User login
Vitiligo
THE COMPARISON
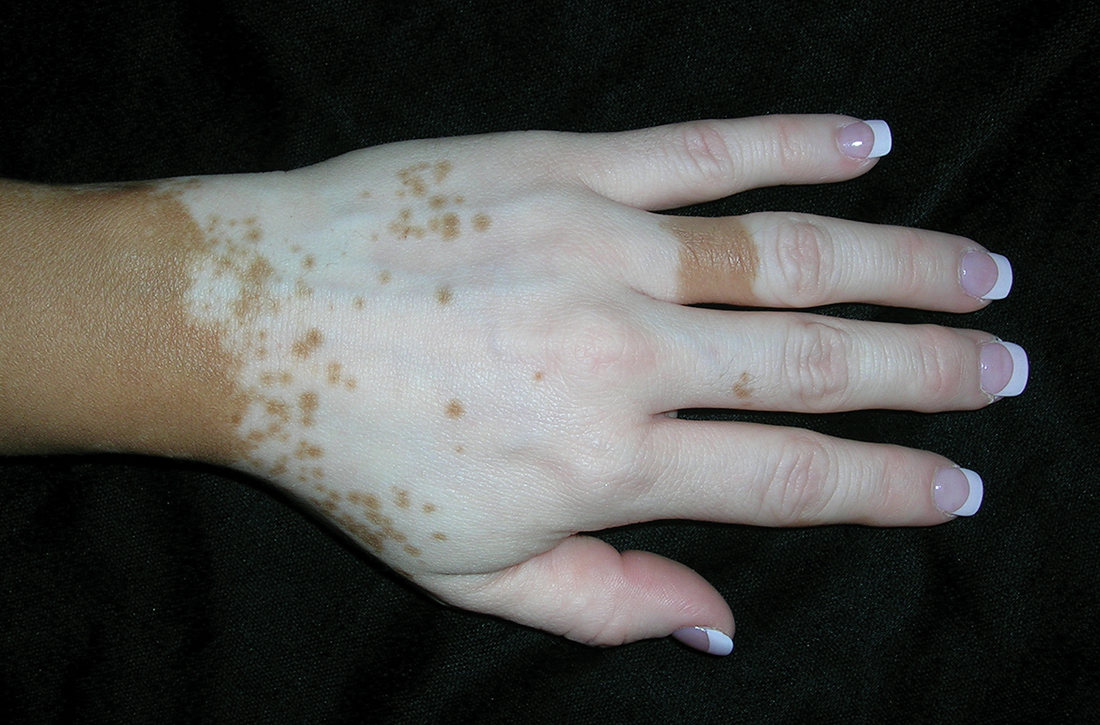
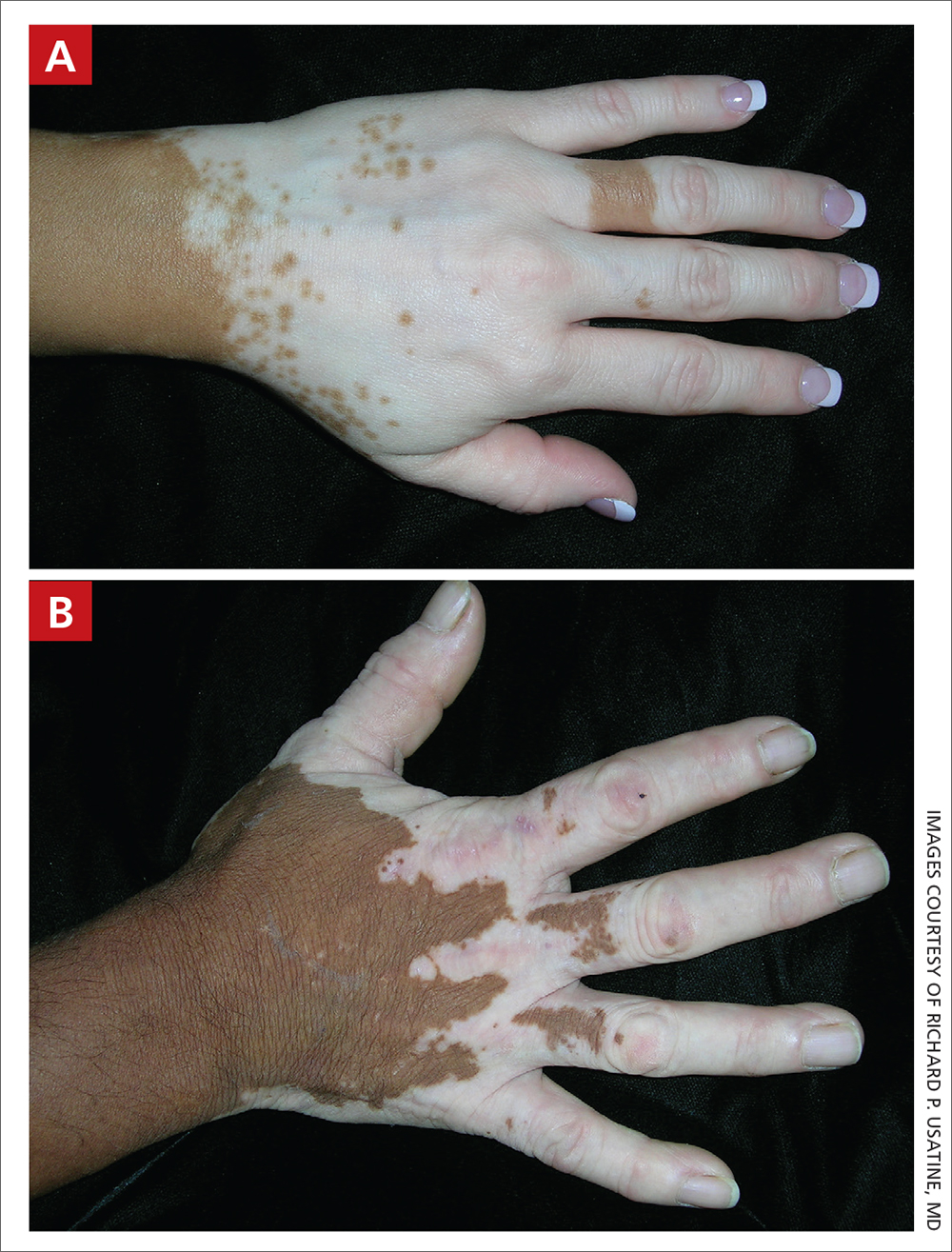
A Vitiligo in a young Hispanic female, which spared the area under a ring. The patient has spotty return of pigment on the hand after narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) treatment.
B Vitiligo on the hand in a young Hispanic male.
Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by areas of depigmented white patches on the skin due to the loss of melanocytes in the epidermis. Various theories on the pathogenesis of vitiligo exist; however, autoimmune destruction of melanocytes remains the leading hypothesis, followed by intrinsic defects in melanocytes.1
Vitiligo is associated with various autoimmune diseases but is most frequently reported in conjunction with thyroid disorders.2
Epidemiology
Vitiligo affects approximately 1% of the US population and up to 8% worldwide.2 There is no difference in prevalence between races or genders. Females typically acquire the disease earlier than males. Onset may occur at any age, although about half of patients will have vitiligo by 20 years of age.1
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Bright white patches are characteristic of vitiligo. The patches typically are asymptomatic and often affect the hands (FIGURES A and B), perioral skin, feet, and scalp, as well as areas more vulnerable to friction and trauma, such as the elbows and knees.2 Trichrome lesions—consisting of varying zones of white (depigmented), lighter brown (hypopigmented), and normal skin—are most commonly seen in individuals with darker skin. Trichrome vitiligo is considered an actively progressing variant of vitiligo.2
An important distinction when making the diagnosis is evaluating for segmental vs nonsegmental vitiligo. Although nonsegmental vitiligo—the more common subtype—is characterized by symmetric distribution and a less predictable course, segmental vitiligo manifests in a localized and unilateral distribution, often avoiding extension past the midline. Segmental vitiligo typically manifests at a younger age and follows a more rapidly stabilizing course.3
Worth noting
Given that stark contrasts between pigmented and depigmented lesions are more prominent in darker skin tones, vitiligo can be more socially stigmatizing and psychologically devastating in these patients.4,5
Continue to: Treatment of vitiligo...
Treatment of vitiligo includes narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) light phototherapy, excimer laser, topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, and surgical melanocyte transplantation.1 In July 2022, ruxolitinib cream 1.5% was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for nonsegmental vitiligo in patients ages 12 years and older.6,7 It is the only FDA-approved therapy for vitiligo. It is thought to work by inhibiting the Janus kinase–signal transducers and activators of the transcription pathway.6 However, topical ruxolitinib is expensive, costing more than $2000 for 60 g.8
Health disparity highlight
A 2021 study reviewing the coverage policies of 15 commercial health care insurance companies, 50 BlueCross BlueShield plans, Medicaid, Medicare, and Veterans Affairs plans found inequities in the insurance coverage patterns for therapies used to treat vitiligo. There were 2 commonly cited reasons for denying coverage for therapies: vitiligo was considered cosmetic and therapies were not FDA approved.7 In comparison, NB-UVB light phototherapy for psoriasis is not considered cosmetic and has a much higher insurance coverage rate.9,10 The out-of-pocket cost for a patient to purchase their own NB-UVB light phototherapy is more than $5000.11 Not all patients of color are economically disadvantaged, but in the United States, Black and Hispanic populations experience disproportionately higher rates of poverty (19% and 17%, respectively) compared to their White counterparts (8%).12
Final thoughts
FDA approval of new drugs or new treatment indications comes after years of research discovery and large-scale trials. This pursuit of new discovery, however, is uneven. Vitiligo has historically been understudied and underfunded for research; this is common among several conditions adversely affecting people of color in the United States.13
1. Rashighi M, Harris JE. Vitiligo pathogenesis and emerging treatments. Dermatol Clin. 2017;35:257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.det. 2016.11.014
2. Alikhan A, Felsten LM, Daly M, et al. Vitiligo: a comprehensive overview part I. introduction, epidemiology, quality of life, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, associations, histopathology, etiology, and work-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:473-491. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.11.061
3. van Geel N, Speeckaert R. Segmental vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2016.11.005
4. Grimes PE, Miller MM. Vitiligo: patient stories, self-esteem, and the psychological burden of disease. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018;4:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.11.005
5. Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Jones H, et al. Psychosocial effects of vitiligo: a systematic literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021; 22:757-774. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00631-6
6. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. News release. US Food and Drug Administration; July 19, 2022. Accessed December 27, 2022. www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical- treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged- 12-and-older
7. Blundell A, Sachar M, Gabel CK, et al. The scope of health insurance coverage of vitiligo treatments in the United States: implications for health care outcomes and disparities in children of color. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):79-85. doi: 10.1111/ pde.14714
8. Opzelura prices, coupons, and patient assistance programs. Drugs.com. Accessed January 10, 2023. www.drugs.com/priceguide/opzelura
9. Bhutani T, Liao W. A practical approach to home UVB phototherapy for the treatment of generalized psoriasis. Pract Dermatol. 2010;7:31-35.
10. Castro Porto Silva Lopes F, Ahmed A. Insurance coverage for phototherapy for vitiligo in comparison to psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine. 2022;6:217-224. doi: 10.25251/skin.6.3.6
11. Smith MP, Ly K, Thibodeaux Q, et al. Home phototherapy for patients with vitiligo: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:451-459. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S185798
12. Shrider EA, Kollar M, Chen F, et al. Income and poverty in the United States: 2020. US Census Bureau. September 14, 2021. Accessed December 27, 2022. www.census.gov/library/publications/2021/demo/p60-273.html
13. Whitton ME, Pinart M, Batchelor J, et al. Interventions for vitiligo. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(1):CD003263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003263.pub4
THE COMPARISON
A Vitiligo in a young Hispanic female, which spared the area under a ring. The patient has spotty return of pigment on the hand after narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) treatment.
B Vitiligo on the hand in a young Hispanic male.

Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by areas of depigmented white patches on the skin due to the loss of melanocytes in the epidermis. Various theories on the pathogenesis of vitiligo exist; however, autoimmune destruction of melanocytes remains the leading hypothesis, followed by intrinsic defects in melanocytes.1
Vitiligo is associated with various autoimmune diseases but is most frequently reported in conjunction with thyroid disorders.2
Epidemiology
Vitiligo affects approximately 1% of the US population and up to 8% worldwide.2 There is no difference in prevalence between races or genders. Females typically acquire the disease earlier than males. Onset may occur at any age, although about half of patients will have vitiligo by 20 years of age.1
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Bright white patches are characteristic of vitiligo. The patches typically are asymptomatic and often affect the hands (FIGURES A and B), perioral skin, feet, and scalp, as well as areas more vulnerable to friction and trauma, such as the elbows and knees.2 Trichrome lesions—consisting of varying zones of white (depigmented), lighter brown (hypopigmented), and normal skin—are most commonly seen in individuals with darker skin. Trichrome vitiligo is considered an actively progressing variant of vitiligo.2
An important distinction when making the diagnosis is evaluating for segmental vs nonsegmental vitiligo. Although nonsegmental vitiligo—the more common subtype—is characterized by symmetric distribution and a less predictable course, segmental vitiligo manifests in a localized and unilateral distribution, often avoiding extension past the midline. Segmental vitiligo typically manifests at a younger age and follows a more rapidly stabilizing course.3
Worth noting
Given that stark contrasts between pigmented and depigmented lesions are more prominent in darker skin tones, vitiligo can be more socially stigmatizing and psychologically devastating in these patients.4,5
Continue to: Treatment of vitiligo...
Treatment of vitiligo includes narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) light phototherapy, excimer laser, topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, and surgical melanocyte transplantation.1 In July 2022, ruxolitinib cream 1.5% was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for nonsegmental vitiligo in patients ages 12 years and older.6,7 It is the only FDA-approved therapy for vitiligo. It is thought to work by inhibiting the Janus kinase–signal transducers and activators of the transcription pathway.6 However, topical ruxolitinib is expensive, costing more than $2000 for 60 g.8
Health disparity highlight
A 2021 study reviewing the coverage policies of 15 commercial health care insurance companies, 50 BlueCross BlueShield plans, Medicaid, Medicare, and Veterans Affairs plans found inequities in the insurance coverage patterns for therapies used to treat vitiligo. There were 2 commonly cited reasons for denying coverage for therapies: vitiligo was considered cosmetic and therapies were not FDA approved.7 In comparison, NB-UVB light phototherapy for psoriasis is not considered cosmetic and has a much higher insurance coverage rate.9,10 The out-of-pocket cost for a patient to purchase their own NB-UVB light phototherapy is more than $5000.11 Not all patients of color are economically disadvantaged, but in the United States, Black and Hispanic populations experience disproportionately higher rates of poverty (19% and 17%, respectively) compared to their White counterparts (8%).12
Final thoughts
FDA approval of new drugs or new treatment indications comes after years of research discovery and large-scale trials. This pursuit of new discovery, however, is uneven. Vitiligo has historically been understudied and underfunded for research; this is common among several conditions adversely affecting people of color in the United States.13
THE COMPARISON
A Vitiligo in a young Hispanic female, which spared the area under a ring. The patient has spotty return of pigment on the hand after narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) treatment.
B Vitiligo on the hand in a young Hispanic male.

Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by areas of depigmented white patches on the skin due to the loss of melanocytes in the epidermis. Various theories on the pathogenesis of vitiligo exist; however, autoimmune destruction of melanocytes remains the leading hypothesis, followed by intrinsic defects in melanocytes.1
Vitiligo is associated with various autoimmune diseases but is most frequently reported in conjunction with thyroid disorders.2
Epidemiology
Vitiligo affects approximately 1% of the US population and up to 8% worldwide.2 There is no difference in prevalence between races or genders. Females typically acquire the disease earlier than males. Onset may occur at any age, although about half of patients will have vitiligo by 20 years of age.1
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Bright white patches are characteristic of vitiligo. The patches typically are asymptomatic and often affect the hands (FIGURES A and B), perioral skin, feet, and scalp, as well as areas more vulnerable to friction and trauma, such as the elbows and knees.2 Trichrome lesions—consisting of varying zones of white (depigmented), lighter brown (hypopigmented), and normal skin—are most commonly seen in individuals with darker skin. Trichrome vitiligo is considered an actively progressing variant of vitiligo.2
An important distinction when making the diagnosis is evaluating for segmental vs nonsegmental vitiligo. Although nonsegmental vitiligo—the more common subtype—is characterized by symmetric distribution and a less predictable course, segmental vitiligo manifests in a localized and unilateral distribution, often avoiding extension past the midline. Segmental vitiligo typically manifests at a younger age and follows a more rapidly stabilizing course.3
Worth noting
Given that stark contrasts between pigmented and depigmented lesions are more prominent in darker skin tones, vitiligo can be more socially stigmatizing and psychologically devastating in these patients.4,5
Continue to: Treatment of vitiligo...
