User login
Early time-restricted eating ups weight loss, but jury still out
, new findings suggest.
Previous studies have produced mixed results regarding the weight-loss potential for intermittent fasting, the practice of alternating eating with extended fasting, and the “time-restricted eating” format, where eating is restricted to a specific, often 10-hour, time window during the day.
In a new randomized clinical trial of 90 people with obesity in which that time window was 7 AM through 3 PM, so 8 hours long, researchers report that “eTRE was more effective for losing weight and lowering diastolic blood pressure than was eating over a period of 12 or more hours at 14 weeks. The eTRE intervention may therefore be an effective treatment for both obesity and hypertension.” The study, by Humaira Jamshed, PhD, of the department of nutrition sciences, University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues, was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Shalender Bhasin, MBBS, points out that the study findings differ from those of a previous trial published in April of 139 adults conducted in China, which did not find a significant weight loss benefit with TRE versus ad lib eating.
“The scientific premise and the preclinical data of the effects of TRE are promising, but the inconsistency among studies renders it difficult to draw strong inferences from these well-conducted but relatively small trials,” notes Dr. Bhasin, of Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Need for larger and longer trials of TRE
Dr. Bhasin says – and the study authors also acknowledge – that much larger randomized clinical trials of longer duration are needed “to comprehensively evaluate the hypothesized benefits and risks of long-term TRE of calorically restricted diets in adults.”
Commenting on the study for the U.K. Science Media Centre, Simon Steenson, PhD, nutrition scientist, British Nutrition Foundation, said “one of the strengths of this new study is the trial design and the number of people who were recruited compared to many of the previous trials to date.”
However, Dr. Steenson also pointed to the prior Chinese research as evidence that the inconsistencies across studies highlight the need for larger and longer trials, with cardiovascular as well as weight-loss endpoints.
Still, Dr. Steenson said, “For individuals who may find that this pattern of eating fits better with their lifestyle and preferences, time-restricted feeding is one option for reducing overall calorie intake that might be a suitable approach for some. Ultimately, it is about finding the best approach to moderate calorie intake that works for each person, as successful and sustained weight loss is about ensuring the diet is feasible to follow in the long-term.”
Differences in weight loss, diastolic BP, but not all measures
The study population included 90 adults seen at the Weight Loss Medicine clinic at the University of Alabama at Birmingham between August 2018 and December 2019. Participants had a body mass index of 30-60 kg/m2, and none had diabetes.
They were randomized to eTRE with the 7 AM to PM eating window or a control schedule with eating across 12 hours or more, mimicking U.S. median mealtimes, at least 6 days a week. All participants received 30-minute weight-loss counseling sessions at baseline and at weeks 2, 6, and 10 and were advised to follow a diet of 500 kcal/day below their resting energy expenditure and exercise 75-150 minutes per week.
The eTRE group adhered with their schedule a mean of 6 days per week, lower than the 6.3 days among controls (P = .03), and adherence declined by about 0.4 days per week in the eTRE group over the 14 weeks (P = .001).
At 14 weeks, both the eTRE group and controls had lost clinically meaningful amounts of weight, at –6.3 kg and –4.0 kg, respectively, but the –2.3 kg difference was significant (P = .002).
However, there was no difference in absolute fat loss (P = .09) or ratio of fat loss to weight loss (P = .43). There were also no significant differences in changes in other body composition parameters, including visceral fat and waist circumference.
Diastolic blood pressure was lowered by an additional 4 mmHg in the eTRE group, compared with controls at 14 weeks (P = .04), but there were no significant differences in systolic blood pressure, heart rate, glucose, A1c levels, insulin levels, measures of insulin resistance, or plasma lipids.
There were no differences between the two groups in self-reported physical activity, energy intake, or dietary macronutrient composition either. However, weight-loss modeling in 77 participants with at least two weight measurements indicated that the eTRE group reduced their intake by about 214 kcal/day, compared with controls (P = .04).
Those in the eTRE group also showed greater improvements in measures of mood disturbance, vigor-activity, fatigue-inertia, and depression-dejection. Other mood and sleep endpoints were similar between groups.
In a secondary analysis of just the 59 participants who completed the study, eTRE was also more effective at reducing body fat (P = .047) and trunk fat (P = .03).
About 41% of the eTRE completers planned to continue the practice after the study concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Jamshed has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bhasin has reported receiving grants to his institution for research on which Dr. Bhasin is the principal investigator from AbbVie and MIB, receiving personal fees from OPKO and Aditum and holding equity interest in FPT and XYOne. Dr. Steenson has declared funding in support of the British Nutrition Foundation that comes from a range of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new findings suggest.
Previous studies have produced mixed results regarding the weight-loss potential for intermittent fasting, the practice of alternating eating with extended fasting, and the “time-restricted eating” format, where eating is restricted to a specific, often 10-hour, time window during the day.
In a new randomized clinical trial of 90 people with obesity in which that time window was 7 AM through 3 PM, so 8 hours long, researchers report that “eTRE was more effective for losing weight and lowering diastolic blood pressure than was eating over a period of 12 or more hours at 14 weeks. The eTRE intervention may therefore be an effective treatment for both obesity and hypertension.” The study, by Humaira Jamshed, PhD, of the department of nutrition sciences, University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues, was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Shalender Bhasin, MBBS, points out that the study findings differ from those of a previous trial published in April of 139 adults conducted in China, which did not find a significant weight loss benefit with TRE versus ad lib eating.
“The scientific premise and the preclinical data of the effects of TRE are promising, but the inconsistency among studies renders it difficult to draw strong inferences from these well-conducted but relatively small trials,” notes Dr. Bhasin, of Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Need for larger and longer trials of TRE
Dr. Bhasin says – and the study authors also acknowledge – that much larger randomized clinical trials of longer duration are needed “to comprehensively evaluate the hypothesized benefits and risks of long-term TRE of calorically restricted diets in adults.”
Commenting on the study for the U.K. Science Media Centre, Simon Steenson, PhD, nutrition scientist, British Nutrition Foundation, said “one of the strengths of this new study is the trial design and the number of people who were recruited compared to many of the previous trials to date.”
However, Dr. Steenson also pointed to the prior Chinese research as evidence that the inconsistencies across studies highlight the need for larger and longer trials, with cardiovascular as well as weight-loss endpoints.
Still, Dr. Steenson said, “For individuals who may find that this pattern of eating fits better with their lifestyle and preferences, time-restricted feeding is one option for reducing overall calorie intake that might be a suitable approach for some. Ultimately, it is about finding the best approach to moderate calorie intake that works for each person, as successful and sustained weight loss is about ensuring the diet is feasible to follow in the long-term.”
Differences in weight loss, diastolic BP, but not all measures
The study population included 90 adults seen at the Weight Loss Medicine clinic at the University of Alabama at Birmingham between August 2018 and December 2019. Participants had a body mass index of 30-60 kg/m2, and none had diabetes.
They were randomized to eTRE with the 7 AM to PM eating window or a control schedule with eating across 12 hours or more, mimicking U.S. median mealtimes, at least 6 days a week. All participants received 30-minute weight-loss counseling sessions at baseline and at weeks 2, 6, and 10 and were advised to follow a diet of 500 kcal/day below their resting energy expenditure and exercise 75-150 minutes per week.
The eTRE group adhered with their schedule a mean of 6 days per week, lower than the 6.3 days among controls (P = .03), and adherence declined by about 0.4 days per week in the eTRE group over the 14 weeks (P = .001).
At 14 weeks, both the eTRE group and controls had lost clinically meaningful amounts of weight, at –6.3 kg and –4.0 kg, respectively, but the –2.3 kg difference was significant (P = .002).
However, there was no difference in absolute fat loss (P = .09) or ratio of fat loss to weight loss (P = .43). There were also no significant differences in changes in other body composition parameters, including visceral fat and waist circumference.
Diastolic blood pressure was lowered by an additional 4 mmHg in the eTRE group, compared with controls at 14 weeks (P = .04), but there were no significant differences in systolic blood pressure, heart rate, glucose, A1c levels, insulin levels, measures of insulin resistance, or plasma lipids.
There were no differences between the two groups in self-reported physical activity, energy intake, or dietary macronutrient composition either. However, weight-loss modeling in 77 participants with at least two weight measurements indicated that the eTRE group reduced their intake by about 214 kcal/day, compared with controls (P = .04).
Those in the eTRE group also showed greater improvements in measures of mood disturbance, vigor-activity, fatigue-inertia, and depression-dejection. Other mood and sleep endpoints were similar between groups.
In a secondary analysis of just the 59 participants who completed the study, eTRE was also more effective at reducing body fat (P = .047) and trunk fat (P = .03).
About 41% of the eTRE completers planned to continue the practice after the study concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Jamshed has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bhasin has reported receiving grants to his institution for research on which Dr. Bhasin is the principal investigator from AbbVie and MIB, receiving personal fees from OPKO and Aditum and holding equity interest in FPT and XYOne. Dr. Steenson has declared funding in support of the British Nutrition Foundation that comes from a range of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new findings suggest.
Previous studies have produced mixed results regarding the weight-loss potential for intermittent fasting, the practice of alternating eating with extended fasting, and the “time-restricted eating” format, where eating is restricted to a specific, often 10-hour, time window during the day.
In a new randomized clinical trial of 90 people with obesity in which that time window was 7 AM through 3 PM, so 8 hours long, researchers report that “eTRE was more effective for losing weight and lowering diastolic blood pressure than was eating over a period of 12 or more hours at 14 weeks. The eTRE intervention may therefore be an effective treatment for both obesity and hypertension.” The study, by Humaira Jamshed, PhD, of the department of nutrition sciences, University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues, was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Shalender Bhasin, MBBS, points out that the study findings differ from those of a previous trial published in April of 139 adults conducted in China, which did not find a significant weight loss benefit with TRE versus ad lib eating.
“The scientific premise and the preclinical data of the effects of TRE are promising, but the inconsistency among studies renders it difficult to draw strong inferences from these well-conducted but relatively small trials,” notes Dr. Bhasin, of Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Need for larger and longer trials of TRE
Dr. Bhasin says – and the study authors also acknowledge – that much larger randomized clinical trials of longer duration are needed “to comprehensively evaluate the hypothesized benefits and risks of long-term TRE of calorically restricted diets in adults.”
Commenting on the study for the U.K. Science Media Centre, Simon Steenson, PhD, nutrition scientist, British Nutrition Foundation, said “one of the strengths of this new study is the trial design and the number of people who were recruited compared to many of the previous trials to date.”
However, Dr. Steenson also pointed to the prior Chinese research as evidence that the inconsistencies across studies highlight the need for larger and longer trials, with cardiovascular as well as weight-loss endpoints.
Still, Dr. Steenson said, “For individuals who may find that this pattern of eating fits better with their lifestyle and preferences, time-restricted feeding is one option for reducing overall calorie intake that might be a suitable approach for some. Ultimately, it is about finding the best approach to moderate calorie intake that works for each person, as successful and sustained weight loss is about ensuring the diet is feasible to follow in the long-term.”
Differences in weight loss, diastolic BP, but not all measures
The study population included 90 adults seen at the Weight Loss Medicine clinic at the University of Alabama at Birmingham between August 2018 and December 2019. Participants had a body mass index of 30-60 kg/m2, and none had diabetes.
They were randomized to eTRE with the 7 AM to PM eating window or a control schedule with eating across 12 hours or more, mimicking U.S. median mealtimes, at least 6 days a week. All participants received 30-minute weight-loss counseling sessions at baseline and at weeks 2, 6, and 10 and were advised to follow a diet of 500 kcal/day below their resting energy expenditure and exercise 75-150 minutes per week.
The eTRE group adhered with their schedule a mean of 6 days per week, lower than the 6.3 days among controls (P = .03), and adherence declined by about 0.4 days per week in the eTRE group over the 14 weeks (P = .001).
At 14 weeks, both the eTRE group and controls had lost clinically meaningful amounts of weight, at –6.3 kg and –4.0 kg, respectively, but the –2.3 kg difference was significant (P = .002).
However, there was no difference in absolute fat loss (P = .09) or ratio of fat loss to weight loss (P = .43). There were also no significant differences in changes in other body composition parameters, including visceral fat and waist circumference.
Diastolic blood pressure was lowered by an additional 4 mmHg in the eTRE group, compared with controls at 14 weeks (P = .04), but there were no significant differences in systolic blood pressure, heart rate, glucose, A1c levels, insulin levels, measures of insulin resistance, or plasma lipids.
There were no differences between the two groups in self-reported physical activity, energy intake, or dietary macronutrient composition either. However, weight-loss modeling in 77 participants with at least two weight measurements indicated that the eTRE group reduced their intake by about 214 kcal/day, compared with controls (P = .04).
Those in the eTRE group also showed greater improvements in measures of mood disturbance, vigor-activity, fatigue-inertia, and depression-dejection. Other mood and sleep endpoints were similar between groups.
In a secondary analysis of just the 59 participants who completed the study, eTRE was also more effective at reducing body fat (P = .047) and trunk fat (P = .03).
About 41% of the eTRE completers planned to continue the practice after the study concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Jamshed has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bhasin has reported receiving grants to his institution for research on which Dr. Bhasin is the principal investigator from AbbVie and MIB, receiving personal fees from OPKO and Aditum and holding equity interest in FPT and XYOne. Dr. Steenson has declared funding in support of the British Nutrition Foundation that comes from a range of sources.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Audit Proof Your Mohs Note
In October 2020, Medicare released an updated guidance to reduce Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) reimbursement issues,1 which initially was released in 2013. This guidance defines the latest performance and documentation requirements that Medicare requires for MMS. Understanding these requirements and making sure that your Mohs surgical reports have all the needed documentation details are critical because auditors from not only Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) but also private insurers and Medicare Advantage plans have adopted these standards and will deny payment for Mohs surgical codes if they are not met. This article provides a review of the updated Medicare requirements to make sure your MMS procedure notes are audit proof.
Notes Must Indicate Mohs Is the Most Appropriate Treatment
I review many of my colleagues’ Mohs notes and can tell you that some of the requirements laid out in the updated guidance typically are already reported by Mohs surgeons in their notes, including the location, number, and size of the lesion or lesions treated and the number of stages performed. However, there are some new requirements that often are not reported by Mohs surgeons that now need to be included. The guidance indicates the following:
The majority of skin cancers can be managed by simple excision or destruction techniques. The medical record of a patient undergoing MMS should clearly show that this procedure was chosen because of the complexity (eg, poorly defined clinical borders, possible deep invasion, prior irradiation), size or location (eg, maximum conservation of tumor-free tissue is important). Medicare will consider reimbursement for MMS for accepted diagnoses and indications, which you must document in the patient’s medical record as being appropriate for MMS and that MMS is the most appropriate choice for the treatment of a particular lesion.1
In my experience, most Mohs notes include some statement that the skin cancer treated is appropriate based on the Mohs appropriate use criteria (AUC) or the AUC score. However, notes should make clear not just that the lesion treated is “appropriate” for MMS but also that it is the most appropriate treatment (eg, why the lesion was not managed by standard excision or destruction technique).
Mohs Surgeon Must Perform the Surgery and Interpret Slides
The updated guidance clearly indicates that MMS may only be performed by a physician who is specifically trained and highly skilled in Mohs techniques and pathologic identification: “Medicare will only reimburse for MMS services when the Mohs surgeon acts as both surgeon and pathologist.”1 Mohs micrographic surgery codes may not be billed if preparation or interpretation of the pathology slides is performed by a physician other than the Mohs surgeon. Operative notes and pathology documentation in the patient’s medical record should clearly show that MMS was performed using an accepted MMS technique in which the physician acts in 2 integrated and distinct capacities—surgeon and pathologist—thereby confirming that the procedure meets the definition of the Current Procedural Terminology code(s).
Furthermore, the Mohs operative report should detail “the number of specimens per stage.”1 I interpret this statement to indicate that the Mohs surgeon should document the number of tissue blocks examined in each stage of Mohs surgery. For example, a statement in the notes such as “the specimen from the first Mohs stage was oriented, mapped, and divided into 4 blocks” should suffice to meet this requirement.
Histologic Description Must Be Included in Mohs Notes
Medicare will require the Mohs surgeon to document “the histology of the specimens taken. That description should include depth of invasion, pathological pattern, cell morphology, and, if present, perineural invasion or presence of scar tissue.”1 Although this histologic description requirement appears daunting, it is common for Mohs surgeons to indicate their pathologic findings on their Mohs map such as “NBCC” next to a red area to indicate “nodular basal cell carcinoma visualized.” A template-based system to translate typical pathologic findings can be employed to rapidly and accurately populate a Mohs note with histologic description such as “NBBC=nodular aggregates of palisaded basaloid epithelial tumor arising from the epidermis forming a palisade with a cleft forming from the adjacent mucinous stroma extending to the mid dermis. Centrally the nuclei become crowded with scattered mitotic figures and necrotic bodies evident.”
Recent Improvement for 1-Stage Mohs Surgeries
The most notable improvement in the
Final Thoughts
Overall, the updated Medicare guidance provides important details in the requirements for performance and documentation of Mohs surgery cases. However, additional critical information will be found in Mohs coverage policies and local coverage determinations (LCDs) from MACs and private insurers.2-4 Each LCD and insurer Mohs payment policy has unique wording and requirements. Coverage of MMS for specific malignant diagnoses, histologic subtypes, locations, and clinical scenarios varies between LCDs; most are based directly on the Mohs AUC, while others have a less specific coverage criteria. To understand the specific documentation and coverage requirements of the MAC for a particular region or private insurer, Mohs surgeons are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the Mohs surgery LCD of their local MAC and coverage policies of their insurers and to ensure their documentation substantiates these requirements. Making sure that your MMS documentation is accurate and complies with Medicare and insurer requirements will keep you out of hot water with auditors and allow reimbursement for this critical skin cancer procedure.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance to reduce Mohs surgery reimbursement issues. MLN Matters. Published October 27, 2020. Accessed July 18, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNMattersArticles/Downloads/SE1318.pdf
- Mohs micrographic surgery policy, professional. United Healthcare website. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.uhcprovider.com/content/dam/provider/docs/public/policies/comm-reimbursement/COMM-Mohs-Micrographic-Surgery-Policy.pdf#:~:text=This%20policy%20describes%20reimbursement%20guidelines%20for%20reporting%20Mohs,CCI%20Editing%20Policy%20and%20the%20Laboratory%20Services%20Policy.
- Clinical UM guideline—Mohs micrographic surgery. Anthem Insurance Companies website. Published October 6, 2021. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.anthem.com/dam/medpolicies/abcbs/active/guidelines/gl_pw_d085074.html
- Local coverage determinations. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Updated July 12, 2022. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Coverage/DeterminationProcess/LCDs
In October 2020, Medicare released an updated guidance to reduce Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) reimbursement issues,1 which initially was released in 2013. This guidance defines the latest performance and documentation requirements that Medicare requires for MMS. Understanding these requirements and making sure that your Mohs surgical reports have all the needed documentation details are critical because auditors from not only Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) but also private insurers and Medicare Advantage plans have adopted these standards and will deny payment for Mohs surgical codes if they are not met. This article provides a review of the updated Medicare requirements to make sure your MMS procedure notes are audit proof.
Notes Must Indicate Mohs Is the Most Appropriate Treatment
I review many of my colleagues’ Mohs notes and can tell you that some of the requirements laid out in the updated guidance typically are already reported by Mohs surgeons in their notes, including the location, number, and size of the lesion or lesions treated and the number of stages performed. However, there are some new requirements that often are not reported by Mohs surgeons that now need to be included. The guidance indicates the following:
The majority of skin cancers can be managed by simple excision or destruction techniques. The medical record of a patient undergoing MMS should clearly show that this procedure was chosen because of the complexity (eg, poorly defined clinical borders, possible deep invasion, prior irradiation), size or location (eg, maximum conservation of tumor-free tissue is important). Medicare will consider reimbursement for MMS for accepted diagnoses and indications, which you must document in the patient’s medical record as being appropriate for MMS and that MMS is the most appropriate choice for the treatment of a particular lesion.1
In my experience, most Mohs notes include some statement that the skin cancer treated is appropriate based on the Mohs appropriate use criteria (AUC) or the AUC score. However, notes should make clear not just that the lesion treated is “appropriate” for MMS but also that it is the most appropriate treatment (eg, why the lesion was not managed by standard excision or destruction technique).
Mohs Surgeon Must Perform the Surgery and Interpret Slides
The updated guidance clearly indicates that MMS may only be performed by a physician who is specifically trained and highly skilled in Mohs techniques and pathologic identification: “Medicare will only reimburse for MMS services when the Mohs surgeon acts as both surgeon and pathologist.”1 Mohs micrographic surgery codes may not be billed if preparation or interpretation of the pathology slides is performed by a physician other than the Mohs surgeon. Operative notes and pathology documentation in the patient’s medical record should clearly show that MMS was performed using an accepted MMS technique in which the physician acts in 2 integrated and distinct capacities—surgeon and pathologist—thereby confirming that the procedure meets the definition of the Current Procedural Terminology code(s).
Furthermore, the Mohs operative report should detail “the number of specimens per stage.”1 I interpret this statement to indicate that the Mohs surgeon should document the number of tissue blocks examined in each stage of Mohs surgery. For example, a statement in the notes such as “the specimen from the first Mohs stage was oriented, mapped, and divided into 4 blocks” should suffice to meet this requirement.
Histologic Description Must Be Included in Mohs Notes
Medicare will require the Mohs surgeon to document “the histology of the specimens taken. That description should include depth of invasion, pathological pattern, cell morphology, and, if present, perineural invasion or presence of scar tissue.”1 Although this histologic description requirement appears daunting, it is common for Mohs surgeons to indicate their pathologic findings on their Mohs map such as “NBCC” next to a red area to indicate “nodular basal cell carcinoma visualized.” A template-based system to translate typical pathologic findings can be employed to rapidly and accurately populate a Mohs note with histologic description such as “NBBC=nodular aggregates of palisaded basaloid epithelial tumor arising from the epidermis forming a palisade with a cleft forming from the adjacent mucinous stroma extending to the mid dermis. Centrally the nuclei become crowded with scattered mitotic figures and necrotic bodies evident.”
Recent Improvement for 1-Stage Mohs Surgeries
The most notable improvement in the
Final Thoughts
Overall, the updated Medicare guidance provides important details in the requirements for performance and documentation of Mohs surgery cases. However, additional critical information will be found in Mohs coverage policies and local coverage determinations (LCDs) from MACs and private insurers.2-4 Each LCD and insurer Mohs payment policy has unique wording and requirements. Coverage of MMS for specific malignant diagnoses, histologic subtypes, locations, and clinical scenarios varies between LCDs; most are based directly on the Mohs AUC, while others have a less specific coverage criteria. To understand the specific documentation and coverage requirements of the MAC for a particular region or private insurer, Mohs surgeons are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the Mohs surgery LCD of their local MAC and coverage policies of their insurers and to ensure their documentation substantiates these requirements. Making sure that your MMS documentation is accurate and complies with Medicare and insurer requirements will keep you out of hot water with auditors and allow reimbursement for this critical skin cancer procedure.
In October 2020, Medicare released an updated guidance to reduce Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) reimbursement issues,1 which initially was released in 2013. This guidance defines the latest performance and documentation requirements that Medicare requires for MMS. Understanding these requirements and making sure that your Mohs surgical reports have all the needed documentation details are critical because auditors from not only Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) but also private insurers and Medicare Advantage plans have adopted these standards and will deny payment for Mohs surgical codes if they are not met. This article provides a review of the updated Medicare requirements to make sure your MMS procedure notes are audit proof.
Notes Must Indicate Mohs Is the Most Appropriate Treatment
I review many of my colleagues’ Mohs notes and can tell you that some of the requirements laid out in the updated guidance typically are already reported by Mohs surgeons in their notes, including the location, number, and size of the lesion or lesions treated and the number of stages performed. However, there are some new requirements that often are not reported by Mohs surgeons that now need to be included. The guidance indicates the following:
The majority of skin cancers can be managed by simple excision or destruction techniques. The medical record of a patient undergoing MMS should clearly show that this procedure was chosen because of the complexity (eg, poorly defined clinical borders, possible deep invasion, prior irradiation), size or location (eg, maximum conservation of tumor-free tissue is important). Medicare will consider reimbursement for MMS for accepted diagnoses and indications, which you must document in the patient’s medical record as being appropriate for MMS and that MMS is the most appropriate choice for the treatment of a particular lesion.1
In my experience, most Mohs notes include some statement that the skin cancer treated is appropriate based on the Mohs appropriate use criteria (AUC) or the AUC score. However, notes should make clear not just that the lesion treated is “appropriate” for MMS but also that it is the most appropriate treatment (eg, why the lesion was not managed by standard excision or destruction technique).
Mohs Surgeon Must Perform the Surgery and Interpret Slides
The updated guidance clearly indicates that MMS may only be performed by a physician who is specifically trained and highly skilled in Mohs techniques and pathologic identification: “Medicare will only reimburse for MMS services when the Mohs surgeon acts as both surgeon and pathologist.”1 Mohs micrographic surgery codes may not be billed if preparation or interpretation of the pathology slides is performed by a physician other than the Mohs surgeon. Operative notes and pathology documentation in the patient’s medical record should clearly show that MMS was performed using an accepted MMS technique in which the physician acts in 2 integrated and distinct capacities—surgeon and pathologist—thereby confirming that the procedure meets the definition of the Current Procedural Terminology code(s).
Furthermore, the Mohs operative report should detail “the number of specimens per stage.”1 I interpret this statement to indicate that the Mohs surgeon should document the number of tissue blocks examined in each stage of Mohs surgery. For example, a statement in the notes such as “the specimen from the first Mohs stage was oriented, mapped, and divided into 4 blocks” should suffice to meet this requirement.
Histologic Description Must Be Included in Mohs Notes
Medicare will require the Mohs surgeon to document “the histology of the specimens taken. That description should include depth of invasion, pathological pattern, cell morphology, and, if present, perineural invasion or presence of scar tissue.”1 Although this histologic description requirement appears daunting, it is common for Mohs surgeons to indicate their pathologic findings on their Mohs map such as “NBCC” next to a red area to indicate “nodular basal cell carcinoma visualized.” A template-based system to translate typical pathologic findings can be employed to rapidly and accurately populate a Mohs note with histologic description such as “NBBC=nodular aggregates of palisaded basaloid epithelial tumor arising from the epidermis forming a palisade with a cleft forming from the adjacent mucinous stroma extending to the mid dermis. Centrally the nuclei become crowded with scattered mitotic figures and necrotic bodies evident.”
