdalene M. Assimon, PharmD, PhD, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization.
The study was published online Oct. 20 in JAMA Cardiology (doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.4234).
Nearly twofold increased risk
The QT interval-prolonging potential of fluoroquinolone antibiotics are well known. However, evidence linking respiratory fluoroquinolones to adverse cardiac outcomes in the hemodialysis population is limited.
These new observational findings are based on a total of 626,322 antibiotic treatment episodes among 264,968 adults (mean age, 61 years; 51% men) receiving in-center hemodialysis – with respiratory fluoroquinolone making up 40.2% of treatment episodes and amoxicillin-based antibiotic treatment episodes making up 59.8%.
The rate of SCD within 5 days of outpatient initiation of a study antibiotic was 105.7 per 100,000 people prescribed a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or moxifloxacin) versus with 40.0 per 100,000 prescribed amoxicillin or amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (weighted hazard ratio: 1.95; 95% confidence interval, 1.57-2.41).
The authors estimate that one additional SCD would occur during a 5-day follow-up period for every 2,273 respiratory fluoroquinolone treatment episodes. Consistent associations were seen when follow-up was extended to 7, 10, and 14 days.
“Our data suggest that curtailing respiratory fluoroquinolone prescribing may be one actionable strategy to mitigate SCD risk in the hemodialysis population. However, the associated absolute risk reduction would be relatively small,” wrote the authors.
They noted that the rate of SCD in the hemodialysis population exceeds that of the general population by more than 20-fold. Most patients undergoing hemodialysis have a least one risk factor for drug-induced QT interval prolongation.
In the current study, nearly 20% of hemodialysis patients prescribed a respiratory fluoroquinolone were taking other medications with known risk for torsades de pointes.
“Our results emphasize the importance of performing a thorough medication review and considering pharmacodynamic drug interactions before prescribing new drug therapies for any condition,” Dr. Assimon and colleagues advised.
They suggest that clinicians consider electrocardiographic monitoring before and during fluoroquinolone therapy in hemodialysis patients, especially in high-risk individuals.
Valuable study
Reached for comment, Ankur Shah, MD, of the division of kidney diseases and hypertension, Brown University, Providence, R.I., called the analysis “valuable” and said the results are “consistent with the known association of cardiac arrhythmias with respiratory fluoroquinolone use in the general population, postulated to be due to increased risk of torsades de pointes from QTc prolongation. This abnormal heart rhythm can lead to sudden cardiac death.
“Notably, the population receiving respiratory fluoroquinolones had a higher incidence of cardiac disease at baseline, but the risk persisted after adjustment for this increased burden of comorbidity,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. He was not involved in the current research.
Dr. Shah cautioned that observational data such as these should be considered more “hypothesis-generating than practice-changing, as there may be unrecognized confounders or differences in the population that received the respiratory fluoroquinolones.
“A prospective randomized trial would provide a definitive answer, but in the interim, caution should be taken in using respiratory fluoroquinolones when local bacterial resistance patterns or patient-specific data offer another option,” Dr. Shah concluded.
Dr. Assimon reported receiving grants from the Renal Research Institute (a subsidiary of Fresenius Medical Care), honoraria from the International Society of Nephrology for serving as a statistical reviewer for Kidney International Reports, and honoraria from the American Society of Nephrology for serving as an editorial fellow for the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. Dr. Shah has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large observational study suggests.
However, in many cases, the absolute risk is relatively small, and the antimicrobial benefits of a fluoroquinolone may outweigh the potential cardiac risks, the researchers say.
“Pathogen-directed treatment of respiratory infections is of the utmost importance. Respiratory fluoroquinolones should be prescribed whenever an amoxicillin-based antibiotic offers suboptimal antimicrobial coverage and clinicians should consider electrocardiographic monitoring,” first author Magdalene M. Assimon, PharmD, PhD, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization.
The study was published online Oct. 20 in JAMA Cardiology (doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.4234).
Nearly twofold increased risk
The QT interval-prolonging potential of fluoroquinolone antibiotics are well known. However, evidence linking respiratory fluoroquinolones to adverse cardiac outcomes in the hemodialysis population is limited.
These new observational findings are based on a total of 626,322 antibiotic treatment episodes among 264,968 adults (mean age, 61 years; 51% men) receiving in-center hemodialysis – with respiratory fluoroquinolone making up 40.2% of treatment episodes and amoxicillin-based antibiotic treatment episodes making up 59.8%.
The rate of SCD within 5 days of outpatient initiation of a study antibiotic was 105.7 per 100,000 people prescribed a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or moxifloxacin) versus with 40.0 per 100,000 prescribed amoxicillin or amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (weighted hazard ratio: 1.95; 95% confidence interval, 1.57-2.41).
The authors estimate that one additional SCD would occur during a 5-day follow-up period for every 2,273 respiratory fluoroquinolone treatment episodes. Consistent associations were seen when follow-up was extended to 7, 10, and 14 days.
“Our data suggest that curtailing respiratory fluoroquinolone prescribing may be one actionable strategy to mitigate SCD risk in the hemodialysis population. However, the associated absolute risk reduction would be relatively small,” wrote the authors.
They noted that the rate of SCD in the hemodialysis population exceeds that of the general population by more than 20-fold. Most patients undergoing hemodialysis have a least one risk factor for drug-induced QT interval prolongation.
In the current study, nearly 20% of hemodialysis patients prescribed a respiratory fluoroquinolone were taking other medications with known risk for torsades de pointes.
