User login
Data Trends 2024: Substance Use Disorder
- Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/sar.s116720
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: a companion infographic. SAMHSA publication no. PEP23-07-01-007. November 13, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42730/2022-nsduh-infographic-report.pdf
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Among the Veteran Population Aged 18 or Older. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt44472/2022-nsduh-pop-slides-veterans.pdf
- Cypel YS, DePhilippis D, Davey VJ. Substance use in U.S. Vietnam War era veterans and nonveterans: results from the Vietnam Era Health Retrospective Observational Study. Subst Use Misuse. 2023;58(7):858-870. doi:10.1080/10826084.2023.2188427
- Otufowora A, Liu Y, Okusanya A, Ogidan A, Okusanya A, Cottler LB. The effect of veteran status and chronic pain on past 30-day sedative use among community-dwelling adult males. J Am Board Fam Med. 2024;37(1):118-128. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2023.230226R2
- Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/sar.s116720
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: a companion infographic. SAMHSA publication no. PEP23-07-01-007. November 13, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42730/2022-nsduh-infographic-report.pdf
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Among the Veteran Population Aged 18 or Older. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt44472/2022-nsduh-pop-slides-veterans.pdf
- Cypel YS, DePhilippis D, Davey VJ. Substance use in U.S. Vietnam War era veterans and nonveterans: results from the Vietnam Era Health Retrospective Observational Study. Subst Use Misuse. 2023;58(7):858-870. doi:10.1080/10826084.2023.2188427
- Otufowora A, Liu Y, Okusanya A, Ogidan A, Okusanya A, Cottler LB. The effect of veteran status and chronic pain on past 30-day sedative use among community-dwelling adult males. J Am Board Fam Med. 2024;37(1):118-128. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2023.230226R2
- Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/sar.s116720
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: a companion infographic. SAMHSA publication no. PEP23-07-01-007. November 13, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42730/2022-nsduh-infographic-report.pdf
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Among the Veteran Population Aged 18 or Older. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt44472/2022-nsduh-pop-slides-veterans.pdf
- Cypel YS, DePhilippis D, Davey VJ. Substance use in U.S. Vietnam War era veterans and nonveterans: results from the Vietnam Era Health Retrospective Observational Study. Subst Use Misuse. 2023;58(7):858-870. doi:10.1080/10826084.2023.2188427
- Otufowora A, Liu Y, Okusanya A, Ogidan A, Okusanya A, Cottler LB. The effect of veteran status and chronic pain on past 30-day sedative use among community-dwelling adult males. J Am Board Fam Med. 2024;37(1):118-128. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2023.230226R2
Automated ERCP Report Card Offers High Accuracy, Minimal Work
offering a real-time gauge of both individual- and institutional-level quality indicators, according to the developers.
The tool boasts an accuracy level exceeding 96%, integrates with multiple electronic health records, and requires minimal additional work time, reported Anmol Singh, MD, of TriStar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
“Implementation of quality indicator tracking remains difficult due to the complexity of ERCP as compared with other endoscopic procedures, resulting in significant limitations in the extraction and synthesis of these data,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “Manual extraction methods such as self-assessment forms and chart reviews are both time intensive and error prone, and current automated extraction methods, such as natural language processing, can require substantial resources to implement and undesirably complicate the endoscopy work flow.”
To overcome these challenges, Dr. Singh and colleagues designed an analytics tool that automatically collects ERCP quality indicators from endoscopy reports with “minimal input” from the endoscopist, and is compatible with “any electronic reporting system.”
Development relied upon endoscopy records from 2,146 ERCPs performed by 12 endoscopists at four facilities. The most common reason for ERCP was choledocholithiasis, followed by malignant and benign biliary stricture. Most common procedures were stent placement and sphincterotomy.
Data were aggregated in a Health Level–7 (HL-7) interface, an international standard system that enables compatibility between different types of electronic health records. Some inputs were entered by the performing endoscopist via drop-down menus.
Next, data were shifted into an analytics suite, which evaluated quality indicators, including cannulation difficulty and success rate, and administration of post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis.
Manual review showed that this approach yielded an accuracy of 96.5%-100%.
Beyond this high level of accuracy, Dr. Singh and colleagues described several reasons why their tool may be superior to previous attempts at an automated ERCP report card.
“Our HL-7–based tool offers several advantages, including versatility via compatibility with multiple types of commercial reporting software and flexibility in customizing the type and aesthetic of the data displayed,” they wrote. “These features improve the user interface, keep costs down, and allow for integration into smaller or nonacademic practice settings.”
They also highlighted how the tool measures quality in relation to procedure indication and difficulty at the provider level.
“Unlike in colonoscopy, where metrics such as adenoma detection rate can be ubiquitously applied to all screening procedures, the difficulty and risk profile of ERCP is inextricably dependent on patient and procedural factors such as indication of the procedure, history of interventions, or history of altered anatomy,” Dr. Singh and colleagues wrote. “Prior studies have shown that both the cost-effectiveness and complication rates of procedures are influenced by procedural indication and complexity. As such, benchmarking an individual provider’s performance necessarily requires the correct procedural context.”
With further optimization, this tool can be integrated into various types of existing endoscopy reporting software at a reasonable cost, and with minimal impact on routine work flow, the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Boston Scientific, Organon, and others.
offering a real-time gauge of both individual- and institutional-level quality indicators, according to the developers.
The tool boasts an accuracy level exceeding 96%, integrates with multiple electronic health records, and requires minimal additional work time, reported Anmol Singh, MD, of TriStar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
“Implementation of quality indicator tracking remains difficult due to the complexity of ERCP as compared with other endoscopic procedures, resulting in significant limitations in the extraction and synthesis of these data,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “Manual extraction methods such as self-assessment forms and chart reviews are both time intensive and error prone, and current automated extraction methods, such as natural language processing, can require substantial resources to implement and undesirably complicate the endoscopy work flow.”
To overcome these challenges, Dr. Singh and colleagues designed an analytics tool that automatically collects ERCP quality indicators from endoscopy reports with “minimal input” from the endoscopist, and is compatible with “any electronic reporting system.”
Development relied upon endoscopy records from 2,146 ERCPs performed by 12 endoscopists at four facilities. The most common reason for ERCP was choledocholithiasis, followed by malignant and benign biliary stricture. Most common procedures were stent placement and sphincterotomy.
Data were aggregated in a Health Level–7 (HL-7) interface, an international standard system that enables compatibility between different types of electronic health records. Some inputs were entered by the performing endoscopist via drop-down menus.
Next, data were shifted into an analytics suite, which evaluated quality indicators, including cannulation difficulty and success rate, and administration of post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis.
Manual review showed that this approach yielded an accuracy of 96.5%-100%.
Beyond this high level of accuracy, Dr. Singh and colleagues described several reasons why their tool may be superior to previous attempts at an automated ERCP report card.
“Our HL-7–based tool offers several advantages, including versatility via compatibility with multiple types of commercial reporting software and flexibility in customizing the type and aesthetic of the data displayed,” they wrote. “These features improve the user interface, keep costs down, and allow for integration into smaller or nonacademic practice settings.”
They also highlighted how the tool measures quality in relation to procedure indication and difficulty at the provider level.
“Unlike in colonoscopy, where metrics such as adenoma detection rate can be ubiquitously applied to all screening procedures, the difficulty and risk profile of ERCP is inextricably dependent on patient and procedural factors such as indication of the procedure, history of interventions, or history of altered anatomy,” Dr. Singh and colleagues wrote. “Prior studies have shown that both the cost-effectiveness and complication rates of procedures are influenced by procedural indication and complexity. As such, benchmarking an individual provider’s performance necessarily requires the correct procedural context.”
With further optimization, this tool can be integrated into various types of existing endoscopy reporting software at a reasonable cost, and with minimal impact on routine work flow, the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Boston Scientific, Organon, and others.
offering a real-time gauge of both individual- and institutional-level quality indicators, according to the developers.
The tool boasts an accuracy level exceeding 96%, integrates with multiple electronic health records, and requires minimal additional work time, reported Anmol Singh, MD, of TriStar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
“Implementation of quality indicator tracking remains difficult due to the complexity of ERCP as compared with other endoscopic procedures, resulting in significant limitations in the extraction and synthesis of these data,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “Manual extraction methods such as self-assessment forms and chart reviews are both time intensive and error prone, and current automated extraction methods, such as natural language processing, can require substantial resources to implement and undesirably complicate the endoscopy work flow.”
To overcome these challenges, Dr. Singh and colleagues designed an analytics tool that automatically collects ERCP quality indicators from endoscopy reports with “minimal input” from the endoscopist, and is compatible with “any electronic reporting system.”
Development relied upon endoscopy records from 2,146 ERCPs performed by 12 endoscopists at four facilities. The most common reason for ERCP was choledocholithiasis, followed by malignant and benign biliary stricture. Most common procedures were stent placement and sphincterotomy.
Data were aggregated in a Health Level–7 (HL-7) interface, an international standard system that enables compatibility between different types of electronic health records. Some inputs were entered by the performing endoscopist via drop-down menus.
Next, data were shifted into an analytics suite, which evaluated quality indicators, including cannulation difficulty and success rate, and administration of post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis.
Manual review showed that this approach yielded an accuracy of 96.5%-100%.
Beyond this high level of accuracy, Dr. Singh and colleagues described several reasons why their tool may be superior to previous attempts at an automated ERCP report card.
“Our HL-7–based tool offers several advantages, including versatility via compatibility with multiple types of commercial reporting software and flexibility in customizing the type and aesthetic of the data displayed,” they wrote. “These features improve the user interface, keep costs down, and allow for integration into smaller or nonacademic practice settings.”
They also highlighted how the tool measures quality in relation to procedure indication and difficulty at the provider level.
“Unlike in colonoscopy, where metrics such as adenoma detection rate can be ubiquitously applied to all screening procedures, the difficulty and risk profile of ERCP is inextricably dependent on patient and procedural factors such as indication of the procedure, history of interventions, or history of altered anatomy,” Dr. Singh and colleagues wrote. “Prior studies have shown that both the cost-effectiveness and complication rates of procedures are influenced by procedural indication and complexity. As such, benchmarking an individual provider’s performance necessarily requires the correct procedural context.”
