User login
Diffuse Urticarial Rash in a Pregnant Patient
The Diagnosis: Pemphigoid Gestationis
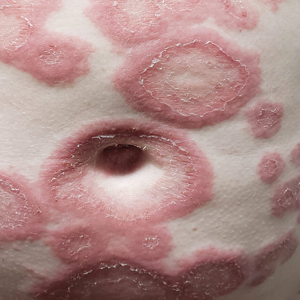
A lesional biopsy showed a subepidermal split with eosinophils and neutrophils. Perilesional biopsy for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) showed linear deposition of 3+ C3 along the basement membrane zone. The clinical, histopathologic, and immunofluorescent findings were consistent with pemphigoid gestationis (PG). Prednisone 1 mg/kg daily was initiated. Her condition continued to worsen, and cyclosporine 250 mg daily was added while prednisone was tapered, with remission of disease.
Pemphigoid gestationis is an autoimmune bullous dermatosis that occurs in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, with an incidence of 1 in 50,000 to 60,000 pregnancies.1 In terms of pathogenesis, aberrant expression of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on placental tissues causes the loss of immune tolerance of the placenta, which leads to the production of antibodies against the placental protein bullous pemphigoid 180.2 Bullous pemphigoid 180 also is a hemidesmosomal protein found in the skin of the mother; therefore, the presence of the circulating antibodies leads to separation at the dermoepidermal junction and vesiculation.
Pemphigoid gestationis is characterized by the sudden eruption of intensely pruritic urticarial papules and plaques, classically with periumbilical involvement. Tense vesicles and bullae can develop. Women with PG have an increased risk for development of Graves disease. Histopathology shows subepidermal vesiculation with a predominance of eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence classically shows linear deposition of C3 along the basement membrane zone. Fetal complications include prematurity and small size for gestational age. Additionally, blisters can be seen in 5% to 10% of neonates due to placental transmission of autoantibodies.3
Frequently PG flares shortly postpartum. Pemphigoid gestationis resolves within 6 months postdelivery but frequently reoccurs in subsequent pregnancies. Mild disease can be treated with mid- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. Severe disease is managed with oral corticosteroids, most commonly prednisone. Refractory disease is managed with azathioprine, cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin, or plasmapheresis.
The differential diagnosis of PG includes other pregnancy-associated dermatoses such as atopic eruption of pregnancy, impetigo herpetiformis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and polymorphous eruption of pregnancy. Atopic eruption of pregnancy is the most common dermatosis of pregnancy and is characterized by an eczematous eruption in patients with an atopic history, typically in the first trimester. Blisters are not seen, and DIF is negative. Impetigo herpetiformis, or pustular psoriasis of pregnancy, is a variant of generalized pustular psoriasis that occurs during pregnancy. Diffuse erythematous patches studded with pustules, rather than vesicles, are seen; DIF is negative. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy presents without primary skin findings and severe pruritus predominantly on the palms and soles, often with secondary excoriations. Polymorphous eruption of pregnancy presents as a polymorphous eruption of urticarial to erythematous papules and plaques commonly originating in striae. In contrast to PG, there is periumbilical sparing, vesiculation is rare, and DIF is negative.
- Shornick JK, Bangert JL, Freeman RG, et al. Herpes gestationis: clinical and histologic features of twenty-eight cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:214-224.
- Sadik CD, Lima AL, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid gestationis: toward a better understanding of the etiopathogenesis. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:378-382.
- Shornick JK, Black MM. Fetal risks in herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:63-68.
The Diagnosis: Pemphigoid Gestationis
A lesional biopsy showed a subepidermal split with eosinophils and neutrophils. Perilesional biopsy for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) showed linear deposition of 3+ C3 along the basement membrane zone. The clinical, histopathologic, and immunofluorescent findings were consistent with pemphigoid gestationis (PG). Prednisone 1 mg/kg daily was initiated. Her condition continued to worsen, and cyclosporine 250 mg daily was added while prednisone was tapered, with remission of disease.
Pemphigoid gestationis is an autoimmune bullous dermatosis that occurs in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, with an incidence of 1 in 50,000 to 60,000 pregnancies.1 In terms of pathogenesis, aberrant expression of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on placental tissues causes the loss of immune tolerance of the placenta, which leads to the production of antibodies against the placental protein bullous pemphigoid 180.2 Bullous pemphigoid 180 also is a hemidesmosomal protein found in the skin of the mother; therefore, the presence of the circulating antibodies leads to separation at the dermoepidermal junction and vesiculation.
Pemphigoid gestationis is characterized by the sudden eruption of intensely pruritic urticarial papules and plaques, classically with periumbilical involvement. Tense vesicles and bullae can develop. Women with PG have an increased risk for development of Graves disease. Histopathology shows subepidermal vesiculation with a predominance of eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence classically shows linear deposition of C3 along the basement membrane zone. Fetal complications include prematurity and small size for gestational age. Additionally, blisters can be seen in 5% to 10% of neonates due to placental transmission of autoantibodies.3
Frequently PG flares shortly postpartum. Pemphigoid gestationis resolves within 6 months postdelivery but frequently reoccurs in subsequent pregnancies. Mild disease can be treated with mid- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. Severe disease is managed with oral corticosteroids, most commonly prednisone. Refractory disease is managed with azathioprine, cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin, or plasmapheresis.
The differential diagnosis of PG includes other pregnancy-associated dermatoses such as atopic eruption of pregnancy, impetigo herpetiformis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and polymorphous eruption of pregnancy. Atopic eruption of pregnancy is the most common dermatosis of pregnancy and is characterized by an eczematous eruption in patients with an atopic history, typically in the first trimester. Blisters are not seen, and DIF is negative. Impetigo herpetiformis, or pustular psoriasis of pregnancy, is a variant of generalized pustular psoriasis that occurs during pregnancy. Diffuse erythematous patches studded with pustules, rather than vesicles, are seen; DIF is negative. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy presents without primary skin findings and severe pruritus predominantly on the palms and soles, often with secondary excoriations. Polymorphous eruption of pregnancy presents as a polymorphous eruption of urticarial to erythematous papules and plaques commonly originating in striae. In contrast to PG, there is periumbilical sparing, vesiculation is rare, and DIF is negative.
The Diagnosis: Pemphigoid Gestationis
A lesional biopsy showed a subepidermal split with eosinophils and neutrophils. Perilesional biopsy for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) showed linear deposition of 3+ C3 along the basement membrane zone. The clinical, histopathologic, and immunofluorescent findings were consistent with pemphigoid gestationis (PG). Prednisone 1 mg/kg daily was initiated. Her condition continued to worsen, and cyclosporine 250 mg daily was added while prednisone was tapered, with remission of disease.
Pemphigoid gestationis is an autoimmune bullous dermatosis that occurs in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, with an incidence of 1 in 50,000 to 60,000 pregnancies.1 In terms of pathogenesis, aberrant expression of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on placental tissues causes the loss of immune tolerance of the placenta, which leads to the production of antibodies against the placental protein bullous pemphigoid 180.2 Bullous pemphigoid 180 also is a hemidesmosomal protein found in the skin of the mother; therefore, the presence of the circulating antibodies leads to separation at the dermoepidermal junction and vesiculation.
Pemphigoid gestationis is characterized by the sudden eruption of intensely pruritic urticarial papules and plaques, classically with periumbilical involvement. Tense vesicles and bullae can develop. Women with PG have an increased risk for development of Graves disease. Histopathology shows subepidermal vesiculation with a predominance of eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence classically shows linear deposition of C3 along the basement membrane zone. Fetal complications include prematurity and small size for gestational age. Additionally, blisters can be seen in 5% to 10% of neonates due to placental transmission of autoantibodies.3
Frequently PG flares shortly postpartum. Pemphigoid gestationis resolves within 6 months postdelivery but frequently reoccurs in subsequent pregnancies. Mild disease can be treated with mid- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. Severe disease is managed with oral corticosteroids, most commonly prednisone. Refractory disease is managed with azathioprine, cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin, or plasmapheresis.
The differential diagnosis of PG includes other pregnancy-associated dermatoses such as atopic eruption of pregnancy, impetigo herpetiformis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and polymorphous eruption of pregnancy. Atopic eruption of pregnancy is the most common dermatosis of pregnancy and is characterized by an eczematous eruption in patients with an atopic history, typically in the first trimester. Blisters are not seen, and DIF is negative. Impetigo herpetiformis, or pustular psoriasis of pregnancy, is a variant of generalized pustular psoriasis that occurs during pregnancy. Diffuse erythematous patches studded with pustules, rather than vesicles, are seen; DIF is negative. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy presents without primary skin findings and severe pruritus predominantly on the palms and soles, often with secondary excoriations. Polymorphous eruption of pregnancy presents as a polymorphous eruption of urticarial to erythematous papules and plaques commonly originating in striae. In contrast to PG, there is periumbilical sparing, vesiculation is rare, and DIF is negative.
- Shornick JK, Bangert JL, Freeman RG, et al. Herpes gestationis: clinical and histologic features of twenty-eight cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:214-224.
- Sadik CD, Lima AL, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid gestationis: toward a better understanding of the etiopathogenesis. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:378-382.
- Shornick JK, Black MM. Fetal risks in herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:63-68.
- Shornick JK, Bangert JL, Freeman RG, et al. Herpes gestationis: clinical and histologic features of twenty-eight cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:214-224.
- Sadik CD, Lima AL, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid gestationis: toward a better understanding of the etiopathogenesis. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:378-382.
- Shornick JK, Black MM. Fetal risks in herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:63-68.
A 29-year-old pregnant woman at 18 weeks and 5 days of gestation presented with a diffuse, pruritic, blistering rash of 5 weeks’ duration that started on the forearms and generalized to affect the trunk, legs, palms, and soles. Physical examination showed diffuse urticarial papules and plaques with small tense vesicles with an annular configuration on the abdomen and marked periumbilical involvement.
Analysis: Surgery may not be better than casting for some wrist fractures
There are around 100,000 adult distal radius fractures in the United Kingdom each year. Current National Health Service guidelines in the United Kingdom recommend using K-wires to stabilize wrist fractures when closed reduction is possible or there is no involvement of the articular surface. This is in contrast to fractures that require open reduction and internal fixation with a plate and screws to align the joint articular surface.
As a result, the use of K-wires for surgical fixation has been increasing since 2010 with a comparable decrease of the use of plates and screws.
Even though fixation with wires can provide reliable functional outcomes for patients after reduction of a displaced wrist fracture, surgery still carries risks for the patient and adds an additional expense. A well-molded plaster cast is a safer and cheaper intervention, but it is unclear if it could provide the same functional outcome as pinning.
Therefore, researchers in the United Kingdom conducted a multicenter, randomized trial among 36 hospitals within the NHS as part of the Distal Radius Acute Fracture Fixation Trial 2 (DRAFFT2). Investigators randomly assigned 500 patients aged 16 years and older with dorsally displaced distal radius fractures to manipulation followed by a molded cast or manipulation followed by surgical fixation with K-wires plus a cast.
The study was published online in BMJ.
At 1 year, there were no significant differences between the groups in Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation (PRWE) scores centered on pain and function.
In an interview, Matthew Costa, PhD, professor of orthopaedic trauma at the University of Oxford (England) and the study’s lead author, said, “If a closed reduction of the fracture can be achieved, clinicians may consider the application of a molded plaster cast as a safe and cost-effective alternative to surgical fixation.”
However, in referencing the data his group published, he did find one thing surprising: “One in eight patients treated with a molded cast required later surgery for loss of fracture position in the first 6 weeks after their injury.”
Dr. Costa added, “This was indeed the key bit of information that patients need when making their decision about surgery. Initial feedback from our patient and public involvement group is that they would be happy to take this chance given that seven out of eight patients didn’t need any form of surgical fixation.”
Philip Blazar, MD, chief of the hand and upper extremity service, Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital in Boston, commended the U.K. authors on completing a challenging randomized controlled trial.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Blazer observed a critical difference between U.K. and U.S. guidelines. “It is important to remember that a sizable number of these patients had surgery,” said Dr. Blazar, who was not involved with the study. “They had pins inserted under an anesthetic, and would not have [had] surgery compared to current practice as recommended by many authorities, including the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeon’s Clinical Practice Guidelines on Distal Radius Fractures.”
Like Dr. Costa, Dr. Blazar expressed concerns about the secondary surgeries in the study group: “27% of patients had a second surgery: 13% in the first 6 weeks after manipulation for loss of reduction, and the remaining 14% had carpal tunnel releases, tendon transfers, tenolysis, and/or capsulectomy for limited range of motion.”
In addition, Dr. Blazar is worried that, although recovery is generally considered to be only 12 months for these type of injuries – the duration of follow-up time in the DRAFFT2 study – “the probable outcome is that in the second 12 months after the injury, there will continue to be more of these types of surgeries.”
Dr. Costa agreed that close follow-up is warranted, “It does suggest that patients treated in a molded cast do need to be followed up carefully to spot those that do need later surgery.”
Still, for Dr. Blazar, the largest takeaway of the study is that, “At 12 months, disability scores between these two groups are not different, but the group treated nonsurgically had 10 times the number of secondary surgeries (27% vs. 2%-3%).”
Moving forward, Dr. Blazar would like to see more specific indications for who would benefit from pinning. He told this news organization, “The greatest limitation is that this study provides no information on which patients with distal radius fractures where reduction is indicated would benefit from surgery. Looking at the details of this study, all patients with displaced fractures from age 16 to the elderly were treated as one indication. My impression is that most surgeons operate on patients taking into account radiographic and patient factors such as age, hand dominance, occupation, overall medical health, and activity level.”
The DRAFFT2 study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme and was supported by NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Blazar and Dr. Costa have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There are around 100,000 adult distal radius fractures in the United Kingdom each year. Current National Health Service guidelines in the United Kingdom recommend using K-wires to stabilize wrist fractures when closed reduction is possible or there is no involvement of the articular surface. This is in contrast to fractures that require open reduction and internal fixation with a plate and screws to align the joint articular surface.
As a result, the use of K-wires for surgical fixation has been increasing since 2010 with a comparable decrease of the use of plates and screws.
Even though fixation with wires can provide reliable functional outcomes for patients after reduction of a displaced wrist fracture, surgery still carries risks for the patient and adds an additional expense. A well-molded plaster cast is a safer and cheaper intervention, but it is unclear if it could provide the same functional outcome as pinning.
Therefore, researchers in the United Kingdom conducted a multicenter, randomized trial among 36 hospitals within the NHS as part of the Distal Radius Acute Fracture Fixation Trial 2 (DRAFFT2). Investigators randomly assigned 500 patients aged 16 years and older with dorsally displaced distal radius fractures to manipulation followed by a molded cast or manipulation followed by surgical fixation with K-wires plus a cast.
The study was published online in BMJ.
At 1 year, there were no significant differences between the groups in Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation (PRWE) scores centered on pain and function.
In an interview, Matthew Costa, PhD, professor of orthopaedic trauma at the University of Oxford (England) and the study’s lead author, said, “If a closed reduction of the fracture can be achieved, clinicians may consider the application of a molded plaster cast as a safe and cost-effective alternative to surgical fixation.”
However, in referencing the data his group published, he did find one thing surprising: “One in eight patients treated with a molded cast required later surgery for loss of fracture position in the first 6 weeks after their injury.”
Dr. Costa added, “This was indeed the key bit of information that patients need when making their decision about surgery. Initial feedback from our patient and public involvement group is that they would be happy to take this chance given that seven out of eight patients didn’t need any form of surgical fixation.”
Philip Blazar, MD, chief of the hand and upper extremity service, Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital in Boston, commended the U.K. authors on completing a challenging randomized controlled trial.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Blazer observed a critical difference between U.K. and U.S. guidelines. “It is important to remember that a sizable number of these patients had surgery,” said Dr. Blazar, who was not involved with the study. “They had pins inserted under an anesthetic, and would not have [had] surgery compared to current practice as recommended by many authorities, including the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeon’s Clinical Practice Guidelines on Distal Radius Fractures.”
Like Dr. Costa, Dr. Blazar expressed concerns about the secondary surgeries in the study group: “27% of patients had a second surgery: 13% in the first 6 weeks after manipulation for loss of reduction, and the remaining 14% had carpal tunnel releases, tendon transfers, tenolysis, and/or capsulectomy for limited range of motion.”
In addition, Dr. Blazar is worried that, although recovery is generally considered to be only 12 months for these type of injuries – the duration of follow-up time in the DRAFFT2 study – “the probable outcome is that in the second 12 months after the injury, there will continue to be more of these types of surgeries.”
Dr. Costa agreed that close follow-up is warranted, “It does suggest that patients treated in a molded cast do need to be followed up carefully to spot those that do need later surgery.”
Still, for Dr. Blazar, the largest takeaway of the study is that, “At 12 months, disability scores between these two groups are not different, but the group treated nonsurgically had 10 times the number of secondary surgeries (27% vs. 2%-3%).”
Moving forward, Dr. Blazar would like to see more specific indications for who would benefit from pinning. He told this news organization, “The greatest limitation is that this study provides no information on which patients with distal radius fractures where reduction is indicated would benefit from surgery. Looking at the details of this study, all patients with displaced fractures from age 16 to the elderly were treated as one indication. My impression is that most surgeons operate on patients taking into account radiographic and patient factors such as age, hand dominance, occupation, overall medical health, and activity level.”
The DRAFFT2 study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme and was supported by NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Blazar and Dr. Costa have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There are around 100,000 adult distal radius fractures in the United Kingdom each year. Current National Health Service guidelines in the United Kingdom recommend using K-wires to stabilize wrist fractures when closed reduction is possible or there is no involvement of the articular surface. This is in contrast to fractures that require open reduction and internal fixation with a plate and screws to align the joint articular surface.
As a result, the use of K-wires for surgical fixation has been increasing since 2010 with a comparable decrease of the use of plates and screws.
Even though fixation with wires can provide reliable functional outcomes for patients after reduction of a displaced wrist fracture, surgery still carries risks for the patient and adds an additional expense. A well-molded plaster cast is a safer and cheaper intervention, but it is unclear if it could provide the same functional outcome as pinning.
Therefore, researchers in the United Kingdom conducted a multicenter, randomized trial among 36 hospitals within the NHS as part of the Distal Radius Acute Fracture Fixation Trial 2 (DRAFFT2). Investigators randomly assigned 500 patients aged 16 years and older with dorsally displaced distal radius fractures to manipulation followed by a molded cast or manipulation followed by surgical fixation with K-wires plus a cast.
The study was published online in BMJ.
At 1 year, there were no significant differences between the groups in Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation (PRWE) scores centered on pain and function.
In an interview, Matthew Costa, PhD, professor of orthopaedic trauma at the University of Oxford (England) and the study’s lead author, said, “If a closed reduction of the fracture can be achieved, clinicians may consider the application of a molded plaster cast as a safe and cost-effective alternative to surgical fixation.”
However, in referencing the data his group published, he did find one thing surprising: “One in eight patients treated with a molded cast required later surgery for loss of fracture position in the first 6 weeks after their injury.”
Dr. Costa added, “This was indeed the key bit of information that patients need when making their decision about surgery. Initial feedback from our patient and public involvement group is that they would be happy to take this chance given that seven out of eight patients didn’t need any form of surgical fixation.”
Philip Blazar, MD, chief of the hand and upper extremity service, Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital in Boston, commended the U.K. authors on completing a challenging randomized controlled trial.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Blazer observed a critical difference between U.K. and U.S. guidelines. “It is important to remember that a sizable number of these patients had surgery,” said Dr. Blazar, who was not involved with the study. “They had pins inserted under an anesthetic, and would not have [had] surgery compared to current practice as recommended by many authorities, including the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeon’s Clinical Practice Guidelines on Distal Radius Fractures.”
Like Dr. Costa, Dr. Blazar expressed concerns about the secondary surgeries in the study group: “27% of patients had a second surgery: 13% in the first 6 weeks after manipulation for loss of reduction, and the remaining 14% had carpal tunnel releases, tendon transfers, tenolysis, and/or capsulectomy for limited range of motion.”
In addition, Dr. Blazar is worried that, although recovery is generally considered to be only 12 months for these type of injuries – the duration of follow-up time in the DRAFFT2 study – “the probable outcome is that in the second 12 months after the injury, there will continue to be more of these types of surgeries.”
Dr. Costa agreed that close follow-up is warranted, “It does suggest that patients treated in a molded cast do need to be followed up carefully to spot those that do need later surgery.”
Still, for Dr. Blazar, the largest takeaway of the study is that, “At 12 months, disability scores between these two groups are not different, but the group treated nonsurgically had 10 times the number of secondary surgeries (27% vs. 2%-3%).”
Moving forward, Dr. Blazar would like to see more specific indications for who would benefit from pinning. He told this news organization, “The greatest limitation is that this study provides no information on which patients with distal radius fractures where reduction is indicated would benefit from surgery. Looking at the details of this study, all patients with displaced fractures from age 16 to the elderly were treated as one indication. My impression is that most surgeons operate on patients taking into account radiographic and patient factors such as age, hand dominance, occupation, overall medical health, and activity level.”
The DRAFFT2 study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme and was supported by NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Blazar and Dr. Costa have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMJ
The cell that might trigger Alzheimer’s disease
It all started with genetic data. A gene here, a gene there. Eventually the story became clearer: If scientists are to one day find a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, they should look to the immune system.
Over the past couple decades, researchers have identified numerous genes involved in various immune system functions that may also contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. Some of the prime suspects are genes that control microglia, now the focus of intense research in developing new Alzheimer’s drugs.
Microglia are amoeba-like cells that scour the brain for injuries and invaders. They help clear dead or impaired brain cells and literally gobble up invading microbes. Without them, we’d be in trouble.
In a normal brain, a protein called beta-amyloid is cleared away through our lymphatic system by microglia as molecular junk. But sometimes it builds up. Certain gene mutations are one culprit in this toxic accumulation. Traumatic brain injury is another, and, perhaps, impaired microglial function.
One thing everyone agrees on is that in people with Alzheimer’s disease, too much amyloid accumulates between their brain cells and in the vessels that supply the brain with blood. Once amyloid begins to clog networks of neurons, it triggers the accumulation of another protein, called tau, inside of these brain cells. The presence of tau sends microglia and other immune mechanisms into overdrive, resulting in the inflammatory immune response that many experts believe ultimately saps brain vitality in Alzheimer’s disease.
The gene scene
To date, nearly a dozen genes involved in immune and microglial function have been tied to Alzheimer’s disease. The first was CD33, identified in 2008.
“When we got the results, I literally ran to my colleague’s office next door and said, you gotta see this!” said Harvard neuroscientist Rudolph Tanzi. Dr. Tanzi, who goes by Rudy, led the CD33 research. The discovery was quickly named a top medical breakthrough of 2008 by Time magazine.
“We were laughing because what they didn’t know is we had no idea what this gene did,” he joked. But over time, research by Dr. Tanzi and his group revealed that CD33 is a kind of microglial on-off switch, activating the cells as part of an inflammatory pathway.
“We kind of got it all going when it came to the genetics,” he said.
Microglia normally recognize molecular patterns associated with microbes and cellular damage as unwanted. This is how they know to take action – to devour unfamiliar pathogens and dead tissue. Dr. Tanzi believes microglia sense any sign of brain damage as an infection, which causes them to become hyperactive.
Much of our modern human immune system, he explained, evolved many hundreds of thousands of years ago. Our lifespans at the time were far shorter than they are today, and the majority of people didn’t live long enough to develop dementia or the withered brain cells that come with it. So our immune system, he said, assumes any faulty brain tissue is due to a microbe, not dementia. Microglia react aggressively, clearing the area to prevent the spread of infection.
“They say, ‘We better wipe out this part of the brain that’s infected, even if it’s not.’ They don’t know,” quipped Dr. Tanzi. “That’s what causes neuroinflammation. And CD33 turns this response on. The microglia become killers, not just janitors.”
A brake on overactive microglia
If CD33 is the yin, a gene called TREM2 is the yang. Discovered a few years after CD33, TREM2 reins in microglial activation, returning them to their role as cellular housekeepers.
Neurologist David Holtzman, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who studies TREM2, agrees that wherever you find amyloid, tau, or dead brain cells, there are microglia raring to go and ready to scavenge.
“I think at first a lot of people thought these cells were reacting to Alzheimer’s pathology, and not necessarily a cause of the disease,” he said.
It was the discovery of TREM2 on the heels of CD33 that really shifted the thinking, in part because it produces a protein that in the brain is only found in microglia. “Many of us [in the field] immediately said, ‘Look, there’s now a risk factor that is only expressed in microglia. It must be that innate immune cells are important in some way in the pathogenesis of the disease,’ “ he added.
Dr. Holtzman sees microglial activation in impending dementia as a double-edged sword. In the beginning, microglia clear unwanted amyloid to maintain brain health. But once accumulated amyloid and tau have done enough damage, the neuroinflammation that comes with microglial activation does more harm than good. Neurons die en masse and dementia sets in.
But not all researchers are convinced.
Serge Revist, PhD, is a professor in the department of molecular medicine at the Laval University Medical School in Quebec. Based on his lab’s research, he believes that while impaired immune activity is involved in Alzheimer’s disease, it is not the root cause. “I don’t think it is the immune cells that do the damage, I still think it is the beta-amyloid itself,” he said, “In my lab, in mouse studies, we’ve never found that immune cells were directly responsible for killing neurons.”
He does believe that in some patients with Alzheimer’s disease, microglia may not be able to handle the excess amyloid that accumulates in the disease and that developing treatments that improve the ability of microglia and the immune system to clear the protein could be effective.
Microglial medicines
The biological cascade leading to Alzheimer’s disease is a tangled one. Gene variants influencing the accumulation and clearance of amyloid are likely a major contributor. But immune activity caused by early life infection might also be involved, at least in some cases. This infectious theory of Alzheimer’s disease was first proposed by Dr. Tanzi’s now-deceased colleague Robert Moir, PhD. Dr. Tanzi’s group even has evidence that amyloid itself is antimicrobial and evolved to protect us from pathogens, only to become a problem when overactive and aggregated.
And the same goes for microglia, cells whose over-ambition might cause much of the brain degeneration seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
In theory, if a treatment could decrease CD33 activity or increase that of TREM2, doctors might one day may be able to slow or even stop the progression of dementia. Instead of going after amyloid itself – the mechanism behind so many failed investigational Alzheimer’s drugs – a therapy that quells the immune response to amyloid might be the answer in treating dementia.
“There are a number of scientists and companies trying to figure out how to influence genes like TREM2 and CD33 and to both decrease amyloid and act on the downstream consequences of the protein,” said Dr. Holtzman. “All of this is to say that somewhere in the biology that causes Alzheimer’s disease, the immune system is involved.”
It seems that in many cases, the most common form of a dementia might be due to a well-intentioned immune cell going rogue. “I think you’d hear this from basically any researcher worth their salt,” said Dr. Tanzi. “I feel strongly that without microglial activation, you will not get Alzheimer’s disease.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It all started with genetic data. A gene here, a gene there. Eventually the story became clearer: If scientists are to one day find a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, they should look to the immune system.
Over the past couple decades, researchers have identified numerous genes involved in various immune system functions that may also contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. Some of the prime suspects are genes that control microglia, now the focus of intense research in developing new Alzheimer’s drugs.
Microglia are amoeba-like cells that scour the brain for injuries and invaders. They help clear dead or impaired brain cells and literally gobble up invading microbes. Without them, we’d be in trouble.
In a normal brain, a protein called beta-amyloid is cleared away through our lymphatic system by microglia as molecular junk. But sometimes it builds up. Certain gene mutations are one culprit in this toxic accumulation. Traumatic brain injury is another, and, perhaps, impaired microglial function.
One thing everyone agrees on is that in people with Alzheimer’s disease, too much amyloid accumulates between their brain cells and in the vessels that supply the brain with blood. Once amyloid begins to clog networks of neurons, it triggers the accumulation of another protein, called tau, inside of these brain cells. The presence of tau sends microglia and other immune mechanisms into overdrive, resulting in the inflammatory immune response that many experts believe ultimately saps brain vitality in Alzheimer’s disease.
The gene scene
To date, nearly a dozen genes involved in immune and microglial function have been tied to Alzheimer’s disease. The first was CD33, identified in 2008.
“When we got the results, I literally ran to my colleague’s office next door and said, you gotta see this!” said Harvard neuroscientist Rudolph Tanzi. Dr. Tanzi, who goes by Rudy, led the CD33 research. The discovery was quickly named a top medical breakthrough of 2008 by Time magazine.
“We were laughing because what they didn’t know is we had no idea what this gene did,” he joked. But over time, research by Dr. Tanzi and his group revealed that CD33 is a kind of microglial on-off switch, activating the cells as part of an inflammatory pathway.
“We kind of got it all going when it came to the genetics,” he said.
Microglia normally recognize molecular patterns associated with microbes and cellular damage as unwanted. This is how they know to take action – to devour unfamiliar pathogens and dead tissue. Dr. Tanzi believes microglia sense any sign of brain damage as an infection, which causes them to become hyperactive.
Much of our modern human immune system, he explained, evolved many hundreds of thousands of years ago. Our lifespans at the time were far shorter than they are today, and the majority of people didn’t live long enough to develop dementia or the withered brain cells that come with it. So our immune system, he said, assumes any faulty brain tissue is due to a microbe, not dementia. Microglia react aggressively, clearing the area to prevent the spread of infection.
“They say, ‘We better wipe out this part of the brain that’s infected, even if it’s not.’ They don’t know,” quipped Dr. Tanzi. “That’s what causes neuroinflammation. And CD33 turns this response on. The microglia become killers, not just janitors.”
A brake on overactive microglia
If CD33 is the yin, a gene called TREM2 is the yang. Discovered a few years after CD33, TREM2 reins in microglial activation, returning them to their role as cellular housekeepers.
Neurologist David Holtzman, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who studies TREM2, agrees that wherever you find amyloid, tau, or dead brain cells, there are microglia raring to go and ready to scavenge.
“I think at first a lot of people thought these cells were reacting to Alzheimer’s pathology, and not necessarily a cause of the disease,” he said.
It was the discovery of TREM2 on the heels of CD33 that really shifted the thinking, in part because it produces a protein that in the brain is only found in microglia. “Many of us [in the field] immediately said, ‘Look, there’s now a risk factor that is only expressed in microglia. It must be that innate immune cells are important in some way in the pathogenesis of the disease,’ “ he added.
Dr. Holtzman sees microglial activation in impending dementia as a double-edged sword. In the beginning, microglia clear unwanted amyloid to maintain brain health. But once accumulated amyloid and tau have done enough damage, the neuroinflammation that comes with microglial activation does more harm than good. Neurons die en masse and dementia sets in.
But not all researchers are convinced.
Serge Revist, PhD, is a professor in the department of molecular medicine at the Laval University Medical School in Quebec. Based on his lab’s research, he believes that while impaired immune activity is involved in Alzheimer’s disease, it is not the root cause. “I don’t think it is the immune cells that do the damage, I still think it is the beta-amyloid itself,” he said, “In my lab, in mouse studies, we’ve never found that immune cells were directly responsible for killing neurons.”
He does believe that in some patients with Alzheimer’s disease, microglia may not be able to handle the excess amyloid that accumulates in the disease and that developing treatments that improve the ability of microglia and the immune system to clear the protein could be effective.
Microglial medicines
The biological cascade leading to Alzheimer’s disease is a tangled one. Gene variants influencing the accumulation and clearance of amyloid are likely a major contributor. But immune activity caused by early life infection might also be involved, at least in some cases. This infectious theory of Alzheimer’s disease was first proposed by Dr. Tanzi’s now-deceased colleague Robert Moir, PhD. Dr. Tanzi’s group even has evidence that amyloid itself is antimicrobial and evolved to protect us from pathogens, only to become a problem when overactive and aggregated.
And the same goes for microglia, cells whose over-ambition might cause much of the brain degeneration seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
In theory, if a treatment could decrease CD33 activity or increase that of TREM2, doctors might one day may be able to slow or even stop the progression of dementia. Instead of going after amyloid itself – the mechanism behind so many failed investigational Alzheimer’s drugs – a therapy that quells the immune response to amyloid might be the answer in treating dementia.
“There are a number of scientists and companies trying to figure out how to influence genes like TREM2 and CD33 and to both decrease amyloid and act on the downstream consequences of the protein,” said Dr. Holtzman. “All of this is to say that somewhere in the biology that causes Alzheimer’s disease, the immune system is involved.”
It seems that in many cases, the most common form of a dementia might be due to a well-intentioned immune cell going rogue. “I think you’d hear this from basically any researcher worth their salt,” said Dr. Tanzi. “I feel strongly that without microglial activation, you will not get Alzheimer’s disease.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It all started with genetic data. A gene here, a gene there. Eventually the story became clearer: If scientists are to one day find a cure for Alzheimer’s disease, they should look to the immune system.
Over the past couple decades, researchers have identified numerous genes involved in various immune system functions that may also contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. Some of the prime suspects are genes that control microglia, now the focus of intense research in developing new Alzheimer’s drugs.
Microglia are amoeba-like cells that scour the brain for injuries and invaders. They help clear dead or impaired brain cells and literally gobble up invading microbes. Without them, we’d be in trouble.
In a normal brain, a protein called beta-amyloid is cleared away through our lymphatic system by microglia as molecular junk. But sometimes it builds up. Certain gene mutations are one culprit in this toxic accumulation. Traumatic brain injury is another, and, perhaps, impaired microglial function.
One thing everyone agrees on is that in people with Alzheimer’s disease, too much amyloid accumulates between their brain cells and in the vessels that supply the brain with blood. Once amyloid begins to clog networks of neurons, it triggers the accumulation of another protein, called tau, inside of these brain cells. The presence of tau sends microglia and other immune mechanisms into overdrive, resulting in the inflammatory immune response that many experts believe ultimately saps brain vitality in Alzheimer’s disease.
The gene scene
To date, nearly a dozen genes involved in immune and microglial function have been tied to Alzheimer’s disease. The first was CD33, identified in 2008.
“When we got the results, I literally ran to my colleague’s office next door and said, you gotta see this!” said Harvard neuroscientist Rudolph Tanzi. Dr. Tanzi, who goes by Rudy, led the CD33 research. The discovery was quickly named a top medical breakthrough of 2008 by Time magazine.
“We were laughing because what they didn’t know is we had no idea what this gene did,” he joked. But over time, research by Dr. Tanzi and his group revealed that CD33 is a kind of microglial on-off switch, activating the cells as part of an inflammatory pathway.
“We kind of got it all going when it came to the genetics,” he said.
Microglia normally recognize molecular patterns associated with microbes and cellular damage as unwanted. This is how they know to take action – to devour unfamiliar pathogens and dead tissue. Dr. Tanzi believes microglia sense any sign of brain damage as an infection, which causes them to become hyperactive.
Much of our modern human immune system, he explained, evolved many hundreds of thousands of years ago. Our lifespans at the time were far shorter than they are today, and the majority of people didn’t live long enough to develop dementia or the withered brain cells that come with it. So our immune system, he said, assumes any faulty brain tissue is due to a microbe, not dementia. Microglia react aggressively, clearing the area to prevent the spread of infection.
“They say, ‘We better wipe out this part of the brain that’s infected, even if it’s not.’ They don’t know,” quipped Dr. Tanzi. “That’s what causes neuroinflammation. And CD33 turns this response on. The microglia become killers, not just janitors.”
A brake on overactive microglia
If CD33 is the yin, a gene called TREM2 is the yang. Discovered a few years after CD33, TREM2 reins in microglial activation, returning them to their role as cellular housekeepers.
Neurologist David Holtzman, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who studies TREM2, agrees that wherever you find amyloid, tau, or dead brain cells, there are microglia raring to go and ready to scavenge.
“I think at first a lot of people thought these cells were reacting to Alzheimer’s pathology, and not necessarily a cause of the disease,” he said.
It was the discovery of TREM2 on the heels of CD33 that really shifted the thinking, in part because it produces a protein that in the brain is only found in microglia. “Many of us [in the field] immediately said, ‘Look, there’s now a risk factor that is only expressed in microglia. It must be that innate immune cells are important in some way in the pathogenesis of the disease,’ “ he added.
Dr. Holtzman sees microglial activation in impending dementia as a double-edged sword. In the beginning, microglia clear unwanted amyloid to maintain brain health. But once accumulated amyloid and tau have done enough damage, the neuroinflammation that comes with microglial activation does more harm than good. Neurons die en masse and dementia sets in.
But not all researchers are convinced.
Serge Revist, PhD, is a professor in the department of molecular medicine at the Laval University Medical School in Quebec. Based on his lab’s research, he believes that while impaired immune activity is involved in Alzheimer’s disease, it is not the root cause. “I don’t think it is the immune cells that do the damage, I still think it is the beta-amyloid itself,” he said, “In my lab, in mouse studies, we’ve never found that immune cells were directly responsible for killing neurons.”
He does believe that in some patients with Alzheimer’s disease, microglia may not be able to handle the excess amyloid that accumulates in the disease and that developing treatments that improve the ability of microglia and the immune system to clear the protein could be effective.
Microglial medicines
The biological cascade leading to Alzheimer’s disease is a tangled one. Gene variants influencing the accumulation and clearance of amyloid are likely a major contributor. But immune activity caused by early life infection might also be involved, at least in some cases. This infectious theory of Alzheimer’s disease was first proposed by Dr. Tanzi’s now-deceased colleague Robert Moir, PhD. Dr. Tanzi’s group even has evidence that amyloid itself is antimicrobial and evolved to protect us from pathogens, only to become a problem when overactive and aggregated.
And the same goes for microglia, cells whose over-ambition might cause much of the brain degeneration seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
In theory, if a treatment could decrease CD33 activity or increase that of TREM2, doctors might one day may be able to slow or even stop the progression of dementia. Instead of going after amyloid itself – the mechanism behind so many failed investigational Alzheimer’s drugs – a therapy that quells the immune response to amyloid might be the answer in treating dementia.
“There are a number of scientists and companies trying to figure out how to influence genes like TREM2 and CD33 and to both decrease amyloid and act on the downstream consequences of the protein,” said Dr. Holtzman. “All of this is to say that somewhere in the biology that causes Alzheimer’s disease, the immune system is involved.”
It seems that in many cases, the most common form of a dementia might be due to a well-intentioned immune cell going rogue. “I think you’d hear this from basically any researcher worth their salt,” said Dr. Tanzi. “I feel strongly that without microglial activation, you will not get Alzheimer’s disease.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychedelic therapy and suicide: A myth busted?
A commonly held belief that classic psychedelic therapy can trigger suicidal thoughts, actions, or other types of self-harm is not supported by research, and, in fact, the opposite may be true.
Results from a meta-analysis of individual patient data showed that psychedelic therapy was associated with large, acute, and sustained decreases in suicidality across a range of clinical patient populations.
“ It gives us a better understanding of the effects of psychedelics on suicidality in the context of clinical trials,” study investigator Cory Weissman, MD, department of psychiatry, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
The evidence suggests psychedelic therapy “may reduce suicidal ideation when administered in the appropriate setting and offered to carefully screened patients,” Dr. Weissman said.
The findings were published online Jan. 18 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
More research needed
The analysis included seven psychedelic therapy clinical trials that had data on suicidality. Five of the trials used psilocybin plus psychotherapy and two used ayahuasca plus psychotherapy. All seven trials had a “low” risk of bias.
Patients included in the trials had treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD), recurrent MDD, AIDS-related demoralization, and distress related to life-threatening cancer.
The meta-analytic results showed significant decreases in suicidality at all acute time points (80 to 240 minutes post administration) and at most post-acute time points (1 day to 4 months post administration).
Effect sizes for reductions in suicidality were “large” at all acute time points, with standardized mean differences (SMD) ranging from -1.48 to -1.72, and remained large from 1 day to 3-4 months after therapy (SMD range, -1.50 to -2.36).
At 6 months, the effect size for reductions in suicidality with psychedelic therapy was “medium” (SMD, -0.65).
Large effect sizes for reductions in suicidality occurred across the different patient populations represented in the trial, the investigators note.
No study reported any suicide-related adverse events because of administration of a psychedelic. There were also “very few” acute (6.5%) or postacute (3.0%) elevations in suicidality, “providing support for the safety of psychedelic therapy within controlled contexts,” the researchers write.
They caution, however, that large controlled trials that specifically evaluate the effect of psychedelic therapy on suicidality are needed.
Promising avenue
In an accompanying editorial, Daniel Grossman, BS, and Peter Hendricks, PhD, department of health behavior, University of Alabama at Birmingham, note that results of this review warrant “optimism” for use of psychedelics for treatment of suicidality.
Based on this study and others, classic psychedelic therapy for suicidality appears to be a “promising avenue” for further investigation, they write.
However, research and anecdotes about increased suicidality and other self-harm attributed to psychedelic therapy, “though evidently rare, remain a critical concern” for further research to address, Dr. Grossman and Dr. Hendricks add.
The hope is that future research “clarifies who is most subject to these risks, what factors best identify them, and how best to navigate their treatment safely,” they write.
The meta-analysis had no funding. Dr. Weissman receives funding from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation and serves on the advisory board of GoodCap Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Hendricks is on the scientific advisory board of Bright Minds Biosciences, Eleusis Benefit Corporation, and Rest Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A commonly held belief that classic psychedelic therapy can trigger suicidal thoughts, actions, or other types of self-harm is not supported by research, and, in fact, the opposite may be true.
Results from a meta-analysis of individual patient data showed that psychedelic therapy was associated with large, acute, and sustained decreases in suicidality across a range of clinical patient populations.
“ It gives us a better understanding of the effects of psychedelics on suicidality in the context of clinical trials,” study investigator Cory Weissman, MD, department of psychiatry, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
The evidence suggests psychedelic therapy “may reduce suicidal ideation when administered in the appropriate setting and offered to carefully screened patients,” Dr. Weissman said.
The findings were published online Jan. 18 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
More research needed
The analysis included seven psychedelic therapy clinical trials that had data on suicidality. Five of the trials used psilocybin plus psychotherapy and two used ayahuasca plus psychotherapy. All seven trials had a “low” risk of bias.
Patients included in the trials had treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD), recurrent MDD, AIDS-related demoralization, and distress related to life-threatening cancer.
The meta-analytic results showed significant decreases in suicidality at all acute time points (80 to 240 minutes post administration) and at most post-acute time points (1 day to 4 months post administration).
Effect sizes for reductions in suicidality were “large” at all acute time points, with standardized mean differences (SMD) ranging from -1.48 to -1.72, and remained large from 1 day to 3-4 months after therapy (SMD range, -1.50 to -2.36).
At 6 months, the effect size for reductions in suicidality with psychedelic therapy was “medium” (SMD, -0.65).
Large effect sizes for reductions in suicidality occurred across the different patient populations represented in the trial, the investigators note.
No study reported any suicide-related adverse events because of administration of a psychedelic. There were also “very few” acute (6.5%) or postacute (3.0%) elevations in suicidality, “providing support for the safety of psychedelic therapy within controlled contexts,” the researchers write.
They caution, however, that large controlled trials that specifically evaluate the effect of psychedelic therapy on suicidality are needed.
Promising avenue
In an accompanying editorial, Daniel Grossman, BS, and Peter Hendricks, PhD, department of health behavior, University of Alabama at Birmingham, note that results of this review warrant “optimism” for use of psychedelics for treatment of suicidality.
Based on this study and others, classic psychedelic therapy for suicidality appears to be a “promising avenue” for further investigation, they write.
However, research and anecdotes about increased suicidality and other self-harm attributed to psychedelic therapy, “though evidently rare, remain a critical concern” for further research to address, Dr. Grossman and Dr. Hendricks add.
The hope is that future research “clarifies who is most subject to these risks, what factors best identify them, and how best to navigate their treatment safely,” they write.
The meta-analysis had no funding. Dr. Weissman receives funding from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation and serves on the advisory board of GoodCap Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Hendricks is on the scientific advisory board of Bright Minds Biosciences, Eleusis Benefit Corporation, and Rest Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A commonly held belief that classic psychedelic therapy can trigger suicidal thoughts, actions, or other types of self-harm is not supported by research, and, in fact, the opposite may be true.
Results from a meta-analysis of individual patient data showed that psychedelic therapy was associated with large, acute, and sustained decreases in suicidality across a range of clinical patient populations.
“ It gives us a better understanding of the effects of psychedelics on suicidality in the context of clinical trials,” study investigator Cory Weissman, MD, department of psychiatry, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
The evidence suggests psychedelic therapy “may reduce suicidal ideation when administered in the appropriate setting and offered to carefully screened patients,” Dr. Weissman said.
The findings were published online Jan. 18 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
More research needed
The analysis included seven psychedelic therapy clinical trials that had data on suicidality. Five of the trials used psilocybin plus psychotherapy and two used ayahuasca plus psychotherapy. All seven trials had a “low” risk of bias.
Patients included in the trials had treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD), recurrent MDD, AIDS-related demoralization, and distress related to life-threatening cancer.
The meta-analytic results showed significant decreases in suicidality at all acute time points (80 to 240 minutes post administration) and at most post-acute time points (1 day to 4 months post administration).
Effect sizes for reductions in suicidality were “large” at all acute time points, with standardized mean differences (SMD) ranging from -1.48 to -1.72, and remained large from 1 day to 3-4 months after therapy (SMD range, -1.50 to -2.36).
At 6 months, the effect size for reductions in suicidality with psychedelic therapy was “medium” (SMD, -0.65).
Large effect sizes for reductions in suicidality occurred across the different patient populations represented in the trial, the investigators note.
No study reported any suicide-related adverse events because of administration of a psychedelic. There were also “very few” acute (6.5%) or postacute (3.0%) elevations in suicidality, “providing support for the safety of psychedelic therapy within controlled contexts,” the researchers write.
They caution, however, that large controlled trials that specifically evaluate the effect of psychedelic therapy on suicidality are needed.
Promising avenue
In an accompanying editorial, Daniel Grossman, BS, and Peter Hendricks, PhD, department of health behavior, University of Alabama at Birmingham, note that results of this review warrant “optimism” for use of psychedelics for treatment of suicidality.
Based on this study and others, classic psychedelic therapy for suicidality appears to be a “promising avenue” for further investigation, they write.
However, research and anecdotes about increased suicidality and other self-harm attributed to psychedelic therapy, “though evidently rare, remain a critical concern” for further research to address, Dr. Grossman and Dr. Hendricks add.
The hope is that future research “clarifies who is most subject to these risks, what factors best identify them, and how best to navigate their treatment safely,” they write.
The meta-analysis had no funding. Dr. Weissman receives funding from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation and serves on the advisory board of GoodCap Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Hendricks is on the scientific advisory board of Bright Minds Biosciences, Eleusis Benefit Corporation, and Rest Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Motherhood and mortality: Navigating miscarriages as a physician
One clinic morning in an office visit, I stood next to the door talking, hand on the doorknob ready to exit. My elderly patient was sitting in the chair next to the door, family member in another, as I attempted my exit. Suddenly, as if looking for something, my patient locked her gaze to my abdomen and began to slowly advance herself forward, eyes squinting for a better view. She had found something. Poke, poke, poke. Three pokes in quick succession into my apparently protruding abdomen stoked an internal horror that I dared not release onto my face. How in the hell could she know? My heart sank – the signs were still there.
“There’s something in there,” she said with a seasoned certainty.
“No there’s not,” I said trying hard to hide any emotion.
“Yes, there is,” she said flatly.
“Grannie, no there isn’t,” her family member interrupted, unknowingly saving me. I thanked them again and quickly left the room.
My patient had the ongoings of slowly progressing dementia. Little did she know she was right. Maybe she had known something in another time and space. Either way, I wasn’t prepared to tell the story. She wasn’t prepared to fully understand.
I tried to forge on to see the next patient. Tears began welling in both eyes. I tilted my head back slightly to prevent the water from falling. I wanted to feel offended, but she couldn’t have known the war my body was fighting at the time. I had not yet shared the pregnancy news with this particular patient, and yet her knowing was telling in a sense. I’m learning that the old folks always know.
I was at work, actively having yet another miscarriage. This was the second of two. This most recent time, we found out at 9 weeks that our baby had stopped growing about a week or so earlier. Cue the denial. Cue the rage. Cue the devastation.
Thinking back, with each pregnancy discovery, we did not wait the customary 3 months before telling anyone. Just about everyone knew. We were immediately excited to start sharing with friends, family, coworkers, and even patients early on. We knew the risks in my 40-something age group but were quintessentially optimistic.
I am a family medicine physician with expert-level knowledge and clinical experiences in women’s health counseling, contraception, conception, and pregnancy. In my training, I’ve delivered babies, been elbow-deep searching for wayward tissue from bleeding uteri, and sutured gaping vaginal lacerations. I’ve cried with new mothers at the end of long labors. I’ve been bear-hugged by doting new fathers. I have an abundance of medical knowledge, and yet the pain and struggle of miscarriage over the past 2.5 years has twice reduced me to absolute pieces. There was no course to teach me how to navigate loss within my own body, no textbook to study so that I could test out of the experience. Life hit us dead-on, and I was broken.
I can say that the experience of a miscarriage does not get easier with each subsequent loss. At least for me, the emotions were always raw and tender. Each one was a new gash to my emotional and physical health. My sanity bled out. I was physically exhausted. The struggles of being a health care worker in the midst of a global pandemic I’m sure did not help the situation. My first miscarriage was just before the start of the pandemic. I was in New York visiting family and after dinner at Tavern on the Green, of all places, when I began showing signs. Two days later, I was at the coffee station in our clinic cafeteria adding my cream and sugar when my ob.gyn.’s office called. The hCG levels were probably too low; a miscarriage was likely. I kept my composure, walked out of the cafeteria, got my car keys, went to my car, and proceeded to scream at the top of my lungs for a few minutes. Afterward, I went back to finish up my work and canceled my clinic for the rest of the day.
For my second miscarriage, I was laying in my doctor’s office getting an ultrasound. I had started bleeding the previous day but thought that the subchorionic hemorrhage noted on the last ultrasound might be the culprit. The bleeding was light. That’s the thing about being a pregnant physician: We know too much. The image on the screen looked abnormal, the remnants a ghost of its former self. I knew something was wrong but held out some hope. She searched and turned and pressed the transducer into my belly for a seemingly better view. She apologized for not finding the heartbeat. How is this happening again?
So how does one get through the loss of multiple pregnancies? I know my husband and I worked hard to get through each loss. We did all the right things a good therapist would recommend: Be present in the moment, go with your feelings, allow yourself to feel everything. There were no wrong emotions. Little by little we grieved and healed, grieved and healed. Having a successful pregnancy did help. Miracles are not promised but I believe we were sent one, and her name is Giavonna Barbara. Bookended by miscarriages, she has made me realize just how precious and delicate life really is. She is our absolute world and joy.
I’ve learned twice now that men mourn differently than women. Not any less, just in a different way. There is a pain in the silence that often goes unvocalized, but it is of no less value. My husband and I allowed each other to heal in our own unique ways, and that has made all of the difference. I think I knew I was doing okay when one day I found something funny and I let out the heartiest laugh my belly could muster. A different purpose was renewed. Tears were harder to come by. Hope for the future again sprung eternal. Life went on and so did we.
Looking back, I realize that having a miscarriage and working as a physician in the middle of a global pandemic pushed me to my emotional and physical limits. There is a second-guessing of sorts that occurs. Did the miscarriage happen because I was under so much stress at work? It had happened in the past, was this going to continue to happen?
I can say that I was great at compartmentalizing emotions. I’d try and box them away until I got off of work and then turn them on like a switch once I hit the driver’s seat. It’s easy as a busy physician with so many patients to see, messages to return, notes to write, students and residents to teach, and programs to run to completely tune out the thought of mourning. Temporarily anyway. Work was actually a welcome distraction at times. A purpose. The journey to healing is individualized and can’t be rushed. I like to think that I heal a little bit more every day thinking about the losses and gains that I’ve had. I’m grateful for the experience and growth.
In 2022, I’m looking forward to continuing my healing journey among the twists and turns of the pandemic. I now bring a different level of understanding and empathy to my patients who are undergoing or who have undergone a miscarriage. There will always be a piece of me that viscerally mourns with them. We have a hidden shared experience. I believe I am a better physician because of those lessons learned from my own personal tragedy. Now, I look forward to sharing big belly laughs with my family and friends and savoring the small, quiet moments with my husband and daughter.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One clinic morning in an office visit, I stood next to the door talking, hand on the doorknob ready to exit. My elderly patient was sitting in the chair next to the door, family member in another, as I attempted my exit. Suddenly, as if looking for something, my patient locked her gaze to my abdomen and began to slowly advance herself forward, eyes squinting for a better view. She had found something. Poke, poke, poke. Three pokes in quick succession into my apparently protruding abdomen stoked an internal horror that I dared not release onto my face. How in the hell could she know? My heart sank – the signs were still there.
“There’s something in there,” she said with a seasoned certainty.
“No there’s not,” I said trying hard to hide any emotion.
“Yes, there is,” she said flatly.
“Grannie, no there isn’t,” her family member interrupted, unknowingly saving me. I thanked them again and quickly left the room.
My patient had the ongoings of slowly progressing dementia. Little did she know she was right. Maybe she had known something in another time and space. Either way, I wasn’t prepared to tell the story. She wasn’t prepared to fully understand.
I tried to forge on to see the next patient. Tears began welling in both eyes. I tilted my head back slightly to prevent the water from falling. I wanted to feel offended, but she couldn’t have known the war my body was fighting at the time. I had not yet shared the pregnancy news with this particular patient, and yet her knowing was telling in a sense. I’m learning that the old folks always know.
I was at work, actively having yet another miscarriage. This was the second of two. This most recent time, we found out at 9 weeks that our baby had stopped growing about a week or so earlier. Cue the denial. Cue the rage. Cue the devastation.
Thinking back, with each pregnancy discovery, we did not wait the customary 3 months before telling anyone. Just about everyone knew. We were immediately excited to start sharing with friends, family, coworkers, and even patients early on. We knew the risks in my 40-something age group but were quintessentially optimistic.
I am a family medicine physician with expert-level knowledge and clinical experiences in women’s health counseling, contraception, conception, and pregnancy. In my training, I’ve delivered babies, been elbow-deep searching for wayward tissue from bleeding uteri, and sutured gaping vaginal lacerations. I’ve cried with new mothers at the end of long labors. I’ve been bear-hugged by doting new fathers. I have an abundance of medical knowledge, and yet the pain and struggle of miscarriage over the past 2.5 years has twice reduced me to absolute pieces. There was no course to teach me how to navigate loss within my own body, no textbook to study so that I could test out of the experience. Life hit us dead-on, and I was broken.
I can say that the experience of a miscarriage does not get easier with each subsequent loss. At least for me, the emotions were always raw and tender. Each one was a new gash to my emotional and physical health. My sanity bled out. I was physically exhausted. The struggles of being a health care worker in the midst of a global pandemic I’m sure did not help the situation. My first miscarriage was just before the start of the pandemic. I was in New York visiting family and after dinner at Tavern on the Green, of all places, when I began showing signs. Two days later, I was at the coffee station in our clinic cafeteria adding my cream and sugar when my ob.gyn.’s office called. The hCG levels were probably too low; a miscarriage was likely. I kept my composure, walked out of the cafeteria, got my car keys, went to my car, and proceeded to scream at the top of my lungs for a few minutes. Afterward, I went back to finish up my work and canceled my clinic for the rest of the day.
For my second miscarriage, I was laying in my doctor’s office getting an ultrasound. I had started bleeding the previous day but thought that the subchorionic hemorrhage noted on the last ultrasound might be the culprit. The bleeding was light. That’s the thing about being a pregnant physician: We know too much. The image on the screen looked abnormal, the remnants a ghost of its former self. I knew something was wrong but held out some hope. She searched and turned and pressed the transducer into my belly for a seemingly better view. She apologized for not finding the heartbeat. How is this happening again?
So how does one get through the loss of multiple pregnancies? I know my husband and I worked hard to get through each loss. We did all the right things a good therapist would recommend: Be present in the moment, go with your feelings, allow yourself to feel everything. There were no wrong emotions. Little by little we grieved and healed, grieved and healed. Having a successful pregnancy did help. Miracles are not promised but I believe we were sent one, and her name is Giavonna Barbara. Bookended by miscarriages, she has made me realize just how precious and delicate life really is. She is our absolute world and joy.
I’ve learned twice now that men mourn differently than women. Not any less, just in a different way. There is a pain in the silence that often goes unvocalized, but it is of no less value. My husband and I allowed each other to heal in our own unique ways, and that has made all of the difference. I think I knew I was doing okay when one day I found something funny and I let out the heartiest laugh my belly could muster. A different purpose was renewed. Tears were harder to come by. Hope for the future again sprung eternal. Life went on and so did we.
Looking back, I realize that having a miscarriage and working as a physician in the middle of a global pandemic pushed me to my emotional and physical limits. There is a second-guessing of sorts that occurs. Did the miscarriage happen because I was under so much stress at work? It had happened in the past, was this going to continue to happen?
I can say that I was great at compartmentalizing emotions. I’d try and box them away until I got off of work and then turn them on like a switch once I hit the driver’s seat. It’s easy as a busy physician with so many patients to see, messages to return, notes to write, students and residents to teach, and programs to run to completely tune out the thought of mourning. Temporarily anyway. Work was actually a welcome distraction at times. A purpose. The journey to healing is individualized and can’t be rushed. I like to think that I heal a little bit more every day thinking about the losses and gains that I’ve had. I’m grateful for the experience and growth.
In 2022, I’m looking forward to continuing my healing journey among the twists and turns of the pandemic. I now bring a different level of understanding and empathy to my patients who are undergoing or who have undergone a miscarriage. There will always be a piece of me that viscerally mourns with them. We have a hidden shared experience. I believe I am a better physician because of those lessons learned from my own personal tragedy. Now, I look forward to sharing big belly laughs with my family and friends and savoring the small, quiet moments with my husband and daughter.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One clinic morning in an office visit, I stood next to the door talking, hand on the doorknob ready to exit. My elderly patient was sitting in the chair next to the door, family member in another, as I attempted my exit. Suddenly, as if looking for something, my patient locked her gaze to my abdomen and began to slowly advance herself forward, eyes squinting for a better view. She had found something. Poke, poke, poke. Three pokes in quick succession into my apparently protruding abdomen stoked an internal horror that I dared not release onto my face. How in the hell could she know? My heart sank – the signs were still there.
“There’s something in there,” she said with a seasoned certainty.
“No there’s not,” I said trying hard to hide any emotion.
“Yes, there is,” she said flatly.
“Grannie, no there isn’t,” her family member interrupted, unknowingly saving me. I thanked them again and quickly left the room.
My patient had the ongoings of slowly progressing dementia. Little did she know she was right. Maybe she had known something in another time and space. Either way, I wasn’t prepared to tell the story. She wasn’t prepared to fully understand.
I tried to forge on to see the next patient. Tears began welling in both eyes. I tilted my head back slightly to prevent the water from falling. I wanted to feel offended, but she couldn’t have known the war my body was fighting at the time. I had not yet shared the pregnancy news with this particular patient, and yet her knowing was telling in a sense. I’m learning that the old folks always know.
I was at work, actively having yet another miscarriage. This was the second of two. This most recent time, we found out at 9 weeks that our baby had stopped growing about a week or so earlier. Cue the denial. Cue the rage. Cue the devastation.
Thinking back, with each pregnancy discovery, we did not wait the customary 3 months before telling anyone. Just about everyone knew. We were immediately excited to start sharing with friends, family, coworkers, and even patients early on. We knew the risks in my 40-something age group but were quintessentially optimistic.
I am a family medicine physician with expert-level knowledge and clinical experiences in women’s health counseling, contraception, conception, and pregnancy. In my training, I’ve delivered babies, been elbow-deep searching for wayward tissue from bleeding uteri, and sutured gaping vaginal lacerations. I’ve cried with new mothers at the end of long labors. I’ve been bear-hugged by doting new fathers. I have an abundance of medical knowledge, and yet the pain and struggle of miscarriage over the past 2.5 years has twice reduced me to absolute pieces. There was no course to teach me how to navigate loss within my own body, no textbook to study so that I could test out of the experience. Life hit us dead-on, and I was broken.
I can say that the experience of a miscarriage does not get easier with each subsequent loss. At least for me, the emotions were always raw and tender. Each one was a new gash to my emotional and physical health. My sanity bled out. I was physically exhausted. The struggles of being a health care worker in the midst of a global pandemic I’m sure did not help the situation. My first miscarriage was just before the start of the pandemic. I was in New York visiting family and after dinner at Tavern on the Green, of all places, when I began showing signs. Two days later, I was at the coffee station in our clinic cafeteria adding my cream and sugar when my ob.gyn.’s office called. The hCG levels were probably too low; a miscarriage was likely. I kept my composure, walked out of the cafeteria, got my car keys, went to my car, and proceeded to scream at the top of my lungs for a few minutes. Afterward, I went back to finish up my work and canceled my clinic for the rest of the day.
For my second miscarriage, I was laying in my doctor’s office getting an ultrasound. I had started bleeding the previous day but thought that the subchorionic hemorrhage noted on the last ultrasound might be the culprit. The bleeding was light. That’s the thing about being a pregnant physician: We know too much. The image on the screen looked abnormal, the remnants a ghost of its former self. I knew something was wrong but held out some hope. She searched and turned and pressed the transducer into my belly for a seemingly better view. She apologized for not finding the heartbeat. How is this happening again?
So how does one get through the loss of multiple pregnancies? I know my husband and I worked hard to get through each loss. We did all the right things a good therapist would recommend: Be present in the moment, go with your feelings, allow yourself to feel everything. There were no wrong emotions. Little by little we grieved and healed, grieved and healed. Having a successful pregnancy did help. Miracles are not promised but I believe we were sent one, and her name is Giavonna Barbara. Bookended by miscarriages, she has made me realize just how precious and delicate life really is. She is our absolute world and joy.
I’ve learned twice now that men mourn differently than women. Not any less, just in a different way. There is a pain in the silence that often goes unvocalized, but it is of no less value. My husband and I allowed each other to heal in our own unique ways, and that has made all of the difference. I think I knew I was doing okay when one day I found something funny and I let out the heartiest laugh my belly could muster. A different purpose was renewed. Tears were harder to come by. Hope for the future again sprung eternal. Life went on and so did we.
Looking back, I realize that having a miscarriage and working as a physician in the middle of a global pandemic pushed me to my emotional and physical limits. There is a second-guessing of sorts that occurs. Did the miscarriage happen because I was under so much stress at work? It had happened in the past, was this going to continue to happen?
I can say that I was great at compartmentalizing emotions. I’d try and box them away until I got off of work and then turn them on like a switch once I hit the driver’s seat. It’s easy as a busy physician with so many patients to see, messages to return, notes to write, students and residents to teach, and programs to run to completely tune out the thought of mourning. Temporarily anyway. Work was actually a welcome distraction at times. A purpose. The journey to healing is individualized and can’t be rushed. I like to think that I heal a little bit more every day thinking about the losses and gains that I’ve had. I’m grateful for the experience and growth.
In 2022, I’m looking forward to continuing my healing journey among the twists and turns of the pandemic. I now bring a different level of understanding and empathy to my patients who are undergoing or who have undergone a miscarriage. There will always be a piece of me that viscerally mourns with them. We have a hidden shared experience. I believe I am a better physician because of those lessons learned from my own personal tragedy. Now, I look forward to sharing big belly laughs with my family and friends and savoring the small, quiet moments with my husband and daughter.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Jeremiah Stamler, pioneer of preventive cardiology, dies at 102
On the occasion of his 100th birthday, The Washington Post wrote of the trailblazing cardiologist and scientist Jeremiah Dr. Stamler, MD: “You may not know him, but he may have saved your life.”
Hyperbole, it was not.
Over a career spanning more than 70 years, Dr. Stamler transformed medicine and the public’s understanding of diet and lifestyle in cardiovascular health and helped introduce the concept of readily measured ‘risk factors’ such as cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
Dr. Stamler, the founding chair and a professor emeritus of preventive medicine at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, died Wednesday at his home in Sag Harbor, New York, at age 102.
“It is no exaggeration to say that few people in history have had as great an impact on human health,” Donald Lloyd-Jones, MD, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Feinberg and president of the American Heart Association, said in a statement.
“Jerry was a giant intellect who founded the fields of cardiovascular epidemiology and preventive cardiology and led [the way] in defining new prevention concepts right up until his last days,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added in a statement issued by the university.
Tom Frieden, MD, former director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, tweeted, “Jerry and my father did research on sodium together in the early 1950s. He was a giant in the field of public health, and we’re still benefiting from his brilliance and dedication.”
Roger Blumenthal, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, tweeted, “R.I.P., Dr. Jeremiah Stamler, ‘the father of preventive cardiology,’ dies at 102 – a true legendary force for health.”
The son of Russian immigrants, Dr. Stamler was born in Brooklyn in 1919 and received a bachelor’s degree from Columbia University and a medical degree from State University of New York.
Discharged from the U.S. Army with the rank of captain, Dr. Stamler and his first wife, Rose, herself a distinguished cardiology researcher, moved to Chicago in 1947 and began researching nutrition and atherosclerosis under pioneering cardiology researcher Louis N. Katz, MD, ultimately showing that atherosclerosis could be introduced by changing the diet of chickens. She died in 1998.
Dr. Stamler also worked for Chicago’s Public Health Department in the 1950s, starting a rheumatic fever prevention program for children and the Chicago Coronary Prevention Evaluation Program, working with higher-risk middle-aged men.
Dr. Stamler’s international INTERSALT study established an independent relationship between blood pressure and increased sodium intake, as well as body mass index and heavy alcohol intake. First published in 1988, the research faced opposition from fellow scientists and the food industry alike.
In a 2006 interview, Dr. Stamler said he and fellow researchers began pressing the American Heart Association in the late 1950s to adopt a public policy of support to improve lifestyles, including smoking cessation and better nutrition. “It took some doing. The AHA was initially reluctant and was under pressure from industry.”
Their efforts were rewarded with the AHA’s first statement on smoking in 1959 and first statement on diet in 1960, whereas, Dr. Stamler noted, “the first World Health Organization statement did not come out until the 1980s.”
Philip Greenland, MD, professor of cardiology and former chair of preventive medicine at Northwestern, described Dr. Stamler as a “force for truth that never backed down when confronted by others who did not share his passion for truth and the best science.”
“I loved working with him since I always knew he would make our research better, clearer, more relevant, and more impactful,” he said in the AHA statement.
A lifelong activist and opponent of the Vietnam War, Dr. Stamler was subpoenaed in May 1965 by the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) along with his nutritionist-assistant Yolanda Hall. Rather than pleading the Fifth Amendment against self-incrimination, Dr. Stamler and Ms. Hall refused to testify before the committee and were charged with contempt of Congress.
With the help of local attorneys, Dr. Stamler filed a civil suit against the HUAC, charging that its mandate was unconstitutional. After 8½ years of litigation that went all the way to the Supreme Court, the government agreed to drop its indictment against Dr. Stamler and he dropped his civil suit against the committee.
A year after the Stamler v. Willis case ended, the House voted to terminate the HUAC. In an essay detailing the high-profile case, Henry Blackburn quipped, “They simply did not know who they were taking on when they tagged ol’ Jerry Stamler.”
“Dr. Stamler’s exceptional science was paralleled by his remarkable humanity. He was a champion of our best American ideals, he was fearless when facing the status quo, and he was tireless in the pursuit of what was right and just. He remains a beacon for all that is noble in medicine,” said Clyde Yancy, MD, MSc, Northwestern’s chair of cardiology.
Over the course of his career, Dr. Stamler published more than 670 peer-reviewed papers, 22 books and monographs, and his work has been cited more than 56,000 times. A committed mentor, Dr. Stamler was the 2014 recipient of the AHA’s Eugene Braunwald Academic Mentorship Award.
A lifelong proponent of the Mediterranean diet, Dr. Stamler divided his time between New York, a home in Italy, and Chicago, with his wife Gloria Beckerman Stamler, whom he married in 2004 and who preceded him in death.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the occasion of his 100th birthday, The Washington Post wrote of the trailblazing cardiologist and scientist Jeremiah Dr. Stamler, MD: “You may not know him, but he may have saved your life.”
Hyperbole, it was not.
Over a career spanning more than 70 years, Dr. Stamler transformed medicine and the public’s understanding of diet and lifestyle in cardiovascular health and helped introduce the concept of readily measured ‘risk factors’ such as cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
Dr. Stamler, the founding chair and a professor emeritus of preventive medicine at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, died Wednesday at his home in Sag Harbor, New York, at age 102.
“It is no exaggeration to say that few people in history have had as great an impact on human health,” Donald Lloyd-Jones, MD, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Feinberg and president of the American Heart Association, said in a statement.
“Jerry was a giant intellect who founded the fields of cardiovascular epidemiology and preventive cardiology and led [the way] in defining new prevention concepts right up until his last days,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added in a statement issued by the university.
Tom Frieden, MD, former director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, tweeted, “Jerry and my father did research on sodium together in the early 1950s. He was a giant in the field of public health, and we’re still benefiting from his brilliance and dedication.”
Roger Blumenthal, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, tweeted, “R.I.P., Dr. Jeremiah Stamler, ‘the father of preventive cardiology,’ dies at 102 – a true legendary force for health.”
The son of Russian immigrants, Dr. Stamler was born in Brooklyn in 1919 and received a bachelor’s degree from Columbia University and a medical degree from State University of New York.
Discharged from the U.S. Army with the rank of captain, Dr. Stamler and his first wife, Rose, herself a distinguished cardiology researcher, moved to Chicago in 1947 and began researching nutrition and atherosclerosis under pioneering cardiology researcher Louis N. Katz, MD, ultimately showing that atherosclerosis could be introduced by changing the diet of chickens. She died in 1998.
Dr. Stamler also worked for Chicago’s Public Health Department in the 1950s, starting a rheumatic fever prevention program for children and the Chicago Coronary Prevention Evaluation Program, working with higher-risk middle-aged men.
Dr. Stamler’s international INTERSALT study established an independent relationship between blood pressure and increased sodium intake, as well as body mass index and heavy alcohol intake. First published in 1988, the research faced opposition from fellow scientists and the food industry alike.
In a 2006 interview, Dr. Stamler said he and fellow researchers began pressing the American Heart Association in the late 1950s to adopt a public policy of support to improve lifestyles, including smoking cessation and better nutrition. “It took some doing. The AHA was initially reluctant and was under pressure from industry.”
Their efforts were rewarded with the AHA’s first statement on smoking in 1959 and first statement on diet in 1960, whereas, Dr. Stamler noted, “the first World Health Organization statement did not come out until the 1980s.”
Philip Greenland, MD, professor of cardiology and former chair of preventive medicine at Northwestern, described Dr. Stamler as a “force for truth that never backed down when confronted by others who did not share his passion for truth and the best science.”
“I loved working with him since I always knew he would make our research better, clearer, more relevant, and more impactful,” he said in the AHA statement.
A lifelong activist and opponent of the Vietnam War, Dr. Stamler was subpoenaed in May 1965 by the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) along with his nutritionist-assistant Yolanda Hall. Rather than pleading the Fifth Amendment against self-incrimination, Dr. Stamler and Ms. Hall refused to testify before the committee and were charged with contempt of Congress.
With the help of local attorneys, Dr. Stamler filed a civil suit against the HUAC, charging that its mandate was unconstitutional. After 8½ years of litigation that went all the way to the Supreme Court, the government agreed to drop its indictment against Dr. Stamler and he dropped his civil suit against the committee.
A year after the Stamler v. Willis case ended, the House voted to terminate the HUAC. In an essay detailing the high-profile case, Henry Blackburn quipped, “They simply did not know who they were taking on when they tagged ol’ Jerry Stamler.”
“Dr. Stamler’s exceptional science was paralleled by his remarkable humanity. He was a champion of our best American ideals, he was fearless when facing the status quo, and he was tireless in the pursuit of what was right and just. He remains a beacon for all that is noble in medicine,” said Clyde Yancy, MD, MSc, Northwestern’s chair of cardiology.
Over the course of his career, Dr. Stamler published more than 670 peer-reviewed papers, 22 books and monographs, and his work has been cited more than 56,000 times. A committed mentor, Dr. Stamler was the 2014 recipient of the AHA’s Eugene Braunwald Academic Mentorship Award.
A lifelong proponent of the Mediterranean diet, Dr. Stamler divided his time between New York, a home in Italy, and Chicago, with his wife Gloria Beckerman Stamler, whom he married in 2004 and who preceded him in death.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the occasion of his 100th birthday, The Washington Post wrote of the trailblazing cardiologist and scientist Jeremiah Dr. Stamler, MD: “You may not know him, but he may have saved your life.”
Hyperbole, it was not.
Over a career spanning more than 70 years, Dr. Stamler transformed medicine and the public’s understanding of diet and lifestyle in cardiovascular health and helped introduce the concept of readily measured ‘risk factors’ such as cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
Dr. Stamler, the founding chair and a professor emeritus of preventive medicine at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, died Wednesday at his home in Sag Harbor, New York, at age 102.
“It is no exaggeration to say that few people in history have had as great an impact on human health,” Donald Lloyd-Jones, MD, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Feinberg and president of the American Heart Association, said in a statement.
“Jerry was a giant intellect who founded the fields of cardiovascular epidemiology and preventive cardiology and led [the way] in defining new prevention concepts right up until his last days,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added in a statement issued by the university.
Tom Frieden, MD, former director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, tweeted, “Jerry and my father did research on sodium together in the early 1950s. He was a giant in the field of public health, and we’re still benefiting from his brilliance and dedication.”
Roger Blumenthal, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, tweeted, “R.I.P., Dr. Jeremiah Stamler, ‘the father of preventive cardiology,’ dies at 102 – a true legendary force for health.”
The son of Russian immigrants, Dr. Stamler was born in Brooklyn in 1919 and received a bachelor’s degree from Columbia University and a medical degree from State University of New York.
Discharged from the U.S. Army with the rank of captain, Dr. Stamler and his first wife, Rose, herself a distinguished cardiology researcher, moved to Chicago in 1947 and began researching nutrition and atherosclerosis under pioneering cardiology researcher Louis N. Katz, MD, ultimately showing that atherosclerosis could be introduced by changing the diet of chickens. She died in 1998.
Dr. Stamler also worked for Chicago’s Public Health Department in the 1950s, starting a rheumatic fever prevention program for children and the Chicago Coronary Prevention Evaluation Program, working with higher-risk middle-aged men.
Dr. Stamler’s international INTERSALT study established an independent relationship between blood pressure and increased sodium intake, as well as body mass index and heavy alcohol intake. First published in 1988, the research faced opposition from fellow scientists and the food industry alike.
In a 2006 interview, Dr. Stamler said he and fellow researchers began pressing the American Heart Association in the late 1950s to adopt a public policy of support to improve lifestyles, including smoking cessation and better nutrition. “It took some doing. The AHA was initially reluctant and was under pressure from industry.”
Their efforts were rewarded with the AHA’s first statement on smoking in 1959 and first statement on diet in 1960, whereas, Dr. Stamler noted, “the first World Health Organization statement did not come out until the 1980s.”
Philip Greenland, MD, professor of cardiology and former chair of preventive medicine at Northwestern, described Dr. Stamler as a “force for truth that never backed down when confronted by others who did not share his passion for truth and the best science.”
“I loved working with him since I always knew he would make our research better, clearer, more relevant, and more impactful,” he said in the AHA statement.
A lifelong activist and opponent of the Vietnam War, Dr. Stamler was subpoenaed in May 1965 by the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) along with his nutritionist-assistant Yolanda Hall. Rather than pleading the Fifth Amendment against self-incrimination, Dr. Stamler and Ms. Hall refused to testify before the committee and were charged with contempt of Congress.
With the help of local attorneys, Dr. Stamler filed a civil suit against the HUAC, charging that its mandate was unconstitutional. After 8½ years of litigation that went all the way to the Supreme Court, the government agreed to drop its indictment against Dr. Stamler and he dropped his civil suit against the committee.
A year after the Stamler v. Willis case ended, the House voted to terminate the HUAC. In an essay detailing the high-profile case, Henry Blackburn quipped, “They simply did not know who they were taking on when they tagged ol’ Jerry Stamler.”
“Dr. Stamler’s exceptional science was paralleled by his remarkable humanity. He was a champion of our best American ideals, he was fearless when facing the status quo, and he was tireless in the pursuit of what was right and just. He remains a beacon for all that is noble in medicine,” said Clyde Yancy, MD, MSc, Northwestern’s chair of cardiology.
Over the course of his career, Dr. Stamler published more than 670 peer-reviewed papers, 22 books and monographs, and his work has been cited more than 56,000 times. A committed mentor, Dr. Stamler was the 2014 recipient of the AHA’s Eugene Braunwald Academic Mentorship Award.
A lifelong proponent of the Mediterranean diet, Dr. Stamler divided his time between New York, a home in Italy, and Chicago, with his wife Gloria Beckerman Stamler, whom he married in 2004 and who preceded him in death.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What docs don’t know about the Disabilities Act can hurt them and patients
Lisa Iezzoni, MD, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a disability researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, has used a wheelchair for more than 30 years because of multiple sclerosis. When she visits her primary care doctor, she doesn’t get weighed because the scales are not wheelchair accessible.
This failure to weigh her and other patients in wheelchairs could lead to serious medical problems. Weight is used to monitor a person’s overall health and prenatal health and to determine accurate doses for medications such as some chemotherapies, said Dr. Iezzoni.
In another situation, a man who used a wheelchair said that his primary care doctor never got him out of it for a complete physical exam. The patient later developed lymphoma, which first appeared in his groin. The doctor should have accommodated his disability and used a height-adjustable exam table or a portable lift to transfer him onto the table.
When physicians don’t provide access to medical care that patients with disabilities need, they put themselves at greater risk of lawsuits, fines, and settlements.
Yet, a new study in Health Affairs suggests that a large percentage of doctors are not fully aware of what they are legally required to do.
Under federal nondiscrimination laws (Americans With Disabilities Act, American Rehabilitation Act, and ADA Amendments Act), medical practices must provide equal access to people with disabilities, accommodate their disability-related needs, and not refuse them medical services because of their disabilities, say disability experts.
Where doctors go wrong with disability laws
What doctors don’t know about providing reasonable accommodations makes them vulnerable to lawsuits, which worries more than two-thirds of the 714 outpatient doctors surveyed.
Not only are they required to provide reasonable accommodations, but they also have to pay for them, the researchers said. One-fifth of the surveyed doctors said they didn’t know that practice owners have to pay.
More than one practice has made patients pay for services needed for their disability, such as sign language interpreters – the patients later complained this violated the ADA to enforcement agencies.
Doctors also don’t know that they have to collaborate with patients to determine what reasonable accommodations they need – over two-thirds of those surveyed said they didn’t know it was a joint responsibility, the study found.
When doctors fail to accommodate patients’ disability needs, they engage in discrimination and violate the ADA, says Elizabeth Pendo, JD, a coauthor of the study and the Joseph J. Simeone Professor of Law at Saint Louis University.
The Department of Justice has investigated several patient complaints of alleged disability discrimination recently and resolved the disputes with agreements and small fines in some cases. “The goal is not to get large financial settlements but to work with practices to get the correct procedures in place to be compliant,” said Ms. Pendo.
Physicians would be wise to check out whether their practices are as accessible as they think. Even if there’s a ramp to the office building, the parking lot may not have a van-accessible space or enough handicapped parking signs, or the exam room may be too narrow for a wheelchair to navigate.
These practices violated the ADA and agreed to make changes:
- Hamden, Conn., has two buildings that patients with physical disabilities couldn’t easily enter. The physician owners agreed to change the buildings’ entrances and access routes and add features to make it easier to use examination rooms and restrooms and the check-in and check-out areas.
- Seven medical offices in Riverside, Calif., failed to communicate effectively with deaf and hard-of-hearing patients. They should have had a qualified sign language interpreter, an assistive listening device, or another appropriate aid or service available to a deaf patient and her family. Instead, the office relied on a video remote interpretation system that often failed to work. The agreement requires the clinic to provide those aids and services to patients and their companions who are deaf or hard of hearing, advertise their availability, assess each patient who is deaf or hard of hearing to determine the best aids and services for their needs, and pay $5,000 in compensation to the complainant and a $1,000 civil penalty to the United States.
- Springfield, Mass., refused to provide full joint replacements to two patients being treated with buprenorphine, a medication used to treat opioid use disorder. Rather than accommodate the patients, the surgeons referred them elsewhere because they were uncomfortable with the postoperative pain management protocol for patients prescribed buprenorphine. “The Americans With Disabilities Act protects health care access for people under medical treatment for opioid use disorder,” said Acting U.S. Attorney Nathaniel R. Mendell. “Health care providers must comply with the ADA, even when doing so is inconvenient or makes them uncomfortable.” The agreement requires the practice to adopt a nondiscrimination policy, provide training on the ADA and opioid use disorder, and pay two complainants $15,000 each for pain and suffering.
The DOJ has filed civil lawsuits against medical practices when they failed to resolve the allegations. Recent cases include an ophthalmology practice with 24 facilities in Arizona that refused to help transfer patients in wheelchairs to surgery tables for eye surgery and required them to pay for transfer support services and two obstetricians-gynecologists in Bakersfield, Calif., who refused to provide routine medical care to a patient because of her HIV status.
What doctors should know
Many people tend to think of a person with a disability as being in a wheelchair. But the ADA has a very broad definition of disability, which includes any physical or mental impairment that substantially limits any major life activity, said Ms. Pendo.
“It was amended in 2008 to clarify that the definition includes people with chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer, cognitive and neurological disorders, substance abuse disorders, vision and hearing loss, and learning and other disabilities,” she said.
That means that doctors have to accommodate many types of disabilities, which can be challenging. The ADA only specifies that fixed structures need to be accessible, such as parking lots, driveways, and buildings, said Dr. Iezzoni.
When it comes to “reasonable accommodations,” doctors should decide that on a case-by-case basis, she said.
“We can say based on our study that 71% of doctors don’t know the right way to think about the accommodations – they don’t know they need to talk to patients so they can explain to them exactly what they need to accommodate their disability,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Doctors are also required to provide effective communication for patients with sensory or cognitive disabilities, which can depend on the severity, said Ms. Pendo. Is the person deaf or hard of hearing, blind or partially sighted – is the dementia mild or severe?
“The requirement is there, but what that looks like will vary by patient. That’s what’s challenging,” said Ms. Pendo.
Dr. Iezzoni recommends that doctor’s offices ask patients whether they need special help or individual assistance when they make appointments and enter their responses in their records. She also suggests that patients be asked at follow-up appointments whether they still need the same help or not.
“Disabilities can change over time – a person with bad arthritis may need help getting onto an exam table, but later get a knee or hip replacement that is effective and no longer need that help,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Benefits outweigh costs
Physicians have made progress in meeting the ADA’s physical accessibility requirements, said Dr. Iezzoni. “The literature suggests that doctors have done a good job at fixing the structural barriers people with mobility issues face, such as ramps and bathrooms.”
However, there are exceptions in rural older buildings which can be harder to retrofit for wheelchair accessibility, she said. “I recall interviewing a rural doctor several years ago who said that he knew his patients well and when a patient visits with mobility problems, he goes down and carries the patient up the steps to his office. My response was that is not respectful of the patient or safe for the patient or you. That doctor has since changed the location of his practice,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Some doctors may resist paying for accessible medical equipment because of cost, but she said the benefits are worth it. These include preventing staff injuries when they transfer patients and being used by patients with temporary disabilities and aging people with bad knees, backs, hearing and sight. In addition, businesses may be eligible for federal and state tax credits.
Dr. Iezzoni recently visited her doctor where they finally got height-adjustable exam tables. “I asked the assistant, who really likes these tables? She said it’s the elderly ladies of short stature – the table is lowered and they sit down and get on it.”
But, Dr. Iezonni’s main message to doctors is that patients with disabilities deserve equal quality of care. “Just because we have a disability doesn’t mean we should get worse care than other people. It’s a matter of professionalism that doctors should want to give the same quality care to all their patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lisa Iezzoni, MD, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a disability researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, has used a wheelchair for more than 30 years because of multiple sclerosis. When she visits her primary care doctor, she doesn’t get weighed because the scales are not wheelchair accessible.
This failure to weigh her and other patients in wheelchairs could lead to serious medical problems. Weight is used to monitor a person’s overall health and prenatal health and to determine accurate doses for medications such as some chemotherapies, said Dr. Iezzoni.
In another situation, a man who used a wheelchair said that his primary care doctor never got him out of it for a complete physical exam. The patient later developed lymphoma, which first appeared in his groin. The doctor should have accommodated his disability and used a height-adjustable exam table or a portable lift to transfer him onto the table.
When physicians don’t provide access to medical care that patients with disabilities need, they put themselves at greater risk of lawsuits, fines, and settlements.
Yet, a new study in Health Affairs suggests that a large percentage of doctors are not fully aware of what they are legally required to do.
Under federal nondiscrimination laws (Americans With Disabilities Act, American Rehabilitation Act, and ADA Amendments Act), medical practices must provide equal access to people with disabilities, accommodate their disability-related needs, and not refuse them medical services because of their disabilities, say disability experts.
Where doctors go wrong with disability laws
What doctors don’t know about providing reasonable accommodations makes them vulnerable to lawsuits, which worries more than two-thirds of the 714 outpatient doctors surveyed.
Not only are they required to provide reasonable accommodations, but they also have to pay for them, the researchers said. One-fifth of the surveyed doctors said they didn’t know that practice owners have to pay.
More than one practice has made patients pay for services needed for their disability, such as sign language interpreters – the patients later complained this violated the ADA to enforcement agencies.
Doctors also don’t know that they have to collaborate with patients to determine what reasonable accommodations they need – over two-thirds of those surveyed said they didn’t know it was a joint responsibility, the study found.
When doctors fail to accommodate patients’ disability needs, they engage in discrimination and violate the ADA, says Elizabeth Pendo, JD, a coauthor of the study and the Joseph J. Simeone Professor of Law at Saint Louis University.
The Department of Justice has investigated several patient complaints of alleged disability discrimination recently and resolved the disputes with agreements and small fines in some cases. “The goal is not to get large financial settlements but to work with practices to get the correct procedures in place to be compliant,” said Ms. Pendo.
Physicians would be wise to check out whether their practices are as accessible as they think. Even if there’s a ramp to the office building, the parking lot may not have a van-accessible space or enough handicapped parking signs, or the exam room may be too narrow for a wheelchair to navigate.
These practices violated the ADA and agreed to make changes:
- Hamden, Conn., has two buildings that patients with physical disabilities couldn’t easily enter. The physician owners agreed to change the buildings’ entrances and access routes and add features to make it easier to use examination rooms and restrooms and the check-in and check-out areas.
- Seven medical offices in Riverside, Calif., failed to communicate effectively with deaf and hard-of-hearing patients. They should have had a qualified sign language interpreter, an assistive listening device, or another appropriate aid or service available to a deaf patient and her family. Instead, the office relied on a video remote interpretation system that often failed to work. The agreement requires the clinic to provide those aids and services to patients and their companions who are deaf or hard of hearing, advertise their availability, assess each patient who is deaf or hard of hearing to determine the best aids and services for their needs, and pay $5,000 in compensation to the complainant and a $1,000 civil penalty to the United States.
- Springfield, Mass., refused to provide full joint replacements to two patients being treated with buprenorphine, a medication used to treat opioid use disorder. Rather than accommodate the patients, the surgeons referred them elsewhere because they were uncomfortable with the postoperative pain management protocol for patients prescribed buprenorphine. “The Americans With Disabilities Act protects health care access for people under medical treatment for opioid use disorder,” said Acting U.S. Attorney Nathaniel R. Mendell. “Health care providers must comply with the ADA, even when doing so is inconvenient or makes them uncomfortable.” The agreement requires the practice to adopt a nondiscrimination policy, provide training on the ADA and opioid use disorder, and pay two complainants $15,000 each for pain and suffering.
The DOJ has filed civil lawsuits against medical practices when they failed to resolve the allegations. Recent cases include an ophthalmology practice with 24 facilities in Arizona that refused to help transfer patients in wheelchairs to surgery tables for eye surgery and required them to pay for transfer support services and two obstetricians-gynecologists in Bakersfield, Calif., who refused to provide routine medical care to a patient because of her HIV status.
What doctors should know
Many people tend to think of a person with a disability as being in a wheelchair. But the ADA has a very broad definition of disability, which includes any physical or mental impairment that substantially limits any major life activity, said Ms. Pendo.
“It was amended in 2008 to clarify that the definition includes people with chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer, cognitive and neurological disorders, substance abuse disorders, vision and hearing loss, and learning and other disabilities,” she said.
That means that doctors have to accommodate many types of disabilities, which can be challenging. The ADA only specifies that fixed structures need to be accessible, such as parking lots, driveways, and buildings, said Dr. Iezzoni.
When it comes to “reasonable accommodations,” doctors should decide that on a case-by-case basis, she said.
“We can say based on our study that 71% of doctors don’t know the right way to think about the accommodations – they don’t know they need to talk to patients so they can explain to them exactly what they need to accommodate their disability,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Doctors are also required to provide effective communication for patients with sensory or cognitive disabilities, which can depend on the severity, said Ms. Pendo. Is the person deaf or hard of hearing, blind or partially sighted – is the dementia mild or severe?
“The requirement is there, but what that looks like will vary by patient. That’s what’s challenging,” said Ms. Pendo.
Dr. Iezzoni recommends that doctor’s offices ask patients whether they need special help or individual assistance when they make appointments and enter their responses in their records. She also suggests that patients be asked at follow-up appointments whether they still need the same help or not.
“Disabilities can change over time – a person with bad arthritis may need help getting onto an exam table, but later get a knee or hip replacement that is effective and no longer need that help,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Benefits outweigh costs
Physicians have made progress in meeting the ADA’s physical accessibility requirements, said Dr. Iezzoni. “The literature suggests that doctors have done a good job at fixing the structural barriers people with mobility issues face, such as ramps and bathrooms.”
However, there are exceptions in rural older buildings which can be harder to retrofit for wheelchair accessibility, she said. “I recall interviewing a rural doctor several years ago who said that he knew his patients well and when a patient visits with mobility problems, he goes down and carries the patient up the steps to his office. My response was that is not respectful of the patient or safe for the patient or you. That doctor has since changed the location of his practice,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Some doctors may resist paying for accessible medical equipment because of cost, but she said the benefits are worth it. These include preventing staff injuries when they transfer patients and being used by patients with temporary disabilities and aging people with bad knees, backs, hearing and sight. In addition, businesses may be eligible for federal and state tax credits.
Dr. Iezzoni recently visited her doctor where they finally got height-adjustable exam tables. “I asked the assistant, who really likes these tables? She said it’s the elderly ladies of short stature – the table is lowered and they sit down and get on it.”
But, Dr. Iezonni’s main message to doctors is that patients with disabilities deserve equal quality of care. “Just because we have a disability doesn’t mean we should get worse care than other people. It’s a matter of professionalism that doctors should want to give the same quality care to all their patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lisa Iezzoni, MD, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a disability researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, has used a wheelchair for more than 30 years because of multiple sclerosis. When she visits her primary care doctor, she doesn’t get weighed because the scales are not wheelchair accessible.
This failure to weigh her and other patients in wheelchairs could lead to serious medical problems. Weight is used to monitor a person’s overall health and prenatal health and to determine accurate doses for medications such as some chemotherapies, said Dr. Iezzoni.
In another situation, a man who used a wheelchair said that his primary care doctor never got him out of it for a complete physical exam. The patient later developed lymphoma, which first appeared in his groin. The doctor should have accommodated his disability and used a height-adjustable exam table or a portable lift to transfer him onto the table.
When physicians don’t provide access to medical care that patients with disabilities need, they put themselves at greater risk of lawsuits, fines, and settlements.
Yet, a new study in Health Affairs suggests that a large percentage of doctors are not fully aware of what they are legally required to do.
Under federal nondiscrimination laws (Americans With Disabilities Act, American Rehabilitation Act, and ADA Amendments Act), medical practices must provide equal access to people with disabilities, accommodate their disability-related needs, and not refuse them medical services because of their disabilities, say disability experts.
Where doctors go wrong with disability laws
What doctors don’t know about providing reasonable accommodations makes them vulnerable to lawsuits, which worries more than two-thirds of the 714 outpatient doctors surveyed.
Not only are they required to provide reasonable accommodations, but they also have to pay for them, the researchers said. One-fifth of the surveyed doctors said they didn’t know that practice owners have to pay.
More than one practice has made patients pay for services needed for their disability, such as sign language interpreters – the patients later complained this violated the ADA to enforcement agencies.
Doctors also don’t know that they have to collaborate with patients to determine what reasonable accommodations they need – over two-thirds of those surveyed said they didn’t know it was a joint responsibility, the study found.
When doctors fail to accommodate patients’ disability needs, they engage in discrimination and violate the ADA, says Elizabeth Pendo, JD, a coauthor of the study and the Joseph J. Simeone Professor of Law at Saint Louis University.
The Department of Justice has investigated several patient complaints of alleged disability discrimination recently and resolved the disputes with agreements and small fines in some cases. “The goal is not to get large financial settlements but to work with practices to get the correct procedures in place to be compliant,” said Ms. Pendo.
Physicians would be wise to check out whether their practices are as accessible as they think. Even if there’s a ramp to the office building, the parking lot may not have a van-accessible space or enough handicapped parking signs, or the exam room may be too narrow for a wheelchair to navigate.
These practices violated the ADA and agreed to make changes:
- Hamden, Conn., has two buildings that patients with physical disabilities couldn’t easily enter. The physician owners agreed to change the buildings’ entrances and access routes and add features to make it easier to use examination rooms and restrooms and the check-in and check-out areas.
- Seven medical offices in Riverside, Calif., failed to communicate effectively with deaf and hard-of-hearing patients. They should have had a qualified sign language interpreter, an assistive listening device, or another appropriate aid or service available to a deaf patient and her family. Instead, the office relied on a video remote interpretation system that often failed to work. The agreement requires the clinic to provide those aids and services to patients and their companions who are deaf or hard of hearing, advertise their availability, assess each patient who is deaf or hard of hearing to determine the best aids and services for their needs, and pay $5,000 in compensation to the complainant and a $1,000 civil penalty to the United States.
- Springfield, Mass., refused to provide full joint replacements to two patients being treated with buprenorphine, a medication used to treat opioid use disorder. Rather than accommodate the patients, the surgeons referred them elsewhere because they were uncomfortable with the postoperative pain management protocol for patients prescribed buprenorphine. “The Americans With Disabilities Act protects health care access for people under medical treatment for opioid use disorder,” said Acting U.S. Attorney Nathaniel R. Mendell. “Health care providers must comply with the ADA, even when doing so is inconvenient or makes them uncomfortable.” The agreement requires the practice to adopt a nondiscrimination policy, provide training on the ADA and opioid use disorder, and pay two complainants $15,000 each for pain and suffering.
The DOJ has filed civil lawsuits against medical practices when they failed to resolve the allegations. Recent cases include an ophthalmology practice with 24 facilities in Arizona that refused to help transfer patients in wheelchairs to surgery tables for eye surgery and required them to pay for transfer support services and two obstetricians-gynecologists in Bakersfield, Calif., who refused to provide routine medical care to a patient because of her HIV status.
What doctors should know
Many people tend to think of a person with a disability as being in a wheelchair. But the ADA has a very broad definition of disability, which includes any physical or mental impairment that substantially limits any major life activity, said Ms. Pendo.
“It was amended in 2008 to clarify that the definition includes people with chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer, cognitive and neurological disorders, substance abuse disorders, vision and hearing loss, and learning and other disabilities,” she said.
That means that doctors have to accommodate many types of disabilities, which can be challenging. The ADA only specifies that fixed structures need to be accessible, such as parking lots, driveways, and buildings, said Dr. Iezzoni.
When it comes to “reasonable accommodations,” doctors should decide that on a case-by-case basis, she said.
“We can say based on our study that 71% of doctors don’t know the right way to think about the accommodations – they don’t know they need to talk to patients so they can explain to them exactly what they need to accommodate their disability,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Doctors are also required to provide effective communication for patients with sensory or cognitive disabilities, which can depend on the severity, said Ms. Pendo. Is the person deaf or hard of hearing, blind or partially sighted – is the dementia mild or severe?
“The requirement is there, but what that looks like will vary by patient. That’s what’s challenging,” said Ms. Pendo.
Dr. Iezzoni recommends that doctor’s offices ask patients whether they need special help or individual assistance when they make appointments and enter their responses in their records. She also suggests that patients be asked at follow-up appointments whether they still need the same help or not.
“Disabilities can change over time – a person with bad arthritis may need help getting onto an exam table, but later get a knee or hip replacement that is effective and no longer need that help,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Benefits outweigh costs
Physicians have made progress in meeting the ADA’s physical accessibility requirements, said Dr. Iezzoni. “The literature suggests that doctors have done a good job at fixing the structural barriers people with mobility issues face, such as ramps and bathrooms.”
However, there are exceptions in rural older buildings which can be harder to retrofit for wheelchair accessibility, she said. “I recall interviewing a rural doctor several years ago who said that he knew his patients well and when a patient visits with mobility problems, he goes down and carries the patient up the steps to his office. My response was that is not respectful of the patient or safe for the patient or you. That doctor has since changed the location of his practice,” said Dr. Iezzoni.
Some doctors may resist paying for accessible medical equipment because of cost, but she said the benefits are worth it. These include preventing staff injuries when they transfer patients and being used by patients with temporary disabilities and aging people with bad knees, backs, hearing and sight. In addition, businesses may be eligible for federal and state tax credits.
Dr. Iezzoni recently visited her doctor where they finally got height-adjustable exam tables. “I asked the assistant, who really likes these tables? She said it’s the elderly ladies of short stature – the table is lowered and they sit down and get on it.”
But, Dr. Iezonni’s main message to doctors is that patients with disabilities deserve equal quality of care. “Just because we have a disability doesn’t mean we should get worse care than other people. It’s a matter of professionalism that doctors should want to give the same quality care to all their patients.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID-19: The Omicron tide may have turned
The Omicron-fueled surge appears to have peaked as new cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the first time since late November 2021, dipping back below the 1 million mark for the week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total number of cases in children was up to 11.4 million as of Jan. 27, with children representing 18.6% of all cases reported since the pandemic started, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
As children remain the largest reservoir of unvaccinated Americans, their share of the COVID case load continues to rise quickly. Just 2 weeks ago, children made up 17.8% of the cumulative number of cases, and at the end of December it was 17.4%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that trends for admissions and emergency department visits reflect the decline in new cases. New admissions of children aged 0-17 years with diagnosed COVID-19 peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 population on Jan. 15 and were down to 0.95 per 100,000 on Jan. 29.
Daily ED visits for COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, peaked at 13.9% on Jan. 14 for children aged 0-11 years and on Jan. 9 for both 12- to 15-year-olds (14.1%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (13.8%). By Jan. 28, the rates were down to 5.6% (0-11), 3.1% (12-15), and 3.3% (16-17), the CDC reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
Trends involving more severe illness support observations that Omicron is milder than earlier variants. Children hospitalized with COVID-19 were less likely to be admitted to an intensive care unit over the last 2 months than during the Delta surge in the late summer and early fall or during the winter of 2020-2021, the CDC said based on data from the BD Insights Research Database, which includes 229,000 patients and 267 hospitals.
Those data show that the highest monthly rate occurred early on, in May of 2020, when 27.8% of children with COVID-19 ended up in the ICU. The rates for December 2021 and January 2022, by comparison, were 11.0% and 11.3%, respectively, the CDC said.
Vaccination lags in younger children
As reports surface about Pfizer-BioNTech filing an emergency use request to extend vaccine coverage to children aged 6 months to 5 years, it does appear that prevention efforts could use the proverbial shot in the arm.
As of Jan. 30, just 30.4% of children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine, and only 21.6% are fully vaccinated. At a comparable point in their timeline – just short of 3 months after approval – the respective numbers for children aged 12-15 were about 42% and 31%, CDC data show.
In the younger group, both initial doses and completions rose slightly in the first 2 weeks of January but then dropped in each of the last 2 weeks. There was a more significant surge in interest among the 12- to 17-year-olds in mid-January, but the last full week of the month brought declines of more than 50% in both measures, according to a separate AAP analysis.
The Omicron-fueled surge appears to have peaked as new cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the first time since late November 2021, dipping back below the 1 million mark for the week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total number of cases in children was up to 11.4 million as of Jan. 27, with children representing 18.6% of all cases reported since the pandemic started, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
As children remain the largest reservoir of unvaccinated Americans, their share of the COVID case load continues to rise quickly. Just 2 weeks ago, children made up 17.8% of the cumulative number of cases, and at the end of December it was 17.4%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that trends for admissions and emergency department visits reflect the decline in new cases. New admissions of children aged 0-17 years with diagnosed COVID-19 peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 population on Jan. 15 and were down to 0.95 per 100,000 on Jan. 29.
Daily ED visits for COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, peaked at 13.9% on Jan. 14 for children aged 0-11 years and on Jan. 9 for both 12- to 15-year-olds (14.1%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (13.8%). By Jan. 28, the rates were down to 5.6% (0-11), 3.1% (12-15), and 3.3% (16-17), the CDC reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
Trends involving more severe illness support observations that Omicron is milder than earlier variants. Children hospitalized with COVID-19 were less likely to be admitted to an intensive care unit over the last 2 months than during the Delta surge in the late summer and early fall or during the winter of 2020-2021, the CDC said based on data from the BD Insights Research Database, which includes 229,000 patients and 267 hospitals.
Those data show that the highest monthly rate occurred early on, in May of 2020, when 27.8% of children with COVID-19 ended up in the ICU. The rates for December 2021 and January 2022, by comparison, were 11.0% and 11.3%, respectively, the CDC said.
Vaccination lags in younger children
As reports surface about Pfizer-BioNTech filing an emergency use request to extend vaccine coverage to children aged 6 months to 5 years, it does appear that prevention efforts could use the proverbial shot in the arm.
As of Jan. 30, just 30.4% of children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine, and only 21.6% are fully vaccinated. At a comparable point in their timeline – just short of 3 months after approval – the respective numbers for children aged 12-15 were about 42% and 31%, CDC data show.
In the younger group, both initial doses and completions rose slightly in the first 2 weeks of January but then dropped in each of the last 2 weeks. There was a more significant surge in interest among the 12- to 17-year-olds in mid-January, but the last full week of the month brought declines of more than 50% in both measures, according to a separate AAP analysis.
The Omicron-fueled surge appears to have peaked as new cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the first time since late November 2021, dipping back below the 1 million mark for the week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total number of cases in children was up to 11.4 million as of Jan. 27, with children representing 18.6% of all cases reported since the pandemic started, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
As children remain the largest reservoir of unvaccinated Americans, their share of the COVID case load continues to rise quickly. Just 2 weeks ago, children made up 17.8% of the cumulative number of cases, and at the end of December it was 17.4%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that trends for admissions and emergency department visits reflect the decline in new cases. New admissions of children aged 0-17 years with diagnosed COVID-19 peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 population on Jan. 15 and were down to 0.95 per 100,000 on Jan. 29.
Daily ED visits for COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, peaked at 13.9% on Jan. 14 for children aged 0-11 years and on Jan. 9 for both 12- to 15-year-olds (14.1%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (13.8%). By Jan. 28, the rates were down to 5.6% (0-11), 3.1% (12-15), and 3.3% (16-17), the CDC reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
Trends involving more severe illness support observations that Omicron is milder than earlier variants. Children hospitalized with COVID-19 were less likely to be admitted to an intensive care unit over the last 2 months than during the Delta surge in the late summer and early fall or during the winter of 2020-2021, the CDC said based on data from the BD Insights Research Database, which includes 229,000 patients and 267 hospitals.
Those data show that the highest monthly rate occurred early on, in May of 2020, when 27.8% of children with COVID-19 ended up in the ICU. The rates for December 2021 and January 2022, by comparison, were 11.0% and 11.3%, respectively, the CDC said.
Vaccination lags in younger children
As reports surface about Pfizer-BioNTech filing an emergency use request to extend vaccine coverage to children aged 6 months to 5 years, it does appear that prevention efforts could use the proverbial shot in the arm.
As of Jan. 30, just 30.4% of children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine, and only 21.6% are fully vaccinated. At a comparable point in their timeline – just short of 3 months after approval – the respective numbers for children aged 12-15 were about 42% and 31%, CDC data show.
In the younger group, both initial doses and completions rose slightly in the first 2 weeks of January but then dropped in each of the last 2 weeks. There was a more significant surge in interest among the 12- to 17-year-olds in mid-January, but the last full week of the month brought declines of more than 50% in both measures, according to a separate AAP analysis.
CDC issues new pneumococcal vaccine recommendations for adults
The recommendations, voted on by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) in October and made final in January with publication in the agency’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), call for use of the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV15; Vaxneuvance, Merck Sharp & Dohme) or 20-valent PCV (PREVNAR20; Wyeth Pharmaceuticals).
The recommendations apply to PCV-naive adults in the United States who are either aged 65 years or older, or who are aged 19-64 years and have underlying conditions such as diabetes, chronic heart or liver disease, or HIV, and have not previously received a PCV or whose previous vaccination history is unknown.
If the PCV15 vaccine is used, a subsequent dose of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23; Pneumovax23, Merck Sharp & Dohme) should be provided, typically at least 1 year later, under the recommendations.
As reported by this news organization, PCV15 and PREVNAR20 received approval from the Food and Drug Administration last July.
Those approvals provided an impetus for the revised recommendations, “offer[ing] an opportunity to review the existing recommendations and available data,” Miwako Kobayashi, MD, first author of the MMWR report and a medical epidemiologist with the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, CDC, in Atlanta, said in an interview.
“As part of that process, ACIP strived to simplify the recommendations,” she said.
The previous recommendations called for the PCV13 vaccine and the PPSV23 and had varying conditions (depending on certain age and risk groups) that added complexity to the process. Under the new approach, the same recommendation applies regardless of specific medical conditions or other risk factors.
“With the simplified recommendation for adults 19 through 64, we expect coverage may increase among this population,” Dr. Kobayashi said.
Compared with the PCV13 vaccine, PREVNAR20 protects against seven additional serotypes involved in cases of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) and pneumonia, which are responsible for up to 40% of all cases of pneumococcal disease and related deaths in the United States.
While the PREVNAR20 includes five more pneumococcal serotypes than PCV15, the
CDC does not recommend one over the other, Dr. Kobayashi noted.
More than 90% of cases of adult IPD involve older adults and adults with chronic medical conditions or immunocompromising conditions, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, or cochlear implants, the MMWR report notes.
Commenting on the recommendations, Amit A. Shah, MD, a geriatrician with the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Ariz., underscored the need for clinicians to be proactive in recommending the vaccines to those patients.
“Despite only needing one vaccine dose after turning 65 to be considered vaccinated, only about 70% of people in this group have received any pneumococcal vaccination,” he said in an interview. “This percentage has not increased much over the past several years.”
The new approach should help change that, he said.
“These new recommendations are a significant simplification from the prior confusing and challenging-to-implement recommendations from 2019,” Dr. Shah explained.
Among the 2019 recommendations was a stipulation for “shared decision-making” with PCV13, and a conversation that often only complicated matters, he noted.
“Patients and providers alike had confusion about this since it was not a clear-cut ‘yes, give it’ or ‘no, do not give it any longer’ recommendation.”
“Now that this new recommendation will require no extra time for a discussion in the clinic, and just a simple ‘it’s time for your pneumonia shot’ offer, this may become more feasible,” Dr. Shah added. “In addition, removal of the shared decision-making stipulation allows for this immunization to be easily protocolized in the clinic, similar to automatic offers to the flu vaccine for patients each year.”
According to the CDC, pneumococcal pneumonia causes an estimated 150,000 hospitalizations each year in the United States, while pneumococcal meningitis and bacteremia killed approximately 3,250 people in the United States in 2019.
“Clinicians are patients’ most trusted resource when it comes to vaccine recommendations,” Dr. Kobayashi said. “We encourage all clinicians to recommend pneumococcal vaccines when indicated.”
Dr. Kobayashi and Dr. Shah have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The recommendations, voted on by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) in October and made final in January with publication in the agency’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), call for use of the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV15; Vaxneuvance, Merck Sharp & Dohme) or 20-valent PCV (PREVNAR20; Wyeth Pharmaceuticals).
The recommendations apply to PCV-naive adults in the United States who are either aged 65 years or older, or who are aged 19-64 years and have underlying conditions such as diabetes, chronic heart or liver disease, or HIV, and have not previously received a PCV or whose previous vaccination history is unknown.
If the PCV15 vaccine is used, a subsequent dose of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23; Pneumovax23, Merck Sharp & Dohme) should be provided, typically at least 1 year later, under the recommendations.
As reported by this news organization, PCV15 and PREVNAR20 received approval from the Food and Drug Administration last July.
Those approvals provided an impetus for the revised recommendations, “offer[ing] an opportunity to review the existing recommendations and available data,” Miwako Kobayashi, MD, first author of the MMWR report and a medical epidemiologist with the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, CDC, in Atlanta, said in an interview.
“As part of that process, ACIP strived to simplify the recommendations,” she said.
The previous recommendations called for the PCV13 vaccine and the PPSV23 and had varying conditions (depending on certain age and risk groups) that added complexity to the process. Under the new approach, the same recommendation applies regardless of specific medical conditions or other risk factors.
“With the simplified recommendation for adults 19 through 64, we expect coverage may increase among this population,” Dr. Kobayashi said.
Compared with the PCV13 vaccine, PREVNAR20 protects against seven additional serotypes involved in cases of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) and pneumonia, which are responsible for up to 40% of all cases of pneumococcal disease and related deaths in the United States.
While the PREVNAR20 includes five more pneumococcal serotypes than PCV15, the
CDC does not recommend one over the other, Dr. Kobayashi noted.
More than 90% of cases of adult IPD involve older adults and adults with chronic medical conditions or immunocompromising conditions, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, or cochlear implants, the MMWR report notes.
Commenting on the recommendations, Amit A. Shah, MD, a geriatrician with the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Ariz., underscored the need for clinicians to be proactive in recommending the vaccines to those patients.
“Despite only needing one vaccine dose after turning 65 to be considered vaccinated, only about 70% of people in this group have received any pneumococcal vaccination,” he said in an interview. “This percentage has not increased much over the past several years.”
The new approach should help change that, he said.
“These new recommendations are a significant simplification from the prior confusing and challenging-to-implement recommendations from 2019,” Dr. Shah explained.
Among the 2019 recommendations was a stipulation for “shared decision-making” with PCV13, and a conversation that often only complicated matters, he noted.
“Patients and providers alike had confusion about this since it was not a clear-cut ‘yes, give it’ or ‘no, do not give it any longer’ recommendation.”
“Now that this new recommendation will require no extra time for a discussion in the clinic, and just a simple ‘it’s time for your pneumonia shot’ offer, this may become more feasible,” Dr. Shah added. “In addition, removal of the shared decision-making stipulation allows for this immunization to be easily protocolized in the clinic, similar to automatic offers to the flu vaccine for patients each year.”
According to the CDC, pneumococcal pneumonia causes an estimated 150,000 hospitalizations each year in the United States, while pneumococcal meningitis and bacteremia killed approximately 3,250 people in the United States in 2019.
“Clinicians are patients’ most trusted resource when it comes to vaccine recommendations,” Dr. Kobayashi said. “We encourage all clinicians to recommend pneumococcal vaccines when indicated.”
Dr. Kobayashi and Dr. Shah have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The recommendations, voted on by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) in October and made final in January with publication in the agency’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), call for use of the 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV15; Vaxneuvance, Merck Sharp & Dohme) or 20-valent PCV (PREVNAR20; Wyeth Pharmaceuticals).
The recommendations apply to PCV-naive adults in the United States who are either aged 65 years or older, or who are aged 19-64 years and have underlying conditions such as diabetes, chronic heart or liver disease, or HIV, and have not previously received a PCV or whose previous vaccination history is unknown.
If the PCV15 vaccine is used, a subsequent dose of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23; Pneumovax23, Merck Sharp & Dohme) should be provided, typically at least 1 year later, under the recommendations.
As reported by this news organization, PCV15 and PREVNAR20 received approval from the Food and Drug Administration last July.
Those approvals provided an impetus for the revised recommendations, “offer[ing] an opportunity to review the existing recommendations and available data,” Miwako Kobayashi, MD, first author of the MMWR report and a medical epidemiologist with the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, CDC, in Atlanta, said in an interview.
“As part of that process, ACIP strived to simplify the recommendations,” she said.
The previous recommendations called for the PCV13 vaccine and the PPSV23 and had varying conditions (depending on certain age and risk groups) that added complexity to the process. Under the new approach, the same recommendation applies regardless of specific medical conditions or other risk factors.
“With the simplified recommendation for adults 19 through 64, we expect coverage may increase among this population,” Dr. Kobayashi said.
Compared with the PCV13 vaccine, PREVNAR20 protects against seven additional serotypes involved in cases of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) and pneumonia, which are responsible for up to 40% of all cases of pneumococcal disease and related deaths in the United States.
While the PREVNAR20 includes five more pneumococcal serotypes than PCV15, the
CDC does not recommend one over the other, Dr. Kobayashi noted.
More than 90% of cases of adult IPD involve older adults and adults with chronic medical conditions or immunocompromising conditions, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, or cochlear implants, the MMWR report notes.
Commenting on the recommendations, Amit A. Shah, MD, a geriatrician with the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Ariz., underscored the need for clinicians to be proactive in recommending the vaccines to those patients.
“Despite only needing one vaccine dose after turning 65 to be considered vaccinated, only about 70% of people in this group have received any pneumococcal vaccination,” he said in an interview. “This percentage has not increased much over the past several years.”
The new approach should help change that, he said.
“These new recommendations are a significant simplification from the prior confusing and challenging-to-implement recommendations from 2019,” Dr. Shah explained.
Among the 2019 recommendations was a stipulation for “shared decision-making” with PCV13, and a conversation that often only complicated matters, he noted.
“Patients and providers alike had confusion about this since it was not a clear-cut ‘yes, give it’ or ‘no, do not give it any longer’ recommendation.”
“Now that this new recommendation will require no extra time for a discussion in the clinic, and just a simple ‘it’s time for your pneumonia shot’ offer, this may become more feasible,” Dr. Shah added. “In addition, removal of the shared decision-making stipulation allows for this immunization to be easily protocolized in the clinic, similar to automatic offers to the flu vaccine for patients each year.”
According to the CDC, pneumococcal pneumonia causes an estimated 150,000 hospitalizations each year in the United States, while pneumococcal meningitis and bacteremia killed approximately 3,250 people in the United States in 2019.
“Clinicians are patients’ most trusted resource when it comes to vaccine recommendations,” Dr. Kobayashi said. “We encourage all clinicians to recommend pneumococcal vaccines when indicated.”
Dr. Kobayashi and Dr. Shah have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE MMWR
Newly approved drug improves sleep onset in insomnia
In the first of two studies, a 50-mg dose of daridorexant was associated with a reduction in latency to persistent sleep (LPS) of 11.7 minutes at month 3 versus placebo. The drug also was associated with improved daytime function.
Based on these results, the Food and Drug Administration approved daridorexant for the treatment of insomnia in adults earlier in January.
“The study shows that it is a really good drug that works differently from most other drugs,” said Emmanuel Mignot, MD, PhD, professor of sleep medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “It’s more specific to sleep,” Dr. Mignot added.
The findings were published in the February issue of The Lancet Neurology.
Two trials, three doses
Daridorexant is a dual orexin receptor antagonist intended to reduce excessive wakefulness. The investigators hypothesized that, because of its therapeutic target, the drug would not cause sleepiness on the morning after administration.
To examine daridorexant’s safety and efficacy, the researchers conducted two double-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trials. Eligible participants were aged 18 years or older, had moderate to severe insomnia disorder, and had a self-reported history of disturbed sleep at least 3 nights per week for at least 3 months before screening.
In study 1, investigators randomly assigned participants in groups of equal size to daridorexant 25 mg, 50 mg, or placebo. In study 2, participants were randomly assigned to daridorexant 10 mg, 25 mg, or placebo.
During a placebo run-in period, participants underwent polysomnography on two consecutive nights to define baseline values. At the end of months 1 and 3 of the treatment period, participants again underwent 2 nights of polysomnography. A final night of polysomnography occurred during the placebo run-out period.
Self-assessments included the Insomnia Daytime Symptoms and Impacts Questionnaire (IDSIQ). This questionnaire, to which participants responded daily, is designed to measure the daytime impairments related to insomnia. The IDSIQ questions focus on sleepiness, mood, alertness, and cognition.
The study’s primary endpoints were change from baseline in wake after sleep onset (WASO) and LPS at months 1 and 3. Secondary endpoints were change from baseline in self-reported total sleep time and change in the IDSIQ sleepiness domain score at months 1 and 3.
The investigators enrolled 930 participants in study 1 and 924 in study 2. In each study, more than two-thirds of participants were women, 39% were aged 65 or older, and demographic and baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups.
Dose-dependent effects
At month 1 in study 1, WASO was reduced by 22.8 minutes (P < .0001) in patients who received the 50-mg dose and by 12.2 minutes (P < .0001) in the 25-mg dose. At month 3, WASO was reduced by 18.3 minutes (P < .0001) in those assigned to 50 mg and by 11.9 minutes (P < .0001) in those assigned to 25 mg.
LPS was reduced by 11.4 minutes (P < .0001) at month 1 and by 11.7 minutes (P < .0001) at month 3 with the 50-mg dose versus placebo. LPS was reduced by 8.3 minutes (P = .0005) at month 1 and by 7.6 minutes (P = .0015) at month 3 with the 25-mg dose versus placebo.
At both time points, self-reported total sleep time was significantly increased and the IDSIQ sleepiness score significantly improved with the 50-mg dose. The 25-mg dose was associated with significant improvements in self-reported total sleep time at both time points, but not with significant improvements in IDSIQ sleepiness score.
In study 2, the 25-mg dose was associated with significant reductions in WASO at month 1 (11.6 minutes, P = .0001) and month 3 (10.3 minutes, P = .0028) compared with placebo. The 25-mg dose was not associated with significant differences in LPS at either time point, however.
Similarly, the 25-mg dose was associated with improvements in self-reported total sleep time, but not with the IDSIQ sleepiness score. The 10-mg dose was not associated with improvements on any endpoint compared with placebo.
Longer studies needed
In an accompanying editorial, Kai Spiegelhalder, PhD, University of Freiburg, Germany, and colleagues pointed out that although insomnia disorder is defined by self-reported difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, none of the primary or secondary endpoints in these trials addressed these symptoms.
However, Dr. Mignot noted the use of the IDSIQ scale is the most interesting aspect of the study. Although difficulty with concentration and mood impairment are major symptoms of insomnia, they are often neglected. “This drug was reversing the daytime impairment that insomniacs have,” said Dr. Mignot. “We now need to systematically study people not only for the effect on sleep, but also that it makes them feel better the day after.”
He added that most of the current hypnotics were not developed to treat insomnia. Daridorexant, in contrast, targets the wake-promoting orexin system. “It works more selectively on sleep and not on other things. Most of the other sleeping pills have more complex effects on the brain,” Dr. Mignot said.
Commenting on the study, John Winkelman, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the low prevalence of side effects associated with daridorexant was remarkable. “This is not what most of the benzodiazepine receptor agonists looked like,” said Dr. Winkelman, who was not involved with the research.
Many insomnia drugs affect transmitter systems that are widespread in the brain, thus provoking side effects. But orexin-receptor antagonists “don’t seem to produce a lot of side effects,” he noted.
Although the study duration was reasonable, longer studies will be necessary, he added. “And it would be nice to see comparative data. Prescribers want to see some context.” said Dr. Winkelman.
The study was funded by Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Mignot reported receiving research or clinical trial funding from Axsome, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Avadel, Apple, Huami, Sunovion, and Takeda. He has also received consulting fees or speakers’ conference reimbursement from Idorsia, Centessa Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Avadel, Dreem, and Takeda. Dr. Winkelman has consulted for Idorsia and has participated in investigator-initiated studies supported by Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first of two studies, a 50-mg dose of daridorexant was associated with a reduction in latency to persistent sleep (LPS) of 11.7 minutes at month 3 versus placebo. The drug also was associated with improved daytime function.
Based on these results, the Food and Drug Administration approved daridorexant for the treatment of insomnia in adults earlier in January.
“The study shows that it is a really good drug that works differently from most other drugs,” said Emmanuel Mignot, MD, PhD, professor of sleep medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “It’s more specific to sleep,” Dr. Mignot added.
The findings were published in the February issue of The Lancet Neurology.
Two trials, three doses
Daridorexant is a dual orexin receptor antagonist intended to reduce excessive wakefulness. The investigators hypothesized that, because of its therapeutic target, the drug would not cause sleepiness on the morning after administration.
To examine daridorexant’s safety and efficacy, the researchers conducted two double-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trials. Eligible participants were aged 18 years or older, had moderate to severe insomnia disorder, and had a self-reported history of disturbed sleep at least 3 nights per week for at least 3 months before screening.
In study 1, investigators randomly assigned participants in groups of equal size to daridorexant 25 mg, 50 mg, or placebo. In study 2, participants were randomly assigned to daridorexant 10 mg, 25 mg, or placebo.
During a placebo run-in period, participants underwent polysomnography on two consecutive nights to define baseline values. At the end of months 1 and 3 of the treatment period, participants again underwent 2 nights of polysomnography. A final night of polysomnography occurred during the placebo run-out period.
Self-assessments included the Insomnia Daytime Symptoms and Impacts Questionnaire (IDSIQ). This questionnaire, to which participants responded daily, is designed to measure the daytime impairments related to insomnia. The IDSIQ questions focus on sleepiness, mood, alertness, and cognition.
The study’s primary endpoints were change from baseline in wake after sleep onset (WASO) and LPS at months 1 and 3. Secondary endpoints were change from baseline in self-reported total sleep time and change in the IDSIQ sleepiness domain score at months 1 and 3.
The investigators enrolled 930 participants in study 1 and 924 in study 2. In each study, more than two-thirds of participants were women, 39% were aged 65 or older, and demographic and baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups.
Dose-dependent effects
At month 1 in study 1, WASO was reduced by 22.8 minutes (P < .0001) in patients who received the 50-mg dose and by 12.2 minutes (P < .0001) in the 25-mg dose. At month 3, WASO was reduced by 18.3 minutes (P < .0001) in those assigned to 50 mg and by 11.9 minutes (P < .0001) in those assigned to 25 mg.
LPS was reduced by 11.4 minutes (P < .0001) at month 1 and by 11.7 minutes (P < .0001) at month 3 with the 50-mg dose versus placebo. LPS was reduced by 8.3 minutes (P = .0005) at month 1 and by 7.6 minutes (P = .0015) at month 3 with the 25-mg dose versus placebo.
At both time points, self-reported total sleep time was significantly increased and the IDSIQ sleepiness score significantly improved with the 50-mg dose. The 25-mg dose was associated with significant improvements in self-reported total sleep time at both time points, but not with significant improvements in IDSIQ sleepiness score.
In study 2, the 25-mg dose was associated with significant reductions in WASO at month 1 (11.6 minutes, P = .0001) and month 3 (10.3 minutes, P = .0028) compared with placebo. The 25-mg dose was not associated with significant differences in LPS at either time point, however.
Similarly, the 25-mg dose was associated with improvements in self-reported total sleep time, but not with the IDSIQ sleepiness score. The 10-mg dose was not associated with improvements on any endpoint compared with placebo.
Longer studies needed
In an accompanying editorial, Kai Spiegelhalder, PhD, University of Freiburg, Germany, and colleagues pointed out that although insomnia disorder is defined by self-reported difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, none of the primary or secondary endpoints in these trials addressed these symptoms.
However, Dr. Mignot noted the use of the IDSIQ scale is the most interesting aspect of the study. Although difficulty with concentration and mood impairment are major symptoms of insomnia, they are often neglected. “This drug was reversing the daytime impairment that insomniacs have,” said Dr. Mignot. “We now need to systematically study people not only for the effect on sleep, but also that it makes them feel better the day after.”
He added that most of the current hypnotics were not developed to treat insomnia. Daridorexant, in contrast, targets the wake-promoting orexin system. “It works more selectively on sleep and not on other things. Most of the other sleeping pills have more complex effects on the brain,” Dr. Mignot said.
Commenting on the study, John Winkelman, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the low prevalence of side effects associated with daridorexant was remarkable. “This is not what most of the benzodiazepine receptor agonists looked like,” said Dr. Winkelman, who was not involved with the research.
Many insomnia drugs affect transmitter systems that are widespread in the brain, thus provoking side effects. But orexin-receptor antagonists “don’t seem to produce a lot of side effects,” he noted.
Although the study duration was reasonable, longer studies will be necessary, he added. “And it would be nice to see comparative data. Prescribers want to see some context.” said Dr. Winkelman.
The study was funded by Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Mignot reported receiving research or clinical trial funding from Axsome, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Avadel, Apple, Huami, Sunovion, and Takeda. He has also received consulting fees or speakers’ conference reimbursement from Idorsia, Centessa Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Avadel, Dreem, and Takeda. Dr. Winkelman has consulted for Idorsia and has participated in investigator-initiated studies supported by Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first of two studies, a 50-mg dose of daridorexant was associated with a reduction in latency to persistent sleep (LPS) of 11.7 minutes at month 3 versus placebo. The drug also was associated with improved daytime function.
Based on these results, the Food and Drug Administration approved daridorexant for the treatment of insomnia in adults earlier in January.
“The study shows that it is a really good drug that works differently from most other drugs,” said Emmanuel Mignot, MD, PhD, professor of sleep medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “It’s more specific to sleep,” Dr. Mignot added.
The findings were published in the February issue of The Lancet Neurology.
Two trials, three doses
Daridorexant is a dual orexin receptor antagonist intended to reduce excessive wakefulness. The investigators hypothesized that, because of its therapeutic target, the drug would not cause sleepiness on the morning after administration.
To examine daridorexant’s safety and efficacy, the researchers conducted two double-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trials. Eligible participants were aged 18 years or older, had moderate to severe insomnia disorder, and had a self-reported history of disturbed sleep at least 3 nights per week for at least 3 months before screening.
In study 1, investigators randomly assigned participants in groups of equal size to daridorexant 25 mg, 50 mg, or placebo. In study 2, participants were randomly assigned to daridorexant 10 mg, 25 mg, or placebo.
During a placebo run-in period, participants underwent polysomnography on two consecutive nights to define baseline values. At the end of months 1 and 3 of the treatment period, participants again underwent 2 nights of polysomnography. A final night of polysomnography occurred during the placebo run-out period.
Self-assessments included the Insomnia Daytime Symptoms and Impacts Questionnaire (IDSIQ). This questionnaire, to which participants responded daily, is designed to measure the daytime impairments related to insomnia. The IDSIQ questions focus on sleepiness, mood, alertness, and cognition.
The study’s primary endpoints were change from baseline in wake after sleep onset (WASO) and LPS at months 1 and 3. Secondary endpoints were change from baseline in self-reported total sleep time and change in the IDSIQ sleepiness domain score at months 1 and 3.
The investigators enrolled 930 participants in study 1 and 924 in study 2. In each study, more than two-thirds of participants were women, 39% were aged 65 or older, and demographic and baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups.
Dose-dependent effects
At month 1 in study 1, WASO was reduced by 22.8 minutes (P < .0001) in patients who received the 50-mg dose and by 12.2 minutes (P < .0001) in the 25-mg dose. At month 3, WASO was reduced by 18.3 minutes (P < .0001) in those assigned to 50 mg and by 11.9 minutes (P < .0001) in those assigned to 25 mg.
LPS was reduced by 11.4 minutes (P < .0001) at month 1 and by 11.7 minutes (P < .0001) at month 3 with the 50-mg dose versus placebo. LPS was reduced by 8.3 minutes (P = .0005) at month 1 and by 7.6 minutes (P = .0015) at month 3 with the 25-mg dose versus placebo.
At both time points, self-reported total sleep time was significantly increased and the IDSIQ sleepiness score significantly improved with the 50-mg dose. The 25-mg dose was associated with significant improvements in self-reported total sleep time at both time points, but not with significant improvements in IDSIQ sleepiness score.
In study 2, the 25-mg dose was associated with significant reductions in WASO at month 1 (11.6 minutes, P = .0001) and month 3 (10.3 minutes, P = .0028) compared with placebo. The 25-mg dose was not associated with significant differences in LPS at either time point, however.
Similarly, the 25-mg dose was associated with improvements in self-reported total sleep time, but not with the IDSIQ sleepiness score. The 10-mg dose was not associated with improvements on any endpoint compared with placebo.
Longer studies needed
In an accompanying editorial, Kai Spiegelhalder, PhD, University of Freiburg, Germany, and colleagues pointed out that although insomnia disorder is defined by self-reported difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, none of the primary or secondary endpoints in these trials addressed these symptoms.
However, Dr. Mignot noted the use of the IDSIQ scale is the most interesting aspect of the study. Although difficulty with concentration and mood impairment are major symptoms of insomnia, they are often neglected. “This drug was reversing the daytime impairment that insomniacs have,” said Dr. Mignot. “We now need to systematically study people not only for the effect on sleep, but also that it makes them feel better the day after.”
He added that most of the current hypnotics were not developed to treat insomnia. Daridorexant, in contrast, targets the wake-promoting orexin system. “It works more selectively on sleep and not on other things. Most of the other sleeping pills have more complex effects on the brain,” Dr. Mignot said.
Commenting on the study, John Winkelman, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the low prevalence of side effects associated with daridorexant was remarkable. “This is not what most of the benzodiazepine receptor agonists looked like,” said Dr. Winkelman, who was not involved with the research.
Many insomnia drugs affect transmitter systems that are widespread in the brain, thus provoking side effects. But orexin-receptor antagonists “don’t seem to produce a lot of side effects,” he noted.
Although the study duration was reasonable, longer studies will be necessary, he added. “And it would be nice to see comparative data. Prescribers want to see some context.” said Dr. Winkelman.
The study was funded by Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Mignot reported receiving research or clinical trial funding from Axsome, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Avadel, Apple, Huami, Sunovion, and Takeda. He has also received consulting fees or speakers’ conference reimbursement from Idorsia, Centessa Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Avadel, Dreem, and Takeda. Dr. Winkelman has consulted for Idorsia and has participated in investigator-initiated studies supported by Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET NEUROLOGY