User login
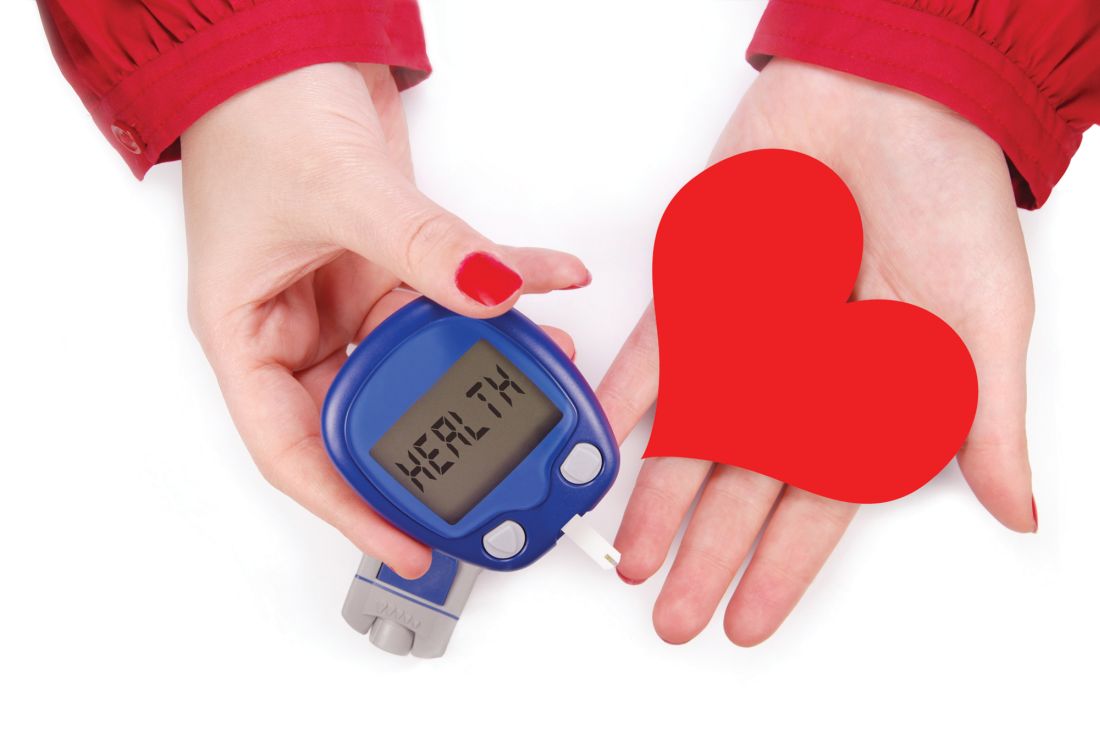
AHA advice for diabetes patients to stay heart healthy
A new document from the American Heart Association summarizes the latest research on cardiovascular risk factor management in type 2 diabetes, including medications, lifestyle, and social determinants of health.
Despite the availability of effective therapies for improving cardiovascular risk, in the United States fewer than one in five people with type 2 diabetes and without known cardiovascular disease meet control targets for a combination of A1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and nonsmoking status.
That proportion drops to less than 1 in 10 if body mass index less than 30 kg/m2 is included among the targets, and even less than that among individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, Joshua J. Joseph, MD, and colleagues point out in their paper, published online Jan. 10 in Circulation.
“This new scientific statement is an urgent call to action to follow the latest evidence-based approaches and to develop new best practices to advance type 2 diabetes treatment and care and reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” wrote Dr. Joseph, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors.
The statement is not a guideline but an expert analysis that may inform future clinical practice guidelines, according to a press release from the AHA.
The new statement reviews evidence through June 2020 for lifestyle management of diabetes and weight, glycemic targets and control, blood pressure management, lipid management, antithrombotic therapy, and screening for cardiovascular and renal complications, including imaging. It also discusses the clinical implications of recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of newer glucose-lowering medications.
However, Dr. Joseph and colleagues point out, clinical care and treatment account for just 10%-20% of modifiable contributors to health outcomes. The other 80%-90% relate to social determinants of health, including health-related behaviors, socioeconomic factors, environmental factors, and racism.
“If we are to continue to advance the management of cardiovascular risk factors, we must also address the [social determinants of health] in the delivery of health care,” they noted.
Overall, they advise a patient-centered approach, meaning “reframing our clinical encounters to think about patients as people who live in families, communities, and societies that must be considered in their cardiovascular risk management.”
“People with [type 2 diabetes] face numerous barriers to health including access to care and equitable care, which must be considered when developing individualized care plans with our patients,” Dr. Joseph said in the AHA press release.
Lifestyle, medications for lowering A1c, BP, lipids
For lifestyle management, the authors say, “culturally appropriate recommendations through diabetes self-management education and support and medical nutrition therapy are key to meeting individualized goals for behavioral change and diabetes self-management.”
The document summarizes recommendations from other professional societies regarding glycemic targets and glucose lowering medications, i.e., target A1c levels of either < 7% or < 6.5% for the majority, with adjustments based on individual factors, such as life expectancy. It advises on use of metformin as first-line therapy followed by a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist for those with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
“Cost may be a barrier to taking some [type 2 diabetes] medications as prescribed; however, many of these medications are now more commonly covered by more health insurance plans,” Dr. Joseph said.
“Another barrier is recognition by patients that these newer [type 2 diabetes] medications are also effective in reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease.”
Blood pressure treatment guidelines differ between those of the AHA/American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), most notably that the AHA/ACC guidelines advise a general target of < 130/80 mm Hg, whereas ADA advises < 140/90 mm Hg or < 130/80 mm Hg for those with high risk if it can be safely achieved.
The decision should be “patient-centered with shared decision-making,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues advised.
For lipid-lowering, the document cites the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, which include advising statins as first-line therapy for both primary and secondary prevention in diabetes, with highest intensity statins used in those at highest risk. But again, treatment should be individualized, and other agents should be used for patients in whom statins don’t work or aren’t tolerated.
And while use of antiplatelets – that is, aspirin – is well established as secondary prevention in type 2 diabetes, given new data suggesting that the risk for major bleeding could outweigh the benefits for primary prevention, “the relative benefits of antithrombotic approaches need to be weighed carefully against risks using a patient-centered approach,” the authors advised.
Among the many imaging tests available to facilitate cardiovascular risk stratification in type 2 diabetes, coronary artery calcification (CAC) CT screening is one of the few with sufficient data to support routine use in selected patients. The National Lipid Association, for example, recommends escalation to high-intensity statin for CAC > 100.
“One avenue to continue to address and advance diabetes management is through breaking down the four walls of the clinic or hospital through community engagement, clinic-to-community connections, and academic-community-government partnerships that may help address and support modifiable lifestyle behaviors such as physical activity, nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management,” Dr. Joseph concluded.
The AHA receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations, including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers, and other companies, also make donations and fund AHA programs and events. The AHA’s strict policies prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers, and health insurance providers and the AHA’s financial information are available on the association’s website. Dr. Joseph has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new document from the American Heart Association summarizes the latest research on cardiovascular risk factor management in type 2 diabetes, including medications, lifestyle, and social determinants of health.
Despite the availability of effective therapies for improving cardiovascular risk, in the United States fewer than one in five people with type 2 diabetes and without known cardiovascular disease meet control targets for a combination of A1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and nonsmoking status.
That proportion drops to less than 1 in 10 if body mass index less than 30 kg/m2 is included among the targets, and even less than that among individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, Joshua J. Joseph, MD, and colleagues point out in their paper, published online Jan. 10 in Circulation.
“This new scientific statement is an urgent call to action to follow the latest evidence-based approaches and to develop new best practices to advance type 2 diabetes treatment and care and reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” wrote Dr. Joseph, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors.
The statement is not a guideline but an expert analysis that may inform future clinical practice guidelines, according to a press release from the AHA.
The new statement reviews evidence through June 2020 for lifestyle management of diabetes and weight, glycemic targets and control, blood pressure management, lipid management, antithrombotic therapy, and screening for cardiovascular and renal complications, including imaging. It also discusses the clinical implications of recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of newer glucose-lowering medications.
However, Dr. Joseph and colleagues point out, clinical care and treatment account for just 10%-20% of modifiable contributors to health outcomes. The other 80%-90% relate to social determinants of health, including health-related behaviors, socioeconomic factors, environmental factors, and racism.
“If we are to continue to advance the management of cardiovascular risk factors, we must also address the [social determinants of health] in the delivery of health care,” they noted.
Overall, they advise a patient-centered approach, meaning “reframing our clinical encounters to think about patients as people who live in families, communities, and societies that must be considered in their cardiovascular risk management.”
“People with [type 2 diabetes] face numerous barriers to health including access to care and equitable care, which must be considered when developing individualized care plans with our patients,” Dr. Joseph said in the AHA press release.
Lifestyle, medications for lowering A1c, BP, lipids
For lifestyle management, the authors say, “culturally appropriate recommendations through diabetes self-management education and support and medical nutrition therapy are key to meeting individualized goals for behavioral change and diabetes self-management.”
The document summarizes recommendations from other professional societies regarding glycemic targets and glucose lowering medications, i.e., target A1c levels of either < 7% or < 6.5% for the majority, with adjustments based on individual factors, such as life expectancy. It advises on use of metformin as first-line therapy followed by a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist for those with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
“Cost may be a barrier to taking some [type 2 diabetes] medications as prescribed; however, many of these medications are now more commonly covered by more health insurance plans,” Dr. Joseph said.
“Another barrier is recognition by patients that these newer [type 2 diabetes] medications are also effective in reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease.”
Blood pressure treatment guidelines differ between those of the AHA/American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), most notably that the AHA/ACC guidelines advise a general target of < 130/80 mm Hg, whereas ADA advises < 140/90 mm Hg or < 130/80 mm Hg for those with high risk if it can be safely achieved.
The decision should be “patient-centered with shared decision-making,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues advised.
For lipid-lowering, the document cites the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, which include advising statins as first-line therapy for both primary and secondary prevention in diabetes, with highest intensity statins used in those at highest risk. But again, treatment should be individualized, and other agents should be used for patients in whom statins don’t work or aren’t tolerated.
And while use of antiplatelets – that is, aspirin – is well established as secondary prevention in type 2 diabetes, given new data suggesting that the risk for major bleeding could outweigh the benefits for primary prevention, “the relative benefits of antithrombotic approaches need to be weighed carefully against risks using a patient-centered approach,” the authors advised.
Among the many imaging tests available to facilitate cardiovascular risk stratification in type 2 diabetes, coronary artery calcification (CAC) CT screening is one of the few with sufficient data to support routine use in selected patients. The National Lipid Association, for example, recommends escalation to high-intensity statin for CAC > 100.
“One avenue to continue to address and advance diabetes management is through breaking down the four walls of the clinic or hospital through community engagement, clinic-to-community connections, and academic-community-government partnerships that may help address and support modifiable lifestyle behaviors such as physical activity, nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management,” Dr. Joseph concluded.
The AHA receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations, including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers, and other companies, also make donations and fund AHA programs and events. The AHA’s strict policies prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers, and health insurance providers and the AHA’s financial information are available on the association’s website. Dr. Joseph has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new document from the American Heart Association summarizes the latest research on cardiovascular risk factor management in type 2 diabetes, including medications, lifestyle, and social determinants of health.
Despite the availability of effective therapies for improving cardiovascular risk, in the United States fewer than one in five people with type 2 diabetes and without known cardiovascular disease meet control targets for a combination of A1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and nonsmoking status.
That proportion drops to less than 1 in 10 if body mass index less than 30 kg/m2 is included among the targets, and even less than that among individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, Joshua J. Joseph, MD, and colleagues point out in their paper, published online Jan. 10 in Circulation.
“This new scientific statement is an urgent call to action to follow the latest evidence-based approaches and to develop new best practices to advance type 2 diabetes treatment and care and reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” wrote Dr. Joseph, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors.
The statement is not a guideline but an expert analysis that may inform future clinical practice guidelines, according to a press release from the AHA.
The new statement reviews evidence through June 2020 for lifestyle management of diabetes and weight, glycemic targets and control, blood pressure management, lipid management, antithrombotic therapy, and screening for cardiovascular and renal complications, including imaging. It also discusses the clinical implications of recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of newer glucose-lowering medications.
However, Dr. Joseph and colleagues point out, clinical care and treatment account for just 10%-20% of modifiable contributors to health outcomes. The other 80%-90% relate to social determinants of health, including health-related behaviors, socioeconomic factors, environmental factors, and racism.
“If we are to continue to advance the management of cardiovascular risk factors, we must also address the [social determinants of health] in the delivery of health care,” they noted.
Overall, they advise a patient-centered approach, meaning “reframing our clinical encounters to think about patients as people who live in families, communities, and societies that must be considered in their cardiovascular risk management.”
“People with [type 2 diabetes] face numerous barriers to health including access to care and equitable care, which must be considered when developing individualized care plans with our patients,” Dr. Joseph said in the AHA press release.
Lifestyle, medications for lowering A1c, BP, lipids
For lifestyle management, the authors say, “culturally appropriate recommendations through diabetes self-management education and support and medical nutrition therapy are key to meeting individualized goals for behavioral change and diabetes self-management.”
The document summarizes recommendations from other professional societies regarding glycemic targets and glucose lowering medications, i.e., target A1c levels of either < 7% or < 6.5% for the majority, with adjustments based on individual factors, such as life expectancy. It advises on use of metformin as first-line therapy followed by a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist for those with established cardiovascular disease or risk factors.
“Cost may be a barrier to taking some [type 2 diabetes] medications as prescribed; however, many of these medications are now more commonly covered by more health insurance plans,” Dr. Joseph said.
“Another barrier is recognition by patients that these newer [type 2 diabetes] medications are also effective in reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and kidney disease.”
Blood pressure treatment guidelines differ between those of the AHA/American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), most notably that the AHA/ACC guidelines advise a general target of < 130/80 mm Hg, whereas ADA advises < 140/90 mm Hg or < 130/80 mm Hg for those with high risk if it can be safely achieved.
The decision should be “patient-centered with shared decision-making,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues advised.
For lipid-lowering, the document cites the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, which include advising statins as first-line therapy for both primary and secondary prevention in diabetes, with highest intensity statins used in those at highest risk. But again, treatment should be individualized, and other agents should be used for patients in whom statins don’t work or aren’t tolerated.
And while use of antiplatelets – that is, aspirin – is well established as secondary prevention in type 2 diabetes, given new data suggesting that the risk for major bleeding could outweigh the benefits for primary prevention, “the relative benefits of antithrombotic approaches need to be weighed carefully against risks using a patient-centered approach,” the authors advised.
Among the many imaging tests available to facilitate cardiovascular risk stratification in type 2 diabetes, coronary artery calcification (CAC) CT screening is one of the few with sufficient data to support routine use in selected patients. The National Lipid Association, for example, recommends escalation to high-intensity statin for CAC > 100.
“One avenue to continue to address and advance diabetes management is through breaking down the four walls of the clinic or hospital through community engagement, clinic-to-community connections, and academic-community-government partnerships that may help address and support modifiable lifestyle behaviors such as physical activity, nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management,” Dr. Joseph concluded.
The AHA receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations, including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers, and other companies, also make donations and fund AHA programs and events. The AHA’s strict policies prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers, and health insurance providers and the AHA’s financial information are available on the association’s website. Dr. Joseph has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PA name change bad for patients and the profession
Physician assistants (PAs) are angry with me, and with good reason. I had the audacity to lump them together with nurse practitioners (NPs) in my book “Patients at Risk,” an act which one highly placed PA leader called “distasteful” in a private conversation with me.
