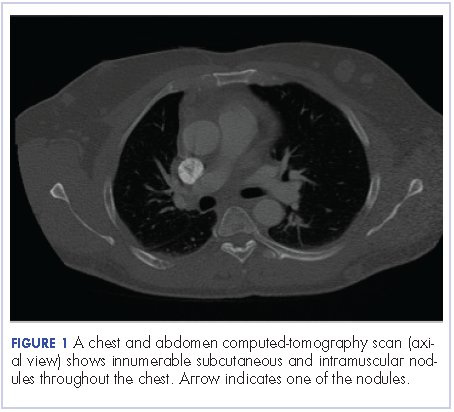
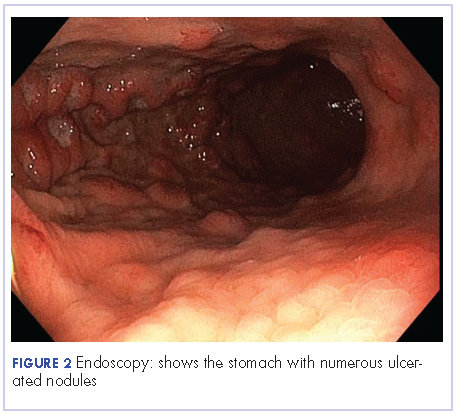
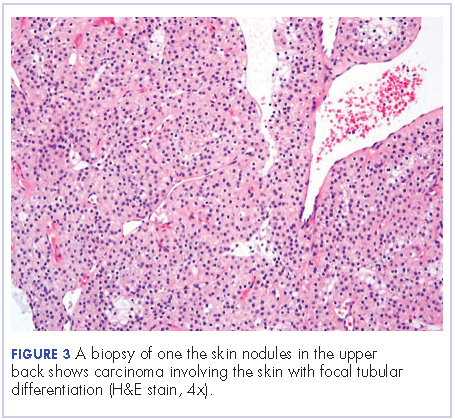
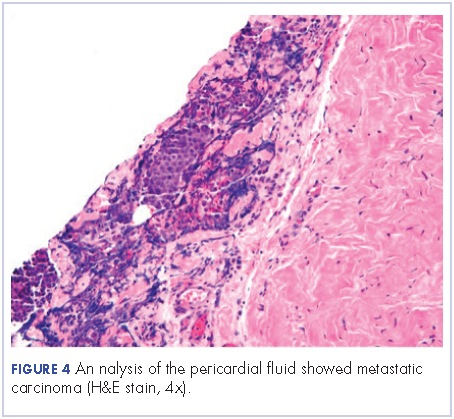
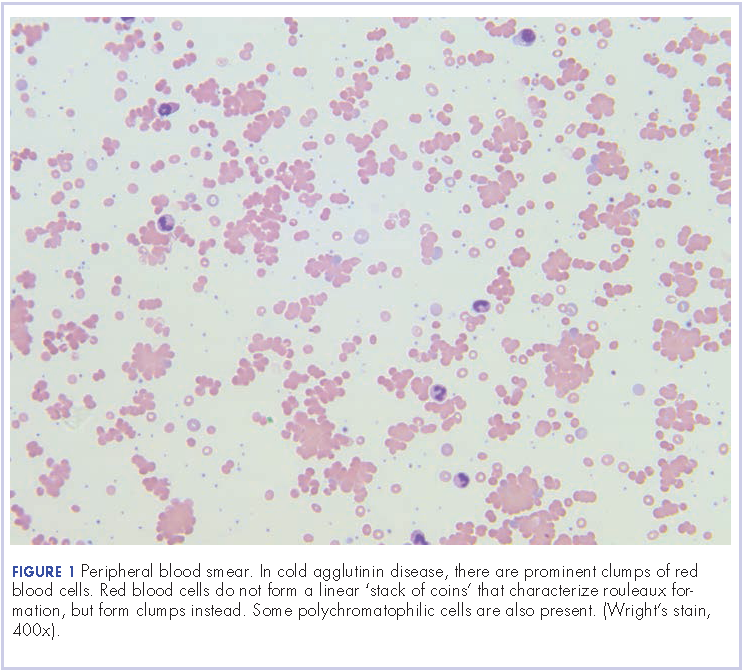
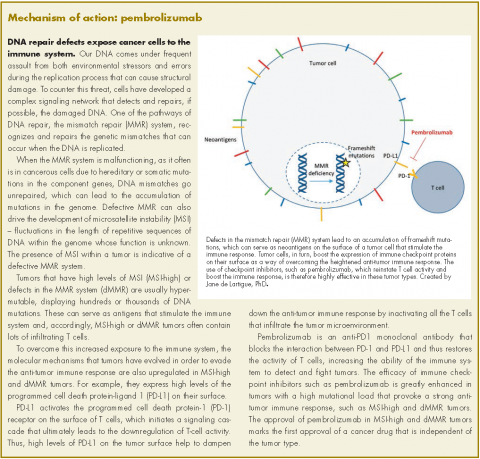
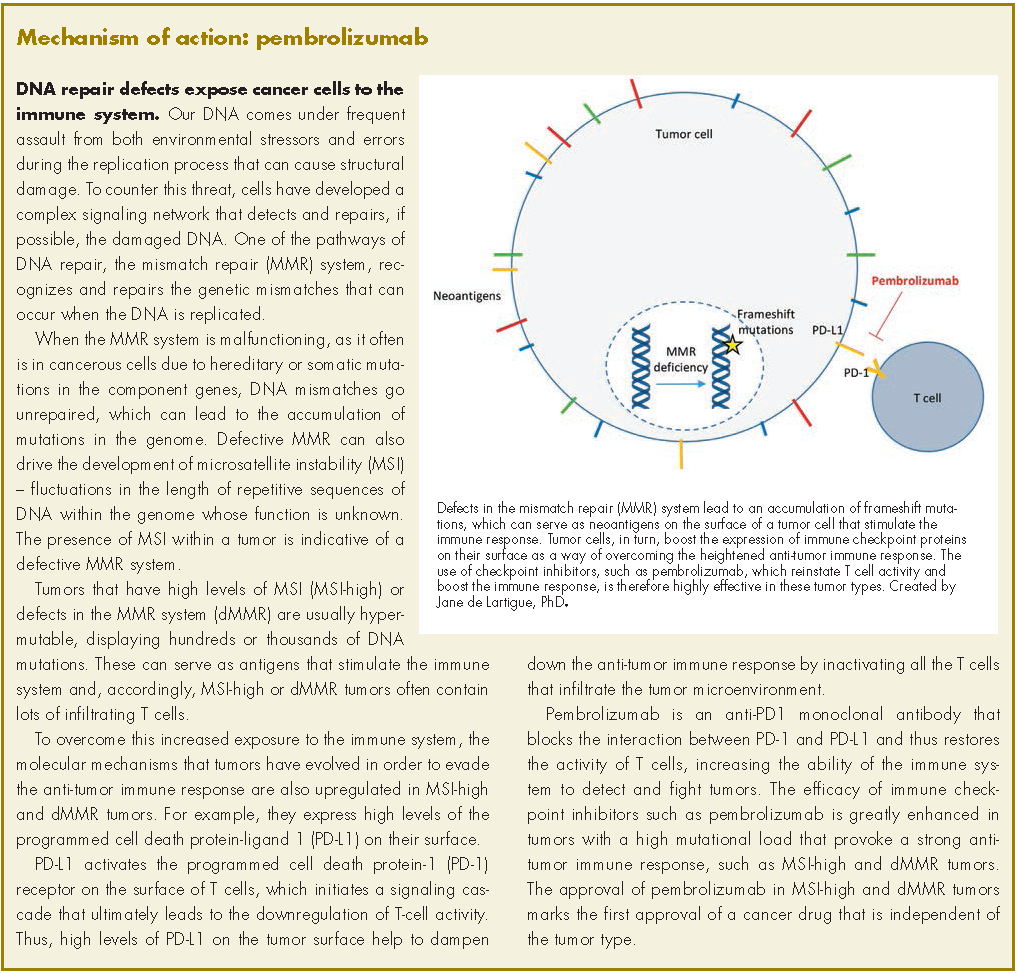
User login
The impact of combining human and online supportive resources for prostate cancer patients
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in men. 1 Treatment choices for prostate cancer are perhaps more varied than for many other cancers, with surgery, external beam radiation therapy, and brachytherapy all widely used, a number of adjuvant and nonstandard therapy options available, as well as the possibility of not immediately treating the cancer – the “active surveillance” option.
Biochemical failure rates do not differ between the 3 main treatments,2 but each exposes patients to the risk of side effects, including impotence, incontinence, rectal injury, and operative mortality. Recovery can be gradual and will not always involve a return to baseline functioning.3 Quality-of-life comparisons observed covariate-controlled decreases in varying specific aspects of quality of life for each of the treatments.4
Surgery, brachytherapy, and external beam radiation therapy have each shown advantages over other treatments on at least some specific aspect, but disadvantages on others.4 Ongoing surveillance of a cancer left in place has become a more common option in part because of the disadvantages of traditional treatment and because of the growing recognition that sensitive diagnosis techniques often locate cancers that might not be life threatening. Recent reviews and reasonably long-term trials portray active surveillance as a valid alternative to surgery and radiation in many cases, with little difference in life expectancy and cancer-related quality of life, and possibly some reduction in health system cost.5-7
Prostate cancer patients cope with these uncertainties and decisions in many ways,8 often using multiple coping behaviors,9 but coping almost always includes seeking information and social support, as well as active problem-solving, to make informed treatment decisions consistent with their values.
Unfortunately, prostate patients often do not receive or use needed information. McGregor10 reported that patients were aware of their incomplete understanding of their disease and treatment options. Findings from several studies suggest that patients often perceive that clinicians inform them about the disease and treatment options but then send them home unprepared to deal with such things as incontinence or difficulties with sexual functioning.11
Similarly, previous research demonstrates the benefits of social support for prostate cancer patients who receive it, but also that overall they are underserved.12,13 Male cancer patients are generally far less likely to seek support and health information than are female patients. And when patients with prostate cancer do participate in online cancer support groups, they are more likely to exchange information, whereas breast cancer patients provide support for each other.14
Mentoring
Some responses to these knowledge and support gaps pair newly diagnosed patients with survivors willing to be a guide, coach, and a source of information, as in the American Cancer Society’s (ACS’s) Man-to-Man support groups.15 Peer mentors may have a sophisticated level of understanding from their own experiences with medical literature and the health care system, but this cannot be assumed. Another mentoring model is expert-based, exemplified by the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI’s) cancer information specialist at the Cancer Information Service (CIS) and a similar system at the ACS. These telephone services allow for responsiveness to the caller’s needs, existing knowledge, and the caller’s readiness for information. The CIS specialist can also introduce important information the caller might not have known to ask about.16
However, not all problems presented by callers can be solved in a single conversation. Callers are encouraged to call back with additional questions or when their situation changes, but speaking with the same specialist is not facilitated, so it is hard for a second call to build upon the first. Combining the expertise of the cancer information specialist with the ongoing and proactive contact and support typical of the lay guide/mentor/navigator could be more effective. Here a CIS-trained information specialist called prostate patients multiple times over the intervention period to help them deal with information seeking and interpretation. In a previous study with breast cancer patients, a mentor of this sort improved patient information competence and emotional processing.17
Interactive resources
Online resources allow cancer patients self-paced and self-directed access to information and support anonymously and at any time. However, this can be more complicated than it might at first seem. With the complexities of the prostate cancer diagnosis, the multiple treatment options, and the uncertain but potentially serious effects of the treatments themselves, the amount of potentially relevant information is quite large. Then, because individuals will value differentially the attributes of treatments, their consequences, or even notions of risk and gain, a system must be able to respond appropriately to a range of very different people. Beyond this, as prostate cancer patients move from the shock of a cancer diagnosis to the problems of interpreting its details, to making treatment decisions, to dealing with problems of recovery, and then re-establishing what is a “new normal” for them, an individual’s demands on a system vary as well. Comprehensive and integrated systems of services meet the varying needs of their users at different times and different situations.18,19 The systems approach not only makes it far easier for users to find what they need, it may also encourage them to see connections between physical, emotional, and social aspects of their illness. Versions of the system used in the present study – CHESS, or Comprehensive Health Enhancement Support System – have been effective supporting patients with AIDS and breast and lung cancers, and teens with asthma.16,20
Study goals and hypotheses
Given the success of the 2 aforementioned approaches, we wanted to compare how CHESS and ongoing contact with a human cancer information mentor in patients with prostate cancer would affect both several general aspects of quality of life and 1 specific to prostate cancer. We also examined differences in the patients’ information competence, quality of life, and social support. There was no a priori expectation that one intervention would be superior to the other, but any differences found could be important to policy decisions, given their quite-different cost and scalability.
More importantly, the primary hypothesis of the study was that patients with access to both CHESS and a mentor would experience substantially better outcomes than those with access to either intervention alone, because each had the potential to enhance the other’s benefits. For example, a patient could read CHESS material and come to the mentor much better prepared. By referring the user to specific parts of CHESS for basic information, the mentor could use calls to address more complex issues, or help interpret and evaluate difficult issues. In addition, because CHESS provides the mentor information about changes in the patient’s treatments, symptoms, and CHESS use, in the combined condition the cancer information mentor can know much more about the patient than when working alone. We also expected that the mentor would stimulate the kind of diverse use of CHESS services we have found to be most effective
Because both mentoring and CHESS have consistently produced positive quality of life effects on their own, compared to controls, there is no reasonable expectation that negative effects of a combined condition could occur and should be tested for. Thus, the study was powered for 1-tailed significance in the comparison between the combined condition and either intervention alone, a procedure used consistently in previous studies of CHESS components or combined conditions. However, since the research question comparing the 2 interventions alone had no such strong history it was tested 2-tailed.
Methods
Recruitment
Study recruitment was conducted from January 1, 2007 to September 30, 2008 at the University of Wisconsin’s Paul P Carbone Comprehensive Cancer Center in Madison, Hartford Hospital’s Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center in Hartford, Connecticut, and The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
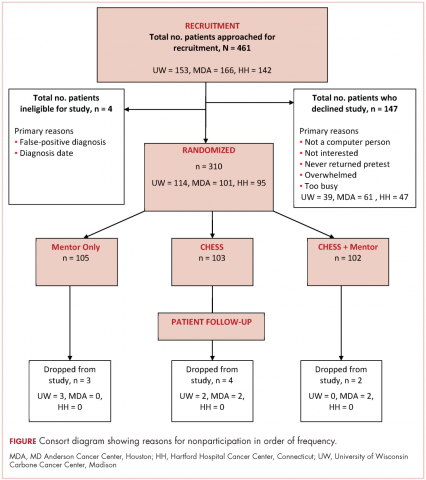
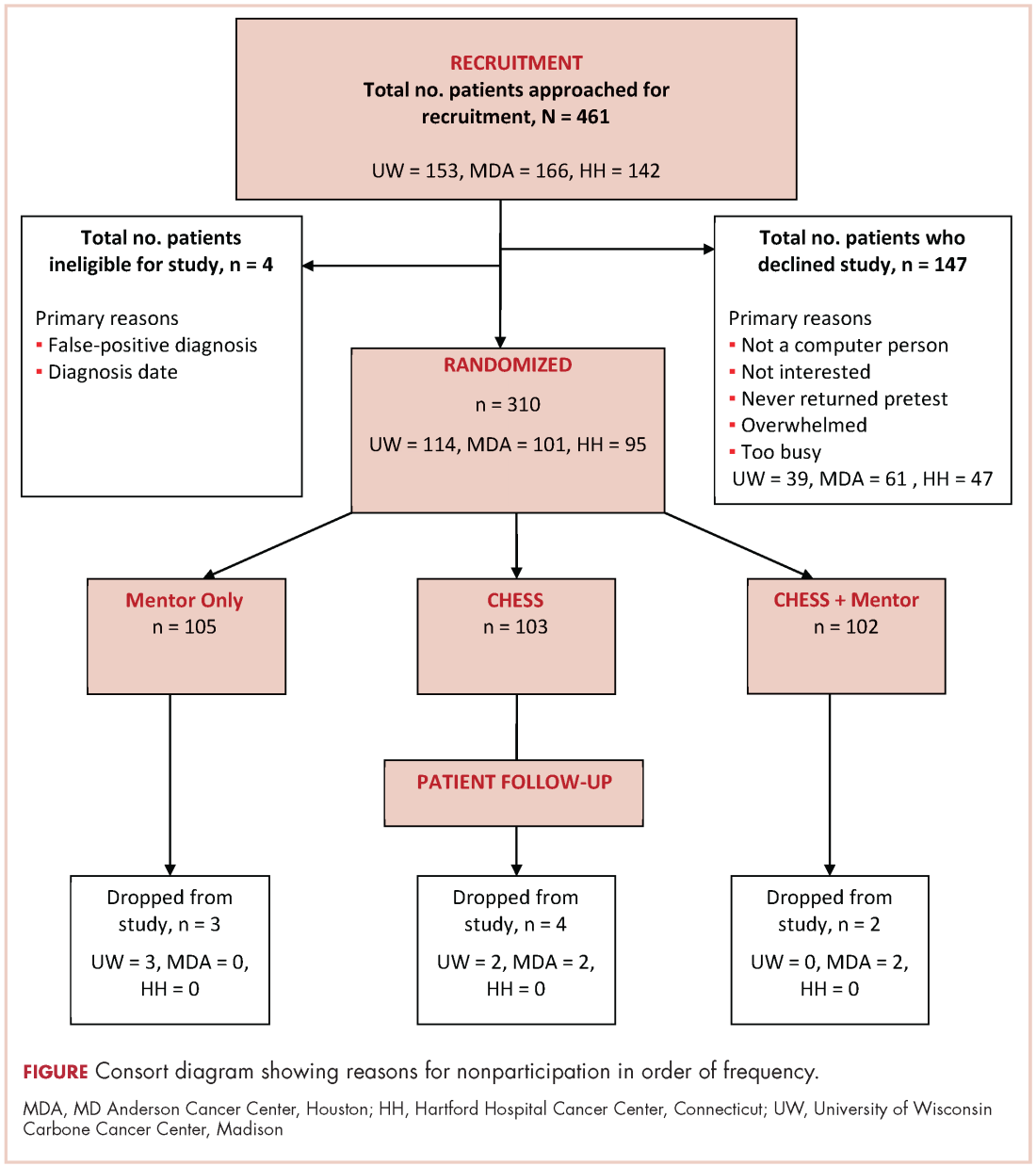
A total of 461 patients were invited to participate in the study. Of those patients, 147 declined to participate, 4 were excluded, and 310 were randomized to access to CHESS only, access to a human mentor only, or access to CHESS and a mentor (CHESS+Mentor) during the 6-month intervention period, which provided adequate power (>.80) for effects of moderate size (Figure 1). Randomization was done with a computer-generated list that site study managers accessed on a patient-by-patient basis, with experimental conditions blocked within sites.
Recruitment was done by posting brochures about the study at the relevant locations and devising standardized recruitment scripts for clinical staff to use when talking to patients about the study. Staff at all sites invited patients they thought might be eligible to learn more about the study. As appropriate, staff members then reviewed informed consent and HIPAA information, explained the interventions, answered patient questions, obtained written consent, collected complete patient contact and computer access information, and provided patients the baseline questionnaires.
The standard inclusion criteria were: men older than 17 years, being able to read and understand English, and being within 2 months of a diagnosis of primary prostate cancer (stage 1 or 2) at the time of recruitment. Despite the 2-month window, few men had begun treatment before pretest. Only 9 of the 310 participants reported having already had surgery (7 prostatectomies, 2 implants), so participants may be fairly characterized as beginning the study in time to benefit from interventions during most stages of their experience with prostate cancer.
Interventions
To provide an equal baseline, all of the participants were given access to the Internet, which is becoming a de facto standard for information access. Internet access charges were paid for all participants during the 6-month intervention period, and computers were loaned to those who did not have a personal computer. All of the participants were offered training on using the computer, particularly with Google search procedures so that they could access resources on prostate cancer.
Participants assigned to the CHESS or CHESS+Mentor conditions were also offered training in using CHESS (basically a guided tour), which typically took about 30 minutes on the telephone but was occasionally done in-person.
CHESS intervention. In creating CHESS for prostate cancer patients, a combination of patient needs assessments, focus groups with patients and family members, and clinician expertise helped us identify the needs, coping mechanisms, and relevant medical information to help patients respond to the disease. An article describing development of the CHESS Prostate Cancer Module22 presents how those different services address patient needs for information, communication, and support, or build skills.
Most of these services were present in CHESS for other diseases, but several were newly created to meet needs of prostate cancer patients and partners, such as a decision map tool and a module on managing sexual problems.22 Also, patients expressed frustration at being overwhelmed by the volume of information and said they would prefer to focus only on what was most relevant, so we created an alternative navigation structure on the CHESS homepage. Using terms suggested by focus groups of prostate cancer survivors and their spouses, we devised a navigation structure called Step-by-Step that identified 6 typical sequential steps of men’s experience with prostate cancer. Clicking on a step would take a patient to a menu focused on actions and considerations specific to that disease step, links to information most relevant at that step, and suggested questions to ask oneself and one’s doctor.
Mentor intervention. The cancer information mentor who made most of the calls to patients was an experienced information specialist with the Cancer Information Service and had served as the expert for the CHESS Ask an Expert service for 6 years. She was highly knowledgeable about prostate cancer and patient information needs. Her additional training for this study focused on taking advantage of repeated contacts with the participants and how to set limits to avoid any semblance of psychological counseling. At recruitment, we made clear that a male mentor was also available if the participant would prefer to discuss sensitive topics with another man. The male mentor was experienced in the Man-to-Man program and received additional training for this role, but he was used for only 1% of all contacts.
During calls, the mentor had Internet access to a range of NCI, ACS, and other resources. She could help interpret information the participant already possessed as well as refer him to other public resources, including those on the Internet. CHESS software designers created an additional interface for the mentor that handled call scheduling and allowed her to record the topics of conversations, her responses and recommendations, and her overall ratings of patient preparedness and satisfaction. Using this interface allowed the mentor to quickly review a participant’s status and focus the conversation on issues raised by past conversations or scheduled treatment events. The mentor calls were audiorecorded and reviewed frequently by the project director during the early months of intervention and less frequently thereafter to ensure adherence to the protocol.
The mentor telephoned weekly during the first month of intervention, then twice during the second month, and once a month during the final 4 months of the intervention (ie, 10 scheduled calls, though patients could also initiate additional calls). Calls were scheduled through a combination of telephone contact and e-mail according to the patient’s preference. Call length ranged from 5 minutes to an hour, with the average about 12 minutes (the first call tended to be considerably longer, and was scheduled for 45 minutes). About 10%-15% of participants in the Mentor conditions initiated calls to the mentor to obtain additional support, and about 15% of scheduled calls in fact took place as e-mail exchanges. A few calls were missed because of scheduling difficulties, and some participants stopped scheduling the last few calls, but the average number of full calls or e-mails was 6.41 per participant.
CHESS+Mentor intervention. For the CHESS+Mentor condition, the interactions and resources used were similar to those of the Mentor-only condition, but the interface also provided the mentor with a summary of the participant’s recent CHESS use and any concerns reported to CHESS, which helped the mentor assess knowledge and make tailored recommendations. The mentor could also refer participants to specific resources within CHESS, aided by knowledge of what parts of CHESS had or had not been used.
Assessment methods
Patients were given surveys at the baseline visit to complete and mail back to research staff before randomization. Follow-up surveys were mailed to patients at 2, 6, 12, and 24 weeks post intervention access, and patients returned the surveys by mail. Patient withdrawal rates were about 3%.
Measures
Outcomes. This study included 4 measures of quality of life (an average of relevant portions of the World Health Organization’s Quality of Life (WHOQOL) measure, Emotional and Functional Well-being, and a prostate-cancer specific index, the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC). We also tested group differences on 5 more specific outcomes that were likely to be proximal rather than distal effects of the interventions: Cancer Information Competence, Health care Competence, Social Support, Bonding (with other patients), and Positive Coping.
Quality of life. Quality of life was measured by combining the psychological, social, and overall dimensions of the WHOQOL measures.23 Each of the 11 items was assessed with a 5-point scale, and the mean of those answers was the overall score.
Emotional well-being. Respondents answered 6 items of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Prostate
Functional well-being. Respondents indicated how often they experienced each of the seven functional well-being subscale items of the FACT-Prostate.24
Prostate cancer patient functioning. We used the EPIC to measure of 3 of 4 domains of prostate cancer patient functioning: urinary, bowel, and sexual (omitting hormonal).25 The EPIC measures frequency and subjective degree of being a problem of several aspects in each domain. We then summed scores across the domains and transformed linearly to a 0-100 scale, with higher scores representing better functioning.
Cancer information competence. Five cancer information competence items, measured on a 5-point scale, assessed a participant’s perception about whether he could find and effectively and use health information, and were summed to create a single score.20
Social support. Six 5-point social support items assessed the informational and emotional support provided by friends, family, coworkers, and others, and were summed to create a single score.20
Health care competence. Five 5-point health care competence items assessed a patient’s comfort and activation level dealing with physicians and health care situations, and were summed to create a single score.20
Positive coping. Coping strategies were measured with the Brief Cope, a shorter version of the original 60-item COPE scale.26 Positive coping strategy, a predictor of positive adaptation in numerous coping contexts, was measured with the mean score of 4 scales (8 items in all): active coping, planning, positive reframing, and humor.
Bonding. Bonding with other prostate cancer patients was measured with five 5-point items about how frequently participants connected with and got information and support from other men with prostate cancer.27
User vs nonuser. Intent-to-treat analyses compared the assigned conditions. However, because CHESS use was self-selected and available at any time whereas mentor calls were scheduled and initiated by another person, the proportion actually using the interventions was quite different.
Since a participant assigned access to CHESS had to select the URL, even a single entry to the system was counted as use. Of 198 participants assigned to either the CHESS or CHESS+Mentor conditions, 43 (22%) never logged in and were classified as nonusers.
Because the mentor scheduled calls and attempted repeatedly to complete scheduled calls, the patient was in a reactive position, and the decision not to use the mentor’s services could come at the earliest at the end of a first completed call. However, after examining call notes and consulting with the mentors, it was clear that opting not to receive mentoring typically occurred at the second call. Furthermore, much (though not all) of the first call was typically taken up with getting acquainted and scheduling issues, so that defining “nonuse” as 2 or fewer completed calls was most faithful to what actually happened. Of 202 participants assigned access to a mentor, 16 (8%) were thus defined as nonusers.
Results
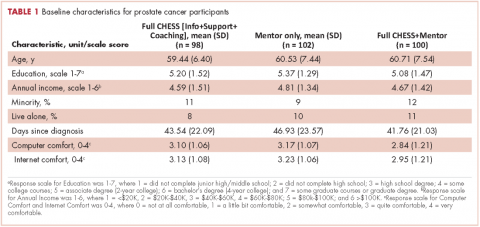
Overall, the participants were about 60 years of age and had some college education and middle-class incomes (Table 1). Only about 10% were minorities or lived alone, and their comfort using computers and the Internet was at or above the “quite comfortable” level. None of groups differed significantly from any other.
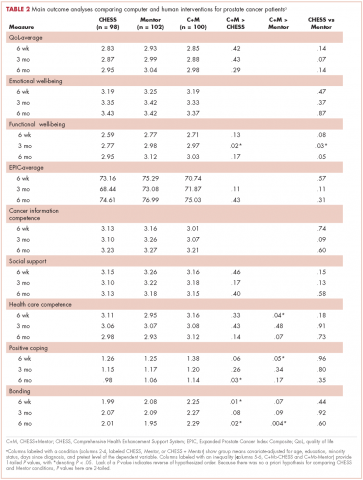
The 2 primary hypotheses of the study were that participants in the combined condition would manifest higher outcome scores than those with either intervention alone. Table 2 displays group means at 3 posttest intervals, controlling for theoretically chosen covariates (age, education, and minority status) and pretest levels of the dependent variable. The table also summarizes tests examining the hypotheses and the comparison of CHESS and Mentor conditions. The 4 quality-of-life scores appear first, followed by 5 more specific outcomes that are perhaps more proximal effects of these interventions.