Recent Improvement for 1-Stage Mohs Surgeries
The most notable improvement in the
Final Thoughts
Overall, the updated Medicare guidance provides important details in the requirements for performance and documentation of Mohs surgery cases. However, additional critical information will be found in Mohs coverage policies and local coverage determinations (LCDs) from MACs and private insurers.2-4 Each LCD and insurer Mohs payment policy has unique wording and requirements. Coverage of MMS for specific malignant diagnoses, histologic subtypes, locations, and clinical scenarios varies between LCDs; most are based directly on the Mohs AUC, while others have a less specific coverage criteria. To understand the specific documentation and coverage requirements of the MAC for a particular region or private insurer, Mohs surgeons are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the Mohs surgery LCD of their local MAC and coverage policies of their insurers and to ensure their documentation substantiates these requirements. Making sure that your MMS documentation is accurate and complies with Medicare and insurer requirements will keep you out of hot water with auditors and allow reimbursement for this critical skin cancer procedure.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance to reduce Mohs surgery reimbursement issues. MLN Matters. Published October 27, 2020. Accessed July 18, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNMattersArticles/Downloads/SE1318.pdf
- Mohs micrographic surgery policy, professional. United Healthcare website. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.uhcprovider.com/content/dam/provider/docs/public/policies/comm-reimbursement/COMM-Mohs-Micrographic-Surgery-Policy.pdf#:~:text=This%20policy%20describes%20reimbursement%20guidelines%20for%20reporting%20Mohs,CCI%20Editing%20Policy%20and%20the%20Laboratory%20Services%20Policy.
- Clinical UM guideline—Mohs micrographic surgery. Anthem Insurance Companies website. Published October 6, 2021. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.anthem.com/dam/medpolicies/abcbs/active/guidelines/gl_pw_d085074.html
- Local coverage determinations. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Updated July 12, 2022. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Coverage/DeterminationProcess/LCDs
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance to reduce Mohs surgery reimbursement issues. MLN Matters. Published October 27, 2020. Accessed July 18, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNMattersArticles/Downloads/SE1318.pdf
- Mohs micrographic surgery policy, professional. United Healthcare website. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.uhcprovider.com/content/dam/provider/docs/public/policies/comm-reimbursement/COMM-Mohs-Micrographic-Surgery-Policy.pdf#:~:text=This%20policy%20describes%20reimbursement%20guidelines%20for%20reporting%20Mohs,CCI%20Editing%20Policy%20and%20the%20Laboratory%20Services%20Policy.
- Clinical UM guideline—Mohs micrographic surgery. Anthem Insurance Companies website. Published October 6, 2021. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.anthem.com/dam/medpolicies/abcbs/active/guidelines/gl_pw_d085074.html
- Local coverage determinations. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services website. Updated July 12, 2022. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Coverage/DeterminationProcess/LCDs
Practice Points
- Medicare’s updated guidance for documentation of Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) includes some new requirements that Mohs surgeons should ensure are implemented in their Mohs records.
- Per Medicare guidance, MMS records should include a justification of why MMS was the most appropriate treatment and a description of the histologic findings from the Mohs slides.
- One major improvement with the updated documentation requirements is that if no tumor is visualized in the first stage of MMS, then no histology description of the tumor is required.
James Roberts, MD, trailblazer in EM, dies at age 76
at the age of 76 years. Dr. Roberts was coauthor of the foundational EM text, Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care , and was among the first physicians in the world to be board certified in EM. He was a prominent member of the American College of Emergency Physicians, a long-time contributor and editorial board chair for Emergency Medicine News, and a founding member of the American College of Medical Toxicology. He previously served as chairman of the Mercy Catholic Medical Center emergency department in Philadelphia, and vice chairman of the department of emergency medicine at Drexel University, Philadelphia.
“Dr. Roberts was a prominent EM physician and a pioneer in emergency medicine,” said Robert Glatter, MD, assistant professor of emergency medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.. “He is a revered and respected figure in emergency medicine.” This sentiment was echoed by his colleagues and former students across the EM world.
“How does one describe a unicorn?” Leslie Dye, MD, past president of the ACMT wrote in a tribute to Dr. Roberts on the ACMT website. “There are existing words, but he should have words that belong solely to him. Compassionate, irreverent, brilliant, funny, sarcastic, HUMBLE, modest, kind, inquisitive, and one of the best doctors I have ever met.”
By all accounts, Dr. Roberts lived his life according to words he wrote in a 2018 column for Emergency Medicine News, “How to Be a Good EP.” “Emergency medicine is not just a job, it’s a lifestyle, but there is more to life than medicine. You can never make up a missed championship soccer game, anniversary, birthday, or chance to take your son or daughter fishing. In a heartbeat your children will be on their own and will likely have trouble finding time for you. Remember that you might need a shift off someday, so be ready to help a colleague with a similar request.”
He is survived by a large extended family, including his daughter Martha, son Matthew, and spouse of more than 40 years, Lydia Forte Roberts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
at the age of 76 years. Dr. Roberts was coauthor of the foundational EM text, Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care , and was among the first physicians in the world to be board certified in EM. He was a prominent member of the American College of Emergency Physicians, a long-time contributor and editorial board chair for Emergency Medicine News, and a founding member of the American College of Medical Toxicology. He previously served as chairman of the Mercy Catholic Medical Center emergency department in Philadelphia, and vice chairman of the department of emergency medicine at Drexel University, Philadelphia.
“Dr. Roberts was a prominent EM physician and a pioneer in emergency medicine,” said Robert Glatter, MD, assistant professor of emergency medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.. “He is a revered and respected figure in emergency medicine.” This sentiment was echoed by his colleagues and former students across the EM world.
“How does one describe a unicorn?” Leslie Dye, MD, past president of the ACMT wrote in a tribute to Dr. Roberts on the ACMT website. “There are existing words, but he should have words that belong solely to him. Compassionate, irreverent, brilliant, funny, sarcastic, HUMBLE, modest, kind, inquisitive, and one of the best doctors I have ever met.”
By all accounts, Dr. Roberts lived his life according to words he wrote in a 2018 column for Emergency Medicine News, “How to Be a Good EP.” “Emergency medicine is not just a job, it’s a lifestyle, but there is more to life than medicine. You can never make up a missed championship soccer game, anniversary, birthday, or chance to take your son or daughter fishing. In a heartbeat your children will be on their own and will likely have trouble finding time for you. Remember that you might need a shift off someday, so be ready to help a colleague with a similar request.”
He is survived by a large extended family, including his daughter Martha, son Matthew, and spouse of more than 40 years, Lydia Forte Roberts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
at the age of 76 years. Dr. Roberts was coauthor of the foundational EM text, Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care , and was among the first physicians in the world to be board certified in EM. He was a prominent member of the American College of Emergency Physicians, a long-time contributor and editorial board chair for Emergency Medicine News, and a founding member of the American College of Medical Toxicology. He previously served as chairman of the Mercy Catholic Medical Center emergency department in Philadelphia, and vice chairman of the department of emergency medicine at Drexel University, Philadelphia.
“Dr. Roberts was a prominent EM physician and a pioneer in emergency medicine,” said Robert Glatter, MD, assistant professor of emergency medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.. “He is a revered and respected figure in emergency medicine.” This sentiment was echoed by his colleagues and former students across the EM world.
“How does one describe a unicorn?” Leslie Dye, MD, past president of the ACMT wrote in a tribute to Dr. Roberts on the ACMT website. “There are existing words, but he should have words that belong solely to him. Compassionate, irreverent, brilliant, funny, sarcastic, HUMBLE, modest, kind, inquisitive, and one of the best doctors I have ever met.”
By all accounts, Dr. Roberts lived his life according to words he wrote in a 2018 column for Emergency Medicine News, “How to Be a Good EP.” “Emergency medicine is not just a job, it’s a lifestyle, but there is more to life than medicine. You can never make up a missed championship soccer game, anniversary, birthday, or chance to take your son or daughter fishing. In a heartbeat your children will be on their own and will likely have trouble finding time for you. Remember that you might need a shift off someday, so be ready to help a colleague with a similar request.”
He is survived by a large extended family, including his daughter Martha, son Matthew, and spouse of more than 40 years, Lydia Forte Roberts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Discrepancies in Skin Cancer Screening Reporting Among Patients, Primary Care Physicians, and Patient Medical Records
Keratinocyte carcinoma (KC), or nonmelanoma skin cancer, is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States.1 Basal cell carcinoma comprises the majority of all KCs.2,3 Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common skin cancer, representing approximately 20% of KCs and accounting for the majority of KC-related deaths.4-7 Malignant melanoma represents the majority of all skin cancer–related deaths.8 The incidence of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma in the United States is on the rise and carries substantial morbidity and mortality with notable social and economic burdens.1,8-10
Prevention is necessary to reduce skin cancer morbidity and mortality as well as rising treatment costs. The most commonly used skin cancer screening method among dermatologists is the visual full-body skin examination (FBSE), which is a noninvasive, safe, quick, and cost-effective method of early detection and prevention.11 To effectively confront the growing incidence and health care burden of skin cancer, primary care providers (PCPs) must join dermatologists in conducting FBSEs.12,13
Despite being the predominant means of secondary skin cancer prevention, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued an I rating for insufficient evidence to assess the benefits vs harms of screening the adult general population by PCPs.14,15 A major barrier to studying screening is the lack of a standardized method for conducting and reporting FBSEs.13 Systematic thorough skin examination generally is not performed in the primary care setting.16-18
We aimed to investigate what occurs during an FBSE in the primary care setting and how often they are performed. We examined whether there was potential variation in the execution of the examination, what was perceived by the patient vs reported by the physician, and what was ultimately included in the medical record. Miscommunication between patient and provider regarding performance of FBSEs has previously been noted,17-19 and we sought to characterize and quantify that miscommunication. We hypothesized that there would be lower patient-reported FBSEs compared to physicians and patient medical records. We also hypothesized that there would be variability in how physicians screened for skin cancer.
METHODS
This study was cross-sectional and was conducted based on interviews and a review of medical records at secondary- and tertiary-level units (clinics and hospitals) across the United States. We examined baseline data from a randomized controlled trial of a Web-based skin cancer early detection continuing education course—the Basic Skin Cancer Triage curriculum. Complete details have been described elsewhere.12 This study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Rhode Island Hospital, and Brown University (all in Providence, Rhode Island), as well as those of all recruitment sites.
Data were collected from 2005 to 2008 and included physician online surveys, patient telephone interviews, and patient medical record data abstracted by research assistants. Primary care providers included in the study were general internists, family physicians, or medicine-pediatrics practitioners who were recruited from 4 collaborating centers across the United States in the mid-Atlantic region, Ohio, Kansas, and southern California, and who had been in practice for at least a year. Patients were recruited from participating physician practices and selected by research assistants who traveled to each clinic for coordination, recruitment, and performance of medical record reviews. Patients were selected as having minimal risk of melanoma (eg, no signs of severe photodamage to the skin). Patients completed structured telephone surveys within 1 to 2 weeks of the office visit regarding the practices observed and clinical questions asked during their recent clinical encounter with their PCP.
Measures
Demographics—Demographic variables asked of physicians included age, sex, ethnicity, academic degree (MD vs DO), years in practice, training, and prior dermatology training. Demographic information asked of patients included age, sex, ethnicity, education, and household income.
Physician-Reported Examination and Counseling Variables—Physicians were asked to characterize their clinical practices, prompted by questions regarding performance of FBSEs: “Please think of a typical month and using the scale below, indicate how frequently you perform a total body skin exam during an annual exam (eg, periodic follow-up exam).” Physicians responded to 3 questions on a 5-point scale (1=never, 2=sometimes, 3=about half, 4=often, 5=almost always).
Patient-Reported Examination Variables—Patients also were asked to characterize the skin examination experienced in their clinical encounter with their PCP, including: “During your last visit, as far as you could tell, did your physician: (1) look at the skin on your back? (2) look at the skin on your belly area? (3) look at the skin on the back of your legs?” Patient responses were coded as yes, no, don’t know, or refused. Participants who refused were excluded from analysis; participants who responded are detailed in Table 1. In addition, patients also reported the level of undress with their physician by answering the following question: “During your last medical exam, did you: 1=keep your clothes on; 2=partially undress; 3=totally undress except for undergarments; 4=totally undress, including all undergarments?”
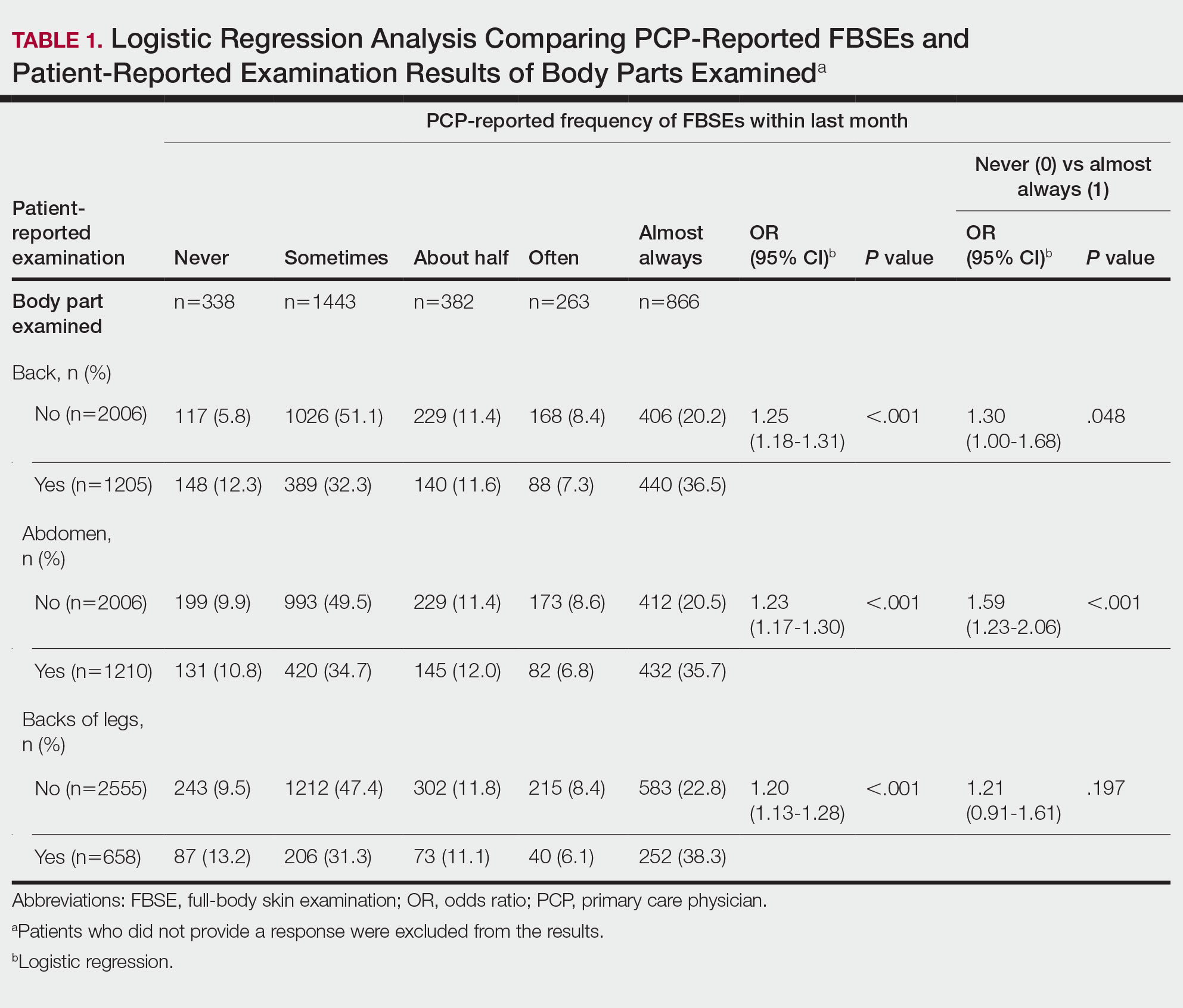
Patient Medical Record–Extracted Data—Research assistants used a structured abstract form to extract the information from the patient’s medical record and graded it as 0 (absence) or 1 (presence) from the medical record.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics included mean and standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables as well as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. Logit/logistic regression analysis was used to predict the odds of patient-reported outcomes that were binary with physician-reported variables as the predictor. Linear regression analysis was used to assess the association between 2 continuous variables. All analyses were conducted using SPSS version 24 (IBM).20 Significance criterion was set at α of .05.
RESULTS Demographics
The final sample included data from 53 physicians and 3343 patients. The study sample mean age (SD) was 50.3 (9.9) years for PCPs (n=53) and 59.8 (16.9) years for patients (n=3343). The physician sample was 36% female and predominantly White (83%). Ninety-one percent of the PCPs had an MD (the remaining had a DO degree), and the mean (SD) years practicing was 21.8 (10.6) years. Seventeen percent of PCPs were trained in internal medicine, 4% in internal medicine and pediatrics, and 79% family medicine; 79% of PCPs had received prior training in dermatology. The patient sample was 58% female, predominantly White (84%), non-Hispanic/Latinx (95%), had completed high school (94%), and earned more than $40,000 annually (66%).
Physician- and Patient-Reported FBSEs
Physicians reported performing FBSEs with variable frequency. Among PCPs who conducted FBSEs with greater frequency, there was a modest increase in the odds that patients reported a particular body part was examined (back: odds ratio [OR], 24.5% [95% CI, 1.18-1.31; P<.001]; abdomen: OR, 23.3% [95% CI, 1.17-1.30; P<.001]; backs of legs: OR, 20.4% [95% CI, 1.13-1.28; P<.001])(Table 1). The patient-reported level of undress during examination was significantly associated with physician-reported FBSE (β=0.16 [95% CI, 0.13-0.18; P<.001])(Table 2).
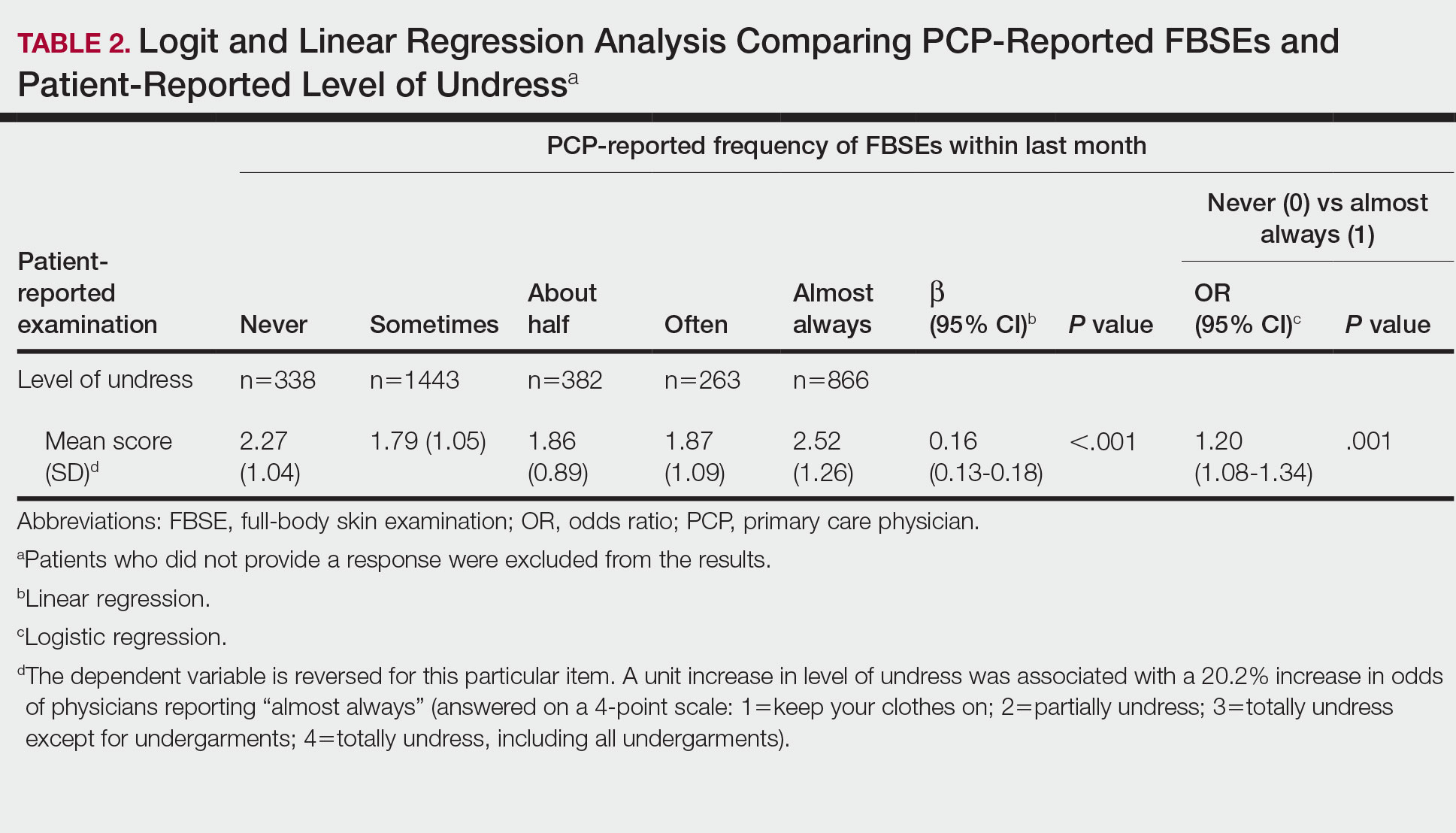
Because of the bimodal distribution of scores in the physician-reported frequency of FBSEs, particularly pertaining to the extreme points of the scale, we further repeated analysis with only the never and almost always groups (Table 1). Primary care providers who reported almost always for FBSE had 29.6% increased odds of patient-reported back examination (95% CI, 1.00-1.68; P=.048) and 59.3% increased odds of patient-reported abdomen examination (95% CI, 1.23-2.06; P<.001). The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined when the PCP reported having never conducted an FBSE were 56%, 40%, and 26%, respectively. The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined when the PCP reported having almost always conducted an FBSE were 52%, 51%, and 30%, respectively. Raw percentages were calculated by dividing the number of "yes" responses by participants for each body part examined by thetotal number of participant responses (“yes” and “no”) for each respective body part. There was no significant change in odds of patient-reported backs of legs examined with PCP-reported never vs almost always conducting an FBSE. In addition, a greater patient-reported level of undress was associated with 20.2% increased odds of PCPs reporting almost always conducting an FBSE (95% CI, 1.08-1.34; P=.001).
FBSEs in Patient Medical Records
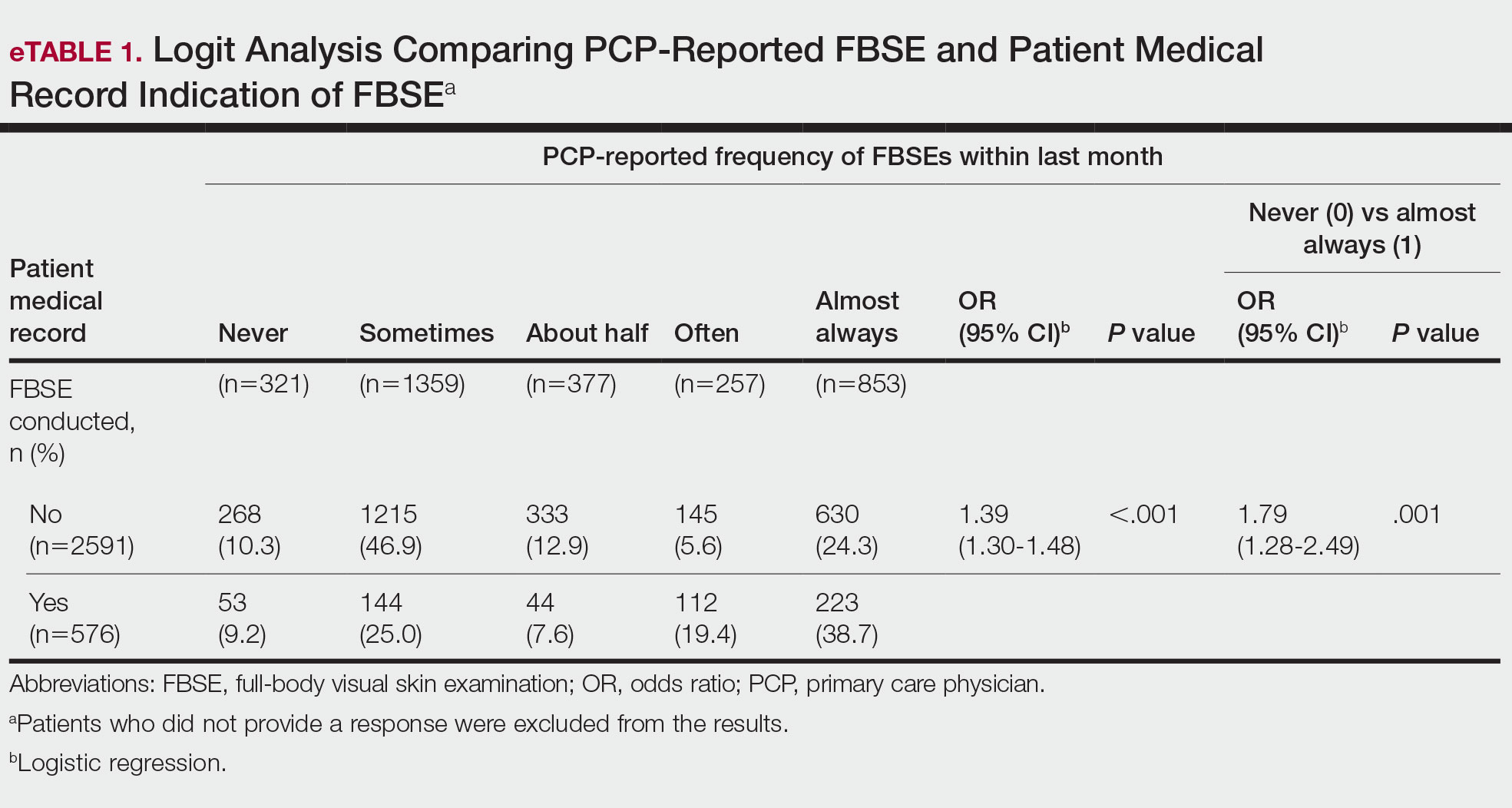
When comparing PCP-reported FBSE and report of FBSE in patient medical records, there was a 39.0% increased odds of the patient medical record indicating FBSE when physicians reported conducting an FBSE with greater frequency (95% CI, 1.30-1.48; P<.001)(eTable 1). When examining PCP-reported never vs almost always conducting an FBSE, a report of almost always was associated with 79.0% increased odds of the patient medical record indicating that an FBSE was conducted (95% CI, 1.28-2.49; P=.001). The raw percentage of the patient medical record indicating an FBSE was conducted when the PCP reported having never conducted an FBSE was 17% and 26% when the PCP reported having almost always conducted an FBSE.
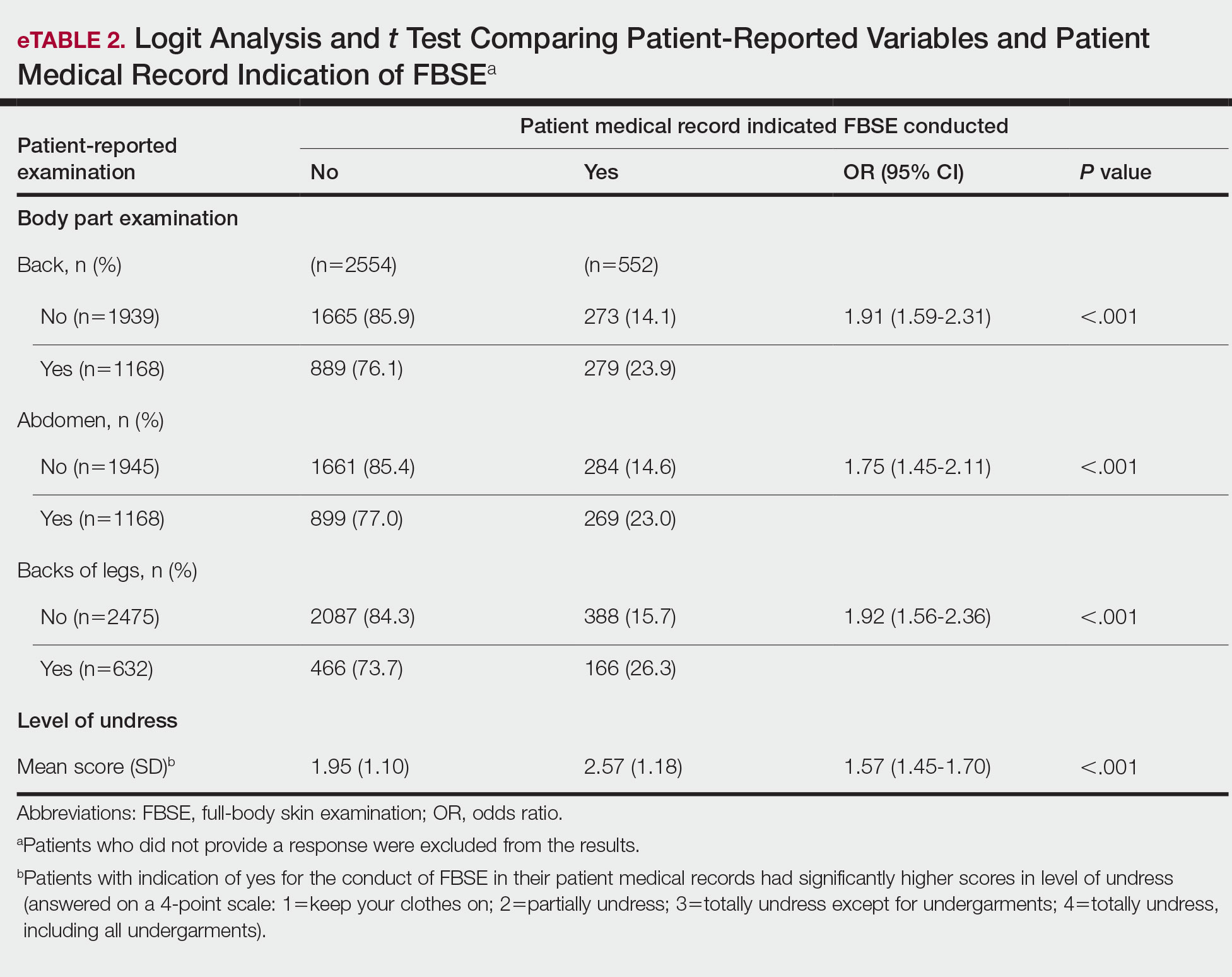
When comparing the patient-reported body part examined with patient FBSE medical record documentation, an indication of yes for FBSE on the patient medical record was associated with a considerable increase in odds that patients reported a particular body part was examined (back: 91.4% [95% CI, 1.59-2.31; P<.001]; abdomen: 75.0% [95% CI, 1.45-2.11; P<.001]; backs of legs: 91.6% [95% CI, 1.56-2.36; P<.001])(eTable 2). The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined vs not examined when the patient medical record indicated an FBSE was completed were 24% vs 14%, 23% vs 15%, and 26% vs 16%, respectively. An increase in patient-reported level of undress was associated with a 57.0% increased odds of their medical record indicating an FBSE was conducted (95% CI, 1.45-1.70; P<.001).
COMMENT How PCPs Perform FBSEs Varies
We found that PCPs performed FBSEs with variable frequency, and among those who did, the patient report of their examination varied considerably (Table 1). There appears to be considerable ambiguity in each of these means of determining the extent to which the skin was inspected for skin cancer, which may render the task of improving such inspection more difficult. We asked patients whether their back, abdomen, and backs of legs were examined as an assessment of some of the variety of areas inspected during an FBSE. During a general well-visit appointment, a patient’s back and abdomen may be examined for multiple reasons. Patients may have misinterpreted elements of the pulmonary, cardiac, abdominal, or musculoskeletal examinations as being part of the FBSE. The back and abdomen—the least specific features of the FBSE—were reported by patients to be the most often examined. Conversely, the backs of the legs—the most specific feature of the FBSE—had the lowest odds of being examined (Table 1).
In addition to the potential limitations of patient awareness of physician activity, our results also could be explained by differences among PCPs in how they performed FBSEs. There is no standardized method of conducting an FBSE. Furthermore, not all medical students and residents are exposed to dermatology training. In our sample of 53 physicians, 79% had reported receiving dermatology training; however, we did not assess the extent to which they had been trained in conducting an FBSE and/or identifying malignant lesions. In an American survey of 659 medical students, more than two-thirds of students had never been trained or never examined a patient for skin cancer.21 In another American survey of 342 internal medicine, family medicine, pediatrics, and obstetrics/gynecology residents across 7 medical schools and 4 residency programs, more than three-quarters of residents had never been trained in skin cancer screening.22 Our findings reflect insufficient and inconsistent training in skin cancer screening and underscore the need for mandatory education to ensure quality FBSEs are performed in the primary care setting.
Frequency of PCPs Performing FBSEs
Similar to prior studies analyzing the frequency of FBSE performance in the primary care setting,16,19,23,24 more than half of our PCP sample reported sometimes to never conducting FBSEs. The percentage of physicians who reported conducting FBSEs in our sample was greater than the proportion reported by the National Health Interview Survey, in which only 8% of patients received an FBSE in the prior year by a PCP or obstetrician/gynecologist,16 but similar to a smaller patient study.19 In that study, 87% of patients, regardless of their skin cancer history, also reported that they would like their PCP to perform an FBSE regularly.19 Although some of our patient participants may have declined an FBSE, it is unlikely that that would have entirely accounted for the relatively low number of PCPs who reported frequently performing FBSEs.
Documentation in Medical Records of FBSEs
Compared to PCP self-reported performance of FBSEs, considerably fewer PCPs marked the patient medical record as having completed an FBSE. Among patients with medical records that indicated an FBSE had been conducted, they reported higher odds of all 3 body parts being examined, the highest being the backs of the legs. Also, when the patient medical record indicated an FBSE had been completed, the odds that the PCP reported an FBSE also were higher. The relatively low medical record documentation of FBSEs highlights the need for more rigorous enforcement of accurate documentation. However, among the cases that were recorded, it appeared that the content of the examinations was more consistent.
Benefits of PCP-Led FBSEs
Although the USPSTF issued an I rating for PCP-led FBSEs,14 multiple national medical societies, including the American Cancer Society,25 American Academy of Dermatology,26 and Skin Cancer Foundation,27 as well as international guidelines in Germany,28 Australia,29,30 and New Zealand,31 recommend regular FBSEs among the general or at-risk population; New Zealand and Australia have the highest incidence and prevalence of melanoma in the world.8 The benefits of physician-led FBSEs on detection of early-stage skin cancer, and in particular, melanoma detection, have been documented in numerous studies.30,32-38 However, the variability and often poor quality of skin screening may contribute in part to the just as numerous null results from prior skin screening studies,15 perpetuating the insufficient status of skin examinations by USPSTF standards.14 Our study underscores both the variability in frequency and content of PCP-administered FBSEs. It also highlights the need for standardization of screening examinations at the medical student, trainee, and physician level.
Study Limitations
The present study has several limitations. First, there was an unknown time lag between the FBSEs and physician self-reported surveys. Similarly, there was a variable time lag between the patient examination encounter and subsequent telephone survey. Both the physician and patient survey data may have been affected by recall bias. Second, patients were not asked directly whether an FBSE had been conducted. Furthermore, patients may not have appreciated whether the body part examined was part of the FBSE or another examination. Also, screenings often were not recorded in the medical record, assuming that the patient report and/or physician report was more accurate than the medical record.
Our study also was limited by demographics; our patient sample was largely comprised of White, educated, US adults, potentially limiting the generalizability of our findings. Conversely, a notable strength of our study was that our participants were recruited from 4 geographically diverse centers. Furthermore, we had a comparatively large sample size of patients and physicians. Also, the independent assessment of provider-reported examinations, objective assessment of medical records, and patient reports of their encounters provides a strong foundation for assessing the independent contributions of each data source.
CONCLUSION
Our study highlights the challenges future studies face in promoting skin cancer screening in the primary care setting. Our findings underscore the need for a standardized FBSE as well as clear clinical expectations regarding skin cancer screening that is expected of PCPs.
As long as skin cancer screening rates remain low in the United States, patients will be subject to potential delays and missed diagnoses, impacting morbidity and mortality.8 There are burgeoning resources and efforts in place to increase skin cancer screening. For example, free validated online training is available for early detection of melanoma and other skin cancers (https://www.visualdx.com/skin-cancer-education/).39-42 Future directions for bolstering screening numbers must focus on educating PCPs about skin cancer prevention and perhaps narrowing the screening population by age-appropriate risk assessments.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the U.S. population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Dourmishev LA, Rusinova D, Botev I. Clinical variants, stages, and management of basal cell carcinoma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:12-17.
- Thompson AK, Kelley BF, Prokop LJ, et al. Risk factors for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:419-428.
- Motaparthi K, Kapil JP, Velazquez EF. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: review of the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Guidelines, Prognostic Factors, and Histopathologic Variants. Adv Anat Pathol. 2017;24:171-194.
- Barton V, Armeson K, Hampras S, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer and risk of all-cause and cancer-related mortality: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309:243-251.
- Weinstock MA, Bogaars HA, Ashley M, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer mortality. a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1194-1197.
- Matthews NH, Li W-Q, Qureshi AA, et al. Epidemiology of melanoma. In: Ward WH, Farma JM, eds. Cutaneous Melanoma: Etiology and Therapy. Codon Publications; 2017:3-22.
- Cakir BO, Adamson P, Cingi C. Epidemiology and economic burden of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2012;20:419-422.
- Guy GP, Machlin SR, Ekwueme DU, et al. Prevalence and costs of skin cancer treatment in the U.S., 2002-2006 and 2007-2011. Am J Prev Med. 2015;48:183-187.
- Losina E, Walensky RP, Geller A, et al. Visual screening for malignant melanoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:21-28.
- Markova A, Weinstock MA, Risica P, et al. Effect of a web-based curriculum on primary care practice: basic skin cancer triage trial. Fam Med. 2013;45:558-568.
- Johnson MM, Leachman SA, Aspinwall LG, et al. Skin cancer screening: recommendations for data-driven screening guidelines and a review of the US Preventive Services Task Force controversy. Melanoma Manag. 2017;4:13-37.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Screening for skin cancer in adults: an updated systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. November 30, 2015. Accessed July 25, 2022. http://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/draft-evidence-review159/skin-cancer-screening2
- Wernli KJ, Henrikson NB, Morrison CC, et al. Screening for skin cancer in adults: updated evidence report and systematic review forthe US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;316:436-447.
- LeBlanc WG, Vidal L, Kirsner RS, et al. Reported skin cancer screening of US adult workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:55-63.
- Federman DG, Concato J, Caralis PV, et al. Screening for skin cancer in primary care settings. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:1423-1425.
- Kirsner RS, Muhkerjee S, Federman DG. Skin cancer screening in primary care: prevalence and barriers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:564-566.
- Federman DG, Kravetz JD, Tobin DG, et al. Full-body skin examinations: the patient’s perspective. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:530-534.
- IBM. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows. IBM Corp; 2015.
- Moore MM, Geller AC, Zhang Z, et al. Skin cancer examination teaching in US medical education. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:439-444.
- Wise E, Singh D, Moore M, et al. Rates of skin cancer screening and prevention counseling by US medical residents. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1131-1136.
- Lakhani NA, Saraiya M, Thompson TD, et al. Total body skin examination for skin cancer screening among U.S. adults from 2000 to 2010. Prev Med. 2014;61:75-80.
- Coups EJ, Geller AC, Weinstock MA, et al. Prevalence and correlates of skin cancer screening among middle-aged and older white adults in the United States. Am J Med. 2010;123:439-445.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2016. Accessed March 13, 2022. https://cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2016/
- American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer incidence rates. Updated April 22, 2022. Accessed August 1, 2022. https://www.aad.org/media/stats-skin-cancer
- Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin cancer prevention. Accessed July 25, 2022. http://skincancer.org/prevention/sun-protection/prevention-guidelines
- Katalinic A, Eisemann N, Waldmann A. Skin cancer screening in Germany. documenting melanoma incidence and mortality from 2008 to 2013. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015;112:629-634.
- Cancer Council Australia. Position statement: screening and early detection of skin cancer. Published July 2014. Accessed July 25, 2022. https://dermcoll.edu.au/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/PosStatEarlyDetectSkinCa.pdf
- Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Guidelines for Preventive Activities in General Practice. 9th ed. The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners; 2016. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.racgp.org.au/download/Documents/Guidelines/Redbook9/17048-Red-Book-9th-Edition.pdf
- Cancer Council Australia and Australian Cancer Network and New Zealand Guidelines Group. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Melanoma in Australia and New Zealand. The Cancer Council Australia and Australian Cancer Network, Sydney and New Zealand Guidelines Group, Wellington; 2008. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.health.govt.nz/system/files/documents/publications/melanoma-guideline-nov08-v2.pdf
- Swetter SM, Pollitt RA, Johnson TM, et al. Behavioral determinants of successful early melanoma detection: role of self and physician skin examination. Cancer. 2012;118:3725-3734.
- Terushkin V, Halpern AC. Melanoma early detection. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:481-500, viii.
- Aitken JF, Elwood M, Baade PD, et al. Clinical whole-body skin examination reduces the incidence of thick melanomas. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:450-458.
- Aitken JF, Elwood JM, Lowe JB, et al. A randomised trial of population screening for melanoma. J Med Screen. 2002;9:33-37.
- Breitbart EW, Waldmann A, Nolte S, et al. Systematic skin cancer screening in Northern Germany. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:201-211.
- Janda M, Lowe JB, Elwood M, et al. Do centralised skin screening clinics increase participation in melanoma screening (Australia)? Cancer Causes Control. 2006;17:161-168.
- Aitken JF, Janda M, Elwood M, et al. Clinical outcomes from skin screening clinics within a community-based melanoma screening program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:105-114.
- Eide MJ, Asgari MM, Fletcher SW, et al. Effects on skills and practice from a web-based skin cancer course for primary care providers. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:648-657.
- Weinstock MA, Ferris LK, Saul MI, et al. Downstream consequences of melanoma screening in a community practice setting: first results. Cancer. 2016;122:3152-3156.
- Matthews NH, Risica PM, Ferris LK, et al. Psychosocial impact of skin biopsies in the setting of melanoma screening: a cross-sectional survey. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:664-665.
- Risica PM, Matthews NH, Dionne L, et al. Psychosocial consequences of skin cancer screening. Prev Med Rep. 2018;10:310-316.
Keratinocyte carcinoma (KC), or nonmelanoma skin cancer, is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States.1 Basal cell carcinoma comprises the majority of all KCs.2,3 Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common skin cancer, representing approximately 20% of KCs and accounting for the majority of KC-related deaths.4-7 Malignant melanoma represents the majority of all skin cancer–related deaths.8 The incidence of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma in the United States is on the rise and carries substantial morbidity and mortality with notable social and economic burdens.1,8-10
Prevention is necessary to reduce skin cancer morbidity and mortality as well as rising treatment costs. The most commonly used skin cancer screening method among dermatologists is the visual full-body skin examination (FBSE), which is a noninvasive, safe, quick, and cost-effective method of early detection and prevention.11 To effectively confront the growing incidence and health care burden of skin cancer, primary care providers (PCPs) must join dermatologists in conducting FBSEs.12,13
Despite being the predominant means of secondary skin cancer prevention, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued an I rating for insufficient evidence to assess the benefits vs harms of screening the adult general population by PCPs.14,15 A major barrier to studying screening is the lack of a standardized method for conducting and reporting FBSEs.13 Systematic thorough skin examination generally is not performed in the primary care setting.16-18
We aimed to investigate what occurs during an FBSE in the primary care setting and how often they are performed. We examined whether there was potential variation in the execution of the examination, what was perceived by the patient vs reported by the physician, and what was ultimately included in the medical record. Miscommunication between patient and provider regarding performance of FBSEs has previously been noted,17-19 and we sought to characterize and quantify that miscommunication. We hypothesized that there would be lower patient-reported FBSEs compared to physicians and patient medical records. We also hypothesized that there would be variability in how physicians screened for skin cancer.
METHODS
This study was cross-sectional and was conducted based on interviews and a review of medical records at secondary- and tertiary-level units (clinics and hospitals) across the United States. We examined baseline data from a randomized controlled trial of a Web-based skin cancer early detection continuing education course—the Basic Skin Cancer Triage curriculum. Complete details have been described elsewhere.12 This study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Rhode Island Hospital, and Brown University (all in Providence, Rhode Island), as well as those of all recruitment sites.
Data were collected from 2005 to 2008 and included physician online surveys, patient telephone interviews, and patient medical record data abstracted by research assistants. Primary care providers included in the study were general internists, family physicians, or medicine-pediatrics practitioners who were recruited from 4 collaborating centers across the United States in the mid-Atlantic region, Ohio, Kansas, and southern California, and who had been in practice for at least a year. Patients were recruited from participating physician practices and selected by research assistants who traveled to each clinic for coordination, recruitment, and performance of medical record reviews. Patients were selected as having minimal risk of melanoma (eg, no signs of severe photodamage to the skin). Patients completed structured telephone surveys within 1 to 2 weeks of the office visit regarding the practices observed and clinical questions asked during their recent clinical encounter with their PCP.
Measures
Demographics—Demographic variables asked of physicians included age, sex, ethnicity, academic degree (MD vs DO), years in practice, training, and prior dermatology training. Demographic information asked of patients included age, sex, ethnicity, education, and household income.
Physician-Reported Examination and Counseling Variables—Physicians were asked to characterize their clinical practices, prompted by questions regarding performance of FBSEs: “Please think of a typical month and using the scale below, indicate how frequently you perform a total body skin exam during an annual exam (eg, periodic follow-up exam).” Physicians responded to 3 questions on a 5-point scale (1=never, 2=sometimes, 3=about half, 4=often, 5=almost always).
Patient-Reported Examination Variables—Patients also were asked to characterize the skin examination experienced in their clinical encounter with their PCP, including: “During your last visit, as far as you could tell, did your physician: (1) look at the skin on your back? (2) look at the skin on your belly area? (3) look at the skin on the back of your legs?” Patient responses were coded as yes, no, don’t know, or refused. Participants who refused were excluded from analysis; participants who responded are detailed in Table 1. In addition, patients also reported the level of undress with their physician by answering the following question: “During your last medical exam, did you: 1=keep your clothes on; 2=partially undress; 3=totally undress except for undergarments; 4=totally undress, including all undergarments?”

Patient Medical Record–Extracted Data—Research assistants used a structured abstract form to extract the information from the patient’s medical record and graded it as 0 (absence) or 1 (presence) from the medical record.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics included mean and standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables as well as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. Logit/logistic regression analysis was used to predict the odds of patient-reported outcomes that were binary with physician-reported variables as the predictor. Linear regression analysis was used to assess the association between 2 continuous variables. All analyses were conducted using SPSS version 24 (IBM).20 Significance criterion was set at α of .05.
RESULTS Demographics
The final sample included data from 53 physicians and 3343 patients. The study sample mean age (SD) was 50.3 (9.9) years for PCPs (n=53) and 59.8 (16.9) years for patients (n=3343). The physician sample was 36% female and predominantly White (83%). Ninety-one percent of the PCPs had an MD (the remaining had a DO degree), and the mean (SD) years practicing was 21.8 (10.6) years. Seventeen percent of PCPs were trained in internal medicine, 4% in internal medicine and pediatrics, and 79% family medicine; 79% of PCPs had received prior training in dermatology. The patient sample was 58% female, predominantly White (84%), non-Hispanic/Latinx (95%), had completed high school (94%), and earned more than $40,000 annually (66%).
Physician- and Patient-Reported FBSEs
Physicians reported performing FBSEs with variable frequency. Among PCPs who conducted FBSEs with greater frequency, there was a modest increase in the odds that patients reported a particular body part was examined (back: odds ratio [OR], 24.5% [95% CI, 1.18-1.31; P<.001]; abdomen: OR, 23.3% [95% CI, 1.17-1.30; P<.001]; backs of legs: OR, 20.4% [95% CI, 1.13-1.28; P<.001])(Table 1). The patient-reported level of undress during examination was significantly associated with physician-reported FBSE (β=0.16 [95% CI, 0.13-0.18; P<.001])(Table 2).

Because of the bimodal distribution of scores in the physician-reported frequency of FBSEs, particularly pertaining to the extreme points of the scale, we further repeated analysis with only the never and almost always groups (Table 1). Primary care providers who reported almost always for FBSE had 29.6% increased odds of patient-reported back examination (95% CI, 1.00-1.68; P=.048) and 59.3% increased odds of patient-reported abdomen examination (95% CI, 1.23-2.06; P<.001). The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined when the PCP reported having never conducted an FBSE were 56%, 40%, and 26%, respectively. The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined when the PCP reported having almost always conducted an FBSE were 52%, 51%, and 30%, respectively. Raw percentages were calculated by dividing the number of "yes" responses by participants for each body part examined by thetotal number of participant responses (“yes” and “no”) for each respective body part. There was no significant change in odds of patient-reported backs of legs examined with PCP-reported never vs almost always conducting an FBSE. In addition, a greater patient-reported level of undress was associated with 20.2% increased odds of PCPs reporting almost always conducting an FBSE (95% CI, 1.08-1.34; P=.001).
FBSEs in Patient Medical Records
When comparing PCP-reported FBSE and report of FBSE in patient medical records, there was a 39.0% increased odds of the patient medical record indicating FBSE when physicians reported conducting an FBSE with greater frequency (95% CI, 1.30-1.48; P<.001)(eTable 1). When examining PCP-reported never vs almost always conducting an FBSE, a report of almost always was associated with 79.0% increased odds of the patient medical record indicating that an FBSE was conducted (95% CI, 1.28-2.49; P=.001). The raw percentage of the patient medical record indicating an FBSE was conducted when the PCP reported having never conducted an FBSE was 17% and 26% when the PCP reported having almost always conducted an FBSE.

When comparing the patient-reported body part examined with patient FBSE medical record documentation, an indication of yes for FBSE on the patient medical record was associated with a considerable increase in odds that patients reported a particular body part was examined (back: 91.4% [95% CI, 1.59-2.31; P<.001]; abdomen: 75.0% [95% CI, 1.45-2.11; P<.001]; backs of legs: 91.6% [95% CI, 1.56-2.36; P<.001])(eTable 2). The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined vs not examined when the patient medical record indicated an FBSE was completed were 24% vs 14%, 23% vs 15%, and 26% vs 16%, respectively. An increase in patient-reported level of undress was associated with a 57.0% increased odds of their medical record indicating an FBSE was conducted (95% CI, 1.45-1.70; P<.001).

COMMENT How PCPs Perform FBSEs Varies
We found that PCPs performed FBSEs with variable frequency, and among those who did, the patient report of their examination varied considerably (Table 1). There appears to be considerable ambiguity in each of these means of determining the extent to which the skin was inspected for skin cancer, which may render the task of improving such inspection more difficult. We asked patients whether their back, abdomen, and backs of legs were examined as an assessment of some of the variety of areas inspected during an FBSE. During a general well-visit appointment, a patient’s back and abdomen may be examined for multiple reasons. Patients may have misinterpreted elements of the pulmonary, cardiac, abdominal, or musculoskeletal examinations as being part of the FBSE. The back and abdomen—the least specific features of the FBSE—were reported by patients to be the most often examined. Conversely, the backs of the legs—the most specific feature of the FBSE—had the lowest odds of being examined (Table 1).
In addition to the potential limitations of patient awareness of physician activity, our results also could be explained by differences among PCPs in how they performed FBSEs. There is no standardized method of conducting an FBSE. Furthermore, not all medical students and residents are exposed to dermatology training. In our sample of 53 physicians, 79% had reported receiving dermatology training; however, we did not assess the extent to which they had been trained in conducting an FBSE and/or identifying malignant lesions. In an American survey of 659 medical students, more than two-thirds of students had never been trained or never examined a patient for skin cancer.21 In another American survey of 342 internal medicine, family medicine, pediatrics, and obstetrics/gynecology residents across 7 medical schools and 4 residency programs, more than three-quarters of residents had never been trained in skin cancer screening.22 Our findings reflect insufficient and inconsistent training in skin cancer screening and underscore the need for mandatory education to ensure quality FBSEs are performed in the primary care setting.