Treatment of vitiligo includes narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) light phototherapy, excimer laser, topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, and surgical melanocyte transplantation.1 In July 2022, ruxolitinib cream 1.5% was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for nonsegmental vitiligo in patients ages 12 years and older.6,7 It is the only FDA-approved therapy for vitiligo. It is thought to work by inhibiting the Janus kinase–signal transducers and activators of the transcription pathway.6 However, topical ruxolitinib is expensive, costing more than $2000 for 60 g.8
Health disparity highlight
A 2021 study reviewing the coverage policies of 15 commercial health care insurance companies, 50 BlueCross BlueShield plans, Medicaid, Medicare, and Veterans Affairs plans found inequities in the insurance coverage patterns for therapies used to treat vitiligo. There were 2 commonly cited reasons for denying coverage for therapies: vitiligo was considered cosmetic and therapies were not FDA approved.7 In comparison, NB-UVB light phototherapy for psoriasis is not considered cosmetic and has a much higher insurance coverage rate.9,10 The out-of-pocket cost for a patient to purchase their own NB-UVB light phototherapy is more than $5000.11 Not all patients of color are economically disadvantaged, but in the United States, Black and Hispanic populations experience disproportionately higher rates of poverty (19% and 17%, respectively) compared to their White counterparts (8%).12
Final thoughts
FDA approval of new drugs or new treatment indications comes after years of research discovery and large-scale trials. This pursuit of new discovery, however, is uneven. Vitiligo has historically been understudied and underfunded for research; this is common among several conditions adversely affecting people of color in the United States.13
1. Rashighi M, Harris JE. Vitiligo pathogenesis and emerging treatments. Dermatol Clin. 2017;35:257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.det. 2016.11.014
2. Alikhan A, Felsten LM, Daly M, et al. Vitiligo: a comprehensive overview part I. introduction, epidemiology, quality of life, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, associations, histopathology, etiology, and work-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:473-491. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.11.061
3. van Geel N, Speeckaert R. Segmental vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2016.11.005
4. Grimes PE, Miller MM. Vitiligo: patient stories, self-esteem, and the psychological burden of disease. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018;4:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.11.005
5. Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Jones H, et al. Psychosocial effects of vitiligo: a systematic literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021; 22:757-774. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00631-6
6. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. News release. US Food and Drug Administration; July 19, 2022. Accessed December 27, 2022. www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical- treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged- 12-and-older
7. Blundell A, Sachar M, Gabel CK, et al. The scope of health insurance coverage of vitiligo treatments in the United States: implications for health care outcomes and disparities in children of color. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):79-85. doi: 10.1111/ pde.14714
8. Opzelura prices, coupons, and patient assistance programs. Drugs.com. Accessed January 10, 2023. www.drugs.com/priceguide/opzelura
9. Bhutani T, Liao W. A practical approach to home UVB phototherapy for the treatment of generalized psoriasis. Pract Dermatol. 2010;7:31-35.
10. Castro Porto Silva Lopes F, Ahmed A. Insurance coverage for phototherapy for vitiligo in comparison to psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine. 2022;6:217-224. doi: 10.25251/skin.6.3.6
11. Smith MP, Ly K, Thibodeaux Q, et al. Home phototherapy for patients with vitiligo: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:451-459. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S185798
12. Shrider EA, Kollar M, Chen F, et al. Income and poverty in the United States: 2020. US Census Bureau. September 14, 2021. Accessed December 27, 2022. www.census.gov/library/publications/2021/demo/p60-273.html
13. Whitton ME, Pinart M, Batchelor J, et al. Interventions for vitiligo. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(1):CD003263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003263.pub4
1. Rashighi M, Harris JE. Vitiligo pathogenesis and emerging treatments. Dermatol Clin. 2017;35:257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.det. 2016.11.014
2. Alikhan A, Felsten LM, Daly M, et al. Vitiligo: a comprehensive overview part I. introduction, epidemiology, quality of life, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, associations, histopathology, etiology, and work-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:473-491. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.11.061
3. van Geel N, Speeckaert R. Segmental vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2016.11.005
4. Grimes PE, Miller MM. Vitiligo: patient stories, self-esteem, and the psychological burden of disease. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018;4:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.11.005
5. Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Jones H, et al. Psychosocial effects of vitiligo: a systematic literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021; 22:757-774. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00631-6
6. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. News release. US Food and Drug Administration; July 19, 2022. Accessed December 27, 2022. www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical- treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged- 12-and-older
7. Blundell A, Sachar M, Gabel CK, et al. The scope of health insurance coverage of vitiligo treatments in the United States: implications for health care outcomes and disparities in children of color. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):79-85. doi: 10.1111/ pde.14714
8. Opzelura prices, coupons, and patient assistance programs. Drugs.com. Accessed January 10, 2023. www.drugs.com/priceguide/opzelura
9. Bhutani T, Liao W. A practical approach to home UVB phototherapy for the treatment of generalized psoriasis. Pract Dermatol. 2010;7:31-35.
10. Castro Porto Silva Lopes F, Ahmed A. Insurance coverage for phototherapy for vitiligo in comparison to psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine. 2022;6:217-224. doi: 10.25251/skin.6.3.6
11. Smith MP, Ly K, Thibodeaux Q, et al. Home phototherapy for patients with vitiligo: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:451-459. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S185798
12. Shrider EA, Kollar M, Chen F, et al. Income and poverty in the United States: 2020. US Census Bureau. September 14, 2021. Accessed December 27, 2022. www.census.gov/library/publications/2021/demo/p60-273.html
13. Whitton ME, Pinart M, Batchelor J, et al. Interventions for vitiligo. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(1):CD003263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003263.pub4
Transgender people in rural America struggle to find doctors willing or able to provide care
For Tammy Rainey, finding a health care provider who knows about gender-affirming care has been a challenge in the rural northern Mississippi town where she lives.
As a transgender woman, Ms. Rainey needs the hormone estrogen, which allows her to physically transition by developing more feminine features. But when she asked her doctor for an estrogen prescription, he said he couldn’t provide that type of care.
“He’s generally a good guy and doesn’t act prejudiced. He gets my name and pronouns right,” said Ms. Rainey. “But when I asked him about hormones, he said, ‘I just don’t feel like I know enough about that. I don’t want to get involved in that.’ ”
So Ms. Rainey drives around 170 miles round trip every 6 months to get a supply of estrogen from a clinic in Memphis, Tenn., to take home with her.
The obstacles Ms. Rainey overcomes to access care illustrate a type of medical inequity that transgender people who live in the rural United States often face: A general lack of education about trans-related care among small-town health professionals who might also be reluctant to learn.
“Medical communities across the country are seeing clearly that there is a knowledge gap in the provision of gender-affirming care,” said Morissa Ladinsky, MD, a pediatrician who co-leads the Youth Multidisciplinary Gender Team at the University of Alabama–Birmingham (UAB).
Accurately counting the number of transgender people in rural America is hindered by a lack of U.S. census data and uniform state data. However, the Movement Advancement Project, a nonprofit organization that advocates for LGBTQ+ issues, used 2014-17 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data from selected ZIP codes in 35 states to estimate that roughly one in six transgender adults in the United States live in a rural area. When that report was released in 2019, there were an estimated 1.4 million transgender people 13 and older nationwide. That number is now at least 1.6 million, according to the Williams Institute, a nonprofit think tank at the UCLA School of Law.
One in three trans people in rural areas experienced discrimination by a health care provider in the year leading up to the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey Report, according to an analysis by MAP. A third of all trans individuals report having to teach their doctors about their health care needs to receive appropriate care, and 62% worry about being negatively judged by a health care provider because of their sexual orientation or gender identity, according to data collected by the Williams Institute and other organizations.
A lack of local rural providers knowledgeable in trans care can mean long drives to gender-affirming clinics in metropolitan areas. Rural trans people are three times as likely as are all transgender adults to travel 25-49 miles for routine care.
In Colorado, for example, many trans people outside Denver struggle to find proper care. Those who do have a trans-inclusive provider are more likely to receive wellness exams, less likely to delay care due to discrimination, and less likely to attempt suicide, according to results from the Colorado Transgender Health Survey published in 2018.
Much of the lack of care experienced by trans people is linked to insufficient education on LGBTQ+ health in medical schools across the country. In 2014, the Association of American Medical Colleges, which represents 170 accredited medical schools in the United States and Canada, released its first curriculum guidelines on caring for LGBTQ+ patients. As of 2018, 76% of medical schools included LGBTQ health themes in their curriculum, with half providing three or fewer classes on this topic.
Perhaps because of this, almost 77% of students from 10 medical schools in New England felt “not competent” or “somewhat not competent” in treating gender minority patients, according to a 2018 pilot study. Another paper, published last year, found that even clinicians who work in trans-friendly clinics lack knowledge about hormones, gender-affirming surgical options, and how to use appropriate pronouns and trans-inclusive language.
Throughout medical school, trans care was only briefly mentioned in endocrinology class, said Justin Bailey, MD, who received his medical degree from UAB in 2021 and is now a resident there. “I don’t want to say the wrong thing or use the wrong pronouns, so I was hesitant and a little bit tepid in my approach to interviewing and treating this population of patients,” he said.
On top of insufficient medical school education, some practicing doctors don’t take the time to teach themselves about trans people, said Kathie Moehlig, founder of TransFamily Support Services, a nonprofit organization that offers a range of services to transgender people and their families. They are very well intentioned yet uneducated when it comes to transgender care, she said.
Some medical schools, like the one at UAB, have pushed for change. Since 2017, Dr. Ladinsky and her colleagues have worked to include trans people in their standardized patient program, which gives medical students hands-on experience and feedback by interacting with “patients” in simulated clinical environments.
For example, a trans individual acting as a patient will simulate acid reflux by pretending to have pain in their stomach and chest. Then, over the course of the examination, they will reveal that they are transgender.
In the early years of this program, some students’ bedside manner would change once the patient’s gender identity was revealed, said Elaine Stephens, a trans woman who participates in UAB’s standardized patient program. “Sometimes they would immediately start asking about sexual activity,” Stephens said.
Since UAB launched its program, students’ reactions have improved significantly, she said.
This progress is being replicated by other medical schools, said Ms. Moehlig. “But it’s a slow start, and these are large institutions that take a long time to move forward.”
Advocates also are working outside medical schools to improve care in rural areas. In Colorado, the nonprofit Extension for Community Health Outcomes, or ECHO Colorado, has been offering monthly virtual classes on gender-affirming care to rural providers since 2020. The classes became so popular that the organization created a 4-week boot camp in 2021 for providers to learn about hormone therapy management, proper terminologies, surgical options, and supporting patients’ mental health.
For many years, doctors failed to recognize the need to learn about gender-affirming care, said Caroline Kirsch, DO, director of osteopathic education at the University of Wyoming Family Medicine Residency Program–Casper. In Casper, this led to “a number of patients traveling to Colorado to access care, which is a large burden for them financially,” said Dr. Kirsch, who has participated in the ECHO Colorado program.
“Things that haven’t been as well taught historically in medical school are things that I think many physicians feel anxious about initially,” she said. “The earlier you learn about this type of care in your career, the more likely you are to see its potential and be less anxious about it.”
Educating more providers about trans-related care has become increasingly vital in recent years as gender-affirming clinics nationwide experience a rise in harassment and threats. For instance, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s Clinic for Transgender Health became the target of far-right hate on social media last year. After growing pressure from Tennessee’s Republican lawmakers, the clinic paused gender-affirmation surgeries on patients younger than 18, potentially leaving many trans individuals without necessary care.
Stephens hopes to see more medical schools include coursework on trans health care. She also wishes for doctors to treat trans people as they would any other patient.
“Just provide quality health care,” she tells the medical students at UAB. “We need health care like everyone else does.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
For Tammy Rainey, finding a health care provider who knows about gender-affirming care has been a challenge in the rural northern Mississippi town where she lives.
As a transgender woman, Ms. Rainey needs the hormone estrogen, which allows her to physically transition by developing more feminine features. But when she asked her doctor for an estrogen prescription, he said he couldn’t provide that type of care.
“He’s generally a good guy and doesn’t act prejudiced. He gets my name and pronouns right,” said Ms. Rainey. “But when I asked him about hormones, he said, ‘I just don’t feel like I know enough about that. I don’t want to get involved in that.’ ”
So Ms. Rainey drives around 170 miles round trip every 6 months to get a supply of estrogen from a clinic in Memphis, Tenn., to take home with her.
The obstacles Ms. Rainey overcomes to access care illustrate a type of medical inequity that transgender people who live in the rural United States often face: A general lack of education about trans-related care among small-town health professionals who might also be reluctant to learn.
“Medical communities across the country are seeing clearly that there is a knowledge gap in the provision of gender-affirming care,” said Morissa Ladinsky, MD, a pediatrician who co-leads the Youth Multidisciplinary Gender Team at the University of Alabama–Birmingham (UAB).
Accurately counting the number of transgender people in rural America is hindered by a lack of U.S. census data and uniform state data. However, the Movement Advancement Project, a nonprofit organization that advocates for LGBTQ+ issues, used 2014-17 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data from selected ZIP codes in 35 states to estimate that roughly one in six transgender adults in the United States live in a rural area. When that report was released in 2019, there were an estimated 1.4 million transgender people 13 and older nationwide. That number is now at least 1.6 million, according to the Williams Institute, a nonprofit think tank at the UCLA School of Law.
One in three trans people in rural areas experienced discrimination by a health care provider in the year leading up to the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey Report, according to an analysis by MAP. A third of all trans individuals report having to teach their doctors about their health care needs to receive appropriate care, and 62% worry about being negatively judged by a health care provider because of their sexual orientation or gender identity, according to data collected by the Williams Institute and other organizations.
A lack of local rural providers knowledgeable in trans care can mean long drives to gender-affirming clinics in metropolitan areas. Rural trans people are three times as likely as are all transgender adults to travel 25-49 miles for routine care.
In Colorado, for example, many trans people outside Denver struggle to find proper care. Those who do have a trans-inclusive provider are more likely to receive wellness exams, less likely to delay care due to discrimination, and less likely to attempt suicide, according to results from the Colorado Transgender Health Survey published in 2018.
Much of the lack of care experienced by trans people is linked to insufficient education on LGBTQ+ health in medical schools across the country. In 2014, the Association of American Medical Colleges, which represents 170 accredited medical schools in the United States and Canada, released its first curriculum guidelines on caring for LGBTQ+ patients. As of 2018, 76% of medical schools included LGBTQ health themes in their curriculum, with half providing three or fewer classes on this topic.
Perhaps because of this, almost 77% of students from 10 medical schools in New England felt “not competent” or “somewhat not competent” in treating gender minority patients, according to a 2018 pilot study. Another paper, published last year, found that even clinicians who work in trans-friendly clinics lack knowledge about hormones, gender-affirming surgical options, and how to use appropriate pronouns and trans-inclusive language.
Throughout medical school, trans care was only briefly mentioned in endocrinology class, said Justin Bailey, MD, who received his medical degree from UAB in 2021 and is now a resident there. “I don’t want to say the wrong thing or use the wrong pronouns, so I was hesitant and a little bit tepid in my approach to interviewing and treating this population of patients,” he said.
On top of insufficient medical school education, some practicing doctors don’t take the time to teach themselves about trans people, said Kathie Moehlig, founder of TransFamily Support Services, a nonprofit organization that offers a range of services to transgender people and their families. They are very well intentioned yet uneducated when it comes to transgender care, she said.
Some medical schools, like the one at UAB, have pushed for change. Since 2017, Dr. Ladinsky and her colleagues have worked to include trans people in their standardized patient program, which gives medical students hands-on experience and feedback by interacting with “patients” in simulated clinical environments.
For example, a trans individual acting as a patient will simulate acid reflux by pretending to have pain in their stomach and chest. Then, over the course of the examination, they will reveal that they are transgender.
In the early years of this program, some students’ bedside manner would change once the patient’s gender identity was revealed, said Elaine Stephens, a trans woman who participates in UAB’s standardized patient program. “Sometimes they would immediately start asking about sexual activity,” Stephens said.
Since UAB launched its program, students’ reactions have improved significantly, she said.
This progress is being replicated by other medical schools, said Ms. Moehlig. “But it’s a slow start, and these are large institutions that take a long time to move forward.”
Advocates also are working outside medical schools to improve care in rural areas. In Colorado, the nonprofit Extension for Community Health Outcomes, or ECHO Colorado, has been offering monthly virtual classes on gender-affirming care to rural providers since 2020. The classes became so popular that the organization created a 4-week boot camp in 2021 for providers to learn about hormone therapy management, proper terminologies, surgical options, and supporting patients’ mental health.
