User login
‘Best’ for most APL patients: Chemo-free regimen
“In a large cohort of patients with APL, the chemo-free combination of ATRA/ATO is confirmed as the best treatment option, prolonging overall and event-free survival and reducing the relapse rate compared with ATRA/chemotherapy,” said first author Maria Teresa Voso, MD, of Tor Vergata University, in Rome, in presenting the findings at the 2023 annual meeting of the European Hematology Association.
APL, though rare, makes up about 10% of new AML cases, and the advent of the chemo-free ATRA-ATO regimen in recent years has transformed the disease, significantly improving survival.
However, with ongoing questions regarding factors associated with treatment benefits based on issues including the level of risk, Dr. Voso and colleagues turned to data from the large European Union–funded HARMONY registry, a big data project that uniquely provides real-world as well as clinical trial findings from diverse APL patient populations.
They identified 937 patients in the registry with newly diagnosed APL between 2007 and 2020 who met the study’s data quality criteria, including 536 (57.2%) patients from two clinical trials, the UK AML-17 and GIMEMA APL0406 trials, and 401 (42.8%) patients from national registries in 6 countries, representing real-world data.
The median duration of follow-up was 5.66 years, with a range of 0-14 years.
The patients had an average age of about 50, which is consistent with the lower age of diagnosis typical of APL, compared with other forms of AML.
Among them, 380 (40.6%) were treated with the ATRA-ATO regimen while 509 (54.3%) received the chemotherapy combination of ATRA-Idarubicin (AIDA).
Overall, 37.8% were determined to be low risk, as assessed by the Sanz risk-score; 42.3% were intermediate risk, and 18.7% were considered high risk. The rate of complete remission among the patients was 87.5%, and 9% had relapsed.
The results showed the 10-year overall survival (OS) rate to be 92% among the chemo-free ATRA-ATO-treated patients versus 75% in the AIDA-treated patients (P = .001).
Likewise, those treated with the chemo-free regimen had a higher event-free survival and a lower cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) versus chemotherapy over 10 years (P < .001 for both).
In further stratifying by risk, patients who were low risk also had greater improvements with the chemo-free regimen in overall survival (P = .004), event-free survival, and CIR versus AIDA treatment (P < .001).
Among high-risk patients, however, only event-free survival was significantly improved in the chemo-free treated patients (P = .046).
Older age stood out as a significant determinant of survival, with patients in the age 50-69 and 70 or over age groups having a significantly lower rate of overall survival and event-free survival, compared with those under 50 years of age (P < .001), with those risks observed regardless of treatment type.
Age was not a significant factor in terms of the incidence of relapse (P = .159).
Clinical trial versus real-world outcomes
Of note, improved outcomes were reported in clinical trials versus real-world data, with overall survival higher in clinical trials among patients receiving the ATRA/ATO chemo-free treatment (P = .025), as well as in those receiving the AIDA chemotherapy (P < .001).
Early death, an uncommon but key concern with APL, usually due to bleeding complications and defined as death occurring within 30 days from APL diagnosis, occurred among 56 patients, or 5.9%, overall, and was significantly higher in the age 50-69 and over 70 groups versus those under 50 (P < .001).
Early death was more common among those with a Sanz high-risk score (15.4%), compared with low or intermediate risk (3.9%; P < .001); however, the risk was no different between the chemo-free (3.4%) and chemotherapy (5.7%) groups, regardless of whether patients had a low or high risk.
The rates of early death were significantly higher in the real-world population (10.2%), compared with patients in clinical trials (2.8%; P < .001), which Dr. Voso noted may be expected, as early deaths in some cases can occur even before a diagnosis is made.
“These patients sometimes come to the ER and if a diagnosis is not made, they may die before even receiving treatment,” she said in a press briefing.
“Indeed, the median time to death among those who had early death in the study was only 10 days, and there were even some patients dying at day 0,” she explained.
“So, it’s very important that not only hematologists but emergency doctors recognize this disease and try to reduce the early death rate.”
Overall, the results all remained consistent after adjustment in a multivariate analysis, Dr. Voso said.
“The multivariate analysis confirmed that increasing age, high Sanz risk score, the real-life treatment scenario, and the chemotherapy-based approach are independently associated with decreased survival,” she said.
The findings underscore that “elderly age and high Sanz risk score significantly impact on the rate of early deaths, irrespective of treatment,” Dr. Voso said.
ATRA/ATO ‘gold standard’ for low/intermediate risk
Commenting on the study, Alessandro Isidori, MD, PhD, a hematologist at AORMN Hospital, in Pesaro, Italy, who moderated the session, noted that the study underscores the greater challenges with higher-risk patients.
“The study did not show a statistical benefit for high-risk patients receiving ATRA/ATO versus AIDA,” he told this news organization, noting that “currently, there are many countries where ATRA/ATO is not approved for use in high-risk APL.”
“In high-risk APL, the AIDA combination should still be preferred to ATRA/ATO,” he said.
Dr. Isidori recommended careful efforts to stratify higher-risk patients who still may benefit from ATRA/ATO.
“The analysis of high-risk patients with white blood cell count as a continuous variable instead of a fixed variable (more or less than 10,000/mmc) may help to discriminate some high-risk patients who could benefit from ATRA/ATO,” he noted.
Overall, however, “ATRA/ATO is the gold standard for low and intermediate risk APL,” he said.
“Although promising, more data are needed to confirm the efficacy of ATRA/ATO in high-risk APL.”
Dr. Voso disclosed ties with companies including Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Astellas, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Isidori reported no disclosures.
“In a large cohort of patients with APL, the chemo-free combination of ATRA/ATO is confirmed as the best treatment option, prolonging overall and event-free survival and reducing the relapse rate compared with ATRA/chemotherapy,” said first author Maria Teresa Voso, MD, of Tor Vergata University, in Rome, in presenting the findings at the 2023 annual meeting of the European Hematology Association.
APL, though rare, makes up about 10% of new AML cases, and the advent of the chemo-free ATRA-ATO regimen in recent years has transformed the disease, significantly improving survival.
However, with ongoing questions regarding factors associated with treatment benefits based on issues including the level of risk, Dr. Voso and colleagues turned to data from the large European Union–funded HARMONY registry, a big data project that uniquely provides real-world as well as clinical trial findings from diverse APL patient populations.
They identified 937 patients in the registry with newly diagnosed APL between 2007 and 2020 who met the study’s data quality criteria, including 536 (57.2%) patients from two clinical trials, the UK AML-17 and GIMEMA APL0406 trials, and 401 (42.8%) patients from national registries in 6 countries, representing real-world data.
The median duration of follow-up was 5.66 years, with a range of 0-14 years.
The patients had an average age of about 50, which is consistent with the lower age of diagnosis typical of APL, compared with other forms of AML.
Among them, 380 (40.6%) were treated with the ATRA-ATO regimen while 509 (54.3%) received the chemotherapy combination of ATRA-Idarubicin (AIDA).
Overall, 37.8% were determined to be low risk, as assessed by the Sanz risk-score; 42.3% were intermediate risk, and 18.7% were considered high risk. The rate of complete remission among the patients was 87.5%, and 9% had relapsed.
The results showed the 10-year overall survival (OS) rate to be 92% among the chemo-free ATRA-ATO-treated patients versus 75% in the AIDA-treated patients (P = .001).
Likewise, those treated with the chemo-free regimen had a higher event-free survival and a lower cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) versus chemotherapy over 10 years (P < .001 for both).
In further stratifying by risk, patients who were low risk also had greater improvements with the chemo-free regimen in overall survival (P = .004), event-free survival, and CIR versus AIDA treatment (P < .001).
Among high-risk patients, however, only event-free survival was significantly improved in the chemo-free treated patients (P = .046).
Older age stood out as a significant determinant of survival, with patients in the age 50-69 and 70 or over age groups having a significantly lower rate of overall survival and event-free survival, compared with those under 50 years of age (P < .001), with those risks observed regardless of treatment type.
Age was not a significant factor in terms of the incidence of relapse (P = .159).
Clinical trial versus real-world outcomes
Of note, improved outcomes were reported in clinical trials versus real-world data, with overall survival higher in clinical trials among patients receiving the ATRA/ATO chemo-free treatment (P = .025), as well as in those receiving the AIDA chemotherapy (P < .001).
Early death, an uncommon but key concern with APL, usually due to bleeding complications and defined as death occurring within 30 days from APL diagnosis, occurred among 56 patients, or 5.9%, overall, and was significantly higher in the age 50-69 and over 70 groups versus those under 50 (P < .001).
Early death was more common among those with a Sanz high-risk score (15.4%), compared with low or intermediate risk (3.9%; P < .001); however, the risk was no different between the chemo-free (3.4%) and chemotherapy (5.7%) groups, regardless of whether patients had a low or high risk.
The rates of early death were significantly higher in the real-world population (10.2%), compared with patients in clinical trials (2.8%; P < .001), which Dr. Voso noted may be expected, as early deaths in some cases can occur even before a diagnosis is made.
“These patients sometimes come to the ER and if a diagnosis is not made, they may die before even receiving treatment,” she said in a press briefing.
“Indeed, the median time to death among those who had early death in the study was only 10 days, and there were even some patients dying at day 0,” she explained.
“So, it’s very important that not only hematologists but emergency doctors recognize this disease and try to reduce the early death rate.”
Overall, the results all remained consistent after adjustment in a multivariate analysis, Dr. Voso said.
“The multivariate analysis confirmed that increasing age, high Sanz risk score, the real-life treatment scenario, and the chemotherapy-based approach are independently associated with decreased survival,” she said.
The findings underscore that “elderly age and high Sanz risk score significantly impact on the rate of early deaths, irrespective of treatment,” Dr. Voso said.
ATRA/ATO ‘gold standard’ for low/intermediate risk
Commenting on the study, Alessandro Isidori, MD, PhD, a hematologist at AORMN Hospital, in Pesaro, Italy, who moderated the session, noted that the study underscores the greater challenges with higher-risk patients.
“The study did not show a statistical benefit for high-risk patients receiving ATRA/ATO versus AIDA,” he told this news organization, noting that “currently, there are many countries where ATRA/ATO is not approved for use in high-risk APL.”
“In high-risk APL, the AIDA combination should still be preferred to ATRA/ATO,” he said.
Dr. Isidori recommended careful efforts to stratify higher-risk patients who still may benefit from ATRA/ATO.
“The analysis of high-risk patients with white blood cell count as a continuous variable instead of a fixed variable (more or less than 10,000/mmc) may help to discriminate some high-risk patients who could benefit from ATRA/ATO,” he noted.
Overall, however, “ATRA/ATO is the gold standard for low and intermediate risk APL,” he said.
“Although promising, more data are needed to confirm the efficacy of ATRA/ATO in high-risk APL.”
Dr. Voso disclosed ties with companies including Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Astellas, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Isidori reported no disclosures.
“In a large cohort of patients with APL, the chemo-free combination of ATRA/ATO is confirmed as the best treatment option, prolonging overall and event-free survival and reducing the relapse rate compared with ATRA/chemotherapy,” said first author Maria Teresa Voso, MD, of Tor Vergata University, in Rome, in presenting the findings at the 2023 annual meeting of the European Hematology Association.
APL, though rare, makes up about 10% of new AML cases, and the advent of the chemo-free ATRA-ATO regimen in recent years has transformed the disease, significantly improving survival.
However, with ongoing questions regarding factors associated with treatment benefits based on issues including the level of risk, Dr. Voso and colleagues turned to data from the large European Union–funded HARMONY registry, a big data project that uniquely provides real-world as well as clinical trial findings from diverse APL patient populations.
They identified 937 patients in the registry with newly diagnosed APL between 2007 and 2020 who met the study’s data quality criteria, including 536 (57.2%) patients from two clinical trials, the UK AML-17 and GIMEMA APL0406 trials, and 401 (42.8%) patients from national registries in 6 countries, representing real-world data.
The median duration of follow-up was 5.66 years, with a range of 0-14 years.
The patients had an average age of about 50, which is consistent with the lower age of diagnosis typical of APL, compared with other forms of AML.
Among them, 380 (40.6%) were treated with the ATRA-ATO regimen while 509 (54.3%) received the chemotherapy combination of ATRA-Idarubicin (AIDA).
Overall, 37.8% were determined to be low risk, as assessed by the Sanz risk-score; 42.3% were intermediate risk, and 18.7% were considered high risk. The rate of complete remission among the patients was 87.5%, and 9% had relapsed.
The results showed the 10-year overall survival (OS) rate to be 92% among the chemo-free ATRA-ATO-treated patients versus 75% in the AIDA-treated patients (P = .001).
Likewise, those treated with the chemo-free regimen had a higher event-free survival and a lower cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) versus chemotherapy over 10 years (P < .001 for both).
In further stratifying by risk, patients who were low risk also had greater improvements with the chemo-free regimen in overall survival (P = .004), event-free survival, and CIR versus AIDA treatment (P < .001).
Among high-risk patients, however, only event-free survival was significantly improved in the chemo-free treated patients (P = .046).
Older age stood out as a significant determinant of survival, with patients in the age 50-69 and 70 or over age groups having a significantly lower rate of overall survival and event-free survival, compared with those under 50 years of age (P < .001), with those risks observed regardless of treatment type.
Age was not a significant factor in terms of the incidence of relapse (P = .159).
Clinical trial versus real-world outcomes
Of note, improved outcomes were reported in clinical trials versus real-world data, with overall survival higher in clinical trials among patients receiving the ATRA/ATO chemo-free treatment (P = .025), as well as in those receiving the AIDA chemotherapy (P < .001).
Early death, an uncommon but key concern with APL, usually due to bleeding complications and defined as death occurring within 30 days from APL diagnosis, occurred among 56 patients, or 5.9%, overall, and was significantly higher in the age 50-69 and over 70 groups versus those under 50 (P < .001).
Early death was more common among those with a Sanz high-risk score (15.4%), compared with low or intermediate risk (3.9%; P < .001); however, the risk was no different between the chemo-free (3.4%) and chemotherapy (5.7%) groups, regardless of whether patients had a low or high risk.
The rates of early death were significantly higher in the real-world population (10.2%), compared with patients in clinical trials (2.8%; P < .001), which Dr. Voso noted may be expected, as early deaths in some cases can occur even before a diagnosis is made.
“These patients sometimes come to the ER and if a diagnosis is not made, they may die before even receiving treatment,” she said in a press briefing.
“Indeed, the median time to death among those who had early death in the study was only 10 days, and there were even some patients dying at day 0,” she explained.
“So, it’s very important that not only hematologists but emergency doctors recognize this disease and try to reduce the early death rate.”
Overall, the results all remained consistent after adjustment in a multivariate analysis, Dr. Voso said.
“The multivariate analysis confirmed that increasing age, high Sanz risk score, the real-life treatment scenario, and the chemotherapy-based approach are independently associated with decreased survival,” she said.
The findings underscore that “elderly age and high Sanz risk score significantly impact on the rate of early deaths, irrespective of treatment,” Dr. Voso said.
ATRA/ATO ‘gold standard’ for low/intermediate risk
Commenting on the study, Alessandro Isidori, MD, PhD, a hematologist at AORMN Hospital, in Pesaro, Italy, who moderated the session, noted that the study underscores the greater challenges with higher-risk patients.
“The study did not show a statistical benefit for high-risk patients receiving ATRA/ATO versus AIDA,” he told this news organization, noting that “currently, there are many countries where ATRA/ATO is not approved for use in high-risk APL.”
“In high-risk APL, the AIDA combination should still be preferred to ATRA/ATO,” he said.
Dr. Isidori recommended careful efforts to stratify higher-risk patients who still may benefit from ATRA/ATO.
“The analysis of high-risk patients with white blood cell count as a continuous variable instead of a fixed variable (more or less than 10,000/mmc) may help to discriminate some high-risk patients who could benefit from ATRA/ATO,” he noted.
Overall, however, “ATRA/ATO is the gold standard for low and intermediate risk APL,” he said.
“Although promising, more data are needed to confirm the efficacy of ATRA/ATO in high-risk APL.”
Dr. Voso disclosed ties with companies including Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Astellas, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Isidori reported no disclosures.
FROM EHA 2023
Hormone therapies still ‘most effective’ in treating menopausal vasomotor symptoms
Despite new options in non–hormone-based treatments,
This recommendation emerged from an updated position statement from the North American Menopause Society in its first review of the scientific literature since 2015. The statement specifically targets nonhormonal management of symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats, which occur in as many as 80% of menopausal women but are undertreated. The statement appears in the June issue of the Journal of The North American Menopause Society.
“Women with contraindications or objections to hormone treatment should be informed by professionals of evidence-based effective nonhormone treatment options,” stated a NAMS advisory panel led by Chrisandra L. Shufelt, MD, MS, professor and chair of the division of general internal medicine and associate director of the Women’s Health Research Center at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. The statement is one of multiple NAMS updates performed at regular intervals, said Dr. Shufelt, also past president of NAMS, in an interview. “But the research has changed, and we wanted to make clinicians aware of new medications. One of our interesting findings was more evidence that off-label use of the nonhormonal overactive bladder drug oxybutynin can lower the rate of hot flashes.”
