User login
White House announces vaccination plans for younger children
States were allowed to begin preordering the shots this week. But they can’t be delivered into kids’ arms until the FDA and CDC sign off. The shots could be available in early November.
“We know millions of parents have been waiting for COVID-19 vaccine for kids in this age group, and should the FDA and CDC authorize the vaccine, we will be ready to get shots in arms,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said at a briefing Oct. 20.
Asked whether announcing plans to deliver a vaccine to children might put pressure on the agencies considering the evidence for their use, Mr. Zients defended the Biden administration’s plans.
“This is the right way to do things: To be operationally ready,” he said. Mr. Zients said they had learned a lesson from the prior administration.
“The decision was made by the FDA and CDC, and the operations weren’t ready. And that meant that adults at the time were not able to receive their vaccines as efficiently, equitably as possible. And this will enable us to be ready for kids,” he said.
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late September from its test of the vaccine in 2,200 children. The company said the shots had a favorable safety profile and generated “robust” antibody responses.
An FDA panel is scheduled to meet on Oct. 26 to consider Pfizer’s application. The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet the following week, on Nov. 2 and 3.
Laying the groundwork
Doctors applauded the advance planning.
“Laying this advance groundwork, ensuring supply is available at physician practices, and that a patient’s own physician is available to answer questions, is critical to the continued success of this rollout,” Gerald Harmon, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a written statement.
The shots planned for children are 10 micrograms, a smaller dose than is given to adults. To be fully immunized, kids get two doses, spaced about 21 days apart. Vaccines for younger children are packaged in smaller vials and injected through smaller needles, too.
The vaccine for younger children will roll out slightly differently than it has for adults and teens. While adults mostly got their COVID-19 vaccines through pop-up mass vaccination sites, health departments, and other community locations, the strategy to get children immunized against COVID is centered on the offices of pediatricians and primary care doctors.
The White House says 25,000 doctors have already signed up to give the vaccines.
The vaccination campaign will get underway at a tough moment for pediatricians.
The voicemail message at Roswell Pediatrics Center in the suburbs north of Atlanta, for instance, warns parents to be patient.
“Due to the current, new COVID-19 surge, we are experiencing extremely high call volume, as well as suffering from the same staffing shortages that most businesses are having,” the message says, adding that they’re working around the clock to answer questions and return phone calls.
Jesse Hackell, MD, says he knows the feeling. He’s the chief operating officer of Pomona Pediatrics in Pomona, N.Y., and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“We’re swamped now by kids who get sent home from school because they sneezed once and they have to be cleared before they can go back to school,” he said. “We’re seeing kids who we don’t need to see in terms of the degree of illness because the school requires them to be cleared [of COVID-19].”
Dr. Hackell has been offering the vaccines to kids ages 12 and up since May. He’s planning to offer it to younger children too.
“Adding the vaccines to it is going to be a challenge, but you know we’ll get up to speed and we’ll make it happen,” he said, adding that pediatricians have done many large-scale vaccination campaigns, like those for the H1N1 influenza vaccine in 2009.
Dr. Hackell helped to draft a new policy in New York that will require COVID-19 vaccines for schoolchildren once they are granted full approval from the FDA. Other states may follow with their own vaccination requirements.
He said ultimately, vaccinating school-age children is going to make them safer, will help prevent the virus from mutating and spreading, and will help society as a whole get back to normal.
“We’re the vaccine experts in pediatrics. This is what we do. It’s a huge part of our practice like no other specialty. If we can’t get it right, how can anyone else be expected to?” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States were allowed to begin preordering the shots this week. But they can’t be delivered into kids’ arms until the FDA and CDC sign off. The shots could be available in early November.
“We know millions of parents have been waiting for COVID-19 vaccine for kids in this age group, and should the FDA and CDC authorize the vaccine, we will be ready to get shots in arms,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said at a briefing Oct. 20.
Asked whether announcing plans to deliver a vaccine to children might put pressure on the agencies considering the evidence for their use, Mr. Zients defended the Biden administration’s plans.
“This is the right way to do things: To be operationally ready,” he said. Mr. Zients said they had learned a lesson from the prior administration.
“The decision was made by the FDA and CDC, and the operations weren’t ready. And that meant that adults at the time were not able to receive their vaccines as efficiently, equitably as possible. And this will enable us to be ready for kids,” he said.
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late September from its test of the vaccine in 2,200 children. The company said the shots had a favorable safety profile and generated “robust” antibody responses.
An FDA panel is scheduled to meet on Oct. 26 to consider Pfizer’s application. The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet the following week, on Nov. 2 and 3.
Laying the groundwork
Doctors applauded the advance planning.
“Laying this advance groundwork, ensuring supply is available at physician practices, and that a patient’s own physician is available to answer questions, is critical to the continued success of this rollout,” Gerald Harmon, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a written statement.
The shots planned for children are 10 micrograms, a smaller dose than is given to adults. To be fully immunized, kids get two doses, spaced about 21 days apart. Vaccines for younger children are packaged in smaller vials and injected through smaller needles, too.
The vaccine for younger children will roll out slightly differently than it has for adults and teens. While adults mostly got their COVID-19 vaccines through pop-up mass vaccination sites, health departments, and other community locations, the strategy to get children immunized against COVID is centered on the offices of pediatricians and primary care doctors.
The White House says 25,000 doctors have already signed up to give the vaccines.
The vaccination campaign will get underway at a tough moment for pediatricians.
The voicemail message at Roswell Pediatrics Center in the suburbs north of Atlanta, for instance, warns parents to be patient.
“Due to the current, new COVID-19 surge, we are experiencing extremely high call volume, as well as suffering from the same staffing shortages that most businesses are having,” the message says, adding that they’re working around the clock to answer questions and return phone calls.
Jesse Hackell, MD, says he knows the feeling. He’s the chief operating officer of Pomona Pediatrics in Pomona, N.Y., and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“We’re swamped now by kids who get sent home from school because they sneezed once and they have to be cleared before they can go back to school,” he said. “We’re seeing kids who we don’t need to see in terms of the degree of illness because the school requires them to be cleared [of COVID-19].”
Dr. Hackell has been offering the vaccines to kids ages 12 and up since May. He’s planning to offer it to younger children too.
“Adding the vaccines to it is going to be a challenge, but you know we’ll get up to speed and we’ll make it happen,” he said, adding that pediatricians have done many large-scale vaccination campaigns, like those for the H1N1 influenza vaccine in 2009.
Dr. Hackell helped to draft a new policy in New York that will require COVID-19 vaccines for schoolchildren once they are granted full approval from the FDA. Other states may follow with their own vaccination requirements.
He said ultimately, vaccinating school-age children is going to make them safer, will help prevent the virus from mutating and spreading, and will help society as a whole get back to normal.
“We’re the vaccine experts in pediatrics. This is what we do. It’s a huge part of our practice like no other specialty. If we can’t get it right, how can anyone else be expected to?” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States were allowed to begin preordering the shots this week. But they can’t be delivered into kids’ arms until the FDA and CDC sign off. The shots could be available in early November.
“We know millions of parents have been waiting for COVID-19 vaccine for kids in this age group, and should the FDA and CDC authorize the vaccine, we will be ready to get shots in arms,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said at a briefing Oct. 20.
Asked whether announcing plans to deliver a vaccine to children might put pressure on the agencies considering the evidence for their use, Mr. Zients defended the Biden administration’s plans.
“This is the right way to do things: To be operationally ready,” he said. Mr. Zients said they had learned a lesson from the prior administration.
“The decision was made by the FDA and CDC, and the operations weren’t ready. And that meant that adults at the time were not able to receive their vaccines as efficiently, equitably as possible. And this will enable us to be ready for kids,” he said.
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late September from its test of the vaccine in 2,200 children. The company said the shots had a favorable safety profile and generated “robust” antibody responses.
An FDA panel is scheduled to meet on Oct. 26 to consider Pfizer’s application. The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet the following week, on Nov. 2 and 3.
Laying the groundwork
Doctors applauded the advance planning.
“Laying this advance groundwork, ensuring supply is available at physician practices, and that a patient’s own physician is available to answer questions, is critical to the continued success of this rollout,” Gerald Harmon, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a written statement.
The shots planned for children are 10 micrograms, a smaller dose than is given to adults. To be fully immunized, kids get two doses, spaced about 21 days apart. Vaccines for younger children are packaged in smaller vials and injected through smaller needles, too.
The vaccine for younger children will roll out slightly differently than it has for adults and teens. While adults mostly got their COVID-19 vaccines through pop-up mass vaccination sites, health departments, and other community locations, the strategy to get children immunized against COVID is centered on the offices of pediatricians and primary care doctors.
The White House says 25,000 doctors have already signed up to give the vaccines.
The vaccination campaign will get underway at a tough moment for pediatricians.
The voicemail message at Roswell Pediatrics Center in the suburbs north of Atlanta, for instance, warns parents to be patient.
“Due to the current, new COVID-19 surge, we are experiencing extremely high call volume, as well as suffering from the same staffing shortages that most businesses are having,” the message says, adding that they’re working around the clock to answer questions and return phone calls.
Jesse Hackell, MD, says he knows the feeling. He’s the chief operating officer of Pomona Pediatrics in Pomona, N.Y., and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“We’re swamped now by kids who get sent home from school because they sneezed once and they have to be cleared before they can go back to school,” he said. “We’re seeing kids who we don’t need to see in terms of the degree of illness because the school requires them to be cleared [of COVID-19].”
Dr. Hackell has been offering the vaccines to kids ages 12 and up since May. He’s planning to offer it to younger children too.
“Adding the vaccines to it is going to be a challenge, but you know we’ll get up to speed and we’ll make it happen,” he said, adding that pediatricians have done many large-scale vaccination campaigns, like those for the H1N1 influenza vaccine in 2009.
Dr. Hackell helped to draft a new policy in New York that will require COVID-19 vaccines for schoolchildren once they are granted full approval from the FDA. Other states may follow with their own vaccination requirements.
He said ultimately, vaccinating school-age children is going to make them safer, will help prevent the virus from mutating and spreading, and will help society as a whole get back to normal.
“We’re the vaccine experts in pediatrics. This is what we do. It’s a huge part of our practice like no other specialty. If we can’t get it right, how can anyone else be expected to?” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Fungal infection can mimic lung cancer metastases
A fungal infection typically seen in the lungs may have a variety of unusual clinical presentations elsewhere in the body, even raising suspicion of cancer in some cases, a medical resident reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
In one recent and unusual presentation, a 58-year-old woman with persistent headaches had skull lesions on computed tomography (CT) was eventually diagnosed with disseminated coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever), a fungal infection endemic to the Southwestern U.S.
The imaging pattern of her head CT was initially concerning for cancer metastasis, according to Sharjeel Israr, MD, a third-year internal medicine resident at Creighton University in Phoenix, Ariz.
However, the subsequent chest CT revealed a suspicious chest mass. A biopsy of that mass led to the correct diagnosis of disseminated coccidioidomycosis, according to Dr. Israr, who presented the case report in an e-poster at the CHEST meeting, which was held virtually this year.
Mistaken identity
Coccidioidomycosis, caused by the fungus Coccidioides, usually affects the lungs, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. However, in severe cases it can spread to other parts of the body. In those cases, it’s referred to as disseminated coccidioidomycosis.
Arizona accounted for about 10,000 out of 18,000 reported Valley fever cases in 2019, according to the latest statistics from the CDC.
Coccidioidomycosis is frequently mistaken not only for cancer, but also for rheumatic conditions and bacterial infections, according to Valley fever specialist John Galgiani, MD, director of the Valley Fever Center for Excellence at the University of Arizona in Tucson.
“Where Valley fever is common, it should very frequently be in the differential for masses that are thought to be cancer,” Dr. Galgiani said in an interview. “This case is a good example of that.”
Challenging case
In an interview, Dr. Israr said the case was challenging to crack despite the fact that Valley fever is very common in Phoenix.
“It was definitely on the differential from the get-go, but it was very, very low our differential, just based on the presentation that she had,” said Dr. Israr.
The patient had history of diabetes and presented with headaches for 4 weeks. However, she had no pulmonary symptoms or meningeal signs, according to Dr. Israr.
A head CT revealed multiple osseous skull lesions and a left temporal lobe lesion.
“The fact that this patient had lesions in the skull, specifically, is something that raised our initial red flags for cancer – especially since she presented with just a headache as her only complaint,” he said.
The imaging pattern was concerning for metastasis, according to Dr. Israr, particularly since a subsequent CT of the chest showed multiple pulmonary nodules plus a 7.7-cm mass in the right lower lobe.
Once the biopsy confirmed coccidioidomycosis, the patient was started on fluconazole 600 mg twice daily, according to Dr. Israr.
Although severe disseminated coccidioidomycosis can be difficult to treat, the lung lesion had decreased in size from 7.7 cm to 4.2 cm about 3 months later, Dr. Israr said.
“At the end of the day, she didn’t have cancer, and it’s something that we’re treating and she’s actually doing better right now,” Dr. Israr said in the interview.
Dr. Israr and coauthors of the case reported they had no relevant relationships to disclose.
A fungal infection typically seen in the lungs may have a variety of unusual clinical presentations elsewhere in the body, even raising suspicion of cancer in some cases, a medical resident reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
In one recent and unusual presentation, a 58-year-old woman with persistent headaches had skull lesions on computed tomography (CT) was eventually diagnosed with disseminated coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever), a fungal infection endemic to the Southwestern U.S.
The imaging pattern of her head CT was initially concerning for cancer metastasis, according to Sharjeel Israr, MD, a third-year internal medicine resident at Creighton University in Phoenix, Ariz.
However, the subsequent chest CT revealed a suspicious chest mass. A biopsy of that mass led to the correct diagnosis of disseminated coccidioidomycosis, according to Dr. Israr, who presented the case report in an e-poster at the CHEST meeting, which was held virtually this year.
Mistaken identity
Coccidioidomycosis, caused by the fungus Coccidioides, usually affects the lungs, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. However, in severe cases it can spread to other parts of the body. In those cases, it’s referred to as disseminated coccidioidomycosis.
Arizona accounted for about 10,000 out of 18,000 reported Valley fever cases in 2019, according to the latest statistics from the CDC.
Coccidioidomycosis is frequently mistaken not only for cancer, but also for rheumatic conditions and bacterial infections, according to Valley fever specialist John Galgiani, MD, director of the Valley Fever Center for Excellence at the University of Arizona in Tucson.
“Where Valley fever is common, it should very frequently be in the differential for masses that are thought to be cancer,” Dr. Galgiani said in an interview. “This case is a good example of that.”
Challenging case
In an interview, Dr. Israr said the case was challenging to crack despite the fact that Valley fever is very common in Phoenix.
“It was definitely on the differential from the get-go, but it was very, very low our differential, just based on the presentation that she had,” said Dr. Israr.
The patient had history of diabetes and presented with headaches for 4 weeks. However, she had no pulmonary symptoms or meningeal signs, according to Dr. Israr.
A head CT revealed multiple osseous skull lesions and a left temporal lobe lesion.
“The fact that this patient had lesions in the skull, specifically, is something that raised our initial red flags for cancer – especially since she presented with just a headache as her only complaint,” he said.
The imaging pattern was concerning for metastasis, according to Dr. Israr, particularly since a subsequent CT of the chest showed multiple pulmonary nodules plus a 7.7-cm mass in the right lower lobe.
Once the biopsy confirmed coccidioidomycosis, the patient was started on fluconazole 600 mg twice daily, according to Dr. Israr.
Although severe disseminated coccidioidomycosis can be difficult to treat, the lung lesion had decreased in size from 7.7 cm to 4.2 cm about 3 months later, Dr. Israr said.
“At the end of the day, she didn’t have cancer, and it’s something that we’re treating and she’s actually doing better right now,” Dr. Israr said in the interview.
Dr. Israr and coauthors of the case reported they had no relevant relationships to disclose.
A fungal infection typically seen in the lungs may have a variety of unusual clinical presentations elsewhere in the body, even raising suspicion of cancer in some cases, a medical resident reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
In one recent and unusual presentation, a 58-year-old woman with persistent headaches had skull lesions on computed tomography (CT) was eventually diagnosed with disseminated coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever), a fungal infection endemic to the Southwestern U.S.
The imaging pattern of her head CT was initially concerning for cancer metastasis, according to Sharjeel Israr, MD, a third-year internal medicine resident at Creighton University in Phoenix, Ariz.
However, the subsequent chest CT revealed a suspicious chest mass. A biopsy of that mass led to the correct diagnosis of disseminated coccidioidomycosis, according to Dr. Israr, who presented the case report in an e-poster at the CHEST meeting, which was held virtually this year.
Mistaken identity
Coccidioidomycosis, caused by the fungus Coccidioides, usually affects the lungs, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. However, in severe cases it can spread to other parts of the body. In those cases, it’s referred to as disseminated coccidioidomycosis.
Arizona accounted for about 10,000 out of 18,000 reported Valley fever cases in 2019, according to the latest statistics from the CDC.
Coccidioidomycosis is frequently mistaken not only for cancer, but also for rheumatic conditions and bacterial infections, according to Valley fever specialist John Galgiani, MD, director of the Valley Fever Center for Excellence at the University of Arizona in Tucson.