“Our results emphasize the importance of performing a thorough medication review and considering pharmacodynamic drug interactions before prescribing new drug therapies for any condition,” Dr. Assimon and colleagues advised.
They suggest that clinicians consider electrocardiographic monitoring before and during fluoroquinolone therapy in hemodialysis patients, especially in high-risk individuals.
Valuable study
Reached for comment, Ankur Shah, MD, of the division of kidney diseases and hypertension, Brown University, Providence, R.I., called the analysis “valuable” and said the results are “consistent with the known association of cardiac arrhythmias with respiratory fluoroquinolone use in the general population, postulated to be due to increased risk of torsades de pointes from QTc prolongation. This abnormal heart rhythm can lead to sudden cardiac death.
“Notably, the population receiving respiratory fluoroquinolones had a higher incidence of cardiac disease at baseline, but the risk persisted after adjustment for this increased burden of comorbidity,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. He was not involved in the current research.
Dr. Shah cautioned that observational data such as these should be considered more “hypothesis-generating than practice-changing, as there may be unrecognized confounders or differences in the population that received the respiratory fluoroquinolones.
“A prospective randomized trial would provide a definitive answer, but in the interim, caution should be taken in using respiratory fluoroquinolones when local bacterial resistance patterns or patient-specific data offer another option,” Dr. Shah concluded.
Dr. Assimon reported receiving grants from the Renal Research Institute (a subsidiary of Fresenius Medical Care), honoraria from the International Society of Nephrology for serving as a statistical reviewer for Kidney International Reports, and honoraria from the American Society of Nephrology for serving as an editorial fellow for the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. Dr. Shah has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large observational study suggests.
However, in many cases, the absolute risk is relatively small, and the antimicrobial benefits of a fluoroquinolone may outweigh the potential cardiac risks, the researchers say.
“Pathogen-directed treatment of respiratory infections is of the utmost importance. Respiratory fluoroquinolones should be prescribed whenever an amoxicillin-based antibiotic offers suboptimal antimicrobial coverage and clinicians should consider electrocardiographic monitoring,” first author Magdalene M. Assimon, PharmD, PhD, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization.
The study was published online Oct. 20 in JAMA Cardiology (doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.4234).
Nearly twofold increased risk
The QT interval-prolonging potential of fluoroquinolone antibiotics are well known. However, evidence linking respiratory fluoroquinolones to adverse cardiac outcomes in the hemodialysis population is limited.
These new observational findings are based on a total of 626,322 antibiotic treatment episodes among 264,968 adults (mean age, 61 years; 51% men) receiving in-center hemodialysis – with respiratory fluoroquinolone making up 40.2% of treatment episodes and amoxicillin-based antibiotic treatment episodes making up 59.8%.
The rate of SCD within 5 days of outpatient initiation of a study antibiotic was 105.7 per 100,000 people prescribed a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or moxifloxacin) versus with 40.0 per 100,000 prescribed amoxicillin or amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (weighted hazard ratio: 1.95; 95% confidence interval, 1.57-2.41).
The authors estimate that one additional SCD would occur during a 5-day follow-up period for every 2,273 respiratory fluoroquinolone treatment episodes. Consistent associations were seen when follow-up was extended to 7, 10, and 14 days.
“Our data suggest that curtailing respiratory fluoroquinolone prescribing may be one actionable strategy to mitigate SCD risk in the hemodialysis population. However, the associated absolute risk reduction would be relatively small,” wrote the authors.
They noted that the rate of SCD in the hemodialysis population exceeds that of the general population by more than 20-fold. Most patients undergoing hemodialysis have a least one risk factor for drug-induced QT interval prolongation.
In the current study, nearly 20% of hemodialysis patients prescribed a respiratory fluoroquinolone were taking other medications with known risk for torsades de pointes.
“Our results emphasize the importance of performing a thorough medication review and considering pharmacodynamic drug interactions before prescribing new drug therapies for any condition,” Dr. Assimon and colleagues advised.
They suggest that clinicians consider electrocardiographic monitoring before and during fluoroquinolone therapy in hemodialysis patients, especially in high-risk individuals.
Valuable study
Reached for comment, Ankur Shah, MD, of the division of kidney diseases and hypertension, Brown University, Providence, R.I., called the analysis “valuable” and said the results are “consistent with the known association of cardiac arrhythmias with respiratory fluoroquinolone use in the general population, postulated to be due to increased risk of torsades de pointes from QTc prolongation. This abnormal heart rhythm can lead to sudden cardiac death.
“Notably, the population receiving respiratory fluoroquinolones had a higher incidence of cardiac disease at baseline, but the risk persisted after adjustment for this increased burden of comorbidity,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. He was not involved in the current research.
Dr. Shah cautioned that observational data such as these should be considered more “hypothesis-generating than practice-changing, as there may be unrecognized confounders or differences in the population that received the respiratory fluoroquinolones.
“A prospective randomized trial would provide a definitive answer, but in the interim, caution should be taken in using respiratory fluoroquinolones when local bacterial resistance patterns or patient-specific data offer another option,” Dr. Shah concluded.
Dr. Assimon reported receiving grants from the Renal Research Institute (a subsidiary of Fresenius Medical Care), honoraria from the International Society of Nephrology for serving as a statistical reviewer for Kidney International Reports, and honoraria from the American Society of Nephrology for serving as an editorial fellow for the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. Dr. Shah has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19-era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time,” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic, Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today, you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician.
