User login
Doctor removes 23 contact lenses from woman’s eye
In a video posted on Instagram, ophthalmologist Katerina Kurteeva, MD, is shown removing contact lenses from a woman’s eye.
“Don’t sleep in your contact lenses!” she warned.
“They were essentially glued together after sitting under the eyelid for a month,” Dr. Kurteeva said in the post.
The patient is doing fine and wants to continue wearing contact lenses, the doctor told the Los Angeles ABC News affiliate, noting that the patient didn’t know how she could have forgotten to take her lenses out.
About 45 million Americans wear contact lenses, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Contact lens usage increases the risk of infections such as microbial keratitis. In severe cases, microbial keratitis can cause blindness or require corneal transplant.
Dr. Kurteeva told the Los Angeles TV station that the cornea becomes desensitized after years of contact lens wear.
“This is essentially a protective feature, because otherwise you’d be really bothered by everyday contact lens wear. After all, it is a foreign body in your eye,” she said. “So when the cornea loses sensitivity, it’s sort of an adjustment, but at the same time, you don’t feel when something is really wrong as acutely.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In a video posted on Instagram, ophthalmologist Katerina Kurteeva, MD, is shown removing contact lenses from a woman’s eye.
“Don’t sleep in your contact lenses!” she warned.
“They were essentially glued together after sitting under the eyelid for a month,” Dr. Kurteeva said in the post.
The patient is doing fine and wants to continue wearing contact lenses, the doctor told the Los Angeles ABC News affiliate, noting that the patient didn’t know how she could have forgotten to take her lenses out.
About 45 million Americans wear contact lenses, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Contact lens usage increases the risk of infections such as microbial keratitis. In severe cases, microbial keratitis can cause blindness or require corneal transplant.
Dr. Kurteeva told the Los Angeles TV station that the cornea becomes desensitized after years of contact lens wear.
“This is essentially a protective feature, because otherwise you’d be really bothered by everyday contact lens wear. After all, it is a foreign body in your eye,” she said. “So when the cornea loses sensitivity, it’s sort of an adjustment, but at the same time, you don’t feel when something is really wrong as acutely.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In a video posted on Instagram, ophthalmologist Katerina Kurteeva, MD, is shown removing contact lenses from a woman’s eye.
“Don’t sleep in your contact lenses!” she warned.
“They were essentially glued together after sitting under the eyelid for a month,” Dr. Kurteeva said in the post.
The patient is doing fine and wants to continue wearing contact lenses, the doctor told the Los Angeles ABC News affiliate, noting that the patient didn’t know how she could have forgotten to take her lenses out.
About 45 million Americans wear contact lenses, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Contact lens usage increases the risk of infections such as microbial keratitis. In severe cases, microbial keratitis can cause blindness or require corneal transplant.
Dr. Kurteeva told the Los Angeles TV station that the cornea becomes desensitized after years of contact lens wear.
“This is essentially a protective feature, because otherwise you’d be really bothered by everyday contact lens wear. After all, it is a foreign body in your eye,” she said. “So when the cornea loses sensitivity, it’s sort of an adjustment, but at the same time, you don’t feel when something is really wrong as acutely.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Reminder that COVID-19 and cancer can be a deadly combo
A new study underscores the importance of COVID-19 and regular COVID-19 testing among adults with a recent cancer diagnosis.
The Indiana statewide study, conducted at the beginning of the pandemic, found that
“This analysis provides additional empirical evidence on the magnitude of risk to patients with cancer whose immune systems are often weakened either by the disease or treatment,” the study team wrote.
The study was published online in JMIR Cancer.
Although evidence has consistently revealed similar findings, the risk of death among unvaccinated people with cancer and COVID-19 has not been nearly as high in previous studies, lead author Brian E. Dixon, PhD, MBA, with Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Indianapolis, said in a statement. Previous studies from China, for instance, reported a two- to threefold greater risk of all-cause mortality among unvaccinated adults with cancer and COVID-19.
A potential reason for this discrepancy, Dr. Dixon noted, is that earlier studies were “generally smaller and made calculations based on data from a single cancer center or health system.”
Another reason is testing for COVID-19 early in the pandemic was limited to symptomatic individuals who may have had more severe infections, possibly leading to an overestimate of the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection, cancer, and all-cause mortality.
In the current analysis, researchers used electronic health records linked to Indiana’s statewide SARS-CoV-2 testing database and state vital records to evaluate the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and all-cause mortality among 41,924 adults newly diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2019, and Dec. 31, 2020.
Most people with cancer were White (78.4%) and about half were male. At the time of diagnosis, 17% had one comorbid condition and about 10% had two or more. Most patients had breast cancer (14%), prostate cancer (13%), or melanoma (13%).
During the study period, 2,894 patients (7%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
In multivariate adjusted analysis, the risk of death among those newly diagnosed with cancer increased by 91% (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.91) during the first year of the pandemic before vaccines were available, compared with the year before (January 2019 to Jan. 14, 2020).
During the pandemic period, the risk of death was roughly threefold higher among adults 65 years old and older, compared with adults 18-44 years old (aHR, 3.35).
When looking at the time from a cancer diagnosis to SARS-CoV-2 infection, infection was associated with an almost sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (aHR, 6.91). Adults 65 years old and older had an almost threefold increased risk of dying, compared with their younger peers (aHR, 2.74).
Dr. Dixon and colleagues also observed an increased risk of death in men with cancer and COVID, compared with women (aHR, 1.23) and those with at least two comorbid conditions versus none (aHR, 2.12). In addition, the risk of dying was 9% higher among Indiana’s rural population than urban dwellers.
Compared with other cancer types, individuals with lung cancer and other digestive cancers had the highest risk of death after SARS-CoV-2 infection (aHR, 1.45 and 1.80, respectively).
“Our findings highlight the increased risk of death for adult cancer patients who test positive for COVID and underscore the importance to cancer patients – including those in remission – of vaccinations, boosters, and regular COVID testing,” Dr. Dixon commented.
“Our results should encourage individuals diagnosed with cancer not only to take preventive action, but also to expeditiously seek out treatments available in the marketplace should they test positive for COVID,” he added.
Support for the study was provided by Indiana University Simon Cancer Center and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study underscores the importance of COVID-19 and regular COVID-19 testing among adults with a recent cancer diagnosis.
The Indiana statewide study, conducted at the beginning of the pandemic, found that
“This analysis provides additional empirical evidence on the magnitude of risk to patients with cancer whose immune systems are often weakened either by the disease or treatment,” the study team wrote.
The study was published online in JMIR Cancer.
Although evidence has consistently revealed similar findings, the risk of death among unvaccinated people with cancer and COVID-19 has not been nearly as high in previous studies, lead author Brian E. Dixon, PhD, MBA, with Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Indianapolis, said in a statement. Previous studies from China, for instance, reported a two- to threefold greater risk of all-cause mortality among unvaccinated adults with cancer and COVID-19.
A potential reason for this discrepancy, Dr. Dixon noted, is that earlier studies were “generally smaller and made calculations based on data from a single cancer center or health system.”
Another reason is testing for COVID-19 early in the pandemic was limited to symptomatic individuals who may have had more severe infections, possibly leading to an overestimate of the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection, cancer, and all-cause mortality.
In the current analysis, researchers used electronic health records linked to Indiana’s statewide SARS-CoV-2 testing database and state vital records to evaluate the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and all-cause mortality among 41,924 adults newly diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2019, and Dec. 31, 2020.
Most people with cancer were White (78.4%) and about half were male. At the time of diagnosis, 17% had one comorbid condition and about 10% had two or more. Most patients had breast cancer (14%), prostate cancer (13%), or melanoma (13%).
During the study period, 2,894 patients (7%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
In multivariate adjusted analysis, the risk of death among those newly diagnosed with cancer increased by 91% (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.91) during the first year of the pandemic before vaccines were available, compared with the year before (January 2019 to Jan. 14, 2020).
During the pandemic period, the risk of death was roughly threefold higher among adults 65 years old and older, compared with adults 18-44 years old (aHR, 3.35).
When looking at the time from a cancer diagnosis to SARS-CoV-2 infection, infection was associated with an almost sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (aHR, 6.91). Adults 65 years old and older had an almost threefold increased risk of dying, compared with their younger peers (aHR, 2.74).
Dr. Dixon and colleagues also observed an increased risk of death in men with cancer and COVID, compared with women (aHR, 1.23) and those with at least two comorbid conditions versus none (aHR, 2.12). In addition, the risk of dying was 9% higher among Indiana’s rural population than urban dwellers.
Compared with other cancer types, individuals with lung cancer and other digestive cancers had the highest risk of death after SARS-CoV-2 infection (aHR, 1.45 and 1.80, respectively).
“Our findings highlight the increased risk of death for adult cancer patients who test positive for COVID and underscore the importance to cancer patients – including those in remission – of vaccinations, boosters, and regular COVID testing,” Dr. Dixon commented.
“Our results should encourage individuals diagnosed with cancer not only to take preventive action, but also to expeditiously seek out treatments available in the marketplace should they test positive for COVID,” he added.
Support for the study was provided by Indiana University Simon Cancer Center and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study underscores the importance of COVID-19 and regular COVID-19 testing among adults with a recent cancer diagnosis.
The Indiana statewide study, conducted at the beginning of the pandemic, found that
“This analysis provides additional empirical evidence on the magnitude of risk to patients with cancer whose immune systems are often weakened either by the disease or treatment,” the study team wrote.
The study was published online in JMIR Cancer.
Although evidence has consistently revealed similar findings, the risk of death among unvaccinated people with cancer and COVID-19 has not been nearly as high in previous studies, lead author Brian E. Dixon, PhD, MBA, with Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Indianapolis, said in a statement. Previous studies from China, for instance, reported a two- to threefold greater risk of all-cause mortality among unvaccinated adults with cancer and COVID-19.
A potential reason for this discrepancy, Dr. Dixon noted, is that earlier studies were “generally smaller and made calculations based on data from a single cancer center or health system.”
Another reason is testing for COVID-19 early in the pandemic was limited to symptomatic individuals who may have had more severe infections, possibly leading to an overestimate of the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection, cancer, and all-cause mortality.
In the current analysis, researchers used electronic health records linked to Indiana’s statewide SARS-CoV-2 testing database and state vital records to evaluate the association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and all-cause mortality among 41,924 adults newly diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2019, and Dec. 31, 2020.
Most people with cancer were White (78.4%) and about half were male. At the time of diagnosis, 17% had one comorbid condition and about 10% had two or more. Most patients had breast cancer (14%), prostate cancer (13%), or melanoma (13%).
During the study period, 2,894 patients (7%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
In multivariate adjusted analysis, the risk of death among those newly diagnosed with cancer increased by 91% (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.91) during the first year of the pandemic before vaccines were available, compared with the year before (January 2019 to Jan. 14, 2020).
During the pandemic period, the risk of death was roughly threefold higher among adults 65 years old and older, compared with adults 18-44 years old (aHR, 3.35).
When looking at the time from a cancer diagnosis to SARS-CoV-2 infection, infection was associated with an almost sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (aHR, 6.91). Adults 65 years old and older had an almost threefold increased risk of dying, compared with their younger peers (aHR, 2.74).
Dr. Dixon and colleagues also observed an increased risk of death in men with cancer and COVID, compared with women (aHR, 1.23) and those with at least two comorbid conditions versus none (aHR, 2.12). In addition, the risk of dying was 9% higher among Indiana’s rural population than urban dwellers.
Compared with other cancer types, individuals with lung cancer and other digestive cancers had the highest risk of death after SARS-CoV-2 infection (aHR, 1.45 and 1.80, respectively).
“Our findings highlight the increased risk of death for adult cancer patients who test positive for COVID and underscore the importance to cancer patients – including those in remission – of vaccinations, boosters, and regular COVID testing,” Dr. Dixon commented.
“Our results should encourage individuals diagnosed with cancer not only to take preventive action, but also to expeditiously seek out treatments available in the marketplace should they test positive for COVID,” he added.
Support for the study was provided by Indiana University Simon Cancer Center and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JMIR CANCER
Phase 3 topline results ‘disappointing’ for novel antidepressant as monotherapy
The negative monotherapy data come on the heels of earlier phase 2 data showing a benefit of REL-1017 when used as add-on therapy for adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).
Despite the monotherapy results, Relmada reported in a release that it is continuing to enroll patients in two other phase 3 trials. However, RELIANCE I and RELIANCE II are assessing the drug only as adjunctive therapy.
“While these RELIANCE III results are disappointing for patients, the need for new, safe, and effective treatments for MDD continues to exist,” Maurizio Fava, MD, psychiatrist in chief at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in the release.
“We look forward to the data from the ongoing RELIANCE I and II trials of REL-1017, a potential new therapy for the adjunctive treatment of MDD,” Dr. Fava added.
REL-1017 is a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel blocker that preferentially targets hyperactive channels while maintaining physiologic glutamatergic neurotransmission. RELIANCE III tested REL-1017 against placebo for 28 days in 232 adults with MDD.
The study did not achieve its primary endpoint, which was a statistically significant improvement in symptoms of depression compared with placebo, as measured by the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) on day 28.
At that time point, the REL-1017 treatment group showed a reduction in MADRS scores of 14.8 points, vs. 13.9 points for the placebo arm.
The placebo response was “higher than expected” – placebo “dramatically” outperformed REL-1017 at some study sites, Relmada said in the release.
The company added that it is “investigating the nature of these results.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The negative monotherapy data come on the heels of earlier phase 2 data showing a benefit of REL-1017 when used as add-on therapy for adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).
Despite the monotherapy results, Relmada reported in a release that it is continuing to enroll patients in two other phase 3 trials. However, RELIANCE I and RELIANCE II are assessing the drug only as adjunctive therapy.
“While these RELIANCE III results are disappointing for patients, the need for new, safe, and effective treatments for MDD continues to exist,” Maurizio Fava, MD, psychiatrist in chief at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in the release.
“We look forward to the data from the ongoing RELIANCE I and II trials of REL-1017, a potential new therapy for the adjunctive treatment of MDD,” Dr. Fava added.
REL-1017 is a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel blocker that preferentially targets hyperactive channels while maintaining physiologic glutamatergic neurotransmission. RELIANCE III tested REL-1017 against placebo for 28 days in 232 adults with MDD.
The study did not achieve its primary endpoint, which was a statistically significant improvement in symptoms of depression compared with placebo, as measured by the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) on day 28.
At that time point, the REL-1017 treatment group showed a reduction in MADRS scores of 14.8 points, vs. 13.9 points for the placebo arm.
The placebo response was “higher than expected” – placebo “dramatically” outperformed REL-1017 at some study sites, Relmada said in the release.
The company added that it is “investigating the nature of these results.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The negative monotherapy data come on the heels of earlier phase 2 data showing a benefit of REL-1017 when used as add-on therapy for adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).
Despite the monotherapy results, Relmada reported in a release that it is continuing to enroll patients in two other phase 3 trials. However, RELIANCE I and RELIANCE II are assessing the drug only as adjunctive therapy.
“While these RELIANCE III results are disappointing for patients, the need for new, safe, and effective treatments for MDD continues to exist,” Maurizio Fava, MD, psychiatrist in chief at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in the release.
“We look forward to the data from the ongoing RELIANCE I and II trials of REL-1017, a potential new therapy for the adjunctive treatment of MDD,” Dr. Fava added.
REL-1017 is a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel blocker that preferentially targets hyperactive channels while maintaining physiologic glutamatergic neurotransmission. RELIANCE III tested REL-1017 against placebo for 28 days in 232 adults with MDD.
The study did not achieve its primary endpoint, which was a statistically significant improvement in symptoms of depression compared with placebo, as measured by the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) on day 28.
At that time point, the REL-1017 treatment group showed a reduction in MADRS scores of 14.8 points, vs. 13.9 points for the placebo arm.
The placebo response was “higher than expected” – placebo “dramatically” outperformed REL-1017 at some study sites, Relmada said in the release.
The company added that it is “investigating the nature of these results.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID tied to spike in deaths in chronic liver disease with diabetes
The COVID-19 pandemic fueled a sharp uptick in deaths related to chronic liver disease and cirrhosis among people with diabetes, largely owing to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), new data show.
“Our observations confirm that COVID-19 had a higher likelihood of impacting vulnerable populations with pre-existing chronic liver diseases and diabetes, with a death rate as high as 10% in individuals with co-existing chronic liver disease and diabetes,” write the authors.
“The inability to attend regular outpatient clinics for close monitoring and treatment accompanied by diversion of health care resources to COVID-19 care may have resulted in the suboptimal or delayed clinical care of individuals with diabetes and chronic liver disease during the COVID-19 pandemic,” they add.
Donghee Kim, MD, PhD, with the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford (Calif.) University School of Medicine, and colleagues report their findings in the journal Digestive and Liver Disease.
Vulnerable group
The researchers used U.S. national mortality data (2017-2020) to estimate chronic liver disease–related mortality trends among individuals with diabetes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Before the pandemic, the quarterly mortality for chronic liver disease remained stable (quarterly percentage change, 0.6%) but then sharply increased during the pandemic (QPC, 8.6%).
A similar trend was seen with cirrhosis-related mortality (QPC, 0.3% before the pandemic vs. 8.4% during the pandemic).
NAFLD and ALD mortality among individuals with diabetes was steadily increasing before the pandemic (QPC, 4.2% and 3.5%, respectively) but showed a more rapid increase during the pandemic (QPC, 9.6% and 7.7%, respectively).
ALD-related mortality in men was more than threefold higher than in women, while NAFLD-related mortality in women was more than twofold higher than in men.
Mortality for hepatitis C virus infection declined before the pandemic (QPC, −3.3%) and remained stable during the pandemic.
COVID-19–related mortality among adults with chronic liver disease and diabetes also rose sharply during the pandemic – from 0.4% in the first quarter of 2020 to 12.9% in the last quarter of 2020 – with no considerable difference between men and women.
Blame it on lockdowns?
Dr. Kim and colleagues say research is needed to better understand the direct and indirect influence of COVID-19 on coexisting chronic liver disease and diabetes.
“It is plausible that psychosocial stress and a higher predisposition to psychiatric disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic can increase the risk of alcohol use disorder and ALD,” they write.
“Furthermore, it is prudent to suspect that COVID-19–related lockdowns may increase the risk of obesity, leading to a higher risk of insulin resistance and metabolic complications, including diabetes and NAFLD. Future studies are needed to improve our understanding of these possible pathogenetic links. More importantly, emergency preparedness or contingency plans must be in place to continue and provide uninterrupted care for chronic ailments during times of disaster,” they add.
The study had no specific funding. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic fueled a sharp uptick in deaths related to chronic liver disease and cirrhosis among people with diabetes, largely owing to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), new data show.
“Our observations confirm that COVID-19 had a higher likelihood of impacting vulnerable populations with pre-existing chronic liver diseases and diabetes, with a death rate as high as 10% in individuals with co-existing chronic liver disease and diabetes,” write the authors.
“The inability to attend regular outpatient clinics for close monitoring and treatment accompanied by diversion of health care resources to COVID-19 care may have resulted in the suboptimal or delayed clinical care of individuals with diabetes and chronic liver disease during the COVID-19 pandemic,” they add.
Donghee Kim, MD, PhD, with the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford (Calif.) University School of Medicine, and colleagues report their findings in the journal Digestive and Liver Disease.
Vulnerable group
The researchers used U.S. national mortality data (2017-2020) to estimate chronic liver disease–related mortality trends among individuals with diabetes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Before the pandemic, the quarterly mortality for chronic liver disease remained stable (quarterly percentage change, 0.6%) but then sharply increased during the pandemic (QPC, 8.6%).
A similar trend was seen with cirrhosis-related mortality (QPC, 0.3% before the pandemic vs. 8.4% during the pandemic).
NAFLD and ALD mortality among individuals with diabetes was steadily increasing before the pandemic (QPC, 4.2% and 3.5%, respectively) but showed a more rapid increase during the pandemic (QPC, 9.6% and 7.7%, respectively).
ALD-related mortality in men was more than threefold higher than in women, while NAFLD-related mortality in women was more than twofold higher than in men.
Mortality for hepatitis C virus infection declined before the pandemic (QPC, −3.3%) and remained stable during the pandemic.
COVID-19–related mortality among adults with chronic liver disease and diabetes also rose sharply during the pandemic – from 0.4% in the first quarter of 2020 to 12.9% in the last quarter of 2020 – with no considerable difference between men and women.
Blame it on lockdowns?
Dr. Kim and colleagues say research is needed to better understand the direct and indirect influence of COVID-19 on coexisting chronic liver disease and diabetes.
“It is plausible that psychosocial stress and a higher predisposition to psychiatric disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic can increase the risk of alcohol use disorder and ALD,” they write.
“Furthermore, it is prudent to suspect that COVID-19–related lockdowns may increase the risk of obesity, leading to a higher risk of insulin resistance and metabolic complications, including diabetes and NAFLD. Future studies are needed to improve our understanding of these possible pathogenetic links. More importantly, emergency preparedness or contingency plans must be in place to continue and provide uninterrupted care for chronic ailments during times of disaster,” they add.
The study had no specific funding. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic fueled a sharp uptick in deaths related to chronic liver disease and cirrhosis among people with diabetes, largely owing to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), new data show.
“Our observations confirm that COVID-19 had a higher likelihood of impacting vulnerable populations with pre-existing chronic liver diseases and diabetes, with a death rate as high as 10% in individuals with co-existing chronic liver disease and diabetes,” write the authors.
“The inability to attend regular outpatient clinics for close monitoring and treatment accompanied by diversion of health care resources to COVID-19 care may have resulted in the suboptimal or delayed clinical care of individuals with diabetes and chronic liver disease during the COVID-19 pandemic,” they add.
Donghee Kim, MD, PhD, with the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford (Calif.) University School of Medicine, and colleagues report their findings in the journal Digestive and Liver Disease.
Vulnerable group
The researchers used U.S. national mortality data (2017-2020) to estimate chronic liver disease–related mortality trends among individuals with diabetes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Before the pandemic, the quarterly mortality for chronic liver disease remained stable (quarterly percentage change, 0.6%) but then sharply increased during the pandemic (QPC, 8.6%).
A similar trend was seen with cirrhosis-related mortality (QPC, 0.3% before the pandemic vs. 8.4% during the pandemic).
NAFLD and ALD mortality among individuals with diabetes was steadily increasing before the pandemic (QPC, 4.2% and 3.5%, respectively) but showed a more rapid increase during the pandemic (QPC, 9.6% and 7.7%, respectively).
ALD-related mortality in men was more than threefold higher than in women, while NAFLD-related mortality in women was more than twofold higher than in men.
Mortality for hepatitis C virus infection declined before the pandemic (QPC, −3.3%) and remained stable during the pandemic.
COVID-19–related mortality among adults with chronic liver disease and diabetes also rose sharply during the pandemic – from 0.4% in the first quarter of 2020 to 12.9% in the last quarter of 2020 – with no considerable difference between men and women.
Blame it on lockdowns?
Dr. Kim and colleagues say research is needed to better understand the direct and indirect influence of COVID-19 on coexisting chronic liver disease and diabetes.
“It is plausible that psychosocial stress and a higher predisposition to psychiatric disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic can increase the risk of alcohol use disorder and ALD,” they write.
“Furthermore, it is prudent to suspect that COVID-19–related lockdowns may increase the risk of obesity, leading to a higher risk of insulin resistance and metabolic complications, including diabetes and NAFLD. Future studies are needed to improve our understanding of these possible pathogenetic links. More importantly, emergency preparedness or contingency plans must be in place to continue and provide uninterrupted care for chronic ailments during times of disaster,” they add.
The study had no specific funding. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
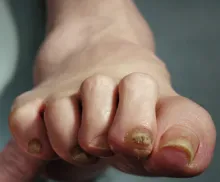
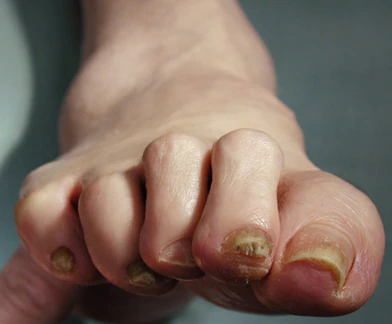
Complaints of foot pain
This patient's physical findings are consistent with a diagnosis of claw toe, which can be caused by diabetes-related peripheral neuropathy.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, diabetes currently affects approximately 537 million adults worldwide. The number of individuals living with diabetes is expected to exceed 640 million by 2030 and 780 million by 2045. In the United States, more than 37 million people are living with diabetes.
Foot complications related to diabetes represent a significant economic and social burden and can profoundly affect a patient's quality of life and medical outcomes. Common diabetes-related foot complications include foot deformity and peripheral neuropathy, both of which increase the risk for ulceration and amputation. The most common deformity is at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). As many as 85% of patients with a history of ulcers and amputation have an MTPJ deformity such as claw toe or hammertoe.
Although they are often grouped together, claw toe and hammertoe have distinct features. Extended MTPJ, flexed proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ), and flexed distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ) are characteristic of claw toe. While hammertoe also has extended MTPJ and flexed PIPJ, the DIPJ is extended rather than flexed. In both cases, the area of high pressure at risk for skin breakdown and ulceration is at the metatarsal head as a result of MTPJ hyperextension deformity.
Prompt detection and care of diabetes-related foot complications can minimize progression and negative consequences on patients' health and quality of life. According to the American Diabetes Association, all patients with diabetes should undergo a comprehensive foot evaluation at least annually to identify risk factors for ulceration and amputation, which include foot deformities, poor glycemic control, peripheral neuropathy, cigarette smoking, preulcerative callus or corn, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease, visual impairment, and a history of ulceration or amputation. When patients present with a history of ulceration or amputation, a foot inspection should be conducted at each visit.
A comprehensive foot evaluation should include inspection of the skin, evaluation of any foot deformities, a neurologic assessment (10-g monofilament testing with at least one other assessment: pinprick, temperature, vibration), and a vascular assessment, including pulses in the legs and feet.
Patients should be educated on risk factors and appropriate management of foot-related complications, including the importance of effective glycemic control and daily monitoring of feet. Treatment may be medical, surgical, or both, as indicated by the individual patient's presentation. Conservative treatment approaches include footwear that is extra wide or deep, avoiding high-heeled and narrow-toed shoes, use of a metatarsal bar or pad, cushioning sleeves or stocking caps with silicon linings, and a longitudinal pad beneath the toes.
Complete recommendations on achieving glycemic control in T2D can be found in the 2022 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care. Guidelines on foot care are also available.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's physical findings are consistent with a diagnosis of claw toe, which can be caused by diabetes-related peripheral neuropathy.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, diabetes currently affects approximately 537 million adults worldwide. The number of individuals living with diabetes is expected to exceed 640 million by 2030 and 780 million by 2045. In the United States, more than 37 million people are living with diabetes.
Foot complications related to diabetes represent a significant economic and social burden and can profoundly affect a patient's quality of life and medical outcomes. Common diabetes-related foot complications include foot deformity and peripheral neuropathy, both of which increase the risk for ulceration and amputation. The most common deformity is at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). As many as 85% of patients with a history of ulcers and amputation have an MTPJ deformity such as claw toe or hammertoe.
Although they are often grouped together, claw toe and hammertoe have distinct features. Extended MTPJ, flexed proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ), and flexed distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ) are characteristic of claw toe. While hammertoe also has extended MTPJ and flexed PIPJ, the DIPJ is extended rather than flexed. In both cases, the area of high pressure at risk for skin breakdown and ulceration is at the metatarsal head as a result of MTPJ hyperextension deformity.
Prompt detection and care of diabetes-related foot complications can minimize progression and negative consequences on patients' health and quality of life. According to the American Diabetes Association, all patients with diabetes should undergo a comprehensive foot evaluation at least annually to identify risk factors for ulceration and amputation, which include foot deformities, poor glycemic control, peripheral neuropathy, cigarette smoking, preulcerative callus or corn, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease, visual impairment, and a history of ulceration or amputation. When patients present with a history of ulceration or amputation, a foot inspection should be conducted at each visit.
A comprehensive foot evaluation should include inspection of the skin, evaluation of any foot deformities, a neurologic assessment (10-g monofilament testing with at least one other assessment: pinprick, temperature, vibration), and a vascular assessment, including pulses in the legs and feet.
Patients should be educated on risk factors and appropriate management of foot-related complications, including the importance of effective glycemic control and daily monitoring of feet. Treatment may be medical, surgical, or both, as indicated by the individual patient's presentation. Conservative treatment approaches include footwear that is extra wide or deep, avoiding high-heeled and narrow-toed shoes, use of a metatarsal bar or pad, cushioning sleeves or stocking caps with silicon linings, and a longitudinal pad beneath the toes.
Complete recommendations on achieving glycemic control in T2D can be found in the 2022 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care. Guidelines on foot care are also available.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's physical findings are consistent with a diagnosis of claw toe, which can be caused by diabetes-related peripheral neuropathy.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, diabetes currently affects approximately 537 million adults worldwide. The number of individuals living with diabetes is expected to exceed 640 million by 2030 and 780 million by 2045. In the United States, more than 37 million people are living with diabetes.
Foot complications related to diabetes represent a significant economic and social burden and can profoundly affect a patient's quality of life and medical outcomes. Common diabetes-related foot complications include foot deformity and peripheral neuropathy, both of which increase the risk for ulceration and amputation. The most common deformity is at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). As many as 85% of patients with a history of ulcers and amputation have an MTPJ deformity such as claw toe or hammertoe.
Although they are often grouped together, claw toe and hammertoe have distinct features. Extended MTPJ, flexed proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ), and flexed distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ) are characteristic of claw toe. While hammertoe also has extended MTPJ and flexed PIPJ, the DIPJ is extended rather than flexed. In both cases, the area of high pressure at risk for skin breakdown and ulceration is at the metatarsal head as a result of MTPJ hyperextension deformity.
Prompt detection and care of diabetes-related foot complications can minimize progression and negative consequences on patients' health and quality of life. According to the American Diabetes Association, all patients with diabetes should undergo a comprehensive foot evaluation at least annually to identify risk factors for ulceration and amputation, which include foot deformities, poor glycemic control, peripheral neuropathy, cigarette smoking, preulcerative callus or corn, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease, visual impairment, and a history of ulceration or amputation. When patients present with a history of ulceration or amputation, a foot inspection should be conducted at each visit.
A comprehensive foot evaluation should include inspection of the skin, evaluation of any foot deformities, a neurologic assessment (10-g monofilament testing with at least one other assessment: pinprick, temperature, vibration), and a vascular assessment, including pulses in the legs and feet.
Patients should be educated on risk factors and appropriate management of foot-related complications, including the importance of effective glycemic control and daily monitoring of feet. Treatment may be medical, surgical, or both, as indicated by the individual patient's presentation. Conservative treatment approaches include footwear that is extra wide or deep, avoiding high-heeled and narrow-toed shoes, use of a metatarsal bar or pad, cushioning sleeves or stocking caps with silicon linings, and a longitudinal pad beneath the toes.
Complete recommendations on achieving glycemic control in T2D can be found in the 2022 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care. Guidelines on foot care are also available.
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Diabetes, Endocrine, and Metabolic Disorders, Eastern Virginia Medical School; EVMS Medical Group, Norfolk, Virginia
Romesh K. Khardori, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 59-year-old woman newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and hypercholesterolemia presents with complaints of foot pain, particularly while wearing shoes. Physical examination reveals an extended metatarsophalangeal joint, a flexed proximal interphalangeal joint, and flexed distal interphalangeal joint. Her toenails are discolored with a yellowish hue, and callus formation is noted over the metatarsal area. The patient reports pain at the tip of the toe from pressure against the point of the distal phalanx. She states that she has not experienced any numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness. Before her recent diabetes diagnosis, the patient had not been receiving regular medical care. The patient's current medications include metformin 500 mg/d, empagliflozin 10 mg/d, and rosuvastatin 10 mg/d.
Children with asymptomatic celiac disease may have severe disease histology
Some pediatric patients with celiac disease whose condition is diagnosed after screening because a first-degree relative has the disease may appear asymptomatic but have severe disease histology, according to a new report.
About half of these patients had no symptoms, but disease histology was as severe as among those screened for other reasons, such as having symptomatic disease or high-risk conditions.
“This data supports current recommendations to screen all first-degree relatives of patients with celiac disease, especially pediatric patients in whom the ramifications of untreated disease may be significant,” wrote Michelle Gould, MD, and colleagues at the University of Toronto and McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The study was published online in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.
Clinical characteristics
The incidence of celiac disease is higher among first-degree relatives of patients with the disease than among the general population, yet the clinical characteristics aren’t well described, the study authors wrote. Determining the clinical, serologic, and histologic phenotype of these patients could help clinicians determine whether continued universal screening of first-degree relatives is appropriate.
Dr. Gould and colleagues conducted a retrospective review of 227 patients diagnosed with celiac disease at McMaster Children’s Hospital between 1996 and 2014. The patients were categorized as being screened for celiac disease because a first-degree relative had the disease or because of other reasons. The other reasons included symptoms consistent with celiac disease or the presence of a high-risk clinical condition for which screening is recommended, such as type 1 diabetes or Down syndrome.
All patients were screened via tissue transglutaminase (tTG-IgA) tests. Positive serology was defined as tTG-IgA greater than the upper limit of normal in the presence of normal IgA immunoglobulin level for age.
The patients who were included in the study had biopsy-proven celiac disease in accordance with the Marsh criteria, which included Marsh III histology, Marsh II histology with positive serology, or Marsh I histology with positive serology and clinical symptoms.
The average age of the patients (144 girls and 83 boys) was 8 years at diagnosis. Among the patients, 49 (21.6%) were screened because a first-degree relative had celiac disease. Of those 49 patients, 24 (49%) were symptomatic, and 25 (51%) were asymptomatic.
By contrast, among the 178 patients who were screened for other reasons, 149 (83.7%) were symptomatic, and 29 (16.3%) were asymptomatic.
There was no significant difference between the patient groups with respect to Marsh score at biopsy and tTG-IgA levels at screening. Among the children who were screened because of family history, Marsh scores were equally severe as among other patients, whether they were symptomatic or not.
In addition, no statistically significant differences were found for other clinical characteristics, including body mass index z-score, weight z-score, height z-score, the presence of anemia, or a low mean corpuscular volume for age.
When comparing the characteristics of those screened because of family history and those screened for other high-risk conditions (type 1 diabetes and Down syndrome), the researchers found that rates of asymptomatic presentation were statistically similar between the groups, as were tissue transglutaminase values, Marsh scores, BMI z-scores, and hemoglobin levels at diagnosis. Although there was a statistical difference between the groups with respect to the mean corpuscular volume values at diagnosis, it was unlikely to be of clinical significance, the authors noted.
At 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years after diagnosis, among patients with repeat tTG-IgA measurements, 93 of 143 patients (65%), 52 of 68 patients (76.5%), and 80 of 90 patients (88.9%) had normal serum tTG-IgA levels, respectively. In comparing the proportion of patients whose tTG-IgA levels were normal, there was no difference between those screened because of family history and those screened for other reasons at any time point after diagnosis.
“This may suggest that the natural history of celiac disease is similar in these two groups following initiation of a gluten-free diet and that there are similar rates of compliance with this therapy regardless of the initial indication for screening,” the study authors wrote.
Clinical implications
Dr. Gould and colleagues noted that celiac disease was considered histologically severe – with a Marsh III score or higher – among nearly all patients whose condition was diagnosed because of family history. Histology was equally severe regardless of whether the patients were symptomatic or asymptomatic at screening – 100% of symptomatic patients had a high score, and 96% of asymptomatic patients had a high score.
“This emphasizes the importance of celiac screening in all patients with first-degree relatives with celiac disease, as symptom status does not predict diagnosis or severity of disease,” they wrote.
Previous studies have indicated that the prevalence of celiac disease is highest among siblings of patients with celiac disease, compared with other types of first-degree relatives, the authors wrote. However, they lacked this information in their records, which would be valuable for analysis in future studies.
In addition, ongoing research should investigate the optimal frequency of screening for first-degree relatives, they noted.
“One study suggests that individuals screened before 10 years of age should have repeat screening in their second decade for a small increased pick-up of diagnoses,” they wrote.
No funding for the study has been reported. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some pediatric patients with celiac disease whose condition is diagnosed after screening because a first-degree relative has the disease may appear asymptomatic but have severe disease histology, according to a new report.
About half of these patients had no symptoms, but disease histology was as severe as among those screened for other reasons, such as having symptomatic disease or high-risk conditions.
“This data supports current recommendations to screen all first-degree relatives of patients with celiac disease, especially pediatric patients in whom the ramifications of untreated disease may be significant,” wrote Michelle Gould, MD, and colleagues at the University of Toronto and McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The study was published online in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.
Clinical characteristics
The incidence of celiac disease is higher among first-degree relatives of patients with the disease than among the general population, yet the clinical characteristics aren’t well described, the study authors wrote. Determining the clinical, serologic, and histologic phenotype of these patients could help clinicians determine whether continued universal screening of first-degree relatives is appropriate.
Dr. Gould and colleagues conducted a retrospective review of 227 patients diagnosed with celiac disease at McMaster Children’s Hospital between 1996 and 2014. The patients were categorized as being screened for celiac disease because a first-degree relative had the disease or because of other reasons. The other reasons included symptoms consistent with celiac disease or the presence of a high-risk clinical condition for which screening is recommended, such as type 1 diabetes or Down syndrome.
All patients were screened via tissue transglutaminase (tTG-IgA) tests. Positive serology was defined as tTG-IgA greater than the upper limit of normal in the presence of normal IgA immunoglobulin level for age.
The patients who were included in the study had biopsy-proven celiac disease in accordance with the Marsh criteria, which included Marsh III histology, Marsh II histology with positive serology, or Marsh I histology with positive serology and clinical symptoms.
The average age of the patients (144 girls and 83 boys) was 8 years at diagnosis. Among the patients, 49 (21.6%) were screened because a first-degree relative had celiac disease. Of those 49 patients, 24 (49%) were symptomatic, and 25 (51%) were asymptomatic.
By contrast, among the 178 patients who were screened for other reasons, 149 (83.7%) were symptomatic, and 29 (16.3%) were asymptomatic.
There was no significant difference between the patient groups with respect to Marsh score at biopsy and tTG-IgA levels at screening. Among the children who were screened because of family history, Marsh scores were equally severe as among other patients, whether they were symptomatic or not.
In addition, no statistically significant differences were found for other clinical characteristics, including body mass index z-score, weight z-score, height z-score, the presence of anemia, or a low mean corpuscular volume for age.
When comparing the characteristics of those screened because of family history and those screened for other high-risk conditions (type 1 diabetes and Down syndrome), the researchers found that rates of asymptomatic presentation were statistically similar between the groups, as were tissue transglutaminase values, Marsh scores, BMI z-scores, and hemoglobin levels at diagnosis. Although there was a statistical difference between the groups with respect to the mean corpuscular volume values at diagnosis, it was unlikely to be of clinical significance, the authors noted.
At 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years after diagnosis, among patients with repeat tTG-IgA measurements, 93 of 143 patients (65%), 52 of 68 patients (76.5%), and 80 of 90 patients (88.9%) had normal serum tTG-IgA levels, respectively. In comparing the proportion of patients whose tTG-IgA levels were normal, there was no difference between those screened because of family history and those screened for other reasons at any time point after diagnosis.
“This may suggest that the natural history of celiac disease is similar in these two groups following initiation of a gluten-free diet and that there are similar rates of compliance with this therapy regardless of the initial indication for screening,” the study authors wrote.
Clinical implications
Dr. Gould and colleagues noted that celiac disease was considered histologically severe – with a Marsh III score or higher – among nearly all patients whose condition was diagnosed because of family history. Histology was equally severe regardless of whether the patients were symptomatic or asymptomatic at screening – 100% of symptomatic patients had a high score, and 96% of asymptomatic patients had a high score.
“This emphasizes the importance of celiac screening in all patients with first-degree relatives with celiac disease, as symptom status does not predict diagnosis or severity of disease,” they wrote.
Previous studies have indicated that the prevalence of celiac disease is highest among siblings of patients with celiac disease, compared with other types of first-degree relatives, the authors wrote. However, they lacked this information in their records, which would be valuable for analysis in future studies.
In addition, ongoing research should investigate the optimal frequency of screening for first-degree relatives, they noted.
“One study suggests that individuals screened before 10 years of age should have repeat screening in their second decade for a small increased pick-up of diagnoses,” they wrote.
No funding for the study has been reported. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some pediatric patients with celiac disease whose condition is diagnosed after screening because a first-degree relative has the disease may appear asymptomatic but have severe disease histology, according to a new report.
About half of these patients had no symptoms, but disease histology was as severe as among those screened for other reasons, such as having symptomatic disease or high-risk conditions.
“This data supports current recommendations to screen all first-degree relatives of patients with celiac disease, especially pediatric patients in whom the ramifications of untreated disease may be significant,” wrote Michelle Gould, MD, and colleagues at the University of Toronto and McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The study was published online in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.
Clinical characteristics
The incidence of celiac disease is higher among first-degree relatives of patients with the disease than among the general population, yet the clinical characteristics aren’t well described, the study authors wrote. Determining the clinical, serologic, and histologic phenotype of these patients could help clinicians determine whether continued universal screening of first-degree relatives is appropriate.
Dr. Gould and colleagues conducted a retrospective review of 227 patients diagnosed with celiac disease at McMaster Children’s Hospital between 1996 and 2014. The patients were categorized as being screened for celiac disease because a first-degree relative had the disease or because of other reasons. The other reasons included symptoms consistent with celiac disease or the presence of a high-risk clinical condition for which screening is recommended, such as type 1 diabetes or Down syndrome.
All patients were screened via tissue transglutaminase (tTG-IgA) tests. Positive serology was defined as tTG-IgA greater than the upper limit of normal in the presence of normal IgA immunoglobulin level for age.
The patients who were included in the study had biopsy-proven celiac disease in accordance with the Marsh criteria, which included Marsh III histology, Marsh II histology with positive serology, or Marsh I histology with positive serology and clinical symptoms.
The average age of the patients (144 girls and 83 boys) was 8 years at diagnosis. Among the patients, 49 (21.6%) were screened because a first-degree relative had celiac disease. Of those 49 patients, 24 (49%) were symptomatic, and 25 (51%) were asymptomatic.
By contrast, among the 178 patients who were screened for other reasons, 149 (83.7%) were symptomatic, and 29 (16.3%) were asymptomatic.
There was no significant difference between the patient groups with respect to Marsh score at biopsy and tTG-IgA levels at screening. Among the children who were screened because of family history, Marsh scores were equally severe as among other patients, whether they were symptomatic or not.
In addition, no statistically significant differences were found for other clinical characteristics, including body mass index z-score, weight z-score, height z-score, the presence of anemia, or a low mean corpuscular volume for age.
When comparing the characteristics of those screened because of family history and those screened for other high-risk conditions (type 1 diabetes and Down syndrome), the researchers found that rates of asymptomatic presentation were statistically similar between the groups, as were tissue transglutaminase values, Marsh scores, BMI z-scores, and hemoglobin levels at diagnosis. Although there was a statistical difference between the groups with respect to the mean corpuscular volume values at diagnosis, it was unlikely to be of clinical significance, the authors noted.
At 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years after diagnosis, among patients with repeat tTG-IgA measurements, 93 of 143 patients (65%), 52 of 68 patients (76.5%), and 80 of 90 patients (88.9%) had normal serum tTG-IgA levels, respectively. In comparing the proportion of patients whose tTG-IgA levels were normal, there was no difference between those screened because of family history and those screened for other reasons at any time point after diagnosis.
“This may suggest that the natural history of celiac disease is similar in these two groups following initiation of a gluten-free diet and that there are similar rates of compliance with this therapy regardless of the initial indication for screening,” the study authors wrote.
Clinical implications
Dr. Gould and colleagues noted that celiac disease was considered histologically severe – with a Marsh III score or higher – among nearly all patients whose condition was diagnosed because of family history. Histology was equally severe regardless of whether the patients were symptomatic or asymptomatic at screening – 100% of symptomatic patients had a high score, and 96% of asymptomatic patients had a high score.
“This emphasizes the importance of celiac screening in all patients with first-degree relatives with celiac disease, as symptom status does not predict diagnosis or severity of disease,” they wrote.
Previous studies have indicated that the prevalence of celiac disease is highest among siblings of patients with celiac disease, compared with other types of first-degree relatives, the authors wrote. However, they lacked this information in their records, which would be valuable for analysis in future studies.
In addition, ongoing research should investigate the optimal frequency of screening for first-degree relatives, they noted.
“One study suggests that individuals screened before 10 years of age should have repeat screening in their second decade for a small increased pick-up of diagnoses,” they wrote.
No funding for the study has been reported. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AND NUTRITION
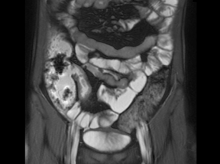
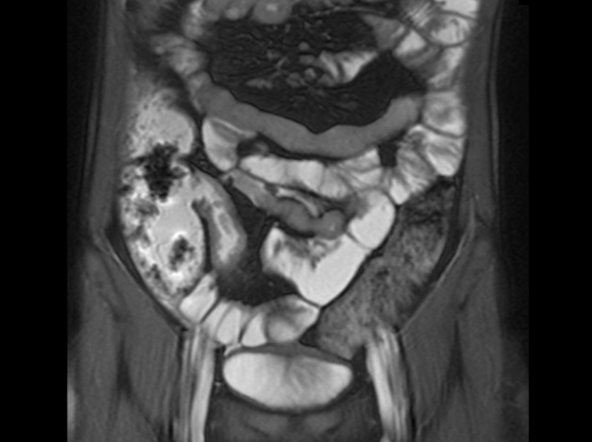
Severe abdominal pain and vomiting
On the basis of the patient’s family history, personal history, and presentation, the likely diagnosis is Crohn disease. Although the disease may be diagnosed at any age, onset shows a bimodal distribution, with the first, more predominant wave occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. Peak global onset is between the ages of 15 and 30. Compared with adult-onset disease, pediatric Crohn disease is associated with a more serious disease course. Patients of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are at higher risk of developing this autoimmune disease than any other ethnic group.
Colonoscopy is the first-line approach for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease. Typical findings in patients with Crohn disease include histologic changes, such as focal crypt irregularity, transmural lymphoid aggregates, fissures and fistulas, and perianal disorders. In the differential diagnosis, ulcerative colitis (UC) must be carefully ruled out. UC involves only the large bowel, rarely causes fistulas, and is frequently seen with bleeding. Crohn disease is characteristically noncontiguous, with linear ulcerations of a cobblestone appearance. In addition, noncaseating granulomas are specific for Crohn disease. Micronutrient and vitamin levels are usually low, as seen in the present case. During workup, fecal calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient in this case may be a candidate for 5-aminosalicylic acid, together with a nutritional plan, used in mild or moderate cases of pediatric Crohn disease. Clinical improvement plus a decrease of fecal calprotectin would be an indication of positive treatment response. Being newly diagnosed, if the patient does not achieve remission after the induction period, he may be at risk for a more complicated disease course. Treatment for Crohn disease in the pediatric setting, as in the adult setting, should be implemented through a step-up approach. Other treatment options for pediatric disease include antibiotics; immunomodulators; and, in moderate-to severe cases, corticosteroids and biologics.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient’s family history, personal history, and presentation, the likely diagnosis is Crohn disease. Although the disease may be diagnosed at any age, onset shows a bimodal distribution, with the first, more predominant wave occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. Peak global onset is between the ages of 15 and 30. Compared with adult-onset disease, pediatric Crohn disease is associated with a more serious disease course. Patients of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are at higher risk of developing this autoimmune disease than any other ethnic group.
Colonoscopy is the first-line approach for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease. Typical findings in patients with Crohn disease include histologic changes, such as focal crypt irregularity, transmural lymphoid aggregates, fissures and fistulas, and perianal disorders. In the differential diagnosis, ulcerative colitis (UC) must be carefully ruled out. UC involves only the large bowel, rarely causes fistulas, and is frequently seen with bleeding. Crohn disease is characteristically noncontiguous, with linear ulcerations of a cobblestone appearance. In addition, noncaseating granulomas are specific for Crohn disease. Micronutrient and vitamin levels are usually low, as seen in the present case. During workup, fecal calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient in this case may be a candidate for 5-aminosalicylic acid, together with a nutritional plan, used in mild or moderate cases of pediatric Crohn disease. Clinical improvement plus a decrease of fecal calprotectin would be an indication of positive treatment response. Being newly diagnosed, if the patient does not achieve remission after the induction period, he may be at risk for a more complicated disease course. Treatment for Crohn disease in the pediatric setting, as in the adult setting, should be implemented through a step-up approach. Other treatment options for pediatric disease include antibiotics; immunomodulators; and, in moderate-to severe cases, corticosteroids and biologics.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient’s family history, personal history, and presentation, the likely diagnosis is Crohn disease. Although the disease may be diagnosed at any age, onset shows a bimodal distribution, with the first, more predominant wave occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. Peak global onset is between the ages of 15 and 30. Compared with adult-onset disease, pediatric Crohn disease is associated with a more serious disease course. Patients of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are at higher risk of developing this autoimmune disease than any other ethnic group.
Colonoscopy is the first-line approach for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease. Typical findings in patients with Crohn disease include histologic changes, such as focal crypt irregularity, transmural lymphoid aggregates, fissures and fistulas, and perianal disorders. In the differential diagnosis, ulcerative colitis (UC) must be carefully ruled out. UC involves only the large bowel, rarely causes fistulas, and is frequently seen with bleeding. Crohn disease is characteristically noncontiguous, with linear ulcerations of a cobblestone appearance. In addition, noncaseating granulomas are specific for Crohn disease. Micronutrient and vitamin levels are usually low, as seen in the present case. During workup, fecal calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient in this case may be a candidate for 5-aminosalicylic acid, together with a nutritional plan, used in mild or moderate cases of pediatric Crohn disease. Clinical improvement plus a decrease of fecal calprotectin would be an indication of positive treatment response. Being newly diagnosed, if the patient does not achieve remission after the induction period, he may be at risk for a more complicated disease course. Treatment for Crohn disease in the pediatric setting, as in the adult setting, should be implemented through a step-up approach. Other treatment options for pediatric disease include antibiotics; immunomodulators; and, in moderate-to severe cases, corticosteroids and biologics.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 12-year-old boy presents to an urgent care center with severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. His height is 5 ft 3 in and weight is 99 lb (BMI 18.7). The patient has a history of chronic diarrhea and reports intermittent abdominal pain that began about 6 months ago. During this time, he has lost about 12 lb, as many foods exacerbate his symptoms, though his mother notes that even plain foods can bother his stomach. Further questioning reveals that his father has moderate Crohn disease (age of onset, 29 years), his sister has celiac disease, and the patient is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. His body temperature is 100.2 °F. Vitamin B12, serum iron, total iron binding capacity, calcium, and magnesium are low. Stool cultures are negative. Ileocolonoscopy shows small aphthous erosions in the large intestine and in the terminal ileum.
New update focuses on acute kidney injury management in cirrhosis
Acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with cirrhosis is potentially preventable, and there are clear steps that can be taken to manage and reverse the condition, concludes a clinical practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
AKI occurs in 47% of patients hospitalized with complications of cirrhosis and in approximately 30% of outpatients with cirrhosis, resulting in a total cost in the United States of $4 billion, explained Patrick S. Kamath, MD, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., one of the authors of this update.
Moreover, Dr. Kamath told this news organization, among patients with cirrhosis and AKI, morbidity and mortality is sevenfold higher in comparison to those without cirrhosis, and repeated episodes of AKI increase the risk of progression to chronic kidney disease.
To provide practical advice for the clinical management of patients with cirrhosis and AKI, the authors conducted an expert review of the best available published evidence and gathered expert opinion.
The update was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Some key takeaways
Among its 14 best practice statements, it describes three situations indicative of AKI:
- A serum creatinine increase of 0.3 mg/dL or more within 48 hours, or
- A serum creatinine increase of 50% or more from baseline, which is a stable serum creatinine in the past 3 months.
- Reduction in urine output of up to 0.5 mL/kg per hour for more than 6 hours.
The update also emphasizes the importance of an accurate diagnosis, inasmuch as not all cases of AKI are due to hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for example. It goes on to advise that the specific type of AKI be identified through medical history and physical examination, as well as with blood biochemistry, urine microscopic examination, urine chemistry, selected urinary biomarkers, and renal ultrasound.
Additionally, it underscores the need to identify and treat infections and to closely monitor fluid status.
Nancy S. Reau, MD, Rush Medical College, Chicago, who was not involved in the update, commented to this news organization that fluid status is important when giving albumin replacement therapy because of the increased risk for pulmonary edema.
She also highlighted that this update advises against transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPSs) as a specific treatment for HRS-AKI, noting that, although the 2022 North American Practice-Based Recommendations for Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Portal Hypertension do not advocate for TIPS for this indication, they also indicated that there was enough evidence to advise against it.
In other key best practice advice statements, the update advises clinicians to hold diuretics and nonselective beta blockers and to discontinue nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
‘Timely’ update
Overall, Dr. Reau believes that the update is “timely, especially in light of the recent [U.S.] approval of terlipressin, which will change our treatment options.”
This update also supports the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) 2021 Practice Guidance guidelines on HRS, she added.
Zobair Younossi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University, Inova Campus, Falls Church, Va., who was not involved in writing the update, told this news organization that the document is important because of the huge increase in mortality among patients with cirrhosis and AKI.
He commented that there has been much advancement in understanding the condition, with updated nomenclature and novel medical treatments, and that this makes the update timely.
Moreover, the update will help clinicians who are involved in the care of patients with cirrhosis, he added.
Dr. Younossi said the update offers a very clearly stated algorithm for how to identify patients whose condition is easily reversible with volume repletion, in comparison with those patients who require medical treatment or even liver transplantation.
“Those things are important because that pathway gives clinicians an idea of how to do this properly,” he said.
“The key for clinicians is to make sure they understand, in the context of cirrhosis, some of the easy things that they can do to prevent AKI,” he continued. He added that the use of NSAIDs in these patients is “going to be problematic.”
Dr. Kamath has a relationship with Sequana Medical. Other authors’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article. Dr. Reau has relationships with Salix and Intercept. Dr. Younossi has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 12/12/2022.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with cirrhosis is potentially preventable, and there are clear steps that can be taken to manage and reverse the condition, concludes a clinical practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
AKI occurs in 47% of patients hospitalized with complications of cirrhosis and in approximately 30% of outpatients with cirrhosis, resulting in a total cost in the United States of $4 billion, explained Patrick S. Kamath, MD, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., one of the authors of this update.
Moreover, Dr. Kamath told this news organization, among patients with cirrhosis and AKI, morbidity and mortality is sevenfold higher in comparison to those without cirrhosis, and repeated episodes of AKI increase the risk of progression to chronic kidney disease.
To provide practical advice for the clinical management of patients with cirrhosis and AKI, the authors conducted an expert review of the best available published evidence and gathered expert opinion.
The update was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Some key takeaways
Among its 14 best practice statements, it describes three situations indicative of AKI:
- A serum creatinine increase of 0.3 mg/dL or more within 48 hours, or
- A serum creatinine increase of 50% or more from baseline, which is a stable serum creatinine in the past 3 months.
- Reduction in urine output of up to 0.5 mL/kg per hour for more than 6 hours.
The update also emphasizes the importance of an accurate diagnosis, inasmuch as not all cases of AKI are due to hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for example. It goes on to advise that the specific type of AKI be identified through medical history and physical examination, as well as with blood biochemistry, urine microscopic examination, urine chemistry, selected urinary biomarkers, and renal ultrasound.
Additionally, it underscores the need to identify and treat infections and to closely monitor fluid status.
Nancy S. Reau, MD, Rush Medical College, Chicago, who was not involved in the update, commented to this news organization that fluid status is important when giving albumin replacement therapy because of the increased risk for pulmonary edema.
She also highlighted that this update advises against transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPSs) as a specific treatment for HRS-AKI, noting that, although the 2022 North American Practice-Based Recommendations for Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Portal Hypertension do not advocate for TIPS for this indication, they also indicated that there was enough evidence to advise against it.
In other key best practice advice statements, the update advises clinicians to hold diuretics and nonselective beta blockers and to discontinue nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
‘Timely’ update
Overall, Dr. Reau believes that the update is “timely, especially in light of the recent [U.S.] approval of terlipressin, which will change our treatment options.”
This update also supports the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) 2021 Practice Guidance guidelines on HRS, she added.
Zobair Younossi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University, Inova Campus, Falls Church, Va., who was not involved in writing the update, told this news organization that the document is important because of the huge increase in mortality among patients with cirrhosis and AKI.
He commented that there has been much advancement in understanding the condition, with updated nomenclature and novel medical treatments, and that this makes the update timely.
Moreover, the update will help clinicians who are involved in the care of patients with cirrhosis, he added.
Dr. Younossi said the update offers a very clearly stated algorithm for how to identify patients whose condition is easily reversible with volume repletion, in comparison with those patients who require medical treatment or even liver transplantation.
“Those things are important because that pathway gives clinicians an idea of how to do this properly,” he said.
“The key for clinicians is to make sure they understand, in the context of cirrhosis, some of the easy things that they can do to prevent AKI,” he continued. He added that the use of NSAIDs in these patients is “going to be problematic.”
Dr. Kamath has a relationship with Sequana Medical. Other authors’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article. Dr. Reau has relationships with Salix and Intercept. Dr. Younossi has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 12/12/2022.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with cirrhosis is potentially preventable, and there are clear steps that can be taken to manage and reverse the condition, concludes a clinical practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
AKI occurs in 47% of patients hospitalized with complications of cirrhosis and in approximately 30% of outpatients with cirrhosis, resulting in a total cost in the United States of $4 billion, explained Patrick S. Kamath, MD, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., one of the authors of this update.
Moreover, Dr. Kamath told this news organization, among patients with cirrhosis and AKI, morbidity and mortality is sevenfold higher in comparison to those without cirrhosis, and repeated episodes of AKI increase the risk of progression to chronic kidney disease.
To provide practical advice for the clinical management of patients with cirrhosis and AKI, the authors conducted an expert review of the best available published evidence and gathered expert opinion.
The update was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Some key takeaways
Among its 14 best practice statements, it describes three situations indicative of AKI:
- A serum creatinine increase of 0.3 mg/dL or more within 48 hours, or
- A serum creatinine increase of 50% or more from baseline, which is a stable serum creatinine in the past 3 months.
- Reduction in urine output of up to 0.5 mL/kg per hour for more than 6 hours.
The update also emphasizes the importance of an accurate diagnosis, inasmuch as not all cases of AKI are due to hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for example. It goes on to advise that the specific type of AKI be identified through medical history and physical examination, as well as with blood biochemistry, urine microscopic examination, urine chemistry, selected urinary biomarkers, and renal ultrasound.
Additionally, it underscores the need to identify and treat infections and to closely monitor fluid status.
Nancy S. Reau, MD, Rush Medical College, Chicago, who was not involved in the update, commented to this news organization that fluid status is important when giving albumin replacement therapy because of the increased risk for pulmonary edema.
She also highlighted that this update advises against transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPSs) as a specific treatment for HRS-AKI, noting that, although the 2022 North American Practice-Based Recommendations for Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Portal Hypertension do not advocate for TIPS for this indication, they also indicated that there was enough evidence to advise against it.
In other key best practice advice statements, the update advises clinicians to hold diuretics and nonselective beta blockers and to discontinue nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
‘Timely’ update
Overall, Dr. Reau believes that the update is “timely, especially in light of the recent [U.S.] approval of terlipressin, which will change our treatment options.”
This update also supports the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) 2021 Practice Guidance guidelines on HRS, she added.
Zobair Younossi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University, Inova Campus, Falls Church, Va., who was not involved in writing the update, told this news organization that the document is important because of the huge increase in mortality among patients with cirrhosis and AKI.
He commented that there has been much advancement in understanding the condition, with updated nomenclature and novel medical treatments, and that this makes the update timely.
Moreover, the update will help clinicians who are involved in the care of patients with cirrhosis, he added.
Dr. Younossi said the update offers a very clearly stated algorithm for how to identify patients whose condition is easily reversible with volume repletion, in comparison with those patients who require medical treatment or even liver transplantation.
“Those things are important because that pathway gives clinicians an idea of how to do this properly,” he said.
“The key for clinicians is to make sure they understand, in the context of cirrhosis, some of the easy things that they can do to prevent AKI,” he continued. He added that the use of NSAIDs in these patients is “going to be problematic.”
Dr. Kamath has a relationship with Sequana Medical. Other authors’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article. Dr. Reau has relationships with Salix and Intercept. Dr. Younossi has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 12/12/2022.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Sexual issues common for GI patients, but docs often avoid topic
VIENNA – Sexual dysfunction in patients with gastrointestinal disorders is undermanaged, with a lack of clinician education, time constraints, and embarrassment preventing constructive discussions to improve patient care and quality of life, according to a new survey.
Overall, 71% of gastroenterologists do not ask their patients about sexual dysfunction, the survey finds.
“While patients with gastrointestinal disorders often experience sexual dysfunction, discussions around the matter are not routine in gastroenterological care,” said Marco Romano, MD, from the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli,” Naples, Italy.
Romano presented the survey findings at this year’s United European Gastroenterology Week meeting.
The research shows not only a clear need for better awareness but also a need to build gastroenterologists’ confidence in addressing sexual dysfunction with their patients, Dr. Romano added.
“Most felt that sexual medicine education and improvement of communication skills within the context of their residency training might be important in order to increase the awareness of sexual dysfunction, to overcome barriers, and to improve care and quality of life for their patients,” reported Dr. Romano. “This will lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment of any sexual problems.”
Respectfully asking the patients if their gastrointestinal disorders interfere with their intimate relationships “is often considered a relief to patients who find that the gastrointestinal problem and the sexual dysfunction are interlinked,” he added.
The findings
The survey was needed because the question of whether gastroenterologists inquire about their patients’ sexual issues had never been assessed, Dr. Romano said.
The researchers sent a cross-sectional, anonymous online survey to members of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Digestive Endoscopy. The questionnaire, designed and informed by a literature review, consisted of 29 single multiple-choice and open-ended questions.
A total of 426 surveys were returned: 335 from experienced gastroenterologists and 91 from residents (less experienced). Of all respondents, 54.7% were men and 45.3% were women.
Even though most gastroenterologists do not ask their patients about sexual dysfunction, the majority want to learn how to manage the issue, the survey found. Of the survey respondents, 80% agreed that it would be useful for gastroenterologists to attend courses dedicated to the problem of sexual dysfunction.
Only 4% of patients report (initiate a dialogue about) the problem, the survey found. Among women aged 40-50 years, the most common complaint reported was dyspareunia (pain on intercourse). In men, the most frequent complaints reported were in the over-40s age group, with 75% citing erectile dysfunction and 45% reporting loss of libido.
The most common gastrointestinal disorders associated with sexual dysfunction are inflammatory bowel diseases (37% of cases), chronic liver diseases (28%), and irritable bowel syndrome (26%), according to the survey.
On the question of whether medications played a role in patients’ sexual dysfunction, nearly 15% of respondents said that prokinetic agents were involved, and 18% thought proton pump inhibitors affect sexual function. Both drug classes are considered responsible for sexual disturbances.
Few gastroenterologists prescribe phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), e.g., Viagra, to treat sexual dysfunction, the survey found. Approximately 90% of respondents said that they never prescribed this class of drugs, preferring to refer patients to an andrologist. Of those who did prescribe PDE5i, significantly fewer residents did compared with experienced gastroenterologists (1.1% vs. 8.8%, respectively; P = .01).
Finally, the biggest reasons why gastroenterologists do not discuss sexual dysfunction are lack of knowledge (80%), insufficient experience (58%), time (44%), and embarrassment (30%).
Practice experience matters
There were some differences among respondents in the experienced group vs. the residents. More men were in the experienced group compared with residents (57.6% vs. 44%, respectively); mean age was 47 years vs. 29 years, respectively; and 71% had 5 or more years of experience in the experienced gastroenterologist group, whereas 78% had 1-5 years of experience among residents.
The survey found that more residents than experienced gastroenterologists “never discussed sexual dysfunction” (38.5% vs. 21.3%, respectively; P = .001) and that more residents than experienced gastroenterologists reported that “patients did not relate their sexual dysfunction to the prescribed therapy” (47.8% vs. 32.5%, respectively; P = .007).
The two groups varied regarding prescription drugs’ role in sexual dysfunction. More experienced gastroenterologists than residents felt that proton pump inhibitors (5.8% vs. 0%, respectively; P = .018) or prokinetics (19.8% vs. 9.5%, respectively; P = .028) might be responsible for some degree of sexual dysfunction.
More residents than experienced doctors felt that other (nongastroenterologic) drugs might contribute to sexual dysfunction in their patients (57.1% vs. 44.7%, respectively; P = .043).
Dr. Romano reported that fewer residents than experienced gastroenterologists referred male patients with sexual dysfunction to an andrologist (frequently/always: 28.1% vs. 44.4%, respectively; P = .004). However, more residents than experienced gastroenterologists disagreed that discussing sexual dysfunction with patients pertains only to specialists (andrologists and gynecologists; 83.5% vs. 71.2%, respectively; P = .018).
Time to step up
Asma Fikree, BMBCh, PhD, of Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, moderated the session. The survey highlights that asking patients about sexual dysfunction is an area for improvement for gastroenterologists, she said.
“We might do it in men and ask about erectile dysfunction, but we are very poor about asking in women,” Dr. Fikree noted.
The pros and cons of different medications should be discussed with patients, she said.
Gastroenterologists need to do a better job of considering how medications can lead to sexual dysfunction and interfere with quality of life, and training would help, she added.
“Some patients might not be very bothered by sexual dysfunction, but others might consider it very important,” Dr. Fikree said. “We should be considering this as part of their treatment and care.”
Dr. Romano and Dr. Fikree report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA – Sexual dysfunction in patients with gastrointestinal disorders is undermanaged, with a lack of clinician education, time constraints, and embarrassment preventing constructive discussions to improve patient care and quality of life, according to a new survey.
Overall, 71% of gastroenterologists do not ask their patients about sexual dysfunction, the survey finds.
“While patients with gastrointestinal disorders often experience sexual dysfunction, discussions around the matter are not routine in gastroenterological care,” said Marco Romano, MD, from the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli,” Naples, Italy.
Romano presented the survey findings at this year’s United European Gastroenterology Week meeting.
The research shows not only a clear need for better awareness but also a need to build gastroenterologists’ confidence in addressing sexual dysfunction with their patients, Dr. Romano added.
“Most felt that sexual medicine education and improvement of communication skills within the context of their residency training might be important in order to increase the awareness of sexual dysfunction, to overcome barriers, and to improve care and quality of life for their patients,” reported Dr. Romano. “This will lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment of any sexual problems.”
Respectfully asking the patients if their gastrointestinal disorders interfere with their intimate relationships “is often considered a relief to patients who find that the gastrointestinal problem and the sexual dysfunction are interlinked,” he added.
The findings
The survey was needed because the question of whether gastroenterologists inquire about their patients’ sexual issues had never been assessed, Dr. Romano said.
The researchers sent a cross-sectional, anonymous online survey to members of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Digestive Endoscopy. The questionnaire, designed and informed by a literature review, consisted of 29 single multiple-choice and open-ended questions.
A total of 426 surveys were returned: 335 from experienced gastroenterologists and 91 from residents (less experienced). Of all respondents, 54.7% were men and 45.3% were women.
Even though most gastroenterologists do not ask their patients about sexual dysfunction, the majority want to learn how to manage the issue, the survey found. Of the survey respondents, 80% agreed that it would be useful for gastroenterologists to attend courses dedicated to the problem of sexual dysfunction.
Only 4% of patients report (initiate a dialogue about) the problem, the survey found. Among women aged 40-50 years, the most common complaint reported was dyspareunia (pain on intercourse). In men, the most frequent complaints reported were in the over-40s age group, with 75% citing erectile dysfunction and 45% reporting loss of libido.
The most common gastrointestinal disorders associated with sexual dysfunction are inflammatory bowel diseases (37% of cases), chronic liver diseases (28%), and irritable bowel syndrome (26%), according to the survey.
On the question of whether medications played a role in patients’ sexual dysfunction, nearly 15% of respondents said that prokinetic agents were involved, and 18% thought proton pump inhibitors affect sexual function. Both drug classes are considered responsible for sexual disturbances.
Few gastroenterologists prescribe phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), e.g., Viagra, to treat sexual dysfunction, the survey found. Approximately 90% of respondents said that they never prescribed this class of drugs, preferring to refer patients to an andrologist. Of those who did prescribe PDE5i, significantly fewer residents did compared with experienced gastroenterologists (1.1% vs. 8.8%, respectively; P = .01).
Finally, the biggest reasons why gastroenterologists do not discuss sexual dysfunction are lack of knowledge (80%), insufficient experience (58%), time (44%), and embarrassment (30%).
Practice experience matters
There were some differences among respondents in the experienced group vs. the residents. More men were in the experienced group compared with residents (57.6% vs. 44%, respectively); mean age was 47 years vs. 29 years, respectively; and 71% had 5 or more years of experience in the experienced gastroenterologist group, whereas 78% had 1-5 years of experience among residents.
The survey found that more residents than experienced gastroenterologists “never discussed sexual dysfunction” (38.5% vs. 21.3%, respectively; P = .001) and that more residents than experienced gastroenterologists reported that “patients did not relate their sexual dysfunction to the prescribed therapy” (47.8% vs. 32.5%, respectively; P = .007).
The two groups varied regarding prescription drugs’ role in sexual dysfunction. More experienced gastroenterologists than residents felt that proton pump inhibitors (5.8% vs. 0%, respectively; P = .018) or prokinetics (19.8% vs. 9.5%, respectively; P = .028) might be responsible for some degree of sexual dysfunction.
More residents than experienced doctors felt that other (nongastroenterologic) drugs might contribute to sexual dysfunction in their patients (57.1% vs. 44.7%, respectively; P = .043).
Dr. Romano reported that fewer residents than experienced gastroenterologists referred male patients with sexual dysfunction to an andrologist (frequently/always: 28.1% vs. 44.4%, respectively; P = .004). However, more residents than experienced gastroenterologists disagreed that discussing sexual dysfunction with patients pertains only to specialists (andrologists and gynecologists; 83.5% vs. 71.2%, respectively; P = .018).
Time to step up
Asma Fikree, BMBCh, PhD, of Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, moderated the session. The survey highlights that asking patients about sexual dysfunction is an area for improvement for gastroenterologists, she said.
“We might do it in men and ask about erectile dysfunction, but we are very poor about asking in women,” Dr. Fikree noted.
The pros and cons of different medications should be discussed with patients, she said.
Gastroenterologists need to do a better job of considering how medications can lead to sexual dysfunction and interfere with quality of life, and training would help, she added.
“Some patients might not be very bothered by sexual dysfunction, but others might consider it very important,” Dr. Fikree said. “We should be considering this as part of their treatment and care.”
Dr. Romano and Dr. Fikree report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA – Sexual dysfunction in patients with gastrointestinal disorders is undermanaged, with a lack of clinician education, time constraints, and embarrassment preventing constructive discussions to improve patient care and quality of life, according to a new survey.
Overall, 71% of gastroenterologists do not ask their patients about sexual dysfunction, the survey finds.
“While patients with gastrointestinal disorders often experience sexual dysfunction, discussions around the matter are not routine in gastroenterological care,” said Marco Romano, MD, from the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli,” Naples, Italy.
Romano presented the survey findings at this year’s United European Gastroenterology Week meeting.
The research shows not only a clear need for better awareness but also a need to build gastroenterologists’ confidence in addressing sexual dysfunction with their patients, Dr. Romano added.
“Most felt that sexual medicine education and improvement of communication skills within the context of their residency training might be important in order to increase the awareness of sexual dysfunction, to overcome barriers, and to improve care and quality of life for their patients,” reported Dr. Romano. “This will lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment of any sexual problems.”
Respectfully asking the patients if their gastrointestinal disorders interfere with their intimate relationships “is often considered a relief to patients who find that the gastrointestinal problem and the sexual dysfunction are interlinked,” he added.
The findings
The survey was needed because the question of whether gastroenterologists inquire about their patients’ sexual issues had never been assessed, Dr. Romano said.
The researchers sent a cross-sectional, anonymous online survey to members of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Digestive Endoscopy. The questionnaire, designed and informed by a literature review, consisted of 29 single multiple-choice and open-ended questions.
A total of 426 surveys were returned: 335 from experienced gastroenterologists and 91 from residents (less experienced). Of all respondents, 54.7% were men and 45.3% were women.
Even though most gastroenterologists do not ask their patients about sexual dysfunction, the majority want to learn how to manage the issue, the survey found. Of the survey respondents, 80% agreed that it would be useful for gastroenterologists to attend courses dedicated to the problem of sexual dysfunction.
Only 4% of patients report (initiate a dialogue about) the problem, the survey found. Among women aged 40-50 years, the most common complaint reported was dyspareunia (pain on intercourse). In men, the most frequent complaints reported were in the over-40s age group, with 75% citing erectile dysfunction and 45% reporting loss of libido.
The most common gastrointestinal disorders associated with sexual dysfunction are inflammatory bowel diseases (37% of cases), chronic liver diseases (28%), and irritable bowel syndrome (26%), according to the survey.
On the question of whether medications played a role in patients’ sexual dysfunction, nearly 15% of respondents said that prokinetic agents were involved, and 18% thought proton pump inhibitors affect sexual function. Both drug classes are considered responsible for sexual disturbances.
Few gastroenterologists prescribe phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), e.g., Viagra, to treat sexual dysfunction, the survey found. Approximately 90% of respondents said that they never prescribed this class of drugs, preferring to refer patients to an andrologist. Of those who did prescribe PDE5i, significantly fewer residents did compared with experienced gastroenterologists (1.1% vs. 8.8%, respectively; P = .01).
Finally, the biggest reasons why gastroenterologists do not discuss sexual dysfunction are lack of knowledge (80%), insufficient experience (58%), time (44%), and embarrassment (30%).
Practice experience matters
There were some differences among respondents in the experienced group vs. the residents. More men were in the experienced group compared with residents (57.6% vs. 44%, respectively); mean age was 47 years vs. 29 years, respectively; and 71% had 5 or more years of experience in the experienced gastroenterologist group, whereas 78% had 1-5 years of experience among residents.
The survey found that more residents than experienced gastroenterologists “never discussed sexual dysfunction” (38.5% vs. 21.3%, respectively; P = .001) and that more residents than experienced gastroenterologists reported that “patients did not relate their sexual dysfunction to the prescribed therapy” (47.8% vs. 32.5%, respectively; P = .007).
The two groups varied regarding prescription drugs’ role in sexual dysfunction. More experienced gastroenterologists than residents felt that proton pump inhibitors (5.8% vs. 0%, respectively; P = .018) or prokinetics (19.8% vs. 9.5%, respectively; P = .028) might be responsible for some degree of sexual dysfunction.
More residents than experienced doctors felt that other (nongastroenterologic) drugs might contribute to sexual dysfunction in their patients (57.1% vs. 44.7%, respectively; P = .043).
Dr. Romano reported that fewer residents than experienced gastroenterologists referred male patients with sexual dysfunction to an andrologist (frequently/always: 28.1% vs. 44.4%, respectively; P = .004). However, more residents than experienced gastroenterologists disagreed that discussing sexual dysfunction with patients pertains only to specialists (andrologists and gynecologists; 83.5% vs. 71.2%, respectively; P = .018).
Time to step up
Asma Fikree, BMBCh, PhD, of Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, moderated the session. The survey highlights that asking patients about sexual dysfunction is an area for improvement for gastroenterologists, she said.
“We might do it in men and ask about erectile dysfunction, but we are very poor about asking in women,” Dr. Fikree noted.
The pros and cons of different medications should be discussed with patients, she said.
Gastroenterologists need to do a better job of considering how medications can lead to sexual dysfunction and interfere with quality of life, and training would help, she added.
“Some patients might not be very bothered by sexual dysfunction, but others might consider it very important,” Dr. Fikree said. “We should be considering this as part of their treatment and care.”
Dr. Romano and Dr. Fikree report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT UEG WEEK 2022
Preexisting mental illness symptoms spiked during pandemic
“Those with preexisting mental health conditions may be particularly vulnerable to these effects because they are more susceptible to experiencing high levels of stress during a crisis and are more likely to experience isolation/despair during confinement compared to the general population,” wrote Danna Ramirez of The Menninger Clinic, Houston, and colleagues.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research , the investigators compared data from 142 adolescents aged 12-17 years and 470 adults aged 18-79 years who were admitted to an inpatient psychiatric hospital in Houston. Of these, 65 adolescents and 235 adults were admitted before the pandemic, and 77 adolescents and 235 adults were admitted during the pandemic.
Clinical outcomes were scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), the Patient Health Questionnaire for Adolescents (PHQ-A), the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale–Short Form (DERS-SF), the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Scale (WHODAS), the World Health Organization Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test (WHOASSIST), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Disturbing Dream and Nightmare Severity Index (DDNSI), and the Suicide Behaviors Questionnaire–Revised (SBQ-R).
Overall, adults admitted during the pandemic had significantly higher levels of anxiety, depression, emotional dysregulation, and disability (P < .001 for all) as well as nightmares (P = .013) compared to those admitted prior to the pandemic.
Among adolescents, measures of anxiety, depression, and sleep quality were significantly higher at admission during the pandemic compared to prior to the pandemic (P = .005, P = .005, and P = .011, respectively)
Reasons for the increase in symptom severity remain unclear, but include the possibility that individuals with preexisting mental illness simply became more ill; or that individuals with symptoms delayed hospital admission out of fear of exposure to COVID-19, which resulted in more severe symptoms at admission, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the primarily White population and the reliance on self-reports, the researchers noted. Another limitation was the lack of differentiation between patients who may have had COVID-19 before hospitalization and those who did not, so the researchers could not determine whether the virus itself played a biological role in symptom severity.
However, the results support data from previous studies and identify increased psychiatry symptom severity for patients admitted for inpatient psychiatry care during the pandemic, they said. Although resources are scarce, the findings emphasize that mental health needs, especially for those with preexisting conditions, should not be overlooked, and continuity and expansion of access to mental health care for all should be prioritized, they concluded.
The study was supported by The Menninger Clinic and The Menninger Clinic Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Those with preexisting mental health conditions may be particularly vulnerable to these effects because they are more susceptible to experiencing high levels of stress during a crisis and are more likely to experience isolation/despair during confinement compared to the general population,” wrote Danna Ramirez of The Menninger Clinic, Houston, and colleagues.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research , the investigators compared data from 142 adolescents aged 12-17 years and 470 adults aged 18-79 years who were admitted to an inpatient psychiatric hospital in Houston. Of these, 65 adolescents and 235 adults were admitted before the pandemic, and 77 adolescents and 235 adults were admitted during the pandemic.
Clinical outcomes were scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), the Patient Health Questionnaire for Adolescents (PHQ-A), the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale–Short Form (DERS-SF), the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Scale (WHODAS), the World Health Organization Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test (WHOASSIST), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Disturbing Dream and Nightmare Severity Index (DDNSI), and the Suicide Behaviors Questionnaire–Revised (SBQ-R).
Overall, adults admitted during the pandemic had significantly higher levels of anxiety, depression, emotional dysregulation, and disability (P < .001 for all) as well as nightmares (P = .013) compared to those admitted prior to the pandemic.
Among adolescents, measures of anxiety, depression, and sleep quality were significantly higher at admission during the pandemic compared to prior to the pandemic (P = .005, P = .005, and P = .011, respectively)
Reasons for the increase in symptom severity remain unclear, but include the possibility that individuals with preexisting mental illness simply became more ill; or that individuals with symptoms delayed hospital admission out of fear of exposure to COVID-19, which resulted in more severe symptoms at admission, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the primarily White population and the reliance on self-reports, the researchers noted. Another limitation was the lack of differentiation between patients who may have had COVID-19 before hospitalization and those who did not, so the researchers could not determine whether the virus itself played a biological role in symptom severity.
However, the results support data from previous studies and identify increased psychiatry symptom severity for patients admitted for inpatient psychiatry care during the pandemic, they said. Although resources are scarce, the findings emphasize that mental health needs, especially for those with preexisting conditions, should not be overlooked, and continuity and expansion of access to mental health care for all should be prioritized, they concluded.
The study was supported by The Menninger Clinic and The Menninger Clinic Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Those with preexisting mental health conditions may be particularly vulnerable to these effects because they are more susceptible to experiencing high levels of stress during a crisis and are more likely to experience isolation/despair during confinement compared to the general population,” wrote Danna Ramirez of The Menninger Clinic, Houston, and colleagues.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research , the investigators compared data from 142 adolescents aged 12-17 years and 470 adults aged 18-79 years who were admitted to an inpatient psychiatric hospital in Houston. Of these, 65 adolescents and 235 adults were admitted before the pandemic, and 77 adolescents and 235 adults were admitted during the pandemic.
Clinical outcomes were scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), the Patient Health Questionnaire for Adolescents (PHQ-A), the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale–Short Form (DERS-SF), the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Scale (WHODAS), the World Health Organization Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test (WHOASSIST), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Disturbing Dream and Nightmare Severity Index (DDNSI), and the Suicide Behaviors Questionnaire–Revised (SBQ-R).
Overall, adults admitted during the pandemic had significantly higher levels of anxiety, depression, emotional dysregulation, and disability (P < .001 for all) as well as nightmares (P = .013) compared to those admitted prior to the pandemic.
Among adolescents, measures of anxiety, depression, and sleep quality were significantly higher at admission during the pandemic compared to prior to the pandemic (P = .005, P = .005, and P = .011, respectively)
Reasons for the increase in symptom severity remain unclear, but include the possibility that individuals with preexisting mental illness simply became more ill; or that individuals with symptoms delayed hospital admission out of fear of exposure to COVID-19, which resulted in more severe symptoms at admission, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the primarily White population and the reliance on self-reports, the researchers noted. Another limitation was the lack of differentiation between patients who may have had COVID-19 before hospitalization and those who did not, so the researchers could not determine whether the virus itself played a biological role in symptom severity.
However, the results support data from previous studies and identify increased psychiatry symptom severity for patients admitted for inpatient psychiatry care during the pandemic, they said. Although resources are scarce, the findings emphasize that mental health needs, especially for those with preexisting conditions, should not be overlooked, and continuity and expansion of access to mental health care for all should be prioritized, they concluded.
The study was supported by The Menninger Clinic and The Menninger Clinic Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PSYCHIATRY RESEARCH