With further optimization, this tool can be integrated into various types of existing endoscopy reporting software at a reasonable cost, and with minimal impact on routine work flow, the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Boston Scientific, Organon, and others.
FROM TECHNIQUES AND INNOVATIONS IN GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
Data Trends 2024: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on traumatic brain injury. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/pubs/docs/va_factsheets/tbi.pdf
- Miles SR, Sayer NA, Belanger HG, et al. Comparing outcomes of the Veterans Health Administration's traumatic brain injury and mental health screening programs: types and frequency of specialty services used. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(1-2):102-111. doi:10.1089/neu.2022.0176
- Pogoda TK, Adams RS, Carlson KF, Dismuke-Greer CE, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Risk of adverse outcomes among veterans who screen positive for traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration but do not complete a comprehensive evaluation: a LIMBIC-CENC study. J Head Trauma Rehabil. Published online June 19, 2023. doi:10.1097/HTR.0000000000000881
- Kinney AR, Yan XD, Schneider AL, et al. Unmet need for outpatient occupational therapy services among veterans with mild traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration: the role of facility characteristics. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(11):1802-1811. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.030
- Clark JMR, Ozturk ED, Chanfreau-Coffinier C, Merritt VC; VA Million Veteran Program. Evaluation of clinical outcomes and employment status in veterans with dual diagnosis of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Qual Life Res. 2024;33(1):229-239. doi:10.1007/s11136-023-03518-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on traumatic brain injury. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/pubs/docs/va_factsheets/tbi.pdf
- Miles SR, Sayer NA, Belanger HG, et al. Comparing outcomes of the Veterans Health Administration's traumatic brain injury and mental health screening programs: types and frequency of specialty services used. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(1-2):102-111. doi:10.1089/neu.2022.0176
- Pogoda TK, Adams RS, Carlson KF, Dismuke-Greer CE, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Risk of adverse outcomes among veterans who screen positive for traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration but do not complete a comprehensive evaluation: a LIMBIC-CENC study. J Head Trauma Rehabil. Published online June 19, 2023. doi:10.1097/HTR.0000000000000881
- Kinney AR, Yan XD, Schneider AL, et al. Unmet need for outpatient occupational therapy services among veterans with mild traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration: the role of facility characteristics. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(11):1802-1811. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.030
- Clark JMR, Ozturk ED, Chanfreau-Coffinier C, Merritt VC; VA Million Veteran Program. Evaluation of clinical outcomes and employment status in veterans with dual diagnosis of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Qual Life Res. 2024;33(1):229-239. doi:10.1007/s11136-023-03518-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on traumatic brain injury. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/pubs/docs/va_factsheets/tbi.pdf
- Miles SR, Sayer NA, Belanger HG, et al. Comparing outcomes of the Veterans Health Administration's traumatic brain injury and mental health screening programs: types and frequency of specialty services used. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(1-2):102-111. doi:10.1089/neu.2022.0176
- Pogoda TK, Adams RS, Carlson KF, Dismuke-Greer CE, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Risk of adverse outcomes among veterans who screen positive for traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration but do not complete a comprehensive evaluation: a LIMBIC-CENC study. J Head Trauma Rehabil. Published online June 19, 2023. doi:10.1097/HTR.0000000000000881
- Kinney AR, Yan XD, Schneider AL, et al. Unmet need for outpatient occupational therapy services among veterans with mild traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration: the role of facility characteristics. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(11):1802-1811. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.030
- Clark JMR, Ozturk ED, Chanfreau-Coffinier C, Merritt VC; VA Million Veteran Program. Evaluation of clinical outcomes and employment status in veterans with dual diagnosis of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Qual Life Res. 2024;33(1):229-239. doi:10.1007/s11136-023-03518-7
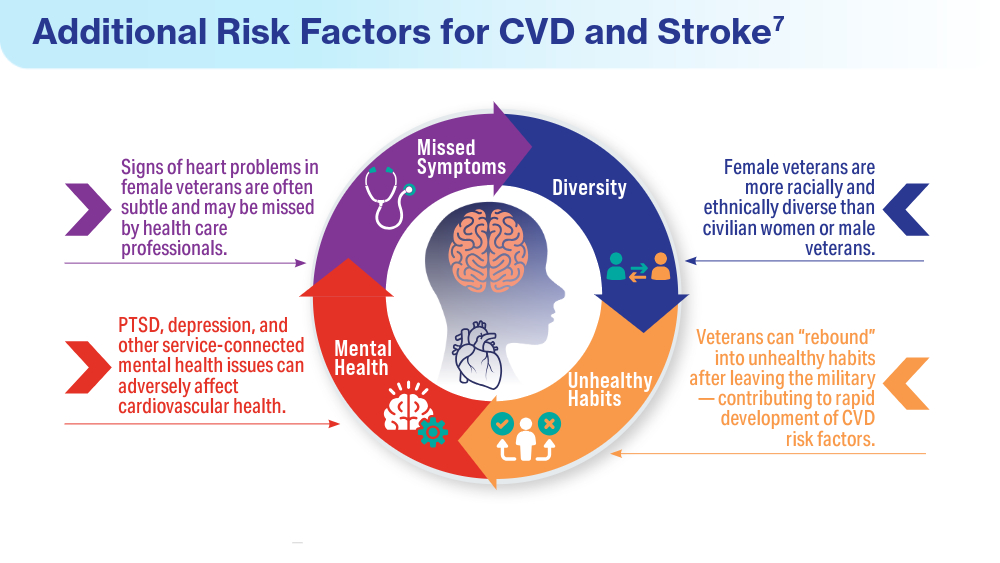
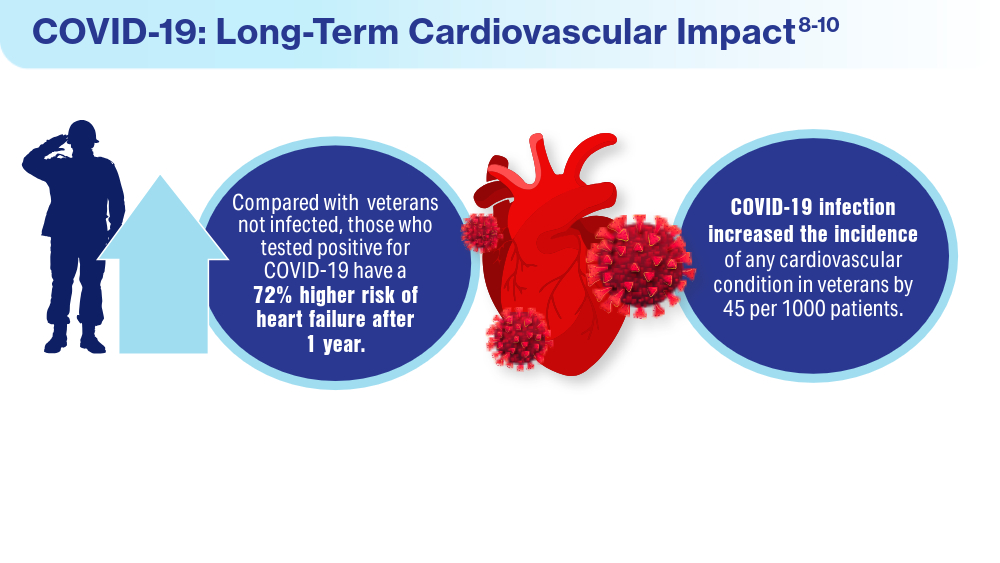
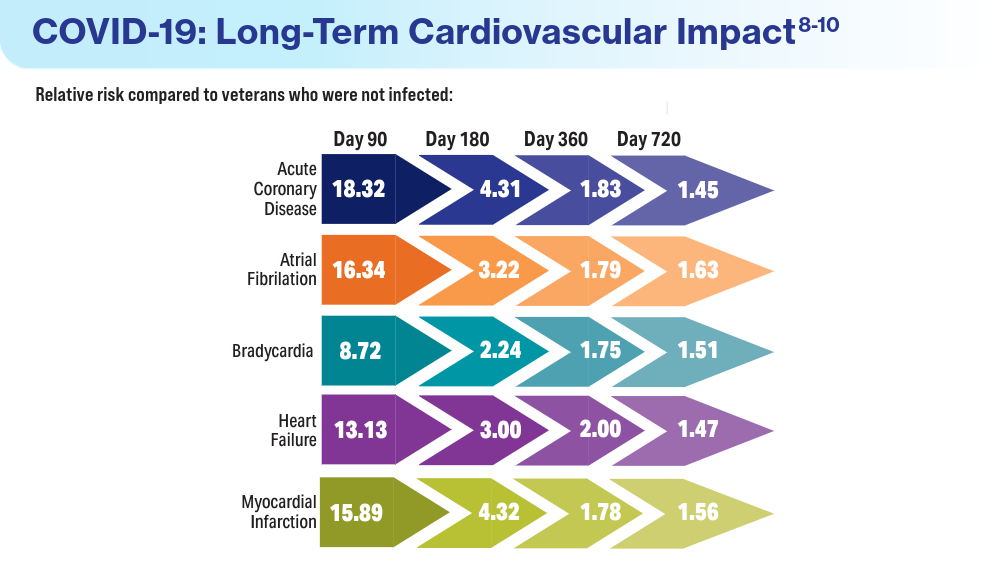
Data Trends 2024: Cardiology
- Boersma P, Cohen RA, Zelaya CE, Moy E. Multiple chronic conditions among veterans and nonveterans: United States, 2015–2018. Natl Health Stat Rep. 2021;(153):1-13. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr153-508.pdf
- Army troops have worse heart health than civilian population, study says. American Heart Association News. June 5, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/06/05/army-troops-have-worse-heart-health-than-civilian-population-study-says
- Haira RS, Kataruka A, Akeroyd JM, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Risk Factor Optimization and Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in US Veterans with Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12:e004817 doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004817
- Merschel M. Gulf War illness may increase risk for heart disease or stroke. American Heart Association News. September 29, 2023. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/09/29/gulf-war-illness-may-increase-risk-for-heart-disease-or-stroke
- Women veterans and heart health. American Heart Association: Go Red for Women. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.goredforwomen.org/en/about-heart-disease-in-women/facts/women-veterans-and-heart-health
- Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2023 Update. American Heart Association Professional Heart Daily. January 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/heart-disease-and-stroke-statistics-2023-update
- Ebrahimi R. Sumner J, Lynch K, et al. Women veterans with PTSD have higher rate of heart disease. American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020, Presentation 314 - P12702. American Heart Association News. November 9, 2020. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/women-veterans-with-ptsd-have-higher-rate-of-heart-disease
- Wadman M. COVID-19 takes serious toll on heart health—a full year after recovery. Science. Updated February 13, 2022. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-takes-serious-toll-heart-health-full-year-after-recovery
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Postacute sequale of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nature Medicine. 2023;29:2347-2357. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02521-2
- Offord C. COVID-19 boosts risks of health problems 2 years later, giant study of veterans says. Science. August 21, 2023. Accessed March 13, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-boosts-risks-health-problems-2-years-later-giant-study-veterans-says
- Boersma P, Cohen RA, Zelaya CE, Moy E. Multiple chronic conditions among veterans and nonveterans: United States, 2015–2018. Natl Health Stat Rep. 2021;(153):1-13. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr153-508.pdf
- Army troops have worse heart health than civilian population, study says. American Heart Association News. June 5, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/06/05/army-troops-have-worse-heart-health-than-civilian-population-study-says
- Haira RS, Kataruka A, Akeroyd JM, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Risk Factor Optimization and Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in US Veterans with Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12:e004817 doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004817
- Merschel M. Gulf War illness may increase risk for heart disease or stroke. American Heart Association News. September 29, 2023. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/09/29/gulf-war-illness-may-increase-risk-for-heart-disease-or-stroke
- Women veterans and heart health. American Heart Association: Go Red for Women. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.goredforwomen.org/en/about-heart-disease-in-women/facts/women-veterans-and-heart-health
- Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2023 Update. American Heart Association Professional Heart Daily. January 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/heart-disease-and-stroke-statistics-2023-update
- Ebrahimi R. Sumner J, Lynch K, et al. Women veterans with PTSD have higher rate of heart disease. American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020, Presentation 314 - P12702. American Heart Association News. November 9, 2020. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/women-veterans-with-ptsd-have-higher-rate-of-heart-disease
- Wadman M. COVID-19 takes serious toll on heart health—a full year after recovery. Science. Updated February 13, 2022. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-takes-serious-toll-heart-health-full-year-after-recovery
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Postacute sequale of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nature Medicine. 2023;29:2347-2357. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02521-2
- Offord C. COVID-19 boosts risks of health problems 2 years later, giant study of veterans says. Science. August 21, 2023. Accessed March 13, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-boosts-risks-health-problems-2-years-later-giant-study-veterans-says
- Boersma P, Cohen RA, Zelaya CE, Moy E. Multiple chronic conditions among veterans and nonveterans: United States, 2015–2018. Natl Health Stat Rep. 2021;(153):1-13. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr153-508.pdf
- Army troops have worse heart health than civilian population, study says. American Heart Association News. June 5, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/06/05/army-troops-have-worse-heart-health-than-civilian-population-study-says
