User login
FBI warns of ‘imminent’ cyberattacks on U.S. hospitals
Amid recent reports of hackers targeting and blackmailing health care systems and even patients, the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies have issued warning of “imminent” cyberattacks on more U.S. hospitals.
A new report released by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, part of the Department of Homeland Security, noted that the FBI and the Department of Health & Human Services have “credible information of an increased and imminent cybercrime threat to U.S. hospitals and health care providers.”
The agencies are urging “timely and reasonable precautions” to protect health care networks from these threats.
As reported, hackers accessed patient records at Vastaamo, Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, and emailed some patients last month demanding €200 in bitcoin or else personal health data would be released online.
In June, the University of California, San Francisco, experienced an information technology (IT) “security incident” that led to the payout of $1.14 million to individuals responsible for a malware attack in exchange for the return of data.
In addition, last week, Sky Lakes Medical Center in Klamath Falls, Ore., released a statement in which it said there had been a ransomware attack on its computer systems. Although “there is no evidence that patient information has been compromised,” some of its systems are still down.
“We’re open for business, it’s just not business as usual,” Tom Hottman, public information officer at Sky Lakes, said in an interview.
Paul S. Appelbaum, MD, Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine, and Law at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview, “People have known for a long time that there are nefarious actors out there.” He said all health care systems should be prepared to deal with these problems.
“In the face of a warning from the FBI, I’d say that’s even more important now,” Dr. Appelbaum added.
‘Malicious cyber actors’
In the new CISA report, the agency noted that it, the FBI, and the HHS have been assessing “malicious cyber actors” targeting health care systems with malware loaders such as TrickBot and BazarLoader, which often lead to data theft, ransomware attacks, and service disruptions.
“The cybercriminal enterprise behind TrickBot, which is likely also the creator of BazarLoader malware, has continued to develop new functionality and tools, increasing the ease, speed, and profitability of victimization,” the report authors wrote.
Phishing campaigns often contain attachments with malware or links to malicious websites. “Loaders start the infection chain by distributing the payload,” the report noted. A backdoor mechanism is then installed on the victim’s device.
In addition to TrickBot and BazarLoader (or BazarBackdoor), the report discussed other malicious tools, including Ryuk and Conti, which are types of ransomware that can infect systems for hackers’ financial gain.
“These issues will be particularly challenging for organizations within the COVID-19 pandemic; therefore, administrators will need to balance this risk when determining their cybersecurity investments,” the agencies wrote.
Dr. Appelbaum said his organization is taking the warning seriously.
“When the report first came out, I received emails from every system that I’m affiliated with warning about it and encouraging me as a member of the medical staff to take the usual prudent precautions,” such as not opening attachments or links from unknown sources, he said.
“The FBI warning has what seems like very reasonable advice, which is that every system should automatically back up their data off site in a separate system that’s differently accessible,” he added.
After a ransomware attack, the most recently entered information may not be backed up and could get lost, but “that’s a lot easier to deal with then losing access to all of your medical records,” said Dr. Appelbaum.
Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., noted that, in answer to the FBI warning, he has heard that many centers, including his own, are warning their clinicians not to open any email attachments at this time.
Recent attacks
UCSF issued a statement noting that malware detected in early June led to the encryption of “a limited number of servers” in its medical school, making them temporarily inaccessible.
“We do not currently believe patient medical records were exposed,” the university said in the statement.
It added that because the encrypted data were necessary for “some of the academic work” conducted at UCSF, they agreed to pay a portion of the ransom demand – about $1.14 million. The hackers then provided a tool that unlocked the encrypted data.
“We continue to cooperate with law enforcement and we appreciate everyone’s understanding that we are limited in what we can share while we continue our investigation,” the statement reads. UCSF declined a request for further comment.
At Sky Lakes Medical Center, computer systems are still down after its ransomware attack, including use of electronic medical records, but the Oregon-based health care system is still seeing patients.
They are “being interviewed old school,” with the admitting process being conducted on paper, “but patient care goes on,” said Mr. Hottman.
In addition to a teaching hospital, Sky Lakes comprises specialty and primary care clinics, including a cancer treatment center. All remain open to patients at this time.
Diagnostic imaging is also continuing, but “getting the image to a place it can be read” has become more complicated, said Mr. Hottman.
“We have some work-arounds in process, and a plan is being assembled that we think will be in place as early as this weekend so that we can get those images read starting next week,” he said.
In addition, “scheduling is a little clunky,” he reported. However, “we have an awesome staff with a good attitude, so there’s still a whole lot we can do.”
He also noted that his institution has reconfirmed that, as of Nov. 4, no patient data had been compromised.
‘Especially chilling’
Targeting hospitals through cyberattacks isn’t new. In 2017, the WannaCry virus affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, including the operating system of the U.K. National Health Service. The cyberattack locked clinicians out of NHS patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
Dr. Appelbaum noted that, as hospital systems become more dependent on the Internet and on electronic communications, they become more vulnerable to data breaches.
“I think it’s clear that there have been concerted efforts lately to undertake attacks on health care IT systems to either hold them hostage, as in a ransomware attack, or to download files and use that information for profit,” he said.
Still, Dr. Vahia noted that contacting patients directly, which occurred in the Finland data breach and blackmail scheme, is something new. It is “especially chilling” that individual psychiatric patients were targeted.
It’s difficult to overstate how big a deal this is, and we should be treating it with the appropriate level of urgency,” he said in an interview.
“It shows how badly things can go wrong when security is compromised; and it should make us take a step back and survey the world of digital health to gain recognition of how much risk there might be that we haven’t really understood before,” Dr. Vahia said.
Clinical tips
Asked whether he had any tips to share with clinicians, Mr. Hottman noted that the best time to have a plan is before something dire happens.
“I would make [the possibility of cyberattacks] part of the emergency preparedness program. What if you don’t have access to computers? What do you do?” It’s important to answer those questions prior to systems going down, he said.
Mr. Hottman reported that after a mechanical failure last year put their computer systems offline for a day, “we started putting all critical information on paper and in a binder,” including phone numbers for the state police.
Dr. Vahia noted that another important step for clinicians “is to just pause and take stock of how digitally dependent” health care is becoming. He also warned that precautions should be taken regarding wearables and apps, as well as for electronic medical records. He noted the importance of strong passwords and two-step verification processes.
Even with the risks, digital technology has had a major impact on health care efficiency. “It’s not perfect, the work is ongoing, and there are big questions that need to be addressed, but in the end, the ability of technology when used right and securely” leads to better patient care, he said.
John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, agreed that digital health care is and will remain very important; but at the same time, security issues need proper attention.
“When you look back at medical hacks that have happened, there’s often a human error behind it. It’s rare for someone to break encryption. I think we have pretty darn good security, but we need to realize that sometimes errors will happen,” he said in an interview.
As an example, Dr. Torous, who is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee, cited phishing emails, which depend on a user clicking a link that can cause a virus to be downloaded into their network.
“You can be cautious, but it takes just one person to download an attachment with a virus in it” to cause disruptions, Dr. Torous said.
Telehealth implications
After its data breach, Vastaamo posted on its website a notice that video is never recorded during the centers’ telehealth sessions, and so patients need not worry that any videos could be leaked online.
Asked whether video is commonly recorded during telehealth sessions in the United States, Dr. Vahia said that he was not aware of sessions being recorded, especially because the amount of the data would be too great to store indefinitely.
Dr. Appelbaum agreed and said that, to his knowledge, no clinicians at Columbia University are recording telehealth sessions. He said that it would represent a privacy threat, and he noted that most health care providers “don’t have the time to go back and watch videos of their interactions with patients.”
In the case of recordings for research purposes, he emphasized that it would be important to get consent and then store the health information offline.
As for other telehealth security risks, Dr. Vahia noted that it is possible that if a computer or device is compromised, an individual could hack into a camera and observe the session. In addition to microphones, “these pose some especially high vulnerabilities,” he said. “Clinicians need to pay attention as to whether the cameras they’re using for telecare are on or if they’re covered when not in use. And they should pay attention to security settings on smartphones and ensure microphones are not turned on as the default.”
Dr. Appelbaum said the HIPAA requires that telehealth sessions be conducted on secure systems, so clinicians need to ascertain whether the system they’re using complies with that rule.
“Particularly people who are not part of larger systems and would not usually take on that responsibility, maybe they’re in private practice or a small group, they really need to check on the security level and on HIPAA compliance and not just assume that it is adequately secure,” he said.
Dr. Appelbaum, who is also a past president of the APA and director of the Center for Law, Ethics, and Psychiatry at Columbia University, noted that the major risk for hospitals after a cyberattack is probably not liability to individual patients.
“It’s much more likely that they would face fines from HIPAA if it’s found that they failed to live up to HIPAA requirements,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid recent reports of hackers targeting and blackmailing health care systems and even patients, the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies have issued warning of “imminent” cyberattacks on more U.S. hospitals.
A new report released by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, part of the Department of Homeland Security, noted that the FBI and the Department of Health & Human Services have “credible information of an increased and imminent cybercrime threat to U.S. hospitals and health care providers.”
The agencies are urging “timely and reasonable precautions” to protect health care networks from these threats.
As reported, hackers accessed patient records at Vastaamo, Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, and emailed some patients last month demanding €200 in bitcoin or else personal health data would be released online.
In June, the University of California, San Francisco, experienced an information technology (IT) “security incident” that led to the payout of $1.14 million to individuals responsible for a malware attack in exchange for the return of data.
In addition, last week, Sky Lakes Medical Center in Klamath Falls, Ore., released a statement in which it said there had been a ransomware attack on its computer systems. Although “there is no evidence that patient information has been compromised,” some of its systems are still down.
“We’re open for business, it’s just not business as usual,” Tom Hottman, public information officer at Sky Lakes, said in an interview.
Paul S. Appelbaum, MD, Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine, and Law at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview, “People have known for a long time that there are nefarious actors out there.” He said all health care systems should be prepared to deal with these problems.
“In the face of a warning from the FBI, I’d say that’s even more important now,” Dr. Appelbaum added.
‘Malicious cyber actors’
In the new CISA report, the agency noted that it, the FBI, and the HHS have been assessing “malicious cyber actors” targeting health care systems with malware loaders such as TrickBot and BazarLoader, which often lead to data theft, ransomware attacks, and service disruptions.
“The cybercriminal enterprise behind TrickBot, which is likely also the creator of BazarLoader malware, has continued to develop new functionality and tools, increasing the ease, speed, and profitability of victimization,” the report authors wrote.
Phishing campaigns often contain attachments with malware or links to malicious websites. “Loaders start the infection chain by distributing the payload,” the report noted. A backdoor mechanism is then installed on the victim’s device.
In addition to TrickBot and BazarLoader (or BazarBackdoor), the report discussed other malicious tools, including Ryuk and Conti, which are types of ransomware that can infect systems for hackers’ financial gain.
“These issues will be particularly challenging for organizations within the COVID-19 pandemic; therefore, administrators will need to balance this risk when determining their cybersecurity investments,” the agencies wrote.
Dr. Appelbaum said his organization is taking the warning seriously.
“When the report first came out, I received emails from every system that I’m affiliated with warning about it and encouraging me as a member of the medical staff to take the usual prudent precautions,” such as not opening attachments or links from unknown sources, he said.
“The FBI warning has what seems like very reasonable advice, which is that every system should automatically back up their data off site in a separate system that’s differently accessible,” he added.
After a ransomware attack, the most recently entered information may not be backed up and could get lost, but “that’s a lot easier to deal with then losing access to all of your medical records,” said Dr. Appelbaum.
Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., noted that, in answer to the FBI warning, he has heard that many centers, including his own, are warning their clinicians not to open any email attachments at this time.
Recent attacks
UCSF issued a statement noting that malware detected in early June led to the encryption of “a limited number of servers” in its medical school, making them temporarily inaccessible.
“We do not currently believe patient medical records were exposed,” the university said in the statement.
It added that because the encrypted data were necessary for “some of the academic work” conducted at UCSF, they agreed to pay a portion of the ransom demand – about $1.14 million. The hackers then provided a tool that unlocked the encrypted data.
“We continue to cooperate with law enforcement and we appreciate everyone’s understanding that we are limited in what we can share while we continue our investigation,” the statement reads. UCSF declined a request for further comment.
At Sky Lakes Medical Center, computer systems are still down after its ransomware attack, including use of electronic medical records, but the Oregon-based health care system is still seeing patients.
They are “being interviewed old school,” with the admitting process being conducted on paper, “but patient care goes on,” said Mr. Hottman.
In addition to a teaching hospital, Sky Lakes comprises specialty and primary care clinics, including a cancer treatment center. All remain open to patients at this time.
Diagnostic imaging is also continuing, but “getting the image to a place it can be read” has become more complicated, said Mr. Hottman.
“We have some work-arounds in process, and a plan is being assembled that we think will be in place as early as this weekend so that we can get those images read starting next week,” he said.
In addition, “scheduling is a little clunky,” he reported. However, “we have an awesome staff with a good attitude, so there’s still a whole lot we can do.”
He also noted that his institution has reconfirmed that, as of Nov. 4, no patient data had been compromised.
‘Especially chilling’
Targeting hospitals through cyberattacks isn’t new. In 2017, the WannaCry virus affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, including the operating system of the U.K. National Health Service. The cyberattack locked clinicians out of NHS patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
Dr. Appelbaum noted that, as hospital systems become more dependent on the Internet and on electronic communications, they become more vulnerable to data breaches.
“I think it’s clear that there have been concerted efforts lately to undertake attacks on health care IT systems to either hold them hostage, as in a ransomware attack, or to download files and use that information for profit,” he said.
Still, Dr. Vahia noted that contacting patients directly, which occurred in the Finland data breach and blackmail scheme, is something new. It is “especially chilling” that individual psychiatric patients were targeted.
It’s difficult to overstate how big a deal this is, and we should be treating it with the appropriate level of urgency,” he said in an interview.
“It shows how badly things can go wrong when security is compromised; and it should make us take a step back and survey the world of digital health to gain recognition of how much risk there might be that we haven’t really understood before,” Dr. Vahia said.
Clinical tips
Asked whether he had any tips to share with clinicians, Mr. Hottman noted that the best time to have a plan is before something dire happens.
“I would make [the possibility of cyberattacks] part of the emergency preparedness program. What if you don’t have access to computers? What do you do?” It’s important to answer those questions prior to systems going down, he said.
Mr. Hottman reported that after a mechanical failure last year put their computer systems offline for a day, “we started putting all critical information on paper and in a binder,” including phone numbers for the state police.
Dr. Vahia noted that another important step for clinicians “is to just pause and take stock of how digitally dependent” health care is becoming. He also warned that precautions should be taken regarding wearables and apps, as well as for electronic medical records. He noted the importance of strong passwords and two-step verification processes.
Even with the risks, digital technology has had a major impact on health care efficiency. “It’s not perfect, the work is ongoing, and there are big questions that need to be addressed, but in the end, the ability of technology when used right and securely” leads to better patient care, he said.
John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, agreed that digital health care is and will remain very important; but at the same time, security issues need proper attention.
“When you look back at medical hacks that have happened, there’s often a human error behind it. It’s rare for someone to break encryption. I think we have pretty darn good security, but we need to realize that sometimes errors will happen,” he said in an interview.
As an example, Dr. Torous, who is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee, cited phishing emails, which depend on a user clicking a link that can cause a virus to be downloaded into their network.
“You can be cautious, but it takes just one person to download an attachment with a virus in it” to cause disruptions, Dr. Torous said.
Telehealth implications
After its data breach, Vastaamo posted on its website a notice that video is never recorded during the centers’ telehealth sessions, and so patients need not worry that any videos could be leaked online.
Asked whether video is commonly recorded during telehealth sessions in the United States, Dr. Vahia said that he was not aware of sessions being recorded, especially because the amount of the data would be too great to store indefinitely.
Dr. Appelbaum agreed and said that, to his knowledge, no clinicians at Columbia University are recording telehealth sessions. He said that it would represent a privacy threat, and he noted that most health care providers “don’t have the time to go back and watch videos of their interactions with patients.”
In the case of recordings for research purposes, he emphasized that it would be important to get consent and then store the health information offline.
As for other telehealth security risks, Dr. Vahia noted that it is possible that if a computer or device is compromised, an individual could hack into a camera and observe the session. In addition to microphones, “these pose some especially high vulnerabilities,” he said. “Clinicians need to pay attention as to whether the cameras they’re using for telecare are on or if they’re covered when not in use. And they should pay attention to security settings on smartphones and ensure microphones are not turned on as the default.”
Dr. Appelbaum said the HIPAA requires that telehealth sessions be conducted on secure systems, so clinicians need to ascertain whether the system they’re using complies with that rule.
“Particularly people who are not part of larger systems and would not usually take on that responsibility, maybe they’re in private practice or a small group, they really need to check on the security level and on HIPAA compliance and not just assume that it is adequately secure,” he said.
Dr. Appelbaum, who is also a past president of the APA and director of the Center for Law, Ethics, and Psychiatry at Columbia University, noted that the major risk for hospitals after a cyberattack is probably not liability to individual patients.
“It’s much more likely that they would face fines from HIPAA if it’s found that they failed to live up to HIPAA requirements,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid recent reports of hackers targeting and blackmailing health care systems and even patients, the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies have issued warning of “imminent” cyberattacks on more U.S. hospitals.
A new report released by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, part of the Department of Homeland Security, noted that the FBI and the Department of Health & Human Services have “credible information of an increased and imminent cybercrime threat to U.S. hospitals and health care providers.”
The agencies are urging “timely and reasonable precautions” to protect health care networks from these threats.
As reported, hackers accessed patient records at Vastaamo, Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, and emailed some patients last month demanding €200 in bitcoin or else personal health data would be released online.
In June, the University of California, San Francisco, experienced an information technology (IT) “security incident” that led to the payout of $1.14 million to individuals responsible for a malware attack in exchange for the return of data.
In addition, last week, Sky Lakes Medical Center in Klamath Falls, Ore., released a statement in which it said there had been a ransomware attack on its computer systems. Although “there is no evidence that patient information has been compromised,” some of its systems are still down.
“We’re open for business, it’s just not business as usual,” Tom Hottman, public information officer at Sky Lakes, said in an interview.
Paul S. Appelbaum, MD, Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine, and Law at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview, “People have known for a long time that there are nefarious actors out there.” He said all health care systems should be prepared to deal with these problems.
“In the face of a warning from the FBI, I’d say that’s even more important now,” Dr. Appelbaum added.
‘Malicious cyber actors’
In the new CISA report, the agency noted that it, the FBI, and the HHS have been assessing “malicious cyber actors” targeting health care systems with malware loaders such as TrickBot and BazarLoader, which often lead to data theft, ransomware attacks, and service disruptions.
“The cybercriminal enterprise behind TrickBot, which is likely also the creator of BazarLoader malware, has continued to develop new functionality and tools, increasing the ease, speed, and profitability of victimization,” the report authors wrote.
Phishing campaigns often contain attachments with malware or links to malicious websites. “Loaders start the infection chain by distributing the payload,” the report noted. A backdoor mechanism is then installed on the victim’s device.
In addition to TrickBot and BazarLoader (or BazarBackdoor), the report discussed other malicious tools, including Ryuk and Conti, which are types of ransomware that can infect systems for hackers’ financial gain.
“These issues will be particularly challenging for organizations within the COVID-19 pandemic; therefore, administrators will need to balance this risk when determining their cybersecurity investments,” the agencies wrote.
Dr. Appelbaum said his organization is taking the warning seriously.
“When the report first came out, I received emails from every system that I’m affiliated with warning about it and encouraging me as a member of the medical staff to take the usual prudent precautions,” such as not opening attachments or links from unknown sources, he said.
“The FBI warning has what seems like very reasonable advice, which is that every system should automatically back up their data off site in a separate system that’s differently accessible,” he added.
After a ransomware attack, the most recently entered information may not be backed up and could get lost, but “that’s a lot easier to deal with then losing access to all of your medical records,” said Dr. Appelbaum.
Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., noted that, in answer to the FBI warning, he has heard that many centers, including his own, are warning their clinicians not to open any email attachments at this time.
Recent attacks
UCSF issued a statement noting that malware detected in early June led to the encryption of “a limited number of servers” in its medical school, making them temporarily inaccessible.
“We do not currently believe patient medical records were exposed,” the university said in the statement.
It added that because the encrypted data were necessary for “some of the academic work” conducted at UCSF, they agreed to pay a portion of the ransom demand – about $1.14 million. The hackers then provided a tool that unlocked the encrypted data.
“We continue to cooperate with law enforcement and we appreciate everyone’s understanding that we are limited in what we can share while we continue our investigation,” the statement reads. UCSF declined a request for further comment.
At Sky Lakes Medical Center, computer systems are still down after its ransomware attack, including use of electronic medical records, but the Oregon-based health care system is still seeing patients.
They are “being interviewed old school,” with the admitting process being conducted on paper, “but patient care goes on,” said Mr. Hottman.
In addition to a teaching hospital, Sky Lakes comprises specialty and primary care clinics, including a cancer treatment center. All remain open to patients at this time.
Diagnostic imaging is also continuing, but “getting the image to a place it can be read” has become more complicated, said Mr. Hottman.
“We have some work-arounds in process, and a plan is being assembled that we think will be in place as early as this weekend so that we can get those images read starting next week,” he said.
In addition, “scheduling is a little clunky,” he reported. However, “we have an awesome staff with a good attitude, so there’s still a whole lot we can do.”
He also noted that his institution has reconfirmed that, as of Nov. 4, no patient data had been compromised.
‘Especially chilling’
Targeting hospitals through cyberattacks isn’t new. In 2017, the WannaCry virus affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, including the operating system of the U.K. National Health Service. The cyberattack locked clinicians out of NHS patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
Dr. Appelbaum noted that, as hospital systems become more dependent on the Internet and on electronic communications, they become more vulnerable to data breaches.
“I think it’s clear that there have been concerted efforts lately to undertake attacks on health care IT systems to either hold them hostage, as in a ransomware attack, or to download files and use that information for profit,” he said.
Still, Dr. Vahia noted that contacting patients directly, which occurred in the Finland data breach and blackmail scheme, is something new. It is “especially chilling” that individual psychiatric patients were targeted.
It’s difficult to overstate how big a deal this is, and we should be treating it with the appropriate level of urgency,” he said in an interview.
“It shows how badly things can go wrong when security is compromised; and it should make us take a step back and survey the world of digital health to gain recognition of how much risk there might be that we haven’t really understood before,” Dr. Vahia said.
Clinical tips
Asked whether he had any tips to share with clinicians, Mr. Hottman noted that the best time to have a plan is before something dire happens.
“I would make [the possibility of cyberattacks] part of the emergency preparedness program. What if you don’t have access to computers? What do you do?” It’s important to answer those questions prior to systems going down, he said.
Mr. Hottman reported that after a mechanical failure last year put their computer systems offline for a day, “we started putting all critical information on paper and in a binder,” including phone numbers for the state police.
Dr. Vahia noted that another important step for clinicians “is to just pause and take stock of how digitally dependent” health care is becoming. He also warned that precautions should be taken regarding wearables and apps, as well as for electronic medical records. He noted the importance of strong passwords and two-step verification processes.
Even with the risks, digital technology has had a major impact on health care efficiency. “It’s not perfect, the work is ongoing, and there are big questions that need to be addressed, but in the end, the ability of technology when used right and securely” leads to better patient care, he said.
John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, agreed that digital health care is and will remain very important; but at the same time, security issues need proper attention.
“When you look back at medical hacks that have happened, there’s often a human error behind it. It’s rare for someone to break encryption. I think we have pretty darn good security, but we need to realize that sometimes errors will happen,” he said in an interview.
As an example, Dr. Torous, who is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee, cited phishing emails, which depend on a user clicking a link that can cause a virus to be downloaded into their network.
“You can be cautious, but it takes just one person to download an attachment with a virus in it” to cause disruptions, Dr. Torous said.
Telehealth implications
After its data breach, Vastaamo posted on its website a notice that video is never recorded during the centers’ telehealth sessions, and so patients need not worry that any videos could be leaked online.
Asked whether video is commonly recorded during telehealth sessions in the United States, Dr. Vahia said that he was not aware of sessions being recorded, especially because the amount of the data would be too great to store indefinitely.
Dr. Appelbaum agreed and said that, to his knowledge, no clinicians at Columbia University are recording telehealth sessions. He said that it would represent a privacy threat, and he noted that most health care providers “don’t have the time to go back and watch videos of their interactions with patients.”
In the case of recordings for research purposes, he emphasized that it would be important to get consent and then store the health information offline.
As for other telehealth security risks, Dr. Vahia noted that it is possible that if a computer or device is compromised, an individual could hack into a camera and observe the session. In addition to microphones, “these pose some especially high vulnerabilities,” he said. “Clinicians need to pay attention as to whether the cameras they’re using for telecare are on or if they’re covered when not in use. And they should pay attention to security settings on smartphones and ensure microphones are not turned on as the default.”
Dr. Appelbaum said the HIPAA requires that telehealth sessions be conducted on secure systems, so clinicians need to ascertain whether the system they’re using complies with that rule.
“Particularly people who are not part of larger systems and would not usually take on that responsibility, maybe they’re in private practice or a small group, they really need to check on the security level and on HIPAA compliance and not just assume that it is adequately secure,” he said.
Dr. Appelbaum, who is also a past president of the APA and director of the Center for Law, Ethics, and Psychiatry at Columbia University, noted that the major risk for hospitals after a cyberattack is probably not liability to individual patients.
“It’s much more likely that they would face fines from HIPAA if it’s found that they failed to live up to HIPAA requirements,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medication adherence challenges and helpers
For most chronic diseases, up to 20%-30% of the pills that are prescribed are not taken. In the case of inhalers for asthma and COPD, patients miss over half of the prescribed doses.
There are many things that contribute to the problem of poor adherence, but people often just simply forget. Thankfully, there are tools designed to help remind patients of what they need to take and when. A survey of apps developed to help patients remember to take their medicines found more than 700 available in Apple and Android app stores.1 Most apps focus on medication alerts, reminders, and medication logs.2 A recent review showed that apps have some – yet limited – effectiveness in increasing adherence, with patient self-reported improvements of 7%-40%.3
Another perhaps more promising area of improving adherence involves high-tech advances in the way medications can be taken. Inhalers are a primary target as they are complicated devices. A patient has to breathe in at the correct time after the inhaler is actuated, and the inhaler works optimally only if the rate of inhalation is sufficient to carry the medication into the lungs.
A number of companies have developed attachments for inhalers (and even inhalers themselves) that can record when the medication is taken through a Bluetooth connection to a patient’s smartphone. These can also assess inspiratory flow. Reminders to take the medication are built into the app, and those reminders disappear if the medication is taken. Patients can receive feedback about the quality of their timing and inspiratory rate to maximize medication delivery to the lungs.4
We learned long ago that it is difficult to take medications three to four times a day, so extended-release tablets were developed to reduce the frequency to once or twice a day. A great deal of work is now being done behind the scenes to develop medications that decrease the need for patients to remember to take their medications. The best examples of this are the long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) devices, specifically IUDs and Nexplanon. Compared with traditional oral contraceptives that need to be taken daily, LARCs reduce the rate of pregnancy by five- to tenfold.
We also now have medications for osteoporosis that can be taken monthly, or even annually. When bisphosphonates were first developed for osteoporosis prevention, they needed to be taken daily. Then a weekly bisphosphonate was developed. Now there is a once-monthly oral bisphosphonate, Ibandronate, and even a once yearly IV bisphosphonate.
Exciting developments have also occurred in the management of diabetes. We may be tempted to take for granted how once-daily long-acting insulin, which releases insulin slowly over the course of a day, has revolutionized the diabetic treatment since its Food and Drug Administration approval in 2000. Yet progress did not end there. The first GLP-1 receptor agonist for diabetes was approved in 2005 and was a twice-a-day medicine. Shortly afterward, a daily GLP-1 was approved, and now there are three once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Several pharmaceutical manufacturers are now working on a once-weekly insulin,5 as well as an implantable GLP-1 receptor agonist that will need to be replaced every 6-12 months.6 Imagine your patient coming in once a year to replace his or her potent glucose lowering medication – one that offers a low incidence of hypoglycemia, maintains glucose control all year long, and requires no adherence to a complicated medication regimen.
Similar technology is being used to develop a once-yearly anti-HIV prophylactic medication delivery system.7 This could help prevent the spread of HIV in areas of the world where it may be difficult for people to take daily medications.7
The many technological advances we have described may help us reduce our likelihood of missing a dose of a medication. We are hopeful that progress in this area will continue, and that one day medication adherence will require even less effort from patients than it does today.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Tabi K et al. Mobile apps for medication management: Review and analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Sep 7(9):13608.
2. Park JYE et al. Mobile phone apps targeting medication adherence: Quality assessment and content analysis of user reviews. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Jan 31;7(1):e11919.
3. Pérez-Jover V et al. Mobile apps for increasing treatment adherence: Systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(6):e12505. doi: 10.2196/12505.
4. 4 Smart inhalers that could be lifesaving for people living with asthma & COPD. MyTherapy, July 11, 2019.
5. Rosenstock J et al. Once-weekly insulin for type 2 diabetes without previous insulin treatment. N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022474.
6. GLP-1 agonists: From 2 daily injections to 1 per week and beyond. DiaTribe, Jan. 10, 2018.
7. Long-acting HIV prevention tools. Hiv.gov, July 20, 2019.
For most chronic diseases, up to 20%-30% of the pills that are prescribed are not taken. In the case of inhalers for asthma and COPD, patients miss over half of the prescribed doses.
There are many things that contribute to the problem of poor adherence, but people often just simply forget. Thankfully, there are tools designed to help remind patients of what they need to take and when. A survey of apps developed to help patients remember to take their medicines found more than 700 available in Apple and Android app stores.1 Most apps focus on medication alerts, reminders, and medication logs.2 A recent review showed that apps have some – yet limited – effectiveness in increasing adherence, with patient self-reported improvements of 7%-40%.3
Another perhaps more promising area of improving adherence involves high-tech advances in the way medications can be taken. Inhalers are a primary target as they are complicated devices. A patient has to breathe in at the correct time after the inhaler is actuated, and the inhaler works optimally only if the rate of inhalation is sufficient to carry the medication into the lungs.
A number of companies have developed attachments for inhalers (and even inhalers themselves) that can record when the medication is taken through a Bluetooth connection to a patient’s smartphone. These can also assess inspiratory flow. Reminders to take the medication are built into the app, and those reminders disappear if the medication is taken. Patients can receive feedback about the quality of their timing and inspiratory rate to maximize medication delivery to the lungs.4
We learned long ago that it is difficult to take medications three to four times a day, so extended-release tablets were developed to reduce the frequency to once or twice a day. A great deal of work is now being done behind the scenes to develop medications that decrease the need for patients to remember to take their medications. The best examples of this are the long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) devices, specifically IUDs and Nexplanon. Compared with traditional oral contraceptives that need to be taken daily, LARCs reduce the rate of pregnancy by five- to tenfold.
We also now have medications for osteoporosis that can be taken monthly, or even annually. When bisphosphonates were first developed for osteoporosis prevention, they needed to be taken daily. Then a weekly bisphosphonate was developed. Now there is a once-monthly oral bisphosphonate, Ibandronate, and even a once yearly IV bisphosphonate.
Exciting developments have also occurred in the management of diabetes. We may be tempted to take for granted how once-daily long-acting insulin, which releases insulin slowly over the course of a day, has revolutionized the diabetic treatment since its Food and Drug Administration approval in 2000. Yet progress did not end there. The first GLP-1 receptor agonist for diabetes was approved in 2005 and was a twice-a-day medicine. Shortly afterward, a daily GLP-1 was approved, and now there are three once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Several pharmaceutical manufacturers are now working on a once-weekly insulin,5 as well as an implantable GLP-1 receptor agonist that will need to be replaced every 6-12 months.6 Imagine your patient coming in once a year to replace his or her potent glucose lowering medication – one that offers a low incidence of hypoglycemia, maintains glucose control all year long, and requires no adherence to a complicated medication regimen.
Similar technology is being used to develop a once-yearly anti-HIV prophylactic medication delivery system.7 This could help prevent the spread of HIV in areas of the world where it may be difficult for people to take daily medications.7
The many technological advances we have described may help us reduce our likelihood of missing a dose of a medication. We are hopeful that progress in this area will continue, and that one day medication adherence will require even less effort from patients than it does today.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Tabi K et al. Mobile apps for medication management: Review and analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Sep 7(9):13608.
2. Park JYE et al. Mobile phone apps targeting medication adherence: Quality assessment and content analysis of user reviews. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Jan 31;7(1):e11919.
3. Pérez-Jover V et al. Mobile apps for increasing treatment adherence: Systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(6):e12505. doi: 10.2196/12505.
4. 4 Smart inhalers that could be lifesaving for people living with asthma & COPD. MyTherapy, July 11, 2019.
5. Rosenstock J et al. Once-weekly insulin for type 2 diabetes without previous insulin treatment. N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022474.
6. GLP-1 agonists: From 2 daily injections to 1 per week and beyond. DiaTribe, Jan. 10, 2018.
7. Long-acting HIV prevention tools. Hiv.gov, July 20, 2019.
For most chronic diseases, up to 20%-30% of the pills that are prescribed are not taken. In the case of inhalers for asthma and COPD, patients miss over half of the prescribed doses.
There are many things that contribute to the problem of poor adherence, but people often just simply forget. Thankfully, there are tools designed to help remind patients of what they need to take and when. A survey of apps developed to help patients remember to take their medicines found more than 700 available in Apple and Android app stores.1 Most apps focus on medication alerts, reminders, and medication logs.2 A recent review showed that apps have some – yet limited – effectiveness in increasing adherence, with patient self-reported improvements of 7%-40%.3
Another perhaps more promising area of improving adherence involves high-tech advances in the way medications can be taken. Inhalers are a primary target as they are complicated devices. A patient has to breathe in at the correct time after the inhaler is actuated, and the inhaler works optimally only if the rate of inhalation is sufficient to carry the medication into the lungs.
A number of companies have developed attachments for inhalers (and even inhalers themselves) that can record when the medication is taken through a Bluetooth connection to a patient’s smartphone. These can also assess inspiratory flow. Reminders to take the medication are built into the app, and those reminders disappear if the medication is taken. Patients can receive feedback about the quality of their timing and inspiratory rate to maximize medication delivery to the lungs.4
We learned long ago that it is difficult to take medications three to four times a day, so extended-release tablets were developed to reduce the frequency to once or twice a day. A great deal of work is now being done behind the scenes to develop medications that decrease the need for patients to remember to take their medications. The best examples of this are the long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) devices, specifically IUDs and Nexplanon. Compared with traditional oral contraceptives that need to be taken daily, LARCs reduce the rate of pregnancy by five- to tenfold.
We also now have medications for osteoporosis that can be taken monthly, or even annually. When bisphosphonates were first developed for osteoporosis prevention, they needed to be taken daily. Then a weekly bisphosphonate was developed. Now there is a once-monthly oral bisphosphonate, Ibandronate, and even a once yearly IV bisphosphonate.
Exciting developments have also occurred in the management of diabetes. We may be tempted to take for granted how once-daily long-acting insulin, which releases insulin slowly over the course of a day, has revolutionized the diabetic treatment since its Food and Drug Administration approval in 2000. Yet progress did not end there. The first GLP-1 receptor agonist for diabetes was approved in 2005 and was a twice-a-day medicine. Shortly afterward, a daily GLP-1 was approved, and now there are three once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Several pharmaceutical manufacturers are now working on a once-weekly insulin,5 as well as an implantable GLP-1 receptor agonist that will need to be replaced every 6-12 months.6 Imagine your patient coming in once a year to replace his or her potent glucose lowering medication – one that offers a low incidence of hypoglycemia, maintains glucose control all year long, and requires no adherence to a complicated medication regimen.
Similar technology is being used to develop a once-yearly anti-HIV prophylactic medication delivery system.7 This could help prevent the spread of HIV in areas of the world where it may be difficult for people to take daily medications.7
The many technological advances we have described may help us reduce our likelihood of missing a dose of a medication. We are hopeful that progress in this area will continue, and that one day medication adherence will require even less effort from patients than it does today.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Tabi K et al. Mobile apps for medication management: Review and analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Sep 7(9):13608.
2. Park JYE et al. Mobile phone apps targeting medication adherence: Quality assessment and content analysis of user reviews. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Jan 31;7(1):e11919.
3. Pérez-Jover V et al. Mobile apps for increasing treatment adherence: Systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(6):e12505. doi: 10.2196/12505.
4. 4 Smart inhalers that could be lifesaving for people living with asthma & COPD. MyTherapy, July 11, 2019.
5. Rosenstock J et al. Once-weekly insulin for type 2 diabetes without previous insulin treatment. N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022474.
6. GLP-1 agonists: From 2 daily injections to 1 per week and beyond. DiaTribe, Jan. 10, 2018.
7. Long-acting HIV prevention tools. Hiv.gov, July 20, 2019.
The Effect of Radium-223 Therapy in Agent Orange-Related Prostate Carcinoma
Patients with metastatic castrate resistant prostate carcinoma (CRPC) have several treatment options, including radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) radionuclide therapy, abiraterone, enzalutamide, and cabazitaxel. Ra-223 therapy has been reported to increase median survival in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma.1,2 However, ERA 223 trial data showed an increase of bone fractures with combination of Ra-223 and abiraterone.3
Agent Orange (AO) exposure has been studied as a potential risk factor for development of prostate carcinoma. AO was a commercially manufactured defoliate that was sprayed extensively during the Vietnam War. Due to a side product of chemical manufacturing, AO was contaminated with the toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a putative carcinogen. These dioxins can enter the food chain through soil contamination. There is enough evidence to link AO to hematologic malignancies and several solid tumors, including prostate carcinoma.4 Although no real estimates exist for what percentage of Vietnam veterans experienced AO exposure, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data showed that about 3 million veterans served in Southeast Asia where AO was used extensively in the combat theater. AO has been reported to be positively associated with a 52% increase in risk of prostate carcinoma detection at initial prostate biopsy.5
There has been no reported study of treatment efficacy in veterans with AO-related prostate carcinoma. We present a retrospective study of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC. The purpose of this study was to compare response to therapy and survival in veterans exposed to agent orange (AO+) vs veterans who were not exposed to (AO-) in a single US Department of Veteran Affairs (VA) medical center.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of veterans with metastatic CRPC to bones who received Ra-223 radionuclide therapy with standard dose of 50 kBq per kg of body weight and other sequential therapies at VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS) from January 2014 to January 2019. The purpose of this study was to measure difference in treatment outcome between AO+ veterans and AO- veterans.
Eligibility Criteria
All veterans had a history that included bone metastasis CRPC. They could have 2 to 3 small lymphadenopathies but not visceral metastasis. They received a minimum of 3 cycles and a maximum of 6 cycles of Ra-223 therapy, which was given in 4-week intervals. Pretreatment criteria was hemoglobin > 10 g/dL, platelet > 100
Statistics
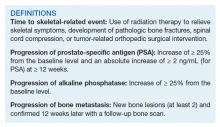
Time to study was calculated from the initiation of Ra-223 therapy. Time to skeletal-related events (SRE), progression of prostate specific antigen (PSA), bone metastasis, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were calculated in months, using unpaired t test with 2-tailed P value. Median survival was calculated in months by Kaplan Meier R log-rank test Definition).
Results
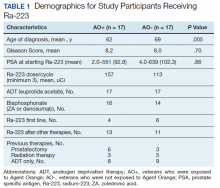
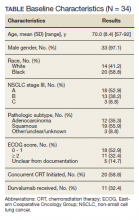
Forty-eight veterans with bone metastasis CRPC received Ra-223 therapy. Of those, 34 veterans were eligible for this retrospective study: 17 AO+ veterans and 17 AO- veterans. Mean age of diagnosis was 62 years (AO+) and 69 years (AO-) (P = .005). Mean Gleason score was 8.2 (AO+) and 8.0 (AO-) (P = .705). Veterans received initial therapy at diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, including radical prostatectomy (6 AO+ and 3 AO-), localized radiation therapy (3 AO+ and 5 AO-), and ADT (8 AO+ and 9 AO-) (Table 1).
Mean PSA at the initiation of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551) and for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639; P = .86). Mean Ra-223 dose per cycle for AO+ and AO- was 157 uCi and 113 uCi, respectively. All 34 veterans received ADT (leuprolide acetate), and 30 veterans (16 AO+ and 14 AO-) received bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid or denosumab). A total of 10 veterans (29%) received Ra-223 as a first-line therapy (4 AO+ and 6 AO-), and 24 veterans (71%) received Ra-223 after hormonal or chemotherapy (13 AO+ and 11 AO-).
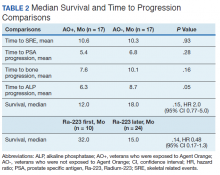
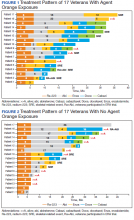
There were 12 SRE (8 AO+ and 4 AO-). Mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Three veterans received concurrent Ra-223 and abiraterone (participated in ERA 223 trial). Two AO+ veterans experienced SRE at 7 months and 11 months, respectively. Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months, respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months, respectively (P = .05). (Table 2). The treatment pattern of AO+ and AO- is depicted on a swimmer plot (Figures 1 and 2).
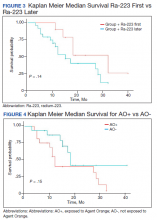
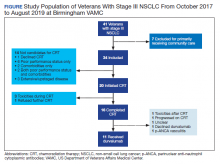
Twenty veterans (58%) had died: 13 AO+ and 7 AO- veterans. Median survival for Ra-223 first and Ra-223 later was was 32 months and 15 months, respectively (P = .14; hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). Overall median survival for AO+ veterans and AO- veterans were 12 months and 18 months, respectively (P = .15; HR, 2.0) (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussions
There has been no reported VA study of using Ra-223 and other therapies (hormonal and chemotherapy) in veterans exposed to AO. This is the first retrospective study to compare the response and survival between AO+ and AO- veterans. Even though this study featured a small sample, it is interesting to note the difference between those 2 populations. There was 1 prior study in veterans with prostate carcinoma using radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in early-stage disease. Everly and colleagues reported that AO+ veterans were less likely to remain biochemically controlled compared with AO- and nonveteran patients with prostate carcinoma.4
Ansbaugh and colleagues reported that AO was associated with a 75% increase in the risk of Gleason ≥ 7 and a 110% increase in Gleason ≥ 8. AO+ veterans are at risk for the detection of high-grade prostate carcinoma. They also tend to have an average age of diagnosis that is 4 to 5 years younger than AO- veterans.6
Our study revealed that AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age (mean 62 years) compared with that of AO- veterans (mean 69 years, P = .005). We also proved that AO veterans have a higher mean Gleason score (8.2) compared with that of AO- veterans (8.0). Veterans received therapy at the time of diagnosis of prostate carcinoma with either radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or ADT with leuprolide acetate. Mean PSA at the start of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551); for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639), which is not statistically significant.
Ra-223, an
In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Parker and colleagues (ALSYMPCA study), 921 patients who had received, were not eligible to receive, or declined docetaxel, in a 2:1 ratio, were randomized to receive 6 injections of Ra-223 or matching placebo.2 Ra-223 significantly improved overall survival (OS) (median, 14.9 months vs 11.3 months) compared with that of placebo. Ra-223 also prolonged the time to the first symptomatic SRE (median, 15.6 months vs 9.8 months), the time to an increase in the total ALP level (median 7.4 months vs 3.8 months), and the time to an increase in the PSA level (median 3.6 months vs 3.4 months).2
In our study, the mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months respectively (P = .05). There is a trend of shorter PSA progression, bone progression, and ALP progression in AO+ veterans, though these were not statistically significant due to small sample population. In our study the median survival in for AO- was 18 months and for AO+ was 12 months, which is comparable with median survival of 14.9 months from the ALSYMPCA study.
There were 12 veterans who developed SREs. All received radiation therapy due to bone progression or impending fracture. AO+ veterans developed more SREs (n = 8) when compared with AO- veterans (n = 4). There were more AO- veterans alive (n = 10) than there were AO+ veterans (n = 4). The plausible explanation of this may be due to the aggressive pattern of prostate carcinoma in AO+ veterans (younger age and higher Gleason score).
VAPHS participated in the ERA trial between 2014 and 2016. The trial enrolled 806 patients who were randomly assigned to receive first-line Ra-223 or placebo in addition to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.3 The study was unblinded prematurely after more fractures and deaths were noted in the Ra-223 and abiraterone group than there were in the placebo and abiraterone group. Median symptomatic SRE was 22.3 months in the Ra-223 group and 26.0 months in the placebo group. Fractures (any grade) occurred in 29% in the Ra-223 group and 11% in the placebo group. It was suggested that Ra-223 could contribute to the risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma. Median OS was 30.7 months in the Ra-223 group and 33.3 months in the placebo group.
We enrolled 3 veterans in the ERA clinical trial. Two AO+ veterans had SREs at 7 months and 11 months. In our study, the median OS for Ra-223 first line was 32 months, which is comparable with median survival of 30.7 months from ERA-223 study. Median survival for Ra-223 later was only 15 months. We recommend veterans with at least 2 to 3-bone metastasis receive Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than second- or third-line setting. In this retrospective study with Ra-223 and other therapies, we proved that AO+ veterans have a worse response and OS when compared with that of AO- veterans.
Conclusions
This is the first VA study to compare the efficacy of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC between AO+ and AO- veterans. AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age and had higher Gleason scores. There was no statistical difference between AO+ and AO- veterans in terms of time to SRE, PSA progression, and bone and ALP progression even though there was a trend of shorter duration in AO+ veterans. There was no median survival difference between veterans who received Ra-223 first vs Ra-223 later as well as between AO+ and AO- veterans, but there was a trend of worse survival in veteran who received Ra-223 later and AO+ veterans.
This study showed that AO+ veterans have a shorter duration of response to therapy and shorter median survival compared with that of AO- veterans. We recommend that veterans should get Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than after hormonal therapy and chemotherapy because their marrows are still intact. We need to investigate further whether veterans that exposed to carcinogen 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) may have different molecular biology and as such may cause inferior efficacy in the treatment of prostate carcinoma.
1. Shore ND. Radium-223 dichloride for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the urologist’s perspective. Urology. 2015;85(4):717-724. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.031
2. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al; ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213-223. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213755
3. Smith M, Parker C, Saad F, et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):e559]. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):408-419. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30860-X
4. Everly L, Merrick GS, Allen ZA, et al. Prostate cancer control and survival in Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange. Brachytherapy. 2009;8(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.08.001
5. Altekruse S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017 Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. 2009. 6. Ansbaugh N, Shannon J, Mori M, Farris PE, Garzotto M. Agent Orange as a risk factor for high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2399-2404. doi:10.1002/cncr.27941
7. Jadvar H, Quinn DI. Targeted α-particle therapy of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(12):966-971. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000290
Patients with metastatic castrate resistant prostate carcinoma (CRPC) have several treatment options, including radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) radionuclide therapy, abiraterone, enzalutamide, and cabazitaxel. Ra-223 therapy has been reported to increase median survival in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma.1,2 However, ERA 223 trial data showed an increase of bone fractures with combination of Ra-223 and abiraterone.3
Agent Orange (AO) exposure has been studied as a potential risk factor for development of prostate carcinoma. AO was a commercially manufactured defoliate that was sprayed extensively during the Vietnam War. Due to a side product of chemical manufacturing, AO was contaminated with the toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a putative carcinogen. These dioxins can enter the food chain through soil contamination. There is enough evidence to link AO to hematologic malignancies and several solid tumors, including prostate carcinoma.4 Although no real estimates exist for what percentage of Vietnam veterans experienced AO exposure, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data showed that about 3 million veterans served in Southeast Asia where AO was used extensively in the combat theater. AO has been reported to be positively associated with a 52% increase in risk of prostate carcinoma detection at initial prostate biopsy.5
There has been no reported study of treatment efficacy in veterans with AO-related prostate carcinoma. We present a retrospective study of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC. The purpose of this study was to compare response to therapy and survival in veterans exposed to agent orange (AO+) vs veterans who were not exposed to (AO-) in a single US Department of Veteran Affairs (VA) medical center.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of veterans with metastatic CRPC to bones who received Ra-223 radionuclide therapy with standard dose of 50 kBq per kg of body weight and other sequential therapies at VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS) from January 2014 to January 2019. The purpose of this study was to measure difference in treatment outcome between AO+ veterans and AO- veterans.
Eligibility Criteria
All veterans had a history that included bone metastasis CRPC. They could have 2 to 3 small lymphadenopathies but not visceral metastasis. They received a minimum of 3 cycles and a maximum of 6 cycles of Ra-223 therapy, which was given in 4-week intervals. Pretreatment criteria was hemoglobin > 10 g/dL, platelet > 100
Statistics
Time to study was calculated from the initiation of Ra-223 therapy. Time to skeletal-related events (SRE), progression of prostate specific antigen (PSA), bone metastasis, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were calculated in months, using unpaired t test with 2-tailed P value. Median survival was calculated in months by Kaplan Meier R log-rank test Definition).
Results
Forty-eight veterans with bone metastasis CRPC received Ra-223 therapy. Of those, 34 veterans were eligible for this retrospective study: 17 AO+ veterans and 17 AO- veterans. Mean age of diagnosis was 62 years (AO+) and 69 years (AO-) (P = .005). Mean Gleason score was 8.2 (AO+) and 8.0 (AO-) (P = .705). Veterans received initial therapy at diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, including radical prostatectomy (6 AO+ and 3 AO-), localized radiation therapy (3 AO+ and 5 AO-), and ADT (8 AO+ and 9 AO-) (Table 1).
Mean PSA at the initiation of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551) and for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639; P = .86). Mean Ra-223 dose per cycle for AO+ and AO- was 157 uCi and 113 uCi, respectively. All 34 veterans received ADT (leuprolide acetate), and 30 veterans (16 AO+ and 14 AO-) received bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid or denosumab). A total of 10 veterans (29%) received Ra-223 as a first-line therapy (4 AO+ and 6 AO-), and 24 veterans (71%) received Ra-223 after hormonal or chemotherapy (13 AO+ and 11 AO-).
There were 12 SRE (8 AO+ and 4 AO-). Mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Three veterans received concurrent Ra-223 and abiraterone (participated in ERA 223 trial). Two AO+ veterans experienced SRE at 7 months and 11 months, respectively. Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months, respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months, respectively (P = .05). (Table 2). The treatment pattern of AO+ and AO- is depicted on a swimmer plot (Figures 1 and 2).
Twenty veterans (58%) had died: 13 AO+ and 7 AO- veterans. Median survival for Ra-223 first and Ra-223 later was was 32 months and 15 months, respectively (P = .14; hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). Overall median survival for AO+ veterans and AO- veterans were 12 months and 18 months, respectively (P = .15; HR, 2.0) (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussions
There has been no reported VA study of using Ra-223 and other therapies (hormonal and chemotherapy) in veterans exposed to AO. This is the first retrospective study to compare the response and survival between AO+ and AO- veterans. Even though this study featured a small sample, it is interesting to note the difference between those 2 populations. There was 1 prior study in veterans with prostate carcinoma using radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in early-stage disease. Everly and colleagues reported that AO+ veterans were less likely to remain biochemically controlled compared with AO- and nonveteran patients with prostate carcinoma.4
Ansbaugh and colleagues reported that AO was associated with a 75% increase in the risk of Gleason ≥ 7 and a 110% increase in Gleason ≥ 8. AO+ veterans are at risk for the detection of high-grade prostate carcinoma. They also tend to have an average age of diagnosis that is 4 to 5 years younger than AO- veterans.6
Our study revealed that AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age (mean 62 years) compared with that of AO- veterans (mean 69 years, P = .005). We also proved that AO veterans have a higher mean Gleason score (8.2) compared with that of AO- veterans (8.0). Veterans received therapy at the time of diagnosis of prostate carcinoma with either radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or ADT with leuprolide acetate. Mean PSA at the start of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551); for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639), which is not statistically significant.
Ra-223, an
In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Parker and colleagues (ALSYMPCA study), 921 patients who had received, were not eligible to receive, or declined docetaxel, in a 2:1 ratio, were randomized to receive 6 injections of Ra-223 or matching placebo.2 Ra-223 significantly improved overall survival (OS) (median, 14.9 months vs 11.3 months) compared with that of placebo. Ra-223 also prolonged the time to the first symptomatic SRE (median, 15.6 months vs 9.8 months), the time to an increase in the total ALP level (median 7.4 months vs 3.8 months), and the time to an increase in the PSA level (median 3.6 months vs 3.4 months).2
In our study, the mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months respectively (P = .05). There is a trend of shorter PSA progression, bone progression, and ALP progression in AO+ veterans, though these were not statistically significant due to small sample population. In our study the median survival in for AO- was 18 months and for AO+ was 12 months, which is comparable with median survival of 14.9 months from the ALSYMPCA study.
There were 12 veterans who developed SREs. All received radiation therapy due to bone progression or impending fracture. AO+ veterans developed more SREs (n = 8) when compared with AO- veterans (n = 4). There were more AO- veterans alive (n = 10) than there were AO+ veterans (n = 4). The plausible explanation of this may be due to the aggressive pattern of prostate carcinoma in AO+ veterans (younger age and higher Gleason score).
VAPHS participated in the ERA trial between 2014 and 2016. The trial enrolled 806 patients who were randomly assigned to receive first-line Ra-223 or placebo in addition to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.3 The study was unblinded prematurely after more fractures and deaths were noted in the Ra-223 and abiraterone group than there were in the placebo and abiraterone group. Median symptomatic SRE was 22.3 months in the Ra-223 group and 26.0 months in the placebo group. Fractures (any grade) occurred in 29% in the Ra-223 group and 11% in the placebo group. It was suggested that Ra-223 could contribute to the risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma. Median OS was 30.7 months in the Ra-223 group and 33.3 months in the placebo group.
We enrolled 3 veterans in the ERA clinical trial. Two AO+ veterans had SREs at 7 months and 11 months. In our study, the median OS for Ra-223 first line was 32 months, which is comparable with median survival of 30.7 months from ERA-223 study. Median survival for Ra-223 later was only 15 months. We recommend veterans with at least 2 to 3-bone metastasis receive Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than second- or third-line setting. In this retrospective study with Ra-223 and other therapies, we proved that AO+ veterans have a worse response and OS when compared with that of AO- veterans.
Conclusions
This is the first VA study to compare the efficacy of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC between AO+ and AO- veterans. AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age and had higher Gleason scores. There was no statistical difference between AO+ and AO- veterans in terms of time to SRE, PSA progression, and bone and ALP progression even though there was a trend of shorter duration in AO+ veterans. There was no median survival difference between veterans who received Ra-223 first vs Ra-223 later as well as between AO+ and AO- veterans, but there was a trend of worse survival in veteran who received Ra-223 later and AO+ veterans.
This study showed that AO+ veterans have a shorter duration of response to therapy and shorter median survival compared with that of AO- veterans. We recommend that veterans should get Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than after hormonal therapy and chemotherapy because their marrows are still intact. We need to investigate further whether veterans that exposed to carcinogen 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) may have different molecular biology and as such may cause inferior efficacy in the treatment of prostate carcinoma.
Patients with metastatic castrate resistant prostate carcinoma (CRPC) have several treatment options, including radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) radionuclide therapy, abiraterone, enzalutamide, and cabazitaxel. Ra-223 therapy has been reported to increase median survival in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma.1,2 However, ERA 223 trial data showed an increase of bone fractures with combination of Ra-223 and abiraterone.3
Agent Orange (AO) exposure has been studied as a potential risk factor for development of prostate carcinoma. AO was a commercially manufactured defoliate that was sprayed extensively during the Vietnam War. Due to a side product of chemical manufacturing, AO was contaminated with the toxin 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a putative carcinogen. These dioxins can enter the food chain through soil contamination. There is enough evidence to link AO to hematologic malignancies and several solid tumors, including prostate carcinoma.4 Although no real estimates exist for what percentage of Vietnam veterans experienced AO exposure, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data showed that about 3 million veterans served in Southeast Asia where AO was used extensively in the combat theater. AO has been reported to be positively associated with a 52% increase in risk of prostate carcinoma detection at initial prostate biopsy.5
There has been no reported study of treatment efficacy in veterans with AO-related prostate carcinoma. We present a retrospective study of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC. The purpose of this study was to compare response to therapy and survival in veterans exposed to agent orange (AO+) vs veterans who were not exposed to (AO-) in a single US Department of Veteran Affairs (VA) medical center.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of veterans with metastatic CRPC to bones who received Ra-223 radionuclide therapy with standard dose of 50 kBq per kg of body weight and other sequential therapies at VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS) from January 2014 to January 2019. The purpose of this study was to measure difference in treatment outcome between AO+ veterans and AO- veterans.
Eligibility Criteria
All veterans had a history that included bone metastasis CRPC. They could have 2 to 3 small lymphadenopathies but not visceral metastasis. They received a minimum of 3 cycles and a maximum of 6 cycles of Ra-223 therapy, which was given in 4-week intervals. Pretreatment criteria was hemoglobin > 10 g/dL, platelet > 100
Statistics
Time to study was calculated from the initiation of Ra-223 therapy. Time to skeletal-related events (SRE), progression of prostate specific antigen (PSA), bone metastasis, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were calculated in months, using unpaired t test with 2-tailed P value. Median survival was calculated in months by Kaplan Meier R log-rank test Definition).
Results
Forty-eight veterans with bone metastasis CRPC received Ra-223 therapy. Of those, 34 veterans were eligible for this retrospective study: 17 AO+ veterans and 17 AO- veterans. Mean age of diagnosis was 62 years (AO+) and 69 years (AO-) (P = .005). Mean Gleason score was 8.2 (AO+) and 8.0 (AO-) (P = .705). Veterans received initial therapy at diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, including radical prostatectomy (6 AO+ and 3 AO-), localized radiation therapy (3 AO+ and 5 AO-), and ADT (8 AO+ and 9 AO-) (Table 1).
Mean PSA at the initiation of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551) and for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639; P = .86). Mean Ra-223 dose per cycle for AO+ and AO- was 157 uCi and 113 uCi, respectively. All 34 veterans received ADT (leuprolide acetate), and 30 veterans (16 AO+ and 14 AO-) received bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid or denosumab). A total of 10 veterans (29%) received Ra-223 as a first-line therapy (4 AO+ and 6 AO-), and 24 veterans (71%) received Ra-223 after hormonal or chemotherapy (13 AO+ and 11 AO-).
There were 12 SRE (8 AO+ and 4 AO-). Mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Three veterans received concurrent Ra-223 and abiraterone (participated in ERA 223 trial). Two AO+ veterans experienced SRE at 7 months and 11 months, respectively. Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months, respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months, respectively (P = .05). (Table 2). The treatment pattern of AO+ and AO- is depicted on a swimmer plot (Figures 1 and 2).
Twenty veterans (58%) had died: 13 AO+ and 7 AO- veterans. Median survival for Ra-223 first and Ra-223 later was was 32 months and 15 months, respectively (P = .14; hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). Overall median survival for AO+ veterans and AO- veterans were 12 months and 18 months, respectively (P = .15; HR, 2.0) (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussions
There has been no reported VA study of using Ra-223 and other therapies (hormonal and chemotherapy) in veterans exposed to AO. This is the first retrospective study to compare the response and survival between AO+ and AO- veterans. Even though this study featured a small sample, it is interesting to note the difference between those 2 populations. There was 1 prior study in veterans with prostate carcinoma using radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in early-stage disease. Everly and colleagues reported that AO+ veterans were less likely to remain biochemically controlled compared with AO- and nonveteran patients with prostate carcinoma.4
Ansbaugh and colleagues reported that AO was associated with a 75% increase in the risk of Gleason ≥ 7 and a 110% increase in Gleason ≥ 8. AO+ veterans are at risk for the detection of high-grade prostate carcinoma. They also tend to have an average age of diagnosis that is 4 to 5 years younger than AO- veterans.6
Our study revealed that AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age (mean 62 years) compared with that of AO- veterans (mean 69 years, P = .005). We also proved that AO veterans have a higher mean Gleason score (8.2) compared with that of AO- veterans (8.0). Veterans received therapy at the time of diagnosis of prostate carcinoma with either radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or ADT with leuprolide acetate. Mean PSA at the start of Ra-223 therapy for AO+ was 92.8 (range, 2-551); for AO- was 102.3 (range, 4-639), which is not statistically significant.
Ra-223, an
In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Parker and colleagues (ALSYMPCA study), 921 patients who had received, were not eligible to receive, or declined docetaxel, in a 2:1 ratio, were randomized to receive 6 injections of Ra-223 or matching placebo.2 Ra-223 significantly improved overall survival (OS) (median, 14.9 months vs 11.3 months) compared with that of placebo. Ra-223 also prolonged the time to the first symptomatic SRE (median, 15.6 months vs 9.8 months), the time to an increase in the total ALP level (median 7.4 months vs 3.8 months), and the time to an increase in the PSA level (median 3.6 months vs 3.4 months).2
In our study, the mean time to SRE for AO+ was 10.6 months and AO- was 10.3 months (P = .93). Mean time to PSA progression for AO+ was 5.4 months and for AO- was 6.8 months (P = .28). Mean time to bone progression for AO+ and for AO- were 7.6 months and 10.1 months respectively (P = .16). Mean time to ALP progression for AO+ and AO- were 6.3 months and 8.7 months respectively (P = .05). There is a trend of shorter PSA progression, bone progression, and ALP progression in AO+ veterans, though these were not statistically significant due to small sample population. In our study the median survival in for AO- was 18 months and for AO+ was 12 months, which is comparable with median survival of 14.9 months from the ALSYMPCA study.
There were 12 veterans who developed SREs. All received radiation therapy due to bone progression or impending fracture. AO+ veterans developed more SREs (n = 8) when compared with AO- veterans (n = 4). There were more AO- veterans alive (n = 10) than there were AO+ veterans (n = 4). The plausible explanation of this may be due to the aggressive pattern of prostate carcinoma in AO+ veterans (younger age and higher Gleason score).
VAPHS participated in the ERA trial between 2014 and 2016. The trial enrolled 806 patients who were randomly assigned to receive first-line Ra-223 or placebo in addition to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.3 The study was unblinded prematurely after more fractures and deaths were noted in the Ra-223 and abiraterone group than there were in the placebo and abiraterone group. Median symptomatic SRE was 22.3 months in the Ra-223 group and 26.0 months in the placebo group. Fractures (any grade) occurred in 29% in the Ra-223 group and 11% in the placebo group. It was suggested that Ra-223 could contribute to the risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with bone metastatic prostate carcinoma. Median OS was 30.7 months in the Ra-223 group and 33.3 months in the placebo group.
We enrolled 3 veterans in the ERA clinical trial. Two AO+ veterans had SREs at 7 months and 11 months. In our study, the median OS for Ra-223 first line was 32 months, which is comparable with median survival of 30.7 months from ERA-223 study. Median survival for Ra-223 later was only 15 months. We recommend veterans with at least 2 to 3-bone metastasis receive Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than second- or third-line setting. In this retrospective study with Ra-223 and other therapies, we proved that AO+ veterans have a worse response and OS when compared with that of AO- veterans.
Conclusions
This is the first VA study to compare the efficacy of Ra-223 and other therapies in metastatic CRPC between AO+ and AO- veterans. AO+ veterans were diagnosed at a younger age and had higher Gleason scores. There was no statistical difference between AO+ and AO- veterans in terms of time to SRE, PSA progression, and bone and ALP progression even though there was a trend of shorter duration in AO+ veterans. There was no median survival difference between veterans who received Ra-223 first vs Ra-223 later as well as between AO+ and AO- veterans, but there was a trend of worse survival in veteran who received Ra-223 later and AO+ veterans.
This study showed that AO+ veterans have a shorter duration of response to therapy and shorter median survival compared with that of AO- veterans. We recommend that veterans should get Ra-223 in the first-line setting rather than after hormonal therapy and chemotherapy because their marrows are still intact. We need to investigate further whether veterans that exposed to carcinogen 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) may have different molecular biology and as such may cause inferior efficacy in the treatment of prostate carcinoma.
1. Shore ND. Radium-223 dichloride for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the urologist’s perspective. Urology. 2015;85(4):717-724. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.031
2. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al; ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213-223. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213755
3. Smith M, Parker C, Saad F, et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):e559]. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):408-419. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30860-X
4. Everly L, Merrick GS, Allen ZA, et al. Prostate cancer control and survival in Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange. Brachytherapy. 2009;8(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.08.001
5. Altekruse S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017 Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. 2009. 6. Ansbaugh N, Shannon J, Mori M, Farris PE, Garzotto M. Agent Orange as a risk factor for high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2399-2404. doi:10.1002/cncr.27941
7. Jadvar H, Quinn DI. Targeted α-particle therapy of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(12):966-971. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000290
1. Shore ND. Radium-223 dichloride for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: the urologist’s perspective. Urology. 2015;85(4):717-724. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.11.031
2. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al; ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213-223. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213755
3. Smith M, Parker C, Saad F, et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial [published correction appears in Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):e559]. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):408-419. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30860-X
4. Everly L, Merrick GS, Allen ZA, et al. Prostate cancer control and survival in Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange. Brachytherapy. 2009;8(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2008.08.001
5. Altekruse S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017 Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. 2009. 6. Ansbaugh N, Shannon J, Mori M, Farris PE, Garzotto M. Agent Orange as a risk factor for high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2399-2404. doi:10.1002/cncr.27941
7. Jadvar H, Quinn DI. Targeted α-particle therapy of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(12):966-971. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000290
Guideline Concordance with Durvalumab in Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single Center Veterans Hospital Experience
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CRT).1 After 2 randomized phase 3 studies in 2017 and 2018 showed significant progression-free and overall survival respectively,2,3 durvalumab became a category 1 recommendation for the above indication per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines.4 Adherence to guidelines have been shown to improve patient survival across several cancer types.5-7 However, guideline adherence rates have been variable across health institutions. Therefore, further study is warranted to evaluate nonadherent practices with the goal of improving the quality of cancer care delivery.8,9
Stage III NSCLC is associated with poor survival rates.10 Concurrent CRT remains the standard of care in patients with good performance status based on clinical trial populations.4 Lung cancer remains a disease of the elderly, with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years.11 Discrepancies in the treatment of lung cancer in older adults can vary widely due to a lack of evidence surrounding the treatment in those who have comorbidities and poor performance status, widening the gap between clinical trial and real-world populations.11
A recent review by Passaro and colleagues revealed that at least 11 pivotal randomized controlled trials have shown the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer. However, these studies have mostly excluded patients with a performance status of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) level ≥ 2.11
Durvalumab is one of many new therapies to enter clinical practice to demonstrate survival benefit, but its use among veterans with stage III NSCLC in adherence with National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines was not robust at the Birmingham Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Alabama. Therefore, we decided to study the level of adherence and to identify barriers to conformity to the category 1 NCCN recommendations.
Methods
The Birmingham VAMC Outpatient Oncology Clinic billing data identified all individuals diagnosed with lung cancer treated between October 2017 and August 2019. Patients who did not have NSCLC that was stage III and unresectable were excluded from our study. Patients who did not receive a majority of their treatment at US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facilities were excluded as well. Each patient’s demographic, functional level, and tumor characteristics during the treatment planning phase and follow-up visits were obtained. Two investigators who evaluated health care provider documentation using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) conducted chart reviews.
The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients who received concurrent CRT and the proportion who received durvalumab consolidation. Our chart review also categorized reasons for nonreceipt of concurrent CRT and subsequent durvalumab. Documented reasons for guideline discordancy were generated empirically and broadly. We noted if documentation was unclear and included reasons for why a veteran was not a candidate for CRT, the presence of toxicities associated with CRT, and a patient’s refusal for therapy despite medical advice. Descriptive data were analyzed for all clinical or demographic characteristics and outcomes.
This was considered an internal quality improvement initiative. As such, Birmingham VAMC did not require institutional review board approval for the study. The facility is accredited by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer.
Results
A total of 41 veterans with stage III NSCLC were identified to have established care in the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic between October 2017 and August 2019. Of these, 7 received the majority of their treatment from community-based non-VA facilities and 14 were not candidates for CRT and were excluded from this study.
The mean (SD) age of study participants was 70.0 (8.4) years (range, 57 to 92 years). Most of the study veterans (33; 97.1%) were male and 20 (58.8%) were African American (Table). Eighteen (53%) of study participants had clinical stage IIIa NSCLC; 19 (56%) showed a squamous subtype of NSCLC. A majority (53%) of the veterans studied were evaluated to be functionally fit with an ECOG status of 0 to 1, although documentation of ECOG status was lacking in 5 (14.7%) patients in the initial treatment planning visit records. It was unclear if performance status had been reevaluated and changes noted over the course of concurrent CRT.
CRT Patients
The relative distribution of veterans who underwent CRT for stage III NSCLC plus the reasons they did not receive guideline-based treatment with durvalumab is shown in the Figure. Fourteen patients (41%) were inappropriate candidates for CRT; the most common reason for this was their poor performance status upon initial evaluation and 3 patients (8.8%) in the study had extensive disease or were upstaged upon follow-up clinic visit.
Twenty (59%) veterans in the study initiated CRT. However, only 16 (47.1%) completed CRT. Those who dropped out of CRT did so because of toxicities that included various cytopenia, gastrointestinal toxicities due to radiation and/or chemotherapy, or failure to thrive.
Durvalumab Treatment
After initiation of CRT, 9 (26.5%) patients did not go on to receive durvalumab. Three patients (8.8%) suffered toxicities during CRT. One study patient was found to have a severe respiratory infection requiring intensive care unit admission. Another study patient was found to have a new sternal lesion on follow-up positron emission tomography. One declined because of a history of severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis, which made durvalumab use unsafe. Three patients (8.8%) declined treatment with CRT or durvalumab because of personal preference. Documentation was unclear as to why durvalumab was prescribed to one patient who had completed CRT.
Discussion
NCCN guidelines on the use of durvalumab in NSCLC are based on the phase 3 PACIFIC placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. This trial, which included only patients with documented performance status of ECOG 0 or 1, reported that grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 30.5% of patients randomized to consolidative durvalumab. Treatment was discontinued in 15.4% of patients due to adverse events.3
Our study examined consolidation therapy with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC with an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1 who had not progressed after 2 or more cycles of definitive concurrent CRT.4 Patients with previous exposure to immunotherapy, a history of immunodeficiency, active infection, unresolved toxicity from CRT, autoimmune disease, and patients who received sequential CRT were excluded.2 Surprisingly, the adherence rate to guidelines was close to 100% with appropriate documentation and justification of CRT initiation and durvalumab use. Five (14.7%) of veterans with unresectable stage III NSCLC did not have clear documentation of ECOG status on initial visit and only 1 veteran who completed CRT did not have clear documentation as to why durvalumab was not provided. Unfortunately, 23 (68.6%) veterans in the study were unable to receive durvalumab, a potentially disease-modifying drug; nearly one-third (10) of veterans were deemed poor candidates for concurrent CRT despite the fact that 52.9% (18) of veterans in the study had a documented ECOG of 0 or 1 on initial evaluation.
Clinical Trials vs Real World
The heterogeneity between anticipated study populations, those who were able to receive durvalumab in the PACIFIC trial, compared with our observed real-world veteran population, likely stems from the lack of information about how comorbidity and fitness can affect the choice of therapeutic intervention in patients with lung cancer.12 In addition, older adults who participated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not representative of the average older adult who presents to medical oncology clinics, making the application of guideline concordant care difficult.13
Similar real-world observations parallel to our analyses have confirmed, complemented and/or refuted findings of RCTs, and have helped impact the treatment of multiple acute and chronic conditions including influenza, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.14
A component of socioeconomic barriers and access to supportive care played roles in the decisions of certain patients who chose not to undergo concurrent CRT despite medical advice. These 2 obstacles also affected the decision making for some in the study when considering the use of durvalumab (administered by a 60-minute IV infusion every 2 weeks for 1 year) per recommended guidelines.1 These hurdles need further study in the context of their effect on quality of life and the difficulties generated by various social determinants of health.
Limitations
Study limitations included the biased and confounding factors previously described about retrospective and nonrandomized observational studies that are controlled for during RCTs.15 Electronic health record data may have been incorrectly collected resulting in missing or wrong data points that affect the validity of our conclusion. Recall bias with regard to documentation by health care providers describing reasons why CRT or durvalumab were not initiated or the patient’s ability to recall previous treatments and report ECOG status or toxicities also may have impacted our findings. Comorbidities and poor performance status, frequently occurring among veterans, negatively impact cancer treatment decisions and may result in a detection bias. For example, tobacco use, cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are notoriously higher in the US veteran population when compared with civilian cohorts.16-18 Also, veterans with poorly controlled depression and posttraumatic stress disorder resulting in functional impairment are a factor.19 Steps were taken to address some of these biases by performing repeat checks of tabulated data and employing 2 independent reviewers to evaluate all relevant clinical documentation, compare results, and reach a consensus.
Conlcusions
This retrospective analysis of adherence to category 1 NCCN guidelines for durvalumab use among patients at the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic reinforced our practice and identified minor deficiencies in documentation that would impact future clinical visits. More importantly, it depicted the massive disparity in treatment candidacy among Birmingham veterans compared with clinical trial populations. Efforts will be made to address factors impacting a veteran’s candidacy for CRT and explore other variables such as socioeconomic barriers to treatment. Multiple complementary tools to assess patients’ frailty, such as the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), are now being used for a variety of disorders including cancers. More robust data and standardization are needed to validate the use of these assessments in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently being evaluated in stage III NSCLC studies and may be implemented as routine practice in the future.12 It is important to distinguish fit from frail veterans with lung cancer for treatment selection. We would like to see the expansion of the eligibility criteria for clinical trials to include patients with a performance status of ECOG 2 in order for results to be truly generalizable to the real-world population. Our hope is that such work will improve not only the quality of lung cancer care, but also the quality of care across multiple tumor types.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage II. Published February 20, 2018. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-durvalumab-after-chemoradiation-unresectable-stage-iii-nsclc
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919-1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342-2350. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809697
4. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer. Version8.2020. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
5. Bristow RE, Chang J, Ziogas A, Campos B, Chavez LR, Anton-Culver H. Impact of National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Centers on ovarian cancer treatment and survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):940-950. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.056
6. Boland GM, Chang GJ, Haynes AB, et al. Association between adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network treatment guidelines and improved survival in patients with colon cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(8):1593-1601. doi:10.1002/cncr.27935
7. Schwentner L, Wöckel A, König J, et al. Adherence to treatment guidelines and survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multi-center cohort study with 9,156 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:487. Published 2013 Oct 21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-487
8. Jazieh A, Alkaiyat MO, Ali Y, Hashim MA, Abdelhafiz N, Al Olayan A. Improving adherence to lung cancer guidelines: a quality improvement project that uses chart review, audit and feedback approach. BMJ Open Qual. 2019;8(3):e000436. Published 2019 Aug 26. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2018-000436
9. Shaverdian N, Offin MD, Rimner A, et al. Utilization and factors precluding the initiation of consolidative durvalumab in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;144:101-104. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.015
10. National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015, Table 15.1 cancer of the lung and bronchus. Accessed October 19, 2020 https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/results_merged/sect_15_lung_bronchus.pdf. Updated September 10, 2018
11. Passaro A, Spitaleri G, Gyawali B, de Marinis F. Immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2: clinical decision making with scant evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(22):1863-1867. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02118
12. Driessen EJM, Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Maas HA, Dingemans AC, van Loon JGM. Study protocol of the NVALT25-ELDAPT trial: selecting the optimal treatment for older patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(6):e849-e852. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.003
13. Schulkes KJ, Nguyen C, van den Bos F, van Elden LJ, Hamaker ME. Selection of Patients in Ongoing Clinical Trials on Lung Cancer. Lung. 2016;194(6):967-974. doi:10.1007/s00408-016-9943-7
14. Blonde L, Khunti K, Harris SB, Meizinger C, Skolnik NS. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician. Adv Ther. 2018;35(11):1763-1774. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y
15. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health. 2007;10(5):326-335. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00186.x
16. Assari S. Veterans and risk of heart disease in the United States: a cohort with 20 years of follow up. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(6):703-709.
17. Shahoumian TA, Phillips BR, Backus LI. Cigarette smoking, reduction and quit attempts: prevalence among veterans with coronary heart disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2016;13:E41. Published 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.5888/pcd13.150282
18. Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
19. Kozel FA, Didehbani N, DeLaRosa B, et al. Factors impacting functional status in veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28(2):112-117. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15070183
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CRT).1 After 2 randomized phase 3 studies in 2017 and 2018 showed significant progression-free and overall survival respectively,2,3 durvalumab became a category 1 recommendation for the above indication per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines.4 Adherence to guidelines have been shown to improve patient survival across several cancer types.5-7 However, guideline adherence rates have been variable across health institutions. Therefore, further study is warranted to evaluate nonadherent practices with the goal of improving the quality of cancer care delivery.8,9
Stage III NSCLC is associated with poor survival rates.10 Concurrent CRT remains the standard of care in patients with good performance status based on clinical trial populations.4 Lung cancer remains a disease of the elderly, with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years.11 Discrepancies in the treatment of lung cancer in older adults can vary widely due to a lack of evidence surrounding the treatment in those who have comorbidities and poor performance status, widening the gap between clinical trial and real-world populations.11
A recent review by Passaro and colleagues revealed that at least 11 pivotal randomized controlled trials have shown the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer. However, these studies have mostly excluded patients with a performance status of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) level ≥ 2.11
Durvalumab is one of many new therapies to enter clinical practice to demonstrate survival benefit, but its use among veterans with stage III NSCLC in adherence with National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines was not robust at the Birmingham Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Alabama. Therefore, we decided to study the level of adherence and to identify barriers to conformity to the category 1 NCCN recommendations.
Methods
The Birmingham VAMC Outpatient Oncology Clinic billing data identified all individuals diagnosed with lung cancer treated between October 2017 and August 2019. Patients who did not have NSCLC that was stage III and unresectable were excluded from our study. Patients who did not receive a majority of their treatment at US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facilities were excluded as well. Each patient’s demographic, functional level, and tumor characteristics during the treatment planning phase and follow-up visits were obtained. Two investigators who evaluated health care provider documentation using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) conducted chart reviews.
The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients who received concurrent CRT and the proportion who received durvalumab consolidation. Our chart review also categorized reasons for nonreceipt of concurrent CRT and subsequent durvalumab. Documented reasons for guideline discordancy were generated empirically and broadly. We noted if documentation was unclear and included reasons for why a veteran was not a candidate for CRT, the presence of toxicities associated with CRT, and a patient’s refusal for therapy despite medical advice. Descriptive data were analyzed for all clinical or demographic characteristics and outcomes.
This was considered an internal quality improvement initiative. As such, Birmingham VAMC did not require institutional review board approval for the study. The facility is accredited by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer.
Results
A total of 41 veterans with stage III NSCLC were identified to have established care in the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic between October 2017 and August 2019. Of these, 7 received the majority of their treatment from community-based non-VA facilities and 14 were not candidates for CRT and were excluded from this study.
The mean (SD) age of study participants was 70.0 (8.4) years (range, 57 to 92 years). Most of the study veterans (33; 97.1%) were male and 20 (58.8%) were African American (Table). Eighteen (53%) of study participants had clinical stage IIIa NSCLC; 19 (56%) showed a squamous subtype of NSCLC. A majority (53%) of the veterans studied were evaluated to be functionally fit with an ECOG status of 0 to 1, although documentation of ECOG status was lacking in 5 (14.7%) patients in the initial treatment planning visit records. It was unclear if performance status had been reevaluated and changes noted over the course of concurrent CRT.
CRT Patients
The relative distribution of veterans who underwent CRT for stage III NSCLC plus the reasons they did not receive guideline-based treatment with durvalumab is shown in the Figure. Fourteen patients (41%) were inappropriate candidates for CRT; the most common reason for this was their poor performance status upon initial evaluation and 3 patients (8.8%) in the study had extensive disease or were upstaged upon follow-up clinic visit.
Twenty (59%) veterans in the study initiated CRT. However, only 16 (47.1%) completed CRT. Those who dropped out of CRT did so because of toxicities that included various cytopenia, gastrointestinal toxicities due to radiation and/or chemotherapy, or failure to thrive.
Durvalumab Treatment
After initiation of CRT, 9 (26.5%) patients did not go on to receive durvalumab. Three patients (8.8%) suffered toxicities during CRT. One study patient was found to have a severe respiratory infection requiring intensive care unit admission. Another study patient was found to have a new sternal lesion on follow-up positron emission tomography. One declined because of a history of severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis, which made durvalumab use unsafe. Three patients (8.8%) declined treatment with CRT or durvalumab because of personal preference. Documentation was unclear as to why durvalumab was prescribed to one patient who had completed CRT.
Discussion
NCCN guidelines on the use of durvalumab in NSCLC are based on the phase 3 PACIFIC placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. This trial, which included only patients with documented performance status of ECOG 0 or 1, reported that grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 30.5% of patients randomized to consolidative durvalumab. Treatment was discontinued in 15.4% of patients due to adverse events.3
Our study examined consolidation therapy with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC with an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1 who had not progressed after 2 or more cycles of definitive concurrent CRT.4 Patients with previous exposure to immunotherapy, a history of immunodeficiency, active infection, unresolved toxicity from CRT, autoimmune disease, and patients who received sequential CRT were excluded.2 Surprisingly, the adherence rate to guidelines was close to 100% with appropriate documentation and justification of CRT initiation and durvalumab use. Five (14.7%) of veterans with unresectable stage III NSCLC did not have clear documentation of ECOG status on initial visit and only 1 veteran who completed CRT did not have clear documentation as to why durvalumab was not provided. Unfortunately, 23 (68.6%) veterans in the study were unable to receive durvalumab, a potentially disease-modifying drug; nearly one-third (10) of veterans were deemed poor candidates for concurrent CRT despite the fact that 52.9% (18) of veterans in the study had a documented ECOG of 0 or 1 on initial evaluation.
Clinical Trials vs Real World
The heterogeneity between anticipated study populations, those who were able to receive durvalumab in the PACIFIC trial, compared with our observed real-world veteran population, likely stems from the lack of information about how comorbidity and fitness can affect the choice of therapeutic intervention in patients with lung cancer.12 In addition, older adults who participated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not representative of the average older adult who presents to medical oncology clinics, making the application of guideline concordant care difficult.13
Similar real-world observations parallel to our analyses have confirmed, complemented and/or refuted findings of RCTs, and have helped impact the treatment of multiple acute and chronic conditions including influenza, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.14
A component of socioeconomic barriers and access to supportive care played roles in the decisions of certain patients who chose not to undergo concurrent CRT despite medical advice. These 2 obstacles also affected the decision making for some in the study when considering the use of durvalumab (administered by a 60-minute IV infusion every 2 weeks for 1 year) per recommended guidelines.1 These hurdles need further study in the context of their effect on quality of life and the difficulties generated by various social determinants of health.
Limitations
Study limitations included the biased and confounding factors previously described about retrospective and nonrandomized observational studies that are controlled for during RCTs.15 Electronic health record data may have been incorrectly collected resulting in missing or wrong data points that affect the validity of our conclusion. Recall bias with regard to documentation by health care providers describing reasons why CRT or durvalumab were not initiated or the patient’s ability to recall previous treatments and report ECOG status or toxicities also may have impacted our findings. Comorbidities and poor performance status, frequently occurring among veterans, negatively impact cancer treatment decisions and may result in a detection bias. For example, tobacco use, cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are notoriously higher in the US veteran population when compared with civilian cohorts.16-18 Also, veterans with poorly controlled depression and posttraumatic stress disorder resulting in functional impairment are a factor.19 Steps were taken to address some of these biases by performing repeat checks of tabulated data and employing 2 independent reviewers to evaluate all relevant clinical documentation, compare results, and reach a consensus.
Conlcusions
This retrospective analysis of adherence to category 1 NCCN guidelines for durvalumab use among patients at the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic reinforced our practice and identified minor deficiencies in documentation that would impact future clinical visits. More importantly, it depicted the massive disparity in treatment candidacy among Birmingham veterans compared with clinical trial populations. Efforts will be made to address factors impacting a veteran’s candidacy for CRT and explore other variables such as socioeconomic barriers to treatment. Multiple complementary tools to assess patients’ frailty, such as the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), are now being used for a variety of disorders including cancers. More robust data and standardization are needed to validate the use of these assessments in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently being evaluated in stage III NSCLC studies and may be implemented as routine practice in the future.12 It is important to distinguish fit from frail veterans with lung cancer for treatment selection. We would like to see the expansion of the eligibility criteria for clinical trials to include patients with a performance status of ECOG 2 in order for results to be truly generalizable to the real-world population. Our hope is that such work will improve not only the quality of lung cancer care, but also the quality of care across multiple tumor types.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy (CRT).1 After 2 randomized phase 3 studies in 2017 and 2018 showed significant progression-free and overall survival respectively,2,3 durvalumab became a category 1 recommendation for the above indication per National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines.4 Adherence to guidelines have been shown to improve patient survival across several cancer types.5-7 However, guideline adherence rates have been variable across health institutions. Therefore, further study is warranted to evaluate nonadherent practices with the goal of improving the quality of cancer care delivery.8,9
Stage III NSCLC is associated with poor survival rates.10 Concurrent CRT remains the standard of care in patients with good performance status based on clinical trial populations.4 Lung cancer remains a disease of the elderly, with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years.11 Discrepancies in the treatment of lung cancer in older adults can vary widely due to a lack of evidence surrounding the treatment in those who have comorbidities and poor performance status, widening the gap between clinical trial and real-world populations.11
A recent review by Passaro and colleagues revealed that at least 11 pivotal randomized controlled trials have shown the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer. However, these studies have mostly excluded patients with a performance status of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) level ≥ 2.11
Durvalumab is one of many new therapies to enter clinical practice to demonstrate survival benefit, but its use among veterans with stage III NSCLC in adherence with National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines was not robust at the Birmingham Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Alabama. Therefore, we decided to study the level of adherence and to identify barriers to conformity to the category 1 NCCN recommendations.
Methods
The Birmingham VAMC Outpatient Oncology Clinic billing data identified all individuals diagnosed with lung cancer treated between October 2017 and August 2019. Patients who did not have NSCLC that was stage III and unresectable were excluded from our study. Patients who did not receive a majority of their treatment at US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facilities were excluded as well. Each patient’s demographic, functional level, and tumor characteristics during the treatment planning phase and follow-up visits were obtained. Two investigators who evaluated health care provider documentation using the VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) conducted chart reviews.
The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients who received concurrent CRT and the proportion who received durvalumab consolidation. Our chart review also categorized reasons for nonreceipt of concurrent CRT and subsequent durvalumab. Documented reasons for guideline discordancy were generated empirically and broadly. We noted if documentation was unclear and included reasons for why a veteran was not a candidate for CRT, the presence of toxicities associated with CRT, and a patient’s refusal for therapy despite medical advice. Descriptive data were analyzed for all clinical or demographic characteristics and outcomes.
This was considered an internal quality improvement initiative. As such, Birmingham VAMC did not require institutional review board approval for the study. The facility is accredited by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer.
Results
A total of 41 veterans with stage III NSCLC were identified to have established care in the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic between October 2017 and August 2019. Of these, 7 received the majority of their treatment from community-based non-VA facilities and 14 were not candidates for CRT and were excluded from this study.
The mean (SD) age of study participants was 70.0 (8.4) years (range, 57 to 92 years). Most of the study veterans (33; 97.1%) were male and 20 (58.8%) were African American (Table). Eighteen (53%) of study participants had clinical stage IIIa NSCLC; 19 (56%) showed a squamous subtype of NSCLC. A majority (53%) of the veterans studied were evaluated to be functionally fit with an ECOG status of 0 to 1, although documentation of ECOG status was lacking in 5 (14.7%) patients in the initial treatment planning visit records. It was unclear if performance status had been reevaluated and changes noted over the course of concurrent CRT.
CRT Patients
The relative distribution of veterans who underwent CRT for stage III NSCLC plus the reasons they did not receive guideline-based treatment with durvalumab is shown in the Figure. Fourteen patients (41%) were inappropriate candidates for CRT; the most common reason for this was their poor performance status upon initial evaluation and 3 patients (8.8%) in the study had extensive disease or were upstaged upon follow-up clinic visit.
Twenty (59%) veterans in the study initiated CRT. However, only 16 (47.1%) completed CRT. Those who dropped out of CRT did so because of toxicities that included various cytopenia, gastrointestinal toxicities due to radiation and/or chemotherapy, or failure to thrive.
Durvalumab Treatment
After initiation of CRT, 9 (26.5%) patients did not go on to receive durvalumab. Three patients (8.8%) suffered toxicities during CRT. One study patient was found to have a severe respiratory infection requiring intensive care unit admission. Another study patient was found to have a new sternal lesion on follow-up positron emission tomography. One declined because of a history of severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis, which made durvalumab use unsafe. Three patients (8.8%) declined treatment with CRT or durvalumab because of personal preference. Documentation was unclear as to why durvalumab was prescribed to one patient who had completed CRT.
Discussion
NCCN guidelines on the use of durvalumab in NSCLC are based on the phase 3 PACIFIC placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. This trial, which included only patients with documented performance status of ECOG 0 or 1, reported that grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 30.5% of patients randomized to consolidative durvalumab. Treatment was discontinued in 15.4% of patients due to adverse events.3
Our study examined consolidation therapy with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC with an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1 who had not progressed after 2 or more cycles of definitive concurrent CRT.4 Patients with previous exposure to immunotherapy, a history of immunodeficiency, active infection, unresolved toxicity from CRT, autoimmune disease, and patients who received sequential CRT were excluded.2 Surprisingly, the adherence rate to guidelines was close to 100% with appropriate documentation and justification of CRT initiation and durvalumab use. Five (14.7%) of veterans with unresectable stage III NSCLC did not have clear documentation of ECOG status on initial visit and only 1 veteran who completed CRT did not have clear documentation as to why durvalumab was not provided. Unfortunately, 23 (68.6%) veterans in the study were unable to receive durvalumab, a potentially disease-modifying drug; nearly one-third (10) of veterans were deemed poor candidates for concurrent CRT despite the fact that 52.9% (18) of veterans in the study had a documented ECOG of 0 or 1 on initial evaluation.
Clinical Trials vs Real World
The heterogeneity between anticipated study populations, those who were able to receive durvalumab in the PACIFIC trial, compared with our observed real-world veteran population, likely stems from the lack of information about how comorbidity and fitness can affect the choice of therapeutic intervention in patients with lung cancer.12 In addition, older adults who participated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are not representative of the average older adult who presents to medical oncology clinics, making the application of guideline concordant care difficult.13
Similar real-world observations parallel to our analyses have confirmed, complemented and/or refuted findings of RCTs, and have helped impact the treatment of multiple acute and chronic conditions including influenza, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.14
A component of socioeconomic barriers and access to supportive care played roles in the decisions of certain patients who chose not to undergo concurrent CRT despite medical advice. These 2 obstacles also affected the decision making for some in the study when considering the use of durvalumab (administered by a 60-minute IV infusion every 2 weeks for 1 year) per recommended guidelines.1 These hurdles need further study in the context of their effect on quality of life and the difficulties generated by various social determinants of health.
Limitations
Study limitations included the biased and confounding factors previously described about retrospective and nonrandomized observational studies that are controlled for during RCTs.15 Electronic health record data may have been incorrectly collected resulting in missing or wrong data points that affect the validity of our conclusion. Recall bias with regard to documentation by health care providers describing reasons why CRT or durvalumab were not initiated or the patient’s ability to recall previous treatments and report ECOG status or toxicities also may have impacted our findings. Comorbidities and poor performance status, frequently occurring among veterans, negatively impact cancer treatment decisions and may result in a detection bias. For example, tobacco use, cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are notoriously higher in the US veteran population when compared with civilian cohorts.16-18 Also, veterans with poorly controlled depression and posttraumatic stress disorder resulting in functional impairment are a factor.19 Steps were taken to address some of these biases by performing repeat checks of tabulated data and employing 2 independent reviewers to evaluate all relevant clinical documentation, compare results, and reach a consensus.
Conlcusions
This retrospective analysis of adherence to category 1 NCCN guidelines for durvalumab use among patients at the Birmingham VAMC Oncology Clinic reinforced our practice and identified minor deficiencies in documentation that would impact future clinical visits. More importantly, it depicted the massive disparity in treatment candidacy among Birmingham veterans compared with clinical trial populations. Efforts will be made to address factors impacting a veteran’s candidacy for CRT and explore other variables such as socioeconomic barriers to treatment. Multiple complementary tools to assess patients’ frailty, such as the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), are now being used for a variety of disorders including cancers. More robust data and standardization are needed to validate the use of these assessments in predicting response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently being evaluated in stage III NSCLC studies and may be implemented as routine practice in the future.12 It is important to distinguish fit from frail veterans with lung cancer for treatment selection. We would like to see the expansion of the eligibility criteria for clinical trials to include patients with a performance status of ECOG 2 in order for results to be truly generalizable to the real-world population. Our hope is that such work will improve not only the quality of lung cancer care, but also the quality of care across multiple tumor types.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage II. Published February 20, 2018. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-durvalumab-after-chemoradiation-unresectable-stage-iii-nsclc
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919-1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342-2350. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809697
4. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer. Version8.2020. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
5. Bristow RE, Chang J, Ziogas A, Campos B, Chavez LR, Anton-Culver H. Impact of National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Centers on ovarian cancer treatment and survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):940-950. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.056
6. Boland GM, Chang GJ, Haynes AB, et al. Association between adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network treatment guidelines and improved survival in patients with colon cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(8):1593-1601. doi:10.1002/cncr.27935
7. Schwentner L, Wöckel A, König J, et al. Adherence to treatment guidelines and survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multi-center cohort study with 9,156 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:487. Published 2013 Oct 21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-487
8. Jazieh A, Alkaiyat MO, Ali Y, Hashim MA, Abdelhafiz N, Al Olayan A. Improving adherence to lung cancer guidelines: a quality improvement project that uses chart review, audit and feedback approach. BMJ Open Qual. 2019;8(3):e000436. Published 2019 Aug 26. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2018-000436
9. Shaverdian N, Offin MD, Rimner A, et al. Utilization and factors precluding the initiation of consolidative durvalumab in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;144:101-104. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.015
10. National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015, Table 15.1 cancer of the lung and bronchus. Accessed October 19, 2020 https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/results_merged/sect_15_lung_bronchus.pdf. Updated September 10, 2018
11. Passaro A, Spitaleri G, Gyawali B, de Marinis F. Immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2: clinical decision making with scant evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(22):1863-1867. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02118
12. Driessen EJM, Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Maas HA, Dingemans AC, van Loon JGM. Study protocol of the NVALT25-ELDAPT trial: selecting the optimal treatment for older patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(6):e849-e852. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.003
13. Schulkes KJ, Nguyen C, van den Bos F, van Elden LJ, Hamaker ME. Selection of Patients in Ongoing Clinical Trials on Lung Cancer. Lung. 2016;194(6):967-974. doi:10.1007/s00408-016-9943-7
14. Blonde L, Khunti K, Harris SB, Meizinger C, Skolnik NS. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician. Adv Ther. 2018;35(11):1763-1774. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y
15. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health. 2007;10(5):326-335. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00186.x
16. Assari S. Veterans and risk of heart disease in the United States: a cohort with 20 years of follow up. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(6):703-709.
17. Shahoumian TA, Phillips BR, Backus LI. Cigarette smoking, reduction and quit attempts: prevalence among veterans with coronary heart disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2016;13:E41. Published 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.5888/pcd13.150282
18. Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
19. Kozel FA, Didehbani N, DeLaRosa B, et al. Factors impacting functional status in veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28(2):112-117. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15070183
1. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage II. Published February 20, 2018. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-durvalumab-after-chemoradiation-unresectable-stage-iii-nsclc
2. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919-1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
3. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342-2350. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809697
4. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer. Version8.2020. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed October 9, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf
5. Bristow RE, Chang J, Ziogas A, Campos B, Chavez LR, Anton-Culver H. Impact of National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Centers on ovarian cancer treatment and survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):940-950. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.056
6. Boland GM, Chang GJ, Haynes AB, et al. Association between adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network treatment guidelines and improved survival in patients with colon cancer. Cancer. 2013;119(8):1593-1601. doi:10.1002/cncr.27935
7. Schwentner L, Wöckel A, König J, et al. Adherence to treatment guidelines and survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multi-center cohort study with 9,156 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:487. Published 2013 Oct 21. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-487
8. Jazieh A, Alkaiyat MO, Ali Y, Hashim MA, Abdelhafiz N, Al Olayan A. Improving adherence to lung cancer guidelines: a quality improvement project that uses chart review, audit and feedback approach. BMJ Open Qual. 2019;8(3):e000436. Published 2019 Aug 26. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2018-000436
9. Shaverdian N, Offin MD, Rimner A, et al. Utilization and factors precluding the initiation of consolidative durvalumab in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;144:101-104. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.015
10. National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015, Table 15.1 cancer of the lung and bronchus. Accessed October 19, 2020 https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/results_merged/sect_15_lung_bronchus.pdf. Updated September 10, 2018
11. Passaro A, Spitaleri G, Gyawali B, de Marinis F. Immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2: clinical decision making with scant evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(22):1863-1867. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02118
12. Driessen EJM, Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Maas HA, Dingemans AC, van Loon JGM. Study protocol of the NVALT25-ELDAPT trial: selecting the optimal treatment for older patients with stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(6):e849-e852. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.003
13. Schulkes KJ, Nguyen C, van den Bos F, van Elden LJ, Hamaker ME. Selection of Patients in Ongoing Clinical Trials on Lung Cancer. Lung. 2016;194(6):967-974. doi:10.1007/s00408-016-9943-7
14. Blonde L, Khunti K, Harris SB, Meizinger C, Skolnik NS. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician. Adv Ther. 2018;35(11):1763-1774. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y
15. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health. 2007;10(5):326-335. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00186.x
16. Assari S. Veterans and risk of heart disease in the United States: a cohort with 20 years of follow up. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(6):703-709.
17. Shahoumian TA, Phillips BR, Backus LI. Cigarette smoking, reduction and quit attempts: prevalence among veterans with coronary heart disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2016;13:E41. Published 2016 Mar 24. doi:10.5888/pcd13.150282
18. Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
19. Kozel FA, Didehbani N, DeLaRosa B, et al. Factors impacting functional status in veterans of recent conflicts with PTSD. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28(2):112-117. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15070183
Psilocybin delivers ‘remarkable’ relief in severe depression
Psilocybin, the psychedelic compound in “magic mushrooms,” rapidly improves symptoms and produces remission in as little as two sessions for patients with major depression, new research suggests.
Results of a small randomized trial showed that treatment with psilocybin was associated with a greater than 50% reduction in depressive symptoms in 67% of study participants. In addition, 71% showed improvement at 4-week follow-up, with more than 50% achieving remission.
“The finding that the majority of people whom we treated showed efficacy was quite a remarkable and gratifying finding and really sets the stage for psilocybin as a treatment for major depression,” senior investigator Roland Griffiths, PhD, Oliver Lee McCabe III Professor in the Neuropsychopharmacology of Consciousness, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a statement.
“Perhaps the most exciting aspect of this as a new therapy is that psilocybin works as a therapeutic intervention with a single session or a few sessions, and then the effects are enduring. In contrast, most conventional treatments for depression ... are given chronically and also have chronic side effects,” added Dr. Griffiths, who is also director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research.
The study was published online Nov.4 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Growing evidence base
As previously reported, psilocybin improves depressive symptoms for patients with cancer. However, these patients might be regarded as having a “reactive depression” to their life-threatening illness, said Dr. Griffiths.
“This study built on that previous research by asking the question, is psilocybin effective in patients who have major depressive disorder, [which is] a much larger population?” he said.
In addition, prior studies of psilocybin-assisted therapy had no control group, lead author Alan Davis, PhD, adjunct assistant professor in the psychedelic research unit, Johns Hopkins University, said in an interview.
The researchers created a control condition by randomly assigning 24 individuals (mean age, 39.8 years; 67% women) who were currently experiencing a moderate or severe major depressive episode to receive either immediate treatment (IT) (n = 13) or delayed treatment (DT) (n = 11).
Participants had longstanding depression, with a mean of 22.4 months in the current depressive episode. They were required to avoid using other antidepressants for 4 weeks prior to screening and up to 4 months following enrollment.
Patients were also required to be medically stable; have no personal/family history of psychotic or bipolar disorders; no past-year alcohol, substance, or nicotine use disorder; and no substantial lifetime or recent use of ketamine or classic hallucinogens.
Depression was measured using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 and the GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (GRID-HAMD). A baseline score of ≥17 was required for enrollment.
Participants received eight preparatory meetings with two session facilitators before the first psilocybin session and then 2-3 hours of follow-up meetings after the psilocybin sessions. In addition, they received 13 sessions of psychotherapy.
After completing these preparatory sessions, they underwent two psilocybin sessions, administered a mean of 1.6 weeks apart.
Participants in the DT group were assessed for depressive symptoms weekly for 8 weeks prior to entering the treatment protocol.
‘Surprising’ findings
Participants in the IT group exhibited significantly lower depression scores on the GRID-HAMD at 1 and 4 weeks after the second psilocybin session in comparison with patients in the DT group during the corresponding weeks.
Moreover, the effect sizes at weeks 5 and 8 were “large” (d = 2.2; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-3.0; and d = 2.6; 95% CI, 1.7-3.6, respectively).
An analysis of outcomes showed that, for all 24 participants, at 1 and at 4 weeks following the psilocybin intervention, 67% and 71% of participants, respectively, had a “clinically significant response” in depressive symptoms; 60% and 56%, respectively, met criteria for remission.
Within-subject T tests likewise revealed significant decreases in depression scores from baseline to 1- and 4-week follow-ups (P < .001; d = 3.6; 95% CI, 2.2-5.0; and P < .001; d = 3.6; 95% CI, 2.2-4.9, respectively).
Importantly, participants experienced no serious adverse effects.
Dr. Griffiths said he was “surprised” by the findings. “We knew that psilocybin would be effective in reactive depression of the type associated with illness, but we did not know that this would be the case in the large number of individuals who qualify for having [major depressive disorder].”
Dr. Davis said the finding “represents a large effect of this treatment among people with major depressive disorder – an approximately 4 times larger effect, compared to studies of antidepressant drugs.”
Dr. Davis noted that psychotherapy was an “essential” component of the study protocol. “ and that this treatment will always have a psychotherapy component and will not be Food and Drug Administration approved as a standalone medication.”
Tipping point
Collin Reiff, MD, clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at New York University noted that because psychedelics are “still stigmatized,” the publication of this study in “one of the highest-impact journals in all of psychiatry suggests that research into psychedelics is now in the mainstream and that the academic psychiatry research community is paying close attention to what is happening.” He described this as a “tipping point.”
Dr. Reiff, who was not involved with the study, noted that research had been conducted on psychedelic compounds until the 1960s, “when they left the research lab and went mainstream, leading to the shutting down and subsequent dormancy of the research for the next 30-40 years.”
Psychedelic research is “undergoing a renaissance and no longer regarded with as much skepticism, but it is important to take our time doing this research so we do not repeat what happened in the 1960s,” said Dr. Reiff.
In an accompanying editorial, Charles F. Reynolds III, MD, endowed professor in geriatric psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pennsylvania, questioned “for whom psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy is appropriate (or not), particularly in patients with depression who are suicidal of have a history of suicide attempt.”
Dr. Reynolds, who is also director of the Aging Institute of UPMC, who was not involved with the study, wrote that “personalizing the management of depression has to entail an understanding of the multiple contexts in which depression occurs, including genetic, developmental, psychosocial, cultural, medical, neurocognitive, and spiritual.”
The study was supported by a crowdsourcing campaign organized by Tim Ferris, as well as by grants from the Riverstyx Foundation. The Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research is funded by the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation and receives support from Tim Ferriss, Matt Mullenweg, Craig Nerenberg, and Blake Mycoskie. It is also supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Davis received support from the NIDA. Dr. Griffiths was partially supported by a NIDA grant. Disclosures for the other authors are listed in the original article. Reiff reports owning stock in Compass Pathways. Dr. Reynolds reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Psilocybin, the psychedelic compound in “magic mushrooms,” rapidly improves symptoms and produces remission in as little as two sessions for patients with major depression, new research suggests.
Results of a small randomized trial showed that treatment with psilocybin was associated with a greater than 50% reduction in depressive symptoms in 67% of study participants. In addition, 71% showed improvement at 4-week follow-up, with more than 50% achieving remission.
“The finding that the majority of people whom we treated showed efficacy was quite a remarkable and gratifying finding and really sets the stage for psilocybin as a treatment for major depression,” senior investigator Roland Griffiths, PhD, Oliver Lee McCabe III Professor in the Neuropsychopharmacology of Consciousness, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a statement.
“Perhaps the most exciting aspect of this as a new therapy is that psilocybin works as a therapeutic intervention with a single session or a few sessions, and then the effects are enduring. In contrast, most conventional treatments for depression ... are given chronically and also have chronic side effects,” added Dr. Griffiths, who is also director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research.
The study was published online Nov.4 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Growing evidence base
As previously reported, psilocybin improves depressive symptoms for patients with cancer. However, these patients might be regarded as having a “reactive depression” to their life-threatening illness, said Dr. Griffiths.
“This study built on that previous research by asking the question, is psilocybin effective in patients who have major depressive disorder, [which is] a much larger population?” he said.
In addition, prior studies of psilocybin-assisted therapy had no control group, lead author Alan Davis, PhD, adjunct assistant professor in the psychedelic research unit, Johns Hopkins University, said in an interview.
The researchers created a control condition by randomly assigning 24 individuals (mean age, 39.8 years; 67% women) who were currently experiencing a moderate or severe major depressive episode to receive either immediate treatment (IT) (n = 13) or delayed treatment (DT) (n = 11).
Participants had longstanding depression, with a mean of 22.4 months in the current depressive episode. They were required to avoid using other antidepressants for 4 weeks prior to screening and up to 4 months following enrollment.
Patients were also required to be medically stable; have no personal/family history of psychotic or bipolar disorders; no past-year alcohol, substance, or nicotine use disorder; and no substantial lifetime or recent use of ketamine or classic hallucinogens.
Depression was measured using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 and the GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (GRID-HAMD). A baseline score of ≥17 was required for enrollment.
Participants received eight preparatory meetings with two session facilitators before the first psilocybin session and then 2-3 hours of follow-up meetings after the psilocybin sessions. In addition, they received 13 sessions of psychotherapy.
After completing these preparatory sessions, they underwent two psilocybin sessions, administered a mean of 1.6 weeks apart.
Participants in the DT group were assessed for depressive symptoms weekly for 8 weeks prior to entering the treatment protocol.
‘Surprising’ findings
Participants in the IT group exhibited significantly lower depression scores on the GRID-HAMD at 1 and 4 weeks after the second psilocybin session in comparison with patients in the DT group during the corresponding weeks.
Moreover, the effect sizes at weeks 5 and 8 were “large” (d = 2.2; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-3.0; and d = 2.6; 95% CI, 1.7-3.6, respectively).
An analysis of outcomes showed that, for all 24 participants, at 1 and at 4 weeks following the psilocybin intervention, 67% and 71% of participants, respectively, had a “clinically significant response” in depressive symptoms; 60% and 56%, respectively, met criteria for remission.
Within-subject T tests likewise revealed significant decreases in depression scores from baseline to 1- and 4-week follow-ups (P < .001; d = 3.6; 95% CI, 2.2-5.0; and P < .001; d = 3.6; 95% CI, 2.2-4.9, respectively).
Importantly, participants experienced no serious adverse effects.
Dr. Griffiths said he was “surprised” by the findings. “We knew that psilocybin would be effective in reactive depression of the type associated with illness, but we did not know that this would be the case in the large number of individuals who qualify for having [major depressive disorder].”
Dr. Davis said the finding “represents a large effect of this treatment among people with major depressive disorder – an approximately 4 times larger effect, compared to studies of antidepressant drugs.”
Dr. Davis noted that psychotherapy was an “essential” component of the study protocol. “ and that this treatment will always have a psychotherapy component and will not be Food and Drug Administration approved as a standalone medication.”
Tipping point
Collin Reiff, MD, clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at New York University noted that because psychedelics are “still stigmatized,” the publication of this study in “one of the highest-impact journals in all of psychiatry suggests that research into psychedelics is now in the mainstream and that the academic psychiatry research community is paying close attention to what is happening.” He described this as a “tipping point.”
Dr. Reiff, who was not involved with the study, noted that research had been conducted on psychedelic compounds until the 1960s, “when they left the research lab and went mainstream, leading to the shutting down and subsequent dormancy of the research for the next 30-40 years.”
Psychedelic research is “undergoing a renaissance and no longer regarded with as much skepticism, but it is important to take our time doing this research so we do not repeat what happened in the 1960s,” said Dr. Reiff.
In an accompanying editorial, Charles F. Reynolds III, MD, endowed professor in geriatric psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pennsylvania, questioned “for whom psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy is appropriate (or not), particularly in patients with depression who are suicidal of have a history of suicide attempt.”
Dr. Reynolds, who is also director of the Aging Institute of UPMC, who was not involved with the study, wrote that “personalizing the management of depression has to entail an understanding of the multiple contexts in which depression occurs, including genetic, developmental, psychosocial, cultural, medical, neurocognitive, and spiritual.”
The study was supported by a crowdsourcing campaign organized by Tim Ferris, as well as by grants from the Riverstyx Foundation. The Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research is funded by the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation and receives support from Tim Ferriss, Matt Mullenweg, Craig Nerenberg, and Blake Mycoskie. It is also supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Davis received support from the NIDA. Dr. Griffiths was partially supported by a NIDA grant. Disclosures for the other authors are listed in the original article. Reiff reports owning stock in Compass Pathways. Dr. Reynolds reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Psilocybin, the psychedelic compound in “magic mushrooms,” rapidly improves symptoms and produces remission in as little as two sessions for patients with major depression, new research suggests.
Results of a small randomized trial showed that treatment with psilocybin was associated with a greater than 50% reduction in depressive symptoms in 67% of study participants. In addition, 71% showed improvement at 4-week follow-up, with more than 50% achieving remission.
“The finding that the majority of people whom we treated showed efficacy was quite a remarkable and gratifying finding and really sets the stage for psilocybin as a treatment for major depression,” senior investigator Roland Griffiths, PhD, Oliver Lee McCabe III Professor in the Neuropsychopharmacology of Consciousness, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a statement.
“Perhaps the most exciting aspect of this as a new therapy is that psilocybin works as a therapeutic intervention with a single session or a few sessions, and then the effects are enduring. In contrast, most conventional treatments for depression ... are given chronically and also have chronic side effects,” added Dr. Griffiths, who is also director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research.
The study was published online Nov.4 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Growing evidence base
As previously reported, psilocybin improves depressive symptoms for patients with cancer. However, these patients might be regarded as having a “reactive depression” to their life-threatening illness, said Dr. Griffiths.
“This study built on that previous research by asking the question, is psilocybin effective in patients who have major depressive disorder, [which is] a much larger population?” he said.
In addition, prior studies of psilocybin-assisted therapy had no control group, lead author Alan Davis, PhD, adjunct assistant professor in the psychedelic research unit, Johns Hopkins University, said in an interview.
The researchers created a control condition by randomly assigning 24 individuals (mean age, 39.8 years; 67% women) who were currently experiencing a moderate or severe major depressive episode to receive either immediate treatment (IT) (n = 13) or delayed treatment (DT) (n = 11).
Participants had longstanding depression, with a mean of 22.4 months in the current depressive episode. They were required to avoid using other antidepressants for 4 weeks prior to screening and up to 4 months following enrollment.
Patients were also required to be medically stable; have no personal/family history of psychotic or bipolar disorders; no past-year alcohol, substance, or nicotine use disorder; and no substantial lifetime or recent use of ketamine or classic hallucinogens.
Depression was measured using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 and the GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (GRID-HAMD). A baseline score of ≥17 was required for enrollment.
Participants received eight preparatory meetings with two session facilitators before the first psilocybin session and then 2-3 hours of follow-up meetings after the psilocybin sessions. In addition, they received 13 sessions of psychotherapy.
After completing these preparatory sessions, they underwent two psilocybin sessions, administered a mean of 1.6 weeks apart.
Participants in the DT group were assessed for depressive symptoms weekly for 8 weeks prior to entering the treatment protocol.
‘Surprising’ findings
Participants in the IT group exhibited significantly lower depression scores on the GRID-HAMD at 1 and 4 weeks after the second psilocybin session in comparison with patients in the DT group during the corresponding weeks.
Moreover, the effect sizes at weeks 5 and 8 were “large” (d = 2.2; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-3.0; and d = 2.6; 95% CI, 1.7-3.6, respectively).
An analysis of outcomes showed that, for all 24 participants, at 1 and at 4 weeks following the psilocybin intervention, 67% and 71% of participants, respectively, had a “clinically significant response” in depressive symptoms; 60% and 56%, respectively, met criteria for remission.
Within-subject T tests likewise revealed significant decreases in depression scores from baseline to 1- and 4-week follow-ups (P < .001; d = 3.6; 95% CI, 2.2-5.0; and P < .001; d = 3.6; 95% CI, 2.2-4.9, respectively).
Importantly, participants experienced no serious adverse effects.
Dr. Griffiths said he was “surprised” by the findings. “We knew that psilocybin would be effective in reactive depression of the type associated with illness, but we did not know that this would be the case in the large number of individuals who qualify for having [major depressive disorder].”
Dr. Davis said the finding “represents a large effect of this treatment among people with major depressive disorder – an approximately 4 times larger effect, compared to studies of antidepressant drugs.”
Dr. Davis noted that psychotherapy was an “essential” component of the study protocol. “ and that this treatment will always have a psychotherapy component and will not be Food and Drug Administration approved as a standalone medication.”
Tipping point
Collin Reiff, MD, clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at New York University noted that because psychedelics are “still stigmatized,” the publication of this study in “one of the highest-impact journals in all of psychiatry suggests that research into psychedelics is now in the mainstream and that the academic psychiatry research community is paying close attention to what is happening.” He described this as a “tipping point.”
Dr. Reiff, who was not involved with the study, noted that research had been conducted on psychedelic compounds until the 1960s, “when they left the research lab and went mainstream, leading to the shutting down and subsequent dormancy of the research for the next 30-40 years.”
Psychedelic research is “undergoing a renaissance and no longer regarded with as much skepticism, but it is important to take our time doing this research so we do not repeat what happened in the 1960s,” said Dr. Reiff.
In an accompanying editorial, Charles F. Reynolds III, MD, endowed professor in geriatric psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pennsylvania, questioned “for whom psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy is appropriate (or not), particularly in patients with depression who are suicidal of have a history of suicide attempt.”
Dr. Reynolds, who is also director of the Aging Institute of UPMC, who was not involved with the study, wrote that “personalizing the management of depression has to entail an understanding of the multiple contexts in which depression occurs, including genetic, developmental, psychosocial, cultural, medical, neurocognitive, and spiritual.”
The study was supported by a crowdsourcing campaign organized by Tim Ferris, as well as by grants from the Riverstyx Foundation. The Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research is funded by the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation and receives support from Tim Ferriss, Matt Mullenweg, Craig Nerenberg, and Blake Mycoskie. It is also supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Davis received support from the NIDA. Dr. Griffiths was partially supported by a NIDA grant. Disclosures for the other authors are listed in the original article. Reiff reports owning stock in Compass Pathways. Dr. Reynolds reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pembrolizumab plus axitinib continues to outshine sunitinib for advanced RCC
Pembrolizumab plus axitinib continued to top sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in an extended follow-up of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 trial.
The trial’s initial results, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2019, showed superior efficacy with the combination. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib was subsequently approved in the United States and elsewhere as first-line treatment for advanced RCC.
The latest results from KEYNOTE-426, published in The Lancet Oncology, show a continued survival benefit with pembrolizumab plus axitinib.
“Overall, the results of this study continue to support pembrolizumab plus axitinib as standard of care in patients with previously untreated advanced renal cell carcinoma,” wrote study author Thomas Powles, MD, of the Queen Mary University and Barts Cancer Centre, London, and colleagues.
However, the new findings “must be read and interpreted together with the existing published literature,” they added. This includes trials of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, avelumab plus axitinib, and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for advanced RCC, all versus sunitinib.
“Given the impossibility of making direct comparisons between the different combinations ... clinical experience and knowledge of the disease and of our patients will be vital to optimize this new therapeutic arsenal and to be able to reach goals that, until a few years ago, were considered unattainable,” wrote authors of a related editorial in The Lancet Oncology.
Trial details and results
KEYNOTE-426 included 861 patients with newly diagnosed stage IV or recurrent metastatic RCC with clear cell histology.
Patients were randomized to sunitinib monotherapy (n = 429) or pembrolizumab plus axitinib (n = 432). Pembrolizumab was given at 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles, and axitinib was given at 5 mg orally twice daily. Sunitinib was given at 50 mg orally once daily for 4 weeks per 6-week cycle.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. The median age was 62 years in the combination arm and 61 years in the sunitinib arm. Most patients were men (71% and 75%, respectively).
At a median follow-up of 30.6 months, the median overall survival (OS) was 35.7 months in the sunitinib arm but not yet reached in the pembrolizumab-axitinib arm (hazard ratio, 0.68, 95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.85, P = .0003).
The updated hazard ratio for OS with the combination wasn’t as robust as the hazard ratio in the initial analysis (0.53), likely in part because 48% of patients in the sunitinib group subsequently received immunotherapy, according to Dr. Powles and colleagues.
The median progression free survival (PFS) was 11.1 months with sunitinib and 15.4 months with the combination (HR, 0.71, 95% CI, 0.60-0.84, P < .0001). The objective response rate was 60% with pembrolizumab plus axitinib and 40% in the sunitinib group (P < .0001).
Risk groups and response criteria
Although patients in the combination arm had better objective response rates and PFS across all risk categories, there was no OS benefit in the favorable-risk subgroup, perhaps because favorable-risk patients have more indolent disease, Dr. Powles and colleagues noted.
Even so, “the pembrolizumab plus axitinib combination achieved a nonnegligible rate of 11% complete responses in favorable-risk cases, suggesting a potential curative role in this setting,” the editorialists wrote.
Dr. Powles and colleagues raised the question of whether RECIST-defined response is adequate to capture the full benefit of the combination.
In a post hoc analysis, the researchers found that change in tumor size was prognostic for OS. Patients in the pembrolizumab-axitinib group with an “at least 80% reduction in target lesions within 6 months of randomization had a durable subsequent overall survival benefit (i.e., 36 months survival), similar to patients who had RECIST-defined complete response,” Dr. Powles and colleagues wrote.
“These data support a hypothesis that durable benefit to an immunotherapy-containing regimen in renal cell cancer is not limited to the subset of complete responders,” the researchers added. “Because RECIST categories might not classify all patients who achieve durable benefit, depth of response might also supplement objective response as an important clinical endpoint.”
Safety and discontinuation
There were no new safety signals and no new treatment-related deaths.
The most frequent grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the combination and sunitinib arms, respectively) were hypertension (22% and 20%), alanine aminotransferase elevations (13% and 3%), and diarrhea (11% and 5%).
Treatment-related adverse events led to pembrolizumab interruption in 44% of patients, axitinib interruption in 62%, and interruption of both in 30%. Treatment-related adverse events led to discontinuation of one or the other drug in about 20% of subjects and both in 7%.
The number of discontinuations and interruptions suggests “caution in optimizing the therapeutic choice in real-world patients,” the editorialists wrote.
“New treatment modalities, including intermittent administrations or an induction phase followed by single-agent maintenance, could be explored in future adaptive clinical trials, with undeniable advantages in terms of reducing clinical and financial toxicity,” they added.
The KEYNOTE-426 study was funded by Merck, maker of pembrolizumab. The investigators and the editorialists disclosed ties to Merck and other companies.
SOURCE: Powles T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2020 Oct. 23. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8.
Pembrolizumab plus axitinib continued to top sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in an extended follow-up of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 trial.
The trial’s initial results, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2019, showed superior efficacy with the combination. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib was subsequently approved in the United States and elsewhere as first-line treatment for advanced RCC.
The latest results from KEYNOTE-426, published in The Lancet Oncology, show a continued survival benefit with pembrolizumab plus axitinib.
“Overall, the results of this study continue to support pembrolizumab plus axitinib as standard of care in patients with previously untreated advanced renal cell carcinoma,” wrote study author Thomas Powles, MD, of the Queen Mary University and Barts Cancer Centre, London, and colleagues.
However, the new findings “must be read and interpreted together with the existing published literature,” they added. This includes trials of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, avelumab plus axitinib, and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for advanced RCC, all versus sunitinib.
“Given the impossibility of making direct comparisons between the different combinations ... clinical experience and knowledge of the disease and of our patients will be vital to optimize this new therapeutic arsenal and to be able to reach goals that, until a few years ago, were considered unattainable,” wrote authors of a related editorial in The Lancet Oncology.
Trial details and results
KEYNOTE-426 included 861 patients with newly diagnosed stage IV or recurrent metastatic RCC with clear cell histology.
Patients were randomized to sunitinib monotherapy (n = 429) or pembrolizumab plus axitinib (n = 432). Pembrolizumab was given at 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles, and axitinib was given at 5 mg orally twice daily. Sunitinib was given at 50 mg orally once daily for 4 weeks per 6-week cycle.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. The median age was 62 years in the combination arm and 61 years in the sunitinib arm. Most patients were men (71% and 75%, respectively).
At a median follow-up of 30.6 months, the median overall survival (OS) was 35.7 months in the sunitinib arm but not yet reached in the pembrolizumab-axitinib arm (hazard ratio, 0.68, 95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.85, P = .0003).
The updated hazard ratio for OS with the combination wasn’t as robust as the hazard ratio in the initial analysis (0.53), likely in part because 48% of patients in the sunitinib group subsequently received immunotherapy, according to Dr. Powles and colleagues.
The median progression free survival (PFS) was 11.1 months with sunitinib and 15.4 months with the combination (HR, 0.71, 95% CI, 0.60-0.84, P < .0001). The objective response rate was 60% with pembrolizumab plus axitinib and 40% in the sunitinib group (P < .0001).
Risk groups and response criteria
Although patients in the combination arm had better objective response rates and PFS across all risk categories, there was no OS benefit in the favorable-risk subgroup, perhaps because favorable-risk patients have more indolent disease, Dr. Powles and colleagues noted.
Even so, “the pembrolizumab plus axitinib combination achieved a nonnegligible rate of 11% complete responses in favorable-risk cases, suggesting a potential curative role in this setting,” the editorialists wrote.
Dr. Powles and colleagues raised the question of whether RECIST-defined response is adequate to capture the full benefit of the combination.
In a post hoc analysis, the researchers found that change in tumor size was prognostic for OS. Patients in the pembrolizumab-axitinib group with an “at least 80% reduction in target lesions within 6 months of randomization had a durable subsequent overall survival benefit (i.e., 36 months survival), similar to patients who had RECIST-defined complete response,” Dr. Powles and colleagues wrote.
“These data support a hypothesis that durable benefit to an immunotherapy-containing regimen in renal cell cancer is not limited to the subset of complete responders,” the researchers added. “Because RECIST categories might not classify all patients who achieve durable benefit, depth of response might also supplement objective response as an important clinical endpoint.”
Safety and discontinuation
There were no new safety signals and no new treatment-related deaths.
The most frequent grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the combination and sunitinib arms, respectively) were hypertension (22% and 20%), alanine aminotransferase elevations (13% and 3%), and diarrhea (11% and 5%).
Treatment-related adverse events led to pembrolizumab interruption in 44% of patients, axitinib interruption in 62%, and interruption of both in 30%. Treatment-related adverse events led to discontinuation of one or the other drug in about 20% of subjects and both in 7%.
The number of discontinuations and interruptions suggests “caution in optimizing the therapeutic choice in real-world patients,” the editorialists wrote.
“New treatment modalities, including intermittent administrations or an induction phase followed by single-agent maintenance, could be explored in future adaptive clinical trials, with undeniable advantages in terms of reducing clinical and financial toxicity,” they added.
The KEYNOTE-426 study was funded by Merck, maker of pembrolizumab. The investigators and the editorialists disclosed ties to Merck and other companies.
SOURCE: Powles T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2020 Oct. 23. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8.
Pembrolizumab plus axitinib continued to top sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in an extended follow-up of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 trial.
The trial’s initial results, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2019, showed superior efficacy with the combination. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib was subsequently approved in the United States and elsewhere as first-line treatment for advanced RCC.
The latest results from KEYNOTE-426, published in The Lancet Oncology, show a continued survival benefit with pembrolizumab plus axitinib.
“Overall, the results of this study continue to support pembrolizumab plus axitinib as standard of care in patients with previously untreated advanced renal cell carcinoma,” wrote study author Thomas Powles, MD, of the Queen Mary University and Barts Cancer Centre, London, and colleagues.
However, the new findings “must be read and interpreted together with the existing published literature,” they added. This includes trials of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, avelumab plus axitinib, and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for advanced RCC, all versus sunitinib.
“Given the impossibility of making direct comparisons between the different combinations ... clinical experience and knowledge of the disease and of our patients will be vital to optimize this new therapeutic arsenal and to be able to reach goals that, until a few years ago, were considered unattainable,” wrote authors of a related editorial in The Lancet Oncology.
Trial details and results
KEYNOTE-426 included 861 patients with newly diagnosed stage IV or recurrent metastatic RCC with clear cell histology.
Patients were randomized to sunitinib monotherapy (n = 429) or pembrolizumab plus axitinib (n = 432). Pembrolizumab was given at 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles, and axitinib was given at 5 mg orally twice daily. Sunitinib was given at 50 mg orally once daily for 4 weeks per 6-week cycle.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. The median age was 62 years in the combination arm and 61 years in the sunitinib arm. Most patients were men (71% and 75%, respectively).
At a median follow-up of 30.6 months, the median overall survival (OS) was 35.7 months in the sunitinib arm but not yet reached in the pembrolizumab-axitinib arm (hazard ratio, 0.68, 95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.85, P = .0003).
The updated hazard ratio for OS with the combination wasn’t as robust as the hazard ratio in the initial analysis (0.53), likely in part because 48% of patients in the sunitinib group subsequently received immunotherapy, according to Dr. Powles and colleagues.
The median progression free survival (PFS) was 11.1 months with sunitinib and 15.4 months with the combination (HR, 0.71, 95% CI, 0.60-0.84, P < .0001). The objective response rate was 60% with pembrolizumab plus axitinib and 40% in the sunitinib group (P < .0001).
Risk groups and response criteria
Although patients in the combination arm had better objective response rates and PFS across all risk categories, there was no OS benefit in the favorable-risk subgroup, perhaps because favorable-risk patients have more indolent disease, Dr. Powles and colleagues noted.
Even so, “the pembrolizumab plus axitinib combination achieved a nonnegligible rate of 11% complete responses in favorable-risk cases, suggesting a potential curative role in this setting,” the editorialists wrote.
Dr. Powles and colleagues raised the question of whether RECIST-defined response is adequate to capture the full benefit of the combination.
In a post hoc analysis, the researchers found that change in tumor size was prognostic for OS. Patients in the pembrolizumab-axitinib group with an “at least 80% reduction in target lesions within 6 months of randomization had a durable subsequent overall survival benefit (i.e., 36 months survival), similar to patients who had RECIST-defined complete response,” Dr. Powles and colleagues wrote.
“These data support a hypothesis that durable benefit to an immunotherapy-containing regimen in renal cell cancer is not limited to the subset of complete responders,” the researchers added. “Because RECIST categories might not classify all patients who achieve durable benefit, depth of response might also supplement objective response as an important clinical endpoint.”
Safety and discontinuation
There were no new safety signals and no new treatment-related deaths.
The most frequent grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the combination and sunitinib arms, respectively) were hypertension (22% and 20%), alanine aminotransferase elevations (13% and 3%), and diarrhea (11% and 5%).
Treatment-related adverse events led to pembrolizumab interruption in 44% of patients, axitinib interruption in 62%, and interruption of both in 30%. Treatment-related adverse events led to discontinuation of one or the other drug in about 20% of subjects and both in 7%.
The number of discontinuations and interruptions suggests “caution in optimizing the therapeutic choice in real-world patients,” the editorialists wrote.
“New treatment modalities, including intermittent administrations or an induction phase followed by single-agent maintenance, could be explored in future adaptive clinical trials, with undeniable advantages in terms of reducing clinical and financial toxicity,” they added.
The KEYNOTE-426 study was funded by Merck, maker of pembrolizumab. The investigators and the editorialists disclosed ties to Merck and other companies.
SOURCE: Powles T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2020 Oct. 23. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8.
FROM LANCET ONCOLOGY
COVID-19–related HCQ shortages affected rheumatology patients worldwide
New data document the global fallout for rheumatology patients when hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) supplies were being diverted to hospitals for COVID-19 patients.
Demand for HCQ soared on evidence-lacking claims that the drug was effective in treating and preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. Further research has since shown HCQ to be ineffective for COVID-19 and potentially harmful to patients.
But during the height of the COVID-19-related hype, patients worldwide with autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, had trouble getting the pills at all or couldn’t get as many as they needed for their chronic conditions.
Emily Sirotich, MSc, a PhD student at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., presented data at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology demonstrating that the severity of shortages differed widely.
Whereas 26.7% of rheumatology patients in Africa and 21.4% in southeast Asia said their pharmacy ran short of HCQ – which was originally developed as an antimalarial drug but has been found effective in treating some rheumatic diseases – only 6.8% of patients in the Americas and 2.1% in European regions reported the shortages.
“There are large regional disparities in access to antimalarials whether they were caused by the COVID-19 pandemic or already existed,” she said in an interview.
Global survey polled patient experience
Ms. Sirotich’s team analyzed data from the Global Rheumatology Alliance Patient Experience Survey.
They found that from 9,393 respondents (average age 46.1 years and 90% female), 3,872 (41.2%) were taking antimalarials. Of these, 230 (6.2% globally) were unable to keep taking the drugs because their pharmacy ran out.
Researchers evaluated the effect of drug shortages on disease activity, mental health, and physical health by comparing mean values with two-sided independent t-tests to identify significant differences.
They found that patients who were unable to obtain antimalarials had significantly higher levels of rheumatic disease activity as well as poorer mental and physical health (all P < .001).
The survey was distributed online through patient support groups and on social media. Patients with rheumatic diseases or their parents anonymously entered data including their rheumatic disease diagnosis, medications, COVID-19 status, and disease outcomes.
Ms. Sirotich said they are currently gathering new data to see if the gaps in access to HCQ persist and whether the physical and mental consequences of not having the medications continue.
Hospitals stockpiled HCQ in the U.S.
Michael Ganio, PharmD, senior director of pharmacy practice and quality at the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP), said in an interview that hospitals in the United States received large amounts of HCQ in late spring and early summer, donated by pharmaceutical companies for COVID-19 before the lack of evidence for efficacy became clear.
Hospitals found themselves sitting on large quantities of HCQ they couldn’t use while prescriptions for rheumatology outpatients were going unfilled.
It is only in recent months that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has given clear direction to hospitals on how to redistribute those supplies, Dr. Ganio said.
“There’s no good real good way to move a product from a hospital to a [drug store] down the street,” he said.
The Food and Drug Administration now lists the HCQ shortages as resolved.
Declined prescriptions have frustrated physicians
Brett Smith, DO, a pediatric and adult rheumatologist in Alcoa, Tenn., said he was frustrated by pharmacies declining his prescriptions for HCQ for patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
“I got notes from pharmacies that I should consider alternative agents,” he said in an interview. But the safety profiles of the alternatives were not as good, he said.
“Hydroxychloroquine has no risk of infection and no risk of malignancy, and they were proposing alternative agents that carry those risks,” he said.
“I had some people with RA who couldn’t get [HCQ] who had a substantial increase in swollen joints and pain without it,” he said.
Dr. Smith said some patients who use HCQ for off-label uses such as certain skin disorders still aren’t getting the drug, as off-label use has been discouraged to make sure those with lupus and RA have enough, he said.
Saira Sheikh, MD, director of the University of North Carolina Rheumatology Lupus Clinic in Chapel Hill, said in an interview that during the summer months pharmacists required additional documentation of the diagnosis of autoimmune disease, resulting in unnecessary delays even when patients had been on the medication for many years.
She said emerging research has found patient-reported barriers to filling prescriptions, interruptions in HCQ treatment, and reported emotional stress and anxiety related to medication access during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This experience with HCQ during the COVID-19 pandemic teaches us that while swift action and progress to address the immediate threats of the pandemic should be commended, it is important that we move forward in a conscious manner, guided by an evidence base that comes from high-quality research, not from rushed judgments based on preliminary studies, or pressure from political leaders,” Dr. Sheikh said.
Ms. Sirotich, Dr. Smith, Dr. Sheikh, and Dr. Ganio have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New data document the global fallout for rheumatology patients when hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) supplies were being diverted to hospitals for COVID-19 patients.
Demand for HCQ soared on evidence-lacking claims that the drug was effective in treating and preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. Further research has since shown HCQ to be ineffective for COVID-19 and potentially harmful to patients.
But during the height of the COVID-19-related hype, patients worldwide with autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, had trouble getting the pills at all or couldn’t get as many as they needed for their chronic conditions.
Emily Sirotich, MSc, a PhD student at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., presented data at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology demonstrating that the severity of shortages differed widely.
Whereas 26.7% of rheumatology patients in Africa and 21.4% in southeast Asia said their pharmacy ran short of HCQ – which was originally developed as an antimalarial drug but has been found effective in treating some rheumatic diseases – only 6.8% of patients in the Americas and 2.1% in European regions reported the shortages.
“There are large regional disparities in access to antimalarials whether they were caused by the COVID-19 pandemic or already existed,” she said in an interview.
Global survey polled patient experience
Ms. Sirotich’s team analyzed data from the Global Rheumatology Alliance Patient Experience Survey.
They found that from 9,393 respondents (average age 46.1 years and 90% female), 3,872 (41.2%) were taking antimalarials. Of these, 230 (6.2% globally) were unable to keep taking the drugs because their pharmacy ran out.
Researchers evaluated the effect of drug shortages on disease activity, mental health, and physical health by comparing mean values with two-sided independent t-tests to identify significant differences.
They found that patients who were unable to obtain antimalarials had significantly higher levels of rheumatic disease activity as well as poorer mental and physical health (all P < .001).
The survey was distributed online through patient support groups and on social media. Patients with rheumatic diseases or their parents anonymously entered data including their rheumatic disease diagnosis, medications, COVID-19 status, and disease outcomes.
Ms. Sirotich said they are currently gathering new data to see if the gaps in access to HCQ persist and whether the physical and mental consequences of not having the medications continue.
Hospitals stockpiled HCQ in the U.S.
Michael Ganio, PharmD, senior director of pharmacy practice and quality at the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP), said in an interview that hospitals in the United States received large amounts of HCQ in late spring and early summer, donated by pharmaceutical companies for COVID-19 before the lack of evidence for efficacy became clear.
Hospitals found themselves sitting on large quantities of HCQ they couldn’t use while prescriptions for rheumatology outpatients were going unfilled.
It is only in recent months that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has given clear direction to hospitals on how to redistribute those supplies, Dr. Ganio said.
“There’s no good real good way to move a product from a hospital to a [drug store] down the street,” he said.
The Food and Drug Administration now lists the HCQ shortages as resolved.
Declined prescriptions have frustrated physicians
Brett Smith, DO, a pediatric and adult rheumatologist in Alcoa, Tenn., said he was frustrated by pharmacies declining his prescriptions for HCQ for patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
“I got notes from pharmacies that I should consider alternative agents,” he said in an interview. But the safety profiles of the alternatives were not as good, he said.
“Hydroxychloroquine has no risk of infection and no risk of malignancy, and they were proposing alternative agents that carry those risks,” he said.
“I had some people with RA who couldn’t get [HCQ] who had a substantial increase in swollen joints and pain without it,” he said.
Dr. Smith said some patients who use HCQ for off-label uses such as certain skin disorders still aren’t getting the drug, as off-label use has been discouraged to make sure those with lupus and RA have enough, he said.
Saira Sheikh, MD, director of the University of North Carolina Rheumatology Lupus Clinic in Chapel Hill, said in an interview that during the summer months pharmacists required additional documentation of the diagnosis of autoimmune disease, resulting in unnecessary delays even when patients had been on the medication for many years.
She said emerging research has found patient-reported barriers to filling prescriptions, interruptions in HCQ treatment, and reported emotional stress and anxiety related to medication access during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This experience with HCQ during the COVID-19 pandemic teaches us that while swift action and progress to address the immediate threats of the pandemic should be commended, it is important that we move forward in a conscious manner, guided by an evidence base that comes from high-quality research, not from rushed judgments based on preliminary studies, or pressure from political leaders,” Dr. Sheikh said.
Ms. Sirotich, Dr. Smith, Dr. Sheikh, and Dr. Ganio have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New data document the global fallout for rheumatology patients when hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) supplies were being diverted to hospitals for COVID-19 patients.
Demand for HCQ soared on evidence-lacking claims that the drug was effective in treating and preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. Further research has since shown HCQ to be ineffective for COVID-19 and potentially harmful to patients.
But during the height of the COVID-19-related hype, patients worldwide with autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, had trouble getting the pills at all or couldn’t get as many as they needed for their chronic conditions.
Emily Sirotich, MSc, a PhD student at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., presented data at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology demonstrating that the severity of shortages differed widely.
Whereas 26.7% of rheumatology patients in Africa and 21.4% in southeast Asia said their pharmacy ran short of HCQ – which was originally developed as an antimalarial drug but has been found effective in treating some rheumatic diseases – only 6.8% of patients in the Americas and 2.1% in European regions reported the shortages.
“There are large regional disparities in access to antimalarials whether they were caused by the COVID-19 pandemic or already existed,” she said in an interview.
Global survey polled patient experience
Ms. Sirotich’s team analyzed data from the Global Rheumatology Alliance Patient Experience Survey.
They found that from 9,393 respondents (average age 46.1 years and 90% female), 3,872 (41.2%) were taking antimalarials. Of these, 230 (6.2% globally) were unable to keep taking the drugs because their pharmacy ran out.
Researchers evaluated the effect of drug shortages on disease activity, mental health, and physical health by comparing mean values with two-sided independent t-tests to identify significant differences.
They found that patients who were unable to obtain antimalarials had significantly higher levels of rheumatic disease activity as well as poorer mental and physical health (all P < .001).
The survey was distributed online through patient support groups and on social media. Patients with rheumatic diseases or their parents anonymously entered data including their rheumatic disease diagnosis, medications, COVID-19 status, and disease outcomes.
Ms. Sirotich said they are currently gathering new data to see if the gaps in access to HCQ persist and whether the physical and mental consequences of not having the medications continue.
Hospitals stockpiled HCQ in the U.S.
Michael Ganio, PharmD, senior director of pharmacy practice and quality at the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP), said in an interview that hospitals in the United States received large amounts of HCQ in late spring and early summer, donated by pharmaceutical companies for COVID-19 before the lack of evidence for efficacy became clear.
Hospitals found themselves sitting on large quantities of HCQ they couldn’t use while prescriptions for rheumatology outpatients were going unfilled.
It is only in recent months that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has given clear direction to hospitals on how to redistribute those supplies, Dr. Ganio said.
“There’s no good real good way to move a product from a hospital to a [drug store] down the street,” he said.
The Food and Drug Administration now lists the HCQ shortages as resolved.
Declined prescriptions have frustrated physicians
Brett Smith, DO, a pediatric and adult rheumatologist in Alcoa, Tenn., said he was frustrated by pharmacies declining his prescriptions for HCQ for patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
“I got notes from pharmacies that I should consider alternative agents,” he said in an interview. But the safety profiles of the alternatives were not as good, he said.
“Hydroxychloroquine has no risk of infection and no risk of malignancy, and they were proposing alternative agents that carry those risks,” he said.
“I had some people with RA who couldn’t get [HCQ] who had a substantial increase in swollen joints and pain without it,” he said.
Dr. Smith said some patients who use HCQ for off-label uses such as certain skin disorders still aren’t getting the drug, as off-label use has been discouraged to make sure those with lupus and RA have enough, he said.
Saira Sheikh, MD, director of the University of North Carolina Rheumatology Lupus Clinic in Chapel Hill, said in an interview that during the summer months pharmacists required additional documentation of the diagnosis of autoimmune disease, resulting in unnecessary delays even when patients had been on the medication for many years.
She said emerging research has found patient-reported barriers to filling prescriptions, interruptions in HCQ treatment, and reported emotional stress and anxiety related to medication access during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This experience with HCQ during the COVID-19 pandemic teaches us that while swift action and progress to address the immediate threats of the pandemic should be commended, it is important that we move forward in a conscious manner, guided by an evidence base that comes from high-quality research, not from rushed judgments based on preliminary studies, or pressure from political leaders,” Dr. Sheikh said.
Ms. Sirotich, Dr. Smith, Dr. Sheikh, and Dr. Ganio have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
First-of-its kind guideline on lipid monitoring in endocrine diseases
Endocrine diseases of any type – not just diabetes – can represent a cardiovascular risk and patients with those disorders should be screened for high cholesterol, according to a new clinical practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
“The simple recommendation to check a lipid panel in patients with endocrine diseases and calculate cardiovascular risk may be practice changing because that is not done routinely,” Connie Newman, MD, chair of the Endocrine Society committee that developed the guideline, said in an interview.
“Usually the focus is on assessment and treatment of the endocrine disease, rather than on assessment and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk,” said Newman, an adjunct professor of medicine in the department of medicine, division of endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism, at New York University.
Whereas diabetes, well-known for its increased cardiovascular risk profile, is commonly addressed in other cardiovascular and cholesterol practice management guidelines, the array of other endocrine diseases are not typically included.
“This guideline is the first of its kind,” Dr. Newman said. “The Endocrine Society has not previously issued a guideline on lipid management in endocrine disorders [and] other organizations have not written guidelines on this topic.
“Rather, guidelines have been written on cholesterol management, but these do not describe cholesterol management in patients with endocrine diseases such as thyroid disease [hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism], Cushing’s syndrome, acromegaly, growth hormone deficiency, menopause, male hypogonadism, and obesity,” she noted.
But these conditions carry a host of cardiovascular risk factors that may require careful monitoring and management.
“Although endocrine hormones, such as thyroid hormone, cortisol, estrogen, testosterone, growth hormone, and insulin, affect pathways for lipid metabolism, physicians lack guidance on lipid abnormalities, cardiovascular risk, and treatment to reduce lipids and cardiovascular risk in patients with endocrine diseases,” she explained.
Vinaya Simha, MD, an internal medicine specialist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agrees that the guideline is notable in addressing an unmet need.
Recommendations that stand out to Dr. Simha include the suggestion of adding eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ethyl ester to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in adults with diabetes or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who have elevated triglyceride levels despite statin treatment.
James L. Rosenzweig, MD, an endocrinologist at Hebrew SeniorLife in Boston, agreed that this is an important addition to an area that needs more guidance.
“Many of these clinical situations can exacerbate dyslipidemia and some also increase the cardiovascular risk to a greater extent in combination with elevated cholesterol and/or triglycerides,” he said in an interview.
“In many cases, treatment of the underlying disorder appropriately can have an important impact in resolving the lipid disorder. In others, more aggressive pharmacological treatment is indicated,” he said.
“I think that this will be a valuable resource, especially for endocrinologists, but it can be used as well by providers in other disciplines.”
Key recommendations for different endocrine conditions
The guideline, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, details those risks and provides evidence-based recommendations on their management and treatment.
Key recommendations include:
- Obtain a lipid panel and evaluate cardiovascular risk factors in all adults with endocrine disorders.
- In patients with and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, start statin therapy in addition to lifestyle modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. “This could mean earlier treatment because other guidelines recommend consideration of therapy at age 40,” Dr. Newman said.
- Statin therapy is also recommended for adults over 40 with with a duration of diabetes of more than 20 years and/or microvascular complications, regardless of their cardiovascular risk score. “This means earlier treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes with statins in order to reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” Dr. Newman noted.
- In patients with hyperlipidemia, rule out as the cause before treating with lipid-lowering medications. And among patients who are found to have hypothyroidism, reevaluate the lipid profile when the patient has thyroid hormone levels in the normal range.
- Adults with persistent endogenous Cushing’s syndrome should have their lipid profile monitored. Statin therapy should be considered in addition to lifestyle modifications, irrespective of the cardiovascular risk score.
- In postmenopausal women, high cholesterol or triglycerides should be treated with statins rather than hormone therapy.
- Evaluate and treat lipids and other cardiovascular risk factors in women who enter menopause early (before the age of 40-45 years).
Nice summary of ‘risk-enhancing’ endocrine disorders
Dr. Simha said in an interview that the new guideline is “probably the first comprehensive statement addressing lipid treatment in patients with a broad range of endocrine disorders besides diabetes.”
“Most of the treatment recommendations are congruent with other current guidelines such as the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association [guidelines], but there is specific mention of which endocrine disorders represent enhanced cardiovascular risk,” she explained.
The new recommendations are notable for including “a nice summary of how different endocrine disorders affect lipid values, and also which endocrine disorders need to be considered as ‘risk-enhancing factors,’ ” Dr. Simha noted.
“The use of EPA in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is novel, compared to the ACC/AHA recommendation. This reflects new data which is now available,” she added.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists also just issued a new algorithm on lipid management and prevention of cardiovascular disease in which treatment of hypertriglyceridemia is emphasized.
In addition, the new Endocrine Society guideline “also mentions an LDL [cholesterol] treatment threshold of 70 mg/dL, and 55 mg/dL in some patient categories, which previous guidelines have not,” Dr. Simha noted.
Overall, Dr. Newman added that the goal of the guideline is to increase awareness of key issues with endocrine diseases that may not necessarily be on clinicians’ radars.
“We hope that it will make a lipid panel and cardiovascular risk evaluation routine in adults with endocrine diseases and cause a greater focus on therapies to reduce heart disease and stroke,” she said.
Dr. Newman, Dr. Simha, and Dr. Rosenzweig reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Endocrine diseases of any type – not just diabetes – can represent a cardiovascular risk and patients with those disorders should be screened for high cholesterol, according to a new clinical practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
“The simple recommendation to check a lipid panel in patients with endocrine diseases and calculate cardiovascular risk may be practice changing because that is not done routinely,” Connie Newman, MD, chair of the Endocrine Society committee that developed the guideline, said in an interview.
“Usually the focus is on assessment and treatment of the endocrine disease, rather than on assessment and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk,” said Newman, an adjunct professor of medicine in the department of medicine, division of endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism, at New York University.
Whereas diabetes, well-known for its increased cardiovascular risk profile, is commonly addressed in other cardiovascular and cholesterol practice management guidelines, the array of other endocrine diseases are not typically included.
“This guideline is the first of its kind,” Dr. Newman said. “The Endocrine Society has not previously issued a guideline on lipid management in endocrine disorders [and] other organizations have not written guidelines on this topic.
“Rather, guidelines have been written on cholesterol management, but these do not describe cholesterol management in patients with endocrine diseases such as thyroid disease [hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism], Cushing’s syndrome, acromegaly, growth hormone deficiency, menopause, male hypogonadism, and obesity,” she noted.
But these conditions carry a host of cardiovascular risk factors that may require careful monitoring and management.
“Although endocrine hormones, such as thyroid hormone, cortisol, estrogen, testosterone, growth hormone, and insulin, affect pathways for lipid metabolism, physicians lack guidance on lipid abnormalities, cardiovascular risk, and treatment to reduce lipids and cardiovascular risk in patients with endocrine diseases,” she explained.
Vinaya Simha, MD, an internal medicine specialist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agrees that the guideline is notable in addressing an unmet need.
Recommendations that stand out to Dr. Simha include the suggestion of adding eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ethyl ester to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in adults with diabetes or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who have elevated triglyceride levels despite statin treatment.
James L. Rosenzweig, MD, an endocrinologist at Hebrew SeniorLife in Boston, agreed that this is an important addition to an area that needs more guidance.
“Many of these clinical situations can exacerbate dyslipidemia and some also increase the cardiovascular risk to a greater extent in combination with elevated cholesterol and/or triglycerides,” he said in an interview.
“In many cases, treatment of the underlying disorder appropriately can have an important impact in resolving the lipid disorder. In others, more aggressive pharmacological treatment is indicated,” he said.
“I think that this will be a valuable resource, especially for endocrinologists, but it can be used as well by providers in other disciplines.”
Key recommendations for different endocrine conditions
The guideline, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, details those risks and provides evidence-based recommendations on their management and treatment.
Key recommendations include:
- Obtain a lipid panel and evaluate cardiovascular risk factors in all adults with endocrine disorders.
- In patients with and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, start statin therapy in addition to lifestyle modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. “This could mean earlier treatment because other guidelines recommend consideration of therapy at age 40,” Dr. Newman said.
- Statin therapy is also recommended for adults over 40 with with a duration of diabetes of more than 20 years and/or microvascular complications, regardless of their cardiovascular risk score. “This means earlier treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes with statins in order to reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” Dr. Newman noted.
- In patients with hyperlipidemia, rule out as the cause before treating with lipid-lowering medications. And among patients who are found to have hypothyroidism, reevaluate the lipid profile when the patient has thyroid hormone levels in the normal range.
- Adults with persistent endogenous Cushing’s syndrome should have their lipid profile monitored. Statin therapy should be considered in addition to lifestyle modifications, irrespective of the cardiovascular risk score.
- In postmenopausal women, high cholesterol or triglycerides should be treated with statins rather than hormone therapy.
- Evaluate and treat lipids and other cardiovascular risk factors in women who enter menopause early (before the age of 40-45 years).
Nice summary of ‘risk-enhancing’ endocrine disorders
Dr. Simha said in an interview that the new guideline is “probably the first comprehensive statement addressing lipid treatment in patients with a broad range of endocrine disorders besides diabetes.”
“Most of the treatment recommendations are congruent with other current guidelines such as the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association [guidelines], but there is specific mention of which endocrine disorders represent enhanced cardiovascular risk,” she explained.
The new recommendations are notable for including “a nice summary of how different endocrine disorders affect lipid values, and also which endocrine disorders need to be considered as ‘risk-enhancing factors,’ ” Dr. Simha noted.
“The use of EPA in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is novel, compared to the ACC/AHA recommendation. This reflects new data which is now available,” she added.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists also just issued a new algorithm on lipid management and prevention of cardiovascular disease in which treatment of hypertriglyceridemia is emphasized.
In addition, the new Endocrine Society guideline “also mentions an LDL [cholesterol] treatment threshold of 70 mg/dL, and 55 mg/dL in some patient categories, which previous guidelines have not,” Dr. Simha noted.
Overall, Dr. Newman added that the goal of the guideline is to increase awareness of key issues with endocrine diseases that may not necessarily be on clinicians’ radars.
“We hope that it will make a lipid panel and cardiovascular risk evaluation routine in adults with endocrine diseases and cause a greater focus on therapies to reduce heart disease and stroke,” she said.
Dr. Newman, Dr. Simha, and Dr. Rosenzweig reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Endocrine diseases of any type – not just diabetes – can represent a cardiovascular risk and patients with those disorders should be screened for high cholesterol, according to a new clinical practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
“The simple recommendation to check a lipid panel in patients with endocrine diseases and calculate cardiovascular risk may be practice changing because that is not done routinely,” Connie Newman, MD, chair of the Endocrine Society committee that developed the guideline, said in an interview.
“Usually the focus is on assessment and treatment of the endocrine disease, rather than on assessment and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk,” said Newman, an adjunct professor of medicine in the department of medicine, division of endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism, at New York University.
Whereas diabetes, well-known for its increased cardiovascular risk profile, is commonly addressed in other cardiovascular and cholesterol practice management guidelines, the array of other endocrine diseases are not typically included.
“This guideline is the first of its kind,” Dr. Newman said. “The Endocrine Society has not previously issued a guideline on lipid management in endocrine disorders [and] other organizations have not written guidelines on this topic.
“Rather, guidelines have been written on cholesterol management, but these do not describe cholesterol management in patients with endocrine diseases such as thyroid disease [hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism], Cushing’s syndrome, acromegaly, growth hormone deficiency, menopause, male hypogonadism, and obesity,” she noted.
But these conditions carry a host of cardiovascular risk factors that may require careful monitoring and management.
“Although endocrine hormones, such as thyroid hormone, cortisol, estrogen, testosterone, growth hormone, and insulin, affect pathways for lipid metabolism, physicians lack guidance on lipid abnormalities, cardiovascular risk, and treatment to reduce lipids and cardiovascular risk in patients with endocrine diseases,” she explained.
Vinaya Simha, MD, an internal medicine specialist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agrees that the guideline is notable in addressing an unmet need.
Recommendations that stand out to Dr. Simha include the suggestion of adding eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ethyl ester to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in adults with diabetes or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who have elevated triglyceride levels despite statin treatment.
James L. Rosenzweig, MD, an endocrinologist at Hebrew SeniorLife in Boston, agreed that this is an important addition to an area that needs more guidance.
“Many of these clinical situations can exacerbate dyslipidemia and some also increase the cardiovascular risk to a greater extent in combination with elevated cholesterol and/or triglycerides,” he said in an interview.
“In many cases, treatment of the underlying disorder appropriately can have an important impact in resolving the lipid disorder. In others, more aggressive pharmacological treatment is indicated,” he said.
“I think that this will be a valuable resource, especially for endocrinologists, but it can be used as well by providers in other disciplines.”
Key recommendations for different endocrine conditions
The guideline, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, details those risks and provides evidence-based recommendations on their management and treatment.
Key recommendations include:
- Obtain a lipid panel and evaluate cardiovascular risk factors in all adults with endocrine disorders.
- In patients with and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, start statin therapy in addition to lifestyle modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. “This could mean earlier treatment because other guidelines recommend consideration of therapy at age 40,” Dr. Newman said.
- Statin therapy is also recommended for adults over 40 with with a duration of diabetes of more than 20 years and/or microvascular complications, regardless of their cardiovascular risk score. “This means earlier treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes with statins in order to reduce cardiovascular disease risk,” Dr. Newman noted.
- In patients with hyperlipidemia, rule out as the cause before treating with lipid-lowering medications. And among patients who are found to have hypothyroidism, reevaluate the lipid profile when the patient has thyroid hormone levels in the normal range.
- Adults with persistent endogenous Cushing’s syndrome should have their lipid profile monitored. Statin therapy should be considered in addition to lifestyle modifications, irrespective of the cardiovascular risk score.
- In postmenopausal women, high cholesterol or triglycerides should be treated with statins rather than hormone therapy.
- Evaluate and treat lipids and other cardiovascular risk factors in women who enter menopause early (before the age of 40-45 years).
Nice summary of ‘risk-enhancing’ endocrine disorders
Dr. Simha said in an interview that the new guideline is “probably the first comprehensive statement addressing lipid treatment in patients with a broad range of endocrine disorders besides diabetes.”
“Most of the treatment recommendations are congruent with other current guidelines such as the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association [guidelines], but there is specific mention of which endocrine disorders represent enhanced cardiovascular risk,” she explained.
The new recommendations are notable for including “a nice summary of how different endocrine disorders affect lipid values, and also which endocrine disorders need to be considered as ‘risk-enhancing factors,’ ” Dr. Simha noted.
“The use of EPA in patients with hypertriglyceridemia is novel, compared to the ACC/AHA recommendation. This reflects new data which is now available,” she added.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists also just issued a new algorithm on lipid management and prevention of cardiovascular disease in which treatment of hypertriglyceridemia is emphasized.
In addition, the new Endocrine Society guideline “also mentions an LDL [cholesterol] treatment threshold of 70 mg/dL, and 55 mg/dL in some patient categories, which previous guidelines have not,” Dr. Simha noted.
Overall, Dr. Newman added that the goal of the guideline is to increase awareness of key issues with endocrine diseases that may not necessarily be on clinicians’ radars.
“We hope that it will make a lipid panel and cardiovascular risk evaluation routine in adults with endocrine diseases and cause a greater focus on therapies to reduce heart disease and stroke,” she said.
Dr. Newman, Dr. Simha, and Dr. Rosenzweig reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Response to “The Other Pandemic: Addiction”
To the Editor: Normally I would skip the editorial; however, the title “The Other Pandemic: Addiction” caught my eye (Fed Pract. 2020;37[10]:440-441). This will, of course, require me going in for eye care in the next couple of days, but my concerns are low. After all, the hook you used wasn’t that big.
Bravo! Your choice to focus on the effects of isolation was a masterful touch. I started skimming with the assumption that you would say something along the lines of ‘COVID bad, everybody depressed, blah, blah.’ But you cut into the abscess of the issue cleanly, exposing the core—isolation “amplifies negative thoughts, dysphoria, and fearful emotions.” A deadly combination for our patients and ourselves.
I have been a physician assistant in the US Army, and as a civilian at Brooke Army Medical Center and US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health Care System. One thing I have seen throughout that time was the effects of isolation on the active duty enlisted young, and even more so on retired older warriors. Throughout the time of our military service, we transfer to many places and make a lot of friends, but more so, we lose track of them over time.
I have cared for many older warriors who cannot get something as simple as a colonoscopy because they do not have someone to drive them home after they have been sedated. Family and friends were scattered over the country, or the world. At the VA, many older warriors come not just for an appointment, but also as a time to socialize and ‘BS’ with those who understand them.
One goal I set for myself many years ago was to have the warrior laughing before they left my office. If I did that, I knew I had made a difference. Thank you for your editorial.
Anthony J Passaniti, PA, USA (ret) [email protected]
To the Editor: Normally I would skip the editorial; however, the title “The Other Pandemic: Addiction” caught my eye (Fed Pract. 2020;37[10]:440-441). This will, of course, require me going in for eye care in the next couple of days, but my concerns are low. After all, the hook you used wasn’t that big.
Bravo! Your choice to focus on the effects of isolation was a masterful touch. I started skimming with the assumption that you would say something along the lines of ‘COVID bad, everybody depressed, blah, blah.’ But you cut into the abscess of the issue cleanly, exposing the core—isolation “amplifies negative thoughts, dysphoria, and fearful emotions.” A deadly combination for our patients and ourselves.
I have been a physician assistant in the US Army, and as a civilian at Brooke Army Medical Center and US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health Care System. One thing I have seen throughout that time was the effects of isolation on the active duty enlisted young, and even more so on retired older warriors. Throughout the time of our military service, we transfer to many places and make a lot of friends, but more so, we lose track of them over time.
I have cared for many older warriors who cannot get something as simple as a colonoscopy because they do not have someone to drive them home after they have been sedated. Family and friends were scattered over the country, or the world. At the VA, many older warriors come not just for an appointment, but also as a time to socialize and ‘BS’ with those who understand them.
One goal I set for myself many years ago was to have the warrior laughing before they left my office. If I did that, I knew I had made a difference. Thank you for your editorial.
Anthony J Passaniti, PA, USA (ret) [email protected]
To the Editor: Normally I would skip the editorial; however, the title “The Other Pandemic: Addiction” caught my eye (Fed Pract. 2020;37[10]:440-441). This will, of course, require me going in for eye care in the next couple of days, but my concerns are low. After all, the hook you used wasn’t that big.
Bravo! Your choice to focus on the effects of isolation was a masterful touch. I started skimming with the assumption that you would say something along the lines of ‘COVID bad, everybody depressed, blah, blah.’ But you cut into the abscess of the issue cleanly, exposing the core—isolation “amplifies negative thoughts, dysphoria, and fearful emotions.” A deadly combination for our patients and ourselves.
I have been a physician assistant in the US Army, and as a civilian at Brooke Army Medical Center and US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health Care System. One thing I have seen throughout that time was the effects of isolation on the active duty enlisted young, and even more so on retired older warriors. Throughout the time of our military service, we transfer to many places and make a lot of friends, but more so, we lose track of them over time.
I have cared for many older warriors who cannot get something as simple as a colonoscopy because they do not have someone to drive them home after they have been sedated. Family and friends were scattered over the country, or the world. At the VA, many older warriors come not just for an appointment, but also as a time to socialize and ‘BS’ with those who understand them.
One goal I set for myself many years ago was to have the warrior laughing before they left my office. If I did that, I knew I had made a difference. Thank you for your editorial.
Anthony J Passaniti, PA, USA (ret) [email protected]
Smartphones can differentiate bipolar from borderline personality disorder
There’s a reason they’re called smartphones.
Indeed, how patients use their smartphones and where they take them provides insight into what has been termed their “digital phenotype.” It’s information that, analyzed correctly, becomes useful in differentiating bipolar disorder from borderline personality disorder, a distinction that’s often challenging in clinical practice, Kate E.A. Saunders, MD, DPhil, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Dr. Saunders, a psychiatrist at the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues have developed a smartphone app enabling patients to briefly characterize their current mood on a daily basis, as well as a machine learning model to analyze this data stream as patients’ moods evolve over time. In their prospective longitudinal Automated Monitoring of Symptom Severity (AMoSS) study of 48 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of bipolar disorder, 31 with borderline personality disorder, and 51 healthy volunteers, the tool correctly classified 75% of participants into the correct diagnostic category on the basis of 20 daily mood ratings (Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Dec 13;81:274. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0334-0).
The app also monitors activity via accelerometry and geolocation to assess an individual’s circadian rest-activity patterns, as well as telephone use and texting behavior. In another report from AMoSS, Dr. Saunders and coinvestigators showed that these patterns also distinguish persons with bipolar disorder from those with borderline personality disorder, who in turn differ from healthy controls (Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 20;91:195. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0526-2).
It doesn’t replace doctors, but clearly it can add to diagnostic accuracy,” she said.
Borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder are common diagnoses with quite different treatment approaches and prognoses. Studies have shown that rates of misdiagnosis of the two disorders are significant. The challenge is that they share overlapping diagnostic criteria, including prominent mood instability, which is difficult to assess reliably in clinical practice. That’s because the assessment relies on retrospective self-report of how patients felt in the past, which is often colored by their present mood state. The smartphone app sidesteps that limitation by having patients rate their mood daily digitally across six categories – anxiety, elation, sadness, anger, irritability, and energy – on a 1-7 scale.
The machine learning model that analyzes this information organizes the voluminous data into what Dr. Saunders called “signatures of mood” and breaks them down using rough path theory, a mathematical concept based upon differential equations. Dr. Saunders and colleagues have demonstrated that the shifting daily mood self-rating patterns can be used not only to sharpen the differential diagnosis between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, but also to predict future mood. Automated analysis of the past 20 previous mood self-ratings predicted the next day’s mood in healthy controls with 89%-98% accuracy, depending upon which of the six mood categories was under scrutiny.
The predictive power in patients with bipolar disorder was also good, ranging from 82% accuracy for the energetic and anxious domains to 90% for the angry mood category. This ability to predict future mood states could have clinical value by assisting bipolar patients in enhancing proactive self-management and managing their mood stability to avoid depressive or manic relapse, although this has yet to be studied.
“For borderline personality disorder the predictive accuracy was not so good – 70%-78% – but perhaps that doesn’t matter,” Dr. Saunders said. “Perhaps that difficulty in predicting mood may actually be quite a useful diagnostic marker.”
‘Mr. Jones, the doctor is ready to see your phone now.’
The app’s accelerometry and geolocation capabilities can also enhance diagnostic accuracy, as has been shown in the AMoSS study.
The geolocation analysis generates data on the places a patient has gone and how much time was spent there. Feeding that information into the machine learning model predicted the presence or absence of depression with 85% accuracy for bipolar disorder, but couldn’t predict depression at all in borderline personality disorder.
“So we get a sense that people with bipolar disorder have behavioral manifestations of their mood symptoms which are much more consistent with one another and appear to change very consistently with their mood state, whereas borderline personality disorder seems to be characterized by something that’s much more unstable and unpredictable – and we can pick up these predictive variables using our smartphones,” Dr. Saunders said.
As depressive symptoms arise in patients with bipolar disorder, affected individuals display much less day-to-day variability in movement as measured by accelerometry. These changes predicted bipolar disorder with 76% specificity and 48% sensitivity.
“That’s OK. But we can’t do that at all in people with borderline personality disorder, again highlighting the fact that behavioral manifestations and symptoms in these groups are very, very different,” Dr. Saunders observed.
In AMoSS, analysis of activity, geolocation, and distal temperature rhythms showed that the individuals with borderline personality disorder displayed evidence of delayed circadian function, with a distinctive rest-activity pattern that differed from persons with bipolar disorder. This delayed circadian function might provide a novel therapeutic target in borderline personality disorder, a condition for which there is a notable lack of effective pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic interventions.
Phone use patterns were revealing. Patients with bipolar disorder had an increased total telephone call frequency relative to the healthy controls, whereas those with borderline personality disorder used text messaging much more frequently, consistent with the notion that borderline patients have difficulty in interpersonal communication.
Smartphone-based diagnostic differentiation between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder isn’t ready for prime time use in clinical practice, Dr. Saunders said. This is groundbreaking work that needs to be refined and replicated in larger studies. There are important ethical and data protection issues that require attention. But patients are gung-ho. Dr. Saunders noted that participant compliance in AMoSS was “extraordinarily good,” at 82%. Moreover, even though the study lasted for 3 months, more than 60% of subjects continued filing mood reports for 12 months.
“Smartphones may also give us an improved understanding of the lived experience of people with mental health problems. That’s certainly the feedback we got a lot from patients. They enjoy using this technology. They feel it’s helpful to be able to show their clinician this is what it’s like for them,” Dr. Saunders said.
Clinical usefulness is limited
The study was interesting as a pilot, and it is technologically very innovative. However, at this stage, it is unclear how the results can be used clinically, said Igor Galynker, MD, PhD, when asked about the findings.
There is a place for using this type of technology for patients living in remote areas, for example. However, Dr. Galynker, director of the Richard and Cynthia Zirinsky Center for Bipolar Disorder in New York, said such technology should be viewed as augmentation rather than as a substitute for face-to-face treatment.
“Typically, if clinicians have enough time to speak to the patient and to take history, they can differentiate between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder: The former is cyclical, the latter is less so. However, this is hard to do without face-to-face contact, or when you only have 10 minutes,” said Dr. Galynker, professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine and director of the Galynker Research and Prevention Laboratory, both at Mount Sinai in New York.
Dr. Saunders’ work is funded by the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Galynker reported receiving funding from the National Institute of Mental Health and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. He has no other disclosures.
SOURCE: ECNP 2020. Session S21.
There’s a reason they’re called smartphones.
Indeed, how patients use their smartphones and where they take them provides insight into what has been termed their “digital phenotype.” It’s information that, analyzed correctly, becomes useful in differentiating bipolar disorder from borderline personality disorder, a distinction that’s often challenging in clinical practice, Kate E.A. Saunders, MD, DPhil, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Dr. Saunders, a psychiatrist at the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues have developed a smartphone app enabling patients to briefly characterize their current mood on a daily basis, as well as a machine learning model to analyze this data stream as patients’ moods evolve over time. In their prospective longitudinal Automated Monitoring of Symptom Severity (AMoSS) study of 48 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of bipolar disorder, 31 with borderline personality disorder, and 51 healthy volunteers, the tool correctly classified 75% of participants into the correct diagnostic category on the basis of 20 daily mood ratings (Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Dec 13;81:274. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0334-0).
The app also monitors activity via accelerometry and geolocation to assess an individual’s circadian rest-activity patterns, as well as telephone use and texting behavior. In another report from AMoSS, Dr. Saunders and coinvestigators showed that these patterns also distinguish persons with bipolar disorder from those with borderline personality disorder, who in turn differ from healthy controls (Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 20;91:195. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0526-2).
It doesn’t replace doctors, but clearly it can add to diagnostic accuracy,” she said.
Borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder are common diagnoses with quite different treatment approaches and prognoses. Studies have shown that rates of misdiagnosis of the two disorders are significant. The challenge is that they share overlapping diagnostic criteria, including prominent mood instability, which is difficult to assess reliably in clinical practice. That’s because the assessment relies on retrospective self-report of how patients felt in the past, which is often colored by their present mood state. The smartphone app sidesteps that limitation by having patients rate their mood daily digitally across six categories – anxiety, elation, sadness, anger, irritability, and energy – on a 1-7 scale.
The machine learning model that analyzes this information organizes the voluminous data into what Dr. Saunders called “signatures of mood” and breaks them down using rough path theory, a mathematical concept based upon differential equations. Dr. Saunders and colleagues have demonstrated that the shifting daily mood self-rating patterns can be used not only to sharpen the differential diagnosis between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, but also to predict future mood. Automated analysis of the past 20 previous mood self-ratings predicted the next day’s mood in healthy controls with 89%-98% accuracy, depending upon which of the six mood categories was under scrutiny.
The predictive power in patients with bipolar disorder was also good, ranging from 82% accuracy for the energetic and anxious domains to 90% for the angry mood category. This ability to predict future mood states could have clinical value by assisting bipolar patients in enhancing proactive self-management and managing their mood stability to avoid depressive or manic relapse, although this has yet to be studied.
“For borderline personality disorder the predictive accuracy was not so good – 70%-78% – but perhaps that doesn’t matter,” Dr. Saunders said. “Perhaps that difficulty in predicting mood may actually be quite a useful diagnostic marker.”
‘Mr. Jones, the doctor is ready to see your phone now.’
The app’s accelerometry and geolocation capabilities can also enhance diagnostic accuracy, as has been shown in the AMoSS study.
The geolocation analysis generates data on the places a patient has gone and how much time was spent there. Feeding that information into the machine learning model predicted the presence or absence of depression with 85% accuracy for bipolar disorder, but couldn’t predict depression at all in borderline personality disorder.
“So we get a sense that people with bipolar disorder have behavioral manifestations of their mood symptoms which are much more consistent with one another and appear to change very consistently with their mood state, whereas borderline personality disorder seems to be characterized by something that’s much more unstable and unpredictable – and we can pick up these predictive variables using our smartphones,” Dr. Saunders said.
As depressive symptoms arise in patients with bipolar disorder, affected individuals display much less day-to-day variability in movement as measured by accelerometry. These changes predicted bipolar disorder with 76% specificity and 48% sensitivity.
“That’s OK. But we can’t do that at all in people with borderline personality disorder, again highlighting the fact that behavioral manifestations and symptoms in these groups are very, very different,” Dr. Saunders observed.
In AMoSS, analysis of activity, geolocation, and distal temperature rhythms showed that the individuals with borderline personality disorder displayed evidence of delayed circadian function, with a distinctive rest-activity pattern that differed from persons with bipolar disorder. This delayed circadian function might provide a novel therapeutic target in borderline personality disorder, a condition for which there is a notable lack of effective pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic interventions.
Phone use patterns were revealing. Patients with bipolar disorder had an increased total telephone call frequency relative to the healthy controls, whereas those with borderline personality disorder used text messaging much more frequently, consistent with the notion that borderline patients have difficulty in interpersonal communication.
Smartphone-based diagnostic differentiation between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder isn’t ready for prime time use in clinical practice, Dr. Saunders said. This is groundbreaking work that needs to be refined and replicated in larger studies. There are important ethical and data protection issues that require attention. But patients are gung-ho. Dr. Saunders noted that participant compliance in AMoSS was “extraordinarily good,” at 82%. Moreover, even though the study lasted for 3 months, more than 60% of subjects continued filing mood reports for 12 months.
“Smartphones may also give us an improved understanding of the lived experience of people with mental health problems. That’s certainly the feedback we got a lot from patients. They enjoy using this technology. They feel it’s helpful to be able to show their clinician this is what it’s like for them,” Dr. Saunders said.
Clinical usefulness is limited
The study was interesting as a pilot, and it is technologically very innovative. However, at this stage, it is unclear how the results can be used clinically, said Igor Galynker, MD, PhD, when asked about the findings.
There is a place for using this type of technology for patients living in remote areas, for example. However, Dr. Galynker, director of the Richard and Cynthia Zirinsky Center for Bipolar Disorder in New York, said such technology should be viewed as augmentation rather than as a substitute for face-to-face treatment.
“Typically, if clinicians have enough time to speak to the patient and to take history, they can differentiate between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder: The former is cyclical, the latter is less so. However, this is hard to do without face-to-face contact, or when you only have 10 minutes,” said Dr. Galynker, professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine and director of the Galynker Research and Prevention Laboratory, both at Mount Sinai in New York.
Dr. Saunders’ work is funded by the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Galynker reported receiving funding from the National Institute of Mental Health and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. He has no other disclosures.
SOURCE: ECNP 2020. Session S21.
There’s a reason they’re called smartphones.
Indeed, how patients use their smartphones and where they take them provides insight into what has been termed their “digital phenotype.” It’s information that, analyzed correctly, becomes useful in differentiating bipolar disorder from borderline personality disorder, a distinction that’s often challenging in clinical practice, Kate E.A. Saunders, MD, DPhil, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Dr. Saunders, a psychiatrist at the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues have developed a smartphone app enabling patients to briefly characterize their current mood on a daily basis, as well as a machine learning model to analyze this data stream as patients’ moods evolve over time. In their prospective longitudinal Automated Monitoring of Symptom Severity (AMoSS) study of 48 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of bipolar disorder, 31 with borderline personality disorder, and 51 healthy volunteers, the tool correctly classified 75% of participants into the correct diagnostic category on the basis of 20 daily mood ratings (Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Dec 13;81:274. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0334-0).
The app also monitors activity via accelerometry and geolocation to assess an individual’s circadian rest-activity patterns, as well as telephone use and texting behavior. In another report from AMoSS, Dr. Saunders and coinvestigators showed that these patterns also distinguish persons with bipolar disorder from those with borderline personality disorder, who in turn differ from healthy controls (Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 20;91:195. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0526-2).
It doesn’t replace doctors, but clearly it can add to diagnostic accuracy,” she said.
Borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder are common diagnoses with quite different treatment approaches and prognoses. Studies have shown that rates of misdiagnosis of the two disorders are significant. The challenge is that they share overlapping diagnostic criteria, including prominent mood instability, which is difficult to assess reliably in clinical practice. That’s because the assessment relies on retrospective self-report of how patients felt in the past, which is often colored by their present mood state. The smartphone app sidesteps that limitation by having patients rate their mood daily digitally across six categories – anxiety, elation, sadness, anger, irritability, and energy – on a 1-7 scale.
The machine learning model that analyzes this information organizes the voluminous data into what Dr. Saunders called “signatures of mood” and breaks them down using rough path theory, a mathematical concept based upon differential equations. Dr. Saunders and colleagues have demonstrated that the shifting daily mood self-rating patterns can be used not only to sharpen the differential diagnosis between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, but also to predict future mood. Automated analysis of the past 20 previous mood self-ratings predicted the next day’s mood in healthy controls with 89%-98% accuracy, depending upon which of the six mood categories was under scrutiny.
The predictive power in patients with bipolar disorder was also good, ranging from 82% accuracy for the energetic and anxious domains to 90% for the angry mood category. This ability to predict future mood states could have clinical value by assisting bipolar patients in enhancing proactive self-management and managing their mood stability to avoid depressive or manic relapse, although this has yet to be studied.
“For borderline personality disorder the predictive accuracy was not so good – 70%-78% – but perhaps that doesn’t matter,” Dr. Saunders said. “Perhaps that difficulty in predicting mood may actually be quite a useful diagnostic marker.”
‘Mr. Jones, the doctor is ready to see your phone now.’
The app’s accelerometry and geolocation capabilities can also enhance diagnostic accuracy, as has been shown in the AMoSS study.
The geolocation analysis generates data on the places a patient has gone and how much time was spent there. Feeding that information into the machine learning model predicted the presence or absence of depression with 85% accuracy for bipolar disorder, but couldn’t predict depression at all in borderline personality disorder.
“So we get a sense that people with bipolar disorder have behavioral manifestations of their mood symptoms which are much more consistent with one another and appear to change very consistently with their mood state, whereas borderline personality disorder seems to be characterized by something that’s much more unstable and unpredictable – and we can pick up these predictive variables using our smartphones,” Dr. Saunders said.
As depressive symptoms arise in patients with bipolar disorder, affected individuals display much less day-to-day variability in movement as measured by accelerometry. These changes predicted bipolar disorder with 76% specificity and 48% sensitivity.
“That’s OK. But we can’t do that at all in people with borderline personality disorder, again highlighting the fact that behavioral manifestations and symptoms in these groups are very, very different,” Dr. Saunders observed.
In AMoSS, analysis of activity, geolocation, and distal temperature rhythms showed that the individuals with borderline personality disorder displayed evidence of delayed circadian function, with a distinctive rest-activity pattern that differed from persons with bipolar disorder. This delayed circadian function might provide a novel therapeutic target in borderline personality disorder, a condition for which there is a notable lack of effective pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic interventions.
Phone use patterns were revealing. Patients with bipolar disorder had an increased total telephone call frequency relative to the healthy controls, whereas those with borderline personality disorder used text messaging much more frequently, consistent with the notion that borderline patients have difficulty in interpersonal communication.
Smartphone-based diagnostic differentiation between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder isn’t ready for prime time use in clinical practice, Dr. Saunders said. This is groundbreaking work that needs to be refined and replicated in larger studies. There are important ethical and data protection issues that require attention. But patients are gung-ho. Dr. Saunders noted that participant compliance in AMoSS was “extraordinarily good,” at 82%. Moreover, even though the study lasted for 3 months, more than 60% of subjects continued filing mood reports for 12 months.
“Smartphones may also give us an improved understanding of the lived experience of people with mental health problems. That’s certainly the feedback we got a lot from patients. They enjoy using this technology. They feel it’s helpful to be able to show their clinician this is what it’s like for them,” Dr. Saunders said.
Clinical usefulness is limited
The study was interesting as a pilot, and it is technologically very innovative. However, at this stage, it is unclear how the results can be used clinically, said Igor Galynker, MD, PhD, when asked about the findings.
There is a place for using this type of technology for patients living in remote areas, for example. However, Dr. Galynker, director of the Richard and Cynthia Zirinsky Center for Bipolar Disorder in New York, said such technology should be viewed as augmentation rather than as a substitute for face-to-face treatment.
“Typically, if clinicians have enough time to speak to the patient and to take history, they can differentiate between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder: The former is cyclical, the latter is less so. However, this is hard to do without face-to-face contact, or when you only have 10 minutes,” said Dr. Galynker, professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine and director of the Galynker Research and Prevention Laboratory, both at Mount Sinai in New York.
Dr. Saunders’ work is funded by the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Galynker reported receiving funding from the National Institute of Mental Health and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. He has no other disclosures.
SOURCE: ECNP 2020. Session S21.
FROM ECNP 2020