The combined condition scored significantly higher than the CHESS-only condition on functional well-being at 3 months, on positive coping at 6 months, and on bonding at both 6 weeks and 6 months. The combined condition scored significantly higher than Mentor-only on health care competence and positive coping at 6 weeks, and on bonding at 6 months. This represents partial but scattered support for the hypotheses. And some comparisons of the combined condition with the Mentor-only condition showed reversals of the predicted relationship (although only cancer information competence at 3 months would have reached statistical significance in a 2-tailed test).
No directional hypotheses were made for the comparison of the 2 interventions (see Table 2 for the results of 2-tailed tests). Participants in the Mentor condition reported significantly higher functional well-being at 3 months, although there were 5 other comparisons in which the Mentor group scored higher at P < .10, and higher than the CHESS group on 22 of the 27 comparisons. Thus, it seemed that the Mentor condition alone might have been a somewhat stronger intervention than CHESS alone.
Discussion
We used a randomized control design to test whether combining computer-based and human interventions would provide greater benefits to prostate cancer patients than either alone, as previous research had shown for breast cancer patients.18 The computer-based resource was CHESS, a repeatedly evaluated integrated system combining information, social support, and interactive tools to help patients manage their response to disease. The human cancer information mentor intervention combined the expertise of NCI’s Cancer Information Service with the repeated contact more typical of peer mentoring. Previous research with breast cancer patients had shown both interventions to provide greater information, support, and quality-of-life benefits than Internet access alone.14 This study also compared outcomes obtained by the separate CHESS and Mentor conditions, but without predicting a direction of difference.
Tests at 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months after intervention found instances in which prostate cancer patients assigned to the combined CHESS+Mentor condition experienced more positive quality of life or other outcomes than those assigned to CHESS or Mentor alone, but those differences were scattered rather than consistent. In the direct comparisons of the separate CHESS and Mentor conditions, significance was even rarer, but outcome scores tended to be higher in the Mentor condition than in the CHESS condition.
We noted that differential uptake of the 2 interventions (92% for Mentor vs 78% for CHESS) made interpreting the intent-to-treat analyses problematic, as the mentor’s control of the call schedule meant that far more patients in that condition actually received at least some intervention than in the CHESS condition, where patients used or did not use CHESS entirely at their own volition. This could have biased results in several ways, such as by underestimating the efficacy of the CHESS condition alone and thus inflating the contrast between CHESS alone and CHESS+Mentor. Or the combined condition might have been less different than the Mentor-only condition than intended, thus making for a conservative test of that comparison. However, post hoc analyses of only those participants who had actually used their assigned interventions (and this led to some reclassification of those originally assigned to the CHESS+Mentor condition) produced results that were little different than the intent-to-treat analysis.
Thus, although the combined condition produced some small advantages over either intervention alone, these advantages did not live up to expectations or to previous experience with breast cancer patients.17 We expected the mentor to be able to reinforce and help interpret what the participants learned from CHESS and their clinicians, and also to advise and direct these patients to be much more effective users of CHESS and other resources. Similarly, we expected that CHESS would make patients much better prepared for mentoring, so that instead of dealing with routine information matters, the mentor could go into greater detail or deal with more complex issues. Their combined effect should have been much larger than each alone, and that was not the case. Perhaps from the prostate cancer patients’ perspective, the 2 interventions seemed to offer similar resources, and a patient benefitted from one or the other but expected no additional gain from attending to both.
The 2 interventions themselves seemed nearly equally effective. The Mentor intervention was significantly stronger than CHESS in only 1 of 27 tests in the intent-to-treat analysis and 2 in the analysis limited to intervention users.
These results for prostate cancer patients are somewhat weaker than those previously reported with breast cancer patients.17 It is possible that prostate cancer patients (or men in general) are less inclined to seek health information, support, and health self-management than breast cancer patients (or women in general), perhaps becaus
Although these interventions were experienced by prostate cancer patients in their homes in natural and familiar ways, any experimental manipulation must acknowledge possible problems with external validity. More important here, our recruitment procedures may have produced self-selection to enter or not enter the study in 2 ways that limit its applicability. First, although we thought that offering Internet access to all participants would make participation more likely, the most frequent reason men gave in declining to join the study was “not a computer person.” Our participants were certainly very comfortable with computers and the Internet, and most used them frequently even before the study. Second, it seems that, except for their prostate cancer, our sample was healthy in other respects, as indicated by the low number of other health care visits or surgeries/hospitalization they reported (and “overwhelmed” and “too busy,” 2 common reasons for declining study participations could also be coming from men with more comorbidities). Thus, our sample was probably more computer literate and healthier than the general population of prostate cancer patients.
Nonetheless, for policymakers deciding what information and support interventions to put in place for prostate cancer patients (or more generally for other cancer patients as well), these results have 2 implications. First, since the combination of the mentor and CHESS produced only small advantages over either alone, the extra effort of doing both seems clearly unwarranted for prostate cancer patients. The somewhat larger advantage of the combined intervention shown for breast cancer patients in previous studiesmight warrant using the combination in some circumstances, but even that is not clear-cut.
Finding that CHESS and the cancer information mentor separately provided essentially equal benefits might seem to suggest that they can be regarded as alternatives. However, computer-based services can be provided much more cheaply and scaled up far more readily than services dependent on one-on-one contacts by a highly trained professional. This may direct health care decision makers first toward computer-based services.
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277-300.
2. Cozzarini C. Low-dose rate brachytherapy, radical prostatectomy, or external-beam radiation therapy for localized prostate carcinoma: The growing dilemma. European Urology. 2011;60(5):894-896.
3. Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1250-1261.
4. Ferrer F, Guedea F, Pardo Y, et al. Quality of life impact of treatments for localized prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2013;108(2):306-313.
5. Cooperberg, MR, Carroll, PR, Klotz, L. Active Surveillance for prostate cancer: progress and promise. J Clin Onc. 2011;29:3669-3676.
6. Hamdy, FC, Donovan JL, Lane JA, et al. 10-year outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1415-1424.
7. Donovan JL, Hamdy FC, Lane JA, et al. Patient-reported outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1425-37.
8. Lavery JF, Clarke VA. Prostate cancer: patients’ spouses’ coping and marital adjustment. Psychol Health Med. 1999;4(3):289-302.
9. Folkman S, Lazarus R. If it changes it must be a process: study of emotion and coping during three stages of a college examination. J Pers Soc Psycol. 1985;48:150-170.
10. McGregor S. What information patients with localized prostate cancer hear and understand. Patient Educ Couns. 2003;49:273-278.
11. Steginga SK, Occhipinti S, Dunn J, Gardiner RA, Heathcote P, Yaxley J. (2001) The supportive care needs of men with prostate cancer (2000). Psychooncology. 2001;10(1):66-75.
12. Gregoire I, Kalogeropoulos D, Corcos J. The effectiveness of a professionally led support group for men with prostate cancer. Urologic Nurs. 1997;17(2):58-66.
13. Katz D, Koppie T, Wu D, et al. Sociodemographic characteristics and health related quality of life in men attending prostate cancer support groups. J Urol. 2002;168:2092-2096.
14. Klemm P, Hurst M, Dearholt S, Trone S. Gender differences on Internet cancer support groups. Comput Nurs. 1999;17(2):65-72.
15. Gray R, Fitch M, Phillips C, Labrecque M, Fergus K. Managing the impact of illness: the experiences of men with prostate cancer and their spouses. J Health Psychol. 2000;5(4):531-548.
16. Thomsen CA, Ter Maat J. Evaluating the Cancer Information Service: a model for health communications. Part 1. J Health Commun. 1998;3(suppl.):1-13.
17. Hawkins RP, Pingree S, Baker TB, et al. Integrating eHealth with human services for breast cancer patients. Transl Behav Med. 2011;1(1):146-154.
18. Strecher V. Internet methods for delivering behavioral and health-related interventions. Ann Rev Clin Psychol. 2007;(3):53-76.
19. Gustafson DH, Hawkins RP, McTavish F, et al. Internet-based interactive support for cancer patients: Are integrated systems better? J Commun. 2008;58(2):238-257.
20. Gustafson DH, Hawkins RP, Boberg EW, et al. CHESS: Ten years of research and development in consumer health informatics for broad populations, including the underserved. Int J Med Inform. 2002;65(3):169-177.
21. Han JY, Hawkins RP, Shaw B, Pingree S, McTavish F, Gustafson D. Unraveling uses and effects of an interactive health communication system. J Broadcast Electron Media. 2009;53(1):1-22.
22. Van Bogaert D, Hawkins RP, Pingree S, Jarrard D. The development of an eHealth tool suite for prostate cancer patients and their partners. J Support Oncol. 2012;10(5):202-208.
23. The WHOQOL Group. Development of the WHOQOL: Rationale and current status. Int J Ment Health. 1994;23:24-56.
24. Esper P, Mo F, Chodak G, Sinner M, Cella D, Pienta KJ. Measuring quality of life in men with prostate cancer using the functional assessment of cancer therapy-prostate instrument. Urology. 1997;50:920-928.
25. Wei JT, Dunn R, Litwin M, Sandler H, Sanda MG. Development and validation of the expanded prostate cancer index composite (EPIC) for comprehensive assessment of health-related quality of life in men with prostate cancer. Urology. 2000;56:899-905.
26. Carver CS. You want to measure coping but your protocol’s too long: consider the brief COPE. Int J Behav Med. 1997;4: 91-100.
27. Gustafson D, McTavish F, Stengle W, et al. Use and impact of eHealth System by low-income women with breast cancer. J Health Commun. 2005;10(suppl 1):219-234.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in men. 1 Treatment choices for prostate cancer are perhaps more varied than for many other cancers, with surgery, external beam radiation therapy, and brachytherapy all widely used, a number of adjuvant and nonstandard therapy options available, as well as the possibility of not immediately treating the cancer – the “active surveillance” option.
Biochemical failure rates do not differ between the 3 main treatments,2 but each exposes patients to the risk of side effects, including impotence, incontinence, rectal injury, and operative mortality. Recovery can be gradual and will not always involve a return to baseline functioning.3 Quality-of-life comparisons observed covariate-controlled decreases in varying specific aspects of quality of life for each of the treatments.4
Surgery, brachytherapy, and external beam radiation therapy have each shown advantages over other treatments on at least some specific aspect, but disadvantages on others.4 Ongoing surveillance of a cancer left in place has become a more common option in part because of the disadvantages of traditional treatment and because of the growing recognition that sensitive diagnosis techniques often locate cancers that might not be life threatening. Recent reviews and reasonably long-term trials portray active surveillance as a valid alternative to surgery and radiation in many cases, with little difference in life expectancy and cancer-related quality of life, and possibly some reduction in health system cost.5-7
Prostate cancer patients cope with these uncertainties and decisions in many ways,8 often using multiple coping behaviors,9 but coping almost always includes seeking information and social support, as well as active problem-solving, to make informed treatment decisions consistent with their values.
Unfortunately, prostate patients often do not receive or use needed information. McGregor10 reported that patients were aware of their incomplete understanding of their disease and treatment options. Findings from several studies suggest that patients often perceive that clinicians inform them about the disease and treatment options but then send them home unprepared to deal with such things as incontinence or difficulties with sexual functioning.11
Similarly, previous research demonstrates the benefits of social support for prostate cancer patients who receive it, but also that overall they are underserved.12,13 Male cancer patients are generally far less likely to seek support and health information than are female patients. And when patients with prostate cancer do participate in online cancer support groups, they are more likely to exchange information, whereas breast cancer patients provide support for each other.14
Mentoring
Some responses to these knowledge and support gaps pair newly diagnosed patients with survivors willing to be a guide, coach, and a source of information, as in the American Cancer Society’s (ACS’s) Man-to-Man support groups.15 Peer mentors may have a sophisticated level of understanding from their own experiences with medical literature and the health care system, but this cannot be assumed. Another mentoring model is expert-based, exemplified by the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI’s) cancer information specialist at the Cancer Information Service (CIS) and a similar system at the ACS. These telephone services allow for responsiveness to the caller’s needs, existing knowledge, and the caller’s readiness for information. The CIS specialist can also introduce important information the caller might not have known to ask about.16
However, not all problems presented by callers can be solved in a single conversation. Callers are encouraged to call back with additional questions or when their situation changes, but speaking with the same specialist is not facilitated, so it is hard for a second call to build upon the first. Combining the expertise of the cancer information specialist with the ongoing and proactive contact and support typical of the lay guide/mentor/navigator could be more effective. Here a CIS-trained information specialist called prostate patients multiple times over the intervention period to help them deal with information seeking and interpretation. In a previous study with breast cancer patients, a mentor of this sort improved patient information competence and emotional processing.17
Interactive resources
Online resources allow cancer patients self-paced and self-directed access to information and support anonymously and at any time. However, this can be more complicated than it might at first seem. With the complexities of the prostate cancer diagnosis, the multiple treatment options, and the uncertain but potentially serious effects of the treatments themselves, the amount of potentially relevant information is quite large. Then, because individuals will value differentially the attributes of treatments, their consequences, or even notions of risk and gain, a system must be able to respond appropriately to a range of very different people. Beyond this, as prostate cancer patients move from the shock of a cancer diagnosis to the problems of interpreting its details, to making treatment decisions, to dealing with problems of recovery, and then re-establishing what is a “new normal” for them, an individual’s demands on a system vary as well. Comprehensive and integrated systems of services meet the varying needs of their users at different times and different situations.18,19 The systems approach not only makes it far easier for users to find what they need, it may also encourage them to see connections between physical, emotional, and social aspects of their illness. Versions of the system used in the present study – CHESS, or Comprehensive Health Enhancement Support System – have been effective supporting patients with AIDS and breast and lung cancers, and teens with asthma.16,20
Study goals and hypotheses
Given the success of the 2 aforementioned approaches, we wanted to compare how CHESS and ongoing contact with a human cancer information mentor in patients with prostate cancer would affect both several general aspects of quality of life and 1 specific to prostate cancer. We also examined differences in the patients’ information competence, quality of life, and social support. There was no a priori expectation that one intervention would be superior to the other, but any differences found could be important to policy decisions, given their quite-different cost and scalability.
More importantly, the primary hypothesis of the study was that patients with access to both CHESS and a mentor would experience substantially better outcomes than those with access to either intervention alone, because each had the potential to enhance the other’s benefits. For example, a patient could read CHESS material and come to the mentor much better prepared. By referring the user to specific parts of CHESS for basic information, the mentor could use calls to address more complex issues, or help interpret and evaluate difficult issues. In addition, because CHESS provides the mentor information about changes in the patient’s treatments, symptoms, and CHESS use, in the combined condition the cancer information mentor can know much more about the patient than when working alone. We also expected that the mentor would stimulate the kind of diverse use of CHESS services we have found to be most effective
Because both mentoring and CHESS have consistently produced positive quality of life effects on their own, compared to controls, there is no reasonable expectation that negative effects of a combined condition could occur and should be tested for. Thus, the study was powered for 1-tailed significance in the comparison between the combined condition and either intervention alone, a procedure used consistently in previous studies of CHESS components or combined conditions. However, since the research question comparing the 2 interventions alone had no such strong history it was tested 2-tailed.
Methods
Recruitment
Study recruitment was conducted from January 1, 2007 to September 30, 2008 at the University of Wisconsin’s Paul P Carbone Comprehensive Cancer Center in Madison, Hartford Hospital’s Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center in Hartford, Connecticut, and The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
A total of 461 patients were invited to participate in the study. Of those patients, 147 declined to participate, 4 were excluded, and 310 were randomized to access to CHESS only, access to a human mentor only, or access to CHESS and a mentor (CHESS+Mentor) during the 6-month intervention period, which provided adequate power (>.80) for effects of moderate size (Figure 1). Randomization was done with a computer-generated list that site study managers accessed on a patient-by-patient basis, with experimental conditions blocked within sites.
Recruitment was done by posting brochures about the study at the relevant locations and devising standardized recruitment scripts for clinical staff to use when talking to patients about the study. Staff at all sites invited patients they thought might be eligible to learn more about the study. As appropriate, staff members then reviewed informed consent and HIPAA information, explained the interventions, answered patient questions, obtained written consent, collected complete patient contact and computer access information, and provided patients the baseline questionnaires.
The standard inclusion criteria were: men older than 17 years, being able to read and understand English, and being within 2 months of a diagnosis of primary prostate cancer (stage 1 or 2) at the time of recruitment. Despite the 2-month window, few men had begun treatment before pretest. Only 9 of the 310 participants reported having already had surgery (7 prostatectomies, 2 implants), so participants may be fairly characterized as beginning the study in time to benefit from interventions during most stages of their experience with prostate cancer.
Interventions
To provide an equal baseline, all of the participants were given access to the Internet, which is becoming a de facto standard for information access. Internet access charges were paid for all participants during the 6-month intervention period, and computers were loaned to those who did not have a personal computer. All of the participants were offered training on using the computer, particularly with Google search procedures so that they could access resources on prostate cancer.
Participants assigned to the CHESS or CHESS+Mentor conditions were also offered training in using CHESS (basically a guided tour), which typically took about 30 minutes on the telephone but was occasionally done in-person.
CHESS intervention. In creating CHESS for prostate cancer patients, a combination of patient needs assessments, focus groups with patients and family members, and clinician expertise helped us identify the needs, coping mechanisms, and relevant medical information to help patients respond to the disease. An article describing development of the CHESS Prostate Cancer Module22 presents how those different services address patient needs for information, communication, and support, or build skills.
Most of these services were present in CHESS for other diseases, but several were newly created to meet needs of prostate cancer patients and partners, such as a decision map tool and a module on managing sexual problems.22 Also, patients expressed frustration at being overwhelmed by the volume of information and said they would prefer to focus only on what was most relevant, so we created an alternative navigation structure on the CHESS homepage. Using terms suggested by focus groups of prostate cancer survivors and their spouses, we devised a navigation structure called Step-by-Step that identified 6 typical sequential steps of men’s experience with prostate cancer. Clicking on a step would take a patient to a menu focused on actions and considerations specific to that disease step, links to information most relevant at that step, and suggested questions to ask oneself and one’s doctor.
Mentor intervention. The cancer information mentor who made most of the calls to patients was an experienced information specialist with the Cancer Information Service and had served as the expert for the CHESS Ask an Expert service for 6 years. She was highly knowledgeable about prostate cancer and patient information needs. Her additional training for this study focused on taking advantage of repeated contacts with the participants and how to set limits to avoid any semblance of psychological counseling. At recruitment, we made clear that a male mentor was also available if the participant would prefer to discuss sensitive topics with another man. The male mentor was experienced in the Man-to-Man program and received additional training for this role, but he was used for only 1% of all contacts.
During calls, the mentor had Internet access to a range of NCI, ACS, and other resources. She could help interpret information the participant already possessed as well as refer him to other public resources, including those on the Internet. CHESS software designers created an additional interface for the mentor that handled call scheduling and allowed her to record the topics of conversations, her responses and recommendations, and her overall ratings of patient preparedness and satisfaction. Using this interface allowed the mentor to quickly review a participant’s status and focus the conversation on issues raised by past conversations or scheduled treatment events. The mentor calls were audiorecorded and reviewed frequently by the project director during the early months of intervention and less frequently thereafter to ensure adherence to the protocol.
The mentor telephoned weekly during the first month of intervention, then twice during the second month, and once a month during the final 4 months of the intervention (ie, 10 scheduled calls, though patients could also initiate additional calls). Calls were scheduled through a combination of telephone contact and e-mail according to the patient’s preference. Call length ranged from 5 minutes to an hour, with the average about 12 minutes (the first call tended to be considerably longer, and was scheduled for 45 minutes). About 10%-15% of participants in the Mentor conditions initiated calls to the mentor to obtain additional support, and about 15% of scheduled calls in fact took place as e-mail exchanges. A few calls were missed because of scheduling difficulties, and some participants stopped scheduling the last few calls, but the average number of full calls or e-mails was 6.41 per participant.
CHESS+Mentor intervention. For the CHESS+Mentor condition, the interactions and resources used were similar to those of the Mentor-only condition, but the interface also provided the mentor with a summary of the participant’s recent CHESS use and any concerns reported to CHESS, which helped the mentor assess knowledge and make tailored recommendations. The mentor could also refer participants to specific resources within CHESS, aided by knowledge of what parts of CHESS had or had not been used.
Assessment methods
Patients were given surveys at the baseline visit to complete and mail back to research staff before randomization. Follow-up surveys were mailed to patients at 2, 6, 12, and 24 weeks post intervention access, and patients returned the surveys by mail. Patient withdrawal rates were about 3%.
Measures
Outcomes. This study included 4 measures of quality of life (an average of relevant portions of the World Health Organization’s Quality of Life (WHOQOL) measure, Emotional and Functional Well-being, and a prostate-cancer specific index, the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC). We also tested group differences on 5 more specific outcomes that were likely to be proximal rather than distal effects of the interventions: Cancer Information Competence, Health care Competence, Social Support, Bonding (with other patients), and Positive Coping.
Quality of life. Quality of life was measured by combining the psychological, social, and overall dimensions of the WHOQOL measures.23 Each of the 11 items was assessed with a 5-point scale, and the mean of those answers was the overall score.
Emotional well-being. Respondents answered 6 items of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Prostate
Functional well-being. Respondents indicated how often they experienced each of the seven functional well-being subscale items of the FACT-Prostate.24
Prostate cancer patient functioning. We used the EPIC to measure of 3 of 4 domains of prostate cancer patient functioning: urinary, bowel, and sexual (omitting hormonal).25 The EPIC measures frequency and subjective degree of being a problem of several aspects in each domain. We then summed scores across the domains and transformed linearly to a 0-100 scale, with higher scores representing better functioning.
Cancer information competence. Five cancer information competence items, measured on a 5-point scale, assessed a participant’s perception about whether he could find and effectively and use health information, and were summed to create a single score.20
Social support. Six 5-point social support items assessed the informational and emotional support provided by friends, family, coworkers, and others, and were summed to create a single score.20
Health care competence. Five 5-point health care competence items assessed a patient’s comfort and activation level dealing with physicians and health care situations, and were summed to create a single score.20
Positive coping. Coping strategies were measured with the Brief Cope, a shorter version of the original 60-item COPE scale.26 Positive coping strategy, a predictor of positive adaptation in numerous coping contexts, was measured with the mean score of 4 scales (8 items in all): active coping, planning, positive reframing, and humor.
Bonding. Bonding with other prostate cancer patients was measured with five 5-point items about how frequently participants connected with and got information and support from other men with prostate cancer.27
User vs nonuser. Intent-to-treat analyses compared the assigned conditions. However, because CHESS use was self-selected and available at any time whereas mentor calls were scheduled and initiated by another person, the proportion actually using the interventions was quite different.
Since a participant assigned access to CHESS had to select the URL, even a single entry to the system was counted as use. Of 198 participants assigned to either the CHESS or CHESS+Mentor conditions, 43 (22%) never logged in and were classified as nonusers.
Because the mentor scheduled calls and attempted repeatedly to complete scheduled calls, the patient was in a reactive position, and the decision not to use the mentor’s services could come at the earliest at the end of a first completed call. However, after examining call notes and consulting with the mentors, it was clear that opting not to receive mentoring typically occurred at the second call. Furthermore, much (though not all) of the first call was typically taken up with getting acquainted and scheduling issues, so that defining “nonuse” as 2 or fewer completed calls was most faithful to what actually happened. Of 202 participants assigned access to a mentor, 16 (8%) were thus defined as nonusers.
Results
Overall, the participants were about 60 years of age and had some college education and middle-class incomes (Table 1). Only about 10% were minorities or lived alone, and their comfort using computers and the Internet was at or above the “quite comfortable” level. None of groups differed significantly from any other.
The 2 primary hypotheses of the study were that participants in the combined condition would manifest higher outcome scores than those with either intervention alone. Table 2 displays group means at 3 posttest intervals, controlling for theoretically chosen covariates (age, education, and minority status) and pretest levels of the dependent variable. The table also summarizes tests examining the hypotheses and the comparison of CHESS and Mentor conditions. The 4 quality-of-life scores appear first, followed by 5 more specific outcomes that are perhaps more proximal effects of these interventions.
The combined condition scored significantly higher than the CHESS-only condition on functional well-being at 3 months, on positive coping at 6 months, and on bonding at both 6 weeks and 6 months. The combined condition scored significantly higher than Mentor-only on health care competence and positive coping at 6 weeks, and on bonding at 6 months. This represents partial but scattered support for the hypotheses. And some comparisons of the combined condition with the Mentor-only condition showed reversals of the predicted relationship (although only cancer information competence at 3 months would have reached statistical significance in a 2-tailed test).
No directional hypotheses were made for the comparison of the 2 interventions (see Table 2 for the results of 2-tailed tests). Participants in the Mentor condition reported significantly higher functional well-being at 3 months, although there were 5 other comparisons in which the Mentor group scored higher at P < .10, and higher than the CHESS group on 22 of the 27 comparisons. Thus, it seemed that the Mentor condition alone might have been a somewhat stronger intervention than CHESS alone.
Discussion
We used a randomized control design to test whether combining computer-based and human interventions would provide greater benefits to prostate cancer patients than either alone, as previous research had shown for breast cancer patients.18 The computer-based resource was CHESS, a repeatedly evaluated integrated system combining information, social support, and interactive tools to help patients manage their response to disease. The human cancer information mentor intervention combined the expertise of NCI’s Cancer Information Service with the repeated contact more typical of peer mentoring. Previous research with breast cancer patients had shown both interventions to provide greater information, support, and quality-of-life benefits than Internet access alone.14 This study also compared outcomes obtained by the separate CHESS and Mentor conditions, but without predicting a direction of difference.
Tests at 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months after intervention found instances in which prostate cancer patients assigned to the combined CHESS+Mentor condition experienced more positive quality of life or other outcomes than those assigned to CHESS or Mentor alone, but those differences were scattered rather than consistent. In the direct comparisons of the separate CHESS and Mentor conditions, significance was even rarer, but outcome scores tended to be higher in the Mentor condition than in the CHESS condition.
We noted that differential uptake of the 2 interventions (92% for Mentor vs 78% for CHESS) made interpreting the intent-to-treat analyses problematic, as the mentor’s control of the call schedule meant that far more patients in that condition actually received at least some intervention than in the CHESS condition, where patients used or did not use CHESS entirely at their own volition. This could have biased results in several ways, such as by underestimating the efficacy of the CHESS condition alone and thus inflating the contrast between CHESS alone and CHESS+Mentor. Or the combined condition might have been less different than the Mentor-only condition than intended, thus making for a conservative test of that comparison. However, post hoc analyses of only those participants who had actually used their assigned interventions (and this led to some reclassification of those originally assigned to the CHESS+Mentor condition) produced results that were little different than the intent-to-treat analysis.
Thus, although the combined condition produced some small advantages over either intervention alone, these advantages did not live up to expectations or to previous experience with breast cancer patients.17 We expected the mentor to be able to reinforce and help interpret what the participants learned from CHESS and their clinicians, and also to advise and direct these patients to be much more effective users of CHESS and other resources. Similarly, we expected that CHESS would make patients much better prepared for mentoring, so that instead of dealing with routine information matters, the mentor could go into greater detail or deal with more complex issues. Their combined effect should have been much larger than each alone, and that was not the case. Perhaps from the prostate cancer patients’ perspective, the 2 interventions seemed to offer similar resources, and a patient benefitted from one or the other but expected no additional gain from attending to both.
The 2 interventions themselves seemed nearly equally effective. The Mentor intervention was significantly stronger than CHESS in only 1 of 27 tests in the intent-to-treat analysis and 2 in the analysis limited to intervention users.
These results for prostate cancer patients are somewhat weaker than those previously reported with breast cancer patients.17 It is possible that prostate cancer patients (or men in general) are less inclined to seek health information, support, and health self-management than breast cancer patients (or women in general), perhaps becaus
Although these interventions were experienced by prostate cancer patients in their homes in natural and familiar ways, any experimental manipulation must acknowledge possible problems with external validity. More important here, our recruitment procedures may have produced self-selection to enter or not enter the study in 2 ways that limit its applicability. First, although we thought that offering Internet access to all participants would make participation more likely, the most frequent reason men gave in declining to join the study was “not a computer person.” Our participants were certainly very comfortable with computers and the Internet, and most used them frequently even before the study. Second, it seems that, except for their prostate cancer, our sample was healthy in other respects, as indicated by the low number of other health care visits or surgeries/hospitalization they reported (and “overwhelmed” and “too busy,” 2 common reasons for declining study participations could also be coming from men with more comorbidities). Thus, our sample was probably more computer literate and healthier than the general population of prostate cancer patients.