Dr. Persampiere is a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at [email protected] or via [email protected].
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19-era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time,” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic, Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today, you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician.
Dr. Persampiere is a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at [email protected] or via [email protected].
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19-era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time,” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic, Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today, you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician.
Dr. Persampiere is a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at [email protected] or via [email protected].
Molluscum Contagiosum Superimposed on Lymphangioma Circumscriptum
To the Editor:
Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system.1 It is postulated to arise from abnormal lymphatic cisterns, and it grows separately from the normal lymphatic system. These cisterns are connected to malformed dermal lymphatic channels, and the contraction of smooth muscles lining cisterns will cause dilatation of connected lymphatic channels in the papillary dermis due to back pressure,1,2 which causes a classic LC manifestation characterized by multiple translucent, sometimes red-brown, small vesicles grouped together. Lymphangioma circumscriptum can be difficult to differentiate from molluscum contagiosum (MC) due to the similar morphology.1 We present a notable case of MC superimposed on LC.
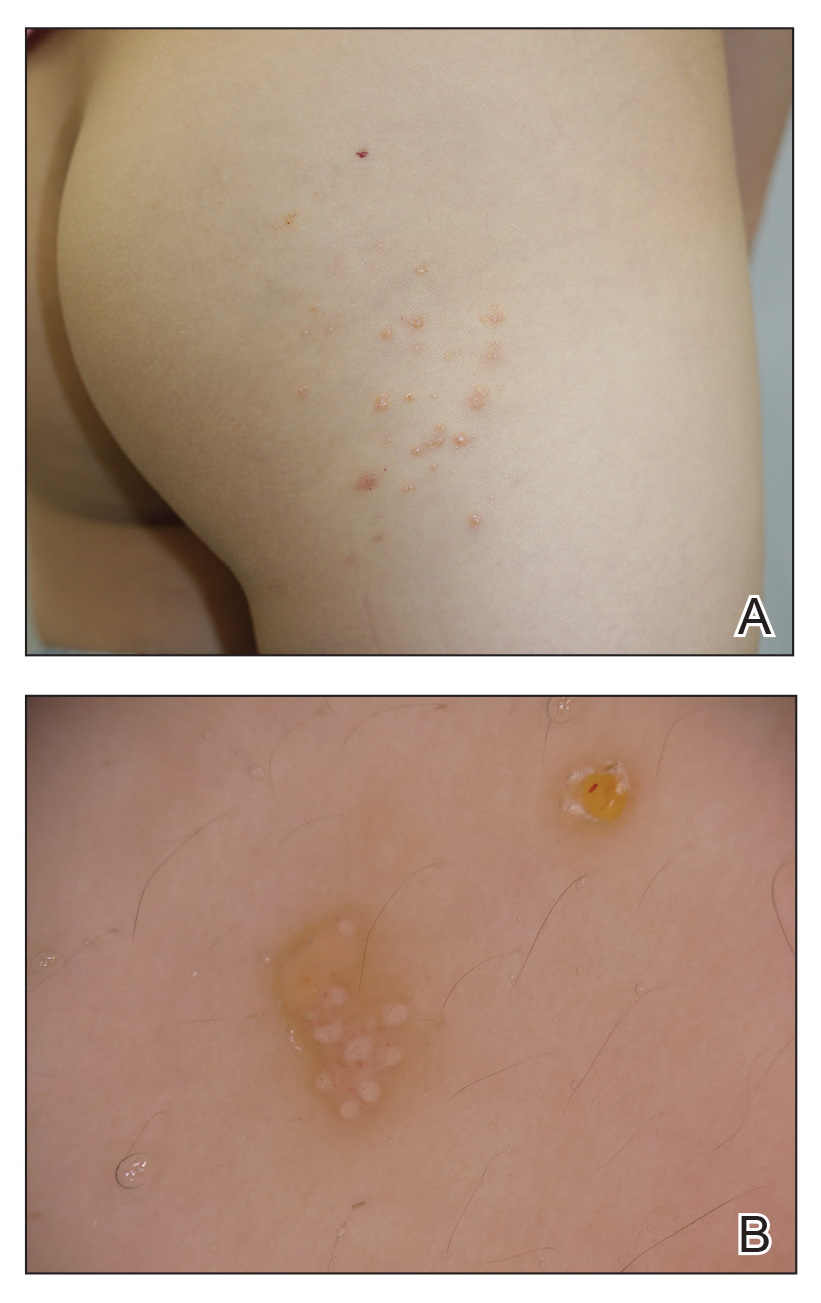
A 6-year-old girl presented with multiple grouped, clear, vesicular papules on the right buttock of 18 months’ duration. Some of the papules showed tiny whitish pearl-like particles on the top (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present elsewhere on the body. She had no underlying disease and did not have a history of procedure, edema, or malformation of the lower extremities. Histopathology from one of the lesions showed dilated cystic lymphatic spaces in the papillary dermis lined with flattened endothelium and cup-shaped downward proliferation of the epidermis with presence of large intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies—features of both LC and MC (Figure 2). We waited 4 additional months for the MC lesions to self-resolve, but they persisted. The patient’s mother strongly requested for their removal, and the residual MC lesions were carefully removed by CO2 laser. To prevent unnecessary physical damage to underlying LC lesions and minimize scarring, we opted to use the CO2 laser and not simple curettage. She currently is under periodic observation with no signs of clinical recurrence of MC, but the LC lesions naturally persisted.