I will admit that PAs have reason to be upset. With competitive acceptance rates including a requirement for extensive health care experience before PA school, standardized training, and at least 2,000 hours of clinical experience before graduation, the profession is a stark contrast to the haphazard training and 500 clinical hours required of NPs today. Further, unlike NPs, who have sought independent practice since the 1980s, PAs have traditionally been close allies with physicians, generally working in a 1:1 supervision model.
The truth is that it hurt to include PAs with NPs in my book. I’ve had my own close relationships with PAs over the years and found the PAs I worked with to be outstanding clinicians. Unfortunately, the profession has given me no choice. Following a model set by the NP profession,
Their efforts began with a change in terminology. “Optimal team practice” (OTP) was supposed to give PAs more flexibility, allowing them to work for hospitals or physician groups rather than under the responsibility of one physician. Not surprisingly, corporations and even academic centers have been quick to take advantage, hiring PAs and placing them in positions without adequate physician support. OTP paved the way for independent practice, as PAs sought and gained independence from any physician supervision in North Dakota, the first state to grant them that right.
Most recently, PAs have determined to change their name entirely, calling themselves physician associates. This move by the American Academy of Physician Assistants is the culmination of a years-long marketing study on how to increase the relevance and improve patient perception of the PA profession. The AAPA decision is expected to galvanize state and local PA organizations to lobby legislators for legal and regulatory changes that allow the use of the “physician associate” title, which is not currently a legal representation of PA licensure.
PAs’ latest attempt at title and branding reform follows years of advocacy to not be referred to as physician extenders or midlevel providers. For example, to gain more public acceptance of the PA model, the profession launched the public relations campaign “Your PA Can,” closely mirroring the “We Choose NPs” media blitz. PAs have also followed other dangerous precedents set by NPs, including 100% online training and a new “Doctor of Medical Science” degree, allowing PAs, as well as NPs, to now be called “doctors.”
I can understand PA reasoning even if I don’t agree with it. PAs are frustrated to be treated as second-class citizens compared with NPs, who have been granted independent practice in half the states in the union despite having a fraction of PA training. Frankly, it’s unfair that NPs are being hired preferentially over PAs simply because of looser legal requirements for physician oversight. The bottom line is that NPs have been more successful at persuading legislators to allow them independence – but that doesn’t make it right for either group.
While PAs have more clinical training upon graduation than NPs, they still have far less than physicians. PAs generally attend a 2-year master’s degree program after college which includes 2,000 hours of hands-on clinical work. By comparison, the average medical student spends 4 years and receives 5,000-6,000 hours of supervised clinical training upon graduation. But this isn’t considered enough for a graduate medical student to practice medicine independently.
Physicians must complete at least 3 years of postgraduate residency training in most states to receive a medical license, and by the time a physician is permitted to practice medicine unsupervised, they will have attained no fewer than 15,000-20,000 hours of supervised clinical practice, with years of specialty-specific training.
Patients want and deserve access to truly physician-led care, but in many parts of the country, physicians are being replaced by nonphysician practitioners to boost corporate profits. In many cases, patients are kept in the dark about the differences in training between the medical professionals now in charge of their care. The American Medical Association and other critics have expressed concern that the proposed title of “physician associate” is likely to further obscure the training and roles of medical professionals, already a source of confusion to patients.
One specific criticism is that a physician associate has historically referred to a physician (MD or DO) in a private practice group who has not yet achieved the status of partner. These physician associates are fully licensed medical doctors who have completed medical school and residency training and are in the process of completing a partnership track with their group to participate fully in financial and administrative processes. This nomenclature is similar to that of attorneys on a partnership track. Thus, the use of the term “physician associate” for someone other than a medical doctor is seen as misleading, particularly to patients who cannot be expected to have familiarity with the differences in training.
Efforts to separate the PA profession from a close-working relationship with a physician are bad not only for patients but for PAs as well. Many PAs who desire physician involvement may find themselves hung out to dry, hired by companies and expected to perform outside of their comfort level. The profession also risks ostracizing physician allies, many of whom have preferentially sought to work with PAs.
My sincere hope is that the PA profession will return to its traditional roots of a physician-PA relationship, a model that has been demonstrated to result in high-quality patient care. When that day comes, I will happily re-title my book. But as long as the AAPA continues to work to remove physicians from the equation, patients are indeed at risk.
Rebekah Bernard, MD, is a family physician in Fort Myers, Florida, and president of Physicians for Patient Protection. She is the coauthor of Patients at Risk: The Rise of the Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant in Healthcare (Irvine, Calif.: Universal Publishers, 2020). She had no relevant financial disclosures. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician assistants (PAs) are angry with me, and with good reason. I had the audacity to lump them together with nurse practitioners (NPs) in my book “Patients at Risk,” an act which one highly placed PA leader called “distasteful” in a private conversation with me.
I will admit that PAs have reason to be upset. With competitive acceptance rates including a requirement for extensive health care experience before PA school, standardized training, and at least 2,000 hours of clinical experience before graduation, the profession is a stark contrast to the haphazard training and 500 clinical hours required of NPs today. Further, unlike NPs, who have sought independent practice since the 1980s, PAs have traditionally been close allies with physicians, generally working in a 1:1 supervision model.
The truth is that it hurt to include PAs with NPs in my book. I’ve had my own close relationships with PAs over the years and found the PAs I worked with to be outstanding clinicians. Unfortunately, the profession has given me no choice. Following a model set by the NP profession,
Their efforts began with a change in terminology. “Optimal team practice” (OTP) was supposed to give PAs more flexibility, allowing them to work for hospitals or physician groups rather than under the responsibility of one physician. Not surprisingly, corporations and even academic centers have been quick to take advantage, hiring PAs and placing them in positions without adequate physician support. OTP paved the way for independent practice, as PAs sought and gained independence from any physician supervision in North Dakota, the first state to grant them that right.
Most recently, PAs have determined to change their name entirely, calling themselves physician associates. This move by the American Academy of Physician Assistants is the culmination of a years-long marketing study on how to increase the relevance and improve patient perception of the PA profession. The AAPA decision is expected to galvanize state and local PA organizations to lobby legislators for legal and regulatory changes that allow the use of the “physician associate” title, which is not currently a legal representation of PA licensure.
PAs’ latest attempt at title and branding reform follows years of advocacy to not be referred to as physician extenders or midlevel providers. For example, to gain more public acceptance of the PA model, the profession launched the public relations campaign “Your PA Can,” closely mirroring the “We Choose NPs” media blitz. PAs have also followed other dangerous precedents set by NPs, including 100% online training and a new “Doctor of Medical Science” degree, allowing PAs, as well as NPs, to now be called “doctors.”
I can understand PA reasoning even if I don’t agree with it. PAs are frustrated to be treated as second-class citizens compared with NPs, who have been granted independent practice in half the states in the union despite having a fraction of PA training. Frankly, it’s unfair that NPs are being hired preferentially over PAs simply because of looser legal requirements for physician oversight. The bottom line is that NPs have been more successful at persuading legislators to allow them independence – but that doesn’t make it right for either group.
While PAs have more clinical training upon graduation than NPs, they still have far less than physicians. PAs generally attend a 2-year master’s degree program after college which includes 2,000 hours of hands-on clinical work. By comparison, the average medical student spends 4 years and receives 5,000-6,000 hours of supervised clinical training upon graduation. But this isn’t considered enough for a graduate medical student to practice medicine independently.
Physicians must complete at least 3 years of postgraduate residency training in most states to receive a medical license, and by the time a physician is permitted to practice medicine unsupervised, they will have attained no fewer than 15,000-20,000 hours of supervised clinical practice, with years of specialty-specific training.
Patients want and deserve access to truly physician-led care, but in many parts of the country, physicians are being replaced by nonphysician practitioners to boost corporate profits. In many cases, patients are kept in the dark about the differences in training between the medical professionals now in charge of their care. The American Medical Association and other critics have expressed concern that the proposed title of “physician associate” is likely to further obscure the training and roles of medical professionals, already a source of confusion to patients.
One specific criticism is that a physician associate has historically referred to a physician (MD or DO) in a private practice group who has not yet achieved the status of partner. These physician associates are fully licensed medical doctors who have completed medical school and residency training and are in the process of completing a partnership track with their group to participate fully in financial and administrative processes. This nomenclature is similar to that of attorneys on a partnership track. Thus, the use of the term “physician associate” for someone other than a medical doctor is seen as misleading, particularly to patients who cannot be expected to have familiarity with the differences in training.
Efforts to separate the PA profession from a close-working relationship with a physician are bad not only for patients but for PAs as well. Many PAs who desire physician involvement may find themselves hung out to dry, hired by companies and expected to perform outside of their comfort level. The profession also risks ostracizing physician allies, many of whom have preferentially sought to work with PAs.
My sincere hope is that the PA profession will return to its traditional roots of a physician-PA relationship, a model that has been demonstrated to result in high-quality patient care. When that day comes, I will happily re-title my book. But as long as the AAPA continues to work to remove physicians from the equation, patients are indeed at risk.
Rebekah Bernard, MD, is a family physician in Fort Myers, Florida, and president of Physicians for Patient Protection. She is the coauthor of Patients at Risk: The Rise of the Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant in Healthcare (Irvine, Calif.: Universal Publishers, 2020). She had no relevant financial disclosures. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician assistants (PAs) are angry with me, and with good reason. I had the audacity to lump them together with nurse practitioners (NPs) in my book “Patients at Risk,” an act which one highly placed PA leader called “distasteful” in a private conversation with me.
I will admit that PAs have reason to be upset. With competitive acceptance rates including a requirement for extensive health care experience before PA school, standardized training, and at least 2,000 hours of clinical experience before graduation, the profession is a stark contrast to the haphazard training and 500 clinical hours required of NPs today. Further, unlike NPs, who have sought independent practice since the 1980s, PAs have traditionally been close allies with physicians, generally working in a 1:1 supervision model.
The truth is that it hurt to include PAs with NPs in my book. I’ve had my own close relationships with PAs over the years and found the PAs I worked with to be outstanding clinicians. Unfortunately, the profession has given me no choice. Following a model set by the NP profession,
Their efforts began with a change in terminology. “Optimal team practice” (OTP) was supposed to give PAs more flexibility, allowing them to work for hospitals or physician groups rather than under the responsibility of one physician. Not surprisingly, corporations and even academic centers have been quick to take advantage, hiring PAs and placing them in positions without adequate physician support. OTP paved the way for independent practice, as PAs sought and gained independence from any physician supervision in North Dakota, the first state to grant them that right.
Most recently, PAs have determined to change their name entirely, calling themselves physician associates. This move by the American Academy of Physician Assistants is the culmination of a years-long marketing study on how to increase the relevance and improve patient perception of the PA profession. The AAPA decision is expected to galvanize state and local PA organizations to lobby legislators for legal and regulatory changes that allow the use of the “physician associate” title, which is not currently a legal representation of PA licensure.
PAs’ latest attempt at title and branding reform follows years of advocacy to not be referred to as physician extenders or midlevel providers. For example, to gain more public acceptance of the PA model, the profession launched the public relations campaign “Your PA Can,” closely mirroring the “We Choose NPs” media blitz. PAs have also followed other dangerous precedents set by NPs, including 100% online training and a new “Doctor of Medical Science” degree, allowing PAs, as well as NPs, to now be called “doctors.”
I can understand PA reasoning even if I don’t agree with it. PAs are frustrated to be treated as second-class citizens compared with NPs, who have been granted independent practice in half the states in the union despite having a fraction of PA training. Frankly, it’s unfair that NPs are being hired preferentially over PAs simply because of looser legal requirements for physician oversight. The bottom line is that NPs have been more successful at persuading legislators to allow them independence – but that doesn’t make it right for either group.
While PAs have more clinical training upon graduation than NPs, they still have far less than physicians. PAs generally attend a 2-year master’s degree program after college which includes 2,000 hours of hands-on clinical work. By comparison, the average medical student spends 4 years and receives 5,000-6,000 hours of supervised clinical training upon graduation. But this isn’t considered enough for a graduate medical student to practice medicine independently.
Physicians must complete at least 3 years of postgraduate residency training in most states to receive a medical license, and by the time a physician is permitted to practice medicine unsupervised, they will have attained no fewer than 15,000-20,000 hours of supervised clinical practice, with years of specialty-specific training.
Patients want and deserve access to truly physician-led care, but in many parts of the country, physicians are being replaced by nonphysician practitioners to boost corporate profits. In many cases, patients are kept in the dark about the differences in training between the medical professionals now in charge of their care. The American Medical Association and other critics have expressed concern that the proposed title of “physician associate” is likely to further obscure the training and roles of medical professionals, already a source of confusion to patients.
One specific criticism is that a physician associate has historically referred to a physician (MD or DO) in a private practice group who has not yet achieved the status of partner. These physician associates are fully licensed medical doctors who have completed medical school and residency training and are in the process of completing a partnership track with their group to participate fully in financial and administrative processes. This nomenclature is similar to that of attorneys on a partnership track. Thus, the use of the term “physician associate” for someone other than a medical doctor is seen as misleading, particularly to patients who cannot be expected to have familiarity with the differences in training.
Efforts to separate the PA profession from a close-working relationship with a physician are bad not only for patients but for PAs as well. Many PAs who desire physician involvement may find themselves hung out to dry, hired by companies and expected to perform outside of their comfort level. The profession also risks ostracizing physician allies, many of whom have preferentially sought to work with PAs.
My sincere hope is that the PA profession will return to its traditional roots of a physician-PA relationship, a model that has been demonstrated to result in high-quality patient care. When that day comes, I will happily re-title my book. But as long as the AAPA continues to work to remove physicians from the equation, patients are indeed at risk.
Rebekah Bernard, MD, is a family physician in Fort Myers, Florida, and president of Physicians for Patient Protection. She is the coauthor of Patients at Risk: The Rise of the Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant in Healthcare (Irvine, Calif.: Universal Publishers, 2020). She had no relevant financial disclosures. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black-owned hospice seeks to bring greater ease in dying to Black families
This time, it didn’t take much persuading for Mary Murphy to embrace home hospice. When her mother was dying from Alzheimer’s disease in 2020, she had been reluctant until she saw what a help it was. So when her husband, Willie, neared the end of his life, she embraced hospice again.
The Murphys’ house in a leafy Nashville, Tenn., neighborhood is their happy place – full of their treasures.
“He’s good to me – buys me anything I want,” she said, as she pulled a milky glass vase out of a floor-to-ceiling cabinet with mirrored shelves.
Willie bought Mary the display case to help her to show off the trinkets she picks up at estate sales.
Down the hall, Willie was lying in their bed, now unable to speak. His heart was giving out.
“You gonna wake up for a minute?” she asked, cradling his head. She patted his back while he cleared his throat. “Cough it out.”
Heart and Soul Hospice is owned and operated by people who share the same cultural background as the patients they aim to serve.
In their application to obtain a certificate of need in Tennessee, the hospice owners made it clear they are Black and intend to serve everyone but will focus on African Americans, who are currently underserved. Tennessee data shows that in Nashville just 19% of hospice patients are Black, although they make up 27% of the capital city’s population.
Though the area already had numerous hospice agencies, regulators granted Heart and Soul permission to operate, based primarily on the value of educating an underserved group.
In Ms. Murphy’s first hospice experience, her mother had been living with dementia for decades. Still, Ms. Murphy had concerns about transitioning her mother to hospice. She felt as if she was giving up on her mom.
“My first thought was death,” she said.
National data shows that Black Medicare patients and their families are not making the move to comfort care as often as white patients are. Roughly 41% of Black Medicare beneficiaries who died in 2019 were enrolled in hospice, compared with 54% of White patients, according to data compiled annually by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
Ms. Murphy’s mother survived nearly 3 years on hospice. The benefit is meant for those in the final 6 months of life, but predicting when the end will come is difficult, especially in cases of dementia. Hospice provides palliative care for the dying and support for caregivers for a long as the process lasts.
Ms. Murphy did most of the caregiving – which can be overwhelming – but hospice helped with a few baths a week, medication in the mail and any medical equipment they needed.
And most important to Ms. Murphy was the emotional support, which came mostly from her hospice nurse.
“Wasn’t no doctor going to come here, hold my hand, stay here until the funeral home came for her,” she said about the day her mother died.
Last year, on the day after Thanksgiving, Willie Murphy died. And the same hospice nurse was at the Murphy home within minutes. She’d already stopped by that morning to check on him and returned as soon as Mary called and told her he wasn’t breathing.
“If you don’t feel like: ‘Oh my God, thank God I have hospice,’ if you can’t say that, then we’re doing something wrong,” said Keisha Mason, Heart and Soul’s director of nursing.
Ms. Mason, like Ms. Murphy, is Black and said that in her view there’s nothing fundamental keeping Black patients from using hospice except learning what the service can offer and that it’s basically free to patients – paid for by Medicare, Medicaid, and most private health plans.
“I say to them, ‘If you see a bill, then call us, because you should not,’” she said.
As Ms. Mason helped launch this new hospice agency, she began using new language, calling hospice more than a Medicare benefit. She describes it as an entitlement.
“Just as you are entitled to unemployment, as you are entitled to Social Security, you are entitled to a hospice benefit,” she said.
The investors in Heart and Soul include David Turner, owner of CNS Hospice in Detroit; Nashville pastor the Rev. Sandy McClain; and André Lee, a former hospital administrator on the campus of Meharry Medical College, a historically Black institution in Nashville.
Mr. Lee and Mr. Turner also started a Black-focused hospice agency in Michigan and have plans to replicate the model in other states.
More families need to consider home hospice as an alternative for end-of-life care, Mr. Lee said. Nursing homes are pricey. And even with Medicare, a hospital bill can be hefty.
“You’ll go in there and they’ll eat you alive,” he said. “I hate to say [something] bad about hospitals, but it’s true.”
Hospice research hasn’t come up with clear reasons to explain the gap between White and Black families’ use of the benefit. Some experts speculate it’s related to spiritual beliefs and widespread mistrust in the medical system because of decades of discrimination.
The hospice industry’s national trade group, the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, released a diversity and inclusion toolkit and a guide to reaching more Black patients. It recommends connecting with influential DJs, partnering with Black pastors and simply hiring more Black nurses.
Bridging the gap is not overly complicated, Mr. Lee said.
“A lot of hospices don’t employ enough Black people,” he said. “We all feel comfortable when you see someone over there that looks like you.”
Well-established hospice agencies have attempted to minimize barriers with their own diversity initiatives. Michelle Drayton of Visiting Nurse Service of New York said her large agency has met with ministers who counsel families dealing with failing health.
“Many of them did not fully understand what hospice was,” she said. “They had many of the same sort of misperceptions.”
Every hospice company, whether it’s an upstart or one of the nation’s oldest, can promote end-of-life education and ease care disparities, Ms. Drayton said. “We’re not just handing out a brochure,” she added.
This story is part of a partnership that includes Nashville Public Radio, NPR, and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
This time, it didn’t take much persuading for Mary Murphy to embrace home hospice. When her mother was dying from Alzheimer’s disease in 2020, she had been reluctant until she saw what a help it was. So when her husband, Willie, neared the end of his life, she embraced hospice again.
The Murphys’ house in a leafy Nashville, Tenn., neighborhood is their happy place – full of their treasures.
“He’s good to me – buys me anything I want,” she said, as she pulled a milky glass vase out of a floor-to-ceiling cabinet with mirrored shelves.
Willie bought Mary the display case to help her to show off the trinkets she picks up at estate sales.
Down the hall, Willie was lying in their bed, now unable to speak. His heart was giving out.
“You gonna wake up for a minute?” she asked, cradling his head. She patted his back while he cleared his throat. “Cough it out.”
Heart and Soul Hospice is owned and operated by people who share the same cultural background as the patients they aim to serve.
In their application to obtain a certificate of need in Tennessee, the hospice owners made it clear they are Black and intend to serve everyone but will focus on African Americans, who are currently underserved. Tennessee data shows that in Nashville just 19% of hospice patients are Black, although they make up 27% of the capital city’s population.
Though the area already had numerous hospice agencies, regulators granted Heart and Soul permission to operate, based primarily on the value of educating an underserved group.
In Ms. Murphy’s first hospice experience, her mother had been living with dementia for decades. Still, Ms. Murphy had concerns about transitioning her mother to hospice. She felt as if she was giving up on her mom.
“My first thought was death,” she said.
National data shows that Black Medicare patients and their families are not making the move to comfort care as often as white patients are. Roughly 41% of Black Medicare beneficiaries who died in 2019 were enrolled in hospice, compared with 54% of White patients, according to data compiled annually by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
Ms. Murphy’s mother survived nearly 3 years on hospice. The benefit is meant for those in the final 6 months of life, but predicting when the end will come is difficult, especially in cases of dementia. Hospice provides palliative care for the dying and support for caregivers for a long as the process lasts.
Ms. Murphy did most of the caregiving – which can be overwhelming – but hospice helped with a few baths a week, medication in the mail and any medical equipment they needed.
And most important to Ms. Murphy was the emotional support, which came mostly from her hospice nurse.
“Wasn’t no doctor going to come here, hold my hand, stay here until the funeral home came for her,” she said about the day her mother died.
Last year, on the day after Thanksgiving, Willie Murphy died. And the same hospice nurse was at the Murphy home within minutes. She’d already stopped by that morning to check on him and returned as soon as Mary called and told her he wasn’t breathing.
“If you don’t feel like: ‘Oh my God, thank God I have hospice,’ if you can’t say that, then we’re doing something wrong,” said Keisha Mason, Heart and Soul’s director of nursing.
Ms. Mason, like Ms. Murphy, is Black and said that in her view there’s nothing fundamental keeping Black patients from using hospice except learning what the service can offer and that it’s basically free to patients – paid for by Medicare, Medicaid, and most private health plans.
“I say to them, ‘If you see a bill, then call us, because you should not,’” she said.
As Ms. Mason helped launch this new hospice agency, she began using new language, calling hospice more than a Medicare benefit. She describes it as an entitlement.
“Just as you are entitled to unemployment, as you are entitled to Social Security, you are entitled to a hospice benefit,” she said.
The investors in Heart and Soul include David Turner, owner of CNS Hospice in Detroit; Nashville pastor the Rev. Sandy McClain; and André Lee, a former hospital administrator on the campus of Meharry Medical College, a historically Black institution in Nashville.
Mr. Lee and Mr. Turner also started a Black-focused hospice agency in Michigan and have plans to replicate the model in other states.
More families need to consider home hospice as an alternative for end-of-life care, Mr. Lee said. Nursing homes are pricey. And even with Medicare, a hospital bill can be hefty.
“You’ll go in there and they’ll eat you alive,” he said. “I hate to say [something] bad about hospitals, but it’s true.”
Hospice research hasn’t come up with clear reasons to explain the gap between White and Black families’ use of the benefit. Some experts speculate it’s related to spiritual beliefs and widespread mistrust in the medical system because of decades of discrimination.
The hospice industry’s national trade group, the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, released a diversity and inclusion toolkit and a guide to reaching more Black patients. It recommends connecting with influential DJs, partnering with Black pastors and simply hiring more Black nurses.
Bridging the gap is not overly complicated, Mr. Lee said.
“A lot of hospices don’t employ enough Black people,” he said. “We all feel comfortable when you see someone over there that looks like you.”
Well-established hospice agencies have attempted to minimize barriers with their own diversity initiatives. Michelle Drayton of Visiting Nurse Service of New York said her large agency has met with ministers who counsel families dealing with failing health.
“Many of them did not fully understand what hospice was,” she said. “They had many of the same sort of misperceptions.”
Every hospice company, whether it’s an upstart or one of the nation’s oldest, can promote end-of-life education and ease care disparities, Ms. Drayton said. “We’re not just handing out a brochure,” she added.
This story is part of a partnership that includes Nashville Public Radio, NPR, and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
This time, it didn’t take much persuading for Mary Murphy to embrace home hospice. When her mother was dying from Alzheimer’s disease in 2020, she had been reluctant until she saw what a help it was. So when her husband, Willie, neared the end of his life, she embraced hospice again.
The Murphys’ house in a leafy Nashville, Tenn., neighborhood is their happy place – full of their treasures.
“He’s good to me – buys me anything I want,” she said, as she pulled a milky glass vase out of a floor-to-ceiling cabinet with mirrored shelves.
Willie bought Mary the display case to help her to show off the trinkets she picks up at estate sales.
Down the hall, Willie was lying in their bed, now unable to speak. His heart was giving out.
“You gonna wake up for a minute?” she asked, cradling his head. She patted his back while he cleared his throat. “Cough it out.”
Heart and Soul Hospice is owned and operated by people who share the same cultural background as the patients they aim to serve.
In their application to obtain a certificate of need in Tennessee, the hospice owners made it clear they are Black and intend to serve everyone but will focus on African Americans, who are currently underserved. Tennessee data shows that in Nashville just 19% of hospice patients are Black, although they make up 27% of the capital city’s population.
Though the area already had numerous hospice agencies, regulators granted Heart and Soul permission to operate, based primarily on the value of educating an underserved group.
In Ms. Murphy’s first hospice experience, her mother had been living with dementia for decades. Still, Ms. Murphy had concerns about transitioning her mother to hospice. She felt as if she was giving up on her mom.
“My first thought was death,” she said.
National data shows that Black Medicare patients and their families are not making the move to comfort care as often as white patients are. Roughly 41% of Black Medicare beneficiaries who died in 2019 were enrolled in hospice, compared with 54% of White patients, according to data compiled annually by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
Ms. Murphy’s mother survived nearly 3 years on hospice. The benefit is meant for those in the final 6 months of life, but predicting when the end will come is difficult, especially in cases of dementia. Hospice provides palliative care for the dying and support for caregivers for a long as the process lasts.
Ms. Murphy did most of the caregiving – which can be overwhelming – but hospice helped with a few baths a week, medication in the mail and any medical equipment they needed.
And most important to Ms. Murphy was the emotional support, which came mostly from her hospice nurse.
“Wasn’t no doctor going to come here, hold my hand, stay here until the funeral home came for her,” she said about the day her mother died.
Last year, on the day after Thanksgiving, Willie Murphy died. And the same hospice nurse was at the Murphy home within minutes. She’d already stopped by that morning to check on him and returned as soon as Mary called and told her he wasn’t breathing.
“If you don’t feel like: ‘Oh my God, thank God I have hospice,’ if you can’t say that, then we’re doing something wrong,” said Keisha Mason, Heart and Soul’s director of nursing.
Ms. Mason, like Ms. Murphy, is Black and said that in her view there’s nothing fundamental keeping Black patients from using hospice except learning what the service can offer and that it’s basically free to patients – paid for by Medicare, Medicaid, and most private health plans.
“I say to them, ‘If you see a bill, then call us, because you should not,’” she said.
As Ms. Mason helped launch this new hospice agency, she began using new language, calling hospice more than a Medicare benefit. She describes it as an entitlement.
“Just as you are entitled to unemployment, as you are entitled to Social Security, you are entitled to a hospice benefit,” she said.
The investors in Heart and Soul include David Turner, owner of CNS Hospice in Detroit; Nashville pastor the Rev. Sandy McClain; and André Lee, a former hospital administrator on the campus of Meharry Medical College, a historically Black institution in Nashville.
Mr. Lee and Mr. Turner also started a Black-focused hospice agency in Michigan and have plans to replicate the model in other states.
More families need to consider home hospice as an alternative for end-of-life care, Mr. Lee said. Nursing homes are pricey. And even with Medicare, a hospital bill can be hefty.
“You’ll go in there and they’ll eat you alive,” he said. “I hate to say [something] bad about hospitals, but it’s true.”
Hospice research hasn’t come up with clear reasons to explain the gap between White and Black families’ use of the benefit. Some experts speculate it’s related to spiritual beliefs and widespread mistrust in the medical system because of decades of discrimination.
The hospice industry’s national trade group, the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, released a diversity and inclusion toolkit and a guide to reaching more Black patients. It recommends connecting with influential DJs, partnering with Black pastors and simply hiring more Black nurses.
Bridging the gap is not overly complicated, Mr. Lee said.
“A lot of hospices don’t employ enough Black people,” he said. “We all feel comfortable when you see someone over there that looks like you.”
Well-established hospice agencies have attempted to minimize barriers with their own diversity initiatives. Michelle Drayton of Visiting Nurse Service of New York said her large agency has met with ministers who counsel families dealing with failing health.
“Many of them did not fully understand what hospice was,” she said. “They had many of the same sort of misperceptions.”
Every hospice company, whether it’s an upstart or one of the nation’s oldest, can promote end-of-life education and ease care disparities, Ms. Drayton said. “We’re not just handing out a brochure,” she added.
This story is part of a partnership that includes Nashville Public Radio, NPR, and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
At-risk Americans become eligible for fourth COVID shot this week
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
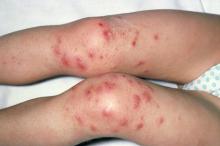
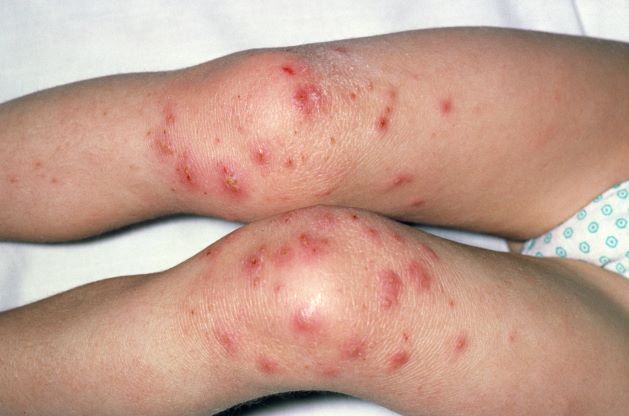
History of AD with progressing flare
The patient is empirically diagnosed with AD complicated by bacterial infection. A skin swab culture is positive for Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
AD is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by pruritus, eczematous lesions, xerosis, and lichenification. Individuals of all ages may be affected by AD, although it normally begins in infancy. Studies suggest that as many as 17.1% of adults and 22.6% of children are affected by AD. The disease is associated with diminished quality of life, sleep disturbance, depression, and anxiety. To further complicate matters, patients with AD have a significantly increased risk for recurrent skin infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
The underlying mechanisms of bacterial infection in AD are multifactorial and involve both host and bacterial factors. Factors implicated in the increased risk for infection in patients with AD include skin barrier defects, suppression of cutaneous innate immunity by type 2 inflammation, S aureus colonization, and cutaneous dysbiosis. Up to 90% of patients with AD are colonized with S aureus. It has been theorized that the host skin microbiota may play a role in protecting against S aureus colonization and infection in patients with AD. Additionally, bacterial virulence factors, such as the superantigens, proteases, and cytolytic phenol‐soluble modulins secreted by S aureus, trigger skin inflammation and may also contribute to bacterial persistence and/or epithelial penetration and infection.
Overt bacterial infection in patients with AD can be recognized by the presence of weeping lesions, honey‐colored crusts, and pustules. However, cutaneous erythema and warmth, oozing associated with edema, and regional lymphadenopathy are seen in both AD exacerbations and in patients with infection, making clinical diagnosis challenging. In addition, anatomical site‐ and skin type-specific features may disguise signs of infection, and the high frequency of S aureus colonization in AD makes positive skin swab culture of suspected infection an unreliable diagnostic tool.
S pyogenes is the second most common cause of skin and soft tissue infections in AD (S aureus is the leading cause, although data suggest that pediatric patients are not likely to be affected by superinfections caused by methicillin-resistant S aureus [MRSA]). S pyogenes may cause infections in patients with AD alone or in combination with S aureus. Patients with these skin infections usually present with pustules or impetigo. The lesions may appear as punched-out erosions with scalloped borders that mimic eczema herpeticum or eczema coxsackium. According to guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology, the presence of purulent exudate and pustules on skin examination may suggest a diagnosis of secondary bacterial infection over inflammation from dermatitis.
The use of systemic antibiotics in the treatment of noninfected AD is not recommended; however, systemic antibiotics can be recommended for patients with clinical evidence of bacterial infection, in addition to standard treatment for AD, including the concurrent application of topical steroids. For patients with AD who have signs and symptoms of systemic illness, hospitalization and empirical intravenous antibiotics are recommended. The antibiotic regimen should provide coverage against S aureus because this is the most frequently identified bacterial pathogen in AD.
When treating critically ill patients, treatment that provides coverage for both MRSA and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA) with vancomycin and an antistaphylococcal beta-lactam is appropriate. In patients with severe but non–life-threatening infections, vancomycin may be used alone as empirical therapy, pending culture results. Clindamycin can also be considered, particularly if there is no concern for an endovascular infection and the local incidence of clindamycin resistance is less than 15%.
Bacteremia triggered by S aureus initially requires the use of a bactericidal intravenous agent. For MRSA, vancomycin is the first-line agent. Cefazolin and nafcillin are both acceptable first-line agents for MSSA, although nafcillin can cause venous irritation and phlebitis when administered peripherally. Among children with S aureus bacteremia, an oral agent to which the isolate is susceptible is appropriate, as long as there are no concerns for ongoing bacteremia or endovascular complications. Duration of therapy should be determined by the clinical response; 7-14 days is usually recommended.
For patients with AD with uncomplicated, nonpurulent skin infection, a beta-lactam antibiotic that covers both S aureus and beta-hemolytic streptococci (eg, cefazolin or cephalexin) may be appropriate pending clinical response or culture and considering local epidemiology and resistance patterns. In patients who present with a skin abscess, history of MRSA colonization, close contacts with a history of skin infections, or recent hospitalization, consideration of coverage for MRSA is recommended. Acceptable oral options for MRSA skin infections in both children and adults include clindamycin, doxycycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and linezolid, assuming that the isolate is susceptible in vitro. Finally, topical mupirocin ointment for 5-10 days is an appropriate treatment for patients with AD with minor, localized skin infections such as impetigo.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier
The patient is empirically diagnosed with AD complicated by bacterial infection. A skin swab culture is positive for Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
AD is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by pruritus, eczematous lesions, xerosis, and lichenification. Individuals of all ages may be affected by AD, although it normally begins in infancy. Studies suggest that as many as 17.1% of adults and 22.6% of children are affected by AD. The disease is associated with diminished quality of life, sleep disturbance, depression, and anxiety. To further complicate matters, patients with AD have a significantly increased risk for recurrent skin infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
The underlying mechanisms of bacterial infection in AD are multifactorial and involve both host and bacterial factors. Factors implicated in the increased risk for infection in patients with AD include skin barrier defects, suppression of cutaneous innate immunity by type 2 inflammation, S aureus colonization, and cutaneous dysbiosis. Up to 90% of patients with AD are colonized with S aureus. It has been theorized that the host skin microbiota may play a role in protecting against S aureus colonization and infection in patients with AD. Additionally, bacterial virulence factors, such as the superantigens, proteases, and cytolytic phenol‐soluble modulins secreted by S aureus, trigger skin inflammation and may also contribute to bacterial persistence and/or epithelial penetration and infection.
Overt bacterial infection in patients with AD can be recognized by the presence of weeping lesions, honey‐colored crusts, and pustules. However, cutaneous erythema and warmth, oozing associated with edema, and regional lymphadenopathy are seen in both AD exacerbations and in patients with infection, making clinical diagnosis challenging. In addition, anatomical site‐ and skin type-specific features may disguise signs of infection, and the high frequency of S aureus colonization in AD makes positive skin swab culture of suspected infection an unreliable diagnostic tool.
S pyogenes is the second most common cause of skin and soft tissue infections in AD (S aureus is the leading cause, although data suggest that pediatric patients are not likely to be affected by superinfections caused by methicillin-resistant S aureus [MRSA]). S pyogenes may cause infections in patients with AD alone or in combination with S aureus. Patients with these skin infections usually present with pustules or impetigo. The lesions may appear as punched-out erosions with scalloped borders that mimic eczema herpeticum or eczema coxsackium. According to guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology, the presence of purulent exudate and pustules on skin examination may suggest a diagnosis of secondary bacterial infection over inflammation from dermatitis.
The use of systemic antibiotics in the treatment of noninfected AD is not recommended; however, systemic antibiotics can be recommended for patients with clinical evidence of bacterial infection, in addition to standard treatment for AD, including the concurrent application of topical steroids. For patients with AD who have signs and symptoms of systemic illness, hospitalization and empirical intravenous antibiotics are recommended. The antibiotic regimen should provide coverage against S aureus because this is the most frequently identified bacterial pathogen in AD.
When treating critically ill patients, treatment that provides coverage for both MRSA and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA) with vancomycin and an antistaphylococcal beta-lactam is appropriate. In patients with severe but non–life-threatening infections, vancomycin may be used alone as empirical therapy, pending culture results. Clindamycin can also be considered, particularly if there is no concern for an endovascular infection and the local incidence of clindamycin resistance is less than 15%.
Bacteremia triggered by S aureus initially requires the use of a bactericidal intravenous agent. For MRSA, vancomycin is the first-line agent. Cefazolin and nafcillin are both acceptable first-line agents for MSSA, although nafcillin can cause venous irritation and phlebitis when administered peripherally. Among children with S aureus bacteremia, an oral agent to which the isolate is susceptible is appropriate, as long as there are no concerns for ongoing bacteremia or endovascular complications. Duration of therapy should be determined by the clinical response; 7-14 days is usually recommended.
For patients with AD with uncomplicated, nonpurulent skin infection, a beta-lactam antibiotic that covers both S aureus and beta-hemolytic streptococci (eg, cefazolin or cephalexin) may be appropriate pending clinical response or culture and considering local epidemiology and resistance patterns. In patients who present with a skin abscess, history of MRSA colonization, close contacts with a history of skin infections, or recent hospitalization, consideration of coverage for MRSA is recommended. Acceptable oral options for MRSA skin infections in both children and adults include clindamycin, doxycycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and linezolid, assuming that the isolate is susceptible in vitro. Finally, topical mupirocin ointment for 5-10 days is an appropriate treatment for patients with AD with minor, localized skin infections such as impetigo.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier
The patient is empirically diagnosed with AD complicated by bacterial infection. A skin swab culture is positive for Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
AD is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by pruritus, eczematous lesions, xerosis, and lichenification. Individuals of all ages may be affected by AD, although it normally begins in infancy. Studies suggest that as many as 17.1% of adults and 22.6% of children are affected by AD. The disease is associated with diminished quality of life, sleep disturbance, depression, and anxiety. To further complicate matters, patients with AD have a significantly increased risk for recurrent skin infections, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
The underlying mechanisms of bacterial infection in AD are multifactorial and involve both host and bacterial factors. Factors implicated in the increased risk for infection in patients with AD include skin barrier defects, suppression of cutaneous innate immunity by type 2 inflammation, S aureus colonization, and cutaneous dysbiosis. Up to 90% of patients with AD are colonized with S aureus. It has been theorized that the host skin microbiota may play a role in protecting against S aureus colonization and infection in patients with AD. Additionally, bacterial virulence factors, such as the superantigens, proteases, and cytolytic phenol‐soluble modulins secreted by S aureus, trigger skin inflammation and may also contribute to bacterial persistence and/or epithelial penetration and infection.
Overt bacterial infection in patients with AD can be recognized by the presence of weeping lesions, honey‐colored crusts, and pustules. However, cutaneous erythema and warmth, oozing associated with edema, and regional lymphadenopathy are seen in both AD exacerbations and in patients with infection, making clinical diagnosis challenging. In addition, anatomical site‐ and skin type-specific features may disguise signs of infection, and the high frequency of S aureus colonization in AD makes positive skin swab culture of suspected infection an unreliable diagnostic tool.
S pyogenes is the second most common cause of skin and soft tissue infections in AD (S aureus is the leading cause, although data suggest that pediatric patients are not likely to be affected by superinfections caused by methicillin-resistant S aureus [MRSA]). S pyogenes may cause infections in patients with AD alone or in combination with S aureus. Patients with these skin infections usually present with pustules or impetigo. The lesions may appear as punched-out erosions with scalloped borders that mimic eczema herpeticum or eczema coxsackium. According to guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology, the presence of purulent exudate and pustules on skin examination may suggest a diagnosis of secondary bacterial infection over inflammation from dermatitis.
The use of systemic antibiotics in the treatment of noninfected AD is not recommended; however, systemic antibiotics can be recommended for patients with clinical evidence of bacterial infection, in addition to standard treatment for AD, including the concurrent application of topical steroids. For patients with AD who have signs and symptoms of systemic illness, hospitalization and empirical intravenous antibiotics are recommended. The antibiotic regimen should provide coverage against S aureus because this is the most frequently identified bacterial pathogen in AD.
When treating critically ill patients, treatment that provides coverage for both MRSA and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA) with vancomycin and an antistaphylococcal beta-lactam is appropriate. In patients with severe but non–life-threatening infections, vancomycin may be used alone as empirical therapy, pending culture results. Clindamycin can also be considered, particularly if there is no concern for an endovascular infection and the local incidence of clindamycin resistance is less than 15%.
Bacteremia triggered by S aureus initially requires the use of a bactericidal intravenous agent. For MRSA, vancomycin is the first-line agent. Cefazolin and nafcillin are both acceptable first-line agents for MSSA, although nafcillin can cause venous irritation and phlebitis when administered peripherally. Among children with S aureus bacteremia, an oral agent to which the isolate is susceptible is appropriate, as long as there are no concerns for ongoing bacteremia or endovascular complications. Duration of therapy should be determined by the clinical response; 7-14 days is usually recommended.
For patients with AD with uncomplicated, nonpurulent skin infection, a beta-lactam antibiotic that covers both S aureus and beta-hemolytic streptococci (eg, cefazolin or cephalexin) may be appropriate pending clinical response or culture and considering local epidemiology and resistance patterns. In patients who present with a skin abscess, history of MRSA colonization, close contacts with a history of skin infections, or recent hospitalization, consideration of coverage for MRSA is recommended. Acceptable oral options for MRSA skin infections in both children and adults include clindamycin, doxycycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and linezolid, assuming that the isolate is susceptible in vitro. Finally, topical mupirocin ointment for 5-10 days is an appropriate treatment for patients with AD with minor, localized skin infections such as impetigo.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier
A 9-year-old girl with a history of moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) presents with a rapidly progressing AD flare. The patient had been stable over the past 6 months with the use of daily emollients. Over the past 36-48 hours, the patient developed pruritic lesions and pustules on her knees and elbows, and erythema and scaling around the eyes. Physical examination reveals a temperature of 101.5°F (38.6°C), a heart rate of 112 beats/min, a respiratory rate of 32 breaths/min, and a blood pressure of 100/95 mm Hg. Physical findings include cutaneous erythema and warmth surrounding the affected areas, pustules with yellow fluid, and regional lymphadenopathy.
Individualize the duration of postpartum magnesium treatment for patients with preeclampsia to best balance the benefits and harms of treatment
Preeclampsia complicates 3% to 8% of pregnancies.1-3 The incidence of preeclampsia is influenced by the clinical characteristics of the pregnant population, including the prevalence of overweight, obesity, chronic hypertension, diabetes, nulliparity, advanced maternal age, multiple gestations, kidney disease, and a history of preeclampsia in a prior pregnancy.4
Magnesium treatment reduces the rate of eclampsia among patients with preeclampsia
For patients with preeclampsia, magnesium treatment reduces the risk of seizure. In the Magpie trial, 9,992 pregnant patients were treated for 24 hours with magnesium or placebo.5 The magnesium treatment regimen was either a 4-g IV bolus over 10 to 15 minutes followed by a continuous infusion of 1 g/hr or an intramuscular regimen (10-g intramuscular loading dose followed by 5 g IM every 4 hours). Eclamptic seizures occurred in 0.8% and 1.9% of patients treated with magnesium or placebo, respectively (relative risk [RR], 0.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.29 to 0.60). Among patients with a multiple gestation, the rate of eclampsia was 2% and 6% in the patients treated with magnesium or placebo, respectively. The number of patients who needed to be treated to prevent one eclamptic event was 63 and 109 for patients with preeclampsia with and without severe features, respectively. Intrapartum treatment with magnesium also reduced the risk of placental abruption from 3.2% for the patients receiving placebo to 2.0% among the patients treated with magnesium (RR, 0.67; 99% CI, 0.45- 0.89). Maternal death was reduced with magnesium treatment compared with placebo (0.2% vs 0.4%), but the difference was not statistically significant.
In the Magpie trial, side effects were reported by 24% and 5% of patients treated with magnesium and placebo, respectively. The most common side effects were flushing, nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness. Of note, magnesium treatment is contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis because it can cause muscle weakness and hypoventilation.6 For patients with preeclampsia and myasthenia gravis, levetiracetam may be utilized to reduce the risk of seizure.6
Duration of postpartum magnesium treatment
There are no studies with a sufficient number of participants to definitively determine the optimal duration of postpartum magnesium therapy. A properly powered study would likely require more than 16,000 to 20,000 participants to identify clinically meaningful differences in the rate of postpartum eclampsia among patients treated with magnesium for 12 or 24 hours.7,8 It is unlikely that such a study will be completed. Hence, the duration of postpartum magnesium must be based on clinical judgment, balancing the risks and benefits of treatment.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends continuing magnesium treatment for 24 hours postpartum. They advise, “For patients requiring cesarean delivery (before the onset of labor), the infusion should ideally begin before surgery and continue during surgery, as well as 24 hours afterwards. For patients who deliver vaginally, the infusion should continue for 24 hours after delivery.”9
Multiple randomized trials have reported on the outcomes associated with 12 hours versus 24 hours of postpartum magnesium therapy (TABLE). Because the rate of postpartum eclamptic seizure is very low, none of the studies were sufficiently powered to provide a definitive answer to the benefits and harms of the shorter versus longer time frame of magnesium therapy.10-15
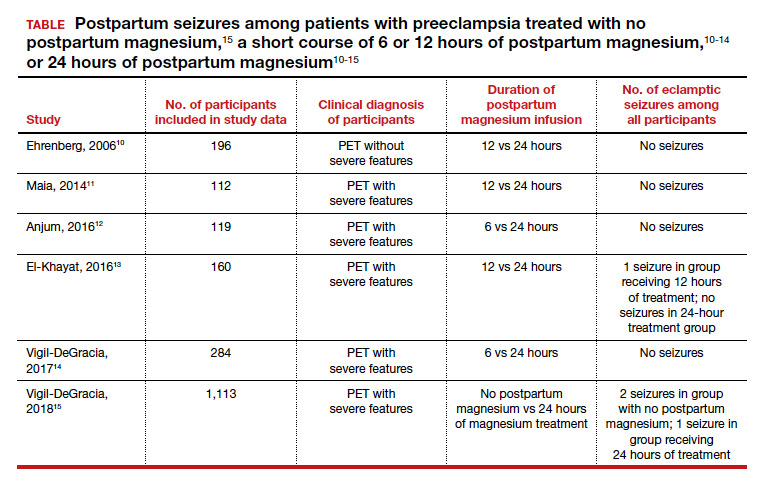
Continue to: The harms of prolonged postpartum magnesium infusion...
The harms of prolonged postpartum magnesium infusion
The harms of prolonging treatment with postpartum magnesium infusion are generally not emphasized in the medical literature. However, side effects that can occur are flushing, nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness, delayed early ambulation, delayed return to full diet, delayed discontinuation of a bladder catheter, and delayed initiation of breastfeeding.5,15 In one large clinical trial, 1,113 patients with preeclampsia with severe features who received intrapartum magnesium for ≥8 hours were randomized after birth to immediate discontinuation of magnesium or continuation of magnesium for 24 hours.15 There was 1 seizure in the group of 555 patients who received 24 hours of postpartum magnesium and 2 seizures in the group of 558 patients who received no magnesium after birth. In this trial, continuation of magnesium postpartum resulted in delayed initiation of breastfeeding and delayed ambulation.15
Balancing the benefits and harms of postpartum magnesium infusion
An important clinical point is that magnesium treatment will not prevent all seizures associated with preeclampsia; in the Magpie trial, among the 5,055 patients with preeclampsia treated with magnesium there were 40 (0.8%) seizures.5 Magnesium treatment will reduce but not eliminate the risk of seizure. Clinicians should have a plan to treat seizures that occur while a woman is being treated with magnesium.
In the absence of high-quality data to guide the duration of postpartum magnesium therapy it is best to use clinical parameters to balance the benefits and harms of postpartum magnesium treatment.16-18 Patients may want to participate in the decision about the duration of postpartum magnesium treatment after receiving counseling about the benefits and harms.
For patients with preeclampsia without severe features, many clinicians are no longer ordering intrapartum magnesium for prevention of seizures because they believe the risk of seizure in patients without severe disease is very low. Hence, these patients will not receive postpartum magnesium treatment unless they evolve to preeclampsia with severe features or develop a “red flag” warning postpartum (see below).
For patients with preeclampsia without severe features who received intrapartum magnesium, after birth, the magnesium infusion could be stopped immediately or within 12 hours of birth. For patients with preeclampsia without severe features, early termination of the magnesium infusion best balances the benefit of seizure reduction with the harms of delayed early ambulation, return to full diet, discontinuation of the bladder catheter, and initiation of breastfeeding.
For patients with preeclampsia with severe features, 24 hours of magnesium may best balance the benefits and harms of treatment. However, if the patient continues to have “red flag” findings, continued magnesium treatment beyond 24 hours may be warranted.
Red flag findings include: an eclamptic seizure before or after birth, ongoing or recurring severe headaches, visual scotomata, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, severe hypertension, oliguria, rising creatinine, or liver transaminases and declining platelet count.
The hypertensive diseases of pregnancy, including preeclampsia often appear suddenly and may evolve rapidly, threatening the health of both mother and fetus. A high level of suspicion that a hypertensive disease might be the cause of vague symptoms such as epigastric discomfort or headache may accelerate early diagnosis. Rapid treatment of severe hypertension with intravenous labetalol and hydralazine, and intrapartum plus postpartum administration of magnesium to prevent placental abruption and eclampsia will optimize patient outcomes. No patient, patient’s family members, or clinician, wants to experience the grief of a preventable maternal, fetal, or newborn death due to hypertension.19 Obstetricians, midwives, labor nurses, obstetrical anesthesiologists and doulas play key roles in preventing maternal, fetal, and newborn morbidity and death from hypertensive diseases of pregnancy. As a team we are the last line of defense protecting the health of our patients. ●
- World Health Organization. WHO International Collaborative Study of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Geographic variation in the incidence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158:80-83.
- Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Incidence of preeclampsia: risk factors and outcomes associated with early- versus late-onset disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:544.e1-e12. doi: 10.1016 /j.ajog.2013.08.019.
- Mayrink K, Souza RT, Feitosa FE, et al. Incidence and risk factors for preeclampsia in a cohort of healthy nulliparous patients: a nested casecontrol study. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9517. doi: 10.1038 /s41598-019-46011-3.
- Bartsch E, Medcalf KE, Park AL, et al. High risk of pre-eclampsia identification group. BMJ. 2016;353:i1753. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1753.
- Altman D, Carroli G, Duley L; The Magpie Trial Collaborative Group. Do patients with preeclampsia, and their babies, benefit from magnesium sulfate? The Magpie Trial: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1877- 1890. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08778-0.
- Lake AJ, Al Hkabbaz A, Keeney R. Severe preeclampsia in the setting of myasthenia gravis. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2017;9204930. doi: 10.1155/2017/9204930.
- Hurd WW, Ventolini G, Stolfi A. Postpartum seizure prophylaxis: using maternal clinical parameters to guide therapy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102: 196-197. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(03)00471-x.
- Scott JR. Safety of eliminating postpartum magnesium sulphate: intriguing but not yet proven. BJOG. 2018;125:1312. doi: 10.1111/1471 -0528.15317.
- Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 222. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e237-e260. doi: 10.1097/AOG .0000000000003891.
- Ehrenberg H, Mercer BM. Abbreviated postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy for patients with mild preeclampsia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:833-888. doi: 10.1097 /01.AOG.0000236493.35347.d8.
- Maia SB, Katz L, Neto CN, et al. Abbreviated (12- hour) versus traditional (24-hour) postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy in severe pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2014;126:260-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2014.03.024.
- Anjum S, Rajaram GP, Bano I. Short-course (6-h) magnesium sulfate therapy in severe preeclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016;293:983-986. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3903-y.
- El-Khayat W, Atef A, Abdelatty S, et al. A novel protocol for postpartum magnesium sulphate in severe pre-eclampsia: a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29: 154-158. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.991915.
- Vigil-De Gracia P, Ramirez R, Duran Y, et al. Magnesium sulfate for 6 vs 24 hours post-delivery in patients who received magnesium sulfate for less than 8 hours before birth: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:241. doi: 10.1186/s12884-017-1424-3.
- Vigil-DeGracia P, Ludmir J, Ng J, et al. Is there benefit to continue magnesium sulphate postpartum in patients receiving magnesium sulphate before delivery? A randomized controlled study. BJOG. 2018;125:1304-1311. doi: 10.1111/1471 -0528.15320.
- Ascarelli MH, Johnson V, May WL, et al. Individually determined postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy with clinical parameters to safety and cost-effectively shorten treatment for preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:952-956. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(98)70195-4.
- Isler CM, Barrilleaux PS, Rinehart BK, et al. Postpartum seizure prophylaxis: using maternal clinical parameters to guide therapy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:66-69. doi: 10.1016/s0029 -7844(02)02317-7.
- Fontenot MT, Lewis DF, Frederick JB, et al. A prospective randomized trial of magnesium sulfate in severe preeclampsia: use of diuresis as a clinical parameter to determine the duration of postpartum therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:1788- 1793. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.12.056.
- Tsigas EZ. The Preeclampsia Foundation: the voice and views of the patient and family. Am J Obstet Gynecol. Epub August 23, 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.053.
Preeclampsia complicates 3% to 8% of pregnancies.1-3 The incidence of preeclampsia is influenced by the clinical characteristics of the pregnant population, including the prevalence of overweight, obesity, chronic hypertension, diabetes, nulliparity, advanced maternal age, multiple gestations, kidney disease, and a history of preeclampsia in a prior pregnancy.4
Magnesium treatment reduces the rate of eclampsia among patients with preeclampsia
For patients with preeclampsia, magnesium treatment reduces the risk of seizure. In the Magpie trial, 9,992 pregnant patients were treated for 24 hours with magnesium or placebo.5 The magnesium treatment regimen was either a 4-g IV bolus over 10 to 15 minutes followed by a continuous infusion of 1 g/hr or an intramuscular regimen (10-g intramuscular loading dose followed by 5 g IM every 4 hours). Eclamptic seizures occurred in 0.8% and 1.9% of patients treated with magnesium or placebo, respectively (relative risk [RR], 0.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.29 to 0.60). Among patients with a multiple gestation, the rate of eclampsia was 2% and 6% in the patients treated with magnesium or placebo, respectively. The number of patients who needed to be treated to prevent one eclamptic event was 63 and 109 for patients with preeclampsia with and without severe features, respectively. Intrapartum treatment with magnesium also reduced the risk of placental abruption from 3.2% for the patients receiving placebo to 2.0% among the patients treated with magnesium (RR, 0.67; 99% CI, 0.45- 0.89). Maternal death was reduced with magnesium treatment compared with placebo (0.2% vs 0.4%), but the difference was not statistically significant.
In the Magpie trial, side effects were reported by 24% and 5% of patients treated with magnesium and placebo, respectively. The most common side effects were flushing, nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness. Of note, magnesium treatment is contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis because it can cause muscle weakness and hypoventilation.6 For patients with preeclampsia and myasthenia gravis, levetiracetam may be utilized to reduce the risk of seizure.6
Duration of postpartum magnesium treatment
There are no studies with a sufficient number of participants to definitively determine the optimal duration of postpartum magnesium therapy. A properly powered study would likely require more than 16,000 to 20,000 participants to identify clinically meaningful differences in the rate of postpartum eclampsia among patients treated with magnesium for 12 or 24 hours.7,8 It is unlikely that such a study will be completed. Hence, the duration of postpartum magnesium must be based on clinical judgment, balancing the risks and benefits of treatment.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends continuing magnesium treatment for 24 hours postpartum. They advise, “For patients requiring cesarean delivery (before the onset of labor), the infusion should ideally begin before surgery and continue during surgery, as well as 24 hours afterwards. For patients who deliver vaginally, the infusion should continue for 24 hours after delivery.”9
Multiple randomized trials have reported on the outcomes associated with 12 hours versus 24 hours of postpartum magnesium therapy (TABLE). Because the rate of postpartum eclamptic seizure is very low, none of the studies were sufficiently powered to provide a definitive answer to the benefits and harms of the shorter versus longer time frame of magnesium therapy.10-15

Continue to: The harms of prolonged postpartum magnesium infusion...
The harms of prolonged postpartum magnesium infusion
The harms of prolonging treatment with postpartum magnesium infusion are generally not emphasized in the medical literature. However, side effects that can occur are flushing, nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness, delayed early ambulation, delayed return to full diet, delayed discontinuation of a bladder catheter, and delayed initiation of breastfeeding.5,15 In one large clinical trial, 1,113 patients with preeclampsia with severe features who received intrapartum magnesium for ≥8 hours were randomized after birth to immediate discontinuation of magnesium or continuation of magnesium for 24 hours.15 There was 1 seizure in the group of 555 patients who received 24 hours of postpartum magnesium and 2 seizures in the group of 558 patients who received no magnesium after birth. In this trial, continuation of magnesium postpartum resulted in delayed initiation of breastfeeding and delayed ambulation.15
Balancing the benefits and harms of postpartum magnesium infusion
An important clinical point is that magnesium treatment will not prevent all seizures associated with preeclampsia; in the Magpie trial, among the 5,055 patients with preeclampsia treated with magnesium there were 40 (0.8%) seizures.5 Magnesium treatment will reduce but not eliminate the risk of seizure. Clinicians should have a plan to treat seizures that occur while a woman is being treated with magnesium.
In the absence of high-quality data to guide the duration of postpartum magnesium therapy it is best to use clinical parameters to balance the benefits and harms of postpartum magnesium treatment.16-18 Patients may want to participate in the decision about the duration of postpartum magnesium treatment after receiving counseling about the benefits and harms.
For patients with preeclampsia without severe features, many clinicians are no longer ordering intrapartum magnesium for prevention of seizures because they believe the risk of seizure in patients without severe disease is very low. Hence, these patients will not receive postpartum magnesium treatment unless they evolve to preeclampsia with severe features or develop a “red flag” warning postpartum (see below).
For patients with preeclampsia without severe features who received intrapartum magnesium, after birth, the magnesium infusion could be stopped immediately or within 12 hours of birth. For patients with preeclampsia without severe features, early termination of the magnesium infusion best balances the benefit of seizure reduction with the harms of delayed early ambulation, return to full diet, discontinuation of the bladder catheter, and initiation of breastfeeding.
For patients with preeclampsia with severe features, 24 hours of magnesium may best balance the benefits and harms of treatment. However, if the patient continues to have “red flag” findings, continued magnesium treatment beyond 24 hours may be warranted.
Red flag findings include: an eclamptic seizure before or after birth, ongoing or recurring severe headaches, visual scotomata, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, severe hypertension, oliguria, rising creatinine, or liver transaminases and declining platelet count.
The hypertensive diseases of pregnancy, including preeclampsia often appear suddenly and may evolve rapidly, threatening the health of both mother and fetus. A high level of suspicion that a hypertensive disease might be the cause of vague symptoms such as epigastric discomfort or headache may accelerate early diagnosis. Rapid treatment of severe hypertension with intravenous labetalol and hydralazine, and intrapartum plus postpartum administration of magnesium to prevent placental abruption and eclampsia will optimize patient outcomes. No patient, patient’s family members, or clinician, wants to experience the grief of a preventable maternal, fetal, or newborn death due to hypertension.19 Obstetricians, midwives, labor nurses, obstetrical anesthesiologists and doulas play key roles in preventing maternal, fetal, and newborn morbidity and death from hypertensive diseases of pregnancy. As a team we are the last line of defense protecting the health of our patients. ●
Preeclampsia complicates 3% to 8% of pregnancies.1-3 The incidence of preeclampsia is influenced by the clinical characteristics of the pregnant population, including the prevalence of overweight, obesity, chronic hypertension, diabetes, nulliparity, advanced maternal age, multiple gestations, kidney disease, and a history of preeclampsia in a prior pregnancy.4
Magnesium treatment reduces the rate of eclampsia among patients with preeclampsia
For patients with preeclampsia, magnesium treatment reduces the risk of seizure. In the Magpie trial, 9,992 pregnant patients were treated for 24 hours with magnesium or placebo.5 The magnesium treatment regimen was either a 4-g IV bolus over 10 to 15 minutes followed by a continuous infusion of 1 g/hr or an intramuscular regimen (10-g intramuscular loading dose followed by 5 g IM every 4 hours). Eclamptic seizures occurred in 0.8% and 1.9% of patients treated with magnesium or placebo, respectively (relative risk [RR], 0.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.29 to 0.60). Among patients with a multiple gestation, the rate of eclampsia was 2% and 6% in the patients treated with magnesium or placebo, respectively. The number of patients who needed to be treated to prevent one eclamptic event was 63 and 109 for patients with preeclampsia with and without severe features, respectively. Intrapartum treatment with magnesium also reduced the risk of placental abruption from 3.2% for the patients receiving placebo to 2.0% among the patients treated with magnesium (RR, 0.67; 99% CI, 0.45- 0.89). Maternal death was reduced with magnesium treatment compared with placebo (0.2% vs 0.4%), but the difference was not statistically significant.
In the Magpie trial, side effects were reported by 24% and 5% of patients treated with magnesium and placebo, respectively. The most common side effects were flushing, nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness. Of note, magnesium treatment is contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis because it can cause muscle weakness and hypoventilation.6 For patients with preeclampsia and myasthenia gravis, levetiracetam may be utilized to reduce the risk of seizure.6
Duration of postpartum magnesium treatment
There are no studies with a sufficient number of participants to definitively determine the optimal duration of postpartum magnesium therapy. A properly powered study would likely require more than 16,000 to 20,000 participants to identify clinically meaningful differences in the rate of postpartum eclampsia among patients treated with magnesium for 12 or 24 hours.7,8 It is unlikely that such a study will be completed. Hence, the duration of postpartum magnesium must be based on clinical judgment, balancing the risks and benefits of treatment.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends continuing magnesium treatment for 24 hours postpartum. They advise, “For patients requiring cesarean delivery (before the onset of labor), the infusion should ideally begin before surgery and continue during surgery, as well as 24 hours afterwards. For patients who deliver vaginally, the infusion should continue for 24 hours after delivery.”9
Multiple randomized trials have reported on the outcomes associated with 12 hours versus 24 hours of postpartum magnesium therapy (TABLE). Because the rate of postpartum eclamptic seizure is very low, none of the studies were sufficiently powered to provide a definitive answer to the benefits and harms of the shorter versus longer time frame of magnesium therapy.10-15

Continue to: The harms of prolonged postpartum magnesium infusion...