- Haira RS, Kataruka A, Akeroyd JM, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Risk Factor Optimization and Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in US Veterans with Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12:e004817 doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004817
- Merschel M. Gulf War illness may increase risk for heart disease or stroke. American Heart Association News. September 29, 2023. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/09/29/gulf-war-illness-may-increase-risk-for-heart-disease-or-stroke
- Women veterans and heart health. American Heart Association: Go Red for Women. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.goredforwomen.org/en/about-heart-disease-in-women/facts/women-veterans-and-heart-health
- Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2023 Update. American Heart Association Professional Heart Daily. January 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/heart-disease-and-stroke-statistics-2023-update
- Ebrahimi R. Sumner J, Lynch K, et al. Women veterans with PTSD have higher rate of heart disease. American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020, Presentation 314 - P12702. American Heart Association News. November 9, 2020. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/women-veterans-with-ptsd-have-higher-rate-of-heart-disease
- Wadman M. COVID-19 takes serious toll on heart health—a full year after recovery. Science. Updated February 13, 2022. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-takes-serious-toll-heart-health-full-year-after-recovery
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Postacute sequale of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nature Medicine. 2023;29:2347-2357. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02521-2
- Offord C. COVID-19 boosts risks of health problems 2 years later, giant study of veterans says. Science. August 21, 2023. Accessed March 13, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-boosts-risks-health-problems-2-years-later-giant-study-veterans-says
FIT Screening Cuts Colorectal Cancer Mortality by One Third
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- In the United States, annual FIT screening is recommended among average-risk adults to reduce the risk for death from CRC, but evidence on its effectiveness is limited.
- Researchers performed a nested case-control study within two large, demographically diverse health systems with long-standing programs of mailing FITs to promote CRC screening efforts.
- They compared 1103 adults who had died of CRC between 2011 and 2017 (cases) with 9608 matched, randomly selected people who were alive and free of CRC (controls).
- Analyses focused on FIT screening completed within 5 years before CRC diagnosis for cases or the corresponding date for controls.
- The primary outcome measured was CRC death overall and by tumor location; secondary analyses assessed CRC death by race and ethnicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- In regression analysis, completing one or more FIT screenings was associated with a 33% lower risk for CRC death overall.
- There was a 42% lower risk for death from left colon and rectum cancers but no significant reduction in mortality from right colon cancers.
- The benefits of FIT screening were observed across racial and ethnic groups, with significant mortality reductions of 63% in non-Hispanic Asian, 42% in non-Hispanic Black, and 29% in non-Hispanic White individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings support the use of strategies for coordinated and equitable large-scale population-based delivery of FIT screening with follow-up of abnormal screening results to help avert preventable premature CRC deaths,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, Center for Health Equity, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Almost one half of study subjects had completed two or more FITs, but the case-control design was not suitable for assessing the impact of repeated screening. The study was conducted prior to the US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation to start screening at age 45 years, so the findings may not directly apply to adults aged 45-49 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Doubeni reported receiving royalties from UpToDate, and additional authors reported receiving grants outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- In the United States, annual FIT screening is recommended among average-risk adults to reduce the risk for death from CRC, but evidence on its effectiveness is limited.
- Researchers performed a nested case-control study within two large, demographically diverse health systems with long-standing programs of mailing FITs to promote CRC screening efforts.
- They compared 1103 adults who had died of CRC between 2011 and 2017 (cases) with 9608 matched, randomly selected people who were alive and free of CRC (controls).
- Analyses focused on FIT screening completed within 5 years before CRC diagnosis for cases or the corresponding date for controls.
- The primary outcome measured was CRC death overall and by tumor location; secondary analyses assessed CRC death by race and ethnicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- In regression analysis, completing one or more FIT screenings was associated with a 33% lower risk for CRC death overall.
- There was a 42% lower risk for death from left colon and rectum cancers but no significant reduction in mortality from right colon cancers.
- The benefits of FIT screening were observed across racial and ethnic groups, with significant mortality reductions of 63% in non-Hispanic Asian, 42% in non-Hispanic Black, and 29% in non-Hispanic White individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings support the use of strategies for coordinated and equitable large-scale population-based delivery of FIT screening with follow-up of abnormal screening results to help avert preventable premature CRC deaths,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, Center for Health Equity, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Almost one half of study subjects had completed two or more FITs, but the case-control design was not suitable for assessing the impact of repeated screening. The study was conducted prior to the US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation to start screening at age 45 years, so the findings may not directly apply to adults aged 45-49 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Doubeni reported receiving royalties from UpToDate, and additional authors reported receiving grants outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- In the United States, annual FIT screening is recommended among average-risk adults to reduce the risk for death from CRC, but evidence on its effectiveness is limited.
- Researchers performed a nested case-control study within two large, demographically diverse health systems with long-standing programs of mailing FITs to promote CRC screening efforts.
- They compared 1103 adults who had died of CRC between 2011 and 2017 (cases) with 9608 matched, randomly selected people who were alive and free of CRC (controls).
- Analyses focused on FIT screening completed within 5 years before CRC diagnosis for cases or the corresponding date for controls.
- The primary outcome measured was CRC death overall and by tumor location; secondary analyses assessed CRC death by race and ethnicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- In regression analysis, completing one or more FIT screenings was associated with a 33% lower risk for CRC death overall.
- There was a 42% lower risk for death from left colon and rectum cancers but no significant reduction in mortality from right colon cancers.
- The benefits of FIT screening were observed across racial and ethnic groups, with significant mortality reductions of 63% in non-Hispanic Asian, 42% in non-Hispanic Black, and 29% in non-Hispanic White individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings support the use of strategies for coordinated and equitable large-scale population-based delivery of FIT screening with follow-up of abnormal screening results to help avert preventable premature CRC deaths,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, Center for Health Equity, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Almost one half of study subjects had completed two or more FITs, but the case-control design was not suitable for assessing the impact of repeated screening. The study was conducted prior to the US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation to start screening at age 45 years, so the findings may not directly apply to adults aged 45-49 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Doubeni reported receiving royalties from UpToDate, and additional authors reported receiving grants outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Biological Pathway May Explain BPA Exposure, Autism Link
BPA is a potent endocrine disruptor found in polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins and has been banned by the Food and Drug Administration for use in baby bottles, sippy cups, and infant formula packaging.
“Exposure to BPA has already been shown in some studies to be associated with subsequent autism in offspring,” lead researcher Anne-Louise Ponsonby, PhD, The Florey Institute, Heidelberg, Australia, said in a statement.
“Our work is important because it demonstrates one of the biological mechanisms potentially involved. BPA can disrupt hormone-controlled male fetal brain development in several ways, including silencing a key enzyme, aromatase, that controls neurohormones and is especially important in fetal male brain development. This appears to be part of the autism puzzle,” she said.
Brain aromatase, encoded by CYP19A1, converts neural androgens to neural estrogens and has been implicated in ASD. Postmortem analyses of men with ASD also show markedly reduced aromatase activity.
The findings were published online in Nature Communications.
New Biological Mechanism
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from the Barwon Infant Study in 1067 infants in Australia. At age 7-11 years, 43 children had a confirmed ASD diagnosis, and 249 infants with Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) data at age 2 years had an autism spectrum problem score above the median.
