User login
When Childhood Cancer Survivors Face Sexual Challenges
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Experts Highlight Challenges That Remain for AI Devices in Triaging Skin Cancer
Emerging according to researchers and dermatologists investigating AI.
While some AI-integrated devices designed to triage skin lesions have emerged, including one that received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance earlier in 2024, it may be some time before AI has a meaningful clinical impact in dermatology and, more specifically, the diagnosis of skin cancer, Ivy Lee, MD, a dermatologist in Pasadena, California, and chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s augmented intelligence committee, told this news organization.
“It hasn’t really translated into clinical practice yet,” Dr. Lee said of AI in dermatology. “There have been significant advances in terms of the technical possibility and feasibility of these tools, but the translation and integration of AI into actual clinical work flows to benefit patients beyond academic research studies has been limited.” More studies and more “easily accessible and digestible information” are needed to evaluate AI tools in dermatologic practice.
“In dermatology, we’re on a cusp with AI,” said Rebecca Hartman, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at the VA Boston Healthcare System and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. “I think it’s going to come and change what we do,” which is especially true for any image-based specialty,” including radiology and pathology, in addition to dermatology.
Dr. Hartman led a study of one of these emerging technologies, the handheld elastic scattering spectroscopy device DermaSensor, which was cleared by the FDA in January for evaluating skin lesions suggestive of skin cancer.
Early AI Devices for Skin Cancer Detection
At the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) meeting in April, a panel explored a number of algorithms with dermatologic applications that use AI to triage skin lesions, including DermaSensor.
Raman spectroscopy, which contains a handheld Raman probe, a diode laser, and a detecting spectrograph. A laser beam — which at 1.56 W/cm2 is below the maximum permissible exposure — focuses on the skin target with a 3.5-mm spot, gathers data on the target, and feeds it back into the unit that houses the algorithm that evaluates the spot analysis. It’s still in the investigative phase. A clinical trial, published almost 5 years ago, demonstrated a sensitivity of 90%-99% and a specificity of 24%-66% for skin cancer.
A dermatoscope called Sklip clips onto a smartphone and performs what company cofounder Alexander Witkowski, MD, PhD, described as an “optical painless virtual biopsy” for at-home use. The device uploads the captured image to an AI platform for analysis. It received FDA breakthrough device designation in 2022. At the ASLMS meeting, Dr. Witkowski said that clinical performance showed the device had a 97% sensitivity and 30% specificity for skin cancer.
DermaSensor, described in the study conducted by Dr. Hartman and others as a noninvasive, point-and-click spectrometer, is a wireless handheld piece that weighs about 10 ounces. The unit captures five recordings to generate a spectral reading, which an algorithm in the software unit analyzes. The study found a sensitivity of 95.5% and specificity of 32.5% for melanoma detection with the device.
The target market for DermaSensor is primary care physicians, and, according to the FDA announcement in January, it is indicated for evaluating skin lesions “suggestive” of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and/or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in patients aged 40 and older to “assist healthcare providers in determining whether to refer a patient to a dermatologist.”
So Many Cases, So Few Dermatologists
In dermatology, AI devices have the potential to streamline the crushing burden of diagnosing skin cancer, said Yun Liu, PhD, a senior staff scientist at Google Research, Mountain View, California, who’s worked on developing machine-learning tools in dermatology among other medical fields. “Many people cannot access dermatology expertise when they most need it, ie, without waiting a long time. This causes substantial morbidity for patients,” Dr. Liu said in an interview.
His own research of an AI-based tool to help primary care physicians and nurse practitioners in teledermatology practices diagnose skin conditions documented the shortage of dermatologists to triage lesions, including a finding that only about one quarter of skin conditions are seen by a specialist and that nonspecialists play a pivotal role in the management of skin lesions.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that about 6.1 million adults are treated for BCC and SCCs each year. The American Medical Association estimates that 13,200 active dermatologists practice in the United States.
Overcoming Barriers to AI in Dermatology
Before AI makes significant inroads in dermatology, clinicians need to see more verifiable data, said Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, assistant professor of biomedical data science and dermatology at Stanford University, Stanford, California. “One of the challenges is having the availability of models that actually improve clinical care because we have some very early prospective trials on different devices, but we don’t have large-scale randomized clinical trials of AI devices showing definitive behaviors such as improved patient outcomes, that it helps curb skin cancer, or it catches it like dermatologists but helps reduce the biopsy load,” she said. “You need good data.”
Another challenge she noted was overcoming biases built into medicine. “A lot of the image-based models are built on datasets depicting skin disease on White skin, and those models don’t work so well on people with brown and black skin, who have historically had worse outcomes and also have been underrepresented in dermatology,” said Dr. Daneshjou, an associate editor of NEJM AI.
There’s also the challenge of getting verified AI models into the clinic. “Similar to many medical AI endeavors, developing a proof-of-concept or research prototype is far easier and faster than bringing the development to real users,” Dr. Liu said. “In particular, it is important to conduct thorough validation studies on various patient populations and settings and understand how these AI tools can best fit into the workflow or patient journey.”
A study published in 2023 documented progress Google made in deploying AI models in retina specialty clinics in India and Thailand, Dr. Liu noted.
Another challenge is to avoid overdiagnosis with these new technologies, Dr. Hartman said. Her group’s study showed the DermaSensor had a positive predictive value of 16% and a negative predictive value of 98.5%. “I think there’s some question about how this will factor into overdiagnosis. Could this actually bombard dermatologists more if the positive predictive value’s only 16%?”
One key to dermatologists accepting AI tools is having a transparent process for validating them, Dr. Lee said. “Even with FDA clearance, we don’t have the transparency we need as clinicians, researchers, and advocates of machine learning and AI in healthcare.”
But, Dr. Lee noted, the FDA in June took a step toward illuminating its validation process when it adopted guiding principles for transparency for machine learning–enabled devices. “Once we can get more access to this information and have more transparency, that’s where we can think about actually about making the decision to implement or not implement into local healthcare settings,” she said. The process was further enabled by a White House executive order in October 2023 on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of AI.
The experience with telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic, when patients and providers quickly embraced the technology to stay connected, serves as a potential template for AI, Dr. Lee noted. “As we’d seen with telehealth through the pandemic, you also need the cultural evolution and the development of the infrastructure around it to actually make sure this is a sustainable implementation and a scalable implementation in healthcare.”
Dr. Lee had no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Hartman received funding from DermaSensor for a study. Dr. Witkowski is a cofounder of Sklip. Dr. Liu is an employee of Google Research. Dr. Daneshjou reported financial relationships with MD Algorithms, Revea, and L’Oreal.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging according to researchers and dermatologists investigating AI.
While some AI-integrated devices designed to triage skin lesions have emerged, including one that received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance earlier in 2024, it may be some time before AI has a meaningful clinical impact in dermatology and, more specifically, the diagnosis of skin cancer, Ivy Lee, MD, a dermatologist in Pasadena, California, and chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s augmented intelligence committee, told this news organization.
“It hasn’t really translated into clinical practice yet,” Dr. Lee said of AI in dermatology. “There have been significant advances in terms of the technical possibility and feasibility of these tools, but the translation and integration of AI into actual clinical work flows to benefit patients beyond academic research studies has been limited.” More studies and more “easily accessible and digestible information” are needed to evaluate AI tools in dermatologic practice.
“In dermatology, we’re on a cusp with AI,” said Rebecca Hartman, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at the VA Boston Healthcare System and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. “I think it’s going to come and change what we do,” which is especially true for any image-based specialty,” including radiology and pathology, in addition to dermatology.
Dr. Hartman led a study of one of these emerging technologies, the handheld elastic scattering spectroscopy device DermaSensor, which was cleared by the FDA in January for evaluating skin lesions suggestive of skin cancer.
Early AI Devices for Skin Cancer Detection
At the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) meeting in April, a panel explored a number of algorithms with dermatologic applications that use AI to triage skin lesions, including DermaSensor.
Raman spectroscopy, which contains a handheld Raman probe, a diode laser, and a detecting spectrograph. A laser beam — which at 1.56 W/cm2 is below the maximum permissible exposure — focuses on the skin target with a 3.5-mm spot, gathers data on the target, and feeds it back into the unit that houses the algorithm that evaluates the spot analysis. It’s still in the investigative phase. A clinical trial, published almost 5 years ago, demonstrated a sensitivity of 90%-99% and a specificity of 24%-66% for skin cancer.
A dermatoscope called Sklip clips onto a smartphone and performs what company cofounder Alexander Witkowski, MD, PhD, described as an “optical painless virtual biopsy” for at-home use. The device uploads the captured image to an AI platform for analysis. It received FDA breakthrough device designation in 2022. At the ASLMS meeting, Dr. Witkowski said that clinical performance showed the device had a 97% sensitivity and 30% specificity for skin cancer.
DermaSensor, described in the study conducted by Dr. Hartman and others as a noninvasive, point-and-click spectrometer, is a wireless handheld piece that weighs about 10 ounces. The unit captures five recordings to generate a spectral reading, which an algorithm in the software unit analyzes. The study found a sensitivity of 95.5% and specificity of 32.5% for melanoma detection with the device.
The target market for DermaSensor is primary care physicians, and, according to the FDA announcement in January, it is indicated for evaluating skin lesions “suggestive” of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and/or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in patients aged 40 and older to “assist healthcare providers in determining whether to refer a patient to a dermatologist.”
So Many Cases, So Few Dermatologists
In dermatology, AI devices have the potential to streamline the crushing burden of diagnosing skin cancer, said Yun Liu, PhD, a senior staff scientist at Google Research, Mountain View, California, who’s worked on developing machine-learning tools in dermatology among other medical fields. “Many people cannot access dermatology expertise when they most need it, ie, without waiting a long time. This causes substantial morbidity for patients,” Dr. Liu said in an interview.
His own research of an AI-based tool to help primary care physicians and nurse practitioners in teledermatology practices diagnose skin conditions documented the shortage of dermatologists to triage lesions, including a finding that only about one quarter of skin conditions are seen by a specialist and that nonspecialists play a pivotal role in the management of skin lesions.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that about 6.1 million adults are treated for BCC and SCCs each year. The American Medical Association estimates that 13,200 active dermatologists practice in the United States.
Overcoming Barriers to AI in Dermatology
Before AI makes significant inroads in dermatology, clinicians need to see more verifiable data, said Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, assistant professor of biomedical data science and dermatology at Stanford University, Stanford, California. “One of the challenges is having the availability of models that actually improve clinical care because we have some very early prospective trials on different devices, but we don’t have large-scale randomized clinical trials of AI devices showing definitive behaviors such as improved patient outcomes, that it helps curb skin cancer, or it catches it like dermatologists but helps reduce the biopsy load,” she said. “You need good data.”
Another challenge she noted was overcoming biases built into medicine. “A lot of the image-based models are built on datasets depicting skin disease on White skin, and those models don’t work so well on people with brown and black skin, who have historically had worse outcomes and also have been underrepresented in dermatology,” said Dr. Daneshjou, an associate editor of NEJM AI.
There’s also the challenge of getting verified AI models into the clinic. “Similar to many medical AI endeavors, developing a proof-of-concept or research prototype is far easier and faster than bringing the development to real users,” Dr. Liu said. “In particular, it is important to conduct thorough validation studies on various patient populations and settings and understand how these AI tools can best fit into the workflow or patient journey.”
A study published in 2023 documented progress Google made in deploying AI models in retina specialty clinics in India and Thailand, Dr. Liu noted.
Another challenge is to avoid overdiagnosis with these new technologies, Dr. Hartman said. Her group’s study showed the DermaSensor had a positive predictive value of 16% and a negative predictive value of 98.5%. “I think there’s some question about how this will factor into overdiagnosis. Could this actually bombard dermatologists more if the positive predictive value’s only 16%?”
