User login
High-efficacy therapies for MS: When and how to use them
Despite better long-term disease outcomes, there are concerns over long-term safety, and some physicians and patients remain wary of these medications.
High-efficacy therapies were the subject of a session at the annual meeting of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ECTRIMS). Key topics included patient selection, timing of escalation to high-efficacy therapies, and initial use of high-efficacy therapies. The session produced a compelling message, according to moderator Patricia Coyle, MD. “I think [the speakers provided] accumulating data that this is a smart thing to do: Use high-efficacy therapies early to get the maximum bang for the buck,” Dr. Coyle said in an interview. She is professor of neurology and director of the MS Comprehensive Care Center at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Consider baseline characteristics
In the first talk, Xavier Montalban, MD, PhD, noted that a statement from the ECTRIMS/EAN (European Academy of Neurology) guideline update in 2021 said that a high-efficacy disease-modifying therapy (DMT) should be considered early in the disease course. A key question is whether any baseline characteristics can be used to select patients, and studies have shown worse prognosis with older age, male sex, low levels of vitamin D, and smoking status, among various other factors.
He presented subgroup analyses from trials of fingolimod and ozanimod, which showed that the drugs did not work as well in patients with poor prognostic factors such as an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of 4 or above and age over 40 years. Lower doses also tend to have less efficacy in males. “If you have [a patient with] bad baseline prognostic factors, you need high-efficacy medication at the right dose, because a lower dose will not work well. It is the same phenomenon for age,” Dr. Montalban said in his talk. On the other hand, he showed the results of a study of ofatumumab and ocrelizumab, both of which showed high efficacy even in patients with poor prognostic factors.
Among patients with secondary progressive MS, clinical or MRI evidence of inflammatory activity is the only poor prognostic factor that appears to be a good predictor of treatment response.
Dr. Montalban also addressed the timing of intervention with DMTs. A study from his group prospectively followed 1,015 patients treated with DMTs. “Interestingly, what we observed is that patients who were treated with DMTs just after the first attack did better than those who were treated after the second attack, and you have to take into consideration that we treat those patients after the first attack, those who had the worst prognostic factors, so treatment was very effective in that sense,” said Dr. Montalban, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Centre of Catalonia at Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona.
Switching DMTs
In the second presentation, Dalia Rotstein, MD, discussed how to incorporate prognostic factors when switching a patient to high-efficacy therapies as a result of new disease activity while on another therapy.
Patients with favorable prognostic factors at baseline may be started out on immunomodulatory therapy. “Essentially, we want to match the intensity of the therapy to the intensity of the disease of the patient in front of us,” Dr. Rotstein said in her talk. Nevertheless, the course of MS is unpredictable, and the first year or two of immunomodulatory therapy can give physicians clues about the longer-term course of the disease. “We need to observe closely for disease activity in the first year, but even up to 2 years on therapy to determine a need for early escalation,” said Dr. Rotstein, assistant professor of medicine at University of Toronto.
For switching to high-efficacy therapies, any relapse, disability progression, or an EDSS change of 1 point or more could be a consideration. MRI indicators are more controversial, but one to three new T2 lesions also could prompt a switch.
Serum neural filament light chain (sNFL) is a useful biomarker for monitoring disease activity as it correlates well with new disease activity within the next year. It can be monitored every 3-4 months and adjusted for clinical factors and monitored for changing levels. A concerning finding can be followed up with an MRI or in-person visit.
When switching to a high-efficacy therapy, it’s important to administer any vaccines well in advance to ensure a good immune response.
When it comes to a washout period, physicians need to consider both the risk of immunosuppression and breakthrough disease activity. “But in general, we’ve observed that we can minimize the duration of the washout when stopping initial immunomodulator therapy to reduce the risk of breakthrough disease activity. We need to pay particular attention to the risk of rebound activity with longer washouts after stopping sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators because the rebound activity can be devastating,” said Dr. Rotstein.
A study of timing of relapses after fingolimod washout, carried out by Dr. Rotstein’s group, found a stark signal. “We observed that when the washout after fingolimod discontinuation was 30 days or more, there is a very high risk of early relapse,” she said.
The case for induction therapy
In the third talk, Gavin Giovannoni, MBBCh, PhD, discussed “flipping the pyramid” – that is, starting patients off immediately with high-efficacy therapies rather than waiting until they progress on other therapies. He likened such a decision to a gambler, because MS patients on less-effective therapy can suffer irreversible, long-term physical consequences, as well as social consequences such as unemployment due to cognitive effects.
“We always tend to put up a graph about the risks and benefits of a specific treatment, and we forget about the risks of untreated or undertreated MS. Keep that in mind when making decisions about high-efficacy therapies,” said Dr. Giovannoni, professor of neurology at Queen Mary University of London.
About 80% of patients on tier 1, or low-efficacy therapies, will have breakthrough activity on MRI within 4 years. Moving up a tier gets to about a 60% rate of breakthrough activity. High-efficacy therapies attain an efficacy of about 80% at 6 months. “If you have MS, you’ve got to realize that if you had to roll the dice, which tier would you want to be in? By putting all of them [on high-efficacy therapies], you’re going to get the majority responding and a few of them will break through,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He presented some real-world evidence to back up the argument: A study comparing outcomes in Sweden and Denmark, which have similar demographics. In Denmark, 7.6% of patients with MS received high-efficacy therapies initially, while in Sweden the proportion was 34.5%. Patients with MS treated in Sweden had a 29% lower probability of progressing to disability (P = .004) and there were 22% fewer discontinuations of DMTs (P < .001). Since that study, the proportion of patients receiving high-efficacy therapies to begin with is closer to 70%. “This is compelling evidence that you want to be on a [high-efficacy therapy] early. If I had MS, I would want to live in Sweden,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
Historical treatments focused on reducing relapses, and more recently on eliminating evidence of inflammatory disease. He said that physicians are prioritizing brain volume loss to improve long-term outcomes in MS, and some are studying long-term disability. “We know that brain volume loss in MS is a prognostic sign both at baseline and at follow-up. It predicts poor outcome, poor cognition and employment, poor quality of life, et cetera,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He cited data from studies of alemtuzumab that showed a significant reduction in brain volume loss. “The rate is about 0.2% per annum, which is kind of getting into the normal range for age-matched controls. Those people who were started off on interferons in the study lost a lot of brain volume in those first 2 years, and that’s irreversible,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He pointed out that studies of hematopoietic stem cell therapy showed similar brain-volume outcomes. “So flipping the pyramid with the two most highly effective therapies almost normalizes brain volume loss in people with MS,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
There is also evidence in other autoimmune diseases that early use of high-efficacy therapies improves outcomes. More aggressive therapy in rheumatoid arthritis has reduced joint replacements by 90%.
“I think you really, really need to give your patients the opportunity of flipping the pyramid. You shouldn’t decide that for them,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
Dr. Coyle has consulted for nearly all pharmaceutical companies developing drugs in the MS space. Dr. Montalban has financial relationships with Biogen Idec, Merck Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Roche, Celgene, Actelion, Mylan, BMS, and Sandoz. Dr. Rotstein has financial ties with Roche Canada, Alexion, Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi Aventis. Dr. Giovannoni has financial ties with AbbVie, Aslan, Atara Bio, Biogen, BMS-Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, GW Pharma, Janssen/J&J, Japanese Tobacco, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, LifNano, Merck & Co., Merck KGaA/EMD Serono, Moderna, Novartis, Sanofi, Roche/Genentech, and Teva.
Despite better long-term disease outcomes, there are concerns over long-term safety, and some physicians and patients remain wary of these medications.
High-efficacy therapies were the subject of a session at the annual meeting of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ECTRIMS). Key topics included patient selection, timing of escalation to high-efficacy therapies, and initial use of high-efficacy therapies. The session produced a compelling message, according to moderator Patricia Coyle, MD. “I think [the speakers provided] accumulating data that this is a smart thing to do: Use high-efficacy therapies early to get the maximum bang for the buck,” Dr. Coyle said in an interview. She is professor of neurology and director of the MS Comprehensive Care Center at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Consider baseline characteristics
In the first talk, Xavier Montalban, MD, PhD, noted that a statement from the ECTRIMS/EAN (European Academy of Neurology) guideline update in 2021 said that a high-efficacy disease-modifying therapy (DMT) should be considered early in the disease course. A key question is whether any baseline characteristics can be used to select patients, and studies have shown worse prognosis with older age, male sex, low levels of vitamin D, and smoking status, among various other factors.
He presented subgroup analyses from trials of fingolimod and ozanimod, which showed that the drugs did not work as well in patients with poor prognostic factors such as an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of 4 or above and age over 40 years. Lower doses also tend to have less efficacy in males. “If you have [a patient with] bad baseline prognostic factors, you need high-efficacy medication at the right dose, because a lower dose will not work well. It is the same phenomenon for age,” Dr. Montalban said in his talk. On the other hand, he showed the results of a study of ofatumumab and ocrelizumab, both of which showed high efficacy even in patients with poor prognostic factors.
Among patients with secondary progressive MS, clinical or MRI evidence of inflammatory activity is the only poor prognostic factor that appears to be a good predictor of treatment response.
Dr. Montalban also addressed the timing of intervention with DMTs. A study from his group prospectively followed 1,015 patients treated with DMTs. “Interestingly, what we observed is that patients who were treated with DMTs just after the first attack did better than those who were treated after the second attack, and you have to take into consideration that we treat those patients after the first attack, those who had the worst prognostic factors, so treatment was very effective in that sense,” said Dr. Montalban, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Centre of Catalonia at Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona.
Switching DMTs
In the second presentation, Dalia Rotstein, MD, discussed how to incorporate prognostic factors when switching a patient to high-efficacy therapies as a result of new disease activity while on another therapy.
Patients with favorable prognostic factors at baseline may be started out on immunomodulatory therapy. “Essentially, we want to match the intensity of the therapy to the intensity of the disease of the patient in front of us,” Dr. Rotstein said in her talk. Nevertheless, the course of MS is unpredictable, and the first year or two of immunomodulatory therapy can give physicians clues about the longer-term course of the disease. “We need to observe closely for disease activity in the first year, but even up to 2 years on therapy to determine a need for early escalation,” said Dr. Rotstein, assistant professor of medicine at University of Toronto.
For switching to high-efficacy therapies, any relapse, disability progression, or an EDSS change of 1 point or more could be a consideration. MRI indicators are more controversial, but one to three new T2 lesions also could prompt a switch.
Serum neural filament light chain (sNFL) is a useful biomarker for monitoring disease activity as it correlates well with new disease activity within the next year. It can be monitored every 3-4 months and adjusted for clinical factors and monitored for changing levels. A concerning finding can be followed up with an MRI or in-person visit.
When switching to a high-efficacy therapy, it’s important to administer any vaccines well in advance to ensure a good immune response.
When it comes to a washout period, physicians need to consider both the risk of immunosuppression and breakthrough disease activity. “But in general, we’ve observed that we can minimize the duration of the washout when stopping initial immunomodulator therapy to reduce the risk of breakthrough disease activity. We need to pay particular attention to the risk of rebound activity with longer washouts after stopping sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators because the rebound activity can be devastating,” said Dr. Rotstein.
A study of timing of relapses after fingolimod washout, carried out by Dr. Rotstein’s group, found a stark signal. “We observed that when the washout after fingolimod discontinuation was 30 days or more, there is a very high risk of early relapse,” she said.
The case for induction therapy
In the third talk, Gavin Giovannoni, MBBCh, PhD, discussed “flipping the pyramid” – that is, starting patients off immediately with high-efficacy therapies rather than waiting until they progress on other therapies. He likened such a decision to a gambler, because MS patients on less-effective therapy can suffer irreversible, long-term physical consequences, as well as social consequences such as unemployment due to cognitive effects.
“We always tend to put up a graph about the risks and benefits of a specific treatment, and we forget about the risks of untreated or undertreated MS. Keep that in mind when making decisions about high-efficacy therapies,” said Dr. Giovannoni, professor of neurology at Queen Mary University of London.
About 80% of patients on tier 1, or low-efficacy therapies, will have breakthrough activity on MRI within 4 years. Moving up a tier gets to about a 60% rate of breakthrough activity. High-efficacy therapies attain an efficacy of about 80% at 6 months. “If you have MS, you’ve got to realize that if you had to roll the dice, which tier would you want to be in? By putting all of them [on high-efficacy therapies], you’re going to get the majority responding and a few of them will break through,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He presented some real-world evidence to back up the argument: A study comparing outcomes in Sweden and Denmark, which have similar demographics. In Denmark, 7.6% of patients with MS received high-efficacy therapies initially, while in Sweden the proportion was 34.5%. Patients with MS treated in Sweden had a 29% lower probability of progressing to disability (P = .004) and there were 22% fewer discontinuations of DMTs (P < .001). Since that study, the proportion of patients receiving high-efficacy therapies to begin with is closer to 70%. “This is compelling evidence that you want to be on a [high-efficacy therapy] early. If I had MS, I would want to live in Sweden,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
Historical treatments focused on reducing relapses, and more recently on eliminating evidence of inflammatory disease. He said that physicians are prioritizing brain volume loss to improve long-term outcomes in MS, and some are studying long-term disability. “We know that brain volume loss in MS is a prognostic sign both at baseline and at follow-up. It predicts poor outcome, poor cognition and employment, poor quality of life, et cetera,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He cited data from studies of alemtuzumab that showed a significant reduction in brain volume loss. “The rate is about 0.2% per annum, which is kind of getting into the normal range for age-matched controls. Those people who were started off on interferons in the study lost a lot of brain volume in those first 2 years, and that’s irreversible,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He pointed out that studies of hematopoietic stem cell therapy showed similar brain-volume outcomes. “So flipping the pyramid with the two most highly effective therapies almost normalizes brain volume loss in people with MS,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
There is also evidence in other autoimmune diseases that early use of high-efficacy therapies improves outcomes. More aggressive therapy in rheumatoid arthritis has reduced joint replacements by 90%.
“I think you really, really need to give your patients the opportunity of flipping the pyramid. You shouldn’t decide that for them,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
Dr. Coyle has consulted for nearly all pharmaceutical companies developing drugs in the MS space. Dr. Montalban has financial relationships with Biogen Idec, Merck Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Roche, Celgene, Actelion, Mylan, BMS, and Sandoz. Dr. Rotstein has financial ties with Roche Canada, Alexion, Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi Aventis. Dr. Giovannoni has financial ties with AbbVie, Aslan, Atara Bio, Biogen, BMS-Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, GW Pharma, Janssen/J&J, Japanese Tobacco, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, LifNano, Merck & Co., Merck KGaA/EMD Serono, Moderna, Novartis, Sanofi, Roche/Genentech, and Teva.
Despite better long-term disease outcomes, there are concerns over long-term safety, and some physicians and patients remain wary of these medications.
High-efficacy therapies were the subject of a session at the annual meeting of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ECTRIMS). Key topics included patient selection, timing of escalation to high-efficacy therapies, and initial use of high-efficacy therapies. The session produced a compelling message, according to moderator Patricia Coyle, MD. “I think [the speakers provided] accumulating data that this is a smart thing to do: Use high-efficacy therapies early to get the maximum bang for the buck,” Dr. Coyle said in an interview. She is professor of neurology and director of the MS Comprehensive Care Center at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
Consider baseline characteristics
In the first talk, Xavier Montalban, MD, PhD, noted that a statement from the ECTRIMS/EAN (European Academy of Neurology) guideline update in 2021 said that a high-efficacy disease-modifying therapy (DMT) should be considered early in the disease course. A key question is whether any baseline characteristics can be used to select patients, and studies have shown worse prognosis with older age, male sex, low levels of vitamin D, and smoking status, among various other factors.
He presented subgroup analyses from trials of fingolimod and ozanimod, which showed that the drugs did not work as well in patients with poor prognostic factors such as an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of 4 or above and age over 40 years. Lower doses also tend to have less efficacy in males. “If you have [a patient with] bad baseline prognostic factors, you need high-efficacy medication at the right dose, because a lower dose will not work well. It is the same phenomenon for age,” Dr. Montalban said in his talk. On the other hand, he showed the results of a study of ofatumumab and ocrelizumab, both of which showed high efficacy even in patients with poor prognostic factors.
Among patients with secondary progressive MS, clinical or MRI evidence of inflammatory activity is the only poor prognostic factor that appears to be a good predictor of treatment response.
Dr. Montalban also addressed the timing of intervention with DMTs. A study from his group prospectively followed 1,015 patients treated with DMTs. “Interestingly, what we observed is that patients who were treated with DMTs just after the first attack did better than those who were treated after the second attack, and you have to take into consideration that we treat those patients after the first attack, those who had the worst prognostic factors, so treatment was very effective in that sense,” said Dr. Montalban, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Centre of Catalonia at Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona.
Switching DMTs
In the second presentation, Dalia Rotstein, MD, discussed how to incorporate prognostic factors when switching a patient to high-efficacy therapies as a result of new disease activity while on another therapy.
Patients with favorable prognostic factors at baseline may be started out on immunomodulatory therapy. “Essentially, we want to match the intensity of the therapy to the intensity of the disease of the patient in front of us,” Dr. Rotstein said in her talk. Nevertheless, the course of MS is unpredictable, and the first year or two of immunomodulatory therapy can give physicians clues about the longer-term course of the disease. “We need to observe closely for disease activity in the first year, but even up to 2 years on therapy to determine a need for early escalation,” said Dr. Rotstein, assistant professor of medicine at University of Toronto.
For switching to high-efficacy therapies, any relapse, disability progression, or an EDSS change of 1 point or more could be a consideration. MRI indicators are more controversial, but one to three new T2 lesions also could prompt a switch.
