User login
Are providers asking about menstrual bleeding before/during anticoagulant therapy?
ORLANDO – A small study suggests health care providers may fail to ask patients about heavy menstrual bleeding before or during treatment with oral anticoagulants.
Researchers performed a chart review at a single center, which indicated that 60% of women were not asked about heavy menstrual bleeding before they were prescribed an oral anticoagulant.
Six months after the women started anticoagulant therapy, 29% required treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding. Charts for the remaining 71% of women contained no information about heavy menstrual bleeding.
“We were unable to distinguish between true absence of heavy menstrual bleeding and absence of reporting,” said Bethany T. Samuelson Bannow, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Dr. Samuelson Bannow presented these findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
She explained that heavy menstrual bleeding is defined as more than 80 mL of blood loss per cycle. It affects 10%-15% of women in their lifetime, and anticoagulants increase the risk of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Studies have shown that heavy menstrual bleeding occurs in 22%-65% of women treated with vitamin K agonists and 20%-27% of women treated with rivaroxaban (Blood. 2017;130[24]:2603-9). However, many anticoagulant studies don’t include heavy menstrual bleeding as an outcome.
To gain more insight, Dr. Samuelson Bannow and colleagues conducted a chart review. Their study included 236 women of reproductive age treated at Oregon Health & Science University between Jan. 1, 2012, and Dec. 31, 2018.
The patients’ median age was 37 years (range, 18-50 years). Most patients (67%) were receiving an oral anticoagulant for venous thromboembolism. The rest were on anticoagulant therapy for arterial thrombosis (6%), atrial fibrillation (6%), a mechanical valve (1%), or “other” reasons (20%).
Dr. Samuelson Bannow said the other group was “almost exclusively women who were receiving prophylaxis” postoperatively or for travel. Most women in this group were receiving rivaroxaban.
Rivaroxaban was the most commonly prescribed anticoagulant in the entire cohort (41%), followed by warfarin (34%) and apixaban (25%).
At the time of anticoagulant prescription, 12% of women reported a history of heavy menstrual bleeding, and 28% did not. For most patients – 60% – there was no discussion of menstrual history documented.
Six months after starting oral anticoagulant therapy, 29% of patients required treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding. For 71% of patients, there was no documentation on the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding was required in 33% of patients on rivaroxaban, 24% of those on apixaban, and 29% of those on warfarin, a significant difference (P less than .001).
“Rates of heavy menstrual bleeding … are higher in rivaroxaban users,” Dr. Samuelson Bannow said. “This is not the first study to demonstrate this. However, [the rate of heavy menstrual bleeding in this study] is still a lot lower than we would expect based on past levels with warfarin. This tells us we’re probably missing a lot of heavy menstrual bleeding. That’s not too surprising considering how few providers are actually asking about the menses.”
Dr. Samuelson Bannow and colleagues disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Samuelson Bannow BT et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 60.
ORLANDO – A small study suggests health care providers may fail to ask patients about heavy menstrual bleeding before or during treatment with oral anticoagulants.
Researchers performed a chart review at a single center, which indicated that 60% of women were not asked about heavy menstrual bleeding before they were prescribed an oral anticoagulant.
Six months after the women started anticoagulant therapy, 29% required treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding. Charts for the remaining 71% of women contained no information about heavy menstrual bleeding.
“We were unable to distinguish between true absence of heavy menstrual bleeding and absence of reporting,” said Bethany T. Samuelson Bannow, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Dr. Samuelson Bannow presented these findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
She explained that heavy menstrual bleeding is defined as more than 80 mL of blood loss per cycle. It affects 10%-15% of women in their lifetime, and anticoagulants increase the risk of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Studies have shown that heavy menstrual bleeding occurs in 22%-65% of women treated with vitamin K agonists and 20%-27% of women treated with rivaroxaban (Blood. 2017;130[24]:2603-9). However, many anticoagulant studies don’t include heavy menstrual bleeding as an outcome.
To gain more insight, Dr. Samuelson Bannow and colleagues conducted a chart review. Their study included 236 women of reproductive age treated at Oregon Health & Science University between Jan. 1, 2012, and Dec. 31, 2018.
The patients’ median age was 37 years (range, 18-50 years). Most patients (67%) were receiving an oral anticoagulant for venous thromboembolism. The rest were on anticoagulant therapy for arterial thrombosis (6%), atrial fibrillation (6%), a mechanical valve (1%), or “other” reasons (20%).
Dr. Samuelson Bannow said the other group was “almost exclusively women who were receiving prophylaxis” postoperatively or for travel. Most women in this group were receiving rivaroxaban.
Rivaroxaban was the most commonly prescribed anticoagulant in the entire cohort (41%), followed by warfarin (34%) and apixaban (25%).
At the time of anticoagulant prescription, 12% of women reported a history of heavy menstrual bleeding, and 28% did not. For most patients – 60% – there was no discussion of menstrual history documented.
Six months after starting oral anticoagulant therapy, 29% of patients required treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding. For 71% of patients, there was no documentation on the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding was required in 33% of patients on rivaroxaban, 24% of those on apixaban, and 29% of those on warfarin, a significant difference (P less than .001).
“Rates of heavy menstrual bleeding … are higher in rivaroxaban users,” Dr. Samuelson Bannow said. “This is not the first study to demonstrate this. However, [the rate of heavy menstrual bleeding in this study] is still a lot lower than we would expect based on past levels with warfarin. This tells us we’re probably missing a lot of heavy menstrual bleeding. That’s not too surprising considering how few providers are actually asking about the menses.”
Dr. Samuelson Bannow and colleagues disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Samuelson Bannow BT et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 60.
ORLANDO – A small study suggests health care providers may fail to ask patients about heavy menstrual bleeding before or during treatment with oral anticoagulants.
Researchers performed a chart review at a single center, which indicated that 60% of women were not asked about heavy menstrual bleeding before they were prescribed an oral anticoagulant.
Six months after the women started anticoagulant therapy, 29% required treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding. Charts for the remaining 71% of women contained no information about heavy menstrual bleeding.
“We were unable to distinguish between true absence of heavy menstrual bleeding and absence of reporting,” said Bethany T. Samuelson Bannow, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Dr. Samuelson Bannow presented these findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
She explained that heavy menstrual bleeding is defined as more than 80 mL of blood loss per cycle. It affects 10%-15% of women in their lifetime, and anticoagulants increase the risk of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Studies have shown that heavy menstrual bleeding occurs in 22%-65% of women treated with vitamin K agonists and 20%-27% of women treated with rivaroxaban (Blood. 2017;130[24]:2603-9). However, many anticoagulant studies don’t include heavy menstrual bleeding as an outcome.
To gain more insight, Dr. Samuelson Bannow and colleagues conducted a chart review. Their study included 236 women of reproductive age treated at Oregon Health & Science University between Jan. 1, 2012, and Dec. 31, 2018.
The patients’ median age was 37 years (range, 18-50 years). Most patients (67%) were receiving an oral anticoagulant for venous thromboembolism. The rest were on anticoagulant therapy for arterial thrombosis (6%), atrial fibrillation (6%), a mechanical valve (1%), or “other” reasons (20%).
Dr. Samuelson Bannow said the other group was “almost exclusively women who were receiving prophylaxis” postoperatively or for travel. Most women in this group were receiving rivaroxaban.
Rivaroxaban was the most commonly prescribed anticoagulant in the entire cohort (41%), followed by warfarin (34%) and apixaban (25%).
At the time of anticoagulant prescription, 12% of women reported a history of heavy menstrual bleeding, and 28% did not. For most patients – 60% – there was no discussion of menstrual history documented.
Six months after starting oral anticoagulant therapy, 29% of patients required treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding. For 71% of patients, there was no documentation on the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding was required in 33% of patients on rivaroxaban, 24% of those on apixaban, and 29% of those on warfarin, a significant difference (P less than .001).
“Rates of heavy menstrual bleeding … are higher in rivaroxaban users,” Dr. Samuelson Bannow said. “This is not the first study to demonstrate this. However, [the rate of heavy menstrual bleeding in this study] is still a lot lower than we would expect based on past levels with warfarin. This tells us we’re probably missing a lot of heavy menstrual bleeding. That’s not too surprising considering how few providers are actually asking about the menses.”
Dr. Samuelson Bannow and colleagues disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Samuelson Bannow BT et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 60.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Liver fibrosis scores predict CV event risk associated with NAFLD
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a prospective observational study had a twofold increase in cardiovascular events, .
At median follow-up of 41.4 months representing 3,044.4 person-years of observation in the Progression of Liver Damage and Cardiometabolic Disorders in NAFLD (PLINIO) study, 58 cardiovascular events (CVEs) were reported in 898 consecutive outpatients who were screened for liver steatosis by ultrasound. The annual rate of CVEs among 643 patients with NAFLD was 2.1%, compared with 1.0% among 255 patients without NAFLD, according to Francesco Baratta, MD, of Clinica Medica, Sapienza University of Rome, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The difference did not meet a priori thresholds for statistical significance (P = .066), but became significant after exclusion of new-onset atrial fibrillation events (annual CVE rates of 1.9% vs. 0.7%; P = .034), and on multivariate analysis, age, male sex, and NAFLD were found to be independently associated with CVE occurrence (hazard ratios, 1.07, 3.20, and 2.73, respectively), the investigators found.
In NAFLD patients, a NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) greater than 0.676 was significantly associated with CVEs after adjustment for comorbidities (HR, 2.29), and a Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score greater than 2.67, a history of cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome predicted incident CVEs (HRs, 4.57, 2.95, and 2.30, respectively). The findings were similar after exclusion of new-onset atrial fibrillation from the composite endpoint (HRs, 2.42 and 4.00, respectively).
“Furthermore, when we analyzed only patients without CVEs at baseline, we found a similar association between liver fibrosis and CVEs,” the researchers wrote, noting that the adjusted HRs for NFS were 2.50 and 4.28, respectively.
In addition to liver-related complications, patients with NAFLD are known to have an increased CVE risk, and while liver fibrosis severity is used to determine prognosis, not all patients can undergo a liver biopsy to assess fibrosis. Therefore, there is a need to identify and validate noninvasive markers of liver fibrosis, but few data exist with respect to the predictive role of noninvasive scoring on CVEs, they said.
The findings of this study suggest the use of the NFS and FIB-4 score may reduce the need for liver biopsy by identifying NAFLD patients at higher risk of having advanced liver fibrosis. They further suggest that liver fibrosis development in patients with NAFLD “may be the result of a long-term exposure to cardiometabolic risk factors such as diabetes,” and that “the concomitant presence of multiple cardiometabolic conditions may induce a chronic low-grade proinflammatory and pro-oxidant status leading to liver inflammation (i.e., macrophage activation) and collagen deposition.”
The findings may also have clinical implications: “The association between liver fibrosis and cardiovascular risk supports a potential role for statin treatment in patients with NAFLD,” they explained.
The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Baratta F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.12.026.
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a prospective observational study had a twofold increase in cardiovascular events, .