One key to dermatologists accepting AI tools is having a transparent process for validating them, Dr. Lee said. “Even with FDA clearance, we don’t have the transparency we need as clinicians, researchers, and advocates of machine learning and AI in healthcare.”
But, Dr. Lee noted, the FDA in June took a step toward illuminating its validation process when it adopted guiding principles for transparency for machine learning–enabled devices. “Once we can get more access to this information and have more transparency, that’s where we can think about actually about making the decision to implement or not implement into local healthcare settings,” she said. The process was further enabled by a White House executive order in October 2023 on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of AI.
The experience with telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic, when patients and providers quickly embraced the technology to stay connected, serves as a potential template for AI, Dr. Lee noted. “As we’d seen with telehealth through the pandemic, you also need the cultural evolution and the development of the infrastructure around it to actually make sure this is a sustainable implementation and a scalable implementation in healthcare.”
Dr. Lee had no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Hartman received funding from DermaSensor for a study. Dr. Witkowski is a cofounder of Sklip. Dr. Liu is an employee of Google Research. Dr. Daneshjou reported financial relationships with MD Algorithms, Revea, and L’Oreal.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging according to researchers and dermatologists investigating AI.
While some AI-integrated devices designed to triage skin lesions have emerged, including one that received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance earlier in 2024, it may be some time before AI has a meaningful clinical impact in dermatology and, more specifically, the diagnosis of skin cancer, Ivy Lee, MD, a dermatologist in Pasadena, California, and chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s augmented intelligence committee, told this news organization.
“It hasn’t really translated into clinical practice yet,” Dr. Lee said of AI in dermatology. “There have been significant advances in terms of the technical possibility and feasibility of these tools, but the translation and integration of AI into actual clinical work flows to benefit patients beyond academic research studies has been limited.” More studies and more “easily accessible and digestible information” are needed to evaluate AI tools in dermatologic practice.
“In dermatology, we’re on a cusp with AI,” said Rebecca Hartman, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at the VA Boston Healthcare System and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. “I think it’s going to come and change what we do,” which is especially true for any image-based specialty,” including radiology and pathology, in addition to dermatology.
Dr. Hartman led a study of one of these emerging technologies, the handheld elastic scattering spectroscopy device DermaSensor, which was cleared by the FDA in January for evaluating skin lesions suggestive of skin cancer.
Early AI Devices for Skin Cancer Detection
At the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) meeting in April, a panel explored a number of algorithms with dermatologic applications that use AI to triage skin lesions, including DermaSensor.
Raman spectroscopy, which contains a handheld Raman probe, a diode laser, and a detecting spectrograph. A laser beam — which at 1.56 W/cm2 is below the maximum permissible exposure — focuses on the skin target with a 3.5-mm spot, gathers data on the target, and feeds it back into the unit that houses the algorithm that evaluates the spot analysis. It’s still in the investigative phase. A clinical trial, published almost 5 years ago, demonstrated a sensitivity of 90%-99% and a specificity of 24%-66% for skin cancer.
A dermatoscope called Sklip clips onto a smartphone and performs what company cofounder Alexander Witkowski, MD, PhD, described as an “optical painless virtual biopsy” for at-home use. The device uploads the captured image to an AI platform for analysis. It received FDA breakthrough device designation in 2022. At the ASLMS meeting, Dr. Witkowski said that clinical performance showed the device had a 97% sensitivity and 30% specificity for skin cancer.
DermaSensor, described in the study conducted by Dr. Hartman and others as a noninvasive, point-and-click spectrometer, is a wireless handheld piece that weighs about 10 ounces. The unit captures five recordings to generate a spectral reading, which an algorithm in the software unit analyzes. The study found a sensitivity of 95.5% and specificity of 32.5% for melanoma detection with the device.
The target market for DermaSensor is primary care physicians, and, according to the FDA announcement in January, it is indicated for evaluating skin lesions “suggestive” of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and/or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in patients aged 40 and older to “assist healthcare providers in determining whether to refer a patient to a dermatologist.”
So Many Cases, So Few Dermatologists
In dermatology, AI devices have the potential to streamline the crushing burden of diagnosing skin cancer, said Yun Liu, PhD, a senior staff scientist at Google Research, Mountain View, California, who’s worked on developing machine-learning tools in dermatology among other medical fields. “Many people cannot access dermatology expertise when they most need it, ie, without waiting a long time. This causes substantial morbidity for patients,” Dr. Liu said in an interview.
His own research of an AI-based tool to help primary care physicians and nurse practitioners in teledermatology practices diagnose skin conditions documented the shortage of dermatologists to triage lesions, including a finding that only about one quarter of skin conditions are seen by a specialist and that nonspecialists play a pivotal role in the management of skin lesions.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that about 6.1 million adults are treated for BCC and SCCs each year. The American Medical Association estimates that 13,200 active dermatologists practice in the United States.
Overcoming Barriers to AI in Dermatology
Before AI makes significant inroads in dermatology, clinicians need to see more verifiable data, said Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, assistant professor of biomedical data science and dermatology at Stanford University, Stanford, California. “One of the challenges is having the availability of models that actually improve clinical care because we have some very early prospective trials on different devices, but we don’t have large-scale randomized clinical trials of AI devices showing definitive behaviors such as improved patient outcomes, that it helps curb skin cancer, or it catches it like dermatologists but helps reduce the biopsy load,” she said. “You need good data.”
Another challenge she noted was overcoming biases built into medicine. “A lot of the image-based models are built on datasets depicting skin disease on White skin, and those models don’t work so well on people with brown and black skin, who have historically had worse outcomes and also have been underrepresented in dermatology,” said Dr. Daneshjou, an associate editor of NEJM AI.
There’s also the challenge of getting verified AI models into the clinic. “Similar to many medical AI endeavors, developing a proof-of-concept or research prototype is far easier and faster than bringing the development to real users,” Dr. Liu said. “In particular, it is important to conduct thorough validation studies on various patient populations and settings and understand how these AI tools can best fit into the workflow or patient journey.”
A study published in 2023 documented progress Google made in deploying AI models in retina specialty clinics in India and Thailand, Dr. Liu noted.
Another challenge is to avoid overdiagnosis with these new technologies, Dr. Hartman said. Her group’s study showed the DermaSensor had a positive predictive value of 16% and a negative predictive value of 98.5%. “I think there’s some question about how this will factor into overdiagnosis. Could this actually bombard dermatologists more if the positive predictive value’s only 16%?”
One key to dermatologists accepting AI tools is having a transparent process for validating them, Dr. Lee said. “Even with FDA clearance, we don’t have the transparency we need as clinicians, researchers, and advocates of machine learning and AI in healthcare.”
But, Dr. Lee noted, the FDA in June took a step toward illuminating its validation process when it adopted guiding principles for transparency for machine learning–enabled devices. “Once we can get more access to this information and have more transparency, that’s where we can think about actually about making the decision to implement or not implement into local healthcare settings,” she said. The process was further enabled by a White House executive order in October 2023 on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of AI.
The experience with telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic, when patients and providers quickly embraced the technology to stay connected, serves as a potential template for AI, Dr. Lee noted. “As we’d seen with telehealth through the pandemic, you also need the cultural evolution and the development of the infrastructure around it to actually make sure this is a sustainable implementation and a scalable implementation in healthcare.”
Dr. Lee had no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Hartman received funding from DermaSensor for a study. Dr. Witkowski is a cofounder of Sklip. Dr. Liu is an employee of Google Research. Dr. Daneshjou reported financial relationships with MD Algorithms, Revea, and L’Oreal.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer: Encouraging Data on Laser Treatment
TOPLINE:
Published
METHODOLOGY:
- Using MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, and www.clinicaltrials.gov, researchers systematically reviewed 50 unique published articles that evaluated the role of laser therapy for NMSC.
- Of the 50 studies, 37 focused on lasers for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), 10 on lasers for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and three on the treatment of both tumor types.
- The analysis was limited to studies published in English from the first data available through May 1, 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Data was strongest for the use of lasers for treating BCC, especially pulsed-dye lasers (PDL). Of 11 unique studies on PDL as monotherapy for managing BCCs, clearance rates ranged from 14.3% to 90.0%.
- For SCCs, 13 studies were identified that evaluated the use of lasers alone or in combination with PDL for treating SCC in situ. Among case reports that used PDL and thulium lasers separately, clearance rates of 100% were reported, while several case series that used the CO2 laser reported response rates that ranged from 61.5% to 100%.
- The best evidence for clearing both BCC and SCC tumors was observed when ablative lasers such as the CO2 or erbium yttrium aluminum garnet are combined with methyl aminolevulinate–photodynamic therapy (PDT) or 5-aminolevulinic acid–PDT, “likely due to increased delivery of the photosensitizing compound to neoplastic cells,” the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Additional investigations with longer follow-up periods are needed to determine optimal laser parameters, number of treatment sessions required, and recurrence rates (using complete histologic analysis through step sectioning) before lasers can fully be adopted into clinical practice,” the authors wrote. “Surgical excision, specifically Mohs micrographic surgery,” they added, “persists as the gold standard for high-risk and cosmetically sensitive tumors, offering the highest cure rates in a single office visit.”
SOURCE:
Amanda Rosenthal, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center in California, and colleagues conducted the review. The study was published in the August 2024 issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Laser therapy is not FDA approved for the treatment of NMSC and remains an alternative treatment option. Also, most published studies focus on BCCs, while studies on cutaneous SCCs are more limited.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Published
METHODOLOGY:
- Using MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, and www.clinicaltrials.gov, researchers systematically reviewed 50 unique published articles that evaluated the role of laser therapy for NMSC.
- Of the 50 studies, 37 focused on lasers for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), 10 on lasers for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and three on the treatment of both tumor types.
- The analysis was limited to studies published in English from the first data available through May 1, 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Data was strongest for the use of lasers for treating BCC, especially pulsed-dye lasers (PDL). Of 11 unique studies on PDL as monotherapy for managing BCCs, clearance rates ranged from 14.3% to 90.0%.
- For SCCs, 13 studies were identified that evaluated the use of lasers alone or in combination with PDL for treating SCC in situ. Among case reports that used PDL and thulium lasers separately, clearance rates of 100% were reported, while several case series that used the CO2 laser reported response rates that ranged from 61.5% to 100%.
- The best evidence for clearing both BCC and SCC tumors was observed when ablative lasers such as the CO2 or erbium yttrium aluminum garnet are combined with methyl aminolevulinate–photodynamic therapy (PDT) or 5-aminolevulinic acid–PDT, “likely due to increased delivery of the photosensitizing compound to neoplastic cells,” the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Additional investigations with longer follow-up periods are needed to determine optimal laser parameters, number of treatment sessions required, and recurrence rates (using complete histologic analysis through step sectioning) before lasers can fully be adopted into clinical practice,” the authors wrote. “Surgical excision, specifically Mohs micrographic surgery,” they added, “persists as the gold standard for high-risk and cosmetically sensitive tumors, offering the highest cure rates in a single office visit.”
SOURCE:
Amanda Rosenthal, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center in California, and colleagues conducted the review. The study was published in the August 2024 issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Laser therapy is not FDA approved for the treatment of NMSC and remains an alternative treatment option. Also, most published studies focus on BCCs, while studies on cutaneous SCCs are more limited.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Published
METHODOLOGY:
- Using MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, and www.clinicaltrials.gov, researchers systematically reviewed 50 unique published articles that evaluated the role of laser therapy for NMSC.
- Of the 50 studies, 37 focused on lasers for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), 10 on lasers for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and three on the treatment of both tumor types.
- The analysis was limited to studies published in English from the first data available through May 1, 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Data was strongest for the use of lasers for treating BCC, especially pulsed-dye lasers (PDL). Of 11 unique studies on PDL as monotherapy for managing BCCs, clearance rates ranged from 14.3% to 90.0%.
- For SCCs, 13 studies were identified that evaluated the use of lasers alone or in combination with PDL for treating SCC in situ. Among case reports that used PDL and thulium lasers separately, clearance rates of 100% were reported, while several case series that used the CO2 laser reported response rates that ranged from 61.5% to 100%.
- The best evidence for clearing both BCC and SCC tumors was observed when ablative lasers such as the CO2 or erbium yttrium aluminum garnet are combined with methyl aminolevulinate–photodynamic therapy (PDT) or 5-aminolevulinic acid–PDT, “likely due to increased delivery of the photosensitizing compound to neoplastic cells,” the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Additional investigations with longer follow-up periods are needed to determine optimal laser parameters, number of treatment sessions required, and recurrence rates (using complete histologic analysis through step sectioning) before lasers can fully be adopted into clinical practice,” the authors wrote. “Surgical excision, specifically Mohs micrographic surgery,” they added, “persists as the gold standard for high-risk and cosmetically sensitive tumors, offering the highest cure rates in a single office visit.”
SOURCE:
Amanda Rosenthal, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center in California, and colleagues conducted the review. The study was published in the August 2024 issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Laser therapy is not FDA approved for the treatment of NMSC and remains an alternative treatment option. Also, most published studies focus on BCCs, while studies on cutaneous SCCs are more limited.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy May Be Overused in Dying Patients With Cancer
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Addressing Depression Reduce Chemo Toxicity in Older Adults?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epidermal Tumors Arising on Donor Sites From Autologous Skin Grafts: A Systematic Review
Skin grafting is a surgical technique used to cover skin defects resulting from the removal of skin tumors, ulcers, or burn injuries.1-3 Complications can occur at both donor and recipient sites and may include bleeding, hematoma/seroma formation, postoperative pain, infection, scarring, paresthesia, skin pigmentation, graft contracture, and graft failure.1,2,4,5 The development of epidermal tumors is not commonly reported among the complications of skin grafting; however, cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites during the postoperative period have been reported.6-12
We performed a systematic review of the literature for cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites in patients undergoing autologous skin graft surgery. We present the clinical characteristics of these cases and discuss the nature of these tumors.
Methods
Search Strategy and Study Selection—A literature search was conducted by 2 independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) for articles published before December 2022 in the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, OpenGrey, Google Scholar, and WorldCat. Search terms included all possible combinations of the following: keratoacanthoma, molluscum sebaceum, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, acanthoma, wart, Merkel cell carcinoma, verruca, Bowen disease, keratosis, skin cancer, cutaneous cancer, skin neoplasia, cutaneous neoplasia, and skin tumor. The literature search terms were selected based on the World Health Organization classification of skin tumors.13 Manual bibliography checks were performed on all eligible search results for possible relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and, if needed, mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). To be included, a study had to report a case(s) of epidermal tumor(s) that was confirmed by histopathology and arose on a graft donor site in a patient receiving autologous skin grafts for any reason. No language, geographic, or report date restrictions were set.
Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis—We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.14 Two independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) retrieved the data from the included studies. We have used the terms case and patient interchangeably, and 1 month was measured as 4 weeks for simplicity. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). The quality of the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers (M.P. and V.P.) using the tool proposed by Murad et al.15
We used descriptive statistical analysis to analyze clinical characteristics of the included cases. We performed separate descriptive analyses based on the most frequently reported types of epidermal tumors and compared the differences between different groups using the Mann-Whitney U test, χ2 test, and Fisher exact test. The level of significance was set at P<.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 29).
Results
Literature Search and Characteristics of Included Studies—The initial literature search identified 1378 studies, which were screened based on title and abstract. After removing duplicate and irrelevant studies and evaluating the full text of eligible studies, 31 studies (4 case series and 27 case reports) were included in the systematic review (Figure).6-12,16-39 Quality assessment of the included studies is presented in Table 1.
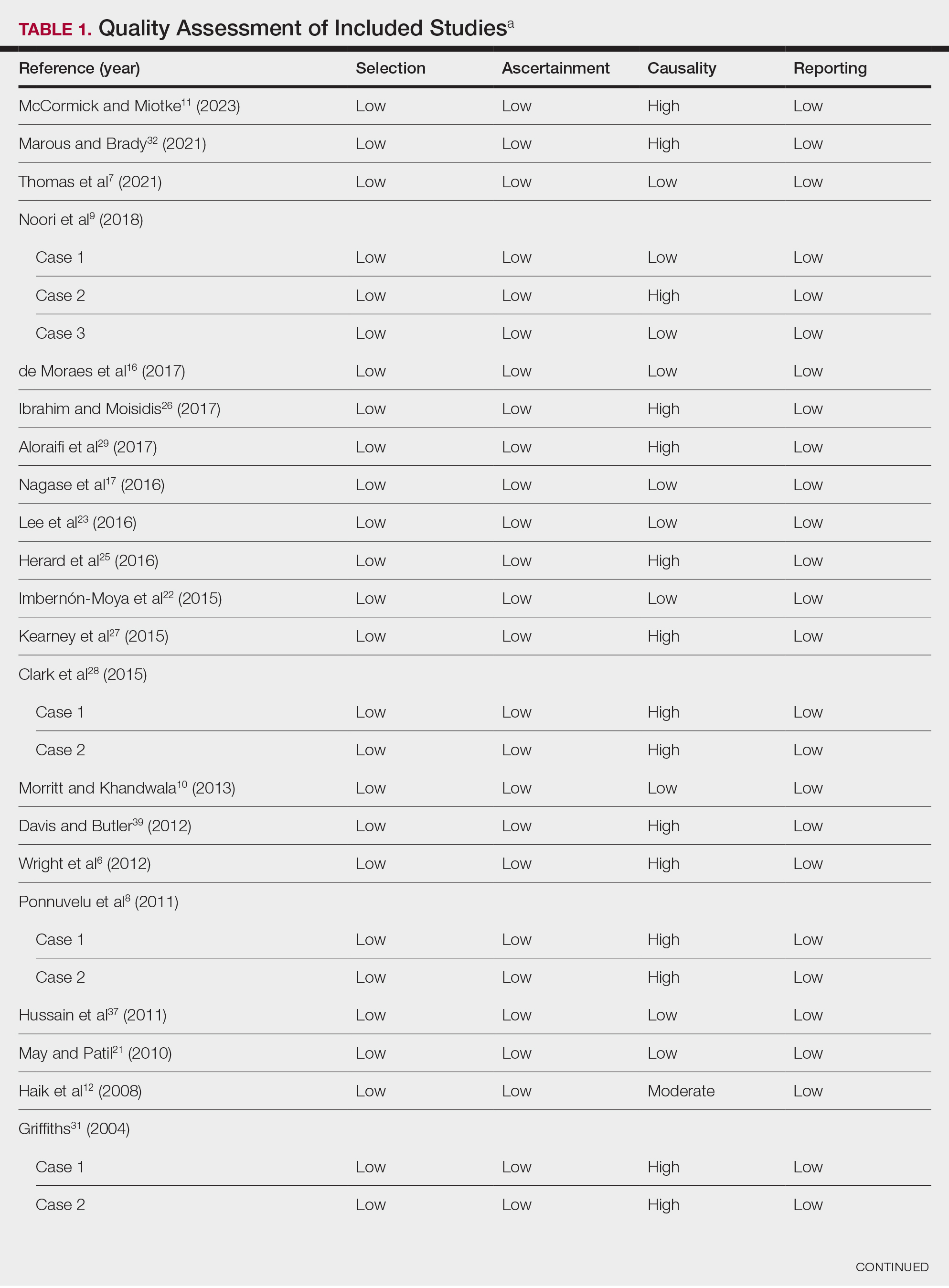
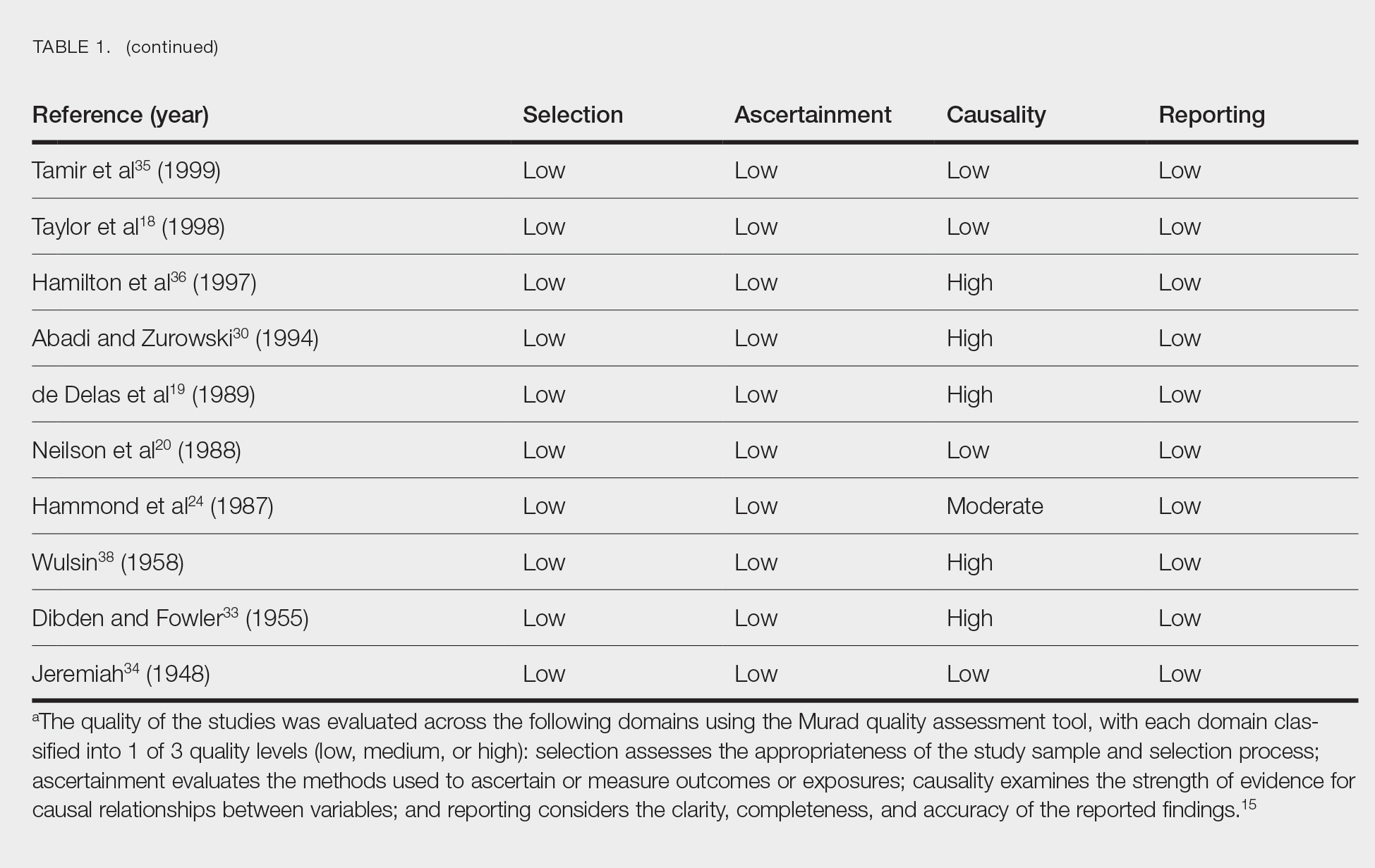
Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients—Our systematic review included 36 patients with a mean age of 63 years and a male to female ratio of 2:1. The 2 most common causes for skin grafting were burn wounds and surgical excision of skin tumors. Most grafts were harvested from the thighs. The development of a solitary lesion on the donor area was reported in two-thirds of the patients, while more than 1 lesion developed in the remaining one-third of patients. The median time to tumor development was 6.5 weeks. In most cases, a split-thickness skin graft was used.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (CSCCs) were found in 23 patients, with well-differentiated CSCCs in 19 of these cases. Additionally, keratoacanthomas (KAs) were found in 10 patients. The majority of patients underwent surgical excision of the tumor. The median follow-up time was 12 months, during which recurrences were noted in a small percentage of cases. Clinical characteristics of included patients are presented in Table 2.
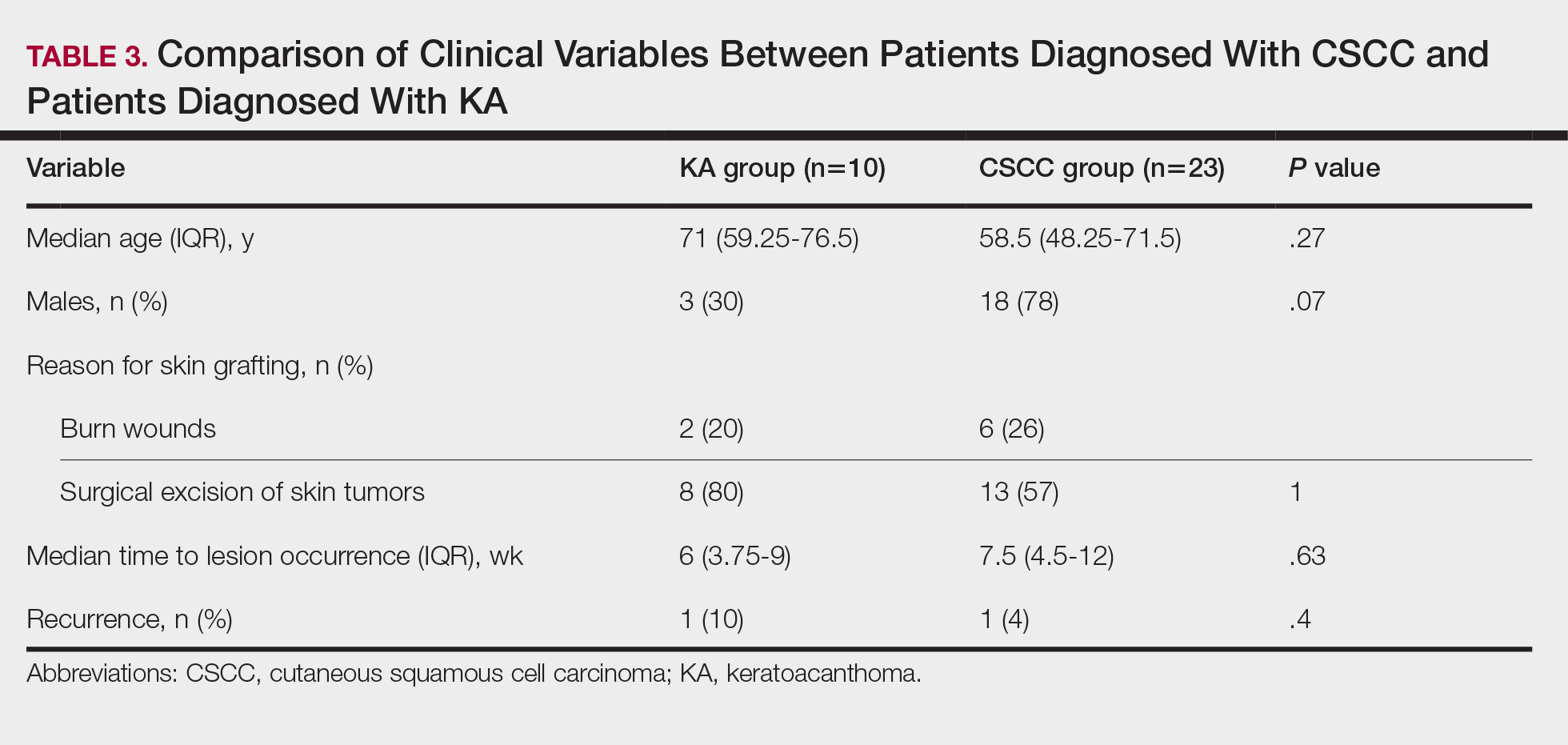
Comment
Reasons for Tumor Development on Skin Graft Donor Sites—The etiology behind epidermal tumor development on graft donor sites is unclear. According to one theory, iatrogenic contamination of the donor site during the removal of a primary epidermal tumor could be responsible. However, contemporary surgical procedures dictate the use of different sets of instruments for separate surgical sites. Moreover, this theory cannot explain the occurrence of epidermal tumors on donor sites in patients who have undergone skin grafting for the repair of burn wounds.37
Another theory suggests that hematogenous and/or lymphatic spread can occur from the site of the primary epidermal tumor to the donor site, which has increased vascularization.16,37 However, this theory also fails to provide an explanation for the development of epidermal tumors in patients who receive skin grafts for burn wounds.
A third theory states that the microenvironment of the donor site is key to tumor development. The donor site undergoes acute inflammation due to the trauma from harvesting the skin graft. According to this theory, acute inflammation could promote neoplastic growth and thus explain the development of epidermal tumors on the donor site.8,26 However, the relationship between acute inflammation and carcinogenesis remains unclear. What is known to date is that the development of CSCC has been documented primarily in chronically inflamed tissues, whereas the development of KA—a variant of CSCC with distinctive and more benign clinical characteristics—can be expected in the setting of acute trauma-related inflammation.13,40,41
Based on our systematic review, we propose that well-differentiated CSCC on graft donor sites might actually be misdiagnosed KA, given that the histopathologic differential diagnosis between CSCC and KA is extremely challenging.42 This hypothesis could explain the development of well-differentiated CSCC and KA on graft donor sites.
Conclusion
Development of CSCC and KA on graft donor sites can be listed among the postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting. Patients and physicians should be aware of this potential complication, and donor sites should be monitored for the occurrence of epidermal tumors.
- Adams DC, Ramsey ML. Grafts in dermatologic surgery: review and update on full- and split-thickness skin grafts, free cartilage grafts, and composite grafts. Dermatologic Surg. 2005;31(8, pt 2):1055-1067. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31831
- Shimizu R, Kishi K. Skin graft. Plast Surg Int. 2012;2012:563493. doi:10.1155/2012/563493
- Reddy S, El-Haddawi F, Fancourt M, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lower limb skin graft failure. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:582080. doi:10.1155/2014/582080
- Coughlin MJ, Dockery GD, Crawford ME, et al. Lower Extremity Soft Tissue & Cutaneous Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders Ltd; 2012.
- Herskovitz I, Hughes OB, Macquhae F, et al. Epidermal skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2016;13(suppl 3):52-56. doi:10.1111/iwj.12631
- Wright H, McKinnell TH, Dunkin C. Recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at remote limb donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1265-1266. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2012.01.022
- Thomas W, Rezzadeh K, Rossi K, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising at a skin graft donor site: case report and review of the literature. Plast Surg Case Stud. 2021;7:2513826X211008425. doi:10.1177/2513826X211008425
- Ponnuvelu G, Ng MFY, Connolly CM, et al. Inflammation to skin malignancy, time to rethink the link: SCC in skin graft donor sites. Surgeon. 2011;9:168-169. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2010.08.006
- Noori VJ, Trehan K, Savetamal A, et al. New onset squamous cell carcinoma in previous split-thickness skin graft donor site. Int J Surg. 2018;52:16-19. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.047
- Morritt DG, Khandwala AR. The development of squamous cell carcinomas in split-thickness skin graft donor sites. Eur J Plast Surg. 2013;36:377-380.
- McCormick M, Miotke S. Squamous cell carcinoma at split thickness skin graft donor site: a case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2023;44:210-213. doi:10.1093/jbcr/irac137
- Haik J, Georgiou I, Farber N, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. Burns. 2008;34:891-893. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2007.06.006
- Elder DE, Massi D, Scolyer RA WR. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. IARC Press; 2018.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264-269, W64. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
- Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ. 2018;23:60-63. doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
- de Moraes LPB, Burchett I, Nicholls S, et al. Large solitary distant metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to skin graft site with complete response following definitive radiotherapy. Int J Bioautomation. 2017;21:103-108.
- Nagase K, Suzuki Y, Misago N, et al. Acute development of keratoacanthoma at a full-thickness skin graft donor site shortly after surgery. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1232-1233. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13368
- Taylor CD, Snelling CF, Nickerson D, et al. Acute development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1998;19:382-385. doi:10.1097/00004630-199809000-00004
- de Delas J, Leache A, Vazquez Doval J, et al. Keratoacanthoma over the donor site of a laminar skin graft. Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1989;17:225-228.
- Neilson D, Emerson DJ, Dunn L. Squamous cell carcinoma of skin developing in a skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1988;41:417-419. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90086-0
- May JT, Patil YJ. Keratoacanthoma-type squamous cell carcinoma developing in a skin graft donor site after tumor extirpation at a distant site. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89:E11-E13.
- Imbernón-Moya A, Vargas-Laguna E, Lobato-Berezo A, et al. Simultaneous onset of basal cell carcinoma over skin graft and donor site. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:244-246. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.05.004
- Lee S, Coutts I, Ryan A, et al. Keratoacanthoma formation after skin grafting: a brief report and pathophysiological hypothesis. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e117-e119. doi:10.1111/ajd.12501
- Hammond JS, Thomsen S, Ward CG. Scar carcinoma arising acutelyin a skin graft donor site. J Trauma. 1987;27:681-683. doi:10.1097/00005373-198706000-00017
- Herard C, Arnaud D, Goga D, et al. Rapid onset of squamous cell carcinoma in a thin skin graft donor site. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143:457-461. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2015.03.027
- Ibrahim A, Moisidis E. Case series: rapidly growing squamous cell carcinoma after cutaneous surgical intervention. JPRAS Open. 2017;14:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2017.08.004
- Kearney L, Dolan RT, Parfrey NA, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a skin graft donor site following melanoma extirpation at a distant site: a case report and review of the literature. JPRAS Open. 2015;3:35-38. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2015.02.002
- Clark MA, Guitart J, Gerami P, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomatous atypical squamous proliferations (KASPs) arising in skin graft sites. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:274-276. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.06.009
- Aloraifi F, Mulgrew S, James NK. Secondary Merkel cell carcinoma arising from a graft donor site. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:167-169. doi:10.1177/1203475416676805
- Abadir R, Zurowski S. Case report: squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in both palms, axillary node, donor skin graft site and both soles—associated hyperkeratosis and porokeratosis. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:507-510. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-797-507
- Griffiths RW. Keratoacanthoma observed. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:485-501. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.007
- Marous M, Brady K. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split thickness skin graft donor site in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatologic Surg. 2021;47:1106-1107. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002955
- Dibden FA, Fowler M. The multiple growth of molluscum sebaceum in donor and recipient sites of skin graft. Aust N Z J Surg. 1955;25:157-159. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05122.x
- Jeremiah BS. Squamous cell carcinoma development on donor area following removal of a split thickness skin graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1948;3:718-721.
- Tamir G, Morgenstern S, Ben-Amitay D, et al. Synchronous appearance of keratoacanthomas in burn scar and skin graft donor site shortly after injury. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 2):870-871. doi:10.1053/jd.1999.v40.a94419
- Hamilton SA, Dickson WA, O’Brien CJ. Keratoacanthoma developing in a split skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:560-561. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91308-4
- Hussain A, Ekwobi C, Watson S. Metastatic implantation squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:690-692. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.06.004
- Wulsin JH. Keratoacanthoma: a benign cutaneous tumors arising in a skin graft donor site. Am Surg. 1958;24:689-692.
- Davis L, Butler D. Acute development of squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB208. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.874
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002;16:217-226, 229; discussion 230-232.
- Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K, Suchorska W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020;25:422-427. doi:10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
- Carr RA, Houghton JP. Histopathologists’ approach to keratoacanthoma: a multisite survey of regional variation in Great Britain and Ireland. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:637-638. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202255
Skin grafting is a surgical technique used to cover skin defects resulting from the removal of skin tumors, ulcers, or burn injuries.1-3 Complications can occur at both donor and recipient sites and may include bleeding, hematoma/seroma formation, postoperative pain, infection, scarring, paresthesia, skin pigmentation, graft contracture, and graft failure.1,2,4,5 The development of epidermal tumors is not commonly reported among the complications of skin grafting; however, cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites during the postoperative period have been reported.6-12
We performed a systematic review of the literature for cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites in patients undergoing autologous skin graft surgery. We present the clinical characteristics of these cases and discuss the nature of these tumors.
Methods
Search Strategy and Study Selection—A literature search was conducted by 2 independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) for articles published before December 2022 in the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, OpenGrey, Google Scholar, and WorldCat. Search terms included all possible combinations of the following: keratoacanthoma, molluscum sebaceum, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, acanthoma, wart, Merkel cell carcinoma, verruca, Bowen disease, keratosis, skin cancer, cutaneous cancer, skin neoplasia, cutaneous neoplasia, and skin tumor. The literature search terms were selected based on the World Health Organization classification of skin tumors.13 Manual bibliography checks were performed on all eligible search results for possible relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and, if needed, mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). To be included, a study had to report a case(s) of epidermal tumor(s) that was confirmed by histopathology and arose on a graft donor site in a patient receiving autologous skin grafts for any reason. No language, geographic, or report date restrictions were set.
Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis—We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.14 Two independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) retrieved the data from the included studies. We have used the terms case and patient interchangeably, and 1 month was measured as 4 weeks for simplicity. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). The quality of the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers (M.P. and V.P.) using the tool proposed by Murad et al.15
We used descriptive statistical analysis to analyze clinical characteristics of the included cases. We performed separate descriptive analyses based on the most frequently reported types of epidermal tumors and compared the differences between different groups using the Mann-Whitney U test, χ2 test, and Fisher exact test. The level of significance was set at P<.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 29).
Results
Literature Search and Characteristics of Included Studies—The initial literature search identified 1378 studies, which were screened based on title and abstract. After removing duplicate and irrelevant studies and evaluating the full text of eligible studies, 31 studies (4 case series and 27 case reports) were included in the systematic review (Figure).6-12,16-39 Quality assessment of the included studies is presented in Table 1.


Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients—Our systematic review included 36 patients with a mean age of 63 years and a male to female ratio of 2:1. The 2 most common causes for skin grafting were burn wounds and surgical excision of skin tumors. Most grafts were harvested from the thighs. The development of a solitary lesion on the donor area was reported in two-thirds of the patients, while more than 1 lesion developed in the remaining one-third of patients. The median time to tumor development was 6.5 weeks. In most cases, a split-thickness skin graft was used.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (CSCCs) were found in 23 patients, with well-differentiated CSCCs in 19 of these cases. Additionally, keratoacanthomas (KAs) were found in 10 patients. The majority of patients underwent surgical excision of the tumor. The median follow-up time was 12 months, during which recurrences were noted in a small percentage of cases. Clinical characteristics of included patients are presented in Table 2.


Comment
Reasons for Tumor Development on Skin Graft Donor Sites—The etiology behind epidermal tumor development on graft donor sites is unclear. According to one theory, iatrogenic contamination of the donor site during the removal of a primary epidermal tumor could be responsible. However, contemporary surgical procedures dictate the use of different sets of instruments for separate surgical sites. Moreover, this theory cannot explain the occurrence of epidermal tumors on donor sites in patients who have undergone skin grafting for the repair of burn wounds.37
Another theory suggests that hematogenous and/or lymphatic spread can occur from the site of the primary epidermal tumor to the donor site, which has increased vascularization.16,37 However, this theory also fails to provide an explanation for the development of epidermal tumors in patients who receive skin grafts for burn wounds.
A third theory states that the microenvironment of the donor site is key to tumor development. The donor site undergoes acute inflammation due to the trauma from harvesting the skin graft. According to this theory, acute inflammation could promote neoplastic growth and thus explain the development of epidermal tumors on the donor site.8,26 However, the relationship between acute inflammation and carcinogenesis remains unclear. What is known to date is that the development of CSCC has been documented primarily in chronically inflamed tissues, whereas the development of KA—a variant of CSCC with distinctive and more benign clinical characteristics—can be expected in the setting of acute trauma-related inflammation.13,40,41
Based on our systematic review, we propose that well-differentiated CSCC on graft donor sites might actually be misdiagnosed KA, given that the histopathologic differential diagnosis between CSCC and KA is extremely challenging.42 This hypothesis could explain the development of well-differentiated CSCC and KA on graft donor sites.
Conclusion
Development of CSCC and KA on graft donor sites can be listed among the postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting. Patients and physicians should be aware of this potential complication, and donor sites should be monitored for the occurrence of epidermal tumors.
Skin grafting is a surgical technique used to cover skin defects resulting from the removal of skin tumors, ulcers, or burn injuries.1-3 Complications can occur at both donor and recipient sites and may include bleeding, hematoma/seroma formation, postoperative pain, infection, scarring, paresthesia, skin pigmentation, graft contracture, and graft failure.1,2,4,5 The development of epidermal tumors is not commonly reported among the complications of skin grafting; however, cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites during the postoperative period have been reported.6-12
We performed a systematic review of the literature for cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites in patients undergoing autologous skin graft surgery. We present the clinical characteristics of these cases and discuss the nature of these tumors.
Methods
Search Strategy and Study Selection—A literature search was conducted by 2 independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) for articles published before December 2022 in the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, OpenGrey, Google Scholar, and WorldCat. Search terms included all possible combinations of the following: keratoacanthoma, molluscum sebaceum, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, acanthoma, wart, Merkel cell carcinoma, verruca, Bowen disease, keratosis, skin cancer, cutaneous cancer, skin neoplasia, cutaneous neoplasia, and skin tumor. The literature search terms were selected based on the World Health Organization classification of skin tumors.13 Manual bibliography checks were performed on all eligible search results for possible relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and, if needed, mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). To be included, a study had to report a case(s) of epidermal tumor(s) that was confirmed by histopathology and arose on a graft donor site in a patient receiving autologous skin grafts for any reason. No language, geographic, or report date restrictions were set.
Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis—We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.14 Two independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) retrieved the data from the included studies. We have used the terms case and patient interchangeably, and 1 month was measured as 4 weeks for simplicity. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). The quality of the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers (M.P. and V.P.) using the tool proposed by Murad et al.15
We used descriptive statistical analysis to analyze clinical characteristics of the included cases. We performed separate descriptive analyses based on the most frequently reported types of epidermal tumors and compared the differences between different groups using the Mann-Whitney U test, χ2 test, and Fisher exact test. The level of significance was set at P<.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 29).
Results
Literature Search and Characteristics of Included Studies—The initial literature search identified 1378 studies, which were screened based on title and abstract. After removing duplicate and irrelevant studies and evaluating the full text of eligible studies, 31 studies (4 case series and 27 case reports) were included in the systematic review (Figure).6-12,16-39 Quality assessment of the included studies is presented in Table 1.


Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients—Our systematic review included 36 patients with a mean age of 63 years and a male to female ratio of 2:1. The 2 most common causes for skin grafting were burn wounds and surgical excision of skin tumors. Most grafts were harvested from the thighs. The development of a solitary lesion on the donor area was reported in two-thirds of the patients, while more than 1 lesion developed in the remaining one-third of patients. The median time to tumor development was 6.5 weeks. In most cases, a split-thickness skin graft was used.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (CSCCs) were found in 23 patients, with well-differentiated CSCCs in 19 of these cases. Additionally, keratoacanthomas (KAs) were found in 10 patients. The majority of patients underwent surgical excision of the tumor. The median follow-up time was 12 months, during which recurrences were noted in a small percentage of cases. Clinical characteristics of included patients are presented in Table 2.


Comment
Reasons for Tumor Development on Skin Graft Donor Sites—The etiology behind epidermal tumor development on graft donor sites is unclear. According to one theory, iatrogenic contamination of the donor site during the removal of a primary epidermal tumor could be responsible. However, contemporary surgical procedures dictate the use of different sets of instruments for separate surgical sites. Moreover, this theory cannot explain the occurrence of epidermal tumors on donor sites in patients who have undergone skin grafting for the repair of burn wounds.37
Another theory suggests that hematogenous and/or lymphatic spread can occur from the site of the primary epidermal tumor to the donor site, which has increased vascularization.16,37 However, this theory also fails to provide an explanation for the development of epidermal tumors in patients who receive skin grafts for burn wounds.
A third theory states that the microenvironment of the donor site is key to tumor development. The donor site undergoes acute inflammation due to the trauma from harvesting the skin graft. According to this theory, acute inflammation could promote neoplastic growth and thus explain the development of epidermal tumors on the donor site.8,26 However, the relationship between acute inflammation and carcinogenesis remains unclear. What is known to date is that the development of CSCC has been documented primarily in chronically inflamed tissues, whereas the development of KA—a variant of CSCC with distinctive and more benign clinical characteristics—can be expected in the setting of acute trauma-related inflammation.13,40,41
Based on our systematic review, we propose that well-differentiated CSCC on graft donor sites might actually be misdiagnosed KA, given that the histopathologic differential diagnosis between CSCC and KA is extremely challenging.42 This hypothesis could explain the development of well-differentiated CSCC and KA on graft donor sites.
Conclusion
Development of CSCC and KA on graft donor sites can be listed among the postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting. Patients and physicians should be aware of this potential complication, and donor sites should be monitored for the occurrence of epidermal tumors.
- Adams DC, Ramsey ML. Grafts in dermatologic surgery: review and update on full- and split-thickness skin grafts, free cartilage grafts, and composite grafts. Dermatologic Surg. 2005;31(8, pt 2):1055-1067. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31831
- Shimizu R, Kishi K. Skin graft. Plast Surg Int. 2012;2012:563493. doi:10.1155/2012/563493
- Reddy S, El-Haddawi F, Fancourt M, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lower limb skin graft failure. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:582080. doi:10.1155/2014/582080
- Coughlin MJ, Dockery GD, Crawford ME, et al. Lower Extremity Soft Tissue & Cutaneous Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders Ltd; 2012.
- Herskovitz I, Hughes OB, Macquhae F, et al. Epidermal skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2016;13(suppl 3):52-56. doi:10.1111/iwj.12631
- Wright H, McKinnell TH, Dunkin C. Recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at remote limb donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1265-1266. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2012.01.022
- Thomas W, Rezzadeh K, Rossi K, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising at a skin graft donor site: case report and review of the literature. Plast Surg Case Stud. 2021;7:2513826X211008425. doi:10.1177/2513826X211008425
- Ponnuvelu G, Ng MFY, Connolly CM, et al. Inflammation to skin malignancy, time to rethink the link: SCC in skin graft donor sites. Surgeon. 2011;9:168-169. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2010.08.006
- Noori VJ, Trehan K, Savetamal A, et al. New onset squamous cell carcinoma in previous split-thickness skin graft donor site. Int J Surg. 2018;52:16-19. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.047
- Morritt DG, Khandwala AR. The development of squamous cell carcinomas in split-thickness skin graft donor sites. Eur J Plast Surg. 2013;36:377-380.
- McCormick M, Miotke S. Squamous cell carcinoma at split thickness skin graft donor site: a case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2023;44:210-213. doi:10.1093/jbcr/irac137
- Haik J, Georgiou I, Farber N, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. Burns. 2008;34:891-893. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2007.06.006
- Elder DE, Massi D, Scolyer RA WR. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. IARC Press; 2018.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264-269, W64. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
- Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ. 2018;23:60-63. doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
- de Moraes LPB, Burchett I, Nicholls S, et al. Large solitary distant metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to skin graft site with complete response following definitive radiotherapy. Int J Bioautomation. 2017;21:103-108.
- Nagase K, Suzuki Y, Misago N, et al. Acute development of keratoacanthoma at a full-thickness skin graft donor site shortly after surgery. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1232-1233. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13368
- Taylor CD, Snelling CF, Nickerson D, et al. Acute development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1998;19:382-385. doi:10.1097/00004630-199809000-00004
- de Delas J, Leache A, Vazquez Doval J, et al. Keratoacanthoma over the donor site of a laminar skin graft. Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1989;17:225-228.
- Neilson D, Emerson DJ, Dunn L. Squamous cell carcinoma of skin developing in a skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1988;41:417-419. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90086-0
- May JT, Patil YJ. Keratoacanthoma-type squamous cell carcinoma developing in a skin graft donor site after tumor extirpation at a distant site. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89:E11-E13.
- Imbernón-Moya A, Vargas-Laguna E, Lobato-Berezo A, et al. Simultaneous onset of basal cell carcinoma over skin graft and donor site. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:244-246. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.05.004
- Lee S, Coutts I, Ryan A, et al. Keratoacanthoma formation after skin grafting: a brief report and pathophysiological hypothesis. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e117-e119. doi:10.1111/ajd.12501
- Hammond JS, Thomsen S, Ward CG. Scar carcinoma arising acutelyin a skin graft donor site. J Trauma. 1987;27:681-683. doi:10.1097/00005373-198706000-00017
- Herard C, Arnaud D, Goga D, et al. Rapid onset of squamous cell carcinoma in a thin skin graft donor site. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143:457-461. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2015.03.027
- Ibrahim A, Moisidis E. Case series: rapidly growing squamous cell carcinoma after cutaneous surgical intervention. JPRAS Open. 2017;14:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2017.08.004
- Kearney L, Dolan RT, Parfrey NA, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a skin graft donor site following melanoma extirpation at a distant site: a case report and review of the literature. JPRAS Open. 2015;3:35-38. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2015.02.002
- Clark MA, Guitart J, Gerami P, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomatous atypical squamous proliferations (KASPs) arising in skin graft sites. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:274-276. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.06.009
- Aloraifi F, Mulgrew S, James NK. Secondary Merkel cell carcinoma arising from a graft donor site. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:167-169. doi:10.1177/1203475416676805
- Abadir R, Zurowski S. Case report: squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in both palms, axillary node, donor skin graft site and both soles—associated hyperkeratosis and porokeratosis. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:507-510. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-797-507
- Griffiths RW. Keratoacanthoma observed. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:485-501. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.007
- Marous M, Brady K. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split thickness skin graft donor site in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatologic Surg. 2021;47:1106-1107. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002955
- Dibden FA, Fowler M. The multiple growth of molluscum sebaceum in donor and recipient sites of skin graft. Aust N Z J Surg. 1955;25:157-159. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05122.x
- Jeremiah BS. Squamous cell carcinoma development on donor area following removal of a split thickness skin graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1948;3:718-721.
- Tamir G, Morgenstern S, Ben-Amitay D, et al. Synchronous appearance of keratoacanthomas in burn scar and skin graft donor site shortly after injury. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 2):870-871. doi:10.1053/jd.1999.v40.a94419
- Hamilton SA, Dickson WA, O’Brien CJ. Keratoacanthoma developing in a split skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:560-561. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91308-4
- Hussain A, Ekwobi C, Watson S. Metastatic implantation squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:690-692. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.06.004
- Wulsin JH. Keratoacanthoma: a benign cutaneous tumors arising in a skin graft donor site. Am Surg. 1958;24:689-692.
- Davis L, Butler D. Acute development of squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB208. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.874
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002;16:217-226, 229; discussion 230-232.
- Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K, Suchorska W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020;25:422-427. doi:10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
- Carr RA, Houghton JP. Histopathologists’ approach to keratoacanthoma: a multisite survey of regional variation in Great Britain and Ireland. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:637-638. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202255
- Adams DC, Ramsey ML. Grafts in dermatologic surgery: review and update on full- and split-thickness skin grafts, free cartilage grafts, and composite grafts. Dermatologic Surg. 2005;31(8, pt 2):1055-1067. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31831
- Shimizu R, Kishi K. Skin graft. Plast Surg Int. 2012;2012:563493. doi:10.1155/2012/563493
- Reddy S, El-Haddawi F, Fancourt M, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lower limb skin graft failure. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:582080. doi:10.1155/2014/582080
- Coughlin MJ, Dockery GD, Crawford ME, et al. Lower Extremity Soft Tissue & Cutaneous Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders Ltd; 2012.
- Herskovitz I, Hughes OB, Macquhae F, et al. Epidermal skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2016;13(suppl 3):52-56. doi:10.1111/iwj.12631
- Wright H, McKinnell TH, Dunkin C. Recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at remote limb donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1265-1266. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2012.01.022
- Thomas W, Rezzadeh K, Rossi K, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising at a skin graft donor site: case report and review of the literature. Plast Surg Case Stud. 2021;7:2513826X211008425. doi:10.1177/2513826X211008425
- Ponnuvelu G, Ng MFY, Connolly CM, et al. Inflammation to skin malignancy, time to rethink the link: SCC in skin graft donor sites. Surgeon. 2011;9:168-169. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2010.08.006
- Noori VJ, Trehan K, Savetamal A, et al. New onset squamous cell carcinoma in previous split-thickness skin graft donor site. Int J Surg. 2018;52:16-19. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.047
- Morritt DG, Khandwala AR. The development of squamous cell carcinomas in split-thickness skin graft donor sites. Eur J Plast Surg. 2013;36:377-380.
- McCormick M, Miotke S. Squamous cell carcinoma at split thickness skin graft donor site: a case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2023;44:210-213. doi:10.1093/jbcr/irac137
- Haik J, Georgiou I, Farber N, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. Burns. 2008;34:891-893. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2007.06.006
- Elder DE, Massi D, Scolyer RA WR. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. IARC Press; 2018.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264-269, W64. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
- Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ. 2018;23:60-63. doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
- de Moraes LPB, Burchett I, Nicholls S, et al. Large solitary distant metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to skin graft site with complete response following definitive radiotherapy. Int J Bioautomation. 2017;21:103-108.
- Nagase K, Suzuki Y, Misago N, et al. Acute development of keratoacanthoma at a full-thickness skin graft donor site shortly after surgery. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1232-1233. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13368
- Taylor CD, Snelling CF, Nickerson D, et al. Acute development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1998;19:382-385. doi:10.1097/00004630-199809000-00004
- de Delas J, Leache A, Vazquez Doval J, et al. Keratoacanthoma over the donor site of a laminar skin graft. Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1989;17:225-228.
- Neilson D, Emerson DJ, Dunn L. Squamous cell carcinoma of skin developing in a skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1988;41:417-419. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90086-0
- May JT, Patil YJ. Keratoacanthoma-type squamous cell carcinoma developing in a skin graft donor site after tumor extirpation at a distant site. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89:E11-E13.
- Imbernón-Moya A, Vargas-Laguna E, Lobato-Berezo A, et al. Simultaneous onset of basal cell carcinoma over skin graft and donor site. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:244-246. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.05.004
- Lee S, Coutts I, Ryan A, et al. Keratoacanthoma formation after skin grafting: a brief report and pathophysiological hypothesis. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e117-e119. doi:10.1111/ajd.12501
- Hammond JS, Thomsen S, Ward CG. Scar carcinoma arising acutelyin a skin graft donor site. J Trauma. 1987;27:681-683. doi:10.1097/00005373-198706000-00017
- Herard C, Arnaud D, Goga D, et al. Rapid onset of squamous cell carcinoma in a thin skin graft donor site. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143:457-461. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2015.03.027
- Ibrahim A, Moisidis E. Case series: rapidly growing squamous cell carcinoma after cutaneous surgical intervention. JPRAS Open. 2017;14:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2017.08.004
- Kearney L, Dolan RT, Parfrey NA, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a skin graft donor site following melanoma extirpation at a distant site: a case report and review of the literature. JPRAS Open. 2015;3:35-38. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2015.02.002
- Clark MA, Guitart J, Gerami P, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomatous atypical squamous proliferations (KASPs) arising in skin graft sites. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:274-276. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.06.009
- Aloraifi F, Mulgrew S, James NK. Secondary Merkel cell carcinoma arising from a graft donor site. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:167-169. doi:10.1177/1203475416676805
- Abadir R, Zurowski S. Case report: squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in both palms, axillary node, donor skin graft site and both soles—associated hyperkeratosis and porokeratosis. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:507-510. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-797-507
- Griffiths RW. Keratoacanthoma observed. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:485-501. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.007
- Marous M, Brady K. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split thickness skin graft donor site in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatologic Surg. 2021;47:1106-1107. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002955
- Dibden FA, Fowler M. The multiple growth of molluscum sebaceum in donor and recipient sites of skin graft. Aust N Z J Surg. 1955;25:157-159. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05122.x
- Jeremiah BS. Squamous cell carcinoma development on donor area following removal of a split thickness skin graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1948;3:718-721.
- Tamir G, Morgenstern S, Ben-Amitay D, et al. Synchronous appearance of keratoacanthomas in burn scar and skin graft donor site shortly after injury. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 2):870-871. doi:10.1053/jd.1999.v40.a94419
- Hamilton SA, Dickson WA, O’Brien CJ. Keratoacanthoma developing in a split skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:560-561. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91308-4
- Hussain A, Ekwobi C, Watson S. Metastatic implantation squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:690-692. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.06.004
- Wulsin JH. Keratoacanthoma: a benign cutaneous tumors arising in a skin graft donor site. Am Surg. 1958;24:689-692.
- Davis L, Butler D. Acute development of squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB208. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.874
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002;16:217-226, 229; discussion 230-232.
- Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K, Suchorska W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020;25:422-427. doi:10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
- Carr RA, Houghton JP. Histopathologists’ approach to keratoacanthoma: a multisite survey of regional variation in Great Britain and Ireland. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:637-638. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202255
Practice Points
- Donor site cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) and keratoacanthoma (KA) can be postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting.
- Surgical excision of donor site CSCC and KA typically is curative.
Saxophone Penis: A Forgotten Manifestation of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
Practice Points
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease.
- Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation.
- Repetitive inflammation within the context of HS may cause structural deformity of the penis, resulting in a saxophone penis.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
FDA Approves First Engineered Cell Therapy for a Solid Tumor
Afami-cel — the first engineered cell therapy for a solid tumor — is indicated specifically for adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy, are positive for several human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), and whose tumors express melanoma-associated antigen A4, as determined by FDA-authorized companion diagnostic devices.
The single-dose treatment targets solid tumors expressing melanoma-associated antigen A4, a protein highly expressed in synovial sarcoma.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer, which affects about 1000 people in the US each year. Malignant cells develop and form a tumor in soft tissues, often in the extremities.
“Adults with metastatic synovial sarcoma, a life-threatening form of cancer, often face limited treatment options in addition to the risk of cancer spread or recurrence,” Nicole Verdun, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Products in the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the agency press release announcing the approval. “Today’s approval represents a significant milestone in the development of an innovative, safe and effective therapy for patients with this rare but potentially fatal disease.”
T-cell receptor therapy, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, involves altering patient T cells to fight cancer. While CAR-T therapy inserts an artificial receptor to target a specific surface protein on cancer cells, the T-cell receptor therapy modifies existing receptors to recognize an array of antigens on the surface of cancer cells — a promising strategy for targeting solid tumors.
The accelerated approval of afami-cel was based on the phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial in 44 patients with synovial sarcoma who received a single infusion of the therapy. The trial had enrolled 52 patients, but 8 did not receive afami-cel, including 3 who died and 1 who withdrew.
According to the FDA announcement, the overall response rate was 43.2%, with a median time to response of 4.9 weeks. The median duration of response was 6 months (95% CI, 4.6 months to not reached). Among patients who responded, 39% had a duration of response of 12 months or longer.
“These results suggest that a one-time treatment with afami-cel has the potential to extend life while allowing responders to go off chemotherapy,” said lead investigator Sandra D’Angelo, MD, a sarcoma specialist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, in a company press release.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning for serious or fatal cytokine release syndrome.
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included cytokine release syndrome, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, infections, pyrexia, constipation, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and edema. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included decreased lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, white cell blood count, red blood cell, and platelet count.
The recommended dose is between 2.68x109 to 10x109 MAGE-A4 T-cell receptor–positive T-cells. The FDA notice specifies not using a leukodepleting filter or prophylactic systemic corticosteroids.
The list price for the one-time therapy is $727,000, according to Fierce Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Afami-cel — the first engineered cell therapy for a solid tumor — is indicated specifically for adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy, are positive for several human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), and whose tumors express melanoma-associated antigen A4, as determined by FDA-authorized companion diagnostic devices.
The single-dose treatment targets solid tumors expressing melanoma-associated antigen A4, a protein highly expressed in synovial sarcoma.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer, which affects about 1000 people in the US each year. Malignant cells develop and form a tumor in soft tissues, often in the extremities.
“Adults with metastatic synovial sarcoma, a life-threatening form of cancer, often face limited treatment options in addition to the risk of cancer spread or recurrence,” Nicole Verdun, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Products in the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the agency press release announcing the approval. “Today’s approval represents a significant milestone in the development of an innovative, safe and effective therapy for patients with this rare but potentially fatal disease.”
T-cell receptor therapy, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, involves altering patient T cells to fight cancer. While CAR-T therapy inserts an artificial receptor to target a specific surface protein on cancer cells, the T-cell receptor therapy modifies existing receptors to recognize an array of antigens on the surface of cancer cells — a promising strategy for targeting solid tumors.
The accelerated approval of afami-cel was based on the phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial in 44 patients with synovial sarcoma who received a single infusion of the therapy. The trial had enrolled 52 patients, but 8 did not receive afami-cel, including 3 who died and 1 who withdrew.
According to the FDA announcement, the overall response rate was 43.2%, with a median time to response of 4.9 weeks. The median duration of response was 6 months (95% CI, 4.6 months to not reached). Among patients who responded, 39% had a duration of response of 12 months or longer.
“These results suggest that a one-time treatment with afami-cel has the potential to extend life while allowing responders to go off chemotherapy,” said lead investigator Sandra D’Angelo, MD, a sarcoma specialist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, in a company press release.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning for serious or fatal cytokine release syndrome.
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included cytokine release syndrome, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, infections, pyrexia, constipation, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and edema. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included decreased lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, white cell blood count, red blood cell, and platelet count.
The recommended dose is between 2.68x109 to 10x109 MAGE-A4 T-cell receptor–positive T-cells. The FDA notice specifies not using a leukodepleting filter or prophylactic systemic corticosteroids.
The list price for the one-time therapy is $727,000, according to Fierce Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Afami-cel — the first engineered cell therapy for a solid tumor — is indicated specifically for adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy, are positive for several human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), and whose tumors express melanoma-associated antigen A4, as determined by FDA-authorized companion diagnostic devices.
The single-dose treatment targets solid tumors expressing melanoma-associated antigen A4, a protein highly expressed in synovial sarcoma.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer, which affects about 1000 people in the US each year. Malignant cells develop and form a tumor in soft tissues, often in the extremities.
“Adults with metastatic synovial sarcoma, a life-threatening form of cancer, often face limited treatment options in addition to the risk of cancer spread or recurrence,” Nicole Verdun, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Products in the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the agency press release announcing the approval. “Today’s approval represents a significant milestone in the development of an innovative, safe and effective therapy for patients with this rare but potentially fatal disease.”
T-cell receptor therapy, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, involves altering patient T cells to fight cancer. While CAR-T therapy inserts an artificial receptor to target a specific surface protein on cancer cells, the T-cell receptor therapy modifies existing receptors to recognize an array of antigens on the surface of cancer cells — a promising strategy for targeting solid tumors.
The accelerated approval of afami-cel was based on the phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial in 44 patients with synovial sarcoma who received a single infusion of the therapy. The trial had enrolled 52 patients, but 8 did not receive afami-cel, including 3 who died and 1 who withdrew.
According to the FDA announcement, the overall response rate was 43.2%, with a median time to response of 4.9 weeks. The median duration of response was 6 months (95% CI, 4.6 months to not reached). Among patients who responded, 39% had a duration of response of 12 months or longer.
“These results suggest that a one-time treatment with afami-cel has the potential to extend life while allowing responders to go off chemotherapy,” said lead investigator Sandra D’Angelo, MD, a sarcoma specialist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, in a company press release.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning for serious or fatal cytokine release syndrome.
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included cytokine release syndrome, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, infections, pyrexia, constipation, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and edema. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included decreased lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, white cell blood count, red blood cell, and platelet count.
The recommended dose is between 2.68x109 to 10x109 MAGE-A4 T-cell receptor–positive T-cells. The FDA notice specifies not using a leukodepleting filter or prophylactic systemic corticosteroids.
The list price for the one-time therapy is $727,000, according to Fierce Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Last 30 Days: How Oncologists’ Choices Affect End-of-Life Cancer Care
TOPLINE:
Patients treated by oncologists in the top quartile for end-of-life prescribing behavior were almost four and a half times more likely to receive end-of-life therapy than those treated by these specialists in the bottom quartile.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, focusing on patients who died of cancer between 2012 and 2017.
- A total of 17,609 patients with breast, lung, colorectal, or prostate cancer were included, treated by 960 oncologists across 388 practices.
- Patients were required to have had at least one systemic cancer therapy claim in the last 180 days of life, with the treating oncologist identified on the basis of the therapy claim closest to the time of death.
- The study used multilevel models to estimate oncologists’ rates of providing cancer therapy in the last 30 days of life, adjusting for patient characteristics and practice variation.
- Functional status was assessed on the basis of paid claims for durable medical equipment in the last 60 months of life, with scores categorized as 0, 1, ≥ 2, or unknown.
TAKEAWAY:
- Oncologists in the 95th percentile for high end-of-life prescribing behavior had a 45% adjusted rate of treating patients in the last 30 days of life, compared with 17% among those in the 5th percentile.
- Patients treated by high end-of-life prescribing oncologists had over four times higher odds of receiving systemic therapy in the last 30 days of life (odds ratio [OR], 4.42; 95% CI, 4.00-4.89).
- Higher end-of-life prescribing oncologists also had a higher proportion of patients hospitalized in the last 30 days of life than low prescribers (58% vs 51.9%).
- No significant association was found between oncologist prescribing behavior and patient race or ethnicity, except for Black patients who had lower odds of receiving treatment (OR, 0.77; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Given calls to rein in overutilization of end-of-life six to eight cancer therapies, our findings highlight an underappreciated area for further research: How treatment discontinuation before death is shaped by oncologists’ unique treatment propensities. Elucidating the reasons for this remarkable variability in oncologist treatment behavior could inform efforts to reduce end-of-life cancer treatment overutilization,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Login S. George, PhD, Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on SEER-Medicare data may limit the generalizability of the findings to patients with Medicare Advantage, private insurance, or Medicaid, as well as younger patients. The lack of data on patient preferences and other health characteristics could confound the results. The study focused on systemic therapies and may not be generalizable to other treatments such as clinical trial drugs, oral therapies, surgery, or radiation. The data from 2012 to 2017 may not reflect more recent trends in cancer treatment.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. George disclosed receiving grants from these organizations. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients treated by oncologists in the top quartile for end-of-life prescribing behavior were almost four and a half times more likely to receive end-of-life therapy than those treated by these specialists in the bottom quartile.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, focusing on patients who died of cancer between 2012 and 2017.
- A total of 17,609 patients with breast, lung, colorectal, or prostate cancer were included, treated by 960 oncologists across 388 practices.
- Patients were required to have had at least one systemic cancer therapy claim in the last 180 days of life, with the treating oncologist identified on the basis of the therapy claim closest to the time of death.
- The study used multilevel models to estimate oncologists’ rates of providing cancer therapy in the last 30 days of life, adjusting for patient characteristics and practice variation.
- Functional status was assessed on the basis of paid claims for durable medical equipment in the last 60 months of life, with scores categorized as 0, 1, ≥ 2, or unknown.
TAKEAWAY:
- Oncologists in the 95th percentile for high end-of-life prescribing behavior had a 45% adjusted rate of treating patients in the last 30 days of life, compared with 17% among those in the 5th percentile.
- Patients treated by high end-of-life prescribing oncologists had over four times higher odds of receiving systemic therapy in the last 30 days of life (odds ratio [OR], 4.42; 95% CI, 4.00-4.89).
- Higher end-of-life prescribing oncologists also had a higher proportion of patients hospitalized in the last 30 days of life than low prescribers (58% vs 51.9%).
- No significant association was found between oncologist prescribing behavior and patient race or ethnicity, except for Black patients who had lower odds of receiving treatment (OR, 0.77; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Given calls to rein in overutilization of end-of-life six to eight cancer therapies, our findings highlight an underappreciated area for further research: How treatment discontinuation before death is shaped by oncologists’ unique treatment propensities. Elucidating the reasons for this remarkable variability in oncologist treatment behavior could inform efforts to reduce end-of-life cancer treatment overutilization,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Login S. George, PhD, Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on SEER-Medicare data may limit the generalizability of the findings to patients with Medicare Advantage, private insurance, or Medicaid, as well as younger patients. The lack of data on patient preferences and other health characteristics could confound the results. The study focused on systemic therapies and may not be generalizable to other treatments such as clinical trial drugs, oral therapies, surgery, or radiation. The data from 2012 to 2017 may not reflect more recent trends in cancer treatment.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. George disclosed receiving grants from these organizations. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients treated by oncologists in the top quartile for end-of-life prescribing behavior were almost four and a half times more likely to receive end-of-life therapy than those treated by these specialists in the bottom quartile.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, focusing on patients who died of cancer between 2012 and 2017.
- A total of 17,609 patients with breast, lung, colorectal, or prostate cancer were included, treated by 960 oncologists across 388 practices.
- Patients were required to have had at least one systemic cancer therapy claim in the last 180 days of life, with the treating oncologist identified on the basis of the therapy claim closest to the time of death.
- The study used multilevel models to estimate oncologists’ rates of providing cancer therapy in the last 30 days of life, adjusting for patient characteristics and practice variation.
- Functional status was assessed on the basis of paid claims for durable medical equipment in the last 60 months of life, with scores categorized as 0, 1, ≥ 2, or unknown.
TAKEAWAY:
- Oncologists in the 95th percentile for high end-of-life prescribing behavior had a 45% adjusted rate of treating patients in the last 30 days of life, compared with 17% among those in the 5th percentile.
- Patients treated by high end-of-life prescribing oncologists had over four times higher odds of receiving systemic therapy in the last 30 days of life (odds ratio [OR], 4.42; 95% CI, 4.00-4.89).
- Higher end-of-life prescribing oncologists also had a higher proportion of patients hospitalized in the last 30 days of life than low prescribers (58% vs 51.9%).
- No significant association was found between oncologist prescribing behavior and patient race or ethnicity, except for Black patients who had lower odds of receiving treatment (OR, 0.77; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Given calls to rein in overutilization of end-of-life six to eight cancer therapies, our findings highlight an underappreciated area for further research: How treatment discontinuation before death is shaped by oncologists’ unique treatment propensities. Elucidating the reasons for this remarkable variability in oncologist treatment behavior could inform efforts to reduce end-of-life cancer treatment overutilization,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Login S. George, PhD, Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on SEER-Medicare data may limit the generalizability of the findings to patients with Medicare Advantage, private insurance, or Medicaid, as well as younger patients. The lack of data on patient preferences and other health characteristics could confound the results. The study focused on systemic therapies and may not be generalizable to other treatments such as clinical trial drugs, oral therapies, surgery, or radiation. The data from 2012 to 2017 may not reflect more recent trends in cancer treatment.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. George disclosed receiving grants from these organizations. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ancient Viruses in Our DNA Hold Clues to Cancer Treatment
according to a fascinating new study in Science Advances. Targeting these viral remnants still lingering in our DNA could lead to more effective cancer treatment with fewer side effects, the researchers said.
The study “gives a better understanding of how gene regulation can be impacted by these ancient retroviral sequences,” said Dixie Mager, PhD, scientist emeritus at the Terry Fox Laboratory at the British Columbia Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (Mager was not involved in the study.)
Long thought to be “junk” DNA with no biologic function, “endogenous retroviruses,” which have mutated over time and lost their ability to create the virus, are now known to regulate genes — allowing some genes to turn on and off. Research in recent years suggests they may play a role in diseases like cancer.
But scientists weren’t exactly sure what that role was, said senior study author Edward Chuong, PhD, a genome biologist at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Most studies have looked at whether endogenous retroviruses code for proteins that influence cancer. But these ancient viral strands usually don’t code for proteins at all.
Dr. Chuong took a different approach. Inspired by scientists who’ve studied how viral remnants regulate positive processes (immunity, brain development, or placenta development), he and his team explored whether some might regulate genes that, once activated, help cancer thrive.
Borrowing from epigenomic analysis data (data on molecules that alter gene expression) for 21 cancers mapped by the Cancer Genome Atlas, the researchers identified 19 virus-derived DNA sequences that bind to regulatory proteins more in cancer cells than in healthy cells. All of these could potentially act as gene regulators that promote cancer.
The researchers homed in on one sequence, called LTR10, because it showed especially high activity in several cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. This DNA segment comes from a virus that entered our ancestors’ genome 30 million years ago, and it’s activated in a third of colorectal cancers.
Using the gene editing technology clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Dr. Chuong’s team silenced LTR10 in colorectal cancer cells, altering the gene sequence so it couldn’t bind to regulatory proteins. Doing so dampened the activity of nearby cancer-promoting genes.
“They still behaved like cancer cells,” Dr. Chuong said. But “it made the cancer cells more susceptible to radiation. That would imply that the presence of that viral ‘switch’ actually helped those cancer cells survive radiation therapy.”
Previously, two studies had found that viral regulators play a role in promoting two types of cancer: Leukemia and prostate cancer. The new study shows these two cases weren’t flukes. All 21 cancers they looked at had at least one of those 19 viral elements, presumably working as cancer enhancers.
The study also identified what activates LTR10 to make it promote cancer. The culprit is a regulator protein called mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, which is overactivated in about 40% of all human cancers.
Some cancer drugs — MAP kinase inhibitors — already target MAP kinase, and they’re often the first ones prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cancer, Dr. Chuong said. As with many cancer treatments, doctors don’t know why they work, just that they do.
“By understanding the mechanisms in the cell, we might be able to make them work better or further optimize their treatment,” he said.
“MAP kinase inhibitors are really like a sledgehammer to the cell,” Dr. Chuong said — meaning they affect many cellular processes, not just those related to cancer.
“If we’re able to say that these viral switches are what’s important, then that could potentially help us develop a more targeted therapy that uses something like CRISPR to silence these viral elements,” he said. Or it could help providers choose a MAP kinase inhibitor from among the dozens available best suited to treat an individual patient and avoid side effects.
Still, whether the findings translate to real cancer patients remains to be seen. “It’s very, very hard to go the final step of showing in a patient that these actually make a difference in the cancer,” Dr. Mager said.
More lab research, human trials, and at least a few years will be needed before this discovery could help treat cancer. “Directly targeting these elements as a therapy would be at least 5 years out,” Dr. Chuong said, “partly because that application would rely on CRISPR epigenome editing technology that is still being developed for clinical use.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a fascinating new study in Science Advances. Targeting these viral remnants still lingering in our DNA could lead to more effective cancer treatment with fewer side effects, the researchers said.
The study “gives a better understanding of how gene regulation can be impacted by these ancient retroviral sequences,” said Dixie Mager, PhD, scientist emeritus at the Terry Fox Laboratory at the British Columbia Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (Mager was not involved in the study.)
Long thought to be “junk” DNA with no biologic function, “endogenous retroviruses,” which have mutated over time and lost their ability to create the virus, are now known to regulate genes — allowing some genes to turn on and off. Research in recent years suggests they may play a role in diseases like cancer.
But scientists weren’t exactly sure what that role was, said senior study author Edward Chuong, PhD, a genome biologist at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Most studies have looked at whether endogenous retroviruses code for proteins that influence cancer. But these ancient viral strands usually don’t code for proteins at all.
Dr. Chuong took a different approach. Inspired by scientists who’ve studied how viral remnants regulate positive processes (immunity, brain development, or placenta development), he and his team explored whether some might regulate genes that, once activated, help cancer thrive.
Borrowing from epigenomic analysis data (data on molecules that alter gene expression) for 21 cancers mapped by the Cancer Genome Atlas, the researchers identified 19 virus-derived DNA sequences that bind to regulatory proteins more in cancer cells than in healthy cells. All of these could potentially act as gene regulators that promote cancer.
The researchers homed in on one sequence, called LTR10, because it showed especially high activity in several cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. This DNA segment comes from a virus that entered our ancestors’ genome 30 million years ago, and it’s activated in a third of colorectal cancers.
Using the gene editing technology clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Dr. Chuong’s team silenced LTR10 in colorectal cancer cells, altering the gene sequence so it couldn’t bind to regulatory proteins. Doing so dampened the activity of nearby cancer-promoting genes.
“They still behaved like cancer cells,” Dr. Chuong said. But “it made the cancer cells more susceptible to radiation. That would imply that the presence of that viral ‘switch’ actually helped those cancer cells survive radiation therapy.”
Previously, two studies had found that viral regulators play a role in promoting two types of cancer: Leukemia and prostate cancer. The new study shows these two cases weren’t flukes. All 21 cancers they looked at had at least one of those 19 viral elements, presumably working as cancer enhancers.
The study also identified what activates LTR10 to make it promote cancer. The culprit is a regulator protein called mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, which is overactivated in about 40% of all human cancers.
Some cancer drugs — MAP kinase inhibitors — already target MAP kinase, and they’re often the first ones prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cancer, Dr. Chuong said. As with many cancer treatments, doctors don’t know why they work, just that they do.
“By understanding the mechanisms in the cell, we might be able to make them work better or further optimize their treatment,” he said.
“MAP kinase inhibitors are really like a sledgehammer to the cell,” Dr. Chuong said — meaning they affect many cellular processes, not just those related to cancer.
“If we’re able to say that these viral switches are what’s important, then that could potentially help us develop a more targeted therapy that uses something like CRISPR to silence these viral elements,” he said. Or it could help providers choose a MAP kinase inhibitor from among the dozens available best suited to treat an individual patient and avoid side effects.
Still, whether the findings translate to real cancer patients remains to be seen. “It’s very, very hard to go the final step of showing in a patient that these actually make a difference in the cancer,” Dr. Mager said.
More lab research, human trials, and at least a few years will be needed before this discovery could help treat cancer. “Directly targeting these elements as a therapy would be at least 5 years out,” Dr. Chuong said, “partly because that application would rely on CRISPR epigenome editing technology that is still being developed for clinical use.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a fascinating new study in Science Advances. Targeting these viral remnants still lingering in our DNA could lead to more effective cancer treatment with fewer side effects, the researchers said.
The study “gives a better understanding of how gene regulation can be impacted by these ancient retroviral sequences,” said Dixie Mager, PhD, scientist emeritus at the Terry Fox Laboratory at the British Columbia Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (Mager was not involved in the study.)
Long thought to be “junk” DNA with no biologic function, “endogenous retroviruses,” which have mutated over time and lost their ability to create the virus, are now known to regulate genes — allowing some genes to turn on and off. Research in recent years suggests they may play a role in diseases like cancer.
But scientists weren’t exactly sure what that role was, said senior study author Edward Chuong, PhD, a genome biologist at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Most studies have looked at whether endogenous retroviruses code for proteins that influence cancer. But these ancient viral strands usually don’t code for proteins at all.
Dr. Chuong took a different approach. Inspired by scientists who’ve studied how viral remnants regulate positive processes (immunity, brain development, or placenta development), he and his team explored whether some might regulate genes that, once activated, help cancer thrive.
Borrowing from epigenomic analysis data (data on molecules that alter gene expression) for 21 cancers mapped by the Cancer Genome Atlas, the researchers identified 19 virus-derived DNA sequences that bind to regulatory proteins more in cancer cells than in healthy cells. All of these could potentially act as gene regulators that promote cancer.
The researchers homed in on one sequence, called LTR10, because it showed especially high activity in several cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. This DNA segment comes from a virus that entered our ancestors’ genome 30 million years ago, and it’s activated in a third of colorectal cancers.
Using the gene editing technology clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Dr. Chuong’s team silenced LTR10 in colorectal cancer cells, altering the gene sequence so it couldn’t bind to regulatory proteins. Doing so dampened the activity of nearby cancer-promoting genes.
“They still behaved like cancer cells,” Dr. Chuong said. But “it made the cancer cells more susceptible to radiation. That would imply that the presence of that viral ‘switch’ actually helped those cancer cells survive radiation therapy.”
Previously, two studies had found that viral regulators play a role in promoting two types of cancer: Leukemia and prostate cancer. The new study shows these two cases weren’t flukes. All 21 cancers they looked at had at least one of those 19 viral elements, presumably working as cancer enhancers.
The study also identified what activates LTR10 to make it promote cancer. The culprit is a regulator protein called mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, which is overactivated in about 40% of all human cancers.
Some cancer drugs — MAP kinase inhibitors — already target MAP kinase, and they’re often the first ones prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cancer, Dr. Chuong said. As with many cancer treatments, doctors don’t know why they work, just that they do.
“By understanding the mechanisms in the cell, we might be able to make them work better or further optimize their treatment,” he said.
“MAP kinase inhibitors are really like a sledgehammer to the cell,” Dr. Chuong said — meaning they affect many cellular processes, not just those related to cancer.
“If we’re able to say that these viral switches are what’s important, then that could potentially help us develop a more targeted therapy that uses something like CRISPR to silence these viral elements,” he said. Or it could help providers choose a MAP kinase inhibitor from among the dozens available best suited to treat an individual patient and avoid side effects.
Still, whether the findings translate to real cancer patients remains to be seen. “It’s very, very hard to go the final step of showing in a patient that these actually make a difference in the cancer,” Dr. Mager said.
More lab research, human trials, and at least a few years will be needed before this discovery could help treat cancer. “Directly targeting these elements as a therapy would be at least 5 years out,” Dr. Chuong said, “partly because that application would rely on CRISPR epigenome editing technology that is still being developed for clinical use.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES