User login
Outcomes After Prolonged ICU Stays in Postoperative Cardiac Surgery Patients
Prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stays, variably defined as > 48 h to > 14 days, are a known complication of cardiac surgery.1-8 Prolonged stays are associated with higher resource utilization and higher mortality.2,3,9-12 Although there are several cardiac surgery risk models that can be used preoperatively to identify patients at risk for prolonged ICU stay, factors that influence outcomes for patients who experience prolonged ICU stays are poorly understood.2,13-19 Little information is available to inform discussions between health care practitioners (HCPs) and patients throughout a prolonged ICU stay, especially those ≥ 7 days.
As cardiac surgical complexity, patient age, and preexisting comorbidities have increased over time, so has the need to provide patients and HCPs with data to inform decision making, enhance prognostication, and set realistic expectations at varying time intervals during prolonged ICU stay. The purpose of this study was to evaluate short- and long-term outcomes in cardiac surgery patients after prolonged ICU stays at relevant time intervals (7, 14, 21, and 28 days) and to determine factors that may predict a patient’s outcome after a prolonged ICU stay.
Methods
The University of Michigan Health System Institutional Review Board approved this study and waived informed consent. We merged the University of Michigan Medical Center Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) database, which is updated periodically with late mortality, with elements of the electronic health record (EHR). Adult patients were included if they had cardiac surgery at the University of Michigan between January 2, 2001, and December 31, 2011. Late mortality was updated through December 1, 2014. Data are presented as frequency (%), mean (SD), and median (IQR) as appropriate. Bivariate comparisons between survivors and nonsurvivors were done with χ2 or Fisher exact test for categorical data, Student t test for continuous normally distributed data, and Wilcoxon rank sum test for continuous not normally distributed data. To determine factors associated with operative mortality (death within 30 days of surgery or hospital discharge, whichever occurred later), we used logistic regression with forward selection. All available factors were initially entered in the models.
Separate logistic models were created based on all data available at days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Final models consisted of factors with statistically significant P values (< .05) and adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% CIs that excluded 1. To determine factors associated with late mortality, we used a Cox proportional hazard model, which used data available at discharge and STS complications. As these complications did not include their timing, they could only be used in models created at discharge and not for days 7, 14, 21, and 28 models. Final models consisted of factors with P values < .05 and 95% CIs of the AORs or the hazard ratios (HRs) that excluded 1. As the EHR did not start recording data until January 2, 2004, and its capture of data remained incomplete for several years, rather than imputing these missing data or excluding these patients, we chose to create an extra categorical level for each factor to represent missing data. For continuous factors with missing data, we first converted the continuous data to terciles and the missing data became the fourth level.20,21
The discrimination of the logistic models were determined by the c-statistic and for the Cox proportional hazards model with the Harrell concordance index (C index). Time trends were assessed with the Cochran-Armitage trend test. P < .05 was deemed statistically significant. Statistics were calculated with SPSS versions 21-23 or SAS 9.4.
Results
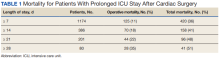
Of 8309 admissions to the ICU after cardiac surgery, 1174 (14%) had ICU stays ≥ 7 days, 386 (5%) ≥ 14 days, 201 (2%) ≥ 21 days, and 80 (0.9%) ≥ 28 days. The prolonged ICU study population was mostly male, White race, with a mean (SD) age of 62 (14) years. Patients had a variety of comorbidities, most notably 61% had hypertension and half had heart failure. Valve surgery (55%) was the most common procedure (n = 651). Twenty-nine percent required > 1 procedure (eAppendix 1).
The operative mortality
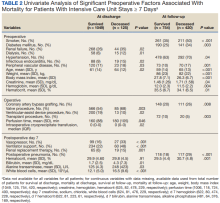
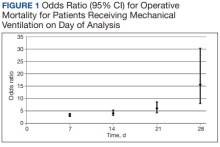
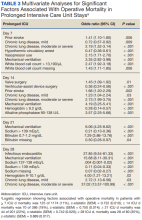
Using multivariable logistic regression to adjust for factors associated with mortality, we found that receiving mechanical ventilation on the day of analysis was associated with increased operative mortality with AOR increasing from 3.35 (95% CI, 2.82-3.98) for
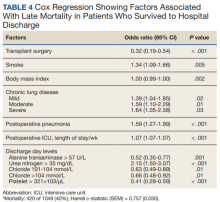
After multivariable Cox regression to adjust for confounders, we found that each postoperative week was associated with a 7% higher hazard of dying (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.07-1.07; P < .001). Postoperative pneumonia was also associated with increased hazard of dying (HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.27-1.99; P < .001),
Discussion
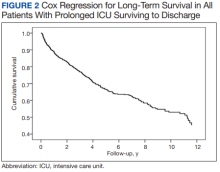
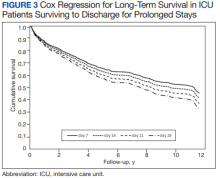
We found that operative mortality increased the longer the patient stayed in the ICU, ranging from 11% for ≥ 7 days to 35% for ≥ 28 days. We further found that in ICU survivors, median (IQR) survival was 10.7 (0.7) years. While previous studies have evaluated prolonged ICU stays, they have been limited by studying limited subpopulations, such as patients who are dependent on dialysis or octogenarians, or used a single cutoff to define prolonged ICU stays, variably defined from > 48 hours to > 14 days.2-7,9-12,22 Our study is similar to others that used ≥ 2 cutoffs.1,8 However, our study was novel by providing 4 cutoffs to improve temporal prediction of hospital outcomes. Unlike a study by Ryan and colleagues, which found no increase in mortality with longer stay (43.5% for ≥ 14 days and 45% for ≥ 28 days), our study findings are similar to those of Yu and colleagues (11.1% mortality for prolonged ICU stays of 1 to 2 weeks, 26.6% for 2 to 4 weeks, and 31% for > 4 weeks) and others (8%, 3 to 14 days; 40%, >14 days; 10%, 1 to 2 weeks; 25.7% > 2 weeks) in finding a progressively increased hospital mortality with longer ICU stays.1,4,5,8 These differences may be related to different ICU populations or to improvements in care since Ryan and colleagues study was conducted.
Fewer studies have evaluated factors associated with mortality in cardiac surgery prolonged ICU stay patients. Our study is similar to other studies that evaluated risk factors by finding associations between a variety of comorbidities and process of care associated with both operative and long-term mortality; however, comparison between these studies is limited by the varying factors analyzed.1,3,5,6,8,9,11 We found that mechanical ventilation on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 was strongly associated with operative mortality, similar to noncardiac surgery patients and cardiac surgery patients.6,23,24 While we found several processes of care, such as catecholamine use and transfusions to be associated with mortality, which is similar to other studies, notably, we did not find an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality.1,25 While there is an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality in ICU patients, its status in cardiac surgery patients with prolonged ICU stays is less clear.26 While Ryan and colleagues found an association between renal replacement therapy and hospital mortality in patients staying ≥ 14 days, they did not find it in patients staying ≥.
28 days.1 Other studies of prolonged ICU stays for cardiac surgery patients have also failed to find an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality.5,6,9 Importantly, practice that expedites liberation from mechanical ventilation, such as fast tracking, daily spontaneous breathing trials, extubation to noninvasive respiratory support, and pulmonary rehabilitation may all have potential to limit mechanical ventilation duration and improve hospital survival and deserve further study.27-29Median (IQR) survival in hospital survivors was 10.7 (0.7) years, which is generally better than previously reported, but similar to that reported by Silberman and colleagues.2,4,6,8,11,12 Differences between these studies may relate to different patient populations within the cardiac surgery ICUs, definitions of prolonged ICU stays, or eras of care. Further study is needed to clarify these discrepancies. We found that cardiac transplantation and obesity were associated with the least risk of dying, while smoking, lung disease, and postoperative pneumonia were independently associated with increased hazard of dying. The obesity paradox, where obesity is protective, has been previously observed in cardiac surgery patients.30
Strengths and Limitations
There are several limitations of this study. This is a single center study, and our patient population and processes of care may differ from other centers, limiting its generalizability. Notably, we do fewer coronary bypass operations and more aortic reconstructions and ventricular assist device insertions than do many other centers. Second, we did not have laboratory values for about one-third of patients (preceded EHR implementation). However, we were able to compensate for this by binning values and including missing data as an extra bin.20,21
The main strength of this study is that we were able to combine disparate records to assess a large number of potential factors associated with both operative and long-term mortality. This produced models that had good to very good discrimination. By producing models at 7, 14, 21, and 28 days to predict operative mortality and a model at discharge, it may help to provide objective data to facilitate conversations with patients and their families. However, further studies to externally validate these models should be conducted.
Conclusions
We found that longer prolonged ICU stays are associated with both operative and late mortality. Receiving mechanical ventilation on days 7, 14, 21, or 28 was strongly associated with operative mortality.
1. Ryan TA, Rady MY, Bashour A, Leventhal M, Lytle B, Starr NJ. Predictors of outcome in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care stay. Chest. 1997;112(4):1035-1042. doi:10.1378/chest.112.4.1035
2. Hein OV, Birnbaum J, Wernecke K, England M, Konertz W, Spies C. Prolonged intensive care unit stay in cardiac surgery: risk factors and long-term-survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81(3):880-885. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.09.077
3. Mahesh B, Choong CK, Goldsmith K, Gerrard C, Nashef SA, Vuylsteke A. Prolonged stay in intensive care unit is a powerful predictor of adverse outcomes after cardiac operations. Ann Thoracic Surg. 2012;94(1):109-116. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.02.010
4. Silberman S, Bitran D, Fink D, Tauber R, Merin O. Very prolonged stay in the intensive care unit after cardiac operations: early results and late survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96(1):15-21. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.01.103
5. Lapar DJ, Gillen JR, Crosby IK, et al. Predictors of operative mortality in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care unit duration. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(6):1116-1123. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.02.028
6. Manji RA, Arora RC, Singal RK, et al. Long-term outcome and predictors of noninstitutionalized survival subsequent to prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgical procedures. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(1):56-63. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.07.004
7. Augustin P, Tanaka S, Chhor V, et al. Prognosis of prolonged intensive care unit stay after aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis in octogenarians. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(6):1555-1561. doi:10.1053/j.jvca.2016.07.029
8. Yu PJ, Cassiere HA, Fishbein J, Esposito RA, Hartman AR. Outcomes of patients with prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(6):1550-1554. doi:10.1053/j.jvca.2016.03.145
9. Bashour CA, Yared JP, Ryan TA, et al. Long-term survival and functional capacity in cardiac surgery patients after prolonged intensive care. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(12):3847-3853. doi:10.1097/00003246-200012000-00018
10. Isgro F, Skuras JA, Kiessling AH, Lehmann A, Saggau W. Survival and quality of life after a long-term intensive care stay. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;50(2):95-99. doi:10.1055/s-2002-26693
11. Williams MR, Wellner RB, Hartnett EA, Hartnett EA, Thornton B, Kavarana MN, Mahapatra R, Oz MC Sladen R. Long-term survival and quality of life in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care unit length of stay. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(5):1472-1478.
12. Lagercrantz E, Lindblom D, Sartipy U. Survival and quality of life in cardiac surgery patients with prolonged intensive care. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89:490-495. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(02)03464-1
13. Edwards FH, Clark RE, Schwartz M. Coronary artery bypass grafting: the Society of Thoracic Surgeons National Database experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;57(1):12-19. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(94)90358-1
14. Lawrence DR, Valencia O, Smith EE, Murday A, Treasure T. Parsonnet score is a good predictor of the duration of intensive care unit stay following cardiac surgery. Heart. 2000;83(4):429-432. doi:10.1136/heart.83.4.429
15. Janssen DP, Noyez L, Wouters C, Brouwer RM. Preoperative prediction of prolonged stay in the intensive care unit for coronary bypass surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;25(2):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.11.005
16. Nilsson J, Algotsson L, Hoglund P, Luhrs C, Brandt J. EuroSCORE predicts intensive care unit stay and costs of open heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78(5):1528-1534. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.060
17. Ghotkar SV, Grayson AD, Fabri BM, Dihmis WC, Pullan DM. Preoperative calculation of risk for prolonged intensive care unit stay following coronary artery bypass grafting. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;1:14. doi:10.1186/1749-8090-1-1418. Messaoudi N, Decocker J, Stockman BA, Bossaert LL, Rodrigus IE. Is EuroSCORE useful in the prediction of extended intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery? Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg. 2009;36(1):35-39. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.02.007
19. Ettema RG, Peelen LM, Schuurmans MJ, Nierich AP, Kalkman CJ, Moons KG. Prediction models for prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery: systematic review and validation study. Circulation. 2010;122(7):682-689. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.926808
20. Engoren M. Does erythrocyte blood transfusion prevent acute kidney injury? Propensity-matched case control analysis. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(5):1126-1133. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e181f70f56
21. UK National Centre for Research Methods. Minimising the effect of missing data. Revised July 22, 2011. Accessed June 28, 2022. www.restore.ac.uk/srme/www/fac/soc/wie/research-new/srme/modules/mod3/9/index.html.
22. Leontyev S, Davierwala PM, Gaube LM, et al. Outcomes of dialysis-dependent patients after cardiac operations in a single-center experience of 483 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(4):1270-1276. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.07.05223. Freundlich RE, Maile MD, Sferra JJ, Jewell ES, Kheterpal S, Engoren M. Complications associated with mortality in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Database. Anesth Analg. 2018;127(1):55-62. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000002799
24. Freundlich RE, Maile MD, Hajjar MM, et al. Years of life lost after complications of coronary artery bypass operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(6):1893-1899. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.09.048
25. Koch CG, Li L, Sessler DI, et al. Duration of red-cell storage and complications after cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(12):1229-1239. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa070403
26. Truche AS, Ragey SP, Souweine B, et al. ICU survival and need of renal replacement therapy with respect to AKI duration in critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2018;8(1):127. doi:10.1186/s13613-018-0467-6
27. Kollef MH, Shapiro SD, Silver P, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of protocol-directed versus physician-directed weaning from mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 1997;25(4):567-574. doi:10.1097/00003246-199704000-00004
28. McWilliams D, Weblin J, Atkins G, et al. Enhancing rehabilitation of mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: a quality improvement project. J Crit Care. 2015;30(1):13-18. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.09.018
29. Hernandez G, Vaquero C, Gonzalez P, et al. Effect of postextubation high-flow nasal cannula vs conventional oxygen therapy on reintubation in low-risk patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1354-1361. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2711
30. Schwann TA, Ramira PS, Engoren MC, et al. Evidence and temporality of the obesity paradox in coronary bypass surgery: an analysis of cause-specific mortality. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;54(5):896-903. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezy207
Prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stays, variably defined as > 48 h to > 14 days, are a known complication of cardiac surgery.1-8 Prolonged stays are associated with higher resource utilization and higher mortality.2,3,9-12 Although there are several cardiac surgery risk models that can be used preoperatively to identify patients at risk for prolonged ICU stay, factors that influence outcomes for patients who experience prolonged ICU stays are poorly understood.2,13-19 Little information is available to inform discussions between health care practitioners (HCPs) and patients throughout a prolonged ICU stay, especially those ≥ 7 days.
As cardiac surgical complexity, patient age, and preexisting comorbidities have increased over time, so has the need to provide patients and HCPs with data to inform decision making, enhance prognostication, and set realistic expectations at varying time intervals during prolonged ICU stay. The purpose of this study was to evaluate short- and long-term outcomes in cardiac surgery patients after prolonged ICU stays at relevant time intervals (7, 14, 21, and 28 days) and to determine factors that may predict a patient’s outcome after a prolonged ICU stay.
Methods
The University of Michigan Health System Institutional Review Board approved this study and waived informed consent. We merged the University of Michigan Medical Center Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) database, which is updated periodically with late mortality, with elements of the electronic health record (EHR). Adult patients were included if they had cardiac surgery at the University of Michigan between January 2, 2001, and December 31, 2011. Late mortality was updated through December 1, 2014. Data are presented as frequency (%), mean (SD), and median (IQR) as appropriate. Bivariate comparisons between survivors and nonsurvivors were done with χ2 or Fisher exact test for categorical data, Student t test for continuous normally distributed data, and Wilcoxon rank sum test for continuous not normally distributed data. To determine factors associated with operative mortality (death within 30 days of surgery or hospital discharge, whichever occurred later), we used logistic regression with forward selection. All available factors were initially entered in the models.
Separate logistic models were created based on all data available at days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Final models consisted of factors with statistically significant P values (< .05) and adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% CIs that excluded 1. To determine factors associated with late mortality, we used a Cox proportional hazard model, which used data available at discharge and STS complications. As these complications did not include their timing, they could only be used in models created at discharge and not for days 7, 14, 21, and 28 models. Final models consisted of factors with P values < .05 and 95% CIs of the AORs or the hazard ratios (HRs) that excluded 1. As the EHR did not start recording data until January 2, 2004, and its capture of data remained incomplete for several years, rather than imputing these missing data or excluding these patients, we chose to create an extra categorical level for each factor to represent missing data. For continuous factors with missing data, we first converted the continuous data to terciles and the missing data became the fourth level.20,21
The discrimination of the logistic models were determined by the c-statistic and for the Cox proportional hazards model with the Harrell concordance index (C index). Time trends were assessed with the Cochran-Armitage trend test. P < .05 was deemed statistically significant. Statistics were calculated with SPSS versions 21-23 or SAS 9.4.
Results
Of 8309 admissions to the ICU after cardiac surgery, 1174 (14%) had ICU stays ≥ 7 days, 386 (5%) ≥ 14 days, 201 (2%) ≥ 21 days, and 80 (0.9%) ≥ 28 days. The prolonged ICU study population was mostly male, White race, with a mean (SD) age of 62 (14) years. Patients had a variety of comorbidities, most notably 61% had hypertension and half had heart failure. Valve surgery (55%) was the most common procedure (n = 651). Twenty-nine percent required > 1 procedure (eAppendix 1).
The operative mortality
Using multivariable logistic regression to adjust for factors associated with mortality, we found that receiving mechanical ventilation on the day of analysis was associated with increased operative mortality with AOR increasing from 3.35 (95% CI, 2.82-3.98) for
After multivariable Cox regression to adjust for confounders, we found that each postoperative week was associated with a 7% higher hazard of dying (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.07-1.07; P < .001). Postoperative pneumonia was also associated with increased hazard of dying (HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.27-1.99; P < .001),
Discussion
We found that operative mortality increased the longer the patient stayed in the ICU, ranging from 11% for ≥ 7 days to 35% for ≥ 28 days. We further found that in ICU survivors, median (IQR) survival was 10.7 (0.7) years. While previous studies have evaluated prolonged ICU stays, they have been limited by studying limited subpopulations, such as patients who are dependent on dialysis or octogenarians, or used a single cutoff to define prolonged ICU stays, variably defined from > 48 hours to > 14 days.2-7,9-12,22 Our study is similar to others that used ≥ 2 cutoffs.1,8 However, our study was novel by providing 4 cutoffs to improve temporal prediction of hospital outcomes. Unlike a study by Ryan and colleagues, which found no increase in mortality with longer stay (43.5% for ≥ 14 days and 45% for ≥ 28 days), our study findings are similar to those of Yu and colleagues (11.1% mortality for prolonged ICU stays of 1 to 2 weeks, 26.6% for 2 to 4 weeks, and 31% for > 4 weeks) and others (8%, 3 to 14 days; 40%, >14 days; 10%, 1 to 2 weeks; 25.7% > 2 weeks) in finding a progressively increased hospital mortality with longer ICU stays.1,4,5,8 These differences may be related to different ICU populations or to improvements in care since Ryan and colleagues study was conducted.
Fewer studies have evaluated factors associated with mortality in cardiac surgery prolonged ICU stay patients. Our study is similar to other studies that evaluated risk factors by finding associations between a variety of comorbidities and process of care associated with both operative and long-term mortality; however, comparison between these studies is limited by the varying factors analyzed.1,3,5,6,8,9,11 We found that mechanical ventilation on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 was strongly associated with operative mortality, similar to noncardiac surgery patients and cardiac surgery patients.6,23,24 While we found several processes of care, such as catecholamine use and transfusions to be associated with mortality, which is similar to other studies, notably, we did not find an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality.1,25 While there is an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality in ICU patients, its status in cardiac surgery patients with prolonged ICU stays is less clear.26 While Ryan and colleagues found an association between renal replacement therapy and hospital mortality in patients staying ≥ 14 days, they did not find it in patients staying ≥.
28 days.1 Other studies of prolonged ICU stays for cardiac surgery patients have also failed to find an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality.5,6,9 Importantly, practice that expedites liberation from mechanical ventilation, such as fast tracking, daily spontaneous breathing trials, extubation to noninvasive respiratory support, and pulmonary rehabilitation may all have potential to limit mechanical ventilation duration and improve hospital survival and deserve further study.27-29Median (IQR) survival in hospital survivors was 10.7 (0.7) years, which is generally better than previously reported, but similar to that reported by Silberman and colleagues.2,4,6,8,11,12 Differences between these studies may relate to different patient populations within the cardiac surgery ICUs, definitions of prolonged ICU stays, or eras of care. Further study is needed to clarify these discrepancies. We found that cardiac transplantation and obesity were associated with the least risk of dying, while smoking, lung disease, and postoperative pneumonia were independently associated with increased hazard of dying. The obesity paradox, where obesity is protective, has been previously observed in cardiac surgery patients.30
Strengths and Limitations
There are several limitations of this study. This is a single center study, and our patient population and processes of care may differ from other centers, limiting its generalizability. Notably, we do fewer coronary bypass operations and more aortic reconstructions and ventricular assist device insertions than do many other centers. Second, we did not have laboratory values for about one-third of patients (preceded EHR implementation). However, we were able to compensate for this by binning values and including missing data as an extra bin.20,21
The main strength of this study is that we were able to combine disparate records to assess a large number of potential factors associated with both operative and long-term mortality. This produced models that had good to very good discrimination. By producing models at 7, 14, 21, and 28 days to predict operative mortality and a model at discharge, it may help to provide objective data to facilitate conversations with patients and their families. However, further studies to externally validate these models should be conducted.
Conclusions
We found that longer prolonged ICU stays are associated with both operative and late mortality. Receiving mechanical ventilation on days 7, 14, 21, or 28 was strongly associated with operative mortality.
Prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stays, variably defined as > 48 h to > 14 days, are a known complication of cardiac surgery.1-8 Prolonged stays are associated with higher resource utilization and higher mortality.2,3,9-12 Although there are several cardiac surgery risk models that can be used preoperatively to identify patients at risk for prolonged ICU stay, factors that influence outcomes for patients who experience prolonged ICU stays are poorly understood.2,13-19 Little information is available to inform discussions between health care practitioners (HCPs) and patients throughout a prolonged ICU stay, especially those ≥ 7 days.
As cardiac surgical complexity, patient age, and preexisting comorbidities have increased over time, so has the need to provide patients and HCPs with data to inform decision making, enhance prognostication, and set realistic expectations at varying time intervals during prolonged ICU stay. The purpose of this study was to evaluate short- and long-term outcomes in cardiac surgery patients after prolonged ICU stays at relevant time intervals (7, 14, 21, and 28 days) and to determine factors that may predict a patient’s outcome after a prolonged ICU stay.
Methods
The University of Michigan Health System Institutional Review Board approved this study and waived informed consent. We merged the University of Michigan Medical Center Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) database, which is updated periodically with late mortality, with elements of the electronic health record (EHR). Adult patients were included if they had cardiac surgery at the University of Michigan between January 2, 2001, and December 31, 2011. Late mortality was updated through December 1, 2014. Data are presented as frequency (%), mean (SD), and median (IQR) as appropriate. Bivariate comparisons between survivors and nonsurvivors were done with χ2 or Fisher exact test for categorical data, Student t test for continuous normally distributed data, and Wilcoxon rank sum test for continuous not normally distributed data. To determine factors associated with operative mortality (death within 30 days of surgery or hospital discharge, whichever occurred later), we used logistic regression with forward selection. All available factors were initially entered in the models.
Separate logistic models were created based on all data available at days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Final models consisted of factors with statistically significant P values (< .05) and adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% CIs that excluded 1. To determine factors associated with late mortality, we used a Cox proportional hazard model, which used data available at discharge and STS complications. As these complications did not include their timing, they could only be used in models created at discharge and not for days 7, 14, 21, and 28 models. Final models consisted of factors with P values < .05 and 95% CIs of the AORs or the hazard ratios (HRs) that excluded 1. As the EHR did not start recording data until January 2, 2004, and its capture of data remained incomplete for several years, rather than imputing these missing data or excluding these patients, we chose to create an extra categorical level for each factor to represent missing data. For continuous factors with missing data, we first converted the continuous data to terciles and the missing data became the fourth level.20,21
The discrimination of the logistic models were determined by the c-statistic and for the Cox proportional hazards model with the Harrell concordance index (C index). Time trends were assessed with the Cochran-Armitage trend test. P < .05 was deemed statistically significant. Statistics were calculated with SPSS versions 21-23 or SAS 9.4.
Results
Of 8309 admissions to the ICU after cardiac surgery, 1174 (14%) had ICU stays ≥ 7 days, 386 (5%) ≥ 14 days, 201 (2%) ≥ 21 days, and 80 (0.9%) ≥ 28 days. The prolonged ICU study population was mostly male, White race, with a mean (SD) age of 62 (14) years. Patients had a variety of comorbidities, most notably 61% had hypertension and half had heart failure. Valve surgery (55%) was the most common procedure (n = 651). Twenty-nine percent required > 1 procedure (eAppendix 1).
The operative mortality
Using multivariable logistic regression to adjust for factors associated with mortality, we found that receiving mechanical ventilation on the day of analysis was associated with increased operative mortality with AOR increasing from 3.35 (95% CI, 2.82-3.98) for
After multivariable Cox regression to adjust for confounders, we found that each postoperative week was associated with a 7% higher hazard of dying (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.07-1.07; P < .001). Postoperative pneumonia was also associated with increased hazard of dying (HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.27-1.99; P < .001),
Discussion
We found that operative mortality increased the longer the patient stayed in the ICU, ranging from 11% for ≥ 7 days to 35% for ≥ 28 days. We further found that in ICU survivors, median (IQR) survival was 10.7 (0.7) years. While previous studies have evaluated prolonged ICU stays, they have been limited by studying limited subpopulations, such as patients who are dependent on dialysis or octogenarians, or used a single cutoff to define prolonged ICU stays, variably defined from > 48 hours to > 14 days.2-7,9-12,22 Our study is similar to others that used ≥ 2 cutoffs.1,8 However, our study was novel by providing 4 cutoffs to improve temporal prediction of hospital outcomes. Unlike a study by Ryan and colleagues, which found no increase in mortality with longer stay (43.5% for ≥ 14 days and 45% for ≥ 28 days), our study findings are similar to those of Yu and colleagues (11.1% mortality for prolonged ICU stays of 1 to 2 weeks, 26.6% for 2 to 4 weeks, and 31% for > 4 weeks) and others (8%, 3 to 14 days; 40%, >14 days; 10%, 1 to 2 weeks; 25.7% > 2 weeks) in finding a progressively increased hospital mortality with longer ICU stays.1,4,5,8 These differences may be related to different ICU populations or to improvements in care since Ryan and colleagues study was conducted.
Fewer studies have evaluated factors associated with mortality in cardiac surgery prolonged ICU stay patients. Our study is similar to other studies that evaluated risk factors by finding associations between a variety of comorbidities and process of care associated with both operative and long-term mortality; however, comparison between these studies is limited by the varying factors analyzed.1,3,5,6,8,9,11 We found that mechanical ventilation on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 was strongly associated with operative mortality, similar to noncardiac surgery patients and cardiac surgery patients.6,23,24 While we found several processes of care, such as catecholamine use and transfusions to be associated with mortality, which is similar to other studies, notably, we did not find an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality.1,25 While there is an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality in ICU patients, its status in cardiac surgery patients with prolonged ICU stays is less clear.26 While Ryan and colleagues found an association between renal replacement therapy and hospital mortality in patients staying ≥ 14 days, they did not find it in patients staying ≥.
28 days.1 Other studies of prolonged ICU stays for cardiac surgery patients have also failed to find an association between renal replacement therapy and mortality.5,6,9 Importantly, practice that expedites liberation from mechanical ventilation, such as fast tracking, daily spontaneous breathing trials, extubation to noninvasive respiratory support, and pulmonary rehabilitation may all have potential to limit mechanical ventilation duration and improve hospital survival and deserve further study.27-29Median (IQR) survival in hospital survivors was 10.7 (0.7) years, which is generally better than previously reported, but similar to that reported by Silberman and colleagues.2,4,6,8,11,12 Differences between these studies may relate to different patient populations within the cardiac surgery ICUs, definitions of prolonged ICU stays, or eras of care. Further study is needed to clarify these discrepancies. We found that cardiac transplantation and obesity were associated with the least risk of dying, while smoking, lung disease, and postoperative pneumonia were independently associated with increased hazard of dying. The obesity paradox, where obesity is protective, has been previously observed in cardiac surgery patients.30
Strengths and Limitations
There are several limitations of this study. This is a single center study, and our patient population and processes of care may differ from other centers, limiting its generalizability. Notably, we do fewer coronary bypass operations and more aortic reconstructions and ventricular assist device insertions than do many other centers. Second, we did not have laboratory values for about one-third of patients (preceded EHR implementation). However, we were able to compensate for this by binning values and including missing data as an extra bin.20,21
The main strength of this study is that we were able to combine disparate records to assess a large number of potential factors associated with both operative and long-term mortality. This produced models that had good to very good discrimination. By producing models at 7, 14, 21, and 28 days to predict operative mortality and a model at discharge, it may help to provide objective data to facilitate conversations with patients and their families. However, further studies to externally validate these models should be conducted.
Conclusions
We found that longer prolonged ICU stays are associated with both operative and late mortality. Receiving mechanical ventilation on days 7, 14, 21, or 28 was strongly associated with operative mortality.
1. Ryan TA, Rady MY, Bashour A, Leventhal M, Lytle B, Starr NJ. Predictors of outcome in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care stay. Chest. 1997;112(4):1035-1042. doi:10.1378/chest.112.4.1035
2. Hein OV, Birnbaum J, Wernecke K, England M, Konertz W, Spies C. Prolonged intensive care unit stay in cardiac surgery: risk factors and long-term-survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81(3):880-885. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.09.077
3. Mahesh B, Choong CK, Goldsmith K, Gerrard C, Nashef SA, Vuylsteke A. Prolonged stay in intensive care unit is a powerful predictor of adverse outcomes after cardiac operations. Ann Thoracic Surg. 2012;94(1):109-116. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.02.010
4. Silberman S, Bitran D, Fink D, Tauber R, Merin O. Very prolonged stay in the intensive care unit after cardiac operations: early results and late survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96(1):15-21. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.01.103
5. Lapar DJ, Gillen JR, Crosby IK, et al. Predictors of operative mortality in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care unit duration. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(6):1116-1123. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.02.028
6. Manji RA, Arora RC, Singal RK, et al. Long-term outcome and predictors of noninstitutionalized survival subsequent to prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgical procedures. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(1):56-63. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.07.004
7. Augustin P, Tanaka S, Chhor V, et al. Prognosis of prolonged intensive care unit stay after aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis in octogenarians. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(6):1555-1561. doi:10.1053/j.jvca.2016.07.029
8. Yu PJ, Cassiere HA, Fishbein J, Esposito RA, Hartman AR. Outcomes of patients with prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(6):1550-1554. doi:10.1053/j.jvca.2016.03.145
9. Bashour CA, Yared JP, Ryan TA, et al. Long-term survival and functional capacity in cardiac surgery patients after prolonged intensive care. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(12):3847-3853. doi:10.1097/00003246-200012000-00018
10. Isgro F, Skuras JA, Kiessling AH, Lehmann A, Saggau W. Survival and quality of life after a long-term intensive care stay. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;50(2):95-99. doi:10.1055/s-2002-26693
11. Williams MR, Wellner RB, Hartnett EA, Hartnett EA, Thornton B, Kavarana MN, Mahapatra R, Oz MC Sladen R. Long-term survival and quality of life in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care unit length of stay. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(5):1472-1478.
12. Lagercrantz E, Lindblom D, Sartipy U. Survival and quality of life in cardiac surgery patients with prolonged intensive care. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89:490-495. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(02)03464-1
13. Edwards FH, Clark RE, Schwartz M. Coronary artery bypass grafting: the Society of Thoracic Surgeons National Database experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;57(1):12-19. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(94)90358-1
14. Lawrence DR, Valencia O, Smith EE, Murday A, Treasure T. Parsonnet score is a good predictor of the duration of intensive care unit stay following cardiac surgery. Heart. 2000;83(4):429-432. doi:10.1136/heart.83.4.429
15. Janssen DP, Noyez L, Wouters C, Brouwer RM. Preoperative prediction of prolonged stay in the intensive care unit for coronary bypass surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;25(2):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.11.005
16. Nilsson J, Algotsson L, Hoglund P, Luhrs C, Brandt J. EuroSCORE predicts intensive care unit stay and costs of open heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78(5):1528-1534. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.060
17. Ghotkar SV, Grayson AD, Fabri BM, Dihmis WC, Pullan DM. Preoperative calculation of risk for prolonged intensive care unit stay following coronary artery bypass grafting. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;1:14. doi:10.1186/1749-8090-1-1418. Messaoudi N, Decocker J, Stockman BA, Bossaert LL, Rodrigus IE. Is EuroSCORE useful in the prediction of extended intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery? Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg. 2009;36(1):35-39. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.02.007
19. Ettema RG, Peelen LM, Schuurmans MJ, Nierich AP, Kalkman CJ, Moons KG. Prediction models for prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery: systematic review and validation study. Circulation. 2010;122(7):682-689. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.926808
20. Engoren M. Does erythrocyte blood transfusion prevent acute kidney injury? Propensity-matched case control analysis. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(5):1126-1133. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e181f70f56
21. UK National Centre for Research Methods. Minimising the effect of missing data. Revised July 22, 2011. Accessed June 28, 2022. www.restore.ac.uk/srme/www/fac/soc/wie/research-new/srme/modules/mod3/9/index.html.
22. Leontyev S, Davierwala PM, Gaube LM, et al. Outcomes of dialysis-dependent patients after cardiac operations in a single-center experience of 483 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(4):1270-1276. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.07.05223. Freundlich RE, Maile MD, Sferra JJ, Jewell ES, Kheterpal S, Engoren M. Complications associated with mortality in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Database. Anesth Analg. 2018;127(1):55-62. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000002799
24. Freundlich RE, Maile MD, Hajjar MM, et al. Years of life lost after complications of coronary artery bypass operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(6):1893-1899. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.09.048
25. Koch CG, Li L, Sessler DI, et al. Duration of red-cell storage and complications after cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(12):1229-1239. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa070403
26. Truche AS, Ragey SP, Souweine B, et al. ICU survival and need of renal replacement therapy with respect to AKI duration in critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2018;8(1):127. doi:10.1186/s13613-018-0467-6
27. Kollef MH, Shapiro SD, Silver P, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of protocol-directed versus physician-directed weaning from mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 1997;25(4):567-574. doi:10.1097/00003246-199704000-00004
28. McWilliams D, Weblin J, Atkins G, et al. Enhancing rehabilitation of mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: a quality improvement project. J Crit Care. 2015;30(1):13-18. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.09.018
29. Hernandez G, Vaquero C, Gonzalez P, et al. Effect of postextubation high-flow nasal cannula vs conventional oxygen therapy on reintubation in low-risk patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1354-1361. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2711
30. Schwann TA, Ramira PS, Engoren MC, et al. Evidence and temporality of the obesity paradox in coronary bypass surgery: an analysis of cause-specific mortality. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;54(5):896-903. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezy207
1. Ryan TA, Rady MY, Bashour A, Leventhal M, Lytle B, Starr NJ. Predictors of outcome in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care stay. Chest. 1997;112(4):1035-1042. doi:10.1378/chest.112.4.1035
2. Hein OV, Birnbaum J, Wernecke K, England M, Konertz W, Spies C. Prolonged intensive care unit stay in cardiac surgery: risk factors and long-term-survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81(3):880-885. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.09.077
3. Mahesh B, Choong CK, Goldsmith K, Gerrard C, Nashef SA, Vuylsteke A. Prolonged stay in intensive care unit is a powerful predictor of adverse outcomes after cardiac operations. Ann Thoracic Surg. 2012;94(1):109-116. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.02.010
4. Silberman S, Bitran D, Fink D, Tauber R, Merin O. Very prolonged stay in the intensive care unit after cardiac operations: early results and late survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96(1):15-21. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.01.103
5. Lapar DJ, Gillen JR, Crosby IK, et al. Predictors of operative mortality in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care unit duration. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(6):1116-1123. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.02.028
6. Manji RA, Arora RC, Singal RK, et al. Long-term outcome and predictors of noninstitutionalized survival subsequent to prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgical procedures. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(1):56-63. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.07.004
7. Augustin P, Tanaka S, Chhor V, et al. Prognosis of prolonged intensive care unit stay after aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis in octogenarians. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(6):1555-1561. doi:10.1053/j.jvca.2016.07.029
8. Yu PJ, Cassiere HA, Fishbein J, Esposito RA, Hartman AR. Outcomes of patients with prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(6):1550-1554. doi:10.1053/j.jvca.2016.03.145
9. Bashour CA, Yared JP, Ryan TA, et al. Long-term survival and functional capacity in cardiac surgery patients after prolonged intensive care. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(12):3847-3853. doi:10.1097/00003246-200012000-00018
10. Isgro F, Skuras JA, Kiessling AH, Lehmann A, Saggau W. Survival and quality of life after a long-term intensive care stay. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;50(2):95-99. doi:10.1055/s-2002-26693
11. Williams MR, Wellner RB, Hartnett EA, Hartnett EA, Thornton B, Kavarana MN, Mahapatra R, Oz MC Sladen R. Long-term survival and quality of life in cardiac surgical patients with prolonged intensive care unit length of stay. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(5):1472-1478.
12. Lagercrantz E, Lindblom D, Sartipy U. Survival and quality of life in cardiac surgery patients with prolonged intensive care. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89:490-495. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(02)03464-1
13. Edwards FH, Clark RE, Schwartz M. Coronary artery bypass grafting: the Society of Thoracic Surgeons National Database experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;57(1):12-19. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(94)90358-1
14. Lawrence DR, Valencia O, Smith EE, Murday A, Treasure T. Parsonnet score is a good predictor of the duration of intensive care unit stay following cardiac surgery. Heart. 2000;83(4):429-432. doi:10.1136/heart.83.4.429
15. Janssen DP, Noyez L, Wouters C, Brouwer RM. Preoperative prediction of prolonged stay in the intensive care unit for coronary bypass surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;25(2):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.11.005
16. Nilsson J, Algotsson L, Hoglund P, Luhrs C, Brandt J. EuroSCORE predicts intensive care unit stay and costs of open heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78(5):1528-1534. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.060
17. Ghotkar SV, Grayson AD, Fabri BM, Dihmis WC, Pullan DM. Preoperative calculation of risk for prolonged intensive care unit stay following coronary artery bypass grafting. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;1:14. doi:10.1186/1749-8090-1-1418. Messaoudi N, Decocker J, Stockman BA, Bossaert LL, Rodrigus IE. Is EuroSCORE useful in the prediction of extended intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery? Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg. 2009;36(1):35-39. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.02.007
19. Ettema RG, Peelen LM, Schuurmans MJ, Nierich AP, Kalkman CJ, Moons KG. Prediction models for prolonged intensive care unit stay after cardiac surgery: systematic review and validation study. Circulation. 2010;122(7):682-689. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.926808
20. Engoren M. Does erythrocyte blood transfusion prevent acute kidney injury? Propensity-matched case control analysis. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(5):1126-1133. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e181f70f56
21. UK National Centre for Research Methods. Minimising the effect of missing data. Revised July 22, 2011. Accessed June 28, 2022. www.restore.ac.uk/srme/www/fac/soc/wie/research-new/srme/modules/mod3/9/index.html.
22. Leontyev S, Davierwala PM, Gaube LM, et al. Outcomes of dialysis-dependent patients after cardiac operations in a single-center experience of 483 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(4):1270-1276. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.07.05223. Freundlich RE, Maile MD, Sferra JJ, Jewell ES, Kheterpal S, Engoren M. Complications associated with mortality in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Database. Anesth Analg. 2018;127(1):55-62. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000002799
24. Freundlich RE, Maile MD, Hajjar MM, et al. Years of life lost after complications of coronary artery bypass operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(6):1893-1899. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.09.048
25. Koch CG, Li L, Sessler DI, et al. Duration of red-cell storage and complications after cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(12):1229-1239. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa070403
26. Truche AS, Ragey SP, Souweine B, et al. ICU survival and need of renal replacement therapy with respect to AKI duration in critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2018;8(1):127. doi:10.1186/s13613-018-0467-6
27. Kollef MH, Shapiro SD, Silver P, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of protocol-directed versus physician-directed weaning from mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 1997;25(4):567-574. doi:10.1097/00003246-199704000-00004
28. McWilliams D, Weblin J, Atkins G, et al. Enhancing rehabilitation of mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: a quality improvement project. J Crit Care. 2015;30(1):13-18. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.09.018
29. Hernandez G, Vaquero C, Gonzalez P, et al. Effect of postextubation high-flow nasal cannula vs conventional oxygen therapy on reintubation in low-risk patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1354-1361. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2711
30. Schwann TA, Ramira PS, Engoren MC, et al. Evidence and temporality of the obesity paradox in coronary bypass surgery: an analysis of cause-specific mortality. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;54(5):896-903. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezy207
NSAIDs for spondyloarthritis may affect time to conception
PHILADELPHIA – Women with spondyloarthritis (SpA) who are desiring pregnancy may want to consider decreasing use or discontinuing use (with supervision) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before conception, new data suggest.
Researchers have found a connection between NSAID use and age and a significantly longer time to conception among women with spondyloarthritis. Sabrina Hamroun, MMed, with the rheumatology department at the University Hospital Cochin, Paris, presented the findings during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
SpA commonly affects women of childbearing age, but data are sparse regarding the effects of disease on fertility.
Patients in the study were taken from the French multicenter cohort GR2 from 2015 to June 2021.
Among the 207 patients with SpA in the cohort, 88 were selected for analysis of time to conception. Of these, 56 patients (63.6%) had a clinical pregnancy during follow-up.
Subfertility group took an average of 16 months to get pregnant
Subfertility was observed in 40 (45.4%) of the women, with an average time to conception of 16.1 months. A woman was considered subfertile if her time to conception was more than 12 months or if she did not become pregnant.
The average preconception Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index score was 2.9 (+/- 2.1), the authors noted. The average age of the participants was 32 years.
Twenty-three patients were treated with NSAIDs, eight with corticosteroids, 12 with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and 61 with biologics.
Researchers adjusted for factors including age, body mass index, disease duration and severity, smoking, form of SpA (axial, peripheral, or both), and medication in the preconception period.
They found significant associations between longer time to conception and age (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.40; P < .001), and a much higher hazard ratio with the use of NSAIDs during preconception (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.15-3.85; P = .01).
Some data unavailable
Ms. Hamroun acknowledged that no data were available on the frequency of sexual intercourse or quality of life, factors that could affect time to conception. Women were asked when they discontinued contraceptive use and actively began trying to become pregnant.
She stated that information on the dose of NSAIDs used by the patients was incomplete, noting, “We were therefore unable to adjust the results of our statistical analyses on the dose used by patients.”
Additionally, because the study participants were patients at tertiary centers in France and had more severe disease, the results may not be generalizable to all women of childbearing age. Patients with less severe SpA are often managed in outpatient settings in France, she said.
When asked about alternatives to NSAIDs, Ms. Hamroun said that anti–tumor necrosis factor agents with low placental passage may be a good alternative “if a woman with long-standing difficulties to conceive needs a regular use of NSAIDs to control disease activity, in the absence of any other cause of subfertility.”
The patient’s age must also be considered, she noted.
“A therapeutic switch may be favored in a woman over 35 years of age, for example, whose fertility is already impaired by age,” Ms. Hamroun said.
As for the mechanism that might explain the effects of NSAIDs on conception, Ms. Hamroun said that prostaglandins are essential to ovulation and embryo implantation and explained that NSAIDs may work against ovulation and result in poor implantation (miscarriage) by blocking prostaglandins.
She pointed out that her results are in line with the ACR’s recommendation to discontinue NSAID use during the preconception period in women with SpA who are having difficulty conceiving.
Control before conception is important
Sinead Maguire, MD, a clinical and research fellow in the Spondylitis Program at Toronto (Ont.) Western Hospital who was not part of the study, said the study highlights the importance of optimizing disease control before conception.
“There are a number of things rheumatologists can do to support our SpA patients when they are trying to conceive,” she told this news organization. “One of the most important issues to address is ensuring their SpA is in remission and continues to remain so. For that reason, if a woman is requiring regular NSAIDs for symptom control, the results of this study might encourage me to consider a biologic agent sooner to ensure remission.”
She urged women who want to become pregnant to discuss medications with their rheumatologist before trying to conceive.
“It is very exciting to see studies such as this so that rheumatologists can provide answers to our patients’ questions with evidence-based advice,” she said.
Ms. Hamroun and several coauthors had no disclosures. Other coauthors disclosed relationships with companies including Merck/MSD, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and/or UCB. Dr. Maguire reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – Women with spondyloarthritis (SpA) who are desiring pregnancy may want to consider decreasing use or discontinuing use (with supervision) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before conception, new data suggest.
Researchers have found a connection between NSAID use and age and a significantly longer time to conception among women with spondyloarthritis. Sabrina Hamroun, MMed, with the rheumatology department at the University Hospital Cochin, Paris, presented the findings during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
SpA commonly affects women of childbearing age, but data are sparse regarding the effects of disease on fertility.
Patients in the study were taken from the French multicenter cohort GR2 from 2015 to June 2021.
Among the 207 patients with SpA in the cohort, 88 were selected for analysis of time to conception. Of these, 56 patients (63.6%) had a clinical pregnancy during follow-up.
Subfertility group took an average of 16 months to get pregnant
Subfertility was observed in 40 (45.4%) of the women, with an average time to conception of 16.1 months. A woman was considered subfertile if her time to conception was more than 12 months or if she did not become pregnant.
The average preconception Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index score was 2.9 (+/- 2.1), the authors noted. The average age of the participants was 32 years.
Twenty-three patients were treated with NSAIDs, eight with corticosteroids, 12 with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and 61 with biologics.
Researchers adjusted for factors including age, body mass index, disease duration and severity, smoking, form of SpA (axial, peripheral, or both), and medication in the preconception period.
They found significant associations between longer time to conception and age (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.40; P < .001), and a much higher hazard ratio with the use of NSAIDs during preconception (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.15-3.85; P = .01).
Some data unavailable
Ms. Hamroun acknowledged that no data were available on the frequency of sexual intercourse or quality of life, factors that could affect time to conception. Women were asked when they discontinued contraceptive use and actively began trying to become pregnant.
She stated that information on the dose of NSAIDs used by the patients was incomplete, noting, “We were therefore unable to adjust the results of our statistical analyses on the dose used by patients.”
Additionally, because the study participants were patients at tertiary centers in France and had more severe disease, the results may not be generalizable to all women of childbearing age. Patients with less severe SpA are often managed in outpatient settings in France, she said.
When asked about alternatives to NSAIDs, Ms. Hamroun said that anti–tumor necrosis factor agents with low placental passage may be a good alternative “if a woman with long-standing difficulties to conceive needs a regular use of NSAIDs to control disease activity, in the absence of any other cause of subfertility.”
The patient’s age must also be considered, she noted.
“A therapeutic switch may be favored in a woman over 35 years of age, for example, whose fertility is already impaired by age,” Ms. Hamroun said.
As for the mechanism that might explain the effects of NSAIDs on conception, Ms. Hamroun said that prostaglandins are essential to ovulation and embryo implantation and explained that NSAIDs may work against ovulation and result in poor implantation (miscarriage) by blocking prostaglandins.
She pointed out that her results are in line with the ACR’s recommendation to discontinue NSAID use during the preconception period in women with SpA who are having difficulty conceiving.
Control before conception is important
Sinead Maguire, MD, a clinical and research fellow in the Spondylitis Program at Toronto (Ont.) Western Hospital who was not part of the study, said the study highlights the importance of optimizing disease control before conception.
“There are a number of things rheumatologists can do to support our SpA patients when they are trying to conceive,” she told this news organization. “One of the most important issues to address is ensuring their SpA is in remission and continues to remain so. For that reason, if a woman is requiring regular NSAIDs for symptom control, the results of this study might encourage me to consider a biologic agent sooner to ensure remission.”
She urged women who want to become pregnant to discuss medications with their rheumatologist before trying to conceive.
“It is very exciting to see studies such as this so that rheumatologists can provide answers to our patients’ questions with evidence-based advice,” she said.
Ms. Hamroun and several coauthors had no disclosures. Other coauthors disclosed relationships with companies including Merck/MSD, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and/or UCB. Dr. Maguire reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – Women with spondyloarthritis (SpA) who are desiring pregnancy may want to consider decreasing use or discontinuing use (with supervision) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before conception, new data suggest.
Researchers have found a connection between NSAID use and age and a significantly longer time to conception among women with spondyloarthritis. Sabrina Hamroun, MMed, with the rheumatology department at the University Hospital Cochin, Paris, presented the findings during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
SpA commonly affects women of childbearing age, but data are sparse regarding the effects of disease on fertility.
Patients in the study were taken from the French multicenter cohort GR2 from 2015 to June 2021.
Among the 207 patients with SpA in the cohort, 88 were selected for analysis of time to conception. Of these, 56 patients (63.6%) had a clinical pregnancy during follow-up.
Subfertility group took an average of 16 months to get pregnant
Subfertility was observed in 40 (45.4%) of the women, with an average time to conception of 16.1 months. A woman was considered subfertile if her time to conception was more than 12 months or if she did not become pregnant.
The average preconception Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index score was 2.9 (+/- 2.1), the authors noted. The average age of the participants was 32 years.
Twenty-three patients were treated with NSAIDs, eight with corticosteroids, 12 with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and 61 with biologics.
Researchers adjusted for factors including age, body mass index, disease duration and severity, smoking, form of SpA (axial, peripheral, or both), and medication in the preconception period.
They found significant associations between longer time to conception and age (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.40; P < .001), and a much higher hazard ratio with the use of NSAIDs during preconception (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.15-3.85; P = .01).
Some data unavailable
Ms. Hamroun acknowledged that no data were available on the frequency of sexual intercourse or quality of life, factors that could affect time to conception. Women were asked when they discontinued contraceptive use and actively began trying to become pregnant.
She stated that information on the dose of NSAIDs used by the patients was incomplete, noting, “We were therefore unable to adjust the results of our statistical analyses on the dose used by patients.”
Additionally, because the study participants were patients at tertiary centers in France and had more severe disease, the results may not be generalizable to all women of childbearing age. Patients with less severe SpA are often managed in outpatient settings in France, she said.
When asked about alternatives to NSAIDs, Ms. Hamroun said that anti–tumor necrosis factor agents with low placental passage may be a good alternative “if a woman with long-standing difficulties to conceive needs a regular use of NSAIDs to control disease activity, in the absence of any other cause of subfertility.”
The patient’s age must also be considered, she noted.
“A therapeutic switch may be favored in a woman over 35 years of age, for example, whose fertility is already impaired by age,” Ms. Hamroun said.
As for the mechanism that might explain the effects of NSAIDs on conception, Ms. Hamroun said that prostaglandins are essential to ovulation and embryo implantation and explained that NSAIDs may work against ovulation and result in poor implantation (miscarriage) by blocking prostaglandins.
She pointed out that her results are in line with the ACR’s recommendation to discontinue NSAID use during the preconception period in women with SpA who are having difficulty conceiving.
Control before conception is important
Sinead Maguire, MD, a clinical and research fellow in the Spondylitis Program at Toronto (Ont.) Western Hospital who was not part of the study, said the study highlights the importance of optimizing disease control before conception.
“There are a number of things rheumatologists can do to support our SpA patients when they are trying to conceive,” she told this news organization. “One of the most important issues to address is ensuring their SpA is in remission and continues to remain so. For that reason, if a woman is requiring regular NSAIDs for symptom control, the results of this study might encourage me to consider a biologic agent sooner to ensure remission.”
She urged women who want to become pregnant to discuss medications with their rheumatologist before trying to conceive.
“It is very exciting to see studies such as this so that rheumatologists can provide answers to our patients’ questions with evidence-based advice,” she said.
Ms. Hamroun and several coauthors had no disclosures. Other coauthors disclosed relationships with companies including Merck/MSD, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and/or UCB. Dr. Maguire reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2022
Combination therapy shows mixed results for scleroderma-related lung disease
PHILADELPHIA – Combining the immunomodulatory agent mycophenolate with the antifibrotic pirfenidone led to more rapid improvement and showed a trend to be more effective than mycophenolate mofetil alone for treating the signs and symptoms of scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease, but the combination therapy came with an increase in side effects, according to results from the Scleroderma Lung Study III.
Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He noted some problems with the study – namely its small size, enrolling only 51 patients, about one-third of its original goal. But he also said it showed a potential signal for efficacy and that the study itself could serve as a “template” for future studies of combination mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus pirfenidone therapy for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
“The pirfenidone patients had quite a bit more GI side effects and photosensitivity, and those are known side effects,” Dr. Khanna said in an interview. “So the combination therapy had more side effects but trends to higher efficacy.”
The design of SLS-III, a phase 2 clinical trial, was a challenge, Dr. Khanna explained. The goal was to enroll 150 SSc-ILD patients who hadn’t had any previous treatment for their disease. Finding those patients proved difficult. “In fact, if you look at the recent history, 70% of the patients with early diffuse scleroderma are on MMF,” he said in his presentation. Compounding low study enrollment was the intervening COVID-19 pandemic, he added.
Testing a faster-acting combination
Nonetheless, the trial managed to enroll 27 patients in the combination therapy group and 24 in the MMF-plus-placebo group and compared their outcomes over 18 months. Study dosing was 1,500 mg MMF twice daily and pirfenidone 801 mg three times daily, titrated to the tolerable dose.
Despite the study’s being underpowered, Dr. Khanna said, it still reported some notable outcomes that merit further investigation. “I think what was intriguing in the study was the long-term benefit in the patient-reported outcomes and the structural changes,” he said in the interview.
Among those notable outcomes was a clinically significant change in forced vital capacity (FVC) percentage for the combination vs. the placebo groups: 2.24% vs. 2.09%. He also noted that the combination group saw a somewhat more robust improvement in FVC at six months: 2.59% (± 0.98%) vs. 0.92% (± 1.1%) in the placebo group.
The combination group showed greater improvements in high-resolution computed tomography-evaluated lung involvement and lung fibrosis and patient-reported outcomes, including a statistically significant 3.67-point greater improvement in PROMIS-29 physical function score (4.42 vs. 0.75).
The patients on combination therapy had higher rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), and seven discontinued one or both study drugs early, all in the combined arm. Four combination therapy patients had six SAEs, compared to two placebo patients with three SAEs. In the combination group, SAEs included chest pain, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, nodular basal cell cancer, marginal zone B cell lymphoma, renal crisis, and dyspnea. SAEs in the placebo group were colitis, COVID-19 and hypoxic respiratory failure.
Study design challenges
Nonetheless, Dr. Khanna said the SLS-III data are consistent with the SLS-II findings, with mean improvements in FVC of 2.24% and 2.1%, respectively.
“The next study may be able to replicate what we tried to do, keeping in mind that there are really no MMF-naive patients who are walking around,” Dr. Khanna said. “So the challenge is about the feasibility of recruiting within a trial vs. trying to show a statistical difference between the drug and placebo.”
This study could serve as a foundation for future studies of MMF in patients with SSc-ILD, Robert Spiera, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “There are lessons to be learned both from the study but also from prior studies looking at MMF use in the background in patients treated with other drugs in clinical trials,” he said.
Dr. Spiera noted that the study had other challenges besides the difficulty in recruiting patients who hadn’t been on MMF therapy. “A great challenge is that the benefit with regard to the impact on the lungs from MMF seems most prominent in the first 6 months to a year to even 2 years that somebody is on the drug,” he said.
The other challenge with this study is that a large proportion of patients had limited systemic disease and relatively lower levels of skin disease compared with other studies of patients on MMF, Dr. Spiera said.
“The optimal treatment of scleroderma-associated lung disease remains a very important and not-adequately met need,” he said. “Particularly, we’re looking for drugs that are tolerable in a patient population that are very prone to GI side effects in general. This study and others have taught us a lot about trial design, and I think more globally this will allow us to move this field forward.”
Dr. Khanna disclosed relationships with Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Janssen Global Services, Prometheus Biosciences, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Genentech/Roche, Theraly, and Pfizer. Genentech provided funding for the study and pirfenidone and placebo drugs at no cost.
Dr. Spiera disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche and Vera.
PHILADELPHIA – Combining the immunomodulatory agent mycophenolate with the antifibrotic pirfenidone led to more rapid improvement and showed a trend to be more effective than mycophenolate mofetil alone for treating the signs and symptoms of scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease, but the combination therapy came with an increase in side effects, according to results from the Scleroderma Lung Study III.
Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He noted some problems with the study – namely its small size, enrolling only 51 patients, about one-third of its original goal. But he also said it showed a potential signal for efficacy and that the study itself could serve as a “template” for future studies of combination mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus pirfenidone therapy for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
“The pirfenidone patients had quite a bit more GI side effects and photosensitivity, and those are known side effects,” Dr. Khanna said in an interview. “So the combination therapy had more side effects but trends to higher efficacy.”
The design of SLS-III, a phase 2 clinical trial, was a challenge, Dr. Khanna explained. The goal was to enroll 150 SSc-ILD patients who hadn’t had any previous treatment for their disease. Finding those patients proved difficult. “In fact, if you look at the recent history, 70% of the patients with early diffuse scleroderma are on MMF,” he said in his presentation. Compounding low study enrollment was the intervening COVID-19 pandemic, he added.
Testing a faster-acting combination
Nonetheless, the trial managed to enroll 27 patients in the combination therapy group and 24 in the MMF-plus-placebo group and compared their outcomes over 18 months. Study dosing was 1,500 mg MMF twice daily and pirfenidone 801 mg three times daily, titrated to the tolerable dose.
Despite the study’s being underpowered, Dr. Khanna said, it still reported some notable outcomes that merit further investigation. “I think what was intriguing in the study was the long-term benefit in the patient-reported outcomes and the structural changes,” he said in the interview.
Among those notable outcomes was a clinically significant change in forced vital capacity (FVC) percentage for the combination vs. the placebo groups: 2.24% vs. 2.09%. He also noted that the combination group saw a somewhat more robust improvement in FVC at six months: 2.59% (± 0.98%) vs. 0.92% (± 1.1%) in the placebo group.
The combination group showed greater improvements in high-resolution computed tomography-evaluated lung involvement and lung fibrosis and patient-reported outcomes, including a statistically significant 3.67-point greater improvement in PROMIS-29 physical function score (4.42 vs. 0.75).
The patients on combination therapy had higher rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), and seven discontinued one or both study drugs early, all in the combined arm. Four combination therapy patients had six SAEs, compared to two placebo patients with three SAEs. In the combination group, SAEs included chest pain, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, nodular basal cell cancer, marginal zone B cell lymphoma, renal crisis, and dyspnea. SAEs in the placebo group were colitis, COVID-19 and hypoxic respiratory failure.
Study design challenges
Nonetheless, Dr. Khanna said the SLS-III data are consistent with the SLS-II findings, with mean improvements in FVC of 2.24% and 2.1%, respectively.
“The next study may be able to replicate what we tried to do, keeping in mind that there are really no MMF-naive patients who are walking around,” Dr. Khanna said. “So the challenge is about the feasibility of recruiting within a trial vs. trying to show a statistical difference between the drug and placebo.”
This study could serve as a foundation for future studies of MMF in patients with SSc-ILD, Robert Spiera, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “There are lessons to be learned both from the study but also from prior studies looking at MMF use in the background in patients treated with other drugs in clinical trials,” he said.
Dr. Spiera noted that the study had other challenges besides the difficulty in recruiting patients who hadn’t been on MMF therapy. “A great challenge is that the benefit with regard to the impact on the lungs from MMF seems most prominent in the first 6 months to a year to even 2 years that somebody is on the drug,” he said.
The other challenge with this study is that a large proportion of patients had limited systemic disease and relatively lower levels of skin disease compared with other studies of patients on MMF, Dr. Spiera said.
“The optimal treatment of scleroderma-associated lung disease remains a very important and not-adequately met need,” he said. “Particularly, we’re looking for drugs that are tolerable in a patient population that are very prone to GI side effects in general. This study and others have taught us a lot about trial design, and I think more globally this will allow us to move this field forward.”
Dr. Khanna disclosed relationships with Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Janssen Global Services, Prometheus Biosciences, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Genentech/Roche, Theraly, and Pfizer. Genentech provided funding for the study and pirfenidone and placebo drugs at no cost.
Dr. Spiera disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche and Vera.
PHILADELPHIA – Combining the immunomodulatory agent mycophenolate with the antifibrotic pirfenidone led to more rapid improvement and showed a trend to be more effective than mycophenolate mofetil alone for treating the signs and symptoms of scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease, but the combination therapy came with an increase in side effects, according to results from the Scleroderma Lung Study III.
Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He noted some problems with the study – namely its small size, enrolling only 51 patients, about one-third of its original goal. But he also said it showed a potential signal for efficacy and that the study itself could serve as a “template” for future studies of combination mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus pirfenidone therapy for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
“The pirfenidone patients had quite a bit more GI side effects and photosensitivity, and those are known side effects,” Dr. Khanna said in an interview. “So the combination therapy had more side effects but trends to higher efficacy.”
The design of SLS-III, a phase 2 clinical trial, was a challenge, Dr. Khanna explained. The goal was to enroll 150 SSc-ILD patients who hadn’t had any previous treatment for their disease. Finding those patients proved difficult. “In fact, if you look at the recent history, 70% of the patients with early diffuse scleroderma are on MMF,” he said in his presentation. Compounding low study enrollment was the intervening COVID-19 pandemic, he added.
Testing a faster-acting combination
Nonetheless, the trial managed to enroll 27 patients in the combination therapy group and 24 in the MMF-plus-placebo group and compared their outcomes over 18 months. Study dosing was 1,500 mg MMF twice daily and pirfenidone 801 mg three times daily, titrated to the tolerable dose.
Despite the study’s being underpowered, Dr. Khanna said, it still reported some notable outcomes that merit further investigation. “I think what was intriguing in the study was the long-term benefit in the patient-reported outcomes and the structural changes,” he said in the interview.
Among those notable outcomes was a clinically significant change in forced vital capacity (FVC) percentage for the combination vs. the placebo groups: 2.24% vs. 2.09%. He also noted that the combination group saw a somewhat more robust improvement in FVC at six months: 2.59% (± 0.98%) vs. 0.92% (± 1.1%) in the placebo group.
The combination group showed greater improvements in high-resolution computed tomography-evaluated lung involvement and lung fibrosis and patient-reported outcomes, including a statistically significant 3.67-point greater improvement in PROMIS-29 physical function score (4.42 vs. 0.75).
The patients on combination therapy had higher rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), and seven discontinued one or both study drugs early, all in the combined arm. Four combination therapy patients had six SAEs, compared to two placebo patients with three SAEs. In the combination group, SAEs included chest pain, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, nodular basal cell cancer, marginal zone B cell lymphoma, renal crisis, and dyspnea. SAEs in the placebo group were colitis, COVID-19 and hypoxic respiratory failure.
Study design challenges
Nonetheless, Dr. Khanna said the SLS-III data are consistent with the SLS-II findings, with mean improvements in FVC of 2.24% and 2.1%, respectively.
“The next study may be able to replicate what we tried to do, keeping in mind that there are really no MMF-naive patients who are walking around,” Dr. Khanna said. “So the challenge is about the feasibility of recruiting within a trial vs. trying to show a statistical difference between the drug and placebo.”
This study could serve as a foundation for future studies of MMF in patients with SSc-ILD, Robert Spiera, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “There are lessons to be learned both from the study but also from prior studies looking at MMF use in the background in patients treated with other drugs in clinical trials,” he said.
Dr. Spiera noted that the study had other challenges besides the difficulty in recruiting patients who hadn’t been on MMF therapy. “A great challenge is that the benefit with regard to the impact on the lungs from MMF seems most prominent in the first 6 months to a year to even 2 years that somebody is on the drug,” he said.
The other challenge with this study is that a large proportion of patients had limited systemic disease and relatively lower levels of skin disease compared with other studies of patients on MMF, Dr. Spiera said.
“The optimal treatment of scleroderma-associated lung disease remains a very important and not-adequately met need,” he said. “Particularly, we’re looking for drugs that are tolerable in a patient population that are very prone to GI side effects in general. This study and others have taught us a lot about trial design, and I think more globally this will allow us to move this field forward.”
Dr. Khanna disclosed relationships with Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Janssen Global Services, Prometheus Biosciences, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Genentech/Roche, Theraly, and Pfizer. Genentech provided funding for the study and pirfenidone and placebo drugs at no cost.
Dr. Spiera disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche and Vera.
AT ACR 2022
Starting a podcast
In my last column, I discussed . At this writing (November 2022), more than 600 million blogs are online, compared with about 2 million podcasts, and relatively few of them are run by physicians. With podcasts, you have a better chance of standing out in a crowded online world.
Starting a podcast is not difficult, but there are several steps you need to go through before launching one.
As with blogging, start by outlining a long-range plan. Your general topic will probably be your specialty, but you will need to narrow your focus to a few specific subjects, such as the problems you see most often, or a subspecialty that you concentrate on. You can always expand your topic later, as you get more popular. Choose a name for your podcast, and purchase a domain name that accurately describes it.
You will also need to choose a hosting service. Numerous inexpensive hosting platforms are available, and a simple Google search will find them for you. Many of them provide free learning materials, helpful creative tools, and customer support to get you through the confusing technical aspects. They can also help you choose a music introduction (to add a bit of polish), and help you piece together your audio segments. Buzzsprout, RSS.com, and Podbean get good reviews on many sites. (As always, I have no financial interest in any company or service mentioned herein.)
Hosting services can assist you in creating a template – a framework that you can reuse each time you record an episode – containing your intro and exit music, tracks for your conversations, etc. This will make your podcasts instantly recognizable each time your listeners tune in.
Many podcasting experts recommend recruiting a co-host. This can be an associate within your practice, a friend who practices elsewhere, or perhaps a resident in an academic setting. You will be able to spread the workload of creating, editing, and promoting. Plus, it is much easier to generate interesting content when two people are having a conversation, rather than one person lecturing from a prepared script. You might also consider having multiple co-hosts, either to expand episodes into group discussions, or to take turns working with you in covering different subjects.
How long you make your podcast is entirely up to you. Some consultants recommend specific time frames, such as 5 minutes (because that’s an average attention span), or 28 minutes (because that’s the average driving commute time). There are short podcasts and long ones; whatever works for you is fine, as long as you don’t drift off the topic. Furthermore, no one says they must all be the same length; when you are finished talking, you are done. And no one says you must stick with one subject throughout. Combining several short segments might hold more listeners’ interest and will make it easier to share small clips on social media.
Content guidelines are similar to those for blogs. Give people content that will be of interest or benefit to them. Talk about subjects – medical and otherwise – that are relevant to your practice or are prominent in the news.
As with blogs, try to avoid polarizing political discussions, and while it’s fine to discuss treatments and procedures that you offer, aggressive solicitation tends to make viewers look elsewhere. Keep any medical advice in general terms; don’t portray any specific patients as examples.
When your podcast is ready, your hosting platform will show you how to submit it to iTunes, and how to submit your podcast RSS feed to other podcast directories. As you upload new episodes, your host will automatically update your RSS feed, so that any directory you are listed on will receive the new episode.
Once you are uploaded, you can use your host’s social sharing tools to spread the word. As with blogs, use social media, such as your practice’s Facebook page, to push podcast updates into patients’ feeds and track relevant Twitter hashtags to find online communities that might be interested in your subject matter. You should also find your episode embed code (which your host will have) and place it in a prominent place on your website so patients can listen directly from there.
Transcriptions are another excellent promotional tool. Search engines will “read” your podcasts and list them in searches. Some podcast hosts will do transcribing for a fee, but there are independent transcription services as well.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
In my last column, I discussed . At this writing (November 2022), more than 600 million blogs are online, compared with about 2 million podcasts, and relatively few of them are run by physicians. With podcasts, you have a better chance of standing out in a crowded online world.
Starting a podcast is not difficult, but there are several steps you need to go through before launching one.
As with blogging, start by outlining a long-range plan. Your general topic will probably be your specialty, but you will need to narrow your focus to a few specific subjects, such as the problems you see most often, or a subspecialty that you concentrate on. You can always expand your topic later, as you get more popular. Choose a name for your podcast, and purchase a domain name that accurately describes it.
You will also need to choose a hosting service. Numerous inexpensive hosting platforms are available, and a simple Google search will find them for you. Many of them provide free learning materials, helpful creative tools, and customer support to get you through the confusing technical aspects. They can also help you choose a music introduction (to add a bit of polish), and help you piece together your audio segments. Buzzsprout, RSS.com, and Podbean get good reviews on many sites. (As always, I have no financial interest in any company or service mentioned herein.)
Hosting services can assist you in creating a template – a framework that you can reuse each time you record an episode – containing your intro and exit music, tracks for your conversations, etc. This will make your podcasts instantly recognizable each time your listeners tune in.
Many podcasting experts recommend recruiting a co-host. This can be an associate within your practice, a friend who practices elsewhere, or perhaps a resident in an academic setting. You will be able to spread the workload of creating, editing, and promoting. Plus, it is much easier to generate interesting content when two people are having a conversation, rather than one person lecturing from a prepared script. You might also consider having multiple co-hosts, either to expand episodes into group discussions, or to take turns working with you in covering different subjects.
How long you make your podcast is entirely up to you. Some consultants recommend specific time frames, such as 5 minutes (because that’s an average attention span), or 28 minutes (because that’s the average driving commute time). There are short podcasts and long ones; whatever works for you is fine, as long as you don’t drift off the topic. Furthermore, no one says they must all be the same length; when you are finished talking, you are done. And no one says you must stick with one subject throughout. Combining several short segments might hold more listeners’ interest and will make it easier to share small clips on social media.
Content guidelines are similar to those for blogs. Give people content that will be of interest or benefit to them. Talk about subjects – medical and otherwise – that are relevant to your practice or are prominent in the news.
As with blogs, try to avoid polarizing political discussions, and while it’s fine to discuss treatments and procedures that you offer, aggressive solicitation tends to make viewers look elsewhere. Keep any medical advice in general terms; don’t portray any specific patients as examples.
When your podcast is ready, your hosting platform will show you how to submit it to iTunes, and how to submit your podcast RSS feed to other podcast directories. As you upload new episodes, your host will automatically update your RSS feed, so that any directory you are listed on will receive the new episode.
Once you are uploaded, you can use your host’s social sharing tools to spread the word. As with blogs, use social media, such as your practice’s Facebook page, to push podcast updates into patients’ feeds and track relevant Twitter hashtags to find online communities that might be interested in your subject matter. You should also find your episode embed code (which your host will have) and place it in a prominent place on your website so patients can listen directly from there.
Transcriptions are another excellent promotional tool. Search engines will “read” your podcasts and list them in searches. Some podcast hosts will do transcribing for a fee, but there are independent transcription services as well.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
In my last column, I discussed . At this writing (November 2022), more than 600 million blogs are online, compared with about 2 million podcasts, and relatively few of them are run by physicians. With podcasts, you have a better chance of standing out in a crowded online world.
Starting a podcast is not difficult, but there are several steps you need to go through before launching one.
As with blogging, start by outlining a long-range plan. Your general topic will probably be your specialty, but you will need to narrow your focus to a few specific subjects, such as the problems you see most often, or a subspecialty that you concentrate on. You can always expand your topic later, as you get more popular. Choose a name for your podcast, and purchase a domain name that accurately describes it.
You will also need to choose a hosting service. Numerous inexpensive hosting platforms are available, and a simple Google search will find them for you. Many of them provide free learning materials, helpful creative tools, and customer support to get you through the confusing technical aspects. They can also help you choose a music introduction (to add a bit of polish), and help you piece together your audio segments. Buzzsprout, RSS.com, and Podbean get good reviews on many sites. (As always, I have no financial interest in any company or service mentioned herein.)
Hosting services can assist you in creating a template – a framework that you can reuse each time you record an episode – containing your intro and exit music, tracks for your conversations, etc. This will make your podcasts instantly recognizable each time your listeners tune in.
Many podcasting experts recommend recruiting a co-host. This can be an associate within your practice, a friend who practices elsewhere, or perhaps a resident in an academic setting. You will be able to spread the workload of creating, editing, and promoting. Plus, it is much easier to generate interesting content when two people are having a conversation, rather than one person lecturing from a prepared script. You might also consider having multiple co-hosts, either to expand episodes into group discussions, or to take turns working with you in covering different subjects.
How long you make your podcast is entirely up to you. Some consultants recommend specific time frames, such as 5 minutes (because that’s an average attention span), or 28 minutes (because that’s the average driving commute time). There are short podcasts and long ones; whatever works for you is fine, as long as you don’t drift off the topic. Furthermore, no one says they must all be the same length; when you are finished talking, you are done. And no one says you must stick with one subject throughout. Combining several short segments might hold more listeners’ interest and will make it easier to share small clips on social media.
Content guidelines are similar to those for blogs. Give people content that will be of interest or benefit to them. Talk about subjects – medical and otherwise – that are relevant to your practice or are prominent in the news.
As with blogs, try to avoid polarizing political discussions, and while it’s fine to discuss treatments and procedures that you offer, aggressive solicitation tends to make viewers look elsewhere. Keep any medical advice in general terms; don’t portray any specific patients as examples.
When your podcast is ready, your hosting platform will show you how to submit it to iTunes, and how to submit your podcast RSS feed to other podcast directories. As you upload new episodes, your host will automatically update your RSS feed, so that any directory you are listed on will receive the new episode.
Once you are uploaded, you can use your host’s social sharing tools to spread the word. As with blogs, use social media, such as your practice’s Facebook page, to push podcast updates into patients’ feeds and track relevant Twitter hashtags to find online communities that might be interested in your subject matter. You should also find your episode embed code (which your host will have) and place it in a prominent place on your website so patients can listen directly from there.
Transcriptions are another excellent promotional tool. Search engines will “read” your podcasts and list them in searches. Some podcast hosts will do transcribing for a fee, but there are independent transcription services as well.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
Combination therapy may boost remission in JIA
Benefit endures at 3 years
PHILADELPHIA – Aggressive therapy using conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in combination with biologic agents early, soon after a child is diagnosed with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), enabled more patients to achieve clinical remission and longer times in inactive disease than more conventional therapeutic approaches, 3-year results of prospective, observational study demonstrated.
The results of The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance STOP-JIA study, which Yukiko Kimura, MD, presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed early combination therapy had benefits, compared with other treatment strategies that were more evident at 3 years than at 1 year of study.
“The STOP-JIA study showed that, after 3 years, patients who started a biologic early on in combination with methotrexate spent more time in inactive disease and achieved clinical remission more often when compared to those started on traditional step-up therapy,” Dr. Kimura, chief of pediatric rheumatology at Hackensack (N.J.) Meridian Health and professor of pediatrics at the Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine, said at a press conference. “This study shows that the treatment of poly-JIA patients receive initially very early on in their disease matters even 3 years after that treatment was started.”
The study compared three CARRA consensus treatment plans (CTP) for untreated pediatric pJIA patients: step-up (SU) – starting conventional synthetic DMARD therapy and adding a biologic if needed after 3 or more months; early-combination (EC) therapy – starting synthetic and biologic DMARDs together; and biologic first (BF) therapy – starting biologic DMARD monotherapy.
Dr. Kimura explained the rationale for the study. “Since biologic treatments were introduced more than 20 years ago, the prognosis for JIA significantly improved. These very effective medicines often work wonders, quickly reducing pain and inflammation in joint disease activity,” she said in the press conference. “What is not known, however, is when is the best time to start these very effective treatments.”
The most common approach is to start with a synthetic DMARD, typically methotrexate, and wait before starting a biologic, Dr. Kimura said.
“But even though methotrexate can work very well by itself, it does not work for every patient, and we don’t know whether waiting months for it to work and then starting a biologic might potentially lessen their effectiveness,” Dr. Kimura added. “We don’t know if there’s a window of opportunity that’s lost while waiting to see whether methotrexate will work.”
The study originally enrolled 400 patients, 297 of whom completed the 3-year visit – 190 in SU, 76 in EC and 31 in BF. At 12 months, the study found no statistically significant difference in clinically inactive disease (CID) between the groups, Dr. Kimura said.
Even at the 3-year visit, the percentage of patients in CID off glucocorticoids and clinical Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score based on 10 joints inactive disease (cJADAS 10 ID) did not differ among the three groups, Dr. Kimura said in presenting the results. “But,” she added, “greater proportions of early-combination CTP group were able to achieve clinical remissions and spend more time with inactive disease in both CID and cJADAS 10.”
A closer look at the outcomes showed some separation between early-combination therapy and the other two treatment plans. The incidence of clinical remission (at any time point over 36 months) was 67.1% in the EC group vs. 49.1% and 47.3%, respectively, in the BF and SU groups, Dr. Kimura said. “The difference between the early-combination and step-up groups was highly significant [P = .007],” she added.
EC also had an edge in the percentage of time patients spent in CID (over 36 months): 39.2% versus 32% and 27.4%, respectively, in the BF and SU groups (P = .006 for EV vs. SU), as well as cJADAS 10 ID (50.6% in EC group vs. 42.8% and 37.5%, respectively in the BF and SU groups; P = .005 for EC vs. SU).
Dr. Kimura said that the STOP JIA trial will continue with longer-term analysis and ongoing monitoring of study patients through the CARRA registry. “These longer-term analyses and readouts will be important because even though the results at 12 months didn’t seem as definitive, it seems the longer we go, the more impact we see of the treatments that were started early on in this disease.”
The findings from this study are “significantly important,” Nina T. Washington, MD, MPH, a pediatric rheumatologist at the University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, and the Mary Bridge Children’s Hospital in Tacoma, Wash., said in an interview. “At least for the past decade we’ve really been advocating towards earlier and aggressive therapy, and that’s what this study shows: the sooner you can treat this disease, the sooner you can attack those joints that are inflamed, the better outcome you give the patient.”
The study also confirms that pediatric rheumatologists are not overtreating patients with pJIA, she added.
“In a sense we’re actually treating and preventing and if you have a child that has arthritis, it’s okay to treat that child,” Dr. Washington said. “For me that’s the most reassuring thing: that I’m not necessarily going overboard. If I have a child with polyarticular JIA and they have multiple inflamed joints and I have the evidence as they’re sitting in front of me, and I treat them. I’m going to give them the best outcome.”
The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute provided study funding. Dr. Kimura is chair of the CARRA JIA disease research committee and cochair of the CARRA Registry and Research Oversight Committee. She disclosed a financial relationship with Genentech. Dr. Washington has no relevant relationships to disclose.
Benefit endures at 3 years
Benefit endures at 3 years
PHILADELPHIA – Aggressive therapy using conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in combination with biologic agents early, soon after a child is diagnosed with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), enabled more patients to achieve clinical remission and longer times in inactive disease than more conventional therapeutic approaches, 3-year results of prospective, observational study demonstrated.
The results of The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance STOP-JIA study, which Yukiko Kimura, MD, presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed early combination therapy had benefits, compared with other treatment strategies that were more evident at 3 years than at 1 year of study.
“The STOP-JIA study showed that, after 3 years, patients who started a biologic early on in combination with methotrexate spent more time in inactive disease and achieved clinical remission more often when compared to those started on traditional step-up therapy,” Dr. Kimura, chief of pediatric rheumatology at Hackensack (N.J.) Meridian Health and professor of pediatrics at the Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine, said at a press conference. “This study shows that the treatment of poly-JIA patients receive initially very early on in their disease matters even 3 years after that treatment was started.”
The study compared three CARRA consensus treatment plans (CTP) for untreated pediatric pJIA patients: step-up (SU) – starting conventional synthetic DMARD therapy and adding a biologic if needed after 3 or more months; early-combination (EC) therapy – starting synthetic and biologic DMARDs together; and biologic first (BF) therapy – starting biologic DMARD monotherapy.
Dr. Kimura explained the rationale for the study. “Since biologic treatments were introduced more than 20 years ago, the prognosis for JIA significantly improved. These very effective medicines often work wonders, quickly reducing pain and inflammation in joint disease activity,” she said in the press conference. “What is not known, however, is when is the best time to start these very effective treatments.”
The most common approach is to start with a synthetic DMARD, typically methotrexate, and wait before starting a biologic, Dr. Kimura said.
“But even though methotrexate can work very well by itself, it does not work for every patient, and we don’t know whether waiting months for it to work and then starting a biologic might potentially lessen their effectiveness,” Dr. Kimura added. “We don’t know if there’s a window of opportunity that’s lost while waiting to see whether methotrexate will work.”
The study originally enrolled 400 patients, 297 of whom completed the 3-year visit – 190 in SU, 76 in EC and 31 in BF. At 12 months, the study found no statistically significant difference in clinically inactive disease (CID) between the groups, Dr. Kimura said.
Even at the 3-year visit, the percentage of patients in CID off glucocorticoids and clinical Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score based on 10 joints inactive disease (cJADAS 10 ID) did not differ among the three groups, Dr. Kimura said in presenting the results. “But,” she added, “greater proportions of early-combination CTP group were able to achieve clinical remissions and spend more time with inactive disease in both CID and cJADAS 10.”
A closer look at the outcomes showed some separation between early-combination therapy and the other two treatment plans. The incidence of clinical remission (at any time point over 36 months) was 67.1% in the EC group vs. 49.1% and 47.3%, respectively, in the BF and SU groups, Dr. Kimura said. “The difference between the early-combination and step-up groups was highly significant [P = .007],” she added.
EC also had an edge in the percentage of time patients spent in CID (over 36 months): 39.2% versus 32% and 27.4%, respectively, in the BF and SU groups (P = .006 for EV vs. SU), as well as cJADAS 10 ID (50.6% in EC group vs. 42.8% and 37.5%, respectively in the BF and SU groups; P = .005 for EC vs. SU).
Dr. Kimura said that the STOP JIA trial will continue with longer-term analysis and ongoing monitoring of study patients through the CARRA registry. “These longer-term analyses and readouts will be important because even though the results at 12 months didn’t seem as definitive, it seems the longer we go, the more impact we see of the treatments that were started early on in this disease.”
The findings from this study are “significantly important,” Nina T. Washington, MD, MPH, a pediatric rheumatologist at the University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, and the Mary Bridge Children’s Hospital in Tacoma, Wash., said in an interview. “At least for the past decade we’ve really been advocating towards earlier and aggressive therapy, and that’s what this study shows: the sooner you can treat this disease, the sooner you can attack those joints that are inflamed, the better outcome you give the patient.”
The study also confirms that pediatric rheumatologists are not overtreating patients with pJIA, she added.
“In a sense we’re actually treating and preventing and if you have a child that has arthritis, it’s okay to treat that child,” Dr. Washington said. “For me that’s the most reassuring thing: that I’m not necessarily going overboard. If I have a child with polyarticular JIA and they have multiple inflamed joints and I have the evidence as they’re sitting in front of me, and I treat them. I’m going to give them the best outcome.”
The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute provided study funding. Dr. Kimura is chair of the CARRA JIA disease research committee and cochair of the CARRA Registry and Research Oversight Committee. She disclosed a financial relationship with Genentech. Dr. Washington has no relevant relationships to disclose.
PHILADELPHIA – Aggressive therapy using conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in combination with biologic agents early, soon after a child is diagnosed with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), enabled more patients to achieve clinical remission and longer times in inactive disease than more conventional therapeutic approaches, 3-year results of prospective, observational study demonstrated.
The results of The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance STOP-JIA study, which Yukiko Kimura, MD, presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed early combination therapy had benefits, compared with other treatment strategies that were more evident at 3 years than at 1 year of study.
“The STOP-JIA study showed that, after 3 years, patients who started a biologic early on in combination with methotrexate spent more time in inactive disease and achieved clinical remission more often when compared to those started on traditional step-up therapy,” Dr. Kimura, chief of pediatric rheumatology at Hackensack (N.J.) Meridian Health and professor of pediatrics at the Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine, said at a press conference. “This study shows that the treatment of poly-JIA patients receive initially very early on in their disease matters even 3 years after that treatment was started.”
The study compared three CARRA consensus treatment plans (CTP) for untreated pediatric pJIA patients: step-up (SU) – starting conventional synthetic DMARD therapy and adding a biologic if needed after 3 or more months; early-combination (EC) therapy – starting synthetic and biologic DMARDs together; and biologic first (BF) therapy – starting biologic DMARD monotherapy.
Dr. Kimura explained the rationale for the study. “Since biologic treatments were introduced more than 20 years ago, the prognosis for JIA significantly improved. These very effective medicines often work wonders, quickly reducing pain and inflammation in joint disease activity,” she said in the press conference. “What is not known, however, is when is the best time to start these very effective treatments.”
The most common approach is to start with a synthetic DMARD, typically methotrexate, and wait before starting a biologic, Dr. Kimura said.
“But even though methotrexate can work very well by itself, it does not work for every patient, and we don’t know whether waiting months for it to work and then starting a biologic might potentially lessen their effectiveness,” Dr. Kimura added. “We don’t know if there’s a window of opportunity that’s lost while waiting to see whether methotrexate will work.”
The study originally enrolled 400 patients, 297 of whom completed the 3-year visit – 190 in SU, 76 in EC and 31 in BF. At 12 months, the study found no statistically significant difference in clinically inactive disease (CID) between the groups, Dr. Kimura said.
Even at the 3-year visit, the percentage of patients in CID off glucocorticoids and clinical Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score based on 10 joints inactive disease (cJADAS 10 ID) did not differ among the three groups, Dr. Kimura said in presenting the results. “But,” she added, “greater proportions of early-combination CTP group were able to achieve clinical remissions and spend more time with inactive disease in both CID and cJADAS 10.”
A closer look at the outcomes showed some separation between early-combination therapy and the other two treatment plans. The incidence of clinical remission (at any time point over 36 months) was 67.1% in the EC group vs. 49.1% and 47.3%, respectively, in the BF and SU groups, Dr. Kimura said. “The difference between the early-combination and step-up groups was highly significant [P = .007],” she added.
EC also had an edge in the percentage of time patients spent in CID (over 36 months): 39.2% versus 32% and 27.4%, respectively, in the BF and SU groups (P = .006 for EV vs. SU), as well as cJADAS 10 ID (50.6% in EC group vs. 42.8% and 37.5%, respectively in the BF and SU groups; P = .005 for EC vs. SU).
Dr. Kimura said that the STOP JIA trial will continue with longer-term analysis and ongoing monitoring of study patients through the CARRA registry. “These longer-term analyses and readouts will be important because even though the results at 12 months didn’t seem as definitive, it seems the longer we go, the more impact we see of the treatments that were started early on in this disease.”
The findings from this study are “significantly important,” Nina T. Washington, MD, MPH, a pediatric rheumatologist at the University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, and the Mary Bridge Children’s Hospital in Tacoma, Wash., said in an interview. “At least for the past decade we’ve really been advocating towards earlier and aggressive therapy, and that’s what this study shows: the sooner you can treat this disease, the sooner you can attack those joints that are inflamed, the better outcome you give the patient.”
The study also confirms that pediatric rheumatologists are not overtreating patients with pJIA, she added.
“In a sense we’re actually treating and preventing and if you have a child that has arthritis, it’s okay to treat that child,” Dr. Washington said. “For me that’s the most reassuring thing: that I’m not necessarily going overboard. If I have a child with polyarticular JIA and they have multiple inflamed joints and I have the evidence as they’re sitting in front of me, and I treat them. I’m going to give them the best outcome.”
The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute provided study funding. Dr. Kimura is chair of the CARRA JIA disease research committee and cochair of the CARRA Registry and Research Oversight Committee. She disclosed a financial relationship with Genentech. Dr. Washington has no relevant relationships to disclose.
AT ACR 2022
Love them or hate them, masks in schools work
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
On March 26, 2022, Hawaii became the last state in the United States to lift its indoor mask mandate. By the time the current school year started, there were essentially no public school mask mandates either.
Whether you viewed the mask as an emblem of stalwart defiance against a rampaging virus, or a scarlet letter emblematic of the overreaches of public policy, you probably aren’t seeing them much anymore.
And yet, the debate about masks still rages. Who was right, who was wrong? Who trusted science, and what does the science even say? If we brought our country into marriage counseling, would we be told it is time to move on? To look forward, not backward? To plan for our bright future together?
Perhaps. But this question isn’t really moot just because masks have largely disappeared in the United States. Variants may emerge that lead to more infection waves – and other pandemics may occur in the future. And so I think it is important to discuss a study that, with quite rigorous analysis, attempts to answer the following question: Did masking in schools lower students’ and teachers’ risk of COVID?
We are talking about this study, appearing in the New England Journal of Medicine. The short version goes like this.
Researchers had access to two important sources of data. One – an accounting of all the teachers and students (more than 300,000 of them) in 79 public, noncharter school districts in Eastern Massachusetts who tested positive for COVID every week. Two – the date that each of those school districts lifted their mask mandates or (in the case of two districts) didn’t.
Right away, I’m sure you’re thinking of potential issues. Districts that kept masks even when the statewide ban was lifted are likely quite a bit different from districts that dropped masks right away. You’re right, of course – hold on to that thought; we’ll get there.
But first – the big question – would districts that kept their masks on longer do better when it comes to the rate of COVID infection?
When everyone was masking, COVID case rates were pretty similar. Statewide mandates are lifted in late February – and most school districts remove their mandates within a few weeks – the black line are the two districts (Boston and Chelsea) where mask mandates remained in place.
Prior to the mask mandate lifting, you see very similar COVID rates in districts that would eventually remove the mandate and those that would not, with a bit of noise around the initial Omicron wave which saw just a huge amount of people get infected.
And then, after the mandate was lifted, separation. Districts that held on to masks longer had lower rates of COVID infection.
In all, over the 15-weeks of the study, there were roughly 12,000 extra cases of COVID in the mask-free school districts, which corresponds to about 35% of the total COVID burden during that time. And, yes, kids do well with COVID – on average. But 12,000 extra cases is enough to translate into a significant number of important clinical outcomes – think hospitalizations and post-COVID syndromes. And of course, maybe most importantly, missed school days. Positive kids were not allowed in class no matter what district they were in.
Okay – I promised we’d address confounders. This was not a cluster-randomized trial, where some school districts had their mandates removed based on the vicissitudes of a virtual coin flip, as much as many of us would have been interested to see that. The decision to remove masks was up to the various school boards – and they had a lot of pressure on them from many different directions. But all we need to worry about is whether any of those things that pressure a school board to keep masks on would ALSO lead to fewer COVID cases. That’s how confounders work, and how you can get false results in a study like this.
And yes – districts that kept the masks on longer were different than those who took them right off. But check out how they were different.
The districts that kept masks on longer had more low-income students. More Black and Latino students. More students per classroom. These are all risk factors that increase the risk of COVID infection. In other words, the confounding here goes in the opposite direction of the results. If anything, these factors should make you more certain that masking works.
The authors also adjusted for other factors – the community transmission of COVID-19, vaccination rates, school district sizes, and so on. No major change in the results.
One concern I addressed to Dr. Ellie Murray, the biostatistician on the study – could districts that removed masks simply have been testing more to compensate, leading to increased capturing of cases?
If anything, the schools that kept masks on were testing more than the schools that took them off – again that would tend to imply that the results are even stronger than what was reported.
Is this a perfect study? Of course not – it’s one study, it’s from one state. And the relatively large effects from keeping masks on for one or 2 weeks require us to really embrace the concept of exponential growth of infections, but, if COVID has taught us anything, it is that small changes in initial conditions can have pretty big effects.
My daughter, who goes to a public school here in Connecticut, unmasked, was home with COVID this past week. She’s fine. But you know what? She missed a week of school. I worked from home to be with her – though I didn’t test positive. And that is a real cost to both of us that I think we need to consider when we consider the value of masks. Yes, they’re annoying – but if they keep kids in school, might they be worth it? Perhaps not for now, as cases aren’t surging. But in the future, be it a particularly concerning variant, or a whole new pandemic, we should not discount the simple, cheap, and apparently beneficial act of wearing masks to decrease transmission.
Dr. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
On March 26, 2022, Hawaii became the last state in the United States to lift its indoor mask mandate. By the time the current school year started, there were essentially no public school mask mandates either.
Whether you viewed the mask as an emblem of stalwart defiance against a rampaging virus, or a scarlet letter emblematic of the overreaches of public policy, you probably aren’t seeing them much anymore.
And yet, the debate about masks still rages. Who was right, who was wrong? Who trusted science, and what does the science even say? If we brought our country into marriage counseling, would we be told it is time to move on? To look forward, not backward? To plan for our bright future together?
Perhaps. But this question isn’t really moot just because masks have largely disappeared in the United States. Variants may emerge that lead to more infection waves – and other pandemics may occur in the future. And so I think it is important to discuss a study that, with quite rigorous analysis, attempts to answer the following question: Did masking in schools lower students’ and teachers’ risk of COVID?
We are talking about this study, appearing in the New England Journal of Medicine. The short version goes like this.
Researchers had access to two important sources of data. One – an accounting of all the teachers and students (more than 300,000 of them) in 79 public, noncharter school districts in Eastern Massachusetts who tested positive for COVID every week. Two – the date that each of those school districts lifted their mask mandates or (in the case of two districts) didn’t.
Right away, I’m sure you’re thinking of potential issues. Districts that kept masks even when the statewide ban was lifted are likely quite a bit different from districts that dropped masks right away. You’re right, of course – hold on to that thought; we’ll get there.
But first – the big question – would districts that kept their masks on longer do better when it comes to the rate of COVID infection?
When everyone was masking, COVID case rates were pretty similar. Statewide mandates are lifted in late February – and most school districts remove their mandates within a few weeks – the black line are the two districts (Boston and Chelsea) where mask mandates remained in place.
Prior to the mask mandate lifting, you see very similar COVID rates in districts that would eventually remove the mandate and those that would not, with a bit of noise around the initial Omicron wave which saw just a huge amount of people get infected.
And then, after the mandate was lifted, separation. Districts that held on to masks longer had lower rates of COVID infection.
In all, over the 15-weeks of the study, there were roughly 12,000 extra cases of COVID in the mask-free school districts, which corresponds to about 35% of the total COVID burden during that time. And, yes, kids do well with COVID – on average. But 12,000 extra cases is enough to translate into a significant number of important clinical outcomes – think hospitalizations and post-COVID syndromes. And of course, maybe most importantly, missed school days. Positive kids were not allowed in class no matter what district they were in.
Okay – I promised we’d address confounders. This was not a cluster-randomized trial, where some school districts had their mandates removed based on the vicissitudes of a virtual coin flip, as much as many of us would have been interested to see that. The decision to remove masks was up to the various school boards – and they had a lot of pressure on them from many different directions. But all we need to worry about is whether any of those things that pressure a school board to keep masks on would ALSO lead to fewer COVID cases. That’s how confounders work, and how you can get false results in a study like this.
And yes – districts that kept the masks on longer were different than those who took them right off. But check out how they were different.
The districts that kept masks on longer had more low-income students. More Black and Latino students. More students per classroom. These are all risk factors that increase the risk of COVID infection. In other words, the confounding here goes in the opposite direction of the results. If anything, these factors should make you more certain that masking works.
The authors also adjusted for other factors – the community transmission of COVID-19, vaccination rates, school district sizes, and so on. No major change in the results.
One concern I addressed to Dr. Ellie Murray, the biostatistician on the study – could districts that removed masks simply have been testing more to compensate, leading to increased capturing of cases?
If anything, the schools that kept masks on were testing more than the schools that took them off – again that would tend to imply that the results are even stronger than what was reported.
Is this a perfect study? Of course not – it’s one study, it’s from one state. And the relatively large effects from keeping masks on for one or 2 weeks require us to really embrace the concept of exponential growth of infections, but, if COVID has taught us anything, it is that small changes in initial conditions can have pretty big effects.
My daughter, who goes to a public school here in Connecticut, unmasked, was home with COVID this past week. She’s fine. But you know what? She missed a week of school. I worked from home to be with her – though I didn’t test positive. And that is a real cost to both of us that I think we need to consider when we consider the value of masks. Yes, they’re annoying – but if they keep kids in school, might they be worth it? Perhaps not for now, as cases aren’t surging. But in the future, be it a particularly concerning variant, or a whole new pandemic, we should not discount the simple, cheap, and apparently beneficial act of wearing masks to decrease transmission.
Dr. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
On March 26, 2022, Hawaii became the last state in the United States to lift its indoor mask mandate. By the time the current school year started, there were essentially no public school mask mandates either.
Whether you viewed the mask as an emblem of stalwart defiance against a rampaging virus, or a scarlet letter emblematic of the overreaches of public policy, you probably aren’t seeing them much anymore.
And yet, the debate about masks still rages. Who was right, who was wrong? Who trusted science, and what does the science even say? If we brought our country into marriage counseling, would we be told it is time to move on? To look forward, not backward? To plan for our bright future together?
Perhaps. But this question isn’t really moot just because masks have largely disappeared in the United States. Variants may emerge that lead to more infection waves – and other pandemics may occur in the future. And so I think it is important to discuss a study that, with quite rigorous analysis, attempts to answer the following question: Did masking in schools lower students’ and teachers’ risk of COVID?
We are talking about this study, appearing in the New England Journal of Medicine. The short version goes like this.
Researchers had access to two important sources of data. One – an accounting of all the teachers and students (more than 300,000 of them) in 79 public, noncharter school districts in Eastern Massachusetts who tested positive for COVID every week. Two – the date that each of those school districts lifted their mask mandates or (in the case of two districts) didn’t.
Right away, I’m sure you’re thinking of potential issues. Districts that kept masks even when the statewide ban was lifted are likely quite a bit different from districts that dropped masks right away. You’re right, of course – hold on to that thought; we’ll get there.
But first – the big question – would districts that kept their masks on longer do better when it comes to the rate of COVID infection?
When everyone was masking, COVID case rates were pretty similar. Statewide mandates are lifted in late February – and most school districts remove their mandates within a few weeks – the black line are the two districts (Boston and Chelsea) where mask mandates remained in place.
Prior to the mask mandate lifting, you see very similar COVID rates in districts that would eventually remove the mandate and those that would not, with a bit of noise around the initial Omicron wave which saw just a huge amount of people get infected.
And then, after the mandate was lifted, separation. Districts that held on to masks longer had lower rates of COVID infection.
In all, over the 15-weeks of the study, there were roughly 12,000 extra cases of COVID in the mask-free school districts, which corresponds to about 35% of the total COVID burden during that time. And, yes, kids do well with COVID – on average. But 12,000 extra cases is enough to translate into a significant number of important clinical outcomes – think hospitalizations and post-COVID syndromes. And of course, maybe most importantly, missed school days. Positive kids were not allowed in class no matter what district they were in.
Okay – I promised we’d address confounders. This was not a cluster-randomized trial, where some school districts had their mandates removed based on the vicissitudes of a virtual coin flip, as much as many of us would have been interested to see that. The decision to remove masks was up to the various school boards – and they had a lot of pressure on them from many different directions. But all we need to worry about is whether any of those things that pressure a school board to keep masks on would ALSO lead to fewer COVID cases. That’s how confounders work, and how you can get false results in a study like this.
And yes – districts that kept the masks on longer were different than those who took them right off. But check out how they were different.
The districts that kept masks on longer had more low-income students. More Black and Latino students. More students per classroom. These are all risk factors that increase the risk of COVID infection. In other words, the confounding here goes in the opposite direction of the results. If anything, these factors should make you more certain that masking works.
The authors also adjusted for other factors – the community transmission of COVID-19, vaccination rates, school district sizes, and so on. No major change in the results.
One concern I addressed to Dr. Ellie Murray, the biostatistician on the study – could districts that removed masks simply have been testing more to compensate, leading to increased capturing of cases?
If anything, the schools that kept masks on were testing more than the schools that took them off – again that would tend to imply that the results are even stronger than what was reported.
Is this a perfect study? Of course not – it’s one study, it’s from one state. And the relatively large effects from keeping masks on for one or 2 weeks require us to really embrace the concept of exponential growth of infections, but, if COVID has taught us anything, it is that small changes in initial conditions can have pretty big effects.
My daughter, who goes to a public school here in Connecticut, unmasked, was home with COVID this past week. She’s fine. But you know what? She missed a week of school. I worked from home to be with her – though I didn’t test positive. And that is a real cost to both of us that I think we need to consider when we consider the value of masks. Yes, they’re annoying – but if they keep kids in school, might they be worth it? Perhaps not for now, as cases aren’t surging. But in the future, be it a particularly concerning variant, or a whole new pandemic, we should not discount the simple, cheap, and apparently beneficial act of wearing masks to decrease transmission.
Dr. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.