User login
Patients exposed to HIV, hepatitis at Massachusetts hospital
The negligent administration of intravenous medications during endoscopy procedures performed between June 14, 2021, and April 19, 2023, at Salem Hospital, located about 20 miles northeast of Boston, has caused a “heightened risk of exposure to these harmful life-altering and life-threatening infections,” according to the lawsuit filed at Suffolk County Superior Court in Boston by Keches Law Group on behalf of plaintiff Melinda Cashman and others.
Although patients were notified in early November of their potential exposure, it could take months or even years to determine if infection has occurred. Attorneys for Ms. Cashman claim that the plaintiff “suffered and will continue to suffer severe emotional distress and anguish” as a result of the associated risks.
The lawyers argue that Ms. Cashman and others like her may “suffer permanent injuries,” along with “extreme anxiety and decreased quality of life.” They are seeking monetary damages to offset disruptions to relationships, increased medical bills, and any mental health therapy required.
Outreach to potentially affected patients began after the hospital was made aware, earlier this year, of an “isolated practice” that could have led to viral transmission, according to a statement from Mass General Brigham, but there is no evidence to date of any infections resulting from this incident. “We sincerely apologize to those who have been impacted and we remain committed to delivering high-quality, compassionate healthcare to our community.”
Hepatitis B and C are both treatable with antiviral mediations, and hepatitis C is curable in 95% of cases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV, although not curable, can be managed with antiretroviral therapy.
Mass General Brigham is working with the Massachusetts Department of Public Health, which will conduct an onsite investigation into quality-control practices. Affected patients can reach out to a clinician-staffed hotline with questions and receive free screening for the viruses, hospital officials report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The negligent administration of intravenous medications during endoscopy procedures performed between June 14, 2021, and April 19, 2023, at Salem Hospital, located about 20 miles northeast of Boston, has caused a “heightened risk of exposure to these harmful life-altering and life-threatening infections,” according to the lawsuit filed at Suffolk County Superior Court in Boston by Keches Law Group on behalf of plaintiff Melinda Cashman and others.
Although patients were notified in early November of their potential exposure, it could take months or even years to determine if infection has occurred. Attorneys for Ms. Cashman claim that the plaintiff “suffered and will continue to suffer severe emotional distress and anguish” as a result of the associated risks.
The lawyers argue that Ms. Cashman and others like her may “suffer permanent injuries,” along with “extreme anxiety and decreased quality of life.” They are seeking monetary damages to offset disruptions to relationships, increased medical bills, and any mental health therapy required.
Outreach to potentially affected patients began after the hospital was made aware, earlier this year, of an “isolated practice” that could have led to viral transmission, according to a statement from Mass General Brigham, but there is no evidence to date of any infections resulting from this incident. “We sincerely apologize to those who have been impacted and we remain committed to delivering high-quality, compassionate healthcare to our community.”
Hepatitis B and C are both treatable with antiviral mediations, and hepatitis C is curable in 95% of cases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV, although not curable, can be managed with antiretroviral therapy.
Mass General Brigham is working with the Massachusetts Department of Public Health, which will conduct an onsite investigation into quality-control practices. Affected patients can reach out to a clinician-staffed hotline with questions and receive free screening for the viruses, hospital officials report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The negligent administration of intravenous medications during endoscopy procedures performed between June 14, 2021, and April 19, 2023, at Salem Hospital, located about 20 miles northeast of Boston, has caused a “heightened risk of exposure to these harmful life-altering and life-threatening infections,” according to the lawsuit filed at Suffolk County Superior Court in Boston by Keches Law Group on behalf of plaintiff Melinda Cashman and others.
Although patients were notified in early November of their potential exposure, it could take months or even years to determine if infection has occurred. Attorneys for Ms. Cashman claim that the plaintiff “suffered and will continue to suffer severe emotional distress and anguish” as a result of the associated risks.
The lawyers argue that Ms. Cashman and others like her may “suffer permanent injuries,” along with “extreme anxiety and decreased quality of life.” They are seeking monetary damages to offset disruptions to relationships, increased medical bills, and any mental health therapy required.
Outreach to potentially affected patients began after the hospital was made aware, earlier this year, of an “isolated practice” that could have led to viral transmission, according to a statement from Mass General Brigham, but there is no evidence to date of any infections resulting from this incident. “We sincerely apologize to those who have been impacted and we remain committed to delivering high-quality, compassionate healthcare to our community.”
Hepatitis B and C are both treatable with antiviral mediations, and hepatitis C is curable in 95% of cases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV, although not curable, can be managed with antiretroviral therapy.
Mass General Brigham is working with the Massachusetts Department of Public Health, which will conduct an onsite investigation into quality-control practices. Affected patients can reach out to a clinician-staffed hotline with questions and receive free screening for the viruses, hospital officials report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ACC/AHA issue updated atrial fibrillation guideline
The American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have issued an updated guideline for preventing and optimally managing atrial fibrillation (AF).
The 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
“The new guideline has important changes,” including a new way to classify AF, Jose Joglar, MD, professor of cardiac electrophysiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and chair of the writing committee, said in an interview.
The previous classification was largely based only on arrhythmia duration and tended to emphasize specific therapeutic interventions rather than a more holistic and multidisciplinary management approach, Dr. Joglar explained.
, from prevention, lifestyle and risk factor modification, screening, and therapy.
Stage 1: At risk for AF due to the presence of risk factors
Stage 2: Pre-AF, with evidence of structural or electrical findings predisposing to AF
Stage 3: AF, including paroxysmal (3A), persistent (3B), long-standing persistent (3C), successful AF ablation (3D)
Stage 4: Permanent AF
The updated guideline recognizes lifestyle and risk factor modification as a “pillar” of AF management and offers “more prescriptive” recommendations, including management of obesity, weight loss, physical activity, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, hypertension, and other comorbidities.
“We should not only be telling patients they need to be healthy, which doesn’t mean much to a patient, we need to tell them precisely what they need to do. For example, how much exercise to do or how much weight to lose to have a benefit,” Dr. Joglar said in an interview.
The good news for many people, he noted, is that coffee, which has had a “bad reputation,” is okay, as the latest data show it doesn’t seem to exacerbate AF.
The new guideline continues to endorse use of the CHA2DS2-VASc score as the predictor of choice to determine the risk of stroke, but it also allows for flexibility to use other calculators when uncertainty exists or when other risk factors, such as kidney disease, need to be included.
With the emergence of “new and consistent” evidence, the guideline also emphasizes the importance of early and continued management of patients with AF with a focus on maintaining sinus rhythm and minimizing AF burden.
Catheter ablation of AF is given a class 1 indication as first-line therapy in selected patients, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
That’s based on recent randomized studies that have shown catheter ablation to be “superior to pharmacological therapy” for rhythm control in appropriately selected patients, Dr. Joglar told this news organization.
“There’s no need to try pharmacological therapies after a discussion between the patient and doctor and they decide that they want to proceed with the most effective intervention,” he added.
The new guideline also upgrades the class of recommendation for left atrial appendage occlusion devices to 2a, compared with the 2019 AF Focused Update, for use of these devices in patients with long-term contraindications to anticoagulation.
It also provides updated recommendations for AF detected via implantable devices and wearables as well as recommendations for patients with AF identified during medical illness or surgery.
Development of the guideline had no commercial funding. Disclosures for the writing group are available with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have issued an updated guideline for preventing and optimally managing atrial fibrillation (AF).
The 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
“The new guideline has important changes,” including a new way to classify AF, Jose Joglar, MD, professor of cardiac electrophysiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and chair of the writing committee, said in an interview.
The previous classification was largely based only on arrhythmia duration and tended to emphasize specific therapeutic interventions rather than a more holistic and multidisciplinary management approach, Dr. Joglar explained.
, from prevention, lifestyle and risk factor modification, screening, and therapy.
Stage 1: At risk for AF due to the presence of risk factors
Stage 2: Pre-AF, with evidence of structural or electrical findings predisposing to AF
Stage 3: AF, including paroxysmal (3A), persistent (3B), long-standing persistent (3C), successful AF ablation (3D)
Stage 4: Permanent AF
The updated guideline recognizes lifestyle and risk factor modification as a “pillar” of AF management and offers “more prescriptive” recommendations, including management of obesity, weight loss, physical activity, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, hypertension, and other comorbidities.
“We should not only be telling patients they need to be healthy, which doesn’t mean much to a patient, we need to tell them precisely what they need to do. For example, how much exercise to do or how much weight to lose to have a benefit,” Dr. Joglar said in an interview.
The good news for many people, he noted, is that coffee, which has had a “bad reputation,” is okay, as the latest data show it doesn’t seem to exacerbate AF.
The new guideline continues to endorse use of the CHA2DS2-VASc score as the predictor of choice to determine the risk of stroke, but it also allows for flexibility to use other calculators when uncertainty exists or when other risk factors, such as kidney disease, need to be included.
With the emergence of “new and consistent” evidence, the guideline also emphasizes the importance of early and continued management of patients with AF with a focus on maintaining sinus rhythm and minimizing AF burden.
Catheter ablation of AF is given a class 1 indication as first-line therapy in selected patients, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
That’s based on recent randomized studies that have shown catheter ablation to be “superior to pharmacological therapy” for rhythm control in appropriately selected patients, Dr. Joglar told this news organization.
“There’s no need to try pharmacological therapies after a discussion between the patient and doctor and they decide that they want to proceed with the most effective intervention,” he added.
The new guideline also upgrades the class of recommendation for left atrial appendage occlusion devices to 2a, compared with the 2019 AF Focused Update, for use of these devices in patients with long-term contraindications to anticoagulation.
It also provides updated recommendations for AF detected via implantable devices and wearables as well as recommendations for patients with AF identified during medical illness or surgery.
Development of the guideline had no commercial funding. Disclosures for the writing group are available with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have issued an updated guideline for preventing and optimally managing atrial fibrillation (AF).
The 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
“The new guideline has important changes,” including a new way to classify AF, Jose Joglar, MD, professor of cardiac electrophysiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and chair of the writing committee, said in an interview.
The previous classification was largely based only on arrhythmia duration and tended to emphasize specific therapeutic interventions rather than a more holistic and multidisciplinary management approach, Dr. Joglar explained.
, from prevention, lifestyle and risk factor modification, screening, and therapy.
Stage 1: At risk for AF due to the presence of risk factors
Stage 2: Pre-AF, with evidence of structural or electrical findings predisposing to AF
Stage 3: AF, including paroxysmal (3A), persistent (3B), long-standing persistent (3C), successful AF ablation (3D)
Stage 4: Permanent AF
The updated guideline recognizes lifestyle and risk factor modification as a “pillar” of AF management and offers “more prescriptive” recommendations, including management of obesity, weight loss, physical activity, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, hypertension, and other comorbidities.
“We should not only be telling patients they need to be healthy, which doesn’t mean much to a patient, we need to tell them precisely what they need to do. For example, how much exercise to do or how much weight to lose to have a benefit,” Dr. Joglar said in an interview.
The good news for many people, he noted, is that coffee, which has had a “bad reputation,” is okay, as the latest data show it doesn’t seem to exacerbate AF.
The new guideline continues to endorse use of the CHA2DS2-VASc score as the predictor of choice to determine the risk of stroke, but it also allows for flexibility to use other calculators when uncertainty exists or when other risk factors, such as kidney disease, need to be included.
With the emergence of “new and consistent” evidence, the guideline also emphasizes the importance of early and continued management of patients with AF with a focus on maintaining sinus rhythm and minimizing AF burden.
Catheter ablation of AF is given a class 1 indication as first-line therapy in selected patients, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
That’s based on recent randomized studies that have shown catheter ablation to be “superior to pharmacological therapy” for rhythm control in appropriately selected patients, Dr. Joglar told this news organization.
“There’s no need to try pharmacological therapies after a discussion between the patient and doctor and they decide that they want to proceed with the most effective intervention,” he added.
The new guideline also upgrades the class of recommendation for left atrial appendage occlusion devices to 2a, compared with the 2019 AF Focused Update, for use of these devices in patients with long-term contraindications to anticoagulation.
It also provides updated recommendations for AF detected via implantable devices and wearables as well as recommendations for patients with AF identified during medical illness or surgery.
Development of the guideline had no commercial funding. Disclosures for the writing group are available with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What is the dark side of GLP-1 receptor agonists?
The approval of the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide for weight regulation in January 2023 ushered in a new era of obesity therapy. In recent months, however,
“When millions of people are treated with medications like semaglutide, even relatively rare side effects occur in a large number of individuals,” Susan Yanovski, MD, codirector of the Office of Obesity Research at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases in Bethesda, Maryland, said in a JAMA news report.
Despite the low incidence of these adverse events and the likelihood that the benefits outweigh these risks in individuals with severe obesity, doctors and patients should be aware of these serious side effects, she added.
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide or liraglutide mimic certain intestinal hormones. Almost all their characteristic side effects involve the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea. However, these are not the rare, severe side effects that are gaining increasing attention.
Severe Gastric Problems
A recent analysis published in JAMA shows that GLP-1 receptor agonists are associated with a ninefold higher risk of pancreatitis, compared with bupropion, an older weight-loss medication. Patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists also had four times more frequent intestinal obstruction and more than three times more frequent gastroparesis. The absolute risks for these complications, however, were less than 1% per year of use.
There were no indications of an increased risk for gallbladder diseases. Acute pancreatitis and acute gallbladder diseases are known complications of GLP-1 receptor agonists.
These results “reinforce that these are effective medications, and all medications have side effects,” said Dr. Yanovski. She emphasized that despite a significant increase in relative risk, however, the absolute risk remains very low.
Anesthetic Complications
In the spring of 2023, reports of patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists and vomiting or aspirating food during anesthesia surfaced in some scientific journals. It was particularly noticeable that some of these patients vomited unusually large amounts of stomach contents, even though they had not eaten anything, as directed by the doctor before the operation.
Experts believe that the slowed gastric emptying intentionally caused by GLP-1 receptor agonists could be responsible for these problems.
The American Society of Anesthesiologists now recommends that patients do not take GLP-1 receptor agonists on the day of surgery and discontinue weekly administered agents like Wegovy 7 days before the procedure.
Increased Suicidality Risk?
In July, case reports of depression and suicidal ideation led the European Medicines Agency to investigate about 150 cases of potential self-harm and suicidal thoughts in patients who had received liraglutide or semaglutide. The review now also includes other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Results of the review process are expected in December.
Dr. Yanovski noted that it is unclear whether these incidents are caused by the drugs, but suicidal thoughts and suicidal behavior have also been observed with other medications for obesity treatment (eg, rimonabant). “It is certainly a good idea to use these medications cautiously in patients with a history of suicidality and monitor the patients accordingly,” she said.
Long-Term Safety
GLP-1 receptor agonists likely need to be used long term, potentially for life, for the effects on body weight to persist. Whether there are side effects and complications that only become apparent over time is currently unknown — especially when these medications are used for weight reduction.
Studies in rodents have suggested an increased risk of medullary thyroid carcinomas. Whether a similar signal exists in humans may only become apparent in many years. In patients who have had medullary thyroid carcinoma themselves or in the family, dulaglutide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist, are contraindicated.
With dual agonists like tirzepatide or even triple agonists like retatrutide (GLP-1/GIP/glucagon), patients can lose significantly more weight than with the monoagonist semaglutide. Gastrointestinal events were also frequent in studies of dual agonists.
Awaiting Guideline Updates
Guidelines for using these new medications are still scarce. “There are clinical guidelines for obesity therapy, but they were all written before the GLP-1 receptor agonists came on the market,” said Dr. Yanovski. “Medical societies are currently working intensively to develop new guidelines to help doctors use these medications safely and effectively in clinical practice.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The approval of the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide for weight regulation in January 2023 ushered in a new era of obesity therapy. In recent months, however,
“When millions of people are treated with medications like semaglutide, even relatively rare side effects occur in a large number of individuals,” Susan Yanovski, MD, codirector of the Office of Obesity Research at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases in Bethesda, Maryland, said in a JAMA news report.
Despite the low incidence of these adverse events and the likelihood that the benefits outweigh these risks in individuals with severe obesity, doctors and patients should be aware of these serious side effects, she added.
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide or liraglutide mimic certain intestinal hormones. Almost all their characteristic side effects involve the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea. However, these are not the rare, severe side effects that are gaining increasing attention.
Severe Gastric Problems
A recent analysis published in JAMA shows that GLP-1 receptor agonists are associated with a ninefold higher risk of pancreatitis, compared with bupropion, an older weight-loss medication. Patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists also had four times more frequent intestinal obstruction and more than three times more frequent gastroparesis. The absolute risks for these complications, however, were less than 1% per year of use.
There were no indications of an increased risk for gallbladder diseases. Acute pancreatitis and acute gallbladder diseases are known complications of GLP-1 receptor agonists.
These results “reinforce that these are effective medications, and all medications have side effects,” said Dr. Yanovski. She emphasized that despite a significant increase in relative risk, however, the absolute risk remains very low.
Anesthetic Complications
In the spring of 2023, reports of patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists and vomiting or aspirating food during anesthesia surfaced in some scientific journals. It was particularly noticeable that some of these patients vomited unusually large amounts of stomach contents, even though they had not eaten anything, as directed by the doctor before the operation.
Experts believe that the slowed gastric emptying intentionally caused by GLP-1 receptor agonists could be responsible for these problems.
The American Society of Anesthesiologists now recommends that patients do not take GLP-1 receptor agonists on the day of surgery and discontinue weekly administered agents like Wegovy 7 days before the procedure.
Increased Suicidality Risk?
In July, case reports of depression and suicidal ideation led the European Medicines Agency to investigate about 150 cases of potential self-harm and suicidal thoughts in patients who had received liraglutide or semaglutide. The review now also includes other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Results of the review process are expected in December.
Dr. Yanovski noted that it is unclear whether these incidents are caused by the drugs, but suicidal thoughts and suicidal behavior have also been observed with other medications for obesity treatment (eg, rimonabant). “It is certainly a good idea to use these medications cautiously in patients with a history of suicidality and monitor the patients accordingly,” she said.
Long-Term Safety
GLP-1 receptor agonists likely need to be used long term, potentially for life, for the effects on body weight to persist. Whether there are side effects and complications that only become apparent over time is currently unknown — especially when these medications are used for weight reduction.
Studies in rodents have suggested an increased risk of medullary thyroid carcinomas. Whether a similar signal exists in humans may only become apparent in many years. In patients who have had medullary thyroid carcinoma themselves or in the family, dulaglutide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist, are contraindicated.
With dual agonists like tirzepatide or even triple agonists like retatrutide (GLP-1/GIP/glucagon), patients can lose significantly more weight than with the monoagonist semaglutide. Gastrointestinal events were also frequent in studies of dual agonists.
Awaiting Guideline Updates
Guidelines for using these new medications are still scarce. “There are clinical guidelines for obesity therapy, but they were all written before the GLP-1 receptor agonists came on the market,” said Dr. Yanovski. “Medical societies are currently working intensively to develop new guidelines to help doctors use these medications safely and effectively in clinical practice.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The approval of the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide for weight regulation in January 2023 ushered in a new era of obesity therapy. In recent months, however,
“When millions of people are treated with medications like semaglutide, even relatively rare side effects occur in a large number of individuals,” Susan Yanovski, MD, codirector of the Office of Obesity Research at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases in Bethesda, Maryland, said in a JAMA news report.
Despite the low incidence of these adverse events and the likelihood that the benefits outweigh these risks in individuals with severe obesity, doctors and patients should be aware of these serious side effects, she added.
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide or liraglutide mimic certain intestinal hormones. Almost all their characteristic side effects involve the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea. However, these are not the rare, severe side effects that are gaining increasing attention.
Severe Gastric Problems
A recent analysis published in JAMA shows that GLP-1 receptor agonists are associated with a ninefold higher risk of pancreatitis, compared with bupropion, an older weight-loss medication. Patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists also had four times more frequent intestinal obstruction and more than three times more frequent gastroparesis. The absolute risks for these complications, however, were less than 1% per year of use.
There were no indications of an increased risk for gallbladder diseases. Acute pancreatitis and acute gallbladder diseases are known complications of GLP-1 receptor agonists.
These results “reinforce that these are effective medications, and all medications have side effects,” said Dr. Yanovski. She emphasized that despite a significant increase in relative risk, however, the absolute risk remains very low.
Anesthetic Complications
In the spring of 2023, reports of patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists and vomiting or aspirating food during anesthesia surfaced in some scientific journals. It was particularly noticeable that some of these patients vomited unusually large amounts of stomach contents, even though they had not eaten anything, as directed by the doctor before the operation.
Experts believe that the slowed gastric emptying intentionally caused by GLP-1 receptor agonists could be responsible for these problems.
The American Society of Anesthesiologists now recommends that patients do not take GLP-1 receptor agonists on the day of surgery and discontinue weekly administered agents like Wegovy 7 days before the procedure.
Increased Suicidality Risk?
In July, case reports of depression and suicidal ideation led the European Medicines Agency to investigate about 150 cases of potential self-harm and suicidal thoughts in patients who had received liraglutide or semaglutide. The review now also includes other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Results of the review process are expected in December.
Dr. Yanovski noted that it is unclear whether these incidents are caused by the drugs, but suicidal thoughts and suicidal behavior have also been observed with other medications for obesity treatment (eg, rimonabant). “It is certainly a good idea to use these medications cautiously in patients with a history of suicidality and monitor the patients accordingly,” she said.
Long-Term Safety
GLP-1 receptor agonists likely need to be used long term, potentially for life, for the effects on body weight to persist. Whether there are side effects and complications that only become apparent over time is currently unknown — especially when these medications are used for weight reduction.
Studies in rodents have suggested an increased risk of medullary thyroid carcinomas. Whether a similar signal exists in humans may only become apparent in many years. In patients who have had medullary thyroid carcinoma themselves or in the family, dulaglutide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist, are contraindicated.
With dual agonists like tirzepatide or even triple agonists like retatrutide (GLP-1/GIP/glucagon), patients can lose significantly more weight than with the monoagonist semaglutide. Gastrointestinal events were also frequent in studies of dual agonists.
Awaiting Guideline Updates
Guidelines for using these new medications are still scarce. “There are clinical guidelines for obesity therapy, but they were all written before the GLP-1 receptor agonists came on the market,” said Dr. Yanovski. “Medical societies are currently working intensively to develop new guidelines to help doctors use these medications safely and effectively in clinical practice.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Networks at CHEST 2023
CHEST 2023 in Honolulu kicked off for Network Leadership during the Council of Networks meeting.
We congratulated our Network leaders – Margaret Pisani, Council of Networks Vice-chair, who was awarded the Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical Care; and Jean Elwing, Chair of the Pulmonary Vascular & Cardiovascular Network, for being awarded the Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary Physiology. CHEST 2023 included excellent educational content by the Networks, including two Network highlights per each of the seven Networks, as well as an Experience CHEST submission from each of the 22 sections.
We also had the opportunity to meet face-to-face at the Network Open Forums, the Network Mixer, and the inaugural Fellow-in-Training Mixer in the Trainee Lounge. We saw a lot of familiar faces at these events, and 182 new individuals also signed up to become Network members.
There will be one final Council of Networks leadership meeting in December prior to our leadership transition in January.
We thank outgoing Network chairs, Dr. Marcos Restrepo of the Chest Infections & Disaster Response Network, Dr. Christopher Carroll of the Critical Care Network, Dr. Debbie Levine of the Diffuse Lung Disease & Lung Transplant Network, and Dr. Carolyn D’Ambrosio of the Sleep Medicine Network, for their leadership and hard work dedicated to the Networks that have greatly benefited from their service.
Cassie Kennedy, MD, FCCP – Chair, Council of Networks
Margaret Pisani, MD, MPH, FCCP – Vice-Chair, Council of Networks
CHEST 2023 in Honolulu kicked off for Network Leadership during the Council of Networks meeting.
We congratulated our Network leaders – Margaret Pisani, Council of Networks Vice-chair, who was awarded the Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical Care; and Jean Elwing, Chair of the Pulmonary Vascular & Cardiovascular Network, for being awarded the Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary Physiology. CHEST 2023 included excellent educational content by the Networks, including two Network highlights per each of the seven Networks, as well as an Experience CHEST submission from each of the 22 sections.
We also had the opportunity to meet face-to-face at the Network Open Forums, the Network Mixer, and the inaugural Fellow-in-Training Mixer in the Trainee Lounge. We saw a lot of familiar faces at these events, and 182 new individuals also signed up to become Network members.
There will be one final Council of Networks leadership meeting in December prior to our leadership transition in January.
We thank outgoing Network chairs, Dr. Marcos Restrepo of the Chest Infections & Disaster Response Network, Dr. Christopher Carroll of the Critical Care Network, Dr. Debbie Levine of the Diffuse Lung Disease & Lung Transplant Network, and Dr. Carolyn D’Ambrosio of the Sleep Medicine Network, for their leadership and hard work dedicated to the Networks that have greatly benefited from their service.
Cassie Kennedy, MD, FCCP – Chair, Council of Networks
Margaret Pisani, MD, MPH, FCCP – Vice-Chair, Council of Networks
CHEST 2023 in Honolulu kicked off for Network Leadership during the Council of Networks meeting.
We congratulated our Network leaders – Margaret Pisani, Council of Networks Vice-chair, who was awarded the Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical Care; and Jean Elwing, Chair of the Pulmonary Vascular & Cardiovascular Network, for being awarded the Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary Physiology. CHEST 2023 included excellent educational content by the Networks, including two Network highlights per each of the seven Networks, as well as an Experience CHEST submission from each of the 22 sections.
We also had the opportunity to meet face-to-face at the Network Open Forums, the Network Mixer, and the inaugural Fellow-in-Training Mixer in the Trainee Lounge. We saw a lot of familiar faces at these events, and 182 new individuals also signed up to become Network members.
There will be one final Council of Networks leadership meeting in December prior to our leadership transition in January.
We thank outgoing Network chairs, Dr. Marcos Restrepo of the Chest Infections & Disaster Response Network, Dr. Christopher Carroll of the Critical Care Network, Dr. Debbie Levine of the Diffuse Lung Disease & Lung Transplant Network, and Dr. Carolyn D’Ambrosio of the Sleep Medicine Network, for their leadership and hard work dedicated to the Networks that have greatly benefited from their service.
Cassie Kennedy, MD, FCCP – Chair, Council of Networks
Margaret Pisani, MD, MPH, FCCP – Vice-Chair, Council of Networks
The 5 things dentists wished physicians weren’t missing
From overlooked gum disease to suspicious lesions, oral health can provide a critical window into broader medical concerns.
A recent statement by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found that dental screenings by primary care doctors may not work well enough to catch patients most at risk of oral health issues.
But dentists say a quick look during regular office visits could help catch health problems.
“Health care providers other than dentists don’t look in the mouth a lot, and if they do, they’re looking past the teeth and mouth into the throat,” said Romesh Nalliah, DDS, MHCM, an associate dean for patient services at the University of Michigan School of Dentistry in Ann Arbor.
“It can be a big ask of primary care physicians, because we already ask a lot of them. But some of these things are very simple – just a quick scan of the mouth – and could be done by other medical office staff.”
Here are five key conditions with oral signs that dentists wish primary care doctors would catch during checkups, which could unlock early detection and treatment:
Diabetes: Within the realm of oral health, type 2 diabetes can leave distinct imprints that dental professionals are trained to watch for. For example, gum disease – marked by inflamed, bleeding gums – can be a sign of the illness. People with diabetes may have a dry mouth, stemming from reduced production of saliva, leading to discomfort, a hard time swallowing, and a higher risk of dental infections. An estimated 34% to 51% of people with diabetes have dry mouth.
Another sign that can show up in the mouth is a fungal infection, such as oral thrush, which can mean the immune system isn’t working well and is often linked to uncontrolled diabetes.
“We know gum disease appears more frequently and more severely in patients with diabetes, and that treating the gum disease can help improve diabetes-related outcomes,” said Marie Jackson, DMD, FAGD, a dentist in Montclair, NJ. “Good oral health habits are just generally beneficial from an overall health perspective.”
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Illnesses like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis have long been recognized for their effect on the gut. However, a lesser-known aspect of these disorders is their potential to show up in the mouth, presenting a unique set of challenges for both patients and health care providers. Some people with IBD have aphthous stomatitis – more commonly known as canker sores. These oral symptoms not only add to discomfort for those with IBD, but also can show that a disease is present.
“Crohn’s disease in particular can cause mouth ulcers that look like sores,” Dr. Jackson said. “Anytime someone comes in for a checkup, we look for red patches, which can be an indicator.”
These ulcers often are shallow and round, and typically are on the soft tissues lining the mouth, such as the inner cheeks, lips, and tongue. IBD and oral ulcers come with inflammation. The body’s immune response can result in an overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, triggering a cascade of events that help cause these painful ulcers.
Heart disease: The mouth may be an unexpected place to find signs of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Heart issues often come with oral symptoms, notably a higher chance of gum disease. The connection lies in the inflammatory nature of both conditions; chronic heart disease may add to an inflammatory response that, in turn, worsens gum inflammation and leads to more severe issues with the teeth and gums. Symptoms such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and gum swelling can serve as early warning signs.
Also, people with gum disease are at a higher risk of issues with their heart and blood vessels. Bacteria in the mouth can enter other areas of the body, including the heart.
“Gum disease provides an open portal to get into the bloodstream,” Dr. Jackson said.
Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis often goes unnoticed until the condition leads to injury. But research shows it can affect the teeth in noticeable ways, including tooth loss and gum disease.
For patients with implants, dentures, and bridges, weak bones may lead to looser-fitting replacements.
Unfortunately, certain medications for osteoporosis, bisphosphonate drugs, also can cause dental issues – something all doctors should be aware of when prescribing any medications, Dr. Nalliah said.
“When a medical office puts someone on a new medication, they should send them to a dentist,” Dr. Nalliah said. “Many of them can cause dry mouth, which can cause decay.”
Oral cancer: Symptoms of oral cancer that may be visible during a doctor visit include a sore on the lip or in the mouth, white or reddish patches on the inside of the mouth, loose teeth, or a lump inside the mouth.
“Anytime I have a patient with a white patch they have not had before, if they have not bitten their tongue, we have them come in again in 2 or 3 weeks, and if it’s still there, we have it biopsied,” Dr. Jackson said. “Oral cancer definitely is on the rise with HPV,” she said.
Oropharynx cancers linked to HPV infection increased yearly by 1.3% in women and by 2.8% in men from 2015 to 2019.
According to the CDC, compared with other cancers, oral and pharyngeal cancer has one of the poorest 5-year survival rates: only 52% of people diagnosed with oral cancer survive 5 years. Only 35% of oral cancer is detected at the earliest stage.
“Most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage of the disease,” Dr. Nalliah said. “Many of those vulnerable people don’t have dental insurance.”
Effects of Oral Hygiene on Overall Health
While some health issues may show up in the mouth, the problems go both ways: Poor oral hygiene can lead to negative health outcomes. Some studies show there may even be a connection between poor oral health and worse brain health.
“What I wish physicians would talk to our patients about is the importance of regular dental visits,” said Ruchi Sahota, DDS, a general family dentist in Fremont, CA, and a consumer adviser for the American Dental Association. “Teeth don’t necessarily hurt until something big is going on. Going to the dentist regularly, brushing at least twice a day, flossing at least once a day, all of these things can contribute to greater overall health.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
From overlooked gum disease to suspicious lesions, oral health can provide a critical window into broader medical concerns.
A recent statement by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found that dental screenings by primary care doctors may not work well enough to catch patients most at risk of oral health issues.
But dentists say a quick look during regular office visits could help catch health problems.
“Health care providers other than dentists don’t look in the mouth a lot, and if they do, they’re looking past the teeth and mouth into the throat,” said Romesh Nalliah, DDS, MHCM, an associate dean for patient services at the University of Michigan School of Dentistry in Ann Arbor.
“It can be a big ask of primary care physicians, because we already ask a lot of them. But some of these things are very simple – just a quick scan of the mouth – and could be done by other medical office staff.”
Here are five key conditions with oral signs that dentists wish primary care doctors would catch during checkups, which could unlock early detection and treatment:
Diabetes: Within the realm of oral health, type 2 diabetes can leave distinct imprints that dental professionals are trained to watch for. For example, gum disease – marked by inflamed, bleeding gums – can be a sign of the illness. People with diabetes may have a dry mouth, stemming from reduced production of saliva, leading to discomfort, a hard time swallowing, and a higher risk of dental infections. An estimated 34% to 51% of people with diabetes have dry mouth.
Another sign that can show up in the mouth is a fungal infection, such as oral thrush, which can mean the immune system isn’t working well and is often linked to uncontrolled diabetes.
“We know gum disease appears more frequently and more severely in patients with diabetes, and that treating the gum disease can help improve diabetes-related outcomes,” said Marie Jackson, DMD, FAGD, a dentist in Montclair, NJ. “Good oral health habits are just generally beneficial from an overall health perspective.”
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Illnesses like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis have long been recognized for their effect on the gut. However, a lesser-known aspect of these disorders is their potential to show up in the mouth, presenting a unique set of challenges for both patients and health care providers. Some people with IBD have aphthous stomatitis – more commonly known as canker sores. These oral symptoms not only add to discomfort for those with IBD, but also can show that a disease is present.
“Crohn’s disease in particular can cause mouth ulcers that look like sores,” Dr. Jackson said. “Anytime someone comes in for a checkup, we look for red patches, which can be an indicator.”
These ulcers often are shallow and round, and typically are on the soft tissues lining the mouth, such as the inner cheeks, lips, and tongue. IBD and oral ulcers come with inflammation. The body’s immune response can result in an overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, triggering a cascade of events that help cause these painful ulcers.
Heart disease: The mouth may be an unexpected place to find signs of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Heart issues often come with oral symptoms, notably a higher chance of gum disease. The connection lies in the inflammatory nature of both conditions; chronic heart disease may add to an inflammatory response that, in turn, worsens gum inflammation and leads to more severe issues with the teeth and gums. Symptoms such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and gum swelling can serve as early warning signs.
Also, people with gum disease are at a higher risk of issues with their heart and blood vessels. Bacteria in the mouth can enter other areas of the body, including the heart.
“Gum disease provides an open portal to get into the bloodstream,” Dr. Jackson said.
Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis often goes unnoticed until the condition leads to injury. But research shows it can affect the teeth in noticeable ways, including tooth loss and gum disease.
For patients with implants, dentures, and bridges, weak bones may lead to looser-fitting replacements.
Unfortunately, certain medications for osteoporosis, bisphosphonate drugs, also can cause dental issues – something all doctors should be aware of when prescribing any medications, Dr. Nalliah said.
“When a medical office puts someone on a new medication, they should send them to a dentist,” Dr. Nalliah said. “Many of them can cause dry mouth, which can cause decay.”
Oral cancer: Symptoms of oral cancer that may be visible during a doctor visit include a sore on the lip or in the mouth, white or reddish patches on the inside of the mouth, loose teeth, or a lump inside the mouth.
“Anytime I have a patient with a white patch they have not had before, if they have not bitten their tongue, we have them come in again in 2 or 3 weeks, and if it’s still there, we have it biopsied,” Dr. Jackson said. “Oral cancer definitely is on the rise with HPV,” she said.
Oropharynx cancers linked to HPV infection increased yearly by 1.3% in women and by 2.8% in men from 2015 to 2019.
According to the CDC, compared with other cancers, oral and pharyngeal cancer has one of the poorest 5-year survival rates: only 52% of people diagnosed with oral cancer survive 5 years. Only 35% of oral cancer is detected at the earliest stage.
“Most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage of the disease,” Dr. Nalliah said. “Many of those vulnerable people don’t have dental insurance.”
Effects of Oral Hygiene on Overall Health
While some health issues may show up in the mouth, the problems go both ways: Poor oral hygiene can lead to negative health outcomes. Some studies show there may even be a connection between poor oral health and worse brain health.
“What I wish physicians would talk to our patients about is the importance of regular dental visits,” said Ruchi Sahota, DDS, a general family dentist in Fremont, CA, and a consumer adviser for the American Dental Association. “Teeth don’t necessarily hurt until something big is going on. Going to the dentist regularly, brushing at least twice a day, flossing at least once a day, all of these things can contribute to greater overall health.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
From overlooked gum disease to suspicious lesions, oral health can provide a critical window into broader medical concerns.
A recent statement by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found that dental screenings by primary care doctors may not work well enough to catch patients most at risk of oral health issues.
But dentists say a quick look during regular office visits could help catch health problems.
“Health care providers other than dentists don’t look in the mouth a lot, and if they do, they’re looking past the teeth and mouth into the throat,” said Romesh Nalliah, DDS, MHCM, an associate dean for patient services at the University of Michigan School of Dentistry in Ann Arbor.
“It can be a big ask of primary care physicians, because we already ask a lot of them. But some of these things are very simple – just a quick scan of the mouth – and could be done by other medical office staff.”
Here are five key conditions with oral signs that dentists wish primary care doctors would catch during checkups, which could unlock early detection and treatment:
Diabetes: Within the realm of oral health, type 2 diabetes can leave distinct imprints that dental professionals are trained to watch for. For example, gum disease – marked by inflamed, bleeding gums – can be a sign of the illness. People with diabetes may have a dry mouth, stemming from reduced production of saliva, leading to discomfort, a hard time swallowing, and a higher risk of dental infections. An estimated 34% to 51% of people with diabetes have dry mouth.
Another sign that can show up in the mouth is a fungal infection, such as oral thrush, which can mean the immune system isn’t working well and is often linked to uncontrolled diabetes.
“We know gum disease appears more frequently and more severely in patients with diabetes, and that treating the gum disease can help improve diabetes-related outcomes,” said Marie Jackson, DMD, FAGD, a dentist in Montclair, NJ. “Good oral health habits are just generally beneficial from an overall health perspective.”
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Illnesses like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis have long been recognized for their effect on the gut. However, a lesser-known aspect of these disorders is their potential to show up in the mouth, presenting a unique set of challenges for both patients and health care providers. Some people with IBD have aphthous stomatitis – more commonly known as canker sores. These oral symptoms not only add to discomfort for those with IBD, but also can show that a disease is present.
“Crohn’s disease in particular can cause mouth ulcers that look like sores,” Dr. Jackson said. “Anytime someone comes in for a checkup, we look for red patches, which can be an indicator.”
These ulcers often are shallow and round, and typically are on the soft tissues lining the mouth, such as the inner cheeks, lips, and tongue. IBD and oral ulcers come with inflammation. The body’s immune response can result in an overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, triggering a cascade of events that help cause these painful ulcers.
Heart disease: The mouth may be an unexpected place to find signs of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Heart issues often come with oral symptoms, notably a higher chance of gum disease. The connection lies in the inflammatory nature of both conditions; chronic heart disease may add to an inflammatory response that, in turn, worsens gum inflammation and leads to more severe issues with the teeth and gums. Symptoms such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and gum swelling can serve as early warning signs.
Also, people with gum disease are at a higher risk of issues with their heart and blood vessels. Bacteria in the mouth can enter other areas of the body, including the heart.
“Gum disease provides an open portal to get into the bloodstream,” Dr. Jackson said.
Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis often goes unnoticed until the condition leads to injury. But research shows it can affect the teeth in noticeable ways, including tooth loss and gum disease.
For patients with implants, dentures, and bridges, weak bones may lead to looser-fitting replacements.
Unfortunately, certain medications for osteoporosis, bisphosphonate drugs, also can cause dental issues – something all doctors should be aware of when prescribing any medications, Dr. Nalliah said.
“When a medical office puts someone on a new medication, they should send them to a dentist,” Dr. Nalliah said. “Many of them can cause dry mouth, which can cause decay.”
Oral cancer: Symptoms of oral cancer that may be visible during a doctor visit include a sore on the lip or in the mouth, white or reddish patches on the inside of the mouth, loose teeth, or a lump inside the mouth.
“Anytime I have a patient with a white patch they have not had before, if they have not bitten their tongue, we have them come in again in 2 or 3 weeks, and if it’s still there, we have it biopsied,” Dr. Jackson said. “Oral cancer definitely is on the rise with HPV,” she said.
Oropharynx cancers linked to HPV infection increased yearly by 1.3% in women and by 2.8% in men from 2015 to 2019.
According to the CDC, compared with other cancers, oral and pharyngeal cancer has one of the poorest 5-year survival rates: only 52% of people diagnosed with oral cancer survive 5 years. Only 35% of oral cancer is detected at the earliest stage.
“Most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage of the disease,” Dr. Nalliah said. “Many of those vulnerable people don’t have dental insurance.”
Effects of Oral Hygiene on Overall Health
While some health issues may show up in the mouth, the problems go both ways: Poor oral hygiene can lead to negative health outcomes. Some studies show there may even be a connection between poor oral health and worse brain health.
“What I wish physicians would talk to our patients about is the importance of regular dental visits,” said Ruchi Sahota, DDS, a general family dentist in Fremont, CA, and a consumer adviser for the American Dental Association. “Teeth don’t necessarily hurt until something big is going on. Going to the dentist regularly, brushing at least twice a day, flossing at least once a day, all of these things can contribute to greater overall health.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Vagus nerve stimulation promising in POTS
TOPLINE:
possibly through decreased antiadrenergic autoantibodies and inflammatory cytokines, and improved cardiac autonomic function, in a small proof-of-concept study.
METHODOLOGY:
The double-blind study included 25 female patients with POTS, a syndrome of orthostatic intolerance (mean age 31 years and 81% Caucasian), who were randomly assigned to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) to the right tragus or sham stimulation to the earlobe, a site devoid of vagal innervation.
After training, patients delivered the tVNS themselves at a frequency of 20 Hz and pulse width of 200 ms during 1-hour daily sessions over 2 months.
At baseline and 2 months, patients underwent a tilt test to determine postural tachycardia; they remained supine for 25 minutes, followed by 10 minutes of standing, as tolerated.
Researchers used electrocardiogram data to examine heart rate and blood samples to assess serum cytokines and antiautonomic autoantibodies.
The primary outcome was a comparison of orthostatic tachycardia (standing – supine) between the two arms at 2 months.
TAKEAWAY:
At 2 months, postural tachycardia was significantly less in the active vs sham arm (mean postural increase in heart rate 17.6 beats/min vs 31.7 beats/min; P = .01).
There was a significant decrease in beta 1-adrenergic receptor (beta 1-AR; P = .01) and alpha-1-AR (P = .04) autoantibody activity in the active vs sham group, which may account at least in part for the reduced orthostatic tachycardia, although the exact mechanisms for this effect have not been clearly defined, the authors said.
Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels were significantly decreased in the active group relative to the sham group (8.3 pg/mL vs 13.9 pg/mL; P = .01).
As for heart rate variability, change in low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) from supine to standing was significantly decreased, and postural change in LF/HF ratio, a surrogate for sympathovagal balance, was significantly lower in the active group compared with the sham group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Collectively, these data suggest that tVNS, a low-cost, low-risk intervention, applied for a short period of time in selected patients with POTS, may result in a significant amelioration of their disease,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Stavros Stavrakis, MD, PhD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology..
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a small sample size, included only females, and extended only up to 2 months. As there was no improvement on the overall score from the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire, researchers can’t conclude tVNS improved patient reported outcomes. The study used 1 hour of daily stimulation but the optimal duration and ideal timing of tVNS is yet to be determined.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, NIH/National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and individual donations from Francie Fitzgerald and family through the OU Foundation Fund. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
possibly through decreased antiadrenergic autoantibodies and inflammatory cytokines, and improved cardiac autonomic function, in a small proof-of-concept study.
METHODOLOGY:
The double-blind study included 25 female patients with POTS, a syndrome of orthostatic intolerance (mean age 31 years and 81% Caucasian), who were randomly assigned to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) to the right tragus or sham stimulation to the earlobe, a site devoid of vagal innervation.
After training, patients delivered the tVNS themselves at a frequency of 20 Hz and pulse width of 200 ms during 1-hour daily sessions over 2 months.
At baseline and 2 months, patients underwent a tilt test to determine postural tachycardia; they remained supine for 25 minutes, followed by 10 minutes of standing, as tolerated.
Researchers used electrocardiogram data to examine heart rate and blood samples to assess serum cytokines and antiautonomic autoantibodies.
The primary outcome was a comparison of orthostatic tachycardia (standing – supine) between the two arms at 2 months.
TAKEAWAY:
At 2 months, postural tachycardia was significantly less in the active vs sham arm (mean postural increase in heart rate 17.6 beats/min vs 31.7 beats/min; P = .01).
There was a significant decrease in beta 1-adrenergic receptor (beta 1-AR; P = .01) and alpha-1-AR (P = .04) autoantibody activity in the active vs sham group, which may account at least in part for the reduced orthostatic tachycardia, although the exact mechanisms for this effect have not been clearly defined, the authors said.
Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels were significantly decreased in the active group relative to the sham group (8.3 pg/mL vs 13.9 pg/mL; P = .01).
As for heart rate variability, change in low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) from supine to standing was significantly decreased, and postural change in LF/HF ratio, a surrogate for sympathovagal balance, was significantly lower in the active group compared with the sham group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Collectively, these data suggest that tVNS, a low-cost, low-risk intervention, applied for a short period of time in selected patients with POTS, may result in a significant amelioration of their disease,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Stavros Stavrakis, MD, PhD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology..
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a small sample size, included only females, and extended only up to 2 months. As there was no improvement on the overall score from the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire, researchers can’t conclude tVNS improved patient reported outcomes. The study used 1 hour of daily stimulation but the optimal duration and ideal timing of tVNS is yet to be determined.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, NIH/National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and individual donations from Francie Fitzgerald and family through the OU Foundation Fund. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
possibly through decreased antiadrenergic autoantibodies and inflammatory cytokines, and improved cardiac autonomic function, in a small proof-of-concept study.
METHODOLOGY:
The double-blind study included 25 female patients with POTS, a syndrome of orthostatic intolerance (mean age 31 years and 81% Caucasian), who were randomly assigned to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) to the right tragus or sham stimulation to the earlobe, a site devoid of vagal innervation.
After training, patients delivered the tVNS themselves at a frequency of 20 Hz and pulse width of 200 ms during 1-hour daily sessions over 2 months.
At baseline and 2 months, patients underwent a tilt test to determine postural tachycardia; they remained supine for 25 minutes, followed by 10 minutes of standing, as tolerated.
Researchers used electrocardiogram data to examine heart rate and blood samples to assess serum cytokines and antiautonomic autoantibodies.
The primary outcome was a comparison of orthostatic tachycardia (standing – supine) between the two arms at 2 months.
TAKEAWAY:
At 2 months, postural tachycardia was significantly less in the active vs sham arm (mean postural increase in heart rate 17.6 beats/min vs 31.7 beats/min; P = .01).
There was a significant decrease in beta 1-adrenergic receptor (beta 1-AR; P = .01) and alpha-1-AR (P = .04) autoantibody activity in the active vs sham group, which may account at least in part for the reduced orthostatic tachycardia, although the exact mechanisms for this effect have not been clearly defined, the authors said.
Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels were significantly decreased in the active group relative to the sham group (8.3 pg/mL vs 13.9 pg/mL; P = .01).
As for heart rate variability, change in low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) from supine to standing was significantly decreased, and postural change in LF/HF ratio, a surrogate for sympathovagal balance, was significantly lower in the active group compared with the sham group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Collectively, these data suggest that tVNS, a low-cost, low-risk intervention, applied for a short period of time in selected patients with POTS, may result in a significant amelioration of their disease,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Stavros Stavrakis, MD, PhD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology..
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a small sample size, included only females, and extended only up to 2 months. As there was no improvement on the overall score from the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire, researchers can’t conclude tVNS improved patient reported outcomes. The study used 1 hour of daily stimulation but the optimal duration and ideal timing of tVNS is yet to be determined.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, NIH/National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and individual donations from Francie Fitzgerald and family through the OU Foundation Fund. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Small-volume blood sample tubes may reduce anemia and transfusions in intensive care
according to a new study. The change does not appear to impair biospecimen sufficiency for lab analysis.
In addition, by reducing blood transfusion during ICU admission by about 10 units per 100 patients, the change may enable hospitals and health systems to sustain blood product supply during ongoing worldwide shortages.
“It doesn’t take long working in a hospital or being a patient or family member to realize how much blood we take to do lab work. As a result, patients may develop anemia and low RBC counts, which can be associated with worse health outcomes,” lead author Deborah Siegal, MD, a hematologist at the Ottawa Hospital and associate professor of medicine at the University of Ottawa, said in an interview.
“Unfortunately, the majority of the blood we take is discarded as waste,” she said. “Here’s an opportunity to move the needle on reducing anemia in hospitalized patients, where the benefit also doesn’t come at a cost.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Reducing Blood Loss
Among ICU patients with critical illness, there is a high prevalence of anemia, Siegal noted. More than 90% of these patients have some degree of anemia after a 3-day stay. Typically, RBC transfusions are given to correct the low blood counts, and as many as 40% of ICU patients receive at least one RBC transfusion. Anemia and RBC transfusion are each associated with adverse outcomes, including higher mortality and longer ICU and hospital stays.
Although anemia in critically ill ICU patients can have several causes, blood sampling can be substantial because of the need to draw multiple tubes several times per day. During 8 days in an ICU, the amount of blood drawn equals about 1 unit of whole blood, the authors noted, and ICU patients often struggle to increase RBC production and compensate for blood loss.
Even then, only 10% of the blood collected is required for lab testing; the remaining 90% is often discarded as waste, the authors noted. Small-volume tubes (1.8 to 3.5 mL), which are designed to draw about 50% less than standard-volume tubes (4 to 6 mL) by using less vacuum strength, are of the same size and cost as standard-volume tubes, and the collection technique is the same. They are produced by the same manufacturers and are compatible with existing lab equipment.
Siegal and colleagues conducted a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial to test the switch to small-volume tubes in 25 adult medical-surgical ICUs in Canada between February 2019 and January 2021. They analyzed data from more than 27,000 patients admitted to the ICU for 48 hours or longer. ICUs were randomly assigned to switch from standard-volume tubes to small-volume tubes for lab testing. The research team primarily assessed RBC transfusion in units per patient per ICU stay, as well as hemoglobin decrease during ICU stay, length of stay in the ICU and hospital, mortality in the ICU and hospital, and specimen tubes with insufficient volume for testing.
In a primary analysis of 21,201 patients, which excluded 6210 patients admitted during the early COVID-19 pandemic, there was no significant difference between tube-volume groups in RBC units per patient per ICU stay (relative risk [RR], 0.91). However, there was an absolute reduction of 7.24 RBC units per 100 patients per ICU stay in the small-volume group.
In addition, in a prespecified secondary analysis of 27,411 patients, RBC units per patient per ICU stay significantly decreased (RR, 0.88) after the switch to small-volume tubes, and there was an absolute reduction of 9.84 RBC units per 100 patients per ICU stay.
Overall, the median decrease in transfusion-adjusted hemoglobin wasn’t significantly different in the primary analysis but was lower in the secondary analysis. The frequency of specimens with insufficient volume for testing was low (≤0.03%) before and after the transition to small-volume tubes.
About 36,000 units of blood were given to ICU patients during the study period. The use of small-volume tubes may have saved about 1500 RBC units, the authors estimated.
“This could be an important way to help preserve the supply of blood products for patients who need them, including those undergoing cancer treatment, surgery, trauma, or other medical illnesses,” Siegal said. “The other great aspect is that this was implemented by people on the ground in the ICUs, and it’s still in use in most of those hospitals today.”
The investigators noted the need to study the switch in other patient populations, such as non-ICU hospitalized patients or outpatient settings. For instance, ICU patients often have central venous or arterial catheters for blood draws, but small-volume tubes can be used with venipuncture and could lead to additional benefits there as well.
Implementing Change
Commenting on the findings for this article, Lisa Hicks, MD, a hematologist at St. Michael’s Hospital and associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said, “Routinely collecting smaller volumes of blood for diagnostic testing appears to be feasible and does not cause problems with inadequate sampling. Whether this strategy decreases transfusion is more complicated.” Hicks did not participate in the study.
“At the end of the day, we still don’t know with certainty whether reduced-volume blood collection tubes decrease transfusion burden in ICU patients — it’s possible that there are so many other factors driving down hemoglobin in this population that the impact of blood collection volume is modest to negligible,” she said. “On the other hand, it’s also possible that there is an important impact that was masked by the relatively short ICU stays in the included population.”
Hicks has researched ways to reduce unnecessary diagnostic phlebotomy in ICUs. She and colleagues found that targeting clinicians’ test ordering behavior can decrease blood draws and RBC transfusions.
“What we now know, thanks to Siegal et al, is that we don’t need to collect nearly as much blood from our ICU patients as we do, raising the question of which strategy should really be standard,” she said. “My vote goes for more blood in the patient and less in the bin.”
The study was funded by a peer-reviewed grant from the Academic Health Sciences Centers AFP Innovation Fund/Hamilton Academic Health Sciences Organization and the Hamilton Health Sciences Research Institute through the Population Health Research Institute. Siegal, who is supported by a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Anticoagulant Management of Cardiovascular Disease, reported honoraria for presentations paid indirectly to her institution from BMS-Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Servier, and Roche outside of the submitted work. Hicks reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study. The change does not appear to impair biospecimen sufficiency for lab analysis.
In addition, by reducing blood transfusion during ICU admission by about 10 units per 100 patients, the change may enable hospitals and health systems to sustain blood product supply during ongoing worldwide shortages.
“It doesn’t take long working in a hospital or being a patient or family member to realize how much blood we take to do lab work. As a result, patients may develop anemia and low RBC counts, which can be associated with worse health outcomes,” lead author Deborah Siegal, MD, a hematologist at the Ottawa Hospital and associate professor of medicine at the University of Ottawa, said in an interview.
“Unfortunately, the majority of the blood we take is discarded as waste,” she said. “Here’s an opportunity to move the needle on reducing anemia in hospitalized patients, where the benefit also doesn’t come at a cost.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Reducing Blood Loss
Among ICU patients with critical illness, there is a high prevalence of anemia, Siegal noted. More than 90% of these patients have some degree of anemia after a 3-day stay. Typically, RBC transfusions are given to correct the low blood counts, and as many as 40% of ICU patients receive at least one RBC transfusion. Anemia and RBC transfusion are each associated with adverse outcomes, including higher mortality and longer ICU and hospital stays.
Although anemia in critically ill ICU patients can have several causes, blood sampling can be substantial because of the need to draw multiple tubes several times per day. During 8 days in an ICU, the amount of blood drawn equals about 1 unit of whole blood, the authors noted, and ICU patients often struggle to increase RBC production and compensate for blood loss.
Even then, only 10% of the blood collected is required for lab testing; the remaining 90% is often discarded as waste, the authors noted. Small-volume tubes (1.8 to 3.5 mL), which are designed to draw about 50% less than standard-volume tubes (4 to 6 mL) by using less vacuum strength, are of the same size and cost as standard-volume tubes, and the collection technique is the same. They are produced by the same manufacturers and are compatible with existing lab equipment.
Siegal and colleagues conducted a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial to test the switch to small-volume tubes in 25 adult medical-surgical ICUs in Canada between February 2019 and January 2021. They analyzed data from more than 27,000 patients admitted to the ICU for 48 hours or longer. ICUs were randomly assigned to switch from standard-volume tubes to small-volume tubes for lab testing. The research team primarily assessed RBC transfusion in units per patient per ICU stay, as well as hemoglobin decrease during ICU stay, length of stay in the ICU and hospital, mortality in the ICU and hospital, and specimen tubes with insufficient volume for testing.
In a primary analysis of 21,201 patients, which excluded 6210 patients admitted during the early COVID-19 pandemic, there was no significant difference between tube-volume groups in RBC units per patient per ICU stay (relative risk [RR], 0.91). However, there was an absolute reduction of 7.24 RBC units per 100 patients per ICU stay in the small-volume group.
In addition, in a prespecified secondary analysis of 27,411 patients, RBC units per patient per ICU stay significantly decreased (RR, 0.88) after the switch to small-volume tubes, and there was an absolute reduction of 9.84 RBC units per 100 patients per ICU stay.
Overall, the median decrease in transfusion-adjusted hemoglobin wasn’t significantly different in the primary analysis but was lower in the secondary analysis. The frequency of specimens with insufficient volume for testing was low (≤0.03%) before and after the transition to small-volume tubes.
About 36,000 units of blood were given to ICU patients during the study period. The use of small-volume tubes may have saved about 1500 RBC units, the authors estimated.
“This could be an important way to help preserve the supply of blood products for patients who need them, including those undergoing cancer treatment, surgery, trauma, or other medical illnesses,” Siegal said. “The other great aspect is that this was implemented by people on the ground in the ICUs, and it’s still in use in most of those hospitals today.”
The investigators noted the need to study the switch in other patient populations, such as non-ICU hospitalized patients or outpatient settings. For instance, ICU patients often have central venous or arterial catheters for blood draws, but small-volume tubes can be used with venipuncture and could lead to additional benefits there as well.
Implementing Change
Commenting on the findings for this article, Lisa Hicks, MD, a hematologist at St. Michael’s Hospital and associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said, “Routinely collecting smaller volumes of blood for diagnostic testing appears to be feasible and does not cause problems with inadequate sampling. Whether this strategy decreases transfusion is more complicated.” Hicks did not participate in the study.
“At the end of the day, we still don’t know with certainty whether reduced-volume blood collection tubes decrease transfusion burden in ICU patients — it’s possible that there are so many other factors driving down hemoglobin in this population that the impact of blood collection volume is modest to negligible,” she said. “On the other hand, it’s also possible that there is an important impact that was masked by the relatively short ICU stays in the included population.”
Hicks has researched ways to reduce unnecessary diagnostic phlebotomy in ICUs. She and colleagues found that targeting clinicians’ test ordering behavior can decrease blood draws and RBC transfusions.
“What we now know, thanks to Siegal et al, is that we don’t need to collect nearly as much blood from our ICU patients as we do, raising the question of which strategy should really be standard,” she said. “My vote goes for more blood in the patient and less in the bin.”
The study was funded by a peer-reviewed grant from the Academic Health Sciences Centers AFP Innovation Fund/Hamilton Academic Health Sciences Organization and the Hamilton Health Sciences Research Institute through the Population Health Research Institute. Siegal, who is supported by a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Anticoagulant Management of Cardiovascular Disease, reported honoraria for presentations paid indirectly to her institution from BMS-Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Servier, and Roche outside of the submitted work. Hicks reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study. The change does not appear to impair biospecimen sufficiency for lab analysis.
In addition, by reducing blood transfusion during ICU admission by about 10 units per 100 patients, the change may enable hospitals and health systems to sustain blood product supply during ongoing worldwide shortages.
“It doesn’t take long working in a hospital or being a patient or family member to realize how much blood we take to do lab work. As a result, patients may develop anemia and low RBC counts, which can be associated with worse health outcomes,” lead author Deborah Siegal, MD, a hematologist at the Ottawa Hospital and associate professor of medicine at the University of Ottawa, said in an interview.
“Unfortunately, the majority of the blood we take is discarded as waste,” she said. “Here’s an opportunity to move the needle on reducing anemia in hospitalized patients, where the benefit also doesn’t come at a cost.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Reducing Blood Loss
Among ICU patients with critical illness, there is a high prevalence of anemia, Siegal noted. More than 90% of these patients have some degree of anemia after a 3-day stay. Typically, RBC transfusions are given to correct the low blood counts, and as many as 40% of ICU patients receive at least one RBC transfusion. Anemia and RBC transfusion are each associated with adverse outcomes, including higher mortality and longer ICU and hospital stays.
Although anemia in critically ill ICU patients can have several causes, blood sampling can be substantial because of the need to draw multiple tubes several times per day. During 8 days in an ICU, the amount of blood drawn equals about 1 unit of whole blood, the authors noted, and ICU patients often struggle to increase RBC production and compensate for blood loss.
Even then, only 10% of the blood collected is required for lab testing; the remaining 90% is often discarded as waste, the authors noted. Small-volume tubes (1.8 to 3.5 mL), which are designed to draw about 50% less than standard-volume tubes (4 to 6 mL) by using less vacuum strength, are of the same size and cost as standard-volume tubes, and the collection technique is the same. They are produced by the same manufacturers and are compatible with existing lab equipment.
Siegal and colleagues conducted a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial to test the switch to small-volume tubes in 25 adult medical-surgical ICUs in Canada between February 2019 and January 2021. They analyzed data from more than 27,000 patients admitted to the ICU for 48 hours or longer. ICUs were randomly assigned to switch from standard-volume tubes to small-volume tubes for lab testing. The research team primarily assessed RBC transfusion in units per patient per ICU stay, as well as hemoglobin decrease during ICU stay, length of stay in the ICU and hospital, mortality in the ICU and hospital, and specimen tubes with insufficient volume for testing.
In a primary analysis of 21,201 patients, which excluded 6210 patients admitted during the early COVID-19 pandemic, there was no significant difference between tube-volume groups in RBC units per patient per ICU stay (relative risk [RR], 0.91). However, there was an absolute reduction of 7.24 RBC units per 100 patients per ICU stay in the small-volume group.
In addition, in a prespecified secondary analysis of 27,411 patients, RBC units per patient per ICU stay significantly decreased (RR, 0.88) after the switch to small-volume tubes, and there was an absolute reduction of 9.84 RBC units per 100 patients per ICU stay.
Overall, the median decrease in transfusion-adjusted hemoglobin wasn’t significantly different in the primary analysis but was lower in the secondary analysis. The frequency of specimens with insufficient volume for testing was low (≤0.03%) before and after the transition to small-volume tubes.
About 36,000 units of blood were given to ICU patients during the study period. The use of small-volume tubes may have saved about 1500 RBC units, the authors estimated.
“This could be an important way to help preserve the supply of blood products for patients who need them, including those undergoing cancer treatment, surgery, trauma, or other medical illnesses,” Siegal said. “The other great aspect is that this was implemented by people on the ground in the ICUs, and it’s still in use in most of those hospitals today.”
The investigators noted the need to study the switch in other patient populations, such as non-ICU hospitalized patients or outpatient settings. For instance, ICU patients often have central venous or arterial catheters for blood draws, but small-volume tubes can be used with venipuncture and could lead to additional benefits there as well.
Implementing Change
Commenting on the findings for this article, Lisa Hicks, MD, a hematologist at St. Michael’s Hospital and associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said, “Routinely collecting smaller volumes of blood for diagnostic testing appears to be feasible and does not cause problems with inadequate sampling. Whether this strategy decreases transfusion is more complicated.” Hicks did not participate in the study.
“At the end of the day, we still don’t know with certainty whether reduced-volume blood collection tubes decrease transfusion burden in ICU patients — it’s possible that there are so many other factors driving down hemoglobin in this population that the impact of blood collection volume is modest to negligible,” she said. “On the other hand, it’s also possible that there is an important impact that was masked by the relatively short ICU stays in the included population.”
Hicks has researched ways to reduce unnecessary diagnostic phlebotomy in ICUs. She and colleagues found that targeting clinicians’ test ordering behavior can decrease blood draws and RBC transfusions.
“What we now know, thanks to Siegal et al, is that we don’t need to collect nearly as much blood from our ICU patients as we do, raising the question of which strategy should really be standard,” she said. “My vote goes for more blood in the patient and less in the bin.”
The study was funded by a peer-reviewed grant from the Academic Health Sciences Centers AFP Innovation Fund/Hamilton Academic Health Sciences Organization and the Hamilton Health Sciences Research Institute through the Population Health Research Institute. Siegal, who is supported by a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Anticoagulant Management of Cardiovascular Disease, reported honoraria for presentations paid indirectly to her institution from BMS-Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Servier, and Roche outside of the submitted work. Hicks reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
ASCO details how to manage ongoing cancer drug shortage
As of November 30, the US Food and Drug Administration lists 16 commonly used oncology drugs currently in shortage, including methotrexate, capecitabine, vinblastine, carboplatin, and cisplatin, along with another 13 discontinued agents.
The ASCO guidance, which is updated regularly on ASCO’s drug shortage website, covers dozens of clinical situations involving breast, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, gynecologic, thoracic, and head & neck cancers, as well as Hodgkin lymphoma.
The recommendations, published earlier in JCO Oncology Practice, represent the work of a Drug Shortages Advisory Group with over 40 oncologists, ethicists, and patient advocates brought together by ASCO in collaboration with the Society for Gynecologic Oncology.
In the guidance, the advisory group also provides some context about why these shortage issues have persisted, including a paucity of generic options, quality control issues, and reluctance among manufacturers to produce older drugs with slim profit margins.
And “while ASCO continues to work to address the root causes of the shortages, this guidance document aims to support clinicians, as they navigate the complexities of treatment planning amid the drug shortage, and patients with cancer who are already enduring physical and emotional hardships,” the advisory group writes.
The overall message in the guidance: conserve oncology drugs in limited supply to use when needed most.
The recommendations highlight alternative regimens, when available, and what to do in situations when there are no alternatives, advice that has become particularly relevant for the oncology workhorses cisplatin and carboplatin.
More generally, when ranges of acceptable doses and dose frequencies exist for drugs in short supply, clinicians should opt for the lowest dose at the longest interval. Dose rounding and multi-use vials should also be used to eliminate waste, and alternatives should be used whenever possible. If an alternative agent with similar efficacy and safety is available, the agent in limited supply should not be ordered.
In certain settings where no reasonable alternatives to platinum regimens exist, the advisory group recommends patients travel to where platinum agents are available. The group noted this strategy specifically for patients with non–small cell lung cancer or testicular germ cell cancers, but also acknowledged that this option “may cause additional financial toxicity, hardship, and distress.”
Other, more granular advice includes holding carboplatin in reserve for patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer on neoadjuvant therapy who don’t respond well to upfront doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and pembrolizumab.
In addition to providing strategies to manage the ongoing cancer drug shortages, ASCO advises counseling for patients and clinicians struggling with the “psychological or moral distress” from the ongoing shortages.
“Unfortunately, drug shortages place the patient and the provider in a challenging situation, possibly resulting in inferior outcomes, delayed or denied care, and increased adverse events,” the advisory group writes. “ASCO will continue to respond to the oncology drug shortage crisis through policy and advocacy efforts, provide ethical guidance for allocation and prioritization decisions, and maintain shortage-specific clinical guidance as long as necessary.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As of November 30, the US Food and Drug Administration lists 16 commonly used oncology drugs currently in shortage, including methotrexate, capecitabine, vinblastine, carboplatin, and cisplatin, along with another 13 discontinued agents.
The ASCO guidance, which is updated regularly on ASCO’s drug shortage website, covers dozens of clinical situations involving breast, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, gynecologic, thoracic, and head & neck cancers, as well as Hodgkin lymphoma.
The recommendations, published earlier in JCO Oncology Practice, represent the work of a Drug Shortages Advisory Group with over 40 oncologists, ethicists, and patient advocates brought together by ASCO in collaboration with the Society for Gynecologic Oncology.
In the guidance, the advisory group also provides some context about why these shortage issues have persisted, including a paucity of generic options, quality control issues, and reluctance among manufacturers to produce older drugs with slim profit margins.
And “while ASCO continues to work to address the root causes of the shortages, this guidance document aims to support clinicians, as they navigate the complexities of treatment planning amid the drug shortage, and patients with cancer who are already enduring physical and emotional hardships,” the advisory group writes.
The overall message in the guidance: conserve oncology drugs in limited supply to use when needed most.
The recommendations highlight alternative regimens, when available, and what to do in situations when there are no alternatives, advice that has become particularly relevant for the oncology workhorses cisplatin and carboplatin.
More generally, when ranges of acceptable doses and dose frequencies exist for drugs in short supply, clinicians should opt for the lowest dose at the longest interval. Dose rounding and multi-use vials should also be used to eliminate waste, and alternatives should be used whenever possible. If an alternative agent with similar efficacy and safety is available, the agent in limited supply should not be ordered.
In certain settings where no reasonable alternatives to platinum regimens exist, the advisory group recommends patients travel to where platinum agents are available. The group noted this strategy specifically for patients with non–small cell lung cancer or testicular germ cell cancers, but also acknowledged that this option “may cause additional financial toxicity, hardship, and distress.”
Other, more granular advice includes holding carboplatin in reserve for patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer on neoadjuvant therapy who don’t respond well to upfront doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and pembrolizumab.
In addition to providing strategies to manage the ongoing cancer drug shortages, ASCO advises counseling for patients and clinicians struggling with the “psychological or moral distress” from the ongoing shortages.
“Unfortunately, drug shortages place the patient and the provider in a challenging situation, possibly resulting in inferior outcomes, delayed or denied care, and increased adverse events,” the advisory group writes. “ASCO will continue to respond to the oncology drug shortage crisis through policy and advocacy efforts, provide ethical guidance for allocation and prioritization decisions, and maintain shortage-specific clinical guidance as long as necessary.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As of November 30, the US Food and Drug Administration lists 16 commonly used oncology drugs currently in shortage, including methotrexate, capecitabine, vinblastine, carboplatin, and cisplatin, along with another 13 discontinued agents.
The ASCO guidance, which is updated regularly on ASCO’s drug shortage website, covers dozens of clinical situations involving breast, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, gynecologic, thoracic, and head & neck cancers, as well as Hodgkin lymphoma.
The recommendations, published earlier in JCO Oncology Practice, represent the work of a Drug Shortages Advisory Group with over 40 oncologists, ethicists, and patient advocates brought together by ASCO in collaboration with the Society for Gynecologic Oncology.
In the guidance, the advisory group also provides some context about why these shortage issues have persisted, including a paucity of generic options, quality control issues, and reluctance among manufacturers to produce older drugs with slim profit margins.
And “while ASCO continues to work to address the root causes of the shortages, this guidance document aims to support clinicians, as they navigate the complexities of treatment planning amid the drug shortage, and patients with cancer who are already enduring physical and emotional hardships,” the advisory group writes.
The overall message in the guidance: conserve oncology drugs in limited supply to use when needed most.
The recommendations highlight alternative regimens, when available, and what to do in situations when there are no alternatives, advice that has become particularly relevant for the oncology workhorses cisplatin and carboplatin.
More generally, when ranges of acceptable doses and dose frequencies exist for drugs in short supply, clinicians should opt for the lowest dose at the longest interval. Dose rounding and multi-use vials should also be used to eliminate waste, and alternatives should be used whenever possible. If an alternative agent with similar efficacy and safety is available, the agent in limited supply should not be ordered.
In certain settings where no reasonable alternatives to platinum regimens exist, the advisory group recommends patients travel to where platinum agents are available. The group noted this strategy specifically for patients with non–small cell lung cancer or testicular germ cell cancers, but also acknowledged that this option “may cause additional financial toxicity, hardship, and distress.”
Other, more granular advice includes holding carboplatin in reserve for patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer on neoadjuvant therapy who don’t respond well to upfront doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and pembrolizumab.
In addition to providing strategies to manage the ongoing cancer drug shortages, ASCO advises counseling for patients and clinicians struggling with the “psychological or moral distress” from the ongoing shortages.
“Unfortunately, drug shortages place the patient and the provider in a challenging situation, possibly resulting in inferior outcomes, delayed or denied care, and increased adverse events,” the advisory group writes. “ASCO will continue to respond to the oncology drug shortage crisis through policy and advocacy efforts, provide ethical guidance for allocation and prioritization decisions, and maintain shortage-specific clinical guidance as long as necessary.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JCO ONCOLOGY PRACTICE
Transapical valve replacement relieves mitral regurgitation
, relief of mitral regurgitation, and increases in cardiac hemodynamics and quality of life sustained at 1 year.
Further, patients with severe mitral annular calcification (MAC) showed improvements in hemodynamics, functional status, and quality of life after the procedure.
With 70 centers participating in the Tendyne SUMMIT trial, the first 100 trial roll-in patients accrued from the first one or two patients from each site without previous Tendyne TMVR experience.
“For this new procedure, with new operators, there was no intraprocedural mortality, and procedural survival was 100%,” co-primary investigator Jason Rogers, MD, of the University of California Davis Medical Center, Sacramento, told attendees at a Late-Breaking Clinical Science session at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
“The survival was 74% at 12 months. The valve was very effective at eliminating much regurgitation, and 96.5% of patients had either zero or 1+ at a year, and 97% at 30 days had no mitral regurgitation,” he reported. As follow-up was during the COVID-19 pandemic, several of the deaths were attributed to COVID.
Device and trial designs
The Tendyne TMVR is placed through the cardiac apex. It has an outer frame contoured to comport with the shape of the native mitral valve. Inside is a circular, self-expanding, tri-leaflet bioprosthetic valve.
A unique aspect of the design is a tether attached to the outflow side of the valve to allow positioning and control of the valve. At the end of the tether is an apical pad that is placed over the apical access site to control bleeding. The device is currently limited to investigational use in the United States.
The trial enrolled patients with grade III/IV MR or severe MAC if valve anatomy was deemed amenable to transcatheter repair or met MitraClip indications and if these treatments were considered more appropriate than surgery.
Dr. Rogers reported on the first 100 roll-in (early experimental) patients who received Tendyne TMVR. There was a separate severe MAC cohort receiving Tendyne implantation (N = 103). A further 1:1 randomized study of 382 patients compared Tendyne investigational treatment with a MitraClip control group.
At baseline, the 100 roll-in patients had an average age of 75 years, 54% were men, 46% had a frailty score of 2 or greater, and 41% had been hospitalized in the prior 12 months for heart failure. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 48.6% ± 10.3%.
Improved cardiac function
Procedural survival was 100%, technical success 94%, and valve implantation occurred in 97%. Of the first 100 patients, 26 had died by 1 year, and two withdrew consent, leaving 72 for evaluation.
Immediate post-procedure survival was 98%, 87.9% at 3 months, 83.7% at 6 months, and 74.3% at 1 year. MR severity decreased from 29% 3+ and 69% 4+ at baseline to 96.5% 0/1+ and 3.5% 2+ at 1 year.
Cumulative adverse outcomes at 1 year were 27% all-cause mortality, 21.6% cardiovascular mortality, 5.4% all-cause stroke, 2.3% myocardial infarction (MI), 2.2% post-operative mitral reintervention, no major but 2.3% minor device thrombosis, and 32.4% major bleeding.
Most adverse events occurred peri-procedurally or within the first month, representing, “I think, a new procedure with new operators and a high real risk population,” Dr. Rogers said.
Echocardiography at 1 year compared with baseline showed significant changes with decreases in left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV), increases in cardiac output (CO) and forward stroke volume, and no change in mitral valve gradient or left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) gradient. New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification decreased from 69% class III/IV at baseline to 20% at 1 year, at which point 80% of patients were in class I/II.
“There was a consistent and steady improvement in KCCQ [Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire] score, as expected, as patients recovered from this invasive procedure,” Dr. Rogers said. The 1-year score was 68.7, representing fair to good quality of life.
Outcomes with severe MAC
After screening for MR 3+ or greater, severe mitral stenosis, or moderate MR plus mitral stenosis, 103 eligible patients were treated with the Tendyne device. The median MAC volume of the cohort was 4000 mm3, with a maximum of 38,000 mm3.
Patients averaged 78 years old, 44.7% male, 55.3% had a frailty score of 2 or greater, 73.8% were in NYHA class III or greater, and 29.1% had been hospitalized within the prior 12 months for heart failure. Grade III or IV MR severity was present in 89%, with MR being primary in 90.3% of patients, and 10.7% had severe mitral stenosis.
Tendyne procedure survival was 98.1%, technical success was 94.2%, and valves were implanted in all patients. Emergency surgery or other intervention was required in 5.8%.
As co-presenter of the SUMMIT results, Vinod Thourani, MD, of the Piedmont Heart Institute in Atlanta, said at 30 days there was 6.8% all-cause mortality, all of it cardiovascular. There was one disabling stroke, one MI, no device thrombosis, and 21.4% major bleeding.
“At 1 month, there was less than grade 1 mitral regurgitation in all patients,” he reported, vs. 89% grade 3+/4+ at baseline. “At 1 month, it was an improvement in the NYHA classification to almost 70% in class I or II, which was improved from baseline of 26% in NYHA class I or II.”
Hemodynamic parameters all showed improvement, with a reduction in LVEF, LVEDV, and mitral valve gradient and increases in CO and forward stroke volume. There was no significant increase in LVOT gradient.
There was a small improvement in the KCCQ quality of life score from a baseline score of 49.2 to 52.3 at 30 days. “We’re expecting the KCCQ overall score to improve on 1 year follow up since the patients [are] still recovering from their thoracotomy incision,” Dr. Thourani predicted.
The primary endpoint will be evaluated at 1 year post procedure, he said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
No good option
Designated discussant Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, first thanked the presenters for their trial, saying, “What an absolute pleasure to be a mitral surgeon at a meeting where you’re presenting a solution for something that we find incredibly challenging. There’s no good transcatheter option for MAC. There’s no great surgical option for MAC.”
She noted the small size of the MAC cohort and asked what drove failure in patient screening, starting with 474 patients, identifying 120 who would be eligible, and enrolling 103 in the MAC cohort. The presenters identified neo-LVOT, the residual LVOT created after implanting the mitral valve prosthesis. Screening also eliminated patients with a too large or too small annulus.
Dr. Thourani said in Europe, surgeons have used anterior leaflet splitting before Tendyne, which may help to expand the population of eligible patients, but no leaflet modification was allowed in the SUMMIT trial.
Dr. Chikwe then pointed to the six deaths in the MAC arm and 11 deaths in the roll-in arm and asked about the mechanism of these deaths. “Was it [that] the 22% major bleeding is transapical? Really the Achilles heel of this procedure? Is this something that could become a transcatheter device?”
“We call it a transcatheter procedure, but it’s very much a surgical procedure,” Dr. Rogers answered. “And, you know, despite having great experienced sites...many surgeons don’t deal with the apex very much.” Furthermore, catheter insertion can lead to bleeding complications.
He noted that the roll-in patients were the first one or two cases at each site, and there have been improvements with site experience. The apical pads assist in hemostasis. He said the current design of the Tendyne catheter-delivered valve does not allow it to be adapted to a transfemoral transseptal approach.
Dr. Rogers is a consultant to and co-national principal investigator of the SUMMIT Pivotal Trial for Abbott. He is a consultant to Boston Scientific and a consultant/equity holder in Laminar. Dr. Thourani has received grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Artivion, AtriCure, Boston Scientific, Croivalve, Edwards Lifesciences, JenaValve, Medtronic, and Trisol; consultant fees/honoraria from Abbott Vascular, Artivion, AtriCure, Boston Scientific, Croivalve, and Edwards Lifesciences; and has an executive role/ownership interest in DASI Simulations. Dr. Chikwe reports no relevant financial relationships. The SUMMIT trial was sponsored by Abbott.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, relief of mitral regurgitation, and increases in cardiac hemodynamics and quality of life sustained at 1 year.
Further, patients with severe mitral annular calcification (MAC) showed improvements in hemodynamics, functional status, and quality of life after the procedure.
With 70 centers participating in the Tendyne SUMMIT trial, the first 100 trial roll-in patients accrued from the first one or two patients from each site without previous Tendyne TMVR experience.
“For this new procedure, with new operators, there was no intraprocedural mortality, and procedural survival was 100%,” co-primary investigator Jason Rogers, MD, of the University of California Davis Medical Center, Sacramento, told attendees at a Late-Breaking Clinical Science session at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
“The survival was 74% at 12 months. The valve was very effective at eliminating much regurgitation, and 96.5% of patients had either zero or 1+ at a year, and 97% at 30 days had no mitral regurgitation,” he reported. As follow-up was during the COVID-19 pandemic, several of the deaths were attributed to COVID.
Device and trial designs
The Tendyne TMVR is placed through the cardiac apex. It has an outer frame contoured to comport with the shape of the native mitral valve. Inside is a circular, self-expanding, tri-leaflet bioprosthetic valve.
A unique aspect of the design is a tether attached to the outflow side of the valve to allow positioning and control of the valve. At the end of the tether is an apical pad that is placed over the apical access site to control bleeding. The device is currently limited to investigational use in the United States.
The trial enrolled patients with grade III/IV MR or severe MAC if valve anatomy was deemed amenable to transcatheter repair or met MitraClip indications and if these treatments were considered more appropriate than surgery.
Dr. Rogers reported on the first 100 roll-in (early experimental) patients who received Tendyne TMVR. There was a separate severe MAC cohort receiving Tendyne implantation (N = 103). A further 1:1 randomized study of 382 patients compared Tendyne investigational treatment with a MitraClip control group.
At baseline, the 100 roll-in patients had an average age of 75 years, 54% were men, 46% had a frailty score of 2 or greater, and 41% had been hospitalized in the prior 12 months for heart failure. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 48.6% ± 10.3%.
Improved cardiac function
Procedural survival was 100%, technical success 94%, and valve implantation occurred in 97%. Of the first 100 patients, 26 had died by 1 year, and two withdrew consent, leaving 72 for evaluation.
Immediate post-procedure survival was 98%, 87.9% at 3 months, 83.7% at 6 months, and 74.3% at 1 year. MR severity decreased from 29% 3+ and 69% 4+ at baseline to 96.5% 0/1+ and 3.5% 2+ at 1 year.
Cumulative adverse outcomes at 1 year were 27% all-cause mortality, 21.6% cardiovascular mortality, 5.4% all-cause stroke, 2.3% myocardial infarction (MI), 2.2% post-operative mitral reintervention, no major but 2.3% minor device thrombosis, and 32.4% major bleeding.
Most adverse events occurred peri-procedurally or within the first month, representing, “I think, a new procedure with new operators and a high real risk population,” Dr. Rogers said.
Echocardiography at 1 year compared with baseline showed significant changes with decreases in left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV), increases in cardiac output (CO) and forward stroke volume, and no change in mitral valve gradient or left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) gradient. New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification decreased from 69% class III/IV at baseline to 20% at 1 year, at which point 80% of patients were in class I/II.
“There was a consistent and steady improvement in KCCQ [Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire] score, as expected, as patients recovered from this invasive procedure,” Dr. Rogers said. The 1-year score was 68.7, representing fair to good quality of life.
Outcomes with severe MAC
After screening for MR 3+ or greater, severe mitral stenosis, or moderate MR plus mitral stenosis, 103 eligible patients were treated with the Tendyne device. The median MAC volume of the cohort was 4000 mm3, with a maximum of 38,000 mm3.
Patients averaged 78 years old, 44.7% male, 55.3% had a frailty score of 2 or greater, 73.8% were in NYHA class III or greater, and 29.1% had been hospitalized within the prior 12 months for heart failure. Grade III or IV MR severity was present in 89%, with MR being primary in 90.3% of patients, and 10.7% had severe mitral stenosis.
Tendyne procedure survival was 98.1%, technical success was 94.2%, and valves were implanted in all patients. Emergency surgery or other intervention was required in 5.8%.
As co-presenter of the SUMMIT results, Vinod Thourani, MD, of the Piedmont Heart Institute in Atlanta, said at 30 days there was 6.8% all-cause mortality, all of it cardiovascular. There was one disabling stroke, one MI, no device thrombosis, and 21.4% major bleeding.
“At 1 month, there was less than grade 1 mitral regurgitation in all patients,” he reported, vs. 89% grade 3+/4+ at baseline. “At 1 month, it was an improvement in the NYHA classification to almost 70% in class I or II, which was improved from baseline of 26% in NYHA class I or II.”
Hemodynamic parameters all showed improvement, with a reduction in LVEF, LVEDV, and mitral valve gradient and increases in CO and forward stroke volume. There was no significant increase in LVOT gradient.
There was a small improvement in the KCCQ quality of life score from a baseline score of 49.2 to 52.3 at 30 days. “We’re expecting the KCCQ overall score to improve on 1 year follow up since the patients [are] still recovering from their thoracotomy incision,” Dr. Thourani predicted.
The primary endpoint will be evaluated at 1 year post procedure, he said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
No good option
Designated discussant Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, first thanked the presenters for their trial, saying, “What an absolute pleasure to be a mitral surgeon at a meeting where you’re presenting a solution for something that we find incredibly challenging. There’s no good transcatheter option for MAC. There’s no great surgical option for MAC.”
She noted the small size of the MAC cohort and asked what drove failure in patient screening, starting with 474 patients, identifying 120 who would be eligible, and enrolling 103 in the MAC cohort. The presenters identified neo-LVOT, the residual LVOT created after implanting the mitral valve prosthesis. Screening also eliminated patients with a too large or too small annulus.
Dr. Thourani said in Europe, surgeons have used anterior leaflet splitting before Tendyne, which may help to expand the population of eligible patients, but no leaflet modification was allowed in the SUMMIT trial.
Dr. Chikwe then pointed to the six deaths in the MAC arm and 11 deaths in the roll-in arm and asked about the mechanism of these deaths. “Was it [that] the 22% major bleeding is transapical? Really the Achilles heel of this procedure? Is this something that could become a transcatheter device?”
“We call it a transcatheter procedure, but it’s very much a surgical procedure,” Dr. Rogers answered. “And, you know, despite having great experienced sites...many surgeons don’t deal with the apex very much.” Furthermore, catheter insertion can lead to bleeding complications.
He noted that the roll-in patients were the first one or two cases at each site, and there have been improvements with site experience. The apical pads assist in hemostasis. He said the current design of the Tendyne catheter-delivered valve does not allow it to be adapted to a transfemoral transseptal approach.
Dr. Rogers is a consultant to and co-national principal investigator of the SUMMIT Pivotal Trial for Abbott. He is a consultant to Boston Scientific and a consultant/equity holder in Laminar. Dr. Thourani has received grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Artivion, AtriCure, Boston Scientific, Croivalve, Edwards Lifesciences, JenaValve, Medtronic, and Trisol; consultant fees/honoraria from Abbott Vascular, Artivion, AtriCure, Boston Scientific, Croivalve, and Edwards Lifesciences; and has an executive role/ownership interest in DASI Simulations. Dr. Chikwe reports no relevant financial relationships. The SUMMIT trial was sponsored by Abbott.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, relief of mitral regurgitation, and increases in cardiac hemodynamics and quality of life sustained at 1 year.
Further, patients with severe mitral annular calcification (MAC) showed improvements in hemodynamics, functional status, and quality of life after the procedure.
With 70 centers participating in the Tendyne SUMMIT trial, the first 100 trial roll-in patients accrued from the first one or two patients from each site without previous Tendyne TMVR experience.
“For this new procedure, with new operators, there was no intraprocedural mortality, and procedural survival was 100%,” co-primary investigator Jason Rogers, MD, of the University of California Davis Medical Center, Sacramento, told attendees at a Late-Breaking Clinical Science session at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
“The survival was 74% at 12 months. The valve was very effective at eliminating much regurgitation, and 96.5% of patients had either zero or 1+ at a year, and 97% at 30 days had no mitral regurgitation,” he reported. As follow-up was during the COVID-19 pandemic, several of the deaths were attributed to COVID.
Device and trial designs
The Tendyne TMVR is placed through the cardiac apex. It has an outer frame contoured to comport with the shape of the native mitral valve. Inside is a circular, self-expanding, tri-leaflet bioprosthetic valve.
A unique aspect of the design is a tether attached to the outflow side of the valve to allow positioning and control of the valve. At the end of the tether is an apical pad that is placed over the apical access site to control bleeding. The device is currently limited to investigational use in the United States.
The trial enrolled patients with grade III/IV MR or severe MAC if valve anatomy was deemed amenable to transcatheter repair or met MitraClip indications and if these treatments were considered more appropriate than surgery.
Dr. Rogers reported on the first 100 roll-in (early experimental) patients who received Tendyne TMVR. There was a separate severe MAC cohort receiving Tendyne implantation (N = 103). A further 1:1 randomized study of 382 patients compared Tendyne investigational treatment with a MitraClip control group.
At baseline, the 100 roll-in patients had an average age of 75 years, 54% were men, 46% had a frailty score of 2 or greater, and 41% had been hospitalized in the prior 12 months for heart failure. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 48.6% ± 10.3%.
Improved cardiac function
Procedural survival was 100%, technical success 94%, and valve implantation occurred in 97%. Of the first 100 patients, 26 had died by 1 year, and two withdrew consent, leaving 72 for evaluation.
Immediate post-procedure survival was 98%, 87.9% at 3 months, 83.7% at 6 months, and 74.3% at 1 year. MR severity decreased from 29% 3+ and 69% 4+ at baseline to 96.5% 0/1+ and 3.5% 2+ at 1 year.
Cumulative adverse outcomes at 1 year were 27% all-cause mortality, 21.6% cardiovascular mortality, 5.4% all-cause stroke, 2.3% myocardial infarction (MI), 2.2% post-operative mitral reintervention, no major but 2.3% minor device thrombosis, and 32.4% major bleeding.
Most adverse events occurred peri-procedurally or within the first month, representing, “I think, a new procedure with new operators and a high real risk population,” Dr. Rogers said.
Echocardiography at 1 year compared with baseline showed significant changes with decreases in left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV), increases in cardiac output (CO) and forward stroke volume, and no change in mitral valve gradient or left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) gradient. New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification decreased from 69% class III/IV at baseline to 20% at 1 year, at which point 80% of patients were in class I/II.
“There was a consistent and steady improvement in KCCQ [Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire] score, as expected, as patients recovered from this invasive procedure,” Dr. Rogers said. The 1-year score was 68.7, representing fair to good quality of life.
Outcomes with severe MAC
After screening for MR 3+ or greater, severe mitral stenosis, or moderate MR plus mitral stenosis, 103 eligible patients were treated with the Tendyne device. The median MAC volume of the cohort was 4000 mm3, with a maximum of 38,000 mm3.
Patients averaged 78 years old, 44.7% male, 55.3% had a frailty score of 2 or greater, 73.8% were in NYHA class III or greater, and 29.1% had been hospitalized within the prior 12 months for heart failure. Grade III or IV MR severity was present in 89%, with MR being primary in 90.3% of patients, and 10.7% had severe mitral stenosis.
Tendyne procedure survival was 98.1%, technical success was 94.2%, and valves were implanted in all patients. Emergency surgery or other intervention was required in 5.8%.
As co-presenter of the SUMMIT results, Vinod Thourani, MD, of the Piedmont Heart Institute in Atlanta, said at 30 days there was 6.8% all-cause mortality, all of it cardiovascular. There was one disabling stroke, one MI, no device thrombosis, and 21.4% major bleeding.
“At 1 month, there was less than grade 1 mitral regurgitation in all patients,” he reported, vs. 89% grade 3+/4+ at baseline. “At 1 month, it was an improvement in the NYHA classification to almost 70% in class I or II, which was improved from baseline of 26% in NYHA class I or II.”
Hemodynamic parameters all showed improvement, with a reduction in LVEF, LVEDV, and mitral valve gradient and increases in CO and forward stroke volume. There was no significant increase in LVOT gradient.
There was a small improvement in the KCCQ quality of life score from a baseline score of 49.2 to 52.3 at 30 days. “We’re expecting the KCCQ overall score to improve on 1 year follow up since the patients [are] still recovering from their thoracotomy incision,” Dr. Thourani predicted.
The primary endpoint will be evaluated at 1 year post procedure, he said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
No good option
Designated discussant Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, first thanked the presenters for their trial, saying, “What an absolute pleasure to be a mitral surgeon at a meeting where you’re presenting a solution for something that we find incredibly challenging. There’s no good transcatheter option for MAC. There’s no great surgical option for MAC.”
She noted the small size of the MAC cohort and asked what drove failure in patient screening, starting with 474 patients, identifying 120 who would be eligible, and enrolling 103 in the MAC cohort. The presenters identified neo-LVOT, the residual LVOT created after implanting the mitral valve prosthesis. Screening also eliminated patients with a too large or too small annulus.
Dr. Thourani said in Europe, surgeons have used anterior leaflet splitting before Tendyne, which may help to expand the population of eligible patients, but no leaflet modification was allowed in the SUMMIT trial.
Dr. Chikwe then pointed to the six deaths in the MAC arm and 11 deaths in the roll-in arm and asked about the mechanism of these deaths. “Was it [that] the 22% major bleeding is transapical? Really the Achilles heel of this procedure? Is this something that could become a transcatheter device?”
“We call it a transcatheter procedure, but it’s very much a surgical procedure,” Dr. Rogers answered. “And, you know, despite having great experienced sites...many surgeons don’t deal with the apex very much.” Furthermore, catheter insertion can lead to bleeding complications.
He noted that the roll-in patients were the first one or two cases at each site, and there have been improvements with site experience. The apical pads assist in hemostasis. He said the current design of the Tendyne catheter-delivered valve does not allow it to be adapted to a transfemoral transseptal approach.
Dr. Rogers is a consultant to and co-national principal investigator of the SUMMIT Pivotal Trial for Abbott. He is a consultant to Boston Scientific and a consultant/equity holder in Laminar. Dr. Thourani has received grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Artivion, AtriCure, Boston Scientific, Croivalve, Edwards Lifesciences, JenaValve, Medtronic, and Trisol; consultant fees/honoraria from Abbott Vascular, Artivion, AtriCure, Boston Scientific, Croivalve, and Edwards Lifesciences; and has an executive role/ownership interest in DASI Simulations. Dr. Chikwe reports no relevant financial relationships. The SUMMIT trial was sponsored by Abbott.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM TCT 2023
Delirious mania: Presentation, pathogenesis, and management
Delirious mania is a syndrome characterized by the acute onset of severe hyperactivity, psychosis, catatonia, and intermittent confusion. While there have been growing reports of this phenomenon over the last 2 decades, it remains poorly recognized and understood.1,2 There is no widely accepted nosology for delirious mania and the condition is absent from DSM-5, which magnifies the difficulties in making a timely diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may result in a detrimental outcome.2,3 Delirious mania has also been labeled as lethal catatonia, specific febrile delirium, hyperactive or exhaustive mania, and Bell’s mania.2,4,5 The characterization and diagnosis of this condition have a long and inconsistent history (Box1,6-11).
Box
Delirious mania was originally recognized in 1849 by Luther Bell in McLean Hospital after he observed 40 cases that were uniquely distinct from 1,700 other cases from 1836 to 1849.6 He described these patients as being suddenly confused, demonstrating unprovoked combativeness, remarkable decreased need for sleep, excessive motor restlessness, extreme fearfulness, and certain physiological signs, including rapid pulse and sweating. Bell was limited to the psychiatric treatment of his time, which largely was confined to physical restraints. Approximately three-fourths of these patients died.6
Following Bell’s report, this syndrome remained unexplored and rarely described. Some researchers postulated that the development of confusion was a natural progression of late-phase mania in close to 20% of patients.7 However, this did not account for the rapid onset of symptoms as well as certain unexplained movement abnormalities. In 1980, Bond8 presented 3 cases that were similar in nature to Bell’s depiction: acute onset with extraordinary irritability, withdrawal, delirium, and mania.
For the next 2 decades, delirious mania was seldom reported in the literature. The term was often reserved to illustrate when a patient had nothing more than mania with features of delirium.9
By 1996, catatonia became better recognized in its wide array of symptomology and diagnostic scales.10,11 In 1999, in addition to the sudden onset of excitement, paranoia, grandiosity, and disorientation, Fink1 reported catatonic signs including negativism, stereotypy, posturing, grimacing, and echo phenomena in patients with delirious mania. He identified its sensitive response to electroconvulsive therapy.
Delirious mania continues to be met with incertitude in clinical practice, and numerous inconsistencies have been reported in the literature. For example, some cases that have been reported as delirious mania had more evidence of primary delirium due to another medical condition or primary mania.12,13 Other cases have demonstrated swift improvement of symptoms after monotherapy with antipsychotics without a trial of benzodiazepines or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT); the exclusion of a sudden onset questions the validity of the diagnosis and promotes the use of less efficacious treatments.14,15 Other reports have confirmed that the diagnosis is missed when certain symptoms are more predominant, such as a thought disorder (acute schizophrenia), grandiosity and delusional ideation (bipolar disorder [BD]), and less commonly assessed catatonic signs (ambitendency, automatic obedience). These symptoms are mistakenly attributed to the respective disease.1,16 This especially holds true when delirious mania is initially diagnosed as a primary psychosis, which leads to the administration of antipsychotics.17 Other cases have reported that delirious mania was resistant to treatment, but ECT was never pursued.18
In this review, we provide a more comprehensive perspective of the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management of delirious mania. We searched PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “delirious mania,” “delirious mania AND catatonia,” or “manic delirium.” Most articles we found were case reports, case series, or retrospective chart reviews. There were no systematic reviews, meta analyses, or randomized control trials (RCTs). The 12 articles included in this review consist of 7 individual case reports, 4 case series, and 1 retrospective chart review that describe a total of 36 cases (Table1,2,5,17,19-26).
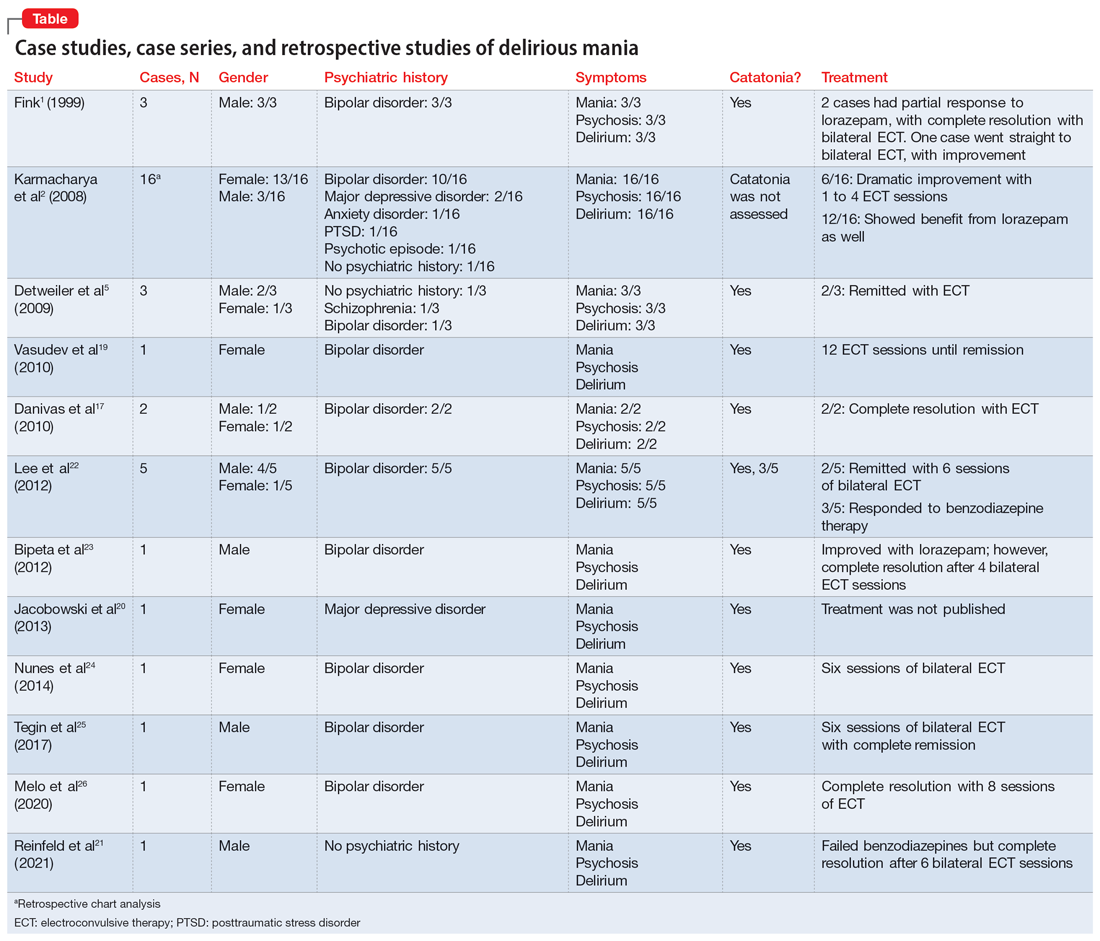
Clinical presentation: What to look for
Patients with delirious mania typically develop symptoms extremely rapidly. In virtually all published literature, symptoms were reported to emerge within hours to days and consisted of severe forms of mania, psychosis, and delirium; 100% of the cases in our review had these symptoms. Commonly reported symptoms were:
- intense excitement
- emotional lability
- grandiose delusions
- profound insomnia
- pressured and rapid speech
- auditory and visual hallucinations
- hypersexuality
- thought disorganization.
Exquisite paranoia can also result in violent aggression (and may require the use of physical restraints). Patients may confine themselves to very small spaces (such as a closet) in response to the intense paranoia. Impairments in various neurocognitive domains—including inability to focus; disorientation; language and visuospatial disturbances; difficulty with shifting and sustaining attention; and short-term memory impairments—have been reported. Patients often cannot recall the events during the episode.1,2,5,27,28
Catatonia has been closely associated with delirious mania.29 Features of excited catatonia—such as excessive motor activity, negativism, grimacing, posturing, echolalia, echopraxia, stereotypy, automatic obedience, verbigeration, combativeness, impulsivity, and rigidity—typically accompany delirious mania.1,5,10,19,27
In addition to these symptoms, patients may engage in specific behaviors. They may exhibit inappropriate toileting such as smearing feces on walls or in bags, fecal or urinary incontinence, disrobing or running naked in public places, or pouring liquid on the floor or on one’s head.1,2
Continue to: Of the 36 cases...
Of the 36 cases reported in the literature we reviewed, 20 (55%) were female. Most patients had an underlining psychiatric condition, including BD (72%), major depressive disorder (8%), and schizophrenia (2%). Three patients had no psychiatric history.
Physical examination
On initial presentation, a patient with delirious mania may be dehydrated, with dry mucous membranes, pale conjunctiva, tongue dryness, and poor skin turgor.28,30 Due to excessive motor activity, diaphoresis with tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, and fever may be present.31
Certain basic cognitive tasks should be assessed to determine the patient’s orientation to place, date, and time. Assess if the patient can recall recent events, names of objects, or perform serial 7s; clock drawing capabilities also should be ascertained.1,2,5 A Mini-Mental State Examination is useful.32
The Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale should be used to elicit features of catatonia, such as waxy flexibility, negativism, gegenhalten, mitgehen, catalepsy, ambitendency, automatic obedience, and grasp reflex.10
Laboratory findings are nonspecific
Although no specific laboratory findings are associated with delirious mania, bloodwork and imaging are routinely investigated, especially if delirium characteristics are most striking. A complete blood count, chemistries, hepatic panel, thyroid functioning, blood and/or urine cultures, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), and urinalysis can be ordered. Head imaging such as MRI and CT to rule out intracranial pathology are typically performed.19 However, the diagnosis of delirious mania is based on the presence of the phenotypic features, by verification of catatonia, and by the responsiveness to the treatment delivered.29
Continue to: Pathogenisis: Several hypotheses
Pathogenesis: Several hypotheses
The pathogenesis of delirious mania is not well understood. There are several postulations but no salient theory. Most patients with delirious mania have an underlying systemic medical or psychiatric condition.
Mood disorders. Patients with BD or schizoaffective disorder are especially susceptible to delirious mania. The percentage of manic patients who present with delirious mania varies by study. One study suggested approximately 19% have features of the phenomenon,33 while others estimated 15% to 25%.34 Elias et al35 calculated that 15% of patients with mania succumb to manic exhaustion; from this it can be reasonably concluded that these were cases of misdiagnosed delirious mania.
Delirium hypothesis. Patients with delirious mania typically have features of delirium, including fluctuation of consciousness, disorientation, and/or poor sleep-wake cycle.36 During rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep, memory circuits are fortified. When there is a substantial loss of REM and non-REM sleep, these circuits become faulty, even after 1 night. Pathological brain waves on EEG reflect the inability to reinforce the memory circuits. Patients with these waves may develop hallucinations, bizarre delusions, and altered sensorium. ECT reduces the pathological slow wave morphologies, thus restoring the synaptic maintenance and correcting the incompetent circuitry. This can explain the robust and rapid response of ECT in a patient with delirious mania.37,38
Neurotransmitter hypothesis. It has been shown that in patients with delirious mania there is dysregulation of dopamine transport, which leads to dopamine overflow in the synapse. In contrast to a drug effect (ie, cocaine or methamphetamine) that acts by inhibiting dopamine reuptake, dopamine overflow in delirious mania is caused by the loss of dopamine transporter regulation. This results in a dysfunctional dopaminergic state that precipitates an acute state of delirium and agitation.39,40
Serotonin plays a role in mood disorders, including mania and depression.41,42 More specifically, serotonin has been implicated in impulsivity and aggression as shown by reduced levels of CSF 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and depletion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).43
Continue to: Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission...
Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission are known to occur in delirium and catatonia. In delirium, GABA signaling is increased, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and melatonin release, thus impairing the sleep-wake cycle.44 Deficiencies in acetylcholine and melatonin are seen as well as excess of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine and glutamate.45 Conversely, in catatonia, functional imaging studies found decreased GABA-A binding in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, parietal, and motor cortical regions.46 A study analyzing 10 catatonic patients found decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex compared to psychiatric and healthy controls.47
Other neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) have been hypothesized to be hyperactive, causing downstream dysregulation of GABA functioning.48 However, the exact connection between delirious mania and all these receptors and neurotransmitters remains unknown.
Encephalitis hypothesis. The relationship between delirious mania and autoimmune encephalitis suggests delirious mania has etiologies other than a primary psychiatric illness. In a 2020 retrospective study49 that analyzed 79 patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 25.3% met criteria for delirious mania, and 95% of these patients had catatonic features. Dalmau et al50 found that in many cases, patients tend to respond to ECT; in a cases series of 3 patients, 2 responded to benzodiazepines.
COVID-19 hypothesis. The SARS-CoV-2 virion has been associated with many neuropsychiatric complications, including mood, psychotic, and neurocognitive disorders.51,52 There also have been cases of COVID-19–induced catatonia.53-55 One case of delirious mania in a patient with COVID-19 has been reported.21 The general mechanism has been proposed to be related to the stimulation of the proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, which the virus produces in large quantities.56 These cytokines have been linked to psychosis and other psychiatric disorders.57 The patient with COVID-19–induced delirious mania had elevated inflammatory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer, which supports a proinflammatory state. This patient had a complete resolution of symptoms with ECT.21
Management: Benzodiazepines and ECT
A step-by-step algorithm for managing delirious mania is outlined in the Figure. Regardless of the underlining etiology, management of delirious mania consists of benzodiazepines (lorazepam and diazepam); prompt use of ECT, particularly for patients who do not improve with large doses of lorazepam; or (if applicable) continued treatment of the underlining medical condition, which does not preclude the use of benzodiazepines or ECT. Recent reports27,58 have described details for using ECT for delirious mania, highlighting the use of high-energy dosing, bilateral electrode placement, and frequent sessions.
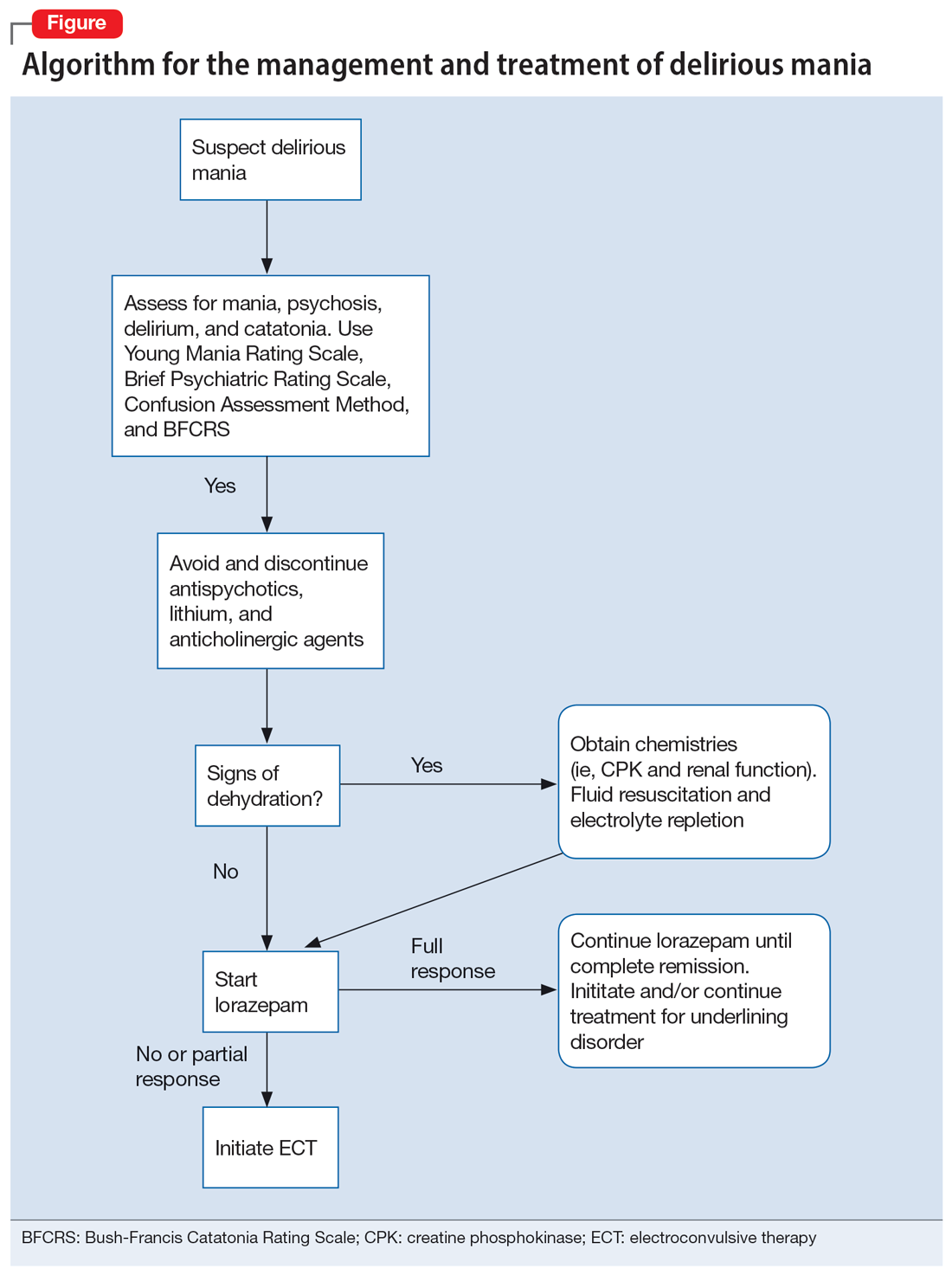
Continue to: Knowing which medications...
Knowing which medications to avoid is as important as knowing which agents to administer. Be vigilant in avoiding high-potency antipsychotics, as these medications can worsen extrapyramidal symptoms and may precipitate seizures or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).28 Anticholinergic agents should also be avoided because they worsen confusion. Although lithium is effective in BD, in delirious mania, high doses of lithium and haloperidol may cause severe encephalopathic syndromes, with symptoms that can include lethargy, tremors, cerebellar dysfunction, and worsened confusion; it may also cause widespread and irreversible brain damage.59
Due to long periods of hyperactivity, withdrawal, and diaphoresis, patients with delirious mania may be severely dehydrated with metabolic derangements, including elevated CPK due to rhabdomyolysis from prolonged exertion, IM antipsychotics, or rigidity. To prevent acute renal failure, this must be immediately addressed with rapid fluid resuscitation and electrolyte repletion.61
Benzodiazepines. The rapid use of lorazepam should be initiated when delirious mania is suspected. Doses of 6 to 20 mg have been reported to be effective if tolerated.5,20 Typically, high-dose lorazepam will not have the sedative effect that would normally occur in a patient who does not have delirious mania.2 Lorazepam should be titrated until full resolution of symptoms. Doses up to 30 mg have been reported as effective and tolerable.62 In our literature review, 50% of patients (18/36) responded or partially responded to lorazepam. However, only 3 case reports documented a complete remission with lorazepam, and many patients needed ECT for remission of symptoms.
ECT is generally reserved for patients who are not helped by benzodiazepine therapy, which is estimated to be up to 20%.5 ECT is highly effective in delirious mania, with remission rates ranging from 80% to 100%.1 ECT is also effective in acute nondelirious mania (comparable to depression); however, it is only used in a small minority of cases (0.2% to 12%).35 In our review, 58% of cases (21/36) reported using ECT, and in all cases it resulted in complete remission.
A dramatic improvement can be seen even after a single ECT session, though most patients show improvement after 4 sessions or 3 to 7 days.1,2,5 In our review, most patients received 4 to 12 sessions until achieving complete remission.
Continue to: No RCTs have evaluated...
No RCTs have evaluated ECT electrode placement in patients with delirious mania. However, several RCTs have investigated electrode placement in patients with acute nondelirious mania. Hiremani et al63 found that bitemporal placement had a more rapid response rate than bifrontal placement, but there was no overall difference in response rate. Barekatain et al64 found no difference between these 2 bilateral approaches. Many of the delirious mania cases report using a bilateral placement (including 42% of the ECT cases in our review) due to the emergent need for rapid relief of symptoms, which is especially necessary if the patient is experiencing hemodynamic instability, excessive violence, risk for self-harm, worsening delirium, or resistance to lorazepam.
Prognosis: Often fatal if left untreated
Patients with delirious mania are at high risk to progress to a more severe form of NMS or malignant catatonia. Therefore, high-potency antipsychotics should be avoided; mortality can be elevated from 60% without antipsychotics to 78% with antipsychotics.4 Some researchers estimate 75% to 78% of cases of delirious mania can be fatal if left untreated.3,6
Bottom Line
Delirious mania is routinely mistaken for more conventional manic or psychotic disorders. Clinicians need to be able to rapidly recognize the symptoms of this syndrome, which include mania, psychosis, delirium, and possible catatonia, so they can avoid administering toxic agents and instead initiate effective treatments such as benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Related Resources
- Arsan C, Baker C, Wong J, et al. Delirious mania: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(1):20f02744. doi:10.4088/PCC.20f02744
- Lamba G, Kennedy EA, Vu CP. Case report: ECT for delirious mania. Clinical Psychiatry News. December 14, 2021. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/249909/bipolar-disorder/case-report-ect-delirious-mania
Drug Brand Names
Diazepam • Valium
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
1. Fink M. Delirious mania. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1(1):54-60.
2. Karmacharya R, England ML, Ongür D. Delirious mania: clinical features and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2008;109(3):312-316.
3. Friedman RS, Mufson MJ, Eisenberg TD, et al. Medically and psychiatrically ill: the challenge of delirious mania. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003;11(2):91-98.
4. Mann SC, Caroff SN, Bleier HR, et al. Lethal catatonia. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(11):1374-1381.
5. Detweiler MB, Mehra A, Rowell T, et al. Delirious mania and malignant catatonia: a report of 3 cases and review. Psychiatr Q. 2009;80(1):23-40.
6. Bell L. On a form of disease resembling some advanced stages of mania and fever. American Journal of Insanity. 1849;6(2):97-127.
7. Carlson GA, Goodwin FK. The stages of mania. A longitudinal analysis of the manic episode. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;28(2):221-228.
8. Bond TC. Recognition of acute delirious mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(5):553-554.
9. Hutchinson G, David A. Manic pseudo-delirium - two case reports. Behav Neurol. 1997;10(1):21-23.
10. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. I. Rating scale and standardized examination. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):129-136.
11. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. II. Treatment with lorazepam and electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):137-143.
12. Cordeiro CR, Saraiva R, Côrte-Real B, et al. When the bell rings: clinical features of Bell’s mania. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19l02511. doi:10.4088/PCC.19l02511
13. Yeo LX, Kuo TC, Hu KC, et al. Lurasidone-induced delirious mania. Am J Ther. 2019;26(6):e786-e787.
14. Jung WY, Lee BD. Quetiapine treatment for delirious mania in a military soldier. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;12(2):PCC.09l00830. doi:10.4088/PCC.09l00830yel
15. Wahid N, Chin G, Turner AH, et al. Clinical response of clozapine as a treatment for delirious mania. Ment Illn. 2017;9(2):7182. doi:10.4081/mi.2017.7182
16. Taylor MA, Fink M. Catatonia in psychiatric classification: a home of its own. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(7):1233-1241.
17. Danivas V, Behere RV, Varambally S, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of delirious mania: a report of 2 patients. J ECT. 2010;26(4):278-279.
18. O’Callaghan N, McDonald C, Hallahan B. Delirious mania intractable to treatment. Ir J Psychol Med. 2016;33(2):129-132.
19. Vasudev K, Grunze H. What works for delirious catatonic mania? BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0220102713. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2713
20. Jacobowski NL, Heckers S, Bobo WV. Delirious mania: detection, diagnosis, and clinical management in the acute setting. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19(1):15-28.
21. Reinfeld S, Yacoub A. A case of delirious mania induced by COVID-19 treated with electroconvulsive therapy. J ECT. 2021;37(4):e38-e39.
22. Lee BS, Huang SS, Hsu WY, et al. Clinical features of delirious mania: a series of five cases and a brief literature review. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:65. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-65
23. Bipeta R, Khan MA. Delirious mania: can we get away with this concept? A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:720354. doi:10.1155/2012/720354
24. Nunes AL, Cheniaux E. Delirium and mania with catatonic features in a Brazilian patient: response to ECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26(1):E1-E3.
25. Tegin C, Kalayil G, Lippmann S. Electroconvulsive therapy and delirious catatonic mania. J ECT. 2017;33(4):e33-e34.
26. Melo AL, Serra M. Delirious mania and catatonia. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22(6):647-649.
27. Fink M. Expanding the catatonia tent: recognizing electroconvulsive therapy responsive syndromes. J ECT. 2021;37(2):77-79.
28. Fink M. Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Guide for Professionals and Their Patients. Oxford University Press; 2009.
29. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251 Suppl 1:I8-I13.
30. Vivanti A, Harvey K, Ash S, et al. Clinical assessment of dehydration in older people admitted to hospital: what are the strongest indicators? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(3):340-355.
31. Ware MR, Feller DB, Hall KL. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: diagnosis and management. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018;20(1):17r02185. doi:10.4088/PCC.17r0218
32. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189-198.
33. Taylor MA, Abrams R. The phenomenology of mania. A new look at some old patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;29(4):520-522.
34. Klerman GL. The spectrum of mania. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(1):11-20.
35. Elias A, Thomas N, Sackeim HA. Electroconvulsive therapy in mania: a review of 80 years of clinical experience. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(3):229-239.
36. Thom RP, Levy-Carrick NC, Bui M, et al. Delirium. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(10):785-793.
37. Charlton BG, Kavanau JL. Delirium and psychotic symptoms--an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58(1):24-27.
38. Kramp P, Bolwig TG. Electroconvulsive therapy in acute delirious states. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(4):368-371.
39. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
40. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
41. Charney DS. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 14:11-14.
42. Shiah IS, Yatham LN. Serotonin in mania and in the mechanism of action of mood stabilizers: a review of clinical studies. Bipolar Disord. 2000;2(2):77-92.
43. Dalley JW, Roiser JP. Dopamine, serotonin and impulsivity. Neuroscience. 2012;215:42-58.
44. Maldonado JR. Pathoetiological model of delirium: a comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of delirium and an evidence-based approach to prevention and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):789-856, ix.
45. Maldonado JR. Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(12):1190-1222.
46. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
47. Northoff G, Steinke R, Czcervenka C, et al. Decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex in akinetic catatonia: investigation of in vivo benzodiazepine receptor binding. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(4):445-450.
48. Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(4):371-380.
49. Restrepo-Martínez M, Chacón-González J, Bayliss L, et al. Delirious mania as a neuropsychiatric presentation in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(1):64-69.
50. Dalmau J, Armangué T, Planagumà J, et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1045-1057.
51. Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A. Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):261.
52. Iqbal Y, Al Abdulla MA, Albrahim S, et al. Psychiatric presentation of patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective review of 50 consecutive patients seen by a consultation-liaison psychiatry team. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(5):e109.
53. Gouse BM, Spears WE, Nieves Archibald A, et al. Catatonia in a hospitalized patient with COVID-19 and proposed immune-mediated mechanism. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:529-530.
54. Caan MP, Lim CT, Howard M. A case of catatonia in a man with COVID-19. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(5):556-560.
55. Zain SM, Muthukanagaraj P, Rahman N. Excited catatonia - a delayed neuropsychiatric complication of COVID-19 infection. Cureus. 2021;13(3):e13891.
56. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: a review. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(11):1619-1629.
57. Radhakrishnan R, Kaser M, Guloksuz S. The link between the immune system, environment, and psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2017;43(4):693-697.
58. Fink M, Kellner CH, McCall WV. Optimizing ECT technique in treating catatonia. J ECT. 2016;32(3):149-150.
59. Cohen WJ, Cohen NH. Lithium carbonate, haloperidol, and irreversible brain damage. JAMA. 1974;230(9):1283-1287.
60. Davis MJ, de Nesnera A, Folks DG. Confused and nearly naked after going on spending sprees. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(7):56-62.
61. Stanley M, Chippa V, Aeddula NR, et al. Rhabdomyolysis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
62. Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(11):1173-1177.
63. Hiremani RM, Thirthalli J, Tharayil BS, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled study comparing short-term efficacy of bifrontal and bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in acute mania. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):701-707.
64. Barekatain M, Jahangard L, Haghighi M, et al. Bifrontal versus bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in severe manic patients. J ECT. 2008;24(3):199-202.
Delirious mania is a syndrome characterized by the acute onset of severe hyperactivity, psychosis, catatonia, and intermittent confusion. While there have been growing reports of this phenomenon over the last 2 decades, it remains poorly recognized and understood.1,2 There is no widely accepted nosology for delirious mania and the condition is absent from DSM-5, which magnifies the difficulties in making a timely diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may result in a detrimental outcome.2,3 Delirious mania has also been labeled as lethal catatonia, specific febrile delirium, hyperactive or exhaustive mania, and Bell’s mania.2,4,5 The characterization and diagnosis of this condition have a long and inconsistent history (Box1,6-11).
Box
Delirious mania was originally recognized in 1849 by Luther Bell in McLean Hospital after he observed 40 cases that were uniquely distinct from 1,700 other cases from 1836 to 1849.6 He described these patients as being suddenly confused, demonstrating unprovoked combativeness, remarkable decreased need for sleep, excessive motor restlessness, extreme fearfulness, and certain physiological signs, including rapid pulse and sweating. Bell was limited to the psychiatric treatment of his time, which largely was confined to physical restraints. Approximately three-fourths of these patients died.6
Following Bell’s report, this syndrome remained unexplored and rarely described. Some researchers postulated that the development of confusion was a natural progression of late-phase mania in close to 20% of patients.7 However, this did not account for the rapid onset of symptoms as well as certain unexplained movement abnormalities. In 1980, Bond8 presented 3 cases that were similar in nature to Bell’s depiction: acute onset with extraordinary irritability, withdrawal, delirium, and mania.
For the next 2 decades, delirious mania was seldom reported in the literature. The term was often reserved to illustrate when a patient had nothing more than mania with features of delirium.9
By 1996, catatonia became better recognized in its wide array of symptomology and diagnostic scales.10,11 In 1999, in addition to the sudden onset of excitement, paranoia, grandiosity, and disorientation, Fink1 reported catatonic signs including negativism, stereotypy, posturing, grimacing, and echo phenomena in patients with delirious mania. He identified its sensitive response to electroconvulsive therapy.
Delirious mania continues to be met with incertitude in clinical practice, and numerous inconsistencies have been reported in the literature. For example, some cases that have been reported as delirious mania had more evidence of primary delirium due to another medical condition or primary mania.12,13 Other cases have demonstrated swift improvement of symptoms after monotherapy with antipsychotics without a trial of benzodiazepines or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT); the exclusion of a sudden onset questions the validity of the diagnosis and promotes the use of less efficacious treatments.14,15 Other reports have confirmed that the diagnosis is missed when certain symptoms are more predominant, such as a thought disorder (acute schizophrenia), grandiosity and delusional ideation (bipolar disorder [BD]), and less commonly assessed catatonic signs (ambitendency, automatic obedience). These symptoms are mistakenly attributed to the respective disease.1,16 This especially holds true when delirious mania is initially diagnosed as a primary psychosis, which leads to the administration of antipsychotics.17 Other cases have reported that delirious mania was resistant to treatment, but ECT was never pursued.18
In this review, we provide a more comprehensive perspective of the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management of delirious mania. We searched PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “delirious mania,” “delirious mania AND catatonia,” or “manic delirium.” Most articles we found were case reports, case series, or retrospective chart reviews. There were no systematic reviews, meta analyses, or randomized control trials (RCTs). The 12 articles included in this review consist of 7 individual case reports, 4 case series, and 1 retrospective chart review that describe a total of 36 cases (Table1,2,5,17,19-26).

Clinical presentation: What to look for
Patients with delirious mania typically develop symptoms extremely rapidly. In virtually all published literature, symptoms were reported to emerge within hours to days and consisted of severe forms of mania, psychosis, and delirium; 100% of the cases in our review had these symptoms. Commonly reported symptoms were:
- intense excitement
- emotional lability
- grandiose delusions
- profound insomnia
- pressured and rapid speech
- auditory and visual hallucinations
- hypersexuality
- thought disorganization.
Exquisite paranoia can also result in violent aggression (and may require the use of physical restraints). Patients may confine themselves to very small spaces (such as a closet) in response to the intense paranoia. Impairments in various neurocognitive domains—including inability to focus; disorientation; language and visuospatial disturbances; difficulty with shifting and sustaining attention; and short-term memory impairments—have been reported. Patients often cannot recall the events during the episode.1,2,5,27,28
Catatonia has been closely associated with delirious mania.29 Features of excited catatonia—such as excessive motor activity, negativism, grimacing, posturing, echolalia, echopraxia, stereotypy, automatic obedience, verbigeration, combativeness, impulsivity, and rigidity—typically accompany delirious mania.1,5,10,19,27
In addition to these symptoms, patients may engage in specific behaviors. They may exhibit inappropriate toileting such as smearing feces on walls or in bags, fecal or urinary incontinence, disrobing or running naked in public places, or pouring liquid on the floor or on one’s head.1,2
Continue to: Of the 36 cases...
Of the 36 cases reported in the literature we reviewed, 20 (55%) were female. Most patients had an underlining psychiatric condition, including BD (72%), major depressive disorder (8%), and schizophrenia (2%). Three patients had no psychiatric history.
Physical examination
On initial presentation, a patient with delirious mania may be dehydrated, with dry mucous membranes, pale conjunctiva, tongue dryness, and poor skin turgor.28,30 Due to excessive motor activity, diaphoresis with tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, and fever may be present.31
Certain basic cognitive tasks should be assessed to determine the patient’s orientation to place, date, and time. Assess if the patient can recall recent events, names of objects, or perform serial 7s; clock drawing capabilities also should be ascertained.1,2,5 A Mini-Mental State Examination is useful.32
The Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale should be used to elicit features of catatonia, such as waxy flexibility, negativism, gegenhalten, mitgehen, catalepsy, ambitendency, automatic obedience, and grasp reflex.10
Laboratory findings are nonspecific
Although no specific laboratory findings are associated with delirious mania, bloodwork and imaging are routinely investigated, especially if delirium characteristics are most striking. A complete blood count, chemistries, hepatic panel, thyroid functioning, blood and/or urine cultures, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), and urinalysis can be ordered. Head imaging such as MRI and CT to rule out intracranial pathology are typically performed.19 However, the diagnosis of delirious mania is based on the presence of the phenotypic features, by verification of catatonia, and by the responsiveness to the treatment delivered.29
Continue to: Pathogenisis: Several hypotheses
Pathogenesis: Several hypotheses
The pathogenesis of delirious mania is not well understood. There are several postulations but no salient theory. Most patients with delirious mania have an underlying systemic medical or psychiatric condition.
Mood disorders. Patients with BD or schizoaffective disorder are especially susceptible to delirious mania. The percentage of manic patients who present with delirious mania varies by study. One study suggested approximately 19% have features of the phenomenon,33 while others estimated 15% to 25%.34 Elias et al35 calculated that 15% of patients with mania succumb to manic exhaustion; from this it can be reasonably concluded that these were cases of misdiagnosed delirious mania.
Delirium hypothesis. Patients with delirious mania typically have features of delirium, including fluctuation of consciousness, disorientation, and/or poor sleep-wake cycle.36 During rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep, memory circuits are fortified. When there is a substantial loss of REM and non-REM sleep, these circuits become faulty, even after 1 night. Pathological brain waves on EEG reflect the inability to reinforce the memory circuits. Patients with these waves may develop hallucinations, bizarre delusions, and altered sensorium. ECT reduces the pathological slow wave morphologies, thus restoring the synaptic maintenance and correcting the incompetent circuitry. This can explain the robust and rapid response of ECT in a patient with delirious mania.37,38
Neurotransmitter hypothesis. It has been shown that in patients with delirious mania there is dysregulation of dopamine transport, which leads to dopamine overflow in the synapse. In contrast to a drug effect (ie, cocaine or methamphetamine) that acts by inhibiting dopamine reuptake, dopamine overflow in delirious mania is caused by the loss of dopamine transporter regulation. This results in a dysfunctional dopaminergic state that precipitates an acute state of delirium and agitation.39,40
Serotonin plays a role in mood disorders, including mania and depression.41,42 More specifically, serotonin has been implicated in impulsivity and aggression as shown by reduced levels of CSF 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and depletion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).43
Continue to: Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission...
Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission are known to occur in delirium and catatonia. In delirium, GABA signaling is increased, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and melatonin release, thus impairing the sleep-wake cycle.44 Deficiencies in acetylcholine and melatonin are seen as well as excess of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine and glutamate.45 Conversely, in catatonia, functional imaging studies found decreased GABA-A binding in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, parietal, and motor cortical regions.46 A study analyzing 10 catatonic patients found decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex compared to psychiatric and healthy controls.47
Other neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) have been hypothesized to be hyperactive, causing downstream dysregulation of GABA functioning.48 However, the exact connection between delirious mania and all these receptors and neurotransmitters remains unknown.
Encephalitis hypothesis. The relationship between delirious mania and autoimmune encephalitis suggests delirious mania has etiologies other than a primary psychiatric illness. In a 2020 retrospective study49 that analyzed 79 patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 25.3% met criteria for delirious mania, and 95% of these patients had catatonic features. Dalmau et al50 found that in many cases, patients tend to respond to ECT; in a cases series of 3 patients, 2 responded to benzodiazepines.
COVID-19 hypothesis. The SARS-CoV-2 virion has been associated with many neuropsychiatric complications, including mood, psychotic, and neurocognitive disorders.51,52 There also have been cases of COVID-19–induced catatonia.53-55 One case of delirious mania in a patient with COVID-19 has been reported.21 The general mechanism has been proposed to be related to the stimulation of the proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, which the virus produces in large quantities.56 These cytokines have been linked to psychosis and other psychiatric disorders.57 The patient with COVID-19–induced delirious mania had elevated inflammatory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer, which supports a proinflammatory state. This patient had a complete resolution of symptoms with ECT.21
Management: Benzodiazepines and ECT
A step-by-step algorithm for managing delirious mania is outlined in the Figure. Regardless of the underlining etiology, management of delirious mania consists of benzodiazepines (lorazepam and diazepam); prompt use of ECT, particularly for patients who do not improve with large doses of lorazepam; or (if applicable) continued treatment of the underlining medical condition, which does not preclude the use of benzodiazepines or ECT. Recent reports27,58 have described details for using ECT for delirious mania, highlighting the use of high-energy dosing, bilateral electrode placement, and frequent sessions.

Continue to: Knowing which medications...
Knowing which medications to avoid is as important as knowing which agents to administer. Be vigilant in avoiding high-potency antipsychotics, as these medications can worsen extrapyramidal symptoms and may precipitate seizures or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).28 Anticholinergic agents should also be avoided because they worsen confusion. Although lithium is effective in BD, in delirious mania, high doses of lithium and haloperidol may cause severe encephalopathic syndromes, with symptoms that can include lethargy, tremors, cerebellar dysfunction, and worsened confusion; it may also cause widespread and irreversible brain damage.59
Due to long periods of hyperactivity, withdrawal, and diaphoresis, patients with delirious mania may be severely dehydrated with metabolic derangements, including elevated CPK due to rhabdomyolysis from prolonged exertion, IM antipsychotics, or rigidity. To prevent acute renal failure, this must be immediately addressed with rapid fluid resuscitation and electrolyte repletion.61
Benzodiazepines. The rapid use of lorazepam should be initiated when delirious mania is suspected. Doses of 6 to 20 mg have been reported to be effective if tolerated.5,20 Typically, high-dose lorazepam will not have the sedative effect that would normally occur in a patient who does not have delirious mania.2 Lorazepam should be titrated until full resolution of symptoms. Doses up to 30 mg have been reported as effective and tolerable.62 In our literature review, 50% of patients (18/36) responded or partially responded to lorazepam. However, only 3 case reports documented a complete remission with lorazepam, and many patients needed ECT for remission of symptoms.
ECT is generally reserved for patients who are not helped by benzodiazepine therapy, which is estimated to be up to 20%.5 ECT is highly effective in delirious mania, with remission rates ranging from 80% to 100%.1 ECT is also effective in acute nondelirious mania (comparable to depression); however, it is only used in a small minority of cases (0.2% to 12%).35 In our review, 58% of cases (21/36) reported using ECT, and in all cases it resulted in complete remission.
A dramatic improvement can be seen even after a single ECT session, though most patients show improvement after 4 sessions or 3 to 7 days.1,2,5 In our review, most patients received 4 to 12 sessions until achieving complete remission.
Continue to: No RCTs have evaluated...
No RCTs have evaluated ECT electrode placement in patients with delirious mania. However, several RCTs have investigated electrode placement in patients with acute nondelirious mania. Hiremani et al63 found that bitemporal placement had a more rapid response rate than bifrontal placement, but there was no overall difference in response rate. Barekatain et al64 found no difference between these 2 bilateral approaches. Many of the delirious mania cases report using a bilateral placement (including 42% of the ECT cases in our review) due to the emergent need for rapid relief of symptoms, which is especially necessary if the patient is experiencing hemodynamic instability, excessive violence, risk for self-harm, worsening delirium, or resistance to lorazepam.
Prognosis: Often fatal if left untreated
Patients with delirious mania are at high risk to progress to a more severe form of NMS or malignant catatonia. Therefore, high-potency antipsychotics should be avoided; mortality can be elevated from 60% without antipsychotics to 78% with antipsychotics.4 Some researchers estimate 75% to 78% of cases of delirious mania can be fatal if left untreated.3,6
Bottom Line
Delirious mania is routinely mistaken for more conventional manic or psychotic disorders. Clinicians need to be able to rapidly recognize the symptoms of this syndrome, which include mania, psychosis, delirium, and possible catatonia, so they can avoid administering toxic agents and instead initiate effective treatments such as benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Related Resources
- Arsan C, Baker C, Wong J, et al. Delirious mania: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(1):20f02744. doi:10.4088/PCC.20f02744
- Lamba G, Kennedy EA, Vu CP. Case report: ECT for delirious mania. Clinical Psychiatry News. December 14, 2021. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/249909/bipolar-disorder/case-report-ect-delirious-mania
Drug Brand Names
Diazepam • Valium
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Delirious mania is a syndrome characterized by the acute onset of severe hyperactivity, psychosis, catatonia, and intermittent confusion. While there have been growing reports of this phenomenon over the last 2 decades, it remains poorly recognized and understood.1,2 There is no widely accepted nosology for delirious mania and the condition is absent from DSM-5, which magnifies the difficulties in making a timely diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may result in a detrimental outcome.2,3 Delirious mania has also been labeled as lethal catatonia, specific febrile delirium, hyperactive or exhaustive mania, and Bell’s mania.2,4,5 The characterization and diagnosis of this condition have a long and inconsistent history (Box1,6-11).
Box
Delirious mania was originally recognized in 1849 by Luther Bell in McLean Hospital after he observed 40 cases that were uniquely distinct from 1,700 other cases from 1836 to 1849.6 He described these patients as being suddenly confused, demonstrating unprovoked combativeness, remarkable decreased need for sleep, excessive motor restlessness, extreme fearfulness, and certain physiological signs, including rapid pulse and sweating. Bell was limited to the psychiatric treatment of his time, which largely was confined to physical restraints. Approximately three-fourths of these patients died.6
Following Bell’s report, this syndrome remained unexplored and rarely described. Some researchers postulated that the development of confusion was a natural progression of late-phase mania in close to 20% of patients.7 However, this did not account for the rapid onset of symptoms as well as certain unexplained movement abnormalities. In 1980, Bond8 presented 3 cases that were similar in nature to Bell’s depiction: acute onset with extraordinary irritability, withdrawal, delirium, and mania.
For the next 2 decades, delirious mania was seldom reported in the literature. The term was often reserved to illustrate when a patient had nothing more than mania with features of delirium.9
By 1996, catatonia became better recognized in its wide array of symptomology and diagnostic scales.10,11 In 1999, in addition to the sudden onset of excitement, paranoia, grandiosity, and disorientation, Fink1 reported catatonic signs including negativism, stereotypy, posturing, grimacing, and echo phenomena in patients with delirious mania. He identified its sensitive response to electroconvulsive therapy.
Delirious mania continues to be met with incertitude in clinical practice, and numerous inconsistencies have been reported in the literature. For example, some cases that have been reported as delirious mania had more evidence of primary delirium due to another medical condition or primary mania.12,13 Other cases have demonstrated swift improvement of symptoms after monotherapy with antipsychotics without a trial of benzodiazepines or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT); the exclusion of a sudden onset questions the validity of the diagnosis and promotes the use of less efficacious treatments.14,15 Other reports have confirmed that the diagnosis is missed when certain symptoms are more predominant, such as a thought disorder (acute schizophrenia), grandiosity and delusional ideation (bipolar disorder [BD]), and less commonly assessed catatonic signs (ambitendency, automatic obedience). These symptoms are mistakenly attributed to the respective disease.1,16 This especially holds true when delirious mania is initially diagnosed as a primary psychosis, which leads to the administration of antipsychotics.17 Other cases have reported that delirious mania was resistant to treatment, but ECT was never pursued.18
In this review, we provide a more comprehensive perspective of the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management of delirious mania. We searched PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “delirious mania,” “delirious mania AND catatonia,” or “manic delirium.” Most articles we found were case reports, case series, or retrospective chart reviews. There were no systematic reviews, meta analyses, or randomized control trials (RCTs). The 12 articles included in this review consist of 7 individual case reports, 4 case series, and 1 retrospective chart review that describe a total of 36 cases (Table1,2,5,17,19-26).

Clinical presentation: What to look for
Patients with delirious mania typically develop symptoms extremely rapidly. In virtually all published literature, symptoms were reported to emerge within hours to days and consisted of severe forms of mania, psychosis, and delirium; 100% of the cases in our review had these symptoms. Commonly reported symptoms were:
- intense excitement
- emotional lability
- grandiose delusions
- profound insomnia
- pressured and rapid speech
- auditory and visual hallucinations
- hypersexuality
- thought disorganization.
Exquisite paranoia can also result in violent aggression (and may require the use of physical restraints). Patients may confine themselves to very small spaces (such as a closet) in response to the intense paranoia. Impairments in various neurocognitive domains—including inability to focus; disorientation; language and visuospatial disturbances; difficulty with shifting and sustaining attention; and short-term memory impairments—have been reported. Patients often cannot recall the events during the episode.1,2,5,27,28
Catatonia has been closely associated with delirious mania.29 Features of excited catatonia—such as excessive motor activity, negativism, grimacing, posturing, echolalia, echopraxia, stereotypy, automatic obedience, verbigeration, combativeness, impulsivity, and rigidity—typically accompany delirious mania.1,5,10,19,27
In addition to these symptoms, patients may engage in specific behaviors. They may exhibit inappropriate toileting such as smearing feces on walls or in bags, fecal or urinary incontinence, disrobing or running naked in public places, or pouring liquid on the floor or on one’s head.1,2
Continue to: Of the 36 cases...
Of the 36 cases reported in the literature we reviewed, 20 (55%) were female. Most patients had an underlining psychiatric condition, including BD (72%), major depressive disorder (8%), and schizophrenia (2%). Three patients had no psychiatric history.
Physical examination
On initial presentation, a patient with delirious mania may be dehydrated, with dry mucous membranes, pale conjunctiva, tongue dryness, and poor skin turgor.28,30 Due to excessive motor activity, diaphoresis with tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, and fever may be present.31
Certain basic cognitive tasks should be assessed to determine the patient’s orientation to place, date, and time. Assess if the patient can recall recent events, names of objects, or perform serial 7s; clock drawing capabilities also should be ascertained.1,2,5 A Mini-Mental State Examination is useful.32
The Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale should be used to elicit features of catatonia, such as waxy flexibility, negativism, gegenhalten, mitgehen, catalepsy, ambitendency, automatic obedience, and grasp reflex.10
Laboratory findings are nonspecific
Although no specific laboratory findings are associated with delirious mania, bloodwork and imaging are routinely investigated, especially if delirium characteristics are most striking. A complete blood count, chemistries, hepatic panel, thyroid functioning, blood and/or urine cultures, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), and urinalysis can be ordered. Head imaging such as MRI and CT to rule out intracranial pathology are typically performed.19 However, the diagnosis of delirious mania is based on the presence of the phenotypic features, by verification of catatonia, and by the responsiveness to the treatment delivered.29
Continue to: Pathogenisis: Several hypotheses
Pathogenesis: Several hypotheses
The pathogenesis of delirious mania is not well understood. There are several postulations but no salient theory. Most patients with delirious mania have an underlying systemic medical or psychiatric condition.
Mood disorders. Patients with BD or schizoaffective disorder are especially susceptible to delirious mania. The percentage of manic patients who present with delirious mania varies by study. One study suggested approximately 19% have features of the phenomenon,33 while others estimated 15% to 25%.34 Elias et al35 calculated that 15% of patients with mania succumb to manic exhaustion; from this it can be reasonably concluded that these were cases of misdiagnosed delirious mania.
Delirium hypothesis. Patients with delirious mania typically have features of delirium, including fluctuation of consciousness, disorientation, and/or poor sleep-wake cycle.36 During rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep, memory circuits are fortified. When there is a substantial loss of REM and non-REM sleep, these circuits become faulty, even after 1 night. Pathological brain waves on EEG reflect the inability to reinforce the memory circuits. Patients with these waves may develop hallucinations, bizarre delusions, and altered sensorium. ECT reduces the pathological slow wave morphologies, thus restoring the synaptic maintenance and correcting the incompetent circuitry. This can explain the robust and rapid response of ECT in a patient with delirious mania.37,38
Neurotransmitter hypothesis. It has been shown that in patients with delirious mania there is dysregulation of dopamine transport, which leads to dopamine overflow in the synapse. In contrast to a drug effect (ie, cocaine or methamphetamine) that acts by inhibiting dopamine reuptake, dopamine overflow in delirious mania is caused by the loss of dopamine transporter regulation. This results in a dysfunctional dopaminergic state that precipitates an acute state of delirium and agitation.39,40
Serotonin plays a role in mood disorders, including mania and depression.41,42 More specifically, serotonin has been implicated in impulsivity and aggression as shown by reduced levels of CSF 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and depletion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).43
Continue to: Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission...
Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission are known to occur in delirium and catatonia. In delirium, GABA signaling is increased, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and melatonin release, thus impairing the sleep-wake cycle.44 Deficiencies in acetylcholine and melatonin are seen as well as excess of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine and glutamate.45 Conversely, in catatonia, functional imaging studies found decreased GABA-A binding in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, parietal, and motor cortical regions.46 A study analyzing 10 catatonic patients found decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex compared to psychiatric and healthy controls.47
Other neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) have been hypothesized to be hyperactive, causing downstream dysregulation of GABA functioning.48 However, the exact connection between delirious mania and all these receptors and neurotransmitters remains unknown.
Encephalitis hypothesis. The relationship between delirious mania and autoimmune encephalitis suggests delirious mania has etiologies other than a primary psychiatric illness. In a 2020 retrospective study49 that analyzed 79 patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 25.3% met criteria for delirious mania, and 95% of these patients had catatonic features. Dalmau et al50 found that in many cases, patients tend to respond to ECT; in a cases series of 3 patients, 2 responded to benzodiazepines.
COVID-19 hypothesis. The SARS-CoV-2 virion has been associated with many neuropsychiatric complications, including mood, psychotic, and neurocognitive disorders.51,52 There also have been cases of COVID-19–induced catatonia.53-55 One case of delirious mania in a patient with COVID-19 has been reported.21 The general mechanism has been proposed to be related to the stimulation of the proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, which the virus produces in large quantities.56 These cytokines have been linked to psychosis and other psychiatric disorders.57 The patient with COVID-19–induced delirious mania had elevated inflammatory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer, which supports a proinflammatory state. This patient had a complete resolution of symptoms with ECT.21
Management: Benzodiazepines and ECT
A step-by-step algorithm for managing delirious mania is outlined in the Figure. Regardless of the underlining etiology, management of delirious mania consists of benzodiazepines (lorazepam and diazepam); prompt use of ECT, particularly for patients who do not improve with large doses of lorazepam; or (if applicable) continued treatment of the underlining medical condition, which does not preclude the use of benzodiazepines or ECT. Recent reports27,58 have described details for using ECT for delirious mania, highlighting the use of high-energy dosing, bilateral electrode placement, and frequent sessions.

Continue to: Knowing which medications...
Knowing which medications to avoid is as important as knowing which agents to administer. Be vigilant in avoiding high-potency antipsychotics, as these medications can worsen extrapyramidal symptoms and may precipitate seizures or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).28 Anticholinergic agents should also be avoided because they worsen confusion. Although lithium is effective in BD, in delirious mania, high doses of lithium and haloperidol may cause severe encephalopathic syndromes, with symptoms that can include lethargy, tremors, cerebellar dysfunction, and worsened confusion; it may also cause widespread and irreversible brain damage.59
Due to long periods of hyperactivity, withdrawal, and diaphoresis, patients with delirious mania may be severely dehydrated with metabolic derangements, including elevated CPK due to rhabdomyolysis from prolonged exertion, IM antipsychotics, or rigidity. To prevent acute renal failure, this must be immediately addressed with rapid fluid resuscitation and electrolyte repletion.61
Benzodiazepines. The rapid use of lorazepam should be initiated when delirious mania is suspected. Doses of 6 to 20 mg have been reported to be effective if tolerated.5,20 Typically, high-dose lorazepam will not have the sedative effect that would normally occur in a patient who does not have delirious mania.2 Lorazepam should be titrated until full resolution of symptoms. Doses up to 30 mg have been reported as effective and tolerable.62 In our literature review, 50% of patients (18/36) responded or partially responded to lorazepam. However, only 3 case reports documented a complete remission with lorazepam, and many patients needed ECT for remission of symptoms.
ECT is generally reserved for patients who are not helped by benzodiazepine therapy, which is estimated to be up to 20%.5 ECT is highly effective in delirious mania, with remission rates ranging from 80% to 100%.1 ECT is also effective in acute nondelirious mania (comparable to depression); however, it is only used in a small minority of cases (0.2% to 12%).35 In our review, 58% of cases (21/36) reported using ECT, and in all cases it resulted in complete remission.
A dramatic improvement can be seen even after a single ECT session, though most patients show improvement after 4 sessions or 3 to 7 days.1,2,5 In our review, most patients received 4 to 12 sessions until achieving complete remission.
Continue to: No RCTs have evaluated...
No RCTs have evaluated ECT electrode placement in patients with delirious mania. However, several RCTs have investigated electrode placement in patients with acute nondelirious mania. Hiremani et al63 found that bitemporal placement had a more rapid response rate than bifrontal placement, but there was no overall difference in response rate. Barekatain et al64 found no difference between these 2 bilateral approaches. Many of the delirious mania cases report using a bilateral placement (including 42% of the ECT cases in our review) due to the emergent need for rapid relief of symptoms, which is especially necessary if the patient is experiencing hemodynamic instability, excessive violence, risk for self-harm, worsening delirium, or resistance to lorazepam.
Prognosis: Often fatal if left untreated
Patients with delirious mania are at high risk to progress to a more severe form of NMS or malignant catatonia. Therefore, high-potency antipsychotics should be avoided; mortality can be elevated from 60% without antipsychotics to 78% with antipsychotics.4 Some researchers estimate 75% to 78% of cases of delirious mania can be fatal if left untreated.3,6
Bottom Line
Delirious mania is routinely mistaken for more conventional manic or psychotic disorders. Clinicians need to be able to rapidly recognize the symptoms of this syndrome, which include mania, psychosis, delirium, and possible catatonia, so they can avoid administering toxic agents and instead initiate effective treatments such as benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Related Resources
- Arsan C, Baker C, Wong J, et al. Delirious mania: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(1):20f02744. doi:10.4088/PCC.20f02744
- Lamba G, Kennedy EA, Vu CP. Case report: ECT for delirious mania. Clinical Psychiatry News. December 14, 2021. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/249909/bipolar-disorder/case-report-ect-delirious-mania
Drug Brand Names
Diazepam • Valium
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
1. Fink M. Delirious mania. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1(1):54-60.
2. Karmacharya R, England ML, Ongür D. Delirious mania: clinical features and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2008;109(3):312-316.
3. Friedman RS, Mufson MJ, Eisenberg TD, et al. Medically and psychiatrically ill: the challenge of delirious mania. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003;11(2):91-98.
4. Mann SC, Caroff SN, Bleier HR, et al. Lethal catatonia. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(11):1374-1381.
5. Detweiler MB, Mehra A, Rowell T, et al. Delirious mania and malignant catatonia: a report of 3 cases and review. Psychiatr Q. 2009;80(1):23-40.
6. Bell L. On a form of disease resembling some advanced stages of mania and fever. American Journal of Insanity. 1849;6(2):97-127.
7. Carlson GA, Goodwin FK. The stages of mania. A longitudinal analysis of the manic episode. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;28(2):221-228.
8. Bond TC. Recognition of acute delirious mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(5):553-554.
9. Hutchinson G, David A. Manic pseudo-delirium - two case reports. Behav Neurol. 1997;10(1):21-23.
10. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. I. Rating scale and standardized examination. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):129-136.
11. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. II. Treatment with lorazepam and electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):137-143.
12. Cordeiro CR, Saraiva R, Côrte-Real B, et al. When the bell rings: clinical features of Bell’s mania. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19l02511. doi:10.4088/PCC.19l02511
13. Yeo LX, Kuo TC, Hu KC, et al. Lurasidone-induced delirious mania. Am J Ther. 2019;26(6):e786-e787.
14. Jung WY, Lee BD. Quetiapine treatment for delirious mania in a military soldier. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;12(2):PCC.09l00830. doi:10.4088/PCC.09l00830yel
15. Wahid N, Chin G, Turner AH, et al. Clinical response of clozapine as a treatment for delirious mania. Ment Illn. 2017;9(2):7182. doi:10.4081/mi.2017.7182
16. Taylor MA, Fink M. Catatonia in psychiatric classification: a home of its own. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(7):1233-1241.
17. Danivas V, Behere RV, Varambally S, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of delirious mania: a report of 2 patients. J ECT. 2010;26(4):278-279.
18. O’Callaghan N, McDonald C, Hallahan B. Delirious mania intractable to treatment. Ir J Psychol Med. 2016;33(2):129-132.
19. Vasudev K, Grunze H. What works for delirious catatonic mania? BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0220102713. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2713
20. Jacobowski NL, Heckers S, Bobo WV. Delirious mania: detection, diagnosis, and clinical management in the acute setting. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19(1):15-28.
21. Reinfeld S, Yacoub A. A case of delirious mania induced by COVID-19 treated with electroconvulsive therapy. J ECT. 2021;37(4):e38-e39.
22. Lee BS, Huang SS, Hsu WY, et al. Clinical features of delirious mania: a series of five cases and a brief literature review. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:65. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-65
23. Bipeta R, Khan MA. Delirious mania: can we get away with this concept? A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:720354. doi:10.1155/2012/720354
24. Nunes AL, Cheniaux E. Delirium and mania with catatonic features in a Brazilian patient: response to ECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26(1):E1-E3.
25. Tegin C, Kalayil G, Lippmann S. Electroconvulsive therapy and delirious catatonic mania. J ECT. 2017;33(4):e33-e34.
26. Melo AL, Serra M. Delirious mania and catatonia. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22(6):647-649.
27. Fink M. Expanding the catatonia tent: recognizing electroconvulsive therapy responsive syndromes. J ECT. 2021;37(2):77-79.
28. Fink M. Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Guide for Professionals and Their Patients. Oxford University Press; 2009.
29. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251 Suppl 1:I8-I13.
30. Vivanti A, Harvey K, Ash S, et al. Clinical assessment of dehydration in older people admitted to hospital: what are the strongest indicators? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(3):340-355.
31. Ware MR, Feller DB, Hall KL. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: diagnosis and management. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018;20(1):17r02185. doi:10.4088/PCC.17r0218
32. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189-198.
33. Taylor MA, Abrams R. The phenomenology of mania. A new look at some old patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;29(4):520-522.
34. Klerman GL. The spectrum of mania. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(1):11-20.
35. Elias A, Thomas N, Sackeim HA. Electroconvulsive therapy in mania: a review of 80 years of clinical experience. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(3):229-239.
36. Thom RP, Levy-Carrick NC, Bui M, et al. Delirium. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(10):785-793.
37. Charlton BG, Kavanau JL. Delirium and psychotic symptoms--an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58(1):24-27.
38. Kramp P, Bolwig TG. Electroconvulsive therapy in acute delirious states. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(4):368-371.
39. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
40. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
41. Charney DS. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 14:11-14.
42. Shiah IS, Yatham LN. Serotonin in mania and in the mechanism of action of mood stabilizers: a review of clinical studies. Bipolar Disord. 2000;2(2):77-92.
43. Dalley JW, Roiser JP. Dopamine, serotonin and impulsivity. Neuroscience. 2012;215:42-58.
44. Maldonado JR. Pathoetiological model of delirium: a comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of delirium and an evidence-based approach to prevention and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):789-856, ix.
45. Maldonado JR. Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(12):1190-1222.
46. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
47. Northoff G, Steinke R, Czcervenka C, et al. Decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex in akinetic catatonia: investigation of in vivo benzodiazepine receptor binding. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(4):445-450.
48. Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(4):371-380.
49. Restrepo-Martínez M, Chacón-González J, Bayliss L, et al. Delirious mania as a neuropsychiatric presentation in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(1):64-69.
50. Dalmau J, Armangué T, Planagumà J, et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1045-1057.
51. Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A. Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):261.
52. Iqbal Y, Al Abdulla MA, Albrahim S, et al. Psychiatric presentation of patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective review of 50 consecutive patients seen by a consultation-liaison psychiatry team. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(5):e109.
53. Gouse BM, Spears WE, Nieves Archibald A, et al. Catatonia in a hospitalized patient with COVID-19 and proposed immune-mediated mechanism. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:529-530.
54. Caan MP, Lim CT, Howard M. A case of catatonia in a man with COVID-19. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(5):556-560.
55. Zain SM, Muthukanagaraj P, Rahman N. Excited catatonia - a delayed neuropsychiatric complication of COVID-19 infection. Cureus. 2021;13(3):e13891.
56. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: a review. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(11):1619-1629.
57. Radhakrishnan R, Kaser M, Guloksuz S. The link between the immune system, environment, and psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2017;43(4):693-697.
58. Fink M, Kellner CH, McCall WV. Optimizing ECT technique in treating catatonia. J ECT. 2016;32(3):149-150.
59. Cohen WJ, Cohen NH. Lithium carbonate, haloperidol, and irreversible brain damage. JAMA. 1974;230(9):1283-1287.
60. Davis MJ, de Nesnera A, Folks DG. Confused and nearly naked after going on spending sprees. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(7):56-62.
61. Stanley M, Chippa V, Aeddula NR, et al. Rhabdomyolysis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
62. Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(11):1173-1177.
63. Hiremani RM, Thirthalli J, Tharayil BS, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled study comparing short-term efficacy of bifrontal and bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in acute mania. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):701-707.
64. Barekatain M, Jahangard L, Haghighi M, et al. Bifrontal versus bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in severe manic patients. J ECT. 2008;24(3):199-202.
1. Fink M. Delirious mania. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1(1):54-60.
2. Karmacharya R, England ML, Ongür D. Delirious mania: clinical features and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2008;109(3):312-316.
3. Friedman RS, Mufson MJ, Eisenberg TD, et al. Medically and psychiatrically ill: the challenge of delirious mania. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003;11(2):91-98.
4. Mann SC, Caroff SN, Bleier HR, et al. Lethal catatonia. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(11):1374-1381.
5. Detweiler MB, Mehra A, Rowell T, et al. Delirious mania and malignant catatonia: a report of 3 cases and review. Psychiatr Q. 2009;80(1):23-40.
6. Bell L. On a form of disease resembling some advanced stages of mania and fever. American Journal of Insanity. 1849;6(2):97-127.
7. Carlson GA, Goodwin FK. The stages of mania. A longitudinal analysis of the manic episode. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;28(2):221-228.
8. Bond TC. Recognition of acute delirious mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(5):553-554.
9. Hutchinson G, David A. Manic pseudo-delirium - two case reports. Behav Neurol. 1997;10(1):21-23.
10. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. I. Rating scale and standardized examination. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):129-136.
11. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. II. Treatment with lorazepam and electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):137-143.
12. Cordeiro CR, Saraiva R, Côrte-Real B, et al. When the bell rings: clinical features of Bell’s mania. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19l02511. doi:10.4088/PCC.19l02511
13. Yeo LX, Kuo TC, Hu KC, et al. Lurasidone-induced delirious mania. Am J Ther. 2019;26(6):e786-e787.
14. Jung WY, Lee BD. Quetiapine treatment for delirious mania in a military soldier. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;12(2):PCC.09l00830. doi:10.4088/PCC.09l00830yel
15. Wahid N, Chin G, Turner AH, et al. Clinical response of clozapine as a treatment for delirious mania. Ment Illn. 2017;9(2):7182. doi:10.4081/mi.2017.7182
16. Taylor MA, Fink M. Catatonia in psychiatric classification: a home of its own. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(7):1233-1241.
17. Danivas V, Behere RV, Varambally S, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of delirious mania: a report of 2 patients. J ECT. 2010;26(4):278-279.
18. O’Callaghan N, McDonald C, Hallahan B. Delirious mania intractable to treatment. Ir J Psychol Med. 2016;33(2):129-132.
19. Vasudev K, Grunze H. What works for delirious catatonic mania? BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0220102713. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2713
20. Jacobowski NL, Heckers S, Bobo WV. Delirious mania: detection, diagnosis, and clinical management in the acute setting. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19(1):15-28.
21. Reinfeld S, Yacoub A. A case of delirious mania induced by COVID-19 treated with electroconvulsive therapy. J ECT. 2021;37(4):e38-e39.
22. Lee BS, Huang SS, Hsu WY, et al. Clinical features of delirious mania: a series of five cases and a brief literature review. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:65. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-65
23. Bipeta R, Khan MA. Delirious mania: can we get away with this concept? A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:720354. doi:10.1155/2012/720354
24. Nunes AL, Cheniaux E. Delirium and mania with catatonic features in a Brazilian patient: response to ECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26(1):E1-E3.
25. Tegin C, Kalayil G, Lippmann S. Electroconvulsive therapy and delirious catatonic mania. J ECT. 2017;33(4):e33-e34.
26. Melo AL, Serra M. Delirious mania and catatonia. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22(6):647-649.
27. Fink M. Expanding the catatonia tent: recognizing electroconvulsive therapy responsive syndromes. J ECT. 2021;37(2):77-79.
28. Fink M. Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Guide for Professionals and Their Patients. Oxford University Press; 2009.
29. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251 Suppl 1:I8-I13.
30. Vivanti A, Harvey K, Ash S, et al. Clinical assessment of dehydration in older people admitted to hospital: what are the strongest indicators? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(3):340-355.
31. Ware MR, Feller DB, Hall KL. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: diagnosis and management. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018;20(1):17r02185. doi:10.4088/PCC.17r0218
32. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189-198.
33. Taylor MA, Abrams R. The phenomenology of mania. A new look at some old patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;29(4):520-522.
34. Klerman GL. The spectrum of mania. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(1):11-20.
35. Elias A, Thomas N, Sackeim HA. Electroconvulsive therapy in mania: a review of 80 years of clinical experience. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(3):229-239.
36. Thom RP, Levy-Carrick NC, Bui M, et al. Delirium. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(10):785-793.
37. Charlton BG, Kavanau JL. Delirium and psychotic symptoms--an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58(1):24-27.
38. Kramp P, Bolwig TG. Electroconvulsive therapy in acute delirious states. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(4):368-371.
39. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
40. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
41. Charney DS. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 14:11-14.
42. Shiah IS, Yatham LN. Serotonin in mania and in the mechanism of action of mood stabilizers: a review of clinical studies. Bipolar Disord. 2000;2(2):77-92.
43. Dalley JW, Roiser JP. Dopamine, serotonin and impulsivity. Neuroscience. 2012;215:42-58.
44. Maldonado JR. Pathoetiological model of delirium: a comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of delirium and an evidence-based approach to prevention and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):789-856, ix.
45. Maldonado JR. Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(12):1190-1222.
46. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
47. Northoff G, Steinke R, Czcervenka C, et al. Decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex in akinetic catatonia: investigation of in vivo benzodiazepine receptor binding. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(4):445-450.
48. Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(4):371-380.
49. Restrepo-Martínez M, Chacón-González J, Bayliss L, et al. Delirious mania as a neuropsychiatric presentation in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(1):64-69.
50. Dalmau J, Armangué T, Planagumà J, et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1045-1057.
51. Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A. Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):261.
52. Iqbal Y, Al Abdulla MA, Albrahim S, et al. Psychiatric presentation of patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective review of 50 consecutive patients seen by a consultation-liaison psychiatry team. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(5):e109.
53. Gouse BM, Spears WE, Nieves Archibald A, et al. Catatonia in a hospitalized patient with COVID-19 and proposed immune-mediated mechanism. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:529-530.
54. Caan MP, Lim CT, Howard M. A case of catatonia in a man with COVID-19. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(5):556-560.
55. Zain SM, Muthukanagaraj P, Rahman N. Excited catatonia - a delayed neuropsychiatric complication of COVID-19 infection. Cureus. 2021;13(3):e13891.
56. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: a review. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(11):1619-1629.
57. Radhakrishnan R, Kaser M, Guloksuz S. The link between the immune system, environment, and psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2017;43(4):693-697.
58. Fink M, Kellner CH, McCall WV. Optimizing ECT technique in treating catatonia. J ECT. 2016;32(3):149-150.
59. Cohen WJ, Cohen NH. Lithium carbonate, haloperidol, and irreversible brain damage. JAMA. 1974;230(9):1283-1287.
60. Davis MJ, de Nesnera A, Folks DG. Confused and nearly naked after going on spending sprees. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(7):56-62.
61. Stanley M, Chippa V, Aeddula NR, et al. Rhabdomyolysis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
62. Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(11):1173-1177.
63. Hiremani RM, Thirthalli J, Tharayil BS, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled study comparing short-term efficacy of bifrontal and bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in acute mania. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):701-707.
64. Barekatain M, Jahangard L, Haghighi M, et al. Bifrontal versus bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in severe manic patients. J ECT. 2008;24(3):199-202.
