User login
Dr. Gloviczki: Of Ties, VAM and a New Challenge
On Wednesday morning, the Society for Vascular Surgery bumped into SVS Past President Dr. Peter Gloviczki. Here’s what we learned about one of our leaders – who is stepping into a new role with the Society – and his participation at VAM this year.
The first thing to note is that he was wearing the very first SVS tie! “It’s the one I designed,” he said.
Dr. Gloviczki is about to start his term, with Dr. Peter Lawrence, as editors-in-chief of the Journal of Vascular Surgery. “We’re very excited,” he said. “We have a new cover and a new format."
The two are expanding the Journal to include much more public media, Dr. Gloviczki said. They have set up a recording studio (National Harbor 1), and after participants give their presentations at VAM, they can record a five-minute video of his or her presentation, Dr. Gloviczki said. When their articles of original research are published, these interviews will be posted online on JVS, SVS and YouTube websites.
As for what he hopes to take from VAM this year: “I’m looking for ideas, for new topics we can include in the Journal. There are differences between European and U.S. colleagues on how to treat vascular disease. I want to learn about that.”
And how many VAMs has he attended? “Almost all of them,” he allowed.
On Wednesday morning, the Society for Vascular Surgery bumped into SVS Past President Dr. Peter Gloviczki. Here’s what we learned about one of our leaders – who is stepping into a new role with the Society – and his participation at VAM this year.
The first thing to note is that he was wearing the very first SVS tie! “It’s the one I designed,” he said.
Dr. Gloviczki is about to start his term, with Dr. Peter Lawrence, as editors-in-chief of the Journal of Vascular Surgery. “We’re very excited,” he said. “We have a new cover and a new format."
The two are expanding the Journal to include much more public media, Dr. Gloviczki said. They have set up a recording studio (National Harbor 1), and after participants give their presentations at VAM, they can record a five-minute video of his or her presentation, Dr. Gloviczki said. When their articles of original research are published, these interviews will be posted online on JVS, SVS and YouTube websites.
As for what he hopes to take from VAM this year: “I’m looking for ideas, for new topics we can include in the Journal. There are differences between European and U.S. colleagues on how to treat vascular disease. I want to learn about that.”
And how many VAMs has he attended? “Almost all of them,” he allowed.
On Wednesday morning, the Society for Vascular Surgery bumped into SVS Past President Dr. Peter Gloviczki. Here’s what we learned about one of our leaders – who is stepping into a new role with the Society – and his participation at VAM this year.
The first thing to note is that he was wearing the very first SVS tie! “It’s the one I designed,” he said.
Dr. Gloviczki is about to start his term, with Dr. Peter Lawrence, as editors-in-chief of the Journal of Vascular Surgery. “We’re very excited,” he said. “We have a new cover and a new format."
The two are expanding the Journal to include much more public media, Dr. Gloviczki said. They have set up a recording studio (National Harbor 1), and after participants give their presentations at VAM, they can record a five-minute video of his or her presentation, Dr. Gloviczki said. When their articles of original research are published, these interviews will be posted online on JVS, SVS and YouTube websites.
As for what he hopes to take from VAM this year: “I’m looking for ideas, for new topics we can include in the Journal. There are differences between European and U.S. colleagues on how to treat vascular disease. I want to learn about that.”
And how many VAMs has he attended? “Almost all of them,” he allowed.
Vandetanib shows variable response, toxicity in RET-positive NSCLC
CHICAGO – The RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib shows marked yet variable antitumor activity and toxicity in patients whose RET-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was unsuccessfully treated with chemotherapy, according to results of two small phase II trials presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The overall response rates were 53% and 61% in two independent trials conducted by Dr. Takashi Seto of the National Kyushu Cancer Center, Japan, and by Dr. Se-Hoon Lee of Sungkyunkwan University, South Korea, respectively.
Compared to previous studies with other RET inhibitors, though all had small cohorts, there were many similarities in response rates. Progression-free survival was the most variable, but was much higher in the cabozantinib data reported at the 2015 ASCO annual meeting, according to moderator Dr. Karen Reckamp of the City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, Calif. “Vandetanib may have lower response rates than some of the others,” she said.
RET is a tyrosine kinase domain that fuses to and undergoes rearrangements with KIF5B and CCDC6 genes. This fusion and subsequent rearrangement results in ligand-dependent dimerization, which causes tumor growth. RET rearrangements were first identified in thyroid cancers.
“RET fusions were identified as new driver oncogenes of NSCLC in 2012 and observed in 1%-2% of all NSCLC,” Dr. Seto said. “Non–small cell lung cancer with RET rearrangement is regarded as a unique entity in terms of pathogenesis,” said Dr. Lee. There are currently multiple RET inhibitors in various stages of development.
In the trial headed by Dr. Seto, the Japanese genetic screening network was utilized to identify 34 NSCLC patients with RET rearrangements. Among the 34 patients, 17 met the eligibility requirements of having failed at least one prior chemotherapy treatment. Of those 17 patients, the median age was 59 years, 74% were female, all had adenocarcinomas, and 68% were nonsmokers.
All 17 patients received vandetanib at a dose of 300 mg once daily. The overall response rate was 53% (90% confidence interval, 31-74), and the disease control rate was 88%. The median progression-free survival was 4.7 months (90% CI, 2.8-8.3).
There was a marked difference in overall response rate and progression-free survival among RET fusion subtypes. For CCDC6-RET, the overall response was 83% and the progression-free survival was 8.3 months. For KIF5B-RET, the overall response was 20% with a median progression-free survival of 2.9 months.
Dr. Seto noted that there was no known biological explanation for the observed discrepancy in response rate or survival.
Dr. Seto reported that the safety profile was similar to previous reports. Four patients ended treatment due to adverse events while 16 experienced dose interruptions due to treatment-related toxicities. The most common grade three and four toxicities were hypertension (58%), rash (16%), and diarrhea (11%).
In the trial headed by Dr. Lee, 18 patients with RET rearrangements (confirmed by fluorescent in situ hybridization) met the eligibility requirement of having failed platinum-based chemotherapy. The median age of the cohort was 55 years, and 33% were female.
Similar to Dr. Seto’s study, all 18 patients received vandetanib at 300 mg once daily. Of the 18 patient cohort, 17% achieved partial remission and 44% achieved stable disease. Seven patients had no remission or stabilization. There were no treatment-related mortalities or grade 4 adverse events. Two grade 3 adverse events were reported.
“Looking at these two studies together, I think the important thing about the characteristics you see [is] that the age range is very similar [with a] median in the 50’s,” commented Dr. Reckamp. “The male to female ratio is actually opposite in both so [this] can occur in both men and women. The smoking status, interestingly is similar in both, where about a third of patients were former smokers. Most of the patients had adenocarcinoma. Many of these patients were highly previously treated. Only the Seto group looked at RET fusion partner, which may be important in looking at efficacy for these agents.” Vandetanib is a “challenging drug to tolerate,” Dr. Reckamp also noted.
“Is there a preferred RET inhibitor in small cell lung cancer?” Dr. Reckamp asked. “There are many RET inhibitors approved for other cancer types at this point, and they are multitargeted tyrosine kinases. In small studies they have similar efficacy. Toxicities vary because of the off-target effects, and most of the [treatment] decisions were made based on potential toxicities rather than differing efficacy. So none is really differentiated as the best choice, and it is unlikely that we are going to have the trials to evaluate them head to head.”
Dr. Reckamp suggested that “most patients with adenocarcinoma” should be tested for RET rearrangements. “Both men and women, both smokers and nonsmokers. And if you don’t test, you won’t find it. And if you don’t find it, you won’t be able to treat.” Dr. Reckamp also noted that next generation sequencing (NGS) should be the preferred method of identifying RET status because NGS uses less tissue, provides genetic sequencing, and allows for the identification of binding partners.
“Does targeting RET improve patient outcomes?” she continued. “Because that is really the question we need to answer if we need to move forward with RET inhibition for lung cancer. So there are variable response rates, less than other inhibitors of other oncogenic-driven tumors, that’s for sure... But if you look at the data, and these are [for] heavily pretreated patients for the most part, the response rates are better than second-line cytotoxic chemotherapy that we have had in the past and similar to unselected checkpoint inhibition. So there is potential for improving outcomes, and again if we don’t know someone is RET, we potentially are not going to offer a treatment that could help them live longer or better.”
When asked how she would treat a newly-diagnosed patient with RET-positive NSCLC, Dr. Reckamp said she would treat with first-line chemotherapy rather than a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) but would enroll the patient in whatever TKI trial was ongoing at that point in time.
“There are multiple trials that are ongoing,” Dr. Reckamp said. “It is unlikely that a comparison trial will be completed and so we are going to have to look at these trials next to each other and differentiate based on toxicity [and] perceived efficacy.”
Specifically, Dr. Reckamp believes the medical community needs to move toward “universal testing” for RET status in lung cancer patients. Resistance and combination therapies will also need to be assessed in future studies.
“RET is important in lung cancer, and should be targeted. We now need to find the best way to do that,” Dr. Reckamp concluded.
The trial headed by Dr. Seto was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria and research funding from multiple companies including AstraZeneca. The trial headed by Dr. Lee was funded by AstraZeneca Korea. Dr. Lee reported having a consulting or advisory role and receiving honoraria and research funding from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech.
CHICAGO – The RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib shows marked yet variable antitumor activity and toxicity in patients whose RET-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was unsuccessfully treated with chemotherapy, according to results of two small phase II trials presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The overall response rates were 53% and 61% in two independent trials conducted by Dr. Takashi Seto of the National Kyushu Cancer Center, Japan, and by Dr. Se-Hoon Lee of Sungkyunkwan University, South Korea, respectively.
Compared to previous studies with other RET inhibitors, though all had small cohorts, there were many similarities in response rates. Progression-free survival was the most variable, but was much higher in the cabozantinib data reported at the 2015 ASCO annual meeting, according to moderator Dr. Karen Reckamp of the City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, Calif. “Vandetanib may have lower response rates than some of the others,” she said.
RET is a tyrosine kinase domain that fuses to and undergoes rearrangements with KIF5B and CCDC6 genes. This fusion and subsequent rearrangement results in ligand-dependent dimerization, which causes tumor growth. RET rearrangements were first identified in thyroid cancers.
“RET fusions were identified as new driver oncogenes of NSCLC in 2012 and observed in 1%-2% of all NSCLC,” Dr. Seto said. “Non–small cell lung cancer with RET rearrangement is regarded as a unique entity in terms of pathogenesis,” said Dr. Lee. There are currently multiple RET inhibitors in various stages of development.
In the trial headed by Dr. Seto, the Japanese genetic screening network was utilized to identify 34 NSCLC patients with RET rearrangements. Among the 34 patients, 17 met the eligibility requirements of having failed at least one prior chemotherapy treatment. Of those 17 patients, the median age was 59 years, 74% were female, all had adenocarcinomas, and 68% were nonsmokers.
All 17 patients received vandetanib at a dose of 300 mg once daily. The overall response rate was 53% (90% confidence interval, 31-74), and the disease control rate was 88%. The median progression-free survival was 4.7 months (90% CI, 2.8-8.3).
There was a marked difference in overall response rate and progression-free survival among RET fusion subtypes. For CCDC6-RET, the overall response was 83% and the progression-free survival was 8.3 months. For KIF5B-RET, the overall response was 20% with a median progression-free survival of 2.9 months.
Dr. Seto noted that there was no known biological explanation for the observed discrepancy in response rate or survival.
Dr. Seto reported that the safety profile was similar to previous reports. Four patients ended treatment due to adverse events while 16 experienced dose interruptions due to treatment-related toxicities. The most common grade three and four toxicities were hypertension (58%), rash (16%), and diarrhea (11%).
In the trial headed by Dr. Lee, 18 patients with RET rearrangements (confirmed by fluorescent in situ hybridization) met the eligibility requirement of having failed platinum-based chemotherapy. The median age of the cohort was 55 years, and 33% were female.
Similar to Dr. Seto’s study, all 18 patients received vandetanib at 300 mg once daily. Of the 18 patient cohort, 17% achieved partial remission and 44% achieved stable disease. Seven patients had no remission or stabilization. There were no treatment-related mortalities or grade 4 adverse events. Two grade 3 adverse events were reported.
“Looking at these two studies together, I think the important thing about the characteristics you see [is] that the age range is very similar [with a] median in the 50’s,” commented Dr. Reckamp. “The male to female ratio is actually opposite in both so [this] can occur in both men and women. The smoking status, interestingly is similar in both, where about a third of patients were former smokers. Most of the patients had adenocarcinoma. Many of these patients were highly previously treated. Only the Seto group looked at RET fusion partner, which may be important in looking at efficacy for these agents.” Vandetanib is a “challenging drug to tolerate,” Dr. Reckamp also noted.
“Is there a preferred RET inhibitor in small cell lung cancer?” Dr. Reckamp asked. “There are many RET inhibitors approved for other cancer types at this point, and they are multitargeted tyrosine kinases. In small studies they have similar efficacy. Toxicities vary because of the off-target effects, and most of the [treatment] decisions were made based on potential toxicities rather than differing efficacy. So none is really differentiated as the best choice, and it is unlikely that we are going to have the trials to evaluate them head to head.”
Dr. Reckamp suggested that “most patients with adenocarcinoma” should be tested for RET rearrangements. “Both men and women, both smokers and nonsmokers. And if you don’t test, you won’t find it. And if you don’t find it, you won’t be able to treat.” Dr. Reckamp also noted that next generation sequencing (NGS) should be the preferred method of identifying RET status because NGS uses less tissue, provides genetic sequencing, and allows for the identification of binding partners.
“Does targeting RET improve patient outcomes?” she continued. “Because that is really the question we need to answer if we need to move forward with RET inhibition for lung cancer. So there are variable response rates, less than other inhibitors of other oncogenic-driven tumors, that’s for sure... But if you look at the data, and these are [for] heavily pretreated patients for the most part, the response rates are better than second-line cytotoxic chemotherapy that we have had in the past and similar to unselected checkpoint inhibition. So there is potential for improving outcomes, and again if we don’t know someone is RET, we potentially are not going to offer a treatment that could help them live longer or better.”
When asked how she would treat a newly-diagnosed patient with RET-positive NSCLC, Dr. Reckamp said she would treat with first-line chemotherapy rather than a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) but would enroll the patient in whatever TKI trial was ongoing at that point in time.
“There are multiple trials that are ongoing,” Dr. Reckamp said. “It is unlikely that a comparison trial will be completed and so we are going to have to look at these trials next to each other and differentiate based on toxicity [and] perceived efficacy.”
Specifically, Dr. Reckamp believes the medical community needs to move toward “universal testing” for RET status in lung cancer patients. Resistance and combination therapies will also need to be assessed in future studies.
“RET is important in lung cancer, and should be targeted. We now need to find the best way to do that,” Dr. Reckamp concluded.
The trial headed by Dr. Seto was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria and research funding from multiple companies including AstraZeneca. The trial headed by Dr. Lee was funded by AstraZeneca Korea. Dr. Lee reported having a consulting or advisory role and receiving honoraria and research funding from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech.
CHICAGO – The RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib shows marked yet variable antitumor activity and toxicity in patients whose RET-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was unsuccessfully treated with chemotherapy, according to results of two small phase II trials presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The overall response rates were 53% and 61% in two independent trials conducted by Dr. Takashi Seto of the National Kyushu Cancer Center, Japan, and by Dr. Se-Hoon Lee of Sungkyunkwan University, South Korea, respectively.
Compared to previous studies with other RET inhibitors, though all had small cohorts, there were many similarities in response rates. Progression-free survival was the most variable, but was much higher in the cabozantinib data reported at the 2015 ASCO annual meeting, according to moderator Dr. Karen Reckamp of the City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, Calif. “Vandetanib may have lower response rates than some of the others,” she said.
RET is a tyrosine kinase domain that fuses to and undergoes rearrangements with KIF5B and CCDC6 genes. This fusion and subsequent rearrangement results in ligand-dependent dimerization, which causes tumor growth. RET rearrangements were first identified in thyroid cancers.
“RET fusions were identified as new driver oncogenes of NSCLC in 2012 and observed in 1%-2% of all NSCLC,” Dr. Seto said. “Non–small cell lung cancer with RET rearrangement is regarded as a unique entity in terms of pathogenesis,” said Dr. Lee. There are currently multiple RET inhibitors in various stages of development.
In the trial headed by Dr. Seto, the Japanese genetic screening network was utilized to identify 34 NSCLC patients with RET rearrangements. Among the 34 patients, 17 met the eligibility requirements of having failed at least one prior chemotherapy treatment. Of those 17 patients, the median age was 59 years, 74% were female, all had adenocarcinomas, and 68% were nonsmokers.
All 17 patients received vandetanib at a dose of 300 mg once daily. The overall response rate was 53% (90% confidence interval, 31-74), and the disease control rate was 88%. The median progression-free survival was 4.7 months (90% CI, 2.8-8.3).
There was a marked difference in overall response rate and progression-free survival among RET fusion subtypes. For CCDC6-RET, the overall response was 83% and the progression-free survival was 8.3 months. For KIF5B-RET, the overall response was 20% with a median progression-free survival of 2.9 months.
Dr. Seto noted that there was no known biological explanation for the observed discrepancy in response rate or survival.
Dr. Seto reported that the safety profile was similar to previous reports. Four patients ended treatment due to adverse events while 16 experienced dose interruptions due to treatment-related toxicities. The most common grade three and four toxicities were hypertension (58%), rash (16%), and diarrhea (11%).
In the trial headed by Dr. Lee, 18 patients with RET rearrangements (confirmed by fluorescent in situ hybridization) met the eligibility requirement of having failed platinum-based chemotherapy. The median age of the cohort was 55 years, and 33% were female.
Similar to Dr. Seto’s study, all 18 patients received vandetanib at 300 mg once daily. Of the 18 patient cohort, 17% achieved partial remission and 44% achieved stable disease. Seven patients had no remission or stabilization. There were no treatment-related mortalities or grade 4 adverse events. Two grade 3 adverse events were reported.
“Looking at these two studies together, I think the important thing about the characteristics you see [is] that the age range is very similar [with a] median in the 50’s,” commented Dr. Reckamp. “The male to female ratio is actually opposite in both so [this] can occur in both men and women. The smoking status, interestingly is similar in both, where about a third of patients were former smokers. Most of the patients had adenocarcinoma. Many of these patients were highly previously treated. Only the Seto group looked at RET fusion partner, which may be important in looking at efficacy for these agents.” Vandetanib is a “challenging drug to tolerate,” Dr. Reckamp also noted.
“Is there a preferred RET inhibitor in small cell lung cancer?” Dr. Reckamp asked. “There are many RET inhibitors approved for other cancer types at this point, and they are multitargeted tyrosine kinases. In small studies they have similar efficacy. Toxicities vary because of the off-target effects, and most of the [treatment] decisions were made based on potential toxicities rather than differing efficacy. So none is really differentiated as the best choice, and it is unlikely that we are going to have the trials to evaluate them head to head.”
Dr. Reckamp suggested that “most patients with adenocarcinoma” should be tested for RET rearrangements. “Both men and women, both smokers and nonsmokers. And if you don’t test, you won’t find it. And if you don’t find it, you won’t be able to treat.” Dr. Reckamp also noted that next generation sequencing (NGS) should be the preferred method of identifying RET status because NGS uses less tissue, provides genetic sequencing, and allows for the identification of binding partners.
“Does targeting RET improve patient outcomes?” she continued. “Because that is really the question we need to answer if we need to move forward with RET inhibition for lung cancer. So there are variable response rates, less than other inhibitors of other oncogenic-driven tumors, that’s for sure... But if you look at the data, and these are [for] heavily pretreated patients for the most part, the response rates are better than second-line cytotoxic chemotherapy that we have had in the past and similar to unselected checkpoint inhibition. So there is potential for improving outcomes, and again if we don’t know someone is RET, we potentially are not going to offer a treatment that could help them live longer or better.”
When asked how she would treat a newly-diagnosed patient with RET-positive NSCLC, Dr. Reckamp said she would treat with first-line chemotherapy rather than a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) but would enroll the patient in whatever TKI trial was ongoing at that point in time.
“There are multiple trials that are ongoing,” Dr. Reckamp said. “It is unlikely that a comparison trial will be completed and so we are going to have to look at these trials next to each other and differentiate based on toxicity [and] perceived efficacy.”
Specifically, Dr. Reckamp believes the medical community needs to move toward “universal testing” for RET status in lung cancer patients. Resistance and combination therapies will also need to be assessed in future studies.
“RET is important in lung cancer, and should be targeted. We now need to find the best way to do that,” Dr. Reckamp concluded.
The trial headed by Dr. Seto was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria and research funding from multiple companies including AstraZeneca. The trial headed by Dr. Lee was funded by AstraZeneca Korea. Dr. Lee reported having a consulting or advisory role and receiving honoraria and research funding from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech.
AT THE 2016 ASCO ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Vandetanib shows marked yet variable anti-tumor activity and toxicity in patients with RET-rearranged NSCLC.
Major finding: The overall response rates were 53% and 61% in two independent trials.
Data source: Two independently-conducted multicenter phase II trials of patients with RET-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.
Disclosures: The trial headed by Dr. Seto was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria and research funding from multiple companies including AstraZeneca. The trial headed by Dr. Lee was funded by AstraZeneca Korea Ltd. Dr. Lee reported having a consulting or advisory role and receiving honoraria and research funding from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech.
We Must Lead on BEST-CLI Trial, Enroll Patients: Dr. Conte
Dr. Michael Conte issued an urgent call Thursday for vascular surgeons to enroll patients in the BEST-CLI Trial, designed to answer this question: What’s the best treatment for advanced critical limb ischemia?
“This is a key opportunity to define optimal care for patients with critical limb-threatening ischemia,” said Dr. Conte to the audience at the E. Stanley Crawford Critical Issues Forum. “Vascular surgeons are the dominant providers, and we must be the leaders.”
Investigators hope to enroll 2,100 patients; to date the trial is at “barely one-third of that enrollment,” he said.
The National Institutes of Health is closely monitoring the trial, officially the “Best Endovascular vs. Best Surgical Therapy in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia” trial, he said, adding, “and we must execute on this important opportunity.
“Most importantly, the trial will help us define an evidenced-based standard of care. Vascular surgeons must play a leading role in this landmark trial,” he said.
To participate and learn more, visit: www.bestcli.com.
Dr. Michael Conte issued an urgent call Thursday for vascular surgeons to enroll patients in the BEST-CLI Trial, designed to answer this question: What’s the best treatment for advanced critical limb ischemia?
“This is a key opportunity to define optimal care for patients with critical limb-threatening ischemia,” said Dr. Conte to the audience at the E. Stanley Crawford Critical Issues Forum. “Vascular surgeons are the dominant providers, and we must be the leaders.”
Investigators hope to enroll 2,100 patients; to date the trial is at “barely one-third of that enrollment,” he said.
The National Institutes of Health is closely monitoring the trial, officially the “Best Endovascular vs. Best Surgical Therapy in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia” trial, he said, adding, “and we must execute on this important opportunity.
“Most importantly, the trial will help us define an evidenced-based standard of care. Vascular surgeons must play a leading role in this landmark trial,” he said.
To participate and learn more, visit: www.bestcli.com.
Dr. Michael Conte issued an urgent call Thursday for vascular surgeons to enroll patients in the BEST-CLI Trial, designed to answer this question: What’s the best treatment for advanced critical limb ischemia?
“This is a key opportunity to define optimal care for patients with critical limb-threatening ischemia,” said Dr. Conte to the audience at the E. Stanley Crawford Critical Issues Forum. “Vascular surgeons are the dominant providers, and we must be the leaders.”
Investigators hope to enroll 2,100 patients; to date the trial is at “barely one-third of that enrollment,” he said.
The National Institutes of Health is closely monitoring the trial, officially the “Best Endovascular vs. Best Surgical Therapy in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia” trial, he said, adding, “and we must execute on this important opportunity.
“Most importantly, the trial will help us define an evidenced-based standard of care. Vascular surgeons must play a leading role in this landmark trial,” he said.
To participate and learn more, visit: www.bestcli.com.
Mogamulizumab achieves objective responses in relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma
CHICAGO – The anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody mogamulizumab was superior to other investigator-selected therapies for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL), based on results from 71 patients in a prospective, multicenter, randomized study reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Commonly used cytotoxic regimens provided limited therapeutic benefit for these patients, but mogamulizumab resulted in an objective response rate that supports its therapeutic potential in this setting, reported Dr. Adrienne Alise Phillips of New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College, New York.
A malignancy of T-cells infected with HTLV-1, ATL has a poor prognosis with a median overall survival of less than 3 months in patients with relapsed/refractory disease. CCR4 is expressed in over 90% of ATL patients, and mogamulizumab is approved in Japan for ATL as well as for peripheral T-cell lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
The 71 patients in the study were from the United States, the European Union and Latin America. The study is the largest randomized clinical trial of relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma thus far conducted. The patients were randomized in 2:1 fashion 47:24 patients) to mogamulizumab, 1.0 mg/kg, given weekly for the first 4-week cycle and then biweekly, or to one of three investigator choice regimens [gemcitabine and oxaliplatin, DHAP (dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin), or pralatrexate]. Patients who were in the investigator-choice arm and whose disease progressed were permitted to cross over to mogamulizumab.
The primary endpoint was objective response rate based on modified Tsukasaki criteria and assessed by the treating investigator and in blinded fashion by independent review.
The objective response rate in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 23.4% (11 of 47) by independent review and 34% (16 of 47) by the treating investigator. In the investigator choice group, the overall response rate was 2 of 24 by independent review and 0 of 24 by the treating investigator.
The confirmed objective response rate after 1 month in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 10.6% by independent review and 14.9% by the treating investigator; there were no confirmed responses in the investigator-choice arm. Of 18 patients who crossed over to mogamulizumab, 3 responded. The median duration of response for mogamulizumab was 5 months; one patient had a complete response that lasted over 9 months and the survival data are not yet mature.
Mogamulizumab had few drug-related adverse events, primarily infusion reactions (46.8%), rash/drug eruption (25.5%) and infections (14.9%).
Dr. Phillips disclosed ties to Celgene, Genentech, and Takeda, as well as research funding from Kyowa Hakko Kirin, the sponsor of the study.
On Twitter @maryjodales

|
| Mary Jo Dales/Frontline Medical News Dr. Sonali M. Smith |
Mogamulizumab was superior to investigator’s choice therapy in the largest prospective randomized trial of this very rare disease. Approximately one-third of patients responded, while the response to investigator’s choice therapies was zero. The potential impact of mogamulizumab on T-cell regulation is intriguing. Could it have applications in other T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas?
Dr. Sonali M. Smith is with the University of Chicago and was the invited discussant of the study.

|
| Mary Jo Dales/Frontline Medical News Dr. Sonali M. Smith |
Mogamulizumab was superior to investigator’s choice therapy in the largest prospective randomized trial of this very rare disease. Approximately one-third of patients responded, while the response to investigator’s choice therapies was zero. The potential impact of mogamulizumab on T-cell regulation is intriguing. Could it have applications in other T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas?
Dr. Sonali M. Smith is with the University of Chicago and was the invited discussant of the study.

|
| Mary Jo Dales/Frontline Medical News Dr. Sonali M. Smith |
Mogamulizumab was superior to investigator’s choice therapy in the largest prospective randomized trial of this very rare disease. Approximately one-third of patients responded, while the response to investigator’s choice therapies was zero. The potential impact of mogamulizumab on T-cell regulation is intriguing. Could it have applications in other T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas?
Dr. Sonali M. Smith is with the University of Chicago and was the invited discussant of the study.
CHICAGO – The anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody mogamulizumab was superior to other investigator-selected therapies for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL), based on results from 71 patients in a prospective, multicenter, randomized study reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Commonly used cytotoxic regimens provided limited therapeutic benefit for these patients, but mogamulizumab resulted in an objective response rate that supports its therapeutic potential in this setting, reported Dr. Adrienne Alise Phillips of New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College, New York.
A malignancy of T-cells infected with HTLV-1, ATL has a poor prognosis with a median overall survival of less than 3 months in patients with relapsed/refractory disease. CCR4 is expressed in over 90% of ATL patients, and mogamulizumab is approved in Japan for ATL as well as for peripheral T-cell lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
The 71 patients in the study were from the United States, the European Union and Latin America. The study is the largest randomized clinical trial of relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma thus far conducted. The patients were randomized in 2:1 fashion 47:24 patients) to mogamulizumab, 1.0 mg/kg, given weekly for the first 4-week cycle and then biweekly, or to one of three investigator choice regimens [gemcitabine and oxaliplatin, DHAP (dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin), or pralatrexate]. Patients who were in the investigator-choice arm and whose disease progressed were permitted to cross over to mogamulizumab.
The primary endpoint was objective response rate based on modified Tsukasaki criteria and assessed by the treating investigator and in blinded fashion by independent review.
The objective response rate in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 23.4% (11 of 47) by independent review and 34% (16 of 47) by the treating investigator. In the investigator choice group, the overall response rate was 2 of 24 by independent review and 0 of 24 by the treating investigator.
The confirmed objective response rate after 1 month in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 10.6% by independent review and 14.9% by the treating investigator; there were no confirmed responses in the investigator-choice arm. Of 18 patients who crossed over to mogamulizumab, 3 responded. The median duration of response for mogamulizumab was 5 months; one patient had a complete response that lasted over 9 months and the survival data are not yet mature.
Mogamulizumab had few drug-related adverse events, primarily infusion reactions (46.8%), rash/drug eruption (25.5%) and infections (14.9%).
Dr. Phillips disclosed ties to Celgene, Genentech, and Takeda, as well as research funding from Kyowa Hakko Kirin, the sponsor of the study.
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – The anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody mogamulizumab was superior to other investigator-selected therapies for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL), based on results from 71 patients in a prospective, multicenter, randomized study reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Commonly used cytotoxic regimens provided limited therapeutic benefit for these patients, but mogamulizumab resulted in an objective response rate that supports its therapeutic potential in this setting, reported Dr. Adrienne Alise Phillips of New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College, New York.
A malignancy of T-cells infected with HTLV-1, ATL has a poor prognosis with a median overall survival of less than 3 months in patients with relapsed/refractory disease. CCR4 is expressed in over 90% of ATL patients, and mogamulizumab is approved in Japan for ATL as well as for peripheral T-cell lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
The 71 patients in the study were from the United States, the European Union and Latin America. The study is the largest randomized clinical trial of relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma thus far conducted. The patients were randomized in 2:1 fashion 47:24 patients) to mogamulizumab, 1.0 mg/kg, given weekly for the first 4-week cycle and then biweekly, or to one of three investigator choice regimens [gemcitabine and oxaliplatin, DHAP (dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin), or pralatrexate]. Patients who were in the investigator-choice arm and whose disease progressed were permitted to cross over to mogamulizumab.
The primary endpoint was objective response rate based on modified Tsukasaki criteria and assessed by the treating investigator and in blinded fashion by independent review.
The objective response rate in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 23.4% (11 of 47) by independent review and 34% (16 of 47) by the treating investigator. In the investigator choice group, the overall response rate was 2 of 24 by independent review and 0 of 24 by the treating investigator.
The confirmed objective response rate after 1 month in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 10.6% by independent review and 14.9% by the treating investigator; there were no confirmed responses in the investigator-choice arm. Of 18 patients who crossed over to mogamulizumab, 3 responded. The median duration of response for mogamulizumab was 5 months; one patient had a complete response that lasted over 9 months and the survival data are not yet mature.
Mogamulizumab had few drug-related adverse events, primarily infusion reactions (46.8%), rash/drug eruption (25.5%) and infections (14.9%).
Dr. Phillips disclosed ties to Celgene, Genentech, and Takeda, as well as research funding from Kyowa Hakko Kirin, the sponsor of the study.
On Twitter @maryjodales
AT THE 2016 ASCO ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: The anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody mogamulizumab was superior to other investigator-selected therapies for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma.
Major finding: The confirmed objective response rate after 1 month in the mogamulizumab-treated group was 10.6% by independent review and 14.9% by the treating investigator; there were no confirmed responses in the investigator-choice arm.
Data source: Prospective, multicenter, randomized study of 71 patients from the United States, the European Union, and Latin America.
Disclosures: Dr. Phillips disclosed ties to Celgene, Genentech, and Takeda, as well as research funding from Kyowa Hakko Kirin, the sponsor of the study.
Crawford Forum: Clarifying SFA-Popliteal Treatment Options
“In a follow-up to Peter Lawrence’s Presidential Address last year about appropriateness of care, I have selected the topic ‘In Search of Clarity – SFA-Popliteal Interventions for Claudication,’” said Dr. Ronald Fairman, in his introduction to the 2016 Crawford Critical Issues Forum.
Each year, the Vascular Annual Meeting is highlighted by the Forum, which is moderated and organized by the incoming SVS president. This year, Dr. Fairman, of the University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, assembled six speakers from a variety of disciplines to address the treatment of claudication as an area of concern for vascular specialists in an era of changing interventional technology and medical therapies.
Dr. Mary McDermott, of Northwestern University, Chicago, discussed the growing area of exercise training for claudication. She pointed out that numerous studies have demonstrated the value of supervised treadmill exercise, but more recent research is focusing on a more achievable goal of home exercise walking coupled to behavioral counseling and monitoring as an effective method of treatment.
The medical management of claudication was addressed by Dr. Elizabeth Ratchford, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She pointed out that medical management focuses on the two aspects: Live Longer and Feel Better, with the current focus on the former due primarily to the lack of drugs that can affect the latter.
Dr. Michael S. Conte, of the University of California San Francisco, detailed the variety of interventions available, and addressed current guidelines and best practices. “Vascular surgeons are now the predominant specialty doing peripheral interventions,” said Dr. Conte. “Our guidelines suggest that firstline therapy should be exercise, either supervised or home-based. But importantly, we were the first to suggest that maybe there should be some threshold, such that patients should have a reasonable chance of at least 50% improvement that lasts for at least two years,” for any intervention.
Dr. Peter Schneider, Kaiser Permanente Medical Group, Honolulu, provided the example of the Kaiser Model for using technology. He pointed out that having to make a strong case for using a new technology before it was implemented was a good check on the introduction of new methods into practice.
How to make decisions on treatment in community practice was addressed by Dr. Dennis Gable, of Texas Vascular Associates, Dallas. After detailing the various issues involved, he concluded that there was no great difference between the treatment concerns of private and academic practice, other than the greater opportunity to participate in clinical trials that academia provides.
And finally, Robert M. Zwolak, MD, PhD, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, dealt with the always thorny issue of the financial side of treating claudication. He pointed out that the difference between reimbursement to hospitals as compared with office-based practice is complex and can go either way depending on the type of treatment, he pointed out. “Supervised exercise is effective for claudication, but it is not covered by Medicare; percutaneous lower extremity intervention is expensive, but is covered by Medicare,” he said, pointing out the complexity of the issue.
“In a follow-up to Peter Lawrence’s Presidential Address last year about appropriateness of care, I have selected the topic ‘In Search of Clarity – SFA-Popliteal Interventions for Claudication,’” said Dr. Ronald Fairman, in his introduction to the 2016 Crawford Critical Issues Forum.
Each year, the Vascular Annual Meeting is highlighted by the Forum, which is moderated and organized by the incoming SVS president. This year, Dr. Fairman, of the University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, assembled six speakers from a variety of disciplines to address the treatment of claudication as an area of concern for vascular specialists in an era of changing interventional technology and medical therapies.
Dr. Mary McDermott, of Northwestern University, Chicago, discussed the growing area of exercise training for claudication. She pointed out that numerous studies have demonstrated the value of supervised treadmill exercise, but more recent research is focusing on a more achievable goal of home exercise walking coupled to behavioral counseling and monitoring as an effective method of treatment.
The medical management of claudication was addressed by Dr. Elizabeth Ratchford, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She pointed out that medical management focuses on the two aspects: Live Longer and Feel Better, with the current focus on the former due primarily to the lack of drugs that can affect the latter.
Dr. Michael S. Conte, of the University of California San Francisco, detailed the variety of interventions available, and addressed current guidelines and best practices. “Vascular surgeons are now the predominant specialty doing peripheral interventions,” said Dr. Conte. “Our guidelines suggest that firstline therapy should be exercise, either supervised or home-based. But importantly, we were the first to suggest that maybe there should be some threshold, such that patients should have a reasonable chance of at least 50% improvement that lasts for at least two years,” for any intervention.
Dr. Peter Schneider, Kaiser Permanente Medical Group, Honolulu, provided the example of the Kaiser Model for using technology. He pointed out that having to make a strong case for using a new technology before it was implemented was a good check on the introduction of new methods into practice.
How to make decisions on treatment in community practice was addressed by Dr. Dennis Gable, of Texas Vascular Associates, Dallas. After detailing the various issues involved, he concluded that there was no great difference between the treatment concerns of private and academic practice, other than the greater opportunity to participate in clinical trials that academia provides.
And finally, Robert M. Zwolak, MD, PhD, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, dealt with the always thorny issue of the financial side of treating claudication. He pointed out that the difference between reimbursement to hospitals as compared with office-based practice is complex and can go either way depending on the type of treatment, he pointed out. “Supervised exercise is effective for claudication, but it is not covered by Medicare; percutaneous lower extremity intervention is expensive, but is covered by Medicare,” he said, pointing out the complexity of the issue.
“In a follow-up to Peter Lawrence’s Presidential Address last year about appropriateness of care, I have selected the topic ‘In Search of Clarity – SFA-Popliteal Interventions for Claudication,’” said Dr. Ronald Fairman, in his introduction to the 2016 Crawford Critical Issues Forum.
Each year, the Vascular Annual Meeting is highlighted by the Forum, which is moderated and organized by the incoming SVS president. This year, Dr. Fairman, of the University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, assembled six speakers from a variety of disciplines to address the treatment of claudication as an area of concern for vascular specialists in an era of changing interventional technology and medical therapies.
Dr. Mary McDermott, of Northwestern University, Chicago, discussed the growing area of exercise training for claudication. She pointed out that numerous studies have demonstrated the value of supervised treadmill exercise, but more recent research is focusing on a more achievable goal of home exercise walking coupled to behavioral counseling and monitoring as an effective method of treatment.
The medical management of claudication was addressed by Dr. Elizabeth Ratchford, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She pointed out that medical management focuses on the two aspects: Live Longer and Feel Better, with the current focus on the former due primarily to the lack of drugs that can affect the latter.
Dr. Michael S. Conte, of the University of California San Francisco, detailed the variety of interventions available, and addressed current guidelines and best practices. “Vascular surgeons are now the predominant specialty doing peripheral interventions,” said Dr. Conte. “Our guidelines suggest that firstline therapy should be exercise, either supervised or home-based. But importantly, we were the first to suggest that maybe there should be some threshold, such that patients should have a reasonable chance of at least 50% improvement that lasts for at least two years,” for any intervention.
Dr. Peter Schneider, Kaiser Permanente Medical Group, Honolulu, provided the example of the Kaiser Model for using technology. He pointed out that having to make a strong case for using a new technology before it was implemented was a good check on the introduction of new methods into practice.
How to make decisions on treatment in community practice was addressed by Dr. Dennis Gable, of Texas Vascular Associates, Dallas. After detailing the various issues involved, he concluded that there was no great difference between the treatment concerns of private and academic practice, other than the greater opportunity to participate in clinical trials that academia provides.
And finally, Robert M. Zwolak, MD, PhD, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, dealt with the always thorny issue of the financial side of treating claudication. He pointed out that the difference between reimbursement to hospitals as compared with office-based practice is complex and can go either way depending on the type of treatment, he pointed out. “Supervised exercise is effective for claudication, but it is not covered by Medicare; percutaneous lower extremity intervention is expensive, but is covered by Medicare,” he said, pointing out the complexity of the issue.
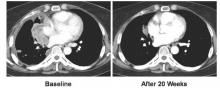
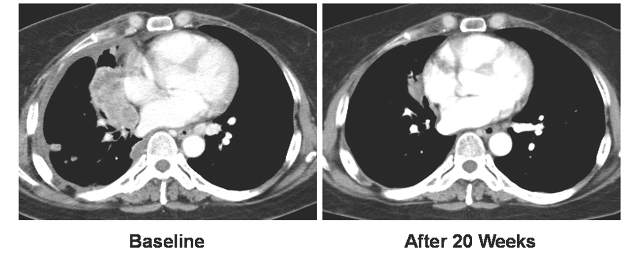
Preoperative chemotherapy improves survival in patients with large anorectal GIST
LOS ANGELES – The size of anorectal gastrointestinal stroma tumors is the most important determinant of survival following resection, results from an analysis of national data showed.
In addition, preoperative chemotherapy appears to improve survival rate in patients with tumors 5 cm in size or greater.
Anorectal gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare, making up about 3% of all GIST cases, lead study author Dr. Alexander T. Hawkins reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. However, “optimal management remains elusive with questions regarding the role of local excision and the use of preoperative chemotherapy,” said Dr. Hawkins of the section of colon and rectal surgery at Washington University in St. Louis.
In an effort to determine the impact of tumor size, the benefits of using neoadjuvant imatinib, and the impact of a surgical approach, the researchers used the National Cancer Database (NCD) to identify 333 cases of anorectal GIST from 1998 through 2012. The NCD collects data from more than 1,500 cancer centers in the United States, and it’s estimated to account for 70% of all newly diagnosed cases of cancer.
The mean age of patients was 62 years, the median tumor size was 4 cm, 47% had a high-grade tumor, six presented with metastatic disease, and the overall 5-year survival rate was 78%. Of the 333 cases, 163 underwent local excision, 158 underwent radical excision, and 12 had no resection data. Of the radical excision cases, 89 had tumors of 5 cm in size or larger, while 69 had tumors of less than 5 cm in size.
Tumors treated with local resection tended to be smaller, compared with those treated by radical resection (a median of 2.5 cm vs. a median of 6.2 cm, respectively; P less than .001). Bivariate analysis revealed that patients who underwent treatment with local resection had a shorter hospital length of stay (a median of 0 vs. 7 days; P less than .001), but similar rates of 30-day readmission (5.5% vs. 4.4%, P = .65), 30-day mortality (0.6% vs. 1.3%, P = .54) and 90-day mortality (1.2% vs. 2.5%, P = .38). The rates of 5-year survival were higher in the local resection group (80.1% vs. 74.1%, P = .04).
Multivariable survival analysis revealed that advanced age (HR, 2.41) and tumor size greater than 5 cm (HR 2.48; P = .004) were associated with increased mortality. When Dr. Hawkins and his associates evaluated the role of chemotherapy, patients who received preoperative chemotherapy had a 5-year survival of 76.7%, compared with 50.4% in those who did not (P = .04). However, in this same group, chemotherapy did not improve the rate of margin-negative resection (80% vs. 78.6%, P = .88).
Dr. Hawkins also reported that, compared with patients who underwent radical resection, those who underwent local resection had lower rates of preoperative chemotherapy (9.2% vs. 25.3%, respectively; P = .0001) and smaller median tumor size (2.5 cm vs. 6.2 cm, P less than .0001). For tumors smaller than 5 cm in size, there was no difference in 5-year survival by surgical approach (82.3% vs. 82.6%, P = .71).
“Size in the most important determinant of survival after resection of anorectal GIST,” Dr. Hawkins concluded. “For smaller tumors, local excision may be an adequate therapy. Perhaps our most important finding is that preoperative chemotherapy appears to result in improved survival for large tumors treated with radical resection.”
Dr. Hawkins reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – The size of anorectal gastrointestinal stroma tumors is the most important determinant of survival following resection, results from an analysis of national data showed.
In addition, preoperative chemotherapy appears to improve survival rate in patients with tumors 5 cm in size or greater.
Anorectal gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare, making up about 3% of all GIST cases, lead study author Dr. Alexander T. Hawkins reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. However, “optimal management remains elusive with questions regarding the role of local excision and the use of preoperative chemotherapy,” said Dr. Hawkins of the section of colon and rectal surgery at Washington University in St. Louis.
In an effort to determine the impact of tumor size, the benefits of using neoadjuvant imatinib, and the impact of a surgical approach, the researchers used the National Cancer Database (NCD) to identify 333 cases of anorectal GIST from 1998 through 2012. The NCD collects data from more than 1,500 cancer centers in the United States, and it’s estimated to account for 70% of all newly diagnosed cases of cancer.
The mean age of patients was 62 years, the median tumor size was 4 cm, 47% had a high-grade tumor, six presented with metastatic disease, and the overall 5-year survival rate was 78%. Of the 333 cases, 163 underwent local excision, 158 underwent radical excision, and 12 had no resection data. Of the radical excision cases, 89 had tumors of 5 cm in size or larger, while 69 had tumors of less than 5 cm in size.
Tumors treated with local resection tended to be smaller, compared with those treated by radical resection (a median of 2.5 cm vs. a median of 6.2 cm, respectively; P less than .001). Bivariate analysis revealed that patients who underwent treatment with local resection had a shorter hospital length of stay (a median of 0 vs. 7 days; P less than .001), but similar rates of 30-day readmission (5.5% vs. 4.4%, P = .65), 30-day mortality (0.6% vs. 1.3%, P = .54) and 90-day mortality (1.2% vs. 2.5%, P = .38). The rates of 5-year survival were higher in the local resection group (80.1% vs. 74.1%, P = .04).
Multivariable survival analysis revealed that advanced age (HR, 2.41) and tumor size greater than 5 cm (HR 2.48; P = .004) were associated with increased mortality. When Dr. Hawkins and his associates evaluated the role of chemotherapy, patients who received preoperative chemotherapy had a 5-year survival of 76.7%, compared with 50.4% in those who did not (P = .04). However, in this same group, chemotherapy did not improve the rate of margin-negative resection (80% vs. 78.6%, P = .88).
Dr. Hawkins also reported that, compared with patients who underwent radical resection, those who underwent local resection had lower rates of preoperative chemotherapy (9.2% vs. 25.3%, respectively; P = .0001) and smaller median tumor size (2.5 cm vs. 6.2 cm, P less than .0001). For tumors smaller than 5 cm in size, there was no difference in 5-year survival by surgical approach (82.3% vs. 82.6%, P = .71).
“Size in the most important determinant of survival after resection of anorectal GIST,” Dr. Hawkins concluded. “For smaller tumors, local excision may be an adequate therapy. Perhaps our most important finding is that preoperative chemotherapy appears to result in improved survival for large tumors treated with radical resection.”
Dr. Hawkins reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – The size of anorectal gastrointestinal stroma tumors is the most important determinant of survival following resection, results from an analysis of national data showed.
In addition, preoperative chemotherapy appears to improve survival rate in patients with tumors 5 cm in size or greater.
Anorectal gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare, making up about 3% of all GIST cases, lead study author Dr. Alexander T. Hawkins reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. However, “optimal management remains elusive with questions regarding the role of local excision and the use of preoperative chemotherapy,” said Dr. Hawkins of the section of colon and rectal surgery at Washington University in St. Louis.
In an effort to determine the impact of tumor size, the benefits of using neoadjuvant imatinib, and the impact of a surgical approach, the researchers used the National Cancer Database (NCD) to identify 333 cases of anorectal GIST from 1998 through 2012. The NCD collects data from more than 1,500 cancer centers in the United States, and it’s estimated to account for 70% of all newly diagnosed cases of cancer.
The mean age of patients was 62 years, the median tumor size was 4 cm, 47% had a high-grade tumor, six presented with metastatic disease, and the overall 5-year survival rate was 78%. Of the 333 cases, 163 underwent local excision, 158 underwent radical excision, and 12 had no resection data. Of the radical excision cases, 89 had tumors of 5 cm in size or larger, while 69 had tumors of less than 5 cm in size.
Tumors treated with local resection tended to be smaller, compared with those treated by radical resection (a median of 2.5 cm vs. a median of 6.2 cm, respectively; P less than .001). Bivariate analysis revealed that patients who underwent treatment with local resection had a shorter hospital length of stay (a median of 0 vs. 7 days; P less than .001), but similar rates of 30-day readmission (5.5% vs. 4.4%, P = .65), 30-day mortality (0.6% vs. 1.3%, P = .54) and 90-day mortality (1.2% vs. 2.5%, P = .38). The rates of 5-year survival were higher in the local resection group (80.1% vs. 74.1%, P = .04).
Multivariable survival analysis revealed that advanced age (HR, 2.41) and tumor size greater than 5 cm (HR 2.48; P = .004) were associated with increased mortality. When Dr. Hawkins and his associates evaluated the role of chemotherapy, patients who received preoperative chemotherapy had a 5-year survival of 76.7%, compared with 50.4% in those who did not (P = .04). However, in this same group, chemotherapy did not improve the rate of margin-negative resection (80% vs. 78.6%, P = .88).
Dr. Hawkins also reported that, compared with patients who underwent radical resection, those who underwent local resection had lower rates of preoperative chemotherapy (9.2% vs. 25.3%, respectively; P = .0001) and smaller median tumor size (2.5 cm vs. 6.2 cm, P less than .0001). For tumors smaller than 5 cm in size, there was no difference in 5-year survival by surgical approach (82.3% vs. 82.6%, P = .71).
“Size in the most important determinant of survival after resection of anorectal GIST,” Dr. Hawkins concluded. “For smaller tumors, local excision may be an adequate therapy. Perhaps our most important finding is that preoperative chemotherapy appears to result in improved survival for large tumors treated with radical resection.”
Dr. Hawkins reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT THE ASCRS ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Anorectal gastrointestinal stroma tumors greater than 5 cm in size were associated with worse survival.
Major finding: Anorectal gastrointestinal stroma tumors greater than 5 cm in size were associated with increased mortality (HR 2.48; P = .004).
Data source: A review of National Cancer Database records to identify 333 cases of anorectal GIST from 1998 through 2012.
Disclosures: Dr. Hawkins reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Scenes from the Vascular Annual Meeting
Beyond the Plenary Sessions and scientific abstract presentations, there were many exciting events in which to participate and presentations to attend throughout the Vascular Annual Meeting, including sessions especially planned for residents and students. These photos capture some of the action:
Beyond the Plenary Sessions and scientific abstract presentations, there were many exciting events in which to participate and presentations to attend throughout the Vascular Annual Meeting, including sessions especially planned for residents and students. These photos capture some of the action:
Beyond the Plenary Sessions and scientific abstract presentations, there were many exciting events in which to participate and presentations to attend throughout the Vascular Annual Meeting, including sessions especially planned for residents and students. These photos capture some of the action:
VIDEO: Smoking, excess weight hinder sustained remission in early RA
LONDON – Tobacco use and excess weight can make it harder to achieve sustained remission in the treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis, according to findings from more than 1,000 patients in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) multicenter, prospective study.
Aggressive treatment that starts soon after diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is important for the absence of disease activity, which is the hallmark of sustained remission. But the reality is a success rate of less than 50% in the first 3 years with physical deterioration continuing thereafter. “Excess weight and smoking are two risk factors for developing RA. We were interested in seeing if they might also affect how well people responded to treatment,” said Susan Bartlett, Ph.D., a clinical psychologist at McGill University in Montreal.
At the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, Dr. Bartlett and colleagues reported on a cohort of 1,008 early RA patients who were enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) multicenter, prospective study and followed from around the time of diagnosis through the first 3 years of treatment to estimate the time it took until they achieved sustained remission, defined as having a 28-joint Disease Activity Score less than 2.6 for two consecutive visits.
Mean age of the patients (72% female, 81% white) was early 50s. Overall, 30% of females and 47% of males were overweight, one-third of both genders were obese, and 15%-20% smoked. Treatment at entry included methotrexate in mono- or combination therapy in about three-quarters of the patients, with steroids used in about half and biologics used sparingly.
The proportion of patients in sustained remission was 38% at 3 years, with a median time to remission of 11.3 months. “That finding wasn’t surprising because that is generally what is found in most studies of early RA. However, when we looked more closely at who was and wasn’t achieving remission, we found that people who smoked and those who were overweight or obese were much less likely than their nonsmoking, normal-weight peers to be in sustained remission,” Dr. Bartlett said in a pre-congress interview.
After adjustment for factors that could affect response to treatment – including age, race, disability status, pain, and early medications used – smoking (P = .046) and excess weight (P = .003) were associated with a poorer likelihood of achieving sustained remission. While more men than women were overweight or obese, the effects of weight and smoking appeared to be more problematic for women (P = .02).
An average nonsmoking male with a healthy body mass index (BMI; 25 kg/m2 or less) had about a 41% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 15% for an obese male smoker. A nonsmoking female with a healthy BMI had a 27% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 10% for an obese female smoker. Probabilities of sustained remission were also lower for overweight men and women, Dr. Bartlett reported.
Smoking and obesity have already been linked with an increased likelihood of developing RA, which in turn increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and premature death. The latest data suggest that both smoking and extra weight – including overweight and obese as defined by BMI – may also independently influence the success of treatment. “Our data suggest that if you have RA, it’s important to take the medications that your doctor has prescribed. If you smoke, you need to stop. And if you’re carrying extra weight, not only is that placing a greater demand on already vulnerable joints, it may also be making your RA treatment less effective,” Dr. Bartlett said.
These lifestyle modifications can be challenging for some people with RA, she said in the interview. Clinicians can help by considering lifestyle behaviors that lead to chronic diseases and poorer outcomes in addition to their more traditional view of diagnosis and treatment, she said, adding that patients and clinicians should know that even a small amount of weight loss can improve health and may improve response to therapy.
Well controlled clinical trials will be needed to better understand the benefits of weight control and smoking cessation on response to RA treatment. Also, why women who smoke and are overweight are at more of a disadvantage than their male counterparts is unknown. “As we begin putting these pieces together, we may learn valuable information that helps us to better control and ultimately cure RA,” said Dr. Bartlett.
The researchers had no conflicts of interest to declare.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
LONDON – Tobacco use and excess weight can make it harder to achieve sustained remission in the treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis, according to findings from more than 1,000 patients in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) multicenter, prospective study.
Aggressive treatment that starts soon after diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is important for the absence of disease activity, which is the hallmark of sustained remission. But the reality is a success rate of less than 50% in the first 3 years with physical deterioration continuing thereafter. “Excess weight and smoking are two risk factors for developing RA. We were interested in seeing if they might also affect how well people responded to treatment,” said Susan Bartlett, Ph.D., a clinical psychologist at McGill University in Montreal.
At the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, Dr. Bartlett and colleagues reported on a cohort of 1,008 early RA patients who were enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) multicenter, prospective study and followed from around the time of diagnosis through the first 3 years of treatment to estimate the time it took until they achieved sustained remission, defined as having a 28-joint Disease Activity Score less than 2.6 for two consecutive visits.
Mean age of the patients (72% female, 81% white) was early 50s. Overall, 30% of females and 47% of males were overweight, one-third of both genders were obese, and 15%-20% smoked. Treatment at entry included methotrexate in mono- or combination therapy in about three-quarters of the patients, with steroids used in about half and biologics used sparingly.
The proportion of patients in sustained remission was 38% at 3 years, with a median time to remission of 11.3 months. “That finding wasn’t surprising because that is generally what is found in most studies of early RA. However, when we looked more closely at who was and wasn’t achieving remission, we found that people who smoked and those who were overweight or obese were much less likely than their nonsmoking, normal-weight peers to be in sustained remission,” Dr. Bartlett said in a pre-congress interview.
After adjustment for factors that could affect response to treatment – including age, race, disability status, pain, and early medications used – smoking (P = .046) and excess weight (P = .003) were associated with a poorer likelihood of achieving sustained remission. While more men than women were overweight or obese, the effects of weight and smoking appeared to be more problematic for women (P = .02).
An average nonsmoking male with a healthy body mass index (BMI; 25 kg/m2 or less) had about a 41% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 15% for an obese male smoker. A nonsmoking female with a healthy BMI had a 27% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 10% for an obese female smoker. Probabilities of sustained remission were also lower for overweight men and women, Dr. Bartlett reported.
Smoking and obesity have already been linked with an increased likelihood of developing RA, which in turn increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and premature death. The latest data suggest that both smoking and extra weight – including overweight and obese as defined by BMI – may also independently influence the success of treatment. “Our data suggest that if you have RA, it’s important to take the medications that your doctor has prescribed. If you smoke, you need to stop. And if you’re carrying extra weight, not only is that placing a greater demand on already vulnerable joints, it may also be making your RA treatment less effective,” Dr. Bartlett said.
These lifestyle modifications can be challenging for some people with RA, she said in the interview. Clinicians can help by considering lifestyle behaviors that lead to chronic diseases and poorer outcomes in addition to their more traditional view of diagnosis and treatment, she said, adding that patients and clinicians should know that even a small amount of weight loss can improve health and may improve response to therapy.
Well controlled clinical trials will be needed to better understand the benefits of weight control and smoking cessation on response to RA treatment. Also, why women who smoke and are overweight are at more of a disadvantage than their male counterparts is unknown. “As we begin putting these pieces together, we may learn valuable information that helps us to better control and ultimately cure RA,” said Dr. Bartlett.
The researchers had no conflicts of interest to declare.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
LONDON – Tobacco use and excess weight can make it harder to achieve sustained remission in the treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis, according to findings from more than 1,000 patients in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) multicenter, prospective study.
Aggressive treatment that starts soon after diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is important for the absence of disease activity, which is the hallmark of sustained remission. But the reality is a success rate of less than 50% in the first 3 years with physical deterioration continuing thereafter. “Excess weight and smoking are two risk factors for developing RA. We were interested in seeing if they might also affect how well people responded to treatment,” said Susan Bartlett, Ph.D., a clinical psychologist at McGill University in Montreal.
At the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, Dr. Bartlett and colleagues reported on a cohort of 1,008 early RA patients who were enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) multicenter, prospective study and followed from around the time of diagnosis through the first 3 years of treatment to estimate the time it took until they achieved sustained remission, defined as having a 28-joint Disease Activity Score less than 2.6 for two consecutive visits.
Mean age of the patients (72% female, 81% white) was early 50s. Overall, 30% of females and 47% of males were overweight, one-third of both genders were obese, and 15%-20% smoked. Treatment at entry included methotrexate in mono- or combination therapy in about three-quarters of the patients, with steroids used in about half and biologics used sparingly.
The proportion of patients in sustained remission was 38% at 3 years, with a median time to remission of 11.3 months. “That finding wasn’t surprising because that is generally what is found in most studies of early RA. However, when we looked more closely at who was and wasn’t achieving remission, we found that people who smoked and those who were overweight or obese were much less likely than their nonsmoking, normal-weight peers to be in sustained remission,” Dr. Bartlett said in a pre-congress interview.
After adjustment for factors that could affect response to treatment – including age, race, disability status, pain, and early medications used – smoking (P = .046) and excess weight (P = .003) were associated with a poorer likelihood of achieving sustained remission. While more men than women were overweight or obese, the effects of weight and smoking appeared to be more problematic for women (P = .02).
An average nonsmoking male with a healthy body mass index (BMI; 25 kg/m2 or less) had about a 41% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 15% for an obese male smoker. A nonsmoking female with a healthy BMI had a 27% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 10% for an obese female smoker. Probabilities of sustained remission were also lower for overweight men and women, Dr. Bartlett reported.
Smoking and obesity have already been linked with an increased likelihood of developing RA, which in turn increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and premature death. The latest data suggest that both smoking and extra weight – including overweight and obese as defined by BMI – may also independently influence the success of treatment. “Our data suggest that if you have RA, it’s important to take the medications that your doctor has prescribed. If you smoke, you need to stop. And if you’re carrying extra weight, not only is that placing a greater demand on already vulnerable joints, it may also be making your RA treatment less effective,” Dr. Bartlett said.
These lifestyle modifications can be challenging for some people with RA, she said in the interview. Clinicians can help by considering lifestyle behaviors that lead to chronic diseases and poorer outcomes in addition to their more traditional view of diagnosis and treatment, she said, adding that patients and clinicians should know that even a small amount of weight loss can improve health and may improve response to therapy.
Well controlled clinical trials will be needed to better understand the benefits of weight control and smoking cessation on response to RA treatment. Also, why women who smoke and are overweight are at more of a disadvantage than their male counterparts is unknown. “As we begin putting these pieces together, we may learn valuable information that helps us to better control and ultimately cure RA,” said Dr. Bartlett.
The researchers had no conflicts of interest to declare.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
AT THE EULAR CONGRESS 2016
Key clinical point: The latest data suggest that both smoking and extra weight – including overweight and obese as defined by BMI – may independently influence the success of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
Major finding: A nonsmoking female with a healthy BMI had a 27% probability of achieving sustained remission within 3 years, compared with 10% for an obese female smoker.
Data source: A prospective study of 1,008 patients with early RA in the prospective, multicenter CATCH study.
Disclosures: The researchers had no conflicts of interest to declare.
Teriflunomide effective for faster-advancing MS
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – The approved once-daily oral immunomodulator teriflunomide is effective in reducing relapse, and worsening of relapsing forms, of multiple sclerosis (RMS) in patients with faster-advancing disease.
The findings from a post hoc pooled subgroup analysis of patients in the TEMSO and TOWER randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trials presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers expand the efficacy of teriflunomide to a broad spectrum of patients with RMS.
The pooled analysis examined the outcomes of treatment with two doses of teriflunomide in all patients (n = 2,257) and in a subgroup of patients with faster-advancing MS (n = 1,184) according to disease severity using a baseline Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score (MSSS) of 5 as a cutoff. The group with faster-advancing disease included 405 who received placebo, 396 treated with teriflunomide 7 mg, and 383 treated with teriflunomide 14 mg.
The 1,184 patients with faster-advancing MS were comparable to the other 1,073 patients in terms of age, sex, MS subtype, and number of relapses in the prior year. Baseline characteristics of the faster-advancing MS patients treated with placebo and both teriflunomide doses were comparable.
Relative to the placebo group, the annualized relapse rate in patients with faster-advancing MS was significantly reduced by both doses of teriflunomide, with a relative risk reduction of 30.3% for the 7-mg dose (P = .0002) and 37.5% for the 14-mg dose (P less than .0001). Time to first relapse was also reduced by teriflunomide 14 mg and 7 mg, with reductions in relapse risk of 43.2% (P less than .0001) and 28.8% (P = .0014), respectively, compared with placebo.
The higher dose of teriflunomide was effective in reducing the worsening of disability at greater than or equal to 12 weeks and 24 weeks, with reductions, compared with placebo, of 40.3% (P = .0076) and 46.1% (P = .0110), respectively.
The results were consistent with data reported in the individual TEMSO and TOWER trials, and prior analyses of the pooled data.
“These results indicate that teriflunomide is not only effective for MS patients with relatively mild disease, but also with rather more aggressive disease. Teriflunomide, a well-tolerated and convenient once-daily tablet, is a very reasonable option for this population,” said the presenter, Dr. Aaron E. Miller of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Teriflunomide is approved for relapsing-remitting MS in many countries, including the United States and the European Union. The TEMSO and TOWER trials were pivotal in securing approval. The trials had a similar design, except for the absence of magnetic resonance imaging evaluation in TOWER.
The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Miller disclosed consulting fees from Accordant Health Services, Acorda Therapeutics, Alkermes, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, GlaxoSmithKline, Mallinckrodt Paharmaceuticals/Questor, Novartis, Roche, and Teva, and grant/research support from Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Questor, Roche, and Sanofi.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – The approved once-daily oral immunomodulator teriflunomide is effective in reducing relapse, and worsening of relapsing forms, of multiple sclerosis (RMS) in patients with faster-advancing disease.
The findings from a post hoc pooled subgroup analysis of patients in the TEMSO and TOWER randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trials presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers expand the efficacy of teriflunomide to a broad spectrum of patients with RMS.
The pooled analysis examined the outcomes of treatment with two doses of teriflunomide in all patients (n = 2,257) and in a subgroup of patients with faster-advancing MS (n = 1,184) according to disease severity using a baseline Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score (MSSS) of 5 as a cutoff. The group with faster-advancing disease included 405 who received placebo, 396 treated with teriflunomide 7 mg, and 383 treated with teriflunomide 14 mg.
The 1,184 patients with faster-advancing MS were comparable to the other 1,073 patients in terms of age, sex, MS subtype, and number of relapses in the prior year. Baseline characteristics of the faster-advancing MS patients treated with placebo and both teriflunomide doses were comparable.
Relative to the placebo group, the annualized relapse rate in patients with faster-advancing MS was significantly reduced by both doses of teriflunomide, with a relative risk reduction of 30.3% for the 7-mg dose (P = .0002) and 37.5% for the 14-mg dose (P less than .0001). Time to first relapse was also reduced by teriflunomide 14 mg and 7 mg, with reductions in relapse risk of 43.2% (P less than .0001) and 28.8% (P = .0014), respectively, compared with placebo.
The higher dose of teriflunomide was effective in reducing the worsening of disability at greater than or equal to 12 weeks and 24 weeks, with reductions, compared with placebo, of 40.3% (P = .0076) and 46.1% (P = .0110), respectively.
The results were consistent with data reported in the individual TEMSO and TOWER trials, and prior analyses of the pooled data.
“These results indicate that teriflunomide is not only effective for MS patients with relatively mild disease, but also with rather more aggressive disease. Teriflunomide, a well-tolerated and convenient once-daily tablet, is a very reasonable option for this population,” said the presenter, Dr. Aaron E. Miller of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Teriflunomide is approved for relapsing-remitting MS in many countries, including the United States and the European Union. The TEMSO and TOWER trials were pivotal in securing approval. The trials had a similar design, except for the absence of magnetic resonance imaging evaluation in TOWER.
The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Miller disclosed consulting fees from Accordant Health Services, Acorda Therapeutics, Alkermes, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, GlaxoSmithKline, Mallinckrodt Paharmaceuticals/Questor, Novartis, Roche, and Teva, and grant/research support from Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Questor, Roche, and Sanofi.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – The approved once-daily oral immunomodulator teriflunomide is effective in reducing relapse, and worsening of relapsing forms, of multiple sclerosis (RMS) in patients with faster-advancing disease.
The findings from a post hoc pooled subgroup analysis of patients in the TEMSO and TOWER randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trials presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers expand the efficacy of teriflunomide to a broad spectrum of patients with RMS.
The pooled analysis examined the outcomes of treatment with two doses of teriflunomide in all patients (n = 2,257) and in a subgroup of patients with faster-advancing MS (n = 1,184) according to disease severity using a baseline Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score (MSSS) of 5 as a cutoff. The group with faster-advancing disease included 405 who received placebo, 396 treated with teriflunomide 7 mg, and 383 treated with teriflunomide 14 mg.
The 1,184 patients with faster-advancing MS were comparable to the other 1,073 patients in terms of age, sex, MS subtype, and number of relapses in the prior year. Baseline characteristics of the faster-advancing MS patients treated with placebo and both teriflunomide doses were comparable.
Relative to the placebo group, the annualized relapse rate in patients with faster-advancing MS was significantly reduced by both doses of teriflunomide, with a relative risk reduction of 30.3% for the 7-mg dose (P = .0002) and 37.5% for the 14-mg dose (P less than .0001). Time to first relapse was also reduced by teriflunomide 14 mg and 7 mg, with reductions in relapse risk of 43.2% (P less than .0001) and 28.8% (P = .0014), respectively, compared with placebo.
The higher dose of teriflunomide was effective in reducing the worsening of disability at greater than or equal to 12 weeks and 24 weeks, with reductions, compared with placebo, of 40.3% (P = .0076) and 46.1% (P = .0110), respectively.
The results were consistent with data reported in the individual TEMSO and TOWER trials, and prior analyses of the pooled data.
“These results indicate that teriflunomide is not only effective for MS patients with relatively mild disease, but also with rather more aggressive disease. Teriflunomide, a well-tolerated and convenient once-daily tablet, is a very reasonable option for this population,” said the presenter, Dr. Aaron E. Miller of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Teriflunomide is approved for relapsing-remitting MS in many countries, including the United States and the European Union. The TEMSO and TOWER trials were pivotal in securing approval. The trials had a similar design, except for the absence of magnetic resonance imaging evaluation in TOWER.
The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Miller disclosed consulting fees from Accordant Health Services, Acorda Therapeutics, Alkermes, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, GlaxoSmithKline, Mallinckrodt Paharmaceuticals/Questor, Novartis, Roche, and Teva, and grant/research support from Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Questor, Roche, and Sanofi.
AT THE CMSC ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Teriflunomide is effective for patients with faster-advancing MS.
Major finding: Teriflunomide at 14 mg and 7 mg reduced the annualized relapse rate of patients with fast-advancing relapsing-remitting MS (MSSS greater than 5) by 43.2% and 28.8%, respectively, compared with placebo.
Data source: A pooled analysis of patients from the TEMSO and TOWER randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trials.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Miller disclosed consulting fees from Accordant Health Services, Acorda Therapeutics, Alkermes, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, GlaxoSmithKline, Mallinckrodt Paharmaceuticals/Questor, Novartis, Roche, and Teva, and grant/research support from Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Questor, Roche, and Sanofi.
Diagnosis, treatment of gout lag behind prevalence
LONDON – The prevalence of gout is increasing and to prevent an epidemic, rheumatologists and other physicians need to diagnose and treat cases promptly and better explain the treatment process to their patients, according to a Swedish expert on the disease.
“It’s a disease for which we understand the mechanisms, we know how to diagnose it, and we have had good treatments for the last 50 years,” said Dr. Lennart Jacobsson, professor of rheumatology at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden. “Despite that, we don’t treat it properly. It’s difficult to understand why that is the case, why there is such a lack of knowledge and such a lack of willingness to pursue treatment.”
Gout is the most common nondegenerative inflammatory joint disease, exemplified by a prevalence of 0.9%-2.5% in Europe and 3.9% in the United States. The incidence is increasing along with factors such as the aging population, as well as lifestyle changes such as rising body mass index and physical inactivity, Dr. Jacobsson said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“It’s the same story everywhere,” he said. “Gout is underdiagnosed, it’s diagnosed late, and once it’s diagnosed people don’t get treated with urate-lowering therapy, which aims at the heart of the disease. If they are treated, treatment often is discontinued, which we think is largely due to lack of education and information to patients.”
Urate crystals can build up over as much as a decade before a person experiences a first gout attack, Dr. Jacobsson said. “It can take 3-5 years of effective treatment to get rid of those masses within the body. Over that time, especially at the beginning, patients may still have gout attacks, which they often interpret as side effects of the medication or a misinterpretation that it doesn’t work because they’re not properly informed that medication needs to be a long-term treatment.”
Close to 10% of men aged 70-80 years have gout, he said, but it’s still unclear how many of those have mild, moderate, or severe disease. It’s also not well studied how gout itself can affect health-related quality of life and costs to society. “You can easily imagine that the costs are pretty large, however, and they will increase,” he said.
Gout is interrelated with several metabolic syndrome disorders such as obesity, hypertension, and diabetes, Dr. Jacobsson said: “If you have renal disease, you have higher uric acid levels and can more easily get gout, but from having high uric acid levels you may also get decreased renal function, so it’s sort of circular. The same is true of gout and hypertension.”
Once considered a disease of the wealthy, Dr. Jacobsson said, gout has recently been shown to be associated with lower income and socioeconomic class, as is the case for many other chronic diseases. There are still large opportunities for improvements regarding early detection and the initiation of urate-lowering therapy, he said, as well as counseling patients on lifestyle improvements.
“We know what to do, we have the tools, and we should start using them more effectively,” he said. “It’s really very simple, but that message has to get through. It’s an increasing problem, and it’s bad not just for the joints but also for quality of life and comorbidities.”
Dr. Jacobsson reported no relevant financial disclosures.
LONDON – The prevalence of gout is increasing and to prevent an epidemic, rheumatologists and other physicians need to diagnose and treat cases promptly and better explain the treatment process to their patients, according to a Swedish expert on the disease.
“It’s a disease for which we understand the mechanisms, we know how to diagnose it, and we have had good treatments for the last 50 years,” said Dr. Lennart Jacobsson, professor of rheumatology at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden. “Despite that, we don’t treat it properly. It’s difficult to understand why that is the case, why there is such a lack of knowledge and such a lack of willingness to pursue treatment.”
Gout is the most common nondegenerative inflammatory joint disease, exemplified by a prevalence of 0.9%-2.5% in Europe and 3.9% in the United States. The incidence is increasing along with factors such as the aging population, as well as lifestyle changes such as rising body mass index and physical inactivity, Dr. Jacobsson said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“It’s the same story everywhere,” he said. “Gout is underdiagnosed, it’s diagnosed late, and once it’s diagnosed people don’t get treated with urate-lowering therapy, which aims at the heart of the disease. If they are treated, treatment often is discontinued, which we think is largely due to lack of education and information to patients.”
Urate crystals can build up over as much as a decade before a person experiences a first gout attack, Dr. Jacobsson said. “It can take 3-5 years of effective treatment to get rid of those masses within the body. Over that time, especially at the beginning, patients may still have gout attacks, which they often interpret as side effects of the medication or a misinterpretation that it doesn’t work because they’re not properly informed that medication needs to be a long-term treatment.”
Close to 10% of men aged 70-80 years have gout, he said, but it’s still unclear how many of those have mild, moderate, or severe disease. It’s also not well studied how gout itself can affect health-related quality of life and costs to society. “You can easily imagine that the costs are pretty large, however, and they will increase,” he said.
Gout is interrelated with several metabolic syndrome disorders such as obesity, hypertension, and diabetes, Dr. Jacobsson said: “If you have renal disease, you have higher uric acid levels and can more easily get gout, but from having high uric acid levels you may also get decreased renal function, so it’s sort of circular. The same is true of gout and hypertension.”
Once considered a disease of the wealthy, Dr. Jacobsson said, gout has recently been shown to be associated with lower income and socioeconomic class, as is the case for many other chronic diseases. There are still large opportunities for improvements regarding early detection and the initiation of urate-lowering therapy, he said, as well as counseling patients on lifestyle improvements.
“We know what to do, we have the tools, and we should start using them more effectively,” he said. “It’s really very simple, but that message has to get through. It’s an increasing problem, and it’s bad not just for the joints but also for quality of life and comorbidities.”
Dr. Jacobsson reported no relevant financial disclosures.
LONDON – The prevalence of gout is increasing and to prevent an epidemic, rheumatologists and other physicians need to diagnose and treat cases promptly and better explain the treatment process to their patients, according to a Swedish expert on the disease.
“It’s a disease for which we understand the mechanisms, we know how to diagnose it, and we have had good treatments for the last 50 years,” said Dr. Lennart Jacobsson, professor of rheumatology at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden. “Despite that, we don’t treat it properly. It’s difficult to understand why that is the case, why there is such a lack of knowledge and such a lack of willingness to pursue treatment.”
Gout is the most common nondegenerative inflammatory joint disease, exemplified by a prevalence of 0.9%-2.5% in Europe and 3.9% in the United States. The incidence is increasing along with factors such as the aging population, as well as lifestyle changes such as rising body mass index and physical inactivity, Dr. Jacobsson said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“It’s the same story everywhere,” he said. “Gout is underdiagnosed, it’s diagnosed late, and once it’s diagnosed people don’t get treated with urate-lowering therapy, which aims at the heart of the disease. If they are treated, treatment often is discontinued, which we think is largely due to lack of education and information to patients.”
Urate crystals can build up over as much as a decade before a person experiences a first gout attack, Dr. Jacobsson said. “It can take 3-5 years of effective treatment to get rid of those masses within the body. Over that time, especially at the beginning, patients may still have gout attacks, which they often interpret as side effects of the medication or a misinterpretation that it doesn’t work because they’re not properly informed that medication needs to be a long-term treatment.”
Close to 10% of men aged 70-80 years have gout, he said, but it’s still unclear how many of those have mild, moderate, or severe disease. It’s also not well studied how gout itself can affect health-related quality of life and costs to society. “You can easily imagine that the costs are pretty large, however, and they will increase,” he said.
Gout is interrelated with several metabolic syndrome disorders such as obesity, hypertension, and diabetes, Dr. Jacobsson said: “If you have renal disease, you have higher uric acid levels and can more easily get gout, but from having high uric acid levels you may also get decreased renal function, so it’s sort of circular. The same is true of gout and hypertension.”
Once considered a disease of the wealthy, Dr. Jacobsson said, gout has recently been shown to be associated with lower income and socioeconomic class, as is the case for many other chronic diseases. There are still large opportunities for improvements regarding early detection and the initiation of urate-lowering therapy, he said, as well as counseling patients on lifestyle improvements.
“We know what to do, we have the tools, and we should start using them more effectively,” he said. “It’s really very simple, but that message has to get through. It’s an increasing problem, and it’s bad not just for the joints but also for quality of life and comorbidities.”
Dr. Jacobsson reported no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE EULAR 2016 CONGRESS