At median follow-up of 41.4 months representing 3,044.4 person-years of observation in the Progression of Liver Damage and Cardiometabolic Disorders in NAFLD (PLINIO) study, 58 cardiovascular events (CVEs) were reported in 898 consecutive outpatients who were screened for liver steatosis by ultrasound. The annual rate of CVEs among 643 patients with NAFLD was 2.1%, compared with 1.0% among 255 patients without NAFLD, according to Francesco Baratta, MD, of Clinica Medica, Sapienza University of Rome, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The difference did not meet a priori thresholds for statistical significance (P = .066), but became significant after exclusion of new-onset atrial fibrillation events (annual CVE rates of 1.9% vs. 0.7%; P = .034), and on multivariate analysis, age, male sex, and NAFLD were found to be independently associated with CVE occurrence (hazard ratios, 1.07, 3.20, and 2.73, respectively), the investigators found.
In NAFLD patients, a NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) greater than 0.676 was significantly associated with CVEs after adjustment for comorbidities (HR, 2.29), and a Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score greater than 2.67, a history of cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome predicted incident CVEs (HRs, 4.57, 2.95, and 2.30, respectively). The findings were similar after exclusion of new-onset atrial fibrillation from the composite endpoint (HRs, 2.42 and 4.00, respectively).
“Furthermore, when we analyzed only patients without CVEs at baseline, we found a similar association between liver fibrosis and CVEs,” the researchers wrote, noting that the adjusted HRs for NFS were 2.50 and 4.28, respectively.
In addition to liver-related complications, patients with NAFLD are known to have an increased CVE risk, and while liver fibrosis severity is used to determine prognosis, not all patients can undergo a liver biopsy to assess fibrosis. Therefore, there is a need to identify and validate noninvasive markers of liver fibrosis, but few data exist with respect to the predictive role of noninvasive scoring on CVEs, they said.
The findings of this study suggest the use of the NFS and FIB-4 score may reduce the need for liver biopsy by identifying NAFLD patients at higher risk of having advanced liver fibrosis. They further suggest that liver fibrosis development in patients with NAFLD “may be the result of a long-term exposure to cardiometabolic risk factors such as diabetes,” and that “the concomitant presence of multiple cardiometabolic conditions may induce a chronic low-grade proinflammatory and pro-oxidant status leading to liver inflammation (i.e., macrophage activation) and collagen deposition.”
The findings may also have clinical implications: “The association between liver fibrosis and cardiovascular risk supports a potential role for statin treatment in patients with NAFLD,” they explained.
The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Baratta F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.12.026.
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a prospective observational study had a twofold increase in cardiovascular events, .
At median follow-up of 41.4 months representing 3,044.4 person-years of observation in the Progression of Liver Damage and Cardiometabolic Disorders in NAFLD (PLINIO) study, 58 cardiovascular events (CVEs) were reported in 898 consecutive outpatients who were screened for liver steatosis by ultrasound. The annual rate of CVEs among 643 patients with NAFLD was 2.1%, compared with 1.0% among 255 patients without NAFLD, according to Francesco Baratta, MD, of Clinica Medica, Sapienza University of Rome, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The difference did not meet a priori thresholds for statistical significance (P = .066), but became significant after exclusion of new-onset atrial fibrillation events (annual CVE rates of 1.9% vs. 0.7%; P = .034), and on multivariate analysis, age, male sex, and NAFLD were found to be independently associated with CVE occurrence (hazard ratios, 1.07, 3.20, and 2.73, respectively), the investigators found.
In NAFLD patients, a NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) greater than 0.676 was significantly associated with CVEs after adjustment for comorbidities (HR, 2.29), and a Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score greater than 2.67, a history of cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome predicted incident CVEs (HRs, 4.57, 2.95, and 2.30, respectively). The findings were similar after exclusion of new-onset atrial fibrillation from the composite endpoint (HRs, 2.42 and 4.00, respectively).
“Furthermore, when we analyzed only patients without CVEs at baseline, we found a similar association between liver fibrosis and CVEs,” the researchers wrote, noting that the adjusted HRs for NFS were 2.50 and 4.28, respectively.
In addition to liver-related complications, patients with NAFLD are known to have an increased CVE risk, and while liver fibrosis severity is used to determine prognosis, not all patients can undergo a liver biopsy to assess fibrosis. Therefore, there is a need to identify and validate noninvasive markers of liver fibrosis, but few data exist with respect to the predictive role of noninvasive scoring on CVEs, they said.
The findings of this study suggest the use of the NFS and FIB-4 score may reduce the need for liver biopsy by identifying NAFLD patients at higher risk of having advanced liver fibrosis. They further suggest that liver fibrosis development in patients with NAFLD “may be the result of a long-term exposure to cardiometabolic risk factors such as diabetes,” and that “the concomitant presence of multiple cardiometabolic conditions may induce a chronic low-grade proinflammatory and pro-oxidant status leading to liver inflammation (i.e., macrophage activation) and collagen deposition.”
The findings may also have clinical implications: “The association between liver fibrosis and cardiovascular risk supports a potential role for statin treatment in patients with NAFLD,” they explained.
The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Baratta F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.12.026.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Rash on hands and feet
Lichenoid dermatoses are a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical presentations. The term “lichenoid” refers to the popular lesions of certain skin disorders of which lichen planus (LP) is the prototype. The papules are shiny, flat topped, polygonal, of different sizes, and occur in clusters creating a pattern that resembles lichen growing on a rock. Lichenoid eruptions are quite common in children and can result from many different origins. In most instances the precise mechanism of disease is not known, although it is usually believed to be immunologic in nature. Certain disorders are common in children, whereas others more often affect the adult population.
Lichen striatus, lichen nitidus (LN), and lichen spinulosus are lichenoid lesions that are more common in children than adults.
LN – as seen in the patient described here – is an uncommon benign inflammatory skin disease, primarily of children. Individual lesions are sharply demarcated, pinpoint to pinhead sized, round or polygonal, and strikingly monomorphous in nature. The papules are usually flesh colored, however, the color varies from yellow and brown to violet hues depending on the background color of the patient’s skin. This variation in color is in contrast with LP which is characteristically violaceous. The surfaces of the papules are flat, shiny, and slightly elevated. They may have a fine scale or a hyperkeratotic plug. The lesions tend to occur in groups, primarily on the abdomen, chest, glans penis, and upper extremities. The Koebner phenomenon is observed and is a hallmark for the disorder. LN is generally asymptomatic, unlike LP, which is exceedingly pruritic.
The cause of LN is unknown; however, it has been proposed that LN, in particular generalized LN, may be associated with immune alterations in the patient. The course of LN is slowly progressive with a tendency toward remission. The lesions can remain stationary for years; however, they sometimes disappear spontaneously and completely.
The differential diagnosis of LN beyond the entities discussed above includes frictional lichenoid eruption, lichenoid drug eruption, LP, and keratosis pilaris.
LP is the classic lichenoid eruption. It is rare in children and occurs most frequently in individuals aged 30-60 years. LP usually manifests as an extremely pruritic eruption of flat-topped polygonal and violaceous papules that often have fine linear white scales known as Wickham striae. The distribution is usually bilateral and symmetric with most of the papules and plaques located on the legs, flexor wrists, neck, and genitalia. The lesions may exhibit the Koebner phenomenon, appearing in a linear pattern along the site of a scratch. Generally, in childhood cases there is reported itching, and oral and nail lesions are less common.
Frictional lichenoid eruption occurs in childhood. The lesions consist of lichenoid papules with regular borders 1-2 mm in diameter that generally are asymptomatic, although they may be mildly pruritic. The papules are found in a very characteristic distribution with almost exclusive involvement of the backs of the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees with occasional involvement of the extensor forearms and cheeks. This disorder occurs in predisposed children who have been exposed to significant frictional force during play, and typically resolves spontaneously after removal of the stimulus.
Keratosis pilaris is a rash that usually is found on the outer areas of the upper arms, upper thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. It consists of small bumps that are flesh colored to red. The bumps generally don’t hurt or itch.
The lack of symptoms and spontaneous healing have rendered treatment unnecessary in most cases. LN generally is self-limiting, thus treatment may not be necessary. However, topical treatment with mid- to high-potency corticosteroids has hastened resolution of lesions in some children, as have topical dinitrochlorobenzene and systemic treatment with psoralens, astemizole, etretinate, and psoralen-UVA.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Eichenfield nor Dr. Bhatti has any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
Pickert A. Cutis. 2012 Sep;90(3):E1-3. https://mdedge-files-live.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0900300E1.pdf Tziotzios C et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Nov;79(5):789-804. Tilly JJ et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
Lichenoid dermatoses are a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical presentations. The term “lichenoid” refers to the popular lesions of certain skin disorders of which lichen planus (LP) is the prototype. The papules are shiny, flat topped, polygonal, of different sizes, and occur in clusters creating a pattern that resembles lichen growing on a rock. Lichenoid eruptions are quite common in children and can result from many different origins. In most instances the precise mechanism of disease is not known, although it is usually believed to be immunologic in nature. Certain disorders are common in children, whereas others more often affect the adult population.
Lichen striatus, lichen nitidus (LN), and lichen spinulosus are lichenoid lesions that are more common in children than adults.
LN – as seen in the patient described here – is an uncommon benign inflammatory skin disease, primarily of children. Individual lesions are sharply demarcated, pinpoint to pinhead sized, round or polygonal, and strikingly monomorphous in nature. The papules are usually flesh colored, however, the color varies from yellow and brown to violet hues depending on the background color of the patient’s skin. This variation in color is in contrast with LP which is characteristically violaceous. The surfaces of the papules are flat, shiny, and slightly elevated. They may have a fine scale or a hyperkeratotic plug. The lesions tend to occur in groups, primarily on the abdomen, chest, glans penis, and upper extremities. The Koebner phenomenon is observed and is a hallmark for the disorder. LN is generally asymptomatic, unlike LP, which is exceedingly pruritic.
The cause of LN is unknown; however, it has been proposed that LN, in particular generalized LN, may be associated with immune alterations in the patient. The course of LN is slowly progressive with a tendency toward remission. The lesions can remain stationary for years; however, they sometimes disappear spontaneously and completely.
The differential diagnosis of LN beyond the entities discussed above includes frictional lichenoid eruption, lichenoid drug eruption, LP, and keratosis pilaris.
LP is the classic lichenoid eruption. It is rare in children and occurs most frequently in individuals aged 30-60 years. LP usually manifests as an extremely pruritic eruption of flat-topped polygonal and violaceous papules that often have fine linear white scales known as Wickham striae. The distribution is usually bilateral and symmetric with most of the papules and plaques located on the legs, flexor wrists, neck, and genitalia. The lesions may exhibit the Koebner phenomenon, appearing in a linear pattern along the site of a scratch. Generally, in childhood cases there is reported itching, and oral and nail lesions are less common.
Frictional lichenoid eruption occurs in childhood. The lesions consist of lichenoid papules with regular borders 1-2 mm in diameter that generally are asymptomatic, although they may be mildly pruritic. The papules are found in a very characteristic distribution with almost exclusive involvement of the backs of the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees with occasional involvement of the extensor forearms and cheeks. This disorder occurs in predisposed children who have been exposed to significant frictional force during play, and typically resolves spontaneously after removal of the stimulus.
Keratosis pilaris is a rash that usually is found on the outer areas of the upper arms, upper thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. It consists of small bumps that are flesh colored to red. The bumps generally don’t hurt or itch.
The lack of symptoms and spontaneous healing have rendered treatment unnecessary in most cases. LN generally is self-limiting, thus treatment may not be necessary. However, topical treatment with mid- to high-potency corticosteroids has hastened resolution of lesions in some children, as have topical dinitrochlorobenzene and systemic treatment with psoralens, astemizole, etretinate, and psoralen-UVA.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Eichenfield nor Dr. Bhatti has any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
Pickert A. Cutis. 2012 Sep;90(3):E1-3. https://mdedge-files-live.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0900300E1.pdf Tziotzios C et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Nov;79(5):789-804. Tilly JJ et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
Lichenoid dermatoses are a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical presentations. The term “lichenoid” refers to the popular lesions of certain skin disorders of which lichen planus (LP) is the prototype. The papules are shiny, flat topped, polygonal, of different sizes, and occur in clusters creating a pattern that resembles lichen growing on a rock. Lichenoid eruptions are quite common in children and can result from many different origins. In most instances the precise mechanism of disease is not known, although it is usually believed to be immunologic in nature. Certain disorders are common in children, whereas others more often affect the adult population.
Lichen striatus, lichen nitidus (LN), and lichen spinulosus are lichenoid lesions that are more common in children than adults.
LN – as seen in the patient described here – is an uncommon benign inflammatory skin disease, primarily of children. Individual lesions are sharply demarcated, pinpoint to pinhead sized, round or polygonal, and strikingly monomorphous in nature. The papules are usually flesh colored, however, the color varies from yellow and brown to violet hues depending on the background color of the patient’s skin. This variation in color is in contrast with LP which is characteristically violaceous. The surfaces of the papules are flat, shiny, and slightly elevated. They may have a fine scale or a hyperkeratotic plug. The lesions tend to occur in groups, primarily on the abdomen, chest, glans penis, and upper extremities. The Koebner phenomenon is observed and is a hallmark for the disorder. LN is generally asymptomatic, unlike LP, which is exceedingly pruritic.
The cause of LN is unknown; however, it has been proposed that LN, in particular generalized LN, may be associated with immune alterations in the patient. The course of LN is slowly progressive with a tendency toward remission. The lesions can remain stationary for years; however, they sometimes disappear spontaneously and completely.
The differential diagnosis of LN beyond the entities discussed above includes frictional lichenoid eruption, lichenoid drug eruption, LP, and keratosis pilaris.
LP is the classic lichenoid eruption. It is rare in children and occurs most frequently in individuals aged 30-60 years. LP usually manifests as an extremely pruritic eruption of flat-topped polygonal and violaceous papules that often have fine linear white scales known as Wickham striae. The distribution is usually bilateral and symmetric with most of the papules and plaques located on the legs, flexor wrists, neck, and genitalia. The lesions may exhibit the Koebner phenomenon, appearing in a linear pattern along the site of a scratch. Generally, in childhood cases there is reported itching, and oral and nail lesions are less common.
Frictional lichenoid eruption occurs in childhood. The lesions consist of lichenoid papules with regular borders 1-2 mm in diameter that generally are asymptomatic, although they may be mildly pruritic. The papules are found in a very characteristic distribution with almost exclusive involvement of the backs of the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees with occasional involvement of the extensor forearms and cheeks. This disorder occurs in predisposed children who have been exposed to significant frictional force during play, and typically resolves spontaneously after removal of the stimulus.
Keratosis pilaris is a rash that usually is found on the outer areas of the upper arms, upper thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. It consists of small bumps that are flesh colored to red. The bumps generally don’t hurt or itch.
The lack of symptoms and spontaneous healing have rendered treatment unnecessary in most cases. LN generally is self-limiting, thus treatment may not be necessary. However, topical treatment with mid- to high-potency corticosteroids has hastened resolution of lesions in some children, as have topical dinitrochlorobenzene and systemic treatment with psoralens, astemizole, etretinate, and psoralen-UVA.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Eichenfield nor Dr. Bhatti has any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
Pickert A. Cutis. 2012 Sep;90(3):E1-3. https://mdedge-files-live.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0900300E1.pdf Tziotzios C et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Nov;79(5):789-804. Tilly JJ et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
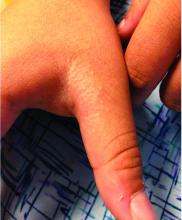
A 9-year-old healthy Kuwaiti male with no significant past medical history presents with a rash on his hands and feet that has been present for 3 years.
His mother reports that he has been seen by dermatologists in various countries and was last seen by a dermatologist in Kuwait 3 years ago. At that time, he was told that it was dryness and advised to not shower daily. Since then he has been taking showers three times weekly and using Cetaphil once weekly without improvement. He was seen by his pediatrician 6 months ago, diagnosed with xerosis, and was given hydrocortisone 2.5% to use twice daily, again without any improvement.
The rash is not itchy, and he has no oral lesions or nail involvement. Exam revealed lichenoid papules on bilateral dorsal hands and feet, bilateral upper arms, bilateral axilla, lower abdomen, and left upper chest.
Chin There, Done That—Now What?
ANSWER
The correct answer is to perform a 3-mm punch biopsy (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
When the history and physical exam fail to point to a clear diagnosis, skin biopsy can answer a very basic question: What is the pathophysiologic process associated with the lesions? The information thus obtained doesn’t always produce a blinking neon sign of a diagnosis, but at a minimum, it can rule out a great number of things, such as cancer or infection.
More often, the types of cells seen, and the patterns in which they are arranged, tell us a great deal. In this case, accumulations of monocytes, macrophages, and activated T-lymphocytes were arranged in circular patterns, but there was no evidence of necrosis (caseation), which can be seen in tubercular granulomas. Stains performed to identify mycobacterial organisms were negative. These findings established the diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis, a granulomatous disease thought to represent a reaction to an unknown antigen (eg, a microorganism) or environmental substance. It is far more common in those with darker skin types.
Although this patient’s disease was confined to the skin, sarcoidosis can affect virtually any other organ in the body—in particular, the lungs, kidneys, liver, nervous system, or even the eyes. For this reason, patients with sarcoidosis are usually referred to pulmonology for a workup intended to rule out systemic involvement and to other specialists as symptoms dictate.
Many cases of sarcoidosis remit on their own, without treatment. When treatment is initiated, the 2 most commonly used medications are systemic glucocorticoids and/or methotrexate. Both drugs have been associated with serious adverse effects and should only be prescribed by experienced providers.
This combination was prescribed for the case patient, who obtained rapid relief. Blood work (complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel) was within normal limits prior to and during treatment, and the pulmonologist pronounced her free of lung involvement.
ANSWER
The correct answer is to perform a 3-mm punch biopsy (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
When the history and physical exam fail to point to a clear diagnosis, skin biopsy can answer a very basic question: What is the pathophysiologic process associated with the lesions? The information thus obtained doesn’t always produce a blinking neon sign of a diagnosis, but at a minimum, it can rule out a great number of things, such as cancer or infection.
More often, the types of cells seen, and the patterns in which they are arranged, tell us a great deal. In this case, accumulations of monocytes, macrophages, and activated T-lymphocytes were arranged in circular patterns, but there was no evidence of necrosis (caseation), which can be seen in tubercular granulomas. Stains performed to identify mycobacterial organisms were negative. These findings established the diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis, a granulomatous disease thought to represent a reaction to an unknown antigen (eg, a microorganism) or environmental substance. It is far more common in those with darker skin types.
Although this patient’s disease was confined to the skin, sarcoidosis can affect virtually any other organ in the body—in particular, the lungs, kidneys, liver, nervous system, or even the eyes. For this reason, patients with sarcoidosis are usually referred to pulmonology for a workup intended to rule out systemic involvement and to other specialists as symptoms dictate.
Many cases of sarcoidosis remit on their own, without treatment. When treatment is initiated, the 2 most commonly used medications are systemic glucocorticoids and/or methotrexate. Both drugs have been associated with serious adverse effects and should only be prescribed by experienced providers.
This combination was prescribed for the case patient, who obtained rapid relief. Blood work (complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel) was within normal limits prior to and during treatment, and the pulmonologist pronounced her free of lung involvement.
ANSWER
The correct answer is to perform a 3-mm punch biopsy (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
When the history and physical exam fail to point to a clear diagnosis, skin biopsy can answer a very basic question: What is the pathophysiologic process associated with the lesions? The information thus obtained doesn’t always produce a blinking neon sign of a diagnosis, but at a minimum, it can rule out a great number of things, such as cancer or infection.
More often, the types of cells seen, and the patterns in which they are arranged, tell us a great deal. In this case, accumulations of monocytes, macrophages, and activated T-lymphocytes were arranged in circular patterns, but there was no evidence of necrosis (caseation), which can be seen in tubercular granulomas. Stains performed to identify mycobacterial organisms were negative. These findings established the diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis, a granulomatous disease thought to represent a reaction to an unknown antigen (eg, a microorganism) or environmental substance. It is far more common in those with darker skin types.
Although this patient’s disease was confined to the skin, sarcoidosis can affect virtually any other organ in the body—in particular, the lungs, kidneys, liver, nervous system, or even the eyes. For this reason, patients with sarcoidosis are usually referred to pulmonology for a workup intended to rule out systemic involvement and to other specialists as symptoms dictate.
Many cases of sarcoidosis remit on their own, without treatment. When treatment is initiated, the 2 most commonly used medications are systemic glucocorticoids and/or methotrexate. Both drugs have been associated with serious adverse effects and should only be prescribed by experienced providers.
This combination was prescribed for the case patient, who obtained rapid relief. Blood work (complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel) was within normal limits prior to and during treatment, and the pulmonologist pronounced her free of lung involvement.
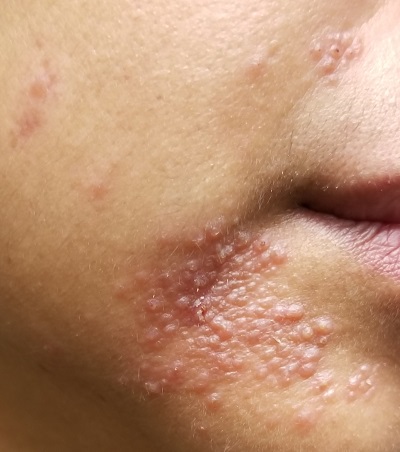
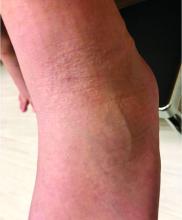
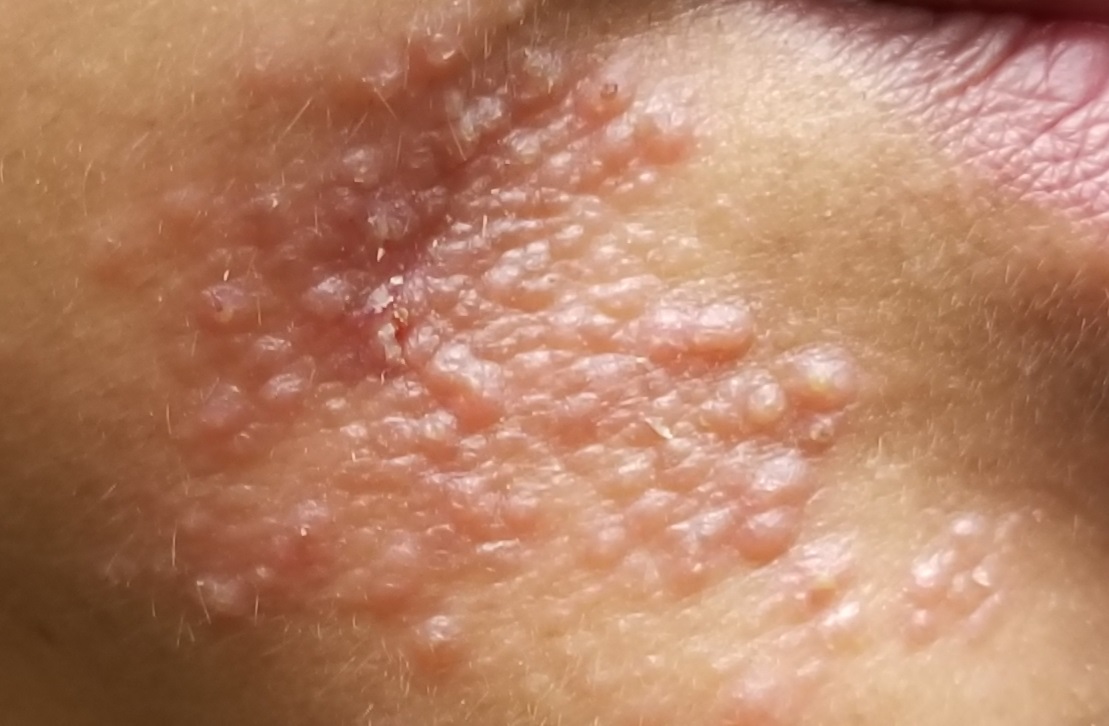
A 51-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for evaluation of a facial rash that has been present, on and off, for years. It usually affects her right chin and perioral area but occasionally manifests with smaller yet similar lesions elsewhere on the face. The lesions are slightly itchy, but the patient’s main concern is their impact on her appearance.
She has consulted several primary care providers over the years, all of whom initially diagnosed and treated for acne—to no avail. This was typically followed by a recommendation to try an OTC topical product, such as an antifungal (tolnaftate and clotrimazole), hydrocortisone 1%, or triple-antibiotic cream—again, without improvement. At no point was a biopsy suggested.
Examination reveals a dense cluster of papules covering a 5×4-cm section of the right chin and perioral area. Although the lesions appear vesicular, they are in fact solid but soft, shiny, and confluent. The papules are about the same color as her type IV skin. There are no comedones or pustules.
No adenopathy is detected in the region. There is no involvement of the adjacent oral mucosal surfaces.
The patient’s skin elsewhere is unremarkable, and in general, she appears to be in good health (certainly in no distress). She claims to be healthy otherwise, with no fever, malaise, joint pain, fatigue, or shortness of breath. No one else in her household is similarly affected.
Framingham: Exercise lessens cardiometabolic risk of poor diet
PHILADELPHIA – Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week as recommended in national guidelines appears to mitigate the cardiometabolic risks associated with poor diet quality in middle-aged and older adults, according to an analysis of Framingham Heart Study data.
“Our findings suggest adherence to physical activity guidelines may have a protective effect on cardiometabolic health regardless of diet quality,” Joowon Lee, PhD, declared at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He presented separate cross-sectional analyses of the risks of metabolic syndrome in 2,379 middle-aged participants in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored Framingham (Mass.) Third Generation Study and 1,180 older participants in the Framingham Offspring Study.
The two analyses showed the same thing across a broad age spectrum: The highest prevalence of metabolic syndrome as defined by Adult Treatment Panel III criteria was present among those individuals who got less than 150 minutes of physical activity per week and were also in the lowest tertile in terms of diet quality, while the lowest prevalence of metabolic syndrome occurred in participants in the top tertile for diet quality who engaged in at least 150 minutes per week of moderate to vigorous physical activity in accord with the Department of Health & Human Services 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
In both the middle-aged and older populations, optimal physical activity – that is, at least 150 minutes per week – appeared to override the adverse impact of suboptimal diet quality. Physically active individuals with moderate or even poor diet quality had a significantly lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome than did the reference group constituted by participants with poor diet quality who didn’t exercise for 150 minutes per week.
But the converse didn’t hold true: Individuals with optimal diet quality who didn’t reach the physical activity threshold had no reduction in metabolic syndrome, compared with the reference group, according to Dr. Lee of Boston University.
For example, among the Framingham Offspring Study participants, whose mean age was 69 years at the time of their ninth formal examination in 2014, the prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 59% in those who got less than 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity weekly as assessed by accelerometer and who were also in the lowest tertile for diet quality as self-reported on the DGAI-2010 (Dietary Guidelines Adherence Index) semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. The relative risk of metabolic syndrome was reduced by 61% in participants with both optimal physical activity and diet quality, by 49% in those with at least 150 minutes of physical activity but only moderate diet quality, and by 39% in those with optimal exercise and poor diet quality. In contrast, individuals in the top or middle tertiles for diet quality who didn’t meet the physical activity standard had a metabolic syndrome rate that wasn’t significantly lower than the reference group.
Dr. Lee observed that his analyses are best viewed as hypothesis generating. Their cross-sectional format precludes firm conclusions as to causality.
His findings prompted session comoderator Satyam Sarma, MD, of the University of Texas, Dallas, to make one of the most memorable comments heard at AHA 2019: that the Framingham findings suggest it may be possible to outrun a bad diet.
Dr. Lee reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, supported by Boston University.
SOURCE: Lee J. AHA 2019, Abstract RF244.
PHILADELPHIA – Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week as recommended in national guidelines appears to mitigate the cardiometabolic risks associated with poor diet quality in middle-aged and older adults, according to an analysis of Framingham Heart Study data.
“Our findings suggest adherence to physical activity guidelines may have a protective effect on cardiometabolic health regardless of diet quality,” Joowon Lee, PhD, declared at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He presented separate cross-sectional analyses of the risks of metabolic syndrome in 2,379 middle-aged participants in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored Framingham (Mass.) Third Generation Study and 1,180 older participants in the Framingham Offspring Study.
The two analyses showed the same thing across a broad age spectrum: The highest prevalence of metabolic syndrome as defined by Adult Treatment Panel III criteria was present among those individuals who got less than 150 minutes of physical activity per week and were also in the lowest tertile in terms of diet quality, while the lowest prevalence of metabolic syndrome occurred in participants in the top tertile for diet quality who engaged in at least 150 minutes per week of moderate to vigorous physical activity in accord with the Department of Health & Human Services 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
In both the middle-aged and older populations, optimal physical activity – that is, at least 150 minutes per week – appeared to override the adverse impact of suboptimal diet quality. Physically active individuals with moderate or even poor diet quality had a significantly lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome than did the reference group constituted by participants with poor diet quality who didn’t exercise for 150 minutes per week.
But the converse didn’t hold true: Individuals with optimal diet quality who didn’t reach the physical activity threshold had no reduction in metabolic syndrome, compared with the reference group, according to Dr. Lee of Boston University.
For example, among the Framingham Offspring Study participants, whose mean age was 69 years at the time of their ninth formal examination in 2014, the prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 59% in those who got less than 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity weekly as assessed by accelerometer and who were also in the lowest tertile for diet quality as self-reported on the DGAI-2010 (Dietary Guidelines Adherence Index) semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. The relative risk of metabolic syndrome was reduced by 61% in participants with both optimal physical activity and diet quality, by 49% in those with at least 150 minutes of physical activity but only moderate diet quality, and by 39% in those with optimal exercise and poor diet quality. In contrast, individuals in the top or middle tertiles for diet quality who didn’t meet the physical activity standard had a metabolic syndrome rate that wasn’t significantly lower than the reference group.
Dr. Lee observed that his analyses are best viewed as hypothesis generating. Their cross-sectional format precludes firm conclusions as to causality.
His findings prompted session comoderator Satyam Sarma, MD, of the University of Texas, Dallas, to make one of the most memorable comments heard at AHA 2019: that the Framingham findings suggest it may be possible to outrun a bad diet.
Dr. Lee reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, supported by Boston University.
SOURCE: Lee J. AHA 2019, Abstract RF244.
PHILADELPHIA – Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week as recommended in national guidelines appears to mitigate the cardiometabolic risks associated with poor diet quality in middle-aged and older adults, according to an analysis of Framingham Heart Study data.
“Our findings suggest adherence to physical activity guidelines may have a protective effect on cardiometabolic health regardless of diet quality,” Joowon Lee, PhD, declared at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He presented separate cross-sectional analyses of the risks of metabolic syndrome in 2,379 middle-aged participants in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored Framingham (Mass.) Third Generation Study and 1,180 older participants in the Framingham Offspring Study.
The two analyses showed the same thing across a broad age spectrum: The highest prevalence of metabolic syndrome as defined by Adult Treatment Panel III criteria was present among those individuals who got less than 150 minutes of physical activity per week and were also in the lowest tertile in terms of diet quality, while the lowest prevalence of metabolic syndrome occurred in participants in the top tertile for diet quality who engaged in at least 150 minutes per week of moderate to vigorous physical activity in accord with the Department of Health & Human Services 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
In both the middle-aged and older populations, optimal physical activity – that is, at least 150 minutes per week – appeared to override the adverse impact of suboptimal diet quality. Physically active individuals with moderate or even poor diet quality had a significantly lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome than did the reference group constituted by participants with poor diet quality who didn’t exercise for 150 minutes per week.
But the converse didn’t hold true: Individuals with optimal diet quality who didn’t reach the physical activity threshold had no reduction in metabolic syndrome, compared with the reference group, according to Dr. Lee of Boston University.
For example, among the Framingham Offspring Study participants, whose mean age was 69 years at the time of their ninth formal examination in 2014, the prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 59% in those who got less than 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity weekly as assessed by accelerometer and who were also in the lowest tertile for diet quality as self-reported on the DGAI-2010 (Dietary Guidelines Adherence Index) semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. The relative risk of metabolic syndrome was reduced by 61% in participants with both optimal physical activity and diet quality, by 49% in those with at least 150 minutes of physical activity but only moderate diet quality, and by 39% in those with optimal exercise and poor diet quality. In contrast, individuals in the top or middle tertiles for diet quality who didn’t meet the physical activity standard had a metabolic syndrome rate that wasn’t significantly lower than the reference group.
Dr. Lee observed that his analyses are best viewed as hypothesis generating. Their cross-sectional format precludes firm conclusions as to causality.
His findings prompted session comoderator Satyam Sarma, MD, of the University of Texas, Dallas, to make one of the most memorable comments heard at AHA 2019: that the Framingham findings suggest it may be possible to outrun a bad diet.
Dr. Lee reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, supported by Boston University.
SOURCE: Lee J. AHA 2019, Abstract RF244.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019
Frequent lab testing is common, but low-yield, for isotretinoin patients
Abnormalities in lipids, liver enzymes, and blood counts were rare, and
In a review of 1,863 patients receiving isotretinoin, there were no cases of grade 4 abnormalities of lipids, liver enzymes, or complete blood count (CBC). Further, fewer than 1% of patients had grade 2-3 laboratory abnormalities, and no patients had cholesterol or CBC abnormalities of grade 3 or higher.
The retrospective cohort study used an electronic database to identify patients who were prescribed isotretinoin for acne from 2007 to 2017, with inclusion criteria structured to “increase the likelihood of capturing a complete course of isotretinoin therapy,” wrote John Barbieri, MD, and coauthors. The database allowed the investigators to group lab values into baseline testing, and testing by month of therapy for individual deidentified patient records.
Dr. Barbieri, a dermatologist and postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and coinvestigators found that over half of all patients had baseline triglyceride, total cholesterol, AST, ALT, and platelet and white blood cell count levels.
Though the number of patients who had any of these levels checked in a given month of treatment declined over time, as did the total number of patients still on isotretinoin therapy, monthly AST and ALT monitoring occurred in 37.6%-58.5% of patients. Monthly triglyceride monitoring was conducted in between 39.6% and 61.4% of participants, and CBCs were obtained in 26.8%-37.4% of participants.
In terms of the abnormalities that were seen, grade 1 triglyceride elevations of 150-300 mg/dL were present in about 13% of patients at baseline, rising to 39% of participants who were still receiving isotretinoin at month 6. However, grade 2 elevations of up to 500 mg/dL were seen in 1.4% of patients at baseline and 2.4%-5.6% of patients during subsequent months.
Grade 1 liver enzyme abnormalities of less than three times the upper limit of normal values were seen at baseline in under 4% of patients, and in no more than 6.7% of patients through the course of treatment.
Leukopenia of between 3 x 103/mcL and the lower limit of normal occurred in 4.1% of baseline tests and in 6.6%-10.1% of tests in subsequent months. Grade 1 thrombocytopenia (values between 75 x 103/mcL and the lower limit of normal) occurred in 1.9% of baseline tests and no more than 2.9% of tests in the following months.
The results, wrote Dr. Barbieri and coauthors, affirm that most patients fare well on isotretinoin, and frequent laboratory testing is likely to be low-yield. Even using relatively low Medicare reimbursement rates for these tests yielded an estimated $134 in per-patient charges for the studied population. If baseline lipid and liver functions were followed only by repeat testing when peak isotretinoin dose was reached, charges would drop to about $87 per patient. Using the iPLEDGE database figures, this would save $17.4 million in monitoring costs annually, they wrote.
They also calculated that the monitoring regimen they observed puts the cost of detecting one single grade 3 hepatic enzyme elevation at $6,000; one grade 3 triglyceride elevation would cost $7,750.
Of the patients, 49% were female, the median age was 18.2 years, and the median duration of isotretinoin therapy was under 5 months (148 days). Nearly 90% of patients were white and non-Hispanic; 2.5% were black.
The data used for the analysis did not give the investigators access to clinician notes, but they did observe that, even when abnormal test values were seen, isotretinoin prescribing continued. This, they added, pointed toward reassuring clinical scenarios, even in cases of abnormal lab values.
“These findings are consistent with prior studies and suggest that extensive laboratory monitoring observed in this population may be of low value,” concluded Dr. Barbieri and colleagues. “In addition, changes to lipid levels observed in this study typically occurred during the first 2-3 months of therapy before stabilizing, which is consistent with findings in prior studies.”
The investigators noted that, despite mounting evidence of isotretinoin’s safety, there was no trend toward decreased CBC testing over the decade-long period of the study, and there were only “modest” decreases in hepatic enzyme and lipid monitoring. They called for an awareness campaign on the part of professional societies, and consideration for “more specific guideline recommendations” that may ease the testing burden on the adolescent and young adult population receiving isotretinoin.
The study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health, and Dr. Barbieri receives partial salary support from Pfizer through a grant to the University of Pennsylvania. He has received support for unrelated work from Eli Lilly and Novartis. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Barbieri J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82(1):72-9.
Abnormalities in lipids, liver enzymes, and blood counts were rare, and
In a review of 1,863 patients receiving isotretinoin, there were no cases of grade 4 abnormalities of lipids, liver enzymes, or complete blood count (CBC). Further, fewer than 1% of patients had grade 2-3 laboratory abnormalities, and no patients had cholesterol or CBC abnormalities of grade 3 or higher.
The retrospective cohort study used an electronic database to identify patients who were prescribed isotretinoin for acne from 2007 to 2017, with inclusion criteria structured to “increase the likelihood of capturing a complete course of isotretinoin therapy,” wrote John Barbieri, MD, and coauthors. The database allowed the investigators to group lab values into baseline testing, and testing by month of therapy for individual deidentified patient records.
Dr. Barbieri, a dermatologist and postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and coinvestigators found that over half of all patients had baseline triglyceride, total cholesterol, AST, ALT, and platelet and white blood cell count levels.
Though the number of patients who had any of these levels checked in a given month of treatment declined over time, as did the total number of patients still on isotretinoin therapy, monthly AST and ALT monitoring occurred in 37.6%-58.5% of patients. Monthly triglyceride monitoring was conducted in between 39.6% and 61.4% of participants, and CBCs were obtained in 26.8%-37.4% of participants.
In terms of the abnormalities that were seen, grade 1 triglyceride elevations of 150-300 mg/dL were present in about 13% of patients at baseline, rising to 39% of participants who were still receiving isotretinoin at month 6. However, grade 2 elevations of up to 500 mg/dL were seen in 1.4% of patients at baseline and 2.4%-5.6% of patients during subsequent months.
Grade 1 liver enzyme abnormalities of less than three times the upper limit of normal values were seen at baseline in under 4% of patients, and in no more than 6.7% of patients through the course of treatment.
Leukopenia of between 3 x 103/mcL and the lower limit of normal occurred in 4.1% of baseline tests and in 6.6%-10.1% of tests in subsequent months. Grade 1 thrombocytopenia (values between 75 x 103/mcL and the lower limit of normal) occurred in 1.9% of baseline tests and no more than 2.9% of tests in the following months.
The results, wrote Dr. Barbieri and coauthors, affirm that most patients fare well on isotretinoin, and frequent laboratory testing is likely to be low-yield. Even using relatively low Medicare reimbursement rates for these tests yielded an estimated $134 in per-patient charges for the studied population. If baseline lipid and liver functions were followed only by repeat testing when peak isotretinoin dose was reached, charges would drop to about $87 per patient. Using the iPLEDGE database figures, this would save $17.4 million in monitoring costs annually, they wrote.
They also calculated that the monitoring regimen they observed puts the cost of detecting one single grade 3 hepatic enzyme elevation at $6,000; one grade 3 triglyceride elevation would cost $7,750.
Of the patients, 49% were female, the median age was 18.2 years, and the median duration of isotretinoin therapy was under 5 months (148 days). Nearly 90% of patients were white and non-Hispanic; 2.5% were black.
The data used for the analysis did not give the investigators access to clinician notes, but they did observe that, even when abnormal test values were seen, isotretinoin prescribing continued. This, they added, pointed toward reassuring clinical scenarios, even in cases of abnormal lab values.
“These findings are consistent with prior studies and suggest that extensive laboratory monitoring observed in this population may be of low value,” concluded Dr. Barbieri and colleagues. “In addition, changes to lipid levels observed in this study typically occurred during the first 2-3 months of therapy before stabilizing, which is consistent with findings in prior studies.”
The investigators noted that, despite mounting evidence of isotretinoin’s safety, there was no trend toward decreased CBC testing over the decade-long period of the study, and there were only “modest” decreases in hepatic enzyme and lipid monitoring. They called for an awareness campaign on the part of professional societies, and consideration for “more specific guideline recommendations” that may ease the testing burden on the adolescent and young adult population receiving isotretinoin.
The study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health, and Dr. Barbieri receives partial salary support from Pfizer through a grant to the University of Pennsylvania. He has received support for unrelated work from Eli Lilly and Novartis. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Barbieri J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82(1):72-9.
Abnormalities in lipids, liver enzymes, and blood counts were rare, and
In a review of 1,863 patients receiving isotretinoin, there were no cases of grade 4 abnormalities of lipids, liver enzymes, or complete blood count (CBC). Further, fewer than 1% of patients had grade 2-3 laboratory abnormalities, and no patients had cholesterol or CBC abnormalities of grade 3 or higher.
The retrospective cohort study used an electronic database to identify patients who were prescribed isotretinoin for acne from 2007 to 2017, with inclusion criteria structured to “increase the likelihood of capturing a complete course of isotretinoin therapy,” wrote John Barbieri, MD, and coauthors. The database allowed the investigators to group lab values into baseline testing, and testing by month of therapy for individual deidentified patient records.
Dr. Barbieri, a dermatologist and postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and coinvestigators found that over half of all patients had baseline triglyceride, total cholesterol, AST, ALT, and platelet and white blood cell count levels.
Though the number of patients who had any of these levels checked in a given month of treatment declined over time, as did the total number of patients still on isotretinoin therapy, monthly AST and ALT monitoring occurred in 37.6%-58.5% of patients. Monthly triglyceride monitoring was conducted in between 39.6% and 61.4% of participants, and CBCs were obtained in 26.8%-37.4% of participants.
In terms of the abnormalities that were seen, grade 1 triglyceride elevations of 150-300 mg/dL were present in about 13% of patients at baseline, rising to 39% of participants who were still receiving isotretinoin at month 6. However, grade 2 elevations of up to 500 mg/dL were seen in 1.4% of patients at baseline and 2.4%-5.6% of patients during subsequent months.
Grade 1 liver enzyme abnormalities of less than three times the upper limit of normal values were seen at baseline in under 4% of patients, and in no more than 6.7% of patients through the course of treatment.
Leukopenia of between 3 x 103/mcL and the lower limit of normal occurred in 4.1% of baseline tests and in 6.6%-10.1% of tests in subsequent months. Grade 1 thrombocytopenia (values between 75 x 103/mcL and the lower limit of normal) occurred in 1.9% of baseline tests and no more than 2.9% of tests in the following months.
The results, wrote Dr. Barbieri and coauthors, affirm that most patients fare well on isotretinoin, and frequent laboratory testing is likely to be low-yield. Even using relatively low Medicare reimbursement rates for these tests yielded an estimated $134 in per-patient charges for the studied population. If baseline lipid and liver functions were followed only by repeat testing when peak isotretinoin dose was reached, charges would drop to about $87 per patient. Using the iPLEDGE database figures, this would save $17.4 million in monitoring costs annually, they wrote.
They also calculated that the monitoring regimen they observed puts the cost of detecting one single grade 3 hepatic enzyme elevation at $6,000; one grade 3 triglyceride elevation would cost $7,750.
Of the patients, 49% were female, the median age was 18.2 years, and the median duration of isotretinoin therapy was under 5 months (148 days). Nearly 90% of patients were white and non-Hispanic; 2.5% were black.
The data used for the analysis did not give the investigators access to clinician notes, but they did observe that, even when abnormal test values were seen, isotretinoin prescribing continued. This, they added, pointed toward reassuring clinical scenarios, even in cases of abnormal lab values.
“These findings are consistent with prior studies and suggest that extensive laboratory monitoring observed in this population may be of low value,” concluded Dr. Barbieri and colleagues. “In addition, changes to lipid levels observed in this study typically occurred during the first 2-3 months of therapy before stabilizing, which is consistent with findings in prior studies.”
The investigators noted that, despite mounting evidence of isotretinoin’s safety, there was no trend toward decreased CBC testing over the decade-long period of the study, and there were only “modest” decreases in hepatic enzyme and lipid monitoring. They called for an awareness campaign on the part of professional societies, and consideration for “more specific guideline recommendations” that may ease the testing burden on the adolescent and young adult population receiving isotretinoin.
The study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health, and Dr. Barbieri receives partial salary support from Pfizer through a grant to the University of Pennsylvania. He has received support for unrelated work from Eli Lilly and Novartis. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Barbieri J et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82(1):72-9.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
February 2020 – ICYMI
Gastroenterology
November 2019
Clip closure after resection of large colorectal lesions with substantial risk of bleeding. Albéniz E et al. 2019 Nov;157(5):1213-21.e4. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.037.
Tumor seeding during colonoscopy as a possible cause for metachronous colorectal cancer. Backes Y et al. 2019 Nov;157(5):1222-32.e4. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.062.
December 2019
How to “DEAL” with disruptive physician behavior. Junga Z et al. 2019 Dec;157(6):1469-72. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.021.
Effect of sex, age, and positivity threshold on fecal immunochemical test accuracy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Selby K et al. 2019 Dec;(6):1494-505. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.023.
January 2020
How to approach burnout among gastroenterology fellows. DeCross AJ 2020 Jan;158(1):32-5. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.032.
Efficacy and safety of peppermint oil in a randomized, double-blind trial of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Weerts ZZRM et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):123-36. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.026.
Validation of a machine learning model that outperforms clinical risk scoring systems for upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Shung DL et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):160-7. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.009.
Efficacy and safety of early vs elective colonoscopy for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Niikura R et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):168-75.e6. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.010.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
November 2019
Medical professional liability in gastroenterology: Understanding the claims landscape and proposed mechanisms for reform. Adams MA and John I. Allen. 2019 Nov;17(12):2392-6.e1. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.002.
Optimizing use of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score, Fibrosis-4 score, and liver stiffness measurement to identify patients with advanced fibrosis. Chan W-K et al. 2019 Nov;17(12):2570-80.e37. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.006.
December 2019
Clinical and molecular features of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancers. Samadder NJ et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2731-9.e2. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.02.040.
Neurologic deficits in patients with newly diagnosed celiac disease are frequent and linked with autoimmunity to transglutaminase 6. Hadjivassiliou M et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2678-86.e2. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.014.
Increased risk of death in first year after liver transplantation among patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis vs liver disease of other etiologies. Nagai S et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2759-68.e5. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.033.
January 2020
Incorporating high value care into gastroenterology fellowship training. Shah BJ and Janice H. Jou. 2020 Jan;18(1):11-3. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.040.
Association of obesity with colonic diverticulosis in women. Peery AF et al. 2020 Jan;18(1):107-14.e1. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.058.
Endocuff vision reduces inspection time without decreasing lesion detection: A clinical randomized trial. Rex DK et al. 2020 Jan;18(1):158-62.e1 doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.01.015.
Gastroenterology
November 2019
Clip closure after resection of large colorectal lesions with substantial risk of bleeding. Albéniz E et al. 2019 Nov;157(5):1213-21.e4. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.037.
Tumor seeding during colonoscopy as a possible cause for metachronous colorectal cancer. Backes Y et al. 2019 Nov;157(5):1222-32.e4. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.062.
December 2019
How to “DEAL” with disruptive physician behavior. Junga Z et al. 2019 Dec;157(6):1469-72. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.021.
Effect of sex, age, and positivity threshold on fecal immunochemical test accuracy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Selby K et al. 2019 Dec;(6):1494-505. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.023.
January 2020
How to approach burnout among gastroenterology fellows. DeCross AJ 2020 Jan;158(1):32-5. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.032.
Efficacy and safety of peppermint oil in a randomized, double-blind trial of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Weerts ZZRM et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):123-36. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.026.
Validation of a machine learning model that outperforms clinical risk scoring systems for upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Shung DL et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):160-7. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.009.
Efficacy and safety of early vs elective colonoscopy for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Niikura R et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):168-75.e6. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.010.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
November 2019
Medical professional liability in gastroenterology: Understanding the claims landscape and proposed mechanisms for reform. Adams MA and John I. Allen. 2019 Nov;17(12):2392-6.e1. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.002.
Optimizing use of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score, Fibrosis-4 score, and liver stiffness measurement to identify patients with advanced fibrosis. Chan W-K et al. 2019 Nov;17(12):2570-80.e37. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.006.
December 2019
Clinical and molecular features of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancers. Samadder NJ et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2731-9.e2. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.02.040.
Neurologic deficits in patients with newly diagnosed celiac disease are frequent and linked with autoimmunity to transglutaminase 6. Hadjivassiliou M et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2678-86.e2. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.014.
Increased risk of death in first year after liver transplantation among patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis vs liver disease of other etiologies. Nagai S et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2759-68.e5. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.033.
January 2020
Incorporating high value care into gastroenterology fellowship training. Shah BJ and Janice H. Jou. 2020 Jan;18(1):11-3. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.040.
Association of obesity with colonic diverticulosis in women. Peery AF et al. 2020 Jan;18(1):107-14.e1. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.058.
Endocuff vision reduces inspection time without decreasing lesion detection: A clinical randomized trial. Rex DK et al. 2020 Jan;18(1):158-62.e1 doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.01.015.
Gastroenterology
November 2019
Clip closure after resection of large colorectal lesions with substantial risk of bleeding. Albéniz E et al. 2019 Nov;157(5):1213-21.e4. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.037.
Tumor seeding during colonoscopy as a possible cause for metachronous colorectal cancer. Backes Y et al. 2019 Nov;157(5):1222-32.e4. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.062.
December 2019
How to “DEAL” with disruptive physician behavior. Junga Z et al. 2019 Dec;157(6):1469-72. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.021.
Effect of sex, age, and positivity threshold on fecal immunochemical test accuracy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Selby K et al. 2019 Dec;(6):1494-505. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.023.
January 2020
How to approach burnout among gastroenterology fellows. DeCross AJ 2020 Jan;158(1):32-5. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.032.
Efficacy and safety of peppermint oil in a randomized, double-blind trial of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Weerts ZZRM et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):123-36. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.026.
Validation of a machine learning model that outperforms clinical risk scoring systems for upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Shung DL et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):160-7. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.009.
Efficacy and safety of early vs elective colonoscopy for acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Niikura R et al. 2020 Jan;158(1):168-75.e6. doi. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.010.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
November 2019
Medical professional liability in gastroenterology: Understanding the claims landscape and proposed mechanisms for reform. Adams MA and John I. Allen. 2019 Nov;17(12):2392-6.e1. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.002.
Optimizing use of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score, Fibrosis-4 score, and liver stiffness measurement to identify patients with advanced fibrosis. Chan W-K et al. 2019 Nov;17(12):2570-80.e37. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.006.
December 2019
Clinical and molecular features of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancers. Samadder NJ et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2731-9.e2. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.02.040.
Neurologic deficits in patients with newly diagnosed celiac disease are frequent and linked with autoimmunity to transglutaminase 6. Hadjivassiliou M et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2678-86.e2. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.014.
Increased risk of death in first year after liver transplantation among patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis vs liver disease of other etiologies. Nagai S et al. 2019 Dec;17(12):2759-68.e5. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.033.
January 2020
Incorporating high value care into gastroenterology fellowship training. Shah BJ and Janice H. Jou. 2020 Jan;18(1):11-3. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.040.
Association of obesity with colonic diverticulosis in women. Peery AF et al. 2020 Jan;18(1):107-14.e1. doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.058.
Endocuff vision reduces inspection time without decreasing lesion detection: A clinical randomized trial. Rex DK et al. 2020 Jan;18(1):158-62.e1 doi. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.01.015.
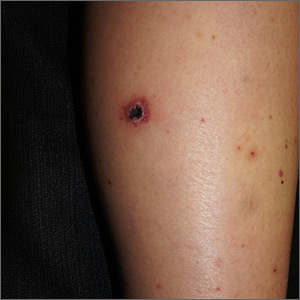
Rash on legs and abdomen
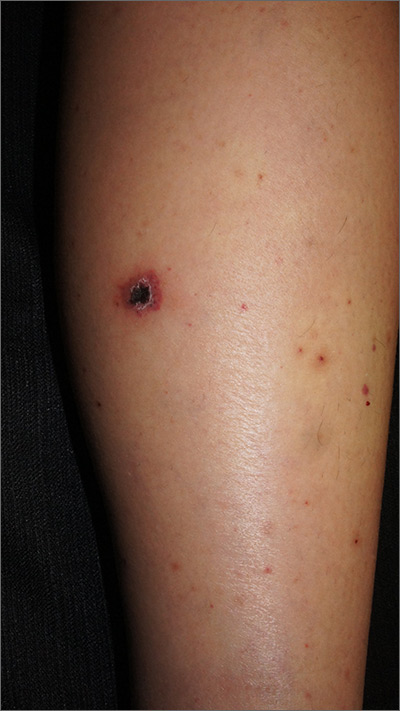
The rash was consistent with nonblanching purpura. Two punch biopsies were performed for hematoxylin and eosin stain and direct immunofluorescence, which were consistent with IgA mediated small vessel vasculitis, or Henoch-Schoenlein purpura.
IgA small vessel vasculitis commonly occurs in children after a transient viral illness or as an allergic reaction to a medication. Nonblanching purpura occurs because small vessels have been cracked open by neutrophils and lymphocytes and leaked blood cells outside of the vascular circulation. Pressure fails to move these cells downstream, and thus, the skin does not blanch.
Joint pain is common, as is a self-resolving IgA mediated nephropathy. Approximately 1% to 3% of children will progress to end stage renal disease. IgA vasculitis also occurs in adults, with a higher portion developing nephropathy. In adults, lesions that present on the abdomen are suspected to correspond with gravity dependency and the total burden of IgA, leading to a higher risk for nephropathy.
The differential diagnosis of purpura is broad, but includes leukocytoclastic vasculitis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis, capillaritis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
The patient in this case was given topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment to treat the rash. She returned 3 weeks later and her blood pressure was 160/105 mm Hg and she had protein and blood in her urine. The FP recommended a renal biopsy, which confirmed severe IgA nephropathy and end stage renal failure. She was given systemic steroids and ultimately received a renal transplant. Her outcome was atypical and unfortunate. Usually IgA vasculitis is benign and self-resolves with rest. Even when nephropathy is present, it typically resolves over weeks to months.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
Audemard-Verger A, Terrier B, Dechartres A, et al. French Vasculitis Study Group. Characteristics and management of IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein) in adults: data from 260 patients included in a French multicenter retrospective survey. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69:1862-1870.

The rash was consistent with nonblanching purpura. Two punch biopsies were performed for hematoxylin and eosin stain and direct immunofluorescence, which were consistent with IgA mediated small vessel vasculitis, or Henoch-Schoenlein purpura.
IgA small vessel vasculitis commonly occurs in children after a transient viral illness or as an allergic reaction to a medication. Nonblanching purpura occurs because small vessels have been cracked open by neutrophils and lymphocytes and leaked blood cells outside of the vascular circulation. Pressure fails to move these cells downstream, and thus, the skin does not blanch.
Joint pain is common, as is a self-resolving IgA mediated nephropathy. Approximately 1% to 3% of children will progress to end stage renal disease. IgA vasculitis also occurs in adults, with a higher portion developing nephropathy. In adults, lesions that present on the abdomen are suspected to correspond with gravity dependency and the total burden of IgA, leading to a higher risk for nephropathy.
The differential diagnosis of purpura is broad, but includes leukocytoclastic vasculitis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis, capillaritis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
The patient in this case was given topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment to treat the rash. She returned 3 weeks later and her blood pressure was 160/105 mm Hg and she had protein and blood in her urine. The FP recommended a renal biopsy, which confirmed severe IgA nephropathy and end stage renal failure. She was given systemic steroids and ultimately received a renal transplant. Her outcome was atypical and unfortunate. Usually IgA vasculitis is benign and self-resolves with rest. Even when nephropathy is present, it typically resolves over weeks to months.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

The rash was consistent with nonblanching purpura. Two punch biopsies were performed for hematoxylin and eosin stain and direct immunofluorescence, which were consistent with IgA mediated small vessel vasculitis, or Henoch-Schoenlein purpura.
IgA small vessel vasculitis commonly occurs in children after a transient viral illness or as an allergic reaction to a medication. Nonblanching purpura occurs because small vessels have been cracked open by neutrophils and lymphocytes and leaked blood cells outside of the vascular circulation. Pressure fails to move these cells downstream, and thus, the skin does not blanch.
Joint pain is common, as is a self-resolving IgA mediated nephropathy. Approximately 1% to 3% of children will progress to end stage renal disease. IgA vasculitis also occurs in adults, with a higher portion developing nephropathy. In adults, lesions that present on the abdomen are suspected to correspond with gravity dependency and the total burden of IgA, leading to a higher risk for nephropathy.
The differential diagnosis of purpura is broad, but includes leukocytoclastic vasculitis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis, capillaritis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
The patient in this case was given topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment to treat the rash. She returned 3 weeks later and her blood pressure was 160/105 mm Hg and she had protein and blood in her urine. The FP recommended a renal biopsy, which confirmed severe IgA nephropathy and end stage renal failure. She was given systemic steroids and ultimately received a renal transplant. Her outcome was atypical and unfortunate. Usually IgA vasculitis is benign and self-resolves with rest. Even when nephropathy is present, it typically resolves over weeks to months.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
Audemard-Verger A, Terrier B, Dechartres A, et al. French Vasculitis Study Group. Characteristics and management of IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein) in adults: data from 260 patients included in a French multicenter retrospective survey. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69:1862-1870.
Audemard-Verger A, Terrier B, Dechartres A, et al. French Vasculitis Study Group. Characteristics and management of IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein) in adults: data from 260 patients included in a French multicenter retrospective survey. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69:1862-1870.
Cherry concentrate fails for gout flares
Tart cherry concentrate had no impact on gout flares over a 28-day period, based on data from 50 adult patients.
Urate-lowering therapy is part of gout management, and previous studies have suggested that tart cherry concentrate lowers sodium urate within hours in healthy volunteers and to a nonsignificant extent over 120 days in patients with gout, but “the optimal dose of tart cherry concentrate for either a serum urate effect on or flare prevention is unknown,” wrote Lisa K. Stamp, MD, of the University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand, and colleagues.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers randomized 50 adults with gout and baseline serum urate levels greater than 0.36 mmol/L (6 mg/dL) to receive one of four doses of tart cherry juice concentrate (7.5 mL, 15 mL, 22.5 mL, or 30 mL) or a placebo twice daily for 28 days. Half of the participants were taking allopurinol and half were not taking any urate-lowering therapy.
After 28 days, patients who received cherry juice showed no significant changes in serum urate regardless of whether they were also taking allopurinol. In addition, cherry juice at any dose had no significant effect on reducing the serum urate area under the curve and no apparent impact on measures including urine urate excretion, change in urinary anthocyanins, and frequency of gout flares, compared with placebo. However, the cherry juice was well tolerated, and 84% of the study participants said they would recommend it to a friend as a method of gout prevention.
The researchers collected blood samples at baseline, and at 1, 3, and 5 hours after consuming cherry juice, and on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28. “If there is an effect of cherry concentrate on gout flares over a longer time period, it is not likely to be mediated by reduction in serum urate,” the researchers said.
Of 24 adverse events reported during the study, 18 occurred in patients taking cherry juice at all dosage levels, and one case of hyperglycemia was potentially related to cherry concentrate. No serious adverse events associated with tart cherry concentrate occurred during the study period.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to blind the study because participants prepared their doses at home, and the lack of data on the exact contents of the cherry juice concentrate used in the study, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that tart cherry concentrate has no effect on serum urate concentration or urinary urate excretion, which make it unlikely to be useful in reducing gout flares, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Stamp LK et al. Rheumatology. 2019 Dec 31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez606.
Tart cherry concentrate had no impact on gout flares over a 28-day period, based on data from 50 adult patients.
Urate-lowering therapy is part of gout management, and previous studies have suggested that tart cherry concentrate lowers sodium urate within hours in healthy volunteers and to a nonsignificant extent over 120 days in patients with gout, but “the optimal dose of tart cherry concentrate for either a serum urate effect on or flare prevention is unknown,” wrote Lisa K. Stamp, MD, of the University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand, and colleagues.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers randomized 50 adults with gout and baseline serum urate levels greater than 0.36 mmol/L (6 mg/dL) to receive one of four doses of tart cherry juice concentrate (7.5 mL, 15 mL, 22.5 mL, or 30 mL) or a placebo twice daily for 28 days. Half of the participants were taking allopurinol and half were not taking any urate-lowering therapy.
After 28 days, patients who received cherry juice showed no significant changes in serum urate regardless of whether they were also taking allopurinol. In addition, cherry juice at any dose had no significant effect on reducing the serum urate area under the curve and no apparent impact on measures including urine urate excretion, change in urinary anthocyanins, and frequency of gout flares, compared with placebo. However, the cherry juice was well tolerated, and 84% of the study participants said they would recommend it to a friend as a method of gout prevention.
The researchers collected blood samples at baseline, and at 1, 3, and 5 hours after consuming cherry juice, and on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28. “If there is an effect of cherry concentrate on gout flares over a longer time period, it is not likely to be mediated by reduction in serum urate,” the researchers said.
Of 24 adverse events reported during the study, 18 occurred in patients taking cherry juice at all dosage levels, and one case of hyperglycemia was potentially related to cherry concentrate. No serious adverse events associated with tart cherry concentrate occurred during the study period.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to blind the study because participants prepared their doses at home, and the lack of data on the exact contents of the cherry juice concentrate used in the study, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that tart cherry concentrate has no effect on serum urate concentration or urinary urate excretion, which make it unlikely to be useful in reducing gout flares, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Stamp LK et al. Rheumatology. 2019 Dec 31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez606.
Tart cherry concentrate had no impact on gout flares over a 28-day period, based on data from 50 adult patients.
Urate-lowering therapy is part of gout management, and previous studies have suggested that tart cherry concentrate lowers sodium urate within hours in healthy volunteers and to a nonsignificant extent over 120 days in patients with gout, but “the optimal dose of tart cherry concentrate for either a serum urate effect on or flare prevention is unknown,” wrote Lisa K. Stamp, MD, of the University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand, and colleagues.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers randomized 50 adults with gout and baseline serum urate levels greater than 0.36 mmol/L (6 mg/dL) to receive one of four doses of tart cherry juice concentrate (7.5 mL, 15 mL, 22.5 mL, or 30 mL) or a placebo twice daily for 28 days. Half of the participants were taking allopurinol and half were not taking any urate-lowering therapy.
After 28 days, patients who received cherry juice showed no significant changes in serum urate regardless of whether they were also taking allopurinol. In addition, cherry juice at any dose had no significant effect on reducing the serum urate area under the curve and no apparent impact on measures including urine urate excretion, change in urinary anthocyanins, and frequency of gout flares, compared with placebo. However, the cherry juice was well tolerated, and 84% of the study participants said they would recommend it to a friend as a method of gout prevention.
The researchers collected blood samples at baseline, and at 1, 3, and 5 hours after consuming cherry juice, and on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28. “If there is an effect of cherry concentrate on gout flares over a longer time period, it is not likely to be mediated by reduction in serum urate,” the researchers said.
Of 24 adverse events reported during the study, 18 occurred in patients taking cherry juice at all dosage levels, and one case of hyperglycemia was potentially related to cherry concentrate. No serious adverse events associated with tart cherry concentrate occurred during the study period.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to blind the study because participants prepared their doses at home, and the lack of data on the exact contents of the cherry juice concentrate used in the study, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that tart cherry concentrate has no effect on serum urate concentration or urinary urate excretion, which make it unlikely to be useful in reducing gout flares, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Stamp LK et al. Rheumatology. 2019 Dec 31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez606.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
UKALL14: Rituximab improves EFS in B-ALL, but four doses not enough
ORLANDO – Adding rituximab to standard induction chemotherapy in adults with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) appears to improve event-free survival, but four doses are insufficient, according to the first analysis from the randomized, phase 3 UKALL14 trial.
The findings also suggest that the significant event-free survival (EFS) benefit of adding 16-18 doses of rituximab in B-ALL patients, as demonstrated in “the recent and very important” GRAALL-2005/R study, may be generalizable to B-precursor ALL patients regardless of Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome status or CD20-positive expression level, Adele K. Fielding, MBBS, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Unlike GRAALL-2005/R (NCT00327678), which included only patients with greater than 20% of ALL blasts expressing CD20 and with Ph-negative ALL, UKALL14 (NCT01085617) included B-ALL patients regardless of Ph chromosome status or CD20 expression level, explained Dr. Fielding of the Cancer Institute, University College London.
Overall, EFS rates among patients in the UKALL14 study at a median follow-up of 40.5 months were 41.9% in 288 patients randomized to receive standard-of-care chemotherapy (SOC), and 48.7% among 289 randomized to receive SOC plus rituximab, but the difference was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.88; P = .28), she said.
“Likewise there was a nonsignificant improvement in 3-year event-free survival and in median event-free survival in the rituximab arms, but these differences did not meet our predetermined criteria,” she added.
Similarly, the overall survival findings showed slight, but non–statistically significant improvement in the rituximab arms (HR, 0.9; P = .39). The 3-year and median overall survival outcomes appeared to favor rituximab, but “this was not the magnitude of benefit that we were seeking in our study,” she said.
However, while a preplanned subgroup analysis by cytogenetic and other risk groups, as well as by cell surface CD20 expression, did not reveal any significant interactions for EFS, they did show that the percentage of blasts expressing CD20 was a strong independent poor prognostic factor.
A cutoff of 11.6%, compared with the 20% typically used, was found to be ideal based on the Youden Index, which determines the best balance between sensitivity and specificity.
“Interestingly, in addition to this, we did not find any impact of CD20 expression on response to rituximab,” Dr. Fielding noted.
Further, outcomes analyses by post–induction treatment assignment showed that, in patients who received myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplant, “there was a large and statistically significant benefit to [adding rituximab], she said.
Landmark analysis showed an EFS hazard ratio of 0.48 at the time of transplant (P = .037), she said, noting that the SOC and SOC plus rituximab arms were well matched among this subset of patients.
The difference appeared to relate to relapse risk (HR, .38), but on an intention-to-treat analysis including all patients under age 40 years, the difference was “no longer quite so pronounced.”
“We do not understand the biological basis for this finding,” Dr. Fielding said, noting that it wasn’t explained by differences in graft-versus-host disease or infection. “This difference was not apparent in patients who received or were intended to receive reduced-intensity allogeneic conditioning.”
A multivariable analysis did not show a significant treatment effect, but did show “the same trend toward a better outcome in the rituximab arm,” she added.
UKALL14 subjects were adults aged 25-65 years with de novo ALL, regardless of Ph status or cell surface CD20 expression, who were recruited from 70 centers in the United Kingdom between December 2010 and July 2017. Those randomized to standard of care received a standard four-drug induction after a steroid prephase – with or without four doses of rituximab.
After a second induction, patients underwent risk assessment; low-risk patients were treated on the SOC arm and received high-dose methotrexate and additional pegylated asparaginase followed by four cycles of consolidation therapy. This was followed by 2 years of maintenance treatment.
High-risk patients with a sibling or fully matched unrelated donor available underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant, with those aged 40 years and younger receiving myeloablative conditioning and those over 40 years receiving reduced-intensity conditioning.
Most patients in the SOC plus rituximab arm received all four doses of rituximab, and the treatment arms were well-balanced with respect to risk characteristics, Dr. Fielding said, adding that no differences were noted in adverse events or mortality between the arms.
There is strong rationale for studying rituximab in ALL, she noted. For example, rituximab is safe to add to chemotherapy, and it has potential relevance at any level of CD20 expression, she said, explaining the basis for the study. Indeed, the findings support its use in this setting.
“Rituximab benefits patients with ALL,” she said. “But in our hands, four doses is insufficient to realize the full benefit.”
Dr. Fielding is a consultant for Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte.
SOURCE: Marks D et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 739.
ORLANDO – Adding rituximab to standard induction chemotherapy in adults with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) appears to improve event-free survival, but four doses are insufficient, according to the first analysis from the randomized, phase 3 UKALL14 trial.
The findings also suggest that the significant event-free survival (EFS) benefit of adding 16-18 doses of rituximab in B-ALL patients, as demonstrated in “the recent and very important” GRAALL-2005/R study, may be generalizable to B-precursor ALL patients regardless of Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome status or CD20-positive expression level, Adele K. Fielding, MBBS, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Unlike GRAALL-2005/R (NCT00327678), which included only patients with greater than 20% of ALL blasts expressing CD20 and with Ph-negative ALL, UKALL14 (NCT01085617) included B-ALL patients regardless of Ph chromosome status or CD20 expression level, explained Dr. Fielding of the Cancer Institute, University College London.
Overall, EFS rates among patients in the UKALL14 study at a median follow-up of 40.5 months were 41.9% in 288 patients randomized to receive standard-of-care chemotherapy (SOC), and 48.7% among 289 randomized to receive SOC plus rituximab, but the difference was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.88; P = .28), she said.
“Likewise there was a nonsignificant improvement in 3-year event-free survival and in median event-free survival in the rituximab arms, but these differences did not meet our predetermined criteria,” she added.
Similarly, the overall survival findings showed slight, but non–statistically significant improvement in the rituximab arms (HR, 0.9; P = .39). The 3-year and median overall survival outcomes appeared to favor rituximab, but “this was not the magnitude of benefit that we were seeking in our study,” she said.
However, while a preplanned subgroup analysis by cytogenetic and other risk groups, as well as by cell surface CD20 expression, did not reveal any significant interactions for EFS, they did show that the percentage of blasts expressing CD20 was a strong independent poor prognostic factor.
A cutoff of 11.6%, compared with the 20% typically used, was found to be ideal based on the Youden Index, which determines the best balance between sensitivity and specificity.
“Interestingly, in addition to this, we did not find any impact of CD20 expression on response to rituximab,” Dr. Fielding noted.
Further, outcomes analyses by post–induction treatment assignment showed that, in patients who received myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplant, “there was a large and statistically significant benefit to [adding rituximab], she said.
Landmark analysis showed an EFS hazard ratio of 0.48 at the time of transplant (P = .037), she said, noting that the SOC and SOC plus rituximab arms were well matched among this subset of patients.
The difference appeared to relate to relapse risk (HR, .38), but on an intention-to-treat analysis including all patients under age 40 years, the difference was “no longer quite so pronounced.”
“We do not understand the biological basis for this finding,” Dr. Fielding said, noting that it wasn’t explained by differences in graft-versus-host disease or infection. “This difference was not apparent in patients who received or were intended to receive reduced-intensity allogeneic conditioning.”
A multivariable analysis did not show a significant treatment effect, but did show “the same trend toward a better outcome in the rituximab arm,” she added.
UKALL14 subjects were adults aged 25-65 years with de novo ALL, regardless of Ph status or cell surface CD20 expression, who were recruited from 70 centers in the United Kingdom between December 2010 and July 2017. Those randomized to standard of care received a standard four-drug induction after a steroid prephase – with or without four doses of rituximab.
After a second induction, patients underwent risk assessment; low-risk patients were treated on the SOC arm and received high-dose methotrexate and additional pegylated asparaginase followed by four cycles of consolidation therapy. This was followed by 2 years of maintenance treatment.
High-risk patients with a sibling or fully matched unrelated donor available underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant, with those aged 40 years and younger receiving myeloablative conditioning and those over 40 years receiving reduced-intensity conditioning.
Most patients in the SOC plus rituximab arm received all four doses of rituximab, and the treatment arms were well-balanced with respect to risk characteristics, Dr. Fielding said, adding that no differences were noted in adverse events or mortality between the arms.
There is strong rationale for studying rituximab in ALL, she noted. For example, rituximab is safe to add to chemotherapy, and it has potential relevance at any level of CD20 expression, she said, explaining the basis for the study. Indeed, the findings support its use in this setting.
“Rituximab benefits patients with ALL,” she said. “But in our hands, four doses is insufficient to realize the full benefit.”
Dr. Fielding is a consultant for Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte.
SOURCE: Marks D et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 739.
ORLANDO – Adding rituximab to standard induction chemotherapy in adults with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) appears to improve event-free survival, but four doses are insufficient, according to the first analysis from the randomized, phase 3 UKALL14 trial.
The findings also suggest that the significant event-free survival (EFS) benefit of adding 16-18 doses of rituximab in B-ALL patients, as demonstrated in “the recent and very important” GRAALL-2005/R study, may be generalizable to B-precursor ALL patients regardless of Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome status or CD20-positive expression level, Adele K. Fielding, MBBS, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Unlike GRAALL-2005/R (NCT00327678), which included only patients with greater than 20% of ALL blasts expressing CD20 and with Ph-negative ALL, UKALL14 (NCT01085617) included B-ALL patients regardless of Ph chromosome status or CD20 expression level, explained Dr. Fielding of the Cancer Institute, University College London.
Overall, EFS rates among patients in the UKALL14 study at a median follow-up of 40.5 months were 41.9% in 288 patients randomized to receive standard-of-care chemotherapy (SOC), and 48.7% among 289 randomized to receive SOC plus rituximab, but the difference was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.88; P = .28), she said.
“Likewise there was a nonsignificant improvement in 3-year event-free survival and in median event-free survival in the rituximab arms, but these differences did not meet our predetermined criteria,” she added.
Similarly, the overall survival findings showed slight, but non–statistically significant improvement in the rituximab arms (HR, 0.9; P = .39). The 3-year and median overall survival outcomes appeared to favor rituximab, but “this was not the magnitude of benefit that we were seeking in our study,” she said.
However, while a preplanned subgroup analysis by cytogenetic and other risk groups, as well as by cell surface CD20 expression, did not reveal any significant interactions for EFS, they did show that the percentage of blasts expressing CD20 was a strong independent poor prognostic factor.
A cutoff of 11.6%, compared with the 20% typically used, was found to be ideal based on the Youden Index, which determines the best balance between sensitivity and specificity.
“Interestingly, in addition to this, we did not find any impact of CD20 expression on response to rituximab,” Dr. Fielding noted.
Further, outcomes analyses by post–induction treatment assignment showed that, in patients who received myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplant, “there was a large and statistically significant benefit to [adding rituximab], she said.
Landmark analysis showed an EFS hazard ratio of 0.48 at the time of transplant (P = .037), she said, noting that the SOC and SOC plus rituximab arms were well matched among this subset of patients.
The difference appeared to relate to relapse risk (HR, .38), but on an intention-to-treat analysis including all patients under age 40 years, the difference was “no longer quite so pronounced.”
“We do not understand the biological basis for this finding,” Dr. Fielding said, noting that it wasn’t explained by differences in graft-versus-host disease or infection. “This difference was not apparent in patients who received or were intended to receive reduced-intensity allogeneic conditioning.”
A multivariable analysis did not show a significant treatment effect, but did show “the same trend toward a better outcome in the rituximab arm,” she added.
UKALL14 subjects were adults aged 25-65 years with de novo ALL, regardless of Ph status or cell surface CD20 expression, who were recruited from 70 centers in the United Kingdom between December 2010 and July 2017. Those randomized to standard of care received a standard four-drug induction after a steroid prephase – with or without four doses of rituximab.
After a second induction, patients underwent risk assessment; low-risk patients were treated on the SOC arm and received high-dose methotrexate and additional pegylated asparaginase followed by four cycles of consolidation therapy. This was followed by 2 years of maintenance treatment.
High-risk patients with a sibling or fully matched unrelated donor available underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant, with those aged 40 years and younger receiving myeloablative conditioning and those over 40 years receiving reduced-intensity conditioning.
Most patients in the SOC plus rituximab arm received all four doses of rituximab, and the treatment arms were well-balanced with respect to risk characteristics, Dr. Fielding said, adding that no differences were noted in adverse events or mortality between the arms.
There is strong rationale for studying rituximab in ALL, she noted. For example, rituximab is safe to add to chemotherapy, and it has potential relevance at any level of CD20 expression, she said, explaining the basis for the study. Indeed, the findings support its use in this setting.
“Rituximab benefits patients with ALL,” she said. “But in our hands, four doses is insufficient to realize the full benefit.”
Dr. Fielding is a consultant for Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte.
SOURCE: Marks D et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 739.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019