Serum neural filament light chain (sNFL) is a useful biomarker for monitoring disease activity as it correlates well with new disease activity within the next year. It can be monitored every 3-4 months and adjusted for clinical factors and monitored for changing levels. A concerning finding can be followed up with an MRI or in-person visit.
When switching to a high-efficacy therapy, it’s important to administer any vaccines well in advance to ensure a good immune response.
When it comes to a washout period, physicians need to consider both the risk of immunosuppression and breakthrough disease activity. “But in general, we’ve observed that we can minimize the duration of the washout when stopping initial immunomodulator therapy to reduce the risk of breakthrough disease activity. We need to pay particular attention to the risk of rebound activity with longer washouts after stopping sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators because the rebound activity can be devastating,” said Dr. Rotstein.
A study of timing of relapses after fingolimod washout, carried out by Dr. Rotstein’s group, found a stark signal. “We observed that when the washout after fingolimod discontinuation was 30 days or more, there is a very high risk of early relapse,” she said.
The case for induction therapy
In the third talk, Gavin Giovannoni, MBBCh, PhD, discussed “flipping the pyramid” – that is, starting patients off immediately with high-efficacy therapies rather than waiting until they progress on other therapies. He likened such a decision to a gambler, because MS patients on less-effective therapy can suffer irreversible, long-term physical consequences, as well as social consequences such as unemployment due to cognitive effects.
“We always tend to put up a graph about the risks and benefits of a specific treatment, and we forget about the risks of untreated or undertreated MS. Keep that in mind when making decisions about high-efficacy therapies,” said Dr. Giovannoni, professor of neurology at Queen Mary University of London.
About 80% of patients on tier 1, or low-efficacy therapies, will have breakthrough activity on MRI within 4 years. Moving up a tier gets to about a 60% rate of breakthrough activity. High-efficacy therapies attain an efficacy of about 80% at 6 months. “If you have MS, you’ve got to realize that if you had to roll the dice, which tier would you want to be in? By putting all of them [on high-efficacy therapies], you’re going to get the majority responding and a few of them will break through,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He presented some real-world evidence to back up the argument: A study comparing outcomes in Sweden and Denmark, which have similar demographics. In Denmark, 7.6% of patients with MS received high-efficacy therapies initially, while in Sweden the proportion was 34.5%. Patients with MS treated in Sweden had a 29% lower probability of progressing to disability (P = .004) and there were 22% fewer discontinuations of DMTs (P < .001). Since that study, the proportion of patients receiving high-efficacy therapies to begin with is closer to 70%. “This is compelling evidence that you want to be on a [high-efficacy therapy] early. If I had MS, I would want to live in Sweden,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
Historical treatments focused on reducing relapses, and more recently on eliminating evidence of inflammatory disease. He said that physicians are prioritizing brain volume loss to improve long-term outcomes in MS, and some are studying long-term disability. “We know that brain volume loss in MS is a prognostic sign both at baseline and at follow-up. It predicts poor outcome, poor cognition and employment, poor quality of life, et cetera,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He cited data from studies of alemtuzumab that showed a significant reduction in brain volume loss. “The rate is about 0.2% per annum, which is kind of getting into the normal range for age-matched controls. Those people who were started off on interferons in the study lost a lot of brain volume in those first 2 years, and that’s irreversible,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
He pointed out that studies of hematopoietic stem cell therapy showed similar brain-volume outcomes. “So flipping the pyramid with the two most highly effective therapies almost normalizes brain volume loss in people with MS,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
There is also evidence in other autoimmune diseases that early use of high-efficacy therapies improves outcomes. More aggressive therapy in rheumatoid arthritis has reduced joint replacements by 90%.
“I think you really, really need to give your patients the opportunity of flipping the pyramid. You shouldn’t decide that for them,” said Dr. Giovannoni.
Dr. Coyle has consulted for nearly all pharmaceutical companies developing drugs in the MS space. Dr. Montalban has financial relationships with Biogen Idec, Merck Serono, Genentech, Genzyme, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Roche, Celgene, Actelion, Mylan, BMS, and Sandoz. Dr. Rotstein has financial ties with Roche Canada, Alexion, Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi Aventis. Dr. Giovannoni has financial ties with AbbVie, Aslan, Atara Bio, Biogen, BMS-Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, GW Pharma, Janssen/J&J, Japanese Tobacco, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, LifNano, Merck & Co., Merck KGaA/EMD Serono, Moderna, Novartis, Sanofi, Roche/Genentech, and Teva.
FROM ECTRIMS 2022
In childhood sickle cell disease stroke prevention is key
CINCINNATI – Sickle cell disease is well known for its associated anemia, but patients experience a range of other complications as well. These include vision and kidney problems, delayed growth, susceptibility to infection, and pain.
Another issue, not always as well recognized, is a considerably heightened risk for childhood stroke. “, and there’s also an elevated risk of five times the general population in adults with sickle cell disease,” said Lori Jordan, MD, PhD, in an interview.
At the 2022 annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society, Dr. Jordan spoke about stroke as a complication of sickle cell disease, and the role that neurologists can play in preventing primary or secondary strokes. “At least in children, studies have shown that if we screen and identify patients who are at highest risk of stroke, there are primary prevention therapies – usually implemented by hematologists, but that neurologists often are involved with – both monitoring for cognitive effects of silent cerebral infarct and also with treating patients who unfortunately still have an acute stroke,” said Dr. Jordan, who is an associate professor of pediatrics, neurology, and radiology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She also is director of the pediatric stroke program at Vanderbilt.
Time is of the essence
“In general, stroke in children is rare, but it’s more common in sickle cell disease, so it’s really important for providers to know that stroke risk is higher in those patients, particularly in those children, and then identify it and treat it earlier. Time is of the essence, and if we can give them the same therapeutics that we give the general stroke population, then time really becomes a factor, so it’s important that people know that it’s an issue for this population,” said Eboni Lance, MD, PhD, who coordinated the session where Dr. Jordan spoke.
Sickle cell disease is caused by a double mutation in the gene encoding the hemoglobin gene, producing the altered sickle hemoglobin (hemoglobin S). The change causes the hemoglobin proteins to tend to stick to one another, which can lead red blood cells to adopt a sickle-like shape. The sickle-shaped blood cells in turn have a tendency to aggregate and can block blood flow or lead to endothelial injury. Symptoms of stroke in children can include hemiparesis, aphasia, and seizure, but they can also be silent.
If no preventive is employed, one in nine with sickle cell disease will experience a stroke by the age of 19. Cerebrovascular symptoms are the most frequent debilitating complication of the condition. Nearly 40% of patients with sickle cell disease will have a silent cerebral infarct by age 18, as will 50% by age 30. Silent strokes have been associated with worse educational attainment and a greater need for educational special services.
Factors contributing to stroke in children with sickle cell disease include anemia and a low blood oxygen count, reduced oxygen affinity of hemoglobin variant, and cerebral vasculopathy. An estimated 10%-15% of young adults with sickle cell disease have severe intracranial stenosis.
Primary and secondary stroke prevention strategies
The dire consequences of stroke in this patient population underline the importance of primary stroke prevention, which requires the use of transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound. It has been validated as a tool to screen for initial stroke risk in children with no history of stroke. High velocity measured on TCD indicates a narrowed blood vessel or elevated blood that is compensating for anemia. It adds up to a “struggling brain,” said Dr. Jordan, during her talk. If the TCD ultrasound velocity is greater than 200 cm/sec (or 170 cm/sec, depending on nonimaging versus imaging TCD), the TWiTCH trial showed that seven monthly transfusions is the number needed to treat to prevent one stroke. After 1 year, patients can be switched from transfusions to hydroxyurea if the patient has no significant intracranial stenosis. Hydroxyurea boosts both fetal and total hemoglobin, and also counters inflammation.
Following an acute stroke or transient ischemic attack, patients should receive a transfusion within 2 hours of presenting in the health care setting. American Society of Hematology guidelines recommend exchange transfusion rather than a simple transfusion. A simple transfusion can be initiated if an exchange transfusion is not available within 2 hours and hemoglobin values are less than 8.5 g/dL, to be followed by performance of exchange transfusion when available.
For chronic secondary stroke prevention, transfusions should be performed approximately monthly with the goal of maintaining hemoglobin above 9 g/dL at all times, as well as suppressing hemoglobin S levels to 30% or less of total hemoglobin.
Sudden, severe headache is a potential harbinger of complications like aneurysm, which occurs 10-fold more often among patients with sickle cell disease than the general population. It could also indicate increased intracranial pressure or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Treatment of acute headache in sickle cell disease should avoid use of triptans, since vasoconstriction can counter the increased cerebral blood flow that compensates for anemia. Gabapentin and amitriptyline are good treatment choices.
New-onset seizures are a potential sign of stroke or posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy (PRES) in patients with sickle cell disease. Urgent MRI should be considered for all new-onset seizures. If blood pressure is high, PRES may be present. Seizures may also be an indicator of a previous brain injury.
Dr. Jordan has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Lance has served on an advisory board for Novartis.
CINCINNATI – Sickle cell disease is well known for its associated anemia, but patients experience a range of other complications as well. These include vision and kidney problems, delayed growth, susceptibility to infection, and pain.
Another issue, not always as well recognized, is a considerably heightened risk for childhood stroke. “, and there’s also an elevated risk of five times the general population in adults with sickle cell disease,” said Lori Jordan, MD, PhD, in an interview.
At the 2022 annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society, Dr. Jordan spoke about stroke as a complication of sickle cell disease, and the role that neurologists can play in preventing primary or secondary strokes. “At least in children, studies have shown that if we screen and identify patients who are at highest risk of stroke, there are primary prevention therapies – usually implemented by hematologists, but that neurologists often are involved with – both monitoring for cognitive effects of silent cerebral infarct and also with treating patients who unfortunately still have an acute stroke,” said Dr. Jordan, who is an associate professor of pediatrics, neurology, and radiology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She also is director of the pediatric stroke program at Vanderbilt.
Time is of the essence
“In general, stroke in children is rare, but it’s more common in sickle cell disease, so it’s really important for providers to know that stroke risk is higher in those patients, particularly in those children, and then identify it and treat it earlier. Time is of the essence, and if we can give them the same therapeutics that we give the general stroke population, then time really becomes a factor, so it’s important that people know that it’s an issue for this population,” said Eboni Lance, MD, PhD, who coordinated the session where Dr. Jordan spoke.
Sickle cell disease is caused by a double mutation in the gene encoding the hemoglobin gene, producing the altered sickle hemoglobin (hemoglobin S). The change causes the hemoglobin proteins to tend to stick to one another, which can lead red blood cells to adopt a sickle-like shape. The sickle-shaped blood cells in turn have a tendency to aggregate and can block blood flow or lead to endothelial injury. Symptoms of stroke in children can include hemiparesis, aphasia, and seizure, but they can also be silent.
If no preventive is employed, one in nine with sickle cell disease will experience a stroke by the age of 19. Cerebrovascular symptoms are the most frequent debilitating complication of the condition. Nearly 40% of patients with sickle cell disease will have a silent cerebral infarct by age 18, as will 50% by age 30. Silent strokes have been associated with worse educational attainment and a greater need for educational special services.
Factors contributing to stroke in children with sickle cell disease include anemia and a low blood oxygen count, reduced oxygen affinity of hemoglobin variant, and cerebral vasculopathy. An estimated 10%-15% of young adults with sickle cell disease have severe intracranial stenosis.
Primary and secondary stroke prevention strategies
The dire consequences of stroke in this patient population underline the importance of primary stroke prevention, which requires the use of transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound. It has been validated as a tool to screen for initial stroke risk in children with no history of stroke. High velocity measured on TCD indicates a narrowed blood vessel or elevated blood that is compensating for anemia. It adds up to a “struggling brain,” said Dr. Jordan, during her talk. If the TCD ultrasound velocity is greater than 200 cm/sec (or 170 cm/sec, depending on nonimaging versus imaging TCD), the TWiTCH trial showed that seven monthly transfusions is the number needed to treat to prevent one stroke. After 1 year, patients can be switched from transfusions to hydroxyurea if the patient has no significant intracranial stenosis. Hydroxyurea boosts both fetal and total hemoglobin, and also counters inflammation.
Following an acute stroke or transient ischemic attack, patients should receive a transfusion within 2 hours of presenting in the health care setting. American Society of Hematology guidelines recommend exchange transfusion rather than a simple transfusion. A simple transfusion can be initiated if an exchange transfusion is not available within 2 hours and hemoglobin values are less than 8.5 g/dL, to be followed by performance of exchange transfusion when available.
For chronic secondary stroke prevention, transfusions should be performed approximately monthly with the goal of maintaining hemoglobin above 9 g/dL at all times, as well as suppressing hemoglobin S levels to 30% or less of total hemoglobin.
Sudden, severe headache is a potential harbinger of complications like aneurysm, which occurs 10-fold more often among patients with sickle cell disease than the general population. It could also indicate increased intracranial pressure or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Treatment of acute headache in sickle cell disease should avoid use of triptans, since vasoconstriction can counter the increased cerebral blood flow that compensates for anemia. Gabapentin and amitriptyline are good treatment choices.
New-onset seizures are a potential sign of stroke or posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy (PRES) in patients with sickle cell disease. Urgent MRI should be considered for all new-onset seizures. If blood pressure is high, PRES may be present. Seizures may also be an indicator of a previous brain injury.
Dr. Jordan has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Lance has served on an advisory board for Novartis.
CINCINNATI – Sickle cell disease is well known for its associated anemia, but patients experience a range of other complications as well. These include vision and kidney problems, delayed growth, susceptibility to infection, and pain.
Another issue, not always as well recognized, is a considerably heightened risk for childhood stroke. “, and there’s also an elevated risk of five times the general population in adults with sickle cell disease,” said Lori Jordan, MD, PhD, in an interview.
At the 2022 annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society, Dr. Jordan spoke about stroke as a complication of sickle cell disease, and the role that neurologists can play in preventing primary or secondary strokes. “At least in children, studies have shown that if we screen and identify patients who are at highest risk of stroke, there are primary prevention therapies – usually implemented by hematologists, but that neurologists often are involved with – both monitoring for cognitive effects of silent cerebral infarct and also with treating patients who unfortunately still have an acute stroke,” said Dr. Jordan, who is an associate professor of pediatrics, neurology, and radiology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She also is director of the pediatric stroke program at Vanderbilt.
Time is of the essence
“In general, stroke in children is rare, but it’s more common in sickle cell disease, so it’s really important for providers to know that stroke risk is higher in those patients, particularly in those children, and then identify it and treat it earlier. Time is of the essence, and if we can give them the same therapeutics that we give the general stroke population, then time really becomes a factor, so it’s important that people know that it’s an issue for this population,” said Eboni Lance, MD, PhD, who coordinated the session where Dr. Jordan spoke.
Sickle cell disease is caused by a double mutation in the gene encoding the hemoglobin gene, producing the altered sickle hemoglobin (hemoglobin S). The change causes the hemoglobin proteins to tend to stick to one another, which can lead red blood cells to adopt a sickle-like shape. The sickle-shaped blood cells in turn have a tendency to aggregate and can block blood flow or lead to endothelial injury. Symptoms of stroke in children can include hemiparesis, aphasia, and seizure, but they can also be silent.
If no preventive is employed, one in nine with sickle cell disease will experience a stroke by the age of 19. Cerebrovascular symptoms are the most frequent debilitating complication of the condition. Nearly 40% of patients with sickle cell disease will have a silent cerebral infarct by age 18, as will 50% by age 30. Silent strokes have been associated with worse educational attainment and a greater need for educational special services.
Factors contributing to stroke in children with sickle cell disease include anemia and a low blood oxygen count, reduced oxygen affinity of hemoglobin variant, and cerebral vasculopathy. An estimated 10%-15% of young adults with sickle cell disease have severe intracranial stenosis.
Primary and secondary stroke prevention strategies
The dire consequences of stroke in this patient population underline the importance of primary stroke prevention, which requires the use of transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound. It has been validated as a tool to screen for initial stroke risk in children with no history of stroke. High velocity measured on TCD indicates a narrowed blood vessel or elevated blood that is compensating for anemia. It adds up to a “struggling brain,” said Dr. Jordan, during her talk. If the TCD ultrasound velocity is greater than 200 cm/sec (or 170 cm/sec, depending on nonimaging versus imaging TCD), the TWiTCH trial showed that seven monthly transfusions is the number needed to treat to prevent one stroke. After 1 year, patients can be switched from transfusions to hydroxyurea if the patient has no significant intracranial stenosis. Hydroxyurea boosts both fetal and total hemoglobin, and also counters inflammation.
Following an acute stroke or transient ischemic attack, patients should receive a transfusion within 2 hours of presenting in the health care setting. American Society of Hematology guidelines recommend exchange transfusion rather than a simple transfusion. A simple transfusion can be initiated if an exchange transfusion is not available within 2 hours and hemoglobin values are less than 8.5 g/dL, to be followed by performance of exchange transfusion when available.
For chronic secondary stroke prevention, transfusions should be performed approximately monthly with the goal of maintaining hemoglobin above 9 g/dL at all times, as well as suppressing hemoglobin S levels to 30% or less of total hemoglobin.
Sudden, severe headache is a potential harbinger of complications like aneurysm, which occurs 10-fold more often among patients with sickle cell disease than the general population. It could also indicate increased intracranial pressure or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Treatment of acute headache in sickle cell disease should avoid use of triptans, since vasoconstriction can counter the increased cerebral blood flow that compensates for anemia. Gabapentin and amitriptyline are good treatment choices.
New-onset seizures are a potential sign of stroke or posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy (PRES) in patients with sickle cell disease. Urgent MRI should be considered for all new-onset seizures. If blood pressure is high, PRES may be present. Seizures may also be an indicator of a previous brain injury.
Dr. Jordan has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Lance has served on an advisory board for Novartis.
FROM CNS 2022
Two biologics equally effective for extraintestinal manifestations of IBD
Vedolizumab (Entyvio) and ustekinumab (Stelara) appear to be equally effective for extraintestinal manifestation (EIM) of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to results of a retrospective study published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Between 25% and 40% of patients with IBD experience EIM, which reduces quality of life, according to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. EIM commonly involves the joints, skin, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. Anemia is another extraintestinal complication.
Until now, it’s been unclear whether vedolizumab and ustekinumab are equally effective for treating EIM.
Vedolizumab specifically targets the gastrointestinal tract, a potential disadvantage in reducing EIM, while ustekinumab is thought to have a systemic effect, a potential treatment advantage, Moran Livne-Margolin, MD, and colleagues, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, point out.
To investigate, they included 111 adults with IBD who were treated at the medical center between 2015 and 2021 – 53 with vedolizumab and 58 with ustekinumab. Before starting treatment, all of them had active EIM, most commonly arthralgia (84%).
After 6 weeks of treatment, 66% of patients in both groups had a clinical response to their intestinal disease.
After 14 and 26 weeks of treatment, clinical response rates were 59% and 50%, respectively, with vedolizumab, and 48% and 41%, respectively, with ustekinumab.
Over 52 weeks, both biologics were equally effective against the intestinal disease, with clinical response rates of 42% with vedolizumab and 44% with ustekinumab.
A similar pattern emerged when looking at improvement in EIM.
At week 6, 44% of patients taking vedolizumab and 35% taking ustekinumab had improvement in EIM, with no significant difference between the two biologics (P = .4).
At week 14, rates of improvement in EIM were 43% for vedolizumab and 33% for ustekinumab (P = .39); at 26 weeks, rates were 39% and 33%, respectively (P = .6); and at 52 weeks, rates were 34% and 36% (P = .9).
Researchers also found a significant positive correlation between improvement of the intestinal disease and clinical improvement of EIM at each time point.
Ustekinumab is usually preferred in patients with EIM, Dr. Livne-Margolin and colleagues note. But their findings “may raise some questions whether ustekinumab is, in fact, a better choice in those specific patients.”
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and small cohort size.
Additionally, vedolizumab is given intravenously in the clinic and mandates patients to have a routine checkup every 1-2 months, whereas ustekinumab can be given at home. As a result, data were missing on some of the patients treated with ustekinumab during the follow-up.
Another limitation is that most of the patients had articular complaints with a small presentation of other EIM.
Also, most of the patients had Crohn’s disease, with only one patient with ulcerative colitis in the ustekinumab group, compared with 12 in the vedolizumab group.
Finally, patients treated with ustekinumab had more experience with anti-TNF treatment, compared with the vedolizumab group, which might have influenced the results with a negative bias toward ustekinumab.
The study had no specific funding. Three authors have disclosed relationships with Janssen, which makes ustekinumab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vedolizumab (Entyvio) and ustekinumab (Stelara) appear to be equally effective for extraintestinal manifestation (EIM) of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to results of a retrospective study published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Between 25% and 40% of patients with IBD experience EIM, which reduces quality of life, according to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. EIM commonly involves the joints, skin, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. Anemia is another extraintestinal complication.
Until now, it’s been unclear whether vedolizumab and ustekinumab are equally effective for treating EIM.
Vedolizumab specifically targets the gastrointestinal tract, a potential disadvantage in reducing EIM, while ustekinumab is thought to have a systemic effect, a potential treatment advantage, Moran Livne-Margolin, MD, and colleagues, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, point out.
To investigate, they included 111 adults with IBD who were treated at the medical center between 2015 and 2021 – 53 with vedolizumab and 58 with ustekinumab. Before starting treatment, all of them had active EIM, most commonly arthralgia (84%).
After 6 weeks of treatment, 66% of patients in both groups had a clinical response to their intestinal disease.
After 14 and 26 weeks of treatment, clinical response rates were 59% and 50%, respectively, with vedolizumab, and 48% and 41%, respectively, with ustekinumab.
Over 52 weeks, both biologics were equally effective against the intestinal disease, with clinical response rates of 42% with vedolizumab and 44% with ustekinumab.
A similar pattern emerged when looking at improvement in EIM.
At week 6, 44% of patients taking vedolizumab and 35% taking ustekinumab had improvement in EIM, with no significant difference between the two biologics (P = .4).
At week 14, rates of improvement in EIM were 43% for vedolizumab and 33% for ustekinumab (P = .39); at 26 weeks, rates were 39% and 33%, respectively (P = .6); and at 52 weeks, rates were 34% and 36% (P = .9).
Researchers also found a significant positive correlation between improvement of the intestinal disease and clinical improvement of EIM at each time point.
Ustekinumab is usually preferred in patients with EIM, Dr. Livne-Margolin and colleagues note. But their findings “may raise some questions whether ustekinumab is, in fact, a better choice in those specific patients.”
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and small cohort size.
Additionally, vedolizumab is given intravenously in the clinic and mandates patients to have a routine checkup every 1-2 months, whereas ustekinumab can be given at home. As a result, data were missing on some of the patients treated with ustekinumab during the follow-up.
Another limitation is that most of the patients had articular complaints with a small presentation of other EIM.
Also, most of the patients had Crohn’s disease, with only one patient with ulcerative colitis in the ustekinumab group, compared with 12 in the vedolizumab group.
Finally, patients treated with ustekinumab had more experience with anti-TNF treatment, compared with the vedolizumab group, which might have influenced the results with a negative bias toward ustekinumab.
The study had no specific funding. Three authors have disclosed relationships with Janssen, which makes ustekinumab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vedolizumab (Entyvio) and ustekinumab (Stelara) appear to be equally effective for extraintestinal manifestation (EIM) of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to results of a retrospective study published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Between 25% and 40% of patients with IBD experience EIM, which reduces quality of life, according to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. EIM commonly involves the joints, skin, bones, eyes, kidney, and liver. Anemia is another extraintestinal complication.
Until now, it’s been unclear whether vedolizumab and ustekinumab are equally effective for treating EIM.
Vedolizumab specifically targets the gastrointestinal tract, a potential disadvantage in reducing EIM, while ustekinumab is thought to have a systemic effect, a potential treatment advantage, Moran Livne-Margolin, MD, and colleagues, Chaim Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, point out.
To investigate, they included 111 adults with IBD who were treated at the medical center between 2015 and 2021 – 53 with vedolizumab and 58 with ustekinumab. Before starting treatment, all of them had active EIM, most commonly arthralgia (84%).
After 6 weeks of treatment, 66% of patients in both groups had a clinical response to their intestinal disease.
After 14 and 26 weeks of treatment, clinical response rates were 59% and 50%, respectively, with vedolizumab, and 48% and 41%, respectively, with ustekinumab.
Over 52 weeks, both biologics were equally effective against the intestinal disease, with clinical response rates of 42% with vedolizumab and 44% with ustekinumab.
A similar pattern emerged when looking at improvement in EIM.
At week 6, 44% of patients taking vedolizumab and 35% taking ustekinumab had improvement in EIM, with no significant difference between the two biologics (P = .4).
At week 14, rates of improvement in EIM were 43% for vedolizumab and 33% for ustekinumab (P = .39); at 26 weeks, rates were 39% and 33%, respectively (P = .6); and at 52 weeks, rates were 34% and 36% (P = .9).
Researchers also found a significant positive correlation between improvement of the intestinal disease and clinical improvement of EIM at each time point.
Ustekinumab is usually preferred in patients with EIM, Dr. Livne-Margolin and colleagues note. But their findings “may raise some questions whether ustekinumab is, in fact, a better choice in those specific patients.”
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and small cohort size.
Additionally, vedolizumab is given intravenously in the clinic and mandates patients to have a routine checkup every 1-2 months, whereas ustekinumab can be given at home. As a result, data were missing on some of the patients treated with ustekinumab during the follow-up.
Another limitation is that most of the patients had articular complaints with a small presentation of other EIM.
Also, most of the patients had Crohn’s disease, with only one patient with ulcerative colitis in the ustekinumab group, compared with 12 in the vedolizumab group.
Finally, patients treated with ustekinumab had more experience with anti-TNF treatment, compared with the vedolizumab group, which might have influenced the results with a negative bias toward ustekinumab.
The study had no specific funding. Three authors have disclosed relationships with Janssen, which makes ustekinumab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIGESTIVE AND LIVER DISEASE
Anatomic site influences ropivacaine duration during dermatologic surgery
DENVER – , results from a single-center study showed.
Ropivacaine is a long-acting anesthetic that may be used as a substitute for the more commonly local anesthetics such as lidocaine or bupivacaine in dermatologic surgery, lead study author Kira Minkis, MD, PhD, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, where the study results were presented during an oral abstract session. By comparison, ropivacaine has been reported to have a faster onset, similar duration in the range of 6-14 hours, less pain upon injection, and inherent vasoconstrictive properties.
“With tumescent anesthesia, studies have previously shown that the rate and absorption of anesthetics is influenced by the site of administration,” said Dr. Minkis, director of Mohs and dermatologic surgery at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. “In studies comparing absorption of local anesthetics in tumescent anesthesia by regions that differ in vascularity, peak serum concentrations are greater and rise more rapidly after use in the head and neck compared to the trunk and extremities. However, no studies to date have compared the duration of ropivacaine in highly vascularized tissue or compared duration between regions that differ in vascularity.” The aim of the study, she noted, was to characterize the difference in duration of ropivacaine’s effects between anatomic regions of rich and comparably poor vascularity, such as the face and extremities, respectively.
Dr. Minkis and her colleagues recruited 17 women and 12 men with a mean age of 72 years who underwent Mohs surgery on the nose or the shin at Weill Cornell Medicine. Patients were anesthetized at each site with a subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mL of ropivacaine, 0.2%. Sensation was determined by pinprick prior to injection, at baseline, and every 15 minutes until sensation returned or surgery concluded. The primary endpoint was time to return of pinprick sensation.
The researchers found that the duration of ropivacaine was significantly shorter on the nose (a median of 60 minutes) than on the shin (a median of 210 minutes). In fact, the upper limit of the range of duration at the shin was not determinable because 22 of the 29 (76%) of participants did not regain sensation on the shin prior to leaving the surgical suite and concluding the study. The proportion of study participants who regained sensation within 1 hour was 76% among those who were treated on the nose vs. 3% of those who were treated on the shin (P < .0001).
“With durations of up to 6-14 hours reported, our results indicate a strikingly shorter duration of local anesthesia in highly vascularized tissue,” Dr. Minkis said. “The brevity of local anesthesia is even more surprising given the intrinsic vasoconstrictive properties of ropivacaine. Often, we co-administer epinephrine to achieve vasoconstriction and reduce local blood flow, thus prolonging local concentrations of the anesthetic with the added benefit of reducing bleeding during surgery. The short duration we’ve observed in our study is emphasized in using a potent, long-acting local anesthetic with vasoconstrictive properties that otherwise should attenuate the effects of high local vascularity.”
In other findings, patients with history of hypertension were more likely to regain sensation on the nose by 60 minutes but this did not reach statistical significance (P = .079). Other comorbidities including underlying anxiety/depression, diabetes, and kidney disease did not significantly impact duration of ropivacaine action on the nose. The same held true for patients who were treated on the shin.
“We highlight an inconsistency between the reported duration of a long-lasting local anesthetic and the short-lived anesthesia experienced by our patients in a highly vascularized region,” Dr. Minkis said. “In practice, adjunctive use of a long-acting anesthetic to prolong anesthesia is common, which may provide relief from multiple injections of shorter-acting lidocaine. However, the duration of Mohs surgery can be unpredictable. Extended wait times between stages may exceed the duration we’ve observed in this study.”
In addition, she continued, “pain is frequently reported on postoperative days 0 to 3, leading some to recommend the use of long-acting local anesthetics to prevent overprescription or a gap in pain coverage. This emphasizes a gap in effective pain control, but also an opportunity to improve our patients’ surgical and recovery experiences.”
Impact on practice
Keith L. Duffy, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who was asked to comment on the study, said that in light of current local anesthetic shortages and back orders, “we dermatologic surgeons have been experimenting with different anesthetics and concentrations that we can use in our patients. Ropivacaine may become the anesthetic of choice for many of our practices given its inherent properties.”
The duration of anesthetic effects by anatomic location in this study is “actually more impressive than I would have suspected as a practicing Mohs surgeon. The results of this study will immediately impact my Mohs surgery clinic,” he said, adding that he hoped that Dr. Minkis and others “will expand on this study to include more patients, different anesthetics, and more anatomic locations.”
Dr. Minkis acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center design and the fact that there were too few observations of medical and clinical characteristics for subgroup analysis.
She and Dr. Duffy reported having no financial disclosures.
DENVER – , results from a single-center study showed.
Ropivacaine is a long-acting anesthetic that may be used as a substitute for the more commonly local anesthetics such as lidocaine or bupivacaine in dermatologic surgery, lead study author Kira Minkis, MD, PhD, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, where the study results were presented during an oral abstract session. By comparison, ropivacaine has been reported to have a faster onset, similar duration in the range of 6-14 hours, less pain upon injection, and inherent vasoconstrictive properties.
“With tumescent anesthesia, studies have previously shown that the rate and absorption of anesthetics is influenced by the site of administration,” said Dr. Minkis, director of Mohs and dermatologic surgery at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. “In studies comparing absorption of local anesthetics in tumescent anesthesia by regions that differ in vascularity, peak serum concentrations are greater and rise more rapidly after use in the head and neck compared to the trunk and extremities. However, no studies to date have compared the duration of ropivacaine in highly vascularized tissue or compared duration between regions that differ in vascularity.” The aim of the study, she noted, was to characterize the difference in duration of ropivacaine’s effects between anatomic regions of rich and comparably poor vascularity, such as the face and extremities, respectively.
Dr. Minkis and her colleagues recruited 17 women and 12 men with a mean age of 72 years who underwent Mohs surgery on the nose or the shin at Weill Cornell Medicine. Patients were anesthetized at each site with a subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mL of ropivacaine, 0.2%. Sensation was determined by pinprick prior to injection, at baseline, and every 15 minutes until sensation returned or surgery concluded. The primary endpoint was time to return of pinprick sensation.
The researchers found that the duration of ropivacaine was significantly shorter on the nose (a median of 60 minutes) than on the shin (a median of 210 minutes). In fact, the upper limit of the range of duration at the shin was not determinable because 22 of the 29 (76%) of participants did not regain sensation on the shin prior to leaving the surgical suite and concluding the study. The proportion of study participants who regained sensation within 1 hour was 76% among those who were treated on the nose vs. 3% of those who were treated on the shin (P < .0001).
“With durations of up to 6-14 hours reported, our results indicate a strikingly shorter duration of local anesthesia in highly vascularized tissue,” Dr. Minkis said. “The brevity of local anesthesia is even more surprising given the intrinsic vasoconstrictive properties of ropivacaine. Often, we co-administer epinephrine to achieve vasoconstriction and reduce local blood flow, thus prolonging local concentrations of the anesthetic with the added benefit of reducing bleeding during surgery. The short duration we’ve observed in our study is emphasized in using a potent, long-acting local anesthetic with vasoconstrictive properties that otherwise should attenuate the effects of high local vascularity.”
In other findings, patients with history of hypertension were more likely to regain sensation on the nose by 60 minutes but this did not reach statistical significance (P = .079). Other comorbidities including underlying anxiety/depression, diabetes, and kidney disease did not significantly impact duration of ropivacaine action on the nose. The same held true for patients who were treated on the shin.
“We highlight an inconsistency between the reported duration of a long-lasting local anesthetic and the short-lived anesthesia experienced by our patients in a highly vascularized region,” Dr. Minkis said. “In practice, adjunctive use of a long-acting anesthetic to prolong anesthesia is common, which may provide relief from multiple injections of shorter-acting lidocaine. However, the duration of Mohs surgery can be unpredictable. Extended wait times between stages may exceed the duration we’ve observed in this study.”
In addition, she continued, “pain is frequently reported on postoperative days 0 to 3, leading some to recommend the use of long-acting local anesthetics to prevent overprescription or a gap in pain coverage. This emphasizes a gap in effective pain control, but also an opportunity to improve our patients’ surgical and recovery experiences.”
Impact on practice
Keith L. Duffy, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who was asked to comment on the study, said that in light of current local anesthetic shortages and back orders, “we dermatologic surgeons have been experimenting with different anesthetics and concentrations that we can use in our patients. Ropivacaine may become the anesthetic of choice for many of our practices given its inherent properties.”
The duration of anesthetic effects by anatomic location in this study is “actually more impressive than I would have suspected as a practicing Mohs surgeon. The results of this study will immediately impact my Mohs surgery clinic,” he said, adding that he hoped that Dr. Minkis and others “will expand on this study to include more patients, different anesthetics, and more anatomic locations.”
Dr. Minkis acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center design and the fact that there were too few observations of medical and clinical characteristics for subgroup analysis.
She and Dr. Duffy reported having no financial disclosures.
DENVER – , results from a single-center study showed.
Ropivacaine is a long-acting anesthetic that may be used as a substitute for the more commonly local anesthetics such as lidocaine or bupivacaine in dermatologic surgery, lead study author Kira Minkis, MD, PhD, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, where the study results were presented during an oral abstract session. By comparison, ropivacaine has been reported to have a faster onset, similar duration in the range of 6-14 hours, less pain upon injection, and inherent vasoconstrictive properties.
“With tumescent anesthesia, studies have previously shown that the rate and absorption of anesthetics is influenced by the site of administration,” said Dr. Minkis, director of Mohs and dermatologic surgery at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. “In studies comparing absorption of local anesthetics in tumescent anesthesia by regions that differ in vascularity, peak serum concentrations are greater and rise more rapidly after use in the head and neck compared to the trunk and extremities. However, no studies to date have compared the duration of ropivacaine in highly vascularized tissue or compared duration between regions that differ in vascularity.” The aim of the study, she noted, was to characterize the difference in duration of ropivacaine’s effects between anatomic regions of rich and comparably poor vascularity, such as the face and extremities, respectively.
Dr. Minkis and her colleagues recruited 17 women and 12 men with a mean age of 72 years who underwent Mohs surgery on the nose or the shin at Weill Cornell Medicine. Patients were anesthetized at each site with a subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mL of ropivacaine, 0.2%. Sensation was determined by pinprick prior to injection, at baseline, and every 15 minutes until sensation returned or surgery concluded. The primary endpoint was time to return of pinprick sensation.
The researchers found that the duration of ropivacaine was significantly shorter on the nose (a median of 60 minutes) than on the shin (a median of 210 minutes). In fact, the upper limit of the range of duration at the shin was not determinable because 22 of the 29 (76%) of participants did not regain sensation on the shin prior to leaving the surgical suite and concluding the study. The proportion of study participants who regained sensation within 1 hour was 76% among those who were treated on the nose vs. 3% of those who were treated on the shin (P < .0001).
“With durations of up to 6-14 hours reported, our results indicate a strikingly shorter duration of local anesthesia in highly vascularized tissue,” Dr. Minkis said. “The brevity of local anesthesia is even more surprising given the intrinsic vasoconstrictive properties of ropivacaine. Often, we co-administer epinephrine to achieve vasoconstriction and reduce local blood flow, thus prolonging local concentrations of the anesthetic with the added benefit of reducing bleeding during surgery. The short duration we’ve observed in our study is emphasized in using a potent, long-acting local anesthetic with vasoconstrictive properties that otherwise should attenuate the effects of high local vascularity.”
In other findings, patients with history of hypertension were more likely to regain sensation on the nose by 60 minutes but this did not reach statistical significance (P = .079). Other comorbidities including underlying anxiety/depression, diabetes, and kidney disease did not significantly impact duration of ropivacaine action on the nose. The same held true for patients who were treated on the shin.
“We highlight an inconsistency between the reported duration of a long-lasting local anesthetic and the short-lived anesthesia experienced by our patients in a highly vascularized region,” Dr. Minkis said. “In practice, adjunctive use of a long-acting anesthetic to prolong anesthesia is common, which may provide relief from multiple injections of shorter-acting lidocaine. However, the duration of Mohs surgery can be unpredictable. Extended wait times between stages may exceed the duration we’ve observed in this study.”
In addition, she continued, “pain is frequently reported on postoperative days 0 to 3, leading some to recommend the use of long-acting local anesthetics to prevent overprescription or a gap in pain coverage. This emphasizes a gap in effective pain control, but also an opportunity to improve our patients’ surgical and recovery experiences.”
Impact on practice
Keith L. Duffy, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who was asked to comment on the study, said that in light of current local anesthetic shortages and back orders, “we dermatologic surgeons have been experimenting with different anesthetics and concentrations that we can use in our patients. Ropivacaine may become the anesthetic of choice for many of our practices given its inherent properties.”
The duration of anesthetic effects by anatomic location in this study is “actually more impressive than I would have suspected as a practicing Mohs surgeon. The results of this study will immediately impact my Mohs surgery clinic,” he said, adding that he hoped that Dr. Minkis and others “will expand on this study to include more patients, different anesthetics, and more anatomic locations.”
Dr. Minkis acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center design and the fact that there were too few observations of medical and clinical characteristics for subgroup analysis.
She and Dr. Duffy reported having no financial disclosures.
AT ASDS 2022
Decoding mechanisms of diabetic embryopathy suggests therapeutic targets
Before the introduction of insulin, there were few reported cases of pregnancy complicated by diabetes because women with the disease too often did not live to childbearing age, and when they did, they were often counseled to terminate their pregnancies. Perinatal and maternal mortality in the limited number of reported pregnancies were 70% and 40%, respectively,1 making the risks of continuing the pregnancy quite high.
After insulin became available, maternal mortality dropped dramatically, down to a few percent. Perinatal mortality also declined, but it took several decades to achieve a similar magnitude of reduction.2 Today, with insulin therapy and tight glucose control as well as improved perinatal care, almost all women with diabetes can contemplate pregnancy with greater hope for normal outcomes.
Problems persist, however. Maternal diabetes continues to cause a variety of adverse outcomes, including infants large for gestational age, prematurity, and structural birth defects. Birth defects and prematurity, in fact, are the top causes of the unacceptably high infant mortality rate in the United States – a rate that is about 70% higher than the average in comparable developed countries.3
Infant mortality is considered an indicator of population health and of the development of a country; to reduce its rate, we must address these two areas.
Women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are five times more likely to have a child with birth defects than are nondiabetic women.4 Up to 10% of women with preexisting diabetes will have fetuses with a major congenital malformation.5
Over the years we have been striving in our Center for Birth Defects Research to understand the pathomechanisms and the molecular and epigenetic alterations behind the high rates of birth defects in the offspring of women with preexisting diabetes. We have focused on heart defects and neural tube defects (particularly the latter), which together cause significant mortality, morbidity, disability, and human suffering.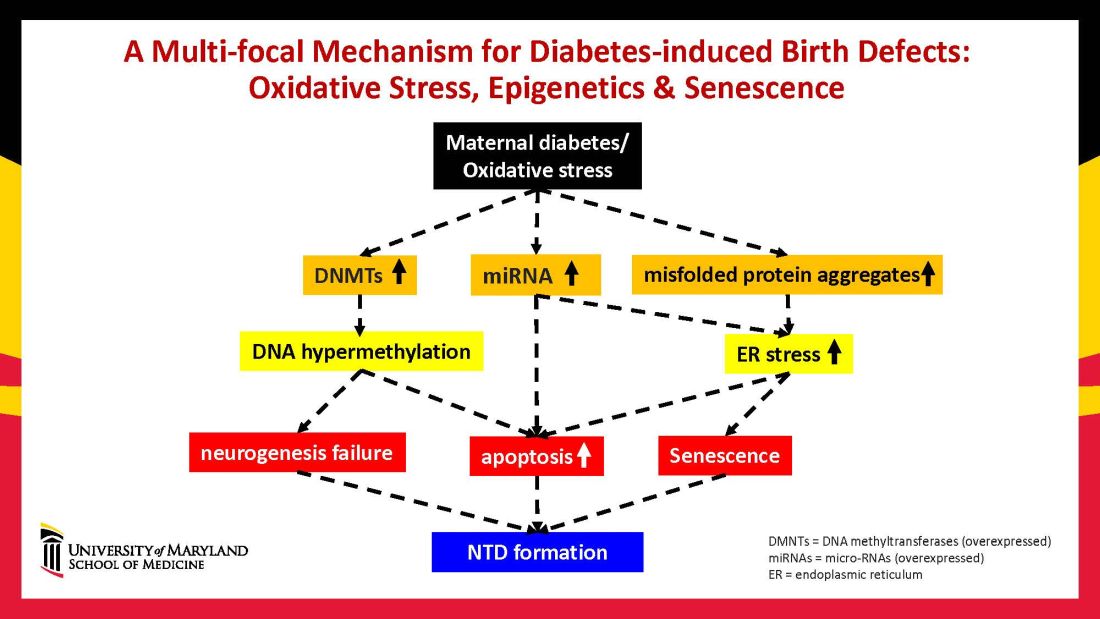
Using animal models that mimic human diabetic pregnancy, we have made significant strides in our understanding of the mechanisms, uncovering molecular pathways involving oxidative stress, senescence/premature cellular aging, and epigenetic modifications (Figure 1). Understanding these pathways is providing us, in turn, with potential therapeutic targets and approaches that may be used in the future to prevent birth defects in women who enter pregnancy with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Unraveling the role of oxidative stress
Our mouse models accurately reflect the human conditions of diabetes in pregnancy and diabetic embryopathy. Offspring of mice with type 1 and type 2 diabetes have a similarly higher rate of neural tube defects and congenital heart disease, compared to mice without diabetes. We observe a similar incidence of anencephaly and spina bifida, and of cardiac septation defects in the mouse embryo hearts, for instance.
A primary mechanism and causal event of diabetic embryopathy is hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in embryonic cells. Excessive cell death in the neural epithelium or in the developing heart leads to abnormal organogenesis and dysfunctional developmental events that cause birth defects. We have identified pathways leading to apoptosis, and have found that many of these pathways crosstalk with each other.
Hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress – one of these pathways – by causing sustained generation of reactive oxygen species. The cells’ mitochondrial function is significantly impaired by the hyperglycemia response, and this diabetes-induced mitochondrial dysfunction further increases the production of reactive oxygen species and a weakening of the endogenous cellular antioxidant systems, both of which then exacerbate oxidative stress.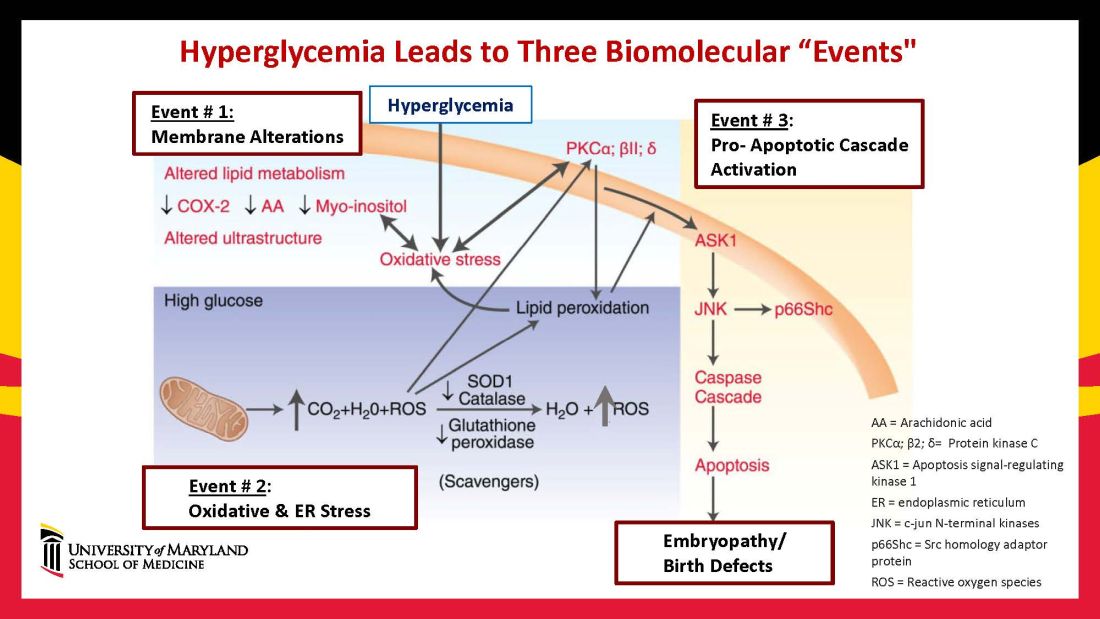
Our research has detailed what happens downstream. We’ve learned that oxidative stress in embryos exposed to maternal diabetes activates a cascade of proapoptotic kinase signaling molecules – for example, protein kinase C isoforms such as PKCalpha; apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; and c-Jun-N-terminal kinases – that ultimately lead to abnormal cell death in the neuroepithelium before neural tube closure (Figure 2).5
Hyperglycemia also alters membrane biochemistry in the developing embryo, suppressing lipids including arachidonic acid and myoinositol, and induces the elevation of other molecules that cause newly synthesized proteins to be misfolded. A build-up of misfolded/unfolded proteins triggers or exacerbates endoplasmic reticulum stress, which, like oxidative stress, plays a role in the activation of proapoptotic kinase signaling and apoptosis.6
When we’ve deleted genes for some of the proapoptotic kinase–signaling intermediates, or otherwise inhibited oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stresses, we’ve been able to ameliorate neural cell apoptosis and the formation of neural tube defects. Studying the processes both forward and backward gives us confidence that the pathways are real and important, and that altering the pathways can alter the outcomes.
Reduced autophagy and induction of cellular senescence
Just as mitochondria are negatively affected by hyperglycemic conditions, so are autophagosomes – organelles that play a key role in removing abnormal or damaged stem cells and cellular components (including unfolded protein aggregates) and in maintaining cellular homeostasis. A high level of autophagy is essential for neural tube closure as well as cardiac morphogenesis.
In our models, maternal diabetes significantly suppressed the process of autophagy in neuroepithelial cells. We have identified responsible molecular intermediates and a key regulating gene for autophagy impairment and have found that deletion of the gene restores autophagy and reduces the development of neural tube defects.4 Administration of a naturally occurring compound, trehalose, which reactivates autophagy, had a similar effect.7Exposure to hyperglycemia not only causes cell death and suppresses autophagy, it also impairs other aspects of cellular function. More recently, we have shown that cells in the neuroepithelium become quiescent and cease proliferating. The quiescent cells, those cells with premature aging markers, also produce cytokines that influence the functioning and development of neighboring cells, causing additional cell death.
All told, premature senescence in the neuroepithelium adversely affects the neurulation process, leading to neural tube defects. In our mouse model, the senomorphic agent rapamycin suppressed cellular senescence, reduced the number of apoptotic neuroepithelial cells, and reduced the formation of neural tube defects.8
The role of epigenetics, future interventions
Epigenetics – the process by which gene expression and function can be modified by environmental conditions without modification of the DNA sequence – has become an additional area of focus in diabetic embryopathy. Our lab has studied the overexpression of both DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) that cause DNA hypermethylation, and of microRNAs (miRNAs) that can suppress gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Both are considered to be primary epigenetic mechanisms involved in human diseases and it appears that they are influential in the incidence of birth defects in diabetic mothers.
In our mouse models, maternal diabetes induces DNA hypermethylation via the increase of DNMTs, leading to the silencing of genes essential for neural tube closure and formation of the developing heart. MiRNAs also play a role; in addition to finding altered DNMT activity in the neural epithelium and other tissues of diabetes-exposed embryos, we also found altered miRNA expression. By deleting miRNA genes or by inhibiting DNMT activity through treatment with antioxidants, we saw significant reductions in birth defects.
In one study of the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), we demonstrated inhibition of diabetes-elevated DNMT expression and activity and suppression of DNA hypermethylation. The expression of genes essential for neural tube closure was restored, with a subsequent reduction in neural tube defects from 29.5% to 2% in embryos treated with EGCG.9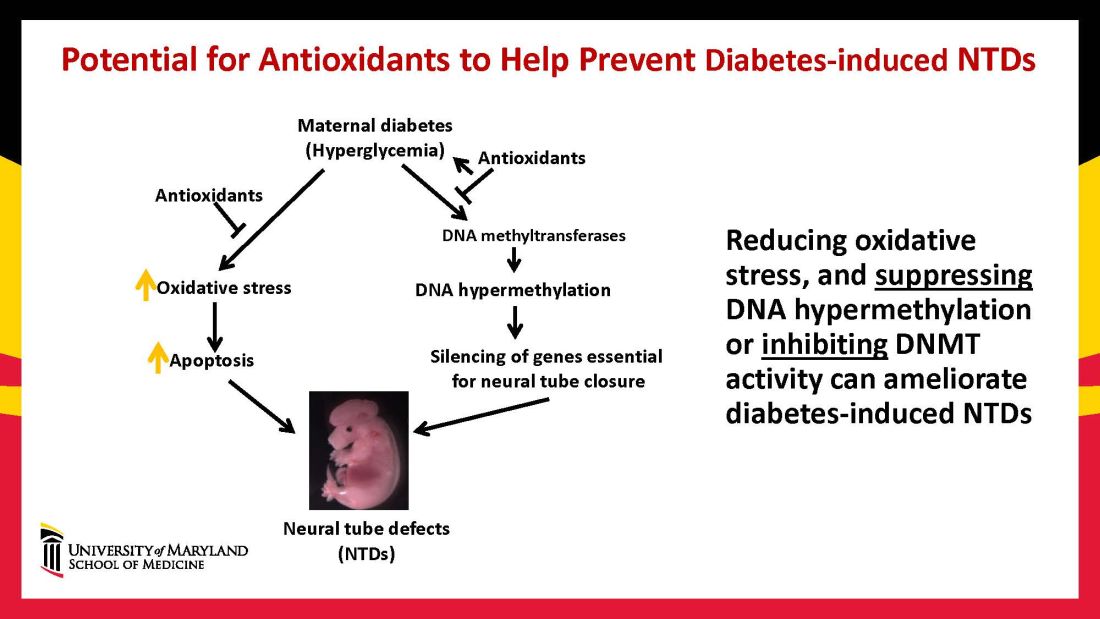
Our interventions to reverse or alter the mechanisms and pathways leading to birth defects have not only helped prove causation, but have given us hope for the future. Antioxidants are among the compounds that could be used as dietary supplements during pregnancy to prevent structural birth defects (Figure 3). Other compounds could activate the process of autophagy (for example, trehalose) and antisenescence compounds similar to rapamycin could be used to reduce numbers of senescent cells in the neuroepithelium or the developing heart.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang reported no relevant disclosures.
Dr. Reece, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist, is dean emeritus of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, former university executive vice president, endowed professor and director of CARTI, and codirector of the Center for Birth Defects.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022
References
1. Z Zhiyong and Reece EA. Clin Lab Med. 2013;33(2)207-33.
2. Reece EA and Coustan DR. Diabetes and obesity in women. Wolters Kluwer: 2019. 4th ed. (https://www.amazon.com/Diabetes-Obesity-Women-Albert-Reece/dp/1496390547).
3. The Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker. www.healthsystemtracker.org.
4. Wang F et al. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:15182.
5. Yang P et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(5):569-79.
6. Li X et al. Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):599-608.
7. Xu C et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Sep 1;305(5):E667-78.
8. Xu C et al. Sci Adv. 2021;7(27):eabf5089.
9. Zhong J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;215(3):368.e1-10.
Before the introduction of insulin, there were few reported cases of pregnancy complicated by diabetes because women with the disease too often did not live to childbearing age, and when they did, they were often counseled to terminate their pregnancies. Perinatal and maternal mortality in the limited number of reported pregnancies were 70% and 40%, respectively,1 making the risks of continuing the pregnancy quite high.
After insulin became available, maternal mortality dropped dramatically, down to a few percent. Perinatal mortality also declined, but it took several decades to achieve a similar magnitude of reduction.2 Today, with insulin therapy and tight glucose control as well as improved perinatal care, almost all women with diabetes can contemplate pregnancy with greater hope for normal outcomes.
Problems persist, however. Maternal diabetes continues to cause a variety of adverse outcomes, including infants large for gestational age, prematurity, and structural birth defects. Birth defects and prematurity, in fact, are the top causes of the unacceptably high infant mortality rate in the United States – a rate that is about 70% higher than the average in comparable developed countries.3
Infant mortality is considered an indicator of population health and of the development of a country; to reduce its rate, we must address these two areas.
Women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are five times more likely to have a child with birth defects than are nondiabetic women.4 Up to 10% of women with preexisting diabetes will have fetuses with a major congenital malformation.5
Over the years we have been striving in our Center for Birth Defects Research to understand the pathomechanisms and the molecular and epigenetic alterations behind the high rates of birth defects in the offspring of women with preexisting diabetes. We have focused on heart defects and neural tube defects (particularly the latter), which together cause significant mortality, morbidity, disability, and human suffering.
Using animal models that mimic human diabetic pregnancy, we have made significant strides in our understanding of the mechanisms, uncovering molecular pathways involving oxidative stress, senescence/premature cellular aging, and epigenetic modifications (Figure 1). Understanding these pathways is providing us, in turn, with potential therapeutic targets and approaches that may be used in the future to prevent birth defects in women who enter pregnancy with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Unraveling the role of oxidative stress
Our mouse models accurately reflect the human conditions of diabetes in pregnancy and diabetic embryopathy. Offspring of mice with type 1 and type 2 diabetes have a similarly higher rate of neural tube defects and congenital heart disease, compared to mice without diabetes. We observe a similar incidence of anencephaly and spina bifida, and of cardiac septation defects in the mouse embryo hearts, for instance.
A primary mechanism and causal event of diabetic embryopathy is hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in embryonic cells. Excessive cell death in the neural epithelium or in the developing heart leads to abnormal organogenesis and dysfunctional developmental events that cause birth defects. We have identified pathways leading to apoptosis, and have found that many of these pathways crosstalk with each other.
Hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress – one of these pathways – by causing sustained generation of reactive oxygen species. The cells’ mitochondrial function is significantly impaired by the hyperglycemia response, and this diabetes-induced mitochondrial dysfunction further increases the production of reactive oxygen species and a weakening of the endogenous cellular antioxidant systems, both of which then exacerbate oxidative stress.
Our research has detailed what happens downstream. We’ve learned that oxidative stress in embryos exposed to maternal diabetes activates a cascade of proapoptotic kinase signaling molecules – for example, protein kinase C isoforms such as PKCalpha; apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; and c-Jun-N-terminal kinases – that ultimately lead to abnormal cell death in the neuroepithelium before neural tube closure (Figure 2).5
Hyperglycemia also alters membrane biochemistry in the developing embryo, suppressing lipids including arachidonic acid and myoinositol, and induces the elevation of other molecules that cause newly synthesized proteins to be misfolded. A build-up of misfolded/unfolded proteins triggers or exacerbates endoplasmic reticulum stress, which, like oxidative stress, plays a role in the activation of proapoptotic kinase signaling and apoptosis.6
When we’ve deleted genes for some of the proapoptotic kinase–signaling intermediates, or otherwise inhibited oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stresses, we’ve been able to ameliorate neural cell apoptosis and the formation of neural tube defects. Studying the processes both forward and backward gives us confidence that the pathways are real and important, and that altering the pathways can alter the outcomes.
Reduced autophagy and induction of cellular senescence
Just as mitochondria are negatively affected by hyperglycemic conditions, so are autophagosomes – organelles that play a key role in removing abnormal or damaged stem cells and cellular components (including unfolded protein aggregates) and in maintaining cellular homeostasis. A high level of autophagy is essential for neural tube closure as well as cardiac morphogenesis.
In our models, maternal diabetes significantly suppressed the process of autophagy in neuroepithelial cells. We have identified responsible molecular intermediates and a key regulating gene for autophagy impairment and have found that deletion of the gene restores autophagy and reduces the development of neural tube defects.4 Administration of a naturally occurring compound, trehalose, which reactivates autophagy, had a similar effect.7Exposure to hyperglycemia not only causes cell death and suppresses autophagy, it also impairs other aspects of cellular function. More recently, we have shown that cells in the neuroepithelium become quiescent and cease proliferating. The quiescent cells, those cells with premature aging markers, also produce cytokines that influence the functioning and development of neighboring cells, causing additional cell death.
All told, premature senescence in the neuroepithelium adversely affects the neurulation process, leading to neural tube defects. In our mouse model, the senomorphic agent rapamycin suppressed cellular senescence, reduced the number of apoptotic neuroepithelial cells, and reduced the formation of neural tube defects.8
The role of epigenetics, future interventions
Epigenetics – the process by which gene expression and function can be modified by environmental conditions without modification of the DNA sequence – has become an additional area of focus in diabetic embryopathy. Our lab has studied the overexpression of both DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) that cause DNA hypermethylation, and of microRNAs (miRNAs) that can suppress gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Both are considered to be primary epigenetic mechanisms involved in human diseases and it appears that they are influential in the incidence of birth defects in diabetic mothers.
In our mouse models, maternal diabetes induces DNA hypermethylation via the increase of DNMTs, leading to the silencing of genes essential for neural tube closure and formation of the developing heart. MiRNAs also play a role; in addition to finding altered DNMT activity in the neural epithelium and other tissues of diabetes-exposed embryos, we also found altered miRNA expression. By deleting miRNA genes or by inhibiting DNMT activity through treatment with antioxidants, we saw significant reductions in birth defects.
In one study of the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), we demonstrated inhibition of diabetes-elevated DNMT expression and activity and suppression of DNA hypermethylation. The expression of genes essential for neural tube closure was restored, with a subsequent reduction in neural tube defects from 29.5% to 2% in embryos treated with EGCG.9
Our interventions to reverse or alter the mechanisms and pathways leading to birth defects have not only helped prove causation, but have given us hope for the future. Antioxidants are among the compounds that could be used as dietary supplements during pregnancy to prevent structural birth defects (Figure 3). Other compounds could activate the process of autophagy (for example, trehalose) and antisenescence compounds similar to rapamycin could be used to reduce numbers of senescent cells in the neuroepithelium or the developing heart.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang reported no relevant disclosures.
Dr. Reece, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist, is dean emeritus of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, former university executive vice president, endowed professor and director of CARTI, and codirector of the Center for Birth Defects.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022
References
1. Z Zhiyong and Reece EA. Clin Lab Med. 2013;33(2)207-33.
2. Reece EA and Coustan DR. Diabetes and obesity in women. Wolters Kluwer: 2019. 4th ed. (https://www.amazon.com/Diabetes-Obesity-Women-Albert-Reece/dp/1496390547).
3. The Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker. www.healthsystemtracker.org.
4. Wang F et al. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:15182.
5. Yang P et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(5):569-79.
6. Li X et al. Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):599-608.
7. Xu C et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Sep 1;305(5):E667-78.
8. Xu C et al. Sci Adv. 2021;7(27):eabf5089.
9. Zhong J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;215(3):368.e1-10.
Before the introduction of insulin, there were few reported cases of pregnancy complicated by diabetes because women with the disease too often did not live to childbearing age, and when they did, they were often counseled to terminate their pregnancies. Perinatal and maternal mortality in the limited number of reported pregnancies were 70% and 40%, respectively,1 making the risks of continuing the pregnancy quite high.
After insulin became available, maternal mortality dropped dramatically, down to a few percent. Perinatal mortality also declined, but it took several decades to achieve a similar magnitude of reduction.2 Today, with insulin therapy and tight glucose control as well as improved perinatal care, almost all women with diabetes can contemplate pregnancy with greater hope for normal outcomes.
Problems persist, however. Maternal diabetes continues to cause a variety of adverse outcomes, including infants large for gestational age, prematurity, and structural birth defects. Birth defects and prematurity, in fact, are the top causes of the unacceptably high infant mortality rate in the United States – a rate that is about 70% higher than the average in comparable developed countries.3
Infant mortality is considered an indicator of population health and of the development of a country; to reduce its rate, we must address these two areas.
Women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are five times more likely to have a child with birth defects than are nondiabetic women.4 Up to 10% of women with preexisting diabetes will have fetuses with a major congenital malformation.5
Over the years we have been striving in our Center for Birth Defects Research to understand the pathomechanisms and the molecular and epigenetic alterations behind the high rates of birth defects in the offspring of women with preexisting diabetes. We have focused on heart defects and neural tube defects (particularly the latter), which together cause significant mortality, morbidity, disability, and human suffering.
Using animal models that mimic human diabetic pregnancy, we have made significant strides in our understanding of the mechanisms, uncovering molecular pathways involving oxidative stress, senescence/premature cellular aging, and epigenetic modifications (Figure 1). Understanding these pathways is providing us, in turn, with potential therapeutic targets and approaches that may be used in the future to prevent birth defects in women who enter pregnancy with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Unraveling the role of oxidative stress
Our mouse models accurately reflect the human conditions of diabetes in pregnancy and diabetic embryopathy. Offspring of mice with type 1 and type 2 diabetes have a similarly higher rate of neural tube defects and congenital heart disease, compared to mice without diabetes. We observe a similar incidence of anencephaly and spina bifida, and of cardiac septation defects in the mouse embryo hearts, for instance.
A primary mechanism and causal event of diabetic embryopathy is hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in embryonic cells. Excessive cell death in the neural epithelium or in the developing heart leads to abnormal organogenesis and dysfunctional developmental events that cause birth defects. We have identified pathways leading to apoptosis, and have found that many of these pathways crosstalk with each other.
Hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress – one of these pathways – by causing sustained generation of reactive oxygen species. The cells’ mitochondrial function is significantly impaired by the hyperglycemia response, and this diabetes-induced mitochondrial dysfunction further increases the production of reactive oxygen species and a weakening of the endogenous cellular antioxidant systems, both of which then exacerbate oxidative stress.
Our research has detailed what happens downstream. We’ve learned that oxidative stress in embryos exposed to maternal diabetes activates a cascade of proapoptotic kinase signaling molecules – for example, protein kinase C isoforms such as PKCalpha; apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; and c-Jun-N-terminal kinases – that ultimately lead to abnormal cell death in the neuroepithelium before neural tube closure (Figure 2).5
Hyperglycemia also alters membrane biochemistry in the developing embryo, suppressing lipids including arachidonic acid and myoinositol, and induces the elevation of other molecules that cause newly synthesized proteins to be misfolded. A build-up of misfolded/unfolded proteins triggers or exacerbates endoplasmic reticulum stress, which, like oxidative stress, plays a role in the activation of proapoptotic kinase signaling and apoptosis.6
When we’ve deleted genes for some of the proapoptotic kinase–signaling intermediates, or otherwise inhibited oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stresses, we’ve been able to ameliorate neural cell apoptosis and the formation of neural tube defects. Studying the processes both forward and backward gives us confidence that the pathways are real and important, and that altering the pathways can alter the outcomes.
Reduced autophagy and induction of cellular senescence
Just as mitochondria are negatively affected by hyperglycemic conditions, so are autophagosomes – organelles that play a key role in removing abnormal or damaged stem cells and cellular components (including unfolded protein aggregates) and in maintaining cellular homeostasis. A high level of autophagy is essential for neural tube closure as well as cardiac morphogenesis.
In our models, maternal diabetes significantly suppressed the process of autophagy in neuroepithelial cells. We have identified responsible molecular intermediates and a key regulating gene for autophagy impairment and have found that deletion of the gene restores autophagy and reduces the development of neural tube defects.4 Administration of a naturally occurring compound, trehalose, which reactivates autophagy, had a similar effect.7Exposure to hyperglycemia not only causes cell death and suppresses autophagy, it also impairs other aspects of cellular function. More recently, we have shown that cells in the neuroepithelium become quiescent and cease proliferating. The quiescent cells, those cells with premature aging markers, also produce cytokines that influence the functioning and development of neighboring cells, causing additional cell death.
All told, premature senescence in the neuroepithelium adversely affects the neurulation process, leading to neural tube defects. In our mouse model, the senomorphic agent rapamycin suppressed cellular senescence, reduced the number of apoptotic neuroepithelial cells, and reduced the formation of neural tube defects.8
The role of epigenetics, future interventions
Epigenetics – the process by which gene expression and function can be modified by environmental conditions without modification of the DNA sequence – has become an additional area of focus in diabetic embryopathy. Our lab has studied the overexpression of both DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) that cause DNA hypermethylation, and of microRNAs (miRNAs) that can suppress gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Both are considered to be primary epigenetic mechanisms involved in human diseases and it appears that they are influential in the incidence of birth defects in diabetic mothers.
In our mouse models, maternal diabetes induces DNA hypermethylation via the increase of DNMTs, leading to the silencing of genes essential for neural tube closure and formation of the developing heart. MiRNAs also play a role; in addition to finding altered DNMT activity in the neural epithelium and other tissues of diabetes-exposed embryos, we also found altered miRNA expression. By deleting miRNA genes or by inhibiting DNMT activity through treatment with antioxidants, we saw significant reductions in birth defects.
In one study of the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), we demonstrated inhibition of diabetes-elevated DNMT expression and activity and suppression of DNA hypermethylation. The expression of genes essential for neural tube closure was restored, with a subsequent reduction in neural tube defects from 29.5% to 2% in embryos treated with EGCG.9
Our interventions to reverse or alter the mechanisms and pathways leading to birth defects have not only helped prove causation, but have given us hope for the future. Antioxidants are among the compounds that could be used as dietary supplements during pregnancy to prevent structural birth defects (Figure 3). Other compounds could activate the process of autophagy (for example, trehalose) and antisenescence compounds similar to rapamycin could be used to reduce numbers of senescent cells in the neuroepithelium or the developing heart.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang reported no relevant disclosures.
Dr. Reece, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist, is dean emeritus of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, former university executive vice president, endowed professor and director of CARTI, and codirector of the Center for Birth Defects.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022
References
1. Z Zhiyong and Reece EA. Clin Lab Med. 2013;33(2)207-33.
2. Reece EA and Coustan DR. Diabetes and obesity in women. Wolters Kluwer: 2019. 4th ed. (https://www.amazon.com/Diabetes-Obesity-Women-Albert-Reece/dp/1496390547).
3. The Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker. www.healthsystemtracker.org.
4. Wang F et al. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:15182.
5. Yang P et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(5):569-79.
6. Li X et al. Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):599-608.
7. Xu C et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Sep 1;305(5):E667-78.
8. Xu C et al. Sci Adv. 2021;7(27):eabf5089.
9. Zhong J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;215(3):368.e1-10.
Discoveries in diabetic embryogenesis
Many issues surrounding pregnancy care of women with preexisting diabetes remain challenging, especially in light of the relentless increase in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and globally. Rising rates of death and severe morbidity in diabetic women have continued despite significant advances in insulin pharmacology and administration technology.
However, despite these advances in glucose monitoring and insulin administration, fetal mortality and childhood morbidity rates continue to climb. This is because critical fetal structural anomalies arise from developmental errors occurring in the embryonic period – between 2 and 13 weeks of gestation – a time when most women with preexisting diabetes are just entering into prenatal care, often with suboptimal glycemic control.
Thus, significant future progress in reducing fetal mortality and childhood disability in infants of diabetic mothers will depend upon effective interventions in the first trimester while embryogenesis and critical organ formation are underway.
In this issue of Ob.Gyn. News, the editor of Master Class in Obstetrics, E. Albert Reece MD, PhD, MBA, steps into the role of coauthor. He and his research colleague Peixin Yang, PhD, present exciting insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying structural birth defects in infants of diabetic mothers – especially cardiac and neural tube defects – and also provide a glimpse into some potentially effective maternal pharmacologic interventions. After appropriate human trials, these interventions could be effectively applied from the time of a positive pregnancy test with potentially dramatic results.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang, who lead the Center for the Study of Birth Defects at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, share their impressive accumulation of data from embryos of pregnant diabetic rodents. They demonstrate convincingly that, in first-trimester rodent embryos, maternal hyperglycemia induces excessive apoptosis, which in turn leads to structural defects in critical fetal organs. They further found that maternal hyperglycemia reduces embryonic autophagosomes – the developmentally essential organelles that remove abnormal or damaged cells during embryo formation.
These investigators also identified reactivators of these organelles which, when administered maternally in the first trimester, significantly reduced the incidence of neural tube defects. Thus, for optimal development of diabetes-affected embryos, first-trimester administration of reactivators of autophagy could offer a significant, life-changing intervention in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Moore is professor emeritus of maternal-fetal medicine and chair emeritus in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at UC San Diego Health. He reported no disclosures.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
Many issues surrounding pregnancy care of women with preexisting diabetes remain challenging, especially in light of the relentless increase in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and globally. Rising rates of death and severe morbidity in diabetic women have continued despite significant advances in insulin pharmacology and administration technology.
However, despite these advances in glucose monitoring and insulin administration, fetal mortality and childhood morbidity rates continue to climb. This is because critical fetal structural anomalies arise from developmental errors occurring in the embryonic period – between 2 and 13 weeks of gestation – a time when most women with preexisting diabetes are just entering into prenatal care, often with suboptimal glycemic control.
Thus, significant future progress in reducing fetal mortality and childhood disability in infants of diabetic mothers will depend upon effective interventions in the first trimester while embryogenesis and critical organ formation are underway.
In this issue of Ob.Gyn. News, the editor of Master Class in Obstetrics, E. Albert Reece MD, PhD, MBA, steps into the role of coauthor. He and his research colleague Peixin Yang, PhD, present exciting insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying structural birth defects in infants of diabetic mothers – especially cardiac and neural tube defects – and also provide a glimpse into some potentially effective maternal pharmacologic interventions. After appropriate human trials, these interventions could be effectively applied from the time of a positive pregnancy test with potentially dramatic results.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang, who lead the Center for the Study of Birth Defects at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, share their impressive accumulation of data from embryos of pregnant diabetic rodents. They demonstrate convincingly that, in first-trimester rodent embryos, maternal hyperglycemia induces excessive apoptosis, which in turn leads to structural defects in critical fetal organs. They further found that maternal hyperglycemia reduces embryonic autophagosomes – the developmentally essential organelles that remove abnormal or damaged cells during embryo formation.
These investigators also identified reactivators of these organelles which, when administered maternally in the first trimester, significantly reduced the incidence of neural tube defects. Thus, for optimal development of diabetes-affected embryos, first-trimester administration of reactivators of autophagy could offer a significant, life-changing intervention in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Moore is professor emeritus of maternal-fetal medicine and chair emeritus in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at UC San Diego Health. He reported no disclosures.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
Many issues surrounding pregnancy care of women with preexisting diabetes remain challenging, especially in light of the relentless increase in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and globally. Rising rates of death and severe morbidity in diabetic women have continued despite significant advances in insulin pharmacology and administration technology.
However, despite these advances in glucose monitoring and insulin administration, fetal mortality and childhood morbidity rates continue to climb. This is because critical fetal structural anomalies arise from developmental errors occurring in the embryonic period – between 2 and 13 weeks of gestation – a time when most women with preexisting diabetes are just entering into prenatal care, often with suboptimal glycemic control.
Thus, significant future progress in reducing fetal mortality and childhood disability in infants of diabetic mothers will depend upon effective interventions in the first trimester while embryogenesis and critical organ formation are underway.
In this issue of Ob.Gyn. News, the editor of Master Class in Obstetrics, E. Albert Reece MD, PhD, MBA, steps into the role of coauthor. He and his research colleague Peixin Yang, PhD, present exciting insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying structural birth defects in infants of diabetic mothers – especially cardiac and neural tube defects – and also provide a glimpse into some potentially effective maternal pharmacologic interventions. After appropriate human trials, these interventions could be effectively applied from the time of a positive pregnancy test with potentially dramatic results.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang, who lead the Center for the Study of Birth Defects at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, share their impressive accumulation of data from embryos of pregnant diabetic rodents. They demonstrate convincingly that, in first-trimester rodent embryos, maternal hyperglycemia induces excessive apoptosis, which in turn leads to structural defects in critical fetal organs. They further found that maternal hyperglycemia reduces embryonic autophagosomes – the developmentally essential organelles that remove abnormal or damaged cells during embryo formation.
These investigators also identified reactivators of these organelles which, when administered maternally in the first trimester, significantly reduced the incidence of neural tube defects. Thus, for optimal development of diabetes-affected embryos, first-trimester administration of reactivators of autophagy could offer a significant, life-changing intervention in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Moore is professor emeritus of maternal-fetal medicine and chair emeritus in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at UC San Diego Health. He reported no disclosures.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
First-in-class device for facial wrinkles, tightening hits the market
DENVER – .
“It’s early yet, but I have treated dozens of patients with this device, and they have been happy with the results,” Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “This is a new technique that offers the ability to remove a significant amount of damaged, lax skin without concern for scarring,” he said.
A brainchild of dermatologists and plastic surgeons at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, the first-in-class device is cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of moderate and severe wrinkles in the mid and lower face in adults aged 22 years or older with Fitzpatrick skin types I-IV. It features a proprietary needle design that makes a series of high throughput microexcisions in epidermal and dermal tissue, with minimal downtime and without using thermal energy.
“It doesn’t do anything equivalent to a facelift, but the concept is a facelift by thousands of micro-punch excisions,” said Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital. “Rather than pulling up the skin and lifting it and cutting the excess skin like we do with a facelift, we are creating thousands of smaller-scale tissue removals with immediate closures to do the same thing. The micro-cores are about the size of a 22-gauge needle and there is no scarring due to the small size of these tissue extractions.”
The device features needle cartridges capable of excising up to 24,000 cores per treatment. According to data from Cytrellis, the manufacturer, the equivalent of about 2 inches of skin can be removed during the procedure, which typically takes fewer than 30 minutes to perform. “There is no heat whatsoever,” Dr. Avram said. “In my experience, it especially helps with jawline definition, the lower medial cheek excess skin, and accordion lines in that area.”
In a pivotal trial of the device, 51 patients with mid to lower face wrinkles (moderately deep or deep wrinkles with well-defined edges) were treated 2-3 times with 7%-8% skin removal and up to a 5-mm needle coring depth). The investigators found that 40% of study participants achieved an improvement of 2 grades on the Lemperle Wrinkle Severity Scale and that the rate of overall satisfaction (slightly, somewhat, and extremely satisfied) was 86%.
In addition, 90% showed improvement of treated sites on the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale, and 70% were comfortable enough to go out in public or return to work 3 days after treatment. Common side effects that can occur immediately post treatment include redness, swelling, and pinpoint bleeding, which typically clear in a few days.
Dr. Avram, immediate past president of the ASDS, has posted videos to his Instagram feed that show him treating patients with the Ellacor device and he admits that the procedure looks painful. “There are all these tear emojis and people cursing me out,” he said, referring to responses from his Instagram followers.
Proper local anesthesia prior to treatment is key. “I perform nerve blocks and infiltrate the skin,” he said. “You have to cover the whole treatment area. If you don’t, then it’s going to hurt. The average pain score is 1.9 out of 10. The highest pain score I’ve gotten from a patient is a 3 out of 10.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Merz, Sciton, and Soliton, and has ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis.
DENVER – .
“It’s early yet, but I have treated dozens of patients with this device, and they have been happy with the results,” Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “This is a new technique that offers the ability to remove a significant amount of damaged, lax skin without concern for scarring,” he said.
A brainchild of dermatologists and plastic surgeons at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, the first-in-class device is cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of moderate and severe wrinkles in the mid and lower face in adults aged 22 years or older with Fitzpatrick skin types I-IV. It features a proprietary needle design that makes a series of high throughput microexcisions in epidermal and dermal tissue, with minimal downtime and without using thermal energy.
“It doesn’t do anything equivalent to a facelift, but the concept is a facelift by thousands of micro-punch excisions,” said Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital. “Rather than pulling up the skin and lifting it and cutting the excess skin like we do with a facelift, we are creating thousands of smaller-scale tissue removals with immediate closures to do the same thing. The micro-cores are about the size of a 22-gauge needle and there is no scarring due to the small size of these tissue extractions.”
The device features needle cartridges capable of excising up to 24,000 cores per treatment. According to data from Cytrellis, the manufacturer, the equivalent of about 2 inches of skin can be removed during the procedure, which typically takes fewer than 30 minutes to perform. “There is no heat whatsoever,” Dr. Avram said. “In my experience, it especially helps with jawline definition, the lower medial cheek excess skin, and accordion lines in that area.”
In a pivotal trial of the device, 51 patients with mid to lower face wrinkles (moderately deep or deep wrinkles with well-defined edges) were treated 2-3 times with 7%-8% skin removal and up to a 5-mm needle coring depth). The investigators found that 40% of study participants achieved an improvement of 2 grades on the Lemperle Wrinkle Severity Scale and that the rate of overall satisfaction (slightly, somewhat, and extremely satisfied) was 86%.
In addition, 90% showed improvement of treated sites on the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale, and 70% were comfortable enough to go out in public or return to work 3 days after treatment. Common side effects that can occur immediately post treatment include redness, swelling, and pinpoint bleeding, which typically clear in a few days.
Dr. Avram, immediate past president of the ASDS, has posted videos to his Instagram feed that show him treating patients with the Ellacor device and he admits that the procedure looks painful. “There are all these tear emojis and people cursing me out,” he said, referring to responses from his Instagram followers.
Proper local anesthesia prior to treatment is key. “I perform nerve blocks and infiltrate the skin,” he said. “You have to cover the whole treatment area. If you don’t, then it’s going to hurt. The average pain score is 1.9 out of 10. The highest pain score I’ve gotten from a patient is a 3 out of 10.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Merz, Sciton, and Soliton, and has ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis.
DENVER – .
“It’s early yet, but I have treated dozens of patients with this device, and they have been happy with the results,” Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “This is a new technique that offers the ability to remove a significant amount of damaged, lax skin without concern for scarring,” he said.
A brainchild of dermatologists and plastic surgeons at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, the first-in-class device is cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of moderate and severe wrinkles in the mid and lower face in adults aged 22 years or older with Fitzpatrick skin types I-IV. It features a proprietary needle design that makes a series of high throughput microexcisions in epidermal and dermal tissue, with minimal downtime and without using thermal energy.
“It doesn’t do anything equivalent to a facelift, but the concept is a facelift by thousands of micro-punch excisions,” said Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital. “Rather than pulling up the skin and lifting it and cutting the excess skin like we do with a facelift, we are creating thousands of smaller-scale tissue removals with immediate closures to do the same thing. The micro-cores are about the size of a 22-gauge needle and there is no scarring due to the small size of these tissue extractions.”
The device features needle cartridges capable of excising up to 24,000 cores per treatment. According to data from Cytrellis, the manufacturer, the equivalent of about 2 inches of skin can be removed during the procedure, which typically takes fewer than 30 minutes to perform. “There is no heat whatsoever,” Dr. Avram said. “In my experience, it especially helps with jawline definition, the lower medial cheek excess skin, and accordion lines in that area.”
In a pivotal trial of the device, 51 patients with mid to lower face wrinkles (moderately deep or deep wrinkles with well-defined edges) were treated 2-3 times with 7%-8% skin removal and up to a 5-mm needle coring depth). The investigators found that 40% of study participants achieved an improvement of 2 grades on the Lemperle Wrinkle Severity Scale and that the rate of overall satisfaction (slightly, somewhat, and extremely satisfied) was 86%.
In addition, 90% showed improvement of treated sites on the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale, and 70% were comfortable enough to go out in public or return to work 3 days after treatment. Common side effects that can occur immediately post treatment include redness, swelling, and pinpoint bleeding, which typically clear in a few days.
Dr. Avram, immediate past president of the ASDS, has posted videos to his Instagram feed that show him treating patients with the Ellacor device and he admits that the procedure looks painful. “There are all these tear emojis and people cursing me out,” he said, referring to responses from his Instagram followers.
Proper local anesthesia prior to treatment is key. “I perform nerve blocks and infiltrate the skin,” he said. “You have to cover the whole treatment area. If you don’t, then it’s going to hurt. The average pain score is 1.9 out of 10. The highest pain score I’ve gotten from a patient is a 3 out of 10.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Merz, Sciton, and Soliton, and has ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis.
AT ASDS 2022
Many specialists are on the wrong side of the patient-jargon relationship
Doctor, doctor, gimme the news. I got a bad case of misidentifying you
There are a lot of medical specialties out there. A lot. Everything from allergists to urologists, with something like 150 subspecialties grouped in among the larger specialties. Can you name every one? Do you know what they do?
The point is, telling a patient or anyone in the general public that you’re an ophthalmologist may not be as helpful as you might think, if a recent study is to be believed. In a survey of 204 adults, conducted at the Minnesota State Fair of all places, researchers asked volunteers to define 14 different specialties, as well as five medical seniority titles.
The results were less than stellar. While more than 90% of people correctly defined what cardiologists and dermatologists do, 6 of the other 12 specialists were correctly identified by less than half of those surveyed. Nephrology was at the bottom, correctly identified by just 20% of the fair-attending public, followed by internists (21%), intensivists (29%), hospitalists (31%), pulmonologists (43%), and neonatologists at 48%. The hospitalists are particularly concerning. They’re doctors, but in hospitals. How hard is that? (Yes, it’s obviously more complicated than that, but still.)
The general public didn’t fare much better when it came to correctly lining up the order of progression from medical student to attending. Just 12% managed to place all five in the correct order of med student, intern, senior resident, fellow, then attending, with senior resident proving especially troublesome. More than 40% put senior resident at the end, compared with 27% for attending. Which does make a certain amount of sense, since it has senior in the name.
While the results speak for themselves – maybe elaborate on what the heck your fancy title actually means – it’s too bad the researchers didn’t throw in something really tricky. If two-thirds of the population can’t identify a hospitalist, just imagine how many people would misidentify an otolaryngologist.
Beach-to-table sand could fight obesity
People are always looking for the new weight loss solution. Whether it’s to just look good in a new pair of jeans or reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, there are millions of diets and exercise routines out here. We’re here to tell you that the next new therapy to reduce fat comes from a very unsuspecting place: Sand.
Like sand from the beach and desert, sand? Well, yes and no.
The research involved engineered porous silica particles made from sand that are designed to have a high surface area. Investigators used a two-step GI model in which gastric digestion was modeled for 30 minutes, followed by a 60-minute intestinal phase, to show that the porous silica particles helped prevent fat and sugar adsorption within the GI tract.
By mimicking the gastrointestinal environment during digestion of a high-fat, high-carb meal, the researchers found that the porous silica created an “anti-obesity effect” by restricting the adsorption of those fats and carbohydrates.
Okay, but how is that on the tummy? Much gentler on the stomach than a drug such as orlistat, said senior researcher Paul Joyce, PhD, of the University of South Australia, Adelaide, who noted the lack of effective therapies without side effects, such as bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, that deter people from treatment.
Obesity affects over 1.9 billion people worldwide, so the researchers think this could be a breakthrough. Reducing obesity may be one of the most preventable ways to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other weight-related chronic conditions. A treatment solution this simple could be the answer to this global health crisis.
Who would have thought the solution would be as simple as sand? But how would the sand get in our stomachs? Do we sprinkle it on our food? Mix it in during cooking? Or will the sand come in pill form? We sure hope it’s that third one.
I am Reliebo. I am here to help you
Halloween is almost here, and the LOTME staff has been trying to make the office look as scary as possible: Headless vampires, ghost clowns, Ted Cruz, gray tombstones, pink hearts, green clovers, red balloons. Wait a second, those last three are Lucky Charms marshmallows, aren’t they? We’ll use those some other time.
What are we not using to decorate? Well, besides marshmallows from cereal, we’re not using Reliebo. That’s what we’re not using. Reliebo is a cute little fuzzy robot, and is not at all scary. Reliebo was designed to be the opposite of scary. Reliebo “may reduce fear as well as alleviate the perception of pain during medical treatments, including vaccinations,” senior author Fumihide Tanaka, PhD, of the University of Tsukuba (Japan) said in a written statement.
The soft, fur-covered robot contains small airbags that can inflate in response to hand movements. When study participants were subjected to a moderate heat stimulus on one arm, those who held the robot with the other arm experienced less pain than those who did not have a Reliebo.
The results also were encouraging when Dr. Tanaka and associates measured the levels of oxytocin and cortisol (biomarkers for stress) from the subjects’ saliva samples and evaluated their fear of injections and their psychological state before and after the experiments.
After looking at that photo of Reliebo for a while, though, we have to admit that we’re having a bit of a rethink about its cuteness. Is it cute, or weird-looking? An office full of fuzzy little inflating robots just could be seriously creepy. Please don’t tell the rest of the staff about this. We want to surprise them on Monday.
Doctor, doctor, gimme the news. I got a bad case of misidentifying you
There are a lot of medical specialties out there. A lot. Everything from allergists to urologists, with something like 150 subspecialties grouped in among the larger specialties. Can you name every one? Do you know what they do?
The point is, telling a patient or anyone in the general public that you’re an ophthalmologist may not be as helpful as you might think, if a recent study is to be believed. In a survey of 204 adults, conducted at the Minnesota State Fair of all places, researchers asked volunteers to define 14 different specialties, as well as five medical seniority titles.
The results were less than stellar. While more than 90% of people correctly defined what cardiologists and dermatologists do, 6 of the other 12 specialists were correctly identified by less than half of those surveyed. Nephrology was at the bottom, correctly identified by just 20% of the fair-attending public, followed by internists (21%), intensivists (29%), hospitalists (31%), pulmonologists (43%), and neonatologists at 48%. The hospitalists are particularly concerning. They’re doctors, but in hospitals. How hard is that? (Yes, it’s obviously more complicated than that, but still.)
The general public didn’t fare much better when it came to correctly lining up the order of progression from medical student to attending. Just 12% managed to place all five in the correct order of med student, intern, senior resident, fellow, then attending, with senior resident proving especially troublesome. More than 40% put senior resident at the end, compared with 27% for attending. Which does make a certain amount of sense, since it has senior in the name.
While the results speak for themselves – maybe elaborate on what the heck your fancy title actually means – it’s too bad the researchers didn’t throw in something really tricky. If two-thirds of the population can’t identify a hospitalist, just imagine how many people would misidentify an otolaryngologist.
Beach-to-table sand could fight obesity
People are always looking for the new weight loss solution. Whether it’s to just look good in a new pair of jeans or reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, there are millions of diets and exercise routines out here. We’re here to tell you that the next new therapy to reduce fat comes from a very unsuspecting place: Sand.
Like sand from the beach and desert, sand? Well, yes and no.
The research involved engineered porous silica particles made from sand that are designed to have a high surface area. Investigators used a two-step GI model in which gastric digestion was modeled for 30 minutes, followed by a 60-minute intestinal phase, to show that the porous silica particles helped prevent fat and sugar adsorption within the GI tract.
By mimicking the gastrointestinal environment during digestion of a high-fat, high-carb meal, the researchers found that the porous silica created an “anti-obesity effect” by restricting the adsorption of those fats and carbohydrates.
Okay, but how is that on the tummy? Much gentler on the stomach than a drug such as orlistat, said senior researcher Paul Joyce, PhD, of the University of South Australia, Adelaide, who noted the lack of effective therapies without side effects, such as bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, that deter people from treatment.
Obesity affects over 1.9 billion people worldwide, so the researchers think this could be a breakthrough. Reducing obesity may be one of the most preventable ways to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other weight-related chronic conditions. A treatment solution this simple could be the answer to this global health crisis.
Who would have thought the solution would be as simple as sand? But how would the sand get in our stomachs? Do we sprinkle it on our food? Mix it in during cooking? Or will the sand come in pill form? We sure hope it’s that third one.
I am Reliebo. I am here to help you
Halloween is almost here, and the LOTME staff has been trying to make the office look as scary as possible: Headless vampires, ghost clowns, Ted Cruz, gray tombstones, pink hearts, green clovers, red balloons. Wait a second, those last three are Lucky Charms marshmallows, aren’t they? We’ll use those some other time.
What are we not using to decorate? Well, besides marshmallows from cereal, we’re not using Reliebo. That’s what we’re not using. Reliebo is a cute little fuzzy robot, and is not at all scary. Reliebo was designed to be the opposite of scary. Reliebo “may reduce fear as well as alleviate the perception of pain during medical treatments, including vaccinations,” senior author Fumihide Tanaka, PhD, of the University of Tsukuba (Japan) said in a written statement.
The soft, fur-covered robot contains small airbags that can inflate in response to hand movements. When study participants were subjected to a moderate heat stimulus on one arm, those who held the robot with the other arm experienced less pain than those who did not have a Reliebo.
The results also were encouraging when Dr. Tanaka and associates measured the levels of oxytocin and cortisol (biomarkers for stress) from the subjects’ saliva samples and evaluated their fear of injections and their psychological state before and after the experiments.
After looking at that photo of Reliebo for a while, though, we have to admit that we’re having a bit of a rethink about its cuteness. Is it cute, or weird-looking? An office full of fuzzy little inflating robots just could be seriously creepy. Please don’t tell the rest of the staff about this. We want to surprise them on Monday.
Doctor, doctor, gimme the news. I got a bad case of misidentifying you
There are a lot of medical specialties out there. A lot. Everything from allergists to urologists, with something like 150 subspecialties grouped in among the larger specialties. Can you name every one? Do you know what they do?
The point is, telling a patient or anyone in the general public that you’re an ophthalmologist may not be as helpful as you might think, if a recent study is to be believed. In a survey of 204 adults, conducted at the Minnesota State Fair of all places, researchers asked volunteers to define 14 different specialties, as well as five medical seniority titles.
The results were less than stellar. While more than 90% of people correctly defined what cardiologists and dermatologists do, 6 of the other 12 specialists were correctly identified by less than half of those surveyed. Nephrology was at the bottom, correctly identified by just 20% of the fair-attending public, followed by internists (21%), intensivists (29%), hospitalists (31%), pulmonologists (43%), and neonatologists at 48%. The hospitalists are particularly concerning. They’re doctors, but in hospitals. How hard is that? (Yes, it’s obviously more complicated than that, but still.)
The general public didn’t fare much better when it came to correctly lining up the order of progression from medical student to attending. Just 12% managed to place all five in the correct order of med student, intern, senior resident, fellow, then attending, with senior resident proving especially troublesome. More than 40% put senior resident at the end, compared with 27% for attending. Which does make a certain amount of sense, since it has senior in the name.
While the results speak for themselves – maybe elaborate on what the heck your fancy title actually means – it’s too bad the researchers didn’t throw in something really tricky. If two-thirds of the population can’t identify a hospitalist, just imagine how many people would misidentify an otolaryngologist.
Beach-to-table sand could fight obesity
People are always looking for the new weight loss solution. Whether it’s to just look good in a new pair of jeans or reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, there are millions of diets and exercise routines out here. We’re here to tell you that the next new therapy to reduce fat comes from a very unsuspecting place: Sand.
Like sand from the beach and desert, sand? Well, yes and no.
The research involved engineered porous silica particles made from sand that are designed to have a high surface area. Investigators used a two-step GI model in which gastric digestion was modeled for 30 minutes, followed by a 60-minute intestinal phase, to show that the porous silica particles helped prevent fat and sugar adsorption within the GI tract.
By mimicking the gastrointestinal environment during digestion of a high-fat, high-carb meal, the researchers found that the porous silica created an “anti-obesity effect” by restricting the adsorption of those fats and carbohydrates.
Okay, but how is that on the tummy? Much gentler on the stomach than a drug such as orlistat, said senior researcher Paul Joyce, PhD, of the University of South Australia, Adelaide, who noted the lack of effective therapies without side effects, such as bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, that deter people from treatment.
Obesity affects over 1.9 billion people worldwide, so the researchers think this could be a breakthrough. Reducing obesity may be one of the most preventable ways to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other weight-related chronic conditions. A treatment solution this simple could be the answer to this global health crisis.
Who would have thought the solution would be as simple as sand? But how would the sand get in our stomachs? Do we sprinkle it on our food? Mix it in during cooking? Or will the sand come in pill form? We sure hope it’s that third one.
I am Reliebo. I am here to help you
Halloween is almost here, and the LOTME staff has been trying to make the office look as scary as possible: Headless vampires, ghost clowns, Ted Cruz, gray tombstones, pink hearts, green clovers, red balloons. Wait a second, those last three are Lucky Charms marshmallows, aren’t they? We’ll use those some other time.
What are we not using to decorate? Well, besides marshmallows from cereal, we’re not using Reliebo. That’s what we’re not using. Reliebo is a cute little fuzzy robot, and is not at all scary. Reliebo was designed to be the opposite of scary. Reliebo “may reduce fear as well as alleviate the perception of pain during medical treatments, including vaccinations,” senior author Fumihide Tanaka, PhD, of the University of Tsukuba (Japan) said in a written statement.
The soft, fur-covered robot contains small airbags that can inflate in response to hand movements. When study participants were subjected to a moderate heat stimulus on one arm, those who held the robot with the other arm experienced less pain than those who did not have a Reliebo.
The results also were encouraging when Dr. Tanaka and associates measured the levels of oxytocin and cortisol (biomarkers for stress) from the subjects’ saliva samples and evaluated their fear of injections and their psychological state before and after the experiments.
After looking at that photo of Reliebo for a while, though, we have to admit that we’re having a bit of a rethink about its cuteness. Is it cute, or weird-looking? An office full of fuzzy little inflating robots just could be seriously creepy. Please don’t tell the rest of the staff about this. We want to surprise them on Monday.
‘Financial toxicity’: Harsh side effect of cancer care
When 32-year-old Brittany Dicks was diagnosed with stage II triple negative breast cancer in January 2022, she wasn’t worried about the cost of treatment. A medical assistant in Charleston, S.C., Ms. Dicks had full-time employment with health benefits.
But when she wasn’t able to work for several months because of chemotherapy and its side effects, Ms. Dicks lost her job. Her health insurance coverage ended in May. And although she filed for Medicaid at the beginning of June, it wasn’t approved until September.
Meanwhile, Ms. Dicks still needed treatment. She estimates that she ran up close to $20,000 in medical debt while finishing chemotherapy during the 4 months she was uninsured.
The surgeon she had seen since her diagnosis terminated her care when she could no longer pay her bills. That left her delaying a much-needed mastectomy.
“I don’t sleep at night,” said Ms. Dicks, a single mother of two young kids, ages 3 and 11. “Mentally, I’m drained. Just because I have cancer, doesn’t mean the bills aren’t due every month.”
As soon as she felt well enough over the summer, she started working as a part-time delivery driver for DoorDash to help pay for food and gas.
But that was just a Band-Aid. Even when her new insurance kicked in, covering the costs of daily life remained a struggle.
Ms. Dicks is still in deep medical debt. Her Medicaid has covered new medical expenses, and she hopes Medicaid will reimburse her for the debt she incurred over the summer while she waited for her coverage to kick in. So far, though, Medicaid has not touched her $20,000 debt.
“I fear that I’m not going to be able to dig out of this hole,” Ms. Dicks said.
Researchers who study the financial impacts of cancer have a term for Ms. Dicks’ experience: financial toxicity.
Financial toxicity is a catchall term for the burden many Americans with cancer experience.
“Financial toxicity is a multidimensional concept. There’s both a material burden and a psychosocial one,” said Grace Li Smith, MD, PhD, MPH, a radiation oncologist at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Researchers are also now beginning to understand the psychological effects these financial burdens can have on patients and their family.
“Financial toxicity is not unique to the patient,” said Dr. Li Smith. It “very directly impacts the whole family or household.”
Stifling financial pressures
Early in her career, Dr. Li Smith was already seeing how her patients’ worries extended beyond their physical disease.
One of Dr. Li Smith’s first patients told her their greatest worry wasn’t whether the treatment would work or what physical toxicity to expect, it was how they would pay for their care.
“There was much more anxiety and true distress about the financial burden than about the treatment itself,” Dr. Li Smith recalled.
This fear about the costs of cancer care is well founded. In the United States, cancer treatment costs reached an estimated $150 billion in 2020 and continue to rise. Patients shoulder a significant portion of that burden – with one study estimating that patients paid $21 billion for their cancer care in 2019.
The burden is often compounded by decreased income. Between 40% and 85% of patients with cancer needed to take time off work or quit their jobs during treatment. And for those, like Dicks, who find themselves with no insurance, out-of-pocket costs can quickly skyrocket.
In fact, one study of newly diagnosed cancer patients over age 50 reported that more than 42% of patients fully depleted their financial assets and around 30% incurred debt by the second year of their diagnosis.
Younger adults may be even more financially vulnerable. A study of patients in Washington found that those under 65 – which represent about half of cancer cases – were two to five times more likely to declare bankruptcy than patients over 65.
Dr. Li Smith and colleagues have found that younger patients aged 18-64 experienced greater monetary hardships, which meant less money for food, worse adherence to medications, as well as greater distress and anxiety overall. In fact, younger adults were over 4.5 times more likely to encounter severe financial toxicity, compared with older adults, and about 4 times more likely to experience severe psychological effects from this burden.
The distress, if left unchecked, can spiral out of control.
Molly MacDonald had just gone through a financially devastating divorce in 2005 when she was diagnosed with breast cancer. Recently out of work and dealing with a $1,300 monthly COBRA premium, the mother of five had no financial safety net. She risked having her car repossessed and her utilities shut off.
“I gave tentative thought to how I could take my life and make it look like an accident,” said Ms. MacDonald. “I thought the kids would be better off without me.”
For some, the loss of income can be even more worrisome than the medical bills. Some patients may go back to work during treatment, often against medical advice.
When Stephanie Caputo, 43, of Monroe, N.J., began treatment for stage III breast cancer in 2021, her physician recommended she stop working. Treatment would make her immunocompromised, and her job in a medical clinic could expose her to harmful pathogens, including the coronavirus.
Ms. Caputo went on disability and received $900 every 2 weeks. But that wasn’t enough to pay her mortgage, let alone cover her other monthly expenses as a single mother of 4 teenagers.
After finishing chemotherapy, and during radiation, Ms. Caputo went back to work, part time, against her doctor’s advice.
“My doctor is telling me I can’t work, but I also can’t have my house go into default,” said Ms. Caputo.
But being on her feet through 12-hour shifts made treatment side effects, especially back and joint pain, kick into overdrive. “The physicality of my job was really difficult to tolerate,” she said.
The physical burden was too great to take on more work, but the extra money also wasn’t enough to keep her afloat. Fortunately, her brother stepped in and covered 6 months of her mortgage payments.
Financial toxicity impacts families
Although financial toxicity research to date has largely focused on the patient, researchers are also starting to understand that family members and caregivers often share in the burden.
“We are just at the beginning of realizing that this is a real problem,” said Fumiko Chino, MD, a radiation oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
Dr. Chino and colleagues recently showed that family members of patients with cancer were more likely to delay or forgo medical care than family members of people without cancer. The study found the effect was greatest among family members of younger adults with cancer.
“The caregiver and family burden related to cancer diagnosis and treatment is really underappreciated,” said Dr. Chino. “Family members and caregivers are neglecting their own health concerns, passing up career opportunities, struggling with financial concerns.”
Dr. Chino speaks from personal experience. When her fiancé, later husband, was diagnosed with neuroendocrine carcinoma in 2005, Dr. Chino quit her job as art director at a television production company to take care of him.
The couple, both in their 20s, struggled to afford his care. Dr. Chino put her own dental, medical, and mental health care on hold. She never, for instance, went to physical therapy to address injuries sustained sleeping in hospital chairs and moving around her husband who was over 6 feet tall. At one point, she walked with a limp.
Dr. Chino’s husband passed away in 2007, and even 15 years later, her injury from sleeping in hospital chairs remains “a significant physical burden,” she said. But like many caregivers “I wasn’t really thinking about my own health.”
Danielle Hadfield, 35, an ED nurse in Rochester, N.Y., also delayed her own care when her mom got sick.
Ms. Hadfield quit her job shortly after her mom was diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma in August 2020. Ms. Hadfield knew her mom, who lived 3.5 hours away in Albany, N.Y., would need a lot of care in the upcoming months.
“I knew this was going to be the last year or so of her life, and I wanted to be there for her,” said Ms. Hadfield.
When Ms. Hadfield quit her job, she and her husband – who was self-employed – purchased health insurance coverage through the New York state marketplace. The monthly insurance payments for Ms. Hadfield, who was pregnant with her second child, her husband, and their toddler cost as much as the family’s monthly mortgage payments.
In addition to providing childcare for her young daughter and making frequent trips to Albany, Ms. Hadfield began a side business as a legal nurse consultant, working mostly at night, to replace a portion of her lost income. During this time, she began to experience pain attacks that would migrate through her body along with intermittent tongue and facial numbness. She ignored these health issues for nearly a year, until after her mother died in November 2021.
Only after her mother passed away did Ms. Hadfield begin seeking answers to her own pain. In September 2022, she finally got them. She had a nerve condition called small-fiber sensory neuropathy.
But even with a diagnosis, she is still facing more tests to root out the cause and understand the best treatment.
Is help out there?
What can physicians do to help patients and families at risk for financial toxicity?
Specific guidelines for dealing with financial toxicity do not exist in most professional guidelines, nor are there standard screening tools to identify it, said Dr. Li Smith.
These gaps put pressure on physicians to ask about financial barriers and concerns, but most do not know how to broach the topic or how to help. “Physicians may not know how to fix the problem or what resources exist,” Dr. Li Smith said.
Patients and family members, on the other hand, are often reluctant to bring up cost with physicians. Some may be ashamed to talk about their financial problems while others may fear doing so will prevent them from being offered the best possible treatments, said Ms. MacDonald.
But, experts say, financial toxicity needs to be dealt with head on. That means involving financial navigators or counselors and social workers who can, for instance, help patients and families find financial support for their basic living expenses.
From a research perspective, more clinical trials should include financial toxicity outcomes, said Joshua Palmer, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Dr. Palmer and colleagues recently showed that the number of radiation therapy clinical trials including financial toxicity endpoints increased significantly from 2001 to 2020, though the absolute rate of inclusion remains low, at roughly 1.5% of radiation therapy-based clinical trials including financial toxicity endpoints from 2016 to 2020.
“Financial burden is part of the broader discussion about shared decision-making,” said Dr. Palmer.
In shared decision-making, physicians discuss the risks and benefits of different treatment options, empowering the patient to make an informed choice with the physician.
What we want to avoid is patients feeling like they will get inferior care, if they have financial barriers, said Dr. Palmer.
And every little bit can help. In 2006, Ms. MacDonald started the Pink Fund – a nonprofit to help patients with cancer cover nonmedical cost-of-living expenses. Both Ms. Caputo and Ms. Dicks received grants from the Pink Fund. For Ms. Caputo, the funds covered 2 months of car payments and for Ms. Dicks, it covered 2 months of rent.
While the one-time grant was a big help, said Ms. Dicks, “cancer is an everyday thing.” And “we all deserve peace of mind” when trying to heal.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When 32-year-old Brittany Dicks was diagnosed with stage II triple negative breast cancer in January 2022, she wasn’t worried about the cost of treatment. A medical assistant in Charleston, S.C., Ms. Dicks had full-time employment with health benefits.
But when she wasn’t able to work for several months because of chemotherapy and its side effects, Ms. Dicks lost her job. Her health insurance coverage ended in May. And although she filed for Medicaid at the beginning of June, it wasn’t approved until September.
Meanwhile, Ms. Dicks still needed treatment. She estimates that she ran up close to $20,000 in medical debt while finishing chemotherapy during the 4 months she was uninsured.
The surgeon she had seen since her diagnosis terminated her care when she could no longer pay her bills. That left her delaying a much-needed mastectomy.
“I don’t sleep at night,” said Ms. Dicks, a single mother of two young kids, ages 3 and 11. “Mentally, I’m drained. Just because I have cancer, doesn’t mean the bills aren’t due every month.”
As soon as she felt well enough over the summer, she started working as a part-time delivery driver for DoorDash to help pay for food and gas.
But that was just a Band-Aid. Even when her new insurance kicked in, covering the costs of daily life remained a struggle.
Ms. Dicks is still in deep medical debt. Her Medicaid has covered new medical expenses, and she hopes Medicaid will reimburse her for the debt she incurred over the summer while she waited for her coverage to kick in. So far, though, Medicaid has not touched her $20,000 debt.
“I fear that I’m not going to be able to dig out of this hole,” Ms. Dicks said.
Researchers who study the financial impacts of cancer have a term for Ms. Dicks’ experience: financial toxicity.
Financial toxicity is a catchall term for the burden many Americans with cancer experience.
“Financial toxicity is a multidimensional concept. There’s both a material burden and a psychosocial one,” said Grace Li Smith, MD, PhD, MPH, a radiation oncologist at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Researchers are also now beginning to understand the psychological effects these financial burdens can have on patients and their family.
“Financial toxicity is not unique to the patient,” said Dr. Li Smith. It “very directly impacts the whole family or household.”
Stifling financial pressures
Early in her career, Dr. Li Smith was already seeing how her patients’ worries extended beyond their physical disease.
One of Dr. Li Smith’s first patients told her their greatest worry wasn’t whether the treatment would work or what physical toxicity to expect, it was how they would pay for their care.
“There was much more anxiety and true distress about the financial burden than about the treatment itself,” Dr. Li Smith recalled.
This fear about the costs of cancer care is well founded. In the United States, cancer treatment costs reached an estimated $150 billion in 2020 and continue to rise. Patients shoulder a significant portion of that burden – with one study estimating that patients paid $21 billion for their cancer care in 2019.
The burden is often compounded by decreased income. Between 40% and 85% of patients with cancer needed to take time off work or quit their jobs during treatment. And for those, like Dicks, who find themselves with no insurance, out-of-pocket costs can quickly skyrocket.
In fact, one study of newly diagnosed cancer patients over age 50 reported that more than 42% of patients fully depleted their financial assets and around 30% incurred debt by the second year of their diagnosis.
Younger adults may be even more financially vulnerable. A study of patients in Washington found that those under 65 – which represent about half of cancer cases – were two to five times more likely to declare bankruptcy than patients over 65.
Dr. Li Smith and colleagues have found that younger patients aged 18-64 experienced greater monetary hardships, which meant less money for food, worse adherence to medications, as well as greater distress and anxiety overall. In fact, younger adults were over 4.5 times more likely to encounter severe financial toxicity, compared with older adults, and about 4 times more likely to experience severe psychological effects from this burden.
The distress, if left unchecked, can spiral out of control.
Molly MacDonald had just gone through a financially devastating divorce in 2005 when she was diagnosed with breast cancer. Recently out of work and dealing with a $1,300 monthly COBRA premium, the mother of five had no financial safety net. She risked having her car repossessed and her utilities shut off.
“I gave tentative thought to how I could take my life and make it look like an accident,” said Ms. MacDonald. “I thought the kids would be better off without me.”
For some, the loss of income can be even more worrisome than the medical bills. Some patients may go back to work during treatment, often against medical advice.
When Stephanie Caputo, 43, of Monroe, N.J., began treatment for stage III breast cancer in 2021, her physician recommended she stop working. Treatment would make her immunocompromised, and her job in a medical clinic could expose her to harmful pathogens, including the coronavirus.
Ms. Caputo went on disability and received $900 every 2 weeks. But that wasn’t enough to pay her mortgage, let alone cover her other monthly expenses as a single mother of 4 teenagers.
After finishing chemotherapy, and during radiation, Ms. Caputo went back to work, part time, against her doctor’s advice.
“My doctor is telling me I can’t work, but I also can’t have my house go into default,” said Ms. Caputo.
But being on her feet through 12-hour shifts made treatment side effects, especially back and joint pain, kick into overdrive. “The physicality of my job was really difficult to tolerate,” she said.
The physical burden was too great to take on more work, but the extra money also wasn’t enough to keep her afloat. Fortunately, her brother stepped in and covered 6 months of her mortgage payments.
Financial toxicity impacts families
Although financial toxicity research to date has largely focused on the patient, researchers are also starting to understand that family members and caregivers often share in the burden.
“We are just at the beginning of realizing that this is a real problem,” said Fumiko Chino, MD, a radiation oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
Dr. Chino and colleagues recently showed that family members of patients with cancer were more likely to delay or forgo medical care than family members of people without cancer. The study found the effect was greatest among family members of younger adults with cancer.
“The caregiver and family burden related to cancer diagnosis and treatment is really underappreciated,” said Dr. Chino. “Family members and caregivers are neglecting their own health concerns, passing up career opportunities, struggling with financial concerns.”
Dr. Chino speaks from personal experience. When her fiancé, later husband, was diagnosed with neuroendocrine carcinoma in 2005, Dr. Chino quit her job as art director at a television production company to take care of him.
The couple, both in their 20s, struggled to afford his care. Dr. Chino put her own dental, medical, and mental health care on hold. She never, for instance, went to physical therapy to address injuries sustained sleeping in hospital chairs and moving around her husband who was over 6 feet tall. At one point, she walked with a limp.
Dr. Chino’s husband passed away in 2007, and even 15 years later, her injury from sleeping in hospital chairs remains “a significant physical burden,” she said. But like many caregivers “I wasn’t really thinking about my own health.”
Danielle Hadfield, 35, an ED nurse in Rochester, N.Y., also delayed her own care when her mom got sick.
Ms. Hadfield quit her job shortly after her mom was diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma in August 2020. Ms. Hadfield knew her mom, who lived 3.5 hours away in Albany, N.Y., would need a lot of care in the upcoming months.
“I knew this was going to be the last year or so of her life, and I wanted to be there for her,” said Ms. Hadfield.
When Ms. Hadfield quit her job, she and her husband – who was self-employed – purchased health insurance coverage through the New York state marketplace. The monthly insurance payments for Ms. Hadfield, who was pregnant with her second child, her husband, and their toddler cost as much as the family’s monthly mortgage payments.
In addition to providing childcare for her young daughter and making frequent trips to Albany, Ms. Hadfield began a side business as a legal nurse consultant, working mostly at night, to replace a portion of her lost income. During this time, she began to experience pain attacks that would migrate through her body along with intermittent tongue and facial numbness. She ignored these health issues for nearly a year, until after her mother died in November 2021.
Only after her mother passed away did Ms. Hadfield begin seeking answers to her own pain. In September 2022, she finally got them. She had a nerve condition called small-fiber sensory neuropathy.
But even with a diagnosis, she is still facing more tests to root out the cause and understand the best treatment.
Is help out there?
What can physicians do to help patients and families at risk for financial toxicity?
Specific guidelines for dealing with financial toxicity do not exist in most professional guidelines, nor are there standard screening tools to identify it, said Dr. Li Smith.
These gaps put pressure on physicians to ask about financial barriers and concerns, but most do not know how to broach the topic or how to help. “Physicians may not know how to fix the problem or what resources exist,” Dr. Li Smith said.
Patients and family members, on the other hand, are often reluctant to bring up cost with physicians. Some may be ashamed to talk about their financial problems while others may fear doing so will prevent them from being offered the best possible treatments, said Ms. MacDonald.
But, experts say, financial toxicity needs to be dealt with head on. That means involving financial navigators or counselors and social workers who can, for instance, help patients and families find financial support for their basic living expenses.
From a research perspective, more clinical trials should include financial toxicity outcomes, said Joshua Palmer, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Dr. Palmer and colleagues recently showed that the number of radiation therapy clinical trials including financial toxicity endpoints increased significantly from 2001 to 2020, though the absolute rate of inclusion remains low, at roughly 1.5% of radiation therapy-based clinical trials including financial toxicity endpoints from 2016 to 2020.
“Financial burden is part of the broader discussion about shared decision-making,” said Dr. Palmer.
In shared decision-making, physicians discuss the risks and benefits of different treatment options, empowering the patient to make an informed choice with the physician.
What we want to avoid is patients feeling like they will get inferior care, if they have financial barriers, said Dr. Palmer.
And every little bit can help. In 2006, Ms. MacDonald started the Pink Fund – a nonprofit to help patients with cancer cover nonmedical cost-of-living expenses. Both Ms. Caputo and Ms. Dicks received grants from the Pink Fund. For Ms. Caputo, the funds covered 2 months of car payments and for Ms. Dicks, it covered 2 months of rent.
While the one-time grant was a big help, said Ms. Dicks, “cancer is an everyday thing.” And “we all deserve peace of mind” when trying to heal.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When 32-year-old Brittany Dicks was diagnosed with stage II triple negative breast cancer in January 2022, she wasn’t worried about the cost of treatment. A medical assistant in Charleston, S.C., Ms. Dicks had full-time employment with health benefits.
But when she wasn’t able to work for several months because of chemotherapy and its side effects, Ms. Dicks lost her job. Her health insurance coverage ended in May. And although she filed for Medicaid at the beginning of June, it wasn’t approved until September.
Meanwhile, Ms. Dicks still needed treatment. She estimates that she ran up close to $20,000 in medical debt while finishing chemotherapy during the 4 months she was uninsured.
The surgeon she had seen since her diagnosis terminated her care when she could no longer pay her bills. That left her delaying a much-needed mastectomy.
“I don’t sleep at night,” said Ms. Dicks, a single mother of two young kids, ages 3 and 11. “Mentally, I’m drained. Just because I have cancer, doesn’t mean the bills aren’t due every month.”
As soon as she felt well enough over the summer, she started working as a part-time delivery driver for DoorDash to help pay for food and gas.
But that was just a Band-Aid. Even when her new insurance kicked in, covering the costs of daily life remained a struggle.
Ms. Dicks is still in deep medical debt. Her Medicaid has covered new medical expenses, and she hopes Medicaid will reimburse her for the debt she incurred over the summer while she waited for her coverage to kick in. So far, though, Medicaid has not touched her $20,000 debt.
“I fear that I’m not going to be able to dig out of this hole,” Ms. Dicks said.
Researchers who study the financial impacts of cancer have a term for Ms. Dicks’ experience: financial toxicity.
Financial toxicity is a catchall term for the burden many Americans with cancer experience.
“Financial toxicity is a multidimensional concept. There’s both a material burden and a psychosocial one,” said Grace Li Smith, MD, PhD, MPH, a radiation oncologist at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Researchers are also now beginning to understand the psychological effects these financial burdens can have on patients and their family.
“Financial toxicity is not unique to the patient,” said Dr. Li Smith. It “very directly impacts the whole family or household.”
Stifling financial pressures
Early in her career, Dr. Li Smith was already seeing how her patients’ worries extended beyond their physical disease.
One of Dr. Li Smith’s first patients told her their greatest worry wasn’t whether the treatment would work or what physical toxicity to expect, it was how they would pay for their care.
“There was much more anxiety and true distress about the financial burden than about the treatment itself,” Dr. Li Smith recalled.
This fear about the costs of cancer care is well founded. In the United States, cancer treatment costs reached an estimated $150 billion in 2020 and continue to rise. Patients shoulder a significant portion of that burden – with one study estimating that patients paid $21 billion for their cancer care in 2019.
The burden is often compounded by decreased income. Between 40% and 85% of patients with cancer needed to take time off work or quit their jobs during treatment. And for those, like Dicks, who find themselves with no insurance, out-of-pocket costs can quickly skyrocket.
In fact, one study of newly diagnosed cancer patients over age 50 reported that more than 42% of patients fully depleted their financial assets and around 30% incurred debt by the second year of their diagnosis.
Younger adults may be even more financially vulnerable. A study of patients in Washington found that those under 65 – which represent about half of cancer cases – were two to five times more likely to declare bankruptcy than patients over 65.
Dr. Li Smith and colleagues have found that younger patients aged 18-64 experienced greater monetary hardships, which meant less money for food, worse adherence to medications, as well as greater distress and anxiety overall. In fact, younger adults were over 4.5 times more likely to encounter severe financial toxicity, compared with older adults, and about 4 times more likely to experience severe psychological effects from this burden.
The distress, if left unchecked, can spiral out of control.
Molly MacDonald had just gone through a financially devastating divorce in 2005 when she was diagnosed with breast cancer. Recently out of work and dealing with a $1,300 monthly COBRA premium, the mother of five had no financial safety net. She risked having her car repossessed and her utilities shut off.
“I gave tentative thought to how I could take my life and make it look like an accident,” said Ms. MacDonald. “I thought the kids would be better off without me.”
For some, the loss of income can be even more worrisome than the medical bills. Some patients may go back to work during treatment, often against medical advice.
When Stephanie Caputo, 43, of Monroe, N.J., began treatment for stage III breast cancer in 2021, her physician recommended she stop working. Treatment would make her immunocompromised, and her job in a medical clinic could expose her to harmful pathogens, including the coronavirus.
Ms. Caputo went on disability and received $900 every 2 weeks. But that wasn’t enough to pay her mortgage, let alone cover her other monthly expenses as a single mother of 4 teenagers.
After finishing chemotherapy, and during radiation, Ms. Caputo went back to work, part time, against her doctor’s advice.
“My doctor is telling me I can’t work, but I also can’t have my house go into default,” said Ms. Caputo.
But being on her feet through 12-hour shifts made treatment side effects, especially back and joint pain, kick into overdrive. “The physicality of my job was really difficult to tolerate,” she said.
The physical burden was too great to take on more work, but the extra money also wasn’t enough to keep her afloat. Fortunately, her brother stepped in and covered 6 months of her mortgage payments.
Financial toxicity impacts families
Although financial toxicity research to date has largely focused on the patient, researchers are also starting to understand that family members and caregivers often share in the burden.
“We are just at the beginning of realizing that this is a real problem,” said Fumiko Chino, MD, a radiation oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
Dr. Chino and colleagues recently showed that family members of patients with cancer were more likely to delay or forgo medical care than family members of people without cancer. The study found the effect was greatest among family members of younger adults with cancer.
“The caregiver and family burden related to cancer diagnosis and treatment is really underappreciated,” said Dr. Chino. “Family members and caregivers are neglecting their own health concerns, passing up career opportunities, struggling with financial concerns.”
Dr. Chino speaks from personal experience. When her fiancé, later husband, was diagnosed with neuroendocrine carcinoma in 2005, Dr. Chino quit her job as art director at a television production company to take care of him.
The couple, both in their 20s, struggled to afford his care. Dr. Chino put her own dental, medical, and mental health care on hold. She never, for instance, went to physical therapy to address injuries sustained sleeping in hospital chairs and moving around her husband who was over 6 feet tall. At one point, she walked with a limp.
Dr. Chino’s husband passed away in 2007, and even 15 years later, her injury from sleeping in hospital chairs remains “a significant physical burden,” she said. But like many caregivers “I wasn’t really thinking about my own health.”
Danielle Hadfield, 35, an ED nurse in Rochester, N.Y., also delayed her own care when her mom got sick.
Ms. Hadfield quit her job shortly after her mom was diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma in August 2020. Ms. Hadfield knew her mom, who lived 3.5 hours away in Albany, N.Y., would need a lot of care in the upcoming months.
“I knew this was going to be the last year or so of her life, and I wanted to be there for her,” said Ms. Hadfield.
When Ms. Hadfield quit her job, she and her husband – who was self-employed – purchased health insurance coverage through the New York state marketplace. The monthly insurance payments for Ms. Hadfield, who was pregnant with her second child, her husband, and their toddler cost as much as the family’s monthly mortgage payments.
In addition to providing childcare for her young daughter and making frequent trips to Albany, Ms. Hadfield began a side business as a legal nurse consultant, working mostly at night, to replace a portion of her lost income. During this time, she began to experience pain attacks that would migrate through her body along with intermittent tongue and facial numbness. She ignored these health issues for nearly a year, until after her mother died in November 2021.
Only after her mother passed away did Ms. Hadfield begin seeking answers to her own pain. In September 2022, she finally got them. She had a nerve condition called small-fiber sensory neuropathy.
But even with a diagnosis, she is still facing more tests to root out the cause and understand the best treatment.
Is help out there?
What can physicians do to help patients and families at risk for financial toxicity?
Specific guidelines for dealing with financial toxicity do not exist in most professional guidelines, nor are there standard screening tools to identify it, said Dr. Li Smith.
These gaps put pressure on physicians to ask about financial barriers and concerns, but most do not know how to broach the topic or how to help. “Physicians may not know how to fix the problem or what resources exist,” Dr. Li Smith said.
Patients and family members, on the other hand, are often reluctant to bring up cost with physicians. Some may be ashamed to talk about their financial problems while others may fear doing so will prevent them from being offered the best possible treatments, said Ms. MacDonald.
But, experts say, financial toxicity needs to be dealt with head on. That means involving financial navigators or counselors and social workers who can, for instance, help patients and families find financial support for their basic living expenses.
From a research perspective, more clinical trials should include financial toxicity outcomes, said Joshua Palmer, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Dr. Palmer and colleagues recently showed that the number of radiation therapy clinical trials including financial toxicity endpoints increased significantly from 2001 to 2020, though the absolute rate of inclusion remains low, at roughly 1.5% of radiation therapy-based clinical trials including financial toxicity endpoints from 2016 to 2020.
“Financial burden is part of the broader discussion about shared decision-making,” said Dr. Palmer.
In shared decision-making, physicians discuss the risks and benefits of different treatment options, empowering the patient to make an informed choice with the physician.
What we want to avoid is patients feeling like they will get inferior care, if they have financial barriers, said Dr. Palmer.
And every little bit can help. In 2006, Ms. MacDonald started the Pink Fund – a nonprofit to help patients with cancer cover nonmedical cost-of-living expenses. Both Ms. Caputo and Ms. Dicks received grants from the Pink Fund. For Ms. Caputo, the funds covered 2 months of car payments and for Ms. Dicks, it covered 2 months of rent.
While the one-time grant was a big help, said Ms. Dicks, “cancer is an everyday thing.” And “we all deserve peace of mind” when trying to heal.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Bugs, drugs, and the placenta
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.