Nonetheless, for policymakers deciding what information and support interventions to put in place for prostate cancer patients (or more generally for other cancer patients as well), these results have 2 implications. First, since the combination of the mentor and CHESS produced only small advantages over either alone, the extra effort of doing both seems clearly unwarranted for prostate cancer patients. The somewhat larger advantage of the combined intervention shown for breast cancer patients in previous studiesmight warrant using the combination in some circumstances, but even that is not clear-cut.
Finding that CHESS and the cancer information mentor separately provided essentially equal benefits might seem to suggest that they can be regarded as alternatives. However, computer-based services can be provided much more cheaply and scaled up far more readily than services dependent on one-on-one contacts by a highly trained professional. This may direct health care decision makers first toward computer-based services.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in men. 1 Treatment choices for prostate cancer are perhaps more varied than for many other cancers, with surgery, external beam radiation therapy, and brachytherapy all widely used, a number of adjuvant and nonstandard therapy options available, as well as the possibility of not immediately treating the cancer – the “active surveillance” option.
Biochemical failure rates do not differ between the 3 main treatments,2 but each exposes patients to the risk of side effects, including impotence, incontinence, rectal injury, and operative mortality. Recovery can be gradual and will not always involve a return to baseline functioning.3 Quality-of-life comparisons observed covariate-controlled decreases in varying specific aspects of quality of life for each of the treatments.4
Surgery, brachytherapy, and external beam radiation therapy have each shown advantages over other treatments on at least some specific aspect, but disadvantages on others.4 Ongoing surveillance of a cancer left in place has become a more common option in part because of the disadvantages of traditional treatment and because of the growing recognition that sensitive diagnosis techniques often locate cancers that might not be life threatening. Recent reviews and reasonably long-term trials portray active surveillance as a valid alternative to surgery and radiation in many cases, with little difference in life expectancy and cancer-related quality of life, and possibly some reduction in health system cost.5-7
Prostate cancer patients cope with these uncertainties and decisions in many ways,8 often using multiple coping behaviors,9 but coping almost always includes seeking information and social support, as well as active problem-solving, to make informed treatment decisions consistent with their values.
Unfortunately, prostate patients often do not receive or use needed information. McGregor10 reported that patients were aware of their incomplete understanding of their disease and treatment options. Findings from several studies suggest that patients often perceive that clinicians inform them about the disease and treatment options but then send them home unprepared to deal with such things as incontinence or difficulties with sexual functioning.11
Similarly, previous research demonstrates the benefits of social support for prostate cancer patients who receive it, but also that overall they are underserved.12,13 Male cancer patients are generally far less likely to seek support and health information than are female patients. And when patients with prostate cancer do participate in online cancer support groups, they are more likely to exchange information, whereas breast cancer patients provide support for each other.14
Mentoring
Some responses to these knowledge and support gaps pair newly diagnosed patients with survivors willing to be a guide, coach, and a source of information, as in the American Cancer Society’s (ACS’s) Man-to-Man support groups.15 Peer mentors may have a sophisticated level of understanding from their own experiences with medical literature and the health care system, but this cannot be assumed. Another mentoring model is expert-based, exemplified by the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI’s) cancer information specialist at the Cancer Information Service (CIS) and a similar system at the ACS. These telephone services allow for responsiveness to the caller’s needs, existing knowledge, and the caller’s readiness for information. The CIS specialist can also introduce important information the caller might not have known to ask about.16
However, not all problems presented by callers can be solved in a single conversation. Callers are encouraged to call back with additional questions or when their situation changes, but speaking with the same specialist is not facilitated, so it is hard for a second call to build upon the first. Combining the expertise of the cancer information specialist with the ongoing and proactive contact and support typical of the lay guide/mentor/navigator could be more effective. Here a CIS-trained information specialist called prostate patients multiple times over the intervention period to help them deal with information seeking and interpretation. In a previous study with breast cancer patients, a mentor of this sort improved patient information competence and emotional processing.17
Interactive resources
Online resources allow cancer patients self-paced and self-directed access to information and support anonymously and at any time. However, this can be more complicated than it might at first seem. With the complexities of the prostate cancer diagnosis, the multiple treatment options, and the uncertain but potentially serious effects of the treatments themselves, the amount of potentially relevant information is quite large. Then, because individuals will value differentially the attributes of treatments, their consequences, or even notions of risk and gain, a system must be able to respond appropriately to a range of very different people. Beyond this, as prostate cancer patients move from the shock of a cancer diagnosis to the problems of interpreting its details, to making treatment decisions, to dealing with problems of recovery, and then re-establishing what is a “new normal” for them, an individual’s demands on a system vary as well. Comprehensive and integrated systems of services meet the varying needs of their users at different times and different situations.18,19 The systems approach not only makes it far easier for users to find what they need, it may also encourage them to see connections between physical, emotional, and social aspects of their illness. Versions of the system used in the present study – CHESS, or Comprehensive Health Enhancement Support System – have been effective supporting patients with AIDS and breast and lung cancers, and teens with asthma.16,20
Study goals and hypotheses
Given the success of the 2 aforementioned approaches, we wanted to compare how CHESS and ongoing contact with a human cancer information mentor in patients with prostate cancer would affect both several general aspects of quality of life and 1 specific to prostate cancer. We also examined differences in the patients’ information competence, quality of life, and social support. There was no a priori expectation that one intervention would be superior to the other, but any differences found could be important to policy decisions, given their quite-different cost and scalability.
More importantly, the primary hypothesis of the study was that patients with access to both CHESS and a mentor would experience substantially better outcomes than those with access to either intervention alone, because each had the potential to enhance the other’s benefits. For example, a patient could read CHESS material and come to the mentor much better prepared. By referring the user to specific parts of CHESS for basic information, the mentor could use calls to address more complex issues, or help interpret and evaluate difficult issues. In addition, because CHESS provides the mentor information about changes in the patient’s treatments, symptoms, and CHESS use, in the combined condition the cancer information mentor can know much more about the patient than when working alone. We also expected that the mentor would stimulate the kind of diverse use of CHESS services we have found to be most effective
Because both mentoring and CHESS have consistently produced positive quality of life effects on their own, compared to controls, there is no reasonable expectation that negative effects of a combined condition could occur and should be tested for. Thus, the study was powered for 1-tailed significance in the comparison between the combined condition and either intervention alone, a procedure used consistently in previous studies of CHESS components or combined conditions. However, since the research question comparing the 2 interventions alone had no such strong history it was tested 2-tailed.
Methods
Recruitment
Study recruitment was conducted from January 1, 2007 to September 30, 2008 at the University of Wisconsin’s Paul P Carbone Comprehensive Cancer Center in Madison, Hartford Hospital’s Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center in Hartford, Connecticut, and The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
A total of 461 patients were invited to participate in the study. Of those patients, 147 declined to participate, 4 were excluded, and 310 were randomized to access to CHESS only, access to a human mentor only, or access to CHESS and a mentor (CHESS+Mentor) during the 6-month intervention period, which provided adequate power (>.80) for effects of moderate size (Figure 1). Randomization was done with a computer-generated list that site study managers accessed on a patient-by-patient basis, with experimental conditions blocked within sites.
Recruitment was done by posting brochures about the study at the relevant locations and devising standardized recruitment scripts for clinical staff to use when talking to patients about the study. Staff at all sites invited patients they thought might be eligible to learn more about the study. As appropriate, staff members then reviewed informed consent and HIPAA information, explained the interventions, answered patient questions, obtained written consent, collected complete patient contact and computer access information, and provided patients the baseline questionnaires.
The standard inclusion criteria were: men older than 17 years, being able to read and understand English, and being within 2 months of a diagnosis of primary prostate cancer (stage 1 or 2) at the time of recruitment. Despite the 2-month window, few men had begun treatment before pretest. Only 9 of the 310 participants reported having already had surgery (7 prostatectomies, 2 implants), so participants may be fairly characterized as beginning the study in time to benefit from interventions during most stages of their experience with prostate cancer.
Interventions
To provide an equal baseline, all of the participants were given access to the Internet, which is becoming a de facto standard for information access. Internet access charges were paid for all participants during the 6-month intervention period, and computers were loaned to those who did not have a personal computer. All of the participants were offered training on using the computer, particularly with Google search procedures so that they could access resources on prostate cancer.
Participants assigned to the CHESS or CHESS+Mentor conditions were also offered training in using CHESS (basically a guided tour), which typically took about 30 minutes on the telephone but was occasionally done in-person.
CHESS intervention. In creating CHESS for prostate cancer patients, a combination of patient needs assessments, focus groups with patients and family members, and clinician expertise helped us identify the needs, coping mechanisms, and relevant medical information to help patients respond to the disease. An article describing development of the CHESS Prostate Cancer Module22 presents how those different services address patient needs for information, communication, and support, or build skills.
Most of these services were present in CHESS for other diseases, but several were newly created to meet needs of prostate cancer patients and partners, such as a decision map tool and a module on managing sexual problems.22 Also, patients expressed frustration at being overwhelmed by the volume of information and said they would prefer to focus only on what was most relevant, so we created an alternative navigation structure on the CHESS homepage. Using terms suggested by focus groups of prostate cancer survivors and their spouses, we devised a navigation structure called Step-by-Step that identified 6 typical sequential steps of men’s experience with prostate cancer. Clicking on a step would take a patient to a menu focused on actions and considerations specific to that disease step, links to information most relevant at that step, and suggested questions to ask oneself and one’s doctor.
Mentor intervention. The cancer information mentor who made most of the calls to patients was an experienced information specialist with the Cancer Information Service and had served as the expert for the CHESS Ask an Expert service for 6 years. She was highly knowledgeable about prostate cancer and patient information needs. Her additional training for this study focused on taking advantage of repeated contacts with the participants and how to set limits to avoid any semblance of psychological counseling. At recruitment, we made clear that a male mentor was also available if the participant would prefer to discuss sensitive topics with another man. The male mentor was experienced in the Man-to-Man program and received additional training for this role, but he was used for only 1% of all contacts.
During calls, the mentor had Internet access to a range of NCI, ACS, and other resources. She could help interpret information the participant already possessed as well as refer him to other public resources, including those on the Internet. CHESS software designers created an additional interface for the mentor that handled call scheduling and allowed her to record the topics of conversations, her responses and recommendations, and her overall ratings of patient preparedness and satisfaction. Using this interface allowed the mentor to quickly review a participant’s status and focus the conversation on issues raised by past conversations or scheduled treatment events. The mentor calls were audiorecorded and reviewed frequently by the project director during the early months of intervention and less frequently thereafter to ensure adherence to the protocol.
The mentor telephoned weekly during the first month of intervention, then twice during the second month, and once a month during the final 4 months of the intervention (ie, 10 scheduled calls, though patients could also initiate additional calls). Calls were scheduled through a combination of telephone contact and e-mail according to the patient’s preference. Call length ranged from 5 minutes to an hour, with the average about 12 minutes (the first call tended to be considerably longer, and was scheduled for 45 minutes). About 10%-15% of participants in the Mentor conditions initiated calls to the mentor to obtain additional support, and about 15% of scheduled calls in fact took place as e-mail exchanges. A few calls were missed because of scheduling difficulties, and some participants stopped scheduling the last few calls, but the average number of full calls or e-mails was 6.41 per participant.
CHESS+Mentor intervention. For the CHESS+Mentor condition, the interactions and resources used were similar to those of the Mentor-only condition, but the interface also provided the mentor with a summary of the participant’s recent CHESS use and any concerns reported to CHESS, which helped the mentor assess knowledge and make tailored recommendations. The mentor could also refer participants to specific resources within CHESS, aided by knowledge of what parts of CHESS had or had not been used.
Assessment methods
Patients were given surveys at the baseline visit to complete and mail back to research staff before randomization. Follow-up surveys were mailed to patients at 2, 6, 12, and 24 weeks post intervention access, and patients returned the surveys by mail. Patient withdrawal rates were about 3%.
Measures
Outcomes. This study included 4 measures of quality of life (an average of relevant portions of the World Health Organization’s Quality of Life (WHOQOL) measure, Emotional and Functional Well-being, and a prostate-cancer specific index, the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC). We also tested group differences on 5 more specific outcomes that were likely to be proximal rather than distal effects of the interventions: Cancer Information Competence, Health care Competence, Social Support, Bonding (with other patients), and Positive Coping.
Quality of life. Quality of life was measured by combining the psychological, social, and overall dimensions of the WHOQOL measures.23 Each of the 11 items was assessed with a 5-point scale, and the mean of those answers was the overall score.
Emotional well-being. Respondents answered 6 items of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Prostate
Functional well-being. Respondents indicated how often they experienced each of the seven functional well-being subscale items of the FACT-Prostate.24
Prostate cancer patient functioning. We used the EPIC to measure of 3 of 4 domains of prostate cancer patient functioning: urinary, bowel, and sexual (omitting hormonal).25 The EPIC measures frequency and subjective degree of being a problem of several aspects in each domain. We then summed scores across the domains and transformed linearly to a 0-100 scale, with higher scores representing better functioning.
Cancer information competence. Five cancer information competence items, measured on a 5-point scale, assessed a participant’s perception about whether he could find and effectively and use health information, and were summed to create a single score.20
Social support. Six 5-point social support items assessed the informational and emotional support provided by friends, family, coworkers, and others, and were summed to create a single score.20
Health care competence. Five 5-point health care competence items assessed a patient’s comfort and activation level dealing with physicians and health care situations, and were summed to create a single score.20
Positive coping. Coping strategies were measured with the Brief Cope, a shorter version of the original 60-item COPE scale.26 Positive coping strategy, a predictor of positive adaptation in numerous coping contexts, was measured with the mean score of 4 scales (8 items in all): active coping, planning, positive reframing, and humor.
Bonding. Bonding with other prostate cancer patients was measured with five 5-point items about how frequently participants connected with and got information and support from other men with prostate cancer.27
User vs nonuser. Intent-to-treat analyses compared the assigned conditions. However, because CHESS use was self-selected and available at any time whereas mentor calls were scheduled and initiated by another person, the proportion actually using the interventions was quite different.
Since a participant assigned access to CHESS had to select the URL, even a single entry to the system was counted as use. Of 198 participants assigned to either the CHESS or CHESS+Mentor conditions, 43 (22%) never logged in and were classified as nonusers.
Because the mentor scheduled calls and attempted repeatedly to complete scheduled calls, the patient was in a reactive position, and the decision not to use the mentor’s services could come at the earliest at the end of a first completed call. However, after examining call notes and consulting with the mentors, it was clear that opting not to receive mentoring typically occurred at the second call. Furthermore, much (though not all) of the first call was typically taken up with getting acquainted and scheduling issues, so that defining “nonuse” as 2 or fewer completed calls was most faithful to what actually happened. Of 202 participants assigned access to a mentor, 16 (8%) were thus defined as nonusers.
Results
Overall, the participants were about 60 years of age and had some college education and middle-class incomes (Table 1). Only about 10% were minorities or lived alone, and their comfort using computers and the Internet was at or above the “quite comfortable” level. None of groups differed significantly from any other.
The 2 primary hypotheses of the study were that participants in the combined condition would manifest higher outcome scores than those with either intervention alone. Table 2 displays group means at 3 posttest intervals, controlling for theoretically chosen covariates (age, education, and minority status) and pretest levels of the dependent variable. The table also summarizes tests examining the hypotheses and the comparison of CHESS and Mentor conditions. The 4 quality-of-life scores appear first, followed by 5 more specific outcomes that are perhaps more proximal effects of these interventions.
The combined condition scored significantly higher than the CHESS-only condition on functional well-being at 3 months, on positive coping at 6 months, and on bonding at both 6 weeks and 6 months. The combined condition scored significantly higher than Mentor-only on health care competence and positive coping at 6 weeks, and on bonding at 6 months. This represents partial but scattered support for the hypotheses. And some comparisons of the combined condition with the Mentor-only condition showed reversals of the predicted relationship (although only cancer information competence at 3 months would have reached statistical significance in a 2-tailed test).
No directional hypotheses were made for the comparison of the 2 interventions (see Table 2 for the results of 2-tailed tests). Participants in the Mentor condition reported significantly higher functional well-being at 3 months, although there were 5 other comparisons in which the Mentor group scored higher at P < .10, and higher than the CHESS group on 22 of the 27 comparisons. Thus, it seemed that the Mentor condition alone might have been a somewhat stronger intervention than CHESS alone.
Discussion
We used a randomized control design to test whether combining computer-based and human interventions would provide greater benefits to prostate cancer patients than either alone, as previous research had shown for breast cancer patients.18 The computer-based resource was CHESS, a repeatedly evaluated integrated system combining information, social support, and interactive tools to help patients manage their response to disease. The human cancer information mentor intervention combined the expertise of NCI’s Cancer Information Service with the repeated contact more typical of peer mentoring. Previous research with breast cancer patients had shown both interventions to provide greater information, support, and quality-of-life benefits than Internet access alone.14 This study also compared outcomes obtained by the separate CHESS and Mentor conditions, but without predicting a direction of difference.
Tests at 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months after intervention found instances in which prostate cancer patients assigned to the combined CHESS+Mentor condition experienced more positive quality of life or other outcomes than those assigned to CHESS or Mentor alone, but those differences were scattered rather than consistent. In the direct comparisons of the separate CHESS and Mentor conditions, significance was even rarer, but outcome scores tended to be higher in the Mentor condition than in the CHESS condition.
We noted that differential uptake of the 2 interventions (92% for Mentor vs 78% for CHESS) made interpreting the intent-to-treat analyses problematic, as the mentor’s control of the call schedule meant that far more patients in that condition actually received at least some intervention than in the CHESS condition, where patients used or did not use CHESS entirely at their own volition. This could have biased results in several ways, such as by underestimating the efficacy of the CHESS condition alone and thus inflating the contrast between CHESS alone and CHESS+Mentor. Or the combined condition might have been less different than the Mentor-only condition than intended, thus making for a conservative test of that comparison. However, post hoc analyses of only those participants who had actually used their assigned interventions (and this led to some reclassification of those originally assigned to the CHESS+Mentor condition) produced results that were little different than the intent-to-treat analysis.
Thus, although the combined condition produced some small advantages over either intervention alone, these advantages did not live up to expectations or to previous experience with breast cancer patients.17 We expected the mentor to be able to reinforce and help interpret what the participants learned from CHESS and their clinicians, and also to advise and direct these patients to be much more effective users of CHESS and other resources. Similarly, we expected that CHESS would make patients much better prepared for mentoring, so that instead of dealing with routine information matters, the mentor could go into greater detail or deal with more complex issues. Their combined effect should have been much larger than each alone, and that was not the case. Perhaps from the prostate cancer patients’ perspective, the 2 interventions seemed to offer similar resources, and a patient benefitted from one or the other but expected no additional gain from attending to both.
The 2 interventions themselves seemed nearly equally effective. The Mentor intervention was significantly stronger than CHESS in only 1 of 27 tests in the intent-to-treat analysis and 2 in the analysis limited to intervention users.
These results for prostate cancer patients are somewhat weaker than those previously reported with breast cancer patients.17 It is possible that prostate cancer patients (or men in general) are less inclined to seek health information, support, and health self-management than breast cancer patients (or women in general), perhaps becaus
Although these interventions were experienced by prostate cancer patients in their homes in natural and familiar ways, any experimental manipulation must acknowledge possible problems with external validity. More important here, our recruitment procedures may have produced self-selection to enter or not enter the study in 2 ways that limit its applicability. First, although we thought that offering Internet access to all participants would make participation more likely, the most frequent reason men gave in declining to join the study was “not a computer person.” Our participants were certainly very comfortable with computers and the Internet, and most used them frequently even before the study. Second, it seems that, except for their prostate cancer, our sample was healthy in other respects, as indicated by the low number of other health care visits or surgeries/hospitalization they reported (and “overwhelmed” and “too busy,” 2 common reasons for declining study participations could also be coming from men with more comorbidities). Thus, our sample was probably more computer literate and healthier than the general population of prostate cancer patients.
Nonetheless, for policymakers deciding what information and support interventions to put in place for prostate cancer patients (or more generally for other cancer patients as well), these results have 2 implications. First, since the combination of the mentor and CHESS produced only small advantages over either alone, the extra effort of doing both seems clearly unwarranted for prostate cancer patients. The somewhat larger advantage of the combined intervention shown for breast cancer patients in previous studiesmight warrant using the combination in some circumstances, but even that is not clear-cut.
Finding that CHESS and the cancer information mentor separately provided essentially equal benefits might seem to suggest that they can be regarded as alternatives. However, computer-based services can be provided much more cheaply and scaled up far more readily than services dependent on one-on-one contacts by a highly trained professional. This may direct health care decision makers first toward computer-based services.
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277-300.
2. Cozzarini C. Low-dose rate brachytherapy, radical prostatectomy, or external-beam radiation therapy for localized prostate carcinoma: The growing dilemma. European Urology. 2011;60(5):894-896.
3. Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1250-1261.
4. Ferrer F, Guedea F, Pardo Y, et al. Quality of life impact of treatments for localized prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2013;108(2):306-313.
5. Cooperberg, MR, Carroll, PR, Klotz, L. Active Surveillance for prostate cancer: progress and promise. J Clin Onc. 2011;29:3669-3676.
6. Hamdy, FC, Donovan JL, Lane JA, et al. 10-year outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1415-1424.
7. Donovan JL, Hamdy FC, Lane JA, et al. Patient-reported outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1425-37.
8. Lavery JF, Clarke VA. Prostate cancer: patients’ spouses’ coping and marital adjustment. Psychol Health Med. 1999;4(3):289-302.
9. Folkman S, Lazarus R. If it changes it must be a process: study of emotion and coping during three stages of a college examination. J Pers Soc Psycol. 1985;48:150-170.
10. McGregor S. What information patients with localized prostate cancer hear and understand. Patient Educ Couns. 2003;49:273-278.
11. Steginga SK, Occhipinti S, Dunn J, Gardiner RA, Heathcote P, Yaxley J. (2001) The supportive care needs of men with prostate cancer (2000). Psychooncology. 2001;10(1):66-75.
12. Gregoire I, Kalogeropoulos D, Corcos J. The effectiveness of a professionally led support group for men with prostate cancer. Urologic Nurs. 1997;17(2):58-66.
13. Katz D, Koppie T, Wu D, et al. Sociodemographic characteristics and health related quality of life in men attending prostate cancer support groups. J Urol. 2002;168:2092-2096.
14. Klemm P, Hurst M, Dearholt S, Trone S. Gender differences on Internet cancer support groups. Comput Nurs. 1999;17(2):65-72.
15. Gray R, Fitch M, Phillips C, Labrecque M, Fergus K. Managing the impact of illness: the experiences of men with prostate cancer and their spouses. J Health Psychol. 2000;5(4):531-548.
16. Thomsen CA, Ter Maat J. Evaluating the Cancer Information Service: a model for health communications. Part 1. J Health Commun. 1998;3(suppl.):1-13.
17. Hawkins RP, Pingree S, Baker TB, et al. Integrating eHealth with human services for breast cancer patients. Transl Behav Med. 2011;1(1):146-154.
18. Strecher V. Internet methods for delivering behavioral and health-related interventions. Ann Rev Clin Psychol. 2007;(3):53-76.
19. Gustafson DH, Hawkins RP, McTavish F, et al. Internet-based interactive support for cancer patients: Are integrated systems better? J Commun. 2008;58(2):238-257.
20. Gustafson DH, Hawkins RP, Boberg EW, et al. CHESS: Ten years of research and development in consumer health informatics for broad populations, including the underserved. Int J Med Inform. 2002;65(3):169-177.
21. Han JY, Hawkins RP, Shaw B, Pingree S, McTavish F, Gustafson D. Unraveling uses and effects of an interactive health communication system. J Broadcast Electron Media. 2009;53(1):1-22.
22. Van Bogaert D, Hawkins RP, Pingree S, Jarrard D. The development of an eHealth tool suite for prostate cancer patients and their partners. J Support Oncol. 2012;10(5):202-208.
23. The WHOQOL Group. Development of the WHOQOL: Rationale and current status. Int J Ment Health. 1994;23:24-56.
24. Esper P, Mo F, Chodak G, Sinner M, Cella D, Pienta KJ. Measuring quality of life in men with prostate cancer using the functional assessment of cancer therapy-prostate instrument. Urology. 1997;50:920-928.
25. Wei JT, Dunn R, Litwin M, Sandler H, Sanda MG. Development and validation of the expanded prostate cancer index composite (EPIC) for comprehensive assessment of health-related quality of life in men with prostate cancer. Urology. 2000;56:899-905.
26. Carver CS. You want to measure coping but your protocol’s too long: consider the brief COPE. Int J Behav Med. 1997;4: 91-100.
27. Gustafson D, McTavish F, Stengle W, et al. Use and impact of eHealth System by low-income women with breast cancer. J Health Commun. 2005;10(suppl 1):219-234.
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277-300.
2. Cozzarini C. Low-dose rate brachytherapy, radical prostatectomy, or external-beam radiation therapy for localized prostate carcinoma: The growing dilemma. European Urology. 2011;60(5):894-896.
3. Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1250-1261.
4. Ferrer F, Guedea F, Pardo Y, et al. Quality of life impact of treatments for localized prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2013;108(2):306-313.
5. Cooperberg, MR, Carroll, PR, Klotz, L. Active Surveillance for prostate cancer: progress and promise. J Clin Onc. 2011;29:3669-3676.
6. Hamdy, FC, Donovan JL, Lane JA, et al. 10-year outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1415-1424.
7. Donovan JL, Hamdy FC, Lane JA, et al. Patient-reported outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1425-37.
8. Lavery JF, Clarke VA. Prostate cancer: patients’ spouses’ coping and marital adjustment. Psychol Health Med. 1999;4(3):289-302.
9. Folkman S, Lazarus R. If it changes it must be a process: study of emotion and coping during three stages of a college examination. J Pers Soc Psycol. 1985;48:150-170.
10. McGregor S. What information patients with localized prostate cancer hear and understand. Patient Educ Couns. 2003;49:273-278.
11. Steginga SK, Occhipinti S, Dunn J, Gardiner RA, Heathcote P, Yaxley J. (2001) The supportive care needs of men with prostate cancer (2000). Psychooncology. 2001;10(1):66-75.
12. Gregoire I, Kalogeropoulos D, Corcos J. The effectiveness of a professionally led support group for men with prostate cancer. Urologic Nurs. 1997;17(2):58-66.
13. Katz D, Koppie T, Wu D, et al. Sociodemographic characteristics and health related quality of life in men attending prostate cancer support groups. J Urol. 2002;168:2092-2096.
14. Klemm P, Hurst M, Dearholt S, Trone S. Gender differences on Internet cancer support groups. Comput Nurs. 1999;17(2):65-72.
15. Gray R, Fitch M, Phillips C, Labrecque M, Fergus K. Managing the impact of illness: the experiences of men with prostate cancer and their spouses. J Health Psychol. 2000;5(4):531-548.
16. Thomsen CA, Ter Maat J. Evaluating the Cancer Information Service: a model for health communications. Part 1. J Health Commun. 1998;3(suppl.):1-13.
17. Hawkins RP, Pingree S, Baker TB, et al. Integrating eHealth with human services for breast cancer patients. Transl Behav Med. 2011;1(1):146-154.
18. Strecher V. Internet methods for delivering behavioral and health-related interventions. Ann Rev Clin Psychol. 2007;(3):53-76.
19. Gustafson DH, Hawkins RP, McTavish F, et al. Internet-based interactive support for cancer patients: Are integrated systems better? J Commun. 2008;58(2):238-257.
20. Gustafson DH, Hawkins RP, Boberg EW, et al. CHESS: Ten years of research and development in consumer health informatics for broad populations, including the underserved. Int J Med Inform. 2002;65(3):169-177.
21. Han JY, Hawkins RP, Shaw B, Pingree S, McTavish F, Gustafson D. Unraveling uses and effects of an interactive health communication system. J Broadcast Electron Media. 2009;53(1):1-22.
