User login
Is the troll tracker crying wolf?
I’m a big believer in my state’s Prescription Monitoring Program (PMP), perhaps more commonly known as the troll tracker. The ability to quickly access a patient’s controlled prescription records across pharmacies has been enormously helpful in my everyday practice. I rely on it and check it often.
With it I can see if my patients are getting the same drug from other prescribers, pharmacy-shopping, or carrying out other concerning activities. The database helpfully sends me emails alerting me to such conflicts, so I can take prompt action on them.
Unfortunately, the threshold for such emails has gradually crept lower, to where I now get maybe 10 a week.
A lady to whom I gave two Valium tablets to get her through a lumbar spine MRI also got 20 Percocet for the same back pain from her internist … and I get an alert email.
A long-established patient for whom I’ve been prescribing Ativan and Tramadol for years, fills them both every month … and I get an alert email every month (and I’m the only prescriber who has written for him in the last 10 years).
A patient who suffered a painful vertebral fracture, got 10 Norco in the ED, follows with up with me 5 days later, and I write her for 20 more … and I get an email.
Now, I understand what the program is trying to do – and wholeheartedly agree with it – but the problem is that the more email warnings I get the less likely I am to have time to investigate each one. It’s like the boy who cried “wolf!” In fact, it’s probably been over a year since a warning email from the PMP told me something I didn’t already know.
Granted, these emails are sent by a computer, following a rigid set of parameters to do so. The machine doesn’t know I’m aware of the situation, or keep track of case nuances, or even notice that I’m the only prescriber of all the medications involved. It just does what it’s set to do. And the warnings all make it clear that they’re just warnings, and that the treatment is still left to physician’s discretion.
Arizona currently has roughly 18,000 practicing physicians. Granted, not all of them are routinely prescribing controlled agents, but I’d guess at least two-thirds of them are. So it’s safe to assume at least 12,000 doctors here are receiving email warnings with varying degrees of frequency.
At some point, with all the other tasks and hats your average doctor goes through in a day, too many of these warnings – the vast majority of them meaningless – become part of the background noise.
There are only so many hours in a day to see patients, write notes, send prescriptions, review tests, return calls, fill out forms, and all the other things that are part of our days. Having to log into the PMP website to see what’s up every time you get an email from them, especially when the last 20 (or more) warnings that you received were meaningless, gets pushed farther and farther onto the back burner. So when a real warning shows up, it may not got noticed much at all.
Like I said, I believe in and routinely use the state PMP. But it may be time to take a second look at the criteria under which its email warning system operates.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I’m a big believer in my state’s Prescription Monitoring Program (PMP), perhaps more commonly known as the troll tracker. The ability to quickly access a patient’s controlled prescription records across pharmacies has been enormously helpful in my everyday practice. I rely on it and check it often.
With it I can see if my patients are getting the same drug from other prescribers, pharmacy-shopping, or carrying out other concerning activities. The database helpfully sends me emails alerting me to such conflicts, so I can take prompt action on them.
Unfortunately, the threshold for such emails has gradually crept lower, to where I now get maybe 10 a week.
A lady to whom I gave two Valium tablets to get her through a lumbar spine MRI also got 20 Percocet for the same back pain from her internist … and I get an alert email.
A long-established patient for whom I’ve been prescribing Ativan and Tramadol for years, fills them both every month … and I get an alert email every month (and I’m the only prescriber who has written for him in the last 10 years).
A patient who suffered a painful vertebral fracture, got 10 Norco in the ED, follows with up with me 5 days later, and I write her for 20 more … and I get an email.
Now, I understand what the program is trying to do – and wholeheartedly agree with it – but the problem is that the more email warnings I get the less likely I am to have time to investigate each one. It’s like the boy who cried “wolf!” In fact, it’s probably been over a year since a warning email from the PMP told me something I didn’t already know.
Granted, these emails are sent by a computer, following a rigid set of parameters to do so. The machine doesn’t know I’m aware of the situation, or keep track of case nuances, or even notice that I’m the only prescriber of all the medications involved. It just does what it’s set to do. And the warnings all make it clear that they’re just warnings, and that the treatment is still left to physician’s discretion.
Arizona currently has roughly 18,000 practicing physicians. Granted, not all of them are routinely prescribing controlled agents, but I’d guess at least two-thirds of them are. So it’s safe to assume at least 12,000 doctors here are receiving email warnings with varying degrees of frequency.
At some point, with all the other tasks and hats your average doctor goes through in a day, too many of these warnings – the vast majority of them meaningless – become part of the background noise.
There are only so many hours in a day to see patients, write notes, send prescriptions, review tests, return calls, fill out forms, and all the other things that are part of our days. Having to log into the PMP website to see what’s up every time you get an email from them, especially when the last 20 (or more) warnings that you received were meaningless, gets pushed farther and farther onto the back burner. So when a real warning shows up, it may not got noticed much at all.
Like I said, I believe in and routinely use the state PMP. But it may be time to take a second look at the criteria under which its email warning system operates.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I’m a big believer in my state’s Prescription Monitoring Program (PMP), perhaps more commonly known as the troll tracker. The ability to quickly access a patient’s controlled prescription records across pharmacies has been enormously helpful in my everyday practice. I rely on it and check it often.
With it I can see if my patients are getting the same drug from other prescribers, pharmacy-shopping, or carrying out other concerning activities. The database helpfully sends me emails alerting me to such conflicts, so I can take prompt action on them.
Unfortunately, the threshold for such emails has gradually crept lower, to where I now get maybe 10 a week.
A lady to whom I gave two Valium tablets to get her through a lumbar spine MRI also got 20 Percocet for the same back pain from her internist … and I get an alert email.
A long-established patient for whom I’ve been prescribing Ativan and Tramadol for years, fills them both every month … and I get an alert email every month (and I’m the only prescriber who has written for him in the last 10 years).
A patient who suffered a painful vertebral fracture, got 10 Norco in the ED, follows with up with me 5 days later, and I write her for 20 more … and I get an email.
Now, I understand what the program is trying to do – and wholeheartedly agree with it – but the problem is that the more email warnings I get the less likely I am to have time to investigate each one. It’s like the boy who cried “wolf!” In fact, it’s probably been over a year since a warning email from the PMP told me something I didn’t already know.
Granted, these emails are sent by a computer, following a rigid set of parameters to do so. The machine doesn’t know I’m aware of the situation, or keep track of case nuances, or even notice that I’m the only prescriber of all the medications involved. It just does what it’s set to do. And the warnings all make it clear that they’re just warnings, and that the treatment is still left to physician’s discretion.
Arizona currently has roughly 18,000 practicing physicians. Granted, not all of them are routinely prescribing controlled agents, but I’d guess at least two-thirds of them are. So it’s safe to assume at least 12,000 doctors here are receiving email warnings with varying degrees of frequency.
At some point, with all the other tasks and hats your average doctor goes through in a day, too many of these warnings – the vast majority of them meaningless – become part of the background noise.
There are only so many hours in a day to see patients, write notes, send prescriptions, review tests, return calls, fill out forms, and all the other things that are part of our days. Having to log into the PMP website to see what’s up every time you get an email from them, especially when the last 20 (or more) warnings that you received were meaningless, gets pushed farther and farther onto the back burner. So when a real warning shows up, it may not got noticed much at all.
Like I said, I believe in and routinely use the state PMP. But it may be time to take a second look at the criteria under which its email warning system operates.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The authority/accountability balance
Evaluating your career trajectory
I have had the pleasure of working on the Society of Hospital Medicine’s signature Leadership Academies since 2010, and I enjoy working with hospital medicine leaders from around the country every year. I started as a hospital medicine leader in 2000 and served during the unprecedented growth of the field when it was “the most rapidly growing specialty in the history of medicine.”
Most businesses dream of having a year of double-digit growth; my department grew an average of 15% annually for more than 10 years. These unique experiences have taught me many lessons and afforded me the opportunity to watch many stars of hospital medicine rise, as well as to learn from several less-scrupulous leaders about the darker side of hospital politics.
One of the lessons I learned the hard way about hospital politics is striking the “Authority/Accountability balance” in your career. I shared this perspective at the SHM annual conference in 2018, at speaking engagements on the West Coast, and with my leadership group at the academies. I am sharing it with you because the feedback I have received has been very positive.
The Authority/Accountability balance is a tool for evaluating your current career trajectory and measuring if it is set up for success or failure. The essence is that your Authority and Accountability need to be balanced for you to be successful in your career, regardless of your station. Everybody from the hospitalist fresh out of residency to the CEO needs to have Authority and Accountability in balance to be successful. And as you use the tool to measure your own potential for success or failure, learn to apply it to those who report to you.
I believe the rising tide lifts all boats and the success of your subordinates, through mentoring and support, will add to your success. There is another, more cynical view of subordinates that can be identified using the Authority/Accountability balance, which I will address.
Authority
In this construct, “Authority” has a much broader meaning than just the ability to tell people what to do. The ability to tell people what to do is important but not sufficient for success in hospital politics.
Financial resources are essential for a successful Authority/Accountability balance – not only the hardware such as computers, telephones, pagers, and so on, but also clerical support, technical support, and analytic support so that you are getting high-quality data on the performance of the members of your hospital medicine group (HMG). These “soft” resources (clerical, technical, and analytical) are often overlooked as needs that HMG leaders must advocate for; I speak with many HMG leaders who remain under-resourced with “soft” assets. However, being appropriately resourced in these areas can be transformational for a group. Hospitalists don’t like doing clerical work, and if you don’t like a menial job assigned to you, you probably won’t do it very well. Having an unlicensed person dedicated to these clerical activities not only will cost less, but will ensure the job is done better.
Reporting structure is critically important, often overlooked, and historically misaligned in HMGs. When hospital medicine was starting in the late 1990s and early 2000s, rapidly growing hospitalist groups were typically led by young, early-career physicians who had chosen hospital medicine as a career. The problem was that they often lacked the seniority and connections at the executive level to advocate for their HMG. All too often the hospitalist group was tucked in under another department or division which, in turn, reported HMG updates and issues to the board of directors and the CEO.
A common reporting structure in the early days was that a senior member of the medical staff, or group, had once worked in the hospital and therefore “understood” the issues and challenges that the hospitalists were facing. It was up to this physician with seniority and connections to advocate for the hospitalists as they saw fit. The problem was that the hospital landscape was, and is, constantly evolving in innumerable ways. These “once removed” reporting structures for HMGs failed to get the required information on the rapidly changing, and evolving, hospitalist landscape to the desks of executives who had the financial and structural control to address the challenges that the hospitalists in the trenches were facing.
Numerous HMGs failed in the early days of hospital medicine because of this type of misaligned reporting structure. This is a lesson that should not be forgotten: Make sure your HMG leader has a seat at the table where executive decisions are made, including but not limited to the board of directors. To be in balance, you have to be “in the room where it happens.”
Accountability
The outcomes that you are responsible for need to be explicit, appropriately resourced with Authority, and clearly spelled out in your job description. Your job description is a document you should know, own, and revisit regularly with whomever you report to, in order to ensure success.
Once you have the Authority side of the equation appropriately resourced, setting outcomes that are a stretch, but still realistic and achievable within the scope of your position, is critical to your success. It is good to think about short-, medium-, and long-term goals, especially if you are in a leadership role. For example, one expectation you will have, regardless of your station, is that you keep up on your email and answer your phone. These are short-term goals that will often be included in your job description. However, taking on a new hospital contract and making sure that it has 24/7 hospitalist coverage, that all the hospitalists are meeting the geometric mean length of stay, and that all the physicians are having 15 encounters per day doesn’t happen immediately. Long-term goals, such as taking on a new hospital contract, are the big-picture stuff that can make or break the career of an HMG leader. Long-term goals also need to be delineated in the job description, along with specific time stamps and the resources you need to accomplish big ticket items – which are spelled out in the Authority side (that is, physician recruiter, secretary, background checks, and so on).
One of the classic misuses of Accountability is the “Fall Guy” scenario. The Fall Guy scenario is often used by cynical hospital and medical group executives to expand their influence while limiting their liability. In the Fall Guy scenario, the executive is surrounded with junior partners who are underpowered with Authority, and then the executive makes decisions for which the junior partners are Accountable. This allows the senior executive to make risky decisions on behalf of the hospital or medical group without the liability of being held accountable when the decision-making process fails. When the risky, and often ill-informed, decision fails, the junior partner who lacked the Authority to make the decision – but held the Accountability for it – becomes the Fall Guy for the failed endeavor. This is a critical outcome that the Authority/Accountability balance can help you avoid, if you use it wisely and properly.
If you find yourself in the Fall Guy position, it is time for a change. The Authority, the Accountability, or both need to change so that they are in better balance. Or your employer needs to change. Changing employers is an outcome worth avoiding, if at all possible. I have scrutinized thousands of resumes in my career, and frequent job changes always wave a red flag to prospective employers. However, changing jobs remains a crucial option if you are being set up for failure when Authority and Accountability are out of balance.
If you are unable to negotiate for the balance that will allow you to be successful with your current group, remember that HMG leaders are a prized commodity and in short supply. Leaving a group that has been your career is hard, but it is better to leave than stay in a position where you are set up for failure as the Fall Guy. Further, the most effective time to expand your Authority is when you are negotiating the terms of a new position. Changing positions is the nuclear option. However, it is better than becoming the Fall Guy, and a change can create opportunities that will accelerate your career and influence, if done right.
When I talk about Authority/Accountability balance, I always counter the Fall Guy with an ignominious historical figure: General George B. McClellan. General McClellan was the commander of the Army of the Potomac during the early years of the American Civil War. General McClellan had the industrial might of the Union north at his beck and call, as well as extraordinary resources for recruiting and retaining soldiers for his army. At every encounter with General Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia, General McClellan outnumbered them, sometimes by more than two to one. Yet General McClellan was outfoxed repeatedly for the same reason: He failed to take decisive action.
Every time that McClellan failed, he blamed insufficient resources and told President Lincoln that he needed more troops and more equipment to be successful. In summary, while the Fall Guy scenario needs to be avoided, once you are adequately resourced, success requires taking decisive and strategic action, or you will suffer as did General McClellan. Failing to act when you are appropriately resourced can be just as damaging to your career and credibility as allowing yourself to become the Fall Guy.
Job description
Everybody has somebody that they report to, no matter how high up on the executive ladder they have climbed. Even the CEO must report to the board of directors. And that reporting structure usually involves periodic formal reviews. Your formal review is a good time to go over your job description, note what is relevant, remove what is irrelevant, and add new elements that have evolved in importance since your last review.
Job descriptions take many forms, but they always include a list of qualifications. If you have the job, you have the qualifications, so that is not likely to change. You may become more qualified for a higher-level position, but that is an entirely different discussion. I like to think of a well-written job description as including short-term and long-term goals. Short-term goals are usually the daily stuff that keeps operations running smoothly but garners little attention. Examples would include staying current on your emails, answering your phone, organizing meetings, and regularly attending various committees. Even some of these short-term goals can and will change over time. I always enjoyed quality oversight in my department, but as the department and my responsibilities grew, I realized I couldn’t do everything that I wanted to do. I needed to focus on the things only I could do and delegate those things that could be done by someone else, even though I wanted to continue doing them myself. I created a position for a clinical quality officer, and quality oversight moved off of my job description.
Long-term goals are the aspirational items, such as increasing market share, decreasing readmissions, improving patient satisfaction, and the like. Effective leaders are often focused on these aspirational, long-term goals, but they still must effectively execute their short-term goals. Stephen Covey outlines the dilemma with the “time management matrix” in his seminal work “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.” An in-depth discussion is beyond the scope of this article, but the time management matrix places tasks into one of four categories based on urgency and importance, and provides strategies for staying up on short-term goals while continually moving long-term goals forward.If you show up at your review with a list of accomplishments as well as an understanding of how the “time management matrix” affects your responsibilities, your boss will be impressed. It is also worth mentioning that Covey’s first habit is “Proactivity.” He uses the term Proactivity in a much more nuanced form than we typically think of, however. Simply put, Proactivity is the opposite of Reactivity, and it is another invaluable tool for success with those long-term goals that will help you make a name for yourself.
When you show up for your review, be it annual, biannual, or other, be prepared. Not only should you bring your job description and recommendations for how it should be adapted in the changing environment, but also bring examples of your accomplishments since the last review.
I talk with leaders frequently who are hardworking and diligent and hate bragging about their achievements; I get that. At the same time, if you don’t inform your superiors about your successes, there is no guarantee that they will hear about them or understand them in the appropriate context. Bragging about how great you are in the physician’s lounge is annoying; telling your boss about your accomplishments since the last review is critical to maintaining the momentum of past accomplishments. If you are not willing to toot your own horn, there is a very good chance that your horn will remain silent. I don’t think self-promotion comes easily to anyone, and it has to be done with a degree of humility and sensitivity; but it has to be done, so prepare for it.
Look out for yourself and others
We talk about teamwork and collaboration as hospitalists, and SHM is always underscoring the importance of teamwork and highlighting examples of successful teamwork in its many conferences and publications. Most hospital executives are focused on their own careers, however, and many have no reservations about damaging your career (your brand) if they think it will promote theirs. You have to look out for yourself and size up every leadership position you get into.
Physicians can expect their careers to last decades. The average hospital CEO has a tenure of less than 3.5 years, however, and when a new CEO is hired, almost half of chief financial, chief operating, and chief information officers are fired within 9 months. You may be focused on the long-term success of your organization as you plan your career, but many hospital administrators are interested only in short-term gains. It is similar to some members of Congress who are interested only in what they need to do now to win the next election and not in the long-term needs of the country. You should understand this disconnect when dealing with hospital executives, and how you and your credibility can become cannon fodder in their quest for short-term self-preservation.
You have to look out for and take care of yourself as you promote your group. With a better understanding of the Authority/Accountability balance, you have new tools to assess your chances of success and to advocate for yourself so that you and your group can be successful.
Despite my cynicism toward executives in the medical field, I personally advocate for supporting the career development of those around you and advise against furthering your career at the expense of others. Many unscrupulous executives will use this approach, surrounding themselves with Fall Guys, but my experience shows that this is not a sustainable strategy for success. It can lead to short-term gains, but eventually the piper must be paid. Moreover, the most successful medical executives and leaders that I have encountered have been those who genuinely cared about their subordinates, looked out for them, and selflessly promoted their careers.
In the age of social media, tearing others down seems to be the fastest way to get more “likes.” However, I strongly believe that you can’t build up your group, and our profession, just by tearing people down. Lending a helping hand may bring you less attention in the short term, but such action raises your stature, creates loyalty, and leads to sustainable success for the long run.
Dr. McIlraith is the founding chairman of the Hospital Medicine Department at Mercy Medical Group in Sacramento, Calif. He received the SHM Award for Outstanding Service in Hospital Medicine in 2016 and is currently a member of the SHM Practice Management and Awards Committees, as well as the SHM Critical Care Task Force.
Sources
Quinn R. HM Turns 20: A look at the evolution of hospital medicine. The Hospitalist. 2016 August. https://www.the-hospitalist.org/hospitalist/article/121525/hm-turns-20-look-evolution-hospital-medicine
Stephen R. Covey. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change. Simon & Schuster. 1989.
10 Statistics on CEO Turnover, Recruitment. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2020. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-management-administration/10-statistics-on-ceo-turnover-recruitment.html
Evaluating your career trajectory
Evaluating your career trajectory
I have had the pleasure of working on the Society of Hospital Medicine’s signature Leadership Academies since 2010, and I enjoy working with hospital medicine leaders from around the country every year. I started as a hospital medicine leader in 2000 and served during the unprecedented growth of the field when it was “the most rapidly growing specialty in the history of medicine.”
Most businesses dream of having a year of double-digit growth; my department grew an average of 15% annually for more than 10 years. These unique experiences have taught me many lessons and afforded me the opportunity to watch many stars of hospital medicine rise, as well as to learn from several less-scrupulous leaders about the darker side of hospital politics.
One of the lessons I learned the hard way about hospital politics is striking the “Authority/Accountability balance” in your career. I shared this perspective at the SHM annual conference in 2018, at speaking engagements on the West Coast, and with my leadership group at the academies. I am sharing it with you because the feedback I have received has been very positive.
The Authority/Accountability balance is a tool for evaluating your current career trajectory and measuring if it is set up for success or failure. The essence is that your Authority and Accountability need to be balanced for you to be successful in your career, regardless of your station. Everybody from the hospitalist fresh out of residency to the CEO needs to have Authority and Accountability in balance to be successful. And as you use the tool to measure your own potential for success or failure, learn to apply it to those who report to you.
I believe the rising tide lifts all boats and the success of your subordinates, through mentoring and support, will add to your success. There is another, more cynical view of subordinates that can be identified using the Authority/Accountability balance, which I will address.
Authority
In this construct, “Authority” has a much broader meaning than just the ability to tell people what to do. The ability to tell people what to do is important but not sufficient for success in hospital politics.
Financial resources are essential for a successful Authority/Accountability balance – not only the hardware such as computers, telephones, pagers, and so on, but also clerical support, technical support, and analytic support so that you are getting high-quality data on the performance of the members of your hospital medicine group (HMG). These “soft” resources (clerical, technical, and analytical) are often overlooked as needs that HMG leaders must advocate for; I speak with many HMG leaders who remain under-resourced with “soft” assets. However, being appropriately resourced in these areas can be transformational for a group. Hospitalists don’t like doing clerical work, and if you don’t like a menial job assigned to you, you probably won’t do it very well. Having an unlicensed person dedicated to these clerical activities not only will cost less, but will ensure the job is done better.
Reporting structure is critically important, often overlooked, and historically misaligned in HMGs. When hospital medicine was starting in the late 1990s and early 2000s, rapidly growing hospitalist groups were typically led by young, early-career physicians who had chosen hospital medicine as a career. The problem was that they often lacked the seniority and connections at the executive level to advocate for their HMG. All too often the hospitalist group was tucked in under another department or division which, in turn, reported HMG updates and issues to the board of directors and the CEO.
A common reporting structure in the early days was that a senior member of the medical staff, or group, had once worked in the hospital and therefore “understood” the issues and challenges that the hospitalists were facing. It was up to this physician with seniority and connections to advocate for the hospitalists as they saw fit. The problem was that the hospital landscape was, and is, constantly evolving in innumerable ways. These “once removed” reporting structures for HMGs failed to get the required information on the rapidly changing, and evolving, hospitalist landscape to the desks of executives who had the financial and structural control to address the challenges that the hospitalists in the trenches were facing.
Numerous HMGs failed in the early days of hospital medicine because of this type of misaligned reporting structure. This is a lesson that should not be forgotten: Make sure your HMG leader has a seat at the table where executive decisions are made, including but not limited to the board of directors. To be in balance, you have to be “in the room where it happens.”
Accountability
The outcomes that you are responsible for need to be explicit, appropriately resourced with Authority, and clearly spelled out in your job description. Your job description is a document you should know, own, and revisit regularly with whomever you report to, in order to ensure success.
Once you have the Authority side of the equation appropriately resourced, setting outcomes that are a stretch, but still realistic and achievable within the scope of your position, is critical to your success. It is good to think about short-, medium-, and long-term goals, especially if you are in a leadership role. For example, one expectation you will have, regardless of your station, is that you keep up on your email and answer your phone. These are short-term goals that will often be included in your job description. However, taking on a new hospital contract and making sure that it has 24/7 hospitalist coverage, that all the hospitalists are meeting the geometric mean length of stay, and that all the physicians are having 15 encounters per day doesn’t happen immediately. Long-term goals, such as taking on a new hospital contract, are the big-picture stuff that can make or break the career of an HMG leader. Long-term goals also need to be delineated in the job description, along with specific time stamps and the resources you need to accomplish big ticket items – which are spelled out in the Authority side (that is, physician recruiter, secretary, background checks, and so on).
One of the classic misuses of Accountability is the “Fall Guy” scenario. The Fall Guy scenario is often used by cynical hospital and medical group executives to expand their influence while limiting their liability. In the Fall Guy scenario, the executive is surrounded with junior partners who are underpowered with Authority, and then the executive makes decisions for which the junior partners are Accountable. This allows the senior executive to make risky decisions on behalf of the hospital or medical group without the liability of being held accountable when the decision-making process fails. When the risky, and often ill-informed, decision fails, the junior partner who lacked the Authority to make the decision – but held the Accountability for it – becomes the Fall Guy for the failed endeavor. This is a critical outcome that the Authority/Accountability balance can help you avoid, if you use it wisely and properly.
If you find yourself in the Fall Guy position, it is time for a change. The Authority, the Accountability, or both need to change so that they are in better balance. Or your employer needs to change. Changing employers is an outcome worth avoiding, if at all possible. I have scrutinized thousands of resumes in my career, and frequent job changes always wave a red flag to prospective employers. However, changing jobs remains a crucial option if you are being set up for failure when Authority and Accountability are out of balance.
If you are unable to negotiate for the balance that will allow you to be successful with your current group, remember that HMG leaders are a prized commodity and in short supply. Leaving a group that has been your career is hard, but it is better to leave than stay in a position where you are set up for failure as the Fall Guy. Further, the most effective time to expand your Authority is when you are negotiating the terms of a new position. Changing positions is the nuclear option. However, it is better than becoming the Fall Guy, and a change can create opportunities that will accelerate your career and influence, if done right.
When I talk about Authority/Accountability balance, I always counter the Fall Guy with an ignominious historical figure: General George B. McClellan. General McClellan was the commander of the Army of the Potomac during the early years of the American Civil War. General McClellan had the industrial might of the Union north at his beck and call, as well as extraordinary resources for recruiting and retaining soldiers for his army. At every encounter with General Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia, General McClellan outnumbered them, sometimes by more than two to one. Yet General McClellan was outfoxed repeatedly for the same reason: He failed to take decisive action.
Every time that McClellan failed, he blamed insufficient resources and told President Lincoln that he needed more troops and more equipment to be successful. In summary, while the Fall Guy scenario needs to be avoided, once you are adequately resourced, success requires taking decisive and strategic action, or you will suffer as did General McClellan. Failing to act when you are appropriately resourced can be just as damaging to your career and credibility as allowing yourself to become the Fall Guy.
Job description
Everybody has somebody that they report to, no matter how high up on the executive ladder they have climbed. Even the CEO must report to the board of directors. And that reporting structure usually involves periodic formal reviews. Your formal review is a good time to go over your job description, note what is relevant, remove what is irrelevant, and add new elements that have evolved in importance since your last review.
Job descriptions take many forms, but they always include a list of qualifications. If you have the job, you have the qualifications, so that is not likely to change. You may become more qualified for a higher-level position, but that is an entirely different discussion. I like to think of a well-written job description as including short-term and long-term goals. Short-term goals are usually the daily stuff that keeps operations running smoothly but garners little attention. Examples would include staying current on your emails, answering your phone, organizing meetings, and regularly attending various committees. Even some of these short-term goals can and will change over time. I always enjoyed quality oversight in my department, but as the department and my responsibilities grew, I realized I couldn’t do everything that I wanted to do. I needed to focus on the things only I could do and delegate those things that could be done by someone else, even though I wanted to continue doing them myself. I created a position for a clinical quality officer, and quality oversight moved off of my job description.
Long-term goals are the aspirational items, such as increasing market share, decreasing readmissions, improving patient satisfaction, and the like. Effective leaders are often focused on these aspirational, long-term goals, but they still must effectively execute their short-term goals. Stephen Covey outlines the dilemma with the “time management matrix” in his seminal work “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.” An in-depth discussion is beyond the scope of this article, but the time management matrix places tasks into one of four categories based on urgency and importance, and provides strategies for staying up on short-term goals while continually moving long-term goals forward.If you show up at your review with a list of accomplishments as well as an understanding of how the “time management matrix” affects your responsibilities, your boss will be impressed. It is also worth mentioning that Covey’s first habit is “Proactivity.” He uses the term Proactivity in a much more nuanced form than we typically think of, however. Simply put, Proactivity is the opposite of Reactivity, and it is another invaluable tool for success with those long-term goals that will help you make a name for yourself.
When you show up for your review, be it annual, biannual, or other, be prepared. Not only should you bring your job description and recommendations for how it should be adapted in the changing environment, but also bring examples of your accomplishments since the last review.
I talk with leaders frequently who are hardworking and diligent and hate bragging about their achievements; I get that. At the same time, if you don’t inform your superiors about your successes, there is no guarantee that they will hear about them or understand them in the appropriate context. Bragging about how great you are in the physician’s lounge is annoying; telling your boss about your accomplishments since the last review is critical to maintaining the momentum of past accomplishments. If you are not willing to toot your own horn, there is a very good chance that your horn will remain silent. I don’t think self-promotion comes easily to anyone, and it has to be done with a degree of humility and sensitivity; but it has to be done, so prepare for it.
Look out for yourself and others
We talk about teamwork and collaboration as hospitalists, and SHM is always underscoring the importance of teamwork and highlighting examples of successful teamwork in its many conferences and publications. Most hospital executives are focused on their own careers, however, and many have no reservations about damaging your career (your brand) if they think it will promote theirs. You have to look out for yourself and size up every leadership position you get into.
Physicians can expect their careers to last decades. The average hospital CEO has a tenure of less than 3.5 years, however, and when a new CEO is hired, almost half of chief financial, chief operating, and chief information officers are fired within 9 months. You may be focused on the long-term success of your organization as you plan your career, but many hospital administrators are interested only in short-term gains. It is similar to some members of Congress who are interested only in what they need to do now to win the next election and not in the long-term needs of the country. You should understand this disconnect when dealing with hospital executives, and how you and your credibility can become cannon fodder in their quest for short-term self-preservation.
You have to look out for and take care of yourself as you promote your group. With a better understanding of the Authority/Accountability balance, you have new tools to assess your chances of success and to advocate for yourself so that you and your group can be successful.
Despite my cynicism toward executives in the medical field, I personally advocate for supporting the career development of those around you and advise against furthering your career at the expense of others. Many unscrupulous executives will use this approach, surrounding themselves with Fall Guys, but my experience shows that this is not a sustainable strategy for success. It can lead to short-term gains, but eventually the piper must be paid. Moreover, the most successful medical executives and leaders that I have encountered have been those who genuinely cared about their subordinates, looked out for them, and selflessly promoted their careers.
In the age of social media, tearing others down seems to be the fastest way to get more “likes.” However, I strongly believe that you can’t build up your group, and our profession, just by tearing people down. Lending a helping hand may bring you less attention in the short term, but such action raises your stature, creates loyalty, and leads to sustainable success for the long run.
Dr. McIlraith is the founding chairman of the Hospital Medicine Department at Mercy Medical Group in Sacramento, Calif. He received the SHM Award for Outstanding Service in Hospital Medicine in 2016 and is currently a member of the SHM Practice Management and Awards Committees, as well as the SHM Critical Care Task Force.
Sources
Quinn R. HM Turns 20: A look at the evolution of hospital medicine. The Hospitalist. 2016 August. https://www.the-hospitalist.org/hospitalist/article/121525/hm-turns-20-look-evolution-hospital-medicine
Stephen R. Covey. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change. Simon & Schuster. 1989.
10 Statistics on CEO Turnover, Recruitment. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2020. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-management-administration/10-statistics-on-ceo-turnover-recruitment.html
I have had the pleasure of working on the Society of Hospital Medicine’s signature Leadership Academies since 2010, and I enjoy working with hospital medicine leaders from around the country every year. I started as a hospital medicine leader in 2000 and served during the unprecedented growth of the field when it was “the most rapidly growing specialty in the history of medicine.”
Most businesses dream of having a year of double-digit growth; my department grew an average of 15% annually for more than 10 years. These unique experiences have taught me many lessons and afforded me the opportunity to watch many stars of hospital medicine rise, as well as to learn from several less-scrupulous leaders about the darker side of hospital politics.
One of the lessons I learned the hard way about hospital politics is striking the “Authority/Accountability balance” in your career. I shared this perspective at the SHM annual conference in 2018, at speaking engagements on the West Coast, and with my leadership group at the academies. I am sharing it with you because the feedback I have received has been very positive.
The Authority/Accountability balance is a tool for evaluating your current career trajectory and measuring if it is set up for success or failure. The essence is that your Authority and Accountability need to be balanced for you to be successful in your career, regardless of your station. Everybody from the hospitalist fresh out of residency to the CEO needs to have Authority and Accountability in balance to be successful. And as you use the tool to measure your own potential for success or failure, learn to apply it to those who report to you.
I believe the rising tide lifts all boats and the success of your subordinates, through mentoring and support, will add to your success. There is another, more cynical view of subordinates that can be identified using the Authority/Accountability balance, which I will address.
Authority
In this construct, “Authority” has a much broader meaning than just the ability to tell people what to do. The ability to tell people what to do is important but not sufficient for success in hospital politics.
Financial resources are essential for a successful Authority/Accountability balance – not only the hardware such as computers, telephones, pagers, and so on, but also clerical support, technical support, and analytic support so that you are getting high-quality data on the performance of the members of your hospital medicine group (HMG). These “soft” resources (clerical, technical, and analytical) are often overlooked as needs that HMG leaders must advocate for; I speak with many HMG leaders who remain under-resourced with “soft” assets. However, being appropriately resourced in these areas can be transformational for a group. Hospitalists don’t like doing clerical work, and if you don’t like a menial job assigned to you, you probably won’t do it very well. Having an unlicensed person dedicated to these clerical activities not only will cost less, but will ensure the job is done better.
Reporting structure is critically important, often overlooked, and historically misaligned in HMGs. When hospital medicine was starting in the late 1990s and early 2000s, rapidly growing hospitalist groups were typically led by young, early-career physicians who had chosen hospital medicine as a career. The problem was that they often lacked the seniority and connections at the executive level to advocate for their HMG. All too often the hospitalist group was tucked in under another department or division which, in turn, reported HMG updates and issues to the board of directors and the CEO.
A common reporting structure in the early days was that a senior member of the medical staff, or group, had once worked in the hospital and therefore “understood” the issues and challenges that the hospitalists were facing. It was up to this physician with seniority and connections to advocate for the hospitalists as they saw fit. The problem was that the hospital landscape was, and is, constantly evolving in innumerable ways. These “once removed” reporting structures for HMGs failed to get the required information on the rapidly changing, and evolving, hospitalist landscape to the desks of executives who had the financial and structural control to address the challenges that the hospitalists in the trenches were facing.
Numerous HMGs failed in the early days of hospital medicine because of this type of misaligned reporting structure. This is a lesson that should not be forgotten: Make sure your HMG leader has a seat at the table where executive decisions are made, including but not limited to the board of directors. To be in balance, you have to be “in the room where it happens.”
Accountability
The outcomes that you are responsible for need to be explicit, appropriately resourced with Authority, and clearly spelled out in your job description. Your job description is a document you should know, own, and revisit regularly with whomever you report to, in order to ensure success.
Once you have the Authority side of the equation appropriately resourced, setting outcomes that are a stretch, but still realistic and achievable within the scope of your position, is critical to your success. It is good to think about short-, medium-, and long-term goals, especially if you are in a leadership role. For example, one expectation you will have, regardless of your station, is that you keep up on your email and answer your phone. These are short-term goals that will often be included in your job description. However, taking on a new hospital contract and making sure that it has 24/7 hospitalist coverage, that all the hospitalists are meeting the geometric mean length of stay, and that all the physicians are having 15 encounters per day doesn’t happen immediately. Long-term goals, such as taking on a new hospital contract, are the big-picture stuff that can make or break the career of an HMG leader. Long-term goals also need to be delineated in the job description, along with specific time stamps and the resources you need to accomplish big ticket items – which are spelled out in the Authority side (that is, physician recruiter, secretary, background checks, and so on).
One of the classic misuses of Accountability is the “Fall Guy” scenario. The Fall Guy scenario is often used by cynical hospital and medical group executives to expand their influence while limiting their liability. In the Fall Guy scenario, the executive is surrounded with junior partners who are underpowered with Authority, and then the executive makes decisions for which the junior partners are Accountable. This allows the senior executive to make risky decisions on behalf of the hospital or medical group without the liability of being held accountable when the decision-making process fails. When the risky, and often ill-informed, decision fails, the junior partner who lacked the Authority to make the decision – but held the Accountability for it – becomes the Fall Guy for the failed endeavor. This is a critical outcome that the Authority/Accountability balance can help you avoid, if you use it wisely and properly.
If you find yourself in the Fall Guy position, it is time for a change. The Authority, the Accountability, or both need to change so that they are in better balance. Or your employer needs to change. Changing employers is an outcome worth avoiding, if at all possible. I have scrutinized thousands of resumes in my career, and frequent job changes always wave a red flag to prospective employers. However, changing jobs remains a crucial option if you are being set up for failure when Authority and Accountability are out of balance.
If you are unable to negotiate for the balance that will allow you to be successful with your current group, remember that HMG leaders are a prized commodity and in short supply. Leaving a group that has been your career is hard, but it is better to leave than stay in a position where you are set up for failure as the Fall Guy. Further, the most effective time to expand your Authority is when you are negotiating the terms of a new position. Changing positions is the nuclear option. However, it is better than becoming the Fall Guy, and a change can create opportunities that will accelerate your career and influence, if done right.
When I talk about Authority/Accountability balance, I always counter the Fall Guy with an ignominious historical figure: General George B. McClellan. General McClellan was the commander of the Army of the Potomac during the early years of the American Civil War. General McClellan had the industrial might of the Union north at his beck and call, as well as extraordinary resources for recruiting and retaining soldiers for his army. At every encounter with General Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia, General McClellan outnumbered them, sometimes by more than two to one. Yet General McClellan was outfoxed repeatedly for the same reason: He failed to take decisive action.
Every time that McClellan failed, he blamed insufficient resources and told President Lincoln that he needed more troops and more equipment to be successful. In summary, while the Fall Guy scenario needs to be avoided, once you are adequately resourced, success requires taking decisive and strategic action, or you will suffer as did General McClellan. Failing to act when you are appropriately resourced can be just as damaging to your career and credibility as allowing yourself to become the Fall Guy.
Job description
Everybody has somebody that they report to, no matter how high up on the executive ladder they have climbed. Even the CEO must report to the board of directors. And that reporting structure usually involves periodic formal reviews. Your formal review is a good time to go over your job description, note what is relevant, remove what is irrelevant, and add new elements that have evolved in importance since your last review.
Job descriptions take many forms, but they always include a list of qualifications. If you have the job, you have the qualifications, so that is not likely to change. You may become more qualified for a higher-level position, but that is an entirely different discussion. I like to think of a well-written job description as including short-term and long-term goals. Short-term goals are usually the daily stuff that keeps operations running smoothly but garners little attention. Examples would include staying current on your emails, answering your phone, organizing meetings, and regularly attending various committees. Even some of these short-term goals can and will change over time. I always enjoyed quality oversight in my department, but as the department and my responsibilities grew, I realized I couldn’t do everything that I wanted to do. I needed to focus on the things only I could do and delegate those things that could be done by someone else, even though I wanted to continue doing them myself. I created a position for a clinical quality officer, and quality oversight moved off of my job description.
Long-term goals are the aspirational items, such as increasing market share, decreasing readmissions, improving patient satisfaction, and the like. Effective leaders are often focused on these aspirational, long-term goals, but they still must effectively execute their short-term goals. Stephen Covey outlines the dilemma with the “time management matrix” in his seminal work “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.” An in-depth discussion is beyond the scope of this article, but the time management matrix places tasks into one of four categories based on urgency and importance, and provides strategies for staying up on short-term goals while continually moving long-term goals forward.If you show up at your review with a list of accomplishments as well as an understanding of how the “time management matrix” affects your responsibilities, your boss will be impressed. It is also worth mentioning that Covey’s first habit is “Proactivity.” He uses the term Proactivity in a much more nuanced form than we typically think of, however. Simply put, Proactivity is the opposite of Reactivity, and it is another invaluable tool for success with those long-term goals that will help you make a name for yourself.
When you show up for your review, be it annual, biannual, or other, be prepared. Not only should you bring your job description and recommendations for how it should be adapted in the changing environment, but also bring examples of your accomplishments since the last review.
I talk with leaders frequently who are hardworking and diligent and hate bragging about their achievements; I get that. At the same time, if you don’t inform your superiors about your successes, there is no guarantee that they will hear about them or understand them in the appropriate context. Bragging about how great you are in the physician’s lounge is annoying; telling your boss about your accomplishments since the last review is critical to maintaining the momentum of past accomplishments. If you are not willing to toot your own horn, there is a very good chance that your horn will remain silent. I don’t think self-promotion comes easily to anyone, and it has to be done with a degree of humility and sensitivity; but it has to be done, so prepare for it.
Look out for yourself and others
We talk about teamwork and collaboration as hospitalists, and SHM is always underscoring the importance of teamwork and highlighting examples of successful teamwork in its many conferences and publications. Most hospital executives are focused on their own careers, however, and many have no reservations about damaging your career (your brand) if they think it will promote theirs. You have to look out for yourself and size up every leadership position you get into.
Physicians can expect their careers to last decades. The average hospital CEO has a tenure of less than 3.5 years, however, and when a new CEO is hired, almost half of chief financial, chief operating, and chief information officers are fired within 9 months. You may be focused on the long-term success of your organization as you plan your career, but many hospital administrators are interested only in short-term gains. It is similar to some members of Congress who are interested only in what they need to do now to win the next election and not in the long-term needs of the country. You should understand this disconnect when dealing with hospital executives, and how you and your credibility can become cannon fodder in their quest for short-term self-preservation.
You have to look out for and take care of yourself as you promote your group. With a better understanding of the Authority/Accountability balance, you have new tools to assess your chances of success and to advocate for yourself so that you and your group can be successful.
Despite my cynicism toward executives in the medical field, I personally advocate for supporting the career development of those around you and advise against furthering your career at the expense of others. Many unscrupulous executives will use this approach, surrounding themselves with Fall Guys, but my experience shows that this is not a sustainable strategy for success. It can lead to short-term gains, but eventually the piper must be paid. Moreover, the most successful medical executives and leaders that I have encountered have been those who genuinely cared about their subordinates, looked out for them, and selflessly promoted their careers.
In the age of social media, tearing others down seems to be the fastest way to get more “likes.” However, I strongly believe that you can’t build up your group, and our profession, just by tearing people down. Lending a helping hand may bring you less attention in the short term, but such action raises your stature, creates loyalty, and leads to sustainable success for the long run.
Dr. McIlraith is the founding chairman of the Hospital Medicine Department at Mercy Medical Group in Sacramento, Calif. He received the SHM Award for Outstanding Service in Hospital Medicine in 2016 and is currently a member of the SHM Practice Management and Awards Committees, as well as the SHM Critical Care Task Force.
Sources
Quinn R. HM Turns 20: A look at the evolution of hospital medicine. The Hospitalist. 2016 August. https://www.the-hospitalist.org/hospitalist/article/121525/hm-turns-20-look-evolution-hospital-medicine
Stephen R. Covey. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change. Simon & Schuster. 1989.
10 Statistics on CEO Turnover, Recruitment. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2020. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-management-administration/10-statistics-on-ceo-turnover-recruitment.html
Antibody shows promise in eosinophilic gastritis/duodenitis
In a phase 2 trial in eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis, an anti–Siglec-8 antibody greatly reduced populations of eosinophilic cells, and also led to improved symptoms. The sponsoring company, Alkalos, is currently conducting a phase 3 trial in eosinophilic gastritis or duodenitis and a phase 2-3 trial in eosinophilic esophagitis.
The news is welcome to clinicians who treat these rare conditions, since the only current treatment option is steroids. This is particularly challenging because most patients with these conditions present in their 30s and 40s, according to Carol Semrad, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study. She noted that the study’s results were impressive, but it will take a phase 3 trial to convince. It’s also unclear if the clinical benefit tracks with the impressive reduction seen in eosinophil count. “There’s somewhat of a disconnect between symptom reduction and reduction of the eosinophil counts. Sometimes just blocking the inflammation [isn’t enough]. Maybe there is other damage to the bowel.”
Still, “it looks like they have a proof of concept that it’s very effective at blocking the eosinophils and mast cells that are thought to be causing eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis in human disease. That, along with improvement in symptoms, is highly promising, given that we have no other treatment beside steroids,” said Dr. Semrad.
The research, led by Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Ikuo Hirano, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, appeared in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The antibody (lirentelimab) targets sialic acid–binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 8 (Siglec-8), which is an inhibitory receptor found on mature eosinophils and mast cells, and expressed at low levels on basophils. The antibody reduces eosinophil population through natural killer cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity and apoptosis, and other antibodies against the same target have been shown to inhibit activation of mast cells.
At 22 sites across the United States, researchers randomized 65 adults with active, uncontrolled eosinophilic gastritis or eosinophilic duodenitis, or both, to receive four monthly low doses (0.3, 1, 1, and 1 mg/kg) or high-dose lirentelimab (0.3, 1, 3, and 3 mg/kg), or placebo. A total of 10 patients had gastritis, 25 had duodenitis, and 30 had both.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, there was a mean 86% reduction in eosinophil count in patients in the treatment groups, compared with a 9% increase in controls (P < .001). In the per-protocol analysis, there was a 95% reduction versus a 10% increase (P < .001). Of treated patients, 95% had a gastrointestinal eosinophil count of 6 or fewer per high-powered field, compared with 0% in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, 63% of treated patients experienced a treatment response, defined as at least a 30% reduction in total symptom score and at least a 75% reduction in eosinophil count. About 5% of patients had a response in the placebo group (P < .001). The mean percentage change in total symptom score was –48 versus –22 in the placebo group (P = .004). In the per-protocol analysis, 69% responded versus 5% (P < .001). The mean percentage change in total symptom score was –53 versus –24 (P = .001).
91% of patients in the treatment groups experienced at least one adverse event, compared with 82% in the placebo group. About 60% in the treatment group had an infusion-related reaction versus 23% who received placebo; 93% of reactions were mild to moderate. Serious adverse events occurred in 9% of the treatment group and 14% of patients on placebo. The only serious adverse event thought to be related to the drug was a single grade 4 infusion-related event in the high-dose treatment group, which led to discontinuation of the drug and withdrawal from the trial. 86% of patients in the treatment group experienced transient lymphopenia, as did 47% of the placebo group, but there were no clinical consequences.
One potential concern with the therapy is the effect that long-term suppression of eosinophils and mast cells, and to a lesser extent basophils, could have on the immune system. Eosinophils are key to defenses against parasites, so that will need to be looked at in further studies, according to Dr. Semrad: “How is blocking those inflammatory cells going to impact gut function and the ability to fight off certain organisms? That’s going to be one of the real questions.”
The study was funded by Alkalos. Dr. Semrad has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Dellon ES et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2012047.
In a phase 2 trial in eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis, an anti–Siglec-8 antibody greatly reduced populations of eosinophilic cells, and also led to improved symptoms. The sponsoring company, Alkalos, is currently conducting a phase 3 trial in eosinophilic gastritis or duodenitis and a phase 2-3 trial in eosinophilic esophagitis.
The news is welcome to clinicians who treat these rare conditions, since the only current treatment option is steroids. This is particularly challenging because most patients with these conditions present in their 30s and 40s, according to Carol Semrad, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study. She noted that the study’s results were impressive, but it will take a phase 3 trial to convince. It’s also unclear if the clinical benefit tracks with the impressive reduction seen in eosinophil count. “There’s somewhat of a disconnect between symptom reduction and reduction of the eosinophil counts. Sometimes just blocking the inflammation [isn’t enough]. Maybe there is other damage to the bowel.”
Still, “it looks like they have a proof of concept that it’s very effective at blocking the eosinophils and mast cells that are thought to be causing eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis in human disease. That, along with improvement in symptoms, is highly promising, given that we have no other treatment beside steroids,” said Dr. Semrad.
The research, led by Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Ikuo Hirano, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, appeared in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The antibody (lirentelimab) targets sialic acid–binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 8 (Siglec-8), which is an inhibitory receptor found on mature eosinophils and mast cells, and expressed at low levels on basophils. The antibody reduces eosinophil population through natural killer cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity and apoptosis, and other antibodies against the same target have been shown to inhibit activation of mast cells.
At 22 sites across the United States, researchers randomized 65 adults with active, uncontrolled eosinophilic gastritis or eosinophilic duodenitis, or both, to receive four monthly low doses (0.3, 1, 1, and 1 mg/kg) or high-dose lirentelimab (0.3, 1, 3, and 3 mg/kg), or placebo. A total of 10 patients had gastritis, 25 had duodenitis, and 30 had both.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, there was a mean 86% reduction in eosinophil count in patients in the treatment groups, compared with a 9% increase in controls (P < .001). In the per-protocol analysis, there was a 95% reduction versus a 10% increase (P < .001). Of treated patients, 95% had a gastrointestinal eosinophil count of 6 or fewer per high-powered field, compared with 0% in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, 63% of treated patients experienced a treatment response, defined as at least a 30% reduction in total symptom score and at least a 75% reduction in eosinophil count. About 5% of patients had a response in the placebo group (P < .001). The mean percentage change in total symptom score was –48 versus –22 in the placebo group (P = .004). In the per-protocol analysis, 69% responded versus 5% (P < .001). The mean percentage change in total symptom score was –53 versus –24 (P = .001).
91% of patients in the treatment groups experienced at least one adverse event, compared with 82% in the placebo group. About 60% in the treatment group had an infusion-related reaction versus 23% who received placebo; 93% of reactions were mild to moderate. Serious adverse events occurred in 9% of the treatment group and 14% of patients on placebo. The only serious adverse event thought to be related to the drug was a single grade 4 infusion-related event in the high-dose treatment group, which led to discontinuation of the drug and withdrawal from the trial. 86% of patients in the treatment group experienced transient lymphopenia, as did 47% of the placebo group, but there were no clinical consequences.
One potential concern with the therapy is the effect that long-term suppression of eosinophils and mast cells, and to a lesser extent basophils, could have on the immune system. Eosinophils are key to defenses against parasites, so that will need to be looked at in further studies, according to Dr. Semrad: “How is blocking those inflammatory cells going to impact gut function and the ability to fight off certain organisms? That’s going to be one of the real questions.”
The study was funded by Alkalos. Dr. Semrad has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Dellon ES et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2012047.
In a phase 2 trial in eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis, an anti–Siglec-8 antibody greatly reduced populations of eosinophilic cells, and also led to improved symptoms. The sponsoring company, Alkalos, is currently conducting a phase 3 trial in eosinophilic gastritis or duodenitis and a phase 2-3 trial in eosinophilic esophagitis.
The news is welcome to clinicians who treat these rare conditions, since the only current treatment option is steroids. This is particularly challenging because most patients with these conditions present in their 30s and 40s, according to Carol Semrad, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study. She noted that the study’s results were impressive, but it will take a phase 3 trial to convince. It’s also unclear if the clinical benefit tracks with the impressive reduction seen in eosinophil count. “There’s somewhat of a disconnect between symptom reduction and reduction of the eosinophil counts. Sometimes just blocking the inflammation [isn’t enough]. Maybe there is other damage to the bowel.”
Still, “it looks like they have a proof of concept that it’s very effective at blocking the eosinophils and mast cells that are thought to be causing eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis in human disease. That, along with improvement in symptoms, is highly promising, given that we have no other treatment beside steroids,” said Dr. Semrad.
The research, led by Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Ikuo Hirano, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, appeared in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The antibody (lirentelimab) targets sialic acid–binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 8 (Siglec-8), which is an inhibitory receptor found on mature eosinophils and mast cells, and expressed at low levels on basophils. The antibody reduces eosinophil population through natural killer cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity and apoptosis, and other antibodies against the same target have been shown to inhibit activation of mast cells.
At 22 sites across the United States, researchers randomized 65 adults with active, uncontrolled eosinophilic gastritis or eosinophilic duodenitis, or both, to receive four monthly low doses (0.3, 1, 1, and 1 mg/kg) or high-dose lirentelimab (0.3, 1, 3, and 3 mg/kg), or placebo. A total of 10 patients had gastritis, 25 had duodenitis, and 30 had both.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, there was a mean 86% reduction in eosinophil count in patients in the treatment groups, compared with a 9% increase in controls (P < .001). In the per-protocol analysis, there was a 95% reduction versus a 10% increase (P < .001). Of treated patients, 95% had a gastrointestinal eosinophil count of 6 or fewer per high-powered field, compared with 0% in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, 63% of treated patients experienced a treatment response, defined as at least a 30% reduction in total symptom score and at least a 75% reduction in eosinophil count. About 5% of patients had a response in the placebo group (P < .001). The mean percentage change in total symptom score was –48 versus –22 in the placebo group (P = .004). In the per-protocol analysis, 69% responded versus 5% (P < .001). The mean percentage change in total symptom score was –53 versus –24 (P = .001).
91% of patients in the treatment groups experienced at least one adverse event, compared with 82% in the placebo group. About 60% in the treatment group had an infusion-related reaction versus 23% who received placebo; 93% of reactions were mild to moderate. Serious adverse events occurred in 9% of the treatment group and 14% of patients on placebo. The only serious adverse event thought to be related to the drug was a single grade 4 infusion-related event in the high-dose treatment group, which led to discontinuation of the drug and withdrawal from the trial. 86% of patients in the treatment group experienced transient lymphopenia, as did 47% of the placebo group, but there were no clinical consequences.
One potential concern with the therapy is the effect that long-term suppression of eosinophils and mast cells, and to a lesser extent basophils, could have on the immune system. Eosinophils are key to defenses against parasites, so that will need to be looked at in further studies, according to Dr. Semrad: “How is blocking those inflammatory cells going to impact gut function and the ability to fight off certain organisms? That’s going to be one of the real questions.”
The study was funded by Alkalos. Dr. Semrad has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Dellon ES et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2012047.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Inpatient opioid administration associated with postdischarge opioid use
Background: Efforts to reduce and monitor high-risk opioid prescribing have largely focused on outpatient prescribing with less empiric evaluation of inpatient administration. Little is known about the association of inpatient opioid administration and postdischarge opioid use.
Study design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: 12 community and academic hospitals in Pennsylvania.
Synopsis: With electronic health record data from 2010-2014 to evaluate 148,068 opioid-naive patients aged 18 years and older, this study showed a relationship between inpatient opioid administration, specific patterns of inpatient opioid administration, and postdischarge opioid use. Specifically, inpatient opioid administration was associated with a 3.0% increase (95% CI, 2.8%-3.2%) in opioid use at 90 days post discharge. Additionally, inpatient opioid administration within 12 hours of hospital discharge was associated with a 3.6% increase (95% CI, 3.3%-3.9%) in opioid use at 90 days post discharge.
This observational study is prone to potential unmeasured confounders negating any clear causation. Rather, hospitalists should be aware of the increasing focus on inpatient opioid administration as it relates to outpatient opioid use, especially in the setting of the current opioid crisis.
Bottom line: Inpatient opioid administration and administration patterns are associated with 90-day postdischarge opioid use in opioid-naive patients.
Citation: Donohue JM et al. Patterns of opioid administration among opioid-naive inpatients and associations with postdischarge opioid use. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jun 18:171(2):81-90.
Dr. Ledford is a hospitalist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
Background: Efforts to reduce and monitor high-risk opioid prescribing have largely focused on outpatient prescribing with less empiric evaluation of inpatient administration. Little is known about the association of inpatient opioid administration and postdischarge opioid use.
Study design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: 12 community and academic hospitals in Pennsylvania.
Synopsis: With electronic health record data from 2010-2014 to evaluate 148,068 opioid-naive patients aged 18 years and older, this study showed a relationship between inpatient opioid administration, specific patterns of inpatient opioid administration, and postdischarge opioid use. Specifically, inpatient opioid administration was associated with a 3.0% increase (95% CI, 2.8%-3.2%) in opioid use at 90 days post discharge. Additionally, inpatient opioid administration within 12 hours of hospital discharge was associated with a 3.6% increase (95% CI, 3.3%-3.9%) in opioid use at 90 days post discharge.
This observational study is prone to potential unmeasured confounders negating any clear causation. Rather, hospitalists should be aware of the increasing focus on inpatient opioid administration as it relates to outpatient opioid use, especially in the setting of the current opioid crisis.
Bottom line: Inpatient opioid administration and administration patterns are associated with 90-day postdischarge opioid use in opioid-naive patients.
Citation: Donohue JM et al. Patterns of opioid administration among opioid-naive inpatients and associations with postdischarge opioid use. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jun 18:171(2):81-90.
Dr. Ledford is a hospitalist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
Background: Efforts to reduce and monitor high-risk opioid prescribing have largely focused on outpatient prescribing with less empiric evaluation of inpatient administration. Little is known about the association of inpatient opioid administration and postdischarge opioid use.
Study design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: 12 community and academic hospitals in Pennsylvania.
Synopsis: With electronic health record data from 2010-2014 to evaluate 148,068 opioid-naive patients aged 18 years and older, this study showed a relationship between inpatient opioid administration, specific patterns of inpatient opioid administration, and postdischarge opioid use. Specifically, inpatient opioid administration was associated with a 3.0% increase (95% CI, 2.8%-3.2%) in opioid use at 90 days post discharge. Additionally, inpatient opioid administration within 12 hours of hospital discharge was associated with a 3.6% increase (95% CI, 3.3%-3.9%) in opioid use at 90 days post discharge.
This observational study is prone to potential unmeasured confounders negating any clear causation. Rather, hospitalists should be aware of the increasing focus on inpatient opioid administration as it relates to outpatient opioid use, especially in the setting of the current opioid crisis.
Bottom line: Inpatient opioid administration and administration patterns are associated with 90-day postdischarge opioid use in opioid-naive patients.
Citation: Donohue JM et al. Patterns of opioid administration among opioid-naive inpatients and associations with postdischarge opioid use. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jun 18:171(2):81-90.
Dr. Ledford is a hospitalist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
AACE issues ‘cookbook’ algorithm to manage dyslipidemia
A new algorithm on lipid management and prevention of cardiovascular disease from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists* (AACE) and the American College of Endocrinology (ACE) is “a nice cookbook” that many clinicians, especially those who are not lipid experts, will find useful, according to writing committee chair Yehuda Handelsman, MD.
The algorithm, published Oct. 10 in Endocrine Practice as 10 slides, or as part of a more detailed consensus statement, is a companion to the 2017 AACE/ACE guidelines for lipid management and includes more recent information about new therapies.
“What we’re trying to do here is to say, ‘focus on LDL-C, triglycerides, high-risk patients, and lifestyle. Understand all the medications available to you to reduce LDL-C and reduce triglycerides,’ ” Dr. Handelsman, of the Metabolic Institute of America, Tarzana, Calif., explained in an interview.
“We touch on lipoprotein(a), which we still don’t have medication for, but it identifies people at high risk, and we need that.”
Clinicians also need to know “that we’ve got some newer drugs in the market that can manage people who have statin intolerance,” Dr. Handelsman added.
“We introduced new therapies like icosapent ethyl” (Vascepa, Amarin) for hypertriglyceridemia, “when to use it, and how to use it. Even though it was not part of the 2017 guideline, we gave recommendations based on current data in the algorithm.”
Although there is no good evidence that lowering triglycerides reduces heart disease, he continued, many experts believe that the target triglyceride level should be less than 150 mg/dL, and the algorithm explains how to treat to this goal.
“Last, and most importantly, I cannot fail to underscore the fact that lifestyle is very important,” he emphasized.
Robert H. Eckel, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and president of medicine and science at the American Diabetes Association, who was not involved with this algorithm, said in an interview that the algorithm is important since it offers “the clinician or health care practitioner an approach, a kind of a cookbook or application of the guidelines, for how to manage lipid disorders in patients at risk ... It’s geared for the nonexperts too,” he said.
Dyslipidemia treatment summarized in 10 slides
The AACE/ACE algorithm comprises 10 slides, one each for dyslipidemic states, secondary causes of lipid disorders, screening for and assessing lipid disorders and atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD) risk, ASCVD risk categories and treatment goals, lifestyle recommendations, treating LDL-C to goal, managing statin intolerance and safety, management of hypertriglyceridemia and the role of icosapent ethyl, assessment and management of elevated lipoprotein(a), and profiles of medications for dyslipidemia.
The algorithm defines five ASCVD risk categories and recommends increasingly lower LDL-C, non–HDL-C, and apo B target levels with increasing risk, but the same triglyceride target for all.
First, “treatment of lipid disorders begins with lifestyle therapy to improve nutrition, physical activity, weight, and other factors that affect lipids,” the consensus statement authors stress.
Next, “LDL-C has been, and remains, the main focus of efforts to improve lipid profiles in individuals at risk for ASCVD” (see table).
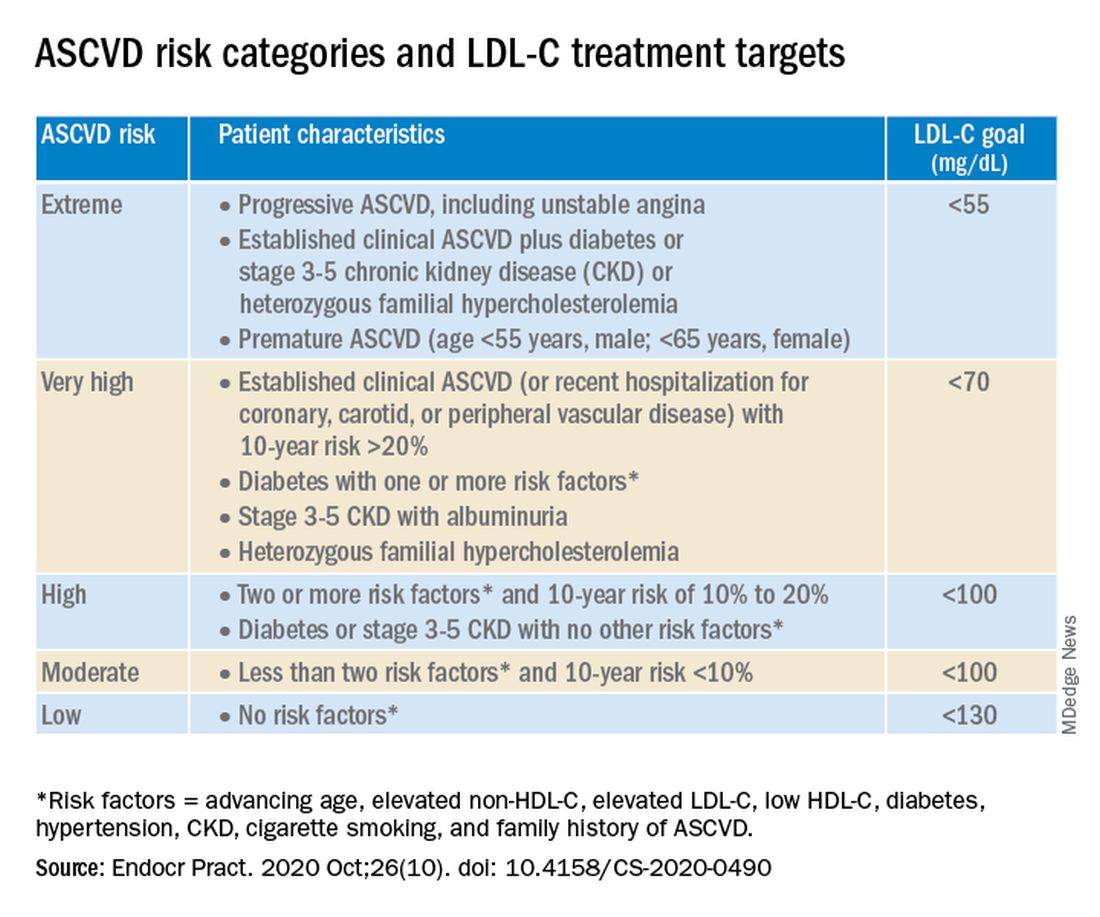
“We stratify [LDL-C] not as a one-treatment-target-for-all,” but rather as extreme, very high, high, moderate, and low ASCVD risk, Dr. Handelsman explained, with different treatment pathways (specified in another slide) to reach different risk-dependent goals.
“Unlike the ACC [American College of Cardiology] guideline, which shows if you want to further reduce LDL after statin give ezetimibe first, we say ‘no’,” he noted. “If somebody has an extreme risk, and you don’t think ezetimibe will get to a goal below 55 mg/dL, you should go first with a PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and only then add ezetimibe or [colesevelam] or other drugs,” he said.
The consensus statement authors expand on this scenario. “Treatment for patients at extreme risk should begin with lifestyle therapy plus a high-intensity statin (atorvastatin 40 to 80 mg or rosuvastatin 20 to 40 mg, or the highest tolerated statin dose) to achieve an LDL-C goal of less than 55 mg/dL.”
“If LDL-C remains above goal after 3 months,” a PCSK9 inhibitor (evolocumab [Repatha, Amgen] or alirocumab [Praluent, Sanofi/Regeneron]), the cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe, or the bile acid sequestrant colesevelam (Welchol, Daiichi Sankyo) or the adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor bempedoic acid (Nexletol, Esperion) “should be added, depending on required LDL-C lowering, and a third agent should be added if the combination fails to achieve the goal.”
However, “because the cost of ezetimibe is low, it may be preferred over PCSK9 inhibitors as second-line therapy to achieve an LDL-C below 70 mg/dL for patients who require no more than 15%-20% further reduction to reach goals.”
For patients at moderate or high risk, lipid management should begin with a moderate-intensity statin and be increased to a high-intensity statin before adding a second lipid-lowering medication to reach an LDL-C below 100 mg/dL.
According to the consensus statement, the desirable goal for triglycerides is less than 150 mg/dL.
In all patients with triglyceride levels of at least 500 mg/dL, statin therapy should be combined with a fibrate, prescription-grade omega-3 fatty acid, and/or niacin to reduce triglycerides.
In any patient with established ASCVD or diabetes with at least 2 ASCVD risk factors and triglycerides of 135-499 mg/dL, icosapent ethyl should be added to a statin to prevent ASCVD events.
Statement aligns with major guidelines
In general, the 2017 AACE/ACE guidelines and algorithm are “pretty similar” to other guidelines such as the 2018 ACC/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for cholesterol management, the 2019 ACC/AHA guidelines for primary prevention of CVD, and the 2019 European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia, according to Dr. Eckel.
They have “all have now taken into consideration the evidence behind PCSK9 inhibitors,” he noted. “That’s important because those drugs have proven to be effective.”
Two differences, he pointed out, are that the 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines suggest that lipoprotein(a) measurement be considered at least once in every adult’s lifetime, and they recommend apo B analysis in people with high triglycerides but normal LDL (or no higher than 100 mg/dL), to identify additional risk.
*AACE changes its name, broadens focus
Shortly after its algorithm was published, AACE announced that it has a new organization name and brand, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, which “more clearly defines AACE as a community of individuals who work together to elevate the practice of clinical endocrinology,” according to an Oct. 20 statement.
The change is meant to acknowledge AACE’s “more modern, inclusive approach to endocrinology that supports multidisciplinary care teams – with endocrinologists leading the way.”
Along with the name change is a new global website. The statement notes that “health care professionals and community members can access all of the valuable clinical content such as guidelines, disease state networks and important education by visiting the pro portal in the top right corner of the site, or by going directly to pro.aace.com.”
Dr. Handelsman discloses that he receives research grant support from Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BMS, Gan & Lee, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi, and he is a consultant and/or speaker for Amarin, BI-Lilly, and Sanofi.
Dr. Eckel has received consultant/advisory board fees from Kowa, Novo Nordisk, and Provention Bio.
A new algorithm on lipid management and prevention of cardiovascular disease from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists* (AACE) and the American College of Endocrinology (ACE) is “a nice cookbook” that many clinicians, especially those who are not lipid experts, will find useful, according to writing committee chair Yehuda Handelsman, MD.
The algorithm, published Oct. 10 in Endocrine Practice as 10 slides, or as part of a more detailed consensus statement, is a companion to the 2017 AACE/ACE guidelines for lipid management and includes more recent information about new therapies.
“What we’re trying to do here is to say, ‘focus on LDL-C, triglycerides, high-risk patients, and lifestyle. Understand all the medications available to you to reduce LDL-C and reduce triglycerides,’ ” Dr. Handelsman, of the Metabolic Institute of America, Tarzana, Calif., explained in an interview.
“We touch on lipoprotein(a), which we still don’t have medication for, but it identifies people at high risk, and we need that.”
Clinicians also need to know “that we’ve got some newer drugs in the market that can manage people who have statin intolerance,” Dr. Handelsman added.
“We introduced new therapies like icosapent ethyl” (Vascepa, Amarin) for hypertriglyceridemia, “when to use it, and how to use it. Even though it was not part of the 2017 guideline, we gave recommendations based on current data in the algorithm.”
Although there is no good evidence that lowering triglycerides reduces heart disease, he continued, many experts believe that the target triglyceride level should be less than 150 mg/dL, and the algorithm explains how to treat to this goal.
“Last, and most importantly, I cannot fail to underscore the fact that lifestyle is very important,” he emphasized.
Robert H. Eckel, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and president of medicine and science at the American Diabetes Association, who was not involved with this algorithm, said in an interview that the algorithm is important since it offers “the clinician or health care practitioner an approach, a kind of a cookbook or application of the guidelines, for how to manage lipid disorders in patients at risk ... It’s geared for the nonexperts too,” he said.
Dyslipidemia treatment summarized in 10 slides
The AACE/ACE algorithm comprises 10 slides, one each for dyslipidemic states, secondary causes of lipid disorders, screening for and assessing lipid disorders and atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD) risk, ASCVD risk categories and treatment goals, lifestyle recommendations, treating LDL-C to goal, managing statin intolerance and safety, management of hypertriglyceridemia and the role of icosapent ethyl, assessment and management of elevated lipoprotein(a), and profiles of medications for dyslipidemia.
The algorithm defines five ASCVD risk categories and recommends increasingly lower LDL-C, non–HDL-C, and apo B target levels with increasing risk, but the same triglyceride target for all.
First, “treatment of lipid disorders begins with lifestyle therapy to improve nutrition, physical activity, weight, and other factors that affect lipids,” the consensus statement authors stress.
Next, “LDL-C has been, and remains, the main focus of efforts to improve lipid profiles in individuals at risk for ASCVD” (see table).

“We stratify [LDL-C] not as a one-treatment-target-for-all,” but rather as extreme, very high, high, moderate, and low ASCVD risk, Dr. Handelsman explained, with different treatment pathways (specified in another slide) to reach different risk-dependent goals.
“Unlike the ACC [American College of Cardiology] guideline, which shows if you want to further reduce LDL after statin give ezetimibe first, we say ‘no’,” he noted. “If somebody has an extreme risk, and you don’t think ezetimibe will get to a goal below 55 mg/dL, you should go first with a PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and only then add ezetimibe or [colesevelam] or other drugs,” he said.
The consensus statement authors expand on this scenario. “Treatment for patients at extreme risk should begin with lifestyle therapy plus a high-intensity statin (atorvastatin 40 to 80 mg or rosuvastatin 20 to 40 mg, or the highest tolerated statin dose) to achieve an LDL-C goal of less than 55 mg/dL.”
“If LDL-C remains above goal after 3 months,” a PCSK9 inhibitor (evolocumab [Repatha, Amgen] or alirocumab [Praluent, Sanofi/Regeneron]), the cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe, or the bile acid sequestrant colesevelam (Welchol, Daiichi Sankyo) or the adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor bempedoic acid (Nexletol, Esperion) “should be added, depending on required LDL-C lowering, and a third agent should be added if the combination fails to achieve the goal.”
However, “because the cost of ezetimibe is low, it may be preferred over PCSK9 inhibitors as second-line therapy to achieve an LDL-C below 70 mg/dL for patients who require no more than 15%-20% further reduction to reach goals.”
For patients at moderate or high risk, lipid management should begin with a moderate-intensity statin and be increased to a high-intensity statin before adding a second lipid-lowering medication to reach an LDL-C below 100 mg/dL.
According to the consensus statement, the desirable goal for triglycerides is less than 150 mg/dL.
In all patients with triglyceride levels of at least 500 mg/dL, statin therapy should be combined with a fibrate, prescription-grade omega-3 fatty acid, and/or niacin to reduce triglycerides.
In any patient with established ASCVD or diabetes with at least 2 ASCVD risk factors and triglycerides of 135-499 mg/dL, icosapent ethyl should be added to a statin to prevent ASCVD events.
Statement aligns with major guidelines
In general, the 2017 AACE/ACE guidelines and algorithm are “pretty similar” to other guidelines such as the 2018 ACC/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for cholesterol management, the 2019 ACC/AHA guidelines for primary prevention of CVD, and the 2019 European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia, according to Dr. Eckel.
They have “all have now taken into consideration the evidence behind PCSK9 inhibitors,” he noted. “That’s important because those drugs have proven to be effective.”
Two differences, he pointed out, are that the 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines suggest that lipoprotein(a) measurement be considered at least once in every adult’s lifetime, and they recommend apo B analysis in people with high triglycerides but normal LDL (or no higher than 100 mg/dL), to identify additional risk.
*AACE changes its name, broadens focus
Shortly after its algorithm was published, AACE announced that it has a new organization name and brand, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, which “more clearly defines AACE as a community of individuals who work together to elevate the practice of clinical endocrinology,” according to an Oct. 20 statement.
The change is meant to acknowledge AACE’s “more modern, inclusive approach to endocrinology that supports multidisciplinary care teams – with endocrinologists leading the way.”
Along with the name change is a new global website. The statement notes that “health care professionals and community members can access all of the valuable clinical content such as guidelines, disease state networks and important education by visiting the pro portal in the top right corner of the site, or by going directly to pro.aace.com.”
Dr. Handelsman discloses that he receives research grant support from Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BMS, Gan & Lee, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi, and he is a consultant and/or speaker for Amarin, BI-Lilly, and Sanofi.
Dr. Eckel has received consultant/advisory board fees from Kowa, Novo Nordisk, and Provention Bio.
A new algorithm on lipid management and prevention of cardiovascular disease from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists* (AACE) and the American College of Endocrinology (ACE) is “a nice cookbook” that many clinicians, especially those who are not lipid experts, will find useful, according to writing committee chair Yehuda Handelsman, MD.
The algorithm, published Oct. 10 in Endocrine Practice as 10 slides, or as part of a more detailed consensus statement, is a companion to the 2017 AACE/ACE guidelines for lipid management and includes more recent information about new therapies.
“What we’re trying to do here is to say, ‘focus on LDL-C, triglycerides, high-risk patients, and lifestyle. Understand all the medications available to you to reduce LDL-C and reduce triglycerides,’ ” Dr. Handelsman, of the Metabolic Institute of America, Tarzana, Calif., explained in an interview.
“We touch on lipoprotein(a), which we still don’t have medication for, but it identifies people at high risk, and we need that.”
Clinicians also need to know “that we’ve got some newer drugs in the market that can manage people who have statin intolerance,” Dr. Handelsman added.
“We introduced new therapies like icosapent ethyl” (Vascepa, Amarin) for hypertriglyceridemia, “when to use it, and how to use it. Even though it was not part of the 2017 guideline, we gave recommendations based on current data in the algorithm.”
Although there is no good evidence that lowering triglycerides reduces heart disease, he continued, many experts believe that the target triglyceride level should be less than 150 mg/dL, and the algorithm explains how to treat to this goal.
“Last, and most importantly, I cannot fail to underscore the fact that lifestyle is very important,” he emphasized.
Robert H. Eckel, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and president of medicine and science at the American Diabetes Association, who was not involved with this algorithm, said in an interview that the algorithm is important since it offers “the clinician or health care practitioner an approach, a kind of a cookbook or application of the guidelines, for how to manage lipid disorders in patients at risk ... It’s geared for the nonexperts too,” he said.
Dyslipidemia treatment summarized in 10 slides
The AACE/ACE algorithm comprises 10 slides, one each for dyslipidemic states, secondary causes of lipid disorders, screening for and assessing lipid disorders and atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD) risk, ASCVD risk categories and treatment goals, lifestyle recommendations, treating LDL-C to goal, managing statin intolerance and safety, management of hypertriglyceridemia and the role of icosapent ethyl, assessment and management of elevated lipoprotein(a), and profiles of medications for dyslipidemia.
The algorithm defines five ASCVD risk categories and recommends increasingly lower LDL-C, non–HDL-C, and apo B target levels with increasing risk, but the same triglyceride target for all.
First, “treatment of lipid disorders begins with lifestyle therapy to improve nutrition, physical activity, weight, and other factors that affect lipids,” the consensus statement authors stress.
Next, “LDL-C has been, and remains, the main focus of efforts to improve lipid profiles in individuals at risk for ASCVD” (see table).

“We stratify [LDL-C] not as a one-treatment-target-for-all,” but rather as extreme, very high, high, moderate, and low ASCVD risk, Dr. Handelsman explained, with different treatment pathways (specified in another slide) to reach different risk-dependent goals.
“Unlike the ACC [American College of Cardiology] guideline, which shows if you want to further reduce LDL after statin give ezetimibe first, we say ‘no’,” he noted. “If somebody has an extreme risk, and you don’t think ezetimibe will get to a goal below 55 mg/dL, you should go first with a PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and only then add ezetimibe or [colesevelam] or other drugs,” he said.
The consensus statement authors expand on this scenario. “Treatment for patients at extreme risk should begin with lifestyle therapy plus a high-intensity statin (atorvastatin 40 to 80 mg or rosuvastatin 20 to 40 mg, or the highest tolerated statin dose) to achieve an LDL-C goal of less than 55 mg/dL.”
“If LDL-C remains above goal after 3 months,” a PCSK9 inhibitor (evolocumab [Repatha, Amgen] or alirocumab [Praluent, Sanofi/Regeneron]), the cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe, or the bile acid sequestrant colesevelam (Welchol, Daiichi Sankyo) or the adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor bempedoic acid (Nexletol, Esperion) “should be added, depending on required LDL-C lowering, and a third agent should be added if the combination fails to achieve the goal.”
However, “because the cost of ezetimibe is low, it may be preferred over PCSK9 inhibitors as second-line therapy to achieve an LDL-C below 70 mg/dL for patients who require no more than 15%-20% further reduction to reach goals.”
For patients at moderate or high risk, lipid management should begin with a moderate-intensity statin and be increased to a high-intensity statin before adding a second lipid-lowering medication to reach an LDL-C below 100 mg/dL.
According to the consensus statement, the desirable goal for triglycerides is less than 150 mg/dL.
In all patients with triglyceride levels of at least 500 mg/dL, statin therapy should be combined with a fibrate, prescription-grade omega-3 fatty acid, and/or niacin to reduce triglycerides.
In any patient with established ASCVD or diabetes with at least 2 ASCVD risk factors and triglycerides of 135-499 mg/dL, icosapent ethyl should be added to a statin to prevent ASCVD events.
Statement aligns with major guidelines
In general, the 2017 AACE/ACE guidelines and algorithm are “pretty similar” to other guidelines such as the 2018 ACC/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for cholesterol management, the 2019 ACC/AHA guidelines for primary prevention of CVD, and the 2019 European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia, according to Dr. Eckel.
They have “all have now taken into consideration the evidence behind PCSK9 inhibitors,” he noted. “That’s important because those drugs have proven to be effective.”
Two differences, he pointed out, are that the 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines suggest that lipoprotein(a) measurement be considered at least once in every adult’s lifetime, and they recommend apo B analysis in people with high triglycerides but normal LDL (or no higher than 100 mg/dL), to identify additional risk.
*AACE changes its name, broadens focus
Shortly after its algorithm was published, AACE announced that it has a new organization name and brand, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, which “more clearly defines AACE as a community of individuals who work together to elevate the practice of clinical endocrinology,” according to an Oct. 20 statement.
The change is meant to acknowledge AACE’s “more modern, inclusive approach to endocrinology that supports multidisciplinary care teams – with endocrinologists leading the way.”
Along with the name change is a new global website. The statement notes that “health care professionals and community members can access all of the valuable clinical content such as guidelines, disease state networks and important education by visiting the pro portal in the top right corner of the site, or by going directly to pro.aace.com.”
Dr. Handelsman discloses that he receives research grant support from Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BMS, Gan & Lee, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi, and he is a consultant and/or speaker for Amarin, BI-Lilly, and Sanofi.
Dr. Eckel has received consultant/advisory board fees from Kowa, Novo Nordisk, and Provention Bio.
Security breach in Finland leads to psychiatric patient blackmail
Hackers have accessed patient records at Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, emailing some patients to pay up or face having their private medical records released online.
Vastaamo treats about 40,000 patients and runs 25 centers across the country. Hackers emailed some of the centers’ patients asking for a blackmail payment of 200 euro in bitcoin, The Guardian reports.
Agencies such as the country’s National Bureau of Investigation are urging victims not to comply with the blackmailers’ demand and instead requesting that patients report these incidents to authorities and turn over incriminating emails. However, some data from patient records have already been released online.
“We deeply regret what happened and on behalf of our [patients] who have been compromised, we apologize for the shortcoming in data security, the consequences and human cost of which have been extremely heavy,” the center said in a statement. They added that the investigation into the situation is ongoing.
‘Sobering reminder’
In a comment, John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said this is “a sobering reminder that any digital data is subject to hacking.”
Torous is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee.
“This is not the first time psychotherapy notes have been targeted and it actually happened, on a smaller scale, in the US in 2017,” he said.
In April of that year, confidential patient record information from a mental health center in Maine, including evaluations, session notes, and names of sex-abuse victims, was listed on the dark web.
Also in April, computer hackers released the WannaCry virus into the operating system of the United Kingdom’s National Health Service, which subsequently locked clinicians out of patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
In addition, in 2016 hackers took Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center in Los Angeles offline for more than a week after demanding a ransom of $3.6 million.
Criminal investigation
For Vastaamo, three of its employees were approached by the blackmailer via email at the end of September, the company reports. These incidents were immediately disclosed and the Central Criminal Police launched a criminal investigation.
In addition, several agencies were contacted, including the Finnish Cyber Security Center, the Data Protection Commission, and a cyber security company.
Investigators believe the breach, which led to the customer database theft, occurred back in November 2018. In addition, security “deficiencies” remained until March 2019.
“We do not know that the database was stolen after November 2018, but it is possible that individual data [have been] viewed or copied,” Vastaamo said in a press release. No additional “vulnerabilities were identified after March 2019.”
The center’s CEO, Ville Tapio, who did not disclose any of these incidents to the parent company and its board of directors, was subsequently fired.
Once the police investigation began, Vastaamo said it was not granted permission by the authorities to communicate the occurrence to its patients. However, after the blackmailer released some patient information online early on Oct. 21, permission to inform patients was granted.
The company noted that the blackmailer has started emailing victims, informing of the data breach, and demanding ransom. So far, the emails have not contained harmful digital content or “malware,” but authorities warn that any attachments should not be opened. The police have requested that such emails be kept so they can be used as evidence.
In a Q&A section on its website, Vastaamo noted that videos are never recorded during its centers’ telehealth sessions and patients should not be concerned about the possibility of leaked videos.
In addition, the cybercrime has not interrupted Vastaamo’s operations.
“The authorities and the response office will do their utmost to find out what happened, to prevent the dissemination of information, and to bring the perpetrators to justice,” the center said.
“The most important task ... is to support customers in the midst of an exceptionally serious and difficult situation,” it added.
“Worst-case scenario”
In a comment, Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., said Vastaamo’s data breach “represents the worst-case scenario for digital health.”
He added that more information is needed about the specifics of the case, including exactly what happened, how the system was hacked, and what information was compromised.
Still, “it raises fundamental questions that healthcare systems, clinicians, and patients everywhere should be asking about what measures are in place to protect electronic medical records and other personal digital information,” said Dr. Vahia.
“This incident also serves as another reminder that the issue of data security and privacy is foundational to digital mental health. Ultimately, without a commitment from all stakeholders to maintaining the strictest levels of security, as well as transparency around how data are handled there will be little to no trust from clinicians or patients,” he said. All of that could prevent digital healthcare from achieving its full potential, he added.
In addition, Dr. Vahia noted that the rapid uptick of telemedicine because of the pandemic has accelerated the use of other forms of digital information in mental healthcare.
“This unfortunate incident should serve as a wake-up call and bring the issue of data protection back firmly into the spotlight,” said Dr. Vahia.
Now that telehealth has become a larger part of clinical practice, said Torous, it’s important for clinicians to be vigilant regarding security procedures.
“Telehealth and digital data are here to stay, and with them new benefits as well as risks. We can continue to work to minimize the risks and protect privacy while ensuring the benefits to patients expand,” he added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hackers have accessed patient records at Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, emailing some patients to pay up or face having their private medical records released online.
Vastaamo treats about 40,000 patients and runs 25 centers across the country. Hackers emailed some of the centers’ patients asking for a blackmail payment of 200 euro in bitcoin, The Guardian reports.
Agencies such as the country’s National Bureau of Investigation are urging victims not to comply with the blackmailers’ demand and instead requesting that patients report these incidents to authorities and turn over incriminating emails. However, some data from patient records have already been released online.
“We deeply regret what happened and on behalf of our [patients] who have been compromised, we apologize for the shortcoming in data security, the consequences and human cost of which have been extremely heavy,” the center said in a statement. They added that the investigation into the situation is ongoing.
‘Sobering reminder’
In a comment, John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said this is “a sobering reminder that any digital data is subject to hacking.”
Torous is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee.
“This is not the first time psychotherapy notes have been targeted and it actually happened, on a smaller scale, in the US in 2017,” he said.
In April of that year, confidential patient record information from a mental health center in Maine, including evaluations, session notes, and names of sex-abuse victims, was listed on the dark web.
Also in April, computer hackers released the WannaCry virus into the operating system of the United Kingdom’s National Health Service, which subsequently locked clinicians out of patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
In addition, in 2016 hackers took Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center in Los Angeles offline for more than a week after demanding a ransom of $3.6 million.
Criminal investigation
For Vastaamo, three of its employees were approached by the blackmailer via email at the end of September, the company reports. These incidents were immediately disclosed and the Central Criminal Police launched a criminal investigation.
In addition, several agencies were contacted, including the Finnish Cyber Security Center, the Data Protection Commission, and a cyber security company.
Investigators believe the breach, which led to the customer database theft, occurred back in November 2018. In addition, security “deficiencies” remained until March 2019.
“We do not know that the database was stolen after November 2018, but it is possible that individual data [have been] viewed or copied,” Vastaamo said in a press release. No additional “vulnerabilities were identified after March 2019.”
The center’s CEO, Ville Tapio, who did not disclose any of these incidents to the parent company and its board of directors, was subsequently fired.
Once the police investigation began, Vastaamo said it was not granted permission by the authorities to communicate the occurrence to its patients. However, after the blackmailer released some patient information online early on Oct. 21, permission to inform patients was granted.
The company noted that the blackmailer has started emailing victims, informing of the data breach, and demanding ransom. So far, the emails have not contained harmful digital content or “malware,” but authorities warn that any attachments should not be opened. The police have requested that such emails be kept so they can be used as evidence.
In a Q&A section on its website, Vastaamo noted that videos are never recorded during its centers’ telehealth sessions and patients should not be concerned about the possibility of leaked videos.
In addition, the cybercrime has not interrupted Vastaamo’s operations.
“The authorities and the response office will do their utmost to find out what happened, to prevent the dissemination of information, and to bring the perpetrators to justice,” the center said.
“The most important task ... is to support customers in the midst of an exceptionally serious and difficult situation,” it added.
“Worst-case scenario”
In a comment, Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., said Vastaamo’s data breach “represents the worst-case scenario for digital health.”
He added that more information is needed about the specifics of the case, including exactly what happened, how the system was hacked, and what information was compromised.
Still, “it raises fundamental questions that healthcare systems, clinicians, and patients everywhere should be asking about what measures are in place to protect electronic medical records and other personal digital information,” said Dr. Vahia.
“This incident also serves as another reminder that the issue of data security and privacy is foundational to digital mental health. Ultimately, without a commitment from all stakeholders to maintaining the strictest levels of security, as well as transparency around how data are handled there will be little to no trust from clinicians or patients,” he said. All of that could prevent digital healthcare from achieving its full potential, he added.
In addition, Dr. Vahia noted that the rapid uptick of telemedicine because of the pandemic has accelerated the use of other forms of digital information in mental healthcare.
“This unfortunate incident should serve as a wake-up call and bring the issue of data protection back firmly into the spotlight,” said Dr. Vahia.
Now that telehealth has become a larger part of clinical practice, said Torous, it’s important for clinicians to be vigilant regarding security procedures.
“Telehealth and digital data are here to stay, and with them new benefits as well as risks. We can continue to work to minimize the risks and protect privacy while ensuring the benefits to patients expand,” he added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hackers have accessed patient records at Finland’s largest private psychotherapy system, emailing some patients to pay up or face having their private medical records released online.
Vastaamo treats about 40,000 patients and runs 25 centers across the country. Hackers emailed some of the centers’ patients asking for a blackmail payment of 200 euro in bitcoin, The Guardian reports.
Agencies such as the country’s National Bureau of Investigation are urging victims not to comply with the blackmailers’ demand and instead requesting that patients report these incidents to authorities and turn over incriminating emails. However, some data from patient records have already been released online.
“We deeply regret what happened and on behalf of our [patients] who have been compromised, we apologize for the shortcoming in data security, the consequences and human cost of which have been extremely heavy,” the center said in a statement. They added that the investigation into the situation is ongoing.
‘Sobering reminder’
In a comment, John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said this is “a sobering reminder that any digital data is subject to hacking.”
Torous is also chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Health and Technology Committee.
“This is not the first time psychotherapy notes have been targeted and it actually happened, on a smaller scale, in the US in 2017,” he said.
In April of that year, confidential patient record information from a mental health center in Maine, including evaluations, session notes, and names of sex-abuse victims, was listed on the dark web.
Also in April, computer hackers released the WannaCry virus into the operating system of the United Kingdom’s National Health Service, which subsequently locked clinicians out of patient records and other digital tools for 3 days.
In addition, in 2016 hackers took Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center in Los Angeles offline for more than a week after demanding a ransom of $3.6 million.
Criminal investigation
For Vastaamo, three of its employees were approached by the blackmailer via email at the end of September, the company reports. These incidents were immediately disclosed and the Central Criminal Police launched a criminal investigation.
In addition, several agencies were contacted, including the Finnish Cyber Security Center, the Data Protection Commission, and a cyber security company.
Investigators believe the breach, which led to the customer database theft, occurred back in November 2018. In addition, security “deficiencies” remained until March 2019.
“We do not know that the database was stolen after November 2018, but it is possible that individual data [have been] viewed or copied,” Vastaamo said in a press release. No additional “vulnerabilities were identified after March 2019.”
The center’s CEO, Ville Tapio, who did not disclose any of these incidents to the parent company and its board of directors, was subsequently fired.
Once the police investigation began, Vastaamo said it was not granted permission by the authorities to communicate the occurrence to its patients. However, after the blackmailer released some patient information online early on Oct. 21, permission to inform patients was granted.
The company noted that the blackmailer has started emailing victims, informing of the data breach, and demanding ransom. So far, the emails have not contained harmful digital content or “malware,” but authorities warn that any attachments should not be opened. The police have requested that such emails be kept so they can be used as evidence.
In a Q&A section on its website, Vastaamo noted that videos are never recorded during its centers’ telehealth sessions and patients should not be concerned about the possibility of leaked videos.
In addition, the cybercrime has not interrupted Vastaamo’s operations.
“The authorities and the response office will do their utmost to find out what happened, to prevent the dissemination of information, and to bring the perpetrators to justice,” the center said.
“The most important task ... is to support customers in the midst of an exceptionally serious and difficult situation,” it added.
“Worst-case scenario”
In a comment, Ipsit Vahia, MD, medical director at the Institute for Technology and Psychiatry at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., said Vastaamo’s data breach “represents the worst-case scenario for digital health.”
He added that more information is needed about the specifics of the case, including exactly what happened, how the system was hacked, and what information was compromised.
Still, “it raises fundamental questions that healthcare systems, clinicians, and patients everywhere should be asking about what measures are in place to protect electronic medical records and other personal digital information,” said Dr. Vahia.
“This incident also serves as another reminder that the issue of data security and privacy is foundational to digital mental health. Ultimately, without a commitment from all stakeholders to maintaining the strictest levels of security, as well as transparency around how data are handled there will be little to no trust from clinicians or patients,” he said. All of that could prevent digital healthcare from achieving its full potential, he added.
In addition, Dr. Vahia noted that the rapid uptick of telemedicine because of the pandemic has accelerated the use of other forms of digital information in mental healthcare.
“This unfortunate incident should serve as a wake-up call and bring the issue of data protection back firmly into the spotlight,” said Dr. Vahia.
Now that telehealth has become a larger part of clinical practice, said Torous, it’s important for clinicians to be vigilant regarding security procedures.
“Telehealth and digital data are here to stay, and with them new benefits as well as risks. We can continue to work to minimize the risks and protect privacy while ensuring the benefits to patients expand,” he added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ODC1 gene linked to newly described neurodevelopmental disorder
but it may be treated with diet modifications and available therapies, according to the researcher whose group first identified the disorder.
Lance Rodan, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, reported on research into ODC1 gain-of-function disorder –named for ornithine decarboxylase 1, the rate-limiting enzyme involved in polyamine synthesis – in the Linda De Meirleir Neurometabolic award lecture at the 2020 CNS-ICNA Conjoint Meeting, held virtually this year. Dr. Rodan and colleagues first described ODC1 disorder in a multicenter case series.
Dr. Rodan noted that dysregulated polyamine levels are associated with cancer, and that ODC1 is expressed “ubiquitously” throughout the body.
Pathophysiology and phenotypes
In an interview, he described the metabolic process more fully. “GI flora can produce putrescine, which is the polyamine that accumulates in excess in the ODC1 gain-of-function disorder. It is yet to be elucidated if decreasing putrescine production by GI flora and/or reducing dietary sources of putrescine may play a role in the management of this disorder.”
In the De Meirleir lecture, Dr. Rodan described four patients from his group’s published case series, all found to have heterozygous de novo variants in the ODC1 gene, along with a fifth patient reported by Caleb Bupp, MD, and colleagues at Michigan State University, East Lansing.
“There’s a recognizable phenotype to this disorder,” Dr. Rodan said. “These individuals have neurodevelopment abnormalities. They may have behavioral concerns. They have low-tone central hypertonia and macrocephaly.”
One of the most distinctive characteristics of ODC1 disorder is alopecia, he said, “which in almost everybody with this condition involves the eyebrows and eyelashes and in some individuals also involves the scalp hair.”
These patients also have what Dr. Rodan called “a common yet subtle facial gestalt.” That can include hypertelorism, spareness of the eyebrows and eyelashes, and a tubular- shaped nose with a short columella and a short philtrum.
They may also have abnormalities of the nails and cryptorchidism, and typically a prenatal history of polyhydramnios, he said.
MRI findings include prominent perivascular spaces, periventricular cysts, abnormal white matter and corpus callosum abnormalities, he said, adding that the fetal case MRI demonstrated subepidermal cysts, white matter cysts in the temporal pole, deficiency of the falx cerebri and abnormal white-matter signals.
Biochemical features of ODC1 disorder include increased N-acetylputrescine levels with normal spermine and spermidine levels, Dr. Rodan said. He also noted that Dr. Bupp’s group reported increased putrescine in fibroblasts and increased ODC1 protein levels in red blood cells.
Dr. Rodan also described possible molecular mechanisms in ODC1 disorder. One was the location of the ODC1 variants: all were reported closely located to truncating variants in the final exon of the ODC1 gene. This allows truncating proteins to survive, adding to the degradation that results in a net gain-of-function of ODC1 enzyme activity.
With regard to pathophysiology of ODC1 disorder, Dr. Rodan noted that research has implicated chronically elevated putrescine levels in the alopecia, a finding animal models support. “Since putrescine is a precursor for gamma-aminobutyric acid, it’s possible perturbed GABA levels may also be involved,” he said. Abnormal modulation N-methyl-D-aspirate receptors may also be involved, he said.
Another hypothesis purports that potential of elevated levels of toxic aldehydes/H2O2 similar to Snyder-Robinson syndrome, the better known polyamine-related neurometabolic disorder. “Along those lines, maybe there’s also a secondary mitochondrial or lysosomal dysfunction, but this is something that’s still being actively studied,” Dr. Rodan said.
Treatment
Because ODC1 disorder was only first described 2 years ago, research into treatment is nascent. “In terms of management, I think one of the more fundamental questions is whether this is more of a static developmental disorder or whether this actually represents a progressive degenerative disorder,” Dr. Rodan said.
One potential treatment that has been explored, he said, is difluoromethylornithine, a synthetic ODC1 inhibitor already Food and Drug Administration approved for African sleeping sickness and as a topical treatment for hirsutism. It is also the subject of ongoing clinical trials in colon cancer and neuroblastoma. Potential side effects include myelosuppression, seizures and hearing loss.
Dr. Rodan noted that a single-center study reported that difluoromethylornithine in a 3-year-old patient with ODC1 disorder reduced ODC protein activity and putrescine to control levels.
Other potential treatments include the natural ODC1 inhibitors agmatine and turmeric/curcumin, flagyl/rifaximin to decrease putrescine production in the gut, a low-dairy diet to lower putrescine levels, and antioxidants. “There could be a role for antioxidant stress similar to what is seen in Snyder-Robinson syndrome,” Dr. Rodan said.
Based on mouse studies, patients with ODC1 may be at risk of skin cancer, so regular skin checks along with sun protection should be part of management, he said. “This also raises the question of whether there should be surveillance for other types of cancer given the role of polyamine in various types of tumors.”
Dr. Rodan has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
but it may be treated with diet modifications and available therapies, according to the researcher whose group first identified the disorder.
Lance Rodan, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, reported on research into ODC1 gain-of-function disorder –named for ornithine decarboxylase 1, the rate-limiting enzyme involved in polyamine synthesis – in the Linda De Meirleir Neurometabolic award lecture at the 2020 CNS-ICNA Conjoint Meeting, held virtually this year. Dr. Rodan and colleagues first described ODC1 disorder in a multicenter case series.
Dr. Rodan noted that dysregulated polyamine levels are associated with cancer, and that ODC1 is expressed “ubiquitously” throughout the body.
Pathophysiology and phenotypes
In an interview, he described the metabolic process more fully. “GI flora can produce putrescine, which is the polyamine that accumulates in excess in the ODC1 gain-of-function disorder. It is yet to be elucidated if decreasing putrescine production by GI flora and/or reducing dietary sources of putrescine may play a role in the management of this disorder.”
In the De Meirleir lecture, Dr. Rodan described four patients from his group’s published case series, all found to have heterozygous de novo variants in the ODC1 gene, along with a fifth patient reported by Caleb Bupp, MD, and colleagues at Michigan State University, East Lansing.
“There’s a recognizable phenotype to this disorder,” Dr. Rodan said. “These individuals have neurodevelopment abnormalities. They may have behavioral concerns. They have low-tone central hypertonia and macrocephaly.”
One of the most distinctive characteristics of ODC1 disorder is alopecia, he said, “which in almost everybody with this condition involves the eyebrows and eyelashes and in some individuals also involves the scalp hair.”
These patients also have what Dr. Rodan called “a common yet subtle facial gestalt.” That can include hypertelorism, spareness of the eyebrows and eyelashes, and a tubular- shaped nose with a short columella and a short philtrum.
They may also have abnormalities of the nails and cryptorchidism, and typically a prenatal history of polyhydramnios, he said.
MRI findings include prominent perivascular spaces, periventricular cysts, abnormal white matter and corpus callosum abnormalities, he said, adding that the fetal case MRI demonstrated subepidermal cysts, white matter cysts in the temporal pole, deficiency of the falx cerebri and abnormal white-matter signals.
Biochemical features of ODC1 disorder include increased N-acetylputrescine levels with normal spermine and spermidine levels, Dr. Rodan said. He also noted that Dr. Bupp’s group reported increased putrescine in fibroblasts and increased ODC1 protein levels in red blood cells.
Dr. Rodan also described possible molecular mechanisms in ODC1 disorder. One was the location of the ODC1 variants: all were reported closely located to truncating variants in the final exon of the ODC1 gene. This allows truncating proteins to survive, adding to the degradation that results in a net gain-of-function of ODC1 enzyme activity.
With regard to pathophysiology of ODC1 disorder, Dr. Rodan noted that research has implicated chronically elevated putrescine levels in the alopecia, a finding animal models support. “Since putrescine is a precursor for gamma-aminobutyric acid, it’s possible perturbed GABA levels may also be involved,” he said. Abnormal modulation N-methyl-D-aspirate receptors may also be involved, he said.
Another hypothesis purports that potential of elevated levels of toxic aldehydes/H2O2 similar to Snyder-Robinson syndrome, the better known polyamine-related neurometabolic disorder. “Along those lines, maybe there’s also a secondary mitochondrial or lysosomal dysfunction, but this is something that’s still being actively studied,” Dr. Rodan said.
Treatment
Because ODC1 disorder was only first described 2 years ago, research into treatment is nascent. “In terms of management, I think one of the more fundamental questions is whether this is more of a static developmental disorder or whether this actually represents a progressive degenerative disorder,” Dr. Rodan said.
One potential treatment that has been explored, he said, is difluoromethylornithine, a synthetic ODC1 inhibitor already Food and Drug Administration approved for African sleeping sickness and as a topical treatment for hirsutism. It is also the subject of ongoing clinical trials in colon cancer and neuroblastoma. Potential side effects include myelosuppression, seizures and hearing loss.
Dr. Rodan noted that a single-center study reported that difluoromethylornithine in a 3-year-old patient with ODC1 disorder reduced ODC protein activity and putrescine to control levels.
Other potential treatments include the natural ODC1 inhibitors agmatine and turmeric/curcumin, flagyl/rifaximin to decrease putrescine production in the gut, a low-dairy diet to lower putrescine levels, and antioxidants. “There could be a role for antioxidant stress similar to what is seen in Snyder-Robinson syndrome,” Dr. Rodan said.
Based on mouse studies, patients with ODC1 may be at risk of skin cancer, so regular skin checks along with sun protection should be part of management, he said. “This also raises the question of whether there should be surveillance for other types of cancer given the role of polyamine in various types of tumors.”
Dr. Rodan has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
but it may be treated with diet modifications and available therapies, according to the researcher whose group first identified the disorder.
Lance Rodan, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, reported on research into ODC1 gain-of-function disorder –named for ornithine decarboxylase 1, the rate-limiting enzyme involved in polyamine synthesis – in the Linda De Meirleir Neurometabolic award lecture at the 2020 CNS-ICNA Conjoint Meeting, held virtually this year. Dr. Rodan and colleagues first described ODC1 disorder in a multicenter case series.
Dr. Rodan noted that dysregulated polyamine levels are associated with cancer, and that ODC1 is expressed “ubiquitously” throughout the body.
Pathophysiology and phenotypes
In an interview, he described the metabolic process more fully. “GI flora can produce putrescine, which is the polyamine that accumulates in excess in the ODC1 gain-of-function disorder. It is yet to be elucidated if decreasing putrescine production by GI flora and/or reducing dietary sources of putrescine may play a role in the management of this disorder.”
In the De Meirleir lecture, Dr. Rodan described four patients from his group’s published case series, all found to have heterozygous de novo variants in the ODC1 gene, along with a fifth patient reported by Caleb Bupp, MD, and colleagues at Michigan State University, East Lansing.
“There’s a recognizable phenotype to this disorder,” Dr. Rodan said. “These individuals have neurodevelopment abnormalities. They may have behavioral concerns. They have low-tone central hypertonia and macrocephaly.”
One of the most distinctive characteristics of ODC1 disorder is alopecia, he said, “which in almost everybody with this condition involves the eyebrows and eyelashes and in some individuals also involves the scalp hair.”
These patients also have what Dr. Rodan called “a common yet subtle facial gestalt.” That can include hypertelorism, spareness of the eyebrows and eyelashes, and a tubular- shaped nose with a short columella and a short philtrum.
They may also have abnormalities of the nails and cryptorchidism, and typically a prenatal history of polyhydramnios, he said.
MRI findings include prominent perivascular spaces, periventricular cysts, abnormal white matter and corpus callosum abnormalities, he said, adding that the fetal case MRI demonstrated subepidermal cysts, white matter cysts in the temporal pole, deficiency of the falx cerebri and abnormal white-matter signals.
Biochemical features of ODC1 disorder include increased N-acetylputrescine levels with normal spermine and spermidine levels, Dr. Rodan said. He also noted that Dr. Bupp’s group reported increased putrescine in fibroblasts and increased ODC1 protein levels in red blood cells.
Dr. Rodan also described possible molecular mechanisms in ODC1 disorder. One was the location of the ODC1 variants: all were reported closely located to truncating variants in the final exon of the ODC1 gene. This allows truncating proteins to survive, adding to the degradation that results in a net gain-of-function of ODC1 enzyme activity.
With regard to pathophysiology of ODC1 disorder, Dr. Rodan noted that research has implicated chronically elevated putrescine levels in the alopecia, a finding animal models support. “Since putrescine is a precursor for gamma-aminobutyric acid, it’s possible perturbed GABA levels may also be involved,” he said. Abnormal modulation N-methyl-D-aspirate receptors may also be involved, he said.
Another hypothesis purports that potential of elevated levels of toxic aldehydes/H2O2 similar to Snyder-Robinson syndrome, the better known polyamine-related neurometabolic disorder. “Along those lines, maybe there’s also a secondary mitochondrial or lysosomal dysfunction, but this is something that’s still being actively studied,” Dr. Rodan said.
Treatment
Because ODC1 disorder was only first described 2 years ago, research into treatment is nascent. “In terms of management, I think one of the more fundamental questions is whether this is more of a static developmental disorder or whether this actually represents a progressive degenerative disorder,” Dr. Rodan said.
One potential treatment that has been explored, he said, is difluoromethylornithine, a synthetic ODC1 inhibitor already Food and Drug Administration approved for African sleeping sickness and as a topical treatment for hirsutism. It is also the subject of ongoing clinical trials in colon cancer and neuroblastoma. Potential side effects include myelosuppression, seizures and hearing loss.
Dr. Rodan noted that a single-center study reported that difluoromethylornithine in a 3-year-old patient with ODC1 disorder reduced ODC protein activity and putrescine to control levels.
Other potential treatments include the natural ODC1 inhibitors agmatine and turmeric/curcumin, flagyl/rifaximin to decrease putrescine production in the gut, a low-dairy diet to lower putrescine levels, and antioxidants. “There could be a role for antioxidant stress similar to what is seen in Snyder-Robinson syndrome,” Dr. Rodan said.
Based on mouse studies, patients with ODC1 may be at risk of skin cancer, so regular skin checks along with sun protection should be part of management, he said. “This also raises the question of whether there should be surveillance for other types of cancer given the role of polyamine in various types of tumors.”
Dr. Rodan has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
FROM CNS-ICNA 2020
COVID-19 treatment: What the NIH recommends
References
- National Institute of Health. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Updated October 22, 2020. Accessed October 28, 2020.
References
- National Institute of Health. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Updated October 22, 2020. Accessed October 28, 2020.
References
- National Institute of Health. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Updated October 22, 2020. Accessed October 28, 2020.
Higher serum omega-3 tied to better outcome after STEMI
Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids was associated with improved prognosis after ST-segment myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a new observational study.
The prospective study, which involved 944 patients with STEMI who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), showed that plasma levels of fatty acids at the time of the STEMI were inversely associated with both incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and cardiovascular readmissions (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 and 0.74 for 1-SD increase; for both, P < .05).
No association was seen for the endpoint of all-cause mortality.
“What we showed is that your consumption of fish and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids before the heart attack impacts your prognosis after the heart attack. It’s a novel approach because it’s not primary prevention or secondary prevention,” said Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, from the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain.
Sala-Vila, co–senior author Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Heart Universitari Germans Trias I Pujol, Barcelona, and first author Iolanda Lázaro, PhD, also from IMIM, reported their findings online Oct. 26 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
It has been established that dietary omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has cardioprotective properties, but observational studies and randomized trials of EPA intake have yielded disparate findings.
This study avoided the usual traps of nutritional epidemiology research – self-reported food diaries and intake questionnaires. For this study, the researchers measured tissue levels of EPA and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) by measuring serum phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels, which reflect dietary intake during the previous 3 or 4 weeks.
This technique, said Sala-Vila, not only provides a more reliable measure of fatty acid intake over time but also avoids measurement errors related to fatty acid content variation.
For example, “The EPA content of a piece of fish eaten in January could be very different from one eaten in June,” explained Sala-Vila.
That said, he acknowledged that this technique, which uses gas chromatography, does not at present have a clear clinical application. “It’s quite difficult just to convert levels of serum-PC EPA into consumption of fatty fish. We feel that the best advice at this point is that given by the American Heart Association to eat two servings of fatty fish a week.”
EPA and ALA: Partners in prevention?
In addition to the findings regarding EPA, the researchers also found that serum-PC ALA was inversely related to all-cause mortality after STEMI (HR, 0.65 for 1-SD increase; P < .05).
A trend was seen for an association between ALA and lower risk for incident MACE (P = .093).
ALA is readily available from inexpensive plant sources (eg, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, soy beans) and has been associated with lower all-cause mortality in high-risk individuals.
This omega-3 fatty acid is often given short shrift in the fatty acid world because of the seven-step enzymatic process needed to convert it into more beneficial forms.
“We know that the conversion of ALA to EPA or DHA [docohexaenoic acid] is marginal, but we decided to include it in the study because we feel that this fatty acid is becoming more important because there are some issues with fish consumption – people are concerned about pollutants and sustainability, and some just don’t like it,” explained Sala-Vila.
“We were shocked to see that the marine-derived and vegetable-derived fatty acids don’t appear to compete, but rather they act synergistically,” said Sala-Villa. The researchers suggested that marine and vegetable omega-3 fatty acids may act as “partners in prevention.”
“We are not metabolically adapted to converting ALA to EPA, but despite this, there is a large body of evidence showing that one way to increase the status of EPA and DHA in our membranes is by eating these sources of fatty acids,” said Sala-Vila.
For almost 20 years, Sala-Vila has been studying how the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 affects disease. Two of his current projects involve studying levels of ALA in red blood cell membranes as a risk factor for ischemic stroke and omega-3 status in individuals with cognitive impairment who are at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Applicable to all patients with atherosclerosis
In comments to theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, Deepak Bhatt, MD, called the study “terrific,” adding that the effort is “as good as it gets” for observational nutrition research.
“I think one has to view these findings in the larger universe of what is really a revolution in omega-3 fatty acid research,” said Bhatt.
This universe, he said, includes a wealth of observational research showing the benefits of omega-3s, two outcome trials – JELIS and REDUCE-IT – that showed the benefits of EPA supplementation, and two imaging studies – EVAPORATE and CHERRY – that showed favorable effects of EPA on the vasculature.
REDUCE-IT, for which Bhatt served as principal investigator, showed that treatment with icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), a high-dose purified form of EPA, led to a 25% relative risk reduction in MACE in an at-risk Western population.
The results, said Bhatt, who co-wrote an editorial that accompanies the current Sala-Vila article, “likely apply to all patients with atherosclerosis or who are at high risk for it” and supports the practice of counseling patients to increase their intake of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
The field may be due for a shake-up, he noted. At next month’s American Heart Association meeting, the results of another trial of another prescription-grade EPA/DHA supplement will be presented, and they are expected to be negative.
AstraZeneca announced in January 2020 the early closure of the STRENGTH trial of Epanova after an interim analysis showed a low likelihood of their product demonstrating benefit in the enrolled population.
Epanova is a fish-oil derived mixture of free fatty acids, primarily EPA and DHA. It is approved in the United States and is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride levels in adults with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. This indication is not affected by the data from the STRENGTH trial, according to a company press release.
Sala-Vila has received grants and support from the California Walnut Commission, including a grant to support part of this study. Bayés-Genís and Bhatt have relationships with a number of companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids was associated with improved prognosis after ST-segment myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a new observational study.
The prospective study, which involved 944 patients with STEMI who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), showed that plasma levels of fatty acids at the time of the STEMI were inversely associated with both incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and cardiovascular readmissions (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 and 0.74 for 1-SD increase; for both, P < .05).
No association was seen for the endpoint of all-cause mortality.
“What we showed is that your consumption of fish and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids before the heart attack impacts your prognosis after the heart attack. It’s a novel approach because it’s not primary prevention or secondary prevention,” said Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, from the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain.
Sala-Vila, co–senior author Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Heart Universitari Germans Trias I Pujol, Barcelona, and first author Iolanda Lázaro, PhD, also from IMIM, reported their findings online Oct. 26 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
It has been established that dietary omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has cardioprotective properties, but observational studies and randomized trials of EPA intake have yielded disparate findings.
This study avoided the usual traps of nutritional epidemiology research – self-reported food diaries and intake questionnaires. For this study, the researchers measured tissue levels of EPA and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) by measuring serum phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels, which reflect dietary intake during the previous 3 or 4 weeks.
This technique, said Sala-Vila, not only provides a more reliable measure of fatty acid intake over time but also avoids measurement errors related to fatty acid content variation.
For example, “The EPA content of a piece of fish eaten in January could be very different from one eaten in June,” explained Sala-Vila.
That said, he acknowledged that this technique, which uses gas chromatography, does not at present have a clear clinical application. “It’s quite difficult just to convert levels of serum-PC EPA into consumption of fatty fish. We feel that the best advice at this point is that given by the American Heart Association to eat two servings of fatty fish a week.”
EPA and ALA: Partners in prevention?
In addition to the findings regarding EPA, the researchers also found that serum-PC ALA was inversely related to all-cause mortality after STEMI (HR, 0.65 for 1-SD increase; P < .05).
A trend was seen for an association between ALA and lower risk for incident MACE (P = .093).
ALA is readily available from inexpensive plant sources (eg, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, soy beans) and has been associated with lower all-cause mortality in high-risk individuals.
This omega-3 fatty acid is often given short shrift in the fatty acid world because of the seven-step enzymatic process needed to convert it into more beneficial forms.
“We know that the conversion of ALA to EPA or DHA [docohexaenoic acid] is marginal, but we decided to include it in the study because we feel that this fatty acid is becoming more important because there are some issues with fish consumption – people are concerned about pollutants and sustainability, and some just don’t like it,” explained Sala-Vila.
“We were shocked to see that the marine-derived and vegetable-derived fatty acids don’t appear to compete, but rather they act synergistically,” said Sala-Villa. The researchers suggested that marine and vegetable omega-3 fatty acids may act as “partners in prevention.”
“We are not metabolically adapted to converting ALA to EPA, but despite this, there is a large body of evidence showing that one way to increase the status of EPA and DHA in our membranes is by eating these sources of fatty acids,” said Sala-Vila.
For almost 20 years, Sala-Vila has been studying how the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 affects disease. Two of his current projects involve studying levels of ALA in red blood cell membranes as a risk factor for ischemic stroke and omega-3 status in individuals with cognitive impairment who are at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Applicable to all patients with atherosclerosis
In comments to theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, Deepak Bhatt, MD, called the study “terrific,” adding that the effort is “as good as it gets” for observational nutrition research.
“I think one has to view these findings in the larger universe of what is really a revolution in omega-3 fatty acid research,” said Bhatt.
This universe, he said, includes a wealth of observational research showing the benefits of omega-3s, two outcome trials – JELIS and REDUCE-IT – that showed the benefits of EPA supplementation, and two imaging studies – EVAPORATE and CHERRY – that showed favorable effects of EPA on the vasculature.
REDUCE-IT, for which Bhatt served as principal investigator, showed that treatment with icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), a high-dose purified form of EPA, led to a 25% relative risk reduction in MACE in an at-risk Western population.
The results, said Bhatt, who co-wrote an editorial that accompanies the current Sala-Vila article, “likely apply to all patients with atherosclerosis or who are at high risk for it” and supports the practice of counseling patients to increase their intake of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
The field may be due for a shake-up, he noted. At next month’s American Heart Association meeting, the results of another trial of another prescription-grade EPA/DHA supplement will be presented, and they are expected to be negative.
AstraZeneca announced in January 2020 the early closure of the STRENGTH trial of Epanova after an interim analysis showed a low likelihood of their product demonstrating benefit in the enrolled population.
Epanova is a fish-oil derived mixture of free fatty acids, primarily EPA and DHA. It is approved in the United States and is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride levels in adults with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. This indication is not affected by the data from the STRENGTH trial, according to a company press release.
Sala-Vila has received grants and support from the California Walnut Commission, including a grant to support part of this study. Bayés-Genís and Bhatt have relationships with a number of companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids was associated with improved prognosis after ST-segment myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a new observational study.
The prospective study, which involved 944 patients with STEMI who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), showed that plasma levels of fatty acids at the time of the STEMI were inversely associated with both incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and cardiovascular readmissions (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 and 0.74 for 1-SD increase; for both, P < .05).
No association was seen for the endpoint of all-cause mortality.
“What we showed is that your consumption of fish and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids before the heart attack impacts your prognosis after the heart attack. It’s a novel approach because it’s not primary prevention or secondary prevention,” said Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, from the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain.
Sala-Vila, co–senior author Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Heart Universitari Germans Trias I Pujol, Barcelona, and first author Iolanda Lázaro, PhD, also from IMIM, reported their findings online Oct. 26 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
It has been established that dietary omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has cardioprotective properties, but observational studies and randomized trials of EPA intake have yielded disparate findings.
This study avoided the usual traps of nutritional epidemiology research – self-reported food diaries and intake questionnaires. For this study, the researchers measured tissue levels of EPA and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) by measuring serum phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels, which reflect dietary intake during the previous 3 or 4 weeks.
This technique, said Sala-Vila, not only provides a more reliable measure of fatty acid intake over time but also avoids measurement errors related to fatty acid content variation.
For example, “The EPA content of a piece of fish eaten in January could be very different from one eaten in June,” explained Sala-Vila.
That said, he acknowledged that this technique, which uses gas chromatography, does not at present have a clear clinical application. “It’s quite difficult just to convert levels of serum-PC EPA into consumption of fatty fish. We feel that the best advice at this point is that given by the American Heart Association to eat two servings of fatty fish a week.”
EPA and ALA: Partners in prevention?
In addition to the findings regarding EPA, the researchers also found that serum-PC ALA was inversely related to all-cause mortality after STEMI (HR, 0.65 for 1-SD increase; P < .05).
A trend was seen for an association between ALA and lower risk for incident MACE (P = .093).
ALA is readily available from inexpensive plant sources (eg, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, soy beans) and has been associated with lower all-cause mortality in high-risk individuals.
This omega-3 fatty acid is often given short shrift in the fatty acid world because of the seven-step enzymatic process needed to convert it into more beneficial forms.
“We know that the conversion of ALA to EPA or DHA [docohexaenoic acid] is marginal, but we decided to include it in the study because we feel that this fatty acid is becoming more important because there are some issues with fish consumption – people are concerned about pollutants and sustainability, and some just don’t like it,” explained Sala-Vila.
“We were shocked to see that the marine-derived and vegetable-derived fatty acids don’t appear to compete, but rather they act synergistically,” said Sala-Villa. The researchers suggested that marine and vegetable omega-3 fatty acids may act as “partners in prevention.”
“We are not metabolically adapted to converting ALA to EPA, but despite this, there is a large body of evidence showing that one way to increase the status of EPA and DHA in our membranes is by eating these sources of fatty acids,” said Sala-Vila.
For almost 20 years, Sala-Vila has been studying how the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 affects disease. Two of his current projects involve studying levels of ALA in red blood cell membranes as a risk factor for ischemic stroke and omega-3 status in individuals with cognitive impairment who are at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Applicable to all patients with atherosclerosis
In comments to theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, Deepak Bhatt, MD, called the study “terrific,” adding that the effort is “as good as it gets” for observational nutrition research.
“I think one has to view these findings in the larger universe of what is really a revolution in omega-3 fatty acid research,” said Bhatt.
This universe, he said, includes a wealth of observational research showing the benefits of omega-3s, two outcome trials – JELIS and REDUCE-IT – that showed the benefits of EPA supplementation, and two imaging studies – EVAPORATE and CHERRY – that showed favorable effects of EPA on the vasculature.
REDUCE-IT, for which Bhatt served as principal investigator, showed that treatment with icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), a high-dose purified form of EPA, led to a 25% relative risk reduction in MACE in an at-risk Western population.
The results, said Bhatt, who co-wrote an editorial that accompanies the current Sala-Vila article, “likely apply to all patients with atherosclerosis or who are at high risk for it” and supports the practice of counseling patients to increase their intake of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
The field may be due for a shake-up, he noted. At next month’s American Heart Association meeting, the results of another trial of another prescription-grade EPA/DHA supplement will be presented, and they are expected to be negative.
AstraZeneca announced in January 2020 the early closure of the STRENGTH trial of Epanova after an interim analysis showed a low likelihood of their product demonstrating benefit in the enrolled population.
Epanova is a fish-oil derived mixture of free fatty acids, primarily EPA and DHA. It is approved in the United States and is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride levels in adults with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. This indication is not affected by the data from the STRENGTH trial, according to a company press release.
Sala-Vila has received grants and support from the California Walnut Commission, including a grant to support part of this study. Bayés-Genís and Bhatt have relationships with a number of companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins may lower risk of colorectal cancer
Statin use may significantly lower the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) in patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), based on a meta-analysis and systematic review.
In more than 15,000 patients with IBD, statin use was associated with a 60% reduced risk of CRC, reported lead author Kevin N. Singh, MD, of NYU Langone Medical Center in New York, and colleagues.
“Statin use has been linked with a risk reduction for cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma, breast, gastric, pancreatic, and biliary tract cancers, but data supporting the use of statins for chemoprevention against CRC is conflicting,” Dr. Singh said during a virtual presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
He noted a 2014 meta-analysis by Lytras and colleagues that reported a 9% CRC risk reduction in statin users who did not have IBD. In patients with IBD, data are scarce, according to Dr. Singh.
To further explore the relationship between statin use and CRC in patients without IBD, the investigators analyzed data from 52 studies, including 8 randomized clinical trials, 17 cohort studies, and 27 case-control studies. Of the 11,459,306 patients involved, approximately 2 million used statins and roughly 9 million did not.
To evaluate the same relationship in patients with IBD, the investigators conducted a separate meta-analysis involving 15,342 patients from 5 observational studies, 1 of which was an unpublished abstract. In the 4 published studies, 1,161 patients used statins while 12,145 did not.
In the non-IBD population, statin use was associated with a 20% reduced risk of CRC (pooled odds ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.88; P less than .001). In patients with IBD, statin use was associated with a 60% CRC risk reduction (pooled OR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.19-0.86, P = .019).
Dr. Singh noted “significant heterogeneity” in both analyses (I2 greater than 75), most prominently in the IBD populations, which he ascribed to “differences in demographic features, ethnic groups, and risk factors for CRC.”
While publication bias was absent from the non-IBD analysis, it was detected in the IBD portion of the study. Dr. Singh said that selection bias may also have been present in the IBD analysis, due to exclusive use of observational studies.
“Prospective trials are needed to confirm the risk reduction of CRC in the IBD population, including whether the effects of statins differ between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease patients,” Dr. Singh said.
Additional analyses are underway, he added, including one that will account for the potentially confounding effect of aspirin use.
According to David E. Kaplan, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, “The finding that statins are associated with reduced CRC in IBD provides additional support for the clinical importance of the antineoplastic effects of statins. This effect has been strongly observed in liver cancer, and is pending prospective validation.”
Dr. Kaplan also offered some mechanistic insight into why statins have an anticancer effect, pointing to “the centrality of cholesterol biosynthesis for development and/or progression of malignancy.”
The investigators and Dr. Kaplan reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Statin use may significantly lower the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) in patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), based on a meta-analysis and systematic review.
In more than 15,000 patients with IBD, statin use was associated with a 60% reduced risk of CRC, reported lead author Kevin N. Singh, MD, of NYU Langone Medical Center in New York, and colleagues.
“Statin use has been linked with a risk reduction for cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma, breast, gastric, pancreatic, and biliary tract cancers, but data supporting the use of statins for chemoprevention against CRC is conflicting,” Dr. Singh said during a virtual presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
He noted a 2014 meta-analysis by Lytras and colleagues that reported a 9% CRC risk reduction in statin users who did not have IBD. In patients with IBD, data are scarce, according to Dr. Singh.
To further explore the relationship between statin use and CRC in patients without IBD, the investigators analyzed data from 52 studies, including 8 randomized clinical trials, 17 cohort studies, and 27 case-control studies. Of the 11,459,306 patients involved, approximately 2 million used statins and roughly 9 million did not.
To evaluate the same relationship in patients with IBD, the investigators conducted a separate meta-analysis involving 15,342 patients from 5 observational studies, 1 of which was an unpublished abstract. In the 4 published studies, 1,161 patients used statins while 12,145 did not.
In the non-IBD population, statin use was associated with a 20% reduced risk of CRC (pooled odds ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.88; P less than .001). In patients with IBD, statin use was associated with a 60% CRC risk reduction (pooled OR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.19-0.86, P = .019).
Dr. Singh noted “significant heterogeneity” in both analyses (I2 greater than 75), most prominently in the IBD populations, which he ascribed to “differences in demographic features, ethnic groups, and risk factors for CRC.”
While publication bias was absent from the non-IBD analysis, it was detected in the IBD portion of the study. Dr. Singh said that selection bias may also have been present in the IBD analysis, due to exclusive use of observational studies.
“Prospective trials are needed to confirm the risk reduction of CRC in the IBD population, including whether the effects of statins differ between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease patients,” Dr. Singh said.
Additional analyses are underway, he added, including one that will account for the potentially confounding effect of aspirin use.
According to David E. Kaplan, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, “The finding that statins are associated with reduced CRC in IBD provides additional support for the clinical importance of the antineoplastic effects of statins. This effect has been strongly observed in liver cancer, and is pending prospective validation.”
Dr. Kaplan also offered some mechanistic insight into why statins have an anticancer effect, pointing to “the centrality of cholesterol biosynthesis for development and/or progression of malignancy.”
The investigators and Dr. Kaplan reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Statin use may significantly lower the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) in patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), based on a meta-analysis and systematic review.
In more than 15,000 patients with IBD, statin use was associated with a 60% reduced risk of CRC, reported lead author Kevin N. Singh, MD, of NYU Langone Medical Center in New York, and colleagues.
“Statin use has been linked with a risk reduction for cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma, breast, gastric, pancreatic, and biliary tract cancers, but data supporting the use of statins for chemoprevention against CRC is conflicting,” Dr. Singh said during a virtual presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
He noted a 2014 meta-analysis by Lytras and colleagues that reported a 9% CRC risk reduction in statin users who did not have IBD. In patients with IBD, data are scarce, according to Dr. Singh.
To further explore the relationship between statin use and CRC in patients without IBD, the investigators analyzed data from 52 studies, including 8 randomized clinical trials, 17 cohort studies, and 27 case-control studies. Of the 11,459,306 patients involved, approximately 2 million used statins and roughly 9 million did not.
To evaluate the same relationship in patients with IBD, the investigators conducted a separate meta-analysis involving 15,342 patients from 5 observational studies, 1 of which was an unpublished abstract. In the 4 published studies, 1,161 patients used statins while 12,145 did not.
In the non-IBD population, statin use was associated with a 20% reduced risk of CRC (pooled odds ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.88; P less than .001). In patients with IBD, statin use was associated with a 60% CRC risk reduction (pooled OR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.19-0.86, P = .019).
Dr. Singh noted “significant heterogeneity” in both analyses (I2 greater than 75), most prominently in the IBD populations, which he ascribed to “differences in demographic features, ethnic groups, and risk factors for CRC.”
While publication bias was absent from the non-IBD analysis, it was detected in the IBD portion of the study. Dr. Singh said that selection bias may also have been present in the IBD analysis, due to exclusive use of observational studies.
“Prospective trials are needed to confirm the risk reduction of CRC in the IBD population, including whether the effects of statins differ between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease patients,” Dr. Singh said.
Additional analyses are underway, he added, including one that will account for the potentially confounding effect of aspirin use.
According to David E. Kaplan, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, “The finding that statins are associated with reduced CRC in IBD provides additional support for the clinical importance of the antineoplastic effects of statins. This effect has been strongly observed in liver cancer, and is pending prospective validation.”
Dr. Kaplan also offered some mechanistic insight into why statins have an anticancer effect, pointing to “the centrality of cholesterol biosynthesis for development and/or progression of malignancy.”
The investigators and Dr. Kaplan reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ACG 2020