Dr. Shufelt noted that many of the current update’s findings align with previous research, and stressed that the therapeutic recommendations apply specifically to VMS. “Not all menopause-related symptoms are vasomotor, however,” she said. “While a lot of the lifestyle options such as cooling techniques and exercise are not recommended for controlling hot flashes, diet and exercise changes can be beneficial for other health reasons.”
Although it’s the most effective option for VMS, hormone therapy is not suitable for women with contraindications such as a previous blood clot, an estrogen-dependent cancer, a family history of such cancers, or a personal preference against hormone use, Dr. Shufelt added, so nonhormonal alternatives are important to prevent women from wasting time and money on ineffective remedies. “Women need to know what works and what doesn’t,” she said.
Recommended nonhormonal therapies
Based on a rigorous review of the scientific evidence to date, NAMS found the following therapies to be effective: cognitive-behavioral therapy; clinical hypnosis; SSRIs and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors – which yield mild to moderate improvements; gabapentin – which lessens the frequency and severity of hot flashes; fezolinetant (Veozah), a novel first-in-class neurokinin B antagonist that was Food and Drug Administration–approved in May for VSM; and oxybutynin, an antimuscarinic, anticholinergic drug, that reduces moderate to severe VMS, although long-term use in older adults may be linked to cognitive decline, weight loss, and stellate ganglion block.
Therapies that were ineffective, associated with adverse effects (AEs), or lacking adequate evidence of efficacy and thus not recommended for VMS included: paced respiration; supplemental and herbal remedies such as black cohosh, milk thistle, and evening primrose; cooling techniques; trigger avoidance; exercise and yoga; mindfulness-based intervention and relaxation; suvorexant, a dual orexin-receptor antagonist used for insomnia; soy foods, extracts, and the soy metabolite equol; cannabinoids; acupuncture; calibration of neural oscillations; chiropractics; clonidine, an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist that is associated with significant AEs with no recent evidence of benefit over placebo; dietary modification; and pregabalin – which is associated with significant AEs and has controlled-substance prescribing restrictions.
Ultimately, clinicians should individualize menopause care to each patient. For example, “if a patient says that avoiding caffeine in the morning stops her from having hot flashes in the afternoon, that’s fine,” Dr. Shufelt said.
HT still most effective
“This statement is excellent, comprehensive, and evidence-based,” commented Jill M. Rabin MD, vice chair of education and development, obstetrics and gynecology, at Northshore University Hospital/LIJ Medical Center in Manhasset, N.Y., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell Health in Hempstead, N.Y.
Dr. Rabin, coauthor of Mind Over Bladder was not involved in compiling the statement.
She agreed that hormone therapy is the most effective option for VMS and regularly prescribes it for suitable candidates in different forms depending on the type and severity of menopausal symptoms. As for nonhormonal options, Dr. Rabin added in an interview, some of those not recommended in the current NAMS statement could yet prove to be effective as more data accumulate. Suvorexant may be one to watch, for instance, but currently there are not enough data on its effectiveness.
“It’s really important to keep up on this nonhormonal research,” Dr. Rabin said. “As the population ages, more and more women will be in the peri- and postmenopausal periods and some have medical reasons for not taking hormone therapy.” It’s important to recommend nonhormonal therapies of proven benefit according to current high-level evidence, she said, “but also to keep your ear to the ground about those still under investigation.”
As for the lifestyle and alternative remedies of unproven benefit, Dr. Rabin added, there’s little harm in trying them. “As far as I know, no one’s ever died of relaxation and paced breathing.” In addition, a patient’s interaction with and sense of control over her own physiology provided by these techniques may be beneficial in themselves.
Dr. Shufelt reported grant support from the National Institutes of Health. Numerous authors reported consulting fees from and other financial ties to private-sector companies. Dr. Rabin had no relevant competing interests to disclose with regard to her comments.
Despite new options in non–hormone-based treatments,
This recommendation emerged from an updated position statement from the North American Menopause Society in its first review of the scientific literature since 2015. The statement specifically targets nonhormonal management of symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats, which occur in as many as 80% of menopausal women but are undertreated. The statement appears in the June issue of the Journal of The North American Menopause Society.
“Women with contraindications or objections to hormone treatment should be informed by professionals of evidence-based effective nonhormone treatment options,” stated a NAMS advisory panel led by Chrisandra L. Shufelt, MD, MS, professor and chair of the division of general internal medicine and associate director of the Women’s Health Research Center at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. The statement is one of multiple NAMS updates performed at regular intervals, said Dr. Shufelt, also past president of NAMS, in an interview. “But the research has changed, and we wanted to make clinicians aware of new medications. One of our interesting findings was more evidence that off-label use of the nonhormonal overactive bladder drug oxybutynin can lower the rate of hot flashes.”
Dr. Shufelt noted that many of the current update’s findings align with previous research, and stressed that the therapeutic recommendations apply specifically to VMS. “Not all menopause-related symptoms are vasomotor, however,” she said. “While a lot of the lifestyle options such as cooling techniques and exercise are not recommended for controlling hot flashes, diet and exercise changes can be beneficial for other health reasons.”
Although it’s the most effective option for VMS, hormone therapy is not suitable for women with contraindications such as a previous blood clot, an estrogen-dependent cancer, a family history of such cancers, or a personal preference against hormone use, Dr. Shufelt added, so nonhormonal alternatives are important to prevent women from wasting time and money on ineffective remedies. “Women need to know what works and what doesn’t,” she said.
Recommended nonhormonal therapies
Based on a rigorous review of the scientific evidence to date, NAMS found the following therapies to be effective: cognitive-behavioral therapy; clinical hypnosis; SSRIs and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors – which yield mild to moderate improvements; gabapentin – which lessens the frequency and severity of hot flashes; fezolinetant (Veozah), a novel first-in-class neurokinin B antagonist that was Food and Drug Administration–approved in May for VSM; and oxybutynin, an antimuscarinic, anticholinergic drug, that reduces moderate to severe VMS, although long-term use in older adults may be linked to cognitive decline, weight loss, and stellate ganglion block.
Therapies that were ineffective, associated with adverse effects (AEs), or lacking adequate evidence of efficacy and thus not recommended for VMS included: paced respiration; supplemental and herbal remedies such as black cohosh, milk thistle, and evening primrose; cooling techniques; trigger avoidance; exercise and yoga; mindfulness-based intervention and relaxation; suvorexant, a dual orexin-receptor antagonist used for insomnia; soy foods, extracts, and the soy metabolite equol; cannabinoids; acupuncture; calibration of neural oscillations; chiropractics; clonidine, an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist that is associated with significant AEs with no recent evidence of benefit over placebo; dietary modification; and pregabalin – which is associated with significant AEs and has controlled-substance prescribing restrictions.
Ultimately, clinicians should individualize menopause care to each patient. For example, “if a patient says that avoiding caffeine in the morning stops her from having hot flashes in the afternoon, that’s fine,” Dr. Shufelt said.
HT still most effective
“This statement is excellent, comprehensive, and evidence-based,” commented Jill M. Rabin MD, vice chair of education and development, obstetrics and gynecology, at Northshore University Hospital/LIJ Medical Center in Manhasset, N.Y., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell Health in Hempstead, N.Y.
Dr. Rabin, coauthor of Mind Over Bladder was not involved in compiling the statement.
She agreed that hormone therapy is the most effective option for VMS and regularly prescribes it for suitable candidates in different forms depending on the type and severity of menopausal symptoms. As for nonhormonal options, Dr. Rabin added in an interview, some of those not recommended in the current NAMS statement could yet prove to be effective as more data accumulate. Suvorexant may be one to watch, for instance, but currently there are not enough data on its effectiveness.
“It’s really important to keep up on this nonhormonal research,” Dr. Rabin said. “As the population ages, more and more women will be in the peri- and postmenopausal periods and some have medical reasons for not taking hormone therapy.” It’s important to recommend nonhormonal therapies of proven benefit according to current high-level evidence, she said, “but also to keep your ear to the ground about those still under investigation.”
As for the lifestyle and alternative remedies of unproven benefit, Dr. Rabin added, there’s little harm in trying them. “As far as I know, no one’s ever died of relaxation and paced breathing.” In addition, a patient’s interaction with and sense of control over her own physiology provided by these techniques may be beneficial in themselves.
Dr. Shufelt reported grant support from the National Institutes of Health. Numerous authors reported consulting fees from and other financial ties to private-sector companies. Dr. Rabin had no relevant competing interests to disclose with regard to her comments.
Despite new options in non–hormone-based treatments,
This recommendation emerged from an updated position statement from the North American Menopause Society in its first review of the scientific literature since 2015. The statement specifically targets nonhormonal management of symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats, which occur in as many as 80% of menopausal women but are undertreated. The statement appears in the June issue of the Journal of The North American Menopause Society.
“Women with contraindications or objections to hormone treatment should be informed by professionals of evidence-based effective nonhormone treatment options,” stated a NAMS advisory panel led by Chrisandra L. Shufelt, MD, MS, professor and chair of the division of general internal medicine and associate director of the Women’s Health Research Center at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. The statement is one of multiple NAMS updates performed at regular intervals, said Dr. Shufelt, also past president of NAMS, in an interview. “But the research has changed, and we wanted to make clinicians aware of new medications. One of our interesting findings was more evidence that off-label use of the nonhormonal overactive bladder drug oxybutynin can lower the rate of hot flashes.”
Dr. Shufelt noted that many of the current update’s findings align with previous research, and stressed that the therapeutic recommendations apply specifically to VMS. “Not all menopause-related symptoms are vasomotor, however,” she said. “While a lot of the lifestyle options such as cooling techniques and exercise are not recommended for controlling hot flashes, diet and exercise changes can be beneficial for other health reasons.”
Although it’s the most effective option for VMS, hormone therapy is not suitable for women with contraindications such as a previous blood clot, an estrogen-dependent cancer, a family history of such cancers, or a personal preference against hormone use, Dr. Shufelt added, so nonhormonal alternatives are important to prevent women from wasting time and money on ineffective remedies. “Women need to know what works and what doesn’t,” she said.
Recommended nonhormonal therapies
Based on a rigorous review of the scientific evidence to date, NAMS found the following therapies to be effective: cognitive-behavioral therapy; clinical hypnosis; SSRIs and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors – which yield mild to moderate improvements; gabapentin – which lessens the frequency and severity of hot flashes; fezolinetant (Veozah), a novel first-in-class neurokinin B antagonist that was Food and Drug Administration–approved in May for VSM; and oxybutynin, an antimuscarinic, anticholinergic drug, that reduces moderate to severe VMS, although long-term use in older adults may be linked to cognitive decline, weight loss, and stellate ganglion block.
Therapies that were ineffective, associated with adverse effects (AEs), or lacking adequate evidence of efficacy and thus not recommended for VMS included: paced respiration; supplemental and herbal remedies such as black cohosh, milk thistle, and evening primrose; cooling techniques; trigger avoidance; exercise and yoga; mindfulness-based intervention and relaxation; suvorexant, a dual orexin-receptor antagonist used for insomnia; soy foods, extracts, and the soy metabolite equol; cannabinoids; acupuncture; calibration of neural oscillations; chiropractics; clonidine, an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist that is associated with significant AEs with no recent evidence of benefit over placebo; dietary modification; and pregabalin – which is associated with significant AEs and has controlled-substance prescribing restrictions.
Ultimately, clinicians should individualize menopause care to each patient. For example, “if a patient says that avoiding caffeine in the morning stops her from having hot flashes in the afternoon, that’s fine,” Dr. Shufelt said.
HT still most effective
“This statement is excellent, comprehensive, and evidence-based,” commented Jill M. Rabin MD, vice chair of education and development, obstetrics and gynecology, at Northshore University Hospital/LIJ Medical Center in Manhasset, N.Y., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell Health in Hempstead, N.Y.
Dr. Rabin, coauthor of Mind Over Bladder was not involved in compiling the statement.
She agreed that hormone therapy is the most effective option for VMS and regularly prescribes it for suitable candidates in different forms depending on the type and severity of menopausal symptoms. As for nonhormonal options, Dr. Rabin added in an interview, some of those not recommended in the current NAMS statement could yet prove to be effective as more data accumulate. Suvorexant may be one to watch, for instance, but currently there are not enough data on its effectiveness.
“It’s really important to keep up on this nonhormonal research,” Dr. Rabin said. “As the population ages, more and more women will be in the peri- and postmenopausal periods and some have medical reasons for not taking hormone therapy.” It’s important to recommend nonhormonal therapies of proven benefit according to current high-level evidence, she said, “but also to keep your ear to the ground about those still under investigation.”
As for the lifestyle and alternative remedies of unproven benefit, Dr. Rabin added, there’s little harm in trying them. “As far as I know, no one’s ever died of relaxation and paced breathing.” In addition, a patient’s interaction with and sense of control over her own physiology provided by these techniques may be beneficial in themselves.
Dr. Shufelt reported grant support from the National Institutes of Health. Numerous authors reported consulting fees from and other financial ties to private-sector companies. Dr. Rabin had no relevant competing interests to disclose with regard to her comments.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE NORTH AMERICAN MENOPAUSE SOCIETY
Systemic lupus erythematosus
THE COMPARISON
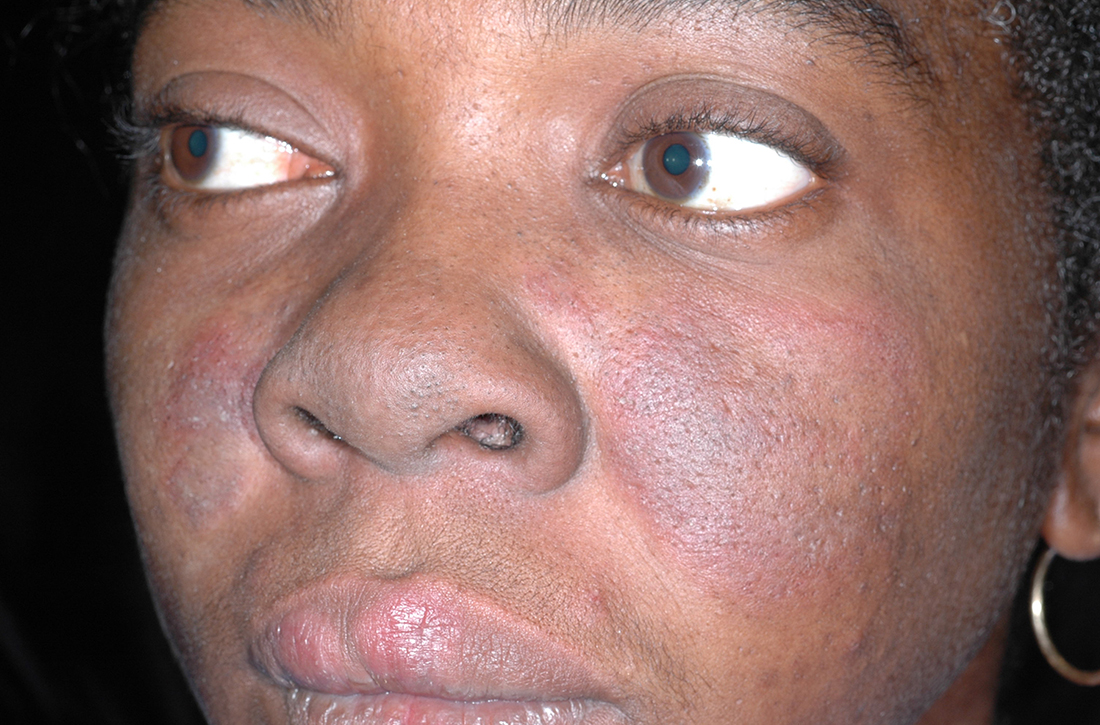
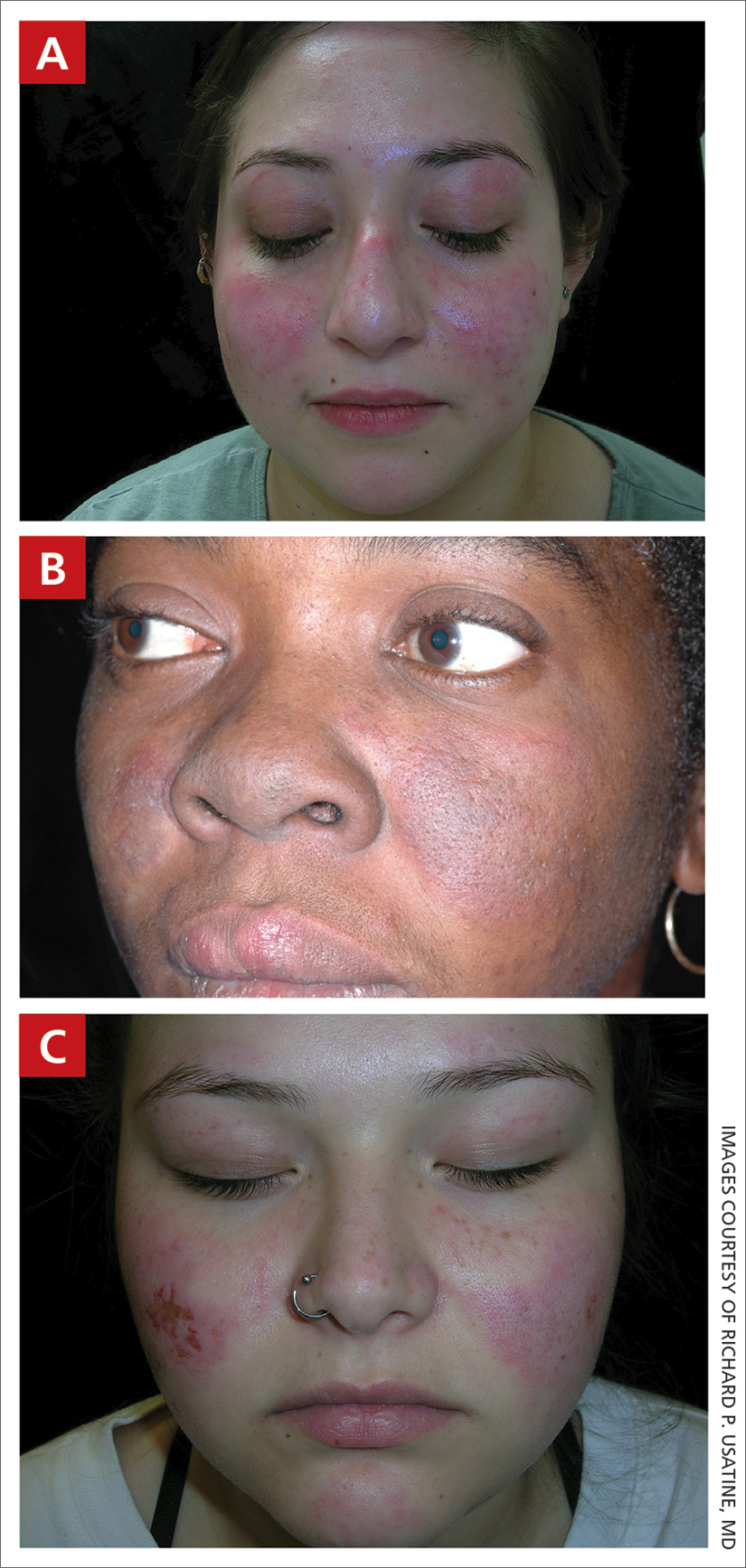
A A 23-year-old White woman with malar erythema from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The erythema also can be seen on the nose and eyelids but spares the nasolabial folds.
B A Black woman with malar erythema and hyperpigmentation from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The nasolabial folds are spared.
C A 19-year-old Latina woman with malar erythema from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The erythema also can be seen on the nose, chin, and eyelids but spares the nasolabial folds. Cutaneous erosions are present on the right cheek as part of the lupus flare.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the kidneys, lungs, brain, and heart, although it is not limited to these organs. Dermatologists and primary care physicians play a critical role in the early identification of SLE (particularly in those with skin of color), as the standardized mortality rate is 2.6-fold higher in patients with SLE compared to the general population.1 The clinical manifestations of SLE vary.
Epidemiology
A meta-analysis of data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Lupus Registry network including 5417 patients revealed a prevalence of 72.8 cases per 100,000 person-years.2 The prevalence was higher in females than males and highest among females identifying as Black. White and Asian/ Pacific Islander females had the lowest prevalence. The American Indian (indigenous)/Alaska Native–identifying population had the highest race-specific SLE estimates among both females and males compared to other racial/ethnic groups.2
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
The diagnosis of SLE is based on clinical and immunologic criteria from the European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology.3,4 An antinuclear antibody titer of 1:80 or higher at least once is required for the diagnosis of SLE, as long as there is not another more likely diagnosis. If it is present, 22 additive weighted classification criteria are considered; each criterion is assigned points, ranging from 2 to 10. Patients with at least 1 clinical criterion and 10 or more points are classified as having SLE. If more than 1 of the criteria are met in a domain, then the one with the highest numerical value is counted.3,4
Aringer et al3,4 outline the criteria and numerical points to make the diagnosis of SLE. The mucocutaneous component of the SLE diagnostic criteria3,4 includes nonscarring alopecia, oral ulcers, subacute cutaneous or discoid lupus erythematosus,5 and acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, with acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus being the highest-weighted criterion in that domain. The other clinical domains are constitutional, hematologic, neuropsychiatric, serosal, musculoskeletal, renal, antiphospholipid antibodies, complement proteins, and SLE-specific antibodies.3,4
The malar (“butterfly”) rash of SLE characteristically includes erythema that spares the nasolabial folds but affects the nasal bridge and cheeks.6 The rash occasionally may be pruritic and painful, lasting days to weeks. Photosensitivity occurs, resulting in rashes or even an overall worsening of SLE symptoms. In those with darker skin tones, erythema may appear violaceous or may not be as readily appreciated.6
Worth noting
- Patients with skin of color are at an increased risk for postinflammatory hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation (pigment alteration), hypertrophic scars, and keloids.7,8
- The mortality rate for those with SLE is high despite early recognition and treatment when compared to the general population.1,9
Health disparity highlight
Those at greatest risk for death from SLE in the United States are those of African descent, Hispanic individuals, men, and those with low socioeconomic status,9 which likely is primarily driven by social determinants of health instead of genetic patterns. Income level, educational attainment, insurance status, and environmental factors10 have farreaching effects, negatively impacting quality of life and even mortality.
1. Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, et al. Overall and cause-specific mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: an updated meta-analysis. Lupus. 2016;25:727-734.
2. Izmirly PM, Parton H, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States: estimates from a meta-analysis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Lupus Registries. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:991-996. doi: 10.1002/art.41632
3. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71:1400-1412. doi: 10.1002/art.40930
4. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1151-1159.
5. Heath CR, Usatine RP. Discoid lupus. Cutis. 2022;109:172-173.
6. Firestein GS, Budd RC, Harris ED Jr, et al, eds. Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 8th ed. Saunders Elsevier; 2008.
7. Nozile W, Adgerson CH, Cohen GF. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus in skin of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:343-349.
8. Cardinali F, Kovacs D, Picardo M. Mechanisms underlying postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: lessons for solar. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2012;139(suppl 4):S148-S152.
9. Ocampo-Piraquive V, Nieto-Aristizábal I, Cañas CA, et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: causes, predictors and interventions. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2018;14:1043-1053. doi: 10.1080/17446 66X.2018.1538789
10. Carter EE, Barr SG, Clarke AE. The global burden of SLE: prevalence, health disparities and socioeconomic impact. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:605-620. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.137
THE COMPARISON
A A 23-year-old White woman with malar erythema from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The erythema also can be seen on the nose and eyelids but spares the nasolabial folds.
B A Black woman with malar erythema and hyperpigmentation from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The nasolabial folds are spared.
C A 19-year-old Latina woman with malar erythema from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The erythema also can be seen on the nose, chin, and eyelids but spares the nasolabial folds. Cutaneous erosions are present on the right cheek as part of the lupus flare.

Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the kidneys, lungs, brain, and heart, although it is not limited to these organs. Dermatologists and primary care physicians play a critical role in the early identification of SLE (particularly in those with skin of color), as the standardized mortality rate is 2.6-fold higher in patients with SLE compared to the general population.1 The clinical manifestations of SLE vary.
Epidemiology
A meta-analysis of data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Lupus Registry network including 5417 patients revealed a prevalence of 72.8 cases per 100,000 person-years.2 The prevalence was higher in females than males and highest among females identifying as Black. White and Asian/ Pacific Islander females had the lowest prevalence. The American Indian (indigenous)/Alaska Native–identifying population had the highest race-specific SLE estimates among both females and males compared to other racial/ethnic groups.2
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
The diagnosis of SLE is based on clinical and immunologic criteria from the European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology.3,4 An antinuclear antibody titer of 1:80 or higher at least once is required for the diagnosis of SLE, as long as there is not another more likely diagnosis. If it is present, 22 additive weighted classification criteria are considered; each criterion is assigned points, ranging from 2 to 10. Patients with at least 1 clinical criterion and 10 or more points are classified as having SLE. If more than 1 of the criteria are met in a domain, then the one with the highest numerical value is counted.3,4
Aringer et al3,4 outline the criteria and numerical points to make the diagnosis of SLE. The mucocutaneous component of the SLE diagnostic criteria3,4 includes nonscarring alopecia, oral ulcers, subacute cutaneous or discoid lupus erythematosus,5 and acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, with acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus being the highest-weighted criterion in that domain. The other clinical domains are constitutional, hematologic, neuropsychiatric, serosal, musculoskeletal, renal, antiphospholipid antibodies, complement proteins, and SLE-specific antibodies.3,4
The malar (“butterfly”) rash of SLE characteristically includes erythema that spares the nasolabial folds but affects the nasal bridge and cheeks.6 The rash occasionally may be pruritic and painful, lasting days to weeks. Photosensitivity occurs, resulting in rashes or even an overall worsening of SLE symptoms. In those with darker skin tones, erythema may appear violaceous or may not be as readily appreciated.6
Worth noting
- Patients with skin of color are at an increased risk for postinflammatory hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation (pigment alteration), hypertrophic scars, and keloids.7,8
- The mortality rate for those with SLE is high despite early recognition and treatment when compared to the general population.1,9
Health disparity highlight
Those at greatest risk for death from SLE in the United States are those of African descent, Hispanic individuals, men, and those with low socioeconomic status,9 which likely is primarily driven by social determinants of health instead of genetic patterns. Income level, educational attainment, insurance status, and environmental factors10 have farreaching effects, negatively impacting quality of life and even mortality.
THE COMPARISON
A A 23-year-old White woman with malar erythema from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The erythema also can be seen on the nose and eyelids but spares the nasolabial folds.
B A Black woman with malar erythema and hyperpigmentation from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The nasolabial folds are spared.
C A 19-year-old Latina woman with malar erythema from acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The erythema also can be seen on the nose, chin, and eyelids but spares the nasolabial folds. Cutaneous erosions are present on the right cheek as part of the lupus flare.

Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the kidneys, lungs, brain, and heart, although it is not limited to these organs. Dermatologists and primary care physicians play a critical role in the early identification of SLE (particularly in those with skin of color), as the standardized mortality rate is 2.6-fold higher in patients with SLE compared to the general population.1 The clinical manifestations of SLE vary.
Epidemiology
A meta-analysis of data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Lupus Registry network including 5417 patients revealed a prevalence of 72.8 cases per 100,000 person-years.2 The prevalence was higher in females than males and highest among females identifying as Black. White and Asian/ Pacific Islander females had the lowest prevalence. The American Indian (indigenous)/Alaska Native–identifying population had the highest race-specific SLE estimates among both females and males compared to other racial/ethnic groups.2
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
The diagnosis of SLE is based on clinical and immunologic criteria from the European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology.3,4 An antinuclear antibody titer of 1:80 or higher at least once is required for the diagnosis of SLE, as long as there is not another more likely diagnosis. If it is present, 22 additive weighted classification criteria are considered; each criterion is assigned points, ranging from 2 to 10. Patients with at least 1 clinical criterion and 10 or more points are classified as having SLE. If more than 1 of the criteria are met in a domain, then the one with the highest numerical value is counted.3,4
Aringer et al3,4 outline the criteria and numerical points to make the diagnosis of SLE. The mucocutaneous component of the SLE diagnostic criteria3,4 includes nonscarring alopecia, oral ulcers, subacute cutaneous or discoid lupus erythematosus,5 and acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, with acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus being the highest-weighted criterion in that domain. The other clinical domains are constitutional, hematologic, neuropsychiatric, serosal, musculoskeletal, renal, antiphospholipid antibodies, complement proteins, and SLE-specific antibodies.3,4
The malar (“butterfly”) rash of SLE characteristically includes erythema that spares the nasolabial folds but affects the nasal bridge and cheeks.6 The rash occasionally may be pruritic and painful, lasting days to weeks. Photosensitivity occurs, resulting in rashes or even an overall worsening of SLE symptoms. In those with darker skin tones, erythema may appear violaceous or may not be as readily appreciated.6
Worth noting
- Patients with skin of color are at an increased risk for postinflammatory hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation (pigment alteration), hypertrophic scars, and keloids.7,8
- The mortality rate for those with SLE is high despite early recognition and treatment when compared to the general population.1,9
Health disparity highlight
Those at greatest risk for death from SLE in the United States are those of African descent, Hispanic individuals, men, and those with low socioeconomic status,9 which likely is primarily driven by social determinants of health instead of genetic patterns. Income level, educational attainment, insurance status, and environmental factors10 have farreaching effects, negatively impacting quality of life and even mortality.
1. Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, et al. Overall and cause-specific mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: an updated meta-analysis. Lupus. 2016;25:727-734.
2. Izmirly PM, Parton H, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States: estimates from a meta-analysis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Lupus Registries. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:991-996. doi: 10.1002/art.41632
3. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71:1400-1412. doi: 10.1002/art.40930
4. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1151-1159.
5. Heath CR, Usatine RP. Discoid lupus. Cutis. 2022;109:172-173.
6. Firestein GS, Budd RC, Harris ED Jr, et al, eds. Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 8th ed. Saunders Elsevier; 2008.
7. Nozile W, Adgerson CH, Cohen GF. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus in skin of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:343-349.
8. Cardinali F, Kovacs D, Picardo M. Mechanisms underlying postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: lessons for solar. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2012;139(suppl 4):S148-S152.
9. Ocampo-Piraquive V, Nieto-Aristizábal I, Cañas CA, et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: causes, predictors and interventions. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2018;14:1043-1053. doi: 10.1080/17446 66X.2018.1538789
10. Carter EE, Barr SG, Clarke AE. The global burden of SLE: prevalence, health disparities and socioeconomic impact. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:605-620. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.137
1. Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, et al. Overall and cause-specific mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: an updated meta-analysis. Lupus. 2016;25:727-734.
2. Izmirly PM, Parton H, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States: estimates from a meta-analysis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Lupus Registries. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:991-996. doi: 10.1002/art.41632
3. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71:1400-1412. doi: 10.1002/art.40930
4. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1151-1159.
5. Heath CR, Usatine RP. Discoid lupus. Cutis. 2022;109:172-173.
6. Firestein GS, Budd RC, Harris ED Jr, et al, eds. Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 8th ed. Saunders Elsevier; 2008.
7. Nozile W, Adgerson CH, Cohen GF. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus in skin of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:343-349.
8. Cardinali F, Kovacs D, Picardo M. Mechanisms underlying postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: lessons for solar. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2012;139(suppl 4):S148-S152.
9. Ocampo-Piraquive V, Nieto-Aristizábal I, Cañas CA, et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: causes, predictors and interventions. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2018;14:1043-1053. doi: 10.1080/17446 66X.2018.1538789
10. Carter EE, Barr SG, Clarke AE. The global burden of SLE: prevalence, health disparities and socioeconomic impact. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:605-620. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.137
Risk threshold may help providers decide on rabies PEP
The model, reported in JAMA Network Open, could help clinicians, particularly those in primary care settings, to more rationally prescribe PEP to people concerned about a potential exposure to the rabies virus (RABV). In the United States, rabies PEP often is given without a comprehensive assessment that considers regional factors as well as species, nature of an attack, and the health and vaccination status of the animal.
Providers err on the side of caution, as rabies infection has a fatality rate near 100%. When exposures are low-risk, however, patients can rack up substantial out-of-pocket expenses or experience unnecessary adverse effects from the series of shots. Those can include injection site reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, and neurological complications.
The authors write that an estimated 55,000 people per year in the United States were treated for potential exposure to RABV in 2017 and 2018, at an estimated cost of more than $3,800 per person treated.
Researchers calculate risk threshold
The researchers, led by Kelly Charniga, PhD, MPH, an infectious disease epidemiologist with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, calculated positivity rates using more than 900,000 animal samples tested for RABV between 2011 and 2020. Other parameters were estimated from surveillance data and the literature and probabilities were estimated using Bayes’ rule.
A convenience sample of state public health officials in all states (excluding Hawaii) plus Washington and Puerto Rico was used to help determine a risk threshold for recommending PEP. Respondents were asked whether they would recommend PEP given 24 standardized exposure scenarios while accounting for local rabies epidemiology.
Their model establishes a risk threshold of 0.0004 for PEP administration, which represents the probability that an animal would test positive for RABV given that a person was exposed, and the probability that a person would die from rabies after exposure to a suspect rabid animal and no PEP. PEP should not be recommended with any value lower than that cutoff.
Alfred DeMaria, DPH, a consultant to the Massachusetts Department of Public Health in Boston, who was not involved with the study, said the work will be particularly helpful for primary care physicians, giving them confidence to not recommend PEP when infection is statistically highly unlikely and thereby to reduce unnecessary and costly measures.
“Concern about rabies is often based on a very unlikely scenario,” Dr. DeMaria said. He gave the example of people coming into primary care worried that they might have been exposed after comforting their dog who had been bitten in a fight with a wild animal.
“Has that ever happened in the history of the human species? Not that we know of,” he said.
Many people also think dogs and other domestic animals are a likely source of rabies, which is not the case in the United States, Dr. DeMaria said.
“In most cases, it is exposure to a raccoon, a skunk, or a bat,” he said. “Most calls are for potential bat exposure, especially in the summer when young bats are flying around and are not very savvy about avoiding humans.”
The authors note the difference between the animals likely to bite and the species that carry RABV: “The most common mammals involved in bite events in the U.S. are dogs, cats, and small rodents. These species, when healthy and provoked into biting, represent some of the lowest risk exposures evaluated in this model.”
The canine rabies variant virus was eliminated in the United States in 2004.
The study authors note that their model should not be used in other countries because “most rabies deaths globally are caused by domestic dogs.”
Health department consultation can reduce inappropriate treatment
Dr. DeMaria said the paper may also convince physicians to consult with their health department for a final recommendation.
The authors note that a 2020 study in Cook County, Ill., found patients who received PEP were about 90% less likely to receive inappropriate treatment if their clinician had consulted with a health department.
“Anything that puts the risk in a context, like this paper does, is helpful,” he said.
Most physicians in the United States will never see a patient with rabies, the authors write, but animal bites are common – resulting in hundreds of thousands of primary care and emergency department visits each year when physicians must decide whether to administer PEP.
The study authors and Dr. DeMaria report no relevant financial relationships.
The model, reported in JAMA Network Open, could help clinicians, particularly those in primary care settings, to more rationally prescribe PEP to people concerned about a potential exposure to the rabies virus (RABV). In the United States, rabies PEP often is given without a comprehensive assessment that considers regional factors as well as species, nature of an attack, and the health and vaccination status of the animal.
Providers err on the side of caution, as rabies infection has a fatality rate near 100%. When exposures are low-risk, however, patients can rack up substantial out-of-pocket expenses or experience unnecessary adverse effects from the series of shots. Those can include injection site reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, and neurological complications.
The authors write that an estimated 55,000 people per year in the United States were treated for potential exposure to RABV in 2017 and 2018, at an estimated cost of more than $3,800 per person treated.
Researchers calculate risk threshold
The researchers, led by Kelly Charniga, PhD, MPH, an infectious disease epidemiologist with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, calculated positivity rates using more than 900,000 animal samples tested for RABV between 2011 and 2020. Other parameters were estimated from surveillance data and the literature and probabilities were estimated using Bayes’ rule.
A convenience sample of state public health officials in all states (excluding Hawaii) plus Washington and Puerto Rico was used to help determine a risk threshold for recommending PEP. Respondents were asked whether they would recommend PEP given 24 standardized exposure scenarios while accounting for local rabies epidemiology.
Their model establishes a risk threshold of 0.0004 for PEP administration, which represents the probability that an animal would test positive for RABV given that a person was exposed, and the probability that a person would die from rabies after exposure to a suspect rabid animal and no PEP. PEP should not be recommended with any value lower than that cutoff.
Alfred DeMaria, DPH, a consultant to the Massachusetts Department of Public Health in Boston, who was not involved with the study, said the work will be particularly helpful for primary care physicians, giving them confidence to not recommend PEP when infection is statistically highly unlikely and thereby to reduce unnecessary and costly measures.
“Concern about rabies is often based on a very unlikely scenario,” Dr. DeMaria said. He gave the example of people coming into primary care worried that they might have been exposed after comforting their dog who had been bitten in a fight with a wild animal.
“Has that ever happened in the history of the human species? Not that we know of,” he said.
Many people also think dogs and other domestic animals are a likely source of rabies, which is not the case in the United States, Dr. DeMaria said.
“In most cases, it is exposure to a raccoon, a skunk, or a bat,” he said. “Most calls are for potential bat exposure, especially in the summer when young bats are flying around and are not very savvy about avoiding humans.”
The authors note the difference between the animals likely to bite and the species that carry RABV: “The most common mammals involved in bite events in the U.S. are dogs, cats, and small rodents. These species, when healthy and provoked into biting, represent some of the lowest risk exposures evaluated in this model.”
The canine rabies variant virus was eliminated in the United States in 2004.
The study authors note that their model should not be used in other countries because “most rabies deaths globally are caused by domestic dogs.”
Health department consultation can reduce inappropriate treatment
Dr. DeMaria said the paper may also convince physicians to consult with their health department for a final recommendation.
The authors note that a 2020 study in Cook County, Ill., found patients who received PEP were about 90% less likely to receive inappropriate treatment if their clinician had consulted with a health department.
“Anything that puts the risk in a context, like this paper does, is helpful,” he said.
Most physicians in the United States will never see a patient with rabies, the authors write, but animal bites are common – resulting in hundreds of thousands of primary care and emergency department visits each year when physicians must decide whether to administer PEP.
The study authors and Dr. DeMaria report no relevant financial relationships.
The model, reported in JAMA Network Open, could help clinicians, particularly those in primary care settings, to more rationally prescribe PEP to people concerned about a potential exposure to the rabies virus (RABV). In the United States, rabies PEP often is given without a comprehensive assessment that considers regional factors as well as species, nature of an attack, and the health and vaccination status of the animal.
Providers err on the side of caution, as rabies infection has a fatality rate near 100%. When exposures are low-risk, however, patients can rack up substantial out-of-pocket expenses or experience unnecessary adverse effects from the series of shots. Those can include injection site reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, and neurological complications.
The authors write that an estimated 55,000 people per year in the United States were treated for potential exposure to RABV in 2017 and 2018, at an estimated cost of more than $3,800 per person treated.
Researchers calculate risk threshold
The researchers, led by Kelly Charniga, PhD, MPH, an infectious disease epidemiologist with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, calculated positivity rates using more than 900,000 animal samples tested for RABV between 2011 and 2020. Other parameters were estimated from surveillance data and the literature and probabilities were estimated using Bayes’ rule.
A convenience sample of state public health officials in all states (excluding Hawaii) plus Washington and Puerto Rico was used to help determine a risk threshold for recommending PEP. Respondents were asked whether they would recommend PEP given 24 standardized exposure scenarios while accounting for local rabies epidemiology.
Their model establishes a risk threshold of 0.0004 for PEP administration, which represents the probability that an animal would test positive for RABV given that a person was exposed, and the probability that a person would die from rabies after exposure to a suspect rabid animal and no PEP. PEP should not be recommended with any value lower than that cutoff.
Alfred DeMaria, DPH, a consultant to the Massachusetts Department of Public Health in Boston, who was not involved with the study, said the work will be particularly helpful for primary care physicians, giving them confidence to not recommend PEP when infection is statistically highly unlikely and thereby to reduce unnecessary and costly measures.
“Concern about rabies is often based on a very unlikely scenario,” Dr. DeMaria said. He gave the example of people coming into primary care worried that they might have been exposed after comforting their dog who had been bitten in a fight with a wild animal.
“Has that ever happened in the history of the human species? Not that we know of,” he said.
Many people also think dogs and other domestic animals are a likely source of rabies, which is not the case in the United States, Dr. DeMaria said.
“In most cases, it is exposure to a raccoon, a skunk, or a bat,” he said. “Most calls are for potential bat exposure, especially in the summer when young bats are flying around and are not very savvy about avoiding humans.”
The authors note the difference between the animals likely to bite and the species that carry RABV: “The most common mammals involved in bite events in the U.S. are dogs, cats, and small rodents. These species, when healthy and provoked into biting, represent some of the lowest risk exposures evaluated in this model.”
The canine rabies variant virus was eliminated in the United States in 2004.
The study authors note that their model should not be used in other countries because “most rabies deaths globally are caused by domestic dogs.”
Health department consultation can reduce inappropriate treatment
Dr. DeMaria said the paper may also convince physicians to consult with their health department for a final recommendation.
The authors note that a 2020 study in Cook County, Ill., found patients who received PEP were about 90% less likely to receive inappropriate treatment if their clinician had consulted with a health department.
“Anything that puts the risk in a context, like this paper does, is helpful,” he said.
Most physicians in the United States will never see a patient with rabies, the authors write, but animal bites are common – resulting in hundreds of thousands of primary care and emergency department visits each year when physicians must decide whether to administer PEP.
The study authors and Dr. DeMaria report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK
Immediate statin after acute stroke reduces disability
MUNICH, GERMANY – without compromising safety, results of the INSPIRES trial show.
The research, presented at the annual European Stroke Organisation Conference, also showed that intensive antiplatelet therapy reduced the risk for recurrent stroke albeit at an increased in bleeding risk versus standard treatment.
The study involved more than 6,000 patients with acute mild ischemic stroke or TIA and intracranial or extracranial atherosclerosis (ICAS/ECAS), who were randomly assigned in a 2 x 2 factorial design to compare intensive versus standard antiplatelet therapy and intensive statin therapy within 24 hours versus waiting up to 72 hours after onset.
Intensive antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel plus aspirin reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days by 21% versus standard single-agent therapy, although it also doubled the risk for moderate to severe bleeding.
Starting intensive statin therapy with atorvastatin within 24 hours of onset had no impact on recurrent stroke risk but did reduce the risk for a poor functional outcome versus waiting up to 72 hours by 16%.
Moreover, it was “safe, with no increased risk of bleeding, hepatotoxicity, or muscle toxicity,” said study presenter Yilong Wang, MD, department of neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, National Clinical Research Center.
There was, however, a suggestion of an interaction between intensive antiplatelet therapy and immediate intensive statin therapy, he noted, with a trend toward increased bleeding vs delaying the start of statin therapy.
Approached for comment, session cochair Carlos Molina, MD, director of the stroke unit and brain hemodynamics in Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, said that the study is “important because when we look at studies of minor stroke and TIA, they are just focused on long-term outcomes in terms of recurrent stroke.”
He said in an interview that “putting statins in the equation and looking at their impact on long-term outcomes, the study demonstrates that statins are associated ... in particular with reductions in disabling stoke, and that’s good.”
Recurrence and progression
Dr. Wang began by highlighting that acute mild stroke and high-risk TIA are common and underestimated, with a relatively high risk for recurrence and progression, often caused by ICAS/ECAS.
Numerous guidelines recommend intensive antiplatelet therapy in the first 24 hours after the event, but Wang pointed out that there is little evidence to support this, and a meta-analysis suggested the window for effective treatment may be up to 72 hours.
In addition, intense statin therapy appears to be beneficial for the secondary prevention of atherosclerotic stroke in the nonacute phase, although there is no evidence for any neuroprotective effects in the acute phase nor for the optimal timing of starting the drugs.
Dr. Wang also noted that there is the potential for an interaction between intensive antiplatelet and statin therapy that could increase the risk for bleeding.
To investigate further, the researchers conducted a multicenter study involving patients aged 35-80 years with acute ischemic stroke or TIA.
The former was defined as an acute single infarction with 50% or greater stenosis of a major intracranial or extracranial artery that “probably account for the infarction and symptoms,” or multiple infarctions of large artery origin, including nonstenotic vulnerable plaques.
Patients were required to have a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 4-5 24 hours or less from acute stoke onset or 0-5 between 24 and 72 hours of onset.
TIA was defined as 50% or more stenosis of major intracranial or extracranial arteries that probably account for the symptoms, and an ABCD2 score for stroke risk of 4 or more within 24-72 hours of onset.
Patients were excluded if they had received dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel or high-intensity statin therapy within 14 days of random assignment or had intravenous thrombolysis or endovascular therapy after acute stroke or TIA onset.
Those included in the trial were randomly assigned in a 2 x 2 factorial design to receive:
- Intensive or dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin plus immediate high-intensity statin therapy with atorvastatin
- Intensive antiplatelet therapy plus delayed high-intensity statin therapy
- Standard antiplatelet therapy with aspirin alone plus immediate high-intensity statin therapy
- Standard antiplatelet therapy plus delayed high-intensity statin therapy
In all, 6,100 patients were enrolled from 222 hospitals in 99 cities across 25 provinces in China. The mean age was 65 years, and 34.6%-37.0% were women. TIA was recorded in 12.2%-14.1% of patients; 19.5%-19.7% had a single acute infarction, and 66.4%-68.1% had acute multiple infarctions.
The time to randomization was 24 hours or less after event onset in 12.5%-13.2% of cases versus 24-48 hours in 41.2%-42.5% and 48 hours or more in 44.9%-45.7% of patients.
The primary efficacy outcome, defined as stroke at 90 days, was significantly less common with intensive versus standard antiplatelet therapy, at a cumulative probability of 9.2% versus 7.3% (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.94; P = .007).
Clopidogrel plus aspirin was also associated with a significant reduction in a composite vascular event of stroke, myocardial infarction, or vascular death versus aspirin alone, at 7.5% versus 9.3% (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.67-0.95, P = .01), as well as a reduction in rates of ischemic stroke (P = .002), and TIA (P = .02).
The primary safety outcome, defined as moderate to severe bleeding on the GUSTO criteria, was increased with intensive antiplatelet therapy, at 0.9% versus 0.4% for aspirin alone (HR, 2.08; 95% CI, 1.07-4.03; P = .02).
Turning to statin use, Dr. Wang showed that there was no significant difference in rates of stroke at 90 days between delayed and immediate intensive therapy, at a cumulative probability of 8.4% versus 8.1% (HR, 0.95; P = .58).
There was also no difference in rates of moderate to severe bleeding, at 0.8% with immediate versus 0.6% for delayed intensive statin therapy (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 0.73-2.54; P = .34).
Dr. Wang reported that there were no significant differences in key secondary efficacy and safety outcomes.
Analysis of the distribution of modified Rankin Scale scores at 90 days, however, indicated that there was a significant reduction in the risk for poor functional outcome, defined as a score of 2-6, with immediate versus delayed statin therapy (odds ratio, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.72-0.99; P = .04).
Finally, it was found that combining dual antiplatelet therapy with immediate intensive statin therapy was associated with an increase in moderate to severe bleeding versus delayed statin therapy, affecting 1.1% versus 0.7% of patients. The association nonetheless did not reach statistical significance (HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 0.78-3.71; P = .18).
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, the Beijing Outstanding Young Scientist Program, the Beijing Youth Scholar Program, and the Beijing Talent Project. The drug was provided by Sanofi and Jialin Pharmaceutical. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
MUNICH, GERMANY – without compromising safety, results of the INSPIRES trial show.
The research, presented at the annual European Stroke Organisation Conference, also showed that intensive antiplatelet therapy reduced the risk for recurrent stroke albeit at an increased in bleeding risk versus standard treatment.
The study involved more than 6,000 patients with acute mild ischemic stroke or TIA and intracranial or extracranial atherosclerosis (ICAS/ECAS), who were randomly assigned in a 2 x 2 factorial design to compare intensive versus standard antiplatelet therapy and intensive statin therapy within 24 hours versus waiting up to 72 hours after onset.
Intensive antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel plus aspirin reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days by 21% versus standard single-agent therapy, although it also doubled the risk for moderate to severe bleeding.
Starting intensive statin therapy with atorvastatin within 24 hours of onset had no impact on recurrent stroke risk but did reduce the risk for a poor functional outcome versus waiting up to 72 hours by 16%.
Moreover, it was “safe, with no increased risk of bleeding, hepatotoxicity, or muscle toxicity,” said study presenter Yilong Wang, MD, department of neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, National Clinical Research Center.
There was, however, a suggestion of an interaction between intensive antiplatelet therapy and immediate intensive statin therapy, he noted, with a trend toward increased bleeding vs delaying the start of statin therapy.
Approached for comment, session cochair Carlos Molina, MD, director of the stroke unit and brain hemodynamics in Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, said that the study is “important because when we look at studies of minor stroke and TIA, they are just focused on long-term outcomes in terms of recurrent stroke.”
He said in an interview that “putting statins in the equation and looking at their impact on long-term outcomes, the study demonstrates that statins are associated ... in particular with reductions in disabling stoke, and that’s good.”
Recurrence and progression
Dr. Wang began by highlighting that acute mild stroke and high-risk TIA are common and underestimated, with a relatively high risk for recurrence and progression, often caused by ICAS/ECAS.
Numerous guidelines recommend intensive antiplatelet therapy in the first 24 hours after the event, but Wang pointed out that there is little evidence to support this, and a meta-analysis suggested the window for effective treatment may be up to 72 hours.
In addition, intense statin therapy appears to be beneficial for the secondary prevention of atherosclerotic stroke in the nonacute phase, although there is no evidence for any neuroprotective effects in the acute phase nor for the optimal timing of starting the drugs.
Dr. Wang also noted that there is the potential for an interaction between intensive antiplatelet and statin therapy that could increase the risk for bleeding.
To investigate further, the researchers conducted a multicenter study involving patients aged 35-80 years with acute ischemic stroke or TIA.
The former was defined as an acute single infarction with 50% or greater stenosis of a major intracranial or extracranial artery that “probably account for the infarction and symptoms,” or multiple infarctions of large artery origin, including nonstenotic vulnerable plaques.
Patients were required to have a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 4-5 24 hours or less from acute stoke onset or 0-5 between 24 and 72 hours of onset.
TIA was defined as 50% or more stenosis of major intracranial or extracranial arteries that probably account for the symptoms, and an ABCD2 score for stroke risk of 4 or more within 24-72 hours of onset.
Patients were excluded if they had received dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel or high-intensity statin therapy within 14 days of random assignment or had intravenous thrombolysis or endovascular therapy after acute stroke or TIA onset.
Those included in the trial were randomly assigned in a 2 x 2 factorial design to receive:
- Intensive or dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin plus immediate high-intensity statin therapy with atorvastatin
- Intensive antiplatelet therapy plus delayed high-intensity statin therapy
- Standard antiplatelet therapy with aspirin alone plus immediate high-intensity statin therapy
- Standard antiplatelet therapy plus delayed high-intensity statin therapy
In all, 6,100 patients were enrolled from 222 hospitals in 99 cities across 25 provinces in China. The mean age was 65 years, and 34.6%-37.0% were women. TIA was recorded in 12.2%-14.1% of patients; 19.5%-19.7% had a single acute infarction, and 66.4%-68.1% had acute multiple infarctions.
The time to randomization was 24 hours or less after event onset in 12.5%-13.2% of cases versus 24-48 hours in 41.2%-42.5% and 48 hours or more in 44.9%-45.7% of patients.
The primary efficacy outcome, defined as stroke at 90 days, was significantly less common with intensive versus standard antiplatelet therapy, at a cumulative probability of 9.2% versus 7.3% (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.94; P = .007).
Clopidogrel plus aspirin was also associated with a significant reduction in a composite vascular event of stroke, myocardial infarction, or vascular death versus aspirin alone, at 7.5% versus 9.3% (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.67-0.95, P = .01), as well as a reduction in rates of ischemic stroke (P = .002), and TIA (P = .02).
The primary safety outcome, defined as moderate to severe bleeding on the GUSTO criteria, was increased with intensive antiplatelet therapy, at 0.9% versus 0.4% for aspirin alone (HR, 2.08; 95% CI, 1.07-4.03; P = .02).
Turning to statin use, Dr. Wang showed that there was no significant difference in rates of stroke at 90 days between delayed and immediate intensive therapy, at a cumulative probability of 8.4% versus 8.1% (HR, 0.95; P = .58).
There was also no difference in rates of moderate to severe bleeding, at 0.8% with immediate versus 0.6% for delayed intensive statin therapy (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 0.73-2.54; P = .34).
Dr. Wang reported that there were no significant differences in key secondary efficacy and safety outcomes.
Analysis of the distribution of modified Rankin Scale scores at 90 days, however, indicated that there was a significant reduction in the risk for poor functional outcome, defined as a score of 2-6, with immediate versus delayed statin therapy (odds ratio, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.72-0.99; P = .04).
Finally, it was found that combining dual antiplatelet therapy with immediate intensive statin therapy was associated with an increase in moderate to severe bleeding versus delayed statin therapy, affecting 1.1% versus 0.7% of patients. The association nonetheless did not reach statistical significance (HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 0.78-3.71; P = .18).
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, the Beijing Outstanding Young Scientist Program, the Beijing Youth Scholar Program, and the Beijing Talent Project. The drug was provided by Sanofi and Jialin Pharmaceutical. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
MUNICH, GERMANY – without compromising safety, results of the INSPIRES trial show.
The research, presented at the annual European Stroke Organisation Conference, also showed that intensive antiplatelet therapy reduced the risk for recurrent stroke albeit at an increased in bleeding risk versus standard treatment.
The study involved more than 6,000 patients with acute mild ischemic stroke or TIA and intracranial or extracranial atherosclerosis (ICAS/ECAS), who were randomly assigned in a 2 x 2 factorial design to compare intensive versus standard antiplatelet therapy and intensive statin therapy within 24 hours versus waiting up to 72 hours after onset.
Intensive antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel plus aspirin reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days by 21% versus standard single-agent therapy, although it also doubled the risk for moderate to severe bleeding.
Starting intensive statin therapy with atorvastatin within 24 hours of onset had no impact on recurrent stroke risk but did reduce the risk for a poor functional outcome versus waiting up to 72 hours by 16%.
Moreover, it was “safe, with no increased risk of bleeding, hepatotoxicity, or muscle toxicity,” said study presenter Yilong Wang, MD, department of neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, National Clinical Research Center.
There was, however, a suggestion of an interaction between intensive antiplatelet therapy and immediate intensive statin therapy, he noted, with a trend toward increased bleeding vs delaying the start of statin therapy.
Approached for comment, session cochair Carlos Molina, MD, director of the stroke unit and brain hemodynamics in Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, said that the study is “important because when we look at studies of minor stroke and TIA, they are just focused on long-term outcomes in terms of recurrent stroke.”
He said in an interview that “putting statins in the equation and looking at their impact on long-term outcomes, the study demonstrates that statins are associated ... in particular with reductions in disabling stoke, and that’s good.”
Recurrence and progression
Dr. Wang began by highlighting that acute mild stroke and high-risk TIA are common and underestimated, with a relatively high risk for recurrence and progression, often caused by ICAS/ECAS.
Numerous guidelines recommend intensive antiplatelet therapy in the first 24 hours after the event, but Wang pointed out that there is little evidence to support this, and a meta-analysis suggested the window for effective treatment may be up to 72 hours.
In addition, intense statin therapy appears to be beneficial for the secondary prevention of atherosclerotic stroke in the nonacute phase, although there is no evidence for any neuroprotective effects in the acute phase nor for the optimal timing of starting the drugs.
Dr. Wang also noted that there is the potential for an interaction between intensive antiplatelet and statin therapy that could increase the risk for bleeding.
To investigate further, the researchers conducted a multicenter study involving patients aged 35-80 years with acute ischemic stroke or TIA.
The former was defined as an acute single infarction with 50% or greater stenosis of a major intracranial or extracranial artery that “probably account for the infarction and symptoms,” or multiple infarctions of large artery origin, including nonstenotic vulnerable plaques.
Patients were required to have a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 4-5 24 hours or less from acute stoke onset or 0-5 between 24 and 72 hours of onset.
TIA was defined as 50% or more stenosis of major intracranial or extracranial arteries that probably account for the symptoms, and an ABCD2 score for stroke risk of 4 or more within 24-72 hours of onset.
Patients were excluded if they had received dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel or high-intensity statin therapy within 14 days of random assignment or had intravenous thrombolysis or endovascular therapy after acute stroke or TIA onset.
Those included in the trial were randomly assigned in a 2 x 2 factorial design to receive:
- Intensive or dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin plus immediate high-intensity statin therapy with atorvastatin
- Intensive antiplatelet therapy plus delayed high-intensity statin therapy
- Standard antiplatelet therapy with aspirin alone plus immediate high-intensity statin therapy
- Standard antiplatelet therapy plus delayed high-intensity statin therapy
In all, 6,100 patients were enrolled from 222 hospitals in 99 cities across 25 provinces in China. The mean age was 65 years, and 34.6%-37.0% were women. TIA was recorded in 12.2%-14.1% of patients; 19.5%-19.7% had a single acute infarction, and 66.4%-68.1% had acute multiple infarctions.
The time to randomization was 24 hours or less after event onset in 12.5%-13.2% of cases versus 24-48 hours in 41.2%-42.5% and 48 hours or more in 44.9%-45.7% of patients.
The primary efficacy outcome, defined as stroke at 90 days, was significantly less common with intensive versus standard antiplatelet therapy, at a cumulative probability of 9.2% versus 7.3% (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.94; P = .007).
Clopidogrel plus aspirin was also associated with a significant reduction in a composite vascular event of stroke, myocardial infarction, or vascular death versus aspirin alone, at 7.5% versus 9.3% (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.67-0.95, P = .01), as well as a reduction in rates of ischemic stroke (P = .002), and TIA (P = .02).
The primary safety outcome, defined as moderate to severe bleeding on the GUSTO criteria, was increased with intensive antiplatelet therapy, at 0.9% versus 0.4% for aspirin alone (HR, 2.08; 95% CI, 1.07-4.03; P = .02).
Turning to statin use, Dr. Wang showed that there was no significant difference in rates of stroke at 90 days between delayed and immediate intensive therapy, at a cumulative probability of 8.4% versus 8.1% (HR, 0.95; P = .58).
There was also no difference in rates of moderate to severe bleeding, at 0.8% with immediate versus 0.6% for delayed intensive statin therapy (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 0.73-2.54; P = .34).
Dr. Wang reported that there were no significant differences in key secondary efficacy and safety outcomes.
Analysis of the distribution of modified Rankin Scale scores at 90 days, however, indicated that there was a significant reduction in the risk for poor functional outcome, defined as a score of 2-6, with immediate versus delayed statin therapy (odds ratio, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.72-0.99; P = .04).
Finally, it was found that combining dual antiplatelet therapy with immediate intensive statin therapy was associated with an increase in moderate to severe bleeding versus delayed statin therapy, affecting 1.1% versus 0.7% of patients. The association nonetheless did not reach statistical significance (HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 0.78-3.71; P = .18).
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, the Beijing Outstanding Young Scientist Program, the Beijing Youth Scholar Program, and the Beijing Talent Project. The drug was provided by Sanofi and Jialin Pharmaceutical. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ESOC 2023
Profile of respiratory bacteria in children younger than 6 months
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
Antibiotic prophylaxis may lower SSIs in skin cancer surgery
Delivering s, compared with not using incision site antibiotics.
The rate of postoperative SSIs was 2.1% in the clindamycin arm, vs. 5.7% in the control arm and 5.3% in the flucloxacillin arm.
“Based on these results, we recommend the routine adoption of incisional microdosed clindamycin for patients undergoing skin cancer surgery,” Maple Goh, MBChB, of the Auckland Regional Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Unit, Auckland, New Zealand, and the coauthors conclude. “This strategy appears suitable for widespread implementation because of the magnitude of the effect observed and the absence of adverse events.”
The study was published online in JAMA Surgery.
Skin cancer surgery carries a high risk of SSIs, which represent costly yet largely preventable complications of surgery. Despite the risk, there’s a lack of evidence from randomized clinical trials of the role of antibiotic prophylaxis in reducing SSI rates among patients undergoing skin cancer surgery. Previous studies have investigated incisional antibiotic prophylaxis to reduce SSIs with Mohs micrographic surgery, but these surgeries represent a relatively small proportion of overall skin cancer surgeries.
To understand whether this benefit extends to more general skin cancer surgeries, investigators recruited patients from a high-volume skin cancer center in New Zealand who were treated from February to July 2019. In the double-blind, prospective PICASSo trial, patients were randomly assigned to receive an incision site injection of buffered local anesthetic alone (control group), buffered local anesthetic with microdoses of flucloxacillin (500 mcg/mL), or buffered local anesthetic with microdoses of clindamycin (500 mcg/mL). The most common surgery type was excision and direct closure (approximately 80% in all arms), and the mean volume injected per length of direct closure was 1.5 mL/cm.
The primary endpoint was the rate of postoperative SSIs, defined as a postoperative wound infection score of 5 or more. The SSI rate was calculated as the number of lesions with SSIs per total number of lesions in the group.
Overall, 681 patients with 1,133 total lesions were included in the study. Compared with the control arm, the rate of postoperative SSIs was nearly threefold lower among patients who received clindamycin, –2.1% (9 of 422) vs. 5.7% (22 of 388) in the control arm (P = .01 for clindamycin vs. control).
However, flucloxacillin did not demonstrate the same effectiveness. The flucloxacillin arm and the control arm demonstrated similar postoperative SSI rates – 5.3% (17 of 323) vs. 5.7%.
The results were similar after adjusting for baseline differences and lesion ulceration.
The researchers also found that the proportion of lesions that required postoperative systemic antibiotics was four times higher among the control arm, in comparison with the clindamycin arm (8% vs. 2.1%; P < .001). It was two times higher than in the flucloxacillin arm (8% vs. 4%; P = .03).
Treatment with microdoses of incisional flucloxacillin and clindamycin was safe and well tolerated.
The researchers speculated that clindamycin’s greater effectiveness may come down to its slightly broader coverage of commonly cultured bacteria in skin and soft tissue infections, including community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clindamycin is known to have more efficacy against anaerobic bacteria that may be lurking in chronically ulcerated skin lesions and is associated with less local tissue inflammation, compared with flucloxacillin.
Overall, “clindamycin was significantly more effective at preventing SSI than flucloxacillin in our study,” the authors conclude. They note that the use of clindamycin as a first-line prophylaxis agent against SSIs for patients undergoing skin cancer surgery is a practical option.
“These results establish evidence-based guidelines for antibiotic prophylaxis in one of the most common surgical interventions performed worldwide, where they have been previously absent,” the researchers say.
The authors of an editorial published with the study underscore other advantages of incisional microdosing with antibiotics.
“One advantage of cutaneous antibiotic administration is improved drug delivery to poorly perfused tissue, which would have limited reach by the systemic circulation,” wrote Amanda R. Sergesketter, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and Scott T. Hollenbeck, MD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“While not evaluated in this study, local antibiotic delivery may be especially relevant to larger and more complex wounds,” the editorialists say. They note that the next step for future studies should be to evaluate prophylaxis in more complex situations.
“Such studies should be considered enthusiastically, given the clearly favorable impact on surgical site infections demonstrated in the PICASSo trial,” Dr. Sergesketter and Dr. Hollenbeck said.
The study was supported by a grant from the New Zealand Health Research Council. Dr. Hollenbeck reported educational grants to Duke University from Allergan, Acelity, Synovis, Integra, Smith & Nephew, Stryker, Cook, KLs Martin, Bard, VOptix, Scanlan, True Digital Surgery, Nautilus, Mitaka, Checkpoint Surgical, and Omniguide, and he is a founder and equity holder for InSoma Bio, a premarket company focused on tissue regeneration.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Delivering s, compared with not using incision site antibiotics.
The rate of postoperative SSIs was 2.1% in the clindamycin arm, vs. 5.7% in the control arm and 5.3% in the flucloxacillin arm.
“Based on these results, we recommend the routine adoption of incisional microdosed clindamycin for patients undergoing skin cancer surgery,” Maple Goh, MBChB, of the Auckland Regional Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Unit, Auckland, New Zealand, and the coauthors conclude. “This strategy appears suitable for widespread implementation because of the magnitude of the effect observed and the absence of adverse events.”
The study was published online in JAMA Surgery.
Skin cancer surgery carries a high risk of SSIs, which represent costly yet largely preventable complications of surgery. Despite the risk, there’s a lack of evidence from randomized clinical trials of the role of antibiotic prophylaxis in reducing SSI rates among patients undergoing skin cancer surgery. Previous studies have investigated incisional antibiotic prophylaxis to reduce SSIs with Mohs micrographic surgery, but these surgeries represent a relatively small proportion of overall skin cancer surgeries.
To understand whether this benefit extends to more general skin cancer surgeries, investigators recruited patients from a high-volume skin cancer center in New Zealand who were treated from February to July 2019. In the double-blind, prospective PICASSo trial, patients were randomly assigned to receive an incision site injection of buffered local anesthetic alone (control group), buffered local anesthetic with microdoses of flucloxacillin (500 mcg/mL), or buffered local anesthetic with microdoses of clindamycin (500 mcg/mL). The most common surgery type was excision and direct closure (approximately 80% in all arms), and the mean volume injected per length of direct closure was 1.5 mL/cm.
The primary endpoint was the rate of postoperative SSIs, defined as a postoperative wound infection score of 5 or more. The SSI rate was calculated as the number of lesions with SSIs per total number of lesions in the group.
Overall, 681 patients with 1,133 total lesions were included in the study. Compared with the control arm, the rate of postoperative SSIs was nearly threefold lower among patients who received clindamycin, –2.1% (9 of 422) vs. 5.7% (22 of 388) in the control arm (P = .01 for clindamycin vs. control).
However, flucloxacillin did not demonstrate the same effectiveness. The flucloxacillin arm and the control arm demonstrated similar postoperative SSI rates – 5.3% (17 of 323) vs. 5.7%.
The results were similar after adjusting for baseline differences and lesion ulceration.
The researchers also found that the proportion of lesions that required postoperative systemic antibiotics was four times higher among the control arm, in comparison with the clindamycin arm (8% vs. 2.1%; P < .001). It was two times higher than in the flucloxacillin arm (8% vs. 4%; P = .03).
Treatment with microdoses of incisional flucloxacillin and clindamycin was safe and well tolerated.
The researchers speculated that clindamycin’s greater effectiveness may come down to its slightly broader coverage of commonly cultured bacteria in skin and soft tissue infections, including community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clindamycin is known to have more efficacy against anaerobic bacteria that may be lurking in chronically ulcerated skin lesions and is associated with less local tissue inflammation, compared with flucloxacillin.
Overall, “clindamycin was significantly more effective at preventing SSI than flucloxacillin in our study,” the authors conclude. They note that the use of clindamycin as a first-line prophylaxis agent against SSIs for patients undergoing skin cancer surgery is a practical option.
“These results establish evidence-based guidelines for antibiotic prophylaxis in one of the most common surgical interventions performed worldwide, where they have been previously absent,” the researchers say.
The authors of an editorial published with the study underscore other advantages of incisional microdosing with antibiotics.
“One advantage of cutaneous antibiotic administration is improved drug delivery to poorly perfused tissue, which would have limited reach by the systemic circulation,” wrote Amanda R. Sergesketter, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and Scott T. Hollenbeck, MD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“While not evaluated in this study, local antibiotic delivery may be especially relevant to larger and more complex wounds,” the editorialists say. They note that the next step for future studies should be to evaluate prophylaxis in more complex situations.
“Such studies should be considered enthusiastically, given the clearly favorable impact on surgical site infections demonstrated in the PICASSo trial,” Dr. Sergesketter and Dr. Hollenbeck said.
The study was supported by a grant from the New Zealand Health Research Council. Dr. Hollenbeck reported educational grants to Duke University from Allergan, Acelity, Synovis, Integra, Smith & Nephew, Stryker, Cook, KLs Martin, Bard, VOptix, Scanlan, True Digital Surgery, Nautilus, Mitaka, Checkpoint Surgical, and Omniguide, and he is a founder and equity holder for InSoma Bio, a premarket company focused on tissue regeneration.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Delivering s, compared with not using incision site antibiotics.
The rate of postoperative SSIs was 2.1% in the clindamycin arm, vs. 5.7% in the control arm and 5.3% in the flucloxacillin arm.
“Based on these results, we recommend the routine adoption of incisional microdosed clindamycin for patients undergoing skin cancer surgery,” Maple Goh, MBChB, of the Auckland Regional Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Unit, Auckland, New Zealand, and the coauthors conclude. “This strategy appears suitable for widespread implementation because of the magnitude of the effect observed and the absence of adverse events.”
The study was published online in JAMA Surgery.
Skin cancer surgery carries a high risk of SSIs, which represent costly yet largely preventable complications of surgery. Despite the risk, there’s a lack of evidence from randomized clinical trials of the role of antibiotic prophylaxis in reducing SSI rates among patients undergoing skin cancer surgery. Previous studies have investigated incisional antibiotic prophylaxis to reduce SSIs with Mohs micrographic surgery, but these surgeries represent a relatively small proportion of overall skin cancer surgeries.
To understand whether this benefit extends to more general skin cancer surgeries, investigators recruited patients from a high-volume skin cancer center in New Zealand who were treated from February to July 2019. In the double-blind, prospective PICASSo trial, patients were randomly assigned to receive an incision site injection of buffered local anesthetic alone (control group), buffered local anesthetic with microdoses of flucloxacillin (500 mcg/mL), or buffered local anesthetic with microdoses of clindamycin (500 mcg/mL). The most common surgery type was excision and direct closure (approximately 80% in all arms), and the mean volume injected per length of direct closure was 1.5 mL/cm.
The primary endpoint was the rate of postoperative SSIs, defined as a postoperative wound infection score of 5 or more. The SSI rate was calculated as the number of lesions with SSIs per total number of lesions in the group.
Overall, 681 patients with 1,133 total lesions were included in the study. Compared with the control arm, the rate of postoperative SSIs was nearly threefold lower among patients who received clindamycin, –2.1% (9 of 422) vs. 5.7% (22 of 388) in the control arm (P = .01 for clindamycin vs. control).
However, flucloxacillin did not demonstrate the same effectiveness. The flucloxacillin arm and the control arm demonstrated similar postoperative SSI rates – 5.3% (17 of 323) vs. 5.7%.
The results were similar after adjusting for baseline differences and lesion ulceration.
The researchers also found that the proportion of lesions that required postoperative systemic antibiotics was four times higher among the control arm, in comparison with the clindamycin arm (8% vs. 2.1%; P < .001). It was two times higher than in the flucloxacillin arm (8% vs. 4%; P = .03).
Treatment with microdoses of incisional flucloxacillin and clindamycin was safe and well tolerated.
The researchers speculated that clindamycin’s greater effectiveness may come down to its slightly broader coverage of commonly cultured bacteria in skin and soft tissue infections, including community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clindamycin is known to have more efficacy against anaerobic bacteria that may be lurking in chronically ulcerated skin lesions and is associated with less local tissue inflammation, compared with flucloxacillin.
Overall, “clindamycin was significantly more effective at preventing SSI than flucloxacillin in our study,” the authors conclude. They note that the use of clindamycin as a first-line prophylaxis agent against SSIs for patients undergoing skin cancer surgery is a practical option.
“These results establish evidence-based guidelines for antibiotic prophylaxis in one of the most common surgical interventions performed worldwide, where they have been previously absent,” the researchers say.
The authors of an editorial published with the study underscore other advantages of incisional microdosing with antibiotics.
“One advantage of cutaneous antibiotic administration is improved drug delivery to poorly perfused tissue, which would have limited reach by the systemic circulation,” wrote Amanda R. Sergesketter, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and Scott T. Hollenbeck, MD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“While not evaluated in this study, local antibiotic delivery may be especially relevant to larger and more complex wounds,” the editorialists say. They note that the next step for future studies should be to evaluate prophylaxis in more complex situations.
“Such studies should be considered enthusiastically, given the clearly favorable impact on surgical site infections demonstrated in the PICASSo trial,” Dr. Sergesketter and Dr. Hollenbeck said.
The study was supported by a grant from the New Zealand Health Research Council. Dr. Hollenbeck reported educational grants to Duke University from Allergan, Acelity, Synovis, Integra, Smith & Nephew, Stryker, Cook, KLs Martin, Bard, VOptix, Scanlan, True Digital Surgery, Nautilus, Mitaka, Checkpoint Surgical, and Omniguide, and he is a founder and equity holder for InSoma Bio, a premarket company focused on tissue regeneration.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Advising patients on AD treatment options: Expert pearls
WASHINGTON –
The question was top of mind for experts who shared their advice during a “Tips and Tricks” session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting. Dupilumab dosing and dupilumab-associated facial redness and ocular disease, self-image issues, topical regimen adherence, and the quantification of disease were among the other topics raised by the experts.
Here are some of their practice pearls.
Treatment decisions, safety concerns
Deciding on a treatment is “kind of confusing ... particularly in the last year ... and it will only get more complicated,” said Raj J. Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “We’re all about some version of shared decision-making, but if all else is equal, sometimes it pays to explicitly ask the patient, what do you want to do?”
Questions about how long a systemic treatment should be tried, both initially and in the long run, are common. “I think that oftentimes we all get antsy about making changes when we’re not getting to the endpoint we want to. And at least in my real-world experience, late responders are a real thing. Sometimes 3-4 months ... isn’t enough,” he said.
Trial extension data show that patients who were nonresponders for various endpoints at 16 weeks are “captured continuously as you go further and further out,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Regarding the long term, “realistically, there’s no perfect time to call it quits.”
Addressing fears about Janus kinase inhibitors can be challenging, he said. “When you’ve identified the right patient and labs are done ... have them take the medication in front of you and hang out,” he advised. “It may sound ridiculous, but for the extremely anxious person it can be a big stress reducer for everyone involved.”
Regarding treatment fears more generally, “asking patients ‘what is the biggest risk of not treating your disease?’ sometimes gets people thinking,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
For parents of children with AD, said Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, risks of not treating can become apparent once treatments are started and benefits are realized. “It’s so easy to focus on the risks of any treatment because they’re right there in black and white, and the risks of not treating are not always as apparent, even though – or maybe because – they live with them every day.”
When treatment is underway, “they see [how] everyone sleeps better, how school performance gets better, how concentration gets better,” said Dr. Sidbury, professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Washington. Seattle, and chief of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
“Always contextualize,” he advised. “As dermatologists, we’re savvy with navigating boxed warnings.”
David Rosmarin, MD, chair of dermatology, at Indiana University, Indianapolis, and formerly vice chair for research and education at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, said he addresses questions about the length of systemic treatment by advising patients: “Why don’t we start taking [the medication] for 3 months and then we’ll take it from there.”
In some pediatric cases, Dr. Rosmarin said, having the child express “what their AD means to them – how it affects them,” and then acknowledging and validating what the child says, is helpful to parents who are concerned about systemic treatments.
Dupilumab in the real world
Some patients on dupilumab do not have a complete response with dosing every 2 weeks and may benefit from more frequent dosing, said Dr. Rosmarin.
“We know from the SOLO-1 and SOLO-2 studies that dupilumab weekly dosing was evaluated. It was only the every-other-week dosing that was approved, and we can see why – in terms of the changes in EASI [Eczema Area and Severity Index] score they’re close to overlapping,” he said.
In real life, however, “some patients benefit from different dosing. It’s important to realize that. I think we all have some patients who may dose more frequently and some who may dose less frequently,” Dr. Rosmarin said.
For a patient who “gets absolutely no response from dupilumab after 3-4 months, I’d switch them to something else. But for those who are partial responders, particularly those who tell me they’re getting itchy before their next dose, they’re the ones who benefit most from doubling the dose to dupilumab weekly,” he said.
For patients who experience dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis, itraconazole may help, Dr. Rosmarin added. “We’re using 200 mg daily for 2 weeks and weekly thereafter, and it helps some of our patients.” The average self-reported improvement was 52% for patients with dupilumab-associated facial redness treated with itraconazole in a retrospective medical record review that he and his colleagues published in 2022.
Dr. Rosmarin pointed to a multicenter prospective cohort study also published in 2022 showing that baseline/pretreatment levels of Malassezia-specific IgE were associated with the development of dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis. The median levels of Malassezia-specific IgE were 32 kUL–1 versus 2.3 kUL–1 in patients who experienced dupilumab-associated facial redness, compared with those who did not.
He said that, while there “may be multiple reasons” for dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis and that “plenty of patients” who don’t have Malassezia-specific IgE develop head and neck dermatitis, “this could be one cause.”
Itraconazole has been shown in his practice to be superior to fluconazole, likely because it has greater anti-inflammatory effects and provides better coverage of Malassezia because it is more lipophilic, said Dr. Rosmarin, who does not test for Malassezia-specific IgE before trying itraconazole.
For dupilumab-associated ocular surface disease, Elaine C. Siegfried, MD, offered her first-line suggestions: warm compresses (such as a microwaved bean bag), bland ocular lubricant (such as preservative-free artificial tears), oral hydration, and if needed and accessible, the prescription ophthalmic solution lifitegrast.
“It’s become an issue – what the dermatologist can do first line,” said Dr. Siegfried, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Saint Louis University and director of the division of pediatric dermatology at Cardinal Glennon Children’s Hospital, St. Louis.
“If these don’t work, then I’ll identify an ophthalmologist who’s knowledgeable about Dupixent-related ocular surface disease,” she said. Selection is “important because they’re not all knowledgeable ... corneal specialists typically have the most knowledge.”
Topical adherence with diffuse xerosis and mild-moderate AD
For patients with diffuse xerosis and mild-moderate AD, especially those who are older and having difficulty with topical regimens, Anna De Benedetto, MD, said she tries to enhance adherence by simplifying the regimen. She asks patients to buy a pound jar of base cream (ceramide base) – “whatever emollient they like” – and mixes into it a high-potency steroid solution. They’re instructed to apply the combined cream once daily for 1-2 weeks, and then three times a week alternating with a nonmedicated cream.
“This way they’re using one [cream] to target the immune system and the skin barrier,” said Dr. De Benedetto, associate professor of dermatology and director of the dermatology clinical trial unit at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center.
‘Wet wrap’ pajamas; self-image for children, teens
Dermatologist Melinda Gooderham, MSc, MD, assistant professor at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and medical director at the SKiN Centre for Dermatology, said that, for widespread and troublesome AD, she advises patients or parents to wet a thin cotton pajama top and bottom and spin it in the dryer “so it’s almost dry but still moist.” Dry, looser pajamas or a light track suit can then be worn over the damp pajamas. “I usually tell [patients] to buy one size up,” she said.
Body dysmorphia is common with skin disease, and its incidence is six times higher in people with eczema than those without the disease, said Dr. Siegfried. “I’ve found that, for patients subjected to AD for a long time,” this is still an issue, “even when you clear their skin.”
For children, teens and their families, the nonprofit organization Made a Masterpiece can be valuable, Dr. Siegfried said. It offers resources from parents, children, psychologists, dermatologists, and others to help manage the emotional, social and spiritual aspects of living with a skin condition.
To use or not to use BSA; environmental counseling
“I think [assessing] body surface area [BSA] is very important in pediatrics and for adolescents [especially in those with moderate to severe disease] because it quantifies the disease for the family,” said Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and vice chair of the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Diego.
“Families live with the disease, but quantification really matters” for understanding the extent and impact of the disease and for motivating families to treat, said Dr. Eichenfield.
(When the disease is markedly diminished in follow-up, knowing the BSA then “helps families to register the improvement and gives positive reinforcement,” Dr. Eichenfeld said after the meeting.)
Young patients can participate, he noted at the meeting. “When I do telemedicine visits, kids can tell me how many hands of eczema they have.”
Dr. Eichenfield also said that he now routinely counsels on the environmental impacts on eczema. For example, “I explain to people that we’re probably going to have a bad wildfire season in California, and it’s the kind of environmental perturbation that may impact some eczema patients,” he said, noting the 2021 study documenting an association of wildfire air pollution from the 2018 California Camp fire with an increase in dermatology clinic visits for AD and itch in San Francisco.
“It helps to keep an eye out for that, and also to be aware of some of the environmental changes,” he said.
Dr. Chovatiya reported ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others. Dr. Sidbury reported ties with Regeneron, UCB, Pfizer, Leo Pharma, and Lilly, among others. Dr. Rosmarin reported ties with AbbVie, Incyte, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others. Dr. Siegfried reported ties with Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, AbbVie, Incyte, Leo, and Pfizer, among others. Dr. De Benedetto reported ties with Incyte, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Sanofi Advent, among others. Dr. Gooderham reported ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, among others. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others.
WASHINGTON –
The question was top of mind for experts who shared their advice during a “Tips and Tricks” session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting. Dupilumab dosing and dupilumab-associated facial redness and ocular disease, self-image issues, topical regimen adherence, and the quantification of disease were among the other topics raised by the experts.
Here are some of their practice pearls.
Treatment decisions, safety concerns
Deciding on a treatment is “kind of confusing ... particularly in the last year ... and it will only get more complicated,” said Raj J. Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “We’re all about some version of shared decision-making, but if all else is equal, sometimes it pays to explicitly ask the patient, what do you want to do?”
Questions about how long a systemic treatment should be tried, both initially and in the long run, are common. “I think that oftentimes we all get antsy about making changes when we’re not getting to the endpoint we want to. And at least in my real-world experience, late responders are a real thing. Sometimes 3-4 months ... isn’t enough,” he said.
Trial extension data show that patients who were nonresponders for various endpoints at 16 weeks are “captured continuously as you go further and further out,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Regarding the long term, “realistically, there’s no perfect time to call it quits.”
Addressing fears about Janus kinase inhibitors can be challenging, he said. “When you’ve identified the right patient and labs are done ... have them take the medication in front of you and hang out,” he advised. “It may sound ridiculous, but for the extremely anxious person it can be a big stress reducer for everyone involved.”
Regarding treatment fears more generally, “asking patients ‘what is the biggest risk of not treating your disease?’ sometimes gets people thinking,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
For parents of children with AD, said Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, risks of not treating can become apparent once treatments are started and benefits are realized. “It’s so easy to focus on the risks of any treatment because they’re right there in black and white, and the risks of not treating are not always as apparent, even though – or maybe because – they live with them every day.”
When treatment is underway, “they see [how] everyone sleeps better, how school performance gets better, how concentration gets better,” said Dr. Sidbury, professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Washington. Seattle, and chief of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
“Always contextualize,” he advised. “As dermatologists, we’re savvy with navigating boxed warnings.”
David Rosmarin, MD, chair of dermatology, at Indiana University, Indianapolis, and formerly vice chair for research and education at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, said he addresses questions about the length of systemic treatment by advising patients: “Why don’t we start taking [the medication] for 3 months and then we’ll take it from there.”
In some pediatric cases, Dr. Rosmarin said, having the child express “what their AD means to them – how it affects them,” and then acknowledging and validating what the child says, is helpful to parents who are concerned about systemic treatments.
Dupilumab in the real world
Some patients on dupilumab do not have a complete response with dosing every 2 weeks and may benefit from more frequent dosing, said Dr. Rosmarin.
“We know from the SOLO-1 and SOLO-2 studies that dupilumab weekly dosing was evaluated. It was only the every-other-week dosing that was approved, and we can see why – in terms of the changes in EASI [Eczema Area and Severity Index] score they’re close to overlapping,” he said.
In real life, however, “some patients benefit from different dosing. It’s important to realize that. I think we all have some patients who may dose more frequently and some who may dose less frequently,” Dr. Rosmarin said.
For a patient who “gets absolutely no response from dupilumab after 3-4 months, I’d switch them to something else. But for those who are partial responders, particularly those who tell me they’re getting itchy before their next dose, they’re the ones who benefit most from doubling the dose to dupilumab weekly,” he said.
For patients who experience dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis, itraconazole may help, Dr. Rosmarin added. “We’re using 200 mg daily for 2 weeks and weekly thereafter, and it helps some of our patients.” The average self-reported improvement was 52% for patients with dupilumab-associated facial redness treated with itraconazole in a retrospective medical record review that he and his colleagues published in 2022.
Dr. Rosmarin pointed to a multicenter prospective cohort study also published in 2022 showing that baseline/pretreatment levels of Malassezia-specific IgE were associated with the development of dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis. The median levels of Malassezia-specific IgE were 32 kUL–1 versus 2.3 kUL–1 in patients who experienced dupilumab-associated facial redness, compared with those who did not.
He said that, while there “may be multiple reasons” for dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis and that “plenty of patients” who don’t have Malassezia-specific IgE develop head and neck dermatitis, “this could be one cause.”
Itraconazole has been shown in his practice to be superior to fluconazole, likely because it has greater anti-inflammatory effects and provides better coverage of Malassezia because it is more lipophilic, said Dr. Rosmarin, who does not test for Malassezia-specific IgE before trying itraconazole.
For dupilumab-associated ocular surface disease, Elaine C. Siegfried, MD, offered her first-line suggestions: warm compresses (such as a microwaved bean bag), bland ocular lubricant (such as preservative-free artificial tears), oral hydration, and if needed and accessible, the prescription ophthalmic solution lifitegrast.
“It’s become an issue – what the dermatologist can do first line,” said Dr. Siegfried, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Saint Louis University and director of the division of pediatric dermatology at Cardinal Glennon Children’s Hospital, St. Louis.
“If these don’t work, then I’ll identify an ophthalmologist who’s knowledgeable about Dupixent-related ocular surface disease,” she said. Selection is “important because they’re not all knowledgeable ... corneal specialists typically have the most knowledge.”
Topical adherence with diffuse xerosis and mild-moderate AD
For patients with diffuse xerosis and mild-moderate AD, especially those who are older and having difficulty with topical regimens, Anna De Benedetto, MD, said she tries to enhance adherence by simplifying the regimen. She asks patients to buy a pound jar of base cream (ceramide base) – “whatever emollient they like” – and mixes into it a high-potency steroid solution. They’re instructed to apply the combined cream once daily for 1-2 weeks, and then three times a week alternating with a nonmedicated cream.
“This way they’re using one [cream] to target the immune system and the skin barrier,” said Dr. De Benedetto, associate professor of dermatology and director of the dermatology clinical trial unit at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center.
‘Wet wrap’ pajamas; self-image for children, teens
Dermatologist Melinda Gooderham, MSc, MD, assistant professor at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and medical director at the SKiN Centre for Dermatology, said that, for widespread and troublesome AD, she advises patients or parents to wet a thin cotton pajama top and bottom and spin it in the dryer “so it’s almost dry but still moist.” Dry, looser pajamas or a light track suit can then be worn over the damp pajamas. “I usually tell [patients] to buy one size up,” she said.
Body dysmorphia is common with skin disease, and its incidence is six times higher in people with eczema than those without the disease, said Dr. Siegfried. “I’ve found that, for patients subjected to AD for a long time,” this is still an issue, “even when you clear their skin.”
For children, teens and their families, the nonprofit organization Made a Masterpiece can be valuable, Dr. Siegfried said. It offers resources from parents, children, psychologists, dermatologists, and others to help manage the emotional, social and spiritual aspects of living with a skin condition.
To use or not to use BSA; environmental counseling
“I think [assessing] body surface area [BSA] is very important in pediatrics and for adolescents [especially in those with moderate to severe disease] because it quantifies the disease for the family,” said Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and vice chair of the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Diego.
“Families live with the disease, but quantification really matters” for understanding the extent and impact of the disease and for motivating families to treat, said Dr. Eichenfield.
(When the disease is markedly diminished in follow-up, knowing the BSA then “helps families to register the improvement and gives positive reinforcement,” Dr. Eichenfeld said after the meeting.)
Young patients can participate, he noted at the meeting. “When I do telemedicine visits, kids can tell me how many hands of eczema they have.”
Dr. Eichenfield also said that he now routinely counsels on the environmental impacts on eczema. For example, “I explain to people that we’re probably going to have a bad wildfire season in California, and it’s the kind of environmental perturbation that may impact some eczema patients,” he said, noting the 2021 study documenting an association of wildfire air pollution from the 2018 California Camp fire with an increase in dermatology clinic visits for AD and itch in San Francisco.
“It helps to keep an eye out for that, and also to be aware of some of the environmental changes,” he said.
Dr. Chovatiya reported ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others. Dr. Sidbury reported ties with Regeneron, UCB, Pfizer, Leo Pharma, and Lilly, among others. Dr. Rosmarin reported ties with AbbVie, Incyte, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others. Dr. Siegfried reported ties with Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, AbbVie, Incyte, Leo, and Pfizer, among others. Dr. De Benedetto reported ties with Incyte, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Sanofi Advent, among others. Dr. Gooderham reported ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, among others. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others.
WASHINGTON –
The question was top of mind for experts who shared their advice during a “Tips and Tricks” session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting. Dupilumab dosing and dupilumab-associated facial redness and ocular disease, self-image issues, topical regimen adherence, and the quantification of disease were among the other topics raised by the experts.
Here are some of their practice pearls.
Treatment decisions, safety concerns
Deciding on a treatment is “kind of confusing ... particularly in the last year ... and it will only get more complicated,” said Raj J. Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “We’re all about some version of shared decision-making, but if all else is equal, sometimes it pays to explicitly ask the patient, what do you want to do?”
Questions about how long a systemic treatment should be tried, both initially and in the long run, are common. “I think that oftentimes we all get antsy about making changes when we’re not getting to the endpoint we want to. And at least in my real-world experience, late responders are a real thing. Sometimes 3-4 months ... isn’t enough,” he said.
Trial extension data show that patients who were nonresponders for various endpoints at 16 weeks are “captured continuously as you go further and further out,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Regarding the long term, “realistically, there’s no perfect time to call it quits.”
Addressing fears about Janus kinase inhibitors can be challenging, he said. “When you’ve identified the right patient and labs are done ... have them take the medication in front of you and hang out,” he advised. “It may sound ridiculous, but for the extremely anxious person it can be a big stress reducer for everyone involved.”
Regarding treatment fears more generally, “asking patients ‘what is the biggest risk of not treating your disease?’ sometimes gets people thinking,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
For parents of children with AD, said Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, risks of not treating can become apparent once treatments are started and benefits are realized. “It’s so easy to focus on the risks of any treatment because they’re right there in black and white, and the risks of not treating are not always as apparent, even though – or maybe because – they live with them every day.”
When treatment is underway, “they see [how] everyone sleeps better, how school performance gets better, how concentration gets better,” said Dr. Sidbury, professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Washington. Seattle, and chief of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
“Always contextualize,” he advised. “As dermatologists, we’re savvy with navigating boxed warnings.”
David Rosmarin, MD, chair of dermatology, at Indiana University, Indianapolis, and formerly vice chair for research and education at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, said he addresses questions about the length of systemic treatment by advising patients: “Why don’t we start taking [the medication] for 3 months and then we’ll take it from there.”
In some pediatric cases, Dr. Rosmarin said, having the child express “what their AD means to them – how it affects them,” and then acknowledging and validating what the child says, is helpful to parents who are concerned about systemic treatments.
Dupilumab in the real world
Some patients on dupilumab do not have a complete response with dosing every 2 weeks and may benefit from more frequent dosing, said Dr. Rosmarin.
“We know from the SOLO-1 and SOLO-2 studies that dupilumab weekly dosing was evaluated. It was only the every-other-week dosing that was approved, and we can see why – in terms of the changes in EASI [Eczema Area and Severity Index] score they’re close to overlapping,” he said.
In real life, however, “some patients benefit from different dosing. It’s important to realize that. I think we all have some patients who may dose more frequently and some who may dose less frequently,” Dr. Rosmarin said.
For a patient who “gets absolutely no response from dupilumab after 3-4 months, I’d switch them to something else. But for those who are partial responders, particularly those who tell me they’re getting itchy before their next dose, they’re the ones who benefit most from doubling the dose to dupilumab weekly,” he said.
For patients who experience dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis, itraconazole may help, Dr. Rosmarin added. “We’re using 200 mg daily for 2 weeks and weekly thereafter, and it helps some of our patients.” The average self-reported improvement was 52% for patients with dupilumab-associated facial redness treated with itraconazole in a retrospective medical record review that he and his colleagues published in 2022.
Dr. Rosmarin pointed to a multicenter prospective cohort study also published in 2022 showing that baseline/pretreatment levels of Malassezia-specific IgE were associated with the development of dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis. The median levels of Malassezia-specific IgE were 32 kUL–1 versus 2.3 kUL–1 in patients who experienced dupilumab-associated facial redness, compared with those who did not.
He said that, while there “may be multiple reasons” for dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis and that “plenty of patients” who don’t have Malassezia-specific IgE develop head and neck dermatitis, “this could be one cause.”
Itraconazole has been shown in his practice to be superior to fluconazole, likely because it has greater anti-inflammatory effects and provides better coverage of Malassezia because it is more lipophilic, said Dr. Rosmarin, who does not test for Malassezia-specific IgE before trying itraconazole.
For dupilumab-associated ocular surface disease, Elaine C. Siegfried, MD, offered her first-line suggestions: warm compresses (such as a microwaved bean bag), bland ocular lubricant (such as preservative-free artificial tears), oral hydration, and if needed and accessible, the prescription ophthalmic solution lifitegrast.
“It’s become an issue – what the dermatologist can do first line,” said Dr. Siegfried, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Saint Louis University and director of the division of pediatric dermatology at Cardinal Glennon Children’s Hospital, St. Louis.
“If these don’t work, then I’ll identify an ophthalmologist who’s knowledgeable about Dupixent-related ocular surface disease,” she said. Selection is “important because they’re not all knowledgeable ... corneal specialists typically have the most knowledge.”
Topical adherence with diffuse xerosis and mild-moderate AD
For patients with diffuse xerosis and mild-moderate AD, especially those who are older and having difficulty with topical regimens, Anna De Benedetto, MD, said she tries to enhance adherence by simplifying the regimen. She asks patients to buy a pound jar of base cream (ceramide base) – “whatever emollient they like” – and mixes into it a high-potency steroid solution. They’re instructed to apply the combined cream once daily for 1-2 weeks, and then three times a week alternating with a nonmedicated cream.
“This way they’re using one [cream] to target the immune system and the skin barrier,” said Dr. De Benedetto, associate professor of dermatology and director of the dermatology clinical trial unit at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center.
‘Wet wrap’ pajamas; self-image for children, teens
Dermatologist Melinda Gooderham, MSc, MD, assistant professor at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and medical director at the SKiN Centre for Dermatology, said that, for widespread and troublesome AD, she advises patients or parents to wet a thin cotton pajama top and bottom and spin it in the dryer “so it’s almost dry but still moist.” Dry, looser pajamas or a light track suit can then be worn over the damp pajamas. “I usually tell [patients] to buy one size up,” she said.
Body dysmorphia is common with skin disease, and its incidence is six times higher in people with eczema than those without the disease, said Dr. Siegfried. “I’ve found that, for patients subjected to AD for a long time,” this is still an issue, “even when you clear their skin.”
For children, teens and their families, the nonprofit organization Made a Masterpiece can be valuable, Dr. Siegfried said. It offers resources from parents, children, psychologists, dermatologists, and others to help manage the emotional, social and spiritual aspects of living with a skin condition.
To use or not to use BSA; environmental counseling
“I think [assessing] body surface area [BSA] is very important in pediatrics and for adolescents [especially in those with moderate to severe disease] because it quantifies the disease for the family,” said Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and vice chair of the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Diego.
“Families live with the disease, but quantification really matters” for understanding the extent and impact of the disease and for motivating families to treat, said Dr. Eichenfield.
(When the disease is markedly diminished in follow-up, knowing the BSA then “helps families to register the improvement and gives positive reinforcement,” Dr. Eichenfeld said after the meeting.)
Young patients can participate, he noted at the meeting. “When I do telemedicine visits, kids can tell me how many hands of eczema they have.”
Dr. Eichenfield also said that he now routinely counsels on the environmental impacts on eczema. For example, “I explain to people that we’re probably going to have a bad wildfire season in California, and it’s the kind of environmental perturbation that may impact some eczema patients,” he said, noting the 2021 study documenting an association of wildfire air pollution from the 2018 California Camp fire with an increase in dermatology clinic visits for AD and itch in San Francisco.
“It helps to keep an eye out for that, and also to be aware of some of the environmental changes,” he said.
Dr. Chovatiya reported ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others. Dr. Sidbury reported ties with Regeneron, UCB, Pfizer, Leo Pharma, and Lilly, among others. Dr. Rosmarin reported ties with AbbVie, Incyte, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others. Dr. Siegfried reported ties with Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, AbbVie, Incyte, Leo, and Pfizer, among others. Dr. De Benedetto reported ties with Incyte, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Sanofi Advent, among others. Dr. Gooderham reported ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, among others. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed ties with AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi, among others.
AT RAD 2023
FDA panel unanimously endorses lecanemab for Alzheimer’s
“Overall, the study demonstrated clearly that this is an effective treatment,” said acting chair Robert C. Alexander, MD, chief scientific officer, Alzheimer’s Prevention Initiative, Banner Alzheimer’s Institute, and research professor, department of psychiatry, University of Arizona, Phoenix, during the meeting.
An intravenous infusion targeting amyloid-beta, lecanemab received accelerated FDA approved earlier in 2023 for the treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The company was required to complete a confirmatory study to verify and describe the product’s clinical benefit.
The Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee met to discuss this phase 3 study (CLARITY-AD). The multicenter, double-blind study included 1,795 patients (mean age, 71 years) who had mild cognitive impairment caused by AD or mild AD dementia.
Delayed progression
Study participants had a broad range of comorbidities, and many were concomitantly receiving other medications. Black people were underrepresented in the study at just 3% of the total cohort.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo or lecanemab 10 mg/kg biweekly. In addition to a placebo-controlled period and safety follow-up, the study has an ongoing extension phase of up to 4 years.
The study met its primary endpoint, showing a highly statistically significant 27% less decline on the Clinical Dementia Rating-Sum of Boxes at 18 months (difference in adjusted mean, –0.45; 95% CI, –0.67 to –0.23; P = .00005).
This was supported by a significant 26% difference on the AD Assessment Scale–Cognitive Subscale with 14 tasks (ADAS-Cog 14).
The drug also affected function, with a 37% decrease, compared with placebo, on the AD Cooperative Study–Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment.
Committee members heard that the results signal delays in disease progression by about 5 months, giving patients more time to live independently and participate in hobbies and interests.
Patients who received the active drug also experienced quality of life benefits. Compared with patients who received placebo, those who took lecanemab had 49% less decline as measured with the European Quality of Life–5 Dimensions scale and 56% less decline as measured by the Quality of Life in AD scale, and caregivers reported less burden.
Lecanemab also affected biomarkers of amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration, providing a biological basis for the treatment effects consistent with slowing of disease progression.
Unanimous support
All six committee members agreed by vote that the study provides evidence of clinical benefit. They variously descried the study and results as “robust,” “compelling,” “well conducted,” “clear and consistent,” and “clinically meaningful.”
In the active treatment group, there was a higher incidence of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs), which can be serious and life-threatening but are usually asymptomatic. In this study, most ARIAs had resolved by 3 months.
