User login
Exercise improves physical and cognitive health in Down syndrome
In the first study of its kind, U.K. and French researchers reported that exercise positively affected physical and cognitive health in persons with Down syndrome. “The findings are significant and offer a crucial challenge to the [Down syndrome] and wider societies,” wrote a team led by Dan Gordon, PhD, associate professor of cardiorespiratory exercise physiology at Anglia Ruskin University in Cambridge, England. “Impact of Prescribed Exercise on the Physical and Cognitive Health of Adults with Down Syndrome: The MinDSets Study” was published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
“Through the simple application of walking, a form of exercise which requires little to no equipment or expense, there were significant increases in cognitive and executive function, reflecting improved capabilities in key attributes of information processing, vigilance, and selective attention,” the researchers wrote.
“Increased cognitive function will help foster increased societal integration and quality of life, which, given that this is the first generation of those with [Down syndrome] to outlive their parents and caregivers, is of importance,” they wrote.
For example, those in an exercise-only intervention arm had an 11.4% improvement on the distance covered in the Six-Minute Walk Test, going from a mean of 498.8 meters before intervention to 522.1 meters afterward. Those in a group that combined group exercise with cognitive training increased the distance walked by 9.9%, or 49.2 meters. Groups that got cognitive training only or no intervention showed no significant changes.
In measures of cognitive function, the exercise group showed a 38% increase in selective attention, with the cognitive and combined groups showing changes for the same measure of 16.5% and 55.3%, respectively. The changes for concentration in the exercise-alone group was 31.5%, while those receiving cognitive training alone or combined exercise plus cognitive training showed improvements in concentration of 21% and 15%, respectively.
Asked why a combination intervention was not superior to exercise alone, Dr. Gordon said in an interview, “Something we’re looking at in the data but can’t fully confirm is that the combined group started to become fatigued due to the double dose of the intervention, and this prevented them in the final tests from doing quite so well as the exercise-alone group. Irrespective of the magnitude of change, any cognitive adaptation observed will be beneficial to this population.”
The evidence for the benefits of exercise on both physical and cognitive health in a non–Down syndrome population are well established, he said, but there were few data on its effect on the Down syndrome population.
One small study showed physical and neurocognitive benefits with resistance training.
“The evidence from previous studies showed increased levels of inactivity and sitting time in Down syndrome individuals compared with non–[Down syndrome] controls, so we hypothesized that exercise, albeit small amounts, would increase their physical fitness,” Dr. Gordon said.
His team also hypothesized that walking would stimulate cognitive development since it requires heightened cognitive engagement compared with inactivity. “What surprised us was the degree of improvement,” Dr. Gordon said.
The process of walking requires the brain to interpret information on a real-time basis from both internal and external cues, he continued. “For most of us this process requires low-level cognitive engagement. However, in the [Down syndrome] population, where motor control is impaired and accompanied by poor muscle tone, walking imposes a heightened cognitive load.” It requires them to concentrate on the action, be aware of their surroundings, and make the right decisions, all of which stimulate areas of the brain that control these functions.
Study details
Eighty-three adult participants were available for final analysis – 67 from North America, 8 from Europe, 5 from Africa, 2 from Asia, and 1 from Australia. The mean age of participants was 27.1 years, 40 were female, and all had caregiver support during the study.
Those unable to visualize information on computer and mobile/tablet screens or to listen to instructions/auditory cues were excluded. All were provided with instructions and a mobile monitoring tool set to record steps completed, distances covered, speeds, and heart rate.
Each was assigned to one of four groups. Exercise intervention-only consisted of 8 weeks of cardiorespiratory exercise defined as either walking or jogging three times a week for 30 minutes. Cognitive training included eight levels (about 20 minutes) of cognitive and executive function exercises six times per week. The combined group completed both the cardiorespiratory and cognitive interventions, while the fourth group acted as controls with no intervention.
According to the authors, the study offers a real-life scenario that can be readily adopted within the Down syndrome community.
This study was commissioned by the Canadian Down Syndrome Society. The authors had no conflicts of interest to declare.
In the first study of its kind, U.K. and French researchers reported that exercise positively affected physical and cognitive health in persons with Down syndrome. “The findings are significant and offer a crucial challenge to the [Down syndrome] and wider societies,” wrote a team led by Dan Gordon, PhD, associate professor of cardiorespiratory exercise physiology at Anglia Ruskin University in Cambridge, England. “Impact of Prescribed Exercise on the Physical and Cognitive Health of Adults with Down Syndrome: The MinDSets Study” was published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
“Through the simple application of walking, a form of exercise which requires little to no equipment or expense, there were significant increases in cognitive and executive function, reflecting improved capabilities in key attributes of information processing, vigilance, and selective attention,” the researchers wrote.
“Increased cognitive function will help foster increased societal integration and quality of life, which, given that this is the first generation of those with [Down syndrome] to outlive their parents and caregivers, is of importance,” they wrote.
For example, those in an exercise-only intervention arm had an 11.4% improvement on the distance covered in the Six-Minute Walk Test, going from a mean of 498.8 meters before intervention to 522.1 meters afterward. Those in a group that combined group exercise with cognitive training increased the distance walked by 9.9%, or 49.2 meters. Groups that got cognitive training only or no intervention showed no significant changes.
In measures of cognitive function, the exercise group showed a 38% increase in selective attention, with the cognitive and combined groups showing changes for the same measure of 16.5% and 55.3%, respectively. The changes for concentration in the exercise-alone group was 31.5%, while those receiving cognitive training alone or combined exercise plus cognitive training showed improvements in concentration of 21% and 15%, respectively.
Asked why a combination intervention was not superior to exercise alone, Dr. Gordon said in an interview, “Something we’re looking at in the data but can’t fully confirm is that the combined group started to become fatigued due to the double dose of the intervention, and this prevented them in the final tests from doing quite so well as the exercise-alone group. Irrespective of the magnitude of change, any cognitive adaptation observed will be beneficial to this population.”
The evidence for the benefits of exercise on both physical and cognitive health in a non–Down syndrome population are well established, he said, but there were few data on its effect on the Down syndrome population.
One small study showed physical and neurocognitive benefits with resistance training.
“The evidence from previous studies showed increased levels of inactivity and sitting time in Down syndrome individuals compared with non–[Down syndrome] controls, so we hypothesized that exercise, albeit small amounts, would increase their physical fitness,” Dr. Gordon said.
His team also hypothesized that walking would stimulate cognitive development since it requires heightened cognitive engagement compared with inactivity. “What surprised us was the degree of improvement,” Dr. Gordon said.
The process of walking requires the brain to interpret information on a real-time basis from both internal and external cues, he continued. “For most of us this process requires low-level cognitive engagement. However, in the [Down syndrome] population, where motor control is impaired and accompanied by poor muscle tone, walking imposes a heightened cognitive load.” It requires them to concentrate on the action, be aware of their surroundings, and make the right decisions, all of which stimulate areas of the brain that control these functions.
Study details
Eighty-three adult participants were available for final analysis – 67 from North America, 8 from Europe, 5 from Africa, 2 from Asia, and 1 from Australia. The mean age of participants was 27.1 years, 40 were female, and all had caregiver support during the study.
Those unable to visualize information on computer and mobile/tablet screens or to listen to instructions/auditory cues were excluded. All were provided with instructions and a mobile monitoring tool set to record steps completed, distances covered, speeds, and heart rate.
Each was assigned to one of four groups. Exercise intervention-only consisted of 8 weeks of cardiorespiratory exercise defined as either walking or jogging three times a week for 30 minutes. Cognitive training included eight levels (about 20 minutes) of cognitive and executive function exercises six times per week. The combined group completed both the cardiorespiratory and cognitive interventions, while the fourth group acted as controls with no intervention.
According to the authors, the study offers a real-life scenario that can be readily adopted within the Down syndrome community.
This study was commissioned by the Canadian Down Syndrome Society. The authors had no conflicts of interest to declare.
In the first study of its kind, U.K. and French researchers reported that exercise positively affected physical and cognitive health in persons with Down syndrome. “The findings are significant and offer a crucial challenge to the [Down syndrome] and wider societies,” wrote a team led by Dan Gordon, PhD, associate professor of cardiorespiratory exercise physiology at Anglia Ruskin University in Cambridge, England. “Impact of Prescribed Exercise on the Physical and Cognitive Health of Adults with Down Syndrome: The MinDSets Study” was published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
“Through the simple application of walking, a form of exercise which requires little to no equipment or expense, there were significant increases in cognitive and executive function, reflecting improved capabilities in key attributes of information processing, vigilance, and selective attention,” the researchers wrote.
“Increased cognitive function will help foster increased societal integration and quality of life, which, given that this is the first generation of those with [Down syndrome] to outlive their parents and caregivers, is of importance,” they wrote.
For example, those in an exercise-only intervention arm had an 11.4% improvement on the distance covered in the Six-Minute Walk Test, going from a mean of 498.8 meters before intervention to 522.1 meters afterward. Those in a group that combined group exercise with cognitive training increased the distance walked by 9.9%, or 49.2 meters. Groups that got cognitive training only or no intervention showed no significant changes.
In measures of cognitive function, the exercise group showed a 38% increase in selective attention, with the cognitive and combined groups showing changes for the same measure of 16.5% and 55.3%, respectively. The changes for concentration in the exercise-alone group was 31.5%, while those receiving cognitive training alone or combined exercise plus cognitive training showed improvements in concentration of 21% and 15%, respectively.
Asked why a combination intervention was not superior to exercise alone, Dr. Gordon said in an interview, “Something we’re looking at in the data but can’t fully confirm is that the combined group started to become fatigued due to the double dose of the intervention, and this prevented them in the final tests from doing quite so well as the exercise-alone group. Irrespective of the magnitude of change, any cognitive adaptation observed will be beneficial to this population.”
The evidence for the benefits of exercise on both physical and cognitive health in a non–Down syndrome population are well established, he said, but there were few data on its effect on the Down syndrome population.
One small study showed physical and neurocognitive benefits with resistance training.
“The evidence from previous studies showed increased levels of inactivity and sitting time in Down syndrome individuals compared with non–[Down syndrome] controls, so we hypothesized that exercise, albeit small amounts, would increase their physical fitness,” Dr. Gordon said.
His team also hypothesized that walking would stimulate cognitive development since it requires heightened cognitive engagement compared with inactivity. “What surprised us was the degree of improvement,” Dr. Gordon said.
The process of walking requires the brain to interpret information on a real-time basis from both internal and external cues, he continued. “For most of us this process requires low-level cognitive engagement. However, in the [Down syndrome] population, where motor control is impaired and accompanied by poor muscle tone, walking imposes a heightened cognitive load.” It requires them to concentrate on the action, be aware of their surroundings, and make the right decisions, all of which stimulate areas of the brain that control these functions.
Study details
Eighty-three adult participants were available for final analysis – 67 from North America, 8 from Europe, 5 from Africa, 2 from Asia, and 1 from Australia. The mean age of participants was 27.1 years, 40 were female, and all had caregiver support during the study.
Those unable to visualize information on computer and mobile/tablet screens or to listen to instructions/auditory cues were excluded. All were provided with instructions and a mobile monitoring tool set to record steps completed, distances covered, speeds, and heart rate.
Each was assigned to one of four groups. Exercise intervention-only consisted of 8 weeks of cardiorespiratory exercise defined as either walking or jogging three times a week for 30 minutes. Cognitive training included eight levels (about 20 minutes) of cognitive and executive function exercises six times per week. The combined group completed both the cardiorespiratory and cognitive interventions, while the fourth group acted as controls with no intervention.
According to the authors, the study offers a real-life scenario that can be readily adopted within the Down syndrome community.
This study was commissioned by the Canadian Down Syndrome Society. The authors had no conflicts of interest to declare.
FROM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH AND PUBLIC HEALTH
Prognostic tool identifies alcohol relapse risk after liver transplant
, based on data from 140 individuals.
Alcohol relapse after liver transplant ranges from 4% to as high as 95% among patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and better tools are needed to identify those at increased risk, Jiten P. Kothadia, MD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, said in a presentation given in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Dr. Kothadia and colleagues evaluated the effectiveness of the Social Determinant Acuity Tool (S-DAT), which stratified patients in terms of successful post-liver transplant outcomes from excellent (S-DAT scores 0-6) to poor candidates (scores 35-40). The S-DAT categories included cognitive function, mental health, social support, coping skills, financial status, compliance, alcohol abuse, substance abuse, reliability, legal issues, understanding the transplant process, and desire for transplant.
The study population included 140 adults with alcoholic liver disease who underwent a liver transplant between January 2016 and November 2021 at a single center. Before surgery, all patients underwent a thorough psychosocial evaluation using the S-DAT. The mean age of the participants was 53.4 years, 107 were male, and 67.9% had abstained from alcohol for more than 6 months prior to transplant.
The primary outcome of post-liver transplant alcohol relapse was defined as any alcohol use regardless of the amount or frequency, based on patient interviews or blood or urine tests.
Overall, the rate of relapse was 23.6%; and the rate within a year was 18.6%. In a multivariate analysis, S-DAT score was a significant predictor of relapse (odds ratio [OR] 1.65, P = .000). Other independent predictors of relapse were post-LT alcohol treatment (OR 7.11, P = .02), smoking history (OR 0.15, P = .03), and marital status (OR 60.28, P = .000). The area under the receiver operative curves (AUROC) for the S-DAT score to predict alcohol relapse within 1 year after LT was 0.77.
The sensitivity of the S-DAT for predicting relapse risk was 96.2%, and specificity was 40.4%; positive and negative predictive values were 26.9% and 97.9%, respectively.
The high sensitivity and negative predictive values of the S-DAT make it a useful screening tool for identifying patients at low risk of alcohol relapse after a liver transplant, Dr. Kothadia said in an interview. “Our score will guide risk-based interventions post-LT to reduce post-LT relapse and improve long-term outcomes.”
The findings included only data from a single center, which may limit generalizability, Dr. Kothadia said. The tool is not yet clinically available, he noted.
“We would like to perform external validation of our S-DAT score as it stresses the importance of these psychosocial variables,” and to confirm the findings in larger, multicenter, prospective clinical trials, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Kothadia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
, based on data from 140 individuals.
Alcohol relapse after liver transplant ranges from 4% to as high as 95% among patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and better tools are needed to identify those at increased risk, Jiten P. Kothadia, MD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, said in a presentation given in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Dr. Kothadia and colleagues evaluated the effectiveness of the Social Determinant Acuity Tool (S-DAT), which stratified patients in terms of successful post-liver transplant outcomes from excellent (S-DAT scores 0-6) to poor candidates (scores 35-40). The S-DAT categories included cognitive function, mental health, social support, coping skills, financial status, compliance, alcohol abuse, substance abuse, reliability, legal issues, understanding the transplant process, and desire for transplant.
The study population included 140 adults with alcoholic liver disease who underwent a liver transplant between January 2016 and November 2021 at a single center. Before surgery, all patients underwent a thorough psychosocial evaluation using the S-DAT. The mean age of the participants was 53.4 years, 107 were male, and 67.9% had abstained from alcohol for more than 6 months prior to transplant.
The primary outcome of post-liver transplant alcohol relapse was defined as any alcohol use regardless of the amount or frequency, based on patient interviews or blood or urine tests.
Overall, the rate of relapse was 23.6%; and the rate within a year was 18.6%. In a multivariate analysis, S-DAT score was a significant predictor of relapse (odds ratio [OR] 1.65, P = .000). Other independent predictors of relapse were post-LT alcohol treatment (OR 7.11, P = .02), smoking history (OR 0.15, P = .03), and marital status (OR 60.28, P = .000). The area under the receiver operative curves (AUROC) for the S-DAT score to predict alcohol relapse within 1 year after LT was 0.77.
The sensitivity of the S-DAT for predicting relapse risk was 96.2%, and specificity was 40.4%; positive and negative predictive values were 26.9% and 97.9%, respectively.
The high sensitivity and negative predictive values of the S-DAT make it a useful screening tool for identifying patients at low risk of alcohol relapse after a liver transplant, Dr. Kothadia said in an interview. “Our score will guide risk-based interventions post-LT to reduce post-LT relapse and improve long-term outcomes.”
The findings included only data from a single center, which may limit generalizability, Dr. Kothadia said. The tool is not yet clinically available, he noted.
“We would like to perform external validation of our S-DAT score as it stresses the importance of these psychosocial variables,” and to confirm the findings in larger, multicenter, prospective clinical trials, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Kothadia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
, based on data from 140 individuals.
Alcohol relapse after liver transplant ranges from 4% to as high as 95% among patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and better tools are needed to identify those at increased risk, Jiten P. Kothadia, MD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, said in a presentation given in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Dr. Kothadia and colleagues evaluated the effectiveness of the Social Determinant Acuity Tool (S-DAT), which stratified patients in terms of successful post-liver transplant outcomes from excellent (S-DAT scores 0-6) to poor candidates (scores 35-40). The S-DAT categories included cognitive function, mental health, social support, coping skills, financial status, compliance, alcohol abuse, substance abuse, reliability, legal issues, understanding the transplant process, and desire for transplant.
The study population included 140 adults with alcoholic liver disease who underwent a liver transplant between January 2016 and November 2021 at a single center. Before surgery, all patients underwent a thorough psychosocial evaluation using the S-DAT. The mean age of the participants was 53.4 years, 107 were male, and 67.9% had abstained from alcohol for more than 6 months prior to transplant.
The primary outcome of post-liver transplant alcohol relapse was defined as any alcohol use regardless of the amount or frequency, based on patient interviews or blood or urine tests.
Overall, the rate of relapse was 23.6%; and the rate within a year was 18.6%. In a multivariate analysis, S-DAT score was a significant predictor of relapse (odds ratio [OR] 1.65, P = .000). Other independent predictors of relapse were post-LT alcohol treatment (OR 7.11, P = .02), smoking history (OR 0.15, P = .03), and marital status (OR 60.28, P = .000). The area under the receiver operative curves (AUROC) for the S-DAT score to predict alcohol relapse within 1 year after LT was 0.77.
The sensitivity of the S-DAT for predicting relapse risk was 96.2%, and specificity was 40.4%; positive and negative predictive values were 26.9% and 97.9%, respectively.
The high sensitivity and negative predictive values of the S-DAT make it a useful screening tool for identifying patients at low risk of alcohol relapse after a liver transplant, Dr. Kothadia said in an interview. “Our score will guide risk-based interventions post-LT to reduce post-LT relapse and improve long-term outcomes.”
The findings included only data from a single center, which may limit generalizability, Dr. Kothadia said. The tool is not yet clinically available, he noted.
