User login
Progressive Eyelash Loss and Scale of the Right Eyelid
The Diagnosis: Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) characterized by folliculotropism and follicular-based lesions. The clinical manifestation of FMF can vary and includes patches, plaques, or tumors resembling nonfolliculotropic MF; acneform lesions including comedones and pustules; or areas of alopecia. Lesions commonly involve the head and neck but also can be seen on the trunk or extremities. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides can be accompanied by pruritus or superimposed secondary infection.
Histologic features of FMF include follicular (perifollicular or intrafollicular) infiltration by atypical T cells showing cerebriform nuclei.1 In early lesions, there may be only mild superficial perivascular inflammation without notable lymphocyte atypia, making diagnosis challenging. 2,3 Mucinous degeneration of the follicles—termed follicular mucinosis—is a common histologic finding in FMF.1,2 Follicular mucinosis is not exclusive to FMF; it can be primary/idiopathic or secondary to underlying inflammatory or neoplastic disorders such as FMF. On immunohistochemistry, FMF most commonly demonstrates a helper T cell phenotype that is positive for CD3 and CD4 and negative for CD8, with aberrant loss of CD7 and variably CD5, which is similar to classic MF. Occasionally, larger CD30+ cells also can be present in the dermis. T-cell gene rearrangement studies will demonstrate T-cell receptor clonality in most cases.2
Many large retrospective cohort studies have suggested that patients with FMF have a worse prognosis than classic MF, with a 5-year survival rate of 62% to 87% for early-stage FMF vs more than 90% for classic patchand plaque-stage MF.4-7 However, a 2016 study suggested histologic evaluation may be able to further differentiate clinically identical cases into indolent and aggressive forms of FMF with considerably different outcomes based on the density of the perifollicular infiltrate.5 The presence of follicular mucinosis has no impact on prognosis compared to cases without follicular mucinosis.1,2
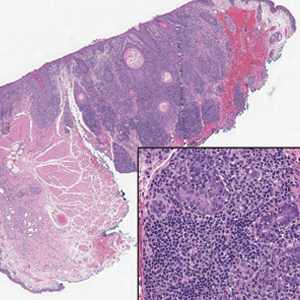
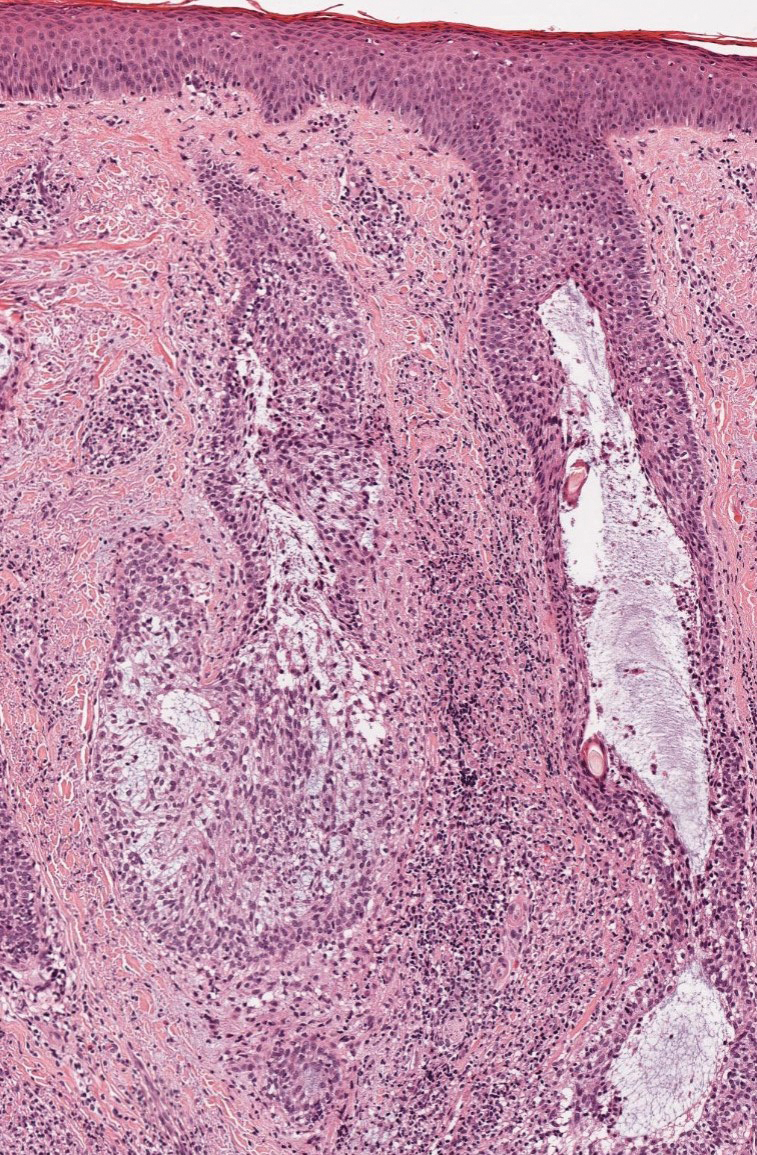
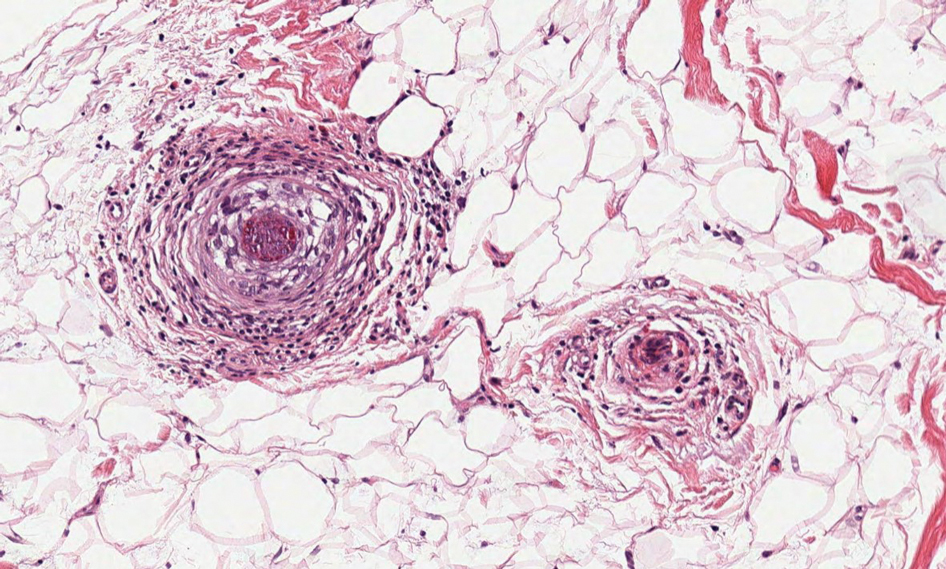
Alopecia mucinosa is characterized by infiltrating, erythematous, scaling plaques localized to the head and neck.8 It is diagnosed clinically, and histopathology shows follicular mucinosis. The terms alopecia mucinosa and follicular mucinosis often are used interchangeably. Over the past few decades, 3 variants have been categorized: primary acute, primary chronic, and secondary. The primary acute form manifests in children and young adults as solitary lesions, which often resolve spontaneously. In contrast, the primary chronic form manifests in older adults as multiple disseminated lesions with a chronic relapsing course.8,9 The secondary form can occur in the setting of other disorders, including lupus erythematosus, hypertrophic lichen planus, alopecia areata, and neoplasms such as MF or Hodgkin lymphoma.9 The histopathologic findings are similar for all types of alopecia mucinosa, with cystic pools of mucin deposition in the sebaceous glands and external root sheath of the follicles as well as associated inflammation composed of lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1).9,10 The inflammatory infiltrate rarely extends into the epidermis or upper portion of the hair follicle. Although histopathology alone cannot reliably distinguish between primary and secondary forms of alopecia mucinosa, MF (including follicular MF) or another underlying cutaneous T-cell lymphoma should be considered if inflammation extends into the upper dermis, epidermis, or follicles or is in a dense bandlike distribution.11 On immunohistochemistry, lymphocytes should show positivity for CD3, CD4, and CD8. The CD4:CD8 ratio often is 1:1 in alopecia mucinosa, while in FMF it is approximately 3:1.10 CD7 commonly is negative but can be present in a small percentage of cases.12 T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies have detected clonality in both primary and secondary alopecia mucinosa and thus cannot be used alone to distinguish between the two.10 Given the overlap in histopathologic and immunohistochemical features of primary and secondary alopecia mucinosa, definitive diagnosis cannot be made with any single modality and should be based on correlating clinical presentation, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analyses.
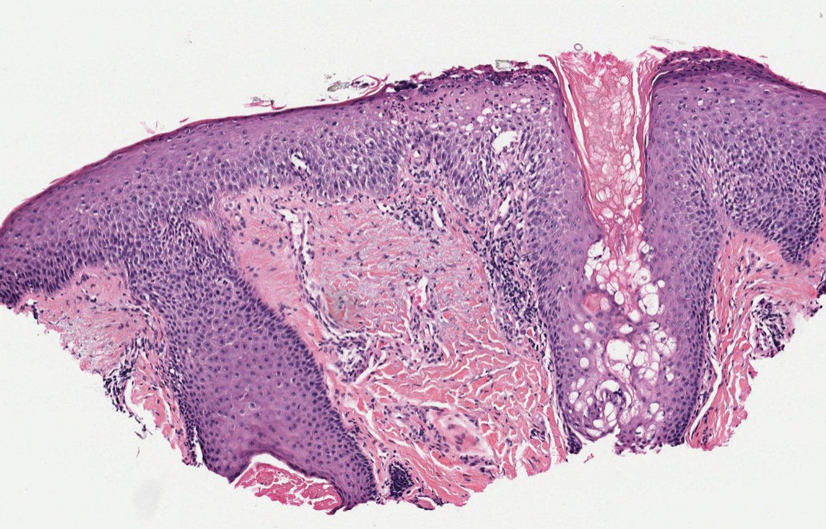
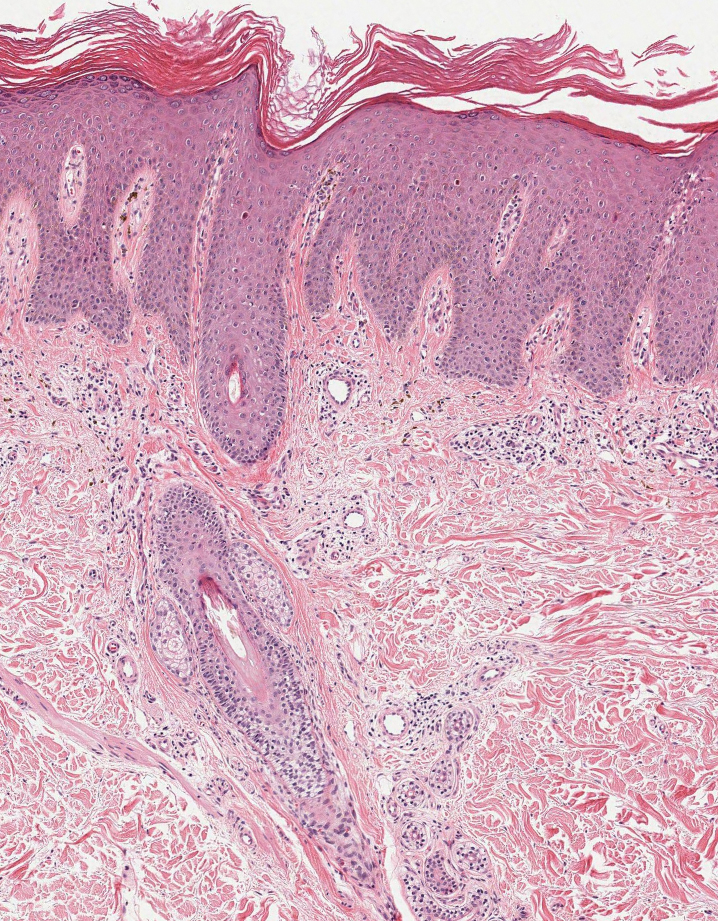
Inflammatory dermatoses including seborrheic dermatitis also are in the differential diagnosis for FMF. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting 1% to 3% of the general population. 13 Patients usually present with scaly and greasy plaques and papules localized to areas with increased sebaceous glands and high sebum production such as the face, scalp, and intertriginous regions. The distribution often is symmetrical, and the severity of disease can vary substantially.13 Sebopsoriasis is an entity with overlapping features of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis, including thicker, more erythematous plaques that are more elevated. Histopathology of seborrheic dermatitis reveals spongiotic inflammation in the epidermis characterized by rounding of the keratinocytes, widening of the intercellular spaces, and accumulation of intracellular edema, causing the formation of clear spaces in the epidermis (Figure 2). Focal parakeratosis, usually in the follicular ostia, and mounds of scaly crust often are present. 14 A periodic acid–Schiff stain should be performed to rule out infectious dermatophytes, which can show similar clinical and histologic features. More chronic cases of seborrheic dermatitis often can take on histologic features of psoriasis, namely epidermal hyperplasia with thinning over dermal papillae, though the hyperplasia in psoriasis is more regular.
Alopecia areata is an immune-mediated disorder characterized by nonscarring hair loss; it affects approximately 0.1% to 0.2% of the general population.15 The pathogenesis involves the premature transition of hair follicles in the anagen (growth) phase to the catagen ( nonproliferative/involution) and telogen (resting) phases, resulting in sudden hair shedding and decreased regrowth. Clinically, it is characterized by asymptomatic hair loss that occurs most frequently on the scalp and other areas of the head, including eyelashes, eyebrows, and facial hair, but also can occur on the extremities. There are several variants; the most common is patchy alopecia, which features smooth circular areas of hair loss that progress over several weeks. Some patients can progress to loss of all scalp hairs (alopecia totalis) or all hairs throughout the body (alopecia universalis). 15 Patients typically will have spontaneous regrowth of hair, with up to 50% of those with limited hair loss recovering within a year.16 The disease has a chronic/ relapsing course, and patients often will have multiple episodes of hair loss. Histopathologic features can vary depending on the stage of disease. In acute cases, a peribulbar lymphocytic infiltrate preferentially involving anagen-stage hair follicles is seen, with associated necrosis, edema, and pigment incontinence (Figure 3).16 In chronic alopecia areata, the inflammation may be less brisk, and follicular miniaturization often is seen. Additionally, increased proportions of catagen- or telogen-stage follicles are present.16,17 On immunohistochemistry, lymphocytes express both CD4 and CD8, with a slightly increased CD4:CD8 ratio in active disease.18
Psoriatic alopecia describes hair loss that occurs in patients with psoriasis. Patients present with scaly, erythematous, psoriasiform plaques or patches, as well as decreased hair density, finer hairs, and increased dystrophic hair bulbs within the psoriatic plaques.19 It often is nonscarring and resolves with therapy, though scarring may occur with secondary infection. Psoriatic alopecia may occur in the setting of classic psoriasis and also may occur in psoriasiform drug eruptions, including those caused by tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.20,21 Histologic features include atrophy of sebaceous glands, epidermal changes with hypogranulosis and psoriasiform hyperplasia, decreased hair follicle density, and neutrophils in the stratum spinosum (Figure 4). There often is associated perifollicular lymphocytic inflammation with small lymphocytes that do not have notable morphologic abnormalities.
- Willemze R, Cerroni L, Kempf W, et al. The 2018 update of the WHO-EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2019;133:1703-1714. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-11-881268
- Malveira MIB, Pascoal G, Gamonal SBL, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: challenging clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical diagnosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5 suppl 1):73-75. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175634
- Flaig MJ, Cerroni L, Schuhmann K, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a histopathologic analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:525- 530. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2001.281006.x
- van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-198. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.2.191
- van Santen S, Roach REJ, van Doorn R, et al. Clinical staging and prognostic factors in folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:992-1000. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.1597
- Lehman JS, Cook-Norris RH, Weed BR, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: single-center study and systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:607-613. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.101
- Gerami P, Rosen S, Kuzel T, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: an aggressive variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:738-746. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.6.738
- Büchner SA, Meier M, Rufli TH. Follicular mucinosis associated with mycosis fungoides. Dermatology. 1991;183:66-67. doi:10.1159/000247639
- Akinsanya AO, Tschen JA. Follicular mucinosis: a case report. Cureus. 2019;11:E4746. doi:10.7759/cureus.4746
- Rongioletti F, De Lucchi S, Meyes D, et al. Follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical and molecular study comparing the primary benign form and the mycosis fungoides-associated follicular mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:15-19. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01338.x
- Khalil J, Kurban M, Abbas O. Follicular mucinosis: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2021;60:159-165. doi:10.1111/ijd.15165
- Zvulunov A, Shkalim V, Ben-Amitai D, et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of alopecia mucinosa/follicular mucinosis and its natural history in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1174-1181. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.04.015
- Dessinioti C, Katsambas A. Seborrheic dermatitis: etiology, risk factors, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:343-351. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.001
- Gupta AK, Bluhm R. Seborrheic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:13-26; quiz 19-20. doi:10.1111/j .1468-3083.2004.00693.x
- Strazzulla LC, Wang EHC, Avila L, et al. Alopecia areata: disease characteristics, clinical evaluation, and new perspectives on pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1-12. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2017.04.1141
- Alkhalifah A, Alsantali A, Wang E, et al. Alopecia areata update: part I. clinical picture, histopathology, and pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:177-88, quiz 189-90. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.10.032
- Whiting DA. Histopathologic features of alopecia areata: a new look. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:1555-1559. doi:10.1001/archderm .139.12.1555
- Todes-Taylor N, Turner R, Wood GS, et al. T cell subpopulations in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11(2 pt 1):216-223. doi:10.1016 /s0190-9622(84)70152-6
- George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721. doi:10.1111/ced.12715
- Afaasiev OK, Zhang CZ, Ruhoy SM. TNF-inhibitor associated psoriatic alopecia: diagnostic utility of sebaceous lobule atrophy. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:563-539. doi:10.1111/cup.12932
- Silva CY, Brown KL, Kurban AK, et al. Psoriatic alopecia—fact or fiction? A clinicohistologic reappraisal. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:611-619. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.100574
The Diagnosis: Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) characterized by folliculotropism and follicular-based lesions. The clinical manifestation of FMF can vary and includes patches, plaques, or tumors resembling nonfolliculotropic MF; acneform lesions including comedones and pustules; or areas of alopecia. Lesions commonly involve the head and neck but also can be seen on the trunk or extremities. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides can be accompanied by pruritus or superimposed secondary infection.
Histologic features of FMF include follicular (perifollicular or intrafollicular) infiltration by atypical T cells showing cerebriform nuclei.1 In early lesions, there may be only mild superficial perivascular inflammation without notable lymphocyte atypia, making diagnosis challenging. 2,3 Mucinous degeneration of the follicles—termed follicular mucinosis—is a common histologic finding in FMF.1,2 Follicular mucinosis is not exclusive to FMF; it can be primary/idiopathic or secondary to underlying inflammatory or neoplastic disorders such as FMF. On immunohistochemistry, FMF most commonly demonstrates a helper T cell phenotype that is positive for CD3 and CD4 and negative for CD8, with aberrant loss of CD7 and variably CD5, which is similar to classic MF. Occasionally, larger CD30+ cells also can be present in the dermis. T-cell gene rearrangement studies will demonstrate T-cell receptor clonality in most cases.2
Many large retrospective cohort studies have suggested that patients with FMF have a worse prognosis than classic MF, with a 5-year survival rate of 62% to 87% for early-stage FMF vs more than 90% for classic patchand plaque-stage MF.4-7 However, a 2016 study suggested histologic evaluation may be able to further differentiate clinically identical cases into indolent and aggressive forms of FMF with considerably different outcomes based on the density of the perifollicular infiltrate.5 The presence of follicular mucinosis has no impact on prognosis compared to cases without follicular mucinosis.1,2
Alopecia mucinosa is characterized by infiltrating, erythematous, scaling plaques localized to the head and neck.8 It is diagnosed clinically, and histopathology shows follicular mucinosis. The terms alopecia mucinosa and follicular mucinosis often are used interchangeably. Over the past few decades, 3 variants have been categorized: primary acute, primary chronic, and secondary. The primary acute form manifests in children and young adults as solitary lesions, which often resolve spontaneously. In contrast, the primary chronic form manifests in older adults as multiple disseminated lesions with a chronic relapsing course.8,9 The secondary form can occur in the setting of other disorders, including lupus erythematosus, hypertrophic lichen planus, alopecia areata, and neoplasms such as MF or Hodgkin lymphoma.9 The histopathologic findings are similar for all types of alopecia mucinosa, with cystic pools of mucin deposition in the sebaceous glands and external root sheath of the follicles as well as associated inflammation composed of lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1).9,10 The inflammatory infiltrate rarely extends into the epidermis or upper portion of the hair follicle. Although histopathology alone cannot reliably distinguish between primary and secondary forms of alopecia mucinosa, MF (including follicular MF) or another underlying cutaneous T-cell lymphoma should be considered if inflammation extends into the upper dermis, epidermis, or follicles or is in a dense bandlike distribution.11 On immunohistochemistry, lymphocytes should show positivity for CD3, CD4, and CD8. The CD4:CD8 ratio often is 1:1 in alopecia mucinosa, while in FMF it is approximately 3:1.10 CD7 commonly is negative but can be present in a small percentage of cases.12 T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies have detected clonality in both primary and secondary alopecia mucinosa and thus cannot be used alone to distinguish between the two.10 Given the overlap in histopathologic and immunohistochemical features of primary and secondary alopecia mucinosa, definitive diagnosis cannot be made with any single modality and should be based on correlating clinical presentation, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analyses.
Inflammatory dermatoses including seborrheic dermatitis also are in the differential diagnosis for FMF. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting 1% to 3% of the general population. 13 Patients usually present with scaly and greasy plaques and papules localized to areas with increased sebaceous glands and high sebum production such as the face, scalp, and intertriginous regions. The distribution often is symmetrical, and the severity of disease can vary substantially.13 Sebopsoriasis is an entity with overlapping features of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis, including thicker, more erythematous plaques that are more elevated. Histopathology of seborrheic dermatitis reveals spongiotic inflammation in the epidermis characterized by rounding of the keratinocytes, widening of the intercellular spaces, and accumulation of intracellular edema, causing the formation of clear spaces in the epidermis (Figure 2). Focal parakeratosis, usually in the follicular ostia, and mounds of scaly crust often are present. 14 A periodic acid–Schiff stain should be performed to rule out infectious dermatophytes, which can show similar clinical and histologic features. More chronic cases of seborrheic dermatitis often can take on histologic features of psoriasis, namely epidermal hyperplasia with thinning over dermal papillae, though the hyperplasia in psoriasis is more regular.

Alopecia areata is an immune-mediated disorder characterized by nonscarring hair loss; it affects approximately 0.1% to 0.2% of the general population.15 The pathogenesis involves the premature transition of hair follicles in the anagen (growth) phase to the catagen ( nonproliferative/involution) and telogen (resting) phases, resulting in sudden hair shedding and decreased regrowth. Clinically, it is characterized by asymptomatic hair loss that occurs most frequently on the scalp and other areas of the head, including eyelashes, eyebrows, and facial hair, but also can occur on the extremities. There are several variants; the most common is patchy alopecia, which features smooth circular areas of hair loss that progress over several weeks. Some patients can progress to loss of all scalp hairs (alopecia totalis) or all hairs throughout the body (alopecia universalis). 15 Patients typically will have spontaneous regrowth of hair, with up to 50% of those with limited hair loss recovering within a year.16 The disease has a chronic/ relapsing course, and patients often will have multiple episodes of hair loss. Histopathologic features can vary depending on the stage of disease. In acute cases, a peribulbar lymphocytic infiltrate preferentially involving anagen-stage hair follicles is seen, with associated necrosis, edema, and pigment incontinence (Figure 3).16 In chronic alopecia areata, the inflammation may be less brisk, and follicular miniaturization often is seen. Additionally, increased proportions of catagen- or telogen-stage follicles are present.16,17 On immunohistochemistry, lymphocytes express both CD4 and CD8, with a slightly increased CD4:CD8 ratio in active disease.18

Psoriatic alopecia describes hair loss that occurs in patients with psoriasis. Patients present with scaly, erythematous, psoriasiform plaques or patches, as well as decreased hair density, finer hairs, and increased dystrophic hair bulbs within the psoriatic plaques.19 It often is nonscarring and resolves with therapy, though scarring may occur with secondary infection. Psoriatic alopecia may occur in the setting of classic psoriasis and also may occur in psoriasiform drug eruptions, including those caused by tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.20,21 Histologic features include atrophy of sebaceous glands, epidermal changes with hypogranulosis and psoriasiform hyperplasia, decreased hair follicle density, and neutrophils in the stratum spinosum (Figure 4). There often is associated perifollicular lymphocytic inflammation with small lymphocytes that do not have notable morphologic abnormalities.


The Diagnosis: Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) characterized by folliculotropism and follicular-based lesions. The clinical manifestation of FMF can vary and includes patches, plaques, or tumors resembling nonfolliculotropic MF; acneform lesions including comedones and pustules; or areas of alopecia. Lesions commonly involve the head and neck but also can be seen on the trunk or extremities. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides can be accompanied by pruritus or superimposed secondary infection.
Histologic features of FMF include follicular (perifollicular or intrafollicular) infiltration by atypical T cells showing cerebriform nuclei.1 In early lesions, there may be only mild superficial perivascular inflammation without notable lymphocyte atypia, making diagnosis challenging. 2,3 Mucinous degeneration of the follicles—termed follicular mucinosis—is a common histologic finding in FMF.1,2 Follicular mucinosis is not exclusive to FMF; it can be primary/idiopathic or secondary to underlying inflammatory or neoplastic disorders such as FMF. On immunohistochemistry, FMF most commonly demonstrates a helper T cell phenotype that is positive for CD3 and CD4 and negative for CD8, with aberrant loss of CD7 and variably CD5, which is similar to classic MF. Occasionally, larger CD30+ cells also can be present in the dermis. T-cell gene rearrangement studies will demonstrate T-cell receptor clonality in most cases.2
Many large retrospective cohort studies have suggested that patients with FMF have a worse prognosis than classic MF, with a 5-year survival rate of 62% to 87% for early-stage FMF vs more than 90% for classic patchand plaque-stage MF.4-7 However, a 2016 study suggested histologic evaluation may be able to further differentiate clinically identical cases into indolent and aggressive forms of FMF with considerably different outcomes based on the density of the perifollicular infiltrate.5 The presence of follicular mucinosis has no impact on prognosis compared to cases without follicular mucinosis.1,2
Alopecia mucinosa is characterized by infiltrating, erythematous, scaling plaques localized to the head and neck.8 It is diagnosed clinically, and histopathology shows follicular mucinosis. The terms alopecia mucinosa and follicular mucinosis often are used interchangeably. Over the past few decades, 3 variants have been categorized: primary acute, primary chronic, and secondary. The primary acute form manifests in children and young adults as solitary lesions, which often resolve spontaneously. In contrast, the primary chronic form manifests in older adults as multiple disseminated lesions with a chronic relapsing course.8,9 The secondary form can occur in the setting of other disorders, including lupus erythematosus, hypertrophic lichen planus, alopecia areata, and neoplasms such as MF or Hodgkin lymphoma.9 The histopathologic findings are similar for all types of alopecia mucinosa, with cystic pools of mucin deposition in the sebaceous glands and external root sheath of the follicles as well as associated inflammation composed of lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1).9,10 The inflammatory infiltrate rarely extends into the epidermis or upper portion of the hair follicle. Although histopathology alone cannot reliably distinguish between primary and secondary forms of alopecia mucinosa, MF (including follicular MF) or another underlying cutaneous T-cell lymphoma should be considered if inflammation extends into the upper dermis, epidermis, or follicles or is in a dense bandlike distribution.11 On immunohistochemistry, lymphocytes should show positivity for CD3, CD4, and CD8. The CD4:CD8 ratio often is 1:1 in alopecia mucinosa, while in FMF it is approximately 3:1.10 CD7 commonly is negative but can be present in a small percentage of cases.12 T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies have detected clonality in both primary and secondary alopecia mucinosa and thus cannot be used alone to distinguish between the two.10 Given the overlap in histopathologic and immunohistochemical features of primary and secondary alopecia mucinosa, definitive diagnosis cannot be made with any single modality and should be based on correlating clinical presentation, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analyses.
Inflammatory dermatoses including seborrheic dermatitis also are in the differential diagnosis for FMF. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting 1% to 3% of the general population. 13 Patients usually present with scaly and greasy plaques and papules localized to areas with increased sebaceous glands and high sebum production such as the face, scalp, and intertriginous regions. The distribution often is symmetrical, and the severity of disease can vary substantially.13 Sebopsoriasis is an entity with overlapping features of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis, including thicker, more erythematous plaques that are more elevated. Histopathology of seborrheic dermatitis reveals spongiotic inflammation in the epidermis characterized by rounding of the keratinocytes, widening of the intercellular spaces, and accumulation of intracellular edema, causing the formation of clear spaces in the epidermis (Figure 2). Focal parakeratosis, usually in the follicular ostia, and mounds of scaly crust often are present. 14 A periodic acid–Schiff stain should be performed to rule out infectious dermatophytes, which can show similar clinical and histologic features. More chronic cases of seborrheic dermatitis often can take on histologic features of psoriasis, namely epidermal hyperplasia with thinning over dermal papillae, though the hyperplasia in psoriasis is more regular.

Alopecia areata is an immune-mediated disorder characterized by nonscarring hair loss; it affects approximately 0.1% to 0.2% of the general population.15 The pathogenesis involves the premature transition of hair follicles in the anagen (growth) phase to the catagen ( nonproliferative/involution) and telogen (resting) phases, resulting in sudden hair shedding and decreased regrowth. Clinically, it is characterized by asymptomatic hair loss that occurs most frequently on the scalp and other areas of the head, including eyelashes, eyebrows, and facial hair, but also can occur on the extremities. There are several variants; the most common is patchy alopecia, which features smooth circular areas of hair loss that progress over several weeks. Some patients can progress to loss of all scalp hairs (alopecia totalis) or all hairs throughout the body (alopecia universalis). 15 Patients typically will have spontaneous regrowth of hair, with up to 50% of those with limited hair loss recovering within a year.16 The disease has a chronic/ relapsing course, and patients often will have multiple episodes of hair loss. Histopathologic features can vary depending on the stage of disease. In acute cases, a peribulbar lymphocytic infiltrate preferentially involving anagen-stage hair follicles is seen, with associated necrosis, edema, and pigment incontinence (Figure 3).16 In chronic alopecia areata, the inflammation may be less brisk, and follicular miniaturization often is seen. Additionally, increased proportions of catagen- or telogen-stage follicles are present.16,17 On immunohistochemistry, lymphocytes express both CD4 and CD8, with a slightly increased CD4:CD8 ratio in active disease.18

Psoriatic alopecia describes hair loss that occurs in patients with psoriasis. Patients present with scaly, erythematous, psoriasiform plaques or patches, as well as decreased hair density, finer hairs, and increased dystrophic hair bulbs within the psoriatic plaques.19 It often is nonscarring and resolves with therapy, though scarring may occur with secondary infection. Psoriatic alopecia may occur in the setting of classic psoriasis and also may occur in psoriasiform drug eruptions, including those caused by tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.20,21 Histologic features include atrophy of sebaceous glands, epidermal changes with hypogranulosis and psoriasiform hyperplasia, decreased hair follicle density, and neutrophils in the stratum spinosum (Figure 4). There often is associated perifollicular lymphocytic inflammation with small lymphocytes that do not have notable morphologic abnormalities.


- Willemze R, Cerroni L, Kempf W, et al. The 2018 update of the WHO-EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2019;133:1703-1714. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-11-881268
- Malveira MIB, Pascoal G, Gamonal SBL, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: challenging clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical diagnosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5 suppl 1):73-75. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175634
- Flaig MJ, Cerroni L, Schuhmann K, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a histopathologic analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:525- 530. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2001.281006.x
- van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-198. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.2.191
- van Santen S, Roach REJ, van Doorn R, et al. Clinical staging and prognostic factors in folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:992-1000. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.1597
- Lehman JS, Cook-Norris RH, Weed BR, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: single-center study and systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:607-613. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.101
- Gerami P, Rosen S, Kuzel T, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: an aggressive variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:738-746. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.6.738
- Büchner SA, Meier M, Rufli TH. Follicular mucinosis associated with mycosis fungoides. Dermatology. 1991;183:66-67. doi:10.1159/000247639
- Akinsanya AO, Tschen JA. Follicular mucinosis: a case report. Cureus. 2019;11:E4746. doi:10.7759/cureus.4746
- Rongioletti F, De Lucchi S, Meyes D, et al. Follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical and molecular study comparing the primary benign form and the mycosis fungoides-associated follicular mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:15-19. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01338.x
- Khalil J, Kurban M, Abbas O. Follicular mucinosis: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2021;60:159-165. doi:10.1111/ijd.15165
- Zvulunov A, Shkalim V, Ben-Amitai D, et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of alopecia mucinosa/follicular mucinosis and its natural history in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1174-1181. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.04.015
- Dessinioti C, Katsambas A. Seborrheic dermatitis: etiology, risk factors, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:343-351. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.001
- Gupta AK, Bluhm R. Seborrheic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:13-26; quiz 19-20. doi:10.1111/j .1468-3083.2004.00693.x
- Strazzulla LC, Wang EHC, Avila L, et al. Alopecia areata: disease characteristics, clinical evaluation, and new perspectives on pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1-12. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2017.04.1141
- Alkhalifah A, Alsantali A, Wang E, et al. Alopecia areata update: part I. clinical picture, histopathology, and pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:177-88, quiz 189-90. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.10.032
- Whiting DA. Histopathologic features of alopecia areata: a new look. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:1555-1559. doi:10.1001/archderm .139.12.1555
- Todes-Taylor N, Turner R, Wood GS, et al. T cell subpopulations in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11(2 pt 1):216-223. doi:10.1016 /s0190-9622(84)70152-6
- George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721. doi:10.1111/ced.12715
- Afaasiev OK, Zhang CZ, Ruhoy SM. TNF-inhibitor associated psoriatic alopecia: diagnostic utility of sebaceous lobule atrophy. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:563-539. doi:10.1111/cup.12932
- Silva CY, Brown KL, Kurban AK, et al. Psoriatic alopecia—fact or fiction? A clinicohistologic reappraisal. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:611-619. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.100574
- Willemze R, Cerroni L, Kempf W, et al. The 2018 update of the WHO-EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2019;133:1703-1714. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-11-881268
- Malveira MIB, Pascoal G, Gamonal SBL, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: challenging clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical diagnosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5 suppl 1):73-75. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175634
- Flaig MJ, Cerroni L, Schuhmann K, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a histopathologic analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:525- 530. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2001.281006.x
- van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-198. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.2.191
- van Santen S, Roach REJ, van Doorn R, et al. Clinical staging and prognostic factors in folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:992-1000. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.1597
- Lehman JS, Cook-Norris RH, Weed BR, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: single-center study and systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:607-613. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.101
- Gerami P, Rosen S, Kuzel T, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: an aggressive variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:738-746. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.6.738
- Büchner SA, Meier M, Rufli TH. Follicular mucinosis associated with mycosis fungoides. Dermatology. 1991;183:66-67. doi:10.1159/000247639
- Akinsanya AO, Tschen JA. Follicular mucinosis: a case report. Cureus. 2019;11:E4746. doi:10.7759/cureus.4746
- Rongioletti F, De Lucchi S, Meyes D, et al. Follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical and molecular study comparing the primary benign form and the mycosis fungoides-associated follicular mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:15-19. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01338.x
- Khalil J, Kurban M, Abbas O. Follicular mucinosis: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2021;60:159-165. doi:10.1111/ijd.15165
- Zvulunov A, Shkalim V, Ben-Amitai D, et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of alopecia mucinosa/follicular mucinosis and its natural history in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1174-1181. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.04.015
- Dessinioti C, Katsambas A. Seborrheic dermatitis: etiology, risk factors, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:343-351. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.001
- Gupta AK, Bluhm R. Seborrheic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:13-26; quiz 19-20. doi:10.1111/j .1468-3083.2004.00693.x
- Strazzulla LC, Wang EHC, Avila L, et al. Alopecia areata: disease characteristics, clinical evaluation, and new perspectives on pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1-12. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2017.04.1141
- Alkhalifah A, Alsantali A, Wang E, et al. Alopecia areata update: part I. clinical picture, histopathology, and pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:177-88, quiz 189-90. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.10.032
- Whiting DA. Histopathologic features of alopecia areata: a new look. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:1555-1559. doi:10.1001/archderm .139.12.1555
- Todes-Taylor N, Turner R, Wood GS, et al. T cell subpopulations in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11(2 pt 1):216-223. doi:10.1016 /s0190-9622(84)70152-6
- George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721. doi:10.1111/ced.12715
- Afaasiev OK, Zhang CZ, Ruhoy SM. TNF-inhibitor associated psoriatic alopecia: diagnostic utility of sebaceous lobule atrophy. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:563-539. doi:10.1111/cup.12932
- Silva CY, Brown KL, Kurban AK, et al. Psoriatic alopecia—fact or fiction? A clinicohistologic reappraisal. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:611-619. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.100574
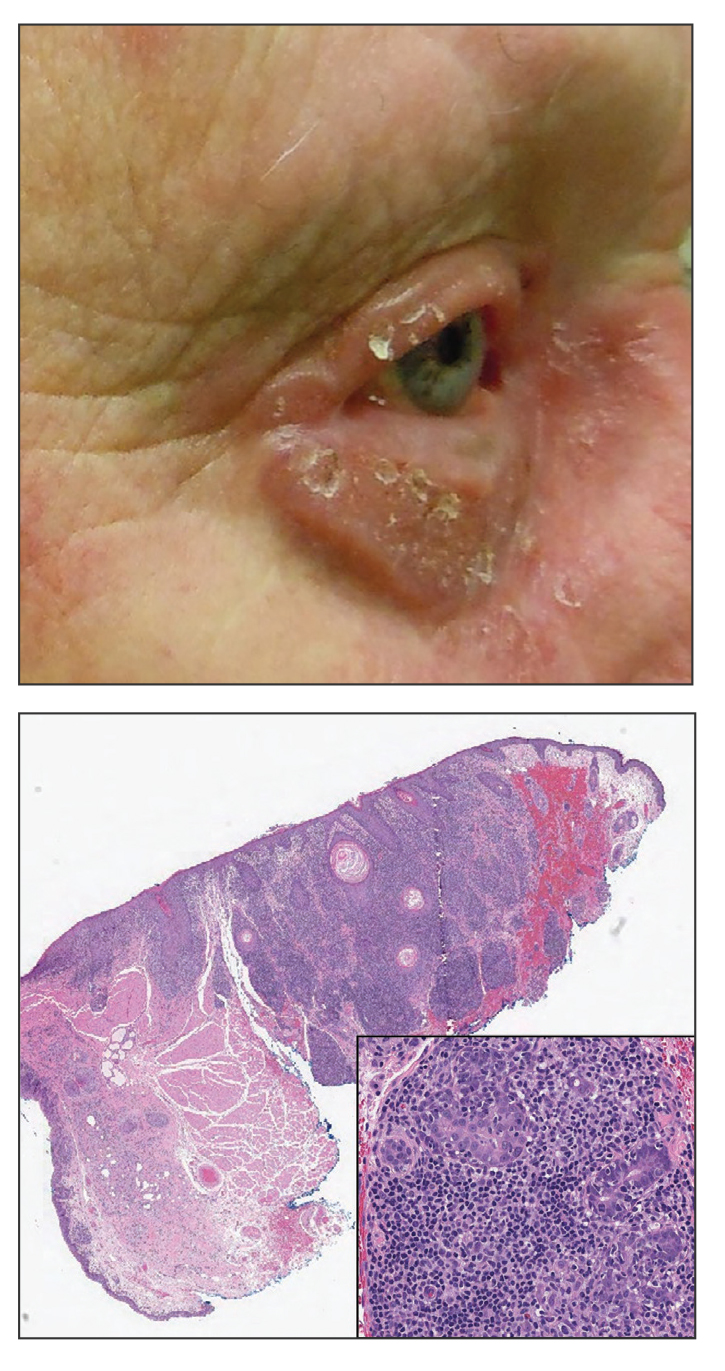
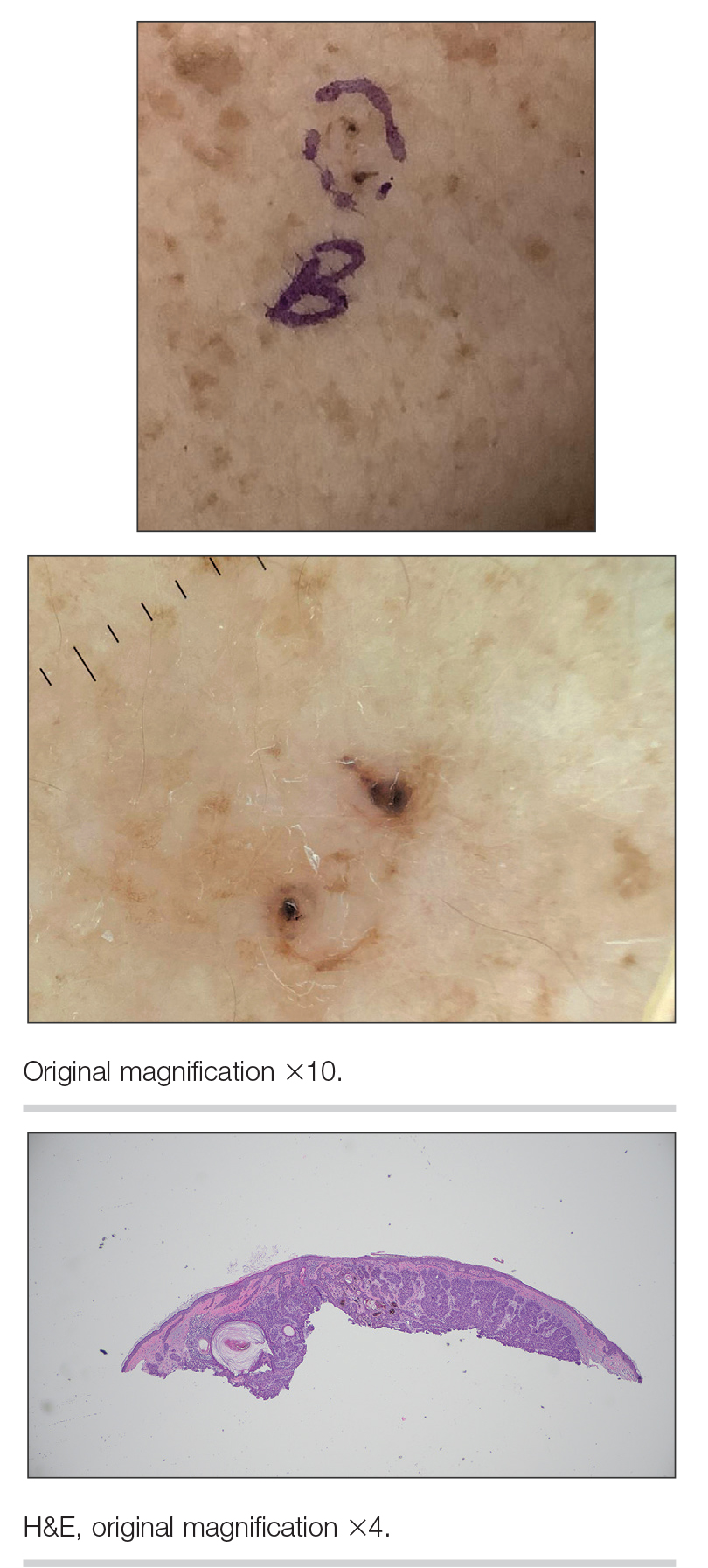
An 88-year-old man presented with progressive eyelash loss and scale involving the right eyelids (top). Dermatopathologic examination was performed (bottom).
Pigmented Lesion on the Left Shoulder in an Older Woman
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
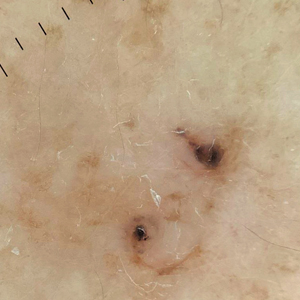
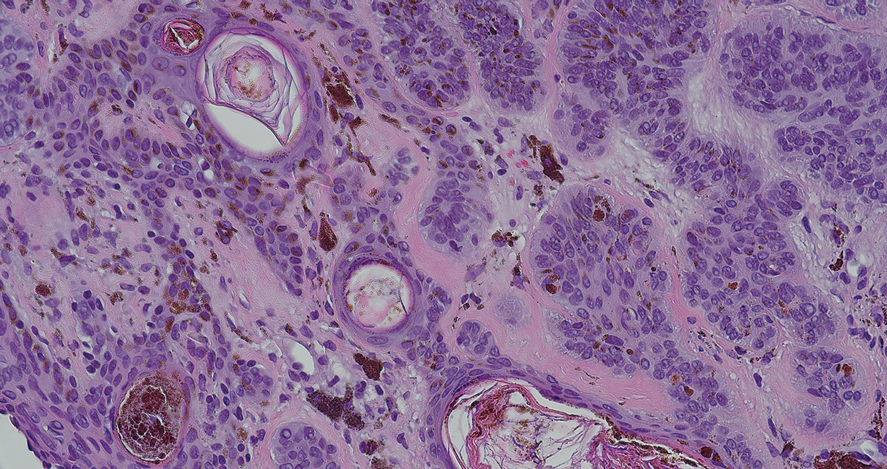
Dermoscopy of our patient’s irregular dark brown papule revealed large blue clustered clods and radial lines converging to a central dot (middle quiz image). Histopathology revealed nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, small horn pseudocysts, and deposits of melanin extending into the dermis (Figure). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of pigmented nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
Nodular BCC represents 60% to 80% of all BCC cases; pigmented BCC represents 6% of BCC cases.1 Basal cell carcinomas frequently manifest as pearly papules with areas of pigment, surface telangiectases, and foci of ulceration. Dermoscopic features include fine arborizing vessels, blue-gray ovoid nests, spoke wheel–like structures, leaflike structures, and focal ulceration.1 Histopathology shows well-defined dermal nodules comprising basaloid epithelial cells with peripheral palisading, mucinous stroma, focal melanin deposits, and surrounding clefting.2 Arborizing vessels correspond to dilated vessels in the dermis.3 Blue-gray ovoid nests are wellcircumscribed ovoid or elongated structures that correspond histologically to well-defined large tumor nests with melanin aggregates invading the dermis. Spoke wheel–like structures are well-circumscribed radial projections connected to a pigmented central axis that correspond histologically to tumor nests near the epidermis and that appear as fingerlike projections with centrally located melanin deposits.3
The differential diagnosis of our patient’s lesion included nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, deep penetrating nevus, and cellular blue nevus. Nodular melanoma is an invasive melanoma that lacks a radial growth phase. Dermoscopically, the more common features are a bluewhite veil, atypical vascular pattern, asymmetric pigmentation, atypical pigment network, and peripheral black globules.4 Histopathology reveals atypical melanocytes and architectural disorder.2 Pigmented nodular BCC also can display dark globules on dermoscopy but typically has smaller and more arborizing blood vessels and does not have a pigmented network. Furthermore, BCC would not have atypical melanocytes on histopathology.4,5
Dermoscopy of lentigo maligna melanoma displays hyperpigmented follicular openings, an annular-granular pattern, pigmented rhomboidal structures, and obliterated hair follicles.6 Histopathology demonstrates epidermal atrophy, increased pigmentation in basal keratinocytes, prominent solar elastosis, and an increased number of melanocytes that extend beyond the epidermis. 7 Pigmented nodular BCC can be distinguished from lentigo maligna melanoma dermoscopically by the presence of arborizing vessels, blue-gray ovoid nests, and lack of a pigment network.
Deep penetrating nevus is a darkly pigmented melanocytic lesion that infiltrates deeply into the reticular dermis.8 Specific dermoscopic features have not been well established; however, a uniformly dark blue or black pattern is common. Histologically, this type of nevus is symmetric and wedge shaped with a broad base extending to the deep dermis and subcutaneous fat.8 Melanocytes do not exhibit atypia or bizarre mitoses. Although pigmented nodular BCC can appear similar to deep penetrating nevus, histologically there will be atypical basaloid epithelial cells in BCC.
Blue nevi clinically appear as a smooth blue-gray lesion with a steel blue ground-glass pattern on dermoscopy. Histopathology shows spindle-shaped melanocytes in the dermis, which distinguishes this lesion from BCC.9
Consider pigmented BCC when a patient presents with a pigmented lesion. Dermoscopy can help appreciate a pigmented BCC by looking for features such as a spoke wheel– like pattern, blue ovoid nests, arborizing blood vessels, and lack of a pigment network. Because pigmented BCC constitutes a small fraction of all BCCs, it is important to be familiar with its presentation and dermoscopic features.
- Heath MS, Bar A. Basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:13-21. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.07.005
- Rastrelli M, Tropea S, Rossi CR, et al. Melanoma: epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. In Vivo. 2014; 28:1005-1012.
- Wozniak-Rito A, Zalaudek I, Rudnicka L. Dermoscopy of basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:241-247. doi:10.1111/ced.13387
- Menzies SW, Moloney FJ, Byth K, et al. Dermoscopic valuation of nodular melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:699-709. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2013.2466
- Pizzichetta MA, Kittler H, Stanganelli I, et al; Italian Melanoma Intergroup. Pigmented nodular melanoma: the predictive value of dermoscopic features using multivariate analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:106-114. doi:10.1111/bjd.13861
- Pralong P, Bathelier E, Dalle S, et al. Dermoscopy of lentigo maligna melanoma: report of 125 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:280-287. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10932.x
- Reed JA, Shea CR. Lentigo maligna: melanoma in situ on chronically sun-damaged skin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:838-841. doi:10.5858/2011-0051-RAIR.1
- Strazzula L, Senna MM, Yasuda M, et al. The deep penetrating nevus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1234-1240. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2014.07.026
- Ferrera G, Argenziano G. Blue nevus. In: Soyer HP, Argenziano G, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Melanocytic Lesions of the Skin. Springer; 2007:78-86.
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Dermoscopy of our patient’s irregular dark brown papule revealed large blue clustered clods and radial lines converging to a central dot (middle quiz image). Histopathology revealed nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, small horn pseudocysts, and deposits of melanin extending into the dermis (Figure). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of pigmented nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
Nodular BCC represents 60% to 80% of all BCC cases; pigmented BCC represents 6% of BCC cases.1 Basal cell carcinomas frequently manifest as pearly papules with areas of pigment, surface telangiectases, and foci of ulceration. Dermoscopic features include fine arborizing vessels, blue-gray ovoid nests, spoke wheel–like structures, leaflike structures, and focal ulceration.1 Histopathology shows well-defined dermal nodules comprising basaloid epithelial cells with peripheral palisading, mucinous stroma, focal melanin deposits, and surrounding clefting.2 Arborizing vessels correspond to dilated vessels in the dermis.3 Blue-gray ovoid nests are wellcircumscribed ovoid or elongated structures that correspond histologically to well-defined large tumor nests with melanin aggregates invading the dermis. Spoke wheel–like structures are well-circumscribed radial projections connected to a pigmented central axis that correspond histologically to tumor nests near the epidermis and that appear as fingerlike projections with centrally located melanin deposits.3
The differential diagnosis of our patient’s lesion included nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, deep penetrating nevus, and cellular blue nevus. Nodular melanoma is an invasive melanoma that lacks a radial growth phase. Dermoscopically, the more common features are a bluewhite veil, atypical vascular pattern, asymmetric pigmentation, atypical pigment network, and peripheral black globules.4 Histopathology reveals atypical melanocytes and architectural disorder.2 Pigmented nodular BCC also can display dark globules on dermoscopy but typically has smaller and more arborizing blood vessels and does not have a pigmented network. Furthermore, BCC would not have atypical melanocytes on histopathology.4,5
Dermoscopy of lentigo maligna melanoma displays hyperpigmented follicular openings, an annular-granular pattern, pigmented rhomboidal structures, and obliterated hair follicles.6 Histopathology demonstrates epidermal atrophy, increased pigmentation in basal keratinocytes, prominent solar elastosis, and an increased number of melanocytes that extend beyond the epidermis. 7 Pigmented nodular BCC can be distinguished from lentigo maligna melanoma dermoscopically by the presence of arborizing vessels, blue-gray ovoid nests, and lack of a pigment network.

Deep penetrating nevus is a darkly pigmented melanocytic lesion that infiltrates deeply into the reticular dermis.8 Specific dermoscopic features have not been well established; however, a uniformly dark blue or black pattern is common. Histologically, this type of nevus is symmetric and wedge shaped with a broad base extending to the deep dermis and subcutaneous fat.8 Melanocytes do not exhibit atypia or bizarre mitoses. Although pigmented nodular BCC can appear similar to deep penetrating nevus, histologically there will be atypical basaloid epithelial cells in BCC.
Blue nevi clinically appear as a smooth blue-gray lesion with a steel blue ground-glass pattern on dermoscopy. Histopathology shows spindle-shaped melanocytes in the dermis, which distinguishes this lesion from BCC.9
Consider pigmented BCC when a patient presents with a pigmented lesion. Dermoscopy can help appreciate a pigmented BCC by looking for features such as a spoke wheel– like pattern, blue ovoid nests, arborizing blood vessels, and lack of a pigment network. Because pigmented BCC constitutes a small fraction of all BCCs, it is important to be familiar with its presentation and dermoscopic features.
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Dermoscopy of our patient’s irregular dark brown papule revealed large blue clustered clods and radial lines converging to a central dot (middle quiz image). Histopathology revealed nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, small horn pseudocysts, and deposits of melanin extending into the dermis (Figure). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of pigmented nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
Nodular BCC represents 60% to 80% of all BCC cases; pigmented BCC represents 6% of BCC cases.1 Basal cell carcinomas frequently manifest as pearly papules with areas of pigment, surface telangiectases, and foci of ulceration. Dermoscopic features include fine arborizing vessels, blue-gray ovoid nests, spoke wheel–like structures, leaflike structures, and focal ulceration.1 Histopathology shows well-defined dermal nodules comprising basaloid epithelial cells with peripheral palisading, mucinous stroma, focal melanin deposits, and surrounding clefting.2 Arborizing vessels correspond to dilated vessels in the dermis.3 Blue-gray ovoid nests are wellcircumscribed ovoid or elongated structures that correspond histologically to well-defined large tumor nests with melanin aggregates invading the dermis. Spoke wheel–like structures are well-circumscribed radial projections connected to a pigmented central axis that correspond histologically to tumor nests near the epidermis and that appear as fingerlike projections with centrally located melanin deposits.3
The differential diagnosis of our patient’s lesion included nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, deep penetrating nevus, and cellular blue nevus. Nodular melanoma is an invasive melanoma that lacks a radial growth phase. Dermoscopically, the more common features are a bluewhite veil, atypical vascular pattern, asymmetric pigmentation, atypical pigment network, and peripheral black globules.4 Histopathology reveals atypical melanocytes and architectural disorder.2 Pigmented nodular BCC also can display dark globules on dermoscopy but typically has smaller and more arborizing blood vessels and does not have a pigmented network. Furthermore, BCC would not have atypical melanocytes on histopathology.4,5
Dermoscopy of lentigo maligna melanoma displays hyperpigmented follicular openings, an annular-granular pattern, pigmented rhomboidal structures, and obliterated hair follicles.6 Histopathology demonstrates epidermal atrophy, increased pigmentation in basal keratinocytes, prominent solar elastosis, and an increased number of melanocytes that extend beyond the epidermis. 7 Pigmented nodular BCC can be distinguished from lentigo maligna melanoma dermoscopically by the presence of arborizing vessels, blue-gray ovoid nests, and lack of a pigment network.

Deep penetrating nevus is a darkly pigmented melanocytic lesion that infiltrates deeply into the reticular dermis.8 Specific dermoscopic features have not been well established; however, a uniformly dark blue or black pattern is common. Histologically, this type of nevus is symmetric and wedge shaped with a broad base extending to the deep dermis and subcutaneous fat.8 Melanocytes do not exhibit atypia or bizarre mitoses. Although pigmented nodular BCC can appear similar to deep penetrating nevus, histologically there will be atypical basaloid epithelial cells in BCC.
Blue nevi clinically appear as a smooth blue-gray lesion with a steel blue ground-glass pattern on dermoscopy. Histopathology shows spindle-shaped melanocytes in the dermis, which distinguishes this lesion from BCC.9
Consider pigmented BCC when a patient presents with a pigmented lesion. Dermoscopy can help appreciate a pigmented BCC by looking for features such as a spoke wheel– like pattern, blue ovoid nests, arborizing blood vessels, and lack of a pigment network. Because pigmented BCC constitutes a small fraction of all BCCs, it is important to be familiar with its presentation and dermoscopic features.
- Heath MS, Bar A. Basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:13-21. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.07.005
- Rastrelli M, Tropea S, Rossi CR, et al. Melanoma: epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. In Vivo. 2014; 28:1005-1012.
- Wozniak-Rito A, Zalaudek I, Rudnicka L. Dermoscopy of basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:241-247. doi:10.1111/ced.13387
- Menzies SW, Moloney FJ, Byth K, et al. Dermoscopic valuation of nodular melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:699-709. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2013.2466
- Pizzichetta MA, Kittler H, Stanganelli I, et al; Italian Melanoma Intergroup. Pigmented nodular melanoma: the predictive value of dermoscopic features using multivariate analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:106-114. doi:10.1111/bjd.13861
- Pralong P, Bathelier E, Dalle S, et al. Dermoscopy of lentigo maligna melanoma: report of 125 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:280-287. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10932.x
- Reed JA, Shea CR. Lentigo maligna: melanoma in situ on chronically sun-damaged skin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:838-841. doi:10.5858/2011-0051-RAIR.1
- Strazzula L, Senna MM, Yasuda M, et al. The deep penetrating nevus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1234-1240. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2014.07.026
- Ferrera G, Argenziano G. Blue nevus. In: Soyer HP, Argenziano G, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Melanocytic Lesions of the Skin. Springer; 2007:78-86.
- Heath MS, Bar A. Basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:13-21. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.07.005
- Rastrelli M, Tropea S, Rossi CR, et al. Melanoma: epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. In Vivo. 2014; 28:1005-1012.
- Wozniak-Rito A, Zalaudek I, Rudnicka L. Dermoscopy of basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:241-247. doi:10.1111/ced.13387
- Menzies SW, Moloney FJ, Byth K, et al. Dermoscopic valuation of nodular melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:699-709. doi:10.1001 /jamadermatol.2013.2466
- Pizzichetta MA, Kittler H, Stanganelli I, et al; Italian Melanoma Intergroup. Pigmented nodular melanoma: the predictive value of dermoscopic features using multivariate analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:106-114. doi:10.1111/bjd.13861
- Pralong P, Bathelier E, Dalle S, et al. Dermoscopy of lentigo maligna melanoma: report of 125 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:280-287. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10932.x
- Reed JA, Shea CR. Lentigo maligna: melanoma in situ on chronically sun-damaged skin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:838-841. doi:10.5858/2011-0051-RAIR.1
- Strazzula L, Senna MM, Yasuda M, et al. The deep penetrating nevus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1234-1240. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2014.07.026
- Ferrera G, Argenziano G. Blue nevus. In: Soyer HP, Argenziano G, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Melanocytic Lesions of the Skin. Springer; 2007:78-86.
A 92-year-old woman presented to dermatology as a new patient for a full-body skin examination. She had a history of sarcoidosis and a liposarcoma that had been excised more than 20 years prior. She had no history of skin cancer; however, her granddaughter recently was diagnosed with melanoma. Physical examination revealed a 5-mm, irregular, dark brown papule on the left shoulder (top) that was evaluated by dermoscopy (middle). A tangential biopsy was performed for histopathologic analysis (bottom).
Trifluridine/tipiracil Plus Bevacizumab: A Game Changer in Late-Stage Refractory mCRC
An elderly gentleman was truly suffering, so his doctor decided to try something new.
“He’d had a number of cumulative side effects after almost two years of IV chemotherapy for his metastatic colon cancer,” said Anuj Patel, MD, a senior physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, recalling his patient. “When we switched him to combination treatment with trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab, he constantly remarked on how well he now felt. He described no side effects from this new regimen.”
Trifluridine/tipiracil (Lonsurf) had been used to treat advanced gastric cancer, while bevacizumab had been therapeutic for a wider range of diseases, including cervical, brain, liver, kidney, gynecological and lung cancers. Used together for treating refractory mCRC, well-known initial findings about their effectiveness have been proven true over time.
“Patients taking both drugs can experience, on average, a life extension of three months,” said Richard M. Goldberg, MD, professor emeritus of the West Virginia University Cancer Institute and director of Fight Colorectal Cancer.
The History of the Combined Therapy’s Approval
The FDA originally approved trifluridine/tipiracil in September 2015 for use in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients eligible to take it had to have been treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) biological therapy, and—if RAS wild-type—an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy, according to data published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The FDA’s August 2023 approval of the trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab combination regimen is for patients meeting the same eligibility requirements.
Another drug, regorafenib, had already been approved by the FDA in September 2012 to treat mCRC. The drug has a wide range of potential side effects, however, including complications relating to the limbs.
“One of my patients tried regorafenib as his initial third- line treatment,” Dr. Goldberg said. “I checked in on him at his farm, and he was sitting in the barn near his tractor.
He had such severe hand-foot syndrome that he could barely walk.”
Trifluridine/tipiracil alone proved to be very helpful in this case. “We switched him to it, and he tolerated it well,” Dr. Goldberg continued. “He got his fields plowed and was on it for months before he passed away. We both felt it kept him going longer.”
A new research review confirms the regimen’s success, determining that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab was associated with improved outcomes compared to therapy solely with trifluridine/tipiracil.
A True Practice Changer
Now that the regimen has been on the market for more than half a year, there are longer-term data available.
Patients on average live within the same timeframe as the patients in the SUNLIGHT study, and many feel physically better on the therapy. “The combination has very quickly shifted the standard of care,” Dr. Goldberg said.
The regimen can also provide significant psychological benefits to patients.
“As patients can maintain good performance status for longer with the combination, it increases the perception of quality of life,” said Jacobo Hincapie-Echeverri, MD, a GI and geriatric oncologist at Orlando Health Cancer Institute in Orlando, Florida.
The regimen is unique too, in that it can help doctors plan additional treatment strategies.
“This current approval, for the combination of trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab, is practice-changing in that it helps clarify the sequence for later treatments for patients with mCRC,” said Dr. Patel, who is also clinical director of the Center for Esophageal and Gastric Cancer and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “Previously, it had been difficult to decide between trifluridine/tipiracil and regorafenib in this setting.”
The fact that the regimen has been shown to give time and improved quality of life to patients in ways regorafenib does not is clarifying. “Now, with the improved outcomes seen, I do think that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab is the better option for most mCRC patients after IV chemotherapies,” Dr. Patel added.
When it comes to his specific experience with prescribing the regimen for his patients, Dr. Patel reported that it’s easier on his patients than other therapies.
“I find that it is generally well tolerated,” he elaborated. “As an oral agent, it is also usually somewhat easier to take (than other delivery methods of medication). These factors are critical for patients who have likely already had at least 2 or 3 prior lines of chemotherapy. I have had many patients with mCRC who, after disease progression on prior IV chemotherapy regimens, have had periods of meaningful disease control – often with fewer and manageable side effects.”
Dr. Goldberg mentioned another benefit.
“The nice thing about the combination of trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab is that in terms of toxicity, there’s very little difference compared to the toxicity of trifluridine/tipiracil used alone.”
Are There Downsides to the Regimen?
The pros are obvious, but the regimen has some cons as well. Medically, patients should have a platelet count over 75,000/mm3 and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) over 1,500/mm3 prior to the start of each cycle, and their liver and renal function should be monitored.
Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer must be also carefully monitored for hematologic adverse events (AEs) , including chemotherapy-associated neutropenia. Biweekly treatments may reduce the risk of AEs as a whole, however, according to research.
The regimen is also expensive – an approximate cost of $8,191 for a 28-day supply. According to a new study, patients managing both AE expenses along with the cost of trifluridine/tipiracil-bevacizumab face a monthly bill of about $17,179.
Some very good news, though: 100% of Medicare drug plans cover trifluridine/tipiracil, with an average copay of $57-$292. Bevacizumab is also covered by Medicare, with a copay as low as $0-$25.
Private insurers do cover the drugs, depending on a patient’s specific plan. However, if a patient’s claim is denied, financial assistance for trifluridine/tipiracil through the drug’s manufacturers may be available for some patients, reducing prescriptions to a zero cost in some cases. Bevacizumab can be made available to patients who may not have health insurance at all, too. Patients can use a financial assistance tool through the drug’s manufacturer to receive up to $25,000 in yearly copay assistance.
What Does the Latest Research on the Regimen Indicate?
In May 2024, two abstracts were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) that explored expanded possible use of trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab as a treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer.
The first abstract studied trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab as upfront treatment for mCRC, adding capecitabine to the regimen.
“It’s a phase 1 study looking at dose findings for the three-drug combination, where the active drug is a chemotherapy agent classified as a fluoropyrimidine ... I would characterize this as a study combining two [fluoropyrimidines] with a single targeted therapy,” Dr. Goldberg said.
“Combining two fluoropyrimidines is an unusual approach, because they tend to have overlapping side effects, and the potential is there for either innate drug resistance to the class of drugs or that the combination of two agents that work by a similar mechanism of action could hasten the development of acquired drug resistance. There is apparently a signal that combining the two chemotherapy agents enhances each other’s activity in cell culture and animal models,” he added.
Ultimately, Dr. Goldberg said he thinks more evidence is needed to prove the regimen’s effectiveness.
“This is a very early study and really provides no information about its potential given that no response data was presented,” he added. “While this is an interesting idea, it is unclear if it will pan out until we see the data on the Phase II study in progress.”
The other abstract looked at the impact of colorectal liver metastases in patients with mCRC who in phase 3 of the SUNLIGHT trial received trifluridine/tipiracil with or without bevacizumab.
“There is not much that is novel here,” Dr. Goldberg said. “The retrospective analysis shows that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab is better than trifluridine/tipiracil alone in the subset of patients with liver metastases, as it was shown to be in the entire patient population. While this is reassuring, it’s not unexpected, especially since the vast majority of people enrolled in the SUNLIGHT trial had liver metastases.”
The Bottom Line
In the future, the potential exists for trifluridine/tipiracil combined with bevacizumab to work in first-line and second-line patients.
“Seventy percent of colorectal cancer patients reach second line treatment right now, but only 30% reach third line treatment — either they become too sick to continue, or choose not to,” Dr. Goldberg said. “The hope is that using these drugs earlier can help more patients reach and prolong treatment.”
It’s also possible that the regimen can be applied in new ways.
“Further research combining trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab with other targeted therapies could yield additional advances for refractory mCRC patients,” Dr. Hincapie-Echeverri said. “The survival benefit of this therapy reinforces the importance of continuing to develop new therapies to improve outcomes in the refractory mCRC setting.”
Dr. Patel’s patient felt lucky to simply live a longer life.
Because of the regimen, “his cancer remained stable for approximately 8 months. Upon its progression, he chose not to pursue any further chemotherapy. He instead expressed his gratitude at having been able to feel more like himself for nearly a year.”
Dr. Patel received research funding in 2017 from Taiho, which manufactures trifluridine/tipiracil. He receives no current funding from Taiho and has no additional conflicts of interest. Dr. Goldberg helped represent Taiho in a patent law dispute regarding Lonsurf for which he was paid, but he is no longer paid by the company. Dr. Hincapie-Echeverri is a speaker for Astellas Pharma, which does not manufacture trifluridine/tipiracil or bevacizumab, and he has no additional conflicts of interest.
An elderly gentleman was truly suffering, so his doctor decided to try something new.
“He’d had a number of cumulative side effects after almost two years of IV chemotherapy for his metastatic colon cancer,” said Anuj Patel, MD, a senior physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, recalling his patient. “When we switched him to combination treatment with trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab, he constantly remarked on how well he now felt. He described no side effects from this new regimen.”
Trifluridine/tipiracil (Lonsurf) had been used to treat advanced gastric cancer, while bevacizumab had been therapeutic for a wider range of diseases, including cervical, brain, liver, kidney, gynecological and lung cancers. Used together for treating refractory mCRC, well-known initial findings about their effectiveness have been proven true over time.
“Patients taking both drugs can experience, on average, a life extension of three months,” said Richard M. Goldberg, MD, professor emeritus of the West Virginia University Cancer Institute and director of Fight Colorectal Cancer.
The History of the Combined Therapy’s Approval
The FDA originally approved trifluridine/tipiracil in September 2015 for use in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients eligible to take it had to have been treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) biological therapy, and—if RAS wild-type—an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy, according to data published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The FDA’s August 2023 approval of the trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab combination regimen is for patients meeting the same eligibility requirements.
Another drug, regorafenib, had already been approved by the FDA in September 2012 to treat mCRC. The drug has a wide range of potential side effects, however, including complications relating to the limbs.
“One of my patients tried regorafenib as his initial third- line treatment,” Dr. Goldberg said. “I checked in on him at his farm, and he was sitting in the barn near his tractor.
He had such severe hand-foot syndrome that he could barely walk.”
Trifluridine/tipiracil alone proved to be very helpful in this case. “We switched him to it, and he tolerated it well,” Dr. Goldberg continued. “He got his fields plowed and was on it for months before he passed away. We both felt it kept him going longer.”
A new research review confirms the regimen’s success, determining that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab was associated with improved outcomes compared to therapy solely with trifluridine/tipiracil.
A True Practice Changer
Now that the regimen has been on the market for more than half a year, there are longer-term data available.
Patients on average live within the same timeframe as the patients in the SUNLIGHT study, and many feel physically better on the therapy. “The combination has very quickly shifted the standard of care,” Dr. Goldberg said.
The regimen can also provide significant psychological benefits to patients.
“As patients can maintain good performance status for longer with the combination, it increases the perception of quality of life,” said Jacobo Hincapie-Echeverri, MD, a GI and geriatric oncologist at Orlando Health Cancer Institute in Orlando, Florida.
The regimen is unique too, in that it can help doctors plan additional treatment strategies.
“This current approval, for the combination of trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab, is practice-changing in that it helps clarify the sequence for later treatments for patients with mCRC,” said Dr. Patel, who is also clinical director of the Center for Esophageal and Gastric Cancer and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “Previously, it had been difficult to decide between trifluridine/tipiracil and regorafenib in this setting.”
The fact that the regimen has been shown to give time and improved quality of life to patients in ways regorafenib does not is clarifying. “Now, with the improved outcomes seen, I do think that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab is the better option for most mCRC patients after IV chemotherapies,” Dr. Patel added.
When it comes to his specific experience with prescribing the regimen for his patients, Dr. Patel reported that it’s easier on his patients than other therapies.
“I find that it is generally well tolerated,” he elaborated. “As an oral agent, it is also usually somewhat easier to take (than other delivery methods of medication). These factors are critical for patients who have likely already had at least 2 or 3 prior lines of chemotherapy. I have had many patients with mCRC who, after disease progression on prior IV chemotherapy regimens, have had periods of meaningful disease control – often with fewer and manageable side effects.”
Dr. Goldberg mentioned another benefit.
“The nice thing about the combination of trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab is that in terms of toxicity, there’s very little difference compared to the toxicity of trifluridine/tipiracil used alone.”
Are There Downsides to the Regimen?
The pros are obvious, but the regimen has some cons as well. Medically, patients should have a platelet count over 75,000/mm3 and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) over 1,500/mm3 prior to the start of each cycle, and their liver and renal function should be monitored.
Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer must be also carefully monitored for hematologic adverse events (AEs) , including chemotherapy-associated neutropenia. Biweekly treatments may reduce the risk of AEs as a whole, however, according to research.
The regimen is also expensive – an approximate cost of $8,191 for a 28-day supply. According to a new study, patients managing both AE expenses along with the cost of trifluridine/tipiracil-bevacizumab face a monthly bill of about $17,179.
Some very good news, though: 100% of Medicare drug plans cover trifluridine/tipiracil, with an average copay of $57-$292. Bevacizumab is also covered by Medicare, with a copay as low as $0-$25.
Private insurers do cover the drugs, depending on a patient’s specific plan. However, if a patient’s claim is denied, financial assistance for trifluridine/tipiracil through the drug’s manufacturers may be available for some patients, reducing prescriptions to a zero cost in some cases. Bevacizumab can be made available to patients who may not have health insurance at all, too. Patients can use a financial assistance tool through the drug’s manufacturer to receive up to $25,000 in yearly copay assistance.
What Does the Latest Research on the Regimen Indicate?
In May 2024, two abstracts were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) that explored expanded possible use of trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab as a treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer.
The first abstract studied trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab as upfront treatment for mCRC, adding capecitabine to the regimen.
“It’s a phase 1 study looking at dose findings for the three-drug combination, where the active drug is a chemotherapy agent classified as a fluoropyrimidine ... I would characterize this as a study combining two [fluoropyrimidines] with a single targeted therapy,” Dr. Goldberg said.
“Combining two fluoropyrimidines is an unusual approach, because they tend to have overlapping side effects, and the potential is there for either innate drug resistance to the class of drugs or that the combination of two agents that work by a similar mechanism of action could hasten the development of acquired drug resistance. There is apparently a signal that combining the two chemotherapy agents enhances each other’s activity in cell culture and animal models,” he added.
Ultimately, Dr. Goldberg said he thinks more evidence is needed to prove the regimen’s effectiveness.
“This is a very early study and really provides no information about its potential given that no response data was presented,” he added. “While this is an interesting idea, it is unclear if it will pan out until we see the data on the Phase II study in progress.”
The other abstract looked at the impact of colorectal liver metastases in patients with mCRC who in phase 3 of the SUNLIGHT trial received trifluridine/tipiracil with or without bevacizumab.
“There is not much that is novel here,” Dr. Goldberg said. “The retrospective analysis shows that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab is better than trifluridine/tipiracil alone in the subset of patients with liver metastases, as it was shown to be in the entire patient population. While this is reassuring, it’s not unexpected, especially since the vast majority of people enrolled in the SUNLIGHT trial had liver metastases.”
The Bottom Line
In the future, the potential exists for trifluridine/tipiracil combined with bevacizumab to work in first-line and second-line patients.
“Seventy percent of colorectal cancer patients reach second line treatment right now, but only 30% reach third line treatment — either they become too sick to continue, or choose not to,” Dr. Goldberg said. “The hope is that using these drugs earlier can help more patients reach and prolong treatment.”
It’s also possible that the regimen can be applied in new ways.
“Further research combining trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab with other targeted therapies could yield additional advances for refractory mCRC patients,” Dr. Hincapie-Echeverri said. “The survival benefit of this therapy reinforces the importance of continuing to develop new therapies to improve outcomes in the refractory mCRC setting.”
Dr. Patel’s patient felt lucky to simply live a longer life.
Because of the regimen, “his cancer remained stable for approximately 8 months. Upon its progression, he chose not to pursue any further chemotherapy. He instead expressed his gratitude at having been able to feel more like himself for nearly a year.”
Dr. Patel received research funding in 2017 from Taiho, which manufactures trifluridine/tipiracil. He receives no current funding from Taiho and has no additional conflicts of interest. Dr. Goldberg helped represent Taiho in a patent law dispute regarding Lonsurf for which he was paid, but he is no longer paid by the company. Dr. Hincapie-Echeverri is a speaker for Astellas Pharma, which does not manufacture trifluridine/tipiracil or bevacizumab, and he has no additional conflicts of interest.
An elderly gentleman was truly suffering, so his doctor decided to try something new.
“He’d had a number of cumulative side effects after almost two years of IV chemotherapy for his metastatic colon cancer,” said Anuj Patel, MD, a senior physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, recalling his patient. “When we switched him to combination treatment with trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab, he constantly remarked on how well he now felt. He described no side effects from this new regimen.”
Trifluridine/tipiracil (Lonsurf) had been used to treat advanced gastric cancer, while bevacizumab had been therapeutic for a wider range of diseases, including cervical, brain, liver, kidney, gynecological and lung cancers. Used together for treating refractory mCRC, well-known initial findings about their effectiveness have been proven true over time.
“Patients taking both drugs can experience, on average, a life extension of three months,” said Richard M. Goldberg, MD, professor emeritus of the West Virginia University Cancer Institute and director of Fight Colorectal Cancer.
The History of the Combined Therapy’s Approval
The FDA originally approved trifluridine/tipiracil in September 2015 for use in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients eligible to take it had to have been treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) biological therapy, and—if RAS wild-type—an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy, according to data published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The FDA’s August 2023 approval of the trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab combination regimen is for patients meeting the same eligibility requirements.
Another drug, regorafenib, had already been approved by the FDA in September 2012 to treat mCRC. The drug has a wide range of potential side effects, however, including complications relating to the limbs.
“One of my patients tried regorafenib as his initial third- line treatment,” Dr. Goldberg said. “I checked in on him at his farm, and he was sitting in the barn near his tractor.
He had such severe hand-foot syndrome that he could barely walk.”
Trifluridine/tipiracil alone proved to be very helpful in this case. “We switched him to it, and he tolerated it well,” Dr. Goldberg continued. “He got his fields plowed and was on it for months before he passed away. We both felt it kept him going longer.”
A new research review confirms the regimen’s success, determining that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab was associated with improved outcomes compared to therapy solely with trifluridine/tipiracil.
A True Practice Changer
Now that the regimen has been on the market for more than half a year, there are longer-term data available.
Patients on average live within the same timeframe as the patients in the SUNLIGHT study, and many feel physically better on the therapy. “The combination has very quickly shifted the standard of care,” Dr. Goldberg said.
The regimen can also provide significant psychological benefits to patients.
“As patients can maintain good performance status for longer with the combination, it increases the perception of quality of life,” said Jacobo Hincapie-Echeverri, MD, a GI and geriatric oncologist at Orlando Health Cancer Institute in Orlando, Florida.
The regimen is unique too, in that it can help doctors plan additional treatment strategies.
“This current approval, for the combination of trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab, is practice-changing in that it helps clarify the sequence for later treatments for patients with mCRC,” said Dr. Patel, who is also clinical director of the Center for Esophageal and Gastric Cancer and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “Previously, it had been difficult to decide between trifluridine/tipiracil and regorafenib in this setting.”
The fact that the regimen has been shown to give time and improved quality of life to patients in ways regorafenib does not is clarifying. “Now, with the improved outcomes seen, I do think that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab is the better option for most mCRC patients after IV chemotherapies,” Dr. Patel added.
When it comes to his specific experience with prescribing the regimen for his patients, Dr. Patel reported that it’s easier on his patients than other therapies.
“I find that it is generally well tolerated,” he elaborated. “As an oral agent, it is also usually somewhat easier to take (than other delivery methods of medication). These factors are critical for patients who have likely already had at least 2 or 3 prior lines of chemotherapy. I have had many patients with mCRC who, after disease progression on prior IV chemotherapy regimens, have had periods of meaningful disease control – often with fewer and manageable side effects.”
Dr. Goldberg mentioned another benefit.
“The nice thing about the combination of trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab is that in terms of toxicity, there’s very little difference compared to the toxicity of trifluridine/tipiracil used alone.”
Are There Downsides to the Regimen?
The pros are obvious, but the regimen has some cons as well. Medically, patients should have a platelet count over 75,000/mm3 and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) over 1,500/mm3 prior to the start of each cycle, and their liver and renal function should be monitored.
Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer must be also carefully monitored for hematologic adverse events (AEs) , including chemotherapy-associated neutropenia. Biweekly treatments may reduce the risk of AEs as a whole, however, according to research.
The regimen is also expensive – an approximate cost of $8,191 for a 28-day supply. According to a new study, patients managing both AE expenses along with the cost of trifluridine/tipiracil-bevacizumab face a monthly bill of about $17,179.
Some very good news, though: 100% of Medicare drug plans cover trifluridine/tipiracil, with an average copay of $57-$292. Bevacizumab is also covered by Medicare, with a copay as low as $0-$25.
Private insurers do cover the drugs, depending on a patient’s specific plan. However, if a patient’s claim is denied, financial assistance for trifluridine/tipiracil through the drug’s manufacturers may be available for some patients, reducing prescriptions to a zero cost in some cases. Bevacizumab can be made available to patients who may not have health insurance at all, too. Patients can use a financial assistance tool through the drug’s manufacturer to receive up to $25,000 in yearly copay assistance.
What Does the Latest Research on the Regimen Indicate?
In May 2024, two abstracts were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) that explored expanded possible use of trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab as a treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer.
The first abstract studied trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab as upfront treatment for mCRC, adding capecitabine to the regimen.
“It’s a phase 1 study looking at dose findings for the three-drug combination, where the active drug is a chemotherapy agent classified as a fluoropyrimidine ... I would characterize this as a study combining two [fluoropyrimidines] with a single targeted therapy,” Dr. Goldberg said.
“Combining two fluoropyrimidines is an unusual approach, because they tend to have overlapping side effects, and the potential is there for either innate drug resistance to the class of drugs or that the combination of two agents that work by a similar mechanism of action could hasten the development of acquired drug resistance. There is apparently a signal that combining the two chemotherapy agents enhances each other’s activity in cell culture and animal models,” he added.
Ultimately, Dr. Goldberg said he thinks more evidence is needed to prove the regimen’s effectiveness.
“This is a very early study and really provides no information about its potential given that no response data was presented,” he added. “While this is an interesting idea, it is unclear if it will pan out until we see the data on the Phase II study in progress.”
The other abstract looked at the impact of colorectal liver metastases in patients with mCRC who in phase 3 of the SUNLIGHT trial received trifluridine/tipiracil with or without bevacizumab.
“There is not much that is novel here,” Dr. Goldberg said. “The retrospective analysis shows that trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab is better than trifluridine/tipiracil alone in the subset of patients with liver metastases, as it was shown to be in the entire patient population. While this is reassuring, it’s not unexpected, especially since the vast majority of people enrolled in the SUNLIGHT trial had liver metastases.”
The Bottom Line
In the future, the potential exists for trifluridine/tipiracil combined with bevacizumab to work in first-line and second-line patients.
“Seventy percent of colorectal cancer patients reach second line treatment right now, but only 30% reach third line treatment — either they become too sick to continue, or choose not to,” Dr. Goldberg said. “The hope is that using these drugs earlier can help more patients reach and prolong treatment.”
It’s also possible that the regimen can be applied in new ways.
“Further research combining trifluridine/tipiracil and bevacizumab with other targeted therapies could yield additional advances for refractory mCRC patients,” Dr. Hincapie-Echeverri said. “The survival benefit of this therapy reinforces the importance of continuing to develop new therapies to improve outcomes in the refractory mCRC setting.”
Dr. Patel’s patient felt lucky to simply live a longer life.
Because of the regimen, “his cancer remained stable for approximately 8 months. Upon its progression, he chose not to pursue any further chemotherapy. He instead expressed his gratitude at having been able to feel more like himself for nearly a year.”
Dr. Patel received research funding in 2017 from Taiho, which manufactures trifluridine/tipiracil. He receives no current funding from Taiho and has no additional conflicts of interest. Dr. Goldberg helped represent Taiho in a patent law dispute regarding Lonsurf for which he was paid, but he is no longer paid by the company. Dr. Hincapie-Echeverri is a speaker for Astellas Pharma, which does not manufacture trifluridine/tipiracil or bevacizumab, and he has no additional conflicts of interest.
Urticaria Linked to Higher Cancer Risk, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should South Park: The End of Obesity Be Required Viewing in Medical School?
Yes, there’s still much to find offensive, but South Park: The End of Obesity, in just 51 minutes, does more to explain some of obesity’s realities, its pharmacotherapy, and weight bias than the mainstream media has done perhaps ever.
The mini-movie follows the plight of Eric Cartman, the fictional South Parkian child with severe obesity.
South Park got everything right. The movie starts in a medical center where discussions with Cartman, his mother, and his doctor make it clear that obesity isn’t something that Cartman chose and is perhaps the most distressing aspect of his life. This certainly echoes study findings which report that quality-of-life scores in children with severe obesity are lower than those of children with newly diagnosed on-treatment cancers. As to how obesity erodes a child’s quality of life, no doubt part of its impact stems from obesity being a top source of schoolyard bullying, which is reflected by Cartman as he imagines his life without it.
Cartman’s mother explains that of course they’ve tried diet and exercise, but that intentional behavior change alone hasn’t been sufficient to sustainably move the scale’s needle — a truth for the vast majority of people with obesity. But here, unlike in many actual doctors’ offices, Cartman’s doctor doesn’t spend time doubting or cajoling; instead, he does his job — which is to inform his patient, without judgment, about a pharmaceutical option that has proved to be beneficial. He accurately describes these medications as ushering in “a whole new era of medicine, a miracle really” that can “help people lose vast amounts of weight.”
The kicker, though, comes next. The doctor explains that insurance companies cover the medications only for patients with diabetes, “so if you can’t afford them, you’re just kind of out of luck.” This is changing somewhat now, at least here in Canada, where two of our main private insurers have changed their base coverages to make antiobesity medications something employers need to opt out of rather than opt into, but certainly they’re not covered by US Medicare for weight management, nor by our version of the same here in Canada.
But even for those who have coverage, there are hoops to jump through, which is highlighted by the incredible efforts made by Cartman and his friends to get his insurance plan to cover the medications. Thwarted at every turn, despite the undeniable benefits of these medications to health and quality of life, they are forced to turn to compounding — a phenomenon certainly pervasive here in North America whereby compounding pharmacies claim to be able to provide glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs with comparable efficacy at a fraction of the price, but without the same rigor of proof of purity or efficacy.
Also covered by South Park is that the GLP-1 analog supply is impacted by use by people who don’t meet approved medical criteria and are using the medications for aesthetic purposes. This speaks to the incredible societal pressure to be thin and to the comfort of some physicians to inappropriately prescribe these medications. This is covered by the subplot of South Park’s weed farmer, Randy, who in turn delivers an important insight into how it feels to use a GLP-1 analog: “I think there’s something wrong with these drugs ... I feel satisfied. With any drugs I want to do more and more, but with these drugs I feel like I want things less. With these drugs you don’t really crave anything.” The sentiment is echoed by Cartman, who exclaims, “I think I’m full. I’ve never known that feeling before in my life, but I’m full.”
It’s remarkable that South Park, a show built on serving up politically incorrect offense, covers obesity and its treatment with more accuracy, nuance, and compassion than does society as a whole. The show notes that obesity is a biological condition (it is), that when it comes to health (in America) “you have to have some f-ing willpower.” But where they explicitly mean having willpower in terms of filing and pursing insurance claims (you do), explains that drug companies are making antiobesity medications more expensive in America than anywhere else in the world (they are), and finally delivers this quote, which, while missing the biological basis of behavior and hunger with respect to obesity, certainly sums up why blame has no place in the discourse:
“We have sugar companies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance companies all just trying to figure out how to make money off our health. It isn’t fair to put the blame on anyone for their weight.”
No, it’s not.
This movie should be required viewing in medical schools.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, department of family medicine, University of Ottawa, and medical director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yes, there’s still much to find offensive, but South Park: The End of Obesity, in just 51 minutes, does more to explain some of obesity’s realities, its pharmacotherapy, and weight bias than the mainstream media has done perhaps ever.
The mini-movie follows the plight of Eric Cartman, the fictional South Parkian child with severe obesity.
South Park got everything right. The movie starts in a medical center where discussions with Cartman, his mother, and his doctor make it clear that obesity isn’t something that Cartman chose and is perhaps the most distressing aspect of his life. This certainly echoes study findings which report that quality-of-life scores in children with severe obesity are lower than those of children with newly diagnosed on-treatment cancers. As to how obesity erodes a child’s quality of life, no doubt part of its impact stems from obesity being a top source of schoolyard bullying, which is reflected by Cartman as he imagines his life without it.
Cartman’s mother explains that of course they’ve tried diet and exercise, but that intentional behavior change alone hasn’t been sufficient to sustainably move the scale’s needle — a truth for the vast majority of people with obesity. But here, unlike in many actual doctors’ offices, Cartman’s doctor doesn’t spend time doubting or cajoling; instead, he does his job — which is to inform his patient, without judgment, about a pharmaceutical option that has proved to be beneficial. He accurately describes these medications as ushering in “a whole new era of medicine, a miracle really” that can “help people lose vast amounts of weight.”
The kicker, though, comes next. The doctor explains that insurance companies cover the medications only for patients with diabetes, “so if you can’t afford them, you’re just kind of out of luck.” This is changing somewhat now, at least here in Canada, where two of our main private insurers have changed their base coverages to make antiobesity medications something employers need to opt out of rather than opt into, but certainly they’re not covered by US Medicare for weight management, nor by our version of the same here in Canada.
But even for those who have coverage, there are hoops to jump through, which is highlighted by the incredible efforts made by Cartman and his friends to get his insurance plan to cover the medications. Thwarted at every turn, despite the undeniable benefits of these medications to health and quality of life, they are forced to turn to compounding — a phenomenon certainly pervasive here in North America whereby compounding pharmacies claim to be able to provide glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs with comparable efficacy at a fraction of the price, but without the same rigor of proof of purity or efficacy.
Also covered by South Park is that the GLP-1 analog supply is impacted by use by people who don’t meet approved medical criteria and are using the medications for aesthetic purposes. This speaks to the incredible societal pressure to be thin and to the comfort of some physicians to inappropriately prescribe these medications. This is covered by the subplot of South Park’s weed farmer, Randy, who in turn delivers an important insight into how it feels to use a GLP-1 analog: “I think there’s something wrong with these drugs ... I feel satisfied. With any drugs I want to do more and more, but with these drugs I feel like I want things less. With these drugs you don’t really crave anything.” The sentiment is echoed by Cartman, who exclaims, “I think I’m full. I’ve never known that feeling before in my life, but I’m full.”
It’s remarkable that South Park, a show built on serving up politically incorrect offense, covers obesity and its treatment with more accuracy, nuance, and compassion than does society as a whole. The show notes that obesity is a biological condition (it is), that when it comes to health (in America) “you have to have some f-ing willpower.” But where they explicitly mean having willpower in terms of filing and pursing insurance claims (you do), explains that drug companies are making antiobesity medications more expensive in America than anywhere else in the world (they are), and finally delivers this quote, which, while missing the biological basis of behavior and hunger with respect to obesity, certainly sums up why blame has no place in the discourse:
“We have sugar companies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance companies all just trying to figure out how to make money off our health. It isn’t fair to put the blame on anyone for their weight.”
No, it’s not.
This movie should be required viewing in medical schools.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, department of family medicine, University of Ottawa, and medical director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yes, there’s still much to find offensive, but South Park: The End of Obesity, in just 51 minutes, does more to explain some of obesity’s realities, its pharmacotherapy, and weight bias than the mainstream media has done perhaps ever.
The mini-movie follows the plight of Eric Cartman, the fictional South Parkian child with severe obesity.
South Park got everything right. The movie starts in a medical center where discussions with Cartman, his mother, and his doctor make it clear that obesity isn’t something that Cartman chose and is perhaps the most distressing aspect of his life. This certainly echoes study findings which report that quality-of-life scores in children with severe obesity are lower than those of children with newly diagnosed on-treatment cancers. As to how obesity erodes a child’s quality of life, no doubt part of its impact stems from obesity being a top source of schoolyard bullying, which is reflected by Cartman as he imagines his life without it.
Cartman’s mother explains that of course they’ve tried diet and exercise, but that intentional behavior change alone hasn’t been sufficient to sustainably move the scale’s needle — a truth for the vast majority of people with obesity. But here, unlike in many actual doctors’ offices, Cartman’s doctor doesn’t spend time doubting or cajoling; instead, he does his job — which is to inform his patient, without judgment, about a pharmaceutical option that has proved to be beneficial. He accurately describes these medications as ushering in “a whole new era of medicine, a miracle really” that can “help people lose vast amounts of weight.”
The kicker, though, comes next. The doctor explains that insurance companies cover the medications only for patients with diabetes, “so if you can’t afford them, you’re just kind of out of luck.” This is changing somewhat now, at least here in Canada, where two of our main private insurers have changed their base coverages to make antiobesity medications something employers need to opt out of rather than opt into, but certainly they’re not covered by US Medicare for weight management, nor by our version of the same here in Canada.
But even for those who have coverage, there are hoops to jump through, which is highlighted by the incredible efforts made by Cartman and his friends to get his insurance plan to cover the medications. Thwarted at every turn, despite the undeniable benefits of these medications to health and quality of life, they are forced to turn to compounding — a phenomenon certainly pervasive here in North America whereby compounding pharmacies claim to be able to provide glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs with comparable efficacy at a fraction of the price, but without the same rigor of proof of purity or efficacy.
Also covered by South Park is that the GLP-1 analog supply is impacted by use by people who don’t meet approved medical criteria and are using the medications for aesthetic purposes. This speaks to the incredible societal pressure to be thin and to the comfort of some physicians to inappropriately prescribe these medications. This is covered by the subplot of South Park’s weed farmer, Randy, who in turn delivers an important insight into how it feels to use a GLP-1 analog: “I think there’s something wrong with these drugs ... I feel satisfied. With any drugs I want to do more and more, but with these drugs I feel like I want things less. With these drugs you don’t really crave anything.” The sentiment is echoed by Cartman, who exclaims, “I think I’m full. I’ve never known that feeling before in my life, but I’m full.”
It’s remarkable that South Park, a show built on serving up politically incorrect offense, covers obesity and its treatment with more accuracy, nuance, and compassion than does society as a whole. The show notes that obesity is a biological condition (it is), that when it comes to health (in America) “you have to have some f-ing willpower.” But where they explicitly mean having willpower in terms of filing and pursing insurance claims (you do), explains that drug companies are making antiobesity medications more expensive in America than anywhere else in the world (they are), and finally delivers this quote, which, while missing the biological basis of behavior and hunger with respect to obesity, certainly sums up why blame has no place in the discourse:
“We have sugar companies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance companies all just trying to figure out how to make money off our health. It isn’t fair to put the blame on anyone for their weight.”
No, it’s not.
This movie should be required viewing in medical schools.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, department of family medicine, University of Ottawa, and medical director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Postpartum Screening Critical for Urinary Symptoms and Related Mental Health
Bothersome urinary symptoms and incontinence at 12 months post partum are common and treatable, so screening for those symptoms as well as associated depression and anxiety is essential, write authors of a new study.
Sonia Bhandari Randhawa, MD, with the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, led the study published in Urogynecology, which identified factors associated with persistent stress urinary incontinence (SUI), marked by leakage from sudden movements such as coughing or jumping; urgency UI (UUI), leakage after a sudden and intense need to urinate, even if the bladder isn’t full; and other overall bothersome urinary symptoms 1 year after delivery.
Associations by Subtype
Dr. Randhawa analyzed data provided by 419 patients (77% Hispanic White and 22% non-Hispanic Black). After multivariable analysis, SUI (n = 136, 32.5%) was significantly associated with greater body mass index (BMI) at the time of delivery and greater depression screening scores. Factors not associated included fetal birth weight, mode of delivery, degree of laceration, and breastfeeding status.
UUI (n = 69, 16.5%) was significantly associated with more births and higher anxiety screening scores. Women with overall urinary symptom bother also had significantly more births and higher anxiety screening scores.
“These findings support the [American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists] recommendations for routine mental health and urinary incontinence screening in the postpartum period,” said Gena Dunivan, MD, director of the Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery at University of Alabama–Birmingham, who was not part of the study. “Routine screening for these issues will hopefully reduce the stigma, allowing more patients to receive the help they deserve.”
1 in 3 Postpartum Patients Affected by Urinary Incontinence
About one third of postpartum patients are affected by urinary incontinence, which is linked with poorer quality of life and mental health outcomes, the authors note.
Estimates of incontinence frequency post partum vary depending on the population studied, differences in subgroups, and definition of urinary incontinence. A strength of the study was its sizable population, made up almost entirely of Hispanic White and non-Hispanic Black women receiving care at a large safety-net hospital.
“This study has important clinical implications for postpartum patients,” the authors write. “Given an array of proven treatment options for both UUI and SUI, maternal health surveillance needs to include routine inquiry about UI to overcome patients’ reluctance for seeking care. Next, as elevated BMI was identified as a risk factor for persistent postpartum SUI, maintaining a healthy weight should be routinely encouraged during antenatal and postpartum clinic visits.”
Lauren Giugale, MD, director of UPMC’s Magee-Womens Hospital Postpartum Pelvic Floor Healing Clinic in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, says an important aspect of the study is that it measured urinary symptoms 1 year after delivery and shows that these symptoms persist. “A lot of studies look more short term,” she noted.
She also pointed to the study’s population of Black and Hispanic women, populations which “have been pretty hard to capture in urogynecology research. It’s important for us to understand these urinary symptoms are affecting those women as well as White women.”
Association With Anxiety
The association between postpartum depression scores and SUI is important, she says, but Dr. Randhawa’s team also “uniquely looked at anxiety scores in postpartum women. They showed an association between anxiety scores and UUI, so there’s certainly a potential impact of postpartum urinary symptoms on maternal mental health and maternal well-being.” The relationship between anxiety and depression and postpartum urinary symptoms is not well understood and warrants further research, she says.
In her role, Dr. Giugale says, she always asks about urinary symptoms, particularly in postpartum women. But she notes that some ob.gyn.s without urogynecology training may not prioritize those questions amid all the other information they need to cover.
She says she tells her residents to ask patients pointedly, “Are you having any urine leakage? Patients may not think it’s a problem that can be addressed. We do patients a disservice when we don’t ask the important questions that might potentially impact patients’ lives.”
The authors and Dr. Giugale and Dr. Dunivan report no relevant financial relationships.
Bothersome urinary symptoms and incontinence at 12 months post partum are common and treatable, so screening for those symptoms as well as associated depression and anxiety is essential, write authors of a new study.
Sonia Bhandari Randhawa, MD, with the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, led the study published in Urogynecology, which identified factors associated with persistent stress urinary incontinence (SUI), marked by leakage from sudden movements such as coughing or jumping; urgency UI (UUI), leakage after a sudden and intense need to urinate, even if the bladder isn’t full; and other overall bothersome urinary symptoms 1 year after delivery.
Associations by Subtype
Dr. Randhawa analyzed data provided by 419 patients (77% Hispanic White and 22% non-Hispanic Black). After multivariable analysis, SUI (n = 136, 32.5%) was significantly associated with greater body mass index (BMI) at the time of delivery and greater depression screening scores. Factors not associated included fetal birth weight, mode of delivery, degree of laceration, and breastfeeding status.
UUI (n = 69, 16.5%) was significantly associated with more births and higher anxiety screening scores. Women with overall urinary symptom bother also had significantly more births and higher anxiety screening scores.
“These findings support the [American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists] recommendations for routine mental health and urinary incontinence screening in the postpartum period,” said Gena Dunivan, MD, director of the Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery at University of Alabama–Birmingham, who was not part of the study. “Routine screening for these issues will hopefully reduce the stigma, allowing more patients to receive the help they deserve.”
1 in 3 Postpartum Patients Affected by Urinary Incontinence
About one third of postpartum patients are affected by urinary incontinence, which is linked with poorer quality of life and mental health outcomes, the authors note.
Estimates of incontinence frequency post partum vary depending on the population studied, differences in subgroups, and definition of urinary incontinence. A strength of the study was its sizable population, made up almost entirely of Hispanic White and non-Hispanic Black women receiving care at a large safety-net hospital.
“This study has important clinical implications for postpartum patients,” the authors write. “Given an array of proven treatment options for both UUI and SUI, maternal health surveillance needs to include routine inquiry about UI to overcome patients’ reluctance for seeking care. Next, as elevated BMI was identified as a risk factor for persistent postpartum SUI, maintaining a healthy weight should be routinely encouraged during antenatal and postpartum clinic visits.”
Lauren Giugale, MD, director of UPMC’s Magee-Womens Hospital Postpartum Pelvic Floor Healing Clinic in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, says an important aspect of the study is that it measured urinary symptoms 1 year after delivery and shows that these symptoms persist. “A lot of studies look more short term,” she noted.
She also pointed to the study’s population of Black and Hispanic women, populations which “have been pretty hard to capture in urogynecology research. It’s important for us to understand these urinary symptoms are affecting those women as well as White women.”
Association With Anxiety
The association between postpartum depression scores and SUI is important, she says, but Dr. Randhawa’s team also “uniquely looked at anxiety scores in postpartum women. They showed an association between anxiety scores and UUI, so there’s certainly a potential impact of postpartum urinary symptoms on maternal mental health and maternal well-being.” The relationship between anxiety and depression and postpartum urinary symptoms is not well understood and warrants further research, she says.
In her role, Dr. Giugale says, she always asks about urinary symptoms, particularly in postpartum women. But she notes that some ob.gyn.s without urogynecology training may not prioritize those questions amid all the other information they need to cover.
She says she tells her residents to ask patients pointedly, “Are you having any urine leakage? Patients may not think it’s a problem that can be addressed. We do patients a disservice when we don’t ask the important questions that might potentially impact patients’ lives.”
The authors and Dr. Giugale and Dr. Dunivan report no relevant financial relationships.
Bothersome urinary symptoms and incontinence at 12 months post partum are common and treatable, so screening for those symptoms as well as associated depression and anxiety is essential, write authors of a new study.
Sonia Bhandari Randhawa, MD, with the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, led the study published in Urogynecology, which identified factors associated with persistent stress urinary incontinence (SUI), marked by leakage from sudden movements such as coughing or jumping; urgency UI (UUI), leakage after a sudden and intense need to urinate, even if the bladder isn’t full; and other overall bothersome urinary symptoms 1 year after delivery.
Associations by Subtype
Dr. Randhawa analyzed data provided by 419 patients (77% Hispanic White and 22% non-Hispanic Black). After multivariable analysis, SUI (n = 136, 32.5%) was significantly associated with greater body mass index (BMI) at the time of delivery and greater depression screening scores. Factors not associated included fetal birth weight, mode of delivery, degree of laceration, and breastfeeding status.
UUI (n = 69, 16.5%) was significantly associated with more births and higher anxiety screening scores. Women with overall urinary symptom bother also had significantly more births and higher anxiety screening scores.
“These findings support the [American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists] recommendations for routine mental health and urinary incontinence screening in the postpartum period,” said Gena Dunivan, MD, director of the Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery at University of Alabama–Birmingham, who was not part of the study. “Routine screening for these issues will hopefully reduce the stigma, allowing more patients to receive the help they deserve.”
1 in 3 Postpartum Patients Affected by Urinary Incontinence
About one third of postpartum patients are affected by urinary incontinence, which is linked with poorer quality of life and mental health outcomes, the authors note.
Estimates of incontinence frequency post partum vary depending on the population studied, differences in subgroups, and definition of urinary incontinence. A strength of the study was its sizable population, made up almost entirely of Hispanic White and non-Hispanic Black women receiving care at a large safety-net hospital.
“This study has important clinical implications for postpartum patients,” the authors write. “Given an array of proven treatment options for both UUI and SUI, maternal health surveillance needs to include routine inquiry about UI to overcome patients’ reluctance for seeking care. Next, as elevated BMI was identified as a risk factor for persistent postpartum SUI, maintaining a healthy weight should be routinely encouraged during antenatal and postpartum clinic visits.”
Lauren Giugale, MD, director of UPMC’s Magee-Womens Hospital Postpartum Pelvic Floor Healing Clinic in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, says an important aspect of the study is that it measured urinary symptoms 1 year after delivery and shows that these symptoms persist. “A lot of studies look more short term,” she noted.
She also pointed to the study’s population of Black and Hispanic women, populations which “have been pretty hard to capture in urogynecology research. It’s important for us to understand these urinary symptoms are affecting those women as well as White women.”
Association With Anxiety
The association between postpartum depression scores and SUI is important, she says, but Dr. Randhawa’s team also “uniquely looked at anxiety scores in postpartum women. They showed an association between anxiety scores and UUI, so there’s certainly a potential impact of postpartum urinary symptoms on maternal mental health and maternal well-being.” The relationship between anxiety and depression and postpartum urinary symptoms is not well understood and warrants further research, she says.
In her role, Dr. Giugale says, she always asks about urinary symptoms, particularly in postpartum women. But she notes that some ob.gyn.s without urogynecology training may not prioritize those questions amid all the other information they need to cover.
She says she tells her residents to ask patients pointedly, “Are you having any urine leakage? Patients may not think it’s a problem that can be addressed. We do patients a disservice when we don’t ask the important questions that might potentially impact patients’ lives.”
The authors and Dr. Giugale and Dr. Dunivan report no relevant financial relationships.
UROGYNECOLOGY
Does An Elevated Lp(a) Call for Low-dose Aspirin?
Should a patient with high lipoprotein (a), or Lp(a), be started on low-dose aspirin?
This is the conundrum facing many physicians and patients, but even getting to that point will require more availability and coverage of tests and a greater appreciation of the risk associated with Lp(a), said cardiologists.
Lp(a): The Silent Risk
On Lp(a) Awareness Day, C. Michael Gibson, MD, MA, CEO of the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Boston, Massachusetts, and PERFUSE took the opportunity to talk about his experiences with testing on X.
The professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, said he was surprised to find that he had a very high calcium score, despite a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level of just 70 mg/dL. Eventually, he found out that he had a “very, very high Lp(a),” which was particularly concerning because his grandfather died of a heart attack at 45 years of age.
But how much risk does that represent?
A 2022 consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) highlighted that epidemiologic and genetic studies “strongly support a causal and continuous association between Lp(a) concentration and cardiovascular outcomes,” even at very low LDL cholesterol levels.
This is because Lp(a) has proinflammatory and proatherosclerotic properties, and high levels are associated with both micro- and macrocalcification of the aortic valve. Findings from a US registry study also suggest the threshold related to increased cardiovascular risk may differ for primary and secondary prevention populations (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Mar 5;83[9]:873-886).
Lp(a) is, however, genetically determined, and there are no drugs available that directly lower levels, although some are on the horizon. In the meantime, the experts behind the consensus statement recommend that all adults be tested at least once in their lifetime.
Testing Cost and Availability
This recommendation has been translated into guidelines in “many, many” countries, said lead author Florian Kronenberg, MD, MAE, Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria, but “we are far away from reaching that goal.”
“We’ve got a real problem,” added Stephen Nicholls, MD, PhD, director of the Victorian Heart Institute and a professor of cardiology at Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, as there is “not a country in the world where there’s good access to Lp(a) testing.”
Dr. Kronenberg said that the consensus statement “created a kind of momentum” toward universal testing.
Ulrich Laufs, MD, PhD, professor and chair, Department of Cardiology, University Hospital Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany, agreed, saying that, overall, Lp(a) testing has “increased dramatically,” albeit from “extremely low levels.”
Dr. Kronenberg believes that “we have to be really patient.” He cited a lack of knowledge among physicians as one of the biggest barriers to greater uptake of testing.
“There is still no appreciation of the role of Lp(a),” agreed Alberico L. Catapano, MD, PhD, director of Cardiovascular Research and of the Lipoproteins and Atherosclerosis Laboratory of IRCCS Multimedica, Milan, Italy, and past president of the EAS.
“That’s why it’s not mentioned” to patients, he said. “What is really needed is to inform physician colleagues that Lp(a) is not only a risk factor but is the cause” of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Dr. Kronenberg said that the pressure for testing can often come from the patient themselves.
Physicians then question why the patient wants to be tested when there are no medications to treat it, he added. “We really tried very hard when we did the consensus paper to say that we should perform the test and give people advice on what to do.”
Dr. Catapano believes that another major obstacle is the cost of the test, which remains high “because very few people do it,” and there is some debate over which test to use.
Taken together, these issues have meant that “payers are really struggling with the idea of funding Lp(a),” said Dr. Nicholls, adding that “there seems to be this fixation on: ‘Well, if you can’t lower Lp(a), why measure it?’ ”
Rather than blame the payers, he says there is a need to educate about the science behind testing and underline that Lp(a) is an “important risk enhancer” for cardiovascular disease.
“Because if we’re going to make people pay out of pocket, then you’re creating a massive equity issue in that only those who can afford the test have it.”
High Lp(a) Now What?
But once the test has been performed, there then comes the question as to what to do about the result.
“Before we get anywhere near an agent that effectively lowers Lp(a) and get it into the clinic, there are lots of things that we can do today,” said Dr. Nicholls.
If someone has an intermediate or high background cardiovascular risk and they have got a high Lp(a) level, they “should be treated more intensively, as we know that high Lp(a) patients do better if their LDL cholesterol and their blood pressure is lower.”
For Dr. Catapano, this means having the “same mindset as you do with [a patient with] high blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, and so on, because it’s exactly the same thing: It’s interacting with your other risk factors to increase your overall risk.”
Dr. Gibson agreed. Through a range of measures, including weight loss and statin therapy, he was able to reduce his overall cardiovascular risk, and his LDL cholesterol level dropped to just 20 mg/dL.
A Role for Aspirin?
It gained added momentum when Pablo Corral, MD, a lipidologist and a professor in the School of Medicine, Pharmacology Department, FASTA University, Mar del Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina, highlighted the issue on X.
He pointed to a recent study, which showed that regular aspirin use was associated with a significantly lower rate of ASCVD mortality in adults without clinical ASCVD but who had elevated Lp(a).
Dr. Nicholls said that, when you “peel away the layers” of the current evidence, there is some suggestion that Lp(a)may be prothrombotic. “So in theory, perhaps aspirin might be maybe more intuitively useful there.”
He noted that the ASPREE primary prevention study found that low-dose aspirin in older adults resulted in a significantly higher risk for major hemorrhage over placebo and did not significantly reduce the risk for cardiovascular disease.
But an analysis he and his colleagues did suggest that aspirin may indeed benefit older individuals if they have elevated Lp(a) genotypes.
An Individual Decision
For Dr. Kronenberg and Dr. Laufs, there is currently a lack of appropriate data to make a recommendation either way, particularly for primary prevention.
They warned that the risk for thrombosis in patients with mildly elevated Lp(a) cannot be discounted, and in most cases either “the existing risk of bleeding exceeds the beneficial effects [of aspirin], or it’s not indicated,” said Dr. Laufs.
“When we make a recommendation, we should have evidence-based data,” Dr. Kronenberg said, but, at the moment, people “somehow put their finger in the air and see” which way the wind is blowing.
Dr. Catapano urged patients to talk to their physician, as even low-dose aspirin is “very potent” at inhibiting platelets.
Dr. Gibson agreed, saying that he is in two minds, as the potential benefit has to be weighed against the bleeding risk.
He personally takes low-dose aspirin because “I know I have a low bleeding risk,” but it is a decision “that has to be taken individually between a patient and their physician.”
Dr. Gibson, Dr. Kronenberg, Dr. Nicholls, and Dr. Catapano all reported conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies and organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should a patient with high lipoprotein (a), or Lp(a), be started on low-dose aspirin?
This is the conundrum facing many physicians and patients, but even getting to that point will require more availability and coverage of tests and a greater appreciation of the risk associated with Lp(a), said cardiologists.
Lp(a): The Silent Risk
On Lp(a) Awareness Day, C. Michael Gibson, MD, MA, CEO of the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Boston, Massachusetts, and PERFUSE took the opportunity to talk about his experiences with testing on X.
The professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, said he was surprised to find that he had a very high calcium score, despite a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level of just 70 mg/dL. Eventually, he found out that he had a “very, very high Lp(a),” which was particularly concerning because his grandfather died of a heart attack at 45 years of age.
But how much risk does that represent?
A 2022 consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) highlighted that epidemiologic and genetic studies “strongly support a causal and continuous association between Lp(a) concentration and cardiovascular outcomes,” even at very low LDL cholesterol levels.
This is because Lp(a) has proinflammatory and proatherosclerotic properties, and high levels are associated with both micro- and macrocalcification of the aortic valve. Findings from a US registry study also suggest the threshold related to increased cardiovascular risk may differ for primary and secondary prevention populations (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Mar 5;83[9]:873-886).
Lp(a) is, however, genetically determined, and there are no drugs available that directly lower levels, although some are on the horizon. In the meantime, the experts behind the consensus statement recommend that all adults be tested at least once in their lifetime.
Testing Cost and Availability
This recommendation has been translated into guidelines in “many, many” countries, said lead author Florian Kronenberg, MD, MAE, Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria, but “we are far away from reaching that goal.”
“We’ve got a real problem,” added Stephen Nicholls, MD, PhD, director of the Victorian Heart Institute and a professor of cardiology at Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, as there is “not a country in the world where there’s good access to Lp(a) testing.”
Dr. Kronenberg said that the consensus statement “created a kind of momentum” toward universal testing.
Ulrich Laufs, MD, PhD, professor and chair, Department of Cardiology, University Hospital Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany, agreed, saying that, overall, Lp(a) testing has “increased dramatically,” albeit from “extremely low levels.”
Dr. Kronenberg believes that “we have to be really patient.” He cited a lack of knowledge among physicians as one of the biggest barriers to greater uptake of testing.
“There is still no appreciation of the role of Lp(a),” agreed Alberico L. Catapano, MD, PhD, director of Cardiovascular Research and of the Lipoproteins and Atherosclerosis Laboratory of IRCCS Multimedica, Milan, Italy, and past president of the EAS.
“That’s why it’s not mentioned” to patients, he said. “What is really needed is to inform physician colleagues that Lp(a) is not only a risk factor but is the cause” of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Dr. Kronenberg said that the pressure for testing can often come from the patient themselves.
Physicians then question why the patient wants to be tested when there are no medications to treat it, he added. “We really tried very hard when we did the consensus paper to say that we should perform the test and give people advice on what to do.”
Dr. Catapano believes that another major obstacle is the cost of the test, which remains high “because very few people do it,” and there is some debate over which test to use.
Taken together, these issues have meant that “payers are really struggling with the idea of funding Lp(a),” said Dr. Nicholls, adding that “there seems to be this fixation on: ‘Well, if you can’t lower Lp(a), why measure it?’ ”
Rather than blame the payers, he says there is a need to educate about the science behind testing and underline that Lp(a) is an “important risk enhancer” for cardiovascular disease.
“Because if we’re going to make people pay out of pocket, then you’re creating a massive equity issue in that only those who can afford the test have it.”
High Lp(a) Now What?
But once the test has been performed, there then comes the question as to what to do about the result.
“Before we get anywhere near an agent that effectively lowers Lp(a) and get it into the clinic, there are lots of things that we can do today,” said Dr. Nicholls.
If someone has an intermediate or high background cardiovascular risk and they have got a high Lp(a) level, they “should be treated more intensively, as we know that high Lp(a) patients do better if their LDL cholesterol and their blood pressure is lower.”
For Dr. Catapano, this means having the “same mindset as you do with [a patient with] high blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, and so on, because it’s exactly the same thing: It’s interacting with your other risk factors to increase your overall risk.”
Dr. Gibson agreed. Through a range of measures, including weight loss and statin therapy, he was able to reduce his overall cardiovascular risk, and his LDL cholesterol level dropped to just 20 mg/dL.
A Role for Aspirin?
It gained added momentum when Pablo Corral, MD, a lipidologist and a professor in the School of Medicine, Pharmacology Department, FASTA University, Mar del Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina, highlighted the issue on X.
He pointed to a recent study, which showed that regular aspirin use was associated with a significantly lower rate of ASCVD mortality in adults without clinical ASCVD but who had elevated Lp(a).
Dr. Nicholls said that, when you “peel away the layers” of the current evidence, there is some suggestion that Lp(a)may be prothrombotic. “So in theory, perhaps aspirin might be maybe more intuitively useful there.”
He noted that the ASPREE primary prevention study found that low-dose aspirin in older adults resulted in a significantly higher risk for major hemorrhage over placebo and did not significantly reduce the risk for cardiovascular disease.
But an analysis he and his colleagues did suggest that aspirin may indeed benefit older individuals if they have elevated Lp(a) genotypes.
An Individual Decision
For Dr. Kronenberg and Dr. Laufs, there is currently a lack of appropriate data to make a recommendation either way, particularly for primary prevention.
They warned that the risk for thrombosis in patients with mildly elevated Lp(a) cannot be discounted, and in most cases either “the existing risk of bleeding exceeds the beneficial effects [of aspirin], or it’s not indicated,” said Dr. Laufs.
“When we make a recommendation, we should have evidence-based data,” Dr. Kronenberg said, but, at the moment, people “somehow put their finger in the air and see” which way the wind is blowing.
Dr. Catapano urged patients to talk to their physician, as even low-dose aspirin is “very potent” at inhibiting platelets.
Dr. Gibson agreed, saying that he is in two minds, as the potential benefit has to be weighed against the bleeding risk.
He personally takes low-dose aspirin because “I know I have a low bleeding risk,” but it is a decision “that has to be taken individually between a patient and their physician.”
Dr. Gibson, Dr. Kronenberg, Dr. Nicholls, and Dr. Catapano all reported conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies and organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should a patient with high lipoprotein (a), or Lp(a), be started on low-dose aspirin?
This is the conundrum facing many physicians and patients, but even getting to that point will require more availability and coverage of tests and a greater appreciation of the risk associated with Lp(a), said cardiologists.
Lp(a): The Silent Risk
On Lp(a) Awareness Day, C. Michael Gibson, MD, MA, CEO of the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Boston, Massachusetts, and PERFUSE took the opportunity to talk about his experiences with testing on X.
The professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, said he was surprised to find that he had a very high calcium score, despite a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level of just 70 mg/dL. Eventually, he found out that he had a “very, very high Lp(a),” which was particularly concerning because his grandfather died of a heart attack at 45 years of age.
But how much risk does that represent?
A 2022 consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) highlighted that epidemiologic and genetic studies “strongly support a causal and continuous association between Lp(a) concentration and cardiovascular outcomes,” even at very low LDL cholesterol levels.
This is because Lp(a) has proinflammatory and proatherosclerotic properties, and high levels are associated with both micro- and macrocalcification of the aortic valve. Findings from a US registry study also suggest the threshold related to increased cardiovascular risk may differ for primary and secondary prevention populations (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Mar 5;83[9]:873-886).
Lp(a) is, however, genetically determined, and there are no drugs available that directly lower levels, although some are on the horizon. In the meantime, the experts behind the consensus statement recommend that all adults be tested at least once in their lifetime.
Testing Cost and Availability
This recommendation has been translated into guidelines in “many, many” countries, said lead author Florian Kronenberg, MD, MAE, Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria, but “we are far away from reaching that goal.”
“We’ve got a real problem,” added Stephen Nicholls, MD, PhD, director of the Victorian Heart Institute and a professor of cardiology at Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, as there is “not a country in the world where there’s good access to Lp(a) testing.”
Dr. Kronenberg said that the consensus statement “created a kind of momentum” toward universal testing.
Ulrich Laufs, MD, PhD, professor and chair, Department of Cardiology, University Hospital Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany, agreed, saying that, overall, Lp(a) testing has “increased dramatically,” albeit from “extremely low levels.”
Dr. Kronenberg believes that “we have to be really patient.” He cited a lack of knowledge among physicians as one of the biggest barriers to greater uptake of testing.
“There is still no appreciation of the role of Lp(a),” agreed Alberico L. Catapano, MD, PhD, director of Cardiovascular Research and of the Lipoproteins and Atherosclerosis Laboratory of IRCCS Multimedica, Milan, Italy, and past president of the EAS.
“That’s why it’s not mentioned” to patients, he said. “What is really needed is to inform physician colleagues that Lp(a) is not only a risk factor but is the cause” of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Dr. Kronenberg said that the pressure for testing can often come from the patient themselves.
Physicians then question why the patient wants to be tested when there are no medications to treat it, he added. “We really tried very hard when we did the consensus paper to say that we should perform the test and give people advice on what to do.”
Dr. Catapano believes that another major obstacle is the cost of the test, which remains high “because very few people do it,” and there is some debate over which test to use.
Taken together, these issues have meant that “payers are really struggling with the idea of funding Lp(a),” said Dr. Nicholls, adding that “there seems to be this fixation on: ‘Well, if you can’t lower Lp(a), why measure it?’ ”
Rather than blame the payers, he says there is a need to educate about the science behind testing and underline that Lp(a) is an “important risk enhancer” for cardiovascular disease.
“Because if we’re going to make people pay out of pocket, then you’re creating a massive equity issue in that only those who can afford the test have it.”
High Lp(a) Now What?
But once the test has been performed, there then comes the question as to what to do about the result.
“Before we get anywhere near an agent that effectively lowers Lp(a) and get it into the clinic, there are lots of things that we can do today,” said Dr. Nicholls.
If someone has an intermediate or high background cardiovascular risk and they have got a high Lp(a) level, they “should be treated more intensively, as we know that high Lp(a) patients do better if their LDL cholesterol and their blood pressure is lower.”
For Dr. Catapano, this means having the “same mindset as you do with [a patient with] high blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, and so on, because it’s exactly the same thing: It’s interacting with your other risk factors to increase your overall risk.”
Dr. Gibson agreed. Through a range of measures, including weight loss and statin therapy, he was able to reduce his overall cardiovascular risk, and his LDL cholesterol level dropped to just 20 mg/dL.
A Role for Aspirin?
It gained added momentum when Pablo Corral, MD, a lipidologist and a professor in the School of Medicine, Pharmacology Department, FASTA University, Mar del Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina, highlighted the issue on X.
He pointed to a recent study, which showed that regular aspirin use was associated with a significantly lower rate of ASCVD mortality in adults without clinical ASCVD but who had elevated Lp(a).
Dr. Nicholls said that, when you “peel away the layers” of the current evidence, there is some suggestion that Lp(a)may be prothrombotic. “So in theory, perhaps aspirin might be maybe more intuitively useful there.”
He noted that the ASPREE primary prevention study found that low-dose aspirin in older adults resulted in a significantly higher risk for major hemorrhage over placebo and did not significantly reduce the risk for cardiovascular disease.
But an analysis he and his colleagues did suggest that aspirin may indeed benefit older individuals if they have elevated Lp(a) genotypes.
An Individual Decision
For Dr. Kronenberg and Dr. Laufs, there is currently a lack of appropriate data to make a recommendation either way, particularly for primary prevention.
They warned that the risk for thrombosis in patients with mildly elevated Lp(a) cannot be discounted, and in most cases either “the existing risk of bleeding exceeds the beneficial effects [of aspirin], or it’s not indicated,” said Dr. Laufs.
“When we make a recommendation, we should have evidence-based data,” Dr. Kronenberg said, but, at the moment, people “somehow put their finger in the air and see” which way the wind is blowing.
Dr. Catapano urged patients to talk to their physician, as even low-dose aspirin is “very potent” at inhibiting platelets.
Dr. Gibson agreed, saying that he is in two minds, as the potential benefit has to be weighed against the bleeding risk.
He personally takes low-dose aspirin because “I know I have a low bleeding risk,” but it is a decision “that has to be taken individually between a patient and their physician.”
Dr. Gibson, Dr. Kronenberg, Dr. Nicholls, and Dr. Catapano all reported conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies and organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLP-1 Thyroid Warning Could Increase Overdiagnosis
ORLANDO, Florida — Clinicians should keep in mind concerns about overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer when prescribing glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs, as the US boxed warning about this risk for this class of medicines for certain tumors in mice could trigger excess screening, an expert endocrinologist said.
Speaking at the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, a professor of medicine at Boston University, Boston, reviewed the different approaches US and European regulators have taken for the GLP-1 drugs. She also explained the current concerns about the wide use of thyroid screening in general and how these intersect with the rapid uptake of the GLP-1 drugs.
said Dr. Pearce, who is also a former board president of the American Thyroid Association (ATA). “We do not want to contribute to this epidemic of overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer.”
The ATA and the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) are among the health organizations that have in recent years sought to boost public awareness of the potential risks for excess screening of thyroid nodules. In 2017, the USPSTF, which influences insurance coverage, recommended against routine screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults. At that time, the incidence of thyroid cancer detection had increased by 4.5% per year over a decade, faster than for any other cancer, but without a corresponding change in the mortality rate, USPSTF said.
“Unequivocally, the thyroid cancer mortality has not kept pace with thyroid cancer detection,” Dr. Pearce said at the ADA meeting. “We’ve been diagnosing a lot of small thyroid cancers that people would otherwise have been destined to die with and not die of.”
Dr. Pearce said clinicians should be careful not to overly restrict access to GLP-1 drugs due to concerns about thyroid cancer — and they should use care in screening nodules.
It’s possible that the weight loss experienced by people taking GLP-1 drugs may make preexisting thyroid nodules more prominent, Dr. Pearce said. It’s also likely that the US boxed warning on thyroid risk on GLP-1 drugs makes clinicians and patients more likely to look for these kinds of growths.
Dr. Pearce urged adherence to guidelines such as the ones the ATA published in 2015 for assessing nodules.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Pearce noted the frequency of CT scans in US medical practice in turning up many incidental thyroid nodules, a finding that can cause some panic for patients and their clinicians.
But it helps to put these findings in context, as by the age of 50, about 40% of women will have at least one thyroid nodule, making this a very common finding, she said.
“The vast majority are not malignant,” Dr. Pearce said. “When you explain this to patients, it alleviates anxiety.”
The US, European Union Differences
In the United States, the label for GLP-1 drugs starts with a boxed warning about thyroid C-cell tumors seen in rodents given these medicines in testing.
It’s unknown if the medicines could cause medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in humans, the label adds. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2, the boxed warning says. This is based largely on data seen in laboratory rats.
“It’s a big black box warning that gets people’s attention,” Dr. Pearce said. “Important to note that if you practice in Europe, you will not be familiar with this labeling because it doesn’t exist there. They’ve never had this warning on the European package.”
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) does include information about the results of rodent studies as part of the discussion of known and potential risks for GLP-1 drugs but has not emphasized it in the same way as the US drug labels do.
For example, the public assessment report posted on the EMA website for semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) notes that nonlethal thyroid C-cell tumors “observed in rodents are a class effect for GLP-1 receptor agonists.” It’s possible that these may be due to a particular sensitivity in rodents, the report said.
“The relevance for humans is considered to be low but cannot be completely excluded,” the EMA report said in the product information section of the report.
There has been ongoing interest in the issue.
The EMA’s Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in October concluded that the available evidence does not support a causal association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.
The EMA’s PRAC safety committee said it began assessing the evidence about a possible connection following the publication of a study in 2022 in the journal Diabetes Care. That paper reported on an analysis that suggested increased risk for all thyroid cancer and medullary thyroid cancer with the use of GLP-1 drugs, particularly after 1-3 years of treatment.
The EMA’s PRAC said that in making its decision, it also considered other published papers on this topic as well as clinical and postmarketing data on GLP-1 drugs.
In an email interview, Jean-Luc Faillie, MD, PhD, corresponding author of the Diabetes Care paper, called for continued “vigilance and prudence in clinical practice” with GLP-1 drugs.
His paper reported on a case-control analysis on the basis of reports from the French national healthcare insurance system database, looking at people who had taken GLP-1 drugs and similar people who had not.
Due to a lack of a specific diagnostic code for medullary thyroid cancers, the researchers used a composite definition combining thyroid cancer diagnosis with several calcitonin tests, a carcinoembryonic antigen test, or a specific treatment (vandetanib) to identify potential cases of this cancer.
It’s possible that this method could have led to overestimation of MTC among the cases of thyroid cancer, wrote Dr. Faillie, who is a professor at France’s Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, and part of its pharmacological vigilance service.
“Nevertheless, it’s crucial to emphasize that any potential overestimation of MTC cases would likely apply equally to both GLP-1 receptor agonist–exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Faillie wrote. “Therefore, it should not significantly impact our main findings regarding the suggested increased risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonist use.”
Dr. Pearce disclosed honoraria for speaking at the Merck China Forum. Dr. Faille and his coauthors reported no conflicts of interest in the publication of their study. Their research was supported by the French Medicines Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, grant 2019S015) in the context of a partnership with the Health Product Epidemiology Scientific Interest Group (EPI-PHARE). The study was part of France’s Drugs Systematized Assessment in Real-Life Environment (DRUGS-SAFEr) research program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Florida — Clinicians should keep in mind concerns about overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer when prescribing glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs, as the US boxed warning about this risk for this class of medicines for certain tumors in mice could trigger excess screening, an expert endocrinologist said.
Speaking at the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, a professor of medicine at Boston University, Boston, reviewed the different approaches US and European regulators have taken for the GLP-1 drugs. She also explained the current concerns about the wide use of thyroid screening in general and how these intersect with the rapid uptake of the GLP-1 drugs.
said Dr. Pearce, who is also a former board president of the American Thyroid Association (ATA). “We do not want to contribute to this epidemic of overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer.”
The ATA and the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) are among the health organizations that have in recent years sought to boost public awareness of the potential risks for excess screening of thyroid nodules. In 2017, the USPSTF, which influences insurance coverage, recommended against routine screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults. At that time, the incidence of thyroid cancer detection had increased by 4.5% per year over a decade, faster than for any other cancer, but without a corresponding change in the mortality rate, USPSTF said.
“Unequivocally, the thyroid cancer mortality has not kept pace with thyroid cancer detection,” Dr. Pearce said at the ADA meeting. “We’ve been diagnosing a lot of small thyroid cancers that people would otherwise have been destined to die with and not die of.”
Dr. Pearce said clinicians should be careful not to overly restrict access to GLP-1 drugs due to concerns about thyroid cancer — and they should use care in screening nodules.
It’s possible that the weight loss experienced by people taking GLP-1 drugs may make preexisting thyroid nodules more prominent, Dr. Pearce said. It’s also likely that the US boxed warning on thyroid risk on GLP-1 drugs makes clinicians and patients more likely to look for these kinds of growths.
Dr. Pearce urged adherence to guidelines such as the ones the ATA published in 2015 for assessing nodules.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Pearce noted the frequency of CT scans in US medical practice in turning up many incidental thyroid nodules, a finding that can cause some panic for patients and their clinicians.
But it helps to put these findings in context, as by the age of 50, about 40% of women will have at least one thyroid nodule, making this a very common finding, she said.
“The vast majority are not malignant,” Dr. Pearce said. “When you explain this to patients, it alleviates anxiety.”
The US, European Union Differences
In the United States, the label for GLP-1 drugs starts with a boxed warning about thyroid C-cell tumors seen in rodents given these medicines in testing.
It’s unknown if the medicines could cause medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in humans, the label adds. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2, the boxed warning says. This is based largely on data seen in laboratory rats.
“It’s a big black box warning that gets people’s attention,” Dr. Pearce said. “Important to note that if you practice in Europe, you will not be familiar with this labeling because it doesn’t exist there. They’ve never had this warning on the European package.”
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) does include information about the results of rodent studies as part of the discussion of known and potential risks for GLP-1 drugs but has not emphasized it in the same way as the US drug labels do.
For example, the public assessment report posted on the EMA website for semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) notes that nonlethal thyroid C-cell tumors “observed in rodents are a class effect for GLP-1 receptor agonists.” It’s possible that these may be due to a particular sensitivity in rodents, the report said.
“The relevance for humans is considered to be low but cannot be completely excluded,” the EMA report said in the product information section of the report.
There has been ongoing interest in the issue.
The EMA’s Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in October concluded that the available evidence does not support a causal association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.
The EMA’s PRAC safety committee said it began assessing the evidence about a possible connection following the publication of a study in 2022 in the journal Diabetes Care. That paper reported on an analysis that suggested increased risk for all thyroid cancer and medullary thyroid cancer with the use of GLP-1 drugs, particularly after 1-3 years of treatment.
The EMA’s PRAC said that in making its decision, it also considered other published papers on this topic as well as clinical and postmarketing data on GLP-1 drugs.
In an email interview, Jean-Luc Faillie, MD, PhD, corresponding author of the Diabetes Care paper, called for continued “vigilance and prudence in clinical practice” with GLP-1 drugs.
His paper reported on a case-control analysis on the basis of reports from the French national healthcare insurance system database, looking at people who had taken GLP-1 drugs and similar people who had not.
Due to a lack of a specific diagnostic code for medullary thyroid cancers, the researchers used a composite definition combining thyroid cancer diagnosis with several calcitonin tests, a carcinoembryonic antigen test, or a specific treatment (vandetanib) to identify potential cases of this cancer.
It’s possible that this method could have led to overestimation of MTC among the cases of thyroid cancer, wrote Dr. Faillie, who is a professor at France’s Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, and part of its pharmacological vigilance service.
“Nevertheless, it’s crucial to emphasize that any potential overestimation of MTC cases would likely apply equally to both GLP-1 receptor agonist–exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Faillie wrote. “Therefore, it should not significantly impact our main findings regarding the suggested increased risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonist use.”
Dr. Pearce disclosed honoraria for speaking at the Merck China Forum. Dr. Faille and his coauthors reported no conflicts of interest in the publication of their study. Their research was supported by the French Medicines Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, grant 2019S015) in the context of a partnership with the Health Product Epidemiology Scientific Interest Group (EPI-PHARE). The study was part of France’s Drugs Systematized Assessment in Real-Life Environment (DRUGS-SAFEr) research program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Florida — Clinicians should keep in mind concerns about overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer when prescribing glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs, as the US boxed warning about this risk for this class of medicines for certain tumors in mice could trigger excess screening, an expert endocrinologist said.
Speaking at the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, a professor of medicine at Boston University, Boston, reviewed the different approaches US and European regulators have taken for the GLP-1 drugs. She also explained the current concerns about the wide use of thyroid screening in general and how these intersect with the rapid uptake of the GLP-1 drugs.
said Dr. Pearce, who is also a former board president of the American Thyroid Association (ATA). “We do not want to contribute to this epidemic of overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer.”
The ATA and the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) are among the health organizations that have in recent years sought to boost public awareness of the potential risks for excess screening of thyroid nodules. In 2017, the USPSTF, which influences insurance coverage, recommended against routine screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults. At that time, the incidence of thyroid cancer detection had increased by 4.5% per year over a decade, faster than for any other cancer, but without a corresponding change in the mortality rate, USPSTF said.
“Unequivocally, the thyroid cancer mortality has not kept pace with thyroid cancer detection,” Dr. Pearce said at the ADA meeting. “We’ve been diagnosing a lot of small thyroid cancers that people would otherwise have been destined to die with and not die of.”
Dr. Pearce said clinicians should be careful not to overly restrict access to GLP-1 drugs due to concerns about thyroid cancer — and they should use care in screening nodules.
It’s possible that the weight loss experienced by people taking GLP-1 drugs may make preexisting thyroid nodules more prominent, Dr. Pearce said. It’s also likely that the US boxed warning on thyroid risk on GLP-1 drugs makes clinicians and patients more likely to look for these kinds of growths.
Dr. Pearce urged adherence to guidelines such as the ones the ATA published in 2015 for assessing nodules.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Pearce noted the frequency of CT scans in US medical practice in turning up many incidental thyroid nodules, a finding that can cause some panic for patients and their clinicians.
But it helps to put these findings in context, as by the age of 50, about 40% of women will have at least one thyroid nodule, making this a very common finding, she said.
“The vast majority are not malignant,” Dr. Pearce said. “When you explain this to patients, it alleviates anxiety.”
The US, European Union Differences
In the United States, the label for GLP-1 drugs starts with a boxed warning about thyroid C-cell tumors seen in rodents given these medicines in testing.
It’s unknown if the medicines could cause medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in humans, the label adds. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2, the boxed warning says. This is based largely on data seen in laboratory rats.
“It’s a big black box warning that gets people’s attention,” Dr. Pearce said. “Important to note that if you practice in Europe, you will not be familiar with this labeling because it doesn’t exist there. They’ve never had this warning on the European package.”
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) does include information about the results of rodent studies as part of the discussion of known and potential risks for GLP-1 drugs but has not emphasized it in the same way as the US drug labels do.
For example, the public assessment report posted on the EMA website for semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) notes that nonlethal thyroid C-cell tumors “observed in rodents are a class effect for GLP-1 receptor agonists.” It’s possible that these may be due to a particular sensitivity in rodents, the report said.
“The relevance for humans is considered to be low but cannot be completely excluded,” the EMA report said in the product information section of the report.
There has been ongoing interest in the issue.
The EMA’s Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in October concluded that the available evidence does not support a causal association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.
The EMA’s PRAC safety committee said it began assessing the evidence about a possible connection following the publication of a study in 2022 in the journal Diabetes Care. That paper reported on an analysis that suggested increased risk for all thyroid cancer and medullary thyroid cancer with the use of GLP-1 drugs, particularly after 1-3 years of treatment.
The EMA’s PRAC said that in making its decision, it also considered other published papers on this topic as well as clinical and postmarketing data on GLP-1 drugs.
In an email interview, Jean-Luc Faillie, MD, PhD, corresponding author of the Diabetes Care paper, called for continued “vigilance and prudence in clinical practice” with GLP-1 drugs.
His paper reported on a case-control analysis on the basis of reports from the French national healthcare insurance system database, looking at people who had taken GLP-1 drugs and similar people who had not.
Due to a lack of a specific diagnostic code for medullary thyroid cancers, the researchers used a composite definition combining thyroid cancer diagnosis with several calcitonin tests, a carcinoembryonic antigen test, or a specific treatment (vandetanib) to identify potential cases of this cancer.
It’s possible that this method could have led to overestimation of MTC among the cases of thyroid cancer, wrote Dr. Faillie, who is a professor at France’s Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, and part of its pharmacological vigilance service.
“Nevertheless, it’s crucial to emphasize that any potential overestimation of MTC cases would likely apply equally to both GLP-1 receptor agonist–exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Faillie wrote. “Therefore, it should not significantly impact our main findings regarding the suggested increased risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonist use.”
Dr. Pearce disclosed honoraria for speaking at the Merck China Forum. Dr. Faille and his coauthors reported no conflicts of interest in the publication of their study. Their research was supported by the French Medicines Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, grant 2019S015) in the context of a partnership with the Health Product Epidemiology Scientific Interest Group (EPI-PHARE). The study was part of France’s Drugs Systematized Assessment in Real-Life Environment (DRUGS-SAFEr) research program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
The State of Skin of Color Centers in the United States: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study
Although individuals with skin of color (SoC) are expected to become at least half of the US population by the year 2044, there remains a paucity of education and exposure to treatment of patients with SoC at many dermatology residency programs across the country.1 One way to improve SoC education has been the formation of specialized clinics, centers, and programs. The first SoC center (SoCC) was established in 1999 at Mount Sinai–St. Luke’s Roosevelt in New York, New York2; since then, at least 13 additional formal SoCCs or SoC specialty clinics (SoCSCs) at US academic dermatology programs have been established.
Skin of color centers serve several important purposes: they improve dermatologic care in patients with SoC, increase research efforts focused on SoC dermatologic conditions, and educate dermatology resident and fellow trainees about SoC. Improving dermatologic care of patients with SoC in the United States is important in providing equitable health care and improving health disparities. Studies have shown that patient-physician racial and cultural concordance can positively impact patient care, increase patient trust and rapport, and improve patient-physician communication, and it can even influence patient decision-making to seek care.3,4 Unfortunately, even though the US population continues to diversify, the racial/ethnic backgrounds of dermatologists do not parallel this trend; Hispanic and Black physicians comprise 18.9% and 13.6% of the general population, respectively, but represent only 4.2% and 3.0% of dermatologists, respectively.5-7 This deficit is mirrored by resident and faculty representation, with Black and Latino representation ranging from 3% to 7%.8-10
Many SoCC’s engage in research focused on dermatologic conditions affecting patients with SoC, which is vital to improving the dermatologic care in this underserved population. Despite increasing recognition of the importance of SoC research, there remains a paucity of clinical trials and research specifically focused on or demonstrating equitable representation of SoC.11,12
The education and training of future dermatologists is another important area that can be improved by SoCCs. A 2008 study involving 63 chief residents showed that approximately half (52.4% [33/63]) of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures, and 30.2% (19/63) reported having a dedicated rotation where they gained specific experience treating patients with SoC.13 A later study in 2022 (N=125) found that 63.2% of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures, and only 11.2% reported having a dedicated rotation where they gained experience treating patients with SoC.14 These findings suggest that in the last 14 years, formal SoC education—specifically SoC clinical training—has not increased sufficiently.
We conducted a cross-sectional survey study to provide an in-depth analysis of SoCCs and SoCSCs in the United States, including their patient care focus, research, and program diversity.
Methods
We conducted an investigator-initiated, multicenter, cross-sectional survey study of all SoCCs in the United States and their respective academic residency programs. Fifteen formal SoCCs and/or SoCSCs were identified by dermatology program websites and an article by Tull et al2 on the state of ethnic skin centers. All programs and centers identified were associated with a dermatology residency program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
A 42-item questionnaire was sent via email to the directors of these centers and clinics with the intent to collect descriptive information about each of the SoCCs, the diversity of the faculty and residents of the associated dermatology department, current research and funding, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and trainee education from March through April 2020. Data were analyzed using Excel and SPSS statistical software to obtain descriptive statistics including the mean value numeric trends across programs.
This study underwent expedited review and was approved by the University of Southern California (Los Angeles, California) institutional review board (IRB #HS-20-00113). Patient consent was not applicable, as no information was collected about patients.
Results
Fourteen directors from SoCCs/SoCSCs completed the questionnaire (93.3% response rate). Most centers were located in urban areas (12/14 [85.71%]), except for 2 in rural or suburban settings (Table). Most of the SoCCs/SoCSCs were located in the South (5/14 [35.71%]), followed by the Northeast (4/14 [28.57%]), West (3/14 [21.43%]), and Midwest (2/14 [14.29%])(Table). Six (42.86%) of the programs had a SoCSC, 3 (21.43%) had a formal SoCC, and 5 (35.71%) had both. Across all centers, the most common population seen and treated was Black/African American followed by Hispanic/Latino and Asian, respectively. The most commonly seen dermatologic conditions were acne, pigmentary disorders, alopecia, and atopic dermatitis (Figure). The most common cosmetic practice performed for patients with SoC was dermatosis papulosa nigra/seborrheic keratosis removal, followed by laser treatments, skin tag removal, chemical peels, and neuromodulator injections, respectively.
Faculty and Resident Demographics and Areas of Focus—The demographics and diversity of the dermatology faculty and residents at each individual institution also were assessed. The average number of full-time faculty at each institution was 19.4 (range, 2–48), while the average number of full-time faculty who identified as underrepresented in medicine (URiM) was 2.1 (range, 0–5). The average number of residents at each institution was 17.1 (range, 10–31), while the average number of URiM residents was 1.7 (range, 1–3).
The average number of full-time faculty members at each SoCC was 1.6 (range, 1–4). The majority of program directors reported having other specialists in their department that also treated dermatologic conditions predominantly affecting patients with SoC (10/14 [71.43%]). The 3 most common areas of expertise were alopecia, including central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA); cutaneous lupus; and traction alopecia (eTable 1).
Faculty SoC Research—Only a minority of programs had active clinical trials related to SoC (5/14 [35.71%]). Clinical research was the most common type of research being conducted (11/14 [78.57%]), followed by basic science/translational (4/14 [28.57%]) and epidemiologic research (2/14 [14.29%]). The most commonly investigated conditions for observational studies included CCCA, keloids/hypertrophic scarring, and atopic dermatitis (eTable 2). Only 8 of 14 programs had formal SoC research opportunities for residents (57.14%), while 9 had opportunities for medical students (64.29%).
Few institutions had internal funding (3/14 [21.43%]) or external funding (4/14 [28.57%]) for SoC research. Extramural fun ding sources included the Skin of Color Society, the Dermatology Foundation, and the Radiation Oncology Institute, as well as industry funding. No federal funding was received by any of the sites.
Skin of Color Education and Diversity Initiatives—All 14 programs had residents rotating through their SoCC and/or SoCSCs. The vast majority (12/14 [85.71%]) indicated resident exposure to clinical training at the SoCC and/or SoCSC during all 3 years of training. Residents at most of the programs spent 1 to 3 months rotating at the SoCC/SoCSC (6/14 [42.86%]). The other programs indicated residents spent 3 to 6 months (3/14 [21.43%]) or longer than 6 months (3/14 [21.4%]), and only 2 programs (14.29%) indicated that residents spent less than 1 month in the SoCC/SoCSC.
The majority of programs offered a SoC didactic curriculum for residents (10/14 [71.43%]), with an average of 3.3 SoC-related lectures per year (range, 0–5). Almost all programs (13/14 [92.86%]) invited SoC specialists from outside institutions as guest lecturers. Half of the programs (7/14 [50.0%]) used a SoC textbook for resident education. Only 3 programs (21.43%) offered at least 1 introductory SoC dermatology lecture as part of the preclinical medical student dermatology curriculum.
Home institution medical students were able to rotate at their respective SoCC/SoCSC at 11 of 14 institutions (78.57%), while visiting students were able to rotate at half of the programs (7/14 [50.0%]). At some programs, rotating at the SoCC/SoCSC was optional and was not formally integrated into the medical student rotation schedule for both home and visiting students (1/14 [7.14%] and 4/14 [28.57%], respectively). A majority of the programs (8/14 [57.14%]) offered scholarships and/or grants for home and/or visiting URiM students to help fund away rotations.
Despite their SoC focus, only half of the programs with SoCCs/SoCSCs had a formal committee focused on diversity and inclusion (7/14 [50.0%]) Additionally, only 5 of 14 (35.71%) programs had any URiM outreach programs with the medical school and/or the local community.
Comment
As the number of SoCCs/SoCSCs in the United States continues to grow, it is important to highlight their programmatic, research, and educational accomplishments to show the benefits of such programs, including their ability to increase access to culturally competent and inclusive care for diverse patient populations. One study found that nearly 92% of patients in the United States seen by dermatologists are White.15 Although studies have shown that Hispanic/Latino and Black patients are less likely to seek care from a dermatologist,16,17 there is no indication that these patients have a lesser need for such specialty care. Additionally, outcomes of common dermatologic conditions often are poorer in SoC populations.15 The dermatologists leading SoCCs/SoCSCs are actively working to reverse these trends, with Black and Hispanic/Latino patients representing the majority of their patients.
Faculty and Resident Demographics and Areas of Focus—Although there are increased diversity efforts in dermatology and the medical profession more broadly, there still is much work to be done. While individuals with SoC now comprise more than 35% of the US population, only 12% of dermatology residents and 6% of academic dermatology faculty identify as either Black or Hispanic/Latino.5,8,10 These numbers are even more discouraging when considering other URiM racial groups such as Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiians or Native American/American Indians who represent 0% and 0.1% of dermatology faculty, respectively.8,10 Academic programs with SoCCs/SoCSCs are working to create a space in which these discrepancies in representation can begin to be addressed. Compared to the national 6.8% rate of URiM faculty at academic institutions, those with SoCCs/SoCSCs report closer to 10% of faculty identifying as URiM.18 Moreover, almost all programs had faculty specialized in at least 1 condition that predominantly affects patients with SoC. This is of critical importance, as the conditions that most commonly affect SoC populations—such as CCCA, hidradenitis suppurativa, and cutaneous lupus—often are understudied, underfunded, underdiagnosed, and undertreated.19-22
Faculty SoC Research—An important step in narrowing the knowledge gap and improving health care disparities in patients with SoC is to increase SoC research and/or to increase the representation of patients with SoC in research studies. In a 2021 study, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms race/ethnicity, dyschromia, atopic dermatitis, and acne was conducted to investigate publications pertaining to the top 3 most common chief concerns in patients with SoC. Only 1.6% of studies analyzed (N=74,941) had a specific focus on SoC.12 A similar study found that among the top 5 dermatology-focused research journals, only 3.4% of all research (N=11,003) on the top 3 most common chief concerns in patients with SOC was conducted in patients with SoC.23 Research efforts focused on dermatologic issues that affect patients with SoC are a priority at SoCCs/SoCSCs. In our study, all respondents indicated that they had at least 1 ongoing observational study; the most commonly studied conditions were CCCA, keloids/hypertrophic scarring, and atopic dermatitis, all of which are conditions that either occur in high frequency or primarily occur in SoC. Only 35.71% (5/14) of respondents had active clinical trials related to SoC, and only 21.43% (3/14) and 28.57% (4/14) had internal and external funding, respectively. Although research efforts are a priority at SoCCs/SoCSCs, our survey study highlights the continued paucity of formal clinical trials as well as funding for SoC-focused research. Improved research efforts for SoC must address these deficits in funding, academic support, and other resources.
It also is of great importance for institutions to provide support for trainees wanting to pursue SoC research. Encouragingly, more than half (57.14%) of SoCCs/SoCSCs have developed formal research opportunities for residents, and nearly 64.29% have formal opportunities for medical students. These efforts to provide early experiences in SoC research are especially impactful by cultivating interest in working with populations with SoC and hopefully inspiring future dermatologists to engage in further SoC research.
SoC Education and Diversity Initiatives—Although it is important to increase representation of URiM physicians in dermatology and to train more SoC specialists, it is imperative that all dermatologists feel comfortable recognizing and treating dermatologic conditions in patients of all skin tones and all racial/ethnic backgrounds; however, many studies suggest that residents not only lack formal didactics and education in SoC, but even more unsettling, they also lack confidence in treating SoC.13,24 However, one study showed that this can be changed; Mhlaba et al25 assessed a SoC curriculum for dermatology residents, and indeed all of the residents indicated that the curriculum improved their ability to treat SoC patients. This deficit in dermatology residency training is specifically addressed by SoCCs/SoCSCs. In our study, all respondents indicated that residents rotate through their centers. Moreover, our study found that most of the academic institutions with SoCCs/SoCSCs provide a SoC didactic curriculum for residents, and almost all of the programs invited SoC specialists to give guest lectures. This is in contrast to a 2022 study showing that 63.2% (N=125) of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures.14 These findings highlight the critical role that SoCCs/SoCSCs can provide in dermatology residency training.
Although SoCCs/SoCSCs have made considerable progress, there is still much room for improvement. Namely, only half of the respondents in our study indicated that their program has formally incorporated a SoC textbook into resident education (eTable 3). Representation of SoC in the textbooks that dermatology residents use is critically important because these images form the foundation of the morphologic aids of diagnosis. Numerous studies have analyzed popular dermatologic textbooks used by residency programs nationwide, finding the number of SoC images across dermatology textbooks ranging from 4% to 18%.26,27 The use of standard dermatology textbooks is not enough to train residents to be competent in diagnosing and treating patients with SoC. There should be a concerted effort across the field of dermatology to encourage the development of a SoC educational curriculum at every academic dermatology program, including SoC textbooks, Kodachromes, and online/electronic resources.
Efforts to increase diversity in dermatology and dermatologic training should start in medical school preclinical curriculums and medical student rotations. Although our survey did not assess current medical student curricula, the benefits of academic institutions with SoCCs/SoCSCs are highlighted by the ability for both home and visiting medical students to rotate through the centers and gain early exposure to SoC dermatology. Most of the programs even provide scholarships and/or grants for URiM students to help fund their rotations, which is of critical importance considering the mounting data that the financial burden of visiting rotations disproportionately affects URiM students.28
Study Limitations—Although we did an extensive search and believe to have correctly identified all 15 formal SoCCs/SoCSCs with a high response rate (93.3%), there are institutions that do not have formalized SoCCs/SoCSCs but are known to serve SoC populations. Likewise, there are private dermatology practices not associated with academic centers that have SoC specialists and positively contribute to SoC patient care, research, and education that were not included in this study. Additionally, the data for this study were collected in 2020 and analyzed in 2021, so it is possible that not all SoCCs, divisions, or clinics were included in this study, particularly if established after 2021.
Conclusion
As the United States continues to diversify, the proportion of patients with SoC will continue to grow, and it is imperative that this racial, ethnic, and cultural diversity is reflected in the dermatology workforce as well as research and training. The current deficits in medical training related to SoC populations and the importance for patients with SoC to find dermatologists who can appropriately treat them is well known.29 Skin of color centers/SoCSCs strive to increase access to care for patients with SoC, improve cultural competency, promote diversity among faculty and trainees, and encourage SoC research and education at all levels. We urge academic dermatology training programs to make SoC education, research, and patient care a departmental priority. Important first steps include departmental diversification at all levels, incorporating SoC into curricula for residents, providing and securing funding for SoC research, and supporting the establishment of more formal SoCCs and/or SoCSCs to help reduce dermatologic health care disparities among patients with SoC and improve health equity.
Appendix

- Colby SL, Jennifer JM. Projections of the size and composition of the U.S. population: 2014 to 2060. United States Census Bureau website. March 3, 2015. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.html
- Tull RZ, Kerby E, Subash JJ, et al. Ethnic skin centers in the United States: where are we in 2020? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1757-1759. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.054
- Shen MJ, Peterson EB, Costas-Muñiz R, et al. The effects of race and racial concordance on patient-physician communication: a systematic review of the literature. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2018;5:117-140. doi:10.1007/s40615-017-0350-4
- Saha S, Beach MC. Impact of physician race on patient decision-making and ratings of physicians: a randomized experiment using video vignettes. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:1084-1091. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05646-z
- Quick Facts: United States. US Census Bureau website. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045221
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.10.044
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.07.001
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table B5. number of active MD residents, by race/ethnicity (alone or in combination) and GME specialty. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/report-residents/2022/table-b5-md-residents-race-ethnicity-and-specialty
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table B6. number of active DO residents, by race/ethnicity (alone or in combination) and GME specialty. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/report-residents/2022/table-b6-do-residents-race-ethnicity-and-specialty
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table 16. U.S. medical school faculty by gender, race/ethnicity, and department, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/media/8456/download
- Chen V, Akhtar S, Zheng C, et al. Assessment of changes in diversity in dermatology clinical trials between 2010-2015 and 2015-2020: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:288-292. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5596
- Montgomery SNB, Elbuluk N. A quantitative analysis of research publications focused on the top chief complaints in patients withskinof color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:241-242. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.031
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.06.024
- Ibraheim MK, Gupta R, Dao H, et al. Evaluating skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: data from a national survey. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:228-233. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.11.015
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3114
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 202;156:312-319. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4818
- Dlova NC, Salkey KS, Callender VD, et al. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: new insights and a call for action. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S54-S56. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.01.004
- Okeke CAV, Perry JD, Simmonds FC, et al. Clinical trials and skin of color: the example of hidradenitis suppurativa. dermatology. 2022;238:180-184. doi:10.1159/000516467
- Robles J, Anim T, Wusu MH, et al. An Approach to Faculty Development for Underrepresented Minorities in Medicine. South Med J. 2021;114(9):579-582. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000001290
- Serrano L, Ulschmid C, Szabo A, et al. Racial disparities of delay in diagnosis and dermatologic care for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;114:613-616. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2022.08.002
- Drenkard C, Lim SS. Update on lupus epidemiology: advancinghealth disparities research through the study of minority populations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31:689-696. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000646
- Militello M, Szeto MD, Presley CL, et al. A quantitative analysis of research publications focused on skin of color: representation in academic dermatology journals. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:E189-E192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.04.053
- Cline A, Winter RP, Kourosh S, et al. Multiethnic training in residency: a survey of dermatology residents. Cutis. 2020;105:310-313.
- Mhlaba JM, Pontes DS, Patterson SS, et al. Evaluation of a skin of color curriculum for dermatology residents. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:786-789. doi:10.36849/JDD.6193
- Adelekun A, Onyekaba G, Lipoff JB. Skin color in dermatology textbooks: an updated evaluation and analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:194-196. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.084
- Harp T, Militello M, McCarver V, et al. Further analysis of skin of color representation in dermatology textbooks used by residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:E39-E41. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.069
- Muzumdar S, Grant-Kels JM, Feng H. Strategies to improve medical student visiting rotations. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:727-728. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.11.001
- Gorbatenko-Roth K, Prose N, Kundu RV, et al. Assessment of Black patients’ perception of their dermatology care. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1129-1134. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2063
Although individuals with skin of color (SoC) are expected to become at least half of the US population by the year 2044, there remains a paucity of education and exposure to treatment of patients with SoC at many dermatology residency programs across the country.1 One way to improve SoC education has been the formation of specialized clinics, centers, and programs. The first SoC center (SoCC) was established in 1999 at Mount Sinai–St. Luke’s Roosevelt in New York, New York2; since then, at least 13 additional formal SoCCs or SoC specialty clinics (SoCSCs) at US academic dermatology programs have been established.
Skin of color centers serve several important purposes: they improve dermatologic care in patients with SoC, increase research efforts focused on SoC dermatologic conditions, and educate dermatology resident and fellow trainees about SoC. Improving dermatologic care of patients with SoC in the United States is important in providing equitable health care and improving health disparities. Studies have shown that patient-physician racial and cultural concordance can positively impact patient care, increase patient trust and rapport, and improve patient-physician communication, and it can even influence patient decision-making to seek care.3,4 Unfortunately, even though the US population continues to diversify, the racial/ethnic backgrounds of dermatologists do not parallel this trend; Hispanic and Black physicians comprise 18.9% and 13.6% of the general population, respectively, but represent only 4.2% and 3.0% of dermatologists, respectively.5-7 This deficit is mirrored by resident and faculty representation, with Black and Latino representation ranging from 3% to 7%.8-10
Many SoCC’s engage in research focused on dermatologic conditions affecting patients with SoC, which is vital to improving the dermatologic care in this underserved population. Despite increasing recognition of the importance of SoC research, there remains a paucity of clinical trials and research specifically focused on or demonstrating equitable representation of SoC.11,12
The education and training of future dermatologists is another important area that can be improved by SoCCs. A 2008 study involving 63 chief residents showed that approximately half (52.4% [33/63]) of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures, and 30.2% (19/63) reported having a dedicated rotation where they gained specific experience treating patients with SoC.13 A later study in 2022 (N=125) found that 63.2% of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures, and only 11.2% reported having a dedicated rotation where they gained experience treating patients with SoC.14 These findings suggest that in the last 14 years, formal SoC education—specifically SoC clinical training—has not increased sufficiently.
We conducted a cross-sectional survey study to provide an in-depth analysis of SoCCs and SoCSCs in the United States, including their patient care focus, research, and program diversity.
Methods
We conducted an investigator-initiated, multicenter, cross-sectional survey study of all SoCCs in the United States and their respective academic residency programs. Fifteen formal SoCCs and/or SoCSCs were identified by dermatology program websites and an article by Tull et al2 on the state of ethnic skin centers. All programs and centers identified were associated with a dermatology residency program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
A 42-item questionnaire was sent via email to the directors of these centers and clinics with the intent to collect descriptive information about each of the SoCCs, the diversity of the faculty and residents of the associated dermatology department, current research and funding, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and trainee education from March through April 2020. Data were analyzed using Excel and SPSS statistical software to obtain descriptive statistics including the mean value numeric trends across programs.
This study underwent expedited review and was approved by the University of Southern California (Los Angeles, California) institutional review board (IRB #HS-20-00113). Patient consent was not applicable, as no information was collected about patients.
Results
Fourteen directors from SoCCs/SoCSCs completed the questionnaire (93.3% response rate). Most centers were located in urban areas (12/14 [85.71%]), except for 2 in rural or suburban settings (Table). Most of the SoCCs/SoCSCs were located in the South (5/14 [35.71%]), followed by the Northeast (4/14 [28.57%]), West (3/14 [21.43%]), and Midwest (2/14 [14.29%])(Table). Six (42.86%) of the programs had a SoCSC, 3 (21.43%) had a formal SoCC, and 5 (35.71%) had both. Across all centers, the most common population seen and treated was Black/African American followed by Hispanic/Latino and Asian, respectively. The most commonly seen dermatologic conditions were acne, pigmentary disorders, alopecia, and atopic dermatitis (Figure). The most common cosmetic practice performed for patients with SoC was dermatosis papulosa nigra/seborrheic keratosis removal, followed by laser treatments, skin tag removal, chemical peels, and neuromodulator injections, respectively.

Faculty and Resident Demographics and Areas of Focus—The demographics and diversity of the dermatology faculty and residents at each individual institution also were assessed. The average number of full-time faculty at each institution was 19.4 (range, 2–48), while the average number of full-time faculty who identified as underrepresented in medicine (URiM) was 2.1 (range, 0–5). The average number of residents at each institution was 17.1 (range, 10–31), while the average number of URiM residents was 1.7 (range, 1–3).

The average number of full-time faculty members at each SoCC was 1.6 (range, 1–4). The majority of program directors reported having other specialists in their department that also treated dermatologic conditions predominantly affecting patients with SoC (10/14 [71.43%]). The 3 most common areas of expertise were alopecia, including central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA); cutaneous lupus; and traction alopecia (eTable 1).
Faculty SoC Research—Only a minority of programs had active clinical trials related to SoC (5/14 [35.71%]). Clinical research was the most common type of research being conducted (11/14 [78.57%]), followed by basic science/translational (4/14 [28.57%]) and epidemiologic research (2/14 [14.29%]). The most commonly investigated conditions for observational studies included CCCA, keloids/hypertrophic scarring, and atopic dermatitis (eTable 2). Only 8 of 14 programs had formal SoC research opportunities for residents (57.14%), while 9 had opportunities for medical students (64.29%).
Few institutions had internal funding (3/14 [21.43%]) or external funding (4/14 [28.57%]) for SoC research. Extramural fun ding sources included the Skin of Color Society, the Dermatology Foundation, and the Radiation Oncology Institute, as well as industry funding. No federal funding was received by any of the sites.
Skin of Color Education and Diversity Initiatives—All 14 programs had residents rotating through their SoCC and/or SoCSCs. The vast majority (12/14 [85.71%]) indicated resident exposure to clinical training at the SoCC and/or SoCSC during all 3 years of training. Residents at most of the programs spent 1 to 3 months rotating at the SoCC/SoCSC (6/14 [42.86%]). The other programs indicated residents spent 3 to 6 months (3/14 [21.43%]) or longer than 6 months (3/14 [21.4%]), and only 2 programs (14.29%) indicated that residents spent less than 1 month in the SoCC/SoCSC.
The majority of programs offered a SoC didactic curriculum for residents (10/14 [71.43%]), with an average of 3.3 SoC-related lectures per year (range, 0–5). Almost all programs (13/14 [92.86%]) invited SoC specialists from outside institutions as guest lecturers. Half of the programs (7/14 [50.0%]) used a SoC textbook for resident education. Only 3 programs (21.43%) offered at least 1 introductory SoC dermatology lecture as part of the preclinical medical student dermatology curriculum.
Home institution medical students were able to rotate at their respective SoCC/SoCSC at 11 of 14 institutions (78.57%), while visiting students were able to rotate at half of the programs (7/14 [50.0%]). At some programs, rotating at the SoCC/SoCSC was optional and was not formally integrated into the medical student rotation schedule for both home and visiting students (1/14 [7.14%] and 4/14 [28.57%], respectively). A majority of the programs (8/14 [57.14%]) offered scholarships and/or grants for home and/or visiting URiM students to help fund away rotations.
Despite their SoC focus, only half of the programs with SoCCs/SoCSCs had a formal committee focused on diversity and inclusion (7/14 [50.0%]) Additionally, only 5 of 14 (35.71%) programs had any URiM outreach programs with the medical school and/or the local community.
Comment
As the number of SoCCs/SoCSCs in the United States continues to grow, it is important to highlight their programmatic, research, and educational accomplishments to show the benefits of such programs, including their ability to increase access to culturally competent and inclusive care for diverse patient populations. One study found that nearly 92% of patients in the United States seen by dermatologists are White.15 Although studies have shown that Hispanic/Latino and Black patients are less likely to seek care from a dermatologist,16,17 there is no indication that these patients have a lesser need for such specialty care. Additionally, outcomes of common dermatologic conditions often are poorer in SoC populations.15 The dermatologists leading SoCCs/SoCSCs are actively working to reverse these trends, with Black and Hispanic/Latino patients representing the majority of their patients.
Faculty and Resident Demographics and Areas of Focus—Although there are increased diversity efforts in dermatology and the medical profession more broadly, there still is much work to be done. While individuals with SoC now comprise more than 35% of the US population, only 12% of dermatology residents and 6% of academic dermatology faculty identify as either Black or Hispanic/Latino.5,8,10 These numbers are even more discouraging when considering other URiM racial groups such as Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiians or Native American/American Indians who represent 0% and 0.1% of dermatology faculty, respectively.8,10 Academic programs with SoCCs/SoCSCs are working to create a space in which these discrepancies in representation can begin to be addressed. Compared to the national 6.8% rate of URiM faculty at academic institutions, those with SoCCs/SoCSCs report closer to 10% of faculty identifying as URiM.18 Moreover, almost all programs had faculty specialized in at least 1 condition that predominantly affects patients with SoC. This is of critical importance, as the conditions that most commonly affect SoC populations—such as CCCA, hidradenitis suppurativa, and cutaneous lupus—often are understudied, underfunded, underdiagnosed, and undertreated.19-22
Faculty SoC Research—An important step in narrowing the knowledge gap and improving health care disparities in patients with SoC is to increase SoC research and/or to increase the representation of patients with SoC in research studies. In a 2021 study, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms race/ethnicity, dyschromia, atopic dermatitis, and acne was conducted to investigate publications pertaining to the top 3 most common chief concerns in patients with SoC. Only 1.6% of studies analyzed (N=74,941) had a specific focus on SoC.12 A similar study found that among the top 5 dermatology-focused research journals, only 3.4% of all research (N=11,003) on the top 3 most common chief concerns in patients with SOC was conducted in patients with SoC.23 Research efforts focused on dermatologic issues that affect patients with SoC are a priority at SoCCs/SoCSCs. In our study, all respondents indicated that they had at least 1 ongoing observational study; the most commonly studied conditions were CCCA, keloids/hypertrophic scarring, and atopic dermatitis, all of which are conditions that either occur in high frequency or primarily occur in SoC. Only 35.71% (5/14) of respondents had active clinical trials related to SoC, and only 21.43% (3/14) and 28.57% (4/14) had internal and external funding, respectively. Although research efforts are a priority at SoCCs/SoCSCs, our survey study highlights the continued paucity of formal clinical trials as well as funding for SoC-focused research. Improved research efforts for SoC must address these deficits in funding, academic support, and other resources.
It also is of great importance for institutions to provide support for trainees wanting to pursue SoC research. Encouragingly, more than half (57.14%) of SoCCs/SoCSCs have developed formal research opportunities for residents, and nearly 64.29% have formal opportunities for medical students. These efforts to provide early experiences in SoC research are especially impactful by cultivating interest in working with populations with SoC and hopefully inspiring future dermatologists to engage in further SoC research.
SoC Education and Diversity Initiatives—Although it is important to increase representation of URiM physicians in dermatology and to train more SoC specialists, it is imperative that all dermatologists feel comfortable recognizing and treating dermatologic conditions in patients of all skin tones and all racial/ethnic backgrounds; however, many studies suggest that residents not only lack formal didactics and education in SoC, but even more unsettling, they also lack confidence in treating SoC.13,24 However, one study showed that this can be changed; Mhlaba et al25 assessed a SoC curriculum for dermatology residents, and indeed all of the residents indicated that the curriculum improved their ability to treat SoC patients. This deficit in dermatology residency training is specifically addressed by SoCCs/SoCSCs. In our study, all respondents indicated that residents rotate through their centers. Moreover, our study found that most of the academic institutions with SoCCs/SoCSCs provide a SoC didactic curriculum for residents, and almost all of the programs invited SoC specialists to give guest lectures. This is in contrast to a 2022 study showing that 63.2% (N=125) of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures.14 These findings highlight the critical role that SoCCs/SoCSCs can provide in dermatology residency training.
Although SoCCs/SoCSCs have made considerable progress, there is still much room for improvement. Namely, only half of the respondents in our study indicated that their program has formally incorporated a SoC textbook into resident education (eTable 3). Representation of SoC in the textbooks that dermatology residents use is critically important because these images form the foundation of the morphologic aids of diagnosis. Numerous studies have analyzed popular dermatologic textbooks used by residency programs nationwide, finding the number of SoC images across dermatology textbooks ranging from 4% to 18%.26,27 The use of standard dermatology textbooks is not enough to train residents to be competent in diagnosing and treating patients with SoC. There should be a concerted effort across the field of dermatology to encourage the development of a SoC educational curriculum at every academic dermatology program, including SoC textbooks, Kodachromes, and online/electronic resources.
Efforts to increase diversity in dermatology and dermatologic training should start in medical school preclinical curriculums and medical student rotations. Although our survey did not assess current medical student curricula, the benefits of academic institutions with SoCCs/SoCSCs are highlighted by the ability for both home and visiting medical students to rotate through the centers and gain early exposure to SoC dermatology. Most of the programs even provide scholarships and/or grants for URiM students to help fund their rotations, which is of critical importance considering the mounting data that the financial burden of visiting rotations disproportionately affects URiM students.28
Study Limitations—Although we did an extensive search and believe to have correctly identified all 15 formal SoCCs/SoCSCs with a high response rate (93.3%), there are institutions that do not have formalized SoCCs/SoCSCs but are known to serve SoC populations. Likewise, there are private dermatology practices not associated with academic centers that have SoC specialists and positively contribute to SoC patient care, research, and education that were not included in this study. Additionally, the data for this study were collected in 2020 and analyzed in 2021, so it is possible that not all SoCCs, divisions, or clinics were included in this study, particularly if established after 2021.
Conclusion
As the United States continues to diversify, the proportion of patients with SoC will continue to grow, and it is imperative that this racial, ethnic, and cultural diversity is reflected in the dermatology workforce as well as research and training. The current deficits in medical training related to SoC populations and the importance for patients with SoC to find dermatologists who can appropriately treat them is well known.29 Skin of color centers/SoCSCs strive to increase access to care for patients with SoC, improve cultural competency, promote diversity among faculty and trainees, and encourage SoC research and education at all levels. We urge academic dermatology training programs to make SoC education, research, and patient care a departmental priority. Important first steps include departmental diversification at all levels, incorporating SoC into curricula for residents, providing and securing funding for SoC research, and supporting the establishment of more formal SoCCs and/or SoCSCs to help reduce dermatologic health care disparities among patients with SoC and improve health equity.
Appendix



Although individuals with skin of color (SoC) are expected to become at least half of the US population by the year 2044, there remains a paucity of education and exposure to treatment of patients with SoC at many dermatology residency programs across the country.1 One way to improve SoC education has been the formation of specialized clinics, centers, and programs. The first SoC center (SoCC) was established in 1999 at Mount Sinai–St. Luke’s Roosevelt in New York, New York2; since then, at least 13 additional formal SoCCs or SoC specialty clinics (SoCSCs) at US academic dermatology programs have been established.
Skin of color centers serve several important purposes: they improve dermatologic care in patients with SoC, increase research efforts focused on SoC dermatologic conditions, and educate dermatology resident and fellow trainees about SoC. Improving dermatologic care of patients with SoC in the United States is important in providing equitable health care and improving health disparities. Studies have shown that patient-physician racial and cultural concordance can positively impact patient care, increase patient trust and rapport, and improve patient-physician communication, and it can even influence patient decision-making to seek care.3,4 Unfortunately, even though the US population continues to diversify, the racial/ethnic backgrounds of dermatologists do not parallel this trend; Hispanic and Black physicians comprise 18.9% and 13.6% of the general population, respectively, but represent only 4.2% and 3.0% of dermatologists, respectively.5-7 This deficit is mirrored by resident and faculty representation, with Black and Latino representation ranging from 3% to 7%.8-10
Many SoCC’s engage in research focused on dermatologic conditions affecting patients with SoC, which is vital to improving the dermatologic care in this underserved population. Despite increasing recognition of the importance of SoC research, there remains a paucity of clinical trials and research specifically focused on or demonstrating equitable representation of SoC.11,12
The education and training of future dermatologists is another important area that can be improved by SoCCs. A 2008 study involving 63 chief residents showed that approximately half (52.4% [33/63]) of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures, and 30.2% (19/63) reported having a dedicated rotation where they gained specific experience treating patients with SoC.13 A later study in 2022 (N=125) found that 63.2% of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures, and only 11.2% reported having a dedicated rotation where they gained experience treating patients with SoC.14 These findings suggest that in the last 14 years, formal SoC education—specifically SoC clinical training—has not increased sufficiently.
We conducted a cross-sectional survey study to provide an in-depth analysis of SoCCs and SoCSCs in the United States, including their patient care focus, research, and program diversity.
Methods
We conducted an investigator-initiated, multicenter, cross-sectional survey study of all SoCCs in the United States and their respective academic residency programs. Fifteen formal SoCCs and/or SoCSCs were identified by dermatology program websites and an article by Tull et al2 on the state of ethnic skin centers. All programs and centers identified were associated with a dermatology residency program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
A 42-item questionnaire was sent via email to the directors of these centers and clinics with the intent to collect descriptive information about each of the SoCCs, the diversity of the faculty and residents of the associated dermatology department, current research and funding, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and trainee education from March through April 2020. Data were analyzed using Excel and SPSS statistical software to obtain descriptive statistics including the mean value numeric trends across programs.
This study underwent expedited review and was approved by the University of Southern California (Los Angeles, California) institutional review board (IRB #HS-20-00113). Patient consent was not applicable, as no information was collected about patients.
Results
Fourteen directors from SoCCs/SoCSCs completed the questionnaire (93.3% response rate). Most centers were located in urban areas (12/14 [85.71%]), except for 2 in rural or suburban settings (Table). Most of the SoCCs/SoCSCs were located in the South (5/14 [35.71%]), followed by the Northeast (4/14 [28.57%]), West (3/14 [21.43%]), and Midwest (2/14 [14.29%])(Table). Six (42.86%) of the programs had a SoCSC, 3 (21.43%) had a formal SoCC, and 5 (35.71%) had both. Across all centers, the most common population seen and treated was Black/African American followed by Hispanic/Latino and Asian, respectively. The most commonly seen dermatologic conditions were acne, pigmentary disorders, alopecia, and atopic dermatitis (Figure). The most common cosmetic practice performed for patients with SoC was dermatosis papulosa nigra/seborrheic keratosis removal, followed by laser treatments, skin tag removal, chemical peels, and neuromodulator injections, respectively.

Faculty and Resident Demographics and Areas of Focus—The demographics and diversity of the dermatology faculty and residents at each individual institution also were assessed. The average number of full-time faculty at each institution was 19.4 (range, 2–48), while the average number of full-time faculty who identified as underrepresented in medicine (URiM) was 2.1 (range, 0–5). The average number of residents at each institution was 17.1 (range, 10–31), while the average number of URiM residents was 1.7 (range, 1–3).

The average number of full-time faculty members at each SoCC was 1.6 (range, 1–4). The majority of program directors reported having other specialists in their department that also treated dermatologic conditions predominantly affecting patients with SoC (10/14 [71.43%]). The 3 most common areas of expertise were alopecia, including central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA); cutaneous lupus; and traction alopecia (eTable 1).
Faculty SoC Research—Only a minority of programs had active clinical trials related to SoC (5/14 [35.71%]). Clinical research was the most common type of research being conducted (11/14 [78.57%]), followed by basic science/translational (4/14 [28.57%]) and epidemiologic research (2/14 [14.29%]). The most commonly investigated conditions for observational studies included CCCA, keloids/hypertrophic scarring, and atopic dermatitis (eTable 2). Only 8 of 14 programs had formal SoC research opportunities for residents (57.14%), while 9 had opportunities for medical students (64.29%).
Few institutions had internal funding (3/14 [21.43%]) or external funding (4/14 [28.57%]) for SoC research. Extramural fun ding sources included the Skin of Color Society, the Dermatology Foundation, and the Radiation Oncology Institute, as well as industry funding. No federal funding was received by any of the sites.
Skin of Color Education and Diversity Initiatives—All 14 programs had residents rotating through their SoCC and/or SoCSCs. The vast majority (12/14 [85.71%]) indicated resident exposure to clinical training at the SoCC and/or SoCSC during all 3 years of training. Residents at most of the programs spent 1 to 3 months rotating at the SoCC/SoCSC (6/14 [42.86%]). The other programs indicated residents spent 3 to 6 months (3/14 [21.43%]) or longer than 6 months (3/14 [21.4%]), and only 2 programs (14.29%) indicated that residents spent less than 1 month in the SoCC/SoCSC.
The majority of programs offered a SoC didactic curriculum for residents (10/14 [71.43%]), with an average of 3.3 SoC-related lectures per year (range, 0–5). Almost all programs (13/14 [92.86%]) invited SoC specialists from outside institutions as guest lecturers. Half of the programs (7/14 [50.0%]) used a SoC textbook for resident education. Only 3 programs (21.43%) offered at least 1 introductory SoC dermatology lecture as part of the preclinical medical student dermatology curriculum.
Home institution medical students were able to rotate at their respective SoCC/SoCSC at 11 of 14 institutions (78.57%), while visiting students were able to rotate at half of the programs (7/14 [50.0%]). At some programs, rotating at the SoCC/SoCSC was optional and was not formally integrated into the medical student rotation schedule for both home and visiting students (1/14 [7.14%] and 4/14 [28.57%], respectively). A majority of the programs (8/14 [57.14%]) offered scholarships and/or grants for home and/or visiting URiM students to help fund away rotations.
Despite their SoC focus, only half of the programs with SoCCs/SoCSCs had a formal committee focused on diversity and inclusion (7/14 [50.0%]) Additionally, only 5 of 14 (35.71%) programs had any URiM outreach programs with the medical school and/or the local community.
Comment
As the number of SoCCs/SoCSCs in the United States continues to grow, it is important to highlight their programmatic, research, and educational accomplishments to show the benefits of such programs, including their ability to increase access to culturally competent and inclusive care for diverse patient populations. One study found that nearly 92% of patients in the United States seen by dermatologists are White.15 Although studies have shown that Hispanic/Latino and Black patients are less likely to seek care from a dermatologist,16,17 there is no indication that these patients have a lesser need for such specialty care. Additionally, outcomes of common dermatologic conditions often are poorer in SoC populations.15 The dermatologists leading SoCCs/SoCSCs are actively working to reverse these trends, with Black and Hispanic/Latino patients representing the majority of their patients.
Faculty and Resident Demographics and Areas of Focus—Although there are increased diversity efforts in dermatology and the medical profession more broadly, there still is much work to be done. While individuals with SoC now comprise more than 35% of the US population, only 12% of dermatology residents and 6% of academic dermatology faculty identify as either Black or Hispanic/Latino.5,8,10 These numbers are even more discouraging when considering other URiM racial groups such as Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiians or Native American/American Indians who represent 0% and 0.1% of dermatology faculty, respectively.8,10 Academic programs with SoCCs/SoCSCs are working to create a space in which these discrepancies in representation can begin to be addressed. Compared to the national 6.8% rate of URiM faculty at academic institutions, those with SoCCs/SoCSCs report closer to 10% of faculty identifying as URiM.18 Moreover, almost all programs had faculty specialized in at least 1 condition that predominantly affects patients with SoC. This is of critical importance, as the conditions that most commonly affect SoC populations—such as CCCA, hidradenitis suppurativa, and cutaneous lupus—often are understudied, underfunded, underdiagnosed, and undertreated.19-22
Faculty SoC Research—An important step in narrowing the knowledge gap and improving health care disparities in patients with SoC is to increase SoC research and/or to increase the representation of patients with SoC in research studies. In a 2021 study, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms race/ethnicity, dyschromia, atopic dermatitis, and acne was conducted to investigate publications pertaining to the top 3 most common chief concerns in patients with SoC. Only 1.6% of studies analyzed (N=74,941) had a specific focus on SoC.12 A similar study found that among the top 5 dermatology-focused research journals, only 3.4% of all research (N=11,003) on the top 3 most common chief concerns in patients with SOC was conducted in patients with SoC.23 Research efforts focused on dermatologic issues that affect patients with SoC are a priority at SoCCs/SoCSCs. In our study, all respondents indicated that they had at least 1 ongoing observational study; the most commonly studied conditions were CCCA, keloids/hypertrophic scarring, and atopic dermatitis, all of which are conditions that either occur in high frequency or primarily occur in SoC. Only 35.71% (5/14) of respondents had active clinical trials related to SoC, and only 21.43% (3/14) and 28.57% (4/14) had internal and external funding, respectively. Although research efforts are a priority at SoCCs/SoCSCs, our survey study highlights the continued paucity of formal clinical trials as well as funding for SoC-focused research. Improved research efforts for SoC must address these deficits in funding, academic support, and other resources.
It also is of great importance for institutions to provide support for trainees wanting to pursue SoC research. Encouragingly, more than half (57.14%) of SoCCs/SoCSCs have developed formal research opportunities for residents, and nearly 64.29% have formal opportunities for medical students. These efforts to provide early experiences in SoC research are especially impactful by cultivating interest in working with populations with SoC and hopefully inspiring future dermatologists to engage in further SoC research.
SoC Education and Diversity Initiatives—Although it is important to increase representation of URiM physicians in dermatology and to train more SoC specialists, it is imperative that all dermatologists feel comfortable recognizing and treating dermatologic conditions in patients of all skin tones and all racial/ethnic backgrounds; however, many studies suggest that residents not only lack formal didactics and education in SoC, but even more unsettling, they also lack confidence in treating SoC.13,24 However, one study showed that this can be changed; Mhlaba et al25 assessed a SoC curriculum for dermatology residents, and indeed all of the residents indicated that the curriculum improved their ability to treat SoC patients. This deficit in dermatology residency training is specifically addressed by SoCCs/SoCSCs. In our study, all respondents indicated that residents rotate through their centers. Moreover, our study found that most of the academic institutions with SoCCs/SoCSCs provide a SoC didactic curriculum for residents, and almost all of the programs invited SoC specialists to give guest lectures. This is in contrast to a 2022 study showing that 63.2% (N=125) of graduating dermatology residents reported receiving SoC-specific didactics, sessions, or lectures.14 These findings highlight the critical role that SoCCs/SoCSCs can provide in dermatology residency training.
Although SoCCs/SoCSCs have made considerable progress, there is still much room for improvement. Namely, only half of the respondents in our study indicated that their program has formally incorporated a SoC textbook into resident education (eTable 3). Representation of SoC in the textbooks that dermatology residents use is critically important because these images form the foundation of the morphologic aids of diagnosis. Numerous studies have analyzed popular dermatologic textbooks used by residency programs nationwide, finding the number of SoC images across dermatology textbooks ranging from 4% to 18%.26,27 The use of standard dermatology textbooks is not enough to train residents to be competent in diagnosing and treating patients with SoC. There should be a concerted effort across the field of dermatology to encourage the development of a SoC educational curriculum at every academic dermatology program, including SoC textbooks, Kodachromes, and online/electronic resources.
Efforts to increase diversity in dermatology and dermatologic training should start in medical school preclinical curriculums and medical student rotations. Although our survey did not assess current medical student curricula, the benefits of academic institutions with SoCCs/SoCSCs are highlighted by the ability for both home and visiting medical students to rotate through the centers and gain early exposure to SoC dermatology. Most of the programs even provide scholarships and/or grants for URiM students to help fund their rotations, which is of critical importance considering the mounting data that the financial burden of visiting rotations disproportionately affects URiM students.28
Study Limitations—Although we did an extensive search and believe to have correctly identified all 15 formal SoCCs/SoCSCs with a high response rate (93.3%), there are institutions that do not have formalized SoCCs/SoCSCs but are known to serve SoC populations. Likewise, there are private dermatology practices not associated with academic centers that have SoC specialists and positively contribute to SoC patient care, research, and education that were not included in this study. Additionally, the data for this study were collected in 2020 and analyzed in 2021, so it is possible that not all SoCCs, divisions, or clinics were included in this study, particularly if established after 2021.
Conclusion
As the United States continues to diversify, the proportion of patients with SoC will continue to grow, and it is imperative that this racial, ethnic, and cultural diversity is reflected in the dermatology workforce as well as research and training. The current deficits in medical training related to SoC populations and the importance for patients with SoC to find dermatologists who can appropriately treat them is well known.29 Skin of color centers/SoCSCs strive to increase access to care for patients with SoC, improve cultural competency, promote diversity among faculty and trainees, and encourage SoC research and education at all levels. We urge academic dermatology training programs to make SoC education, research, and patient care a departmental priority. Important first steps include departmental diversification at all levels, incorporating SoC into curricula for residents, providing and securing funding for SoC research, and supporting the establishment of more formal SoCCs and/or SoCSCs to help reduce dermatologic health care disparities among patients with SoC and improve health equity.
Appendix



- Colby SL, Jennifer JM. Projections of the size and composition of the U.S. population: 2014 to 2060. United States Census Bureau website. March 3, 2015. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.html
- Tull RZ, Kerby E, Subash JJ, et al. Ethnic skin centers in the United States: where are we in 2020? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1757-1759. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.054
- Shen MJ, Peterson EB, Costas-Muñiz R, et al. The effects of race and racial concordance on patient-physician communication: a systematic review of the literature. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2018;5:117-140. doi:10.1007/s40615-017-0350-4
- Saha S, Beach MC. Impact of physician race on patient decision-making and ratings of physicians: a randomized experiment using video vignettes. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:1084-1091. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05646-z
- Quick Facts: United States. US Census Bureau website. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045221
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.10.044
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.07.001
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table B5. number of active MD residents, by race/ethnicity (alone or in combination) and GME specialty. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/report-residents/2022/table-b5-md-residents-race-ethnicity-and-specialty
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table B6. number of active DO residents, by race/ethnicity (alone or in combination) and GME specialty. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/report-residents/2022/table-b6-do-residents-race-ethnicity-and-specialty
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table 16. U.S. medical school faculty by gender, race/ethnicity, and department, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/media/8456/download
- Chen V, Akhtar S, Zheng C, et al. Assessment of changes in diversity in dermatology clinical trials between 2010-2015 and 2015-2020: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:288-292. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5596
- Montgomery SNB, Elbuluk N. A quantitative analysis of research publications focused on the top chief complaints in patients withskinof color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:241-242. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.031
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.06.024
- Ibraheim MK, Gupta R, Dao H, et al. Evaluating skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: data from a national survey. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:228-233. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.11.015
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3114
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 202;156:312-319. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4818
- Dlova NC, Salkey KS, Callender VD, et al. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: new insights and a call for action. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S54-S56. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.01.004
- Okeke CAV, Perry JD, Simmonds FC, et al. Clinical trials and skin of color: the example of hidradenitis suppurativa. dermatology. 2022;238:180-184. doi:10.1159/000516467
- Robles J, Anim T, Wusu MH, et al. An Approach to Faculty Development for Underrepresented Minorities in Medicine. South Med J. 2021;114(9):579-582. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000001290
- Serrano L, Ulschmid C, Szabo A, et al. Racial disparities of delay in diagnosis and dermatologic care for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;114:613-616. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2022.08.002
- Drenkard C, Lim SS. Update on lupus epidemiology: advancinghealth disparities research through the study of minority populations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31:689-696. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000646
- Militello M, Szeto MD, Presley CL, et al. A quantitative analysis of research publications focused on skin of color: representation in academic dermatology journals. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:E189-E192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.04.053
- Cline A, Winter RP, Kourosh S, et al. Multiethnic training in residency: a survey of dermatology residents. Cutis. 2020;105:310-313.
- Mhlaba JM, Pontes DS, Patterson SS, et al. Evaluation of a skin of color curriculum for dermatology residents. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:786-789. doi:10.36849/JDD.6193
- Adelekun A, Onyekaba G, Lipoff JB. Skin color in dermatology textbooks: an updated evaluation and analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:194-196. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.084
- Harp T, Militello M, McCarver V, et al. Further analysis of skin of color representation in dermatology textbooks used by residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:E39-E41. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.069
- Muzumdar S, Grant-Kels JM, Feng H. Strategies to improve medical student visiting rotations. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:727-728. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.11.001
- Gorbatenko-Roth K, Prose N, Kundu RV, et al. Assessment of Black patients’ perception of their dermatology care. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1129-1134. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2063
- Colby SL, Jennifer JM. Projections of the size and composition of the U.S. population: 2014 to 2060. United States Census Bureau website. March 3, 2015. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.html
- Tull RZ, Kerby E, Subash JJ, et al. Ethnic skin centers in the United States: where are we in 2020? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1757-1759. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.054
- Shen MJ, Peterson EB, Costas-Muñiz R, et al. The effects of race and racial concordance on patient-physician communication: a systematic review of the literature. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2018;5:117-140. doi:10.1007/s40615-017-0350-4
- Saha S, Beach MC. Impact of physician race on patient decision-making and ratings of physicians: a randomized experiment using video vignettes. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:1084-1091. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05646-z
- Quick Facts: United States. US Census Bureau website. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045221
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.10.044
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.07.001
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table B5. number of active MD residents, by race/ethnicity (alone or in combination) and GME specialty. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/report-residents/2022/table-b5-md-residents-race-ethnicity-and-specialty
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table B6. number of active DO residents, by race/ethnicity (alone or in combination) and GME specialty. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/report-residents/2022/table-b6-do-residents-race-ethnicity-and-specialty
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Table 16. U.S. medical school faculty by gender, race/ethnicity, and department, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/media/8456/download
- Chen V, Akhtar S, Zheng C, et al. Assessment of changes in diversity in dermatology clinical trials between 2010-2015 and 2015-2020: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:288-292. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5596
- Montgomery SNB, Elbuluk N. A quantitative analysis of research publications focused on the top chief complaints in patients withskinof color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:241-242. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.031
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.06.024
- Ibraheim MK, Gupta R, Dao H, et al. Evaluating skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: data from a national survey. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:228-233. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.11.015
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3114
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 202;156:312-319. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4818
- Dlova NC, Salkey KS, Callender VD, et al. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: new insights and a call for action. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S54-S56. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.01.004
- Okeke CAV, Perry JD, Simmonds FC, et al. Clinical trials and skin of color: the example of hidradenitis suppurativa. dermatology. 2022;238:180-184. doi:10.1159/000516467
- Robles J, Anim T, Wusu MH, et al. An Approach to Faculty Development for Underrepresented Minorities in Medicine. South Med J. 2021;114(9):579-582. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000001290
- Serrano L, Ulschmid C, Szabo A, et al. Racial disparities of delay in diagnosis and dermatologic care for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;114:613-616. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2022.08.002
- Drenkard C, Lim SS. Update on lupus epidemiology: advancinghealth disparities research through the study of minority populations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31:689-696. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000646
- Militello M, Szeto MD, Presley CL, et al. A quantitative analysis of research publications focused on skin of color: representation in academic dermatology journals. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:E189-E192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.04.053
- Cline A, Winter RP, Kourosh S, et al. Multiethnic training in residency: a survey of dermatology residents. Cutis. 2020;105:310-313.
- Mhlaba JM, Pontes DS, Patterson SS, et al. Evaluation of a skin of color curriculum for dermatology residents. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:786-789. doi:10.36849/JDD.6193
- Adelekun A, Onyekaba G, Lipoff JB. Skin color in dermatology textbooks: an updated evaluation and analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:194-196. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.084
- Harp T, Militello M, McCarver V, et al. Further analysis of skin of color representation in dermatology textbooks used by residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:E39-E41. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.069
- Muzumdar S, Grant-Kels JM, Feng H. Strategies to improve medical student visiting rotations. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:727-728. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.11.001
- Gorbatenko-Roth K, Prose N, Kundu RV, et al. Assessment of Black patients’ perception of their dermatology care. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1129-1134. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2063
Practice Points
- Skin of color centers in the United States work to reverse the paucity of research, education, and training in skin of color dermatology and promote the diversification of residents and faculty.
- Skin of color centers expand access to culturally competent and inclusive care for diverse patient populations.
Facial Temperature Can Reveal Age and Disease
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
My oldest daughter is at sleepaway camp for a couple of weeks, and the camp has a photographer who goes around all day taking pictures of the kids, which get uploaded to a private Facebook group. In the past, I would go online every day (or, okay, several times a day) and scroll through all those pictures looking for one that features my kid.
I don’t have to do that anymore. This year, I simply uploaded a picture of my daughter to an app and artificial intelligence (AI) takes care of the rest, recognizing her face amidst the sea of smiling children, and flagging just those photos for me to peruse. It’s amazing, really. And a bit scary.
The fact that facial recognition has penetrated the summer camp market should tell you that the tech is truly ubiquitous. But today we’re going to think a bit more about what AI can do with a picture of your face, because the power of facial recognition is not just skin deep.
What’s got me hot and bothered about facial images is this paper, appearing in Cell Metabolism, which adds a new layer to the standard facial-analysis playbook: facial temperature.
To understand this paper, you need to understand a whole field of research that is developing various different “clocks” for age.
It turns out that age really is just a number. Our cells, our proteins, our biochemistry can be analyzed to give different numbers. These “clocks,” as distinct from the calendar we usually use to measure our age, might have more predictive power than the number itself.
There are numerous molecular clocks, such as telomere length, that not only correlate with calendar age but are superior to calendar age in predicting age-related complications. Testing telomere length typically requires a blood sample — and remains costly. But we can use other sources to estimate age; how about a photo?
I mean, we do this all the time when we meet someone new or, as a physician, when we meet a new patient. I have often written that a patient “appears younger than their stated age,” and we’ve all had the experience of hearing how old someone is and being shocked. I mean, have you seen Sharon Stone recently? She’s 66 years old. Okay — to be fair, there might be some outside help there. But you get the point.
Back to the Cell Metabolism paper. Researchers report on multiple algorithms to obtain an “age” from a picture of an individual’s face.
The first algorithm is pretty straightforward. Researchers collected 2811 images, all of Han Chinese individuals ranging in age from 20 to 90 years, and reconstructed a 3D facial map from those. 
They then trained a convolutional neural network to predict the individuals’ ages from the pictures. It was quite accurate, as you can see here.
In the AI age, this may not seem that impressive. A brief search online turned up dozens of apps that promised to guess my age from a photo.
I sent this rather unflattering picture of myself to ChatGPT which, after initially demurring and saying it was not designed to guess ages, pegged me at somewhere between 35 and 45, which I am taking as a major victory.
But the Cell Metabolism paper goes deeper. Literally. 
And this is where things start to get interesting. Because sure, the visible part of your face can change depending on makeup, expression, plastic surgery, and the like. But the temperature? That’s harder to fake.
It turns out that the temperature distribution in your face changes as you get older. There is a cooling of the nose and the cheeks, for example.
And the researchers could combine all this temperature data to guess someone’s calendar age fairly accurately, though notably not as accurately as the model that just looks at the pictures.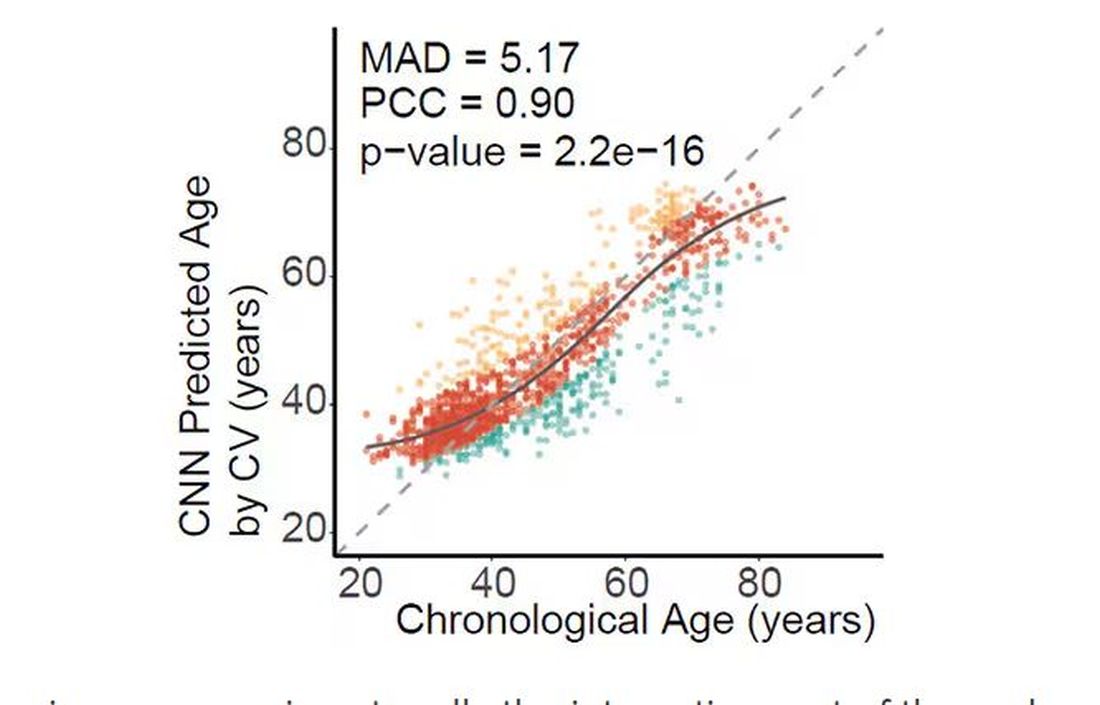
But guessing your age is not really the interesting part of thermal imaging of the face. It’s guessing — or, rather, predicting — the state of your metabolism. All these study participants had extensive metabolic testing performed, as well as detailed analysis of their lifestyle behaviors. And facial images could be used to predict those factors.
For example, the 3D reconstruction of the faces could predict who ate seafood (they tend to look younger than their actual age) compared with who ate poultry and meat (they tend to look older). The thermal imaging could predict who got more sleep (they look younger from a temperature perspective) and who ate more yogurt (also younger-appearing, temperature-wise). Facial temperature patterns could identify those with higher BMI, higher blood pressure, higher fasting glucose.
The researchers used the difference between actual and predicted age as a metric to measure illness as well. You can see here how, on average, individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and even liver cysts are “older,” at least by face temperature.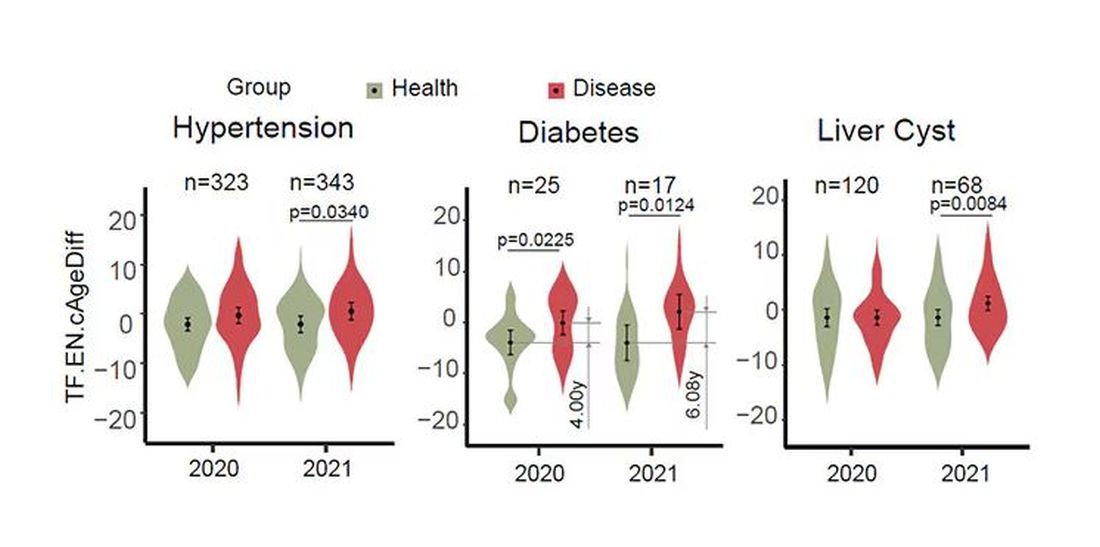
It may even be possible to use facial temperature as biofeedback. In a small study, the researchers measured the difference between facial temperature age and real age before and after 2 weeks of jump-roping. It turns out that 2 weeks of jump-roping can make you look about 5 years younger, at least as judged by a thermal camera. Or like the Predator.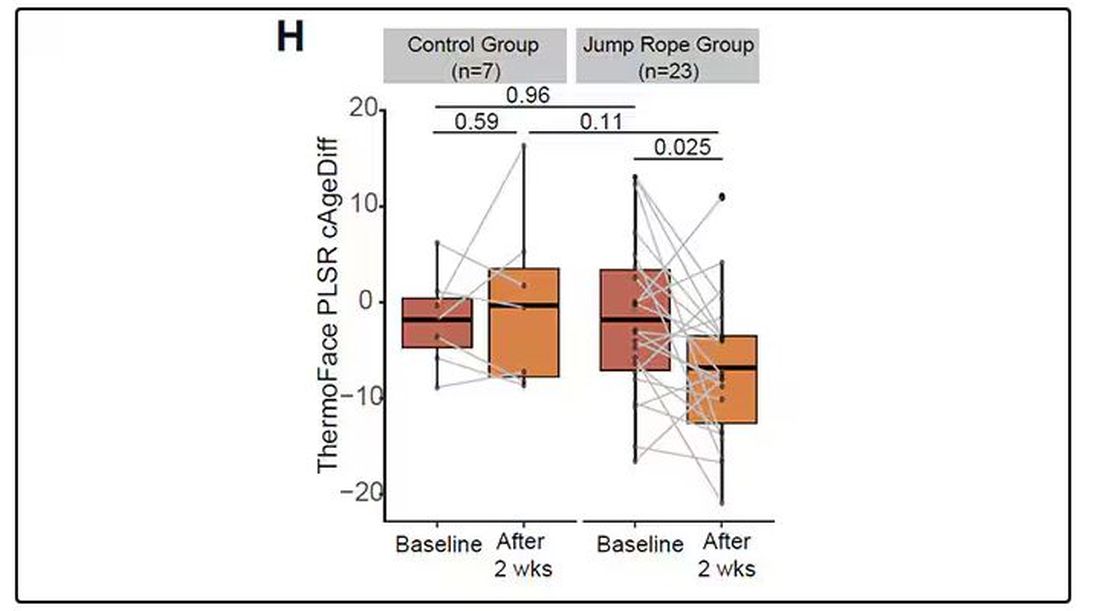
Okay, this is all very cool, but I’m not saying we’ll all be doing facial temperature tests in the near future. No; what this study highlights for me is how much information about ourselves is available to those who know how to decode it. Maybe those data come from the wrinkles in our faces, or the angles of our smiles, or the speed with which we type, or the temperature of our elbows. The data have always been there, actually, but we’ve never had the tools powerful enough to analyze them until now.
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with Star Trek — I know, you’re shocked — and, of course, the famous tricorder, a scanner that could tell everything about someone’s state of health in 5 seconds from 3 feet away. That’s how I thought medicine really would be in the future. Once I got to medical school, I was disabused of that notion. But the age of data, the age of AI, may mean the tricorder age is not actually that far away.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
My oldest daughter is at sleepaway camp for a couple of weeks, and the camp has a photographer who goes around all day taking pictures of the kids, which get uploaded to a private Facebook group. In the past, I would go online every day (or, okay, several times a day) and scroll through all those pictures looking for one that features my kid.
I don’t have to do that anymore. This year, I simply uploaded a picture of my daughter to an app and artificial intelligence (AI) takes care of the rest, recognizing her face amidst the sea of smiling children, and flagging just those photos for me to peruse. It’s amazing, really. And a bit scary.
The fact that facial recognition has penetrated the summer camp market should tell you that the tech is truly ubiquitous. But today we’re going to think a bit more about what AI can do with a picture of your face, because the power of facial recognition is not just skin deep.
What’s got me hot and bothered about facial images is this paper, appearing in Cell Metabolism, which adds a new layer to the standard facial-analysis playbook: facial temperature.
To understand this paper, you need to understand a whole field of research that is developing various different “clocks” for age.
It turns out that age really is just a number. Our cells, our proteins, our biochemistry can be analyzed to give different numbers. These “clocks,” as distinct from the calendar we usually use to measure our age, might have more predictive power than the number itself.
There are numerous molecular clocks, such as telomere length, that not only correlate with calendar age but are superior to calendar age in predicting age-related complications. Testing telomere length typically requires a blood sample — and remains costly. But we can use other sources to estimate age; how about a photo?
I mean, we do this all the time when we meet someone new or, as a physician, when we meet a new patient. I have often written that a patient “appears younger than their stated age,” and we’ve all had the experience of hearing how old someone is and being shocked. I mean, have you seen Sharon Stone recently? She’s 66 years old. Okay — to be fair, there might be some outside help there. But you get the point.
Back to the Cell Metabolism paper. Researchers report on multiple algorithms to obtain an “age” from a picture of an individual’s face.
The first algorithm is pretty straightforward. Researchers collected 2811 images, all of Han Chinese individuals ranging in age from 20 to 90 years, and reconstructed a 3D facial map from those. 
They then trained a convolutional neural network to predict the individuals’ ages from the pictures. It was quite accurate, as you can see here.
In the AI age, this may not seem that impressive. A brief search online turned up dozens of apps that promised to guess my age from a photo.
I sent this rather unflattering picture of myself to ChatGPT which, after initially demurring and saying it was not designed to guess ages, pegged me at somewhere between 35 and 45, which I am taking as a major victory.
But the Cell Metabolism paper goes deeper. Literally. 
And this is where things start to get interesting. Because sure, the visible part of your face can change depending on makeup, expression, plastic surgery, and the like. But the temperature? That’s harder to fake.
It turns out that the temperature distribution in your face changes as you get older. There is a cooling of the nose and the cheeks, for example.
And the researchers could combine all this temperature data to guess someone’s calendar age fairly accurately, though notably not as accurately as the model that just looks at the pictures.
But guessing your age is not really the interesting part of thermal imaging of the face. It’s guessing — or, rather, predicting — the state of your metabolism. All these study participants had extensive metabolic testing performed, as well as detailed analysis of their lifestyle behaviors. And facial images could be used to predict those factors.
For example, the 3D reconstruction of the faces could predict who ate seafood (they tend to look younger than their actual age) compared with who ate poultry and meat (they tend to look older). The thermal imaging could predict who got more sleep (they look younger from a temperature perspective) and who ate more yogurt (also younger-appearing, temperature-wise). Facial temperature patterns could identify those with higher BMI, higher blood pressure, higher fasting glucose.
The researchers used the difference between actual and predicted age as a metric to measure illness as well. You can see here how, on average, individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and even liver cysts are “older,” at least by face temperature.
It may even be possible to use facial temperature as biofeedback. In a small study, the researchers measured the difference between facial temperature age and real age before and after 2 weeks of jump-roping. It turns out that 2 weeks of jump-roping can make you look about 5 years younger, at least as judged by a thermal camera. Or like the Predator.
Okay, this is all very cool, but I’m not saying we’ll all be doing facial temperature tests in the near future. No; what this study highlights for me is how much information about ourselves is available to those who know how to decode it. Maybe those data come from the wrinkles in our faces, or the angles of our smiles, or the speed with which we type, or the temperature of our elbows. The data have always been there, actually, but we’ve never had the tools powerful enough to analyze them until now.
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with Star Trek — I know, you’re shocked — and, of course, the famous tricorder, a scanner that could tell everything about someone’s state of health in 5 seconds from 3 feet away. That’s how I thought medicine really would be in the future. Once I got to medical school, I was disabused of that notion. But the age of data, the age of AI, may mean the tricorder age is not actually that far away.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
My oldest daughter is at sleepaway camp for a couple of weeks, and the camp has a photographer who goes around all day taking pictures of the kids, which get uploaded to a private Facebook group. In the past, I would go online every day (or, okay, several times a day) and scroll through all those pictures looking for one that features my kid.
I don’t have to do that anymore. This year, I simply uploaded a picture of my daughter to an app and artificial intelligence (AI) takes care of the rest, recognizing her face amidst the sea of smiling children, and flagging just those photos for me to peruse. It’s amazing, really. And a bit scary.
The fact that facial recognition has penetrated the summer camp market should tell you that the tech is truly ubiquitous. But today we’re going to think a bit more about what AI can do with a picture of your face, because the power of facial recognition is not just skin deep.
What’s got me hot and bothered about facial images is this paper, appearing in Cell Metabolism, which adds a new layer to the standard facial-analysis playbook: facial temperature.
To understand this paper, you need to understand a whole field of research that is developing various different “clocks” for age.
It turns out that age really is just a number. Our cells, our proteins, our biochemistry can be analyzed to give different numbers. These “clocks,” as distinct from the calendar we usually use to measure our age, might have more predictive power than the number itself.
There are numerous molecular clocks, such as telomere length, that not only correlate with calendar age but are superior to calendar age in predicting age-related complications. Testing telomere length typically requires a blood sample — and remains costly. But we can use other sources to estimate age; how about a photo?
I mean, we do this all the time when we meet someone new or, as a physician, when we meet a new patient. I have often written that a patient “appears younger than their stated age,” and we’ve all had the experience of hearing how old someone is and being shocked. I mean, have you seen Sharon Stone recently? She’s 66 years old. Okay — to be fair, there might be some outside help there. But you get the point.
Back to the Cell Metabolism paper. Researchers report on multiple algorithms to obtain an “age” from a picture of an individual’s face.
The first algorithm is pretty straightforward. Researchers collected 2811 images, all of Han Chinese individuals ranging in age from 20 to 90 years, and reconstructed a 3D facial map from those. 
They then trained a convolutional neural network to predict the individuals’ ages from the pictures. It was quite accurate, as you can see here.
In the AI age, this may not seem that impressive. A brief search online turned up dozens of apps that promised to guess my age from a photo.
I sent this rather unflattering picture of myself to ChatGPT which, after initially demurring and saying it was not designed to guess ages, pegged me at somewhere between 35 and 45, which I am taking as a major victory.
But the Cell Metabolism paper goes deeper. Literally. 
And this is where things start to get interesting. Because sure, the visible part of your face can change depending on makeup, expression, plastic surgery, and the like. But the temperature? That’s harder to fake.
It turns out that the temperature distribution in your face changes as you get older. There is a cooling of the nose and the cheeks, for example.
And the researchers could combine all this temperature data to guess someone’s calendar age fairly accurately, though notably not as accurately as the model that just looks at the pictures.
But guessing your age is not really the interesting part of thermal imaging of the face. It’s guessing — or, rather, predicting — the state of your metabolism. All these study participants had extensive metabolic testing performed, as well as detailed analysis of their lifestyle behaviors. And facial images could be used to predict those factors.
For example, the 3D reconstruction of the faces could predict who ate seafood (they tend to look younger than their actual age) compared with who ate poultry and meat (they tend to look older). The thermal imaging could predict who got more sleep (they look younger from a temperature perspective) and who ate more yogurt (also younger-appearing, temperature-wise). Facial temperature patterns could identify those with higher BMI, higher blood pressure, higher fasting glucose.
The researchers used the difference between actual and predicted age as a metric to measure illness as well. You can see here how, on average, individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and even liver cysts are “older,” at least by face temperature.
It may even be possible to use facial temperature as biofeedback. In a small study, the researchers measured the difference between facial temperature age and real age before and after 2 weeks of jump-roping. It turns out that 2 weeks of jump-roping can make you look about 5 years younger, at least as judged by a thermal camera. Or like the Predator.
Okay, this is all very cool, but I’m not saying we’ll all be doing facial temperature tests in the near future. No; what this study highlights for me is how much information about ourselves is available to those who know how to decode it. Maybe those data come from the wrinkles in our faces, or the angles of our smiles, or the speed with which we type, or the temperature of our elbows. The data have always been there, actually, but we’ve never had the tools powerful enough to analyze them until now.
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with Star Trek — I know, you’re shocked — and, of course, the famous tricorder, a scanner that could tell everything about someone’s state of health in 5 seconds from 3 feet away. That’s how I thought medicine really would be in the future. Once I got to medical school, I was disabused of that notion. But the age of data, the age of AI, may mean the tricorder age is not actually that far away.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.