User login
Why Incorporating Obstetric History Matters for CVD Risk Management in Autoimmune Diseases
NEW YORK — Systemic autoimmune disease is well-recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but less recognized as a cardiovascular risk factor is a history of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, and cardiologists and rheumatologists need to include an obstetric history when managing patients with autoimmune diseases, a specialist in reproductive health in rheumatology told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
“Autoimmune diseases, lupus in particular, increase the risk for both cardiovascular disease and maternal placental syndromes,” Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, a professor at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and a specialist in reproductive health issues in rheumatology patients, told attendees. “For those patients who have complications during pregnancy, it further increases their already increased risk for later cardiovascular disease.”
CVD Risk Double Whammy
A history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and problematic pregnancy can be a double whammy for CVD risk. Dr. Sammaritano cited a 2022 meta-analysis that showed patients with SLE had a 2.5 times greater risk for stroke and almost three times greater risk for myocardial infarction than people without SLE.
Maternal placental syndromes include pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, preeclampsia, premature membrane rupture, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise, Dr. Sammaritano said. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, formerly called adverse pregnancy outcomes, she noted, include gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Pregnancy complications can have an adverse effect on the mother’s postpartum cardiovascular health, Dr. Sammaritano noted, a fact borne out by the cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes population-based retrospective cohort study and a 2007 meta-analysis that found a history of preeclampsia doubles the risk for venous thromboembolism, stroke, and ischemic heart disease up to 15 years after pregnancy.
“It is always important to obtain a reproductive health history from patients with autoimmune diseases,” Dr. Sammaritano told this news organization in an interview. “This is an integral part of any medical history. In the usual setting, this includes not only pregnancy history but also use of contraception in reproductive-aged women. Unplanned pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes in the setting of active or severe autoimmune disease or when teratogenic medications are used.”
Pregnancy history can be a factor in a woman’s cardiovascular health more than 15 years postpartum, even if a woman is no longer planning a pregnancy or is menopausal. “As such, this history is important in assessing every woman’s risk profile for CVD in addition to usual traditional risk factors,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“It is even more important for women with autoimmune disorders, who have been shown to have an already increased risk for CVD independent of their pregnancy history, likely related to a chronic inflammatory state and other autoimmune-related factors such as presence of antiphospholipid antibodies [aPL] or use of corticosteroids.”
Timing of disease onset is also an issue, she said. “In patients with SLE, for example, onset of CVD is much earlier than in the general population,” Dr. Sammaritano said. “As a result, these patients should likely be assessed for risk — both traditional and other risk factors — earlier than the general population, especially if an adverse obstetric history is present.”
At the younger end of the age continuum, women with autoimmune disease, including SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, who are pregnant should be put on guideline-directed low-dose aspirin preeclampsia prophylaxis, Dr. Sammaritano said. “Whether every patient with SLE needs this is still uncertain, but certainly, those with a history of renal disease, hypertension, or aPL antibody clearly do,” she added.
The evidence supporting hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in these patients is controversial, but Dr. Sammaritano noted two meta-analyses, one in 2022 and the other in 2023, that showed that HCQ lowered the risk for preeclampsia in women.
“The clear benefit of HCQ in preventing maternal disease complications, including flare, means we recommend it regardless for all patients with SLE at baseline and during pregnancy [if tolerated],” Dr. Sammaritano said. “The benefit or optimal use of these medications in other autoimmune diseases is less studied and less certain.”
Dr. Sammaritano added in her presentation, “We really need better therapies and, hopefully, those will be on the way, but I think the takeaway message, particularly for practicing rheumatologists and cardiologists, is to ask the question about obstetric history. Many of us don’t. It doesn’t seem relevant in the moment, but it really is in terms of the patient’s long-term risk for cardiovascular disease.”
The Case for Treatment During Pregnancy
Prophylaxis against pregnancy complications in patients with autoimmune disease may be achievable, Taryn Youngstein, MBBS, consultant rheumatologist and codirector of the Centre of Excellence in Vasculitis Research, Imperial College London, London, England, told this news organization after Dr. Sammaritano’s presentation. At the 2023 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, her group reported the safety and effectiveness of continuing tocilizumab in pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis, a large-vessel vasculitis predominantly affecting women of reproductive age.
“What traditionally happens is you would stop the biologic particularly before the third trimester because of safety and concerns that the monoclonal antibody is actively transported across the placenta, which means the baby gets much more concentration of the drug than the mum,” Dr. Youngstein said.
It’s a situation physicians must monitor closely, she said. “The mum is donating their immune system to the baby, but they’re also donating drug.”
“In high-risk patients, we would share decision-making with the patient,” Dr. Youngstein continued. “We have decided it’s too high of a risk for us to stop the drug, so we have been continuing the interleukin-6 [IL-6] inhibitor throughout the entire pregnancy.”
The data from Dr. Youngstein’s group showed that pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis who continued IL-6 inhibition therapy all carried to term with healthy births.
“We’ve shown that it’s relatively safe to do that, but you have to be very careful in monitoring the baby,” she said. This includes not giving the infant any live vaccines at birth because it will have the high levels of IL-6 inhibition, she said.
Dr. Sammaritano and Dr. Youngstein had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Systemic autoimmune disease is well-recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but less recognized as a cardiovascular risk factor is a history of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, and cardiologists and rheumatologists need to include an obstetric history when managing patients with autoimmune diseases, a specialist in reproductive health in rheumatology told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
“Autoimmune diseases, lupus in particular, increase the risk for both cardiovascular disease and maternal placental syndromes,” Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, a professor at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and a specialist in reproductive health issues in rheumatology patients, told attendees. “For those patients who have complications during pregnancy, it further increases their already increased risk for later cardiovascular disease.”
CVD Risk Double Whammy
A history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and problematic pregnancy can be a double whammy for CVD risk. Dr. Sammaritano cited a 2022 meta-analysis that showed patients with SLE had a 2.5 times greater risk for stroke and almost three times greater risk for myocardial infarction than people without SLE.
Maternal placental syndromes include pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, preeclampsia, premature membrane rupture, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise, Dr. Sammaritano said. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, formerly called adverse pregnancy outcomes, she noted, include gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Pregnancy complications can have an adverse effect on the mother’s postpartum cardiovascular health, Dr. Sammaritano noted, a fact borne out by the cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes population-based retrospective cohort study and a 2007 meta-analysis that found a history of preeclampsia doubles the risk for venous thromboembolism, stroke, and ischemic heart disease up to 15 years after pregnancy.
“It is always important to obtain a reproductive health history from patients with autoimmune diseases,” Dr. Sammaritano told this news organization in an interview. “This is an integral part of any medical history. In the usual setting, this includes not only pregnancy history but also use of contraception in reproductive-aged women. Unplanned pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes in the setting of active or severe autoimmune disease or when teratogenic medications are used.”
Pregnancy history can be a factor in a woman’s cardiovascular health more than 15 years postpartum, even if a woman is no longer planning a pregnancy or is menopausal. “As such, this history is important in assessing every woman’s risk profile for CVD in addition to usual traditional risk factors,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“It is even more important for women with autoimmune disorders, who have been shown to have an already increased risk for CVD independent of their pregnancy history, likely related to a chronic inflammatory state and other autoimmune-related factors such as presence of antiphospholipid antibodies [aPL] or use of corticosteroids.”
Timing of disease onset is also an issue, she said. “In patients with SLE, for example, onset of CVD is much earlier than in the general population,” Dr. Sammaritano said. “As a result, these patients should likely be assessed for risk — both traditional and other risk factors — earlier than the general population, especially if an adverse obstetric history is present.”
At the younger end of the age continuum, women with autoimmune disease, including SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, who are pregnant should be put on guideline-directed low-dose aspirin preeclampsia prophylaxis, Dr. Sammaritano said. “Whether every patient with SLE needs this is still uncertain, but certainly, those with a history of renal disease, hypertension, or aPL antibody clearly do,” she added.
The evidence supporting hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in these patients is controversial, but Dr. Sammaritano noted two meta-analyses, one in 2022 and the other in 2023, that showed that HCQ lowered the risk for preeclampsia in women.
“The clear benefit of HCQ in preventing maternal disease complications, including flare, means we recommend it regardless for all patients with SLE at baseline and during pregnancy [if tolerated],” Dr. Sammaritano said. “The benefit or optimal use of these medications in other autoimmune diseases is less studied and less certain.”
Dr. Sammaritano added in her presentation, “We really need better therapies and, hopefully, those will be on the way, but I think the takeaway message, particularly for practicing rheumatologists and cardiologists, is to ask the question about obstetric history. Many of us don’t. It doesn’t seem relevant in the moment, but it really is in terms of the patient’s long-term risk for cardiovascular disease.”
The Case for Treatment During Pregnancy
Prophylaxis against pregnancy complications in patients with autoimmune disease may be achievable, Taryn Youngstein, MBBS, consultant rheumatologist and codirector of the Centre of Excellence in Vasculitis Research, Imperial College London, London, England, told this news organization after Dr. Sammaritano’s presentation. At the 2023 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, her group reported the safety and effectiveness of continuing tocilizumab in pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis, a large-vessel vasculitis predominantly affecting women of reproductive age.
“What traditionally happens is you would stop the biologic particularly before the third trimester because of safety and concerns that the monoclonal antibody is actively transported across the placenta, which means the baby gets much more concentration of the drug than the mum,” Dr. Youngstein said.
It’s a situation physicians must monitor closely, she said. “The mum is donating their immune system to the baby, but they’re also donating drug.”
“In high-risk patients, we would share decision-making with the patient,” Dr. Youngstein continued. “We have decided it’s too high of a risk for us to stop the drug, so we have been continuing the interleukin-6 [IL-6] inhibitor throughout the entire pregnancy.”
The data from Dr. Youngstein’s group showed that pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis who continued IL-6 inhibition therapy all carried to term with healthy births.
“We’ve shown that it’s relatively safe to do that, but you have to be very careful in monitoring the baby,” she said. This includes not giving the infant any live vaccines at birth because it will have the high levels of IL-6 inhibition, she said.
Dr. Sammaritano and Dr. Youngstein had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Systemic autoimmune disease is well-recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but less recognized as a cardiovascular risk factor is a history of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, and cardiologists and rheumatologists need to include an obstetric history when managing patients with autoimmune diseases, a specialist in reproductive health in rheumatology told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
“Autoimmune diseases, lupus in particular, increase the risk for both cardiovascular disease and maternal placental syndromes,” Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, a professor at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and a specialist in reproductive health issues in rheumatology patients, told attendees. “For those patients who have complications during pregnancy, it further increases their already increased risk for later cardiovascular disease.”
CVD Risk Double Whammy
A history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and problematic pregnancy can be a double whammy for CVD risk. Dr. Sammaritano cited a 2022 meta-analysis that showed patients with SLE had a 2.5 times greater risk for stroke and almost three times greater risk for myocardial infarction than people without SLE.
Maternal placental syndromes include pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, preeclampsia, premature membrane rupture, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise, Dr. Sammaritano said. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, formerly called adverse pregnancy outcomes, she noted, include gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Pregnancy complications can have an adverse effect on the mother’s postpartum cardiovascular health, Dr. Sammaritano noted, a fact borne out by the cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes population-based retrospective cohort study and a 2007 meta-analysis that found a history of preeclampsia doubles the risk for venous thromboembolism, stroke, and ischemic heart disease up to 15 years after pregnancy.
“It is always important to obtain a reproductive health history from patients with autoimmune diseases,” Dr. Sammaritano told this news organization in an interview. “This is an integral part of any medical history. In the usual setting, this includes not only pregnancy history but also use of contraception in reproductive-aged women. Unplanned pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes in the setting of active or severe autoimmune disease or when teratogenic medications are used.”
Pregnancy history can be a factor in a woman’s cardiovascular health more than 15 years postpartum, even if a woman is no longer planning a pregnancy or is menopausal. “As such, this history is important in assessing every woman’s risk profile for CVD in addition to usual traditional risk factors,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“It is even more important for women with autoimmune disorders, who have been shown to have an already increased risk for CVD independent of their pregnancy history, likely related to a chronic inflammatory state and other autoimmune-related factors such as presence of antiphospholipid antibodies [aPL] or use of corticosteroids.”
Timing of disease onset is also an issue, she said. “In patients with SLE, for example, onset of CVD is much earlier than in the general population,” Dr. Sammaritano said. “As a result, these patients should likely be assessed for risk — both traditional and other risk factors — earlier than the general population, especially if an adverse obstetric history is present.”
At the younger end of the age continuum, women with autoimmune disease, including SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, who are pregnant should be put on guideline-directed low-dose aspirin preeclampsia prophylaxis, Dr. Sammaritano said. “Whether every patient with SLE needs this is still uncertain, but certainly, those with a history of renal disease, hypertension, or aPL antibody clearly do,” she added.
The evidence supporting hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in these patients is controversial, but Dr. Sammaritano noted two meta-analyses, one in 2022 and the other in 2023, that showed that HCQ lowered the risk for preeclampsia in women.
“The clear benefit of HCQ in preventing maternal disease complications, including flare, means we recommend it regardless for all patients with SLE at baseline and during pregnancy [if tolerated],” Dr. Sammaritano said. “The benefit or optimal use of these medications in other autoimmune diseases is less studied and less certain.”
Dr. Sammaritano added in her presentation, “We really need better therapies and, hopefully, those will be on the way, but I think the takeaway message, particularly for practicing rheumatologists and cardiologists, is to ask the question about obstetric history. Many of us don’t. It doesn’t seem relevant in the moment, but it really is in terms of the patient’s long-term risk for cardiovascular disease.”
The Case for Treatment During Pregnancy
Prophylaxis against pregnancy complications in patients with autoimmune disease may be achievable, Taryn Youngstein, MBBS, consultant rheumatologist and codirector of the Centre of Excellence in Vasculitis Research, Imperial College London, London, England, told this news organization after Dr. Sammaritano’s presentation. At the 2023 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, her group reported the safety and effectiveness of continuing tocilizumab in pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis, a large-vessel vasculitis predominantly affecting women of reproductive age.
“What traditionally happens is you would stop the biologic particularly before the third trimester because of safety and concerns that the monoclonal antibody is actively transported across the placenta, which means the baby gets much more concentration of the drug than the mum,” Dr. Youngstein said.
It’s a situation physicians must monitor closely, she said. “The mum is donating their immune system to the baby, but they’re also donating drug.”
“In high-risk patients, we would share decision-making with the patient,” Dr. Youngstein continued. “We have decided it’s too high of a risk for us to stop the drug, so we have been continuing the interleukin-6 [IL-6] inhibitor throughout the entire pregnancy.”
The data from Dr. Youngstein’s group showed that pregnant women with Takayasu arteritis who continued IL-6 inhibition therapy all carried to term with healthy births.
“We’ve shown that it’s relatively safe to do that, but you have to be very careful in monitoring the baby,” she said. This includes not giving the infant any live vaccines at birth because it will have the high levels of IL-6 inhibition, she said.
Dr. Sammaritano and Dr. Youngstein had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tool May Help Prioritize High-Risk Patients for Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.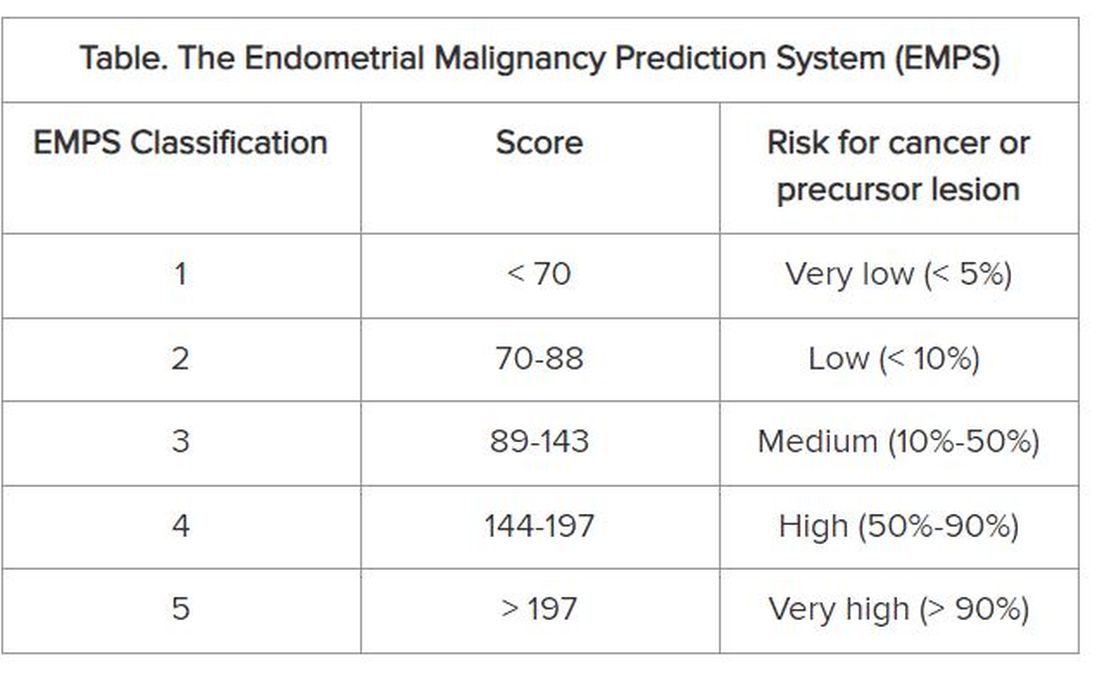
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Associated With Poorer Cognition in Older Adults
Lower urinary tract symptoms were significantly associated with lower scores on measures of cognitive impairment in older adults, based on data from approximately 10,000 individuals.
“We know that lower urinary tract symptoms are very common in aging men and women;” however, older adults often underreport symptoms and avoid seeking treatment, Belinda Williams, MD, of the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
“Evidence also shows us that the incidence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is higher in patients with dementia,” she said. However, the association between cognitive impairment and LUTS has not been well studied, she said.
To address this knowledge gap, Dr. Williams and colleagues reviewed data from older adults with and without LUTS who were enrolled in the REasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) study, a cohort study including 30,239 Black or White adults aged 45 years and older who completed telephone or in-home assessments in 2003-2007 and in 2013-2017.
The study population included 6062 women and 4438 men who responded to questionnaires about LUTS and completed several cognitive tests via telephone in 2019-2010. The tests evaluated verbal fluency, executive function, and memory, and included the Six-Item Screener, Animal Naming, Letter F naming, and word list learning; lower scores indicated poorer cognitive performance.
Participants who met the criteria for LUTS were categorized as having mild, moderate, or severe symptoms.
The researchers controlled for age, race, education, income, and urban/rural setting in a multivariate analysis. The mean ages of the women and men were 69 years and 63 years, respectively; 41% and 32% were Black, 59% and 68% were White.
Overall, 70% of women and 62% of men reported LUTS; 6.2% and 8.2%, respectively, met criteria for cognitive impairment. The association between cognitive impairment and LUTS was statistically significant for all specific tests (P < .01), but not for the global cognitive domain tests.
Black men were more likely to report LUTS than White men, but LUTS reports were similar between Black and White women.
Moderate LUTS was the most common degree of severity for men and women (54% and 64%, respectively).
The most common symptom overall was pre-toilet leakage (urge urinary incontinence), reported by 94% of women and 91% of men. The next most common symptoms for men and women were nocturia and urgency.
“We found that, across the board, in all the cognitive tests, LUTS were associated with lower cognitive test scores,” Dr. Williams said in her presentation. Little differences were seen on the Six-Item Screener, she noted, but when they further analyzed the data using scores lower than 4 to indicate cognitive impairment, they found significant association with LUTS, she said.
The results showing that the presence of LUTS was consistently associated with lower cognitive test scores of verbal fluency, executive function, and memory, are applicable in clinical practice, Dr. Williams said in her presentation.
“Recognizing the subtle changes in cognition among older adults with LUTS may impact treatment decisions,” she said. “For example, we can encourage and advise our patients to be physically and cognitively active and to avoid anticholinergic medications.”
Next steps for research include analyzing longitudinal changes in cognition among participants with and without LUTS, said Dr. Williams.
During a question-and-answer session, Dr. Williams agreed with a comment that incorporating cognitive screening strategies in to LUTS clinical pathways might be helpful, such as conducting a baseline Montreal Cognitive Assessment Test (MoCA) in patients with LUTS. “Periodic repeat MoCAs thereafter can help assess decline in cognition,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Lower urinary tract symptoms were significantly associated with lower scores on measures of cognitive impairment in older adults, based on data from approximately 10,000 individuals.
“We know that lower urinary tract symptoms are very common in aging men and women;” however, older adults often underreport symptoms and avoid seeking treatment, Belinda Williams, MD, of the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
“Evidence also shows us that the incidence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is higher in patients with dementia,” she said. However, the association between cognitive impairment and LUTS has not been well studied, she said.
To address this knowledge gap, Dr. Williams and colleagues reviewed data from older adults with and without LUTS who were enrolled in the REasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) study, a cohort study including 30,239 Black or White adults aged 45 years and older who completed telephone or in-home assessments in 2003-2007 and in 2013-2017.
The study population included 6062 women and 4438 men who responded to questionnaires about LUTS and completed several cognitive tests via telephone in 2019-2010. The tests evaluated verbal fluency, executive function, and memory, and included the Six-Item Screener, Animal Naming, Letter F naming, and word list learning; lower scores indicated poorer cognitive performance.
Participants who met the criteria for LUTS were categorized as having mild, moderate, or severe symptoms.
The researchers controlled for age, race, education, income, and urban/rural setting in a multivariate analysis. The mean ages of the women and men were 69 years and 63 years, respectively; 41% and 32% were Black, 59% and 68% were White.
Overall, 70% of women and 62% of men reported LUTS; 6.2% and 8.2%, respectively, met criteria for cognitive impairment. The association between cognitive impairment and LUTS was statistically significant for all specific tests (P < .01), but not for the global cognitive domain tests.
Black men were more likely to report LUTS than White men, but LUTS reports were similar between Black and White women.
Moderate LUTS was the most common degree of severity for men and women (54% and 64%, respectively).
The most common symptom overall was pre-toilet leakage (urge urinary incontinence), reported by 94% of women and 91% of men. The next most common symptoms for men and women were nocturia and urgency.
“We found that, across the board, in all the cognitive tests, LUTS were associated with lower cognitive test scores,” Dr. Williams said in her presentation. Little differences were seen on the Six-Item Screener, she noted, but when they further analyzed the data using scores lower than 4 to indicate cognitive impairment, they found significant association with LUTS, she said.
The results showing that the presence of LUTS was consistently associated with lower cognitive test scores of verbal fluency, executive function, and memory, are applicable in clinical practice, Dr. Williams said in her presentation.
“Recognizing the subtle changes in cognition among older adults with LUTS may impact treatment decisions,” she said. “For example, we can encourage and advise our patients to be physically and cognitively active and to avoid anticholinergic medications.”
Next steps for research include analyzing longitudinal changes in cognition among participants with and without LUTS, said Dr. Williams.
During a question-and-answer session, Dr. Williams agreed with a comment that incorporating cognitive screening strategies in to LUTS clinical pathways might be helpful, such as conducting a baseline Montreal Cognitive Assessment Test (MoCA) in patients with LUTS. “Periodic repeat MoCAs thereafter can help assess decline in cognition,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Lower urinary tract symptoms were significantly associated with lower scores on measures of cognitive impairment in older adults, based on data from approximately 10,000 individuals.
“We know that lower urinary tract symptoms are very common in aging men and women;” however, older adults often underreport symptoms and avoid seeking treatment, Belinda Williams, MD, of the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
“Evidence also shows us that the incidence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is higher in patients with dementia,” she said. However, the association between cognitive impairment and LUTS has not been well studied, she said.
To address this knowledge gap, Dr. Williams and colleagues reviewed data from older adults with and without LUTS who were enrolled in the REasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) study, a cohort study including 30,239 Black or White adults aged 45 years and older who completed telephone or in-home assessments in 2003-2007 and in 2013-2017.
The study population included 6062 women and 4438 men who responded to questionnaires about LUTS and completed several cognitive tests via telephone in 2019-2010. The tests evaluated verbal fluency, executive function, and memory, and included the Six-Item Screener, Animal Naming, Letter F naming, and word list learning; lower scores indicated poorer cognitive performance.
Participants who met the criteria for LUTS were categorized as having mild, moderate, or severe symptoms.
The researchers controlled for age, race, education, income, and urban/rural setting in a multivariate analysis. The mean ages of the women and men were 69 years and 63 years, respectively; 41% and 32% were Black, 59% and 68% were White.
Overall, 70% of women and 62% of men reported LUTS; 6.2% and 8.2%, respectively, met criteria for cognitive impairment. The association between cognitive impairment and LUTS was statistically significant for all specific tests (P < .01), but not for the global cognitive domain tests.
Black men were more likely to report LUTS than White men, but LUTS reports were similar between Black and White women.
Moderate LUTS was the most common degree of severity for men and women (54% and 64%, respectively).
The most common symptom overall was pre-toilet leakage (urge urinary incontinence), reported by 94% of women and 91% of men. The next most common symptoms for men and women were nocturia and urgency.
“We found that, across the board, in all the cognitive tests, LUTS were associated with lower cognitive test scores,” Dr. Williams said in her presentation. Little differences were seen on the Six-Item Screener, she noted, but when they further analyzed the data using scores lower than 4 to indicate cognitive impairment, they found significant association with LUTS, she said.
The results showing that the presence of LUTS was consistently associated with lower cognitive test scores of verbal fluency, executive function, and memory, are applicable in clinical practice, Dr. Williams said in her presentation.
“Recognizing the subtle changes in cognition among older adults with LUTS may impact treatment decisions,” she said. “For example, we can encourage and advise our patients to be physically and cognitively active and to avoid anticholinergic medications.”
Next steps for research include analyzing longitudinal changes in cognition among participants with and without LUTS, said Dr. Williams.
During a question-and-answer session, Dr. Williams agreed with a comment that incorporating cognitive screening strategies in to LUTS clinical pathways might be helpful, such as conducting a baseline Montreal Cognitive Assessment Test (MoCA) in patients with LUTS. “Periodic repeat MoCAs thereafter can help assess decline in cognition,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AGS 2024
Clinicians Call for Easing FDA Warnings on Low-Dose Estrogen
Charles Powell, MD, said he sometimes has a hard time persuading patients to start on low-dose vaginal estrogen, which can help prevent urinary tract infections and ease other symptoms of menopause.
Many women fear taking these vaginal products because of what Dr. Powell considers excessively strong warnings about the risk for cancer and cardiovascular disease linked to daily estrogen pills that were issued in the early 2000s.
He is advocating for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to remove the boxed warning on low-dose estrogen. His efforts are separate from his roles as an associate professor of urology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, and as a member of the American Urological Association (AUA), Dr. Powell said.
In his quest to find out how to change labeling, Dr. Powell has gained a quick education about drug regulation. He has enlisted Representative Jim Baird (R-IN) and Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) to contact the FDA on his behalf, while congressional staff guided him through the hurdles of getting the warning label changed. For instance, a manufacturer of low-dose estrogen may need to become involved.
“You don’t learn this in med school,” Dr. Powell said in an interview.
With this work, Dr. Powell is wading into a long-standing argument between the FDA and some clinicians and researchers about the potential harms of low-dose estrogen.
He is doing so at a time of increased interest in understanding genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), a term coined a decade ago by the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society to cover “a constellation of conditions” related to urogenital atrophy.
Symptoms of GSM include vaginal dryness and burning and recurrent urinary tract infections.
The federal government in 2022 began a project budgeted with nearly $1 million to review evidence on treatments, including vaginal and low-dose estrogen. The aim is to eventually help the AUA develop clinical guidelines for addressing GSM.
In addition, a bipartisan Senate bill introduced in May calls for authorizing $125 million over 5 years for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund research on menopause. Senator Patty Murray (D-WA), the lead sponsor of the bill, is a longtime advocate for women’s health and serves as chairwoman for the Senate Appropriations Committee, which largely sets the NIH budget.
“The bottom line is, for too long, menopause has been overlooked, underinvested in and left behind,” Sen. Murray said during a May 2 press conference. “It is well past time to stop treating menopause like some kind of secret and start treating it like the major mainstream public health issue it is.”
Evidence Demands
Increased federal funding for menopause research could help efforts to change the warning label on low-dose estrogen, according to JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Dr. Manson was a leader of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a major federally funded research project launched in 1991 to investigate if hormone therapy and diet could protect older women from chronic diseases related to aging.
Before the WHI, clinicians prescribed hormones to prevent cardiovascular disease, based on evidence from earlier research.
But in 2002, a WHI trial that compared estrogen-progestin tablets with placebo was halted early because of disturbing findings, including an association with higher risk for breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Compared with placebo, for every 10,000 women taking estrogen plus progestin annually, incidences of cardiovascular disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and invasive breast cancer were seven to eight times higher.
In January 2003, the FDA announced it would put a boxed warning about cardiovascular risk and cancer risk on estrogen products, reflecting the WHI finding.
The agency at the time said clinicians should work with patients to assess risks and benefits of these products to manage the effects of menopause.
But more news on the potential harms of estrogen followed in 2004: A WHI study comparing estrogen-only pills with placebo produced signals of a small increased risk for stroke, although it also indicated no excess risk for breast cancer for at least 6.8 years of use.
Dr. Manson and the North American Menopause Society in 2016 filed a petition with the FDA to remove the boxed warning that appears on the front of low-dose estrogen products. The group wanted the information on risks moved to the usual warning section of the label.
Two years later, the FDA rejected the petition, citing the absence of “well-controlled studies,” to prove low-dose topical estrogen poses less risk to women than the high-dose pills studied in the WHI.
The FDA told this news organization that it stands by the decisions in its rejection of the petition.
Persuading the FDA to revise the labels on low-dose estrogen products likely will require evidence from randomized, large-scale studies, Dr. Manson said. The agency has not been satisfied to date with findings from other kinds of studies, including observational research.
“Once that evidence is available that the benefit-risk profile is different for different formulations and the evidence is compelling and definitive, that warning should change,” Dr. Manson told this news organization.
But the warning continues to have a chilling effect on patient willingness to use low-dose vaginal estrogen, even with the FDA’s continued endorsement of estrogen for menopause symptoms, clinicians told this news organization.
Risa Kagan, MD, a gynecologist at Sutter Health in Berkeley, California, said in many cases her patients’ partners also need to be reassured. Dr. Kagan said she still sees women who have had to discontinue sexual intercourse because of pain. In some cases, the patients will bring the medicine home only to find that the warnings frighten their spouses.
“The spouse says, ‘Oh my God, I don’t want you to get dementia, to get breast cancer, it’s not worth it, so let’s keep doing outercourse’,” meaning sexual relations without penetration, Dr. Kagan said.
Difficult Messaging
From the initial unveiling of disappointing WHI results, clinicians and researchers have stressed that women could continue using estrogen products for managing symptoms of menopause, even while advising strongly against their continued use with the intention of preventing heart disease.
Newly published findings from follow-ups of WHI participants may give clinicians and patients even more confidence for the use of estrogen products in early menopause.
According to the study, which Dr. Manson coauthored, younger women have a low risk for cardiovascular disease and other associated conditions when taking hormone therapy. Risks attributed to these drugs were less than one additional adverse event per 1000 women annually. This population may also derive significant quality-of-life benefits for symptom relief.
Dr. Manson told this news organization that estrogen in lower doses and delivered through the skin as a patch or gel may further reduce risks.
“The WHI findings should never be used as a reason to deny hormone therapy to women in early menopause with bothersome menopausal symptoms,” Dr. Manson said. “Many women are good candidates for treatment and, in shared decision-making with their clinicians, should be able to receive appropriate and personalized healthcare for their needs.”
But the current FDA warning label makes it difficult to help women understand the risk and benefits of low-dose estrogen, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, medical director at the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
Clinicians now must set aside time to explain the warnings to women when they prescribe low-dose estrogen, Dr. Faubion said.
“The package insert is going to look scary: I prepare women for that because otherwise they often won’t even fill it or use it.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Charles Powell, MD, said he sometimes has a hard time persuading patients to start on low-dose vaginal estrogen, which can help prevent urinary tract infections and ease other symptoms of menopause.
Many women fear taking these vaginal products because of what Dr. Powell considers excessively strong warnings about the risk for cancer and cardiovascular disease linked to daily estrogen pills that were issued in the early 2000s.
He is advocating for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to remove the boxed warning on low-dose estrogen. His efforts are separate from his roles as an associate professor of urology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, and as a member of the American Urological Association (AUA), Dr. Powell said.
In his quest to find out how to change labeling, Dr. Powell has gained a quick education about drug regulation. He has enlisted Representative Jim Baird (R-IN) and Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) to contact the FDA on his behalf, while congressional staff guided him through the hurdles of getting the warning label changed. For instance, a manufacturer of low-dose estrogen may need to become involved.
“You don’t learn this in med school,” Dr. Powell said in an interview.
With this work, Dr. Powell is wading into a long-standing argument between the FDA and some clinicians and researchers about the potential harms of low-dose estrogen.
He is doing so at a time of increased interest in understanding genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), a term coined a decade ago by the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society to cover “a constellation of conditions” related to urogenital atrophy.
Symptoms of GSM include vaginal dryness and burning and recurrent urinary tract infections.
The federal government in 2022 began a project budgeted with nearly $1 million to review evidence on treatments, including vaginal and low-dose estrogen. The aim is to eventually help the AUA develop clinical guidelines for addressing GSM.
In addition, a bipartisan Senate bill introduced in May calls for authorizing $125 million over 5 years for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund research on menopause. Senator Patty Murray (D-WA), the lead sponsor of the bill, is a longtime advocate for women’s health and serves as chairwoman for the Senate Appropriations Committee, which largely sets the NIH budget.
“The bottom line is, for too long, menopause has been overlooked, underinvested in and left behind,” Sen. Murray said during a May 2 press conference. “It is well past time to stop treating menopause like some kind of secret and start treating it like the major mainstream public health issue it is.”
Evidence Demands
Increased federal funding for menopause research could help efforts to change the warning label on low-dose estrogen, according to JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Dr. Manson was a leader of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a major federally funded research project launched in 1991 to investigate if hormone therapy and diet could protect older women from chronic diseases related to aging.
Before the WHI, clinicians prescribed hormones to prevent cardiovascular disease, based on evidence from earlier research.
But in 2002, a WHI trial that compared estrogen-progestin tablets with placebo was halted early because of disturbing findings, including an association with higher risk for breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Compared with placebo, for every 10,000 women taking estrogen plus progestin annually, incidences of cardiovascular disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and invasive breast cancer were seven to eight times higher.
In January 2003, the FDA announced it would put a boxed warning about cardiovascular risk and cancer risk on estrogen products, reflecting the WHI finding.
The agency at the time said clinicians should work with patients to assess risks and benefits of these products to manage the effects of menopause.
But more news on the potential harms of estrogen followed in 2004: A WHI study comparing estrogen-only pills with placebo produced signals of a small increased risk for stroke, although it also indicated no excess risk for breast cancer for at least 6.8 years of use.
Dr. Manson and the North American Menopause Society in 2016 filed a petition with the FDA to remove the boxed warning that appears on the front of low-dose estrogen products. The group wanted the information on risks moved to the usual warning section of the label.
Two years later, the FDA rejected the petition, citing the absence of “well-controlled studies,” to prove low-dose topical estrogen poses less risk to women than the high-dose pills studied in the WHI.
The FDA told this news organization that it stands by the decisions in its rejection of the petition.
Persuading the FDA to revise the labels on low-dose estrogen products likely will require evidence from randomized, large-scale studies, Dr. Manson said. The agency has not been satisfied to date with findings from other kinds of studies, including observational research.
“Once that evidence is available that the benefit-risk profile is different for different formulations and the evidence is compelling and definitive, that warning should change,” Dr. Manson told this news organization.
But the warning continues to have a chilling effect on patient willingness to use low-dose vaginal estrogen, even with the FDA’s continued endorsement of estrogen for menopause symptoms, clinicians told this news organization.
Risa Kagan, MD, a gynecologist at Sutter Health in Berkeley, California, said in many cases her patients’ partners also need to be reassured. Dr. Kagan said she still sees women who have had to discontinue sexual intercourse because of pain. In some cases, the patients will bring the medicine home only to find that the warnings frighten their spouses.
“The spouse says, ‘Oh my God, I don’t want you to get dementia, to get breast cancer, it’s not worth it, so let’s keep doing outercourse’,” meaning sexual relations without penetration, Dr. Kagan said.
Difficult Messaging
From the initial unveiling of disappointing WHI results, clinicians and researchers have stressed that women could continue using estrogen products for managing symptoms of menopause, even while advising strongly against their continued use with the intention of preventing heart disease.
Newly published findings from follow-ups of WHI participants may give clinicians and patients even more confidence for the use of estrogen products in early menopause.
According to the study, which Dr. Manson coauthored, younger women have a low risk for cardiovascular disease and other associated conditions when taking hormone therapy. Risks attributed to these drugs were less than one additional adverse event per 1000 women annually. This population may also derive significant quality-of-life benefits for symptom relief.
Dr. Manson told this news organization that estrogen in lower doses and delivered through the skin as a patch or gel may further reduce risks.
“The WHI findings should never be used as a reason to deny hormone therapy to women in early menopause with bothersome menopausal symptoms,” Dr. Manson said. “Many women are good candidates for treatment and, in shared decision-making with their clinicians, should be able to receive appropriate and personalized healthcare for their needs.”
But the current FDA warning label makes it difficult to help women understand the risk and benefits of low-dose estrogen, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, medical director at the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
Clinicians now must set aside time to explain the warnings to women when they prescribe low-dose estrogen, Dr. Faubion said.
“The package insert is going to look scary: I prepare women for that because otherwise they often won’t even fill it or use it.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Charles Powell, MD, said he sometimes has a hard time persuading patients to start on low-dose vaginal estrogen, which can help prevent urinary tract infections and ease other symptoms of menopause.
Many women fear taking these vaginal products because of what Dr. Powell considers excessively strong warnings about the risk for cancer and cardiovascular disease linked to daily estrogen pills that were issued in the early 2000s.
He is advocating for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to remove the boxed warning on low-dose estrogen. His efforts are separate from his roles as an associate professor of urology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, and as a member of the American Urological Association (AUA), Dr. Powell said.
In his quest to find out how to change labeling, Dr. Powell has gained a quick education about drug regulation. He has enlisted Representative Jim Baird (R-IN) and Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) to contact the FDA on his behalf, while congressional staff guided him through the hurdles of getting the warning label changed. For instance, a manufacturer of low-dose estrogen may need to become involved.
“You don’t learn this in med school,” Dr. Powell said in an interview.
With this work, Dr. Powell is wading into a long-standing argument between the FDA and some clinicians and researchers about the potential harms of low-dose estrogen.
He is doing so at a time of increased interest in understanding genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), a term coined a decade ago by the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society to cover “a constellation of conditions” related to urogenital atrophy.
Symptoms of GSM include vaginal dryness and burning and recurrent urinary tract infections.
The federal government in 2022 began a project budgeted with nearly $1 million to review evidence on treatments, including vaginal and low-dose estrogen. The aim is to eventually help the AUA develop clinical guidelines for addressing GSM.
In addition, a bipartisan Senate bill introduced in May calls for authorizing $125 million over 5 years for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund research on menopause. Senator Patty Murray (D-WA), the lead sponsor of the bill, is a longtime advocate for women’s health and serves as chairwoman for the Senate Appropriations Committee, which largely sets the NIH budget.
“The bottom line is, for too long, menopause has been overlooked, underinvested in and left behind,” Sen. Murray said during a May 2 press conference. “It is well past time to stop treating menopause like some kind of secret and start treating it like the major mainstream public health issue it is.”
Evidence Demands
Increased federal funding for menopause research could help efforts to change the warning label on low-dose estrogen, according to JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Dr. Manson was a leader of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a major federally funded research project launched in 1991 to investigate if hormone therapy and diet could protect older women from chronic diseases related to aging.
Before the WHI, clinicians prescribed hormones to prevent cardiovascular disease, based on evidence from earlier research.
But in 2002, a WHI trial that compared estrogen-progestin tablets with placebo was halted early because of disturbing findings, including an association with higher risk for breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Compared with placebo, for every 10,000 women taking estrogen plus progestin annually, incidences of cardiovascular disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and invasive breast cancer were seven to eight times higher.
In January 2003, the FDA announced it would put a boxed warning about cardiovascular risk and cancer risk on estrogen products, reflecting the WHI finding.
The agency at the time said clinicians should work with patients to assess risks and benefits of these products to manage the effects of menopause.
But more news on the potential harms of estrogen followed in 2004: A WHI study comparing estrogen-only pills with placebo produced signals of a small increased risk for stroke, although it also indicated no excess risk for breast cancer for at least 6.8 years of use.
Dr. Manson and the North American Menopause Society in 2016 filed a petition with the FDA to remove the boxed warning that appears on the front of low-dose estrogen products. The group wanted the information on risks moved to the usual warning section of the label.
Two years later, the FDA rejected the petition, citing the absence of “well-controlled studies,” to prove low-dose topical estrogen poses less risk to women than the high-dose pills studied in the WHI.
The FDA told this news organization that it stands by the decisions in its rejection of the petition.
Persuading the FDA to revise the labels on low-dose estrogen products likely will require evidence from randomized, large-scale studies, Dr. Manson said. The agency has not been satisfied to date with findings from other kinds of studies, including observational research.
“Once that evidence is available that the benefit-risk profile is different for different formulations and the evidence is compelling and definitive, that warning should change,” Dr. Manson told this news organization.
But the warning continues to have a chilling effect on patient willingness to use low-dose vaginal estrogen, even with the FDA’s continued endorsement of estrogen for menopause symptoms, clinicians told this news organization.
Risa Kagan, MD, a gynecologist at Sutter Health in Berkeley, California, said in many cases her patients’ partners also need to be reassured. Dr. Kagan said she still sees women who have had to discontinue sexual intercourse because of pain. In some cases, the patients will bring the medicine home only to find that the warnings frighten their spouses.
“The spouse says, ‘Oh my God, I don’t want you to get dementia, to get breast cancer, it’s not worth it, so let’s keep doing outercourse’,” meaning sexual relations without penetration, Dr. Kagan said.
Difficult Messaging
From the initial unveiling of disappointing WHI results, clinicians and researchers have stressed that women could continue using estrogen products for managing symptoms of menopause, even while advising strongly against their continued use with the intention of preventing heart disease.
Newly published findings from follow-ups of WHI participants may give clinicians and patients even more confidence for the use of estrogen products in early menopause.
According to the study, which Dr. Manson coauthored, younger women have a low risk for cardiovascular disease and other associated conditions when taking hormone therapy. Risks attributed to these drugs were less than one additional adverse event per 1000 women annually. This population may also derive significant quality-of-life benefits for symptom relief.
Dr. Manson told this news organization that estrogen in lower doses and delivered through the skin as a patch or gel may further reduce risks.
“The WHI findings should never be used as a reason to deny hormone therapy to women in early menopause with bothersome menopausal symptoms,” Dr. Manson said. “Many women are good candidates for treatment and, in shared decision-making with their clinicians, should be able to receive appropriate and personalized healthcare for their needs.”
But the current FDA warning label makes it difficult to help women understand the risk and benefits of low-dose estrogen, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, medical director at the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
Clinicians now must set aside time to explain the warnings to women when they prescribe low-dose estrogen, Dr. Faubion said.
“The package insert is going to look scary: I prepare women for that because otherwise they often won’t even fill it or use it.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
In HPV-Positive Head and Neck Cancer, Treatment Is a Quandary
The topic of head and neck cancer is especially timely since the disease is evolving. A hematologist/oncologist with the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) told colleagues that specialists are grappling with how to de-escalate treatment.
Molly Tokaz, MD, of Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care and the University of Washington said tobacco is fading as a cause as fewer people smoke, and that human papillomavirus (HPV) is triggering more cases. HPV-positive patients have better prognoses, raising the prospect that their treatment could be adjusted.
“Instead of increasing the amount of therapy we're giving, we’re trying to peel it back,” she said. “If they’re going to respond no matter what we do, why are we going in with these huge weapons of mass destruction if we can get the same results with something more like a light infantry?”
Tokaz spoke about deescalating therapy at a May 2024 regional AVAHO meeting in Seattle that was focused on head and neck cancer. She elaborated on her presentation in an interview with Federal Practitioner. according to Tokaz, 90% of head and neck cancers are mucosal squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). HPV is associated specifically with nasopharyngeal cancer, which is distinct from SCC, and oropharyngeal cancer, which has been linked to better prognoses.
HPV-positive head and neck cancer is a unique entity with its own epidemiology, clinical prognosis, and treatment. “Patients tend to be younger without the same number of comorbid conditions,” Tokaz said. “Some of them are never smokers or light smokers. So, it's a different demographic than we’ve seen traditionally.”
The bad news is that HPV-associated head and neck cancer numbers are on the rise. Fortunately, outcomes tend to be better for the HPV-positive forms.
As for therapy for head and neck cancer, immunotherapy and targeted therapy play smaller roles than in some other cancers because the form tends to be diagnosed in early stages before metastases appear. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation remain the major treatments. According to Tokaz’s presentation, surgery, or radiation—often with minimal adjuvant chemotherapy—can be appropriate for the earliest stage I and II cases of head and neck SCC. (She noted that HPV-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma has its own staging system.)
Stage I and II cases make up 15% of new diagnoses and have a 5-year survival rate of > 70%. “In the earliest days, our main role was to make radiation work better and reduce it while adding a minimum amount of toxicity mutations,” she said. “Chemotherapy can help, but it’s only demonstrated improvement in overall survival in patients with positive surgical margins and extracapsular extension.”
In Stage III, IVA, and IVB cases, which make up 70% of new diagnoses, chemotherapy plus radiation is recommended. Five-year survival drops to 30% to 50%. Finally, 10% of new diagnoses are Stage IVC, which is incurable and median survival is < 1 year.
Since HPV-positive patients generally have better prognoses, oncologists are considering how to adjust their treatment. However, Tokaz notes that clinical trials have not shown a benefit from less intensive treatment in these patients. “At this point, we still treat them the same way as HPV-negative patients. But it's an ongoing area of research.”
Researchers are also exploring how to optimize regimens in patients ineligible for treatment with the chemotherapy agent cisplatin. “These folks have been traditionally excluded from clinical trials because they’re sicker,” Tokaz explained. “Researchers normally want the fittest and the best patients [in trials]. If you give a drug to someone with a lot of other comorbid conditions, they might not do as well with it, and it makes your drug look bad.”
Figuring out how to treat these patients is an especially urgent task in head and neck cancer because so many patients are frail and have comorbidities. More globally, Tokaz said the rise of HPV-related head and neck cancer highlights the importance of HPV vaccination, which is crucial for preventing cervical and anal cancer in addition to head and neck cancer. “HPV vaccination for children and young adults is crucial.”
Molly Tokaz, MD, reported no relevant financial relationships.
The topic of head and neck cancer is especially timely since the disease is evolving. A hematologist/oncologist with the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) told colleagues that specialists are grappling with how to de-escalate treatment.
Molly Tokaz, MD, of Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care and the University of Washington said tobacco is fading as a cause as fewer people smoke, and that human papillomavirus (HPV) is triggering more cases. HPV-positive patients have better prognoses, raising the prospect that their treatment could be adjusted.
“Instead of increasing the amount of therapy we're giving, we’re trying to peel it back,” she said. “If they’re going to respond no matter what we do, why are we going in with these huge weapons of mass destruction if we can get the same results with something more like a light infantry?”
Tokaz spoke about deescalating therapy at a May 2024 regional AVAHO meeting in Seattle that was focused on head and neck cancer. She elaborated on her presentation in an interview with Federal Practitioner. according to Tokaz, 90% of head and neck cancers are mucosal squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). HPV is associated specifically with nasopharyngeal cancer, which is distinct from SCC, and oropharyngeal cancer, which has been linked to better prognoses.
HPV-positive head and neck cancer is a unique entity with its own epidemiology, clinical prognosis, and treatment. “Patients tend to be younger without the same number of comorbid conditions,” Tokaz said. “Some of them are never smokers or light smokers. So, it's a different demographic than we’ve seen traditionally.”
The bad news is that HPV-associated head and neck cancer numbers are on the rise. Fortunately, outcomes tend to be better for the HPV-positive forms.
As for therapy for head and neck cancer, immunotherapy and targeted therapy play smaller roles than in some other cancers because the form tends to be diagnosed in early stages before metastases appear. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation remain the major treatments. According to Tokaz’s presentation, surgery, or radiation—often with minimal adjuvant chemotherapy—can be appropriate for the earliest stage I and II cases of head and neck SCC. (She noted that HPV-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma has its own staging system.)
Stage I and II cases make up 15% of new diagnoses and have a 5-year survival rate of > 70%. “In the earliest days, our main role was to make radiation work better and reduce it while adding a minimum amount of toxicity mutations,” she said. “Chemotherapy can help, but it’s only demonstrated improvement in overall survival in patients with positive surgical margins and extracapsular extension.”
In Stage III, IVA, and IVB cases, which make up 70% of new diagnoses, chemotherapy plus radiation is recommended. Five-year survival drops to 30% to 50%. Finally, 10% of new diagnoses are Stage IVC, which is incurable and median survival is < 1 year.
Since HPV-positive patients generally have better prognoses, oncologists are considering how to adjust their treatment. However, Tokaz notes that clinical trials have not shown a benefit from less intensive treatment in these patients. “At this point, we still treat them the same way as HPV-negative patients. But it's an ongoing area of research.”
Researchers are also exploring how to optimize regimens in patients ineligible for treatment with the chemotherapy agent cisplatin. “These folks have been traditionally excluded from clinical trials because they’re sicker,” Tokaz explained. “Researchers normally want the fittest and the best patients [in trials]. If you give a drug to someone with a lot of other comorbid conditions, they might not do as well with it, and it makes your drug look bad.”
Figuring out how to treat these patients is an especially urgent task in head and neck cancer because so many patients are frail and have comorbidities. More globally, Tokaz said the rise of HPV-related head and neck cancer highlights the importance of HPV vaccination, which is crucial for preventing cervical and anal cancer in addition to head and neck cancer. “HPV vaccination for children and young adults is crucial.”
Molly Tokaz, MD, reported no relevant financial relationships.
The topic of head and neck cancer is especially timely since the disease is evolving. A hematologist/oncologist with the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) told colleagues that specialists are grappling with how to de-escalate treatment.
Molly Tokaz, MD, of Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care and the University of Washington said tobacco is fading as a cause as fewer people smoke, and that human papillomavirus (HPV) is triggering more cases. HPV-positive patients have better prognoses, raising the prospect that their treatment could be adjusted.
“Instead of increasing the amount of therapy we're giving, we’re trying to peel it back,” she said. “If they’re going to respond no matter what we do, why are we going in with these huge weapons of mass destruction if we can get the same results with something more like a light infantry?”
Tokaz spoke about deescalating therapy at a May 2024 regional AVAHO meeting in Seattle that was focused on head and neck cancer. She elaborated on her presentation in an interview with Federal Practitioner. according to Tokaz, 90% of head and neck cancers are mucosal squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). HPV is associated specifically with nasopharyngeal cancer, which is distinct from SCC, and oropharyngeal cancer, which has been linked to better prognoses.
HPV-positive head and neck cancer is a unique entity with its own epidemiology, clinical prognosis, and treatment. “Patients tend to be younger without the same number of comorbid conditions,” Tokaz said. “Some of them are never smokers or light smokers. So, it's a different demographic than we’ve seen traditionally.”
The bad news is that HPV-associated head and neck cancer numbers are on the rise. Fortunately, outcomes tend to be better for the HPV-positive forms.
As for therapy for head and neck cancer, immunotherapy and targeted therapy play smaller roles than in some other cancers because the form tends to be diagnosed in early stages before metastases appear. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation remain the major treatments. According to Tokaz’s presentation, surgery, or radiation—often with minimal adjuvant chemotherapy—can be appropriate for the earliest stage I and II cases of head and neck SCC. (She noted that HPV-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma has its own staging system.)
Stage I and II cases make up 15% of new diagnoses and have a 5-year survival rate of > 70%. “In the earliest days, our main role was to make radiation work better and reduce it while adding a minimum amount of toxicity mutations,” she said. “Chemotherapy can help, but it’s only demonstrated improvement in overall survival in patients with positive surgical margins and extracapsular extension.”
In Stage III, IVA, and IVB cases, which make up 70% of new diagnoses, chemotherapy plus radiation is recommended. Five-year survival drops to 30% to 50%. Finally, 10% of new diagnoses are Stage IVC, which is incurable and median survival is < 1 year.
Since HPV-positive patients generally have better prognoses, oncologists are considering how to adjust their treatment. However, Tokaz notes that clinical trials have not shown a benefit from less intensive treatment in these patients. “At this point, we still treat them the same way as HPV-negative patients. But it's an ongoing area of research.”
Researchers are also exploring how to optimize regimens in patients ineligible for treatment with the chemotherapy agent cisplatin. “These folks have been traditionally excluded from clinical trials because they’re sicker,” Tokaz explained. “Researchers normally want the fittest and the best patients [in trials]. If you give a drug to someone with a lot of other comorbid conditions, they might not do as well with it, and it makes your drug look bad.”
Figuring out how to treat these patients is an especially urgent task in head and neck cancer because so many patients are frail and have comorbidities. More globally, Tokaz said the rise of HPV-related head and neck cancer highlights the importance of HPV vaccination, which is crucial for preventing cervical and anal cancer in addition to head and neck cancer. “HPV vaccination for children and young adults is crucial.”
Molly Tokaz, MD, reported no relevant financial relationships.
More Rapid Confirmation of an Autism Diagnosis Is Coming to Primary Care
TORONTO — , according to a series of studies presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting.
Accelerated Diagnosis
In one study, 80% of the evaluations were conducted within 6 weeks of patient enrollment, according to Corinna Rea, MD, a clinician in the primary care center at Boston Children’s Hospital as well as an assistant professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
This outcome was drawn from a pilot study with 179 children suspected of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by clinicians in a pediatric clinic. All were under the age of 3 years. In the first step, families completed the Bayley-4 Social-Emotional and Adaptive Behavior Scale.
The next step was a virtual assessment by a trained clinician using the TELE-ADS-PEDs (TAP) tool developed by Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee. Patients and families participated from their homes. The diagnosis of ASD was made by a psychologist using the patient’s history and data provided by the two assessment tools.
Through this approach, the median time to diagnosis was 30 days, according to Dr. Rea. Relative to a median time of 168 days to diagnosis among patients considered likely to have ASD at Dr. Rea’s center in the year prior to this pilot study, the time was reduced significantly (P < .001).
All patients in the study were subsequently evaluated by traditional methods. One hundred percent of the ASD diagnoses were confirmed with traditional assessment.
On the basis of these data, the accelerated approach “seems efficient and quite accurate,” Dr. Rea reported. When family members were surveyed at the end of the pilot study, 60% were satisfied and 28% were moderately satisfied. Although 59% reported that they would have preferred an in-person assessment, approximately 90% agreed the child’s development was mostly or completely captured in the accelerated assessment.
Dr. Rea pointed out that the psychologists participating in this study offered the opinion that home-based assessments are in their experience better than in-person evaluations due to the more natural behavior of the child in their own environment. However, she said that the diagnostic approach in the pilot study is still being modified, and one of the goals is to make virtual assessment more acceptable to the families.
A Commercialized Diagnostic Approach
A similar approach has been commercialized by a firm called As You Are, according to Steven D. Hicks, MD, PhD, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania. Dr. Hicks is a principal in the enterprise, which is also assessing ASD virtually.
Trained pediatricians are evaluating patients with multiple tools in addition to TAP, including the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-V) checklist for ASD. The company, which began offering this diagnostic service in 2022, now employs more than 30 pediatricians who participated in a 1-month training program.
At the 2024 PAS meeting, quality assurance data were presented on 215 (2.2%) of the 9632 children evaluated between February 2023 and March 2024. The diagnostic assessments of these randomly selected children were reviewed by one of three randomly assigned experts (a developmental pediatrician, a child psychologist, or a pediatrician with 7 years’ diagnostic experience) blinded to the initial scoring.
The diagnostic agreement was 94%, according to the data presented, providing a specificity of 90% and a sensitivity of 90% for ASD. The commercialized diagnostic approach is providing a diagnosis in a mean time of 29 days from initial contact, compared with delays that typically exceed 1 year for many children with suspected ASD, according to Dr. Hicks.
Additional Studies Aim at Streamlining Diagnosis
Two additional studies also evaluated strategies to streamline the diagnosis of ASD. Both were positive. In one, the accuracy and time to diagnosis among pediatricians trained in TAP and CARS were compared with those of ASD specialists in a dedicated autism clinic. Both were located at Nemours Children’s Health Center, Wilmington, Delaware.
In this study, presented by Meghan Harrison, DO, an attending pediatrician at Nemours Children’s Health, time to diagnosis among the 39 patients evaluated by pediatricians relative to the 349 patients evaluated at the dedicated ASD center (2.0 vs 5.1 months; P = .001) was significantly shorter. The age at diagnosis in the pediatrician-assessed population (27.5 vs 36.5 months; P < .001) was also significantly younger.
In another study, led by Ashely L. Early, MSW, a clinical social worker at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, switching to a screening tool called the Rapid Interactive Screening Test for Autism in Toddlers (RITA-1) reduced the wait time to evaluation by approximately 5 months relative to previous practice with a more cumbersome screening method.
An ‘Urgent Need’ to Accelerate Diagnosis
In most places in the United States, children suspected of ASD are referred to specialists for confirmation of the diagnosis, which is needed to quality for ASD services, according to Katherine Zuckerman, MD, a professor of pediatrics the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon. Dr. Zuckerman, who was moderator of the session in which all four of these abstracts were presented, explained that there is an urgent need to accelerate the time to diagnosis, which involves long delays for many if not most children with ASD. This is important because treatment and supportive services for ASD are almost always dependent on a diagnosis.
“There are tons of data to show that earlier access to ASD services has important patient benefits, including higher IQs,” she said. Other benefits she listed include a better quality of life for the child and the family.
“It can provide a huge reduction in family stress,” she added, suggesting that early interventions favorably modify the trajectory of the disability over time with accruing benefits.
“The lifetime costs of ASD exceed cancer and most other disease, so there are major implications for the cumulative cost of ASD management,” Dr. Zuckerman said. She suggested that the studies presented at the meeting reflect a likely evolution in who evaluates children for ASD and how quickly the evaluation is performed.
Dr. Rea, Dr. Harrison, Dr. Zuckerman, and Ms. Early reported no potential conflicts of interest. In addition to his executive role in As You Are, Dr. Hicks has financial relationships with Quadrant Biosciences and Spectrum Solutions.
TORONTO — , according to a series of studies presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting.
Accelerated Diagnosis
In one study, 80% of the evaluations were conducted within 6 weeks of patient enrollment, according to Corinna Rea, MD, a clinician in the primary care center at Boston Children’s Hospital as well as an assistant professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
This outcome was drawn from a pilot study with 179 children suspected of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by clinicians in a pediatric clinic. All were under the age of 3 years. In the first step, families completed the Bayley-4 Social-Emotional and Adaptive Behavior Scale.
The next step was a virtual assessment by a trained clinician using the TELE-ADS-PEDs (TAP) tool developed by Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee. Patients and families participated from their homes. The diagnosis of ASD was made by a psychologist using the patient’s history and data provided by the two assessment tools.
Through this approach, the median time to diagnosis was 30 days, according to Dr. Rea. Relative to a median time of 168 days to diagnosis among patients considered likely to have ASD at Dr. Rea’s center in the year prior to this pilot study, the time was reduced significantly (P < .001).
All patients in the study were subsequently evaluated by traditional methods. One hundred percent of the ASD diagnoses were confirmed with traditional assessment.
On the basis of these data, the accelerated approach “seems efficient and quite accurate,” Dr. Rea reported. When family members were surveyed at the end of the pilot study, 60% were satisfied and 28% were moderately satisfied. Although 59% reported that they would have preferred an in-person assessment, approximately 90% agreed the child’s development was mostly or completely captured in the accelerated assessment.
Dr. Rea pointed out that the psychologists participating in this study offered the opinion that home-based assessments are in their experience better than in-person evaluations due to the more natural behavior of the child in their own environment. However, she said that the diagnostic approach in the pilot study is still being modified, and one of the goals is to make virtual assessment more acceptable to the families.
A Commercialized Diagnostic Approach
A similar approach has been commercialized by a firm called As You Are, according to Steven D. Hicks, MD, PhD, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania. Dr. Hicks is a principal in the enterprise, which is also assessing ASD virtually.
Trained pediatricians are evaluating patients with multiple tools in addition to TAP, including the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-V) checklist for ASD. The company, which began offering this diagnostic service in 2022, now employs more than 30 pediatricians who participated in a 1-month training program.
At the 2024 PAS meeting, quality assurance data were presented on 215 (2.2%) of the 9632 children evaluated between February 2023 and March 2024. The diagnostic assessments of these randomly selected children were reviewed by one of three randomly assigned experts (a developmental pediatrician, a child psychologist, or a pediatrician with 7 years’ diagnostic experience) blinded to the initial scoring.
The diagnostic agreement was 94%, according to the data presented, providing a specificity of 90% and a sensitivity of 90% for ASD. The commercialized diagnostic approach is providing a diagnosis in a mean time of 29 days from initial contact, compared with delays that typically exceed 1 year for many children with suspected ASD, according to Dr. Hicks.
Additional Studies Aim at Streamlining Diagnosis
Two additional studies also evaluated strategies to streamline the diagnosis of ASD. Both were positive. In one, the accuracy and time to diagnosis among pediatricians trained in TAP and CARS were compared with those of ASD specialists in a dedicated autism clinic. Both were located at Nemours Children’s Health Center, Wilmington, Delaware.
In this study, presented by Meghan Harrison, DO, an attending pediatrician at Nemours Children’s Health, time to diagnosis among the 39 patients evaluated by pediatricians relative to the 349 patients evaluated at the dedicated ASD center (2.0 vs 5.1 months; P = .001) was significantly shorter. The age at diagnosis in the pediatrician-assessed population (27.5 vs 36.5 months; P < .001) was also significantly younger.
In another study, led by Ashely L. Early, MSW, a clinical social worker at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, switching to a screening tool called the Rapid Interactive Screening Test for Autism in Toddlers (RITA-1) reduced the wait time to evaluation by approximately 5 months relative to previous practice with a more cumbersome screening method.
An ‘Urgent Need’ to Accelerate Diagnosis
In most places in the United States, children suspected of ASD are referred to specialists for confirmation of the diagnosis, which is needed to quality for ASD services, according to Katherine Zuckerman, MD, a professor of pediatrics the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon. Dr. Zuckerman, who was moderator of the session in which all four of these abstracts were presented, explained that there is an urgent need to accelerate the time to diagnosis, which involves long delays for many if not most children with ASD. This is important because treatment and supportive services for ASD are almost always dependent on a diagnosis.
“There are tons of data to show that earlier access to ASD services has important patient benefits, including higher IQs,” she said. Other benefits she listed include a better quality of life for the child and the family.
“It can provide a huge reduction in family stress,” she added, suggesting that early interventions favorably modify the trajectory of the disability over time with accruing benefits.
“The lifetime costs of ASD exceed cancer and most other disease, so there are major implications for the cumulative cost of ASD management,” Dr. Zuckerman said. She suggested that the studies presented at the meeting reflect a likely evolution in who evaluates children for ASD and how quickly the evaluation is performed.
Dr. Rea, Dr. Harrison, Dr. Zuckerman, and Ms. Early reported no potential conflicts of interest. In addition to his executive role in As You Are, Dr. Hicks has financial relationships with Quadrant Biosciences and Spectrum Solutions.
TORONTO — , according to a series of studies presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting.
Accelerated Diagnosis
In one study, 80% of the evaluations were conducted within 6 weeks of patient enrollment, according to Corinna Rea, MD, a clinician in the primary care center at Boston Children’s Hospital as well as an assistant professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
This outcome was drawn from a pilot study with 179 children suspected of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by clinicians in a pediatric clinic. All were under the age of 3 years. In the first step, families completed the Bayley-4 Social-Emotional and Adaptive Behavior Scale.
The next step was a virtual assessment by a trained clinician using the TELE-ADS-PEDs (TAP) tool developed by Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee. Patients and families participated from their homes. The diagnosis of ASD was made by a psychologist using the patient’s history and data provided by the two assessment tools.
Through this approach, the median time to diagnosis was 30 days, according to Dr. Rea. Relative to a median time of 168 days to diagnosis among patients considered likely to have ASD at Dr. Rea’s center in the year prior to this pilot study, the time was reduced significantly (P < .001).
All patients in the study were subsequently evaluated by traditional methods. One hundred percent of the ASD diagnoses were confirmed with traditional assessment.
On the basis of these data, the accelerated approach “seems efficient and quite accurate,” Dr. Rea reported. When family members were surveyed at the end of the pilot study, 60% were satisfied and 28% were moderately satisfied. Although 59% reported that they would have preferred an in-person assessment, approximately 90% agreed the child’s development was mostly or completely captured in the accelerated assessment.
Dr. Rea pointed out that the psychologists participating in this study offered the opinion that home-based assessments are in their experience better than in-person evaluations due to the more natural behavior of the child in their own environment. However, she said that the diagnostic approach in the pilot study is still being modified, and one of the goals is to make virtual assessment more acceptable to the families.
A Commercialized Diagnostic Approach
A similar approach has been commercialized by a firm called As You Are, according to Steven D. Hicks, MD, PhD, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania. Dr. Hicks is a principal in the enterprise, which is also assessing ASD virtually.
Trained pediatricians are evaluating patients with multiple tools in addition to TAP, including the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-V) checklist for ASD. The company, which began offering this diagnostic service in 2022, now employs more than 30 pediatricians who participated in a 1-month training program.
At the 2024 PAS meeting, quality assurance data were presented on 215 (2.2%) of the 9632 children evaluated between February 2023 and March 2024. The diagnostic assessments of these randomly selected children were reviewed by one of three randomly assigned experts (a developmental pediatrician, a child psychologist, or a pediatrician with 7 years’ diagnostic experience) blinded to the initial scoring.
The diagnostic agreement was 94%, according to the data presented, providing a specificity of 90% and a sensitivity of 90% for ASD. The commercialized diagnostic approach is providing a diagnosis in a mean time of 29 days from initial contact, compared with delays that typically exceed 1 year for many children with suspected ASD, according to Dr. Hicks.
Additional Studies Aim at Streamlining Diagnosis
Two additional studies also evaluated strategies to streamline the diagnosis of ASD. Both were positive. In one, the accuracy and time to diagnosis among pediatricians trained in TAP and CARS were compared with those of ASD specialists in a dedicated autism clinic. Both were located at Nemours Children’s Health Center, Wilmington, Delaware.
In this study, presented by Meghan Harrison, DO, an attending pediatrician at Nemours Children’s Health, time to diagnosis among the 39 patients evaluated by pediatricians relative to the 349 patients evaluated at the dedicated ASD center (2.0 vs 5.1 months; P = .001) was significantly shorter. The age at diagnosis in the pediatrician-assessed population (27.5 vs 36.5 months; P < .001) was also significantly younger.
In another study, led by Ashely L. Early, MSW, a clinical social worker at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, switching to a screening tool called the Rapid Interactive Screening Test for Autism in Toddlers (RITA-1) reduced the wait time to evaluation by approximately 5 months relative to previous practice with a more cumbersome screening method.
An ‘Urgent Need’ to Accelerate Diagnosis
In most places in the United States, children suspected of ASD are referred to specialists for confirmation of the diagnosis, which is needed to quality for ASD services, according to Katherine Zuckerman, MD, a professor of pediatrics the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon. Dr. Zuckerman, who was moderator of the session in which all four of these abstracts were presented, explained that there is an urgent need to accelerate the time to diagnosis, which involves long delays for many if not most children with ASD. This is important because treatment and supportive services for ASD are almost always dependent on a diagnosis.
“There are tons of data to show that earlier access to ASD services has important patient benefits, including higher IQs,” she said. Other benefits she listed include a better quality of life for the child and the family.
“It can provide a huge reduction in family stress,” she added, suggesting that early interventions favorably modify the trajectory of the disability over time with accruing benefits.
“The lifetime costs of ASD exceed cancer and most other disease, so there are major implications for the cumulative cost of ASD management,” Dr. Zuckerman said. She suggested that the studies presented at the meeting reflect a likely evolution in who evaluates children for ASD and how quickly the evaluation is performed.
Dr. Rea, Dr. Harrison, Dr. Zuckerman, and Ms. Early reported no potential conflicts of interest. In addition to his executive role in As You Are, Dr. Hicks has financial relationships with Quadrant Biosciences and Spectrum Solutions.
FROM PAS 2024
Post-COVID Mental Health Risks Linger for Veterans
Not surprisingly, anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, and other mental health issues became more prevalent during the COVID-19 pandemic—and after. Studies have found that neurologic and psychiatric sequelae may last up to 6 months following COVID-19 infection.
It appears that COVID-19 infection—even past the acute stage—could put hospitalized patients at risk of exacerbating existing mental health conditions or even developing new conditions. Researchers from Salem Veterans Affairs Health Care System conducted a retrospective observational study from January 1, 2020, through January 1, 2022, of 50,805 veterans hospitalized with COVID-19 and 50,805 patients hospitalized for other reasons.
The researchers found that veterans with COVID-19 group had significantly higher rates of psychiatry-related hospitalization at both 90 and 180 days, as well as a significant increase in the incidence of outpatient mental health visits at 180 days. They also noted a significantly higher risk of new-onset depression and new-onset dementia in the COVID-19 patients at 180 days compared with the non-COVID-19 cohort.
The exact mechanism of the impact of COVID-19 hospitalization on new or worsening depression has yet to be uncovered, the researchers say, but it is known to be complex and interrelated. They point to post-COVID-19 follow-up studies that have found that even mild and asymptomatic infection may lead to cognitive impairment, delirium, extreme fatigue, and clinically relevant mood symptoms. The residual effects of COVID-19 appear to span multiple organ systems.
The researchers also cite current hypotheses about the psychiatric sequelae of COVID-19 that suggest sustained neuroinflammatory processes disrupt the blood-brain barrier, leading to damaged neurons and glia in the brain. In a systematic review, roughly one-third of patients developed neurologic symptoms in the acute phase of the disease, with brain abnormalities “suggestive of COVID-19 etiology.” What’s more, multiple studies have found that anxiety and depression worsen the clinical course of chronic disease, indicating that this mechanism is bidirectional.
Future studies should, among other things include outcomes assessed by COVID-19 disease severity, as well as various psychiatric adverse effects, to enhance provider vigilance and promote closer monitoring.
Not surprisingly, anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, and other mental health issues became more prevalent during the COVID-19 pandemic—and after. Studies have found that neurologic and psychiatric sequelae may last up to 6 months following COVID-19 infection.
It appears that COVID-19 infection—even past the acute stage—could put hospitalized patients at risk of exacerbating existing mental health conditions or even developing new conditions. Researchers from Salem Veterans Affairs Health Care System conducted a retrospective observational study from January 1, 2020, through January 1, 2022, of 50,805 veterans hospitalized with COVID-19 and 50,805 patients hospitalized for other reasons.
The researchers found that veterans with COVID-19 group had significantly higher rates of psychiatry-related hospitalization at both 90 and 180 days, as well as a significant increase in the incidence of outpatient mental health visits at 180 days. They also noted a significantly higher risk of new-onset depression and new-onset dementia in the COVID-19 patients at 180 days compared with the non-COVID-19 cohort.
The exact mechanism of the impact of COVID-19 hospitalization on new or worsening depression has yet to be uncovered, the researchers say, but it is known to be complex and interrelated. They point to post-COVID-19 follow-up studies that have found that even mild and asymptomatic infection may lead to cognitive impairment, delirium, extreme fatigue, and clinically relevant mood symptoms. The residual effects of COVID-19 appear to span multiple organ systems.
The researchers also cite current hypotheses about the psychiatric sequelae of COVID-19 that suggest sustained neuroinflammatory processes disrupt the blood-brain barrier, leading to damaged neurons and glia in the brain. In a systematic review, roughly one-third of patients developed neurologic symptoms in the acute phase of the disease, with brain abnormalities “suggestive of COVID-19 etiology.” What’s more, multiple studies have found that anxiety and depression worsen the clinical course of chronic disease, indicating that this mechanism is bidirectional.
Future studies should, among other things include outcomes assessed by COVID-19 disease severity, as well as various psychiatric adverse effects, to enhance provider vigilance and promote closer monitoring.
Not surprisingly, anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, and other mental health issues became more prevalent during the COVID-19 pandemic—and after. Studies have found that neurologic and psychiatric sequelae may last up to 6 months following COVID-19 infection.
It appears that COVID-19 infection—even past the acute stage—could put hospitalized patients at risk of exacerbating existing mental health conditions or even developing new conditions. Researchers from Salem Veterans Affairs Health Care System conducted a retrospective observational study from January 1, 2020, through January 1, 2022, of 50,805 veterans hospitalized with COVID-19 and 50,805 patients hospitalized for other reasons.
The researchers found that veterans with COVID-19 group had significantly higher rates of psychiatry-related hospitalization at both 90 and 180 days, as well as a significant increase in the incidence of outpatient mental health visits at 180 days. They also noted a significantly higher risk of new-onset depression and new-onset dementia in the COVID-19 patients at 180 days compared with the non-COVID-19 cohort.
The exact mechanism of the impact of COVID-19 hospitalization on new or worsening depression has yet to be uncovered, the researchers say, but it is known to be complex and interrelated. They point to post-COVID-19 follow-up studies that have found that even mild and asymptomatic infection may lead to cognitive impairment, delirium, extreme fatigue, and clinically relevant mood symptoms. The residual effects of COVID-19 appear to span multiple organ systems.
The researchers also cite current hypotheses about the psychiatric sequelae of COVID-19 that suggest sustained neuroinflammatory processes disrupt the blood-brain barrier, leading to damaged neurons and glia in the brain. In a systematic review, roughly one-third of patients developed neurologic symptoms in the acute phase of the disease, with brain abnormalities “suggestive of COVID-19 etiology.” What’s more, multiple studies have found that anxiety and depression worsen the clinical course of chronic disease, indicating that this mechanism is bidirectional.
Future studies should, among other things include outcomes assessed by COVID-19 disease severity, as well as various psychiatric adverse effects, to enhance provider vigilance and promote closer monitoring.
Lower Protein Intake In Midlife May Increase Mortality Risk
Lower intake of dietary protein in midlife was a significant independent predictor of all-cause mortality in later life, based on data from a cohort study of more than 8000 men.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance of dietary protein intake is 0.8 g/kg body weight, but previous studies of the effect of dietary protein on all-cause mortality have yielded inconsistent results, Pedro Joaquin Ayau Aguilar, MD, of the University of Hawaii, Honolulu, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
To better examine these effects, Dr. Aguilar and colleagues reviewed data from 7486 participants in the Kuakini Honolulu Heart Program (HHP), a prospective cohort study of Japanese-American men in Hawaii.
Participants underwent a baseline exam in 1965-1968 at ages 45-68 years and were followed for mortality until December 31, 2022. The researchers created quintiles of dietary protein/kg categorized as plant or animal source, trained dietitians worked with participants to complete a 24-hour diet recall, and the primary outcome was all-cause mortality.
Overall, the mean protein intake in the study population was 1.5 g/kg body weight; the mean animal protein and plant protein intakes were 1.1 g/kg and 0.4 g/kg, respectively.
In an age-adjusted analysis, mortality rates per 1,000 person-years were significantly higher with lower total protein intake, with rates of 39.7 per 1,000 person-years and 36.8 per 1,000 person-years in the first and fifth quintiles, respectively (P < .0001).
Data Show Consistency Across Protein Types
Trends were similar for animal protein and plant protein intake, with mortality rates of 39.6 and 36.5 per 1000 person-years for the first and fifth quintiles, respectively.
“All of these categories had a significant trend, with the lowest quintile showing the highest mortality rate,” Dr. Aguilar said in his presentation.
The study was limited by several factors including the homogeneous population of Japanese men, and the inability to make conclusions about cause and effect, Dr. Aguilar said. However, the results were strengthened by the large cohort, long follow-up, and complete mortality surveillance, he added.
As for the study’s clinical implications, “I believe it adds to the body of evidence on how nutrition impacts health and [the data] can help us better advise our patients on their macronutrient intake to better optimize their health,” Dr. Aguilar said in a question-and-answer session following the presentation.
Looking ahead, “More research is needed to more accurately define which type of protein and in which amounts are optimal for health,” as well as how other macronutrients in different stages of life affect health span and life span, he said.
Although a minimum Recommended Daily Allowance of dietary protein is 0.8 g/kg body weight, the relationship between dietary protein intake and all-cause mortality remains unclear, said Shelly Gray, PharmD, professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, said in an interview.
Dr. Gray, who served as a moderator for the session in which the study was presented, agreed that more research is needed before clinical implications can be discussed.
The study was supported by the Department of Geriatric Medicine, John A. Burns School of Medicine, University of Hawaii; Kuakini Medical Center, Honolulu, Hawaii; and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gray had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Lower intake of dietary protein in midlife was a significant independent predictor of all-cause mortality in later life, based on data from a cohort study of more than 8000 men.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance of dietary protein intake is 0.8 g/kg body weight, but previous studies of the effect of dietary protein on all-cause mortality have yielded inconsistent results, Pedro Joaquin Ayau Aguilar, MD, of the University of Hawaii, Honolulu, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
To better examine these effects, Dr. Aguilar and colleagues reviewed data from 7486 participants in the Kuakini Honolulu Heart Program (HHP), a prospective cohort study of Japanese-American men in Hawaii.
Participants underwent a baseline exam in 1965-1968 at ages 45-68 years and were followed for mortality until December 31, 2022. The researchers created quintiles of dietary protein/kg categorized as plant or animal source, trained dietitians worked with participants to complete a 24-hour diet recall, and the primary outcome was all-cause mortality.
Overall, the mean protein intake in the study population was 1.5 g/kg body weight; the mean animal protein and plant protein intakes were 1.1 g/kg and 0.4 g/kg, respectively.
In an age-adjusted analysis, mortality rates per 1,000 person-years were significantly higher with lower total protein intake, with rates of 39.7 per 1,000 person-years and 36.8 per 1,000 person-years in the first and fifth quintiles, respectively (P < .0001).
Data Show Consistency Across Protein Types
Trends were similar for animal protein and plant protein intake, with mortality rates of 39.6 and 36.5 per 1000 person-years for the first and fifth quintiles, respectively.
“All of these categories had a significant trend, with the lowest quintile showing the highest mortality rate,” Dr. Aguilar said in his presentation.
The study was limited by several factors including the homogeneous population of Japanese men, and the inability to make conclusions about cause and effect, Dr. Aguilar said. However, the results were strengthened by the large cohort, long follow-up, and complete mortality surveillance, he added.
As for the study’s clinical implications, “I believe it adds to the body of evidence on how nutrition impacts health and [the data] can help us better advise our patients on their macronutrient intake to better optimize their health,” Dr. Aguilar said in a question-and-answer session following the presentation.
Looking ahead, “More research is needed to more accurately define which type of protein and in which amounts are optimal for health,” as well as how other macronutrients in different stages of life affect health span and life span, he said.
Although a minimum Recommended Daily Allowance of dietary protein is 0.8 g/kg body weight, the relationship between dietary protein intake and all-cause mortality remains unclear, said Shelly Gray, PharmD, professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, said in an interview.
Dr. Gray, who served as a moderator for the session in which the study was presented, agreed that more research is needed before clinical implications can be discussed.
The study was supported by the Department of Geriatric Medicine, John A. Burns School of Medicine, University of Hawaii; Kuakini Medical Center, Honolulu, Hawaii; and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gray had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Lower intake of dietary protein in midlife was a significant independent predictor of all-cause mortality in later life, based on data from a cohort study of more than 8000 men.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance of dietary protein intake is 0.8 g/kg body weight, but previous studies of the effect of dietary protein on all-cause mortality have yielded inconsistent results, Pedro Joaquin Ayau Aguilar, MD, of the University of Hawaii, Honolulu, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
To better examine these effects, Dr. Aguilar and colleagues reviewed data from 7486 participants in the Kuakini Honolulu Heart Program (HHP), a prospective cohort study of Japanese-American men in Hawaii.
Participants underwent a baseline exam in 1965-1968 at ages 45-68 years and were followed for mortality until December 31, 2022. The researchers created quintiles of dietary protein/kg categorized as plant or animal source, trained dietitians worked with participants to complete a 24-hour diet recall, and the primary outcome was all-cause mortality.
Overall, the mean protein intake in the study population was 1.5 g/kg body weight; the mean animal protein and plant protein intakes were 1.1 g/kg and 0.4 g/kg, respectively.
In an age-adjusted analysis, mortality rates per 1,000 person-years were significantly higher with lower total protein intake, with rates of 39.7 per 1,000 person-years and 36.8 per 1,000 person-years in the first and fifth quintiles, respectively (P < .0001).
Data Show Consistency Across Protein Types
Trends were similar for animal protein and plant protein intake, with mortality rates of 39.6 and 36.5 per 1000 person-years for the first and fifth quintiles, respectively.
“All of these categories had a significant trend, with the lowest quintile showing the highest mortality rate,” Dr. Aguilar said in his presentation.
The study was limited by several factors including the homogeneous population of Japanese men, and the inability to make conclusions about cause and effect, Dr. Aguilar said. However, the results were strengthened by the large cohort, long follow-up, and complete mortality surveillance, he added.
As for the study’s clinical implications, “I believe it adds to the body of evidence on how nutrition impacts health and [the data] can help us better advise our patients on their macronutrient intake to better optimize their health,” Dr. Aguilar said in a question-and-answer session following the presentation.
Looking ahead, “More research is needed to more accurately define which type of protein and in which amounts are optimal for health,” as well as how other macronutrients in different stages of life affect health span and life span, he said.
Although a minimum Recommended Daily Allowance of dietary protein is 0.8 g/kg body weight, the relationship between dietary protein intake and all-cause mortality remains unclear, said Shelly Gray, PharmD, professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, said in an interview.
Dr. Gray, who served as a moderator for the session in which the study was presented, agreed that more research is needed before clinical implications can be discussed.
The study was supported by the Department of Geriatric Medicine, John A. Burns School of Medicine, University of Hawaii; Kuakini Medical Center, Honolulu, Hawaii; and the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gray had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AGS 2024
CVD Risk Rises With Higher NSAID Doses in Ankylosing Spondylitis
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as ischemic heart disease, stroke, and congestive heart failure in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) compared with lower doses.
METHODOLOGY:
- NSAIDs can suppress inflammation and relieve pain in patients with AS, but long-term treatment with NSAIDs poses concerns regarding gastrointestinal and renal toxicities and increased CVD risk.
- This nationwide cohort study used data from the Korean National Health Insurance database to investigate the risk for CVD associated with an increasing NSAID dosage in a real-world AS cohort.
- Investigators recruited 19,775 patients (mean age, 36.1 years; 75% men) with newly diagnosed AS and without any prior CVD between January 2010 and December 2018, among whom 99.7% received NSAID treatment and 30.2% received tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment.
- A time-varying approach was used to assess the NSAID exposure, wherein periods of NSAID use were defined as “NSAID-exposed” and periods longer than 1 month without NSAID use were defined as “NSAID-unexposed.”
- The primary outcome was the composite outcome of ischemic heart disease, stroke, or congestive heart failure.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the follow-up period of 98,290 person-years, 1663 cases of CVD were identified, which included 1157 cases of ischemic heart disease, 301 cases of stroke, and 613 cases of congestive heart failure.
- After adjusting for confounders, each defined daily dose increase in NSAIDs raised the risk for incident CVD by 10% (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.13).
- Similarly, increasing the dose of NSAIDs was associated with an increased risk for ischemic heart disease (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.05-1.11), stroke (aHR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.04-1.15), and congestive heart failure (aHR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.08-1.16).
- The association between increasing NSAID dose and increased CVD risk was consistent across various subgroups, with NSAIDs posing a greater threat to cardiovascular health in women than in men.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “Taken together, these results suggest that increasing the dose of NSAIDs is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk in AS, but that the increased risk might be lower than that in the general population.”
SOURCE:
First author Ji-Won Kim, MD, PhD, of the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, the Republic of Korea, and colleagues had their work published online on April 9 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was of retrospective nature. The levels of acute phase reactants and AS disease activity could not be determined owing to a lack of data in the National Health Insurance database. The accuracy of the diagnosis of cardiovascular outcomes on the basis of the International Classification of Disease codes was also questionable.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as ischemic heart disease, stroke, and congestive heart failure in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) compared with lower doses.
METHODOLOGY:
- NSAIDs can suppress inflammation and relieve pain in patients with AS, but long-term treatment with NSAIDs poses concerns regarding gastrointestinal and renal toxicities and increased CVD risk.
- This nationwide cohort study used data from the Korean National Health Insurance database to investigate the risk for CVD associated with an increasing NSAID dosage in a real-world AS cohort.
- Investigators recruited 19,775 patients (mean age, 36.1 years; 75% men) with newly diagnosed AS and without any prior CVD between January 2010 and December 2018, among whom 99.7% received NSAID treatment and 30.2% received tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment.
- A time-varying approach was used to assess the NSAID exposure, wherein periods of NSAID use were defined as “NSAID-exposed” and periods longer than 1 month without NSAID use were defined as “NSAID-unexposed.”
- The primary outcome was the composite outcome of ischemic heart disease, stroke, or congestive heart failure.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the follow-up period of 98,290 person-years, 1663 cases of CVD were identified, which included 1157 cases of ischemic heart disease, 301 cases of stroke, and 613 cases of congestive heart failure.
- After adjusting for confounders, each defined daily dose increase in NSAIDs raised the risk for incident CVD by 10% (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.13).
- Similarly, increasing the dose of NSAIDs was associated with an increased risk for ischemic heart disease (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.05-1.11), stroke (aHR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.04-1.15), and congestive heart failure (aHR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.08-1.16).
- The association between increasing NSAID dose and increased CVD risk was consistent across various subgroups, with NSAIDs posing a greater threat to cardiovascular health in women than in men.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “Taken together, these results suggest that increasing the dose of NSAIDs is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk in AS, but that the increased risk might be lower than that in the general population.”
SOURCE:
First author Ji-Won Kim, MD, PhD, of the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, the Republic of Korea, and colleagues had their work published online on April 9 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was of retrospective nature. The levels of acute phase reactants and AS disease activity could not be determined owing to a lack of data in the National Health Insurance database. The accuracy of the diagnosis of cardiovascular outcomes on the basis of the International Classification of Disease codes was also questionable.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as ischemic heart disease, stroke, and congestive heart failure in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) compared with lower doses.
METHODOLOGY:
- NSAIDs can suppress inflammation and relieve pain in patients with AS, but long-term treatment with NSAIDs poses concerns regarding gastrointestinal and renal toxicities and increased CVD risk.
- This nationwide cohort study used data from the Korean National Health Insurance database to investigate the risk for CVD associated with an increasing NSAID dosage in a real-world AS cohort.
- Investigators recruited 19,775 patients (mean age, 36.1 years; 75% men) with newly diagnosed AS and without any prior CVD between January 2010 and December 2018, among whom 99.7% received NSAID treatment and 30.2% received tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatment.
- A time-varying approach was used to assess the NSAID exposure, wherein periods of NSAID use were defined as “NSAID-exposed” and periods longer than 1 month without NSAID use were defined as “NSAID-unexposed.”
- The primary outcome was the composite outcome of ischemic heart disease, stroke, or congestive heart failure.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the follow-up period of 98,290 person-years, 1663 cases of CVD were identified, which included 1157 cases of ischemic heart disease, 301 cases of stroke, and 613 cases of congestive heart failure.
- After adjusting for confounders, each defined daily dose increase in NSAIDs raised the risk for incident CVD by 10% (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.13).
- Similarly, increasing the dose of NSAIDs was associated with an increased risk for ischemic heart disease (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.05-1.11), stroke (aHR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.04-1.15), and congestive heart failure (aHR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.08-1.16).
- The association between increasing NSAID dose and increased CVD risk was consistent across various subgroups, with NSAIDs posing a greater threat to cardiovascular health in women than in men.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “Taken together, these results suggest that increasing the dose of NSAIDs is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk in AS, but that the increased risk might be lower than that in the general population.”
SOURCE:
First author Ji-Won Kim, MD, PhD, of the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, the Republic of Korea, and colleagues had their work published online on April 9 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was of retrospective nature. The levels of acute phase reactants and AS disease activity could not be determined owing to a lack of data in the National Health Insurance database. The accuracy of the diagnosis of cardiovascular outcomes on the basis of the International Classification of Disease codes was also questionable.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.