The harms of prolonged postpartum magnesium infusion
The harms of prolonging treatment with postpartum magnesium infusion are generally not emphasized in the medical literature. However, side effects that can occur are flushing, nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness, delayed early ambulation, delayed return to full diet, delayed discontinuation of a bladder catheter, and delayed initiation of breastfeeding.5,15 In one large clinical trial, 1,113 patients with preeclampsia with severe features who received intrapartum magnesium for ≥8 hours were randomized after birth to immediate discontinuation of magnesium or continuation of magnesium for 24 hours.15 There was 1 seizure in the group of 555 patients who received 24 hours of postpartum magnesium and 2 seizures in the group of 558 patients who received no magnesium after birth. In this trial, continuation of magnesium postpartum resulted in delayed initiation of breastfeeding and delayed ambulation.15
Balancing the benefits and harms of postpartum magnesium infusion
An important clinical point is that magnesium treatment will not prevent all seizures associated with preeclampsia; in the Magpie trial, among the 5,055 patients with preeclampsia treated with magnesium there were 40 (0.8%) seizures.5 Magnesium treatment will reduce but not eliminate the risk of seizure. Clinicians should have a plan to treat seizures that occur while a woman is being treated with magnesium.
In the absence of high-quality data to guide the duration of postpartum magnesium therapy it is best to use clinical parameters to balance the benefits and harms of postpartum magnesium treatment.16-18 Patients may want to participate in the decision about the duration of postpartum magnesium treatment after receiving counseling about the benefits and harms.
For patients with preeclampsia without severe features, many clinicians are no longer ordering intrapartum magnesium for prevention of seizures because they believe the risk of seizure in patients without severe disease is very low. Hence, these patients will not receive postpartum magnesium treatment unless they evolve to preeclampsia with severe features or develop a “red flag” warning postpartum (see below).
For patients with preeclampsia without severe features who received intrapartum magnesium, after birth, the magnesium infusion could be stopped immediately or within 12 hours of birth. For patients with preeclampsia without severe features, early termination of the magnesium infusion best balances the benefit of seizure reduction with the harms of delayed early ambulation, return to full diet, discontinuation of the bladder catheter, and initiation of breastfeeding.
For patients with preeclampsia with severe features, 24 hours of magnesium may best balance the benefits and harms of treatment. However, if the patient continues to have “red flag” findings, continued magnesium treatment beyond 24 hours may be warranted.
Red flag findings include: an eclamptic seizure before or after birth, ongoing or recurring severe headaches, visual scotomata, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, severe hypertension, oliguria, rising creatinine, or liver transaminases and declining platelet count.
The hypertensive diseases of pregnancy, including preeclampsia often appear suddenly and may evolve rapidly, threatening the health of both mother and fetus. A high level of suspicion that a hypertensive disease might be the cause of vague symptoms such as epigastric discomfort or headache may accelerate early diagnosis. Rapid treatment of severe hypertension with intravenous labetalol and hydralazine, and intrapartum plus postpartum administration of magnesium to prevent placental abruption and eclampsia will optimize patient outcomes. No patient, patient’s family members, or clinician, wants to experience the grief of a preventable maternal, fetal, or newborn death due to hypertension.19 Obstetricians, midwives, labor nurses, obstetrical anesthesiologists and doulas play key roles in preventing maternal, fetal, and newborn morbidity and death from hypertensive diseases of pregnancy. As a team we are the last line of defense protecting the health of our patients. ●
- World Health Organization. WHO International Collaborative Study of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Geographic variation in the incidence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158:80-83.
- Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Incidence of preeclampsia: risk factors and outcomes associated with early- versus late-onset disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:544.e1-e12. doi: 10.1016 /j.ajog.2013.08.019.
- Mayrink K, Souza RT, Feitosa FE, et al. Incidence and risk factors for preeclampsia in a cohort of healthy nulliparous patients: a nested casecontrol study. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9517. doi: 10.1038 /s41598-019-46011-3.
- Bartsch E, Medcalf KE, Park AL, et al. High risk of pre-eclampsia identification group. BMJ. 2016;353:i1753. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1753.
- Altman D, Carroli G, Duley L; The Magpie Trial Collaborative Group. Do patients with preeclampsia, and their babies, benefit from magnesium sulfate? The Magpie Trial: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1877- 1890. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08778-0.
- Lake AJ, Al Hkabbaz A, Keeney R. Severe preeclampsia in the setting of myasthenia gravis. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2017;9204930. doi: 10.1155/2017/9204930.
- Hurd WW, Ventolini G, Stolfi A. Postpartum seizure prophylaxis: using maternal clinical parameters to guide therapy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102: 196-197. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(03)00471-x.
- Scott JR. Safety of eliminating postpartum magnesium sulphate: intriguing but not yet proven. BJOG. 2018;125:1312. doi: 10.1111/1471 -0528.15317.
- Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 222. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e237-e260. doi: 10.1097/AOG .0000000000003891.
- Ehrenberg H, Mercer BM. Abbreviated postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy for patients with mild preeclampsia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:833-888. doi: 10.1097 /01.AOG.0000236493.35347.d8.
- Maia SB, Katz L, Neto CN, et al. Abbreviated (12- hour) versus traditional (24-hour) postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy in severe pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2014;126:260-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2014.03.024.
- Anjum S, Rajaram GP, Bano I. Short-course (6-h) magnesium sulfate therapy in severe preeclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016;293:983-986. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3903-y.
- El-Khayat W, Atef A, Abdelatty S, et al. A novel protocol for postpartum magnesium sulphate in severe pre-eclampsia: a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29: 154-158. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.991915.
- Vigil-De Gracia P, Ramirez R, Duran Y, et al. Magnesium sulfate for 6 vs 24 hours post-delivery in patients who received magnesium sulfate for less than 8 hours before birth: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:241. doi: 10.1186/s12884-017-1424-3.
- Vigil-DeGracia P, Ludmir J, Ng J, et al. Is there benefit to continue magnesium sulphate postpartum in patients receiving magnesium sulphate before delivery? A randomized controlled study. BJOG. 2018;125:1304-1311. doi: 10.1111/1471 -0528.15320.
- Ascarelli MH, Johnson V, May WL, et al. Individually determined postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy with clinical parameters to safety and cost-effectively shorten treatment for preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:952-956. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(98)70195-4.
- Isler CM, Barrilleaux PS, Rinehart BK, et al. Postpartum seizure prophylaxis: using maternal clinical parameters to guide therapy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:66-69. doi: 10.1016/s0029 -7844(02)02317-7.
- Fontenot MT, Lewis DF, Frederick JB, et al. A prospective randomized trial of magnesium sulfate in severe preeclampsia: use of diuresis as a clinical parameter to determine the duration of postpartum therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:1788- 1793. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.12.056.
- Tsigas EZ. The Preeclampsia Foundation: the voice and views of the patient and family. Am J Obstet Gynecol. Epub August 23, 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.053.
- World Health Organization. WHO International Collaborative Study of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Geographic variation in the incidence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158:80-83.
- Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Incidence of preeclampsia: risk factors and outcomes associated with early- versus late-onset disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:544.e1-e12. doi: 10.1016 /j.ajog.2013.08.019.
- Mayrink K, Souza RT, Feitosa FE, et al. Incidence and risk factors for preeclampsia in a cohort of healthy nulliparous patients: a nested casecontrol study. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9517. doi: 10.1038 /s41598-019-46011-3.
- Bartsch E, Medcalf KE, Park AL, et al. High risk of pre-eclampsia identification group. BMJ. 2016;353:i1753. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1753.
- Altman D, Carroli G, Duley L; The Magpie Trial Collaborative Group. Do patients with preeclampsia, and their babies, benefit from magnesium sulfate? The Magpie Trial: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1877- 1890. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08778-0.
- Lake AJ, Al Hkabbaz A, Keeney R. Severe preeclampsia in the setting of myasthenia gravis. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2017;9204930. doi: 10.1155/2017/9204930.
- Hurd WW, Ventolini G, Stolfi A. Postpartum seizure prophylaxis: using maternal clinical parameters to guide therapy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102: 196-197. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(03)00471-x.
- Scott JR. Safety of eliminating postpartum magnesium sulphate: intriguing but not yet proven. BJOG. 2018;125:1312. doi: 10.1111/1471 -0528.15317.
- Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 222. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e237-e260. doi: 10.1097/AOG .0000000000003891.
- Ehrenberg H, Mercer BM. Abbreviated postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy for patients with mild preeclampsia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:833-888. doi: 10.1097 /01.AOG.0000236493.35347.d8.
- Maia SB, Katz L, Neto CN, et al. Abbreviated (12- hour) versus traditional (24-hour) postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy in severe pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2014;126:260-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2014.03.024.
- Anjum S, Rajaram GP, Bano I. Short-course (6-h) magnesium sulfate therapy in severe preeclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016;293:983-986. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3903-y.
- El-Khayat W, Atef A, Abdelatty S, et al. A novel protocol for postpartum magnesium sulphate in severe pre-eclampsia: a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29: 154-158. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.991915.
- Vigil-De Gracia P, Ramirez R, Duran Y, et al. Magnesium sulfate for 6 vs 24 hours post-delivery in patients who received magnesium sulfate for less than 8 hours before birth: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:241. doi: 10.1186/s12884-017-1424-3.
- Vigil-DeGracia P, Ludmir J, Ng J, et al. Is there benefit to continue magnesium sulphate postpartum in patients receiving magnesium sulphate before delivery? A randomized controlled study. BJOG. 2018;125:1304-1311. doi: 10.1111/1471 -0528.15320.
- Ascarelli MH, Johnson V, May WL, et al. Individually determined postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy with clinical parameters to safety and cost-effectively shorten treatment for preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:952-956. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(98)70195-4.
- Isler CM, Barrilleaux PS, Rinehart BK, et al. Postpartum seizure prophylaxis: using maternal clinical parameters to guide therapy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:66-69. doi: 10.1016/s0029 -7844(02)02317-7.
- Fontenot MT, Lewis DF, Frederick JB, et al. A prospective randomized trial of magnesium sulfate in severe preeclampsia: use of diuresis as a clinical parameter to determine the duration of postpartum therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:1788- 1793. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.12.056.
- Tsigas EZ. The Preeclampsia Foundation: the voice and views of the patient and family. Am J Obstet Gynecol. Epub August 23, 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.053.
Lack of high school education vaccine hesitancy predictor
Lack of a high school education is a predictor of whether a person will be resistant to getting the COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Researchers from the University of North Carolina looked at vaccination rates in 3,142 counties in the U.S. They compared them to population characteristics based on the CDC Social Vulnerability Index.
They found that more than half of the unvaccinated adults in the U.S. with strong vaccine hesitancy had a high school education or less. Vaccine hesitancy was defined as refusal to be vaccinated even if the COVID-19 vaccine was available.
The other main predictor for vaccine hesitancy was concern about vaccine availability and distribution, the researchers said.
“Our study suggests that low education levels are a major contributor to vaccine hesitancy and ultimately vaccination levels,” the authors wrote. The study was published in the American Journal of Infection Control. “Specifically, low vaccination levels were found in communities with a less educated population and with more concern about vaccine uptake capacity, suggesting that education is an ongoing challenge.”
“Our findings suggest that policy makers and community leaders should tailor vaccine information and efforts to those with limited education and specifically address knowledge concerns that are prevalent and likely more modifiable.”
The study was based on data gathered months ago. It says that as of May 9, 2021, 34.7% of the U.S. population was fully vaccinated and that 8% reported a strong unwillingness to get vaccinated.
At press time, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID Data Tracker showed that 62.5% of the U.S. population was fully vaccinated.
According to the study, other consistent characteristics of people who are vaccine hesitant are that they belong to a racial minority, are 65 or older, live in a household with children 18 or younger, or are unemployed.
When asked why they were vaccine hesitant, people gave these reasons: Lack of trust in COVID-19 vaccines (55%), concerns about side effects (48%), and lack of trust in government (46%).
Lack of access to vaccines, often cited in previous studies about resistance to other vaccines, was not cited as a reason for not getting the COVID-19 vaccine.
“COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy is a public health threat,” the researchers concluded. “Since education levels are not easily modifiable, our results suggest that policymakers would be best served by closing knowledge gaps to overcome negative perceptions of the vaccine through tailored interventions.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Lack of a high school education is a predictor of whether a person will be resistant to getting the COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Researchers from the University of North Carolina looked at vaccination rates in 3,142 counties in the U.S. They compared them to population characteristics based on the CDC Social Vulnerability Index.
They found that more than half of the unvaccinated adults in the U.S. with strong vaccine hesitancy had a high school education or less. Vaccine hesitancy was defined as refusal to be vaccinated even if the COVID-19 vaccine was available.
The other main predictor for vaccine hesitancy was concern about vaccine availability and distribution, the researchers said.
“Our study suggests that low education levels are a major contributor to vaccine hesitancy and ultimately vaccination levels,” the authors wrote. The study was published in the American Journal of Infection Control. “Specifically, low vaccination levels were found in communities with a less educated population and with more concern about vaccine uptake capacity, suggesting that education is an ongoing challenge.”
“Our findings suggest that policy makers and community leaders should tailor vaccine information and efforts to those with limited education and specifically address knowledge concerns that are prevalent and likely more modifiable.”
The study was based on data gathered months ago. It says that as of May 9, 2021, 34.7% of the U.S. population was fully vaccinated and that 8% reported a strong unwillingness to get vaccinated.
At press time, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID Data Tracker showed that 62.5% of the U.S. population was fully vaccinated.
According to the study, other consistent characteristics of people who are vaccine hesitant are that they belong to a racial minority, are 65 or older, live in a household with children 18 or younger, or are unemployed.
When asked why they were vaccine hesitant, people gave these reasons: Lack of trust in COVID-19 vaccines (55%), concerns about side effects (48%), and lack of trust in government (46%).
Lack of access to vaccines, often cited in previous studies about resistance to other vaccines, was not cited as a reason for not getting the COVID-19 vaccine.
“COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy is a public health threat,” the researchers concluded. “Since education levels are not easily modifiable, our results suggest that policymakers would be best served by closing knowledge gaps to overcome negative perceptions of the vaccine through tailored interventions.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Lack of a high school education is a predictor of whether a person will be resistant to getting the COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Researchers from the University of North Carolina looked at vaccination rates in 3,142 counties in the U.S. They compared them to population characteristics based on the CDC Social Vulnerability Index.
They found that more than half of the unvaccinated adults in the U.S. with strong vaccine hesitancy had a high school education or less. Vaccine hesitancy was defined as refusal to be vaccinated even if the COVID-19 vaccine was available.
The other main predictor for vaccine hesitancy was concern about vaccine availability and distribution, the researchers said.
“Our study suggests that low education levels are a major contributor to vaccine hesitancy and ultimately vaccination levels,” the authors wrote. The study was published in the American Journal of Infection Control. “Specifically, low vaccination levels were found in communities with a less educated population and with more concern about vaccine uptake capacity, suggesting that education is an ongoing challenge.”
“Our findings suggest that policy makers and community leaders should tailor vaccine information and efforts to those with limited education and specifically address knowledge concerns that are prevalent and likely more modifiable.”
The study was based on data gathered months ago. It says that as of May 9, 2021, 34.7% of the U.S. population was fully vaccinated and that 8% reported a strong unwillingness to get vaccinated.
At press time, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID Data Tracker showed that 62.5% of the U.S. population was fully vaccinated.
According to the study, other consistent characteristics of people who are vaccine hesitant are that they belong to a racial minority, are 65 or older, live in a household with children 18 or younger, or are unemployed.
When asked why they were vaccine hesitant, people gave these reasons: Lack of trust in COVID-19 vaccines (55%), concerns about side effects (48%), and lack of trust in government (46%).
Lack of access to vaccines, often cited in previous studies about resistance to other vaccines, was not cited as a reason for not getting the COVID-19 vaccine.
“COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy is a public health threat,” the researchers concluded. “Since education levels are not easily modifiable, our results suggest that policymakers would be best served by closing knowledge gaps to overcome negative perceptions of the vaccine through tailored interventions.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF INFECTION CONTROL
FDA OKs new adult insomnia med
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual orexin receptor antagonist daridorexant (Quviviq) for the treatment of insomnia in adults, the drug’s manufacturer, Idorsia, has announced.
The FDA’s decision was based partly on a phase 3 trial of adults with moderate to severe insomnia who were randomly assigned to receive 25 or 50 mg of daridorexant or matching placebo. Daridorexant was associated with dose-dependent improvements in wake after sleep onset, total sleep time, and latency to persistent sleep.
Whereas the overall results are very positive, the improvements in daytime functioning are especially “exciting,” Thomas Roth, PhD, director of the Sleep Disorders and Research Center at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, said in an interview.
“That’s sort of a big deal. For me, that’s the biggest deal there is,” said Dr. Roth, who was a consultant on the design of the phase 3 trial and on the interpretation of the data.
The drug will be available in doses of 25 mg and 50 mg, and the FDA has recommended that it be classified as a controlled substance. After it is scheduled by the Drug Enforcement Administration, daridorexant is expected to be made available in May.
Favorable safety profile
Insomnia is a common disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep and by early-morning awakenings. Patients with insomnia often report fatigue, irritability, and difficulty with concentration. The condition can also result in significant problems with work and social activities, thus contributing to anxiety or depression.
As with other dual orexin receptor antagonists, daridorexant competitively binds with both orexin receptors in the lateral hypothalamus to block the activity of orexin in a reversible way. This approach decreases the downstream action of the wake-promoting neurotransmitters that are overactive in patients with insomnia.
The phase 3 trial measured daytime functioning using the new Insomnia Daytime Symptoms and Impacts Questionnaire (IDSIQ), a patient-reported outcome instrument. Daridorexant was associated with significant improvements in daytime function, particularly in sleepiness and mood.
Previous trials of other dual orexin receptor antagonists did not use the IDSIQ as an outcome, so it is not possible to compare daridorexant with those drugs in this respect, Dr. Roth noted. Researchers also have not conducted head-to-head trials of the drug with other dual orexin receptor antagonists.
Daridorexant also had a favorable safety profile and was not associated with rebound insomnia or withdrawal effects. The most common adverse events were headache and somnolence or fatigue.
“They had no effect on sleep stage distribution [and] they had no significant effects on sleep and breathing in people with mild to moderate sleep apnea,” said Dr. Roth, who presented the phase 3 findings at SLEEP 2020.
In addition to serving as a consultant for Idorsia on the trial design and interpretation of results, Dr. Roth has also served as a consultant for other companies that develop sleep agents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual orexin receptor antagonist daridorexant (Quviviq) for the treatment of insomnia in adults, the drug’s manufacturer, Idorsia, has announced.
The FDA’s decision was based partly on a phase 3 trial of adults with moderate to severe insomnia who were randomly assigned to receive 25 or 50 mg of daridorexant or matching placebo. Daridorexant was associated with dose-dependent improvements in wake after sleep onset, total sleep time, and latency to persistent sleep.
Whereas the overall results are very positive, the improvements in daytime functioning are especially “exciting,” Thomas Roth, PhD, director of the Sleep Disorders and Research Center at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, said in an interview.
“That’s sort of a big deal. For me, that’s the biggest deal there is,” said Dr. Roth, who was a consultant on the design of the phase 3 trial and on the interpretation of the data.
The drug will be available in doses of 25 mg and 50 mg, and the FDA has recommended that it be classified as a controlled substance. After it is scheduled by the Drug Enforcement Administration, daridorexant is expected to be made available in May.
Favorable safety profile
Insomnia is a common disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep and by early-morning awakenings. Patients with insomnia often report fatigue, irritability, and difficulty with concentration. The condition can also result in significant problems with work and social activities, thus contributing to anxiety or depression.
As with other dual orexin receptor antagonists, daridorexant competitively binds with both orexin receptors in the lateral hypothalamus to block the activity of orexin in a reversible way. This approach decreases the downstream action of the wake-promoting neurotransmitters that are overactive in patients with insomnia.
The phase 3 trial measured daytime functioning using the new Insomnia Daytime Symptoms and Impacts Questionnaire (IDSIQ), a patient-reported outcome instrument. Daridorexant was associated with significant improvements in daytime function, particularly in sleepiness and mood.
Previous trials of other dual orexin receptor antagonists did not use the IDSIQ as an outcome, so it is not possible to compare daridorexant with those drugs in this respect, Dr. Roth noted. Researchers also have not conducted head-to-head trials of the drug with other dual orexin receptor antagonists.
Daridorexant also had a favorable safety profile and was not associated with rebound insomnia or withdrawal effects. The most common adverse events were headache and somnolence or fatigue.
“They had no effect on sleep stage distribution [and] they had no significant effects on sleep and breathing in people with mild to moderate sleep apnea,” said Dr. Roth, who presented the phase 3 findings at SLEEP 2020.
In addition to serving as a consultant for Idorsia on the trial design and interpretation of results, Dr. Roth has also served as a consultant for other companies that develop sleep agents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual orexin receptor antagonist daridorexant (Quviviq) for the treatment of insomnia in adults, the drug’s manufacturer, Idorsia, has announced.
The FDA’s decision was based partly on a phase 3 trial of adults with moderate to severe insomnia who were randomly assigned to receive 25 or 50 mg of daridorexant or matching placebo. Daridorexant was associated with dose-dependent improvements in wake after sleep onset, total sleep time, and latency to persistent sleep.
Whereas the overall results are very positive, the improvements in daytime functioning are especially “exciting,” Thomas Roth, PhD, director of the Sleep Disorders and Research Center at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, said in an interview.
“That’s sort of a big deal. For me, that’s the biggest deal there is,” said Dr. Roth, who was a consultant on the design of the phase 3 trial and on the interpretation of the data.
The drug will be available in doses of 25 mg and 50 mg, and the FDA has recommended that it be classified as a controlled substance. After it is scheduled by the Drug Enforcement Administration, daridorexant is expected to be made available in May.
Favorable safety profile
Insomnia is a common disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep and by early-morning awakenings. Patients with insomnia often report fatigue, irritability, and difficulty with concentration. The condition can also result in significant problems with work and social activities, thus contributing to anxiety or depression.
As with other dual orexin receptor antagonists, daridorexant competitively binds with both orexin receptors in the lateral hypothalamus to block the activity of orexin in a reversible way. This approach decreases the downstream action of the wake-promoting neurotransmitters that are overactive in patients with insomnia.
The phase 3 trial measured daytime functioning using the new Insomnia Daytime Symptoms and Impacts Questionnaire (IDSIQ), a patient-reported outcome instrument. Daridorexant was associated with significant improvements in daytime function, particularly in sleepiness and mood.
Previous trials of other dual orexin receptor antagonists did not use the IDSIQ as an outcome, so it is not possible to compare daridorexant with those drugs in this respect, Dr. Roth noted. Researchers also have not conducted head-to-head trials of the drug with other dual orexin receptor antagonists.
Daridorexant also had a favorable safety profile and was not associated with rebound insomnia or withdrawal effects. The most common adverse events were headache and somnolence or fatigue.
“They had no effect on sleep stage distribution [and] they had no significant effects on sleep and breathing in people with mild to moderate sleep apnea,” said Dr. Roth, who presented the phase 3 findings at SLEEP 2020.
In addition to serving as a consultant for Idorsia on the trial design and interpretation of results, Dr. Roth has also served as a consultant for other companies that develop sleep agents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 linked to increased diabetes risk in youth
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes among youth, whereas other acute respiratory infections were not, new data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate.
The results from two large U.S. health claims databases were published in an early release in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report by Catherine E. Barrett, PhD, and colleagues of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team and Division of Diabetes Translation.
Clinicians should monitor individuals younger than 18 years in the months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection for new diabetes onset, they advise.
The findings, which are supported by independent studies in adults, “underscore the importance of COVID-19 prevention among all age groups, including vaccination for all eligible children and adolescents, and chronic disease prevention and treatment,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
Diabetes type couldn’t be reliably distinguished from the databases, which is noted as an important study limitation.
“SARS-CoV-2 infection might lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes through complex and differing mechanisms,” they say.
Emerging evidence began to suggest, in mid-2020, that COVID-19 may trigger the onset of diabetes in healthy people. A new global registry was subsequently established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes, called the CoviDiab registry.
Not clear if diabetes after COVID-19 is transient or permanent
From one of the databases used in the new study, known as IQVIA, 80,893 individuals aged younger than 18 years diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 2020 to February 26, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched people during that period who did not have COVID-19 and to prepandemic groups with and without a diagnosis of acute respiratory illness during March 1, 2017, to February 26, 2018.
From the second database, HealthVerity, 439,439 youth diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 1, 2020, to June 28, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched youth without COVID-19. Here, there was no prepandemic comparison group.
Diabetes diagnoses were coded in 0.08% with COVID-19 vs. 0.03% without COVID-19 in IQVIA and in 0.25% vs. 0.19% in HealthVerity.
Thus, new diabetes diagnoses were 166% and 31% more likely to occur in those with COVID-19 in IQVIA and HealthVerity, respectively. And in IQVIA, those with COVID-19 were 116% more likely to develop diabetes than were those with prepandemic acute respiratory illnesses. Those differences were all significant, whereas non–SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections were not associated with diabetes, Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
In both databases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common at diabetes onset among those with, vs. without, COVID-19: 48.5% vs. 13.6% in IQVIA and 40.2% vs. 29.7% in HealthVerity. In IQVIA, 22.0% with prepandemic acute respiratory illness presented with DKA.
Dr. Barrett and colleagues offer several potential explanations for the observed association between COVID-19 and diabetes, including a direct attack on pancreatic beta cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, or via stress hyperglycemia resulting from cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism.
Another possibility is the precipitation to diabetes from prediabetes; the latter is a condition present in one in five U.S. adolescents.
Steroid treatment during hospitalization might have led to transient hyperglycemia, but only 1.5% to 2.2% of diabetes codes were for drug- or chemical-induced diabetes. The majority were for type 1 or 2.
Alternatively, pandemic-associated weight gain might have also contributed to risks for both severe COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes.
“Although this study can provide information on the risk for diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection, additional data are needed to understand underlying pathogenic mechanisms, either those caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection itself or resulting from treatments, and whether a COVID-19–associated diabetes diagnosis is transient or leads to a chronic condition,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes among youth, whereas other acute respiratory infections were not, new data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate.
The results from two large U.S. health claims databases were published in an early release in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report by Catherine E. Barrett, PhD, and colleagues of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team and Division of Diabetes Translation.
Clinicians should monitor individuals younger than 18 years in the months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection for new diabetes onset, they advise.
The findings, which are supported by independent studies in adults, “underscore the importance of COVID-19 prevention among all age groups, including vaccination for all eligible children and adolescents, and chronic disease prevention and treatment,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
Diabetes type couldn’t be reliably distinguished from the databases, which is noted as an important study limitation.
“SARS-CoV-2 infection might lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes through complex and differing mechanisms,” they say.
Emerging evidence began to suggest, in mid-2020, that COVID-19 may trigger the onset of diabetes in healthy people. A new global registry was subsequently established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes, called the CoviDiab registry.
Not clear if diabetes after COVID-19 is transient or permanent
From one of the databases used in the new study, known as IQVIA, 80,893 individuals aged younger than 18 years diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 2020 to February 26, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched people during that period who did not have COVID-19 and to prepandemic groups with and without a diagnosis of acute respiratory illness during March 1, 2017, to February 26, 2018.
From the second database, HealthVerity, 439,439 youth diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 1, 2020, to June 28, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched youth without COVID-19. Here, there was no prepandemic comparison group.
Diabetes diagnoses were coded in 0.08% with COVID-19 vs. 0.03% without COVID-19 in IQVIA and in 0.25% vs. 0.19% in HealthVerity.
Thus, new diabetes diagnoses were 166% and 31% more likely to occur in those with COVID-19 in IQVIA and HealthVerity, respectively. And in IQVIA, those with COVID-19 were 116% more likely to develop diabetes than were those with prepandemic acute respiratory illnesses. Those differences were all significant, whereas non–SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections were not associated with diabetes, Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
In both databases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common at diabetes onset among those with, vs. without, COVID-19: 48.5% vs. 13.6% in IQVIA and 40.2% vs. 29.7% in HealthVerity. In IQVIA, 22.0% with prepandemic acute respiratory illness presented with DKA.
Dr. Barrett and colleagues offer several potential explanations for the observed association between COVID-19 and diabetes, including a direct attack on pancreatic beta cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, or via stress hyperglycemia resulting from cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism.
Another possibility is the precipitation to diabetes from prediabetes; the latter is a condition present in one in five U.S. adolescents.
Steroid treatment during hospitalization might have led to transient hyperglycemia, but only 1.5% to 2.2% of diabetes codes were for drug- or chemical-induced diabetes. The majority were for type 1 or 2.
Alternatively, pandemic-associated weight gain might have also contributed to risks for both severe COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes.
“Although this study can provide information on the risk for diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection, additional data are needed to understand underlying pathogenic mechanisms, either those caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection itself or resulting from treatments, and whether a COVID-19–associated diabetes diagnosis is transient or leads to a chronic condition,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes among youth, whereas other acute respiratory infections were not, new data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate.
The results from two large U.S. health claims databases were published in an early release in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report by Catherine E. Barrett, PhD, and colleagues of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team and Division of Diabetes Translation.
Clinicians should monitor individuals younger than 18 years in the months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection for new diabetes onset, they advise.
The findings, which are supported by independent studies in adults, “underscore the importance of COVID-19 prevention among all age groups, including vaccination for all eligible children and adolescents, and chronic disease prevention and treatment,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
Diabetes type couldn’t be reliably distinguished from the databases, which is noted as an important study limitation.
“SARS-CoV-2 infection might lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes through complex and differing mechanisms,” they say.
Emerging evidence began to suggest, in mid-2020, that COVID-19 may trigger the onset of diabetes in healthy people. A new global registry was subsequently established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes, called the CoviDiab registry.
Not clear if diabetes after COVID-19 is transient or permanent
From one of the databases used in the new study, known as IQVIA, 80,893 individuals aged younger than 18 years diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 2020 to February 26, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched people during that period who did not have COVID-19 and to prepandemic groups with and without a diagnosis of acute respiratory illness during March 1, 2017, to February 26, 2018.
From the second database, HealthVerity, 439,439 youth diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 1, 2020, to June 28, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched youth without COVID-19. Here, there was no prepandemic comparison group.
Diabetes diagnoses were coded in 0.08% with COVID-19 vs. 0.03% without COVID-19 in IQVIA and in 0.25% vs. 0.19% in HealthVerity.
Thus, new diabetes diagnoses were 166% and 31% more likely to occur in those with COVID-19 in IQVIA and HealthVerity, respectively. And in IQVIA, those with COVID-19 were 116% more likely to develop diabetes than were those with prepandemic acute respiratory illnesses. Those differences were all significant, whereas non–SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections were not associated with diabetes, Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
In both databases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common at diabetes onset among those with, vs. without, COVID-19: 48.5% vs. 13.6% in IQVIA and 40.2% vs. 29.7% in HealthVerity. In IQVIA, 22.0% with prepandemic acute respiratory illness presented with DKA.
Dr. Barrett and colleagues offer several potential explanations for the observed association between COVID-19 and diabetes, including a direct attack on pancreatic beta cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, or via stress hyperglycemia resulting from cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism.
Another possibility is the precipitation to diabetes from prediabetes; the latter is a condition present in one in five U.S. adolescents.
Steroid treatment during hospitalization might have led to transient hyperglycemia, but only 1.5% to 2.2% of diabetes codes were for drug- or chemical-induced diabetes. The majority were for type 1 or 2.
Alternatively, pandemic-associated weight gain might have also contributed to risks for both severe COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes.
“Although this study can provide information on the risk for diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection, additional data are needed to understand underlying pathogenic mechanisms, either those caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection itself or resulting from treatments, and whether a COVID-19–associated diabetes diagnosis is transient or leads to a chronic condition,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MMWR
As pandemic regs expire, states get tougher on telehealth: report
Among the most important restrictions that have been reinstated in some states are those barring requirements for insurers to cover telehealth and regulations that prohibit telehealth visits across state lines, unless the physician is licensed in both states.
“Only three states – Arizona, Florida, and Indiana – allow all health care providers to easily practice telehealth across state lines,” says a news release on the think tanks’ report. “Forty-seven others have arbitrary barriers in place that limit patients’ access to specialists and available appointments based purely on residency.”
“Once the [state-based] public health emergency declarations started to end or executive orders were withdrawn, many of the new flexibilities for providers, insurers, and patients were lost overnight,” Vittorio Nastasi, a policy analyst at Reason Foundation and a co-author of the report, says in the news release. “States need to adopt a number of telehealth reforms to provide their residents better access to this safe and effective virtual care.”
On a positive note, the report says, most states have removed the requirement that a patient must first see a provider in person before they can use telehealth services. The exceptions are Tennessee, Alaska, and West Virginia, which require an in-person visit before certain telehealth services can be provided.
In addition, 20 states allow nurse practitioners to conduct telehealth visits without being under the supervision of a physician. Prior to the pandemic, some states allowed only doctors to use telehealth, the report says, but, during the COVID crisis, “the acute shortage of providers in many counties adds to the need for more kinds of providers to be able to use it.”
A number of states place restrictions on the telehealth modalities that can be utilized. Under the definition by the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth includes audio-video visits, remote patient monitoring, and “store and forward” telemedicine, which entails collecting clinical information and sending it to another site for evaluation. The latter method is particularly useful for consultations with specialists, the report notes.
Coverage mandates and payment parity
The report also examines other parameters of telehealth regulations in each state, including whether they have telehealth coverage mandates and whether they require physicians to be paid the same amount for similar types of in-person and telehealth visits.
The report views insurance mandates as beneficial, but not if they require coverage of all virtual services. While telehealth can be a game changer for post-stroke care and for other “treatment-intensive conditions,” the report says, the evidence of better outcomes for other conditions treated through telehealth is far less certain. Therefore, it advises states to “protect flexibility so that new innovative models can emerge.”
Ateev Mehrotra, MD, a professor at Harvard Medical School who studies telehealth, agrees that it offers more value in some clinical situations than in others. “High value is improving quality or outcomes at a reasonable cost,” he told this news organization. “If a telemedicine visit for stroke can save a person’s life and prevent disability, let’s pay for it. A telemedicine visit for a cold may not be necessary. Mom’s chicken soup is fine.”
A little over half of the states still require payment parity, according to the report. While these regulations are intended to promote the use of telehealth, the authors note, they can increase the growth of health care costs. Moreover, they argue, it’s hard to defend equal payments for virtual visits when the overhead required to deliver them – such as office rental, utility, and labor costs – is much lower than that for in-person visits. Also, it makes no sense for health systems to charge facility fees for telehealth visits when these visits can be initiated from anywhere, they say.
Dr. Mehrotra concurs with this view. “If you see someone in your office, your fee includes all the overhead for your office, and it’s a substantial cost,” he says. “For many procedures, it’s more than half of the cost. If you have a telemedicine visit and you’re at home, why would you pay the same amount? The visit may take the same amount of time, but all the money that goes for overhead is not accounted for.”
Telemedicine across state lines
The report’s contention about the difficulty of conducting telehealth encounters across most state lines seems to be at odds with the growth in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for physicians in one compact member state to get licensed in others. Currently, 35 states belong to the compact, Joe Knickrehm, vice president of communications for the Federation of State Medical Boards, told this news organization.
In addition, he says, “12 state boards issue a special purpose license, telemedicine license or certificate, or license to practice medicine across state lines to allow for the practice of telemedicine.”
The catch, Dr. Mehrotra says, is that, despite the streamlining of license applications in compact member states, the fees charged by the state boards are still very high – a point that the report also makes. “If I want to have broad scope of practice, I’d have to pay thousands of dollars to many states. The license fees start to add up. Also, I have to keep track of each state’s CME requirements, which are all different. Keeping up with all of that is an administration burden, and it’s a pain.”
Mr. Knickrehm contends that obtaining multiple licenses via the compact “is generally less expensive for physicians than the cost of requesting transcripts, fingerprints, and other necessary paperwork each time they apply for licensure in a new state. Physicians are seeing the benefits of an expedited process that allows them to begin practicing more quickly [in other states].”
Dr. Mehrotra says he has seen the same retrenchment in state telehealth regulations that the report references. However, he says, “CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] has signaled that at least through 2022 and maybe into 2023, they’ll continue their extensions of telemedicine [pandemic regulations].” After that, Congress would have to decide whether to make the changes permanent.
“Right now, it’s hard for me to see how a payer is going to pull back on telehealth, unless there’s ample evidence of overuse of telehealth,” he argues. “With the public and providers liking telehealth, it’s hard to say on theoretical grounds that we should stop using it. That’s why Medicare and others have extended it and why Congress will too.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the most important restrictions that have been reinstated in some states are those barring requirements for insurers to cover telehealth and regulations that prohibit telehealth visits across state lines, unless the physician is licensed in both states.
“Only three states – Arizona, Florida, and Indiana – allow all health care providers to easily practice telehealth across state lines,” says a news release on the think tanks’ report. “Forty-seven others have arbitrary barriers in place that limit patients’ access to specialists and available appointments based purely on residency.”
“Once the [state-based] public health emergency declarations started to end or executive orders were withdrawn, many of the new flexibilities for providers, insurers, and patients were lost overnight,” Vittorio Nastasi, a policy analyst at Reason Foundation and a co-author of the report, says in the news release. “States need to adopt a number of telehealth reforms to provide their residents better access to this safe and effective virtual care.”
On a positive note, the report says, most states have removed the requirement that a patient must first see a provider in person before they can use telehealth services. The exceptions are Tennessee, Alaska, and West Virginia, which require an in-person visit before certain telehealth services can be provided.
In addition, 20 states allow nurse practitioners to conduct telehealth visits without being under the supervision of a physician. Prior to the pandemic, some states allowed only doctors to use telehealth, the report says, but, during the COVID crisis, “the acute shortage of providers in many counties adds to the need for more kinds of providers to be able to use it.”
A number of states place restrictions on the telehealth modalities that can be utilized. Under the definition by the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth includes audio-video visits, remote patient monitoring, and “store and forward” telemedicine, which entails collecting clinical information and sending it to another site for evaluation. The latter method is particularly useful for consultations with specialists, the report notes.
Coverage mandates and payment parity
The report also examines other parameters of telehealth regulations in each state, including whether they have telehealth coverage mandates and whether they require physicians to be paid the same amount for similar types of in-person and telehealth visits.
The report views insurance mandates as beneficial, but not if they require coverage of all virtual services. While telehealth can be a game changer for post-stroke care and for other “treatment-intensive conditions,” the report says, the evidence of better outcomes for other conditions treated through telehealth is far less certain. Therefore, it advises states to “protect flexibility so that new innovative models can emerge.”
Ateev Mehrotra, MD, a professor at Harvard Medical School who studies telehealth, agrees that it offers more value in some clinical situations than in others. “High value is improving quality or outcomes at a reasonable cost,” he told this news organization. “If a telemedicine visit for stroke can save a person’s life and prevent disability, let’s pay for it. A telemedicine visit for a cold may not be necessary. Mom’s chicken soup is fine.”
A little over half of the states still require payment parity, according to the report. While these regulations are intended to promote the use of telehealth, the authors note, they can increase the growth of health care costs. Moreover, they argue, it’s hard to defend equal payments for virtual visits when the overhead required to deliver them – such as office rental, utility, and labor costs – is much lower than that for in-person visits. Also, it makes no sense for health systems to charge facility fees for telehealth visits when these visits can be initiated from anywhere, they say.
Dr. Mehrotra concurs with this view. “If you see someone in your office, your fee includes all the overhead for your office, and it’s a substantial cost,” he says. “For many procedures, it’s more than half of the cost. If you have a telemedicine visit and you’re at home, why would you pay the same amount? The visit may take the same amount of time, but all the money that goes for overhead is not accounted for.”
Telemedicine across state lines
The report’s contention about the difficulty of conducting telehealth encounters across most state lines seems to be at odds with the growth in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for physicians in one compact member state to get licensed in others. Currently, 35 states belong to the compact, Joe Knickrehm, vice president of communications for the Federation of State Medical Boards, told this news organization.
In addition, he says, “12 state boards issue a special purpose license, telemedicine license or certificate, or license to practice medicine across state lines to allow for the practice of telemedicine.”
The catch, Dr. Mehrotra says, is that, despite the streamlining of license applications in compact member states, the fees charged by the state boards are still very high – a point that the report also makes. “If I want to have broad scope of practice, I’d have to pay thousands of dollars to many states. The license fees start to add up. Also, I have to keep track of each state’s CME requirements, which are all different. Keeping up with all of that is an administration burden, and it’s a pain.”
Mr. Knickrehm contends that obtaining multiple licenses via the compact “is generally less expensive for physicians than the cost of requesting transcripts, fingerprints, and other necessary paperwork each time they apply for licensure in a new state. Physicians are seeing the benefits of an expedited process that allows them to begin practicing more quickly [in other states].”
Dr. Mehrotra says he has seen the same retrenchment in state telehealth regulations that the report references. However, he says, “CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] has signaled that at least through 2022 and maybe into 2023, they’ll continue their extensions of telemedicine [pandemic regulations].” After that, Congress would have to decide whether to make the changes permanent.
“Right now, it’s hard for me to see how a payer is going to pull back on telehealth, unless there’s ample evidence of overuse of telehealth,” he argues. “With the public and providers liking telehealth, it’s hard to say on theoretical grounds that we should stop using it. That’s why Medicare and others have extended it and why Congress will too.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the most important restrictions that have been reinstated in some states are those barring requirements for insurers to cover telehealth and regulations that prohibit telehealth visits across state lines, unless the physician is licensed in both states.
“Only three states – Arizona, Florida, and Indiana – allow all health care providers to easily practice telehealth across state lines,” says a news release on the think tanks’ report. “Forty-seven others have arbitrary barriers in place that limit patients’ access to specialists and available appointments based purely on residency.”
“Once the [state-based] public health emergency declarations started to end or executive orders were withdrawn, many of the new flexibilities for providers, insurers, and patients were lost overnight,” Vittorio Nastasi, a policy analyst at Reason Foundation and a co-author of the report, says in the news release. “States need to adopt a number of telehealth reforms to provide their residents better access to this safe and effective virtual care.”
On a positive note, the report says, most states have removed the requirement that a patient must first see a provider in person before they can use telehealth services. The exceptions are Tennessee, Alaska, and West Virginia, which require an in-person visit before certain telehealth services can be provided.
In addition, 20 states allow nurse practitioners to conduct telehealth visits without being under the supervision of a physician. Prior to the pandemic, some states allowed only doctors to use telehealth, the report says, but, during the COVID crisis, “the acute shortage of providers in many counties adds to the need for more kinds of providers to be able to use it.”
A number of states place restrictions on the telehealth modalities that can be utilized. Under the definition by the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth includes audio-video visits, remote patient monitoring, and “store and forward” telemedicine, which entails collecting clinical information and sending it to another site for evaluation. The latter method is particularly useful for consultations with specialists, the report notes.
Coverage mandates and payment parity
The report also examines other parameters of telehealth regulations in each state, including whether they have telehealth coverage mandates and whether they require physicians to be paid the same amount for similar types of in-person and telehealth visits.
The report views insurance mandates as beneficial, but not if they require coverage of all virtual services. While telehealth can be a game changer for post-stroke care and for other “treatment-intensive conditions,” the report says, the evidence of better outcomes for other conditions treated through telehealth is far less certain. Therefore, it advises states to “protect flexibility so that new innovative models can emerge.”
Ateev Mehrotra, MD, a professor at Harvard Medical School who studies telehealth, agrees that it offers more value in some clinical situations than in others. “High value is improving quality or outcomes at a reasonable cost,” he told this news organization. “If a telemedicine visit for stroke can save a person’s life and prevent disability, let’s pay for it. A telemedicine visit for a cold may not be necessary. Mom’s chicken soup is fine.”
A little over half of the states still require payment parity, according to the report. While these regulations are intended to promote the use of telehealth, the authors note, they can increase the growth of health care costs. Moreover, they argue, it’s hard to defend equal payments for virtual visits when the overhead required to deliver them – such as office rental, utility, and labor costs – is much lower than that for in-person visits. Also, it makes no sense for health systems to charge facility fees for telehealth visits when these visits can be initiated from anywhere, they say.
Dr. Mehrotra concurs with this view. “If you see someone in your office, your fee includes all the overhead for your office, and it’s a substantial cost,” he says. “For many procedures, it’s more than half of the cost. If you have a telemedicine visit and you’re at home, why would you pay the same amount? The visit may take the same amount of time, but all the money that goes for overhead is not accounted for.”
Telemedicine across state lines
The report’s contention about the difficulty of conducting telehealth encounters across most state lines seems to be at odds with the growth in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for physicians in one compact member state to get licensed in others. Currently, 35 states belong to the compact, Joe Knickrehm, vice president of communications for the Federation of State Medical Boards, told this news organization.
In addition, he says, “12 state boards issue a special purpose license, telemedicine license or certificate, or license to practice medicine across state lines to allow for the practice of telemedicine.”
The catch, Dr. Mehrotra says, is that, despite the streamlining of license applications in compact member states, the fees charged by the state boards are still very high – a point that the report also makes. “If I want to have broad scope of practice, I’d have to pay thousands of dollars to many states. The license fees start to add up. Also, I have to keep track of each state’s CME requirements, which are all different. Keeping up with all of that is an administration burden, and it’s a pain.”
Mr. Knickrehm contends that obtaining multiple licenses via the compact “is generally less expensive for physicians than the cost of requesting transcripts, fingerprints, and other necessary paperwork each time they apply for licensure in a new state. Physicians are seeing the benefits of an expedited process that allows them to begin practicing more quickly [in other states].”
Dr. Mehrotra says he has seen the same retrenchment in state telehealth regulations that the report references. However, he says, “CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] has signaled that at least through 2022 and maybe into 2023, they’ll continue their extensions of telemedicine [pandemic regulations].” After that, Congress would have to decide whether to make the changes permanent.
“Right now, it’s hard for me to see how a payer is going to pull back on telehealth, unless there’s ample evidence of overuse of telehealth,” he argues. “With the public and providers liking telehealth, it’s hard to say on theoretical grounds that we should stop using it. That’s why Medicare and others have extended it and why Congress will too.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.