User login
Best practices for an LGBTQ+ friendly medical space
While rainbow-colored flags may wave proudly from hotel balconies and sports arenas, LGBTQ+ patients might still feel some discrimination in the medical space, according to a Center for American Progress survey.
“Despite health care being considered a basic human right by the World Health Organization, it’s common for LGBTQ+ folks to face difficulties not only when trying to access care but also within the walls of the doctor’s office or hospital,” says Samantha Estevez, MD, a reproductive endocrinology and infertility fellow in New York.
In Medscape’s Physicians’ Views on LGBTQ+ Rights Issues Report 2022: Strong Emotions, Contrary Opinions, physicians were asked whether they see disparities in the care LGBTQ+ patients receive in comparison with the care that non-LGBTQ+ patients receive. About 35% of physicians said LGBTQ+ patients receive a different level of care; 52% of respondents younger than 45 said so.
It’s an issue unlikely to be resolved without the medical community’s awareness. With insights from four LGBTQ+ clinicians, here are several steps physicians can take to close the disparity gap.
Update intake forms
Many patient medical forms are populated with checkboxes. These forms may make it easier for patients to share their medical information and for practices to collect data. But unfortunately, they don’t allow for patients to fill in contextual information.
“It’s extremely important for health care professionals to understand the people they are serving,” says Nicholas Grant, PhD, ABPP, president of GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality. Dr. Grant is a board-certified clinical psychologist in Hawaii. “The more accurate we are with our information gathering and paperwork, the more accurate we will be at serving our LGBTQ+ communities.”
Dr. Grant recommends asking open-ended questions, such as the following:
- What is your gender identity?
- What was your assigned sex at birth?
- What pronouns do you prefer?
- What gender(s) are your sexual partners?
However, Frances Grimstad, MD, a Boston-based ob/gyn and GLMA board member, adds this advice: Before revising intake forms, consider their purpose.
“As an ob/gyn, information about a patient’s sexual orientation and their sexual activity is beneficial for my care,” says Dr. Grimstad. “But that information may not be relevant for a physical therapy clinic where most patients are coming in with knee injuries. So, you shouldn’t just place items on your intake forms by default. Instead, clinicians should consider what is relevant to the encounter you’re having and how you are going to use the information.”
Change signage
Take stock of posters and brochures in the office and signs outside restrooms. If they communicate traditional gender roles, then it may be time for a change.
“It’s important to ensure representation of all types of people and families in your office,” says Chase Anderson, MD, an assistant professor of child and adolescent psychiatry in San Francisco.
Hang posters with images of diverse families. Display brochures that address LGBTQ+ health concerns when warranted. And for restrooms, replace traditional binary images with gender-neutral ones. You can also add signage about each bathroom’s purpose, suggests Dr. Grimstad.
“Let’s not just de-gender bathrooms,” she says. “Let’s hang signs that tell if the bathroom has multiple stalls, urinals, or handicap access. Let signage focus on the functions of each bathroom, not gender.”
Ask for feedback
Feedback forms give LBGTQ+ patients a platform to share concerns. For example, consider an email with a linked document that all patients can fill out anonymously. Ask questions such as the following:
- Did you feel affirmed during your appointment? If so, how? If not, how can we improve?
- Did we use the proper pronouns?
- Did signage make you feel like you were in a safe space? What didn’t make you feel safe?
Set up a system with team members to process feedback and implement changes.
Also, if you have a large-scale practice, consider forming an LGBTQ+ community advisory board. “They can offer feedback about your practice’s clinical structure,” Dr. Grimstad tells Medscape.
Hire diverse employees
Building a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to serving the LBGTQ+ community. Team members should reflect your patient population.
“Diversity isn’t a monolith,” says Dr. Grimstad. “It isn’t just racial diversity, or sexual or gender diversity. Even in a town which appears homogeneous in one area of diversity, such as a majority White town, it’s important to remember all the other facets of diversity that exist, such as gender, sexual orientation, cultural diversity.”
A diverse team may offer a surprising boost to your practice. According to a study published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, patient outcomes improve when a more diverse team provides care. In fact, diverse teams fare better in innovation, communication, risk assessment, and financial performance.
Dr. Anderson also recommends allowing team members “to be themselves.” For example, let employees wear their hair in whatever way they prefer or display their tattoos.
“This signals to patients that if staff members can be themselves here, patients can be themselves here, too,” says Dr. Anderson.
Provide training
Medical staff may sometimes feel uncomfortable serving LBGTQ+ patients because of their own biases, attitudes, or lack of knowledge about the community. Regular training can ease their discomfort.
“Make sure all health professionals are trained and educated on the needs of LGBTQ+ patients,” says Dr. Grant. “Understanding their health needs is the provider’s responsibility.”
For basic information, Dr. Anderson recommends visiting The Trevor Project, an organization that serves LGBTQ+ youth. “They’re really good at keeping up with changing verbiage and trends,” says Dr. Anderson.
To strengthen community connections, Dr. Grimstad recommends using trainers from your local area if possible. Do a Google search to find an LGBTQ+ center nearby or in the closest major city. Invite them to staff meetings or ask them to organize a workshop.
By implementing these strategies, you can start building a bridge between your practice and the LGBTQ+ community and provide better care for them as patients.
“Whether it’s knowing about PrEP ... or ensuring staff members are trained in caring for patients with any general or sexual identity, we as doctors and medical professionals must continue to move forward and serve our LGBTQ+ patients in big and small ways,” says Dr. Estevez.
For in-depth training, check the following organizations:
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center at the Fenway Institute provides educational programs and resources to health care organizations.
GLMA has a top 10 health issues webpage that doctors can use to educate themselves and staff members on the LGBTQ+ community’s most urgent health needs.
Alliance for Full Acceptance offers LGBTQ cultural competency training, including a 1-hour awareness class and a 3-hour inclusivity workshop for clinicians.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has compiled a list of training curricula for behavioral health counselors and primary care providers.
UCSF’s Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Resource Center has a list of training and educational materials for medical professionals.
Equality California Institute offers both in-person and virtual training covering basic terminology, data on LGBTQ+ health issues, and how to create an inclusive environment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While rainbow-colored flags may wave proudly from hotel balconies and sports arenas, LGBTQ+ patients might still feel some discrimination in the medical space, according to a Center for American Progress survey.
“Despite health care being considered a basic human right by the World Health Organization, it’s common for LGBTQ+ folks to face difficulties not only when trying to access care but also within the walls of the doctor’s office or hospital,” says Samantha Estevez, MD, a reproductive endocrinology and infertility fellow in New York.
In Medscape’s Physicians’ Views on LGBTQ+ Rights Issues Report 2022: Strong Emotions, Contrary Opinions, physicians were asked whether they see disparities in the care LGBTQ+ patients receive in comparison with the care that non-LGBTQ+ patients receive. About 35% of physicians said LGBTQ+ patients receive a different level of care; 52% of respondents younger than 45 said so.
It’s an issue unlikely to be resolved without the medical community’s awareness. With insights from four LGBTQ+ clinicians, here are several steps physicians can take to close the disparity gap.
Update intake forms
Many patient medical forms are populated with checkboxes. These forms may make it easier for patients to share their medical information and for practices to collect data. But unfortunately, they don’t allow for patients to fill in contextual information.
“It’s extremely important for health care professionals to understand the people they are serving,” says Nicholas Grant, PhD, ABPP, president of GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality. Dr. Grant is a board-certified clinical psychologist in Hawaii. “The more accurate we are with our information gathering and paperwork, the more accurate we will be at serving our LGBTQ+ communities.”
Dr. Grant recommends asking open-ended questions, such as the following:
- What is your gender identity?
- What was your assigned sex at birth?
- What pronouns do you prefer?
- What gender(s) are your sexual partners?
However, Frances Grimstad, MD, a Boston-based ob/gyn and GLMA board member, adds this advice: Before revising intake forms, consider their purpose.
“As an ob/gyn, information about a patient’s sexual orientation and their sexual activity is beneficial for my care,” says Dr. Grimstad. “But that information may not be relevant for a physical therapy clinic where most patients are coming in with knee injuries. So, you shouldn’t just place items on your intake forms by default. Instead, clinicians should consider what is relevant to the encounter you’re having and how you are going to use the information.”
Change signage
Take stock of posters and brochures in the office and signs outside restrooms. If they communicate traditional gender roles, then it may be time for a change.
“It’s important to ensure representation of all types of people and families in your office,” says Chase Anderson, MD, an assistant professor of child and adolescent psychiatry in San Francisco.
Hang posters with images of diverse families. Display brochures that address LGBTQ+ health concerns when warranted. And for restrooms, replace traditional binary images with gender-neutral ones. You can also add signage about each bathroom’s purpose, suggests Dr. Grimstad.
“Let’s not just de-gender bathrooms,” she says. “Let’s hang signs that tell if the bathroom has multiple stalls, urinals, or handicap access. Let signage focus on the functions of each bathroom, not gender.”
Ask for feedback
Feedback forms give LBGTQ+ patients a platform to share concerns. For example, consider an email with a linked document that all patients can fill out anonymously. Ask questions such as the following:
- Did you feel affirmed during your appointment? If so, how? If not, how can we improve?
- Did we use the proper pronouns?
- Did signage make you feel like you were in a safe space? What didn’t make you feel safe?
Set up a system with team members to process feedback and implement changes.
Also, if you have a large-scale practice, consider forming an LGBTQ+ community advisory board. “They can offer feedback about your practice’s clinical structure,” Dr. Grimstad tells Medscape.
Hire diverse employees
Building a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to serving the LBGTQ+ community. Team members should reflect your patient population.
“Diversity isn’t a monolith,” says Dr. Grimstad. “It isn’t just racial diversity, or sexual or gender diversity. Even in a town which appears homogeneous in one area of diversity, such as a majority White town, it’s important to remember all the other facets of diversity that exist, such as gender, sexual orientation, cultural diversity.”
A diverse team may offer a surprising boost to your practice. According to a study published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, patient outcomes improve when a more diverse team provides care. In fact, diverse teams fare better in innovation, communication, risk assessment, and financial performance.
Dr. Anderson also recommends allowing team members “to be themselves.” For example, let employees wear their hair in whatever way they prefer or display their tattoos.
“This signals to patients that if staff members can be themselves here, patients can be themselves here, too,” says Dr. Anderson.
Provide training
Medical staff may sometimes feel uncomfortable serving LBGTQ+ patients because of their own biases, attitudes, or lack of knowledge about the community. Regular training can ease their discomfort.
“Make sure all health professionals are trained and educated on the needs of LGBTQ+ patients,” says Dr. Grant. “Understanding their health needs is the provider’s responsibility.”
For basic information, Dr. Anderson recommends visiting The Trevor Project, an organization that serves LGBTQ+ youth. “They’re really good at keeping up with changing verbiage and trends,” says Dr. Anderson.
To strengthen community connections, Dr. Grimstad recommends using trainers from your local area if possible. Do a Google search to find an LGBTQ+ center nearby or in the closest major city. Invite them to staff meetings or ask them to organize a workshop.
By implementing these strategies, you can start building a bridge between your practice and the LGBTQ+ community and provide better care for them as patients.
“Whether it’s knowing about PrEP ... or ensuring staff members are trained in caring for patients with any general or sexual identity, we as doctors and medical professionals must continue to move forward and serve our LGBTQ+ patients in big and small ways,” says Dr. Estevez.
For in-depth training, check the following organizations:
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center at the Fenway Institute provides educational programs and resources to health care organizations.
GLMA has a top 10 health issues webpage that doctors can use to educate themselves and staff members on the LGBTQ+ community’s most urgent health needs.
Alliance for Full Acceptance offers LGBTQ cultural competency training, including a 1-hour awareness class and a 3-hour inclusivity workshop for clinicians.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has compiled a list of training curricula for behavioral health counselors and primary care providers.
UCSF’s Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Resource Center has a list of training and educational materials for medical professionals.
Equality California Institute offers both in-person and virtual training covering basic terminology, data on LGBTQ+ health issues, and how to create an inclusive environment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While rainbow-colored flags may wave proudly from hotel balconies and sports arenas, LGBTQ+ patients might still feel some discrimination in the medical space, according to a Center for American Progress survey.
“Despite health care being considered a basic human right by the World Health Organization, it’s common for LGBTQ+ folks to face difficulties not only when trying to access care but also within the walls of the doctor’s office or hospital,” says Samantha Estevez, MD, a reproductive endocrinology and infertility fellow in New York.
In Medscape’s Physicians’ Views on LGBTQ+ Rights Issues Report 2022: Strong Emotions, Contrary Opinions, physicians were asked whether they see disparities in the care LGBTQ+ patients receive in comparison with the care that non-LGBTQ+ patients receive. About 35% of physicians said LGBTQ+ patients receive a different level of care; 52% of respondents younger than 45 said so.
It’s an issue unlikely to be resolved without the medical community’s awareness. With insights from four LGBTQ+ clinicians, here are several steps physicians can take to close the disparity gap.
Update intake forms
Many patient medical forms are populated with checkboxes. These forms may make it easier for patients to share their medical information and for practices to collect data. But unfortunately, they don’t allow for patients to fill in contextual information.
“It’s extremely important for health care professionals to understand the people they are serving,” says Nicholas Grant, PhD, ABPP, president of GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality. Dr. Grant is a board-certified clinical psychologist in Hawaii. “The more accurate we are with our information gathering and paperwork, the more accurate we will be at serving our LGBTQ+ communities.”
Dr. Grant recommends asking open-ended questions, such as the following:
- What is your gender identity?
- What was your assigned sex at birth?
- What pronouns do you prefer?
- What gender(s) are your sexual partners?
However, Frances Grimstad, MD, a Boston-based ob/gyn and GLMA board member, adds this advice: Before revising intake forms, consider their purpose.
“As an ob/gyn, information about a patient’s sexual orientation and their sexual activity is beneficial for my care,” says Dr. Grimstad. “But that information may not be relevant for a physical therapy clinic where most patients are coming in with knee injuries. So, you shouldn’t just place items on your intake forms by default. Instead, clinicians should consider what is relevant to the encounter you’re having and how you are going to use the information.”
Change signage
Take stock of posters and brochures in the office and signs outside restrooms. If they communicate traditional gender roles, then it may be time for a change.
“It’s important to ensure representation of all types of people and families in your office,” says Chase Anderson, MD, an assistant professor of child and adolescent psychiatry in San Francisco.
Hang posters with images of diverse families. Display brochures that address LGBTQ+ health concerns when warranted. And for restrooms, replace traditional binary images with gender-neutral ones. You can also add signage about each bathroom’s purpose, suggests Dr. Grimstad.
“Let’s not just de-gender bathrooms,” she says. “Let’s hang signs that tell if the bathroom has multiple stalls, urinals, or handicap access. Let signage focus on the functions of each bathroom, not gender.”
Ask for feedback
Feedback forms give LBGTQ+ patients a platform to share concerns. For example, consider an email with a linked document that all patients can fill out anonymously. Ask questions such as the following:
- Did you feel affirmed during your appointment? If so, how? If not, how can we improve?
- Did we use the proper pronouns?
- Did signage make you feel like you were in a safe space? What didn’t make you feel safe?
Set up a system with team members to process feedback and implement changes.
Also, if you have a large-scale practice, consider forming an LGBTQ+ community advisory board. “They can offer feedback about your practice’s clinical structure,” Dr. Grimstad tells Medscape.
Hire diverse employees
Building a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to serving the LBGTQ+ community. Team members should reflect your patient population.
“Diversity isn’t a monolith,” says Dr. Grimstad. “It isn’t just racial diversity, or sexual or gender diversity. Even in a town which appears homogeneous in one area of diversity, such as a majority White town, it’s important to remember all the other facets of diversity that exist, such as gender, sexual orientation, cultural diversity.”
A diverse team may offer a surprising boost to your practice. According to a study published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, patient outcomes improve when a more diverse team provides care. In fact, diverse teams fare better in innovation, communication, risk assessment, and financial performance.
Dr. Anderson also recommends allowing team members “to be themselves.” For example, let employees wear their hair in whatever way they prefer or display their tattoos.
“This signals to patients that if staff members can be themselves here, patients can be themselves here, too,” says Dr. Anderson.
Provide training
Medical staff may sometimes feel uncomfortable serving LBGTQ+ patients because of their own biases, attitudes, or lack of knowledge about the community. Regular training can ease their discomfort.
“Make sure all health professionals are trained and educated on the needs of LGBTQ+ patients,” says Dr. Grant. “Understanding their health needs is the provider’s responsibility.”
For basic information, Dr. Anderson recommends visiting The Trevor Project, an organization that serves LGBTQ+ youth. “They’re really good at keeping up with changing verbiage and trends,” says Dr. Anderson.
To strengthen community connections, Dr. Grimstad recommends using trainers from your local area if possible. Do a Google search to find an LGBTQ+ center nearby or in the closest major city. Invite them to staff meetings or ask them to organize a workshop.
By implementing these strategies, you can start building a bridge between your practice and the LGBTQ+ community and provide better care for them as patients.
“Whether it’s knowing about PrEP ... or ensuring staff members are trained in caring for patients with any general or sexual identity, we as doctors and medical professionals must continue to move forward and serve our LGBTQ+ patients in big and small ways,” says Dr. Estevez.
For in-depth training, check the following organizations:
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center at the Fenway Institute provides educational programs and resources to health care organizations.
GLMA has a top 10 health issues webpage that doctors can use to educate themselves and staff members on the LGBTQ+ community’s most urgent health needs.
Alliance for Full Acceptance offers LGBTQ cultural competency training, including a 1-hour awareness class and a 3-hour inclusivity workshop for clinicians.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has compiled a list of training curricula for behavioral health counselors and primary care providers.
UCSF’s Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Resource Center has a list of training and educational materials for medical professionals.
Equality California Institute offers both in-person and virtual training covering basic terminology, data on LGBTQ+ health issues, and how to create an inclusive environment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mentorship key to improving GI, hepatology workforce diversity
Increasing mentorship opportunities for gastroenterology and hepatology residents and medical students from populations underrepresented in medicine is essential to increase diversity in the specialty and improve health disparities among patients, according to a special report published simultaneously in Gastroenterology and three other journals.
“This study helps to establish priorities for diversity, equity and inclusion in our field and informs future interventions to improve workforce diversity and eliminate health care disparities among the patients we serve,” Folasade P. May, MD, PhD, MPhil, the study’s corresponding author and an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in a prepared statement.
The report, the result of a partnership between researchers at UCLA and the Intersociety Group on Diversity, reveals the findings of a survey aimed at assessing current perspectives on individuals underrepresented in medicine and health equity within gastroenterology and hepatology. The collaboration involved five gastroenterology professional societies: the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease; American College of Gastroenterology; American Gastroenterological Association; American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
”The current racial and ethnic composition of the GI and hepatology workforce does not reflect the population of patients served or the current matriculants in medicine,” Harman K. Rahal, MD, of UCLA and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and James H. Tabibian, MD, PhD, of UCLA and Olive View–UCLA Medical Center, and colleagues wrote. “As there are several conditions in GI and hepatology with disparities in incidence, treatment, and outcomes, representation of UIM [underrepresented in medicine] individuals is critical to address health disparities.”
The term “underrepresented in medicine” is defined by the Association of American Medical Colleges as “those racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in the medical profession relative to their numbers in the general population.” The authors explained that these groups “have traditionally included Latino (i.e., Latino/a/x), Black (or African American), Native American (namely, American Indian, Alaska Native, and Native Hawaiian), Pacific Islander, and mainland Puerto Rican individuals.”
The five gastroenterology and hepatology societies partnered with investigators at UCLA to develop a 33-question electronic survey “to determine perspectives of current racial, ethnic, and gender diversity within GI and hepatology; to assess current views on interventions needed to increase racial, ethnic, and gender diversity in the field; and to collect data on the experiences of UIM individuals and women in our field,” according to the report’s authors. The survey was then distributed to members of those societies, with 1,219 respondents.
The report found that inadequate representation of people from those underrepresented groups in the education and training pipeline was the most frequently reported barrier to improving racial and ethnic diversity in the field (35.4%), followed by insufficient racial and ethnic minority group representation in professional leadership (27.9%) and insufficient racial and ethnic minority group representation among practicing GI and hepatology professionals in the workplace (26.6%). Only 9% of fellows in GI and hepatology are from groups underrepresented in medicine, according to data from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Furthermore, one study has shown that the proportion of UIM in academic faculty has never exceeded 10% at each academic rank; there has even been a decline recently among junior academic faculty positions. That study also found that only 9% of academic gastroenterologists in the United states identify as underrepresented in medicine, with little change over the last decade.
Potential contributors to this low level of representation, the authors wrote, include “lack of racial and ethnic diversity in the medical training pipeline, nondiverse leadership, bias, racial discrimination, and the notion that UIM physicians may be less likely to promote themselves or be promoted.”
Another potential contributor, however, may be complacency within the field about the need to improve diversity and taking actions to do so.
A majority of White physicians (78%) were very or somewhat satisfied with current levels of workforce diversity, compared with a majority of Black physicians (63%) feeling very or somewhat unsatisfied.
This disconnect was not surprising to Aja McCutchen, MD, a partner at Atlanta Gastroenterology Associates who was not involved in the survey.
“One cannot discount the lived experience of a [person underrepresented in medicine] as it relates to recognizing conscious and unconscious biases, microaggression recognition, and absence of [underrepresented clinicians] in key positions. This is a reality that I do see on a daily basis,” Dr. McCutchen said in an interview.
Only 35% of respondents felt there is “insufficient racial and ethnic representation in education and training,” and just over a quarter (28%) felt the same about representation in leadership. In fact, most respondents (59.7%) thought that racial and ethnic diversity had increased over the past 5 years even though data show no change, the authors noted.
Although Dr. McCutchen appreciated the broad recognition from respondents, regardless of background, to improve diversity in the pipeline, she noted that “retention of current talent and future talent would also require cultural shifts in understanding the challenges of the [underrepresented] members,” Dr. McCutchen said.
Again, however, the majority of the respondents (64.6%) were themselves not members of underrepresented groups. Nearly half the respondents (48.7%) were non-Hispanic White, and one in five (22.5%) were Asian, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander. The remaining respondents, making up less than a third of the total, were Hispanic (10.6%), Black (9.1%), American Indian or Alaskan Native (0.2%), another race/ethnicity (3.3%), or preferred not to answer (5.7%).
Dr. McCutchen said she had mixed feelings about the survey overall.
“On the one hand, I was eager to read the perceptions of survey respondents as it relates to diversity, equity and inclusion in the GI space as very little cross-organizational data exists,” said Dr. McCutchen. “On the other hand, the responses reminded me that there is a lot of work to be done as I expected more dissatisfaction with the current GI workforce in both academia and private practice respondents.”
She was surprised, for example, that nearly three-quarters of the respondents were somewhat or very satisfied, and that a majority thought racial and ethnic diversity had increased.
Studies on provider-patient concordance have shown that patients feel it’s important to share common ground with their physicians particularly in terms of race, ethnicity and language, the authors noted.
“This patient preference underscores the need to recruit and train a more diverse cohort of trainees into GI and hepatology fellowships if the desired goal is to optimize patient care and combat health disparities,” they wrote. They pointed out that cultural understanding can influence how patients perceive their health, symptoms, and concerns, which can then affect providers’ diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations. In turn, patients may have better adherence to treatment recommendations when they share a similar background as their clinician.
“Diversity in medicine also leads to greater diversity in thoughts, better returns on investments, increased scholarly activities related to health equity to name a few,” Dr. McCutchen said.
The top recommendations from respondents for improving representation of currently underrepresented individuals in GI and hepatology were to increase mentorship opportunities for residents (45%) and medical students (43%) from these groups and to increase representation of professionals from these backgrounds in program and professional society leadership (39%). A third of respondents also recommended increasing shadowing opportunities for undergraduate students from these underrepresented populations.
Dr. McCutchen expressed optimism regarding the initiatives to improve diversity, equity and inclusion across the gastroenterology spectrum.
“It is incumbent upon all of us to continue to be the driving force of change, which will be a journey and not a destination,” McCutchen said. “In the future, diversity, equity and inclusion will be the expectation, and we will ultimately move closer to the goal of completely eliminating health care inequities.”
The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute, the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, and Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research Ablon Scholars Program. The authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. McCutchen disclosed relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and Redhill Biopharmaceuticals.
Increasing mentorship opportunities for gastroenterology and hepatology residents and medical students from populations underrepresented in medicine is essential to increase diversity in the specialty and improve health disparities among patients, according to a special report published simultaneously in Gastroenterology and three other journals.
“This study helps to establish priorities for diversity, equity and inclusion in our field and informs future interventions to improve workforce diversity and eliminate health care disparities among the patients we serve,” Folasade P. May, MD, PhD, MPhil, the study’s corresponding author and an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in a prepared statement.
The report, the result of a partnership between researchers at UCLA and the Intersociety Group on Diversity, reveals the findings of a survey aimed at assessing current perspectives on individuals underrepresented in medicine and health equity within gastroenterology and hepatology. The collaboration involved five gastroenterology professional societies: the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease; American College of Gastroenterology; American Gastroenterological Association; American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
”The current racial and ethnic composition of the GI and hepatology workforce does not reflect the population of patients served or the current matriculants in medicine,” Harman K. Rahal, MD, of UCLA and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and James H. Tabibian, MD, PhD, of UCLA and Olive View–UCLA Medical Center, and colleagues wrote. “As there are several conditions in GI and hepatology with disparities in incidence, treatment, and outcomes, representation of UIM [underrepresented in medicine] individuals is critical to address health disparities.”
The term “underrepresented in medicine” is defined by the Association of American Medical Colleges as “those racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in the medical profession relative to their numbers in the general population.” The authors explained that these groups “have traditionally included Latino (i.e., Latino/a/x), Black (or African American), Native American (namely, American Indian, Alaska Native, and Native Hawaiian), Pacific Islander, and mainland Puerto Rican individuals.”
The five gastroenterology and hepatology societies partnered with investigators at UCLA to develop a 33-question electronic survey “to determine perspectives of current racial, ethnic, and gender diversity within GI and hepatology; to assess current views on interventions needed to increase racial, ethnic, and gender diversity in the field; and to collect data on the experiences of UIM individuals and women in our field,” according to the report’s authors. The survey was then distributed to members of those societies, with 1,219 respondents.