“Where Valley fever is common, it should very frequently be in the differential for masses that are thought to be cancer,” Dr. Galgiani said in an interview. “This case is a good example of that.”
Challenging case
In an interview, Dr. Israr said the case was challenging to crack despite the fact that Valley fever is very common in Phoenix.
“It was definitely on the differential from the get-go, but it was very, very low our differential, just based on the presentation that she had,” said Dr. Israr.
The patient had history of diabetes and presented with headaches for 4 weeks. However, she had no pulmonary symptoms or meningeal signs, according to Dr. Israr.
A head CT revealed multiple osseous skull lesions and a left temporal lobe lesion.
“The fact that this patient had lesions in the skull, specifically, is something that raised our initial red flags for cancer – especially since she presented with just a headache as her only complaint,” he said.
The imaging pattern was concerning for metastasis, according to Dr. Israr, particularly since a subsequent CT of the chest showed multiple pulmonary nodules plus a 7.7-cm mass in the right lower lobe.
Once the biopsy confirmed coccidioidomycosis, the patient was started on fluconazole 600 mg twice daily, according to Dr. Israr.
Although severe disseminated coccidioidomycosis can be difficult to treat, the lung lesion had decreased in size from 7.7 cm to 4.2 cm about 3 months later, Dr. Israr said.
“At the end of the day, she didn’t have cancer, and it’s something that we’re treating and she’s actually doing better right now,” Dr. Israr said in the interview.
Dr. Israr and coauthors of the case reported they had no relevant relationships to disclose.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2021
Painful facial abscess
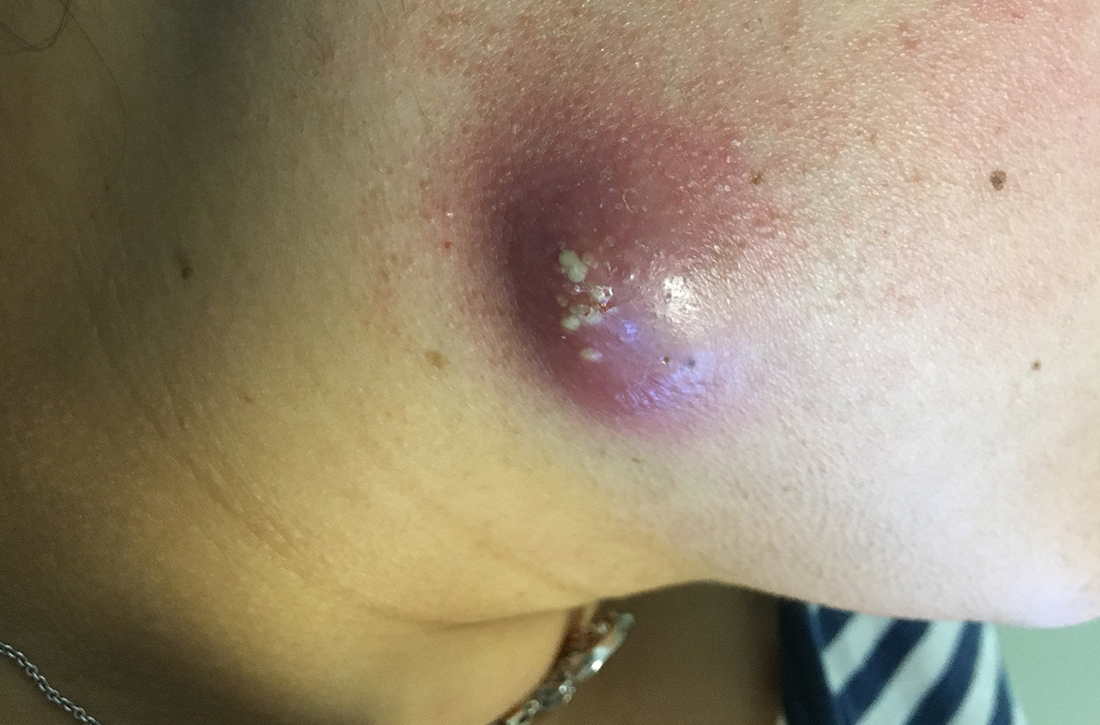
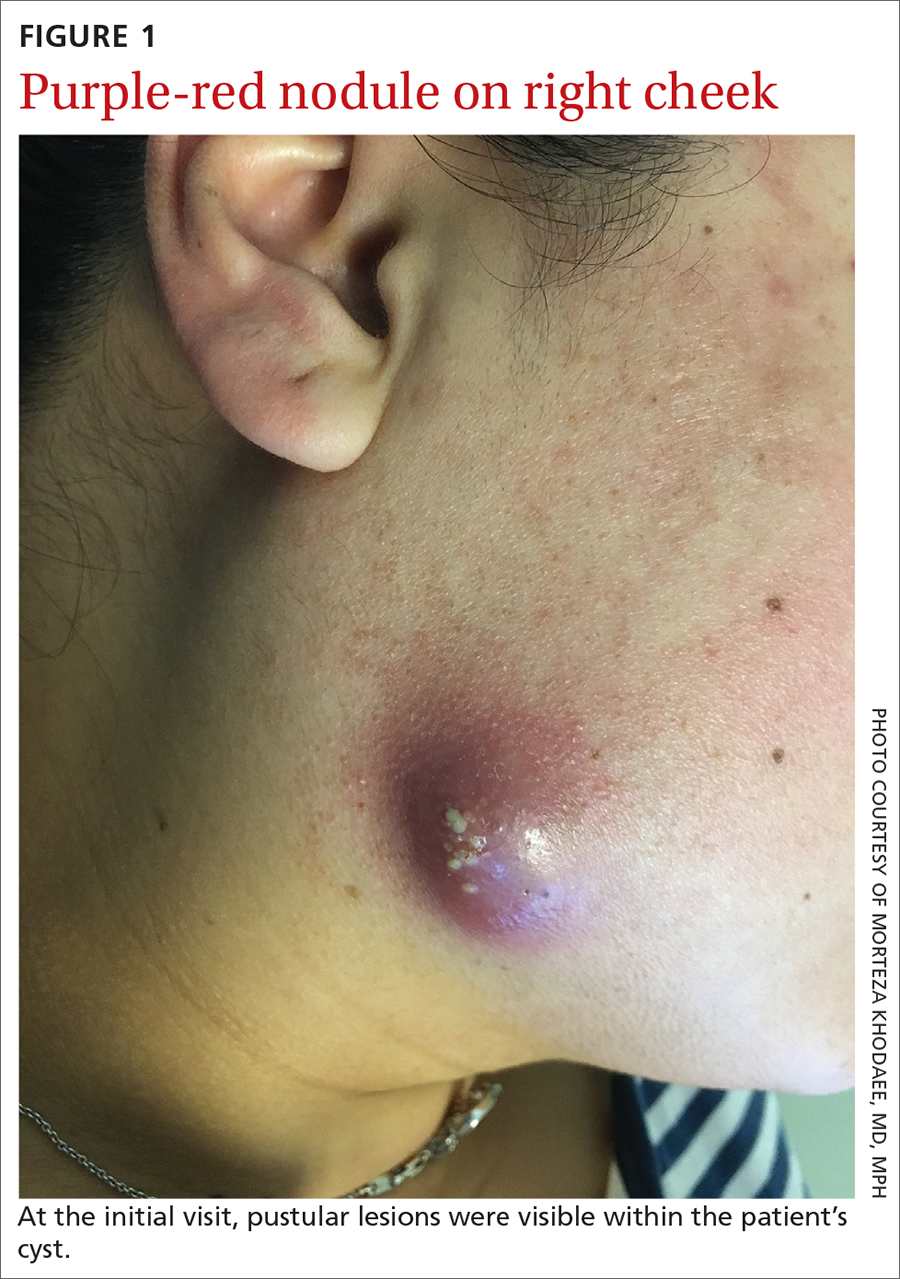
A 35-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a purple-red cyst on her right cheek that had been present for about 4 years but had worsened over the prior 2 weeks (FIGURE 1). She said she was experiencing excruciating pain and that the cyst had purulent drainage. She denied any history of diabetes, dental problems, recent trauma, or an inciting event.
On physical examination, there was no cervical lymphadenopathy, and her vital signs were normal. An incision and drainage procedure was performed. About 2 mL of purulent fluid was extracted and sent for aerobic and anaerobic cultures.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Cervicofacial actinomycosis
Direct Gram stain showed gram-positive cocci, so the patient was started on a 7-day course of cephalexin 500 mg tid. Five days later, the anaerobic culture grew Actinomyces neuii, revealing the diagnosis as cervicofacial actinomycosis; the patient stopped taking cephalexin. The patient was then switched to a 3-month course of amoxicillin 875 mg bid.
Actinomyces are natural inhabitants of the human oropharynx and gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts.1-4 They are filamentous, gram-positive rods with characteristic sulfur granules (although these are not always present).1-4 It is believed that actinomycosis is endogenously acquired from deep tissue either through dental trauma, penetrating wounds, or compound fractures.2,4
The most common presentations of actinomycosis include cervicofacial (sometimes referred to as “lumpy jaw syndrome”), followed by abdominopelvic and thoracic/pulmonary, manifestations.2-4 Primary cutaneous actinomycosis is rare.5-9 Actinomycosis infection often manifests with indolent constitutional symptoms such as fatigue and anorexia.1 Most cases occur in men ages 20 to 60 years, although cases in women are increasingly being reported.2-4
Risk factors include poor dental hygiene or dental procedures, alcoholism, intrauterine device use, immunosuppression, appendicitis, and diverticulitis.2-4 The exact cause of this patient’s actinomycosis was unknown, as she did not have any known risk factors.
Furunculosis and sporotrichosis are part of the differential
Actinomycosis is often called a “great mimicker” due to its ability to masquerade as infection, malignancy, or fungus.1 The differential diagnosis for this patient’s presentation included bacterial soft-tissue infection (eg, furunculosis), infected epidermoid cyst, cutaneous tuberculosis, sporotrichosis, deep fungal infection, and nocardiosis.
Continue to: Furunculosis was initially suspected
Furunculosis was initially suspected, but the original wound culture demonstrated actinomycoses instead of traditional gram-positive bacteria.
A clinical diagnosis
The diagnosis of actinomycosis is usually made clinically, but definitive confirmation requires culture, which can be challenging with a slow-growing facultative or strict anaerobe that may take up to 14 days to appear.2-4 A Gram stain can aid in the diagnosis, but overall, there is a high false-negative rate in identifying actinomycosis.1,3,4
Treatment time can be lengthy, but prognosis is favorable
Unfortunately, there are no randomized controlled studies for treatment of actinomycosis. The majority of evidence for treatment comes from in vitro and clinical case studies.2-4,10 In general, prognosis of actinomycosis is favorable with low mortality, but chronic infection without complete resolution of symptoms can occur.1-4,7,8,10
First-line therapy for actinomycosis is a beta-lactam antibiotic, typically penicillin G or amoxicillin.2-4,10 High doses of prolonged intravenous (IV) and oral antibiotic therapy (2 to 12 months) based on location and complexity are standard.3,11 However, if there is minimal bone involvement and the patient shows rapid improvement, treatment could be shortened to a 4 to 6–week oral regimen.1,11 Surgical intervention can also shorten the required length of antibiotic duration.1,10
Cutaneous actinomycosis Tx. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid has been shown to be an effective treatment for cutaneous actinomycosis, especially if polymicrobial infection is suspected.5,6 Individualized regimens for cutaneous actinomycosis—based on severity, location, and treatment response—are acceptable with close monitoring.1,2,11
Continue to: A lengthy recovery for our patient
A lengthy recovery for our patient
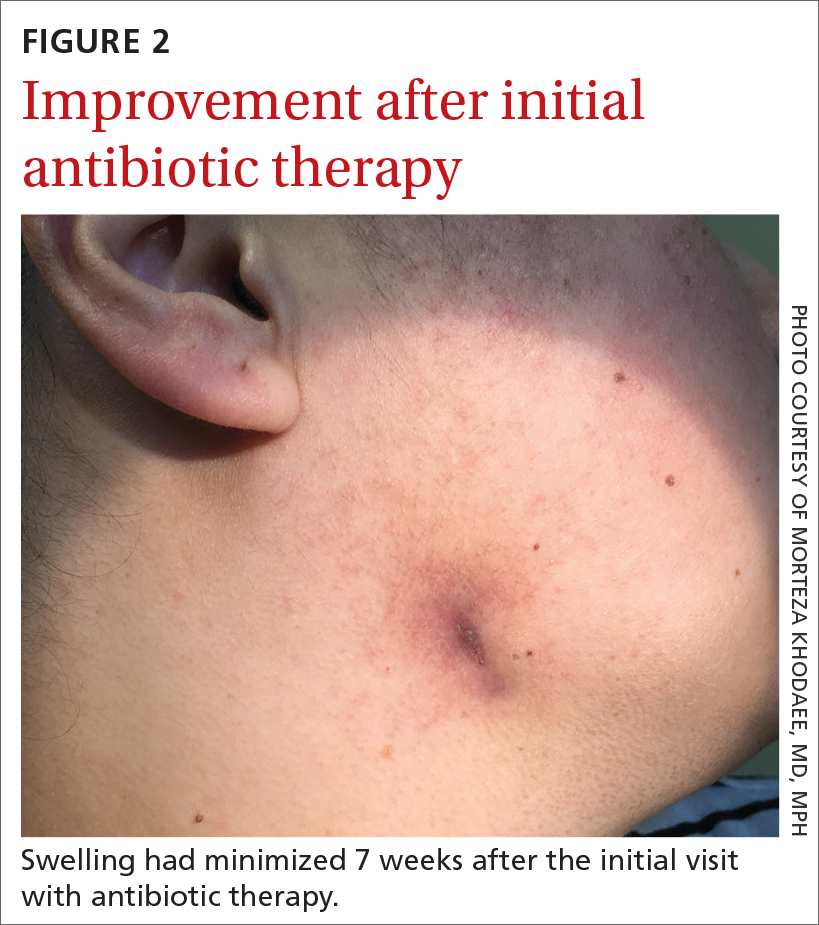
Seven weeks after the initial visit, the patient reported that she had taken only 20 days’ worth of the recommended 3-month course of amoxicillin. Fortunately, the lesion appeared to be healing well with no apparent fluid collection (FIGURE 2).
The patient was then prescribed, and completed, a 3-month course of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid
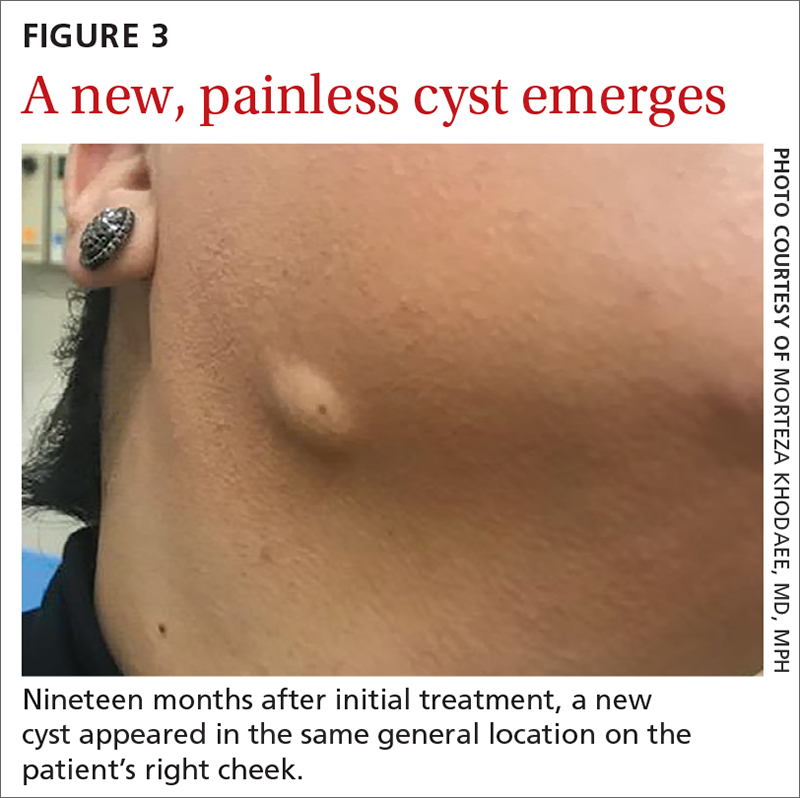
Nineteen months after initial treatment, the lesion reappeared as a painless cyst in a similar location (FIGURE 3). Plastic Surgery incised and drained the lesion and Infectious Diseases continued her on 3 months of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg bid, which she did complete.
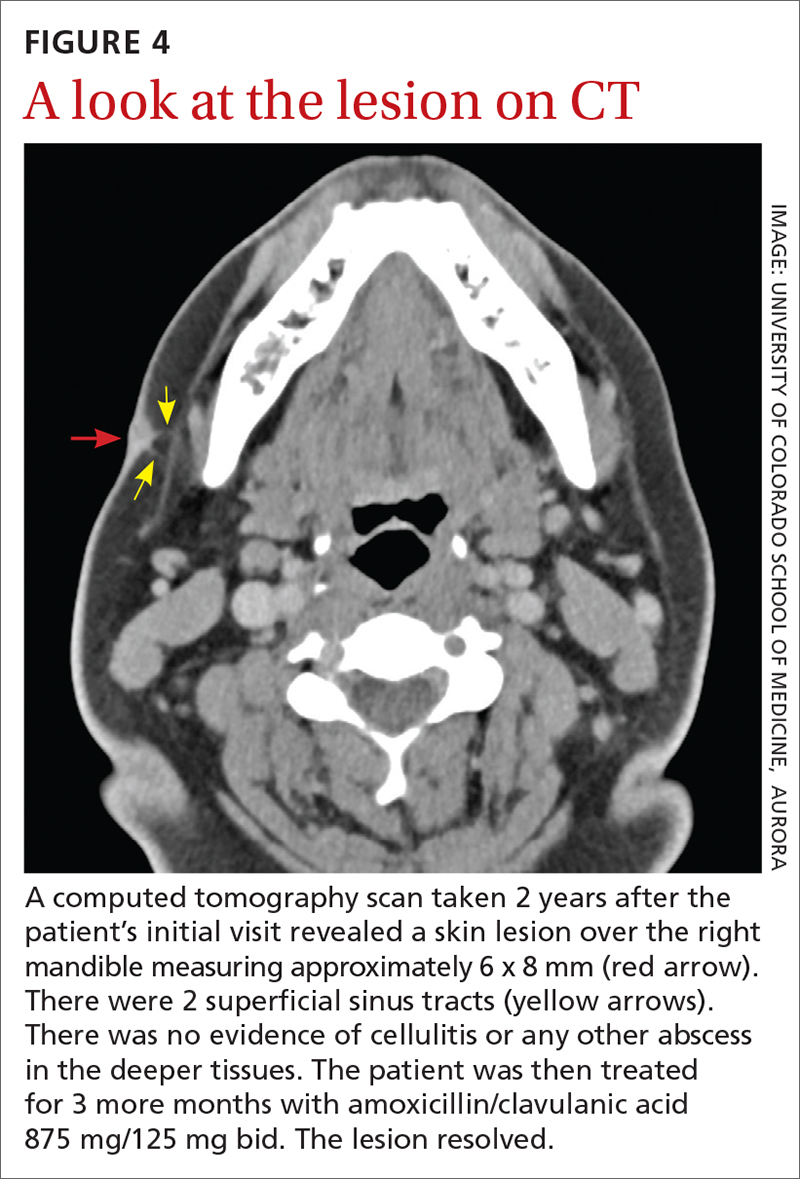
Due to the continued presence of the lesion, a computed tomography scan of the face was ordered 2 years after the initial visit and demonstrated a superficial skin lesion with no mandibular involvement (FIGURE 4). She was then treated with 3 more months of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg bid, with the possibility of deep debridement if not improved. However, debridement was unnecessary as the cyst did not recur.
We believe that the course of this patient’s treatment was protracted because she never took oral antibiotics for more than 3 months at a time, and thus, her infection never completely resolved. In retrospect, we would have treated her more aggressively from the outset.
1. Najmi AH, Najmi IH, Tawhari MMH, et al. Cutaneous actinomycosis and long-term management through using oral and topical antibiotics: a case report. Clin Pract. 2018;8:1102. doi: 10.4081/ cp.2018.1102
2. Sharma S, Hashmi MF, Valentino ID. Actinomycosis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
3. Valour F, Sénécha A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-97. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S39601
4. Wong VK, Turmezei TD, Weston VC. Actinomycosis. BMJ. 2011;343:d6099. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d6099
5. Akhtar M, Zade MP, Shahane PL, et al. Scalp actinomycosis presenting as soft tissue tumour: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;16:99-101. doi: 10.1016/ j.ijscr.2015.09.030
6. Bose M, Ghosh R, Mukherjee K, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis:a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:YD03-5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8286.4591
7. Cataño JC, Gómez Villegas SI. Images in clinical medicine. Cutaneous actinomycosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1773. doi: 10.1056/ NEJMicm1511213
8. Mehta V, Balachandran C. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis on the chest wall. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:13.
9. Piggott SA, Khodaee M. A bump in the groin: cutaneous actinomycosis. J Family Community Med. 2017;24:203. doi: 10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_79_17
10. Bonifaz A, Tirado-Sánchez A, Calderón L, et al. Treatment of cutaneous actinomycosis with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:59-64. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2016.1178373
11. Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;;7:183-197. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S39601
A 35-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a purple-red cyst on her right cheek that had been present for about 4 years but had worsened over the prior 2 weeks (FIGURE 1). She said she was experiencing excruciating pain and that the cyst had purulent drainage. She denied any history of diabetes, dental problems, recent trauma, or an inciting event.
On physical examination, there was no cervical lymphadenopathy, and her vital signs were normal. An incision and drainage procedure was performed. About 2 mL of purulent fluid was extracted and sent for aerobic and anaerobic cultures.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Cervicofacial actinomycosis
Direct Gram stain showed gram-positive cocci, so the patient was started on a 7-day course of cephalexin 500 mg tid. Five days later, the anaerobic culture grew Actinomyces neuii, revealing the diagnosis as cervicofacial actinomycosis; the patient stopped taking cephalexin. The patient was then switched to a 3-month course of amoxicillin 875 mg bid.
Actinomyces are natural inhabitants of the human oropharynx and gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts.1-4 They are filamentous, gram-positive rods with characteristic sulfur granules (although these are not always present).1-4 It is believed that actinomycosis is endogenously acquired from deep tissue either through dental trauma, penetrating wounds, or compound fractures.2,4
The most common presentations of actinomycosis include cervicofacial (sometimes referred to as “lumpy jaw syndrome”), followed by abdominopelvic and thoracic/pulmonary, manifestations.2-4 Primary cutaneous actinomycosis is rare.5-9 Actinomycosis infection often manifests with indolent constitutional symptoms such as fatigue and anorexia.1 Most cases occur in men ages 20 to 60 years, although cases in women are increasingly being reported.2-4
Risk factors include poor dental hygiene or dental procedures, alcoholism, intrauterine device use, immunosuppression, appendicitis, and diverticulitis.2-4 The exact cause of this patient’s actinomycosis was unknown, as she did not have any known risk factors.
Furunculosis and sporotrichosis are part of the differential
Actinomycosis is often called a “great mimicker” due to its ability to masquerade as infection, malignancy, or fungus.1 The differential diagnosis for this patient’s presentation included bacterial soft-tissue infection (eg, furunculosis), infected epidermoid cyst, cutaneous tuberculosis, sporotrichosis, deep fungal infection, and nocardiosis.
Continue to: Furunculosis was initially suspected
Furunculosis was initially suspected, but the original wound culture demonstrated actinomycoses instead of traditional gram-positive bacteria.
A clinical diagnosis
The diagnosis of actinomycosis is usually made clinically, but definitive confirmation requires culture, which can be challenging with a slow-growing facultative or strict anaerobe that may take up to 14 days to appear.2-4 A Gram stain can aid in the diagnosis, but overall, there is a high false-negative rate in identifying actinomycosis.1,3,4
Treatment time can be lengthy, but prognosis is favorable
Unfortunately, there are no randomized controlled studies for treatment of actinomycosis. The majority of evidence for treatment comes from in vitro and clinical case studies.2-4,10 In general, prognosis of actinomycosis is favorable with low mortality, but chronic infection without complete resolution of symptoms can occur.1-4,7,8,10
First-line therapy for actinomycosis is a beta-lactam antibiotic, typically penicillin G or amoxicillin.2-4,10 High doses of prolonged intravenous (IV) and oral antibiotic therapy (2 to 12 months) based on location and complexity are standard.3,11 However, if there is minimal bone involvement and the patient shows rapid improvement, treatment could be shortened to a 4 to 6–week oral regimen.1,11 Surgical intervention can also shorten the required length of antibiotic duration.1,10
Cutaneous actinomycosis Tx. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid has been shown to be an effective treatment for cutaneous actinomycosis, especially if polymicrobial infection is suspected.5,6 Individualized regimens for cutaneous actinomycosis—based on severity, location, and treatment response—are acceptable with close monitoring.1,2,11
Continue to: A lengthy recovery for our patient
A lengthy recovery for our patient
Seven weeks after the initial visit, the patient reported that she had taken only 20 days’ worth of the recommended 3-month course of amoxicillin. Fortunately, the lesion appeared to be healing well with no apparent fluid collection (FIGURE 2).

The patient was then prescribed, and completed, a 3-month course of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid
Nineteen months after initial treatment, the lesion reappeared as a painless cyst in a similar location (FIGURE 3). Plastic Surgery incised and drained the lesion and Infectious Diseases continued her on 3 months of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg bid, which she did complete.

Due to the continued presence of the lesion, a computed tomography scan of the face was ordered 2 years after the initial visit and demonstrated a superficial skin lesion with no mandibular involvement (FIGURE 4). She was then treated with 3 more months of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg bid, with the possibility of deep debridement if not improved. However, debridement was unnecessary as the cyst did not recur.

We believe that the course of this patient’s treatment was protracted because she never took oral antibiotics for more than 3 months at a time, and thus, her infection never completely resolved. In retrospect, we would have treated her more aggressively from the outset.
A 35-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a purple-red cyst on her right cheek that had been present for about 4 years but had worsened over the prior 2 weeks (FIGURE 1). She said she was experiencing excruciating pain and that the cyst had purulent drainage. She denied any history of diabetes, dental problems, recent trauma, or an inciting event.
On physical examination, there was no cervical lymphadenopathy, and her vital signs were normal. An incision and drainage procedure was performed. About 2 mL of purulent fluid was extracted and sent for aerobic and anaerobic cultures.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Cervicofacial actinomycosis
Direct Gram stain showed gram-positive cocci, so the patient was started on a 7-day course of cephalexin 500 mg tid. Five days later, the anaerobic culture grew Actinomyces neuii, revealing the diagnosis as cervicofacial actinomycosis; the patient stopped taking cephalexin. The patient was then switched to a 3-month course of amoxicillin 875 mg bid.
Actinomyces are natural inhabitants of the human oropharynx and gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts.1-4 They are filamentous, gram-positive rods with characteristic sulfur granules (although these are not always present).1-4 It is believed that actinomycosis is endogenously acquired from deep tissue either through dental trauma, penetrating wounds, or compound fractures.2,4
The most common presentations of actinomycosis include cervicofacial (sometimes referred to as “lumpy jaw syndrome”), followed by abdominopelvic and thoracic/pulmonary, manifestations.2-4 Primary cutaneous actinomycosis is rare.5-9 Actinomycosis infection often manifests with indolent constitutional symptoms such as fatigue and anorexia.1 Most cases occur in men ages 20 to 60 years, although cases in women are increasingly being reported.2-4
Risk factors include poor dental hygiene or dental procedures, alcoholism, intrauterine device use, immunosuppression, appendicitis, and diverticulitis.2-4 The exact cause of this patient’s actinomycosis was unknown, as she did not have any known risk factors.
Furunculosis and sporotrichosis are part of the differential
Actinomycosis is often called a “great mimicker” due to its ability to masquerade as infection, malignancy, or fungus.1 The differential diagnosis for this patient’s presentation included bacterial soft-tissue infection (eg, furunculosis), infected epidermoid cyst, cutaneous tuberculosis, sporotrichosis, deep fungal infection, and nocardiosis.
Continue to: Furunculosis was initially suspected
Furunculosis was initially suspected, but the original wound culture demonstrated actinomycoses instead of traditional gram-positive bacteria.
A clinical diagnosis
The diagnosis of actinomycosis is usually made clinically, but definitive confirmation requires culture, which can be challenging with a slow-growing facultative or strict anaerobe that may take up to 14 days to appear.2-4 A Gram stain can aid in the diagnosis, but overall, there is a high false-negative rate in identifying actinomycosis.1,3,4
Treatment time can be lengthy, but prognosis is favorable
Unfortunately, there are no randomized controlled studies for treatment of actinomycosis. The majority of evidence for treatment comes from in vitro and clinical case studies.2-4,10 In general, prognosis of actinomycosis is favorable with low mortality, but chronic infection without complete resolution of symptoms can occur.1-4,7,8,10
First-line therapy for actinomycosis is a beta-lactam antibiotic, typically penicillin G or amoxicillin.2-4,10 High doses of prolonged intravenous (IV) and oral antibiotic therapy (2 to 12 months) based on location and complexity are standard.3,11 However, if there is minimal bone involvement and the patient shows rapid improvement, treatment could be shortened to a 4 to 6–week oral regimen.1,11 Surgical intervention can also shorten the required length of antibiotic duration.1,10
Cutaneous actinomycosis Tx. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid has been shown to be an effective treatment for cutaneous actinomycosis, especially if polymicrobial infection is suspected.5,6 Individualized regimens for cutaneous actinomycosis—based on severity, location, and treatment response—are acceptable with close monitoring.1,2,11
Continue to: A lengthy recovery for our patient
A lengthy recovery for our patient
Seven weeks after the initial visit, the patient reported that she had taken only 20 days’ worth of the recommended 3-month course of amoxicillin. Fortunately, the lesion appeared to be healing well with no apparent fluid collection (FIGURE 2).

The patient was then prescribed, and completed, a 3-month course of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid
Nineteen months after initial treatment, the lesion reappeared as a painless cyst in a similar location (FIGURE 3). Plastic Surgery incised and drained the lesion and Infectious Diseases continued her on 3 months of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg bid, which she did complete.

Due to the continued presence of the lesion, a computed tomography scan of the face was ordered 2 years after the initial visit and demonstrated a superficial skin lesion with no mandibular involvement (FIGURE 4). She was then treated with 3 more months of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg bid, with the possibility of deep debridement if not improved. However, debridement was unnecessary as the cyst did not recur.

We believe that the course of this patient’s treatment was protracted because she never took oral antibiotics for more than 3 months at a time, and thus, her infection never completely resolved. In retrospect, we would have treated her more aggressively from the outset.
1. Najmi AH, Najmi IH, Tawhari MMH, et al. Cutaneous actinomycosis and long-term management through using oral and topical antibiotics: a case report. Clin Pract. 2018;8:1102. doi: 10.4081/ cp.2018.1102
2. Sharma S, Hashmi MF, Valentino ID. Actinomycosis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
3. Valour F, Sénécha A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-97. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S39601
4. Wong VK, Turmezei TD, Weston VC. Actinomycosis. BMJ. 2011;343:d6099. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d6099
5. Akhtar M, Zade MP, Shahane PL, et al. Scalp actinomycosis presenting as soft tissue tumour: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;16:99-101. doi: 10.1016/ j.ijscr.2015.09.030
6. Bose M, Ghosh R, Mukherjee K, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis:a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:YD03-5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8286.4591
7. Cataño JC, Gómez Villegas SI. Images in clinical medicine. Cutaneous actinomycosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1773. doi: 10.1056/ NEJMicm1511213
8. Mehta V, Balachandran C. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis on the chest wall. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:13.
9. Piggott SA, Khodaee M. A bump in the groin: cutaneous actinomycosis. J Family Community Med. 2017;24:203. doi: 10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_79_17
10. Bonifaz A, Tirado-Sánchez A, Calderón L, et al. Treatment of cutaneous actinomycosis with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:59-64. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2016.1178373
11. Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;;7:183-197. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S39601
1. Najmi AH, Najmi IH, Tawhari MMH, et al. Cutaneous actinomycosis and long-term management through using oral and topical antibiotics: a case report. Clin Pract. 2018;8:1102. doi: 10.4081/ cp.2018.1102
2. Sharma S, Hashmi MF, Valentino ID. Actinomycosis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
3. Valour F, Sénécha A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-97. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S39601
4. Wong VK, Turmezei TD, Weston VC. Actinomycosis. BMJ. 2011;343:d6099. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d6099
5. Akhtar M, Zade MP, Shahane PL, et al. Scalp actinomycosis presenting as soft tissue tumour: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;16:99-101. doi: 10.1016/ j.ijscr.2015.09.030
6. Bose M, Ghosh R, Mukherjee K, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis:a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:YD03-5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8286.4591
7. Cataño JC, Gómez Villegas SI. Images in clinical medicine. Cutaneous actinomycosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1773. doi: 10.1056/ NEJMicm1511213
8. Mehta V, Balachandran C. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis on the chest wall. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:13.
9. Piggott SA, Khodaee M. A bump in the groin: cutaneous actinomycosis. J Family Community Med. 2017;24:203. doi: 10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_79_17
10. Bonifaz A, Tirado-Sánchez A, Calderón L, et al. Treatment of cutaneous actinomycosis with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:59-64. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2016.1178373
11. Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;;7:183-197. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S39601
Influenza vaccine update, 2021-22
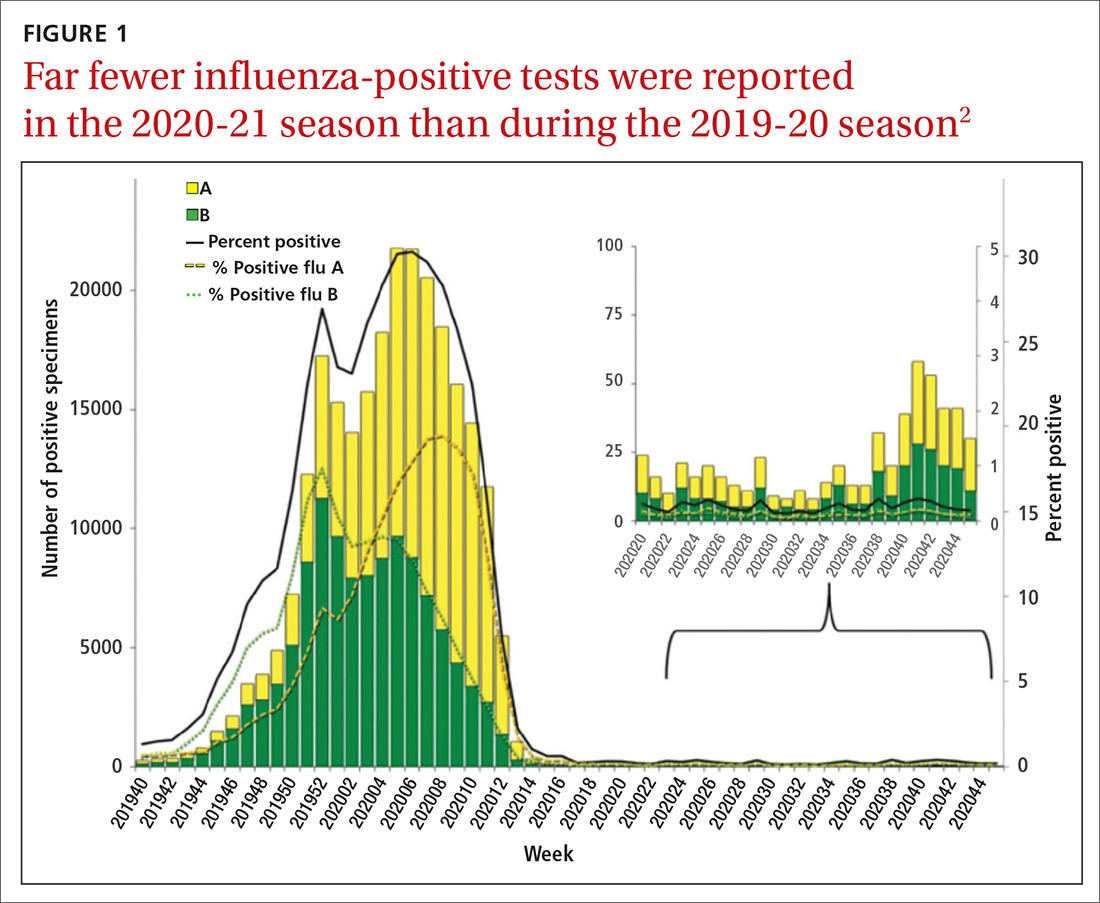
During the 2020-2021 influenza season, fewer cases of influenza were reported than in any previous year since 1997, when data were first recorded.1FIGURE 12 shows the dramatic decline in the number of influenza-positive clinical samples reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during the 2020-2021 influenza season compared with the 2019-2020 season. There was only one pediatric death attributed to influenza in 2020-2021, compared with a mean of 177 per year in the previous 3 seasons.
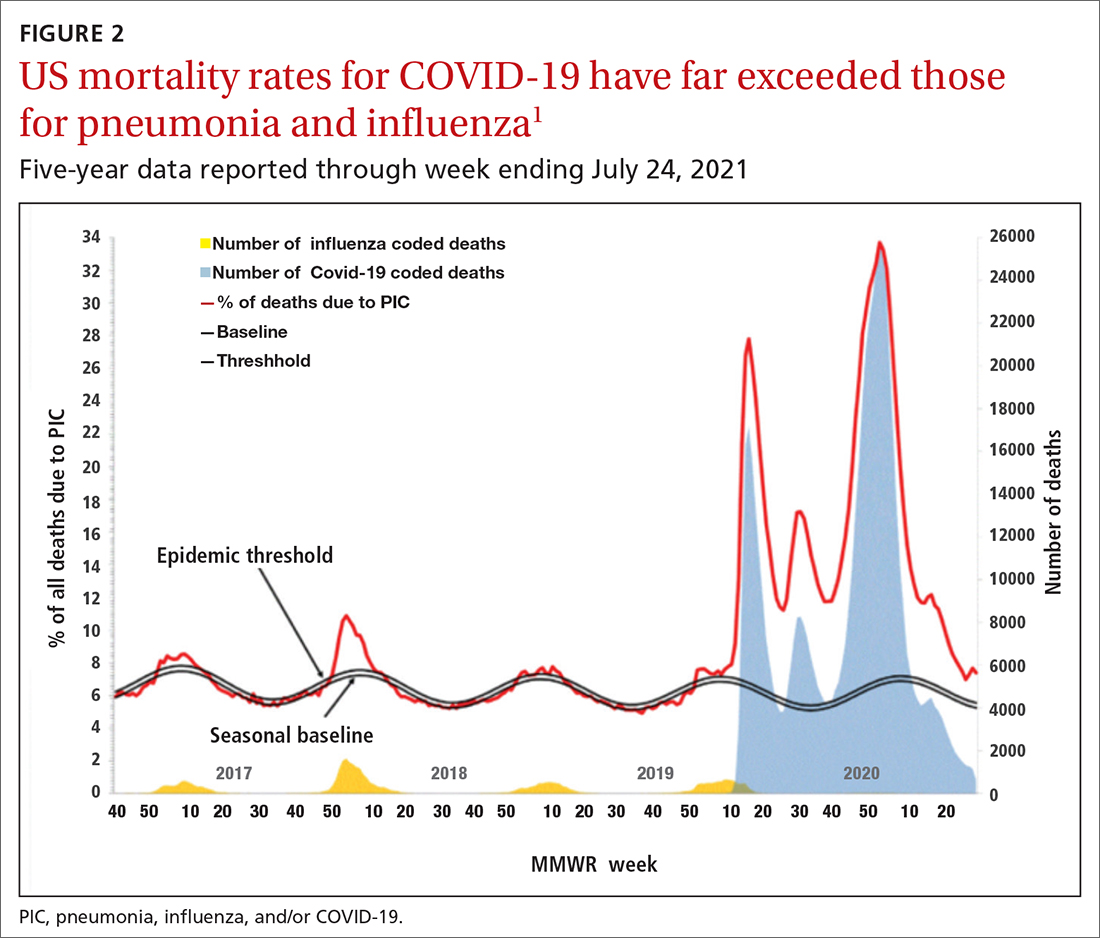
Deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were recorded over a recent 5-year period, with COVID-19 added in early mid-2020 (FIGURE 2).1 Total cumulative deaths for 2020-2021 were extremely high, mostly due to COVID-19. Of the relatively few influenza cases last season, 37.5% were caused by influenza A and 62.5% by influenza B. The extremely low incidence of influenza precludes determining influenza vaccine effectiveness for last season.1
In addition, other common respiratory pathogens—parainfluenza, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, enteroviruses, and common coronaviruses—circulated last winter at historic lows.3 All of these historic lows can be attributed to the measures taken to mitigate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic, including masks, social distancing, closure of certain venues that normally attract large crowds, and the closure of schools with a resulting increase in schooling at home. With the anticipated relaxation of these measures in 2021-2022, we can expect more influenza and other respiratory ailments due to common pathogens.
Updates to influenza vaccine recommendations
At its June 2021 meeting, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) approved the influenza vaccine recommendations for the 2021-2022 season.4 The central recommendation is unchanged: Everyone ≥ 6 months of age should receive a vaccine unless they have a contraindication. Updates to the previous recommendations include the content of the 2021 vaccines, the specific vaccines that will be available for different age groups, the timing of vaccine administration, advice on co-administration with COVID-19 vaccines, and the list of contraindications and precautions based on vaccine type.4
Viral composition of US vaccines for the 2021-22 season
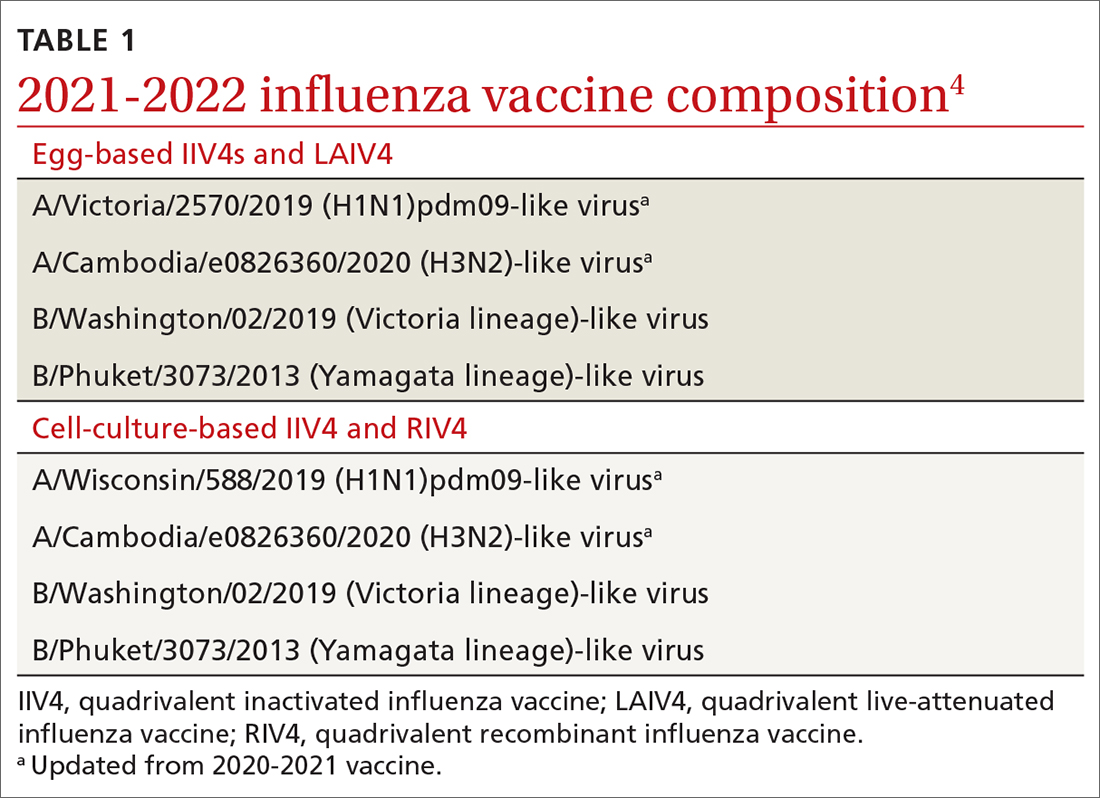
The antigens that will be included in the 2021-2022 influenza vaccines are listed in TABLE 1.4 The B strains are the same as last year; the A strains have been updated. The H3N2 strain is the same in all vaccines, but the H1N1 strain differs based on whether the vaccine is egg based or non-egg based. The advantage of non-egg-based vaccines is that the production process does not take as long and can be delayed in an attempt to better reflect the influenza stains in worldwide circulation.
The influenza vaccines expected to be available for the 2021-22 season
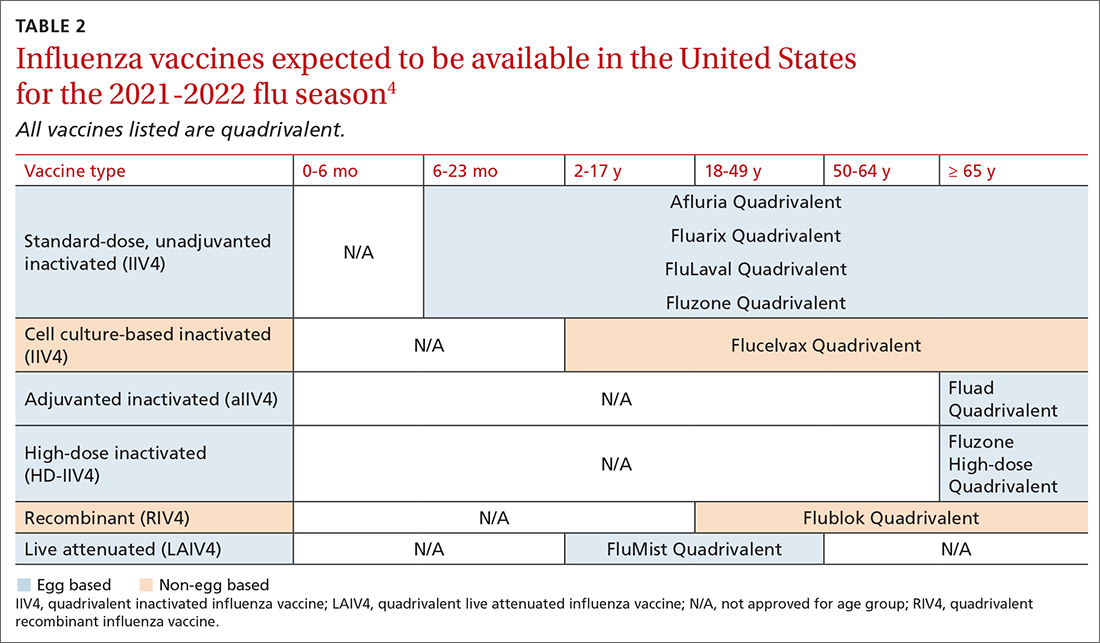
TABLE 24 lists the influenza vaccines approved for use in the United States and the ages for which they are approved.4 All products for 2021-2022 will be quadrivalent, containing 2 type-A and 2 type-B antigens. The only change in age indications is that cell culture–based inactivated influenza vaccine (ccIIV4) (Flucelvax Quadrivalent) is now approved for use starting at age 2 years; previously it was approved starting at age 4 years.4
Timing of vaccination
The onsets and peaks of influenza disease occur at different times each year and can also vary by geographic location. An analysis of 36 influenza seasons starting in 1982 showed that peak activity occurred most frequently in February (15 seasons), followed by December (7 seasons), and January and March (6 seasons each).5 Only once did peak activity occur in October and once in November. This information, along with observational studies showing the waning of influenza vaccine effectiveness after 5 to 6 months, especially in the elderly, informed the ACIP decision to modify their recommendation on the timing of vaccination. The recommendation now states that vaccine should be administered by the end of October and that July and August would have been too early, especially for older adults.
Continue to: Children ages 6 months...
Children ages 6 months through 8 years who have not been vaccinated previously require 2 doses separated by at least 4 weeks, and the first dose should be administered early enough to allow for the second by the end of October.4 Children who require only 1 dose can also receive the vaccine as soon as it is available, as there is less evidence that vaccine effectiveness wanes in children.
Earlier administration is also recommended for pregnant women in their third trimester. Delaying vaccination in this group could result in postpartum administration of the vaccine, thereby depriving infants of protection against influenza illness during their first 6 months after birth.4
Co-administration of influenza and COVID-19 vaccines
Current guidance from the CDC states that COVID-19 vaccines can be co-administered with other vaccines including influenza vaccines.6 However, there are no data by which to judge the efficacy of each vaccine in coadministration or the potential for increased adverse reactions. ACIP advises caution on 2 points: (1) physicians should watch for updated guidance as more information becomes available, and (2) there is the potential for increased reactogenicity after co-administration, especially with the more reactogenic influenza vaccines: adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine (aIIV4) and high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (HD-IIV4). Moreover, these vaccines and the co-administered COVID-19 vaccine should be injected into different limbs.
Contraindications and precautions
Serious allergic reactions to influenza vaccines are rare—about 1.3 incidents per million doses administered.7 However, a previous severe allergic reaction to a particular vaccine or to any component of the vaccine is a contraindication for use of that vaccine. In addition, a history of severe allergic reaction to any influenza vaccine is a contraindication for all egg-based vaccines.
There are 2 precautions for all influenza vaccines: a concurrent moderate or severe acute illness (with or without fever), and a history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receiving any influenza vaccine. An additional precaution for ccIIV4 and recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV4) is a history of severe allergic reaction after administration of any other influenza vaccine. Administration of RIV4 or ccIIV4 to someone with such a history should occur in a medical setting and be supervised by someone who can recognize and treat a severe reaction.
Continue to: Live attenuated influenza vaccine...
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) continues to have a considerably longer list of contraindications, which can be found in the published recommendations for 2021-2022.8
Final advice
The upcoming influenza season has the potential to be clinically challenging with the possibility of co-existing high rates of both COVID-19 and influenza. Recommend both influenza and COVID-19 vaccination to patients. Also, be sure to encourage and practice other preventive measures such as masking in crowds, frequent hand washing, isolation when sick, respiratory hygiene, and (for physicians) selected prescribing of influenza antiviral medications and meticulous office-based infection control practices.9
1. CDC. Weekly U.S. influenza surveillance report. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/index.htm
2. CDC. Weekly archives. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/weeklyarchives2020-2021/WhoNPHL45.html
3. Olsen SJ, Winn AK, Budd AP, et al. Changes in influenza and other respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic — United States, 2020-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1013-1019.
4. Grohskopf L. WG considerations and proposed influenza vaccine recommendations, 2021-22. Presented at the June 24, 2021, meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/03-influenza-grohskopf-508.pdf
5. CDC. The flu season. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/about/season/flu-season.htm
6. CDC. Interim clinical considerations for use of COVID-19 vaccines currently approved or authorized in the United States. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fvaccines%2Fcovid-19%2Finfo-by-product%2Fclinical-considerations.html#Coadministration
7. McNeil MM, Weintraub ES, Duffy J, et al. Risk of anaphylaxis after vaccination in children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:868-878.
8. Grohskopf LA, Alyanak E, Ferdinands JM, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2021–22 influenza season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1-28.
9. CDC. Prevent flu. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/index.html
During the 2020-2021 influenza season, fewer cases of influenza were reported than in any previous year since 1997, when data were first recorded.1FIGURE 12 shows the dramatic decline in the number of influenza-positive clinical samples reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during the 2020-2021 influenza season compared with the 2019-2020 season. There was only one pediatric death attributed to influenza in 2020-2021, compared with a mean of 177 per year in the previous 3 seasons.

Deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were recorded over a recent 5-year period, with COVID-19 added in early mid-2020 (FIGURE 2).1 Total cumulative deaths for 2020-2021 were extremely high, mostly due to COVID-19. Of the relatively few influenza cases last season, 37.5% were caused by influenza A and 62.5% by influenza B. The extremely low incidence of influenza precludes determining influenza vaccine effectiveness for last season.1

In addition, other common respiratory pathogens—parainfluenza, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, enteroviruses, and common coronaviruses—circulated last winter at historic lows.3 All of these historic lows can be attributed to the measures taken to mitigate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic, including masks, social distancing, closure of certain venues that normally attract large crowds, and the closure of schools with a resulting increase in schooling at home. With the anticipated relaxation of these measures in 2021-2022, we can expect more influenza and other respiratory ailments due to common pathogens.
Updates to influenza vaccine recommendations
At its June 2021 meeting, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) approved the influenza vaccine recommendations for the 2021-2022 season.4 The central recommendation is unchanged: Everyone ≥ 6 months of age should receive a vaccine unless they have a contraindication. Updates to the previous recommendations include the content of the 2021 vaccines, the specific vaccines that will be available for different age groups, the timing of vaccine administration, advice on co-administration with COVID-19 vaccines, and the list of contraindications and precautions based on vaccine type.4
Viral composition of US vaccines for the 2021-22 season
The antigens that will be included in the 2021-2022 influenza vaccines are listed in TABLE 1.4 The B strains are the same as last year; the A strains have been updated. The H3N2 strain is the same in all vaccines, but the H1N1 strain differs based on whether the vaccine is egg based or non-egg based. The advantage of non-egg-based vaccines is that the production process does not take as long and can be delayed in an attempt to better reflect the influenza stains in worldwide circulation.

The influenza vaccines expected to be available for the 2021-22 season
TABLE 24 lists the influenza vaccines approved for use in the United States and the ages for which they are approved.4 All products for 2021-2022 will be quadrivalent, containing 2 type-A and 2 type-B antigens. The only change in age indications is that cell culture–based inactivated influenza vaccine (ccIIV4) (Flucelvax Quadrivalent) is now approved for use starting at age 2 years; previously it was approved starting at age 4 years.4

Timing of vaccination
The onsets and peaks of influenza disease occur at different times each year and can also vary by geographic location. An analysis of 36 influenza seasons starting in 1982 showed that peak activity occurred most frequently in February (15 seasons), followed by December (7 seasons), and January and March (6 seasons each).5 Only once did peak activity occur in October and once in November. This information, along with observational studies showing the waning of influenza vaccine effectiveness after 5 to 6 months, especially in the elderly, informed the ACIP decision to modify their recommendation on the timing of vaccination. The recommendation now states that vaccine should be administered by the end of October and that July and August would have been too early, especially for older adults.
Continue to: Children ages 6 months...
Children ages 6 months through 8 years who have not been vaccinated previously require 2 doses separated by at least 4 weeks, and the first dose should be administered early enough to allow for the second by the end of October.4 Children who require only 1 dose can also receive the vaccine as soon as it is available, as there is less evidence that vaccine effectiveness wanes in children.
Earlier administration is also recommended for pregnant women in their third trimester. Delaying vaccination in this group could result in postpartum administration of the vaccine, thereby depriving infants of protection against influenza illness during their first 6 months after birth.4
Co-administration of influenza and COVID-19 vaccines
Current guidance from the CDC states that COVID-19 vaccines can be co-administered with other vaccines including influenza vaccines.6 However, there are no data by which to judge the efficacy of each vaccine in coadministration or the potential for increased adverse reactions. ACIP advises caution on 2 points: (1) physicians should watch for updated guidance as more information becomes available, and (2) there is the potential for increased reactogenicity after co-administration, especially with the more reactogenic influenza vaccines: adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine (aIIV4) and high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (HD-IIV4). Moreover, these vaccines and the co-administered COVID-19 vaccine should be injected into different limbs.
Contraindications and precautions
Serious allergic reactions to influenza vaccines are rare—about 1.3 incidents per million doses administered.7 However, a previous severe allergic reaction to a particular vaccine or to any component of the vaccine is a contraindication for use of that vaccine. In addition, a history of severe allergic reaction to any influenza vaccine is a contraindication for all egg-based vaccines.
There are 2 precautions for all influenza vaccines: a concurrent moderate or severe acute illness (with or without fever), and a history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receiving any influenza vaccine. An additional precaution for ccIIV4 and recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV4) is a history of severe allergic reaction after administration of any other influenza vaccine. Administration of RIV4 or ccIIV4 to someone with such a history should occur in a medical setting and be supervised by someone who can recognize and treat a severe reaction.
Continue to: Live attenuated influenza vaccine...
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) continues to have a considerably longer list of contraindications, which can be found in the published recommendations for 2021-2022.8
Final advice
The upcoming influenza season has the potential to be clinically challenging with the possibility of co-existing high rates of both COVID-19 and influenza. Recommend both influenza and COVID-19 vaccination to patients. Also, be sure to encourage and practice other preventive measures such as masking in crowds, frequent hand washing, isolation when sick, respiratory hygiene, and (for physicians) selected prescribing of influenza antiviral medications and meticulous office-based infection control practices.9
During the 2020-2021 influenza season, fewer cases of influenza were reported than in any previous year since 1997, when data were first recorded.1FIGURE 12 shows the dramatic decline in the number of influenza-positive clinical samples reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during the 2020-2021 influenza season compared with the 2019-2020 season. There was only one pediatric death attributed to influenza in 2020-2021, compared with a mean of 177 per year in the previous 3 seasons.

Deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were recorded over a recent 5-year period, with COVID-19 added in early mid-2020 (FIGURE 2).1 Total cumulative deaths for 2020-2021 were extremely high, mostly due to COVID-19. Of the relatively few influenza cases last season, 37.5% were caused by influenza A and 62.5% by influenza B. The extremely low incidence of influenza precludes determining influenza vaccine effectiveness for last season.1

In addition, other common respiratory pathogens—parainfluenza, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, enteroviruses, and common coronaviruses—circulated last winter at historic lows.3 All of these historic lows can be attributed to the measures taken to mitigate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic, including masks, social distancing, closure of certain venues that normally attract large crowds, and the closure of schools with a resulting increase in schooling at home. With the anticipated relaxation of these measures in 2021-2022, we can expect more influenza and other respiratory ailments due to common pathogens.
Updates to influenza vaccine recommendations
At its June 2021 meeting, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) approved the influenza vaccine recommendations for the 2021-2022 season.4 The central recommendation is unchanged: Everyone ≥ 6 months of age should receive a vaccine unless they have a contraindication. Updates to the previous recommendations include the content of the 2021 vaccines, the specific vaccines that will be available for different age groups, the timing of vaccine administration, advice on co-administration with COVID-19 vaccines, and the list of contraindications and precautions based on vaccine type.4
Viral composition of US vaccines for the 2021-22 season
The antigens that will be included in the 2021-2022 influenza vaccines are listed in TABLE 1.4 The B strains are the same as last year; the A strains have been updated. The H3N2 strain is the same in all vaccines, but the H1N1 strain differs based on whether the vaccine is egg based or non-egg based. The advantage of non-egg-based vaccines is that the production process does not take as long and can be delayed in an attempt to better reflect the influenza stains in worldwide circulation.

The influenza vaccines expected to be available for the 2021-22 season
TABLE 24 lists the influenza vaccines approved for use in the United States and the ages for which they are approved.4 All products for 2021-2022 will be quadrivalent, containing 2 type-A and 2 type-B antigens. The only change in age indications is that cell culture–based inactivated influenza vaccine (ccIIV4) (Flucelvax Quadrivalent) is now approved for use starting at age 2 years; previously it was approved starting at age 4 years.4

Timing of vaccination
The onsets and peaks of influenza disease occur at different times each year and can also vary by geographic location. An analysis of 36 influenza seasons starting in 1982 showed that peak activity occurred most frequently in February (15 seasons), followed by December (7 seasons), and January and March (6 seasons each).5 Only once did peak activity occur in October and once in November. This information, along with observational studies showing the waning of influenza vaccine effectiveness after 5 to 6 months, especially in the elderly, informed the ACIP decision to modify their recommendation on the timing of vaccination. The recommendation now states that vaccine should be administered by the end of October and that July and August would have been too early, especially for older adults.
Continue to: Children ages 6 months...
Children ages 6 months through 8 years who have not been vaccinated previously require 2 doses separated by at least 4 weeks, and the first dose should be administered early enough to allow for the second by the end of October.4 Children who require only 1 dose can also receive the vaccine as soon as it is available, as there is less evidence that vaccine effectiveness wanes in children.
Earlier administration is also recommended for pregnant women in their third trimester. Delaying vaccination in this group could result in postpartum administration of the vaccine, thereby depriving infants of protection against influenza illness during their first 6 months after birth.4
Co-administration of influenza and COVID-19 vaccines
Current guidance from the CDC states that COVID-19 vaccines can be co-administered with other vaccines including influenza vaccines.6 However, there are no data by which to judge the efficacy of each vaccine in coadministration or the potential for increased adverse reactions. ACIP advises caution on 2 points: (1) physicians should watch for updated guidance as more information becomes available, and (2) there is the potential for increased reactogenicity after co-administration, especially with the more reactogenic influenza vaccines: adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine (aIIV4) and high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (HD-IIV4). Moreover, these vaccines and the co-administered COVID-19 vaccine should be injected into different limbs.
Contraindications and precautions
Serious allergic reactions to influenza vaccines are rare—about 1.3 incidents per million doses administered.7 However, a previous severe allergic reaction to a particular vaccine or to any component of the vaccine is a contraindication for use of that vaccine. In addition, a history of severe allergic reaction to any influenza vaccine is a contraindication for all egg-based vaccines.
There are 2 precautions for all influenza vaccines: a concurrent moderate or severe acute illness (with or without fever), and a history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receiving any influenza vaccine. An additional precaution for ccIIV4 and recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV4) is a history of severe allergic reaction after administration of any other influenza vaccine. Administration of RIV4 or ccIIV4 to someone with such a history should occur in a medical setting and be supervised by someone who can recognize and treat a severe reaction.
Continue to: Live attenuated influenza vaccine...
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) continues to have a considerably longer list of contraindications, which can be found in the published recommendations for 2021-2022.8
Final advice
The upcoming influenza season has the potential to be clinically challenging with the possibility of co-existing high rates of both COVID-19 and influenza. Recommend both influenza and COVID-19 vaccination to patients. Also, be sure to encourage and practice other preventive measures such as masking in crowds, frequent hand washing, isolation when sick, respiratory hygiene, and (for physicians) selected prescribing of influenza antiviral medications and meticulous office-based infection control practices.9
1. CDC. Weekly U.S. influenza surveillance report. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/index.htm
2. CDC. Weekly archives. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/weeklyarchives2020-2021/WhoNPHL45.html
3. Olsen SJ, Winn AK, Budd AP, et al. Changes in influenza and other respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic — United States, 2020-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1013-1019.
4. Grohskopf L. WG considerations and proposed influenza vaccine recommendations, 2021-22. Presented at the June 24, 2021, meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/03-influenza-grohskopf-508.pdf
5. CDC. The flu season. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/about/season/flu-season.htm
6. CDC. Interim clinical considerations for use of COVID-19 vaccines currently approved or authorized in the United States. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fvaccines%2Fcovid-19%2Finfo-by-product%2Fclinical-considerations.html#Coadministration
7. McNeil MM, Weintraub ES, Duffy J, et al. Risk of anaphylaxis after vaccination in children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:868-878.
8. Grohskopf LA, Alyanak E, Ferdinands JM, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2021–22 influenza season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1-28.
9. CDC. Prevent flu. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/index.html
1. CDC. Weekly U.S. influenza surveillance report. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/index.htm
2. CDC. Weekly archives. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/weeklyarchives2020-2021/WhoNPHL45.html
3. Olsen SJ, Winn AK, Budd AP, et al. Changes in influenza and other respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic — United States, 2020-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1013-1019.
4. Grohskopf L. WG considerations and proposed influenza vaccine recommendations, 2021-22. Presented at the June 24, 2021, meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/03-influenza-grohskopf-508.pdf
5. CDC. The flu season. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/about/season/flu-season.htm
6. CDC. Interim clinical considerations for use of COVID-19 vaccines currently approved or authorized in the United States. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fvaccines%2Fcovid-19%2Finfo-by-product%2Fclinical-considerations.html#Coadministration
7. McNeil MM, Weintraub ES, Duffy J, et al. Risk of anaphylaxis after vaccination in children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:868-878.
8. Grohskopf LA, Alyanak E, Ferdinands JM, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2021–22 influenza season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1-28.
9. CDC. Prevent flu. Accessed September 23, 2021. www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/index.html
Children and COVID: Vaccinations lower than ever as cases continue to drop
As the COVID-19 vaccine heads toward approval for children under age 12 years, the number of older children receiving it dropped for the 10th consecutive week, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
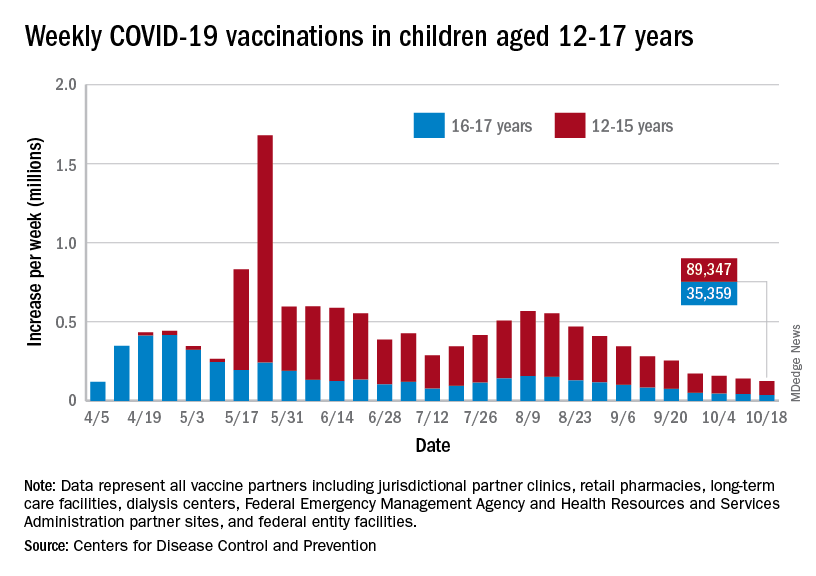
Over 47% of all children aged 12-17 years – that’s close to 12 million eligible individuals – have not received even one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and less than 44% (about 11.1 million) were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 18, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
, when eligibility expanded to include 12- to 15-year-olds, according to the CDC data, which also show that weekly vaccinations have never been lower.
Fortunately, the decline in new cases also continued, as the national total fell for a 6th straight week. There were more than 130,000 child cases reported during the week of Oct. 8-14, compared with 148,000 the previous week and the high of almost 252,000 in late August/early September, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
That brings the cumulative count to 6.18 million, with children accounting for 16.4% of all cases reported since the start of the pandemic. For the week of Oct. 8-14, children represented 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases in the 46 states with up-to-date online dashboards, the AAP and CHA said, noting that New York has never reported age ranges for cases and that Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer.
Current data indicate that child cases in California now exceed 671,000, more than any other state, followed by Florida with 439,000 (the state defines a child as someone aged 0-14 years) and Illinois with 301,000. Vermont has the highest proportion of COVID-19 cases occurring in children (24.3%), with Alaska (24.1%) and South Carolina (23.2%) just behind. The highest rate of cases – 15,569 per 100,000 children – can be found in South Carolina, while the lowest is in Hawaii (4,838 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA reported.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 681 as of Oct. 18, according to the CDC, with the AAP/CHA reporting 558 as of Oct. 14, based on data from 45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. The CDC reports 65,655 admissions since Aug. 1, 2020, in children aged 0-17 years, and the AAP/CHA tally 23,582 since May 5, 2020, among children in 24 states and New York City.
As the COVID-19 vaccine heads toward approval for children under age 12 years, the number of older children receiving it dropped for the 10th consecutive week, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Over 47% of all children aged 12-17 years – that’s close to 12 million eligible individuals – have not received even one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and less than 44% (about 11.1 million) were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 18, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
, when eligibility expanded to include 12- to 15-year-olds, according to the CDC data, which also show that weekly vaccinations have never been lower.
Fortunately, the decline in new cases also continued, as the national total fell for a 6th straight week. There were more than 130,000 child cases reported during the week of Oct. 8-14, compared with 148,000 the previous week and the high of almost 252,000 in late August/early September, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
That brings the cumulative count to 6.18 million, with children accounting for 16.4% of all cases reported since the start of the pandemic. For the week of Oct. 8-14, children represented 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases in the 46 states with up-to-date online dashboards, the AAP and CHA said, noting that New York has never reported age ranges for cases and that Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer.
Current data indicate that child cases in California now exceed 671,000, more than any other state, followed by Florida with 439,000 (the state defines a child as someone aged 0-14 years) and Illinois with 301,000. Vermont has the highest proportion of COVID-19 cases occurring in children (24.3%), with Alaska (24.1%) and South Carolina (23.2%) just behind. The highest rate of cases – 15,569 per 100,000 children – can be found in South Carolina, while the lowest is in Hawaii (4,838 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA reported.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 681 as of Oct. 18, according to the CDC, with the AAP/CHA reporting 558 as of Oct. 14, based on data from 45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. The CDC reports 65,655 admissions since Aug. 1, 2020, in children aged 0-17 years, and the AAP/CHA tally 23,582 since May 5, 2020, among children in 24 states and New York City.
As the COVID-19 vaccine heads toward approval for children under age 12 years, the number of older children receiving it dropped for the 10th consecutive week, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Over 47% of all children aged 12-17 years – that’s close to 12 million eligible individuals – have not received even one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and less than 44% (about 11.1 million) were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 18, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
, when eligibility expanded to include 12- to 15-year-olds, according to the CDC data, which also show that weekly vaccinations have never been lower.
Fortunately, the decline in new cases also continued, as the national total fell for a 6th straight week. There were more than 130,000 child cases reported during the week of Oct. 8-14, compared with 148,000 the previous week and the high of almost 252,000 in late August/early September, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
That brings the cumulative count to 6.18 million, with children accounting for 16.4% of all cases reported since the start of the pandemic. For the week of Oct. 8-14, children represented 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases in the 46 states with up-to-date online dashboards, the AAP and CHA said, noting that New York has never reported age ranges for cases and that Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer.
Current data indicate that child cases in California now exceed 671,000, more than any other state, followed by Florida with 439,000 (the state defines a child as someone aged 0-14 years) and Illinois with 301,000. Vermont has the highest proportion of COVID-19 cases occurring in children (24.3%), with Alaska (24.1%) and South Carolina (23.2%) just behind. The highest rate of cases – 15,569 per 100,000 children – can be found in South Carolina, while the lowest is in Hawaii (4,838 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA reported.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 681 as of Oct. 18, according to the CDC, with the AAP/CHA reporting 558 as of Oct. 14, based on data from 45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. The CDC reports 65,655 admissions since Aug. 1, 2020, in children aged 0-17 years, and the AAP/CHA tally 23,582 since May 5, 2020, among children in 24 states and New York City.
Why toilet paper is the unofficial symbol of anxiety during COVID
How did toilet paper become the unofficial symbol of anxiety during the pandemic? Empty store shelves are a stark reminder of how COVID-19 has taken a toll on people.
At the beginning of the pandemic, stay-at-home orders drove people to buy large amounts of household goods, especially toilet paper. Demand grew to unforeseen heights in March 2020, with $1.45 billion in toilet paper sales in the 4-week period ending March 29, up 112% from the year before, according to IRI, a Chicago-based market research firm.
As the Delta variant drove a COVID-19 resurgence this summer, market research suggests that almost one in two Americans started stockpiling toilet paper again over fears that supply would run out. The higher demand causes ripples through the retail chain, and a growing number of stores are again facing challenges in stocking toilet paper.
Yet there is plenty for everyone if people don’t stockpile too much, according to paper industry market analyst Ronalds Gonzalez, PhD, an associate professor of conversion economics and sustainability at North Carolina State University, Raleigh.
“As long as people buy what they actually need and don’t get into a panic, there won’t be any issue with the supply of hygienic tissue,” he says, adding that “too much” would equate to stockpiling 6-8 months’ worth of toilet paper, as some people did early in the pandemic.
But retailers are worried that history will repeat itself. In late September 2021, warehouse retail giant Costco told Wall Street analysts that it decided to limit customer purchases of essential items like toilet paper and water. Another retailer, Sam’s Club, began limiting customer purchases of supplies like toilet paper at the end of July.
“We are wired to run with the herd,” says Bradley Klontz, PsyD, an associate professor of practice at Creighton University Heider College of Business, Omaha, N.E., who specializes in financial psychology.
“Quite literally, the last person to get to Costco doesn’t get the toilet paper, so when the herd is running in a certain direction, we feel a biological imperative to not be that last person. That fear of scarcity actually creates the experience of scarcity,” he explains.
The science behind the stockpile
People are collectively alerted by photos shared on social media showing store shelves stripped of toilet paper. Those images triggered consumers to rush out and buy bathroom tissue, even if they didn’t need it – and that herd behavior created toilet paper shortages.
Now, a year and half into the pandemic, people are hypervigilant to danger. Any hint of a possible toilet paper shortage can provoke anxiety and the desire to stockpile.
, says Dr. Klontz. He advises people to take a deep breath before buying extra toilet paper and then assess whether it is truly needed.
Deep in our brains is the limbic system, a group of structures that rules over emotions, motivation, reward, learning, memory, and the fight-or-flight response to stress and danger. When a person senses danger, the brain activates hormones to raise blood pressure and heart rate, increase blood flow, and boost the breath rate, making the body ready to fight or flee under threat.
Once everything settles, the body activates chemicals like dopamine that bring on positive feelings of well-being, rewarding that flight-or-fight response. In this way, the brain powerfully reinforces a key survival instinct.
This sequence of experiences and the brain chemistry behind them may explain why people panic-buy toilet paper.
“With toilet paper, my limbic system starts thinking about a perceived threat to safety,” says Julie Pike, PhD, a psychologist in Chapel Hill, N.C., who specializes in anxiety, hoarding, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
She notes that, in stockpiling toilet paper, “we avoid a perceived threat and then we are chemically rewarded” with dopamine. A storage closet full of toilet paper after a perceived threat of scarcity – no matter how unfounded – brings on that satisfied feeling.
When the market shifted
Paper producers make hygiene paper for two markets: the commercial (think: those big rolls of thin paper used in offices, schools, and restaurants) and the consumer (the soft paper you likely use at home). In the spring of 2020, the commercial market plummeted, and the consumer market skyrocketed.
Generally, the consumer toilet paper market is steady. The average American uses about 57 toilet sheets a day and about 50 pounds annually. Grocery stores and other retailers keep just enough toilet paper on hand to meet this steady demand, meaning panic buying at the start of the pandemic quickly depleted stocks. Paper makers had to change production to meet higher consumer demand and fewer commercial buyers.
By the end of the summer of 2020, toilet paper makers had adjusted for the market shift and caught up with demand, as consumers worked through their stockpiles of paper. But retail inventories remain lean because toilet paper doesn’t carry huge profit margins. For this reason, even healthy stocks remain sensitive to sudden shifts in consumer demand, Dr. Gonzalez says.
“If people buy more than they should, then they are just buying from other people,” creating an unnecessary scarcity of toilet paper, he says.
The supply chain
It is true that the supply chain is under unprecedented strain, leading to higher prices for many goods, says Katie Denis, vice president of research and industry narrative at the Consumer Brands Association, Washington, which represents toilet paper makers Georgia-Pacific and Procter & Gamble. Consumers should expect toilet paper to be available, but there may be fewer options for product sizes, she says.
Still, Dr. Gonzalez says consumers should not worry too much about the global supply chain affecting the domestic toilet paper supply. The raw material for toilet paper production is available domestically, and more than 97% of the supply on U.S. retailer shelves is made in the United States, he says.
In modern society, toilet paper is a primary link to civilization, health, and hygiene. While there is no easy substitute, alternatives do exist A bidet, for example, is a device that can spray water on the genital area. Other options are reusable cloths, sponges, baby wipes, napkins, towels, and washcloths.
Human health and hygiene
“Compared to many other items, toilet paper can’t really be replaced,” says Frank H. Farley, PhD, a professor of psychological studies in education at Temple University, who studies human motivation. “It is a unique consumer item that is perceived to be extremely necessary. In that way, it plays into that survivor mentality, that having it is necessary for survival.”
Being without it can truly seem like an existential threat.
New York City emergency planner Ira Tannenbaum advises families to assess their usage of essential household supplies like toilet paper (you can do so through this toilet paper calculator) and keep at least a 1-week supply on hand in case of emergency. New York City has posted recommendations to families for emergency planning, including the guidance to “avoid panic buying.”
Dr. Pike says she would stockpile a bit more, something that could be done gradually, before there’s a panic. She says that if people are tempted to buy more out of anxiety, they should remind themselves that shortages arise because of panicky purchasing.
“Leave some for other families – other people have children and partners and siblings just like us,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
How did toilet paper become the unofficial symbol of anxiety during the pandemic? Empty store shelves are a stark reminder of how COVID-19 has taken a toll on people.
At the beginning of the pandemic, stay-at-home orders drove people to buy large amounts of household goods, especially toilet paper. Demand grew to unforeseen heights in March 2020, with $1.45 billion in toilet paper sales in the 4-week period ending March 29, up 112% from the year before, according to IRI, a Chicago-based market research firm.
As the Delta variant drove a COVID-19 resurgence this summer, market research suggests that almost one in two Americans started stockpiling toilet paper again over fears that supply would run out. The higher demand causes ripples through the retail chain, and a growing number of stores are again facing challenges in stocking toilet paper.
Yet there is plenty for everyone if people don’t stockpile too much, according to paper industry market analyst Ronalds Gonzalez, PhD, an associate professor of conversion economics and sustainability at North Carolina State University, Raleigh.
“As long as people buy what they actually need and don’t get into a panic, there won’t be any issue with the supply of hygienic tissue,” he says, adding that “too much” would equate to stockpiling 6-8 months’ worth of toilet paper, as some people did early in the pandemic.
But retailers are worried that history will repeat itself. In late September 2021, warehouse retail giant Costco told Wall Street analysts that it decided to limit customer purchases of essential items like toilet paper and water. Another retailer, Sam’s Club, began limiting customer purchases of supplies like toilet paper at the end of July.
“We are wired to run with the herd,” says Bradley Klontz, PsyD, an associate professor of practice at Creighton University Heider College of Business, Omaha, N.E., who specializes in financial psychology.
“Quite literally, the last person to get to Costco doesn’t get the toilet paper, so when the herd is running in a certain direction, we feel a biological imperative to not be that last person. That fear of scarcity actually creates the experience of scarcity,” he explains.
The science behind the stockpile
People are collectively alerted by photos shared on social media showing store shelves stripped of toilet paper. Those images triggered consumers to rush out and buy bathroom tissue, even if they didn’t need it – and that herd behavior created toilet paper shortages.
Now, a year and half into the pandemic, people are hypervigilant to danger. Any hint of a possible toilet paper shortage can provoke anxiety and the desire to stockpile.
, says Dr. Klontz. He advises people to take a deep breath before buying extra toilet paper and then assess whether it is truly needed.
Deep in our brains is the limbic system, a group of structures that rules over emotions, motivation, reward, learning, memory, and the fight-or-flight response to stress and danger. When a person senses danger, the brain activates hormones to raise blood pressure and heart rate, increase blood flow, and boost the breath rate, making the body ready to fight or flee under threat.
Once everything settles, the body activates chemicals like dopamine that bring on positive feelings of well-being, rewarding that flight-or-fight response. In this way, the brain powerfully reinforces a key survival instinct.
This sequence of experiences and the brain chemistry behind them may explain why people panic-buy toilet paper.
“With toilet paper, my limbic system starts thinking about a perceived threat to safety,” says Julie Pike, PhD, a psychologist in Chapel Hill, N.C., who specializes in anxiety, hoarding, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
She notes that, in stockpiling toilet paper, “we avoid a perceived threat and then we are chemically rewarded” with dopamine. A storage closet full of toilet paper after a perceived threat of scarcity – no matter how unfounded – brings on that satisfied feeling.
When the market shifted
Paper producers make hygiene paper for two markets: the commercial (think: those big rolls of thin paper used in offices, schools, and restaurants) and the consumer (the soft paper you likely use at home). In the spring of 2020, the commercial market plummeted, and the consumer market skyrocketed.
Generally, the consumer toilet paper market is steady. The average American uses about 57 toilet sheets a day and about 50 pounds annually. Grocery stores and other retailers keep just enough toilet paper on hand to meet this steady demand, meaning panic buying at the start of the pandemic quickly depleted stocks. Paper makers had to change production to meet higher consumer demand and fewer commercial buyers.
By the end of the summer of 2020, toilet paper makers had adjusted for the market shift and caught up with demand, as consumers worked through their stockpiles of paper. But retail inventories remain lean because toilet paper doesn’t carry huge profit margins. For this reason, even healthy stocks remain sensitive to sudden shifts in consumer demand, Dr. Gonzalez says.
“If people buy more than they should, then they are just buying from other people,” creating an unnecessary scarcity of toilet paper, he says.
The supply chain
It is true that the supply chain is under unprecedented strain, leading to higher prices for many goods, says Katie Denis, vice president of research and industry narrative at the Consumer Brands Association, Washington, which represents toilet paper makers Georgia-Pacific and Procter & Gamble. Consumers should expect toilet paper to be available, but there may be fewer options for product sizes, she says.
Still, Dr. Gonzalez says consumers should not worry too much about the global supply chain affecting the domestic toilet paper supply. The raw material for toilet paper production is available domestically, and more than 97% of the supply on U.S. retailer shelves is made in the United States, he says.
In modern society, toilet paper is a primary link to civilization, health, and hygiene. While there is no easy substitute, alternatives do exist A bidet, for example, is a device that can spray water on the genital area. Other options are reusable cloths, sponges, baby wipes, napkins, towels, and washcloths.
Human health and hygiene
“Compared to many other items, toilet paper can’t really be replaced,” says Frank H. Farley, PhD, a professor of psychological studies in education at Temple University, who studies human motivation. “It is a unique consumer item that is perceived to be extremely necessary. In that way, it plays into that survivor mentality, that having it is necessary for survival.”
Being without it can truly seem like an existential threat.
New York City emergency planner Ira Tannenbaum advises families to assess their usage of essential household supplies like toilet paper (you can do so through this toilet paper calculator) and keep at least a 1-week supply on hand in case of emergency. New York City has posted recommendations to families for emergency planning, including the guidance to “avoid panic buying.”
Dr. Pike says she would stockpile a bit more, something that could be done gradually, before there’s a panic. She says that if people are tempted to buy more out of anxiety, they should remind themselves that shortages arise because of panicky purchasing.
“Leave some for other families – other people have children and partners and siblings just like us,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
How did toilet paper become the unofficial symbol of anxiety during the pandemic? Empty store shelves are a stark reminder of how COVID-19 has taken a toll on people.
At the beginning of the pandemic, stay-at-home orders drove people to buy large amounts of household goods, especially toilet paper. Demand grew to unforeseen heights in March 2020, with $1.45 billion in toilet paper sales in the 4-week period ending March 29, up 112% from the year before, according to IRI, a Chicago-based market research firm.
As the Delta variant drove a COVID-19 resurgence this summer, market research suggests that almost one in two Americans started stockpiling toilet paper again over fears that supply would run out. The higher demand causes ripples through the retail chain, and a growing number of stores are again facing challenges in stocking toilet paper.
Yet there is plenty for everyone if people don’t stockpile too much, according to paper industry market analyst Ronalds Gonzalez, PhD, an associate professor of conversion economics and sustainability at North Carolina State University, Raleigh.
“As long as people buy what they actually need and don’t get into a panic, there won’t be any issue with the supply of hygienic tissue,” he says, adding that “too much” would equate to stockpiling 6-8 months’ worth of toilet paper, as some people did early in the pandemic.
But retailers are worried that history will repeat itself. In late September 2021, warehouse retail giant Costco told Wall Street analysts that it decided to limit customer purchases of essential items like toilet paper and water. Another retailer, Sam’s Club, began limiting customer purchases of supplies like toilet paper at the end of July.
“We are wired to run with the herd,” says Bradley Klontz, PsyD, an associate professor of practice at Creighton University Heider College of Business, Omaha, N.E., who specializes in financial psychology.
“Quite literally, the last person to get to Costco doesn’t get the toilet paper, so when the herd is running in a certain direction, we feel a biological imperative to not be that last person. That fear of scarcity actually creates the experience of scarcity,” he explains.
The science behind the stockpile
People are collectively alerted by photos shared on social media showing store shelves stripped of toilet paper. Those images triggered consumers to rush out and buy bathroom tissue, even if they didn’t need it – and that herd behavior created toilet paper shortages.
Now, a year and half into the pandemic, people are hypervigilant to danger. Any hint of a possible toilet paper shortage can provoke anxiety and the desire to stockpile.
, says Dr. Klontz. He advises people to take a deep breath before buying extra toilet paper and then assess whether it is truly needed.
Deep in our brains is the limbic system, a group of structures that rules over emotions, motivation, reward, learning, memory, and the fight-or-flight response to stress and danger. When a person senses danger, the brain activates hormones to raise blood pressure and heart rate, increase blood flow, and boost the breath rate, making the body ready to fight or flee under threat.
Once everything settles, the body activates chemicals like dopamine that bring on positive feelings of well-being, rewarding that flight-or-fight response. In this way, the brain powerfully reinforces a key survival instinct.
This sequence of experiences and the brain chemistry behind them may explain why people panic-buy toilet paper.
“With toilet paper, my limbic system starts thinking about a perceived threat to safety,” says Julie Pike, PhD, a psychologist in Chapel Hill, N.C., who specializes in anxiety, hoarding, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
She notes that, in stockpiling toilet paper, “we avoid a perceived threat and then we are chemically rewarded” with dopamine. A storage closet full of toilet paper after a perceived threat of scarcity – no matter how unfounded – brings on that satisfied feeling.
When the market shifted
Paper producers make hygiene paper for two markets: the commercial (think: those big rolls of thin paper used in offices, schools, and restaurants) and the consumer (the soft paper you likely use at home). In the spring of 2020, the commercial market plummeted, and the consumer market skyrocketed.
Generally, the consumer toilet paper market is steady. The average American uses about 57 toilet sheets a day and about 50 pounds annually. Grocery stores and other retailers keep just enough toilet paper on hand to meet this steady demand, meaning panic buying at the start of the pandemic quickly depleted stocks. Paper makers had to change production to meet higher consumer demand and fewer commercial buyers.
By the end of the summer of 2020, toilet paper makers had adjusted for the market shift and caught up with demand, as consumers worked through their stockpiles of paper. But retail inventories remain lean because toilet paper doesn’t carry huge profit margins. For this reason, even healthy stocks remain sensitive to sudden shifts in consumer demand, Dr. Gonzalez says.
“If people buy more than they should, then they are just buying from other people,” creating an unnecessary scarcity of toilet paper, he says.
The supply chain
It is true that the supply chain is under unprecedented strain, leading to higher prices for many goods, says Katie Denis, vice president of research and industry narrative at the Consumer Brands Association, Washington, which represents toilet paper makers Georgia-Pacific and Procter & Gamble. Consumers should expect toilet paper to be available, but there may be fewer options for product sizes, she says.
Still, Dr. Gonzalez says consumers should not worry too much about the global supply chain affecting the domestic toilet paper supply. The raw material for toilet paper production is available domestically, and more than 97% of the supply on U.S. retailer shelves is made in the United States, he says.
In modern society, toilet paper is a primary link to civilization, health, and hygiene. While there is no easy substitute, alternatives do exist A bidet, for example, is a device that can spray water on the genital area. Other options are reusable cloths, sponges, baby wipes, napkins, towels, and washcloths.
Human health and hygiene
“Compared to many other items, toilet paper can’t really be replaced,” says Frank H. Farley, PhD, a professor of psychological studies in education at Temple University, who studies human motivation. “It is a unique consumer item that is perceived to be extremely necessary. In that way, it plays into that survivor mentality, that having it is necessary for survival.”
Being without it can truly seem like an existential threat.
New York City emergency planner Ira Tannenbaum advises families to assess their usage of essential household supplies like toilet paper (you can do so through this toilet paper calculator) and keep at least a 1-week supply on hand in case of emergency. New York City has posted recommendations to families for emergency planning, including the guidance to “avoid panic buying.”
Dr. Pike says she would stockpile a bit more, something that could be done gradually, before there’s a panic. She says that if people are tempted to buy more out of anxiety, they should remind themselves that shortages arise because of panicky purchasing.
“Leave some for other families – other people have children and partners and siblings just like us,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA expands use of HIV drug to young children
The new lower dose is approved for children weighing from at least 14 kg (30 pounds) to 25 kg (55 pounds) who are virologically suppressed or new to antiretroviral therapy.
“Children living with HIV are in need of effective and accessible formulations of antiretroviral therapy,” said Merdad Parsey, MD, PhD, chief medical officer of Gilead Sciences, the company that produces Biktarvy, in a press release. “The New Drug Application approval is an important step in fulfilling Gilead’s commitment to a goal of bringing pediatric formulations of Biktarvy to children living with HIV around the world,” he said.
Although advances in treatment for pregnant women with HIV have lowered the likelihood of perinatal HIV transmission, pediatric HIV remains a global public health challenge. In 2020, about 1.7 million children younger than 15 years were living with HIV worldwide; 850 children become infected every day.
The approval, announced October 18, expands the use of Biktarvy to younger children. The medication was originally approved in February 2018 for treatment-naive or virologically suppressed adults. In June 2019, the FDA approved updating of the label to include pediatric patients weighing at least 25 kg. This new lower dose of Biktarvy is for a three-drug combo containing bictegravir 30 mg, emtricitabine 120 mg, and tenofovir alafenamide 15 mg. It is given once a day in tablet form.
The most recent expanded indication was based on data from an open-label, single-arm study that included 22 virologically suppressed children living with HIV. After switching to Biktarvy, 91% of participants (20 of 22) remained virologically suppressed at 24 weeks. HIV-1 RNA was not collected for two patients because of «pandemic-related study disruption,» the press release said.
“As children living with HIV will be on therapy for the foreseeable future and from such a young age, there are a number of factors I weigh as a clinician when prescribing the right HIV treatment option to my pediatric patients,” said Carina Rodriguez, MD, the division chief of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of South Florida, who was one of the study investigators. “Finding an efficacious treatment option is paramount, but tolerability and safety are keys to ensuring treatment success. With this expanded approval, clinicians can add Biktarvy to their arsenal of options to help ensure these children maintain virologic suppression with a treatment option that makes sense for them.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new lower dose is approved for children weighing from at least 14 kg (30 pounds) to 25 kg (55 pounds) who are virologically suppressed or new to antiretroviral therapy.
“Children living with HIV are in need of effective and accessible formulations of antiretroviral therapy,” said Merdad Parsey, MD, PhD, chief medical officer of Gilead Sciences, the company that produces Biktarvy, in a press release. “The New Drug Application approval is an important step in fulfilling Gilead’s commitment to a goal of bringing pediatric formulations of Biktarvy to children living with HIV around the world,” he said.
Although advances in treatment for pregnant women with HIV have lowered the likelihood of perinatal HIV transmission, pediatric HIV remains a global public health challenge. In 2020, about 1.7 million children younger than 15 years were living with HIV worldwide; 850 children become infected every day.
The approval, announced October 18, expands the use of Biktarvy to younger children. The medication was originally approved in February 2018 for treatment-naive or virologically suppressed adults. In June 2019, the FDA approved updating of the label to include pediatric patients weighing at least 25 kg. This new lower dose of Biktarvy is for a three-drug combo containing bictegravir 30 mg, emtricitabine 120 mg, and tenofovir alafenamide 15 mg. It is given once a day in tablet form.
The most recent expanded indication was based on data from an open-label, single-arm study that included 22 virologically suppressed children living with HIV. After switching to Biktarvy, 91% of participants (20 of 22) remained virologically suppressed at 24 weeks. HIV-1 RNA was not collected for two patients because of «pandemic-related study disruption,» the press release said.
“As children living with HIV will be on therapy for the foreseeable future and from such a young age, there are a number of factors I weigh as a clinician when prescribing the right HIV treatment option to my pediatric patients,” said Carina Rodriguez, MD, the division chief of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of South Florida, who was one of the study investigators. “Finding an efficacious treatment option is paramount, but tolerability and safety are keys to ensuring treatment success. With this expanded approval, clinicians can add Biktarvy to their arsenal of options to help ensure these children maintain virologic suppression with a treatment option that makes sense for them.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new lower dose is approved for children weighing from at least 14 kg (30 pounds) to 25 kg (55 pounds) who are virologically suppressed or new to antiretroviral therapy.
“Children living with HIV are in need of effective and accessible formulations of antiretroviral therapy,” said Merdad Parsey, MD, PhD, chief medical officer of Gilead Sciences, the company that produces Biktarvy, in a press release. “The New Drug Application approval is an important step in fulfilling Gilead’s commitment to a goal of bringing pediatric formulations of Biktarvy to children living with HIV around the world,” he said.
Although advances in treatment for pregnant women with HIV have lowered the likelihood of perinatal HIV transmission, pediatric HIV remains a global public health challenge. In 2020, about 1.7 million children younger than 15 years were living with HIV worldwide; 850 children become infected every day.
The approval, announced October 18, expands the use of Biktarvy to younger children. The medication was originally approved in February 2018 for treatment-naive or virologically suppressed adults. In June 2019, the FDA approved updating of the label to include pediatric patients weighing at least 25 kg. This new lower dose of Biktarvy is for a three-drug combo containing bictegravir 30 mg, emtricitabine 120 mg, and tenofovir alafenamide 15 mg. It is given once a day in tablet form.
The most recent expanded indication was based on data from an open-label, single-arm study that included 22 virologically suppressed children living with HIV. After switching to Biktarvy, 91% of participants (20 of 22) remained virologically suppressed at 24 weeks. HIV-1 RNA was not collected for two patients because of «pandemic-related study disruption,» the press release said.
“As children living with HIV will be on therapy for the foreseeable future and from such a young age, there are a number of factors I weigh as a clinician when prescribing the right HIV treatment option to my pediatric patients,” said Carina Rodriguez, MD, the division chief of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of South Florida, who was one of the study investigators. “Finding an efficacious treatment option is paramount, but tolerability and safety are keys to ensuring treatment success. With this expanded approval, clinicians can add Biktarvy to their arsenal of options to help ensure these children maintain virologic suppression with a treatment option that makes sense for them.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
States can reserve COVID shots for kids 5-11 this week
States can preorder COVID-19 vaccine doses for younger children this week as they begin to set up vaccination campaigns for ages 5-11.
Vaccine advisory groups for the FDA and CDC are scheduled to discuss and approve the Pfizer shot for kids in the next three weeks. To help states and cities prepare for the rollout, the CDC issued guidance on how to set up expanded vaccination programs.
Immunization program managers can begin ordering doses on Wednesday, according to the guidance. The vials won’t be delivered until the FDA and CDC authorize the shot, but registering now will help federal officials ship doses quickly once they’re available.
Pharmacies in every state will be able to give COVID-19 shots to children, but they can only use doses that are prepared specifically for children. Ages 5-11 will need a 10-microgram dose, which is one-third of the dose administered to ages 12 and older. The guidance warns that doctors should not try to split up or fraction the adult doses.
The CDC guidance also recommends that pediatricians and family practice doctors should serve as primary places to give shots to kids. The document mentions other options, such as vaccination clinics at schools, but doesn’t endorse them as the first choice for vaccinating kids.
The CDC hasn’t yet addressed questions around whether kids should be required to get vaccinated to attend school. The decision will likely be left to state and city officials.
Federal health officials aren’t yet sure how many parents and guardians will seek shots for their younger kids right away, the AP reported. Demand may be high at first for some families, but it may not be as high as when shots first became available for adults, Marcus Plescia, MD, chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, told The Associated Press.
“We’re going to have potentially a very busy, and perhaps modestly chaotic time,” he said.
When vaccines were first authorized for adults, hospitals and pharmacies received priority for ordering shots. Some doctors felt left out. This time, however, the CDC has said that pediatricians will receive higher priority and be able to receive shipments quickly.
As the vaccine rollout begins, health officials should consider logistical concerns to address racial and economic disparities for younger kids, Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and a former acting director of the CDC, told the AP.
If parents or guardians can’t leave work to take their kids to a pharmacy or doctor’s office, for instance, their kids may not receive a shot quickly – or at all.
“It’s really important that we recognize the barriers to vaccinations,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States can preorder COVID-19 vaccine doses for younger children this week as they begin to set up vaccination campaigns for ages 5-11.
Vaccine advisory groups for the FDA and CDC are scheduled to discuss and approve the Pfizer shot for kids in the next three weeks. To help states and cities prepare for the rollout, the CDC issued guidance on how to set up expanded vaccination programs.
Immunization program managers can begin ordering doses on Wednesday, according to the guidance. The vials won’t be delivered until the FDA and CDC authorize the shot, but registering now will help federal officials ship doses quickly once they’re available.
Pharmacies in every state will be able to give COVID-19 shots to children, but they can only use doses that are prepared specifically for children. Ages 5-11 will need a 10-microgram dose, which is one-third of the dose administered to ages 12 and older. The guidance warns that doctors should not try to split up or fraction the adult doses.
The CDC guidance also recommends that pediatricians and family practice doctors should serve as primary places to give shots to kids. The document mentions other options, such as vaccination clinics at schools, but doesn’t endorse them as the first choice for vaccinating kids.
The CDC hasn’t yet addressed questions around whether kids should be required to get vaccinated to attend school. The decision will likely be left to state and city officials.
Federal health officials aren’t yet sure how many parents and guardians will seek shots for their younger kids right away, the AP reported. Demand may be high at first for some families, but it may not be as high as when shots first became available for adults, Marcus Plescia, MD, chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, told The Associated Press.
“We’re going to have potentially a very busy, and perhaps modestly chaotic time,” he said.
When vaccines were first authorized for adults, hospitals and pharmacies received priority for ordering shots. Some doctors felt left out. This time, however, the CDC has said that pediatricians will receive higher priority and be able to receive shipments quickly.
As the vaccine rollout begins, health officials should consider logistical concerns to address racial and economic disparities for younger kids, Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and a former acting director of the CDC, told the AP.
If parents or guardians can’t leave work to take their kids to a pharmacy or doctor’s office, for instance, their kids may not receive a shot quickly – or at all.
“It’s really important that we recognize the barriers to vaccinations,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States can preorder COVID-19 vaccine doses for younger children this week as they begin to set up vaccination campaigns for ages 5-11.
Vaccine advisory groups for the FDA and CDC are scheduled to discuss and approve the Pfizer shot for kids in the next three weeks. To help states and cities prepare for the rollout, the CDC issued guidance on how to set up expanded vaccination programs.
Immunization program managers can begin ordering doses on Wednesday, according to the guidance. The vials won’t be delivered until the FDA and CDC authorize the shot, but registering now will help federal officials ship doses quickly once they’re available.
Pharmacies in every state will be able to give COVID-19 shots to children, but they can only use doses that are prepared specifically for children. Ages 5-11 will need a 10-microgram dose, which is one-third of the dose administered to ages 12 and older. The guidance warns that doctors should not try to split up or fraction the adult doses.
The CDC guidance also recommends that pediatricians and family practice doctors should serve as primary places to give shots to kids. The document mentions other options, such as vaccination clinics at schools, but doesn’t endorse them as the first choice for vaccinating kids.
The CDC hasn’t yet addressed questions around whether kids should be required to get vaccinated to attend school. The decision will likely be left to state and city officials.
Federal health officials aren’t yet sure how many parents and guardians will seek shots for their younger kids right away, the AP reported. Demand may be high at first for some families, but it may not be as high as when shots first became available for adults, Marcus Plescia, MD, chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, told The Associated Press.
“We’re going to have potentially a very busy, and perhaps modestly chaotic time,” he said.
When vaccines were first authorized for adults, hospitals and pharmacies received priority for ordering shots. Some doctors felt left out. This time, however, the CDC has said that pediatricians will receive higher priority and be able to receive shipments quickly.
As the vaccine rollout begins, health officials should consider logistical concerns to address racial and economic disparities for younger kids, Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and a former acting director of the CDC, told the AP.
If parents or guardians can’t leave work to take their kids to a pharmacy or doctor’s office, for instance, their kids may not receive a shot quickly – or at all.
“It’s really important that we recognize the barriers to vaccinations,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves cell-based flu shot for ages 6 months and older
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Flucelvax quadrivalent vaccine for use in children aged 6 months and older, according to a statement from manufacturer Seqirus.
“This approval officially allows all eligible Americans to receive a cell-based influenza vaccine, increasing the potential for greater vaccine effectiveness,” according to the company.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends annual influenza vaccination for all individuals aged 6 months and older without contraindications.
Flucelvax is manufactured using a cell-based process that yields a more precise match to the WHO-selected influenza strains for a given year. This process avoids the variation associated with traditional egg-based vaccines, and offers the potential for greater vaccine effectiveness, according to the company.
The approval was based in part on data from a phase 3 randomized, controlled noninferiority study of children aged 6-47 months. The data are the first for a cell-based flu vaccine in this age group, and were presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting in 2021.
In the immunogenicity study of children aged 6 months through 3 years, described in the package insert, 1,597 children received Flucelvax quadrivalent and 805 received a control quadrivalent vaccine. After 28 days, Flucelvax showed noninferiority to the control quadrivalent against four influenza strains.
The most common side effects with Flucelvax quadrivalent vaccine overall are pain, redness, swelling, or a hardened area at the injection site, headache, low energy, muscle aches, and malaise. Additional side effects reported in children include tenderness or bruising at the injection site, sleepiness, diarrhea, changes in eating habits, and irritability. The vaccine is contraindicated for individuals with allergies to any of its ingredients.
Additional efficacy data on Flucelvax for children and adolescents aged 2-18 years were recently published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Full prescribing information for Flucelvax is available here.
The FDA approval letter is available here.[email protected]
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Flucelvax quadrivalent vaccine for use in children aged 6 months and older, according to a statement from manufacturer Seqirus.
“This approval officially allows all eligible Americans to receive a cell-based influenza vaccine, increasing the potential for greater vaccine effectiveness,” according to the company.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends annual influenza vaccination for all individuals aged 6 months and older without contraindications.
Flucelvax is manufactured using a cell-based process that yields a more precise match to the WHO-selected influenza strains for a given year. This process avoids the variation associated with traditional egg-based vaccines, and offers the potential for greater vaccine effectiveness, according to the company.
The approval was based in part on data from a phase 3 randomized, controlled noninferiority study of children aged 6-47 months. The data are the first for a cell-based flu vaccine in this age group, and were presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting in 2021.
In the immunogenicity study of children aged 6 months through 3 years, described in the package insert, 1,597 children received Flucelvax quadrivalent and 805 received a control quadrivalent vaccine. After 28 days, Flucelvax showed noninferiority to the control quadrivalent against four influenza strains.
The most common side effects with Flucelvax quadrivalent vaccine overall are pain, redness, swelling, or a hardened area at the injection site, headache, low energy, muscle aches, and malaise. Additional side effects reported in children include tenderness or bruising at the injection site, sleepiness, diarrhea, changes in eating habits, and irritability. The vaccine is contraindicated for individuals with allergies to any of its ingredients.
Additional efficacy data on Flucelvax for children and adolescents aged 2-18 years were recently published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Full prescribing information for Flucelvax is available here.
The FDA approval letter is available here.[email protected]
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Flucelvax quadrivalent vaccine for use in children aged 6 months and older, according to a statement from manufacturer Seqirus.
“This approval officially allows all eligible Americans to receive a cell-based influenza vaccine, increasing the potential for greater vaccine effectiveness,” according to the company.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends annual influenza vaccination for all individuals aged 6 months and older without contraindications.
Flucelvax is manufactured using a cell-based process that yields a more precise match to the WHO-selected influenza strains for a given year. This process avoids the variation associated with traditional egg-based vaccines, and offers the potential for greater vaccine effectiveness, according to the company.
The approval was based in part on data from a phase 3 randomized, controlled noninferiority study of children aged 6-47 months. The data are the first for a cell-based flu vaccine in this age group, and were presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting in 2021.
In the immunogenicity study of children aged 6 months through 3 years, described in the package insert, 1,597 children received Flucelvax quadrivalent and 805 received a control quadrivalent vaccine. After 28 days, Flucelvax showed noninferiority to the control quadrivalent against four influenza strains.
The most common side effects with Flucelvax quadrivalent vaccine overall are pain, redness, swelling, or a hardened area at the injection site, headache, low energy, muscle aches, and malaise. Additional side effects reported in children include tenderness or bruising at the injection site, sleepiness, diarrhea, changes in eating habits, and irritability. The vaccine is contraindicated for individuals with allergies to any of its ingredients.
Additional efficacy data on Flucelvax for children and adolescents aged 2-18 years were recently published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Full prescribing information for Flucelvax is available here.
The FDA approval letter is available here.[email protected]
The tryptophan photoproduct FICZ and its effects on the skin
The melatonin precursor tryptophan, an amino acid essential in the human diet, has been shown to display antioxidant effects.1 FICZ (also known as 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole) is a photoproduct of tryptophan that is engendered by exposure to UVB.2 This column discusses the beneficial and detrimental influence of FICZ in skin health.
Antioxidant activity
In 2005, Trommer and Neubert devised a skin lipid model system to screen 47 various compounds (drugs, plant extracts, other plant constituents, and polysaccharides) for topical antioxidative activity in response to UV-induced lipid peroxidation. Among the drugs evaluated, they observed that tryptophan exerted antioxidant effects.3
Wound healing potential
A murine study by Bandeira et al. in 2015 revealed that tryptophan-induced mitigation of the inflammatory response and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase expression may have enhanced skin wound healing in mice who were repeatedly stressed.4
Antifibrotic activity
In 2018, Murai et al. endeavored to clarify the role of FICZ in regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in normal human dermal fibroblasts. They found that FICZ assists in imparting UV-mediated antifibrotic effects through the AHR/MEK/ERK signal pathway in normal human dermal fibroblasts and, thus, shows promise as a therapeutic option for scleroderma.5
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
In 2019, Rodrigues et al. conducted a quantitative analysis of the relative expression of 170 genes involved in various biological processes in the skin biopsies from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by infection with either Leishmania major or L. tropica. They identified tryptophan-2,3-deoxygenase as a restriction factor for the disorder.6
Photosensitizing activity
Park et al. showed that FICZ, a tryptophan photoproduct and endogenous high-affinity aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist, exhibits nanomolar photodynamic activity as a UVA photosensitizer in epidermal keratinocytes and, thus, is possibly operative in human skin.7 Syed and Mukhtar add that FICZ is effective at nanomolar concentrations and that future research may elucidate its applicability against UV-induced adverse effects and inflammatory skin conditions.8
FICZ, oxidative stress, and cancer promotion
FICZ is known to display detrimental, as well as beneficial, influences in skin. The tryptophan photoproduct, comparable to UVB, ligates AhR, generates reactive oxygen species, and strongly photosensitizes for UVA. As Furue et al. note, FICZ upregulates the expression of terminal differentiation molecules (i.e., filaggrin and loricrin via AhR), and its application has been shown to suppress cutaneous inflammation in a psoriasis and dermatitis mouse model.2
In 2016, Reid et al. reported that the protein photodamage brought about by endogenous photosensitizers such as tryptophan tyrosine residues can contribute to the deleterious impact of UVA on human skin.9
In 2018, Tanaka et al. showed that FICZ imparts a cascade of events tantamount in some cases to UVB, as it promoted the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 and boosted reactive oxygen species generation in human HaCaT keratinocytes in an AhR-dependent fashion. They concluded that observing FICZ activity contributes to the understanding of how UVB damages organisms.10
That same year, Murai et al. assessed the effects of FICZ on TGF-beta-mediated ACTA2 and collagen I expression in normal human dermal fibroblasts. They determined that it may act as a key chromophore and one approach to mitigating the effects of photoaging may be to downregulate FICZ signaling.11
A year earlier, Brem et al. showed that the combined effect of FICZ and UVA engendered significant protein damage in HaCaT human keratinocytes, with the oxidation yielded from the combination of FICZ and UVA blocking the removal of potentially mutagenic UVB-induced DNA photolesions by nucleotide excision repair. The researchers concluded that the development of FICZ may raise the risk of incurring skin cancer resulting from sun exposure via the promotion of photochemical impairment of the nucleotide excision repair proteome, which in turn inhibits the removal of UVB-induced DNA lesions.12
Conclusion
However, the tryptophan photoproduct FICZ, which results from UVB exposure, presents as a complicated substance, conferring healthy and harmful effects. Much more research is necessary to determine how best to harness and direct the useful activities of tryptophan and FICZ without incurring damaging effects. Nanotechnology may be one useful avenue of investigation for this purpose.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Trommer H et al. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;55(10):1379-88.
2. Furue M et al. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Feb;154(1):37-41.
3. Trommer H and Neubert RH. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005 Sep 15;8(3):494-506.
4. Bandeira LG et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 9:10(6):e0128439.
5. Murai M et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Jul;91(1):97-103.
6. Rodrigues V et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 4;9:338. eCollection 2019.
7. Park SL et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Jun;135(6):1649-58.
8. Syed DN and Mukhtar H. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Jun;135(6):1478-81.
9. Reid LO et al. Biochemistry. 2016 Aug 30;55(34):4777-86.
10. Tanaka Y et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 25;2018:9298052.
11. Murai M et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Jan;89(1):19-26.
12. Brem R et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 27;7(1):4310.
The melatonin precursor tryptophan, an amino acid essential in the human diet, has been shown to display antioxidant effects.1 FICZ (also known as 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole) is a photoproduct of tryptophan that is engendered by exposure to UVB.2 This column discusses the beneficial and detrimental influence of FICZ in skin health.
Antioxidant activity
In 2005, Trommer and Neubert devised a skin lipid model system to screen 47 various compounds (drugs, plant extracts, other plant constituents, and polysaccharides) for topical antioxidative activity in response to UV-induced lipid peroxidation. Among the drugs evaluated, they observed that tryptophan exerted antioxidant effects.3
Wound healing potential
A murine study by Bandeira et al. in 2015 revealed that tryptophan-induced mitigation of the inflammatory response and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase expression may have enhanced skin wound healing in mice who were repeatedly stressed.4
Antifibrotic activity
In 2018, Murai et al. endeavored to clarify the role of FICZ in regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in normal human dermal fibroblasts. They found that FICZ assists in imparting UV-mediated antifibrotic effects through the AHR/MEK/ERK signal pathway in normal human dermal fibroblasts and, thus, shows promise as a therapeutic option for scleroderma.5
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
In 2019, Rodrigues et al. conducted a quantitative analysis of the relative expression of 170 genes involved in various biological processes in the skin biopsies from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by infection with either Leishmania major or L. tropica. They identified tryptophan-2,3-deoxygenase as a restriction factor for the disorder.6
Photosensitizing activity
Park et al. showed that FICZ, a tryptophan photoproduct and endogenous high-affinity aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist, exhibits nanomolar photodynamic activity as a UVA photosensitizer in epidermal keratinocytes and, thus, is possibly operative in human skin.7 Syed and Mukhtar add that FICZ is effective at nanomolar concentrations and that future research may elucidate its applicability against UV-induced adverse effects and inflammatory skin conditions.8
FICZ, oxidative stress, and cancer promotion
FICZ is known to display detrimental, as well as beneficial, influences in skin. The tryptophan photoproduct, comparable to UVB, ligates AhR, generates reactive oxygen species, and strongly photosensitizes for UVA. As Furue et al. note, FICZ upregulates the expression of terminal differentiation molecules (i.e., filaggrin and loricrin via AhR), and its application has been shown to suppress cutaneous inflammation in a psoriasis and dermatitis mouse model.2
In 2016, Reid et al. reported that the protein photodamage brought about by endogenous photosensitizers such as tryptophan tyrosine residues can contribute to the deleterious impact of UVA on human skin.9
In 2018, Tanaka et al. showed that FICZ imparts a cascade of events tantamount in some cases to UVB, as it promoted the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 and boosted reactive oxygen species generation in human HaCaT keratinocytes in an AhR-dependent fashion. They concluded that observing FICZ activity contributes to the understanding of how UVB damages organisms.10
That same year, Murai et al. assessed the effects of FICZ on TGF-beta-mediated ACTA2 and collagen I expression in normal human dermal fibroblasts. They determined that it may act as a key chromophore and one approach to mitigating the effects of photoaging may be to downregulate FICZ signaling.11
A year earlier, Brem et al. showed that the combined effect of FICZ and UVA engendered significant protein damage in HaCaT human keratinocytes, with the oxidation yielded from the combination of FICZ and UVA blocking the removal of potentially mutagenic UVB-induced DNA photolesions by nucleotide excision repair. The researchers concluded that the development of FICZ may raise the risk of incurring skin cancer resulting from sun exposure via the promotion of photochemical impairment of the nucleotide excision repair proteome, which in turn inhibits the removal of UVB-induced DNA lesions.12
Conclusion
However, the tryptophan photoproduct FICZ, which results from UVB exposure, presents as a complicated substance, conferring healthy and harmful effects. Much more research is necessary to determine how best to harness and direct the useful activities of tryptophan and FICZ without incurring damaging effects. Nanotechnology may be one useful avenue of investigation for this purpose.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Trommer H et al. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;55(10):1379-88.
2. Furue M et al. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Feb;154(1):37-41.
3. Trommer H and Neubert RH. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005 Sep 15;8(3):494-506.
4. Bandeira LG et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 9:10(6):e0128439.
5. Murai M et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Jul;91(1):97-103.
6. Rodrigues V et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 4;9:338. eCollection 2019.
7. Park SL et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Jun;135(6):1649-58.
8. Syed DN and Mukhtar H. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Jun;135(6):1478-81.
9. Reid LO et al. Biochemistry. 2016 Aug 30;55(34):4777-86.
10. Tanaka Y et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 25;2018:9298052.
11. Murai M et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Jan;89(1):19-26.
12. Brem R et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 27;7(1):4310.
The melatonin precursor tryptophan, an amino acid essential in the human diet, has been shown to display antioxidant effects.1 FICZ (also known as 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole) is a photoproduct of tryptophan that is engendered by exposure to UVB.2 This column discusses the beneficial and detrimental influence of FICZ in skin health.
Antioxidant activity
In 2005, Trommer and Neubert devised a skin lipid model system to screen 47 various compounds (drugs, plant extracts, other plant constituents, and polysaccharides) for topical antioxidative activity in response to UV-induced lipid peroxidation. Among the drugs evaluated, they observed that tryptophan exerted antioxidant effects.3
Wound healing potential
A murine study by Bandeira et al. in 2015 revealed that tryptophan-induced mitigation of the inflammatory response and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase expression may have enhanced skin wound healing in mice who were repeatedly stressed.4
Antifibrotic activity
In 2018, Murai et al. endeavored to clarify the role of FICZ in regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in normal human dermal fibroblasts. They found that FICZ assists in imparting UV-mediated antifibrotic effects through the AHR/MEK/ERK signal pathway in normal human dermal fibroblasts and, thus, shows promise as a therapeutic option for scleroderma.5
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
In 2019, Rodrigues et al. conducted a quantitative analysis of the relative expression of 170 genes involved in various biological processes in the skin biopsies from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by infection with either Leishmania major or L. tropica. They identified tryptophan-2,3-deoxygenase as a restriction factor for the disorder.6
Photosensitizing activity
Park et al. showed that FICZ, a tryptophan photoproduct and endogenous high-affinity aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist, exhibits nanomolar photodynamic activity as a UVA photosensitizer in epidermal keratinocytes and, thus, is possibly operative in human skin.7 Syed and Mukhtar add that FICZ is effective at nanomolar concentrations and that future research may elucidate its applicability against UV-induced adverse effects and inflammatory skin conditions.8
FICZ, oxidative stress, and cancer promotion
FICZ is known to display detrimental, as well as beneficial, influences in skin. The tryptophan photoproduct, comparable to UVB, ligates AhR, generates reactive oxygen species, and strongly photosensitizes for UVA. As Furue et al. note, FICZ upregulates the expression of terminal differentiation molecules (i.e., filaggrin and loricrin via AhR), and its application has been shown to suppress cutaneous inflammation in a psoriasis and dermatitis mouse model.2
In 2016, Reid et al. reported that the protein photodamage brought about by endogenous photosensitizers such as tryptophan tyrosine residues can contribute to the deleterious impact of UVA on human skin.9
In 2018, Tanaka et al. showed that FICZ imparts a cascade of events tantamount in some cases to UVB, as it promoted the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 and boosted reactive oxygen species generation in human HaCaT keratinocytes in an AhR-dependent fashion. They concluded that observing FICZ activity contributes to the understanding of how UVB damages organisms.10
That same year, Murai et al. assessed the effects of FICZ on TGF-beta-mediated ACTA2 and collagen I expression in normal human dermal fibroblasts. They determined that it may act as a key chromophore and one approach to mitigating the effects of photoaging may be to downregulate FICZ signaling.11
A year earlier, Brem et al. showed that the combined effect of FICZ and UVA engendered significant protein damage in HaCaT human keratinocytes, with the oxidation yielded from the combination of FICZ and UVA blocking the removal of potentially mutagenic UVB-induced DNA photolesions by nucleotide excision repair. The researchers concluded that the development of FICZ may raise the risk of incurring skin cancer resulting from sun exposure via the promotion of photochemical impairment of the nucleotide excision repair proteome, which in turn inhibits the removal of UVB-induced DNA lesions.12
Conclusion
However, the tryptophan photoproduct FICZ, which results from UVB exposure, presents as a complicated substance, conferring healthy and harmful effects. Much more research is necessary to determine how best to harness and direct the useful activities of tryptophan and FICZ without incurring damaging effects. Nanotechnology may be one useful avenue of investigation for this purpose.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Trommer H et al. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;55(10):1379-88.
2. Furue M et al. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Feb;154(1):37-41.
3. Trommer H and Neubert RH. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005 Sep 15;8(3):494-506.
4. Bandeira LG et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 9:10(6):e0128439.
5. Murai M et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Jul;91(1):97-103.
6. Rodrigues V et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 4;9:338. eCollection 2019.
7. Park SL et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Jun;135(6):1649-58.
8. Syed DN and Mukhtar H. J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Jun;135(6):1478-81.
9. Reid LO et al. Biochemistry. 2016 Aug 30;55(34):4777-86.
10. Tanaka Y et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 25;2018:9298052.
11. Murai M et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Jan;89(1):19-26.
12. Brem R et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 27;7(1):4310.