User login
For urban-based African Americans, proximity to a dermatologist varies by ZIP code
Urban ZIP codes with higher percentages of African American people tend to have fewer dermatologists. In these areas, dermatologists are not able meet the populations’ needs, based on the suggested ratio of patients per dermatologist.
The findings come from an analysis which used U.S. Census data to compare dermatologists’ distribution in urban ZIP codes with high and low representation of African Americans.
“It has been demonstrated that there is a non-uniform geographic distribution of dermatologists, in which they tend to practice in urban settings,” the study’s first author, Nathan Vengalil, MD, said in an interview following the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Furthermore, it is also an unfortunate reality that African Americans suffer from inferior access to care compared to whites across health care. The same is true within dermatology; for example, African Americans face higher morbidity and mortality from melanoma, compared to their white counterparts.”
For the current study, Dr. Vengalil, a recent graduate of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and associates in the university’s department of dermatology drew from 2010 U.S. Census data to identify ZIP codes with populations of 25,000 people and greater, because these should have at least one dermatologist to care for a community of that size (JAMA Dermatology 2017;153[5]:472-3).
Next, they ordered these ZIP codes from low to high concentrations of African American people. Those that fell in the 15th percentile or fewer were categorized as “low” (a total of 370 ZIP codes), while those that fell in the 85th percentile or higher were categorized as “high” (a total of 443 ZIP codes). Following this, the Definitive Healthcare provider database was used to identify the number of dermatologists practicing within each ZIP code and to calculate the average number of people per dermatologist in the “low” and “high” categories.
The researchers found that ZIP codes with high percentage of African American people have an average of 1.02 dermatologists (1 per 39,367 people), which is below the recommended limit of 1 per 25,000 people. Meanwhile, ZIP codes with a low percentage of African American people averaged 2.84 dermatologists (1 per 14,000 people), which is above the adequate limit. “ZIP codes with a low percentage of African Americans had, on average, almost three times more dermatologists than ZIP codes with a high percentage of American Americans,” Dr. Vengalil said. “This means that predominantly African American urban communities may face consequences of low provider availability including longer waits times, decreased diagnosis of skin cancer, and worse health care outcomes.”
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it focused only on the distribution of dermatologists to assess communities’ access to dermatologic care. “It would be interesting to measure how much mid-level providers such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants are able to compensate for the low number of dermatologists in urban ZIP codes with high numbers of African Americans,” Dr. Vengalil said.
The study’s findings suggest that the distribution of dermatologists is not uniform even within the urban environment, especially when comparing areas with different representations of African American persons. “This reveals that lack of provider proximity may contribute to barriers that urban African Americans face in accessing dermatologic care,” he concluded. “Looking toward the future, it will be important to incentivize the development of practice locations in urban African American communities to combat the health disparities of our most underserved patients.”
The study’s other authors were Mio Nakamura, MD, MS, and Yolanda Helfrich, MD. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Vengalil N et al. AAD 20, abstract 16772.
Urban ZIP codes with higher percentages of African American people tend to have fewer dermatologists. In these areas, dermatologists are not able meet the populations’ needs, based on the suggested ratio of patients per dermatologist.
The findings come from an analysis which used U.S. Census data to compare dermatologists’ distribution in urban ZIP codes with high and low representation of African Americans.
“It has been demonstrated that there is a non-uniform geographic distribution of dermatologists, in which they tend to practice in urban settings,” the study’s first author, Nathan Vengalil, MD, said in an interview following the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Furthermore, it is also an unfortunate reality that African Americans suffer from inferior access to care compared to whites across health care. The same is true within dermatology; for example, African Americans face higher morbidity and mortality from melanoma, compared to their white counterparts.”
For the current study, Dr. Vengalil, a recent graduate of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and associates in the university’s department of dermatology drew from 2010 U.S. Census data to identify ZIP codes with populations of 25,000 people and greater, because these should have at least one dermatologist to care for a community of that size (JAMA Dermatology 2017;153[5]:472-3).
Next, they ordered these ZIP codes from low to high concentrations of African American people. Those that fell in the 15th percentile or fewer were categorized as “low” (a total of 370 ZIP codes), while those that fell in the 85th percentile or higher were categorized as “high” (a total of 443 ZIP codes). Following this, the Definitive Healthcare provider database was used to identify the number of dermatologists practicing within each ZIP code and to calculate the average number of people per dermatologist in the “low” and “high” categories.
The researchers found that ZIP codes with high percentage of African American people have an average of 1.02 dermatologists (1 per 39,367 people), which is below the recommended limit of 1 per 25,000 people. Meanwhile, ZIP codes with a low percentage of African American people averaged 2.84 dermatologists (1 per 14,000 people), which is above the adequate limit. “ZIP codes with a low percentage of African Americans had, on average, almost three times more dermatologists than ZIP codes with a high percentage of American Americans,” Dr. Vengalil said. “This means that predominantly African American urban communities may face consequences of low provider availability including longer waits times, decreased diagnosis of skin cancer, and worse health care outcomes.”
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it focused only on the distribution of dermatologists to assess communities’ access to dermatologic care. “It would be interesting to measure how much mid-level providers such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants are able to compensate for the low number of dermatologists in urban ZIP codes with high numbers of African Americans,” Dr. Vengalil said.
The study’s findings suggest that the distribution of dermatologists is not uniform even within the urban environment, especially when comparing areas with different representations of African American persons. “This reveals that lack of provider proximity may contribute to barriers that urban African Americans face in accessing dermatologic care,” he concluded. “Looking toward the future, it will be important to incentivize the development of practice locations in urban African American communities to combat the health disparities of our most underserved patients.”
The study’s other authors were Mio Nakamura, MD, MS, and Yolanda Helfrich, MD. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Vengalil N et al. AAD 20, abstract 16772.
Urban ZIP codes with higher percentages of African American people tend to have fewer dermatologists. In these areas, dermatologists are not able meet the populations’ needs, based on the suggested ratio of patients per dermatologist.
The findings come from an analysis which used U.S. Census data to compare dermatologists’ distribution in urban ZIP codes with high and low representation of African Americans.
“It has been demonstrated that there is a non-uniform geographic distribution of dermatologists, in which they tend to practice in urban settings,” the study’s first author, Nathan Vengalil, MD, said in an interview following the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Furthermore, it is also an unfortunate reality that African Americans suffer from inferior access to care compared to whites across health care. The same is true within dermatology; for example, African Americans face higher morbidity and mortality from melanoma, compared to their white counterparts.”
For the current study, Dr. Vengalil, a recent graduate of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and associates in the university’s department of dermatology drew from 2010 U.S. Census data to identify ZIP codes with populations of 25,000 people and greater, because these should have at least one dermatologist to care for a community of that size (JAMA Dermatology 2017;153[5]:472-3).
Next, they ordered these ZIP codes from low to high concentrations of African American people. Those that fell in the 15th percentile or fewer were categorized as “low” (a total of 370 ZIP codes), while those that fell in the 85th percentile or higher were categorized as “high” (a total of 443 ZIP codes). Following this, the Definitive Healthcare provider database was used to identify the number of dermatologists practicing within each ZIP code and to calculate the average number of people per dermatologist in the “low” and “high” categories.
The researchers found that ZIP codes with high percentage of African American people have an average of 1.02 dermatologists (1 per 39,367 people), which is below the recommended limit of 1 per 25,000 people. Meanwhile, ZIP codes with a low percentage of African American people averaged 2.84 dermatologists (1 per 14,000 people), which is above the adequate limit. “ZIP codes with a low percentage of African Americans had, on average, almost three times more dermatologists than ZIP codes with a high percentage of American Americans,” Dr. Vengalil said. “This means that predominantly African American urban communities may face consequences of low provider availability including longer waits times, decreased diagnosis of skin cancer, and worse health care outcomes.”
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it focused only on the distribution of dermatologists to assess communities’ access to dermatologic care. “It would be interesting to measure how much mid-level providers such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants are able to compensate for the low number of dermatologists in urban ZIP codes with high numbers of African Americans,” Dr. Vengalil said.
The study’s findings suggest that the distribution of dermatologists is not uniform even within the urban environment, especially when comparing areas with different representations of African American persons. “This reveals that lack of provider proximity may contribute to barriers that urban African Americans face in accessing dermatologic care,” he concluded. “Looking toward the future, it will be important to incentivize the development of practice locations in urban African American communities to combat the health disparities of our most underserved patients.”
The study’s other authors were Mio Nakamura, MD, MS, and Yolanda Helfrich, MD. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Vengalil N et al. AAD 20, abstract 16772.
FROM AAD 20
Increased hypothyroidism risk seen in young men with HS
Anna Figueiredo, MD, declared at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The surprise about this finding from a large retrospective case-control study stems from the fact that the elevated risk for hypothyroidism didn’t also extend to younger women with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) nor to patients older than 40 years of either gender, explained Dr. Figueiredo of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago.
She presented a retrospective case-control study based on information extracted from a medical records database of more than 8 million Midwestern adults. Among nearly 141,000 dermatology patients with follow-up in the database for at least 1 year, there were 405 HS patients aged 18-40 years and 327 aged 41-89.
In an age-matched comparison with the dermatology patients without HS, the younger HS cohort was at a significant 1.52-fold increased risk for comorbid hypothyroidism. Upon further stratification by sex, only the younger men with HS were at increased risk. Those patients were at 3.95-fold greater risk for having a diagnosis of hypothyroidism than were age-matched younger male dermatology patients.
Both younger and older HS patients were at numerically increased risk for being diagnosed with hyperthyroidism; however, this difference didn’t approach statistical significance because there were so few cases: a total of just eight in the HS population across the full age spectrum.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory disease with an estimated prevalence of up to 4% in the United States. Growing evidence suggests it is an immune-mediated disorder because the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) has been approved for treatment of HS.
Thyroid disease is also often autoimmune-mediated, but its relationship with HS hasn’t been extensively examined. A recent meta-analysis of five case-control studies concluded that HS was associated with a 1.36-fold increased risk of thyroid disease; however, the Nepalese investigators didn’t distinguish between hypo- and hyperthyroidism (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Feb;82[2]:491-3).
Dr. Figueiredo reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study, which was without commercial support.
Anna Figueiredo, MD, declared at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The surprise about this finding from a large retrospective case-control study stems from the fact that the elevated risk for hypothyroidism didn’t also extend to younger women with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) nor to patients older than 40 years of either gender, explained Dr. Figueiredo of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago.
She presented a retrospective case-control study based on information extracted from a medical records database of more than 8 million Midwestern adults. Among nearly 141,000 dermatology patients with follow-up in the database for at least 1 year, there were 405 HS patients aged 18-40 years and 327 aged 41-89.
In an age-matched comparison with the dermatology patients without HS, the younger HS cohort was at a significant 1.52-fold increased risk for comorbid hypothyroidism. Upon further stratification by sex, only the younger men with HS were at increased risk. Those patients were at 3.95-fold greater risk for having a diagnosis of hypothyroidism than were age-matched younger male dermatology patients.
Both younger and older HS patients were at numerically increased risk for being diagnosed with hyperthyroidism; however, this difference didn’t approach statistical significance because there were so few cases: a total of just eight in the HS population across the full age spectrum.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory disease with an estimated prevalence of up to 4% in the United States. Growing evidence suggests it is an immune-mediated disorder because the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) has been approved for treatment of HS.
Thyroid disease is also often autoimmune-mediated, but its relationship with HS hasn’t been extensively examined. A recent meta-analysis of five case-control studies concluded that HS was associated with a 1.36-fold increased risk of thyroid disease; however, the Nepalese investigators didn’t distinguish between hypo- and hyperthyroidism (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Feb;82[2]:491-3).
Dr. Figueiredo reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study, which was without commercial support.
Anna Figueiredo, MD, declared at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The surprise about this finding from a large retrospective case-control study stems from the fact that the elevated risk for hypothyroidism didn’t also extend to younger women with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) nor to patients older than 40 years of either gender, explained Dr. Figueiredo of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago.
She presented a retrospective case-control study based on information extracted from a medical records database of more than 8 million Midwestern adults. Among nearly 141,000 dermatology patients with follow-up in the database for at least 1 year, there were 405 HS patients aged 18-40 years and 327 aged 41-89.
In an age-matched comparison with the dermatology patients without HS, the younger HS cohort was at a significant 1.52-fold increased risk for comorbid hypothyroidism. Upon further stratification by sex, only the younger men with HS were at increased risk. Those patients were at 3.95-fold greater risk for having a diagnosis of hypothyroidism than were age-matched younger male dermatology patients.
Both younger and older HS patients were at numerically increased risk for being diagnosed with hyperthyroidism; however, this difference didn’t approach statistical significance because there were so few cases: a total of just eight in the HS population across the full age spectrum.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory disease with an estimated prevalence of up to 4% in the United States. Growing evidence suggests it is an immune-mediated disorder because the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) has been approved for treatment of HS.
Thyroid disease is also often autoimmune-mediated, but its relationship with HS hasn’t been extensively examined. A recent meta-analysis of five case-control studies concluded that HS was associated with a 1.36-fold increased risk of thyroid disease; however, the Nepalese investigators didn’t distinguish between hypo- and hyperthyroidism (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Feb;82[2]:491-3).
