User login
Alleviating chemo-related nausea is a huge unmet need
This transcript has been edited for clarity. The transcript and an accompanying video first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is Mark Kris from chilly New York and Memorial Sloan Kettering. Today I want to talk about a recent article in the Journal of Clinical Oncology that reported a study of a new neurokinin-1 antagonist called fosnetupitant. This was a well-conducted trial that demonstrates the noninferiority of IV fosnetupitant when compared with IV fosaprepitant. By their study criteria, fosnetupitant was not inferior.
But my reason for discussing this is that the paper and the trial miss the point for the field right now. Although the authors talk about the prevention of nausea and vomiting in the introduction, in the paper itself and in the abstract results section, there’s not a single mention about the medication’s ability to control nausea, which is the critical issue for our patients today. You have to go into the supplementary data to find it mentioned, and what you find is that the prevention of nausea is 50% for both the control and this new drug. We control nausea in only half of the patients who receive cisplatin in 2022. That is a huge issue.
When you ask patients what are the effects of cancer treatment that they fear most, that concerns them most, it’s nausea and emesis; indeed, nausea has replaced emesis as the biggest concern. And although this trial used emesis as the main endpoint, and it was useful in defining the drug, it was not useful in coming up with a new treatment that addresses a huge need. Further, the authors talk about an advantage to fosnetupitant based on infusion reactions, but it is a difference of 0.3% vs. 3%. They talk about that sort of thing in the abstract and in the discussion section but don’t include nausea as part of the key endpoint of this trial. Again, you had to dig deeply to find out that, frankly, fosnetupitant was no better than the drugs we already have.
The other concerning point is that we do have another drug that works well. If you go to the American Society of Clinical Oncology or National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines for patients receiving high dosages of cisplatin, you find a four-drug regimen, including olanzapine, and that was not used here. Why is olanzapine so critical? It’s an available drug, it’s an inexpensive drug, it’s a safe drug, and it improves nausea by 15%.
So they did this huge trial to show noninferiority, and they neglected to give a drug that could deal with the most serious side effect of cancer therapy – nausea – and improve things by 15%.
A challenge to people in this field: We have to do better. Nausea is a big problem. While noninferiority trials can be helpful for drug development, they’re not really helpful for the field. With a problem of this magnitude, we need better drugs to control nausea. In the meantime, I urge you all to follow the guidelines for high doses of cisplatin. Please use the four-drug regimen that is recommended in the guidelines and widely used in the United States. Going forward, make sure that when we expend huge amounts of energy to develop new agents and report them in our medical journals, that we look for ways to advance care where there are significant gaps in our ability to deliver what we want. Delivering better control of nausea is something we all need to be committed to. It’s a huge unmet need, and I hope future trials will address that need. Our patients will be better for it and we’ll be better in that we’re delivering what patients deserve, what they need, and what they ask for.
Mark G. Kris, MD, is chief of the thoracic oncology service and the William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, and Ariad Pharmaceuticals, and has received research grants from Pfizer, PUMA, and Roche/Genentech.
This transcript has been edited for clarity. The transcript and an accompanying video first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is Mark Kris from chilly New York and Memorial Sloan Kettering. Today I want to talk about a recent article in the Journal of Clinical Oncology that reported a study of a new neurokinin-1 antagonist called fosnetupitant. This was a well-conducted trial that demonstrates the noninferiority of IV fosnetupitant when compared with IV fosaprepitant. By their study criteria, fosnetupitant was not inferior.
But my reason for discussing this is that the paper and the trial miss the point for the field right now. Although the authors talk about the prevention of nausea and vomiting in the introduction, in the paper itself and in the abstract results section, there’s not a single mention about the medication’s ability to control nausea, which is the critical issue for our patients today. You have to go into the supplementary data to find it mentioned, and what you find is that the prevention of nausea is 50% for both the control and this new drug. We control nausea in only half of the patients who receive cisplatin in 2022. That is a huge issue.
When you ask patients what are the effects of cancer treatment that they fear most, that concerns them most, it’s nausea and emesis; indeed, nausea has replaced emesis as the biggest concern. And although this trial used emesis as the main endpoint, and it was useful in defining the drug, it was not useful in coming up with a new treatment that addresses a huge need. Further, the authors talk about an advantage to fosnetupitant based on infusion reactions, but it is a difference of 0.3% vs. 3%. They talk about that sort of thing in the abstract and in the discussion section but don’t include nausea as part of the key endpoint of this trial. Again, you had to dig deeply to find out that, frankly, fosnetupitant was no better than the drugs we already have.
The other concerning point is that we do have another drug that works well. If you go to the American Society of Clinical Oncology or National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines for patients receiving high dosages of cisplatin, you find a four-drug regimen, including olanzapine, and that was not used here. Why is olanzapine so critical? It’s an available drug, it’s an inexpensive drug, it’s a safe drug, and it improves nausea by 15%.
So they did this huge trial to show noninferiority, and they neglected to give a drug that could deal with the most serious side effect of cancer therapy – nausea – and improve things by 15%.
A challenge to people in this field: We have to do better. Nausea is a big problem. While noninferiority trials can be helpful for drug development, they’re not really helpful for the field. With a problem of this magnitude, we need better drugs to control nausea. In the meantime, I urge you all to follow the guidelines for high doses of cisplatin. Please use the four-drug regimen that is recommended in the guidelines and widely used in the United States. Going forward, make sure that when we expend huge amounts of energy to develop new agents and report them in our medical journals, that we look for ways to advance care where there are significant gaps in our ability to deliver what we want. Delivering better control of nausea is something we all need to be committed to. It’s a huge unmet need, and I hope future trials will address that need. Our patients will be better for it and we’ll be better in that we’re delivering what patients deserve, what they need, and what they ask for.
Mark G. Kris, MD, is chief of the thoracic oncology service and the William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, and Ariad Pharmaceuticals, and has received research grants from Pfizer, PUMA, and Roche/Genentech.
This transcript has been edited for clarity. The transcript and an accompanying video first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is Mark Kris from chilly New York and Memorial Sloan Kettering. Today I want to talk about a recent article in the Journal of Clinical Oncology that reported a study of a new neurokinin-1 antagonist called fosnetupitant. This was a well-conducted trial that demonstrates the noninferiority of IV fosnetupitant when compared with IV fosaprepitant. By their study criteria, fosnetupitant was not inferior.
But my reason for discussing this is that the paper and the trial miss the point for the field right now. Although the authors talk about the prevention of nausea and vomiting in the introduction, in the paper itself and in the abstract results section, there’s not a single mention about the medication’s ability to control nausea, which is the critical issue for our patients today. You have to go into the supplementary data to find it mentioned, and what you find is that the prevention of nausea is 50% for both the control and this new drug. We control nausea in only half of the patients who receive cisplatin in 2022. That is a huge issue.
When you ask patients what are the effects of cancer treatment that they fear most, that concerns them most, it’s nausea and emesis; indeed, nausea has replaced emesis as the biggest concern. And although this trial used emesis as the main endpoint, and it was useful in defining the drug, it was not useful in coming up with a new treatment that addresses a huge need. Further, the authors talk about an advantage to fosnetupitant based on infusion reactions, but it is a difference of 0.3% vs. 3%. They talk about that sort of thing in the abstract and in the discussion section but don’t include nausea as part of the key endpoint of this trial. Again, you had to dig deeply to find out that, frankly, fosnetupitant was no better than the drugs we already have.
The other concerning point is that we do have another drug that works well. If you go to the American Society of Clinical Oncology or National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines for patients receiving high dosages of cisplatin, you find a four-drug regimen, including olanzapine, and that was not used here. Why is olanzapine so critical? It’s an available drug, it’s an inexpensive drug, it’s a safe drug, and it improves nausea by 15%.
So they did this huge trial to show noninferiority, and they neglected to give a drug that could deal with the most serious side effect of cancer therapy – nausea – and improve things by 15%.
A challenge to people in this field: We have to do better. Nausea is a big problem. While noninferiority trials can be helpful for drug development, they’re not really helpful for the field. With a problem of this magnitude, we need better drugs to control nausea. In the meantime, I urge you all to follow the guidelines for high doses of cisplatin. Please use the four-drug regimen that is recommended in the guidelines and widely used in the United States. Going forward, make sure that when we expend huge amounts of energy to develop new agents and report them in our medical journals, that we look for ways to advance care where there are significant gaps in our ability to deliver what we want. Delivering better control of nausea is something we all need to be committed to. It’s a huge unmet need, and I hope future trials will address that need. Our patients will be better for it and we’ll be better in that we’re delivering what patients deserve, what they need, and what they ask for.
Mark G. Kris, MD, is chief of the thoracic oncology service and the William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, and Ariad Pharmaceuticals, and has received research grants from Pfizer, PUMA, and Roche/Genentech.
Global pediatric oncology workforce hit hard, but resilient amid pandemic
according to a study that surveyed workers from more than 200 institutions in 79 countries.
A snapshot of the extensive findings reveals that half of participating institutions experienced staffing shortages that had a “major impact” on pediatric cancer care. On the financial front, many respondents pointed to instances of unpaid leave and diminished salary, and others highlighted the psychological toll of providing care, including high rates of burnout and stress. The challenges were evident across high- and low-income countries.
Despite these barriers, pediatric oncology clinicians demonstrated incredible perseverance.
Health care professionals “caring for children with cancer across the world were shown to be incredibly resilient, coming together to continue to provide care even in the direst circumstances,” Elizabeth R. Sniderman, MSN, APRN, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, and colleagues concluded.
The findings, published online Jan. 24, 2022, in Cancer, highlight the global impact of COVID-19 on pediatric oncology clinicians early in the pandemic.
The survey, conducted in summer 2020, included responses from 311 pediatric oncology clinicians who completed a 60-item questionnaire about their experiences of clinical care, resources, and support. The investigators also convened 19 multidisciplinary focus groups who answered questions related to teamwork, communication, and changes to care. Respondents practiced in low- to high-income countries, and included pediatric hematologists and oncologists, nurses, and infectious disease physicians.
Overall, the investigators found that just over half of institutions experienced “major” shortages of clinical staff (108 of 213), and two-thirds experienced reductions in staffing availability (141 of 213). Notably, national income was not associated with this reduction; rather, staffing shortages were more likely to occur in countries with greater COVID-19 incidence and mortality rates.
Respondents reported experiencing threats to their physical health, with half pointing to a lack of necessary personal protective equipment. The financial and psychological toll of the pandemic represented another major stressor, with the effects described across all income levels.
One respondent from Belarus commented on financial concerns, noting that “people don’t really want to admit that they don’t feel well ... they know, that if infected, unpaid self-isolation is waiting for them. Either you don’t go to work for 2 weeks, unpaid, or you go to work for 2 weeks, paid, and endanger all of your colleagues with your infection.”
A respondent from Mexico described the psychological stress: “Honestly, I think that sometimes we put aside the mental health of all of us involved, myself included. I think we were all on the verge of collapse ... practically all the residents who were rotating here told us that they had anxiety attacks, panic attacks, they could not sleep, [and] many of them needed psychiatric medicine.”
Others highlighted feelings of guilt about their ability to provide the highest level of care. An oncologist in the United States noted: “This was a major stress for many providers because [we are] feeling unable to provide the same level of care which we used to provide. And this is what eventually takes a toll.”
And despite these pandemic-related challenges, the study authors found that only 46% of institutions (99 of 213) made psychological support available to staff.
Rays of hope
But it was not all bad news.
Participants also described a greater sense of teamwork, communication, and collegiality throughout the pandemic – “stabilizing elements,” which helped mitigate the many physical, psychological, and financial stressors.
An infection-control physician in Belarus highlighted the importance of receiving “support and encouragement” from colleagues: “When a person gets tired and they have no more enthusiasm, it’s easy to give up and say: ‘I can’t do this anymore.’ But when you see a colleague who tries ... to share the work, and help each other, then you get extra strength.”
An oncologist in South Africa agreed, noting that “everyone has got their sleeves rolled up and are doing the work ... and that’s a testament to everyone that we work with. There was no one that shied away from work or used this as an excuse to do less work.”
An oncologist in Spain described practicing during the pandemic being “one of the best experiences I have had,” explaining that “I have been working in this hospital for ... 25 years, [and] I have never had the feeling of being so informed at all levels.”
Overall, the findings paint a picture of a resilient workforce, and offer lessons about preparedness for future crises, the investigators concluded.
“To protect pediatric oncology providers and their patients, organizations must pay attention to interventions that increase physical, psychological, and financial safety,” the authors stressed. For instance, providing adequate personal protective equipment and vaccines, allowing for time off and rest, and setting up professional psychology services as well as access to peer-support programs can help protect staff.
Although this survey took place relatively early in the pandemic, organizations should take heed of the findings, Lorena V. Baroni, MD, of Hospital J P Garrahan, Buenos Aires, and Eric Bouffet, MD, of The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The results presented in this study should not be taken lightly,” Dr. Baroni and Dr. Bouffet wrote. “The most concerning findings are the physical and psychological impact experienced by pediatric oncology providers.” And perhaps most surprisingly, “the survey did not identify any difference based on country income groups. Participants in both low- and high-income countries described similar oncologic care limitations.”
Overall, these findings “reflect a serious risk that can ultimately affect the care of children and compromise the success of their treatment,” Dr. Baroni and Dr. Bouffet wrote.
This study was supported by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities. The study authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a study that surveyed workers from more than 200 institutions in 79 countries.
A snapshot of the extensive findings reveals that half of participating institutions experienced staffing shortages that had a “major impact” on pediatric cancer care. On the financial front, many respondents pointed to instances of unpaid leave and diminished salary, and others highlighted the psychological toll of providing care, including high rates of burnout and stress. The challenges were evident across high- and low-income countries.
Despite these barriers, pediatric oncology clinicians demonstrated incredible perseverance.
Health care professionals “caring for children with cancer across the world were shown to be incredibly resilient, coming together to continue to provide care even in the direst circumstances,” Elizabeth R. Sniderman, MSN, APRN, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, and colleagues concluded.
The findings, published online Jan. 24, 2022, in Cancer, highlight the global impact of COVID-19 on pediatric oncology clinicians early in the pandemic.
The survey, conducted in summer 2020, included responses from 311 pediatric oncology clinicians who completed a 60-item questionnaire about their experiences of clinical care, resources, and support. The investigators also convened 19 multidisciplinary focus groups who answered questions related to teamwork, communication, and changes to care. Respondents practiced in low- to high-income countries, and included pediatric hematologists and oncologists, nurses, and infectious disease physicians.
Overall, the investigators found that just over half of institutions experienced “major” shortages of clinical staff (108 of 213), and two-thirds experienced reductions in staffing availability (141 of 213). Notably, national income was not associated with this reduction; rather, staffing shortages were more likely to occur in countries with greater COVID-19 incidence and mortality rates.
Respondents reported experiencing threats to their physical health, with half pointing to a lack of necessary personal protective equipment. The financial and psychological toll of the pandemic represented another major stressor, with the effects described across all income levels.
One respondent from Belarus commented on financial concerns, noting that “people don’t really want to admit that they don’t feel well ... they know, that if infected, unpaid self-isolation is waiting for them. Either you don’t go to work for 2 weeks, unpaid, or you go to work for 2 weeks, paid, and endanger all of your colleagues with your infection.”
A respondent from Mexico described the psychological stress: “Honestly, I think that sometimes we put aside the mental health of all of us involved, myself included. I think we were all on the verge of collapse ... practically all the residents who were rotating here told us that they had anxiety attacks, panic attacks, they could not sleep, [and] many of them needed psychiatric medicine.”
Others highlighted feelings of guilt about their ability to provide the highest level of care. An oncologist in the United States noted: “This was a major stress for many providers because [we are] feeling unable to provide the same level of care which we used to provide. And this is what eventually takes a toll.”
And despite these pandemic-related challenges, the study authors found that only 46% of institutions (99 of 213) made psychological support available to staff.
Rays of hope
But it was not all bad news.
Participants also described a greater sense of teamwork, communication, and collegiality throughout the pandemic – “stabilizing elements,” which helped mitigate the many physical, psychological, and financial stressors.
An infection-control physician in Belarus highlighted the importance of receiving “support and encouragement” from colleagues: “When a person gets tired and they have no more enthusiasm, it’s easy to give up and say: ‘I can’t do this anymore.’ But when you see a colleague who tries ... to share the work, and help each other, then you get extra strength.”
An oncologist in South Africa agreed, noting that “everyone has got their sleeves rolled up and are doing the work ... and that’s a testament to everyone that we work with. There was no one that shied away from work or used this as an excuse to do less work.”
An oncologist in Spain described practicing during the pandemic being “one of the best experiences I have had,” explaining that “I have been working in this hospital for ... 25 years, [and] I have never had the feeling of being so informed at all levels.”
Overall, the findings paint a picture of a resilient workforce, and offer lessons about preparedness for future crises, the investigators concluded.
“To protect pediatric oncology providers and their patients, organizations must pay attention to interventions that increase physical, psychological, and financial safety,” the authors stressed. For instance, providing adequate personal protective equipment and vaccines, allowing for time off and rest, and setting up professional psychology services as well as access to peer-support programs can help protect staff.
Although this survey took place relatively early in the pandemic, organizations should take heed of the findings, Lorena V. Baroni, MD, of Hospital J P Garrahan, Buenos Aires, and Eric Bouffet, MD, of The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The results presented in this study should not be taken lightly,” Dr. Baroni and Dr. Bouffet wrote. “The most concerning findings are the physical and psychological impact experienced by pediatric oncology providers.” And perhaps most surprisingly, “the survey did not identify any difference based on country income groups. Participants in both low- and high-income countries described similar oncologic care limitations.”
Overall, these findings “reflect a serious risk that can ultimately affect the care of children and compromise the success of their treatment,” Dr. Baroni and Dr. Bouffet wrote.
This study was supported by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities. The study authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a study that surveyed workers from more than 200 institutions in 79 countries.
A snapshot of the extensive findings reveals that half of participating institutions experienced staffing shortages that had a “major impact” on pediatric cancer care. On the financial front, many respondents pointed to instances of unpaid leave and diminished salary, and others highlighted the psychological toll of providing care, including high rates of burnout and stress. The challenges were evident across high- and low-income countries.
Despite these barriers, pediatric oncology clinicians demonstrated incredible perseverance.
Health care professionals “caring for children with cancer across the world were shown to be incredibly resilient, coming together to continue to provide care even in the direst circumstances,” Elizabeth R. Sniderman, MSN, APRN, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, and colleagues concluded.
The findings, published online Jan. 24, 2022, in Cancer, highlight the global impact of COVID-19 on pediatric oncology clinicians early in the pandemic.
The survey, conducted in summer 2020, included responses from 311 pediatric oncology clinicians who completed a 60-item questionnaire about their experiences of clinical care, resources, and support. The investigators also convened 19 multidisciplinary focus groups who answered questions related to teamwork, communication, and changes to care. Respondents practiced in low- to high-income countries, and included pediatric hematologists and oncologists, nurses, and infectious disease physicians.
Overall, the investigators found that just over half of institutions experienced “major” shortages of clinical staff (108 of 213), and two-thirds experienced reductions in staffing availability (141 of 213). Notably, national income was not associated with this reduction; rather, staffing shortages were more likely to occur in countries with greater COVID-19 incidence and mortality rates.
Respondents reported experiencing threats to their physical health, with half pointing to a lack of necessary personal protective equipment. The financial and psychological toll of the pandemic represented another major stressor, with the effects described across all income levels.
One respondent from Belarus commented on financial concerns, noting that “people don’t really want to admit that they don’t feel well ... they know, that if infected, unpaid self-isolation is waiting for them. Either you don’t go to work for 2 weeks, unpaid, or you go to work for 2 weeks, paid, and endanger all of your colleagues with your infection.”
A respondent from Mexico described the psychological stress: “Honestly, I think that sometimes we put aside the mental health of all of us involved, myself included. I think we were all on the verge of collapse ... practically all the residents who were rotating here told us that they had anxiety attacks, panic attacks, they could not sleep, [and] many of them needed psychiatric medicine.”
Others highlighted feelings of guilt about their ability to provide the highest level of care. An oncologist in the United States noted: “This was a major stress for many providers because [we are] feeling unable to provide the same level of care which we used to provide. And this is what eventually takes a toll.”
And despite these pandemic-related challenges, the study authors found that only 46% of institutions (99 of 213) made psychological support available to staff.
Rays of hope
But it was not all bad news.
Participants also described a greater sense of teamwork, communication, and collegiality throughout the pandemic – “stabilizing elements,” which helped mitigate the many physical, psychological, and financial stressors.
An infection-control physician in Belarus highlighted the importance of receiving “support and encouragement” from colleagues: “When a person gets tired and they have no more enthusiasm, it’s easy to give up and say: ‘I can’t do this anymore.’ But when you see a colleague who tries ... to share the work, and help each other, then you get extra strength.”
An oncologist in South Africa agreed, noting that “everyone has got their sleeves rolled up and are doing the work ... and that’s a testament to everyone that we work with. There was no one that shied away from work or used this as an excuse to do less work.”
An oncologist in Spain described practicing during the pandemic being “one of the best experiences I have had,” explaining that “I have been working in this hospital for ... 25 years, [and] I have never had the feeling of being so informed at all levels.”
Overall, the findings paint a picture of a resilient workforce, and offer lessons about preparedness for future crises, the investigators concluded.
“To protect pediatric oncology providers and their patients, organizations must pay attention to interventions that increase physical, psychological, and financial safety,” the authors stressed. For instance, providing adequate personal protective equipment and vaccines, allowing for time off and rest, and setting up professional psychology services as well as access to peer-support programs can help protect staff.
Although this survey took place relatively early in the pandemic, organizations should take heed of the findings, Lorena V. Baroni, MD, of Hospital J P Garrahan, Buenos Aires, and Eric Bouffet, MD, of The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The results presented in this study should not be taken lightly,” Dr. Baroni and Dr. Bouffet wrote. “The most concerning findings are the physical and psychological impact experienced by pediatric oncology providers.” And perhaps most surprisingly, “the survey did not identify any difference based on country income groups. Participants in both low- and high-income countries described similar oncologic care limitations.”
Overall, these findings “reflect a serious risk that can ultimately affect the care of children and compromise the success of their treatment,” Dr. Baroni and Dr. Bouffet wrote.
This study was supported by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities. The study authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CANCER
Hyperpigmented plaque on back
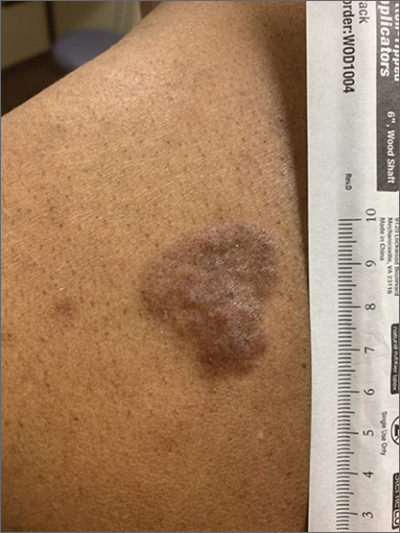
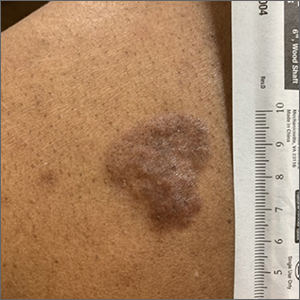
Based on the thickness and size of this irregular lesion, a punch biopsy was performed and confirmed the diagnosis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP).
DFSPs are usually found on the trunk and proximal extremities; they are most often located on the chest and shoulders. The lesion usually manifests as an asymptomatic, firm, and sometimes nodular plaque that may go undiagnosed for years. DFSP is an uncommon mesenchymal tumor with uncertain etiology. It is thought that prior injury to the affected skin may result in a translocation of chromosomes 17 and 22 in skin cells, as this molecular change characterizes the vast majority of DFSPs.
Black patients are more likely than other ethnic populations to develop DFSP and its variants; there is also a slight female predominance.1 Known variants of DFSP include violaceous plaques with telangiectatic atrophic skin, and plaques with dark brown pigmentation called Bednar tumors.1,2
DFSPs are rarely metastatic, but can be locally invasive, so primary treatment consists of wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). There is a higher probability for cure when MMS is utilized to treat DFSPs with the added benefit of minimizing surgical margins and preserving healthy surrounding skin. In the rarer cases of advanced local, unresectable, or metastatic disease, inhibitor therapy with imatinib or radiation therapy may be considered.2 Due to the risk of local recurrence, patients with DFSP should have regular clinical follow-up every 6 months for 5 years, followed by annual lifelong surveillance.1
This patient was referred for MMS and has not yet returned for follow-up evaluation.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Morgan Haynes, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Mendenhall WM, Scarborough MT, Flowers FP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and staging. UpToDate. Updated March 31, 2021. Accessed February 2, 2022. www.uptodate.com/contents/dermatofibrosarcoma-protuberans-epidemiology-pathogenesis-clinical-presentation-diagnosis-and-staging
2. Brooks J, Ramsey ML. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. StatPearls. Updated November 14, 2021. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513305

Based on the thickness and size of this irregular lesion, a punch biopsy was performed and confirmed the diagnosis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP).
DFSPs are usually found on the trunk and proximal extremities; they are most often located on the chest and shoulders. The lesion usually manifests as an asymptomatic, firm, and sometimes nodular plaque that may go undiagnosed for years. DFSP is an uncommon mesenchymal tumor with uncertain etiology. It is thought that prior injury to the affected skin may result in a translocation of chromosomes 17 and 22 in skin cells, as this molecular change characterizes the vast majority of DFSPs.
Black patients are more likely than other ethnic populations to develop DFSP and its variants; there is also a slight female predominance.1 Known variants of DFSP include violaceous plaques with telangiectatic atrophic skin, and plaques with dark brown pigmentation called Bednar tumors.1,2
DFSPs are rarely metastatic, but can be locally invasive, so primary treatment consists of wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). There is a higher probability for cure when MMS is utilized to treat DFSPs with the added benefit of minimizing surgical margins and preserving healthy surrounding skin. In the rarer cases of advanced local, unresectable, or metastatic disease, inhibitor therapy with imatinib or radiation therapy may be considered.2 Due to the risk of local recurrence, patients with DFSP should have regular clinical follow-up every 6 months for 5 years, followed by annual lifelong surveillance.1
This patient was referred for MMS and has not yet returned for follow-up evaluation.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Morgan Haynes, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

Based on the thickness and size of this irregular lesion, a punch biopsy was performed and confirmed the diagnosis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP).
DFSPs are usually found on the trunk and proximal extremities; they are most often located on the chest and shoulders. The lesion usually manifests as an asymptomatic, firm, and sometimes nodular plaque that may go undiagnosed for years. DFSP is an uncommon mesenchymal tumor with uncertain etiology. It is thought that prior injury to the affected skin may result in a translocation of chromosomes 17 and 22 in skin cells, as this molecular change characterizes the vast majority of DFSPs.
Black patients are more likely than other ethnic populations to develop DFSP and its variants; there is also a slight female predominance.1 Known variants of DFSP include violaceous plaques with telangiectatic atrophic skin, and plaques with dark brown pigmentation called Bednar tumors.1,2
DFSPs are rarely metastatic, but can be locally invasive, so primary treatment consists of wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). There is a higher probability for cure when MMS is utilized to treat DFSPs with the added benefit of minimizing surgical margins and preserving healthy surrounding skin. In the rarer cases of advanced local, unresectable, or metastatic disease, inhibitor therapy with imatinib or radiation therapy may be considered.2 Due to the risk of local recurrence, patients with DFSP should have regular clinical follow-up every 6 months for 5 years, followed by annual lifelong surveillance.1
This patient was referred for MMS and has not yet returned for follow-up evaluation.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Morgan Haynes, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Mendenhall WM, Scarborough MT, Flowers FP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and staging. UpToDate. Updated March 31, 2021. Accessed February 2, 2022. www.uptodate.com/contents/dermatofibrosarcoma-protuberans-epidemiology-pathogenesis-clinical-presentation-diagnosis-and-staging
2. Brooks J, Ramsey ML. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. StatPearls. Updated November 14, 2021. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513305
1. Mendenhall WM, Scarborough MT, Flowers FP. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and staging. UpToDate. Updated March 31, 2021. Accessed February 2, 2022. www.uptodate.com/contents/dermatofibrosarcoma-protuberans-epidemiology-pathogenesis-clinical-presentation-diagnosis-and-staging
2. Brooks J, Ramsey ML. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. StatPearls. Updated November 14, 2021. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513305
Missed diagnosis common source of malpractice claims against PCPs
, according to the Medscape Primary Care Physician Malpractice Report 2021. This figure is less than the overall proportion of physicians in all specialties named in a malpractice suit (51%).
More PCPs were part of lawsuits that named multiple parties (34%) than suits that named a individual practitioners (11%). Failure to make a proper diagnosis (41%) was the most common claim in malpractice suits against PCPs, followed by poor outcome/disease progression (26%), complications from treatment/surgery (17%), wrongful death (16%), and failure to treat/delayed treatment (16%).
The report was compiled from an online survey that included more than 4,300 physicians from 29 specialties. The survey was available from May 21, 2021, to August 28, 2021, and included 732 family and internal medicine physicians. Most respondents had practiced medicine for more than 25 years (47%) or from 21-25 years (16%). Almost half of respondents (47%) were aged 60 years or older.
Most PCPs (63%) reported malpractice insurance premiums of less than $20,000 per year, which is more than the overall proportion for all specialists (52%). The typical premium for PCPs was $5,000-$9,999 (26%). Premium payments varied widely by geographic area, with a PCP in New York paying five times as much as a colleague in California, Tennessee, or Ohio would pay to obtain comparable coverage, the survey found.
More than 9 in 10 PCPs (91%) reported being “very surprised” or “somewhat surprised” to having been part of a malpractice suit and reported being upset and anxious: “Feeling betrayed by people to whom I had provided good care, and embarrassed that my colleagues might find out,” as one internist put it. The majority (84%) of PCPs said their lawsuits were unwarranted, in line with perceptions among all specialists (83%).
The largest proportions of cases were settled before trial (35%) or were dismissed within a few months of lawsuit filing (16%). A judge or jury ruled in the plaintiff’s favor only 2% of the time. Seven percent of cases are ongoing, and 3% were settled at trial, according to the survey.
The largest number of cases (40%) took between 1 and 2 years, although 30% were less than a year. Roughly one in four cases (24%) lasted 3-5 years. Almost half (47%) of any monetary payments to plaintiffs were $100,000 or less; one-third of such payments were capped at $500,000.
Two-thirds (68%) of PCPs said that the lawsuit did not negatively affect their careers, and more than one in four (28%) said they now no longer trust patients or that they treat them differently. This change in trust is slightly higher than for specialists overall (24%).
More than 4 in 10 PCPs (41%) said they would have done nothing differently despite being sued. The largest proportion of changes other PCPs would have made included improved documentation (18%) and ordering additional tests as a hedge against a lawsuit (11%); 10% said they should never have taken on the patient in the first place.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the Medscape Primary Care Physician Malpractice Report 2021. This figure is less than the overall proportion of physicians in all specialties named in a malpractice suit (51%).
More PCPs were part of lawsuits that named multiple parties (34%) than suits that named a individual practitioners (11%). Failure to make a proper diagnosis (41%) was the most common claim in malpractice suits against PCPs, followed by poor outcome/disease progression (26%), complications from treatment/surgery (17%), wrongful death (16%), and failure to treat/delayed treatment (16%).
The report was compiled from an online survey that included more than 4,300 physicians from 29 specialties. The survey was available from May 21, 2021, to August 28, 2021, and included 732 family and internal medicine physicians. Most respondents had practiced medicine for more than 25 years (47%) or from 21-25 years (16%). Almost half of respondents (47%) were aged 60 years or older.
Most PCPs (63%) reported malpractice insurance premiums of less than $20,000 per year, which is more than the overall proportion for all specialists (52%). The typical premium for PCPs was $5,000-$9,999 (26%). Premium payments varied widely by geographic area, with a PCP in New York paying five times as much as a colleague in California, Tennessee, or Ohio would pay to obtain comparable coverage, the survey found.
More than 9 in 10 PCPs (91%) reported being “very surprised” or “somewhat surprised” to having been part of a malpractice suit and reported being upset and anxious: “Feeling betrayed by people to whom I had provided good care, and embarrassed that my colleagues might find out,” as one internist put it. The majority (84%) of PCPs said their lawsuits were unwarranted, in line with perceptions among all specialists (83%).
The largest proportions of cases were settled before trial (35%) or were dismissed within a few months of lawsuit filing (16%). A judge or jury ruled in the plaintiff’s favor only 2% of the time. Seven percent of cases are ongoing, and 3% were settled at trial, according to the survey.
The largest number of cases (40%) took between 1 and 2 years, although 30% were less than a year. Roughly one in four cases (24%) lasted 3-5 years. Almost half (47%) of any monetary payments to plaintiffs were $100,000 or less; one-third of such payments were capped at $500,000.
Two-thirds (68%) of PCPs said that the lawsuit did not negatively affect their careers, and more than one in four (28%) said they now no longer trust patients or that they treat them differently. This change in trust is slightly higher than for specialists overall (24%).
More than 4 in 10 PCPs (41%) said they would have done nothing differently despite being sued. The largest proportion of changes other PCPs would have made included improved documentation (18%) and ordering additional tests as a hedge against a lawsuit (11%); 10% said they should never have taken on the patient in the first place.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the Medscape Primary Care Physician Malpractice Report 2021. This figure is less than the overall proportion of physicians in all specialties named in a malpractice suit (51%).
More PCPs were part of lawsuits that named multiple parties (34%) than suits that named a individual practitioners (11%). Failure to make a proper diagnosis (41%) was the most common claim in malpractice suits against PCPs, followed by poor outcome/disease progression (26%), complications from treatment/surgery (17%), wrongful death (16%), and failure to treat/delayed treatment (16%).
The report was compiled from an online survey that included more than 4,300 physicians from 29 specialties. The survey was available from May 21, 2021, to August 28, 2021, and included 732 family and internal medicine physicians. Most respondents had practiced medicine for more than 25 years (47%) or from 21-25 years (16%). Almost half of respondents (47%) were aged 60 years or older.
Most PCPs (63%) reported malpractice insurance premiums of less than $20,000 per year, which is more than the overall proportion for all specialists (52%). The typical premium for PCPs was $5,000-$9,999 (26%). Premium payments varied widely by geographic area, with a PCP in New York paying five times as much as a colleague in California, Tennessee, or Ohio would pay to obtain comparable coverage, the survey found.
More than 9 in 10 PCPs (91%) reported being “very surprised” or “somewhat surprised” to having been part of a malpractice suit and reported being upset and anxious: “Feeling betrayed by people to whom I had provided good care, and embarrassed that my colleagues might find out,” as one internist put it. The majority (84%) of PCPs said their lawsuits were unwarranted, in line with perceptions among all specialists (83%).
The largest proportions of cases were settled before trial (35%) or were dismissed within a few months of lawsuit filing (16%). A judge or jury ruled in the plaintiff’s favor only 2% of the time. Seven percent of cases are ongoing, and 3% were settled at trial, according to the survey.
The largest number of cases (40%) took between 1 and 2 years, although 30% were less than a year. Roughly one in four cases (24%) lasted 3-5 years. Almost half (47%) of any monetary payments to plaintiffs were $100,000 or less; one-third of such payments were capped at $500,000.
Two-thirds (68%) of PCPs said that the lawsuit did not negatively affect their careers, and more than one in four (28%) said they now no longer trust patients or that they treat them differently. This change in trust is slightly higher than for specialists overall (24%).
More than 4 in 10 PCPs (41%) said they would have done nothing differently despite being sued. The largest proportion of changes other PCPs would have made included improved documentation (18%) and ordering additional tests as a hedge against a lawsuit (11%); 10% said they should never have taken on the patient in the first place.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Deaths of despair’ rising, but only in the U.S.
In the United States,
This is not the case in 16 other industrialized nations, however, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, where mortality rates are actually decreasing.
One likely reason is that other countries take better care of their citizens from cradle to grave, authors Peter Sterling, PhD, and Michael Platt, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, wrote in a special communication in JAMA Psychiatry published online Feb. 2.
In the United States, individuals and families often struggle in isolation to navigate the life cycle, whereas other countries offer communal assistance to every life stage, and this support protects individuals and families in the long term, they noted.
The United States could solve this “health crisis” by adopting the best practices of these other nations, they wrote.
U.S. is an outlier
From an anthropological perspective, Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt point out that “hunter-gatherers” prioritized food, comfort, and companionship. When one of these needs is unexpectedly met, the surprise triggers a pulse of the feel-good hormone dopamine.
However, much of modern life offers few opportunities for surprise and dopamine pulses.
“It is the difference between a day’s hard walk to finally encounter and kill a wild pig to feed the family and community versus a quick trip to aisle 7 to select a pork roast in plastic wrap,” Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt noted.
The hunter-gatherers were far more physically active, and cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension were virtually unknown.
The small-scale societies of hunters and gatherers depended on strong family bonds and cooperation with community members.
Modern life is more isolating, often with hours spent alone in front of a computer screen.
Yet the lack of natural dopamine producers in modern society and the increased social isolation is not unique to the United States but holds across the board for industrialized nations.
So why has the United States suffered more deaths of despair?
Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt assert that it comes down to public support other countries provide their citizens across the life span, from prenatal care and quality preschool and elementary school to affordable (or free) education beyond high school.
This support did not require “bloody revolutions, just simple agreements to prepay basic human needs from public funds collected as taxes,” Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt noted.
By adopting some of the best practices pioneered by other wealthy nations, the United States could reduce despair and restore to many the will to live, they added.
However, they caution against the “medicalization” of every identified cause of rising death rates.
“Every symptom of despair has been defined as a disorder or dysregulation within the individual. This incorrectly frames the problem, forcing individuals to grapple on their own,” they wrote.
“It also emphasizes treatment by pharmacology, providing innumerable drugs for anxiety, depression, anger, psychosis, and obesity, plus new drugs to treat addictions to the old drugs. We cannot defeat despair solely with pills – to the contrary, pills will only deepen it,” they added.
Dr. Platt reported receiving grant support from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Charles E. Kaufman Foundation. He is cofounder of Cogwear and a scientific adviser to Neuroflow, Amplio, Blue Horizon International, and Progenity. Dr. Sterling has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the United States,
This is not the case in 16 other industrialized nations, however, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, where mortality rates are actually decreasing.
One likely reason is that other countries take better care of their citizens from cradle to grave, authors Peter Sterling, PhD, and Michael Platt, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, wrote in a special communication in JAMA Psychiatry published online Feb. 2.
In the United States, individuals and families often struggle in isolation to navigate the life cycle, whereas other countries offer communal assistance to every life stage, and this support protects individuals and families in the long term, they noted.
The United States could solve this “health crisis” by adopting the best practices of these other nations, they wrote.
U.S. is an outlier
From an anthropological perspective, Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt point out that “hunter-gatherers” prioritized food, comfort, and companionship. When one of these needs is unexpectedly met, the surprise triggers a pulse of the feel-good hormone dopamine.
However, much of modern life offers few opportunities for surprise and dopamine pulses.
“It is the difference between a day’s hard walk to finally encounter and kill a wild pig to feed the family and community versus a quick trip to aisle 7 to select a pork roast in plastic wrap,” Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt noted.
The hunter-gatherers were far more physically active, and cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension were virtually unknown.
The small-scale societies of hunters and gatherers depended on strong family bonds and cooperation with community members.
Modern life is more isolating, often with hours spent alone in front of a computer screen.
Yet the lack of natural dopamine producers in modern society and the increased social isolation is not unique to the United States but holds across the board for industrialized nations.
So why has the United States suffered more deaths of despair?
Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt assert that it comes down to public support other countries provide their citizens across the life span, from prenatal care and quality preschool and elementary school to affordable (or free) education beyond high school.
This support did not require “bloody revolutions, just simple agreements to prepay basic human needs from public funds collected as taxes,” Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt noted.
By adopting some of the best practices pioneered by other wealthy nations, the United States could reduce despair and restore to many the will to live, they added.
However, they caution against the “medicalization” of every identified cause of rising death rates.
“Every symptom of despair has been defined as a disorder or dysregulation within the individual. This incorrectly frames the problem, forcing individuals to grapple on their own,” they wrote.
“It also emphasizes treatment by pharmacology, providing innumerable drugs for anxiety, depression, anger, psychosis, and obesity, plus new drugs to treat addictions to the old drugs. We cannot defeat despair solely with pills – to the contrary, pills will only deepen it,” they added.
Dr. Platt reported receiving grant support from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Charles E. Kaufman Foundation. He is cofounder of Cogwear and a scientific adviser to Neuroflow, Amplio, Blue Horizon International, and Progenity. Dr. Sterling has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the United States,
This is not the case in 16 other industrialized nations, however, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, where mortality rates are actually decreasing.
One likely reason is that other countries take better care of their citizens from cradle to grave, authors Peter Sterling, PhD, and Michael Platt, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, wrote in a special communication in JAMA Psychiatry published online Feb. 2.
In the United States, individuals and families often struggle in isolation to navigate the life cycle, whereas other countries offer communal assistance to every life stage, and this support protects individuals and families in the long term, they noted.
The United States could solve this “health crisis” by adopting the best practices of these other nations, they wrote.
U.S. is an outlier
From an anthropological perspective, Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt point out that “hunter-gatherers” prioritized food, comfort, and companionship. When one of these needs is unexpectedly met, the surprise triggers a pulse of the feel-good hormone dopamine.
However, much of modern life offers few opportunities for surprise and dopamine pulses.
“It is the difference between a day’s hard walk to finally encounter and kill a wild pig to feed the family and community versus a quick trip to aisle 7 to select a pork roast in plastic wrap,” Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt noted.
The hunter-gatherers were far more physically active, and cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension were virtually unknown.
The small-scale societies of hunters and gatherers depended on strong family bonds and cooperation with community members.
Modern life is more isolating, often with hours spent alone in front of a computer screen.
Yet the lack of natural dopamine producers in modern society and the increased social isolation is not unique to the United States but holds across the board for industrialized nations.
So why has the United States suffered more deaths of despair?
Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt assert that it comes down to public support other countries provide their citizens across the life span, from prenatal care and quality preschool and elementary school to affordable (or free) education beyond high school.
This support did not require “bloody revolutions, just simple agreements to prepay basic human needs from public funds collected as taxes,” Dr. Sterling and Dr. Platt noted.
By adopting some of the best practices pioneered by other wealthy nations, the United States could reduce despair and restore to many the will to live, they added.
However, they caution against the “medicalization” of every identified cause of rising death rates.
“Every symptom of despair has been defined as a disorder or dysregulation within the individual. This incorrectly frames the problem, forcing individuals to grapple on their own,” they wrote.
“It also emphasizes treatment by pharmacology, providing innumerable drugs for anxiety, depression, anger, psychosis, and obesity, plus new drugs to treat addictions to the old drugs. We cannot defeat despair solely with pills – to the contrary, pills will only deepen it,” they added.
Dr. Platt reported receiving grant support from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Charles E. Kaufman Foundation. He is cofounder of Cogwear and a scientific adviser to Neuroflow, Amplio, Blue Horizon International, and Progenity. Dr. Sterling has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antibody mix may prevent COVID symptoms in some asymptomatic people
over 28 days, new research shows.
Results of the study by Meagan P. O’Brien, MD, from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and one of the study’s funders, and coauthors were published online Jan. 14, 2022, in an original investigation in JAMA.
The results suggest new potential for monoclonal antibodies currently used for postexposure prophylaxis and treatment of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2. It has not been clear whether monoclonal antibodies can benefit people with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The trial included 314 participants (mean age, 41 years; 51.6% women). Of the participants, 310 (99.7%) completed the efficacy assessment period, and 204 were asymptomatic and tested negative at baseline and were included in the primary efficacy analysis.
The subcutaneous combination of casirivimab and imdevimab, 1,200 mg (600 mg each), significantly prevented progression to symptomatic disease (29/100 [29.0%] vs. 44/104 [42.3%] with placebo; odds ratio, 0.54 [95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.97]; P = .04; absolute risk difference, −13.3% [95% CI, −26.3% to −0.3%]).
These results were part of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial of close household contacts of a SARS-CoV-2–infected person at 112 sites in the United States, Romania, and Moldova. They were enrolled between July 13, 2020, and Jan. 28, 2021; follow-up ended March 11, 2021.
Asymptomatic people at least 12 years old were eligible if identified within 96 hours of index case positive test collection and were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive one dose of subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab (n = 158), or placebo (n = 156).
COVID-19 vaccination was prohibited before enrollment but was allowed after completing the 28-day efficacy assessment period.
Caution warranted
In an accompanying editorial, however, Jonathan Z. Li, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and Rajesh T. Gandhi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Harvard Medical School, urged caution in interpreting the results.
They wrote that, although monoclonal antibodies are generally used in individuals at high risk for severe COVID-19, this study population was less vulnerable, with an average age of 41, and 30% had no risk for the disease.
“Of the remainder, the most common risk factor was being overweight (which confers less risk than other factors),” the editorialists wrote.
They pointed out, as did the study authors, that enrollment came before the emergence of the Delta and Omicron variants, and that both casirivimab and imdevimab maintain their activity against Delta but not against Omicron.
“While prevention of symptomatic infection has benefits,” they wrote, “the primary goal of monoclonal antibody therapy is to prevent progression to severe disease; however, this trial was unable to assess this outcome because there were only three hospitalizations (all in the placebo group). Also, this study was conducted prior to widespread COVID-19 vaccination; whether monoclonal antibodies have the same benefit in people who have breakthrough infection after vaccination is not known.”
The editorialists highlighted the subcutaneous delivery in this study.
They wrote that Dr. O’Brien and coauthors provide evidence that subcutaneous administration is effective in infected individuals. “However, high serum monoclonal antibody levels are achieved more quickly after intravenous administration than following subcutaneous injection; it is unknown whether intravenous administration might have led to even greater efficacy for individuals with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
The authors of the study also add that, despite efforts to recruit non-White participants, relatively few non-White people were enrolled. Additionally, few adolescents were enrolled.
The sample size was also relatively small, they acknowledge, because of a study design in which the infection status of asymptomatic participants was not confirmed at inclusion.
Several of the authors are employees/stockholders of Regeneron, and have a patent pending, which has been licensed and is receiving royalties. The study was supported by Regeneron and F. Hoffmann–La Roche. This trial was conducted jointly with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the National Institutes of Health. The CoVPN (COVID-19 Prevention Network) is supported by cooperative agreement awards from the NIAID and NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
over 28 days, new research shows.
Results of the study by Meagan P. O’Brien, MD, from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and one of the study’s funders, and coauthors were published online Jan. 14, 2022, in an original investigation in JAMA.
The results suggest new potential for monoclonal antibodies currently used for postexposure prophylaxis and treatment of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2. It has not been clear whether monoclonal antibodies can benefit people with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The trial included 314 participants (mean age, 41 years; 51.6% women). Of the participants, 310 (99.7%) completed the efficacy assessment period, and 204 were asymptomatic and tested negative at baseline and were included in the primary efficacy analysis.
The subcutaneous combination of casirivimab and imdevimab, 1,200 mg (600 mg each), significantly prevented progression to symptomatic disease (29/100 [29.0%] vs. 44/104 [42.3%] with placebo; odds ratio, 0.54 [95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.97]; P = .04; absolute risk difference, −13.3% [95% CI, −26.3% to −0.3%]).
These results were part of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial of close household contacts of a SARS-CoV-2–infected person at 112 sites in the United States, Romania, and Moldova. They were enrolled between July 13, 2020, and Jan. 28, 2021; follow-up ended March 11, 2021.
Asymptomatic people at least 12 years old were eligible if identified within 96 hours of index case positive test collection and were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive one dose of subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab (n = 158), or placebo (n = 156).
COVID-19 vaccination was prohibited before enrollment but was allowed after completing the 28-day efficacy assessment period.
Caution warranted
In an accompanying editorial, however, Jonathan Z. Li, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and Rajesh T. Gandhi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Harvard Medical School, urged caution in interpreting the results.
They wrote that, although monoclonal antibodies are generally used in individuals at high risk for severe COVID-19, this study population was less vulnerable, with an average age of 41, and 30% had no risk for the disease.
“Of the remainder, the most common risk factor was being overweight (which confers less risk than other factors),” the editorialists wrote.
They pointed out, as did the study authors, that enrollment came before the emergence of the Delta and Omicron variants, and that both casirivimab and imdevimab maintain their activity against Delta but not against Omicron.
“While prevention of symptomatic infection has benefits,” they wrote, “the primary goal of monoclonal antibody therapy is to prevent progression to severe disease; however, this trial was unable to assess this outcome because there were only three hospitalizations (all in the placebo group). Also, this study was conducted prior to widespread COVID-19 vaccination; whether monoclonal antibodies have the same benefit in people who have breakthrough infection after vaccination is not known.”
The editorialists highlighted the subcutaneous delivery in this study.
They wrote that Dr. O’Brien and coauthors provide evidence that subcutaneous administration is effective in infected individuals. “However, high serum monoclonal antibody levels are achieved more quickly after intravenous administration than following subcutaneous injection; it is unknown whether intravenous administration might have led to even greater efficacy for individuals with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
The authors of the study also add that, despite efforts to recruit non-White participants, relatively few non-White people were enrolled. Additionally, few adolescents were enrolled.
The sample size was also relatively small, they acknowledge, because of a study design in which the infection status of asymptomatic participants was not confirmed at inclusion.
Several of the authors are employees/stockholders of Regeneron, and have a patent pending, which has been licensed and is receiving royalties. The study was supported by Regeneron and F. Hoffmann–La Roche. This trial was conducted jointly with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the National Institutes of Health. The CoVPN (COVID-19 Prevention Network) is supported by cooperative agreement awards from the NIAID and NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
over 28 days, new research shows.
Results of the study by Meagan P. O’Brien, MD, from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and one of the study’s funders, and coauthors were published online Jan. 14, 2022, in an original investigation in JAMA.
The results suggest new potential for monoclonal antibodies currently used for postexposure prophylaxis and treatment of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2. It has not been clear whether monoclonal antibodies can benefit people with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The trial included 314 participants (mean age, 41 years; 51.6% women). Of the participants, 310 (99.7%) completed the efficacy assessment period, and 204 were asymptomatic and tested negative at baseline and were included in the primary efficacy analysis.
The subcutaneous combination of casirivimab and imdevimab, 1,200 mg (600 mg each), significantly prevented progression to symptomatic disease (29/100 [29.0%] vs. 44/104 [42.3%] with placebo; odds ratio, 0.54 [95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.97]; P = .04; absolute risk difference, −13.3% [95% CI, −26.3% to −0.3%]).
These results were part of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial of close household contacts of a SARS-CoV-2–infected person at 112 sites in the United States, Romania, and Moldova. They were enrolled between July 13, 2020, and Jan. 28, 2021; follow-up ended March 11, 2021.
Asymptomatic people at least 12 years old were eligible if identified within 96 hours of index case positive test collection and were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive one dose of subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab (n = 158), or placebo (n = 156).
COVID-19 vaccination was prohibited before enrollment but was allowed after completing the 28-day efficacy assessment period.
Caution warranted
In an accompanying editorial, however, Jonathan Z. Li, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and Rajesh T. Gandhi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Harvard Medical School, urged caution in interpreting the results.
They wrote that, although monoclonal antibodies are generally used in individuals at high risk for severe COVID-19, this study population was less vulnerable, with an average age of 41, and 30% had no risk for the disease.
“Of the remainder, the most common risk factor was being overweight (which confers less risk than other factors),” the editorialists wrote.
They pointed out, as did the study authors, that enrollment came before the emergence of the Delta and Omicron variants, and that both casirivimab and imdevimab maintain their activity against Delta but not against Omicron.
“While prevention of symptomatic infection has benefits,” they wrote, “the primary goal of monoclonal antibody therapy is to prevent progression to severe disease; however, this trial was unable to assess this outcome because there were only three hospitalizations (all in the placebo group). Also, this study was conducted prior to widespread COVID-19 vaccination; whether monoclonal antibodies have the same benefit in people who have breakthrough infection after vaccination is not known.”
The editorialists highlighted the subcutaneous delivery in this study.
They wrote that Dr. O’Brien and coauthors provide evidence that subcutaneous administration is effective in infected individuals. “However, high serum monoclonal antibody levels are achieved more quickly after intravenous administration than following subcutaneous injection; it is unknown whether intravenous administration might have led to even greater efficacy for individuals with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
The authors of the study also add that, despite efforts to recruit non-White participants, relatively few non-White people were enrolled. Additionally, few adolescents were enrolled.
The sample size was also relatively small, they acknowledge, because of a study design in which the infection status of asymptomatic participants was not confirmed at inclusion.
Several of the authors are employees/stockholders of Regeneron, and have a patent pending, which has been licensed and is receiving royalties. The study was supported by Regeneron and F. Hoffmann–La Roche. This trial was conducted jointly with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the National Institutes of Health. The CoVPN (COVID-19 Prevention Network) is supported by cooperative agreement awards from the NIAID and NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
VARC-3 TAVR technical failure definition ‘highly clinically relevant’
A new study offers early validation of the recently released Valve Academic Research Consortium 3 (VARC-3) definition of technical success after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and highlights its role in patient prognosis.
Results show that one in 10 patients (11.6%) undergoing TAVR with contemporary devices and techniques experiences technical failure, according to VARC-3.
At 30 days, patients with technical failure had significantly higher rates of the composite of cardiovascular (CV) death or stroke (11.5% vs. 3.5%), CV death (6.0% vs. 1.0%), and stroke (7.2% vs. 2.9%), compared with those with technical success.
Technical failure after TAVR was also independently associated with a twofold higher risk for CV death or stroke at 1 year (20.0% vs. 10.3%; hazard ratio, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.37-2.95).
Other independent predictors were history of peripheral artery disease (HR, 1.97), New York Heart Association III or IV disease (HR, 1.86), baseline moderate or greater mitral regurgitation (HR, 1.48), atrial fibrillation (HR, 1.40), and Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted mortality risk (HR, 1.04).
“We were expecting that we were getting better over time with device iterations, with more experience, so we weren’t surprised by the result. But I think what is somewhat surprising is how much of an impact it has on the outcome,” senior study author Thomas Pilgrim, MD, Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland, told this news organization.
The VARC-3 document, introduced last year to some controversy, features a heavier focus on patient outcomes, as well as composite safety and efficacy endpoints. The definition of technical success after TAVR includes freedom from death; successful access, delivery of the device, and retrieval of the delivery system; correct positioning of a prosthetic heart valve into the proper anatomical location; and freedom from surgery or intervention related to the device or to an access-related or cardiac structural complication.
The composite endpoint is meant to replace the VARC-2 definition of “device success,” which also included freedom from death and correct valve positioning but required echocardiographic evaluation. With VARC-3, there is an “immediate measure” of success without having to wait for echocardiography, observed Dr. Pilgrim.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Interventions, TAVR was a technical success in 1,435 of 1,624 (88.4%) patients. Technical failure occurred in 189 patients related to either vascular complications (8.6%) or procedural death or cardiac complications (3.0%).
The VARC-2 endpoint of device success was observed in 66.1% of patients. The high rate of device failure was largely attributed to a 28% incidence of prosthesis-patient mismatch.
“If you use the VARC-2 device success [definition], you include this patient–prosthesis mismatch, the [valve] gradients, [and] regurgitation and then device success is always lower,” Dr. Pilgrim said.
Asked whether the VARC-3 definition may be missing case failures, he replied: “At this stage, we don’t know how important these echocardiographic parameters are for hard clinical endpoints. Maybe the VARC-2 endpoint was too sensitive or the VARC-3 endpoint is not sensitive enough. This is something we just don’t know at this stage.”
Marco Barbanti, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Rodolico Polyclinic University Hospital-San Marco, Catania, Italy, and author of an accompanying editorial, said VARC-3 represents a more accurate indicator of immediate success of the procedure.
“It’s a more pertinent definition according to what really has an impact on prognosis, and, according to the results of this paper, actually, the calibration of this new definition is quite good,” Dr. Barbanti said in an interview.
Patients with VARC-3 technical failure were older, had a higher body mass index, and had more advanced heart failure symptoms than those with technical success. There were no significant differences between the two groups in echocardiographic or CT data, anesthetic strategy, valve type or size, or use of pre- or post-dilation.
All patients underwent TAVR with current balloon-expandable (Sapien 3/Sapien Ultra, Edwards Lifesciences) or self-expanding (Evolut R/PRO [Medtronic], Portico [Abbott], Symetis ACURATE/ACURATE neo [Boston Scientific]) devices between March 2012 and December 2019. A transfemoral approach was used in 92.5% of patients.
In a landmark analysis with the landmark set at 30 days, the effect of technical failure on adverse outcome was limited to the first 30 days (composite endpoint 0-30 days: HR, 3.42; P < .001; 30-360 days: HR, 1.36; P = .266; P for interaction = .002).
At 1 year, the composite of CV death and stroke endpoint occurred in 24.1% of patients with cardiac technical failure, in 18.8% of patients with vascular technical failure, and in 10.3% of patients with technical success.
In multivariate analyses, cardiac and vascular technical failures were independently associated with a 2.6-fold and 1.9-fold increased risk, respectively, for the composite of cardiovascular death and stroke at 1 year.
Female sex, larger device landing zone calcium volume, and earlier procedures (March 2012 to July 2016) were associated with a higher risk for cardiac technical failure, whereas, consistent with previous studies, higher body mass index and use of the Prostar/Manta versus the ProGlide closure device predicted vascular technical failure.
The findings “underscore that technical success is highly clinically relevant and may serve as one of the pivotal endpoints to evaluate the improvement of TAVR or for head-to-head comparisons of new devices in future clinical trials,” the authors conclude.
The findings reflect the experience of a single high-volume center with highly experienced operators in the prospective BERN TAVR registry, however, and may not be generalizable to other heart centers, they note. Although the registry has standardized follow-up, independent analysis of echocardiographic and CT, and independent event adjudication, vascular anatomy was not systematically assessed, and the potential exists for confounding from unmeasured variables.
Dr. Pilgrim reports research grants to the institution from Edwards Lifesciences, Boston Scientific, and Biotronik, personal fees from Biotronik and Boston Scientific, and other from HighLife SAS. Dr. Barbanti is a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study offers early validation of the recently released Valve Academic Research Consortium 3 (VARC-3) definition of technical success after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and highlights its role in patient prognosis.
Results show that one in 10 patients (11.6%) undergoing TAVR with contemporary devices and techniques experiences technical failure, according to VARC-3.
At 30 days, patients with technical failure had significantly higher rates of the composite of cardiovascular (CV) death or stroke (11.5% vs. 3.5%), CV death (6.0% vs. 1.0%), and stroke (7.2% vs. 2.9%), compared with those with technical success.
Technical failure after TAVR was also independently associated with a twofold higher risk for CV death or stroke at 1 year (20.0% vs. 10.3%; hazard ratio, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.37-2.95).
Other independent predictors were history of peripheral artery disease (HR, 1.97), New York Heart Association III or IV disease (HR, 1.86), baseline moderate or greater mitral regurgitation (HR, 1.48), atrial fibrillation (HR, 1.40), and Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted mortality risk (HR, 1.04).
“We were expecting that we were getting better over time with device iterations, with more experience, so we weren’t surprised by the result. But I think what is somewhat surprising is how much of an impact it has on the outcome,” senior study author Thomas Pilgrim, MD, Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland, told this news organization.
The VARC-3 document, introduced last year to some controversy, features a heavier focus on patient outcomes, as well as composite safety and efficacy endpoints. The definition of technical success after TAVR includes freedom from death; successful access, delivery of the device, and retrieval of the delivery system; correct positioning of a prosthetic heart valve into the proper anatomical location; and freedom from surgery or intervention related to the device or to an access-related or cardiac structural complication.
The composite endpoint is meant to replace the VARC-2 definition of “device success,” which also included freedom from death and correct valve positioning but required echocardiographic evaluation. With VARC-3, there is an “immediate measure” of success without having to wait for echocardiography, observed Dr. Pilgrim.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Interventions, TAVR was a technical success in 1,435 of 1,624 (88.4%) patients. Technical failure occurred in 189 patients related to either vascular complications (8.6%) or procedural death or cardiac complications (3.0%).
The VARC-2 endpoint of device success was observed in 66.1% of patients. The high rate of device failure was largely attributed to a 28% incidence of prosthesis-patient mismatch.
“If you use the VARC-2 device success [definition], you include this patient–prosthesis mismatch, the [valve] gradients, [and] regurgitation and then device success is always lower,” Dr. Pilgrim said.
Asked whether the VARC-3 definition may be missing case failures, he replied: “At this stage, we don’t know how important these echocardiographic parameters are for hard clinical endpoints. Maybe the VARC-2 endpoint was too sensitive or the VARC-3 endpoint is not sensitive enough. This is something we just don’t know at this stage.”
Marco Barbanti, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Rodolico Polyclinic University Hospital-San Marco, Catania, Italy, and author of an accompanying editorial, said VARC-3 represents a more accurate indicator of immediate success of the procedure.
“It’s a more pertinent definition according to what really has an impact on prognosis, and, according to the results of this paper, actually, the calibration of this new definition is quite good,” Dr. Barbanti said in an interview.
Patients with VARC-3 technical failure were older, had a higher body mass index, and had more advanced heart failure symptoms than those with technical success. There were no significant differences between the two groups in echocardiographic or CT data, anesthetic strategy, valve type or size, or use of pre- or post-dilation.
All patients underwent TAVR with current balloon-expandable (Sapien 3/Sapien Ultra, Edwards Lifesciences) or self-expanding (Evolut R/PRO [Medtronic], Portico [Abbott], Symetis ACURATE/ACURATE neo [Boston Scientific]) devices between March 2012 and December 2019. A transfemoral approach was used in 92.5% of patients.
In a landmark analysis with the landmark set at 30 days, the effect of technical failure on adverse outcome was limited to the first 30 days (composite endpoint 0-30 days: HR, 3.42; P < .001; 30-360 days: HR, 1.36; P = .266; P for interaction = .002).
At 1 year, the composite of CV death and stroke endpoint occurred in 24.1% of patients with cardiac technical failure, in 18.8% of patients with vascular technical failure, and in 10.3% of patients with technical success.
In multivariate analyses, cardiac and vascular technical failures were independently associated with a 2.6-fold and 1.9-fold increased risk, respectively, for the composite of cardiovascular death and stroke at 1 year.
Female sex, larger device landing zone calcium volume, and earlier procedures (March 2012 to July 2016) were associated with a higher risk for cardiac technical failure, whereas, consistent with previous studies, higher body mass index and use of the Prostar/Manta versus the ProGlide closure device predicted vascular technical failure.
The findings “underscore that technical success is highly clinically relevant and may serve as one of the pivotal endpoints to evaluate the improvement of TAVR or for head-to-head comparisons of new devices in future clinical trials,” the authors conclude.
The findings reflect the experience of a single high-volume center with highly experienced operators in the prospective BERN TAVR registry, however, and may not be generalizable to other heart centers, they note. Although the registry has standardized follow-up, independent analysis of echocardiographic and CT, and independent event adjudication, vascular anatomy was not systematically assessed, and the potential exists for confounding from unmeasured variables.
Dr. Pilgrim reports research grants to the institution from Edwards Lifesciences, Boston Scientific, and Biotronik, personal fees from Biotronik and Boston Scientific, and other from HighLife SAS. Dr. Barbanti is a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study offers early validation of the recently released Valve Academic Research Consortium 3 (VARC-3) definition of technical success after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and highlights its role in patient prognosis.
Results show that one in 10 patients (11.6%) undergoing TAVR with contemporary devices and techniques experiences technical failure, according to VARC-3.
At 30 days, patients with technical failure had significantly higher rates of the composite of cardiovascular (CV) death or stroke (11.5% vs. 3.5%), CV death (6.0% vs. 1.0%), and stroke (7.2% vs. 2.9%), compared with those with technical success.
Technical failure after TAVR was also independently associated with a twofold higher risk for CV death or stroke at 1 year (20.0% vs. 10.3%; hazard ratio, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.37-2.95).
Other independent predictors were history of peripheral artery disease (HR, 1.97), New York Heart Association III or IV disease (HR, 1.86), baseline moderate or greater mitral regurgitation (HR, 1.48), atrial fibrillation (HR, 1.40), and Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted mortality risk (HR, 1.04).
“We were expecting that we were getting better over time with device iterations, with more experience, so we weren’t surprised by the result. But I think what is somewhat surprising is how much of an impact it has on the outcome,” senior study author Thomas Pilgrim, MD, Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland, told this news organization.
The VARC-3 document, introduced last year to some controversy, features a heavier focus on patient outcomes, as well as composite safety and efficacy endpoints. The definition of technical success after TAVR includes freedom from death; successful access, delivery of the device, and retrieval of the delivery system; correct positioning of a prosthetic heart valve into the proper anatomical location; and freedom from surgery or intervention related to the device or to an access-related or cardiac structural complication.
The composite endpoint is meant to replace the VARC-2 definition of “device success,” which also included freedom from death and correct valve positioning but required echocardiographic evaluation. With VARC-3, there is an “immediate measure” of success without having to wait for echocardiography, observed Dr. Pilgrim.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Interventions, TAVR was a technical success in 1,435 of 1,624 (88.4%) patients. Technical failure occurred in 189 patients related to either vascular complications (8.6%) or procedural death or cardiac complications (3.0%).
The VARC-2 endpoint of device success was observed in 66.1% of patients. The high rate of device failure was largely attributed to a 28% incidence of prosthesis-patient mismatch.
“If you use the VARC-2 device success [definition], you include this patient–prosthesis mismatch, the [valve] gradients, [and] regurgitation and then device success is always lower,” Dr. Pilgrim said.
Asked whether the VARC-3 definition may be missing case failures, he replied: “At this stage, we don’t know how important these echocardiographic parameters are for hard clinical endpoints. Maybe the VARC-2 endpoint was too sensitive or the VARC-3 endpoint is not sensitive enough. This is something we just don’t know at this stage.”
Marco Barbanti, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Rodolico Polyclinic University Hospital-San Marco, Catania, Italy, and author of an accompanying editorial, said VARC-3 represents a more accurate indicator of immediate success of the procedure.
“It’s a more pertinent definition according to what really has an impact on prognosis, and, according to the results of this paper, actually, the calibration of this new definition is quite good,” Dr. Barbanti said in an interview.
Patients with VARC-3 technical failure were older, had a higher body mass index, and had more advanced heart failure symptoms than those with technical success. There were no significant differences between the two groups in echocardiographic or CT data, anesthetic strategy, valve type or size, or use of pre- or post-dilation.
All patients underwent TAVR with current balloon-expandable (Sapien 3/Sapien Ultra, Edwards Lifesciences) or self-expanding (Evolut R/PRO [Medtronic], Portico [Abbott], Symetis ACURATE/ACURATE neo [Boston Scientific]) devices between March 2012 and December 2019. A transfemoral approach was used in 92.5% of patients.
In a landmark analysis with the landmark set at 30 days, the effect of technical failure on adverse outcome was limited to the first 30 days (composite endpoint 0-30 days: HR, 3.42; P < .001; 30-360 days: HR, 1.36; P = .266; P for interaction = .002).
At 1 year, the composite of CV death and stroke endpoint occurred in 24.1% of patients with cardiac technical failure, in 18.8% of patients with vascular technical failure, and in 10.3% of patients with technical success.
In multivariate analyses, cardiac and vascular technical failures were independently associated with a 2.6-fold and 1.9-fold increased risk, respectively, for the composite of cardiovascular death and stroke at 1 year.
Female sex, larger device landing zone calcium volume, and earlier procedures (March 2012 to July 2016) were associated with a higher risk for cardiac technical failure, whereas, consistent with previous studies, higher body mass index and use of the Prostar/Manta versus the ProGlide closure device predicted vascular technical failure.
The findings “underscore that technical success is highly clinically relevant and may serve as one of the pivotal endpoints to evaluate the improvement of TAVR or for head-to-head comparisons of new devices in future clinical trials,” the authors conclude.
The findings reflect the experience of a single high-volume center with highly experienced operators in the prospective BERN TAVR registry, however, and may not be generalizable to other heart centers, they note. Although the registry has standardized follow-up, independent analysis of echocardiographic and CT, and independent event adjudication, vascular anatomy was not systematically assessed, and the potential exists for confounding from unmeasured variables.
Dr. Pilgrim reports research grants to the institution from Edwards Lifesciences, Boston Scientific, and Biotronik, personal fees from Biotronik and Boston Scientific, and other from HighLife SAS. Dr. Barbanti is a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS
Future respiratory infection risk raised by early life virus exposure
Many factors influence a child’s subsequent susceptibility to respiratory tract infection (RTI), including breastfeeding, crowded conditions, and exposure to environmental tobacco. Now researchers have found that asymptomatic viral infection in the first days of a baby’s life are linked to a greater risk of respiratory infections in later life.
The new research, published in Nature Microbiology, was conducted as part of the Microbiome Utrecht Infant Study (MUIS), a healthy infant birth cohort study that’s been running for 6 years.
In their study, the authors explained how the respiratory tract is “populated by a specialized microbial ecosystem, which is seeded during and directly following birth,” adding that, “despite recognition of many host and environmental factors known to modulate RTI susceptibility, the mechanism by which a child develops recurrent or severe RTIs, while others remain healthy, remains largely unknown”.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh and University Medical Centre Utrecht (the Netherlands) examined nasal mucosa samples of 114 babies at various times from birth until 12 months of age. They then analyzed the gene activity of the babies’ nasal mucosa, the microbes present in the lining of the nose, and any viruses that infected the children.
Interferon-related mucosal gene activity
The researchers described how the microbiome – the community of microbes in the body – of a newborn baby can be influenced by many things, including delivery method, breastfeeding, antibiotics and the hospital environment. They highlighted how viruses were found to interact with a newborn’s immune system and microbiome in a way that affected both a child’s risk, and number, of subsequent infections.
They explained how when a viral infection was detected in the first days after birth, which they said largely occurred asymptomatically, specific mucosal genes were activated – genes involved with interferons – coinciding with a change in the composition of the microbiome, promoting the growth of potentially harmful microbes.
“The interferon-related gene activity caused by an early first viral infection is thought to create a proinflammatory environment that makes babies susceptible to future infections,” they said, adding that in their study they have demonstrated that “first asymptomatic viral encounters were associated with increased interferon signaling, and preceded the development of disadvantageous respiratory microbiota profiles and clinical RTIs”.
Proinflammatory and microbiologically perturbed environment
Debby Bogaert, PhD, chair of paediatric medicine at the University of Edinburgh, said: “We were surprised to see viral infections occur so early in life, and go mostly unnoticed, probably because the infant’s immune system is in what is known as a state of tolerance after birth. Despite this, these infections seem to affect a normal immune development, which is important to know.”
The authors wrote that their data supports the hypothesis that first viral encounters trigger an interferon-associated proinflammatory environment, which then further drives airway inflammation and symptomatology in a “self-enforcing positive feedback loop”. They said that this “proinflammatory and microbiologically perturbed environment in turn renders an individual more vulnerable to recurrent viral-induced RTIs”.
Wouter de Steenhuijsen, PhD, postdoctoral investigator at University Medical Centre Utrecht, said: “Although further work will be needed to confirm the causality of our findings, the data from this study indicate that early-life encounters with respiratory viruses – especially during the first days of life – may set the tone for subsequent non-beneficial host-microbe interactions, which are related to an infection risk and possibly long term respiratory health.”
Dr. Bogaert added: “Only from birth onwards will an infant start to develop its microbiome. Limiting the number of viral encounters in those first days to weeks of life might be essential for a healthy immune and microbiome development, and consequently long term respiratory health.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Many factors influence a child’s subsequent susceptibility to respiratory tract infection (RTI), including breastfeeding, crowded conditions, and exposure to environmental tobacco. Now researchers have found that asymptomatic viral infection in the first days of a baby’s life are linked to a greater risk of respiratory infections in later life.
The new research, published in Nature Microbiology, was conducted as part of the Microbiome Utrecht Infant Study (MUIS), a healthy infant birth cohort study that’s been running for 6 years.
In their study, the authors explained how the respiratory tract is “populated by a specialized microbial ecosystem, which is seeded during and directly following birth,” adding that, “despite recognition of many host and environmental factors known to modulate RTI susceptibility, the mechanism by which a child develops recurrent or severe RTIs, while others remain healthy, remains largely unknown”.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh and University Medical Centre Utrecht (the Netherlands) examined nasal mucosa samples of 114 babies at various times from birth until 12 months of age. They then analyzed the gene activity of the babies’ nasal mucosa, the microbes present in the lining of the nose, and any viruses that infected the children.
Interferon-related mucosal gene activity
The researchers described how the microbiome – the community of microbes in the body – of a newborn baby can be influenced by many things, including delivery method, breastfeeding, antibiotics and the hospital environment. They highlighted how viruses were found to interact with a newborn’s immune system and microbiome in a way that affected both a child’s risk, and number, of subsequent infections.
They explained how when a viral infection was detected in the first days after birth, which they said largely occurred asymptomatically, specific mucosal genes were activated – genes involved with interferons – coinciding with a change in the composition of the microbiome, promoting the growth of potentially harmful microbes.
“The interferon-related gene activity caused by an early first viral infection is thought to create a proinflammatory environment that makes babies susceptible to future infections,” they said, adding that in their study they have demonstrated that “first asymptomatic viral encounters were associated with increased interferon signaling, and preceded the development of disadvantageous respiratory microbiota profiles and clinical RTIs”.
Proinflammatory and microbiologically perturbed environment
Debby Bogaert, PhD, chair of paediatric medicine at the University of Edinburgh, said: “We were surprised to see viral infections occur so early in life, and go mostly unnoticed, probably because the infant’s immune system is in what is known as a state of tolerance after birth. Despite this, these infections seem to affect a normal immune development, which is important to know.”
The authors wrote that their data supports the hypothesis that first viral encounters trigger an interferon-associated proinflammatory environment, which then further drives airway inflammation and symptomatology in a “self-enforcing positive feedback loop”. They said that this “proinflammatory and microbiologically perturbed environment in turn renders an individual more vulnerable to recurrent viral-induced RTIs”.
Wouter de Steenhuijsen, PhD, postdoctoral investigator at University Medical Centre Utrecht, said: “Although further work will be needed to confirm the causality of our findings, the data from this study indicate that early-life encounters with respiratory viruses – especially during the first days of life – may set the tone for subsequent non-beneficial host-microbe interactions, which are related to an infection risk and possibly long term respiratory health.”
Dr. Bogaert added: “Only from birth onwards will an infant start to develop its microbiome. Limiting the number of viral encounters in those first days to weeks of life might be essential for a healthy immune and microbiome development, and consequently long term respiratory health.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Many factors influence a child’s subsequent susceptibility to respiratory tract infection (RTI), including breastfeeding, crowded conditions, and exposure to environmental tobacco. Now researchers have found that asymptomatic viral infection in the first days of a baby’s life are linked to a greater risk of respiratory infections in later life.
The new research, published in Nature Microbiology, was conducted as part of the Microbiome Utrecht Infant Study (MUIS), a healthy infant birth cohort study that’s been running for 6 years.
In their study, the authors explained how the respiratory tract is “populated by a specialized microbial ecosystem, which is seeded during and directly following birth,” adding that, “despite recognition of many host and environmental factors known to modulate RTI susceptibility, the mechanism by which a child develops recurrent or severe RTIs, while others remain healthy, remains largely unknown”.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh and University Medical Centre Utrecht (the Netherlands) examined nasal mucosa samples of 114 babies at various times from birth until 12 months of age. They then analyzed the gene activity of the babies’ nasal mucosa, the microbes present in the lining of the nose, and any viruses that infected the children.
Interferon-related mucosal gene activity
The researchers described how the microbiome – the community of microbes in the body – of a newborn baby can be influenced by many things, including delivery method, breastfeeding, antibiotics and the hospital environment. They highlighted how viruses were found to interact with a newborn’s immune system and microbiome in a way that affected both a child’s risk, and number, of subsequent infections.
They explained how when a viral infection was detected in the first days after birth, which they said largely occurred asymptomatically, specific mucosal genes were activated – genes involved with interferons – coinciding with a change in the composition of the microbiome, promoting the growth of potentially harmful microbes.
“The interferon-related gene activity caused by an early first viral infection is thought to create a proinflammatory environment that makes babies susceptible to future infections,” they said, adding that in their study they have demonstrated that “first asymptomatic viral encounters were associated with increased interferon signaling, and preceded the development of disadvantageous respiratory microbiota profiles and clinical RTIs”.
Proinflammatory and microbiologically perturbed environment
Debby Bogaert, PhD, chair of paediatric medicine at the University of Edinburgh, said: “We were surprised to see viral infections occur so early in life, and go mostly unnoticed, probably because the infant’s immune system is in what is known as a state of tolerance after birth. Despite this, these infections seem to affect a normal immune development, which is important to know.”
The authors wrote that their data supports the hypothesis that first viral encounters trigger an interferon-associated proinflammatory environment, which then further drives airway inflammation and symptomatology in a “self-enforcing positive feedback loop”. They said that this “proinflammatory and microbiologically perturbed environment in turn renders an individual more vulnerable to recurrent viral-induced RTIs”.
Wouter de Steenhuijsen, PhD, postdoctoral investigator at University Medical Centre Utrecht, said: “Although further work will be needed to confirm the causality of our findings, the data from this study indicate that early-life encounters with respiratory viruses – especially during the first days of life – may set the tone for subsequent non-beneficial host-microbe interactions, which are related to an infection risk and possibly long term respiratory health.”
Dr. Bogaert added: “Only from birth onwards will an infant start to develop its microbiome. Limiting the number of viral encounters in those first days to weeks of life might be essential for a healthy immune and microbiome development, and consequently long term respiratory health.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM NATURE MICROBIOLOGY
Infectious disease pop quiz: Clinical challenge #13 for the ObGyn
For a moderately ill pregnant woman, what is the most appropriate antibiotic combination for inpatient treatment of community-acquired pneumonia?
Continue to the answer...
This patient should be treated with intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g every 24 hours) plus oral or intravenous azithromycin. The appropriate oral dose of azithromycin is 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg daily for 4 doses. The appropriate intravenous dose of azithromycin is 500 mg every 24 hours. The goal is to provide appropriate coverage for the most likely pathogens: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and mycoplasmas. (Antibacterial drugs for community-acquired pneumonia. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2021:63:10-14. Postma DF, van Werkoven CH, van Eldin LJ, et al; CAP-START Study Group. Antibiotic treatment strategies for community acquired pneumonia in adults. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1312-1323.)
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
For a moderately ill pregnant woman, what is the most appropriate antibiotic combination for inpatient treatment of community-acquired pneumonia?
Continue to the answer...
This patient should be treated with intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g every 24 hours) plus oral or intravenous azithromycin. The appropriate oral dose of azithromycin is 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg daily for 4 doses. The appropriate intravenous dose of azithromycin is 500 mg every 24 hours. The goal is to provide appropriate coverage for the most likely pathogens: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and mycoplasmas. (Antibacterial drugs for community-acquired pneumonia. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2021:63:10-14. Postma DF, van Werkoven CH, van Eldin LJ, et al; CAP-START Study Group. Antibiotic treatment strategies for community acquired pneumonia in adults. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1312-1323.)
For a moderately ill pregnant woman, what is the most appropriate antibiotic combination for inpatient treatment of community-acquired pneumonia?
Continue to the answer...
This patient should be treated with intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g every 24 hours) plus oral or intravenous azithromycin. The appropriate oral dose of azithromycin is 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg daily for 4 doses. The appropriate intravenous dose of azithromycin is 500 mg every 24 hours. The goal is to provide appropriate coverage for the most likely pathogens: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and mycoplasmas. (Antibacterial drugs for community-acquired pneumonia. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2021:63:10-14. Postma DF, van Werkoven CH, van Eldin LJ, et al; CAP-START Study Group. Antibiotic treatment strategies for community acquired pneumonia in adults. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1312-1323.)
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
Case report: Male with acute new-onset suicidal ideation tied to SARS-CoV-2
An otherwise healthy 55-year-old male, with no previous psychiatric or medical history, sought care with a family medicine physician for the first time in decades.
Medical symptoms began Oct. 9, 2021, with “some leg weakness and mild sniffles.” Since he was going to be at a public event, he decided to take a PCR test for the SARS-CoV-2 virus on Oct. 13. The patient tested positive.
His symptoms continued to worsen, and he experienced severe body fatigue, sleep disturbance, and lethargy. “A few days after my positive test, the cognitive and physical symptoms dramatically ramped up,” the patient recalled.
Because of those worsening symptoms, on Oct. 20, the patient obtained a new patient appointment with a family medicine physician. After a telemedicine evaluation, the family medicine physician began a multifaceted early outpatient COVID-19 treatment protocol,1 as I (C.M.W.) and colleagues wrote about late last year. However, this treatment began late in the course because of the patient’s initial resistance to seek care.
This early outpatient treatment protocol for COVID-19 included vitamin D3 125 mcg (5,000 ICU), N-acetylcysteine (NAC) 600 mg every day x 30 days; acetylsalicylic acid 325 mg every day x 30 days; azithromycin 250 mg b.i.d. before every meal x 10 days; hydroxychloroquine sulfate 200 mg b.i.d. x 10 days; ivermectin 3 mg, 5 pills daily x 10 days; zinc sulfate 220 mg (50 mg elemental) every day x 30 days; and a prednisone taper (30 mg daily x 3 days, tapering down 5 mg every 3 days). Hydroxyzine 50 mg at bedtime as needed was added for sleep. The patient did not comment to the family physician on any of the psychological or psychiatric symptoms and responded appropriately to questions during the Oct. 20 initial evaluation.
However, he later described that around the time the PCR was positive, For example, he was watching a simple YouTube video for work and “everything was confusing me ... it rattled me, and I couldn’t understand it.” He described his COVID-19 mind as: “The words in my head would come out in a jumbled order, like the message from the words in my brain to my mouth would get crossed. I had trouble spelling and texting. Total cognitive breakdown. I couldn’t do simple mathematics.”
Despite his physical exhaustion, he endured a 3-day period of sleep deprivation. During this time, he recalled looking up at the roof and thinking, “I need to jump off the roof” or thinking, “I might want to throw myself under a bus.” He did not initially reveal his suicidal thoughts to his family medicine physician. After beginning COVID-19 treatment, the patient had two nights of sleep and felt notably improved, and his physical symptoms began to remit. However, the sleeplessness quickly returned “with a vengeance” along with “silly suicidal thoughts.” The thoughts took on a more obsessional quality. For example, he repeatedly thought of jumping out of his second-story bedroom to the living room below and was preoccupied by continually looking at people’s roofs and thinking about jumping. Those thoughts intensified and culminated in his “going missing,” leading his wife to call the police. It was discovered that he had driven to a local bridge and was contemplating jumping off.
After that “going missing” incident, the patient and his wife reached out to their family medicine physician. He reevaluated the patient and, given the new information about the psychiatric symptoms, strongly recommended stat crisis and psychiatric consultation. After discussing the case on the same day, both the family medicine physician and the psychiatrist recommended stat hospital emergency department (ED) assessment on Oct. 29. In the ED, a head CT without contrast at the recommendation of both psychiatrist and family physician, routine electrolytes, CBC with differential, and EKG all were within normal limits. The ED initially discharged him home after crisis evaluation, deciding he was not an imminent risk to himself or others.
The next day, the psychiatrist spoke on the phone with the patient, family medicine physician, and the patient’s wife to arrange an initial assessment. At that time, it remained unclear to all whether the obsessional thoughts had resolved to such a degree that the patient could resist acting upon them. Further, the patient’s sleep architecture had not returned to normal. All agreed another emergency ED assessment was indicated. Ultimately, after voluntary re-evaluation and a difficult hold in the crisis unit, the patient was admitted for psychiatric hospitalization on Oct. 29 and discharged on Nov. 4.
In the psychiatric hospital, venlafaxine XR was started and titrated to 75 mg. The patient was discovered to be hypertensive, and hydrochlorothiazide was started. The discharge diagnosis was major depressive disorder, single episode, severe, without psychotic features.
Posthospitalization course
He was seen for his initial psychiatric outpatient assessment postpsychiatric hospitalization on Nov. 9, as he had not yet been formally evaluated by the psychiatrist because of the emergency situation.
Gabapentin 300 mg by mouth at bedtime was started, and his sleep architecture was restored. The initial plan to titrate venlafaxine XR into dual selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor dose range was terminated, and his psychiatrist considered tapering and discontinuing the venlafaxine XR. A clinical examination, additional history, and collateral data no longer necessarily pointed to an active major depressive disorder or even unspecified depressive disorder, though to be sure, the patient was taking 75 mg of venlafaxine XR. While there were seasonal stressors, historically, nothing had risen to the level of MDD.
The obsessions driving his thoughts to jump off buildings and bridges had completely remitted. His cognitive ability returned to baseline with an ability to focus and perform the complicated tasks of his high-intensity work by the Dec. 8 psychiatric examination, where he was accompanied by his wife. He described feeling like, “I snapped back to like I was before this crazy stuff happened.” His mood was reported as, “Very good; like my old self” and this was confirmed by his wife. His affect was calmer and less tense. He was now using gabapentin sparingly for sleep. We continued to entertain discontinuing the venlafaxine XR, considering this recent severe episode likely driven by the COVID-19 virus. The decision was made to continue venlafaxine XR through the winter rather than discontinuing, remaining on the conservative side of treatment. The patient’s diagnosis was changed from “MDD, single episode,” to “mood disorder due to known physiologic condition (COVID-19) (F06.31) with depressive features; resolving.” At the patient’s follow-up examination on Jan. 5, 2022, he was continuing to do well, stating, “The whole series of crazy events happened to someone else.” The hydrochlorothiazide had been discontinued, and the patient’s blood pressure and pulse were normal at 119/81 and 69, respectively. He had made strategic changes at work to lessen stressors during the typically difficult months.
Discussion
Literature has discussed neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19.2 The cited example questions whether psychiatric symptoms are tied directly to the viral infection or to the “host’s immune response.” We believe our case represents a direct neurocognitive/neuropsychiatric insult due to the COVID-19 infection.
This case presents a 55-year-old male with no previous psychiatric or medical history with new onset significant and debilitating cognitive impairment and obsessive thoughts of throwing himself from his bedroom balcony ending up at a bridge struggling with an irrational thought of jumping; ultimately requiring psychiatric hospitalization for acute suicidal thoughts. The patient’s psychiatric symptoms arose prior to any and all medication treatment. The obsessive thoughts correlated both with the onset of SARS-CoV-2 infection and a period of sleep deprivation subsequent to the infection. A course of steroid treatment and taper were started after the onset of neurocognitive-psychiatric symptoms, though there is close timing. We submit that the patient experienced, as part of the initial neurocognitive psychiatric initiating cascade, a COVID-19–induced sleep deprivation that was not etiologic but part of the process; since, even when sleep returned to normal, it was still several weeks before full cognitive function returned to baseline.
An argument could be made for possible MDD or unspecified depressive disorder, as historically there had been work-related stressors for the patient at this time of year because of the chronological nature of his work; though previously nothing presented with obsessional suicidal thinking and nothing with any cognitive impairment – let alone to this incapacitating degree.
The patient describes his seasonal work much like an accountant’s work at the beginning of each year. In the patient’s case, the months of September and October are historically “nonstop, working days,” which then slow down in the winter months for a period of recuperation. In gathering his past history of symptoms, he denied neurovegetative symptoms to meet full diagnostic criteria for MDD or unspecified depressive disorder, absent this episode in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
We could also consider a contributory negative “organic push” by the viral load and prednisone helping to express an underlying unspecified depression or MDD, but for the profound and unusual presentation. There was little prodrome of depressive symptoms (again, he reported his “typical” extraordinary work burden for this time of year, which is common in his industry).
In this patient, the symptoms have remitted completely. However, the patient is currently taking venlafaxine XR 75 mg. We have considered tapering and discontinuing the venlafaxine – since it is not entirely clear that he needs to be on this medication – so this question remains an open one. We did decide, however, to continue the venlafaxine until after the winter months and to reassess at that time.
Conclusion
The patient presented with new onset psychological and psychiatric symptoms in addition to physiologic symptoms; the former symptoms were not revealed prior to initial family medicine evaluation. As the symptoms worsened, he and his wife sought additional consultation with family physician, psychiatrists, and ED. Steroid treatment may have played a part in exacerbation of symptoms, but the neuropsychiatric cognitive symptoms were present prior to initiation of all pharmacologic and medical treatment. The successful outcome of this case was based upon quick action and collaboration between the family medicine physician, the psychiatrist, and the ED physician. The value of communication, assessment, and action via phone call and text cannot be overstated. Future considerations include further large-scale evaluation of multifaceted early treatment of patients with COVID-19 within the first 72 hours of symptoms to prevent not only hospitalization, morbidity, and mortality, but newly recognized psychological and psychiatric syndromes.3,4
Lastly, fluvoxamine might have been a better choice for adjunctive early treatment of COVID-19.5 As a matter of distinction, if a lingering mood disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder remain a result of SARS-CoV-2 or if one were to start an antidepressant during the course of illness, it would be reasonable to consider fluvoxamine as a potential first-line agent.
Dr. Kohanski is a fellowship trained forensic psychiatrist and a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She maintains a private practice in Somerset, N.J., and is a frequent media commentator and medical podcaster. Dr. Kohanski has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Wax is a residency-trained osteopathic family medicine physician in independent private practice in Mullica Hill, N.J. He has authored multiple papers over 2 decades on topics such as SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 early treatment. He has been a speaker and media host over 2 decades and served on the National Physicians Council on Healthcare Policy’s congressional subcommittee. Dr. Wax has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Dec 30;21(4):517-30.
2. Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jul;87:34-9.
3. Trav Med Infect Dis. 2020 May-Jun 35;10738.
4. Kirsch S. “Early treatment for COVID is key to better outcomes.” Times of India. 2021 May 21.
5. Lancet. 2022 Jan 1;10(1):E42-E51.
An otherwise healthy 55-year-old male, with no previous psychiatric or medical history, sought care with a family medicine physician for the first time in decades.
Medical symptoms began Oct. 9, 2021, with “some leg weakness and mild sniffles.” Since he was going to be at a public event, he decided to take a PCR test for the SARS-CoV-2 virus on Oct. 13. The patient tested positive.
His symptoms continued to worsen, and he experienced severe body fatigue, sleep disturbance, and lethargy. “A few days after my positive test, the cognitive and physical symptoms dramatically ramped up,” the patient recalled.
Because of those worsening symptoms, on Oct. 20, the patient obtained a new patient appointment with a family medicine physician. After a telemedicine evaluation, the family medicine physician began a multifaceted early outpatient COVID-19 treatment protocol,1 as I (C.M.W.) and colleagues wrote about late last year. However, this treatment began late in the course because of the patient’s initial resistance to seek care.
This early outpatient treatment protocol for COVID-19 included vitamin D3 125 mcg (5,000 ICU), N-acetylcysteine (NAC) 600 mg every day x 30 days; acetylsalicylic acid 325 mg every day x 30 days; azithromycin 250 mg b.i.d. before every meal x 10 days; hydroxychloroquine sulfate 200 mg b.i.d. x 10 days; ivermectin 3 mg, 5 pills daily x 10 days; zinc sulfate 220 mg (50 mg elemental) every day x 30 days; and a prednisone taper (30 mg daily x 3 days, tapering down 5 mg every 3 days). Hydroxyzine 50 mg at bedtime as needed was added for sleep. The patient did not comment to the family physician on any of the psychological or psychiatric symptoms and responded appropriately to questions during the Oct. 20 initial evaluation.
However, he later described that around the time the PCR was positive, For example, he was watching a simple YouTube video for work and “everything was confusing me ... it rattled me, and I couldn’t understand it.” He described his COVID-19 mind as: “The words in my head would come out in a jumbled order, like the message from the words in my brain to my mouth would get crossed. I had trouble spelling and texting. Total cognitive breakdown. I couldn’t do simple mathematics.”
Despite his physical exhaustion, he endured a 3-day period of sleep deprivation. During this time, he recalled looking up at the roof and thinking, “I need to jump off the roof” or thinking, “I might want to throw myself under a bus.” He did not initially reveal his suicidal thoughts to his family medicine physician. After beginning COVID-19 treatment, the patient had two nights of sleep and felt notably improved, and his physical symptoms began to remit. However, the sleeplessness quickly returned “with a vengeance” along with “silly suicidal thoughts.” The thoughts took on a more obsessional quality. For example, he repeatedly thought of jumping out of his second-story bedroom to the living room below and was preoccupied by continually looking at people’s roofs and thinking about jumping. Those thoughts intensified and culminated in his “going missing,” leading his wife to call the police. It was discovered that he had driven to a local bridge and was contemplating jumping off.
After that “going missing” incident, the patient and his wife reached out to their family medicine physician. He reevaluated the patient and, given the new information about the psychiatric symptoms, strongly recommended stat crisis and psychiatric consultation. After discussing the case on the same day, both the family medicine physician and the psychiatrist recommended stat hospital emergency department (ED) assessment on Oct. 29. In the ED, a head CT without contrast at the recommendation of both psychiatrist and family physician, routine electrolytes, CBC with differential, and EKG all were within normal limits. The ED initially discharged him home after crisis evaluation, deciding he was not an imminent risk to himself or others.
The next day, the psychiatrist spoke on the phone with the patient, family medicine physician, and the patient’s wife to arrange an initial assessment. At that time, it remained unclear to all whether the obsessional thoughts had resolved to such a degree that the patient could resist acting upon them. Further, the patient’s sleep architecture had not returned to normal. All agreed another emergency ED assessment was indicated. Ultimately, after voluntary re-evaluation and a difficult hold in the crisis unit, the patient was admitted for psychiatric hospitalization on Oct. 29 and discharged on Nov. 4.
In the psychiatric hospital, venlafaxine XR was started and titrated to 75 mg. The patient was discovered to be hypertensive, and hydrochlorothiazide was started. The discharge diagnosis was major depressive disorder, single episode, severe, without psychotic features.
Posthospitalization course
He was seen for his initial psychiatric outpatient assessment postpsychiatric hospitalization on Nov. 9, as he had not yet been formally evaluated by the psychiatrist because of the emergency situation.
Gabapentin 300 mg by mouth at bedtime was started, and his sleep architecture was restored. The initial plan to titrate venlafaxine XR into dual selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor dose range was terminated, and his psychiatrist considered tapering and discontinuing the venlafaxine XR. A clinical examination, additional history, and collateral data no longer necessarily pointed to an active major depressive disorder or even unspecified depressive disorder, though to be sure, the patient was taking 75 mg of venlafaxine XR. While there were seasonal stressors, historically, nothing had risen to the level of MDD.
The obsessions driving his thoughts to jump off buildings and bridges had completely remitted. His cognitive ability returned to baseline with an ability to focus and perform the complicated tasks of his high-intensity work by the Dec. 8 psychiatric examination, where he was accompanied by his wife. He described feeling like, “I snapped back to like I was before this crazy stuff happened.” His mood was reported as, “Very good; like my old self” and this was confirmed by his wife. His affect was calmer and less tense. He was now using gabapentin sparingly for sleep. We continued to entertain discontinuing the venlafaxine XR, considering this recent severe episode likely driven by the COVID-19 virus. The decision was made to continue venlafaxine XR through the winter rather than discontinuing, remaining on the conservative side of treatment. The patient’s diagnosis was changed from “MDD, single episode,” to “mood disorder due to known physiologic condition (COVID-19) (F06.31) with depressive features; resolving.” At the patient’s follow-up examination on Jan. 5, 2022, he was continuing to do well, stating, “The whole series of crazy events happened to someone else.” The hydrochlorothiazide had been discontinued, and the patient’s blood pressure and pulse were normal at 119/81 and 69, respectively. He had made strategic changes at work to lessen stressors during the typically difficult months.
Discussion
Literature has discussed neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19.2 The cited example questions whether psychiatric symptoms are tied directly to the viral infection or to the “host’s immune response.” We believe our case represents a direct neurocognitive/neuropsychiatric insult due to the COVID-19 infection.
This case presents a 55-year-old male with no previous psychiatric or medical history with new onset significant and debilitating cognitive impairment and obsessive thoughts of throwing himself from his bedroom balcony ending up at a bridge struggling with an irrational thought of jumping; ultimately requiring psychiatric hospitalization for acute suicidal thoughts. The patient’s psychiatric symptoms arose prior to any and all medication treatment. The obsessive thoughts correlated both with the onset of SARS-CoV-2 infection and a period of sleep deprivation subsequent to the infection. A course of steroid treatment and taper were started after the onset of neurocognitive-psychiatric symptoms, though there is close timing. We submit that the patient experienced, as part of the initial neurocognitive psychiatric initiating cascade, a COVID-19–induced sleep deprivation that was not etiologic but part of the process; since, even when sleep returned to normal, it was still several weeks before full cognitive function returned to baseline.
An argument could be made for possible MDD or unspecified depressive disorder, as historically there had been work-related stressors for the patient at this time of year because of the chronological nature of his work; though previously nothing presented with obsessional suicidal thinking and nothing with any cognitive impairment – let alone to this incapacitating degree.
The patient describes his seasonal work much like an accountant’s work at the beginning of each year. In the patient’s case, the months of September and October are historically “nonstop, working days,” which then slow down in the winter months for a period of recuperation. In gathering his past history of symptoms, he denied neurovegetative symptoms to meet full diagnostic criteria for MDD or unspecified depressive disorder, absent this episode in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
We could also consider a contributory negative “organic push” by the viral load and prednisone helping to express an underlying unspecified depression or MDD, but for the profound and unusual presentation. There was little prodrome of depressive symptoms (again, he reported his “typical” extraordinary work burden for this time of year, which is common in his industry).
In this patient, the symptoms have remitted completely. However, the patient is currently taking venlafaxine XR 75 mg. We have considered tapering and discontinuing the venlafaxine – since it is not entirely clear that he needs to be on this medication – so this question remains an open one. We did decide, however, to continue the venlafaxine until after the winter months and to reassess at that time.
Conclusion
The patient presented with new onset psychological and psychiatric symptoms in addition to physiologic symptoms; the former symptoms were not revealed prior to initial family medicine evaluation. As the symptoms worsened, he and his wife sought additional consultation with family physician, psychiatrists, and ED. Steroid treatment may have played a part in exacerbation of symptoms, but the neuropsychiatric cognitive symptoms were present prior to initiation of all pharmacologic and medical treatment. The successful outcome of this case was based upon quick action and collaboration between the family medicine physician, the psychiatrist, and the ED physician. The value of communication, assessment, and action via phone call and text cannot be overstated. Future considerations include further large-scale evaluation of multifaceted early treatment of patients with COVID-19 within the first 72 hours of symptoms to prevent not only hospitalization, morbidity, and mortality, but newly recognized psychological and psychiatric syndromes.3,4
Lastly, fluvoxamine might have been a better choice for adjunctive early treatment of COVID-19.5 As a matter of distinction, if a lingering mood disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder remain a result of SARS-CoV-2 or if one were to start an antidepressant during the course of illness, it would be reasonable to consider fluvoxamine as a potential first-line agent.
Dr. Kohanski is a fellowship trained forensic psychiatrist and a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She maintains a private practice in Somerset, N.J., and is a frequent media commentator and medical podcaster. Dr. Kohanski has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Wax is a residency-trained osteopathic family medicine physician in independent private practice in Mullica Hill, N.J. He has authored multiple papers over 2 decades on topics such as SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 early treatment. He has been a speaker and media host over 2 decades and served on the National Physicians Council on Healthcare Policy’s congressional subcommittee. Dr. Wax has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Dec 30;21(4):517-30.
2. Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jul;87:34-9.
3. Trav Med Infect Dis. 2020 May-Jun 35;10738.
4. Kirsch S. “Early treatment for COVID is key to better outcomes.” Times of India. 2021 May 21.
5. Lancet. 2022 Jan 1;10(1):E42-E51.
An otherwise healthy 55-year-old male, with no previous psychiatric or medical history, sought care with a family medicine physician for the first time in decades.
Medical symptoms began Oct. 9, 2021, with “some leg weakness and mild sniffles.” Since he was going to be at a public event, he decided to take a PCR test for the SARS-CoV-2 virus on Oct. 13. The patient tested positive.
His symptoms continued to worsen, and he experienced severe body fatigue, sleep disturbance, and lethargy. “A few days after my positive test, the cognitive and physical symptoms dramatically ramped up,” the patient recalled.
Because of those worsening symptoms, on Oct. 20, the patient obtained a new patient appointment with a family medicine physician. After a telemedicine evaluation, the family medicine physician began a multifaceted early outpatient COVID-19 treatment protocol,1 as I (C.M.W.) and colleagues wrote about late last year. However, this treatment began late in the course because of the patient’s initial resistance to seek care.
This early outpatient treatment protocol for COVID-19 included vitamin D3 125 mcg (5,000 ICU), N-acetylcysteine (NAC) 600 mg every day x 30 days; acetylsalicylic acid 325 mg every day x 30 days; azithromycin 250 mg b.i.d. before every meal x 10 days; hydroxychloroquine sulfate 200 mg b.i.d. x 10 days; ivermectin 3 mg, 5 pills daily x 10 days; zinc sulfate 220 mg (50 mg elemental) every day x 30 days; and a prednisone taper (30 mg daily x 3 days, tapering down 5 mg every 3 days). Hydroxyzine 50 mg at bedtime as needed was added for sleep. The patient did not comment to the family physician on any of the psychological or psychiatric symptoms and responded appropriately to questions during the Oct. 20 initial evaluation.
However, he later described that around the time the PCR was positive, For example, he was watching a simple YouTube video for work and “everything was confusing me ... it rattled me, and I couldn’t understand it.” He described his COVID-19 mind as: “The words in my head would come out in a jumbled order, like the message from the words in my brain to my mouth would get crossed. I had trouble spelling and texting. Total cognitive breakdown. I couldn’t do simple mathematics.”
Despite his physical exhaustion, he endured a 3-day period of sleep deprivation. During this time, he recalled looking up at the roof and thinking, “I need to jump off the roof” or thinking, “I might want to throw myself under a bus.” He did not initially reveal his suicidal thoughts to his family medicine physician. After beginning COVID-19 treatment, the patient had two nights of sleep and felt notably improved, and his physical symptoms began to remit. However, the sleeplessness quickly returned “with a vengeance” along with “silly suicidal thoughts.” The thoughts took on a more obsessional quality. For example, he repeatedly thought of jumping out of his second-story bedroom to the living room below and was preoccupied by continually looking at people’s roofs and thinking about jumping. Those thoughts intensified and culminated in his “going missing,” leading his wife to call the police. It was discovered that he had driven to a local bridge and was contemplating jumping off.
After that “going missing” incident, the patient and his wife reached out to their family medicine physician. He reevaluated the patient and, given the new information about the psychiatric symptoms, strongly recommended stat crisis and psychiatric consultation. After discussing the case on the same day, both the family medicine physician and the psychiatrist recommended stat hospital emergency department (ED) assessment on Oct. 29. In the ED, a head CT without contrast at the recommendation of both psychiatrist and family physician, routine electrolytes, CBC with differential, and EKG all were within normal limits. The ED initially discharged him home after crisis evaluation, deciding he was not an imminent risk to himself or others.
The next day, the psychiatrist spoke on the phone with the patient, family medicine physician, and the patient’s wife to arrange an initial assessment. At that time, it remained unclear to all whether the obsessional thoughts had resolved to such a degree that the patient could resist acting upon them. Further, the patient’s sleep architecture had not returned to normal. All agreed another emergency ED assessment was indicated. Ultimately, after voluntary re-evaluation and a difficult hold in the crisis unit, the patient was admitted for psychiatric hospitalization on Oct. 29 and discharged on Nov. 4.
In the psychiatric hospital, venlafaxine XR was started and titrated to 75 mg. The patient was discovered to be hypertensive, and hydrochlorothiazide was started. The discharge diagnosis was major depressive disorder, single episode, severe, without psychotic features.
Posthospitalization course
He was seen for his initial psychiatric outpatient assessment postpsychiatric hospitalization on Nov. 9, as he had not yet been formally evaluated by the psychiatrist because of the emergency situation.
Gabapentin 300 mg by mouth at bedtime was started, and his sleep architecture was restored. The initial plan to titrate venlafaxine XR into dual selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor dose range was terminated, and his psychiatrist considered tapering and discontinuing the venlafaxine XR. A clinical examination, additional history, and collateral data no longer necessarily pointed to an active major depressive disorder or even unspecified depressive disorder, though to be sure, the patient was taking 75 mg of venlafaxine XR. While there were seasonal stressors, historically, nothing had risen to the level of MDD.
The obsessions driving his thoughts to jump off buildings and bridges had completely remitted. His cognitive ability returned to baseline with an ability to focus and perform the complicated tasks of his high-intensity work by the Dec. 8 psychiatric examination, where he was accompanied by his wife. He described feeling like, “I snapped back to like I was before this crazy stuff happened.” His mood was reported as, “Very good; like my old self” and this was confirmed by his wife. His affect was calmer and less tense. He was now using gabapentin sparingly for sleep. We continued to entertain discontinuing the venlafaxine XR, considering this recent severe episode likely driven by the COVID-19 virus. The decision was made to continue venlafaxine XR through the winter rather than discontinuing, remaining on the conservative side of treatment. The patient’s diagnosis was changed from “MDD, single episode,” to “mood disorder due to known physiologic condition (COVID-19) (F06.31) with depressive features; resolving.” At the patient’s follow-up examination on Jan. 5, 2022, he was continuing to do well, stating, “The whole series of crazy events happened to someone else.” The hydrochlorothiazide had been discontinued, and the patient’s blood pressure and pulse were normal at 119/81 and 69, respectively. He had made strategic changes at work to lessen stressors during the typically difficult months.
Discussion
Literature has discussed neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19.2 The cited example questions whether psychiatric symptoms are tied directly to the viral infection or to the “host’s immune response.” We believe our case represents a direct neurocognitive/neuropsychiatric insult due to the COVID-19 infection.
This case presents a 55-year-old male with no previous psychiatric or medical history with new onset significant and debilitating cognitive impairment and obsessive thoughts of throwing himself from his bedroom balcony ending up at a bridge struggling with an irrational thought of jumping; ultimately requiring psychiatric hospitalization for acute suicidal thoughts. The patient’s psychiatric symptoms arose prior to any and all medication treatment. The obsessive thoughts correlated both with the onset of SARS-CoV-2 infection and a period of sleep deprivation subsequent to the infection. A course of steroid treatment and taper were started after the onset of neurocognitive-psychiatric symptoms, though there is close timing. We submit that the patient experienced, as part of the initial neurocognitive psychiatric initiating cascade, a COVID-19–induced sleep deprivation that was not etiologic but part of the process; since, even when sleep returned to normal, it was still several weeks before full cognitive function returned to baseline.
An argument could be made for possible MDD or unspecified depressive disorder, as historically there had been work-related stressors for the patient at this time of year because of the chronological nature of his work; though previously nothing presented with obsessional suicidal thinking and nothing with any cognitive impairment – let alone to this incapacitating degree.
The patient describes his seasonal work much like an accountant’s work at the beginning of each year. In the patient’s case, the months of September and October are historically “nonstop, working days,” which then slow down in the winter months for a period of recuperation. In gathering his past history of symptoms, he denied neurovegetative symptoms to meet full diagnostic criteria for MDD or unspecified depressive disorder, absent this episode in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
We could also consider a contributory negative “organic push” by the viral load and prednisone helping to express an underlying unspecified depression or MDD, but for the profound and unusual presentation. There was little prodrome of depressive symptoms (again, he reported his “typical” extraordinary work burden for this time of year, which is common in his industry).
In this patient, the symptoms have remitted completely. However, the patient is currently taking venlafaxine XR 75 mg. We have considered tapering and discontinuing the venlafaxine – since it is not entirely clear that he needs to be on this medication – so this question remains an open one. We did decide, however, to continue the venlafaxine until after the winter months and to reassess at that time.
Conclusion
The patient presented with new onset psychological and psychiatric symptoms in addition to physiologic symptoms; the former symptoms were not revealed prior to initial family medicine evaluation. As the symptoms worsened, he and his wife sought additional consultation with family physician, psychiatrists, and ED. Steroid treatment may have played a part in exacerbation of symptoms, but the neuropsychiatric cognitive symptoms were present prior to initiation of all pharmacologic and medical treatment. The successful outcome of this case was based upon quick action and collaboration between the family medicine physician, the psychiatrist, and the ED physician. The value of communication, assessment, and action via phone call and text cannot be overstated. Future considerations include further large-scale evaluation of multifaceted early treatment of patients with COVID-19 within the first 72 hours of symptoms to prevent not only hospitalization, morbidity, and mortality, but newly recognized psychological and psychiatric syndromes.3,4
Lastly, fluvoxamine might have been a better choice for adjunctive early treatment of COVID-19.5 As a matter of distinction, if a lingering mood disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder remain a result of SARS-CoV-2 or if one were to start an antidepressant during the course of illness, it would be reasonable to consider fluvoxamine as a potential first-line agent.
Dr. Kohanski is a fellowship trained forensic psychiatrist and a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She maintains a private practice in Somerset, N.J., and is a frequent media commentator and medical podcaster. Dr. Kohanski has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Wax is a residency-trained osteopathic family medicine physician in independent private practice in Mullica Hill, N.J. He has authored multiple papers over 2 decades on topics such as SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 early treatment. He has been a speaker and media host over 2 decades and served on the National Physicians Council on Healthcare Policy’s congressional subcommittee. Dr. Wax has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Dec 30;21(4):517-30.
2. Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jul;87:34-9.
3. Trav Med Infect Dis. 2020 May-Jun 35;10738.
4. Kirsch S. “Early treatment for COVID is key to better outcomes.” Times of India. 2021 May 21.
5. Lancet. 2022 Jan 1;10(1):E42-E51.