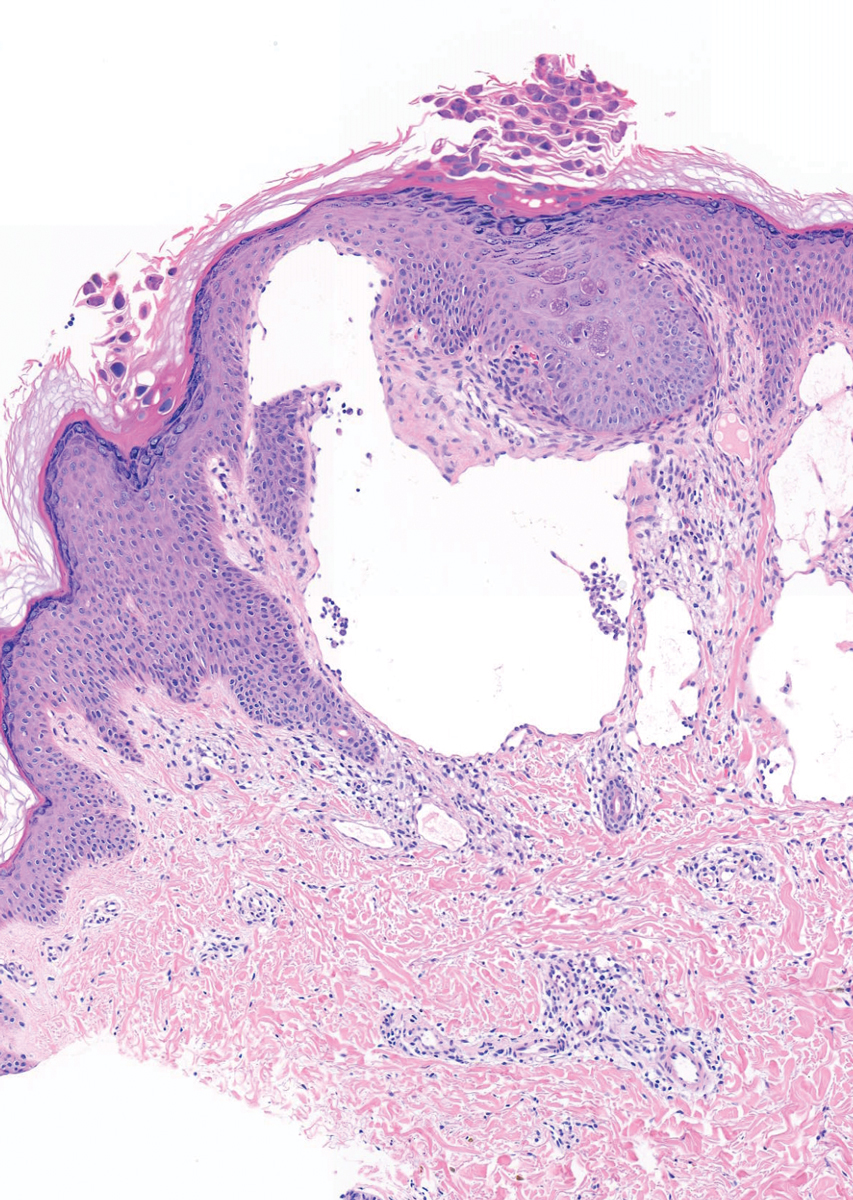
Due to its vesicular and sometimes warty appearance, LC can sometimes be hard to differentiate from MC. In one report, a vesicular plaquelike lesion on the trunk initially was misdiagnosed and treated as MC but was histologically confirmed as LC several years later.3 Our case demonstrates the coexistence of MC and LC. Although this phenomenon may be coincidental, we have not noticed any additional MC lesions on the body and MC only existed over the LC lesions, implying a possible pathophysiologic relationship. It is unlikely that MC might have preceded the development of LC. Although acquired LC exists, it has mostly been reported in the genital region of patients with conditions leading to lymphatic obstruction such as surgery, radiation therapy, malignancy, or serious infections.4 Because our patient developed lesions at an early age without any remarkable medical history, it is likely that she had congenital LC that was secondarily infected by the MC virus. Vesicular lesions in LC are known to rupture easily and may serve as a vulnerable entry site for pathogens. Subsequent secondary bacterial infections are common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most prominent entity.1 However, secondary viral infection rarely is reported. It is possible that the abnormally dilated lymphatic channels of LC that lack communication with the normal lymphatic system have contributed to an LC site-specific vulnerability to MC virus. Further studies and subsequent reports are required to confirm this hypothesis.
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Fatima S, Uddin N, Idrees R, et al. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: clinicopathological spectrum of 29 cases. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:658-661. doi:09.2015/JCPSP.658661
- Patel GA, Siperstein RD, Ragi G, Schwartz RA. Zosteriform lymphangioma circumscriptum. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009;18:179-182.
- Chang MB, Newman CC, Davis MD, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasia (lymphangioma circumscriptum) of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of 11 patients from a single institution and 67 from the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E482-E487. doi:10.1111/ijd.13264
To the Editor:
Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system.1 It is postulated to arise from abnormal lymphatic cisterns, and it grows separately from the normal lymphatic system. These cisterns are connected to malformed dermal lymphatic channels, and the contraction of smooth muscles lining cisterns will cause dilatation of connected lymphatic channels in the papillary dermis due to back pressure,1,2 which causes a classic LC manifestation characterized by multiple translucent, sometimes red-brown, small vesicles grouped together. Lymphangioma circumscriptum can be difficult to differentiate from molluscum contagiosum (MC) due to the similar morphology.1 We present a notable case of MC superimposed on LC.

A 6-year-old girl presented with multiple grouped, clear, vesicular papules on the right buttock of 18 months’ duration. Some of the papules showed tiny whitish pearl-like particles on the top (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present elsewhere on the body. She had no underlying disease and did not have a history of procedure, edema, or malformation of the lower extremities. Histopathology from one of the lesions showed dilated cystic lymphatic spaces in the papillary dermis lined with flattened endothelium and cup-shaped downward proliferation of the epidermis with presence of large intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies—features of both LC and MC (Figure 2). We waited 4 additional months for the MC lesions to self-resolve, but they persisted. The patient’s mother strongly requested for their removal, and the residual MC lesions were carefully removed by CO2 laser. To prevent unnecessary physical damage to underlying LC lesions and minimize scarring, we opted to use the CO2 laser and not simple curettage. She currently is under periodic observation with no signs of clinical recurrence of MC, but the LC lesions naturally persisted.

Due to its vesicular and sometimes warty appearance, LC can sometimes be hard to differentiate from MC. In one report, a vesicular plaquelike lesion on the trunk initially was misdiagnosed and treated as MC but was histologically confirmed as LC several years later.3 Our case demonstrates the coexistence of MC and LC. Although this phenomenon may be coincidental, we have not noticed any additional MC lesions on the body and MC only existed over the LC lesions, implying a possible pathophysiologic relationship. It is unlikely that MC might have preceded the development of LC. Although acquired LC exists, it has mostly been reported in the genital region of patients with conditions leading to lymphatic obstruction such as surgery, radiation therapy, malignancy, or serious infections.4 Because our patient developed lesions at an early age without any remarkable medical history, it is likely that she had congenital LC that was secondarily infected by the MC virus. Vesicular lesions in LC are known to rupture easily and may serve as a vulnerable entry site for pathogens. Subsequent secondary bacterial infections are common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most prominent entity.1 However, secondary viral infection rarely is reported. It is possible that the abnormally dilated lymphatic channels of LC that lack communication with the normal lymphatic system have contributed to an LC site-specific vulnerability to MC virus. Further studies and subsequent reports are required to confirm this hypothesis.
To the Editor:
Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system.1 It is postulated to arise from abnormal lymphatic cisterns, and it grows separately from the normal lymphatic system. These cisterns are connected to malformed dermal lymphatic channels, and the contraction of smooth muscles lining cisterns will cause dilatation of connected lymphatic channels in the papillary dermis due to back pressure,1,2 which causes a classic LC manifestation characterized by multiple translucent, sometimes red-brown, small vesicles grouped together. Lymphangioma circumscriptum can be difficult to differentiate from molluscum contagiosum (MC) due to the similar morphology.1 We present a notable case of MC superimposed on LC.

A 6-year-old girl presented with multiple grouped, clear, vesicular papules on the right buttock of 18 months’ duration. Some of the papules showed tiny whitish pearl-like particles on the top (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present elsewhere on the body. She had no underlying disease and did not have a history of procedure, edema, or malformation of the lower extremities. Histopathology from one of the lesions showed dilated cystic lymphatic spaces in the papillary dermis lined with flattened endothelium and cup-shaped downward proliferation of the epidermis with presence of large intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies—features of both LC and MC (Figure 2). We waited 4 additional months for the MC lesions to self-resolve, but they persisted. The patient’s mother strongly requested for their removal, and the residual MC lesions were carefully removed by CO2 laser. To prevent unnecessary physical damage to underlying LC lesions and minimize scarring, we opted to use the CO2 laser and not simple curettage. She currently is under periodic observation with no signs of clinical recurrence of MC, but the LC lesions naturally persisted.

Due to its vesicular and sometimes warty appearance, LC can sometimes be hard to differentiate from MC. In one report, a vesicular plaquelike lesion on the trunk initially was misdiagnosed and treated as MC but was histologically confirmed as LC several years later.3 Our case demonstrates the coexistence of MC and LC. Although this phenomenon may be coincidental, we have not noticed any additional MC lesions on the body and MC only existed over the LC lesions, implying a possible pathophysiologic relationship. It is unlikely that MC might have preceded the development of LC. Although acquired LC exists, it has mostly been reported in the genital region of patients with conditions leading to lymphatic obstruction such as surgery, radiation therapy, malignancy, or serious infections.4 Because our patient developed lesions at an early age without any remarkable medical history, it is likely that she had congenital LC that was secondarily infected by the MC virus. Vesicular lesions in LC are known to rupture easily and may serve as a vulnerable entry site for pathogens. Subsequent secondary bacterial infections are common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most prominent entity.1 However, secondary viral infection rarely is reported. It is possible that the abnormally dilated lymphatic channels of LC that lack communication with the normal lymphatic system have contributed to an LC site-specific vulnerability to MC virus. Further studies and subsequent reports are required to confirm this hypothesis.
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Fatima S, Uddin N, Idrees R, et al. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: clinicopathological spectrum of 29 cases. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:658-661. doi:09.2015/JCPSP.658661
- Patel GA, Siperstein RD, Ragi G, Schwartz RA. Zosteriform lymphangioma circumscriptum. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009;18:179-182.
