User login
Two COVID-19 outpatient antibody drugs show encouraging results
Two COVID-19 antibody treatments, one developed by Regeneron and the other by Eli Lilly, show promise in the outpatient setting in results released on Oct. 28.
Regeneron, in a randomized, double-blind trial, is assessing the effect of adding its investigational antibody cocktail REGN-COV2 to usual standard of care in comparison with adding placebo to standard of care. A descriptive analysis from the first 275 patients was previously reported. The data described on Oct. 28, which involve an additional 524 patients, show that the trial met all of the first nine endpoints.
Regeneron announced prospective results from its phase 2/3 trial showing REGN-COV2 significantly reduced viral load and patient medical visits, which included hospitalizations, visits to an emergency department, visits for urgent care, and/or physician office/telemedicine visits.
Interest in the cocktail spiked after President Donald Trump extolled its benefits after it was used in his own COVID-19 treatment earlier in October.
Trump received the highest dose of the drug, 8 g, but, according to a Regeneron news release announcing the latest findings, “results showed no significant difference in virologic or clinical efficacy between the REGN-COV2 high dose (8 grams) and low dose (2.4 grams).”
The company described further results of the industry-funded study in the release: “On the primary endpoint, the average daily change in viral load through day 7 (mean time-weighted average change from baseline) in patients with high viral load (defined as greater than107 copies/mL) was a 0.68 log10 copies/mL greater reduction with REGN-COV2 compared to placebo (combined dose groups; P < .0001). There was a 1.08 log greater reduction with REGN-COV2 treatment by day 5, which corresponds to REGN-COV2 patients having, on average, a greater than 10-fold reduction in viral load, compared to placebo.”
The treatment appears to be most effective in patients most at risk, whether because of high viral load, ineffective baseline antibody immune response, or preexisting conditions, according to the researchers.
According to the press release, these results have not been peer reviewed but have been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration, which is reviewing a potential emergency use authorization for the treatment in high-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s treatment and vaccine program, contracted in July with Regeneron for up to 300,000 doses of its antibody cocktail.
Lilly treatment shows drop in hospitalizations, symptoms
Another treatment, also given in the outpatient setting, shows promise as well.
Patients recently diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 who received Eli Lilly’s antibody treatment LY-CoV555 had fewer hospitalizations and symptoms compared with a group that received placebo, an interim analysis of a phase 2 trial indicates.
Peter Chen, MD, with the Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues found that the most profound effects were in the high-risk groups.
The interim findings of the BLAZE-1 study, which was funded by Eli Lilly, were published online October 28 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers randomly assigned 452 patients to receive an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 in one of three doses (700 mg, 2800 mg, or 7000 mg) or placebo.
In the interim analysis, the researchers found that for the entire population, more than 99.97% of viral RNA was eliminated.
For patients who received the 2800-mg dose, the difference from placebo in the decrease from baseline was −0.53 (95% CI, −0.98 to −0.08; P = .02), for a log viral load that was lower by a factor of 3.4. Benefit over placebo was not significant with the other doses.
At day 29, according to the investigators, the percentage of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 was 1.6% (5 of 309 patients) in the treatment group compared with 6.3% (9 of 143 patients) in the placebo group.
Data indicate that the safety profile was similar whether patients received the active treatment or placebo.
“If these results are confirmed in additional analyses in this trial, LY-CoV555 could become a useful treatment for emergency use in patients with recently diagnosed Covid-19,” the authors write.
Deborah Fuller, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, told Medscape Medical News the findings are «exciting» but only part of the treatment solution.
“What’s remarkable about these two studies and others I’ve seen,” she said, “is how consistent they are in terms of the window of time they will be effective, and that’s because they are just targeting the virus itself. They do not have an effect on the inflammation unless they stop the replication early enough.”
The treatments are effective when they are given near the time of diagnosis, she pointed out.
“Once the virus has started that inflammatory cascade in your body, then that train has left the station and you have to deal with the inflammation,” Fuller said.
She says future treatments will likely have to include both the antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and physicians will have to assess what’s best, given the stage of the the patient’s disease.
The trial of REGN-COV2 is funded by Regeneron. The BLAZE-1 study is funded by Eli Lilly. Many of the authors have financial ties to Eli Lilly. Fuller has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two COVID-19 antibody treatments, one developed by Regeneron and the other by Eli Lilly, show promise in the outpatient setting in results released on Oct. 28.
Regeneron, in a randomized, double-blind trial, is assessing the effect of adding its investigational antibody cocktail REGN-COV2 to usual standard of care in comparison with adding placebo to standard of care. A descriptive analysis from the first 275 patients was previously reported. The data described on Oct. 28, which involve an additional 524 patients, show that the trial met all of the first nine endpoints.
Regeneron announced prospective results from its phase 2/3 trial showing REGN-COV2 significantly reduced viral load and patient medical visits, which included hospitalizations, visits to an emergency department, visits for urgent care, and/or physician office/telemedicine visits.
Interest in the cocktail spiked after President Donald Trump extolled its benefits after it was used in his own COVID-19 treatment earlier in October.
Trump received the highest dose of the drug, 8 g, but, according to a Regeneron news release announcing the latest findings, “results showed no significant difference in virologic or clinical efficacy between the REGN-COV2 high dose (8 grams) and low dose (2.4 grams).”
The company described further results of the industry-funded study in the release: “On the primary endpoint, the average daily change in viral load through day 7 (mean time-weighted average change from baseline) in patients with high viral load (defined as greater than107 copies/mL) was a 0.68 log10 copies/mL greater reduction with REGN-COV2 compared to placebo (combined dose groups; P < .0001). There was a 1.08 log greater reduction with REGN-COV2 treatment by day 5, which corresponds to REGN-COV2 patients having, on average, a greater than 10-fold reduction in viral load, compared to placebo.”
The treatment appears to be most effective in patients most at risk, whether because of high viral load, ineffective baseline antibody immune response, or preexisting conditions, according to the researchers.
According to the press release, these results have not been peer reviewed but have been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration, which is reviewing a potential emergency use authorization for the treatment in high-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s treatment and vaccine program, contracted in July with Regeneron for up to 300,000 doses of its antibody cocktail.
Lilly treatment shows drop in hospitalizations, symptoms
Another treatment, also given in the outpatient setting, shows promise as well.
Patients recently diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 who received Eli Lilly’s antibody treatment LY-CoV555 had fewer hospitalizations and symptoms compared with a group that received placebo, an interim analysis of a phase 2 trial indicates.
Peter Chen, MD, with the Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues found that the most profound effects were in the high-risk groups.
The interim findings of the BLAZE-1 study, which was funded by Eli Lilly, were published online October 28 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers randomly assigned 452 patients to receive an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 in one of three doses (700 mg, 2800 mg, or 7000 mg) or placebo.
In the interim analysis, the researchers found that for the entire population, more than 99.97% of viral RNA was eliminated.
For patients who received the 2800-mg dose, the difference from placebo in the decrease from baseline was −0.53 (95% CI, −0.98 to −0.08; P = .02), for a log viral load that was lower by a factor of 3.4. Benefit over placebo was not significant with the other doses.
At day 29, according to the investigators, the percentage of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 was 1.6% (5 of 309 patients) in the treatment group compared with 6.3% (9 of 143 patients) in the placebo group.
Data indicate that the safety profile was similar whether patients received the active treatment or placebo.
“If these results are confirmed in additional analyses in this trial, LY-CoV555 could become a useful treatment for emergency use in patients with recently diagnosed Covid-19,” the authors write.
Deborah Fuller, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, told Medscape Medical News the findings are «exciting» but only part of the treatment solution.
“What’s remarkable about these two studies and others I’ve seen,” she said, “is how consistent they are in terms of the window of time they will be effective, and that’s because they are just targeting the virus itself. They do not have an effect on the inflammation unless they stop the replication early enough.”
The treatments are effective when they are given near the time of diagnosis, she pointed out.
“Once the virus has started that inflammatory cascade in your body, then that train has left the station and you have to deal with the inflammation,” Fuller said.
She says future treatments will likely have to include both the antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and physicians will have to assess what’s best, given the stage of the the patient’s disease.
The trial of REGN-COV2 is funded by Regeneron. The BLAZE-1 study is funded by Eli Lilly. Many of the authors have financial ties to Eli Lilly. Fuller has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two COVID-19 antibody treatments, one developed by Regeneron and the other by Eli Lilly, show promise in the outpatient setting in results released on Oct. 28.
Regeneron, in a randomized, double-blind trial, is assessing the effect of adding its investigational antibody cocktail REGN-COV2 to usual standard of care in comparison with adding placebo to standard of care. A descriptive analysis from the first 275 patients was previously reported. The data described on Oct. 28, which involve an additional 524 patients, show that the trial met all of the first nine endpoints.
Regeneron announced prospective results from its phase 2/3 trial showing REGN-COV2 significantly reduced viral load and patient medical visits, which included hospitalizations, visits to an emergency department, visits for urgent care, and/or physician office/telemedicine visits.
Interest in the cocktail spiked after President Donald Trump extolled its benefits after it was used in his own COVID-19 treatment earlier in October.
Trump received the highest dose of the drug, 8 g, but, according to a Regeneron news release announcing the latest findings, “results showed no significant difference in virologic or clinical efficacy between the REGN-COV2 high dose (8 grams) and low dose (2.4 grams).”
The company described further results of the industry-funded study in the release: “On the primary endpoint, the average daily change in viral load through day 7 (mean time-weighted average change from baseline) in patients with high viral load (defined as greater than107 copies/mL) was a 0.68 log10 copies/mL greater reduction with REGN-COV2 compared to placebo (combined dose groups; P < .0001). There was a 1.08 log greater reduction with REGN-COV2 treatment by day 5, which corresponds to REGN-COV2 patients having, on average, a greater than 10-fold reduction in viral load, compared to placebo.”
The treatment appears to be most effective in patients most at risk, whether because of high viral load, ineffective baseline antibody immune response, or preexisting conditions, according to the researchers.
According to the press release, these results have not been peer reviewed but have been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration, which is reviewing a potential emergency use authorization for the treatment in high-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s treatment and vaccine program, contracted in July with Regeneron for up to 300,000 doses of its antibody cocktail.
Lilly treatment shows drop in hospitalizations, symptoms
Another treatment, also given in the outpatient setting, shows promise as well.
Patients recently diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 who received Eli Lilly’s antibody treatment LY-CoV555 had fewer hospitalizations and symptoms compared with a group that received placebo, an interim analysis of a phase 2 trial indicates.
Peter Chen, MD, with the Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues found that the most profound effects were in the high-risk groups.
The interim findings of the BLAZE-1 study, which was funded by Eli Lilly, were published online October 28 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers randomly assigned 452 patients to receive an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 in one of three doses (700 mg, 2800 mg, or 7000 mg) or placebo.
In the interim analysis, the researchers found that for the entire population, more than 99.97% of viral RNA was eliminated.
For patients who received the 2800-mg dose, the difference from placebo in the decrease from baseline was −0.53 (95% CI, −0.98 to −0.08; P = .02), for a log viral load that was lower by a factor of 3.4. Benefit over placebo was not significant with the other doses.
At day 29, according to the investigators, the percentage of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 was 1.6% (5 of 309 patients) in the treatment group compared with 6.3% (9 of 143 patients) in the placebo group.
Data indicate that the safety profile was similar whether patients received the active treatment or placebo.
“If these results are confirmed in additional analyses in this trial, LY-CoV555 could become a useful treatment for emergency use in patients with recently diagnosed Covid-19,” the authors write.
Deborah Fuller, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, told Medscape Medical News the findings are «exciting» but only part of the treatment solution.
“What’s remarkable about these two studies and others I’ve seen,” she said, “is how consistent they are in terms of the window of time they will be effective, and that’s because they are just targeting the virus itself. They do not have an effect on the inflammation unless they stop the replication early enough.”
The treatments are effective when they are given near the time of diagnosis, she pointed out.
“Once the virus has started that inflammatory cascade in your body, then that train has left the station and you have to deal with the inflammation,” Fuller said.
She says future treatments will likely have to include both the antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and physicians will have to assess what’s best, given the stage of the the patient’s disease.
The trial of REGN-COV2 is funded by Regeneron. The BLAZE-1 study is funded by Eli Lilly. Many of the authors have financial ties to Eli Lilly. Fuller has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No evidence to guide selection of biologic for severe asthma
Although “biologics have been really revolutionary for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma, we still don’t have evidence to know the right drug for the right patient,” said Wendy Moore, MD, of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“You start with your best guess and then switch,” she said in an interview.
There are no real-world contemporary measurements of biologic therapy in the United States at this time, Dr. Moore explained during her presentation of findings from the CHRONICLE trial at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST 2020), held virtually this year.
The agents have different targets: omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E, mepolizumab and reslizumab target interleukin (IL)-5, benralizumab targets the IL-5 receptor, and dupilumab targets the common receptor IL-4 receptor A for IL-4 and IL-13.
When the starting biologic doesn’t get the desired results, there is no evidence to show whether another will work better. What we say is, “This one is not working as well as I’d like, let’s try something new?” said Dr. Moore.
However, when looking at data on patients with severe asthma who change from one biologic to another, “I was actually pleased to see that only 10% are switching,” she said in an interview.
But, she added, “if you add that up with the 8% who are stopping, that means that almost 20% don’t get the clinical response they want.”
CHRONICLE trial
In the ongoing observational CHRONICLE trial, Dr. Moore and colleagues assessed biologic initiations, discontinuations, and switches to a different agent.
All 1,884 study participants had a diagnosis of severe asthma and were being treated by an allergist/immunologist or a pulmonologist. All were taking high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and additional controllers, or had received an Food and Drug Administration–approved monoclonal antibody, systemic corticosteroid, or another systemic immunosuppressant for at least half of the previous 12 months.
In the study cohort, 1,219 participants were receiving one biologic and 27 were receiving two.
Before November 2018, “it was almost universally all benralizumab being prescribed.” An earlier preference was omalizumab, which was prescribed to 99% of patients before November 2015 and to 45% from November 2017 to November 2018.
“As new drugs were introduced, patients were switched if the desired outcome was not achieved,” Dr. Moore explained.
Over the 2-year period from February 2018 to February 2020, 134 patients – about 10% of all participants taking a biologic – made 148 switches to another biologic.
“The most common reasons reported for switching were lack of efficacy, worsening of asthma control, or waning efficacy,” Dr. Moore reported.
Of the 101 patients (8%) who discontinued 106 biologics, reasons cited were a worsening of asthma symptoms, a desire to change to a cheaper medication, and a waning of effectiveness.
“It seems that the biologic used depended on when you started and whether you were prescribed by an immunologist or pulmonologist,” said Dr. Moore. “I don’t think we understand the perfect patient for any one of these drugs.”
Large-population studies need to be done on each of the drugs. “You have to look at who’s the super responder, the partial responder, compared with the nonresponders, for each medication, but those comparative studies are unlikely to happen,” she said.
In her own practice, her 175 patients are “pretty evenly split between dupilumab, benralizumab, and mepolizumab.”
I have opinions on what works, said Dr. Moore, but none of it is evidence-based. “Those with upper airway involvement with chronic sinusitis tend to do better with mepolizumab than benralizumab. My opinion,” she emphasized.
“People with nasal problems may do better with dupilumab and mepolizumab,” she added. “Also in my opinion.
“But more likely, the issue is you have a partial responder who’s on a T2 high drug but has a T2 low problem too.”
PATHWAY study
Findings from the phase 2B PATHWAY study showed that tezepelumab reduced exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled asthma better than inhaled corticosteroids, and improved forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
“Adherence was monitored very carefully,” said investigator Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who presented the PATHWAY data. This could explain, in part, why some patients in the control group “showed improvement from baseline.”
Before switching to a biologic, “we should always consider some of these issues that might contribute to better asthma control, like patient adherence or the inability to use an inhaler properly,” Dr. Corren said.
Some people have never been “shown how to use their inhalers properly,” said Moore. “Some of them come back fine when we show them.”
Dr. Moore has been on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Corren reports receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Although “biologics have been really revolutionary for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma, we still don’t have evidence to know the right drug for the right patient,” said Wendy Moore, MD, of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“You start with your best guess and then switch,” she said in an interview.
There are no real-world contemporary measurements of biologic therapy in the United States at this time, Dr. Moore explained during her presentation of findings from the CHRONICLE trial at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST 2020), held virtually this year.
The agents have different targets: omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E, mepolizumab and reslizumab target interleukin (IL)-5, benralizumab targets the IL-5 receptor, and dupilumab targets the common receptor IL-4 receptor A for IL-4 and IL-13.
When the starting biologic doesn’t get the desired results, there is no evidence to show whether another will work better. What we say is, “This one is not working as well as I’d like, let’s try something new?” said Dr. Moore.
However, when looking at data on patients with severe asthma who change from one biologic to another, “I was actually pleased to see that only 10% are switching,” she said in an interview.
But, she added, “if you add that up with the 8% who are stopping, that means that almost 20% don’t get the clinical response they want.”
CHRONICLE trial
In the ongoing observational CHRONICLE trial, Dr. Moore and colleagues assessed biologic initiations, discontinuations, and switches to a different agent.
All 1,884 study participants had a diagnosis of severe asthma and were being treated by an allergist/immunologist or a pulmonologist. All were taking high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and additional controllers, or had received an Food and Drug Administration–approved monoclonal antibody, systemic corticosteroid, or another systemic immunosuppressant for at least half of the previous 12 months.
In the study cohort, 1,219 participants were receiving one biologic and 27 were receiving two.
Before November 2018, “it was almost universally all benralizumab being prescribed.” An earlier preference was omalizumab, which was prescribed to 99% of patients before November 2015 and to 45% from November 2017 to November 2018.
“As new drugs were introduced, patients were switched if the desired outcome was not achieved,” Dr. Moore explained.
Over the 2-year period from February 2018 to February 2020, 134 patients – about 10% of all participants taking a biologic – made 148 switches to another biologic.
“The most common reasons reported for switching were lack of efficacy, worsening of asthma control, or waning efficacy,” Dr. Moore reported.
Of the 101 patients (8%) who discontinued 106 biologics, reasons cited were a worsening of asthma symptoms, a desire to change to a cheaper medication, and a waning of effectiveness.
“It seems that the biologic used depended on when you started and whether you were prescribed by an immunologist or pulmonologist,” said Dr. Moore. “I don’t think we understand the perfect patient for any one of these drugs.”
Large-population studies need to be done on each of the drugs. “You have to look at who’s the super responder, the partial responder, compared with the nonresponders, for each medication, but those comparative studies are unlikely to happen,” she said.
In her own practice, her 175 patients are “pretty evenly split between dupilumab, benralizumab, and mepolizumab.”
I have opinions on what works, said Dr. Moore, but none of it is evidence-based. “Those with upper airway involvement with chronic sinusitis tend to do better with mepolizumab than benralizumab. My opinion,” she emphasized.
“People with nasal problems may do better with dupilumab and mepolizumab,” she added. “Also in my opinion.
“But more likely, the issue is you have a partial responder who’s on a T2 high drug but has a T2 low problem too.”
PATHWAY study
Findings from the phase 2B PATHWAY study showed that tezepelumab reduced exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled asthma better than inhaled corticosteroids, and improved forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
“Adherence was monitored very carefully,” said investigator Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who presented the PATHWAY data. This could explain, in part, why some patients in the control group “showed improvement from baseline.”
Before switching to a biologic, “we should always consider some of these issues that might contribute to better asthma control, like patient adherence or the inability to use an inhaler properly,” Dr. Corren said.
Some people have never been “shown how to use their inhalers properly,” said Moore. “Some of them come back fine when we show them.”
Dr. Moore has been on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Corren reports receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Although “biologics have been really revolutionary for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma, we still don’t have evidence to know the right drug for the right patient,” said Wendy Moore, MD, of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“You start with your best guess and then switch,” she said in an interview.
There are no real-world contemporary measurements of biologic therapy in the United States at this time, Dr. Moore explained during her presentation of findings from the CHRONICLE trial at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST 2020), held virtually this year.
The agents have different targets: omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E, mepolizumab and reslizumab target interleukin (IL)-5, benralizumab targets the IL-5 receptor, and dupilumab targets the common receptor IL-4 receptor A for IL-4 and IL-13.
When the starting biologic doesn’t get the desired results, there is no evidence to show whether another will work better. What we say is, “This one is not working as well as I’d like, let’s try something new?” said Dr. Moore.
However, when looking at data on patients with severe asthma who change from one biologic to another, “I was actually pleased to see that only 10% are switching,” she said in an interview.
But, she added, “if you add that up with the 8% who are stopping, that means that almost 20% don’t get the clinical response they want.”
CHRONICLE trial
In the ongoing observational CHRONICLE trial, Dr. Moore and colleagues assessed biologic initiations, discontinuations, and switches to a different agent.
All 1,884 study participants had a diagnosis of severe asthma and were being treated by an allergist/immunologist or a pulmonologist. All were taking high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and additional controllers, or had received an Food and Drug Administration–approved monoclonal antibody, systemic corticosteroid, or another systemic immunosuppressant for at least half of the previous 12 months.
In the study cohort, 1,219 participants were receiving one biologic and 27 were receiving two.
Before November 2018, “it was almost universally all benralizumab being prescribed.” An earlier preference was omalizumab, which was prescribed to 99% of patients before November 2015 and to 45% from November 2017 to November 2018.
“As new drugs were introduced, patients were switched if the desired outcome was not achieved,” Dr. Moore explained.
Over the 2-year period from February 2018 to February 2020, 134 patients – about 10% of all participants taking a biologic – made 148 switches to another biologic.
“The most common reasons reported for switching were lack of efficacy, worsening of asthma control, or waning efficacy,” Dr. Moore reported.
Of the 101 patients (8%) who discontinued 106 biologics, reasons cited were a worsening of asthma symptoms, a desire to change to a cheaper medication, and a waning of effectiveness.
“It seems that the biologic used depended on when you started and whether you were prescribed by an immunologist or pulmonologist,” said Dr. Moore. “I don’t think we understand the perfect patient for any one of these drugs.”
Large-population studies need to be done on each of the drugs. “You have to look at who’s the super responder, the partial responder, compared with the nonresponders, for each medication, but those comparative studies are unlikely to happen,” she said.
In her own practice, her 175 patients are “pretty evenly split between dupilumab, benralizumab, and mepolizumab.”
I have opinions on what works, said Dr. Moore, but none of it is evidence-based. “Those with upper airway involvement with chronic sinusitis tend to do better with mepolizumab than benralizumab. My opinion,” she emphasized.
“People with nasal problems may do better with dupilumab and mepolizumab,” she added. “Also in my opinion.
“But more likely, the issue is you have a partial responder who’s on a T2 high drug but has a T2 low problem too.”
PATHWAY study
Findings from the phase 2B PATHWAY study showed that tezepelumab reduced exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled asthma better than inhaled corticosteroids, and improved forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
“Adherence was monitored very carefully,” said investigator Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who presented the PATHWAY data. This could explain, in part, why some patients in the control group “showed improvement from baseline.”
Before switching to a biologic, “we should always consider some of these issues that might contribute to better asthma control, like patient adherence or the inability to use an inhaler properly,” Dr. Corren said.
Some people have never been “shown how to use their inhalers properly,” said Moore. “Some of them come back fine when we show them.”
Dr. Moore has been on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Corren reports receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Adenomyosis: An update on imaging, medical, and surgical treatment
Adenomyosis is a benign disorder, present in 20%-35% of women and characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. The ectopic endometrial tissue appears to cause hypertrophy in the myometrium, resulting in an enlarged globular uterus.
Adenomyosis may present as diffuse or focal involvement within the uterus. When the focal lesion appears to be well defined, it is referred to as an adenomyoma. It is not encapsulated like a fibroid. There may be involvement of the junctional zone of the myometrium – the area between the subendometrial myometrium and the outer myometrium. While the pathogenesis of adenomyosis is unknown, two rigorous theories exist: endomyometrial invagination of the endometrium and de novo from Müllerian rests.
For this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted Keith B. Isaacson, MD, to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of adenomyosis.
Dr. Isaacson is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, Newton, Mass., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is currently in practice specializing in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, where he is the director of the AAGL Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. Dr. Isaacson is a past president of both the AAGL and the Society of Reproductive Surgeons, as well as a published clinical researcher and surgical innovator.
It is a true honor to welcome Dr. Isaacson to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Adenomyosis is a benign disorder, present in 20%-35% of women and characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. The ectopic endometrial tissue appears to cause hypertrophy in the myometrium, resulting in an enlarged globular uterus.
Adenomyosis may present as diffuse or focal involvement within the uterus. When the focal lesion appears to be well defined, it is referred to as an adenomyoma. It is not encapsulated like a fibroid. There may be involvement of the junctional zone of the myometrium – the area between the subendometrial myometrium and the outer myometrium. While the pathogenesis of adenomyosis is unknown, two rigorous theories exist: endomyometrial invagination of the endometrium and de novo from Müllerian rests.
For this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted Keith B. Isaacson, MD, to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of adenomyosis.
Dr. Isaacson is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, Newton, Mass., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is currently in practice specializing in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, where he is the director of the AAGL Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. Dr. Isaacson is a past president of both the AAGL and the Society of Reproductive Surgeons, as well as a published clinical researcher and surgical innovator.
It is a true honor to welcome Dr. Isaacson to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Adenomyosis is a benign disorder, present in 20%-35% of women and characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. The ectopic endometrial tissue appears to cause hypertrophy in the myometrium, resulting in an enlarged globular uterus.
Adenomyosis may present as diffuse or focal involvement within the uterus. When the focal lesion appears to be well defined, it is referred to as an adenomyoma. It is not encapsulated like a fibroid. There may be involvement of the junctional zone of the myometrium – the area between the subendometrial myometrium and the outer myometrium. While the pathogenesis of adenomyosis is unknown, two rigorous theories exist: endomyometrial invagination of the endometrium and de novo from Müllerian rests.
For this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted Keith B. Isaacson, MD, to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of adenomyosis.
Dr. Isaacson is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, Newton, Mass., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is currently in practice specializing in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, where he is the director of the AAGL Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. Dr. Isaacson is a past president of both the AAGL and the Society of Reproductive Surgeons, as well as a published clinical researcher and surgical innovator.
It is a true honor to welcome Dr. Isaacson to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Adenomyosis: While a last resort, surgery remains an option
Adenomyosis causing severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and heavy menstrual bleeding has been thought to affect primarily multiparous women in their mid- to late 40s. Often women who experience pain and heavy bleeding will tolerate their symptoms until they are done with childbearing, at which point they often go on to have a hysterectomy to relieve them of these symptoms. Tissue histology obtained at the time of hysterectomy confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
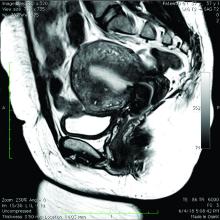
Because the diagnosis is made at the time of hysterectomy, the published incidence and prevalence of adenomyosis is more a reflection of a risk for hysterectomy and not for the disease itself. MRI has been used to evaluate the junctional zone in patients with symptoms of endometriosis. This screen tool is an expensive one, however, and has not been used extensively to evaluate women with symptoms of adenomyosis who are not candidates for a hysterectomy.
Ultrasound studies
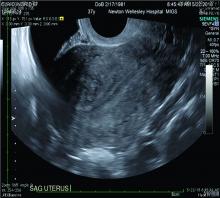
Over the past 5-7 years, numerous studies have been performed that demonstrate ultrasound changes consistent with adenomyosis within the uterus. These changes include asymmetry and heterogeneity of the anterior and posterior myometrium, cystic lesions in the myometrium, ultrasound striations, and streaking and irregular junctional zone thickening seen on 3-D scans.
Our newfound ability to demonstrate changes consistent with adenomyosis by ultrasound – a tool that is much less expensive than MRI and more available to patients – means that we can and should consider adenomyosis in patients suffering from dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, dyspareunia, and infertility – regardless of the patient’s age.
In the last 5 years, adenomyosis has been increasingly recognized as a disorder affecting women of all reproductive ages, including teenagers whose dysmenorrhea disrupts their education and young women undergoing infertility evaluations. In one study, 12% of adolescent girls and young women aged 14–20 years lost days of school or work each month because of dysmenorrhea.1 This disruption is not “normal.”
Several meta-analyses have also demonstrated that ultrasound and MRI changes consistent with adenomyosis can affect embryo implantation rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. The implantation rates can be as low as one half the expected rate without adenomyosis. Additionally, adenomyosis has been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage and preterm delivery.2,3
The clinicians who order and carefully look at the ultrasound themselves, rather than rely on the radiologist to make the diagnosis, will be able to see the changes consistent with adenomyosis. Over time – I anticipate the next several years – a standardized radiologic definition for adenomyosis will evolve, and radiologists will become more familiar with these changes. In the meantime, our patients should not have missed diagnoses.
Considerations for surgery
For the majority of younger patients who are not trying to conceive but want to maintain their fertility, medical treatment with oral contraceptives, progestins, or the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (Mirena) will relieve symptoms. The Mirena IUD has been found in studies of 6-36 months’ treatment duration to decrease the size of the uterus by 25%4 and improve dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia with a low profile of adverse effects in most women.
The Mirena IUD should be considered as a first-line therapy for all women with heavy menstrual bleeding and dyspareunia who want to preserve their fertility.
Patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medical therapy, and do not want to preserve their fertility, may consider hysterectomy, long regarded as the preferred method of treatment. Endometrial ablation can also be considered in those who no longer desire to preserve fertility and are experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. Those with extensive adenomyosis, however, often experience poor results with endometrial ablation and may ultimately require hysterectomy. Endometrial ablation has a history of a high failure rate in women younger than 45 years old.
Patients with adenomyosis who wish to preserve their fertility and cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to hormonal therapy, or those with infertility thought to be caused by adenomyosis, should consider these three management options:
- Do nothing. The embryo implantation rate is not zero with adenomyosis, and we have no data on the number of patients who conceive with adenomyotic changes detected by MRI or ultrasound.
- Pretreat with a GnRH agonist for 2-3 months prior to a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Suppressing the disease prior to an FET seems to increase the implantation rate to what is expected for that patient given her age and other fertility factors.3 While this approach is often successful, an estimated 15%-20% of patients are unable to tolerate GnRH agonist treatment because of its side effects.
- Seek surgical resection of adenomyosis. Unlike uterine fibroids, adenomyosis has no pseudocapsule. When resecting the disease via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy, the process is more of a debulking procedure. Surgical resection should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate hormonal suppression or have failed the other two options.
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision can be challenging because adenomyosis burrows its way through the muscle, is often diffuse, and cannot necessarily be resected with clean margins as can a fibroid. Yet, as demonstrated in a systematic review of 27 observational studies of conservative surgery for adenomyosis – 10 prospective and 17 retrospective studies with a total of almost 1,400 patients and all with adenomyosis confirmed histopathologically – surgery can improve pain, menorrhagia, and adenomyosis-related infertility in a significant number of cases.5
Disease may be resected through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or as we are currently doing with focal disease that is close to the endometrium, hysteroscopy. The type of surgery will depend on the location and characteristics of the disease, and on the surgeon’s skills. The principles are the same with all three approaches: to remove as much diseased tissue – and preserve as much healthy myometrial tissue – as possible and to reconstruct the uterine wall so that it maintains its integrity and can sustain a pregnancy.
The open approach known as the Osada procedure, after Hisao Osada, MD, PhD, in Tokyo, is well described in the literature, with a relatively large number of cases reported in prospective studies. Dr. Osada performs a radical adenomyosis excision with a triple flap method of uterine wall reconstruction. The uterus is bisected in the mid-sagittal plane all the way down through the adenomyosis until the uterine cavity is reached. Excision of the adenomyotic tissue is guided by palpation with the index finger, and a myometrial thickness of 1 cm from the serosa and the endometrium is preserved.
The endometrium is closed, and the myometrial defect is closed with a triple flap method that avoids overlapping suture lines. On one side of the uterus, the myometrium and serosa are sutured in the antero-posterior plane. The seromuscular layer of the opposite side of the uterine wall is then brought over the first seromuscular suture line.6
Others, such as Grigoris H. Grimbizis, MD, PhD, in Greece, have used a laparoscopic approach and closed the myometrium in layers similar to those of a myomectomy.7 There are no comparative trials that demonstrate one technique is superior to the other.
While there are no textbook techniques published for resecting adenomyotic tissue laparoscopically or hysteroscopically from the normal myometrium, there are some general principals the surgeon should keep in mind. Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within myometrium, but biopsy studies have demonstrated that there are relatively few glands and stroma within the diseased tissue. Mostly, the adenomyotic tissue we encounter comprises smooth muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis.
Since there is no pseudocapsule surrounding adenomyotic tissue, the visual cue for the cytoreductive procedure is the presence of normal-appearing myometrium. The normal myometrium can be delineated by palpation with laparoscopic instruments or hysteroscopic loops as it clearly feels less fibrotic and firm than the adenomyotic tissue. For this reason, the adenomyotic tissue is removed in a piecemeal fashion until normal tissue is encountered. (This same philosophy can be applied to removing fibrotic, glandular, or cystic tissue hysteroscopically.)
If the disease involves the inner myometrium, it should resected as this may be very important to restoring normal uterine contractions needed for embryo implantation and development, even if it means entering the cavity laparoscopically.
Hysteroscopically, there is no ability to suture a myometrial defect. This limitation is concerning because the adenomyosis is thought to invade the myometrium and not displace it as seen with monoclonal uterine fibroids. There are no case reports of uterine rupture after hysteroscopic resection of adenomyosis, but the number of cases reported with this type of resection in general is very small.
Laparoscopically, the myometrial defect should be repaired similarly to a myomectomy defect. Chromic or polydioxanone (PDS) suture is appropriate. We have used 2-0 PDS V-loc and a 2-3 layer closure in our laparoscopic cases.
Diffuse adenomyosis can involve the entire anterior or posterior wall of the uterus or both. The surgeon should not attempt to remove all of the disease in this situation and must leave enough tissue, even diseased, to allow for structural integrity during pregnancy. Uterine rupture has not been reported in all published case series and studies, but overall, it is a concern with surgical excision of adenomyosis. An analysis of over 2,000 cases of adenomyomectomies reported worldwide since 1990 shows a uterine rupture rate in the 6% rate, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 7%-72%.8
When the disease is focal and close to the endometrium, as opposed to diffuse and affecting the entire back wall of the uterus, hysteroscopic excision may be an appropriate, less invasive approach.
One of the patients for whom we’ve taken this approach was a 37-year-old patient who presented with a history of six miscarriages, a negative work-up for recurrent pregnancy loss, an enlarged uterus, 8 years of heavy menstrual bleeding, and only mild dysmenorrhea. She had undergone in vitro fertilization with failed embryo transfers but normal genetic screens of the embryos. She was referred with a suspicion of fibroids. An MRI and ultrasound showed heterogeneous myometrium adjacent to the endometrium. This tissue was resected using a bipolar loop electrode until normal myometrium was encountered.
Hysteroscopic resections are currently described in the literature through case reports rather than larger prospective or retrospective studies, and much more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this approach.
At this point in time, while surgery to excise adenomyosis is a last resort and best methods are deliberated, it is still important to appreciate that surgery is an option. Continued infertility is not the only choice, nor is hysterectomy.
References
1. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2014;27:258-65.
2. Minerva Ginecol. 2018 Jun;70(3):295-302.
3. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):483-490.e3.
4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):373.e1-7.
5. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018 Feb;25:265-76.
6. Reproductive BioMed Online. 2011 Jan;22(1):94-9.
7. Fertil Steril. 2014 Feb;101(2):472-87.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018 Mar;109(3):406-17.
Adenomyosis causing severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and heavy menstrual bleeding has been thought to affect primarily multiparous women in their mid- to late 40s. Often women who experience pain and heavy bleeding will tolerate their symptoms until they are done with childbearing, at which point they often go on to have a hysterectomy to relieve them of these symptoms. Tissue histology obtained at the time of hysterectomy confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
Because the diagnosis is made at the time of hysterectomy, the published incidence and prevalence of adenomyosis is more a reflection of a risk for hysterectomy and not for the disease itself. MRI has been used to evaluate the junctional zone in patients with symptoms of endometriosis. This screen tool is an expensive one, however, and has not been used extensively to evaluate women with symptoms of adenomyosis who are not candidates for a hysterectomy.
Ultrasound studies
Over the past 5-7 years, numerous studies have been performed that demonstrate ultrasound changes consistent with adenomyosis within the uterus. These changes include asymmetry and heterogeneity of the anterior and posterior myometrium, cystic lesions in the myometrium, ultrasound striations, and streaking and irregular junctional zone thickening seen on 3-D scans.
Our newfound ability to demonstrate changes consistent with adenomyosis by ultrasound – a tool that is much less expensive than MRI and more available to patients – means that we can and should consider adenomyosis in patients suffering from dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, dyspareunia, and infertility – regardless of the patient’s age.
In the last 5 years, adenomyosis has been increasingly recognized as a disorder affecting women of all reproductive ages, including teenagers whose dysmenorrhea disrupts their education and young women undergoing infertility evaluations. In one study, 12% of adolescent girls and young women aged 14–20 years lost days of school or work each month because of dysmenorrhea.1 This disruption is not “normal.”
Several meta-analyses have also demonstrated that ultrasound and MRI changes consistent with adenomyosis can affect embryo implantation rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. The implantation rates can be as low as one half the expected rate without adenomyosis. Additionally, adenomyosis has been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage and preterm delivery.2,3
The clinicians who order and carefully look at the ultrasound themselves, rather than rely on the radiologist to make the diagnosis, will be able to see the changes consistent with adenomyosis. Over time – I anticipate the next several years – a standardized radiologic definition for adenomyosis will evolve, and radiologists will become more familiar with these changes. In the meantime, our patients should not have missed diagnoses.
Considerations for surgery
For the majority of younger patients who are not trying to conceive but want to maintain their fertility, medical treatment with oral contraceptives, progestins, or the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (Mirena) will relieve symptoms. The Mirena IUD has been found in studies of 6-36 months’ treatment duration to decrease the size of the uterus by 25%4 and improve dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia with a low profile of adverse effects in most women.
The Mirena IUD should be considered as a first-line therapy for all women with heavy menstrual bleeding and dyspareunia who want to preserve their fertility.
Patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medical therapy, and do not want to preserve their fertility, may consider hysterectomy, long regarded as the preferred method of treatment. Endometrial ablation can also be considered in those who no longer desire to preserve fertility and are experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. Those with extensive adenomyosis, however, often experience poor results with endometrial ablation and may ultimately require hysterectomy. Endometrial ablation has a history of a high failure rate in women younger than 45 years old.
Patients with adenomyosis who wish to preserve their fertility and cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to hormonal therapy, or those with infertility thought to be caused by adenomyosis, should consider these three management options:
- Do nothing. The embryo implantation rate is not zero with adenomyosis, and we have no data on the number of patients who conceive with adenomyotic changes detected by MRI or ultrasound.
- Pretreat with a GnRH agonist for 2-3 months prior to a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Suppressing the disease prior to an FET seems to increase the implantation rate to what is expected for that patient given her age and other fertility factors.3 While this approach is often successful, an estimated 15%-20% of patients are unable to tolerate GnRH agonist treatment because of its side effects.
- Seek surgical resection of adenomyosis. Unlike uterine fibroids, adenomyosis has no pseudocapsule. When resecting the disease via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy, the process is more of a debulking procedure. Surgical resection should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate hormonal suppression or have failed the other two options.
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision can be challenging because adenomyosis burrows its way through the muscle, is often diffuse, and cannot necessarily be resected with clean margins as can a fibroid. Yet, as demonstrated in a systematic review of 27 observational studies of conservative surgery for adenomyosis – 10 prospective and 17 retrospective studies with a total of almost 1,400 patients and all with adenomyosis confirmed histopathologically – surgery can improve pain, menorrhagia, and adenomyosis-related infertility in a significant number of cases.5
Disease may be resected through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or as we are currently doing with focal disease that is close to the endometrium, hysteroscopy. The type of surgery will depend on the location and characteristics of the disease, and on the surgeon’s skills. The principles are the same with all three approaches: to remove as much diseased tissue – and preserve as much healthy myometrial tissue – as possible and to reconstruct the uterine wall so that it maintains its integrity and can sustain a pregnancy.
The open approach known as the Osada procedure, after Hisao Osada, MD, PhD, in Tokyo, is well described in the literature, with a relatively large number of cases reported in prospective studies. Dr. Osada performs a radical adenomyosis excision with a triple flap method of uterine wall reconstruction. The uterus is bisected in the mid-sagittal plane all the way down through the adenomyosis until the uterine cavity is reached. Excision of the adenomyotic tissue is guided by palpation with the index finger, and a myometrial thickness of 1 cm from the serosa and the endometrium is preserved.
The endometrium is closed, and the myometrial defect is closed with a triple flap method that avoids overlapping suture lines. On one side of the uterus, the myometrium and serosa are sutured in the antero-posterior plane. The seromuscular layer of the opposite side of the uterine wall is then brought over the first seromuscular suture line.6
Others, such as Grigoris H. Grimbizis, MD, PhD, in Greece, have used a laparoscopic approach and closed the myometrium in layers similar to those of a myomectomy.7 There are no comparative trials that demonstrate one technique is superior to the other.
While there are no textbook techniques published for resecting adenomyotic tissue laparoscopically or hysteroscopically from the normal myometrium, there are some general principals the surgeon should keep in mind. Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within myometrium, but biopsy studies have demonstrated that there are relatively few glands and stroma within the diseased tissue. Mostly, the adenomyotic tissue we encounter comprises smooth muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis.
Since there is no pseudocapsule surrounding adenomyotic tissue, the visual cue for the cytoreductive procedure is the presence of normal-appearing myometrium. The normal myometrium can be delineated by palpation with laparoscopic instruments or hysteroscopic loops as it clearly feels less fibrotic and firm than the adenomyotic tissue. For this reason, the adenomyotic tissue is removed in a piecemeal fashion until normal tissue is encountered. (This same philosophy can be applied to removing fibrotic, glandular, or cystic tissue hysteroscopically.)
If the disease involves the inner myometrium, it should resected as this may be very important to restoring normal uterine contractions needed for embryo implantation and development, even if it means entering the cavity laparoscopically.
Hysteroscopically, there is no ability to suture a myometrial defect. This limitation is concerning because the adenomyosis is thought to invade the myometrium and not displace it as seen with monoclonal uterine fibroids. There are no case reports of uterine rupture after hysteroscopic resection of adenomyosis, but the number of cases reported with this type of resection in general is very small.
Laparoscopically, the myometrial defect should be repaired similarly to a myomectomy defect. Chromic or polydioxanone (PDS) suture is appropriate. We have used 2-0 PDS V-loc and a 2-3 layer closure in our laparoscopic cases.
Diffuse adenomyosis can involve the entire anterior or posterior wall of the uterus or both. The surgeon should not attempt to remove all of the disease in this situation and must leave enough tissue, even diseased, to allow for structural integrity during pregnancy. Uterine rupture has not been reported in all published case series and studies, but overall, it is a concern with surgical excision of adenomyosis. An analysis of over 2,000 cases of adenomyomectomies reported worldwide since 1990 shows a uterine rupture rate in the 6% rate, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 7%-72%.8
When the disease is focal and close to the endometrium, as opposed to diffuse and affecting the entire back wall of the uterus, hysteroscopic excision may be an appropriate, less invasive approach.
One of the patients for whom we’ve taken this approach was a 37-year-old patient who presented with a history of six miscarriages, a negative work-up for recurrent pregnancy loss, an enlarged uterus, 8 years of heavy menstrual bleeding, and only mild dysmenorrhea. She had undergone in vitro fertilization with failed embryo transfers but normal genetic screens of the embryos. She was referred with a suspicion of fibroids. An MRI and ultrasound showed heterogeneous myometrium adjacent to the endometrium. This tissue was resected using a bipolar loop electrode until normal myometrium was encountered.
Hysteroscopic resections are currently described in the literature through case reports rather than larger prospective or retrospective studies, and much more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this approach.
At this point in time, while surgery to excise adenomyosis is a last resort and best methods are deliberated, it is still important to appreciate that surgery is an option. Continued infertility is not the only choice, nor is hysterectomy.
References
1. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2014;27:258-65.
2. Minerva Ginecol. 2018 Jun;70(3):295-302.
3. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):483-490.e3.
4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):373.e1-7.
5. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018 Feb;25:265-76.
6. Reproductive BioMed Online. 2011 Jan;22(1):94-9.
7. Fertil Steril. 2014 Feb;101(2):472-87.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018 Mar;109(3):406-17.
Adenomyosis causing severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and heavy menstrual bleeding has been thought to affect primarily multiparous women in their mid- to late 40s. Often women who experience pain and heavy bleeding will tolerate their symptoms until they are done with childbearing, at which point they often go on to have a hysterectomy to relieve them of these symptoms. Tissue histology obtained at the time of hysterectomy confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
Because the diagnosis is made at the time of hysterectomy, the published incidence and prevalence of adenomyosis is more a reflection of a risk for hysterectomy and not for the disease itself. MRI has been used to evaluate the junctional zone in patients with symptoms of endometriosis. This screen tool is an expensive one, however, and has not been used extensively to evaluate women with symptoms of adenomyosis who are not candidates for a hysterectomy.
Ultrasound studies
Over the past 5-7 years, numerous studies have been performed that demonstrate ultrasound changes consistent with adenomyosis within the uterus. These changes include asymmetry and heterogeneity of the anterior and posterior myometrium, cystic lesions in the myometrium, ultrasound striations, and streaking and irregular junctional zone thickening seen on 3-D scans.
Our newfound ability to demonstrate changes consistent with adenomyosis by ultrasound – a tool that is much less expensive than MRI and more available to patients – means that we can and should consider adenomyosis in patients suffering from dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, dyspareunia, and infertility – regardless of the patient’s age.
In the last 5 years, adenomyosis has been increasingly recognized as a disorder affecting women of all reproductive ages, including teenagers whose dysmenorrhea disrupts their education and young women undergoing infertility evaluations. In one study, 12% of adolescent girls and young women aged 14–20 years lost days of school or work each month because of dysmenorrhea.1 This disruption is not “normal.”
Several meta-analyses have also demonstrated that ultrasound and MRI changes consistent with adenomyosis can affect embryo implantation rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. The implantation rates can be as low as one half the expected rate without adenomyosis. Additionally, adenomyosis has been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage and preterm delivery.2,3
The clinicians who order and carefully look at the ultrasound themselves, rather than rely on the radiologist to make the diagnosis, will be able to see the changes consistent with adenomyosis. Over time – I anticipate the next several years – a standardized radiologic definition for adenomyosis will evolve, and radiologists will become more familiar with these changes. In the meantime, our patients should not have missed diagnoses.
Considerations for surgery
For the majority of younger patients who are not trying to conceive but want to maintain their fertility, medical treatment with oral contraceptives, progestins, or the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (Mirena) will relieve symptoms. The Mirena IUD has been found in studies of 6-36 months’ treatment duration to decrease the size of the uterus by 25%4 and improve dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia with a low profile of adverse effects in most women.
The Mirena IUD should be considered as a first-line therapy for all women with heavy menstrual bleeding and dyspareunia who want to preserve their fertility.
Patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medical therapy, and do not want to preserve their fertility, may consider hysterectomy, long regarded as the preferred method of treatment. Endometrial ablation can also be considered in those who no longer desire to preserve fertility and are experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. Those with extensive adenomyosis, however, often experience poor results with endometrial ablation and may ultimately require hysterectomy. Endometrial ablation has a history of a high failure rate in women younger than 45 years old.
Patients with adenomyosis who wish to preserve their fertility and cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to hormonal therapy, or those with infertility thought to be caused by adenomyosis, should consider these three management options:
- Do nothing. The embryo implantation rate is not zero with adenomyosis, and we have no data on the number of patients who conceive with adenomyotic changes detected by MRI or ultrasound.
- Pretreat with a GnRH agonist for 2-3 months prior to a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Suppressing the disease prior to an FET seems to increase the implantation rate to what is expected for that patient given her age and other fertility factors.3 While this approach is often successful, an estimated 15%-20% of patients are unable to tolerate GnRH agonist treatment because of its side effects.
- Seek surgical resection of adenomyosis. Unlike uterine fibroids, adenomyosis has no pseudocapsule. When resecting the disease via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy, the process is more of a debulking procedure. Surgical resection should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate hormonal suppression or have failed the other two options.
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision can be challenging because adenomyosis burrows its way through the muscle, is often diffuse, and cannot necessarily be resected with clean margins as can a fibroid. Yet, as demonstrated in a systematic review of 27 observational studies of conservative surgery for adenomyosis – 10 prospective and 17 retrospective studies with a total of almost 1,400 patients and all with adenomyosis confirmed histopathologically – surgery can improve pain, menorrhagia, and adenomyosis-related infertility in a significant number of cases.5
Disease may be resected through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or as we are currently doing with focal disease that is close to the endometrium, hysteroscopy. The type of surgery will depend on the location and characteristics of the disease, and on the surgeon’s skills. The principles are the same with all three approaches: to remove as much diseased tissue – and preserve as much healthy myometrial tissue – as possible and to reconstruct the uterine wall so that it maintains its integrity and can sustain a pregnancy.
The open approach known as the Osada procedure, after Hisao Osada, MD, PhD, in Tokyo, is well described in the literature, with a relatively large number of cases reported in prospective studies. Dr. Osada performs a radical adenomyosis excision with a triple flap method of uterine wall reconstruction. The uterus is bisected in the mid-sagittal plane all the way down through the adenomyosis until the uterine cavity is reached. Excision of the adenomyotic tissue is guided by palpation with the index finger, and a myometrial thickness of 1 cm from the serosa and the endometrium is preserved.
The endometrium is closed, and the myometrial defect is closed with a triple flap method that avoids overlapping suture lines. On one side of the uterus, the myometrium and serosa are sutured in the antero-posterior plane. The seromuscular layer of the opposite side of the uterine wall is then brought over the first seromuscular suture line.6
Others, such as Grigoris H. Grimbizis, MD, PhD, in Greece, have used a laparoscopic approach and closed the myometrium in layers similar to those of a myomectomy.7 There are no comparative trials that demonstrate one technique is superior to the other.
While there are no textbook techniques published for resecting adenomyotic tissue laparoscopically or hysteroscopically from the normal myometrium, there are some general principals the surgeon should keep in mind. Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within myometrium, but biopsy studies have demonstrated that there are relatively few glands and stroma within the diseased tissue. Mostly, the adenomyotic tissue we encounter comprises smooth muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis.
Since there is no pseudocapsule surrounding adenomyotic tissue, the visual cue for the cytoreductive procedure is the presence of normal-appearing myometrium. The normal myometrium can be delineated by palpation with laparoscopic instruments or hysteroscopic loops as it clearly feels less fibrotic and firm than the adenomyotic tissue. For this reason, the adenomyotic tissue is removed in a piecemeal fashion until normal tissue is encountered. (This same philosophy can be applied to removing fibrotic, glandular, or cystic tissue hysteroscopically.)
If the disease involves the inner myometrium, it should resected as this may be very important to restoring normal uterine contractions needed for embryo implantation and development, even if it means entering the cavity laparoscopically.
Hysteroscopically, there is no ability to suture a myometrial defect. This limitation is concerning because the adenomyosis is thought to invade the myometrium and not displace it as seen with monoclonal uterine fibroids. There are no case reports of uterine rupture after hysteroscopic resection of adenomyosis, but the number of cases reported with this type of resection in general is very small.
Laparoscopically, the myometrial defect should be repaired similarly to a myomectomy defect. Chromic or polydioxanone (PDS) suture is appropriate. We have used 2-0 PDS V-loc and a 2-3 layer closure in our laparoscopic cases.
Diffuse adenomyosis can involve the entire anterior or posterior wall of the uterus or both. The surgeon should not attempt to remove all of the disease in this situation and must leave enough tissue, even diseased, to allow for structural integrity during pregnancy. Uterine rupture has not been reported in all published case series and studies, but overall, it is a concern with surgical excision of adenomyosis. An analysis of over 2,000 cases of adenomyomectomies reported worldwide since 1990 shows a uterine rupture rate in the 6% rate, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 7%-72%.8
When the disease is focal and close to the endometrium, as opposed to diffuse and affecting the entire back wall of the uterus, hysteroscopic excision may be an appropriate, less invasive approach.
One of the patients for whom we’ve taken this approach was a 37-year-old patient who presented with a history of six miscarriages, a negative work-up for recurrent pregnancy loss, an enlarged uterus, 8 years of heavy menstrual bleeding, and only mild dysmenorrhea. She had undergone in vitro fertilization with failed embryo transfers but normal genetic screens of the embryos. She was referred with a suspicion of fibroids. An MRI and ultrasound showed heterogeneous myometrium adjacent to the endometrium. This tissue was resected using a bipolar loop electrode until normal myometrium was encountered.
Hysteroscopic resections are currently described in the literature through case reports rather than larger prospective or retrospective studies, and much more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this approach.
At this point in time, while surgery to excise adenomyosis is a last resort and best methods are deliberated, it is still important to appreciate that surgery is an option. Continued infertility is not the only choice, nor is hysterectomy.
References
1. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2014;27:258-65.
2. Minerva Ginecol. 2018 Jun;70(3):295-302.
3. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):483-490.e3.
4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):373.e1-7.
5. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018 Feb;25:265-76.
6. Reproductive BioMed Online. 2011 Jan;22(1):94-9.
7. Fertil Steril. 2014 Feb;101(2):472-87.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018 Mar;109(3):406-17.
Skin symptoms common in COVID-19 ‘long-haulers’
for more than 150 days, a new analysis revealed.
Evaluating data from an international registry of COVID-19 patients with dermatologic symptoms, researchers found that retiform purpura rashes are linked to severe COVID-19, with 100% of these patients requiring hospitalization and 82% experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile, pernio/chilblains rashes, dubbed “COVID toes,” are associated with milder disease and a 16% hospitalization rate. For all COVID-19–related skin symptoms, the average duration is 12 days.
“The skin is another organ system that we didn’t know could have long COVID” effects, said principal investigator Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“The skin is really a window into how the body is working overall, so the fact that we could visually see persistent inflammation in long-hauler patients is particularly fascinating and gives us a chance to explore what’s going on,” Dr. Freeman said in an interview. “It certainly makes sense to me, knowing what we know about other organ systems, that there might be some long-lasting inflammation” in the skin as well.
The study is a result of the collaboration between the American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies, the international registry launched this past April. While the study included provider-supplied data from 990 cases spanning 39 countries, the registry now encompasses more than 1,000 patients from 41 countries, Dr. Freeman noted.
Dr. Freeman presented the data at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Many studies have reported dermatologic effects of COVID-19 infection, but information was lacking about duration. The registry represents the largest dataset to date detailing these persistent skin symptoms and offers insight about how COVID-19 can affect many different organ systems even after patients recover from acute infection, Dr. Freeman said.
Eight different types of skin rashes were noted in the study group, of which 303 were lab-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms. Of those, 224 total cases and 90 lab-confirmed cases included information on how long skin symptoms lasted. Lab tests for SARS-CoV-2 included polymerase chain reaction and serum antibody assays.
Dr. Freeman and associates defined “long-haulers” as patients with dermatologic symptoms of COVID-19 lasting 60 days or longer. These “outliers” are likely more prevalent than the registry suggests, she said, since not all providers initially reporting skin symptoms in patients updated that information over time.
“It’s important to understand that the registry is probably significantly underreporting the duration of symptoms and number of long-hauler patients,” she explained. “A registry is often a glimpse into a moment in time to these patients. To combat that, we followed up by email twice with providers to ask if patients’ symptoms were still ongoing or completed.”
Results showed a wide spectrum in average duration of symptoms among lab-confirmed COVID-19 patients, depending on specific rash. Urticaria lasted for a median of 4 days; morbilliform eruptions, 7 days; pernio/chilblains, 10 days; and papulosquamous eruptions, 20 days, with one long-hauler case lasting 70 days.
Five patients with pernio/chilblains were long-haulers, with toe symptoms enduring 60 days or longer. Only one went beyond 133 days with severe pernio and fatigue.
“The fact that we’re not necessarily seeing these long-hauler symptoms across every type of skin rash makes sense,” Dr. Freeman said. “Hives, for example, usually comes on acutely and leaves pretty rapidly. There are no reports of long-hauler hives.”
“That we’re really seeing these long-hauler symptoms in certain skin rashes really suggests that there’s a certain pathophysiology going in within that group of patients,” she added.
Dr. Freeman said not enough data have yet been generated to correlate long-standing COVID-19 skin symptoms with lasting cardiac, neurologic, or other symptoms of prolonged inflammation stemming from the virus.
Meanwhile, an EADV survey of 490 dermatologists revealed that just over one-third have seen patients presenting with skin signs of COVID-19. Moreover, 4% of dermatologists themselves tested positive for the virus.
Dr. Freeman encouraged all frontline clinicians assessing COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms to enter patients into the registry. But despite its strengths, the registry “can’t tell us what percentage of everyone who gets COVID will develop a skin finding or what percentage will be a long-hauler,” she said.
“A registry doesn’t have a denominator, so it’s like a giant case series,” she added.
“It will be very helpful going forward, as many places around the world experience second or third waves of COVID-19, to follow patients prospectively, acknowledge that patients will have symptoms lasting different amounts of time, and be aware these symptoms can occur on the skin,” she said.
Christopher Griffiths, MD, of the University of Manchester (England), praised the international registry as a valuable tool that will help clinicians better manage patients with COVID-19–related skin effects and predict prognosis.
“This has really brought the international dermatology community together, working on a focused goal relevant to all of us around the world,” Dr. Griffiths said in an interview. “It shows the power of communication and collaboration and what can be achieved in a short period of time.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Griffiths disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
for more than 150 days, a new analysis revealed.
Evaluating data from an international registry of COVID-19 patients with dermatologic symptoms, researchers found that retiform purpura rashes are linked to severe COVID-19, with 100% of these patients requiring hospitalization and 82% experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile, pernio/chilblains rashes, dubbed “COVID toes,” are associated with milder disease and a 16% hospitalization rate. For all COVID-19–related skin symptoms, the average duration is 12 days.
“The skin is another organ system that we didn’t know could have long COVID” effects, said principal investigator Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“The skin is really a window into how the body is working overall, so the fact that we could visually see persistent inflammation in long-hauler patients is particularly fascinating and gives us a chance to explore what’s going on,” Dr. Freeman said in an interview. “It certainly makes sense to me, knowing what we know about other organ systems, that there might be some long-lasting inflammation” in the skin as well.
The study is a result of the collaboration between the American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies, the international registry launched this past April. While the study included provider-supplied data from 990 cases spanning 39 countries, the registry now encompasses more than 1,000 patients from 41 countries, Dr. Freeman noted.
Dr. Freeman presented the data at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Many studies have reported dermatologic effects of COVID-19 infection, but information was lacking about duration. The registry represents the largest dataset to date detailing these persistent skin symptoms and offers insight about how COVID-19 can affect many different organ systems even after patients recover from acute infection, Dr. Freeman said.
Eight different types of skin rashes were noted in the study group, of which 303 were lab-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms. Of those, 224 total cases and 90 lab-confirmed cases included information on how long skin symptoms lasted. Lab tests for SARS-CoV-2 included polymerase chain reaction and serum antibody assays.
Dr. Freeman and associates defined “long-haulers” as patients with dermatologic symptoms of COVID-19 lasting 60 days or longer. These “outliers” are likely more prevalent than the registry suggests, she said, since not all providers initially reporting skin symptoms in patients updated that information over time.
“It’s important to understand that the registry is probably significantly underreporting the duration of symptoms and number of long-hauler patients,” she explained. “A registry is often a glimpse into a moment in time to these patients. To combat that, we followed up by email twice with providers to ask if patients’ symptoms were still ongoing or completed.”
Results showed a wide spectrum in average duration of symptoms among lab-confirmed COVID-19 patients, depending on specific rash. Urticaria lasted for a median of 4 days; morbilliform eruptions, 7 days; pernio/chilblains, 10 days; and papulosquamous eruptions, 20 days, with one long-hauler case lasting 70 days.
Five patients with pernio/chilblains were long-haulers, with toe symptoms enduring 60 days or longer. Only one went beyond 133 days with severe pernio and fatigue.
“The fact that we’re not necessarily seeing these long-hauler symptoms across every type of skin rash makes sense,” Dr. Freeman said. “Hives, for example, usually comes on acutely and leaves pretty rapidly. There are no reports of long-hauler hives.”
“That we’re really seeing these long-hauler symptoms in certain skin rashes really suggests that there’s a certain pathophysiology going in within that group of patients,” she added.
Dr. Freeman said not enough data have yet been generated to correlate long-standing COVID-19 skin symptoms with lasting cardiac, neurologic, or other symptoms of prolonged inflammation stemming from the virus.
Meanwhile, an EADV survey of 490 dermatologists revealed that just over one-third have seen patients presenting with skin signs of COVID-19. Moreover, 4% of dermatologists themselves tested positive for the virus.
Dr. Freeman encouraged all frontline clinicians assessing COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms to enter patients into the registry. But despite its strengths, the registry “can’t tell us what percentage of everyone who gets COVID will develop a skin finding or what percentage will be a long-hauler,” she said.
“A registry doesn’t have a denominator, so it’s like a giant case series,” she added.
“It will be very helpful going forward, as many places around the world experience second or third waves of COVID-19, to follow patients prospectively, acknowledge that patients will have symptoms lasting different amounts of time, and be aware these symptoms can occur on the skin,” she said.
Christopher Griffiths, MD, of the University of Manchester (England), praised the international registry as a valuable tool that will help clinicians better manage patients with COVID-19–related skin effects and predict prognosis.
“This has really brought the international dermatology community together, working on a focused goal relevant to all of us around the world,” Dr. Griffiths said in an interview. “It shows the power of communication and collaboration and what can be achieved in a short period of time.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Griffiths disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
for more than 150 days, a new analysis revealed.
Evaluating data from an international registry of COVID-19 patients with dermatologic symptoms, researchers found that retiform purpura rashes are linked to severe COVID-19, with 100% of these patients requiring hospitalization and 82% experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile, pernio/chilblains rashes, dubbed “COVID toes,” are associated with milder disease and a 16% hospitalization rate. For all COVID-19–related skin symptoms, the average duration is 12 days.
“The skin is another organ system that we didn’t know could have long COVID” effects, said principal investigator Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“The skin is really a window into how the body is working overall, so the fact that we could visually see persistent inflammation in long-hauler patients is particularly fascinating and gives us a chance to explore what’s going on,” Dr. Freeman said in an interview. “It certainly makes sense to me, knowing what we know about other organ systems, that there might be some long-lasting inflammation” in the skin as well.
The study is a result of the collaboration between the American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies, the international registry launched this past April. While the study included provider-supplied data from 990 cases spanning 39 countries, the registry now encompasses more than 1,000 patients from 41 countries, Dr. Freeman noted.
Dr. Freeman presented the data at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Many studies have reported dermatologic effects of COVID-19 infection, but information was lacking about duration. The registry represents the largest dataset to date detailing these persistent skin symptoms and offers insight about how COVID-19 can affect many different organ systems even after patients recover from acute infection, Dr. Freeman said.
Eight different types of skin rashes were noted in the study group, of which 303 were lab-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms. Of those, 224 total cases and 90 lab-confirmed cases included information on how long skin symptoms lasted. Lab tests for SARS-CoV-2 included polymerase chain reaction and serum antibody assays.
Dr. Freeman and associates defined “long-haulers” as patients with dermatologic symptoms of COVID-19 lasting 60 days or longer. These “outliers” are likely more prevalent than the registry suggests, she said, since not all providers initially reporting skin symptoms in patients updated that information over time.
“It’s important to understand that the registry is probably significantly underreporting the duration of symptoms and number of long-hauler patients,” she explained. “A registry is often a glimpse into a moment in time to these patients. To combat that, we followed up by email twice with providers to ask if patients’ symptoms were still ongoing or completed.”
Results showed a wide spectrum in average duration of symptoms among lab-confirmed COVID-19 patients, depending on specific rash. Urticaria lasted for a median of 4 days; morbilliform eruptions, 7 days; pernio/chilblains, 10 days; and papulosquamous eruptions, 20 days, with one long-hauler case lasting 70 days.
Five patients with pernio/chilblains were long-haulers, with toe symptoms enduring 60 days or longer. Only one went beyond 133 days with severe pernio and fatigue.
“The fact that we’re not necessarily seeing these long-hauler symptoms across every type of skin rash makes sense,” Dr. Freeman said. “Hives, for example, usually comes on acutely and leaves pretty rapidly. There are no reports of long-hauler hives.”
“That we’re really seeing these long-hauler symptoms in certain skin rashes really suggests that there’s a certain pathophysiology going in within that group of patients,” she added.
Dr. Freeman said not enough data have yet been generated to correlate long-standing COVID-19 skin symptoms with lasting cardiac, neurologic, or other symptoms of prolonged inflammation stemming from the virus.
Meanwhile, an EADV survey of 490 dermatologists revealed that just over one-third have seen patients presenting with skin signs of COVID-19. Moreover, 4% of dermatologists themselves tested positive for the virus.
Dr. Freeman encouraged all frontline clinicians assessing COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms to enter patients into the registry. But despite its strengths, the registry “can’t tell us what percentage of everyone who gets COVID will develop a skin finding or what percentage will be a long-hauler,” she said.
“A registry doesn’t have a denominator, so it’s like a giant case series,” she added.
“It will be very helpful going forward, as many places around the world experience second or third waves of COVID-19, to follow patients prospectively, acknowledge that patients will have symptoms lasting different amounts of time, and be aware these symptoms can occur on the skin,” she said.
Christopher Griffiths, MD, of the University of Manchester (England), praised the international registry as a valuable tool that will help clinicians better manage patients with COVID-19–related skin effects and predict prognosis.
“This has really brought the international dermatology community together, working on a focused goal relevant to all of us around the world,” Dr. Griffiths said in an interview. “It shows the power of communication and collaboration and what can be achieved in a short period of time.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Griffiths disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
For acne in darker skin, judicious use of peeling agents can speed resolution
according to an expert, who cited both published data and empirical experience at the virtual Skin of Color Update 2020.
Because of the risk of exacerbating hyperpigmentation, superficial peels must be used judiciously, but “peels do add some benefit in terms of resolving the hyperpigmentation more rapidly,” Andrew Alexis, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at Mount Sinai Morningside and Mount Sinai West, New York, said at the meeting.
Addressing hyperpigmentation in skin of color is a critical goal. For many patients, the postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) that accompanies acne in Fitzpatrick skin types IV or higher imposes a greater burden than the acne itself.
“PIH is one of the driving forces among patients with darker skin coming to a dermatologist,” said Dr. Alexis, who is also professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Patients often describe these hyperpigmented macules as scars, and they are concerned that they are not reversible.”
In darker skin, the combination of treatments used for acne should address the pathogenic factors that contribute to acne and PIH at the same time, according to Dr. Alexis. He advised describing the goals and the timeline of acne and PIH resolution at the very first visit.
Of these two goals, resolution of PIH is often the more challenging. First-line topical retinoids have anti-inflammatory effects, but Dr. Alexis suggested that additional agents, such as topical antibiotics, topical dapsone, and benzoyl peroxide, are commonly needed to fully control inflammation.
“Topical retinoids serve as the foundation of acne treatment, especially in skin of color due to their dual action on acne and PIH,” he said. However, he added that this needs support with a “well-rounded combination therapy to address as many pathogenic factors as possible.”
One of these factors is subclinical inflammation. Citing studies first initiated at Howard University, Washington, Dr. Alexis said there are now compelling data showing T lymphocyte infiltration and increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines even in clinically uninvolved skin in acne patients with darker skin.
In patients with significant PIH, he considers oral antibiotics for their systemic anti-inflammatory effects, singling out sarecycline as a narrow-spectrum agent with a potent effect on Cutibacterium acnes. This tetracycline, a relatively recent addition to acne treatment options, has specifically been shown to be “superior to placebo across a diverse patient population” that includes those with darker skin tones.
“Another addition that can be leveraged for anti-inflammatory effects is topical minocycline foam. This has also been studied in diverse patient populations and shown to be superior to vehicle,” Dr. Alexis said.
For acne, the response to most of these therapies is relatively rapid, but control of PIH takes longer. After resolution of acne, he considers superficial chemical peels to speed the healing of PIH.
In a small randomized trial he cited, superficial glycolic acid peel added to a modified Kligman formula (hydroquinone 2%, tretinoin 0.05%, and hydrocortisone 1%) provided significantly lower scores in the mean Hyperpigmentation Area and Severity Index at 12 weeks (P = .004) and 21 weeks (P < .001 relative to the Kligman formula alone). Dr. Alexis said he has had the same clinical experience with chemical peels
For many acne patients with darker skin, good results are achieved after four weeks on a multidrug combination with a topical retinoid backbone. One week after stopping the combination, the superficial chemical peel can be started at a very low dose on an every-other-night schedule. If tolerated, the dose can be slowly increased.
Slow up-titration of all topical agents in skin of color, not just superficial chemical peels, is prudent, according to Dr. Alexis. For patients new to retinoids, he also recommended every-other-night dosing to avoid the irritation that might exacerbate PIH. He said the risks of adverse reactions come early. “We need to hold the hands of our patients through the first 2 weeks. Warn of dryness and pealing. Recommend moisturizers and keep the doses low.”
The benefits and risks of acne treatment are different in dark relative to light skin, Dr. Alexis emphasized. He added that a measured approach that includes specific strategies for PIH delivers results.
Providing treatment with a strategy that addresses both acne and PIH, he said, “we can have excellent outcomes time and time again for acne in patients with darker skin types.”
There is an evidence basis for making effective treatment of PIH a specific goal in the treatment of acne. In a study that evaluated the psychosocial impact of PIH in 50 patients with acne, 54% responded that PIH was a source of embarrassment. The study was one of the first to evaluate the impact of PIH as a separate source of impaired quality of life in acne patients.
“To improve the patient’s quality of life, the dermatologist should treat acne and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation at the same time,” said Katlein Franca, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology, University of Miami.
In particular, Dr. Franca, who led the PIH study, suggested that PIH, like acne, is a source of low self-esteem. In regard to PIH, “most patients feel embarrassed about the spots,” she said in an interview.
“Strategies to hide the hyperpigmented spots include the use of makeup and even different hairstyles to cover the affected areas,” she added, indicating that treatments provided to clear PIH as well as acne can remove a source of stress and threat to a sense of well-being.
Dr. Alexis reports financial relationships with many pharmaceutical companies, including those that make acne drugs.
according to an expert, who cited both published data and empirical experience at the virtual Skin of Color Update 2020.
Because of the risk of exacerbating hyperpigmentation, superficial peels must be used judiciously, but “peels do add some benefit in terms of resolving the hyperpigmentation more rapidly,” Andrew Alexis, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at Mount Sinai Morningside and Mount Sinai West, New York, said at the meeting.
Addressing hyperpigmentation in skin of color is a critical goal. For many patients, the postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) that accompanies acne in Fitzpatrick skin types IV or higher imposes a greater burden than the acne itself.
“PIH is one of the driving forces among patients with darker skin coming to a dermatologist,” said Dr. Alexis, who is also professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Patients often describe these hyperpigmented macules as scars, and they are concerned that they are not reversible.”
In darker skin, the combination of treatments used for acne should address the pathogenic factors that contribute to acne and PIH at the same time, according to Dr. Alexis. He advised describing the goals and the timeline of acne and PIH resolution at the very first visit.
Of these two goals, resolution of PIH is often the more challenging. First-line topical retinoids have anti-inflammatory effects, but Dr. Alexis suggested that additional agents, such as topical antibiotics, topical dapsone, and benzoyl peroxide, are commonly needed to fully control inflammation.
“Topical retinoids serve as the foundation of acne treatment, especially in skin of color due to their dual action on acne and PIH,” he said. However, he added that this needs support with a “well-rounded combination therapy to address as many pathogenic factors as possible.”
One of these factors is subclinical inflammation. Citing studies first initiated at Howard University, Washington, Dr. Alexis said there are now compelling data showing T lymphocyte infiltration and increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines even in clinically uninvolved skin in acne patients with darker skin.
In patients with significant PIH, he considers oral antibiotics for their systemic anti-inflammatory effects, singling out sarecycline as a narrow-spectrum agent with a potent effect on Cutibacterium acnes. This tetracycline, a relatively recent addition to acne treatment options, has specifically been shown to be “superior to placebo across a diverse patient population” that includes those with darker skin tones.
“Another addition that can be leveraged for anti-inflammatory effects is topical minocycline foam. This has also been studied in diverse patient populations and shown to be superior to vehicle,” Dr. Alexis said.
For acne, the response to most of these therapies is relatively rapid, but control of PIH takes longer. After resolution of acne, he considers superficial chemical peels to speed the healing of PIH.
In a small randomized trial he cited, superficial glycolic acid peel added to a modified Kligman formula (hydroquinone 2%, tretinoin 0.05%, and hydrocortisone 1%) provided significantly lower scores in the mean Hyperpigmentation Area and Severity Index at 12 weeks (P = .004) and 21 weeks (P < .001 relative to the Kligman formula alone). Dr. Alexis said he has had the same clinical experience with chemical peels
For many acne patients with darker skin, good results are achieved after four weeks on a multidrug combination with a topical retinoid backbone. One week after stopping the combination, the superficial chemical peel can be started at a very low dose on an every-other-night schedule. If tolerated, the dose can be slowly increased.
Slow up-titration of all topical agents in skin of color, not just superficial chemical peels, is prudent, according to Dr. Alexis. For patients new to retinoids, he also recommended every-other-night dosing to avoid the irritation that might exacerbate PIH. He said the risks of adverse reactions come early. “We need to hold the hands of our patients through the first 2 weeks. Warn of dryness and pealing. Recommend moisturizers and keep the doses low.”
The benefits and risks of acne treatment are different in dark relative to light skin, Dr. Alexis emphasized. He added that a measured approach that includes specific strategies for PIH delivers results.
Providing treatment with a strategy that addresses both acne and PIH, he said, “we can have excellent outcomes time and time again for acne in patients with darker skin types.”
There is an evidence basis for making effective treatment of PIH a specific goal in the treatment of acne. In a study that evaluated the psychosocial impact of PIH in 50 patients with acne, 54% responded that PIH was a source of embarrassment. The study was one of the first to evaluate the impact of PIH as a separate source of impaired quality of life in acne patients.
“To improve the patient’s quality of life, the dermatologist should treat acne and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation at the same time,” said Katlein Franca, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology, University of Miami.
In particular, Dr. Franca, who led the PIH study, suggested that PIH, like acne, is a source of low self-esteem. In regard to PIH, “most patients feel embarrassed about the spots,” she said in an interview.
“Strategies to hide the hyperpigmented spots include the use of makeup and even different hairstyles to cover the affected areas,” she added, indicating that treatments provided to clear PIH as well as acne can remove a source of stress and threat to a sense of well-being.
Dr. Alexis reports financial relationships with many pharmaceutical companies, including those that make acne drugs.
according to an expert, who cited both published data and empirical experience at the virtual Skin of Color Update 2020.
Because of the risk of exacerbating hyperpigmentation, superficial peels must be used judiciously, but “peels do add some benefit in terms of resolving the hyperpigmentation more rapidly,” Andrew Alexis, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at Mount Sinai Morningside and Mount Sinai West, New York, said at the meeting.
Addressing hyperpigmentation in skin of color is a critical goal. For many patients, the postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) that accompanies acne in Fitzpatrick skin types IV or higher imposes a greater burden than the acne itself.
“PIH is one of the driving forces among patients with darker skin coming to a dermatologist,” said Dr. Alexis, who is also professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Patients often describe these hyperpigmented macules as scars, and they are concerned that they are not reversible.”
In darker skin, the combination of treatments used for acne should address the pathogenic factors that contribute to acne and PIH at the same time, according to Dr. Alexis. He advised describing the goals and the timeline of acne and PIH resolution at the very first visit.
Of these two goals, resolution of PIH is often the more challenging. First-line topical retinoids have anti-inflammatory effects, but Dr. Alexis suggested that additional agents, such as topical antibiotics, topical dapsone, and benzoyl peroxide, are commonly needed to fully control inflammation.
“Topical retinoids serve as the foundation of acne treatment, especially in skin of color due to their dual action on acne and PIH,” he said. However, he added that this needs support with a “well-rounded combination therapy to address as many pathogenic factors as possible.”
One of these factors is subclinical inflammation. Citing studies first initiated at Howard University, Washington, Dr. Alexis said there are now compelling data showing T lymphocyte infiltration and increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines even in clinically uninvolved skin in acne patients with darker skin.
In patients with significant PIH, he considers oral antibiotics for their systemic anti-inflammatory effects, singling out sarecycline as a narrow-spectrum agent with a potent effect on Cutibacterium acnes. This tetracycline, a relatively recent addition to acne treatment options, has specifically been shown to be “superior to placebo across a diverse patient population” that includes those with darker skin tones.
“Another addition that can be leveraged for anti-inflammatory effects is topical minocycline foam. This has also been studied in diverse patient populations and shown to be superior to vehicle,” Dr. Alexis said.
For acne, the response to most of these therapies is relatively rapid, but control of PIH takes longer. After resolution of acne, he considers superficial chemical peels to speed the healing of PIH.
In a small randomized trial he cited, superficial glycolic acid peel added to a modified Kligman formula (hydroquinone 2%, tretinoin 0.05%, and hydrocortisone 1%) provided significantly lower scores in the mean Hyperpigmentation Area and Severity Index at 12 weeks (P = .004) and 21 weeks (P < .001 relative to the Kligman formula alone). Dr. Alexis said he has had the same clinical experience with chemical peels
For many acne patients with darker skin, good results are achieved after four weeks on a multidrug combination with a topical retinoid backbone. One week after stopping the combination, the superficial chemical peel can be started at a very low dose on an every-other-night schedule. If tolerated, the dose can be slowly increased.
Slow up-titration of all topical agents in skin of color, not just superficial chemical peels, is prudent, according to Dr. Alexis. For patients new to retinoids, he also recommended every-other-night dosing to avoid the irritation that might exacerbate PIH. He said the risks of adverse reactions come early. “We need to hold the hands of our patients through the first 2 weeks. Warn of dryness and pealing. Recommend moisturizers and keep the doses low.”
The benefits and risks of acne treatment are different in dark relative to light skin, Dr. Alexis emphasized. He added that a measured approach that includes specific strategies for PIH delivers results.
Providing treatment with a strategy that addresses both acne and PIH, he said, “we can have excellent outcomes time and time again for acne in patients with darker skin types.”
There is an evidence basis for making effective treatment of PIH a specific goal in the treatment of acne. In a study that evaluated the psychosocial impact of PIH in 50 patients with acne, 54% responded that PIH was a source of embarrassment. The study was one of the first to evaluate the impact of PIH as a separate source of impaired quality of life in acne patients.
“To improve the patient’s quality of life, the dermatologist should treat acne and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation at the same time,” said Katlein Franca, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology, University of Miami.
In particular, Dr. Franca, who led the PIH study, suggested that PIH, like acne, is a source of low self-esteem. In regard to PIH, “most patients feel embarrassed about the spots,” she said in an interview.
“Strategies to hide the hyperpigmented spots include the use of makeup and even different hairstyles to cover the affected areas,” she added, indicating that treatments provided to clear PIH as well as acne can remove a source of stress and threat to a sense of well-being.
Dr. Alexis reports financial relationships with many pharmaceutical companies, including those that make acne drugs.
FROM SOC 2020
Chronic abdominal pain: What to do when a patient presents with it
She reports the pain is about a 7 out of 10, located in the right upper quadrant. The pain does not worsen with food and not relieved with bowel movements. She has no nausea or vomiting. She reports that the pain worsens when she is sitting or standing and is relieved by lying down. Her past medical history includes having had a cholecystectomy in 2016, having hypertension, and having type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The patient’s medications include metformin, lisinopril, and empagliflozin. Her blood pressure was 130/70, and her pulse was 80. An abdominal exam of her found tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant, and no rebound tenderness. Her labs found a white blood cell count of 5.4, a hematocrit of 44%, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 13, a C-reactive protein of 1.0, a bilirubin of .8, an alkaline phosphatase of 100, an aspartate aminotransferase of 30, and an alanine transaminase of 22.
What is the most appropriate next step?
A) Right side up oblique ultrasound.
B) Abdominal CT scan.
C) Upper endoscopy.
D) More detailed physical exam.
The correct answer here is D, a more detailed physical exam is needed. Given the positional nature of this patient’s abdominal pain, an evaluation for an abdominal wall cause is appropriate.
Abdominal wall pain as a cause of chronic abdominal pain is rarely considered, but it really should be. Costanza and colleagues looked at 2,709 patients referred to gastroenterologists for chronic abdominal pain.1 Chronic abdominal wall pain was diagnosed in 137 patients, with the diagnosis unchanged in 97% of these patients after 4 years. Most of the patients were women (four to one), and the diagnosis was almost always unsuspected by the referring physician. Physical exam was helpful in suggesting the diagnosis of abdominal wall pain.
The use of Carnett sign can be helpful. A positive Carnett sign is when abdominal pain increases or remains unchanged with tensing abdomen or when the examiner palpates the tensed abdomen. Thompson and colleagues looked at the outcome of 72 patients with undiagnosed abdominal pain and a positive Carnett sign.2 Despite multiple diagnostic tests and surgeries done on these patients, very few of them had serious underlying pathology.
Thompson and Frances published another study looking at 120 patients presenting to an ED with undiagnosed abdominal pain.3 Twenty-four of the patients had positive abdominal wall tenderness on exam, and of those, only 1 had intra-abdominal pathology.
In another study, 158 patients admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain were evaluated for the presence of abdominal wall pain.4 Fifty-three patients were diagnosed with appendicitis, and 5 had abdominal wall tenderness on exam. Thirty-eight patients had other intra-abdominal pathology, and none of those had abdominal wall tenderness on exam. Of the 67 patients in the study who had nonspecific abdominal pain, 19 had abdominal wall tenderness on exam.
Most physicians do not include evaluation for abdominal wall tenderness as part of their evaluation of patients with abdominal pain. I think looking for this is helpful and, if positive, may lead to a diagnosis, as well as reduce the likelihood of intra-abdominal diagnoses.
What can we do in regard to therapy for patients with an abdominal wall source of pain?
Many patients with abdominal wall pain have anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES). Patient’s with this often have discrete areas of tenderness on exam, often on the lateral edge of the rectus sheath, frequently on the right side of the abdomen. Anesthetic injection at the point of tenderness provides immediate relief for patients with ACNES, and is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.
Boelens and colleagues did injections in 48 patients suspected of having ACNE, randomizing half to receive lidocaine and half to receive saline placebo.5The majority of the patients receiving lidocaine (54%) had a response, compared with 17% of placebo patients (P less than .007).
Greenbaum and colleagues studied 79 patients with chronic abdominal wall pain.6 In this study, 72 of 79 patients had greater than 50% pain relief with anesthetic injection and were followed for a mean of almost 14 months. Only four of these patients ended up having a visceral cause of pain.
Can using injections help pain from ACNES longer term?
Koop and colleagues looked at all published studies in regards to both immediate and longer-term pain relief with injections.7 Both lidocaine injections and injections with lidocaine plus steroids led to long-term pain relief (40%-50% of patients with multiple lidocaine injections and up to 80% with lidocaine plus steroid injections). I think that injections are certainly worth a try in patients with chronic abdominal wall pain.
Pearl
Consider chronic abdominal wall pain in your differential diagnoses for patients with chronic abdominal pain, and use Carnett sign to help with diagnosis.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Costanza CD et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 May;2(5):395-9.
2. Thomson WH et al. Br J Surg. 1991 Feb;78(2):223-5.
3. Thomson H, Francis DM. Lancet. 1977 Nov 19;2(8047):1053-4.
4. Gray DW et al. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1988 Jul;70(4):233-4.
5. Boelens OB et al. Br J Surg. 2013 Jan;100(2):217-21.
6. Greenbaum DS et al. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Sep;39(9):1935-41.
7. Koop H et al. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2016 Jan 29;113(4):51-7.
She reports the pain is about a 7 out of 10, located in the right upper quadrant. The pain does not worsen with food and not relieved with bowel movements. She has no nausea or vomiting. She reports that the pain worsens when she is sitting or standing and is relieved by lying down. Her past medical history includes having had a cholecystectomy in 2016, having hypertension, and having type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The patient’s medications include metformin, lisinopril, and empagliflozin. Her blood pressure was 130/70, and her pulse was 80. An abdominal exam of her found tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant, and no rebound tenderness. Her labs found a white blood cell count of 5.4, a hematocrit of 44%, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 13, a C-reactive protein of 1.0, a bilirubin of .8, an alkaline phosphatase of 100, an aspartate aminotransferase of 30, and an alanine transaminase of 22.
What is the most appropriate next step?
A) Right side up oblique ultrasound.
B) Abdominal CT scan.
C) Upper endoscopy.
D) More detailed physical exam.
The correct answer here is D, a more detailed physical exam is needed. Given the positional nature of this patient’s abdominal pain, an evaluation for an abdominal wall cause is appropriate.
Abdominal wall pain as a cause of chronic abdominal pain is rarely considered, but it really should be. Costanza and colleagues looked at 2,709 patients referred to gastroenterologists for chronic abdominal pain.1 Chronic abdominal wall pain was diagnosed in 137 patients, with the diagnosis unchanged in 97% of these patients after 4 years. Most of the patients were women (four to one), and the diagnosis was almost always unsuspected by the referring physician. Physical exam was helpful in suggesting the diagnosis of abdominal wall pain.
The use of Carnett sign can be helpful. A positive Carnett sign is when abdominal pain increases or remains unchanged with tensing abdomen or when the examiner palpates the tensed abdomen. Thompson and colleagues looked at the outcome of 72 patients with undiagnosed abdominal pain and a positive Carnett sign.2 Despite multiple diagnostic tests and surgeries done on these patients, very few of them had serious underlying pathology.
Thompson and Frances published another study looking at 120 patients presenting to an ED with undiagnosed abdominal pain.3 Twenty-four of the patients had positive abdominal wall tenderness on exam, and of those, only 1 had intra-abdominal pathology.
In another study, 158 patients admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain were evaluated for the presence of abdominal wall pain.4 Fifty-three patients were diagnosed with appendicitis, and 5 had abdominal wall tenderness on exam. Thirty-eight patients had other intra-abdominal pathology, and none of those had abdominal wall tenderness on exam. Of the 67 patients in the study who had nonspecific abdominal pain, 19 had abdominal wall tenderness on exam.
Most physicians do not include evaluation for abdominal wall tenderness as part of their evaluation of patients with abdominal pain. I think looking for this is helpful and, if positive, may lead to a diagnosis, as well as reduce the likelihood of intra-abdominal diagnoses.
What can we do in regard to therapy for patients with an abdominal wall source of pain?
Many patients with abdominal wall pain have anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES). Patient’s with this often have discrete areas of tenderness on exam, often on the lateral edge of the rectus sheath, frequently on the right side of the abdomen. Anesthetic injection at the point of tenderness provides immediate relief for patients with ACNES, and is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.
Boelens and colleagues did injections in 48 patients suspected of having ACNE, randomizing half to receive lidocaine and half to receive saline placebo.5The majority of the patients receiving lidocaine (54%) had a response, compared with 17% of placebo patients (P less than .007).
Greenbaum and colleagues studied 79 patients with chronic abdominal wall pain.6 In this study, 72 of 79 patients had greater than 50% pain relief with anesthetic injection and were followed for a mean of almost 14 months. Only four of these patients ended up having a visceral cause of pain.
Can using injections help pain from ACNES longer term?
Koop and colleagues looked at all published studies in regards to both immediate and longer-term pain relief with injections.7 Both lidocaine injections and injections with lidocaine plus steroids led to long-term pain relief (40%-50% of patients with multiple lidocaine injections and up to 80% with lidocaine plus steroid injections). I think that injections are certainly worth a try in patients with chronic abdominal wall pain.
Pearl
Consider chronic abdominal wall pain in your differential diagnoses for patients with chronic abdominal pain, and use Carnett sign to help with diagnosis.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Costanza CD et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 May;2(5):395-9.
2. Thomson WH et al. Br J Surg. 1991 Feb;78(2):223-5.
3. Thomson H, Francis DM. Lancet. 1977 Nov 19;2(8047):1053-4.
4. Gray DW et al. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1988 Jul;70(4):233-4.
5. Boelens OB et al. Br J Surg. 2013 Jan;100(2):217-21.
6. Greenbaum DS et al. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Sep;39(9):1935-41.
7. Koop H et al. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2016 Jan 29;113(4):51-7.
She reports the pain is about a 7 out of 10, located in the right upper quadrant. The pain does not worsen with food and not relieved with bowel movements. She has no nausea or vomiting. She reports that the pain worsens when she is sitting or standing and is relieved by lying down. Her past medical history includes having had a cholecystectomy in 2016, having hypertension, and having type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The patient’s medications include metformin, lisinopril, and empagliflozin. Her blood pressure was 130/70, and her pulse was 80. An abdominal exam of her found tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant, and no rebound tenderness. Her labs found a white blood cell count of 5.4, a hematocrit of 44%, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 13, a C-reactive protein of 1.0, a bilirubin of .8, an alkaline phosphatase of 100, an aspartate aminotransferase of 30, and an alanine transaminase of 22.
What is the most appropriate next step?
A) Right side up oblique ultrasound.
B) Abdominal CT scan.
C) Upper endoscopy.
D) More detailed physical exam.
The correct answer here is D, a more detailed physical exam is needed. Given the positional nature of this patient’s abdominal pain, an evaluation for an abdominal wall cause is appropriate.
Abdominal wall pain as a cause of chronic abdominal pain is rarely considered, but it really should be. Costanza and colleagues looked at 2,709 patients referred to gastroenterologists for chronic abdominal pain.1 Chronic abdominal wall pain was diagnosed in 137 patients, with the diagnosis unchanged in 97% of these patients after 4 years. Most of the patients were women (four to one), and the diagnosis was almost always unsuspected by the referring physician. Physical exam was helpful in suggesting the diagnosis of abdominal wall pain.
The use of Carnett sign can be helpful. A positive Carnett sign is when abdominal pain increases or remains unchanged with tensing abdomen or when the examiner palpates the tensed abdomen. Thompson and colleagues looked at the outcome of 72 patients with undiagnosed abdominal pain and a positive Carnett sign.2 Despite multiple diagnostic tests and surgeries done on these patients, very few of them had serious underlying pathology.
Thompson and Frances published another study looking at 120 patients presenting to an ED with undiagnosed abdominal pain.3 Twenty-four of the patients had positive abdominal wall tenderness on exam, and of those, only 1 had intra-abdominal pathology.
In another study, 158 patients admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain were evaluated for the presence of abdominal wall pain.4 Fifty-three patients were diagnosed with appendicitis, and 5 had abdominal wall tenderness on exam. Thirty-eight patients had other intra-abdominal pathology, and none of those had abdominal wall tenderness on exam. Of the 67 patients in the study who had nonspecific abdominal pain, 19 had abdominal wall tenderness on exam.
Most physicians do not include evaluation for abdominal wall tenderness as part of their evaluation of patients with abdominal pain. I think looking for this is helpful and, if positive, may lead to a diagnosis, as well as reduce the likelihood of intra-abdominal diagnoses.
What can we do in regard to therapy for patients with an abdominal wall source of pain?
Many patients with abdominal wall pain have anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES). Patient’s with this often have discrete areas of tenderness on exam, often on the lateral edge of the rectus sheath, frequently on the right side of the abdomen. Anesthetic injection at the point of tenderness provides immediate relief for patients with ACNES, and is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.
Boelens and colleagues did injections in 48 patients suspected of having ACNE, randomizing half to receive lidocaine and half to receive saline placebo.5The majority of the patients receiving lidocaine (54%) had a response, compared with 17% of placebo patients (P less than .007).
Greenbaum and colleagues studied 79 patients with chronic abdominal wall pain.6 In this study, 72 of 79 patients had greater than 50% pain relief with anesthetic injection and were followed for a mean of almost 14 months. Only four of these patients ended up having a visceral cause of pain.
Can using injections help pain from ACNES longer term?
Koop and colleagues looked at all published studies in regards to both immediate and longer-term pain relief with injections.7 Both lidocaine injections and injections with lidocaine plus steroids led to long-term pain relief (40%-50% of patients with multiple lidocaine injections and up to 80% with lidocaine plus steroid injections). I think that injections are certainly worth a try in patients with chronic abdominal wall pain.
Pearl
Consider chronic abdominal wall pain in your differential diagnoses for patients with chronic abdominal pain, and use Carnett sign to help with diagnosis.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Costanza CD et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 May;2(5):395-9.
2. Thomson WH et al. Br J Surg. 1991 Feb;78(2):223-5.
3. Thomson H, Francis DM. Lancet. 1977 Nov 19;2(8047):1053-4.
4. Gray DW et al. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1988 Jul;70(4):233-4.
5. Boelens OB et al. Br J Surg. 2013 Jan;100(2):217-21.
6. Greenbaum DS et al. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Sep;39(9):1935-41.
7. Koop H et al. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2016 Jan 29;113(4):51-7.
When First-Line Systemic Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Fails, What Comes Next?
The following is a lightly edited transcript of a virtual roundtable discussion recorded in September 2020. To view the full discussion, go to www.mdedge.com/FedPrac/HCC-Roundtable.
The following is a lightly edited transcript of a virtual roundtable discussion recorded in September 2020. To view the full discussion, go to www.mdedge.com/FedPrac/HCC-Roundtable.
The following is a lightly edited transcript of a virtual roundtable discussion recorded in September 2020. To view the full discussion, go to www.mdedge.com/FedPrac/HCC-Roundtable.
Real-world results with checkpoint inhibitors found inferior to trial results
according to research published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.
However, the research also suggests that real-world patients who receive ICIs achieve longer survival than patients on standard-of-care medications.
“Patients receiving ICIs in real-world practice may differ from those enrolled in trials in a variety of ways, including age, race, performance status, and comorbidity burden,” said study author Jerry S.H. Lee, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Lee noted that only 3%-4% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. In fact, more than half of patients with melanoma and nearly three-quarters of those with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) do not meet criteria for eligibility in clinical trials, he said.
To examine the discrepancies between real-world practice and clinical trials and to better understand which patients receive ICIs in clinical practice, Dr. Lee and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis using electronic health record data from Veterans Administration (VA) facilities nationwide.
The researchers identified 11,888 cancer patients who were treated with ICIs. The cohort included patients who are underrepresented in pivotal clinical trials, including older, non-White, and/or higher disease-burdened patients.
The majority of patients were treated for NSCLC (51.1%), followed by melanoma (14.4%), renal cell carcinoma (RCC; 8.1%), squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (6.8%), urothelial cancer (6.4%), hepatocellular carcinoma (4.5%), and other less common cancer types (8.8%).
Overall survival by indication
In general, median overall survival (OS) in the VA cohort was inferior to median OS reported in clinical trials. However, patients treated with first-line nivolumab for melanoma and second-line pembrolizumab or nivolumab for NSCLC had similar OS in the real-world and trial data.
The researchers did not report exact OS numbers from clinical trials. However, they did report the exact numbers from the VA cohort and show OS differences between the VA cohort and clinical trials graphically.
Among patients in the VA cohort, the median OS was:
- 25.5 months in melanoma patients on first-line nivolumab
- 16.3 months in RCC patients receiving nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 14 months in RCC patients on first-line ipilimumab and nivolumab
- 10.6 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab
- 9.9 months in NSCLC patients receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 9.1 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy
- 6.7 months in urothelial cancer patients receiving ICIs in the second line or higher.
A number of factors may have contributed to the shorter OS observed in the VA cohort, according to the researchers. The VA cohort is predominantly male, is older, and has a higher degree of comorbidity, compared with patients in clinical trials.
In addition, no data are available to determine the cause for discontinuation of therapy, and VA patients may have received ICIs after failing multiple lines of previous therapy, while clinical trials may limit patients to only one or two previous lines of therapy.
After stratifying VA patients by frailty status, the OS among non-frail patients was more similar to the OS reported in clinical trials.
“Real-world outcomes from the VA were more similar when adjusted for frailty, which shows the importance of patient diversity in clinical trials,” Dr. Lee said. He added that the definition of frailty among VA patients included potential injury during combat and therefore differs from a generic frailty definition.
ICIs vs. standard care
The researchers also found that VA patients treated with ICIs had longer OS, compared with a cohort of VA patients receiving standard-of-care therapies.
The median OS was as follows:
- In melanoma patients on first-line treatment – 39.29 months with nivolumab and 5.75 months with chemotherapy (P < .001).
- In RCC patients on first-line treatment – 14.01 months with ipilimumab plus nivolumab and 8.63 months with targeted therapy (P = .051).
- In RCC patients on second-line or greater treatment – 12.43 months with nivolumab and 8.09 months with everolimus (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line therapy – 8.88 months with pembrolizumab and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line combination therapy – 10.59 months with pembrolizumab plus platinum chemotherapy and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on second-line or greater therapy – 10.06 months with pembrolizumab or nivolumab and 6.41 months with docetaxel (P < .001).
- In urothelial cancer patients on second-line or greater therapy – 7.66 months with an ICI and 6.31 months with chemotherapy (P = .043).
Help for treatment decisions
“The real-world survival outcomes not only indicate the breadth of indications but also represent patients who tend not to be eligible for immunotherapy trials, based on their health status,” Dr. Lee said. “We hope this dataset of national-level experience provides practicing oncologists evidence to help patients and family members in the process of decision-making about therapy.”
Real-world data can also inform oncologists who face decisions on whether to prescribe or withhold ICIs and patients who face the financial burden of paying for ICIs, he said.
This dataset will be continually updated. The researchers have already added another 10,000 VA patients who have received immunotherapies in the year since the trial began.
“In a longitudinal way, we plan to examine what causes differences in outcomes and continue to find ways to extend care to veterans with a balance of high quality of life,” Dr. Lee said.
“Patients who participate in clinical trials are, on average, younger and healthier than the general population,” said Bora Youn, PhD, a senior biostatistician at Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., who was not involved in this study.
“In the case of immunotherapies, those with poor performance status and autoimmune conditions are often excluded from trials,” Dr. Youn added. “In the real world, these patients can also receive treatments, and clinicians often need to extrapolate the results from clinical trials. It is therefore important to collect real-world data to understand the effectiveness and safety of these therapies in patients with limited evidence.”
Dr. Youn led a real-world study, published in Cancer, of 1,256 Medicare recipients who were diagnosed with NSCLC and received ICI therapy.
“We found that factors associated with poor prognosis in general, such as squamous histology and failure of aggressive prior treatment, are also predictive of decreased survival among those who initiated immunotherapies. Yet, OS of older patients was relatively comparable to those observed in clinical trials,” Dr. Youn said.
“Understanding the real-world effectiveness of these treatments will help improve the evidence base, especially for those underrepresented in clinical trials. These studies can also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from immunotherapies,” Dr. Youn added.
This study was supported by the VA Office of Research and Development Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Lee and Dr. Youn disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jennifer La et al. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics. 2020:4:918-28.
according to research published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.
However, the research also suggests that real-world patients who receive ICIs achieve longer survival than patients on standard-of-care medications.
“Patients receiving ICIs in real-world practice may differ from those enrolled in trials in a variety of ways, including age, race, performance status, and comorbidity burden,” said study author Jerry S.H. Lee, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Lee noted that only 3%-4% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. In fact, more than half of patients with melanoma and nearly three-quarters of those with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) do not meet criteria for eligibility in clinical trials, he said.
To examine the discrepancies between real-world practice and clinical trials and to better understand which patients receive ICIs in clinical practice, Dr. Lee and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis using electronic health record data from Veterans Administration (VA) facilities nationwide.
The researchers identified 11,888 cancer patients who were treated with ICIs. The cohort included patients who are underrepresented in pivotal clinical trials, including older, non-White, and/or higher disease-burdened patients.
The majority of patients were treated for NSCLC (51.1%), followed by melanoma (14.4%), renal cell carcinoma (RCC; 8.1%), squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (6.8%), urothelial cancer (6.4%), hepatocellular carcinoma (4.5%), and other less common cancer types (8.8%).
Overall survival by indication
In general, median overall survival (OS) in the VA cohort was inferior to median OS reported in clinical trials. However, patients treated with first-line nivolumab for melanoma and second-line pembrolizumab or nivolumab for NSCLC had similar OS in the real-world and trial data.
The researchers did not report exact OS numbers from clinical trials. However, they did report the exact numbers from the VA cohort and show OS differences between the VA cohort and clinical trials graphically.
Among patients in the VA cohort, the median OS was:
- 25.5 months in melanoma patients on first-line nivolumab
- 16.3 months in RCC patients receiving nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 14 months in RCC patients on first-line ipilimumab and nivolumab
- 10.6 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab
- 9.9 months in NSCLC patients receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 9.1 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy
- 6.7 months in urothelial cancer patients receiving ICIs in the second line or higher.
A number of factors may have contributed to the shorter OS observed in the VA cohort, according to the researchers. The VA cohort is predominantly male, is older, and has a higher degree of comorbidity, compared with patients in clinical trials.
In addition, no data are available to determine the cause for discontinuation of therapy, and VA patients may have received ICIs after failing multiple lines of previous therapy, while clinical trials may limit patients to only one or two previous lines of therapy.
After stratifying VA patients by frailty status, the OS among non-frail patients was more similar to the OS reported in clinical trials.
“Real-world outcomes from the VA were more similar when adjusted for frailty, which shows the importance of patient diversity in clinical trials,” Dr. Lee said. He added that the definition of frailty among VA patients included potential injury during combat and therefore differs from a generic frailty definition.
ICIs vs. standard care
The researchers also found that VA patients treated with ICIs had longer OS, compared with a cohort of VA patients receiving standard-of-care therapies.
The median OS was as follows:
- In melanoma patients on first-line treatment – 39.29 months with nivolumab and 5.75 months with chemotherapy (P < .001).
- In RCC patients on first-line treatment – 14.01 months with ipilimumab plus nivolumab and 8.63 months with targeted therapy (P = .051).
- In RCC patients on second-line or greater treatment – 12.43 months with nivolumab and 8.09 months with everolimus (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line therapy – 8.88 months with pembrolizumab and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line combination therapy – 10.59 months with pembrolizumab plus platinum chemotherapy and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on second-line or greater therapy – 10.06 months with pembrolizumab or nivolumab and 6.41 months with docetaxel (P < .001).
- In urothelial cancer patients on second-line or greater therapy – 7.66 months with an ICI and 6.31 months with chemotherapy (P = .043).
Help for treatment decisions
“The real-world survival outcomes not only indicate the breadth of indications but also represent patients who tend not to be eligible for immunotherapy trials, based on their health status,” Dr. Lee said. “We hope this dataset of national-level experience provides practicing oncologists evidence to help patients and family members in the process of decision-making about therapy.”
Real-world data can also inform oncologists who face decisions on whether to prescribe or withhold ICIs and patients who face the financial burden of paying for ICIs, he said.
This dataset will be continually updated. The researchers have already added another 10,000 VA patients who have received immunotherapies in the year since the trial began.
“In a longitudinal way, we plan to examine what causes differences in outcomes and continue to find ways to extend care to veterans with a balance of high quality of life,” Dr. Lee said.
“Patients who participate in clinical trials are, on average, younger and healthier than the general population,” said Bora Youn, PhD, a senior biostatistician at Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., who was not involved in this study.
“In the case of immunotherapies, those with poor performance status and autoimmune conditions are often excluded from trials,” Dr. Youn added. “In the real world, these patients can also receive treatments, and clinicians often need to extrapolate the results from clinical trials. It is therefore important to collect real-world data to understand the effectiveness and safety of these therapies in patients with limited evidence.”
Dr. Youn led a real-world study, published in Cancer, of 1,256 Medicare recipients who were diagnosed with NSCLC and received ICI therapy.
“We found that factors associated with poor prognosis in general, such as squamous histology and failure of aggressive prior treatment, are also predictive of decreased survival among those who initiated immunotherapies. Yet, OS of older patients was relatively comparable to those observed in clinical trials,” Dr. Youn said.
“Understanding the real-world effectiveness of these treatments will help improve the evidence base, especially for those underrepresented in clinical trials. These studies can also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from immunotherapies,” Dr. Youn added.
This study was supported by the VA Office of Research and Development Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Lee and Dr. Youn disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jennifer La et al. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics. 2020:4:918-28.
according to research published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.
However, the research also suggests that real-world patients who receive ICIs achieve longer survival than patients on standard-of-care medications.
“Patients receiving ICIs in real-world practice may differ from those enrolled in trials in a variety of ways, including age, race, performance status, and comorbidity burden,” said study author Jerry S.H. Lee, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Lee noted that only 3%-4% of cancer patients participate in clinical trials. In fact, more than half of patients with melanoma and nearly three-quarters of those with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) do not meet criteria for eligibility in clinical trials, he said.
To examine the discrepancies between real-world practice and clinical trials and to better understand which patients receive ICIs in clinical practice, Dr. Lee and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis using electronic health record data from Veterans Administration (VA) facilities nationwide.
The researchers identified 11,888 cancer patients who were treated with ICIs. The cohort included patients who are underrepresented in pivotal clinical trials, including older, non-White, and/or higher disease-burdened patients.
The majority of patients were treated for NSCLC (51.1%), followed by melanoma (14.4%), renal cell carcinoma (RCC; 8.1%), squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (6.8%), urothelial cancer (6.4%), hepatocellular carcinoma (4.5%), and other less common cancer types (8.8%).
Overall survival by indication
In general, median overall survival (OS) in the VA cohort was inferior to median OS reported in clinical trials. However, patients treated with first-line nivolumab for melanoma and second-line pembrolizumab or nivolumab for NSCLC had similar OS in the real-world and trial data.
The researchers did not report exact OS numbers from clinical trials. However, they did report the exact numbers from the VA cohort and show OS differences between the VA cohort and clinical trials graphically.
Among patients in the VA cohort, the median OS was:
- 25.5 months in melanoma patients on first-line nivolumab
- 16.3 months in RCC patients receiving nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 14 months in RCC patients on first-line ipilimumab and nivolumab
- 10.6 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab
- 9.9 months in NSCLC patients receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab in the second line or higher
- 9.1 months in NSCLC patients on first-line pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy
- 6.7 months in urothelial cancer patients receiving ICIs in the second line or higher.
A number of factors may have contributed to the shorter OS observed in the VA cohort, according to the researchers. The VA cohort is predominantly male, is older, and has a higher degree of comorbidity, compared with patients in clinical trials.
In addition, no data are available to determine the cause for discontinuation of therapy, and VA patients may have received ICIs after failing multiple lines of previous therapy, while clinical trials may limit patients to only one or two previous lines of therapy.
After stratifying VA patients by frailty status, the OS among non-frail patients was more similar to the OS reported in clinical trials.
“Real-world outcomes from the VA were more similar when adjusted for frailty, which shows the importance of patient diversity in clinical trials,” Dr. Lee said. He added that the definition of frailty among VA patients included potential injury during combat and therefore differs from a generic frailty definition.
ICIs vs. standard care
The researchers also found that VA patients treated with ICIs had longer OS, compared with a cohort of VA patients receiving standard-of-care therapies.
The median OS was as follows:
- In melanoma patients on first-line treatment – 39.29 months with nivolumab and 5.75 months with chemotherapy (P < .001).
- In RCC patients on first-line treatment – 14.01 months with ipilimumab plus nivolumab and 8.63 months with targeted therapy (P = .051).
- In RCC patients on second-line or greater treatment – 12.43 months with nivolumab and 8.09 months with everolimus (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line therapy – 8.88 months with pembrolizumab and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on first-line combination therapy – 10.59 months with pembrolizumab plus platinum chemotherapy and 6.38 months with a platinum doublet (P < .001).
- In NSCLC patients on second-line or greater therapy – 10.06 months with pembrolizumab or nivolumab and 6.41 months with docetaxel (P < .001).
- In urothelial cancer patients on second-line or greater therapy – 7.66 months with an ICI and 6.31 months with chemotherapy (P = .043).
Help for treatment decisions
“The real-world survival outcomes not only indicate the breadth of indications but also represent patients who tend not to be eligible for immunotherapy trials, based on their health status,” Dr. Lee said. “We hope this dataset of national-level experience provides practicing oncologists evidence to help patients and family members in the process of decision-making about therapy.”
Real-world data can also inform oncologists who face decisions on whether to prescribe or withhold ICIs and patients who face the financial burden of paying for ICIs, he said.
This dataset will be continually updated. The researchers have already added another 10,000 VA patients who have received immunotherapies in the year since the trial began.
“In a longitudinal way, we plan to examine what causes differences in outcomes and continue to find ways to extend care to veterans with a balance of high quality of life,” Dr. Lee said.
“Patients who participate in clinical trials are, on average, younger and healthier than the general population,” said Bora Youn, PhD, a senior biostatistician at Biogen in Cambridge, Mass., who was not involved in this study.
“In the case of immunotherapies, those with poor performance status and autoimmune conditions are often excluded from trials,” Dr. Youn added. “In the real world, these patients can also receive treatments, and clinicians often need to extrapolate the results from clinical trials. It is therefore important to collect real-world data to understand the effectiveness and safety of these therapies in patients with limited evidence.”
Dr. Youn led a real-world study, published in Cancer, of 1,256 Medicare recipients who were diagnosed with NSCLC and received ICI therapy.
“We found that factors associated with poor prognosis in general, such as squamous histology and failure of aggressive prior treatment, are also predictive of decreased survival among those who initiated immunotherapies. Yet, OS of older patients was relatively comparable to those observed in clinical trials,” Dr. Youn said.
“Understanding the real-world effectiveness of these treatments will help improve the evidence base, especially for those underrepresented in clinical trials. These studies can also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from immunotherapies,” Dr. Youn added.
This study was supported by the VA Office of Research and Development Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Lee and Dr. Youn disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jennifer La et al. JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics. 2020:4:918-28.
FROM JCO CLINICAL CANCER INFORMATICS
October 2020 - What's the diagnosis?
Answer: Celiac hepatitis
Endoscopic biopsy of this severely scalloped duodenal mucosa demonstrated characteristic findings of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, or celiac disease. Celiac disease involvement of the liver is a common extraintestinal manifestation of this immune-mediated disorder, termed celiac hepatitis. Celiac hepatitis affects 40% of adults with celiac disease.1 The pathogenesis is poorly understood, but posited to be related to autoimmunity or toxin-mediated liver injury in the setting of gluten exposure, gut permeability, chronic inflammation, and host susceptibility, among other mechanisms.1-3
Clinical manifestations of celiac hepatitis range from unexplained enzyme elevations in the absence of known liver disease to autoimmune hepatitis to hepatic steatosis, and even cirrhosis.1 The initial presentation can also be elevated liver enzymes in the setting of known celiac disease, without known hepatic disease. Histology of the liver is similarly variable, from a mild or a chronic hepatitis to steatohepatitis and even fibrosis.2 Elevated transaminases less than five times the upper limit of normal when found at celiac diagnosis suggest celiac hepatitis, and do not require further workup.1 For these individuals, response to a gluten-free diet should be monitored and liver chemistries should be repeated at 6–12 months. Persistently elevated aminotransferases should prompt further workup.1 Generally, enzyme elevation and even the histologic appearance of the liver improve after implementation of a gluten-free diet, although not all.2 In celiac hepatitis associated with autoimmune liver disease, immunosuppression may be required in addition to abstaining from gluten.3 Our patient was found to have a tissue transglutaminase level > 100 U/mL (normal, < 4 U/mL). He began a gluten-free diet guided by a nutritionist 4 weeks ago, with rapid improvement in abdominal symptoms, and will be followed to ensure normalization of liver enzymes, which can take up to 1 year.
References
1. Rubio-Tapia A, Murray JA. Liver involvement in celiac disease. Minerva Med. 2008;99:595-604.
2. Majumdar K, Sakhuja P, Puri AS, et al. Coeliac disease and the liver: spectrum of liver histology, serology and treatment response at a tertiary referral centre. J Clin Pathol. 2018;71:412-9.
3. Marciano F, Savoia M, Vajro P. Celiac disease-related hepatic injury: insights into associated conditions and underlying pathomechanisms. Dig Liver Dis. 2016;48:112-9.
Answer: Celiac hepatitis
Endoscopic biopsy of this severely scalloped duodenal mucosa demonstrated characteristic findings of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, or celiac disease. Celiac disease involvement of the liver is a common extraintestinal manifestation of this immune-mediated disorder, termed celiac hepatitis. Celiac hepatitis affects 40% of adults with celiac disease.1 The pathogenesis is poorly understood, but posited to be related to autoimmunity or toxin-mediated liver injury in the setting of gluten exposure, gut permeability, chronic inflammation, and host susceptibility, among other mechanisms.1-3
Clinical manifestations of celiac hepatitis range from unexplained enzyme elevations in the absence of known liver disease to autoimmune hepatitis to hepatic steatosis, and even cirrhosis.1 The initial presentation can also be elevated liver enzymes in the setting of known celiac disease, without known hepatic disease. Histology of the liver is similarly variable, from a mild or a chronic hepatitis to steatohepatitis and even fibrosis.2 Elevated transaminases less than five times the upper limit of normal when found at celiac diagnosis suggest celiac hepatitis, and do not require further workup.1 For these individuals, response to a gluten-free diet should be monitored and liver chemistries should be repeated at 6–12 months. Persistently elevated aminotransferases should prompt further workup.1 Generally, enzyme elevation and even the histologic appearance of the liver improve after implementation of a gluten-free diet, although not all.2 In celiac hepatitis associated with autoimmune liver disease, immunosuppression may be required in addition to abstaining from gluten.3 Our patient was found to have a tissue transglutaminase level > 100 U/mL (normal, < 4 U/mL). He began a gluten-free diet guided by a nutritionist 4 weeks ago, with rapid improvement in abdominal symptoms, and will be followed to ensure normalization of liver enzymes, which can take up to 1 year.
References
1. Rubio-Tapia A, Murray JA. Liver involvement in celiac disease. Minerva Med. 2008;99:595-604.
2. Majumdar K, Sakhuja P, Puri AS, et al. Coeliac disease and the liver: spectrum of liver histology, serology and treatment response at a tertiary referral centre. J Clin Pathol. 2018;71:412-9.
3. Marciano F, Savoia M, Vajro P. Celiac disease-related hepatic injury: insights into associated conditions and underlying pathomechanisms. Dig Liver Dis. 2016;48:112-9.
Answer: Celiac hepatitis
Endoscopic biopsy of this severely scalloped duodenal mucosa demonstrated characteristic findings of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, or celiac disease. Celiac disease involvement of the liver is a common extraintestinal manifestation of this immune-mediated disorder, termed celiac hepatitis. Celiac hepatitis affects 40% of adults with celiac disease.1 The pathogenesis is poorly understood, but posited to be related to autoimmunity or toxin-mediated liver injury in the setting of gluten exposure, gut permeability, chronic inflammation, and host susceptibility, among other mechanisms.1-3
Clinical manifestations of celiac hepatitis range from unexplained enzyme elevations in the absence of known liver disease to autoimmune hepatitis to hepatic steatosis, and even cirrhosis.1 The initial presentation can also be elevated liver enzymes in the setting of known celiac disease, without known hepatic disease. Histology of the liver is similarly variable, from a mild or a chronic hepatitis to steatohepatitis and even fibrosis.2 Elevated transaminases less than five times the upper limit of normal when found at celiac diagnosis suggest celiac hepatitis, and do not require further workup.1 For these individuals, response to a gluten-free diet should be monitored and liver chemistries should be repeated at 6–12 months. Persistently elevated aminotransferases should prompt further workup.1 Generally, enzyme elevation and even the histologic appearance of the liver improve after implementation of a gluten-free diet, although not all.2 In celiac hepatitis associated with autoimmune liver disease, immunosuppression may be required in addition to abstaining from gluten.3 Our patient was found to have a tissue transglutaminase level > 100 U/mL (normal, < 4 U/mL). He began a gluten-free diet guided by a nutritionist 4 weeks ago, with rapid improvement in abdominal symptoms, and will be followed to ensure normalization of liver enzymes, which can take up to 1 year.
References
1. Rubio-Tapia A, Murray JA. Liver involvement in celiac disease. Minerva Med. 2008;99:595-604.
2. Majumdar K, Sakhuja P, Puri AS, et al. Coeliac disease and the liver: spectrum of liver histology, serology and treatment response at a tertiary referral centre. J Clin Pathol. 2018;71:412-9.
3. Marciano F, Savoia M, Vajro P. Celiac disease-related hepatic injury: insights into associated conditions and underlying pathomechanisms. Dig Liver Dis. 2016;48:112-9.
Question: A 24-year-old white man with depression and anxiety disorder is referred for an isolated alanine aminotransferase elevation found by his primary medical doctor on routine blood work. He denies a family history of liver disease, although he does report a family history of lupus. He denies risk factors for viral hepatitis. He drinks about three alcoholic beverages per week. His family is originally from Germany and Ireland. He denies use of over-the-counter medications or supplements beyond a rare use of ibuprofen. His only medication is daily escitalopram. On further questioning he also reports abdominal pain. The abdominal pain is described as dull, constant, right upper quadrant pain near his rib cage. The pain occasionally becomes worse if he eats fast foods. He also notes a 3-month history of bloating and alternating bowel habits between diarrhea and constipation.
Physical examination is notable for unremarkable vital signs and a normal body mass index. He has no stigmata of chronic liver disease or hepatomegaly. He has normal bowel sounds without any tenderness to palpation. An in-office FibroScan is normal with a value of 3 kPa. Aspartate aminotransferase is 33 U/L (normal, 10-40 U/L). Viral serologies are notable for nonreactive hepatitis B surface antigen, surface antibody, and core antibody. Hepatitis C virus RNA is undetectable. Ferritin, iron, and creatine kinase are normal. Thyroid-stimulating hormone, antimitochondrial antibody, and antinuclear antibody are negative. Ceruloplasmin is normal and alpha-1 antitrypsin showed MZ phenotype. An abdominal ultrasound scan shows a normal size liver, normal echotexture, and sludge in the gallbladder, without any intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile duct dilation. The extrahepatic bile duct diameter is 0.3 cm.
Antismooth muscle and quantitative immunoglobulin tests were ordered. An endoscopy is performed for abdominal pain, and duodenal endoscopic and histologic images are provided.