The report found that inadequate representation of people from those underrepresented groups in the education and training pipeline was the most frequently reported barrier to improving racial and ethnic diversity in the field (35.4%), followed by insufficient racial and ethnic minority group representation in professional leadership (27.9%) and insufficient racial and ethnic minority group representation among practicing GI and hepatology professionals in the workplace (26.6%). Only 9% of fellows in GI and hepatology are from groups underrepresented in medicine, according to data from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Furthermore, one study has shown that the proportion of UIM in academic faculty has never exceeded 10% at each academic rank; there has even been a decline recently among junior academic faculty positions. That study also found that only 9% of academic gastroenterologists in the United states identify as underrepresented in medicine, with little change over the last decade.
Potential contributors to this low level of representation, the authors wrote, include “lack of racial and ethnic diversity in the medical training pipeline, nondiverse leadership, bias, racial discrimination, and the notion that UIM physicians may be less likely to promote themselves or be promoted.”
Another potential contributor, however, may be complacency within the field about the need to improve diversity and taking actions to do so.
A majority of White physicians (78%) were very or somewhat satisfied with current levels of workforce diversity, compared with a majority of Black physicians (63%) feeling very or somewhat unsatisfied.
This disconnect was not surprising to Aja McCutchen, MD, a partner at Atlanta Gastroenterology Associates who was not involved in the survey.
“One cannot discount the lived experience of a [person underrepresented in medicine] as it relates to recognizing conscious and unconscious biases, microaggression recognition, and absence of [underrepresented clinicians] in key positions. This is a reality that I do see on a daily basis,” Dr. McCutchen said in an interview.
Only 35% of respondents felt there is “insufficient racial and ethnic representation in education and training,” and just over a quarter (28%) felt the same about representation in leadership. In fact, most respondents (59.7%) thought that racial and ethnic diversity had increased over the past 5 years even though data show no change, the authors noted.
Although Dr. McCutchen appreciated the broad recognition from respondents, regardless of background, to improve diversity in the pipeline, she noted that “retention of current talent and future talent would also require cultural shifts in understanding the challenges of the [underrepresented] members,” Dr. McCutchen said.
Again, however, the majority of the respondents (64.6%) were themselves not members of underrepresented groups. Nearly half the respondents (48.7%) were non-Hispanic White, and one in five (22.5%) were Asian, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander. The remaining respondents, making up less than a third of the total, were Hispanic (10.6%), Black (9.1%), American Indian or Alaskan Native (0.2%), another race/ethnicity (3.3%), or preferred not to answer (5.7%).
Dr. McCutchen said she had mixed feelings about the survey overall.
“On the one hand, I was eager to read the perceptions of survey respondents as it relates to diversity, equity and inclusion in the GI space as very little cross-organizational data exists,” said Dr. McCutchen. “On the other hand, the responses reminded me that there is a lot of work to be done as I expected more dissatisfaction with the current GI workforce in both academia and private practice respondents.”
She was surprised, for example, that nearly three-quarters of the respondents were somewhat or very satisfied, and that a majority thought racial and ethnic diversity had increased.
Studies on provider-patient concordance have shown that patients feel it’s important to share common ground with their physicians particularly in terms of race, ethnicity and language, the authors noted.
“This patient preference underscores the need to recruit and train a more diverse cohort of trainees into GI and hepatology fellowships if the desired goal is to optimize patient care and combat health disparities,” they wrote. They pointed out that cultural understanding can influence how patients perceive their health, symptoms, and concerns, which can then affect providers’ diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations. In turn, patients may have better adherence to treatment recommendations when they share a similar background as their clinician.
“Diversity in medicine also leads to greater diversity in thoughts, better returns on investments, increased scholarly activities related to health equity to name a few,” Dr. McCutchen said.
The top recommendations from respondents for improving representation of currently underrepresented individuals in GI and hepatology were to increase mentorship opportunities for residents (45%) and medical students (43%) from these groups and to increase representation of professionals from these backgrounds in program and professional society leadership (39%). A third of respondents also recommended increasing shadowing opportunities for undergraduate students from these underrepresented populations.
Dr. McCutchen expressed optimism regarding the initiatives to improve diversity, equity and inclusion across the gastroenterology spectrum.
“It is incumbent upon all of us to continue to be the driving force of change, which will be a journey and not a destination,” McCutchen said. “In the future, diversity, equity and inclusion will be the expectation, and we will ultimately move closer to the goal of completely eliminating health care inequities.”
The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute, the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, and Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research Ablon Scholars Program. The authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. McCutchen disclosed relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and Redhill Biopharmaceuticals.
Increasing mentorship opportunities for gastroenterology and hepatology residents and medical students from populations underrepresented in medicine is essential to increase diversity in the specialty and improve health disparities among patients, according to a special report published simultaneously in Gastroenterology and three other journals.
“This study helps to establish priorities for diversity, equity and inclusion in our field and informs future interventions to improve workforce diversity and eliminate health care disparities among the patients we serve,” Folasade P. May, MD, PhD, MPhil, the study’s corresponding author and an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in a prepared statement.
The report, the result of a partnership between researchers at UCLA and the Intersociety Group on Diversity, reveals the findings of a survey aimed at assessing current perspectives on individuals underrepresented in medicine and health equity within gastroenterology and hepatology. The collaboration involved five gastroenterology professional societies: the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease; American College of Gastroenterology; American Gastroenterological Association; American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
”The current racial and ethnic composition of the GI and hepatology workforce does not reflect the population of patients served or the current matriculants in medicine,” Harman K. Rahal, MD, of UCLA and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and James H. Tabibian, MD, PhD, of UCLA and Olive View–UCLA Medical Center, and colleagues wrote. “As there are several conditions in GI and hepatology with disparities in incidence, treatment, and outcomes, representation of UIM [underrepresented in medicine] individuals is critical to address health disparities.”
The term “underrepresented in medicine” is defined by the Association of American Medical Colleges as “those racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in the medical profession relative to their numbers in the general population.” The authors explained that these groups “have traditionally included Latino (i.e., Latino/a/x), Black (or African American), Native American (namely, American Indian, Alaska Native, and Native Hawaiian), Pacific Islander, and mainland Puerto Rican individuals.”
The five gastroenterology and hepatology societies partnered with investigators at UCLA to develop a 33-question electronic survey “to determine perspectives of current racial, ethnic, and gender diversity within GI and hepatology; to assess current views on interventions needed to increase racial, ethnic, and gender diversity in the field; and to collect data on the experiences of UIM individuals and women in our field,” according to the report’s authors. The survey was then distributed to members of those societies, with 1,219 respondents.
The report found that inadequate representation of people from those underrepresented groups in the education and training pipeline was the most frequently reported barrier to improving racial and ethnic diversity in the field (35.4%), followed by insufficient racial and ethnic minority group representation in professional leadership (27.9%) and insufficient racial and ethnic minority group representation among practicing GI and hepatology professionals in the workplace (26.6%). Only 9% of fellows in GI and hepatology are from groups underrepresented in medicine, according to data from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Furthermore, one study has shown that the proportion of UIM in academic faculty has never exceeded 10% at each academic rank; there has even been a decline recently among junior academic faculty positions. That study also found that only 9% of academic gastroenterologists in the United states identify as underrepresented in medicine, with little change over the last decade.
Potential contributors to this low level of representation, the authors wrote, include “lack of racial and ethnic diversity in the medical training pipeline, nondiverse leadership, bias, racial discrimination, and the notion that UIM physicians may be less likely to promote themselves or be promoted.”
Another potential contributor, however, may be complacency within the field about the need to improve diversity and taking actions to do so.
A majority of White physicians (78%) were very or somewhat satisfied with current levels of workforce diversity, compared with a majority of Black physicians (63%) feeling very or somewhat unsatisfied.
This disconnect was not surprising to Aja McCutchen, MD, a partner at Atlanta Gastroenterology Associates who was not involved in the survey.
“One cannot discount the lived experience of a [person underrepresented in medicine] as it relates to recognizing conscious and unconscious biases, microaggression recognition, and absence of [underrepresented clinicians] in key positions. This is a reality that I do see on a daily basis,” Dr. McCutchen said in an interview.
Only 35% of respondents felt there is “insufficient racial and ethnic representation in education and training,” and just over a quarter (28%) felt the same about representation in leadership. In fact, most respondents (59.7%) thought that racial and ethnic diversity had increased over the past 5 years even though data show no change, the authors noted.
Although Dr. McCutchen appreciated the broad recognition from respondents, regardless of background, to improve diversity in the pipeline, she noted that “retention of current talent and future talent would also require cultural shifts in understanding the challenges of the [underrepresented] members,” Dr. McCutchen said.
Again, however, the majority of the respondents (64.6%) were themselves not members of underrepresented groups. Nearly half the respondents (48.7%) were non-Hispanic White, and one in five (22.5%) were Asian, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander. The remaining respondents, making up less than a third of the total, were Hispanic (10.6%), Black (9.1%), American Indian or Alaskan Native (0.2%), another race/ethnicity (3.3%), or preferred not to answer (5.7%).
Dr. McCutchen said she had mixed feelings about the survey overall.
“On the one hand, I was eager to read the perceptions of survey respondents as it relates to diversity, equity and inclusion in the GI space as very little cross-organizational data exists,” said Dr. McCutchen. “On the other hand, the responses reminded me that there is a lot of work to be done as I expected more dissatisfaction with the current GI workforce in both academia and private practice respondents.”
She was surprised, for example, that nearly three-quarters of the respondents were somewhat or very satisfied, and that a majority thought racial and ethnic diversity had increased.
Studies on provider-patient concordance have shown that patients feel it’s important to share common ground with their physicians particularly in terms of race, ethnicity and language, the authors noted.
“This patient preference underscores the need to recruit and train a more diverse cohort of trainees into GI and hepatology fellowships if the desired goal is to optimize patient care and combat health disparities,” they wrote. They pointed out that cultural understanding can influence how patients perceive their health, symptoms, and concerns, which can then affect providers’ diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations. In turn, patients may have better adherence to treatment recommendations when they share a similar background as their clinician.
“Diversity in medicine also leads to greater diversity in thoughts, better returns on investments, increased scholarly activities related to health equity to name a few,” Dr. McCutchen said.
The top recommendations from respondents for improving representation of currently underrepresented individuals in GI and hepatology were to increase mentorship opportunities for residents (45%) and medical students (43%) from these groups and to increase representation of professionals from these backgrounds in program and professional society leadership (39%). A third of respondents also recommended increasing shadowing opportunities for undergraduate students from these underrepresented populations.
Dr. McCutchen expressed optimism regarding the initiatives to improve diversity, equity and inclusion across the gastroenterology spectrum.
“It is incumbent upon all of us to continue to be the driving force of change, which will be a journey and not a destination,” McCutchen said. “In the future, diversity, equity and inclusion will be the expectation, and we will ultimately move closer to the goal of completely eliminating health care inequities.”
The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute, the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, and Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research Ablon Scholars Program. The authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. McCutchen disclosed relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and Redhill Biopharmaceuticals.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Pregnant, postpartum women with disabilities at higher risk for violence
Pregnant or postpartum women with disabilities are at relatively high risk of experiencing violence, often from the people closest to them, new research suggests.
The researchers set out to measure risk of interpersonal violence, which the World Health Organization defines as “the intentional use of physical force or power against an individual by an intimate partner, family member, or other community member.”
Hilary K. Brown, PhD, with the department of health & society, University of Toronto, led the study published online in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Large, population-based dataset
The population study included people 15-49 years old with births in Ontario from 2004 to 2019. They included 147,414 people with physical disabilities; 47,459 people with intellectual disabilities; 2,557 with developmental disabilities; and 9,598 with multiple disabilities.
The control group was 1,594,441 million people without disabilities.
The outcome measured was “any emergency department visit, hospital admission, or death related to physical, sexual, or psychological violence between fertilization and 365 days post partum.”
Researchers found that the adjusted relative risk of interpersonal violence for those with disabilities, compared with those with no disabilities was 1.40 (95% confidence interval, 1.31-1.50) in those with physical disabilities; 2.39 (95% CI, 1.98-2.88) in those with intellectual or developmental disabilities; and 1.96 (95% CI, 1.66-2.30) in those with multiple disabilities.
History of violence means higher risk
Those with a history of interpersonal violence and a disability were at particularly high risk for perinatal violence.
The authors note that pregnancy is a high-risk period for interpersonal violence for all women, particularly by an intimate partner.
“More than 30% of intimate partner violence begins during pregnancy, and preexisting violence tends to escalate perinatally,” they write.
The authors cite previous research that found women with disabilities experience higher rates of abuse overall and by an intimate partner – two to four times rates reported by those without disabilities.
Opportunities for provider intervention
Since the period surrounding pregnancy is a time of increased contact with medical providers and resources, there may be opportunities for identifying abuse and providing interventions.
Those might include better screening, access to violence-related information and services, and education of health care professionals to support people with disabilities. For example, “Tools used for violence screening perinatally do not include items about forms of violence that are unique to individuals with disabilities, such as refusal to assist with activities of daily living.”
The authors add: “[G]iven that the strongest risk factor for interpersonal violence in the perinatal period, particularly in those with disabilities, was a prepregnancy history of interpersonal violence, our findings suggest that more could be done before pregnancy to offer screening and support at the index encounter.”
Violence can lead to adverse outcomes
Implications are important as the violence can result in barriers to care and adverse perinatal outcomes.
Jeanne L. Alhusen, PhD, CRNP, RN, University of Virginia Medical Center professor of nursing and associate dean for research, was not part of this research but wrote a paper earlier this year on the subject and had similar conclusions.
She said before this study by Brown et al., “our understanding of the risk of violence by disability type throughout the perinatal period, on a population-based level, was quite limited.”
With the size of this dataset, she said, this paper provides critical information for health care providers. It extends physicians’ ability to examine risk of violence by disability type as well as these patients’ risk of experiencing different types of violence.
She pointed out that the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) recently incorporated a disability supplement that allows better understanding of pregnancy risks in people with disabilities.
“It will be critical that U.S. states continue to incorporate the disability questions into their PRAMS administration [because] without that information, persons with disabilities will continue to experience unconscionable inequities,” she said.
Barriers to equitable care
Dr. Alhusen added that people with disabilities experience significant barriers in accessing equitable care – both at the provider and the system level.
She said it is critical that we recognize and address the sexual and reproductive health needs of all persons with disability. “This includes screening every person for violence and [ensuring] the tools we utilize are accessible and include items specific to disability-related abuse. In our qualitative studies, we have heard from pregnant persons that they were never screened or that they were screened with their abusive partner sitting next to them.”
Screening questions to ask
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists provides examples of screening questions that are specific to people with disabilities such as asking if a partner has ever prevented the individual from using an assistive device (for example, a wheelchair, cane, or respirator) or refused to help with an important personal need, such as taking medication or getting out of bed.
“For many reasons, people with disabilities are less likely to disclose violence, and health care professionals are less likely to ask them about it,” said coauthor of the current study, Yona Lunsky, PhD, clinician-scientist, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, in a statement. Based on the findings, she said, she hopes clinicians will see the need to develop disability-informed screening tools to capture abuse and identify the appropriate resources for this population before, during, and after pregnancy.
Coauthor Dr. Natasha Saunders receives an honorarium from the BMJ Group (Archives of Diseases in Childhood). Coauthor Dr. Simone N. Vigod receives royalties from UpToDate for authorship of materials related to depression and pregnancy. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Alhusen reported no relevant financial relationships.
Pregnant or postpartum women with disabilities are at relatively high risk of experiencing violence, often from the people closest to them, new research suggests.
The researchers set out to measure risk of interpersonal violence, which the World Health Organization defines as “the intentional use of physical force or power against an individual by an intimate partner, family member, or other community member.”
Hilary K. Brown, PhD, with the department of health & society, University of Toronto, led the study published online in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Large, population-based dataset
The population study included people 15-49 years old with births in Ontario from 2004 to 2019. They included 147,414 people with physical disabilities; 47,459 people with intellectual disabilities; 2,557 with developmental disabilities; and 9,598 with multiple disabilities.
The control group was 1,594,441 million people without disabilities.
The outcome measured was “any emergency department visit, hospital admission, or death related to physical, sexual, or psychological violence between fertilization and 365 days post partum.”
Researchers found that the adjusted relative risk of interpersonal violence for those with disabilities, compared with those with no disabilities was 1.40 (95% confidence interval, 1.31-1.50) in those with physical disabilities; 2.39 (95% CI, 1.98-2.88) in those with intellectual or developmental disabilities; and 1.96 (95% CI, 1.66-2.30) in those with multiple disabilities.
History of violence means higher risk
Those with a history of interpersonal violence and a disability were at particularly high risk for perinatal violence.
The authors note that pregnancy is a high-risk period for interpersonal violence for all women, particularly by an intimate partner.
“More than 30% of intimate partner violence begins during pregnancy, and preexisting violence tends to escalate perinatally,” they write.
The authors cite previous research that found women with disabilities experience higher rates of abuse overall and by an intimate partner – two to four times rates reported by those without disabilities.
Opportunities for provider intervention
Since the period surrounding pregnancy is a time of increased contact with medical providers and resources, there may be opportunities for identifying abuse and providing interventions.
Those might include better screening, access to violence-related information and services, and education of health care professionals to support people with disabilities. For example, “Tools used for violence screening perinatally do not include items about forms of violence that are unique to individuals with disabilities, such as refusal to assist with activities of daily living.”
The authors add: “[G]iven that the strongest risk factor for interpersonal violence in the perinatal period, particularly in those with disabilities, was a prepregnancy history of interpersonal violence, our findings suggest that more could be done before pregnancy to offer screening and support at the index encounter.”
Violence can lead to adverse outcomes
Implications are important as the violence can result in barriers to care and adverse perinatal outcomes.
Jeanne L. Alhusen, PhD, CRNP, RN, University of Virginia Medical Center professor of nursing and associate dean for research, was not part of this research but wrote a paper earlier this year on the subject and had similar conclusions.
She said before this study by Brown et al., “our understanding of the risk of violence by disability type throughout the perinatal period, on a population-based level, was quite limited.”
With the size of this dataset, she said, this paper provides critical information for health care providers. It extends physicians’ ability to examine risk of violence by disability type as well as these patients’ risk of experiencing different types of violence.
She pointed out that the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) recently incorporated a disability supplement that allows better understanding of pregnancy risks in people with disabilities.
“It will be critical that U.S. states continue to incorporate the disability questions into their PRAMS administration [because] without that information, persons with disabilities will continue to experience unconscionable inequities,” she said.
Barriers to equitable care
Dr. Alhusen added that people with disabilities experience significant barriers in accessing equitable care – both at the provider and the system level.
She said it is critical that we recognize and address the sexual and reproductive health needs of all persons with disability. “This includes screening every person for violence and [ensuring] the tools we utilize are accessible and include items specific to disability-related abuse. In our qualitative studies, we have heard from pregnant persons that they were never screened or that they were screened with their abusive partner sitting next to them.”
Screening questions to ask
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists provides examples of screening questions that are specific to people with disabilities such as asking if a partner has ever prevented the individual from using an assistive device (for example, a wheelchair, cane, or respirator) or refused to help with an important personal need, such as taking medication or getting out of bed.
“For many reasons, people with disabilities are less likely to disclose violence, and health care professionals are less likely to ask them about it,” said coauthor of the current study, Yona Lunsky, PhD, clinician-scientist, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, in a statement. Based on the findings, she said, she hopes clinicians will see the need to develop disability-informed screening tools to capture abuse and identify the appropriate resources for this population before, during, and after pregnancy.
Coauthor Dr. Natasha Saunders receives an honorarium from the BMJ Group (Archives of Diseases in Childhood). Coauthor Dr. Simone N. Vigod receives royalties from UpToDate for authorship of materials related to depression and pregnancy. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Alhusen reported no relevant financial relationships.
Pregnant or postpartum women with disabilities are at relatively high risk of experiencing violence, often from the people closest to them, new research suggests.
The researchers set out to measure risk of interpersonal violence, which the World Health Organization defines as “the intentional use of physical force or power against an individual by an intimate partner, family member, or other community member.”
Hilary K. Brown, PhD, with the department of health & society, University of Toronto, led the study published online in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Large, population-based dataset
The population study included people 15-49 years old with births in Ontario from 2004 to 2019. They included 147,414 people with physical disabilities; 47,459 people with intellectual disabilities; 2,557 with developmental disabilities; and 9,598 with multiple disabilities.
The control group was 1,594,441 million people without disabilities.
The outcome measured was “any emergency department visit, hospital admission, or death related to physical, sexual, or psychological violence between fertilization and 365 days post partum.”
Researchers found that the adjusted relative risk of interpersonal violence for those with disabilities, compared with those with no disabilities was 1.40 (95% confidence interval, 1.31-1.50) in those with physical disabilities; 2.39 (95% CI, 1.98-2.88) in those with intellectual or developmental disabilities; and 1.96 (95% CI, 1.66-2.30) in those with multiple disabilities.
History of violence means higher risk
Those with a history of interpersonal violence and a disability were at particularly high risk for perinatal violence.
The authors note that pregnancy is a high-risk period for interpersonal violence for all women, particularly by an intimate partner.
“More than 30% of intimate partner violence begins during pregnancy, and preexisting violence tends to escalate perinatally,” they write.
The authors cite previous research that found women with disabilities experience higher rates of abuse overall and by an intimate partner – two to four times rates reported by those without disabilities.
Opportunities for provider intervention
Since the period surrounding pregnancy is a time of increased contact with medical providers and resources, there may be opportunities for identifying abuse and providing interventions.
Those might include better screening, access to violence-related information and services, and education of health care professionals to support people with disabilities. For example, “Tools used for violence screening perinatally do not include items about forms of violence that are unique to individuals with disabilities, such as refusal to assist with activities of daily living.”
The authors add: “[G]iven that the strongest risk factor for interpersonal violence in the perinatal period, particularly in those with disabilities, was a prepregnancy history of interpersonal violence, our findings suggest that more could be done before pregnancy to offer screening and support at the index encounter.”
Violence can lead to adverse outcomes
Implications are important as the violence can result in barriers to care and adverse perinatal outcomes.
Jeanne L. Alhusen, PhD, CRNP, RN, University of Virginia Medical Center professor of nursing and associate dean for research, was not part of this research but wrote a paper earlier this year on the subject and had similar conclusions.
She said before this study by Brown et al., “our understanding of the risk of violence by disability type throughout the perinatal period, on a population-based level, was quite limited.”
With the size of this dataset, she said, this paper provides critical information for health care providers. It extends physicians’ ability to examine risk of violence by disability type as well as these patients’ risk of experiencing different types of violence.
She pointed out that the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) recently incorporated a disability supplement that allows better understanding of pregnancy risks in people with disabilities.
“It will be critical that U.S. states continue to incorporate the disability questions into their PRAMS administration [because] without that information, persons with disabilities will continue to experience unconscionable inequities,” she said.
Barriers to equitable care
Dr. Alhusen added that people with disabilities experience significant barriers in accessing equitable care – both at the provider and the system level.
She said it is critical that we recognize and address the sexual and reproductive health needs of all persons with disability. “This includes screening every person for violence and [ensuring] the tools we utilize are accessible and include items specific to disability-related abuse. In our qualitative studies, we have heard from pregnant persons that they were never screened or that they were screened with their abusive partner sitting next to them.”
Screening questions to ask
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists provides examples of screening questions that are specific to people with disabilities such as asking if a partner has ever prevented the individual from using an assistive device (for example, a wheelchair, cane, or respirator) or refused to help with an important personal need, such as taking medication or getting out of bed.
“For many reasons, people with disabilities are less likely to disclose violence, and health care professionals are less likely to ask them about it,” said coauthor of the current study, Yona Lunsky, PhD, clinician-scientist, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, in a statement. Based on the findings, she said, she hopes clinicians will see the need to develop disability-informed screening tools to capture abuse and identify the appropriate resources for this population before, during, and after pregnancy.
Coauthor Dr. Natasha Saunders receives an honorarium from the BMJ Group (Archives of Diseases in Childhood). Coauthor Dr. Simone N. Vigod receives royalties from UpToDate for authorship of materials related to depression and pregnancy. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Alhusen reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Tinea capitis
THE COMPARISON
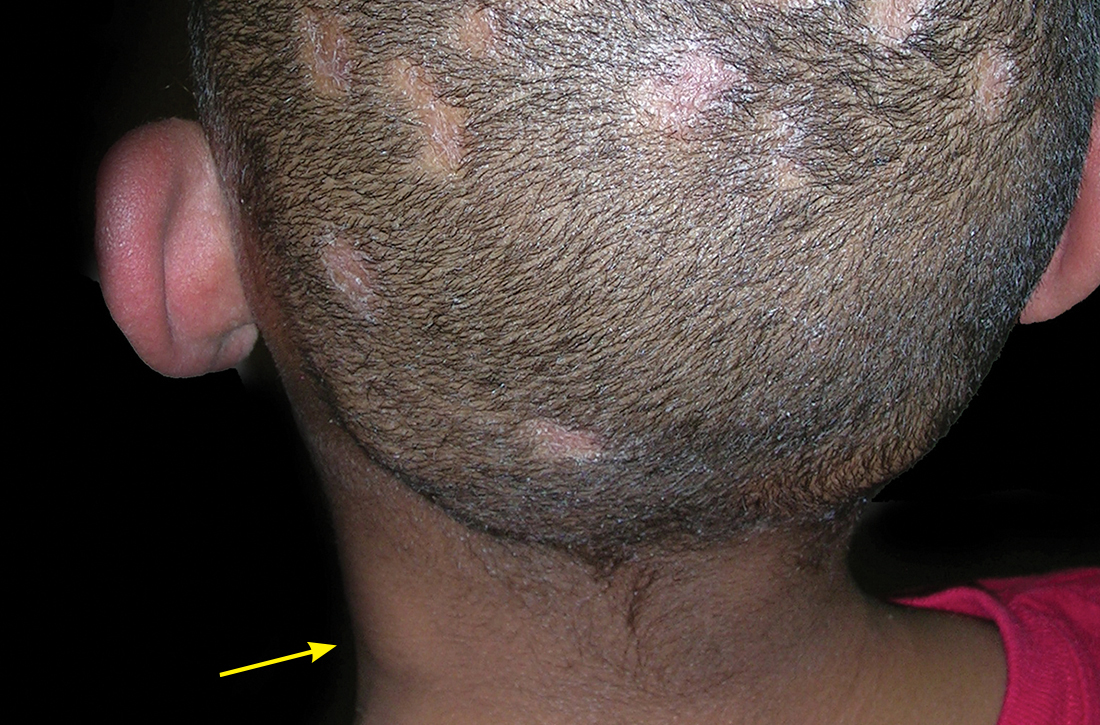
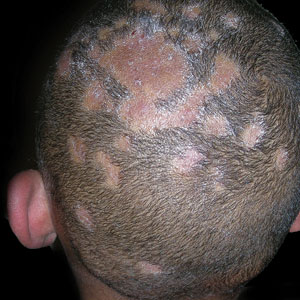
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.
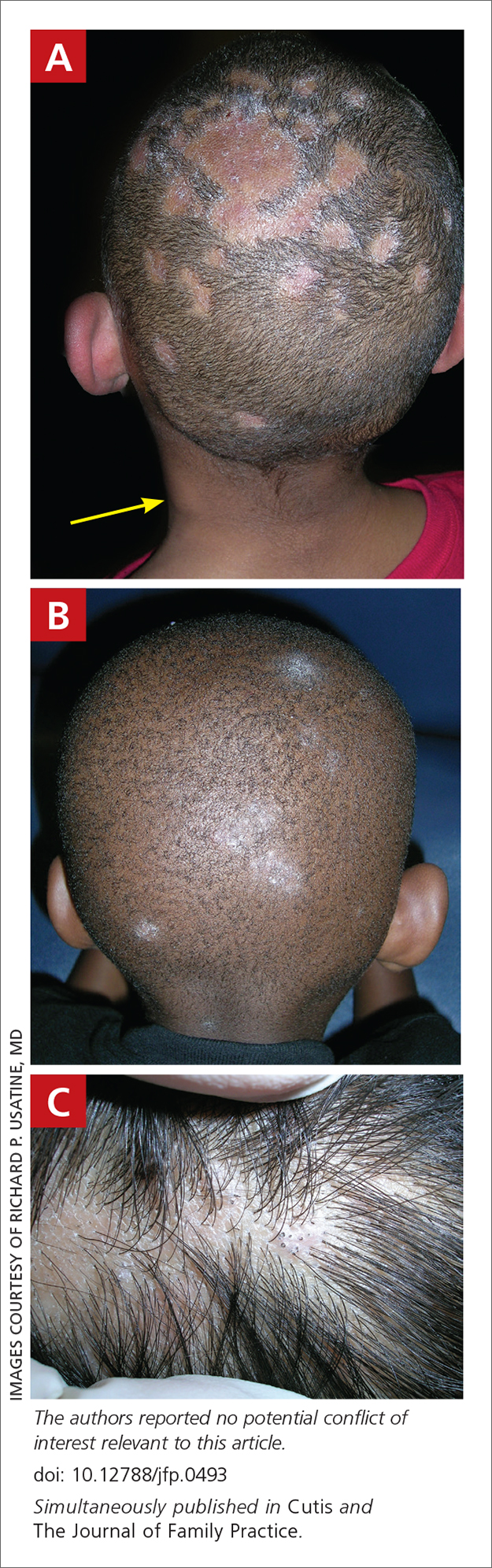
Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) caused by M canis. M canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations:
- broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp
- diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis
- well-demarcated annular plaques
- exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation
- scalp pruritus
- occipital scalp lymphadenopathy.
Worth noting
Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp. However, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to false-negative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5
Health disparity highlight
A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
1. Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15088
2. Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-2522
3. Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
4. Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
5. Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi: 10.1111/pde.14092
6. Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.

Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) caused by M canis. M canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations:
- broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp
- diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis
- well-demarcated annular plaques
- exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation
- scalp pruritus
- occipital scalp lymphadenopathy.
Worth noting
Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp. However, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to false-negative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5
Health disparity highlight
A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.

Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) caused by M canis. M canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations:
- broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp
- diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis
- well-demarcated annular plaques
- exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation
- scalp pruritus
- occipital scalp lymphadenopathy.
Worth noting
Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp. However, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to false-negative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5
Health disparity highlight
A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
1. Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15088
2. Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-2522
3. Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
4. Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
5. Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi: 10.1111/pde.14092
6. Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
1. Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15088
2. Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-2522
3. Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
4. Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
5. Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi: 10.1111/pde.14092
6. Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
Tinea Capitis
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.
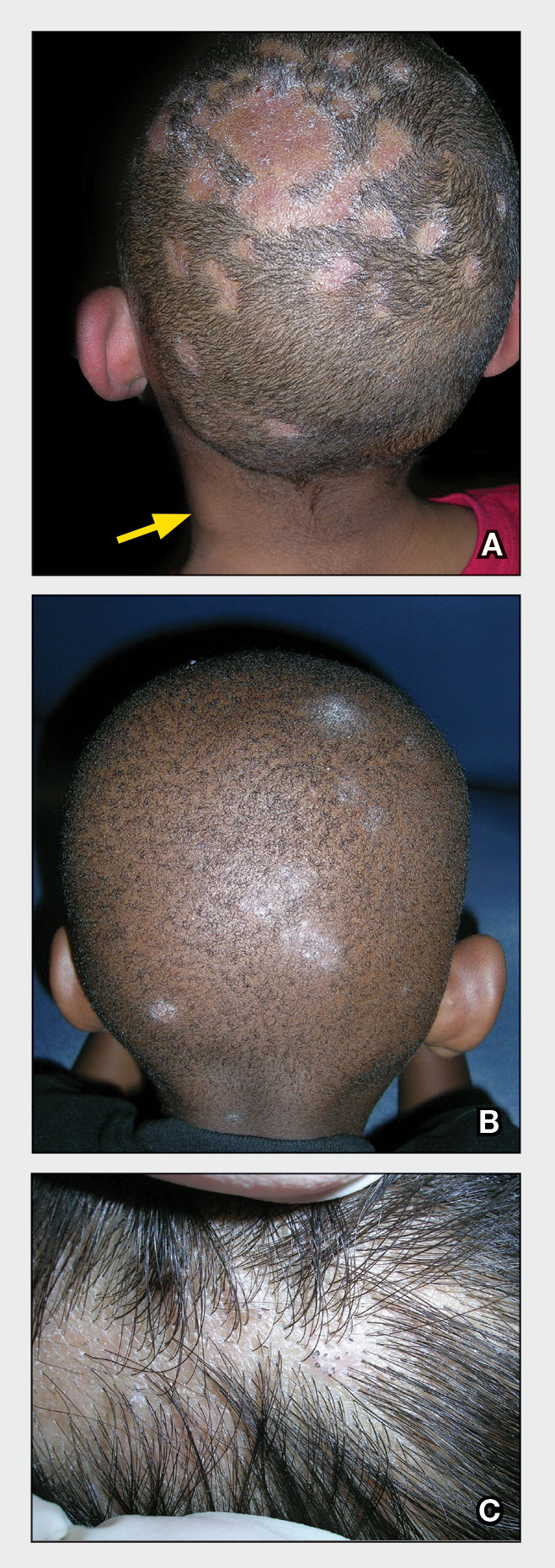
Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) such as M canis. Microsporum canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations: • broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp • diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis • well-demarcated annular plaques • exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation • scalp pruritus • occipital scalp lymphadenopathy. Worth noting Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp; however, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to falsenegative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5 Health disparity highlight A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management [published online July 12, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi:10.1111/jdv.15088
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study [published online April 19, 2010]. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2522
- Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
- Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
- Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015 [published online January 20, 2020]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi:10.1111 /pde.14092
- Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria [published online April 16, 2008]. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.

Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) such as M canis. Microsporum canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations: • broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp • diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis • well-demarcated annular plaques • exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation • scalp pruritus • occipital scalp lymphadenopathy. Worth noting Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp; however, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to falsenegative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5 Health disparity highlight A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.

Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) such as M canis. Microsporum canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations: • broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp • diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis • well-demarcated annular plaques • exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation • scalp pruritus • occipital scalp lymphadenopathy. Worth noting Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp; however, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to falsenegative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5 Health disparity highlight A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management [published online July 12, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi:10.1111/jdv.15088
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study [published online April 19, 2010]. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2522
- Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
- Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
- Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015 [published online January 20, 2020]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi:10.1111 /pde.14092
- Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria [published online April 16, 2008]. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management [published online July 12, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi:10.1111/jdv.15088
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study [published online April 19, 2010]. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2522
- Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
- Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
- Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015 [published online January 20, 2020]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi:10.1111 /pde.14092
- Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria [published online April 16, 2008]. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
The CROWNing Event on Hair Loss in Women of Color: A Framework for Advocacy and Community Engagement (FACE) Survey Analysis
Hair loss is a primary reason why women with skin of color seek dermatologic care.1-3 In addition to physical disfigurement, patients with hair loss are more likely to report feelings of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem compared to the general population.4 There is a critical gap in advocacy efforts and educational information intended for women with skin of color. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) has 6 main public health programs (https://www.aad.org/public/public-health) and 8 stated advocacy priorities (https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities) but none of them focus on outreach to minority communities.
Historically, hair in patients with skin of color also has been a systemic tangible target for race-based discrimination. The Create a Respectful and Open World for Natural Hair (CROWN) Act was passed to protect against discrimination based on race-based hairstyles in schools and workplaces.5 Health care providers play an important role in advocating for their patients, but studies have shown that barriers to effective advocacy include a lack of knowledge, resources, or time.6-8 Virtual advocacy events improve participants’ understanding and interest in community engagement and advocacy.6,7 With the mission to engage, educate, and empower women with skin of color and the dermatologists who treat them, the Virginia Dermatology Society hosted the virtual CROWNing Event on Hair Loss in Women of Color in July 2021. We believe that this event, as well as this column, can serve as a template to improve advocacy and educational efforts for additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized or underserved populations. Survey data were collected and analyzed to establish a baseline of awareness and understanding of hair loss in women with skin of color and to evaluate the impact of a virtual event on participants’ empowerment and familiarity with resources for this population.
Methods
The Virginia Dermatology Society organized a virtual event focused on hair loss and practical political advocacy for women with skin of color. As members of the Virginia Dermatology Society and as part of the planning and execution of this event, the authors engaged relevant stakeholder organizations and collaborated with faculty at a local historically Black university to create a targeted, culturally sensitive communication strategy known as the Framework for Advocacy and Community Engagement (FACE) model (Figure). The agenda included presentations by 2 patients of color living with a hair loss disorder, a dermatologist with experience in advocacy, a Virginia state legislator, and a dermatologic hair loss expert, followed by a final question-and-answer session.
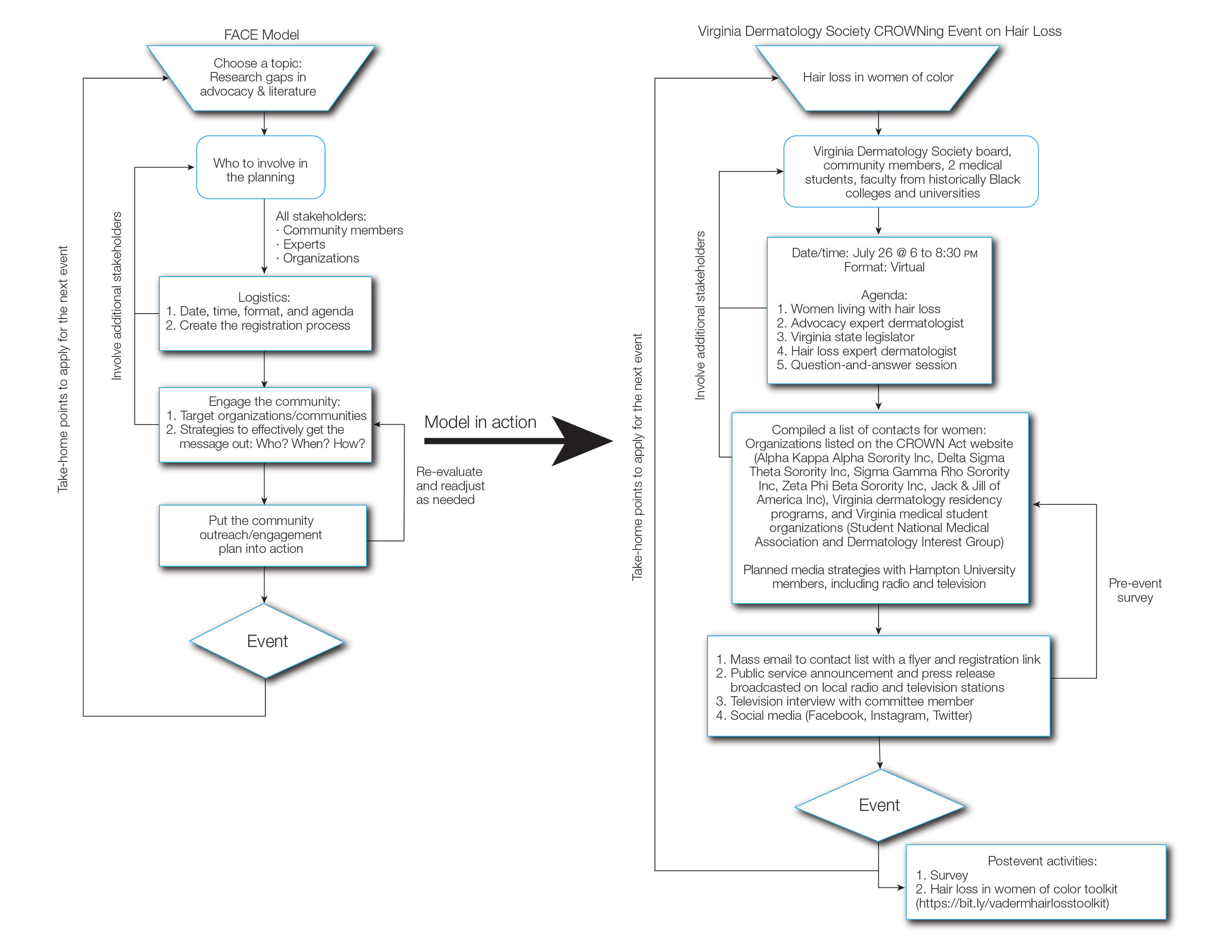
We created pre- and postevent Likert scale surveys assessing participant attitudes, knowledge, and awareness surrounding hair loss that were distributed electronically to all 399 registrants before and after the event, respectively. The responses were analyzed using a Mann-Whitney U test.
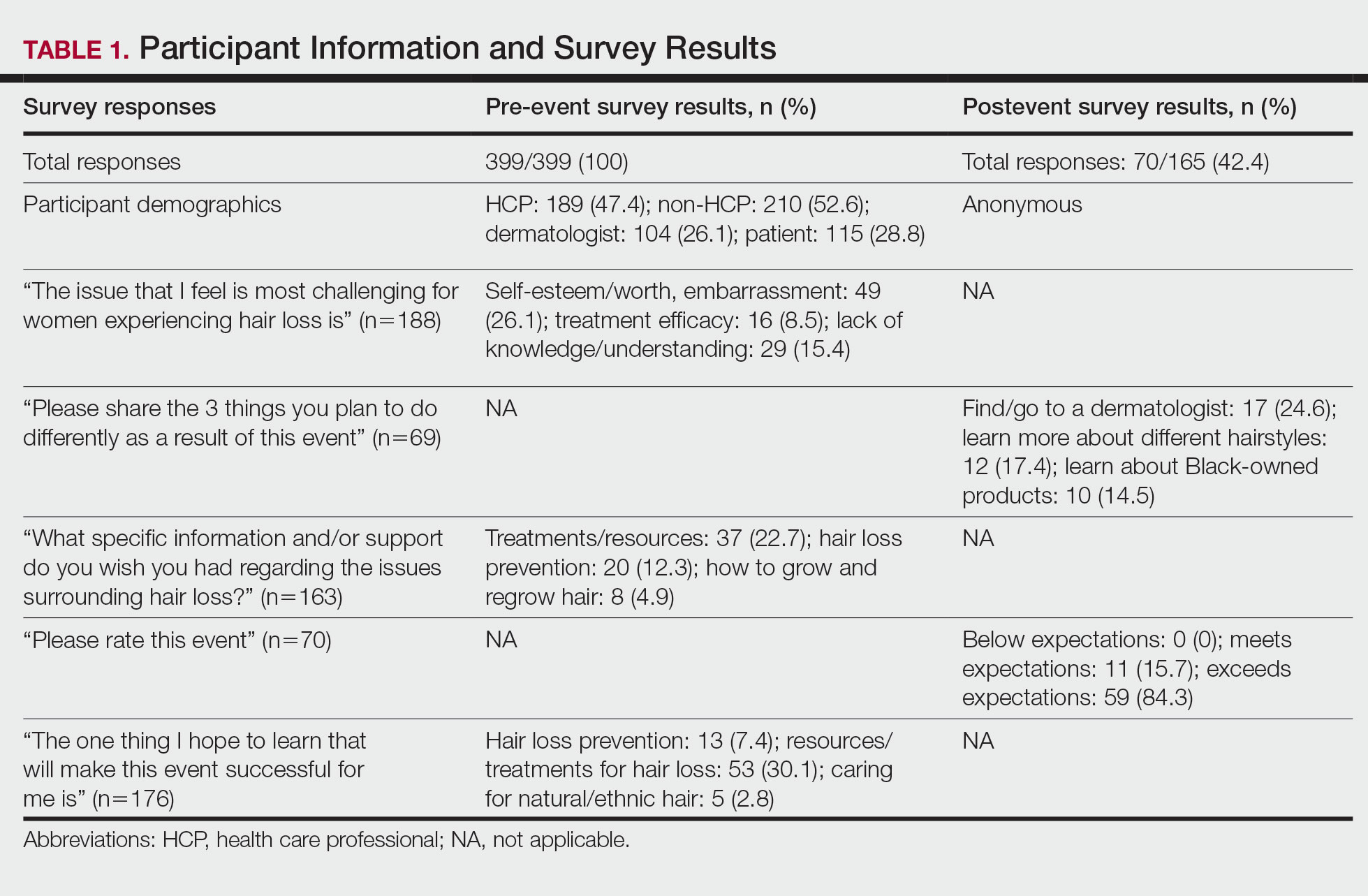
Based on preliminary pre-event survey data, we created a resource toolkit (https://bit.ly/vadermhairlosstoolkit) for distribution to both patients and physicians. The toolkit included articles about evaluating, diagnosing, and treating different types of hair loss that would be beneficial for dermatologists, as well as informational articles, online resources, and videos that would be helpful to patients.
Of the 399 registrants, 165 (41.4%) attended the live virtual event. The postevent survey was completed by 70 (42.4%) participants and showed that familiarity with resources and treatments (z=−3.34, P=.0008) and feelings of empowerment (z=−3.55, P=.0004) significantly increased from before the event (Table 2). Participants indicated that the event exceeded (84.3%) or met (15.7%) their expectations.
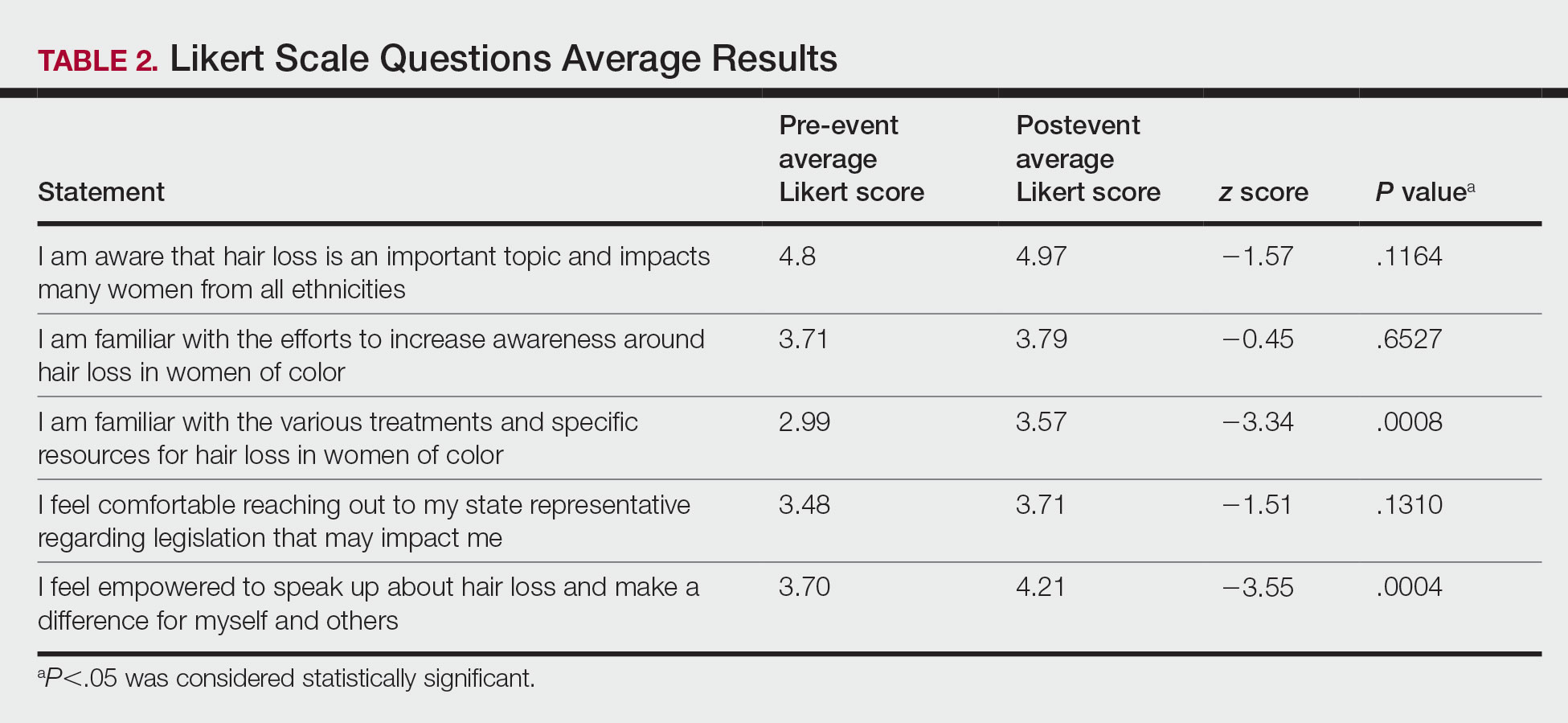
Comment
Hair Loss Is Prevalent in Skin of Color Patients—Alopecia is the fourth most common reason women with skin of color seek care from a dermatologist, accounting for 8.3% of all visits in a study of 1412 patient visits; however, it was not among the leading 10 diagnoses made during visits for White patients.3 Traction alopecia, discoid lupus erythematosus, and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia occur more commonly in Black women,9 many of whom do not feel their dermatologists understand hair in this population.10,11 Lack of skin of color education in medical school and dermatology residency programs has been reported and must be improved to eliminate the knowledge gaps, acquire cultural competence, and improve all aspects of care for patients with skin of color.11-14 Our survey results similarly demonstrated that only 66% of board-certified dermatologists reported being familiar with the various and specific resources and treatments for hair loss in women of color. Improved understanding of hair in patients of color is a first step in diagnosing and treating hair loss.15 Expertise of dermatologists in skin of color improves the dermatology experience of patients of color.11
Hair loss is more than a cosmetic issue, and it is essential that it is regarded as such. Patients with hair loss have an increased prevalence of depression and anxiety compared to the general population and report lower self-esteem, heightened self-consciousness, and loss of confidence.4,9 Historically, the lives of patients of color have been drastically affected by society’s perceptions of their skin color and hairstyle.16
Hair-Based Discrimination in the Workplace—To compound the problem, hair also is a common target of race-based discrimination behind the illusion of “professionalism.” Hair-based discrimination keeps people of color out of professional workplaces; for instance, women of color are more likely to be sent home due to hair appearance than White women.5 The CROWN Act, created in 2019, extends statutory protection to hair texture and protective hairstyles such as braids, locs, twists, and knots in the workplace and public schools to protect against discrimination due to race-based hairstyles. The CROWN Act provides an opportunity for dermatologists to support legislation that protects patients of color and the fundamental human right to nondiscrimination. As societal pressure for damaging hair practices such as hot combing or chemical relaxants decreases, patient outcomes will improve.5
How to Support the CROWN Act—There are various meaningful ways for dermatologists to support the CROWN act, including but not limited to signing petitions, sending letters of support to elected representatives, joining the CROWN Coalition, raising awareness and educating the public through social media, vocalizing against hair discrimination in our own workplaces and communities, and asking patients about their experiences with hair discrimination.5 In addition to advocacy, other antiracist actions suggested to improve health equity include creating curricula on racial inequity and increasing diversity in dermatology.16
There are many advocacy and public health campaigns promoted on the AAD website; however, despite the AAD’s formation of the Access to Dermatologic Care Task Force (ATDCTF) with the goal to raise awareness among dermatologists of health disparities affecting marginalized and underserved populations and to develop policies that increase access to care for these groups, there are still critical gaps in advocacy and information.13 This gap in both advocacy and understanding of hair loss conditions in women of color is one reason the CROWNing Event in July 2021 was held, and we believe this event along with this column can serve as a template for addressing additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized or underserved populations.
Dermatologists can play a vital role in advocating for skin and hair needs in all patient populations from the personal or clinical encounter level to population-level policy legislation.5,8 As experts in skin and hair, dermatologists are best prepared to assume leadership in addressing racial health inequities, educating the public, and improving awareness.5,16 Dermatologists must be able to diagnose and manage skin conditions in people of color.12 However, health advocacy should extend beyond changes to health behavior or health interventions and instead address the root causes of systemic issues that drive disparate health outcomes.6 Every dermatologist has a contribution to make; it is time for us to acknowledge that patients’ ailments neither begin nor end at the clinic door.8,16 As dermatologists, we must speak out against the racial inequities and discriminatory policies affecting the lives of patients of color.16
Although the CROWNing event should be considered successful, reflection in hindsight has allowed us to find ways to improve the impact of future events, including incorporating more lay members of the respective community in the planning process, allocating more time during the event programming for questions, and streamlining the distribution of pre-event and postevent surveys to better gauge knowledge retention among participants and gain crucial feedback for future event planning.
How to Use the FACE Model—We believe that the FACE model (Figure) can help providers engage lay members of the community with additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized and underserved populations. We recommend that future organizers engage stakeholders early during the design, planning, and implementation phases to ensure that the community’s most pressing needs are addressed. Dermatologists possess the knowledge and influence to serve as powerful advocates and champions for health equity. As physicians on the front lines of dermatologic health, we are uniquely positioned to engage and partner with patients through educational and advocacy events such as ours. Similarly, informed and empowered patients can advocate for policies and be proponents for greater research funding.5 We call on the AAD and other dermatologic organizations to expand community outreach and advocacy efforts to include underserved and underrepresented populations.
Acknowledgments—The authors would like to thank and acknowledge the faculty at Hampton University (Hampton, Virginia)—specifically Ms. B. DáVida Plummer, MA—for assistance with communication strategies, including organizing the radio and television announcements and proofreading the public service announcements. We also would like to thank other CROWNing Event Planning Committee members, including Natalia Mendoza, MD (Newport News, Virginia); Farhaad Riyaz, MD (Gainesville, Virginia); Deborah Elder, MD (Charlottesville, Virginia); and David Rowe, MD (Charlottesville, Virginia), as well as Sandra Ring, MS, CCLS, CNP (Chicago, Illinois), from the AAD and the various speakers at the event, including the 2 patients; Victoria Barbosa, MD, MPH, MBA (Chicago, Illinois); Avery LaChance, MD, MPH (Boston, Massachusetts); and Senator Lionell Spruill Sr (Chesapeake, Virginia). We acknowledge Marieke K. Jones, PhD, at the Claude Moore Health Sciences Library at the University of Virginia (Charlottesville, Virginia), for her statistical expertise.
- Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3(suppl 1):S21-S37. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.02.006
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Jamerson TA, Aguh C. An approach to patients with alopecia. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:599-610. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2021.04.002
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Tran A, Gohara M. Community engagement matters: a call for greater advocacy in dermatology. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:189-190. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.01.008
- Yu Z, Moustafa D, Kwak R, et al. Engaging in advocacy during medical training: assessing the impact of a virtual COVID-19-focused state advocacy day [published online January 13, 2021]. Postgrad Med J. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139362
- Earnest MA, Wong SL, Federico SG. Perspective: physician advocacy: what is it and how do we do it? Acad Med J Assoc Am Med Coll. 2010;85:63-67. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181c40d40
- Raffi J, Suresh R, Agbai O. Clinical recognition and management of alopecia in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;5:314-319. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2019.08.005
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care, and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Gorbatenko-Roth K, Prose N, Kundu RV, et al. Assessment of Black patients’ perception of their dermatology care. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1129-1134. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2063
- Ebede T, Papier A. Disparities in dermatology educational resources. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:687-690. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.068
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Taylor SC. Meeting the unique dermatologic needs of black patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1109-1110. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1963
- Dlova NC, Salkey KS, Callender VD, et al. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: new insights and a call for action. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S54-S56. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.01.004
- Smith RJ, Oliver BU. Advocating for Black lives—a call to dermatologists to dismantle institutionalized racism and address racial health inequities. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:155-156. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.4392
Hair loss is a primary reason why women with skin of color seek dermatologic care.1-3 In addition to physical disfigurement, patients with hair loss are more likely to report feelings of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem compared to the general population.4 There is a critical gap in advocacy efforts and educational information intended for women with skin of color. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) has 6 main public health programs (https://www.aad.org/public/public-health) and 8 stated advocacy priorities (https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities) but none of them focus on outreach to minority communities.
Historically, hair in patients with skin of color also has been a systemic tangible target for race-based discrimination. The Create a Respectful and Open World for Natural Hair (CROWN) Act was passed to protect against discrimination based on race-based hairstyles in schools and workplaces.5 Health care providers play an important role in advocating for their patients, but studies have shown that barriers to effective advocacy include a lack of knowledge, resources, or time.6-8 Virtual advocacy events improve participants’ understanding and interest in community engagement and advocacy.6,7 With the mission to engage, educate, and empower women with skin of color and the dermatologists who treat them, the Virginia Dermatology Society hosted the virtual CROWNing Event on Hair Loss in Women of Color in July 2021. We believe that this event, as well as this column, can serve as a template to improve advocacy and educational efforts for additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized or underserved populations. Survey data were collected and analyzed to establish a baseline of awareness and understanding of hair loss in women with skin of color and to evaluate the impact of a virtual event on participants’ empowerment and familiarity with resources for this population.
Methods
The Virginia Dermatology Society organized a virtual event focused on hair loss and practical political advocacy for women with skin of color. As members of the Virginia Dermatology Society and as part of the planning and execution of this event, the authors engaged relevant stakeholder organizations and collaborated with faculty at a local historically Black university to create a targeted, culturally sensitive communication strategy known as the Framework for Advocacy and Community Engagement (FACE) model (Figure). The agenda included presentations by 2 patients of color living with a hair loss disorder, a dermatologist with experience in advocacy, a Virginia state legislator, and a dermatologic hair loss expert, followed by a final question-and-answer session.

We created pre- and postevent Likert scale surveys assessing participant attitudes, knowledge, and awareness surrounding hair loss that were distributed electronically to all 399 registrants before and after the event, respectively. The responses were analyzed using a Mann-Whitney U test.

Based on preliminary pre-event survey data, we created a resource toolkit (https://bit.ly/vadermhairlosstoolkit) for distribution to both patients and physicians. The toolkit included articles about evaluating, diagnosing, and treating different types of hair loss that would be beneficial for dermatologists, as well as informational articles, online resources, and videos that would be helpful to patients.
Of the 399 registrants, 165 (41.4%) attended the live virtual event. The postevent survey was completed by 70 (42.4%) participants and showed that familiarity with resources and treatments (z=−3.34, P=.0008) and feelings of empowerment (z=−3.55, P=.0004) significantly increased from before the event (Table 2). Participants indicated that the event exceeded (84.3%) or met (15.7%) their expectations.

Comment
Hair Loss Is Prevalent in Skin of Color Patients—Alopecia is the fourth most common reason women with skin of color seek care from a dermatologist, accounting for 8.3% of all visits in a study of 1412 patient visits; however, it was not among the leading 10 diagnoses made during visits for White patients.3 Traction alopecia, discoid lupus erythematosus, and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia occur more commonly in Black women,9 many of whom do not feel their dermatologists understand hair in this population.10,11 Lack of skin of color education in medical school and dermatology residency programs has been reported and must be improved to eliminate the knowledge gaps, acquire cultural competence, and improve all aspects of care for patients with skin of color.11-14 Our survey results similarly demonstrated that only 66% of board-certified dermatologists reported being familiar with the various and specific resources and treatments for hair loss in women of color. Improved understanding of hair in patients of color is a first step in diagnosing and treating hair loss.15 Expertise of dermatologists in skin of color improves the dermatology experience of patients of color.11
Hair loss is more than a cosmetic issue, and it is essential that it is regarded as such. Patients with hair loss have an increased prevalence of depression and anxiety compared to the general population and report lower self-esteem, heightened self-consciousness, and loss of confidence.4,9 Historically, the lives of patients of color have been drastically affected by society’s perceptions of their skin color and hairstyle.16
Hair-Based Discrimination in the Workplace—To compound the problem, hair also is a common target of race-based discrimination behind the illusion of “professionalism.” Hair-based discrimination keeps people of color out of professional workplaces; for instance, women of color are more likely to be sent home due to hair appearance than White women.5 The CROWN Act, created in 2019, extends statutory protection to hair texture and protective hairstyles such as braids, locs, twists, and knots in the workplace and public schools to protect against discrimination due to race-based hairstyles. The CROWN Act provides an opportunity for dermatologists to support legislation that protects patients of color and the fundamental human right to nondiscrimination. As societal pressure for damaging hair practices such as hot combing or chemical relaxants decreases, patient outcomes will improve.5
How to Support the CROWN Act—There are various meaningful ways for dermatologists to support the CROWN act, including but not limited to signing petitions, sending letters of support to elected representatives, joining the CROWN Coalition, raising awareness and educating the public through social media, vocalizing against hair discrimination in our own workplaces and communities, and asking patients about their experiences with hair discrimination.5 In addition to advocacy, other antiracist actions suggested to improve health equity include creating curricula on racial inequity and increasing diversity in dermatology.16
There are many advocacy and public health campaigns promoted on the AAD website; however, despite the AAD’s formation of the Access to Dermatologic Care Task Force (ATDCTF) with the goal to raise awareness among dermatologists of health disparities affecting marginalized and underserved populations and to develop policies that increase access to care for these groups, there are still critical gaps in advocacy and information.13 This gap in both advocacy and understanding of hair loss conditions in women of color is one reason the CROWNing Event in July 2021 was held, and we believe this event along with this column can serve as a template for addressing additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized or underserved populations.
Dermatologists can play a vital role in advocating for skin and hair needs in all patient populations from the personal or clinical encounter level to population-level policy legislation.5,8 As experts in skin and hair, dermatologists are best prepared to assume leadership in addressing racial health inequities, educating the public, and improving awareness.5,16 Dermatologists must be able to diagnose and manage skin conditions in people of color.12 However, health advocacy should extend beyond changes to health behavior or health interventions and instead address the root causes of systemic issues that drive disparate health outcomes.6 Every dermatologist has a contribution to make; it is time for us to acknowledge that patients’ ailments neither begin nor end at the clinic door.8,16 As dermatologists, we must speak out against the racial inequities and discriminatory policies affecting the lives of patients of color.16
Although the CROWNing event should be considered successful, reflection in hindsight has allowed us to find ways to improve the impact of future events, including incorporating more lay members of the respective community in the planning process, allocating more time during the event programming for questions, and streamlining the distribution of pre-event and postevent surveys to better gauge knowledge retention among participants and gain crucial feedback for future event planning.
How to Use the FACE Model—We believe that the FACE model (Figure) can help providers engage lay members of the community with additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized and underserved populations. We recommend that future organizers engage stakeholders early during the design, planning, and implementation phases to ensure that the community’s most pressing needs are addressed. Dermatologists possess the knowledge and influence to serve as powerful advocates and champions for health equity. As physicians on the front lines of dermatologic health, we are uniquely positioned to engage and partner with patients through educational and advocacy events such as ours. Similarly, informed and empowered patients can advocate for policies and be proponents for greater research funding.5 We call on the AAD and other dermatologic organizations to expand community outreach and advocacy efforts to include underserved and underrepresented populations.
Acknowledgments—The authors would like to thank and acknowledge the faculty at Hampton University (Hampton, Virginia)—specifically Ms. B. DáVida Plummer, MA—for assistance with communication strategies, including organizing the radio and television announcements and proofreading the public service announcements. We also would like to thank other CROWNing Event Planning Committee members, including Natalia Mendoza, MD (Newport News, Virginia); Farhaad Riyaz, MD (Gainesville, Virginia); Deborah Elder, MD (Charlottesville, Virginia); and David Rowe, MD (Charlottesville, Virginia), as well as Sandra Ring, MS, CCLS, CNP (Chicago, Illinois), from the AAD and the various speakers at the event, including the 2 patients; Victoria Barbosa, MD, MPH, MBA (Chicago, Illinois); Avery LaChance, MD, MPH (Boston, Massachusetts); and Senator Lionell Spruill Sr (Chesapeake, Virginia). We acknowledge Marieke K. Jones, PhD, at the Claude Moore Health Sciences Library at the University of Virginia (Charlottesville, Virginia), for her statistical expertise.
Hair loss is a primary reason why women with skin of color seek dermatologic care.1-3 In addition to physical disfigurement, patients with hair loss are more likely to report feelings of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem compared to the general population.4 There is a critical gap in advocacy efforts and educational information intended for women with skin of color. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) has 6 main public health programs (https://www.aad.org/public/public-health) and 8 stated advocacy priorities (https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities) but none of them focus on outreach to minority communities.
Historically, hair in patients with skin of color also has been a systemic tangible target for race-based discrimination. The Create a Respectful and Open World for Natural Hair (CROWN) Act was passed to protect against discrimination based on race-based hairstyles in schools and workplaces.5 Health care providers play an important role in advocating for their patients, but studies have shown that barriers to effective advocacy include a lack of knowledge, resources, or time.6-8 Virtual advocacy events improve participants’ understanding and interest in community engagement and advocacy.6,7 With the mission to engage, educate, and empower women with skin of color and the dermatologists who treat them, the Virginia Dermatology Society hosted the virtual CROWNing Event on Hair Loss in Women of Color in July 2021. We believe that this event, as well as this column, can serve as a template to improve advocacy and educational efforts for additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized or underserved populations. Survey data were collected and analyzed to establish a baseline of awareness and understanding of hair loss in women with skin of color and to evaluate the impact of a virtual event on participants’ empowerment and familiarity with resources for this population.
Methods
The Virginia Dermatology Society organized a virtual event focused on hair loss and practical political advocacy for women with skin of color. As members of the Virginia Dermatology Society and as part of the planning and execution of this event, the authors engaged relevant stakeholder organizations and collaborated with faculty at a local historically Black university to create a targeted, culturally sensitive communication strategy known as the Framework for Advocacy and Community Engagement (FACE) model (Figure). The agenda included presentations by 2 patients of color living with a hair loss disorder, a dermatologist with experience in advocacy, a Virginia state legislator, and a dermatologic hair loss expert, followed by a final question-and-answer session.

We created pre- and postevent Likert scale surveys assessing participant attitudes, knowledge, and awareness surrounding hair loss that were distributed electronically to all 399 registrants before and after the event, respectively. The responses were analyzed using a Mann-Whitney U test.

Based on preliminary pre-event survey data, we created a resource toolkit (https://bit.ly/vadermhairlosstoolkit) for distribution to both patients and physicians. The toolkit included articles about evaluating, diagnosing, and treating different types of hair loss that would be beneficial for dermatologists, as well as informational articles, online resources, and videos that would be helpful to patients.
Of the 399 registrants, 165 (41.4%) attended the live virtual event. The postevent survey was completed by 70 (42.4%) participants and showed that familiarity with resources and treatments (z=−3.34, P=.0008) and feelings of empowerment (z=−3.55, P=.0004) significantly increased from before the event (Table 2). Participants indicated that the event exceeded (84.3%) or met (15.7%) their expectations.

Comment
Hair Loss Is Prevalent in Skin of Color Patients—Alopecia is the fourth most common reason women with skin of color seek care from a dermatologist, accounting for 8.3% of all visits in a study of 1412 patient visits; however, it was not among the leading 10 diagnoses made during visits for White patients.3 Traction alopecia, discoid lupus erythematosus, and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia occur more commonly in Black women,9 many of whom do not feel their dermatologists understand hair in this population.10,11 Lack of skin of color education in medical school and dermatology residency programs has been reported and must be improved to eliminate the knowledge gaps, acquire cultural competence, and improve all aspects of care for patients with skin of color.11-14 Our survey results similarly demonstrated that only 66% of board-certified dermatologists reported being familiar with the various and specific resources and treatments for hair loss in women of color. Improved understanding of hair in patients of color is a first step in diagnosing and treating hair loss.15 Expertise of dermatologists in skin of color improves the dermatology experience of patients of color.11
Hair loss is more than a cosmetic issue, and it is essential that it is regarded as such. Patients with hair loss have an increased prevalence of depression and anxiety compared to the general population and report lower self-esteem, heightened self-consciousness, and loss of confidence.4,9 Historically, the lives of patients of color have been drastically affected by society’s perceptions of their skin color and hairstyle.16
Hair-Based Discrimination in the Workplace—To compound the problem, hair also is a common target of race-based discrimination behind the illusion of “professionalism.” Hair-based discrimination keeps people of color out of professional workplaces; for instance, women of color are more likely to be sent home due to hair appearance than White women.5 The CROWN Act, created in 2019, extends statutory protection to hair texture and protective hairstyles such as braids, locs, twists, and knots in the workplace and public schools to protect against discrimination due to race-based hairstyles. The CROWN Act provides an opportunity for dermatologists to support legislation that protects patients of color and the fundamental human right to nondiscrimination. As societal pressure for damaging hair practices such as hot combing or chemical relaxants decreases, patient outcomes will improve.5
How to Support the CROWN Act—There are various meaningful ways for dermatologists to support the CROWN act, including but not limited to signing petitions, sending letters of support to elected representatives, joining the CROWN Coalition, raising awareness and educating the public through social media, vocalizing against hair discrimination in our own workplaces and communities, and asking patients about their experiences with hair discrimination.5 In addition to advocacy, other antiracist actions suggested to improve health equity include creating curricula on racial inequity and increasing diversity in dermatology.16
There are many advocacy and public health campaigns promoted on the AAD website; however, despite the AAD’s formation of the Access to Dermatologic Care Task Force (ATDCTF) with the goal to raise awareness among dermatologists of health disparities affecting marginalized and underserved populations and to develop policies that increase access to care for these groups, there are still critical gaps in advocacy and information.13 This gap in both advocacy and understanding of hair loss conditions in women of color is one reason the CROWNing Event in July 2021 was held, and we believe this event along with this column can serve as a template for addressing additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized or underserved populations.
Dermatologists can play a vital role in advocating for skin and hair needs in all patient populations from the personal or clinical encounter level to population-level policy legislation.5,8 As experts in skin and hair, dermatologists are best prepared to assume leadership in addressing racial health inequities, educating the public, and improving awareness.5,16 Dermatologists must be able to diagnose and manage skin conditions in people of color.12 However, health advocacy should extend beyond changes to health behavior or health interventions and instead address the root causes of systemic issues that drive disparate health outcomes.6 Every dermatologist has a contribution to make; it is time for us to acknowledge that patients’ ailments neither begin nor end at the clinic door.8,16 As dermatologists, we must speak out against the racial inequities and discriminatory policies affecting the lives of patients of color.16
Although the CROWNing event should be considered successful, reflection in hindsight has allowed us to find ways to improve the impact of future events, including incorporating more lay members of the respective community in the planning process, allocating more time during the event programming for questions, and streamlining the distribution of pre-event and postevent surveys to better gauge knowledge retention among participants and gain crucial feedback for future event planning.
How to Use the FACE Model—We believe that the FACE model (Figure) can help providers engage lay members of the community with additional topics and diseases that affect marginalized and underserved populations. We recommend that future organizers engage stakeholders early during the design, planning, and implementation phases to ensure that the community’s most pressing needs are addressed. Dermatologists possess the knowledge and influence to serve as powerful advocates and champions for health equity. As physicians on the front lines of dermatologic health, we are uniquely positioned to engage and partner with patients through educational and advocacy events such as ours. Similarly, informed and empowered patients can advocate for policies and be proponents for greater research funding.5 We call on the AAD and other dermatologic organizations to expand community outreach and advocacy efforts to include underserved and underrepresented populations.
Acknowledgments—The authors would like to thank and acknowledge the faculty at Hampton University (Hampton, Virginia)—specifically Ms. B. DáVida Plummer, MA—for assistance with communication strategies, including organizing the radio and television announcements and proofreading the public service announcements. We also would like to thank other CROWNing Event Planning Committee members, including Natalia Mendoza, MD (Newport News, Virginia); Farhaad Riyaz, MD (Gainesville, Virginia); Deborah Elder, MD (Charlottesville, Virginia); and David Rowe, MD (Charlottesville, Virginia), as well as Sandra Ring, MS, CCLS, CNP (Chicago, Illinois), from the AAD and the various speakers at the event, including the 2 patients; Victoria Barbosa, MD, MPH, MBA (Chicago, Illinois); Avery LaChance, MD, MPH (Boston, Massachusetts); and Senator Lionell Spruill Sr (Chesapeake, Virginia). We acknowledge Marieke K. Jones, PhD, at the Claude Moore Health Sciences Library at the University of Virginia (Charlottesville, Virginia), for her statistical expertise.
- Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3(suppl 1):S21-S37. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.02.006
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Jamerson TA, Aguh C. An approach to patients with alopecia. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:599-610. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2021.04.002
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Tran A, Gohara M. Community engagement matters: a call for greater advocacy in dermatology. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:189-190. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.01.008
- Yu Z, Moustafa D, Kwak R, et al. Engaging in advocacy during medical training: assessing the impact of a virtual COVID-19-focused state advocacy day [published online January 13, 2021]. Postgrad Med J. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139362
- Earnest MA, Wong SL, Federico SG. Perspective: physician advocacy: what is it and how do we do it? Acad Med J Assoc Am Med Coll. 2010;85:63-67. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181c40d40
- Raffi J, Suresh R, Agbai O. Clinical recognition and management of alopecia in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;5:314-319. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2019.08.005
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care, and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Gorbatenko-Roth K, Prose N, Kundu RV, et al. Assessment of Black patients’ perception of their dermatology care. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1129-1134. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2063
- Ebede T, Papier A. Disparities in dermatology educational resources. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:687-690. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.068
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Taylor SC. Meeting the unique dermatologic needs of black patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1109-1110. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1963
- Dlova NC, Salkey KS, Callender VD, et al. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: new insights and a call for action. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S54-S56. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.01.004
- Smith RJ, Oliver BU. Advocating for Black lives—a call to dermatologists to dismantle institutionalized racism and address racial health inequities. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:155-156. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.4392
- Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3(suppl 1):S21-S37. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.02.006
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Jamerson TA, Aguh C. An approach to patients with alopecia. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:599-610. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2021.04.002
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Tran A, Gohara M. Community engagement matters: a call for greater advocacy in dermatology. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:189-190. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.01.008
- Yu Z, Moustafa D, Kwak R, et al. Engaging in advocacy during medical training: assessing the impact of a virtual COVID-19-focused state advocacy day [published online January 13, 2021]. Postgrad Med J. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139362
- Earnest MA, Wong SL, Federico SG. Perspective: physician advocacy: what is it and how do we do it? Acad Med J Assoc Am Med Coll. 2010;85:63-67. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181c40d40
- Raffi J, Suresh R, Agbai O. Clinical recognition and management of alopecia in women of color. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;5:314-319. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2019.08.005
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care, and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Gorbatenko-Roth K, Prose N, Kundu RV, et al. Assessment of Black patients’ perception of their dermatology care. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1129-1134. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2063
- Ebede T, Papier A. Disparities in dermatology educational resources. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:687-690. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.068
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Taylor SC. Meeting the unique dermatologic needs of black patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1109-1110. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1963
- Dlova NC, Salkey KS, Callender VD, et al. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: new insights and a call for action. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S54-S56. doi:10.1016/j.jisp.2017.01.004
- Smith RJ, Oliver BU. Advocating for Black lives—a call to dermatologists to dismantle institutionalized racism and address racial health inequities. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:155-156. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.4392
Practice Points
- Hair loss is associated with low self-esteem in women with skin of color; therefore, it is important to both acknowledge the social and psychological impacts of hair loss in this population and provide educational resources and community events that address patient concerns.
- There is a deficit of dermatology advocacy efforts that address conditions affecting patients with skin of color. Highlighting this disparity is the first step to catalyzing change.
- Dermatologists are responsible for advocating for women with skin of color and for addressing the social issues that impact their quality of life.
- The Framework for Advocacy and Community Efforts (FACE) model is a template for others to use when planning community engagement and advocacy efforts.
Learning Experiences in LGBT Health During Dermatology Residency
Approximately 4.5% of adults within the United States identify as members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) community.1 This is an umbrella term inclusive of all individuals identifying as nonheterosexual or noncisgender. Although the LGBT community has increasingly become more recognized and accepted by society over time, health care disparities persist and have been well documented in the literature.2-4 Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact LGBT health, as many health concerns in this population are cutaneous, such as sun-protection behaviors, side effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming procedures, and cutaneous manifestations of sexually transmitted infections.5-7
An education gap has been demonstrated in both medical students and resident physicians regarding LGBT health and cultural competency. In a large-scale, multi-institutional survey study published in 2015, approximately two-thirds of medical students rated their schools’ LGBT curriculum as fair, poor, or very poor.8 Additional studies have echoed these results and have demonstrated not only the need but the desire for additional training on LGBT issues in medical school.9-11 The Association of American Medical Colleges has begun implementing curricular and institutional changes to fulfill this need.12,13
The LGBT education gap has been shown to extend into residency training. Multiple studies performed within a variety of medical specialties have demonstrated that resident physicians receive insufficient training in LGBT health issues, lack comfort in caring for LGBT patients, and would benefit from dedicated curricula on these topics.14-18 Currently, the 2022 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines related to LGBT health are minimal and nonspecific.19
Ensuring that dermatology trainees are well equipped to manage these issues while providing culturally competent care to LGBT patients is paramount. However, research suggests that dedicated training on these topics likely is insufficient. A survey study of dermatology residency program directors (N=90) revealed that although 81% (72/89) viewed training in LGBT health as either very important or somewhat important, 46% (41/90) of programs did not dedicate any time to this content and 37% (33/90) only dedicated 1 to 2 hours per year.20
To further explore this potential education gap, we surveyed dermatology residents directly to better understand LGBT education within residency training, resident preparedness to care for LGBT patients, and outness/discrimination of LGBT-identifying residents. We believe this study should drive future research on the development and implementation of LGBT-specific curricula in dermatology training programs.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey study of dermatology residents in the United States was conducted. The study was deemed exempt from review by The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) institutional review board. Survey responses were collected from October 7, 2020, to November 13, 2020. Qualtrics software was used to create the 20-question survey, which included a combination of categorical, dichotomous, and optional free-text questions related to patient demographics, LGBT training experiences, perceived areas of curriculum improvement, comfort level managing LGBT health issues, and personal experiences. Some questions were adapted from prior surveys.15,21 Validated survey tools used included the 2020 US Census to collect information regarding race and ethnicity, the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory to measure outness regarding sexual orientation, and select questions from the 2020 Association of American Medical Colleges Medical School Graduation Questionnaire regarding discrimination.22-24
The survey was distributed to current allopathic and osteopathic dermatology residents by a variety of methods, including emails to program director and program coordinator listserves. The survey also was posted in the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group on LGBTQ Health October 2020 newsletter, as well as dermatology social media groups, including a messaging forum limited to dermatology residents, a Facebook group open to dermatologists and dermatology residents, and the Facebook group of the Gay and Lesbian Dermatology Association. Current dermatology residents, including those in combined dermatology and internal medicine programs, were included. Individuals who had been accepted to dermatology training programs but had not yet started were excluded. A follow-up email was sent to the program director listserve approximately 3 weeks after the initial distribution.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed in Qualtrics and Microsoft Excel using descriptive statistics. Stata software (Stata 15.1, StataCorp) was used to perform a Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test to compare the means of education level and feelings of preparedness.
Results
Demographics of Respondents—A total of 126 responses were recorded, 12 of which were blank and were removed from the database. A total of 114 dermatology residents’ responses were collected in Qualtrics and analyzed; 91 completed the entire survey (an 80% completion rate). Based on the 2020-2021 ACGME data listing, there were 1612 dermatology residents in the United States, which is an estimated response rate of 7% (114/1612).25 The eTable outlines the demographics of the survey respondents. Most were cisgender females (60%), followed by cisgender males (35%); the remainder preferred not to answer. Regarding sexual orientation, 77% identified as straight or heterosexual; 17% as gay, lesbian, or homosexual; 1% as queer; and 1% as bisexual. The training programs were in 26 states, the majority of which were in the Midwest (34%) and in urban settings (69%). A wide range of postgraduate levels and residency sizes were represented in the survey.
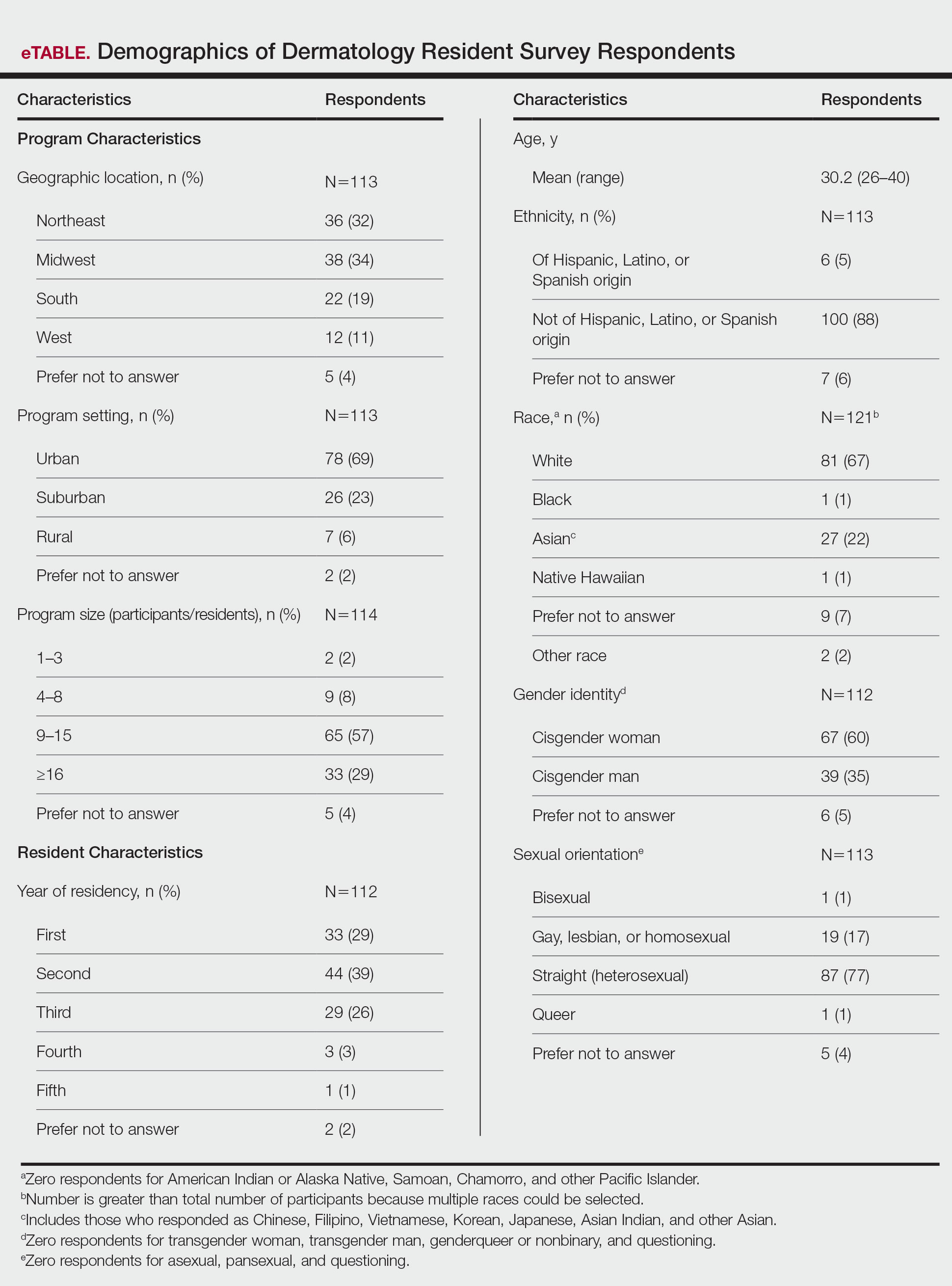
LGBT Education—Fifty-one percent of respondents reported that their programs offer 1 hour or less of LGBT-related curricula per year; 34% reported no time dedicated to this topic. A small portion of residents (5%) reported 10 or more hours of LGBT education per year. Residents also were asked the average number of hours of LGBT education they thought they should receive. The discrepancy between these measures can be visualized in Figure 1. The median hours of education received was 1 hour (IQR, 0–4 hours), whereas the median hours of education desired was 4 hours (IQR, 2–5 hours). The most common and most helpful methods of education reported were clinical experiences with faculty or patients and live lectures.
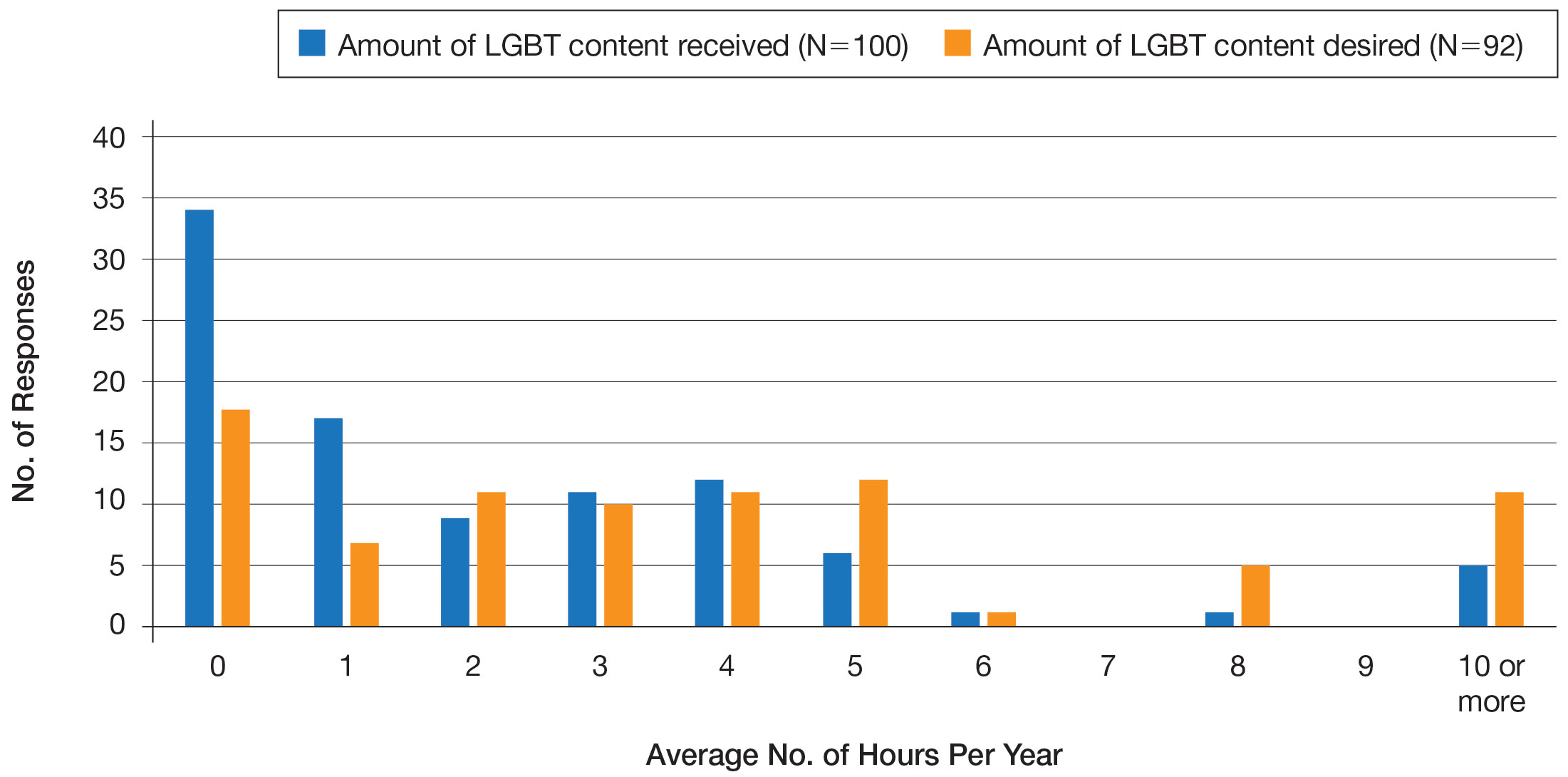
Overall, 45% of survey respondents felt that LGBT topics were covered poorly or not at all in dermatology residency, whereas 26% thought the coverage was good or excellent. The topics that residents were most likely to report receiving good or excellent coverage were dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS (70%) and sexually transmitted diseases in LGBT patients (48%). The topics that were most likely to be reported as not taught or poorly taught included dermatologic concerns associated with puberty blockers (71%), body image (58%), dermatologic concerns associated with gender-affirming surgery (55%), skin cancer risk (53%), taking an LGBT-oriented history and physical examination (52%), and effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy on the skin (50%). A detailed breakdown of coverage level by topic can be found in Figure 2.
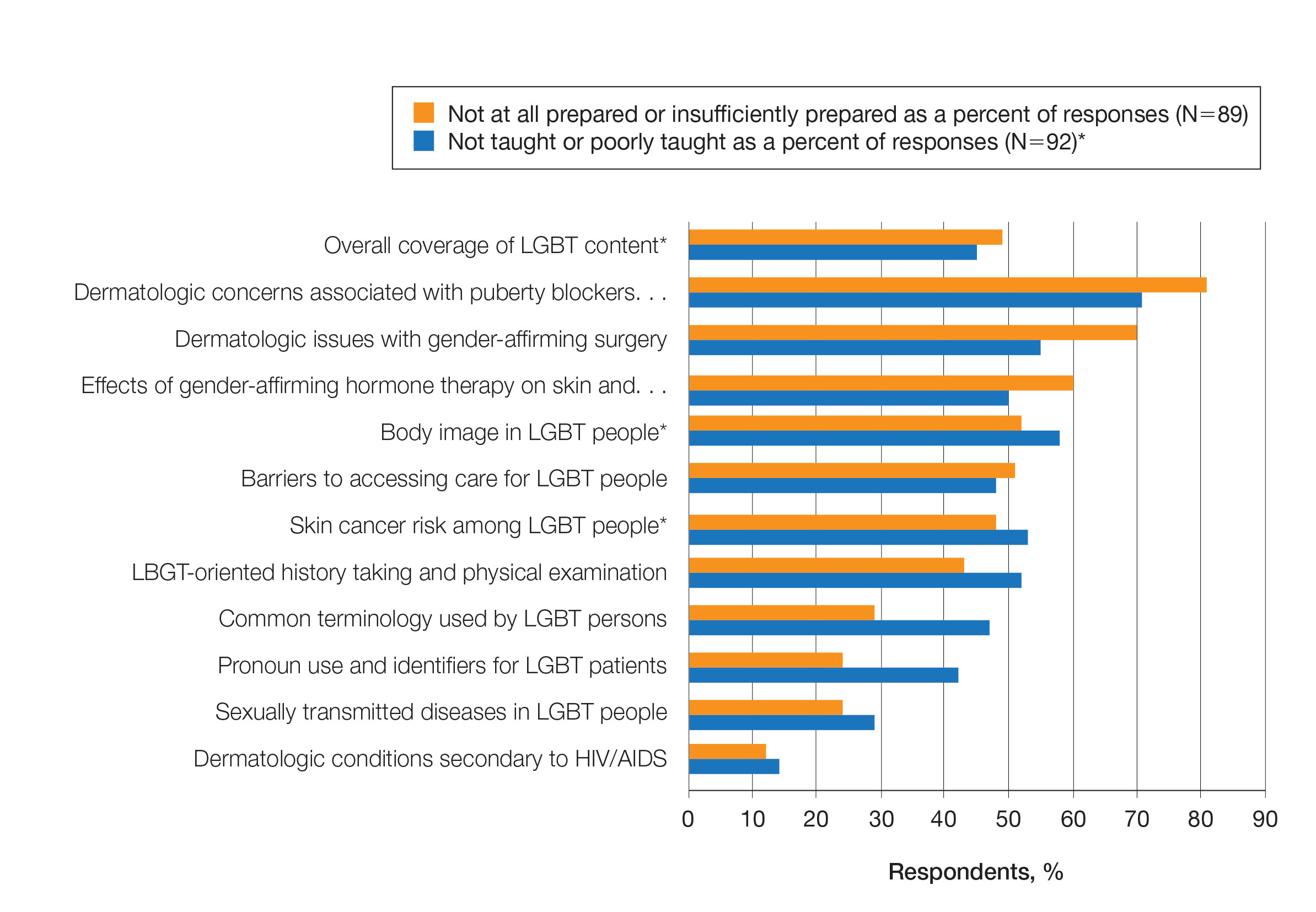
Preparedness to Care for LGBT Patients—Only 68% of survey respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable treating LGBT patients. Furthermore, 49% of dermatology residents reported that they feel not at all prepared or insufficiently prepared to provide care to LGBT individuals (Figure 2), and 60% believed that LGBT training needed to be improved at their residency programs.
There was a significant association between reported level of education and feelings of preparedness. A high ranking of provided education was associated with higher levels of feeling prepared to care for LGBT patients (Kruskal-Wallis rank test, P<.001).
Discrimination/Outness—Approximately one-fourth (24%; 4/17) of nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported that they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation in the workplace. One respondent commented that they were less “out” at their residency program due to fear of discrimination. Nearly one-third of the overall group of dermatology residents surveyed (29%; 27/92) reported that they had witnessed inappropriate or discriminatory comments about LGBT persons made by employees or staff at their programs. Most residents surveyed (96%; 88/92) agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians.
There were 18 nonheterosexual dermatologyresidents who completed the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory.23 In general, respondents reported that they were more “out” with friends and family than work peers and were least “out” with work supervisors and strangers.
Comment
Dermatology Residents Desire More Time on LGBT Health—This cross-sectional survey study explored dermatology residents’ educational experiences with LGBT health during residency training. Similar studies have been performed in other specialties, including a study from 2019 surveying emergency medicine residents that demonstrated residents find caring for LGBT patients more challenging.15 Another 2019 study surveying psychiatry residents found that 42.4% (N=99) reported no coverage of LGBT topics.18 Our study is unique in that it surveyed dermatology residents directly regarding this topic. Although most dermatology program directors view LGBT dermatologic health as an important topic, a prior study revealed that many programs are lacking dedicated LGBT educational experiences. The most common barriers reported were insufficient time in the didactic schedule and lack of experienced faculty.20
Our study revealed that dermatology residents overall tend to agree with residents from other specialties and dermatology program directors. Most of the dermatology residents surveyed reported desiring more time per year spent on LGBT health education than they receive, and 60% expressed that LGBT educational experiences need to be improved at their residency programs. Education on and subsequent comfort level with LGBT health issues varied by subtopic, with most residents feeling comfortable dealing with dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and less comfortable with topics such as puberty blockers, gender-affirming surgery and hormone therapy, body image, and skin cancer risk.
Overall, LGBT health training is viewed as important and in need of improvement by both program directors and residents, yet implementation lags at many programs. A small proportion of the represented programs are excelling in this area—just over 5% of respondents reported receiving 10 or more hours of LGBT-relevant education per year, and approximately 26% of residents felt that LGBT coverage was good or excellent at their programs. Our study showed a clear relationship between feelings of preparedness and education level. The lack of LGBT education at some dermatology residency programs translated into a large portion of dermatology residents feeling ill equipped to care for LGBT patients after graduation—nearly 50% of those surveyed reported feeling insufficiently prepared to care for the LGBT community.
Discrimination in Residency Programs—Dermatology residency programs also are not free from sexual orientation–related and gender identity–related workplace discrimination. Although 96% of dermatology residents reported that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians, 24% of nonheterosexual respondents stated they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation, and 29% of the overall group of dermatology residents had witnessed discriminatory comments to LGBT individuals at their programs. In addition, some nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported being less “out” with their workplace supervisors and strangers, such as patients, than with their family and friends, and 50% of this group reported that their sexual identity was not openly discussed with their workplace supervisors. It has been demonstrated that individuals are more likely to “come out” in perceived LGBT-friendly workplace environments and that being “out” positively impacts psychological health because of the effects of perceived social support and self-coherence.26,27
Study Strengths and Limitations—Strengths of this study include the modest sample size of dermatology residents that participated, high completion rate, and the anonymity of the survey. Limitations include the risk of sampling bias by posting the survey on LGBT-specific groups. The survey also took place in the fall, so the results may not accurately reflect programs that cover this material later in the academic year. Lastly, not all survey questions were validated.
Implementing Change in Residency Programs—Although the results of this study exposed the need for increasing LGBT education in dermatology residency, they do not provide guidelines for the best strategy to begin implementing change. A study from 2020 provides some guidance for incorporating LGBT health training into dermatology residency programs through a combination of curricular modifications and climate optimization.28 Additional future research should focus on the best methods for preparing dermatology residents to care for this population. In this study, residents reported that the most effective teaching methods were real encounters with LGBT patients or faculty educated on LGBT health as well as live lectures from experts. There also appeared to be a correlation between hours spent on LGBT health, including various subtopics, and residents’ perceived preparedness in these areas. Potential actionable items include clarifying the ACGME guidelines on LGBT health topics; increasing the sexual and gender diversity of the faculty, staff, residents, and patients; and dedicating additional didactic and clinical time to LGBT topics and experiences.
Conclusion
This survey study of dermatology residents regarding LGBT learning experiences in residency training provided evidence that dermatology residents as a whole are not adequately taught LGBT health topics and therefore feel unprepared to take care of this patient population. Additionally, most residents desire improvement of LGBT health education and training. Further studies focusing on the best methods for implementing LGBT-specific curricula are needed.
- Newport F. In U.S., estimate of LGBT population rises to 4.5%. Gallup. May 22, 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://news.gallup.com/poll/234863/estimate-lgbt-population-rises.aspx
- Hafeez H, Zeshan M, Tahir MA, et al. Health care disparities among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9:E1184.
- Gonzales G, Henning-Smith C. Barriers to care among transgender and gender nonconforming adults. Millbank Q. 2017;95:726-748.
- Quinn GP, Sanchez JA, Sutton SK, et al. Cancer and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:384-400.
- Sullivan P, Trinidad J, Hamann D. Issues in transgender dermatology: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:438-447.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: terminology, demographics, health disparities, and approaches to care. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:581-589.
- White W, Brenman S, Paradis E, et al. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care: medical students’ preparedness and comfort. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27:254-263.
- Nama N, MacPherson P, Sampson M, et al. Medical students’ perception of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) discrimination in their learning environment and their self-reported comfort level for caring for LGBT patients: a survey study. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1-8.
- Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1193-1201.
- Cherabie J, Nilsen K, Houssayni S. Transgender health medical education intervention and its effects on beliefs, attitudes, comfort, and knowledge. Kans J Med. 2018;11:106-109.
- Integrating LGBT and DSD content into medical school curricula. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published November 2015. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/equity-diversity-inclusion/lgbt-health-resources/videos/curricula-integration
- Cooper MB, Chacko M, Christner J. Incorporating LGBT health in an undergraduate medical education curriculum through the construct of social determinants of health. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10781.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Moreno-Walton L, et al. The prevalence of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender health education and training in emergency medicine residency programs: what do we know? Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:608-611.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Heron SL, et al. Attitudes, behavior, and comfort of emergency medicine residents in caring for LGBT patients: what do we know? AEM Educ Train. 2019;3:129-135.
- Hirschtritt ME, Noy G, Haller E, et al. LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:41-45.
- Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Spagnoletti C, et al. Comprehensive curriculum for internal medicine residents on primary care of patients identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16:10875.
- Zonana J, Batchelder S, Pula J, et al. Comment on: LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:547-548.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Dermatology. Revised June 12, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2022.pdf
- Jia JL, Nord KM, Sarin KY, et al. Sexual and gender minority curricula within US dermatology residency programs. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:593-594.
- Mansh M, White W, Gee-Tong L, et al. Sexual and gender minority identity disclosure during undergraduate medical education: “in the closet” in medical school. Acad Med. 2015;90:634-644.
- US Census Bureau. 2020 Census Informational Questionnaire. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial/2020/technical-documentation/questionnaires-and-instructions/questionnaires/2020-informational-questionnaire-english_DI-Q1.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Fassinger RE. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66-90.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2020 All Schools Summary Report. Published July 2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/media/46851/download
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book: Academic Year 2019-2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2019-2020_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Jackson SD, Sheets RL. Sexual orientation self-presentation among bisexual-identified women and men: patterns and predictors. Arch Sex Behav. 2017;46:1465-1479.
- Tatum AK. Workplace climate and job satisfaction: a test of social cognitive career theory (SCCT)’s workplace self-management model with sexual minority employees. Semantic Scholar. 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Workplace-Climate-and-Job-Satisfaction%3A-A-Test-of-Tatum/5af75ab70acfb73c54e34b95597576d30e07df12
- Fakhoury JW, Daveluy S. Incorporating lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender training into a residency program. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:285-292.
Approximately 4.5% of adults within the United States identify as members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) community.1 This is an umbrella term inclusive of all individuals identifying as nonheterosexual or noncisgender. Although the LGBT community has increasingly become more recognized and accepted by society over time, health care disparities persist and have been well documented in the literature.2-4 Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact LGBT health, as many health concerns in this population are cutaneous, such as sun-protection behaviors, side effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming procedures, and cutaneous manifestations of sexually transmitted infections.5-7
An education gap has been demonstrated in both medical students and resident physicians regarding LGBT health and cultural competency. In a large-scale, multi-institutional survey study published in 2015, approximately two-thirds of medical students rated their schools’ LGBT curriculum as fair, poor, or very poor.8 Additional studies have echoed these results and have demonstrated not only the need but the desire for additional training on LGBT issues in medical school.9-11 The Association of American Medical Colleges has begun implementing curricular and institutional changes to fulfill this need.12,13
The LGBT education gap has been shown to extend into residency training. Multiple studies performed within a variety of medical specialties have demonstrated that resident physicians receive insufficient training in LGBT health issues, lack comfort in caring for LGBT patients, and would benefit from dedicated curricula on these topics.14-18 Currently, the 2022 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines related to LGBT health are minimal and nonspecific.19
Ensuring that dermatology trainees are well equipped to manage these issues while providing culturally competent care to LGBT patients is paramount. However, research suggests that dedicated training on these topics likely is insufficient. A survey study of dermatology residency program directors (N=90) revealed that although 81% (72/89) viewed training in LGBT health as either very important or somewhat important, 46% (41/90) of programs did not dedicate any time to this content and 37% (33/90) only dedicated 1 to 2 hours per year.20
To further explore this potential education gap, we surveyed dermatology residents directly to better understand LGBT education within residency training, resident preparedness to care for LGBT patients, and outness/discrimination of LGBT-identifying residents. We believe this study should drive future research on the development and implementation of LGBT-specific curricula in dermatology training programs.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey study of dermatology residents in the United States was conducted. The study was deemed exempt from review by The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) institutional review board. Survey responses were collected from October 7, 2020, to November 13, 2020. Qualtrics software was used to create the 20-question survey, which included a combination of categorical, dichotomous, and optional free-text questions related to patient demographics, LGBT training experiences, perceived areas of curriculum improvement, comfort level managing LGBT health issues, and personal experiences. Some questions were adapted from prior surveys.15,21 Validated survey tools used included the 2020 US Census to collect information regarding race and ethnicity, the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory to measure outness regarding sexual orientation, and select questions from the 2020 Association of American Medical Colleges Medical School Graduation Questionnaire regarding discrimination.22-24
The survey was distributed to current allopathic and osteopathic dermatology residents by a variety of methods, including emails to program director and program coordinator listserves. The survey also was posted in the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group on LGBTQ Health October 2020 newsletter, as well as dermatology social media groups, including a messaging forum limited to dermatology residents, a Facebook group open to dermatologists and dermatology residents, and the Facebook group of the Gay and Lesbian Dermatology Association. Current dermatology residents, including those in combined dermatology and internal medicine programs, were included. Individuals who had been accepted to dermatology training programs but had not yet started were excluded. A follow-up email was sent to the program director listserve approximately 3 weeks after the initial distribution.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed in Qualtrics and Microsoft Excel using descriptive statistics. Stata software (Stata 15.1, StataCorp) was used to perform a Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test to compare the means of education level and feelings of preparedness.
Results
Demographics of Respondents—A total of 126 responses were recorded, 12 of which were blank and were removed from the database. A total of 114 dermatology residents’ responses were collected in Qualtrics and analyzed; 91 completed the entire survey (an 80% completion rate). Based on the 2020-2021 ACGME data listing, there were 1612 dermatology residents in the United States, which is an estimated response rate of 7% (114/1612).25 The eTable outlines the demographics of the survey respondents. Most were cisgender females (60%), followed by cisgender males (35%); the remainder preferred not to answer. Regarding sexual orientation, 77% identified as straight or heterosexual; 17% as gay, lesbian, or homosexual; 1% as queer; and 1% as bisexual. The training programs were in 26 states, the majority of which were in the Midwest (34%) and in urban settings (69%). A wide range of postgraduate levels and residency sizes were represented in the survey.

LGBT Education—Fifty-one percent of respondents reported that their programs offer 1 hour or less of LGBT-related curricula per year; 34% reported no time dedicated to this topic. A small portion of residents (5%) reported 10 or more hours of LGBT education per year. Residents also were asked the average number of hours of LGBT education they thought they should receive. The discrepancy between these measures can be visualized in Figure 1. The median hours of education received was 1 hour (IQR, 0–4 hours), whereas the median hours of education desired was 4 hours (IQR, 2–5 hours). The most common and most helpful methods of education reported were clinical experiences with faculty or patients and live lectures.

Overall, 45% of survey respondents felt that LGBT topics were covered poorly or not at all in dermatology residency, whereas 26% thought the coverage was good or excellent. The topics that residents were most likely to report receiving good or excellent coverage were dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS (70%) and sexually transmitted diseases in LGBT patients (48%). The topics that were most likely to be reported as not taught or poorly taught included dermatologic concerns associated with puberty blockers (71%), body image (58%), dermatologic concerns associated with gender-affirming surgery (55%), skin cancer risk (53%), taking an LGBT-oriented history and physical examination (52%), and effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy on the skin (50%). A detailed breakdown of coverage level by topic can be found in Figure 2.

Preparedness to Care for LGBT Patients—Only 68% of survey respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable treating LGBT patients. Furthermore, 49% of dermatology residents reported that they feel not at all prepared or insufficiently prepared to provide care to LGBT individuals (Figure 2), and 60% believed that LGBT training needed to be improved at their residency programs.
There was a significant association between reported level of education and feelings of preparedness. A high ranking of provided education was associated with higher levels of feeling prepared to care for LGBT patients (Kruskal-Wallis rank test, P<.001).
Discrimination/Outness—Approximately one-fourth (24%; 4/17) of nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported that they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation in the workplace. One respondent commented that they were less “out” at their residency program due to fear of discrimination. Nearly one-third of the overall group of dermatology residents surveyed (29%; 27/92) reported that they had witnessed inappropriate or discriminatory comments about LGBT persons made by employees or staff at their programs. Most residents surveyed (96%; 88/92) agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians.
There were 18 nonheterosexual dermatologyresidents who completed the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory.23 In general, respondents reported that they were more “out” with friends and family than work peers and were least “out” with work supervisors and strangers.
Comment
Dermatology Residents Desire More Time on LGBT Health—This cross-sectional survey study explored dermatology residents’ educational experiences with LGBT health during residency training. Similar studies have been performed in other specialties, including a study from 2019 surveying emergency medicine residents that demonstrated residents find caring for LGBT patients more challenging.15 Another 2019 study surveying psychiatry residents found that 42.4% (N=99) reported no coverage of LGBT topics.18 Our study is unique in that it surveyed dermatology residents directly regarding this topic. Although most dermatology program directors view LGBT dermatologic health as an important topic, a prior study revealed that many programs are lacking dedicated LGBT educational experiences. The most common barriers reported were insufficient time in the didactic schedule and lack of experienced faculty.20
Our study revealed that dermatology residents overall tend to agree with residents from other specialties and dermatology program directors. Most of the dermatology residents surveyed reported desiring more time per year spent on LGBT health education than they receive, and 60% expressed that LGBT educational experiences need to be improved at their residency programs. Education on and subsequent comfort level with LGBT health issues varied by subtopic, with most residents feeling comfortable dealing with dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and less comfortable with topics such as puberty blockers, gender-affirming surgery and hormone therapy, body image, and skin cancer risk.
Overall, LGBT health training is viewed as important and in need of improvement by both program directors and residents, yet implementation lags at many programs. A small proportion of the represented programs are excelling in this area—just over 5% of respondents reported receiving 10 or more hours of LGBT-relevant education per year, and approximately 26% of residents felt that LGBT coverage was good or excellent at their programs. Our study showed a clear relationship between feelings of preparedness and education level. The lack of LGBT education at some dermatology residency programs translated into a large portion of dermatology residents feeling ill equipped to care for LGBT patients after graduation—nearly 50% of those surveyed reported feeling insufficiently prepared to care for the LGBT community.
Discrimination in Residency Programs—Dermatology residency programs also are not free from sexual orientation–related and gender identity–related workplace discrimination. Although 96% of dermatology residents reported that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians, 24% of nonheterosexual respondents stated they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation, and 29% of the overall group of dermatology residents had witnessed discriminatory comments to LGBT individuals at their programs. In addition, some nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported being less “out” with their workplace supervisors and strangers, such as patients, than with their family and friends, and 50% of this group reported that their sexual identity was not openly discussed with their workplace supervisors. It has been demonstrated that individuals are more likely to “come out” in perceived LGBT-friendly workplace environments and that being “out” positively impacts psychological health because of the effects of perceived social support and self-coherence.26,27
Study Strengths and Limitations—Strengths of this study include the modest sample size of dermatology residents that participated, high completion rate, and the anonymity of the survey. Limitations include the risk of sampling bias by posting the survey on LGBT-specific groups. The survey also took place in the fall, so the results may not accurately reflect programs that cover this material later in the academic year. Lastly, not all survey questions were validated.
Implementing Change in Residency Programs—Although the results of this study exposed the need for increasing LGBT education in dermatology residency, they do not provide guidelines for the best strategy to begin implementing change. A study from 2020 provides some guidance for incorporating LGBT health training into dermatology residency programs through a combination of curricular modifications and climate optimization.28 Additional future research should focus on the best methods for preparing dermatology residents to care for this population. In this study, residents reported that the most effective teaching methods were real encounters with LGBT patients or faculty educated on LGBT health as well as live lectures from experts. There also appeared to be a correlation between hours spent on LGBT health, including various subtopics, and residents’ perceived preparedness in these areas. Potential actionable items include clarifying the ACGME guidelines on LGBT health topics; increasing the sexual and gender diversity of the faculty, staff, residents, and patients; and dedicating additional didactic and clinical time to LGBT topics and experiences.
Conclusion
This survey study of dermatology residents regarding LGBT learning experiences in residency training provided evidence that dermatology residents as a whole are not adequately taught LGBT health topics and therefore feel unprepared to take care of this patient population. Additionally, most residents desire improvement of LGBT health education and training. Further studies focusing on the best methods for implementing LGBT-specific curricula are needed.
Approximately 4.5% of adults within the United States identify as members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) community.1 This is an umbrella term inclusive of all individuals identifying as nonheterosexual or noncisgender. Although the LGBT community has increasingly become more recognized and accepted by society over time, health care disparities persist and have been well documented in the literature.2-4 Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact LGBT health, as many health concerns in this population are cutaneous, such as sun-protection behaviors, side effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming procedures, and cutaneous manifestations of sexually transmitted infections.5-7
An education gap has been demonstrated in both medical students and resident physicians regarding LGBT health and cultural competency. In a large-scale, multi-institutional survey study published in 2015, approximately two-thirds of medical students rated their schools’ LGBT curriculum as fair, poor, or very poor.8 Additional studies have echoed these results and have demonstrated not only the need but the desire for additional training on LGBT issues in medical school.9-11 The Association of American Medical Colleges has begun implementing curricular and institutional changes to fulfill this need.12,13
The LGBT education gap has been shown to extend into residency training. Multiple studies performed within a variety of medical specialties have demonstrated that resident physicians receive insufficient training in LGBT health issues, lack comfort in caring for LGBT patients, and would benefit from dedicated curricula on these topics.14-18 Currently, the 2022 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines related to LGBT health are minimal and nonspecific.19
Ensuring that dermatology trainees are well equipped to manage these issues while providing culturally competent care to LGBT patients is paramount. However, research suggests that dedicated training on these topics likely is insufficient. A survey study of dermatology residency program directors (N=90) revealed that although 81% (72/89) viewed training in LGBT health as either very important or somewhat important, 46% (41/90) of programs did not dedicate any time to this content and 37% (33/90) only dedicated 1 to 2 hours per year.20
To further explore this potential education gap, we surveyed dermatology residents directly to better understand LGBT education within residency training, resident preparedness to care for LGBT patients, and outness/discrimination of LGBT-identifying residents. We believe this study should drive future research on the development and implementation of LGBT-specific curricula in dermatology training programs.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey study of dermatology residents in the United States was conducted. The study was deemed exempt from review by The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) institutional review board. Survey responses were collected from October 7, 2020, to November 13, 2020. Qualtrics software was used to create the 20-question survey, which included a combination of categorical, dichotomous, and optional free-text questions related to patient demographics, LGBT training experiences, perceived areas of curriculum improvement, comfort level managing LGBT health issues, and personal experiences. Some questions were adapted from prior surveys.15,21 Validated survey tools used included the 2020 US Census to collect information regarding race and ethnicity, the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory to measure outness regarding sexual orientation, and select questions from the 2020 Association of American Medical Colleges Medical School Graduation Questionnaire regarding discrimination.22-24
The survey was distributed to current allopathic and osteopathic dermatology residents by a variety of methods, including emails to program director and program coordinator listserves. The survey also was posted in the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group on LGBTQ Health October 2020 newsletter, as well as dermatology social media groups, including a messaging forum limited to dermatology residents, a Facebook group open to dermatologists and dermatology residents, and the Facebook group of the Gay and Lesbian Dermatology Association. Current dermatology residents, including those in combined dermatology and internal medicine programs, were included. Individuals who had been accepted to dermatology training programs but had not yet started were excluded. A follow-up email was sent to the program director listserve approximately 3 weeks after the initial distribution.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed in Qualtrics and Microsoft Excel using descriptive statistics. Stata software (Stata 15.1, StataCorp) was used to perform a Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test to compare the means of education level and feelings of preparedness.
Results
Demographics of Respondents—A total of 126 responses were recorded, 12 of which were blank and were removed from the database. A total of 114 dermatology residents’ responses were collected in Qualtrics and analyzed; 91 completed the entire survey (an 80% completion rate). Based on the 2020-2021 ACGME data listing, there were 1612 dermatology residents in the United States, which is an estimated response rate of 7% (114/1612).25 The eTable outlines the demographics of the survey respondents. Most were cisgender females (60%), followed by cisgender males (35%); the remainder preferred not to answer. Regarding sexual orientation, 77% identified as straight or heterosexual; 17% as gay, lesbian, or homosexual; 1% as queer; and 1% as bisexual. The training programs were in 26 states, the majority of which were in the Midwest (34%) and in urban settings (69%). A wide range of postgraduate levels and residency sizes were represented in the survey.

LGBT Education—Fifty-one percent of respondents reported that their programs offer 1 hour or less of LGBT-related curricula per year; 34% reported no time dedicated to this topic. A small portion of residents (5%) reported 10 or more hours of LGBT education per year. Residents also were asked the average number of hours of LGBT education they thought they should receive. The discrepancy between these measures can be visualized in Figure 1. The median hours of education received was 1 hour (IQR, 0–4 hours), whereas the median hours of education desired was 4 hours (IQR, 2–5 hours). The most common and most helpful methods of education reported were clinical experiences with faculty or patients and live lectures.

Overall, 45% of survey respondents felt that LGBT topics were covered poorly or not at all in dermatology residency, whereas 26% thought the coverage was good or excellent. The topics that residents were most likely to report receiving good or excellent coverage were dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS (70%) and sexually transmitted diseases in LGBT patients (48%). The topics that were most likely to be reported as not taught or poorly taught included dermatologic concerns associated with puberty blockers (71%), body image (58%), dermatologic concerns associated with gender-affirming surgery (55%), skin cancer risk (53%), taking an LGBT-oriented history and physical examination (52%), and effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy on the skin (50%). A detailed breakdown of coverage level by topic can be found in Figure 2.

Preparedness to Care for LGBT Patients—Only 68% of survey respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable treating LGBT patients. Furthermore, 49% of dermatology residents reported that they feel not at all prepared or insufficiently prepared to provide care to LGBT individuals (Figure 2), and 60% believed that LGBT training needed to be improved at their residency programs.
There was a significant association between reported level of education and feelings of preparedness. A high ranking of provided education was associated with higher levels of feeling prepared to care for LGBT patients (Kruskal-Wallis rank test, P<.001).
Discrimination/Outness—Approximately one-fourth (24%; 4/17) of nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported that they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation in the workplace. One respondent commented that they were less “out” at their residency program due to fear of discrimination. Nearly one-third of the overall group of dermatology residents surveyed (29%; 27/92) reported that they had witnessed inappropriate or discriminatory comments about LGBT persons made by employees or staff at their programs. Most residents surveyed (96%; 88/92) agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians.
There were 18 nonheterosexual dermatologyresidents who completed the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory.23 In general, respondents reported that they were more “out” with friends and family than work peers and were least “out” with work supervisors and strangers.
Comment
Dermatology Residents Desire More Time on LGBT Health—This cross-sectional survey study explored dermatology residents’ educational experiences with LGBT health during residency training. Similar studies have been performed in other specialties, including a study from 2019 surveying emergency medicine residents that demonstrated residents find caring for LGBT patients more challenging.15 Another 2019 study surveying psychiatry residents found that 42.4% (N=99) reported no coverage of LGBT topics.18 Our study is unique in that it surveyed dermatology residents directly regarding this topic. Although most dermatology program directors view LGBT dermatologic health as an important topic, a prior study revealed that many programs are lacking dedicated LGBT educational experiences. The most common barriers reported were insufficient time in the didactic schedule and lack of experienced faculty.20
Our study revealed that dermatology residents overall tend to agree with residents from other specialties and dermatology program directors. Most of the dermatology residents surveyed reported desiring more time per year spent on LGBT health education than they receive, and 60% expressed that LGBT educational experiences need to be improved at their residency programs. Education on and subsequent comfort level with LGBT health issues varied by subtopic, with most residents feeling comfortable dealing with dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and less comfortable with topics such as puberty blockers, gender-affirming surgery and hormone therapy, body image, and skin cancer risk.
Overall, LGBT health training is viewed as important and in need of improvement by both program directors and residents, yet implementation lags at many programs. A small proportion of the represented programs are excelling in this area—just over 5% of respondents reported receiving 10 or more hours of LGBT-relevant education per year, and approximately 26% of residents felt that LGBT coverage was good or excellent at their programs. Our study showed a clear relationship between feelings of preparedness and education level. The lack of LGBT education at some dermatology residency programs translated into a large portion of dermatology residents feeling ill equipped to care for LGBT patients after graduation—nearly 50% of those surveyed reported feeling insufficiently prepared to care for the LGBT community.
Discrimination in Residency Programs—Dermatology residency programs also are not free from sexual orientation–related and gender identity–related workplace discrimination. Although 96% of dermatology residents reported that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians, 24% of nonheterosexual respondents stated they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation, and 29% of the overall group of dermatology residents had witnessed discriminatory comments to LGBT individuals at their programs. In addition, some nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported being less “out” with their workplace supervisors and strangers, such as patients, than with their family and friends, and 50% of this group reported that their sexual identity was not openly discussed with their workplace supervisors. It has been demonstrated that individuals are more likely to “come out” in perceived LGBT-friendly workplace environments and that being “out” positively impacts psychological health because of the effects of perceived social support and self-coherence.26,27
Study Strengths and Limitations—Strengths of this study include the modest sample size of dermatology residents that participated, high completion rate, and the anonymity of the survey. Limitations include the risk of sampling bias by posting the survey on LGBT-specific groups. The survey also took place in the fall, so the results may not accurately reflect programs that cover this material later in the academic year. Lastly, not all survey questions were validated.
Implementing Change in Residency Programs—Although the results of this study exposed the need for increasing LGBT education in dermatology residency, they do not provide guidelines for the best strategy to begin implementing change. A study from 2020 provides some guidance for incorporating LGBT health training into dermatology residency programs through a combination of curricular modifications and climate optimization.28 Additional future research should focus on the best methods for preparing dermatology residents to care for this population. In this study, residents reported that the most effective teaching methods were real encounters with LGBT patients or faculty educated on LGBT health as well as live lectures from experts. There also appeared to be a correlation between hours spent on LGBT health, including various subtopics, and residents’ perceived preparedness in these areas. Potential actionable items include clarifying the ACGME guidelines on LGBT health topics; increasing the sexual and gender diversity of the faculty, staff, residents, and patients; and dedicating additional didactic and clinical time to LGBT topics and experiences.
Conclusion
This survey study of dermatology residents regarding LGBT learning experiences in residency training provided evidence that dermatology residents as a whole are not adequately taught LGBT health topics and therefore feel unprepared to take care of this patient population. Additionally, most residents desire improvement of LGBT health education and training. Further studies focusing on the best methods for implementing LGBT-specific curricula are needed.
- Newport F. In U.S., estimate of LGBT population rises to 4.5%. Gallup. May 22, 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://news.gallup.com/poll/234863/estimate-lgbt-population-rises.aspx
- Hafeez H, Zeshan M, Tahir MA, et al. Health care disparities among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9:E1184.
- Gonzales G, Henning-Smith C. Barriers to care among transgender and gender nonconforming adults. Millbank Q. 2017;95:726-748.
- Quinn GP, Sanchez JA, Sutton SK, et al. Cancer and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:384-400.
- Sullivan P, Trinidad J, Hamann D. Issues in transgender dermatology: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:438-447.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: terminology, demographics, health disparities, and approaches to care. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:581-589.
- White W, Brenman S, Paradis E, et al. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care: medical students’ preparedness and comfort. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27:254-263.
- Nama N, MacPherson P, Sampson M, et al. Medical students’ perception of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) discrimination in their learning environment and their self-reported comfort level for caring for LGBT patients: a survey study. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1-8.
- Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1193-1201.
- Cherabie J, Nilsen K, Houssayni S. Transgender health medical education intervention and its effects on beliefs, attitudes, comfort, and knowledge. Kans J Med. 2018;11:106-109.
- Integrating LGBT and DSD content into medical school curricula. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published November 2015. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/equity-diversity-inclusion/lgbt-health-resources/videos/curricula-integration
- Cooper MB, Chacko M, Christner J. Incorporating LGBT health in an undergraduate medical education curriculum through the construct of social determinants of health. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10781.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Moreno-Walton L, et al. The prevalence of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender health education and training in emergency medicine residency programs: what do we know? Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:608-611.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Heron SL, et al. Attitudes, behavior, and comfort of emergency medicine residents in caring for LGBT patients: what do we know? AEM Educ Train. 2019;3:129-135.
- Hirschtritt ME, Noy G, Haller E, et al. LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:41-45.
- Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Spagnoletti C, et al. Comprehensive curriculum for internal medicine residents on primary care of patients identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16:10875.
- Zonana J, Batchelder S, Pula J, et al. Comment on: LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:547-548.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Dermatology. Revised June 12, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2022.pdf
- Jia JL, Nord KM, Sarin KY, et al. Sexual and gender minority curricula within US dermatology residency programs. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:593-594.
- Mansh M, White W, Gee-Tong L, et al. Sexual and gender minority identity disclosure during undergraduate medical education: “in the closet” in medical school. Acad Med. 2015;90:634-644.
- US Census Bureau. 2020 Census Informational Questionnaire. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial/2020/technical-documentation/questionnaires-and-instructions/questionnaires/2020-informational-questionnaire-english_DI-Q1.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Fassinger RE. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66-90.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2020 All Schools Summary Report. Published July 2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/media/46851/download
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book: Academic Year 2019-2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2019-2020_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Jackson SD, Sheets RL. Sexual orientation self-presentation among bisexual-identified women and men: patterns and predictors. Arch Sex Behav. 2017;46:1465-1479.
- Tatum AK. Workplace climate and job satisfaction: a test of social cognitive career theory (SCCT)’s workplace self-management model with sexual minority employees. Semantic Scholar. 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Workplace-Climate-and-Job-Satisfaction%3A-A-Test-of-Tatum/5af75ab70acfb73c54e34b95597576d30e07df12
- Fakhoury JW, Daveluy S. Incorporating lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender training into a residency program. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:285-292.
- Newport F. In U.S., estimate of LGBT population rises to 4.5%. Gallup. May 22, 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://news.gallup.com/poll/234863/estimate-lgbt-population-rises.aspx
- Hafeez H, Zeshan M, Tahir MA, et al. Health care disparities among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9:E1184.
- Gonzales G, Henning-Smith C. Barriers to care among transgender and gender nonconforming adults. Millbank Q. 2017;95:726-748.
- Quinn GP, Sanchez JA, Sutton SK, et al. Cancer and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:384-400.
- Sullivan P, Trinidad J, Hamann D. Issues in transgender dermatology: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:438-447.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: terminology, demographics, health disparities, and approaches to care. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:581-589.
- White W, Brenman S, Paradis E, et al. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care: medical students’ preparedness and comfort. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27:254-263.
- Nama N, MacPherson P, Sampson M, et al. Medical students’ perception of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) discrimination in their learning environment and their self-reported comfort level for caring for LGBT patients: a survey study. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1-8.
- Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1193-1201.
- Cherabie J, Nilsen K, Houssayni S. Transgender health medical education intervention and its effects on beliefs, attitudes, comfort, and knowledge. Kans J Med. 2018;11:106-109.
- Integrating LGBT and DSD content into medical school curricula. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published November 2015. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/equity-diversity-inclusion/lgbt-health-resources/videos/curricula-integration
- Cooper MB, Chacko M, Christner J. Incorporating LGBT health in an undergraduate medical education curriculum through the construct of social determinants of health. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10781.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Moreno-Walton L, et al. The prevalence of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender health education and training in emergency medicine residency programs: what do we know? Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:608-611.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Heron SL, et al. Attitudes, behavior, and comfort of emergency medicine residents in caring for LGBT patients: what do we know? AEM Educ Train. 2019;3:129-135.
- Hirschtritt ME, Noy G, Haller E, et al. LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:41-45.
- Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Spagnoletti C, et al. Comprehensive curriculum for internal medicine residents on primary care of patients identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16:10875.
- Zonana J, Batchelder S, Pula J, et al. Comment on: LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:547-548.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Dermatology. Revised June 12, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2022.pdf
- Jia JL, Nord KM, Sarin KY, et al. Sexual and gender minority curricula within US dermatology residency programs. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:593-594.
- Mansh M, White W, Gee-Tong L, et al. Sexual and gender minority identity disclosure during undergraduate medical education: “in the closet” in medical school. Acad Med. 2015;90:634-644.
- US Census Bureau. 2020 Census Informational Questionnaire. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial/2020/technical-documentation/questionnaires-and-instructions/questionnaires/2020-informational-questionnaire-english_DI-Q1.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Fassinger RE. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66-90.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2020 All Schools Summary Report. Published July 2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/media/46851/download
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book: Academic Year 2019-2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2019-2020_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Jackson SD, Sheets RL. Sexual orientation self-presentation among bisexual-identified women and men: patterns and predictors. Arch Sex Behav. 2017;46:1465-1479.
- Tatum AK. Workplace climate and job satisfaction: a test of social cognitive career theory (SCCT)’s workplace self-management model with sexual minority employees. Semantic Scholar. 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Workplace-Climate-and-Job-Satisfaction%3A-A-Test-of-Tatum/5af75ab70acfb73c54e34b95597576d30e07df12
- Fakhoury JW, Daveluy S. Incorporating lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender training into a residency program. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:285-292.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) health since many health concerns in this population are cutaneous.
- Improving LGBT health education and training in dermatology residency likely will increase dermatology residents' comfort level in treating this population.
Racial disparities in preventive services use seen among patients with spina bifida or cerebral palsy
Black adults also had lower odds of having a bone density screening, compared with White adults. Plus, comorbidities were highest among the Black patients, according to the paper, which was published in Annals of Family Medicine.
Elham Mahmoudi, PhD, and her coauthors examined private insurance claims from 11,635 patients with cerebral palsy (CP) or spina bifida over ten years from 2007 to 2017. The researchers analyzed comorbidities and compared the rates of different psychological, cardiometabolic, and musculoskeletal conditions among these patients.
Only 23% of Hispanic participants and 18% of Black participants attended an annual wellness visit, compared with 32% of the White participants.
Only 1% of Black and 2% of White participants received any bone density screening (odds ratio = 0.54, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.31-0.95), a service that is essential for catching a patient’s potential risk for osteoporosis and fractures.
According to the researchers, patients accessed services such as bone density scans, cholesterol assessments, diabetes screenings, and annual wellness visits less than recommended for people with those chronic conditions.
“People with spina bifida and cerebral palsy have complex care needs. We know through our work that chronic conditions are much higher among them compared with adults without disabilities,” Dr. Mahmoudi, associate professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “I was surprised to see even with private insurance, the rate of using preventative services is so low among White people and minority populations.”
Comorbidities highest in Black participants
Black adults had the highest comorbidity score of 2.5, and Hispanic adults had the lowest comorbidity score of 1.8. For White adults in the study, the comorbidity score was 2.0.
Osteoporosis, a common concern for people with spina bifida or cerebral palsy, was detected in around 4% of all participants. Osteoarthritis was detected in 13.38% of Black participants, versus 8.53% of Hispanic participants and 11.09% of White participants.
Diabetes and hypertension were more common among Black participants than among Hispanic and White participants. The percentages of Black patients with hypertension and diabetes were 16.5% and 39.89%, respectively. Among the Hispanic and White adults, the percentages with hypertension were 22.3% and 28.2%, respectively, according to the paper.
Disparities in access
Jamil Paden, racial and health equity manager at the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation, said getting access to literature, transportation, tables, chairs, weigh scales, and imaging equipment that accommodate the needs of people with disabilities are some of the biggest challenges for people with disabilities who are trying to receive care.
“It’s not a one size fits all, we have to recognize that if someone doesn’t see themselves in a particular place, then it makes it more challenging for them to feel comfortable speaking up and saying things about their health, which would prevent a person from saying something early on,” Mr. Paden said in an interview. “That particular issue will continue to grow and become more of a health risk, or health challenge down the line.”
Mr. Paden emphasized intersections between class, race, and circumstances which can, together, make health care less equitable for people with disabilities, especially in underserved communities and communities of color. He urged health care providers to distance their practices from a “one size fits all” approach to treatment and engage in their patients’ individual lives and communities.
“It’s not enough to just say, Hey, you have a disability. So let me treat your disability ... You have to recognize that although a patient may have a dire diagnosis, they also are a person of color, and they have to navigate different aspects of life from their counterparts,” he said.
Dr. Mahmoudi said patient and provider understanding of the disability is often lacking. She recommended advocating for patients, noting that giving both patients and providers the tools to further educate themselves and apply that to their regular visits is a good first step.
“Just having access to a facility doesn’t mean they will get the services they need. Preventative services that are recommended for people with disabilities differ from the general population. Providers should be educated about that and the patient needs to be educated about that,” she added.
“Patients who do not approach clinicians get lost in the system. Maybe many facilities are not disability friendly, or they need health literacy. If they don’t know they are at risk for osteoporosis, for example, then they won’t ask,” Dr. Mahmoudi said.
The study was funded by The National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research. Dr. Mahmoudi and Mr. Paden report no relevant financial relationships.
Black adults also had lower odds of having a bone density screening, compared with White adults. Plus, comorbidities were highest among the Black patients, according to the paper, which was published in Annals of Family Medicine.
Elham Mahmoudi, PhD, and her coauthors examined private insurance claims from 11,635 patients with cerebral palsy (CP) or spina bifida over ten years from 2007 to 2017. The researchers analyzed comorbidities and compared the rates of different psychological, cardiometabolic, and musculoskeletal conditions among these patients.
Only 23% of Hispanic participants and 18% of Black participants attended an annual wellness visit, compared with 32% of the White participants.
Only 1% of Black and 2% of White participants received any bone density screening (odds ratio = 0.54, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.31-0.95), a service that is essential for catching a patient’s potential risk for osteoporosis and fractures.
According to the researchers, patients accessed services such as bone density scans, cholesterol assessments, diabetes screenings, and annual wellness visits less than recommended for people with those chronic conditions.
“People with spina bifida and cerebral palsy have complex care needs. We know through our work that chronic conditions are much higher among them compared with adults without disabilities,” Dr. Mahmoudi, associate professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “I was surprised to see even with private insurance, the rate of using preventative services is so low among White people and minority populations.”
Comorbidities highest in Black participants
Black adults had the highest comorbidity score of 2.5, and Hispanic adults had the lowest comorbidity score of 1.8. For White adults in the study, the comorbidity score was 2.0.
Osteoporosis, a common concern for people with spina bifida or cerebral palsy, was detected in around 4% of all participants. Osteoarthritis was detected in 13.38% of Black participants, versus 8.53% of Hispanic participants and 11.09% of White participants.
Diabetes and hypertension were more common among Black participants than among Hispanic and White participants. The percentages of Black patients with hypertension and diabetes were 16.5% and 39.89%, respectively. Among the Hispanic and White adults, the percentages with hypertension were 22.3% and 28.2%, respectively, according to the paper.
Disparities in access
Jamil Paden, racial and health equity manager at the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation, said getting access to literature, transportation, tables, chairs, weigh scales, and imaging equipment that accommodate the needs of people with disabilities are some of the biggest challenges for people with disabilities who are trying to receive care.
“It’s not a one size fits all, we have to recognize that if someone doesn’t see themselves in a particular place, then it makes it more challenging for them to feel comfortable speaking up and saying things about their health, which would prevent a person from saying something early on,” Mr. Paden said in an interview. “That particular issue will continue to grow and become more of a health risk, or health challenge down the line.”
Mr. Paden emphasized intersections between class, race, and circumstances which can, together, make health care less equitable for people with disabilities, especially in underserved communities and communities of color. He urged health care providers to distance their practices from a “one size fits all” approach to treatment and engage in their patients’ individual lives and communities.
“It’s not enough to just say, Hey, you have a disability. So let me treat your disability ... You have to recognize that although a patient may have a dire diagnosis, they also are a person of color, and they have to navigate different aspects of life from their counterparts,” he said.
Dr. Mahmoudi said patient and provider understanding of the disability is often lacking. She recommended advocating for patients, noting that giving both patients and providers the tools to further educate themselves and apply that to their regular visits is a good first step.
“Just having access to a facility doesn’t mean they will get the services they need. Preventative services that are recommended for people with disabilities differ from the general population. Providers should be educated about that and the patient needs to be educated about that,” she added.
“Patients who do not approach clinicians get lost in the system. Maybe many facilities are not disability friendly, or they need health literacy. If they don’t know they are at risk for osteoporosis, for example, then they won’t ask,” Dr. Mahmoudi said.
The study was funded by The National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research. Dr. Mahmoudi and Mr. Paden report no relevant financial relationships.
Black adults also had lower odds of having a bone density screening, compared with White adults. Plus, comorbidities were highest among the Black patients, according to the paper, which was published in Annals of Family Medicine.
Elham Mahmoudi, PhD, and her coauthors examined private insurance claims from 11,635 patients with cerebral palsy (CP) or spina bifida over ten years from 2007 to 2017. The researchers analyzed comorbidities and compared the rates of different psychological, cardiometabolic, and musculoskeletal conditions among these patients.
Only 23% of Hispanic participants and 18% of Black participants attended an annual wellness visit, compared with 32% of the White participants.
Only 1% of Black and 2% of White participants received any bone density screening (odds ratio = 0.54, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.31-0.95), a service that is essential for catching a patient’s potential risk for osteoporosis and fractures.
According to the researchers, patients accessed services such as bone density scans, cholesterol assessments, diabetes screenings, and annual wellness visits less than recommended for people with those chronic conditions.
“People with spina bifida and cerebral palsy have complex care needs. We know through our work that chronic conditions are much higher among them compared with adults without disabilities,” Dr. Mahmoudi, associate professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “I was surprised to see even with private insurance, the rate of using preventative services is so low among White people and minority populations.”
Comorbidities highest in Black participants
Black adults had the highest comorbidity score of 2.5, and Hispanic adults had the lowest comorbidity score of 1.8. For White adults in the study, the comorbidity score was 2.0.
Osteoporosis, a common concern for people with spina bifida or cerebral palsy, was detected in around 4% of all participants. Osteoarthritis was detected in 13.38% of Black participants, versus 8.53% of Hispanic participants and 11.09% of White participants.
Diabetes and hypertension were more common among Black participants than among Hispanic and White participants. The percentages of Black patients with hypertension and diabetes were 16.5% and 39.89%, respectively. Among the Hispanic and White adults, the percentages with hypertension were 22.3% and 28.2%, respectively, according to the paper.
Disparities in access
Jamil Paden, racial and health equity manager at the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation, said getting access to literature, transportation, tables, chairs, weigh scales, and imaging equipment that accommodate the needs of people with disabilities are some of the biggest challenges for people with disabilities who are trying to receive care.
“It’s not a one size fits all, we have to recognize that if someone doesn’t see themselves in a particular place, then it makes it more challenging for them to feel comfortable speaking up and saying things about their health, which would prevent a person from saying something early on,” Mr. Paden said in an interview. “That particular issue will continue to grow and become more of a health risk, or health challenge down the line.”
Mr. Paden emphasized intersections between class, race, and circumstances which can, together, make health care less equitable for people with disabilities, especially in underserved communities and communities of color. He urged health care providers to distance their practices from a “one size fits all” approach to treatment and engage in their patients’ individual lives and communities.
“It’s not enough to just say, Hey, you have a disability. So let me treat your disability ... You have to recognize that although a patient may have a dire diagnosis, they also are a person of color, and they have to navigate different aspects of life from their counterparts,” he said.
Dr. Mahmoudi said patient and provider understanding of the disability is often lacking. She recommended advocating for patients, noting that giving both patients and providers the tools to further educate themselves and apply that to their regular visits is a good first step.
“Just having access to a facility doesn’t mean they will get the services they need. Preventative services that are recommended for people with disabilities differ from the general population. Providers should be educated about that and the patient needs to be educated about that,” she added.
“Patients who do not approach clinicians get lost in the system. Maybe many facilities are not disability friendly, or they need health literacy. If they don’t know they are at risk for osteoporosis, for example, then they won’t ask,” Dr. Mahmoudi said.
The study was funded by The National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research. Dr. Mahmoudi and Mr. Paden report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ANNALS OF FAMILY MEDICINE
Dr. Birds-n-Bees: How physicians are taking up the sex ed slack
An athletic coach stands in front of a packed gym full of high school students.
“Don’t have sex,” he instructs, “because you will get pregnant and die. Don’t have sex in the missionary position. Don’t have sex standing up. Just don’t do it, promise? Okay, everybody take some rubbers.”
Sad to say, this scene from the 2004 movie “Mean Girls” bears a striking resemblance to the actual sex education courses taught in schools across the United States today. In fact, things may have gotten measurably worse.
National data recently published by the Guttmacher Institute showed that adolescents were less likely to receive adequate sex education from 2015 to 2019 than they were in 1995. Only half of kids aged 15-19 received sex education that met minimum standards recommended by the Department of Health & Human Services, and fewer than half were given this information before having sex for the first time. With such a vast learning gap, it is no surprise that the United States has some of the highest rates of teenage pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections in the developed world.
Concerned and motivated by this need for sex education, physicians and other medical professionals are stepping in to fill the void, offering sexual health information through a range of methods to students of all ages (some a lot older than one may think). It is a calling that takes them outside their hospitals and exam rooms into workshops and through educational materials, video, and social media content created from scratch.
“The fact that we’re able to go in and provide factual, scientific, important information that can affect the trajectory of someone’s life is powerful,” said Julia Rossen, part of a contingent of med students at Brown University, Providence, R.I., who now teach sex ed as an elective.
Their goals are not just about protecting health. Many are also teaching about other topics commonly ignored in sex education classes, such as consent, pleasure, LGBTQ+ identities, and cultural competence. There is a mutually beneficial relationship, they say, between their sex education work and their medical practice.
Changing the status quo
A jumble of state laws govern how and when schools should offer sex education courses. Individual school districts often make the final decisions about their content, creating even more inconsistent standards. Only 29 states and the District of Columbia mandate sex education, and 13 of those do not require that it be medically accurate. Abstinence-only education, which has been shown to be ineffective, is exclusively taught in 16 states.
Without formal instruction, many young people must learn about sex from family members, who may be unwilling, or they may share knowledge between themselves, which is often incorrect, or navigate the limitless information and misinformation available on the internet.
The consequences of this were apparent to several medical students at Brown University in 2013. At the time, the rate of teenage pregnancy across Rhode Island was 1 in 100, but in the small city of Central Falls, it was 1 in 25. Aiming to improve this, the group created a comprehensive sex education program for a Central Falls middle school that was taught by medical student volunteers.
The Sex Ed by Brown Med program continues today. It consists of eight in-person sessions. Topics include anatomy, contraception, STIs, sexual decision-making, consent, sexual violence, and sexual and gender identity. Through this program, as well as other factors, the Central Falls teenage pregnancy rate declined to 1.6 in 100 from 2016 to 2020, according to the Rhode Island Department of Health.
“Historically, sexual education has been politicized,” said Ms. Rossen, one of the current program leaders. “It’s been at the discretion of a lot of different factors that aren’t under the control of the communities that are actually receiving the education.”
Among seventh graders, the teachers say they encounter different levels of maturity. But they feel that the kids are more receptive and open with younger adults who, like them, are still students. Some volunteers recall the flaws in their own sex education, particularly regarding topics such as consent and gender and sexual identity, and they believe middle school is the time to begin the sexual health conversation. “By the time you’re talking to college-age students, it’s pretty much too late,” said another group leader, Benjamin Stone.
Mr. Stone feels that practicing having these often-awkward discussions enhances their clinical skills as physicians. “Sex and sexual history are part of the comprehensive medical interview. People want to have these conversations, and they’re looking for someone to open the door. The kids are excited that we’re opening that door for them. And I think patients feel the same way.”
Conquering social media
Opening the door has been more like releasing a floodgate for Danielle Jones, MD, an ob.gyn. physician who is originally from Texas but who moved to New Zealand in 2021. Known on social media as “Mama Doctor Jones,” she has garnered more than 3 million followers across YouTube, TikTok, Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook. Dr. Jones produces short, friendly, entertaining videos on a range of reproductive health and sex education topics. They appeal to an adolescent audience hungry for a trustworthy voice on issues such as,: “5 ‘Strange’ Things Your Vagina Does That Are NORMAL” and “Condom Broke ... Now What?”
Dr. Jones uses her platform to debunk some of the misleading and inaccurate sexual health information being taught in classrooms, by other social media influencers, and that is found on the internet in general. Her no-nonsense-style videos call out such myths as being unable to pee with a tampon in, Plan B emergency contraception causing abortions, and COVID-19 vaccines damaging fertility.
“The way sex ed is done in the U.S. in most places is continuing the taboo by making it a one-time discussion or health class,” said Dr. Jones, “particularly if boys and girls are separated. That doesn’t further communication between people or foster an environment where it’s okay to discuss your body and puberty and changes in sexual health in general. And if you can’t talk about it in educational spaces, you’re certainly not going to be comfortable talking about that in a one-on-one situation with another 16-year-old.”
Taking on other taboos, Dr. Jones has been outspoken about abortion and the consequences of the recent Supreme Court decision, both as an ethical issue and a medical one that endangers lives. Raised in a deeply religious family, Dr. Jones said she was indoctrinated with antiabortion views, and it took time for her thinking to evolve “from a scientific and humanistic standpoint.” While working in a Texas private practice, Dr. Jones described being unable to mention abortion online because of fear of losing her patients and for her own safety.
Now free of those constraints, Dr. Jones feels that her videos can be important resources for teachers who may have little health training. And she is enthusiastic about the complementary relationship between her social media work and her clinical practice. “There are conversations I have all the time in the clinic where patients tell me: ‘Nobody’s ever really had this conversation in this way with me. Thank you for explaining that,’ ” said Dr. Jones. “And then I think: ‘Well, now I’ll have it with a hundred thousand other people too.’ ”
Promoting pleasure
While not an ob.gyn., discussing sexuality with patients has become a focus for Evelin Dacker, MD, a family physician in Salem, Ore. Dr. Dacker is certified in functional medicine, which takes a holistic and integrative approach. During her training she had a sudden realization: Sexuality had not been discussed at any point during her medical education.
“I recognized that this was a huge gap in how we deal with a person as a human,” Dr. Dacker explained. “Since sexuality plays a role in so many aspects of our humanness, not just having sex.”
Dr. Dacker believes in rethinking sexuality as a fundamental part of overall health, as vital as nutrition or blood pressure. Outside her medical practice, she teaches classes and workshops on sexual health and sex positivity for young adults and other physicians. She has also developed an educational framework for sexual health topics. Dr. Dacker said she frequently confronts the idea that sexuality is only about engaging with another person. She disagrees. Using food as a metaphor, she argues that just as the pleasure of eating something is purely for oneself, sexuality belongs to the individual.
Sexuality can also be a tool for pleasure, which Dr. Dacker believes plays an essential role in physical health. “Pleasure is a medicine,” Dr. Dacker said. “I actually prescribe self-pleasure practices to my patients, so they can start owning it within themselves. Make sure you get 7-8 hours of sleep, do some breathing exercises to help bring down your stress, and do self-pleasure so that you can integrate into your body better.”
She added that the impact of prioritizing one’s own desires, needs, and boundaries can transform how people view their sexuality. Her adult students frequently ask: “Why wasn’t I taught this as a teenager?”
Speaking of adult students – An older generation learns new tricks
While the teen cohort is usually the focus, the lack of sex education in previous decades – and the way sexual culture has evolved in that time – have an impact on older groups. Among U.S. adults aged 55 and older, the rate of STIs has more than doubled in the past 10 years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While the majority of STI cases still occur among teenagers and young adults, the consistent increase in STIs among older persons is cause for concern among physicians and researchers.
The issue worries Shannon Dowler, MD, a family physician in western North Carolina and chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid. Dr. Dowler, who has practiced in an STI clinic throughout her career, began seeing more and more older adults with chlamydia, herpes, and other STIs. Dowler cites several factors behind the rise, including the growing retirement community population, the availability of pharmaceuticals for sexual dysfunction, and the “hook-up culture” that is active on dating apps, which research shows are regularly used by more than a third of adults older than 55.
Dr. Dowler also sees a lack of communication about sexual health between physicians and their older patients. “Older adults are more likely to be in relationship with their physician outside the exam room, especially if they’re in a small community,” Dr. Dowler said. “Sometimes they aren’t as comfortable sharing what their risks are. But we are guilty in medicine all the time of not asking. We assume someone’s older so they’re not having sex anymore. But, in fact, they are, and we’re not taking the time to say: ‘Let’s talk about your sex life. Are you at risk for anything? Are you having any difficulties with sex?’ We tend to avoid it as a health care culture.”
In contrast, Dr. Dowler said she talks about sexual health with anyone who will listen. She teaches classes in private schools and universities and for church youth groups and other physicians. She often finds that public schools are not interested, which she attributes to fear of her discussing things “outside the rule book.”
Dr. Dowler takes creative approaches. In 2017, she released a hip-hop video, “STD’s Never Get Old,” in which she raps about safe sex for older adults. Her video went viral, was mentioned by several news outlets, and received over 50,000 views on YouTube. Dr. Dowler’s latest project is a book, “Never Too Late: Your Guide to Safer Sex after 60,” which is scheduled for publication on Valentine’s Day, 2023.
“It’s sex ed for seniors,” she explained. “It’s that gym class that some people got – I won’t say everyone got – in high school. This is the version for older adults who didn’t get that. There are new infections now that didn’t exist when they had sex education, if they had sex education.”
A big subject requires a big mission
For others in the sex education field, physicians are allies in their fight against agendas designed to obstruct or erode sex education. Alison Macklin, director of policy and advocacy at SIECUS: Sex Ed for Social Change, formerly the Sexuality Information and Education Council of the United States, sees this struggle playing out in school boards and state legislatures across the country. For every comprehensive sex education bill passed or school district victory, there is yet another blocked proposal or restrictive law somewhere else.
Ms. Macklin urged doctors to get more involved locally and to expand their knowledge of sexual health issues by reaching out to organizations such as Planned Parenthood and to be “hyper vigilant” in their own communities.
“Doctors are trusted. People really respect what they have to say,” Ms. Macklin said. “And this is an important time for them to speak up.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An athletic coach stands in front of a packed gym full of high school students.
“Don’t have sex,” he instructs, “because you will get pregnant and die. Don’t have sex in the missionary position. Don’t have sex standing up. Just don’t do it, promise? Okay, everybody take some rubbers.”
Sad to say, this scene from the 2004 movie “Mean Girls” bears a striking resemblance to the actual sex education courses taught in schools across the United States today. In fact, things may have gotten measurably worse.
National data recently published by the Guttmacher Institute showed that adolescents were less likely to receive adequate sex education from 2015 to 2019 than they were in 1995. Only half of kids aged 15-19 received sex education that met minimum standards recommended by the Department of Health & Human Services, and fewer than half were given this information before having sex for the first time. With such a vast learning gap, it is no surprise that the United States has some of the highest rates of teenage pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections in the developed world.
Concerned and motivated by this need for sex education, physicians and other medical professionals are stepping in to fill the void, offering sexual health information through a range of methods to students of all ages (some a lot older than one may think). It is a calling that takes them outside their hospitals and exam rooms into workshops and through educational materials, video, and social media content created from scratch.
“The fact that we’re able to go in and provide factual, scientific, important information that can affect the trajectory of someone’s life is powerful,” said Julia Rossen, part of a contingent of med students at Brown University, Providence, R.I., who now teach sex ed as an elective.
Their goals are not just about protecting health. Many are also teaching about other topics commonly ignored in sex education classes, such as consent, pleasure, LGBTQ+ identities, and cultural competence. There is a mutually beneficial relationship, they say, between their sex education work and their medical practice.
Changing the status quo
A jumble of state laws govern how and when schools should offer sex education courses. Individual school districts often make the final decisions about their content, creating even more inconsistent standards. Only 29 states and the District of Columbia mandate sex education, and 13 of those do not require that it be medically accurate. Abstinence-only education, which has been shown to be ineffective, is exclusively taught in 16 states.
Without formal instruction, many young people must learn about sex from family members, who may be unwilling, or they may share knowledge between themselves, which is often incorrect, or navigate the limitless information and misinformation available on the internet.
The consequences of this were apparent to several medical students at Brown University in 2013. At the time, the rate of teenage pregnancy across Rhode Island was 1 in 100, but in the small city of Central Falls, it was 1 in 25. Aiming to improve this, the group created a comprehensive sex education program for a Central Falls middle school that was taught by medical student volunteers.
The Sex Ed by Brown Med program continues today. It consists of eight in-person sessions. Topics include anatomy, contraception, STIs, sexual decision-making, consent, sexual violence, and sexual and gender identity. Through this program, as well as other factors, the Central Falls teenage pregnancy rate declined to 1.6 in 100 from 2016 to 2020, according to the Rhode Island Department of Health.
“Historically, sexual education has been politicized,” said Ms. Rossen, one of the current program leaders. “It’s been at the discretion of a lot of different factors that aren’t under the control of the communities that are actually receiving the education.”
Among seventh graders, the teachers say they encounter different levels of maturity. But they feel that the kids are more receptive and open with younger adults who, like them, are still students. Some volunteers recall the flaws in their own sex education, particularly regarding topics such as consent and gender and sexual identity, and they believe middle school is the time to begin the sexual health conversation. “By the time you’re talking to college-age students, it’s pretty much too late,” said another group leader, Benjamin Stone.
Mr. Stone feels that practicing having these often-awkward discussions enhances their clinical skills as physicians. “Sex and sexual history are part of the comprehensive medical interview. People want to have these conversations, and they’re looking for someone to open the door. The kids are excited that we’re opening that door for them. And I think patients feel the same way.”
Conquering social media
Opening the door has been more like releasing a floodgate for Danielle Jones, MD, an ob.gyn. physician who is originally from Texas but who moved to New Zealand in 2021. Known on social media as “Mama Doctor Jones,” she has garnered more than 3 million followers across YouTube, TikTok, Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook. Dr. Jones produces short, friendly, entertaining videos on a range of reproductive health and sex education topics. They appeal to an adolescent audience hungry for a trustworthy voice on issues such as,: “5 ‘Strange’ Things Your Vagina Does That Are NORMAL” and “Condom Broke ... Now What?”
Dr. Jones uses her platform to debunk some of the misleading and inaccurate sexual health information being taught in classrooms, by other social media influencers, and that is found on the internet in general. Her no-nonsense-style videos call out such myths as being unable to pee with a tampon in, Plan B emergency contraception causing abortions, and COVID-19 vaccines damaging fertility.
“The way sex ed is done in the U.S. in most places is continuing the taboo by making it a one-time discussion or health class,” said Dr. Jones, “particularly if boys and girls are separated. That doesn’t further communication between people or foster an environment where it’s okay to discuss your body and puberty and changes in sexual health in general. And if you can’t talk about it in educational spaces, you’re certainly not going to be comfortable talking about that in a one-on-one situation with another 16-year-old.”
Taking on other taboos, Dr. Jones has been outspoken about abortion and the consequences of the recent Supreme Court decision, both as an ethical issue and a medical one that endangers lives. Raised in a deeply religious family, Dr. Jones said she was indoctrinated with antiabortion views, and it took time for her thinking to evolve “from a scientific and humanistic standpoint.” While working in a Texas private practice, Dr. Jones described being unable to mention abortion online because of fear of losing her patients and for her own safety.
Now free of those constraints, Dr. Jones feels that her videos can be important resources for teachers who may have little health training. And she is enthusiastic about the complementary relationship between her social media work and her clinical practice. “There are conversations I have all the time in the clinic where patients tell me: ‘Nobody’s ever really had this conversation in this way with me. Thank you for explaining that,’ ” said Dr. Jones. “And then I think: ‘Well, now I’ll have it with a hundred thousand other people too.’ ”
Promoting pleasure
While not an ob.gyn., discussing sexuality with patients has become a focus for Evelin Dacker, MD, a family physician in Salem, Ore. Dr. Dacker is certified in functional medicine, which takes a holistic and integrative approach. During her training she had a sudden realization: Sexuality had not been discussed at any point during her medical education.
“I recognized that this was a huge gap in how we deal with a person as a human,” Dr. Dacker explained. “Since sexuality plays a role in so many aspects of our humanness, not just having sex.”
Dr. Dacker believes in rethinking sexuality as a fundamental part of overall health, as vital as nutrition or blood pressure. Outside her medical practice, she teaches classes and workshops on sexual health and sex positivity for young adults and other physicians. She has also developed an educational framework for sexual health topics. Dr. Dacker said she frequently confronts the idea that sexuality is only about engaging with another person. She disagrees. Using food as a metaphor, she argues that just as the pleasure of eating something is purely for oneself, sexuality belongs to the individual.
Sexuality can also be a tool for pleasure, which Dr. Dacker believes plays an essential role in physical health. “Pleasure is a medicine,” Dr. Dacker said. “I actually prescribe self-pleasure practices to my patients, so they can start owning it within themselves. Make sure you get 7-8 hours of sleep, do some breathing exercises to help bring down your stress, and do self-pleasure so that you can integrate into your body better.”
She added that the impact of prioritizing one’s own desires, needs, and boundaries can transform how people view their sexuality. Her adult students frequently ask: “Why wasn’t I taught this as a teenager?”
Speaking of adult students – An older generation learns new tricks
While the teen cohort is usually the focus, the lack of sex education in previous decades – and the way sexual culture has evolved in that time – have an impact on older groups. Among U.S. adults aged 55 and older, the rate of STIs has more than doubled in the past 10 years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While the majority of STI cases still occur among teenagers and young adults, the consistent increase in STIs among older persons is cause for concern among physicians and researchers.
The issue worries Shannon Dowler, MD, a family physician in western North Carolina and chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid. Dr. Dowler, who has practiced in an STI clinic throughout her career, began seeing more and more older adults with chlamydia, herpes, and other STIs. Dowler cites several factors behind the rise, including the growing retirement community population, the availability of pharmaceuticals for sexual dysfunction, and the “hook-up culture” that is active on dating apps, which research shows are regularly used by more than a third of adults older than 55.
Dr. Dowler also sees a lack of communication about sexual health between physicians and their older patients. “Older adults are more likely to be in relationship with their physician outside the exam room, especially if they’re in a small community,” Dr. Dowler said. “Sometimes they aren’t as comfortable sharing what their risks are. But we are guilty in medicine all the time of not asking. We assume someone’s older so they’re not having sex anymore. But, in fact, they are, and we’re not taking the time to say: ‘Let’s talk about your sex life. Are you at risk for anything? Are you having any difficulties with sex?’ We tend to avoid it as a health care culture.”
In contrast, Dr. Dowler said she talks about sexual health with anyone who will listen. She teaches classes in private schools and universities and for church youth groups and other physicians. She often finds that public schools are not interested, which she attributes to fear of her discussing things “outside the rule book.”
Dr. Dowler takes creative approaches. In 2017, she released a hip-hop video, “STD’s Never Get Old,” in which she raps about safe sex for older adults. Her video went viral, was mentioned by several news outlets, and received over 50,000 views on YouTube. Dr. Dowler’s latest project is a book, “Never Too Late: Your Guide to Safer Sex after 60,” which is scheduled for publication on Valentine’s Day, 2023.
“It’s sex ed for seniors,” she explained. “It’s that gym class that some people got – I won’t say everyone got – in high school. This is the version for older adults who didn’t get that. There are new infections now that didn’t exist when they had sex education, if they had sex education.”
A big subject requires a big mission
For others in the sex education field, physicians are allies in their fight against agendas designed to obstruct or erode sex education. Alison Macklin, director of policy and advocacy at SIECUS: Sex Ed for Social Change, formerly the Sexuality Information and Education Council of the United States, sees this struggle playing out in school boards and state legislatures across the country. For every comprehensive sex education bill passed or school district victory, there is yet another blocked proposal or restrictive law somewhere else.
Ms. Macklin urged doctors to get more involved locally and to expand their knowledge of sexual health issues by reaching out to organizations such as Planned Parenthood and to be “hyper vigilant” in their own communities.
“Doctors are trusted. People really respect what they have to say,” Ms. Macklin said. “And this is an important time for them to speak up.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An athletic coach stands in front of a packed gym full of high school students.
“Don’t have sex,” he instructs, “because you will get pregnant and die. Don’t have sex in the missionary position. Don’t have sex standing up. Just don’t do it, promise? Okay, everybody take some rubbers.”
Sad to say, this scene from the 2004 movie “Mean Girls” bears a striking resemblance to the actual sex education courses taught in schools across the United States today. In fact, things may have gotten measurably worse.
National data recently published by the Guttmacher Institute showed that adolescents were less likely to receive adequate sex education from 2015 to 2019 than they were in 1995. Only half of kids aged 15-19 received sex education that met minimum standards recommended by the Department of Health & Human Services, and fewer than half were given this information before having sex for the first time. With such a vast learning gap, it is no surprise that the United States has some of the highest rates of teenage pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections in the developed world.
Concerned and motivated by this need for sex education, physicians and other medical professionals are stepping in to fill the void, offering sexual health information through a range of methods to students of all ages (some a lot older than one may think). It is a calling that takes them outside their hospitals and exam rooms into workshops and through educational materials, video, and social media content created from scratch.
“The fact that we’re able to go in and provide factual, scientific, important information that can affect the trajectory of someone’s life is powerful,” said Julia Rossen, part of a contingent of med students at Brown University, Providence, R.I., who now teach sex ed as an elective.
Their goals are not just about protecting health. Many are also teaching about other topics commonly ignored in sex education classes, such as consent, pleasure, LGBTQ+ identities, and cultural competence. There is a mutually beneficial relationship, they say, between their sex education work and their medical practice.
Changing the status quo
A jumble of state laws govern how and when schools should offer sex education courses. Individual school districts often make the final decisions about their content, creating even more inconsistent standards. Only 29 states and the District of Columbia mandate sex education, and 13 of those do not require that it be medically accurate. Abstinence-only education, which has been shown to be ineffective, is exclusively taught in 16 states.
Without formal instruction, many young people must learn about sex from family members, who may be unwilling, or they may share knowledge between themselves, which is often incorrect, or navigate the limitless information and misinformation available on the internet.
The consequences of this were apparent to several medical students at Brown University in 2013. At the time, the rate of teenage pregnancy across Rhode Island was 1 in 100, but in the small city of Central Falls, it was 1 in 25. Aiming to improve this, the group created a comprehensive sex education program for a Central Falls middle school that was taught by medical student volunteers.
The Sex Ed by Brown Med program continues today. It consists of eight in-person sessions. Topics include anatomy, contraception, STIs, sexual decision-making, consent, sexual violence, and sexual and gender identity. Through this program, as well as other factors, the Central Falls teenage pregnancy rate declined to 1.6 in 100 from 2016 to 2020, according to the Rhode Island Department of Health.
“Historically, sexual education has been politicized,” said Ms. Rossen, one of the current program leaders. “It’s been at the discretion of a lot of different factors that aren’t under the control of the communities that are actually receiving the education.”
Among seventh graders, the teachers say they encounter different levels of maturity. But they feel that the kids are more receptive and open with younger adults who, like them, are still students. Some volunteers recall the flaws in their own sex education, particularly regarding topics such as consent and gender and sexual identity, and they believe middle school is the time to begin the sexual health conversation. “By the time you’re talking to college-age students, it’s pretty much too late,” said another group leader, Benjamin Stone.
Mr. Stone feels that practicing having these often-awkward discussions enhances their clinical skills as physicians. “Sex and sexual history are part of the comprehensive medical interview. People want to have these conversations, and they’re looking for someone to open the door. The kids are excited that we’re opening that door for them. And I think patients feel the same way.”
Conquering social media
Opening the door has been more like releasing a floodgate for Danielle Jones, MD, an ob.gyn. physician who is originally from Texas but who moved to New Zealand in 2021. Known on social media as “Mama Doctor Jones,” she has garnered more than 3 million followers across YouTube, TikTok, Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook. Dr. Jones produces short, friendly, entertaining videos on a range of reproductive health and sex education topics. They appeal to an adolescent audience hungry for a trustworthy voice on issues such as,: “5 ‘Strange’ Things Your Vagina Does That Are NORMAL” and “Condom Broke ... Now What?”
Dr. Jones uses her platform to debunk some of the misleading and inaccurate sexual health information being taught in classrooms, by other social media influencers, and that is found on the internet in general. Her no-nonsense-style videos call out such myths as being unable to pee with a tampon in, Plan B emergency contraception causing abortions, and COVID-19 vaccines damaging fertility.
“The way sex ed is done in the U.S. in most places is continuing the taboo by making it a one-time discussion or health class,” said Dr. Jones, “particularly if boys and girls are separated. That doesn’t further communication between people or foster an environment where it’s okay to discuss your body and puberty and changes in sexual health in general. And if you can’t talk about it in educational spaces, you’re certainly not going to be comfortable talking about that in a one-on-one situation with another 16-year-old.”
Taking on other taboos, Dr. Jones has been outspoken about abortion and the consequences of the recent Supreme Court decision, both as an ethical issue and a medical one that endangers lives. Raised in a deeply religious family, Dr. Jones said she was indoctrinated with antiabortion views, and it took time for her thinking to evolve “from a scientific and humanistic standpoint.” While working in a Texas private practice, Dr. Jones described being unable to mention abortion online because of fear of losing her patients and for her own safety.
Now free of those constraints, Dr. Jones feels that her videos can be important resources for teachers who may have little health training. And she is enthusiastic about the complementary relationship between her social media work and her clinical practice. “There are conversations I have all the time in the clinic where patients tell me: ‘Nobody’s ever really had this conversation in this way with me. Thank you for explaining that,’ ” said Dr. Jones. “And then I think: ‘Well, now I’ll have it with a hundred thousand other people too.’ ”
Promoting pleasure
While not an ob.gyn., discussing sexuality with patients has become a focus for Evelin Dacker, MD, a family physician in Salem, Ore. Dr. Dacker is certified in functional medicine, which takes a holistic and integrative approach. During her training she had a sudden realization: Sexuality had not been discussed at any point during her medical education.
“I recognized that this was a huge gap in how we deal with a person as a human,” Dr. Dacker explained. “Since sexuality plays a role in so many aspects of our humanness, not just having sex.”
Dr. Dacker believes in rethinking sexuality as a fundamental part of overall health, as vital as nutrition or blood pressure. Outside her medical practice, she teaches classes and workshops on sexual health and sex positivity for young adults and other physicians. She has also developed an educational framework for sexual health topics. Dr. Dacker said she frequently confronts the idea that sexuality is only about engaging with another person. She disagrees. Using food as a metaphor, she argues that just as the pleasure of eating something is purely for oneself, sexuality belongs to the individual.
Sexuality can also be a tool for pleasure, which Dr. Dacker believes plays an essential role in physical health. “Pleasure is a medicine,” Dr. Dacker said. “I actually prescribe self-pleasure practices to my patients, so they can start owning it within themselves. Make sure you get 7-8 hours of sleep, do some breathing exercises to help bring down your stress, and do self-pleasure so that you can integrate into your body better.”
She added that the impact of prioritizing one’s own desires, needs, and boundaries can transform how people view their sexuality. Her adult students frequently ask: “Why wasn’t I taught this as a teenager?”
Speaking of adult students – An older generation learns new tricks
While the teen cohort is usually the focus, the lack of sex education in previous decades – and the way sexual culture has evolved in that time – have an impact on older groups. Among U.S. adults aged 55 and older, the rate of STIs has more than doubled in the past 10 years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While the majority of STI cases still occur among teenagers and young adults, the consistent increase in STIs among older persons is cause for concern among physicians and researchers.
The issue worries Shannon Dowler, MD, a family physician in western North Carolina and chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid. Dr. Dowler, who has practiced in an STI clinic throughout her career, began seeing more and more older adults with chlamydia, herpes, and other STIs. Dowler cites several factors behind the rise, including the growing retirement community population, the availability of pharmaceuticals for sexual dysfunction, and the “hook-up culture” that is active on dating apps, which research shows are regularly used by more than a third of adults older than 55.
Dr. Dowler also sees a lack of communication about sexual health between physicians and their older patients. “Older adults are more likely to be in relationship with their physician outside the exam room, especially if they’re in a small community,” Dr. Dowler said. “Sometimes they aren’t as comfortable sharing what their risks are. But we are guilty in medicine all the time of not asking. We assume someone’s older so they’re not having sex anymore. But, in fact, they are, and we’re not taking the time to say: ‘Let’s talk about your sex life. Are you at risk for anything? Are you having any difficulties with sex?’ We tend to avoid it as a health care culture.”
In contrast, Dr. Dowler said she talks about sexual health with anyone who will listen. She teaches classes in private schools and universities and for church youth groups and other physicians. She often finds that public schools are not interested, which she attributes to fear of her discussing things “outside the rule book.”
Dr. Dowler takes creative approaches. In 2017, she released a hip-hop video, “STD’s Never Get Old,” in which she raps about safe sex for older adults. Her video went viral, was mentioned by several news outlets, and received over 50,000 views on YouTube. Dr. Dowler’s latest project is a book, “Never Too Late: Your Guide to Safer Sex after 60,” which is scheduled for publication on Valentine’s Day, 2023.
“It’s sex ed for seniors,” she explained. “It’s that gym class that some people got – I won’t say everyone got – in high school. This is the version for older adults who didn’t get that. There are new infections now that didn’t exist when they had sex education, if they had sex education.”
A big subject requires a big mission
For others in the sex education field, physicians are allies in their fight against agendas designed to obstruct or erode sex education. Alison Macklin, director of policy and advocacy at SIECUS: Sex Ed for Social Change, formerly the Sexuality Information and Education Council of the United States, sees this struggle playing out in school boards and state legislatures across the country. For every comprehensive sex education bill passed or school district victory, there is yet another blocked proposal or restrictive law somewhere else.
Ms. Macklin urged doctors to get more involved locally and to expand their knowledge of sexual health issues by reaching out to organizations such as Planned Parenthood and to be “hyper vigilant” in their own communities.
“Doctors are trusted. People really respect what they have to say,” Ms. Macklin said. “And this is an important time for them to speak up.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Noted oncologist ponders death, life, care inequities
In 2020, he published a book aimed at cancer specialists and their patients on how to die “with hope and dignity,” titled “Between Life and Death” (Penguin Random House India).
When Dr. Patel, the CEO of Carolina Blood and Cancer Care Associates in Rock Hill, S.C., became president of the Washington-based Community Oncology Alliance 2 years ago, he stepped into a leadership role in community oncology. As an advocate for health care payment reform on Capitol Hill, the South Carolina legislature, and within his own practice, Dr. Patel has long worked to eliminate disparities in U.S. cancer care.
This news organization spoke with Dr. Patel about his unusual career path.
Question: Your father had a great influence on you. Can you tell us more about him?
Answer: My dad was a hermit and a saint. He lost his dad when he was 4 years old and moved to the big city with his cousins. When he was 9 or so, he got a message saying that his mum was very ill. So, he and his cousin raised some money, got a doctor and one of those old, rugged jeeps, and they started driving to the village, but rains had destroyed the road. So, without penicillin, his mum died of pneumonia.
He felt that roads and doctor access were the two big factors that could have saved her life. He eventually became the Superintending Engineer for four districts in Gujarat State, building roads connecting every village, but he never gave up his simplistic, minimalist life.
When I was in elementary school, every other weekend my dad would literally dump me at the Mahatma Gandhi Ashram and come back in 2 hours. So, I’m looking at Gandhi’s cabinets, his pictures, reading about his life. So, my formative years were born in that.
Q: I read that you were intending to become an engineer and join the space race. How did your father nudge you toward medicine?
A: When I was 9 years old, my favorite movie hero died of cancer. To comfort me, my father inserted the idea into my brain: When you grow up, you can become a doctor to cure cancer. So, when I finished high school, I was 24th in the state and had an option to go to the space school in India. On the day when I was going for the interview, I could see tears in my father’s eyes, and he said, You know what, boy? I thought you’re going to become a doctor and cure cancer. So, to honor him, I went to med school instead.

Q: I understand that your father also triggered your interest in photography?
A: I started photographing Kutchi tribal people in 1977, after I bought a camera from a famous architect [Hasmukh Patel], while traveling with my dad. And then my dad bought me a motorcycle, so I started riding myself. From the time I entered med school in 1978 until I finished my residency in 1987, I made several trips following Kutchi migrant families and livestock. They leave their homeland in Kutch [district] during summer in search of grass and water to keep their livestock alive and walk across the state from the desert of Kutch all the way to central Gujarat until monsoon begins. Then they return, only to resume the journey next year. I would catch them along their journey, would talk to them, drink tea and eat millet crepes with them.

In 1984, between Dr. Patel’s medical school and residency, the Lions Club in his hometown, Ahmedabad, India, sponsored him and three buddies to document people and wildlife in Gujarat state. Traveling by motorcycle, the four friends stayed for free with local families by knocking on doors and explaining that they were medical students. Dr. Patel’s photographs were exhibited by the Lions Club of Ahmedabad and at India’s top art institution, the Lalit Kala gallery.
In the 3rd year of his internal-medicine residency in Bombay (now Mumbai), Dr. Patel approached a national newspaper, The Indian Express, for work. He was immediately sent on assignment to cover a cholera epidemic and filed his story and photographs the following day. He worked as a photojournalist and subeditor for a year.
Q: Among all your thousands of pictures, do you have a favorite?
A: There were two photos of Kutchi people that touched me. There was one photo of a lady. All of her worldly belongings were in the picture and a smile on her face showed that we don’t need so many things to be happy. The second photo is of an elderly lady shifting her water pan on her head to a younger family member. And a little girl looks up with a look of curiosity: Will I be doing this when I grow up? We seek so much materialistic happiness. But when you look at the curiosity, smiles, and happiness [in these photos], you realize we could have a lot of happiness in minimalism, as well.
Q: After you finished your residency in Ahmedabad, how did you get started in oncology?
A: In 1986, Ahmedabad City and Gujarat State did not have structured training programs in oncology, so I went to Bombay [Mumbai], where Dr. B.C. Mehta, a true legend and pioneer in India, had started hematology-oncology training. I was a post-doc research fellow with him for a little over a year but when I started seeing patients, I had to answer to myself, Am I doing everything I can to help these people? I saw that the U.K. had one of the best training programs in hem malignancy, so I started applying. Then something happened that was almost like a miracle.
In April 1992, Dr. Patel was working at the Institute of Kidney Diseases in Ahmedabad. One afternoon, just as the clinic was closing for siesta, a family brought in a young girl. She had drug-induced thrombocytopenia and needed an immediate transfusion. The father offered to sell his wedding ring to pay Dr. Patel if he would supervise the treatment and stay by the girl’s side. Dr. Patel told the man to keep his ring, then he remained in the office with the child. At 4 p.m., the office phone rang. It was Dr. H.K. Parikh, an eminent British physician who was wintering in India and needed to make a medical appointment for his wife. On a normal day, Dr. Patel would have missed the call.
“This is how I got to meet Dr. Parikh, out of the blue,” said Dr. Patel. “His wife came to the office for 6 weeks and after 6 weeks, he said, You’re a smart guy; you should come to England. That was in April. I sent a resume and all the usual paperwork. On July 16, 1992, at 2 in the morning, I got a call from the U.K. saying, Your job is confirmed. I’m going to fax your appointment through the Royal College of Physicians, and you’re coming to Manchester to work with us. I’d been sponsored by the Overseas Doctors Training Program.
“So, it turns out that if I’d declined to see that patient and declined to stay in my clinic that afternoon, if I’d declined to see this doctor’s wife, I would never have been in the U.K. And that opened up the doors for me. I like that story because I’ve found that standing up for people who do not have a voice, who do not have hope, always leads to what is destined for me.”
Q: After working as a registrar in the United Kingdom 4 years, you found yourself in the United States and, once again, had to train as an internist. What was new about U.S. oncology?
A: I took 3 years to get recertified in Jamaica Hospital in Queens, then became a fellow in hematology-oncology at the Thomas Jefferson in Philadelphia. My U.K. training was all based on hematological malignancy. In the United States, I shifted into solid tumors.
Q: You have a long history of advocating for affordable oncology at the community, state, and federal level, and you recently launched a disparities initiative in your center called NOLA (No One Left Alone). What was the trigger for NOLA?
A: In the spring of 2020, when we started seeing the COVID surge and the difference in mortality rate between the multiple races, at the same time I saw the AACR [American Association for Cancer Research] 2020 disparity report showing that 34% of cancer deaths are preventable – one in three – if we took care of disparities. The same year, the Community Oncology Alliance asked me to become the president. So, I felt that there is something herding me, leading me, to this position. Eighty percent of cancer patients are treated in community clinics like ours. It put the onus on me to do something.
I learned from Gandhi that I cannot depend on government, I cannot depend on the policy, I have to act myself.
I said, I would not worry about making money, I would rather lose funding on this. So, we started. I read 400+ papers; I spent over 1,000 hours reading about disparities. And I realized that it’s not complicated. There are five pillars to eliminate disparity: access to care for financial reasons, access to biomarker testing or precision medicine, access to social determinants of health, access to cancer screening, and trials. If we focus on these five, we can at least bring that number from 34% to 20%, if not lower.
So, we put that plan in place. I dedicated three employees whose only role is to ensure that not a single patient has to take financial burden from my practice. And we showed it’s doable.
This has now become my mission for the last quarter of my life.
In 2020, Dr. Patel published a book on dying well titled “Between Life and Death.” It’s framed as a series of his conversations with a former patient, Harry Falls. Harry wanted to understand death better, so Dr. Patel narrated five patient stories, drawing the threads together to help Harry face the inevitable. Dr. Patel now uses a similar approach to train clinicians on having meaningful end-of-life conversations with patients.
Q: Why did you feel the need to write a book about dying?
A: The more I’ve witnessed, the more I’m convinced that there are things that we don’t know about this process, which needs to be explored much more. However, I do feel that there’s a power within all of us to steer the process of leaving this world.
Before I sat down with Harry, I loved to counsel patients, but I didn’t have any structural ideas. It was Harry himself who told me that I now had a simple way to explain dying to a much larger audience.
Q: What is your secret for fitting everything into your life?
A: I’ll tell you, it’s very simple. If I put my soul, heart, mind, actions, and language on the one plane and don’t let my brain and conditioning influence my choices, then I live in the moment. Whenever I let my conditioned mind take all the decisions, those are crooked, because you know, we’re selfish creatures – we can use what we call the convenient lie to hide inconvenient truth. And I try not to do that. I mean, it’s been a journey. It didn’t come overnight. I learned. And I feel that over all these years, the only thing that rewarded me, that opened the door of where I am today, was pure, selfless process, whether it’s the act of talking, speaking, or doing.
In 2020, he published a book aimed at cancer specialists and their patients on how to die “with hope and dignity,” titled “Between Life and Death” (Penguin Random House India).
When Dr. Patel, the CEO of Carolina Blood and Cancer Care Associates in Rock Hill, S.C., became president of the Washington-based Community Oncology Alliance 2 years ago, he stepped into a leadership role in community oncology. As an advocate for health care payment reform on Capitol Hill, the South Carolina legislature, and within his own practice, Dr. Patel has long worked to eliminate disparities in U.S. cancer care.
This news organization spoke with Dr. Patel about his unusual career path.
Question: Your father had a great influence on you. Can you tell us more about him?
Answer: My dad was a hermit and a saint. He lost his dad when he was 4 years old and moved to the big city with his cousins. When he was 9 or so, he got a message saying that his mum was very ill. So, he and his cousin raised some money, got a doctor and one of those old, rugged jeeps, and they started driving to the village, but rains had destroyed the road. So, without penicillin, his mum died of pneumonia.
He felt that roads and doctor access were the two big factors that could have saved her life. He eventually became the Superintending Engineer for four districts in Gujarat State, building roads connecting every village, but he never gave up his simplistic, minimalist life.
When I was in elementary school, every other weekend my dad would literally dump me at the Mahatma Gandhi Ashram and come back in 2 hours. So, I’m looking at Gandhi’s cabinets, his pictures, reading about his life. So, my formative years were born in that.
Q: I read that you were intending to become an engineer and join the space race. How did your father nudge you toward medicine?
A: When I was 9 years old, my favorite movie hero died of cancer. To comfort me, my father inserted the idea into my brain: When you grow up, you can become a doctor to cure cancer. So, when I finished high school, I was 24th in the state and had an option to go to the space school in India. On the day when I was going for the interview, I could see tears in my father’s eyes, and he said, You know what, boy? I thought you’re going to become a doctor and cure cancer. So, to honor him, I went to med school instead.

Q: I understand that your father also triggered your interest in photography?
A: I started photographing Kutchi tribal people in 1977, after I bought a camera from a famous architect [Hasmukh Patel], while traveling with my dad. And then my dad bought me a motorcycle, so I started riding myself. From the time I entered med school in 1978 until I finished my residency in 1987, I made several trips following Kutchi migrant families and livestock. They leave their homeland in Kutch [district] during summer in search of grass and water to keep their livestock alive and walk across the state from the desert of Kutch all the way to central Gujarat until monsoon begins. Then they return, only to resume the journey next year. I would catch them along their journey, would talk to them, drink tea and eat millet crepes with them.

In 1984, between Dr. Patel’s medical school and residency, the Lions Club in his hometown, Ahmedabad, India, sponsored him and three buddies to document people and wildlife in Gujarat state. Traveling by motorcycle, the four friends stayed for free with local families by knocking on doors and explaining that they were medical students. Dr. Patel’s photographs were exhibited by the Lions Club of Ahmedabad and at India’s top art institution, the Lalit Kala gallery.
In the 3rd year of his internal-medicine residency in Bombay (now Mumbai), Dr. Patel approached a national newspaper, The Indian Express, for work. He was immediately sent on assignment to cover a cholera epidemic and filed his story and photographs the following day. He worked as a photojournalist and subeditor for a year.
Q: Among all your thousands of pictures, do you have a favorite?
A: There were two photos of Kutchi people that touched me. There was one photo of a lady. All of her worldly belongings were in the picture and a smile on her face showed that we don’t need so many things to be happy. The second photo is of an elderly lady shifting her water pan on her head to a younger family member. And a little girl looks up with a look of curiosity: Will I be doing this when I grow up? We seek so much materialistic happiness. But when you look at the curiosity, smiles, and happiness [in these photos], you realize we could have a lot of happiness in minimalism, as well.
Q: After you finished your residency in Ahmedabad, how did you get started in oncology?
A: In 1986, Ahmedabad City and Gujarat State did not have structured training programs in oncology, so I went to Bombay [Mumbai], where Dr. B.C. Mehta, a true legend and pioneer in India, had started hematology-oncology training. I was a post-doc research fellow with him for a little over a year but when I started seeing patients, I had to answer to myself, Am I doing everything I can to help these people? I saw that the U.K. had one of the best training programs in hem malignancy, so I started applying. Then something happened that was almost like a miracle.
In April 1992, Dr. Patel was working at the Institute of Kidney Diseases in Ahmedabad. One afternoon, just as the clinic was closing for siesta, a family brought in a young girl. She had drug-induced thrombocytopenia and needed an immediate transfusion. The father offered to sell his wedding ring to pay Dr. Patel if he would supervise the treatment and stay by the girl’s side. Dr. Patel told the man to keep his ring, then he remained in the office with the child. At 4 p.m., the office phone rang. It was Dr. H.K. Parikh, an eminent British physician who was wintering in India and needed to make a medical appointment for his wife. On a normal day, Dr. Patel would have missed the call.
“This is how I got to meet Dr. Parikh, out of the blue,” said Dr. Patel. “His wife came to the office for 6 weeks and after 6 weeks, he said, You’re a smart guy; you should come to England. That was in April. I sent a resume and all the usual paperwork. On July 16, 1992, at 2 in the morning, I got a call from the U.K. saying, Your job is confirmed. I’m going to fax your appointment through the Royal College of Physicians, and you’re coming to Manchester to work with us. I’d been sponsored by the Overseas Doctors Training Program.
“So, it turns out that if I’d declined to see that patient and declined to stay in my clinic that afternoon, if I’d declined to see this doctor’s wife, I would never have been in the U.K. And that opened up the doors for me. I like that story because I’ve found that standing up for people who do not have a voice, who do not have hope, always leads to what is destined for me.”
Q: After working as a registrar in the United Kingdom 4 years, you found yourself in the United States and, once again, had to train as an internist. What was new about U.S. oncology?
A: I took 3 years to get recertified in Jamaica Hospital in Queens, then became a fellow in hematology-oncology at the Thomas Jefferson in Philadelphia. My U.K. training was all based on hematological malignancy. In the United States, I shifted into solid tumors.
Q: You have a long history of advocating for affordable oncology at the community, state, and federal level, and you recently launched a disparities initiative in your center called NOLA (No One Left Alone). What was the trigger for NOLA?
A: In the spring of 2020, when we started seeing the COVID surge and the difference in mortality rate between the multiple races, at the same time I saw the AACR [American Association for Cancer Research] 2020 disparity report showing that 34% of cancer deaths are preventable – one in three – if we took care of disparities. The same year, the Community Oncology Alliance asked me to become the president. So, I felt that there is something herding me, leading me, to this position. Eighty percent of cancer patients are treated in community clinics like ours. It put the onus on me to do something.
I learned from Gandhi that I cannot depend on government, I cannot depend on the policy, I have to act myself.
I said, I would not worry about making money, I would rather lose funding on this. So, we started. I read 400+ papers; I spent over 1,000 hours reading about disparities. And I realized that it’s not complicated. There are five pillars to eliminate disparity: access to care for financial reasons, access to biomarker testing or precision medicine, access to social determinants of health, access to cancer screening, and trials. If we focus on these five, we can at least bring that number from 34% to 20%, if not lower.
So, we put that plan in place. I dedicated three employees whose only role is to ensure that not a single patient has to take financial burden from my practice. And we showed it’s doable.
This has now become my mission for the last quarter of my life.
In 2020, Dr. Patel published a book on dying well titled “Between Life and Death.” It’s framed as a series of his conversations with a former patient, Harry Falls. Harry wanted to understand death better, so Dr. Patel narrated five patient stories, drawing the threads together to help Harry face the inevitable. Dr. Patel now uses a similar approach to train clinicians on having meaningful end-of-life conversations with patients.
Q: Why did you feel the need to write a book about dying?
A: The more I’ve witnessed, the more I’m convinced that there are things that we don’t know about this process, which needs to be explored much more. However, I do feel that there’s a power within all of us to steer the process of leaving this world.
Before I sat down with Harry, I loved to counsel patients, but I didn’t have any structural ideas. It was Harry himself who told me that I now had a simple way to explain dying to a much larger audience.
Q: What is your secret for fitting everything into your life?
A: I’ll tell you, it’s very simple. If I put my soul, heart, mind, actions, and language on the one plane and don’t let my brain and conditioning influence my choices, then I live in the moment. Whenever I let my conditioned mind take all the decisions, those are crooked, because you know, we’re selfish creatures – we can use what we call the convenient lie to hide inconvenient truth. And I try not to do that. I mean, it’s been a journey. It didn’t come overnight. I learned. And I feel that over all these years, the only thing that rewarded me, that opened the door of where I am today, was pure, selfless process, whether it’s the act of talking, speaking, or doing.
In 2020, he published a book aimed at cancer specialists and their patients on how to die “with hope and dignity,” titled “Between Life and Death” (Penguin Random House India).
When Dr. Patel, the CEO of Carolina Blood and Cancer Care Associates in Rock Hill, S.C., became president of the Washington-based Community Oncology Alliance 2 years ago, he stepped into a leadership role in community oncology. As an advocate for health care payment reform on Capitol Hill, the South Carolina legislature, and within his own practice, Dr. Patel has long worked to eliminate disparities in U.S. cancer care.
This news organization spoke with Dr. Patel about his unusual career path.
Question: Your father had a great influence on you. Can you tell us more about him?
Answer: My dad was a hermit and a saint. He lost his dad when he was 4 years old and moved to the big city with his cousins. When he was 9 or so, he got a message saying that his mum was very ill. So, he and his cousin raised some money, got a doctor and one of those old, rugged jeeps, and they started driving to the village, but rains had destroyed the road. So, without penicillin, his mum died of pneumonia.
He felt that roads and doctor access were the two big factors that could have saved her life. He eventually became the Superintending Engineer for four districts in Gujarat State, building roads connecting every village, but he never gave up his simplistic, minimalist life.
When I was in elementary school, every other weekend my dad would literally dump me at the Mahatma Gandhi Ashram and come back in 2 hours. So, I’m looking at Gandhi’s cabinets, his pictures, reading about his life. So, my formative years were born in that.
Q: I read that you were intending to become an engineer and join the space race. How did your father nudge you toward medicine?
A: When I was 9 years old, my favorite movie hero died of cancer. To comfort me, my father inserted the idea into my brain: When you grow up, you can become a doctor to cure cancer. So, when I finished high school, I was 24th in the state and had an option to go to the space school in India. On the day when I was going for the interview, I could see tears in my father’s eyes, and he said, You know what, boy? I thought you’re going to become a doctor and cure cancer. So, to honor him, I went to med school instead.

Q: I understand that your father also triggered your interest in photography?
A: I started photographing Kutchi tribal people in 1977, after I bought a camera from a famous architect [Hasmukh Patel], while traveling with my dad. And then my dad bought me a motorcycle, so I started riding myself. From the time I entered med school in 1978 until I finished my residency in 1987, I made several trips following Kutchi migrant families and livestock. They leave their homeland in Kutch [district] during summer in search of grass and water to keep their livestock alive and walk across the state from the desert of Kutch all the way to central Gujarat until monsoon begins. Then they return, only to resume the journey next year. I would catch them along their journey, would talk to them, drink tea and eat millet crepes with them.

In 1984, between Dr. Patel’s medical school and residency, the Lions Club in his hometown, Ahmedabad, India, sponsored him and three buddies to document people and wildlife in Gujarat state. Traveling by motorcycle, the four friends stayed for free with local families by knocking on doors and explaining that they were medical students. Dr. Patel’s photographs were exhibited by the Lions Club of Ahmedabad and at India’s top art institution, the Lalit Kala gallery.
In the 3rd year of his internal-medicine residency in Bombay (now Mumbai), Dr. Patel approached a national newspaper, The Indian Express, for work. He was immediately sent on assignment to cover a cholera epidemic and filed his story and photographs the following day. He worked as a photojournalist and subeditor for a year.
Q: Among all your thousands of pictures, do you have a favorite?
A: There were two photos of Kutchi people that touched me. There was one photo of a lady. All of her worldly belongings were in the picture and a smile on her face showed that we don’t need so many things to be happy. The second photo is of an elderly lady shifting her water pan on her head to a younger family member. And a little girl looks up with a look of curiosity: Will I be doing this when I grow up? We seek so much materialistic happiness. But when you look at the curiosity, smiles, and happiness [in these photos], you realize we could have a lot of happiness in minimalism, as well.
Q: After you finished your residency in Ahmedabad, how did you get started in oncology?
A: In 1986, Ahmedabad City and Gujarat State did not have structured training programs in oncology, so I went to Bombay [Mumbai], where Dr. B.C. Mehta, a true legend and pioneer in India, had started hematology-oncology training. I was a post-doc research fellow with him for a little over a year but when I started seeing patients, I had to answer to myself, Am I doing everything I can to help these people? I saw that the U.K. had one of the best training programs in hem malignancy, so I started applying. Then something happened that was almost like a miracle.
In April 1992, Dr. Patel was working at the Institute of Kidney Diseases in Ahmedabad. One afternoon, just as the clinic was closing for siesta, a family brought in a young girl. She had drug-induced thrombocytopenia and needed an immediate transfusion. The father offered to sell his wedding ring to pay Dr. Patel if he would supervise the treatment and stay by the girl’s side. Dr. Patel told the man to keep his ring, then he remained in the office with the child. At 4 p.m., the office phone rang. It was Dr. H.K. Parikh, an eminent British physician who was wintering in India and needed to make a medical appointment for his wife. On a normal day, Dr. Patel would have missed the call.
“This is how I got to meet Dr. Parikh, out of the blue,” said Dr. Patel. “His wife came to the office for 6 weeks and after 6 weeks, he said, You’re a smart guy; you should come to England. That was in April. I sent a resume and all the usual paperwork. On July 16, 1992, at 2 in the morning, I got a call from the U.K. saying, Your job is confirmed. I’m going to fax your appointment through the Royal College of Physicians, and you’re coming to Manchester to work with us. I’d been sponsored by the Overseas Doctors Training Program.
“So, it turns out that if I’d declined to see that patient and declined to stay in my clinic that afternoon, if I’d declined to see this doctor’s wife, I would never have been in the U.K. And that opened up the doors for me. I like that story because I’ve found that standing up for people who do not have a voice, who do not have hope, always leads to what is destined for me.”
Q: After working as a registrar in the United Kingdom 4 years, you found yourself in the United States and, once again, had to train as an internist. What was new about U.S. oncology?
A: I took 3 years to get recertified in Jamaica Hospital in Queens, then became a fellow in hematology-oncology at the Thomas Jefferson in Philadelphia. My U.K. training was all based on hematological malignancy. In the United States, I shifted into solid tumors.
Q: You have a long history of advocating for affordable oncology at the community, state, and federal level, and you recently launched a disparities initiative in your center called NOLA (No One Left Alone). What was the trigger for NOLA?
A: In the spring of 2020, when we started seeing the COVID surge and the difference in mortality rate between the multiple races, at the same time I saw the AACR [American Association for Cancer Research] 2020 disparity report showing that 34% of cancer deaths are preventable – one in three – if we took care of disparities. The same year, the Community Oncology Alliance asked me to become the president. So, I felt that there is something herding me, leading me, to this position. Eighty percent of cancer patients are treated in community clinics like ours. It put the onus on me to do something.
I learned from Gandhi that I cannot depend on government, I cannot depend on the policy, I have to act myself.
I said, I would not worry about making money, I would rather lose funding on this. So, we started. I read 400+ papers; I spent over 1,000 hours reading about disparities. And I realized that it’s not complicated. There are five pillars to eliminate disparity: access to care for financial reasons, access to biomarker testing or precision medicine, access to social determinants of health, access to cancer screening, and trials. If we focus on these five, we can at least bring that number from 34% to 20%, if not lower.
So, we put that plan in place. I dedicated three employees whose only role is to ensure that not a single patient has to take financial burden from my practice. And we showed it’s doable.
This has now become my mission for the last quarter of my life.
In 2020, Dr. Patel published a book on dying well titled “Between Life and Death.” It’s framed as a series of his conversations with a former patient, Harry Falls. Harry wanted to understand death better, so Dr. Patel narrated five patient stories, drawing the threads together to help Harry face the inevitable. Dr. Patel now uses a similar approach to train clinicians on having meaningful end-of-life conversations with patients.
Q: Why did you feel the need to write a book about dying?
A: The more I’ve witnessed, the more I’m convinced that there are things that we don’t know about this process, which needs to be explored much more. However, I do feel that there’s a power within all of us to steer the process of leaving this world.
Before I sat down with Harry, I loved to counsel patients, but I didn’t have any structural ideas. It was Harry himself who told me that I now had a simple way to explain dying to a much larger audience.
Q: What is your secret for fitting everything into your life?
A: I’ll tell you, it’s very simple. If I put my soul, heart, mind, actions, and language on the one plane and don’t let my brain and conditioning influence my choices, then I live in the moment. Whenever I let my conditioned mind take all the decisions, those are crooked, because you know, we’re selfish creatures – we can use what we call the convenient lie to hide inconvenient truth. And I try not to do that. I mean, it’s been a journey. It didn’t come overnight. I learned. And I feel that over all these years, the only thing that rewarded me, that opened the door of where I am today, was pure, selfless process, whether it’s the act of talking, speaking, or doing.