For many years, doctors failed to recognize the need to learn about gender-affirming care, said Caroline Kirsch, DO, director of osteopathic education at the University of Wyoming Family Medicine Residency Program–Casper. In Casper, this led to “a number of patients traveling to Colorado to access care, which is a large burden for them financially,” said Dr. Kirsch, who has participated in the ECHO Colorado program.
“Things that haven’t been as well taught historically in medical school are things that I think many physicians feel anxious about initially,” she said. “The earlier you learn about this type of care in your career, the more likely you are to see its potential and be less anxious about it.”
Educating more providers about trans-related care has become increasingly vital in recent years as gender-affirming clinics nationwide experience a rise in harassment and threats. For instance, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s Clinic for Transgender Health became the target of far-right hate on social media last year. After growing pressure from Tennessee’s Republican lawmakers, the clinic paused gender-affirmation surgeries on patients younger than 18, potentially leaving many trans individuals without necessary care.
Stephens hopes to see more medical schools include coursework on trans health care. She also wishes for doctors to treat trans people as they would any other patient.
“Just provide quality health care,” she tells the medical students at UAB. “We need health care like everyone else does.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
For Tammy Rainey, finding a health care provider who knows about gender-affirming care has been a challenge in the rural northern Mississippi town where she lives.
As a transgender woman, Ms. Rainey needs the hormone estrogen, which allows her to physically transition by developing more feminine features. But when she asked her doctor for an estrogen prescription, he said he couldn’t provide that type of care.
“He’s generally a good guy and doesn’t act prejudiced. He gets my name and pronouns right,” said Ms. Rainey. “But when I asked him about hormones, he said, ‘I just don’t feel like I know enough about that. I don’t want to get involved in that.’ ”
So Ms. Rainey drives around 170 miles round trip every 6 months to get a supply of estrogen from a clinic in Memphis, Tenn., to take home with her.
The obstacles Ms. Rainey overcomes to access care illustrate a type of medical inequity that transgender people who live in the rural United States often face: A general lack of education about trans-related care among small-town health professionals who might also be reluctant to learn.
“Medical communities across the country are seeing clearly that there is a knowledge gap in the provision of gender-affirming care,” said Morissa Ladinsky, MD, a pediatrician who co-leads the Youth Multidisciplinary Gender Team at the University of Alabama–Birmingham (UAB).
Accurately counting the number of transgender people in rural America is hindered by a lack of U.S. census data and uniform state data. However, the Movement Advancement Project, a nonprofit organization that advocates for LGBTQ+ issues, used 2014-17 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data from selected ZIP codes in 35 states to estimate that roughly one in six transgender adults in the United States live in a rural area. When that report was released in 2019, there were an estimated 1.4 million transgender people 13 and older nationwide. That number is now at least 1.6 million, according to the Williams Institute, a nonprofit think tank at the UCLA School of Law.
One in three trans people in rural areas experienced discrimination by a health care provider in the year leading up to the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey Report, according to an analysis by MAP. A third of all trans individuals report having to teach their doctors about their health care needs to receive appropriate care, and 62% worry about being negatively judged by a health care provider because of their sexual orientation or gender identity, according to data collected by the Williams Institute and other organizations.
A lack of local rural providers knowledgeable in trans care can mean long drives to gender-affirming clinics in metropolitan areas. Rural trans people are three times as likely as are all transgender adults to travel 25-49 miles for routine care.
In Colorado, for example, many trans people outside Denver struggle to find proper care. Those who do have a trans-inclusive provider are more likely to receive wellness exams, less likely to delay care due to discrimination, and less likely to attempt suicide, according to results from the Colorado Transgender Health Survey published in 2018.
Much of the lack of care experienced by trans people is linked to insufficient education on LGBTQ+ health in medical schools across the country. In 2014, the Association of American Medical Colleges, which represents 170 accredited medical schools in the United States and Canada, released its first curriculum guidelines on caring for LGBTQ+ patients. As of 2018, 76% of medical schools included LGBTQ health themes in their curriculum, with half providing three or fewer classes on this topic.
Perhaps because of this, almost 77% of students from 10 medical schools in New England felt “not competent” or “somewhat not competent” in treating gender minority patients, according to a 2018 pilot study. Another paper, published last year, found that even clinicians who work in trans-friendly clinics lack knowledge about hormones, gender-affirming surgical options, and how to use appropriate pronouns and trans-inclusive language.
Throughout medical school, trans care was only briefly mentioned in endocrinology class, said Justin Bailey, MD, who received his medical degree from UAB in 2021 and is now a resident there. “I don’t want to say the wrong thing or use the wrong pronouns, so I was hesitant and a little bit tepid in my approach to interviewing and treating this population of patients,” he said.
On top of insufficient medical school education, some practicing doctors don’t take the time to teach themselves about trans people, said Kathie Moehlig, founder of TransFamily Support Services, a nonprofit organization that offers a range of services to transgender people and their families. They are very well intentioned yet uneducated when it comes to transgender care, she said.
Some medical schools, like the one at UAB, have pushed for change. Since 2017, Dr. Ladinsky and her colleagues have worked to include trans people in their standardized patient program, which gives medical students hands-on experience and feedback by interacting with “patients” in simulated clinical environments.
For example, a trans individual acting as a patient will simulate acid reflux by pretending to have pain in their stomach and chest. Then, over the course of the examination, they will reveal that they are transgender.
In the early years of this program, some students’ bedside manner would change once the patient’s gender identity was revealed, said Elaine Stephens, a trans woman who participates in UAB’s standardized patient program. “Sometimes they would immediately start asking about sexual activity,” Stephens said.
Since UAB launched its program, students’ reactions have improved significantly, she said.
This progress is being replicated by other medical schools, said Ms. Moehlig. “But it’s a slow start, and these are large institutions that take a long time to move forward.”
Advocates also are working outside medical schools to improve care in rural areas. In Colorado, the nonprofit Extension for Community Health Outcomes, or ECHO Colorado, has been offering monthly virtual classes on gender-affirming care to rural providers since 2020. The classes became so popular that the organization created a 4-week boot camp in 2021 for providers to learn about hormone therapy management, proper terminologies, surgical options, and supporting patients’ mental health.
For many years, doctors failed to recognize the need to learn about gender-affirming care, said Caroline Kirsch, DO, director of osteopathic education at the University of Wyoming Family Medicine Residency Program–Casper. In Casper, this led to “a number of patients traveling to Colorado to access care, which is a large burden for them financially,” said Dr. Kirsch, who has participated in the ECHO Colorado program.
“Things that haven’t been as well taught historically in medical school are things that I think many physicians feel anxious about initially,” she said. “The earlier you learn about this type of care in your career, the more likely you are to see its potential and be less anxious about it.”
Educating more providers about trans-related care has become increasingly vital in recent years as gender-affirming clinics nationwide experience a rise in harassment and threats. For instance, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s Clinic for Transgender Health became the target of far-right hate on social media last year. After growing pressure from Tennessee’s Republican lawmakers, the clinic paused gender-affirmation surgeries on patients younger than 18, potentially leaving many trans individuals without necessary care.
Stephens hopes to see more medical schools include coursework on trans health care. She also wishes for doctors to treat trans people as they would any other patient.
“Just provide quality health care,” she tells the medical students at UAB. “We need health care like everyone else does.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Disability in medicine: My experience
What does a doctor look like? Throughout history, this concept has shifted due to societal norms and increased access to medical education. Today, the idea of a physician has expanded to incorporate a myriad of people; however, stigma still exists in medicine regarding mental illness and disability. I would like to share my personal journey through high school, college, medical school, and now residency, and how my identity and struggles have shaped me into the physician I am today. There are few conversations around disability—especially disability and mental health—in medicine, and through my own advocacy, I have met many students with disability who feel that medical school is unattainable. Additionally, I have met many medical students, residents, and pre-health advisors who are happy for the experience to learn more about a marginalized group in medicine. My hope in sharing my story is to offer a space for conversation about intersectionality within medical communities and how physicians and physicians in training can facilitate that change, regardless of their position or specialty. Additionally, I hope to shed light on the unique mental health needs of patients with disabilities and how mental health clinicians can address those needs.
Perceived weaknesses turned into strengths
“Why do you walk like that?” “What is that brace on your leg?” The early years of my childhood were marked by these questions and others like them. I was the kid with the limp, the kid with a brace on his leg, and the kid who disappeared multiple times a week for doctor’s appointments or physical therapy. I learned to deflect these questions or give nebulous answers about an accident or injury. The reality is that I was born with cerebral palsy (CP). My CP manifested as hemiparesis on the left side of my body. I was in aggressive physical therapy throughout childhood, received Botox injections for muscle spasticity, and underwent corrective surgery on my left leg to straighten my foot. In childhood, the diagnosis meant nothing more than 2 words that sounded like they belonged to superheroes in comic books. Even with supportive parents and family, I kept my disability a secret, much like the powers and abilities of my favorite superheroes.
However, like all great origin stories, what I once thought were weaknesses turned out to be strengths that pushed me through college, medical school, and now psychiatry residency. Living with a disability has shaped how I see the world and relate to my patients. My experience has helped me connect to my patients in ways others might not. These properties are important in any physician but vital in psychiatry, where many patients feel neglected or stigmatized; this is another reason there should be more doctors with disabilities in medicine. Unfortunately, systemic barriers are still in place that disincentivize those with a disability from pursuing careers in medicine. Stories like mine are important to inspire a reexamination of what a physician should be and how medicine, patients, and communities benefit from this change.
My experience through medical school
My path to psychiatry and residency was shaped by my early experience with the medical field and treatment. From the early days of my diagnosis at age 4, I was told that my brain was “wired differently” and that, because of this disruption in circuitry, I would have difficulty with physical activity. I grew to appreciate the intricacies of the brain and pathology to understand my body. With greater understanding came the existential realization that I would live with a disability for the rest of my life. Rather than dream of a future where I would be “normal,” I focused on adapting my life to my normal. An unfortunate reality of this normal was that no doctor would be able to relate to me, and my health care would focus on limitations rather than possibilities.
I focused on school as a distraction and slowly warmed to the idea of pursuing medicine as a career. The seed was planted years prior by the numerous doctors’ visits and procedures, and was cultivated by a desire to understand pathologies and offer treatment to patients from the perspective of a patient. When I applied to medical school, I did not know how to address my CP. Living as a person with CP was a core reason for my decision to pursue medicine, but I was afraid that a disclosure of disability would preclude any admission to medical school. Research into programs offered little guidance because most institutions only listed vague “physical expectations” of each student. There were times I doubted if I would be accepted anywhere. Many programs I reached out to about my situation seemed unenthusiastic about the prospect of a student with CP, and when I brought up my CP in interviews, the reaction was often of surprise and an admission that they had forgotten about “that part” of my application. Fortunately, I was accepted to medical school, but still struggled with the fear that one day I would be found out and not allowed to continue. No one in my class or school was like me, and a meeting with an Americans with Disabilities Act coordinator who asked me to reexamine the physical competencies of the school before advancing to clinical clerkships only further reinforced this fear. I decided to fly under the radar and not say anything about my disability to my attendings. I slowly worked my way through clerkships by making do with adapted ways to perform procedures and exams with additional practice and maneuvering at home. I found myself drawn to psychiatry because of the similarities I saw in the patients and myself. I empathized with how the patients struggled with chronic conditions that left them feeling separated from society and how they felt that their diagnosis was something they needed to hide. When medical school ended and I decided to pursue psychiatry, I wanted to share my story to inspire others with a disability to consider medicine as a career given their unique experiences. My experience thus far has been uplifting as my journey has echoed so many others.
A need for greater representation
Disability representation in medicine is needed more than ever. According to the CDC, >60 million adults in the United States (1 in 4) live with a disability.1 Although the physical health disparities are often discussed, there is less conversation surrounding mental health for individuals with disabilities. A 2018 study by Cree et al2 found that approximately 17.4 million adults with disabilities experienced frequent mental distress, defined as reporting ≥14 mentally unhealthy days in the past 30 days. Furthermore, compared to individuals without a disability, those with a disability are statistically more likely to have suicidal ideation, suicidal planning, and suicide attempts.3 One way to address this disparity is to recruit medical students with disabilities to become physicians with disabilities. Evidence suggests that physicians who are members of groups that are underrepresented in medicine are more likely to deliver care to underrepresented patients.4 However, medical schools and institutions have been slow to address the disparity. A 2019 survey found an estimated 4.6% of medical students responded “yes” when asked if they had a disability, with most students reporting a psychological or attention/hyperactive disorder.5 Existing barriers include restrictive language surrounding technical standards influenced by long-standing vestiges of what a physician should be.6
An opportunity to connect with patients
I now do not see myself as having a secret identity to hide. Although my CP does not give me any superpowers, it has given me the opportunity to connect with my patients and serve as an example of why medical school recruitment and admissions should expand. Psychiatrists have been on the forefront of change in medicine and can shift the perception of a physician. In doing so, we not only enrich our field but also the lives of our patients who may need it most.
1. Okoro CA, Hollis ND, Cyrus AC, et al. Prevalence of disabilities and health care access by disability status and type among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(32):882-887.
2. Cree RA, Okoro CA, Zack MM, et al. Frequent mental distress among adults, by disability status, disability type, and selected characteristics—United States 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1238-1243.
3. Marlow NM, Xie Z, Tanner R, et al. Association between disability and suicide-related outcomes among US adults. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(6):852-862.
4. Thurmond VB, Kirch DG. Impact of minority physicians on health care. South Med J. 1998;91(11):1009-1013.
5. Meeks LM, Case B, Herzer K, et al. Change in prevalence of disabilities and accommodation practices among US medical schools, 2016 vs 2019. JAMA. 2019;322(20):2022-2024.
6. Stauffer C, Case B, Moreland CJ, et al. Technical standards from newly established medical schools: a review of disability inclusive practices. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205211072763.
What does a doctor look like? Throughout history, this concept has shifted due to societal norms and increased access to medical education. Today, the idea of a physician has expanded to incorporate a myriad of people; however, stigma still exists in medicine regarding mental illness and disability. I would like to share my personal journey through high school, college, medical school, and now residency, and how my identity and struggles have shaped me into the physician I am today. There are few conversations around disability—especially disability and mental health—in medicine, and through my own advocacy, I have met many students with disability who feel that medical school is unattainable. Additionally, I have met many medical students, residents, and pre-health advisors who are happy for the experience to learn more about a marginalized group in medicine. My hope in sharing my story is to offer a space for conversation about intersectionality within medical communities and how physicians and physicians in training can facilitate that change, regardless of their position or specialty. Additionally, I hope to shed light on the unique mental health needs of patients with disabilities and how mental health clinicians can address those needs.
Perceived weaknesses turned into strengths
“Why do you walk like that?” “What is that brace on your leg?” The early years of my childhood were marked by these questions and others like them. I was the kid with the limp, the kid with a brace on his leg, and the kid who disappeared multiple times a week for doctor’s appointments or physical therapy. I learned to deflect these questions or give nebulous answers about an accident or injury. The reality is that I was born with cerebral palsy (CP). My CP manifested as hemiparesis on the left side of my body. I was in aggressive physical therapy throughout childhood, received Botox injections for muscle spasticity, and underwent corrective surgery on my left leg to straighten my foot. In childhood, the diagnosis meant nothing more than 2 words that sounded like they belonged to superheroes in comic books. Even with supportive parents and family, I kept my disability a secret, much like the powers and abilities of my favorite superheroes.
However, like all great origin stories, what I once thought were weaknesses turned out to be strengths that pushed me through college, medical school, and now psychiatry residency. Living with a disability has shaped how I see the world and relate to my patients. My experience has helped me connect to my patients in ways others might not. These properties are important in any physician but vital in psychiatry, where many patients feel neglected or stigmatized; this is another reason there should be more doctors with disabilities in medicine. Unfortunately, systemic barriers are still in place that disincentivize those with a disability from pursuing careers in medicine. Stories like mine are important to inspire a reexamination of what a physician should be and how medicine, patients, and communities benefit from this change.
My experience through medical school
My path to psychiatry and residency was shaped by my early experience with the medical field and treatment. From the early days of my diagnosis at age 4, I was told that my brain was “wired differently” and that, because of this disruption in circuitry, I would have difficulty with physical activity. I grew to appreciate the intricacies of the brain and pathology to understand my body. With greater understanding came the existential realization that I would live with a disability for the rest of my life. Rather than dream of a future where I would be “normal,” I focused on adapting my life to my normal. An unfortunate reality of this normal was that no doctor would be able to relate to me, and my health care would focus on limitations rather than possibilities.