22. Van Bogaert D, Hawkins RP, Pingree S, Jarrard D. The development of an eHealth tool suite for prostate cancer patients and their partners. J Support Oncol. 2012;10(5):202-208.
23. The WHOQOL Group. Development of the WHOQOL: Rationale and current status. Int J Ment Health. 1994;23:24-56.
24. Esper P, Mo F, Chodak G, Sinner M, Cella D, Pienta KJ. Measuring quality of life in men with prostate cancer using the functional assessment of cancer therapy-prostate instrument. Urology. 1997;50:920-928.
25. Wei JT, Dunn R, Litwin M, Sandler H, Sanda MG. Development and validation of the expanded prostate cancer index composite (EPIC) for comprehensive assessment of health-related quality of life in men with prostate cancer. Urology. 2000;56:899-905.
26. Carver CS. You want to measure coping but your protocol’s too long: consider the brief COPE. Int J Behav Med. 1997;4: 91-100.
27. Gustafson D, McTavish F, Stengle W, et al. Use and impact of eHealth System by low-income women with breast cancer. J Health Commun. 2005;10(suppl 1):219-234.
Metastatic eccrine carcinoma with stomach and pericardial involvement
Skin adnexal tumors (SAT) are rare tumors that make up about 1%-2% of all cutaneous malignancies. They represent a various group of benign and malignant tumors that arise from skin adnexal epithelial structures: hair follicle, pilosebaceous unit, and apocrine or eccrine sweat glands. Although this derivation provides a practical basis for classification, some tumors may exhibit a mixed or more than one line of differentiation, rendering precise classification of those neoplasms difficult, and such cases should be categorized according to prevailing phenotype. In this report, we present a patient with metastatic eccrine carcinoma. Clinical experience for metastatic disease treatment is derived from a few reports, and there are no universal treatment guidelines. Given the few reported cases and the absence of randomized clinical trials for these patients, it is important to collect clinical experiences.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old African man presented with a 5-week history of multiple nontender subcutaneous skin nodules all over his body except for his palms and soles, and associated with generalized itching. He had a mass in the sole of his right foot 35 years previously in another country. The mass had recurred 15 years later and was excised again. The exact etiology of the mass was unknown to the patient. He had no other medical problems. He was on no medications and did not smoke, drink, or use recreational drugs.
His vital signs on admission were normal. Examination was significant for innumerable superficial skin nodules in the scalp, back, torso, and abdomen. The largest was in the neck and measured 4 x 2 cm. A firm right inguinal mass of 7 x 4 cm was palpable. An abdominal exam revealed large ascites but no organomegaly.
The results of laboratory tests were significant for hyponatremia 126 mEq/L (normal, 135-145), hypercalcemia of 12.2 mg/dL (8.5-10.5), with normal phosphorous of 2.5 mg/dL (2.5-4.5), parathyroid of 11.5 pg/ml (6-65), and low vitamin D level of <7 ng/ml (30-100). Other test results were: carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), 4.36 ng/ml (0.00-2.99); alpha fetoprotein, 2.39 IU/ml (0.00-9.0); calcium 11.6 mg/dL (8.5-10.2); lactate dehydrogenase, 325 U/L (85-210); aspartate aminotransferase, 59 U/L (0-40); alanine aminotransferase 43 U/L (5-35); alkaline phosphatase, 65 u/L (50-120); albumin, 2.7 g/dL (3.8-5.2); white blood cell count, 14.1 k/uL (4.4-10.6); h
A chest and abdomen computed-tomography scan on presentation showed presence of innumerable subcutaneous and intramuscular nodules throughout the chest, abdomen, and pelvis (Figure 1).
Extensive peritoneal carcinomatosis in addition to moderate ascites and perivascular lymphadenopathy were evident in the abdomen cuts. Remarkably, multiple lytic, osseous metastases were seen with subacute pathologic fracture of right fourth rib in addition to mediastinal lymphadenopathy with small pericardial effusion in the chest cuts. The right thigh mass was described as a large lobulated solid and cystic mass. Ascitic fluid analysis was negative for malignant cells. Biopsy of one the skin nodules in the upper back showed carcinoma involving the skin with focal tubular differentiation (Figure 2).
Immunohistochemical stains were positive for p63, epithelial membrane antigen, high molecular weight keratin, and p40. The lesional cells were negative for CEA, bcl-2, Ber-Ep4, CK7, and CK20. The profile was compatible with a skin adnexal carcinoma of sweat gland origin. The groin lymph node showed eccrine acrospiroma.
The patient underwent an upper endoscopy to assess for recurrent vomiting and it revealed diffuse areas of large erythematous ulcerated nodules noted in the cardia, fundus, and body of the stomach (Figure 3). A biopsy of the gastric nodules revealed gastric mucosa with metastatic carcinoma.
After a thorough review of the literature, he was started on palliative chemotherapy 13 days after initial presentation with docetaxel 75 mg/m2, carboplatin AUC 5 (470 mg), and 5-FU (5-fluorouracil, 750 mg/m2) over 24 hours on days 1 through 5. However, on day 2 of the chemotherapy, he became hypotensive and was found to have cardiac tamponade. He underwent an emergent pericardial window procedure. Analysis of the pericardial fluid was consistent with metastatic carcinoma (Figure 4). Chemotherapy was discontinued while he remained hypotensive requiring multiple vasopressors. His clinical condition did not improve and he passed away 27 days from initial presentation.
Discussion
Sweat gland carcinomas are very rare malignant tumors of the adnexal epithelial structures of the skin, sebaceous, hair follicle, apocrine or eccrine glands that were first described by Cornil in 1865.1 They occur primarily in adult patients, with a peak incidence in fifth and sixth decades of life.2,3 The etiology is unknown, but some cases have been reported to be a consequence of radiation therapy.4 They are almost always an incidental histologic diagnosis.2,5 The tumors usually appear as single nodule, and multinodularity usually associated with both local and metastatic disease.6 There are no characteristic findings to suggest that a particular nodule may represent sweat gland carcinoma, and even if sweat gland tumor is suspected, benign counterparts are more common.
Eccrine carcinoma is the most aggressive among skin adnexal tumors. They can arise on the lower limbs, trunk, head and neck, scalp and ears, upper extremities, abdomen, and genital sites.7
The cells of eccrine sweat glands express low molecular weight keratin, epithelial membrane antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen, as well as S100 protein, smooth muscle actin, p63, calponin, cytokeratin 14, and bcl-2.8 Skin tumors with eccrine differentiation may stain for estrogen and progesterone, which has important clinical implications because those patients can be treated with hormonal therapy.9 Positivity for estrogen receptors does not differentiate cutaneous eccrine tumors from cutaneous metastases of breast cancers.8,9 Androgen receptor evaluation in these cases can help distinguish between the two.10 Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) is expressed in 3.5% of skin adnexal tumors.11
The molecular pathogenesis of malignant adnexal tumors is not clear, but overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p16 has been described as a common feature in eccrine carcinomas.12
Prognostic factors for sweat gland carcinoma are difficult to identify, because of the small number of reported cases. The likely prognostic factors include size, histological type, lymph node involvement, and presence of distant metastasis. Absent of lymph node involvement correlates with 10-year disease-free survival rate of 56%, which falls to 9% if nodes are involved.13
There are no uniform guidelines for the treatment sweat gland carcinomas, and the clinical experience described in the literature is the only source of available information.
The treatment of choice of all subtypes of localized sweat gland carcinomas is wide surgical excision with broad tumor margins, given the propensity for local recurrences along with regional lymph node dissection in the presence of clinically positive nodes. Prophylactic lymph node resection does not seem to improve survival or decrease recurrence rates.7 The use of adjuvant radiotherapy to prevent local recurrence also is not well established. One report suggested radiosensitivity of these tumors, and adjuvant radiation was therefore recommended in high-risk cases (ie, large tumors of 5 cm and positive surgical margins of 1 cm) and moderate to poorly differentiated tumors with lymphovascular invasion.14 Adjuvant radiation to the involved lymph node basin is suggested in the setting of extranodal extension or extensive involvement, that is, 4 lymph nodes.15 The role of lymphadenectomy has not been adequately addressed in the literature.
The role of chemotherapy in metastatic disease is not clear, but sweat gland carcinomas are considered chemoresistant (Table). Several combinations have been used with short-term responses. In one case treated with doxorubicin, mitomycin, vincristine, and 5-FU followed by maintenance therapy, the patient achieved a complete response that lasted for 16 months.16 In another report, the treatment response was 2 years with treatment consisted of anthracyclin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and bloemycin.17 Other combinations used in the literature include carboplatin and paclitaxel, which led to prolonged remission.14 Cisplatin and 5-FU, or cisplatin plus cetuximab have been reported but with discouraging results.18 Results to taxanes showed conflicting results.19,20
Hormonal therapy can be effective in cases in which estrogen and progesterone receptors are expressed, which can range from 19%-30% of eccrine sweat gland carcinomas.21,22 Two cases have reported complete regression of lymph nodes in patients with metastatic disease, and in 1 patient relief from pain caused by bone metastases with durable response of around 3 years.23,24 a
Experience with targeted therapy is very limited. Sunitinib has been reported to have some activity in metastatic adnexal tumors as a second-line therapy in 2 patients, with disease control for 8 and 10 months respectively.25 Trastuzumab has been reported as having activity in 1 patient with strong HER2 expression (IHC score of 3+, denoting HER2 positivity), with complete regression of metastatic tumor. Upon progression in the same patient, a combination of lapatinib and capecitabine also showed positive response.26
In conclusion, metastatic sweat gland tumors treatment has not been standardized because of a dearth of reports in the literatures. Its early identification and complete excision gives the best chance of a cure. Neither chemotherapy nor radiation therapy has been proven to be of clinical benefit in treating metastatic disease.
1. Gates O, Warren S, Warvi WN. Tumors of sweat glands. Am J Pathol. 1943;19(4):591-631.
2. Mitts DL, Smith MT, Russell L, Bannayan GA, Cruz AB. Sweat gland carcinoma: a clinico-pathological reappraisal. J Surg Oncol. 1976;8(1):23-29.
3. Panoussopoulos D, Darom A, Lazaris AC, Misthos P, Papadimitriou K, Androulakis G. Sweat gland carcinoma with multiple local recurrences: a case report. Adv Clin Path. 1999;3(3):63-68.
4. Marone U, Caracò C, Anniciello AM, et al. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma : report of a case and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:32.
5. Yildirim S, Aköz T, Akan M, Ege GA. De novo malignant eccrine spiradenoma with an interesting and unusual location. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27(4):417-420.
6. Shaw M, McKee PH, Lowe D, Black MM. Malignant eccrine poroma: a study of twenty-seven cases. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107(6):675-680.
7. De Iuliis F, Amoroso L, Taglieri L, et al. Chemotherapy of rare skin adnexal tumors: a review of literature. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(10):5263-5268.
8. Alsaad KO, Obaidat NA, Ghazarian D. Skin adnexal neoplasms – part 1: an approach to tumours of the pilosebaceous unit. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60(2):129-144.
9. Serhrouchni KI, Harmouch T, Chbani L, et al. Eccrine carcinoma : a rare cutaneous neoplasm. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3570399/. Published online February 4, 2013. Accessed October 11, 2017.
10. Shidham VB, Komorowski RA, Machhi JK. Androgen receptor expression in metastatic adenocarcinoma in females favors a breast primary. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1601970/. Published online October 4, 2006. Accessed October 11, 2017.
11. Hiatt KM, Pillow JL, Smoller BR. Her-2 expression in cutaneous eccrine and apocrine neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2004;17(1):28-32.
12. Gu L-H, Ichiki Y, Kitajima Y. Aberrant expression of p16 and RB protein in eccrine porocarcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29(8):473-479.
13. el-Domeiri AA, Brasfield RD, Huvos AG, Strong EW. Sweat gland carcinoma: a clinico-pathologic study of 83 patients. Ann Surg. 1971;173(2):270-274.
14. Tlemcani K, Levine D, Smith R V, et al. Metastatic apocrine carcinoma of the scalp: prolonged response to systemic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(24):e412-e414.
15. Chamberlain RS, Huber K, White JC, Travaglino-Parda R. Apocrine gland carcinoma of the axilla: review of the literature and recommendations for treatment. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999;22(2):131-135.
16. Gutermuth J, Audring H, Voit C, Trefzer U, Haas N. Antitumour activity of paclitaxel and interferon-alpha in a case of metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18(4):477-479.
17. Mezger J, Remberger K, Schalhorn A, Wohlrab A, Wilmanns W. Treatment of metastatic sweat gland carcinoma by a four drug combination chemotherapy: response in two cases. Med Oncol Tumor Pharmacother. 1986;3(1):29-34.
18. Aaribi I, Mohtaram A, Ben Ameur El Youbi M, et al. Successful management of metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/crionm/2013/282536/. Published 2013. Accessed October 10, 2017.
19. Shiohara J, Koga H, Uhara H, Takata M, Saida T. Eccrine porocarcinoma: clinical and pathological studies of 12 cases. J Dermatol. 2007;34(8):516-522.
20. Swanson PE, Mazoujian G, Mills SE, Campbell RJ, Wick MR. Immunoreactivity for estrogen receptor protein in sweat gland tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991;15(9):835-841.
21. Busam KJ, Tan LK, Granter SR, et al. Epidermal growth factor, estrogen, and progesterone receptor expression in primary sweat gland carcinomas and primary and metastatic mammary carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 1999;12(8):786-793.
22. Sridhar KS, Benedetto P, Otrakji CL, Charyulu KK. Response of eccrine adenocarcinoma to tamoxifen. Cancer. 1989;64(2):366-370.
23. Daniel SJ, Nader R, Kost K, Hüttner I. Facial sweat gland carcinoma metastasizing to neck nodes: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(12):1495-1498.
24. Battistella M, Mateus C, Lassau N, et al. Sunitinib efficacy in the treatment of metastatic skin adnexal carcinomas: report of two patients with hidradenocarcinoma and trichoblastic carcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24(2):199-203.
25. Hidaka T, Fujimura T, Watabe A, et al. Successful treatment of HER-2-positive metastatic apocrine carcinoma of the skin with lapatinib and capecitabine. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(6):654-655.
26. Mandaliya H, Nordman I. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma: a rare case of successful treatment. Case Rep Oncol. 2016;9(2):454-456.
27. de Bree E, Volalakis E, Tsetis D, et al. Treatment of advanced malignant eccrine poroma with locoregional chemotherapy. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152(5):1051-1055.
28. Bahl A, Sharma DN, Julka PK, Das A, Rath GK. Sweat gland carcinoma with lung metastases. J Cancer Res Ther. 2(4):209-211.
29. Wang X-X, Wang H-Y, Zheng J-N, Sui J-C. Primary cutaneous sweat gland carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 10(2):390-392.
Skin adnexal tumors (SAT) are rare tumors that make up about 1%-2% of all cutaneous malignancies. They represent a various group of benign and malignant tumors that arise from skin adnexal epithelial structures: hair follicle, pilosebaceous unit, and apocrine or eccrine sweat glands. Although this derivation provides a practical basis for classification, some tumors may exhibit a mixed or more than one line of differentiation, rendering precise classification of those neoplasms difficult, and such cases should be categorized according to prevailing phenotype. In this report, we present a patient with metastatic eccrine carcinoma. Clinical experience for metastatic disease treatment is derived from a few reports, and there are no universal treatment guidelines. Given the few reported cases and the absence of randomized clinical trials for these patients, it is important to collect clinical experiences.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old African man presented with a 5-week history of multiple nontender subcutaneous skin nodules all over his body except for his palms and soles, and associated with generalized itching. He had a mass in the sole of his right foot 35 years previously in another country. The mass had recurred 15 years later and was excised again. The exact etiology of the mass was unknown to the patient. He had no other medical problems. He was on no medications and did not smoke, drink, or use recreational drugs.
His vital signs on admission were normal. Examination was significant for innumerable superficial skin nodules in the scalp, back, torso, and abdomen. The largest was in the neck and measured 4 x 2 cm. A firm right inguinal mass of 7 x 4 cm was palpable. An abdominal exam revealed large ascites but no organomegaly.
The results of laboratory tests were significant for hyponatremia 126 mEq/L (normal, 135-145), hypercalcemia of 12.2 mg/dL (8.5-10.5), with normal phosphorous of 2.5 mg/dL (2.5-4.5), parathyroid of 11.5 pg/ml (6-65), and low vitamin D level of <7 ng/ml (30-100). Other test results were: carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), 4.36 ng/ml (0.00-2.99); alpha fetoprotein, 2.39 IU/ml (0.00-9.0); calcium 11.6 mg/dL (8.5-10.2); lactate dehydrogenase, 325 U/L (85-210); aspartate aminotransferase, 59 U/L (0-40); alanine aminotransferase 43 U/L (5-35); alkaline phosphatase, 65 u/L (50-120); albumin, 2.7 g/dL (3.8-5.2); white blood cell count, 14.1 k/uL (4.4-10.6); h
A chest and abdomen computed-tomography scan on presentation showed presence of innumerable subcutaneous and intramuscular nodules throughout the chest, abdomen, and pelvis (Figure 1).
Extensive peritoneal carcinomatosis in addition to moderate ascites and perivascular lymphadenopathy were evident in the abdomen cuts. Remarkably, multiple lytic, osseous metastases were seen with subacute pathologic fracture of right fourth rib in addition to mediastinal lymphadenopathy with small pericardial effusion in the chest cuts. The right thigh mass was described as a large lobulated solid and cystic mass. Ascitic fluid analysis was negative for malignant cells. Biopsy of one the skin nodules in the upper back showed carcinoma involving the skin with focal tubular differentiation (Figure 2).
Immunohistochemical stains were positive for p63, epithelial membrane antigen, high molecular weight keratin, and p40. The lesional cells were negative for CEA, bcl-2, Ber-Ep4, CK7, and CK20. The profile was compatible with a skin adnexal carcinoma of sweat gland origin. The groin lymph node showed eccrine acrospiroma.
The patient underwent an upper endoscopy to assess for recurrent vomiting and it revealed diffuse areas of large erythematous ulcerated nodules noted in the cardia, fundus, and body of the stomach (Figure 3). A biopsy of the gastric nodules revealed gastric mucosa with metastatic carcinoma.
After a thorough review of the literature, he was started on palliative chemotherapy 13 days after initial presentation with docetaxel 75 mg/m2, carboplatin AUC 5 (470 mg), and 5-FU (5-fluorouracil, 750 mg/m2) over 24 hours on days 1 through 5. However, on day 2 of the chemotherapy, he became hypotensive and was found to have cardiac tamponade. He underwent an emergent pericardial window procedure. Analysis of the pericardial fluid was consistent with metastatic carcinoma (Figure 4). Chemotherapy was discontinued while he remained hypotensive requiring multiple vasopressors. His clinical condition did not improve and he passed away 27 days from initial presentation.
Discussion
Sweat gland carcinomas are very rare malignant tumors of the adnexal epithelial structures of the skin, sebaceous, hair follicle, apocrine or eccrine glands that were first described by Cornil in 1865.1 They occur primarily in adult patients, with a peak incidence in fifth and sixth decades of life.2,3 The etiology is unknown, but some cases have been reported to be a consequence of radiation therapy.4 They are almost always an incidental histologic diagnosis.2,5 The tumors usually appear as single nodule, and multinodularity usually associated with both local and metastatic disease.6 There are no characteristic findings to suggest that a particular nodule may represent sweat gland carcinoma, and even if sweat gland tumor is suspected, benign counterparts are more common.
Eccrine carcinoma is the most aggressive among skin adnexal tumors. They can arise on the lower limbs, trunk, head and neck, scalp and ears, upper extremities, abdomen, and genital sites.7
The cells of eccrine sweat glands express low molecular weight keratin, epithelial membrane antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen, as well as S100 protein, smooth muscle actin, p63, calponin, cytokeratin 14, and bcl-2.8 Skin tumors with eccrine differentiation may stain for estrogen and progesterone, which has important clinical implications because those patients can be treated with hormonal therapy.9 Positivity for estrogen receptors does not differentiate cutaneous eccrine tumors from cutaneous metastases of breast cancers.8,9 Androgen receptor evaluation in these cases can help distinguish between the two.10 Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) is expressed in 3.5% of skin adnexal tumors.11
The molecular pathogenesis of malignant adnexal tumors is not clear, but overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p16 has been described as a common feature in eccrine carcinomas.12
Prognostic factors for sweat gland carcinoma are difficult to identify, because of the small number of reported cases. The likely prognostic factors include size, histological type, lymph node involvement, and presence of distant metastasis. Absent of lymph node involvement correlates with 10-year disease-free survival rate of 56%, which falls to 9% if nodes are involved.13
There are no uniform guidelines for the treatment sweat gland carcinomas, and the clinical experience described in the literature is the only source of available information.
The treatment of choice of all subtypes of localized sweat gland carcinomas is wide surgical excision with broad tumor margins, given the propensity for local recurrences along with regional lymph node dissection in the presence of clinically positive nodes. Prophylactic lymph node resection does not seem to improve survival or decrease recurrence rates.7 The use of adjuvant radiotherapy to prevent local recurrence also is not well established. One report suggested radiosensitivity of these tumors, and adjuvant radiation was therefore recommended in high-risk cases (ie, large tumors of 5 cm and positive surgical margins of 1 cm) and moderate to poorly differentiated tumors with lymphovascular invasion.14 Adjuvant radiation to the involved lymph node basin is suggested in the setting of extranodal extension or extensive involvement, that is, 4 lymph nodes.15 The role of lymphadenectomy has not been adequately addressed in the literature.
The role of chemotherapy in metastatic disease is not clear, but sweat gland carcinomas are considered chemoresistant (Table). Several combinations have been used with short-term responses. In one case treated with doxorubicin, mitomycin, vincristine, and 5-FU followed by maintenance therapy, the patient achieved a complete response that lasted for 16 months.16 In another report, the treatment response was 2 years with treatment consisted of anthracyclin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and bloemycin.17 Other combinations used in the literature include carboplatin and paclitaxel, which led to prolonged remission.14 Cisplatin and 5-FU, or cisplatin plus cetuximab have been reported but with discouraging results.18 Results to taxanes showed conflicting results.19,20
Hormonal therapy can be effective in cases in which estrogen and progesterone receptors are expressed, which can range from 19%-30% of eccrine sweat gland carcinomas.21,22 Two cases have reported complete regression of lymph nodes in patients with metastatic disease, and in 1 patient relief from pain caused by bone metastases with durable response of around 3 years.23,24 a
Experience with targeted therapy is very limited. Sunitinib has been reported to have some activity in metastatic adnexal tumors as a second-line therapy in 2 patients, with disease control for 8 and 10 months respectively.25 Trastuzumab has been reported as having activity in 1 patient with strong HER2 expression (IHC score of 3+, denoting HER2 positivity), with complete regression of metastatic tumor. Upon progression in the same patient, a combination of lapatinib and capecitabine also showed positive response.26
In conclusion, metastatic sweat gland tumors treatment has not been standardized because of a dearth of reports in the literatures. Its early identification and complete excision gives the best chance of a cure. Neither chemotherapy nor radiation therapy has been proven to be of clinical benefit in treating metastatic disease.
Skin adnexal tumors (SAT) are rare tumors that make up about 1%-2% of all cutaneous malignancies. They represent a various group of benign and malignant tumors that arise from skin adnexal epithelial structures: hair follicle, pilosebaceous unit, and apocrine or eccrine sweat glands. Although this derivation provides a practical basis for classification, some tumors may exhibit a mixed or more than one line of differentiation, rendering precise classification of those neoplasms difficult, and such cases should be categorized according to prevailing phenotype. In this report, we present a patient with metastatic eccrine carcinoma. Clinical experience for metastatic disease treatment is derived from a few reports, and there are no universal treatment guidelines. Given the few reported cases and the absence of randomized clinical trials for these patients, it is important to collect clinical experiences.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old African man presented with a 5-week history of multiple nontender subcutaneous skin nodules all over his body except for his palms and soles, and associated with generalized itching. He had a mass in the sole of his right foot 35 years previously in another country. The mass had recurred 15 years later and was excised again. The exact etiology of the mass was unknown to the patient. He had no other medical problems. He was on no medications and did not smoke, drink, or use recreational drugs.
His vital signs on admission were normal. Examination was significant for innumerable superficial skin nodules in the scalp, back, torso, and abdomen. The largest was in the neck and measured 4 x 2 cm. A firm right inguinal mass of 7 x 4 cm was palpable. An abdominal exam revealed large ascites but no organomegaly.
The results of laboratory tests were significant for hyponatremia 126 mEq/L (normal, 135-145), hypercalcemia of 12.2 mg/dL (8.5-10.5), with normal phosphorous of 2.5 mg/dL (2.5-4.5), parathyroid of 11.5 pg/ml (6-65), and low vitamin D level of <7 ng/ml (30-100). Other test results were: carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), 4.36 ng/ml (0.00-2.99); alpha fetoprotein, 2.39 IU/ml (0.00-9.0); calcium 11.6 mg/dL (8.5-10.2); lactate dehydrogenase, 325 U/L (85-210); aspartate aminotransferase, 59 U/L (0-40); alanine aminotransferase 43 U/L (5-35); alkaline phosphatase, 65 u/L (50-120); albumin, 2.7 g/dL (3.8-5.2); white blood cell count, 14.1 k/uL (4.4-10.6); h
A chest and abdomen computed-tomography scan on presentation showed presence of innumerable subcutaneous and intramuscular nodules throughout the chest, abdomen, and pelvis (Figure 1).
Extensive peritoneal carcinomatosis in addition to moderate ascites and perivascular lymphadenopathy were evident in the abdomen cuts. Remarkably, multiple lytic, osseous metastases were seen with subacute pathologic fracture of right fourth rib in addition to mediastinal lymphadenopathy with small pericardial effusion in the chest cuts. The right thigh mass was described as a large lobulated solid and cystic mass. Ascitic fluid analysis was negative for malignant cells. Biopsy of one the skin nodules in the upper back showed carcinoma involving the skin with focal tubular differentiation (Figure 2).
Immunohistochemical stains were positive for p63, epithelial membrane antigen, high molecular weight keratin, and p40. The lesional cells were negative for CEA, bcl-2, Ber-Ep4, CK7, and CK20. The profile was compatible with a skin adnexal carcinoma of sweat gland origin. The groin lymph node showed eccrine acrospiroma.
The patient underwent an upper endoscopy to assess for recurrent vomiting and it revealed diffuse areas of large erythematous ulcerated nodules noted in the cardia, fundus, and body of the stomach (Figure 3). A biopsy of the gastric nodules revealed gastric mucosa with metastatic carcinoma.
After a thorough review of the literature, he was started on palliative chemotherapy 13 days after initial presentation with docetaxel 75 mg/m2, carboplatin AUC 5 (470 mg), and 5-FU (5-fluorouracil, 750 mg/m2) over 24 hours on days 1 through 5. However, on day 2 of the chemotherapy, he became hypotensive and was found to have cardiac tamponade. He underwent an emergent pericardial window procedure. Analysis of the pericardial fluid was consistent with metastatic carcinoma (Figure 4). Chemotherapy was discontinued while he remained hypotensive requiring multiple vasopressors. His clinical condition did not improve and he passed away 27 days from initial presentation.
Discussion
Sweat gland carcinomas are very rare malignant tumors of the adnexal epithelial structures of the skin, sebaceous, hair follicle, apocrine or eccrine glands that were first described by Cornil in 1865.1 They occur primarily in adult patients, with a peak incidence in fifth and sixth decades of life.2,3 The etiology is unknown, but some cases have been reported to be a consequence of radiation therapy.4 They are almost always an incidental histologic diagnosis.2,5 The tumors usually appear as single nodule, and multinodularity usually associated with both local and metastatic disease.6 There are no characteristic findings to suggest that a particular nodule may represent sweat gland carcinoma, and even if sweat gland tumor is suspected, benign counterparts are more common.