Frequency of PCPs Performing FBSEs
Similar to prior studies analyzing the frequency of FBSE performance in the primary care setting,16,19,23,24 more than half of our PCP sample reported sometimes to never conducting FBSEs. The percentage of physicians who reported conducting FBSEs in our sample was greater than the proportion reported by the National Health Interview Survey, in which only 8% of patients received an FBSE in the prior year by a PCP or obstetrician/gynecologist,16 but similar to a smaller patient study.19 In that study, 87% of patients, regardless of their skin cancer history, also reported that they would like their PCP to perform an FBSE regularly.19 Although some of our patient participants may have declined an FBSE, it is unlikely that that would have entirely accounted for the relatively low number of PCPs who reported frequently performing FBSEs.
Documentation in Medical Records of FBSEs
Compared to PCP self-reported performance of FBSEs, considerably fewer PCPs marked the patient medical record as having completed an FBSE. Among patients with medical records that indicated an FBSE had been conducted, they reported higher odds of all 3 body parts being examined, the highest being the backs of the legs. Also, when the patient medical record indicated an FBSE had been completed, the odds that the PCP reported an FBSE also were higher. The relatively low medical record documentation of FBSEs highlights the need for more rigorous enforcement of accurate documentation. However, among the cases that were recorded, it appeared that the content of the examinations was more consistent.
Benefits of PCP-Led FBSEs
Although the USPSTF issued an I rating for PCP-led FBSEs,14 multiple national medical societies, including the American Cancer Society,25 American Academy of Dermatology,26 and Skin Cancer Foundation,27 as well as international guidelines in Germany,28 Australia,29,30 and New Zealand,31 recommend regular FBSEs among the general or at-risk population; New Zealand and Australia have the highest incidence and prevalence of melanoma in the world.8 The benefits of physician-led FBSEs on detection of early-stage skin cancer, and in particular, melanoma detection, have been documented in numerous studies.30,32-38 However, the variability and often poor quality of skin screening may contribute in part to the just as numerous null results from prior skin screening studies,15 perpetuating the insufficient status of skin examinations by USPSTF standards.14 Our study underscores both the variability in frequency and content of PCP-administered FBSEs. It also highlights the need for standardization of screening examinations at the medical student, trainee, and physician level.
Study Limitations
The present study has several limitations. First, there was an unknown time lag between the FBSEs and physician self-reported surveys. Similarly, there was a variable time lag between the patient examination encounter and subsequent telephone survey. Both the physician and patient survey data may have been affected by recall bias. Second, patients were not asked directly whether an FBSE had been conducted. Furthermore, patients may not have appreciated whether the body part examined was part of the FBSE or another examination. Also, screenings often were not recorded in the medical record, assuming that the patient report and/or physician report was more accurate than the medical record.
Our study also was limited by demographics; our patient sample was largely comprised of White, educated, US adults, potentially limiting the generalizability of our findings. Conversely, a notable strength of our study was that our participants were recruited from 4 geographically diverse centers. Furthermore, we had a comparatively large sample size of patients and physicians. Also, the independent assessment of provider-reported examinations, objective assessment of medical records, and patient reports of their encounters provides a strong foundation for assessing the independent contributions of each data source.
CONCLUSION
Our study highlights the challenges future studies face in promoting skin cancer screening in the primary care setting. Our findings underscore the need for a standardized FBSE as well as clear clinical expectations regarding skin cancer screening that is expected of PCPs.
As long as skin cancer screening rates remain low in the United States, patients will be subject to potential delays and missed diagnoses, impacting morbidity and mortality.8 There are burgeoning resources and efforts in place to increase skin cancer screening. For example, free validated online training is available for early detection of melanoma and other skin cancers (https://www.visualdx.com/skin-cancer-education/).39-42 Future directions for bolstering screening numbers must focus on educating PCPs about skin cancer prevention and perhaps narrowing the screening population by age-appropriate risk assessments.
Keratinocyte carcinoma (KC), or nonmelanoma skin cancer, is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States.1 Basal cell carcinoma comprises the majority of all KCs.2,3 Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common skin cancer, representing approximately 20% of KCs and accounting for the majority of KC-related deaths.4-7 Malignant melanoma represents the majority of all skin cancer–related deaths.8 The incidence of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma in the United States is on the rise and carries substantial morbidity and mortality with notable social and economic burdens.1,8-10
Prevention is necessary to reduce skin cancer morbidity and mortality as well as rising treatment costs. The most commonly used skin cancer screening method among dermatologists is the visual full-body skin examination (FBSE), which is a noninvasive, safe, quick, and cost-effective method of early detection and prevention.11 To effectively confront the growing incidence and health care burden of skin cancer, primary care providers (PCPs) must join dermatologists in conducting FBSEs.12,13
Despite being the predominant means of secondary skin cancer prevention, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued an I rating for insufficient evidence to assess the benefits vs harms of screening the adult general population by PCPs.14,15 A major barrier to studying screening is the lack of a standardized method for conducting and reporting FBSEs.13 Systematic thorough skin examination generally is not performed in the primary care setting.16-18
We aimed to investigate what occurs during an FBSE in the primary care setting and how often they are performed. We examined whether there was potential variation in the execution of the examination, what was perceived by the patient vs reported by the physician, and what was ultimately included in the medical record. Miscommunication between patient and provider regarding performance of FBSEs has previously been noted,17-19 and we sought to characterize and quantify that miscommunication. We hypothesized that there would be lower patient-reported FBSEs compared to physicians and patient medical records. We also hypothesized that there would be variability in how physicians screened for skin cancer.
METHODS
This study was cross-sectional and was conducted based on interviews and a review of medical records at secondary- and tertiary-level units (clinics and hospitals) across the United States. We examined baseline data from a randomized controlled trial of a Web-based skin cancer early detection continuing education course—the Basic Skin Cancer Triage curriculum. Complete details have been described elsewhere.12 This study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Rhode Island Hospital, and Brown University (all in Providence, Rhode Island), as well as those of all recruitment sites.
Data were collected from 2005 to 2008 and included physician online surveys, patient telephone interviews, and patient medical record data abstracted by research assistants. Primary care providers included in the study were general internists, family physicians, or medicine-pediatrics practitioners who were recruited from 4 collaborating centers across the United States in the mid-Atlantic region, Ohio, Kansas, and southern California, and who had been in practice for at least a year. Patients were recruited from participating physician practices and selected by research assistants who traveled to each clinic for coordination, recruitment, and performance of medical record reviews. Patients were selected as having minimal risk of melanoma (eg, no signs of severe photodamage to the skin). Patients completed structured telephone surveys within 1 to 2 weeks of the office visit regarding the practices observed and clinical questions asked during their recent clinical encounter with their PCP.
Measures
Demographics—Demographic variables asked of physicians included age, sex, ethnicity, academic degree (MD vs DO), years in practice, training, and prior dermatology training. Demographic information asked of patients included age, sex, ethnicity, education, and household income.
Physician-Reported Examination and Counseling Variables—Physicians were asked to characterize their clinical practices, prompted by questions regarding performance of FBSEs: “Please think of a typical month and using the scale below, indicate how frequently you perform a total body skin exam during an annual exam (eg, periodic follow-up exam).” Physicians responded to 3 questions on a 5-point scale (1=never, 2=sometimes, 3=about half, 4=often, 5=almost always).
Patient-Reported Examination Variables—Patients also were asked to characterize the skin examination experienced in their clinical encounter with their PCP, including: “During your last visit, as far as you could tell, did your physician: (1) look at the skin on your back? (2) look at the skin on your belly area? (3) look at the skin on the back of your legs?” Patient responses were coded as yes, no, don’t know, or refused. Participants who refused were excluded from analysis; participants who responded are detailed in Table 1. In addition, patients also reported the level of undress with their physician by answering the following question: “During your last medical exam, did you: 1=keep your clothes on; 2=partially undress; 3=totally undress except for undergarments; 4=totally undress, including all undergarments?”

Patient Medical Record–Extracted Data—Research assistants used a structured abstract form to extract the information from the patient’s medical record and graded it as 0 (absence) or 1 (presence) from the medical record.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics included mean and standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables as well as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. Logit/logistic regression analysis was used to predict the odds of patient-reported outcomes that were binary with physician-reported variables as the predictor. Linear regression analysis was used to assess the association between 2 continuous variables. All analyses were conducted using SPSS version 24 (IBM).20 Significance criterion was set at α of .05.
RESULTS Demographics
The final sample included data from 53 physicians and 3343 patients. The study sample mean age (SD) was 50.3 (9.9) years for PCPs (n=53) and 59.8 (16.9) years for patients (n=3343). The physician sample was 36% female and predominantly White (83%). Ninety-one percent of the PCPs had an MD (the remaining had a DO degree), and the mean (SD) years practicing was 21.8 (10.6) years. Seventeen percent of PCPs were trained in internal medicine, 4% in internal medicine and pediatrics, and 79% family medicine; 79% of PCPs had received prior training in dermatology. The patient sample was 58% female, predominantly White (84%), non-Hispanic/Latinx (95%), had completed high school (94%), and earned more than $40,000 annually (66%).
Physician- and Patient-Reported FBSEs
Physicians reported performing FBSEs with variable frequency. Among PCPs who conducted FBSEs with greater frequency, there was a modest increase in the odds that patients reported a particular body part was examined (back: odds ratio [OR], 24.5% [95% CI, 1.18-1.31; P<.001]; abdomen: OR, 23.3% [95% CI, 1.17-1.30; P<.001]; backs of legs: OR, 20.4% [95% CI, 1.13-1.28; P<.001])(Table 1). The patient-reported level of undress during examination was significantly associated with physician-reported FBSE (β=0.16 [95% CI, 0.13-0.18; P<.001])(Table 2).

Because of the bimodal distribution of scores in the physician-reported frequency of FBSEs, particularly pertaining to the extreme points of the scale, we further repeated analysis with only the never and almost always groups (Table 1). Primary care providers who reported almost always for FBSE had 29.6% increased odds of patient-reported back examination (95% CI, 1.00-1.68; P=.048) and 59.3% increased odds of patient-reported abdomen examination (95% CI, 1.23-2.06; P<.001). The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined when the PCP reported having never conducted an FBSE were 56%, 40%, and 26%, respectively. The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined when the PCP reported having almost always conducted an FBSE were 52%, 51%, and 30%, respectively. Raw percentages were calculated by dividing the number of "yes" responses by participants for each body part examined by thetotal number of participant responses (“yes” and “no”) for each respective body part. There was no significant change in odds of patient-reported backs of legs examined with PCP-reported never vs almost always conducting an FBSE. In addition, a greater patient-reported level of undress was associated with 20.2% increased odds of PCPs reporting almost always conducting an FBSE (95% CI, 1.08-1.34; P=.001).
FBSEs in Patient Medical Records
When comparing PCP-reported FBSE and report of FBSE in patient medical records, there was a 39.0% increased odds of the patient medical record indicating FBSE when physicians reported conducting an FBSE with greater frequency (95% CI, 1.30-1.48; P<.001)(eTable 1). When examining PCP-reported never vs almost always conducting an FBSE, a report of almost always was associated with 79.0% increased odds of the patient medical record indicating that an FBSE was conducted (95% CI, 1.28-2.49; P=.001). The raw percentage of the patient medical record indicating an FBSE was conducted when the PCP reported having never conducted an FBSE was 17% and 26% when the PCP reported having almost always conducted an FBSE.

When comparing the patient-reported body part examined with patient FBSE medical record documentation, an indication of yes for FBSE on the patient medical record was associated with a considerable increase in odds that patients reported a particular body part was examined (back: 91.4% [95% CI, 1.59-2.31; P<.001]; abdomen: 75.0% [95% CI, 1.45-2.11; P<.001]; backs of legs: 91.6% [95% CI, 1.56-2.36; P<.001])(eTable 2). The raw percentages of patients who reported having their back, abdomen, and backs of legs examined vs not examined when the patient medical record indicated an FBSE was completed were 24% vs 14%, 23% vs 15%, and 26% vs 16%, respectively. An increase in patient-reported level of undress was associated with a 57.0% increased odds of their medical record indicating an FBSE was conducted (95% CI, 1.45-1.70; P<.001).

COMMENT How PCPs Perform FBSEs Varies
We found that PCPs performed FBSEs with variable frequency, and among those who did, the patient report of their examination varied considerably (Table 1). There appears to be considerable ambiguity in each of these means of determining the extent to which the skin was inspected for skin cancer, which may render the task of improving such inspection more difficult. We asked patients whether their back, abdomen, and backs of legs were examined as an assessment of some of the variety of areas inspected during an FBSE. During a general well-visit appointment, a patient’s back and abdomen may be examined for multiple reasons. Patients may have misinterpreted elements of the pulmonary, cardiac, abdominal, or musculoskeletal examinations as being part of the FBSE. The back and abdomen—the least specific features of the FBSE—were reported by patients to be the most often examined. Conversely, the backs of the legs—the most specific feature of the FBSE—had the lowest odds of being examined (Table 1).
In addition to the potential limitations of patient awareness of physician activity, our results also could be explained by differences among PCPs in how they performed FBSEs. There is no standardized method of conducting an FBSE. Furthermore, not all medical students and residents are exposed to dermatology training. In our sample of 53 physicians, 79% had reported receiving dermatology training; however, we did not assess the extent to which they had been trained in conducting an FBSE and/or identifying malignant lesions. In an American survey of 659 medical students, more than two-thirds of students had never been trained or never examined a patient for skin cancer.21 In another American survey of 342 internal medicine, family medicine, pediatrics, and obstetrics/gynecology residents across 7 medical schools and 4 residency programs, more than three-quarters of residents had never been trained in skin cancer screening.22 Our findings reflect insufficient and inconsistent training in skin cancer screening and underscore the need for mandatory education to ensure quality FBSEs are performed in the primary care setting.
Frequency of PCPs Performing FBSEs
Similar to prior studies analyzing the frequency of FBSE performance in the primary care setting,16,19,23,24 more than half of our PCP sample reported sometimes to never conducting FBSEs. The percentage of physicians who reported conducting FBSEs in our sample was greater than the proportion reported by the National Health Interview Survey, in which only 8% of patients received an FBSE in the prior year by a PCP or obstetrician/gynecologist,16 but similar to a smaller patient study.19 In that study, 87% of patients, regardless of their skin cancer history, also reported that they would like their PCP to perform an FBSE regularly.19 Although some of our patient participants may have declined an FBSE, it is unlikely that that would have entirely accounted for the relatively low number of PCPs who reported frequently performing FBSEs.
Documentation in Medical Records of FBSEs
Compared to PCP self-reported performance of FBSEs, considerably fewer PCPs marked the patient medical record as having completed an FBSE. Among patients with medical records that indicated an FBSE had been conducted, they reported higher odds of all 3 body parts being examined, the highest being the backs of the legs. Also, when the patient medical record indicated an FBSE had been completed, the odds that the PCP reported an FBSE also were higher. The relatively low medical record documentation of FBSEs highlights the need for more rigorous enforcement of accurate documentation. However, among the cases that were recorded, it appeared that the content of the examinations was more consistent.
Benefits of PCP-Led FBSEs
Although the USPSTF issued an I rating for PCP-led FBSEs,14 multiple national medical societies, including the American Cancer Society,25 American Academy of Dermatology,26 and Skin Cancer Foundation,27 as well as international guidelines in Germany,28 Australia,29,30 and New Zealand,31 recommend regular FBSEs among the general or at-risk population; New Zealand and Australia have the highest incidence and prevalence of melanoma in the world.8 The benefits of physician-led FBSEs on detection of early-stage skin cancer, and in particular, melanoma detection, have been documented in numerous studies.30,32-38 However, the variability and often poor quality of skin screening may contribute in part to the just as numerous null results from prior skin screening studies,15 perpetuating the insufficient status of skin examinations by USPSTF standards.14 Our study underscores both the variability in frequency and content of PCP-administered FBSEs. It also highlights the need for standardization of screening examinations at the medical student, trainee, and physician level.
Study Limitations
The present study has several limitations. First, there was an unknown time lag between the FBSEs and physician self-reported surveys. Similarly, there was a variable time lag between the patient examination encounter and subsequent telephone survey. Both the physician and patient survey data may have been affected by recall bias. Second, patients were not asked directly whether an FBSE had been conducted. Furthermore, patients may not have appreciated whether the body part examined was part of the FBSE or another examination. Also, screenings often were not recorded in the medical record, assuming that the patient report and/or physician report was more accurate than the medical record.
Our study also was limited by demographics; our patient sample was largely comprised of White, educated, US adults, potentially limiting the generalizability of our findings. Conversely, a notable strength of our study was that our participants were recruited from 4 geographically diverse centers. Furthermore, we had a comparatively large sample size of patients and physicians. Also, the independent assessment of provider-reported examinations, objective assessment of medical records, and patient reports of their encounters provides a strong foundation for assessing the independent contributions of each data source.
CONCLUSION
Our study highlights the challenges future studies face in promoting skin cancer screening in the primary care setting. Our findings underscore the need for a standardized FBSE as well as clear clinical expectations regarding skin cancer screening that is expected of PCPs.
As long as skin cancer screening rates remain low in the United States, patients will be subject to potential delays and missed diagnoses, impacting morbidity and mortality.8 There are burgeoning resources and efforts in place to increase skin cancer screening. For example, free validated online training is available for early detection of melanoma and other skin cancers (https://www.visualdx.com/skin-cancer-education/).39-42 Future directions for bolstering screening numbers must focus on educating PCPs about skin cancer prevention and perhaps narrowing the screening population by age-appropriate risk assessments.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the U.S. population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Dourmishev LA, Rusinova D, Botev I. Clinical variants, stages, and management of basal cell carcinoma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:12-17.
- Thompson AK, Kelley BF, Prokop LJ, et al. Risk factors for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:419-428.
- Motaparthi K, Kapil JP, Velazquez EF. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: review of the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Guidelines, Prognostic Factors, and Histopathologic Variants. Adv Anat Pathol. 2017;24:171-194.
- Barton V, Armeson K, Hampras S, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer and risk of all-cause and cancer-related mortality: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309:243-251.
- Weinstock MA, Bogaars HA, Ashley M, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer mortality. a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1194-1197.
- Matthews NH, Li W-Q, Qureshi AA, et al. Epidemiology of melanoma. In: Ward WH, Farma JM, eds. Cutaneous Melanoma: Etiology and Therapy. Codon Publications; 2017:3-22.
- Cakir BO, Adamson P, Cingi C. Epidemiology and economic burden of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2012;20:419-422.
- Guy GP, Machlin SR, Ekwueme DU, et al. Prevalence and costs of skin cancer treatment in the U.S., 2002-2006 and 2007-2011. Am J Prev Med. 2015;48:183-187.
- Losina E, Walensky RP, Geller A, et al. Visual screening for malignant melanoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:21-28.
- Markova A, Weinstock MA, Risica P, et al. Effect of a web-based curriculum on primary care practice: basic skin cancer triage trial. Fam Med. 2013;45:558-568.
- Johnson MM, Leachman SA, Aspinwall LG, et al. Skin cancer screening: recommendations for data-driven screening guidelines and a review of the US Preventive Services Task Force controversy. Melanoma Manag. 2017;4:13-37.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Screening for skin cancer in adults: an updated systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. November 30, 2015. Accessed July 25, 2022. http://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/draft-evidence-review159/skin-cancer-screening2
- Wernli KJ, Henrikson NB, Morrison CC, et al. Screening for skin cancer in adults: updated evidence report and systematic review forthe US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;316:436-447.
- LeBlanc WG, Vidal L, Kirsner RS, et al. Reported skin cancer screening of US adult workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:55-63.
- Federman DG, Concato J, Caralis PV, et al. Screening for skin cancer in primary care settings. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:1423-1425.
- Kirsner RS, Muhkerjee S, Federman DG. Skin cancer screening in primary care: prevalence and barriers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:564-566.
- Federman DG, Kravetz JD, Tobin DG, et al. Full-body skin examinations: the patient’s perspective. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:530-534.
- IBM. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows. IBM Corp; 2015.
- Moore MM, Geller AC, Zhang Z, et al. Skin cancer examination teaching in US medical education. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:439-444.
- Wise E, Singh D, Moore M, et al. Rates of skin cancer screening and prevention counseling by US medical residents. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1131-1136.
- Lakhani NA, Saraiya M, Thompson TD, et al. Total body skin examination for skin cancer screening among U.S. adults from 2000 to 2010. Prev Med. 2014;61:75-80.
- Coups EJ, Geller AC, Weinstock MA, et al. Prevalence and correlates of skin cancer screening among middle-aged and older white adults in the United States. Am J Med. 2010;123:439-445.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2016. Accessed March 13, 2022. https://cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2016/
- American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer incidence rates. Updated April 22, 2022. Accessed August 1, 2022. https://www.aad.org/media/stats-skin-cancer
- Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin cancer prevention. Accessed July 25, 2022. http://skincancer.org/prevention/sun-protection/prevention-guidelines
- Katalinic A, Eisemann N, Waldmann A. Skin cancer screening in Germany. documenting melanoma incidence and mortality from 2008 to 2013. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015;112:629-634.
- Cancer Council Australia. Position statement: screening and early detection of skin cancer. Published July 2014. Accessed July 25, 2022. https://dermcoll.edu.au/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/PosStatEarlyDetectSkinCa.pdf
- Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Guidelines for Preventive Activities in General Practice. 9th ed. The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners; 2016. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.racgp.org.au/download/Documents/Guidelines/Redbook9/17048-Red-Book-9th-Edition.pdf
- Cancer Council Australia and Australian Cancer Network and New Zealand Guidelines Group. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Melanoma in Australia and New Zealand. The Cancer Council Australia and Australian Cancer Network, Sydney and New Zealand Guidelines Group, Wellington; 2008. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.health.govt.nz/system/files/documents/publications/melanoma-guideline-nov08-v2.pdf
- Swetter SM, Pollitt RA, Johnson TM, et al. Behavioral determinants of successful early melanoma detection: role of self and physician skin examination. Cancer. 2012;118:3725-3734.
- Terushkin V, Halpern AC. Melanoma early detection. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:481-500, viii.
- Aitken JF, Elwood M, Baade PD, et al. Clinical whole-body skin examination reduces the incidence of thick melanomas. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:450-458.
- Aitken JF, Elwood JM, Lowe JB, et al. A randomised trial of population screening for melanoma. J Med Screen. 2002;9:33-37.
- Breitbart EW, Waldmann A, Nolte S, et al. Systematic skin cancer screening in Northern Germany. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:201-211.
- Janda M, Lowe JB, Elwood M, et al. Do centralised skin screening clinics increase participation in melanoma screening (Australia)? Cancer Causes Control. 2006;17:161-168.
- Aitken JF, Janda M, Elwood M, et al. Clinical outcomes from skin screening clinics within a community-based melanoma screening program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:105-114.
- Eide MJ, Asgari MM, Fletcher SW, et al. Effects on skills and practice from a web-based skin cancer course for primary care providers. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:648-657.
- Weinstock MA, Ferris LK, Saul MI, et al. Downstream consequences of melanoma screening in a community practice setting: first results. Cancer. 2016;122:3152-3156.
- Matthews NH, Risica PM, Ferris LK, et al. Psychosocial impact of skin biopsies in the setting of melanoma screening: a cross-sectional survey. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:664-665.
- Risica PM, Matthews NH, Dionne L, et al. Psychosocial consequences of skin cancer screening. Prev Med Rep. 2018;10:310-316.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the U.S. population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Dourmishev LA, Rusinova D, Botev I. Clinical variants, stages, and management of basal cell carcinoma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:12-17.
- Thompson AK, Kelley BF, Prokop LJ, et al. Risk factors for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:419-428.
- Motaparthi K, Kapil JP, Velazquez EF. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: review of the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Guidelines, Prognostic Factors, and Histopathologic Variants. Adv Anat Pathol. 2017;24:171-194.
- Barton V, Armeson K, Hampras S, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer and risk of all-cause and cancer-related mortality: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017;309:243-251.
- Weinstock MA, Bogaars HA, Ashley M, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer mortality. a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1194-1197.
- Matthews NH, Li W-Q, Qureshi AA, et al. Epidemiology of melanoma. In: Ward WH, Farma JM, eds. Cutaneous Melanoma: Etiology and Therapy. Codon Publications; 2017:3-22.
- Cakir BO, Adamson P, Cingi C. Epidemiology and economic burden of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2012;20:419-422.
- Guy GP, Machlin SR, Ekwueme DU, et al. Prevalence and costs of skin cancer treatment in the U.S., 2002-2006 and 2007-2011. Am J Prev Med. 2015;48:183-187.
- Losina E, Walensky RP, Geller A, et al. Visual screening for malignant melanoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:21-28.
- Markova A, Weinstock MA, Risica P, et al. Effect of a web-based curriculum on primary care practice: basic skin cancer triage trial. Fam Med. 2013;45:558-568.
- Johnson MM, Leachman SA, Aspinwall LG, et al. Skin cancer screening: recommendations for data-driven screening guidelines and a review of the US Preventive Services Task Force controversy. Melanoma Manag. 2017;4:13-37.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Screening for skin cancer in adults: an updated systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. November 30, 2015. Accessed July 25, 2022. http://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/draft-evidence-review159/skin-cancer-screening2
- Wernli KJ, Henrikson NB, Morrison CC, et al. Screening for skin cancer in adults: updated evidence report and systematic review forthe US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;316:436-447.
- LeBlanc WG, Vidal L, Kirsner RS, et al. Reported skin cancer screening of US adult workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:55-63.
- Federman DG, Concato J, Caralis PV, et al. Screening for skin cancer in primary care settings. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:1423-1425.
- Kirsner RS, Muhkerjee S, Federman DG. Skin cancer screening in primary care: prevalence and barriers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:564-566.
- Federman DG, Kravetz JD, Tobin DG, et al. Full-body skin examinations: the patient’s perspective. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:530-534.
- IBM. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows. IBM Corp; 2015.
- Moore MM, Geller AC, Zhang Z, et al. Skin cancer examination teaching in US medical education. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:439-444.
- Wise E, Singh D, Moore M, et al. Rates of skin cancer screening and prevention counseling by US medical residents. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1131-1136.
- Lakhani NA, Saraiya M, Thompson TD, et al. Total body skin examination for skin cancer screening among U.S. adults from 2000 to 2010. Prev Med. 2014;61:75-80.
- Coups EJ, Geller AC, Weinstock MA, et al. Prevalence and correlates of skin cancer screening among middle-aged and older white adults in the United States. Am J Med. 2010;123:439-445.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2016. Accessed March 13, 2022. https://cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2016/
- American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer incidence rates. Updated April 22, 2022. Accessed August 1, 2022. https://www.aad.org/media/stats-skin-cancer
- Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin cancer prevention. Accessed July 25, 2022. http://skincancer.org/prevention/sun-protection/prevention-guidelines
- Katalinic A, Eisemann N, Waldmann A. Skin cancer screening in Germany. documenting melanoma incidence and mortality from 2008 to 2013. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015;112:629-634.
- Cancer Council Australia. Position statement: screening and early detection of skin cancer. Published July 2014. Accessed July 25, 2022. https://dermcoll.edu.au/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/PosStatEarlyDetectSkinCa.pdf
- Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Guidelines for Preventive Activities in General Practice. 9th ed. The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners; 2016. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.racgp.org.au/download/Documents/Guidelines/Redbook9/17048-Red-Book-9th-Edition.pdf
- Cancer Council Australia and Australian Cancer Network and New Zealand Guidelines Group. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Melanoma in Australia and New Zealand. The Cancer Council Australia and Australian Cancer Network, Sydney and New Zealand Guidelines Group, Wellington; 2008. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://www.health.govt.nz/system/files/documents/publications/melanoma-guideline-nov08-v2.pdf
- Swetter SM, Pollitt RA, Johnson TM, et al. Behavioral determinants of successful early melanoma detection: role of self and physician skin examination. Cancer. 2012;118:3725-3734.
- Terushkin V, Halpern AC. Melanoma early detection. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:481-500, viii.
- Aitken JF, Elwood M, Baade PD, et al. Clinical whole-body skin examination reduces the incidence of thick melanomas. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:450-458.
- Aitken JF, Elwood JM, Lowe JB, et al. A randomised trial of population screening for melanoma. J Med Screen. 2002;9:33-37.
- Breitbart EW, Waldmann A, Nolte S, et al. Systematic skin cancer screening in Northern Germany. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:201-211.
- Janda M, Lowe JB, Elwood M, et al. Do centralised skin screening clinics increase participation in melanoma screening (Australia)? Cancer Causes Control. 2006;17:161-168.
- Aitken JF, Janda M, Elwood M, et al. Clinical outcomes from skin screening clinics within a community-based melanoma screening program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:105-114.
- Eide MJ, Asgari MM, Fletcher SW, et al. Effects on skills and practice from a web-based skin cancer course for primary care providers. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:648-657.
- Weinstock MA, Ferris LK, Saul MI, et al. Downstream consequences of melanoma screening in a community practice setting: first results. Cancer. 2016;122:3152-3156.
- Matthews NH, Risica PM, Ferris LK, et al. Psychosocial impact of skin biopsies in the setting of melanoma screening: a cross-sectional survey. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:664-665.
- Risica PM, Matthews NH, Dionne L, et al. Psychosocial consequences of skin cancer screening. Prev Med Rep. 2018;10:310-316.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatologists should be aware of the variability in practice and execution of full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) among primary care providers and offer comprehensive examinations for every patient.
- Variability in reporting and execution of FBSEs may impact the continued US Preventive Services Task Force I rating in their guidelines and promotion of skin cancer screening in the primary care setting.
How to Address Scar Pincushioning and Webbing of the Nasal Dorsum Using Surgical Defatting and Z-plasty
Practice Gap
Nonmelanoma skin cancer is the most common cancer, typically growing in sun-exposed areas. As such, the nasal area is a common site of onset, constituting approximately 25% of cases. Surgical excision of these cancers generally has a high cure rate.1
Although complete excision of the tumor is the primary goal of the dermatologic surgeon, achieving a cosmetically satisfactory scar also is important. As a prominent feature of the face, any irregularities to the nose are easily noticeable.2 The subsequent scar may exhibit features that are less than ideal and cause notable stress to the patient.
When a scar presents with several complications, using a single surgical technique may not sufficiently address all defects. As a result, it can be challenging for the surgeon to decide which combination of methods among the myriad of nonsurgical and surgical options for scar revision will produce the best cosmetic outcome.
Case and Technique
A 76-year-old man presented 1 year after he underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for squamous cell carcinoma on the nasal dorsum. The tumor cleared after 1 stage and was repaired using a bilateral V-Y advancement flap. Postoperatively, the patient developed pincushioning of the flap, atrophic scarring inferior to the flap, and webbing of the pivotal restraint point at the nasal root (Figures 1A and 1B). We opted to address the pincushioning and nasal root webbing by defatting the flap and performing Z-plasty, respectively.
Pincushioning—Pincushioning of a flap arises due to contraction and lymphedema at the edge of the repair. It is seen more often in nasal repairs due to the limited availability of surrounding skin and changes in skin texture from rhinion to tip.3 To combat this in our patient, an incision was made around the site of the original flap, surrounding tissue was undermined, and the flap was reflected back. Subcutaneous tissue was removed with scissors. The flap was then laid back into the defect, and the subcutaneous tissue and dermis were closed with interrupted buried vertical mattress sutures. The epidermis was closed in a simple running fashion.
Webbing—Webbing of a scar also may develop from the contractile wound-healing process.4 Z-plasty commonly is used to camouflage a linear or contracted scar, increase skin availability in an area, or alter scar direction to better align with skin-tension lines.5,6 In our patient, we incised the webbing of the nasal root along the vertical scar. Two arms were drawn at each end of the scar at a 60° angle (Figure 2); the side arms were drawn equal in length and incised vertically. Full-thickness skin flaps were then undermined at the level of subcutaneous fat, creating 2 triangular flaps. Adequate undermining of the surrounding subcutaneous tissue was performed to achieve proper mobilization of the flaps, which allowed for flap transposition to occur without tension and therefore for proper redirection of the scar.6 The flaps were secured using buried vertical mattress sutures and simple running sutures. Using too many buried interrupted sutures can cause vascular compromise of the fragile tips of the Z and should be avoided.3
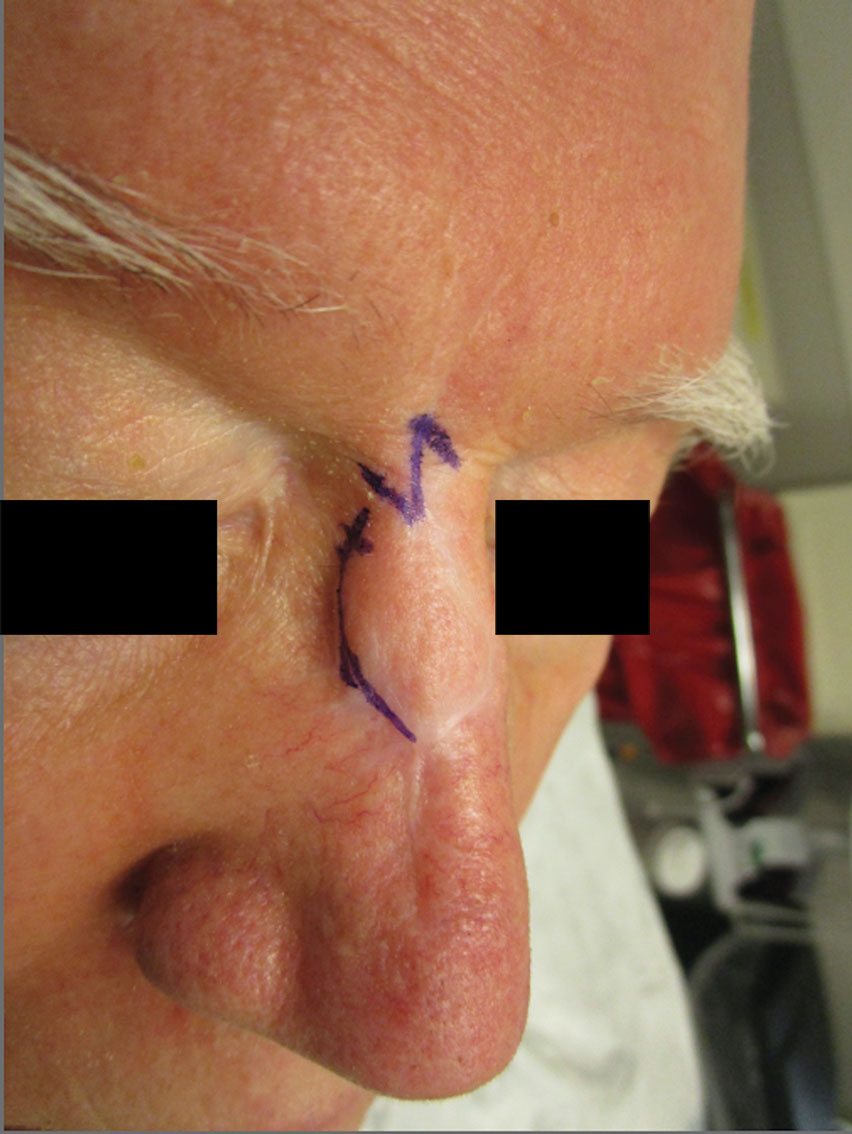
At 4-month postoperative follow-up, the cosmetic outcome was judged satisfactory (Figure 1C).
Practice Implications
In our patient, pincushioning of the flap was easily addressed by defatting the area. However, doing just this would not have sufficed and necessitated another surgical technique—the Z-plasty—which needed to be designed carefully. The larger the angle between the side arms and central limb, the greater directional change and scar length that is gained (Figure 3). As a result, longer limbs and a greater angle could advantageously break up the scar line but consequently would lengthen the scar considerably. Therefore, if the scar was longer or the skin was inelastic, multiple Z-plasty procedures may have been preferred.
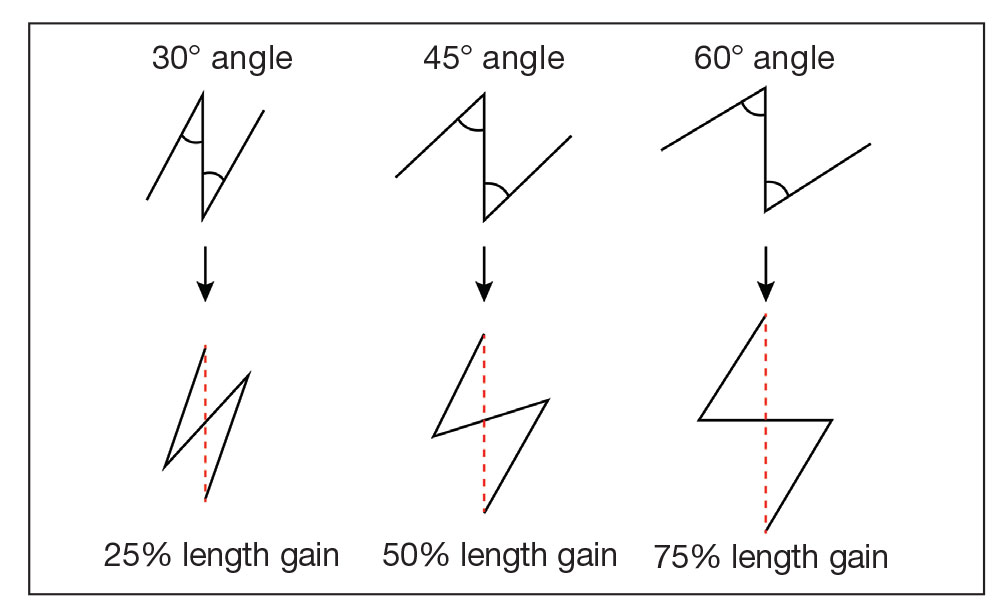
Additionally, for each central limb, both mirror-image options for peripheral arms were considered, with the optimal choice being the one that allowed for final scar lines to mimic relaxed skin-tension lines. Accuracy of the incisions was critical and was assessed by drawing a line between the free ends of the lateral limbs of the Z; this line should pass perpendicularly through the midpoint of the central limb. Last, as with other transposition flap options, Z-plasty has the potential to create a trapdoor or pincushion effect; we reduced this risk by wide undermining to establish an even contraction plate.6
When planning the revision, we considered multiple approaches to achieve the best aesthetic outcome in 1 stage. Had there been notable depression in the scar, we may have used a full-thickness skin graft. If the skin surface was lumpy and uneven, dermabrasion or a laser may have been utilized. Another consideration was to avoid using intralesional steroids, which could have made the already atrophied portions of the scar worse.
Overall, the surgical plan that we chose took into consideration the patient’s nasal anatomic structure, the combination of scar defects, the patient’s desires, and the tools available.
Final Thoughts
The ideal scar is inconspicuous, does not impair the function of surrounding structures, and blends well with adjacent skin.5 Consequently, the combination of pincushioning and webbing of a scar, especially in the nasal area, can pose a surgical challenge to the surgeon and can cause severe anxiety in the patient. In those circumstances, a single surgical technique is not likely to produce the revision with the best cosmetic outcome. Therefore, the synergy of 2 or more surgical techniques with proper planning and meticulous selection may be necessary. A broad knowledge of various scar revision techniques increases the surgeon’s capability to create the ideal scar.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank the case patient for granting permission to publish this information.
- Arginelli F, Salgarelli AC, Ferrari B, et al. Crescentic flap for the reconstruction of the nose after skin cancer resection. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44:703-707. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2016.02.008
- Helml G, von Gregory HF, Amr A, et al. One-stage nasal soft tissue reconstruction with local flaps. Facial Plast Surg. 2014;30:260-267. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1376871
- Woodard CR. Complications in facial flap surgery. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2013;21:599-604. doi:10.1016/j.fsc.2013.07.009
- Brissett AE, Sherris DA. Scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. Facial Plast Surg. 2001;17:263-272. doi:10.1055/s-2001-18827
- A, B, MA. Surgical principles for achieving a functional and cosmetically acceptable scar. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013;104:17-28. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2011.12.010
- Aasi SZ. Z-plasty made simple. Dermatol Res Pract. 2010;2010:982623. doi:10.1155/2010/982623
Practice Gap
Nonmelanoma skin cancer is the most common cancer, typically growing in sun-exposed areas. As such, the nasal area is a common site of onset, constituting approximately 25% of cases. Surgical excision of these cancers generally has a high cure rate.1
Although complete excision of the tumor is the primary goal of the dermatologic surgeon, achieving a cosmetically satisfactory scar also is important. As a prominent feature of the face, any irregularities to the nose are easily noticeable.2 The subsequent scar may exhibit features that are less than ideal and cause notable stress to the patient.
When a scar presents with several complications, using a single surgical technique may not sufficiently address all defects. As a result, it can be challenging for the surgeon to decide which combination of methods among the myriad of nonsurgical and surgical options for scar revision will produce the best cosmetic outcome.
Case and Technique
A 76-year-old man presented 1 year after he underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for squamous cell carcinoma on the nasal dorsum. The tumor cleared after 1 stage and was repaired using a bilateral V-Y advancement flap. Postoperatively, the patient developed pincushioning of the flap, atrophic scarring inferior to the flap, and webbing of the pivotal restraint point at the nasal root (Figures 1A and 1B). We opted to address the pincushioning and nasal root webbing by defatting the flap and performing Z-plasty, respectively.

Pincushioning—Pincushioning of a flap arises due to contraction and lymphedema at the edge of the repair. It is seen more often in nasal repairs due to the limited availability of surrounding skin and changes in skin texture from rhinion to tip.3 To combat this in our patient, an incision was made around the site of the original flap, surrounding tissue was undermined, and the flap was reflected back. Subcutaneous tissue was removed with scissors. The flap was then laid back into the defect, and the subcutaneous tissue and dermis were closed with interrupted buried vertical mattress sutures. The epidermis was closed in a simple running fashion.
Webbing—Webbing of a scar also may develop from the contractile wound-healing process.4 Z-plasty commonly is used to camouflage a linear or contracted scar, increase skin availability in an area, or alter scar direction to better align with skin-tension lines.5,6 In our patient, we incised the webbing of the nasal root along the vertical scar. Two arms were drawn at each end of the scar at a 60° angle (Figure 2); the side arms were drawn equal in length and incised vertically. Full-thickness skin flaps were then undermined at the level of subcutaneous fat, creating 2 triangular flaps. Adequate undermining of the surrounding subcutaneous tissue was performed to achieve proper mobilization of the flaps, which allowed for flap transposition to occur without tension and therefore for proper redirection of the scar.6 The flaps were secured using buried vertical mattress sutures and simple running sutures. Using too many buried interrupted sutures can cause vascular compromise of the fragile tips of the Z and should be avoided.3

At 4-month postoperative follow-up, the cosmetic outcome was judged satisfactory (Figure 1C).
Practice Implications
In our patient, pincushioning of the flap was easily addressed by defatting the area. However, doing just this would not have sufficed and necessitated another surgical technique—the Z-plasty—which needed to be designed carefully. The larger the angle between the side arms and central limb, the greater directional change and scar length that is gained (Figure 3). As a result, longer limbs and a greater angle could advantageously break up the scar line but consequently would lengthen the scar considerably. Therefore, if the scar was longer or the skin was inelastic, multiple Z-plasty procedures may have been preferred.

Additionally, for each central limb, both mirror-image options for peripheral arms were considered, with the optimal choice being the one that allowed for final scar lines to mimic relaxed skin-tension lines. Accuracy of the incisions was critical and was assessed by drawing a line between the free ends of the lateral limbs of the Z; this line should pass perpendicularly through the midpoint of the central limb. Last, as with other transposition flap options, Z-plasty has the potential to create a trapdoor or pincushion effect; we reduced this risk by wide undermining to establish an even contraction plate.6
When planning the revision, we considered multiple approaches to achieve the best aesthetic outcome in 1 stage. Had there been notable depression in the scar, we may have used a full-thickness skin graft. If the skin surface was lumpy and uneven, dermabrasion or a laser may have been utilized. Another consideration was to avoid using intralesional steroids, which could have made the already atrophied portions of the scar worse.
Overall, the surgical plan that we chose took into consideration the patient’s nasal anatomic structure, the combination of scar defects, the patient’s desires, and the tools available.
Final Thoughts
The ideal scar is inconspicuous, does not impair the function of surrounding structures, and blends well with adjacent skin.5 Consequently, the combination of pincushioning and webbing of a scar, especially in the nasal area, can pose a surgical challenge to the surgeon and can cause severe anxiety in the patient. In those circumstances, a single surgical technique is not likely to produce the revision with the best cosmetic outcome. Therefore, the synergy of 2 or more surgical techniques with proper planning and meticulous selection may be necessary. A broad knowledge of various scar revision techniques increases the surgeon’s capability to create the ideal scar.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank the case patient for granting permission to publish this information.
Practice Gap
Nonmelanoma skin cancer is the most common cancer, typically growing in sun-exposed areas. As such, the nasal area is a common site of onset, constituting approximately 25% of cases. Surgical excision of these cancers generally has a high cure rate.1
Although complete excision of the tumor is the primary goal of the dermatologic surgeon, achieving a cosmetically satisfactory scar also is important. As a prominent feature of the face, any irregularities to the nose are easily noticeable.2 The subsequent scar may exhibit features that are less than ideal and cause notable stress to the patient.
When a scar presents with several complications, using a single surgical technique may not sufficiently address all defects. As a result, it can be challenging for the surgeon to decide which combination of methods among the myriad of nonsurgical and surgical options for scar revision will produce the best cosmetic outcome.
Case and Technique
A 76-year-old man presented 1 year after he underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for squamous cell carcinoma on the nasal dorsum. The tumor cleared after 1 stage and was repaired using a bilateral V-Y advancement flap. Postoperatively, the patient developed pincushioning of the flap, atrophic scarring inferior to the flap, and webbing of the pivotal restraint point at the nasal root (Figures 1A and 1B). We opted to address the pincushioning and nasal root webbing by defatting the flap and performing Z-plasty, respectively.

Pincushioning—Pincushioning of a flap arises due to contraction and lymphedema at the edge of the repair. It is seen more often in nasal repairs due to the limited availability of surrounding skin and changes in skin texture from rhinion to tip.3 To combat this in our patient, an incision was made around the site of the original flap, surrounding tissue was undermined, and the flap was reflected back. Subcutaneous tissue was removed with scissors. The flap was then laid back into the defect, and the subcutaneous tissue and dermis were closed with interrupted buried vertical mattress sutures. The epidermis was closed in a simple running fashion.
Webbing—Webbing of a scar also may develop from the contractile wound-healing process.4 Z-plasty commonly is used to camouflage a linear or contracted scar, increase skin availability in an area, or alter scar direction to better align with skin-tension lines.5,6 In our patient, we incised the webbing of the nasal root along the vertical scar. Two arms were drawn at each end of the scar at a 60° angle (Figure 2); the side arms were drawn equal in length and incised vertically. Full-thickness skin flaps were then undermined at the level of subcutaneous fat, creating 2 triangular flaps. Adequate undermining of the surrounding subcutaneous tissue was performed to achieve proper mobilization of the flaps, which allowed for flap transposition to occur without tension and therefore for proper redirection of the scar.6 The flaps were secured using buried vertical mattress sutures and simple running sutures. Using too many buried interrupted sutures can cause vascular compromise of the fragile tips of the Z and should be avoided.3

At 4-month postoperative follow-up, the cosmetic outcome was judged satisfactory (Figure 1C).
Practice Implications
In our patient, pincushioning of the flap was easily addressed by defatting the area. However, doing just this would not have sufficed and necessitated another surgical technique—the Z-plasty—which needed to be designed carefully. The larger the angle between the side arms and central limb, the greater directional change and scar length that is gained (Figure 3). As a result, longer limbs and a greater angle could advantageously break up the scar line but consequently would lengthen the scar considerably. Therefore, if the scar was longer or the skin was inelastic, multiple Z-plasty procedures may have been preferred.

Additionally, for each central limb, both mirror-image options for peripheral arms were considered, with the optimal choice being the one that allowed for final scar lines to mimic relaxed skin-tension lines. Accuracy of the incisions was critical and was assessed by drawing a line between the free ends of the lateral limbs of the Z; this line should pass perpendicularly through the midpoint of the central limb. Last, as with other transposition flap options, Z-plasty has the potential to create a trapdoor or pincushion effect; we reduced this risk by wide undermining to establish an even contraction plate.6
When planning the revision, we considered multiple approaches to achieve the best aesthetic outcome in 1 stage. Had there been notable depression in the scar, we may have used a full-thickness skin graft. If the skin surface was lumpy and uneven, dermabrasion or a laser may have been utilized. Another consideration was to avoid using intralesional steroids, which could have made the already atrophied portions of the scar worse.
Overall, the surgical plan that we chose took into consideration the patient’s nasal anatomic structure, the combination of scar defects, the patient’s desires, and the tools available.
Final Thoughts
The ideal scar is inconspicuous, does not impair the function of surrounding structures, and blends well with adjacent skin.5 Consequently, the combination of pincushioning and webbing of a scar, especially in the nasal area, can pose a surgical challenge to the surgeon and can cause severe anxiety in the patient. In those circumstances, a single surgical technique is not likely to produce the revision with the best cosmetic outcome. Therefore, the synergy of 2 or more surgical techniques with proper planning and meticulous selection may be necessary. A broad knowledge of various scar revision techniques increases the surgeon’s capability to create the ideal scar.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank the case patient for granting permission to publish this information.
- Arginelli F, Salgarelli AC, Ferrari B, et al. Crescentic flap for the reconstruction of the nose after skin cancer resection. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44:703-707. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2016.02.008
- Helml G, von Gregory HF, Amr A, et al. One-stage nasal soft tissue reconstruction with local flaps. Facial Plast Surg. 2014;30:260-267. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1376871
- Woodard CR. Complications in facial flap surgery. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2013;21:599-604. doi:10.1016/j.fsc.2013.07.009
- Brissett AE, Sherris DA. Scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. Facial Plast Surg. 2001;17:263-272. doi:10.1055/s-2001-18827
- A, B, MA. Surgical principles for achieving a functional and cosmetically acceptable scar. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013;104:17-28. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2011.12.010
- Aasi SZ. Z-plasty made simple. Dermatol Res Pract. 2010;2010:982623. doi:10.1155/2010/982623
- Arginelli F, Salgarelli AC, Ferrari B, et al. Crescentic flap for the reconstruction of the nose after skin cancer resection. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44:703-707. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2016.02.008
- Helml G, von Gregory HF, Amr A, et al. One-stage nasal soft tissue reconstruction with local flaps. Facial Plast Surg. 2014;30:260-267. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1376871
- Woodard CR. Complications in facial flap surgery. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2013;21:599-604. doi:10.1016/j.fsc.2013.07.009
- Brissett AE, Sherris DA. Scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. Facial Plast Surg. 2001;17:263-272. doi:10.1055/s-2001-18827
- A, B, MA. Surgical principles for achieving a functional and cosmetically acceptable scar. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013;104:17-28. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2011.12.010
- Aasi SZ. Z-plasty made simple. Dermatol Res Pract. 2010;2010:982623. doi:10.1155/2010/982623
Does cannabis help with menopause symptoms?
Many women with symptoms of menopause are turning to cannabis for help, researchers have found, despite a lack of evidence that the drug works for these issues.
In a survey of perimenopausal and menopausal women who said they’ve used cannabis, nearly 80% said they use medical marijuana to alleviate symptoms such as sleep disturbances, hot flashes, and mood swings.
“Increasingly, we see greater numbers of individuals exploiting the use of cannabis and cannabinoids for lots of conditions. We realized there was no long-term data on how women were treating themselves for conditions like menopause,” said Staci Gruber, PhD, director of the Marijuana Investigations for Neuroscientific Discovery (MIND) program at McLean Hospital, an affiliate of Harvard Medical School, Boston, who led the study.
Dr. Gruber and her colleagues surveyed 131 perimenopausal and 127 postmenopausal women about their use of cannabis, identifying them through targeted advertising and social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Reddit.
The survey, published in Menopause, found 83.5% reported habitual cannabis use and 86% said they were current users. Around half of the women reported mixed medical/recreational use; 30.8% reported recreational use only and 17.7% said they only used medical forms of the drug.
The three most common modes of cannabis use were smoking a joint, bowl, or bong (84.3%); using edibles (78.3%);, and vaping oils (52.6%).
The researchers found that women in perimenopause reported markedly worse symptoms than did those in menopause, and these women tended to use a wider variety of cannabis products.
Dr. Gruber said clinicians should be asking their menopausal patients if they use cannabis to alleviate their symptoms.
Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, a women’s health expert at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and Jacksonville, Fla., said the looming question is whether cannabis in fact works in these patients.
“What we need is to figure out whether it works for women, and that hasn’t been studied yet,” she said.
Dr. Faubion, medical director for the North American Menopause Society, said the society is now conducting a review of worldwide data on nonhormonal treatments for symptoms of menopause. The report, which will examine the most current research on the effects of cannabis, hypnosis, diet, exercise, acupuncture, yoga, and meditation, will be released in 2023, she said.
Dr. Gruber said she hopes her group’s research will open the doors to more detailed explorations of how strains of cannabis and their levels of cannabidiol, a chemical compound in cannabis plants, and tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive component in cannabis, affect the symptoms women experience from menopause. Clinical trials for products aimed at specific symptoms also will be important, she added.
“We have a paucity of data from primary care clinicians,” Dr. Gruber said. “We, as researchers and clinicians, should be providing women with the research to make informed choices.”
The study was supported by private donations to the MIND program at McLean Hospital. No funding sources were involved in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Dr. Gruber reported grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Foria/Praxis Ventures, and Charlotte’s Web. She reported personal fees from the Coalition for Cannabis Policy, Education and Regulation; Beth Israel Deaconess; Fenway Health; Greenwich Biosciences Cannabis Education Working Group; and National Academy of Neuropsychology outside the submitted work. Dr. Faubion reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many women with symptoms of menopause are turning to cannabis for help, researchers have found, despite a lack of evidence that the drug works for these issues.
In a survey of perimenopausal and menopausal women who said they’ve used cannabis, nearly 80% said they use medical marijuana to alleviate symptoms such as sleep disturbances, hot flashes, and mood swings.
“Increasingly, we see greater numbers of individuals exploiting the use of cannabis and cannabinoids for lots of conditions. We realized there was no long-term data on how women were treating themselves for conditions like menopause,” said Staci Gruber, PhD, director of the Marijuana Investigations for Neuroscientific Discovery (MIND) program at McLean Hospital, an affiliate of Harvard Medical School, Boston, who led the study.
Dr. Gruber and her colleagues surveyed 131 perimenopausal and 127 postmenopausal women about their use of cannabis, identifying them through targeted advertising and social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Reddit.
The survey, published in Menopause, found 83.5% reported habitual cannabis use and 86% said they were current users. Around half of the women reported mixed medical/recreational use; 30.8% reported recreational use only and 17.7% said they only used medical forms of the drug.
The three most common modes of cannabis use were smoking a joint, bowl, or bong (84.3%); using edibles (78.3%);, and vaping oils (52.6%).
The researchers found that women in perimenopause reported markedly worse symptoms than did those in menopause, and these women tended to use a wider variety of cannabis products.
Dr. Gruber said clinicians should be asking their menopausal patients if they use cannabis to alleviate their symptoms.
Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, a women’s health expert at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and Jacksonville, Fla., said the looming question is whether cannabis in fact works in these patients.
“What we need is to figure out whether it works for women, and that hasn’t been studied yet,” she said.
Dr. Faubion, medical director for the North American Menopause Society, said the society is now conducting a review of worldwide data on nonhormonal treatments for symptoms of menopause. The report, which will examine the most current research on the effects of cannabis, hypnosis, diet, exercise, acupuncture, yoga, and meditation, will be released in 2023, she said.
Dr. Gruber said she hopes her group’s research will open the doors to more detailed explorations of how strains of cannabis and their levels of cannabidiol, a chemical compound in cannabis plants, and tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive component in cannabis, affect the symptoms women experience from menopause. Clinical trials for products aimed at specific symptoms also will be important, she added.
“We have a paucity of data from primary care clinicians,” Dr. Gruber said. “We, as researchers and clinicians, should be providing women with the research to make informed choices.”
The study was supported by private donations to the MIND program at McLean Hospital. No funding sources were involved in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Dr. Gruber reported grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Foria/Praxis Ventures, and Charlotte’s Web. She reported personal fees from the Coalition for Cannabis Policy, Education and Regulation; Beth Israel Deaconess; Fenway Health; Greenwich Biosciences Cannabis Education Working Group; and National Academy of Neuropsychology outside the submitted work. Dr. Faubion reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many women with symptoms of menopause are turning to cannabis for help, researchers have found, despite a lack of evidence that the drug works for these issues.
In a survey of perimenopausal and menopausal women who said they’ve used cannabis, nearly 80% said they use medical marijuana to alleviate symptoms such as sleep disturbances, hot flashes, and mood swings.
“Increasingly, we see greater numbers of individuals exploiting the use of cannabis and cannabinoids for lots of conditions. We realized there was no long-term data on how women were treating themselves for conditions like menopause,” said Staci Gruber, PhD, director of the Marijuana Investigations for Neuroscientific Discovery (MIND) program at McLean Hospital, an affiliate of Harvard Medical School, Boston, who led the study.
Dr. Gruber and her colleagues surveyed 131 perimenopausal and 127 postmenopausal women about their use of cannabis, identifying them through targeted advertising and social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Reddit.
The survey, published in Menopause, found 83.5% reported habitual cannabis use and 86% said they were current users. Around half of the women reported mixed medical/recreational use; 30.8% reported recreational use only and 17.7% said they only used medical forms of the drug.
The three most common modes of cannabis use were smoking a joint, bowl, or bong (84.3%); using edibles (78.3%);, and vaping oils (52.6%).
The researchers found that women in perimenopause reported markedly worse symptoms than did those in menopause, and these women tended to use a wider variety of cannabis products.
Dr. Gruber said clinicians should be asking their menopausal patients if they use cannabis to alleviate their symptoms.
Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, a women’s health expert at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and Jacksonville, Fla., said the looming question is whether cannabis in fact works in these patients.
“What we need is to figure out whether it works for women, and that hasn’t been studied yet,” she said.
Dr. Faubion, medical director for the North American Menopause Society, said the society is now conducting a review of worldwide data on nonhormonal treatments for symptoms of menopause. The report, which will examine the most current research on the effects of cannabis, hypnosis, diet, exercise, acupuncture, yoga, and meditation, will be released in 2023, she said.
Dr. Gruber said she hopes her group’s research will open the doors to more detailed explorations of how strains of cannabis and their levels of cannabidiol, a chemical compound in cannabis plants, and tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive component in cannabis, affect the symptoms women experience from menopause. Clinical trials for products aimed at specific symptoms also will be important, she added.
“We have a paucity of data from primary care clinicians,” Dr. Gruber said. “We, as researchers and clinicians, should be providing women with the research to make informed choices.”
The study was supported by private donations to the MIND program at McLean Hospital. No funding sources were involved in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Dr. Gruber reported grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Foria/Praxis Ventures, and Charlotte’s Web. She reported personal fees from the Coalition for Cannabis Policy, Education and Regulation; Beth Israel Deaconess; Fenway Health; Greenwich Biosciences Cannabis Education Working Group; and National Academy of Neuropsychology outside the submitted work. Dr. Faubion reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ACR makes changes to adult, pediatric vaccinations guidance
Patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases may need additional vaccines or different versions of vaccines they were not previously recommended to receive, according to updated guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) on vaccinations for these patients. The new guidelines pertain to routine vaccinations for adults and children and are based on the most current evidence. They include recommendations on whether to hold certain medications before or after vaccination. They do not include recommendations regarding COVID-19 vaccines.
For guidance on COVID-19 vaccine timing and frequency, the ACR directs physicians to the CDC’s recommendations for people with mild or severe immunosuppression and the ACR’s previous clinical guidance summary on the topic, last revised in February 2022. The recommendations in the new guidance differ from ACR’s guidance on COVID-19 vaccines on whether and when to hold immunosuppressive medications when patients receive nonlive vaccines. The new guidelines now align more closely with those of EULAR, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the CDC’s recommendations for human papillomavirus (HPV), pneumococcal, and shingles vaccines.
Vaccinations in this population are particularly important because “a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in those with rheumatic diseases is infections, due to the detrimental impact immunosuppression has on the ability for the patient to properly clear the pathogen,” Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at Washington University, St. Louis, told this news organization. While immunosuppressive medications are the most common reason patients with these conditions may have impaired immune function, “some of our patients with autoimmune disease also have a preexisting immunodeficiency that can inherently blunt immune responses to either infection or vaccination,” Dr. Kim explained.
“The authors of the guidelines have done a really nice job of making distinct recommendations based on the mechanism of action of various immunosuppressive medications,” Dr. Kim said. “This helps simplify the process of deciding the timing of vaccination for the health provider, especially for those on multiple immunosuppressives who represent an important proportion of our patients with rheumatic diseases.”
The main change to the guidelines for children, aside from those related to flu vaccination, is in regard to rotavirus vaccination for infants exposed to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors or rituximab in utero. Infants prenatally exposed to rituximab should not receive the rotavirus vaccine until they are older than 6 months. Those exposed prenatally to TNF inhibitors should receive the rotavirus vaccine on time, according to the CDC schedule for all infants.
The new rotavirus recommendations follow data showing that immune responses to rotavirus are blunted in those with infliximab exposure, according to Dr. Kim.
“Thus, this poses a serious theoretical risk in newborns with mothers on [a TNF inhibitor] of ineffective clearance of rotavirus infections,” Dr. Kim said in an interview. “While rotavirus infections are quite common with typically self-limiting disease, sometimes requiring hydration to counteract diarrhea-induced dehydration, this can become severe in these newborns that have [a TNF inhibitor] in their system.”
For adults, the ACR issued the following expanded indications for four vaccines for patients currently taking immunosuppressive medication:
- Patients aged 18 and older should receive the recombinant zoster vaccine against shingles.
- For patients aged 27-44 who weren’t previously vaccinated against HPV, the HPV vaccine is “conditionally recommended.”
- Patients younger than 65 should receive the pneumococcal vaccine.
- Patients aged 19-64 are conditionally recommended to receive the high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine rather than the regular-dose flu vaccine.
The guidelines also conditionally recommend that all patients aged 65 and older who have rheumatic or musculoskeletal diseases receive the high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine, regardless of whether they are taking immunosuppressive medication. Another new conditional recommendation is to give multiple vaccinations to patients on the same day, rather than give individual vaccines on different days.
The guidelines make conditional recommendations regarding flu and nonlive attenuated vaccines for those taking methotrexate, rituximab, or glucocorticoids. Methotrexate should be held for 2 weeks after flu vaccination as long as disease activity allows it, but patients who are taking methotrexate should continue taking it for any other nonlive attenuated vaccinations.
“Non-rheumatology providers, such as general pediatricians and internists, are encouraged to give the influenza vaccination and then consult with the patient’s rheumatology provider about holding methotrexate to avoid a missed vaccination opportunity,” the guidelines state.
Patients taking rituximab should receive the flu vaccine on schedule and continue taking rituximab. However, for these patients, the guidelines recommend to “delay any subsequent rituximab dosing for at least two weeks after influenza vaccination if disease activity allows.”
“Because of the relatively short time period between the rollout of the influenza vaccine and its season, we can’t always wait to time the B-cell depletion dosage,” Dr. Kim said. “Also, it is not always easy to synchronize the patient’s B-cell depletion dosing schedule to the influenza vaccine rollout. Thus, we now just recommend getting the influenza vaccine regardless of the patient’s last B-cell depletion dosage despite its known strong attenuation of optimal immune responses.”
For other nonlive attenuated vaccines, providers should time vaccination for when the next rituximab dose is due and then hold the drug for at least 2 weeks thereafter, providing time for the B cells to mount a response before rituximab depletes B cells again.
Patients taking less than 20 mg of prednisone daily should still receive the flu vaccine and other nonlive attenuated vaccines. Those taking 20 mg or more of prednisone each day should still receive the flu vaccine, but other vaccines should be deferred until their dose of glucocorticoids has been tapered down to less than 20 mg daily.
Patients taking all other immunosuppressive medications should continue taking them for the flu vaccine and other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, but it is conditionally recommended that live attenuated vaccines be deferred. For any patient with a rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease, regardless of disease activity, it is conditionally recommended that all routine nonlive attenuated vaccines be administered.
For live attenuated virus vaccines, the ACR provides a chart on which immunosuppressive medications to hold and for how long. Glucocorticoids, methotrexate, azathioprine, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, calcineurin inhibitors, and oral cyclophosphamide should all be held 4 weeks before and 4 weeks after administration of a live attenuated vaccine. For those taking JAK inhibitors, the medication should be halted 1 week before administration of a live vaccine and should continue to be withheld for 4 weeks after.
For most other biologics, the ACR recommends holding the medication for one dosing interval before the live vaccine and 4 weeks thereafter. The main exception is rituximab, which should be held for 6 months before a live vaccine and then for 4 more weeks thereafter.
For patients receiving intravenous immunoglobulin, the drug should be held for 8-11 months before they are administered a live attenuated vaccine, depending on the dosage, and then 4 weeks after vaccination, regardless of dosage.
To reassure people with rheumatic disease who may have anxiety or concerns about receiving immunizations, whether taking immunosuppressive medication or not, Dr. Kim said it’s important to provide lots of education to patients.
“Fear and emotion have replaced facts, and data as a leading factor in decision-making, as seen with COVID-19,” Dr. Kim said. “The reality is that a small minority of people will have any issues with most vaccines, which include disease flares, adverse events, or acquisition of an autoimmune disease. We are not saying there is zero risk, rather, that the risk is quite small. This is where shared decision-making between the health care provider and the patient must be done effectively to enable the patient to properly weigh risk versus benefit.”
Dr. Kim has relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Kypha, Pfizer, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Exagen Diagnostics, and Foghorn Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases may need additional vaccines or different versions of vaccines they were not previously recommended to receive, according to updated guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) on vaccinations for these patients. The new guidelines pertain to routine vaccinations for adults and children and are based on the most current evidence. They include recommendations on whether to hold certain medications before or after vaccination. They do not include recommendations regarding COVID-19 vaccines.
For guidance on COVID-19 vaccine timing and frequency, the ACR directs physicians to the CDC’s recommendations for people with mild or severe immunosuppression and the ACR’s previous clinical guidance summary on the topic, last revised in February 2022. The recommendations in the new guidance differ from ACR’s guidance on COVID-19 vaccines on whether and when to hold immunosuppressive medications when patients receive nonlive vaccines. The new guidelines now align more closely with those of EULAR, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the CDC’s recommendations for human papillomavirus (HPV), pneumococcal, and shingles vaccines.
Vaccinations in this population are particularly important because “a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in those with rheumatic diseases is infections, due to the detrimental impact immunosuppression has on the ability for the patient to properly clear the pathogen,” Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at Washington University, St. Louis, told this news organization. While immunosuppressive medications are the most common reason patients with these conditions may have impaired immune function, “some of our patients with autoimmune disease also have a preexisting immunodeficiency that can inherently blunt immune responses to either infection or vaccination,” Dr. Kim explained.
“The authors of the guidelines have done a really nice job of making distinct recommendations based on the mechanism of action of various immunosuppressive medications,” Dr. Kim said. “This helps simplify the process of deciding the timing of vaccination for the health provider, especially for those on multiple immunosuppressives who represent an important proportion of our patients with rheumatic diseases.”
The main change to the guidelines for children, aside from those related to flu vaccination, is in regard to rotavirus vaccination for infants exposed to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors or rituximab in utero. Infants prenatally exposed to rituximab should not receive the rotavirus vaccine until they are older than 6 months. Those exposed prenatally to TNF inhibitors should receive the rotavirus vaccine on time, according to the CDC schedule for all infants.
The new rotavirus recommendations follow data showing that immune responses to rotavirus are blunted in those with infliximab exposure, according to Dr. Kim.
“Thus, this poses a serious theoretical risk in newborns with mothers on [a TNF inhibitor] of ineffective clearance of rotavirus infections,” Dr. Kim said in an interview. “While rotavirus infections are quite common with typically self-limiting disease, sometimes requiring hydration to counteract diarrhea-induced dehydration, this can become severe in these newborns that have [a TNF inhibitor] in their system.”
For adults, the ACR issued the following expanded indications for four vaccines for patients currently taking immunosuppressive medication:
- Patients aged 18 and older should receive the recombinant zoster vaccine against shingles.
- For patients aged 27-44 who weren’t previously vaccinated against HPV, the HPV vaccine is “conditionally recommended.”
- Patients younger than 65 should receive the pneumococcal vaccine.
- Patients aged 19-64 are conditionally recommended to receive the high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine rather than the regular-dose flu vaccine.
The guidelines also conditionally recommend that all patients aged 65 and older who have rheumatic or musculoskeletal diseases receive the high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine, regardless of whether they are taking immunosuppressive medication. Another new conditional recommendation is to give multiple vaccinations to patients on the same day, rather than give individual vaccines on different days.
The guidelines make conditional recommendations regarding flu and nonlive attenuated vaccines for those taking methotrexate, rituximab, or glucocorticoids. Methotrexate should be held for 2 weeks after flu vaccination as long as disease activity allows it, but patients who are taking methotrexate should continue taking it for any other nonlive attenuated vaccinations.
“Non-rheumatology providers, such as general pediatricians and internists, are encouraged to give the influenza vaccination and then consult with the patient’s rheumatology provider about holding methotrexate to avoid a missed vaccination opportunity,” the guidelines state.
Patients taking rituximab should receive the flu vaccine on schedule and continue taking rituximab. However, for these patients, the guidelines recommend to “delay any subsequent rituximab dosing for at least two weeks after influenza vaccination if disease activity allows.”
“Because of the relatively short time period between the rollout of the influenza vaccine and its season, we can’t always wait to time the B-cell depletion dosage,” Dr. Kim said. “Also, it is not always easy to synchronize the patient’s B-cell depletion dosing schedule to the influenza vaccine rollout. Thus, we now just recommend getting the influenza vaccine regardless of the patient’s last B-cell depletion dosage despite its known strong attenuation of optimal immune responses.”
For other nonlive attenuated vaccines, providers should time vaccination for when the next rituximab dose is due and then hold the drug for at least 2 weeks thereafter, providing time for the B cells to mount a response before rituximab depletes B cells again.
Patients taking less than 20 mg of prednisone daily should still receive the flu vaccine and other nonlive attenuated vaccines. Those taking 20 mg or more of prednisone each day should still receive the flu vaccine, but other vaccines should be deferred until their dose of glucocorticoids has been tapered down to less than 20 mg daily.
Patients taking all other immunosuppressive medications should continue taking them for the flu vaccine and other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, but it is conditionally recommended that live attenuated vaccines be deferred. For any patient with a rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease, regardless of disease activity, it is conditionally recommended that all routine nonlive attenuated vaccines be administered.
For live attenuated virus vaccines, the ACR provides a chart on which immunosuppressive medications to hold and for how long. Glucocorticoids, methotrexate, azathioprine, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, calcineurin inhibitors, and oral cyclophosphamide should all be held 4 weeks before and 4 weeks after administration of a live attenuated vaccine. For those taking JAK inhibitors, the medication should be halted 1 week before administration of a live vaccine and should continue to be withheld for 4 weeks after.
For most other biologics, the ACR recommends holding the medication for one dosing interval before the live vaccine and 4 weeks thereafter. The main exception is rituximab, which should be held for 6 months before a live vaccine and then for 4 more weeks thereafter.
For patients receiving intravenous immunoglobulin, the drug should be held for 8-11 months before they are administered a live attenuated vaccine, depending on the dosage, and then 4 weeks after vaccination, regardless of dosage.
To reassure people with rheumatic disease who may have anxiety or concerns about receiving immunizations, whether taking immunosuppressive medication or not, Dr. Kim said it’s important to provide lots of education to patients.
“Fear and emotion have replaced facts, and data as a leading factor in decision-making, as seen with COVID-19,” Dr. Kim said. “The reality is that a small minority of people will have any issues with most vaccines, which include disease flares, adverse events, or acquisition of an autoimmune disease. We are not saying there is zero risk, rather, that the risk is quite small. This is where shared decision-making between the health care provider and the patient must be done effectively to enable the patient to properly weigh risk versus benefit.”
Dr. Kim has relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Kypha, Pfizer, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Exagen Diagnostics, and Foghorn Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases may need additional vaccines or different versions of vaccines they were not previously recommended to receive, according to updated guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) on vaccinations for these patients. The new guidelines pertain to routine vaccinations for adults and children and are based on the most current evidence. They include recommendations on whether to hold certain medications before or after vaccination. They do not include recommendations regarding COVID-19 vaccines.
For guidance on COVID-19 vaccine timing and frequency, the ACR directs physicians to the CDC’s recommendations for people with mild or severe immunosuppression and the ACR’s previous clinical guidance summary on the topic, last revised in February 2022. The recommendations in the new guidance differ from ACR’s guidance on COVID-19 vaccines on whether and when to hold immunosuppressive medications when patients receive nonlive vaccines. The new guidelines now align more closely with those of EULAR, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the CDC’s recommendations for human papillomavirus (HPV), pneumococcal, and shingles vaccines.
Vaccinations in this population are particularly important because “a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in those with rheumatic diseases is infections, due to the detrimental impact immunosuppression has on the ability for the patient to properly clear the pathogen,” Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at Washington University, St. Louis, told this news organization. While immunosuppressive medications are the most common reason patients with these conditions may have impaired immune function, “some of our patients with autoimmune disease also have a preexisting immunodeficiency that can inherently blunt immune responses to either infection or vaccination,” Dr. Kim explained.
“The authors of the guidelines have done a really nice job of making distinct recommendations based on the mechanism of action of various immunosuppressive medications,” Dr. Kim said. “This helps simplify the process of deciding the timing of vaccination for the health provider, especially for those on multiple immunosuppressives who represent an important proportion of our patients with rheumatic diseases.”
The main change to the guidelines for children, aside from those related to flu vaccination, is in regard to rotavirus vaccination for infants exposed to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors or rituximab in utero. Infants prenatally exposed to rituximab should not receive the rotavirus vaccine until they are older than 6 months. Those exposed prenatally to TNF inhibitors should receive the rotavirus vaccine on time, according to the CDC schedule for all infants.
The new rotavirus recommendations follow data showing that immune responses to rotavirus are blunted in those with infliximab exposure, according to Dr. Kim.
“Thus, this poses a serious theoretical risk in newborns with mothers on [a TNF inhibitor] of ineffective clearance of rotavirus infections,” Dr. Kim said in an interview. “While rotavirus infections are quite common with typically self-limiting disease, sometimes requiring hydration to counteract diarrhea-induced dehydration, this can become severe in these newborns that have [a TNF inhibitor] in their system.”
For adults, the ACR issued the following expanded indications for four vaccines for patients currently taking immunosuppressive medication:
- Patients aged 18 and older should receive the recombinant zoster vaccine against shingles.
- For patients aged 27-44 who weren’t previously vaccinated against HPV, the HPV vaccine is “conditionally recommended.”
- Patients younger than 65 should receive the pneumococcal vaccine.
- Patients aged 19-64 are conditionally recommended to receive the high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine rather than the regular-dose flu vaccine.
The guidelines also conditionally recommend that all patients aged 65 and older who have rheumatic or musculoskeletal diseases receive the high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine, regardless of whether they are taking immunosuppressive medication. Another new conditional recommendation is to give multiple vaccinations to patients on the same day, rather than give individual vaccines on different days.
The guidelines make conditional recommendations regarding flu and nonlive attenuated vaccines for those taking methotrexate, rituximab, or glucocorticoids. Methotrexate should be held for 2 weeks after flu vaccination as long as disease activity allows it, but patients who are taking methotrexate should continue taking it for any other nonlive attenuated vaccinations.
“Non-rheumatology providers, such as general pediatricians and internists, are encouraged to give the influenza vaccination and then consult with the patient’s rheumatology provider about holding methotrexate to avoid a missed vaccination opportunity,” the guidelines state.
Patients taking rituximab should receive the flu vaccine on schedule and continue taking rituximab. However, for these patients, the guidelines recommend to “delay any subsequent rituximab dosing for at least two weeks after influenza vaccination if disease activity allows.”
“Because of the relatively short time period between the rollout of the influenza vaccine and its season, we can’t always wait to time the B-cell depletion dosage,” Dr. Kim said. “Also, it is not always easy to synchronize the patient’s B-cell depletion dosing schedule to the influenza vaccine rollout. Thus, we now just recommend getting the influenza vaccine regardless of the patient’s last B-cell depletion dosage despite its known strong attenuation of optimal immune responses.”
For other nonlive attenuated vaccines, providers should time vaccination for when the next rituximab dose is due and then hold the drug for at least 2 weeks thereafter, providing time for the B cells to mount a response before rituximab depletes B cells again.
Patients taking less than 20 mg of prednisone daily should still receive the flu vaccine and other nonlive attenuated vaccines. Those taking 20 mg or more of prednisone each day should still receive the flu vaccine, but other vaccines should be deferred until their dose of glucocorticoids has been tapered down to less than 20 mg daily.
Patients taking all other immunosuppressive medications should continue taking them for the flu vaccine and other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, but it is conditionally recommended that live attenuated vaccines be deferred. For any patient with a rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease, regardless of disease activity, it is conditionally recommended that all routine nonlive attenuated vaccines be administered.
For live attenuated virus vaccines, the ACR provides a chart on which immunosuppressive medications to hold and for how long. Glucocorticoids, methotrexate, azathioprine, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, calcineurin inhibitors, and oral cyclophosphamide should all be held 4 weeks before and 4 weeks after administration of a live attenuated vaccine. For those taking JAK inhibitors, the medication should be halted 1 week before administration of a live vaccine and should continue to be withheld for 4 weeks after.
For most other biologics, the ACR recommends holding the medication for one dosing interval before the live vaccine and 4 weeks thereafter. The main exception is rituximab, which should be held for 6 months before a live vaccine and then for 4 more weeks thereafter.
For patients receiving intravenous immunoglobulin, the drug should be held for 8-11 months before they are administered a live attenuated vaccine, depending on the dosage, and then 4 weeks after vaccination, regardless of dosage.
To reassure people with rheumatic disease who may have anxiety or concerns about receiving immunizations, whether taking immunosuppressive medication or not, Dr. Kim said it’s important to provide lots of education to patients.
“Fear and emotion have replaced facts, and data as a leading factor in decision-making, as seen with COVID-19,” Dr. Kim said. “The reality is that a small minority of people will have any issues with most vaccines, which include disease flares, adverse events, or acquisition of an autoimmune disease. We are not saying there is zero risk, rather, that the risk is quite small. This is where shared decision-making between the health care provider and the patient must be done effectively to enable the patient to properly weigh risk versus benefit.”
Dr. Kim has relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Kypha, Pfizer, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Exagen Diagnostics, and Foghorn Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New ILD, asthma, and COPD trials
This column presents a sampling of new and still-recruiting trials of interest to pulmonologists and their patients.
Trials are selected based primarily on these conditions: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/interstitial lung disease; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); asthma; cystic fibrosis; infectious lung diseases; pulmonary artery hypertension; and lung cancer. Links to the studies and contact information are provided for each.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/interstitial lung disease
A Study to Evaluate Long-term Safety of Nintedanib in Children and Adolescents With Interstitial Lung Disease (InPedILD™-ON): NCT05285982
This nonrandomized, phase 3 study is open to children and adolescents between 6 and 17 years old who have interstitial lung disease with lung fibrosis. It is designed to test how well long-term treatment with nintedanib (a drug already used to treat lung fibrosis in adults) is tolerated in children and adolescents.
A total of 60 study participants will take nintedanib capsules twice a day for at least 2 years or until nintedanib or other treatment options become available outside of the study. There will be 9-11 site visits during the first 2 years and site visits every 3 months afterward.
Study physicians will collect information on any health problems of the participants. The primary outcome measure will be the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events.
Location: 26 locations in the United States and internationally
Sponsor: Boehringer Ingelheim
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: April 2022
Expected completion Date: May 2026
Asthma
A Phase 2, Single-Dose, Randomized, Active and Placebo Controlled, Four-Period, Cross-Over Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Intranasal Epinephrine After Administration of ARS-1 or Albuterol in Subjects With Persistent Asthma: NCT05363670
ARS-1 is a novel aqueous formulation of epinephrine nasal spray. The primary outcomes of this study will be the effect of ARS-1 versus albuterol and placebo from baseline to 1 hour on the difference in forced expiratory volume in 1 second based on area under the curve.
A total of 30 study participants (ages 12-65 years) will be recruited.
Location: Three U.S. locations in Florida, Maryland, and Ohio.
Sponsor: ARS Pharmaceuticals
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: July 2022
Expected completion Date: November 2022
COPD
Treatment of Pneumocystitis in COPD (the TOPIC Study): NCT05418777
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, the primary outcome will be to determine if treating Pneumocystis jirovecii in acute exacerbations of COPD with confirmed P. jirovecii colonization has a beneficial clinical impact. As a secondary goal of the study, it will be determined if the addition of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) to standard of care can decolonize these patients and if the decolonization is durable for at least 3 months.
A total of 30 participants aged 40-89 years will be randomized to receive either a suspension with the equivalent of one double-strength TMP-SMX or a suspension with placebo by mouth every 12 hours. If the participant is discharged prior to completing the 10-day course of the medication, they will be sent home with the remaining study medication and a medication diary which will be collected.
Location: William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Mich.
Sponsor: William Beaumont Hospitals
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: July 2022
Expected completion Date: August 2023
Inter-lobar Fissure Completion in Patients With Failed Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (SAVED-1): NCT05257681
This study is intended to be a pilot prospective controlled clinical trial to evaluate the potential role of a lung fissure completion with pleural adhesiolysis strategy (experimental intervention) in severe emphysema/COPD patients with failed bronchoscopic lung volume reduction via the use of endobronchial valves therapy.
In 20 select patients (ages 40-75 years), the lung fissure completion with adhesiolysis strategy will be performed by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery guided stapling along the lung fissures to reduce collateral ventilation with adhesions removal. The primary outcomes will be to prove that interlobar fissures can be completed to at least 95% in severe emphysema patients with previously failed bronchoscopic lung volume reduction over a 2 year period and the occurrence of adverse events in that period. The surgery will be considered feasible if the target inter-lobar fissure can be completed in at least 90% of the patients enrolled. Secondary outcomes over 2 years will include quality of life improvement and the percentage of patients with significant changes in pulmonary function testing.
Location: Beth Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
Sponsor: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: May 2022
Expected completion Date: May 2024
This column presents a sampling of new and still-recruiting trials of interest to pulmonologists and their patients.
Trials are selected based primarily on these conditions: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/interstitial lung disease; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); asthma; cystic fibrosis; infectious lung diseases; pulmonary artery hypertension; and lung cancer. Links to the studies and contact information are provided for each.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/interstitial lung disease
A Study to Evaluate Long-term Safety of Nintedanib in Children and Adolescents With Interstitial Lung Disease (InPedILD™-ON): NCT05285982
This nonrandomized, phase 3 study is open to children and adolescents between 6 and 17 years old who have interstitial lung disease with lung fibrosis. It is designed to test how well long-term treatment with nintedanib (a drug already used to treat lung fibrosis in adults) is tolerated in children and adolescents.
A total of 60 study participants will take nintedanib capsules twice a day for at least 2 years or until nintedanib or other treatment options become available outside of the study. There will be 9-11 site visits during the first 2 years and site visits every 3 months afterward.
Study physicians will collect information on any health problems of the participants. The primary outcome measure will be the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events.
Location: 26 locations in the United States and internationally
Sponsor: Boehringer Ingelheim
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: April 2022
Expected completion Date: May 2026
Asthma
A Phase 2, Single-Dose, Randomized, Active and Placebo Controlled, Four-Period, Cross-Over Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Intranasal Epinephrine After Administration of ARS-1 or Albuterol in Subjects With Persistent Asthma: NCT05363670
ARS-1 is a novel aqueous formulation of epinephrine nasal spray. The primary outcomes of this study will be the effect of ARS-1 versus albuterol and placebo from baseline to 1 hour on the difference in forced expiratory volume in 1 second based on area under the curve.
A total of 30 study participants (ages 12-65 years) will be recruited.
Location: Three U.S. locations in Florida, Maryland, and Ohio.
Sponsor: ARS Pharmaceuticals
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: July 2022
Expected completion Date: November 2022
COPD
Treatment of Pneumocystitis in COPD (the TOPIC Study): NCT05418777
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, the primary outcome will be to determine if treating Pneumocystis jirovecii in acute exacerbations of COPD with confirmed P. jirovecii colonization has a beneficial clinical impact. As a secondary goal of the study, it will be determined if the addition of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) to standard of care can decolonize these patients and if the decolonization is durable for at least 3 months.
A total of 30 participants aged 40-89 years will be randomized to receive either a suspension with the equivalent of one double-strength TMP-SMX or a suspension with placebo by mouth every 12 hours. If the participant is discharged prior to completing the 10-day course of the medication, they will be sent home with the remaining study medication and a medication diary which will be collected.
Location: William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Mich.
Sponsor: William Beaumont Hospitals
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: July 2022
Expected completion Date: August 2023
Inter-lobar Fissure Completion in Patients With Failed Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (SAVED-1): NCT05257681
This study is intended to be a pilot prospective controlled clinical trial to evaluate the potential role of a lung fissure completion with pleural adhesiolysis strategy (experimental intervention) in severe emphysema/COPD patients with failed bronchoscopic lung volume reduction via the use of endobronchial valves therapy.
In 20 select patients (ages 40-75 years), the lung fissure completion with adhesiolysis strategy will be performed by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery guided stapling along the lung fissures to reduce collateral ventilation with adhesions removal. The primary outcomes will be to prove that interlobar fissures can be completed to at least 95% in severe emphysema patients with previously failed bronchoscopic lung volume reduction over a 2 year period and the occurrence of adverse events in that period. The surgery will be considered feasible if the target inter-lobar fissure can be completed in at least 90% of the patients enrolled. Secondary outcomes over 2 years will include quality of life improvement and the percentage of patients with significant changes in pulmonary function testing.
Location: Beth Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
Sponsor: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: May 2022
Expected completion Date: May 2024
This column presents a sampling of new and still-recruiting trials of interest to pulmonologists and their patients.
Trials are selected based primarily on these conditions: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/interstitial lung disease; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); asthma; cystic fibrosis; infectious lung diseases; pulmonary artery hypertension; and lung cancer. Links to the studies and contact information are provided for each.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/interstitial lung disease
A Study to Evaluate Long-term Safety of Nintedanib in Children and Adolescents With Interstitial Lung Disease (InPedILD™-ON): NCT05285982
This nonrandomized, phase 3 study is open to children and adolescents between 6 and 17 years old who have interstitial lung disease with lung fibrosis. It is designed to test how well long-term treatment with nintedanib (a drug already used to treat lung fibrosis in adults) is tolerated in children and adolescents.
A total of 60 study participants will take nintedanib capsules twice a day for at least 2 years or until nintedanib or other treatment options become available outside of the study. There will be 9-11 site visits during the first 2 years and site visits every 3 months afterward.
Study physicians will collect information on any health problems of the participants. The primary outcome measure will be the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events.
Location: 26 locations in the United States and internationally
Sponsor: Boehringer Ingelheim
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: April 2022
Expected completion Date: May 2026
Asthma
A Phase 2, Single-Dose, Randomized, Active and Placebo Controlled, Four-Period, Cross-Over Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Intranasal Epinephrine After Administration of ARS-1 or Albuterol in Subjects With Persistent Asthma: NCT05363670
ARS-1 is a novel aqueous formulation of epinephrine nasal spray. The primary outcomes of this study will be the effect of ARS-1 versus albuterol and placebo from baseline to 1 hour on the difference in forced expiratory volume in 1 second based on area under the curve.
A total of 30 study participants (ages 12-65 years) will be recruited.
Location: Three U.S. locations in Florida, Maryland, and Ohio.
Sponsor: ARS Pharmaceuticals
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: July 2022
Expected completion Date: November 2022
COPD
Treatment of Pneumocystitis in COPD (the TOPIC Study): NCT05418777
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, the primary outcome will be to determine if treating Pneumocystis jirovecii in acute exacerbations of COPD with confirmed P. jirovecii colonization has a beneficial clinical impact. As a secondary goal of the study, it will be determined if the addition of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) to standard of care can decolonize these patients and if the decolonization is durable for at least 3 months.
A total of 30 participants aged 40-89 years will be randomized to receive either a suspension with the equivalent of one double-strength TMP-SMX or a suspension with placebo by mouth every 12 hours. If the participant is discharged prior to completing the 10-day course of the medication, they will be sent home with the remaining study medication and a medication diary which will be collected.
Location: William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Mich.
Sponsor: William Beaumont Hospitals
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: July 2022
Expected completion Date: August 2023
Inter-lobar Fissure Completion in Patients With Failed Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (SAVED-1): NCT05257681
This study is intended to be a pilot prospective controlled clinical trial to evaluate the potential role of a lung fissure completion with pleural adhesiolysis strategy (experimental intervention) in severe emphysema/COPD patients with failed bronchoscopic lung volume reduction via the use of endobronchial valves therapy.
In 20 select patients (ages 40-75 years), the lung fissure completion with adhesiolysis strategy will be performed by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery guided stapling along the lung fissures to reduce collateral ventilation with adhesions removal. The primary outcomes will be to prove that interlobar fissures can be completed to at least 95% in severe emphysema patients with previously failed bronchoscopic lung volume reduction over a 2 year period and the occurrence of adverse events in that period. The surgery will be considered feasible if the target inter-lobar fissure can be completed in at least 90% of the patients enrolled. Secondary outcomes over 2 years will include quality of life improvement and the percentage of patients with significant changes in pulmonary function testing.
Location: Beth Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
Sponsor: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Contact: [email protected]
Study start date: May 2022
Expected completion Date: May 2024
Patients and doctors trapped in a gray zone when abortion laws and emergency care mandate conflict
Each week, Kim Puterbaugh, MD, sees several pregnant patients at a Cleveland hospital who are experiencing complications involving bleeding or infection. The ob.gyn. has to make quick decisions about how to treat them, including whether to remove the dead or dying fetus to protect the health and life of the mother. Leaving in place a fetus that has no chance of survival dramatically increases the chance of maternal infection and permanent injury.
But now her medical decisions are complicated by Ohio’s new abortion law, which generally prohibits abortions after 6 weeks of pregnancy if cardiac activity is detected in the embryo or fetus – which can persist for hours or days even if a pregnancy has no chance of progressing. Given the new law, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center has streamlined its system of having an administrator and legal team on call for Dr. Puterbaugh and other physicians if anyone questions whether the planned treatment is allowed under the law.
Since the Supreme Court erased the constitutional right to abortion in June, Dr. Puterbaugh said these cases put her and doctors like her in an impossible position – squeezing doctors between antiabortion laws in Ohio and other states and the federal Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act. That 1986 law requires hospitals and physicians to provide screening and stabilizing treatment – including abortion, if necessary – in emergency situations.
“It’s a challenge to balance both those two things,” said Dr. Puterbaugh, president of the Society of OB/GYN Hospitalists. “But it’s not really a challenge to me because, in my mind, the life and health of the mother always comes first.”
The Biden administration argues that EMTALA trumps state abortion bans in emergency situations. On Aug. 2, the Department of Justice filed a federal lawsuit challenging an Idaho law that bans abortion in nearly all circumstances. The suit claims the law would make it a criminal offense for medical providers to comply with EMTALA’s requirement to provide abortion, if needed, for women experiencing emergency pregnancy complications.
In a July policy guidance and letter, the Department of Health & Human Services reaffirmed that EMTALA requires hospitals and physicians to offer life- or health-saving medical services, including abortion, in emergency situations. The letter refers to situations such as ectopic pregnancies, severe blood pressure spikes known as preeclampsia, and premature ruptures of the membrane causing a woman’s water to break before her pregnancy is viable.
The guidance stressed that this federal requirement supersedes any state laws that bar abortion, and that hospitals and physicians who don’t comply with the federal mandate could face civil fines and termination from the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
There are no known reports so far of EMTALA investigations arising from denial of emergency care in pregnancy situations.
But elected officials in states that have sharply restricted abortion disagree with the federal judgment. Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton sued the Biden administration in July to prevent the federal government from using the EMTALA law to require abortions in emergency cases. The suit claims that EMTALA doesn’t specifically mandate particular medical procedures such as abortion.
Abortion foes argue that state antiabortion laws already include adequate exceptions when a pregnant woman’s life or health is in danger. John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, said one of Texas’ laws specifies that treatment for ectopic pregnancies or miscarriages is not prohibited. In addition, the law defines a medical emergency allowing abortion as a condition in which a woman is at serious risk of a “substantial impairment of a major bodily function.”
Mr. Seago blamed the news media and medical associations for deliberately sowing confusion about the laws. “The law is very clear,” he said.
Legal wrangling aside, in practice, physicians and hospital lawyers say much depends on the interpretation of vaguely worded exceptions in state abortion bans, and that’s further complicated by the existence of contradictory laws, such as those banning abortion based on cardiac activity. And medical providers don’t want to risk criminal prosecution, fines, and loss of licensure if someone accuses them of violating these confusing laws.
Louise Joy, an attorney in Austin, Tex., who represents hospitals and other health care providers, said her clients perhaps are being overly cautious, but that’s not surprising. “I try to encourage them to do the right thing, but I can’t assure them they’ll be risk free.”
A lot hinges on when a pregnancy-ending complication is deemed an emergency, a moment that is hard to define. Some Missouri women have come to the hospital ED with mild cramping and bleeding and were found to have an ectopic pregnancy that hadn’t ruptured yet, colleagues have told Alison Haddock, MD, a Houston emergency physician who chairs the board of the American College of Emergency Physicians. The standard treatment is to provide the drug methotrexate, which can terminate a pregnancy.
“You’re stable until it ruptures, then it becomes unstable,” she said. “But how unstable do you need to be? The woman’s life is not clearly at risk yet. It’s not clear if EMTALA applies. There will be a lot of gray areas that make it really tough for emergency physicians who want to do what’s right for patients without violating any laws.”
Physicians and hospital attorneys are hoping for clearer federal guidance and guarantees of protection from state prosecutors who might oppose their medical judgment on political grounds.
“This is when we need the federal government to step up and say: ‘Doctors, you must provide the standard of care, and we will prevent the prosecution of anyone who is following appropriate medical practices and doing the right thing for patients,” Ms. Joy said.
They are also hoping that the federal government will proactively investigate without waiting for complaints from individuals whenever appropriate emergency medical care might have been withheld because of the new laws. The New York Times reported in July that a 35-year-old woman in the Dallas–Fort Worth area was denied a dilation and evacuation procedure for her first-trimester miscarriage, despite severe pain and bleeding. The hospital reportedly sent her home with advice to return if she was bleeding heavily. The hospital did not respond to a request for comment for this article.
“If a hospital has a policy saying that when the correct medical procedure for a woman in the emergency department is abortion but physicians can’t do that, that’s a violation of EMTALA that CMS should find actionable,” said Thomas Barker, a former general counsel for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services who advises hospitals on EMTALA compliance issues.
In another potential EMTALA case, Valerie Williams, MD, reported that, after Louisiana implemented its near-total ban on abortion with criminal penalties, her hospital in the New Orleans area blocked her from performing a dilation and evacuation procedure on a pregnant patient whose water broke at 16 weeks. The patient was forced to go through a painful, hours-long labor to deliver a nonviable fetus, with heavy loss of blood.
“This was the first time in my 15-year career that I could not give a patient the care they needed,” Dr. Williams wrote in a court affidavit as part of a case seeking to block the state’s abortion law. “This is a travesty.”
But CMS often relies on state agencies to investigate alleged EMTALA violations. That raises questions about how seriously those investigations will be conducted in states where officials have embraced strict limits on any medical services they deem abortion related.
In July, the Texas Medical Association warned that hospitals are pressing doctors to send pregnant patients with complications home, to wait until they expel the fetus – known as expectant management – rather than treating them at the hospital to remove the fetal remains, according to The Dallas Morning News. In a letter to the Texas Medical Board, the medical association said delayed or denied care risks patients’ future reproductive ability and poses a serious risk to their immediate health.
A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that, after Texas implemented its tight abortion restrictions in September, patients with pregnancy complications experienced much worse outcomes than similar patients in states without abortion bans. Of those treated with expectant management at two major Dallas hospitals, 57% suffered serious complications such as bleeding and infection, compared with 33% who chose immediate pregnancy termination in other states.
Ob.gyns. and emergency physicians say they expect to be on the phone frequently with lawyers to get advice on complying with state antiabortion laws while they are seeing pregnant patients with emergency and near-emergency complications.
“This will endanger women’s lives, no question about it,” Dr. Puterbaugh said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Each week, Kim Puterbaugh, MD, sees several pregnant patients at a Cleveland hospital who are experiencing complications involving bleeding or infection. The ob.gyn. has to make quick decisions about how to treat them, including whether to remove the dead or dying fetus to protect the health and life of the mother. Leaving in place a fetus that has no chance of survival dramatically increases the chance of maternal infection and permanent injury.
But now her medical decisions are complicated by Ohio’s new abortion law, which generally prohibits abortions after 6 weeks of pregnancy if cardiac activity is detected in the embryo or fetus – which can persist for hours or days even if a pregnancy has no chance of progressing. Given the new law, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center has streamlined its system of having an administrator and legal team on call for Dr. Puterbaugh and other physicians if anyone questions whether the planned treatment is allowed under the law.
Since the Supreme Court erased the constitutional right to abortion in June, Dr. Puterbaugh said these cases put her and doctors like her in an impossible position – squeezing doctors between antiabortion laws in Ohio and other states and the federal Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act. That 1986 law requires hospitals and physicians to provide screening and stabilizing treatment – including abortion, if necessary – in emergency situations.
“It’s a challenge to balance both those two things,” said Dr. Puterbaugh, president of the Society of OB/GYN Hospitalists. “But it’s not really a challenge to me because, in my mind, the life and health of the mother always comes first.”
The Biden administration argues that EMTALA trumps state abortion bans in emergency situations. On Aug. 2, the Department of Justice filed a federal lawsuit challenging an Idaho law that bans abortion in nearly all circumstances. The suit claims the law would make it a criminal offense for medical providers to comply with EMTALA’s requirement to provide abortion, if needed, for women experiencing emergency pregnancy complications.
In a July policy guidance and letter, the Department of Health & Human Services reaffirmed that EMTALA requires hospitals and physicians to offer life- or health-saving medical services, including abortion, in emergency situations. The letter refers to situations such as ectopic pregnancies, severe blood pressure spikes known as preeclampsia, and premature ruptures of the membrane causing a woman’s water to break before her pregnancy is viable.
The guidance stressed that this federal requirement supersedes any state laws that bar abortion, and that hospitals and physicians who don’t comply with the federal mandate could face civil fines and termination from the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
There are no known reports so far of EMTALA investigations arising from denial of emergency care in pregnancy situations.
But elected officials in states that have sharply restricted abortion disagree with the federal judgment. Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton sued the Biden administration in July to prevent the federal government from using the EMTALA law to require abortions in emergency cases. The suit claims that EMTALA doesn’t specifically mandate particular medical procedures such as abortion.
Abortion foes argue that state antiabortion laws already include adequate exceptions when a pregnant woman’s life or health is in danger. John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, said one of Texas’ laws specifies that treatment for ectopic pregnancies or miscarriages is not prohibited. In addition, the law defines a medical emergency allowing abortion as a condition in which a woman is at serious risk of a “substantial impairment of a major bodily function.”
Mr. Seago blamed the news media and medical associations for deliberately sowing confusion about the laws. “The law is very clear,” he said.
Legal wrangling aside, in practice, physicians and hospital lawyers say much depends on the interpretation of vaguely worded exceptions in state abortion bans, and that’s further complicated by the existence of contradictory laws, such as those banning abortion based on cardiac activity. And medical providers don’t want to risk criminal prosecution, fines, and loss of licensure if someone accuses them of violating these confusing laws.
Louise Joy, an attorney in Austin, Tex., who represents hospitals and other health care providers, said her clients perhaps are being overly cautious, but that’s not surprising. “I try to encourage them to do the right thing, but I can’t assure them they’ll be risk free.”
A lot hinges on when a pregnancy-ending complication is deemed an emergency, a moment that is hard to define. Some Missouri women have come to the hospital ED with mild cramping and bleeding and were found to have an ectopic pregnancy that hadn’t ruptured yet, colleagues have told Alison Haddock, MD, a Houston emergency physician who chairs the board of the American College of Emergency Physicians. The standard treatment is to provide the drug methotrexate, which can terminate a pregnancy.
“You’re stable until it ruptures, then it becomes unstable,” she said. “But how unstable do you need to be? The woman’s life is not clearly at risk yet. It’s not clear if EMTALA applies. There will be a lot of gray areas that make it really tough for emergency physicians who want to do what’s right for patients without violating any laws.”
Physicians and hospital attorneys are hoping for clearer federal guidance and guarantees of protection from state prosecutors who might oppose their medical judgment on political grounds.
“This is when we need the federal government to step up and say: ‘Doctors, you must provide the standard of care, and we will prevent the prosecution of anyone who is following appropriate medical practices and doing the right thing for patients,” Ms. Joy said.
They are also hoping that the federal government will proactively investigate without waiting for complaints from individuals whenever appropriate emergency medical care might have been withheld because of the new laws. The New York Times reported in July that a 35-year-old woman in the Dallas–Fort Worth area was denied a dilation and evacuation procedure for her first-trimester miscarriage, despite severe pain and bleeding. The hospital reportedly sent her home with advice to return if she was bleeding heavily. The hospital did not respond to a request for comment for this article.
“If a hospital has a policy saying that when the correct medical procedure for a woman in the emergency department is abortion but physicians can’t do that, that’s a violation of EMTALA that CMS should find actionable,” said Thomas Barker, a former general counsel for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services who advises hospitals on EMTALA compliance issues.
In another potential EMTALA case, Valerie Williams, MD, reported that, after Louisiana implemented its near-total ban on abortion with criminal penalties, her hospital in the New Orleans area blocked her from performing a dilation and evacuation procedure on a pregnant patient whose water broke at 16 weeks. The patient was forced to go through a painful, hours-long labor to deliver a nonviable fetus, with heavy loss of blood.
“This was the first time in my 15-year career that I could not give a patient the care they needed,” Dr. Williams wrote in a court affidavit as part of a case seeking to block the state’s abortion law. “This is a travesty.”
But CMS often relies on state agencies to investigate alleged EMTALA violations. That raises questions about how seriously those investigations will be conducted in states where officials have embraced strict limits on any medical services they deem abortion related.
In July, the Texas Medical Association warned that hospitals are pressing doctors to send pregnant patients with complications home, to wait until they expel the fetus – known as expectant management – rather than treating them at the hospital to remove the fetal remains, according to The Dallas Morning News. In a letter to the Texas Medical Board, the medical association said delayed or denied care risks patients’ future reproductive ability and poses a serious risk to their immediate health.
A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that, after Texas implemented its tight abortion restrictions in September, patients with pregnancy complications experienced much worse outcomes than similar patients in states without abortion bans. Of those treated with expectant management at two major Dallas hospitals, 57% suffered serious complications such as bleeding and infection, compared with 33% who chose immediate pregnancy termination in other states.
Ob.gyns. and emergency physicians say they expect to be on the phone frequently with lawyers to get advice on complying with state antiabortion laws while they are seeing pregnant patients with emergency and near-emergency complications.
“This will endanger women’s lives, no question about it,” Dr. Puterbaugh said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Each week, Kim Puterbaugh, MD, sees several pregnant patients at a Cleveland hospital who are experiencing complications involving bleeding or infection. The ob.gyn. has to make quick decisions about how to treat them, including whether to remove the dead or dying fetus to protect the health and life of the mother. Leaving in place a fetus that has no chance of survival dramatically increases the chance of maternal infection and permanent injury.
But now her medical decisions are complicated by Ohio’s new abortion law, which generally prohibits abortions after 6 weeks of pregnancy if cardiac activity is detected in the embryo or fetus – which can persist for hours or days even if a pregnancy has no chance of progressing. Given the new law, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center has streamlined its system of having an administrator and legal team on call for Dr. Puterbaugh and other physicians if anyone questions whether the planned treatment is allowed under the law.
Since the Supreme Court erased the constitutional right to abortion in June, Dr. Puterbaugh said these cases put her and doctors like her in an impossible position – squeezing doctors between antiabortion laws in Ohio and other states and the federal Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act. That 1986 law requires hospitals and physicians to provide screening and stabilizing treatment – including abortion, if necessary – in emergency situations.
“It’s a challenge to balance both those two things,” said Dr. Puterbaugh, president of the Society of OB/GYN Hospitalists. “But it’s not really a challenge to me because, in my mind, the life and health of the mother always comes first.”
The Biden administration argues that EMTALA trumps state abortion bans in emergency situations. On Aug. 2, the Department of Justice filed a federal lawsuit challenging an Idaho law that bans abortion in nearly all circumstances. The suit claims the law would make it a criminal offense for medical providers to comply with EMTALA’s requirement to provide abortion, if needed, for women experiencing emergency pregnancy complications.
In a July policy guidance and letter, the Department of Health & Human Services reaffirmed that EMTALA requires hospitals and physicians to offer life- or health-saving medical services, including abortion, in emergency situations. The letter refers to situations such as ectopic pregnancies, severe blood pressure spikes known as preeclampsia, and premature ruptures of the membrane causing a woman’s water to break before her pregnancy is viable.
The guidance stressed that this federal requirement supersedes any state laws that bar abortion, and that hospitals and physicians who don’t comply with the federal mandate could face civil fines and termination from the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
There are no known reports so far of EMTALA investigations arising from denial of emergency care in pregnancy situations.
But elected officials in states that have sharply restricted abortion disagree with the federal judgment. Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton sued the Biden administration in July to prevent the federal government from using the EMTALA law to require abortions in emergency cases. The suit claims that EMTALA doesn’t specifically mandate particular medical procedures such as abortion.
Abortion foes argue that state antiabortion laws already include adequate exceptions when a pregnant woman’s life or health is in danger. John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, said one of Texas’ laws specifies that treatment for ectopic pregnancies or miscarriages is not prohibited. In addition, the law defines a medical emergency allowing abortion as a condition in which a woman is at serious risk of a “substantial impairment of a major bodily function.”
Mr. Seago blamed the news media and medical associations for deliberately sowing confusion about the laws. “The law is very clear,” he said.
Legal wrangling aside, in practice, physicians and hospital lawyers say much depends on the interpretation of vaguely worded exceptions in state abortion bans, and that’s further complicated by the existence of contradictory laws, such as those banning abortion based on cardiac activity. And medical providers don’t want to risk criminal prosecution, fines, and loss of licensure if someone accuses them of violating these confusing laws.
Louise Joy, an attorney in Austin, Tex., who represents hospitals and other health care providers, said her clients perhaps are being overly cautious, but that’s not surprising. “I try to encourage them to do the right thing, but I can’t assure them they’ll be risk free.”
A lot hinges on when a pregnancy-ending complication is deemed an emergency, a moment that is hard to define. Some Missouri women have come to the hospital ED with mild cramping and bleeding and were found to have an ectopic pregnancy that hadn’t ruptured yet, colleagues have told Alison Haddock, MD, a Houston emergency physician who chairs the board of the American College of Emergency Physicians. The standard treatment is to provide the drug methotrexate, which can terminate a pregnancy.
“You’re stable until it ruptures, then it becomes unstable,” she said. “But how unstable do you need to be? The woman’s life is not clearly at risk yet. It’s not clear if EMTALA applies. There will be a lot of gray areas that make it really tough for emergency physicians who want to do what’s right for patients without violating any laws.”
Physicians and hospital attorneys are hoping for clearer federal guidance and guarantees of protection from state prosecutors who might oppose their medical judgment on political grounds.
“This is when we need the federal government to step up and say: ‘Doctors, you must provide the standard of care, and we will prevent the prosecution of anyone who is following appropriate medical practices and doing the right thing for patients,” Ms. Joy said.
They are also hoping that the federal government will proactively investigate without waiting for complaints from individuals whenever appropriate emergency medical care might have been withheld because of the new laws. The New York Times reported in July that a 35-year-old woman in the Dallas–Fort Worth area was denied a dilation and evacuation procedure for her first-trimester miscarriage, despite severe pain and bleeding. The hospital reportedly sent her home with advice to return if she was bleeding heavily. The hospital did not respond to a request for comment for this article.
“If a hospital has a policy saying that when the correct medical procedure for a woman in the emergency department is abortion but physicians can’t do that, that’s a violation of EMTALA that CMS should find actionable,” said Thomas Barker, a former general counsel for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services who advises hospitals on EMTALA compliance issues.
In another potential EMTALA case, Valerie Williams, MD, reported that, after Louisiana implemented its near-total ban on abortion with criminal penalties, her hospital in the New Orleans area blocked her from performing a dilation and evacuation procedure on a pregnant patient whose water broke at 16 weeks. The patient was forced to go through a painful, hours-long labor to deliver a nonviable fetus, with heavy loss of blood.
“This was the first time in my 15-year career that I could not give a patient the care they needed,” Dr. Williams wrote in a court affidavit as part of a case seeking to block the state’s abortion law. “This is a travesty.”
But CMS often relies on state agencies to investigate alleged EMTALA violations. That raises questions about how seriously those investigations will be conducted in states where officials have embraced strict limits on any medical services they deem abortion related.
In July, the Texas Medical Association warned that hospitals are pressing doctors to send pregnant patients with complications home, to wait until they expel the fetus – known as expectant management – rather than treating them at the hospital to remove the fetal remains, according to The Dallas Morning News. In a letter to the Texas Medical Board, the medical association said delayed or denied care risks patients’ future reproductive ability and poses a serious risk to their immediate health.
A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that, after Texas implemented its tight abortion restrictions in September, patients with pregnancy complications experienced much worse outcomes than similar patients in states without abortion bans. Of those treated with expectant management at two major Dallas hospitals, 57% suffered serious complications such as bleeding and infection, compared with 33% who chose immediate pregnancy termination in other states.
Ob.gyns. and emergency physicians say they expect to be on the phone frequently with lawyers to get advice on complying with state antiabortion laws while they are seeing pregnant patients with emergency and near-emergency complications.
“This will endanger women’s lives, no question about it,” Dr. Puterbaugh said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Clinicians can help people with severe ME/CFS, even unseen
People who are severely ill with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) are often too sick to leave home, but clinicians can still support them in many ways, experts say.
Approximately 250,000 people in the United Kingdom (0.2%-0.4%) have ME/CFS – where it’s called “ME.” As many as 2.5 million in the United States have it. Those numbers are expected to dramatically increase with the addition of people with long COVID. An estimated 25% of patients with the condition are so severely impaired that they are housebound or bedbound to the point where they’re unable to attend medical office visits. There are very few data about them because they’re typically unable to participate in studies.
Speaking at the annual meeting of the International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (IACFS/ME), patient advocate Helen Baxter, of the U.K. charity 25% ME Group, presented a case series of five patients bedbound with ME/CFS who became severely malnourished because of delays in the placement of feeding tubes. The delays occurred because it was not recognized that the patients were unable to eat. The inability to eat may be due to a variety of factors, including gastrointestinal dysfunction, dysphagia, nausea, or lack of sufficient energy to eat or drink.
A report of those cases was included in a special issue of Healthcare, devoted to the topic of severe and very severe ME/CFS. The issue, which was published in April 2021, included 25 articles on the pathophysiology of severe ME/CFS, ways that clinicians can support patients who are too sick to make office visits, and psychosocial aspects of the condition that result from physical debilitation.
Two additional articles by specialist physicians aim to counter the skepticism about ME/CFS that has long persisted among some in the medical community.
“ME/CFS is under-researched and has historically received insufficient funding for research, particularly when compared to other chronic conditions, such as multiple sclerosis. And most of the research that has been done about it has focused on patients who are able to attend clinics. Patients with severe ME/CFS have largely been excluded from research due to the severity of their illness and are often described as ‘hard to reach.’ Consequently, research into severe ME is very limited,” Ms. Baxter said.
Asked to comment, Lucinda Bateman, MD, founder and director of the Bateman Horne Center, Salt Lake City, told this news organization, “It’s a big gap, even in the knowledgeable community. The research is totally skewed towards people who can get up and go participate in research. ... I don’t think most clinicians have any idea how sick people can get with ME/CFS.”
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET), which is commonly used in research, is intended to elicit objective biomarker responses. Such testing, which is considered the gold standard for determining disability, is impossible for the most severely ill patients with ME/CFS and is potentially harmful to these patients because of the hallmark postexertional malaise (PEM) phenomenon, Dr. Bateman noted.
“If we want to use CPET for research, we have to remember that it harms people to some degree and that we’re only studying the people who aren’t as sick. ... It’s one of the reasons I’ve been aggressively pursuing medical education about orthostatic testing, because it’s a clear objective marker, not as deleterious, and potentially leads to treatment options,” she said.
Misdiagnosis, treatment delays led to life-threatening malnutrition
The five patients that Ms. Baxter presented had become severely malnourished and dehydrated. There was evidence of clinical inertia for each of them.
“All were judged to have anorexia nervosa, and psychiatrists were involved, which was an added delay to starting tube feeding. ... In each case, the doctors resorted to making inappropriate psychological diagnoses without positive evidence of psychopathology, failing to recognize the significance of the malnutrition,” Ms. Baxter said. (Urgent tube feeding would have been warranted even had anorexia nervosa been the correct diagnosis, she pointed out.)
Once the problem was finally recognized, “all participants saw an improvement in their situation following the allocation of a home enteral nutrition dietician.”
At the IACFS/ME conference, Ms. Baxter described the painstaking methods used for gathering information, which were described in the same journal. These involved a combination of online, telephone, and text communications with patients or their caregivers. Efforts were made to avoid overtaxing the patients and triggering PEM.
“An early warning system needs to be put in place for patients with severe ME so that when they or their representatives become aware of the development of problems with oral intake, prompt action is taken, and tube feeding started, thereby avoiding undernutrition in patients with very severe ME,” Ms. Baxter and colleagues write.
Indeed, coauthor and semiretired pediatric ME/CFS specialist physician Nigel Speight, of Durham, United Kingdom, said in an interview, “In most of my patients, I used tube feeding early simply to avoid using unnecessary energy and causing stress to the patient.”
Dr. Speight added, “Patients can also die from sheer weakness leading to lack of respiratory drive. Also, and very understandably, some commit suicide.”
Caring for the patient with severe or very severe ME/CFS
Appearing in the special issue is an article entitled, “Caring for the Patient with Severe or Very Severe Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome”. It was authored by a multidisciplinary group led by Jose G. Montoya, MD, of the Jack S. Remington Laboratory for Specialty Diagnostics, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Calif.
In that article, four levels of severity are defined: mild, moderate, severe, and very severe. Included in the “severe” category are patients who are mostly homebound and whose activities of daily living are limited. They may have severe cognitive difficulties. Patients in the “very severe” caregory are bedbound and are unable to care for themselves.
Clinical features include more extreme versions of the core ME/CFS criteria: profound fatigue/weakness, PEM, unrefreshing sleep, orthostatic intolerance, and cognitive impairment. Additional symptoms in those with severe/very severe ME can include extreme hypersensitivity to light, sound, touch, and/or odors. Even small amounts of physical, mental, emotional, and orthostatic stressors can trigger PEM and increased weakness.
The authors recommend a “patient-centered, collaborative approach that is grounded in compassion and respect for the patient in all interactions,” and they provide lists of steps providers can take. These include seeing patients at home if possible and considerations regarding that care, such as partnering with the patient’s caregivers and other health care providers, who may include physical and occupational therapists, home health nurses, and social workers who understand the condition. Home visits by optometrists or ophthalmologists and dentists may be required.
Documenting limitations in activities of daily living is particularly important for helping patients to obtain homecare and disability benefits, Dr. Montoya and colleagues say.
Clinicians should investigate any medical problems that may be amenable to treatment, including orthostatic intolerance, pain, sleep difficulties, comorbidities, or gastrointestinal problems. For patients with pain, bloating, and diarrhea who are found on assessment to have mast cell activation disorder (MCAD), a trial of sodium cromoglicate may be tried, Ms. Baxter told this news organization.
Nonmedical problems that may be contributing to the patient’s morbidity should also be assessed, including a lack of caretaking, social services, transportation, food, and/or supportive devices, such as wheelchairs, bedpans, feeding tubes, and catheters.
The article provides additional detailed recommendations regarding pharmacologic treatments, follow-up visits – in-person or virtual – and hospitalization, as well as recommendations for energy conservation and management.
A section titled Practical Considerations for Busy Providers includes advice to be aware of any regulatory or insurance requirements for providing home visits and to maximize reimbursement by diagnosing any comorbidities, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or MCAD.
Dr. Speight, who authored an article in the special issue on the management of ME in children, called the article by Dr. Montoya and colleagues “absolutely excellent,” and added his own advice, which included not “overinvestigating to cover your back but at the expense of causing stress to the patient” and considering a trial of immunoglobulin.
Importantly, Dr. Speight stressed, “avoid referral to psychiatrists unless specifically indicated for additional psychiatric morbidity; in which case, make clear that the psychiatrist accepts [that the] basic illness is medical.”
He also advised that clinicians stop using the term “chronic fatigue syndrome” because it suggests the illness is mild and/or psychosomatic. “Maybe the United States should embrace the term ME once and for all,” he said.
Dr. Baxter, Dr. Speight, and Dr. Montoya have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bateman is conducting research for Terra Biological.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who are severely ill with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) are often too sick to leave home, but clinicians can still support them in many ways, experts say.
Approximately 250,000 people in the United Kingdom (0.2%-0.4%) have ME/CFS – where it’s called “ME.” As many as 2.5 million in the United States have it. Those numbers are expected to dramatically increase with the addition of people with long COVID. An estimated 25% of patients with the condition are so severely impaired that they are housebound or bedbound to the point where they’re unable to attend medical office visits. There are very few data about them because they’re typically unable to participate in studies.
Speaking at the annual meeting of the International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (IACFS/ME), patient advocate Helen Baxter, of the U.K. charity 25% ME Group, presented a case series of five patients bedbound with ME/CFS who became severely malnourished because of delays in the placement of feeding tubes. The delays occurred because it was not recognized that the patients were unable to eat. The inability to eat may be due to a variety of factors, including gastrointestinal dysfunction, dysphagia, nausea, or lack of sufficient energy to eat or drink.
A report of those cases was included in a special issue of Healthcare, devoted to the topic of severe and very severe ME/CFS. The issue, which was published in April 2021, included 25 articles on the pathophysiology of severe ME/CFS, ways that clinicians can support patients who are too sick to make office visits, and psychosocial aspects of the condition that result from physical debilitation.
Two additional articles by specialist physicians aim to counter the skepticism about ME/CFS that has long persisted among some in the medical community.
“ME/CFS is under-researched and has historically received insufficient funding for research, particularly when compared to other chronic conditions, such as multiple sclerosis. And most of the research that has been done about it has focused on patients who are able to attend clinics. Patients with severe ME/CFS have largely been excluded from research due to the severity of their illness and are often described as ‘hard to reach.’ Consequently, research into severe ME is very limited,” Ms. Baxter said.
Asked to comment, Lucinda Bateman, MD, founder and director of the Bateman Horne Center, Salt Lake City, told this news organization, “It’s a big gap, even in the knowledgeable community. The research is totally skewed towards people who can get up and go participate in research. ... I don’t think most clinicians have any idea how sick people can get with ME/CFS.”
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET), which is commonly used in research, is intended to elicit objective biomarker responses. Such testing, which is considered the gold standard for determining disability, is impossible for the most severely ill patients with ME/CFS and is potentially harmful to these patients because of the hallmark postexertional malaise (PEM) phenomenon, Dr. Bateman noted.
“If we want to use CPET for research, we have to remember that it harms people to some degree and that we’re only studying the people who aren’t as sick. ... It’s one of the reasons I’ve been aggressively pursuing medical education about orthostatic testing, because it’s a clear objective marker, not as deleterious, and potentially leads to treatment options,” she said.
Misdiagnosis, treatment delays led to life-threatening malnutrition
The five patients that Ms. Baxter presented had become severely malnourished and dehydrated. There was evidence of clinical inertia for each of them.
“All were judged to have anorexia nervosa, and psychiatrists were involved, which was an added delay to starting tube feeding. ... In each case, the doctors resorted to making inappropriate psychological diagnoses without positive evidence of psychopathology, failing to recognize the significance of the malnutrition,” Ms. Baxter said. (Urgent tube feeding would have been warranted even had anorexia nervosa been the correct diagnosis, she pointed out.)
Once the problem was finally recognized, “all participants saw an improvement in their situation following the allocation of a home enteral nutrition dietician.”
At the IACFS/ME conference, Ms. Baxter described the painstaking methods used for gathering information, which were described in the same journal. These involved a combination of online, telephone, and text communications with patients or their caregivers. Efforts were made to avoid overtaxing the patients and triggering PEM.
“An early warning system needs to be put in place for patients with severe ME so that when they or their representatives become aware of the development of problems with oral intake, prompt action is taken, and tube feeding started, thereby avoiding undernutrition in patients with very severe ME,” Ms. Baxter and colleagues write.
Indeed, coauthor and semiretired pediatric ME/CFS specialist physician Nigel Speight, of Durham, United Kingdom, said in an interview, “In most of my patients, I used tube feeding early simply to avoid using unnecessary energy and causing stress to the patient.”
Dr. Speight added, “Patients can also die from sheer weakness leading to lack of respiratory drive. Also, and very understandably, some commit suicide.”
Caring for the patient with severe or very severe ME/CFS
Appearing in the special issue is an article entitled, “Caring for the Patient with Severe or Very Severe Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome”. It was authored by a multidisciplinary group led by Jose G. Montoya, MD, of the Jack S. Remington Laboratory for Specialty Diagnostics, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Calif.
In that article, four levels of severity are defined: mild, moderate, severe, and very severe. Included in the “severe” category are patients who are mostly homebound and whose activities of daily living are limited. They may have severe cognitive difficulties. Patients in the “very severe” caregory are bedbound and are unable to care for themselves.
Clinical features include more extreme versions of the core ME/CFS criteria: profound fatigue/weakness, PEM, unrefreshing sleep, orthostatic intolerance, and cognitive impairment. Additional symptoms in those with severe/very severe ME can include extreme hypersensitivity to light, sound, touch, and/or odors. Even small amounts of physical, mental, emotional, and orthostatic stressors can trigger PEM and increased weakness.
The authors recommend a “patient-centered, collaborative approach that is grounded in compassion and respect for the patient in all interactions,” and they provide lists of steps providers can take. These include seeing patients at home if possible and considerations regarding that care, such as partnering with the patient’s caregivers and other health care providers, who may include physical and occupational therapists, home health nurses, and social workers who understand the condition. Home visits by optometrists or ophthalmologists and dentists may be required.
Documenting limitations in activities of daily living is particularly important for helping patients to obtain homecare and disability benefits, Dr. Montoya and colleagues say.
Clinicians should investigate any medical problems that may be amenable to treatment, including orthostatic intolerance, pain, sleep difficulties, comorbidities, or gastrointestinal problems. For patients with pain, bloating, and diarrhea who are found on assessment to have mast cell activation disorder (MCAD), a trial of sodium cromoglicate may be tried, Ms. Baxter told this news organization.
Nonmedical problems that may be contributing to the patient’s morbidity should also be assessed, including a lack of caretaking, social services, transportation, food, and/or supportive devices, such as wheelchairs, bedpans, feeding tubes, and catheters.
The article provides additional detailed recommendations regarding pharmacologic treatments, follow-up visits – in-person or virtual – and hospitalization, as well as recommendations for energy conservation and management.
A section titled Practical Considerations for Busy Providers includes advice to be aware of any regulatory or insurance requirements for providing home visits and to maximize reimbursement by diagnosing any comorbidities, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or MCAD.
Dr. Speight, who authored an article in the special issue on the management of ME in children, called the article by Dr. Montoya and colleagues “absolutely excellent,” and added his own advice, which included not “overinvestigating to cover your back but at the expense of causing stress to the patient” and considering a trial of immunoglobulin.
Importantly, Dr. Speight stressed, “avoid referral to psychiatrists unless specifically indicated for additional psychiatric morbidity; in which case, make clear that the psychiatrist accepts [that the] basic illness is medical.”
He also advised that clinicians stop using the term “chronic fatigue syndrome” because it suggests the illness is mild and/or psychosomatic. “Maybe the United States should embrace the term ME once and for all,” he said.
Dr. Baxter, Dr. Speight, and Dr. Montoya have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bateman is conducting research for Terra Biological.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who are severely ill with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) are often too sick to leave home, but clinicians can still support them in many ways, experts say.
Approximately 250,000 people in the United Kingdom (0.2%-0.4%) have ME/CFS – where it’s called “ME.” As many as 2.5 million in the United States have it. Those numbers are expected to dramatically increase with the addition of people with long COVID. An estimated 25% of patients with the condition are so severely impaired that they are housebound or bedbound to the point where they’re unable to attend medical office visits. There are very few data about them because they’re typically unable to participate in studies.
Speaking at the annual meeting of the International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (IACFS/ME), patient advocate Helen Baxter, of the U.K. charity 25% ME Group, presented a case series of five patients bedbound with ME/CFS who became severely malnourished because of delays in the placement of feeding tubes. The delays occurred because it was not recognized that the patients were unable to eat. The inability to eat may be due to a variety of factors, including gastrointestinal dysfunction, dysphagia, nausea, or lack of sufficient energy to eat or drink.
A report of those cases was included in a special issue of Healthcare, devoted to the topic of severe and very severe ME/CFS. The issue, which was published in April 2021, included 25 articles on the pathophysiology of severe ME/CFS, ways that clinicians can support patients who are too sick to make office visits, and psychosocial aspects of the condition that result from physical debilitation.
Two additional articles by specialist physicians aim to counter the skepticism about ME/CFS that has long persisted among some in the medical community.
“ME/CFS is under-researched and has historically received insufficient funding for research, particularly when compared to other chronic conditions, such as multiple sclerosis. And most of the research that has been done about it has focused on patients who are able to attend clinics. Patients with severe ME/CFS have largely been excluded from research due to the severity of their illness and are often described as ‘hard to reach.’ Consequently, research into severe ME is very limited,” Ms. Baxter said.
Asked to comment, Lucinda Bateman, MD, founder and director of the Bateman Horne Center, Salt Lake City, told this news organization, “It’s a big gap, even in the knowledgeable community. The research is totally skewed towards people who can get up and go participate in research. ... I don’t think most clinicians have any idea how sick people can get with ME/CFS.”
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET), which is commonly used in research, is intended to elicit objective biomarker responses. Such testing, which is considered the gold standard for determining disability, is impossible for the most severely ill patients with ME/CFS and is potentially harmful to these patients because of the hallmark postexertional malaise (PEM) phenomenon, Dr. Bateman noted.
“If we want to use CPET for research, we have to remember that it harms people to some degree and that we’re only studying the people who aren’t as sick. ... It’s one of the reasons I’ve been aggressively pursuing medical education about orthostatic testing, because it’s a clear objective marker, not as deleterious, and potentially leads to treatment options,” she said.
Misdiagnosis, treatment delays led to life-threatening malnutrition
The five patients that Ms. Baxter presented had become severely malnourished and dehydrated. There was evidence of clinical inertia for each of them.
“All were judged to have anorexia nervosa, and psychiatrists were involved, which was an added delay to starting tube feeding. ... In each case, the doctors resorted to making inappropriate psychological diagnoses without positive evidence of psychopathology, failing to recognize the significance of the malnutrition,” Ms. Baxter said. (Urgent tube feeding would have been warranted even had anorexia nervosa been the correct diagnosis, she pointed out.)
Once the problem was finally recognized, “all participants saw an improvement in their situation following the allocation of a home enteral nutrition dietician.”
At the IACFS/ME conference, Ms. Baxter described the painstaking methods used for gathering information, which were described in the same journal. These involved a combination of online, telephone, and text communications with patients or their caregivers. Efforts were made to avoid overtaxing the patients and triggering PEM.
“An early warning system needs to be put in place for patients with severe ME so that when they or their representatives become aware of the development of problems with oral intake, prompt action is taken, and tube feeding started, thereby avoiding undernutrition in patients with very severe ME,” Ms. Baxter and colleagues write.
Indeed, coauthor and semiretired pediatric ME/CFS specialist physician Nigel Speight, of Durham, United Kingdom, said in an interview, “In most of my patients, I used tube feeding early simply to avoid using unnecessary energy and causing stress to the patient.”
Dr. Speight added, “Patients can also die from sheer weakness leading to lack of respiratory drive. Also, and very understandably, some commit suicide.”
Caring for the patient with severe or very severe ME/CFS
Appearing in the special issue is an article entitled, “Caring for the Patient with Severe or Very Severe Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome”. It was authored by a multidisciplinary group led by Jose G. Montoya, MD, of the Jack S. Remington Laboratory for Specialty Diagnostics, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Calif.
In that article, four levels of severity are defined: mild, moderate, severe, and very severe. Included in the “severe” category are patients who are mostly homebound and whose activities of daily living are limited. They may have severe cognitive difficulties. Patients in the “very severe” caregory are bedbound and are unable to care for themselves.
Clinical features include more extreme versions of the core ME/CFS criteria: profound fatigue/weakness, PEM, unrefreshing sleep, orthostatic intolerance, and cognitive impairment. Additional symptoms in those with severe/very severe ME can include extreme hypersensitivity to light, sound, touch, and/or odors. Even small amounts of physical, mental, emotional, and orthostatic stressors can trigger PEM and increased weakness.
The authors recommend a “patient-centered, collaborative approach that is grounded in compassion and respect for the patient in all interactions,” and they provide lists of steps providers can take. These include seeing patients at home if possible and considerations regarding that care, such as partnering with the patient’s caregivers and other health care providers, who may include physical and occupational therapists, home health nurses, and social workers who understand the condition. Home visits by optometrists or ophthalmologists and dentists may be required.
Documenting limitations in activities of daily living is particularly important for helping patients to obtain homecare and disability benefits, Dr. Montoya and colleagues say.
Clinicians should investigate any medical problems that may be amenable to treatment, including orthostatic intolerance, pain, sleep difficulties, comorbidities, or gastrointestinal problems. For patients with pain, bloating, and diarrhea who are found on assessment to have mast cell activation disorder (MCAD), a trial of sodium cromoglicate may be tried, Ms. Baxter told this news organization.
Nonmedical problems that may be contributing to the patient’s morbidity should also be assessed, including a lack of caretaking, social services, transportation, food, and/or supportive devices, such as wheelchairs, bedpans, feeding tubes, and catheters.
The article provides additional detailed recommendations regarding pharmacologic treatments, follow-up visits – in-person or virtual – and hospitalization, as well as recommendations for energy conservation and management.
A section titled Practical Considerations for Busy Providers includes advice to be aware of any regulatory or insurance requirements for providing home visits and to maximize reimbursement by diagnosing any comorbidities, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or MCAD.
Dr. Speight, who authored an article in the special issue on the management of ME in children, called the article by Dr. Montoya and colleagues “absolutely excellent,” and added his own advice, which included not “overinvestigating to cover your back but at the expense of causing stress to the patient” and considering a trial of immunoglobulin.
Importantly, Dr. Speight stressed, “avoid referral to psychiatrists unless specifically indicated for additional psychiatric morbidity; in which case, make clear that the psychiatrist accepts [that the] basic illness is medical.”
He also advised that clinicians stop using the term “chronic fatigue syndrome” because it suggests the illness is mild and/or psychosomatic. “Maybe the United States should embrace the term ME once and for all,” he said.
Dr. Baxter, Dr. Speight, and Dr. Montoya have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bateman is conducting research for Terra Biological.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM IACFS/ME 2022