I focused on school as a distraction and slowly warmed to the idea of pursuing medicine as a career. The seed was planted years prior by the numerous doctors’ visits and procedures, and was cultivated by a desire to understand pathologies and offer treatment to patients from the perspective of a patient. When I applied to medical school, I did not know how to address my CP. Living as a person with CP was a core reason for my decision to pursue medicine, but I was afraid that a disclosure of disability would preclude any admission to medical school. Research into programs offered little guidance because most institutions only listed vague “physical expectations” of each student. There were times I doubted if I would be accepted anywhere. Many programs I reached out to about my situation seemed unenthusiastic about the prospect of a student with CP, and when I brought up my CP in interviews, the reaction was often of surprise and an admission that they had forgotten about “that part” of my application. Fortunately, I was accepted to medical school, but still struggled with the fear that one day I would be found out and not allowed to continue. No one in my class or school was like me, and a meeting with an Americans with Disabilities Act coordinator who asked me to reexamine the physical competencies of the school before advancing to clinical clerkships only further reinforced this fear. I decided to fly under the radar and not say anything about my disability to my attendings. I slowly worked my way through clerkships by making do with adapted ways to perform procedures and exams with additional practice and maneuvering at home. I found myself drawn to psychiatry because of the similarities I saw in the patients and myself. I empathized with how the patients struggled with chronic conditions that left them feeling separated from society and how they felt that their diagnosis was something they needed to hide. When medical school ended and I decided to pursue psychiatry, I wanted to share my story to inspire others with a disability to consider medicine as a career given their unique experiences. My experience thus far has been uplifting as my journey has echoed so many others.
A need for greater representation
Disability representation in medicine is needed more than ever. According to the CDC, >60 million adults in the United States (1 in 4) live with a disability.1 Although the physical health disparities are often discussed, there is less conversation surrounding mental health for individuals with disabilities. A 2018 study by Cree et al2 found that approximately 17.4 million adults with disabilities experienced frequent mental distress, defined as reporting ≥14 mentally unhealthy days in the past 30 days. Furthermore, compared to individuals without a disability, those with a disability are statistically more likely to have suicidal ideation, suicidal planning, and suicide attempts.3 One way to address this disparity is to recruit medical students with disabilities to become physicians with disabilities. Evidence suggests that physicians who are members of groups that are underrepresented in medicine are more likely to deliver care to underrepresented patients.4 However, medical schools and institutions have been slow to address the disparity. A 2019 survey found an estimated 4.6% of medical students responded “yes” when asked if they had a disability, with most students reporting a psychological or attention/hyperactive disorder.5 Existing barriers include restrictive language surrounding technical standards influenced by long-standing vestiges of what a physician should be.6
An opportunity to connect with patients
I now do not see myself as having a secret identity to hide. Although my CP does not give me any superpowers, it has given me the opportunity to connect with my patients and serve as an example of why medical school recruitment and admissions should expand. Psychiatrists have been on the forefront of change in medicine and can shift the perception of a physician. In doing so, we not only enrich our field but also the lives of our patients who may need it most.
What does a doctor look like? Throughout history, this concept has shifted due to societal norms and increased access to medical education. Today, the idea of a physician has expanded to incorporate a myriad of people; however, stigma still exists in medicine regarding mental illness and disability. I would like to share my personal journey through high school, college, medical school, and now residency, and how my identity and struggles have shaped me into the physician I am today. There are few conversations around disability—especially disability and mental health—in medicine, and through my own advocacy, I have met many students with disability who feel that medical school is unattainable. Additionally, I have met many medical students, residents, and pre-health advisors who are happy for the experience to learn more about a marginalized group in medicine. My hope in sharing my story is to offer a space for conversation about intersectionality within medical communities and how physicians and physicians in training can facilitate that change, regardless of their position or specialty. Additionally, I hope to shed light on the unique mental health needs of patients with disabilities and how mental health clinicians can address those needs.
Perceived weaknesses turned into strengths
“Why do you walk like that?” “What is that brace on your leg?” The early years of my childhood were marked by these questions and others like them. I was the kid with the limp, the kid with a brace on his leg, and the kid who disappeared multiple times a week for doctor’s appointments or physical therapy. I learned to deflect these questions or give nebulous answers about an accident or injury. The reality is that I was born with cerebral palsy (CP). My CP manifested as hemiparesis on the left side of my body. I was in aggressive physical therapy throughout childhood, received Botox injections for muscle spasticity, and underwent corrective surgery on my left leg to straighten my foot. In childhood, the diagnosis meant nothing more than 2 words that sounded like they belonged to superheroes in comic books. Even with supportive parents and family, I kept my disability a secret, much like the powers and abilities of my favorite superheroes.
However, like all great origin stories, what I once thought were weaknesses turned out to be strengths that pushed me through college, medical school, and now psychiatry residency. Living with a disability has shaped how I see the world and relate to my patients. My experience has helped me connect to my patients in ways others might not. These properties are important in any physician but vital in psychiatry, where many patients feel neglected or stigmatized; this is another reason there should be more doctors with disabilities in medicine. Unfortunately, systemic barriers are still in place that disincentivize those with a disability from pursuing careers in medicine. Stories like mine are important to inspire a reexamination of what a physician should be and how medicine, patients, and communities benefit from this change.
My experience through medical school
My path to psychiatry and residency was shaped by my early experience with the medical field and treatment. From the early days of my diagnosis at age 4, I was told that my brain was “wired differently” and that, because of this disruption in circuitry, I would have difficulty with physical activity. I grew to appreciate the intricacies of the brain and pathology to understand my body. With greater understanding came the existential realization that I would live with a disability for the rest of my life. Rather than dream of a future where I would be “normal,” I focused on adapting my life to my normal. An unfortunate reality of this normal was that no doctor would be able to relate to me, and my health care would focus on limitations rather than possibilities.
I focused on school as a distraction and slowly warmed to the idea of pursuing medicine as a career. The seed was planted years prior by the numerous doctors’ visits and procedures, and was cultivated by a desire to understand pathologies and offer treatment to patients from the perspective of a patient. When I applied to medical school, I did not know how to address my CP. Living as a person with CP was a core reason for my decision to pursue medicine, but I was afraid that a disclosure of disability would preclude any admission to medical school. Research into programs offered little guidance because most institutions only listed vague “physical expectations” of each student. There were times I doubted if I would be accepted anywhere. Many programs I reached out to about my situation seemed unenthusiastic about the prospect of a student with CP, and when I brought up my CP in interviews, the reaction was often of surprise and an admission that they had forgotten about “that part” of my application. Fortunately, I was accepted to medical school, but still struggled with the fear that one day I would be found out and not allowed to continue. No one in my class or school was like me, and a meeting with an Americans with Disabilities Act coordinator who asked me to reexamine the physical competencies of the school before advancing to clinical clerkships only further reinforced this fear. I decided to fly under the radar and not say anything about my disability to my attendings. I slowly worked my way through clerkships by making do with adapted ways to perform procedures and exams with additional practice and maneuvering at home. I found myself drawn to psychiatry because of the similarities I saw in the patients and myself. I empathized with how the patients struggled with chronic conditions that left them feeling separated from society and how they felt that their diagnosis was something they needed to hide. When medical school ended and I decided to pursue psychiatry, I wanted to share my story to inspire others with a disability to consider medicine as a career given their unique experiences. My experience thus far has been uplifting as my journey has echoed so many others.
A need for greater representation
Disability representation in medicine is needed more than ever. According to the CDC, >60 million adults in the United States (1 in 4) live with a disability.1 Although the physical health disparities are often discussed, there is less conversation surrounding mental health for individuals with disabilities. A 2018 study by Cree et al2 found that approximately 17.4 million adults with disabilities experienced frequent mental distress, defined as reporting ≥14 mentally unhealthy days in the past 30 days. Furthermore, compared to individuals without a disability, those with a disability are statistically more likely to have suicidal ideation, suicidal planning, and suicide attempts.3 One way to address this disparity is to recruit medical students with disabilities to become physicians with disabilities. Evidence suggests that physicians who are members of groups that are underrepresented in medicine are more likely to deliver care to underrepresented patients.4 However, medical schools and institutions have been slow to address the disparity. A 2019 survey found an estimated 4.6% of medical students responded “yes” when asked if they had a disability, with most students reporting a psychological or attention/hyperactive disorder.5 Existing barriers include restrictive language surrounding technical standards influenced by long-standing vestiges of what a physician should be.6
An opportunity to connect with patients
I now do not see myself as having a secret identity to hide. Although my CP does not give me any superpowers, it has given me the opportunity to connect with my patients and serve as an example of why medical school recruitment and admissions should expand. Psychiatrists have been on the forefront of change in medicine and can shift the perception of a physician. In doing so, we not only enrich our field but also the lives of our patients who may need it most.
1. Okoro CA, Hollis ND, Cyrus AC, et al. Prevalence of disabilities and health care access by disability status and type among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(32):882-887.
2. Cree RA, Okoro CA, Zack MM, et al. Frequent mental distress among adults, by disability status, disability type, and selected characteristics—United States 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1238-1243.
3. Marlow NM, Xie Z, Tanner R, et al. Association between disability and suicide-related outcomes among US adults. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(6):852-862.
4. Thurmond VB, Kirch DG. Impact of minority physicians on health care. South Med J. 1998;91(11):1009-1013.
5. Meeks LM, Case B, Herzer K, et al. Change in prevalence of disabilities and accommodation practices among US medical schools, 2016 vs 2019. JAMA. 2019;322(20):2022-2024.
6. Stauffer C, Case B, Moreland CJ, et al. Technical standards from newly established medical schools: a review of disability inclusive practices. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205211072763.
1. Okoro CA, Hollis ND, Cyrus AC, et al. Prevalence of disabilities and health care access by disability status and type among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(32):882-887.
2. Cree RA, Okoro CA, Zack MM, et al. Frequent mental distress among adults, by disability status, disability type, and selected characteristics—United States 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1238-1243.
3. Marlow NM, Xie Z, Tanner R, et al. Association between disability and suicide-related outcomes among US adults. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(6):852-862.
4. Thurmond VB, Kirch DG. Impact of minority physicians on health care. South Med J. 1998;91(11):1009-1013.
5. Meeks LM, Case B, Herzer K, et al. Change in prevalence of disabilities and accommodation practices among US medical schools, 2016 vs 2019. JAMA. 2019;322(20):2022-2024.
6. Stauffer C, Case B, Moreland CJ, et al. Technical standards from newly established medical schools: a review of disability inclusive practices. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205211072763.
Physician sues AMA for defamation over 2022 election controversy
If Willarda Edwards, MD, MBA, had won her 2022 campaign for president-elect of the American Medical Association (AMA), she would have been the second Black woman to head the group.
The lawsuit sheds light on the power dynamics of a politically potent organization that has more than 271,000 members and holds assets of $1.2 billion. The AMA president is one of the most visible figures in American medicine.
“The AMA impugned Dr. Edwards with these false charges, which destroyed her candidacy and irreparably damaged her reputation,” according to the complaint, which was filed Nov. 9, 2022, in Baltimore County Circuit Court. The case was later moved to federal court.
The AMA “previously rejected our attempt to resolve this matter without litigation,” Dr. Edwards’ attorney, Timothy Maloney, told this news organization. An AMA spokesman said the organization had no comment on Dr. Edwards’ suit.
Dr. Edwards is a past president of the National Medical Association, MedChi, the Baltimore City Medical Society, the Monumental City Medical Society, and the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America. She joined the AMA in 1994 and has served as a trustee since 2016.
As chair of the AMA Task Force on Health Equity, “she helped lead the way in consensus building and driving action that in 2019 resulted in the AMA House of Delegates establishing the AMA Center on Health Equity,” according to her AMA bio page.
‘Quid pro quo’ alleged
In June 2022, Dr. Edwards was one of three individuals running to be AMA president-elect.
According to Dr. Edwards’ complaint, she was “incorrectly advised by colleagues” that Virginia urologist William Reha, MD, had decided not to seek the AMA vice-speakership in 2023. This was important because both Dr. Edwards and Dr. Reha were in the Southeastern delegation. It could be in Dr. Edwards’ favor if Dr. Reha was not running, as it would mean one less leadership candidate from the same region.
Dr. Edwards called Dr. Reha on June 6 to discuss the matter. When they talked, Dr. Reha allegedly recorded the call without Dr. Edwards’ knowledge or permission – a felony in Maryland – and also steered her toward discussions about how his decision could benefit her campaign, according to the complaint.
The suit alleges that Dr. Reha’s questions were “clearly calculated to draw some statements by Dr. Edwards that he could use later to thwart her candidacy and to benefit her opponent.”
On June 10, at the AMA’s House of Delegates meeting in Chicago, Dr. Edwards was taken aside and questioned by members of the AMA’s Election Campaign Committee, according to the complaint. They accused her of “vote trading” but did not provide any evidence or a copy of a complaint they said had been filed against her, the suit said.
Dr. Edwards was given no opportunity to produce her own evidence or rebut the accusations, the suit alleges.
Just before the delegates started formal business on June 13, House Speaker Bruce Scott, MD, read a statement to the assembly saying that a complaint of a possible campaign violation had been filed against Dr. Edwards.
Dr. Scott told the delegates that “committee members interviewed the complainant and multiple other individuals said to have knowledge of the circumstances. In addition to conducting multiple interviews, the committee reviewed evidence that was deemed credible and corroborated that a campaign violation did in fact occur,” according to the complaint.
The supposed violation: A “quid pro quo” in which an unnamed delegation would support Dr. Edwards’ current candidacy, and the Southeastern delegation would support a future candidate from that other unnamed delegation.
Dr. Edwards was given a short opportunity to speak, in which she denied any violations.
According to a news report, Dr. Edwards said, “I’ve been in the House of Delegates for 30 years, and you know me as a process person – a person who truly believes in the process and trying to follow the complexities of our election campaign.”
The lawsuit alleges that “this defamatory conduct was repeated the next day to more than 600 delegates just minutes prior to the casting of votes, when Dr Scott repeated these allegations.”
Dr. Edwards lost the election.
AMA: Nothing more to add
The suit alleges that neither the Election Campaign Committee nor the AMA itself has made any accusers or complaints available to Dr. Edwards and that it has not provided any audio or written evidence of her alleged violation.
In July, the AMA’s Southeastern delegation told its membership, “We continue to maintain that Willarda was ‘set up’ ... The whole affair lacked any reasonable semblance of due process.”
The delegation has filed a counter claim against the AMA seeking “to address this lack of due process as well as the reputational harm” to the delegation.
The AMA said that it has nothing it can produce. “The Speaker of the House presented a verbal report to the attending delegates,” said a spokesman. “The Speaker’s report remains the only remarks from an AMA officer, and no additional remarks can be expected at this time.”
He added that there “is no official transcript of the Speaker’s report.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If Willarda Edwards, MD, MBA, had won her 2022 campaign for president-elect of the American Medical Association (AMA), she would have been the second Black woman to head the group.
The lawsuit sheds light on the power dynamics of a politically potent organization that has more than 271,000 members and holds assets of $1.2 billion. The AMA president is one of the most visible figures in American medicine.
“The AMA impugned Dr. Edwards with these false charges, which destroyed her candidacy and irreparably damaged her reputation,” according to the complaint, which was filed Nov. 9, 2022, in Baltimore County Circuit Court. The case was later moved to federal court.
The AMA “previously rejected our attempt to resolve this matter without litigation,” Dr. Edwards’ attorney, Timothy Maloney, told this news organization. An AMA spokesman said the organization had no comment on Dr. Edwards’ suit.
Dr. Edwards is a past president of the National Medical Association, MedChi, the Baltimore City Medical Society, the Monumental City Medical Society, and the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America. She joined the AMA in 1994 and has served as a trustee since 2016.
As chair of the AMA Task Force on Health Equity, “she helped lead the way in consensus building and driving action that in 2019 resulted in the AMA House of Delegates establishing the AMA Center on Health Equity,” according to her AMA bio page.
‘Quid pro quo’ alleged
In June 2022, Dr. Edwards was one of three individuals running to be AMA president-elect.
According to Dr. Edwards’ complaint, she was “incorrectly advised by colleagues” that Virginia urologist William Reha, MD, had decided not to seek the AMA vice-speakership in 2023. This was important because both Dr. Edwards and Dr. Reha were in the Southeastern delegation. It could be in Dr. Edwards’ favor if Dr. Reha was not running, as it would mean one less leadership candidate from the same region.
Dr. Edwards called Dr. Reha on June 6 to discuss the matter. When they talked, Dr. Reha allegedly recorded the call without Dr. Edwards’ knowledge or permission – a felony in Maryland – and also steered her toward discussions about how his decision could benefit her campaign, according to the complaint.
The suit alleges that Dr. Reha’s questions were “clearly calculated to draw some statements by Dr. Edwards that he could use later to thwart her candidacy and to benefit her opponent.”
On June 10, at the AMA’s House of Delegates meeting in Chicago, Dr. Edwards was taken aside and questioned by members of the AMA’s Election Campaign Committee, according to the complaint. They accused her of “vote trading” but did not provide any evidence or a copy of a complaint they said had been filed against her, the suit said.