The researchers developed a CYP19A1 genetic score for aromatase activity based on five single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with lower estrogen levels. Among 595 children with prenatal BPA and CBCL, those with three or more variants were classified as “low aromatase activity” and the remaining were classified as “high.”
In regression analyses, boys with low aromatase activity and high prenatal BPA exposure (top quartile > 2.18 µg/L) were 3.5 times more likely to have autism symptoms at age 2 years (odds ratio [OR], 3.56; 95% CI, 1.13-11.22).
The odds of a confirmed ASD diagnosis were six times higher at age 9 years only in men with low aromatase activity (OR, 6.24; 95% CI, 1.02-38.26).
The researchers also found that higher BPA levels predicted higher methylation in cord blood across the CYP19A1 brain promoter PI.f region (P = .009).
To replicate the findings, data were used from the Columbia Centre for Children’s Health Study–Mothers and Newborns cohort in the United States. Once again, the BPA level was associated with hypermethylation of the aromatase brain promoter PI.f (P = .0089).
In both cohorts, there was evidence that the effect of increased BPA on brain-derived neurotrophic factor hypermethylation was mediated partly through higher aromatase gene methylation (P = .001).
To validate the findings, the researchers examined human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell lines and found aromatase protein levels were more than halved in the presence of BPA 50 µg/L (P = .01).
Additionally, mouse studies showed that male mice exposed to BPA 50 µg/L mid-gestation and male aromatase knockout mice — but not female mice — had social behavior deficits, such as interacting with a strange mouse, as well as structural and functional brain changes.
“We found that BPA suppresses the aromatase enzyme and is associated with anatomical, neurologic, and behavioral changes in the male mice that may be consistent with autism spectrum disorder,” Wah Chin Boon, PhD, co–lead researcher and research fellow, also with The Florey Institute, said in a statement.
“This is the first time a biological pathway has been identified that might help explain the connection between autism and BPA,” she said.
“In this study, not only were the levels of BPA higher than most people would be exposed to, but in at least one of the experiments the mice were injected with BPA directly, whereas humans would be exposed via food and drink,” observed Oliver Jones, PhD, MSc, professor of chemistry, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia. “If you ingest the food, it undergoes metabolism before it gets to the bloodstream, which reduces the effective dose.”
Dr. Jones said further studies with larger numbers of participants measuring BPA throughout pregnancy and other chemicals the mother and child were exposed to are needed to be sure of any such link. “Just because there is a possible mechanism in place does not automatically mean that it is activated,” he said.
Dr. Ponsonby pointed out that BPA and other endocrine-disrupting chemicals are “almost impossible for individuals to avoid” and can enter the body through plastic food and drink packaging, home renovation fumes, and sources such as cosmetics.
Fatty Acid Helpful?
Building on earlier observations that 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10HDA) may have estrogenic modulating activities, the researchers conducted additional studies suggesting that 10HDA may be effective as a competitive ligand that could counteract the effects of BPA on estrogen signaling within cells.
Further, among 3-week-old mice pups prenatally exposed to BPA, daily injections of 10HDA for 3 weeks showed striking and significant improvements in social interaction. Stopping 10HDA resulted in a deficit in social interaction that was again ameliorated by subsequent 10HDA treatment.
“10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid shows early indications of potential in activating opposing biological pathways to improve autism-like characteristics when administered to animals that have been prenatally exposed to BPA,” Dr. Boon said. “It warrants further studies to see whether this potential treatment could be realized in humans.”
Reached for comment, Dr. Jones said “the human studies are not strong at all,” in large part because BPA levels were tested only once at 36 weeks in the BIS cohort.
“I would argue that if BPA is in the urine, it has been excreted and is no longer in the bloodstream, thus not able to affect the child,” he said. “I’d also argue that a single measurement at 36 weeks cannot give you any idea of the mother’s exposure to BPA over the rest of the pregnancy or what the child was exposed to after birth.”
The study was funded by the Minderoo Foundation, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Australian Research Council, and numerous other sponsors. Dr. Boon is a coinventor on “Methods of treating neurodevelopmental diseases and disorders” and is a board member of Meizon Innovation Holdings. Dr. Ponsonby is a scientific adviser to Meizon Innovation Holdings. The remaining authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BPA is a potent endocrine disruptor found in polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins and has been banned by the Food and Drug Administration for use in baby bottles, sippy cups, and infant formula packaging.
“Exposure to BPA has already been shown in some studies to be associated with subsequent autism in offspring,” lead researcher Anne-Louise Ponsonby, PhD, The Florey Institute, Heidelberg, Australia, said in a statement.
“Our work is important because it demonstrates one of the biological mechanisms potentially involved. BPA can disrupt hormone-controlled male fetal brain development in several ways, including silencing a key enzyme, aromatase, that controls neurohormones and is especially important in fetal male brain development. This appears to be part of the autism puzzle,” she said.
Brain aromatase, encoded by CYP19A1, converts neural androgens to neural estrogens and has been implicated in ASD. Postmortem analyses of men with ASD also show markedly reduced aromatase activity.
The findings were published online in Nature Communications.
New Biological Mechanism
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from the Barwon Infant Study in 1067 infants in Australia. At age 7-11 years, 43 children had a confirmed ASD diagnosis, and 249 infants with Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) data at age 2 years had an autism spectrum problem score above the median.
The researchers developed a CYP19A1 genetic score for aromatase activity based on five single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with lower estrogen levels. Among 595 children with prenatal BPA and CBCL, those with three or more variants were classified as “low aromatase activity” and the remaining were classified as “high.”
In regression analyses, boys with low aromatase activity and high prenatal BPA exposure (top quartile > 2.18 µg/L) were 3.5 times more likely to have autism symptoms at age 2 years (odds ratio [OR], 3.56; 95% CI, 1.13-11.22).
The odds of a confirmed ASD diagnosis were six times higher at age 9 years only in men with low aromatase activity (OR, 6.24; 95% CI, 1.02-38.26).
The researchers also found that higher BPA levels predicted higher methylation in cord blood across the CYP19A1 brain promoter PI.f region (P = .009).
To replicate the findings, data were used from the Columbia Centre for Children’s Health Study–Mothers and Newborns cohort in the United States. Once again, the BPA level was associated with hypermethylation of the aromatase brain promoter PI.f (P = .0089).
In both cohorts, there was evidence that the effect of increased BPA on brain-derived neurotrophic factor hypermethylation was mediated partly through higher aromatase gene methylation (P = .001).
To validate the findings, the researchers examined human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell lines and found aromatase protein levels were more than halved in the presence of BPA 50 µg/L (P = .01).
Additionally, mouse studies showed that male mice exposed to BPA 50 µg/L mid-gestation and male aromatase knockout mice — but not female mice — had social behavior deficits, such as interacting with a strange mouse, as well as structural and functional brain changes.
“We found that BPA suppresses the aromatase enzyme and is associated with anatomical, neurologic, and behavioral changes in the male mice that may be consistent with autism spectrum disorder,” Wah Chin Boon, PhD, co–lead researcher and research fellow, also with The Florey Institute, said in a statement.
“This is the first time a biological pathway has been identified that might help explain the connection between autism and BPA,” she said.
“In this study, not only were the levels of BPA higher than most people would be exposed to, but in at least one of the experiments the mice were injected with BPA directly, whereas humans would be exposed via food and drink,” observed Oliver Jones, PhD, MSc, professor of chemistry, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia. “If you ingest the food, it undergoes metabolism before it gets to the bloodstream, which reduces the effective dose.”
Dr. Jones said further studies with larger numbers of participants measuring BPA throughout pregnancy and other chemicals the mother and child were exposed to are needed to be sure of any such link. “Just because there is a possible mechanism in place does not automatically mean that it is activated,” he said.
Dr. Ponsonby pointed out that BPA and other endocrine-disrupting chemicals are “almost impossible for individuals to avoid” and can enter the body through plastic food and drink packaging, home renovation fumes, and sources such as cosmetics.
Fatty Acid Helpful?
Building on earlier observations that 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10HDA) may have estrogenic modulating activities, the researchers conducted additional studies suggesting that 10HDA may be effective as a competitive ligand that could counteract the effects of BPA on estrogen signaling within cells.
Further, among 3-week-old mice pups prenatally exposed to BPA, daily injections of 10HDA for 3 weeks showed striking and significant improvements in social interaction. Stopping 10HDA resulted in a deficit in social interaction that was again ameliorated by subsequent 10HDA treatment.
“10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid shows early indications of potential in activating opposing biological pathways to improve autism-like characteristics when administered to animals that have been prenatally exposed to BPA,” Dr. Boon said. “It warrants further studies to see whether this potential treatment could be realized in humans.”
Reached for comment, Dr. Jones said “the human studies are not strong at all,” in large part because BPA levels were tested only once at 36 weeks in the BIS cohort.
“I would argue that if BPA is in the urine, it has been excreted and is no longer in the bloodstream, thus not able to affect the child,” he said. “I’d also argue that a single measurement at 36 weeks cannot give you any idea of the mother’s exposure to BPA over the rest of the pregnancy or what the child was exposed to after birth.”
The study was funded by the Minderoo Foundation, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Australian Research Council, and numerous other sponsors. Dr. Boon is a coinventor on “Methods of treating neurodevelopmental diseases and disorders” and is a board member of Meizon Innovation Holdings. Dr. Ponsonby is a scientific adviser to Meizon Innovation Holdings. The remaining authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BPA is a potent endocrine disruptor found in polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins and has been banned by the Food and Drug Administration for use in baby bottles, sippy cups, and infant formula packaging.
“Exposure to BPA has already been shown in some studies to be associated with subsequent autism in offspring,” lead researcher Anne-Louise Ponsonby, PhD, The Florey Institute, Heidelberg, Australia, said in a statement.
“Our work is important because it demonstrates one of the biological mechanisms potentially involved. BPA can disrupt hormone-controlled male fetal brain development in several ways, including silencing a key enzyme, aromatase, that controls neurohormones and is especially important in fetal male brain development. This appears to be part of the autism puzzle,” she said.
Brain aromatase, encoded by CYP19A1, converts neural androgens to neural estrogens and has been implicated in ASD. Postmortem analyses of men with ASD also show markedly reduced aromatase activity.
The findings were published online in Nature Communications.