Dr. Figueiredo reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study, which was without commercial support.
FROM AAD 20
Race and race relations: Be curious, not furious
Racism has been around for a very long time, and we still have a long way to go to eradicate it, in all of its forms. Racism can be subtle, such as not offering employment to a fully qualified candidate or lowering your level of care because of the color of a person’s skin. Also, you never know if the future will place you in the same position as that of the person you are discriminating against or excluding. Diversity through the mixture of cultures and races is what provides a richness to our communities and our country.
No matter what race we may be, we all are human and deserve to be treated and respected as such. The patient you misunderstood, feared, or dismissed could be the same person who helps you become a better physician. For instance, one of my teenage patients of Chinese descent confessed one day that she was feeling depressed, sometimes to the point of suicidal ideation. However, she was adamant that I not report this condition to her parents. From her, I learned that mental illness, such as depression, are taboo subjects in Asian cultures. This information enabled me to be more sensitive with handling this patient’s condition and treatment.
In many cities across America, people have been protesting the recent tragic death of Mr. George Floyd, an African American man killed by a white police officer. In the past few months, unfortunately, we have seen similar cases of racist acts against African Americans. Sadly, this is nothing new.
There are examples of racist acts against other racial groups as well. Since the coronavirus pandemic became global news, Asian Americans have faced a wave of intense xenophobia in the United States. Be mindful that one race suffering injustice in one country could themselves be racist against another group given the opportunity. An example of this was reported in an April 16, 2020, article in the Los Angeles Times. The events took place in Guangzhou, China. The article reported that Africans living there were harassed, targeted, and evicted from their homes in the port city following the positive COVID-19 tests of five Nigerians. Instead of imposing quarantine based on contact history, China’s response has been based on race amid the coronavirus crisis. Stories like this remind us that racism is not just black and white, but can occur by any dominant culture against the minority. To be clear, not everyone is a racist.
Fear of the unknown causes misunderstanding and weakens the relationship between a pediatrician and the patient. Instead, let us “be curious and not furious.”1 We may look different on the outside, but inside we are all human, with feelings, desires, and dreams. An example of being misunderstood is commonly observed as others stereotype African American populations. For example, an African American mother may be described as rude, loud, and disrespectful by those in your office. Such labeling fails to take the time necessary to understand the other’s perspective, and it dismisses her. Why might she be acting this way? What false assumptions are you making? How would you react if you were frequently disrespected or dismissed? How would you react if you had to worry about being physically harmed? Your visage could appear to be angry or guarded – not exactly welcoming or pleasant. It is much easier to quickly dismiss such a patient and not be sincerely interested in what she or her child’s medical needs may be. Such a disposition only results in frustrating outcomes and the destruction of trust between a patient and the provider.
Although I encounter racism daily in my work, I strive to put aside those violations as I treat my patients and interact with their parents. The decision to be inquisitive and empathetic is a conscious one, which can disarm strangers, allowing for trust to be built. It can engender a smile as well.
Teachers frequently refer parents to us when their children are having learning or behavioral difficulties in school. One challenging case for me involved a Latino boy with learning difficulties. The mother, who does not speak English, had been struggling with getting help for her son. I decided to attend a meeting for the patient’s Individualized Education Plan (IEP) at his school (an IEP is a requirement of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA). My presence at the meeting, given that I am also fluent in Spanish, provided a bridge in communication between the parent and the teachers. Moreover, my presence persuaded the patient’s teachers to be more aggressive in designing an individualized plan to truly help my patient. Latino and African American students commonly suffer from disparities in health and education. In my own practice, I also work toward improving disparities within Latino and African American communities through medical education initiatives. There is so much we, as pediatricians, can do to advocate for these communities.
The absence of empathy leading to the killing of Mr. Floyd admittedly is not the same as what generates an inadequate IEP or the desire to avoid a “loud” parent. Even so, any lack of empathy lowers the quality of patient care. It takes conscious effort to be open to helping someone you do not innately understand. Quality pediatric care cannot happen where racism and misunderstanding exist between a patient and provider. Until we truly stop being selfish, the issue of racism will continue to resurface. One impactful way the majority population can help people of color is by not being a bystander to injustice. Inaction makes you an accomplice to the racist act. We must be brave – “be curious, not furious.” Remember that an injustice to one culture eventually becomes an injustice against us all. Being open to what is different, new, or not well known is how a culture becomes richer and even better.
Dr. Mba Wright is a primary care pediatrician practicing in Sacramento, Calif., for more than 14 years. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
1. “Going the Distance: Finding and Keeping Lifelong Love” (New York, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1991).
Racism has been around for a very long time, and we still have a long way to go to eradicate it, in all of its forms. Racism can be subtle, such as not offering employment to a fully qualified candidate or lowering your level of care because of the color of a person’s skin. Also, you never know if the future will place you in the same position as that of the person you are discriminating against or excluding. Diversity through the mixture of cultures and races is what provides a richness to our communities and our country.
No matter what race we may be, we all are human and deserve to be treated and respected as such. The patient you misunderstood, feared, or dismissed could be the same person who helps you become a better physician. For instance, one of my teenage patients of Chinese descent confessed one day that she was feeling depressed, sometimes to the point of suicidal ideation. However, she was adamant that I not report this condition to her parents. From her, I learned that mental illness, such as depression, are taboo subjects in Asian cultures. This information enabled me to be more sensitive with handling this patient’s condition and treatment.
In many cities across America, people have been protesting the recent tragic death of Mr. George Floyd, an African American man killed by a white police officer. In the past few months, unfortunately, we have seen similar cases of racist acts against African Americans. Sadly, this is nothing new.
There are examples of racist acts against other racial groups as well. Since the coronavirus pandemic became global news, Asian Americans have faced a wave of intense xenophobia in the United States. Be mindful that one race suffering injustice in one country could themselves be racist against another group given the opportunity. An example of this was reported in an April 16, 2020, article in the Los Angeles Times. The events took place in Guangzhou, China. The article reported that Africans living there were harassed, targeted, and evicted from their homes in the port city following the positive COVID-19 tests of five Nigerians. Instead of imposing quarantine based on contact history, China’s response has been based on race amid the coronavirus crisis. Stories like this remind us that racism is not just black and white, but can occur by any dominant culture against the minority. To be clear, not everyone is a racist.
Fear of the unknown causes misunderstanding and weakens the relationship between a pediatrician and the patient. Instead, let us “be curious and not furious.”1 We may look different on the outside, but inside we are all human, with feelings, desires, and dreams. An example of being misunderstood is commonly observed as others stereotype African American populations. For example, an African American mother may be described as rude, loud, and disrespectful by those in your office. Such labeling fails to take the time necessary to understand the other’s perspective, and it dismisses her. Why might she be acting this way? What false assumptions are you making? How would you react if you were frequently disrespected or dismissed? How would you react if you had to worry about being physically harmed? Your visage could appear to be angry or guarded – not exactly welcoming or pleasant. It is much easier to quickly dismiss such a patient and not be sincerely interested in what she or her child’s medical needs may be. Such a disposition only results in frustrating outcomes and the destruction of trust between a patient and the provider.
Although I encounter racism daily in my work, I strive to put aside those violations as I treat my patients and interact with their parents. The decision to be inquisitive and empathetic is a conscious one, which can disarm strangers, allowing for trust to be built. It can engender a smile as well.
Teachers frequently refer parents to us when their children are having learning or behavioral difficulties in school. One challenging case for me involved a Latino boy with learning difficulties. The mother, who does not speak English, had been struggling with getting help for her son. I decided to attend a meeting for the patient’s Individualized Education Plan (IEP) at his school (an IEP is a requirement of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA). My presence at the meeting, given that I am also fluent in Spanish, provided a bridge in communication between the parent and the teachers. Moreover, my presence persuaded the patient’s teachers to be more aggressive in designing an individualized plan to truly help my patient. Latino and African American students commonly suffer from disparities in health and education. In my own practice, I also work toward improving disparities within Latino and African American communities through medical education initiatives. There is so much we, as pediatricians, can do to advocate for these communities.
The absence of empathy leading to the killing of Mr. Floyd admittedly is not the same as what generates an inadequate IEP or the desire to avoid a “loud” parent. Even so, any lack of empathy lowers the quality of patient care. It takes conscious effort to be open to helping someone you do not innately understand. Quality pediatric care cannot happen where racism and misunderstanding exist between a patient and provider. Until we truly stop being selfish, the issue of racism will continue to resurface. One impactful way the majority population can help people of color is by not being a bystander to injustice. Inaction makes you an accomplice to the racist act. We must be brave – “be curious, not furious.” Remember that an injustice to one culture eventually becomes an injustice against us all. Being open to what is different, new, or not well known is how a culture becomes richer and even better.
Dr. Mba Wright is a primary care pediatrician practicing in Sacramento, Calif., for more than 14 years. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
1. “Going the Distance: Finding and Keeping Lifelong Love” (New York, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1991).
Racism has been around for a very long time, and we still have a long way to go to eradicate it, in all of its forms. Racism can be subtle, such as not offering employment to a fully qualified candidate or lowering your level of care because of the color of a person’s skin. Also, you never know if the future will place you in the same position as that of the person you are discriminating against or excluding. Diversity through the mixture of cultures and races is what provides a richness to our communities and our country.
No matter what race we may be, we all are human and deserve to be treated and respected as such. The patient you misunderstood, feared, or dismissed could be the same person who helps you become a better physician. For instance, one of my teenage patients of Chinese descent confessed one day that she was feeling depressed, sometimes to the point of suicidal ideation. However, she was adamant that I not report this condition to her parents. From her, I learned that mental illness, such as depression, are taboo subjects in Asian cultures. This information enabled me to be more sensitive with handling this patient’s condition and treatment.
In many cities across America, people have been protesting the recent tragic death of Mr. George Floyd, an African American man killed by a white police officer. In the past few months, unfortunately, we have seen similar cases of racist acts against African Americans. Sadly, this is nothing new.
There are examples of racist acts against other racial groups as well. Since the coronavirus pandemic became global news, Asian Americans have faced a wave of intense xenophobia in the United States. Be mindful that one race suffering injustice in one country could themselves be racist against another group given the opportunity. An example of this was reported in an April 16, 2020, article in the Los Angeles Times. The events took place in Guangzhou, China. The article reported that Africans living there were harassed, targeted, and evicted from their homes in the port city following the positive COVID-19 tests of five Nigerians. Instead of imposing quarantine based on contact history, China’s response has been based on race amid the coronavirus crisis. Stories like this remind us that racism is not just black and white, but can occur by any dominant culture against the minority. To be clear, not everyone is a racist.
Fear of the unknown causes misunderstanding and weakens the relationship between a pediatrician and the patient. Instead, let us “be curious and not furious.”1 We may look different on the outside, but inside we are all human, with feelings, desires, and dreams. An example of being misunderstood is commonly observed as others stereotype African American populations. For example, an African American mother may be described as rude, loud, and disrespectful by those in your office. Such labeling fails to take the time necessary to understand the other’s perspective, and it dismisses her. Why might she be acting this way? What false assumptions are you making? How would you react if you were frequently disrespected or dismissed? How would you react if you had to worry about being physically harmed? Your visage could appear to be angry or guarded – not exactly welcoming or pleasant. It is much easier to quickly dismiss such a patient and not be sincerely interested in what she or her child’s medical needs may be. Such a disposition only results in frustrating outcomes and the destruction of trust between a patient and the provider.
Although I encounter racism daily in my work, I strive to put aside those violations as I treat my patients and interact with their parents. The decision to be inquisitive and empathetic is a conscious one, which can disarm strangers, allowing for trust to be built. It can engender a smile as well.
Teachers frequently refer parents to us when their children are having learning or behavioral difficulties in school. One challenging case for me involved a Latino boy with learning difficulties. The mother, who does not speak English, had been struggling with getting help for her son. I decided to attend a meeting for the patient’s Individualized Education Plan (IEP) at his school (an IEP is a requirement of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA). My presence at the meeting, given that I am also fluent in Spanish, provided a bridge in communication between the parent and the teachers. Moreover, my presence persuaded the patient’s teachers to be more aggressive in designing an individualized plan to truly help my patient. Latino and African American students commonly suffer from disparities in health and education. In my own practice, I also work toward improving disparities within Latino and African American communities through medical education initiatives. There is so much we, as pediatricians, can do to advocate for these communities.
The absence of empathy leading to the killing of Mr. Floyd admittedly is not the same as what generates an inadequate IEP or the desire to avoid a “loud” parent. Even so, any lack of empathy lowers the quality of patient care. It takes conscious effort to be open to helping someone you do not innately understand. Quality pediatric care cannot happen where racism and misunderstanding exist between a patient and provider. Until we truly stop being selfish, the issue of racism will continue to resurface. One impactful way the majority population can help people of color is by not being a bystander to injustice. Inaction makes you an accomplice to the racist act. We must be brave – “be curious, not furious.” Remember that an injustice to one culture eventually becomes an injustice against us all. Being open to what is different, new, or not well known is how a culture becomes richer and even better.
Dr. Mba Wright is a primary care pediatrician practicing in Sacramento, Calif., for more than 14 years. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
1. “Going the Distance: Finding and Keeping Lifelong Love” (New York, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1991).
Belimumab safely improved renal function in lupus nephritis patients
compared with control patients who only received standard therapy, in a randomized, multicenter trial with 446 evaluable patients, a finding that may help extend this treatment to a new group of lupus patients.
“The largest” treatment study of lupus nephritis reported to date showed that belimumab, approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for treating patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), administered at a standard dosage of 10 mg intravenously every 4 weeks, “significantly improved multiple lupus nephritis renal responses versus standard therapy alone while maintaining an acceptable safety profile,” Richard A. Furie, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
The study’s primary endpoint was a composite measure that Dr. Furie and associates called the Primary Endpoint Renal Response, which required patients to have achieved a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio of 0.7 or less (compared with an enrollment level of 1.0 or greater), an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 60 mL/min/1.73 kg/m2 and no more than 20% below its preflare level, and continuation on the assigned treatment regimen. After 104 weeks on this treatment, which followed a 60-day induction phase that included treatment with a high-dose glucocorticoid, the percentages of patients who met the Primary Endpoint Renal Response criteria were 32% in the control arm who received standard treatment at the discretion of their treating clinicians plus placebo infusions and 43% in patients who received belimumab infusions in addition to their standard care. This calculated out to a 55% relative increase in this response with belimumab, a statistically significant result, reported Dr. Furie, professor of medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and chief of rheumatology at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.
Patients who received belimumab also had similar and statistically significant levels of improvement for several secondary endpoints, including one called Complete Renal Response, which required a protein-to-creatinine ratio of no greater than 0.5, an eGFR of at least 90 mL/min per 1.73 kg/m2 and no more than 10% below its preflare level, and maintaining the assigned treatment. The Complete Renal Response after 104 weeks was 20% among control patients and 30% among those maintained on belimumab, a 74% relative improvement that was statistically significant. The total percentage of patients with any renal-related event after 104 weeks was 28% among the control patients and 16% among those who received belimumab, a statistically significant difference.
“The fact that the primary and all key secondary endpoints were successfully attained is a major accomplishment in lupus nephritis as well as in any SLE study,” Dr. Furie said in an interview. The study’s 2-year design “provided insight into the durability of the response,” and the steady divergence of the endpoint events in the two study arms beginning after about 24 weeks into the randomized phase “provided data regarding the rapidity of onset of action.” Collectively, the endpoints “mimic our real-life treatment goals: reduce disease activity, prevent flares, preserve renal function, lower steroid treatment, and do it all safely,” he concluded.
Results confirm benefit to subset of patients
“Belimumab is a safe and effective treatment for a significant subset of patients with lupus. We already knew that. Now we have even more confirmation,” commented Joan T. Merrill, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center and a rheumatologist who specializes in SLE at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, both in Oklahoma City. “There have already been at least four international trials demonstrating belimumab’s efficacy in general lupus. Some patients in these earlier trials had nephritis, so it should not be surprising to see similar results in a trial restricted to patients with active nephritis, given the drug’s mechanism of action. Belimumab has repeatedly shown early and sustained benefits above what background treatments achieve, and belimumab has also proven to be safe to add to standard-of-care treatments,” she said in an interview.
The BLISS-LN (Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Patients With Active Lupus Nephritis) study enrolled patients at any of 118 centers in 20 countries, including the United States. All patients enrolled in the trial were adults with biopsy-confirmed, clinically active lupus nephritis and a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio of at least 1.0, and need for induction therapy. The 60-day induction run-in phase began with high-dose glucocorticoids plus either cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), followed by maintenance on low-dose glucocorticoids and either azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil. Nearly three-quarters of patients received mycophenolate mofetil–based induction. Once treatment with either belimumab or placebo began in the study’s main phase, the glucocorticoid dosage had to drop with tapering to no more than 10 mg/day within 24 weeks or the patient was considered a treatment failure.
Thoughts on current and future use of belimumab
The current labeled indication for belimumab is for “treatment of patients aged 5 years and older with active, autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus who are receiving standard therapy,” an inclusive SLE population, but the label also adds this caveat: “Limitations of use: The efficacy of Benlysta has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus.” According to Dr. Furie’s report, GlaxoSmithKline, the company that markets belimumab, plans to seek a labeled indication for lupus nephritis for the drug during 2020.
“I doubt the drug is widely used as yet in clinical practice for lupus nephritis,” although it is being prescribed to selected SLE patients in current, routine practice, said Dr. Merrill, a coinvestigator on some belimumab studies. What also remains unknown is the efficacy of belimumab monotherapy. “We don’t know which subset of patients might benefit from belimumab alone,” she noted. Nor is it known whether belimumab treatment of patients with SLE but without lupus nephritis will forestall later development of lupus nephritis.
“With the introduction of the subcutaneous formulation a few years ago, there has been greater belimumab use” overall in patients with SLE, said Dr. Furie, and with a safety and efficacy record now established in five separate, reported studies in addition to the new BLISS-LN study: BLISS-52, BLISS-76, BLISS-SC, BLISS-NE ASIA, and PLUTO. “The pivotal studies [BLISS-52 and BLISS-76] were done in patients with SLE but without nephritis in need of aggressive induction therapy. About 15% of the trial cohorts had low-level renal involvement,” and post hoc analyses suggested that the benefit in those patients was similar to patients without renal involvement, which led to the BLISS-LN study. “In theory, no SLE patients with high-level nephritis should be on belimumab at this time,” based on its labeling, although some SLE patients with low-level renal disease may now receive the drug because they also have other affected organs, such as skin and joints, Dr. Furie said.
“These are encouraging results,” commented George K. Bertsias, MD, a rheumatologist and SLE specialist at the University of Crete in Heraklion, Greece. He particularly cited the “significant effect from add-on belimumab” on top of treatment with mycophenolate mofetil, an “established and effective treatment for lupus nephritis. The data provide additional evidence for the efficacy of belimumab in SLE, and also in lupus nephritis,” he said in an interview, and “having an official labeled indication for active nephritis will enhance use of the drug” in such patients. “Considering the favorable effects of the drug on SLE, especially preventing major flares, and on lupus nephritis it is possible that the drug will be particularly suitable for SLE patients who are at high risk for developing lupus nephritis, although such an effect remains to be determined.” Until now, belimumab has generally been prescribed to SLE patients who have disease manifestations in organs outside of the kidneys, he noted.
BLISS-LN was sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Furie is a consultant to and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline, and several of the study’s coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Merrill has been a consultant to GlaxoSmithKline as well as to several other companies and has been a coinvestigator on belimumab studies. Dr. Bertsias has been a consultant to Novartis and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline.
SOURCE: Furie RA et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:103, Abstract OP0164.
compared with control patients who only received standard therapy, in a randomized, multicenter trial with 446 evaluable patients, a finding that may help extend this treatment to a new group of lupus patients.
“The largest” treatment study of lupus nephritis reported to date showed that belimumab, approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for treating patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), administered at a standard dosage of 10 mg intravenously every 4 weeks, “significantly improved multiple lupus nephritis renal responses versus standard therapy alone while maintaining an acceptable safety profile,” Richard A. Furie, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
The study’s primary endpoint was a composite measure that Dr. Furie and associates called the Primary Endpoint Renal Response, which required patients to have achieved a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio of 0.7 or less (compared with an enrollment level of 1.0 or greater), an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 60 mL/min/1.73 kg/m2 and no more than 20% below its preflare level, and continuation on the assigned treatment regimen. After 104 weeks on this treatment, which followed a 60-day induction phase that included treatment with a high-dose glucocorticoid, the percentages of patients who met the Primary Endpoint Renal Response criteria were 32% in the control arm who received standard treatment at the discretion of their treating clinicians plus placebo infusions and 43% in patients who received belimumab infusions in addition to their standard care. This calculated out to a 55% relative increase in this response with belimumab, a statistically significant result, reported Dr. Furie, professor of medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and chief of rheumatology at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.
Patients who received belimumab also had similar and statistically significant levels of improvement for several secondary endpoints, including one called Complete Renal Response, which required a protein-to-creatinine ratio of no greater than 0.5, an eGFR of at least 90 mL/min per 1.73 kg/m2 and no more than 10% below its preflare level, and maintaining the assigned treatment. The Complete Renal Response after 104 weeks was 20% among control patients and 30% among those maintained on belimumab, a 74% relative improvement that was statistically significant. The total percentage of patients with any renal-related event after 104 weeks was 28% among the control patients and 16% among those who received belimumab, a statistically significant difference.
“The fact that the primary and all key secondary endpoints were successfully attained is a major accomplishment in lupus nephritis as well as in any SLE study,” Dr. Furie said in an interview. The study’s 2-year design “provided insight into the durability of the response,” and the steady divergence of the endpoint events in the two study arms beginning after about 24 weeks into the randomized phase “provided data regarding the rapidity of onset of action.” Collectively, the endpoints “mimic our real-life treatment goals: reduce disease activity, prevent flares, preserve renal function, lower steroid treatment, and do it all safely,” he concluded.
Results confirm benefit to subset of patients
“Belimumab is a safe and effective treatment for a significant subset of patients with lupus. We already knew that. Now we have even more confirmation,” commented Joan T. Merrill, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center and a rheumatologist who specializes in SLE at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, both in Oklahoma City. “There have already been at least four international trials demonstrating belimumab’s efficacy in general lupus. Some patients in these earlier trials had nephritis, so it should not be surprising to see similar results in a trial restricted to patients with active nephritis, given the drug’s mechanism of action. Belimumab has repeatedly shown early and sustained benefits above what background treatments achieve, and belimumab has also proven to be safe to add to standard-of-care treatments,” she said in an interview.
The BLISS-LN (Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Patients With Active Lupus Nephritis) study enrolled patients at any of 118 centers in 20 countries, including the United States. All patients enrolled in the trial were adults with biopsy-confirmed, clinically active lupus nephritis and a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio of at least 1.0, and need for induction therapy. The 60-day induction run-in phase began with high-dose glucocorticoids plus either cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), followed by maintenance on low-dose glucocorticoids and either azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil. Nearly three-quarters of patients received mycophenolate mofetil–based induction. Once treatment with either belimumab or placebo began in the study’s main phase, the glucocorticoid dosage had to drop with tapering to no more than 10 mg/day within 24 weeks or the patient was considered a treatment failure.
Thoughts on current and future use of belimumab
The current labeled indication for belimumab is for “treatment of patients aged 5 years and older with active, autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus who are receiving standard therapy,” an inclusive SLE population, but the label also adds this caveat: “Limitations of use: The efficacy of Benlysta has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus.” According to Dr. Furie’s report, GlaxoSmithKline, the company that markets belimumab, plans to seek a labeled indication for lupus nephritis for the drug during 2020.
“I doubt the drug is widely used as yet in clinical practice for lupus nephritis,” although it is being prescribed to selected SLE patients in current, routine practice, said Dr. Merrill, a coinvestigator on some belimumab studies. What also remains unknown is the efficacy of belimumab monotherapy. “We don’t know which subset of patients might benefit from belimumab alone,” she noted. Nor is it known whether belimumab treatment of patients with SLE but without lupus nephritis will forestall later development of lupus nephritis.
“With the introduction of the subcutaneous formulation a few years ago, there has been greater belimumab use” overall in patients with SLE, said Dr. Furie, and with a safety and efficacy record now established in five separate, reported studies in addition to the new BLISS-LN study: BLISS-52, BLISS-76, BLISS-SC, BLISS-NE ASIA, and PLUTO. “The pivotal studies [BLISS-52 and BLISS-76] were done in patients with SLE but without nephritis in need of aggressive induction therapy. About 15% of the trial cohorts had low-level renal involvement,” and post hoc analyses suggested that the benefit in those patients was similar to patients without renal involvement, which led to the BLISS-LN study. “In theory, no SLE patients with high-level nephritis should be on belimumab at this time,” based on its labeling, although some SLE patients with low-level renal disease may now receive the drug because they also have other affected organs, such as skin and joints, Dr. Furie said.
“These are encouraging results,” commented George K. Bertsias, MD, a rheumatologist and SLE specialist at the University of Crete in Heraklion, Greece. He particularly cited the “significant effect from add-on belimumab” on top of treatment with mycophenolate mofetil, an “established and effective treatment for lupus nephritis. The data provide additional evidence for the efficacy of belimumab in SLE, and also in lupus nephritis,” he said in an interview, and “having an official labeled indication for active nephritis will enhance use of the drug” in such patients. “Considering the favorable effects of the drug on SLE, especially preventing major flares, and on lupus nephritis it is possible that the drug will be particularly suitable for SLE patients who are at high risk for developing lupus nephritis, although such an effect remains to be determined.” Until now, belimumab has generally been prescribed to SLE patients who have disease manifestations in organs outside of the kidneys, he noted.
BLISS-LN was sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Furie is a consultant to and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline, and several of the study’s coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Merrill has been a consultant to GlaxoSmithKline as well as to several other companies and has been a coinvestigator on belimumab studies. Dr. Bertsias has been a consultant to Novartis and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline.
SOURCE: Furie RA et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:103, Abstract OP0164.
compared with control patients who only received standard therapy, in a randomized, multicenter trial with 446 evaluable patients, a finding that may help extend this treatment to a new group of lupus patients.
“The largest” treatment study of lupus nephritis reported to date showed that belimumab, approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for treating patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), administered at a standard dosage of 10 mg intravenously every 4 weeks, “significantly improved multiple lupus nephritis renal responses versus standard therapy alone while maintaining an acceptable safety profile,” Richard A. Furie, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
The study’s primary endpoint was a composite measure that Dr. Furie and associates called the Primary Endpoint Renal Response, which required patients to have achieved a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio of 0.7 or less (compared with an enrollment level of 1.0 or greater), an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 60 mL/min/1.73 kg/m2 and no more than 20% below its preflare level, and continuation on the assigned treatment regimen. After 104 weeks on this treatment, which followed a 60-day induction phase that included treatment with a high-dose glucocorticoid, the percentages of patients who met the Primary Endpoint Renal Response criteria were 32% in the control arm who received standard treatment at the discretion of their treating clinicians plus placebo infusions and 43% in patients who received belimumab infusions in addition to their standard care. This calculated out to a 55% relative increase in this response with belimumab, a statistically significant result, reported Dr. Furie, professor of medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and chief of rheumatology at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.
Patients who received belimumab also had similar and statistically significant levels of improvement for several secondary endpoints, including one called Complete Renal Response, which required a protein-to-creatinine ratio of no greater than 0.5, an eGFR of at least 90 mL/min per 1.73 kg/m2 and no more than 10% below its preflare level, and maintaining the assigned treatment. The Complete Renal Response after 104 weeks was 20% among control patients and 30% among those maintained on belimumab, a 74% relative improvement that was statistically significant. The total percentage of patients with any renal-related event after 104 weeks was 28% among the control patients and 16% among those who received belimumab, a statistically significant difference.
“The fact that the primary and all key secondary endpoints were successfully attained is a major accomplishment in lupus nephritis as well as in any SLE study,” Dr. Furie said in an interview. The study’s 2-year design “provided insight into the durability of the response,” and the steady divergence of the endpoint events in the two study arms beginning after about 24 weeks into the randomized phase “provided data regarding the rapidity of onset of action.” Collectively, the endpoints “mimic our real-life treatment goals: reduce disease activity, prevent flares, preserve renal function, lower steroid treatment, and do it all safely,” he concluded.
Results confirm benefit to subset of patients
“Belimumab is a safe and effective treatment for a significant subset of patients with lupus. We already knew that. Now we have even more confirmation,” commented Joan T. Merrill, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center and a rheumatologist who specializes in SLE at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, both in Oklahoma City. “There have already been at least four international trials demonstrating belimumab’s efficacy in general lupus. Some patients in these earlier trials had nephritis, so it should not be surprising to see similar results in a trial restricted to patients with active nephritis, given the drug’s mechanism of action. Belimumab has repeatedly shown early and sustained benefits above what background treatments achieve, and belimumab has also proven to be safe to add to standard-of-care treatments,” she said in an interview.
The BLISS-LN (Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Patients With Active Lupus Nephritis) study enrolled patients at any of 118 centers in 20 countries, including the United States. All patients enrolled in the trial were adults with biopsy-confirmed, clinically active lupus nephritis and a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio of at least 1.0, and need for induction therapy. The 60-day induction run-in phase began with high-dose glucocorticoids plus either cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), followed by maintenance on low-dose glucocorticoids and either azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil. Nearly three-quarters of patients received mycophenolate mofetil–based induction. Once treatment with either belimumab or placebo began in the study’s main phase, the glucocorticoid dosage had to drop with tapering to no more than 10 mg/day within 24 weeks or the patient was considered a treatment failure.
Thoughts on current and future use of belimumab
The current labeled indication for belimumab is for “treatment of patients aged 5 years and older with active, autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus who are receiving standard therapy,” an inclusive SLE population, but the label also adds this caveat: “Limitations of use: The efficacy of Benlysta has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus.” According to Dr. Furie’s report, GlaxoSmithKline, the company that markets belimumab, plans to seek a labeled indication for lupus nephritis for the drug during 2020.
“I doubt the drug is widely used as yet in clinical practice for lupus nephritis,” although it is being prescribed to selected SLE patients in current, routine practice, said Dr. Merrill, a coinvestigator on some belimumab studies. What also remains unknown is the efficacy of belimumab monotherapy. “We don’t know which subset of patients might benefit from belimumab alone,” she noted. Nor is it known whether belimumab treatment of patients with SLE but without lupus nephritis will forestall later development of lupus nephritis.
“With the introduction of the subcutaneous formulation a few years ago, there has been greater belimumab use” overall in patients with SLE, said Dr. Furie, and with a safety and efficacy record now established in five separate, reported studies in addition to the new BLISS-LN study: BLISS-52, BLISS-76, BLISS-SC, BLISS-NE ASIA, and PLUTO. “The pivotal studies [BLISS-52 and BLISS-76] were done in patients with SLE but without nephritis in need of aggressive induction therapy. About 15% of the trial cohorts had low-level renal involvement,” and post hoc analyses suggested that the benefit in those patients was similar to patients without renal involvement, which led to the BLISS-LN study. “In theory, no SLE patients with high-level nephritis should be on belimumab at this time,” based on its labeling, although some SLE patients with low-level renal disease may now receive the drug because they also have other affected organs, such as skin and joints, Dr. Furie said.
“These are encouraging results,” commented George K. Bertsias, MD, a rheumatologist and SLE specialist at the University of Crete in Heraklion, Greece. He particularly cited the “significant effect from add-on belimumab” on top of treatment with mycophenolate mofetil, an “established and effective treatment for lupus nephritis. The data provide additional evidence for the efficacy of belimumab in SLE, and also in lupus nephritis,” he said in an interview, and “having an official labeled indication for active nephritis will enhance use of the drug” in such patients. “Considering the favorable effects of the drug on SLE, especially preventing major flares, and on lupus nephritis it is possible that the drug will be particularly suitable for SLE patients who are at high risk for developing lupus nephritis, although such an effect remains to be determined.” Until now, belimumab has generally been prescribed to SLE patients who have disease manifestations in organs outside of the kidneys, he noted.
BLISS-LN was sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Furie is a consultant to and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline, and several of the study’s coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Merrill has been a consultant to GlaxoSmithKline as well as to several other companies and has been a coinvestigator on belimumab studies. Dr. Bertsias has been a consultant to Novartis and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline.
SOURCE: Furie RA et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79[suppl 1]:103, Abstract OP0164.
FROM THE EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS
More phase 3 data reported for abrocitinib for atopic dermatitis
Melinda Gooderham, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The positive results of this 391-patient, international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial mirror those previously reported in the identically designed JADE-MONO-1 pivotal phase 3 trial, noted Dr. Gooderham, medical director of the SKiN Centre for Dermatology and a dermatologist at Queen’s University in Kingston, Ont.
Participants in JADE-MONO-2 were randomized 2:2:1 to abrocitinib at 200 mg once daily, 100 mg once daily, or placebo for 12 weeks. The coprimary endpoint of skin clearance as reflected in an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) with an improvement of at least two grades at week 12 was achieved in 38.1% and 28.4% of patients on 200 and 100 mg of the JAK-1 inhibitor, respectively, compared with 9.1% of placebo-treated controls. The other coprimary endpoint – significant improvement in disease extent as defined by at least a 75% reduction from baseline in Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75 response) at 12 weeks – was reached in 61% of patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg/day, 44.5% on 100 mg/day, and 10.4% of controls.
A key secondary endpoint was improvement in itch based on at least a 4-point improvement at week 12 on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale from a mean baseline score of 7. This outcome was reached by 55.3% of patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg, 45.2% on 100 mg, and 11.5% on placebo. Of note, the reduction in itch was impressively fast, with significant separation from placebo occurring within the first 24 hours of the study, after just a single dose of abrocitinib. By week 2, roughly one-third of patients on high-dose and one-quarter of those on low-dose abrocitinib had already reached the itch endpoint, the dermatologist continued.
The improvement in pruritus scores in abrocitinib-treated patients was accompanied by significantly greater gains on validated measures of quality of life, another secondary endpoint. The EASI-90 response rate, yet another key secondary outcome, was 37.7% with abrocitinib at 200 mg, 23.9% with 100 mg, and 3.9% with placebo.
The safety profile of abrocitinib was essentially the same as for placebo with the exception of a 3.2% incidence of thrombocytopenia in patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg/day; no cases occurred in controls or patients on abrocitinib at 100 mg/day. Although venous thromboembolism has arisen as a potential concern in clinical trials of oral JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis, there were no cases in JADE-MONO-2. A long-term safety extension study in JADE-MONO participants is underway.
In an interview, Dr. Gooderham said that, based on the phase 2 study data that’s available for upadacitinib, another JAK-1-selective oral agent, abrocitinib and upadacitinib appear to be in the same ballpark with respect to efficacy as defined by IGA response, EASI improvement, and itch relief.
“The JAK-1 selectivity does seem to offer some advantage in levels of response over more broad JAK inhibition, such as with baritinib,” she added.
Asked how she foresees abrocitinib fitting into clinical practice, should it win regulatory approval for treatment of atopic dermatitis, Dr. Gooderham said it might be considered on a par with the injectable interleukin-4 and -13 inhibitor dupilumab (Dupixent) as next-line therapy after failure on topical therapy or as an option in patients who haven’t responded to or could not tolerate dupilumab. Abrocitinib will be an attractive option for patients who prefer oral therapy and will be an especially appealing medication in patients with a strong itch component to their atopic dermatitis, she added.
The results of JADE COMPARE, a phase 3, head-to-head randomized comparison of abrocitinib and dupilumab, are expected to be presented later this year at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. Pfizer has announced the key results, reporting that the JAK inhibitor at 200 mg/day achieved significantly greater improvements than dupilumab in the coprimary IGA and EASI-75 endpoints at 12 weeks.
JADE-MONO-2 was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Gooderham reported receiving research grants from that company and close to two dozen others.
The JADE-MONO-2 results have been published online (JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 3;e201406. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1406).
Melinda Gooderham, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The positive results of this 391-patient, international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial mirror those previously reported in the identically designed JADE-MONO-1 pivotal phase 3 trial, noted Dr. Gooderham, medical director of the SKiN Centre for Dermatology and a dermatologist at Queen’s University in Kingston, Ont.
Participants in JADE-MONO-2 were randomized 2:2:1 to abrocitinib at 200 mg once daily, 100 mg once daily, or placebo for 12 weeks. The coprimary endpoint of skin clearance as reflected in an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) with an improvement of at least two grades at week 12 was achieved in 38.1% and 28.4% of patients on 200 and 100 mg of the JAK-1 inhibitor, respectively, compared with 9.1% of placebo-treated controls. The other coprimary endpoint – significant improvement in disease extent as defined by at least a 75% reduction from baseline in Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75 response) at 12 weeks – was reached in 61% of patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg/day, 44.5% on 100 mg/day, and 10.4% of controls.
A key secondary endpoint was improvement in itch based on at least a 4-point improvement at week 12 on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale from a mean baseline score of 7. This outcome was reached by 55.3% of patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg, 45.2% on 100 mg, and 11.5% on placebo. Of note, the reduction in itch was impressively fast, with significant separation from placebo occurring within the first 24 hours of the study, after just a single dose of abrocitinib. By week 2, roughly one-third of patients on high-dose and one-quarter of those on low-dose abrocitinib had already reached the itch endpoint, the dermatologist continued.
The improvement in pruritus scores in abrocitinib-treated patients was accompanied by significantly greater gains on validated measures of quality of life, another secondary endpoint. The EASI-90 response rate, yet another key secondary outcome, was 37.7% with abrocitinib at 200 mg, 23.9% with 100 mg, and 3.9% with placebo.
The safety profile of abrocitinib was essentially the same as for placebo with the exception of a 3.2% incidence of thrombocytopenia in patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg/day; no cases occurred in controls or patients on abrocitinib at 100 mg/day. Although venous thromboembolism has arisen as a potential concern in clinical trials of oral JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis, there were no cases in JADE-MONO-2. A long-term safety extension study in JADE-MONO participants is underway.
In an interview, Dr. Gooderham said that, based on the phase 2 study data that’s available for upadacitinib, another JAK-1-selective oral agent, abrocitinib and upadacitinib appear to be in the same ballpark with respect to efficacy as defined by IGA response, EASI improvement, and itch relief.
“The JAK-1 selectivity does seem to offer some advantage in levels of response over more broad JAK inhibition, such as with baritinib,” she added.
Asked how she foresees abrocitinib fitting into clinical practice, should it win regulatory approval for treatment of atopic dermatitis, Dr. Gooderham said it might be considered on a par with the injectable interleukin-4 and -13 inhibitor dupilumab (Dupixent) as next-line therapy after failure on topical therapy or as an option in patients who haven’t responded to or could not tolerate dupilumab. Abrocitinib will be an attractive option for patients who prefer oral therapy and will be an especially appealing medication in patients with a strong itch component to their atopic dermatitis, she added.
The results of JADE COMPARE, a phase 3, head-to-head randomized comparison of abrocitinib and dupilumab, are expected to be presented later this year at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. Pfizer has announced the key results, reporting that the JAK inhibitor at 200 mg/day achieved significantly greater improvements than dupilumab in the coprimary IGA and EASI-75 endpoints at 12 weeks.
JADE-MONO-2 was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Gooderham reported receiving research grants from that company and close to two dozen others.
The JADE-MONO-2 results have been published online (JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 3;e201406. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1406).
Melinda Gooderham, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The positive results of this 391-patient, international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial mirror those previously reported in the identically designed JADE-MONO-1 pivotal phase 3 trial, noted Dr. Gooderham, medical director of the SKiN Centre for Dermatology and a dermatologist at Queen’s University in Kingston, Ont.
Participants in JADE-MONO-2 were randomized 2:2:1 to abrocitinib at 200 mg once daily, 100 mg once daily, or placebo for 12 weeks. The coprimary endpoint of skin clearance as reflected in an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) with an improvement of at least two grades at week 12 was achieved in 38.1% and 28.4% of patients on 200 and 100 mg of the JAK-1 inhibitor, respectively, compared with 9.1% of placebo-treated controls. The other coprimary endpoint – significant improvement in disease extent as defined by at least a 75% reduction from baseline in Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75 response) at 12 weeks – was reached in 61% of patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg/day, 44.5% on 100 mg/day, and 10.4% of controls.
A key secondary endpoint was improvement in itch based on at least a 4-point improvement at week 12 on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale from a mean baseline score of 7. This outcome was reached by 55.3% of patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg, 45.2% on 100 mg, and 11.5% on placebo. Of note, the reduction in itch was impressively fast, with significant separation from placebo occurring within the first 24 hours of the study, after just a single dose of abrocitinib. By week 2, roughly one-third of patients on high-dose and one-quarter of those on low-dose abrocitinib had already reached the itch endpoint, the dermatologist continued.
The improvement in pruritus scores in abrocitinib-treated patients was accompanied by significantly greater gains on validated measures of quality of life, another secondary endpoint. The EASI-90 response rate, yet another key secondary outcome, was 37.7% with abrocitinib at 200 mg, 23.9% with 100 mg, and 3.9% with placebo.
The safety profile of abrocitinib was essentially the same as for placebo with the exception of a 3.2% incidence of thrombocytopenia in patients on abrocitinib at 200 mg/day; no cases occurred in controls or patients on abrocitinib at 100 mg/day. Although venous thromboembolism has arisen as a potential concern in clinical trials of oral JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis, there were no cases in JADE-MONO-2. A long-term safety extension study in JADE-MONO participants is underway.
In an interview, Dr. Gooderham said that, based on the phase 2 study data that’s available for upadacitinib, another JAK-1-selective oral agent, abrocitinib and upadacitinib appear to be in the same ballpark with respect to efficacy as defined by IGA response, EASI improvement, and itch relief.
“The JAK-1 selectivity does seem to offer some advantage in levels of response over more broad JAK inhibition, such as with baritinib,” she added.
Asked how she foresees abrocitinib fitting into clinical practice, should it win regulatory approval for treatment of atopic dermatitis, Dr. Gooderham said it might be considered on a par with the injectable interleukin-4 and -13 inhibitor dupilumab (Dupixent) as next-line therapy after failure on topical therapy or as an option in patients who haven’t responded to or could not tolerate dupilumab. Abrocitinib will be an attractive option for patients who prefer oral therapy and will be an especially appealing medication in patients with a strong itch component to their atopic dermatitis, she added.
The results of JADE COMPARE, a phase 3, head-to-head randomized comparison of abrocitinib and dupilumab, are expected to be presented later this year at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. Pfizer has announced the key results, reporting that the JAK inhibitor at 200 mg/day achieved significantly greater improvements than dupilumab in the coprimary IGA and EASI-75 endpoints at 12 weeks.
JADE-MONO-2 was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Gooderham reported receiving research grants from that company and close to two dozen others.
The JADE-MONO-2 results have been published online (JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 3;e201406. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1406).
FROM AAD 20
Asthma leads spending on avoidable pediatric inpatient stays
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
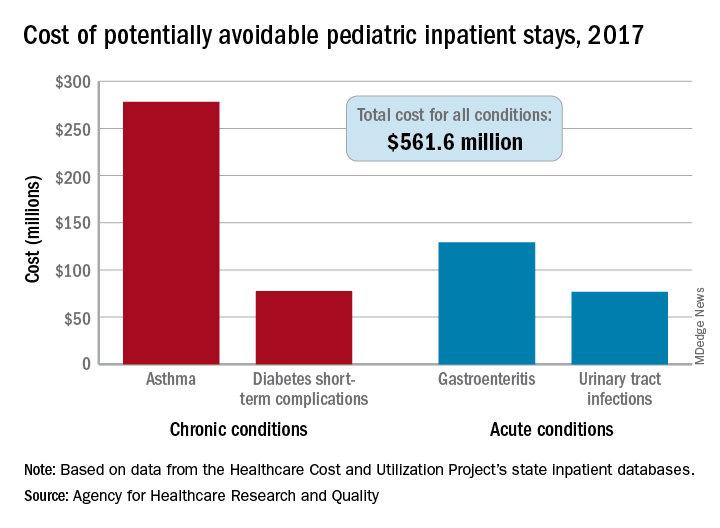
The cost of potentially avoidable visits for asthma that year was $278 million, versus $284 million combined for the other three conditions “that evidence suggests may be avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Those three other conditions are diabetes short-term complications, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Neonatal stays were excluded from the analysis, Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ noted.
The state inpatient databases of the AHRQ’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project included 1.4 million inpatient stays among children aged 3 months to 17 years in 2017, of which 8% (108,300) were deemed potentially preventable. Hospital charges for the preventable stays came to $561.6 million, or 3% of the $20 billion in total costs for all nonneonatal stays, they said.
Rates of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (159 per 100,000 population), gastroenteritis (90 per 100,000), and UTIs (41 per 100,000) were highest for children aged 0-4 years and generally decreased with age, but diabetes stays increased with age, rising from 12 per 100,000 in children aged 5-9 years to 38 per 100,000 for those 15-17 years old, the researchers said.
Black children had a much higher rate of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (218 per 100,000) than did Hispanic children (74), Asian/Pacific Islander children (46), or white children (43), but children classified as other race/ethnicity were higher still: 380 per 100,000. Rates for children classified as other race/ethnicity were highest for the other three conditions as well, they reported.
Comparisons by sex for the four conditions ended up in a 2-2 tie: Girls had higher rates for diabetes (28 vs. 23) and UTIs (35 vs. 8), and boys had higher rates for asthma (96 vs. 67) and gastroenteritis (38 vs. 35), Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang reported.
SOURCE: McDermott KW, Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

The cost of potentially avoidable visits for asthma that year was $278 million, versus $284 million combined for the other three conditions “that evidence suggests may be avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Those three other conditions are diabetes short-term complications, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Neonatal stays were excluded from the analysis, Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ noted.
The state inpatient databases of the AHRQ’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project included 1.4 million inpatient stays among children aged 3 months to 17 years in 2017, of which 8% (108,300) were deemed potentially preventable. Hospital charges for the preventable stays came to $561.6 million, or 3% of the $20 billion in total costs for all nonneonatal stays, they said.
Rates of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (159 per 100,000 population), gastroenteritis (90 per 100,000), and UTIs (41 per 100,000) were highest for children aged 0-4 years and generally decreased with age, but diabetes stays increased with age, rising from 12 per 100,000 in children aged 5-9 years to 38 per 100,000 for those 15-17 years old, the researchers said.
Black children had a much higher rate of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (218 per 100,000) than did Hispanic children (74), Asian/Pacific Islander children (46), or white children (43), but children classified as other race/ethnicity were higher still: 380 per 100,000. Rates for children classified as other race/ethnicity were highest for the other three conditions as well, they reported.
Comparisons by sex for the four conditions ended up in a 2-2 tie: Girls had higher rates for diabetes (28 vs. 23) and UTIs (35 vs. 8), and boys had higher rates for asthma (96 vs. 67) and gastroenteritis (38 vs. 35), Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang reported.
SOURCE: McDermott KW, Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

The cost of potentially avoidable visits for asthma that year was $278 million, versus $284 million combined for the other three conditions “that evidence suggests may be avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Those three other conditions are diabetes short-term complications, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Neonatal stays were excluded from the analysis, Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ noted.
The state inpatient databases of the AHRQ’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project included 1.4 million inpatient stays among children aged 3 months to 17 years in 2017, of which 8% (108,300) were deemed potentially preventable. Hospital charges for the preventable stays came to $561.6 million, or 3% of the $20 billion in total costs for all nonneonatal stays, they said.
Rates of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (159 per 100,000 population), gastroenteritis (90 per 100,000), and UTIs (41 per 100,000) were highest for children aged 0-4 years and generally decreased with age, but diabetes stays increased with age, rising from 12 per 100,000 in children aged 5-9 years to 38 per 100,000 for those 15-17 years old, the researchers said.
Black children had a much higher rate of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (218 per 100,000) than did Hispanic children (74), Asian/Pacific Islander children (46), or white children (43), but children classified as other race/ethnicity were higher still: 380 per 100,000. Rates for children classified as other race/ethnicity were highest for the other three conditions as well, they reported.
Comparisons by sex for the four conditions ended up in a 2-2 tie: Girls had higher rates for diabetes (28 vs. 23) and UTIs (35 vs. 8), and boys had higher rates for asthma (96 vs. 67) and gastroenteritis (38 vs. 35), Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang reported.
SOURCE: McDermott KW, Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
FDA gives thumbs up to tazemetostat for follicular lymphoma
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval of the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (Tazverik, Epizyme, Inc) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in adult patients with tumors harboring an EZH2 mutation.
Eligible patients must have already received at least two prior systemic therapies and have tumors that are positive for an EZH2 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA has also approved the cobas EZH2 Mutation Test (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc) as a companion diagnostic test for tazemetostat.
The new indication is also for adult patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have no other satisfactory alternative treatment options.
“In our view, there remains no clear standard of care in the relapsed and/or refractory [follicular lymphoma] population, as not all patients benefit from today’s available therapies,” said Shefali Agarwal, MD, chief medical officer of Epizyme, in a company press release. “Based on this label, physicians will have the ability to use their clinical discretion to prescribe tazemetostat for their relapsed or refractory patients regardless of EZH2 mutational status and without regard to a specific line of treatment where other options are not satisfactory.”
This accelerated approval is based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials, the FDA notes.
Tazemetostat acts as an inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase. Earlier this year, the drug was approved for the treatment of metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma in cases in which complete resection is not possible. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action and is the first to be indicated for epithelioid sarcoma.
Promising Efficacy in Phase 2 Trial
The new approval for use in follicular lymphoma was based on results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial involving patients who had experienced disease progression after being treated with at least two prior systemic regimens. The cohort was divided into two treatment groups: One group consisted of 45 patients with EZH2-activating mutations, the other included 54 patients with wild-type EZH2.
All patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg administered orally twice a day. The primary efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response, in accordance with International Working Group Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma criteria.
The median duration of follow-up was 22 months for patients with EZH2-activating mutations and 36 months for those with wild-type tumors.
Among the 45 patients with an EZH2-activating mutation, the median number of lines of prior systemic therapy was 2.0 (range, 1 – 11). In 49% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 49%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate was 69%; 12% of patients achieved a complete response, and 57% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 10.9 months and ongoing.
In the cohort of 54 patients with wild-type EZH2, the median number previous therapies was 3.0 (range, 1 – 8); in 59% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 41%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate to tazemetostat treatment was 34%; 4% of patients achieved a complete response, and 30% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 13 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients. The most common were fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, and abdominal pain. Eight patients (8%) discontinued treatment during the trial because of adverse events. There were no reported deaths. No black box warnings have been published, and there are no contraindications.
“The durable responses observed with this drug are notable in the context of the safety profile and route of oral, at-home administration, and will offer an important new option for physicians as we care for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma,” said John Leonard, MD, in a company press release. He is associate dean for clinical research and Richard T. Silver Distinguished Professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Meyer Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and an investigator in the ongoing phase 1b/3 confirmatory trial for tazemetostat.
“Follicular lymphoma remains an incurable disease, and even with the availability of new drugs in recent years, there have remained important unmet needs in the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” he commented.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval of the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (Tazverik, Epizyme, Inc) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in adult patients with tumors harboring an EZH2 mutation.
Eligible patients must have already received at least two prior systemic therapies and have tumors that are positive for an EZH2 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA has also approved the cobas EZH2 Mutation Test (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc) as a companion diagnostic test for tazemetostat.
The new indication is also for adult patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have no other satisfactory alternative treatment options.
“In our view, there remains no clear standard of care in the relapsed and/or refractory [follicular lymphoma] population, as not all patients benefit from today’s available therapies,” said Shefali Agarwal, MD, chief medical officer of Epizyme, in a company press release. “Based on this label, physicians will have the ability to use their clinical discretion to prescribe tazemetostat for their relapsed or refractory patients regardless of EZH2 mutational status and without regard to a specific line of treatment where other options are not satisfactory.”
This accelerated approval is based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials, the FDA notes.
Tazemetostat acts as an inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase. Earlier this year, the drug was approved for the treatment of metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma in cases in which complete resection is not possible. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action and is the first to be indicated for epithelioid sarcoma.
Promising Efficacy in Phase 2 Trial
The new approval for use in follicular lymphoma was based on results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial involving patients who had experienced disease progression after being treated with at least two prior systemic regimens. The cohort was divided into two treatment groups: One group consisted of 45 patients with EZH2-activating mutations, the other included 54 patients with wild-type EZH2.
All patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg administered orally twice a day. The primary efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response, in accordance with International Working Group Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma criteria.
The median duration of follow-up was 22 months for patients with EZH2-activating mutations and 36 months for those with wild-type tumors.
Among the 45 patients with an EZH2-activating mutation, the median number of lines of prior systemic therapy was 2.0 (range, 1 – 11). In 49% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 49%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate was 69%; 12% of patients achieved a complete response, and 57% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 10.9 months and ongoing.
In the cohort of 54 patients with wild-type EZH2, the median number previous therapies was 3.0 (range, 1 – 8); in 59% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 41%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate to tazemetostat treatment was 34%; 4% of patients achieved a complete response, and 30% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 13 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients. The most common were fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, and abdominal pain. Eight patients (8%) discontinued treatment during the trial because of adverse events. There were no reported deaths. No black box warnings have been published, and there are no contraindications.
“The durable responses observed with this drug are notable in the context of the safety profile and route of oral, at-home administration, and will offer an important new option for physicians as we care for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma,” said John Leonard, MD, in a company press release. He is associate dean for clinical research and Richard T. Silver Distinguished Professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Meyer Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and an investigator in the ongoing phase 1b/3 confirmatory trial for tazemetostat.
“Follicular lymphoma remains an incurable disease, and even with the availability of new drugs in recent years, there have remained important unmet needs in the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” he commented.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted accelerated approval of the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (Tazverik, Epizyme, Inc) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in adult patients with tumors harboring an EZH2 mutation.
Eligible patients must have already received at least two prior systemic therapies and have tumors that are positive for an EZH2 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA has also approved the cobas EZH2 Mutation Test (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc) as a companion diagnostic test for tazemetostat.
The new indication is also for adult patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have no other satisfactory alternative treatment options.
“In our view, there remains no clear standard of care in the relapsed and/or refractory [follicular lymphoma] population, as not all patients benefit from today’s available therapies,” said Shefali Agarwal, MD, chief medical officer of Epizyme, in a company press release. “Based on this label, physicians will have the ability to use their clinical discretion to prescribe tazemetostat for their relapsed or refractory patients regardless of EZH2 mutational status and without regard to a specific line of treatment where other options are not satisfactory.”
This accelerated approval is based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials, the FDA notes.
Tazemetostat acts as an inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase. Earlier this year, the drug was approved for the treatment of metastatic or locally advanced epithelioid sarcoma in cases in which complete resection is not possible. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action and is the first to be indicated for epithelioid sarcoma.
Promising Efficacy in Phase 2 Trial
The new approval for use in follicular lymphoma was based on results from an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 2 clinical trial involving patients who had experienced disease progression after being treated with at least two prior systemic regimens. The cohort was divided into two treatment groups: One group consisted of 45 patients with EZH2-activating mutations, the other included 54 patients with wild-type EZH2.
All patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg administered orally twice a day. The primary efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response, in accordance with International Working Group Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma criteria.
The median duration of follow-up was 22 months for patients with EZH2-activating mutations and 36 months for those with wild-type tumors.
Among the 45 patients with an EZH2-activating mutation, the median number of lines of prior systemic therapy was 2.0 (range, 1 – 11). In 49% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 49%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate was 69%; 12% of patients achieved a complete response, and 57% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 10.9 months and ongoing.
In the cohort of 54 patients with wild-type EZH2, the median number previous therapies was 3.0 (range, 1 – 8); in 59% of patients, disease was refractory to rituximab, and in 41%, it was refractory to the patient’s last therapy.
The overall response rate to tazemetostat treatment was 34%; 4% of patients achieved a complete response, and 30% achieved a partial response. The median duration of response was 13 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients. The most common were fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, and abdominal pain. Eight patients (8%) discontinued treatment during the trial because of adverse events. There were no reported deaths. No black box warnings have been published, and there are no contraindications.
“The durable responses observed with this drug are notable in the context of the safety profile and route of oral, at-home administration, and will offer an important new option for physicians as we care for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma,” said John Leonard, MD, in a company press release. He is associate dean for clinical research and Richard T. Silver Distinguished Professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Meyer Cancer Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and an investigator in the ongoing phase 1b/3 confirmatory trial for tazemetostat.
“Follicular lymphoma remains an incurable disease, and even with the availability of new drugs in recent years, there have remained important unmet needs in the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” he commented.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiology care ups CV monitoring, BP control in HER2+ breast cancer
Specialty care from a cardiologist may confer clinical benefits for women with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with trastuzumab, a new study suggests.
Over 48 months of follow-up, results showed cardiology involvement prior to starting trastuzumab was associated with a higher rate of guideline-recommended cardiovascular (CV) monitoring and better systolic blood pressure (BP) control.
Trastuzumab is commonly used to treat HER2-positive breast cancer, which accounts for 20% of all breast cancers. But it carries a boxed warning for decreased left ventricular ejection fraction and heart failure (HF), and interval monitoring with echocardiography is recommended for all patients receiving the monoclonal antibody.
For the study, investigators analyzed electronic health records from 1,047 patients (mean age, 54 years) who received trastuzumab between January 2009 and July 2018 in the University of Pennsylvania health system, Philadelphia. Anthracyclines were used as part of treatment in 15% of patients.
Guideline-adherent cardiovascular monitoring was defined as echocardiography assessment in the 4 months before the initiation of trastuzumab and at least every 4 months during therapy.
Overall, 28% of patients visited a cardiology or cardio-oncology provider beginning 3 months before the baseline visit until the last contact date, the authors reported in JACC: CardioOncology.
Pre-existing HF, atrial fibrillation, and anthracycline treatment were independently associated with a cardiology visit either at baseline or during follow-up.
Patients who interacted with cardiologists, compared with those who did not, had more guideline-adherent cardiac monitoring (76.4% vs 60.1%; P = .007) and cardiac biomarker testing with troponin or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (27.8% vs 13.8%; P = .001).
The use of guideline-adherent cardiac monitoring was 36% to 46% in previous studies of patients with breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab-based therapy, the authors note.
Among the 5,815 echocardiographic procedures for which data on provider specialty were documented, most of the orders were authorized by oncologists (approximately 84% in those with no cardiology involvement and approximately 79% in those with cardiology involvement before trastuzumab initiation).
CV risk parameters
Cardiology involvement was associated with an average 1.5 mm Hg lower systolic BP, independent of baseline systolic BP and antihypertensive medication use (95% confidence interval, –2.9 to –0.1; P = .035).
The effect size was greater in patients with baseline hypertension, who had an average 2.7 mm Hg drop in systolic BP (95% CI, –4.6 to –0.7; P = .007) and were more likely to attain a target systolic BP below 140 mm Hg (odds ratio, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.74; P = .016).
Body mass index (BMI) did not budge significantly in the overall population when cardiologists were involved, but it dropped 0.5 kg/m2 in women who were overweight or obese at baseline.
“I think the results are encouraging,” senior author Bonnie Ky, MD, MSCE, University of Pennsylvania, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “These are modest changes but they are significant.”
These types of changes have been associated with significant reductions in cardiovascular disease risk over time in larger clinical trials, she noted. For example, a 2 mm Hg reduction in systolic BP has been linked to a 10% reduction in stroke mortality and a 7% reduction in ischemic heart disease mortality in middle-aged adults.
“We do think they are important and speak to more aggressive risk factor modification under the care of a specialist,” said Ky, who is also editor-in-chief of JACC: CardioOncology.
This broader role for cardiologists is particularly important given the burden of pre-existing CVD and CVD risk factors in patients with cancer and survivors. In the study, the baseline prevalence of hypertension was 40.6%, dyslipidemia 23.1%, HF 3.2%, atrial fibrillation 1.7%, and diabetes 5.9%.
“Ideally, collaboration between cardiology and oncology can improve the ability to cure a patient’s cancer while minimizing the risk of adverse cardiovascular occurrences,” Erica L. Mayer, MD, MPH, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “Optimization of all cardiovascular parameters, including blood pressure, lipids, and weight, may allow a patient to protect her heart health while becoming a healthy cancer survivor.”
When asked about the 28% cardiology involvement at a U.S. cancer center with one of the most well-developed cardio-oncology programs, she said “the linkage with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, as well as the likelihood of low incidence of cardiovascular disease, in the study population may have led to what appears to be a lower percentage of patients interacting with cardiology at baseline.”
In an accompanying editorial, Mayer says a case can be made from the findings that patients with pre-existing CV disease or at high risk for adverse CV events with cancer therapy should receive multidisciplinary care that involves a cardiologist. “However, for young, otherwise healthy patients with breast cancer with few or no cardiovascular risk factors, the benefits of [additional] subspecialty care may be less clear.”
Further, the rationale supporting the recommended frequency of cardiac monitoring may not be as “compelling” in this group, given the very low incidence of baseline cardiac dysfunction or cardiac events, particularly when treated with nonanthracycline regimens, she writes.
The findings are a call for further study and more personalized medicine, agreed Ky.
“I think there’s a need absolutely for established guidelines and/or expert consensus statements about who should be referred so patients can be referred more systematically,” she said. “Referral to cardiologists, however, is certainly a function of risk factors. Part of the challenge is identifying who will derive the most benefit from cardiovascular care.
“There are some obvious cases: Patients with heart failure and patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease should be under the regular care of a cardiologist,” Ky added. “But there’s certainly a gray zone, especially as it relates, for example, to patients with hypertension and cardiovascular risk factors. It’s not a ‘one size fits all,’ and I believe it is a matter of defining who is at increased CV risk and who would derive the greatest clinical benefit.”
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have developed a clinical risk–prediction algorithm and are investigating both clinical- and biomarker-guided strategies to identify and treat patients at greatest risk of developing left ventricular declines and cardiac dysfunction with exposure to cancer therapies. “These studies are one step forward, but they will all need to be externally validated,” Ky said.
Ky and Mayer reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specialty care from a cardiologist may confer clinical benefits for women with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with trastuzumab, a new study suggests.
Over 48 months of follow-up, results showed cardiology involvement prior to starting trastuzumab was associated with a higher rate of guideline-recommended cardiovascular (CV) monitoring and better systolic blood pressure (BP) control.
Trastuzumab is commonly used to treat HER2-positive breast cancer, which accounts for 20% of all breast cancers. But it carries a boxed warning for decreased left ventricular ejection fraction and heart failure (HF), and interval monitoring with echocardiography is recommended for all patients receiving the monoclonal antibody.
For the study, investigators analyzed electronic health records from 1,047 patients (mean age, 54 years) who received trastuzumab between January 2009 and July 2018 in the University of Pennsylvania health system, Philadelphia. Anthracyclines were used as part of treatment in 15% of patients.
Guideline-adherent cardiovascular monitoring was defined as echocardiography assessment in the 4 months before the initiation of trastuzumab and at least every 4 months during therapy.
Overall, 28% of patients visited a cardiology or cardio-oncology provider beginning 3 months before the baseline visit until the last contact date, the authors reported in JACC: CardioOncology.
Pre-existing HF, atrial fibrillation, and anthracycline treatment were independently associated with a cardiology visit either at baseline or during follow-up.
Patients who interacted with cardiologists, compared with those who did not, had more guideline-adherent cardiac monitoring (76.4% vs 60.1%; P = .007) and cardiac biomarker testing with troponin or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (27.8% vs 13.8%; P = .001).
The use of guideline-adherent cardiac monitoring was 36% to 46% in previous studies of patients with breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab-based therapy, the authors note.
Among the 5,815 echocardiographic procedures for which data on provider specialty were documented, most of the orders were authorized by oncologists (approximately 84% in those with no cardiology involvement and approximately 79% in those with cardiology involvement before trastuzumab initiation).
CV risk parameters
Cardiology involvement was associated with an average 1.5 mm Hg lower systolic BP, independent of baseline systolic BP and antihypertensive medication use (95% confidence interval, –2.9 to –0.1; P = .035).
The effect size was greater in patients with baseline hypertension, who had an average 2.7 mm Hg drop in systolic BP (95% CI, –4.6 to –0.7; P = .007) and were more likely to attain a target systolic BP below 140 mm Hg (odds ratio, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.74; P = .016).
Body mass index (BMI) did not budge significantly in the overall population when cardiologists were involved, but it dropped 0.5 kg/m2 in women who were overweight or obese at baseline.
“I think the results are encouraging,” senior author Bonnie Ky, MD, MSCE, University of Pennsylvania, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “These are modest changes but they are significant.”
These types of changes have been associated with significant reductions in cardiovascular disease risk over time in larger clinical trials, she noted. For example, a 2 mm Hg reduction in systolic BP has been linked to a 10% reduction in stroke mortality and a 7% reduction in ischemic heart disease mortality in middle-aged adults.
“We do think they are important and speak to more aggressive risk factor modification under the care of a specialist,” said Ky, who is also editor-in-chief of JACC: CardioOncology.
This broader role for cardiologists is particularly important given the burden of pre-existing CVD and CVD risk factors in patients with cancer and survivors. In the study, the baseline prevalence of hypertension was 40.6%, dyslipidemia 23.1%, HF 3.2%, atrial fibrillation 1.7%, and diabetes 5.9%.
“Ideally, collaboration between cardiology and oncology can improve the ability to cure a patient’s cancer while minimizing the risk of adverse cardiovascular occurrences,” Erica L. Mayer, MD, MPH, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “Optimization of all cardiovascular parameters, including blood pressure, lipids, and weight, may allow a patient to protect her heart health while becoming a healthy cancer survivor.”
When asked about the 28% cardiology involvement at a U.S. cancer center with one of the most well-developed cardio-oncology programs, she said “the linkage with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, as well as the likelihood of low incidence of cardiovascular disease, in the study population may have led to what appears to be a lower percentage of patients interacting with cardiology at baseline.”
In an accompanying editorial, Mayer says a case can be made from the findings that patients with pre-existing CV disease or at high risk for adverse CV events with cancer therapy should receive multidisciplinary care that involves a cardiologist. “However, for young, otherwise healthy patients with breast cancer with few or no cardiovascular risk factors, the benefits of [additional] subspecialty care may be less clear.”
Further, the rationale supporting the recommended frequency of cardiac monitoring may not be as “compelling” in this group, given the very low incidence of baseline cardiac dysfunction or cardiac events, particularly when treated with nonanthracycline regimens, she writes.
The findings are a call for further study and more personalized medicine, agreed Ky.
“I think there’s a need absolutely for established guidelines and/or expert consensus statements about who should be referred so patients can be referred more systematically,” she said. “Referral to cardiologists, however, is certainly a function of risk factors. Part of the challenge is identifying who will derive the most benefit from cardiovascular care.
“There are some obvious cases: Patients with heart failure and patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease should be under the regular care of a cardiologist,” Ky added. “But there’s certainly a gray zone, especially as it relates, for example, to patients with hypertension and cardiovascular risk factors. It’s not a ‘one size fits all,’ and I believe it is a matter of defining who is at increased CV risk and who would derive the greatest clinical benefit.”
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have developed a clinical risk–prediction algorithm and are investigating both clinical- and biomarker-guided strategies to identify and treat patients at greatest risk of developing left ventricular declines and cardiac dysfunction with exposure to cancer therapies. “These studies are one step forward, but they will all need to be externally validated,” Ky said.
Ky and Mayer reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specialty care from a cardiologist may confer clinical benefits for women with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with trastuzumab, a new study suggests.
Over 48 months of follow-up, results showed cardiology involvement prior to starting trastuzumab was associated with a higher rate of guideline-recommended cardiovascular (CV) monitoring and better systolic blood pressure (BP) control.
Trastuzumab is commonly used to treat HER2-positive breast cancer, which accounts for 20% of all breast cancers. But it carries a boxed warning for decreased left ventricular ejection fraction and heart failure (HF), and interval monitoring with echocardiography is recommended for all patients receiving the monoclonal antibody.
For the study, investigators analyzed electronic health records from 1,047 patients (mean age, 54 years) who received trastuzumab between January 2009 and July 2018 in the University of Pennsylvania health system, Philadelphia. Anthracyclines were used as part of treatment in 15% of patients.
Guideline-adherent cardiovascular monitoring was defined as echocardiography assessment in the 4 months before the initiation of trastuzumab and at least every 4 months during therapy.
Overall, 28% of patients visited a cardiology or cardio-oncology provider beginning 3 months before the baseline visit until the last contact date, the authors reported in JACC: CardioOncology.
Pre-existing HF, atrial fibrillation, and anthracycline treatment were independently associated with a cardiology visit either at baseline or during follow-up.
Patients who interacted with cardiologists, compared with those who did not, had more guideline-adherent cardiac monitoring (76.4% vs 60.1%; P = .007) and cardiac biomarker testing with troponin or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (27.8% vs 13.8%; P = .001).
The use of guideline-adherent cardiac monitoring was 36% to 46% in previous studies of patients with breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab-based therapy, the authors note.
Among the 5,815 echocardiographic procedures for which data on provider specialty were documented, most of the orders were authorized by oncologists (approximately 84% in those with no cardiology involvement and approximately 79% in those with cardiology involvement before trastuzumab initiation).
CV risk parameters
Cardiology involvement was associated with an average 1.5 mm Hg lower systolic BP, independent of baseline systolic BP and antihypertensive medication use (95% confidence interval, –2.9 to –0.1; P = .035).
The effect size was greater in patients with baseline hypertension, who had an average 2.7 mm Hg drop in systolic BP (95% CI, –4.6 to –0.7; P = .007) and were more likely to attain a target systolic BP below 140 mm Hg (odds ratio, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.74; P = .016).
Body mass index (BMI) did not budge significantly in the overall population when cardiologists were involved, but it dropped 0.5 kg/m2 in women who were overweight or obese at baseline.
“I think the results are encouraging,” senior author Bonnie Ky, MD, MSCE, University of Pennsylvania, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “These are modest changes but they are significant.”
These types of changes have been associated with significant reductions in cardiovascular disease risk over time in larger clinical trials, she noted. For example, a 2 mm Hg reduction in systolic BP has been linked to a 10% reduction in stroke mortality and a 7% reduction in ischemic heart disease mortality in middle-aged adults.
“We do think they are important and speak to more aggressive risk factor modification under the care of a specialist,” said Ky, who is also editor-in-chief of JACC: CardioOncology.
This broader role for cardiologists is particularly important given the burden of pre-existing CVD and CVD risk factors in patients with cancer and survivors. In the study, the baseline prevalence of hypertension was 40.6%, dyslipidemia 23.1%, HF 3.2%, atrial fibrillation 1.7%, and diabetes 5.9%.
“Ideally, collaboration between cardiology and oncology can improve the ability to cure a patient’s cancer while minimizing the risk of adverse cardiovascular occurrences,” Erica L. Mayer, MD, MPH, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “Optimization of all cardiovascular parameters, including blood pressure, lipids, and weight, may allow a patient to protect her heart health while becoming a healthy cancer survivor.”
When asked about the 28% cardiology involvement at a U.S. cancer center with one of the most well-developed cardio-oncology programs, she said “the linkage with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, as well as the likelihood of low incidence of cardiovascular disease, in the study population may have led to what appears to be a lower percentage of patients interacting with cardiology at baseline.”
In an accompanying editorial, Mayer says a case can be made from the findings that patients with pre-existing CV disease or at high risk for adverse CV events with cancer therapy should receive multidisciplinary care that involves a cardiologist. “However, for young, otherwise healthy patients with breast cancer with few or no cardiovascular risk factors, the benefits of [additional] subspecialty care may be less clear.”
Further, the rationale supporting the recommended frequency of cardiac monitoring may not be as “compelling” in this group, given the very low incidence of baseline cardiac dysfunction or cardiac events, particularly when treated with nonanthracycline regimens, she writes.
The findings are a call for further study and more personalized medicine, agreed Ky.
“I think there’s a need absolutely for established guidelines and/or expert consensus statements about who should be referred so patients can be referred more systematically,” she said. “Referral to cardiologists, however, is certainly a function of risk factors. Part of the challenge is identifying who will derive the most benefit from cardiovascular care.
“There are some obvious cases: Patients with heart failure and patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease should be under the regular care of a cardiologist,” Ky added. “But there’s certainly a gray zone, especially as it relates, for example, to patients with hypertension and cardiovascular risk factors. It’s not a ‘one size fits all,’ and I believe it is a matter of defining who is at increased CV risk and who would derive the greatest clinical benefit.”
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have developed a clinical risk–prediction algorithm and are investigating both clinical- and biomarker-guided strategies to identify and treat patients at greatest risk of developing left ventricular declines and cardiac dysfunction with exposure to cancer therapies. “These studies are one step forward, but they will all need to be externally validated,” Ky said.
Ky and Mayer reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding CGRP to Botox is safe and effective for migraine prevention
Investigators found the CGRP-mAbs significantly reduced the number of headache days and pain severity with adverse event rates similar to those reported in previous trials of these medications.
“The addition of a CGRP monoclonal antibody provided statistically significantly fewer monthly headache days,” said study investigator Fred Cohen, MD, an internal medicine resident physician at Montefiore Health System, New York. “However, this was a retrospective chart review, which is hindered by elements such as recall bias. Therefore, future prospective studies are warranted for higher quality data.”
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
Fewer headache days
Although Botox is associated with significant clinical improvement in chronic migraine, it often fails to adequately control headache frequency and additional medications are needed.
The CGRP-mAbs fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and erenumab, have recently been approved for migraine prevention, with results from clinical trials demonstrating they are effective for both chronic and episodic migraine. However, patients treated with Botox were excluded from these trials and to date there are no data on combination treatment with Botox and CGRP-mAbs.
To determine whether adjunctive treatment with CGRP-mAbs augments Botox therapy in chronic migraine the investigators conducted a retrospective chart review of patients receiving Botox and prescribed a CGRP-mAb.
Eligible patients met the International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition, criteria for chronic migraine; were age 18 years or older; and presented at a single headache center between May 2018 and May 2019. Patients who received another new therapy during the study or those taking CGRP-mAb treatment for less than 2 months were excluded.
The study’s primary outcome was change in the number of reported monthly headache days, and change in pain severity was the secondary outcome.
The final analysis included data on 153 patients. The population’s mean age was 47.1 years, and 139 patients (90.8%) were women. In all, 89 patients (58.0%) received erenumab (35 received 70 mg and 54 received 140 mg), 51 (33.0%) received galcanezumab, and 13 (9.0%) received fremanezumab.
Overall, 114 (74.5%) patients reported a decrease in monthly headache days or pain severity. In the group of 66 patients for whom quantitative data were available, the average number of monthly headache days before Botox treatment was 25.7. After Botox treatment, patients had an average decrease of 10.9 monthly headache days, a 42.4% reduction, so on average study participants continued to have an average of 14.8 monthly headache days.
After treatment with a CGRP-mAb the number decreased by 5.6 additional days (37.8%). Patients receiving combined therapy had an average of 9.1 monthly headache days. The total decrease from baseline was 16.6 fewer monthly headache days, a 64.6% reduction.
The number of headache days per month was reduced to 9.3 for erenumab and galcanezumab and 5.8 for fremanezumab. However, few patients in the study took fremanezumab so this result had less statistical power than the results for the other CGRP-mAbs.
A total of 13 patients (8.5%) reported side effects associated with the CGRP-mAbs, which included constipation, injection-site reaction, and fatigue.
More evidence is needed
Commenting on the findings, Peter McAllister, MD, medical director of the New England Institute for Neurology and Headache in Stamford, Conn., said the study’s main limitation is that it is a retrospective chart review, which yields lower level evidence than a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Dr. McAllister, who was not involved in the research, also noted that the sample size was small, particularly with respect to fremanezumab.
“This study, despite its limitations, shows that addition of a monoclonal antibody to onabotulinumtoxinA is safe and well tolerated, and may confer additional reduction in migraine or headache days. The authors correctly state that more evidence via prospective study is warranted,” said Dr. McAllister, who is also chief medical officer of the New England Institute for Clinical Research and was not involved in the investigation.
Dr. Cohen has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. McAllister was an investigator in the PREEMPT trial of onabotulinumtoxinA, as well as in all of the phase 3 monoclonal antibody studies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found the CGRP-mAbs significantly reduced the number of headache days and pain severity with adverse event rates similar to those reported in previous trials of these medications.
“The addition of a CGRP monoclonal antibody provided statistically significantly fewer monthly headache days,” said study investigator Fred Cohen, MD, an internal medicine resident physician at Montefiore Health System, New York. “However, this was a retrospective chart review, which is hindered by elements such as recall bias. Therefore, future prospective studies are warranted for higher quality data.”
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
Fewer headache days
Although Botox is associated with significant clinical improvement in chronic migraine, it often fails to adequately control headache frequency and additional medications are needed.
The CGRP-mAbs fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and erenumab, have recently been approved for migraine prevention, with results from clinical trials demonstrating they are effective for both chronic and episodic migraine. However, patients treated with Botox were excluded from these trials and to date there are no data on combination treatment with Botox and CGRP-mAbs.
To determine whether adjunctive treatment with CGRP-mAbs augments Botox therapy in chronic migraine the investigators conducted a retrospective chart review of patients receiving Botox and prescribed a CGRP-mAb.
Eligible patients met the International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition, criteria for chronic migraine; were age 18 years or older; and presented at a single headache center between May 2018 and May 2019. Patients who received another new therapy during the study or those taking CGRP-mAb treatment for less than 2 months were excluded.
The study’s primary outcome was change in the number of reported monthly headache days, and change in pain severity was the secondary outcome.
The final analysis included data on 153 patients. The population’s mean age was 47.1 years, and 139 patients (90.8%) were women. In all, 89 patients (58.0%) received erenumab (35 received 70 mg and 54 received 140 mg), 51 (33.0%) received galcanezumab, and 13 (9.0%) received fremanezumab.
Overall, 114 (74.5%) patients reported a decrease in monthly headache days or pain severity. In the group of 66 patients for whom quantitative data were available, the average number of monthly headache days before Botox treatment was 25.7. After Botox treatment, patients had an average decrease of 10.9 monthly headache days, a 42.4% reduction, so on average study participants continued to have an average of 14.8 monthly headache days.
After treatment with a CGRP-mAb the number decreased by 5.6 additional days (37.8%). Patients receiving combined therapy had an average of 9.1 monthly headache days. The total decrease from baseline was 16.6 fewer monthly headache days, a 64.6% reduction.
The number of headache days per month was reduced to 9.3 for erenumab and galcanezumab and 5.8 for fremanezumab. However, few patients in the study took fremanezumab so this result had less statistical power than the results for the other CGRP-mAbs.
A total of 13 patients (8.5%) reported side effects associated with the CGRP-mAbs, which included constipation, injection-site reaction, and fatigue.
More evidence is needed
Commenting on the findings, Peter McAllister, MD, medical director of the New England Institute for Neurology and Headache in Stamford, Conn., said the study’s main limitation is that it is a retrospective chart review, which yields lower level evidence than a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Dr. McAllister, who was not involved in the research, also noted that the sample size was small, particularly with respect to fremanezumab.
“This study, despite its limitations, shows that addition of a monoclonal antibody to onabotulinumtoxinA is safe and well tolerated, and may confer additional reduction in migraine or headache days. The authors correctly state that more evidence via prospective study is warranted,” said Dr. McAllister, who is also chief medical officer of the New England Institute for Clinical Research and was not involved in the investigation.
Dr. Cohen has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. McAllister was an investigator in the PREEMPT trial of onabotulinumtoxinA, as well as in all of the phase 3 monoclonal antibody studies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found the CGRP-mAbs significantly reduced the number of headache days and pain severity with adverse event rates similar to those reported in previous trials of these medications.
“The addition of a CGRP monoclonal antibody provided statistically significantly fewer monthly headache days,” said study investigator Fred Cohen, MD, an internal medicine resident physician at Montefiore Health System, New York. “However, this was a retrospective chart review, which is hindered by elements such as recall bias. Therefore, future prospective studies are warranted for higher quality data.”
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
Fewer headache days
Although Botox is associated with significant clinical improvement in chronic migraine, it often fails to adequately control headache frequency and additional medications are needed.
The CGRP-mAbs fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and erenumab, have recently been approved for migraine prevention, with results from clinical trials demonstrating they are effective for both chronic and episodic migraine. However, patients treated with Botox were excluded from these trials and to date there are no data on combination treatment with Botox and CGRP-mAbs.
To determine whether adjunctive treatment with CGRP-mAbs augments Botox therapy in chronic migraine the investigators conducted a retrospective chart review of patients receiving Botox and prescribed a CGRP-mAb.
Eligible patients met the International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition, criteria for chronic migraine; were age 18 years or older; and presented at a single headache center between May 2018 and May 2019. Patients who received another new therapy during the study or those taking CGRP-mAb treatment for less than 2 months were excluded.
The study’s primary outcome was change in the number of reported monthly headache days, and change in pain severity was the secondary outcome.
The final analysis included data on 153 patients. The population’s mean age was 47.1 years, and 139 patients (90.8%) were women. In all, 89 patients (58.0%) received erenumab (35 received 70 mg and 54 received 140 mg), 51 (33.0%) received galcanezumab, and 13 (9.0%) received fremanezumab.
Overall, 114 (74.5%) patients reported a decrease in monthly headache days or pain severity. In the group of 66 patients for whom quantitative data were available, the average number of monthly headache days before Botox treatment was 25.7. After Botox treatment, patients had an average decrease of 10.9 monthly headache days, a 42.4% reduction, so on average study participants continued to have an average of 14.8 monthly headache days.
After treatment with a CGRP-mAb the number decreased by 5.6 additional days (37.8%). Patients receiving combined therapy had an average of 9.1 monthly headache days. The total decrease from baseline was 16.6 fewer monthly headache days, a 64.6% reduction.
The number of headache days per month was reduced to 9.3 for erenumab and galcanezumab and 5.8 for fremanezumab. However, few patients in the study took fremanezumab so this result had less statistical power than the results for the other CGRP-mAbs.
A total of 13 patients (8.5%) reported side effects associated with the CGRP-mAbs, which included constipation, injection-site reaction, and fatigue.
More evidence is needed
Commenting on the findings, Peter McAllister, MD, medical director of the New England Institute for Neurology and Headache in Stamford, Conn., said the study’s main limitation is that it is a retrospective chart review, which yields lower level evidence than a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Dr. McAllister, who was not involved in the research, also noted that the sample size was small, particularly with respect to fremanezumab.
“This study, despite its limitations, shows that addition of a monoclonal antibody to onabotulinumtoxinA is safe and well tolerated, and may confer additional reduction in migraine or headache days. The authors correctly state that more evidence via prospective study is warranted,” said Dr. McAllister, who is also chief medical officer of the New England Institute for Clinical Research and was not involved in the investigation.
Dr. Cohen has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. McAllister was an investigator in the PREEMPT trial of onabotulinumtoxinA, as well as in all of the phase 3 monoclonal antibody studies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHS 2020
Minority-serving hospitals had similar survival after liver cancer surgery
Overall survival after liver cancer surgery was similar regardless of whether patients were treated at minority-serving hospitals or at hospitals with proportionally fewer African American or Hispanic patients, investigators have found.
“[T]reatment of racial minorities is largely restricted to a subset of hospitals, often referred to as minority-serving hospitals. We sought to examine whether racial and ethnic minorities with hepatocellular carcinoma receive their surgical care at minority-serving hospitals, and whether treatment at minority-serving hospitals is associated with differences in overall survival,” explained Winta T. Mehtsun, MD, MPH, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and associates in an abstract released as part of the annual Digestive Disease Week.®
Hepatocellular carcinoma continues to have a low 5-year survival rate and exhibits marked racial and ethnic disparities in diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. In a recent study of Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) data, African American patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were significantly younger at diagnosis, were more likely to have metastatic disease, and were less likely to receive surgical treatment compared with whites (Am J Prevent Med 2018;55:S40-48). Among patients with early-stage liver cancer, Hispanic and African American patients are less likely to receive curative therapy and die sooner, on average, than do other patients (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:551-9).
Minority-serving hospitals also have improved significantly less over time on measures of critical care, length of stay, and mortality, but whether these issues extend to hepatocellular carcinoma remains unclear. Therefore, Dr. Mehtsun and her associates studied all 2,609 patients in the National Cancer Database who received surgical resection (not transplantation or local therapy) for nonmetastatic hepatocellular carcinoma between 2004 and 2014. They compared survival at minority-serving hospitals – those in the top 10% based on the proportion of patients who were African American or Hispanic – with survival at other hospitals.
“There was no association between minority-serving hospital and overall survival,” the researchers reported (multivariable hazard ratio for death, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-1.11). In contrast, survival was significantly shorter among patients with more advanced disease (HR, 2.5; 95% CI, 2.1-2.8), patients who were treated at a community cancer program (HR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.3-2.4), and patients whose Charlson Comorbidity Index was greater than 2 (HR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.1-1.4).
Stage at diagnosis, comorbidities, and sex were not significantly related to hospital type, the investigators noted. A total of 298 patients (11%) were treated at minority-serving hospitals. Patients treated at minority-serving hospitals were significantly more likely to be uninsured (11% vs. 4% at other hospitals) and significantly less likely to be treated at an academic center (55% vs. 69%; both P less than .001).
Dr. Mehtsun reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehtsun WT et al. DDW 2020, Abstract Tu2043.
Overall survival after liver cancer surgery was similar regardless of whether patients were treated at minority-serving hospitals or at hospitals with proportionally fewer African American or Hispanic patients, investigators have found.
“[T]reatment of racial minorities is largely restricted to a subset of hospitals, often referred to as minority-serving hospitals. We sought to examine whether racial and ethnic minorities with hepatocellular carcinoma receive their surgical care at minority-serving hospitals, and whether treatment at minority-serving hospitals is associated with differences in overall survival,” explained Winta T. Mehtsun, MD, MPH, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and associates in an abstract released as part of the annual Digestive Disease Week.®
Hepatocellular carcinoma continues to have a low 5-year survival rate and exhibits marked racial and ethnic disparities in diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. In a recent study of Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) data, African American patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were significantly younger at diagnosis, were more likely to have metastatic disease, and were less likely to receive surgical treatment compared with whites (Am J Prevent Med 2018;55:S40-48). Among patients with early-stage liver cancer, Hispanic and African American patients are less likely to receive curative therapy and die sooner, on average, than do other patients (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:551-9).
Minority-serving hospitals also have improved significantly less over time on measures of critical care, length of stay, and mortality, but whether these issues extend to hepatocellular carcinoma remains unclear. Therefore, Dr. Mehtsun and her associates studied all 2,609 patients in the National Cancer Database who received surgical resection (not transplantation or local therapy) for nonmetastatic hepatocellular carcinoma between 2004 and 2014. They compared survival at minority-serving hospitals – those in the top 10% based on the proportion of patients who were African American or Hispanic – with survival at other hospitals.
“There was no association between minority-serving hospital and overall survival,” the researchers reported (multivariable hazard ratio for death, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-1.11). In contrast, survival was significantly shorter among patients with more advanced disease (HR, 2.5; 95% CI, 2.1-2.8), patients who were treated at a community cancer program (HR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.3-2.4), and patients whose Charlson Comorbidity Index was greater than 2 (HR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.1-1.4).
Stage at diagnosis, comorbidities, and sex were not significantly related to hospital type, the investigators noted. A total of 298 patients (11%) were treated at minority-serving hospitals. Patients treated at minority-serving hospitals were significantly more likely to be uninsured (11% vs. 4% at other hospitals) and significantly less likely to be treated at an academic center (55% vs. 69%; both P less than .001).
Dr. Mehtsun reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehtsun WT et al. DDW 2020, Abstract Tu2043.
Overall survival after liver cancer surgery was similar regardless of whether patients were treated at minority-serving hospitals or at hospitals with proportionally fewer African American or Hispanic patients, investigators have found.
“[T]reatment of racial minorities is largely restricted to a subset of hospitals, often referred to as minority-serving hospitals. We sought to examine whether racial and ethnic minorities with hepatocellular carcinoma receive their surgical care at minority-serving hospitals, and whether treatment at minority-serving hospitals is associated with differences in overall survival,” explained Winta T. Mehtsun, MD, MPH, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and associates in an abstract released as part of the annual Digestive Disease Week.®
Hepatocellular carcinoma continues to have a low 5-year survival rate and exhibits marked racial and ethnic disparities in diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. In a recent study of Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) data, African American patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were significantly younger at diagnosis, were more likely to have metastatic disease, and were less likely to receive surgical treatment compared with whites (Am J Prevent Med 2018;55:S40-48). Among patients with early-stage liver cancer, Hispanic and African American patients are less likely to receive curative therapy and die sooner, on average, than do other patients (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:551-9).
Minority-serving hospitals also have improved significantly less over time on measures of critical care, length of stay, and mortality, but whether these issues extend to hepatocellular carcinoma remains unclear. Therefore, Dr. Mehtsun and her associates studied all 2,609 patients in the National Cancer Database who received surgical resection (not transplantation or local therapy) for nonmetastatic hepatocellular carcinoma between 2004 and 2014. They compared survival at minority-serving hospitals – those in the top 10% based on the proportion of patients who were African American or Hispanic – with survival at other hospitals.
“There was no association between minority-serving hospital and overall survival,” the researchers reported (multivariable hazard ratio for death, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-1.11). In contrast, survival was significantly shorter among patients with more advanced disease (HR, 2.5; 95% CI, 2.1-2.8), patients who were treated at a community cancer program (HR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.3-2.4), and patients whose Charlson Comorbidity Index was greater than 2 (HR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.1-1.4).
Stage at diagnosis, comorbidities, and sex were not significantly related to hospital type, the investigators noted. A total of 298 patients (11%) were treated at minority-serving hospitals. Patients treated at minority-serving hospitals were significantly more likely to be uninsured (11% vs. 4% at other hospitals) and significantly less likely to be treated at an academic center (55% vs. 69%; both P less than .001).
Dr. Mehtsun reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehtsun WT et al. DDW 2020, Abstract Tu2043.
FROM DDW 2020