Dr. Edwards was given no opportunity to produce her own evidence or rebut the accusations, the suit alleges.
Just before the delegates started formal business on June 13, House Speaker Bruce Scott, MD, read a statement to the assembly saying that a complaint of a possible campaign violation had been filed against Dr. Edwards.
Dr. Scott told the delegates that “committee members interviewed the complainant and multiple other individuals said to have knowledge of the circumstances. In addition to conducting multiple interviews, the committee reviewed evidence that was deemed credible and corroborated that a campaign violation did in fact occur,” according to the complaint.
The supposed violation: A “quid pro quo” in which an unnamed delegation would support Dr. Edwards’ current candidacy, and the Southeastern delegation would support a future candidate from that other unnamed delegation.
Dr. Edwards was given a short opportunity to speak, in which she denied any violations.
According to a news report, Dr. Edwards said, “I’ve been in the House of Delegates for 30 years, and you know me as a process person – a person who truly believes in the process and trying to follow the complexities of our election campaign.”
The lawsuit alleges that “this defamatory conduct was repeated the next day to more than 600 delegates just minutes prior to the casting of votes, when Dr Scott repeated these allegations.”
Dr. Edwards lost the election.
AMA: Nothing more to add
The suit alleges that neither the Election Campaign Committee nor the AMA itself has made any accusers or complaints available to Dr. Edwards and that it has not provided any audio or written evidence of her alleged violation.
In July, the AMA’s Southeastern delegation told its membership, “We continue to maintain that Willarda was ‘set up’ ... The whole affair lacked any reasonable semblance of due process.”
The delegation has filed a counter claim against the AMA seeking “to address this lack of due process as well as the reputational harm” to the delegation.
The AMA said that it has nothing it can produce. “The Speaker of the House presented a verbal report to the attending delegates,” said a spokesman. “The Speaker’s report remains the only remarks from an AMA officer, and no additional remarks can be expected at this time.”
He added that there “is no official transcript of the Speaker’s report.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If Willarda Edwards, MD, MBA, had won her 2022 campaign for president-elect of the American Medical Association (AMA), she would have been the second Black woman to head the group.
The lawsuit sheds light on the power dynamics of a politically potent organization that has more than 271,000 members and holds assets of $1.2 billion. The AMA president is one of the most visible figures in American medicine.
“The AMA impugned Dr. Edwards with these false charges, which destroyed her candidacy and irreparably damaged her reputation,” according to the complaint, which was filed Nov. 9, 2022, in Baltimore County Circuit Court. The case was later moved to federal court.
The AMA “previously rejected our attempt to resolve this matter without litigation,” Dr. Edwards’ attorney, Timothy Maloney, told this news organization. An AMA spokesman said the organization had no comment on Dr. Edwards’ suit.
Dr. Edwards is a past president of the National Medical Association, MedChi, the Baltimore City Medical Society, the Monumental City Medical Society, and the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America. She joined the AMA in 1994 and has served as a trustee since 2016.
As chair of the AMA Task Force on Health Equity, “she helped lead the way in consensus building and driving action that in 2019 resulted in the AMA House of Delegates establishing the AMA Center on Health Equity,” according to her AMA bio page.
‘Quid pro quo’ alleged
In June 2022, Dr. Edwards was one of three individuals running to be AMA president-elect.
According to Dr. Edwards’ complaint, she was “incorrectly advised by colleagues” that Virginia urologist William Reha, MD, had decided not to seek the AMA vice-speakership in 2023. This was important because both Dr. Edwards and Dr. Reha were in the Southeastern delegation. It could be in Dr. Edwards’ favor if Dr. Reha was not running, as it would mean one less leadership candidate from the same region.
Dr. Edwards called Dr. Reha on June 6 to discuss the matter. When they talked, Dr. Reha allegedly recorded the call without Dr. Edwards’ knowledge or permission – a felony in Maryland – and also steered her toward discussions about how his decision could benefit her campaign, according to the complaint.
The suit alleges that Dr. Reha’s questions were “clearly calculated to draw some statements by Dr. Edwards that he could use later to thwart her candidacy and to benefit her opponent.”
On June 10, at the AMA’s House of Delegates meeting in Chicago, Dr. Edwards was taken aside and questioned by members of the AMA’s Election Campaign Committee, according to the complaint. They accused her of “vote trading” but did not provide any evidence or a copy of a complaint they said had been filed against her, the suit said.
Dr. Edwards was given no opportunity to produce her own evidence or rebut the accusations, the suit alleges.
Just before the delegates started formal business on June 13, House Speaker Bruce Scott, MD, read a statement to the assembly saying that a complaint of a possible campaign violation had been filed against Dr. Edwards.
Dr. Scott told the delegates that “committee members interviewed the complainant and multiple other individuals said to have knowledge of the circumstances. In addition to conducting multiple interviews, the committee reviewed evidence that was deemed credible and corroborated that a campaign violation did in fact occur,” according to the complaint.
The supposed violation: A “quid pro quo” in which an unnamed delegation would support Dr. Edwards’ current candidacy, and the Southeastern delegation would support a future candidate from that other unnamed delegation.
Dr. Edwards was given a short opportunity to speak, in which she denied any violations.
According to a news report, Dr. Edwards said, “I’ve been in the House of Delegates for 30 years, and you know me as a process person – a person who truly believes in the process and trying to follow the complexities of our election campaign.”
The lawsuit alleges that “this defamatory conduct was repeated the next day to more than 600 delegates just minutes prior to the casting of votes, when Dr Scott repeated these allegations.”
Dr. Edwards lost the election.
AMA: Nothing more to add
The suit alleges that neither the Election Campaign Committee nor the AMA itself has made any accusers or complaints available to Dr. Edwards and that it has not provided any audio or written evidence of her alleged violation.
In July, the AMA’s Southeastern delegation told its membership, “We continue to maintain that Willarda was ‘set up’ ... The whole affair lacked any reasonable semblance of due process.”
The delegation has filed a counter claim against the AMA seeking “to address this lack of due process as well as the reputational harm” to the delegation.
The AMA said that it has nothing it can produce. “The Speaker of the House presented a verbal report to the attending delegates,” said a spokesman. “The Speaker’s report remains the only remarks from an AMA officer, and no additional remarks can be expected at this time.”
He added that there “is no official transcript of the Speaker’s report.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mothers with disabilities less likely to start breastfeeding
Mothers with intellectual or developmental disabilities are less likely to initiate breastfeeding and to receive in-hospital breastfeeding support than are those without a disability, new data suggest.
In a population-based cohort study of more than 600,000 mothers, patients with an intellectual or developmental disability were about 18% less likely to have a chance to initiate breastfeeding during their hospital stay.
“Overall, we did see lower rates of breastfeeding practices and supports in people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, as well as those with multiple disabilities, compared to people without disabilities,” study author Hilary K. Brown, PhD, assistant professor of health and society at University of Toronto Scarborough in Ontario, told this news organization.
The study was published in The Lancet Public Health.
Disparities in breastfeeding
“There hasn’t been a lot of research on breastfeeding outcomes in people with disabilities,” said Dr. Brown, who noted that the study outcomes were based on the WHO-UNICEF Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative guidelines. “There have been a number of qualitative studies that have suggested that they do experience barriers accessing care related to breastfeeding and different challenges related to breastfeeding. But as far as quantitative outcomes, there has only been a handful of studies.”
To examine these outcomes, the investigators analyzed health administrative data from Ontario. They included in their analysis all birthing parents aged 15-49 years who had a single live birth between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018. Patients with a physical disability, sensory disability, intellectual or developmental disability, or two or more disabilities were identified via diagnostic algorithms and were compared with individuals without disabilities with respect to the opportunity to initiate breastfeeding, to engage in in-hospital breastfeeding, to engage in exclusive breastfeeding at hospital discharge, to have skin-to-skin contact, and to be provided with breastfeeding assistance.
The investigators considered a physical disability to encompass conditions such as congenital anomalies, musculoskeletal disorders, neurologic disorders, or permanent injuries. They defined sensory disability as hearing loss or vision loss. Intellectual or developmental disability was defined as having autism spectrum disorder, chromosomal anomaly, fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, or other intellectual disability. Patients with multiple disabilities had two or more of these conditions.
The study population included 634,111 birthing parents, of whom 54,476 (8.6%) had a physical disability, 19,227 (3.0%) had a sensory disability, 1,048 (0.2%) had an intellectual or developmental disability, 4,050 (0.6%) had multiple disabilities, and 555,310 (87.6%) had no disability.
The investigators found that patients with intellectual or developmental disabilities were less likely than were those without a disability to have an opportunity to initiate breastfeeding (adjusted relative risk [aRR], 0.82), to engage in any in-hospital breastfeeding (aRR, 0.85), to be breastfeeding exclusively at hospital discharge (aRR, 0.73), to have skin-to-skin contact (aRR, 0.90), and to receive breastfeeding assistance (aRR, 0.85) compared with patients without a disability.
They also found that individuals with multiple disabilities were less likely to have an opportunity to initiate breastfeeding (aRR, 0.93), to engage in any in-hospital breastfeeding (aRR, 0.93), to be exclusively breastfeeding at hospital discharge (aRR, 0.90), to have skin-to-skin contact (aRR, 0.93), and to receive breastfeeding assistance (aRR, 0.95) compared with patients without a disability.
An understudied population
Commenting on the study, Lori Feldman-Winter, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics at Rowan University in Camden, N.J., said that one of its strengths is that it included patients who may be excluded from studies of breastfeeding practices. The finding of few differences in breastfeeding practices and supports for people with physical and sensory disabilities, compared with those without disabilities, was positive, she added.
“This is an understudied population, and it is important to call out that there may be practices related to breastfeeding care that suffer, due to implicit bias regarding persons with intellectual and multiple disabilities,” said Dr. Feldman-Winter. “The good news is that other disabilities did not show the same disparities. This study also shows how important it is to measure potential gaps in care across multiple sociodemographic and other variables, such as disabilities, to ensure equitable and inclusive care.”
Health care professionals need to be aware of disparities in breastfeeding care, she added. They need to be open to exploring potential biases when it comes to providing equitable care.
R. Douglas Wilson, MD, president of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada and professor emeritus of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Calgary in Alberta, noted that the size of the cohort represents a strength of the study and that the findings suggest the possible need for closer follow-up of a new mother who is breastfeeding and who has an intellectual disability or multiple disabilities.
“You might keep that patient in hospital for an extra day, and then the home care nurse may look in on them more frequently than they would for someone who does not need that extra oversight,” said Dr. Wilson. When their patients are pregnant, obstetricians and gynecologists can find out whether their patients intend to breastfeed and put them in touch with nurses or lactation consultants to assist them, he added.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canada Research Chairs Program. Dr. Brown, Dr. Feldman-Winter, and Dr. Wilson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mothers with intellectual or developmental disabilities are less likely to initiate breastfeeding and to receive in-hospital breastfeeding support than are those without a disability, new data suggest.
In a population-based cohort study of more than 600,000 mothers, patients with an intellectual or developmental disability were about 18% less likely to have a chance to initiate breastfeeding during their hospital stay.
“Overall, we did see lower rates of breastfeeding practices and supports in people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, as well as those with multiple disabilities, compared to people without disabilities,” study author Hilary K. Brown, PhD, assistant professor of health and society at University of Toronto Scarborough in Ontario, told this news organization.
The study was published in The Lancet Public Health.
Disparities in breastfeeding
“There hasn’t been a lot of research on breastfeeding outcomes in people with disabilities,” said Dr. Brown, who noted that the study outcomes were based on the WHO-UNICEF Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative guidelines. “There have been a number of qualitative studies that have suggested that they do experience barriers accessing care related to breastfeeding and different challenges related to breastfeeding. But as far as quantitative outcomes, there has only been a handful of studies.”
To examine these outcomes, the investigators analyzed health administrative data from Ontario. They included in their analysis all birthing parents aged 15-49 years who had a single live birth between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018. Patients with a physical disability, sensory disability, intellectual or developmental disability, or two or more disabilities were identified via diagnostic algorithms and were compared with individuals without disabilities with respect to the opportunity to initiate breastfeeding, to engage in in-hospital breastfeeding, to engage in exclusive breastfeeding at hospital discharge, to have skin-to-skin contact, and to be provided with breastfeeding assistance.
The investigators considered a physical disability to encompass conditions such as congenital anomalies, musculoskeletal disorders, neurologic disorders, or permanent injuries. They defined sensory disability as hearing loss or vision loss. Intellectual or developmental disability was defined as having autism spectrum disorder, chromosomal anomaly, fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, or other intellectual disability. Patients with multiple disabilities had two or more of these conditions.
The study population included 634,111 birthing parents, of whom 54,476 (8.6%) had a physical disability, 19,227 (3.0%) had a sensory disability, 1,048 (0.2%) had an intellectual or developmental disability, 4,050 (0.6%) had multiple disabilities, and 555,310 (87.6%) had no disability.
The investigators found that patients with intellectual or developmental disabilities were less likely than were those without a disability to have an opportunity to initiate breastfeeding (adjusted relative risk [aRR], 0.82), to engage in any in-hospital breastfeeding (aRR, 0.85), to be breastfeeding exclusively at hospital discharge (aRR, 0.73), to have skin-to-skin contact (aRR, 0.90), and to receive breastfeeding assistance (aRR, 0.85) compared with patients without a disability.
They also found that individuals with multiple disabilities were less likely to have an opportunity to initiate breastfeeding (aRR, 0.93), to engage in any in-hospital breastfeeding (aRR, 0.93), to be exclusively breastfeeding at hospital discharge (aRR, 0.90), to have skin-to-skin contact (aRR, 0.93), and to receive breastfeeding assistance (aRR, 0.95) compared with patients without a disability.
An understudied population
Commenting on the study, Lori Feldman-Winter, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics at Rowan University in Camden, N.J., said that one of its strengths is that it included patients who may be excluded from studies of breastfeeding practices. The finding of few differences in breastfeeding practices and supports for people with physical and sensory disabilities, compared with those without disabilities, was positive, she added.
“This is an understudied population, and it is important to call out that there may be practices related to breastfeeding care that suffer, due to implicit bias regarding persons with intellectual and multiple disabilities,” said Dr. Feldman-Winter. “The good news is that other disabilities did not show the same disparities. This study also shows how important it is to measure potential gaps in care across multiple sociodemographic and other variables, such as disabilities, to ensure equitable and inclusive care.”
Health care professionals need to be aware of disparities in breastfeeding care, she added. They need to be open to exploring potential biases when it comes to providing equitable care.
R. Douglas Wilson, MD, president of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada and professor emeritus of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Calgary in Alberta, noted that the size of the cohort represents a strength of the study and that the findings suggest the possible need for closer follow-up of a new mother who is breastfeeding and who has an intellectual disability or multiple disabilities.
“You might keep that patient in hospital for an extra day, and then the home care nurse may look in on them more frequently than they would for someone who does not need that extra oversight,” said Dr. Wilson. When their patients are pregnant, obstetricians and gynecologists can find out whether their patients intend to breastfeed and put them in touch with nurses or lactation consultants to assist them, he added.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canada Research Chairs Program. Dr. Brown, Dr. Feldman-Winter, and Dr. Wilson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mothers with intellectual or developmental disabilities are less likely to initiate breastfeeding and to receive in-hospital breastfeeding support than are those without a disability, new data suggest.
In a population-based cohort study of more than 600,000 mothers, patients with an intellectual or developmental disability were about 18% less likely to have a chance to initiate breastfeeding during their hospital stay.
“Overall, we did see lower rates of breastfeeding practices and supports in people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, as well as those with multiple disabilities, compared to people without disabilities,” study author Hilary K. Brown, PhD, assistant professor of health and society at University of Toronto Scarborough in Ontario, told this news organization.
The study was published in The Lancet Public Health.
Disparities in breastfeeding
“There hasn’t been a lot of research on breastfeeding outcomes in people with disabilities,” said Dr. Brown, who noted that the study outcomes were based on the WHO-UNICEF Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative guidelines. “There have been a number of qualitative studies that have suggested that they do experience barriers accessing care related to breastfeeding and different challenges related to breastfeeding. But as far as quantitative outcomes, there has only been a handful of studies.”
To examine these outcomes, the investigators analyzed health administrative data from Ontario. They included in their analysis all birthing parents aged 15-49 years who had a single live birth between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018. Patients with a physical disability, sensory disability, intellectual or developmental disability, or two or more disabilities were identified via diagnostic algorithms and were compared with individuals without disabilities with respect to the opportunity to initiate breastfeeding, to engage in in-hospital breastfeeding, to engage in exclusive breastfeeding at hospital discharge, to have skin-to-skin contact, and to be provided with breastfeeding assistance.
The investigators considered a physical disability to encompass conditions such as congenital anomalies, musculoskeletal disorders, neurologic disorders, or permanent injuries. They defined sensory disability as hearing loss or vision loss. Intellectual or developmental disability was defined as having autism spectrum disorder, chromosomal anomaly, fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, or other intellectual disability. Patients with multiple disabilities had two or more of these conditions.
The study population included 634,111 birthing parents, of whom 54,476 (8.6%) had a physical disability, 19,227 (3.0%) had a sensory disability, 1,048 (0.2%) had an intellectual or developmental disability, 4,050 (0.6%) had multiple disabilities, and 555,310 (87.6%) had no disability.
The investigators found that patients with intellectual or developmental disabilities were less likely than were those without a disability to have an opportunity to initiate breastfeeding (adjusted relative risk [aRR], 0.82), to engage in any in-hospital breastfeeding (aRR, 0.85), to be breastfeeding exclusively at hospital discharge (aRR, 0.73), to have skin-to-skin contact (aRR, 0.90), and to receive breastfeeding assistance (aRR, 0.85) compared with patients without a disability.
They also found that individuals with multiple disabilities were less likely to have an opportunity to initiate breastfeeding (aRR, 0.93), to engage in any in-hospital breastfeeding (aRR, 0.93), to be exclusively breastfeeding at hospital discharge (aRR, 0.90), to have skin-to-skin contact (aRR, 0.93), and to receive breastfeeding assistance (aRR, 0.95) compared with patients without a disability.
An understudied population
Commenting on the study, Lori Feldman-Winter, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics at Rowan University in Camden, N.J., said that one of its strengths is that it included patients who may be excluded from studies of breastfeeding practices. The finding of few differences in breastfeeding practices and supports for people with physical and sensory disabilities, compared with those without disabilities, was positive, she added.
“This is an understudied population, and it is important to call out that there may be practices related to breastfeeding care that suffer, due to implicit bias regarding persons with intellectual and multiple disabilities,” said Dr. Feldman-Winter. “The good news is that other disabilities did not show the same disparities. This study also shows how important it is to measure potential gaps in care across multiple sociodemographic and other variables, such as disabilities, to ensure equitable and inclusive care.”
Health care professionals need to be aware of disparities in breastfeeding care, she added. They need to be open to exploring potential biases when it comes to providing equitable care.
R. Douglas Wilson, MD, president of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada and professor emeritus of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Calgary in Alberta, noted that the size of the cohort represents a strength of the study and that the findings suggest the possible need for closer follow-up of a new mother who is breastfeeding and who has an intellectual disability or multiple disabilities.
“You might keep that patient in hospital for an extra day, and then the home care nurse may look in on them more frequently than they would for someone who does not need that extra oversight,” said Dr. Wilson. When their patients are pregnant, obstetricians and gynecologists can find out whether their patients intend to breastfeed and put them in touch with nurses or lactation consultants to assist them, he added.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canada Research Chairs Program. Dr. Brown, Dr. Feldman-Winter, and Dr. Wilson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET PUBLIC HEALTH
Black Veterans Disproportionately Denied VA Benefits
Black veterans are less likely to have their benefits claims processed and paid than are their White peers because of systemic problems within the US Department of Veterans Affairs, according to a lawsuit filed against the agency.
“A Black veteran who served honorably can walk into the VA, file a disability claim, and be at a significantly higher likelihood of having that claim denied,” said Adam Henderson, a student working with the Yale Law School Veterans Legal Services Clinic, one of several groups connected to the lawsuit.
“The VA has denied countless meritorious applications of Black veterans and thus deprived them and their families of the support that they are entitled to.”
The suit, filed in federal court by the clinic on behalf of Vietnam War veteran Conley Monk Jr., asks for “redress for the harms caused by the failure of VA staff and leaders to administer these benefits programs in a manner free from racial discrimination against Black veterans.”
In a press conference announcing the lawsuit, the effort received backing from Sen. Richard Blumenthal (D, Connecticut) who called it an “unacceptable” situation.
“Black veterans are denied benefits at a very significantly disproportionate rate,” he said. “We know the results. We want to know the reason why.”
The suit stems from an analysis of VA claims records released by the department following an earlier legal action. Between 2001 and 2020, the average denial rate for disability claims filed for Black veterans was 29.5%, significantly above the 24.2% for White veterans.
Attorneys allege the problems date back even further and that VA officials should have known about the racial disparities in the system from previous complaints.
“The negligence of VA leadership, and their failure to train, supervise, monitor and instruct agency officials to take steps to identify and correct racial disparities, led to systematic benefits obstruction for Black veterans,” the suit states.
Monk is a Black disabled Marine Corps veteran who previously sued the military to overturn his less-than-honorable military discharge due to complications from undiagnosed posttraumatic stress disorder.
He was subsequently granted access to a host of veterans benefits but not to retroactive payouts for claims he was denied in the 1970s.
“They didn’t fully compensate me or my family,” he said. “I wasn’t able to give my kids my educational benefits. We should have been receiving checks while they were growing up.”
Along with potential past benefits for Monk, individuals involved with the lawsuit said the move could force the VA to reassess thousands of other unfairly dismissed cases. “For decades [the US government] has allowed racially discriminatory practices to obstruct Black veterans from easily accessing veterans housing, education, and health care benefits with wide-reaching economic consequences for Black veterans and their families,” said Richard Brookshire, executive director of the Black Veterans Project.
“This lawsuit reckons with the shameful history of racism by the Department of Veteran Affairs and seeks to redress long-standing improprieties reverberating across generations of Black military service.”
In a statement, VA press secretary Terrence Hayes did not directly respond to the lawsuit but noted that “throughout history, there have been unacceptable disparities in both VA benefits decisions and military discharge status due to racism, which have wrongly left Black veterans without access to VA care and benefits.”
“We are actively working to right these wrongs, and we will stop at nothing to ensure that all Black veterans get the VA services they have earned and deserve,” he said. “We are currently studying racial disparities in benefits claims decisions, and we will publish the results of that study as soon as they are available.”
Hayes said the department has already begun targeted outreach to Black veterans to help them with claims and is “taking steps to ensure that our claims process combats institutional racism, rather than perpetuating it.”
Black veterans are less likely to have their benefits claims processed and paid than are their White peers because of systemic problems within the US Department of Veterans Affairs, according to a lawsuit filed against the agency.
“A Black veteran who served honorably can walk into the VA, file a disability claim, and be at a significantly higher likelihood of having that claim denied,” said Adam Henderson, a student working with the Yale Law School Veterans Legal Services Clinic, one of several groups connected to the lawsuit.
“The VA has denied countless meritorious applications of Black veterans and thus deprived them and their families of the support that they are entitled to.”
The suit, filed in federal court by the clinic on behalf of Vietnam War veteran Conley Monk Jr., asks for “redress for the harms caused by the failure of VA staff and leaders to administer these benefits programs in a manner free from racial discrimination against Black veterans.”
In a press conference announcing the lawsuit, the effort received backing from Sen. Richard Blumenthal (D, Connecticut) who called it an “unacceptable” situation.
“Black veterans are denied benefits at a very significantly disproportionate rate,” he said. “We know the results. We want to know the reason why.”
The suit stems from an analysis of VA claims records released by the department following an earlier legal action. Between 2001 and 2020, the average denial rate for disability claims filed for Black veterans was 29.5%, significantly above the 24.2% for White veterans.
Attorneys allege the problems date back even further and that VA officials should have known about the racial disparities in the system from previous complaints.
“The negligence of VA leadership, and their failure to train, supervise, monitor and instruct agency officials to take steps to identify and correct racial disparities, led to systematic benefits obstruction for Black veterans,” the suit states.
Monk is a Black disabled Marine Corps veteran who previously sued the military to overturn his less-than-honorable military discharge due to complications from undiagnosed posttraumatic stress disorder.
He was subsequently granted access to a host of veterans benefits but not to retroactive payouts for claims he was denied in the 1970s.
“They didn’t fully compensate me or my family,” he said. “I wasn’t able to give my kids my educational benefits. We should have been receiving checks while they were growing up.”
Along with potential past benefits for Monk, individuals involved with the lawsuit said the move could force the VA to reassess thousands of other unfairly dismissed cases. “For decades [the US government] has allowed racially discriminatory practices to obstruct Black veterans from easily accessing veterans housing, education, and health care benefits with wide-reaching economic consequences for Black veterans and their families,” said Richard Brookshire, executive director of the Black Veterans Project.
“This lawsuit reckons with the shameful history of racism by the Department of Veteran Affairs and seeks to redress long-standing improprieties reverberating across generations of Black military service.”
In a statement, VA press secretary Terrence Hayes did not directly respond to the lawsuit but noted that “throughout history, there have been unacceptable disparities in both VA benefits decisions and military discharge status due to racism, which have wrongly left Black veterans without access to VA care and benefits.”
“We are actively working to right these wrongs, and we will stop at nothing to ensure that all Black veterans get the VA services they have earned and deserve,” he said. “We are currently studying racial disparities in benefits claims decisions, and we will publish the results of that study as soon as they are available.”
Hayes said the department has already begun targeted outreach to Black veterans to help them with claims and is “taking steps to ensure that our claims process combats institutional racism, rather than perpetuating it.”
Black veterans are less likely to have their benefits claims processed and paid than are their White peers because of systemic problems within the US Department of Veterans Affairs, according to a lawsuit filed against the agency.
“A Black veteran who served honorably can walk into the VA, file a disability claim, and be at a significantly higher likelihood of having that claim denied,” said Adam Henderson, a student working with the Yale Law School Veterans Legal Services Clinic, one of several groups connected to the lawsuit.
“The VA has denied countless meritorious applications of Black veterans and thus deprived them and their families of the support that they are entitled to.”
The suit, filed in federal court by the clinic on behalf of Vietnam War veteran Conley Monk Jr., asks for “redress for the harms caused by the failure of VA staff and leaders to administer these benefits programs in a manner free from racial discrimination against Black veterans.”
In a press conference announcing the lawsuit, the effort received backing from Sen. Richard Blumenthal (D, Connecticut) who called it an “unacceptable” situation.
“Black veterans are denied benefits at a very significantly disproportionate rate,” he said. “We know the results. We want to know the reason why.”
The suit stems from an analysis of VA claims records released by the department following an earlier legal action. Between 2001 and 2020, the average denial rate for disability claims filed for Black veterans was 29.5%, significantly above the 24.2% for White veterans.
Attorneys allege the problems date back even further and that VA officials should have known about the racial disparities in the system from previous complaints.
“The negligence of VA leadership, and their failure to train, supervise, monitor and instruct agency officials to take steps to identify and correct racial disparities, led to systematic benefits obstruction for Black veterans,” the suit states.
Monk is a Black disabled Marine Corps veteran who previously sued the military to overturn his less-than-honorable military discharge due to complications from undiagnosed posttraumatic stress disorder.
He was subsequently granted access to a host of veterans benefits but not to retroactive payouts for claims he was denied in the 1970s.
“They didn’t fully compensate me or my family,” he said. “I wasn’t able to give my kids my educational benefits. We should have been receiving checks while they were growing up.”
Along with potential past benefits for Monk, individuals involved with the lawsuit said the move could force the VA to reassess thousands of other unfairly dismissed cases. “For decades [the US government] has allowed racially discriminatory practices to obstruct Black veterans from easily accessing veterans housing, education, and health care benefits with wide-reaching economic consequences for Black veterans and their families,” said Richard Brookshire, executive director of the Black Veterans Project.
“This lawsuit reckons with the shameful history of racism by the Department of Veteran Affairs and seeks to redress long-standing improprieties reverberating across generations of Black military service.”
In a statement, VA press secretary Terrence Hayes did not directly respond to the lawsuit but noted that “throughout history, there have been unacceptable disparities in both VA benefits decisions and military discharge status due to racism, which have wrongly left Black veterans without access to VA care and benefits.”
“We are actively working to right these wrongs, and we will stop at nothing to ensure that all Black veterans get the VA services they have earned and deserve,” he said. “We are currently studying racial disparities in benefits claims decisions, and we will publish the results of that study as soon as they are available.”
Hayes said the department has already begun targeted outreach to Black veterans to help them with claims and is “taking steps to ensure that our claims process combats institutional racism, rather than perpetuating it.”
By the numbers: Cardiology slow to add women, IMGs join more quickly
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.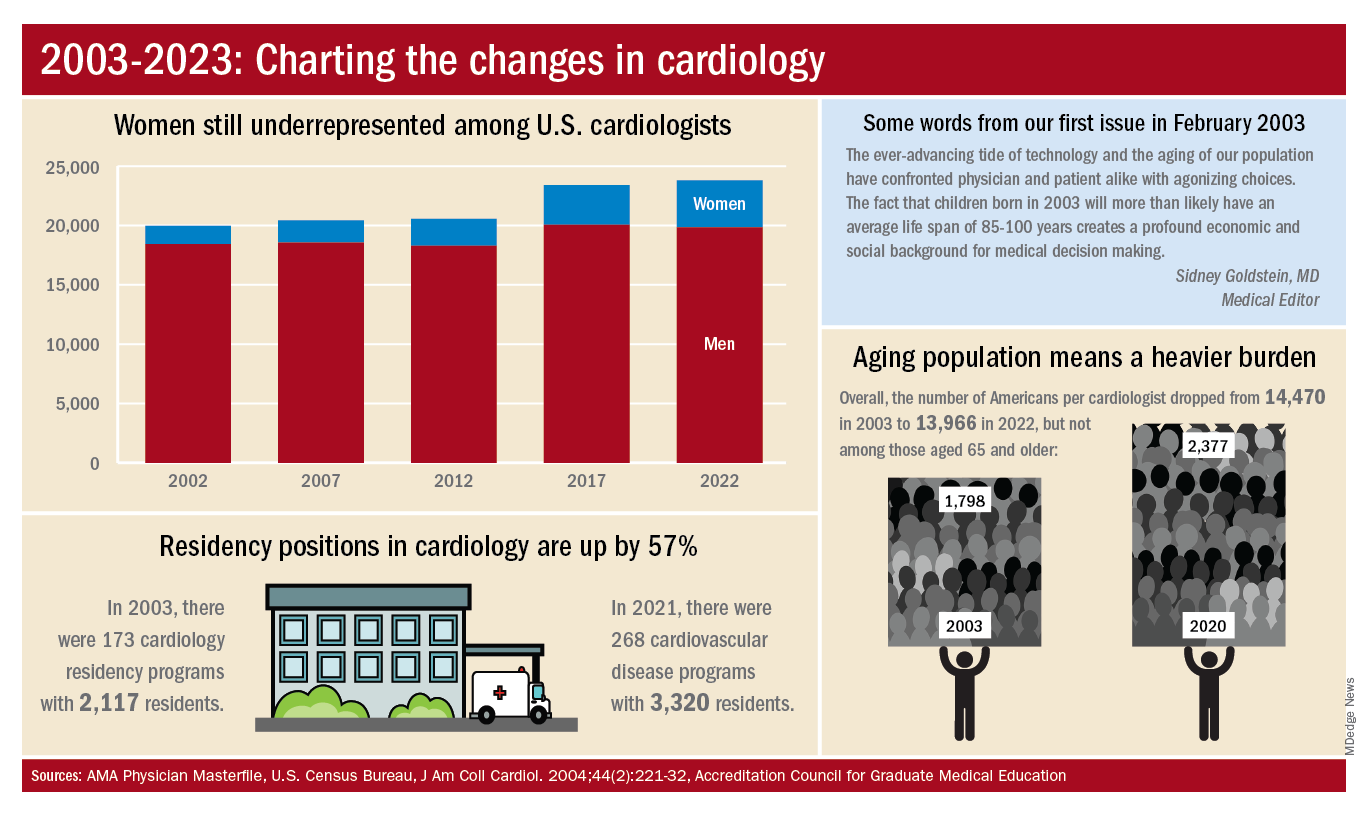
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Hyperpigmented Papules on the Tongue of a Child
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
A 9-year-old Black boy presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of dark spots on the tongue. The family first noted these spots 5 months prior and reported that they remained stable during that time. The patient’s medical history was notable for autism spectrum disorder and multiple food allergies. His family history was negative for similar oral pigmentation or other pigmentary anomalies. A review of systems was positive only for selective eating and rare nosebleeds. Physical examination revealed numerous dark brown, pinpoint papules across the dorsal aspect of the tongue. No hyperpigmentation of the buccal mucosae, lips, palms, or soles was identified. Several light brown streaks were present on the fingernails and toenails, consistent with longitudinal melanonychia. A prior complete blood cell count was within reference range.