Eccrine carcinoma is the most aggressive among skin adnexal tumors. They can arise on the lower limbs, trunk, head and neck, scalp and ears, upper extremities, abdomen, and genital sites.7
The cells of eccrine sweat glands express low molecular weight keratin, epithelial membrane antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen, as well as S100 protein, smooth muscle actin, p63, calponin, cytokeratin 14, and bcl-2.8 Skin tumors with eccrine differentiation may stain for estrogen and progesterone, which has important clinical implications because those patients can be treated with hormonal therapy.9 Positivity for estrogen receptors does not differentiate cutaneous eccrine tumors from cutaneous metastases of breast cancers.8,9 Androgen receptor evaluation in these cases can help distinguish between the two.10 Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) is expressed in 3.5% of skin adnexal tumors.11
The molecular pathogenesis of malignant adnexal tumors is not clear, but overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p16 has been described as a common feature in eccrine carcinomas.12
Prognostic factors for sweat gland carcinoma are difficult to identify, because of the small number of reported cases. The likely prognostic factors include size, histological type, lymph node involvement, and presence of distant metastasis. Absent of lymph node involvement correlates with 10-year disease-free survival rate of 56%, which falls to 9% if nodes are involved.13
There are no uniform guidelines for the treatment sweat gland carcinomas, and the clinical experience described in the literature is the only source of available information.
The treatment of choice of all subtypes of localized sweat gland carcinomas is wide surgical excision with broad tumor margins, given the propensity for local recurrences along with regional lymph node dissection in the presence of clinically positive nodes. Prophylactic lymph node resection does not seem to improve survival or decrease recurrence rates.7 The use of adjuvant radiotherapy to prevent local recurrence also is not well established. One report suggested radiosensitivity of these tumors, and adjuvant radiation was therefore recommended in high-risk cases (ie, large tumors of 5 cm and positive surgical margins of 1 cm) and moderate to poorly differentiated tumors with lymphovascular invasion.14 Adjuvant radiation to the involved lymph node basin is suggested in the setting of extranodal extension or extensive involvement, that is, 4 lymph nodes.15 The role of lymphadenectomy has not been adequately addressed in the literature.
The role of chemotherapy in metastatic disease is not clear, but sweat gland carcinomas are considered chemoresistant (Table). Several combinations have been used with short-term responses. In one case treated with doxorubicin, mitomycin, vincristine, and 5-FU followed by maintenance therapy, the patient achieved a complete response that lasted for 16 months.16 In another report, the treatment response was 2 years with treatment consisted of anthracyclin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and bloemycin.17 Other combinations used in the literature include carboplatin and paclitaxel, which led to prolonged remission.14 Cisplatin and 5-FU, or cisplatin plus cetuximab have been reported but with discouraging results.18 Results to taxanes showed conflicting results.19,20
Hormonal therapy can be effective in cases in which estrogen and progesterone receptors are expressed, which can range from 19%-30% of eccrine sweat gland carcinomas.21,22 Two cases have reported complete regression of lymph nodes in patients with metastatic disease, and in 1 patient relief from pain caused by bone metastases with durable response of around 3 years.23,24 a
Experience with targeted therapy is very limited. Sunitinib has been reported to have some activity in metastatic adnexal tumors as a second-line therapy in 2 patients, with disease control for 8 and 10 months respectively.25 Trastuzumab has been reported as having activity in 1 patient with strong HER2 expression (IHC score of 3+, denoting HER2 positivity), with complete regression of metastatic tumor. Upon progression in the same patient, a combination of lapatinib and capecitabine also showed positive response.26
In conclusion, metastatic sweat gland tumors treatment has not been standardized because of a dearth of reports in the literatures. Its early identification and complete excision gives the best chance of a cure. Neither chemotherapy nor radiation therapy has been proven to be of clinical benefit in treating metastatic disease.
1. Gates O, Warren S, Warvi WN. Tumors of sweat glands. Am J Pathol. 1943;19(4):591-631.
2. Mitts DL, Smith MT, Russell L, Bannayan GA, Cruz AB. Sweat gland carcinoma: a clinico-pathological reappraisal. J Surg Oncol. 1976;8(1):23-29.
3. Panoussopoulos D, Darom A, Lazaris AC, Misthos P, Papadimitriou K, Androulakis G. Sweat gland carcinoma with multiple local recurrences: a case report. Adv Clin Path. 1999;3(3):63-68.
4. Marone U, Caracò C, Anniciello AM, et al. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma : report of a case and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:32.
5. Yildirim S, Aköz T, Akan M, Ege GA. De novo malignant eccrine spiradenoma with an interesting and unusual location. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27(4):417-420.
6. Shaw M, McKee PH, Lowe D, Black MM. Malignant eccrine poroma: a study of twenty-seven cases. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107(6):675-680.
7. De Iuliis F, Amoroso L, Taglieri L, et al. Chemotherapy of rare skin adnexal tumors: a review of literature. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(10):5263-5268.
8. Alsaad KO, Obaidat NA, Ghazarian D. Skin adnexal neoplasms – part 1: an approach to tumours of the pilosebaceous unit. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60(2):129-144.
9. Serhrouchni KI, Harmouch T, Chbani L, et al. Eccrine carcinoma : a rare cutaneous neoplasm. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3570399/. Published online February 4, 2013. Accessed October 11, 2017.
10. Shidham VB, Komorowski RA, Machhi JK. Androgen receptor expression in metastatic adenocarcinoma in females favors a breast primary. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1601970/. Published online October 4, 2006. Accessed October 11, 2017.
11. Hiatt KM, Pillow JL, Smoller BR. Her-2 expression in cutaneous eccrine and apocrine neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2004;17(1):28-32.
12. Gu L-H, Ichiki Y, Kitajima Y. Aberrant expression of p16 and RB protein in eccrine porocarcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29(8):473-479.
13. el-Domeiri AA, Brasfield RD, Huvos AG, Strong EW. Sweat gland carcinoma: a clinico-pathologic study of 83 patients. Ann Surg. 1971;173(2):270-274.
14. Tlemcani K, Levine D, Smith R V, et al. Metastatic apocrine carcinoma of the scalp: prolonged response to systemic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(24):e412-e414.
15. Chamberlain RS, Huber K, White JC, Travaglino-Parda R. Apocrine gland carcinoma of the axilla: review of the literature and recommendations for treatment. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999;22(2):131-135.
16. Gutermuth J, Audring H, Voit C, Trefzer U, Haas N. Antitumour activity of paclitaxel and interferon-alpha in a case of metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18(4):477-479.
17. Mezger J, Remberger K, Schalhorn A, Wohlrab A, Wilmanns W. Treatment of metastatic sweat gland carcinoma by a four drug combination chemotherapy: response in two cases. Med Oncol Tumor Pharmacother. 1986;3(1):29-34.
18. Aaribi I, Mohtaram A, Ben Ameur El Youbi M, et al. Successful management of metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/crionm/2013/282536/. Published 2013. Accessed October 10, 2017.
19. Shiohara J, Koga H, Uhara H, Takata M, Saida T. Eccrine porocarcinoma: clinical and pathological studies of 12 cases. J Dermatol. 2007;34(8):516-522.
20. Swanson PE, Mazoujian G, Mills SE, Campbell RJ, Wick MR. Immunoreactivity for estrogen receptor protein in sweat gland tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991;15(9):835-841.
21. Busam KJ, Tan LK, Granter SR, et al. Epidermal growth factor, estrogen, and progesterone receptor expression in primary sweat gland carcinomas and primary and metastatic mammary carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 1999;12(8):786-793.
22. Sridhar KS, Benedetto P, Otrakji CL, Charyulu KK. Response of eccrine adenocarcinoma to tamoxifen. Cancer. 1989;64(2):366-370.
23. Daniel SJ, Nader R, Kost K, Hüttner I. Facial sweat gland carcinoma metastasizing to neck nodes: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(12):1495-1498.
24. Battistella M, Mateus C, Lassau N, et al. Sunitinib efficacy in the treatment of metastatic skin adnexal carcinomas: report of two patients with hidradenocarcinoma and trichoblastic carcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24(2):199-203.
25. Hidaka T, Fujimura T, Watabe A, et al. Successful treatment of HER-2-positive metastatic apocrine carcinoma of the skin with lapatinib and capecitabine. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(6):654-655.
26. Mandaliya H, Nordman I. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma: a rare case of successful treatment. Case Rep Oncol. 2016;9(2):454-456.
27. de Bree E, Volalakis E, Tsetis D, et al. Treatment of advanced malignant eccrine poroma with locoregional chemotherapy. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152(5):1051-1055.
28. Bahl A, Sharma DN, Julka PK, Das A, Rath GK. Sweat gland carcinoma with lung metastases. J Cancer Res Ther. 2(4):209-211.
29. Wang X-X, Wang H-Y, Zheng J-N, Sui J-C. Primary cutaneous sweat gland carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 10(2):390-392.
1. Gates O, Warren S, Warvi WN. Tumors of sweat glands. Am J Pathol. 1943;19(4):591-631.
2. Mitts DL, Smith MT, Russell L, Bannayan GA, Cruz AB. Sweat gland carcinoma: a clinico-pathological reappraisal. J Surg Oncol. 1976;8(1):23-29.
3. Panoussopoulos D, Darom A, Lazaris AC, Misthos P, Papadimitriou K, Androulakis G. Sweat gland carcinoma with multiple local recurrences: a case report. Adv Clin Path. 1999;3(3):63-68.
4. Marone U, Caracò C, Anniciello AM, et al. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma : report of a case and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:32.
5. Yildirim S, Aköz T, Akan M, Ege GA. De novo malignant eccrine spiradenoma with an interesting and unusual location. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27(4):417-420.
6. Shaw M, McKee PH, Lowe D, Black MM. Malignant eccrine poroma: a study of twenty-seven cases. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107(6):675-680.
7. De Iuliis F, Amoroso L, Taglieri L, et al. Chemotherapy of rare skin adnexal tumors: a review of literature. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(10):5263-5268.
8. Alsaad KO, Obaidat NA, Ghazarian D. Skin adnexal neoplasms – part 1: an approach to tumours of the pilosebaceous unit. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60(2):129-144.
9. Serhrouchni KI, Harmouch T, Chbani L, et al. Eccrine carcinoma : a rare cutaneous neoplasm. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3570399/. Published online February 4, 2013. Accessed October 11, 2017.
10. Shidham VB, Komorowski RA, Machhi JK. Androgen receptor expression in metastatic adenocarcinoma in females favors a breast primary. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1601970/. Published online October 4, 2006. Accessed October 11, 2017.
11. Hiatt KM, Pillow JL, Smoller BR. Her-2 expression in cutaneous eccrine and apocrine neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2004;17(1):28-32.
12. Gu L-H, Ichiki Y, Kitajima Y. Aberrant expression of p16 and RB protein in eccrine porocarcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29(8):473-479.
13. el-Domeiri AA, Brasfield RD, Huvos AG, Strong EW. Sweat gland carcinoma: a clinico-pathologic study of 83 patients. Ann Surg. 1971;173(2):270-274.
14. Tlemcani K, Levine D, Smith R V, et al. Metastatic apocrine carcinoma of the scalp: prolonged response to systemic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(24):e412-e414.
15. Chamberlain RS, Huber K, White JC, Travaglino-Parda R. Apocrine gland carcinoma of the axilla: review of the literature and recommendations for treatment. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999;22(2):131-135.
16. Gutermuth J, Audring H, Voit C, Trefzer U, Haas N. Antitumour activity of paclitaxel and interferon-alpha in a case of metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18(4):477-479.
17. Mezger J, Remberger K, Schalhorn A, Wohlrab A, Wilmanns W. Treatment of metastatic sweat gland carcinoma by a four drug combination chemotherapy: response in two cases. Med Oncol Tumor Pharmacother. 1986;3(1):29-34.
18. Aaribi I, Mohtaram A, Ben Ameur El Youbi M, et al. Successful management of metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/crionm/2013/282536/. Published 2013. Accessed October 10, 2017.
19. Shiohara J, Koga H, Uhara H, Takata M, Saida T. Eccrine porocarcinoma: clinical and pathological studies of 12 cases. J Dermatol. 2007;34(8):516-522.
20. Swanson PE, Mazoujian G, Mills SE, Campbell RJ, Wick MR. Immunoreactivity for estrogen receptor protein in sweat gland tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991;15(9):835-841.
21. Busam KJ, Tan LK, Granter SR, et al. Epidermal growth factor, estrogen, and progesterone receptor expression in primary sweat gland carcinomas and primary and metastatic mammary carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 1999;12(8):786-793.
22. Sridhar KS, Benedetto P, Otrakji CL, Charyulu KK. Response of eccrine adenocarcinoma to tamoxifen. Cancer. 1989;64(2):366-370.
23. Daniel SJ, Nader R, Kost K, Hüttner I. Facial sweat gland carcinoma metastasizing to neck nodes: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(12):1495-1498.
24. Battistella M, Mateus C, Lassau N, et al. Sunitinib efficacy in the treatment of metastatic skin adnexal carcinomas: report of two patients with hidradenocarcinoma and trichoblastic carcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24(2):199-203.
25. Hidaka T, Fujimura T, Watabe A, et al. Successful treatment of HER-2-positive metastatic apocrine carcinoma of the skin with lapatinib and capecitabine. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(6):654-655.
26. Mandaliya H, Nordman I. Metastatic eccrine porocarcinoma: a rare case of successful treatment. Case Rep Oncol. 2016;9(2):454-456.
27. de Bree E, Volalakis E, Tsetis D, et al. Treatment of advanced malignant eccrine poroma with locoregional chemotherapy. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152(5):1051-1055.
28. Bahl A, Sharma DN, Julka PK, Das A, Rath GK. Sweat gland carcinoma with lung metastases. J Cancer Res Ther. 2(4):209-211.
29. Wang X-X, Wang H-Y, Zheng J-N, Sui J-C. Primary cutaneous sweat gland carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 10(2):390-392.
Cold hemolytic anemia: a rare complication of influenza A
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is characterized by the temperature at which the auto-antibody has the greatest avidity for the target red cell antigen, either warm or cold forms. It is detected by a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) also known as the direct Coombs test. DAT is used to determine if red cells have been coated in vivo with immunoglobulin, complement, or both.1 Some causes of a positive DAT include hemolytic transfusion reactions, hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, AIHA, and drug-induced immune hemolysis.
Case presentation and summary
A 58-year-old woman from Brazil with past medical history only significant for cholecystectomy and cesarean section had been visiting in United States for 2 months when she presented to an outside hospital with fever, shortness of breath, and syncope that had resulted in a foot injury. She reported she had been feeling short of breath and had a nonproductive cough and malaise for about 2 weeks before presentation with sick contacts at home. On admission it was noted that she had a hemoglobin level of 7.7 g/dL (normal, 12.0-15.5 g/dL; MCV, 94 fL), total bilirubin of 2.14 mg/dL (normal, 0.2-1.0 mg/dL), and lactate dehydrogenase of 523 U/L (normal, 81-234 U/L). There were no signs of bleeding on her examination. Her DAT was positive and moderate red blood cell agglutination was reported. During the first admission at the outside hospital she was diagnosed with influenza A and completed a full course of oseltamivir (75 mg po twice daily for 5 days). A chest X-ray was negative for infiltrates and showed that the patient’s lung fields were clear. She was transfused 2 units of packed red blood cells with response in hemoglobin up to 9.8 g/dL. The patient was treated with dexamethasone (4 mg IV Q8) as an inpatient and was discharged on a prednisone taper (40 mg, with taper by 10 mg every 3 days) with hemoglobin of 8.1 g/dL.
The patient continued to have nonproductive cough, dyspnea, fevers, chills, and generalized weakness, when she returned to the same outside hospital’s emergency department 2 days after her discharge. At that time, it was noted that she had leucocytosis (white blood cell count, 34.6 x 109 per L), a hemoglobin level of 6.8 g/dL, and her total bilirubin level was 6.9 mg/dL. Her hemodynamics were unstable and she was admitted to their intensive care unit. The results of a chest X-ray revealed right lung consolidation.
The day after this admission, her hemoglobin level fell to 4.7 g/dL, and she was transfused 2 units of packed red blood cells before being transferred to our hospital. A chest X-ray at our hospital confirmed a right lung infiltrate. Vancomycin (1,250 mg IV Q12), levaquin (750 mg IV Q24), and maxipime (1 g IV Q12) were initiated for pneumonia and the patient was transferred to our hospital’s intensive care unit. She was afebrile at 98.3°F, her pulse rate was 84 beats per minute, she was tachypneic with respiratory rate of 26 breaths per minute, her blood pressure was 98/51 mmHg, and she had an oxygen saturation of 99% on 2L oxygen via nasal cannula.
On physical examination she was noted to have scleral icterus and was in mild respiratory distress. A chest X-ray revealed a patchy opacity in the right mid to lower lung. Her initial complete blood panel revealed anemia, with hemoglobin, 6.3 g/dL; white blood cell count, 27 x 109 per L; and platelets, 533 x 109 per L. The patient was then transfused another 2 units of packed red blood cells. She was given intravenous hydration, acetaminophen, and albuterol nebulizer treatments as supportive care. She was provided with blankets to keep warm. In addition to her antibiotics, she was also given prednisone 70 mg for her respiratory symptoms.
Further tests revealed haptoglobin, <30 mg/dL (normal, 36-195 mg/dL); lactate dehydrogenase, 371 U/L (normal, 98-192 U/L); and complements C3, 90 mg/dL (normal, 79-152 mg/dL) and C4, <8 mg/dL (normal, 18-55 mg/dL). Her DAT was positive, and agglutination was seen on peripheral smear (Figure 1). This was her second positive DAT as she had positive one at the outside hospital initially. Her tests for mycoplasma pneumonia, the PCR and IgM, were negative, as were the Monospot for mononucleosis and the ANA for autoimmune disorders. Her cold agglutinin titer was 1:256 (normal, no agglutination <1:64). The patient’s repeat respiratory viral panel was negative given recent full treatment for her influenza A at the previous hospital. Her blood and urine cultures were negative.
The patient was given antibiotics (vancomycin 1,250 mg IV Q12, cefepime 2 g IV Q8, and azithromycin 500 mg daily) for her pneumonia. Her respiratory status improved, and she was transferred to general medical floors after the first day of her admission. Her total bilirubin trended down to 1.9 mg/dL. She remained on prednisone 70 mg daily.
The patient remained in the hospital for an additional 6 days before being discharged home on prednisone. She wanted to return to her home country of Brazil as soon as she was able to and said she would seek outpatient follow-up there with a hematologist. At the time of her discharge, her hemoglobin was 6.6 g/dL and her reticulocyte count, 6.0%. Figures 2 and 3 illustrate her hemoglobin and reticulocyte trend during her admission at our hospital.
Discussion
The incidence of cold AIHA or cold agglutinin disease (CAD) occurs about 4 per 1 million people and commonly affects women more often than men.2 The cause of CAD can be subdivided into primary, idiopathic, or secondary causes, which can include infections, malignancies, or benign diseases.3,4 Primary CAD is a chronic disorder that is generally seen in older women. Secondary CAD can be associated with B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders, such as Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and infectious agents such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae and mononucleosis caused by Epstein-Barr virus.
Mild hemolysis or acrocyanosis may occur with exposure to cold. The blood smear in CAD demonstrates red blood cell agglutination or clumping, polychromasia, and an absence of spherocytosis. In general, most cases require no treatment, but cytotoxic agents or rituximab can be used to treat more severe cases. Appropriate treatment for infectious causes of CAD includes supportive care aimed at the underlying disease process. In addition, it is helpful to keep the patient warm. There is no role for steroid therapy in CAD unlike in warm AIHA. However, our patient was symptomatic from her pneumonia, so we added steroids to help with her pulmonary insult.
The patient had a cold agglutinin titer of 1:256. Titers of 1:32 or higher are considered elevated by this technique. Elevated titers are generally rarely seen except in primary atypical pneumonia due to either M. pneumoniae, influenza A, influenza B, parainfluenza, and adenovirus, and in certain hemolytic anemias. Low titers of cold agglutinins have been demonstrated in malaria, peripheral vascular disease, and common respiratory diseases.
Warm AIHA is caused by IgG antibody activities at body temperature or at 98.6°F. They may or may not bind complement and are removed from circulation by the spleen. Cold AIHA is due to IgM antibodies coating red cells at lower temperatures. They bind complement and lead to red blood cell destruction of agglutinated cells. If the antibody is active at temperatures approaching 98.6°F, clinically significant intravascular and sometimes extravascular complement-mediated hemolysis occur in the liver.5
The incidence of warm AIHA occurs about 10 per 1 million people and affects women twice often as men.2 It can be primary or idiopathic, or associated with various underlying conditions, including autoimmune disorders, immunodeficiency syndromes, lymphoproliferative disorders, other malignancies, and certain drugs. In more severe cases, jaundice and splenomegaly may occur. The blood smear in warm AIHA demonstrates variable spherocytosis, polychromasia, and rare erythrophagocytosis. Treatment usually includes steroids, cytotoxic agents, and splenectomy in severe cases.
There have been few case reports describing influenza as a cause of cold agglutinin hemolytic anemia. Chen and colleagues reported a case of influenza A infection in a 22-month-old boy.6Schoindre and colleagues reported the case of a 60-year-old woman infected with influenza A H1N1 virus who died from CAD.7 Shizuma reported the case of a 67-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis who developed a mixed hemolytic anemia and was positive for influenza A.8Our patient presented with influenza A, which had been diagnosed by respiratory virus panel at a different hospital, and she was anemic at the time of presentation to the outside hospital, with a positive DAT test. She was treated for influenza A with a full course of osltamivir and then returned with complaints of worsening fatigue and was again noted to be anemic with the development of patchy opacities on chest X-ray. The patient was subsequently transferred to our hospital and remained anemic during the course of her treatment. She received supportive care for her underlying influenza A and had symptomatic improvement. She ultimately decided the she would like to pursue further treatment in her native country and was discharged.
In conclusion, this case represents a rare complication of a common illness. Few cases of influenza causing hemolytic anemia have been reported in the literature. There have been reports of oseltamivir causing hemolytic anemia, but our patient presented with evidence of hemolytic anemia before initiation of the medication. In all the aforementioned cases, the patients died as a result of comorbid conditions. Our patient was stable enough to be discharged from the hospital after treatment of her comorbid conditions.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank David Henry, MD, at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, for sharing this case and for his guidance during this patient’s treatment.
1. Roback JD, Grossman BJ, Harris T, Hillyer CD. Technical manual [17th ed]. Bethesda, MD; American Association of Blood Banks; 2011.
2. Jaffee ES, Harris NL, Vardiman JW, Campo E, Arber DA. Hematopathology. St. Louis, MO; Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
3. Feizi T. Monotypic cold agglutinins in infection by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nature. 1967;215(5100):540-542.
4. Horwitz CA, Moulds J, Henle W, et al. Cold agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis and heterophil-antibody-negative mononucleosis-like syndromes. Blood. 1977;50(2):195-202.
5. Hsi ED, editor. Hematopathology [3rd ed]. Philadelphia, PA; Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
6. Chen H, Jia XL, Gao HM, Qian SY. Comorbid presentation of severe novel influenza A (H1N1) and Evans syndrome: a case report. Chin Med J. 2011;124(11):1743-1746.
7. Schoindre Y, Bollée G, Dumont MD, Lesavre P, Servais A. Cold agglutinin syndrome associated with a 2009 influenza A H1N1 infection. http://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(10)00482-1/fulltext. Published February 2011. Accessed October 10, 2017.
8. [Article in Japanese] Shizuma T. [A case of autoimmune hemolytic anemia caused by type A influenza infection in a patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2010;84(3):296-299.
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is characterized by the temperature at which the auto-antibody has the greatest avidity for the target red cell antigen, either warm or cold forms. It is detected by a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) also known as the direct Coombs test. DAT is used to determine if red cells have been coated in vivo with immunoglobulin, complement, or both.1 Some causes of a positive DAT include hemolytic transfusion reactions, hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, AIHA, and drug-induced immune hemolysis.
Case presentation and summary
A 58-year-old woman from Brazil with past medical history only significant for cholecystectomy and cesarean section had been visiting in United States for 2 months when she presented to an outside hospital with fever, shortness of breath, and syncope that had resulted in a foot injury. She reported she had been feeling short of breath and had a nonproductive cough and malaise for about 2 weeks before presentation with sick contacts at home. On admission it was noted that she had a hemoglobin level of 7.7 g/dL (normal, 12.0-15.5 g/dL; MCV, 94 fL), total bilirubin of 2.14 mg/dL (normal, 0.2-1.0 mg/dL), and lactate dehydrogenase of 523 U/L (normal, 81-234 U/L). There were no signs of bleeding on her examination. Her DAT was positive and moderate red blood cell agglutination was reported. During the first admission at the outside hospital she was diagnosed with influenza A and completed a full course of oseltamivir (75 mg po twice daily for 5 days). A chest X-ray was negative for infiltrates and showed that the patient’s lung fields were clear. She was transfused 2 units of packed red blood cells with response in hemoglobin up to 9.8 g/dL. The patient was treated with dexamethasone (4 mg IV Q8) as an inpatient and was discharged on a prednisone taper (40 mg, with taper by 10 mg every 3 days) with hemoglobin of 8.1 g/dL.
The patient continued to have nonproductive cough, dyspnea, fevers, chills, and generalized weakness, when she returned to the same outside hospital’s emergency department 2 days after her discharge. At that time, it was noted that she had leucocytosis (white blood cell count, 34.6 x 109 per L), a hemoglobin level of 6.8 g/dL, and her total bilirubin level was 6.9 mg/dL. Her hemodynamics were unstable and she was admitted to their intensive care unit. The results of a chest X-ray revealed right lung consolidation.
The day after this admission, her hemoglobin level fell to 4.7 g/dL, and she was transfused 2 units of packed red blood cells before being transferred to our hospital. A chest X-ray at our hospital confirmed a right lung infiltrate. Vancomycin (1,250 mg IV Q12), levaquin (750 mg IV Q24), and maxipime (1 g IV Q12) were initiated for pneumonia and the patient was transferred to our hospital’s intensive care unit. She was afebrile at 98.3°F, her pulse rate was 84 beats per minute, she was tachypneic with respiratory rate of 26 breaths per minute, her blood pressure was 98/51 mmHg, and she had an oxygen saturation of 99% on 2L oxygen via nasal cannula.
On physical examination she was noted to have scleral icterus and was in mild respiratory distress. A chest X-ray revealed a patchy opacity in the right mid to lower lung. Her initial complete blood panel revealed anemia, with hemoglobin, 6.3 g/dL; white blood cell count, 27 x 109 per L; and platelets, 533 x 109 per L. The patient was then transfused another 2 units of packed red blood cells. She was given intravenous hydration, acetaminophen, and albuterol nebulizer treatments as supportive care. She was provided with blankets to keep warm. In addition to her antibiotics, she was also given prednisone 70 mg for her respiratory symptoms.
Further tests revealed haptoglobin, <30 mg/dL (normal, 36-195 mg/dL); lactate dehydrogenase, 371 U/L (normal, 98-192 U/L); and complements C3, 90 mg/dL (normal, 79-152 mg/dL) and C4, <8 mg/dL (normal, 18-55 mg/dL). Her DAT was positive, and agglutination was seen on peripheral smear (Figure 1). This was her second positive DAT as she had positive one at the outside hospital initially. Her tests for mycoplasma pneumonia, the PCR and IgM, were negative, as were the Monospot for mononucleosis and the ANA for autoimmune disorders. Her cold agglutinin titer was 1:256 (normal, no agglutination <1:64). The patient’s repeat respiratory viral panel was negative given recent full treatment for her influenza A at the previous hospital. Her blood and urine cultures were negative.
The patient was given antibiotics (vancomycin 1,250 mg IV Q12, cefepime 2 g IV Q8, and azithromycin 500 mg daily) for her pneumonia. Her respiratory status improved, and she was transferred to general medical floors after the first day of her admission. Her total bilirubin trended down to 1.9 mg/dL. She remained on prednisone 70 mg daily.
The patient remained in the hospital for an additional 6 days before being discharged home on prednisone. She wanted to return to her home country of Brazil as soon as she was able to and said she would seek outpatient follow-up there with a hematologist. At the time of her discharge, her hemoglobin was 6.6 g/dL and her reticulocyte count, 6.0%. Figures 2 and 3 illustrate her hemoglobin and reticulocyte trend during her admission at our hospital.
Discussion
The incidence of cold AIHA or cold agglutinin disease (CAD) occurs about 4 per 1 million people and commonly affects women more often than men.2 The cause of CAD can be subdivided into primary, idiopathic, or secondary causes, which can include infections, malignancies, or benign diseases.3,4 Primary CAD is a chronic disorder that is generally seen in older women. Secondary CAD can be associated with B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders, such as Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and infectious agents such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae and mononucleosis caused by Epstein-Barr virus.
Mild hemolysis or acrocyanosis may occur with exposure to cold. The blood smear in CAD demonstrates red blood cell agglutination or clumping, polychromasia, and an absence of spherocytosis. In general, most cases require no treatment, but cytotoxic agents or rituximab can be used to treat more severe cases. Appropriate treatment for infectious causes of CAD includes supportive care aimed at the underlying disease process. In addition, it is helpful to keep the patient warm. There is no role for steroid therapy in CAD unlike in warm AIHA. However, our patient was symptomatic from her pneumonia, so we added steroids to help with her pulmonary insult.
The patient had a cold agglutinin titer of 1:256. Titers of 1:32 or higher are considered elevated by this technique. Elevated titers are generally rarely seen except in primary atypical pneumonia due to either M. pneumoniae, influenza A, influenza B, parainfluenza, and adenovirus, and in certain hemolytic anemias. Low titers of cold agglutinins have been demonstrated in malaria, peripheral vascular disease, and common respiratory diseases.
Warm AIHA is caused by IgG antibody activities at body temperature or at 98.6°F. They may or may not bind complement and are removed from circulation by the spleen. Cold AIHA is due to IgM antibodies coating red cells at lower temperatures. They bind complement and lead to red blood cell destruction of agglutinated cells. If the antibody is active at temperatures approaching 98.6°F, clinically significant intravascular and sometimes extravascular complement-mediated hemolysis occur in the liver.5
The incidence of warm AIHA occurs about 10 per 1 million people and affects women twice often as men.2 It can be primary or idiopathic, or associated with various underlying conditions, including autoimmune disorders, immunodeficiency syndromes, lymphoproliferative disorders, other malignancies, and certain drugs. In more severe cases, jaundice and splenomegaly may occur. The blood smear in warm AIHA demonstrates variable spherocytosis, polychromasia, and rare erythrophagocytosis. Treatment usually includes steroids, cytotoxic agents, and splenectomy in severe cases.
There have been few case reports describing influenza as a cause of cold agglutinin hemolytic anemia. Chen and colleagues reported a case of influenza A infection in a 22-month-old boy.6Schoindre and colleagues reported the case of a 60-year-old woman infected with influenza A H1N1 virus who died from CAD.7 Shizuma reported the case of a 67-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis who developed a mixed hemolytic anemia and was positive for influenza A.8Our patient presented with influenza A, which had been diagnosed by respiratory virus panel at a different hospital, and she was anemic at the time of presentation to the outside hospital, with a positive DAT test. She was treated for influenza A with a full course of osltamivir and then returned with complaints of worsening fatigue and was again noted to be anemic with the development of patchy opacities on chest X-ray. The patient was subsequently transferred to our hospital and remained anemic during the course of her treatment. She received supportive care for her underlying influenza A and had symptomatic improvement. She ultimately decided the she would like to pursue further treatment in her native country and was discharged.
In conclusion, this case represents a rare complication of a common illness. Few cases of influenza causing hemolytic anemia have been reported in the literature. There have been reports of oseltamivir causing hemolytic anemia, but our patient presented with evidence of hemolytic anemia before initiation of the medication. In all the aforementioned cases, the patients died as a result of comorbid conditions. Our patient was stable enough to be discharged from the hospital after treatment of her comorbid conditions.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank David Henry, MD, at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, for sharing this case and for his guidance during this patient’s treatment.
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is characterized by the temperature at which the auto-antibody has the greatest avidity for the target red cell antigen, either warm or cold forms. It is detected by a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) also known as the direct Coombs test. DAT is used to determine if red cells have been coated in vivo with immunoglobulin, complement, or both.1 Some causes of a positive DAT include hemolytic transfusion reactions, hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, AIHA, and drug-induced immune hemolysis.
Case presentation and summary
A 58-year-old woman from Brazil with past medical history only significant for cholecystectomy and cesarean section had been visiting in United States for 2 months when she presented to an outside hospital with fever, shortness of breath, and syncope that had resulted in a foot injury. She reported she had been feeling short of breath and had a nonproductive cough and malaise for about 2 weeks before presentation with sick contacts at home. On admission it was noted that she had a hemoglobin level of 7.7 g/dL (normal, 12.0-15.5 g/dL; MCV, 94 fL), total bilirubin of 2.14 mg/dL (normal, 0.2-1.0 mg/dL), and lactate dehydrogenase of 523 U/L (normal, 81-234 U/L). There were no signs of bleeding on her examination. Her DAT was positive and moderate red blood cell agglutination was reported. During the first admission at the outside hospital she was diagnosed with influenza A and completed a full course of oseltamivir (75 mg po twice daily for 5 days). A chest X-ray was negative for infiltrates and showed that the patient’s lung fields were clear. She was transfused 2 units of packed red blood cells with response in hemoglobin up to 9.8 g/dL. The patient was treated with dexamethasone (4 mg IV Q8) as an inpatient and was discharged on a prednisone taper (40 mg, with taper by 10 mg every 3 days) with hemoglobin of 8.1 g/dL.
The patient continued to have nonproductive cough, dyspnea, fevers, chills, and generalized weakness, when she returned to the same outside hospital’s emergency department 2 days after her discharge. At that time, it was noted that she had leucocytosis (white blood cell count, 34.6 x 109 per L), a hemoglobin level of 6.8 g/dL, and her total bilirubin level was 6.9 mg/dL. Her hemodynamics were unstable and she was admitted to their intensive care unit. The results of a chest X-ray revealed right lung consolidation.
The day after this admission, her hemoglobin level fell to 4.7 g/dL, and she was transfused 2 units of packed red blood cells before being transferred to our hospital. A chest X-ray at our hospital confirmed a right lung infiltrate. Vancomycin (1,250 mg IV Q12), levaquin (750 mg IV Q24), and maxipime (1 g IV Q12) were initiated for pneumonia and the patient was transferred to our hospital’s intensive care unit. She was afebrile at 98.3°F, her pulse rate was 84 beats per minute, she was tachypneic with respiratory rate of 26 breaths per minute, her blood pressure was 98/51 mmHg, and she had an oxygen saturation of 99% on 2L oxygen via nasal cannula.
On physical examination she was noted to have scleral icterus and was in mild respiratory distress. A chest X-ray revealed a patchy opacity in the right mid to lower lung. Her initial complete blood panel revealed anemia, with hemoglobin, 6.3 g/dL; white blood cell count, 27 x 109 per L; and platelets, 533 x 109 per L. The patient was then transfused another 2 units of packed red blood cells. She was given intravenous hydration, acetaminophen, and albuterol nebulizer treatments as supportive care. She was provided with blankets to keep warm. In addition to her antibiotics, she was also given prednisone 70 mg for her respiratory symptoms.
Further tests revealed haptoglobin, <30 mg/dL (normal, 36-195 mg/dL); lactate dehydrogenase, 371 U/L (normal, 98-192 U/L); and complements C3, 90 mg/dL (normal, 79-152 mg/dL) and C4, <8 mg/dL (normal, 18-55 mg/dL). Her DAT was positive, and agglutination was seen on peripheral smear (Figure 1). This was her second positive DAT as she had positive one at the outside hospital initially. Her tests for mycoplasma pneumonia, the PCR and IgM, were negative, as were the Monospot for mononucleosis and the ANA for autoimmune disorders. Her cold agglutinin titer was 1:256 (normal, no agglutination <1:64). The patient’s repeat respiratory viral panel was negative given recent full treatment for her influenza A at the previous hospital. Her blood and urine cultures were negative.
The patient was given antibiotics (vancomycin 1,250 mg IV Q12, cefepime 2 g IV Q8, and azithromycin 500 mg daily) for her pneumonia. Her respiratory status improved, and she was transferred to general medical floors after the first day of her admission. Her total bilirubin trended down to 1.9 mg/dL. She remained on prednisone 70 mg daily.
The patient remained in the hospital for an additional 6 days before being discharged home on prednisone. She wanted to return to her home country of Brazil as soon as she was able to and said she would seek outpatient follow-up there with a hematologist. At the time of her discharge, her hemoglobin was 6.6 g/dL and her reticulocyte count, 6.0%. Figures 2 and 3 illustrate her hemoglobin and reticulocyte trend during her admission at our hospital.
Discussion
The incidence of cold AIHA or cold agglutinin disease (CAD) occurs about 4 per 1 million people and commonly affects women more often than men.2 The cause of CAD can be subdivided into primary, idiopathic, or secondary causes, which can include infections, malignancies, or benign diseases.3,4 Primary CAD is a chronic disorder that is generally seen in older women. Secondary CAD can be associated with B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders, such as Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and infectious agents such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae and mononucleosis caused by Epstein-Barr virus.
Mild hemolysis or acrocyanosis may occur with exposure to cold. The blood smear in CAD demonstrates red blood cell agglutination or clumping, polychromasia, and an absence of spherocytosis. In general, most cases require no treatment, but cytotoxic agents or rituximab can be used to treat more severe cases. Appropriate treatment for infectious causes of CAD includes supportive care aimed at the underlying disease process. In addition, it is helpful to keep the patient warm. There is no role for steroid therapy in CAD unlike in warm AIHA. However, our patient was symptomatic from her pneumonia, so we added steroids to help with her pulmonary insult.
The patient had a cold agglutinin titer of 1:256. Titers of 1:32 or higher are considered elevated by this technique. Elevated titers are generally rarely seen except in primary atypical pneumonia due to either M. pneumoniae, influenza A, influenza B, parainfluenza, and adenovirus, and in certain hemolytic anemias. Low titers of cold agglutinins have been demonstrated in malaria, peripheral vascular disease, and common respiratory diseases.
Warm AIHA is caused by IgG antibody activities at body temperature or at 98.6°F. They may or may not bind complement and are removed from circulation by the spleen. Cold AIHA is due to IgM antibodies coating red cells at lower temperatures. They bind complement and lead to red blood cell destruction of agglutinated cells. If the antibody is active at temperatures approaching 98.6°F, clinically significant intravascular and sometimes extravascular complement-mediated hemolysis occur in the liver.5
The incidence of warm AIHA occurs about 10 per 1 million people and affects women twice often as men.2 It can be primary or idiopathic, or associated with various underlying conditions, including autoimmune disorders, immunodeficiency syndromes, lymphoproliferative disorders, other malignancies, and certain drugs. In more severe cases, jaundice and splenomegaly may occur. The blood smear in warm AIHA demonstrates variable spherocytosis, polychromasia, and rare erythrophagocytosis. Treatment usually includes steroids, cytotoxic agents, and splenectomy in severe cases.
There have been few case reports describing influenza as a cause of cold agglutinin hemolytic anemia. Chen and colleagues reported a case of influenza A infection in a 22-month-old boy.6Schoindre and colleagues reported the case of a 60-year-old woman infected with influenza A H1N1 virus who died from CAD.7 Shizuma reported the case of a 67-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis who developed a mixed hemolytic anemia and was positive for influenza A.8Our patient presented with influenza A, which had been diagnosed by respiratory virus panel at a different hospital, and she was anemic at the time of presentation to the outside hospital, with a positive DAT test. She was treated for influenza A with a full course of osltamivir and then returned with complaints of worsening fatigue and was again noted to be anemic with the development of patchy opacities on chest X-ray. The patient was subsequently transferred to our hospital and remained anemic during the course of her treatment. She received supportive care for her underlying influenza A and had symptomatic improvement. She ultimately decided the she would like to pursue further treatment in her native country and was discharged.
In conclusion, this case represents a rare complication of a common illness. Few cases of influenza causing hemolytic anemia have been reported in the literature. There have been reports of oseltamivir causing hemolytic anemia, but our patient presented with evidence of hemolytic anemia before initiation of the medication. In all the aforementioned cases, the patients died as a result of comorbid conditions. Our patient was stable enough to be discharged from the hospital after treatment of her comorbid conditions.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank David Henry, MD, at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, for sharing this case and for his guidance during this patient’s treatment.
1. Roback JD, Grossman BJ, Harris T, Hillyer CD. Technical manual [17th ed]. Bethesda, MD; American Association of Blood Banks; 2011.
2. Jaffee ES, Harris NL, Vardiman JW, Campo E, Arber DA. Hematopathology. St. Louis, MO; Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
3. Feizi T. Monotypic cold agglutinins in infection by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nature. 1967;215(5100):540-542.
4. Horwitz CA, Moulds J, Henle W, et al. Cold agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis and heterophil-antibody-negative mononucleosis-like syndromes. Blood. 1977;50(2):195-202.
5. Hsi ED, editor. Hematopathology [3rd ed]. Philadelphia, PA; Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
6. Chen H, Jia XL, Gao HM, Qian SY. Comorbid presentation of severe novel influenza A (H1N1) and Evans syndrome: a case report. Chin Med J. 2011;124(11):1743-1746.
7. Schoindre Y, Bollée G, Dumont MD, Lesavre P, Servais A. Cold agglutinin syndrome associated with a 2009 influenza A H1N1 infection. http://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(10)00482-1/fulltext. Published February 2011. Accessed October 10, 2017.
8. [Article in Japanese] Shizuma T. [A case of autoimmune hemolytic anemia caused by type A influenza infection in a patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2010;84(3):296-299.
1. Roback JD, Grossman BJ, Harris T, Hillyer CD. Technical manual [17th ed]. Bethesda, MD; American Association of Blood Banks; 2011.
2. Jaffee ES, Harris NL, Vardiman JW, Campo E, Arber DA. Hematopathology. St. Louis, MO; Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
3. Feizi T. Monotypic cold agglutinins in infection by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nature. 1967;215(5100):540-542.
4. Horwitz CA, Moulds J, Henle W, et al. Cold agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis and heterophil-antibody-negative mononucleosis-like syndromes. Blood. 1977;50(2):195-202.
5. Hsi ED, editor. Hematopathology [3rd ed]. Philadelphia, PA; Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
6. Chen H, Jia XL, Gao HM, Qian SY. Comorbid presentation of severe novel influenza A (H1N1) and Evans syndrome: a case report. Chin Med J. 2011;124(11):1743-1746.
7. Schoindre Y, Bollée G, Dumont MD, Lesavre P, Servais A. Cold agglutinin syndrome associated with a 2009 influenza A H1N1 infection. http://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(10)00482-1/fulltext. Published February 2011. Accessed October 10, 2017.
8. [Article in Japanese] Shizuma T. [A case of autoimmune hemolytic anemia caused by type A influenza infection in a patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2010;84(3):296-299.
Pembrolizumab for dMMR/MSI-H tumors marks first tumor agnostic FDA approval
The United States Food and Drug Administration’s approval earlier this year of pembrolizumab marks the first tumor agnostic indication for a cancer drug.1,2 Accelerated approval was granted for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with any unresectable or metastatic solid tumor that displays mismatch repair deficiencies (dMMR) or high levels of microsatellite instability (MSI-H) and who have progressed after previous treatment and have no satisfactory alternatives. It is also approved specifically for patients with MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer (CRC) that has progressed after treatment with a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan.
Pembrolizumab is a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) receptor inhibitor that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligand, PD-L1, restoring the activity of tumor-infiltrating T cells and boosting the anti-tumor immune response. It is thought to be particularly effective in dMMR/MSI-H tumors because they have a high mutational load and therefore display an abundance of antigens on their surfaces to provoke an immune response.
Approval for the drug was based on the demonstration of durable responses in 149 patients with MSI-H or dMMR cancers across 5 uncontrolled, multicohort, multicenter, single-arm trials. In all, 90 of the patients had CRC, and the remaining 59 patients had 1 of 14 other cancer types that included endometrial, biliary, gastric or gastroesophageal, pancreatic, and breast cancers.
Patients in these trials received pembrolizumab at 1 of 2 different doses, either 200 mg every 3 weeks or 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks, until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression that was symptomatic, rapidly progressive, required urgent intervention, or coincided with a decline in performance status. Treatment was administered for a maximum of 2 years. Patients with an active autoimmune disease or a medical condition that required immunosuppression were ineligible for treatment in all 5 studies.
The median age of enrolled patients was 55 years; 56% were men; 77% white, 19% Asian, 2% black; 98% had metastatic or unresectable disease; and all had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status of 0 or 1 (range, 0-5, where 0 denotes full activity and 1, restricted in physically strenuous activity but ambulatory). MSI-H and MMR status were identified prospectively using polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical analyses, respectively.
The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR), according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1), as assessed by blinded independent central radiologist review, and response duration. The ORR across all five studies
The safety profile was consistent with previously reported safety data for pembrolizumab. The most common adverse events included fatigue, pruritus, diarrhea, decreased appetite, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, and nausea.
The prescribing information includes a “limitation of use” that states that pembroliumab’s safety and efficacy haven’t been established in pediatric patients with MSI-H cancers of the central nervous system.3 It also details warnings and precautions about immune-mediated toxicities, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and renal dysfunction, among others.
Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of these toxicities and treated appropriately. Treatment should be withheld and corticosteroids should be administered for grade 2 or higher pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, and nephritis; and corticosteroids and hormone replacement as clinically indicated for endocrinopathies. It should also be withheld for aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels >3-5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) or total bilirubin levels >1.5-3 times ULN.
Pembrolizumab should be permanently discontinued upon grade 3, 4, or recurrent grade 2 pneumonitis, colitis, nephritis/renal dysfunction, and endocrinopathies or for AST or ALT levels >5 times ULN or total bilirubin levels >3 times ULN. For patients with liver metastases who begin treatment with grade 2 AST or ALT, treatment should be permanently discontinued following increases of more than 50%, relative to baseline, that last for at least 1 week.
Health care providers should also bear in mind that pembrolizumab can, more rarely, cause other immune-mediated toxicities, such as arthritis and exfoliative rash that may require treatment and, based on its mechanism of action, pembrolizumab can also cause fetal harm. Patients with reproductive potential should be advised of the implications. Pembrolizumab is marketed as Keytruda by Merck & Co Inc.
1. United States Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for tissue/site agnostic indication. US FDA Web site. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/ approveddrugs/ucm560040.htm. Last updated May 30, 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
2. Merck. News Release. FDA Approves Merck’s KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab) for Adult and Pediatric Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic, Microsatellite Instability-High (MSI-H) or Mismatch Repair De[1]cient (dMMR) Solid Tumors. http://www.mrknewsroom. com/news-release/prescription-medicine-news/fda-approvesmercks- keytruda-pembrolizumab-adult-and-pediatr. Last updated May 23, 2017. Accessed July 17, 2017.
3. Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for injection, for intravenous use. Prescribing information. Merck & Co Inc. https://www.merck.com/ product/usa/pi_circulars/k/keytruda/keytruda_pi.pdf. Posted May 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
The United States Food and Drug Administration’s approval earlier this year of pembrolizumab marks the first tumor agnostic indication for a cancer drug.1,2 Accelerated approval was granted for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with any unresectable or metastatic solid tumor that displays mismatch repair deficiencies (dMMR) or high levels of microsatellite instability (MSI-H) and who have progressed after previous treatment and have no satisfactory alternatives. It is also approved specifically for patients with MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer (CRC) that has progressed after treatment with a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan.
Pembrolizumab is a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) receptor inhibitor that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligand, PD-L1, restoring the activity of tumor-infiltrating T cells and boosting the anti-tumor immune response. It is thought to be particularly effective in dMMR/MSI-H tumors because they have a high mutational load and therefore display an abundance of antigens on their surfaces to provoke an immune response.
Approval for the drug was based on the demonstration of durable responses in 149 patients with MSI-H or dMMR cancers across 5 uncontrolled, multicohort, multicenter, single-arm trials. In all, 90 of the patients had CRC, and the remaining 59 patients had 1 of 14 other cancer types that included endometrial, biliary, gastric or gastroesophageal, pancreatic, and breast cancers.
Patients in these trials received pembrolizumab at 1 of 2 different doses, either 200 mg every 3 weeks or 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks, until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression that was symptomatic, rapidly progressive, required urgent intervention, or coincided with a decline in performance status. Treatment was administered for a maximum of 2 years. Patients with an active autoimmune disease or a medical condition that required immunosuppression were ineligible for treatment in all 5 studies.
The median age of enrolled patients was 55 years; 56% were men; 77% white, 19% Asian, 2% black; 98% had metastatic or unresectable disease; and all had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status of 0 or 1 (range, 0-5, where 0 denotes full activity and 1, restricted in physically strenuous activity but ambulatory). MSI-H and MMR status were identified prospectively using polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical analyses, respectively.
The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR), according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1), as assessed by blinded independent central radiologist review, and response duration. The ORR across all five studies
The safety profile was consistent with previously reported safety data for pembrolizumab. The most common adverse events included fatigue, pruritus, diarrhea, decreased appetite, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, and nausea.
The prescribing information includes a “limitation of use” that states that pembroliumab’s safety and efficacy haven’t been established in pediatric patients with MSI-H cancers of the central nervous system.3 It also details warnings and precautions about immune-mediated toxicities, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and renal dysfunction, among others.
Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of these toxicities and treated appropriately. Treatment should be withheld and corticosteroids should be administered for grade 2 or higher pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, and nephritis; and corticosteroids and hormone replacement as clinically indicated for endocrinopathies. It should also be withheld for aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels >3-5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) or total bilirubin levels >1.5-3 times ULN.
Pembrolizumab should be permanently discontinued upon grade 3, 4, or recurrent grade 2 pneumonitis, colitis, nephritis/renal dysfunction, and endocrinopathies or for AST or ALT levels >5 times ULN or total bilirubin levels >3 times ULN. For patients with liver metastases who begin treatment with grade 2 AST or ALT, treatment should be permanently discontinued following increases of more than 50%, relative to baseline, that last for at least 1 week.
Health care providers should also bear in mind that pembrolizumab can, more rarely, cause other immune-mediated toxicities, such as arthritis and exfoliative rash that may require treatment and, based on its mechanism of action, pembrolizumab can also cause fetal harm. Patients with reproductive potential should be advised of the implications. Pembrolizumab is marketed as Keytruda by Merck & Co Inc.
The United States Food and Drug Administration’s approval earlier this year of pembrolizumab marks the first tumor agnostic indication for a cancer drug.1,2 Accelerated approval was granted for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with any unresectable or metastatic solid tumor that displays mismatch repair deficiencies (dMMR) or high levels of microsatellite instability (MSI-H) and who have progressed after previous treatment and have no satisfactory alternatives. It is also approved specifically for patients with MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer (CRC) that has progressed after treatment with a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan.
Pembrolizumab is a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) receptor inhibitor that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligand, PD-L1, restoring the activity of tumor-infiltrating T cells and boosting the anti-tumor immune response. It is thought to be particularly effective in dMMR/MSI-H tumors because they have a high mutational load and therefore display an abundance of antigens on their surfaces to provoke an immune response.
Approval for the drug was based on the demonstration of durable responses in 149 patients with MSI-H or dMMR cancers across 5 uncontrolled, multicohort, multicenter, single-arm trials. In all, 90 of the patients had CRC, and the remaining 59 patients had 1 of 14 other cancer types that included endometrial, biliary, gastric or gastroesophageal, pancreatic, and breast cancers.
Patients in these trials received pembrolizumab at 1 of 2 different doses, either 200 mg every 3 weeks or 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks, until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression that was symptomatic, rapidly progressive, required urgent intervention, or coincided with a decline in performance status. Treatment was administered for a maximum of 2 years. Patients with an active autoimmune disease or a medical condition that required immunosuppression were ineligible for treatment in all 5 studies.
The median age of enrolled patients was 55 years; 56% were men; 77% white, 19% Asian, 2% black; 98% had metastatic or unresectable disease; and all had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status of 0 or 1 (range, 0-5, where 0 denotes full activity and 1, restricted in physically strenuous activity but ambulatory). MSI-H and MMR status were identified prospectively using polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical analyses, respectively.
The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR), according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1), as assessed by blinded independent central radiologist review, and response duration. The ORR across all five studies
The safety profile was consistent with previously reported safety data for pembrolizumab. The most common adverse events included fatigue, pruritus, diarrhea, decreased appetite, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, and nausea.
The prescribing information includes a “limitation of use” that states that pembroliumab’s safety and efficacy haven’t been established in pediatric patients with MSI-H cancers of the central nervous system.3 It also details warnings and precautions about immune-mediated toxicities, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and renal dysfunction, among others.
Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of these toxicities and treated appropriately. Treatment should be withheld and corticosteroids should be administered for grade 2 or higher pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, and nephritis; and corticosteroids and hormone replacement as clinically indicated for endocrinopathies. It should also be withheld for aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels >3-5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) or total bilirubin levels >1.5-3 times ULN.
Pembrolizumab should be permanently discontinued upon grade 3, 4, or recurrent grade 2 pneumonitis, colitis, nephritis/renal dysfunction, and endocrinopathies or for AST or ALT levels >5 times ULN or total bilirubin levels >3 times ULN. For patients with liver metastases who begin treatment with grade 2 AST or ALT, treatment should be permanently discontinued following increases of more than 50%, relative to baseline, that last for at least 1 week.
Health care providers should also bear in mind that pembrolizumab can, more rarely, cause other immune-mediated toxicities, such as arthritis and exfoliative rash that may require treatment and, based on its mechanism of action, pembrolizumab can also cause fetal harm. Patients with reproductive potential should be advised of the implications. Pembrolizumab is marketed as Keytruda by Merck & Co Inc.
1. United States Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for tissue/site agnostic indication. US FDA Web site. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/ approveddrugs/ucm560040.htm. Last updated May 30, 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
2. Merck. News Release. FDA Approves Merck’s KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab) for Adult and Pediatric Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic, Microsatellite Instability-High (MSI-H) or Mismatch Repair De[1]cient (dMMR) Solid Tumors. http://www.mrknewsroom. com/news-release/prescription-medicine-news/fda-approvesmercks- keytruda-pembrolizumab-adult-and-pediatr. Last updated May 23, 2017. Accessed July 17, 2017.
3. Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for injection, for intravenous use. Prescribing information. Merck & Co Inc. https://www.merck.com/ product/usa/pi_circulars/k/keytruda/keytruda_pi.pdf. Posted May 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
1. United States Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for tissue/site agnostic indication. US FDA Web site. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/ approveddrugs/ucm560040.htm. Last updated May 30, 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
2. Merck. News Release. FDA Approves Merck’s KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab) for Adult and Pediatric Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic, Microsatellite Instability-High (MSI-H) or Mismatch Repair De[1]cient (dMMR) Solid Tumors. http://www.mrknewsroom. com/news-release/prescription-medicine-news/fda-approvesmercks- keytruda-pembrolizumab-adult-and-pediatr. Last updated May 23, 2017. Accessed July 17, 2017.
3. Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for injection, for intravenous use. Prescribing information. Merck & Co Inc. https://www.merck.com/ product/usa/pi_circulars/k/keytruda/keytruda_pi.pdf. Posted May 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
Brigatinib approval yields additional treatment options for crizotinib-resistant, ALK-positive NSCLC patients
The accelerated approval by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor brigatinib, marked the fourth approved drug in this class.1 The most recent approval expands the available treatment options for patients with metastatic ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease is no longer responding to the first-line ALK inhibitor crizotinib. The FDA based its decision on the results of the phase 2 ALTA trial, in which a significant proportion of patients experienced tumor shrinkage.2
The pivotal trial was a noncomparative, 2-arm, open-label, multicenter study that was carried out during June 2014-September 2015 at 71 centers across 18 countries. Eligible patients were 18 years or older, with locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC, disease progression while taking crizotinib, at least 1 measurable lesion, adequate organ and hematologic function, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of ≤2 (range, 0-5, where 0 means the patient is fully active, and 2, ambulatory and capable of all self-care but not able to carry out any work activities).
Patients were excluded from the trial if they had received previous ALK inhibitor therapy, other than crizotinib, or had received crizotinib within 3 days of the first dose of brigatinib, or they had received chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or investigational drugs within 14 days or monoclonal antibody therapy within 30 days of the first dose of the study drug. Anyone with a history or the presence of pulmonary interstitial disease or drug-related pneumonitis or symptomatic central nervous system (CNS) metastases that were neurologically unstable or required an increasing dose of corticosteroids was also ineligible.
A total of 222 patients were randomized to receive one of two brigatinib doses, either 90 mg daily or 180 mg daily after a 7-day lead-in at 90 mg (the latter to help mitigate pulmonary adverse events observed in previous studies). Randomization was stratified according to baseline brain metastases (present or absent) and best investigator-assessed response to crizotinib (complete response [CR] or partial response [PR] vs other or unknown)
Chest and abdomen imaging by computed-tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast were performed to assess disease at screening and every 8 weeks through cycle 15, and then every 12 weeks until disease progression. Contrast-enhanced brain MRI was carried out at screening and repeated after baseline for the 68% of patients who had CNS metastases at the time of enrollment.
The primary endpoint was confirmed investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1), and secondary endpoints included CNS response, duration of response (DoR), progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS, respectively). ORRs for the 90-mg and 180-mg doses were 48% and 53%, respectively. Responses occurred quickly and were durable in both arms; after a median follow-up of 8 months, median DoR was 13.8 months for both doses. Among the patients with brain metastases, the intracranial response rates for the two doses were 42% and 67%, respectively, notable because of the poor ability of crizotinib to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
Other secondary outcomes also favored the 180-mg dose. Investigator-assessed PFS for the 90-mg and 180-mg doses were 9.2 months and 12.9 months, respectively, and estimated 1-year OS was 71% and 80%, respectively, the latter representing a nonstatistically significant 43% reduction in the risk of death with the 180 mg dose. There were 4 confirmed CRs in the 180-mg arm and 1 in the 90-mg arm.
The safety of brigatinib was evaluated in 219 patients who received at least 1 dose of brigatinib. Treatment was discontinued in 8% of patients in the 180-mg arm and 3% in the 90-mg arm because of adverse events (AEs). The most common AEs were nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, cough, and headache, and visual disturbances also occurred. The most common serious AEs were pneumonia and interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis.
The prescribing information details warnings and precautions about these and other potential toxicities, including hypertension, bradycardia, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and pancreatic enzyme elevation, and hyperglycemia.3 Patients should be monitored for new or worsening respiratory symptoms, especially during the first week of initiating brigatinib treatment; blood pressure should be controlled before treatment initiation and monitored after 2 weeks and at least monthly thereafter; heart rate and blood pressure should be monitored frequently; patients should be advised to report any visual symptoms, or any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness; CPK, lipase, and amylase levels should be monitored during treatment, and fasting glucose tested before starting treatment and periodically thereafter.
Brigatinib should be withheld in any patient with new or worsening respiratory symptoms, for grade 3 hypertension despite optimal antihypertensive therapy, for symptomatic bradycardia, for patients with new or worsening visual symptoms of grade 2 or above, for grade 3 or 4 CPK or pancreatic enzyme elevation, or if adequate hyperglycemia control cannot be achieved. Treatment should be permanently discontinued for grade 3 or 4 or recurrent interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, grade 4 or recurrent grade 3 hypertension, life-threatening bradycardia, and grade 4 visual disturbance.
Based on its mechanism of action, brigatinib can cause fetal harm and patients of reproductive potential should be advised of the risks and necessary precautions. Brigatinib is marketed as Alunbrig. It was discovered by Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, which was acquired by Takeda in February 2017.
1. United States Food and Drug Administration. Brigatinib. US FDA Web site. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm555841.htm. Last updated April 28, 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017
2. Kim D-W, Tiseo M, Ahn M-J, Reckamp KL, et al. Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non–small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(22):2490-2498.
3. Alunbrig (brigatinib) tablets, for oral use. Prescribing information. Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc. https://www.alunbrig.com/assets/pi.pdf. Posted April 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
The accelerated approval by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor brigatinib, marked the fourth approved drug in this class.1 The most recent approval expands the available treatment options for patients with metastatic ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease is no longer responding to the first-line ALK inhibitor crizotinib. The FDA based its decision on the results of the phase 2 ALTA trial, in which a significant proportion of patients experienced tumor shrinkage.2
The pivotal trial was a noncomparative, 2-arm, open-label, multicenter study that was carried out during June 2014-September 2015 at 71 centers across 18 countries. Eligible patients were 18 years or older, with locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC, disease progression while taking crizotinib, at least 1 measurable lesion, adequate organ and hematologic function, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of ≤2 (range, 0-5, where 0 means the patient is fully active, and 2, ambulatory and capable of all self-care but not able to carry out any work activities).
Patients were excluded from the trial if they had received previous ALK inhibitor therapy, other than crizotinib, or had received crizotinib within 3 days of the first dose of brigatinib, or they had received chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or investigational drugs within 14 days or monoclonal antibody therapy within 30 days of the first dose of the study drug. Anyone with a history or the presence of pulmonary interstitial disease or drug-related pneumonitis or symptomatic central nervous system (CNS) metastases that were neurologically unstable or required an increasing dose of corticosteroids was also ineligible.
A total of 222 patients were randomized to receive one of two brigatinib doses, either 90 mg daily or 180 mg daily after a 7-day lead-in at 90 mg (the latter to help mitigate pulmonary adverse events observed in previous studies). Randomization was stratified according to baseline brain metastases (present or absent) and best investigator-assessed response to crizotinib (complete response [CR] or partial response [PR] vs other or unknown)
Chest and abdomen imaging by computed-tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast were performed to assess disease at screening and every 8 weeks through cycle 15, and then every 12 weeks until disease progression. Contrast-enhanced brain MRI was carried out at screening and repeated after baseline for the 68% of patients who had CNS metastases at the time of enrollment.
The primary endpoint was confirmed investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1), and secondary endpoints included CNS response, duration of response (DoR), progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS, respectively). ORRs for the 90-mg and 180-mg doses were 48% and 53%, respectively. Responses occurred quickly and were durable in both arms; after a median follow-up of 8 months, median DoR was 13.8 months for both doses. Among the patients with brain metastases, the intracranial response rates for the two doses were 42% and 67%, respectively, notable because of the poor ability of crizotinib to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
Other secondary outcomes also favored the 180-mg dose. Investigator-assessed PFS for the 90-mg and 180-mg doses were 9.2 months and 12.9 months, respectively, and estimated 1-year OS was 71% and 80%, respectively, the latter representing a nonstatistically significant 43% reduction in the risk of death with the 180 mg dose. There were 4 confirmed CRs in the 180-mg arm and 1 in the 90-mg arm.
The safety of brigatinib was evaluated in 219 patients who received at least 1 dose of brigatinib. Treatment was discontinued in 8% of patients in the 180-mg arm and 3% in the 90-mg arm because of adverse events (AEs). The most common AEs were nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, cough, and headache, and visual disturbances also occurred. The most common serious AEs were pneumonia and interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis.
The prescribing information details warnings and precautions about these and other potential toxicities, including hypertension, bradycardia, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and pancreatic enzyme elevation, and hyperglycemia.3 Patients should be monitored for new or worsening respiratory symptoms, especially during the first week of initiating brigatinib treatment; blood pressure should be controlled before treatment initiation and monitored after 2 weeks and at least monthly thereafter; heart rate and blood pressure should be monitored frequently; patients should be advised to report any visual symptoms, or any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness; CPK, lipase, and amylase levels should be monitored during treatment, and fasting glucose tested before starting treatment and periodically thereafter.
Brigatinib should be withheld in any patient with new or worsening respiratory symptoms, for grade 3 hypertension despite optimal antihypertensive therapy, for symptomatic bradycardia, for patients with new or worsening visual symptoms of grade 2 or above, for grade 3 or 4 CPK or pancreatic enzyme elevation, or if adequate hyperglycemia control cannot be achieved. Treatment should be permanently discontinued for grade 3 or 4 or recurrent interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, grade 4 or recurrent grade 3 hypertension, life-threatening bradycardia, and grade 4 visual disturbance.
Based on its mechanism of action, brigatinib can cause fetal harm and patients of reproductive potential should be advised of the risks and necessary precautions. Brigatinib is marketed as Alunbrig. It was discovered by Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, which was acquired by Takeda in February 2017.
The accelerated approval by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor brigatinib, marked the fourth approved drug in this class.1 The most recent approval expands the available treatment options for patients with metastatic ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease is no longer responding to the first-line ALK inhibitor crizotinib. The FDA based its decision on the results of the phase 2 ALTA trial, in which a significant proportion of patients experienced tumor shrinkage.2
The pivotal trial was a noncomparative, 2-arm, open-label, multicenter study that was carried out during June 2014-September 2015 at 71 centers across 18 countries. Eligible patients were 18 years or older, with locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC, disease progression while taking crizotinib, at least 1 measurable lesion, adequate organ and hematologic function, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of ≤2 (range, 0-5, where 0 means the patient is fully active, and 2, ambulatory and capable of all self-care but not able to carry out any work activities).
Patients were excluded from the trial if they had received previous ALK inhibitor therapy, other than crizotinib, or had received crizotinib within 3 days of the first dose of brigatinib, or they had received chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or investigational drugs within 14 days or monoclonal antibody therapy within 30 days of the first dose of the study drug. Anyone with a history or the presence of pulmonary interstitial disease or drug-related pneumonitis or symptomatic central nervous system (CNS) metastases that were neurologically unstable or required an increasing dose of corticosteroids was also ineligible.
A total of 222 patients were randomized to receive one of two brigatinib doses, either 90 mg daily or 180 mg daily after a 7-day lead-in at 90 mg (the latter to help mitigate pulmonary adverse events observed in previous studies). Randomization was stratified according to baseline brain metastases (present or absent) and best investigator-assessed response to crizotinib (complete response [CR] or partial response [PR] vs other or unknown)
Chest and abdomen imaging by computed-tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast were performed to assess disease at screening and every 8 weeks through cycle 15, and then every 12 weeks until disease progression. Contrast-enhanced brain MRI was carried out at screening and repeated after baseline for the 68% of patients who had CNS metastases at the time of enrollment.
The primary endpoint was confirmed investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1), and secondary endpoints included CNS response, duration of response (DoR), progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS, respectively). ORRs for the 90-mg and 180-mg doses were 48% and 53%, respectively. Responses occurred quickly and were durable in both arms; after a median follow-up of 8 months, median DoR was 13.8 months for both doses. Among the patients with brain metastases, the intracranial response rates for the two doses were 42% and 67%, respectively, notable because of the poor ability of crizotinib to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
Other secondary outcomes also favored the 180-mg dose. Investigator-assessed PFS for the 90-mg and 180-mg doses were 9.2 months and 12.9 months, respectively, and estimated 1-year OS was 71% and 80%, respectively, the latter representing a nonstatistically significant 43% reduction in the risk of death with the 180 mg dose. There were 4 confirmed CRs in the 180-mg arm and 1 in the 90-mg arm.
The safety of brigatinib was evaluated in 219 patients who received at least 1 dose of brigatinib. Treatment was discontinued in 8% of patients in the 180-mg arm and 3% in the 90-mg arm because of adverse events (AEs). The most common AEs were nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, cough, and headache, and visual disturbances also occurred. The most common serious AEs were pneumonia and interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis.
The prescribing information details warnings and precautions about these and other potential toxicities, including hypertension, bradycardia, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and pancreatic enzyme elevation, and hyperglycemia.3 Patients should be monitored for new or worsening respiratory symptoms, especially during the first week of initiating brigatinib treatment; blood pressure should be controlled before treatment initiation and monitored after 2 weeks and at least monthly thereafter; heart rate and blood pressure should be monitored frequently; patients should be advised to report any visual symptoms, or any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness; CPK, lipase, and amylase levels should be monitored during treatment, and fasting glucose tested before starting treatment and periodically thereafter.
Brigatinib should be withheld in any patient with new or worsening respiratory symptoms, for grade 3 hypertension despite optimal antihypertensive therapy, for symptomatic bradycardia, for patients with new or worsening visual symptoms of grade 2 or above, for grade 3 or 4 CPK or pancreatic enzyme elevation, or if adequate hyperglycemia control cannot be achieved. Treatment should be permanently discontinued for grade 3 or 4 or recurrent interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, grade 4 or recurrent grade 3 hypertension, life-threatening bradycardia, and grade 4 visual disturbance.
Based on its mechanism of action, brigatinib can cause fetal harm and patients of reproductive potential should be advised of the risks and necessary precautions. Brigatinib is marketed as Alunbrig. It was discovered by Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, which was acquired by Takeda in February 2017.
1. United States Food and Drug Administration. Brigatinib. US FDA Web site. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm555841.htm. Last updated April 28, 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017
2. Kim D-W, Tiseo M, Ahn M-J, Reckamp KL, et al. Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non–small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(22):2490-2498.
3. Alunbrig (brigatinib) tablets, for oral use. Prescribing information. Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc. https://www.alunbrig.com/assets/pi.pdf. Posted April 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
1. United States Food and Drug Administration. Brigatinib. US FDA Web site. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm555841.htm. Last updated April 28, 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017
2. Kim D-W, Tiseo M, Ahn M-J, Reckamp KL, et al. Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non–small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(22):2490-2498.
3. Alunbrig (brigatinib) tablets, for oral use. Prescribing information. Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc. https://www.alunbrig.com/assets/pi.pdf. Posted April 2017. Accessed July 15, 2017.
Primary analysis confirms interim findings of CTL019 in DLBCL
ATLANTA—The first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy approved in the US to treat children and young adults with leukemia is also producing high response rates in lymphoma, according to investigators of the JULIET trial.
They reported that tisagenlecleucel (formerly CTL019) produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 53% and a complete response (CR) rate of 40% in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Additionally, researchers say the stability in the response rate at 3 and 6 months—38% and 37%, respectively—indicates the durability of the therapy.
At 3 months, 32% of patients who achieved CR remained in CR. At 6 months, 30% remained in CR.
Researchers believe these results confirm the durable clinical benefit reported previously.
Stephen J. Schuster, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, presented the JULIET data at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 577).
“Only about half of relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients are eligible for transplant,” Dr Schuster said. “[O]f those patients, only about a half respond to salvage chemotherapy, and a significant number of patients relapse post-transplant. So there is really a large unmet need for these patients, and CAR T-cell therapy is a potential agent [for them].”
The JULIET trial was a global, single-arm, phase 2 trial evaluating tisagenlecleucel in DLBCL patients. Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah™) consists of CAR T cells with a CD19 antigen-binding domain, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta signaling domain.
The trial was conducted at 27 sites in 10 countries across North America, Europe, Australia, and Asia. There were 2 centralized manufacturing sites, one in Europe and one in the US.
Patients had to be 18 years or older, have had 2 or more prior lines of therapy for DLBCL, and have progressive disease or be ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant (auto-SCT). They could not have had any prior anti-CD19 therapy, and they could not have any central nervous system involvement.
The primary endpoint was best ORR using Lugano criteria with assessment by an independent review committee. Secondary endpoints included duration of response, overall survival (OS), and safety.
Study design and enrollment
Patients were screened and underwent apheresis with cryopreservation of their leukapheresis products during screening, which “allowed for enrollment of all eligible patients,” Dr Schuster said.
Patients could receive bridging chemotherapy while they awaited the manufacture of the CAR T cells.
“What’s important to note is that, early on in the trial, there was a shortage of manufacturing capacity, and this led to a longer-than-anticipated interval between enrollment and treatment,” Dr Schuster said. “This interval decreased as manufacturing capacity improved throughout the trial.”
When their CAR T cells were ready, patients were restaged, lymphodepleted, and received the tisagenlecleucel infusion. The dose ranged from 0.6 x 108 to 6.0 x 108 CAR-positive T cells.
The infusion could be conducted on an inpatient or outpatient basis at the investigator’s discretion, Dr Schuster said.
As of the data cutoff in March 2017, investigators enrolled 147 patients and infused 99 with tisagenlecleucel.
Forty-three patients discontinued before infusion, 9 because of an inability to manufacture the T-cell product and 34 due to death (n=16), physician decision (n=12), patient decision (n=3), adverse event (n=2), and protocol deviation (n=1). Five patients were pending infusion.
There were 81 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up or earlier disease progression evaluable for response.
Patient characteristics
Patients were a median age of 56 (range, 22–76), and 23% were 65 or older. All had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, 80% had DLBCL, and 19% had transformed follicular lymphoma.
Fifteen percent had double or triple hits in CMYC, BCL2, and BCL6 genes, and 52% had germinal center B-cell type disease.
Forty-four percent had 2 prior lines of therapy, 31% had 3 prior lines of therapy, and 19% had 4 to 6 prior lines of therapy. All were either refractory to or relapsed from their last therapy.
Forty-seven percent had undergone prior auto-SCT.
Eighty-nine of the 99 patients infused with tisagenlecleucel received bridging therapy, and 92 received lymphodepleting therapy.
Twenty-six patients were infused as outpatients, and 20 remained as outpatients for 3 or more days after the infusion.
Efficacy
The trial met its primary endpoint with an ORR of 53% tested against the null hypothesis of 20% or less. Forty percent of patients achieved a CR, and 14% had a partial response.
The ORR was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, lines of prior antineoplastic therapy, cell of origin, and rearranged MYC/BCL2/BCL6.
“The durability of response, however, which is really the message, is shown by the stability between 3- and 6-month response rates, 38% and 37%, respectively,” Dr Schuster said. “The response rate at 3 months is really indicative of the long-term benefit of this treatment approach.”
The investigators observed no apparent relationship between tumor response at month 3 and dose. And they observed responses at all dose levels.
The very early response may be due, to a certain extent, to the chemotherapy, according to Dr Schuster.
“The effect of the T cells becomes evident as you follow these patients over time,” he said.
The median duration of response and overall response have not been reached. And 74% of patients were relapse-free at 6 months.
“Importantly, almost all the complete responders at month 3 remained in complete response,” Dr Schuster said.
Safety
Adverse events of special interest that occurred within 8 weeks of the infusion included:
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS)—58% all grades, 15% grade 3, 8% grade 4
- Neurologic events—21% all grades, 8% grade 3, 4% grade 4
- Prolonged cytopenia—36% all grades, 15% grade 3, 12% grade 4
- Infections—34% all grades, 18% grade 3, 2% grade 4
- Febrile neutropenia—13% all grades, 11% grade 3, 2% grade 4
No deaths occurred due to tisagenlecleucel, CRS, or cerebral edema.
Fifty-seven patients developed CRS. The median time to onset of CRS was 3 days (range, 1–9), and the median duration of CRS was 7 days (range, 2–30).
Twenty-eight percent of patients developed hypotension that required intervention, 6% requiring high-dose vasopressors. Eight percent were intubated, and 16% received anticytokine therapy—15% with tocilizumab and 11% with corticosteroids.
Investigators did not observe a relationship between dose and neurological events. However, they did detect a higher probability of CRS with the higher doses of tisagenlecleucel.
They also noted that dose and exposure were independent.
Dr Schuster indicated that these data are the basis for global regulatory submissions.
Manufacture of tisagenlecleucel was centralized, and investigators believe the trial shows the feasibility of global distribution of CAR T-cell therapy using cryopreserved apheresis and centralized manufacturing.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, the sponsor of the trial, is now able to commercially manufacture the CAR T cells in 22 days.
Dr Schuster disclosed research funding and consulting fees from Novartis and Celgene. ![]()
ATLANTA—The first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy approved in the US to treat children and young adults with leukemia is also producing high response rates in lymphoma, according to investigators of the JULIET trial.
They reported that tisagenlecleucel (formerly CTL019) produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 53% and a complete response (CR) rate of 40% in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Additionally, researchers say the stability in the response rate at 3 and 6 months—38% and 37%, respectively—indicates the durability of the therapy.
At 3 months, 32% of patients who achieved CR remained in CR. At 6 months, 30% remained in CR.
Researchers believe these results confirm the durable clinical benefit reported previously.
Stephen J. Schuster, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, presented the JULIET data at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 577).
“Only about half of relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients are eligible for transplant,” Dr Schuster said. “[O]f those patients, only about a half respond to salvage chemotherapy, and a significant number of patients relapse post-transplant. So there is really a large unmet need for these patients, and CAR T-cell therapy is a potential agent [for them].”
The JULIET trial was a global, single-arm, phase 2 trial evaluating tisagenlecleucel in DLBCL patients. Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah™) consists of CAR T cells with a CD19 antigen-binding domain, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta signaling domain.
The trial was conducted at 27 sites in 10 countries across North America, Europe, Australia, and Asia. There were 2 centralized manufacturing sites, one in Europe and one in the US.
Patients had to be 18 years or older, have had 2 or more prior lines of therapy for DLBCL, and have progressive disease or be ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant (auto-SCT). They could not have had any prior anti-CD19 therapy, and they could not have any central nervous system involvement.
The primary endpoint was best ORR using Lugano criteria with assessment by an independent review committee. Secondary endpoints included duration of response, overall survival (OS), and safety.
Study design and enrollment
Patients were screened and underwent apheresis with cryopreservation of their leukapheresis products during screening, which “allowed for enrollment of all eligible patients,” Dr Schuster said.
Patients could receive bridging chemotherapy while they awaited the manufacture of the CAR T cells.
“What’s important to note is that, early on in the trial, there was a shortage of manufacturing capacity, and this led to a longer-than-anticipated interval between enrollment and treatment,” Dr Schuster said. “This interval decreased as manufacturing capacity improved throughout the trial.”
When their CAR T cells were ready, patients were restaged, lymphodepleted, and received the tisagenlecleucel infusion. The dose ranged from 0.6 x 108 to 6.0 x 108 CAR-positive T cells.
The infusion could be conducted on an inpatient or outpatient basis at the investigator’s discretion, Dr Schuster said.
As of the data cutoff in March 2017, investigators enrolled 147 patients and infused 99 with tisagenlecleucel.
Forty-three patients discontinued before infusion, 9 because of an inability to manufacture the T-cell product and 34 due to death (n=16), physician decision (n=12), patient decision (n=3), adverse event (n=2), and protocol deviation (n=1). Five patients were pending infusion.
There were 81 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up or earlier disease progression evaluable for response.
Patient characteristics
Patients were a median age of 56 (range, 22–76), and 23% were 65 or older. All had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, 80% had DLBCL, and 19% had transformed follicular lymphoma.
Fifteen percent had double or triple hits in CMYC, BCL2, and BCL6 genes, and 52% had germinal center B-cell type disease.
Forty-four percent had 2 prior lines of therapy, 31% had 3 prior lines of therapy, and 19% had 4 to 6 prior lines of therapy. All were either refractory to or relapsed from their last therapy.
Forty-seven percent had undergone prior auto-SCT.
Eighty-nine of the 99 patients infused with tisagenlecleucel received bridging therapy, and 92 received lymphodepleting therapy.
Twenty-six patients were infused as outpatients, and 20 remained as outpatients for 3 or more days after the infusion.
Efficacy
The trial met its primary endpoint with an ORR of 53% tested against the null hypothesis of 20% or less. Forty percent of patients achieved a CR, and 14% had a partial response.
The ORR was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, lines of prior antineoplastic therapy, cell of origin, and rearranged MYC/BCL2/BCL6.
“The durability of response, however, which is really the message, is shown by the stability between 3- and 6-month response rates, 38% and 37%, respectively,” Dr Schuster said. “The response rate at 3 months is really indicative of the long-term benefit of this treatment approach.”
The investigators observed no apparent relationship between tumor response at month 3 and dose. And they observed responses at all dose levels.
The very early response may be due, to a certain extent, to the chemotherapy, according to Dr Schuster.
“The effect of the T cells becomes evident as you follow these patients over time,” he said.
The median duration of response and overall response have not been reached. And 74% of patients were relapse-free at 6 months.
“Importantly, almost all the complete responders at month 3 remained in complete response,” Dr Schuster said.
Safety
Adverse events of special interest that occurred within 8 weeks of the infusion included:
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS)—58% all grades, 15% grade 3, 8% grade 4
- Neurologic events—21% all grades, 8% grade 3, 4% grade 4
- Prolonged cytopenia—36% all grades, 15% grade 3, 12% grade 4
- Infections—34% all grades, 18% grade 3, 2% grade 4
- Febrile neutropenia—13% all grades, 11% grade 3, 2% grade 4
No deaths occurred due to tisagenlecleucel, CRS, or cerebral edema.
Fifty-seven patients developed CRS. The median time to onset of CRS was 3 days (range, 1–9), and the median duration of CRS was 7 days (range, 2–30).
Twenty-eight percent of patients developed hypotension that required intervention, 6% requiring high-dose vasopressors. Eight percent were intubated, and 16% received anticytokine therapy—15% with tocilizumab and 11% with corticosteroids.
Investigators did not observe a relationship between dose and neurological events. However, they did detect a higher probability of CRS with the higher doses of tisagenlecleucel.
They also noted that dose and exposure were independent.
Dr Schuster indicated that these data are the basis for global regulatory submissions.
Manufacture of tisagenlecleucel was centralized, and investigators believe the trial shows the feasibility of global distribution of CAR T-cell therapy using cryopreserved apheresis and centralized manufacturing.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, the sponsor of the trial, is now able to commercially manufacture the CAR T cells in 22 days.
Dr Schuster disclosed research funding and consulting fees from Novartis and Celgene. ![]()
ATLANTA—The first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy approved in the US to treat children and young adults with leukemia is also producing high response rates in lymphoma, according to investigators of the JULIET trial.
They reported that tisagenlecleucel (formerly CTL019) produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 53% and a complete response (CR) rate of 40% in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Additionally, researchers say the stability in the response rate at 3 and 6 months—38% and 37%, respectively—indicates the durability of the therapy.
At 3 months, 32% of patients who achieved CR remained in CR. At 6 months, 30% remained in CR.
Researchers believe these results confirm the durable clinical benefit reported previously.
Stephen J. Schuster, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, presented the JULIET data at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 577).
“Only about half of relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients are eligible for transplant,” Dr Schuster said. “[O]f those patients, only about a half respond to salvage chemotherapy, and a significant number of patients relapse post-transplant. So there is really a large unmet need for these patients, and CAR T-cell therapy is a potential agent [for them].”
The JULIET trial was a global, single-arm, phase 2 trial evaluating tisagenlecleucel in DLBCL patients. Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah™) consists of CAR T cells with a CD19 antigen-binding domain, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta signaling domain.
The trial was conducted at 27 sites in 10 countries across North America, Europe, Australia, and Asia. There were 2 centralized manufacturing sites, one in Europe and one in the US.
Patients had to be 18 years or older, have had 2 or more prior lines of therapy for DLBCL, and have progressive disease or be ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant (auto-SCT). They could not have had any prior anti-CD19 therapy, and they could not have any central nervous system involvement.
The primary endpoint was best ORR using Lugano criteria with assessment by an independent review committee. Secondary endpoints included duration of response, overall survival (OS), and safety.
Study design and enrollment
Patients were screened and underwent apheresis with cryopreservation of their leukapheresis products during screening, which “allowed for enrollment of all eligible patients,” Dr Schuster said.
Patients could receive bridging chemotherapy while they awaited the manufacture of the CAR T cells.
“What’s important to note is that, early on in the trial, there was a shortage of manufacturing capacity, and this led to a longer-than-anticipated interval between enrollment and treatment,” Dr Schuster said. “This interval decreased as manufacturing capacity improved throughout the trial.”
When their CAR T cells were ready, patients were restaged, lymphodepleted, and received the tisagenlecleucel infusion. The dose ranged from 0.6 x 108 to 6.0 x 108 CAR-positive T cells.
The infusion could be conducted on an inpatient or outpatient basis at the investigator’s discretion, Dr Schuster said.
As of the data cutoff in March 2017, investigators enrolled 147 patients and infused 99 with tisagenlecleucel.
Forty-three patients discontinued before infusion, 9 because of an inability to manufacture the T-cell product and 34 due to death (n=16), physician decision (n=12), patient decision (n=3), adverse event (n=2), and protocol deviation (n=1). Five patients were pending infusion.
There were 81 patients with at least 3 months of follow-up or earlier disease progression evaluable for response.
Patient characteristics
Patients were a median age of 56 (range, 22–76), and 23% were 65 or older. All had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, 80% had DLBCL, and 19% had transformed follicular lymphoma.
Fifteen percent had double or triple hits in CMYC, BCL2, and BCL6 genes, and 52% had germinal center B-cell type disease.
Forty-four percent had 2 prior lines of therapy, 31% had 3 prior lines of therapy, and 19% had 4 to 6 prior lines of therapy. All were either refractory to or relapsed from their last therapy.
Forty-seven percent had undergone prior auto-SCT.
Eighty-nine of the 99 patients infused with tisagenlecleucel received bridging therapy, and 92 received lymphodepleting therapy.
Twenty-six patients were infused as outpatients, and 20 remained as outpatients for 3 or more days after the infusion.
Efficacy
The trial met its primary endpoint with an ORR of 53% tested against the null hypothesis of 20% or less. Forty percent of patients achieved a CR, and 14% had a partial response.
The ORR was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, lines of prior antineoplastic therapy, cell of origin, and rearranged MYC/BCL2/BCL6.
“The durability of response, however, which is really the message, is shown by the stability between 3- and 6-month response rates, 38% and 37%, respectively,” Dr Schuster said. “The response rate at 3 months is really indicative of the long-term benefit of this treatment approach.”
The investigators observed no apparent relationship between tumor response at month 3 and dose. And they observed responses at all dose levels.
The very early response may be due, to a certain extent, to the chemotherapy, according to Dr Schuster.
“The effect of the T cells becomes evident as you follow these patients over time,” he said.
The median duration of response and overall response have not been reached. And 74% of patients were relapse-free at 6 months.
“Importantly, almost all the complete responders at month 3 remained in complete response,” Dr Schuster said.
Safety
Adverse events of special interest that occurred within 8 weeks of the infusion included:
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS)—58% all grades, 15% grade 3, 8% grade 4
- Neurologic events—21% all grades, 8% grade 3, 4% grade 4
- Prolonged cytopenia—36% all grades, 15% grade 3, 12% grade 4
- Infections—34% all grades, 18% grade 3, 2% grade 4
- Febrile neutropenia—13% all grades, 11% grade 3, 2% grade 4
No deaths occurred due to tisagenlecleucel, CRS, or cerebral edema.
Fifty-seven patients developed CRS. The median time to onset of CRS was 3 days (range, 1–9), and the median duration of CRS was 7 days (range, 2–30).
Twenty-eight percent of patients developed hypotension that required intervention, 6% requiring high-dose vasopressors. Eight percent were intubated, and 16% received anticytokine therapy—15% with tocilizumab and 11% with corticosteroids.
Investigators did not observe a relationship between dose and neurological events. However, they did detect a higher probability of CRS with the higher doses of tisagenlecleucel.
They also noted that dose and exposure were independent.
Dr Schuster indicated that these data are the basis for global regulatory submissions.
Manufacture of tisagenlecleucel was centralized, and investigators believe the trial shows the feasibility of global distribution of CAR T-cell therapy using cryopreserved apheresis and centralized manufacturing.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, the sponsor of the trial, is now able to commercially manufacture the CAR T cells in 22 days.
Dr Schuster disclosed research funding and consulting fees from Novartis and Celgene. ![]()
CRP drives bone destruction in myeloma, team says
New research suggests that C-reactive protein (CRP) drives multiple myeloma (MM) to destroy bone.
Researchers found that CRP accelerated the onset of bone destruction and made bone damage more severe in mouse models of MM.
The team also observed an association between elevated serum CRP levels and greater degree of bone damage in newly diagnosed MM patients.
The researchers therefore believe that CRP might be targeted to prevent or treat MM-associated bone disease.
Qing Yi, MD, PhD, of the Lerner Research Institute at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, and his colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers noted that high levels of circulating CRP have been associated with poor prognosis in many cancers, including MM.
In a previous study, the team found that CRP enhanced MM cell proliferation under stressed conditions and protected MM cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis.
Now, the researchers have found that CRP activates MM cells to promote osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction.
In experiments with mouse models, the team found that CRP promoted MM-cell-mediated lytic bone disease. The researchers said CRP enhanced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity.
In vitro experiments showed that CRP stimulates MM cells to produce osteoclast activators such as RANKL, MCP-1, and MIP-1a.
Further investigation revealed that CRP binds to CD32 on MM cells. This activates a pathway mediated by the kinase p38 MAPK and the transcription factor Twist, which increases MM cells’ production of osteolytic cytokines.
Finally, the researchers analyzed samples from newly diagnosed MM patients.
The team found that serum CRP levels “significantly and positively” correlated with the number of bone lesions patients had. And CRP was abundant in lesion biopsies from individuals with severe skeletal disease. ![]()
New research suggests that C-reactive protein (CRP) drives multiple myeloma (MM) to destroy bone.
Researchers found that CRP accelerated the onset of bone destruction and made bone damage more severe in mouse models of MM.
The team also observed an association between elevated serum CRP levels and greater degree of bone damage in newly diagnosed MM patients.
The researchers therefore believe that CRP might be targeted to prevent or treat MM-associated bone disease.
Qing Yi, MD, PhD, of the Lerner Research Institute at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, and his colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers noted that high levels of circulating CRP have been associated with poor prognosis in many cancers, including MM.
In a previous study, the team found that CRP enhanced MM cell proliferation under stressed conditions and protected MM cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis.
Now, the researchers have found that CRP activates MM cells to promote osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction.
In experiments with mouse models, the team found that CRP promoted MM-cell-mediated lytic bone disease. The researchers said CRP enhanced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity.
In vitro experiments showed that CRP stimulates MM cells to produce osteoclast activators such as RANKL, MCP-1, and MIP-1a.
Further investigation revealed that CRP binds to CD32 on MM cells. This activates a pathway mediated by the kinase p38 MAPK and the transcription factor Twist, which increases MM cells’ production of osteolytic cytokines.
Finally, the researchers analyzed samples from newly diagnosed MM patients.
The team found that serum CRP levels “significantly and positively” correlated with the number of bone lesions patients had. And CRP was abundant in lesion biopsies from individuals with severe skeletal disease. ![]()
New research suggests that C-reactive protein (CRP) drives multiple myeloma (MM) to destroy bone.
Researchers found that CRP accelerated the onset of bone destruction and made bone damage more severe in mouse models of MM.
The team also observed an association between elevated serum CRP levels and greater degree of bone damage in newly diagnosed MM patients.
The researchers therefore believe that CRP might be targeted to prevent or treat MM-associated bone disease.
Qing Yi, MD, PhD, of the Lerner Research Institute at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, and his colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers noted that high levels of circulating CRP have been associated with poor prognosis in many cancers, including MM.
In a previous study, the team found that CRP enhanced MM cell proliferation under stressed conditions and protected MM cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis.
Now, the researchers have found that CRP activates MM cells to promote osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction.
In experiments with mouse models, the team found that CRP promoted MM-cell-mediated lytic bone disease. The researchers said CRP enhanced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity.
In vitro experiments showed that CRP stimulates MM cells to produce osteoclast activators such as RANKL, MCP-1, and MIP-1a.
Further investigation revealed that CRP binds to CD32 on MM cells. This activates a pathway mediated by the kinase p38 MAPK and the transcription factor Twist, which increases MM cells’ production of osteolytic cytokines.
Finally, the researchers analyzed samples from newly diagnosed MM patients.
The team found that serum CRP levels “significantly and positively” correlated with the number of bone lesions patients had. And CRP was abundant in lesion biopsies from individuals with severe skeletal disease. ![]()
Providers endorse medical marijuana for kids with cancer
A survey of nearly 300 US medical providers revealed that many were open to helping children with cancer access medical marijuana (MM).
However, most of the providers surveyed did not know state-specific regulations pertaining to MM.
Providers who were legally eligible to certify (ETC) for MM were less open to endorsing its use.
The lack of standards on formulations, dosing, and potency of MM was identified as the greatest barrier to recommending MM for children with cancer.
Kelly Michelson, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago in Illinois, and her colleagues reported these findings in Pediatrics.
The researchers used a 32-item survey to assess MM practices, knowledge, attitudes, and barriers for pediatric oncology providers in Illinois, Massachusetts, and Washington.
The survey was sent to providers at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, Seattle Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, and Lurie Children’s Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders.
There were 288 respondents, and 33% were legally ETC for MM. Eighty-six percent of ETC providers were physicians, and 14% were nurse practitioners or physician assistants.
Of the non-ETC providers, 89% were nurses, 8% were nurse practitioners or physician assistants, 2% were psychosocial providers, and 2% were “other” providers.
Thirty percent of all providers said they had received at least 1 request for MM in the previous month. And 14% of these providers facilitated patient access to MM.
Ninety-two percent of providers said they were willing to help pediatric cancer patients access MM. Fifty-seven percent of providers approved of patients smoking MM, 89% approved of oral formulations, 67% approved of using MM as cancer-directed therapy, and 92% approved of using MM to manage symptoms.
Fifty-nine percent of providers knew that MM is against federal laws, and 86% knew that their state had legalized MM, but only 5% knew state-specific regulations.
ETC providers were less likely to report willingness to help patients access MM. These providers were also less likely to approve of MM use by smoking, oral formulations, as cancer-directed therapy, or to manage symptoms.
“It is not surprising that providers who are eligible to certify for medical marijuana were more cautious about recommending it, given that their licensure could be jeopardized due to federal prohibition,” Dr Michelson said.
“Institutional policies also may have influenced their attitudes. Lurie Children’s, for example, prohibits pediatric providers from facilitating medical marijuana access in accordance with the federal law, even though it is legal in Illinois.”
Most providers considered MM more permissible for use in children with advanced cancer or near the end of life than in earlier stages of cancer treatment. This is consistent with the current American Academy of Pediatrics position that sanctions MM use for “children with life-limiting or seriously debilitating conditions.”
Only 2% of providers reported that MM was never appropriate for a child with cancer.
Most providers (63%) were not concerned about substance abuse in children who receive MM or about being prosecuted for helping patients access MM (80%).
The greatest concern (listed by 46% of providers) was the absence of standards around prescribing MM to children with cancer.
“In addition to unclear dosage guidelines, the lack of high quality scientific data that medical marijuana benefits outweigh possible harm is a huge concern for providers accustomed to evidence-based practice,” Dr Michelson said. “We need rigorously designed clinical trials on the use of medical marijuana in children with cancer.” ![]()
A survey of nearly 300 US medical providers revealed that many were open to helping children with cancer access medical marijuana (MM).
However, most of the providers surveyed did not know state-specific regulations pertaining to MM.
Providers who were legally eligible to certify (ETC) for MM were less open to endorsing its use.
The lack of standards on formulations, dosing, and potency of MM was identified as the greatest barrier to recommending MM for children with cancer.
Kelly Michelson, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago in Illinois, and her colleagues reported these findings in Pediatrics.
The researchers used a 32-item survey to assess MM practices, knowledge, attitudes, and barriers for pediatric oncology providers in Illinois, Massachusetts, and Washington.
The survey was sent to providers at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, Seattle Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, and Lurie Children’s Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders.
There were 288 respondents, and 33% were legally ETC for MM. Eighty-six percent of ETC providers were physicians, and 14% were nurse practitioners or physician assistants.
Of the non-ETC providers, 89% were nurses, 8% were nurse practitioners or physician assistants, 2% were psychosocial providers, and 2% were “other” providers.
Thirty percent of all providers said they had received at least 1 request for MM in the previous month. And 14% of these providers facilitated patient access to MM.
Ninety-two percent of providers said they were willing to help pediatric cancer patients access MM. Fifty-seven percent of providers approved of patients smoking MM, 89% approved of oral formulations, 67% approved of using MM as cancer-directed therapy, and 92% approved of using MM to manage symptoms.
Fifty-nine percent of providers knew that MM is against federal laws, and 86% knew that their state had legalized MM, but only 5% knew state-specific regulations.
ETC providers were less likely to report willingness to help patients access MM. These providers were also less likely to approve of MM use by smoking, oral formulations, as cancer-directed therapy, or to manage symptoms.
“It is not surprising that providers who are eligible to certify for medical marijuana were more cautious about recommending it, given that their licensure could be jeopardized due to federal prohibition,” Dr Michelson said.
“Institutional policies also may have influenced their attitudes. Lurie Children’s, for example, prohibits pediatric providers from facilitating medical marijuana access in accordance with the federal law, even though it is legal in Illinois.”
Most providers considered MM more permissible for use in children with advanced cancer or near the end of life than in earlier stages of cancer treatment. This is consistent with the current American Academy of Pediatrics position that sanctions MM use for “children with life-limiting or seriously debilitating conditions.”
Only 2% of providers reported that MM was never appropriate for a child with cancer.
Most providers (63%) were not concerned about substance abuse in children who receive MM or about being prosecuted for helping patients access MM (80%).
The greatest concern (listed by 46% of providers) was the absence of standards around prescribing MM to children with cancer.
“In addition to unclear dosage guidelines, the lack of high quality scientific data that medical marijuana benefits outweigh possible harm is a huge concern for providers accustomed to evidence-based practice,” Dr Michelson said. “We need rigorously designed clinical trials on the use of medical marijuana in children with cancer.” ![]()
A survey of nearly 300 US medical providers revealed that many were open to helping children with cancer access medical marijuana (MM).
However, most of the providers surveyed did not know state-specific regulations pertaining to MM.
Providers who were legally eligible to certify (ETC) for MM were less open to endorsing its use.
The lack of standards on formulations, dosing, and potency of MM was identified as the greatest barrier to recommending MM for children with cancer.
Kelly Michelson, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago in Illinois, and her colleagues reported these findings in Pediatrics.
The researchers used a 32-item survey to assess MM practices, knowledge, attitudes, and barriers for pediatric oncology providers in Illinois, Massachusetts, and Washington.
The survey was sent to providers at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, Seattle Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, and Lurie Children’s Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders.
There were 288 respondents, and 33% were legally ETC for MM. Eighty-six percent of ETC providers were physicians, and 14% were nurse practitioners or physician assistants.
Of the non-ETC providers, 89% were nurses, 8% were nurse practitioners or physician assistants, 2% were psychosocial providers, and 2% were “other” providers.
Thirty percent of all providers said they had received at least 1 request for MM in the previous month. And 14% of these providers facilitated patient access to MM.
Ninety-two percent of providers said they were willing to help pediatric cancer patients access MM. Fifty-seven percent of providers approved of patients smoking MM, 89% approved of oral formulations, 67% approved of using MM as cancer-directed therapy, and 92% approved of using MM to manage symptoms.
Fifty-nine percent of providers knew that MM is against federal laws, and 86% knew that their state had legalized MM, but only 5% knew state-specific regulations.
ETC providers were less likely to report willingness to help patients access MM. These providers were also less likely to approve of MM use by smoking, oral formulations, as cancer-directed therapy, or to manage symptoms.
“It is not surprising that providers who are eligible to certify for medical marijuana were more cautious about recommending it, given that their licensure could be jeopardized due to federal prohibition,” Dr Michelson said.
“Institutional policies also may have influenced their attitudes. Lurie Children’s, for example, prohibits pediatric providers from facilitating medical marijuana access in accordance with the federal law, even though it is legal in Illinois.”
Most providers considered MM more permissible for use in children with advanced cancer or near the end of life than in earlier stages of cancer treatment. This is consistent with the current American Academy of Pediatrics position that sanctions MM use for “children with life-limiting or seriously debilitating conditions.”
Only 2% of providers reported that MM was never appropriate for a child with cancer.
Most providers (63%) were not concerned about substance abuse in children who receive MM or about being prosecuted for helping patients access MM (80%).
The greatest concern (listed by 46% of providers) was the absence of standards around prescribing MM to children with cancer.
“In addition to unclear dosage guidelines, the lack of high quality scientific data that medical marijuana benefits outweigh possible harm is a huge concern for providers accustomed to evidence-based practice,” Dr Michelson said. “We need rigorously designed clinical trials on the use of medical marijuana in children with cancer.” ![]()
Bladder Complications in MS
Q) My patient has multiple sclerosis and complains of feeling weaker, but denies urinary symptoms. Why have I been told to check for urinary tract infection and not just administer steroids?
Bladder complications are extremely common in patients living with multiple sclerosis (MS), occurring in around 80% of this population.1 These complications—which include urinary urgency, failure to fully empty the bladder, incontinence, and difficulty getting to a toilet in time—can increase risk for urinary tract infection (UTI). And because many patients with MS also have sensory problems (eg, neurogenic bladder), they do not always present with the hallmark UTI symptoms of burning or pain with urination.
Often, presenting symptoms include generalized weakness, increased spasticity, or intensified neurologic issues. These can lead patients to believe they are having a relapse, when in fact, a UTI is causing a pseudoexacerbation of their baseline neurologic issues. In addition, frequent nocturia can disrupt sleep and further contribute to MS-related fatigue. Patients may self-induce dehydration by limiting their daytime fluid intake in an effort to avoid bathroom visits.1

In partnership with urology colleagues, you can help mitigate bladder complications in patients with MS; this can entail use of medication or interventions such as in-and-out or straight catheterization, timed voids, Botox, or pelvic floor physical therapy. Behavior modifications—ie, minimizing caffeine intake, limiting alcohol consumption, and stopping fluids early in the evening—can also be beneficial.1,2
Before initiating bladder medication, it is important to review potential adverse effects with the patient. It’s also crucial to ensure that patients are fully emptying their bladders before starting anticholinergic medications, as these can worsen retention.
Which treatment should you choose? Insurance companies tend to prefer generic, older-generation anticholinergics, but bear in mind that these can cause or contribute to cognitive issues (which many patients with MS already have).3 Another medication, such as mirabegron, may be preferable; it’s less likely than anticholinergics to cause dry mouth, which may help with compliance. Also, be aware that anticholinergics can cause blurred vision, which might lead patients to believe they are having optic neuritis or another MS-related visual change.4
That said, it is possible for patients to have a relapse and a UTI simultaneously. Due to potential adverse effects, it is essential to balance the risks and benefits of steroid therapy. Steroids could worsen an untreated infection and may not be appropriate for the patient’s symptoms or chief complaint.
Addressing bladder symptoms can not only help prevent UTIs but can also improve skin integrity, sleep quality, independence, and overall quality of life. A thorough exam and history-taking can alleviate secondary and tertiary urinary complications, as well as avoid unnecessary use of corticosteroids. -DRB
Denise R. Bruen, MSN, APRN-BC, MSCN
University of Virgina, Charlottesville
1. Sheehan J. Coping with MS bladder dysfunction. www.everydayhealth.com/multiple-sclerosis/symptoms/coping-with-bladder-dysfunction/. Accessed November 18, 2017.
2. Mayo Clinic. Bladder control: medications for urinary problems. www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/in-depth/bladder-control-problems/art-20044220. Accessed November 18, 2017.
3. Staskin DR, Zoltan E. Anticholinergics and central nervous system effects: are we confused? Rev Urol. 2007;9(4):191-196.
4. Geller EJ, Crane AK, Wells EC, et al. Effect of anticholinergic use for the treatment of overactive bladder on cognitive function in post-menopausal women. Clin Drug Investig. 2012;32(10):697-705.
Q) My patient has multiple sclerosis and complains of feeling weaker, but denies urinary symptoms. Why have I been told to check for urinary tract infection and not just administer steroids?
Bladder complications are extremely common in patients living with multiple sclerosis (MS), occurring in around 80% of this population.1 These complications—which include urinary urgency, failure to fully empty the bladder, incontinence, and difficulty getting to a toilet in time—can increase risk for urinary tract infection (UTI). And because many patients with MS also have sensory problems (eg, neurogenic bladder), they do not always present with the hallmark UTI symptoms of burning or pain with urination.
Often, presenting symptoms include generalized weakness, increased spasticity, or intensified neurologic issues. These can lead patients to believe they are having a relapse, when in fact, a UTI is causing a pseudoexacerbation of their baseline neurologic issues. In addition, frequent nocturia can disrupt sleep and further contribute to MS-related fatigue. Patients may self-induce dehydration by limiting their daytime fluid intake in an effort to avoid bathroom visits.1

In partnership with urology colleagues, you can help mitigate bladder complications in patients with MS; this can entail use of medication or interventions such as in-and-out or straight catheterization, timed voids, Botox, or pelvic floor physical therapy. Behavior modifications—ie, minimizing caffeine intake, limiting alcohol consumption, and stopping fluids early in the evening—can also be beneficial.1,2
Before initiating bladder medication, it is important to review potential adverse effects with the patient. It’s also crucial to ensure that patients are fully emptying their bladders before starting anticholinergic medications, as these can worsen retention.
Which treatment should you choose? Insurance companies tend to prefer generic, older-generation anticholinergics, but bear in mind that these can cause or contribute to cognitive issues (which many patients with MS already have).3 Another medication, such as mirabegron, may be preferable; it’s less likely than anticholinergics to cause dry mouth, which may help with compliance. Also, be aware that anticholinergics can cause blurred vision, which might lead patients to believe they are having optic neuritis or another MS-related visual change.4
That said, it is possible for patients to have a relapse and a UTI simultaneously. Due to potential adverse effects, it is essential to balance the risks and benefits of steroid therapy. Steroids could worsen an untreated infection and may not be appropriate for the patient’s symptoms or chief complaint.
Addressing bladder symptoms can not only help prevent UTIs but can also improve skin integrity, sleep quality, independence, and overall quality of life. A thorough exam and history-taking can alleviate secondary and tertiary urinary complications, as well as avoid unnecessary use of corticosteroids. -DRB
Denise R. Bruen, MSN, APRN-BC, MSCN
University of Virgina, Charlottesville
Q) My patient has multiple sclerosis and complains of feeling weaker, but denies urinary symptoms. Why have I been told to check for urinary tract infection and not just administer steroids?
Bladder complications are extremely common in patients living with multiple sclerosis (MS), occurring in around 80% of this population.1 These complications—which include urinary urgency, failure to fully empty the bladder, incontinence, and difficulty getting to a toilet in time—can increase risk for urinary tract infection (UTI). And because many patients with MS also have sensory problems (eg, neurogenic bladder), they do not always present with the hallmark UTI symptoms of burning or pain with urination.
Often, presenting symptoms include generalized weakness, increased spasticity, or intensified neurologic issues. These can lead patients to believe they are having a relapse, when in fact, a UTI is causing a pseudoexacerbation of their baseline neurologic issues. In addition, frequent nocturia can disrupt sleep and further contribute to MS-related fatigue. Patients may self-induce dehydration by limiting their daytime fluid intake in an effort to avoid bathroom visits.1

In partnership with urology colleagues, you can help mitigate bladder complications in patients with MS; this can entail use of medication or interventions such as in-and-out or straight catheterization, timed voids, Botox, or pelvic floor physical therapy. Behavior modifications—ie, minimizing caffeine intake, limiting alcohol consumption, and stopping fluids early in the evening—can also be beneficial.1,2
Before initiating bladder medication, it is important to review potential adverse effects with the patient. It’s also crucial to ensure that patients are fully emptying their bladders before starting anticholinergic medications, as these can worsen retention.
Which treatment should you choose? Insurance companies tend to prefer generic, older-generation anticholinergics, but bear in mind that these can cause or contribute to cognitive issues (which many patients with MS already have).3 Another medication, such as mirabegron, may be preferable; it’s less likely than anticholinergics to cause dry mouth, which may help with compliance. Also, be aware that anticholinergics can cause blurred vision, which might lead patients to believe they are having optic neuritis or another MS-related visual change.4
That said, it is possible for patients to have a relapse and a UTI simultaneously. Due to potential adverse effects, it is essential to balance the risks and benefits of steroid therapy. Steroids could worsen an untreated infection and may not be appropriate for the patient’s symptoms or chief complaint.
Addressing bladder symptoms can not only help prevent UTIs but can also improve skin integrity, sleep quality, independence, and overall quality of life. A thorough exam and history-taking can alleviate secondary and tertiary urinary complications, as well as avoid unnecessary use of corticosteroids. -DRB
Denise R. Bruen, MSN, APRN-BC, MSCN
University of Virgina, Charlottesville
1. Sheehan J. Coping with MS bladder dysfunction. www.everydayhealth.com/multiple-sclerosis/symptoms/coping-with-bladder-dysfunction/. Accessed November 18, 2017.
2. Mayo Clinic. Bladder control: medications for urinary problems. www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/in-depth/bladder-control-problems/art-20044220. Accessed November 18, 2017.
3. Staskin DR, Zoltan E. Anticholinergics and central nervous system effects: are we confused? Rev Urol. 2007;9(4):191-196.
4. Geller EJ, Crane AK, Wells EC, et al. Effect of anticholinergic use for the treatment of overactive bladder on cognitive function in post-menopausal women. Clin Drug Investig. 2012;32(10):697-705.
1. Sheehan J. Coping with MS bladder dysfunction. www.everydayhealth.com/multiple-sclerosis/symptoms/coping-with-bladder-dysfunction/. Accessed November 18, 2017.
2. Mayo Clinic. Bladder control: medications for urinary problems. www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/in-depth/bladder-control-problems/art-20044220. Accessed November 18, 2017.
3. Staskin DR, Zoltan E. Anticholinergics and central nervous system effects: are we confused? Rev Urol. 2007;9(4):191-196.
4. Geller EJ, Crane AK, Wells EC, et al. Effect of anticholinergic use for the treatment of overactive bladder on cognitive function in post-menopausal women. Clin Drug Investig. 2012;32(10):697-705.
You aren’t (necessarily) a walking petri dish!
Clinical question: Does exposure to a patient with a multidrug-resistant organism result in colonization of a health care provider?
Background: Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) are growing threats in our hospitals, particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and resistant gram-negative bacteria. The role of the health care team in preventing infection transmission is paramount. If a team member who is caring for a patient with an MDRO or handling lab specimens becomes colonized with these bacteria, he or she could potentially transmit them to the next patient.
Setting: Large academic research hospital.
Synopsis: Staff submitted self-collected rectal swabs, which were then cultured for MDROs. 379 health care personnel (which they defined as having had self-reported exposure to MDROs) were compared with 376 staff members in the control group, who reported no exposure to MDROs. There was a nonsignificant difference between growth of multidrug-resistant organisms between the groups (4.0% vs 3.2%).
Bottom line: This study suggests that occupational exposure to an MDRO does not result in subsequent colonization of the health care provider and may not be a major risk factor for nosocomial transmission.
Citation: Decker BK et al. Healthcare personnel intestinal colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017 May 12. pii:S1198-743X(17)30270-7.
Dr. Sata is a medical instructor, Duke University Hospital.
Clinical question: Does exposure to a patient with a multidrug-resistant organism result in colonization of a health care provider?
Background: Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) are growing threats in our hospitals, particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and resistant gram-negative bacteria. The role of the health care team in preventing infection transmission is paramount. If a team member who is caring for a patient with an MDRO or handling lab specimens becomes colonized with these bacteria, he or she could potentially transmit them to the next patient.
Setting: Large academic research hospital.
Synopsis: Staff submitted self-collected rectal swabs, which were then cultured for MDROs. 379 health care personnel (which they defined as having had self-reported exposure to MDROs) were compared with 376 staff members in the control group, who reported no exposure to MDROs. There was a nonsignificant difference between growth of multidrug-resistant organisms between the groups (4.0% vs 3.2%).
Bottom line: This study suggests that occupational exposure to an MDRO does not result in subsequent colonization of the health care provider and may not be a major risk factor for nosocomial transmission.
Citation: Decker BK et al. Healthcare personnel intestinal colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017 May 12. pii:S1198-743X(17)30270-7.
Dr. Sata is a medical instructor, Duke University Hospital.
Clinical question: Does exposure to a patient with a multidrug-resistant organism result in colonization of a health care provider?
Background: Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) are growing threats in our hospitals, particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and resistant gram-negative bacteria. The role of the health care team in preventing infection transmission is paramount. If a team member who is caring for a patient with an MDRO or handling lab specimens becomes colonized with these bacteria, he or she could potentially transmit them to the next patient.
Setting: Large academic research hospital.
Synopsis: Staff submitted self-collected rectal swabs, which were then cultured for MDROs. 379 health care personnel (which they defined as having had self-reported exposure to MDROs) were compared with 376 staff members in the control group, who reported no exposure to MDROs. There was a nonsignificant difference between growth of multidrug-resistant organisms between the groups (4.0% vs 3.2%).
Bottom line: This study suggests that occupational exposure to an MDRO does not result in subsequent colonization of the health care provider and may not be a major risk factor for nosocomial transmission.
Citation: Decker BK et al. Healthcare personnel intestinal colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017 May 12. pii:S1198-743X(17)30270-7.
Dr. Sata is a medical instructor, Duke University Hospital.