- Chang MB, Newman CC, Davis MD, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasia (lymphangioma circumscriptum) of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of 11 patients from a single institution and 67 from the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E482-E487. doi:10.1111/ijd.13264
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Fatima S, Uddin N, Idrees R, et al. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: clinicopathological spectrum of 29 cases. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:658-661. doi:09.2015/JCPSP.658661
- Patel GA, Siperstein RD, Ragi G, Schwartz RA. Zosteriform lymphangioma circumscriptum. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009;18:179-182.
- Chang MB, Newman CC, Davis MD, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasia (lymphangioma circumscriptum) of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of 11 patients from a single institution and 67 from the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E482-E487. doi:10.1111/ijd.13264
Practice Points
- Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system that can be misdiagnosed as molluscum contagiosum (MC).
- Secondary infection of LC is common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common entity, but MC virus also can be secondarily infected.
ACIP recommends Shingrix for younger immunocompromised adults; updates pneumococcal vaccine guidance
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee of Immunization Practices has voted to recommend Shingrix (zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted) for the prevention of shingles in immunodeficient or immunosuppressed adults aged 19 or older. The recommendation was approved Oct. 20 by a unanimous vote.
Shingles is a reactivation of varicella zoster virus (VZV), the virus that causes chickenpox. There are about 1 million cases of shingles in the United States every year, according to CDC estimates, and one in three Americans will develop shingles over their lifetime. While adults older than 50 are one of the most vulnerable groups to reinfection – with about 99% having been infected with VZV – a weakened immune system is another common risk factor.
The Food and Drug Administration originally approved Shingrix in 2017 for the prevention of shingles in adults over 50; in July of this year, the vaccine was approved for immunodeficient adults aged 18 or older. The approval and subsequent recommendation by ACIP were based on clinical studies of Shingrix in adults being treated for hematologic malignancies or those who had undergone an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
According to a press statement from the FDA, “Further safety and immunogenicity data were generated in adults who were, or were anticipated to be, immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to known disease or therapy, including patients with HIV, solid tumors, and renal transplants.”
For adults with functional immune systems, Shingrix is administered in two doses, 2-6 months apart. For immunocompromised individuals, the second dose can be given 1-2 months after the first dose.
During the same meeting, ACIP also voted to recommend pneumococcal vaccines for routine use in adults older than 65 and in adults aged 19-64 with chronic conditions such as diabetes, chronic heart disease, chronic liver disease, and HIV, and disease risk factors like smoking and alcoholism. The recommendation only applies to those who have not received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine or whose vaccination history is unknown. The recommendation states that qualifying adults should be vaccinated with the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Vaxneuvance followed by Pneumovax23, or a single dose of the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Prevnar 20.
These ACIP recommendations will now be sent to the directors of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services for review and approval. If approved, the recommendations are considered finalized and will be published in a future Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee of Immunization Practices has voted to recommend Shingrix (zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted) for the prevention of shingles in immunodeficient or immunosuppressed adults aged 19 or older. The recommendation was approved Oct. 20 by a unanimous vote.
Shingles is a reactivation of varicella zoster virus (VZV), the virus that causes chickenpox. There are about 1 million cases of shingles in the United States every year, according to CDC estimates, and one in three Americans will develop shingles over their lifetime. While adults older than 50 are one of the most vulnerable groups to reinfection – with about 99% having been infected with VZV – a weakened immune system is another common risk factor.
The Food and Drug Administration originally approved Shingrix in 2017 for the prevention of shingles in adults over 50; in July of this year, the vaccine was approved for immunodeficient adults aged 18 or older. The approval and subsequent recommendation by ACIP were based on clinical studies of Shingrix in adults being treated for hematologic malignancies or those who had undergone an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
According to a press statement from the FDA, “Further safety and immunogenicity data were generated in adults who were, or were anticipated to be, immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to known disease or therapy, including patients with HIV, solid tumors, and renal transplants.”
For adults with functional immune systems, Shingrix is administered in two doses, 2-6 months apart. For immunocompromised individuals, the second dose can be given 1-2 months after the first dose.
During the same meeting, ACIP also voted to recommend pneumococcal vaccines for routine use in adults older than 65 and in adults aged 19-64 with chronic conditions such as diabetes, chronic heart disease, chronic liver disease, and HIV, and disease risk factors like smoking and alcoholism. The recommendation only applies to those who have not received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine or whose vaccination history is unknown. The recommendation states that qualifying adults should be vaccinated with the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Vaxneuvance followed by Pneumovax23, or a single dose of the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Prevnar 20.
These ACIP recommendations will now be sent to the directors of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services for review and approval. If approved, the recommendations are considered finalized and will be published in a future Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee of Immunization Practices has voted to recommend Shingrix (zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted) for the prevention of shingles in immunodeficient or immunosuppressed adults aged 19 or older. The recommendation was approved Oct. 20 by a unanimous vote.
Shingles is a reactivation of varicella zoster virus (VZV), the virus that causes chickenpox. There are about 1 million cases of shingles in the United States every year, according to CDC estimates, and one in three Americans will develop shingles over their lifetime. While adults older than 50 are one of the most vulnerable groups to reinfection – with about 99% having been infected with VZV – a weakened immune system is another common risk factor.
The Food and Drug Administration originally approved Shingrix in 2017 for the prevention of shingles in adults over 50; in July of this year, the vaccine was approved for immunodeficient adults aged 18 or older. The approval and subsequent recommendation by ACIP were based on clinical studies of Shingrix in adults being treated for hematologic malignancies or those who had undergone an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
According to a press statement from the FDA, “Further safety and immunogenicity data were generated in adults who were, or were anticipated to be, immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to known disease or therapy, including patients with HIV, solid tumors, and renal transplants.”
For adults with functional immune systems, Shingrix is administered in two doses, 2-6 months apart. For immunocompromised individuals, the second dose can be given 1-2 months after the first dose.
During the same meeting, ACIP also voted to recommend pneumococcal vaccines for routine use in adults older than 65 and in adults aged 19-64 with chronic conditions such as diabetes, chronic heart disease, chronic liver disease, and HIV, and disease risk factors like smoking and alcoholism. The recommendation only applies to those who have not received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine or whose vaccination history is unknown. The recommendation states that qualifying adults should be vaccinated with the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Vaxneuvance followed by Pneumovax23, or a single dose of the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine Prevnar 20.
These ACIP recommendations will now be sent to the directors of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services for review and approval. If approved, the recommendations are considered finalized and will be published in a future Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sepsis multiplies in-hospital mortality risk in COPD
Although slightly fewer than 1% of hospitalizations for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are complicated by sepsis, this complication increases the risk for in-hospital mortality fivefold, investigators who studied a representative national sample found.
Among nearly 7 million hospitalizations in which the primary diagnosis was COPD, nearly 65,000 (0.93%) patients experienced sepsis as a complication. In all, 31% of patients with COPD and sepsis were discharged from the hospital to another care facility, and 19% of patients died in hospital, report Harshil Shah, MD, from Guthrie Corning (N.Y.) Hospital and colleagues.
“Our study highlights the need for better risk stratification in patients with COPD developing sepsis to improve the outcomes. Further studies are warranted to consider factoring some of the modifiable factors into account and to ameliorate the outcomes of sepsis during COPD hospitalizations,” Dr. Shah and colleagues write in a poster presented during the at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians, held virtually this year.
COPD has been associated with increased risk for sepsis because of the use of corticosteroids, underlying comorbidities, and, potentially, because of impaired barrier function, the authors note.
Nationwide sample
To determine the effects of sepsis and predictors of poor outcomes among patients hospitalized for COPD, the investigators used standard diagnostic codes to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of COPD from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample for the period 2007 through 2018 and sepsis from codes in secondary fields in the International Classification of Diseases (9th/10th Editions) Clinical Modification.
They identified a total of 6,940,615 hospitalizations in which the primary diagnosis was COPD; in 64,748 of those cases, sepsis was a complication.
As noted, the in-hospital death rate, one of two primary outcomes, was 19% for patients with COPD and sepsis, and the rate of discharge to other facilities was 31%.
In analysis adjusted for confounding factors, sepsis was associated with an odds ratio for mortality of 4.9 (P < .01) and an OR for discharge to a facility of 2.2 (P < .01).
With regard to trends, the investigators saw that, although the adjusted odds for in-hospital mortality remained stable over time, discharge to facilities increased significantly. In 2007, the adjusted OR was 2.2, whereas in 2018, it was 2.6 (P for trend = .02).
Predictors of in-hospital mortality among patients with sepsis included increasing age (OR, not shown), White ethnicity (OR, 1.2), treatment in the Northeast region (OR, 1.4), disseminated intravascular coagulation (OR, 3.7), pneumococcal infection (OR, 1.2), congestive heart failure (OR, 1.2), and renal failure (OR, 1.4; P < .01 for all comparisons).
Mortality risk for many patients
A COPD specialist who was not involved in the study told this news organization that sepsis is an uncommon but serious complication, not just for patients with COPD but also for those with other severe illnesses.
“Sepsis has a high risk for mortality whether a person has COPD or not,” commented David M. Mannino III MD, FCCP, FERS, professor of medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, and a cofounder and co–medical director of the COPD Foundation.
“It’s not surprising that sepsis is lethal in this population; the question is, if you have COPD, are you more likely to have sepsis? And I think the answer is probably yes. The connection there is that people with COPD have a higher risk for pneumonia, and pneumonia itself is probably one of the biggest risk factors, or certainly an important risk factor, for the development of sepsis,” he said in an interview.
It would be interesting to see the relationship between sepsis and in-hospital mortality for patients with other chronic diseases or people without COPD, he said, and he would have liked to have seen more detailed information about trends over time than Dr. Shah and colleagues provided.
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. Shah and colleagues and Dr. Mannino have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although slightly fewer than 1% of hospitalizations for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are complicated by sepsis, this complication increases the risk for in-hospital mortality fivefold, investigators who studied a representative national sample found.
Among nearly 7 million hospitalizations in which the primary diagnosis was COPD, nearly 65,000 (0.93%) patients experienced sepsis as a complication. In all, 31% of patients with COPD and sepsis were discharged from the hospital to another care facility, and 19% of patients died in hospital, report Harshil Shah, MD, from Guthrie Corning (N.Y.) Hospital and colleagues.
“Our study highlights the need for better risk stratification in patients with COPD developing sepsis to improve the outcomes. Further studies are warranted to consider factoring some of the modifiable factors into account and to ameliorate the outcomes of sepsis during COPD hospitalizations,” Dr. Shah and colleagues write in a poster presented during the at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians, held virtually this year.
COPD has been associated with increased risk for sepsis because of the use of corticosteroids, underlying comorbidities, and, potentially, because of impaired barrier function, the authors note.
Nationwide sample
To determine the effects of sepsis and predictors of poor outcomes among patients hospitalized for COPD, the investigators used standard diagnostic codes to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of COPD from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample for the period 2007 through 2018 and sepsis from codes in secondary fields in the International Classification of Diseases (9th/10th Editions) Clinical Modification.
They identified a total of 6,940,615 hospitalizations in which the primary diagnosis was COPD; in 64,748 of those cases, sepsis was a complication.
As noted, the in-hospital death rate, one of two primary outcomes, was 19% for patients with COPD and sepsis, and the rate of discharge to other facilities was 31%.
In analysis adjusted for confounding factors, sepsis was associated with an odds ratio for mortality of 4.9 (P < .01) and an OR for discharge to a facility of 2.2 (P < .01).
With regard to trends, the investigators saw that, although the adjusted odds for in-hospital mortality remained stable over time, discharge to facilities increased significantly. In 2007, the adjusted OR was 2.2, whereas in 2018, it was 2.6 (P for trend = .02).
Predictors of in-hospital mortality among patients with sepsis included increasing age (OR, not shown), White ethnicity (OR, 1.2), treatment in the Northeast region (OR, 1.4), disseminated intravascular coagulation (OR, 3.7), pneumococcal infection (OR, 1.2), congestive heart failure (OR, 1.2), and renal failure (OR, 1.4; P < .01 for all comparisons).
Mortality risk for many patients
A COPD specialist who was not involved in the study told this news organization that sepsis is an uncommon but serious complication, not just for patients with COPD but also for those with other severe illnesses.
“Sepsis has a high risk for mortality whether a person has COPD or not,” commented David M. Mannino III MD, FCCP, FERS, professor of medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, and a cofounder and co–medical director of the COPD Foundation.
“It’s not surprising that sepsis is lethal in this population; the question is, if you have COPD, are you more likely to have sepsis? And I think the answer is probably yes. The connection there is that people with COPD have a higher risk for pneumonia, and pneumonia itself is probably one of the biggest risk factors, or certainly an important risk factor, for the development of sepsis,” he said in an interview.
It would be interesting to see the relationship between sepsis and in-hospital mortality for patients with other chronic diseases or people without COPD, he said, and he would have liked to have seen more detailed information about trends over time than Dr. Shah and colleagues provided.
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. Shah and colleagues and Dr. Mannino have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although slightly fewer than 1% of hospitalizations for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are complicated by sepsis, this complication increases the risk for in-hospital mortality fivefold, investigators who studied a representative national sample found.
Among nearly 7 million hospitalizations in which the primary diagnosis was COPD, nearly 65,000 (0.93%) patients experienced sepsis as a complication. In all, 31% of patients with COPD and sepsis were discharged from the hospital to another care facility, and 19% of patients died in hospital, report Harshil Shah, MD, from Guthrie Corning (N.Y.) Hospital and colleagues.
“Our study highlights the need for better risk stratification in patients with COPD developing sepsis to improve the outcomes. Further studies are warranted to consider factoring some of the modifiable factors into account and to ameliorate the outcomes of sepsis during COPD hospitalizations,” Dr. Shah and colleagues write in a poster presented during the at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians, held virtually this year.
COPD has been associated with increased risk for sepsis because of the use of corticosteroids, underlying comorbidities, and, potentially, because of impaired barrier function, the authors note.
Nationwide sample
To determine the effects of sepsis and predictors of poor outcomes among patients hospitalized for COPD, the investigators used standard diagnostic codes to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of COPD from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample for the period 2007 through 2018 and sepsis from codes in secondary fields in the International Classification of Diseases (9th/10th Editions) Clinical Modification.
They identified a total of 6,940,615 hospitalizations in which the primary diagnosis was COPD; in 64,748 of those cases, sepsis was a complication.
As noted, the in-hospital death rate, one of two primary outcomes, was 19% for patients with COPD and sepsis, and the rate of discharge to other facilities was 31%.
In analysis adjusted for confounding factors, sepsis was associated with an odds ratio for mortality of 4.9 (P < .01) and an OR for discharge to a facility of 2.2 (P < .01).
With regard to trends, the investigators saw that, although the adjusted odds for in-hospital mortality remained stable over time, discharge to facilities increased significantly. In 2007, the adjusted OR was 2.2, whereas in 2018, it was 2.6 (P for trend = .02).
Predictors of in-hospital mortality among patients with sepsis included increasing age (OR, not shown), White ethnicity (OR, 1.2), treatment in the Northeast region (OR, 1.4), disseminated intravascular coagulation (OR, 3.7), pneumococcal infection (OR, 1.2), congestive heart failure (OR, 1.2), and renal failure (OR, 1.4; P < .01 for all comparisons).
Mortality risk for many patients
A COPD specialist who was not involved in the study told this news organization that sepsis is an uncommon but serious complication, not just for patients with COPD but also for those with other severe illnesses.
“Sepsis has a high risk for mortality whether a person has COPD or not,” commented David M. Mannino III MD, FCCP, FERS, professor of medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, and a cofounder and co–medical director of the COPD Foundation.
“It’s not surprising that sepsis is lethal in this population; the question is, if you have COPD, are you more likely to have sepsis? And I think the answer is probably yes. The connection there is that people with COPD have a higher risk for pneumonia, and pneumonia itself is probably one of the biggest risk factors, or certainly an important risk factor, for the development of sepsis,” he said in an interview.
It would be interesting to see the relationship between sepsis and in-hospital mortality for patients with other chronic diseases or people without COPD, he said, and he would have liked to have seen more detailed information about trends over time than Dr. Shah and colleagues provided.
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. Shah and colleagues and Dr. Mannino have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.