Alopecia Areata in Skin of Color Patients: New Considerations Sparked by the Approval of Baricitinib
With the introduction of the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved medication for alopecia areata (AA)—the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, baricitinib—there is an important focus on this disease in the literature and for practicing dermatologists. Known by all as an autoimmune genetic disease that causes relapsing and remitting nonscarring hair loss, AA is a condition where the psychological burden has been less widely recognized. Patients with AA have reported lower health-related quality of life scores compared to patients with other skin conditions, including psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. In addition, a lesser amount of scalp coverage is negatively correlated to health-related quality of life scores.1 Patients with AA also have a 39% lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.2 The treatment of AA has been a hodgepodge of topical, intralesional, and systemic agents, all with indirect immunosuppressive or anagen prolongation effects. Now that there is an approved therapy for AA with more treatments likely to be approved in the near future, there must be a focus on real-world outcomes. With the dawn of a new era in the treatment of AA as well as new information showcasing an altered prevalence of AA in skin of color, highlighting disparities among this population may help ease challenges dermatologic providers will face.
Efficacy of Baricitinib in Different Races and Ethnicities
How will patients of different races and ethnicities respond to this new treatment, and how will their emotional health be affected? The 2 phase 3 pivotal trials showing efficacy of baricitinib in AA included Black and Latino patients but not in a way that is representative of the US population.3 Until recently, the most commonly used prevalence of AA in the United States was from the NHANES I study completed between 1971 and 1974, which was between 0.1% and 0.2%4 with minimal focus on race and ethnicity. Recent studies suggest that there may be increased prevalence of this condition in Black patients in the United States. These new findings raise concern around access to care and treatment and the need to tailor psychosocial interventions for populations that may not currently have these supports.
A large cross-sectional study published in 2020 demonstrated that these data remained similar, with a lifetime prevalence of 0.21%.5 Of the 45,016 participants—representative of the US population based on the 2015 US Census—the average age of AA patients was 41.2 years, with 61.3% being White and not of Hispanic origin.5 In recent years, other studies have challenged the narrative that AA predominantly affects White patients.6-8 A different cross-sectional study utilizing National Alopecia Areata Registry data from 2002 to 2016 suggested that Black patients have greater odds of developing AA.6 In this study of 2645 cases of AA, the odds ratios of developing the condition were 1.36 for Blacks, 0.53 for Asians, and 0.83 for Hispanics compared with the referent White population. These results were consistent through the varying subtypes of AA.6 In a reply to these findings, Gonzalez and Fleischer7 analyzed data from the 2007 to 2016 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database with a focus on racial and ethnic prevalence of AA. This study concluded that Latino and non-White individuals had an increased likelihood of clinician visits for AA compared with White individuals.7
More evidence of the Black predominance of AA was demonstrated in a study published in 2018. In this large-scale study, 63,960 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and 88,368 women from the Nurses’ Health Study II (NHSII) were included to examine prevalence of disease among these US women.8 Analysis showed increased odds of AA based on self-reported race in Black and Hispanic women. Lifetime incidence of AA was greater in Black women, with 2.63 and 5.23 in NHS and NHSII, respectively. It was hypothesized that hairstyling practices in Black and Hispanic women may cause AA to be more noticeable,8 which may drive patients to seek medical evaluation.
Feaster and McMichael9 published information on the epidemiology of AA in a busy hair loss clinic. This retrospective single-institution study of 265 pediatric and adult Black patients with AA seen over a 5-year period showed that patients aged 18 to 34 years were most likely to present for care, which accounted for 35.8% of the study population, followed by patients aged 10 to 17 years, which accounted for 15.1%. This study also found that females were the larger segment of AA patients, with an increased distribution of disease in young patients. Most of these patients (68.2%) had patchy hair loss, and the ophiasis pattern was seen in 15.1%.9 Although the pathogenesis of AA is linked to autoimmunity,10 the leading cause for these epidemiologic findings of increased prevalence in Black patients is still uncertain.
Baricitinib for AA
In June 2022, the FDA announced the first biologic drug approved for the treatment of AA—baricitinib. Baricitinib is an oral, selective, reversible inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2.3 The phase 3 trials for baricitinib—BRAVE-AA1 (N=654) and BRAVE-AA2 (N=546)—were conducted between March 2019 and May 2020. In these double-blind, parallel-group, randomized, placebo-controlled trials, 33% of the patient population receiving baricitinib accomplished 80% or more scalp coverage at 36 weeks. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score also decreased to 20 or less in 36 weeks. The BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials consisted of a total of 1200 patients, with only 98 identifying as Black. Of these 98 patients, 33 were randomly selected to receive placebo.3 With studies now suggesting that Black individuals have greater odds of AA compared with White individuals6 and Black patients being more likely to seek medical care for AA,7 the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 study population did not allow for significant comparative data for Black patients. These studies did not document Latino patient involvement.3 Future studies in AA must recruit a diversified group of study participants to better reflect the patients with an increased likelihood of presenting with AA.
Other Treatments on the Horizon
Baricitinib likely will remain alone in its class for only a short time. Phase 3 trials have been completed for ritlecitinib, brepocitinib, and deuruxolitinib for AA. Ritlecitinib, an irreversible inhibitor of JAK3 and the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) kinase family, has met all end points in a phase 2b/3 study.11 Brepocitinib is an oral tyrosine kinase 2/JAK1 inhibitor,12 and deuruxolitinib is an investigational JAK1/2 inhibitor for AA.13
Insurance Coverage Considerations and Health Care Disparities
Prior authorizations have been the initial step for many drugs in varying fields of medical practice. A study completed in 2016 suggested that insurance coverage for biologics used in the treatment of psoriasis was becoming increasingly difficult.14 Prior authorization requirement rates increased from 16% of patients in 2009 to 75% in 2014. The decision time also increased from 3.7 days in 2009 to 6.7 days in 2014. The most common reason for delay in decisions and denials was due to step therapy.14 Insurance companies wanted many patients to try less expensive treatment options prior to “stepping up” to more expensive treatments. Although this may be the case in the treatment of psoriasis, the role of step therapy is unclear for patients with AA because there is only 1 FDA-approved medication. This sets out an ambiguous future for our patients with AA and approval for baricitinib.
The time required for the correspondence between insurance companies, clinic staff, and patients for drug approval may delay treatments, and not all providers have enough staff to coordinate and perform this work. For Black patients, who may present more frequently and with more severe disease,7 this could lead to a health care disparity due to the likelihood of the increased need for biologic treatment. Because Black patients have an increased likelihood of being uninsured or underinsured,15 this further decreases the chances of the most severe AA patients receiving the most helpful medication for their condition.
Many pharmaceutical companies have drug cost assistance programs that aim to provide support covering expensive medications for patients unable to afford them. Although this is a good first step, treatment with any JAK inhibitor potentially can be lifelong. Regarding the social determinants of health, it is known that access to medications does not solely depend on cost. Transportation and access to qualified health professionals are among the issues that create barriers to health care. Instilling long-term practices to ensure equal access to JAK inhibitors and treatment of AA may be the cornerstone to treating AA with equity. Whether we require pharmaceutical companies to make sure all patients have equal access to medications or provide community resources to hairstylists and federally qualified health centers, raising awareness and advocating for and creating attainable access to treatment modalities is imperative to providing well-rounded care to a diverse population.
- Liu LY, King BA, Craiglow BG. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among patients with alopecia areata (AA): a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:806-812.e3.
- Colón EA, Popkin MK, Callies AL, et al. Lifetime prevalence of psychiatric disorders in patients with alopecia areata. Compr Psychiatry. 1991;32:245-251.
- King B, Ohyama M, Kwon O, et al. Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib for alopecia areata. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1687-1699. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110343
- Safavi K. Prevalence of alopecia areata in the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:702. doi:10.1001/archderm.1992.01680150136027
- Benigno M, Anastassopoulos KP, Mostaghimi A, et al. A large cross-sectional survey study of the prevalence of alopecia areata in the United States. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:259-266.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Gonzalez T, Fleischer AB Jr. Reply to: racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States [published online March 3, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E295-E296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.063
- Thompson JM, Park MK, Qureshi AA, et al. Race and alopecia areata amongst US women. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2018;19:S47-S50.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123. doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.01.033
- Barahmani N, de Andrade M, Slusser JP, et al. Human leukocyte antigen class II alleles are associated with risk of alopecia areata. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:240-243.
- Xu H, Jesson MI, Seneviratne UI, et al. PF-06651600, a dual JAK3/TEC family kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14:1235-1242.
- Fensome A, Ambler CM, Arnold E, et al. Dual inhibition of TYK2and JAK1 for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: discovery of((S)-2,2-difluorocyclopropyl)((1 R,5 S)-3-(2-((1-methyl-1 H-pyrazol-4-yl) amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-3,8-diazabicyclo3.2.1octan-8-yl)methanone (PF-06700841). J Med Chem. 2018;61:8597-8612.
- King B, Mesinkovska N, Mirmirani P, et al. Phase 2 randomized, dose-ranging trial of CTP-543, a selective Janus kinase inhibitor, in moderate-to-severe alopecia areata [published online March 29, 2022]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:306-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.03.045
- Abdelnabi M, Patel A, Rengifo-Pardo M, et al. Insurance coverage of biologics for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a retrospective, observational 5-year chart review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:421-424. doi:10.1007/s40257-016-0194-4
- Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Health insurance coverage and access to care among black Americans: recent trends and key challenges (Issue Brief No. HP-2022-07). February 22, 2022. Accessed December 21, 2022. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/08307d793263d5069fdd6504385e22f8/black-americans-coverages-access-ib.pdf
With the introduction of the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved medication for alopecia areata (AA)—the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, baricitinib—there is an important focus on this disease in the literature and for practicing dermatologists. Known by all as an autoimmune genetic disease that causes relapsing and remitting nonscarring hair loss, AA is a condition where the psychological burden has been less widely recognized. Patients with AA have reported lower health-related quality of life scores compared to patients with other skin conditions, including psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. In addition, a lesser amount of scalp coverage is negatively correlated to health-related quality of life scores.1 Patients with AA also have a 39% lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.2 The treatment of AA has been a hodgepodge of topical, intralesional, and systemic agents, all with indirect immunosuppressive or anagen prolongation effects. Now that there is an approved therapy for AA with more treatments likely to be approved in the near future, there must be a focus on real-world outcomes. With the dawn of a new era in the treatment of AA as well as new information showcasing an altered prevalence of AA in skin of color, highlighting disparities among this population may help ease challenges dermatologic providers will face.
Efficacy of Baricitinib in Different Races and Ethnicities
How will patients of different races and ethnicities respond to this new treatment, and how will their emotional health be affected? The 2 phase 3 pivotal trials showing efficacy of baricitinib in AA included Black and Latino patients but not in a way that is representative of the US population.3 Until recently, the most commonly used prevalence of AA in the United States was from the NHANES I study completed between 1971 and 1974, which was between 0.1% and 0.2%4 with minimal focus on race and ethnicity. Recent studies suggest that there may be increased prevalence of this condition in Black patients in the United States. These new findings raise concern around access to care and treatment and the need to tailor psychosocial interventions for populations that may not currently have these supports.
A large cross-sectional study published in 2020 demonstrated that these data remained similar, with a lifetime prevalence of 0.21%.5 Of the 45,016 participants—representative of the US population based on the 2015 US Census—the average age of AA patients was 41.2 years, with 61.3% being White and not of Hispanic origin.5 In recent years, other studies have challenged the narrative that AA predominantly affects White patients.6-8 A different cross-sectional study utilizing National Alopecia Areata Registry data from 2002 to 2016 suggested that Black patients have greater odds of developing AA.6 In this study of 2645 cases of AA, the odds ratios of developing the condition were 1.36 for Blacks, 0.53 for Asians, and 0.83 for Hispanics compared with the referent White population. These results were consistent through the varying subtypes of AA.6 In a reply to these findings, Gonzalez and Fleischer7 analyzed data from the 2007 to 2016 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database with a focus on racial and ethnic prevalence of AA. This study concluded that Latino and non-White individuals had an increased likelihood of clinician visits for AA compared with White individuals.7
More evidence of the Black predominance of AA was demonstrated in a study published in 2018. In this large-scale study, 63,960 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and 88,368 women from the Nurses’ Health Study II (NHSII) were included to examine prevalence of disease among these US women.8 Analysis showed increased odds of AA based on self-reported race in Black and Hispanic women. Lifetime incidence of AA was greater in Black women, with 2.63 and 5.23 in NHS and NHSII, respectively. It was hypothesized that hairstyling practices in Black and Hispanic women may cause AA to be more noticeable,8 which may drive patients to seek medical evaluation.
Feaster and McMichael9 published information on the epidemiology of AA in a busy hair loss clinic. This retrospective single-institution study of 265 pediatric and adult Black patients with AA seen over a 5-year period showed that patients aged 18 to 34 years were most likely to present for care, which accounted for 35.8% of the study population, followed by patients aged 10 to 17 years, which accounted for 15.1%. This study also found that females were the larger segment of AA patients, with an increased distribution of disease in young patients. Most of these patients (68.2%) had patchy hair loss, and the ophiasis pattern was seen in 15.1%.9 Although the pathogenesis of AA is linked to autoimmunity,10 the leading cause for these epidemiologic findings of increased prevalence in Black patients is still uncertain.
Baricitinib for AA
In June 2022, the FDA announced the first biologic drug approved for the treatment of AA—baricitinib. Baricitinib is an oral, selective, reversible inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2.3 The phase 3 trials for baricitinib—BRAVE-AA1 (N=654) and BRAVE-AA2 (N=546)—were conducted between March 2019 and May 2020. In these double-blind, parallel-group, randomized, placebo-controlled trials, 33% of the patient population receiving baricitinib accomplished 80% or more scalp coverage at 36 weeks. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score also decreased to 20 or less in 36 weeks. The BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials consisted of a total of 1200 patients, with only 98 identifying as Black. Of these 98 patients, 33 were randomly selected to receive placebo.3 With studies now suggesting that Black individuals have greater odds of AA compared with White individuals6 and Black patients being more likely to seek medical care for AA,7 the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 study population did not allow for significant comparative data for Black patients. These studies did not document Latino patient involvement.3 Future studies in AA must recruit a diversified group of study participants to better reflect the patients with an increased likelihood of presenting with AA.
Other Treatments on the Horizon
Baricitinib likely will remain alone in its class for only a short time. Phase 3 trials have been completed for ritlecitinib, brepocitinib, and deuruxolitinib for AA. Ritlecitinib, an irreversible inhibitor of JAK3 and the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) kinase family, has met all end points in a phase 2b/3 study.11 Brepocitinib is an oral tyrosine kinase 2/JAK1 inhibitor,12 and deuruxolitinib is an investigational JAK1/2 inhibitor for AA.13
Insurance Coverage Considerations and Health Care Disparities
Prior authorizations have been the initial step for many drugs in varying fields of medical practice. A study completed in 2016 suggested that insurance coverage for biologics used in the treatment of psoriasis was becoming increasingly difficult.14 Prior authorization requirement rates increased from 16% of patients in 2009 to 75% in 2014. The decision time also increased from 3.7 days in 2009 to 6.7 days in 2014. The most common reason for delay in decisions and denials was due to step therapy.14 Insurance companies wanted many patients to try less expensive treatment options prior to “stepping up” to more expensive treatments. Although this may be the case in the treatment of psoriasis, the role of step therapy is unclear for patients with AA because there is only 1 FDA-approved medication. This sets out an ambiguous future for our patients with AA and approval for baricitinib.
The time required for the correspondence between insurance companies, clinic staff, and patients for drug approval may delay treatments, and not all providers have enough staff to coordinate and perform this work. For Black patients, who may present more frequently and with more severe disease,7 this could lead to a health care disparity due to the likelihood of the increased need for biologic treatment. Because Black patients have an increased likelihood of being uninsured or underinsured,15 this further decreases the chances of the most severe AA patients receiving the most helpful medication for their condition.
Many pharmaceutical companies have drug cost assistance programs that aim to provide support covering expensive medications for patients unable to afford them. Although this is a good first step, treatment with any JAK inhibitor potentially can be lifelong. Regarding the social determinants of health, it is known that access to medications does not solely depend on cost. Transportation and access to qualified health professionals are among the issues that create barriers to health care. Instilling long-term practices to ensure equal access to JAK inhibitors and treatment of AA may be the cornerstone to treating AA with equity. Whether we require pharmaceutical companies to make sure all patients have equal access to medications or provide community resources to hairstylists and federally qualified health centers, raising awareness and advocating for and creating attainable access to treatment modalities is imperative to providing well-rounded care to a diverse population.
With the introduction of the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved medication for alopecia areata (AA)—the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, baricitinib—there is an important focus on this disease in the literature and for practicing dermatologists. Known by all as an autoimmune genetic disease that causes relapsing and remitting nonscarring hair loss, AA is a condition where the psychological burden has been less widely recognized. Patients with AA have reported lower health-related quality of life scores compared to patients with other skin conditions, including psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. In addition, a lesser amount of scalp coverage is negatively correlated to health-related quality of life scores.1 Patients with AA also have a 39% lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.2 The treatment of AA has been a hodgepodge of topical, intralesional, and systemic agents, all with indirect immunosuppressive or anagen prolongation effects. Now that there is an approved therapy for AA with more treatments likely to be approved in the near future, there must be a focus on real-world outcomes. With the dawn of a new era in the treatment of AA as well as new information showcasing an altered prevalence of AA in skin of color, highlighting disparities among this population may help ease challenges dermatologic providers will face.
Efficacy of Baricitinib in Different Races and Ethnicities
How will patients of different races and ethnicities respond to this new treatment, and how will their emotional health be affected? The 2 phase 3 pivotal trials showing efficacy of baricitinib in AA included Black and Latino patients but not in a way that is representative of the US population.3 Until recently, the most commonly used prevalence of AA in the United States was from the NHANES I study completed between 1971 and 1974, which was between 0.1% and 0.2%4 with minimal focus on race and ethnicity. Recent studies suggest that there may be increased prevalence of this condition in Black patients in the United States. These new findings raise concern around access to care and treatment and the need to tailor psychosocial interventions for populations that may not currently have these supports.
A large cross-sectional study published in 2020 demonstrated that these data remained similar, with a lifetime prevalence of 0.21%.5 Of the 45,016 participants—representative of the US population based on the 2015 US Census—the average age of AA patients was 41.2 years, with 61.3% being White and not of Hispanic origin.5 In recent years, other studies have challenged the narrative that AA predominantly affects White patients.6-8 A different cross-sectional study utilizing National Alopecia Areata Registry data from 2002 to 2016 suggested that Black patients have greater odds of developing AA.6 In this study of 2645 cases of AA, the odds ratios of developing the condition were 1.36 for Blacks, 0.53 for Asians, and 0.83 for Hispanics compared with the referent White population. These results were consistent through the varying subtypes of AA.6 In a reply to these findings, Gonzalez and Fleischer7 analyzed data from the 2007 to 2016 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database with a focus on racial and ethnic prevalence of AA. This study concluded that Latino and non-White individuals had an increased likelihood of clinician visits for AA compared with White individuals.7
More evidence of the Black predominance of AA was demonstrated in a study published in 2018. In this large-scale study, 63,960 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and 88,368 women from the Nurses’ Health Study II (NHSII) were included to examine prevalence of disease among these US women.8 Analysis showed increased odds of AA based on self-reported race in Black and Hispanic women. Lifetime incidence of AA was greater in Black women, with 2.63 and 5.23 in NHS and NHSII, respectively. It was hypothesized that hairstyling practices in Black and Hispanic women may cause AA to be more noticeable,8 which may drive patients to seek medical evaluation.
Feaster and McMichael9 published information on the epidemiology of AA in a busy hair loss clinic. This retrospective single-institution study of 265 pediatric and adult Black patients with AA seen over a 5-year period showed that patients aged 18 to 34 years were most likely to present for care, which accounted for 35.8% of the study population, followed by patients aged 10 to 17 years, which accounted for 15.1%. This study also found that females were the larger segment of AA patients, with an increased distribution of disease in young patients. Most of these patients (68.2%) had patchy hair loss, and the ophiasis pattern was seen in 15.1%.9 Although the pathogenesis of AA is linked to autoimmunity,10 the leading cause for these epidemiologic findings of increased prevalence in Black patients is still uncertain.
Baricitinib for AA
In June 2022, the FDA announced the first biologic drug approved for the treatment of AA—baricitinib. Baricitinib is an oral, selective, reversible inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2.3 The phase 3 trials for baricitinib—BRAVE-AA1 (N=654) and BRAVE-AA2 (N=546)—were conducted between March 2019 and May 2020. In these double-blind, parallel-group, randomized, placebo-controlled trials, 33% of the patient population receiving baricitinib accomplished 80% or more scalp coverage at 36 weeks. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score also decreased to 20 or less in 36 weeks. The BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials consisted of a total of 1200 patients, with only 98 identifying as Black. Of these 98 patients, 33 were randomly selected to receive placebo.3 With studies now suggesting that Black individuals have greater odds of AA compared with White individuals6 and Black patients being more likely to seek medical care for AA,7 the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 study population did not allow for significant comparative data for Black patients. These studies did not document Latino patient involvement.3 Future studies in AA must recruit a diversified group of study participants to better reflect the patients with an increased likelihood of presenting with AA.
Other Treatments on the Horizon
Baricitinib likely will remain alone in its class for only a short time. Phase 3 trials have been completed for ritlecitinib, brepocitinib, and deuruxolitinib for AA. Ritlecitinib, an irreversible inhibitor of JAK3 and the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) kinase family, has met all end points in a phase 2b/3 study.11 Brepocitinib is an oral tyrosine kinase 2/JAK1 inhibitor,12 and deuruxolitinib is an investigational JAK1/2 inhibitor for AA.13
Insurance Coverage Considerations and Health Care Disparities
Prior authorizations have been the initial step for many drugs in varying fields of medical practice. A study completed in 2016 suggested that insurance coverage for biologics used in the treatment of psoriasis was becoming increasingly difficult.14 Prior authorization requirement rates increased from 16% of patients in 2009 to 75% in 2014. The decision time also increased from 3.7 days in 2009 to 6.7 days in 2014. The most common reason for delay in decisions and denials was due to step therapy.14 Insurance companies wanted many patients to try less expensive treatment options prior to “stepping up” to more expensive treatments. Although this may be the case in the treatment of psoriasis, the role of step therapy is unclear for patients with AA because there is only 1 FDA-approved medication. This sets out an ambiguous future for our patients with AA and approval for baricitinib.
The time required for the correspondence between insurance companies, clinic staff, and patients for drug approval may delay treatments, and not all providers have enough staff to coordinate and perform this work. For Black patients, who may present more frequently and with more severe disease,7 this could lead to a health care disparity due to the likelihood of the increased need for biologic treatment. Because Black patients have an increased likelihood of being uninsured or underinsured,15 this further decreases the chances of the most severe AA patients receiving the most helpful medication for their condition.
Many pharmaceutical companies have drug cost assistance programs that aim to provide support covering expensive medications for patients unable to afford them. Although this is a good first step, treatment with any JAK inhibitor potentially can be lifelong. Regarding the social determinants of health, it is known that access to medications does not solely depend on cost. Transportation and access to qualified health professionals are among the issues that create barriers to health care. Instilling long-term practices to ensure equal access to JAK inhibitors and treatment of AA may be the cornerstone to treating AA with equity. Whether we require pharmaceutical companies to make sure all patients have equal access to medications or provide community resources to hairstylists and federally qualified health centers, raising awareness and advocating for and creating attainable access to treatment modalities is imperative to providing well-rounded care to a diverse population.
- Liu LY, King BA, Craiglow BG. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among patients with alopecia areata (AA): a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:806-812.e3.
- Colón EA, Popkin MK, Callies AL, et al. Lifetime prevalence of psychiatric disorders in patients with alopecia areata. Compr Psychiatry. 1991;32:245-251.
- King B, Ohyama M, Kwon O, et al. Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib for alopecia areata. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1687-1699. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110343
- Safavi K. Prevalence of alopecia areata in the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:702. doi:10.1001/archderm.1992.01680150136027
- Benigno M, Anastassopoulos KP, Mostaghimi A, et al. A large cross-sectional survey study of the prevalence of alopecia areata in the United States. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:259-266.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Gonzalez T, Fleischer AB Jr. Reply to: racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States [published online March 3, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E295-E296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.063
- Thompson JM, Park MK, Qureshi AA, et al. Race and alopecia areata amongst US women. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2018;19:S47-S50.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123. doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.01.033
- Barahmani N, de Andrade M, Slusser JP, et al. Human leukocyte antigen class II alleles are associated with risk of alopecia areata. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:240-243.
- Xu H, Jesson MI, Seneviratne UI, et al. PF-06651600, a dual JAK3/TEC family kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14:1235-1242.
- Fensome A, Ambler CM, Arnold E, et al. Dual inhibition of TYK2and JAK1 for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: discovery of((S)-2,2-difluorocyclopropyl)((1 R,5 S)-3-(2-((1-methyl-1 H-pyrazol-4-yl) amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-3,8-diazabicyclo3.2.1octan-8-yl)methanone (PF-06700841). J Med Chem. 2018;61:8597-8612.
- King B, Mesinkovska N, Mirmirani P, et al. Phase 2 randomized, dose-ranging trial of CTP-543, a selective Janus kinase inhibitor, in moderate-to-severe alopecia areata [published online March 29, 2022]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:306-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.03.045
- Abdelnabi M, Patel A, Rengifo-Pardo M, et al. Insurance coverage of biologics for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a retrospective, observational 5-year chart review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:421-424. doi:10.1007/s40257-016-0194-4
- Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Health insurance coverage and access to care among black Americans: recent trends and key challenges (Issue Brief No. HP-2022-07). February 22, 2022. Accessed December 21, 2022. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/08307d793263d5069fdd6504385e22f8/black-americans-coverages-access-ib.pdf
- Liu LY, King BA, Craiglow BG. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among patients with alopecia areata (AA): a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:806-812.e3.
- Colón EA, Popkin MK, Callies AL, et al. Lifetime prevalence of psychiatric disorders in patients with alopecia areata. Compr Psychiatry. 1991;32:245-251.
- King B, Ohyama M, Kwon O, et al. Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib for alopecia areata. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1687-1699. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110343
- Safavi K. Prevalence of alopecia areata in the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:702. doi:10.1001/archderm.1992.01680150136027
- Benigno M, Anastassopoulos KP, Mostaghimi A, et al. A large cross-sectional survey study of the prevalence of alopecia areata in the United States. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:259-266.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Gonzalez T, Fleischer AB Jr. Reply to: racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States [published online March 3, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E295-E296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.063
- Thompson JM, Park MK, Qureshi AA, et al. Race and alopecia areata amongst US women. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2018;19:S47-S50.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123. doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.01.033
- Barahmani N, de Andrade M, Slusser JP, et al. Human leukocyte antigen class II alleles are associated with risk of alopecia areata. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:240-243.
- Xu H, Jesson MI, Seneviratne UI, et al. PF-06651600, a dual JAK3/TEC family kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14:1235-1242.
- Fensome A, Ambler CM, Arnold E, et al. Dual inhibition of TYK2and JAK1 for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: discovery of((S)-2,2-difluorocyclopropyl)((1 R,5 S)-3-(2-((1-methyl-1 H-pyrazol-4-yl) amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-3,8-diazabicyclo3.2.1octan-8-yl)methanone (PF-06700841). J Med Chem. 2018;61:8597-8612.
- King B, Mesinkovska N, Mirmirani P, et al. Phase 2 randomized, dose-ranging trial of CTP-543, a selective Janus kinase inhibitor, in moderate-to-severe alopecia areata [published online March 29, 2022]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:306-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.03.045
- Abdelnabi M, Patel A, Rengifo-Pardo M, et al. Insurance coverage of biologics for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a retrospective, observational 5-year chart review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:421-424. doi:10.1007/s40257-016-0194-4
- Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Health insurance coverage and access to care among black Americans: recent trends and key challenges (Issue Brief No. HP-2022-07). February 22, 2022. Accessed December 21, 2022. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/08307d793263d5069fdd6504385e22f8/black-americans-coverages-access-ib.pdf
Study evaluates features of alopecia areata in Hispanic/Latinx patients
.
Those are among key findings from a retrospective analysis of Hispanic/Latinx patients at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) by Natasha Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, of UCI’s department of dermatology, and her coauthors. The findings were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A recent study examined the epidemiology of alopecia areata (AA) in Black patients, wrote Dr. Mesinkovska and coauthors Celine Phong, a UCI medical student, and Amy J. McMichael, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. “A similar unmet need exists to describe the characteristics of AA in Hispanic/Latinx (H/L) patients, the prevalent majority in California,” they added.
Drawing from chart reviews, ICD codes, and documented physical exams, they retrospectively identified 197 Hispanic/Latinx patients diagnosed with AA at UCI between 2015 and 2022, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
Nearly two-thirds of patients with alopecia were female (63%), and their mean age at diagnosis was 33 years. Most patients (79%) presented with patchy pattern AA, 13% had diffuse pattern AA, and only 12% had eyebrow, eyelash, or beard involvement. The most common comorbidity in patients overall was atopy (24%), including allergic rhinitis (12%), asthma (10%), and/or atopic dermatitis (7%).
The authors found that 18% of patients had one or more coexisting autoimmune conditions, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (9%) and thyroid disease (6%). No patients had celiac disease, myasthenia gravis, or inflammatory bowel disease, but 43% had another dermatologic condition.
In other findings, 22% of patients had vitamin D deficiency, 20% had hyperlipidemia, 18% had obesity, 16% had gastroesophageal reflux disease, and 12% had anemia. At the same time, depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders were identified in 14% of patients.
“Interestingly, the most common autoimmune comorbidity in H/L was rheumatoid arthritis, compared to thyroid disease in Black patients and overall AA patients,” the authors wrote. “This finding may be a reflection of a larger trend, as rheumatoid arthritis in the H/L population has been on the rise.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study including its small sample size and lack of a control group, and reported having no financial disclosures.
.
Those are among key findings from a retrospective analysis of Hispanic/Latinx patients at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) by Natasha Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, of UCI’s department of dermatology, and her coauthors. The findings were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A recent study examined the epidemiology of alopecia areata (AA) in Black patients, wrote Dr. Mesinkovska and coauthors Celine Phong, a UCI medical student, and Amy J. McMichael, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. “A similar unmet need exists to describe the characteristics of AA in Hispanic/Latinx (H/L) patients, the prevalent majority in California,” they added.
Drawing from chart reviews, ICD codes, and documented physical exams, they retrospectively identified 197 Hispanic/Latinx patients diagnosed with AA at UCI between 2015 and 2022, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
Nearly two-thirds of patients with alopecia were female (63%), and their mean age at diagnosis was 33 years. Most patients (79%) presented with patchy pattern AA, 13% had diffuse pattern AA, and only 12% had eyebrow, eyelash, or beard involvement. The most common comorbidity in patients overall was atopy (24%), including allergic rhinitis (12%), asthma (10%), and/or atopic dermatitis (7%).
The authors found that 18% of patients had one or more coexisting autoimmune conditions, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (9%) and thyroid disease (6%). No patients had celiac disease, myasthenia gravis, or inflammatory bowel disease, but 43% had another dermatologic condition.
In other findings, 22% of patients had vitamin D deficiency, 20% had hyperlipidemia, 18% had obesity, 16% had gastroesophageal reflux disease, and 12% had anemia. At the same time, depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders were identified in 14% of patients.
“Interestingly, the most common autoimmune comorbidity in H/L was rheumatoid arthritis, compared to thyroid disease in Black patients and overall AA patients,” the authors wrote. “This finding may be a reflection of a larger trend, as rheumatoid arthritis in the H/L population has been on the rise.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study including its small sample size and lack of a control group, and reported having no financial disclosures.
.
Those are among key findings from a retrospective analysis of Hispanic/Latinx patients at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) by Natasha Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, of UCI’s department of dermatology, and her coauthors. The findings were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A recent study examined the epidemiology of alopecia areata (AA) in Black patients, wrote Dr. Mesinkovska and coauthors Celine Phong, a UCI medical student, and Amy J. McMichael, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. “A similar unmet need exists to describe the characteristics of AA in Hispanic/Latinx (H/L) patients, the prevalent majority in California,” they added.
Drawing from chart reviews, ICD codes, and documented physical exams, they retrospectively identified 197 Hispanic/Latinx patients diagnosed with AA at UCI between 2015 and 2022, including alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
Nearly two-thirds of patients with alopecia were female (63%), and their mean age at diagnosis was 33 years. Most patients (79%) presented with patchy pattern AA, 13% had diffuse pattern AA, and only 12% had eyebrow, eyelash, or beard involvement. The most common comorbidity in patients overall was atopy (24%), including allergic rhinitis (12%), asthma (10%), and/or atopic dermatitis (7%).
The authors found that 18% of patients had one or more coexisting autoimmune conditions, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (9%) and thyroid disease (6%). No patients had celiac disease, myasthenia gravis, or inflammatory bowel disease, but 43% had another dermatologic condition.
In other findings, 22% of patients had vitamin D deficiency, 20% had hyperlipidemia, 18% had obesity, 16% had gastroesophageal reflux disease, and 12% had anemia. At the same time, depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders were identified in 14% of patients.
“Interestingly, the most common autoimmune comorbidity in H/L was rheumatoid arthritis, compared to thyroid disease in Black patients and overall AA patients,” the authors wrote. “This finding may be a reflection of a larger trend, as rheumatoid arthritis in the H/L population has been on the rise.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study including its small sample size and lack of a control group, and reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY