User login
Disseminated Erythematous-Violet Edematous Plaques and Necrotic Nodules
The Diagnosis: Histiocytoid Sweet Syndrome
The patient was admitted for clinical study and treatment monitoring. During the first 72 hours of admittance, the lesions and general malaise further developed along with C-reactive protein elevation (126 mg/L). Administration of intravenous prednisone at a dosage of 1 mg/kg daily was accompanied by substantial improvement after 1 week of treatment, with subsequent follow-up and outpatient monitoring. An underlying neoplasia was ruled out after review of medical history, physical examination, complete blood cell count, chest radiography, abdominal ultrasonography, colonoscopy, and bone marrow aspiration.

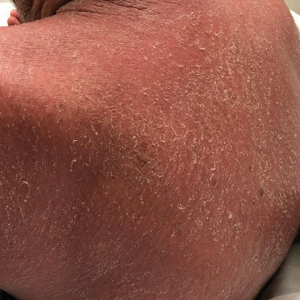
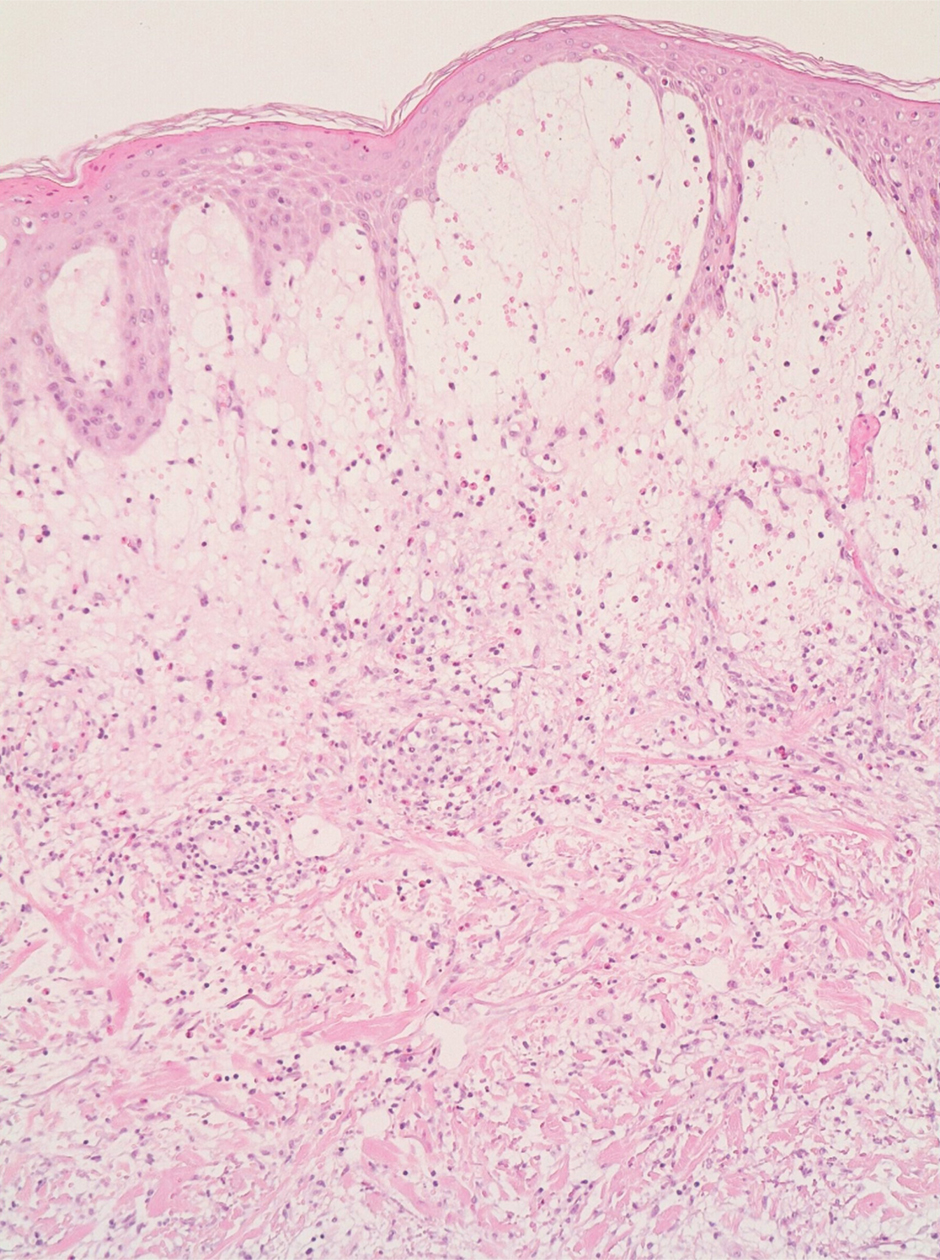
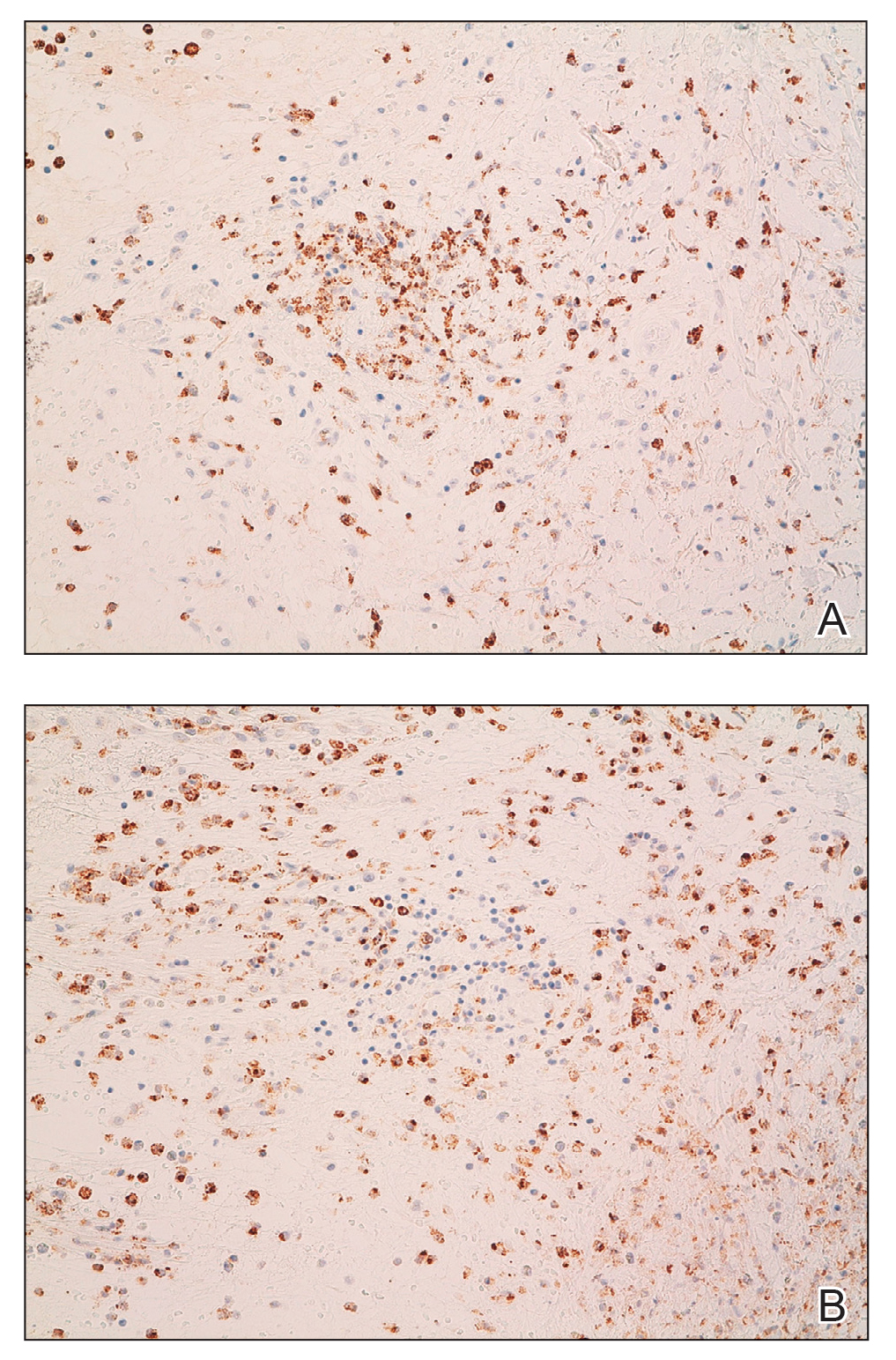
A 4-mm skin biopsy was performed from a lesion on the neck (Figure 1). Histology revealed a dermis with prominent edema alongside superficial, deep, and periadnexal perivascular inflammatory infiltrates, as well as predominant lymphocytes and cells with a histiocytoid profile (Figure 2). These findings were accompanied by isolated neutrophil foci. The absence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis was noted. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that the histiocyte population was positive for myeloperoxidase and CD68, which categorized them as immature cells of myeloid origin (Figure 3). Clinical and histopathologic findings led to a definitive diagnosis of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome (SS). Sweet syndrome consists of a neutrophilic dermatosis profile. Clinically, it manifests as a sudden onset of painful nodules and plaques accompanied by fever, malaise, and leukocytosis.
Histiocytoid SS is a rare histologic variant of SS initially described by Requena et al1 in 2005. In histiocytoid SS, the main inflammatory infiltrates are promyelocytes and myelocytes.2 Immunohistochemistry shows positivity for myeloperoxidase, CD15, CD43, CD45, CD68, MAC-386, and HAM56.1 The diagnosis is determined by exclusion after adequate clinical and histopathologic correlation, which also should exclude other diagnoses such as leukemia cutis and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis.3 Histiocytoid SS may be related to an increased risk for underlying malignancy. Haber et al4 performed a systematic review in which they concluded that approximately 40% of patients newly diagnosed with histiocytoid SS subsequently were diagnosed or already were diagnosed with a hematologic or solid cancer vs 21% in the classical neutrophilic infiltrate of SS (NSS). Histiocytoid SS more commonly was associated with myelodysplastic syndrome (46% vs 2.5% in NSS) and hematologic malignancies (42.5% vs 25% in SS).
The initial differential diagnoses include inflammatory dermatoses, infections, neoplasms, and systemic diseases. In exudative erythema multiforme, early lesions are composed of typical target lesions with mucosal involvement in 25% to 60% of patients.5 Erythema elevatum diutinum is a chronic dermatosis characterized by asymptomatic papules and red-violet nodules. The most characteristic histologic finding is leukocytoclastic vasculitis.6 The absence of vasculitis is part of the major diagnostic criteria for SS.7 Wells syndrome is associated with general malaise, and edematous and erythematous-violet plaques or nodules appear on the limbs; however, it frequently is associated with eosinophilia in peripheral blood, and histology shows that the main cell population of the inflammatory infiltrate also is eosinophilic.8 Painful, superficial, and erosive blisters appear preferentially on the face and backs of the arms in bullous pyoderma gangrenosum. It usually is not associated with the typical systemic manifestations of SS (ie, fever, arthralgia, damage to target organs). On histopathology, the neutrophilic infiltrate is accompanied by subepidermal vesicles.9
Histiocytoid SS responds dramatically to corticosteroids. Other first-line treatments that avoid use of corticosteroids are colchicine, dapsone, and potassium iodide. Multiple treatments were attempted in our patient, including corticosteroids, methotrexate, dapsone, colchicine, and anakinra. Despite patients responding well to treatment, a possible underlying neoplasm, most frequently of hematologic origin, must be excluded.10
- Requena L, Kutzner H, Palmedo G, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a dermal infiltration of immature neutrophilic granulocytes. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:834-842. doi:10.1001/archderm.141.7.834
- Alegría-Landa V, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Santos-Briz A, et al. Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:651-659. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6092
- Llamas-Velasco M, Concha-Garzón MJ, Fraga J, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome related to bortezomib: a mimicker of cutaneous infiltration by myeloma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015; 81:305-306. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.152743
- Haber R, Feghali J, El Gemayel M. Risk of malignancy in histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a systematic review and reappraisal [published online February 21, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:661-663. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.048
- Sokumbi O, Wetter DA. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: a review for the practicing dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:889-902. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05348.x
- Newburger J, Schmieder GJ. Erythema elevatum diutinum. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov /books/NBK448069/
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Weins AB, Biedermann T, Weiss T, et al. Wells syndrome. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:989-993. doi:10.1111/ddg.13132
- Powell FC, Su WP, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: classification and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:395-409; quiz 410-412. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90428-4
- Villarreal-Villarreal CD, Ocampo-Candiani J, Villarreal-Martínez A. Sweet syndrome: a review and update. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107:369-378. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2015.12.001
The Diagnosis: Histiocytoid Sweet Syndrome
The patient was admitted for clinical study and treatment monitoring. During the first 72 hours of admittance, the lesions and general malaise further developed along with C-reactive protein elevation (126 mg/L). Administration of intravenous prednisone at a dosage of 1 mg/kg daily was accompanied by substantial improvement after 1 week of treatment, with subsequent follow-up and outpatient monitoring. An underlying neoplasia was ruled out after review of medical history, physical examination, complete blood cell count, chest radiography, abdominal ultrasonography, colonoscopy, and bone marrow aspiration.

A 4-mm skin biopsy was performed from a lesion on the neck (Figure 1). Histology revealed a dermis with prominent edema alongside superficial, deep, and periadnexal perivascular inflammatory infiltrates, as well as predominant lymphocytes and cells with a histiocytoid profile (Figure 2). These findings were accompanied by isolated neutrophil foci. The absence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis was noted. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that the histiocyte population was positive for myeloperoxidase and CD68, which categorized them as immature cells of myeloid origin (Figure 3). Clinical and histopathologic findings led to a definitive diagnosis of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome (SS). Sweet syndrome consists of a neutrophilic dermatosis profile. Clinically, it manifests as a sudden onset of painful nodules and plaques accompanied by fever, malaise, and leukocytosis.

Histiocytoid SS is a rare histologic variant of SS initially described by Requena et al1 in 2005. In histiocytoid SS, the main inflammatory infiltrates are promyelocytes and myelocytes.2 Immunohistochemistry shows positivity for myeloperoxidase, CD15, CD43, CD45, CD68, MAC-386, and HAM56.1 The diagnosis is determined by exclusion after adequate clinical and histopathologic correlation, which also should exclude other diagnoses such as leukemia cutis and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis.3 Histiocytoid SS may be related to an increased risk for underlying malignancy. Haber et al4 performed a systematic review in which they concluded that approximately 40% of patients newly diagnosed with histiocytoid SS subsequently were diagnosed or already were diagnosed with a hematologic or solid cancer vs 21% in the classical neutrophilic infiltrate of SS (NSS). Histiocytoid SS more commonly was associated with myelodysplastic syndrome (46% vs 2.5% in NSS) and hematologic malignancies (42.5% vs 25% in SS).

The initial differential diagnoses include inflammatory dermatoses, infections, neoplasms, and systemic diseases. In exudative erythema multiforme, early lesions are composed of typical target lesions with mucosal involvement in 25% to 60% of patients.5 Erythema elevatum diutinum is a chronic dermatosis characterized by asymptomatic papules and red-violet nodules. The most characteristic histologic finding is leukocytoclastic vasculitis.6 The absence of vasculitis is part of the major diagnostic criteria for SS.7 Wells syndrome is associated with general malaise, and edematous and erythematous-violet plaques or nodules appear on the limbs; however, it frequently is associated with eosinophilia in peripheral blood, and histology shows that the main cell population of the inflammatory infiltrate also is eosinophilic.8 Painful, superficial, and erosive blisters appear preferentially on the face and backs of the arms in bullous pyoderma gangrenosum. It usually is not associated with the typical systemic manifestations of SS (ie, fever, arthralgia, damage to target organs). On histopathology, the neutrophilic infiltrate is accompanied by subepidermal vesicles.9
Histiocytoid SS responds dramatically to corticosteroids. Other first-line treatments that avoid use of corticosteroids are colchicine, dapsone, and potassium iodide. Multiple treatments were attempted in our patient, including corticosteroids, methotrexate, dapsone, colchicine, and anakinra. Despite patients responding well to treatment, a possible underlying neoplasm, most frequently of hematologic origin, must be excluded.10
The Diagnosis: Histiocytoid Sweet Syndrome
The patient was admitted for clinical study and treatment monitoring. During the first 72 hours of admittance, the lesions and general malaise further developed along with C-reactive protein elevation (126 mg/L). Administration of intravenous prednisone at a dosage of 1 mg/kg daily was accompanied by substantial improvement after 1 week of treatment, with subsequent follow-up and outpatient monitoring. An underlying neoplasia was ruled out after review of medical history, physical examination, complete blood cell count, chest radiography, abdominal ultrasonography, colonoscopy, and bone marrow aspiration.

A 4-mm skin biopsy was performed from a lesion on the neck (Figure 1). Histology revealed a dermis with prominent edema alongside superficial, deep, and periadnexal perivascular inflammatory infiltrates, as well as predominant lymphocytes and cells with a histiocytoid profile (Figure 2). These findings were accompanied by isolated neutrophil foci. The absence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis was noted. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that the histiocyte population was positive for myeloperoxidase and CD68, which categorized them as immature cells of myeloid origin (Figure 3). Clinical and histopathologic findings led to a definitive diagnosis of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome (SS). Sweet syndrome consists of a neutrophilic dermatosis profile. Clinically, it manifests as a sudden onset of painful nodules and plaques accompanied by fever, malaise, and leukocytosis.

Histiocytoid SS is a rare histologic variant of SS initially described by Requena et al1 in 2005. In histiocytoid SS, the main inflammatory infiltrates are promyelocytes and myelocytes.2 Immunohistochemistry shows positivity for myeloperoxidase, CD15, CD43, CD45, CD68, MAC-386, and HAM56.1 The diagnosis is determined by exclusion after adequate clinical and histopathologic correlation, which also should exclude other diagnoses such as leukemia cutis and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis.3 Histiocytoid SS may be related to an increased risk for underlying malignancy. Haber et al4 performed a systematic review in which they concluded that approximately 40% of patients newly diagnosed with histiocytoid SS subsequently were diagnosed or already were diagnosed with a hematologic or solid cancer vs 21% in the classical neutrophilic infiltrate of SS (NSS). Histiocytoid SS more commonly was associated with myelodysplastic syndrome (46% vs 2.5% in NSS) and hematologic malignancies (42.5% vs 25% in SS).

The initial differential diagnoses include inflammatory dermatoses, infections, neoplasms, and systemic diseases. In exudative erythema multiforme, early lesions are composed of typical target lesions with mucosal involvement in 25% to 60% of patients.5 Erythema elevatum diutinum is a chronic dermatosis characterized by asymptomatic papules and red-violet nodules. The most characteristic histologic finding is leukocytoclastic vasculitis.6 The absence of vasculitis is part of the major diagnostic criteria for SS.7 Wells syndrome is associated with general malaise, and edematous and erythematous-violet plaques or nodules appear on the limbs; however, it frequently is associated with eosinophilia in peripheral blood, and histology shows that the main cell population of the inflammatory infiltrate also is eosinophilic.8 Painful, superficial, and erosive blisters appear preferentially on the face and backs of the arms in bullous pyoderma gangrenosum. It usually is not associated with the typical systemic manifestations of SS (ie, fever, arthralgia, damage to target organs). On histopathology, the neutrophilic infiltrate is accompanied by subepidermal vesicles.9
Histiocytoid SS responds dramatically to corticosteroids. Other first-line treatments that avoid use of corticosteroids are colchicine, dapsone, and potassium iodide. Multiple treatments were attempted in our patient, including corticosteroids, methotrexate, dapsone, colchicine, and anakinra. Despite patients responding well to treatment, a possible underlying neoplasm, most frequently of hematologic origin, must be excluded.10
- Requena L, Kutzner H, Palmedo G, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a dermal infiltration of immature neutrophilic granulocytes. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:834-842. doi:10.1001/archderm.141.7.834
- Alegría-Landa V, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Santos-Briz A, et al. Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:651-659. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6092
- Llamas-Velasco M, Concha-Garzón MJ, Fraga J, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome related to bortezomib: a mimicker of cutaneous infiltration by myeloma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015; 81:305-306. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.152743
- Haber R, Feghali J, El Gemayel M. Risk of malignancy in histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a systematic review and reappraisal [published online February 21, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:661-663. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.048
- Sokumbi O, Wetter DA. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: a review for the practicing dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:889-902. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05348.x
- Newburger J, Schmieder GJ. Erythema elevatum diutinum. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov /books/NBK448069/
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Weins AB, Biedermann T, Weiss T, et al. Wells syndrome. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:989-993. doi:10.1111/ddg.13132
- Powell FC, Su WP, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: classification and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:395-409; quiz 410-412. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90428-4
- Villarreal-Villarreal CD, Ocampo-Candiani J, Villarreal-Martínez A. Sweet syndrome: a review and update. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107:369-378. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2015.12.001
- Requena L, Kutzner H, Palmedo G, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a dermal infiltration of immature neutrophilic granulocytes. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:834-842. doi:10.1001/archderm.141.7.834
- Alegría-Landa V, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Santos-Briz A, et al. Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular features of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:651-659. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6092
- Llamas-Velasco M, Concha-Garzón MJ, Fraga J, et al. Histiocytoid Sweet syndrome related to bortezomib: a mimicker of cutaneous infiltration by myeloma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015; 81:305-306. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.152743
- Haber R, Feghali J, El Gemayel M. Risk of malignancy in histiocytoid Sweet syndrome: a systematic review and reappraisal [published online February 21, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:661-663. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.048
- Sokumbi O, Wetter DA. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: a review for the practicing dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:889-902. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05348.x
- Newburger J, Schmieder GJ. Erythema elevatum diutinum. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov /books/NBK448069/
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Weins AB, Biedermann T, Weiss T, et al. Wells syndrome. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:989-993. doi:10.1111/ddg.13132
- Powell FC, Su WP, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: classification and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:395-409; quiz 410-412. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90428-4
- Villarreal-Villarreal CD, Ocampo-Candiani J, Villarreal-Martínez A. Sweet syndrome: a review and update. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107:369-378. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2015.12.001
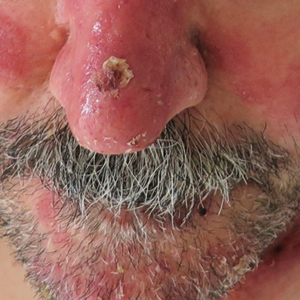
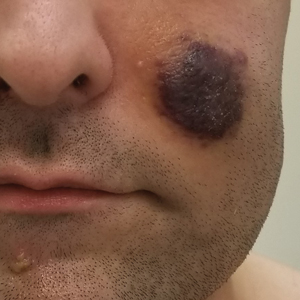
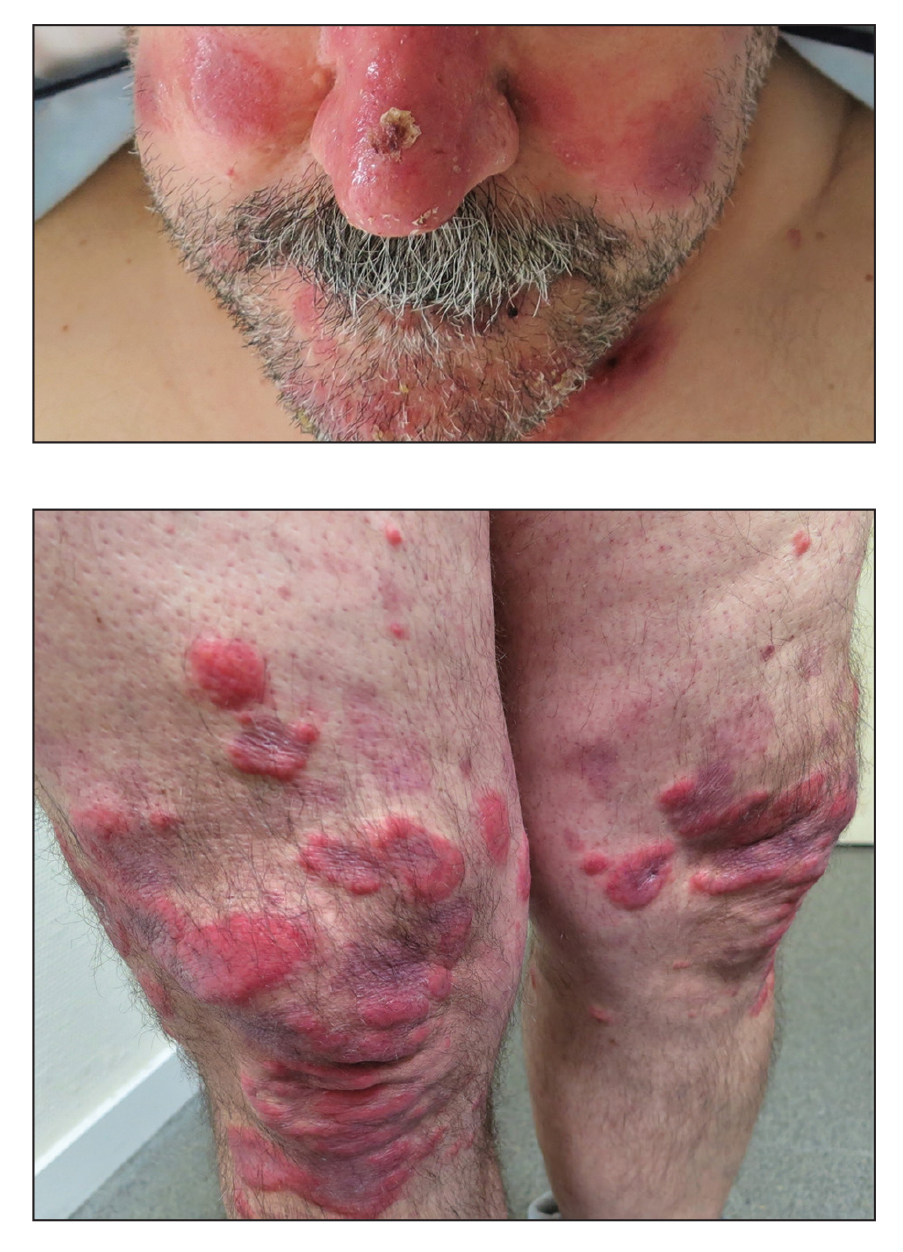
A 53-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a fever and painful skin lesions of 2 days’ duration. He reported a medical history of an upper respiratory infection 4 weeks prior. Physical examination was notable for erythematous-violet edematous papules, necrotic lesions, and pseudovesicles located on the face (top), head, neck, arms, and legs (bottom). Hemorrhagic splinters were evidenced in multiple nail sections. Urgent blood work revealed microcytic anemia (hemoglobin, 12.6 g/dL [reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL]) and elevated C-reactive protein (58 mg/L [reference range, 0.0–5.0 mg/L]).
Improved follow-up needed to find late-stage pancreatic cancers
A relatively large number of late-stage pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs) are detected during follow-up surveillance, yet no single patient- or protocol-specific factor appears to be significantly associated with detecting late-stage disease during this period, according to a new systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
The researchers, led by Ankit Chhoda, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., wrote in Gastroenterology that interval progression in high-risk individuals “highlights the need for improved follow-up methodology with higher accuracy to detect prognostically significant and treatable lesions.”
Individuals at high risk for PDAC are encouraged to undergo routine surveillance for the disease because early detection and resection of T1N0M0 PDAC and high-grade precursors may improve survival outcomes. According to Dr. Chhoda and colleagues, challenges of interval progression of cancers during the surveillance period for gastrointestinal malignancies have been well described in the general and at-risk patient populations. Previous studies, the authors explained, have not scrutinized the issues associated with late-stage PDACs detected during follow-up surveillance.
“Late-stage PDACs necessitate critical appraisal of current follow-up strategies to detect successful targets and perform timely resections,” the authors wrote. The researchers added that the diagnosis of late-stage PDACs during follow-up emphasizes the need for implementing “quality measures to avoid preventable causes, including surveillance adherence and diagnostic errors.”
To understand the incidence rates of late-stage PDACs during follow-up in high-risk individuals, Dr. Chhoda and researchers performed a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of data that included follow-up strategies for early PDAC detection among a high-risk population.
Outcomes of interest for the analysis included the overall diagnosis of advanced neoplasia as well as surveillance-detected/interval late-stage PDACs (T2–4N0M0/metastatic stage PDAC) during follow-up. The investigators defined surveillance-detected and interval late-stage PDACs as late-stage PDACs that were detected during surveillance and as those presenting symptomatically between visits, respectively.
The researchers also performed metaregression of the incidence rates of late-stage PDACs to examine the relationship with clinicoradiologic features in high-risk individuals.
A total of 13 studies on surveillance in 2,169 high-risk individuals were included in the systematic review, while 12 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Across studies, high-risk individuals were followed for over 7,302.72 patient-years for the purposes of detecting incident lesions or progression of preexisting pancreatic abnormalities.
In all high-risk individuals who underwent follow-up, the investigators identified a total yield of advanced neoplasia of 53. This total yield consisted of 7 high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms, 7 high-grade intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, and 39 PDACs. According to the meta-analysis, the cumulative incidence of advanced neoplasia was 3.3 (95% confidence interval, 0.6-7.4; P < .001) per 1,000 patient-years. During follow-up, the cumulative incidence of surveillance-detected/interval late-stage PDACs was 1.7 per 1,000 patient-years (95% CI, 0.2-4.0; P = .03).
In a separate analysis, the investigators sought to identify the relationship between the modality of follow-up imaging and late-stage PDAC incidence. Imaging modalities used during follow-up were mostly cross-sectional imaging, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging with cholangiopancreatography (n = 4) or endoscopic ultrasound and cross-sectional modalities (n = 8).
The investigators found no significant associations between late-stage PDACs and surveillance imaging, baseline pancreatic morphology, study location, genetic background, gender, or age. Incidence of late-stage PDACs in studies with mostly cross-sectional imaging was 0.7 per 1,000 patient-years (95% CI, 0.0-8.0). This incidence rate was lower than that reported with EUS and cross-sectional modalities (2.5 per 1,000 patient-years; 95% CI, 0.6-5.4), but this difference was not statistically significant (P = .2).
No significant difference was found during follow-up in the incidence of late-stage PDACs between high-risk individuals with baseline pancreatic abnormalities (0.0 no significant difference; 95% CI, 0.0-0.3) vs. high-risk individuals with normal baseline (0.9 per 1,000 patient-years; 95% CI, 0.0-2.8) (P = .9).
Most studies included in the analysis did not report on diagnostic errors and surveillance adherence, the researchers wrote. Nonadherence to surveillance as well as delays in surveillance accounted for four late-stage PDACs, and surveillance cessation and/or delays were reported in 4 out of 19 high-risk individuals. There was limited information on symptoms, presentation timing, site of lesion, and surveillance adherence, which the investigators indicated prevented a formal meta-analysis.
In their summary, the study authors noted that in clinical practice there is a need for improved quality measures and adherence to surveillance programs to reduce the risk of diagnostic errors. The authors stated that evidence on the impact of these quality measures “on surveillance outcomes will not only improve quality of surveillance practices, but also enrich our communication with patients who undergo surveillance.”
The researchers reported no conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry, and the study did not receive any funding.
A relatively large number of late-stage pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs) are detected during follow-up surveillance, yet no single patient- or protocol-specific factor appears to be significantly associated with detecting late-stage disease during this period, according to a new systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
The researchers, led by Ankit Chhoda, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., wrote in Gastroenterology that interval progression in high-risk individuals “highlights the need for improved follow-up methodology with higher accuracy to detect prognostically significant and treatable lesions.”
Individuals at high risk for PDAC are encouraged to undergo routine surveillance for the disease because early detection and resection of T1N0M0 PDAC and high-grade precursors may improve survival outcomes. According to Dr. Chhoda and colleagues, challenges of interval progression of cancers during the surveillance period for gastrointestinal malignancies have been well described in the general and at-risk patient populations. Previous studies, the authors explained, have not scrutinized the issues associated with late-stage PDACs detected during follow-up surveillance.
“Late-stage PDACs necessitate critical appraisal of current follow-up strategies to detect successful targets and perform timely resections,” the authors wrote. The researchers added that the diagnosis of late-stage PDACs during follow-up emphasizes the need for implementing “quality measures to avoid preventable causes, including surveillance adherence and diagnostic errors.”
To understand the incidence rates of late-stage PDACs during follow-up in high-risk individuals, Dr. Chhoda and researchers performed a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of data that included follow-up strategies for early PDAC detection among a high-risk population.
Outcomes of interest for the analysis included the overall diagnosis of advanced neoplasia as well as surveillance-detected/interval late-stage PDACs (T2–4N0M0/metastatic stage PDAC) during follow-up. The investigators defined surveillance-detected and interval late-stage PDACs as late-stage PDACs that were detected during surveillance and as those presenting symptomatically between visits, respectively.
The researchers also performed metaregression of the incidence rates of late-stage PDACs to examine the relationship with clinicoradiologic features in high-risk individuals.
A total of 13 studies on surveillance in 2,169 high-risk individuals were included in the systematic review, while 12 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Across studies, high-risk individuals were followed for over 7,302.72 patient-years for the purposes of detecting incident lesions or progression of preexisting pancreatic abnormalities.
In all high-risk individuals who underwent follow-up, the investigators identified a total yield of advanced neoplasia of 53. This total yield consisted of 7 high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms, 7 high-grade intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, and 39 PDACs. According to the meta-analysis, the cumulative incidence of advanced neoplasia was 3.3 (95% confidence interval, 0.6-7.4; P < .001) per 1,000 patient-years. During follow-up, the cumulative incidence of surveillance-detected/interval late-stage PDACs was 1.7 per 1,000 patient-years (95% CI, 0.2-4.0; P = .03).
In a separate analysis, the investigators sought to identify the relationship between the modality of follow-up imaging and late-stage PDAC incidence. Imaging modalities used during follow-up were mostly cross-sectional imaging, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging with cholangiopancreatography (n = 4) or endoscopic ultrasound and cross-sectional modalities (n = 8).
The investigators found no significant associations between late-stage PDACs and surveillance imaging, baseline pancreatic morphology, study location, genetic background, gender, or age. Incidence of late-stage PDACs in studies with mostly cross-sectional imaging was 0.7 per 1,000 patient-years (95% CI, 0.0-8.0). This incidence rate was lower than that reported with EUS and cross-sectional modalities (2.5 per 1,000 patient-years; 95% CI, 0.6-5.4), but this difference was not statistically significant (P = .2).
No significant difference was found during follow-up in the incidence of late-stage PDACs between high-risk individuals with baseline pancreatic abnormalities (0.0 no significant difference; 95% CI, 0.0-0.3) vs. high-risk individuals with normal baseline (0.9 per 1,000 patient-years; 95% CI, 0.0-2.8) (P = .9).
Most studies included in the analysis did not report on diagnostic errors and surveillance adherence, the researchers wrote. Nonadherence to surveillance as well as delays in surveillance accounted for four late-stage PDACs, and surveillance cessation and/or delays were reported in 4 out of 19 high-risk individuals. There was limited information on symptoms, presentation timing, site of lesion, and surveillance adherence, which the investigators indicated prevented a formal meta-analysis.
In their summary, the study authors noted that in clinical practice there is a need for improved quality measures and adherence to surveillance programs to reduce the risk of diagnostic errors. The authors stated that evidence on the impact of these quality measures “on surveillance outcomes will not only improve quality of surveillance practices, but also enrich our communication with patients who undergo surveillance.”
The researchers reported no conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry, and the study did not receive any funding.
A relatively large number of late-stage pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs) are detected during follow-up surveillance, yet no single patient- or protocol-specific factor appears to be significantly associated with detecting late-stage disease during this period, according to a new systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
The researchers, led by Ankit Chhoda, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., wrote in Gastroenterology that interval progression in high-risk individuals “highlights the need for improved follow-up methodology with higher accuracy to detect prognostically significant and treatable lesions.”
Individuals at high risk for PDAC are encouraged to undergo routine surveillance for the disease because early detection and resection of T1N0M0 PDAC and high-grade precursors may improve survival outcomes. According to Dr. Chhoda and colleagues, challenges of interval progression of cancers during the surveillance period for gastrointestinal malignancies have been well described in the general and at-risk patient populations. Previous studies, the authors explained, have not scrutinized the issues associated with late-stage PDACs detected during follow-up surveillance.
“Late-stage PDACs necessitate critical appraisal of current follow-up strategies to detect successful targets and perform timely resections,” the authors wrote. The researchers added that the diagnosis of late-stage PDACs during follow-up emphasizes the need for implementing “quality measures to avoid preventable causes, including surveillance adherence and diagnostic errors.”
To understand the incidence rates of late-stage PDACs during follow-up in high-risk individuals, Dr. Chhoda and researchers performed a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of data that included follow-up strategies for early PDAC detection among a high-risk population.
Outcomes of interest for the analysis included the overall diagnosis of advanced neoplasia as well as surveillance-detected/interval late-stage PDACs (T2–4N0M0/metastatic stage PDAC) during follow-up. The investigators defined surveillance-detected and interval late-stage PDACs as late-stage PDACs that were detected during surveillance and as those presenting symptomatically between visits, respectively.
The researchers also performed metaregression of the incidence rates of late-stage PDACs to examine the relationship with clinicoradiologic features in high-risk individuals.
A total of 13 studies on surveillance in 2,169 high-risk individuals were included in the systematic review, while 12 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Across studies, high-risk individuals were followed for over 7,302.72 patient-years for the purposes of detecting incident lesions or progression of preexisting pancreatic abnormalities.
In all high-risk individuals who underwent follow-up, the investigators identified a total yield of advanced neoplasia of 53. This total yield consisted of 7 high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms, 7 high-grade intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, and 39 PDACs. According to the meta-analysis, the cumulative incidence of advanced neoplasia was 3.3 (95% confidence interval, 0.6-7.4; P < .001) per 1,000 patient-years. During follow-up, the cumulative incidence of surveillance-detected/interval late-stage PDACs was 1.7 per 1,000 patient-years (95% CI, 0.2-4.0; P = .03).
In a separate analysis, the investigators sought to identify the relationship between the modality of follow-up imaging and late-stage PDAC incidence. Imaging modalities used during follow-up were mostly cross-sectional imaging, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging with cholangiopancreatography (n = 4) or endoscopic ultrasound and cross-sectional modalities (n = 8).
The investigators found no significant associations between late-stage PDACs and surveillance imaging, baseline pancreatic morphology, study location, genetic background, gender, or age. Incidence of late-stage PDACs in studies with mostly cross-sectional imaging was 0.7 per 1,000 patient-years (95% CI, 0.0-8.0). This incidence rate was lower than that reported with EUS and cross-sectional modalities (2.5 per 1,000 patient-years; 95% CI, 0.6-5.4), but this difference was not statistically significant (P = .2).
No significant difference was found during follow-up in the incidence of late-stage PDACs between high-risk individuals with baseline pancreatic abnormalities (0.0 no significant difference; 95% CI, 0.0-0.3) vs. high-risk individuals with normal baseline (0.9 per 1,000 patient-years; 95% CI, 0.0-2.8) (P = .9).
Most studies included in the analysis did not report on diagnostic errors and surveillance adherence, the researchers wrote. Nonadherence to surveillance as well as delays in surveillance accounted for four late-stage PDACs, and surveillance cessation and/or delays were reported in 4 out of 19 high-risk individuals. There was limited information on symptoms, presentation timing, site of lesion, and surveillance adherence, which the investigators indicated prevented a formal meta-analysis.
In their summary, the study authors noted that in clinical practice there is a need for improved quality measures and adherence to surveillance programs to reduce the risk of diagnostic errors. The authors stated that evidence on the impact of these quality measures “on surveillance outcomes will not only improve quality of surveillance practices, but also enrich our communication with patients who undergo surveillance.”
The researchers reported no conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry, and the study did not receive any funding.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Intranasal oxytocin shows early promise for cocaine dependence
Intranasal oxytocin (INOT) is showing early promise as a treatment for cocaine dependence, new research suggests.
Results of a small 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with cocaine use disorder showed a high level of abstinence in those who received INOT beginning 2 weeks after treatment initiation.
“In this population of cocaine-dependent individuals in a community clinic setting, , compared to placebo,” lead author Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, a Teaneck, N.J.–based psychiatrist, said in an interview.
On the other hand, “the findings were paradoxical because there was a greater dropout rate in the intranasal oxytocin group after week 1, suggesting that oxytocin might have a biphasic effect, which should be addressed in future studies,” added Dr. Raby, who was an adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry, division on substance abuse, Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, when the trial was conducted.
The study was published in the March issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence Reports.
‘Crying need’
“Focus on stress reactivity in addiction and on the loss of social norms among drug users has generated interest in oxytocin, due to its purported role in these traits and regulation of stress,” the authors wrote.
Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that regulates autonomic functions. Previous research in cannabis users suggests it may have a role in treating addiction by reportedly reducing cravings. In addition, earlier research also suggests it cuts stress reactivity and state anger in cocaine users.
A previous trial of INOT showed it decreased cocaine craving, and additional research has revealed recurrent cocaine use results in lower endogenous oxytocin levels and depleted oxytocin in the hypothalamus and amygdala.
“The bias of my work is to look for simple, nonaddictive medicinal approaches that can be used in the community settings, because that’s where the greatest crying need lies and where most problems from drug addiction occur,” said Dr. Raby.
“There has been long-standing interest in how the brain adaptive systems, or so-called ‘stress systems,’ adjust in the face of drug dependence in general, and the main focus of the study has been to understand this response and use the insight from these adaptations to develop medicinal treatments for drug abuse, particularly cocaine dependence,” he added.
To investigate the potential for INOT to promote abstinence from cocaine, the researchers randomized 26 patients with cocaine use disorder (73% male, mean [SD] age, 50.2 [5.4] years). Most participants had been using cocaine on a regular basis for about 25 years, and baseline average days of cocaine use was 11.1 (5.7) during the 30 days prior to study entry.
At a baseline, the researchers collected participants’ medical history and conducted a physical examination, urine toxicology, electrocardiogram, comprehensive metabolic panel, and complete blood count. They used the MINI International Neuropsychiatric Interview to confirm the diagnosis of cocaine dependence.
The study began with a 7-day inpatient abstinence induction stage, after which participants were randomized to receive either INOT 24 IU or intranasal placebo (n = 15 and n = 11, respectively).
Patients attended the clinic three times per week. At each visit, they completed the cocaine craving scale, the Perceived Stress Scale, and the Clinician Global Inventory (all self-reports), as well as the Time Line Follow Back (TLFB) to document cocaine use.
Participants were trained to self-administer an intranasal solution at home, with compliance monitored in two ways – staff observed self-administration of the randomized medication at the time of clinic visits and weighed the “at home bottle.”
Cocaine use was determined via urine toxicology and TLFB self-report.
Threshold period
INOT did not induce ≥ 3 weeks of continuous abstinence. However, beginning with week 3, the odds of weekly abstinence increased dramatically in the INOT group, from 4.61 (95% confidence interval,1.05, 20.3) to 15.0 (1.18, 190.2) by week 6 (t = 2.12, P = .037).
The overall medication group by time interaction across all 6 weeks was not significant (F1,69 = 1.73, P = .19); but when the interaction was removed, the difference between the overall effect of medication (INOT vs. placebo) over all 6 weeks “reached trend-level significance” (F1,70) = 3.42, P = .07).
The subjective rating outcomes (cravings, perceived stress, cocaine dependence, and depression) “did not show a significant medication group by time interaction effect,” the authors reported, although stress-induced cravings did tend toward a significant difference between the groups.
Half of the patients did not complete the full 6 weeks. Of those who discontinued, 85% came from the INOT group and 15% from the placebo group. Of the 11 who dropped out from the treatment group, seven were abstinent at the time of discontinuation for ≥ 1 week.
There were no significant differences in rates of reported side effects between the two groups.
“This study highlights some promise that perhaps there is a threshold period of time you need to cross, after which time oxytocin could really be really helpful as acute or maintenance medication,” said Dr. Raby. The short study duration might have been a disadvantage. “We might have seen better results if the study had been 8 or 12 weeks in duration.”
Using motivational approaches during the early phase – e.g., psychotherapy or a voucher system – might increase adherence, and then “after this initial lag, we might see a more therapeutic effect,” he suggested.
Dr. Raby noted that his group studied stress hormone secretions in the cocaine-dependent study participants during the 7-day induction period and that the findings, when published, could shed light on this latency period. “Cocaine dependence creates adaptations in the stress system,” he said.
‘Nice first step’
Commenting on the study, Jane Joseph, PhD, professor in the department of neurosciences and director of the neuroimaging division at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said it is “nice to see a clinical trial using oxytocin in cocaine dependence [because] preclinical research has shown fairly convincing effects of oxytocin in reducing craving or stress in the context of cocaine seeking, but findings are rather mixed in human studies.”
Dr. Joseph, who was not involved with the study, said her group’s research showed oxytocin to be the most helpful for men with cocaine use disorder who reported childhood trauma, while for women, oxytocin “seemed to worsen their reactivity to cocaine cues.”
She said the current study is a “nice first step” and suggested that future research should include larger sample sizes to “address some of the individual variability in the response to oxytocin by examining sex differences or trauma history.”
The study was supported by an award from the National Institute of Drug Abuse. Dr. Raby and coauthors and Dr. Joseph have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Intranasal oxytocin (INOT) is showing early promise as a treatment for cocaine dependence, new research suggests.
Results of a small 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with cocaine use disorder showed a high level of abstinence in those who received INOT beginning 2 weeks after treatment initiation.
“In this population of cocaine-dependent individuals in a community clinic setting, , compared to placebo,” lead author Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, a Teaneck, N.J.–based psychiatrist, said in an interview.
On the other hand, “the findings were paradoxical because there was a greater dropout rate in the intranasal oxytocin group after week 1, suggesting that oxytocin might have a biphasic effect, which should be addressed in future studies,” added Dr. Raby, who was an adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry, division on substance abuse, Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, when the trial was conducted.
The study was published in the March issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence Reports.
‘Crying need’
“Focus on stress reactivity in addiction and on the loss of social norms among drug users has generated interest in oxytocin, due to its purported role in these traits and regulation of stress,” the authors wrote.
Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that regulates autonomic functions. Previous research in cannabis users suggests it may have a role in treating addiction by reportedly reducing cravings. In addition, earlier research also suggests it cuts stress reactivity and state anger in cocaine users.
A previous trial of INOT showed it decreased cocaine craving, and additional research has revealed recurrent cocaine use results in lower endogenous oxytocin levels and depleted oxytocin in the hypothalamus and amygdala.
“The bias of my work is to look for simple, nonaddictive medicinal approaches that can be used in the community settings, because that’s where the greatest crying need lies and where most problems from drug addiction occur,” said Dr. Raby.
“There has been long-standing interest in how the brain adaptive systems, or so-called ‘stress systems,’ adjust in the face of drug dependence in general, and the main focus of the study has been to understand this response and use the insight from these adaptations to develop medicinal treatments for drug abuse, particularly cocaine dependence,” he added.
To investigate the potential for INOT to promote abstinence from cocaine, the researchers randomized 26 patients with cocaine use disorder (73% male, mean [SD] age, 50.2 [5.4] years). Most participants had been using cocaine on a regular basis for about 25 years, and baseline average days of cocaine use was 11.1 (5.7) during the 30 days prior to study entry.
At a baseline, the researchers collected participants’ medical history and conducted a physical examination, urine toxicology, electrocardiogram, comprehensive metabolic panel, and complete blood count. They used the MINI International Neuropsychiatric Interview to confirm the diagnosis of cocaine dependence.
The study began with a 7-day inpatient abstinence induction stage, after which participants were randomized to receive either INOT 24 IU or intranasal placebo (n = 15 and n = 11, respectively).
Patients attended the clinic three times per week. At each visit, they completed the cocaine craving scale, the Perceived Stress Scale, and the Clinician Global Inventory (all self-reports), as well as the Time Line Follow Back (TLFB) to document cocaine use.
Participants were trained to self-administer an intranasal solution at home, with compliance monitored in two ways – staff observed self-administration of the randomized medication at the time of clinic visits and weighed the “at home bottle.”
Cocaine use was determined via urine toxicology and TLFB self-report.
Threshold period
INOT did not induce ≥ 3 weeks of continuous abstinence. However, beginning with week 3, the odds of weekly abstinence increased dramatically in the INOT group, from 4.61 (95% confidence interval,1.05, 20.3) to 15.0 (1.18, 190.2) by week 6 (t = 2.12, P = .037).
The overall medication group by time interaction across all 6 weeks was not significant (F1,69 = 1.73, P = .19); but when the interaction was removed, the difference between the overall effect of medication (INOT vs. placebo) over all 6 weeks “reached trend-level significance” (F1,70) = 3.42, P = .07).
The subjective rating outcomes (cravings, perceived stress, cocaine dependence, and depression) “did not show a significant medication group by time interaction effect,” the authors reported, although stress-induced cravings did tend toward a significant difference between the groups.
Half of the patients did not complete the full 6 weeks. Of those who discontinued, 85% came from the INOT group and 15% from the placebo group. Of the 11 who dropped out from the treatment group, seven were abstinent at the time of discontinuation for ≥ 1 week.
There were no significant differences in rates of reported side effects between the two groups.
“This study highlights some promise that perhaps there is a threshold period of time you need to cross, after which time oxytocin could really be really helpful as acute or maintenance medication,” said Dr. Raby. The short study duration might have been a disadvantage. “We might have seen better results if the study had been 8 or 12 weeks in duration.”
Using motivational approaches during the early phase – e.g., psychotherapy or a voucher system – might increase adherence, and then “after this initial lag, we might see a more therapeutic effect,” he suggested.
Dr. Raby noted that his group studied stress hormone secretions in the cocaine-dependent study participants during the 7-day induction period and that the findings, when published, could shed light on this latency period. “Cocaine dependence creates adaptations in the stress system,” he said.
‘Nice first step’
Commenting on the study, Jane Joseph, PhD, professor in the department of neurosciences and director of the neuroimaging division at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said it is “nice to see a clinical trial using oxytocin in cocaine dependence [because] preclinical research has shown fairly convincing effects of oxytocin in reducing craving or stress in the context of cocaine seeking, but findings are rather mixed in human studies.”
Dr. Joseph, who was not involved with the study, said her group’s research showed oxytocin to be the most helpful for men with cocaine use disorder who reported childhood trauma, while for women, oxytocin “seemed to worsen their reactivity to cocaine cues.”
She said the current study is a “nice first step” and suggested that future research should include larger sample sizes to “address some of the individual variability in the response to oxytocin by examining sex differences or trauma history.”
The study was supported by an award from the National Institute of Drug Abuse. Dr. Raby and coauthors and Dr. Joseph have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Intranasal oxytocin (INOT) is showing early promise as a treatment for cocaine dependence, new research suggests.
Results of a small 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with cocaine use disorder showed a high level of abstinence in those who received INOT beginning 2 weeks after treatment initiation.
“In this population of cocaine-dependent individuals in a community clinic setting, , compared to placebo,” lead author Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, a Teaneck, N.J.–based psychiatrist, said in an interview.
On the other hand, “the findings were paradoxical because there was a greater dropout rate in the intranasal oxytocin group after week 1, suggesting that oxytocin might have a biphasic effect, which should be addressed in future studies,” added Dr. Raby, who was an adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry, division on substance abuse, Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, when the trial was conducted.
The study was published in the March issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence Reports.
‘Crying need’
“Focus on stress reactivity in addiction and on the loss of social norms among drug users has generated interest in oxytocin, due to its purported role in these traits and regulation of stress,” the authors wrote.
Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that regulates autonomic functions. Previous research in cannabis users suggests it may have a role in treating addiction by reportedly reducing cravings. In addition, earlier research also suggests it cuts stress reactivity and state anger in cocaine users.
A previous trial of INOT showed it decreased cocaine craving, and additional research has revealed recurrent cocaine use results in lower endogenous oxytocin levels and depleted oxytocin in the hypothalamus and amygdala.
“The bias of my work is to look for simple, nonaddictive medicinal approaches that can be used in the community settings, because that’s where the greatest crying need lies and where most problems from drug addiction occur,” said Dr. Raby.
“There has been long-standing interest in how the brain adaptive systems, or so-called ‘stress systems,’ adjust in the face of drug dependence in general, and the main focus of the study has been to understand this response and use the insight from these adaptations to develop medicinal treatments for drug abuse, particularly cocaine dependence,” he added.
To investigate the potential for INOT to promote abstinence from cocaine, the researchers randomized 26 patients with cocaine use disorder (73% male, mean [SD] age, 50.2 [5.4] years). Most participants had been using cocaine on a regular basis for about 25 years, and baseline average days of cocaine use was 11.1 (5.7) during the 30 days prior to study entry.
At a baseline, the researchers collected participants’ medical history and conducted a physical examination, urine toxicology, electrocardiogram, comprehensive metabolic panel, and complete blood count. They used the MINI International Neuropsychiatric Interview to confirm the diagnosis of cocaine dependence.
The study began with a 7-day inpatient abstinence induction stage, after which participants were randomized to receive either INOT 24 IU or intranasal placebo (n = 15 and n = 11, respectively).
Patients attended the clinic three times per week. At each visit, they completed the cocaine craving scale, the Perceived Stress Scale, and the Clinician Global Inventory (all self-reports), as well as the Time Line Follow Back (TLFB) to document cocaine use.
Participants were trained to self-administer an intranasal solution at home, with compliance monitored in two ways – staff observed self-administration of the randomized medication at the time of clinic visits and weighed the “at home bottle.”
Cocaine use was determined via urine toxicology and TLFB self-report.
Threshold period
INOT did not induce ≥ 3 weeks of continuous abstinence. However, beginning with week 3, the odds of weekly abstinence increased dramatically in the INOT group, from 4.61 (95% confidence interval,1.05, 20.3) to 15.0 (1.18, 190.2) by week 6 (t = 2.12, P = .037).
The overall medication group by time interaction across all 6 weeks was not significant (F1,69 = 1.73, P = .19); but when the interaction was removed, the difference between the overall effect of medication (INOT vs. placebo) over all 6 weeks “reached trend-level significance” (F1,70) = 3.42, P = .07).
The subjective rating outcomes (cravings, perceived stress, cocaine dependence, and depression) “did not show a significant medication group by time interaction effect,” the authors reported, although stress-induced cravings did tend toward a significant difference between the groups.
Half of the patients did not complete the full 6 weeks. Of those who discontinued, 85% came from the INOT group and 15% from the placebo group. Of the 11 who dropped out from the treatment group, seven were abstinent at the time of discontinuation for ≥ 1 week.
There were no significant differences in rates of reported side effects between the two groups.
“This study highlights some promise that perhaps there is a threshold period of time you need to cross, after which time oxytocin could really be really helpful as acute or maintenance medication,” said Dr. Raby. The short study duration might have been a disadvantage. “We might have seen better results if the study had been 8 or 12 weeks in duration.”
Using motivational approaches during the early phase – e.g., psychotherapy or a voucher system – might increase adherence, and then “after this initial lag, we might see a more therapeutic effect,” he suggested.
Dr. Raby noted that his group studied stress hormone secretions in the cocaine-dependent study participants during the 7-day induction period and that the findings, when published, could shed light on this latency period. “Cocaine dependence creates adaptations in the stress system,” he said.
‘Nice first step’
Commenting on the study, Jane Joseph, PhD, professor in the department of neurosciences and director of the neuroimaging division at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said it is “nice to see a clinical trial using oxytocin in cocaine dependence [because] preclinical research has shown fairly convincing effects of oxytocin in reducing craving or stress in the context of cocaine seeking, but findings are rather mixed in human studies.”
Dr. Joseph, who was not involved with the study, said her group’s research showed oxytocin to be the most helpful for men with cocaine use disorder who reported childhood trauma, while for women, oxytocin “seemed to worsen their reactivity to cocaine cues.”
She said the current study is a “nice first step” and suggested that future research should include larger sample sizes to “address some of the individual variability in the response to oxytocin by examining sex differences or trauma history.”
The study was supported by an award from the National Institute of Drug Abuse. Dr. Raby and coauthors and Dr. Joseph have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DRUG AND ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE REPORTS
Community Care Program Lacks Essential Data for Health Care Decisions
In 2014, amidst stories of delays at Veterans Health Administration facilities, Congress established the Veterans Choice Program, which expanded access to private sector health care practitioners. When the program expired in 2018, lawmakers replaced it with the Veterans Community Care Program (VCCP) as part of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks Act (38 USC § 1703 MISSION Act). Since then, the VCCP has grown exponentially; 34% of current veteran health care visits are with private clinicians.
Along with broader private sector access, the MISSION Act also mandated the creation of quality-of-care standards for both VA and VCCP, and stipulated that data be compiled and made available to “provide covered veterans relevant comparative information to make informed decisions regarding their health care.” Two-and-a-half years later, data about the quality of VCCP care remains largely unknown.
Access to Care Website
In the lead up to the MISSION Act, the VA launched its Access to Care website, an online tool that publishes institutional performance data on key metrics so that veterans can make “more informed choices about where, when, and how they receive their health care.” Following the bill’s passage, the VA added a MISSION Act Quality Standards section, which includes results of 27 conventional quality measures for every VA facility. These scores are posted alongside data of regional facilities.
This trailblazing tool is exceedingly comprehensive. Yet, multiple website gaps compromise its utility for veterans deliberating whether to obtain VCCP care, including:
- Data isn’t about VCCP care. The hospitals are selected because they are local, not whether they participate in VCCP. Further, it appears that aggregate scores include non-VCCP facilities.
- Missing conditions/treatments. While the website contains quality scores for an ample range of procedures, it lacks information for many conditions that disproportionately affect veterans. A veteran with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or traumatic brain injury (TBI), for example, has no data to check.
- Skewed comparison population. Private sector practitioners primarily treat nonveteran patients, a population that is, on average, healthier and of higher socioeconomic status when compared with VA patients. Outcomes differ, for example, when patients have coexisting mental illness or homelessness. For VCCP scores to be beneficial for comparisons, they should derive from treated veterans or be accurately risk-adjusted.
- Tangential measures. The Institute of Medicine defined health care quality as “improvement of outcomes.” Patients considering health care options benefit from information about treatment effectiveness and symptom reduction. But because obtaining that quality data is labor intensive, proxy measures are substituted. For example, the measure advising smokers to quit is the closest the website comes to reporting on the quality of mental health care.
High-Performers
The VA initiated a second means to inform veterans about the quality of furnished care. Specifically, they guided third-party administrators (TPAs)—TriWest Healthcare Alliance and Optum—in creating algorithms designating that VCCP individual clinicians, practice groups, and hospitals can be deemed high performing providers (HPPs). The algorithms are calculated using a mix of Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS), Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), and Blue Health Intelligence (BHI) primary and specialty care measures. The designations are intended to be accessible to local VA community care schedulers to connect veterans with HPPs.
Many aspects of the HPP system are not yet public, including the measures that comprise the algorithms and when the designations will become operational. From what is publicly discoverable about HPP designations, there are crucial gaps like those on the Access to Care website. Behavioral and mental health conditions, for instance, are intentionally excluded in HPP monitoring. HPP algorithms draw from care provided to the general population; an HPP’s patient panel may contain no veterans (with their common comorbidities) at all. Most limiting, there’s no expectation that VCCP clinicians be high performing. Of the 1.2 million program clinicians treating veterans as of November 2020, only a nominal 13.4% were HPP.
After studying the HPP system, VA Partnered Evidence-based Policy Resource Center acknowledged that “it remains unclear whether the quality metrics and referral system result in higher quality of care for VA patients or whether the program improves veteran health.”
Quality of VCCP Mental Health Treatment
The MISSION Act mandated the VA to “establish standards and requirements for the provision of care by non-VA health care practitioners in clinical areas for which the Department of Veterans Affairs has special expertise, including PTSD, military sexual trauma-related conditions (MST), and TBI.” This requirement arose from a recognition that mental health care provided in the private sector pales in comparison to the VA’s rigorous evidence-based training, consultation, case review and care delivery. For example, over 8500 VA clinicians have received training in evidence-based cognitive processing therapy and/or prolonged exposure therapy for PTSD.
The MISSION Act also mandated that VCCP providers must “fulfill training requirements established by the Secretary on how to deliver evidence-based treatments in the clinical areas for which the Department of Veterans Affairs has special expertise” before furnishing care pursuant to a contract with the VA. However, the VA elected to disregard the directive, and left it up to VCCP clinician’s discretion whether to obtain training or proficiency.
Two bills introduced in Congress in 2021 aim to uphold these vital mandates for the VCCP program. The Veterans’ Culturally Competent Care Act requires VCCP mental health practitioners to take courses on the evaluation and management of suicide, PTSD, TBI, and MST. The Lethal Means Safety Training Act aligns VCCP clinicians suicide prevention training with existing VA standards.
Recommendations to Assure the Quality of VCCP Care
With review and revision of VCCP quality standards now underway, the following remedial actions are recommended:
- VCCP metrics must be compiled using data on veterans’ care, not the general population, and be published on the Access to Care website. This indispensable information is published on the website for VA care but not for VCCP. Unless VCCP is required to track their veterans, apples-to-apples comparisons of quality of care will remain difficult to attain. Supplemental research that directly contrasts quality of VA to VCCP care should be posted. For example, a 2021 study of enrolled veterans brought by ambulance to VA or community emergency rooms found that all 170 VA medical centers had lower comparative death rates.
- VCCP providers should be held to the same quality standards as those applied to VA clinicians. In a 2020 critical issue update on implementation of the MISSION Act, major veterans service organizations (VSOs) recommended that competency, training, and quality standards for non-VA community clinicians must be equivalent to benchmarks expected of VA clinicians. That includes credentials, initial and follow-up training, diagnostic screening, care-delivery, and documentation standards. Enacting the Veterans’ Culturally Competent Care Act and the Lethal Means Safety Training Act would begin to meet the MISSION Act’s clear statutory language.
- The VA and VCCP should add quality information about major diagnostic categories. This will allow veterans to make informed decisions about their personal condition. For most health diagnoses, there is no searchable listing by disorder.
- Quality assessments should be realigned to focus on outcome measures. For prospective patients, outcome results provide the most meaningful basis for comparing and selecting clinicians. Proxy measures may have little bearing on whether veterans receive effective care. (As Albert Einstein’s famously observed, “Not everything that can be counted counts.”). Also, the specific measures used for a clinician’s HPP designation should be delineated.
- The VA must enforce the MISSION Act’s instruction to renew or cancel contracts based on demonstrated quality of care. As VSOs emphasized, “if the private sector is unwilling or unable to match the VA’s access and quality standards, the VA must consider whether it needs to find new community partners.”
Seventeen billion dollars is spent yearly on purchased health care whose quality remains indeterminate. Ironclad commitments are needed from Congress and the VA to ensure that the effectiveness of, and standards for, veterans care options in the private sector match that in the VA.
In 2014, amidst stories of delays at Veterans Health Administration facilities, Congress established the Veterans Choice Program, which expanded access to private sector health care practitioners. When the program expired in 2018, lawmakers replaced it with the Veterans Community Care Program (VCCP) as part of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks Act (38 USC § 1703 MISSION Act). Since then, the VCCP has grown exponentially; 34% of current veteran health care visits are with private clinicians.
Along with broader private sector access, the MISSION Act also mandated the creation of quality-of-care standards for both VA and VCCP, and stipulated that data be compiled and made available to “provide covered veterans relevant comparative information to make informed decisions regarding their health care.” Two-and-a-half years later, data about the quality of VCCP care remains largely unknown.
Access to Care Website
In the lead up to the MISSION Act, the VA launched its Access to Care website, an online tool that publishes institutional performance data on key metrics so that veterans can make “more informed choices about where, when, and how they receive their health care.” Following the bill’s passage, the VA added a MISSION Act Quality Standards section, which includes results of 27 conventional quality measures for every VA facility. These scores are posted alongside data of regional facilities.
This trailblazing tool is exceedingly comprehensive. Yet, multiple website gaps compromise its utility for veterans deliberating whether to obtain VCCP care, including:
- Data isn’t about VCCP care. The hospitals are selected because they are local, not whether they participate in VCCP. Further, it appears that aggregate scores include non-VCCP facilities.
- Missing conditions/treatments. While the website contains quality scores for an ample range of procedures, it lacks information for many conditions that disproportionately affect veterans. A veteran with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or traumatic brain injury (TBI), for example, has no data to check.
- Skewed comparison population. Private sector practitioners primarily treat nonveteran patients, a population that is, on average, healthier and of higher socioeconomic status when compared with VA patients. Outcomes differ, for example, when patients have coexisting mental illness or homelessness. For VCCP scores to be beneficial for comparisons, they should derive from treated veterans or be accurately risk-adjusted.
- Tangential measures. The Institute of Medicine defined health care quality as “improvement of outcomes.” Patients considering health care options benefit from information about treatment effectiveness and symptom reduction. But because obtaining that quality data is labor intensive, proxy measures are substituted. For example, the measure advising smokers to quit is the closest the website comes to reporting on the quality of mental health care.
High-Performers
The VA initiated a second means to inform veterans about the quality of furnished care. Specifically, they guided third-party administrators (TPAs)—TriWest Healthcare Alliance and Optum—in creating algorithms designating that VCCP individual clinicians, practice groups, and hospitals can be deemed high performing providers (HPPs). The algorithms are calculated using a mix of Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS), Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), and Blue Health Intelligence (BHI) primary and specialty care measures. The designations are intended to be accessible to local VA community care schedulers to connect veterans with HPPs.
Many aspects of the HPP system are not yet public, including the measures that comprise the algorithms and when the designations will become operational. From what is publicly discoverable about HPP designations, there are crucial gaps like those on the Access to Care website. Behavioral and mental health conditions, for instance, are intentionally excluded in HPP monitoring. HPP algorithms draw from care provided to the general population; an HPP’s patient panel may contain no veterans (with their common comorbidities) at all. Most limiting, there’s no expectation that VCCP clinicians be high performing. Of the 1.2 million program clinicians treating veterans as of November 2020, only a nominal 13.4% were HPP.
After studying the HPP system, VA Partnered Evidence-based Policy Resource Center acknowledged that “it remains unclear whether the quality metrics and referral system result in higher quality of care for VA patients or whether the program improves veteran health.”
Quality of VCCP Mental Health Treatment
The MISSION Act mandated the VA to “establish standards and requirements for the provision of care by non-VA health care practitioners in clinical areas for which the Department of Veterans Affairs has special expertise, including PTSD, military sexual trauma-related conditions (MST), and TBI.” This requirement arose from a recognition that mental health care provided in the private sector pales in comparison to the VA’s rigorous evidence-based training, consultation, case review and care delivery. For example, over 8500 VA clinicians have received training in evidence-based cognitive processing therapy and/or prolonged exposure therapy for PTSD.
The MISSION Act also mandated that VCCP providers must “fulfill training requirements established by the Secretary on how to deliver evidence-based treatments in the clinical areas for which the Department of Veterans Affairs has special expertise” before furnishing care pursuant to a contract with the VA. However, the VA elected to disregard the directive, and left it up to VCCP clinician’s discretion whether to obtain training or proficiency.
Two bills introduced in Congress in 2021 aim to uphold these vital mandates for the VCCP program. The Veterans’ Culturally Competent Care Act requires VCCP mental health practitioners to take courses on the evaluation and management of suicide, PTSD, TBI, and MST. The Lethal Means Safety Training Act aligns VCCP clinicians suicide prevention training with existing VA standards.
Recommendations to Assure the Quality of VCCP Care
With review and revision of VCCP quality standards now underway, the following remedial actions are recommended:
- VCCP metrics must be compiled using data on veterans’ care, not the general population, and be published on the Access to Care website. This indispensable information is published on the website for VA care but not for VCCP. Unless VCCP is required to track their veterans, apples-to-apples comparisons of quality of care will remain difficult to attain. Supplemental research that directly contrasts quality of VA to VCCP care should be posted. For example, a 2021 study of enrolled veterans brought by ambulance to VA or community emergency rooms found that all 170 VA medical centers had lower comparative death rates.
- VCCP providers should be held to the same quality standards as those applied to VA clinicians. In a 2020 critical issue update on implementation of the MISSION Act, major veterans service organizations (VSOs) recommended that competency, training, and quality standards for non-VA community clinicians must be equivalent to benchmarks expected of VA clinicians. That includes credentials, initial and follow-up training, diagnostic screening, care-delivery, and documentation standards. Enacting the Veterans’ Culturally Competent Care Act and the Lethal Means Safety Training Act would begin to meet the MISSION Act’s clear statutory language.
- The VA and VCCP should add quality information about major diagnostic categories. This will allow veterans to make informed decisions about their personal condition. For most health diagnoses, there is no searchable listing by disorder.
- Quality assessments should be realigned to focus on outcome measures. For prospective patients, outcome results provide the most meaningful basis for comparing and selecting clinicians. Proxy measures may have little bearing on whether veterans receive effective care. (As Albert Einstein’s famously observed, “Not everything that can be counted counts.”). Also, the specific measures used for a clinician’s HPP designation should be delineated.
- The VA must enforce the MISSION Act’s instruction to renew or cancel contracts based on demonstrated quality of care. As VSOs emphasized, “if the private sector is unwilling or unable to match the VA’s access and quality standards, the VA must consider whether it needs to find new community partners.”
Seventeen billion dollars is spent yearly on purchased health care whose quality remains indeterminate. Ironclad commitments are needed from Congress and the VA to ensure that the effectiveness of, and standards for, veterans care options in the private sector match that in the VA.
In 2014, amidst stories of delays at Veterans Health Administration facilities, Congress established the Veterans Choice Program, which expanded access to private sector health care practitioners. When the program expired in 2018, lawmakers replaced it with the Veterans Community Care Program (VCCP) as part of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks Act (38 USC § 1703 MISSION Act). Since then, the VCCP has grown exponentially; 34% of current veteran health care visits are with private clinicians.
Along with broader private sector access, the MISSION Act also mandated the creation of quality-of-care standards for both VA and VCCP, and stipulated that data be compiled and made available to “provide covered veterans relevant comparative information to make informed decisions regarding their health care.” Two-and-a-half years later, data about the quality of VCCP care remains largely unknown.
Access to Care Website
In the lead up to the MISSION Act, the VA launched its Access to Care website, an online tool that publishes institutional performance data on key metrics so that veterans can make “more informed choices about where, when, and how they receive their health care.” Following the bill’s passage, the VA added a MISSION Act Quality Standards section, which includes results of 27 conventional quality measures for every VA facility. These scores are posted alongside data of regional facilities.
This trailblazing tool is exceedingly comprehensive. Yet, multiple website gaps compromise its utility for veterans deliberating whether to obtain VCCP care, including:
- Data isn’t about VCCP care. The hospitals are selected because they are local, not whether they participate in VCCP. Further, it appears that aggregate scores include non-VCCP facilities.
- Missing conditions/treatments. While the website contains quality scores for an ample range of procedures, it lacks information for many conditions that disproportionately affect veterans. A veteran with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or traumatic brain injury (TBI), for example, has no data to check.
- Skewed comparison population. Private sector practitioners primarily treat nonveteran patients, a population that is, on average, healthier and of higher socioeconomic status when compared with VA patients. Outcomes differ, for example, when patients have coexisting mental illness or homelessness. For VCCP scores to be beneficial for comparisons, they should derive from treated veterans or be accurately risk-adjusted.
- Tangential measures. The Institute of Medicine defined health care quality as “improvement of outcomes.” Patients considering health care options benefit from information about treatment effectiveness and symptom reduction. But because obtaining that quality data is labor intensive, proxy measures are substituted. For example, the measure advising smokers to quit is the closest the website comes to reporting on the quality of mental health care.
High-Performers
The VA initiated a second means to inform veterans about the quality of furnished care. Specifically, they guided third-party administrators (TPAs)—TriWest Healthcare Alliance and Optum—in creating algorithms designating that VCCP individual clinicians, practice groups, and hospitals can be deemed high performing providers (HPPs). The algorithms are calculated using a mix of Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS), Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), and Blue Health Intelligence (BHI) primary and specialty care measures. The designations are intended to be accessible to local VA community care schedulers to connect veterans with HPPs.
Many aspects of the HPP system are not yet public, including the measures that comprise the algorithms and when the designations will become operational. From what is publicly discoverable about HPP designations, there are crucial gaps like those on the Access to Care website. Behavioral and mental health conditions, for instance, are intentionally excluded in HPP monitoring. HPP algorithms draw from care provided to the general population; an HPP’s patient panel may contain no veterans (with their common comorbidities) at all. Most limiting, there’s no expectation that VCCP clinicians be high performing. Of the 1.2 million program clinicians treating veterans as of November 2020, only a nominal 13.4% were HPP.
After studying the HPP system, VA Partnered Evidence-based Policy Resource Center acknowledged that “it remains unclear whether the quality metrics and referral system result in higher quality of care for VA patients or whether the program improves veteran health.”
Quality of VCCP Mental Health Treatment
The MISSION Act mandated the VA to “establish standards and requirements for the provision of care by non-VA health care practitioners in clinical areas for which the Department of Veterans Affairs has special expertise, including PTSD, military sexual trauma-related conditions (MST), and TBI.” This requirement arose from a recognition that mental health care provided in the private sector pales in comparison to the VA’s rigorous evidence-based training, consultation, case review and care delivery. For example, over 8500 VA clinicians have received training in evidence-based cognitive processing therapy and/or prolonged exposure therapy for PTSD.
The MISSION Act also mandated that VCCP providers must “fulfill training requirements established by the Secretary on how to deliver evidence-based treatments in the clinical areas for which the Department of Veterans Affairs has special expertise” before furnishing care pursuant to a contract with the VA. However, the VA elected to disregard the directive, and left it up to VCCP clinician’s discretion whether to obtain training or proficiency.
Two bills introduced in Congress in 2021 aim to uphold these vital mandates for the VCCP program. The Veterans’ Culturally Competent Care Act requires VCCP mental health practitioners to take courses on the evaluation and management of suicide, PTSD, TBI, and MST. The Lethal Means Safety Training Act aligns VCCP clinicians suicide prevention training with existing VA standards.
Recommendations to Assure the Quality of VCCP Care
With review and revision of VCCP quality standards now underway, the following remedial actions are recommended:
- VCCP metrics must be compiled using data on veterans’ care, not the general population, and be published on the Access to Care website. This indispensable information is published on the website for VA care but not for VCCP. Unless VCCP is required to track their veterans, apples-to-apples comparisons of quality of care will remain difficult to attain. Supplemental research that directly contrasts quality of VA to VCCP care should be posted. For example, a 2021 study of enrolled veterans brought by ambulance to VA or community emergency rooms found that all 170 VA medical centers had lower comparative death rates.
- VCCP providers should be held to the same quality standards as those applied to VA clinicians. In a 2020 critical issue update on implementation of the MISSION Act, major veterans service organizations (VSOs) recommended that competency, training, and quality standards for non-VA community clinicians must be equivalent to benchmarks expected of VA clinicians. That includes credentials, initial and follow-up training, diagnostic screening, care-delivery, and documentation standards. Enacting the Veterans’ Culturally Competent Care Act and the Lethal Means Safety Training Act would begin to meet the MISSION Act’s clear statutory language.
- The VA and VCCP should add quality information about major diagnostic categories. This will allow veterans to make informed decisions about their personal condition. For most health diagnoses, there is no searchable listing by disorder.
- Quality assessments should be realigned to focus on outcome measures. For prospective patients, outcome results provide the most meaningful basis for comparing and selecting clinicians. Proxy measures may have little bearing on whether veterans receive effective care. (As Albert Einstein’s famously observed, “Not everything that can be counted counts.”). Also, the specific measures used for a clinician’s HPP designation should be delineated.
- The VA must enforce the MISSION Act’s instruction to renew or cancel contracts based on demonstrated quality of care. As VSOs emphasized, “if the private sector is unwilling or unable to match the VA’s access and quality standards, the VA must consider whether it needs to find new community partners.”
Seventeen billion dollars is spent yearly on purchased health care whose quality remains indeterminate. Ironclad commitments are needed from Congress and the VA to ensure that the effectiveness of, and standards for, veterans care options in the private sector match that in the VA.
Indurated Violaceous Lesions on the Face, Trunk, and Legs
The Diagnosis: Kaposi Sarcoma
A punch biopsy of a lesion on the right side of the back revealed a diffuse, poorly circumscribed, spindle cell neoplasm of the papillary and reticular dermis with associated vascular and pseudovascular spaces distended by erythrocytes (Figure 1). Immunostaining was positive for human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)(Figure 2), ETS-related gene, CD31, and CD34 and negative for pan cytokeratin, confirming the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma (KS). Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures were negative. The patient was tested for HIV and referred to infectious disease and oncology. He subsequently was found to have HIV with a viral load greater than 1 million copies. He was started on antiretroviral therapy and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis. Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis showed bilateral, multifocal, perihilar, flame-shaped consolidations suggestive of KS. The patient later disclosed having an intermittent dry cough of more than a year’s duration with occasional bright red blood per rectum after bowel movements. After workup, the patient was found to have cytomegalovirus esophagitis/gastritis and candidal esophagitis that were treated with valganciclovir and fluconazole, respectively.
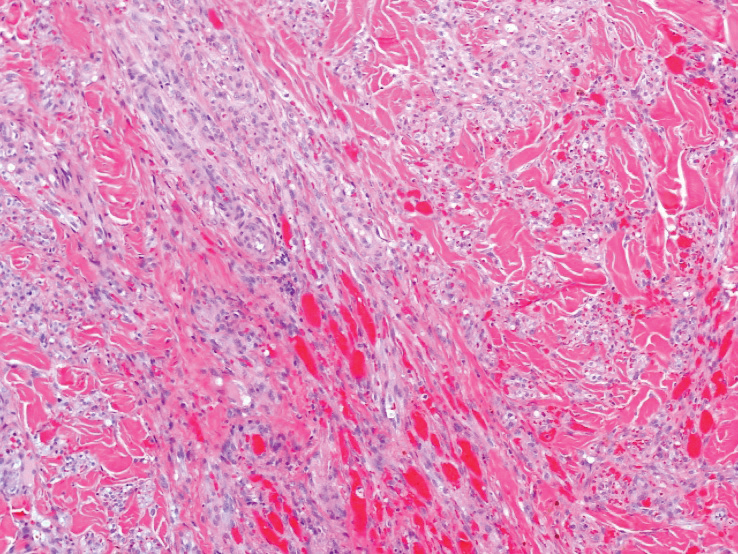
Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative, AIDSdefining disease associated with HHV-8. There are 4 types of KS as defined by the populations they affect. AIDS-associated KS occurs in individuals with HIV, as seen in our patient. It often is accompanied by extensive mucocutaneous and visceral lesions, as well as systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and diarrhea.1 Classic KS is a variant that presents in older men of Mediterranean, Eastern European, and South American descent. Cutaneous lesions typically are distributed on the lower extremities.2,3 Endemic (African) KS is seen in HIV-negative children and young adults in equatorial Africa. It most commonly affects the lower extremities or lymph nodes and usually follows a more aggressive course.2 Lastly, iatrogenic KS is associated with immunosuppressive medications or conditions, such as organ transplantation, chemotherapy, and rheumatologic disorders.3,4
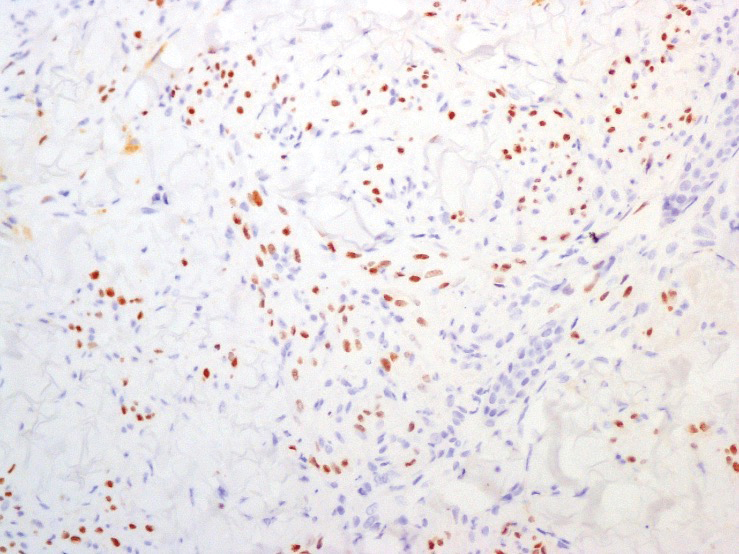
Kaposi sarcoma commonly presents as violaceous or dark red macules, patches, papules, plaques, and nodules on various parts of the body (Figure 3). Lesions typically begin as macules and progress into plaques or nodules. Our patient presented as a deceptively healthy young man with lesions at various stages of development. In addition to the skin and oral mucosa, the lungs, lymph nodes, and gastrointestinal tract commonly are involved in AIDS-associated KS.5 Patients may experience symptoms of internal involvement, including bleeding, hematochezia, odynophagia, or dyspnea.
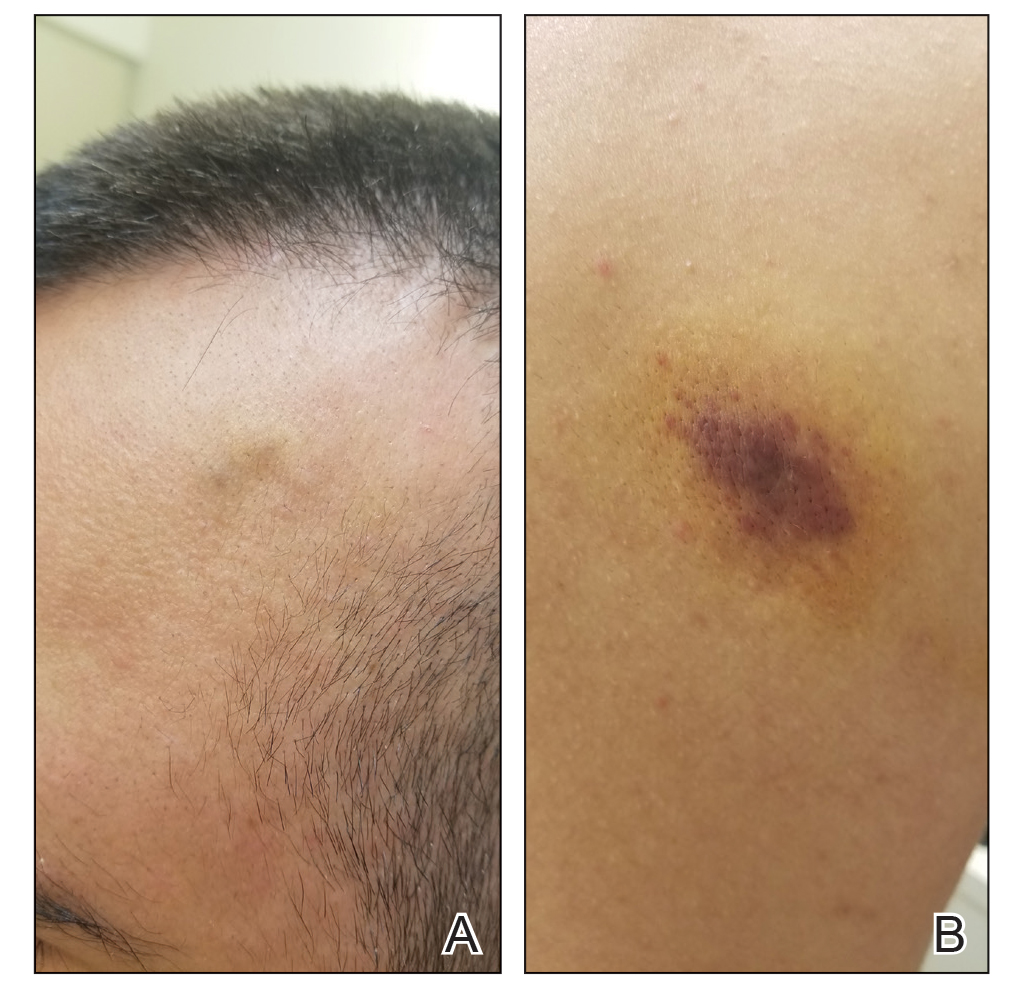
The differential diagnosis includes conditions that can mimic KS, including bacillary angiomatosis, angioinvasive fungal disease, sarcoid, and other malignancies. A skin biopsy is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of KS. Histopathology shows a vascular proliferation in the dermis and spindle cell proliferation.6 Kaposi sarcoma stains positively for factor VIII–related antigen, CD31, and CD34.2 Additionally, staining for HHV-8 gene products, such as latency-associated nuclear antigen 1, is helpful in differentiating KS from other conditions.7
In HIV-associated KS, the mainstay of treatment is initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Typically, as the CD4 count rises with treatment, the tumor burden classic KS, effective treatment options include recurrent cryotherapy or intralesional chemotherapeutics, such as vincristine, for localized lesions; for widespread disease, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin or radiation have been found to be effective options. Lastly, for patients with iatrogenic KS, reducing immunosuppressive medications is a reasonable first step in management. If this does not yield adequate improvement, transitioning from calcineurin inhibitors (eg, cyclosporine) to proliferation signal inhibitors (eg, sirolimus) may lead to resolution.7
- Friedman-Kien AE, Saltzman BR. Clinical manifestations of classical, endemic African, and epidemic AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1237-1250.
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294.
- Vangipuram R, Tyring SK. Epidemiology of Kaposi sarcoma: review and description of the nonepidemic variant. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:538-542.
- Klepp O, Dahl O, Stenwig JT. Association of Kaposi’s sarcoma and prior immunosuppressive therapy. a 5‐year material of Kaposi’s sarcoma in Norway. Cancer. 1978;42:2626-2630.
- Lemlich G, Schwam L, Lebwohl M. Kaposi’s sarcoma and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: postmortem findings in twenty-four cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:319-325.
- Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:10.
- Curtiss P, Strazzulla LC, Friedman-Kien AE. An update on Kaposi’s sarcoma: epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2016;6:465-470.
The Diagnosis: Kaposi Sarcoma
A punch biopsy of a lesion on the right side of the back revealed a diffuse, poorly circumscribed, spindle cell neoplasm of the papillary and reticular dermis with associated vascular and pseudovascular spaces distended by erythrocytes (Figure 1). Immunostaining was positive for human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)(Figure 2), ETS-related gene, CD31, and CD34 and negative for pan cytokeratin, confirming the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma (KS). Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures were negative. The patient was tested for HIV and referred to infectious disease and oncology. He subsequently was found to have HIV with a viral load greater than 1 million copies. He was started on antiretroviral therapy and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis. Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis showed bilateral, multifocal, perihilar, flame-shaped consolidations suggestive of KS. The patient later disclosed having an intermittent dry cough of more than a year’s duration with occasional bright red blood per rectum after bowel movements. After workup, the patient was found to have cytomegalovirus esophagitis/gastritis and candidal esophagitis that were treated with valganciclovir and fluconazole, respectively.

Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative, AIDSdefining disease associated with HHV-8. There are 4 types of KS as defined by the populations they affect. AIDS-associated KS occurs in individuals with HIV, as seen in our patient. It often is accompanied by extensive mucocutaneous and visceral lesions, as well as systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and diarrhea.1 Classic KS is a variant that presents in older men of Mediterranean, Eastern European, and South American descent. Cutaneous lesions typically are distributed on the lower extremities.2,3 Endemic (African) KS is seen in HIV-negative children and young adults in equatorial Africa. It most commonly affects the lower extremities or lymph nodes and usually follows a more aggressive course.2 Lastly, iatrogenic KS is associated with immunosuppressive medications or conditions, such as organ transplantation, chemotherapy, and rheumatologic disorders.3,4

Kaposi sarcoma commonly presents as violaceous or dark red macules, patches, papules, plaques, and nodules on various parts of the body (Figure 3). Lesions typically begin as macules and progress into plaques or nodules. Our patient presented as a deceptively healthy young man with lesions at various stages of development. In addition to the skin and oral mucosa, the lungs, lymph nodes, and gastrointestinal tract commonly are involved in AIDS-associated KS.5 Patients may experience symptoms of internal involvement, including bleeding, hematochezia, odynophagia, or dyspnea.

The differential diagnosis includes conditions that can mimic KS, including bacillary angiomatosis, angioinvasive fungal disease, sarcoid, and other malignancies. A skin biopsy is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of KS. Histopathology shows a vascular proliferation in the dermis and spindle cell proliferation.6 Kaposi sarcoma stains positively for factor VIII–related antigen, CD31, and CD34.2 Additionally, staining for HHV-8 gene products, such as latency-associated nuclear antigen 1, is helpful in differentiating KS from other conditions.7
In HIV-associated KS, the mainstay of treatment is initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Typically, as the CD4 count rises with treatment, the tumor burden classic KS, effective treatment options include recurrent cryotherapy or intralesional chemotherapeutics, such as vincristine, for localized lesions; for widespread disease, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin or radiation have been found to be effective options. Lastly, for patients with iatrogenic KS, reducing immunosuppressive medications is a reasonable first step in management. If this does not yield adequate improvement, transitioning from calcineurin inhibitors (eg, cyclosporine) to proliferation signal inhibitors (eg, sirolimus) may lead to resolution.7
The Diagnosis: Kaposi Sarcoma
A punch biopsy of a lesion on the right side of the back revealed a diffuse, poorly circumscribed, spindle cell neoplasm of the papillary and reticular dermis with associated vascular and pseudovascular spaces distended by erythrocytes (Figure 1). Immunostaining was positive for human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)(Figure 2), ETS-related gene, CD31, and CD34 and negative for pan cytokeratin, confirming the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma (KS). Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures were negative. The patient was tested for HIV and referred to infectious disease and oncology. He subsequently was found to have HIV with a viral load greater than 1 million copies. He was started on antiretroviral therapy and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis. Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis showed bilateral, multifocal, perihilar, flame-shaped consolidations suggestive of KS. The patient later disclosed having an intermittent dry cough of more than a year’s duration with occasional bright red blood per rectum after bowel movements. After workup, the patient was found to have cytomegalovirus esophagitis/gastritis and candidal esophagitis that were treated with valganciclovir and fluconazole, respectively.

Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative, AIDSdefining disease associated with HHV-8. There are 4 types of KS as defined by the populations they affect. AIDS-associated KS occurs in individuals with HIV, as seen in our patient. It often is accompanied by extensive mucocutaneous and visceral lesions, as well as systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and diarrhea.1 Classic KS is a variant that presents in older men of Mediterranean, Eastern European, and South American descent. Cutaneous lesions typically are distributed on the lower extremities.2,3 Endemic (African) KS is seen in HIV-negative children and young adults in equatorial Africa. It most commonly affects the lower extremities or lymph nodes and usually follows a more aggressive course.2 Lastly, iatrogenic KS is associated with immunosuppressive medications or conditions, such as organ transplantation, chemotherapy, and rheumatologic disorders.3,4

Kaposi sarcoma commonly presents as violaceous or dark red macules, patches, papules, plaques, and nodules on various parts of the body (Figure 3). Lesions typically begin as macules and progress into plaques or nodules. Our patient presented as a deceptively healthy young man with lesions at various stages of development. In addition to the skin and oral mucosa, the lungs, lymph nodes, and gastrointestinal tract commonly are involved in AIDS-associated KS.5 Patients may experience symptoms of internal involvement, including bleeding, hematochezia, odynophagia, or dyspnea.

The differential diagnosis includes conditions that can mimic KS, including bacillary angiomatosis, angioinvasive fungal disease, sarcoid, and other malignancies. A skin biopsy is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of KS. Histopathology shows a vascular proliferation in the dermis and spindle cell proliferation.6 Kaposi sarcoma stains positively for factor VIII–related antigen, CD31, and CD34.2 Additionally, staining for HHV-8 gene products, such as latency-associated nuclear antigen 1, is helpful in differentiating KS from other conditions.7
In HIV-associated KS, the mainstay of treatment is initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Typically, as the CD4 count rises with treatment, the tumor burden classic KS, effective treatment options include recurrent cryotherapy or intralesional chemotherapeutics, such as vincristine, for localized lesions; for widespread disease, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin or radiation have been found to be effective options. Lastly, for patients with iatrogenic KS, reducing immunosuppressive medications is a reasonable first step in management. If this does not yield adequate improvement, transitioning from calcineurin inhibitors (eg, cyclosporine) to proliferation signal inhibitors (eg, sirolimus) may lead to resolution.7
- Friedman-Kien AE, Saltzman BR. Clinical manifestations of classical, endemic African, and epidemic AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1237-1250.
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294.
- Vangipuram R, Tyring SK. Epidemiology of Kaposi sarcoma: review and description of the nonepidemic variant. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:538-542.
- Klepp O, Dahl O, Stenwig JT. Association of Kaposi’s sarcoma and prior immunosuppressive therapy. a 5‐year material of Kaposi’s sarcoma in Norway. Cancer. 1978;42:2626-2630.
- Lemlich G, Schwam L, Lebwohl M. Kaposi’s sarcoma and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: postmortem findings in twenty-four cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:319-325.
- Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:10.
- Curtiss P, Strazzulla LC, Friedman-Kien AE. An update on Kaposi’s sarcoma: epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2016;6:465-470.
- Friedman-Kien AE, Saltzman BR. Clinical manifestations of classical, endemic African, and epidemic AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1237-1250.
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294.
- Vangipuram R, Tyring SK. Epidemiology of Kaposi sarcoma: review and description of the nonepidemic variant. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:538-542.
- Klepp O, Dahl O, Stenwig JT. Association of Kaposi’s sarcoma and prior immunosuppressive therapy. a 5‐year material of Kaposi’s sarcoma in Norway. Cancer. 1978;42:2626-2630.
- Lemlich G, Schwam L, Lebwohl M. Kaposi’s sarcoma and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: postmortem findings in twenty-four cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:319-325.
- Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:10.
- Curtiss P, Strazzulla LC, Friedman-Kien AE. An update on Kaposi’s sarcoma: epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2016;6:465-470.
A 25-year-old man with no notable medical history presented to the dermatology clinic with growing selfdescribed cysts on the face, trunk, and legs of 6 months’ duration. The lesions started as bruiselike discolorations and progressed to become firm nodules and inflamed masses. Some were minimally itchy and sensitive to touch, but there was no history of bleeding or drainage. The patient denied any new or recent environmental or animal exposures, use of illicit drugs, or travel correlating with the rash onset. He denied any prior treatments. He reported being in his normal state of health and was not taking any medications. Physical examination revealed indurated, violaceous, purpuric subcutaneous nodules, plaques, and masses on the forehead, cheek (top), jaw, flank, axillae (bottom), and back.
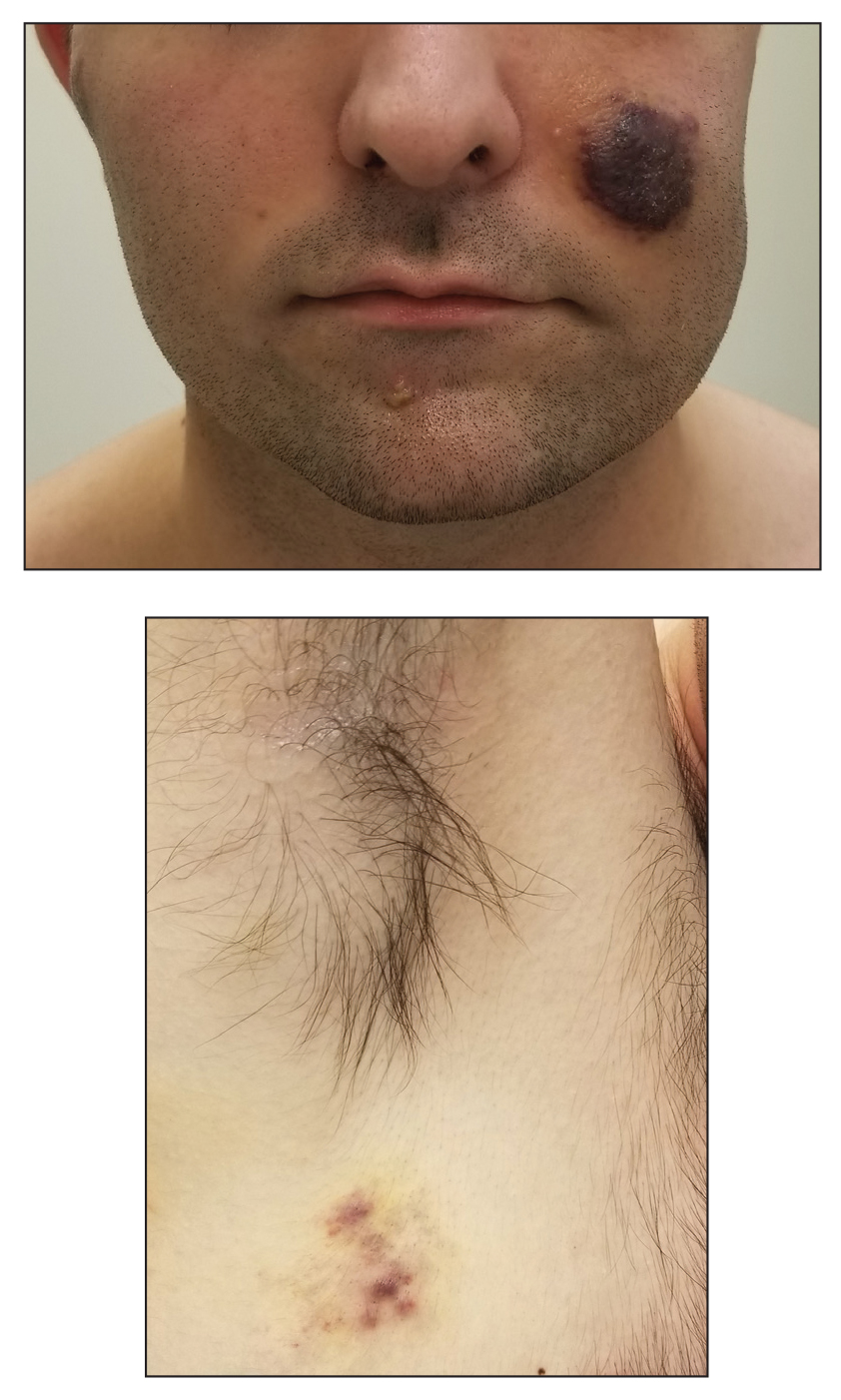
Mosquito nets do prevent malaria, longitudinal study confirms
It seems obvious that increased use of mosquito bed nets in sub-Saharan Africa would decrease the incidence of malaria, but a lingering question remained:
Malaria from Plasmodium falciparum infection exacts a significant toll in sub-Saharan Africa. According to the World Health Organization, there were about 228 million cases and 602,000 deaths from malaria in 2020 alone. About 80% of those deaths were in children less than 5 years old. In some areas, as many as 5% of children die from malaria by age 5.
Efforts to reduce the burden of malaria have been ongoing for decades. In the 1990s, insecticide-treated nets were shown to reduce illness and deaths from malaria in children.
As a result, the use of bed nets has grown significantly. In 2000, only 5% of households in sub-Saharan Africa had a net in the house. By 2020, that number had risen to 65%. From 2004 to 2019 about 1.9 billion nets were distributed in this region. The nets are estimated to have prevented more than 663 million malaria cases between 2000 and 2015.
As described in the NEJM report, public health researchers conducted a 22-year prospective longitudinal cohort study in rural southern Tanzania following 6,706 children born between 1998 and 2000. Initially, home visits were made every 4 months from May 1998 to April 2003. Remarkably, in 2019, they were able to verify the status of fully 89% of those people by reaching out to families and community/village leaders.
Günther Fink, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology and household economics, University of Basel (Switzerland), explained the approach and primary findings to this news organization. The analysis looked at three main groups – children whose parents said they always slept under treated nets, those who slept protected most of the time, and those who spent less than half the time under bed nets. The hazard ratio for death was 0.57 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.72) for the first two groups, compared with the least protected. The corresponding hazard ratio between age 5 and adulthood was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.58-1.49).
The findings confirmed what they had suspected. Dr. Fink summarized simply, “If you always slept under a net, you did much better than if you never slept under the net. If you slept [under a net] more than half of the time, it was much better than if you slept [under a net] less than half the time.” So the more time children slept under bed nets, the less likely they were to acquire malaria. Dr. Fink stressed that the findings showing protective efficacy persisted into adulthood. “It seems just having a healthier early life actually makes you more resilient against other future infections.”
One of the theoretical concerns was that using nets would delay developing functional immunity and that there might be an increase in mortality seen later. This study showed that did not happen.
An accompanying commentary noted that there was some potential that families receiving nets were better off than those that didn’t but concluded that such confounding had been accounted for in other analyses.
Mark Wilson, ScD, professor emeritus of epidemiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, concurred. He told this news organization that the study was “very well designed,” and the researchers “did a fantastic job” in tracking patients 20 years later.
“This is astounding!” he added. “It’s very rare to find this amount of follow-up.”
Dr. Fink’s conclusion? “Bed nets protect you in the short run, and being protected in the short run is also beneficial in the long run. There is no evidence that protecting kids in early childhood is weakening them in any way. So we should keep doing this.”
Dr. Fink and Dr. Wilson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It seems obvious that increased use of mosquito bed nets in sub-Saharan Africa would decrease the incidence of malaria, but a lingering question remained:
Malaria from Plasmodium falciparum infection exacts a significant toll in sub-Saharan Africa. According to the World Health Organization, there were about 228 million cases and 602,000 deaths from malaria in 2020 alone. About 80% of those deaths were in children less than 5 years old. In some areas, as many as 5% of children die from malaria by age 5.
Efforts to reduce the burden of malaria have been ongoing for decades. In the 1990s, insecticide-treated nets were shown to reduce illness and deaths from malaria in children.
As a result, the use of bed nets has grown significantly. In 2000, only 5% of households in sub-Saharan Africa had a net in the house. By 2020, that number had risen to 65%. From 2004 to 2019 about 1.9 billion nets were distributed in this region. The nets are estimated to have prevented more than 663 million malaria cases between 2000 and 2015.
As described in the NEJM report, public health researchers conducted a 22-year prospective longitudinal cohort study in rural southern Tanzania following 6,706 children born between 1998 and 2000. Initially, home visits were made every 4 months from May 1998 to April 2003. Remarkably, in 2019, they were able to verify the status of fully 89% of those people by reaching out to families and community/village leaders.
Günther Fink, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology and household economics, University of Basel (Switzerland), explained the approach and primary findings to this news organization. The analysis looked at three main groups – children whose parents said they always slept under treated nets, those who slept protected most of the time, and those who spent less than half the time under bed nets. The hazard ratio for death was 0.57 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.72) for the first two groups, compared with the least protected. The corresponding hazard ratio between age 5 and adulthood was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.58-1.49).
The findings confirmed what they had suspected. Dr. Fink summarized simply, “If you always slept under a net, you did much better than if you never slept under the net. If you slept [under a net] more than half of the time, it was much better than if you slept [under a net] less than half the time.” So the more time children slept under bed nets, the less likely they were to acquire malaria. Dr. Fink stressed that the findings showing protective efficacy persisted into adulthood. “It seems just having a healthier early life actually makes you more resilient against other future infections.”
One of the theoretical concerns was that using nets would delay developing functional immunity and that there might be an increase in mortality seen later. This study showed that did not happen.
An accompanying commentary noted that there was some potential that families receiving nets were better off than those that didn’t but concluded that such confounding had been accounted for in other analyses.
Mark Wilson, ScD, professor emeritus of epidemiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, concurred. He told this news organization that the study was “very well designed,” and the researchers “did a fantastic job” in tracking patients 20 years later.
“This is astounding!” he added. “It’s very rare to find this amount of follow-up.”
Dr. Fink’s conclusion? “Bed nets protect you in the short run, and being protected in the short run is also beneficial in the long run. There is no evidence that protecting kids in early childhood is weakening them in any way. So we should keep doing this.”
Dr. Fink and Dr. Wilson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It seems obvious that increased use of mosquito bed nets in sub-Saharan Africa would decrease the incidence of malaria, but a lingering question remained:
Malaria from Plasmodium falciparum infection exacts a significant toll in sub-Saharan Africa. According to the World Health Organization, there were about 228 million cases and 602,000 deaths from malaria in 2020 alone. About 80% of those deaths were in children less than 5 years old. In some areas, as many as 5% of children die from malaria by age 5.
Efforts to reduce the burden of malaria have been ongoing for decades. In the 1990s, insecticide-treated nets were shown to reduce illness and deaths from malaria in children.
As a result, the use of bed nets has grown significantly. In 2000, only 5% of households in sub-Saharan Africa had a net in the house. By 2020, that number had risen to 65%. From 2004 to 2019 about 1.9 billion nets were distributed in this region. The nets are estimated to have prevented more than 663 million malaria cases between 2000 and 2015.
As described in the NEJM report, public health researchers conducted a 22-year prospective longitudinal cohort study in rural southern Tanzania following 6,706 children born between 1998 and 2000. Initially, home visits were made every 4 months from May 1998 to April 2003. Remarkably, in 2019, they were able to verify the status of fully 89% of those people by reaching out to families and community/village leaders.
Günther Fink, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology and household economics, University of Basel (Switzerland), explained the approach and primary findings to this news organization. The analysis looked at three main groups – children whose parents said they always slept under treated nets, those who slept protected most of the time, and those who spent less than half the time under bed nets. The hazard ratio for death was 0.57 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.72) for the first two groups, compared with the least protected. The corresponding hazard ratio between age 5 and adulthood was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.58-1.49).
The findings confirmed what they had suspected. Dr. Fink summarized simply, “If you always slept under a net, you did much better than if you never slept under the net. If you slept [under a net] more than half of the time, it was much better than if you slept [under a net] less than half the time.” So the more time children slept under bed nets, the less likely they were to acquire malaria. Dr. Fink stressed that the findings showing protective efficacy persisted into adulthood. “It seems just having a healthier early life actually makes you more resilient against other future infections.”
One of the theoretical concerns was that using nets would delay developing functional immunity and that there might be an increase in mortality seen later. This study showed that did not happen.
An accompanying commentary noted that there was some potential that families receiving nets were better off than those that didn’t but concluded that such confounding had been accounted for in other analyses.
Mark Wilson, ScD, professor emeritus of epidemiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, concurred. He told this news organization that the study was “very well designed,” and the researchers “did a fantastic job” in tracking patients 20 years later.
“This is astounding!” he added. “It’s very rare to find this amount of follow-up.”
Dr. Fink’s conclusion? “Bed nets protect you in the short run, and being protected in the short run is also beneficial in the long run. There is no evidence that protecting kids in early childhood is weakening them in any way. So we should keep doing this.”
Dr. Fink and Dr. Wilson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
IBD classification needs an upgrade
The current clinical classification tools for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are suboptimal, and revision beyond the broad categories of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) could improve trial design, research, and ultimately patient outcomes, according to the authors of a recent review.
“Despite clear improvements in our understanding of disease biology and increasing treatment options, we still face an important therapeutic ceiling [in IBD],” wrote Bram Verstockt, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
“In part, our limited therapeutic successes can be attributed to the disease heterogeneity of IBD: There is not one CD, nor a single UC phenotype,” therefore, a revision of the current systems based on better understanding of IBD is needed, the researchers said.
In a review article published in Gastroenterology, the researchers identified clinical features important to IBD heterogeneity, examined limitations of the current classifications, and proposed improvements.
Characterizing a complex condition
IBD diagnosis is challenging not only because of the overlapping phenotypes, but because other pathologies, including infections, can mimic IBD, the authors noted.
Age of onset should be considered in characterizing IBD, they wrote. Notably, patients with late-onset CD should be distinguished from elderly patients who have had CD for years. The authors cited research showing that “the development of IBD at extremes of age are specific sub-groups that require a different clinical recognition and clinical management,” and that large sample sizes and unbiased statistical methods are needed to define subgroups of IBD patients.
Current CD classification (the Montreal Classification) involves disease location, disease behavior, and age at diagnosis, and considers four phenotypes within disease location: involvement of the ileum, involvement of the colon, involvement of both the ileum and the colon, or isolated upper disease.* “Recently, there has been notable interest in the differential response rates among ileal predominant CD compared to colonic CD,” the authors wrote. Consequently, they proposed a revision of CD classification based on location. Genetic data appear to support this revision. In an IBD genotype-phenotype study including nearly 30,000 patients, three loci (NOD2, MHC, MST1 3p21) were strongly associated with disease location, they said. Other emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota may vary according to disease location. The authors identified clinical aspects of CD classification based on disease location that distinguish small bowel predominant CD versus colonic predominant CD. Ileal disease patients have shown an increased risk for undergoing surgery, while those with colonic involvement have an increased risk for developing extraintestinal manifestations.
They also emphasized the value of considering rectal inflammation, which significantly impacts surgical procedures in CD.
Standard UC classification is based on macroscopic disease in the colon at the time of inflammation, the authors said. Although this approach allows for quick assessment of a patient’s risk of colectomy, the authors proposed improvements, including the use of serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify patients at highest risk for colectomy and colon cancer based on inflammation. The authors also suggested that patients with refractory proctitis be enrolled in UC clinical trials or in studies focusing on refractory proctitis in particular.
The pelvic pouch has become the most often performed surgical procedure for patients undergoing colectomy, but there is no agreement on classification of inflammatory pelvic pouch disorders, and studies of etiology and treatment are lacking, the authors noted. They advised a clinical assessment based on symptoms, including stool frequency, urgency, and incontinence. They also suggested that afferent limb ulcers of erosions should be classified separately from pouch inflammation.
The authors ended by noting that extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) that occur in up to half of IBD patients may or may not be directly related to intestinal disease, and may represent a different phenotype, and the presence and type of EIM should be included in a revised IBD classification system, they said.
The authors emphasized that continuing to refer to IBD as only CD and UC “does a great disservice to our attempts to better understand IBD pathogenesis and to improve clinical patient management.”
They concluded: “Although revised clinical classification tools alone will not be sufficient and should be complemented by deeper and more detailed study into molecular subclassification of disease, the considerations here could be used as a springboard toward improved trial design, future translational research approaches and better treatment outcomes for patients.”
Review reflects complexity of IBD and challenges of change
The review is important at this time because of the growing recognition that IBD, while traditionally categorized as either UC or CD, is most likely composed of a range of heterogeneous conditions involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Jatin Roper, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Evidence that our current classification of IBD is suboptimal comes from both the wide range of clinical phenotypes as well as complexity in genetic markers that are associated with IBD,” he said. “It is well accepted in the gastroenterology community that IBD is a complex condition; so it is surprising to me that the dichotomy of UC vs. Crohn’s disease has rarely been challenged,” said Dr. Roper. “The authors of this review should be commended for raising the question of whether IBD deserves a more nuanced classification system that reflects the growing recognition of the wide heterogeneity of patient presentations and genetics,” he said.
“Challenging medical definitions is inherently difficult because patient diagnoses, treatment plans, as well as decades of clinical research have been based on well-accepted disease categories. Another major challenge in reclassification is that the course of IBD can vary greatly over time in the same patient in severity, range, and complexity, and potentially includes many disease subtypes noted by the authors of this review,” he added. “Therefore, I believe that the current system of dividing IBD in UC and CD is here to stay until subtypes based on mechanisms of disease pathogenesis are discovered.
“Additional research is needed to understand the molecular basis of IBD,” Dr. Roper emphasized. “Recent advances in RNA expression and proteomics at the single cell level may reveal distinct cell types or cell functions in tissues from IBD patients that may help us understand clinical phenotype or response to therapy.”
The study received no outside funding. The authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Biogen, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Takeda, and Truvion. Dr. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Help your patients better understand their IBD treatment options by sharing AGA’s patient education, “Living with IBD,” in the AGA GI Patient Center at www.gastro.org/IBD.
*Correction, 4/11/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the Montreal Classification.
The current clinical classification tools for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are suboptimal, and revision beyond the broad categories of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) could improve trial design, research, and ultimately patient outcomes, according to the authors of a recent review.
“Despite clear improvements in our understanding of disease biology and increasing treatment options, we still face an important therapeutic ceiling [in IBD],” wrote Bram Verstockt, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
“In part, our limited therapeutic successes can be attributed to the disease heterogeneity of IBD: There is not one CD, nor a single UC phenotype,” therefore, a revision of the current systems based on better understanding of IBD is needed, the researchers said.
In a review article published in Gastroenterology, the researchers identified clinical features important to IBD heterogeneity, examined limitations of the current classifications, and proposed improvements.
Characterizing a complex condition
IBD diagnosis is challenging not only because of the overlapping phenotypes, but because other pathologies, including infections, can mimic IBD, the authors noted.
Age of onset should be considered in characterizing IBD, they wrote. Notably, patients with late-onset CD should be distinguished from elderly patients who have had CD for years. The authors cited research showing that “the development of IBD at extremes of age are specific sub-groups that require a different clinical recognition and clinical management,” and that large sample sizes and unbiased statistical methods are needed to define subgroups of IBD patients.
Current CD classification (the Montreal Classification) involves disease location, disease behavior, and age at diagnosis, and considers four phenotypes within disease location: involvement of the ileum, involvement of the colon, involvement of both the ileum and the colon, or isolated upper disease.* “Recently, there has been notable interest in the differential response rates among ileal predominant CD compared to colonic CD,” the authors wrote. Consequently, they proposed a revision of CD classification based on location. Genetic data appear to support this revision. In an IBD genotype-phenotype study including nearly 30,000 patients, three loci (NOD2, MHC, MST1 3p21) were strongly associated with disease location, they said. Other emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota may vary according to disease location. The authors identified clinical aspects of CD classification based on disease location that distinguish small bowel predominant CD versus colonic predominant CD. Ileal disease patients have shown an increased risk for undergoing surgery, while those with colonic involvement have an increased risk for developing extraintestinal manifestations.
They also emphasized the value of considering rectal inflammation, which significantly impacts surgical procedures in CD.
Standard UC classification is based on macroscopic disease in the colon at the time of inflammation, the authors said. Although this approach allows for quick assessment of a patient’s risk of colectomy, the authors proposed improvements, including the use of serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify patients at highest risk for colectomy and colon cancer based on inflammation. The authors also suggested that patients with refractory proctitis be enrolled in UC clinical trials or in studies focusing on refractory proctitis in particular.
The pelvic pouch has become the most often performed surgical procedure for patients undergoing colectomy, but there is no agreement on classification of inflammatory pelvic pouch disorders, and studies of etiology and treatment are lacking, the authors noted. They advised a clinical assessment based on symptoms, including stool frequency, urgency, and incontinence. They also suggested that afferent limb ulcers of erosions should be classified separately from pouch inflammation.
The authors ended by noting that extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) that occur in up to half of IBD patients may or may not be directly related to intestinal disease, and may represent a different phenotype, and the presence and type of EIM should be included in a revised IBD classification system, they said.
The authors emphasized that continuing to refer to IBD as only CD and UC “does a great disservice to our attempts to better understand IBD pathogenesis and to improve clinical patient management.”
They concluded: “Although revised clinical classification tools alone will not be sufficient and should be complemented by deeper and more detailed study into molecular subclassification of disease, the considerations here could be used as a springboard toward improved trial design, future translational research approaches and better treatment outcomes for patients.”
Review reflects complexity of IBD and challenges of change
The review is important at this time because of the growing recognition that IBD, while traditionally categorized as either UC or CD, is most likely composed of a range of heterogeneous conditions involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Jatin Roper, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Evidence that our current classification of IBD is suboptimal comes from both the wide range of clinical phenotypes as well as complexity in genetic markers that are associated with IBD,” he said. “It is well accepted in the gastroenterology community that IBD is a complex condition; so it is surprising to me that the dichotomy of UC vs. Crohn’s disease has rarely been challenged,” said Dr. Roper. “The authors of this review should be commended for raising the question of whether IBD deserves a more nuanced classification system that reflects the growing recognition of the wide heterogeneity of patient presentations and genetics,” he said.
“Challenging medical definitions is inherently difficult because patient diagnoses, treatment plans, as well as decades of clinical research have been based on well-accepted disease categories. Another major challenge in reclassification is that the course of IBD can vary greatly over time in the same patient in severity, range, and complexity, and potentially includes many disease subtypes noted by the authors of this review,” he added. “Therefore, I believe that the current system of dividing IBD in UC and CD is here to stay until subtypes based on mechanisms of disease pathogenesis are discovered.
“Additional research is needed to understand the molecular basis of IBD,” Dr. Roper emphasized. “Recent advances in RNA expression and proteomics at the single cell level may reveal distinct cell types or cell functions in tissues from IBD patients that may help us understand clinical phenotype or response to therapy.”
The study received no outside funding. The authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Biogen, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Takeda, and Truvion. Dr. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Help your patients better understand their IBD treatment options by sharing AGA’s patient education, “Living with IBD,” in the AGA GI Patient Center at www.gastro.org/IBD.
*Correction, 4/11/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the Montreal Classification.
The current clinical classification tools for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are suboptimal, and revision beyond the broad categories of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) could improve trial design, research, and ultimately patient outcomes, according to the authors of a recent review.
“Despite clear improvements in our understanding of disease biology and increasing treatment options, we still face an important therapeutic ceiling [in IBD],” wrote Bram Verstockt, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
“In part, our limited therapeutic successes can be attributed to the disease heterogeneity of IBD: There is not one CD, nor a single UC phenotype,” therefore, a revision of the current systems based on better understanding of IBD is needed, the researchers said.
In a review article published in Gastroenterology, the researchers identified clinical features important to IBD heterogeneity, examined limitations of the current classifications, and proposed improvements.
Characterizing a complex condition
IBD diagnosis is challenging not only because of the overlapping phenotypes, but because other pathologies, including infections, can mimic IBD, the authors noted.
Age of onset should be considered in characterizing IBD, they wrote. Notably, patients with late-onset CD should be distinguished from elderly patients who have had CD for years. The authors cited research showing that “the development of IBD at extremes of age are specific sub-groups that require a different clinical recognition and clinical management,” and that large sample sizes and unbiased statistical methods are needed to define subgroups of IBD patients.
Current CD classification (the Montreal Classification) involves disease location, disease behavior, and age at diagnosis, and considers four phenotypes within disease location: involvement of the ileum, involvement of the colon, involvement of both the ileum and the colon, or isolated upper disease.* “Recently, there has been notable interest in the differential response rates among ileal predominant CD compared to colonic CD,” the authors wrote. Consequently, they proposed a revision of CD classification based on location. Genetic data appear to support this revision. In an IBD genotype-phenotype study including nearly 30,000 patients, three loci (NOD2, MHC, MST1 3p21) were strongly associated with disease location, they said. Other emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota may vary according to disease location. The authors identified clinical aspects of CD classification based on disease location that distinguish small bowel predominant CD versus colonic predominant CD. Ileal disease patients have shown an increased risk for undergoing surgery, while those with colonic involvement have an increased risk for developing extraintestinal manifestations.
They also emphasized the value of considering rectal inflammation, which significantly impacts surgical procedures in CD.
Standard UC classification is based on macroscopic disease in the colon at the time of inflammation, the authors said. Although this approach allows for quick assessment of a patient’s risk of colectomy, the authors proposed improvements, including the use of serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify patients at highest risk for colectomy and colon cancer based on inflammation. The authors also suggested that patients with refractory proctitis be enrolled in UC clinical trials or in studies focusing on refractory proctitis in particular.
The pelvic pouch has become the most often performed surgical procedure for patients undergoing colectomy, but there is no agreement on classification of inflammatory pelvic pouch disorders, and studies of etiology and treatment are lacking, the authors noted. They advised a clinical assessment based on symptoms, including stool frequency, urgency, and incontinence. They also suggested that afferent limb ulcers of erosions should be classified separately from pouch inflammation.
The authors ended by noting that extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) that occur in up to half of IBD patients may or may not be directly related to intestinal disease, and may represent a different phenotype, and the presence and type of EIM should be included in a revised IBD classification system, they said.
The authors emphasized that continuing to refer to IBD as only CD and UC “does a great disservice to our attempts to better understand IBD pathogenesis and to improve clinical patient management.”
They concluded: “Although revised clinical classification tools alone will not be sufficient and should be complemented by deeper and more detailed study into molecular subclassification of disease, the considerations here could be used as a springboard toward improved trial design, future translational research approaches and better treatment outcomes for patients.”
Review reflects complexity of IBD and challenges of change
The review is important at this time because of the growing recognition that IBD, while traditionally categorized as either UC or CD, is most likely composed of a range of heterogeneous conditions involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Jatin Roper, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Evidence that our current classification of IBD is suboptimal comes from both the wide range of clinical phenotypes as well as complexity in genetic markers that are associated with IBD,” he said. “It is well accepted in the gastroenterology community that IBD is a complex condition; so it is surprising to me that the dichotomy of UC vs. Crohn’s disease has rarely been challenged,” said Dr. Roper. “The authors of this review should be commended for raising the question of whether IBD deserves a more nuanced classification system that reflects the growing recognition of the wide heterogeneity of patient presentations and genetics,” he said.
“Challenging medical definitions is inherently difficult because patient diagnoses, treatment plans, as well as decades of clinical research have been based on well-accepted disease categories. Another major challenge in reclassification is that the course of IBD can vary greatly over time in the same patient in severity, range, and complexity, and potentially includes many disease subtypes noted by the authors of this review,” he added. “Therefore, I believe that the current system of dividing IBD in UC and CD is here to stay until subtypes based on mechanisms of disease pathogenesis are discovered.
“Additional research is needed to understand the molecular basis of IBD,” Dr. Roper emphasized. “Recent advances in RNA expression and proteomics at the single cell level may reveal distinct cell types or cell functions in tissues from IBD patients that may help us understand clinical phenotype or response to therapy.”
The study received no outside funding. The authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Biogen, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Takeda, and Truvion. Dr. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Help your patients better understand their IBD treatment options by sharing AGA’s patient education, “Living with IBD,” in the AGA GI Patient Center at www.gastro.org/IBD.
*Correction, 4/11/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the Montreal Classification.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
IBD classification needs an upgrade
The current clinical classification tools for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are suboptimal, and revision beyond the broad categories of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) could improve trial design, research, and ultimately patient outcomes, according to the authors of a recent review.
“Despite clear improvements in our understanding of disease biology and increasing treatment options, we still face an important therapeutic ceiling [in IBD],” wrote Bram Verstockt, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
“In part, our limited therapeutic successes can be attributed to the disease heterogeneity of IBD: There is not one CD, nor a single UC phenotype,” therefore, a revision of the current systems based on better understanding of IBD is needed, the researchers said.
In a review article published in Gastroenterology, the researchers identified clinical features important to IBD heterogeneity, examined limitations of the current classifications, and proposed improvements.
Characterizing a complex condition
IBD diagnosis is challenging not only because of the overlapping phenotypes, but because other pathologies, including infections, can mimic IBD, the authors noted.
Age of onset should be considered in characterizing IBD, they wrote. Notably, patients with late-onset CD should be distinguished from elderly patients who have had CD for years. The authors cited research showing that “the development of IBD at extremes of age are specific sub-groups that require a different clinical recognition and clinical management,” and that large sample sizes and unbiased statistical methods are needed to define subgroups of IBD patients.
Current CD classification (the Montreal Classification) involves disease location, disease behavior, and age at diagnosis, and considers four phenotypes within disease location: involvement of the ileum, involvement of the colon, involvement of both the ileum and the colon, or isolated upper disease.* “Recently, there has been notable interest in the differential response rates among ileal predominant CD compared to colonic CD,” the authors wrote. Consequently, they proposed a revision of CD classification based on location. Genetic data appear to support this revision. In an IBD genotype-phenotype study including nearly 30,000 patients, three loci (NOD2, MHC, MST1 3p21) were strongly associated with disease location, they said. Other emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota may vary according to disease location. The authors identified clinical aspects of CD classification based on disease location that distinguish small bowel predominant CD versus colonic predominant CD. Ileal disease patients have shown an increased risk for undergoing surgery, while those with colonic involvement have an increased risk for developing extraintestinal manifestations.
They also emphasized the value of considering rectal inflammation, which significantly impacts surgical procedures in CD.
Standard UC classification is based on macroscopic disease in the colon at the time of inflammation, the authors said. Although this approach allows for quick assessment of a patient’s risk of colectomy, the authors proposed improvements, including the use of serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify patients at highest risk for colectomy and colon cancer based on inflammation. The authors also suggested that patients with refractory proctitis be enrolled in UC clinical trials or in studies focusing on refractory proctitis in particular.
The pelvic pouch has become the most often performed surgical procedure for patients undergoing colectomy, but there is no agreement on classification of inflammatory pelvic pouch disorders, and studies of etiology and treatment are lacking, the authors noted. They advised a clinical assessment based on symptoms, including stool frequency, urgency, and incontinence. They also suggested that afferent limb ulcers of erosions should be classified separately from pouch inflammation.
The authors ended by noting that extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) that occur in up to half of IBD patients may or may not be directly related to intestinal disease, and may represent a different phenotype, and the presence and type of EIM should be included in a revised IBD classification system, they said.
The authors emphasized that continuing to refer to IBD as only CD and UC “does a great disservice to our attempts to better understand IBD pathogenesis and to improve clinical patient management.”
They concluded: “Although revised clinical classification tools alone will not be sufficient and should be complemented by deeper and more detailed study into molecular subclassification of disease, the considerations here could be used as a springboard toward improved trial design, future translational research approaches and better treatment outcomes for patients.”
Review reflects complexity of IBD and challenges of change
The review is important at this time because of the growing recognition that IBD, while traditionally categorized as either UC or CD, is most likely composed of a range of heterogeneous conditions involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Jatin Roper, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Evidence that our current classification of IBD is suboptimal comes from both the wide range of clinical phenotypes as well as complexity in genetic markers that are associated with IBD,” he said. “It is well accepted in the gastroenterology community that IBD is a complex condition; so it is surprising to me that the dichotomy of UC vs. Crohn’s disease has rarely been challenged,” said Dr. Roper. “The authors of this review should be commended for raising the question of whether IBD deserves a more nuanced classification system that reflects the growing recognition of the wide heterogeneity of patient presentations and genetics,” he said.
“Challenging medical definitions is inherently difficult because patient diagnoses, treatment plans, as well as decades of clinical research have been based on well-accepted disease categories. Another major challenge in reclassification is that the course of IBD can vary greatly over time in the same patient in severity, range, and complexity, and potentially includes many disease subtypes noted by the authors of this review,” he added. “Therefore, I believe that the current system of dividing IBD in UC and CD is here to stay until subtypes based on mechanisms of disease pathogenesis are discovered.
“Additional research is needed to understand the molecular basis of IBD,” Dr. Roper emphasized. “Recent advances in RNA expression and proteomics at the single cell level may reveal distinct cell types or cell functions in tissues from IBD patients that may help us understand clinical phenotype or response to therapy.”
The study received no outside funding. The authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Biogen, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Takeda, and Truvion. Dr. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Correction, 4/13/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the Montreal Classification.
The current clinical classification tools for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are suboptimal, and revision beyond the broad categories of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) could improve trial design, research, and ultimately patient outcomes, according to the authors of a recent review.
“Despite clear improvements in our understanding of disease biology and increasing treatment options, we still face an important therapeutic ceiling [in IBD],” wrote Bram Verstockt, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
“In part, our limited therapeutic successes can be attributed to the disease heterogeneity of IBD: There is not one CD, nor a single UC phenotype,” therefore, a revision of the current systems based on better understanding of IBD is needed, the researchers said.
In a review article published in Gastroenterology, the researchers identified clinical features important to IBD heterogeneity, examined limitations of the current classifications, and proposed improvements.
Characterizing a complex condition
IBD diagnosis is challenging not only because of the overlapping phenotypes, but because other pathologies, including infections, can mimic IBD, the authors noted.
Age of onset should be considered in characterizing IBD, they wrote. Notably, patients with late-onset CD should be distinguished from elderly patients who have had CD for years. The authors cited research showing that “the development of IBD at extremes of age are specific sub-groups that require a different clinical recognition and clinical management,” and that large sample sizes and unbiased statistical methods are needed to define subgroups of IBD patients.
Current CD classification (the Montreal Classification) involves disease location, disease behavior, and age at diagnosis, and considers four phenotypes within disease location: involvement of the ileum, involvement of the colon, involvement of both the ileum and the colon, or isolated upper disease.* “Recently, there has been notable interest in the differential response rates among ileal predominant CD compared to colonic CD,” the authors wrote. Consequently, they proposed a revision of CD classification based on location. Genetic data appear to support this revision. In an IBD genotype-phenotype study including nearly 30,000 patients, three loci (NOD2, MHC, MST1 3p21) were strongly associated with disease location, they said. Other emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota may vary according to disease location. The authors identified clinical aspects of CD classification based on disease location that distinguish small bowel predominant CD versus colonic predominant CD. Ileal disease patients have shown an increased risk for undergoing surgery, while those with colonic involvement have an increased risk for developing extraintestinal manifestations.
They also emphasized the value of considering rectal inflammation, which significantly impacts surgical procedures in CD.
Standard UC classification is based on macroscopic disease in the colon at the time of inflammation, the authors said. Although this approach allows for quick assessment of a patient’s risk of colectomy, the authors proposed improvements, including the use of serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify patients at highest risk for colectomy and colon cancer based on inflammation. The authors also suggested that patients with refractory proctitis be enrolled in UC clinical trials or in studies focusing on refractory proctitis in particular.
The pelvic pouch has become the most often performed surgical procedure for patients undergoing colectomy, but there is no agreement on classification of inflammatory pelvic pouch disorders, and studies of etiology and treatment are lacking, the authors noted. They advised a clinical assessment based on symptoms, including stool frequency, urgency, and incontinence. They also suggested that afferent limb ulcers of erosions should be classified separately from pouch inflammation.
The authors ended by noting that extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) that occur in up to half of IBD patients may or may not be directly related to intestinal disease, and may represent a different phenotype, and the presence and type of EIM should be included in a revised IBD classification system, they said.
The authors emphasized that continuing to refer to IBD as only CD and UC “does a great disservice to our attempts to better understand IBD pathogenesis and to improve clinical patient management.”
They concluded: “Although revised clinical classification tools alone will not be sufficient and should be complemented by deeper and more detailed study into molecular subclassification of disease, the considerations here could be used as a springboard toward improved trial design, future translational research approaches and better treatment outcomes for patients.”
Review reflects complexity of IBD and challenges of change
The review is important at this time because of the growing recognition that IBD, while traditionally categorized as either UC or CD, is most likely composed of a range of heterogeneous conditions involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Jatin Roper, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Evidence that our current classification of IBD is suboptimal comes from both the wide range of clinical phenotypes as well as complexity in genetic markers that are associated with IBD,” he said. “It is well accepted in the gastroenterology community that IBD is a complex condition; so it is surprising to me that the dichotomy of UC vs. Crohn’s disease has rarely been challenged,” said Dr. Roper. “The authors of this review should be commended for raising the question of whether IBD deserves a more nuanced classification system that reflects the growing recognition of the wide heterogeneity of patient presentations and genetics,” he said.
“Challenging medical definitions is inherently difficult because patient diagnoses, treatment plans, as well as decades of clinical research have been based on well-accepted disease categories. Another major challenge in reclassification is that the course of IBD can vary greatly over time in the same patient in severity, range, and complexity, and potentially includes many disease subtypes noted by the authors of this review,” he added. “Therefore, I believe that the current system of dividing IBD in UC and CD is here to stay until subtypes based on mechanisms of disease pathogenesis are discovered.
“Additional research is needed to understand the molecular basis of IBD,” Dr. Roper emphasized. “Recent advances in RNA expression and proteomics at the single cell level may reveal distinct cell types or cell functions in tissues from IBD patients that may help us understand clinical phenotype or response to therapy.”
The study received no outside funding. The authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Biogen, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Takeda, and Truvion. Dr. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Correction, 4/13/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the Montreal Classification.
The current clinical classification tools for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are suboptimal, and revision beyond the broad categories of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) could improve trial design, research, and ultimately patient outcomes, according to the authors of a recent review.
“Despite clear improvements in our understanding of disease biology and increasing treatment options, we still face an important therapeutic ceiling [in IBD],” wrote Bram Verstockt, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
“In part, our limited therapeutic successes can be attributed to the disease heterogeneity of IBD: There is not one CD, nor a single UC phenotype,” therefore, a revision of the current systems based on better understanding of IBD is needed, the researchers said.
In a review article published in Gastroenterology, the researchers identified clinical features important to IBD heterogeneity, examined limitations of the current classifications, and proposed improvements.
Characterizing a complex condition
IBD diagnosis is challenging not only because of the overlapping phenotypes, but because other pathologies, including infections, can mimic IBD, the authors noted.
Age of onset should be considered in characterizing IBD, they wrote. Notably, patients with late-onset CD should be distinguished from elderly patients who have had CD for years. The authors cited research showing that “the development of IBD at extremes of age are specific sub-groups that require a different clinical recognition and clinical management,” and that large sample sizes and unbiased statistical methods are needed to define subgroups of IBD patients.
Current CD classification (the Montreal Classification) involves disease location, disease behavior, and age at diagnosis, and considers four phenotypes within disease location: involvement of the ileum, involvement of the colon, involvement of both the ileum and the colon, or isolated upper disease.* “Recently, there has been notable interest in the differential response rates among ileal predominant CD compared to colonic CD,” the authors wrote. Consequently, they proposed a revision of CD classification based on location. Genetic data appear to support this revision. In an IBD genotype-phenotype study including nearly 30,000 patients, three loci (NOD2, MHC, MST1 3p21) were strongly associated with disease location, they said. Other emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota may vary according to disease location. The authors identified clinical aspects of CD classification based on disease location that distinguish small bowel predominant CD versus colonic predominant CD. Ileal disease patients have shown an increased risk for undergoing surgery, while those with colonic involvement have an increased risk for developing extraintestinal manifestations.
They also emphasized the value of considering rectal inflammation, which significantly impacts surgical procedures in CD.
Standard UC classification is based on macroscopic disease in the colon at the time of inflammation, the authors said. Although this approach allows for quick assessment of a patient’s risk of colectomy, the authors proposed improvements, including the use of serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify patients at highest risk for colectomy and colon cancer based on inflammation. The authors also suggested that patients with refractory proctitis be enrolled in UC clinical trials or in studies focusing on refractory proctitis in particular.
The pelvic pouch has become the most often performed surgical procedure for patients undergoing colectomy, but there is no agreement on classification of inflammatory pelvic pouch disorders, and studies of etiology and treatment are lacking, the authors noted. They advised a clinical assessment based on symptoms, including stool frequency, urgency, and incontinence. They also suggested that afferent limb ulcers of erosions should be classified separately from pouch inflammation.
The authors ended by noting that extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) that occur in up to half of IBD patients may or may not be directly related to intestinal disease, and may represent a different phenotype, and the presence and type of EIM should be included in a revised IBD classification system, they said.
The authors emphasized that continuing to refer to IBD as only CD and UC “does a great disservice to our attempts to better understand IBD pathogenesis and to improve clinical patient management.”
They concluded: “Although revised clinical classification tools alone will not be sufficient and should be complemented by deeper and more detailed study into molecular subclassification of disease, the considerations here could be used as a springboard toward improved trial design, future translational research approaches and better treatment outcomes for patients.”
Review reflects complexity of IBD and challenges of change
The review is important at this time because of the growing recognition that IBD, while traditionally categorized as either UC or CD, is most likely composed of a range of heterogeneous conditions involving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Jatin Roper, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Evidence that our current classification of IBD is suboptimal comes from both the wide range of clinical phenotypes as well as complexity in genetic markers that are associated with IBD,” he said. “It is well accepted in the gastroenterology community that IBD is a complex condition; so it is surprising to me that the dichotomy of UC vs. Crohn’s disease has rarely been challenged,” said Dr. Roper. “The authors of this review should be commended for raising the question of whether IBD deserves a more nuanced classification system that reflects the growing recognition of the wide heterogeneity of patient presentations and genetics,” he said.
“Challenging medical definitions is inherently difficult because patient diagnoses, treatment plans, as well as decades of clinical research have been based on well-accepted disease categories. Another major challenge in reclassification is that the course of IBD can vary greatly over time in the same patient in severity, range, and complexity, and potentially includes many disease subtypes noted by the authors of this review,” he added. “Therefore, I believe that the current system of dividing IBD in UC and CD is here to stay until subtypes based on mechanisms of disease pathogenesis are discovered.
“Additional research is needed to understand the molecular basis of IBD,” Dr. Roper emphasized. “Recent advances in RNA expression and proteomics at the single cell level may reveal distinct cell types or cell functions in tissues from IBD patients that may help us understand clinical phenotype or response to therapy.”
The study received no outside funding. The authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Biogen, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Takeda, and Truvion. Dr. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Correction, 4/13/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the Montreal Classification.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
FDA approves 2-month dosing of injectable HIV drug Cabenuva
Cabenuva was first approved by the FDA in January 2021 to be administered once monthly to treat HIV-1 infection in virologically suppressed adults. The medication was the first injectable complete antiretroviral regimen approved by the FDA.
Cabenuva can replace a current treatment in virologically suppressed adults on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and no known or suspected resistance to rilpivirine and cabotegravir, the Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson said in a press release. Janssen and ViiV Healthcare codeveloped the injectable antiretroviral medication Cabenuva.
The expanded label approval “marks an important step forward in advancing the treatment landscape for people living with HIV,” said Candice Long, the president of infectious diseases and vaccines at Janssen Therapeutics, in a Feb. 1 press release. “With this milestone, adults living with HIV have a treatment option that further reduces the frequency of medication.”
This expanded approval was based on global clinical trial of 1,045 adults with HIV-1, which found Cabenuva administered every 8 weeks (3 mL dose of both cabotegravir and rilpivirine) to be noninferior to the 4-week regimen (2 mL dose of both medicines). At week 48 of the trial, the proportion of participants with viral loads above 50 copies per milliliter was 1.7% in the 2-month arm and 1.0% in the 1-month arm. The study found that rates of virological suppression were similar for both the 1-month and 2-month regimens (93.5% and 94.3%, respectively).
The most common side effects were injection site reactions, pyrexia, fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, sleep disorders, dizziness, and rash. Adverse reactions reported in individuals receiving the regimen every 2 months or once monthly were similar. Cabenuva is contraindicated for patients with a hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine or for those receiving carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, rifapentine, St. John’s wort, and more than one dose of systemic dexamethasone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cabenuva was first approved by the FDA in January 2021 to be administered once monthly to treat HIV-1 infection in virologically suppressed adults. The medication was the first injectable complete antiretroviral regimen approved by the FDA.
Cabenuva can replace a current treatment in virologically suppressed adults on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and no known or suspected resistance to rilpivirine and cabotegravir, the Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson said in a press release. Janssen and ViiV Healthcare codeveloped the injectable antiretroviral medication Cabenuva.
The expanded label approval “marks an important step forward in advancing the treatment landscape for people living with HIV,” said Candice Long, the president of infectious diseases and vaccines at Janssen Therapeutics, in a Feb. 1 press release. “With this milestone, adults living with HIV have a treatment option that further reduces the frequency of medication.”
This expanded approval was based on global clinical trial of 1,045 adults with HIV-1, which found Cabenuva administered every 8 weeks (3 mL dose of both cabotegravir and rilpivirine) to be noninferior to the 4-week regimen (2 mL dose of both medicines). At week 48 of the trial, the proportion of participants with viral loads above 50 copies per milliliter was 1.7% in the 2-month arm and 1.0% in the 1-month arm. The study found that rates of virological suppression were similar for both the 1-month and 2-month regimens (93.5% and 94.3%, respectively).
The most common side effects were injection site reactions, pyrexia, fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, sleep disorders, dizziness, and rash. Adverse reactions reported in individuals receiving the regimen every 2 months or once monthly were similar. Cabenuva is contraindicated for patients with a hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine or for those receiving carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, rifapentine, St. John’s wort, and more than one dose of systemic dexamethasone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cabenuva was first approved by the FDA in January 2021 to be administered once monthly to treat HIV-1 infection in virologically suppressed adults. The medication was the first injectable complete antiretroviral regimen approved by the FDA.
Cabenuva can replace a current treatment in virologically suppressed adults on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and no known or suspected resistance to rilpivirine and cabotegravir, the Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson said in a press release. Janssen and ViiV Healthcare codeveloped the injectable antiretroviral medication Cabenuva.
The expanded label approval “marks an important step forward in advancing the treatment landscape for people living with HIV,” said Candice Long, the president of infectious diseases and vaccines at Janssen Therapeutics, in a Feb. 1 press release. “With this milestone, adults living with HIV have a treatment option that further reduces the frequency of medication.”
This expanded approval was based on global clinical trial of 1,045 adults with HIV-1, which found Cabenuva administered every 8 weeks (3 mL dose of both cabotegravir and rilpivirine) to be noninferior to the 4-week regimen (2 mL dose of both medicines). At week 48 of the trial, the proportion of participants with viral loads above 50 copies per milliliter was 1.7% in the 2-month arm and 1.0% in the 1-month arm. The study found that rates of virological suppression were similar for both the 1-month and 2-month regimens (93.5% and 94.3%, respectively).
The most common side effects were injection site reactions, pyrexia, fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, sleep disorders, dizziness, and rash. Adverse reactions reported in individuals receiving the regimen every 2 months or once monthly were similar. Cabenuva is contraindicated for patients with a hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine or for those receiving carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, rifapentine, St. John’s wort, and more than one dose of systemic dexamethasone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Concurrent Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Vulgaris: Implications for Targeted Biologic Therapy
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with notable elevation in helper T cell (TH) production of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A.1 Upon binding of IL-17A to IL-17 receptors in the skin, an inflammatory cascade is triggered, resulting in the classic clinical appearance of psoriasis. Moderate to severe psoriasis often is managed by suppressing TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation using targeted immune therapy such as secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor.2 Atopic dermatitis (AD), another chronic inflammatory dermatosis, is associated with substantial elevation in TH2-mediated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-4.3 Dupilumab, which interacts with IL-4R, disrupts the IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways and demonstrates considerable efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe AD.4
A case series has shown that suppression of the TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation of psoriasis may paradoxically result in the development of TH2-mediated AD.5 Similarly, a recent case report described a patient who developed psoriasis following treatment of AD with dupilumab.6 Herein, we describe a patient with a history of psoriasis that was well controlled with secukinumab who developed severe refractory erythrodermic AD that resolved with dupilumab treatment. Following clearance of AD with dupilumab, he exhibited psoriasis recurrence.
Case Report
A 39-year-old man with a lifelong history of psoriasis was admitted to the hospital for management of severe erythroderma. Four years prior, secukinumab was initiated for treatment of psoriasis, resulting in excellent clinical response. He discontinued secukinumab after 2 years of treatment because of insurance coverage issues and managed his condition with only topical corticosteroids. He restarted secukinumab 10 months before admission because of a psoriasis flare. Shortly after resuming secukinumab, he developed a severe exfoliative erythroderma that was not responsive to corticosteroids, etanercept, methotrexate, or ustekinumab.
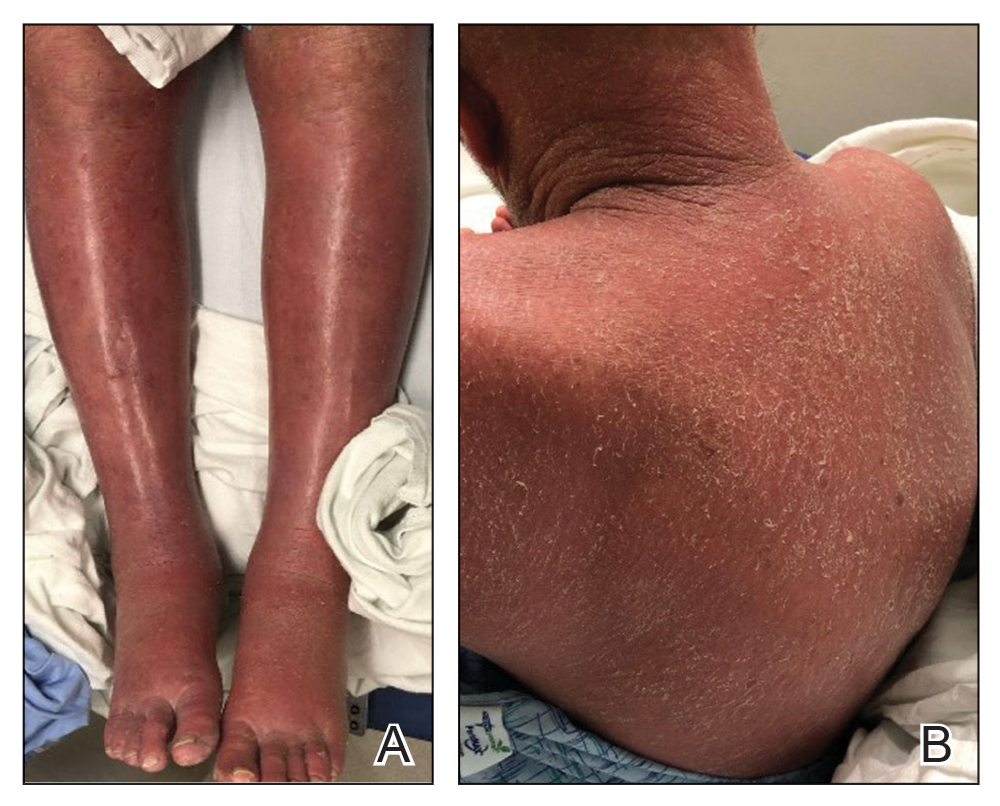
On initial presentation, physical examination revealed diffuse erythema and scaling with associated edema of the face, trunk, and extremities (Figure 1). A biopsy from the patient’s right arm demonstrated a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered eosinophils consistent with spongiotic dermatitis (Figure 2). Cyclosporine 225 mg twice daily and topical corticosteroids were started.
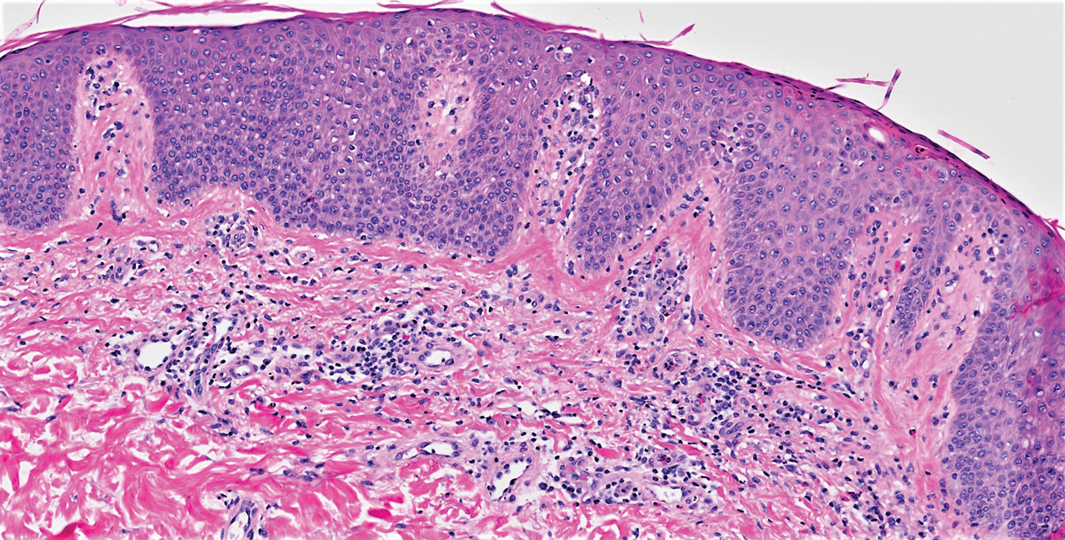
Over the next several months, the patient had several admissions secondary to recurrent skin abscesses in the setting of refractory erythroderma. He underwent trials of infliximab, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, guselkumab, and acitretin with minimal improvement. He underwent an extensive laboratory and radiologic workup, which was notable for cyclical peripheral eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels correlating with the erythroderma flares. A second biopsy was obtained and continued to demonstrate changes consistent with AD.
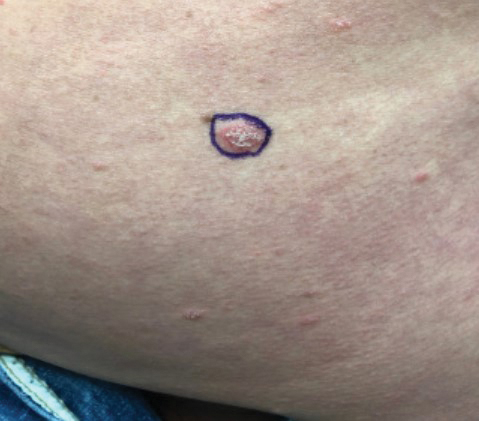
Four months after the initial hospitalization, all psoriasis medications were stopped, and the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg/2 mL every 2 weeks and an 8-week oral prednisone taper. This combination led to notable clinical improvement and resolution of peripheral eosinophilia. Several months after disease remission, he began to develop worsening erythema and pruritus on the trunk and extremities, followed by the development of new psoriatic lesions (Figure 3) with a biopsy consistent with psoriasis (Figure 4). The patient was continued on dupilumab, but cyclosporine was added. The patient self-discontinued dupilumab owing to injection-site discomfort and has been slowly weaning off oral cyclosporine with 1 to 2 remaining eczematous plaques and 1 to 2 psoriatic plaques managed by topical corticosteroids.
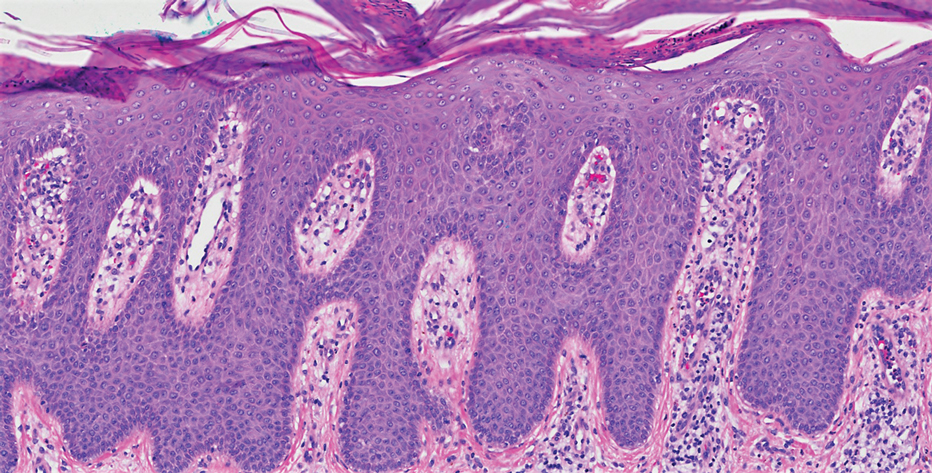
Comment
We present a patient with psoriasis that was well controlled on secukinumab who developed severe AD following treatment with secukinumab. The AD resolved following treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. However, after several months of treatment with dupilumab alone, he began to develop psoriatic lesions again. This case supports findings in a case series describing the development of AD in patients with psoriasis treated with IL-17 inhibitors5 and a recent case report describing a patient with AD who developed psoriasis following treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor.6
Recognized adverse effects demonstrate biologic medications’ contributions to both normal as well as aberrant immunologic responses. For example, IL-17 plays an essential role in innate and adaptive immune responses against infections at mucosal and cutaneous interfaces, as demonstrated by chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in patients with genetic defects in IL-17–related pathways.7 Similarly, in patients taking IL-17 antagonists, an increase in the incidence of Candida infections has been observed.8 In patients with concurrent psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with IL-17 inhibitors is contraindicated due to the risk of exacerbating the IBD. This observation is somewhat paradoxical, as increased IL-17 release by TH17 cells is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.9 Interestingly, it is now thought that IL-17 may play a protective role in T-cell–driven intestinal inflammation through induction of protective intestinal epithelial gene expression and increased mucosal defense against gut microbes, explaining the worsening of IBD in patients on IL-17 inhibitors.10 These adverse effects illustrate the complicated and varied roles biologic medications play in immunologic response.
Given that TH1 and TH2 exert opposing immune mechanisms, it is uncommon for psoriasis and AD to coexist in a single patient. However, patients who exhibit concurrent findings may represent a unique population in which psoriasis and AD coexist, perhaps because of an underlying genetic predisposition. Moreover, targeted treatment of pathways unique to these disease processes may result in paradoxical flaring of the nontargeted pathway. It also is possible that inhibition of a specific T-cell pathway in a subset of patients will result in an immunologic imbalance, favoring increased activity of the opposing pathway in the absence of coexisting disease. In the case presented here, the findings may be explained by secukinumab’s inhibition of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation, which resulted in a shift to a TH2-mediated inflammatory response manifesting as AD, as well as dupilumab’s inhibition of TH2-mediated inflammation, which caused a shift back to TH1-mediated inflammatory pathways. Additionally, for patients with changing morphologies exacerbated by biologic medications, alternative diagnoses, such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, may be considered.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of secukinumab-induced AD in a patient with psoriasis that resolved following several months of treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. Subsequently, this same patient developed re-emergence of psoriatic lesions with continued use of dupilumab, which was eventually discontinued by the patient despite appropriate disease control. In addition to illustrating the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of 2 common inflammatory dermatologic conditions, this case highlights how pharmacologic interventions targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences. Further investigation into the effects of targeted biologics on the TH1/TH2 immune axis is warranted to better understand the mechanism and possible implications of the phenotypic switching presented in this case.
- Diani M, Altomare G, Reali E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7692024.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-338.
- van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, et al. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:389-394.
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:130-139.
- Lai FYX, Higgins E, Smith CH, et al. Morphologic switch from psoriasiform to eczematous dermatitis after anti-IL-17 therapy: a case series. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1082-1084.
- Varma A, Levitt J. Dupilumab-induced phenotype switching from atopic dermatitis to psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:217-218.
- Ling Y, Puel A. IL-17 and infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(suppl 1):34-40.
- Saunte DM, Mrowietz U, Puig L, et al. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:47-62.
- Hölttä V, Klemetti P, Sipponen T, et al. IL-23/IL-17 immunity as a hallmark of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1175-1184.
- Smith MK, Pai J, Panaccione R, et al. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-interleukin-17 blockade (ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:162.
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with notable elevation in helper T cell (TH) production of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A.1 Upon binding of IL-17A to IL-17 receptors in the skin, an inflammatory cascade is triggered, resulting in the classic clinical appearance of psoriasis. Moderate to severe psoriasis often is managed by suppressing TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation using targeted immune therapy such as secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor.2 Atopic dermatitis (AD), another chronic inflammatory dermatosis, is associated with substantial elevation in TH2-mediated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-4.3 Dupilumab, which interacts with IL-4R, disrupts the IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways and demonstrates considerable efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe AD.4
A case series has shown that suppression of the TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation of psoriasis may paradoxically result in the development of TH2-mediated AD.5 Similarly, a recent case report described a patient who developed psoriasis following treatment of AD with dupilumab.6 Herein, we describe a patient with a history of psoriasis that was well controlled with secukinumab who developed severe refractory erythrodermic AD that resolved with dupilumab treatment. Following clearance of AD with dupilumab, he exhibited psoriasis recurrence.
Case Report
A 39-year-old man with a lifelong history of psoriasis was admitted to the hospital for management of severe erythroderma. Four years prior, secukinumab was initiated for treatment of psoriasis, resulting in excellent clinical response. He discontinued secukinumab after 2 years of treatment because of insurance coverage issues and managed his condition with only topical corticosteroids. He restarted secukinumab 10 months before admission because of a psoriasis flare. Shortly after resuming secukinumab, he developed a severe exfoliative erythroderma that was not responsive to corticosteroids, etanercept, methotrexate, or ustekinumab.

On initial presentation, physical examination revealed diffuse erythema and scaling with associated edema of the face, trunk, and extremities (Figure 1). A biopsy from the patient’s right arm demonstrated a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered eosinophils consistent with spongiotic dermatitis (Figure 2). Cyclosporine 225 mg twice daily and topical corticosteroids were started.

Over the next several months, the patient had several admissions secondary to recurrent skin abscesses in the setting of refractory erythroderma. He underwent trials of infliximab, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, guselkumab, and acitretin with minimal improvement. He underwent an extensive laboratory and radiologic workup, which was notable for cyclical peripheral eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels correlating with the erythroderma flares. A second biopsy was obtained and continued to demonstrate changes consistent with AD.

Four months after the initial hospitalization, all psoriasis medications were stopped, and the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg/2 mL every 2 weeks and an 8-week oral prednisone taper. This combination led to notable clinical improvement and resolution of peripheral eosinophilia. Several months after disease remission, he began to develop worsening erythema and pruritus on the trunk and extremities, followed by the development of new psoriatic lesions (Figure 3) with a biopsy consistent with psoriasis (Figure 4). The patient was continued on dupilumab, but cyclosporine was added. The patient self-discontinued dupilumab owing to injection-site discomfort and has been slowly weaning off oral cyclosporine with 1 to 2 remaining eczematous plaques and 1 to 2 psoriatic plaques managed by topical corticosteroids.

Comment
We present a patient with psoriasis that was well controlled on secukinumab who developed severe AD following treatment with secukinumab. The AD resolved following treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. However, after several months of treatment with dupilumab alone, he began to develop psoriatic lesions again. This case supports findings in a case series describing the development of AD in patients with psoriasis treated with IL-17 inhibitors5 and a recent case report describing a patient with AD who developed psoriasis following treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor.6
Recognized adverse effects demonstrate biologic medications’ contributions to both normal as well as aberrant immunologic responses. For example, IL-17 plays an essential role in innate and adaptive immune responses against infections at mucosal and cutaneous interfaces, as demonstrated by chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in patients with genetic defects in IL-17–related pathways.7 Similarly, in patients taking IL-17 antagonists, an increase in the incidence of Candida infections has been observed.8 In patients with concurrent psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with IL-17 inhibitors is contraindicated due to the risk of exacerbating the IBD. This observation is somewhat paradoxical, as increased IL-17 release by TH17 cells is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.9 Interestingly, it is now thought that IL-17 may play a protective role in T-cell–driven intestinal inflammation through induction of protective intestinal epithelial gene expression and increased mucosal defense against gut microbes, explaining the worsening of IBD in patients on IL-17 inhibitors.10 These adverse effects illustrate the complicated and varied roles biologic medications play in immunologic response.
Given that TH1 and TH2 exert opposing immune mechanisms, it is uncommon for psoriasis and AD to coexist in a single patient. However, patients who exhibit concurrent findings may represent a unique population in which psoriasis and AD coexist, perhaps because of an underlying genetic predisposition. Moreover, targeted treatment of pathways unique to these disease processes may result in paradoxical flaring of the nontargeted pathway. It also is possible that inhibition of a specific T-cell pathway in a subset of patients will result in an immunologic imbalance, favoring increased activity of the opposing pathway in the absence of coexisting disease. In the case presented here, the findings may be explained by secukinumab’s inhibition of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation, which resulted in a shift to a TH2-mediated inflammatory response manifesting as AD, as well as dupilumab’s inhibition of TH2-mediated inflammation, which caused a shift back to TH1-mediated inflammatory pathways. Additionally, for patients with changing morphologies exacerbated by biologic medications, alternative diagnoses, such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, may be considered.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of secukinumab-induced AD in a patient with psoriasis that resolved following several months of treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. Subsequently, this same patient developed re-emergence of psoriatic lesions with continued use of dupilumab, which was eventually discontinued by the patient despite appropriate disease control. In addition to illustrating the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of 2 common inflammatory dermatologic conditions, this case highlights how pharmacologic interventions targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences. Further investigation into the effects of targeted biologics on the TH1/TH2 immune axis is warranted to better understand the mechanism and possible implications of the phenotypic switching presented in this case.
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with notable elevation in helper T cell (TH) production of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A.1 Upon binding of IL-17A to IL-17 receptors in the skin, an inflammatory cascade is triggered, resulting in the classic clinical appearance of psoriasis. Moderate to severe psoriasis often is managed by suppressing TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation using targeted immune therapy such as secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor.2 Atopic dermatitis (AD), another chronic inflammatory dermatosis, is associated with substantial elevation in TH2-mediated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-4.3 Dupilumab, which interacts with IL-4R, disrupts the IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways and demonstrates considerable efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe AD.4
A case series has shown that suppression of the TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation of psoriasis may paradoxically result in the development of TH2-mediated AD.5 Similarly, a recent case report described a patient who developed psoriasis following treatment of AD with dupilumab.6 Herein, we describe a patient with a history of psoriasis that was well controlled with secukinumab who developed severe refractory erythrodermic AD that resolved with dupilumab treatment. Following clearance of AD with dupilumab, he exhibited psoriasis recurrence.
Case Report
A 39-year-old man with a lifelong history of psoriasis was admitted to the hospital for management of severe erythroderma. Four years prior, secukinumab was initiated for treatment of psoriasis, resulting in excellent clinical response. He discontinued secukinumab after 2 years of treatment because of insurance coverage issues and managed his condition with only topical corticosteroids. He restarted secukinumab 10 months before admission because of a psoriasis flare. Shortly after resuming secukinumab, he developed a severe exfoliative erythroderma that was not responsive to corticosteroids, etanercept, methotrexate, or ustekinumab.

On initial presentation, physical examination revealed diffuse erythema and scaling with associated edema of the face, trunk, and extremities (Figure 1). A biopsy from the patient’s right arm demonstrated a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered eosinophils consistent with spongiotic dermatitis (Figure 2). Cyclosporine 225 mg twice daily and topical corticosteroids were started.

Over the next several months, the patient had several admissions secondary to recurrent skin abscesses in the setting of refractory erythroderma. He underwent trials of infliximab, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, guselkumab, and acitretin with minimal improvement. He underwent an extensive laboratory and radiologic workup, which was notable for cyclical peripheral eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels correlating with the erythroderma flares. A second biopsy was obtained and continued to demonstrate changes consistent with AD.

Four months after the initial hospitalization, all psoriasis medications were stopped, and the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg/2 mL every 2 weeks and an 8-week oral prednisone taper. This combination led to notable clinical improvement and resolution of peripheral eosinophilia. Several months after disease remission, he began to develop worsening erythema and pruritus on the trunk and extremities, followed by the development of new psoriatic lesions (Figure 3) with a biopsy consistent with psoriasis (Figure 4). The patient was continued on dupilumab, but cyclosporine was added. The patient self-discontinued dupilumab owing to injection-site discomfort and has been slowly weaning off oral cyclosporine with 1 to 2 remaining eczematous plaques and 1 to 2 psoriatic plaques managed by topical corticosteroids.

Comment
We present a patient with psoriasis that was well controlled on secukinumab who developed severe AD following treatment with secukinumab. The AD resolved following treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. However, after several months of treatment with dupilumab alone, he began to develop psoriatic lesions again. This case supports findings in a case series describing the development of AD in patients with psoriasis treated with IL-17 inhibitors5 and a recent case report describing a patient with AD who developed psoriasis following treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor.6
Recognized adverse effects demonstrate biologic medications’ contributions to both normal as well as aberrant immunologic responses. For example, IL-17 plays an essential role in innate and adaptive immune responses against infections at mucosal and cutaneous interfaces, as demonstrated by chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in patients with genetic defects in IL-17–related pathways.7 Similarly, in patients taking IL-17 antagonists, an increase in the incidence of Candida infections has been observed.8 In patients with concurrent psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with IL-17 inhibitors is contraindicated due to the risk of exacerbating the IBD. This observation is somewhat paradoxical, as increased IL-17 release by TH17 cells is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.9 Interestingly, it is now thought that IL-17 may play a protective role in T-cell–driven intestinal inflammation through induction of protective intestinal epithelial gene expression and increased mucosal defense against gut microbes, explaining the worsening of IBD in patients on IL-17 inhibitors.10 These adverse effects illustrate the complicated and varied roles biologic medications play in immunologic response.
Given that TH1 and TH2 exert opposing immune mechanisms, it is uncommon for psoriasis and AD to coexist in a single patient. However, patients who exhibit concurrent findings may represent a unique population in which psoriasis and AD coexist, perhaps because of an underlying genetic predisposition. Moreover, targeted treatment of pathways unique to these disease processes may result in paradoxical flaring of the nontargeted pathway. It also is possible that inhibition of a specific T-cell pathway in a subset of patients will result in an immunologic imbalance, favoring increased activity of the opposing pathway in the absence of coexisting disease. In the case presented here, the findings may be explained by secukinumab’s inhibition of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation, which resulted in a shift to a TH2-mediated inflammatory response manifesting as AD, as well as dupilumab’s inhibition of TH2-mediated inflammation, which caused a shift back to TH1-mediated inflammatory pathways. Additionally, for patients with changing morphologies exacerbated by biologic medications, alternative diagnoses, such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, may be considered.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of secukinumab-induced AD in a patient with psoriasis that resolved following several months of treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. Subsequently, this same patient developed re-emergence of psoriatic lesions with continued use of dupilumab, which was eventually discontinued by the patient despite appropriate disease control. In addition to illustrating the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of 2 common inflammatory dermatologic conditions, this case highlights how pharmacologic interventions targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences. Further investigation into the effects of targeted biologics on the TH1/TH2 immune axis is warranted to better understand the mechanism and possible implications of the phenotypic switching presented in this case.
- Diani M, Altomare G, Reali E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7692024.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-338.
- van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, et al. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:389-394.
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:130-139.
- Lai FYX, Higgins E, Smith CH, et al. Morphologic switch from psoriasiform to eczematous dermatitis after anti-IL-17 therapy: a case series. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1082-1084.
- Varma A, Levitt J. Dupilumab-induced phenotype switching from atopic dermatitis to psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:217-218.
- Ling Y, Puel A. IL-17 and infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(suppl 1):34-40.
- Saunte DM, Mrowietz U, Puig L, et al. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:47-62.
- Hölttä V, Klemetti P, Sipponen T, et al. IL-23/IL-17 immunity as a hallmark of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1175-1184.
- Smith MK, Pai J, Panaccione R, et al. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-interleukin-17 blockade (ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:162.
- Diani M, Altomare G, Reali E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7692024.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-338.
- van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, et al. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:389-394.
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:130-139.
- Lai FYX, Higgins E, Smith CH, et al. Morphologic switch from psoriasiform to eczematous dermatitis after anti-IL-17 therapy: a case series. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1082-1084.
- Varma A, Levitt J. Dupilumab-induced phenotype switching from atopic dermatitis to psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:217-218.
- Ling Y, Puel A. IL-17 and infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(suppl 1):34-40.
- Saunte DM, Mrowietz U, Puig L, et al. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:47-62.
- Hölttä V, Klemetti P, Sipponen T, et al. IL-23/IL-17 immunity as a hallmark of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1175-1184.
- Smith MK, Pai J, Panaccione R, et al. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-interleukin-17 blockade (ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:162.
Practice Points
- Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris, a helper T cell TH1/TH17-mediated skin condition, with secukinumab may result in phenotypic switching to TH2-mediated atopic dermatitis.
- Atopic dermatitis responds well to dupilumab but may result in phenotypic switching to psoriasis.
- Biologic therapies targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences on the TH1/TH2 immune axis.