Deaths occurred in 0.8% of the placebo and 0.7% of the treatment group. Dean Follmann, PhD, assistant director for biostatistics, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md., noted that the numbers of deaths and serious adverse events were “quite similar” in the two groups.
“And for serious ARIA, there was an imbalance favoring placebo, but overall, these were pretty rare,” he said.
Subgroup concerns
Committee members discussed the risk/benefit profile for three subgroups of patients – those with apolipoprotein E4 (apo E4) allele, patients taking an anticoagulant, and those with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
In the apo E4 group, the study’s primary endpoint did not favor the drug, but secondary endpoints did.
“I think the general feeling [for apo E4 status] is that the risk/benefit still remains favorable, especially when looking across multiple endpoints,” said Dr. Alexander.
However, some members supported recommending genetic testing before initiating the drug.
The views were more diverse for the use of lecanemab in the presence of an anticoagulant, which may increase the risk for cerebral hemorrhage. Some committee members strongly recommended that these patients not receive lecanemab, while others highlighted the need for more information, owing to uncertainties about the risks.
With respect to CAA, most members supported the idea of considering use of the drug in the presence of this condition, but only after discussing the risks with patients and their families and in the presence of a robust reporting system.
An Alzheimer’s Association representative was in attendance during the public hearing portion of the meeting to express support for traditional approval of lecanemab for people with early AD.
The association strongly favors full Medicare coverage for FDA-approved AD treatments. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has determined that AD treatments receiving traditional FDA approval will be covered if clinicians register and enter data in a registry.
“While this is an important signal that CMS wants to improve access to FDA-approved treatments, registry as a condition of coverage is an unnecessary and potentially harmful barrier,” said the Alzheimer’s Association in a press release following the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Overall, the study demonstrated clearly that this is an effective treatment,” said acting chair Robert C. Alexander, MD, chief scientific officer, Alzheimer’s Prevention Initiative, Banner Alzheimer’s Institute, and research professor, department of psychiatry, University of Arizona, Phoenix, during the meeting.
An intravenous infusion targeting amyloid-beta, lecanemab received accelerated FDA approved earlier in 2023 for the treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The company was required to complete a confirmatory study to verify and describe the product’s clinical benefit.
The Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee met to discuss this phase 3 study (CLARITY-AD). The multicenter, double-blind study included 1,795 patients (mean age, 71 years) who had mild cognitive impairment caused by AD or mild AD dementia.
Delayed progression
Study participants had a broad range of comorbidities, and many were concomitantly receiving other medications. Black people were underrepresented in the study at just 3% of the total cohort.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo or lecanemab 10 mg/kg biweekly. In addition to a placebo-controlled period and safety follow-up, the study has an ongoing extension phase of up to 4 years.
The study met its primary endpoint, showing a highly statistically significant 27% less decline on the Clinical Dementia Rating-Sum of Boxes at 18 months (difference in adjusted mean, –0.45; 95% CI, –0.67 to –0.23; P = .00005).
This was supported by a significant 26% difference on the AD Assessment Scale–Cognitive Subscale with 14 tasks (ADAS-Cog 14).
The drug also affected function, with a 37% decrease, compared with placebo, on the AD Cooperative Study–Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment.
Committee members heard that the results signal delays in disease progression by about 5 months, giving patients more time to live independently and participate in hobbies and interests.
Patients who received the active drug also experienced quality of life benefits. Compared with patients who received placebo, those who took lecanemab had 49% less decline as measured with the European Quality of Life–5 Dimensions scale and 56% less decline as measured by the Quality of Life in AD scale, and caregivers reported less burden.
Lecanemab also affected biomarkers of amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration, providing a biological basis for the treatment effects consistent with slowing of disease progression.
Unanimous support
All six committee members agreed by vote that the study provides evidence of clinical benefit. They variously descried the study and results as “robust,” “compelling,” “well conducted,” “clear and consistent,” and “clinically meaningful.”
In the active treatment group, there was a higher incidence of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs), which can be serious and life-threatening but are usually asymptomatic. In this study, most ARIAs had resolved by 3 months.
Deaths occurred in 0.8% of the placebo and 0.7% of the treatment group. Dean Follmann, PhD, assistant director for biostatistics, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md., noted that the numbers of deaths and serious adverse events were “quite similar” in the two groups.
“And for serious ARIA, there was an imbalance favoring placebo, but overall, these were pretty rare,” he said.
Subgroup concerns
Committee members discussed the risk/benefit profile for three subgroups of patients – those with apolipoprotein E4 (apo E4) allele, patients taking an anticoagulant, and those with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
In the apo E4 group, the study’s primary endpoint did not favor the drug, but secondary endpoints did.
“I think the general feeling [for apo E4 status] is that the risk/benefit still remains favorable, especially when looking across multiple endpoints,” said Dr. Alexander.
However, some members supported recommending genetic testing before initiating the drug.
The views were more diverse for the use of lecanemab in the presence of an anticoagulant, which may increase the risk for cerebral hemorrhage. Some committee members strongly recommended that these patients not receive lecanemab, while others highlighted the need for more information, owing to uncertainties about the risks.
With respect to CAA, most members supported the idea of considering use of the drug in the presence of this condition, but only after discussing the risks with patients and their families and in the presence of a robust reporting system.
An Alzheimer’s Association representative was in attendance during the public hearing portion of the meeting to express support for traditional approval of lecanemab for people with early AD.
The association strongly favors full Medicare coverage for FDA-approved AD treatments. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has determined that AD treatments receiving traditional FDA approval will be covered if clinicians register and enter data in a registry.
“While this is an important signal that CMS wants to improve access to FDA-approved treatments, registry as a condition of coverage is an unnecessary and potentially harmful barrier,” said the Alzheimer’s Association in a press release following the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Overall, the study demonstrated clearly that this is an effective treatment,” said acting chair Robert C. Alexander, MD, chief scientific officer, Alzheimer’s Prevention Initiative, Banner Alzheimer’s Institute, and research professor, department of psychiatry, University of Arizona, Phoenix, during the meeting.
An intravenous infusion targeting amyloid-beta, lecanemab received accelerated FDA approved earlier in 2023 for the treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The company was required to complete a confirmatory study to verify and describe the product’s clinical benefit.
The Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee met to discuss this phase 3 study (CLARITY-AD). The multicenter, double-blind study included 1,795 patients (mean age, 71 years) who had mild cognitive impairment caused by AD or mild AD dementia.
Delayed progression
Study participants had a broad range of comorbidities, and many were concomitantly receiving other medications. Black people were underrepresented in the study at just 3% of the total cohort.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo or lecanemab 10 mg/kg biweekly. In addition to a placebo-controlled period and safety follow-up, the study has an ongoing extension phase of up to 4 years.
The study met its primary endpoint, showing a highly statistically significant 27% less decline on the Clinical Dementia Rating-Sum of Boxes at 18 months (difference in adjusted mean, –0.45; 95% CI, –0.67 to –0.23; P = .00005).
This was supported by a significant 26% difference on the AD Assessment Scale–Cognitive Subscale with 14 tasks (ADAS-Cog 14).
The drug also affected function, with a 37% decrease, compared with placebo, on the AD Cooperative Study–Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment.
Committee members heard that the results signal delays in disease progression by about 5 months, giving patients more time to live independently and participate in hobbies and interests.
Patients who received the active drug also experienced quality of life benefits. Compared with patients who received placebo, those who took lecanemab had 49% less decline as measured with the European Quality of Life–5 Dimensions scale and 56% less decline as measured by the Quality of Life in AD scale, and caregivers reported less burden.
Lecanemab also affected biomarkers of amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration, providing a biological basis for the treatment effects consistent with slowing of disease progression.
Unanimous support
All six committee members agreed by vote that the study provides evidence of clinical benefit. They variously descried the study and results as “robust,” “compelling,” “well conducted,” “clear and consistent,” and “clinically meaningful.”
In the active treatment group, there was a higher incidence of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs), which can be serious and life-threatening but are usually asymptomatic. In this study, most ARIAs had resolved by 3 months.
Deaths occurred in 0.8% of the placebo and 0.7% of the treatment group. Dean Follmann, PhD, assistant director for biostatistics, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md., noted that the numbers of deaths and serious adverse events were “quite similar” in the two groups.
“And for serious ARIA, there was an imbalance favoring placebo, but overall, these were pretty rare,” he said.
Subgroup concerns
Committee members discussed the risk/benefit profile for three subgroups of patients – those with apolipoprotein E4 (apo E4) allele, patients taking an anticoagulant, and those with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
In the apo E4 group, the study’s primary endpoint did not favor the drug, but secondary endpoints did.
“I think the general feeling [for apo E4 status] is that the risk/benefit still remains favorable, especially when looking across multiple endpoints,” said Dr. Alexander.
However, some members supported recommending genetic testing before initiating the drug.
The views were more diverse for the use of lecanemab in the presence of an anticoagulant, which may increase the risk for cerebral hemorrhage. Some committee members strongly recommended that these patients not receive lecanemab, while others highlighted the need for more information, owing to uncertainties about the risks.
With respect to CAA, most members supported the idea of considering use of the drug in the presence of this condition, but only after discussing the risks with patients and their families and in the presence of a robust reporting system.
An Alzheimer’s Association representative was in attendance during the public hearing portion of the meeting to express support for traditional approval of lecanemab for people with early AD.
The association strongly favors full Medicare coverage for FDA-approved AD treatments. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has determined that AD treatments receiving traditional FDA approval will be covered if clinicians register and enter data in a registry.
“While this is an important signal that CMS wants to improve access to FDA-approved treatments, registry as a condition of coverage is an unnecessary and potentially harmful barrier,” said the Alzheimer’s Association in a press release following the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 7-year-old male has a bumpy rash on the chin for several months
Given the presentation and the unique location of the lesions he was diagnosed with follicular keratosis of the chin (FKC).
This is a rare and poorly understood condition that can be present in older children and young teenagers. In the cases reported by Kanzaki et al.1 were two boys who presented with the condition; it was thought to be associated with rubbing of the chin with their hands when watching TV or reading. The author described improvement with habit change. This condition is usually described in boys, and some cases presented in brothers,2 suggesting a genetic predisposition. Some reports lack a history of rubbing or trauma to the area.
Histopathologic evaluation of the lesions demonstrates dilated hair follicles containing keratotic basophilic material without any signs of inflammation.
The lesions can be confused with keratosis pilaris (KP). Keratosis pilaris can be described in association with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis, which were not present in our patient. The lesions usually present on the sides of the cheeks and lateral region of the arms and legs. Compared with follicular keratosis, KP lesions usually present with associated perifollicular erythema. Our patient did not present with lesions on the cheeks or the sides of the arms or legs. Milia can present on the chin of children, usually if there is history of rubbing or trauma, or on a scar. Milia are micro keratin cysts, usually seen in areas of the face. Lichen spinulous is described as rough small follicular papules that present in oval or circular patches that can grow up to 5 cm and spread rapidly. They usually present on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, neck, abdomen, and knees. These lesions are thought to be secondary to infections, have been associated with atopy, and have been seen in patients with atopic dermatitis. There is a probable genetic predisposition. The lesions are usually treated with gentle soaps and moisturizer containing keratolytics like urea or salicylic acid, and in some cases topical retinoids can also be tried. Follicular mucinosis can also present similarly to keratosis follicularis. The lesions present as scaly plaques or as grouped skin color papules on the face, scalp, or the neck that can also be associated with hair loss. Sometimes a biopsy needs to be done to be able to distinguish it from follicular keratosis. There is an increase of mucin around hair follicles and sebaceous glands with associated inflammation and degeneration of the follicular structures. In patients with primary follicular mucinosis the lesions can resolve spontaneously in a couple of years. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids, oral antibiotics like macrolides or tetracyclines, dapsone, and phototherapy.
KFC can be treated with vitamin D analogues. It is usually unresponsive to corticosteroids, keratolytic lotions, and retinoids. Our patient was prescribed calcipotriene.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego
References
1. Kanzaki T et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(1):134-5.
2. Buechner AA et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Jan 1;154(1):111-2.
Given the presentation and the unique location of the lesions he was diagnosed with follicular keratosis of the chin (FKC).
This is a rare and poorly understood condition that can be present in older children and young teenagers. In the cases reported by Kanzaki et al.1 were two boys who presented with the condition; it was thought to be associated with rubbing of the chin with their hands when watching TV or reading. The author described improvement with habit change. This condition is usually described in boys, and some cases presented in brothers,2 suggesting a genetic predisposition. Some reports lack a history of rubbing or trauma to the area.
Histopathologic evaluation of the lesions demonstrates dilated hair follicles containing keratotic basophilic material without any signs of inflammation.
The lesions can be confused with keratosis pilaris (KP). Keratosis pilaris can be described in association with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis, which were not present in our patient. The lesions usually present on the sides of the cheeks and lateral region of the arms and legs. Compared with follicular keratosis, KP lesions usually present with associated perifollicular erythema. Our patient did not present with lesions on the cheeks or the sides of the arms or legs. Milia can present on the chin of children, usually if there is history of rubbing or trauma, or on a scar. Milia are micro keratin cysts, usually seen in areas of the face. Lichen spinulous is described as rough small follicular papules that present in oval or circular patches that can grow up to 5 cm and spread rapidly. They usually present on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, neck, abdomen, and knees. These lesions are thought to be secondary to infections, have been associated with atopy, and have been seen in patients with atopic dermatitis. There is a probable genetic predisposition. The lesions are usually treated with gentle soaps and moisturizer containing keratolytics like urea or salicylic acid, and in some cases topical retinoids can also be tried. Follicular mucinosis can also present similarly to keratosis follicularis. The lesions present as scaly plaques or as grouped skin color papules on the face, scalp, or the neck that can also be associated with hair loss. Sometimes a biopsy needs to be done to be able to distinguish it from follicular keratosis. There is an increase of mucin around hair follicles and sebaceous glands with associated inflammation and degeneration of the follicular structures. In patients with primary follicular mucinosis the lesions can resolve spontaneously in a couple of years. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids, oral antibiotics like macrolides or tetracyclines, dapsone, and phototherapy.
KFC can be treated with vitamin D analogues. It is usually unresponsive to corticosteroids, keratolytic lotions, and retinoids. Our patient was prescribed calcipotriene.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego
References
1. Kanzaki T et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(1):134-5.
2. Buechner AA et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Jan 1;154(1):111-2.
Given the presentation and the unique location of the lesions he was diagnosed with follicular keratosis of the chin (FKC).
This is a rare and poorly understood condition that can be present in older children and young teenagers. In the cases reported by Kanzaki et al.1 were two boys who presented with the condition; it was thought to be associated with rubbing of the chin with their hands when watching TV or reading. The author described improvement with habit change. This condition is usually described in boys, and some cases presented in brothers,2 suggesting a genetic predisposition. Some reports lack a history of rubbing or trauma to the area.
Histopathologic evaluation of the lesions demonstrates dilated hair follicles containing keratotic basophilic material without any signs of inflammation.
The lesions can be confused with keratosis pilaris (KP). Keratosis pilaris can be described in association with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis, which were not present in our patient. The lesions usually present on the sides of the cheeks and lateral region of the arms and legs. Compared with follicular keratosis, KP lesions usually present with associated perifollicular erythema. Our patient did not present with lesions on the cheeks or the sides of the arms or legs. Milia can present on the chin of children, usually if there is history of rubbing or trauma, or on a scar. Milia are micro keratin cysts, usually seen in areas of the face. Lichen spinulous is described as rough small follicular papules that present in oval or circular patches that can grow up to 5 cm and spread rapidly. They usually present on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, neck, abdomen, and knees. These lesions are thought to be secondary to infections, have been associated with atopy, and have been seen in patients with atopic dermatitis. There is a probable genetic predisposition. The lesions are usually treated with gentle soaps and moisturizer containing keratolytics like urea or salicylic acid, and in some cases topical retinoids can also be tried. Follicular mucinosis can also present similarly to keratosis follicularis. The lesions present as scaly plaques or as grouped skin color papules on the face, scalp, or the neck that can also be associated with hair loss. Sometimes a biopsy needs to be done to be able to distinguish it from follicular keratosis. There is an increase of mucin around hair follicles and sebaceous glands with associated inflammation and degeneration of the follicular structures. In patients with primary follicular mucinosis the lesions can resolve spontaneously in a couple of years. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids, oral antibiotics like macrolides or tetracyclines, dapsone, and phototherapy.
KFC can be treated with vitamin D analogues. It is usually unresponsive to corticosteroids, keratolytic lotions, and retinoids. Our patient was prescribed calcipotriene.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego
References
1. Kanzaki T et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(1):134-5.
2. Buechner AA et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Jan 1;154(1):111-2.
He is a healthy child with no past medical history. He is not taking any medications.
On physical exam he has follicular hyperkeratotic papules on the chin. No lesions on the axilla or thighs.