“We would like to perform external validation of our S-DAT score as it stresses the importance of these psychosocial variables,” and to confirm the findings in larger, multicenter, prospective clinical trials, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Kothadia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ACG 2023
New Therapies in Melanoma: Current Trends, Evolving Paradigms, and Future Perspectives
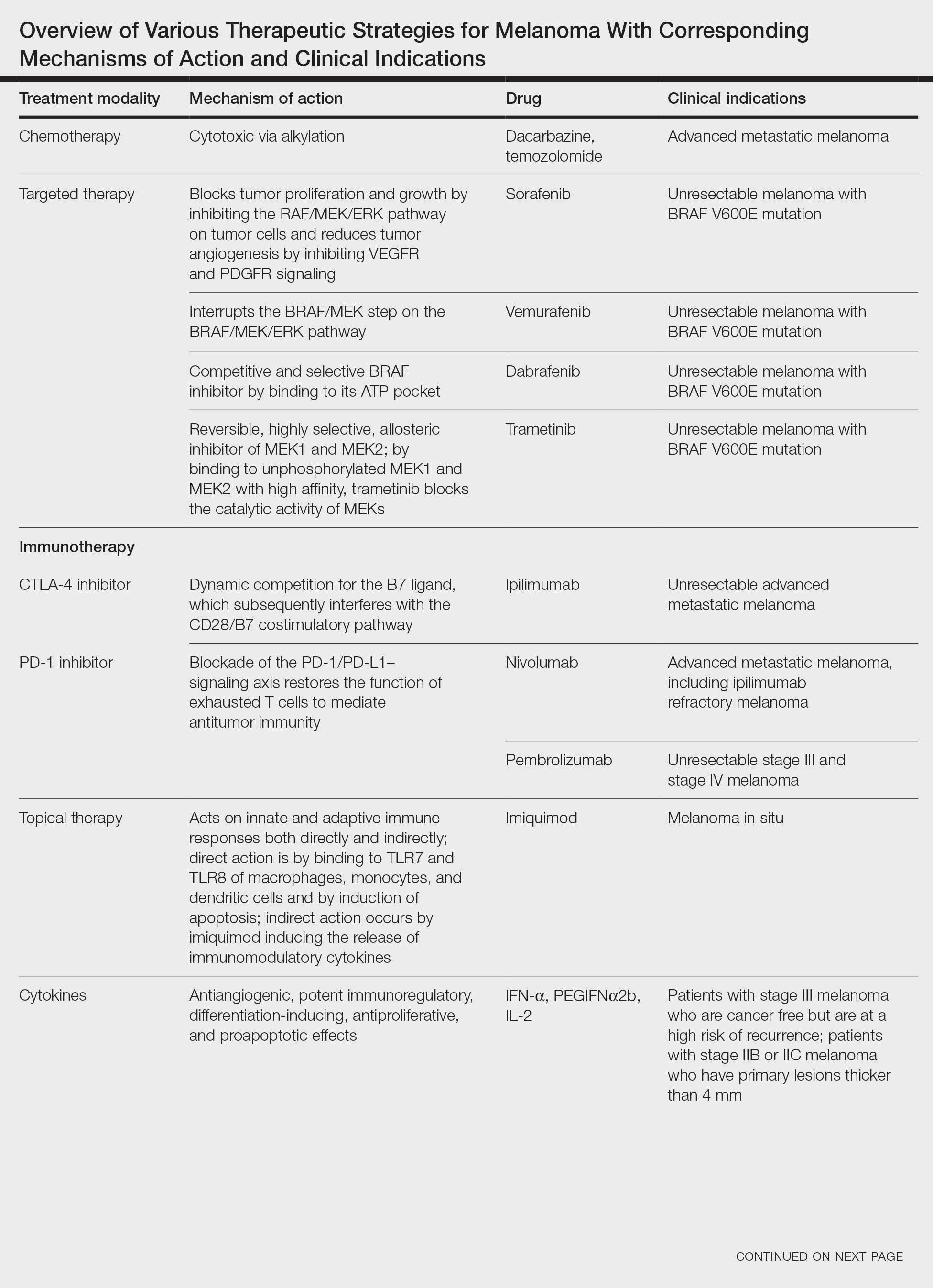
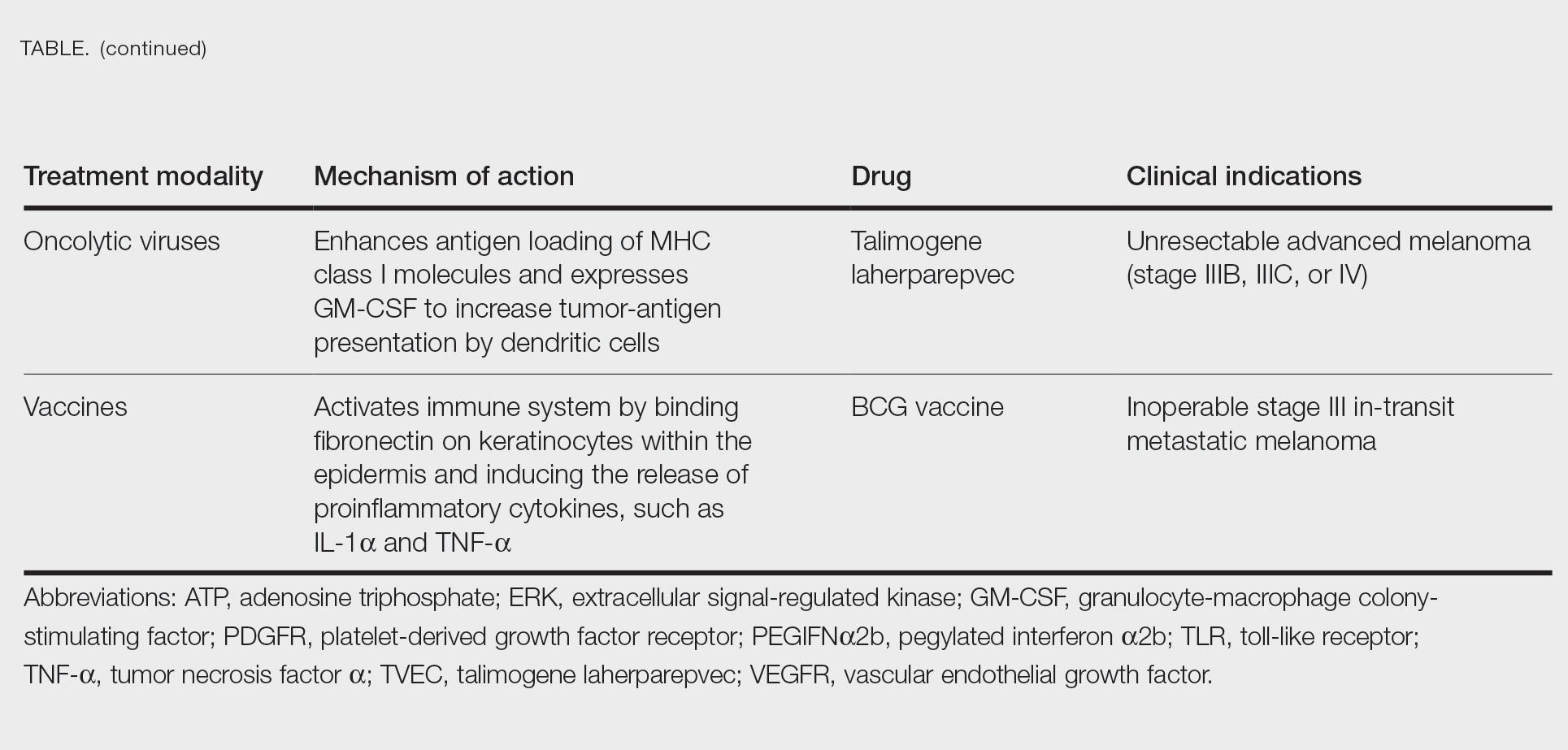
Cutaneous malignant melanoma represents an aggressive form of skin cancer, with 132,000 new cases of melanoma and 50,000 melanoma-related deaths diagnosed worldwide each year.1 In recent decades, major progress has been made in the treatment of melanoma, especially metastatic and advanced-stage disease. Approval of new treatments, such as immunotherapy with anti–PD-1 (pembrolizumab and nivolumab) and anti–CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) antibodies, has revolutionized therapeutic strategies (Figure 1). Molecularly, melanoma has the highest mutational burden among solid tumors. Approximately 40% of melanomas harbor the BRAF V600 mutation, leading to constitutive activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway.2 The other described genomic subtypes are mutated RAS (accounting for approximately 28% of cases), mutated NF1 (approximately 14% of cases), and triple wild type, though these other subtypes have not been as successfully targeted with therapy to date.3 Dual inhibition of this pathway using combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors confers high response rates and survival benefit, though efficacy in metastatic patients often is limited by development of resistance. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved 3 combinations of targeted therapy in unresectable tumors: dabrafenib and trametinib, vemurafenib and cobimetinib, and encorafenib and binimetinib. The oncolytic herpesvirus talimogene laherparepvec also has received FDA approval for local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with recurrent melanoma after initial surgery.2
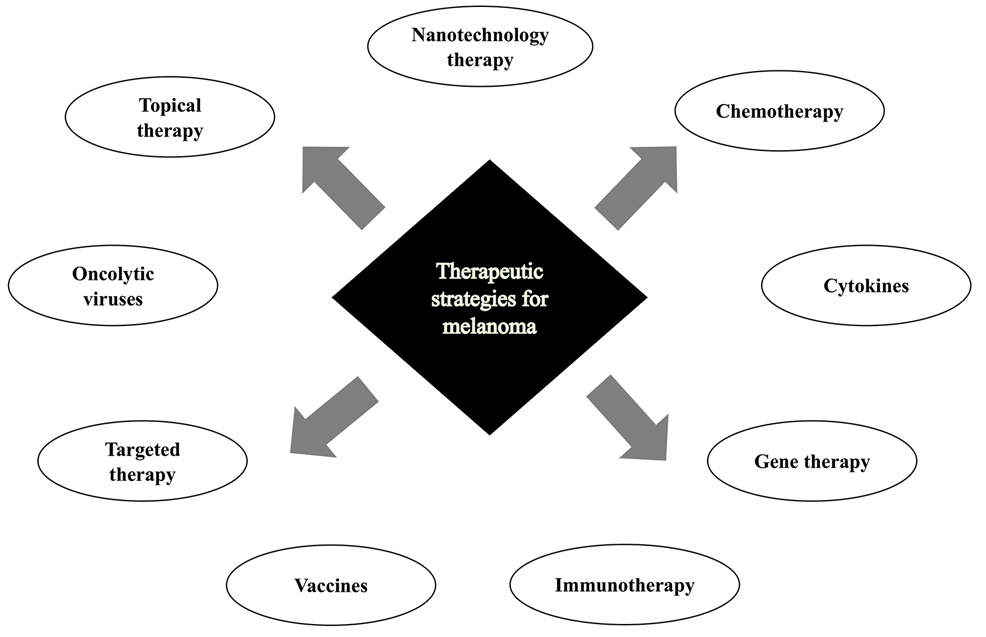
In this review, we explore new therapeutic agents and novel combinations that are being tested in early-phase clinical trials (Table). We discuss newer promising tools such as nanotechnology to develop nanosystems that act as drug carriers and/or light absorbents to potentially improve therapy outcomes. Finally, we highlight challenges such as management after resistance and intervention with novel immunotherapies and the lack of predictive biomarkers to stratify patients to targeted treatments after primary treatment failure.
Targeted Therapies
Vemurafenib was approved by the FDA in 2011 and was the first BRAF-targeted therapy approved for the treatment of melanoma based on a 48% response rate and a 63% reduction in the risk for death vs dacarbazine chemotherapy.4 Despite a rapid and clinically significant initial response, progression-free survival (PFS) was only 5.3 months, which is indicative of the rapid development of resistance with monotherapy through MAPK reactivation. As a result, combined BRAF and MEK inhibition was introduced and is now the standard of care for targeted therapy in melanoma. Treatment with dabrafenib and trametinib, vemurafenib and cobimetinib, or encorafenib and binimetinib is associated with prolonged PFS and overall survival (OS) compared to BRAF inhibitor monotherapy, with response rates exceeding 60% and a complete response rate of 10% to 18%.5 Recently, combining atezolizumab with vemurafenib and cobimetinib was shown to improve PFS compared to combined targeted therapy.6 Targeted therapy usually is given as first-line treatment to symptomatic patients with a high tumor burden because the response may be more rapid than the response to immunotherapy. Ultimately, most patients with advanced BRAF-mutated melanoma receive both targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
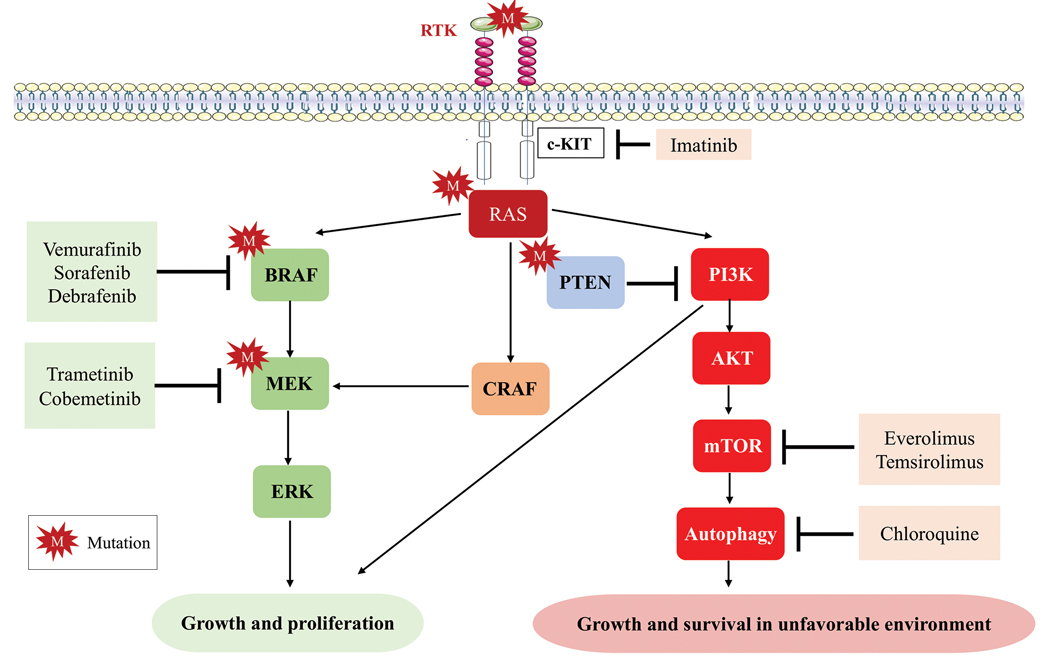
Mutations of KIT (encoding proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase) activate intracellular MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways (Figure 2).7 KIT mutations are found in mucosal and acral melanomas as well as chronically sun-damaged skin, with frequencies of 39%, 36%, and 28%, respectively. Imatinib was associated with a 53% response rate and PFS of 3.9 months among patients with KIT-mutated melanoma but failed to cause regression in melanomas with KIT amplification.8
Anti–CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
CTLA-4 is a protein found on T cells that binds with another protein, B7, preventing T cells from killing cancer cells. Hence, blockade of CTLA-4 antibody avoids the immunosuppressive state of lymphocytes, strengthening their antitumor action.9 Ipilimumab, an anti–CTLA-4 antibody, demonstrated improvement in median OS for management of unresectable or metastatic stage IV melanoma, resulting in its FDA approval.8 A combination of ipilimumab with dacarbazine in stage IV melanoma showed notable improvement of OS.10 Similarly, tremelimumab showed evidence of tumor regression in a phase 1 trial but with more severe immune-related side effects compared with ipilimumab.11 A second study on patients with stage IV melanoma treated with tremelimumab as first-line therapy in comparison with dacarbazine demonstrated differences in OS that were not statistically significant, though there was a longer duration of an objective response in patients treated with tremelimumab (35.8 months) compared with patients responding to dacarbazine (13.7 months).12
Anti–PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
PD-1 is a transmembrane protein with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory signaling, identified as an apoptosis-associated molecule.13 Upon activation, it is expressed on the cell surface of CD4, CD8, B lymphocytes, natural killer cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells.14 PD-L1, the ligand of PD-1, is constitutively expressed on different hematopoietic cells, as well as on fibroblasts, endothelial cells, mesenchymal cells, neurons, and keratinocytes.15,16 Reactivation of effector T lymphocytes by PD-1:PD-L1 pathway inhibition has shown clinically significant therapeutic relevance.17 The PD-1:PD-L1 interaction is active only in the presence of T- or B-cell antigen receptor cross-link. This interaction prevents PI3K/AKT signaling and MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway activation with the net result of lymphocytic functional exhaustion.18,19 PD-L1 blockade is shown to have better clinical benefit and minor toxicity compared to anti–CTLA-4 therapy. Treatment with anti-PD1 nivolumab in a phase 1b clinical trial (N=107) demonstrated highly specific action, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in 32% of patients with advanced melanoma.20 These promising results led to the FDA approval of nivolumab for the treatment of patients with advanced and unresponsive melanoma. A recent clinical trial combining ipilimumab and nivolumab resulted in an impressive increase of PFS compared with ipilimumab monotherapy (11.5 months vs 2.9 months).21 Similarly, treatment with pembrolizumab in advanced melanoma demonstrated improvement in PFS and OS compared with anti–CTLA-4 therapy,22,23 which resulted in FDA approval of pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced melanoma in patients previously treated with ipilimumab or BRAF inhibitors in BRAF V600 mutation–positive patients.24
Lymphocyte-Activated Gene 3–Targeted Therapies
Nanotechnology in Melanoma Therapy
The use of nanotechnology represents one of the newer alternative therapies employed for treatment of melanoma and is especially gaining interest due to reduced adverse effects in comparison with other conventional treatments for melanoma. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems precisely target tumor cells and improve the effect of both the conventional and innovative antineoplastic treatment.27,31 Tumor vasculature differs from normal tissues by being discontinuous and having interspersed small gaps/holes that allow nanoparticles to exit the circulation and enter and accumulate in the tumor tissue, leading to enhanced and targeted release of the antineoplastic drug to tumor cells.32 This mechanism is called the enhanced permeability and retention effect.33
Another mechanism by which nanoparticles work is ligand-based targeting in which ligands such as monoclonal antibodies, peptides, and nucleic acids located on the surface of nanoparticles can bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of tumor cells and lead to targeted delivery of the drug.34 Nanomaterials used for melanoma treatment include vesicular systems such as liposomes and niosomes, polymeric nanoparticles, noble metal-based nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, dendrimers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructures, lipid carriers, and microneedles. In melanoma, nanoparticles can be used to enhance targeted delivery of drugs, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Cai et al35 described usage of scaffolds in delivery systems. Tumor-associated antigens, adjuvant drugs, and chemical agents that influence the tumor microenvironment can be loaded onto these scaffolding agents. In a study by Zhu et al,36 photosensitizer chlorin e6 and immunoadjuvant aluminum hydroxide were used as a novel nanosystem that effectively destroyed tumor cells and induced a strong systemic antitumor response. IL-2 is a cytokine produced by B or T lymphocytes. Its use in melanoma has been limited by a severe adverse effect profile and lack of complete response in most patients. Cytokine-containing nanogels have been found to selectively release IL-2 in response to activation of T-cell receptors, and a mouse model in melanoma showed better response compared to free IL-1 and no adverse systemic effects.37
Nanovaccines represent another interesting novel immunotherapy modality. A study by Conniot et al38 showed that nanoparticles can be used in the treatment of melanoma. Nanoparticles made of biodegradable polymer were loaded with Melan-A/MART-1 (26–35 A27L) MHC class I-restricted peptide (MHC class I antigen), and the limited peptide MHC class II Melan-A/MART-1 51–73 (MHC class II antigen) and grafted with mannose that was then combined with an anti–PD-L1 antibody and injected into mouse models. This combination resulted in T-cell infiltration at early stages and increased infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Ibrutinib, a myeloid-derived suppressor cell inhibitor, was added and demonstrated marked tumor remission and prolonged survival.38
Overexpression of certain microRNAs (miRNAs), especially miR-204-5p and miR-199b-5p, has been shown to inhibit growth of melanoma cells in vitro, both alone and in combination with MAPK inhibitors, but these miRNAs are easily degradable in body fluids. Lipid nanoparticles can bind these miRNAs and have been shown to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and improve efficacy of BRAF and MEK inhibitors.39
Triple-Combination Therapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti–PD-1 or anti–CTLA-4 drugs have become the standard of care in treatment of advanced melanoma. Approximately 40% to 50% of cases of melanoma harbor BRAF mutations, and patients with these mutations could benefit from BRAF and MEK inhibitors. Data from clinical trials on BRAF and MEK inhibitors even showed initial high objective response rates, but the response was short-lived, and there was frequent acquired resistance.40 With ICIs, the major limitation was primary resistance, with only 50% of patients initially responding.41 Studies on murine models demonstrated that BRAF-mutated tumors had decreased expression of IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor α, and CD40 ligand on CD4+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and increased accumulation of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, leading to a protumor microenvironment. BRAF and MEK pathway inhibition were found to improve intratumoral CD4+ T-cell activity, leading to improved antitumor T-cell responses.42 Because of this enhanced immune response by BRAF and MEK inhibitors, it was hypothesized and later supported by clinical research that a combination of these targeted treatments and ICIs can have a synergistic effect, leading to increased antitumor activity.43 A randomized phase 2 clinical trial (KEYNOTE-022) in which the treatment group was given pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib and the control group was treated with dabrafenib and trametinib showed increased medial OS in the treatment group vs the control group (46.3 months vs 26.3 months) and more frequent complete response in the treatment group vs the control group (20% vs 15%).44 In the IMspire150 phase 3 clinical trial, patients with advanced stage IIIC to IV BRAF-mutant melanoma were treated with either a triple combination of the PDL-1 inhibitor atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib or vemurafenib and cobimetinib. Although the objective response rate was similar in both groups, the median duration of response was longer in the triplet group compared with the doublet group (21 months vs 12.6 months). Given these results, the FDA approved the triple-combination therapy with atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib. Although triple-combination therapy has shown promising results, it is expected that there will be an increase in the frequency of treatment-related adverse effects. In the phase 3 COMBi-I study, patients with advanced stage IIIC to IV BRAF V600E mutant cutaneous melanoma were treated with either a combination of spartalizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib or just dabrafenib and trametinib. Although the objective response rates were not significantly different (69% vs 64%), there was increased frequency of treatment-related adverse effects in patients receiving triple-combination therapy.43 As more follow-up data come out of these ongoing clinical trials, benefits of triple-combination therapy and its adverse effect profile will be more definitely established.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
One of the major roadblocks in the treatment of melanoma is the failure of response to ICI with CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in a large patient population, which has resulted in the need for new biomarkers that can act as potential therapeutic targets. Further, the main underlying factor for both adjuvant and neoadjuvant approaches remains the selection of patients, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the number of patients exposed to potentially toxic treatments without gaining clinical benefit. Clinical and pathological factors (eg, Breslow thickness, ulceration, the number of positive lymph nodes) play a role in stratifying patients as per risk of recurrence.45 Similarly, peripheral blood biomarkers have been proposed as prognostic tools for high-risk stage II and III melanoma, including markers of systemic inflammation previously explored in the metastatic setting.46 However, the use of these parameters has not been validated for clinical practice. Currently, despite promising results of BRAF and MEK inhibitors and therapeutic ICIs, as well as IL-2 or interferon alfa, treatment options in metastatic melanoma are limited because of its high heterogeneity, problematic patient stratification, and high genetic mutational rate. Recently, the role of epigenetic modifications andmiRNAs in melanoma progression and metastatic spread has been described. Silencing of CDKN2A locus and encoding for p16INK4A and p14ARF by DNA methylation are noted in 27% and 57% of metastatic melanomas, respectively, which enables melanoma cells to escape from growth arrest and apoptosis generated by Rb protein and p53 pathways.47 Demethylation of these and other tumor suppressor genes with proapoptotic function (eg, RASSF1A and tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand) can restore cell death pathways, though future clinical studies in melanoma are warranted.48
- Geller AC, Clapp RW, Sober AJ, et al. Melanoma epidemic: an analysis of six decades of data from the Connecticut Tumor Registry. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:4172-4178.
- Moreira A, Heinzerling L, Bhardwaj N, et al. Current melanoma treatments: where do we stand? Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:221.
- Watson IR, Wu C-J, Zou L, et al. Genomic classification of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Res. 2015;75(15 Suppl):2972.
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2507-2516.
- Hamid O, Cowey CL, Offner M, et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of approved combination BRAF and MEK inhibitor regimens for BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:1642.
- Gutzmer R, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, et al. Atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib as first-line treatment for unresectable advanced BRAFV600 mutation-positive melanoma (IMspire150): primary analysis of the randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1835-1844.
- Reddy BY, Miller DM, Tsao H. Somatic driver mutations in melanoma. Cancer. 2017;123(suppl 11):2104-2117.
- Hodi FS, Corless CL, Giobbie-Hurder A, et al. Imatinib for melanomas harboring mutationally activated or amplified KIT arising on mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3182-3190.
- Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J. A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:65-97.
- Maverakis E, Cornelius LA, Bowen GM, et al. Metastatic melanoma—a review of current and future treatment options. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:516-524.
- Ribas A, Chesney JA, Gordon MS, et al. Safety profile and pharmacokinetic analyses of the anti-CTLA4 antibody tremelimumab administered as a one hour infusion. J Transl Med. 2012;10:1-6.
- Ribas A, Puzanov I, Dummer R, et al. Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:908-918.
- BG Neel, Gu H, Pao L. The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:284-293.
- Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, et al. Induced expression of PD‐1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992;11:3887-3895.
- Yamazaki T, Akiba H, Iwai H, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC. J Immunol. 2002;169:5538-5545.
- Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ et al. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677-704.
- Blank C, Kuball J, Voelkl S, et al. Blockade of PD‐L1 (B7‐H1) augments human tumor‐specific T cell responses in vitro. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:317-327.
- Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, et al. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9543-9553.
- Patsoukis N, Brown J, Petkova V, et al. Selective effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras pathways regulate molecular components of the cell cycle and inhibit T cell proliferation. Sci Signal. 2012;5:ra46.
- Topalian SL, Sznol M, McDermott DF, et al. Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1020-1030.
- Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:375-384.
- Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:320-330.
- Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2006-2017.
- Burns MC, O’Donnell A, Puzanov I. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Exp Opin Orphan Drugs. 2016;4:867-873.
- F Triebel. LAG-3: a regulator of T-cell and DC responses and its use in therapeutic vaccination. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:619-622.
- Maruhashi T, Sugiura D, Okazaki I-M, et al. LAG-3: from molecular functions to clinical applications. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001014.
- Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, et al. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:20-37.
- Tawbi HA, Schadendorf D, Lipson EJ, et al. Relatlimab and nivolumab versus nivolumab in untreated advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:24-34.
- US Food and Drug Administration approves first LAG-3-blocking antibody combination, Opdualag™ (nivolumab and relatlimab-rmbw), as treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Press release. Bristol Myers Squibb. March 18, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2023. https://news.bms.com/news/details/2022/U.S.-Food-and-Drug-Administration-Approves-First-LAG-3-Blocking-Antibody-Combination-Opdualag-nivolumab-and-relatlimab-rmbw-as-Treatment-for-Patients-with-Unresectable-or-Metastatic-Melanoma/default.aspx
- Zhao B-W, Zhang F-Y, Wang Y, et al. LAG3-PD1 or CTLA4-PD1 inhibition in advanced melanoma: indirect cross comparisons of the CheckMate-067 and RELATIVITY-047 trials. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:4975.
- Jin C, Wang K, Oppong-Gyebi A, et al. Application of nanotechnology in cancer diagnosis and therapy-a mini-review. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:2964-2973.
- Maeda H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2015;91:3-6.
- Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J, et al. Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor targeting. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:812-818.
- Beiu C, Giurcaneanu C, Grumezescu AM, et al. Nanosystems for improved targeted therapies in melanoma. J Clin Med. 2020;9:318.
- Cai L, Xu J, Yang Z, et al. Engineered biomaterials for cancer immunotherapy. MedComm. 2020;1:35-46.
- Zhu Y, Xue J, Chen W, et al. Albumin-biomineralized nanoparticles to synergize phototherapy and immunotherapy against melanoma. J Control Release. 2020;322:300-311.
- Zhang Y, Li N, Suh H, et al. Nanoparticle anchoring targets immune agonists to tumors enabling anti-cancer immunity without systemic toxicity. Nat Commun. 2018;9:6.
- Conniot J, Scomparin A, Peres C, et al. Immunization with mannosylated nanovaccines and inhibition of the immune-suppressing microenvironment sensitizes melanoma to immune checkpoint modulators. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14:891-901.
- Fattore L, Campani V, Ruggiero CF, et al. In vitro biophysical and biological characterization of lipid nanoparticles co-encapsulating oncosuppressors miR-199b-5p and miR-204-5p as potentiators of target therapy in metastatic melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1930.
- Welti M, Dimitriou F, Gutzmer R, et al. Triple combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors and BRAF/MEK inhibitors in BRAF V600 melanoma: current status and future perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:5489.
- Khair DO, Bax HJ, Mele S, et al. Combining immune checkpoint inhibitors: established and emerging targets and strategies to improve outcomes in melanoma. Front Immunol. 2019;10:453.
- Ho P-C, Meeth KM, Tsui Y-C, et al. Immune-based antitumor effects of BRAF inhibitors rely on signaling by CD40L and IFNγBRAF inhibitor-induced antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3205-3217.
- Dummer R, Sandhu SK, Miller WH, et al. A phase II, multicenter study of encorafenib/binimetinib followed by a rational triple-combination after progression in patients with advanced BRAF V600-mutated melanoma (LOGIC2). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15 suppl):10022.
- Ferrucci PF, Di Giacomo AM, Del Vecchio M, et al. KEYNOTE-022 part 3: a randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study of pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib in BRAF-mutant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001806.
- Madu MF, Schopman JH, Berger DM, et al. Clinical prognostic markers in stage IIIC melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116:244-251.
- Davis JL, Langan RC, Panageas KS, et al. Elevated blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: a readily available biomarker associated with death due to disease in high risk nonmetastatic melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:1989-1996.
- Freedberg DE, Rigas SH, Russak J, et al. Frequent p16-independent inactivation of p14ARF in human melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:784-795.
- Sigalotti L, Covre A, Fratta E, et al. Epigenetics of human cutaneous melanoma: setting the stage for new therapeutic strategies. J Transl Med. 2010;8:1-22.
Cutaneous malignant melanoma represents an aggressive form of skin cancer, with 132,000 new cases of melanoma and 50,000 melanoma-related deaths diagnosed worldwide each year.1 In recent decades, major progress has been made in the treatment of melanoma, especially metastatic and advanced-stage disease. Approval of new treatments, such as immunotherapy with anti–PD-1 (pembrolizumab and nivolumab) and anti–CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) antibodies, has revolutionized therapeutic strategies (Figure 1). Molecularly, melanoma has the highest mutational burden among solid tumors. Approximately 40% of melanomas harbor the BRAF V600 mutation, leading to constitutive activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway.2 The other described genomic subtypes are mutated RAS (accounting for approximately 28% of cases), mutated NF1 (approximately 14% of cases), and triple wild type, though these other subtypes have not been as successfully targeted with therapy to date.3 Dual inhibition of this pathway using combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors confers high response rates and survival benefit, though efficacy in metastatic patients often is limited by development of resistance. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved 3 combinations of targeted therapy in unresectable tumors: dabrafenib and trametinib, vemurafenib and cobimetinib, and encorafenib and binimetinib. The oncolytic herpesvirus talimogene laherparepvec also has received FDA approval for local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with recurrent melanoma after initial surgery.2

In this review, we explore new therapeutic agents and novel combinations that are being tested in early-phase clinical trials (Table). We discuss newer promising tools such as nanotechnology to develop nanosystems that act as drug carriers and/or light absorbents to potentially improve therapy outcomes. Finally, we highlight challenges such as management after resistance and intervention with novel immunotherapies and the lack of predictive biomarkers to stratify patients to targeted treatments after primary treatment failure.


Targeted Therapies
Vemurafenib was approved by the FDA in 2011 and was the first BRAF-targeted therapy approved for the treatment of melanoma based on a 48% response rate and a 63% reduction in the risk for death vs dacarbazine chemotherapy.4 Despite a rapid and clinically significant initial response, progression-free survival (PFS) was only 5.3 months, which is indicative of the rapid development of resistance with monotherapy through MAPK reactivation. As a result, combined BRAF and MEK inhibition was introduced and is now the standard of care for targeted therapy in melanoma. Treatment with dabrafenib and trametinib, vemurafenib and cobimetinib, or encorafenib and binimetinib is associated with prolonged PFS and overall survival (OS) compared to BRAF inhibitor monotherapy, with response rates exceeding 60% and a complete response rate of 10% to 18%.5 Recently, combining atezolizumab with vemurafenib and cobimetinib was shown to improve PFS compared to combined targeted therapy.6 Targeted therapy usually is given as first-line treatment to symptomatic patients with a high tumor burden because the response may be more rapid than the response to immunotherapy. Ultimately, most patients with advanced BRAF-mutated melanoma receive both targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Mutations of KIT (encoding proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase) activate intracellular MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways (Figure 2).7 KIT mutations are found in mucosal and acral melanomas as well as chronically sun-damaged skin, with frequencies of 39%, 36%, and 28%, respectively. Imatinib was associated with a 53% response rate and PFS of 3.9 months among patients with KIT-mutated melanoma but failed to cause regression in melanomas with KIT amplification.8

Anti–CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
CTLA-4 is a protein found on T cells that binds with another protein, B7, preventing T cells from killing cancer cells. Hence, blockade of CTLA-4 antibody avoids the immunosuppressive state of lymphocytes, strengthening their antitumor action.9 Ipilimumab, an anti–CTLA-4 antibody, demonstrated improvement in median OS for management of unresectable or metastatic stage IV melanoma, resulting in its FDA approval.8 A combination of ipilimumab with dacarbazine in stage IV melanoma showed notable improvement of OS.10 Similarly, tremelimumab showed evidence of tumor regression in a phase 1 trial but with more severe immune-related side effects compared with ipilimumab.11 A second study on patients with stage IV melanoma treated with tremelimumab as first-line therapy in comparison with dacarbazine demonstrated differences in OS that were not statistically significant, though there was a longer duration of an objective response in patients treated with tremelimumab (35.8 months) compared with patients responding to dacarbazine (13.7 months).12
Anti–PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
PD-1 is a transmembrane protein with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory signaling, identified as an apoptosis-associated molecule.13 Upon activation, it is expressed on the cell surface of CD4, CD8, B lymphocytes, natural killer cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells.14 PD-L1, the ligand of PD-1, is constitutively expressed on different hematopoietic cells, as well as on fibroblasts, endothelial cells, mesenchymal cells, neurons, and keratinocytes.15,16 Reactivation of effector T lymphocytes by PD-1:PD-L1 pathway inhibition has shown clinically significant therapeutic relevance.17 The PD-1:PD-L1 interaction is active only in the presence of T- or B-cell antigen receptor cross-link. This interaction prevents PI3K/AKT signaling and MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway activation with the net result of lymphocytic functional exhaustion.18,19 PD-L1 blockade is shown to have better clinical benefit and minor toxicity compared to anti–CTLA-4 therapy. Treatment with anti-PD1 nivolumab in a phase 1b clinical trial (N=107) demonstrated highly specific action, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in 32% of patients with advanced melanoma.20 These promising results led to the FDA approval of nivolumab for the treatment of patients with advanced and unresponsive melanoma. A recent clinical trial combining ipilimumab and nivolumab resulted in an impressive increase of PFS compared with ipilimumab monotherapy (11.5 months vs 2.9 months).21 Similarly, treatment with pembrolizumab in advanced melanoma demonstrated improvement in PFS and OS compared with anti–CTLA-4 therapy,22,23 which resulted in FDA approval of pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced melanoma in patients previously treated with ipilimumab or BRAF inhibitors in BRAF V600 mutation–positive patients.24
Lymphocyte-Activated Gene 3–Targeted Therapies
Nanotechnology in Melanoma Therapy
The use of nanotechnology represents one of the newer alternative therapies employed for treatment of melanoma and is especially gaining interest due to reduced adverse effects in comparison with other conventional treatments for melanoma. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems precisely target tumor cells and improve the effect of both the conventional and innovative antineoplastic treatment.27,31 Tumor vasculature differs from normal tissues by being discontinuous and having interspersed small gaps/holes that allow nanoparticles to exit the circulation and enter and accumulate in the tumor tissue, leading to enhanced and targeted release of the antineoplastic drug to tumor cells.32 This mechanism is called the enhanced permeability and retention effect.33
Another mechanism by which nanoparticles work is ligand-based targeting in which ligands such as monoclonal antibodies, peptides, and nucleic acids located on the surface of nanoparticles can bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of tumor cells and lead to targeted delivery of the drug.34 Nanomaterials used for melanoma treatment include vesicular systems such as liposomes and niosomes, polymeric nanoparticles, noble metal-based nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, dendrimers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructures, lipid carriers, and microneedles. In melanoma, nanoparticles can be used to enhance targeted delivery of drugs, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Cai et al35 described usage of scaffolds in delivery systems. Tumor-associated antigens, adjuvant drugs, and chemical agents that influence the tumor microenvironment can be loaded onto these scaffolding agents. In a study by Zhu et al,36 photosensitizer chlorin e6 and immunoadjuvant aluminum hydroxide were used as a novel nanosystem that effectively destroyed tumor cells and induced a strong systemic antitumor response. IL-2 is a cytokine produced by B or T lymphocytes. Its use in melanoma has been limited by a severe adverse effect profile and lack of complete response in most patients. Cytokine-containing nanogels have been found to selectively release IL-2 in response to activation of T-cell receptors, and a mouse model in melanoma showed better response compared to free IL-1 and no adverse systemic effects.37
Nanovaccines represent another interesting novel immunotherapy modality. A study by Conniot et al38 showed that nanoparticles can be used in the treatment of melanoma. Nanoparticles made of biodegradable polymer were loaded with Melan-A/MART-1 (26–35 A27L) MHC class I-restricted peptide (MHC class I antigen), and the limited peptide MHC class II Melan-A/MART-1 51–73 (MHC class II antigen) and grafted with mannose that was then combined with an anti–PD-L1 antibody and injected into mouse models. This combination resulted in T-cell infiltration at early stages and increased infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Ibrutinib, a myeloid-derived suppressor cell inhibitor, was added and demonstrated marked tumor remission and prolonged survival.38
Overexpression of certain microRNAs (miRNAs), especially miR-204-5p and miR-199b-5p, has been shown to inhibit growth of melanoma cells in vitro, both alone and in combination with MAPK inhibitors, but these miRNAs are easily degradable in body fluids. Lipid nanoparticles can bind these miRNAs and have been shown to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and improve efficacy of BRAF and MEK inhibitors.39
Triple-Combination Therapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti–PD-1 or anti–CTLA-4 drugs have become the standard of care in treatment of advanced melanoma. Approximately 40% to 50% of cases of melanoma harbor BRAF mutations, and patients with these mutations could benefit from BRAF and MEK inhibitors. Data from clinical trials on BRAF and MEK inhibitors even showed initial high objective response rates, but the response was short-lived, and there was frequent acquired resistance.40 With ICIs, the major limitation was primary resistance, with only 50% of patients initially responding.41 Studies on murine models demonstrated that BRAF-mutated tumors had decreased expression of IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor α, and CD40 ligand on CD4+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and increased accumulation of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, leading to a protumor microenvironment. BRAF and MEK pathway inhibition were found to improve intratumoral CD4+ T-cell activity, leading to improved antitumor T-cell responses.42 Because of this enhanced immune response by BRAF and MEK inhibitors, it was hypothesized and later supported by clinical research that a combination of these targeted treatments and ICIs can have a synergistic effect, leading to increased antitumor activity.43 A randomized phase 2 clinical trial (KEYNOTE-022) in which the treatment group was given pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib and the control group was treated with dabrafenib and trametinib showed increased medial OS in the treatment group vs the control group (46.3 months vs 26.3 months) and more frequent complete response in the treatment group vs the control group (20% vs 15%).44 In the IMspire150 phase 3 clinical trial, patients with advanced stage IIIC to IV BRAF-mutant melanoma were treated with either a triple combination of the PDL-1 inhibitor atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib or vemurafenib and cobimetinib. Although the objective response rate was similar in both groups, the median duration of response was longer in the triplet group compared with the doublet group (21 months vs 12.6 months). Given these results, the FDA approved the triple-combination therapy with atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib. Although triple-combination therapy has shown promising results, it is expected that there will be an increase in the frequency of treatment-related adverse effects. In the phase 3 COMBi-I study, patients with advanced stage IIIC to IV BRAF V600E mutant cutaneous melanoma were treated with either a combination of spartalizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib or just dabrafenib and trametinib. Although the objective response rates were not significantly different (69% vs 64%), there was increased frequency of treatment-related adverse effects in patients receiving triple-combination therapy.43 As more follow-up data come out of these ongoing clinical trials, benefits of triple-combination therapy and its adverse effect profile will be more definitely established.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
One of the major roadblocks in the treatment of melanoma is the failure of response to ICI with CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in a large patient population, which has resulted in the need for new biomarkers that can act as potential therapeutic targets. Further, the main underlying factor for both adjuvant and neoadjuvant approaches remains the selection of patients, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the number of patients exposed to potentially toxic treatments without gaining clinical benefit. Clinical and pathological factors (eg, Breslow thickness, ulceration, the number of positive lymph nodes) play a role in stratifying patients as per risk of recurrence.45 Similarly, peripheral blood biomarkers have been proposed as prognostic tools for high-risk stage II and III melanoma, including markers of systemic inflammation previously explored in the metastatic setting.46 However, the use of these parameters has not been validated for clinical practice. Currently, despite promising results of BRAF and MEK inhibitors and therapeutic ICIs, as well as IL-2 or interferon alfa, treatment options in metastatic melanoma are limited because of its high heterogeneity, problematic patient stratification, and high genetic mutational rate. Recently, the role of epigenetic modifications andmiRNAs in melanoma progression and metastatic spread has been described. Silencing of CDKN2A locus and encoding for p16INK4A and p14ARF by DNA methylation are noted in 27% and 57% of metastatic melanomas, respectively, which enables melanoma cells to escape from growth arrest and apoptosis generated by Rb protein and p53 pathways.47 Demethylation of these and other tumor suppressor genes with proapoptotic function (eg, RASSF1A and tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand) can restore cell death pathways, though future clinical studies in melanoma are warranted.48
Cutaneous malignant melanoma represents an aggressive form of skin cancer, with 132,000 new cases of melanoma and 50,000 melanoma-related deaths diagnosed worldwide each year.1 In recent decades, major progress has been made in the treatment of melanoma, especially metastatic and advanced-stage disease. Approval of new treatments, such as immunotherapy with anti–PD-1 (pembrolizumab and nivolumab) and anti–CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) antibodies, has revolutionized therapeutic strategies (Figure 1). Molecularly, melanoma has the highest mutational burden among solid tumors. Approximately 40% of melanomas harbor the BRAF V600 mutation, leading to constitutive activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway.2 The other described genomic subtypes are mutated RAS (accounting for approximately 28% of cases), mutated NF1 (approximately 14% of cases), and triple wild type, though these other subtypes have not been as successfully targeted with therapy to date.3 Dual inhibition of this pathway using combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors confers high response rates and survival benefit, though efficacy in metastatic patients often is limited by development of resistance. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved 3 combinations of targeted therapy in unresectable tumors: dabrafenib and trametinib, vemurafenib and cobimetinib, and encorafenib and binimetinib. The oncolytic herpesvirus talimogene laherparepvec also has received FDA approval for local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with recurrent melanoma after initial surgery.2

In this review, we explore new therapeutic agents and novel combinations that are being tested in early-phase clinical trials (Table). We discuss newer promising tools such as nanotechnology to develop nanosystems that act as drug carriers and/or light absorbents to potentially improve therapy outcomes. Finally, we highlight challenges such as management after resistance and intervention with novel immunotherapies and the lack of predictive biomarkers to stratify patients to targeted treatments after primary treatment failure.


Targeted Therapies
Vemurafenib was approved by the FDA in 2011 and was the first BRAF-targeted therapy approved for the treatment of melanoma based on a 48% response rate and a 63% reduction in the risk for death vs dacarbazine chemotherapy.4 Despite a rapid and clinically significant initial response, progression-free survival (PFS) was only 5.3 months, which is indicative of the rapid development of resistance with monotherapy through MAPK reactivation. As a result, combined BRAF and MEK inhibition was introduced and is now the standard of care for targeted therapy in melanoma. Treatment with dabrafenib and trametinib, vemurafenib and cobimetinib, or encorafenib and binimetinib is associated with prolonged PFS and overall survival (OS) compared to BRAF inhibitor monotherapy, with response rates exceeding 60% and a complete response rate of 10% to 18%.5 Recently, combining atezolizumab with vemurafenib and cobimetinib was shown to improve PFS compared to combined targeted therapy.6 Targeted therapy usually is given as first-line treatment to symptomatic patients with a high tumor burden because the response may be more rapid than the response to immunotherapy. Ultimately, most patients with advanced BRAF-mutated melanoma receive both targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Mutations of KIT (encoding proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase) activate intracellular MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways (Figure 2).7 KIT mutations are found in mucosal and acral melanomas as well as chronically sun-damaged skin, with frequencies of 39%, 36%, and 28%, respectively. Imatinib was associated with a 53% response rate and PFS of 3.9 months among patients with KIT-mutated melanoma but failed to cause regression in melanomas with KIT amplification.8

Anti–CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
CTLA-4 is a protein found on T cells that binds with another protein, B7, preventing T cells from killing cancer cells. Hence, blockade of CTLA-4 antibody avoids the immunosuppressive state of lymphocytes, strengthening their antitumor action.9 Ipilimumab, an anti–CTLA-4 antibody, demonstrated improvement in median OS for management of unresectable or metastatic stage IV melanoma, resulting in its FDA approval.8 A combination of ipilimumab with dacarbazine in stage IV melanoma showed notable improvement of OS.10 Similarly, tremelimumab showed evidence of tumor regression in a phase 1 trial but with more severe immune-related side effects compared with ipilimumab.11 A second study on patients with stage IV melanoma treated with tremelimumab as first-line therapy in comparison with dacarbazine demonstrated differences in OS that were not statistically significant, though there was a longer duration of an objective response in patients treated with tremelimumab (35.8 months) compared with patients responding to dacarbazine (13.7 months).12
Anti–PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
PD-1 is a transmembrane protein with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory signaling, identified as an apoptosis-associated molecule.13 Upon activation, it is expressed on the cell surface of CD4, CD8, B lymphocytes, natural killer cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells.14 PD-L1, the ligand of PD-1, is constitutively expressed on different hematopoietic cells, as well as on fibroblasts, endothelial cells, mesenchymal cells, neurons, and keratinocytes.15,16 Reactivation of effector T lymphocytes by PD-1:PD-L1 pathway inhibition has shown clinically significant therapeutic relevance.17 The PD-1:PD-L1 interaction is active only in the presence of T- or B-cell antigen receptor cross-link. This interaction prevents PI3K/AKT signaling and MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway activation with the net result of lymphocytic functional exhaustion.18,19 PD-L1 blockade is shown to have better clinical benefit and minor toxicity compared to anti–CTLA-4 therapy. Treatment with anti-PD1 nivolumab in a phase 1b clinical trial (N=107) demonstrated highly specific action, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in 32% of patients with advanced melanoma.20 These promising results led to the FDA approval of nivolumab for the treatment of patients with advanced and unresponsive melanoma. A recent clinical trial combining ipilimumab and nivolumab resulted in an impressive increase of PFS compared with ipilimumab monotherapy (11.5 months vs 2.9 months).21 Similarly, treatment with pembrolizumab in advanced melanoma demonstrated improvement in PFS and OS compared with anti–CTLA-4 therapy,22,23 which resulted in FDA approval of pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced melanoma in patients previously treated with ipilimumab or BRAF inhibitors in BRAF V600 mutation–positive patients.24
Lymphocyte-Activated Gene 3–Targeted Therapies
Nanotechnology in Melanoma Therapy
The use of nanotechnology represents one of the newer alternative therapies employed for treatment of melanoma and is especially gaining interest due to reduced adverse effects in comparison with other conventional treatments for melanoma. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems precisely target tumor cells and improve the effect of both the conventional and innovative antineoplastic treatment.27,31 Tumor vasculature differs from normal tissues by being discontinuous and having interspersed small gaps/holes that allow nanoparticles to exit the circulation and enter and accumulate in the tumor tissue, leading to enhanced and targeted release of the antineoplastic drug to tumor cells.32 This mechanism is called the enhanced permeability and retention effect.33
Another mechanism by which nanoparticles work is ligand-based targeting in which ligands such as monoclonal antibodies, peptides, and nucleic acids located on the surface of nanoparticles can bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of tumor cells and lead to targeted delivery of the drug.34 Nanomaterials used for melanoma treatment include vesicular systems such as liposomes and niosomes, polymeric nanoparticles, noble metal-based nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, dendrimers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructures, lipid carriers, and microneedles. In melanoma, nanoparticles can be used to enhance targeted delivery of drugs, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Cai et al35 described usage of scaffolds in delivery systems. Tumor-associated antigens, adjuvant drugs, and chemical agents that influence the tumor microenvironment can be loaded onto these scaffolding agents. In a study by Zhu et al,36 photosensitizer chlorin e6 and immunoadjuvant aluminum hydroxide were used as a novel nanosystem that effectively destroyed tumor cells and induced a strong systemic antitumor response. IL-2 is a cytokine produced by B or T lymphocytes. Its use in melanoma has been limited by a severe adverse effect profile and lack of complete response in most patients. Cytokine-containing nanogels have been found to selectively release IL-2 in response to activation of T-cell receptors, and a mouse model in melanoma showed better response compared to free IL-1 and no adverse systemic effects.37
Nanovaccines represent another interesting novel immunotherapy modality. A study by Conniot et al38 showed that nanoparticles can be used in the treatment of melanoma. Nanoparticles made of biodegradable polymer were loaded with Melan-A/MART-1 (26–35 A27L) MHC class I-restricted peptide (MHC class I antigen), and the limited peptide MHC class II Melan-A/MART-1 51–73 (MHC class II antigen) and grafted with mannose that was then combined with an anti–PD-L1 antibody and injected into mouse models. This combination resulted in T-cell infiltration at early stages and increased infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Ibrutinib, a myeloid-derived suppressor cell inhibitor, was added and demonstrated marked tumor remission and prolonged survival.38
Overexpression of certain microRNAs (miRNAs), especially miR-204-5p and miR-199b-5p, has been shown to inhibit growth of melanoma cells in vitro, both alone and in combination with MAPK inhibitors, but these miRNAs are easily degradable in body fluids. Lipid nanoparticles can bind these miRNAs and have been shown to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and improve efficacy of BRAF and MEK inhibitors.39
Triple-Combination Therapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti–PD-1 or anti–CTLA-4 drugs have become the standard of care in treatment of advanced melanoma. Approximately 40% to 50% of cases of melanoma harbor BRAF mutations, and patients with these mutations could benefit from BRAF and MEK inhibitors. Data from clinical trials on BRAF and MEK inhibitors even showed initial high objective response rates, but the response was short-lived, and there was frequent acquired resistance.40 With ICIs, the major limitation was primary resistance, with only 50% of patients initially responding.41 Studies on murine models demonstrated that BRAF-mutated tumors had decreased expression of IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor α, and CD40 ligand on CD4+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and increased accumulation of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, leading to a protumor microenvironment. BRAF and MEK pathway inhibition were found to improve intratumoral CD4+ T-cell activity, leading to improved antitumor T-cell responses.42 Because of this enhanced immune response by BRAF and MEK inhibitors, it was hypothesized and later supported by clinical research that a combination of these targeted treatments and ICIs can have a synergistic effect, leading to increased antitumor activity.43 A randomized phase 2 clinical trial (KEYNOTE-022) in which the treatment group was given pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib and the control group was treated with dabrafenib and trametinib showed increased medial OS in the treatment group vs the control group (46.3 months vs 26.3 months) and more frequent complete response in the treatment group vs the control group (20% vs 15%).44 In the IMspire150 phase 3 clinical trial, patients with advanced stage IIIC to IV BRAF-mutant melanoma were treated with either a triple combination of the PDL-1 inhibitor atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib or vemurafenib and cobimetinib. Although the objective response rate was similar in both groups, the median duration of response was longer in the triplet group compared with the doublet group (21 months vs 12.6 months). Given these results, the FDA approved the triple-combination therapy with atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib. Although triple-combination therapy has shown promising results, it is expected that there will be an increase in the frequency of treatment-related adverse effects. In the phase 3 COMBi-I study, patients with advanced stage IIIC to IV BRAF V600E mutant cutaneous melanoma were treated with either a combination of spartalizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib or just dabrafenib and trametinib. Although the objective response rates were not significantly different (69% vs 64%), there was increased frequency of treatment-related adverse effects in patients receiving triple-combination therapy.43 As more follow-up data come out of these ongoing clinical trials, benefits of triple-combination therapy and its adverse effect profile will be more definitely established.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
One of the major roadblocks in the treatment of melanoma is the failure of response to ICI with CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in a large patient population, which has resulted in the need for new biomarkers that can act as potential therapeutic targets. Further, the main underlying factor for both adjuvant and neoadjuvant approaches remains the selection of patients, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the number of patients exposed to potentially toxic treatments without gaining clinical benefit. Clinical and pathological factors (eg, Breslow thickness, ulceration, the number of positive lymph nodes) play a role in stratifying patients as per risk of recurrence.45 Similarly, peripheral blood biomarkers have been proposed as prognostic tools for high-risk stage II and III melanoma, including markers of systemic inflammation previously explored in the metastatic setting.46 However, the use of these parameters has not been validated for clinical practice. Currently, despite promising results of BRAF and MEK inhibitors and therapeutic ICIs, as well as IL-2 or interferon alfa, treatment options in metastatic melanoma are limited because of its high heterogeneity, problematic patient stratification, and high genetic mutational rate. Recently, the role of epigenetic modifications andmiRNAs in melanoma progression and metastatic spread has been described. Silencing of CDKN2A locus and encoding for p16INK4A and p14ARF by DNA methylation are noted in 27% and 57% of metastatic melanomas, respectively, which enables melanoma cells to escape from growth arrest and apoptosis generated by Rb protein and p53 pathways.47 Demethylation of these and other tumor suppressor genes with proapoptotic function (eg, RASSF1A and tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand) can restore cell death pathways, though future clinical studies in melanoma are warranted.48
- Geller AC, Clapp RW, Sober AJ, et al. Melanoma epidemic: an analysis of six decades of data from the Connecticut Tumor Registry. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:4172-4178.
- Moreira A, Heinzerling L, Bhardwaj N, et al. Current melanoma treatments: where do we stand? Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:221.
- Watson IR, Wu C-J, Zou L, et al. Genomic classification of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Res. 2015;75(15 Suppl):2972.
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2507-2516.
- Hamid O, Cowey CL, Offner M, et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of approved combination BRAF and MEK inhibitor regimens for BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:1642.
- Gutzmer R, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, et al. Atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib as first-line treatment for unresectable advanced BRAFV600 mutation-positive melanoma (IMspire150): primary analysis of the randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1835-1844.
- Reddy BY, Miller DM, Tsao H. Somatic driver mutations in melanoma. Cancer. 2017;123(suppl 11):2104-2117.
- Hodi FS, Corless CL, Giobbie-Hurder A, et al. Imatinib for melanomas harboring mutationally activated or amplified KIT arising on mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3182-3190.
- Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J. A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:65-97.
- Maverakis E, Cornelius LA, Bowen GM, et al. Metastatic melanoma—a review of current and future treatment options. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:516-524.
- Ribas A, Chesney JA, Gordon MS, et al. Safety profile and pharmacokinetic analyses of the anti-CTLA4 antibody tremelimumab administered as a one hour infusion. J Transl Med. 2012;10:1-6.
- Ribas A, Puzanov I, Dummer R, et al. Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:908-918.
- BG Neel, Gu H, Pao L. The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:284-293.
- Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, et al. Induced expression of PD‐1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992;11:3887-3895.
- Yamazaki T, Akiba H, Iwai H, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC. J Immunol. 2002;169:5538-5545.
- Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ et al. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677-704.
- Blank C, Kuball J, Voelkl S, et al. Blockade of PD‐L1 (B7‐H1) augments human tumor‐specific T cell responses in vitro. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:317-327.
- Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, et al. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9543-9553.
- Patsoukis N, Brown J, Petkova V, et al. Selective effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras pathways regulate molecular components of the cell cycle and inhibit T cell proliferation. Sci Signal. 2012;5:ra46.
- Topalian SL, Sznol M, McDermott DF, et al. Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1020-1030.
- Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:375-384.
- Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:320-330.
- Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2006-2017.
- Burns MC, O’Donnell A, Puzanov I. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Exp Opin Orphan Drugs. 2016;4:867-873.
- F Triebel. LAG-3: a regulator of T-cell and DC responses and its use in therapeutic vaccination. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:619-622.
- Maruhashi T, Sugiura D, Okazaki I-M, et al. LAG-3: from molecular functions to clinical applications. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001014.
- Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, et al. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:20-37.
- Tawbi HA, Schadendorf D, Lipson EJ, et al. Relatlimab and nivolumab versus nivolumab in untreated advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:24-34.
- US Food and Drug Administration approves first LAG-3-blocking antibody combination, Opdualag™ (nivolumab and relatlimab-rmbw), as treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Press release. Bristol Myers Squibb. March 18, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2023. https://news.bms.com/news/details/2022/U.S.-Food-and-Drug-Administration-Approves-First-LAG-3-Blocking-Antibody-Combination-Opdualag-nivolumab-and-relatlimab-rmbw-as-Treatment-for-Patients-with-Unresectable-or-Metastatic-Melanoma/default.aspx
- Zhao B-W, Zhang F-Y, Wang Y, et al. LAG3-PD1 or CTLA4-PD1 inhibition in advanced melanoma: indirect cross comparisons of the CheckMate-067 and RELATIVITY-047 trials. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:4975.
- Jin C, Wang K, Oppong-Gyebi A, et al. Application of nanotechnology in cancer diagnosis and therapy-a mini-review. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:2964-2973.
- Maeda H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2015;91:3-6.
- Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J, et al. Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor targeting. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:812-818.
- Beiu C, Giurcaneanu C, Grumezescu AM, et al. Nanosystems for improved targeted therapies in melanoma. J Clin Med. 2020;9:318.
- Cai L, Xu J, Yang Z, et al. Engineered biomaterials for cancer immunotherapy. MedComm. 2020;1:35-46.
- Zhu Y, Xue J, Chen W, et al. Albumin-biomineralized nanoparticles to synergize phototherapy and immunotherapy against melanoma. J Control Release. 2020;322:300-311.
- Zhang Y, Li N, Suh H, et al. Nanoparticle anchoring targets immune agonists to tumors enabling anti-cancer immunity without systemic toxicity. Nat Commun. 2018;9:6.
- Conniot J, Scomparin A, Peres C, et al. Immunization with mannosylated nanovaccines and inhibition of the immune-suppressing microenvironment sensitizes melanoma to immune checkpoint modulators. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14:891-901.
- Fattore L, Campani V, Ruggiero CF, et al. In vitro biophysical and biological characterization of lipid nanoparticles co-encapsulating oncosuppressors miR-199b-5p and miR-204-5p as potentiators of target therapy in metastatic melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1930.
- Welti M, Dimitriou F, Gutzmer R, et al. Triple combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors and BRAF/MEK inhibitors in BRAF V600 melanoma: current status and future perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:5489.
- Khair DO, Bax HJ, Mele S, et al. Combining immune checkpoint inhibitors: established and emerging targets and strategies to improve outcomes in melanoma. Front Immunol. 2019;10:453.
- Ho P-C, Meeth KM, Tsui Y-C, et al. Immune-based antitumor effects of BRAF inhibitors rely on signaling by CD40L and IFNγBRAF inhibitor-induced antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3205-3217.
- Dummer R, Sandhu SK, Miller WH, et al. A phase II, multicenter study of encorafenib/binimetinib followed by a rational triple-combination after progression in patients with advanced BRAF V600-mutated melanoma (LOGIC2). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15 suppl):10022.
- Ferrucci PF, Di Giacomo AM, Del Vecchio M, et al. KEYNOTE-022 part 3: a randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study of pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib in BRAF-mutant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001806.
- Madu MF, Schopman JH, Berger DM, et al. Clinical prognostic markers in stage IIIC melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116:244-251.
- Davis JL, Langan RC, Panageas KS, et al. Elevated blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: a readily available biomarker associated with death due to disease in high risk nonmetastatic melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:1989-1996.
- Freedberg DE, Rigas SH, Russak J, et al. Frequent p16-independent inactivation of p14ARF in human melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:784-795.
- Sigalotti L, Covre A, Fratta E, et al. Epigenetics of human cutaneous melanoma: setting the stage for new therapeutic strategies. J Transl Med. 2010;8:1-22.
- Geller AC, Clapp RW, Sober AJ, et al. Melanoma epidemic: an analysis of six decades of data from the Connecticut Tumor Registry. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:4172-4178.
- Moreira A, Heinzerling L, Bhardwaj N, et al. Current melanoma treatments: where do we stand? Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:221.
- Watson IR, Wu C-J, Zou L, et al. Genomic classification of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Res. 2015;75(15 Suppl):2972.
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2507-2516.
- Hamid O, Cowey CL, Offner M, et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of approved combination BRAF and MEK inhibitor regimens for BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:1642.
- Gutzmer R, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, et al. Atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib as first-line treatment for unresectable advanced BRAFV600 mutation-positive melanoma (IMspire150): primary analysis of the randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1835-1844.
- Reddy BY, Miller DM, Tsao H. Somatic driver mutations in melanoma. Cancer. 2017;123(suppl 11):2104-2117.
- Hodi FS, Corless CL, Giobbie-Hurder A, et al. Imatinib for melanomas harboring mutationally activated or amplified KIT arising on mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3182-3190.
- Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J. A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:65-97.
- Maverakis E, Cornelius LA, Bowen GM, et al. Metastatic melanoma—a review of current and future treatment options. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:516-524.
- Ribas A, Chesney JA, Gordon MS, et al. Safety profile and pharmacokinetic analyses of the anti-CTLA4 antibody tremelimumab administered as a one hour infusion. J Transl Med. 2012;10:1-6.
- Ribas A, Puzanov I, Dummer R, et al. Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:908-918.
- BG Neel, Gu H, Pao L. The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:284-293.
- Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, et al. Induced expression of PD‐1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992;11:3887-3895.
- Yamazaki T, Akiba H, Iwai H, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC. J Immunol. 2002;169:5538-5545.
- Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ et al. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677-704.
- Blank C, Kuball J, Voelkl S, et al. Blockade of PD‐L1 (B7‐H1) augments human tumor‐specific T cell responses in vitro. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:317-327.
- Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, et al. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9543-9553.
- Patsoukis N, Brown J, Petkova V, et al. Selective effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras pathways regulate molecular components of the cell cycle and inhibit T cell proliferation. Sci Signal. 2012;5:ra46.
- Topalian SL, Sznol M, McDermott DF, et al. Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1020-1030.
- Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:375-384.
- Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:320-330.
- Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2006-2017.
- Burns MC, O’Donnell A, Puzanov I. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Exp Opin Orphan Drugs. 2016;4:867-873.
- F Triebel. LAG-3: a regulator of T-cell and DC responses and its use in therapeutic vaccination. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:619-622.
- Maruhashi T, Sugiura D, Okazaki I-M, et al. LAG-3: from molecular functions to clinical applications. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001014.
- Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, et al. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:20-37.
- Tawbi HA, Schadendorf D, Lipson EJ, et al. Relatlimab and nivolumab versus nivolumab in untreated advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:24-34.
- US Food and Drug Administration approves first LAG-3-blocking antibody combination, Opdualag™ (nivolumab and relatlimab-rmbw), as treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Press release. Bristol Myers Squibb. March 18, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2023. https://news.bms.com/news/details/2022/U.S.-Food-and-Drug-Administration-Approves-First-LAG-3-Blocking-Antibody-Combination-Opdualag-nivolumab-and-relatlimab-rmbw-as-Treatment-for-Patients-with-Unresectable-or-Metastatic-Melanoma/default.aspx
- Zhao B-W, Zhang F-Y, Wang Y, et al. LAG3-PD1 or CTLA4-PD1 inhibition in advanced melanoma: indirect cross comparisons of the CheckMate-067 and RELATIVITY-047 trials. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:4975.
- Jin C, Wang K, Oppong-Gyebi A, et al. Application of nanotechnology in cancer diagnosis and therapy-a mini-review. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:2964-2973.
- Maeda H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2015;91:3-6.
- Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J, et al. Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor targeting. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:812-818.
- Beiu C, Giurcaneanu C, Grumezescu AM, et al. Nanosystems for improved targeted therapies in melanoma. J Clin Med. 2020;9:318.
- Cai L, Xu J, Yang Z, et al. Engineered biomaterials for cancer immunotherapy. MedComm. 2020;1:35-46.
- Zhu Y, Xue J, Chen W, et al. Albumin-biomineralized nanoparticles to synergize phototherapy and immunotherapy against melanoma. J Control Release. 2020;322:300-311.
- Zhang Y, Li N, Suh H, et al. Nanoparticle anchoring targets immune agonists to tumors enabling anti-cancer immunity without systemic toxicity. Nat Commun. 2018;9:6.
- Conniot J, Scomparin A, Peres C, et al. Immunization with mannosylated nanovaccines and inhibition of the immune-suppressing microenvironment sensitizes melanoma to immune checkpoint modulators. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14:891-901.
- Fattore L, Campani V, Ruggiero CF, et al. In vitro biophysical and biological characterization of lipid nanoparticles co-encapsulating oncosuppressors miR-199b-5p and miR-204-5p as potentiators of target therapy in metastatic melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1930.
- Welti M, Dimitriou F, Gutzmer R, et al. Triple combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors and BRAF/MEK inhibitors in BRAF V600 melanoma: current status and future perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:5489.
- Khair DO, Bax HJ, Mele S, et al. Combining immune checkpoint inhibitors: established and emerging targets and strategies to improve outcomes in melanoma. Front Immunol. 2019;10:453.
- Ho P-C, Meeth KM, Tsui Y-C, et al. Immune-based antitumor effects of BRAF inhibitors rely on signaling by CD40L and IFNγBRAF inhibitor-induced antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3205-3217.
- Dummer R, Sandhu SK, Miller WH, et al. A phase II, multicenter study of encorafenib/binimetinib followed by a rational triple-combination after progression in patients with advanced BRAF V600-mutated melanoma (LOGIC2). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15 suppl):10022.
- Ferrucci PF, Di Giacomo AM, Del Vecchio M, et al. KEYNOTE-022 part 3: a randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study of pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib in BRAF-mutant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001806.
- Madu MF, Schopman JH, Berger DM, et al. Clinical prognostic markers in stage IIIC melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116:244-251.
- Davis JL, Langan RC, Panageas KS, et al. Elevated blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: a readily available biomarker associated with death due to disease in high risk nonmetastatic melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:1989-1996.
- Freedberg DE, Rigas SH, Russak J, et al. Frequent p16-independent inactivation of p14ARF in human melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:784-795.
- Sigalotti L, Covre A, Fratta E, et al. Epigenetics of human cutaneous melanoma: setting the stage for new therapeutic strategies. J Transl Med. 2010;8:1-22.
Practice Points
- Immune checkpoint inhibition has resulted in a paradigm shift for the treatment of metastatic melanoma.
- Alternative therapies with novel targets such as lymphocyte-activated gene 3 aim to overcome resistance to the usual immune targets such asPD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4.
- Newer promising tools such as nanotechnology are being added to the growing armamentarium of melanoma treatment strategies.
COVID vaccination protects B cell–deficient patients through T-cell responses
TOPLINE:
In individuals with low B-cell counts, T cells have enhanced responses to COVID-19 vaccination and may help prevent severe disease after infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- How the immune systems of B cell–deficient patients respond to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination is not fully understood.
- Researchers evaluated anti–SARS-CoV-2 T-cell responses in 33 patients treated with rituximab (RTX), 12 patients with common variable immune deficiency, and 44 controls.
- The study analyzed effector and memory CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 after infection and vaccination.
TAKEAWAY:
- All B cell–deficient individuals (those treated with RTX or those with a diagnosis of common variable immune deficiency) had increased effector and memory T-cell responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, compared with controls.
- Patients treated with RTX who were vaccinated against COVID-19 had 4.8-fold reduced odds of moderate or severe disease. (These data were not available for patients with common variable immune deficiency.)
- RTX treatment was associated with a decrease in preexisting T-cell immunity in unvaccinated patients, regardless of prior infection with SARS-CoV-2.
- This association was not found in vaccinated patients treated with RTX.
IN PRACTICE:
“[These findings] provide support for vaccination in this vulnerable population and demonstrate the potential benefit of vaccine-induced CD8+ T-cell responses on reducing disease severity from SARS-CoV-2 infection in the absence of spike protein–specific antibodies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online on November 29 in Science Translational Medicine. The first author is Reza Zonozi, MD, who conducted the research while at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is now in private practice in northern Virginia.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers did not obtain specimens from patients with common variable immune deficiency after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Only a small subset of immunophenotyped participants had subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Ragon Institute of Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Harvard Medical School, the Mark and Lisa Schwartz Foundation and E. Schwartz; the Lambertus Family Foundation; and S. Edgerly and P. Edgerly. Four authors reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Merck, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In individuals with low B-cell counts, T cells have enhanced responses to COVID-19 vaccination and may help prevent severe disease after infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- How the immune systems of B cell–deficient patients respond to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination is not fully understood.
- Researchers evaluated anti–SARS-CoV-2 T-cell responses in 33 patients treated with rituximab (RTX), 12 patients with common variable immune deficiency, and 44 controls.
- The study analyzed effector and memory CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 after infection and vaccination.
TAKEAWAY:
- All B cell–deficient individuals (those treated with RTX or those with a diagnosis of common variable immune deficiency) had increased effector and memory T-cell responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, compared with controls.
- Patients treated with RTX who were vaccinated against COVID-19 had 4.8-fold reduced odds of moderate or severe disease. (These data were not available for patients with common variable immune deficiency.)
- RTX treatment was associated with a decrease in preexisting T-cell immunity in unvaccinated patients, regardless of prior infection with SARS-CoV-2.
- This association was not found in vaccinated patients treated with RTX.
IN PRACTICE:
“[These findings] provide support for vaccination in this vulnerable population and demonstrate the potential benefit of vaccine-induced CD8+ T-cell responses on reducing disease severity from SARS-CoV-2 infection in the absence of spike protein–specific antibodies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online on November 29 in Science Translational Medicine. The first author is Reza Zonozi, MD, who conducted the research while at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is now in private practice in northern Virginia.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers did not obtain specimens from patients with common variable immune deficiency after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Only a small subset of immunophenotyped participants had subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Ragon Institute of Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Harvard Medical School, the Mark and Lisa Schwartz Foundation and E. Schwartz; the Lambertus Family Foundation; and S. Edgerly and P. Edgerly. Four authors reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Merck, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In individuals with low B-cell counts, T cells have enhanced responses to COVID-19 vaccination and may help prevent severe disease after infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- How the immune systems of B cell–deficient patients respond to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination is not fully understood.
- Researchers evaluated anti–SARS-CoV-2 T-cell responses in 33 patients treated with rituximab (RTX), 12 patients with common variable immune deficiency, and 44 controls.
- The study analyzed effector and memory CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 after infection and vaccination.
TAKEAWAY:
- All B cell–deficient individuals (those treated with RTX or those with a diagnosis of common variable immune deficiency) had increased effector and memory T-cell responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, compared with controls.
- Patients treated with RTX who were vaccinated against COVID-19 had 4.8-fold reduced odds of moderate or severe disease. (These data were not available for patients with common variable immune deficiency.)
- RTX treatment was associated with a decrease in preexisting T-cell immunity in unvaccinated patients, regardless of prior infection with SARS-CoV-2.
- This association was not found in vaccinated patients treated with RTX.
IN PRACTICE:
“[These findings] provide support for vaccination in this vulnerable population and demonstrate the potential benefit of vaccine-induced CD8+ T-cell responses on reducing disease severity from SARS-CoV-2 infection in the absence of spike protein–specific antibodies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online on November 29 in Science Translational Medicine. The first author is Reza Zonozi, MD, who conducted the research while at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is now in private practice in northern Virginia.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers did not obtain specimens from patients with common variable immune deficiency after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Only a small subset of immunophenotyped participants had subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Ragon Institute of Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Harvard Medical School, the Mark and Lisa Schwartz Foundation and E. Schwartz; the Lambertus Family Foundation; and S. Edgerly and P. Edgerly. Four authors reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Merck, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rheumatology Match Day results for 2024 follow trends of past years
While adult rheumatology programs continue to have high match rates, pediatric rheumatology programs remain less popular.
The National Residency Matching Program (NRMP) reported on Nov. 29 that rheumatology filled 124 of 127 programs (97.6%), with 273 (98.9%) of 276 positions filled. Comparatively, pediatric rheumatology filled 21 out of 38 programs (55%) and 32 (61.5%) of 52 positions.
This year, the number of programs and positions across all specialties rose by 3%, whereas the number of applications only rose by 0.4% (35 additional applicants).
“The growth of fellowship programs and positions in the Match reflect training opportunities and the future workforce trends of medical subspecialties,” said NRMP President Donna Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, in a statement. “While the increase in applicant numbers did not keep pace with the increase in positions this year, the Match rate for applicants remains strong at 82%.”
In adult rheumatology, matched applicants included 117 MD graduates, 86 foreign applicants, 38 DO graduates, and 32 U.S. citizen international medical graduates. A total of 348 applicants preferred the specialty, and 78% matched to rheumatology, whereas 2% matched to a different specialty. Another 70 applicants (20%) did not match to any program.
In pediatric rheumatology, matched applicants included 23 MD graduates, 6 DO graduates, and 3 foreign applicants. All applicants who preferred pediatric rheumatology matched to a program.
Adult rheumatology was one of several specialties that filled over 95% of positions. The other specialties that matched at that rate were allergy and immunology, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology, critical care medicine, gastroenterology, hematology and oncology, and pulmonary/critical care. Interventional Pulmonology and Oncology was the only specialty to achieve a 100% fill rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While adult rheumatology programs continue to have high match rates, pediatric rheumatology programs remain less popular.
The National Residency Matching Program (NRMP) reported on Nov. 29 that rheumatology filled 124 of 127 programs (97.6%), with 273 (98.9%) of 276 positions filled. Comparatively, pediatric rheumatology filled 21 out of 38 programs (55%) and 32 (61.5%) of 52 positions.
This year, the number of programs and positions across all specialties rose by 3%, whereas the number of applications only rose by 0.4% (35 additional applicants).
“The growth of fellowship programs and positions in the Match reflect training opportunities and the future workforce trends of medical subspecialties,” said NRMP President Donna Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, in a statement. “While the increase in applicant numbers did not keep pace with the increase in positions this year, the Match rate for applicants remains strong at 82%.”
In adult rheumatology, matched applicants included 117 MD graduates, 86 foreign applicants, 38 DO graduates, and 32 U.S. citizen international medical graduates. A total of 348 applicants preferred the specialty, and 78% matched to rheumatology, whereas 2% matched to a different specialty. Another 70 applicants (20%) did not match to any program.
In pediatric rheumatology, matched applicants included 23 MD graduates, 6 DO graduates, and 3 foreign applicants. All applicants who preferred pediatric rheumatology matched to a program.
Adult rheumatology was one of several specialties that filled over 95% of positions. The other specialties that matched at that rate were allergy and immunology, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology, critical care medicine, gastroenterology, hematology and oncology, and pulmonary/critical care. Interventional Pulmonology and Oncology was the only specialty to achieve a 100% fill rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While adult rheumatology programs continue to have high match rates, pediatric rheumatology programs remain less popular.
The National Residency Matching Program (NRMP) reported on Nov. 29 that rheumatology filled 124 of 127 programs (97.6%), with 273 (98.9%) of 276 positions filled. Comparatively, pediatric rheumatology filled 21 out of 38 programs (55%) and 32 (61.5%) of 52 positions.
This year, the number of programs and positions across all specialties rose by 3%, whereas the number of applications only rose by 0.4% (35 additional applicants).
“The growth of fellowship programs and positions in the Match reflect training opportunities and the future workforce trends of medical subspecialties,” said NRMP President Donna Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, in a statement. “While the increase in applicant numbers did not keep pace with the increase in positions this year, the Match rate for applicants remains strong at 82%.”
In adult rheumatology, matched applicants included 117 MD graduates, 86 foreign applicants, 38 DO graduates, and 32 U.S. citizen international medical graduates. A total of 348 applicants preferred the specialty, and 78% matched to rheumatology, whereas 2% matched to a different specialty. Another 70 applicants (20%) did not match to any program.
In pediatric rheumatology, matched applicants included 23 MD graduates, 6 DO graduates, and 3 foreign applicants. All applicants who preferred pediatric rheumatology matched to a program.
Adult rheumatology was one of several specialties that filled over 95% of positions. The other specialties that matched at that rate were allergy and immunology, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology, critical care medicine, gastroenterology, hematology and oncology, and pulmonary/critical care. Interventional Pulmonology and Oncology was the only specialty to achieve a 100% fill rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telemedicine not yet on par with in-person visits for rheumatology patients
TOPLINE:
Patients report higher satisfaction with in-person rheumatology visits over telemedicine appointments, according to new research.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators recruited established patients at rheumatology clinics at two tertiary medical centers (the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the University of California, San Francisco) from August 2021 to November 2022.
- 501 patients were randomly assigned to have in-person or telehealth appointments.
- After their visits, patients rated satisfaction using a 10-point Likert scale.
- The investigators compared the two visit types with regard to high post-visit satisfaction (score of 9 or 10).
TAKEAWAY:
- 90.1% of the patients who received in-person appointments were highly satisfied with their visit, compared with 76.7% of the telemedicine group.
- Nearly half of the telemedicine group (47.7%) said they would prefer an in-person visit for their next appointment, and 55.6% of the in-person group wanted the same type of visit for their next encounter.
- Less than 1 in 5 people in either group said they preferred telemedicine for their next visit.
- There was no difference between the two groups in self-efficacy for managing medications or medication adherence.
IN PRACTICE:
There was high satisfaction in both groups, but patients tended to prefer in-person to telemedicine visits for their rheumatology care.
SOURCE:
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology by lead author Lesley E. Jackson, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population was mostly female (84%) and from one geographic area.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding was provided by the Rheumatology Research Foundation Innovative Research Award. The authors disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Pfizer, and several other biopharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients report higher satisfaction with in-person rheumatology visits over telemedicine appointments, according to new research.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators recruited established patients at rheumatology clinics at two tertiary medical centers (the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the University of California, San Francisco) from August 2021 to November 2022.
- 501 patients were randomly assigned to have in-person or telehealth appointments.
- After their visits, patients rated satisfaction using a 10-point Likert scale.
- The investigators compared the two visit types with regard to high post-visit satisfaction (score of 9 or 10).
TAKEAWAY:
- 90.1% of the patients who received in-person appointments were highly satisfied with their visit, compared with 76.7% of the telemedicine group.
- Nearly half of the telemedicine group (47.7%) said they would prefer an in-person visit for their next appointment, and 55.6% of the in-person group wanted the same type of visit for their next encounter.
- Less than 1 in 5 people in either group said they preferred telemedicine for their next visit.
- There was no difference between the two groups in self-efficacy for managing medications or medication adherence.
IN PRACTICE:
There was high satisfaction in both groups, but patients tended to prefer in-person to telemedicine visits for their rheumatology care.
SOURCE:
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology by lead author Lesley E. Jackson, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population was mostly female (84%) and from one geographic area.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding was provided by the Rheumatology Research Foundation Innovative Research Award. The authors disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Pfizer, and several other biopharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients report higher satisfaction with in-person rheumatology visits over telemedicine appointments, according to new research.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators recruited established patients at rheumatology clinics at two tertiary medical centers (the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the University of California, San Francisco) from August 2021 to November 2022.
- 501 patients were randomly assigned to have in-person or telehealth appointments.
- After their visits, patients rated satisfaction using a 10-point Likert scale.
- The investigators compared the two visit types with regard to high post-visit satisfaction (score of 9 or 10).
TAKEAWAY:
- 90.1% of the patients who received in-person appointments were highly satisfied with their visit, compared with 76.7% of the telemedicine group.
- Nearly half of the telemedicine group (47.7%) said they would prefer an in-person visit for their next appointment, and 55.6% of the in-person group wanted the same type of visit for their next encounter.
- Less than 1 in 5 people in either group said they preferred telemedicine for their next visit.
- There was no difference between the two groups in self-efficacy for managing medications or medication adherence.
IN PRACTICE:
There was high satisfaction in both groups, but patients tended to prefer in-person to telemedicine visits for their rheumatology care.
SOURCE:
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology by lead author Lesley E. Jackson, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population was mostly female (84%) and from one geographic area.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding was provided by the Rheumatology Research Foundation Innovative Research Award. The authors disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Pfizer, and several other biopharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pancreatic cystic neoplasms rarely turn cancerous, study shows
, based on a retrospective cohort study from Mayo Clinic.
These findings, if validated in a larger population, could challenge current surveillance practices for IPMNs, reported researchers who were led by Shounak Majumder, MD, a gastroenterologist in the pancreas clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Among intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) that were Fukuoka negative at baseline, fewer than 10% developed worrisome or high-risk features on follow-up. Pancreatic cancer development in IPMN was a rare event overall,” the authors wrote.
“Current international consensus guidelines for the management of IPMNs recommend image-based surveillance with the aim to detect clinical and imaging features of advanced neoplasia,” the authors wrote. Yet “there are no population-based estimates of the burden of pancreatic cancer in individuals with IPMNs or the proportion of pancreatic cancers that develop from or adjacent to an IPMN.”
Researchers aimed to address this knowledge gap with a population-based cohort study. Drawing data from the Rochester Epidemiology Project, which includes longitudinal medical records from residents of Olmsted County, Minn., investigators identified two cohorts. The first group comprised 2,114 patients 50 years old or older who had undergone abdominal CT scans between 2000 and 2015, among whom 231 (10.9%) had IPMNs. The second cohort included 320 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer between 2000 and 2019, among whom 31 (9.8%) had IPMNs.
Further analysis showed that 81% of the patients with IPMNs in the first cohort lacked Fukuoka high-risk or worrisome features. Within this subgroup, the incidence rate of pancreatic cancer per 100 years was not significantly different than among individuals without IPMNs.
“Although the risk of IPMN-PC is has been extensively described, our population-based study further demonstrates that most IPMNs did not progress in Fukuoka stage and did not transform into pancreatic cancer, a similar message was expressed by the current American Gastroenterological Association pancreatic cyst guidelines, published in 2015, and studies published in 2022 and 2016,” the investigators wrote.
Analyzing the cohort of 320 patients with pancreatic cancer showed those with IPMNs had significantly better outcomes than those without IPMNs, including longer survival and lower rate of metastatic disease upon diagnosis. These findings align with previous research, the investigators wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Stefano Crippa, MD, PhD, of Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, and colleagues offered their perspective on the findings.
“Although results of this study should be validated in larger cohorts, they represent useful clinical data from an unselected population-based cohort that helps challenge current IPMN surveillance policies that recommend lifetime active surveillance for all fit individuals,” they wrote. “Currently, we can use follow-up data from studies like this one to identify patients with IPMNs who are not at risk of progression based on clinical-radiological parameters. We can furthermore start selecting subgroups of patients with limited life expectancy due to age or comorbidities to be considered for surveillance discontinuation.”
Timothy Louis Frankel, MD, a gastrointestinal surgeon at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, specializing in malignancies, said the findings are most useful for reassuring patients who have been diagnosed with an IPMN.
“The real take-home message is that in the absence of worrisome features people [with an IPMN] should feel comfortable that their risk is no higher than the general population for developing pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Frankel said in an interview.
Before any changes to surveillance can be considered, however, Dr. Frankel echoed the investigators’ call for a larger study, noting the relatively small population, most of whom (92%) were White.
“We do know that pancreas cancer and pancreas diseases vary significantly by race,” Dr. Frankel said. “So we do need to be a little bit cautious about changing the way that we manage patients based on a fairly homogeneous subset.”
He also pointed out that two patients had IPMNs that developed increased risk over time.
“They actually went from no risk features to having features that put them at risk,” Dr. Frankel said. “Those are patients who were saved by surveillance. So I’m not sure that this study was necessarily designed to let us know if and when we can stop following these lesions.”
Study authors had no relevant disclosures. The editorial writers reported no conflicts of interest.
, based on a retrospective cohort study from Mayo Clinic.
These findings, if validated in a larger population, could challenge current surveillance practices for IPMNs, reported researchers who were led by Shounak Majumder, MD, a gastroenterologist in the pancreas clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Among intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) that were Fukuoka negative at baseline, fewer than 10% developed worrisome or high-risk features on follow-up. Pancreatic cancer development in IPMN was a rare event overall,” the authors wrote.
“Current international consensus guidelines for the management of IPMNs recommend image-based surveillance with the aim to detect clinical and imaging features of advanced neoplasia,” the authors wrote. Yet “there are no population-based estimates of the burden of pancreatic cancer in individuals with IPMNs or the proportion of pancreatic cancers that develop from or adjacent to an IPMN.”
Researchers aimed to address this knowledge gap with a population-based cohort study. Drawing data from the Rochester Epidemiology Project, which includes longitudinal medical records from residents of Olmsted County, Minn., investigators identified two cohorts. The first group comprised 2,114 patients 50 years old or older who had undergone abdominal CT scans between 2000 and 2015, among whom 231 (10.9%) had IPMNs. The second cohort included 320 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer between 2000 and 2019, among whom 31 (9.8%) had IPMNs.
Further analysis showed that 81% of the patients with IPMNs in the first cohort lacked Fukuoka high-risk or worrisome features. Within this subgroup, the incidence rate of pancreatic cancer per 100 years was not significantly different than among individuals without IPMNs.
“Although the risk of IPMN-PC is has been extensively described, our population-based study further demonstrates that most IPMNs did not progress in Fukuoka stage and did not transform into pancreatic cancer, a similar message was expressed by the current American Gastroenterological Association pancreatic cyst guidelines, published in 2015, and studies published in 2022 and 2016,” the investigators wrote.
Analyzing the cohort of 320 patients with pancreatic cancer showed those with IPMNs had significantly better outcomes than those without IPMNs, including longer survival and lower rate of metastatic disease upon diagnosis. These findings align with previous research, the investigators wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Stefano Crippa, MD, PhD, of Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, and colleagues offered their perspective on the findings.
“Although results of this study should be validated in larger cohorts, they represent useful clinical data from an unselected population-based cohort that helps challenge current IPMN surveillance policies that recommend lifetime active surveillance for all fit individuals,” they wrote. “Currently, we can use follow-up data from studies like this one to identify patients with IPMNs who are not at risk of progression based on clinical-radiological parameters. We can furthermore start selecting subgroups of patients with limited life expectancy due to age or comorbidities to be considered for surveillance discontinuation.”
Timothy Louis Frankel, MD, a gastrointestinal surgeon at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, specializing in malignancies, said the findings are most useful for reassuring patients who have been diagnosed with an IPMN.
“The real take-home message is that in the absence of worrisome features people [with an IPMN] should feel comfortable that their risk is no higher than the general population for developing pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Frankel said in an interview.
Before any changes to surveillance can be considered, however, Dr. Frankel echoed the investigators’ call for a larger study, noting the relatively small population, most of whom (92%) were White.
“We do know that pancreas cancer and pancreas diseases vary significantly by race,” Dr. Frankel said. “So we do need to be a little bit cautious about changing the way that we manage patients based on a fairly homogeneous subset.”
He also pointed out that two patients had IPMNs that developed increased risk over time.
“They actually went from no risk features to having features that put them at risk,” Dr. Frankel said. “Those are patients who were saved by surveillance. So I’m not sure that this study was necessarily designed to let us know if and when we can stop following these lesions.”
Study authors had no relevant disclosures. The editorial writers reported no conflicts of interest.
, based on a retrospective cohort study from Mayo Clinic.
These findings, if validated in a larger population, could challenge current surveillance practices for IPMNs, reported researchers who were led by Shounak Majumder, MD, a gastroenterologist in the pancreas clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“Among intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) that were Fukuoka negative at baseline, fewer than 10% developed worrisome or high-risk features on follow-up. Pancreatic cancer development in IPMN was a rare event overall,” the authors wrote.
“Current international consensus guidelines for the management of IPMNs recommend image-based surveillance with the aim to detect clinical and imaging features of advanced neoplasia,” the authors wrote. Yet “there are no population-based estimates of the burden of pancreatic cancer in individuals with IPMNs or the proportion of pancreatic cancers that develop from or adjacent to an IPMN.”
Researchers aimed to address this knowledge gap with a population-based cohort study. Drawing data from the Rochester Epidemiology Project, which includes longitudinal medical records from residents of Olmsted County, Minn., investigators identified two cohorts. The first group comprised 2,114 patients 50 years old or older who had undergone abdominal CT scans between 2000 and 2015, among whom 231 (10.9%) had IPMNs. The second cohort included 320 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer between 2000 and 2019, among whom 31 (9.8%) had IPMNs.
Further analysis showed that 81% of the patients with IPMNs in the first cohort lacked Fukuoka high-risk or worrisome features. Within this subgroup, the incidence rate of pancreatic cancer per 100 years was not significantly different than among individuals without IPMNs.
“Although the risk of IPMN-PC is has been extensively described, our population-based study further demonstrates that most IPMNs did not progress in Fukuoka stage and did not transform into pancreatic cancer, a similar message was expressed by the current American Gastroenterological Association pancreatic cyst guidelines, published in 2015, and studies published in 2022 and 2016,” the investigators wrote.
Analyzing the cohort of 320 patients with pancreatic cancer showed those with IPMNs had significantly better outcomes than those without IPMNs, including longer survival and lower rate of metastatic disease upon diagnosis. These findings align with previous research, the investigators wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Stefano Crippa, MD, PhD, of Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, and colleagues offered their perspective on the findings.
“Although results of this study should be validated in larger cohorts, they represent useful clinical data from an unselected population-based cohort that helps challenge current IPMN surveillance policies that recommend lifetime active surveillance for all fit individuals,” they wrote. “Currently, we can use follow-up data from studies like this one to identify patients with IPMNs who are not at risk of progression based on clinical-radiological parameters. We can furthermore start selecting subgroups of patients with limited life expectancy due to age or comorbidities to be considered for surveillance discontinuation.”
Timothy Louis Frankel, MD, a gastrointestinal surgeon at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, specializing in malignancies, said the findings are most useful for reassuring patients who have been diagnosed with an IPMN.
“The real take-home message is that in the absence of worrisome features people [with an IPMN] should feel comfortable that their risk is no higher than the general population for developing pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Frankel said in an interview.
Before any changes to surveillance can be considered, however, Dr. Frankel echoed the investigators’ call for a larger study, noting the relatively small population, most of whom (92%) were White.
“We do know that pancreas cancer and pancreas diseases vary significantly by race,” Dr. Frankel said. “So we do need to be a little bit cautious about changing the way that we manage patients based on a fairly homogeneous subset.”
He also pointed out that two patients had IPMNs that developed increased risk over time.
“They actually went from no risk features to having features that put them at risk,” Dr. Frankel said. “Those are patients who were saved by surveillance. So I’m not sure that this study was necessarily designed to let us know if and when we can stop following these lesions.”
Study authors had no relevant disclosures. The editorial writers reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Time to stop routine maintenance therapy in myeloma?
For more than 10 years, ongoing treatment with lenalidomide following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has been the unchallenged gold standard.
The new findings were from the MASTER study, published in The Lancet Haematology, along with an invited commentary by Dr. Derman. In MASTER, patients who showed no evidence of disease after transplantation and two phases of consolidation therapy had the opportunity to avoid lenalidomide maintenance.
In the lenalidomide-free group, just 9% of patients without high-risk chromosome abnormalities or just one HRCA progressed within 2 years. About 47% of patients with two or more HRCAs progressed within 2 years.
The MASTER authors concluded that modern regimens of induction plus ASCT/consolidation might be good enough for many patients. Avoiding maintenance therapy “lead to most patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma reaching an MRD [minimal residual disease]-free, treatment-free state with a low risk of disease progression.” They also cautioned that the approach was “not optimal” for high-risk patients.
“We have been indoctrinated into continuous therapy,” said lead author Luciano Costa, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “This was a reasonable approach at the time when [induction and consolidation] therapy was not as effective.”
Lenalidomide for post-ASCT maintenance became a guideline standard following a pivotal study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2012. The study showed that lenalidomide maintenance after transplantation almost doubled the time to progression (P < .001) and improved survival (P = .03).
Shaji Kumar, MD, is chair of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Multiple Myeloma Guidelines and professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Dr. Kumar said that the MASTER results alone are not sufficient to change current guidelines because the study was a single-arm, uncontrolled, phase 2 trial. However, there are “multiple reasons why we would like to stop treatment at some point in time,” Dr. Kumar said.
“Quality of life, the financial cost, and the toxicity are three main reasons why we would like to discontinue the maintenance or give maintenance only for the amount of time that a patient needs it,” Dr. Kumar added. “So then the question comes up, how do we identify the people who need long term treatment versus the people who don’t?”
“Response” in MM is conventionally classified by criteria laid down by the International Myeloma Working Group. However, the MASTER trial made use of a different measure: MRD negativity, in which myeloma cells can no longer be detected in bone-marrow aspirate at a level of 1 in 100,000 (10–5) or, in some studies, 1 in 1 million (10–6).
MRD is a rare bird in oncology: A surrogate endpoint that provides answers faster than progression-free survival or overall survival but is a reliable guide to both. In 2020 a team headed by Nikhil Munshi, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, published a large meta-analysis showing that a negative MRD in a patient with MM was significantly prognostic for both progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.33; P < .001) and overall survival (HR, 0.45; P < .001).
In an interview from 2022, Dr. Munshi explained that patients with MRD negativity are not necessarily “cured”: “Simply, physiologically, it means that if a patient has one [myeloma] cell in a million, that cell is going to take a much longer time to grow up to be myeloma.”
In MASTER, which was based at five U.S. academic medical centers, 81% of participants (96/118) achieved MRD negativity at the 10–5 cutoff. Eighty-four people (71%) had two consecutive MRD-negative results and did not go on to lenalidomide maintenance. Instead, they were monitored with lab tests every 8 weeks for the first 24 weeks and every 16 weeks thereafter and assessed for any changes in MRD after 6 months and 18 months.
The median age in MASTER was 61 years, 43% were women, and 20% were non-Hispanic Black. About 20% of participants had two or more HRCAs, 37% had one HRCA, and 43% had no HRCAs. All participants had four 28-day cycles of induction with Dara-KRd (daratumumab, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone). This was followed by ASCT and up to two phases of consolidation with Dara-KRd.
MASTER is not the only study to show that MRD-guided discontinuation of lenalidomide seems feasible in some patients. In November 2023, Spanish researchers published a study in Blood testing a combination of lenalidomide, dexamethasone, and ixazomib. The trial allowed MRD-negative patients to stop therapy after 2 years. Progression was 17.2% over the following 4 years in the group that dropped maintenance, which included high-risk patients. The authors concluded that their results “support the safety of maintenance therapy discontinuation in patients with negative MRD at 2 years.”
These two trials are conspicuous by their rarity.
Said Dr. Derman: “We haven’t done a great job until recently of designing trials that look into discontinuation.”
Both Dr. Derman and Dr. Costa raised the elephant in the room: industry funding.
“Maintenance therapy is big business,” said Dr. Derman. He added that he had experienced problems in the past obtaining industry funding for research that involved stopping therapy.
Dr. Costa, coauthor of the MASTER trial, agreed in part: “Most pharmaceutical companies do not embark on trials like this because they’re primarily doing registration trials.” MASTER garnered some industry funding, however, and Dr. Costa found that encouraging.
How much money is at stake? In other words, what are the financial savings if patients with zero to one HRCAs who are MRD negative start to take treatment holidays from lenalidomide maintenance?
In the United States in 2019 approximately 6,410 patients received ASCT. The MASTER publication stated that “around 85%” of newly diagnosed MM patients have zero to one HRCAs and that 73% of these patients were able to stop therapy in the trial. This suggests that, each year, approximately 4,000 new patients might be eligible to avoid lenalidomide after ASCT.
The price tag of lenalidomide is approximately $20,000 per month in the United States, according to Dr. Derman. A cohort of 4,000 patients avoiding lenalidomide each year represents lost revenue of $80 million per month or almost $1 billion per year. And this does not take into account patients already on lenalidomide from previous years – or sales outside the United States. The MM multiple research pipeline reflects a lack of enthusiasm for paring down maintenance.
There are currently 229 interventional clinical studies in MM taking place nationwide. Of these, just three trials are testing what happens when patients stop therapy in the post-ASCT setting and none of the three is sponsored by industry (NCT04108624, NCT05091372, and NCT04071457). (All data from clinicaltrials.gov; search covered phase 2, 3, or 4 studies still accruing data; descriptions hand-checked; search terms: maintenance/consolidation/post-ASCT.)
Dr. Derman said that it is “incumbent on investigators” to carry out the studies to identify who is eligible to stop therapy because industry is “probably always going to err on the side of treating more.”
Sergio Giralt, MD, head of the adult bone marrow transplant service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, was an author of the key 2012 study that enshrined lenalidomide maintenance in the guidelines. Dr. Giralt expressed concerns about the single-arm design of MASTER and said he would like to see a randomized study where some patients continued treatment and others stopped.
Dr. Giralt cautioned: “If you’re MRD negative, the chances of having to deal with your disease in the next 5 years is one in five.” Physicians could certainly “have a conversation” with patients who are MRD negative about stopping therapy, but this would need to be weighed against the need for bone-marrow biopsies every 3-6 months to check progress. (In MASTER, MRD was checked at 6 and 18 months.)
Dr. Kumar believes that “we need to pursue the concept of decreasing the duration of treatment.” However, newer immunotherapies may be the answer: “Who knows? That may be the future, that we will do more of this hit-and-run approach rather than trying to keep them persistently on something.”
Dr. Derman said: “I personally think that the data is already there ... [MASTER] shows that perhaps this notion of indefinite maintenance therapy is one that really has to go by the wayside ... patients should have the option to consider with their physician [the chance to] potentially discontinue treatment.”
For 15 years, relentless lenalidomide maintenance has “quite rightly been the strongest pillar of therapy”, said Dr. Costa. “But for patients, this is not something that they easily embrace – it’s not ideal that you are going to have to take therapy for the rest of your life.”
Dr. Costa concluded: “I don’t think we had a single patient who was reluctant to stop therapy.”
Dr. Munshi reported relationships with Adaptive, Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Karyopharm, Legend, Millennium, Novartis, Pfizer, and he is the scientific founder of Oncopep and DCT. Dr. Derman disclosed ties with Janssen, Cota, and BMS. Dr. Costa reported ties with Amgen, Cota, Janssen, BMS, AbbVie, Ionis, Genentech, Sanofi, Karyopharm, AstraZeneca, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Takeda, and Pfizer. Dr. Kumar declared relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GlaxoSmithKline, Karyopharm, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and BeiGene. Dr. Giralt reported ties with Amgen, CSL Behring, Caladrius, Celgene, Ceramedix, ExpertConnect, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Karyopharm, Kite Pharmaceuticals, Magnolia Innovation, Novartis, Omeros, Pfizer, Physicians’ Education Resource, Sanofi, TRM Oncology, and Xcenda.
For more than 10 years, ongoing treatment with lenalidomide following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has been the unchallenged gold standard.
The new findings were from the MASTER study, published in The Lancet Haematology, along with an invited commentary by Dr. Derman. In MASTER, patients who showed no evidence of disease after transplantation and two phases of consolidation therapy had the opportunity to avoid lenalidomide maintenance.
In the lenalidomide-free group, just 9% of patients without high-risk chromosome abnormalities or just one HRCA progressed within 2 years. About 47% of patients with two or more HRCAs progressed within 2 years.
The MASTER authors concluded that modern regimens of induction plus ASCT/consolidation might be good enough for many patients. Avoiding maintenance therapy “lead to most patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma reaching an MRD [minimal residual disease]-free, treatment-free state with a low risk of disease progression.” They also cautioned that the approach was “not optimal” for high-risk patients.
“We have been indoctrinated into continuous therapy,” said lead author Luciano Costa, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “This was a reasonable approach at the time when [induction and consolidation] therapy was not as effective.”
Lenalidomide for post-ASCT maintenance became a guideline standard following a pivotal study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2012. The study showed that lenalidomide maintenance after transplantation almost doubled the time to progression (P < .001) and improved survival (P = .03).
Shaji Kumar, MD, is chair of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Multiple Myeloma Guidelines and professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Dr. Kumar said that the MASTER results alone are not sufficient to change current guidelines because the study was a single-arm, uncontrolled, phase 2 trial. However, there are “multiple reasons why we would like to stop treatment at some point in time,” Dr. Kumar said.
“Quality of life, the financial cost, and the toxicity are three main reasons why we would like to discontinue the maintenance or give maintenance only for the amount of time that a patient needs it,” Dr. Kumar added. “So then the question comes up, how do we identify the people who need long term treatment versus the people who don’t?”
“Response” in MM is conventionally classified by criteria laid down by the International Myeloma Working Group. However, the MASTER trial made use of a different measure: MRD negativity, in which myeloma cells can no longer be detected in bone-marrow aspirate at a level of 1 in 100,000 (10–5) or, in some studies, 1 in 1 million (10–6).
MRD is a rare bird in oncology: A surrogate endpoint that provides answers faster than progression-free survival or overall survival but is a reliable guide to both. In 2020 a team headed by Nikhil Munshi, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, published a large meta-analysis showing that a negative MRD in a patient with MM was significantly prognostic for both progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.33; P < .001) and overall survival (HR, 0.45; P < .001).
In an interview from 2022, Dr. Munshi explained that patients with MRD negativity are not necessarily “cured”: “Simply, physiologically, it means that if a patient has one [myeloma] cell in a million, that cell is going to take a much longer time to grow up to be myeloma.”
In MASTER, which was based at five U.S. academic medical centers, 81% of participants (96/118) achieved MRD negativity at the 10–5 cutoff. Eighty-four people (71%) had two consecutive MRD-negative results and did not go on to lenalidomide maintenance. Instead, they were monitored with lab tests every 8 weeks for the first 24 weeks and every 16 weeks thereafter and assessed for any changes in MRD after 6 months and 18 months.
The median age in MASTER was 61 years, 43% were women, and 20% were non-Hispanic Black. About 20% of participants had two or more HRCAs, 37% had one HRCA, and 43% had no HRCAs. All participants had four 28-day cycles of induction with Dara-KRd (daratumumab, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone). This was followed by ASCT and up to two phases of consolidation with Dara-KRd.
MASTER is not the only study to show that MRD-guided discontinuation of lenalidomide seems feasible in some patients. In November 2023, Spanish researchers published a study in Blood testing a combination of lenalidomide, dexamethasone, and ixazomib. The trial allowed MRD-negative patients to stop therapy after 2 years. Progression was 17.2% over the following 4 years in the group that dropped maintenance, which included high-risk patients. The authors concluded that their results “support the safety of maintenance therapy discontinuation in patients with negative MRD at 2 years.”
These two trials are conspicuous by their rarity.
Said Dr. Derman: “We haven’t done a great job until recently of designing trials that look into discontinuation.”
Both Dr. Derman and Dr. Costa raised the elephant in the room: industry funding.
“Maintenance therapy is big business,” said Dr. Derman. He added that he had experienced problems in the past obtaining industry funding for research that involved stopping therapy.
Dr. Costa, coauthor of the MASTER trial, agreed in part: “Most pharmaceutical companies do not embark on trials like this because they’re primarily doing registration trials.” MASTER garnered some industry funding, however, and Dr. Costa found that encouraging.
How much money is at stake? In other words, what are the financial savings if patients with zero to one HRCAs who are MRD negative start to take treatment holidays from lenalidomide maintenance?
In the United States in 2019 approximately 6,410 patients received ASCT. The MASTER publication stated that “around 85%” of newly diagnosed MM patients have zero to one HRCAs and that 73% of these patients were able to stop therapy in the trial. This suggests that, each year, approximately 4,000 new patients might be eligible to avoid lenalidomide after ASCT.
The price tag of lenalidomide is approximately $20,000 per month in the United States, according to Dr. Derman. A cohort of 4,000 patients avoiding lenalidomide each year represents lost revenue of $80 million per month or almost $1 billion per year. And this does not take into account patients already on lenalidomide from previous years – or sales outside the United States. The MM multiple research pipeline reflects a lack of enthusiasm for paring down maintenance.
There are currently 229 interventional clinical studies in MM taking place nationwide. Of these, just three trials are testing what happens when patients stop therapy in the post-ASCT setting and none of the three is sponsored by industry (NCT04108624, NCT05091372, and NCT04071457). (All data from clinicaltrials.gov; search covered phase 2, 3, or 4 studies still accruing data; descriptions hand-checked; search terms: maintenance/consolidation/post-ASCT.)
Dr. Derman said that it is “incumbent on investigators” to carry out the studies to identify who is eligible to stop therapy because industry is “probably always going to err on the side of treating more.”
Sergio Giralt, MD, head of the adult bone marrow transplant service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, was an author of the key 2012 study that enshrined lenalidomide maintenance in the guidelines. Dr. Giralt expressed concerns about the single-arm design of MASTER and said he would like to see a randomized study where some patients continued treatment and others stopped.
Dr. Giralt cautioned: “If you’re MRD negative, the chances of having to deal with your disease in the next 5 years is one in five.” Physicians could certainly “have a conversation” with patients who are MRD negative about stopping therapy, but this would need to be weighed against the need for bone-marrow biopsies every 3-6 months to check progress. (In MASTER, MRD was checked at 6 and 18 months.)
Dr. Kumar believes that “we need to pursue the concept of decreasing the duration of treatment.” However, newer immunotherapies may be the answer: “Who knows? That may be the future, that we will do more of this hit-and-run approach rather than trying to keep them persistently on something.”
Dr. Derman said: “I personally think that the data is already there ... [MASTER] shows that perhaps this notion of indefinite maintenance therapy is one that really has to go by the wayside ... patients should have the option to consider with their physician [the chance to] potentially discontinue treatment.”
For 15 years, relentless lenalidomide maintenance has “quite rightly been the strongest pillar of therapy”, said Dr. Costa. “But for patients, this is not something that they easily embrace – it’s not ideal that you are going to have to take therapy for the rest of your life.”
Dr. Costa concluded: “I don’t think we had a single patient who was reluctant to stop therapy.”
Dr. Munshi reported relationships with Adaptive, Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Karyopharm, Legend, Millennium, Novartis, Pfizer, and he is the scientific founder of Oncopep and DCT. Dr. Derman disclosed ties with Janssen, Cota, and BMS. Dr. Costa reported ties with Amgen, Cota, Janssen, BMS, AbbVie, Ionis, Genentech, Sanofi, Karyopharm, AstraZeneca, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Takeda, and Pfizer. Dr. Kumar declared relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GlaxoSmithKline, Karyopharm, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and BeiGene. Dr. Giralt reported ties with Amgen, CSL Behring, Caladrius, Celgene, Ceramedix, ExpertConnect, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Karyopharm, Kite Pharmaceuticals, Magnolia Innovation, Novartis, Omeros, Pfizer, Physicians’ Education Resource, Sanofi, TRM Oncology, and Xcenda.
For more than 10 years, ongoing treatment with lenalidomide following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has been the unchallenged gold standard.
The new findings were from the MASTER study, published in The Lancet Haematology, along with an invited commentary by Dr. Derman. In MASTER, patients who showed no evidence of disease after transplantation and two phases of consolidation therapy had the opportunity to avoid lenalidomide maintenance.
In the lenalidomide-free group, just 9% of patients without high-risk chromosome abnormalities or just one HRCA progressed within 2 years. About 47% of patients with two or more HRCAs progressed within 2 years.
The MASTER authors concluded that modern regimens of induction plus ASCT/consolidation might be good enough for many patients. Avoiding maintenance therapy “lead to most patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma reaching an MRD [minimal residual disease]-free, treatment-free state with a low risk of disease progression.” They also cautioned that the approach was “not optimal” for high-risk patients.
“We have been indoctrinated into continuous therapy,” said lead author Luciano Costa, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “This was a reasonable approach at the time when [induction and consolidation] therapy was not as effective.”
Lenalidomide for post-ASCT maintenance became a guideline standard following a pivotal study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2012. The study showed that lenalidomide maintenance after transplantation almost doubled the time to progression (P < .001) and improved survival (P = .03).
Shaji Kumar, MD, is chair of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Multiple Myeloma Guidelines and professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Dr. Kumar said that the MASTER results alone are not sufficient to change current guidelines because the study was a single-arm, uncontrolled, phase 2 trial. However, there are “multiple reasons why we would like to stop treatment at some point in time,” Dr. Kumar said.
“Quality of life, the financial cost, and the toxicity are three main reasons why we would like to discontinue the maintenance or give maintenance only for the amount of time that a patient needs it,” Dr. Kumar added. “So then the question comes up, how do we identify the people who need long term treatment versus the people who don’t?”
“Response” in MM is conventionally classified by criteria laid down by the International Myeloma Working Group. However, the MASTER trial made use of a different measure: MRD negativity, in which myeloma cells can no longer be detected in bone-marrow aspirate at a level of 1 in 100,000 (10–5) or, in some studies, 1 in 1 million (10–6).
MRD is a rare bird in oncology: A surrogate endpoint that provides answers faster than progression-free survival or overall survival but is a reliable guide to both. In 2020 a team headed by Nikhil Munshi, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, published a large meta-analysis showing that a negative MRD in a patient with MM was significantly prognostic for both progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.33; P < .001) and overall survival (HR, 0.45; P < .001).
In an interview from 2022, Dr. Munshi explained that patients with MRD negativity are not necessarily “cured”: “Simply, physiologically, it means that if a patient has one [myeloma] cell in a million, that cell is going to take a much longer time to grow up to be myeloma.”
In MASTER, which was based at five U.S. academic medical centers, 81% of participants (96/118) achieved MRD negativity at the 10–5 cutoff. Eighty-four people (71%) had two consecutive MRD-negative results and did not go on to lenalidomide maintenance. Instead, they were monitored with lab tests every 8 weeks for the first 24 weeks and every 16 weeks thereafter and assessed for any changes in MRD after 6 months and 18 months.
The median age in MASTER was 61 years, 43% were women, and 20% were non-Hispanic Black. About 20% of participants had two or more HRCAs, 37% had one HRCA, and 43% had no HRCAs. All participants had four 28-day cycles of induction with Dara-KRd (daratumumab, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone). This was followed by ASCT and up to two phases of consolidation with Dara-KRd.
MASTER is not the only study to show that MRD-guided discontinuation of lenalidomide seems feasible in some patients. In November 2023, Spanish researchers published a study in Blood testing a combination of lenalidomide, dexamethasone, and ixazomib. The trial allowed MRD-negative patients to stop therapy after 2 years. Progression was 17.2% over the following 4 years in the group that dropped maintenance, which included high-risk patients. The authors concluded that their results “support the safety of maintenance therapy discontinuation in patients with negative MRD at 2 years.”
These two trials are conspicuous by their rarity.
Said Dr. Derman: “We haven’t done a great job until recently of designing trials that look into discontinuation.”
Both Dr. Derman and Dr. Costa raised the elephant in the room: industry funding.
“Maintenance therapy is big business,” said Dr. Derman. He added that he had experienced problems in the past obtaining industry funding for research that involved stopping therapy.
Dr. Costa, coauthor of the MASTER trial, agreed in part: “Most pharmaceutical companies do not embark on trials like this because they’re primarily doing registration trials.” MASTER garnered some industry funding, however, and Dr. Costa found that encouraging.
How much money is at stake? In other words, what are the financial savings if patients with zero to one HRCAs who are MRD negative start to take treatment holidays from lenalidomide maintenance?
In the United States in 2019 approximately 6,410 patients received ASCT. The MASTER publication stated that “around 85%” of newly diagnosed MM patients have zero to one HRCAs and that 73% of these patients were able to stop therapy in the trial. This suggests that, each year, approximately 4,000 new patients might be eligible to avoid lenalidomide after ASCT.
The price tag of lenalidomide is approximately $20,000 per month in the United States, according to Dr. Derman. A cohort of 4,000 patients avoiding lenalidomide each year represents lost revenue of $80 million per month or almost $1 billion per year. And this does not take into account patients already on lenalidomide from previous years – or sales outside the United States. The MM multiple research pipeline reflects a lack of enthusiasm for paring down maintenance.
There are currently 229 interventional clinical studies in MM taking place nationwide. Of these, just three trials are testing what happens when patients stop therapy in the post-ASCT setting and none of the three is sponsored by industry (NCT04108624, NCT05091372, and NCT04071457). (All data from clinicaltrials.gov; search covered phase 2, 3, or 4 studies still accruing data; descriptions hand-checked; search terms: maintenance/consolidation/post-ASCT.)
Dr. Derman said that it is “incumbent on investigators” to carry out the studies to identify who is eligible to stop therapy because industry is “probably always going to err on the side of treating more.”
Sergio Giralt, MD, head of the adult bone marrow transplant service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, was an author of the key 2012 study that enshrined lenalidomide maintenance in the guidelines. Dr. Giralt expressed concerns about the single-arm design of MASTER and said he would like to see a randomized study where some patients continued treatment and others stopped.
Dr. Giralt cautioned: “If you’re MRD negative, the chances of having to deal with your disease in the next 5 years is one in five.” Physicians could certainly “have a conversation” with patients who are MRD negative about stopping therapy, but this would need to be weighed against the need for bone-marrow biopsies every 3-6 months to check progress. (In MASTER, MRD was checked at 6 and 18 months.)
Dr. Kumar believes that “we need to pursue the concept of decreasing the duration of treatment.” However, newer immunotherapies may be the answer: “Who knows? That may be the future, that we will do more of this hit-and-run approach rather than trying to keep them persistently on something.”
Dr. Derman said: “I personally think that the data is already there ... [MASTER] shows that perhaps this notion of indefinite maintenance therapy is one that really has to go by the wayside ... patients should have the option to consider with their physician [the chance to] potentially discontinue treatment.”
For 15 years, relentless lenalidomide maintenance has “quite rightly been the strongest pillar of therapy”, said Dr. Costa. “But for patients, this is not something that they easily embrace – it’s not ideal that you are going to have to take therapy for the rest of your life.”
Dr. Costa concluded: “I don’t think we had a single patient who was reluctant to stop therapy.”
Dr. Munshi reported relationships with Adaptive, Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Karyopharm, Legend, Millennium, Novartis, Pfizer, and he is the scientific founder of Oncopep and DCT. Dr. Derman disclosed ties with Janssen, Cota, and BMS. Dr. Costa reported ties with Amgen, Cota, Janssen, BMS, AbbVie, Ionis, Genentech, Sanofi, Karyopharm, AstraZeneca, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Takeda, and Pfizer. Dr. Kumar declared relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GlaxoSmithKline, Karyopharm, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and BeiGene. Dr. Giralt reported ties with Amgen, CSL Behring, Caladrius, Celgene, Ceramedix, ExpertConnect, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Karyopharm, Kite Pharmaceuticals, Magnolia Innovation, Novartis, Omeros, Pfizer, Physicians’ Education Resource, Sanofi, TRM Oncology, and Xcenda.
Neutrophilic Dermatosis of the Dorsal Hand: A Distinctive Variant of Sweet Syndrome
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is an uncommon reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a painful, enlarging, ulcerative nodule. It often is misdiagnosed and initially treated as an infection. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, it is associated with underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, and malignancies. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is considered a subset of Sweet syndrome (SS); we highlight similarities and differences between NDDH and SS, reporting the case of a 66-year-old man without systemic symptoms who developed NDDH on the right hand.
A 66-year-old man presented with a progressively enlarging, painful, ulcerative, 2-cm nodule on the right hand following mechanical trauma 2 weeks prior (Figure 1). He was afebrile with no remarkable medical history. Laboratory evaluation revealed an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 20 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 3.52 mg/dL (reference range, 0-0.5 mg/dL) without leukocytosis; both were not remarkably elevated when adjusted for age.1,2 The clinical differential diagnosis was broad and included pyoderma with evolving cellulitis, neutrophilic dermatosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, subcutaneous or deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma, and metastasis. Due to the rapid development of the lesion, initial treatment focused on a bacterial infection, but there was no improvement on antibiotics and wound cultures were negative. The ulcerative nodule was biopsied, and histopathology demonstrated abundant neutrophilic inflammation, endothelial swelling, and leukocytoclasis without microorganisms (Figure 2). Tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative. A diagnosis of NDDH was made based on clinical and histologic findings. The wound improved with a 3-week course of oral prednisone.
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is a subset of reactive neutrophilic dermatoses, which includes SS (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) and pyoderma gangrenosum. It is described as a localized variant of SS, with similar associated underlying inflammatory, neoplastic conditions and laboratory findings.3 However, NDDH has characteristic features that differ from classic SS. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand typically presents as painful papules, pustules, or ulcers that progress to become larger ulcers, plaques, and nodules. The clinical appearance may more closely resemble pyoderma gangrenosum or atypical SS, with ulceration frequently present. Pathergy also may be demonstrated in NDDH, similar to our patient. The average age of presentation for NDDH is 60 years, which is older than the average age for SS or pyoderma gangrenosum.3 Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, NDDH responds well to oral steroids or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants such as dapsone, colchicine, azathioprine, or tetracycline antibiotics.4
The criteria for SS are well established5,6 and may be used for the diagnosis of NDDH, taking into account the localization of lesions to the dorsal aspect of the hands. The diagnostic criteria for SS include fulfillment of both major and at least 2 of 4 minor criteria. The 2 major criteria include rapid presentation of skin lesions and neutrophilic dermal infiltrate on biopsy. Minor criteria are defined as the following: (1) preceding nonspecific respiratory or gastrointestinal tract infection, inflammatory conditions, underlying malignancy, or pregnancy; (2) fever; (3) excellent response to steroids; and (4) 3 of the 4 of the following laboratory abnormalities: elevated CRP, ESR, leukocytosis, or left shift in complete blood cell count. Our patient met both major criteria and only 1 minor criterion—excellent response to systemic corticosteroids. Nofal et al7 advocated for revised diagnostic criteria for SS, with one suggestion utilizing only the 2 major criteria being necessary for diagnosis. Given that serum inflammatory markers may not be as elevated in NDDH compared to SS,3,7,8 meeting the major criteria alone may be a better way to diagnose NDDH, as in our patient.
Our patient presented with an expanding ulcerating nodule on the hand that elicited a wide list of differential diagnoses to include infections and neoplasms. Rapid development, localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, and treatment resistance to antibiotics may help the clinician consider a diagnosis of NDDH, which should be confirmed by a biopsy. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, an underlying malignancy or inflammatory condition should be sought out. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand responds well to systemic steroids, though recurrences may occur.
- Miller A, Green M, Robinson D. Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med (Clinical Res Ed). 1983;286:226.
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik A, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Zielenkiewicz M, et al. Inflammatory markers change with age, but do not fall beyond reported normal ranges. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64:249-254.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Gaulding J, Kohen LL. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76(6 suppl 1):AB178.
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-356.
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Nofal A, Abdelmaksoud A, Amer H, et al. Sweet’s syndrome: diagnostic criteria revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:1081-1088.
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Acral manifestations of Sweet syndrome (neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands). Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:81-84.
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is an uncommon reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a painful, enlarging, ulcerative nodule. It often is misdiagnosed and initially treated as an infection. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, it is associated with underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, and malignancies. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is considered a subset of Sweet syndrome (SS); we highlight similarities and differences between NDDH and SS, reporting the case of a 66-year-old man without systemic symptoms who developed NDDH on the right hand.

A 66-year-old man presented with a progressively enlarging, painful, ulcerative, 2-cm nodule on the right hand following mechanical trauma 2 weeks prior (Figure 1). He was afebrile with no remarkable medical history. Laboratory evaluation revealed an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 20 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 3.52 mg/dL (reference range, 0-0.5 mg/dL) without leukocytosis; both were not remarkably elevated when adjusted for age.1,2 The clinical differential diagnosis was broad and included pyoderma with evolving cellulitis, neutrophilic dermatosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, subcutaneous or deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma, and metastasis. Due to the rapid development of the lesion, initial treatment focused on a bacterial infection, but there was no improvement on antibiotics and wound cultures were negative. The ulcerative nodule was biopsied, and histopathology demonstrated abundant neutrophilic inflammation, endothelial swelling, and leukocytoclasis without microorganisms (Figure 2). Tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative. A diagnosis of NDDH was made based on clinical and histologic findings. The wound improved with a 3-week course of oral prednisone.

Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is a subset of reactive neutrophilic dermatoses, which includes SS (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) and pyoderma gangrenosum. It is described as a localized variant of SS, with similar associated underlying inflammatory, neoplastic conditions and laboratory findings.3 However, NDDH has characteristic features that differ from classic SS. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand typically presents as painful papules, pustules, or ulcers that progress to become larger ulcers, plaques, and nodules. The clinical appearance may more closely resemble pyoderma gangrenosum or atypical SS, with ulceration frequently present. Pathergy also may be demonstrated in NDDH, similar to our patient. The average age of presentation for NDDH is 60 years, which is older than the average age for SS or pyoderma gangrenosum.3 Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, NDDH responds well to oral steroids or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants such as dapsone, colchicine, azathioprine, or tetracycline antibiotics.4
The criteria for SS are well established5,6 and may be used for the diagnosis of NDDH, taking into account the localization of lesions to the dorsal aspect of the hands. The diagnostic criteria for SS include fulfillment of both major and at least 2 of 4 minor criteria. The 2 major criteria include rapid presentation of skin lesions and neutrophilic dermal infiltrate on biopsy. Minor criteria are defined as the following: (1) preceding nonspecific respiratory or gastrointestinal tract infection, inflammatory conditions, underlying malignancy, or pregnancy; (2) fever; (3) excellent response to steroids; and (4) 3 of the 4 of the following laboratory abnormalities: elevated CRP, ESR, leukocytosis, or left shift in complete blood cell count. Our patient met both major criteria and only 1 minor criterion—excellent response to systemic corticosteroids. Nofal et al7 advocated for revised diagnostic criteria for SS, with one suggestion utilizing only the 2 major criteria being necessary for diagnosis. Given that serum inflammatory markers may not be as elevated in NDDH compared to SS,3,7,8 meeting the major criteria alone may be a better way to diagnose NDDH, as in our patient.
Our patient presented with an expanding ulcerating nodule on the hand that elicited a wide list of differential diagnoses to include infections and neoplasms. Rapid development, localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, and treatment resistance to antibiotics may help the clinician consider a diagnosis of NDDH, which should be confirmed by a biopsy. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, an underlying malignancy or inflammatory condition should be sought out. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand responds well to systemic steroids, though recurrences may occur.
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is an uncommon reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a painful, enlarging, ulcerative nodule. It often is misdiagnosed and initially treated as an infection. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, it is associated with underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, and malignancies. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is considered a subset of Sweet syndrome (SS); we highlight similarities and differences between NDDH and SS, reporting the case of a 66-year-old man without systemic symptoms who developed NDDH on the right hand.

A 66-year-old man presented with a progressively enlarging, painful, ulcerative, 2-cm nodule on the right hand following mechanical trauma 2 weeks prior (Figure 1). He was afebrile with no remarkable medical history. Laboratory evaluation revealed an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 20 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 3.52 mg/dL (reference range, 0-0.5 mg/dL) without leukocytosis; both were not remarkably elevated when adjusted for age.1,2 The clinical differential diagnosis was broad and included pyoderma with evolving cellulitis, neutrophilic dermatosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, subcutaneous or deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma, and metastasis. Due to the rapid development of the lesion, initial treatment focused on a bacterial infection, but there was no improvement on antibiotics and wound cultures were negative. The ulcerative nodule was biopsied, and histopathology demonstrated abundant neutrophilic inflammation, endothelial swelling, and leukocytoclasis without microorganisms (Figure 2). Tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative. A diagnosis of NDDH was made based on clinical and histologic findings. The wound improved with a 3-week course of oral prednisone.

Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is a subset of reactive neutrophilic dermatoses, which includes SS (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) and pyoderma gangrenosum. It is described as a localized variant of SS, with similar associated underlying inflammatory, neoplastic conditions and laboratory findings.3 However, NDDH has characteristic features that differ from classic SS. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand typically presents as painful papules, pustules, or ulcers that progress to become larger ulcers, plaques, and nodules. The clinical appearance may more closely resemble pyoderma gangrenosum or atypical SS, with ulceration frequently present. Pathergy also may be demonstrated in NDDH, similar to our patient. The average age of presentation for NDDH is 60 years, which is older than the average age for SS or pyoderma gangrenosum.3 Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, NDDH responds well to oral steroids or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants such as dapsone, colchicine, azathioprine, or tetracycline antibiotics.4
The criteria for SS are well established5,6 and may be used for the diagnosis of NDDH, taking into account the localization of lesions to the dorsal aspect of the hands. The diagnostic criteria for SS include fulfillment of both major and at least 2 of 4 minor criteria. The 2 major criteria include rapid presentation of skin lesions and neutrophilic dermal infiltrate on biopsy. Minor criteria are defined as the following: (1) preceding nonspecific respiratory or gastrointestinal tract infection, inflammatory conditions, underlying malignancy, or pregnancy; (2) fever; (3) excellent response to steroids; and (4) 3 of the 4 of the following laboratory abnormalities: elevated CRP, ESR, leukocytosis, or left shift in complete blood cell count. Our patient met both major criteria and only 1 minor criterion—excellent response to systemic corticosteroids. Nofal et al7 advocated for revised diagnostic criteria for SS, with one suggestion utilizing only the 2 major criteria being necessary for diagnosis. Given that serum inflammatory markers may not be as elevated in NDDH compared to SS,3,7,8 meeting the major criteria alone may be a better way to diagnose NDDH, as in our patient.
Our patient presented with an expanding ulcerating nodule on the hand that elicited a wide list of differential diagnoses to include infections and neoplasms. Rapid development, localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, and treatment resistance to antibiotics may help the clinician consider a diagnosis of NDDH, which should be confirmed by a biopsy. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, an underlying malignancy or inflammatory condition should be sought out. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand responds well to systemic steroids, though recurrences may occur.
- Miller A, Green M, Robinson D. Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med (Clinical Res Ed). 1983;286:226.
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik A, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Zielenkiewicz M, et al. Inflammatory markers change with age, but do not fall beyond reported normal ranges. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64:249-254.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Gaulding J, Kohen LL. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76(6 suppl 1):AB178.
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-356.
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Nofal A, Abdelmaksoud A, Amer H, et al. Sweet’s syndrome: diagnostic criteria revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:1081-1088.
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Acral manifestations of Sweet syndrome (neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands). Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:81-84.
- Miller A, Green M, Robinson D. Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med (Clinical Res Ed). 1983;286:226.
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik A, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Zielenkiewicz M, et al. Inflammatory markers change with age, but do not fall beyond reported normal ranges. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64:249-254.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Gaulding J, Kohen LL. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76(6 suppl 1):AB178.
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-356.
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Nofal A, Abdelmaksoud A, Amer H, et al. Sweet’s syndrome: diagnostic criteria revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:1081-1088.
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Acral manifestations of Sweet syndrome (neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands). Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:81-84.
Practice Points
- Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is a reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that includes Sweet syndrome (SS) and pyoderma gangrenosum.
- Localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, presence of ulcerative nodules, and older age at onset are characteristic features of NDDH.
- Meeting the major criteria alone for SS may be a more sensitive way to diagnose NDDH, as serum inflammatory markers may not be remarkably elevated in this condition.
Two novel choices for resection defect repair show similar success
shows new research presented in October at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) Annual Scientific Meeting.
“We know from previous data that defect closure is beneficial, and reduces complications such as delayed bleeding and delayed perforation,” said Salmaan A. Jawaid, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, in a presentation at the meeting.
In the past, defect closure was relatively straightforward; however, “the characteristics of these defects are evolving,” and defects are increasing in size, complexity, and number of locations, he said.
In response, management of resection defects has shifted from a one-step closure to a two-step process with approximation of the widest mucosal edges first, followed by complete resection bed closure, Dr. Jawaid said.
Two novel through the scope (TTS) tissue approximation devices used for the closure of large endoscopic resection defects – the dual-action tissue clip (DAT) and the TTS tack/suture device (TSD) – have not been directly compared on the basis of efficacy and cost, he said.
In the current study, Dr. Jawaid and colleagues randomized 56 adults undergoing tissue approximation and defect closure after endoscopic resection to DAT (31 patients) or TSD (25 patients). The patients were treated at a single center between August 2022 and May 2023 for closures of endoscopic resection defects including gastric, duodenum, and colon lesions greater than 20 mm wide and greater than 30 mm long.
The primary outcomes were technical success of tissue approximation and tissue approximation costs. Secondary outcomes were technical success of complete closure, closure costs, and speed of approximation and closure, as well as safety outcomes. Tissue approximation was defined as less than 15 mm of visible resection bed at the widest margin, and complete closure was defined as no visible resection bed.
Tissue approximation rates were not significantly different between the TSD and DAT groups (88% vs. 83.9%, P = .92). However, approximation cost was significantly lower for DAT compared to TSD ($673.1 vs. $973.6; P = .002).
Similarly, complete closure rates were not significantly different between the TSD and DAT groups (92% vs. 93.5%, P = .83), but closure cost/mm2 was significantly lower for DAT compared to TSD ($1.0/mm2 vs. $1.6/mm2; P = .002).
Notably, the three DAT failures (60%) underwent successful tissue approximation with TSD, and the single TSD failure (33%) underwent successful tissue approximation using DAT.
In terms of speed, the averages for both tissue approximation time and closure speed were significantly faster in the DAT group, compared with the TSD group (12.2 minutes vs. 4 minutes, P < .0001; 72.7 mm2/min vs. 153.5 mm2/min; P = .003).
“The DAT clip was three times faster than the TSD,” Dr. Jawaid said in his presentation. Adverse events including device-related events, post–electrocautery syndrome, and delayed bleeding were similarly low with both devices. However, the DAT can be less effective in some circumstances, such as a closed space or difficult location. In the cases of duodenal defects, TSD was able to approximate all, but DAT was unable to approximate any. Reasons for DAT clip failure in these cases included the resection bed being too large and tissue tearing upon grasping. In the TSD group, the presence of looping was associated with failures for cecum and colon defects.
Data may inform device decisions
“This was an important study conducted to evaluate the different scope devices for defect closure,” said Anita Afzali, MD, MPH, AGAF, a gastroenterologist specializing in inflammatory bowel disease and is executive vice chair of internal medicine at the University of Cincinnati.
“These devices have an impact on risk for delayed bleeding and perforation,” said Dr. Afzali, who served as moderator of the session in which the study was presented.
“With different items now available for defect closure, this randomized controlled study provides guidance on which TTS approximation device should be considered, and help determine effectiveness of defect closure,” she said.
“The results of this randomized controlled trial were very informative,” Dr. Afzali said. The data indicated that both DAT and TSD achieved similar rates of tissue approximation and complete closure, but “what was interesting was that one TSD is equivalent to two DAT for tissue approximation. Further, tissue approximation was three times faster with DAT, and complete closure costs were lower in the DAT-treated group.”
In clinical practice, “the study was able to help identify scenarios, such as resection beds involving greater than 50% circumference or defects located in the duodenum, where TSD is preferred over DAT for defect closure. These suggested scenarios are also important for clinical practice and device considerations,” Dr. Afzali said. “Additional studies with use of both devices, TSD and DAT simultaneously on a defect site may be needed to further assist endoscopists in defect management.”
The study was limited by the small size and use of data from a single center.
However, “based on our interim data, both devices are equally effective for tissue approximation of large endoscopic defects,” and facilitate complete defect closure, Dr. Jawaid said.
Ultimately, “both devices have a role,” with DAT being faster and likely more cost effective, while TSD is likely preferable for defects in the duodenum and those with a circumference greater than 50%, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Jawaid disclosed a consultancy with Boston Scientific, ConMed, CREO Speedboat, and DiLumen. Dr. Afzali disclosed numerous relationships with pharma including having served as an advisor/consultant for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Eli Lilly, and Gilead, among others.
shows new research presented in October at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) Annual Scientific Meeting.
“We know from previous data that defect closure is beneficial, and reduces complications such as delayed bleeding and delayed perforation,” said Salmaan A. Jawaid, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, in a presentation at the meeting.
In the past, defect closure was relatively straightforward; however, “the characteristics of these defects are evolving,” and defects are increasing in size, complexity, and number of locations, he said.
In response, management of resection defects has shifted from a one-step closure to a two-step process with approximation of the widest mucosal edges first, followed by complete resection bed closure, Dr. Jawaid said.
Two novel through the scope (TTS) tissue approximation devices used for the closure of large endoscopic resection defects – the dual-action tissue clip (DAT) and the TTS tack/suture device (TSD) – have not been directly compared on the basis of efficacy and cost, he said.
In the current study, Dr. Jawaid and colleagues randomized 56 adults undergoing tissue approximation and defect closure after endoscopic resection to DAT (31 patients) or TSD (25 patients). The patients were treated at a single center between August 2022 and May 2023 for closures of endoscopic resection defects including gastric, duodenum, and colon lesions greater than 20 mm wide and greater than 30 mm long.
The primary outcomes were technical success of tissue approximation and tissue approximation costs. Secondary outcomes were technical success of complete closure, closure costs, and speed of approximation and closure, as well as safety outcomes. Tissue approximation was defined as less than 15 mm of visible resection bed at the widest margin, and complete closure was defined as no visible resection bed.
Tissue approximation rates were not significantly different between the TSD and DAT groups (88% vs. 83.9%, P = .92). However, approximation cost was significantly lower for DAT compared to TSD ($673.1 vs. $973.6; P = .002).
Similarly, complete closure rates were not significantly different between the TSD and DAT groups (92% vs. 93.5%, P = .83), but closure cost/mm2 was significantly lower for DAT compared to TSD ($1.0/mm2 vs. $1.6/mm2; P = .002).
Notably, the three DAT failures (60%) underwent successful tissue approximation with TSD, and the single TSD failure (33%) underwent successful tissue approximation using DAT.
In terms of speed, the averages for both tissue approximation time and closure speed were significantly faster in the DAT group, compared with the TSD group (12.2 minutes vs. 4 minutes, P < .0001; 72.7 mm2/min vs. 153.5 mm2/min; P = .003).
“The DAT clip was three times faster than the TSD,” Dr. Jawaid said in his presentation. Adverse events including device-related events, post–electrocautery syndrome, and delayed bleeding were similarly low with both devices. However, the DAT can be less effective in some circumstances, such as a closed space or difficult location. In the cases of duodenal defects, TSD was able to approximate all, but DAT was unable to approximate any. Reasons for DAT clip failure in these cases included the resection bed being too large and tissue tearing upon grasping. In the TSD group, the presence of looping was associated with failures for cecum and colon defects.
Data may inform device decisions
“This was an important study conducted to evaluate the different scope devices for defect closure,” said Anita Afzali, MD, MPH, AGAF, a gastroenterologist specializing in inflammatory bowel disease and is executive vice chair of internal medicine at the University of Cincinnati.
“These devices have an impact on risk for delayed bleeding and perforation,” said Dr. Afzali, who served as moderator of the session in which the study was presented.
“With different items now available for defect closure, this randomized controlled study provides guidance on which TTS approximation device should be considered, and help determine effectiveness of defect closure,” she said.
“The results of this randomized controlled trial were very informative,” Dr. Afzali said. The data indicated that both DAT and TSD achieved similar rates of tissue approximation and complete closure, but “what was interesting was that one TSD is equivalent to two DAT for tissue approximation. Further, tissue approximation was three times faster with DAT, and complete closure costs were lower in the DAT-treated group.”
In clinical practice, “the study was able to help identify scenarios, such as resection beds involving greater than 50% circumference or defects located in the duodenum, where TSD is preferred over DAT for defect closure. These suggested scenarios are also important for clinical practice and device considerations,” Dr. Afzali said. “Additional studies with use of both devices, TSD and DAT simultaneously on a defect site may be needed to further assist endoscopists in defect management.”
The study was limited by the small size and use of data from a single center.
However, “based on our interim data, both devices are equally effective for tissue approximation of large endoscopic defects,” and facilitate complete defect closure, Dr. Jawaid said.
Ultimately, “both devices have a role,” with DAT being faster and likely more cost effective, while TSD is likely preferable for defects in the duodenum and those with a circumference greater than 50%, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Jawaid disclosed a consultancy with Boston Scientific, ConMed, CREO Speedboat, and DiLumen. Dr. Afzali disclosed numerous relationships with pharma including having served as an advisor/consultant for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Eli Lilly, and Gilead, among others.
shows new research presented in October at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) Annual Scientific Meeting.
“We know from previous data that defect closure is beneficial, and reduces complications such as delayed bleeding and delayed perforation,” said Salmaan A. Jawaid, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, in a presentation at the meeting.
In the past, defect closure was relatively straightforward; however, “the characteristics of these defects are evolving,” and defects are increasing in size, complexity, and number of locations, he said.
In response, management of resection defects has shifted from a one-step closure to a two-step process with approximation of the widest mucosal edges first, followed by complete resection bed closure, Dr. Jawaid said.
Two novel through the scope (TTS) tissue approximation devices used for the closure of large endoscopic resection defects – the dual-action tissue clip (DAT) and the TTS tack/suture device (TSD) – have not been directly compared on the basis of efficacy and cost, he said.
In the current study, Dr. Jawaid and colleagues randomized 56 adults undergoing tissue approximation and defect closure after endoscopic resection to DAT (31 patients) or TSD (25 patients). The patients were treated at a single center between August 2022 and May 2023 for closures of endoscopic resection defects including gastric, duodenum, and colon lesions greater than 20 mm wide and greater than 30 mm long.
The primary outcomes were technical success of tissue approximation and tissue approximation costs. Secondary outcomes were technical success of complete closure, closure costs, and speed of approximation and closure, as well as safety outcomes. Tissue approximation was defined as less than 15 mm of visible resection bed at the widest margin, and complete closure was defined as no visible resection bed.
Tissue approximation rates were not significantly different between the TSD and DAT groups (88% vs. 83.9%, P = .92). However, approximation cost was significantly lower for DAT compared to TSD ($673.1 vs. $973.6; P = .002).
Similarly, complete closure rates were not significantly different between the TSD and DAT groups (92% vs. 93.5%, P = .83), but closure cost/mm2 was significantly lower for DAT compared to TSD ($1.0/mm2 vs. $1.6/mm2; P = .002).
Notably, the three DAT failures (60%) underwent successful tissue approximation with TSD, and the single TSD failure (33%) underwent successful tissue approximation using DAT.
In terms of speed, the averages for both tissue approximation time and closure speed were significantly faster in the DAT group, compared with the TSD group (12.2 minutes vs. 4 minutes, P < .0001; 72.7 mm2/min vs. 153.5 mm2/min; P = .003).
“The DAT clip was three times faster than the TSD,” Dr. Jawaid said in his presentation. Adverse events including device-related events, post–electrocautery syndrome, and delayed bleeding were similarly low with both devices. However, the DAT can be less effective in some circumstances, such as a closed space or difficult location. In the cases of duodenal defects, TSD was able to approximate all, but DAT was unable to approximate any. Reasons for DAT clip failure in these cases included the resection bed being too large and tissue tearing upon grasping. In the TSD group, the presence of looping was associated with failures for cecum and colon defects.
Data may inform device decisions
“This was an important study conducted to evaluate the different scope devices for defect closure,” said Anita Afzali, MD, MPH, AGAF, a gastroenterologist specializing in inflammatory bowel disease and is executive vice chair of internal medicine at the University of Cincinnati.
“These devices have an impact on risk for delayed bleeding and perforation,” said Dr. Afzali, who served as moderator of the session in which the study was presented.
“With different items now available for defect closure, this randomized controlled study provides guidance on which TTS approximation device should be considered, and help determine effectiveness of defect closure,” she said.
“The results of this randomized controlled trial were very informative,” Dr. Afzali said. The data indicated that both DAT and TSD achieved similar rates of tissue approximation and complete closure, but “what was interesting was that one TSD is equivalent to two DAT for tissue approximation. Further, tissue approximation was three times faster with DAT, and complete closure costs were lower in the DAT-treated group.”
In clinical practice, “the study was able to help identify scenarios, such as resection beds involving greater than 50% circumference or defects located in the duodenum, where TSD is preferred over DAT for defect closure. These suggested scenarios are also important for clinical practice and device considerations,” Dr. Afzali said. “Additional studies with use of both devices, TSD and DAT simultaneously on a defect site may be needed to further assist endoscopists in defect management.”
The study was limited by the small size and use of data from a single center.
However, “based on our interim data, both devices are equally effective for tissue approximation of large endoscopic defects,” and facilitate complete defect closure, Dr. Jawaid said.
Ultimately, “both devices have a role,” with DAT being faster and likely more cost effective, while TSD is likely preferable for defects in the duodenum and those with a circumference greater than 50%, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Jawaid disclosed a consultancy with Boston Scientific, ConMed, CREO Speedboat, and DiLumen. Dr. Afzali disclosed numerous relationships with pharma including having served as an advisor/consultant for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Eli Lilly, and Gilead, among others.
FROM ACG 2023






