User login
Family Not Flourishing? The Hidden Issue of Food Insecurity and How We Can Help
As pediatric providers we are dedicated to helping children have optimal health. And what could be more basic to health than having enough food? Yet, even in one of the richest countries on the planet, as much as 25% of US families are reported to have “food insecurity.”
What does this mean? The US Department of Agriculture (USDA), the agency tracking and addressing food issues, defines food security as “marginal” when there are one or two indications, typically anxiety over food sufficiency or shortage of food even with little or no alteration of diet or intake. “Low” includes reduced quality, variety, or desirability of the diet but little or no reduced intake. When eating patterns are disrupted and intake is reduced, this is considered “very low food security.” “Hunger” refers to an individual’s physiological state when prolonged, involuntary lack of food results in discomfort, illness, weakness, or pain beyond the usual uneasy sensation. Pediatric researchers include in the definition lack of access to enough food for an active and healthy life. I will use the common term “food insecurity” here.
Children under 3 years old in homes with food insecurity have been found to be sick more often, recover more slowly from illness, and be hospitalized more frequently. Deficiencies in nutrition vary by age, with children under 6 having low vegetable intake and low iron, ages 6-11 excess sugary food intake and lower bone density in boys, and adolescents, although harder to measure, had low iron.
Physical and Mental Effects of Food Insecurity
Associated with food insecurity in the home are more developmental delays in children 4-36 months old. Beyond that, children of all ages have lower cognitive indicators, dysregulated behavior, and emotional distress than those in homes with secure food access. These are persisting deficits: kindergarten children with food insecurity have lower math and reading abilities over at least 4 years.
Mental health is also affected by food insecurity. Reviews of multiple studies of children from preschool through adolescence show more child hyperactivity, emotional dysregulation, anxiety, depression, and stress beyond those attributable to their mother’s depression and anxiety. Food insecurity in the early years is associated with mental health issues even into adolescence. School aged children and youth are well aware of the family’s struggle with food access, even when their parents do not realize this. In addition to the anxiety and depression, they may feel shame or be socially ostracized. They may eat less, or choose low-quality foods to cope. Adolescents experiencing food insecurity report greater dysthymia and suicidal ideation. It is unknown whether these mental health difficulties are due to the stress, shame, or decreased intake of macronutrients important to emotional regulation or all of these. One implication is that pediatric providers should also screen for food insecurity as well as other social drivers of health (SDOH) when addressing developmental, behavioral, or mental health issues, not just at well visits.
While we worry about effects for the child, impact of food insecurity on caregivers is significant for parenting as well as adult well-being beginning prenatally. First trimester food insecurity is associated with increased maternal stress at 2 months postpartum and lower bonding scores at 6 months, although this is moderated by social support. The stress of food insecurity and other SDoH present are associated with parental depression, anxiety, and toxic stress, making optimal parenting difficult. Caregivers experiencing insecure food access worry most about their children and may reduce their own eating and food quality to spare the child. More than 30% of families indicated that they had to choose between paying for food and paying for medicine or medical care, jeopardizing their health, making this an important point of discussion for us as well.
Quality Versus Quantity
The total amount of food is not the only factor in adequate child nutrition. Healthy foods usually cost more and also may not be conveniently available. There are so called “food deserts,” areas with few/no full-service grocery stores, and also “food swamps” where unhealthy foods (eg fast food) are more available than healthy options. Life stress, higher in low-income populations, increases the impulse to consume sweet or high-fat “comfort foods” (we all know this!) due to the rush of calories and quick satiety. Children may be influenced in their food choices by media messages about non-nutritious foods. All of these may explain the association of food insecurity with obesity in both children and adults. It also sets them up for lifetime health problems of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular conditions, especially in racial and ethnic minority groups and the poor.
The Larger Picture
Obvious to us all, low income is the main reason for inadequate access to enough or good quality food. Over 60% of families with food insecurity had incomes below the poverty threshold in 2013. Households without children are half as likely to be food insecure. But as 30% of food-insecure households have incomes above the eligibility cut offs for food programs — typically 130% of poverty for Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) or 185% for Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) — it is clear the problem is not related solely to poverty. Even small changes in income or expenses, such as a car breaking down, or heating or medical bills, can quickly result in inability to afford food, especially in areas of high food costs. This is particularly true for immigrant, large, and single-parent families and those with less education. Federal food programs do not cover all food needs for every family.
But we can’t tell if a child lives in a family with food insecurity by whether the child is thin, dropping growth percentiles, or receiving Medicaid insurance. Parents, and even youth, may be reluctant to tell us that they do not have enough to eat out of pride, fear, of prejudice, being reported to a contentious ex, being detected as an illegal immigrant, or even reported for neglect and having their child removed. Because of the suffering and impacts of food insecurity on child well-being, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) published a Policy Statement in 2015, reaffirmed in 2021, recommending screening for food insecurity at all well visits and a toolkit to help. The USDA 18-item Household Food Security Scale (HFSS) has been the gold-standard screen, but affirmative answers to either of the 2-item Hunger Vital Sign (HVS) questionnaire identifies food insecurity with a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 83% compared with the HFSS. The questions ask how often the following were true in the past year: 1) “We worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more” and 2) “The food we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to buy more.” This brief screen is now recommended and practical.
Screening for Food Insecurity
All set to manage food insecurity in your practice, then? Not exactly. Screening is only useful if it results in access to food. A study in a majority low-income clinic found that parents reported food insecurity 7% of the time when the clinician asked the HVS questions versus 45% when they self-reported on paper. Parent focus groups revealed reasons for the discrepant underreporting to the clinician: shame, concerns about stigma, and fear of the child being taken away. They felt more comfortable reporting about their child than about their own family situation. When asked what the clinician did that helped them disclose food insecurity, the caregivers cited strong interpersonal skills, open body language, and empathy. They also requested being given resources for other social issues, not just food insecurity. Clinic staff found paper screening inconvenient and recommended using tablet devices (such as with CHADIS that also scores and provides interviewing help, education, and local resource listings). Clinicians found the need for a follow-up conversation time consuming. Clinic staff thought screening could be facilitated by clinician’s initiating conversations, taking care about children present, and normalizing the screen as applying to all. Caregivers wanted know the use and privacy of the information. This same clinic referred the caregivers to a Benefits Data Trust with a goal of enrolling them in food programs. Of the food insecure, 55% were referred but only one third could be reached by phone with three attempts by the benefits group. Subsequent enrollment of those reached had barriers of verification requirements, wait times, and perceived mistreatment. The program concluded that this difficult two-step process of screening and referral would be improved by an integrated system of screening and enrollment in public benefits. Provision of information about free local food resources is also important, as 84% of those already receiving SNAP benefits remained food insecure.
Offering Assistance
To assist families where food insecurity is found, we need to understand the options of services both for referrals and advocacy. The AAP toolkit is designed to help. For pregnant and postpartum women and children 0-5 years in families with income less than 130% of the poverty level, the WIC program provides electronic cards to purchase approved categories of healthy food from participating vendors. For families with incomes less than 185% of the poverty level, the SNAP program, formerly called food stamps, provides benefits. There are other programs including free and reduced cost National School Breakfast and/or Lunch programs (best when open to all), Child and Adult Care Food Program for institutions (which may include medical offices), and Summer Food Service Programs providing lunch at community sites. Since not all food-insecure families are eligible for the above services, it is important that we are ready to provide information about local food banks, pantries, and low- or no-cost produce programs (see Healthy Food Bank Hub, Feeding America, 2-1-1, or FindHelp.org).
As pediatric providers we have a special opportunity and responsibility to expand our capabilities for sensitively addressing and advocating for help for food insecurity to improve the outlook for the families under our care.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
As pediatric providers we are dedicated to helping children have optimal health. And what could be more basic to health than having enough food? Yet, even in one of the richest countries on the planet, as much as 25% of US families are reported to have “food insecurity.”
What does this mean? The US Department of Agriculture (USDA), the agency tracking and addressing food issues, defines food security as “marginal” when there are one or two indications, typically anxiety over food sufficiency or shortage of food even with little or no alteration of diet or intake. “Low” includes reduced quality, variety, or desirability of the diet but little or no reduced intake. When eating patterns are disrupted and intake is reduced, this is considered “very low food security.” “Hunger” refers to an individual’s physiological state when prolonged, involuntary lack of food results in discomfort, illness, weakness, or pain beyond the usual uneasy sensation. Pediatric researchers include in the definition lack of access to enough food for an active and healthy life. I will use the common term “food insecurity” here.
Children under 3 years old in homes with food insecurity have been found to be sick more often, recover more slowly from illness, and be hospitalized more frequently. Deficiencies in nutrition vary by age, with children under 6 having low vegetable intake and low iron, ages 6-11 excess sugary food intake and lower bone density in boys, and adolescents, although harder to measure, had low iron.
Physical and Mental Effects of Food Insecurity
Associated with food insecurity in the home are more developmental delays in children 4-36 months old. Beyond that, children of all ages have lower cognitive indicators, dysregulated behavior, and emotional distress than those in homes with secure food access. These are persisting deficits: kindergarten children with food insecurity have lower math and reading abilities over at least 4 years.
Mental health is also affected by food insecurity. Reviews of multiple studies of children from preschool through adolescence show more child hyperactivity, emotional dysregulation, anxiety, depression, and stress beyond those attributable to their mother’s depression and anxiety. Food insecurity in the early years is associated with mental health issues even into adolescence. School aged children and youth are well aware of the family’s struggle with food access, even when their parents do not realize this. In addition to the anxiety and depression, they may feel shame or be socially ostracized. They may eat less, or choose low-quality foods to cope. Adolescents experiencing food insecurity report greater dysthymia and suicidal ideation. It is unknown whether these mental health difficulties are due to the stress, shame, or decreased intake of macronutrients important to emotional regulation or all of these. One implication is that pediatric providers should also screen for food insecurity as well as other social drivers of health (SDOH) when addressing developmental, behavioral, or mental health issues, not just at well visits.
While we worry about effects for the child, impact of food insecurity on caregivers is significant for parenting as well as adult well-being beginning prenatally. First trimester food insecurity is associated with increased maternal stress at 2 months postpartum and lower bonding scores at 6 months, although this is moderated by social support. The stress of food insecurity and other SDoH present are associated with parental depression, anxiety, and toxic stress, making optimal parenting difficult. Caregivers experiencing insecure food access worry most about their children and may reduce their own eating and food quality to spare the child. More than 30% of families indicated that they had to choose between paying for food and paying for medicine or medical care, jeopardizing their health, making this an important point of discussion for us as well.
Quality Versus Quantity
The total amount of food is not the only factor in adequate child nutrition. Healthy foods usually cost more and also may not be conveniently available. There are so called “food deserts,” areas with few/no full-service grocery stores, and also “food swamps” where unhealthy foods (eg fast food) are more available than healthy options. Life stress, higher in low-income populations, increases the impulse to consume sweet or high-fat “comfort foods” (we all know this!) due to the rush of calories and quick satiety. Children may be influenced in their food choices by media messages about non-nutritious foods. All of these may explain the association of food insecurity with obesity in both children and adults. It also sets them up for lifetime health problems of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular conditions, especially in racial and ethnic minority groups and the poor.
The Larger Picture
Obvious to us all, low income is the main reason for inadequate access to enough or good quality food. Over 60% of families with food insecurity had incomes below the poverty threshold in 2013. Households without children are half as likely to be food insecure. But as 30% of food-insecure households have incomes above the eligibility cut offs for food programs — typically 130% of poverty for Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) or 185% for Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) — it is clear the problem is not related solely to poverty. Even small changes in income or expenses, such as a car breaking down, or heating or medical bills, can quickly result in inability to afford food, especially in areas of high food costs. This is particularly true for immigrant, large, and single-parent families and those with less education. Federal food programs do not cover all food needs for every family.
But we can’t tell if a child lives in a family with food insecurity by whether the child is thin, dropping growth percentiles, or receiving Medicaid insurance. Parents, and even youth, may be reluctant to tell us that they do not have enough to eat out of pride, fear, of prejudice, being reported to a contentious ex, being detected as an illegal immigrant, or even reported for neglect and having their child removed. Because of the suffering and impacts of food insecurity on child well-being, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) published a Policy Statement in 2015, reaffirmed in 2021, recommending screening for food insecurity at all well visits and a toolkit to help. The USDA 18-item Household Food Security Scale (HFSS) has been the gold-standard screen, but affirmative answers to either of the 2-item Hunger Vital Sign (HVS) questionnaire identifies food insecurity with a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 83% compared with the HFSS. The questions ask how often the following were true in the past year: 1) “We worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more” and 2) “The food we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to buy more.” This brief screen is now recommended and practical.
Screening for Food Insecurity
All set to manage food insecurity in your practice, then? Not exactly. Screening is only useful if it results in access to food. A study in a majority low-income clinic found that parents reported food insecurity 7% of the time when the clinician asked the HVS questions versus 45% when they self-reported on paper. Parent focus groups revealed reasons for the discrepant underreporting to the clinician: shame, concerns about stigma, and fear of the child being taken away. They felt more comfortable reporting about their child than about their own family situation. When asked what the clinician did that helped them disclose food insecurity, the caregivers cited strong interpersonal skills, open body language, and empathy. They also requested being given resources for other social issues, not just food insecurity. Clinic staff found paper screening inconvenient and recommended using tablet devices (such as with CHADIS that also scores and provides interviewing help, education, and local resource listings). Clinicians found the need for a follow-up conversation time consuming. Clinic staff thought screening could be facilitated by clinician’s initiating conversations, taking care about children present, and normalizing the screen as applying to all. Caregivers wanted know the use and privacy of the information. This same clinic referred the caregivers to a Benefits Data Trust with a goal of enrolling them in food programs. Of the food insecure, 55% were referred but only one third could be reached by phone with three attempts by the benefits group. Subsequent enrollment of those reached had barriers of verification requirements, wait times, and perceived mistreatment. The program concluded that this difficult two-step process of screening and referral would be improved by an integrated system of screening and enrollment in public benefits. Provision of information about free local food resources is also important, as 84% of those already receiving SNAP benefits remained food insecure.
Offering Assistance
To assist families where food insecurity is found, we need to understand the options of services both for referrals and advocacy. The AAP toolkit is designed to help. For pregnant and postpartum women and children 0-5 years in families with income less than 130% of the poverty level, the WIC program provides electronic cards to purchase approved categories of healthy food from participating vendors. For families with incomes less than 185% of the poverty level, the SNAP program, formerly called food stamps, provides benefits. There are other programs including free and reduced cost National School Breakfast and/or Lunch programs (best when open to all), Child and Adult Care Food Program for institutions (which may include medical offices), and Summer Food Service Programs providing lunch at community sites. Since not all food-insecure families are eligible for the above services, it is important that we are ready to provide information about local food banks, pantries, and low- or no-cost produce programs (see Healthy Food Bank Hub, Feeding America, 2-1-1, or FindHelp.org).
As pediatric providers we have a special opportunity and responsibility to expand our capabilities for sensitively addressing and advocating for help for food insecurity to improve the outlook for the families under our care.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
As pediatric providers we are dedicated to helping children have optimal health. And what could be more basic to health than having enough food? Yet, even in one of the richest countries on the planet, as much as 25% of US families are reported to have “food insecurity.”
What does this mean? The US Department of Agriculture (USDA), the agency tracking and addressing food issues, defines food security as “marginal” when there are one or two indications, typically anxiety over food sufficiency or shortage of food even with little or no alteration of diet or intake. “Low” includes reduced quality, variety, or desirability of the diet but little or no reduced intake. When eating patterns are disrupted and intake is reduced, this is considered “very low food security.” “Hunger” refers to an individual’s physiological state when prolonged, involuntary lack of food results in discomfort, illness, weakness, or pain beyond the usual uneasy sensation. Pediatric researchers include in the definition lack of access to enough food for an active and healthy life. I will use the common term “food insecurity” here.
Children under 3 years old in homes with food insecurity have been found to be sick more often, recover more slowly from illness, and be hospitalized more frequently. Deficiencies in nutrition vary by age, with children under 6 having low vegetable intake and low iron, ages 6-11 excess sugary food intake and lower bone density in boys, and adolescents, although harder to measure, had low iron.
Physical and Mental Effects of Food Insecurity
Associated with food insecurity in the home are more developmental delays in children 4-36 months old. Beyond that, children of all ages have lower cognitive indicators, dysregulated behavior, and emotional distress than those in homes with secure food access. These are persisting deficits: kindergarten children with food insecurity have lower math and reading abilities over at least 4 years.
Mental health is also affected by food insecurity. Reviews of multiple studies of children from preschool through adolescence show more child hyperactivity, emotional dysregulation, anxiety, depression, and stress beyond those attributable to their mother’s depression and anxiety. Food insecurity in the early years is associated with mental health issues even into adolescence. School aged children and youth are well aware of the family’s struggle with food access, even when their parents do not realize this. In addition to the anxiety and depression, they may feel shame or be socially ostracized. They may eat less, or choose low-quality foods to cope. Adolescents experiencing food insecurity report greater dysthymia and suicidal ideation. It is unknown whether these mental health difficulties are due to the stress, shame, or decreased intake of macronutrients important to emotional regulation or all of these. One implication is that pediatric providers should also screen for food insecurity as well as other social drivers of health (SDOH) when addressing developmental, behavioral, or mental health issues, not just at well visits.
While we worry about effects for the child, impact of food insecurity on caregivers is significant for parenting as well as adult well-being beginning prenatally. First trimester food insecurity is associated with increased maternal stress at 2 months postpartum and lower bonding scores at 6 months, although this is moderated by social support. The stress of food insecurity and other SDoH present are associated with parental depression, anxiety, and toxic stress, making optimal parenting difficult. Caregivers experiencing insecure food access worry most about their children and may reduce their own eating and food quality to spare the child. More than 30% of families indicated that they had to choose between paying for food and paying for medicine or medical care, jeopardizing their health, making this an important point of discussion for us as well.
Quality Versus Quantity
The total amount of food is not the only factor in adequate child nutrition. Healthy foods usually cost more and also may not be conveniently available. There are so called “food deserts,” areas with few/no full-service grocery stores, and also “food swamps” where unhealthy foods (eg fast food) are more available than healthy options. Life stress, higher in low-income populations, increases the impulse to consume sweet or high-fat “comfort foods” (we all know this!) due to the rush of calories and quick satiety. Children may be influenced in their food choices by media messages about non-nutritious foods. All of these may explain the association of food insecurity with obesity in both children and adults. It also sets them up for lifetime health problems of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular conditions, especially in racial and ethnic minority groups and the poor.
The Larger Picture
Obvious to us all, low income is the main reason for inadequate access to enough or good quality food. Over 60% of families with food insecurity had incomes below the poverty threshold in 2013. Households without children are half as likely to be food insecure. But as 30% of food-insecure households have incomes above the eligibility cut offs for food programs — typically 130% of poverty for Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) or 185% for Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) — it is clear the problem is not related solely to poverty. Even small changes in income or expenses, such as a car breaking down, or heating or medical bills, can quickly result in inability to afford food, especially in areas of high food costs. This is particularly true for immigrant, large, and single-parent families and those with less education. Federal food programs do not cover all food needs for every family.
But we can’t tell if a child lives in a family with food insecurity by whether the child is thin, dropping growth percentiles, or receiving Medicaid insurance. Parents, and even youth, may be reluctant to tell us that they do not have enough to eat out of pride, fear, of prejudice, being reported to a contentious ex, being detected as an illegal immigrant, or even reported for neglect and having their child removed. Because of the suffering and impacts of food insecurity on child well-being, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) published a Policy Statement in 2015, reaffirmed in 2021, recommending screening for food insecurity at all well visits and a toolkit to help. The USDA 18-item Household Food Security Scale (HFSS) has been the gold-standard screen, but affirmative answers to either of the 2-item Hunger Vital Sign (HVS) questionnaire identifies food insecurity with a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 83% compared with the HFSS. The questions ask how often the following were true in the past year: 1) “We worried whether our food would run out before we got money to buy more” and 2) “The food we bought just didn’t last and we didn’t have money to buy more.” This brief screen is now recommended and practical.
Screening for Food Insecurity
All set to manage food insecurity in your practice, then? Not exactly. Screening is only useful if it results in access to food. A study in a majority low-income clinic found that parents reported food insecurity 7% of the time when the clinician asked the HVS questions versus 45% when they self-reported on paper. Parent focus groups revealed reasons for the discrepant underreporting to the clinician: shame, concerns about stigma, and fear of the child being taken away. They felt more comfortable reporting about their child than about their own family situation. When asked what the clinician did that helped them disclose food insecurity, the caregivers cited strong interpersonal skills, open body language, and empathy. They also requested being given resources for other social issues, not just food insecurity. Clinic staff found paper screening inconvenient and recommended using tablet devices (such as with CHADIS that also scores and provides interviewing help, education, and local resource listings). Clinicians found the need for a follow-up conversation time consuming. Clinic staff thought screening could be facilitated by clinician’s initiating conversations, taking care about children present, and normalizing the screen as applying to all. Caregivers wanted know the use and privacy of the information. This same clinic referred the caregivers to a Benefits Data Trust with a goal of enrolling them in food programs. Of the food insecure, 55% were referred but only one third could be reached by phone with three attempts by the benefits group. Subsequent enrollment of those reached had barriers of verification requirements, wait times, and perceived mistreatment. The program concluded that this difficult two-step process of screening and referral would be improved by an integrated system of screening and enrollment in public benefits. Provision of information about free local food resources is also important, as 84% of those already receiving SNAP benefits remained food insecure.
Offering Assistance
To assist families where food insecurity is found, we need to understand the options of services both for referrals and advocacy. The AAP toolkit is designed to help. For pregnant and postpartum women and children 0-5 years in families with income less than 130% of the poverty level, the WIC program provides electronic cards to purchase approved categories of healthy food from participating vendors. For families with incomes less than 185% of the poverty level, the SNAP program, formerly called food stamps, provides benefits. There are other programs including free and reduced cost National School Breakfast and/or Lunch programs (best when open to all), Child and Adult Care Food Program for institutions (which may include medical offices), and Summer Food Service Programs providing lunch at community sites. Since not all food-insecure families are eligible for the above services, it is important that we are ready to provide information about local food banks, pantries, and low- or no-cost produce programs (see Healthy Food Bank Hub, Feeding America, 2-1-1, or FindHelp.org).
As pediatric providers we have a special opportunity and responsibility to expand our capabilities for sensitively addressing and advocating for help for food insecurity to improve the outlook for the families under our care.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Data Trends 2024: Dermatology
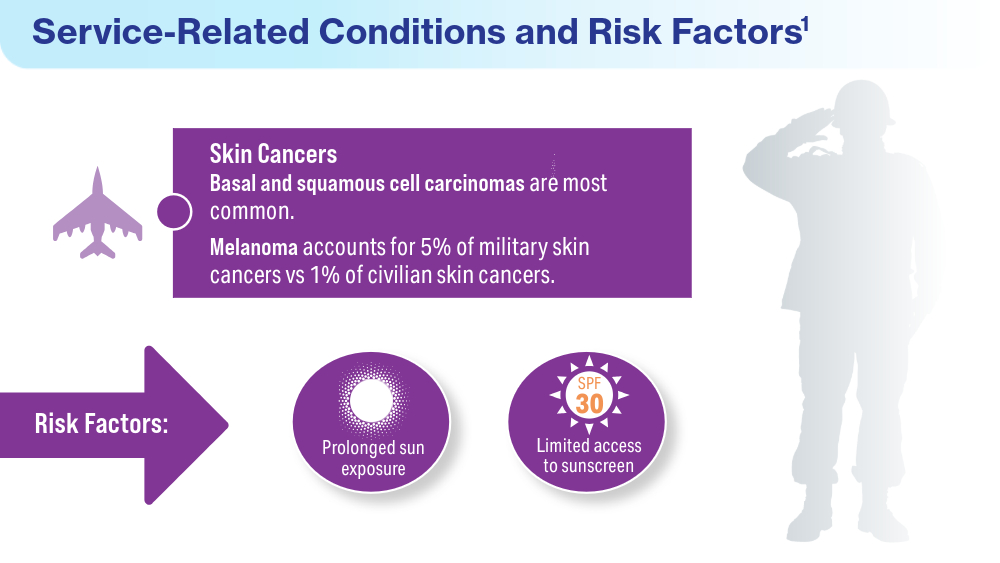
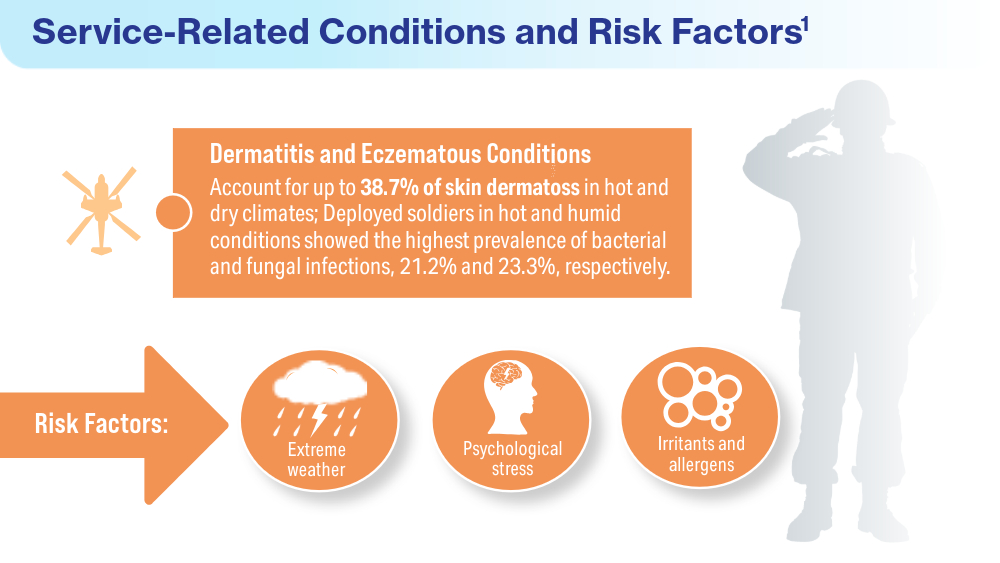
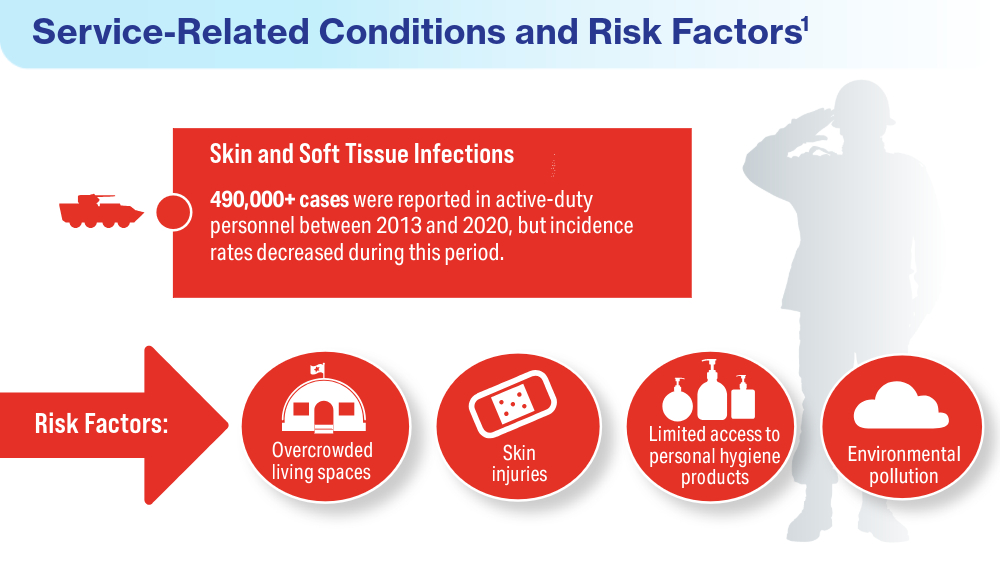
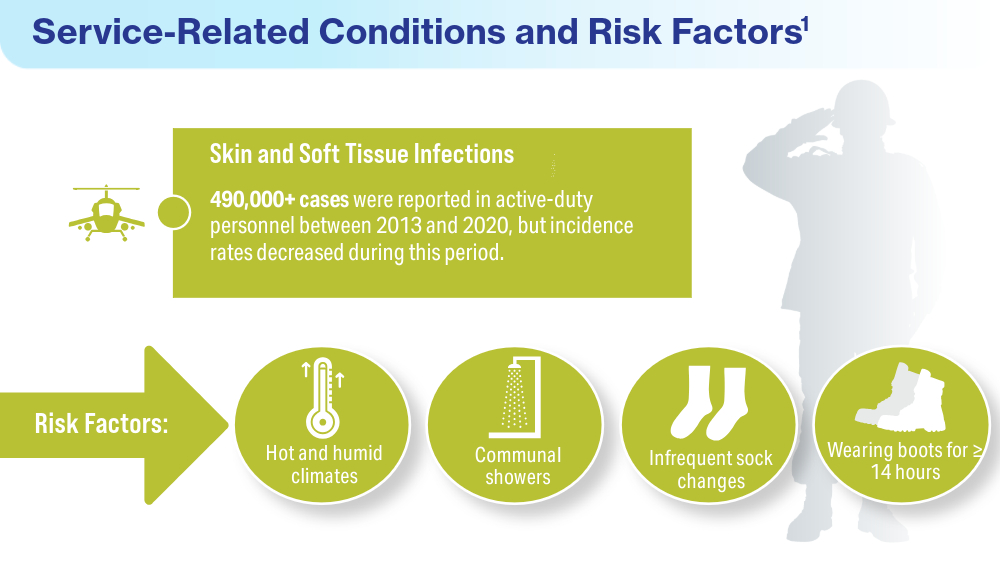
Singal A, Lipner SR. A review of skin disease in military soldiers: challenges and potential solutions. Ann Medicine. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
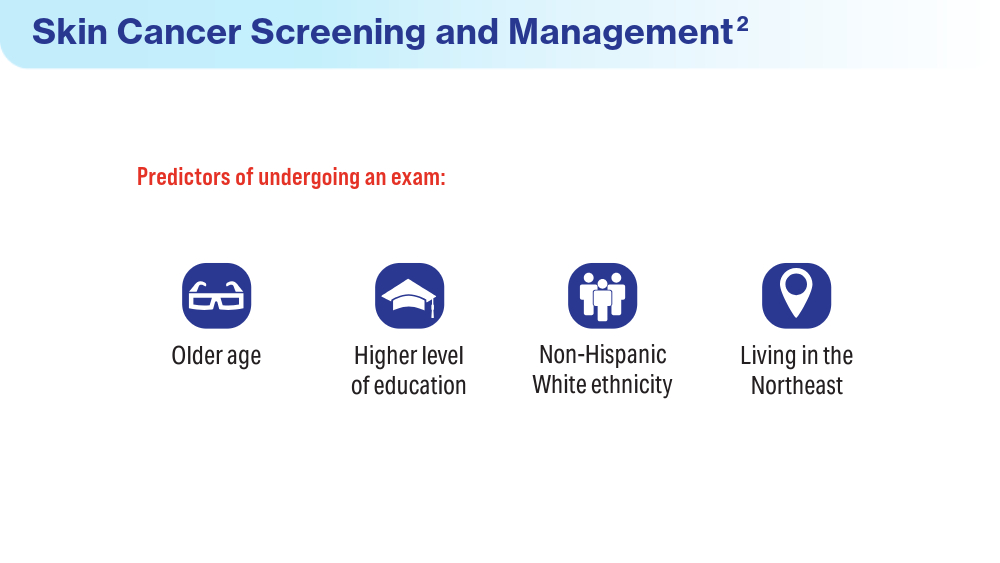
Coups EJ, Xu B, Heckman CJ, Manne SL, Stapleton JL. Physician skin cancer screening among U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health Interview Survey. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0251785. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0251785
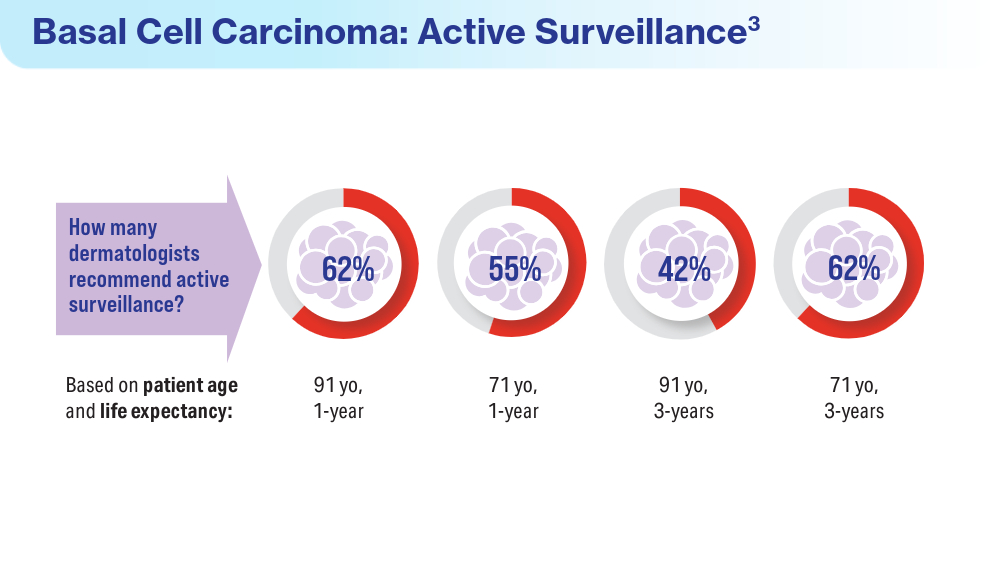
Van Egmond S, de Vere Hunt I, Cai ZR, et al. The perspectives of 606 US dermatologists on active surveillance for low-risk basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2023;188(1):136-137. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljac002
Singal A, Lipner SR. A review of skin disease in military soldiers: challenges and potential solutions. Ann Medicine. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
Coups EJ, Xu B, Heckman CJ, Manne SL, Stapleton JL. Physician skin cancer screening among U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health Interview Survey. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0251785. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0251785
Van Egmond S, de Vere Hunt I, Cai ZR, et al. The perspectives of 606 US dermatologists on active surveillance for low-risk basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2023;188(1):136-137. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljac002
Singal A, Lipner SR. A review of skin disease in military soldiers: challenges and potential solutions. Ann Medicine. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
Coups EJ, Xu B, Heckman CJ, Manne SL, Stapleton JL. Physician skin cancer screening among U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health Interview Survey. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0251785. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0251785
Van Egmond S, de Vere Hunt I, Cai ZR, et al. The perspectives of 606 US dermatologists on active surveillance for low-risk basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2023;188(1):136-137. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljac002
Data Trends 2024: VA Overview
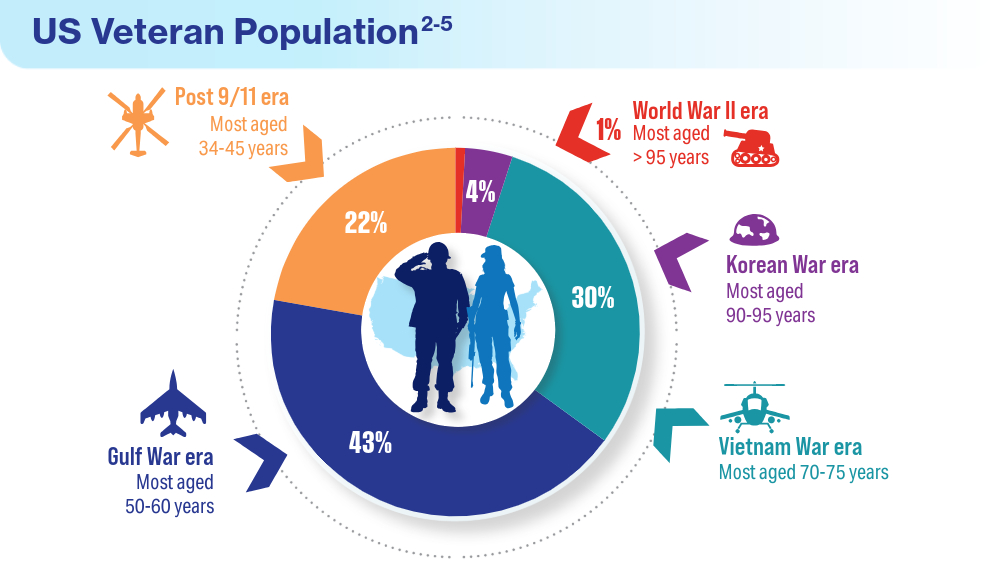
- Shaeffer K. The changing face of America’s veteran population. Pew Research Center. Published November 2023. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/11/08/the-changing-face-of-americas-veteran-population/
US Congress Joint Economic Committee. 10 Key facts about veterans of the post-9/11 era. November 2015. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.jec.senate.gov/public/_cache/files/db43918e-66f0-4096-8704-ffde681459cd/veterans-day-fact-sheet-2015-final.pdf
US Census Bureau. Census Bureau releases new report on veterans. June 2, 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2020/veterans-report.html
Harington KM, Quaden R, Steele L, et al; on behalf of the Va Million Veteran Program. The Million Veteran Program 1990-1991 Gulf War era survey: an evaluation of veteran response, characteristics, and representativeness of the Gulf War era veteran population. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024;21(1):72. doi:10.3390/ijerph21010072
Vespa J. Aging veterans: American's veteran population in later life. American community survey reports. July 2023. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2023/acs/acs-54.pdf
Amaral EFL, Pollard MS, Mendelsohn J, Cefalu M. Current and future demographics of the veteran population, 2014–2024, Project MUSE. Popul Rev. 2018;57(1):28-60. doi:10.1353/prv.2018.0002
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development Service. Rural vs. urban ambulatory health care: a systematic review. May 2011. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/ambulatory-REPORT.pdf
Boscarino JJ, Figley CR, Adams RE, Urosevich TG, Kirchner HL, Boscarino JA. Mental health status in veterans residing in rural versus non-rural areas: results from the Veterans’ Health Study. Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):44. doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00272-6
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. VA research on rural health. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/rural_health.cfm
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
Gawron LM, Pettey WBP, Redd AM, Suo Y, Gundlapalli AV. Distance to Veterans Administration medical centers as a barrier to specialty care for homeless women veterans. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2017;238:112-115.
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Health Equity. National veteran health equity report 2021. Focus on Veterans Health Administration patient experience and health care quality. Updated February 15, 2023. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.va.gov/healthequity/nvher.asp
US Government Accountability Office. VA health care: Office of Rural Health efforts and recommendations for improvement. Published January 11, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-24-107245
Syracuse University, D’aniello Institute for Veterans & Military Families. The employment situation of veterans. January 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://ivmf.syracuse.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/IVMF-Employment-Situation-of-Veterans-January-released-February-2024.pdf
Blue Star Families. 2018 Military Family Lifestyle Survey, executive summary. 2018. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://bluestarfam.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/2018MFLS-Executive-Summary-DIGITAL-FINAL.pdf
Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/SAR.S116720
US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Homeless Programs. Point-in-Time (PIT) Count. Updated January 3, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HOMELESS/pit_count.asp
US Department of Labor Statistics. TED: The economics daily. January 16, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2024/unemployment-rate-at-3-7-percent-in-december-2023.htm
Parker K, Igielnik R, Barroso A, Cilluffo A. The American veteran experience and the post-9/11 generation. Pew Research Center. September 10, 2019. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2019/09/PSDT.10.09.19_veteransexperiences_full.report.pdf
VA aims to house 41,000 homeless veterans in 2024. Government Executive. March 14, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.govexec.com/management/2024/03/va-aims-house-41000-homeless-veterans-2024/394933
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Committee to Evaluate the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. Evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. National Academies Press; 2018. doi:10.17226/24915
Meffert BN, Morabito DM, Sawicki DA, et al. US veterans who do and do not utilize Veterans Affairs health care services: demographic, military, medical, and psychosocial characteristics. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(1):18m02350. doi:10.4088/PCC.18m02350
American Association of Suicidology. 2023 National veteran suicide prevention annual report. February 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://suicidology.org/2024/02/06/2023-national-veteran-suicide-prevention-annual-report/
US Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans Affairs fiscal years 2022-28 strategic plan. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/va-strategic-plan-2022-2028.pdf
- Shaeffer K. The changing face of America’s veteran population. Pew Research Center. Published November 2023. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/11/08/the-changing-face-of-americas-veteran-population/
US Congress Joint Economic Committee. 10 Key facts about veterans of the post-9/11 era. November 2015. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.jec.senate.gov/public/_cache/files/db43918e-66f0-4096-8704-ffde681459cd/veterans-day-fact-sheet-2015-final.pdf
US Census Bureau. Census Bureau releases new report on veterans. June 2, 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2020/veterans-report.html
Harington KM, Quaden R, Steele L, et al; on behalf of the Va Million Veteran Program. The Million Veteran Program 1990-1991 Gulf War era survey: an evaluation of veteran response, characteristics, and representativeness of the Gulf War era veteran population. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024;21(1):72. doi:10.3390/ijerph21010072
Vespa J. Aging veterans: American's veteran population in later life. American community survey reports. July 2023. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2023/acs/acs-54.pdf
Amaral EFL, Pollard MS, Mendelsohn J, Cefalu M. Current and future demographics of the veteran population, 2014–2024, Project MUSE. Popul Rev. 2018;57(1):28-60. doi:10.1353/prv.2018.0002
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development Service. Rural vs. urban ambulatory health care: a systematic review. May 2011. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/ambulatory-REPORT.pdf
Boscarino JJ, Figley CR, Adams RE, Urosevich TG, Kirchner HL, Boscarino JA. Mental health status in veterans residing in rural versus non-rural areas: results from the Veterans’ Health Study. Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):44. doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00272-6
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. VA research on rural health. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/rural_health.cfm
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
Gawron LM, Pettey WBP, Redd AM, Suo Y, Gundlapalli AV. Distance to Veterans Administration medical centers as a barrier to specialty care for homeless women veterans. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2017;238:112-115.
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Health Equity. National veteran health equity report 2021. Focus on Veterans Health Administration patient experience and health care quality. Updated February 15, 2023. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.va.gov/healthequity/nvher.asp
US Government Accountability Office. VA health care: Office of Rural Health efforts and recommendations for improvement. Published January 11, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-24-107245
Syracuse University, D’aniello Institute for Veterans & Military Families. The employment situation of veterans. January 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://ivmf.syracuse.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/IVMF-Employment-Situation-of-Veterans-January-released-February-2024.pdf
Blue Star Families. 2018 Military Family Lifestyle Survey, executive summary. 2018. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://bluestarfam.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/2018MFLS-Executive-Summary-DIGITAL-FINAL.pdf
Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/SAR.S116720
US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Homeless Programs. Point-in-Time (PIT) Count. Updated January 3, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HOMELESS/pit_count.asp
US Department of Labor Statistics. TED: The economics daily. January 16, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2024/unemployment-rate-at-3-7-percent-in-december-2023.htm
Parker K, Igielnik R, Barroso A, Cilluffo A. The American veteran experience and the post-9/11 generation. Pew Research Center. September 10, 2019. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2019/09/PSDT.10.09.19_veteransexperiences_full.report.pdf
VA aims to house 41,000 homeless veterans in 2024. Government Executive. March 14, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.govexec.com/management/2024/03/va-aims-house-41000-homeless-veterans-2024/394933
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Committee to Evaluate the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. Evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. National Academies Press; 2018. doi:10.17226/24915
Meffert BN, Morabito DM, Sawicki DA, et al. US veterans who do and do not utilize Veterans Affairs health care services: demographic, military, medical, and psychosocial characteristics. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(1):18m02350. doi:10.4088/PCC.18m02350
American Association of Suicidology. 2023 National veteran suicide prevention annual report. February 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://suicidology.org/2024/02/06/2023-national-veteran-suicide-prevention-annual-report/
US Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans Affairs fiscal years 2022-28 strategic plan. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/va-strategic-plan-2022-2028.pdf
- Shaeffer K. The changing face of America’s veteran population. Pew Research Center. Published November 2023. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/11/08/the-changing-face-of-americas-veteran-population/
US Congress Joint Economic Committee. 10 Key facts about veterans of the post-9/11 era. November 2015. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.jec.senate.gov/public/_cache/files/db43918e-66f0-4096-8704-ffde681459cd/veterans-day-fact-sheet-2015-final.pdf
US Census Bureau. Census Bureau releases new report on veterans. June 2, 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2020/veterans-report.html
Harington KM, Quaden R, Steele L, et al; on behalf of the Va Million Veteran Program. The Million Veteran Program 1990-1991 Gulf War era survey: an evaluation of veteran response, characteristics, and representativeness of the Gulf War era veteran population. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024;21(1):72. doi:10.3390/ijerph21010072
Vespa J. Aging veterans: American's veteran population in later life. American community survey reports. July 2023. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2023/acs/acs-54.pdf
Amaral EFL, Pollard MS, Mendelsohn J, Cefalu M. Current and future demographics of the veteran population, 2014–2024, Project MUSE. Popul Rev. 2018;57(1):28-60. doi:10.1353/prv.2018.0002
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development Service. Rural vs. urban ambulatory health care: a systematic review. May 2011. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/ambulatory-REPORT.pdf
Boscarino JJ, Figley CR, Adams RE, Urosevich TG, Kirchner HL, Boscarino JA. Mental health status in veterans residing in rural versus non-rural areas: results from the Veterans’ Health Study. Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):44. doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00272-6
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. VA research on rural health. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/rural_health.cfm
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
Gawron LM, Pettey WBP, Redd AM, Suo Y, Gundlapalli AV. Distance to Veterans Administration medical centers as a barrier to specialty care for homeless women veterans. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2017;238:112-115.
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Health Equity. National veteran health equity report 2021. Focus on Veterans Health Administration patient experience and health care quality. Updated February 15, 2023. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.va.gov/healthequity/nvher.asp
US Government Accountability Office. VA health care: Office of Rural Health efforts and recommendations for improvement. Published January 11, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-24-107245
Syracuse University, D’aniello Institute for Veterans & Military Families. The employment situation of veterans. January 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://ivmf.syracuse.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/IVMF-Employment-Situation-of-Veterans-January-released-February-2024.pdf
Blue Star Families. 2018 Military Family Lifestyle Survey, executive summary. 2018. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://bluestarfam.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/2018MFLS-Executive-Summary-DIGITAL-FINAL.pdf
Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/SAR.S116720
US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Homeless Programs. Point-in-Time (PIT) Count. Updated January 3, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HOMELESS/pit_count.asp
US Department of Labor Statistics. TED: The economics daily. January 16, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2024/unemployment-rate-at-3-7-percent-in-december-2023.htm
Parker K, Igielnik R, Barroso A, Cilluffo A. The American veteran experience and the post-9/11 generation. Pew Research Center. September 10, 2019. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2019/09/PSDT.10.09.19_veteransexperiences_full.report.pdf
VA aims to house 41,000 homeless veterans in 2024. Government Executive. March 14, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://www.govexec.com/management/2024/03/va-aims-house-41000-homeless-veterans-2024/394933
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Committee to Evaluate the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. Evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. National Academies Press; 2018. doi:10.17226/24915
Meffert BN, Morabito DM, Sawicki DA, et al. US veterans who do and do not utilize Veterans Affairs health care services: demographic, military, medical, and psychosocial characteristics. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(1):18m02350. doi:10.4088/PCC.18m02350
American Association of Suicidology. 2023 National veteran suicide prevention annual report. February 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://suicidology.org/2024/02/06/2023-national-veteran-suicide-prevention-annual-report/
US Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans Affairs fiscal years 2022-28 strategic plan. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/va-strategic-plan-2022-2028.pdf
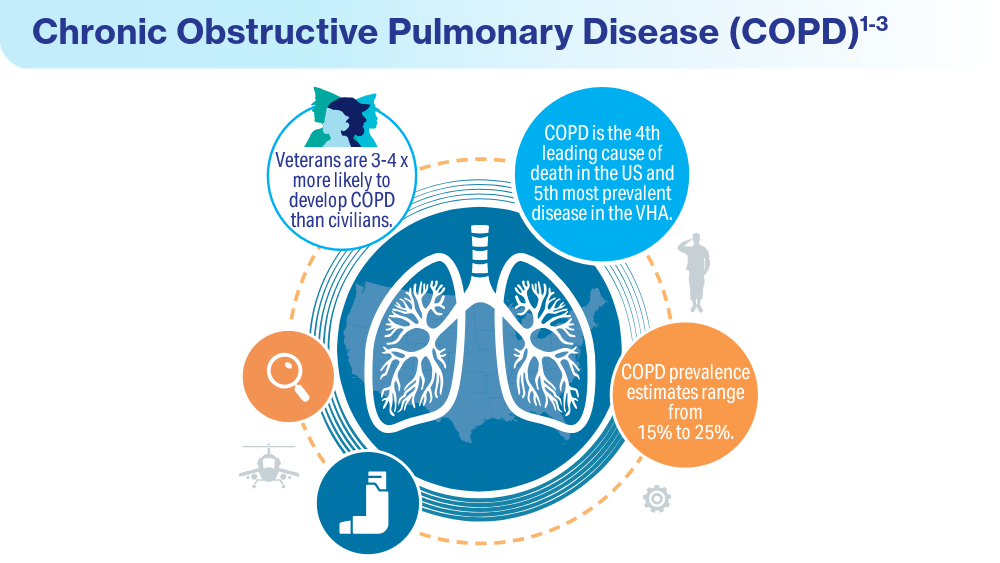
Data Trends 2024: Depression and PTSD
- Inoue C, Shawler E, Jordan CH, Moore MJ, Jackson CA. Veteran and military mental health issues. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572092/
- Panaite V, Cohen NJ, Luter SL, et al. Mental health treatment utilization patterns among 108,457 Afghanistan and Iraq veterans with depression. Psychol Serv. 2024 Feb 1. doi:10.1037/ser0000819
- Holder N, Holliday R, Ranney RM, et al. Relationship of social determinants of health with symptom severity among veterans and non-veterans with probable posttraumatic stress disorder or depression. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2023;58(10):1523-1534. doi:10.1007/s00127-023-02478-0
- Merians AN, Gross G, Spoont MR, Bellamy CD, Harpaz-Rotem I, Pietrzak RH. Racial and ethnic mental health disparities in U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;161:71-76. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.005
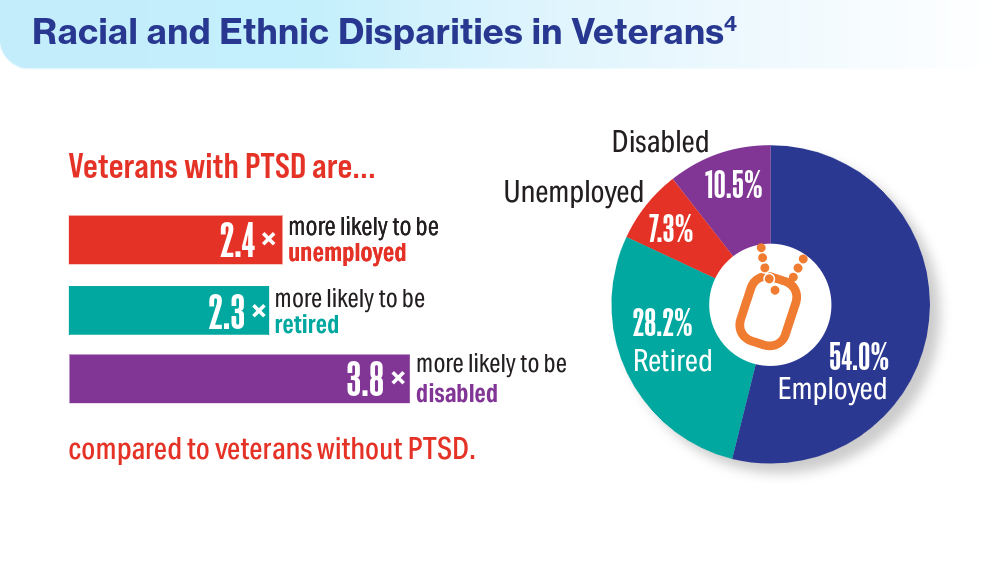
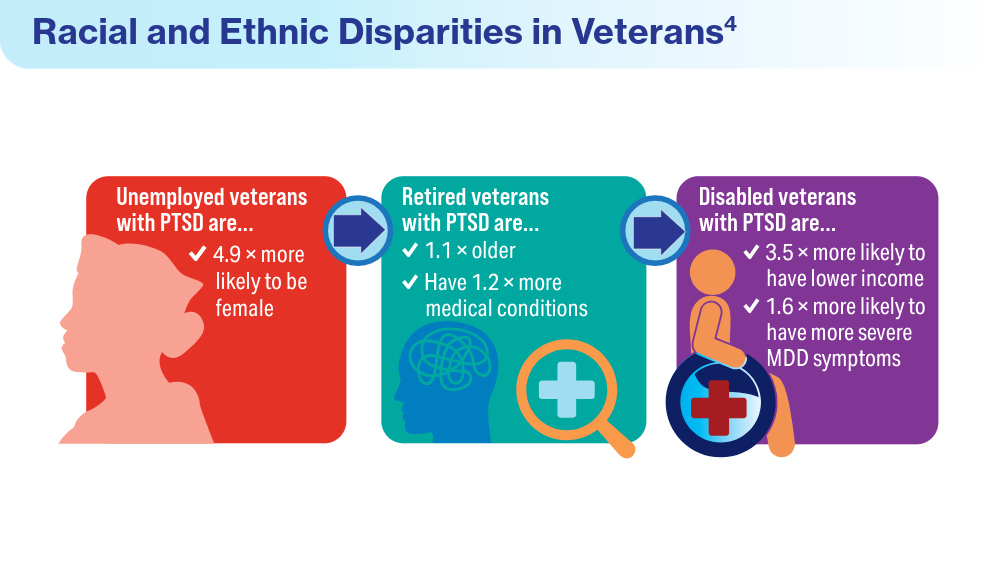
- Fischer IC, Schnurr PP, Pietrzak RH. Employment status among US military veterans with a history of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36(6):1167-1175. doi:10.1002/jts.22977
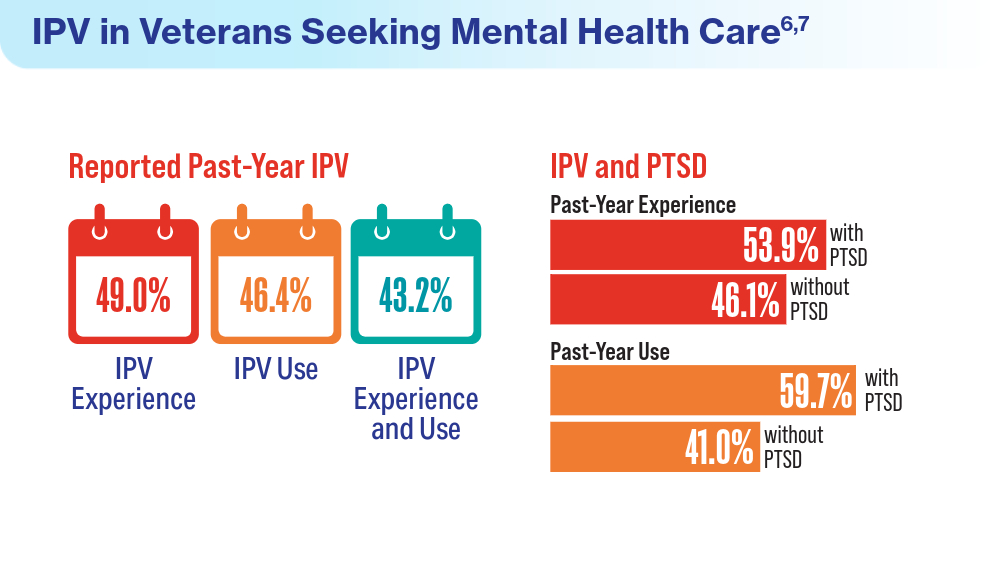
- Portnoy GA, Relyea MR, Presseau C, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence experience and use in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2337685. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37685
- Cowlishaw S, Freijah I, Kartal D, et al. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) in Military and Veteran Populations: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Surveys and Population Screening Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8853. Published 2022 Jul 21. doi:10.3390/ijerph19148853
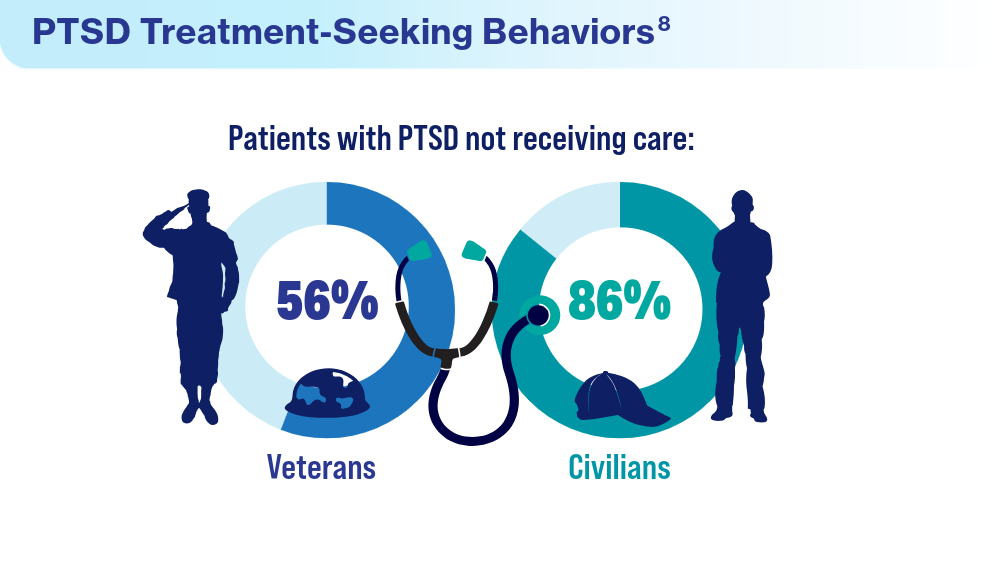
- Ranney RM, Maguen S, Bernhard PA, et al. Treatment utilization for posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of veterans and nonveterans. Med Care. 2023;61(2):87-94. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001793
- Inoue C, Shawler E, Jordan CH, Moore MJ, Jackson CA. Veteran and military mental health issues. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572092/
- Panaite V, Cohen NJ, Luter SL, et al. Mental health treatment utilization patterns among 108,457 Afghanistan and Iraq veterans with depression. Psychol Serv. 2024 Feb 1. doi:10.1037/ser0000819
- Holder N, Holliday R, Ranney RM, et al. Relationship of social determinants of health with symptom severity among veterans and non-veterans with probable posttraumatic stress disorder or depression. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2023;58(10):1523-1534. doi:10.1007/s00127-023-02478-0
- Merians AN, Gross G, Spoont MR, Bellamy CD, Harpaz-Rotem I, Pietrzak RH. Racial and ethnic mental health disparities in U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;161:71-76. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.005
- Fischer IC, Schnurr PP, Pietrzak RH. Employment status among US military veterans with a history of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36(6):1167-1175. doi:10.1002/jts.22977
- Portnoy GA, Relyea MR, Presseau C, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence experience and use in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2337685. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37685
- Cowlishaw S, Freijah I, Kartal D, et al. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) in Military and Veteran Populations: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Surveys and Population Screening Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8853. Published 2022 Jul 21. doi:10.3390/ijerph19148853
- Ranney RM, Maguen S, Bernhard PA, et al. Treatment utilization for posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of veterans and nonveterans. Med Care. 2023;61(2):87-94. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001793
- Inoue C, Shawler E, Jordan CH, Moore MJ, Jackson CA. Veteran and military mental health issues. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572092/
- Panaite V, Cohen NJ, Luter SL, et al. Mental health treatment utilization patterns among 108,457 Afghanistan and Iraq veterans with depression. Psychol Serv. 2024 Feb 1. doi:10.1037/ser0000819
- Holder N, Holliday R, Ranney RM, et al. Relationship of social determinants of health with symptom severity among veterans and non-veterans with probable posttraumatic stress disorder or depression. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2023;58(10):1523-1534. doi:10.1007/s00127-023-02478-0
- Merians AN, Gross G, Spoont MR, Bellamy CD, Harpaz-Rotem I, Pietrzak RH. Racial and ethnic mental health disparities in U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;161:71-76. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.005
- Fischer IC, Schnurr PP, Pietrzak RH. Employment status among US military veterans with a history of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36(6):1167-1175. doi:10.1002/jts.22977
- Portnoy GA, Relyea MR, Presseau C, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence experience and use in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2337685. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37685
- Cowlishaw S, Freijah I, Kartal D, et al. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) in Military and Veteran Populations: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Surveys and Population Screening Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8853. Published 2022 Jul 21. doi:10.3390/ijerph19148853
- Ranney RM, Maguen S, Bernhard PA, et al. Treatment utilization for posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of veterans and nonveterans. Med Care. 2023;61(2):87-94. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001793
Data Trends 2024: Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Rein DB, Wittenborn JS, Burke-Conte Z, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the US in 2019. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022;140(12):1202-1208. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.4401
- Fleckenstein M, Schmitz-Valckenberg S, Chakravarthy U. Age-related macular degeneration: a review. JAMA. 2024;331(2):147-157. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26074
- Meer EA, Targ S, Zhang N, Hoggatt KJ, Mehta KM, Brodie F. Age-related macular degeneration injection frequency: effects of distance traveled and travel support. Retina. 2024;44(2):230-236. doi:10.1097/IAE.0000000000003947
- Bhisitkul RB, Mendes TS, Rofagha S, et al. Macular atrophy progression and 7-year vision outcomes in subjects from the ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON studies: the SEVEN-UP study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159(5):915-24.e2. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2015.01.032
- Rein DB, Wittenborn JS, Burke-Conte Z, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the US in 2019. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022;140(12):1202-1208. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.4401
- Fleckenstein M, Schmitz-Valckenberg S, Chakravarthy U. Age-related macular degeneration: a review. JAMA. 2024;331(2):147-157. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26074
- Meer EA, Targ S, Zhang N, Hoggatt KJ, Mehta KM, Brodie F. Age-related macular degeneration injection frequency: effects of distance traveled and travel support. Retina. 2024;44(2):230-236. doi:10.1097/IAE.0000000000003947
- Bhisitkul RB, Mendes TS, Rofagha S, et al. Macular atrophy progression and 7-year vision outcomes in subjects from the ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON studies: the SEVEN-UP study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159(5):915-24.e2. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2015.01.032
- Rein DB, Wittenborn JS, Burke-Conte Z, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the US in 2019. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022;140(12):1202-1208. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.4401
- Fleckenstein M, Schmitz-Valckenberg S, Chakravarthy U. Age-related macular degeneration: a review. JAMA. 2024;331(2):147-157. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26074
- Meer EA, Targ S, Zhang N, Hoggatt KJ, Mehta KM, Brodie F. Age-related macular degeneration injection frequency: effects of distance traveled and travel support. Retina. 2024;44(2):230-236. doi:10.1097/IAE.0000000000003947
- Bhisitkul RB, Mendes TS, Rofagha S, et al. Macular atrophy progression and 7-year vision outcomes in subjects from the ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON studies: the SEVEN-UP study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159(5):915-24.e2. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2015.01.032
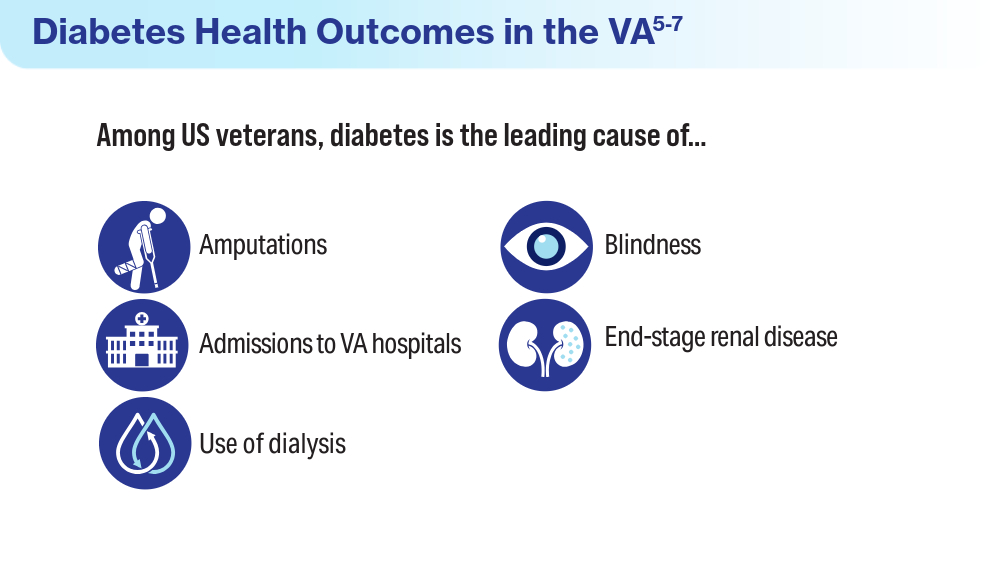
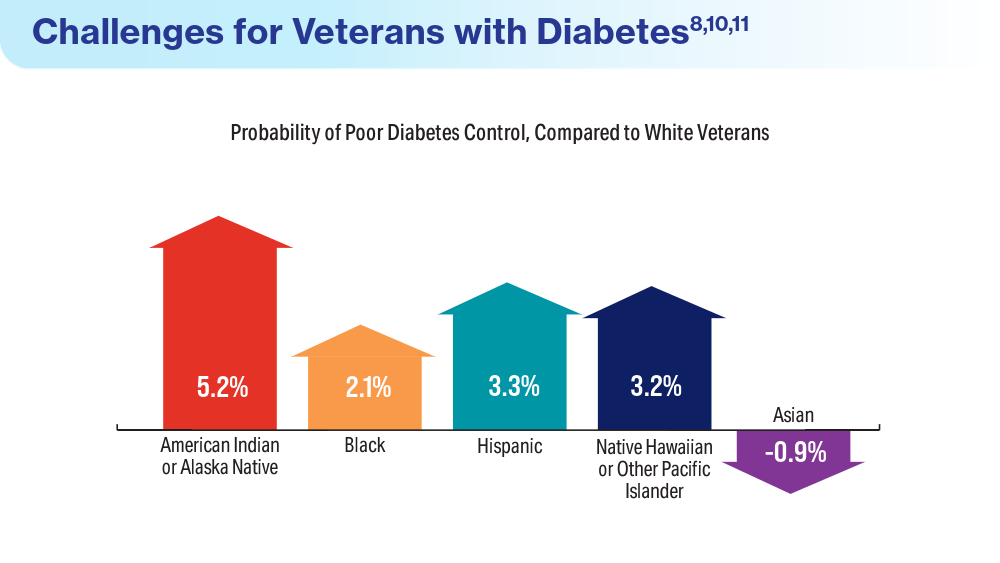
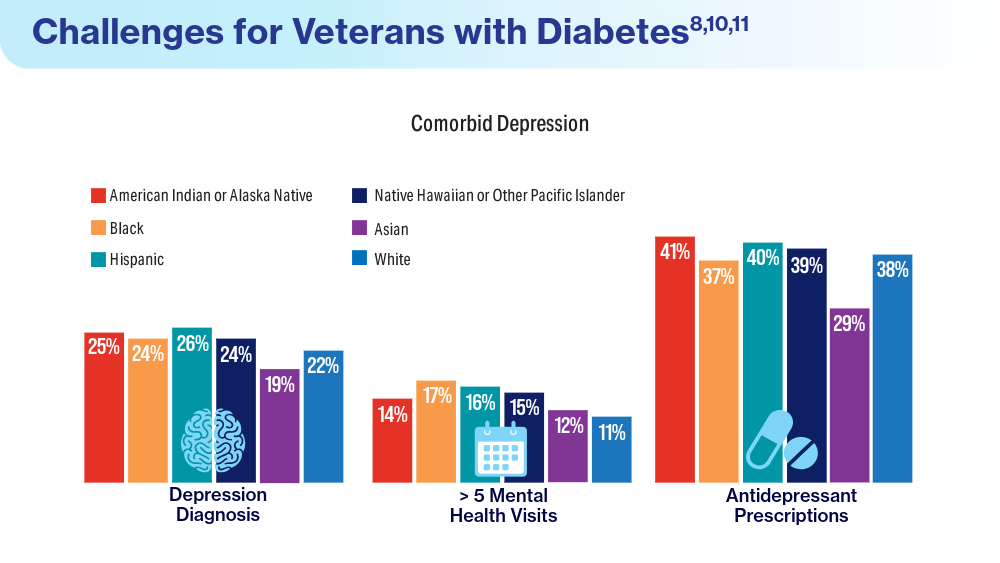
Data Trends 2024: Diabetes
- Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al; for the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. 2024 Heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149(8):e347-e913. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209
- Utech A. VA supports veterans who have type 2 diabetes. VA News. August 18, 2022. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://news.va.gov/107579/va-supportsveterans-who-have-type-2-diabetes/
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, Shanmugam R, Kruse CS, Fulton LV. Obesity and morbidity risk in the U.S. veteran. Healthcare (Basel). 2020;8(3):191. doi:10.3390/healthcare8030191
- Briskin A. Obesity and diabetes: causes, treatments, and stigma. diaTribe. October 4, 2021. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://diatribe.org/obesity-and-diabetescauses-
treatments-and-stigma - Leonard C, Sayre G, Williams S, et al. Understanding the experience of veterans who require lower limb amputation in the Veterans Health Administration. PLOS One. 2022;17(3):e0265620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0265620
- Armstrong DG. Diabetic foot ulcers: a silent killer of veterans. Stat News. November 11, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.statnews.com/2019/11/11/diabetic-foot-ulcers-veterans-silent-killer/
- Koleda EW. The veteran diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) epidemic: a U.S. Department of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) services review. TreatNOW. October 2022. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://treatnow.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/The-VA-Diabetic-Foot-Ulcer-Epidemic-10-14-22.pdf
- CDC identifies diabetes belt. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/46013
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Updated June 7, 2024. Accessed June 19, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/veteran_population.asp
- Avramovic S, Alemi F, Kanchi R, et al. US Veterans Administration diabetes risk (VADR) national cohort: cohort profile. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e039489. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039489
- Breland JY, Tseng CH, Toyama J, Washington DL. Influence of depression on racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes control. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2023;11(6):e003612. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003612
- Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al; for the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. 2024 Heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149(8):e347-e913. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209
- Utech A. VA supports veterans who have type 2 diabetes. VA News. August 18, 2022. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://news.va.gov/107579/va-supportsveterans-who-have-type-2-diabetes/
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, Shanmugam R, Kruse CS, Fulton LV. Obesity and morbidity risk in the U.S. veteran. Healthcare (Basel). 2020;8(3):191. doi:10.3390/healthcare8030191
- Briskin A. Obesity and diabetes: causes, treatments, and stigma. diaTribe. October 4, 2021. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://diatribe.org/obesity-and-diabetescauses-
treatments-and-stigma - Leonard C, Sayre G, Williams S, et al. Understanding the experience of veterans who require lower limb amputation in the Veterans Health Administration. PLOS One. 2022;17(3):e0265620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0265620
- Armstrong DG. Diabetic foot ulcers: a silent killer of veterans. Stat News. November 11, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.statnews.com/2019/11/11/diabetic-foot-ulcers-veterans-silent-killer/
- Koleda EW. The veteran diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) epidemic: a U.S. Department of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) services review. TreatNOW. October 2022. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://treatnow.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/The-VA-Diabetic-Foot-Ulcer-Epidemic-10-14-22.pdf
- CDC identifies diabetes belt. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/46013
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Updated June 7, 2024. Accessed June 19, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/veteran_population.asp
- Avramovic S, Alemi F, Kanchi R, et al. US Veterans Administration diabetes risk (VADR) national cohort: cohort profile. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e039489. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039489
- Breland JY, Tseng CH, Toyama J, Washington DL. Influence of depression on racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes control. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2023;11(6):e003612. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003612
- Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al; for the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. 2024 Heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149(8):e347-e913. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209
- Utech A. VA supports veterans who have type 2 diabetes. VA News. August 18, 2022. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://news.va.gov/107579/va-supportsveterans-who-have-type-2-diabetes/
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, Shanmugam R, Kruse CS, Fulton LV. Obesity and morbidity risk in the U.S. veteran. Healthcare (Basel). 2020;8(3):191. doi:10.3390/healthcare8030191
- Briskin A. Obesity and diabetes: causes, treatments, and stigma. diaTribe. October 4, 2021. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://diatribe.org/obesity-and-diabetescauses-
treatments-and-stigma - Leonard C, Sayre G, Williams S, et al. Understanding the experience of veterans who require lower limb amputation in the Veterans Health Administration. PLOS One. 2022;17(3):e0265620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0265620
- Armstrong DG. Diabetic foot ulcers: a silent killer of veterans. Stat News. November 11, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.statnews.com/2019/11/11/diabetic-foot-ulcers-veterans-silent-killer/
- Koleda EW. The veteran diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) epidemic: a U.S. Department of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) services review. TreatNOW. October 2022. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://treatnow.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/The-VA-Diabetic-Foot-Ulcer-Epidemic-10-14-22.pdf
- CDC identifies diabetes belt. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/46013
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Updated June 7, 2024. Accessed June 19, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/veteran_population.asp
- Avramovic S, Alemi F, Kanchi R, et al. US Veterans Administration diabetes risk (VADR) national cohort: cohort profile. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e039489. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039489
- Breland JY, Tseng CH, Toyama J, Washington DL. Influence of depression on racial and ethnic disparities in diabetes control. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2023;11(6):e003612. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003612
As CGM Benefit Data Accrue, Primary Care Use Expands
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — As increasing data show benefit for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices beyond just insulin-treated diabetes, efforts are being made to optimize the use of CGM in primary care settings.
Currently, Medicare and most private insurers cover CGM for people with diabetes who use insulin, regardless of the type of diabetes or the type of insulin, and for those with a history of severe hypoglycemia. Data are increasingly showing benefit for people who don’t use insulin. As of now, with the exception of some state Medicaid beneficiaries, the majority must pay out of pocket.
Such use is expected to grow with the upcoming availability of two new over-the-counter CGMs, Dexcom’s Stelo and Abbott’s Libre Rio, both made for people with diabetes who don’t use insulin. (Abbott will also launch the Lingo, a wellness CGM for people without diabetes.)
This means that CGM will become increasingly prevalent in primary care, where there is currently a great deal of variability in the capacity to manage and use the data generated by the devices to improve diabetes management, experts said during an oral abstract session at the recent American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions and in interviews with this news organization.
“It’s picking up steam, and there’s a lot more visibility of CGM in primary care and a lot more people prescribing it,” Thomas W. Martens, MD, medical director of the International Diabetes Center at HealthPartners Institute, Minneapolis, told this news organization. He noted that the recent switch in many cases of CGM from billing as durable medical equipment to pharmacy has made prescribing easier, while television advertising has increased demand.
But still unclear, he noted, is how the CGM data are being used. “The question is, are prescriptions just being sent out and people using it like a finger-stick blood glucose monitor, or is primary care really using the data to move diabetes forward? I think that’s where a lot of the work on dissemination and implementation is going. How do we really make this a useful tool for optimizing diabetes care?”
Informing Food Choice, Treatment Intensification
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Martens presented topline data from a randomized multicenter controlled trial funded by Abbott, examining the effect of CGM use on guiding food choices and other behaviors in 72 adults with type 2 diabetes who were not using insulin but who were using other glucose-lowering medications.
At 3 months, with no medication changes, there was a significant overall 26% reduction in time spent above 180 mg/dL (P < .0001), which didn›t differ significantly between those randomized to CGM alone or in conjunction with a food logging app. Both groups also experienced a significant 1.1% reduction in A1c (P < .0001) and about a 4-lb weight loss (P = .014 for CGM alone, P = .0032 for CGM + app).
“The win for people not on insulin is you can see the impact of food choices really quickly with a CGM ... and then perhaps modify that to improve postprandial hyperglycemia,” Dr. Martens said.
And for the clinician, “not everybody with type 2 diabetes not on insulin can get where they need to be just by changing their diets. The CGM is a pretty good tool for knowing when you need to advance therapy.”
Diabetes Care and Education Specialists (DCESs) Assist CGM Use
Another speaker at the ADA meeting, Sean M. Oser, MD, director of the Practice Innovation Program and associated director of the Primary Care Diabetes Lab at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado, noted that 90% of adults with type 2 diabetes and 50% with type 1 diabetes receive their diabetes care in primary care settings.
“CGM is increasingly becoming standard of care in diabetes ... But [primary care providers] remain relatively untrained about CGM ... What I’m concerned about is the disparity disparities in who has access and who does not. We really need to bring our primary care colleagues along,” he said.
Dr. Oser described tools he and his wife, Tamara K. Oser, MD, professor in the Department of Family Medicine at the same institution, developed in conjunction with the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), including the Transformation in Practice series (TIPS).
The PREPARE 4 CGM study examined the use of three different strategies for incorporating CGM into primary care settings: Either use of AAFP TIPS alone, TIPS plus practice facilitation services by coaches who assist the practice in implementing new workflows, or referral to a virtual CGM initiation service (virCIS) with a virtual CGM workshop that Dr. Oser and Dr. Oser also developed.
Of the 76 Colorado primary care practices participating (out of 60 planned), the 46 who chose AAFP TIPS were randomized to either the AAFP TIPS alone or to TIPS + practice facilitation. The other 30 chose virCIS with the onetime CGM basics webinar. The fact that more practices than anticipated were recruited for the study suggests that “primary care interest in CGM is very high. They want to learn,” Dr. Oser noted.
Of the 51 practice characteristics investigated, only one, the presence of a DCES, in the practice, was significantly associated with the choice of CGM implementation strategy. Of the 16 practices with access to a DCES, all of them chose self-initiation with CGM using TIPS. But of the 60 practices without a DCES, half chose the virCIS.
“We know that 36% of primary care practices have access to a DCES within the clinic, part-time or full-time, and that’s not enough, I would argue,” Dr. Oser said.
Indeed, Dr. Martens told this news organization that those professionals, formerly called “diabetes educators,” often aren’t available in primary care settings, especially in rural areas. “Unfortunately, they are not well reimbursed. A lot of care systems don’t employ as many as they ideally should because it tends not to be a moneymaker ... Something’s got to change with reimbursement for the cognitive aspects of diabetes management.”
Dr. Oser said his team’s next steps include completion of the virCIS operations, analysis of the effectiveness of the three implantation strategies in practice- and patient-level outcomes, a cost analysis of the three strategies, and further development of toolkits to assist in these efforts.
“One of our goals is to keep people at their primary care home, where they want to be ... Diabetes knows no borders. People should have access wherever they are,” Dr. Oser concluded in his ADA talk.
What Predicts Primary Care CGM Prescribing?
Further clues about effective strategies to improve CGM prescribing in primary care were provided in a study presented by Jovan Milosavljevic, MD, a second-year endocrinology fellow at the Fleischer Institute for Diabetes and Metabolism, Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York.
He began by noting that there are currently 61.5 million diabetes visits annually in primary care compared with 32.0 million in specialty care and that there is a shortage of endocrinologists in the face of the rising number of people diagnosed with diabetes. “Primary care will continue to be the only point of care for most people with diabetes. So, standard-of-care treatment such as CGM must enter routine primary care practice to impact population-level health outcomes.”
Electronic health record data were examined for 39,710 patients with type 2 diabetes seen at 13 primary care sites affiliated with Montefiore Medical Center, a large safety net hospital in New York, where CGM is widely covered by public insurance. Between July 31, 2020, and July 31, 2023, a total of 3503, or just 8.8%, were prescribed CGM by a primary care provider.
Those with CGM prescribed were younger than those without (59.7 vs 62.7 years), about 40% of both groups were Hispanic or Black, and a majority were English-speaking: 84.5% of those prescribed CGM spoke English, while only 13.1% spoke Spanish. Over half (59.1%) of those prescribed CGM had commercial insurance, while only 11.2% had Medicaid and 29.7% had Medicare.
More patients with CGM prescribed had providers with more than 10 years in practice: 72.5% vs 64.5% with no CGM.
Not surprisingly, those with CGM prescribed were more likely on insulin — 21% using just basal and 35% on multiple daily injections. Those prescribed CGM had higher A1c levels before CGM prescription: 9.2% vs 7.2% for those not prescribed CGM.
No racial or ethnic bias was found in the relationships between CGM use and insulin use, provider experience, engagement with care, and A1c. However, there were differences by age, sex, and spoken language.
For example, the Hispanic group aged 65 years and older was less likely than those younger to be prescribed CGM, but this wasn’t seen in other ethnic groups. In fact, older White people were slightly more likely to have CGM prescribed. Spanish-speaking patients were about 43% less likely to have CGM prescribed than were English-speaking patients.
These findings suggest a dual approach might work best for improving CGM prescribing in primary care. “We can leverage the knowledge that some of these factors are independent of bias and promote clinical and evidence-based guidelines for CGM. Additionally, we should focus on physicians in training,” Dr. Milosavljevic said.
At the same time, “we need to tackle systemic inequity in prescription processes,” with measures such as improving prescription workflows, supporting prior authorization, and using patient hands-on support for older adults and Spanish-speaking individuals, he said.
In a message to this news organization, Tamara K. Oser, MD, wrote, “Disparities in CGM and other diabetes technology are prevalent and multifactorial. In addition to insurance barriers, implicit bias also plays a large role. Shared decision-making should always be used when deciding to prescribe diabetes technologies.”
The PREPARE 4 CGM study is evaluating willingness to pay for CGM, she noted.
“Even patients without insurance might want to purchase one sensor every few months to empower them to learn more about how food and exercise affect their glucose or to help assess the need for [adjusting] diabetes medications. It is an exciting time for people living with diabetes. Primary care, endocrinology, device manufacturers, and insurers should all do their part to assure increased access to these evidence-based technologies.”
Dr. Martens’ employer has received funds on his behalf for research and speaking support from Dexcom, Abbott Diabetes Care, Medtronic, Insulet, Tandem, Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, and Novo Nordisk, and for consulting from Sanofi and Eli Lilly and Company. He is employed by the nonprofit HealthPartners Institute dba International Diabetes Center and received no personal income from these activities.
The Osers have received advisory board consulting fees (through the University of Colorado) from Dexcom, Medscape Medical News, Ascensia, and Blue Circle Health and research grants (through the University of Colorado) from National Institute of Nursing Research, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Helmsley Charitable Trust, Abbott Diabetes, Dexcom, and Insulet. They do not own stocks in any device or pharmaceutical company.
Dr. Milosavljevic’s work was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Advancing Translational Science and Einstein-Montefiore Clinical and Translational Science Awards. He had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — As increasing data show benefit for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices beyond just insulin-treated diabetes, efforts are being made to optimize the use of CGM in primary care settings.
Currently, Medicare and most private insurers cover CGM for people with diabetes who use insulin, regardless of the type of diabetes or the type of insulin, and for those with a history of severe hypoglycemia. Data are increasingly showing benefit for people who don’t use insulin. As of now, with the exception of some state Medicaid beneficiaries, the majority must pay out of pocket.
Such use is expected to grow with the upcoming availability of two new over-the-counter CGMs, Dexcom’s Stelo and Abbott’s Libre Rio, both made for people with diabetes who don’t use insulin. (Abbott will also launch the Lingo, a wellness CGM for people without diabetes.)
This means that CGM will become increasingly prevalent in primary care, where there is currently a great deal of variability in the capacity to manage and use the data generated by the devices to improve diabetes management, experts said during an oral abstract session at the recent American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions and in interviews with this news organization.
“It’s picking up steam, and there’s a lot more visibility of CGM in primary care and a lot more people prescribing it,” Thomas W. Martens, MD, medical director of the International Diabetes Center at HealthPartners Institute, Minneapolis, told this news organization. He noted that the recent switch in many cases of CGM from billing as durable medical equipment to pharmacy has made prescribing easier, while television advertising has increased demand.
But still unclear, he noted, is how the CGM data are being used. “The question is, are prescriptions just being sent out and people using it like a finger-stick blood glucose monitor, or is primary care really using the data to move diabetes forward? I think that’s where a lot of the work on dissemination and implementation is going. How do we really make this a useful tool for optimizing diabetes care?”
Informing Food Choice, Treatment Intensification
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Martens presented topline data from a randomized multicenter controlled trial funded by Abbott, examining the effect of CGM use on guiding food choices and other behaviors in 72 adults with type 2 diabetes who were not using insulin but who were using other glucose-lowering medications.
At 3 months, with no medication changes, there was a significant overall 26% reduction in time spent above 180 mg/dL (P < .0001), which didn›t differ significantly between those randomized to CGM alone or in conjunction with a food logging app. Both groups also experienced a significant 1.1% reduction in A1c (P < .0001) and about a 4-lb weight loss (P = .014 for CGM alone, P = .0032 for CGM + app).
“The win for people not on insulin is you can see the impact of food choices really quickly with a CGM ... and then perhaps modify that to improve postprandial hyperglycemia,” Dr. Martens said.
And for the clinician, “not everybody with type 2 diabetes not on insulin can get where they need to be just by changing their diets. The CGM is a pretty good tool for knowing when you need to advance therapy.”
Diabetes Care and Education Specialists (DCESs) Assist CGM Use
Another speaker at the ADA meeting, Sean M. Oser, MD, director of the Practice Innovation Program and associated director of the Primary Care Diabetes Lab at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado, noted that 90% of adults with type 2 diabetes and 50% with type 1 diabetes receive their diabetes care in primary care settings.
“CGM is increasingly becoming standard of care in diabetes ... But [primary care providers] remain relatively untrained about CGM ... What I’m concerned about is the disparity disparities in who has access and who does not. We really need to bring our primary care colleagues along,” he said.
Dr. Oser described tools he and his wife, Tamara K. Oser, MD, professor in the Department of Family Medicine at the same institution, developed in conjunction with the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), including the Transformation in Practice series (TIPS).
The PREPARE 4 CGM study examined the use of three different strategies for incorporating CGM into primary care settings: Either use of AAFP TIPS alone, TIPS plus practice facilitation services by coaches who assist the practice in implementing new workflows, or referral to a virtual CGM initiation service (virCIS) with a virtual CGM workshop that Dr. Oser and Dr. Oser also developed.
Of the 76 Colorado primary care practices participating (out of 60 planned), the 46 who chose AAFP TIPS were randomized to either the AAFP TIPS alone or to TIPS + practice facilitation. The other 30 chose virCIS with the onetime CGM basics webinar. The fact that more practices than anticipated were recruited for the study suggests that “primary care interest in CGM is very high. They want to learn,” Dr. Oser noted.
Of the 51 practice characteristics investigated, only one, the presence of a DCES, in the practice, was significantly associated with the choice of CGM implementation strategy. Of the 16 practices with access to a DCES, all of them chose self-initiation with CGM using TIPS. But of the 60 practices without a DCES, half chose the virCIS.
“We know that 36% of primary care practices have access to a DCES within the clinic, part-time or full-time, and that’s not enough, I would argue,” Dr. Oser said.
Indeed, Dr. Martens told this news organization that those professionals, formerly called “diabetes educators,” often aren’t available in primary care settings, especially in rural areas. “Unfortunately, they are not well reimbursed. A lot of care systems don’t employ as many as they ideally should because it tends not to be a moneymaker ... Something’s got to change with reimbursement for the cognitive aspects of diabetes management.”
Dr. Oser said his team’s next steps include completion of the virCIS operations, analysis of the effectiveness of the three implantation strategies in practice- and patient-level outcomes, a cost analysis of the three strategies, and further development of toolkits to assist in these efforts.
“One of our goals is to keep people at their primary care home, where they want to be ... Diabetes knows no borders. People should have access wherever they are,” Dr. Oser concluded in his ADA talk.
What Predicts Primary Care CGM Prescribing?
Further clues about effective strategies to improve CGM prescribing in primary care were provided in a study presented by Jovan Milosavljevic, MD, a second-year endocrinology fellow at the Fleischer Institute for Diabetes and Metabolism, Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York.
He began by noting that there are currently 61.5 million diabetes visits annually in primary care compared with 32.0 million in specialty care and that there is a shortage of endocrinologists in the face of the rising number of people diagnosed with diabetes. “Primary care will continue to be the only point of care for most people with diabetes. So, standard-of-care treatment such as CGM must enter routine primary care practice to impact population-level health outcomes.”
Electronic health record data were examined for 39,710 patients with type 2 diabetes seen at 13 primary care sites affiliated with Montefiore Medical Center, a large safety net hospital in New York, where CGM is widely covered by public insurance. Between July 31, 2020, and July 31, 2023, a total of 3503, or just 8.8%, were prescribed CGM by a primary care provider.
Those with CGM prescribed were younger than those without (59.7 vs 62.7 years), about 40% of both groups were Hispanic or Black, and a majority were English-speaking: 84.5% of those prescribed CGM spoke English, while only 13.1% spoke Spanish. Over half (59.1%) of those prescribed CGM had commercial insurance, while only 11.2% had Medicaid and 29.7% had Medicare.
More patients with CGM prescribed had providers with more than 10 years in practice: 72.5% vs 64.5% with no CGM.
Not surprisingly, those with CGM prescribed were more likely on insulin — 21% using just basal and 35% on multiple daily injections. Those prescribed CGM had higher A1c levels before CGM prescription: 9.2% vs 7.2% for those not prescribed CGM.
No racial or ethnic bias was found in the relationships between CGM use and insulin use, provider experience, engagement with care, and A1c. However, there were differences by age, sex, and spoken language.
For example, the Hispanic group aged 65 years and older was less likely than those younger to be prescribed CGM, but this wasn’t seen in other ethnic groups. In fact, older White people were slightly more likely to have CGM prescribed. Spanish-speaking patients were about 43% less likely to have CGM prescribed than were English-speaking patients.
These findings suggest a dual approach might work best for improving CGM prescribing in primary care. “We can leverage the knowledge that some of these factors are independent of bias and promote clinical and evidence-based guidelines for CGM. Additionally, we should focus on physicians in training,” Dr. Milosavljevic said.
At the same time, “we need to tackle systemic inequity in prescription processes,” with measures such as improving prescription workflows, supporting prior authorization, and using patient hands-on support for older adults and Spanish-speaking individuals, he said.
In a message to this news organization, Tamara K. Oser, MD, wrote, “Disparities in CGM and other diabetes technology are prevalent and multifactorial. In addition to insurance barriers, implicit bias also plays a large role. Shared decision-making should always be used when deciding to prescribe diabetes technologies.”
The PREPARE 4 CGM study is evaluating willingness to pay for CGM, she noted.
“Even patients without insurance might want to purchase one sensor every few months to empower them to learn more about how food and exercise affect their glucose or to help assess the need for [adjusting] diabetes medications. It is an exciting time for people living with diabetes. Primary care, endocrinology, device manufacturers, and insurers should all do their part to assure increased access to these evidence-based technologies.”
Dr. Martens’ employer has received funds on his behalf for research and speaking support from Dexcom, Abbott Diabetes Care, Medtronic, Insulet, Tandem, Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, and Novo Nordisk, and for consulting from Sanofi and Eli Lilly and Company. He is employed by the nonprofit HealthPartners Institute dba International Diabetes Center and received no personal income from these activities.
The Osers have received advisory board consulting fees (through the University of Colorado) from Dexcom, Medscape Medical News, Ascensia, and Blue Circle Health and research grants (through the University of Colorado) from National Institute of Nursing Research, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Helmsley Charitable Trust, Abbott Diabetes, Dexcom, and Insulet. They do not own stocks in any device or pharmaceutical company.
Dr. Milosavljevic’s work was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Advancing Translational Science and Einstein-Montefiore Clinical and Translational Science Awards. He had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — As increasing data show benefit for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices beyond just insulin-treated diabetes, efforts are being made to optimize the use of CGM in primary care settings.
Currently, Medicare and most private insurers cover CGM for people with diabetes who use insulin, regardless of the type of diabetes or the type of insulin, and for those with a history of severe hypoglycemia. Data are increasingly showing benefit for people who don’t use insulin. As of now, with the exception of some state Medicaid beneficiaries, the majority must pay out of pocket.
Such use is expected to grow with the upcoming availability of two new over-the-counter CGMs, Dexcom’s Stelo and Abbott’s Libre Rio, both made for people with diabetes who don’t use insulin. (Abbott will also launch the Lingo, a wellness CGM for people without diabetes.)
This means that CGM will become increasingly prevalent in primary care, where there is currently a great deal of variability in the capacity to manage and use the data generated by the devices to improve diabetes management, experts said during an oral abstract session at the recent American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions and in interviews with this news organization.
“It’s picking up steam, and there’s a lot more visibility of CGM in primary care and a lot more people prescribing it,” Thomas W. Martens, MD, medical director of the International Diabetes Center at HealthPartners Institute, Minneapolis, told this news organization. He noted that the recent switch in many cases of CGM from billing as durable medical equipment to pharmacy has made prescribing easier, while television advertising has increased demand.
But still unclear, he noted, is how the CGM data are being used. “The question is, are prescriptions just being sent out and people using it like a finger-stick blood glucose monitor, or is primary care really using the data to move diabetes forward? I think that’s where a lot of the work on dissemination and implementation is going. How do we really make this a useful tool for optimizing diabetes care?”
Informing Food Choice, Treatment Intensification
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Martens presented topline data from a randomized multicenter controlled trial funded by Abbott, examining the effect of CGM use on guiding food choices and other behaviors in 72 adults with type 2 diabetes who were not using insulin but who were using other glucose-lowering medications.
At 3 months, with no medication changes, there was a significant overall 26% reduction in time spent above 180 mg/dL (P < .0001), which didn›t differ significantly between those randomized to CGM alone or in conjunction with a food logging app. Both groups also experienced a significant 1.1% reduction in A1c (P < .0001) and about a 4-lb weight loss (P = .014 for CGM alone, P = .0032 for CGM + app).
“The win for people not on insulin is you can see the impact of food choices really quickly with a CGM ... and then perhaps modify that to improve postprandial hyperglycemia,” Dr. Martens said.
And for the clinician, “not everybody with type 2 diabetes not on insulin can get where they need to be just by changing their diets. The CGM is a pretty good tool for knowing when you need to advance therapy.”
Diabetes Care and Education Specialists (DCESs) Assist CGM Use
Another speaker at the ADA meeting, Sean M. Oser, MD, director of the Practice Innovation Program and associated director of the Primary Care Diabetes Lab at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado, noted that 90% of adults with type 2 diabetes and 50% with type 1 diabetes receive their diabetes care in primary care settings.
“CGM is increasingly becoming standard of care in diabetes ... But [primary care providers] remain relatively untrained about CGM ... What I’m concerned about is the disparity disparities in who has access and who does not. We really need to bring our primary care colleagues along,” he said.
Dr. Oser described tools he and his wife, Tamara K. Oser, MD, professor in the Department of Family Medicine at the same institution, developed in conjunction with the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), including the Transformation in Practice series (TIPS).
The PREPARE 4 CGM study examined the use of three different strategies for incorporating CGM into primary care settings: Either use of AAFP TIPS alone, TIPS plus practice facilitation services by coaches who assist the practice in implementing new workflows, or referral to a virtual CGM initiation service (virCIS) with a virtual CGM workshop that Dr. Oser and Dr. Oser also developed.
Of the 76 Colorado primary care practices participating (out of 60 planned), the 46 who chose AAFP TIPS were randomized to either the AAFP TIPS alone or to TIPS + practice facilitation. The other 30 chose virCIS with the onetime CGM basics webinar. The fact that more practices than anticipated were recruited for the study suggests that “primary care interest in CGM is very high. They want to learn,” Dr. Oser noted.
Of the 51 practice characteristics investigated, only one, the presence of a DCES, in the practice, was significantly associated with the choice of CGM implementation strategy. Of the 16 practices with access to a DCES, all of them chose self-initiation with CGM using TIPS. But of the 60 practices without a DCES, half chose the virCIS.
“We know that 36% of primary care practices have access to a DCES within the clinic, part-time or full-time, and that’s not enough, I would argue,” Dr. Oser said.
Indeed, Dr. Martens told this news organization that those professionals, formerly called “diabetes educators,” often aren’t available in primary care settings, especially in rural areas. “Unfortunately, they are not well reimbursed. A lot of care systems don’t employ as many as they ideally should because it tends not to be a moneymaker ... Something’s got to change with reimbursement for the cognitive aspects of diabetes management.”
Dr. Oser said his team’s next steps include completion of the virCIS operations, analysis of the effectiveness of the three implantation strategies in practice- and patient-level outcomes, a cost analysis of the three strategies, and further development of toolkits to assist in these efforts.
“One of our goals is to keep people at their primary care home, where they want to be ... Diabetes knows no borders. People should have access wherever they are,” Dr. Oser concluded in his ADA talk.
What Predicts Primary Care CGM Prescribing?
Further clues about effective strategies to improve CGM prescribing in primary care were provided in a study presented by Jovan Milosavljevic, MD, a second-year endocrinology fellow at the Fleischer Institute for Diabetes and Metabolism, Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York.
He began by noting that there are currently 61.5 million diabetes visits annually in primary care compared with 32.0 million in specialty care and that there is a shortage of endocrinologists in the face of the rising number of people diagnosed with diabetes. “Primary care will continue to be the only point of care for most people with diabetes. So, standard-of-care treatment such as CGM must enter routine primary care practice to impact population-level health outcomes.”
Electronic health record data were examined for 39,710 patients with type 2 diabetes seen at 13 primary care sites affiliated with Montefiore Medical Center, a large safety net hospital in New York, where CGM is widely covered by public insurance. Between July 31, 2020, and July 31, 2023, a total of 3503, or just 8.8%, were prescribed CGM by a primary care provider.
Those with CGM prescribed were younger than those without (59.7 vs 62.7 years), about 40% of both groups were Hispanic or Black, and a majority were English-speaking: 84.5% of those prescribed CGM spoke English, while only 13.1% spoke Spanish. Over half (59.1%) of those prescribed CGM had commercial insurance, while only 11.2% had Medicaid and 29.7% had Medicare.
More patients with CGM prescribed had providers with more than 10 years in practice: 72.5% vs 64.5% with no CGM.
Not surprisingly, those with CGM prescribed were more likely on insulin — 21% using just basal and 35% on multiple daily injections. Those prescribed CGM had higher A1c levels before CGM prescription: 9.2% vs 7.2% for those not prescribed CGM.
No racial or ethnic bias was found in the relationships between CGM use and insulin use, provider experience, engagement with care, and A1c. However, there were differences by age, sex, and spoken language.
For example, the Hispanic group aged 65 years and older was less likely than those younger to be prescribed CGM, but this wasn’t seen in other ethnic groups. In fact, older White people were slightly more likely to have CGM prescribed. Spanish-speaking patients were about 43% less likely to have CGM prescribed than were English-speaking patients.
These findings suggest a dual approach might work best for improving CGM prescribing in primary care. “We can leverage the knowledge that some of these factors are independent of bias and promote clinical and evidence-based guidelines for CGM. Additionally, we should focus on physicians in training,” Dr. Milosavljevic said.
At the same time, “we need to tackle systemic inequity in prescription processes,” with measures such as improving prescription workflows, supporting prior authorization, and using patient hands-on support for older adults and Spanish-speaking individuals, he said.
In a message to this news organization, Tamara K. Oser, MD, wrote, “Disparities in CGM and other diabetes technology are prevalent and multifactorial. In addition to insurance barriers, implicit bias also plays a large role. Shared decision-making should always be used when deciding to prescribe diabetes technologies.”
The PREPARE 4 CGM study is evaluating willingness to pay for CGM, she noted.
“Even patients without insurance might want to purchase one sensor every few months to empower them to learn more about how food and exercise affect their glucose or to help assess the need for [adjusting] diabetes medications. It is an exciting time for people living with diabetes. Primary care, endocrinology, device manufacturers, and insurers should all do their part to assure increased access to these evidence-based technologies.”
Dr. Martens’ employer has received funds on his behalf for research and speaking support from Dexcom, Abbott Diabetes Care, Medtronic, Insulet, Tandem, Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, and Novo Nordisk, and for consulting from Sanofi and Eli Lilly and Company. He is employed by the nonprofit HealthPartners Institute dba International Diabetes Center and received no personal income from these activities.
The Osers have received advisory board consulting fees (through the University of Colorado) from Dexcom, Medscape Medical News, Ascensia, and Blue Circle Health and research grants (through the University of Colorado) from National Institute of Nursing Research, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the Helmsley Charitable Trust, Abbott Diabetes, Dexcom, and Insulet. They do not own stocks in any device or pharmaceutical company.
Dr. Milosavljevic’s work was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Advancing Translational Science and Einstein-Montefiore Clinical and Translational Science Awards. He had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
Data Trends 2024: Respiratory Health
- McVeigh C, Reid J, Carvalho P. Healthcare professionals’ views of palliative care for American war veterans with non-malignant respiratory disease living in a rural area: a qualitative study. BMC Palliat Care. 2019;18(1):22. doi:10.1186/s12904-019-0408-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Study finds uptick in lung disease in recent veterans. May 23, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0516-3.cfm
- Sanders JW, Putnam SD, Frankart C, et al. Impact of illness and non-combat injury during Operations Iraqi Freedom and Enduring Freedom (Afghanistan). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73(4):713-719.
- Trupin L, Schmajuk G, Ying D, Yelin E, Blanc PD. Military service and COPD risk. Chest. 2022;162(4):792-795. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.04.016
- Bastian LA. Pain-related anxiety intervention for smokers with chronic pain: a comparative effectiveness trial of smoking cessation counseling for veterans. Veteran’s Health Systems Research, IIR 15-092-HSR Study. Published January 2022. Accessed April 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/research/abstracts.cfm?Project_ID=2141704797
- Rivera AC, Powell TM, Boyko EJ, et al; for the Millennium Cohort Study Team. New-onset asthma and combat deployment: findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(10):2136-2144. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy112
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to Military Bases With Open Burn Pits and Respiratory and Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- McVeigh C, Reid J, Carvalho P. Healthcare professionals’ views of palliative care for American war veterans with non-malignant respiratory disease living in a rural area: a qualitative study. BMC Palliat Care. 2019;18(1):22. doi:10.1186/s12904-019-0408-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Study finds uptick in lung disease in recent veterans. May 23, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0516-3.cfm
- Sanders JW, Putnam SD, Frankart C, et al. Impact of illness and non-combat injury during Operations Iraqi Freedom and Enduring Freedom (Afghanistan). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73(4):713-719.
- Trupin L, Schmajuk G, Ying D, Yelin E, Blanc PD. Military service and COPD risk. Chest. 2022;162(4):792-795. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.04.016
- Bastian LA. Pain-related anxiety intervention for smokers with chronic pain: a comparative effectiveness trial of smoking cessation counseling for veterans. Veteran’s Health Systems Research, IIR 15-092-HSR Study. Published January 2022. Accessed April 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/research/abstracts.cfm?Project_ID=2141704797
- Rivera AC, Powell TM, Boyko EJ, et al; for the Millennium Cohort Study Team. New-onset asthma and combat deployment: findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(10):2136-2144. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy112
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to Military Bases With Open Burn Pits and Respiratory and Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- McVeigh C, Reid J, Carvalho P. Healthcare professionals’ views of palliative care for American war veterans with non-malignant respiratory disease living in a rural area: a qualitative study. BMC Palliat Care. 2019;18(1):22. doi:10.1186/s12904-019-0408-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Study finds uptick in lung disease in recent veterans. May 23, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0516-3.cfm
- Sanders JW, Putnam SD, Frankart C, et al. Impact of illness and non-combat injury during Operations Iraqi Freedom and Enduring Freedom (Afghanistan). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73(4):713-719.
- Trupin L, Schmajuk G, Ying D, Yelin E, Blanc PD. Military service and COPD risk. Chest. 2022;162(4):792-795. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.04.016
- Bastian LA. Pain-related anxiety intervention for smokers with chronic pain: a comparative effectiveness trial of smoking cessation counseling for veterans. Veteran’s Health Systems Research, IIR 15-092-HSR Study. Published January 2022. Accessed April 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/research/abstracts.cfm?Project_ID=2141704797
- Rivera AC, Powell TM, Boyko EJ, et al; for the Millennium Cohort Study Team. New-onset asthma and combat deployment: findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(10):2136-2144. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy112
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to Military Bases With Open Burn Pits and Respiratory and Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
Are We Relying Too Much on BMI to Diagnose Obesity?
Gary* is a 60-year-old race car driver with a history of insulin resistance, elevated cholesterol, and severe reflux. His wife sent him to me when his snoring became so loud and “violent” that she could no longer sleep in the same bedroom.
She was desperate to help him lose weight in a sustained fashion. All his previous efforts were short-lived due to his self-described pizza and burger addiction. At 5 ft 9 in and 180 lb, his body mass index (BMI) was approximately 26.5 (normal is 18.5-24.9).
On exam, his arms and legs were relatively thin, but he had a hard, protuberant belly. Given his body habits, comorbidities, and family history of early heart disease, I was worried that his weight would eventually become life-threatening. Solely on the basis of BMI criteria, however, he is not considered to be at high risk.
This begs the question, are we relying too much on BMI and ignoring central adiposity (ie, belly fat) and comorbid conditions when identifying at-risk patients?
The European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) argues exactly this point in its new guidelines published in July 2024. Titled “A New Framework for the Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Obesity in Adults,” the guidelines assert that obesity should be redefined as a chronic and relapsing adiposity-based disease which may start off as asymptomatic but often becomes life-threatening.
The guidelines further argue that BMI does not appropriately predict cardiometabolic risk in patients with BMI < 35. Instead, in such patients we should incorporate the use of waist-to-height ratios to reflect the potentially deleterious presence of increased visceral fat. It expands the definition of high-risk patients to include those with BMI > 25 and a waist-to-height ratio > 0.5.
It also suggests that DEXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) or bioimpedance testing be used when BMI results are ambiguous. The European guidelines recommend considering screening more routinely for eating disorders (with psychometric testing) and depression. The guidelines highlight the importance of long-term goals and of physical activity, nutrition, and psychological support in addition to pharmaceutical treatments.
On the basis of these new guidelines, I attempted to start Gary on Wegovy (semaglutide) along with sending him to a health coach, dietitian, and trainer. Unfortunately, despite documenting a waist-to-height ratio of > 0.6 and elevated fat percentage of just over 30% using bioimpedance, my prior authorization and appeal were summarily rejected by his insurance provider.
In the United States, pharmacotherapy is typically approved for patients with a BMI of 27 or higher with a comorbidity (like high blood pressure or elevated cholesterol levels) or a BMI over 30. This clearly highlights the need for updated criteria for weight loss medication. Thank goodness for compounded semaglutide to fill this void until the medical world catches up with the EASO guidelines.
Now on compounded semaglutide, Gary has lost 15 lb. His once rounded belly is nearly flat, and he has a normal waist-to-height ratio. While his dietary choices still leave something to be desired, his portion sizes are much smaller. His snoring has improved considerably. His most recent bioimpedance testing showed a reduced fat percentage of just under 25%.
*Patient’s name has been changed
Caroline Messer, MD, is Clinical Assistant Professor, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, and Associate Professor, Hofstra School of Medicine, both in New York. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gary* is a 60-year-old race car driver with a history of insulin resistance, elevated cholesterol, and severe reflux. His wife sent him to me when his snoring became so loud and “violent” that she could no longer sleep in the same bedroom.
She was desperate to help him lose weight in a sustained fashion. All his previous efforts were short-lived due to his self-described pizza and burger addiction. At 5 ft 9 in and 180 lb, his body mass index (BMI) was approximately 26.5 (normal is 18.5-24.9).
On exam, his arms and legs were relatively thin, but he had a hard, protuberant belly. Given his body habits, comorbidities, and family history of early heart disease, I was worried that his weight would eventually become life-threatening. Solely on the basis of BMI criteria, however, he is not considered to be at high risk.
This begs the question, are we relying too much on BMI and ignoring central adiposity (ie, belly fat) and comorbid conditions when identifying at-risk patients?
The European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) argues exactly this point in its new guidelines published in July 2024. Titled “A New Framework for the Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Obesity in Adults,” the guidelines assert that obesity should be redefined as a chronic and relapsing adiposity-based disease which may start off as asymptomatic but often becomes life-threatening.
The guidelines further argue that BMI does not appropriately predict cardiometabolic risk in patients with BMI < 35. Instead, in such patients we should incorporate the use of waist-to-height ratios to reflect the potentially deleterious presence of increased visceral fat. It expands the definition of high-risk patients to include those with BMI > 25 and a waist-to-height ratio > 0.5.
It also suggests that DEXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) or bioimpedance testing be used when BMI results are ambiguous. The European guidelines recommend considering screening more routinely for eating disorders (with psychometric testing) and depression. The guidelines highlight the importance of long-term goals and of physical activity, nutrition, and psychological support in addition to pharmaceutical treatments.
On the basis of these new guidelines, I attempted to start Gary on Wegovy (semaglutide) along with sending him to a health coach, dietitian, and trainer. Unfortunately, despite documenting a waist-to-height ratio of > 0.6 and elevated fat percentage of just over 30% using bioimpedance, my prior authorization and appeal were summarily rejected by his insurance provider.
In the United States, pharmacotherapy is typically approved for patients with a BMI of 27 or higher with a comorbidity (like high blood pressure or elevated cholesterol levels) or a BMI over 30. This clearly highlights the need for updated criteria for weight loss medication. Thank goodness for compounded semaglutide to fill this void until the medical world catches up with the EASO guidelines.
Now on compounded semaglutide, Gary has lost 15 lb. His once rounded belly is nearly flat, and he has a normal waist-to-height ratio. While his dietary choices still leave something to be desired, his portion sizes are much smaller. His snoring has improved considerably. His most recent bioimpedance testing showed a reduced fat percentage of just under 25%.
*Patient’s name has been changed
Caroline Messer, MD, is Clinical Assistant Professor, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, and Associate Professor, Hofstra School of Medicine, both in New York. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gary* is a 60-year-old race car driver with a history of insulin resistance, elevated cholesterol, and severe reflux. His wife sent him to me when his snoring became so loud and “violent” that she could no longer sleep in the same bedroom.
She was desperate to help him lose weight in a sustained fashion. All his previous efforts were short-lived due to his self-described pizza and burger addiction. At 5 ft 9 in and 180 lb, his body mass index (BMI) was approximately 26.5 (normal is 18.5-24.9).
On exam, his arms and legs were relatively thin, but he had a hard, protuberant belly. Given his body habits, comorbidities, and family history of early heart disease, I was worried that his weight would eventually become life-threatening. Solely on the basis of BMI criteria, however, he is not considered to be at high risk.
This begs the question, are we relying too much on BMI and ignoring central adiposity (ie, belly fat) and comorbid conditions when identifying at-risk patients?
The European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) argues exactly this point in its new guidelines published in July 2024. Titled “A New Framework for the Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Obesity in Adults,” the guidelines assert that obesity should be redefined as a chronic and relapsing adiposity-based disease which may start off as asymptomatic but often becomes life-threatening.
The guidelines further argue that BMI does not appropriately predict cardiometabolic risk in patients with BMI < 35. Instead, in such patients we should incorporate the use of waist-to-height ratios to reflect the potentially deleterious presence of increased visceral fat. It expands the definition of high-risk patients to include those with BMI > 25 and a waist-to-height ratio > 0.5.
It also suggests that DEXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) or bioimpedance testing be used when BMI results are ambiguous. The European guidelines recommend considering screening more routinely for eating disorders (with psychometric testing) and depression. The guidelines highlight the importance of long-term goals and of physical activity, nutrition, and psychological support in addition to pharmaceutical treatments.
On the basis of these new guidelines, I attempted to start Gary on Wegovy (semaglutide) along with sending him to a health coach, dietitian, and trainer. Unfortunately, despite documenting a waist-to-height ratio of > 0.6 and elevated fat percentage of just over 30% using bioimpedance, my prior authorization and appeal were summarily rejected by his insurance provider.
In the United States, pharmacotherapy is typically approved for patients with a BMI of 27 or higher with a comorbidity (like high blood pressure or elevated cholesterol levels) or a BMI over 30. This clearly highlights the need for updated criteria for weight loss medication. Thank goodness for compounded semaglutide to fill this void until the medical world catches up with the EASO guidelines.
Now on compounded semaglutide, Gary has lost 15 lb. His once rounded belly is nearly flat, and he has a normal waist-to-height ratio. While his dietary choices still leave something to be desired, his portion sizes are much smaller. His snoring has improved considerably. His most recent bioimpedance testing showed a reduced fat percentage of just under 25%.
*Patient’s name has been changed
Caroline Messer, MD, is Clinical Assistant Professor, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, and Associate Professor, Hofstra School of Medicine, both in New York. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in Ten Chronic Pain Patients May Develop Opioid Use Disorder
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.