User login
Restrictive, vegan-based diet linked to fewer RA symptoms
A . After 16 weeks, the mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) decreased from 4.5 to 2.5 (P < .001), and the mean number of swollen joints dipped from 7.0 to 3.3 (P = .03).
The study was published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. It’s not clear whether the vegan diet or the restriction of trigger foods – or both or neither – was helpful. Significant weight loss in the diet group could have played a role in reducing symptoms.
Still, the dietary strategy is “a life-changing experience for people,” lead author Neal D. Barnard, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor of medicine at George Washington University, Washington, D.C, and president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, said in an interview. “Doctors should know about it, and they should try it themselves.”
The researchers launched the study to determine the feasibility of a “practical and easy-to-prescribe diet” without caloric limits, Dr. Barnard said. “People have done a variety of studies where they’ve looked at diet changes, often with fasting, and the quality has been variable.”
There’s no consensus in the medical literature on which dietary approach is best for patients with RA. A 2021 systematic review by Philippa and colleagues found positive results for the Mediterranean diet, high doses of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D supplementation, and sodium restriction. Fasting had significant but temporary effects, and the reviewers noted “outcomes from vegetarian, elimination, peptide, or elemental diets suggested that responses are very individualized.”
For the new randomized, crossover study, researchers assigned 44 women to one of two diet phases. After 16 weeks, they had a 4-week washout period, then began the other 16-week phase. A total of 32 patients completed the study, and they had a mean age of 57 years. Overall, 66% were White, 16% were Black, and 79% held a college degree or graduate degree.
In the 16-week intervention phase, participants went on a low-fat vegan diet. After 4 weeks, they eliminated common RA trigger foods such as grains with gluten, nuts, citrus fruits, and chocolate. After week 7, the subjects added back the trigger foods one by one, keeping them in their diet if they didn’t seem to cause pain.
In the 16-week placebo phase, the women took a supplement that they were told contained omega-3 oils and vitamin E. However, the amounts of omega-3 and vitamin E were very low and had no apparent effect.
Participants in the diet phase attended weekly 1-hour dietary support-group sessions. Thirty-two women completed the full study.
Average DAS28 scores fell in the diet phase, compared with the supplement phase (treatment effect, 1.8 [95% confidence interval [CI], 3.2 to 0.4]; P = .01), as did swollen joints (treatment effect, –4.2 [95% CI, –8.3 to –0.1], P = .047).
While the researchers reported dips in the DAS28 score and swollen joints, “the reductions in the number of painful and tender joints did not reach statistical significance (treatment effects, –4.1 [95% CI, –8.7 to +0.5]; P = .08; and –1.8 [95% CI, –5.5 to +1.9]; P = .41, respectively).”
Mean body weight fell by 6.5 kg among those in the diet group, while those in the placebo group gained 0.8 kg (treatment effect, –7.3 kg [95% CI, –9.4 to –5.1]; P < .001).
The researchers noted “the presumed mechanisms by which diets such [as this intervention strategy] reduce joint symptoms relate to the removal of inflammatory elements of an omnivorous diet, the presence of anti-inflammatory constituents in a plant-based diet, and diet-induced reductions in gut permeability that may, in turn, reduce the passage of antigens into circulation.”
Patients tolerate the diet well, Dr. Barnard said. “It’s practical for day-to-day life, and you don’t have to check into a fasting hospital.”
The message for physicians, he said, is to encourage patients to try changing their eating patterns before turning to medication. “It’s a good idea for anyone to have a chance to try a diet change,” he said. “You’ll know within a matter of weeks whether it will work.”
Vegan diets are also cheaper than diets with meat and dairy, he added.
The study has various limitations. It began with 44 participants, but 12 failed to complete it for various reasons. Four participants who were assigned to the diet phase first refused to resume their regular diets during the next phase. It’s not clear if the lost weight is most responsible for the diet’s benefits, Harvard Medical School rheumatologist Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH, said in an interview. In his review of the study findings, Dr. Solomon said that another possibility is that certain aspects of the diet – and not the full diet – were responsible.
“I am sure that motivated patients could follow such a diet,” he said, “but first we should determine if the specific diet was the key issue or whether weight loss was more important.”
The study was funded by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. Dr. Barnard disclosed royalties and honoraria from books, articles, and lectures on nutrition and health.
A . After 16 weeks, the mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) decreased from 4.5 to 2.5 (P < .001), and the mean number of swollen joints dipped from 7.0 to 3.3 (P = .03).
The study was published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. It’s not clear whether the vegan diet or the restriction of trigger foods – or both or neither – was helpful. Significant weight loss in the diet group could have played a role in reducing symptoms.
Still, the dietary strategy is “a life-changing experience for people,” lead author Neal D. Barnard, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor of medicine at George Washington University, Washington, D.C, and president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, said in an interview. “Doctors should know about it, and they should try it themselves.”
The researchers launched the study to determine the feasibility of a “practical and easy-to-prescribe diet” without caloric limits, Dr. Barnard said. “People have done a variety of studies where they’ve looked at diet changes, often with fasting, and the quality has been variable.”
There’s no consensus in the medical literature on which dietary approach is best for patients with RA. A 2021 systematic review by Philippa and colleagues found positive results for the Mediterranean diet, high doses of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D supplementation, and sodium restriction. Fasting had significant but temporary effects, and the reviewers noted “outcomes from vegetarian, elimination, peptide, or elemental diets suggested that responses are very individualized.”
For the new randomized, crossover study, researchers assigned 44 women to one of two diet phases. After 16 weeks, they had a 4-week washout period, then began the other 16-week phase. A total of 32 patients completed the study, and they had a mean age of 57 years. Overall, 66% were White, 16% were Black, and 79% held a college degree or graduate degree.
In the 16-week intervention phase, participants went on a low-fat vegan diet. After 4 weeks, they eliminated common RA trigger foods such as grains with gluten, nuts, citrus fruits, and chocolate. After week 7, the subjects added back the trigger foods one by one, keeping them in their diet if they didn’t seem to cause pain.
In the 16-week placebo phase, the women took a supplement that they were told contained omega-3 oils and vitamin E. However, the amounts of omega-3 and vitamin E were very low and had no apparent effect.
Participants in the diet phase attended weekly 1-hour dietary support-group sessions. Thirty-two women completed the full study.
Average DAS28 scores fell in the diet phase, compared with the supplement phase (treatment effect, 1.8 [95% confidence interval [CI], 3.2 to 0.4]; P = .01), as did swollen joints (treatment effect, –4.2 [95% CI, –8.3 to –0.1], P = .047).
While the researchers reported dips in the DAS28 score and swollen joints, “the reductions in the number of painful and tender joints did not reach statistical significance (treatment effects, –4.1 [95% CI, –8.7 to +0.5]; P = .08; and –1.8 [95% CI, –5.5 to +1.9]; P = .41, respectively).”
Mean body weight fell by 6.5 kg among those in the diet group, while those in the placebo group gained 0.8 kg (treatment effect, –7.3 kg [95% CI, –9.4 to –5.1]; P < .001).
The researchers noted “the presumed mechanisms by which diets such [as this intervention strategy] reduce joint symptoms relate to the removal of inflammatory elements of an omnivorous diet, the presence of anti-inflammatory constituents in a plant-based diet, and diet-induced reductions in gut permeability that may, in turn, reduce the passage of antigens into circulation.”
Patients tolerate the diet well, Dr. Barnard said. “It’s practical for day-to-day life, and you don’t have to check into a fasting hospital.”
The message for physicians, he said, is to encourage patients to try changing their eating patterns before turning to medication. “It’s a good idea for anyone to have a chance to try a diet change,” he said. “You’ll know within a matter of weeks whether it will work.”
Vegan diets are also cheaper than diets with meat and dairy, he added.
The study has various limitations. It began with 44 participants, but 12 failed to complete it for various reasons. Four participants who were assigned to the diet phase first refused to resume their regular diets during the next phase. It’s not clear if the lost weight is most responsible for the diet’s benefits, Harvard Medical School rheumatologist Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH, said in an interview. In his review of the study findings, Dr. Solomon said that another possibility is that certain aspects of the diet – and not the full diet – were responsible.
“I am sure that motivated patients could follow such a diet,” he said, “but first we should determine if the specific diet was the key issue or whether weight loss was more important.”
The study was funded by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. Dr. Barnard disclosed royalties and honoraria from books, articles, and lectures on nutrition and health.
A . After 16 weeks, the mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) decreased from 4.5 to 2.5 (P < .001), and the mean number of swollen joints dipped from 7.0 to 3.3 (P = .03).
The study was published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. It’s not clear whether the vegan diet or the restriction of trigger foods – or both or neither – was helpful. Significant weight loss in the diet group could have played a role in reducing symptoms.
Still, the dietary strategy is “a life-changing experience for people,” lead author Neal D. Barnard, MD, an internal medicine specialist and adjunct professor of medicine at George Washington University, Washington, D.C, and president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, said in an interview. “Doctors should know about it, and they should try it themselves.”
The researchers launched the study to determine the feasibility of a “practical and easy-to-prescribe diet” without caloric limits, Dr. Barnard said. “People have done a variety of studies where they’ve looked at diet changes, often with fasting, and the quality has been variable.”
There’s no consensus in the medical literature on which dietary approach is best for patients with RA. A 2021 systematic review by Philippa and colleagues found positive results for the Mediterranean diet, high doses of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D supplementation, and sodium restriction. Fasting had significant but temporary effects, and the reviewers noted “outcomes from vegetarian, elimination, peptide, or elemental diets suggested that responses are very individualized.”
For the new randomized, crossover study, researchers assigned 44 women to one of two diet phases. After 16 weeks, they had a 4-week washout period, then began the other 16-week phase. A total of 32 patients completed the study, and they had a mean age of 57 years. Overall, 66% were White, 16% were Black, and 79% held a college degree or graduate degree.
In the 16-week intervention phase, participants went on a low-fat vegan diet. After 4 weeks, they eliminated common RA trigger foods such as grains with gluten, nuts, citrus fruits, and chocolate. After week 7, the subjects added back the trigger foods one by one, keeping them in their diet if they didn’t seem to cause pain.
In the 16-week placebo phase, the women took a supplement that they were told contained omega-3 oils and vitamin E. However, the amounts of omega-3 and vitamin E were very low and had no apparent effect.
Participants in the diet phase attended weekly 1-hour dietary support-group sessions. Thirty-two women completed the full study.
Average DAS28 scores fell in the diet phase, compared with the supplement phase (treatment effect, 1.8 [95% confidence interval [CI], 3.2 to 0.4]; P = .01), as did swollen joints (treatment effect, –4.2 [95% CI, –8.3 to –0.1], P = .047).
While the researchers reported dips in the DAS28 score and swollen joints, “the reductions in the number of painful and tender joints did not reach statistical significance (treatment effects, –4.1 [95% CI, –8.7 to +0.5]; P = .08; and –1.8 [95% CI, –5.5 to +1.9]; P = .41, respectively).”
Mean body weight fell by 6.5 kg among those in the diet group, while those in the placebo group gained 0.8 kg (treatment effect, –7.3 kg [95% CI, –9.4 to –5.1]; P < .001).
The researchers noted “the presumed mechanisms by which diets such [as this intervention strategy] reduce joint symptoms relate to the removal of inflammatory elements of an omnivorous diet, the presence of anti-inflammatory constituents in a plant-based diet, and diet-induced reductions in gut permeability that may, in turn, reduce the passage of antigens into circulation.”
Patients tolerate the diet well, Dr. Barnard said. “It’s practical for day-to-day life, and you don’t have to check into a fasting hospital.”
The message for physicians, he said, is to encourage patients to try changing their eating patterns before turning to medication. “It’s a good idea for anyone to have a chance to try a diet change,” he said. “You’ll know within a matter of weeks whether it will work.”
Vegan diets are also cheaper than diets with meat and dairy, he added.
The study has various limitations. It began with 44 participants, but 12 failed to complete it for various reasons. Four participants who were assigned to the diet phase first refused to resume their regular diets during the next phase. It’s not clear if the lost weight is most responsible for the diet’s benefits, Harvard Medical School rheumatologist Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH, said in an interview. In his review of the study findings, Dr. Solomon said that another possibility is that certain aspects of the diet – and not the full diet – were responsible.
“I am sure that motivated patients could follow such a diet,” he said, “but first we should determine if the specific diet was the key issue or whether weight loss was more important.”
The study was funded by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. Dr. Barnard disclosed royalties and honoraria from books, articles, and lectures on nutrition and health.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF LIFESTYLE MEDICINE
Psychiatric illness associated with eosinophilic esophagitis
People with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) may run an increased risk of mood disorders, anxiety, and ADHD and should be screened for those conditions, researchers say.
“It’s important to know that there is an elevated risk of those diagnoses, so you have that in mind when you treat your patients. You can assess their quality of life and the status of their mental state,” said lead author Lovisa Röjler, MD, a pediatrician and doctoral student at Örebro (Sweden) University Hospital.
“Psychiatric disorders are not found with a blood sample or radiology examination,” she said in an interview.
The study was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Elevated risk found
Previous studies into the relationship between EoE and anxiety and depression have conflicting conclusions.
In the hope of shedding further light, Dr. Röjler and colleagues analyzed data from Sweden’s ESPRESSO cohort, which consists of more than 6 million biopsy samples from the gastrointestinal tract that were collected from throughout the country during the years 1965-2017.
They identified 1,458 people with EoE who had not experienced psychiatric events before being diagnosed with EoE. Of these, 70% had dysphagia, and 58% had food impaction.
In the study, up to 5 reference persons (6,436 people) without EoE who were identified from the Swedish Total Population Register were matched to the patients with EoE by age, sex, county, and year of diagnosis.
Among the people with EoE, there were 106 events of psychiatric disease, at an incidence of 15.96 per 1,000 person-years versus 10.93 per 1,000 person-years (331 events) among those without EoE. This 50% increased risk for psychiatric illness for people with EoE was statistically significant (hazard ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.87).
To adjust for genetic and environmental confounding factors, the researchers compared the rate of psychiatric events among 1,055 people with EoE with that of siblings who did not have EoE (1,699 people). There were 74 events of psychiatric disease among the siblings (8.99 per 1000 person-years). From this the researchers calculated a 62% increased risk of psychiatric events for those with EoE (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.14-2.31).
There was no difference in risk for psychiatric disorders by educational attainment, though people for whom there were no data on education were at increased risk.
There was also no difference in psychiatric risk associated with the use of steroids or proton pump inhibitors for EoE, though these medications have sometimes been linked to psychiatric disorders.
After adjusting for inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and asthma, the researchers still found an increased risk of psychiatric events. Also, the people who had EoE were no more likely than the reference persons to have had psychiatric events before their diagnosis, suggesting that EoE caused the psychiatric events rather than the other way around.
Previous researchers have found a similar association with psychiatric illness in people with celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. The researchers speculated that people with EoE might develop psychiatric illnesses because their symptoms and treatments, such as restrictive diets, cause stress and chronic pain and thereby cause problems with education, work, and social and economic status.
Dr. Röjler recommended that clinicians use questionnaires to identify mood disorders and ADHD in their patients and then refer them to a mental health professional.
Screen for psychiatric disorders
Tiffany Taft, PsyD, a research associate professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, agreed that patients with EoE should be screened more often for psychiatric disorders.
“We’ve found that symptom-specific anxiety is prevalent and associated with other outcomes, like quality of life, so it may not be the typical anxiety that you would diagnose from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,” Dr. Taft said in an interview.
While anxiety is not likely to trigger EoE, it can worsen the symptoms, she said. Sometimes helping patients make the connection between their mental health and EoE can address the anxiety itself.
“Education is good enough for a certain chunk of patients,” Dr. Taft said.
Other patients benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy, which gives them a more realistic understanding of their situation.
“We also add in relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery to calm down the stress response in the body, which is part of that brain-gut connection that enhances symptom severity,” she said.
Some patients prefer medications, or they rely on medication because that is what their insurance provides, she said, adding that most patients do best with a combination of medication and talk therapy.
Ideally, people with these disorders would be referred to someone such as herself, a psychotherapist with a specialty in gastroenterology, Dr. Taft said. But there are not many people in that subspecialty, so if a gastroenterology psychologist is not available, a psychologist who specializes in treating mental illness associated with chronic diseases is a good second choice.
The study was funded by Örebro County Council and Karolinska Institutet. Dr. Röjler and Dr. Taft reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) may run an increased risk of mood disorders, anxiety, and ADHD and should be screened for those conditions, researchers say.
“It’s important to know that there is an elevated risk of those diagnoses, so you have that in mind when you treat your patients. You can assess their quality of life and the status of their mental state,” said lead author Lovisa Röjler, MD, a pediatrician and doctoral student at Örebro (Sweden) University Hospital.
“Psychiatric disorders are not found with a blood sample or radiology examination,” she said in an interview.
The study was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Elevated risk found
Previous studies into the relationship between EoE and anxiety and depression have conflicting conclusions.
In the hope of shedding further light, Dr. Röjler and colleagues analyzed data from Sweden’s ESPRESSO cohort, which consists of more than 6 million biopsy samples from the gastrointestinal tract that were collected from throughout the country during the years 1965-2017.
They identified 1,458 people with EoE who had not experienced psychiatric events before being diagnosed with EoE. Of these, 70% had dysphagia, and 58% had food impaction.
In the study, up to 5 reference persons (6,436 people) without EoE who were identified from the Swedish Total Population Register were matched to the patients with EoE by age, sex, county, and year of diagnosis.
Among the people with EoE, there were 106 events of psychiatric disease, at an incidence of 15.96 per 1,000 person-years versus 10.93 per 1,000 person-years (331 events) among those without EoE. This 50% increased risk for psychiatric illness for people with EoE was statistically significant (hazard ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.87).
To adjust for genetic and environmental confounding factors, the researchers compared the rate of psychiatric events among 1,055 people with EoE with that of siblings who did not have EoE (1,699 people). There were 74 events of psychiatric disease among the siblings (8.99 per 1000 person-years). From this the researchers calculated a 62% increased risk of psychiatric events for those with EoE (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.14-2.31).
There was no difference in risk for psychiatric disorders by educational attainment, though people for whom there were no data on education were at increased risk.
There was also no difference in psychiatric risk associated with the use of steroids or proton pump inhibitors for EoE, though these medications have sometimes been linked to psychiatric disorders.
After adjusting for inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and asthma, the researchers still found an increased risk of psychiatric events. Also, the people who had EoE were no more likely than the reference persons to have had psychiatric events before their diagnosis, suggesting that EoE caused the psychiatric events rather than the other way around.
Previous researchers have found a similar association with psychiatric illness in people with celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. The researchers speculated that people with EoE might develop psychiatric illnesses because their symptoms and treatments, such as restrictive diets, cause stress and chronic pain and thereby cause problems with education, work, and social and economic status.
Dr. Röjler recommended that clinicians use questionnaires to identify mood disorders and ADHD in their patients and then refer them to a mental health professional.
Screen for psychiatric disorders
Tiffany Taft, PsyD, a research associate professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, agreed that patients with EoE should be screened more often for psychiatric disorders.
“We’ve found that symptom-specific anxiety is prevalent and associated with other outcomes, like quality of life, so it may not be the typical anxiety that you would diagnose from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,” Dr. Taft said in an interview.
While anxiety is not likely to trigger EoE, it can worsen the symptoms, she said. Sometimes helping patients make the connection between their mental health and EoE can address the anxiety itself.
“Education is good enough for a certain chunk of patients,” Dr. Taft said.
Other patients benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy, which gives them a more realistic understanding of their situation.
“We also add in relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery to calm down the stress response in the body, which is part of that brain-gut connection that enhances symptom severity,” she said.
Some patients prefer medications, or they rely on medication because that is what their insurance provides, she said, adding that most patients do best with a combination of medication and talk therapy.
Ideally, people with these disorders would be referred to someone such as herself, a psychotherapist with a specialty in gastroenterology, Dr. Taft said. But there are not many people in that subspecialty, so if a gastroenterology psychologist is not available, a psychologist who specializes in treating mental illness associated with chronic diseases is a good second choice.
The study was funded by Örebro County Council and Karolinska Institutet. Dr. Röjler and Dr. Taft reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) may run an increased risk of mood disorders, anxiety, and ADHD and should be screened for those conditions, researchers say.
“It’s important to know that there is an elevated risk of those diagnoses, so you have that in mind when you treat your patients. You can assess their quality of life and the status of their mental state,” said lead author Lovisa Röjler, MD, a pediatrician and doctoral student at Örebro (Sweden) University Hospital.
“Psychiatric disorders are not found with a blood sample or radiology examination,” she said in an interview.
The study was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Elevated risk found
Previous studies into the relationship between EoE and anxiety and depression have conflicting conclusions.
In the hope of shedding further light, Dr. Röjler and colleagues analyzed data from Sweden’s ESPRESSO cohort, which consists of more than 6 million biopsy samples from the gastrointestinal tract that were collected from throughout the country during the years 1965-2017.
They identified 1,458 people with EoE who had not experienced psychiatric events before being diagnosed with EoE. Of these, 70% had dysphagia, and 58% had food impaction.
In the study, up to 5 reference persons (6,436 people) without EoE who were identified from the Swedish Total Population Register were matched to the patients with EoE by age, sex, county, and year of diagnosis.
Among the people with EoE, there were 106 events of psychiatric disease, at an incidence of 15.96 per 1,000 person-years versus 10.93 per 1,000 person-years (331 events) among those without EoE. This 50% increased risk for psychiatric illness for people with EoE was statistically significant (hazard ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.87).
To adjust for genetic and environmental confounding factors, the researchers compared the rate of psychiatric events among 1,055 people with EoE with that of siblings who did not have EoE (1,699 people). There were 74 events of psychiatric disease among the siblings (8.99 per 1000 person-years). From this the researchers calculated a 62% increased risk of psychiatric events for those with EoE (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.14-2.31).
There was no difference in risk for psychiatric disorders by educational attainment, though people for whom there were no data on education were at increased risk.
There was also no difference in psychiatric risk associated with the use of steroids or proton pump inhibitors for EoE, though these medications have sometimes been linked to psychiatric disorders.
After adjusting for inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and asthma, the researchers still found an increased risk of psychiatric events. Also, the people who had EoE were no more likely than the reference persons to have had psychiatric events before their diagnosis, suggesting that EoE caused the psychiatric events rather than the other way around.
Previous researchers have found a similar association with psychiatric illness in people with celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. The researchers speculated that people with EoE might develop psychiatric illnesses because their symptoms and treatments, such as restrictive diets, cause stress and chronic pain and thereby cause problems with education, work, and social and economic status.
Dr. Röjler recommended that clinicians use questionnaires to identify mood disorders and ADHD in their patients and then refer them to a mental health professional.
Screen for psychiatric disorders
Tiffany Taft, PsyD, a research associate professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, agreed that patients with EoE should be screened more often for psychiatric disorders.
“We’ve found that symptom-specific anxiety is prevalent and associated with other outcomes, like quality of life, so it may not be the typical anxiety that you would diagnose from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,” Dr. Taft said in an interview.
While anxiety is not likely to trigger EoE, it can worsen the symptoms, she said. Sometimes helping patients make the connection between their mental health and EoE can address the anxiety itself.
“Education is good enough for a certain chunk of patients,” Dr. Taft said.
Other patients benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy, which gives them a more realistic understanding of their situation.
“We also add in relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery to calm down the stress response in the body, which is part of that brain-gut connection that enhances symptom severity,” she said.
Some patients prefer medications, or they rely on medication because that is what their insurance provides, she said, adding that most patients do best with a combination of medication and talk therapy.
Ideally, people with these disorders would be referred to someone such as herself, a psychotherapist with a specialty in gastroenterology, Dr. Taft said. But there are not many people in that subspecialty, so if a gastroenterology psychologist is not available, a psychologist who specializes in treating mental illness associated with chronic diseases is a good second choice.
The study was funded by Örebro County Council and Karolinska Institutet. Dr. Röjler and Dr. Taft reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
Trans women in female sports: A sports scientist’s take
An interview with Ross Tucker, PhD
When Lia Thomas won the women’s 500-yard freestyle at the 2022 NCAA Division 1 swimming championships, the issue of trans women’s participation in female sports ignited national headlines.
which prohibit trans women’s participation.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Let’s start with the proinclusion argument that there are always advantages in sports.
That’s true. The whole point of sports is to recognize people who have advantages and reward them for it. By the time this argument comes out, people have already accepted that males have advantages, right?
Some do, some don’t.
If someone uses this argument to say that we should allow trans women, basically biological males, to compete in women’s sports, they’ve implicitly accepted that there are advantages. Otherwise, what advantage are you talking about?
They would say it’s like the advantage Michael Phelps has because of his wingspan.
To answer that, you have to start by asking why women’s sports exist.
Women’s sports exist because we recognize that male physiology has biological differences that create performance advantages. Women’s sports exist to ensure that male advantages are excluded. If you allow male advantage in, you’re allowing something to cross into a category that specifically tries to exclude it. That makes the advantage possessed by trans women conceptually and substantively different from an advantage that’s possessed by Michael Phelps because his advantage doesn’t cross a category boundary line.
If someone wants to allow natural advantages to be celebrated in sports, they’re arguing against the existence of any categories, because every single category in sports is trying to filter out certain advantages.
Weight categories in boxing exist to get rid of the advantage of being stronger, taller, with greater reach. Paralympic categories filter out the natural advantage that someone has if, for example, they are only mildly affected by cerebral palsy, compared with more severely affected.
If someone wants to allow natural advantages, they’re making an argument for all advantages to be eliminated from regulation, and we would end up with sports dominated by males between the ages of 20 and 28.
There are some people suggesting open categories by height and weight.
The problem is that for any height, males will be stronger, faster, more powerful than females. For any mass, and we know this because weightlifting has categories by mass, males lift about 30% heavier than females. They’ll be about 10%-15% faster at the same height and weight.
There’d be one or two sports where you might have some women, like gymnastics. Otherwise you would have to create categories that are so small – say, under 100 pounds. But in every other category, most sports would be completely dominated by males.
It’s not a viable solution for me unless we as a society are satisfied with filtering out women.
Another argument is that if trans women have an advantage, then they would be dominating.
That one misunderstands how you assess advantage. For a trans woman to win, she still has to be good enough at the base level without the advantage, in order to parlay that advantage into winning the women’s events.
If I was in the Tour de France and you gave me a bicycle with a 100-watt motor, I wouldn’t win the Tour de France. I’d do better than I would have done without it, but I wouldn’t win. Does my failure to win prove that motors don’t give an advantage? Of course not. My failure says more about my base level of performance than it does about the motor.
In terms of trans athletes, the retention of biological attributes creates the retention of performance advantages, which means that the person’s ranking relative to their peers’ will go up when they compare themselves to women rather than men. Someone who’s ranked 500 might improve to the 250s, but you still won’t see them on a podium.
It’s the change in performance that matters, not the final outcome.
Wasn’t Lia Thomas ranked in the 500s in the men’s division?
There’s some dispute as to whether it was 460 or 550 in the 200- and 65th in the 500-yard freestyle. But the concept is the same and we can use that case because we know the percentage performance change.
As Will Thomas, the performance was 4:18 in the 500-yard freestyle. As Lia Thomas, it’s 4:33. Ms. Thomas has slowed by 5.8% as a result of testosterone suppression. That’s fairly typical; most studies so far suggest performance impairments in that range.
The thing is that the male-female gap in swimming times is 10%-12% on average. That means that Ms. Thomas has retained about half the male advantage.
In strength events, for instance, weightlifting, where the gap is 30% or more, if you lost 10%, you’d still retain a 20% advantage and you’d jump more ranking places.
The retention of about half the male advantage is enough for No. 1 in the NCAA, but it’s not enough to move Ms. Thomas to No. 1 in the world.
The record set by Katie Ledecky in the 500 freestyle is 4:24. Thomas swam 4:18 as a man so could only afford to lose about 1% to be the record holder in women’s swimming.
When Ms. Thomas was beaten by cisgender women in other events, your point is that’s just because her baseline (pretransition) time wasn’t good enough.
Exactly. Are your performances in men’s sports close enough to the best woman such that you can turn that retained advantage into dominance, winning in women’s sports?
If the answer to that is yes, then you get Thomas in the 500. If the answer to that is not quite, then you get Thomas in the other distances.
On your podcast, you expressed frustration at having to keep debunking these arguments. Why do you think they persist?
There are a few things in play. There are nuances around the idea of advantage that people from outside sports don’t always appreciate.
But then the second thing comes into play and that’s the fact that this is an emotive issue. If you come to this debate wanting trans inclusion, then you reject the idea that it’s unfair. You will dismiss everything I’ve just said.
There’s a third thing. When people invoke the Phelps wingspan argument, they haven’t thought through the implications. If you could sit them down and say: “Okay. If you want to get rid of regulating natural advantages, then we would get rid of male and female categories,” what do you think would happen then?
They may still support inclusion because that’s their world view, but at least they’re honest now and understand the implications. But most people don’t go through that process.
I get that men are faster but I was shocked at how many are faster than elite women – for example, Allyson Felix.
There’s an amazing visual representation of that.
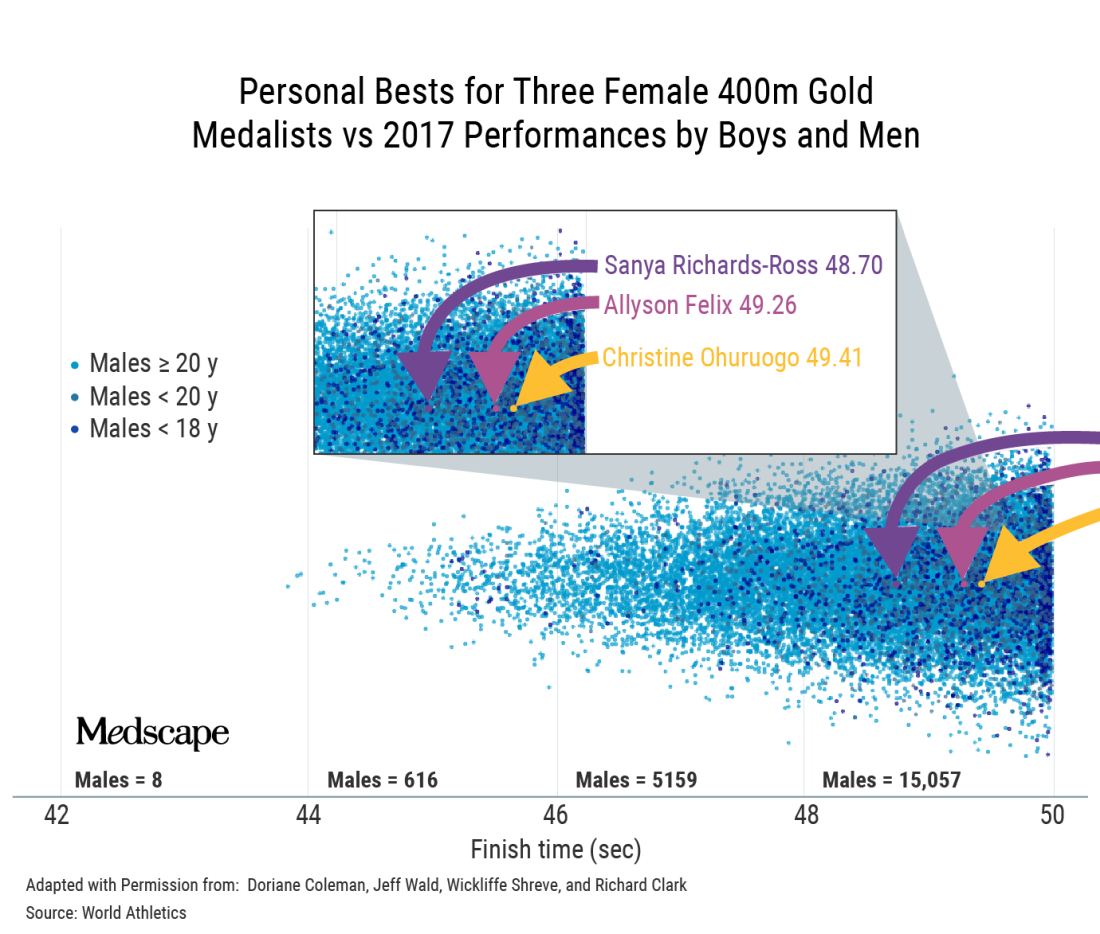
That’s a classic example where, if you’re immersed in sports, it becomes intuitive. If you’re not, you do a double-take and think, is that right? Position determines perspective.
Do you think some of it is because we’re constantly told that girls and women can do anything?
It’s a paradox that is difficult for people to get their minds around because in most walks of life, we can say that women can do anything. Of course, it’s arguably more difficult for women to become CEOs of Fortune 500 companies. This is a work in progress.
But sports are different. In sports, it’s not possible to directly compare male and female, and then tell girls they can be the best at whatever in the whole human race. That’s the uniqueness of sports and the reason categories exist in the first place. The biology does matter.
Speaking of biology, you’ve said that the focus on testosterone levels is a bit of a red herring.
Yes. The authorities were looking for a solution.
They grabbed onto the idea that lowering testosterone was the solution and perpetuated that as the mechanism by which we would ensure fairness. The problem is that my concentration of testosterone today is only a tiny part of the story.
I’ve been exposed to testosterone my whole life. My twin sister has not. There are many differences between us, but in terms of sports, the main biological difference is not that my testosterone is higher today; it’s that my testosterone has been higher my whole life. It’s the work done by that hormone over many years that makes a difference.
The key issue is, has this body, this physiology, been exposed to and benefited in the sports context, from male hormones – yes or no?
If your answer is yes, then that body belongs in male sports. With gender identity, we want to accommodate as far as possible, but we can’t take away that difference. That’s where we create this collision of rights between trans women and women.
Ultimately, your point is that we can’t have both fairness and inclusion.
When we sat down to do the World Rugby trans guidance, we had an epiphany: It doesn’t matter which way we go; we’re going to face hostility.
Once you accept that there are two parties that are affected and one of them will always be unhappy, then you start to see that fairness and inclusion can’t be balanced.
What about Joanna Harper’s proposal to make rules case by case and sport by sport?
First, it could be tricky legally because you’re effectively discriminating against some people within a subset of a subset. You’re going to end up saying to some trans women: “You can play because you don’t pose a safety or fairness issue.” But to another: “You can’t because you’re too strong.”
Then the problem is, how do you do that screening? It’s not like you can measure half a dozen variables and then have an algorithm spit out a performance level that tells you that this trans woman can compete here safely and fairly. It’s a theoretical solution that is practically impossible.
At a conference in Boston recently, Joanna said that when there are no medals, prize money, scholarships, or record times, we should allow inclusion. But just because a woman isn’t winning medals or going to the Olympics doesn’t mean there’s not considerable value for her if she were to make her school team, for instance.
There are only 11 places on the soccer field, eight lanes in a swimming pool. The moment you allow someone in, you potentially exclude someone else. And that happens everywhere, not only at the elite level.
Would you ever make a distinction between elite and subelite?
One of the beauties of sports is that it’s a meritocracy; it functions on a pathway system. I don’t think the level matters if you can track that this person’s presence denied a place on the team or a place at the competition to someone else.
With Lia Thomas, it’s not only denying the silver medalist gold or fourth place a bronze; it’s also the fact that there are only so many places at that meet. For some, that was their ambition and they weren’t able to realize it.
Now, a lot of sports are played outside that pathway. Say your local tennis club has a social league. There is little there to stand in the way of inclusion. Although I’m mindful that there may be a women’s league where it does matter to them.
We can try to accommodate trans women when the stakes are not high, provided that two requirements are met: One is that there’s no disruption to the selection/meritocracy pathway; and the second key point is that women must be okay with that inclusion, particularly if there are safety considerations, but even if it’s just a fairness consideration.
That’s where it gets tricky, because there are bigoted people in the world. Unfortunately, sometimes it’s difficult to tell whether people are using scientific arguments to prop up bigotry or whether they are genuine.
Joanna Harper has said that if you support inclusion, you have to be okay with trans women winning.
Winning the summer tennis league is not winning in the same sense as winning at the NCAA.
But the moment winning means selection and performance pathways, then I think we have to draw a line. The moment participation disrupts the natural order in sports, then it’s a problem.
In World Rugby, we proposed open competitions lower in contact to deal with the safety concerns. That was rejected by the trans community because they felt it was othering – that we were trying to squeeze them off to the side.
If you offered me one of two choices: no participation, or inclusion and they have to be able to win, I’d go for the former.
How did you get involved in this topic?
I got involved because I testified in the Caster Semenya case at the Court of Arbitration for Sport.
That is not a transgender issue; it’s a difference of sex development issue. What it has in common is the question of what to do with male-bodied biological advantage in sports.
When World Rugby joined the Olympic Games, we followed the IOC transgender policy. In 2019, it became apparent from the latest research that male advantage isn’t removed by testosterone suppression. We decided to delete the previous policy and make a new one.
The latest IOC policy is kind of no policy; it leaves it up to the governing bodies for each sport.
The one element of progress in what the IOC released, and it really is the only one, is that they’ve recognized that sports have to manage three imperatives: fairness, inclusion, and safety.
The 2015 IOC document says something like “sports should strive to be as inclusive as possible, but the overriding objective remains to guarantee a fair competition.” Basically, fair competition was nonnegotiable and must be guaranteed.
Of course, that policy allowed for testosterone suppression, and you’d have a difficult time convincing a physiologist that lowering testosterone guarantees fair competition.
Where there is merit in the current policy is that it’s clear that sports like rugby, boxing, taekwondo, and judo have a different equation with respect to safety, fairness, and inclusion than sports like equestrian, shooting, and archery. I think that’s wise to acknowledge.
However, the IOC policy doesn’t do anything to lead. In fact, what they said was extraordinary: There should be no presumption of advantage. If there’s no presumption of advantage for male-bodied athletes, then why do they persist with two categories? If there’s no presumption of advantage for trans women, are they saying that gender identity removes the advantage? We know that’s not true. We know that at the very least, you should presume that there is some advantage. How you manage it is up to you, but you can’t say that it’s not there.
This is a hostile debate. Have you ever thought: Maybe I’ll just shut up and stick to other sports topics?
Big time. The Lia Thomas case brought out a lot of vitriol. From about 2017, the situation we had with Ms. Thomas was predictable. The problem is that 95% of the world didn’t know this was happening and were taken by surprise.
The number of people who have opinions has exploded. A lot wade in without much thought. I’ve seen people question Lia Thomas’s motives. Presumably, Lia Thomas is trans, identifies as a woman, and therefore thinks she belongs in women’s sports. But I’ve seen people saying she only wants to swim in women’s sports because she knows she’ll win. And that’s not the worst of it. I’ve seen people saying Lia Thomas is only identifying as a woman so she can get into women’s changing rooms.
I don’t see how that helps the conversation. It just polarizes to the point that neither side is listening to the other. Before it was the trans community that wasn’t interested in talking about the idea of advantage, fairness, and safety. Their position is that trans women are women; how do you even have a discussion when they’ve got that dogma as their foundation?
Now, unfortunately, on the other side, we’re seeing unnecessary offensive tactics. For example, I’ve referred to Lia Thomas as “she.” I’ll have people shouting at me for using “she.” You’ve got to pick your battles, and that’s not the one you want to be fighting, in my opinion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An interview with Ross Tucker, PhD
An interview with Ross Tucker, PhD
When Lia Thomas won the women’s 500-yard freestyle at the 2022 NCAA Division 1 swimming championships, the issue of trans women’s participation in female sports ignited national headlines.
which prohibit trans women’s participation.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Let’s start with the proinclusion argument that there are always advantages in sports.
That’s true. The whole point of sports is to recognize people who have advantages and reward them for it. By the time this argument comes out, people have already accepted that males have advantages, right?
Some do, some don’t.
If someone uses this argument to say that we should allow trans women, basically biological males, to compete in women’s sports, they’ve implicitly accepted that there are advantages. Otherwise, what advantage are you talking about?
They would say it’s like the advantage Michael Phelps has because of his wingspan.
To answer that, you have to start by asking why women’s sports exist.
Women’s sports exist because we recognize that male physiology has biological differences that create performance advantages. Women’s sports exist to ensure that male advantages are excluded. If you allow male advantage in, you’re allowing something to cross into a category that specifically tries to exclude it. That makes the advantage possessed by trans women conceptually and substantively different from an advantage that’s possessed by Michael Phelps because his advantage doesn’t cross a category boundary line.
If someone wants to allow natural advantages to be celebrated in sports, they’re arguing against the existence of any categories, because every single category in sports is trying to filter out certain advantages.
Weight categories in boxing exist to get rid of the advantage of being stronger, taller, with greater reach. Paralympic categories filter out the natural advantage that someone has if, for example, they are only mildly affected by cerebral palsy, compared with more severely affected.
If someone wants to allow natural advantages, they’re making an argument for all advantages to be eliminated from regulation, and we would end up with sports dominated by males between the ages of 20 and 28.
There are some people suggesting open categories by height and weight.
The problem is that for any height, males will be stronger, faster, more powerful than females. For any mass, and we know this because weightlifting has categories by mass, males lift about 30% heavier than females. They’ll be about 10%-15% faster at the same height and weight.
There’d be one or two sports where you might have some women, like gymnastics. Otherwise you would have to create categories that are so small – say, under 100 pounds. But in every other category, most sports would be completely dominated by males.
It’s not a viable solution for me unless we as a society are satisfied with filtering out women.
Another argument is that if trans women have an advantage, then they would be dominating.
That one misunderstands how you assess advantage. For a trans woman to win, she still has to be good enough at the base level without the advantage, in order to parlay that advantage into winning the women’s events.
If I was in the Tour de France and you gave me a bicycle with a 100-watt motor, I wouldn’t win the Tour de France. I’d do better than I would have done without it, but I wouldn’t win. Does my failure to win prove that motors don’t give an advantage? Of course not. My failure says more about my base level of performance than it does about the motor.
In terms of trans athletes, the retention of biological attributes creates the retention of performance advantages, which means that the person’s ranking relative to their peers’ will go up when they compare themselves to women rather than men. Someone who’s ranked 500 might improve to the 250s, but you still won’t see them on a podium.
It’s the change in performance that matters, not the final outcome.
Wasn’t Lia Thomas ranked in the 500s in the men’s division?
There’s some dispute as to whether it was 460 or 550 in the 200- and 65th in the 500-yard freestyle. But the concept is the same and we can use that case because we know the percentage performance change.
As Will Thomas, the performance was 4:18 in the 500-yard freestyle. As Lia Thomas, it’s 4:33. Ms. Thomas has slowed by 5.8% as a result of testosterone suppression. That’s fairly typical; most studies so far suggest performance impairments in that range.
The thing is that the male-female gap in swimming times is 10%-12% on average. That means that Ms. Thomas has retained about half the male advantage.
In strength events, for instance, weightlifting, where the gap is 30% or more, if you lost 10%, you’d still retain a 20% advantage and you’d jump more ranking places.
The retention of about half the male advantage is enough for No. 1 in the NCAA, but it’s not enough to move Ms. Thomas to No. 1 in the world.
The record set by Katie Ledecky in the 500 freestyle is 4:24. Thomas swam 4:18 as a man so could only afford to lose about 1% to be the record holder in women’s swimming.
When Ms. Thomas was beaten by cisgender women in other events, your point is that’s just because her baseline (pretransition) time wasn’t good enough.
Exactly. Are your performances in men’s sports close enough to the best woman such that you can turn that retained advantage into dominance, winning in women’s sports?
If the answer to that is yes, then you get Thomas in the 500. If the answer to that is not quite, then you get Thomas in the other distances.
On your podcast, you expressed frustration at having to keep debunking these arguments. Why do you think they persist?
There are a few things in play. There are nuances around the idea of advantage that people from outside sports don’t always appreciate.
But then the second thing comes into play and that’s the fact that this is an emotive issue. If you come to this debate wanting trans inclusion, then you reject the idea that it’s unfair. You will dismiss everything I’ve just said.
There’s a third thing. When people invoke the Phelps wingspan argument, they haven’t thought through the implications. If you could sit them down and say: “Okay. If you want to get rid of regulating natural advantages, then we would get rid of male and female categories,” what do you think would happen then?
They may still support inclusion because that’s their world view, but at least they’re honest now and understand the implications. But most people don’t go through that process.
I get that men are faster but I was shocked at how many are faster than elite women – for example, Allyson Felix.
There’s an amazing visual representation of that.

That’s a classic example where, if you’re immersed in sports, it becomes intuitive. If you’re not, you do a double-take and think, is that right? Position determines perspective.
Do you think some of it is because we’re constantly told that girls and women can do anything?
It’s a paradox that is difficult for people to get their minds around because in most walks of life, we can say that women can do anything. Of course, it’s arguably more difficult for women to become CEOs of Fortune 500 companies. This is a work in progress.
But sports are different. In sports, it’s not possible to directly compare male and female, and then tell girls they can be the best at whatever in the whole human race. That’s the uniqueness of sports and the reason categories exist in the first place. The biology does matter.
Speaking of biology, you’ve said that the focus on testosterone levels is a bit of a red herring.
Yes. The authorities were looking for a solution.
They grabbed onto the idea that lowering testosterone was the solution and perpetuated that as the mechanism by which we would ensure fairness. The problem is that my concentration of testosterone today is only a tiny part of the story.
I’ve been exposed to testosterone my whole life. My twin sister has not. There are many differences between us, but in terms of sports, the main biological difference is not that my testosterone is higher today; it’s that my testosterone has been higher my whole life. It’s the work done by that hormone over many years that makes a difference.
The key issue is, has this body, this physiology, been exposed to and benefited in the sports context, from male hormones – yes or no?
If your answer is yes, then that body belongs in male sports. With gender identity, we want to accommodate as far as possible, but we can’t take away that difference. That’s where we create this collision of rights between trans women and women.
Ultimately, your point is that we can’t have both fairness and inclusion.
When we sat down to do the World Rugby trans guidance, we had an epiphany: It doesn’t matter which way we go; we’re going to face hostility.
Once you accept that there are two parties that are affected and one of them will always be unhappy, then you start to see that fairness and inclusion can’t be balanced.
What about Joanna Harper’s proposal to make rules case by case and sport by sport?
First, it could be tricky legally because you’re effectively discriminating against some people within a subset of a subset. You’re going to end up saying to some trans women: “You can play because you don’t pose a safety or fairness issue.” But to another: “You can’t because you’re too strong.”
Then the problem is, how do you do that screening? It’s not like you can measure half a dozen variables and then have an algorithm spit out a performance level that tells you that this trans woman can compete here safely and fairly. It’s a theoretical solution that is practically impossible.
At a conference in Boston recently, Joanna said that when there are no medals, prize money, scholarships, or record times, we should allow inclusion. But just because a woman isn’t winning medals or going to the Olympics doesn’t mean there’s not considerable value for her if she were to make her school team, for instance.
There are only 11 places on the soccer field, eight lanes in a swimming pool. The moment you allow someone in, you potentially exclude someone else. And that happens everywhere, not only at the elite level.
Would you ever make a distinction between elite and subelite?
One of the beauties of sports is that it’s a meritocracy; it functions on a pathway system. I don’t think the level matters if you can track that this person’s presence denied a place on the team or a place at the competition to someone else.
With Lia Thomas, it’s not only denying the silver medalist gold or fourth place a bronze; it’s also the fact that there are only so many places at that meet. For some, that was their ambition and they weren’t able to realize it.
Now, a lot of sports are played outside that pathway. Say your local tennis club has a social league. There is little there to stand in the way of inclusion. Although I’m mindful that there may be a women’s league where it does matter to them.
We can try to accommodate trans women when the stakes are not high, provided that two requirements are met: One is that there’s no disruption to the selection/meritocracy pathway; and the second key point is that women must be okay with that inclusion, particularly if there are safety considerations, but even if it’s just a fairness consideration.
That’s where it gets tricky, because there are bigoted people in the world. Unfortunately, sometimes it’s difficult to tell whether people are using scientific arguments to prop up bigotry or whether they are genuine.
Joanna Harper has said that if you support inclusion, you have to be okay with trans women winning.
Winning the summer tennis league is not winning in the same sense as winning at the NCAA.
But the moment winning means selection and performance pathways, then I think we have to draw a line. The moment participation disrupts the natural order in sports, then it’s a problem.
In World Rugby, we proposed open competitions lower in contact to deal with the safety concerns. That was rejected by the trans community because they felt it was othering – that we were trying to squeeze them off to the side.
If you offered me one of two choices: no participation, or inclusion and they have to be able to win, I’d go for the former.
How did you get involved in this topic?
I got involved because I testified in the Caster Semenya case at the Court of Arbitration for Sport.
That is not a transgender issue; it’s a difference of sex development issue. What it has in common is the question of what to do with male-bodied biological advantage in sports.
When World Rugby joined the Olympic Games, we followed the IOC transgender policy. In 2019, it became apparent from the latest research that male advantage isn’t removed by testosterone suppression. We decided to delete the previous policy and make a new one.
The latest IOC policy is kind of no policy; it leaves it up to the governing bodies for each sport.
The one element of progress in what the IOC released, and it really is the only one, is that they’ve recognized that sports have to manage three imperatives: fairness, inclusion, and safety.
The 2015 IOC document says something like “sports should strive to be as inclusive as possible, but the overriding objective remains to guarantee a fair competition.” Basically, fair competition was nonnegotiable and must be guaranteed.
Of course, that policy allowed for testosterone suppression, and you’d have a difficult time convincing a physiologist that lowering testosterone guarantees fair competition.
Where there is merit in the current policy is that it’s clear that sports like rugby, boxing, taekwondo, and judo have a different equation with respect to safety, fairness, and inclusion than sports like equestrian, shooting, and archery. I think that’s wise to acknowledge.
However, the IOC policy doesn’t do anything to lead. In fact, what they said was extraordinary: There should be no presumption of advantage. If there’s no presumption of advantage for male-bodied athletes, then why do they persist with two categories? If there’s no presumption of advantage for trans women, are they saying that gender identity removes the advantage? We know that’s not true. We know that at the very least, you should presume that there is some advantage. How you manage it is up to you, but you can’t say that it’s not there.
This is a hostile debate. Have you ever thought: Maybe I’ll just shut up and stick to other sports topics?
Big time. The Lia Thomas case brought out a lot of vitriol. From about 2017, the situation we had with Ms. Thomas was predictable. The problem is that 95% of the world didn’t know this was happening and were taken by surprise.
The number of people who have opinions has exploded. A lot wade in without much thought. I’ve seen people question Lia Thomas’s motives. Presumably, Lia Thomas is trans, identifies as a woman, and therefore thinks she belongs in women’s sports. But I’ve seen people saying she only wants to swim in women’s sports because she knows she’ll win. And that’s not the worst of it. I’ve seen people saying Lia Thomas is only identifying as a woman so she can get into women’s changing rooms.
I don’t see how that helps the conversation. It just polarizes to the point that neither side is listening to the other. Before it was the trans community that wasn’t interested in talking about the idea of advantage, fairness, and safety. Their position is that trans women are women; how do you even have a discussion when they’ve got that dogma as their foundation?
Now, unfortunately, on the other side, we’re seeing unnecessary offensive tactics. For example, I’ve referred to Lia Thomas as “she.” I’ll have people shouting at me for using “she.” You’ve got to pick your battles, and that’s not the one you want to be fighting, in my opinion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Lia Thomas won the women’s 500-yard freestyle at the 2022 NCAA Division 1 swimming championships, the issue of trans women’s participation in female sports ignited national headlines.
which prohibit trans women’s participation.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Let’s start with the proinclusion argument that there are always advantages in sports.
That’s true. The whole point of sports is to recognize people who have advantages and reward them for it. By the time this argument comes out, people have already accepted that males have advantages, right?
Some do, some don’t.
If someone uses this argument to say that we should allow trans women, basically biological males, to compete in women’s sports, they’ve implicitly accepted that there are advantages. Otherwise, what advantage are you talking about?
They would say it’s like the advantage Michael Phelps has because of his wingspan.
To answer that, you have to start by asking why women’s sports exist.
Women’s sports exist because we recognize that male physiology has biological differences that create performance advantages. Women’s sports exist to ensure that male advantages are excluded. If you allow male advantage in, you’re allowing something to cross into a category that specifically tries to exclude it. That makes the advantage possessed by trans women conceptually and substantively different from an advantage that’s possessed by Michael Phelps because his advantage doesn’t cross a category boundary line.
If someone wants to allow natural advantages to be celebrated in sports, they’re arguing against the existence of any categories, because every single category in sports is trying to filter out certain advantages.
Weight categories in boxing exist to get rid of the advantage of being stronger, taller, with greater reach. Paralympic categories filter out the natural advantage that someone has if, for example, they are only mildly affected by cerebral palsy, compared with more severely affected.
If someone wants to allow natural advantages, they’re making an argument for all advantages to be eliminated from regulation, and we would end up with sports dominated by males between the ages of 20 and 28.
There are some people suggesting open categories by height and weight.
The problem is that for any height, males will be stronger, faster, more powerful than females. For any mass, and we know this because weightlifting has categories by mass, males lift about 30% heavier than females. They’ll be about 10%-15% faster at the same height and weight.
There’d be one or two sports where you might have some women, like gymnastics. Otherwise you would have to create categories that are so small – say, under 100 pounds. But in every other category, most sports would be completely dominated by males.
It’s not a viable solution for me unless we as a society are satisfied with filtering out women.
Another argument is that if trans women have an advantage, then they would be dominating.
That one misunderstands how you assess advantage. For a trans woman to win, she still has to be good enough at the base level without the advantage, in order to parlay that advantage into winning the women’s events.
If I was in the Tour de France and you gave me a bicycle with a 100-watt motor, I wouldn’t win the Tour de France. I’d do better than I would have done without it, but I wouldn’t win. Does my failure to win prove that motors don’t give an advantage? Of course not. My failure says more about my base level of performance than it does about the motor.
In terms of trans athletes, the retention of biological attributes creates the retention of performance advantages, which means that the person’s ranking relative to their peers’ will go up when they compare themselves to women rather than men. Someone who’s ranked 500 might improve to the 250s, but you still won’t see them on a podium.
It’s the change in performance that matters, not the final outcome.
Wasn’t Lia Thomas ranked in the 500s in the men’s division?
There’s some dispute as to whether it was 460 or 550 in the 200- and 65th in the 500-yard freestyle. But the concept is the same and we can use that case because we know the percentage performance change.
As Will Thomas, the performance was 4:18 in the 500-yard freestyle. As Lia Thomas, it’s 4:33. Ms. Thomas has slowed by 5.8% as a result of testosterone suppression. That’s fairly typical; most studies so far suggest performance impairments in that range.
The thing is that the male-female gap in swimming times is 10%-12% on average. That means that Ms. Thomas has retained about half the male advantage.
In strength events, for instance, weightlifting, where the gap is 30% or more, if you lost 10%, you’d still retain a 20% advantage and you’d jump more ranking places.
The retention of about half the male advantage is enough for No. 1 in the NCAA, but it’s not enough to move Ms. Thomas to No. 1 in the world.
The record set by Katie Ledecky in the 500 freestyle is 4:24. Thomas swam 4:18 as a man so could only afford to lose about 1% to be the record holder in women’s swimming.
When Ms. Thomas was beaten by cisgender women in other events, your point is that’s just because her baseline (pretransition) time wasn’t good enough.
Exactly. Are your performances in men’s sports close enough to the best woman such that you can turn that retained advantage into dominance, winning in women’s sports?
If the answer to that is yes, then you get Thomas in the 500. If the answer to that is not quite, then you get Thomas in the other distances.
On your podcast, you expressed frustration at having to keep debunking these arguments. Why do you think they persist?
There are a few things in play. There are nuances around the idea of advantage that people from outside sports don’t always appreciate.
But then the second thing comes into play and that’s the fact that this is an emotive issue. If you come to this debate wanting trans inclusion, then you reject the idea that it’s unfair. You will dismiss everything I’ve just said.
There’s a third thing. When people invoke the Phelps wingspan argument, they haven’t thought through the implications. If you could sit them down and say: “Okay. If you want to get rid of regulating natural advantages, then we would get rid of male and female categories,” what do you think would happen then?
They may still support inclusion because that’s their world view, but at least they’re honest now and understand the implications. But most people don’t go through that process.
I get that men are faster but I was shocked at how many are faster than elite women – for example, Allyson Felix.
There’s an amazing visual representation of that.

That’s a classic example where, if you’re immersed in sports, it becomes intuitive. If you’re not, you do a double-take and think, is that right? Position determines perspective.
Do you think some of it is because we’re constantly told that girls and women can do anything?
It’s a paradox that is difficult for people to get their minds around because in most walks of life, we can say that women can do anything. Of course, it’s arguably more difficult for women to become CEOs of Fortune 500 companies. This is a work in progress.
But sports are different. In sports, it’s not possible to directly compare male and female, and then tell girls they can be the best at whatever in the whole human race. That’s the uniqueness of sports and the reason categories exist in the first place. The biology does matter.
Speaking of biology, you’ve said that the focus on testosterone levels is a bit of a red herring.
Yes. The authorities were looking for a solution.
They grabbed onto the idea that lowering testosterone was the solution and perpetuated that as the mechanism by which we would ensure fairness. The problem is that my concentration of testosterone today is only a tiny part of the story.
I’ve been exposed to testosterone my whole life. My twin sister has not. There are many differences between us, but in terms of sports, the main biological difference is not that my testosterone is higher today; it’s that my testosterone has been higher my whole life. It’s the work done by that hormone over many years that makes a difference.
The key issue is, has this body, this physiology, been exposed to and benefited in the sports context, from male hormones – yes or no?
If your answer is yes, then that body belongs in male sports. With gender identity, we want to accommodate as far as possible, but we can’t take away that difference. That’s where we create this collision of rights between trans women and women.
Ultimately, your point is that we can’t have both fairness and inclusion.
When we sat down to do the World Rugby trans guidance, we had an epiphany: It doesn’t matter which way we go; we’re going to face hostility.
Once you accept that there are two parties that are affected and one of them will always be unhappy, then you start to see that fairness and inclusion can’t be balanced.
What about Joanna Harper’s proposal to make rules case by case and sport by sport?
First, it could be tricky legally because you’re effectively discriminating against some people within a subset of a subset. You’re going to end up saying to some trans women: “You can play because you don’t pose a safety or fairness issue.” But to another: “You can’t because you’re too strong.”
Then the problem is, how do you do that screening? It’s not like you can measure half a dozen variables and then have an algorithm spit out a performance level that tells you that this trans woman can compete here safely and fairly. It’s a theoretical solution that is practically impossible.
At a conference in Boston recently, Joanna said that when there are no medals, prize money, scholarships, or record times, we should allow inclusion. But just because a woman isn’t winning medals or going to the Olympics doesn’t mean there’s not considerable value for her if she were to make her school team, for instance.
There are only 11 places on the soccer field, eight lanes in a swimming pool. The moment you allow someone in, you potentially exclude someone else. And that happens everywhere, not only at the elite level.
Would you ever make a distinction between elite and subelite?
One of the beauties of sports is that it’s a meritocracy; it functions on a pathway system. I don’t think the level matters if you can track that this person’s presence denied a place on the team or a place at the competition to someone else.
With Lia Thomas, it’s not only denying the silver medalist gold or fourth place a bronze; it’s also the fact that there are only so many places at that meet. For some, that was their ambition and they weren’t able to realize it.
Now, a lot of sports are played outside that pathway. Say your local tennis club has a social league. There is little there to stand in the way of inclusion. Although I’m mindful that there may be a women’s league where it does matter to them.
We can try to accommodate trans women when the stakes are not high, provided that two requirements are met: One is that there’s no disruption to the selection/meritocracy pathway; and the second key point is that women must be okay with that inclusion, particularly if there are safety considerations, but even if it’s just a fairness consideration.
That’s where it gets tricky, because there are bigoted people in the world. Unfortunately, sometimes it’s difficult to tell whether people are using scientific arguments to prop up bigotry or whether they are genuine.
Joanna Harper has said that if you support inclusion, you have to be okay with trans women winning.
Winning the summer tennis league is not winning in the same sense as winning at the NCAA.
But the moment winning means selection and performance pathways, then I think we have to draw a line. The moment participation disrupts the natural order in sports, then it’s a problem.
In World Rugby, we proposed open competitions lower in contact to deal with the safety concerns. That was rejected by the trans community because they felt it was othering – that we were trying to squeeze them off to the side.
If you offered me one of two choices: no participation, or inclusion and they have to be able to win, I’d go for the former.
How did you get involved in this topic?
I got involved because I testified in the Caster Semenya case at the Court of Arbitration for Sport.
That is not a transgender issue; it’s a difference of sex development issue. What it has in common is the question of what to do with male-bodied biological advantage in sports.
When World Rugby joined the Olympic Games, we followed the IOC transgender policy. In 2019, it became apparent from the latest research that male advantage isn’t removed by testosterone suppression. We decided to delete the previous policy and make a new one.
The latest IOC policy is kind of no policy; it leaves it up to the governing bodies for each sport.
The one element of progress in what the IOC released, and it really is the only one, is that they’ve recognized that sports have to manage three imperatives: fairness, inclusion, and safety.
The 2015 IOC document says something like “sports should strive to be as inclusive as possible, but the overriding objective remains to guarantee a fair competition.” Basically, fair competition was nonnegotiable and must be guaranteed.
Of course, that policy allowed for testosterone suppression, and you’d have a difficult time convincing a physiologist that lowering testosterone guarantees fair competition.
Where there is merit in the current policy is that it’s clear that sports like rugby, boxing, taekwondo, and judo have a different equation with respect to safety, fairness, and inclusion than sports like equestrian, shooting, and archery. I think that’s wise to acknowledge.
However, the IOC policy doesn’t do anything to lead. In fact, what they said was extraordinary: There should be no presumption of advantage. If there’s no presumption of advantage for male-bodied athletes, then why do they persist with two categories? If there’s no presumption of advantage for trans women, are they saying that gender identity removes the advantage? We know that’s not true. We know that at the very least, you should presume that there is some advantage. How you manage it is up to you, but you can’t say that it’s not there.
This is a hostile debate. Have you ever thought: Maybe I’ll just shut up and stick to other sports topics?
Big time. The Lia Thomas case brought out a lot of vitriol. From about 2017, the situation we had with Ms. Thomas was predictable. The problem is that 95% of the world didn’t know this was happening and were taken by surprise.
The number of people who have opinions has exploded. A lot wade in without much thought. I’ve seen people question Lia Thomas’s motives. Presumably, Lia Thomas is trans, identifies as a woman, and therefore thinks she belongs in women’s sports. But I’ve seen people saying she only wants to swim in women’s sports because she knows she’ll win. And that’s not the worst of it. I’ve seen people saying Lia Thomas is only identifying as a woman so she can get into women’s changing rooms.
I don’t see how that helps the conversation. It just polarizes to the point that neither side is listening to the other. Before it was the trans community that wasn’t interested in talking about the idea of advantage, fairness, and safety. Their position is that trans women are women; how do you even have a discussion when they’ve got that dogma as their foundation?
Now, unfortunately, on the other side, we’re seeing unnecessary offensive tactics. For example, I’ve referred to Lia Thomas as “she.” I’ll have people shouting at me for using “she.” You’ve got to pick your battles, and that’s not the one you want to be fighting, in my opinion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Age, skin cancer risks for ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid identified
that may result in treatment interruption or cessation.
Investigators in Boston report that among patients receiving ICIs, being aged 70 years or older and having skin cancer are both significant risk factors for bullous pemphigoid. On the plus side, ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid also appears to be a marker for improved tumor responses to therapy.
In a nested case-control study of 5,636 patients with cancer who received either a programmed death 1 inhibitor such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or nivolumab (Opdivo) or a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4 inhibitor such as ipilimumab (Yervoy), 35 patients (0.6%) developed bullous pemphigoid. The study by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and colleagues was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
“What is interesting is that 0.6 is a small number, but we’re seeing bullous pemphigoid at considerably higher frequency than is expected in the general population,” Dr. LeBoeuf said in an interview.
And although bullous pemphigoid has the potential to disrupt ICI therapy, it also appears to be a marker for a favorable tumor response, the investigators found.
Their findings suggest that management of bullous pemphigoid for patients receiving ICIs should focus on early identification and management with therapies directed at the specific toxicity, Dr. LeBoeuf said.
“When you make a specific diagnosis like bullous pemphigoid, then you can treat that specific disease with very targeted therapies, such as omalizumab or dupilumab or rituximab – things that are not globally immune suppressing like steroid or other T-cell–depleting agents. Studies have shown that depleting B cells with anti-CD20 agents is not detrimental to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy,” she said.
Dermatologic AEs common
About 40% of patients with cancer treated with ICIs experience immune-related dermatologic adverse events (AEs) that can range from mild rashes and hair and nail changes to uncommon but life-threatening complications, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a form of toxic epidermal necrolysis, according to members of a European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology task force.
“The desirable, immune-mediated oncologic response is often achieved at the cost of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may potentially affect any organ system,” they wrote in a position statement on the management of ICI-derived dermatologic adverse events.
Dr. LeBoeuf and colleagues note that, while reported risk factors for idiopathic bullous pemphigoid include advanced age, type 2 diabetes, use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, cerebrovascular disease, and neurocognitive disease, risk factors for bullous pemphigoid and other adverse dermatologic events associated with ICIs are less well known.
Study details
To identify risk factors for bullous pemphigoid in patients receiving ICI, the investigators performed a case-control study nested within a retrospective cohort study.
They evaluated records for all patients in the three Harvard-affiliated hospitals to identify patients with ICI-associated bullous pemphigoid from October 2014 through December 2020. Control persons were all patients in the Dana-Farber cancer registry who received ICIs during the study period.
The investigators chose age at ICI initiation (69 years and younger or 70 years and older), sex, ICI agents, and cancer type as potential risk factors.
They used propensity score matching based on age, cancer type, ICI agent, and number of ICI cycles to match two control persons with each case patient.
Of the 5,636 patients treated with ICIs during the study period, 35 (0.6%) developed bullous pemphigoid. The median age was 72.8 years, and 71.4% were men.
In a multivariate logistic regression model that included 2,955 patients with complete data in the cancer registry, factors significantly associated with developing bullous pemphigoid included age 70 years or older (odds ratio, 2.32; P = .01), having melanoma (OR, 3.21; P < .001), and having nonmelanoma skin cancer (OR, 8.32; P < .001).
In comparing the 35 case patients with their matched control patients, a complete or partial response at first restaging imaging was significantly associated with developing bullous pemphigoid (OR, 3.37; P = .01). In addition, there was a higher likelihood of tumor responses to ICIs among patients with bullous pemphigoid, compared with matched control patients (objective response rate, 82.9% vs. 61.4%; P = .03).
Prudent toxicity management
Ryan Sullivan, MD, who treats patients with skin cancer at Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston, but was not involved in the study, commented that the findings raise questions about the relationship between skin cancers and immune-related adverse events.
“It is compelling that bullous pemphigoid is a skin toxicity and is more common to happen in skin cancer patients,” he noted. “That’s a very interesting finding, and the reason that it’s interesting is that it’s harder to understand why a presumably antibody-mediated side effect would be more likely to have that cross-reactivity where the tumor started and where the toxicity happened,” he said in an interview.
He noted that the benefits of ICIs for patients with skin cancers far outweigh the risks of dermatologic adverse events such as bullous pemphigoid and that ICI-associated events require judicious management.
“This is true across the spectrum of toxicities: There are clear manifestations of toxicity that we should be more thoughtful about what’s driving them, more thoughtful about what it is, and more thoughtful about treating them, other than just pouring steroids into patients in industrial doses and hoping that everything’s going to be OK,” he said.
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. LeBoeuf reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study and personal fees for serving as a consultant for several companies outside the study. Coauthor Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, is associate editor of JAMA Dermatology but was not involved in study selection or evaluation for publication. Dr. Sullivan disclosed consulting for ICI makers Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that may result in treatment interruption or cessation.
Investigators in Boston report that among patients receiving ICIs, being aged 70 years or older and having skin cancer are both significant risk factors for bullous pemphigoid. On the plus side, ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid also appears to be a marker for improved tumor responses to therapy.
In a nested case-control study of 5,636 patients with cancer who received either a programmed death 1 inhibitor such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or nivolumab (Opdivo) or a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4 inhibitor such as ipilimumab (Yervoy), 35 patients (0.6%) developed bullous pemphigoid. The study by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and colleagues was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
“What is interesting is that 0.6 is a small number, but we’re seeing bullous pemphigoid at considerably higher frequency than is expected in the general population,” Dr. LeBoeuf said in an interview.
And although bullous pemphigoid has the potential to disrupt ICI therapy, it also appears to be a marker for a favorable tumor response, the investigators found.
Their findings suggest that management of bullous pemphigoid for patients receiving ICIs should focus on early identification and management with therapies directed at the specific toxicity, Dr. LeBoeuf said.
“When you make a specific diagnosis like bullous pemphigoid, then you can treat that specific disease with very targeted therapies, such as omalizumab or dupilumab or rituximab – things that are not globally immune suppressing like steroid or other T-cell–depleting agents. Studies have shown that depleting B cells with anti-CD20 agents is not detrimental to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy,” she said.
Dermatologic AEs common
About 40% of patients with cancer treated with ICIs experience immune-related dermatologic adverse events (AEs) that can range from mild rashes and hair and nail changes to uncommon but life-threatening complications, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a form of toxic epidermal necrolysis, according to members of a European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology task force.
“The desirable, immune-mediated oncologic response is often achieved at the cost of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may potentially affect any organ system,” they wrote in a position statement on the management of ICI-derived dermatologic adverse events.
Dr. LeBoeuf and colleagues note that, while reported risk factors for idiopathic bullous pemphigoid include advanced age, type 2 diabetes, use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, cerebrovascular disease, and neurocognitive disease, risk factors for bullous pemphigoid and other adverse dermatologic events associated with ICIs are less well known.
Study details
To identify risk factors for bullous pemphigoid in patients receiving ICI, the investigators performed a case-control study nested within a retrospective cohort study.
They evaluated records for all patients in the three Harvard-affiliated hospitals to identify patients with ICI-associated bullous pemphigoid from October 2014 through December 2020. Control persons were all patients in the Dana-Farber cancer registry who received ICIs during the study period.
The investigators chose age at ICI initiation (69 years and younger or 70 years and older), sex, ICI agents, and cancer type as potential risk factors.
They used propensity score matching based on age, cancer type, ICI agent, and number of ICI cycles to match two control persons with each case patient.
Of the 5,636 patients treated with ICIs during the study period, 35 (0.6%) developed bullous pemphigoid. The median age was 72.8 years, and 71.4% were men.
In a multivariate logistic regression model that included 2,955 patients with complete data in the cancer registry, factors significantly associated with developing bullous pemphigoid included age 70 years or older (odds ratio, 2.32; P = .01), having melanoma (OR, 3.21; P < .001), and having nonmelanoma skin cancer (OR, 8.32; P < .001).
In comparing the 35 case patients with their matched control patients, a complete or partial response at first restaging imaging was significantly associated with developing bullous pemphigoid (OR, 3.37; P = .01). In addition, there was a higher likelihood of tumor responses to ICIs among patients with bullous pemphigoid, compared with matched control patients (objective response rate, 82.9% vs. 61.4%; P = .03).
Prudent toxicity management
Ryan Sullivan, MD, who treats patients with skin cancer at Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston, but was not involved in the study, commented that the findings raise questions about the relationship between skin cancers and immune-related adverse events.
“It is compelling that bullous pemphigoid is a skin toxicity and is more common to happen in skin cancer patients,” he noted. “That’s a very interesting finding, and the reason that it’s interesting is that it’s harder to understand why a presumably antibody-mediated side effect would be more likely to have that cross-reactivity where the tumor started and where the toxicity happened,” he said in an interview.
He noted that the benefits of ICIs for patients with skin cancers far outweigh the risks of dermatologic adverse events such as bullous pemphigoid and that ICI-associated events require judicious management.
“This is true across the spectrum of toxicities: There are clear manifestations of toxicity that we should be more thoughtful about what’s driving them, more thoughtful about what it is, and more thoughtful about treating them, other than just pouring steroids into patients in industrial doses and hoping that everything’s going to be OK,” he said.
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. LeBoeuf reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study and personal fees for serving as a consultant for several companies outside the study. Coauthor Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, is associate editor of JAMA Dermatology but was not involved in study selection or evaluation for publication. Dr. Sullivan disclosed consulting for ICI makers Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that may result in treatment interruption or cessation.
Investigators in Boston report that among patients receiving ICIs, being aged 70 years or older and having skin cancer are both significant risk factors for bullous pemphigoid. On the plus side, ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid also appears to be a marker for improved tumor responses to therapy.
In a nested case-control study of 5,636 patients with cancer who received either a programmed death 1 inhibitor such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or nivolumab (Opdivo) or a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4 inhibitor such as ipilimumab (Yervoy), 35 patients (0.6%) developed bullous pemphigoid. The study by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and colleagues was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
“What is interesting is that 0.6 is a small number, but we’re seeing bullous pemphigoid at considerably higher frequency than is expected in the general population,” Dr. LeBoeuf said in an interview.
And although bullous pemphigoid has the potential to disrupt ICI therapy, it also appears to be a marker for a favorable tumor response, the investigators found.
Their findings suggest that management of bullous pemphigoid for patients receiving ICIs should focus on early identification and management with therapies directed at the specific toxicity, Dr. LeBoeuf said.
“When you make a specific diagnosis like bullous pemphigoid, then you can treat that specific disease with very targeted therapies, such as omalizumab or dupilumab or rituximab – things that are not globally immune suppressing like steroid or other T-cell–depleting agents. Studies have shown that depleting B cells with anti-CD20 agents is not detrimental to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy,” she said.
Dermatologic AEs common
About 40% of patients with cancer treated with ICIs experience immune-related dermatologic adverse events (AEs) that can range from mild rashes and hair and nail changes to uncommon but life-threatening complications, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a form of toxic epidermal necrolysis, according to members of a European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology task force.
“The desirable, immune-mediated oncologic response is often achieved at the cost of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may potentially affect any organ system,” they wrote in a position statement on the management of ICI-derived dermatologic adverse events.
Dr. LeBoeuf and colleagues note that, while reported risk factors for idiopathic bullous pemphigoid include advanced age, type 2 diabetes, use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, cerebrovascular disease, and neurocognitive disease, risk factors for bullous pemphigoid and other adverse dermatologic events associated with ICIs are less well known.
Study details
To identify risk factors for bullous pemphigoid in patients receiving ICI, the investigators performed a case-control study nested within a retrospective cohort study.
They evaluated records for all patients in the three Harvard-affiliated hospitals to identify patients with ICI-associated bullous pemphigoid from October 2014 through December 2020. Control persons were all patients in the Dana-Farber cancer registry who received ICIs during the study period.
The investigators chose age at ICI initiation (69 years and younger or 70 years and older), sex, ICI agents, and cancer type as potential risk factors.
They used propensity score matching based on age, cancer type, ICI agent, and number of ICI cycles to match two control persons with each case patient.
Of the 5,636 patients treated with ICIs during the study period, 35 (0.6%) developed bullous pemphigoid. The median age was 72.8 years, and 71.4% were men.
In a multivariate logistic regression model that included 2,955 patients with complete data in the cancer registry, factors significantly associated with developing bullous pemphigoid included age 70 years or older (odds ratio, 2.32; P = .01), having melanoma (OR, 3.21; P < .001), and having nonmelanoma skin cancer (OR, 8.32; P < .001).
In comparing the 35 case patients with their matched control patients, a complete or partial response at first restaging imaging was significantly associated with developing bullous pemphigoid (OR, 3.37; P = .01). In addition, there was a higher likelihood of tumor responses to ICIs among patients with bullous pemphigoid, compared with matched control patients (objective response rate, 82.9% vs. 61.4%; P = .03).
Prudent toxicity management
Ryan Sullivan, MD, who treats patients with skin cancer at Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston, but was not involved in the study, commented that the findings raise questions about the relationship between skin cancers and immune-related adverse events.
“It is compelling that bullous pemphigoid is a skin toxicity and is more common to happen in skin cancer patients,” he noted. “That’s a very interesting finding, and the reason that it’s interesting is that it’s harder to understand why a presumably antibody-mediated side effect would be more likely to have that cross-reactivity where the tumor started and where the toxicity happened,” he said in an interview.
He noted that the benefits of ICIs for patients with skin cancers far outweigh the risks of dermatologic adverse events such as bullous pemphigoid and that ICI-associated events require judicious management.
“This is true across the spectrum of toxicities: There are clear manifestations of toxicity that we should be more thoughtful about what’s driving them, more thoughtful about what it is, and more thoughtful about treating them, other than just pouring steroids into patients in industrial doses and hoping that everything’s going to be OK,” he said.
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. LeBoeuf reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study and personal fees for serving as a consultant for several companies outside the study. Coauthor Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, is associate editor of JAMA Dermatology but was not involved in study selection or evaluation for publication. Dr. Sullivan disclosed consulting for ICI makers Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Gun violence now leading cause of death for U.S. children
In 2020, 4,357 children aged 1-19, or approximately 6 in 100,000, died from a gun-related injury, the researchers reported, modestly exceeding the number for auto accidents (3,913) and greatly exceeding deaths caused by suffocation (1,411) or drowning (966).
To observers of gun violence in this country, the grim statistical marker has been all but inevitable. Gunshots were the second-leading cause of death in 2016 among children aged 1-19, the researchers reported. But sharp rises in such fatalities since then, especially in 2020 as the COVID-19 pandemic began, pushed the death toll above all other causes among Americans in this age group.
Guns accounted for more than 45,000 deaths among all age groups in 2020, also a record, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although gun deaths rose across nearly every racial and ethnic group, the increase was greatest among Black children. In this group, firearms accounted for more than 15 deaths per 100,000 children in 2020 – up from about 12 such deaths in 2019.
Homicide was the leading cause of gun deaths, followed by suicide and then accidental shootings, although the reason for some deaths could not be determined, according to the researchers.
The researchers reported their findings in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Gun deaths among children are preventable, both researchers and advocates said.
“There are ways to reduce injuries without banning guns,” said Jason Goldstick, PhD, a statistician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who led the study.
Dr. Goldstick pointed to significant investments in car vehicle safety as a model for policy makers to follow today for making gun injuries less frequent and deadly.
“More people drive today than in the 1970s, and motor vehicle–related injury rates are much lower,” Dr. Goldstick said. Innovations like seatbelt laws and changes in how cars are built have made them less deadly during a crash. Similar innovations are possible in how guns are managed.
More than 4.6 million U.S. children live in homes with unsecured firearms, according to Shannon Watts of the advocacy organization Moms Demand Action. “Securely storing firearms unloaded, locked and separate from ammunition is a simple yet lifesaving action that all gun owners should follow – and lawmakers should require,” she said in a statement to this news organization.
“The effects of gun violence ripple far beyond the child who was struck by a bullet,” said Sarah Burd-Sharps, the senior director of research for the advocacy organization Everytown for Gun Safety. Children might grieve their friends who are now lost or worry that they will be next.
The data in this study aren’t surprising, Ms. Burd-Sharps said, given the large number of homes in which guns are unsecured and the sharp rise in gun sales during the pandemic. On average one child per day in the United States accesses an unsecured gun that ends up injuring or killing themself or someone else.
“Gun owners want to be responsible. These deaths are really preventable,” Ms. Burd-Sharps said. In addition to securing ammunition and firearms separately, she recommended wider use of biometric guns that can only be used by someone with a specific fingerprint. If a young person got ahold of such a gun, even if it was loaded, they couldn’t use it.
The researchers reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2020, 4,357 children aged 1-19, or approximately 6 in 100,000, died from a gun-related injury, the researchers reported, modestly exceeding the number for auto accidents (3,913) and greatly exceeding deaths caused by suffocation (1,411) or drowning (966).
To observers of gun violence in this country, the grim statistical marker has been all but inevitable. Gunshots were the second-leading cause of death in 2016 among children aged 1-19, the researchers reported. But sharp rises in such fatalities since then, especially in 2020 as the COVID-19 pandemic began, pushed the death toll above all other causes among Americans in this age group.
Guns accounted for more than 45,000 deaths among all age groups in 2020, also a record, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although gun deaths rose across nearly every racial and ethnic group, the increase was greatest among Black children. In this group, firearms accounted for more than 15 deaths per 100,000 children in 2020 – up from about 12 such deaths in 2019.
Homicide was the leading cause of gun deaths, followed by suicide and then accidental shootings, although the reason for some deaths could not be determined, according to the researchers.
The researchers reported their findings in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Gun deaths among children are preventable, both researchers and advocates said.
“There are ways to reduce injuries without banning guns,” said Jason Goldstick, PhD, a statistician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who led the study.
Dr. Goldstick pointed to significant investments in car vehicle safety as a model for policy makers to follow today for making gun injuries less frequent and deadly.
“More people drive today than in the 1970s, and motor vehicle–related injury rates are much lower,” Dr. Goldstick said. Innovations like seatbelt laws and changes in how cars are built have made them less deadly during a crash. Similar innovations are possible in how guns are managed.
More than 4.6 million U.S. children live in homes with unsecured firearms, according to Shannon Watts of the advocacy organization Moms Demand Action. “Securely storing firearms unloaded, locked and separate from ammunition is a simple yet lifesaving action that all gun owners should follow – and lawmakers should require,” she said in a statement to this news organization.
“The effects of gun violence ripple far beyond the child who was struck by a bullet,” said Sarah Burd-Sharps, the senior director of research for the advocacy organization Everytown for Gun Safety. Children might grieve their friends who are now lost or worry that they will be next.
The data in this study aren’t surprising, Ms. Burd-Sharps said, given the large number of homes in which guns are unsecured and the sharp rise in gun sales during the pandemic. On average one child per day in the United States accesses an unsecured gun that ends up injuring or killing themself or someone else.
“Gun owners want to be responsible. These deaths are really preventable,” Ms. Burd-Sharps said. In addition to securing ammunition and firearms separately, she recommended wider use of biometric guns that can only be used by someone with a specific fingerprint. If a young person got ahold of such a gun, even if it was loaded, they couldn’t use it.
The researchers reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2020, 4,357 children aged 1-19, or approximately 6 in 100,000, died from a gun-related injury, the researchers reported, modestly exceeding the number for auto accidents (3,913) and greatly exceeding deaths caused by suffocation (1,411) or drowning (966).
To observers of gun violence in this country, the grim statistical marker has been all but inevitable. Gunshots were the second-leading cause of death in 2016 among children aged 1-19, the researchers reported. But sharp rises in such fatalities since then, especially in 2020 as the COVID-19 pandemic began, pushed the death toll above all other causes among Americans in this age group.
Guns accounted for more than 45,000 deaths among all age groups in 2020, also a record, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although gun deaths rose across nearly every racial and ethnic group, the increase was greatest among Black children. In this group, firearms accounted for more than 15 deaths per 100,000 children in 2020 – up from about 12 such deaths in 2019.
Homicide was the leading cause of gun deaths, followed by suicide and then accidental shootings, although the reason for some deaths could not be determined, according to the researchers.
The researchers reported their findings in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Gun deaths among children are preventable, both researchers and advocates said.
“There are ways to reduce injuries without banning guns,” said Jason Goldstick, PhD, a statistician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who led the study.
Dr. Goldstick pointed to significant investments in car vehicle safety as a model for policy makers to follow today for making gun injuries less frequent and deadly.
“More people drive today than in the 1970s, and motor vehicle–related injury rates are much lower,” Dr. Goldstick said. Innovations like seatbelt laws and changes in how cars are built have made them less deadly during a crash. Similar innovations are possible in how guns are managed.
More than 4.6 million U.S. children live in homes with unsecured firearms, according to Shannon Watts of the advocacy organization Moms Demand Action. “Securely storing firearms unloaded, locked and separate from ammunition is a simple yet lifesaving action that all gun owners should follow – and lawmakers should require,” she said in a statement to this news organization.
“The effects of gun violence ripple far beyond the child who was struck by a bullet,” said Sarah Burd-Sharps, the senior director of research for the advocacy organization Everytown for Gun Safety. Children might grieve their friends who are now lost or worry that they will be next.
The data in this study aren’t surprising, Ms. Burd-Sharps said, given the large number of homes in which guns are unsecured and the sharp rise in gun sales during the pandemic. On average one child per day in the United States accesses an unsecured gun that ends up injuring or killing themself or someone else.
“Gun owners want to be responsible. These deaths are really preventable,” Ms. Burd-Sharps said. In addition to securing ammunition and firearms separately, she recommended wider use of biometric guns that can only be used by someone with a specific fingerprint. If a young person got ahold of such a gun, even if it was loaded, they couldn’t use it.
The researchers reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Infectious disease pop quiz: Clinical challenge #24 for the ObGyn
What are the 2 most likely causes for persistent fever in a patient who is being treated with antibiotics for postcesarean endometritis?
Continue to the answer...
The 2 most likely causes of a poor response to treatment for postcesarean endometritis are a resistant microorganism and wound infection. Less common causes of persistent postoperative fever include septic pelvic vein thrombophlebitis, pelvic abscess, retained products of conception, reactivation of a connective tissue disorder, and drug fever.
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
What are the 2 most likely causes for persistent fever in a patient who is being treated with antibiotics for postcesarean endometritis?
Continue to the answer...
The 2 most likely causes of a poor response to treatment for postcesarean endometritis are a resistant microorganism and wound infection. Less common causes of persistent postoperative fever include septic pelvic vein thrombophlebitis, pelvic abscess, retained products of conception, reactivation of a connective tissue disorder, and drug fever.
What are the 2 most likely causes for persistent fever in a patient who is being treated with antibiotics for postcesarean endometritis?
Continue to the answer...
The 2 most likely causes of a poor response to treatment for postcesarean endometritis are a resistant microorganism and wound infection. Less common causes of persistent postoperative fever include septic pelvic vein thrombophlebitis, pelvic abscess, retained products of conception, reactivation of a connective tissue disorder, and drug fever.
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
- Duff P. Maternal and perinatal infections: bacterial. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021:1124-1146.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TJ, et al. Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:862-919.
TNF inhibitors prior to surgery safe in patients with IBD: Study
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can safely take tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) prior to abdominal surgery, a prospective, multicenter, observational study confirms.
The researchers found that exposure to TNFi in the 12 weeks prior to surgery was not associated with an increased risk of either overall infections or surgical site infections (SSI).
The findings should be “very reassuring” for clinicians, lead author Benjamin L. Cohen, MD, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, told this news organization. “In the past, when clinicians were unsure about the safety of using these drugs in the perioperative period, they may have delayed surgeries or stopped medications unnecessarily.”
“For me, the key take-home point of this study is that we need to plan the timing and management of medications around surgery based on factors other than the use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in most patients,” Dr. Cohen continued.
Ultimately, “we will help change practice in how we manage patients with IBD having surgery,” he said.
The research was published online in Gastroenterology.
No increased postop infection risk
The Prospective Cohort of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease Patients Undergoing Surgery to Identify Risk Factors for Post-Operative Infection I (PUCCINI) trial enrolled patients with IBD from 17 sites participating in the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Clinical Research Alliance between September 2014 and June 2017.
Patients had Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or indeterminate colitis, as determined by standard criteria, and planned to undergo intra-abdominal surgery or had undergone intra-abdominal surgery in the preceding 4 days.
Among the 947 patients enrolled, 47.8% were women. All were aged 18 years or older. The median disease duration was 10 years; 34.4% of patients had undergone prior bowel resection, and a further 17.5% had undergone other abdominal surgery.
Systemic corticosteroid use within 2 weeks of surgery was reported by 40.9% of patients, and 42.3% had used antibiotics.
TNFi exposure within the 12 weeks prior to surgery was reported by 40.3% of patients. Adalimumab and infliximab were the most commonly used drugs. Among those who had not used TNFi prior to surgery, 23.7% were TNFi-naive, and 36.0% had used them in the past.
The researchers report that there was no significant difference in the rate of postoperative infections between patients who reported using TNFi in the 12 weeks prior to surgery and those who did not (18.1% vs. 20.2%; P = .469). There was also no difference in SSI, as defined using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria, between the two groups (12.0% vs 12.6%; P = .889).
Multivariate analysis revealed that current TNFi exposure was not associated with any infection, at an odds ratio versus no exposure of 1.050 (P = .80), or with SSI, at an odds ratio of 1.249 (P = .34).
In contrast, preoperative corticosteroid exposure, prior bowel resection, and current smoking were associated with any infection and with SSI.
Approached for comment, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that the current findings are consistent with those of previous studies and that their relevance extends beyond abdominal surgery.
In the past, when surgeons were “confronted with a patient on a TNF blocker, even if it’s orthopedic or plastic surgery, they recommended against using a TNF blocker or operating at the end of the cycle when the drug levels are low,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Hanauer said such practice gets clinicians into a “bind because you’ve got a patient, for instance, who’s got a blockage with Crohn’s disease ... but the only way you could manage them when the TNFi was out of their system was with steroids, which is worse” in terms of postoperative infection risk, he explained.
Prospective studies important
The researchers note that up to 50% of patients with IBD are exposed to TNFi prior to their first surgery. They also note that there is concern that preoperative treatment with these and other immunosuppressive medications may increase the risk of postoperative infections.
However, the evidence is inconsistent, they write, so whether to continue or stop the drugs prior to surgery remains controversial.
“A lot of the initial studies in the perioperative population were single-center and retrospective for the most part,” Dr. Cohen said, adding that the studies used different modes of assessment and followed different time frames.
“So, there’s a lot of heterogeneity,” he said.
In addition, early studies of TNFi were often conducted with patients who were very ill and who had started receiving the drug right before surgery, and they sometimes had a complication Dr. Cohen said. “But you don’t know if that’s because of the drug itself or because of many other factors associated with them being very sick, such as being on steroids, being very malnourished, or having other complications of disease.”
It is difficult to control for such risk factors in retrospective analyses because the information is not always available from medical records, he said. “That’s why it’s so important to study clinical questions like this in a prospective manner.”
Dr. Cohen added that it is important that studies such as theirs continue to be undertaken as new drugs become available.
“We’re entering an era of rapidly expanding drug discovery, so we’re going to have new medications available for use in our patients with IBD,” he explained. “It’s important that we continue to build prospective cohorts to look at questions such as the safety of medications in the perioperative period, rather than solely relying on retrospective data.”
The study was funded by a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation Senior Research Award. Dr. Cohen reports relationships with AbbVie, Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Sublimity Therapeutics, Target RWE, Janssen, Ferring, AlphaSigma, and Takeda. Other authors report numerous financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer reports relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Pfizer, Amgen, Genentech, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can safely take tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) prior to abdominal surgery, a prospective, multicenter, observational study confirms.
The researchers found that exposure to TNFi in the 12 weeks prior to surgery was not associated with an increased risk of either overall infections or surgical site infections (SSI).
The findings should be “very reassuring” for clinicians, lead author Benjamin L. Cohen, MD, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, told this news organization. “In the past, when clinicians were unsure about the safety of using these drugs in the perioperative period, they may have delayed surgeries or stopped medications unnecessarily.”
“For me, the key take-home point of this study is that we need to plan the timing and management of medications around surgery based on factors other than the use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in most patients,” Dr. Cohen continued.
Ultimately, “we will help change practice in how we manage patients with IBD having surgery,” he said.
The research was published online in Gastroenterology.
No increased postop infection risk
The Prospective Cohort of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease Patients Undergoing Surgery to Identify Risk Factors for Post-Operative Infection I (PUCCINI) trial enrolled patients with IBD from 17 sites participating in the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Clinical Research Alliance between September 2014 and June 2017.
Patients had Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or indeterminate colitis, as determined by standard criteria, and planned to undergo intra-abdominal surgery or had undergone intra-abdominal surgery in the preceding 4 days.
Among the 947 patients enrolled, 47.8% were women. All were aged 18 years or older. The median disease duration was 10 years; 34.4% of patients had undergone prior bowel resection, and a further 17.5% had undergone other abdominal surgery.
Systemic corticosteroid use within 2 weeks of surgery was reported by 40.9% of patients, and 42.3% had used antibiotics.
TNFi exposure within the 12 weeks prior to surgery was reported by 40.3% of patients. Adalimumab and infliximab were the most commonly used drugs. Among those who had not used TNFi prior to surgery, 23.7% were TNFi-naive, and 36.0% had used them in the past.
The researchers report that there was no significant difference in the rate of postoperative infections between patients who reported using TNFi in the 12 weeks prior to surgery and those who did not (18.1% vs. 20.2%; P = .469). There was also no difference in SSI, as defined using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria, between the two groups (12.0% vs 12.6%; P = .889).
Multivariate analysis revealed that current TNFi exposure was not associated with any infection, at an odds ratio versus no exposure of 1.050 (P = .80), or with SSI, at an odds ratio of 1.249 (P = .34).
In contrast, preoperative corticosteroid exposure, prior bowel resection, and current smoking were associated with any infection and with SSI.
Approached for comment, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that the current findings are consistent with those of previous studies and that their relevance extends beyond abdominal surgery.
In the past, when surgeons were “confronted with a patient on a TNF blocker, even if it’s orthopedic or plastic surgery, they recommended against using a TNF blocker or operating at the end of the cycle when the drug levels are low,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Hanauer said such practice gets clinicians into a “bind because you’ve got a patient, for instance, who’s got a blockage with Crohn’s disease ... but the only way you could manage them when the TNFi was out of their system was with steroids, which is worse” in terms of postoperative infection risk, he explained.
Prospective studies important
The researchers note that up to 50% of patients with IBD are exposed to TNFi prior to their first surgery. They also note that there is concern that preoperative treatment with these and other immunosuppressive medications may increase the risk of postoperative infections.
However, the evidence is inconsistent, they write, so whether to continue or stop the drugs prior to surgery remains controversial.
“A lot of the initial studies in the perioperative population were single-center and retrospective for the most part,” Dr. Cohen said, adding that the studies used different modes of assessment and followed different time frames.
“So, there’s a lot of heterogeneity,” he said.
In addition, early studies of TNFi were often conducted with patients who were very ill and who had started receiving the drug right before surgery, and they sometimes had a complication Dr. Cohen said. “But you don’t know if that’s because of the drug itself or because of many other factors associated with them being very sick, such as being on steroids, being very malnourished, or having other complications of disease.”
It is difficult to control for such risk factors in retrospective analyses because the information is not always available from medical records, he said. “That’s why it’s so important to study clinical questions like this in a prospective manner.”
Dr. Cohen added that it is important that studies such as theirs continue to be undertaken as new drugs become available.
“We’re entering an era of rapidly expanding drug discovery, so we’re going to have new medications available for use in our patients with IBD,” he explained. “It’s important that we continue to build prospective cohorts to look at questions such as the safety of medications in the perioperative period, rather than solely relying on retrospective data.”
The study was funded by a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation Senior Research Award. Dr. Cohen reports relationships with AbbVie, Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Sublimity Therapeutics, Target RWE, Janssen, Ferring, AlphaSigma, and Takeda. Other authors report numerous financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer reports relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Pfizer, Amgen, Genentech, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can safely take tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) prior to abdominal surgery, a prospective, multicenter, observational study confirms.
The researchers found that exposure to TNFi in the 12 weeks prior to surgery was not associated with an increased risk of either overall infections or surgical site infections (SSI).
The findings should be “very reassuring” for clinicians, lead author Benjamin L. Cohen, MD, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, told this news organization. “In the past, when clinicians were unsure about the safety of using these drugs in the perioperative period, they may have delayed surgeries or stopped medications unnecessarily.”
“For me, the key take-home point of this study is that we need to plan the timing and management of medications around surgery based on factors other than the use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in most patients,” Dr. Cohen continued.
Ultimately, “we will help change practice in how we manage patients with IBD having surgery,” he said.
The research was published online in Gastroenterology.
No increased postop infection risk
The Prospective Cohort of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease Patients Undergoing Surgery to Identify Risk Factors for Post-Operative Infection I (PUCCINI) trial enrolled patients with IBD from 17 sites participating in the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Clinical Research Alliance between September 2014 and June 2017.
Patients had Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or indeterminate colitis, as determined by standard criteria, and planned to undergo intra-abdominal surgery or had undergone intra-abdominal surgery in the preceding 4 days.
Among the 947 patients enrolled, 47.8% were women. All were aged 18 years or older. The median disease duration was 10 years; 34.4% of patients had undergone prior bowel resection, and a further 17.5% had undergone other abdominal surgery.
Systemic corticosteroid use within 2 weeks of surgery was reported by 40.9% of patients, and 42.3% had used antibiotics.
TNFi exposure within the 12 weeks prior to surgery was reported by 40.3% of patients. Adalimumab and infliximab were the most commonly used drugs. Among those who had not used TNFi prior to surgery, 23.7% were TNFi-naive, and 36.0% had used them in the past.
The researchers report that there was no significant difference in the rate of postoperative infections between patients who reported using TNFi in the 12 weeks prior to surgery and those who did not (18.1% vs. 20.2%; P = .469). There was also no difference in SSI, as defined using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria, between the two groups (12.0% vs 12.6%; P = .889).
Multivariate analysis revealed that current TNFi exposure was not associated with any infection, at an odds ratio versus no exposure of 1.050 (P = .80), or with SSI, at an odds ratio of 1.249 (P = .34).
In contrast, preoperative corticosteroid exposure, prior bowel resection, and current smoking were associated with any infection and with SSI.
Approached for comment, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that the current findings are consistent with those of previous studies and that their relevance extends beyond abdominal surgery.
In the past, when surgeons were “confronted with a patient on a TNF blocker, even if it’s orthopedic or plastic surgery, they recommended against using a TNF blocker or operating at the end of the cycle when the drug levels are low,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Hanauer said such practice gets clinicians into a “bind because you’ve got a patient, for instance, who’s got a blockage with Crohn’s disease ... but the only way you could manage them when the TNFi was out of their system was with steroids, which is worse” in terms of postoperative infection risk, he explained.
Prospective studies important
The researchers note that up to 50% of patients with IBD are exposed to TNFi prior to their first surgery. They also note that there is concern that preoperative treatment with these and other immunosuppressive medications may increase the risk of postoperative infections.
However, the evidence is inconsistent, they write, so whether to continue or stop the drugs prior to surgery remains controversial.
“A lot of the initial studies in the perioperative population were single-center and retrospective for the most part,” Dr. Cohen said, adding that the studies used different modes of assessment and followed different time frames.
“So, there’s a lot of heterogeneity,” he said.
In addition, early studies of TNFi were often conducted with patients who were very ill and who had started receiving the drug right before surgery, and they sometimes had a complication Dr. Cohen said. “But you don’t know if that’s because of the drug itself or because of many other factors associated with them being very sick, such as being on steroids, being very malnourished, or having other complications of disease.”
It is difficult to control for such risk factors in retrospective analyses because the information is not always available from medical records, he said. “That’s why it’s so important to study clinical questions like this in a prospective manner.”
Dr. Cohen added that it is important that studies such as theirs continue to be undertaken as new drugs become available.
“We’re entering an era of rapidly expanding drug discovery, so we’re going to have new medications available for use in our patients with IBD,” he explained. “It’s important that we continue to build prospective cohorts to look at questions such as the safety of medications in the perioperative period, rather than solely relying on retrospective data.”
The study was funded by a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation Senior Research Award. Dr. Cohen reports relationships with AbbVie, Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Sublimity Therapeutics, Target RWE, Janssen, Ferring, AlphaSigma, and Takeda. Other authors report numerous financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer reports relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Pfizer, Amgen, Genentech, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Internet intervention improved insomnia in Black women
Data from previous studies suggest that women are up to 40% more likely to experience insomnia disorder compared with men, Eric S. Zhou, PhD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues wrote. The risk is even higher among Black women, but research on tailored treatments for this particular population has been limited.
In their study, published in JAMA Psychiatry, the researchers recruited women with elevated insomnia symptoms who were enrolled in the Black Women’s Health Study, an ongoing national, longitudinal research cohort in the United States. Participants were recruited between October 2019 and June 2020.The participants were randomized to an Internet-delivered behavior intervention (108 women), a stakeholder-informed Internet intervention tailored to Black women (110 women), or non-Internet patient education about sleep (115 women).
The Internet intervention, known as Sleep Healthy Using the Internet (SHUTi), was a 6-session program lasting 45-60 minutes per session and delivered over 6-9 weeks. The program included core elements of cognitive behavioral therapy and took into account information provided by patients about their baseline sleep function, treatment adherence, and sleep progress.
The tailored version of SHUTi for Black women (SHUTi-BWHS) was similar, but included Black actors for video vignettes and the inclusion of content about the cultural and social contexts in which insomnia often occurs for Black women, such while managing neighborhood noise and or living in crowded environments.
A third group received standard patient education material about sleep through a noninteractive website, and served as the control group.
The primary outcome of insomnia severity was measured using the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), a 0- to 28-point scale. Scores for the ISI are based on responses to seven questions, including some that ask participants to rate the severity of their insomnia symptoms.
Clinically significant improvement in insomnia was defined as a reduction in score of more than 7 points. Patients were assessed at baseline, at 9 weeks, and again at approximately 6 months.
Significantly greater reductions in insomnia severity seen in intervention groups vs. control group
Overall, women randomized to SHUTi or SHUTi-BWHS) reported a significantly greater reduction in insomnia symptoms from baseline to 6 months, compared with the control group (P < .001), with ISI score decreases of 10.0, 9.3, and 3.6, respectively. No statistically significant differences in ISI score changes appeared between the between the SHUTi-BWHS and SHUTi groups.
Also, significantly more women in the SHUTi-BWHS group than in the SHUTi group completed the intervention (78.2% vs. 64.8%).
Treatment response was similar between the SHUTI-BWHS and SHUTi groups; 47.3% and 46.3%, respectively, had a decrease in ISI score of more than 7 points. In addition, 37% of women in the SHUTi-BWHS and 38% of women in the SHUTi groups reached ISI scores of less than 8 points, defined as full resolution of insomnia, by the last follow-up visit.
Both the SHUTi and SHUTi-BWHS interventions had dramatic effects on insomnia, but the increased number of women who completed the intervention in the SHUTi-BWHS group supports the value of tailored intervention, the researchers noted. “Similar to prior SHUTi trials, there was a direct association between the participant’s level of intervention engagement and their improvement in sleep.”
The average age of the participants was 60 years, 62% were single, and 44% had a graduate degree or higher. Approximately 5% were being actively treated for sleep apnea.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively high socioeconomic status of the study participants, lack of data on medical mistrust, and inability to detect smaller differences between SHUTi and SHUTi-BWHS, the researchers noted.
Choose Internet-based CBT first for insomnia
“This was an excellent paper that sought to see the relative efficacy of standard version of Internet-delivered CBT-I [cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia] versus a culturally tailored version for Black women,” said Neil Skolnik, MD, professor of family and community medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, in an interview. “The trial confirmed that, compared with sleep education, which was used as the control, Internet-delivered CBT-I is effective in the treatment of insomnia.”
“These results demonstrate two important things,” said Dr. Skolnik. “The most important is that Internet-delivered CBT-I works, and since it is both safe and effective, should be the first-line therapy for patients who want treatment for insomnia.”
Secondly, “the fact that more people completed culturally tailored versions suggests that, when culturally tailored versions are available, their use is preferable, as it might facilitate a higher proportion of patients being successful in their insomnia treatment,” he added.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. The Black Women’s Health Study is supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Zhou disclosed support from both PCORI and the NCI during the study. Dr. Skolnik, who was not involved in the study, disclosed serving on the advisory board for Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. He is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News.
Data from previous studies suggest that women are up to 40% more likely to experience insomnia disorder compared with men, Eric S. Zhou, PhD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues wrote. The risk is even higher among Black women, but research on tailored treatments for this particular population has been limited.
In their study, published in JAMA Psychiatry, the researchers recruited women with elevated insomnia symptoms who were enrolled in the Black Women’s Health Study, an ongoing national, longitudinal research cohort in the United States. Participants were recruited between October 2019 and June 2020.The participants were randomized to an Internet-delivered behavior intervention (108 women), a stakeholder-informed Internet intervention tailored to Black women (110 women), or non-Internet patient education about sleep (115 women).
The Internet intervention, known as Sleep Healthy Using the Internet (SHUTi), was a 6-session program lasting 45-60 minutes per session and delivered over 6-9 weeks. The program included core elements of cognitive behavioral therapy and took into account information provided by patients about their baseline sleep function, treatment adherence, and sleep progress.
The tailored version of SHUTi for Black women (SHUTi-BWHS) was similar, but included Black actors for video vignettes and the inclusion of content about the cultural and social contexts in which insomnia often occurs for Black women, such while managing neighborhood noise and or living in crowded environments.
A third group received standard patient education material about sleep through a noninteractive website, and served as the control group.
The primary outcome of insomnia severity was measured using the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), a 0- to 28-point scale. Scores for the ISI are based on responses to seven questions, including some that ask participants to rate the severity of their insomnia symptoms.
Clinically significant improvement in insomnia was defined as a reduction in score of more than 7 points. Patients were assessed at baseline, at 9 weeks, and again at approximately 6 months.
Significantly greater reductions in insomnia severity seen in intervention groups vs. control group
Overall, women randomized to SHUTi or SHUTi-BWHS) reported a significantly greater reduction in insomnia symptoms from baseline to 6 months, compared with the control group (P < .001), with ISI score decreases of 10.0, 9.3, and 3.6, respectively. No statistically significant differences in ISI score changes appeared between the between the SHUTi-BWHS and SHUTi groups.
Also, significantly more women in the SHUTi-BWHS group than in the SHUTi group completed the intervention (78.2% vs. 64.8%).
Treatment response was similar between the SHUTI-BWHS and SHUTi groups; 47.3% and 46.3%, respectively, had a decrease in ISI score of more than 7 points. In addition, 37% of women in the SHUTi-BWHS and 38% of women in the SHUTi groups reached ISI scores of less than 8 points, defined as full resolution of insomnia, by the last follow-up visit.
Both the SHUTi and SHUTi-BWHS interventions had dramatic effects on insomnia, but the increased number of women who completed the intervention in the SHUTi-BWHS group supports the value of tailored intervention, the researchers noted. “Similar to prior SHUTi trials, there was a direct association between the participant’s level of intervention engagement and their improvement in sleep.”
The average age of the participants was 60 years, 62% were single, and 44% had a graduate degree or higher. Approximately 5% were being actively treated for sleep apnea.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively high socioeconomic status of the study participants, lack of data on medical mistrust, and inability to detect smaller differences between SHUTi and SHUTi-BWHS, the researchers noted.
Choose Internet-based CBT first for insomnia
“This was an excellent paper that sought to see the relative efficacy of standard version of Internet-delivered CBT-I [cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia] versus a culturally tailored version for Black women,” said Neil Skolnik, MD, professor of family and community medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, in an interview. “The trial confirmed that, compared with sleep education, which was used as the control, Internet-delivered CBT-I is effective in the treatment of insomnia.”
“These results demonstrate two important things,” said Dr. Skolnik. “The most important is that Internet-delivered CBT-I works, and since it is both safe and effective, should be the first-line therapy for patients who want treatment for insomnia.”
Secondly, “the fact that more people completed culturally tailored versions suggests that, when culturally tailored versions are available, their use is preferable, as it might facilitate a higher proportion of patients being successful in their insomnia treatment,” he added.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. The Black Women’s Health Study is supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Zhou disclosed support from both PCORI and the NCI during the study. Dr. Skolnik, who was not involved in the study, disclosed serving on the advisory board for Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. He is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News.
Data from previous studies suggest that women are up to 40% more likely to experience insomnia disorder compared with men, Eric S. Zhou, PhD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues wrote. The risk is even higher among Black women, but research on tailored treatments for this particular population has been limited.
In their study, published in JAMA Psychiatry, the researchers recruited women with elevated insomnia symptoms who were enrolled in the Black Women’s Health Study, an ongoing national, longitudinal research cohort in the United States. Participants were recruited between October 2019 and June 2020.The participants were randomized to an Internet-delivered behavior intervention (108 women), a stakeholder-informed Internet intervention tailored to Black women (110 women), or non-Internet patient education about sleep (115 women).
The Internet intervention, known as Sleep Healthy Using the Internet (SHUTi), was a 6-session program lasting 45-60 minutes per session and delivered over 6-9 weeks. The program included core elements of cognitive behavioral therapy and took into account information provided by patients about their baseline sleep function, treatment adherence, and sleep progress.
The tailored version of SHUTi for Black women (SHUTi-BWHS) was similar, but included Black actors for video vignettes and the inclusion of content about the cultural and social contexts in which insomnia often occurs for Black women, such while managing neighborhood noise and or living in crowded environments.
A third group received standard patient education material about sleep through a noninteractive website, and served as the control group.
The primary outcome of insomnia severity was measured using the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), a 0- to 28-point scale. Scores for the ISI are based on responses to seven questions, including some that ask participants to rate the severity of their insomnia symptoms.
Clinically significant improvement in insomnia was defined as a reduction in score of more than 7 points. Patients were assessed at baseline, at 9 weeks, and again at approximately 6 months.
Significantly greater reductions in insomnia severity seen in intervention groups vs. control group
Overall, women randomized to SHUTi or SHUTi-BWHS) reported a significantly greater reduction in insomnia symptoms from baseline to 6 months, compared with the control group (P < .001), with ISI score decreases of 10.0, 9.3, and 3.6, respectively. No statistically significant differences in ISI score changes appeared between the between the SHUTi-BWHS and SHUTi groups.
Also, significantly more women in the SHUTi-BWHS group than in the SHUTi group completed the intervention (78.2% vs. 64.8%).
Treatment response was similar between the SHUTI-BWHS and SHUTi groups; 47.3% and 46.3%, respectively, had a decrease in ISI score of more than 7 points. In addition, 37% of women in the SHUTi-BWHS and 38% of women in the SHUTi groups reached ISI scores of less than 8 points, defined as full resolution of insomnia, by the last follow-up visit.
Both the SHUTi and SHUTi-BWHS interventions had dramatic effects on insomnia, but the increased number of women who completed the intervention in the SHUTi-BWHS group supports the value of tailored intervention, the researchers noted. “Similar to prior SHUTi trials, there was a direct association between the participant’s level of intervention engagement and their improvement in sleep.”
The average age of the participants was 60 years, 62% were single, and 44% had a graduate degree or higher. Approximately 5% were being actively treated for sleep apnea.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively high socioeconomic status of the study participants, lack of data on medical mistrust, and inability to detect smaller differences between SHUTi and SHUTi-BWHS, the researchers noted.
Choose Internet-based CBT first for insomnia
“This was an excellent paper that sought to see the relative efficacy of standard version of Internet-delivered CBT-I [cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia] versus a culturally tailored version for Black women,” said Neil Skolnik, MD, professor of family and community medicine at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, in an interview. “The trial confirmed that, compared with sleep education, which was used as the control, Internet-delivered CBT-I is effective in the treatment of insomnia.”
“These results demonstrate two important things,” said Dr. Skolnik. “The most important is that Internet-delivered CBT-I works, and since it is both safe and effective, should be the first-line therapy for patients who want treatment for insomnia.”
Secondly, “the fact that more people completed culturally tailored versions suggests that, when culturally tailored versions are available, their use is preferable, as it might facilitate a higher proportion of patients being successful in their insomnia treatment,” he added.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. The Black Women’s Health Study is supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Zhou disclosed support from both PCORI and the NCI during the study. Dr. Skolnik, who was not involved in the study, disclosed serving on the advisory board for Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. He is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Physician assistant pleads not guilty to murdering fellow PA
Jacob L. Klein, 40, of Wirtz, Va., was charged with second-degree murder at the Town of New Scotland Court in New York following the discovery the previous week of 35-year-old Philip Rabadi, another PA. Mr. Rabadi was discovered on the garage floor of his New Scotland home, the Albany County Sheriff’s Office said in a press release.
Mr. Rabadi’s arms were bound and he suffered multiple stab wounds and body mutilation, authorities reported. Mr. Klein allegedly had been stalking Mr. Rabadi and his wife, Elana Z. Radin, for 3 days prior to the homicide after driving the 600 miles from Virginia to New Scotland. Ms. Radin had once been Mr. Klein’s girlfriend, according to a report in the Times Union in Albany, N.Y.
Mr. Klein was being held without bail in the Albany County Correctional Facility and a preliminary hearing was set for April 25. Mr. Klein had been extradited from Virginia April 20, the press release stated. He had been apprehended there April 15 as a fugitive on an arrest warrant, according to authorities.
Ms. Radin and Mr. Rabadi were married last September and worked as surgical PAs together at St. Peter’s Hospital in Albany, and “sincerely loved working with one another,” according to Mr. Rabadi’s obituary. They missed each other if they weren’t working together, the obituary stated.
“I know an endless amount of love and strength is being sent my way,” Ms. Radin said in a Facebook post. “These words do not come close to completely encompassing Phil, but they are mine and I’d like to share them.” The obituary she created, reposted on Facebook, was accompanied by photos of the happy couple at their recent wedding.
“Philip was a shining bright light in this world. He was kind, endlessly charismatic, funny, intelligent, patient, and an immediate friend to all. His smile was breathtaking, and his laugh was infectious. Philip was simply a magnetic person. To have known him was a genuine gift in this lifetime.”
The Albany County Sheriff’s Office received a call to check the welfare of Mr. Rabadi after he failed to show up for work last week, according to the press release. Deputies and family members found Mr. Rabadi dead, the release stated.
Ms. Radin reportedly called 911 and arrived at the home with her father-in-law about the same time as the deputies, according to People magazine.
A St. Peter’s Health Partners spokesperson, in an email to this news organization, shared the health system’s reaction to the incident: “The news of Philip Rabadi’s passing leaves us with a deep sadness and heavy hearts...In a memo to colleagues, our senior leaders offered their condolences to Philip’s family and loved ones, mourning the tragic passing of our colleague and friend.”
The response continued, “As a healthcare organization, it is our mission to care for those in need. Right now, many of our own are struggling. Grief counseling services are being made available to colleagues should they need additional support.”
A scholarship was established for PA students in Mr. Rabadi’s name at his alma mater, Albany Medical College.
Meanwhile a search of Mr. Klein’s professional history shows he held a PA license in Syracuse, N.Y., until 2018 and his current license in Virginia was renewed in February.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jacob L. Klein, 40, of Wirtz, Va., was charged with second-degree murder at the Town of New Scotland Court in New York following the discovery the previous week of 35-year-old Philip Rabadi, another PA. Mr. Rabadi was discovered on the garage floor of his New Scotland home, the Albany County Sheriff’s Office said in a press release.
Mr. Rabadi’s arms were bound and he suffered multiple stab wounds and body mutilation, authorities reported. Mr. Klein allegedly had been stalking Mr. Rabadi and his wife, Elana Z. Radin, for 3 days prior to the homicide after driving the 600 miles from Virginia to New Scotland. Ms. Radin had once been Mr. Klein’s girlfriend, according to a report in the Times Union in Albany, N.Y.
Mr. Klein was being held without bail in the Albany County Correctional Facility and a preliminary hearing was set for April 25. Mr. Klein had been extradited from Virginia April 20, the press release stated. He had been apprehended there April 15 as a fugitive on an arrest warrant, according to authorities.
Ms. Radin and Mr. Rabadi were married last September and worked as surgical PAs together at St. Peter’s Hospital in Albany, and “sincerely loved working with one another,” according to Mr. Rabadi’s obituary. They missed each other if they weren’t working together, the obituary stated.
“I know an endless amount of love and strength is being sent my way,” Ms. Radin said in a Facebook post. “These words do not come close to completely encompassing Phil, but they are mine and I’d like to share them.” The obituary she created, reposted on Facebook, was accompanied by photos of the happy couple at their recent wedding.
“Philip was a shining bright light in this world. He was kind, endlessly charismatic, funny, intelligent, patient, and an immediate friend to all. His smile was breathtaking, and his laugh was infectious. Philip was simply a magnetic person. To have known him was a genuine gift in this lifetime.”
The Albany County Sheriff’s Office received a call to check the welfare of Mr. Rabadi after he failed to show up for work last week, according to the press release. Deputies and family members found Mr. Rabadi dead, the release stated.
Ms. Radin reportedly called 911 and arrived at the home with her father-in-law about the same time as the deputies, according to People magazine.
A St. Peter’s Health Partners spokesperson, in an email to this news organization, shared the health system’s reaction to the incident: “The news of Philip Rabadi’s passing leaves us with a deep sadness and heavy hearts...In a memo to colleagues, our senior leaders offered their condolences to Philip’s family and loved ones, mourning the tragic passing of our colleague and friend.”
The response continued, “As a healthcare organization, it is our mission to care for those in need. Right now, many of our own are struggling. Grief counseling services are being made available to colleagues should they need additional support.”
A scholarship was established for PA students in Mr. Rabadi’s name at his alma mater, Albany Medical College.
Meanwhile a search of Mr. Klein’s professional history shows he held a PA license in Syracuse, N.Y., until 2018 and his current license in Virginia was renewed in February.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jacob L. Klein, 40, of Wirtz, Va., was charged with second-degree murder at the Town of New Scotland Court in New York following the discovery the previous week of 35-year-old Philip Rabadi, another PA. Mr. Rabadi was discovered on the garage floor of his New Scotland home, the Albany County Sheriff’s Office said in a press release.
Mr. Rabadi’s arms were bound and he suffered multiple stab wounds and body mutilation, authorities reported. Mr. Klein allegedly had been stalking Mr. Rabadi and his wife, Elana Z. Radin, for 3 days prior to the homicide after driving the 600 miles from Virginia to New Scotland. Ms. Radin had once been Mr. Klein’s girlfriend, according to a report in the Times Union in Albany, N.Y.
Mr. Klein was being held without bail in the Albany County Correctional Facility and a preliminary hearing was set for April 25. Mr. Klein had been extradited from Virginia April 20, the press release stated. He had been apprehended there April 15 as a fugitive on an arrest warrant, according to authorities.
Ms. Radin and Mr. Rabadi were married last September and worked as surgical PAs together at St. Peter’s Hospital in Albany, and “sincerely loved working with one another,” according to Mr. Rabadi’s obituary. They missed each other if they weren’t working together, the obituary stated.
“I know an endless amount of love and strength is being sent my way,” Ms. Radin said in a Facebook post. “These words do not come close to completely encompassing Phil, but they are mine and I’d like to share them.” The obituary she created, reposted on Facebook, was accompanied by photos of the happy couple at their recent wedding.
“Philip was a shining bright light in this world. He was kind, endlessly charismatic, funny, intelligent, patient, and an immediate friend to all. His smile was breathtaking, and his laugh was infectious. Philip was simply a magnetic person. To have known him was a genuine gift in this lifetime.”
The Albany County Sheriff’s Office received a call to check the welfare of Mr. Rabadi after he failed to show up for work last week, according to the press release. Deputies and family members found Mr. Rabadi dead, the release stated.
Ms. Radin reportedly called 911 and arrived at the home with her father-in-law about the same time as the deputies, according to People magazine.
A St. Peter’s Health Partners spokesperson, in an email to this news organization, shared the health system’s reaction to the incident: “The news of Philip Rabadi’s passing leaves us with a deep sadness and heavy hearts...In a memo to colleagues, our senior leaders offered their condolences to Philip’s family and loved ones, mourning the tragic passing of our colleague and friend.”
The response continued, “As a healthcare organization, it is our mission to care for those in need. Right now, many of our own are struggling. Grief counseling services are being made available to colleagues should they need additional support.”
A scholarship was established for PA students in Mr. Rabadi’s name at his alma mater, Albany Medical College.
Meanwhile a search of Mr. Klein’s professional history shows he held a PA license in Syracuse, N.Y., until 2018 and his current license in Virginia was renewed in February.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
You want me to tan my WHAT, Tucker Carlson?
Did you hear the one about the TV host suggesting men get their testicles tanned?
The nutty idea dropped into the lexicon last weekend thanks to Fox News commentator Tucker Carlson.
He aired a promo for a show about an alleged decline of manhood. It featured shirtless, muscled men doing macho things like shooting automatic rifles and wrestling, and a naked man rather triumphantly exposing his crotch to a red-light device made to look like some sort of charging station.
The guest also said he’s heard of something he called “bromeopathy” for people who are suspicious of “mainstream” information. Yes, it’s a combination of the slang term “bro” and the practice of homeopathic medicine.
So, men of America, do you really need to start zapping your privates like Mr. Carlson seems to suggest?
Doctors say the answer is simple: Absolutely not.
‘No legitimate evidence’
“There is no legitimate evidence that this type of treatment is effective in improving testosterone levels,” says Petar Bajic MD, a urologist at the Cleveland Clinic who specializes in men’s health and testosterone.
The red light wouldn’t even be able to penetrate the body deep enough to reach the, uhm, targets, he said, citing “no scientific basis” for Mr. Tucker’s claims that we should be “open minded” about this kind of thing.
“It’s not only a waste of time but also a waste of money,” Dr. Bajic says. “There is a large amount of research and high-quality studies” into treating low testosterone, which is produced primarily in the testicles. “We have very effective and proven treatments available, and this is simply not one of them.”
Testosterone is an important hormone that contributes to masculine physical characteristics, “such as muscle mass and strength, and growth of facial and body hair,” according to the Mayo Clinic. It’s important for bone density, sperm production, erectile function, and more.
As men age, testosterone levels often drop, lowering energy and sexual function while causing weight gain and muscle loss.
If men experience some of these symptoms or become curious about their testosterone levels, they shouldn’t self-diagnose or rely on two guys promoting a TV show, Dr. Bajic says.
Instead, they should see their primary care doctor for a simple blood test, he says. Patient and doctor can decide on treatments, which commonly include:
- Topical gels
- Arm patches
- Injections into the muscle of the leg or the fatty tissue of the belly
- Pellets placed under the skin
Diet, exercise, sleep, and other factors play a role.
‘So much misinformation’
The men’s health consumer market is bloated with products promising to raise testosterone levels and help men boost their bedroom performance, among other claims.
But they’re usually based on nothing more than marketing, and erectile disfunction is more commonly caused by reduced blood flow than a lack of testosterone, Dr. Bajic says.
“It all comes down to looking at all of these as a consumer and as a patient ... with a critical eye. There’s always a new ‘cure all’ for whatever your ailment is,” he says.
Testosterone levels change throughout the day. It’s thought to be produced during REM sleep, which can be diminished by alcohol use and other factors.
“All these things are related,” Dr. Bajic said, so there’s no reason to flash a light where it’s usually not seen – especially since neither the safety nor efficacy of testicle tanning has been established.
Oregon urologist Ashley Winter, MD, got into the Twitter fray about Carlson’s comments.
“Also, by definition you CANNOT have data on testicle tanning because you cannot TAN an internal organ,” she said on the social media network. “Tanning your scrotal sack and calling it ‘testicle tanning,’ is like tanning your abdominal skin and calling it ‘liver tanning.’”
What advocates say
What do proponents of red light therapy say? A Men’s Health article claims red light “works to stimulate ATP production, increase energy available to the cell and in particular, increase the activity of the Leydig cells in your testes, which are the cells responsible for testosterone production.”
The article also helpfully points out: “It’s important to note that there are currently no light therapy devices on the market cleared by FDA for the enhanced production of testosterone LED-based therapy.” And many lamps sold for red light therapy can get so hot that they damage the skin.
The author ordered a Joovv device, which Mr. Carlson’s “fitness professional” guest name-dropped. They range from $600 to almost $10,000. He liked the way it felt and said it seemed to improve his sexual performance.
Still a hard sell
Atlanta dermatologist Emily de Golian, MD, says tanning genitalia can be dangerous to the skin.
“There is no such thing as a safe tan, all tanning is indicative of sun damage in the skin and is the body’s effort to shield the DNA from further damage, and tanning increases the risk of skin cancer,” she says. “Scrotal skin is particularly delicate and sensitive to sun exposure, and the risk of sunburn, which further increases the risk of skin cancer, is high.”
Mat Rezaei, founder and CEO of UPGUYS, which provides erectile disfunction medicine, says, “UV light has no negative or positive response to balancing testosterone deficiency.”
Even frequent Fox guest Kid Rock wasn’t buying into the idea.
“Dude, stop! Testicle tanning? Come on,” Mr. Rock said to Mr. Carlson. “I mean, I haven’t heard anything that good in a long time.”
“Open your mind,” said Mr. Carlson as he laughed along with the musician.
Kid Rock replied, “I’m starting a punk rock band and it’s called Testicle Tanning. That’s the end of it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Did you hear the one about the TV host suggesting men get their testicles tanned?
The nutty idea dropped into the lexicon last weekend thanks to Fox News commentator Tucker Carlson.
He aired a promo for a show about an alleged decline of manhood. It featured shirtless, muscled men doing macho things like shooting automatic rifles and wrestling, and a naked man rather triumphantly exposing his crotch to a red-light device made to look like some sort of charging station.
The guest also said he’s heard of something he called “bromeopathy” for people who are suspicious of “mainstream” information. Yes, it’s a combination of the slang term “bro” and the practice of homeopathic medicine.
So, men of America, do you really need to start zapping your privates like Mr. Carlson seems to suggest?
Doctors say the answer is simple: Absolutely not.
‘No legitimate evidence’
“There is no legitimate evidence that this type of treatment is effective in improving testosterone levels,” says Petar Bajic MD, a urologist at the Cleveland Clinic who specializes in men’s health and testosterone.
The red light wouldn’t even be able to penetrate the body deep enough to reach the, uhm, targets, he said, citing “no scientific basis” for Mr. Tucker’s claims that we should be “open minded” about this kind of thing.
“It’s not only a waste of time but also a waste of money,” Dr. Bajic says. “There is a large amount of research and high-quality studies” into treating low testosterone, which is produced primarily in the testicles. “We have very effective and proven treatments available, and this is simply not one of them.”
Testosterone is an important hormone that contributes to masculine physical characteristics, “such as muscle mass and strength, and growth of facial and body hair,” according to the Mayo Clinic. It’s important for bone density, sperm production, erectile function, and more.
As men age, testosterone levels often drop, lowering energy and sexual function while causing weight gain and muscle loss.
If men experience some of these symptoms or become curious about their testosterone levels, they shouldn’t self-diagnose or rely on two guys promoting a TV show, Dr. Bajic says.
Instead, they should see their primary care doctor for a simple blood test, he says. Patient and doctor can decide on treatments, which commonly include:
- Topical gels
- Arm patches
- Injections into the muscle of the leg or the fatty tissue of the belly
- Pellets placed under the skin
Diet, exercise, sleep, and other factors play a role.
‘So much misinformation’
The men’s health consumer market is bloated with products promising to raise testosterone levels and help men boost their bedroom performance, among other claims.
But they’re usually based on nothing more than marketing, and erectile disfunction is more commonly caused by reduced blood flow than a lack of testosterone, Dr. Bajic says.
“It all comes down to looking at all of these as a consumer and as a patient ... with a critical eye. There’s always a new ‘cure all’ for whatever your ailment is,” he says.
Testosterone levels change throughout the day. It’s thought to be produced during REM sleep, which can be diminished by alcohol use and other factors.
“All these things are related,” Dr. Bajic said, so there’s no reason to flash a light where it’s usually not seen – especially since neither the safety nor efficacy of testicle tanning has been established.
Oregon urologist Ashley Winter, MD, got into the Twitter fray about Carlson’s comments.
“Also, by definition you CANNOT have data on testicle tanning because you cannot TAN an internal organ,” she said on the social media network. “Tanning your scrotal sack and calling it ‘testicle tanning,’ is like tanning your abdominal skin and calling it ‘liver tanning.’”
What advocates say
What do proponents of red light therapy say? A Men’s Health article claims red light “works to stimulate ATP production, increase energy available to the cell and in particular, increase the activity of the Leydig cells in your testes, which are the cells responsible for testosterone production.”
The article also helpfully points out: “It’s important to note that there are currently no light therapy devices on the market cleared by FDA for the enhanced production of testosterone LED-based therapy.” And many lamps sold for red light therapy can get so hot that they damage the skin.
The author ordered a Joovv device, which Mr. Carlson’s “fitness professional” guest name-dropped. They range from $600 to almost $10,000. He liked the way it felt and said it seemed to improve his sexual performance.
Still a hard sell
Atlanta dermatologist Emily de Golian, MD, says tanning genitalia can be dangerous to the skin.
“There is no such thing as a safe tan, all tanning is indicative of sun damage in the skin and is the body’s effort to shield the DNA from further damage, and tanning increases the risk of skin cancer,” she says. “Scrotal skin is particularly delicate and sensitive to sun exposure, and the risk of sunburn, which further increases the risk of skin cancer, is high.”
Mat Rezaei, founder and CEO of UPGUYS, which provides erectile disfunction medicine, says, “UV light has no negative or positive response to balancing testosterone deficiency.”
Even frequent Fox guest Kid Rock wasn’t buying into the idea.
“Dude, stop! Testicle tanning? Come on,” Mr. Rock said to Mr. Carlson. “I mean, I haven’t heard anything that good in a long time.”
“Open your mind,” said Mr. Carlson as he laughed along with the musician.
Kid Rock replied, “I’m starting a punk rock band and it’s called Testicle Tanning. That’s the end of it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Did you hear the one about the TV host suggesting men get their testicles tanned?
The nutty idea dropped into the lexicon last weekend thanks to Fox News commentator Tucker Carlson.
He aired a promo for a show about an alleged decline of manhood. It featured shirtless, muscled men doing macho things like shooting automatic rifles and wrestling, and a naked man rather triumphantly exposing his crotch to a red-light device made to look like some sort of charging station.
The guest also said he’s heard of something he called “bromeopathy” for people who are suspicious of “mainstream” information. Yes, it’s a combination of the slang term “bro” and the practice of homeopathic medicine.
So, men of America, do you really need to start zapping your privates like Mr. Carlson seems to suggest?
Doctors say the answer is simple: Absolutely not.
‘No legitimate evidence’
“There is no legitimate evidence that this type of treatment is effective in improving testosterone levels,” says Petar Bajic MD, a urologist at the Cleveland Clinic who specializes in men’s health and testosterone.
The red light wouldn’t even be able to penetrate the body deep enough to reach the, uhm, targets, he said, citing “no scientific basis” for Mr. Tucker’s claims that we should be “open minded” about this kind of thing.
“It’s not only a waste of time but also a waste of money,” Dr. Bajic says. “There is a large amount of research and high-quality studies” into treating low testosterone, which is produced primarily in the testicles. “We have very effective and proven treatments available, and this is simply not one of them.”
Testosterone is an important hormone that contributes to masculine physical characteristics, “such as muscle mass and strength, and growth of facial and body hair,” according to the Mayo Clinic. It’s important for bone density, sperm production, erectile function, and more.
As men age, testosterone levels often drop, lowering energy and sexual function while causing weight gain and muscle loss.
If men experience some of these symptoms or become curious about their testosterone levels, they shouldn’t self-diagnose or rely on two guys promoting a TV show, Dr. Bajic says.
Instead, they should see their primary care doctor for a simple blood test, he says. Patient and doctor can decide on treatments, which commonly include:
- Topical gels
- Arm patches
- Injections into the muscle of the leg or the fatty tissue of the belly
- Pellets placed under the skin
Diet, exercise, sleep, and other factors play a role.
‘So much misinformation’
The men’s health consumer market is bloated with products promising to raise testosterone levels and help men boost their bedroom performance, among other claims.
But they’re usually based on nothing more than marketing, and erectile disfunction is more commonly caused by reduced blood flow than a lack of testosterone, Dr. Bajic says.
“It all comes down to looking at all of these as a consumer and as a patient ... with a critical eye. There’s always a new ‘cure all’ for whatever your ailment is,” he says.
Testosterone levels change throughout the day. It’s thought to be produced during REM sleep, which can be diminished by alcohol use and other factors.
“All these things are related,” Dr. Bajic said, so there’s no reason to flash a light where it’s usually not seen – especially since neither the safety nor efficacy of testicle tanning has been established.
Oregon urologist Ashley Winter, MD, got into the Twitter fray about Carlson’s comments.
“Also, by definition you CANNOT have data on testicle tanning because you cannot TAN an internal organ,” she said on the social media network. “Tanning your scrotal sack and calling it ‘testicle tanning,’ is like tanning your abdominal skin and calling it ‘liver tanning.’”
What advocates say
What do proponents of red light therapy say? A Men’s Health article claims red light “works to stimulate ATP production, increase energy available to the cell and in particular, increase the activity of the Leydig cells in your testes, which are the cells responsible for testosterone production.”
The article also helpfully points out: “It’s important to note that there are currently no light therapy devices on the market cleared by FDA for the enhanced production of testosterone LED-based therapy.” And many lamps sold for red light therapy can get so hot that they damage the skin.
The author ordered a Joovv device, which Mr. Carlson’s “fitness professional” guest name-dropped. They range from $600 to almost $10,000. He liked the way it felt and said it seemed to improve his sexual performance.
Still a hard sell
Atlanta dermatologist Emily de Golian, MD, says tanning genitalia can be dangerous to the skin.
“There is no such thing as a safe tan, all tanning is indicative of sun damage in the skin and is the body’s effort to shield the DNA from further damage, and tanning increases the risk of skin cancer,” she says. “Scrotal skin is particularly delicate and sensitive to sun exposure, and the risk of sunburn, which further increases the risk of skin cancer, is high.”
Mat Rezaei, founder and CEO of UPGUYS, which provides erectile disfunction medicine, says, “UV light has no negative or positive response to balancing testosterone deficiency.”
Even frequent Fox guest Kid Rock wasn’t buying into the idea.
“Dude, stop! Testicle tanning? Come on,” Mr. Rock said to Mr. Carlson. “I mean, I haven’t heard anything that good in a long time.”
“Open your mind,” said Mr. Carlson as he laughed along with the musician.
Kid Rock replied, “I’m starting a punk rock band and it’s called Testicle Tanning. That’s the end of it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.