New Biological Mechanism
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from the Barwon Infant Study in 1067 infants in Australia. At age 7-11 years, 43 children had a confirmed ASD diagnosis, and 249 infants with Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) data at age 2 years had an autism spectrum problem score above the median.
The researchers developed a CYP19A1 genetic score for aromatase activity based on five single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with lower estrogen levels. Among 595 children with prenatal BPA and CBCL, those with three or more variants were classified as “low aromatase activity” and the remaining were classified as “high.”
In regression analyses, boys with low aromatase activity and high prenatal BPA exposure (top quartile > 2.18 µg/L) were 3.5 times more likely to have autism symptoms at age 2 years (odds ratio [OR], 3.56; 95% CI, 1.13-11.22).
The odds of a confirmed ASD diagnosis were six times higher at age 9 years only in men with low aromatase activity (OR, 6.24; 95% CI, 1.02-38.26).
The researchers also found that higher BPA levels predicted higher methylation in cord blood across the CYP19A1 brain promoter PI.f region (P = .009).
To replicate the findings, data were used from the Columbia Centre for Children’s Health Study–Mothers and Newborns cohort in the United States. Once again, the BPA level was associated with hypermethylation of the aromatase brain promoter PI.f (P = .0089).
In both cohorts, there was evidence that the effect of increased BPA on brain-derived neurotrophic factor hypermethylation was mediated partly through higher aromatase gene methylation (P = .001).
To validate the findings, the researchers examined human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell lines and found aromatase protein levels were more than halved in the presence of BPA 50 µg/L (P = .01).
Additionally, mouse studies showed that male mice exposed to BPA 50 µg/L mid-gestation and male aromatase knockout mice — but not female mice — had social behavior deficits, such as interacting with a strange mouse, as well as structural and functional brain changes.
“We found that BPA suppresses the aromatase enzyme and is associated with anatomical, neurologic, and behavioral changes in the male mice that may be consistent with autism spectrum disorder,” Wah Chin Boon, PhD, co–lead researcher and research fellow, also with The Florey Institute, said in a statement.
“This is the first time a biological pathway has been identified that might help explain the connection between autism and BPA,” she said.
“In this study, not only were the levels of BPA higher than most people would be exposed to, but in at least one of the experiments the mice were injected with BPA directly, whereas humans would be exposed via food and drink,” observed Oliver Jones, PhD, MSc, professor of chemistry, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia. “If you ingest the food, it undergoes metabolism before it gets to the bloodstream, which reduces the effective dose.”
Dr. Jones said further studies with larger numbers of participants measuring BPA throughout pregnancy and other chemicals the mother and child were exposed to are needed to be sure of any such link. “Just because there is a possible mechanism in place does not automatically mean that it is activated,” he said.
Dr. Ponsonby pointed out that BPA and other endocrine-disrupting chemicals are “almost impossible for individuals to avoid” and can enter the body through plastic food and drink packaging, home renovation fumes, and sources such as cosmetics.
Fatty Acid Helpful?
Building on earlier observations that 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10HDA) may have estrogenic modulating activities, the researchers conducted additional studies suggesting that 10HDA may be effective as a competitive ligand that could counteract the effects of BPA on estrogen signaling within cells.
Further, among 3-week-old mice pups prenatally exposed to BPA, daily injections of 10HDA for 3 weeks showed striking and significant improvements in social interaction. Stopping 10HDA resulted in a deficit in social interaction that was again ameliorated by subsequent 10HDA treatment.
“10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid shows early indications of potential in activating opposing biological pathways to improve autism-like characteristics when administered to animals that have been prenatally exposed to BPA,” Dr. Boon said. “It warrants further studies to see whether this potential treatment could be realized in humans.”
Reached for comment, Dr. Jones said “the human studies are not strong at all,” in large part because BPA levels were tested only once at 36 weeks in the BIS cohort.
“I would argue that if BPA is in the urine, it has been excreted and is no longer in the bloodstream, thus not able to affect the child,” he said. “I’d also argue that a single measurement at 36 weeks cannot give you any idea of the mother’s exposure to BPA over the rest of the pregnancy or what the child was exposed to after birth.”
The study was funded by the Minderoo Foundation, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Australian Research Council, and numerous other sponsors. Dr. Boon is a coinventor on “Methods of treating neurodevelopmental diseases and disorders” and is a board member of Meizon Innovation Holdings. Dr. Ponsonby is a scientific adviser to Meizon Innovation Holdings. The remaining authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
When Does Different Types of Organ Damage From Lupus Occur? Long-Term Study Sheds Light
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is SNRI Treatment of Fibromyalgia Working? Look at Sleep Patterns
Not a morning person? For patients with fibromyalgia, the answer to that question could be a clue about their treatment response with a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), suggested a new cross-sectional study published in Rheumatology International.
Compared with patients who had 30% or more pain relief after 8 or more weeks on an SNRI (duloxetine, venlafaxine, or milnacipran), those with less pain relief reported rougher mornings and worse sleep overall. Morningness, morning affect, diurnal dysrhythmia, anytime wakeability, overall sleep quality, subjective sleep quality and disturbances, sleep medication use, and daytime dysfunction were all predictors of nonresponse to SNRI treatment.
“The observed chronobiological characteristics of patients resistant to SNRI treatment are important because they can be targeted with adjunctive circadian interventions, ie, morning light therapy, in order to normalize circadian rhythms and improve sleep, and in effect, overcome the resistance to treatment and alleviate [the] patient’s pain,” said study author Anna Julia Krupa, MD, a psychiatrist and research assistant in the Department of Affective Disorders at Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland.
Fibromyalgia symptoms like sleep disturbance, low mood, fatigue, stiffness, cognitive impairment, and anxiety are often interlinked in positive feedback loops, meaning that the presence of one symptom (ie, sleep problems or depression) exacerbates the other (ie, pain or anxiety), Dr. Krupa said. While SNRIs can reduce pain, anxiety, and depression, they don’t directly improve sleep. Sometimes, pain relief smooths out minor sleep problems, but not always.
“Therefore, if circadian rhythm disruptions and sleep problems are significant, they may constitute a factor which limits SNRI effects on pain in people with fibromyalgia,” Dr. Krupa said.
With 60 patients with fibromyalgia (30 responsive to treatment and 30 nonresponsive to treatment) and 30 healthy controls, this was a small study, noted Daniel G. Arkfeld, MD, DDS, a rheumatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. However, “sleep is probably one of the most difficult things in fibromyalgia, and it definitely needs to be targeted.”
Decades of research suggest that important neurochemicals, like growth hormone, are released in deep sleep. “We know that sleep disturbances and time frame and release of neurochemicals [are] all super important in fibromyalgia,” he said.
Side effects of medication could be another factor at play here. As with any drug, the side effects of SNRIs vary widely from person to person, but palpitations, tremulousness, and insomnia are common, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, internal medicine/rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain & Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“SNRIs are often ‘activating’ because of the increase in norepinephrine,” Dr. Clauw said. “This is often helpful for symptoms such as fatigue and memory problems — but could worsen sleep.”
That’s why he always recommends that patients take an SNRI in the morning, not at night. Try that and the following tips to help patients with fibromyalgia sleep better and feel better, too.
Start with the basics. It’s worth reminding patients about the tried-and-true tips like going to bed and waking up at the same time every day and keeping your bedroom quiet and dark. “Patients should first try ‘sleep hygiene’ strategies,” said Dr. Clauw. “If that doesn’t help then cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be very helpful.”
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CBT for insomnia helped patients with fibromyalgia improve sleep quality, pain, anxiety, and depression compared with nonpharmacologic treatments. And if that doesn’t help? “If need be, they can try nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, eg, tricyclics or gabapentinoids taken at bedtime,” said Dr. Clauw.
Help them fall in love with exercise. A personalized approach to exercise can help patients with fibromyalgia feel better, suggested a study review in Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Exercise can also help reset the circadian clock. Morning activity helps night owls get on an earlier schedule, suggested a study review published in Physical Activity and Nutrition.
Consider yoga, tai chi, or qigong. A study review published in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism suggested mind-body and combined exercises help improve sleep for people with fibromyalgia, while aerobic or strength training alone does not. One explanation is that mind-body exercises might do more than other types to tamp down sympathetic-excitatory overactivation in fibromyalgia, the researchers said. Use this handy guide from the European Pain Federation to help you start the exercise conversation.
Talk about sleep alongside other aspects of fibromyalgia. Psychoeducation for fibromyalgia often includes information about the distinction between acute and chronic pain, the nature of fibromyalgia syndrome, disease-contributing factors, safe and effective treatments, symptoms and characteristics, and coping strategies, according to a study review in the journal Behavioral Sciences. “As a psychiatrist and someone who often consults patients with fibromyalgia, I would also add the information about links between pain and mood, anxiety as well as sleep,” said Dr. Krupa.
Try morning light. Use light to shift circadian rhythms, suggested Dr. Krupa. People who struggle in the morning might benefit from 30-60 minutes of morning light therapy immediately after waking using a 10,000-lux light box or light glasses, as suggested by a study review from the University of Michigan.
Help them get off the night shift. “Fibromyalgia patients probably shouldn’t work the night shift and throw their circadian rhythm off,” said Dr. Arkfeld. Depending on a patient’s work and financial circumstances, a job change might not be possible, but consider writing a note to the patient’s employer asking them to switch the patient to the day shift. Dr. Arkfeld said this approach has worked for some of his patients.
Refer them for a sleep study. Many patients with fibromyalgia have obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep disorders that require additional intervention. “Sleep studies are important to kind of define the actual sleep problem that’s occurring as well, whether it’s the stage for interruption of sleep or sleep apnea or wakefulness,” said Dr. Arkfeld.
The study was funded by Jagiellonian University Medical College. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Not a morning person? For patients with fibromyalgia, the answer to that question could be a clue about their treatment response with a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), suggested a new cross-sectional study published in Rheumatology International.
Compared with patients who had 30% or more pain relief after 8 or more weeks on an SNRI (duloxetine, venlafaxine, or milnacipran), those with less pain relief reported rougher mornings and worse sleep overall. Morningness, morning affect, diurnal dysrhythmia, anytime wakeability, overall sleep quality, subjective sleep quality and disturbances, sleep medication use, and daytime dysfunction were all predictors of nonresponse to SNRI treatment.
“The observed chronobiological characteristics of patients resistant to SNRI treatment are important because they can be targeted with adjunctive circadian interventions, ie, morning light therapy, in order to normalize circadian rhythms and improve sleep, and in effect, overcome the resistance to treatment and alleviate [the] patient’s pain,” said study author Anna Julia Krupa, MD, a psychiatrist and research assistant in the Department of Affective Disorders at Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland.
Fibromyalgia symptoms like sleep disturbance, low mood, fatigue, stiffness, cognitive impairment, and anxiety are often interlinked in positive feedback loops, meaning that the presence of one symptom (ie, sleep problems or depression) exacerbates the other (ie, pain or anxiety), Dr. Krupa said. While SNRIs can reduce pain, anxiety, and depression, they don’t directly improve sleep. Sometimes, pain relief smooths out minor sleep problems, but not always.
“Therefore, if circadian rhythm disruptions and sleep problems are significant, they may constitute a factor which limits SNRI effects on pain in people with fibromyalgia,” Dr. Krupa said.
With 60 patients with fibromyalgia (30 responsive to treatment and 30 nonresponsive to treatment) and 30 healthy controls, this was a small study, noted Daniel G. Arkfeld, MD, DDS, a rheumatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. However, “sleep is probably one of the most difficult things in fibromyalgia, and it definitely needs to be targeted.”
Decades of research suggest that important neurochemicals, like growth hormone, are released in deep sleep. “We know that sleep disturbances and time frame and release of neurochemicals [are] all super important in fibromyalgia,” he said.
Side effects of medication could be another factor at play here. As with any drug, the side effects of SNRIs vary widely from person to person, but palpitations, tremulousness, and insomnia are common, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, internal medicine/rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain & Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“SNRIs are often ‘activating’ because of the increase in norepinephrine,” Dr. Clauw said. “This is often helpful for symptoms such as fatigue and memory problems — but could worsen sleep.”
That’s why he always recommends that patients take an SNRI in the morning, not at night. Try that and the following tips to help patients with fibromyalgia sleep better and feel better, too.
Start with the basics. It’s worth reminding patients about the tried-and-true tips like going to bed and waking up at the same time every day and keeping your bedroom quiet and dark. “Patients should first try ‘sleep hygiene’ strategies,” said Dr. Clauw. “If that doesn’t help then cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be very helpful.”
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CBT for insomnia helped patients with fibromyalgia improve sleep quality, pain, anxiety, and depression compared with nonpharmacologic treatments. And if that doesn’t help? “If need be, they can try nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, eg, tricyclics or gabapentinoids taken at bedtime,” said Dr. Clauw.
Help them fall in love with exercise. A personalized approach to exercise can help patients with fibromyalgia feel better, suggested a study review in Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Exercise can also help reset the circadian clock. Morning activity helps night owls get on an earlier schedule, suggested a study review published in Physical Activity and Nutrition.
Consider yoga, tai chi, or qigong. A study review published in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism suggested mind-body and combined exercises help improve sleep for people with fibromyalgia, while aerobic or strength training alone does not. One explanation is that mind-body exercises might do more than other types to tamp down sympathetic-excitatory overactivation in fibromyalgia, the researchers said. Use this handy guide from the European Pain Federation to help you start the exercise conversation.
Talk about sleep alongside other aspects of fibromyalgia. Psychoeducation for fibromyalgia often includes information about the distinction between acute and chronic pain, the nature of fibromyalgia syndrome, disease-contributing factors, safe and effective treatments, symptoms and characteristics, and coping strategies, according to a study review in the journal Behavioral Sciences. “As a psychiatrist and someone who often consults patients with fibromyalgia, I would also add the information about links between pain and mood, anxiety as well as sleep,” said Dr. Krupa.
Try morning light. Use light to shift circadian rhythms, suggested Dr. Krupa. People who struggle in the morning might benefit from 30-60 minutes of morning light therapy immediately after waking using a 10,000-lux light box or light glasses, as suggested by a study review from the University of Michigan.
Help them get off the night shift. “Fibromyalgia patients probably shouldn’t work the night shift and throw their circadian rhythm off,” said Dr. Arkfeld. Depending on a patient’s work and financial circumstances, a job change might not be possible, but consider writing a note to the patient’s employer asking them to switch the patient to the day shift. Dr. Arkfeld said this approach has worked for some of his patients.
Refer them for a sleep study. Many patients with fibromyalgia have obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep disorders that require additional intervention. “Sleep studies are important to kind of define the actual sleep problem that’s occurring as well, whether it’s the stage for interruption of sleep or sleep apnea or wakefulness,” said Dr. Arkfeld.
The study was funded by Jagiellonian University Medical College. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Not a morning person? For patients with fibromyalgia, the answer to that question could be a clue about their treatment response with a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), suggested a new cross-sectional study published in Rheumatology International.
Compared with patients who had 30% or more pain relief after 8 or more weeks on an SNRI (duloxetine, venlafaxine, or milnacipran), those with less pain relief reported rougher mornings and worse sleep overall. Morningness, morning affect, diurnal dysrhythmia, anytime wakeability, overall sleep quality, subjective sleep quality and disturbances, sleep medication use, and daytime dysfunction were all predictors of nonresponse to SNRI treatment.
“The observed chronobiological characteristics of patients resistant to SNRI treatment are important because they can be targeted with adjunctive circadian interventions, ie, morning light therapy, in order to normalize circadian rhythms and improve sleep, and in effect, overcome the resistance to treatment and alleviate [the] patient’s pain,” said study author Anna Julia Krupa, MD, a psychiatrist and research assistant in the Department of Affective Disorders at Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland.
Fibromyalgia symptoms like sleep disturbance, low mood, fatigue, stiffness, cognitive impairment, and anxiety are often interlinked in positive feedback loops, meaning that the presence of one symptom (ie, sleep problems or depression) exacerbates the other (ie, pain or anxiety), Dr. Krupa said. While SNRIs can reduce pain, anxiety, and depression, they don’t directly improve sleep. Sometimes, pain relief smooths out minor sleep problems, but not always.
“Therefore, if circadian rhythm disruptions and sleep problems are significant, they may constitute a factor which limits SNRI effects on pain in people with fibromyalgia,” Dr. Krupa said.
With 60 patients with fibromyalgia (30 responsive to treatment and 30 nonresponsive to treatment) and 30 healthy controls, this was a small study, noted Daniel G. Arkfeld, MD, DDS, a rheumatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. However, “sleep is probably one of the most difficult things in fibromyalgia, and it definitely needs to be targeted.”
Decades of research suggest that important neurochemicals, like growth hormone, are released in deep sleep. “We know that sleep disturbances and time frame and release of neurochemicals [are] all super important in fibromyalgia,” he said.
Side effects of medication could be another factor at play here. As with any drug, the side effects of SNRIs vary widely from person to person, but palpitations, tremulousness, and insomnia are common, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, internal medicine/rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain & Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“SNRIs are often ‘activating’ because of the increase in norepinephrine,” Dr. Clauw said. “This is often helpful for symptoms such as fatigue and memory problems — but could worsen sleep.”
That’s why he always recommends that patients take an SNRI in the morning, not at night. Try that and the following tips to help patients with fibromyalgia sleep better and feel better, too.
Start with the basics. It’s worth reminding patients about the tried-and-true tips like going to bed and waking up at the same time every day and keeping your bedroom quiet and dark. “Patients should first try ‘sleep hygiene’ strategies,” said Dr. Clauw. “If that doesn’t help then cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be very helpful.”
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CBT for insomnia helped patients with fibromyalgia improve sleep quality, pain, anxiety, and depression compared with nonpharmacologic treatments. And if that doesn’t help? “If need be, they can try nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, eg, tricyclics or gabapentinoids taken at bedtime,” said Dr. Clauw.
Help them fall in love with exercise. A personalized approach to exercise can help patients with fibromyalgia feel better, suggested a study review in Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Exercise can also help reset the circadian clock. Morning activity helps night owls get on an earlier schedule, suggested a study review published in Physical Activity and Nutrition.
Consider yoga, tai chi, or qigong. A study review published in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism suggested mind-body and combined exercises help improve sleep for people with fibromyalgia, while aerobic or strength training alone does not. One explanation is that mind-body exercises might do more than other types to tamp down sympathetic-excitatory overactivation in fibromyalgia, the researchers said. Use this handy guide from the European Pain Federation to help you start the exercise conversation.
Talk about sleep alongside other aspects of fibromyalgia. Psychoeducation for fibromyalgia often includes information about the distinction between acute and chronic pain, the nature of fibromyalgia syndrome, disease-contributing factors, safe and effective treatments, symptoms and characteristics, and coping strategies, according to a study review in the journal Behavioral Sciences. “As a psychiatrist and someone who often consults patients with fibromyalgia, I would also add the information about links between pain and mood, anxiety as well as sleep,” said Dr. Krupa.
Try morning light. Use light to shift circadian rhythms, suggested Dr. Krupa. People who struggle in the morning might benefit from 30-60 minutes of morning light therapy immediately after waking using a 10,000-lux light box or light glasses, as suggested by a study review from the University of Michigan.
Help them get off the night shift. “Fibromyalgia patients probably shouldn’t work the night shift and throw their circadian rhythm off,” said Dr. Arkfeld. Depending on a patient’s work and financial circumstances, a job change might not be possible, but consider writing a note to the patient’s employer asking them to switch the patient to the day shift. Dr. Arkfeld said this approach has worked for some of his patients.
Refer them for a sleep study. Many patients with fibromyalgia have obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep disorders that require additional intervention. “Sleep studies are important to kind of define the actual sleep problem that’s occurring as well, whether it’s the stage for interruption of sleep or sleep apnea or wakefulness,” said Dr. Arkfeld.
The study was funded by Jagiellonian University Medical College. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY INTERNATIONAL
Methotrexate Shows Signs of Relieving Painful Knee Osteoarthritis
TOPLINE:
The antimetabolite and immunosuppressant methotrexate, taken orally and in addition to usual analgesia, alleviates pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a phase 3 randomized controlled trial among 155 patients in the United Kingdom with painful radiographic knee osteoarthritis and an inadequate response to their current medication (PROMOTE trial).
- Patients were assigned to oral methotrexate once weekly (6-week escalation from 10 to 25 mg) or placebo for 12 months, added to usual analgesia.
- The main outcome was average knee pain at 6 months on a numerical rating scale from 0 to 10.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 6 months, mean scores for knee pain had decreased by 1.3 points in the methotrexate group and 0.6 points in the placebo group (difference by intention to treat, 0.79 points; P = .030).
- The former also saw greater benefit in terms of Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index scores for stiffness (difference, 0.60 points; P = .045) and physical function (difference, 5.01 points; P = .008).
- Differences between groups were no longer significant at 12 months.
- Benefit of methotrexate appeared to be dose related.
- The groups were similar with respect to nausea and diarrhea; four serious adverse events (two per group) were deemed unrelated to study treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“Further work is required to understand adequate methotrexate dosing, whether benefits are greater in those with elevated systemic inflammation levels, and to consider cost-effectiveness before introducing this therapy for a potentially large population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sarah R. Kingsbury, PhD, University of Leeds and National Institute for Health and Care Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre, Leeds, England, and was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included a decrease in methotrexate dose between 6 and 12 months, nonallowance of switching to subcutaneous drug for intolerance, and a lack of assessment of the effectiveness of blinding.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Versus Arthritis, a charity that supports people with arthritis. Some authors reported affiliations with Versus Arthritis and/or companies that develop drugs for arthritis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The antimetabolite and immunosuppressant methotrexate, taken orally and in addition to usual analgesia, alleviates pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a phase 3 randomized controlled trial among 155 patients in the United Kingdom with painful radiographic knee osteoarthritis and an inadequate response to their current medication (PROMOTE trial).
- Patients were assigned to oral methotrexate once weekly (6-week escalation from 10 to 25 mg) or placebo for 12 months, added to usual analgesia.
- The main outcome was average knee pain at 6 months on a numerical rating scale from 0 to 10.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 6 months, mean scores for knee pain had decreased by 1.3 points in the methotrexate group and 0.6 points in the placebo group (difference by intention to treat, 0.79 points; P = .030).
- The former also saw greater benefit in terms of Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index scores for stiffness (difference, 0.60 points; P = .045) and physical function (difference, 5.01 points; P = .008).
- Differences between groups were no longer significant at 12 months.
- Benefit of methotrexate appeared to be dose related.
- The groups were similar with respect to nausea and diarrhea; four serious adverse events (two per group) were deemed unrelated to study treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“Further work is required to understand adequate methotrexate dosing, whether benefits are greater in those with elevated systemic inflammation levels, and to consider cost-effectiveness before introducing this therapy for a potentially large population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sarah R. Kingsbury, PhD, University of Leeds and National Institute for Health and Care Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre, Leeds, England, and was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included a decrease in methotrexate dose between 6 and 12 months, nonallowance of switching to subcutaneous drug for intolerance, and a lack of assessment of the effectiveness of blinding.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Versus Arthritis, a charity that supports people with arthritis. Some authors reported affiliations with Versus Arthritis and/or companies that develop drugs for arthritis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The antimetabolite and immunosuppressant methotrexate, taken orally and in addition to usual analgesia, alleviates pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a phase 3 randomized controlled trial among 155 patients in the United Kingdom with painful radiographic knee osteoarthritis and an inadequate response to their current medication (PROMOTE trial).
- Patients were assigned to oral methotrexate once weekly (6-week escalation from 10 to 25 mg) or placebo for 12 months, added to usual analgesia.
- The main outcome was average knee pain at 6 months on a numerical rating scale from 0 to 10.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 6 months, mean scores for knee pain had decreased by 1.3 points in the methotrexate group and 0.6 points in the placebo group (difference by intention to treat, 0.79 points; P = .030).
- The former also saw greater benefit in terms of Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index scores for stiffness (difference, 0.60 points; P = .045) and physical function (difference, 5.01 points; P = .008).
- Differences between groups were no longer significant at 12 months.
- Benefit of methotrexate appeared to be dose related.
- The groups were similar with respect to nausea and diarrhea; four serious adverse events (two per group) were deemed unrelated to study treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“Further work is required to understand adequate methotrexate dosing, whether benefits are greater in those with elevated systemic inflammation levels, and to consider cost-effectiveness before introducing this therapy for a potentially large population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sarah R. Kingsbury, PhD, University of Leeds and National Institute for Health and Care Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre, Leeds, England, and was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included a decrease in methotrexate dose between 6 and 12 months, nonallowance of switching to subcutaneous drug for intolerance, and a lack of assessment of the effectiveness of blinding.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Versus Arthritis, a charity that supports people with arthritis. Some authors reported affiliations with Versus Arthritis and/or companies that develop drugs for arthritis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Common Is Pediatric Emergency Mistriage?
, according to a multicenter retrospective study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also identified gender, age, race, ethnicity, and comorbidity disparities in those who were undertriaged.
The researchers found that only 34.1% of visits were correctly triaged while 58.5% were overtriaged and 7.4% were undertriaged. The findings were based on analysis of more than 1 million pediatric emergency visits over a 5-year period that used the Emergency Severity Index (ESI) version 4 for triage.
“The ESI had poor sensitivity in identifying a critically ill pediatric patient, and undertriage occurred in 1 in 14 children,” wrote Dana R. Sax, MD, a senior emergency physician at The Permanente Medical Group in northern California, and her colleagues.

“More than 90% of pediatric visits were assigned a mid to low triage acuity category, and actual resource use and care intensity frequently did not align with ESI predictions,” the authors wrote. “Our findings highlight an opportunity to improve triage for pediatric patients to mitigate critical undertriage, optimize resource decisions, standardize processes across time and setting, and promote more equitable care.”
The authors added that the study findings are currently being used by the Permanente system “to develop standardized triage education across centers to improve early identification of high-risk patients.”
Disparities in Emergency Care
The results underscore the need for more work to address disparities in emergency care, wrote Warren D. Frankenberger, PhD, RN, a nurse scientist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and two colleagues in an accompanying editorial.
“Decisions in triage can have significant downstream effects on subsequent care during the ED visit,” they wrote in their editorial. “Given that the triage process in most instances is fully executed by nurses, nurse researchers are in a key position to evaluate these and other covariates to influence further improvements in triage.” They suggested that use of clinical decision support tools and artificial intelligence (AI) may improve the triage process, albeit with the caveat that AI often relies on models with pre-existing historical bias that may perpetuate structural inequalities.
Study Methodology
The researchers analyzed 1,016,816 pediatric visits at 21 emergency departments in Kaiser Permanente Northern California between January 2016 and December 2020. The patients were an average 7 years old, and 47% were female. The researchers excluded visits that lacked ESI data or had incomplete ED time variables as well as those with patients who left against medical advice, were not seen, or were transferred from another ED.
The study relied on novel definitions of ESI undertriage and overtriage developed through a modified Delphi process by a team of four emergency physicians, one pediatric emergency physician, two emergency nurses, and one pediatric ICU physician. The definition involved comparing ESI levels to the clinical outcomes and resource use.
Resources included laboratory analysis, electrocardiography, radiography, CT, MRI, diagnostic ultrasonography (not point of care), angiography, IV fluids, and IV, intramuscular, or nebulized medications. Resources did not include “oral medications, tetanus immunizations, point-of-care testing, history and physical examination, saline or heparin lock, prescription refills, simple wound care, crutches, splints, and slings.”
Level 1 events were those requiring time-sensitive, critical intervention, including high-risk sepsis. Level 2 events included most level 1 events that occurred after the first hour (except operating room admission or hospital transfer) as well as respiratory therapy, toxicology consult, lumbar puncture, suicidality as chief concern, at least 2 doses of albuterol or continuous albuterol nebulization, a skeletal survey x-ray order, and medical social work consult with an ED length of stay of at least 2 hours. Level 3 events included IV mediation order, any CT order, OR admission or hospital transfer after one hour, or any pediatric hospitalist consult.
Analyzing the ED Visits
Overtriaged cases were ESI level 1 or 2 cases in which fewer than 2 resources were used; level 3 cases where fewer than 2 resources were used and no level 1 or 2 events occurred; and level 4 cases where no resources were used.
Undertriaged cases were defined as the following:
- ESI level 5 cases where any resource was used and any level 1, 2, or 3 events occurred.
- Level 4 cases where more than 1 resource was used and any level 1, 2, or 3 events occurred.
- Level 3 cases where any level 1 event occurred, more than one level 2 event occurred, or any level 2 event occurred and more than one additional ED resource type was used.
- Level 2 cases where any level 1 event occurred.
About half the visits (51%) were assigned ESI 3, which was the category with the highest proportion of mistriage. After adjusting for study facility and triage vital signs, the researchers found that children age 6 and older were more likely to be undertriaged than those younger than 6, particularly those age 15 and older (relative risk [RR], 1.36).
Undertriage was also modestly more likely with male patients (female patients’ RR, 0.93), patients with comorbidities (RR, 1.11-1.2), patients who arrived by ambulance (RR, 1.04), and patients who were Asian (RR, 1.10), Black (RR, 1.05), or Hispanic (RR, 1.04). Undertriage became gradually less likely with each additional year in the study period, with an RR of 0.89 in 2019 and 2020.
Among the study’s limitations were use of ESI version 4, instead of the currently used 5, and the omission of common procedures from the outcome definition that “may systematically bias the analysis toward overtriage,” the editorial noted. The authors also did not include pain as a variable in the analysis, which can often indicate patient acuity.
Further, this study was unable to include covariates identified in other research that may influence clinical decision-making, such as “the presenting illness or injury, children with complex medical needs, and language proficiency,” Dr. Frankenberger and colleagues wrote. “Furthermore, environmental stressors, such as ED volume and crowding, can influence how a nurse prioritizes care and may increase bias in decision-making and/or increase practice variability.”
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) Community Health program. One author had consulting payments from CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care, and six of the authors have received grant funding from the KPNC Community Health program. The editorial authors reported no conflicts of interest.
, according to a multicenter retrospective study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also identified gender, age, race, ethnicity, and comorbidity disparities in those who were undertriaged.
The researchers found that only 34.1% of visits were correctly triaged while 58.5% were overtriaged and 7.4% were undertriaged. The findings were based on analysis of more than 1 million pediatric emergency visits over a 5-year period that used the Emergency Severity Index (ESI) version 4 for triage.
“The ESI had poor sensitivity in identifying a critically ill pediatric patient, and undertriage occurred in 1 in 14 children,” wrote Dana R. Sax, MD, a senior emergency physician at The Permanente Medical Group in northern California, and her colleagues.

“More than 90% of pediatric visits were assigned a mid to low triage acuity category, and actual resource use and care intensity frequently did not align with ESI predictions,” the authors wrote. “Our findings highlight an opportunity to improve triage for pediatric patients to mitigate critical undertriage, optimize resource decisions, standardize processes across time and setting, and promote more equitable care.”
The authors added that the study findings are currently being used by the Permanente system “to develop standardized triage education across centers to improve early identification of high-risk patients.”
Disparities in Emergency Care
The results underscore the need for more work to address disparities in emergency care, wrote Warren D. Frankenberger, PhD, RN, a nurse scientist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and two colleagues in an accompanying editorial.
“Decisions in triage can have significant downstream effects on subsequent care during the ED visit,” they wrote in their editorial. “Given that the triage process in most instances is fully executed by nurses, nurse researchers are in a key position to evaluate these and other covariates to influence further improvements in triage.” They suggested that use of clinical decision support tools and artificial intelligence (AI) may improve the triage process, albeit with the caveat that AI often relies on models with pre-existing historical bias that may perpetuate structural inequalities.
Study Methodology
The researchers analyzed 1,016,816 pediatric visits at 21 emergency departments in Kaiser Permanente Northern California between January 2016 and December 2020. The patients were an average 7 years old, and 47% were female. The researchers excluded visits that lacked ESI data or had incomplete ED time variables as well as those with patients who left against medical advice, were not seen, or were transferred from another ED.
The study relied on novel definitions of ESI undertriage and overtriage developed through a modified Delphi process by a team of four emergency physicians, one pediatric emergency physician, two emergency nurses, and one pediatric ICU physician. The definition involved comparing ESI levels to the clinical outcomes and resource use.
Resources included laboratory analysis, electrocardiography, radiography, CT, MRI, diagnostic ultrasonography (not point of care), angiography, IV fluids, and IV, intramuscular, or nebulized medications. Resources did not include “oral medications, tetanus immunizations, point-of-care testing, history and physical examination, saline or heparin lock, prescription refills, simple wound care, crutches, splints, and slings.”
Level 1 events were those requiring time-sensitive, critical intervention, including high-risk sepsis. Level 2 events included most level 1 events that occurred after the first hour (except operating room admission or hospital transfer) as well as respiratory therapy, toxicology consult, lumbar puncture, suicidality as chief concern, at least 2 doses of albuterol or continuous albuterol nebulization, a skeletal survey x-ray order, and medical social work consult with an ED length of stay of at least 2 hours. Level 3 events included IV mediation order, any CT order, OR admission or hospital transfer after one hour, or any pediatric hospitalist consult.
Analyzing the ED Visits
Overtriaged cases were ESI level 1 or 2 cases in which fewer than 2 resources were used; level 3 cases where fewer than 2 resources were used and no level 1 or 2 events occurred; and level 4 cases where no resources were used.
Undertriaged cases were defined as the following:
- ESI level 5 cases where any resource was used and any level 1, 2, or 3 events occurred.
- Level 4 cases where more than 1 resource was used and any level 1, 2, or 3 events occurred.
- Level 3 cases where any level 1 event occurred, more than one level 2 event occurred, or any level 2 event occurred and more than one additional ED resource type was used.
- Level 2 cases where any level 1 event occurred.
About half the visits (51%) were assigned ESI 3, which was the category with the highest proportion of mistriage. After adjusting for study facility and triage vital signs, the researchers found that children age 6 and older were more likely to be undertriaged than those younger than 6, particularly those age 15 and older (relative risk [RR], 1.36).
Undertriage was also modestly more likely with male patients (female patients’ RR, 0.93), patients with comorbidities (RR, 1.11-1.2), patients who arrived by ambulance (RR, 1.04), and patients who were Asian (RR, 1.10), Black (RR, 1.05), or Hispanic (RR, 1.04). Undertriage became gradually less likely with each additional year in the study period, with an RR of 0.89 in 2019 and 2020.
Among the study’s limitations were use of ESI version 4, instead of the currently used 5, and the omission of common procedures from the outcome definition that “may systematically bias the analysis toward overtriage,” the editorial noted. The authors also did not include pain as a variable in the analysis, which can often indicate patient acuity.
Further, this study was unable to include covariates identified in other research that may influence clinical decision-making, such as “the presenting illness or injury, children with complex medical needs, and language proficiency,” Dr. Frankenberger and colleagues wrote. “Furthermore, environmental stressors, such as ED volume and crowding, can influence how a nurse prioritizes care and may increase bias in decision-making and/or increase practice variability.”
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) Community Health program. One author had consulting payments from CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care, and six of the authors have received grant funding from the KPNC Community Health program. The editorial authors reported no conflicts of interest.
, according to a multicenter retrospective study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also identified gender, age, race, ethnicity, and comorbidity disparities in those who were undertriaged.
The researchers found that only 34.1% of visits were correctly triaged while 58.5% were overtriaged and 7.4% were undertriaged. The findings were based on analysis of more than 1 million pediatric emergency visits over a 5-year period that used the Emergency Severity Index (ESI) version 4 for triage.
“The ESI had poor sensitivity in identifying a critically ill pediatric patient, and undertriage occurred in 1 in 14 children,” wrote Dana R. Sax, MD, a senior emergency physician at The Permanente Medical Group in northern California, and her colleagues.

“More than 90% of pediatric visits were assigned a mid to low triage acuity category, and actual resource use and care intensity frequently did not align with ESI predictions,” the authors wrote. “Our findings highlight an opportunity to improve triage for pediatric patients to mitigate critical undertriage, optimize resource decisions, standardize processes across time and setting, and promote more equitable care.”
The authors added that the study findings are currently being used by the Permanente system “to develop standardized triage education across centers to improve early identification of high-risk patients.”
Disparities in Emergency Care
The results underscore the need for more work to address disparities in emergency care, wrote Warren D. Frankenberger, PhD, RN, a nurse scientist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and two colleagues in an accompanying editorial.
“Decisions in triage can have significant downstream effects on subsequent care during the ED visit,” they wrote in their editorial. “Given that the triage process in most instances is fully executed by nurses, nurse researchers are in a key position to evaluate these and other covariates to influence further improvements in triage.” They suggested that use of clinical decision support tools and artificial intelligence (AI) may improve the triage process, albeit with the caveat that AI often relies on models with pre-existing historical bias that may perpetuate structural inequalities.
Study Methodology
The researchers analyzed 1,016,816 pediatric visits at 21 emergency departments in Kaiser Permanente Northern California between January 2016 and December 2020. The patients were an average 7 years old, and 47% were female. The researchers excluded visits that lacked ESI data or had incomplete ED time variables as well as those with patients who left against medical advice, were not seen, or were transferred from another ED.
The study relied on novel definitions of ESI undertriage and overtriage developed through a modified Delphi process by a team of four emergency physicians, one pediatric emergency physician, two emergency nurses, and one pediatric ICU physician. The definition involved comparing ESI levels to the clinical outcomes and resource use.
Resources included laboratory analysis, electrocardiography, radiography, CT, MRI, diagnostic ultrasonography (not point of care), angiography, IV fluids, and IV, intramuscular, or nebulized medications. Resources did not include “oral medications, tetanus immunizations, point-of-care testing, history and physical examination, saline or heparin lock, prescription refills, simple wound care, crutches, splints, and slings.”
Level 1 events were those requiring time-sensitive, critical intervention, including high-risk sepsis. Level 2 events included most level 1 events that occurred after the first hour (except operating room admission or hospital transfer) as well as respiratory therapy, toxicology consult, lumbar puncture, suicidality as chief concern, at least 2 doses of albuterol or continuous albuterol nebulization, a skeletal survey x-ray order, and medical social work consult with an ED length of stay of at least 2 hours. Level 3 events included IV mediation order, any CT order, OR admission or hospital transfer after one hour, or any pediatric hospitalist consult.
Analyzing the ED Visits
Overtriaged cases were ESI level 1 or 2 cases in which fewer than 2 resources were used; level 3 cases where fewer than 2 resources were used and no level 1 or 2 events occurred; and level 4 cases where no resources were used.
Undertriaged cases were defined as the following:
- ESI level 5 cases where any resource was used and any level 1, 2, or 3 events occurred.
- Level 4 cases where more than 1 resource was used and any level 1, 2, or 3 events occurred.
- Level 3 cases where any level 1 event occurred, more than one level 2 event occurred, or any level 2 event occurred and more than one additional ED resource type was used.
- Level 2 cases where any level 1 event occurred.
About half the visits (51%) were assigned ESI 3, which was the category with the highest proportion of mistriage. After adjusting for study facility and triage vital signs, the researchers found that children age 6 and older were more likely to be undertriaged than those younger than 6, particularly those age 15 and older (relative risk [RR], 1.36).
Undertriage was also modestly more likely with male patients (female patients’ RR, 0.93), patients with comorbidities (RR, 1.11-1.2), patients who arrived by ambulance (RR, 1.04), and patients who were Asian (RR, 1.10), Black (RR, 1.05), or Hispanic (RR, 1.04). Undertriage became gradually less likely with each additional year in the study period, with an RR of 0.89 in 2019 and 2020.
Among the study’s limitations were use of ESI version 4, instead of the currently used 5, and the omission of common procedures from the outcome definition that “may systematically bias the analysis toward overtriage,” the editorial noted. The authors also did not include pain as a variable in the analysis, which can often indicate patient acuity.
Further, this study was unable to include covariates identified in other research that may influence clinical decision-making, such as “the presenting illness or injury, children with complex medical needs, and language proficiency,” Dr. Frankenberger and colleagues wrote. “Furthermore, environmental stressors, such as ED volume and crowding, can influence how a nurse prioritizes care and may increase bias in decision-making and/or increase practice variability.”
The study was funded by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) Community Health program. One author had consulting payments from CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care, and six of the authors have received grant funding from the KPNC Community Health program. The editorial authors reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS