User login
The Shield Sign of Cutaneous Metastases Is Associated With Carcinoma Hemorrhagiectoides
To the Editor:
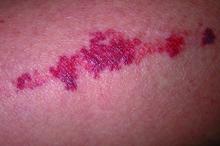
We read with interest the Case Letter from Wang et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15) of a 60-year-old man whose metastatic salivary duct adenocarcinoma manifested with the shield sign as well as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. Cutaneous metastases have seldom been described in association with salivary duct carcinoma.2-7 In addition, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign has not been commonly reported.5,8-12
Salivary duct carcinoma—an uncommon head and neck malignancy characterized by androgen receptor expression—rarely is associated with cutaneous metastases. Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, metastatic, salivary duct carcinoma, and/or skin, including the patient described by Wang et al,1 there have been 8 individuals with cutaneous metastases from this cancer. The morphology of the cutaneous metastases has varied from angiomatous to angiokeratomalike (black and keratotic) papules, bullae, macules (red), papules and nodules (erythematous and scaly), plaques (cellulitislike and confluent that were purpuric, hemorrhagic, and violaceous), pseudovesicles, purpuric papules, subcutaneous nodules, and an ulcer (superficial and mimicked a basal cell carcinoma).1-7 Remarkably, 4 of 8 patients (50%) with salivary duct carcinoma cutaneous metastases presented with a shield sign,5,7 including the case reported by Wang et al.1
The shield sign is a distinctive clinical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis.10 It was named to describe the skin metastases located predominantly on the chest area that would be covered by a medieval knight’s shield5,10,12; metastatic lesions also have been noted on the proximal arm and/or the upper back in a similar distribution.8,9 To date, based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms breast cancer, carcinoma, hemorrhagiectoides, metastases, salivary duct carcinoma, shield, and/or sign, the shield sign has been described in 6 patients with cutaneous metastases either from salivary duct carcinoma (4 patients)1,5,7 or breast cancer (2 patients).8,9 The shield sign pathologically corresponds to carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides, an inflammatory pattern of cutaneous metastases.5,11
Inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma has 3 distinctive clinical and pathologic manifestations.11 Carcinoma erysipelatoides and carcinoma telangiectoides were the earlier described variants.11 In 2012, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides was described as the third pattern of inflammatory cutaneous metastasis.5
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, which clinically mimics cutaneous streptococcal cellulitis, appears as a well-defined erythematous patch or plaque; the tumor cells can be found in the lymphatic vessels and either are absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma telangiectoides, which clinically mimics idiopathic telangiectases, appears as an erythematous patch with prominent telangiectases; the tumor cells can be found in the blood vessels and are either absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides appears as purpuric or violaceous indurated plaques; the tumor cells are not only found in the blood vessels, in the lymphatic vessels, or both, but also can be mildly to extensively present in the dermis.5,10,11
In conclusion, the shield sign is a unique presentation of inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, which is associated with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The clinical features of the infiltrated plaques correspond to the presence of tumor cells in the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the dermis; in addition, the purpuric and violaceous appearance correlates with the presence of extravasated erythrocytes or hemorrhage in the dermis. To date, half of the patients with skin metastases from salivary duct carcinoma have presented with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign.
Authors’ Response
We appreciate and welcome the comments provided by the authors. Drawing attention to unusual pathologic manifestations of cutaneous metastatic salivary duct carcinoma manifesting with the shield sign, the authors present a comprehensive review of 3 distinctive presentations: carcinoma erysipelatoides, carcinoma telangiectoides, and carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The inclusion of these variants enriches the discussion and makes this letter a valuable addition to the literature on cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, particularly metastatic salivary duct carcinoma.
Xintong Wang, MD; William H. Westra, MD
From the Department of Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
- Wang X, Vyas NS, Alghamdi AA, et al. Cutaneous presentation of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma. Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15.
- Pollock JL, Catalano E. Metastatic ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland in a patient with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1098-1099.
- Pollock JL. Metastatic carcinoma of the parotid gland resembling carcinoma of the breast. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:1093.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Anderson JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Shin JY, Eun DH, Lee JY, et al. A case of cutaneous metastases of salivary duct carcinoma mimicking radiation recall dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2020;32:436-438.
- Aravena RC, Aravena DC, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hn3z850.
- Smith KA, Basko-Plluska J, Kothari AD, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cutis. 2020;105:E20-E22.
- Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Cutaneous metastatic cancer: carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides presenting as the shield sign. Cureus. 2021;13:e12627.
- Cohen PR. Pleomorphic appearance of breast cancer cutaneous metastases. Cureus. 2021;13:e20301.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Kurzrock R. Tumor lysis syndrome: introduction of a cutaneous variant and a new classification system. Cureus. 2021;13:e13816.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Case Letter from Wang et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15) of a 60-year-old man whose metastatic salivary duct adenocarcinoma manifested with the shield sign as well as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. Cutaneous metastases have seldom been described in association with salivary duct carcinoma.2-7 In addition, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign has not been commonly reported.5,8-12
Salivary duct carcinoma—an uncommon head and neck malignancy characterized by androgen receptor expression—rarely is associated with cutaneous metastases. Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, metastatic, salivary duct carcinoma, and/or skin, including the patient described by Wang et al,1 there have been 8 individuals with cutaneous metastases from this cancer. The morphology of the cutaneous metastases has varied from angiomatous to angiokeratomalike (black and keratotic) papules, bullae, macules (red), papules and nodules (erythematous and scaly), plaques (cellulitislike and confluent that were purpuric, hemorrhagic, and violaceous), pseudovesicles, purpuric papules, subcutaneous nodules, and an ulcer (superficial and mimicked a basal cell carcinoma).1-7 Remarkably, 4 of 8 patients (50%) with salivary duct carcinoma cutaneous metastases presented with a shield sign,5,7 including the case reported by Wang et al.1
The shield sign is a distinctive clinical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis.10 It was named to describe the skin metastases located predominantly on the chest area that would be covered by a medieval knight’s shield5,10,12; metastatic lesions also have been noted on the proximal arm and/or the upper back in a similar distribution.8,9 To date, based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms breast cancer, carcinoma, hemorrhagiectoides, metastases, salivary duct carcinoma, shield, and/or sign, the shield sign has been described in 6 patients with cutaneous metastases either from salivary duct carcinoma (4 patients)1,5,7 or breast cancer (2 patients).8,9 The shield sign pathologically corresponds to carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides, an inflammatory pattern of cutaneous metastases.5,11
Inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma has 3 distinctive clinical and pathologic manifestations.11 Carcinoma erysipelatoides and carcinoma telangiectoides were the earlier described variants.11 In 2012, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides was described as the third pattern of inflammatory cutaneous metastasis.5
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, which clinically mimics cutaneous streptococcal cellulitis, appears as a well-defined erythematous patch or plaque; the tumor cells can be found in the lymphatic vessels and either are absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma telangiectoides, which clinically mimics idiopathic telangiectases, appears as an erythematous patch with prominent telangiectases; the tumor cells can be found in the blood vessels and are either absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides appears as purpuric or violaceous indurated plaques; the tumor cells are not only found in the blood vessels, in the lymphatic vessels, or both, but also can be mildly to extensively present in the dermis.5,10,11
In conclusion, the shield sign is a unique presentation of inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, which is associated with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The clinical features of the infiltrated plaques correspond to the presence of tumor cells in the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the dermis; in addition, the purpuric and violaceous appearance correlates with the presence of extravasated erythrocytes or hemorrhage in the dermis. To date, half of the patients with skin metastases from salivary duct carcinoma have presented with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign.
Authors’ Response
We appreciate and welcome the comments provided by the authors. Drawing attention to unusual pathologic manifestations of cutaneous metastatic salivary duct carcinoma manifesting with the shield sign, the authors present a comprehensive review of 3 distinctive presentations: carcinoma erysipelatoides, carcinoma telangiectoides, and carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The inclusion of these variants enriches the discussion and makes this letter a valuable addition to the literature on cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, particularly metastatic salivary duct carcinoma.
Xintong Wang, MD; William H. Westra, MD
From the Department of Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Case Letter from Wang et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15) of a 60-year-old man whose metastatic salivary duct adenocarcinoma manifested with the shield sign as well as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. Cutaneous metastases have seldom been described in association with salivary duct carcinoma.2-7 In addition, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign has not been commonly reported.5,8-12
Salivary duct carcinoma—an uncommon head and neck malignancy characterized by androgen receptor expression—rarely is associated with cutaneous metastases. Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, metastatic, salivary duct carcinoma, and/or skin, including the patient described by Wang et al,1 there have been 8 individuals with cutaneous metastases from this cancer. The morphology of the cutaneous metastases has varied from angiomatous to angiokeratomalike (black and keratotic) papules, bullae, macules (red), papules and nodules (erythematous and scaly), plaques (cellulitislike and confluent that were purpuric, hemorrhagic, and violaceous), pseudovesicles, purpuric papules, subcutaneous nodules, and an ulcer (superficial and mimicked a basal cell carcinoma).1-7 Remarkably, 4 of 8 patients (50%) with salivary duct carcinoma cutaneous metastases presented with a shield sign,5,7 including the case reported by Wang et al.1
The shield sign is a distinctive clinical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis.10 It was named to describe the skin metastases located predominantly on the chest area that would be covered by a medieval knight’s shield5,10,12; metastatic lesions also have been noted on the proximal arm and/or the upper back in a similar distribution.8,9 To date, based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms breast cancer, carcinoma, hemorrhagiectoides, metastases, salivary duct carcinoma, shield, and/or sign, the shield sign has been described in 6 patients with cutaneous metastases either from salivary duct carcinoma (4 patients)1,5,7 or breast cancer (2 patients).8,9 The shield sign pathologically corresponds to carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides, an inflammatory pattern of cutaneous metastases.5,11
Inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma has 3 distinctive clinical and pathologic manifestations.11 Carcinoma erysipelatoides and carcinoma telangiectoides were the earlier described variants.11 In 2012, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides was described as the third pattern of inflammatory cutaneous metastasis.5
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, which clinically mimics cutaneous streptococcal cellulitis, appears as a well-defined erythematous patch or plaque; the tumor cells can be found in the lymphatic vessels and either are absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma telangiectoides, which clinically mimics idiopathic telangiectases, appears as an erythematous patch with prominent telangiectases; the tumor cells can be found in the blood vessels and are either absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides appears as purpuric or violaceous indurated plaques; the tumor cells are not only found in the blood vessels, in the lymphatic vessels, or both, but also can be mildly to extensively present in the dermis.5,10,11
In conclusion, the shield sign is a unique presentation of inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, which is associated with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The clinical features of the infiltrated plaques correspond to the presence of tumor cells in the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the dermis; in addition, the purpuric and violaceous appearance correlates with the presence of extravasated erythrocytes or hemorrhage in the dermis. To date, half of the patients with skin metastases from salivary duct carcinoma have presented with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign.
Authors’ Response
We appreciate and welcome the comments provided by the authors. Drawing attention to unusual pathologic manifestations of cutaneous metastatic salivary duct carcinoma manifesting with the shield sign, the authors present a comprehensive review of 3 distinctive presentations: carcinoma erysipelatoides, carcinoma telangiectoides, and carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The inclusion of these variants enriches the discussion and makes this letter a valuable addition to the literature on cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, particularly metastatic salivary duct carcinoma.
Xintong Wang, MD; William H. Westra, MD
From the Department of Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
- Wang X, Vyas NS, Alghamdi AA, et al. Cutaneous presentation of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma. Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15.
- Pollock JL, Catalano E. Metastatic ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland in a patient with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1098-1099.
- Pollock JL. Metastatic carcinoma of the parotid gland resembling carcinoma of the breast. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:1093.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Anderson JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Shin JY, Eun DH, Lee JY, et al. A case of cutaneous metastases of salivary duct carcinoma mimicking radiation recall dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2020;32:436-438.
- Aravena RC, Aravena DC, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hn3z850.
- Smith KA, Basko-Plluska J, Kothari AD, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cutis. 2020;105:E20-E22.
- Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Cutaneous metastatic cancer: carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides presenting as the shield sign. Cureus. 2021;13:e12627.
- Cohen PR. Pleomorphic appearance of breast cancer cutaneous metastases. Cureus. 2021;13:e20301.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Kurzrock R. Tumor lysis syndrome: introduction of a cutaneous variant and a new classification system. Cureus. 2021;13:e13816.
- Wang X, Vyas NS, Alghamdi AA, et al. Cutaneous presentation of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma. Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15.
- Pollock JL, Catalano E. Metastatic ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland in a patient with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1098-1099.
- Pollock JL. Metastatic carcinoma of the parotid gland resembling carcinoma of the breast. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:1093.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Anderson JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Shin JY, Eun DH, Lee JY, et al. A case of cutaneous metastases of salivary duct carcinoma mimicking radiation recall dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2020;32:436-438.
- Aravena RC, Aravena DC, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hn3z850.
- Smith KA, Basko-Plluska J, Kothari AD, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cutis. 2020;105:E20-E22.
- Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Cutaneous metastatic cancer: carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides presenting as the shield sign. Cureus. 2021;13:e12627.
- Cohen PR. Pleomorphic appearance of breast cancer cutaneous metastases. Cureus. 2021;13:e20301.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Kurzrock R. Tumor lysis syndrome: introduction of a cutaneous variant and a new classification system. Cureus. 2021;13:e13816.
Safety Standards a Top Priority for ASLMS President
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, began her term as president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) during the organization’s annual meeting in April 2024.
After earning her medical degree from Albany Medical College, Albany, New York, Dr. Ortiz, a native of Los Angeles, completed her dermatology residency training at the University of California, Irvine, and the university’s Beckman Laser Institute. Next, she completed a laser and cosmetic dermatology fellowship at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, all in Boston, and acquired additional fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Dr. Ortiz is currently director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and a clinical professor of dermatology at UCSD.
She has authored more than 60 publications on new innovations in cutaneous surgery and is a frequent speaker at meetings of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), and ASLMS, and she cochairs the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in San Diego. Dr. Ortiz has received several awards, including the 2024 Castle Connolly Top Doctor Award and the Exceptional Women in Medicine Award; Newsweek America’s Best Dermatologists; the ASLMS Dr. Horace Furumoto Young Investigator Award, the ASLMS Best of Session Award for Cutaneous Applications, and the ASDS President’s Outstanding Service Award. Her primary research focuses on the laser treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
In an interview, Dr. Ortiz spoke about her goals as ASLMS president and other topics related to dermatology.
Who inspired you most to become a doctor?
I’ve wanted to become a doctor for as long as I can remember. My fascination with science and the idea of helping people improve their health were driving forces. However, my biggest influence early on was my uncle, who was a pediatrician. His dedication and passion for medicine deeply inspired me and solidified my desire to pursue a career in healthcare.
I understand that a bout with chickenpox as a teenager influenced your decision to specialize in dermatology.
It’s an interesting and somewhat humorous story. When I was 18, I contracted chickenpox and ended up with scars on my face. It was a tough experience as a teenager, but it’s fascinating how such events can shape your life. In my quest for help, I opened the Yellow Pages and randomly chose a dermatologist nearby, who turned out to be Gary Lask, MD, director of lasers at UCLA [University of California, Los Angeles]. During our visit, I mentioned that I was premed, and he encouraged me to consider dermatology. About 6 years later, as a second-year medical student, I realized my passion for dermatology. I reached out to Dr. Lask and told him: “You were right. I want to be a dermatologist. Now, you have to help me get in!” Today, he remains my mentor, and I am deeply grateful for his guidance and support on this journey.
One of the initiatives for your term as ASLMS president includes a focus on safety standards for lasers and energy-based devices. Why is this important now?
Working at the university, I frequently encounter severe complications arising from the improper use of lasers and energy-based devices. As these procedures gain popularity, more providers are offering them, yet often without adequate training. As the world’s premier laser society, it is our duty to ensure patient safety. In the ever-evolving field of laser medicine, it is crucial that we continually strive to enhance the regulation of laser usage, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care with minimal risk.
One of the suggestions you have for the safety initiative is to offer a rigorous laser safety certification course with continuing education opportunities as a way foster a culture of heightened safety standards. Please explain what would be included in such a course and how it would align with current efforts to report adverse events such as the ASDS-Northwestern University Cutaneous Procedures Adverse Events Reporting (CAPER) registry and the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Program.
A laser safety certification task force has been established to determine the best approach for developing a comprehensive course. The task force aims to assess the necessity of a formal safety certification in our industry, identify the resources needed to support such a certification, establish general safety protocols to form the content foundation, address potential legal concerns, and outline the process for formal certification program recognition. This exploratory work is expected to conclude by the end of the year. The proposed course may include modules on the fundamentals of laser physics, safe operation techniques, patient selection and management, and emergency protocols. Continuing education opportunities would be considered to keep practitioners updated on the latest advancements and safety protocols in laser medicine, thereby fostering a culture of heightened safety standards.
Another initiative for your term is the rollout of a tattoo removal program for former gang members based on the UCSD Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program. Please tell us more about your vision for this national program.
UCSD Dermatology, in collaboration with UCSD Global Health, has been involved in the Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program for the past decade. This initiative supports and rehabilitates former gang members by offering laser tattoo removal, helping them reintegrate into society. My vision is to equip our members with the necessary protocols to implement this outreach initiative in their own communities. By providing opportunities for reform and growth, we aim to foster safer and more inclusive communities nationwide.
You were one of the first clinicians to use a laser to treat basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Who are the ideal candidates for this procedure? Is the technique ready for wide clinical adoption? If not, what kind of studies are needed to make it so?
My research passion lies in optimizing laser treatments for BCC. During my fellowship with R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Mathew Avram, MD, at the MGH Wellman Center for Photomedicine, we conducted a pilot study using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, achieving a 92% clearance rate after one treatment. Inspired by these results, we conducted a larger multicenter study, which demonstrated a 90% clearance rate after a single treatment. I now incorporate this technique into my daily practice. The ideal candidates for this procedure are patients with BCC that do not meet the Mohs Appropriate Use Criteria, such as those with nodular or superficial BCC subtypes on the body, individuals who are poor surgical candidates, or those who are surgically exhausted. However, I do not recommend this treatment for patients who are primarily concerned about facial scarring, particularly younger individuals; in such cases, Mohs surgery still remains the preferred option. While I believe this technique is ready for broader clinical adoption, it requires an understanding of laser endpoints. We are also exploring antibody-targeted gold nanorods to enhance the selectivity and standardization of the treatment.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
My patients are my greatest inspiration. Their trust and dedication motivate me to stay at the forefront of dermatologic advancements, ensuring I provide the most cutting-edge and safe treatments possible. Their commitment drives my relentless pursuit of continuous learning and innovation in the field.
What’s the best advice you can give to female dermatologists seeking leadership positions at the local, state, or national level?
My best advice is to have the courage to ask for what you seek. Societies are always looking for members who are eager to participate and contribute. If you express your interest in becoming more involved, there is likely a position available for you. The more you are willing to contribute to a society, the more likely you will be noticed and excel into higher leadership positions. Take initiative, show your commitment, and don’t hesitate to step forward when opportunities arise.
What’s the one tried-and-true laser- or energy-based procedure that you consider a “must” for your dermatology practice? And why?
Determining a single “must-have” laser- or energy-based procedure is a challenging question as it greatly depends on the specific needs of your patient population. However, one of the most common concerns among patients involves issues like redness and pigmentation. Therefore, having a versatile laser or an intense pulsed light device that effectively targets both red and brown pigmentation is indispensable for most practices.
In your view, what are the top three trends in aesthetic dermatology?
Over the years, I have observed several key trends in aesthetic dermatology:
- Minimally invasive procedures. There is a growing preference for less invasive treatments. Patients increasingly desire minimal downtime while still achieving significant results.
- Advancements in laser and energy-based devices for darker skin. There have been substantial advancements in technologies that are safer and more effective for darker skin tones. These developments play a crucial role in addressing diverse patient needs and providing inclusive dermatologic care.
- Natural aesthetic. I am hopeful that the trend toward an overdone appearance is fading. There seems to be a shift back towards a more natural and conservative aesthetic, emphasizing subtle enhancements over dramatic changes.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
I am most excited to see how artificial intelligence and robotics play a role in energy-based devices.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is also cochair of the MOAS.
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, began her term as president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) during the organization’s annual meeting in April 2024.
After earning her medical degree from Albany Medical College, Albany, New York, Dr. Ortiz, a native of Los Angeles, completed her dermatology residency training at the University of California, Irvine, and the university’s Beckman Laser Institute. Next, she completed a laser and cosmetic dermatology fellowship at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, all in Boston, and acquired additional fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Dr. Ortiz is currently director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and a clinical professor of dermatology at UCSD.
She has authored more than 60 publications on new innovations in cutaneous surgery and is a frequent speaker at meetings of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), and ASLMS, and she cochairs the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in San Diego. Dr. Ortiz has received several awards, including the 2024 Castle Connolly Top Doctor Award and the Exceptional Women in Medicine Award; Newsweek America’s Best Dermatologists; the ASLMS Dr. Horace Furumoto Young Investigator Award, the ASLMS Best of Session Award for Cutaneous Applications, and the ASDS President’s Outstanding Service Award. Her primary research focuses on the laser treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
In an interview, Dr. Ortiz spoke about her goals as ASLMS president and other topics related to dermatology.
Who inspired you most to become a doctor?
I’ve wanted to become a doctor for as long as I can remember. My fascination with science and the idea of helping people improve their health were driving forces. However, my biggest influence early on was my uncle, who was a pediatrician. His dedication and passion for medicine deeply inspired me and solidified my desire to pursue a career in healthcare.
I understand that a bout with chickenpox as a teenager influenced your decision to specialize in dermatology.
It’s an interesting and somewhat humorous story. When I was 18, I contracted chickenpox and ended up with scars on my face. It was a tough experience as a teenager, but it’s fascinating how such events can shape your life. In my quest for help, I opened the Yellow Pages and randomly chose a dermatologist nearby, who turned out to be Gary Lask, MD, director of lasers at UCLA [University of California, Los Angeles]. During our visit, I mentioned that I was premed, and he encouraged me to consider dermatology. About 6 years later, as a second-year medical student, I realized my passion for dermatology. I reached out to Dr. Lask and told him: “You were right. I want to be a dermatologist. Now, you have to help me get in!” Today, he remains my mentor, and I am deeply grateful for his guidance and support on this journey.
One of the initiatives for your term as ASLMS president includes a focus on safety standards for lasers and energy-based devices. Why is this important now?
Working at the university, I frequently encounter severe complications arising from the improper use of lasers and energy-based devices. As these procedures gain popularity, more providers are offering them, yet often without adequate training. As the world’s premier laser society, it is our duty to ensure patient safety. In the ever-evolving field of laser medicine, it is crucial that we continually strive to enhance the regulation of laser usage, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care with minimal risk.
One of the suggestions you have for the safety initiative is to offer a rigorous laser safety certification course with continuing education opportunities as a way foster a culture of heightened safety standards. Please explain what would be included in such a course and how it would align with current efforts to report adverse events such as the ASDS-Northwestern University Cutaneous Procedures Adverse Events Reporting (CAPER) registry and the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Program.
A laser safety certification task force has been established to determine the best approach for developing a comprehensive course. The task force aims to assess the necessity of a formal safety certification in our industry, identify the resources needed to support such a certification, establish general safety protocols to form the content foundation, address potential legal concerns, and outline the process for formal certification program recognition. This exploratory work is expected to conclude by the end of the year. The proposed course may include modules on the fundamentals of laser physics, safe operation techniques, patient selection and management, and emergency protocols. Continuing education opportunities would be considered to keep practitioners updated on the latest advancements and safety protocols in laser medicine, thereby fostering a culture of heightened safety standards.
Another initiative for your term is the rollout of a tattoo removal program for former gang members based on the UCSD Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program. Please tell us more about your vision for this national program.
UCSD Dermatology, in collaboration with UCSD Global Health, has been involved in the Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program for the past decade. This initiative supports and rehabilitates former gang members by offering laser tattoo removal, helping them reintegrate into society. My vision is to equip our members with the necessary protocols to implement this outreach initiative in their own communities. By providing opportunities for reform and growth, we aim to foster safer and more inclusive communities nationwide.
You were one of the first clinicians to use a laser to treat basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Who are the ideal candidates for this procedure? Is the technique ready for wide clinical adoption? If not, what kind of studies are needed to make it so?
My research passion lies in optimizing laser treatments for BCC. During my fellowship with R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Mathew Avram, MD, at the MGH Wellman Center for Photomedicine, we conducted a pilot study using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, achieving a 92% clearance rate after one treatment. Inspired by these results, we conducted a larger multicenter study, which demonstrated a 90% clearance rate after a single treatment. I now incorporate this technique into my daily practice. The ideal candidates for this procedure are patients with BCC that do not meet the Mohs Appropriate Use Criteria, such as those with nodular or superficial BCC subtypes on the body, individuals who are poor surgical candidates, or those who are surgically exhausted. However, I do not recommend this treatment for patients who are primarily concerned about facial scarring, particularly younger individuals; in such cases, Mohs surgery still remains the preferred option. While I believe this technique is ready for broader clinical adoption, it requires an understanding of laser endpoints. We are also exploring antibody-targeted gold nanorods to enhance the selectivity and standardization of the treatment.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
My patients are my greatest inspiration. Their trust and dedication motivate me to stay at the forefront of dermatologic advancements, ensuring I provide the most cutting-edge and safe treatments possible. Their commitment drives my relentless pursuit of continuous learning and innovation in the field.
What’s the best advice you can give to female dermatologists seeking leadership positions at the local, state, or national level?
My best advice is to have the courage to ask for what you seek. Societies are always looking for members who are eager to participate and contribute. If you express your interest in becoming more involved, there is likely a position available for you. The more you are willing to contribute to a society, the more likely you will be noticed and excel into higher leadership positions. Take initiative, show your commitment, and don’t hesitate to step forward when opportunities arise.
What’s the one tried-and-true laser- or energy-based procedure that you consider a “must” for your dermatology practice? And why?
Determining a single “must-have” laser- or energy-based procedure is a challenging question as it greatly depends on the specific needs of your patient population. However, one of the most common concerns among patients involves issues like redness and pigmentation. Therefore, having a versatile laser or an intense pulsed light device that effectively targets both red and brown pigmentation is indispensable for most practices.
In your view, what are the top three trends in aesthetic dermatology?
Over the years, I have observed several key trends in aesthetic dermatology:
- Minimally invasive procedures. There is a growing preference for less invasive treatments. Patients increasingly desire minimal downtime while still achieving significant results.
- Advancements in laser and energy-based devices for darker skin. There have been substantial advancements in technologies that are safer and more effective for darker skin tones. These developments play a crucial role in addressing diverse patient needs and providing inclusive dermatologic care.
- Natural aesthetic. I am hopeful that the trend toward an overdone appearance is fading. There seems to be a shift back towards a more natural and conservative aesthetic, emphasizing subtle enhancements over dramatic changes.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
I am most excited to see how artificial intelligence and robotics play a role in energy-based devices.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is also cochair of the MOAS.
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, began her term as president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) during the organization’s annual meeting in April 2024.
After earning her medical degree from Albany Medical College, Albany, New York, Dr. Ortiz, a native of Los Angeles, completed her dermatology residency training at the University of California, Irvine, and the university’s Beckman Laser Institute. Next, she completed a laser and cosmetic dermatology fellowship at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, all in Boston, and acquired additional fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Dr. Ortiz is currently director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and a clinical professor of dermatology at UCSD.
She has authored more than 60 publications on new innovations in cutaneous surgery and is a frequent speaker at meetings of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), and ASLMS, and she cochairs the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in San Diego. Dr. Ortiz has received several awards, including the 2024 Castle Connolly Top Doctor Award and the Exceptional Women in Medicine Award; Newsweek America’s Best Dermatologists; the ASLMS Dr. Horace Furumoto Young Investigator Award, the ASLMS Best of Session Award for Cutaneous Applications, and the ASDS President’s Outstanding Service Award. Her primary research focuses on the laser treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
In an interview, Dr. Ortiz spoke about her goals as ASLMS president and other topics related to dermatology.
Who inspired you most to become a doctor?
I’ve wanted to become a doctor for as long as I can remember. My fascination with science and the idea of helping people improve their health were driving forces. However, my biggest influence early on was my uncle, who was a pediatrician. His dedication and passion for medicine deeply inspired me and solidified my desire to pursue a career in healthcare.
I understand that a bout with chickenpox as a teenager influenced your decision to specialize in dermatology.
It’s an interesting and somewhat humorous story. When I was 18, I contracted chickenpox and ended up with scars on my face. It was a tough experience as a teenager, but it’s fascinating how such events can shape your life. In my quest for help, I opened the Yellow Pages and randomly chose a dermatologist nearby, who turned out to be Gary Lask, MD, director of lasers at UCLA [University of California, Los Angeles]. During our visit, I mentioned that I was premed, and he encouraged me to consider dermatology. About 6 years later, as a second-year medical student, I realized my passion for dermatology. I reached out to Dr. Lask and told him: “You were right. I want to be a dermatologist. Now, you have to help me get in!” Today, he remains my mentor, and I am deeply grateful for his guidance and support on this journey.
One of the initiatives for your term as ASLMS president includes a focus on safety standards for lasers and energy-based devices. Why is this important now?
Working at the university, I frequently encounter severe complications arising from the improper use of lasers and energy-based devices. As these procedures gain popularity, more providers are offering them, yet often without adequate training. As the world’s premier laser society, it is our duty to ensure patient safety. In the ever-evolving field of laser medicine, it is crucial that we continually strive to enhance the regulation of laser usage, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care with minimal risk.
One of the suggestions you have for the safety initiative is to offer a rigorous laser safety certification course with continuing education opportunities as a way foster a culture of heightened safety standards. Please explain what would be included in such a course and how it would align with current efforts to report adverse events such as the ASDS-Northwestern University Cutaneous Procedures Adverse Events Reporting (CAPER) registry and the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Program.
A laser safety certification task force has been established to determine the best approach for developing a comprehensive course. The task force aims to assess the necessity of a formal safety certification in our industry, identify the resources needed to support such a certification, establish general safety protocols to form the content foundation, address potential legal concerns, and outline the process for formal certification program recognition. This exploratory work is expected to conclude by the end of the year. The proposed course may include modules on the fundamentals of laser physics, safe operation techniques, patient selection and management, and emergency protocols. Continuing education opportunities would be considered to keep practitioners updated on the latest advancements and safety protocols in laser medicine, thereby fostering a culture of heightened safety standards.
Another initiative for your term is the rollout of a tattoo removal program for former gang members based on the UCSD Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program. Please tell us more about your vision for this national program.
UCSD Dermatology, in collaboration with UCSD Global Health, has been involved in the Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program for the past decade. This initiative supports and rehabilitates former gang members by offering laser tattoo removal, helping them reintegrate into society. My vision is to equip our members with the necessary protocols to implement this outreach initiative in their own communities. By providing opportunities for reform and growth, we aim to foster safer and more inclusive communities nationwide.
You were one of the first clinicians to use a laser to treat basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Who are the ideal candidates for this procedure? Is the technique ready for wide clinical adoption? If not, what kind of studies are needed to make it so?
My research passion lies in optimizing laser treatments for BCC. During my fellowship with R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Mathew Avram, MD, at the MGH Wellman Center for Photomedicine, we conducted a pilot study using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, achieving a 92% clearance rate after one treatment. Inspired by these results, we conducted a larger multicenter study, which demonstrated a 90% clearance rate after a single treatment. I now incorporate this technique into my daily practice. The ideal candidates for this procedure are patients with BCC that do not meet the Mohs Appropriate Use Criteria, such as those with nodular or superficial BCC subtypes on the body, individuals who are poor surgical candidates, or those who are surgically exhausted. However, I do not recommend this treatment for patients who are primarily concerned about facial scarring, particularly younger individuals; in such cases, Mohs surgery still remains the preferred option. While I believe this technique is ready for broader clinical adoption, it requires an understanding of laser endpoints. We are also exploring antibody-targeted gold nanorods to enhance the selectivity and standardization of the treatment.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
My patients are my greatest inspiration. Their trust and dedication motivate me to stay at the forefront of dermatologic advancements, ensuring I provide the most cutting-edge and safe treatments possible. Their commitment drives my relentless pursuit of continuous learning and innovation in the field.
What’s the best advice you can give to female dermatologists seeking leadership positions at the local, state, or national level?
My best advice is to have the courage to ask for what you seek. Societies are always looking for members who are eager to participate and contribute. If you express your interest in becoming more involved, there is likely a position available for you. The more you are willing to contribute to a society, the more likely you will be noticed and excel into higher leadership positions. Take initiative, show your commitment, and don’t hesitate to step forward when opportunities arise.
What’s the one tried-and-true laser- or energy-based procedure that you consider a “must” for your dermatology practice? And why?
Determining a single “must-have” laser- or energy-based procedure is a challenging question as it greatly depends on the specific needs of your patient population. However, one of the most common concerns among patients involves issues like redness and pigmentation. Therefore, having a versatile laser or an intense pulsed light device that effectively targets both red and brown pigmentation is indispensable for most practices.
In your view, what are the top three trends in aesthetic dermatology?
Over the years, I have observed several key trends in aesthetic dermatology:
- Minimally invasive procedures. There is a growing preference for less invasive treatments. Patients increasingly desire minimal downtime while still achieving significant results.
- Advancements in laser and energy-based devices for darker skin. There have been substantial advancements in technologies that are safer and more effective for darker skin tones. These developments play a crucial role in addressing diverse patient needs and providing inclusive dermatologic care.
- Natural aesthetic. I am hopeful that the trend toward an overdone appearance is fading. There seems to be a shift back towards a more natural and conservative aesthetic, emphasizing subtle enhancements over dramatic changes.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
I am most excited to see how artificial intelligence and robotics play a role in energy-based devices.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is also cochair of the MOAS.
Pilot Study Finds Experimental CBD Cream Decreases UVA Skin Damage
, results from a small prospective pilot study showed.
“This study hopefully reinvigorates interest in the utilization of whether it be plant-based, human-derived, or synthetic cannabinoids in the management of dermatologic disease,” one of the study investigators, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization. The study was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
For the prospective, single-center, pilot trial, which is believed to be the first of its kind, 19 volunteers aged 22-65 with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III applied either a nano-encapsulated CBD cream or a vehicle cream to blind spots on the skin of the buttocks twice daily for 14 days. Next, researchers applied a minimal erythema dose of UV radiation to the treated skin areas for 30 minutes. After 24 hours, they visually inspected the treated areas to clinically compare the erythema. They also performed five 4-mm punch biopsies from UVA- and non-UVA–exposed treatment sites on each buttock, as well as from an untreated control site that was at least 5 cm away from the treated left buttock.
At 24 hours, 21% of study participants showed less redness on CBD-treated skin compared with control-treated skin, while histology showed that CBD-treated skin demonstrated reduced UVA-induced epidermal hyperplasia compared with control-treated skin (a mean 11.3% change from baseline vs 28.7%, respectively; P = .01). In other findings, application of CBD cream reduced DNA damage and DNA mutations associated with UVA-induced skin aging/damage and ultimately skin cancer.
In addition, the CBD-treated skin samples had a reduction in the UVA-associated increase in the premutagenic marker 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and a reduction of two major UVA-induced mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with skin photoaging.
The research, Dr. Friedman noted, “took a village of collaborators and almost 3 years to pull together,” including collaborating with his long-standing mentor, Brian Berman, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, and a study coauthor. The study “demonstrated that purposeful delivery of CBD using an established nanoparticle platform ... can have a quantifiable impact on preventing the expected DNA damage and cellular injury one should see from UVA exposure,” said Dr. Friedman, who codeveloped the nanoparticle platform with his father, Joel M. Friedman, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City.
“Never before has a dermatologic study on topical cannabinoids dove so deeply into the biological impact of this natural ingredient to highlight its potential, here, as a mitigation strategy for unprotected exposure to prevent the downstream sequelae of UV radiation,” Dr. Friedman said.
In the paper, he and his coauthors acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its small sample size and the single-center design.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he coinvented the nanoparticle technology used in the trial. Dr. Berman is a consultant at MINO Labs, which funded the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures. The study was done in collaboration with the Center for Clinical and Cosmetic Research in Aventura, Florida.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results from a small prospective pilot study showed.
“This study hopefully reinvigorates interest in the utilization of whether it be plant-based, human-derived, or synthetic cannabinoids in the management of dermatologic disease,” one of the study investigators, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization. The study was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
For the prospective, single-center, pilot trial, which is believed to be the first of its kind, 19 volunteers aged 22-65 with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III applied either a nano-encapsulated CBD cream or a vehicle cream to blind spots on the skin of the buttocks twice daily for 14 days. Next, researchers applied a minimal erythema dose of UV radiation to the treated skin areas for 30 minutes. After 24 hours, they visually inspected the treated areas to clinically compare the erythema. They also performed five 4-mm punch biopsies from UVA- and non-UVA–exposed treatment sites on each buttock, as well as from an untreated control site that was at least 5 cm away from the treated left buttock.
At 24 hours, 21% of study participants showed less redness on CBD-treated skin compared with control-treated skin, while histology showed that CBD-treated skin demonstrated reduced UVA-induced epidermal hyperplasia compared with control-treated skin (a mean 11.3% change from baseline vs 28.7%, respectively; P = .01). In other findings, application of CBD cream reduced DNA damage and DNA mutations associated with UVA-induced skin aging/damage and ultimately skin cancer.
In addition, the CBD-treated skin samples had a reduction in the UVA-associated increase in the premutagenic marker 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and a reduction of two major UVA-induced mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with skin photoaging.
The research, Dr. Friedman noted, “took a village of collaborators and almost 3 years to pull together,” including collaborating with his long-standing mentor, Brian Berman, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, and a study coauthor. The study “demonstrated that purposeful delivery of CBD using an established nanoparticle platform ... can have a quantifiable impact on preventing the expected DNA damage and cellular injury one should see from UVA exposure,” said Dr. Friedman, who codeveloped the nanoparticle platform with his father, Joel M. Friedman, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City.
“Never before has a dermatologic study on topical cannabinoids dove so deeply into the biological impact of this natural ingredient to highlight its potential, here, as a mitigation strategy for unprotected exposure to prevent the downstream sequelae of UV radiation,” Dr. Friedman said.
In the paper, he and his coauthors acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its small sample size and the single-center design.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he coinvented the nanoparticle technology used in the trial. Dr. Berman is a consultant at MINO Labs, which funded the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures. The study was done in collaboration with the Center for Clinical and Cosmetic Research in Aventura, Florida.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results from a small prospective pilot study showed.
“This study hopefully reinvigorates interest in the utilization of whether it be plant-based, human-derived, or synthetic cannabinoids in the management of dermatologic disease,” one of the study investigators, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization. The study was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
For the prospective, single-center, pilot trial, which is believed to be the first of its kind, 19 volunteers aged 22-65 with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III applied either a nano-encapsulated CBD cream or a vehicle cream to blind spots on the skin of the buttocks twice daily for 14 days. Next, researchers applied a minimal erythema dose of UV radiation to the treated skin areas for 30 minutes. After 24 hours, they visually inspected the treated areas to clinically compare the erythema. They also performed five 4-mm punch biopsies from UVA- and non-UVA–exposed treatment sites on each buttock, as well as from an untreated control site that was at least 5 cm away from the treated left buttock.
At 24 hours, 21% of study participants showed less redness on CBD-treated skin compared with control-treated skin, while histology showed that CBD-treated skin demonstrated reduced UVA-induced epidermal hyperplasia compared with control-treated skin (a mean 11.3% change from baseline vs 28.7%, respectively; P = .01). In other findings, application of CBD cream reduced DNA damage and DNA mutations associated with UVA-induced skin aging/damage and ultimately skin cancer.
In addition, the CBD-treated skin samples had a reduction in the UVA-associated increase in the premutagenic marker 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and a reduction of two major UVA-induced mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with skin photoaging.
The research, Dr. Friedman noted, “took a village of collaborators and almost 3 years to pull together,” including collaborating with his long-standing mentor, Brian Berman, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, and a study coauthor. The study “demonstrated that purposeful delivery of CBD using an established nanoparticle platform ... can have a quantifiable impact on preventing the expected DNA damage and cellular injury one should see from UVA exposure,” said Dr. Friedman, who codeveloped the nanoparticle platform with his father, Joel M. Friedman, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City.
“Never before has a dermatologic study on topical cannabinoids dove so deeply into the biological impact of this natural ingredient to highlight its potential, here, as a mitigation strategy for unprotected exposure to prevent the downstream sequelae of UV radiation,” Dr. Friedman said.
In the paper, he and his coauthors acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its small sample size and the single-center design.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he coinvented the nanoparticle technology used in the trial. Dr. Berman is a consultant at MINO Labs, which funded the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures. The study was done in collaboration with the Center for Clinical and Cosmetic Research in Aventura, Florida.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Study Finds Varying Skin Cancer Rates Based on Sexual Orientation
Addressing dynamics of each SM subgroup will require increasingly tailored prevention, screening, and research efforts, the study authors said.
“We identified specific subgroups within the sexual minority community who are at higher risk for skin cancer, specifically White gay males and Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black SM men and women — particularly individuals who identify as bisexual,” senior author Matthew Mansh, MD, said in an interview. He is an assistant professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Using data of adults in the US general population from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from January 2014 to December 2021, investigators included more than 1.5 million respondents. The proportions of SM women and men (who self-identified as bisexual, lesbian, gay, “something else,” or other) were 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
Lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher among SM men than among heterosexual men (7.4% vs 6.8%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16). In analyses stratified by racial and ethnic group, AORs for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM men vs their heterosexual counterparts were 2.18 and 3.81, respectively. The corresponding figures for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM women were 2.33 and 2.46, respectively.
When investigators combined all minority respondents along gender lines, lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher in bisexual men (aOR, 3.94), bisexual women (aOR, 1.51), and women identifying as something else or other (aOR, 2.70) than in their heterosexual peers.
“I wasn’t expecting that Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black SMs would be at higher risk for skin cancer,” Dr. Mansh said. Even if these groups have more behavioral risk factors for UV radiation (UVR) exposure, he explained, UVR exposure is less strongly linked with skin cancer in darker skin than in lighter skin. Reasons for the counterintuitive finding could include different screening habits among SM people of different racial and ethnic groups, he said, and analyzing such factors will require further research.
Although some effect sizes were modest, the authors wrote, their findings may have important implications for population-based research and public health efforts aimed at early skin cancer detection and prevention. Presently, the United States lacks established guidelines for skin cancer screening. In a 2023 statement published in JAMA, the US Preventive Services Task Force said that there is insufficient evidence to determine the benefit-harm balance of skin cancer screening in asymptomatic people.
“So there has been a lot of recent talk and a need to identify which subset groups of patients might be higher risk for skin cancer and might benefit from more screening,” Dr. Mansh said in an interview. “Understanding more about the high-risk demographic and clinical features that predispose someone to skin cancer helps identify these high-risk populations that could be used to develop better screening guidelines.”
Identifying groups at a higher risk for skin cancer also allows experts to design more targeted counseling or public health interventions focused on these groups, Dr. Mansh added. Absent screening guidelines, experts emphasize changing modifiable risk factors such as UVR exposure, smoking, and alcohol use. “And we know that the message that might change behaviors in a cisgender heterosexual man might be different than in a gay White male or a Hispanic bisexual male.”
A 2017 review showed that interventions to reduce behaviors involving UVR exposure, such as indoor tanning, among young cisgender women focused largely on aging and appearance-based concerns. A 2019 study showed that messages focused on avoiding skin cancer may help motivate SM men to reduce tanning behaviors.
Furthermore, said Dr. Mansh, all electronic health record products available in the United States must provide data fields for sexual orientation. “I don’t believe many dermatologists, depending on the setting, collect that information routinely. Integrating sexual orientation and/or gender identity data into patient intake forms so that it can be integrated into the electronic health record is probably very helpful, not only for your clinical practice but also for future research studies.”
Asked to comment on the results, Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, who was not involved with the study, said that its impact on clinical practice will be challenging to ascertain. She is chief of dermatology with the VA Boston Healthcare System, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, all in Boston, Massachusetts.
“The study found significant adjusted odds ratios,” Dr. Hartman explained, “but for some of the different populations, the overall lifetime rate of skin cancer is still quite low.” For example, 1.0% for SM non-Hispanic Black men or a difference of 2.1% vs 1.8% in SM Hispanic women. “Thus, I am not sure specific screening recommendations are warranted, although some populations, such as Hispanic sexual minority males, seemed to have a much higher risk (3.8-fold on adjusted analysis) that warrants further investigation.”
For now, she advised assessing patients’ risks for skin cancer based on well-established risk factors such as sun exposure/indoor tanning, skin phototype, immunosuppression, and age.
Dr. Mansh reported no relevant conflicts or funding sources for the study. Dr. Hartman reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Addressing dynamics of each SM subgroup will require increasingly tailored prevention, screening, and research efforts, the study authors said.
“We identified specific subgroups within the sexual minority community who are at higher risk for skin cancer, specifically White gay males and Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black SM men and women — particularly individuals who identify as bisexual,” senior author Matthew Mansh, MD, said in an interview. He is an assistant professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Using data of adults in the US general population from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from January 2014 to December 2021, investigators included more than 1.5 million respondents. The proportions of SM women and men (who self-identified as bisexual, lesbian, gay, “something else,” or other) were 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
Lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher among SM men than among heterosexual men (7.4% vs 6.8%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16). In analyses stratified by racial and ethnic group, AORs for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM men vs their heterosexual counterparts were 2.18 and 3.81, respectively. The corresponding figures for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM women were 2.33 and 2.46, respectively.
When investigators combined all minority respondents along gender lines, lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher in bisexual men (aOR, 3.94), bisexual women (aOR, 1.51), and women identifying as something else or other (aOR, 2.70) than in their heterosexual peers.
“I wasn’t expecting that Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black SMs would be at higher risk for skin cancer,” Dr. Mansh said. Even if these groups have more behavioral risk factors for UV radiation (UVR) exposure, he explained, UVR exposure is less strongly linked with skin cancer in darker skin than in lighter skin. Reasons for the counterintuitive finding could include different screening habits among SM people of different racial and ethnic groups, he said, and analyzing such factors will require further research.
Although some effect sizes were modest, the authors wrote, their findings may have important implications for population-based research and public health efforts aimed at early skin cancer detection and prevention. Presently, the United States lacks established guidelines for skin cancer screening. In a 2023 statement published in JAMA, the US Preventive Services Task Force said that there is insufficient evidence to determine the benefit-harm balance of skin cancer screening in asymptomatic people.
“So there has been a lot of recent talk and a need to identify which subset groups of patients might be higher risk for skin cancer and might benefit from more screening,” Dr. Mansh said in an interview. “Understanding more about the high-risk demographic and clinical features that predispose someone to skin cancer helps identify these high-risk populations that could be used to develop better screening guidelines.”
Identifying groups at a higher risk for skin cancer also allows experts to design more targeted counseling or public health interventions focused on these groups, Dr. Mansh added. Absent screening guidelines, experts emphasize changing modifiable risk factors such as UVR exposure, smoking, and alcohol use. “And we know that the message that might change behaviors in a cisgender heterosexual man might be different than in a gay White male or a Hispanic bisexual male.”
A 2017 review showed that interventions to reduce behaviors involving UVR exposure, such as indoor tanning, among young cisgender women focused largely on aging and appearance-based concerns. A 2019 study showed that messages focused on avoiding skin cancer may help motivate SM men to reduce tanning behaviors.
Furthermore, said Dr. Mansh, all electronic health record products available in the United States must provide data fields for sexual orientation. “I don’t believe many dermatologists, depending on the setting, collect that information routinely. Integrating sexual orientation and/or gender identity data into patient intake forms so that it can be integrated into the electronic health record is probably very helpful, not only for your clinical practice but also for future research studies.”
Asked to comment on the results, Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, who was not involved with the study, said that its impact on clinical practice will be challenging to ascertain. She is chief of dermatology with the VA Boston Healthcare System, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, all in Boston, Massachusetts.
“The study found significant adjusted odds ratios,” Dr. Hartman explained, “but for some of the different populations, the overall lifetime rate of skin cancer is still quite low.” For example, 1.0% for SM non-Hispanic Black men or a difference of 2.1% vs 1.8% in SM Hispanic women. “Thus, I am not sure specific screening recommendations are warranted, although some populations, such as Hispanic sexual minority males, seemed to have a much higher risk (3.8-fold on adjusted analysis) that warrants further investigation.”
For now, she advised assessing patients’ risks for skin cancer based on well-established risk factors such as sun exposure/indoor tanning, skin phototype, immunosuppression, and age.
Dr. Mansh reported no relevant conflicts or funding sources for the study. Dr. Hartman reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Addressing dynamics of each SM subgroup will require increasingly tailored prevention, screening, and research efforts, the study authors said.
“We identified specific subgroups within the sexual minority community who are at higher risk for skin cancer, specifically White gay males and Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black SM men and women — particularly individuals who identify as bisexual,” senior author Matthew Mansh, MD, said in an interview. He is an assistant professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Using data of adults in the US general population from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from January 2014 to December 2021, investigators included more than 1.5 million respondents. The proportions of SM women and men (who self-identified as bisexual, lesbian, gay, “something else,” or other) were 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
Lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher among SM men than among heterosexual men (7.4% vs 6.8%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16). In analyses stratified by racial and ethnic group, AORs for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM men vs their heterosexual counterparts were 2.18 and 3.81, respectively. The corresponding figures for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic SM women were 2.33 and 2.46, respectively.
When investigators combined all minority respondents along gender lines, lifetime skin cancer prevalence was higher in bisexual men (aOR, 3.94), bisexual women (aOR, 1.51), and women identifying as something else or other (aOR, 2.70) than in their heterosexual peers.
“I wasn’t expecting that Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black SMs would be at higher risk for skin cancer,” Dr. Mansh said. Even if these groups have more behavioral risk factors for UV radiation (UVR) exposure, he explained, UVR exposure is less strongly linked with skin cancer in darker skin than in lighter skin. Reasons for the counterintuitive finding could include different screening habits among SM people of different racial and ethnic groups, he said, and analyzing such factors will require further research.
Although some effect sizes were modest, the authors wrote, their findings may have important implications for population-based research and public health efforts aimed at early skin cancer detection and prevention. Presently, the United States lacks established guidelines for skin cancer screening. In a 2023 statement published in JAMA, the US Preventive Services Task Force said that there is insufficient evidence to determine the benefit-harm balance of skin cancer screening in asymptomatic people.
“So there has been a lot of recent talk and a need to identify which subset groups of patients might be higher risk for skin cancer and might benefit from more screening,” Dr. Mansh said in an interview. “Understanding more about the high-risk demographic and clinical features that predispose someone to skin cancer helps identify these high-risk populations that could be used to develop better screening guidelines.”
Identifying groups at a higher risk for skin cancer also allows experts to design more targeted counseling or public health interventions focused on these groups, Dr. Mansh added. Absent screening guidelines, experts emphasize changing modifiable risk factors such as UVR exposure, smoking, and alcohol use. “And we know that the message that might change behaviors in a cisgender heterosexual man might be different than in a gay White male or a Hispanic bisexual male.”
A 2017 review showed that interventions to reduce behaviors involving UVR exposure, such as indoor tanning, among young cisgender women focused largely on aging and appearance-based concerns. A 2019 study showed that messages focused on avoiding skin cancer may help motivate SM men to reduce tanning behaviors.
Furthermore, said Dr. Mansh, all electronic health record products available in the United States must provide data fields for sexual orientation. “I don’t believe many dermatologists, depending on the setting, collect that information routinely. Integrating sexual orientation and/or gender identity data into patient intake forms so that it can be integrated into the electronic health record is probably very helpful, not only for your clinical practice but also for future research studies.”
Asked to comment on the results, Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, who was not involved with the study, said that its impact on clinical practice will be challenging to ascertain. She is chief of dermatology with the VA Boston Healthcare System, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, all in Boston, Massachusetts.
“The study found significant adjusted odds ratios,” Dr. Hartman explained, “but for some of the different populations, the overall lifetime rate of skin cancer is still quite low.” For example, 1.0% for SM non-Hispanic Black men or a difference of 2.1% vs 1.8% in SM Hispanic women. “Thus, I am not sure specific screening recommendations are warranted, although some populations, such as Hispanic sexual minority males, seemed to have a much higher risk (3.8-fold on adjusted analysis) that warrants further investigation.”
For now, she advised assessing patients’ risks for skin cancer based on well-established risk factors such as sun exposure/indoor tanning, skin phototype, immunosuppression, and age.
Dr. Mansh reported no relevant conflicts or funding sources for the study. Dr. Hartman reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Dermatoporosis in Older Adults: A Condition That Requires Holistic, Creative Management
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Greater Transparency of Oncologists’ Pharma Relationships Needed
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
FROM ASCO 2024
Barriers to Mohs Micrographic Surgery in Japanese Patients With Basal Cell Carcinoma
Margin-controlled surgery for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the lower lip was first performed by Dr. Frederic Mohs on June 30, 1936. Since then, thousands of skin cancer surgeons have refined and adopted the technique. Due to the high cure rate and sparing of normal tissue, Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has become the gold standard treatment for facial and special-site nonmelanoma skin cancer worldwide. Mohs micrographic surgery is performed on more than 876,000 tumors annually in the United States.1 Among 3.5 million Americans diagnosed with nonmelanoma skin cancer in 2006, one-quarter were treated with MMS.2 In Japan, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin malignancy, with an incidence of 3.34 cases per 100,000 individuals; SCC is the second most common, with an incidence of 2.5 cases per 100,000 individuals.3
The essential element that makes MMS unique is the careful microscopic examination of the entire margin of the removed specimen. Tissue processing is done with careful en face orientation to ensure that circumferential and deep margins are entirely visible. The surgeon interprets the slides and proceeds to remove the additional tumor as necessary. Because the same physician performs both the surgery and the pathologic assessment throughout the procedure, a precise correlation between the microscopic and surgical findings can be made. The surgeon can begin with smaller margins, removing minimal healthy tissue while removing all the cancer cells, which results in the smallest-possible skin defect and the best prognosis for the malignancy (Figure 1).
At the only facility in Japan offering MMS, the lead author (S.S.) has treated 52 lesions with MMS in 46 patients (2020-2022). Of these patients, 40 were White, 5 were Japanese, and 1 was of African descent. In this case series, we present 5 Japanese patients who had BCC treated with MMS.
Case Series
Patient 1—A 50-year-old Japanese woman presented to dermatology with a brown papule on the nasal tip of 1.25 year’s duration (Figure 2). A biopsy revealed infiltrative BCC (Figure 3), and the patient was referred to the dermatology department at a nearby university hospital. Because the BCC was an aggressive variant, wide local excision (WLE) with subsequent flap reconstruction was recommended as well as radiation therapy. The patient learned about MMS through an internet search and refused both options, seeking MMS treatment at our clinic. Although Japanese health insurance does not cover MMS, the patient had supplemental private insurance that did cover the cost. She provided consent to undergo the procedure. Physical examination revealed a 7.5×6-mm, brown-red macule with ill-defined borders on the tip of the nose. We used a 1.5-mm margin for the first stage of MMS (Figure 4A). The frozen section revealed that the tumor had been entirely excised in the first stage, leaving only a 10.5×9-mm skin defect that was reconstructed with a Dufourmentel flap (Figure 4B). No signs of recurrence were noted at 3.5-year follow-up, and the cosmetic outcome was favorable (Figure 4C). National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend a margin greater than 4 mm for infiltrative BCCs4; therefore, our technique reduced the total defect by at least 4 mm in a cosmetically sensitive area. The patient also did not need radiation therapy, which reduced morbidity. She continues to be recurrence free at 3.5-year follow-up.
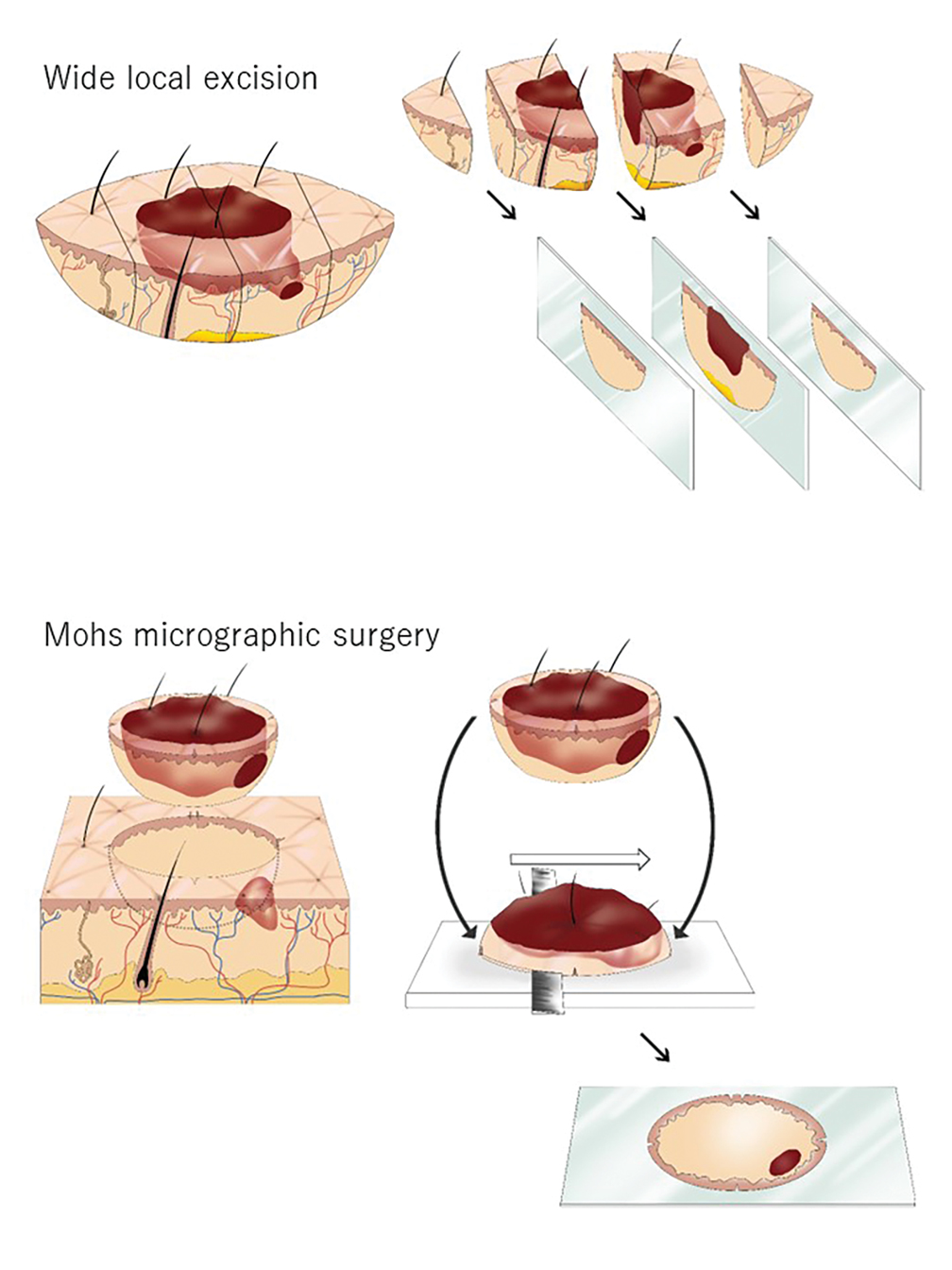
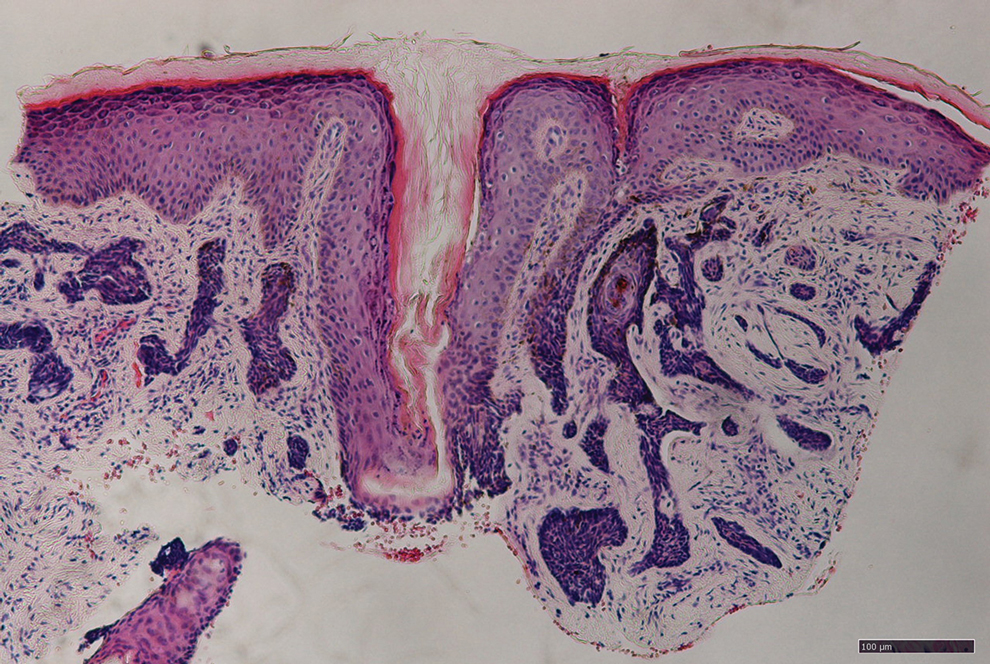
Patient 2—A 63-year-old Japanese man presented to dermatology with a brown macule on the right lower eyelid of 2 years’ duration. A biopsy of the lesion was positive for nodular BCC. After being advised to undergo WLE and extensive reconstruction with plastic surgery, the patient learned of MMS through an internet search and found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm brown macule on the right lower eyelid. The patient had supplemental private insurance that covered the cost of MMS, and he provided consent for the procedure. A 1.5-mm margin was taken for the first stage, resulting in a 10×8-mm defect superficial to the orbicularis oculi muscle. The frozen section revealed residual tumor exposure in the dermis at the 9- to 10-o’clock position. A second-stage excision was performed to remove an additional 1.5 mm of skin at the 9- to 12-o’clock position with a thin layer of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The subsequent histologic examination revealed no residual BCC, and the final 13×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a rotation flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 2.5-year follow-up with an excellent cosmetic outcome.
Patient 3—A 73-year-old Japanese man presented to a local university dermatology clinic with a new papule on the nose. The dermatologist suggested WLE with 4-mm margins and reconstruction of the skin defect 2 weeks later by a plastic surgeon. The patient was not satisfied with the proposed surgical plan, which led him to learn about MMS on the internet; he subsequently found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 4×3.5-mm brown papule on the tip of the nose. He understood the nature of MMS and chose to pay out-of-pocket because Japanese health insurance did not cover the procedure. We used a 2-mm margin for the first stage, which created a 7.5×7-mm skin defect. The frozen section pathology revealed no residual BCC at the cut surface. The skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 4—A 45-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a papule on the right side of the nose of 1 year’s duration. A biopsy revealed the lesion was a nodular BCC. The dermatologist recommended WLE at a general hospital, but the patient refused after learning about MMS. He subsequently made an appointment with our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×4-mm white papule on the right side of the nose. The patient had private insurance that covered the cost of MMS. The first stage was performed with 1.5-mm margins and was clear of residual tumor. A Limberg rhombic flap from the adjacent cheek was used to repair the final 10×7-mm skin defect. There were no signs of recurrence at 1 year and 9 months’ follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 5—A 76-year-old Japanese woman presented to a university hospital near Tokyo with a black papule on the left cutaneous lip of 5 years’ duration. A biopsy revealed nodular BCC, and WLE with flap reconstruction was recommended. The patient’s son learned about MMS through internet research and referred her to our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm black papule on the left upper lip. The patient’s private insurance covered the cost of MMS, and she consented to the procedure. We used a 2-mm initial margin, and the immediate frozen section revealed no signs of BCC at the cut surface. The 11×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Comment
We presented 5 cases of MMS in Japanese patients with BCC. More than 7000 new cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer occur every year in Japan.3 Only 0.04% of these cases—the 5 cases presented here—were treated with MMS in Japan in 2020 and 2021, in contrast to 25% in the United States in 2006.2
MMS vs Other BCC Treatments—Mohs micrographic surgery offers 2 distinct advantages over conventional excision: an improved cure rate while achieving a smaller final defect size, generally leading to better cosmetic outcomes. Overall 5-year recurrence rates of BCC are 10% for conventional surgical excision vs 1% for MMS, while the recurrence rates for SCC are 8% and 3%, respectively.5 A study of well-demarcated BCCs smaller than 2 cm that were treated with MMS with 2-mm increments revealed that 95% of the cases were free of malignancy within a 4-mm margin of the normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor.6 Several articles have reported a 95% cure rate or higher with conventional excision of localized BCC,7 but 4- to 5-mm excision margins are required, resulting in a greater skin defect and a lower cure rate compared to MMS.
Aggressive subtypes of BCC have a higher recurrence rate. Rowe et al8 reported the following 5-year recurrence rates: 5.6% for MMS, 17.4% for conventional surgical excision, 40.0% for curettage and electrodesiccation, and 9.8% for radiation therapy. Primary BCCs with high-risk histologic subtypes has a 10-year recurrence rate of 4.4% with MMS vs 12.2% with conventional excision.9 These findings reveal that MMS yields a better prognosis compared to traditional treatment methods for recurrent BCCs and BCCs of high-risk histologic subtypes.
The primary reason for the excellent cure rate seen in MMS is the ability to perform complete margin assessment. Peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) is crucial in achieving high cure rates with narrow margins. In WLE (Figure 1), vertical sectioning (also known as bread-loafing) does not achieve direct visualization of the entire surgical margin, as this technique only evaluates random sections and does not achieve PDEMA.10 The bread-loafing method is used almost exclusively in Japan and visualizes only 0.1% of the entire margin compared to 100% with MMS.11 Beyond the superior cure rate, the MMS technique often yields smaller final defects compared to WLE. All 5 of our patients achieved complete tumor removal while sparing more normal tissue compared to conventional WLE, which takes at least a 4-mm margin in all directions.
Barriers to Adopting MMS in Japan—There are many barriers to the broader adoption of MMS in Japan. A guideline of the Japanese Dermatological Association says, MMS “is complicated, requires special training for acquisition, and requires time and labor for implementation of a series of processes, and it has not gained wide acceptance in Japan because of these disadvantages.”3 There currently are no MMS training programs in Japan. We refute this statement from the Japanese Dermatological Association because, in our experience, only 1 surgeon plus a single histotechnician familiar with MMS is sufficient for a facility to offer the procedure (the lead author of this study [S.S.] acts as both the surgeon and the histotechnician). Another misconception among some physicians in Japan is that cancer on ethnically Japanese skin is uniquely suited to excision without microscopic verification of tumor clearance because the borders of the tumors are easily identified, which was based on good cure rates for the excision of well-demarcated pigmented BCCs in a Japanese cohort. This study of a Japanese cohort investigated the specimens with the conventional bread-loafing technique but not with the PDEMA.12
Eighty percent (4/5) of our patients presented with nodular BCC, and only 1 required a second stage. In comparison, we also treated 16 White patients with nodular BCC with MMS during the same period, and 31% (5/16) required more than 1 stage, with 1 patient requiring 3 stages. This cohort, however, is too small to demonstrate a statistically significant difference (S.S., unpublished data, 2020-2022).
A study in Singapore reported the postsurgical complication rate and 5-year recurrence rate for 481 tumors (92% BCC and 7.5% SCC). The median follow-up duration after MMS was 36 months, and the recurrence rate was 0.6%. The postsurgical complications included 11 (2.3%) cases with superficial tip necrosis of surgical flaps/grafts, 2 (0.4%) with mild wound dehiscence, 1 (0.2%) with minor surgical site bleeding, and 1 (0.2%) with minor wound infection.13 This study supports the notion that MMS is equally effective for Asian patients.
Awareness of MMS in Japan is lacking, and most Japanese dermatologists do not know about the technique. All 5 patients in our case series asked their dermatologists about alternative treatment options and were not offered MMS. In each case, the patients learned of the technique through internet research.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for MMS in Japan is another barrier. Because the national health insurance does not reimburse for MMS, the procedure is relatively unavailable to most Japanese citizens who cannot pay out-of-pocket for the treatment and do not have supplemental insurance. Mohs micrographic surgery may seem expensive compared to WLE followed by repair; however, in the authors’ experience, in Japan, excision without MMS may require general sedation and multiple surgeries to reconstruct larger skin defects, leading to greater morbidity and risk for the patient.
Conclusion
Mohs micrographic surgery in Japan is in its infancy, and further studies showing recurrence rates and long-term prognosis are needed. Such data should help increase awareness of MMS among Japanese physicians as an excellent treatment option for their patients. Furthermore, as Japan becomes more heterogenous as a society and the US Military increases its presence in the region, the need for MMS is likely to increase.
Acknowledgments—We appreciate the proofreading support by Mark Bivens, MBA, MSc (Tokyo, Japan), as well as the technical support from Ben Tallon, MBChB, and Robyn Mason (both in Tauranga, New Zealand) to start MMS at our clinic.
- Asgari MM, Olson J, Alam M. Needs assessment for Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.010
- Connolly SM, Baker DR, Baker DR, et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: a report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:531-550.
- Ansai SI, Umebayashi Y, Katsumata N, et al. Japanese Dermatological Association Guidelines: outlines of guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 2020. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E288-E311.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et at. Basal cell skin cancer, version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21:1181-1203. doi:10.6004/jncn.2023.0056
- Snow SN, Gunkel J. Mohs surgery. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:2445-2455. doi:10.1016/b978-0-070-94171-3.00041-7
- Wolf DJ, Zitelli JA. Surgical margins for basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:340-344.
- Quazi SJ, Aslam N, Saleem H, et al. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12:E9211.
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day Jus CL. Mohs surgery is the treatment of choice for recurrent (previously treated) basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:424-431.
- Van Loo, Mosterd K, Krekels GA. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:3011-3020.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:1382-1394.
- Hui AM, Jacobson M, Markowitz O, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:503-515.
- Ito T, Inatomi Y, Nagae K, et al. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1828-1831.
- Ho WYB, Zhao X, Tan WPM. Mohs micrographic surgery in Singapore: a long-term follow-up review. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021;50:922-923.
Margin-controlled surgery for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the lower lip was first performed by Dr. Frederic Mohs on June 30, 1936. Since then, thousands of skin cancer surgeons have refined and adopted the technique. Due to the high cure rate and sparing of normal tissue, Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has become the gold standard treatment for facial and special-site nonmelanoma skin cancer worldwide. Mohs micrographic surgery is performed on more than 876,000 tumors annually in the United States.1 Among 3.5 million Americans diagnosed with nonmelanoma skin cancer in 2006, one-quarter were treated with MMS.2 In Japan, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin malignancy, with an incidence of 3.34 cases per 100,000 individuals; SCC is the second most common, with an incidence of 2.5 cases per 100,000 individuals.3
The essential element that makes MMS unique is the careful microscopic examination of the entire margin of the removed specimen. Tissue processing is done with careful en face orientation to ensure that circumferential and deep margins are entirely visible. The surgeon interprets the slides and proceeds to remove the additional tumor as necessary. Because the same physician performs both the surgery and the pathologic assessment throughout the procedure, a precise correlation between the microscopic and surgical findings can be made. The surgeon can begin with smaller margins, removing minimal healthy tissue while removing all the cancer cells, which results in the smallest-possible skin defect and the best prognosis for the malignancy (Figure 1).
At the only facility in Japan offering MMS, the lead author (S.S.) has treated 52 lesions with MMS in 46 patients (2020-2022). Of these patients, 40 were White, 5 were Japanese, and 1 was of African descent. In this case series, we present 5 Japanese patients who had BCC treated with MMS.
Case Series
Patient 1—A 50-year-old Japanese woman presented to dermatology with a brown papule on the nasal tip of 1.25 year’s duration (Figure 2). A biopsy revealed infiltrative BCC (Figure 3), and the patient was referred to the dermatology department at a nearby university hospital. Because the BCC was an aggressive variant, wide local excision (WLE) with subsequent flap reconstruction was recommended as well as radiation therapy. The patient learned about MMS through an internet search and refused both options, seeking MMS treatment at our clinic. Although Japanese health insurance does not cover MMS, the patient had supplemental private insurance that did cover the cost. She provided consent to undergo the procedure. Physical examination revealed a 7.5×6-mm, brown-red macule with ill-defined borders on the tip of the nose. We used a 1.5-mm margin for the first stage of MMS (Figure 4A). The frozen section revealed that the tumor had been entirely excised in the first stage, leaving only a 10.5×9-mm skin defect that was reconstructed with a Dufourmentel flap (Figure 4B). No signs of recurrence were noted at 3.5-year follow-up, and the cosmetic outcome was favorable (Figure 4C). National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend a margin greater than 4 mm for infiltrative BCCs4; therefore, our technique reduced the total defect by at least 4 mm in a cosmetically sensitive area. The patient also did not need radiation therapy, which reduced morbidity. She continues to be recurrence free at 3.5-year follow-up.




Patient 2—A 63-year-old Japanese man presented to dermatology with a brown macule on the right lower eyelid of 2 years’ duration. A biopsy of the lesion was positive for nodular BCC. After being advised to undergo WLE and extensive reconstruction with plastic surgery, the patient learned of MMS through an internet search and found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm brown macule on the right lower eyelid. The patient had supplemental private insurance that covered the cost of MMS, and he provided consent for the procedure. A 1.5-mm margin was taken for the first stage, resulting in a 10×8-mm defect superficial to the orbicularis oculi muscle. The frozen section revealed residual tumor exposure in the dermis at the 9- to 10-o’clock position. A second-stage excision was performed to remove an additional 1.5 mm of skin at the 9- to 12-o’clock position with a thin layer of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The subsequent histologic examination revealed no residual BCC, and the final 13×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a rotation flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 2.5-year follow-up with an excellent cosmetic outcome.
Patient 3—A 73-year-old Japanese man presented to a local university dermatology clinic with a new papule on the nose. The dermatologist suggested WLE with 4-mm margins and reconstruction of the skin defect 2 weeks later by a plastic surgeon. The patient was not satisfied with the proposed surgical plan, which led him to learn about MMS on the internet; he subsequently found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 4×3.5-mm brown papule on the tip of the nose. He understood the nature of MMS and chose to pay out-of-pocket because Japanese health insurance did not cover the procedure. We used a 2-mm margin for the first stage, which created a 7.5×7-mm skin defect. The frozen section pathology revealed no residual BCC at the cut surface. The skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 4—A 45-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a papule on the right side of the nose of 1 year’s duration. A biopsy revealed the lesion was a nodular BCC. The dermatologist recommended WLE at a general hospital, but the patient refused after learning about MMS. He subsequently made an appointment with our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×4-mm white papule on the right side of the nose. The patient had private insurance that covered the cost of MMS. The first stage was performed with 1.5-mm margins and was clear of residual tumor. A Limberg rhombic flap from the adjacent cheek was used to repair the final 10×7-mm skin defect. There were no signs of recurrence at 1 year and 9 months’ follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 5—A 76-year-old Japanese woman presented to a university hospital near Tokyo with a black papule on the left cutaneous lip of 5 years’ duration. A biopsy revealed nodular BCC, and WLE with flap reconstruction was recommended. The patient’s son learned about MMS through internet research and referred her to our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm black papule on the left upper lip. The patient’s private insurance covered the cost of MMS, and she consented to the procedure. We used a 2-mm initial margin, and the immediate frozen section revealed no signs of BCC at the cut surface. The 11×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Comment
We presented 5 cases of MMS in Japanese patients with BCC. More than 7000 new cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer occur every year in Japan.3 Only 0.04% of these cases—the 5 cases presented here—were treated with MMS in Japan in 2020 and 2021, in contrast to 25% in the United States in 2006.2
MMS vs Other BCC Treatments—Mohs micrographic surgery offers 2 distinct advantages over conventional excision: an improved cure rate while achieving a smaller final defect size, generally leading to better cosmetic outcomes. Overall 5-year recurrence rates of BCC are 10% for conventional surgical excision vs 1% for MMS, while the recurrence rates for SCC are 8% and 3%, respectively.5 A study of well-demarcated BCCs smaller than 2 cm that were treated with MMS with 2-mm increments revealed that 95% of the cases were free of malignancy within a 4-mm margin of the normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor.6 Several articles have reported a 95% cure rate or higher with conventional excision of localized BCC,7 but 4- to 5-mm excision margins are required, resulting in a greater skin defect and a lower cure rate compared to MMS.
Aggressive subtypes of BCC have a higher recurrence rate. Rowe et al8 reported the following 5-year recurrence rates: 5.6% for MMS, 17.4% for conventional surgical excision, 40.0% for curettage and electrodesiccation, and 9.8% for radiation therapy. Primary BCCs with high-risk histologic subtypes has a 10-year recurrence rate of 4.4% with MMS vs 12.2% with conventional excision.9 These findings reveal that MMS yields a better prognosis compared to traditional treatment methods for recurrent BCCs and BCCs of high-risk histologic subtypes.
The primary reason for the excellent cure rate seen in MMS is the ability to perform complete margin assessment. Peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) is crucial in achieving high cure rates with narrow margins. In WLE (Figure 1), vertical sectioning (also known as bread-loafing) does not achieve direct visualization of the entire surgical margin, as this technique only evaluates random sections and does not achieve PDEMA.10 The bread-loafing method is used almost exclusively in Japan and visualizes only 0.1% of the entire margin compared to 100% with MMS.11 Beyond the superior cure rate, the MMS technique often yields smaller final defects compared to WLE. All 5 of our patients achieved complete tumor removal while sparing more normal tissue compared to conventional WLE, which takes at least a 4-mm margin in all directions.
Barriers to Adopting MMS in Japan—There are many barriers to the broader adoption of MMS in Japan. A guideline of the Japanese Dermatological Association says, MMS “is complicated, requires special training for acquisition, and requires time and labor for implementation of a series of processes, and it has not gained wide acceptance in Japan because of these disadvantages.”3 There currently are no MMS training programs in Japan. We refute this statement from the Japanese Dermatological Association because, in our experience, only 1 surgeon plus a single histotechnician familiar with MMS is sufficient for a facility to offer the procedure (the lead author of this study [S.S.] acts as both the surgeon and the histotechnician). Another misconception among some physicians in Japan is that cancer on ethnically Japanese skin is uniquely suited to excision without microscopic verification of tumor clearance because the borders of the tumors are easily identified, which was based on good cure rates for the excision of well-demarcated pigmented BCCs in a Japanese cohort. This study of a Japanese cohort investigated the specimens with the conventional bread-loafing technique but not with the PDEMA.12
Eighty percent (4/5) of our patients presented with nodular BCC, and only 1 required a second stage. In comparison, we also treated 16 White patients with nodular BCC with MMS during the same period, and 31% (5/16) required more than 1 stage, with 1 patient requiring 3 stages. This cohort, however, is too small to demonstrate a statistically significant difference (S.S., unpublished data, 2020-2022).
A study in Singapore reported the postsurgical complication rate and 5-year recurrence rate for 481 tumors (92% BCC and 7.5% SCC). The median follow-up duration after MMS was 36 months, and the recurrence rate was 0.6%. The postsurgical complications included 11 (2.3%) cases with superficial tip necrosis of surgical flaps/grafts, 2 (0.4%) with mild wound dehiscence, 1 (0.2%) with minor surgical site bleeding, and 1 (0.2%) with minor wound infection.13 This study supports the notion that MMS is equally effective for Asian patients.
Awareness of MMS in Japan is lacking, and most Japanese dermatologists do not know about the technique. All 5 patients in our case series asked their dermatologists about alternative treatment options and were not offered MMS. In each case, the patients learned of the technique through internet research.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for MMS in Japan is another barrier. Because the national health insurance does not reimburse for MMS, the procedure is relatively unavailable to most Japanese citizens who cannot pay out-of-pocket for the treatment and do not have supplemental insurance. Mohs micrographic surgery may seem expensive compared to WLE followed by repair; however, in the authors’ experience, in Japan, excision without MMS may require general sedation and multiple surgeries to reconstruct larger skin defects, leading to greater morbidity and risk for the patient.
Conclusion
Mohs micrographic surgery in Japan is in its infancy, and further studies showing recurrence rates and long-term prognosis are needed. Such data should help increase awareness of MMS among Japanese physicians as an excellent treatment option for their patients. Furthermore, as Japan becomes more heterogenous as a society and the US Military increases its presence in the region, the need for MMS is likely to increase.
Acknowledgments—We appreciate the proofreading support by Mark Bivens, MBA, MSc (Tokyo, Japan), as well as the technical support from Ben Tallon, MBChB, and Robyn Mason (both in Tauranga, New Zealand) to start MMS at our clinic.
Margin-controlled surgery for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the lower lip was first performed by Dr. Frederic Mohs on June 30, 1936. Since then, thousands of skin cancer surgeons have refined and adopted the technique. Due to the high cure rate and sparing of normal tissue, Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has become the gold standard treatment for facial and special-site nonmelanoma skin cancer worldwide. Mohs micrographic surgery is performed on more than 876,000 tumors annually in the United States.1 Among 3.5 million Americans diagnosed with nonmelanoma skin cancer in 2006, one-quarter were treated with MMS.2 In Japan, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin malignancy, with an incidence of 3.34 cases per 100,000 individuals; SCC is the second most common, with an incidence of 2.5 cases per 100,000 individuals.3
The essential element that makes MMS unique is the careful microscopic examination of the entire margin of the removed specimen. Tissue processing is done with careful en face orientation to ensure that circumferential and deep margins are entirely visible. The surgeon interprets the slides and proceeds to remove the additional tumor as necessary. Because the same physician performs both the surgery and the pathologic assessment throughout the procedure, a precise correlation between the microscopic and surgical findings can be made. The surgeon can begin with smaller margins, removing minimal healthy tissue while removing all the cancer cells, which results in the smallest-possible skin defect and the best prognosis for the malignancy (Figure 1).
At the only facility in Japan offering MMS, the lead author (S.S.) has treated 52 lesions with MMS in 46 patients (2020-2022). Of these patients, 40 were White, 5 were Japanese, and 1 was of African descent. In this case series, we present 5 Japanese patients who had BCC treated with MMS.
Case Series
Patient 1—A 50-year-old Japanese woman presented to dermatology with a brown papule on the nasal tip of 1.25 year’s duration (Figure 2). A biopsy revealed infiltrative BCC (Figure 3), and the patient was referred to the dermatology department at a nearby university hospital. Because the BCC was an aggressive variant, wide local excision (WLE) with subsequent flap reconstruction was recommended as well as radiation therapy. The patient learned about MMS through an internet search and refused both options, seeking MMS treatment at our clinic. Although Japanese health insurance does not cover MMS, the patient had supplemental private insurance that did cover the cost. She provided consent to undergo the procedure. Physical examination revealed a 7.5×6-mm, brown-red macule with ill-defined borders on the tip of the nose. We used a 1.5-mm margin for the first stage of MMS (Figure 4A). The frozen section revealed that the tumor had been entirely excised in the first stage, leaving only a 10.5×9-mm skin defect that was reconstructed with a Dufourmentel flap (Figure 4B). No signs of recurrence were noted at 3.5-year follow-up, and the cosmetic outcome was favorable (Figure 4C). National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend a margin greater than 4 mm for infiltrative BCCs4; therefore, our technique reduced the total defect by at least 4 mm in a cosmetically sensitive area. The patient also did not need radiation therapy, which reduced morbidity. She continues to be recurrence free at 3.5-year follow-up.




Patient 2—A 63-year-old Japanese man presented to dermatology with a brown macule on the right lower eyelid of 2 years’ duration. A biopsy of the lesion was positive for nodular BCC. After being advised to undergo WLE and extensive reconstruction with plastic surgery, the patient learned of MMS through an internet search and found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm brown macule on the right lower eyelid. The patient had supplemental private insurance that covered the cost of MMS, and he provided consent for the procedure. A 1.5-mm margin was taken for the first stage, resulting in a 10×8-mm defect superficial to the orbicularis oculi muscle. The frozen section revealed residual tumor exposure in the dermis at the 9- to 10-o’clock position. A second-stage excision was performed to remove an additional 1.5 mm of skin at the 9- to 12-o’clock position with a thin layer of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The subsequent histologic examination revealed no residual BCC, and the final 13×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a rotation flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 2.5-year follow-up with an excellent cosmetic outcome.
Patient 3—A 73-year-old Japanese man presented to a local university dermatology clinic with a new papule on the nose. The dermatologist suggested WLE with 4-mm margins and reconstruction of the skin defect 2 weeks later by a plastic surgeon. The patient was not satisfied with the proposed surgical plan, which led him to learn about MMS on the internet; he subsequently found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 4×3.5-mm brown papule on the tip of the nose. He understood the nature of MMS and chose to pay out-of-pocket because Japanese health insurance did not cover the procedure. We used a 2-mm margin for the first stage, which created a 7.5×7-mm skin defect. The frozen section pathology revealed no residual BCC at the cut surface. The skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 4—A 45-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a papule on the right side of the nose of 1 year’s duration. A biopsy revealed the lesion was a nodular BCC. The dermatologist recommended WLE at a general hospital, but the patient refused after learning about MMS. He subsequently made an appointment with our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×4-mm white papule on the right side of the nose. The patient had private insurance that covered the cost of MMS. The first stage was performed with 1.5-mm margins and was clear of residual tumor. A Limberg rhombic flap from the adjacent cheek was used to repair the final 10×7-mm skin defect. There were no signs of recurrence at 1 year and 9 months’ follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 5—A 76-year-old Japanese woman presented to a university hospital near Tokyo with a black papule on the left cutaneous lip of 5 years’ duration. A biopsy revealed nodular BCC, and WLE with flap reconstruction was recommended. The patient’s son learned about MMS through internet research and referred her to our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm black papule on the left upper lip. The patient’s private insurance covered the cost of MMS, and she consented to the procedure. We used a 2-mm initial margin, and the immediate frozen section revealed no signs of BCC at the cut surface. The 11×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Comment
We presented 5 cases of MMS in Japanese patients with BCC. More than 7000 new cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer occur every year in Japan.3 Only 0.04% of these cases—the 5 cases presented here—were treated with MMS in Japan in 2020 and 2021, in contrast to 25% in the United States in 2006.2
MMS vs Other BCC Treatments—Mohs micrographic surgery offers 2 distinct advantages over conventional excision: an improved cure rate while achieving a smaller final defect size, generally leading to better cosmetic outcomes. Overall 5-year recurrence rates of BCC are 10% for conventional surgical excision vs 1% for MMS, while the recurrence rates for SCC are 8% and 3%, respectively.5 A study of well-demarcated BCCs smaller than 2 cm that were treated with MMS with 2-mm increments revealed that 95% of the cases were free of malignancy within a 4-mm margin of the normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor.6 Several articles have reported a 95% cure rate or higher with conventional excision of localized BCC,7 but 4- to 5-mm excision margins are required, resulting in a greater skin defect and a lower cure rate compared to MMS.
Aggressive subtypes of BCC have a higher recurrence rate. Rowe et al8 reported the following 5-year recurrence rates: 5.6% for MMS, 17.4% for conventional surgical excision, 40.0% for curettage and electrodesiccation, and 9.8% for radiation therapy. Primary BCCs with high-risk histologic subtypes has a 10-year recurrence rate of 4.4% with MMS vs 12.2% with conventional excision.9 These findings reveal that MMS yields a better prognosis compared to traditional treatment methods for recurrent BCCs and BCCs of high-risk histologic subtypes.
The primary reason for the excellent cure rate seen in MMS is the ability to perform complete margin assessment. Peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) is crucial in achieving high cure rates with narrow margins. In WLE (Figure 1), vertical sectioning (also known as bread-loafing) does not achieve direct visualization of the entire surgical margin, as this technique only evaluates random sections and does not achieve PDEMA.10 The bread-loafing method is used almost exclusively in Japan and visualizes only 0.1% of the entire margin compared to 100% with MMS.11 Beyond the superior cure rate, the MMS technique often yields smaller final defects compared to WLE. All 5 of our patients achieved complete tumor removal while sparing more normal tissue compared to conventional WLE, which takes at least a 4-mm margin in all directions.
Barriers to Adopting MMS in Japan—There are many barriers to the broader adoption of MMS in Japan. A guideline of the Japanese Dermatological Association says, MMS “is complicated, requires special training for acquisition, and requires time and labor for implementation of a series of processes, and it has not gained wide acceptance in Japan because of these disadvantages.”3 There currently are no MMS training programs in Japan. We refute this statement from the Japanese Dermatological Association because, in our experience, only 1 surgeon plus a single histotechnician familiar with MMS is sufficient for a facility to offer the procedure (the lead author of this study [S.S.] acts as both the surgeon and the histotechnician). Another misconception among some physicians in Japan is that cancer on ethnically Japanese skin is uniquely suited to excision without microscopic verification of tumor clearance because the borders of the tumors are easily identified, which was based on good cure rates for the excision of well-demarcated pigmented BCCs in a Japanese cohort. This study of a Japanese cohort investigated the specimens with the conventional bread-loafing technique but not with the PDEMA.12
Eighty percent (4/5) of our patients presented with nodular BCC, and only 1 required a second stage. In comparison, we also treated 16 White patients with nodular BCC with MMS during the same period, and 31% (5/16) required more than 1 stage, with 1 patient requiring 3 stages. This cohort, however, is too small to demonstrate a statistically significant difference (S.S., unpublished data, 2020-2022).
A study in Singapore reported the postsurgical complication rate and 5-year recurrence rate for 481 tumors (92% BCC and 7.5% SCC). The median follow-up duration after MMS was 36 months, and the recurrence rate was 0.6%. The postsurgical complications included 11 (2.3%) cases with superficial tip necrosis of surgical flaps/grafts, 2 (0.4%) with mild wound dehiscence, 1 (0.2%) with minor surgical site bleeding, and 1 (0.2%) with minor wound infection.13 This study supports the notion that MMS is equally effective for Asian patients.
Awareness of MMS in Japan is lacking, and most Japanese dermatologists do not know about the technique. All 5 patients in our case series asked their dermatologists about alternative treatment options and were not offered MMS. In each case, the patients learned of the technique through internet research.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for MMS in Japan is another barrier. Because the national health insurance does not reimburse for MMS, the procedure is relatively unavailable to most Japanese citizens who cannot pay out-of-pocket for the treatment and do not have supplemental insurance. Mohs micrographic surgery may seem expensive compared to WLE followed by repair; however, in the authors’ experience, in Japan, excision without MMS may require general sedation and multiple surgeries to reconstruct larger skin defects, leading to greater morbidity and risk for the patient.
Conclusion
Mohs micrographic surgery in Japan is in its infancy, and further studies showing recurrence rates and long-term prognosis are needed. Such data should help increase awareness of MMS among Japanese physicians as an excellent treatment option for their patients. Furthermore, as Japan becomes more heterogenous as a society and the US Military increases its presence in the region, the need for MMS is likely to increase.
Acknowledgments—We appreciate the proofreading support by Mark Bivens, MBA, MSc (Tokyo, Japan), as well as the technical support from Ben Tallon, MBChB, and Robyn Mason (both in Tauranga, New Zealand) to start MMS at our clinic.
- Asgari MM, Olson J, Alam M. Needs assessment for Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.010
- Connolly SM, Baker DR, Baker DR, et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: a report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:531-550.
- Ansai SI, Umebayashi Y, Katsumata N, et al. Japanese Dermatological Association Guidelines: outlines of guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 2020. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E288-E311.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et at. Basal cell skin cancer, version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21:1181-1203. doi:10.6004/jncn.2023.0056
- Snow SN, Gunkel J. Mohs surgery. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:2445-2455. doi:10.1016/b978-0-070-94171-3.00041-7
- Wolf DJ, Zitelli JA. Surgical margins for basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:340-344.
- Quazi SJ, Aslam N, Saleem H, et al. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12:E9211.
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day Jus CL. Mohs surgery is the treatment of choice for recurrent (previously treated) basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:424-431.
- Van Loo, Mosterd K, Krekels GA. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:3011-3020.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:1382-1394.
- Hui AM, Jacobson M, Markowitz O, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:503-515.
- Ito T, Inatomi Y, Nagae K, et al. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1828-1831.
- Ho WYB, Zhao X, Tan WPM. Mohs micrographic surgery in Singapore: a long-term follow-up review. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021;50:922-923.
- Asgari MM, Olson J, Alam M. Needs assessment for Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.010
- Connolly SM, Baker DR, Baker DR, et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: a report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:531-550.
- Ansai SI, Umebayashi Y, Katsumata N, et al. Japanese Dermatological Association Guidelines: outlines of guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 2020. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E288-E311.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et at. Basal cell skin cancer, version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21:1181-1203. doi:10.6004/jncn.2023.0056
- Snow SN, Gunkel J. Mohs surgery. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:2445-2455. doi:10.1016/b978-0-070-94171-3.00041-7
- Wolf DJ, Zitelli JA. Surgical margins for basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:340-344.
- Quazi SJ, Aslam N, Saleem H, et al. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12:E9211.
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day Jus CL. Mohs surgery is the treatment of choice for recurrent (previously treated) basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:424-431.
- Van Loo, Mosterd K, Krekels GA. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:3011-3020.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:1382-1394.
- Hui AM, Jacobson M, Markowitz O, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:503-515.
- Ito T, Inatomi Y, Nagae K, et al. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1828-1831.
- Ho WYB, Zhao X, Tan WPM. Mohs micrographic surgery in Singapore: a long-term follow-up review. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021;50:922-923.
Practice Points
- Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a safe and effective treatment method for nonmelanoma skin cancer. In some cases, this procedure is superior to standard wide local excision and repair.
- For the broader adaptation of this vital technique in Japan—where MMS is not well established—increased awareness of treatment outcomes among Japanese physicians is needed.
Should Cancer Trial Eligibility Become More Inclusive?
The study, published online in Clinical Cancer Research, highlighted the potential benefits of broadening eligibility criteria for clinical trials.
“It is well known that results in an ‘ideal’ population do not always translate to the real-world population,” senior author Hans Gelderblom, MD, chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, said in a press release. “Eligibility criteria are often too strict, and educated exemptions by experienced investigators can help individual patients, especially in a last-resort trial.”
Although experts have expressed interest in improving trial inclusivity, it’s unclear how doing so might impact treatment safety and efficacy.
In the Drug Rediscovery Protocol (DRUP), Dr. Gelderblom and colleagues examined the impact of broadening trial eligibility on patient outcomes. DRUP is an ongoing Dutch national, multicenter, pan-cancer, nonrandomized clinical trial in which patients are treated off-label with approved molecularly targeted or immunotherapies.
In the trial, 1019 patients with treatment-refractory disease were matched to one of the available study drugs based on their tumor molecular profile and enrolled in parallel cohorts. Cohorts were defined by tumor type, molecular profile, and study drug.
Among these patients, 82 patients — 8% of the cohort — were granted waivers to participate. Most waivers (45%) were granted as exceptions to general- or drug-related eligibility criteria, often because of out-of-range lab results. Other categories included treatment and testing exceptions, as well as out-of-window testing.
The researchers then compared safety and efficacy outcomes between the 82 participants granted waivers and the 937 who did not receive waivers.
Overall, Dr. Gelderblom’s team found that the rate of serious adverse events was similar between patients who received a waiver and those who did not: 39% vs 41%, respectively.
A relationship between waivers and serious adverse events was deemed “unlikely” for 86% of patients and “possible” for 14%. In two cases concerning a direct relationship, for instance, patients who received waivers for decreased hemoglobin levels developed anemia.
The rate of clinical benefit — defined as an objective response or stable disease for at least 16 weeks — was similar between the groups. Overall, 40% of patients who received a waiver (33 of 82) had a clinical benefit vs 33% of patients without a waiver (P = .43). Median overall survival for patients that received a waiver was also similar — 11 months in the waiver group and 8 months in the nonwaiver group (hazard ratio, 0.87; P = .33).
“Safety and clinical benefit were preserved in patients for whom a waiver was granted,” the authors concluded.
The study had several limitations. The diversity of cancer types, treatments, and reasons for protocol exemptions precluded subgroup analyses. In addition, because the decision to grant waivers depended in large part on the likelihood of clinical benefit, “it is possible that patients who received waivers were positively selected for clinical benefit compared with the general study population,” the authors wrote.
So, “although the clinical benefit rate of the patient group for whom a waiver was granted appears to be slightly higher, this difference might be explained by the selection process of the central study team, in which each waiver request was carefully considered, weighing the risks and potential benefits for the patient in question,” the authors explained.
Overall, “these findings advocate for a broader and more inclusive design when establishing novel trials, paving the way for a more effective and tailored application of cancer therapies in patients with advanced or refractory disease,” Dr. Gelderblom said.
Commenting on the study, Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, said that “relaxing eligibility criteria is important, and I support this. Trials should include patients that are more representative of the real-world, so that results are generalizable.”
However, “the paper overemphasized efficacy,” said Dr. Gyawali, from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. The sample size of waiver-granted patients was small, plus “the clinical benefit rate is not a marker of efficacy.
“The response rate is somewhat better, but for a heterogeneous study with multiple targets and drugs, it is difficult to say much about treatment effects here,” Dr. Gyawali added. Overall, “we shouldn’t read too much into treatment benefits based on these numbers.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Stelvio for Life Foundation, the Dutch Cancer Society, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, pharma&, Eisai Co., Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Gelderblom declared no conflicts of interest, and Dr. Gyawali declared no conflicts of interest related to his comment.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, published online in Clinical Cancer Research, highlighted the potential benefits of broadening eligibility criteria for clinical trials.
“It is well known that results in an ‘ideal’ population do not always translate to the real-world population,” senior author Hans Gelderblom, MD, chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, said in a press release. “Eligibility criteria are often too strict, and educated exemptions by experienced investigators can help individual patients, especially in a last-resort trial.”
Although experts have expressed interest in improving trial inclusivity, it’s unclear how doing so might impact treatment safety and efficacy.
In the Drug Rediscovery Protocol (DRUP), Dr. Gelderblom and colleagues examined the impact of broadening trial eligibility on patient outcomes. DRUP is an ongoing Dutch national, multicenter, pan-cancer, nonrandomized clinical trial in which patients are treated off-label with approved molecularly targeted or immunotherapies.
In the trial, 1019 patients with treatment-refractory disease were matched to one of the available study drugs based on their tumor molecular profile and enrolled in parallel cohorts. Cohorts were defined by tumor type, molecular profile, and study drug.
Among these patients, 82 patients — 8% of the cohort — were granted waivers to participate. Most waivers (45%) were granted as exceptions to general- or drug-related eligibility criteria, often because of out-of-range lab results. Other categories included treatment and testing exceptions, as well as out-of-window testing.
The researchers then compared safety and efficacy outcomes between the 82 participants granted waivers and the 937 who did not receive waivers.
Overall, Dr. Gelderblom’s team found that the rate of serious adverse events was similar between patients who received a waiver and those who did not: 39% vs 41%, respectively.
A relationship between waivers and serious adverse events was deemed “unlikely” for 86% of patients and “possible” for 14%. In two cases concerning a direct relationship, for instance, patients who received waivers for decreased hemoglobin levels developed anemia.
The rate of clinical benefit — defined as an objective response or stable disease for at least 16 weeks — was similar between the groups. Overall, 40% of patients who received a waiver (33 of 82) had a clinical benefit vs 33% of patients without a waiver (P = .43). Median overall survival for patients that received a waiver was also similar — 11 months in the waiver group and 8 months in the nonwaiver group (hazard ratio, 0.87; P = .33).
“Safety and clinical benefit were preserved in patients for whom a waiver was granted,” the authors concluded.
The study had several limitations. The diversity of cancer types, treatments, and reasons for protocol exemptions precluded subgroup analyses. In addition, because the decision to grant waivers depended in large part on the likelihood of clinical benefit, “it is possible that patients who received waivers were positively selected for clinical benefit compared with the general study population,” the authors wrote.
So, “although the clinical benefit rate of the patient group for whom a waiver was granted appears to be slightly higher, this difference might be explained by the selection process of the central study team, in which each waiver request was carefully considered, weighing the risks and potential benefits for the patient in question,” the authors explained.
Overall, “these findings advocate for a broader and more inclusive design when establishing novel trials, paving the way for a more effective and tailored application of cancer therapies in patients with advanced or refractory disease,” Dr. Gelderblom said.
Commenting on the study, Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, said that “relaxing eligibility criteria is important, and I support this. Trials should include patients that are more representative of the real-world, so that results are generalizable.”
However, “the paper overemphasized efficacy,” said Dr. Gyawali, from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. The sample size of waiver-granted patients was small, plus “the clinical benefit rate is not a marker of efficacy.
“The response rate is somewhat better, but for a heterogeneous study with multiple targets and drugs, it is difficult to say much about treatment effects here,” Dr. Gyawali added. Overall, “we shouldn’t read too much into treatment benefits based on these numbers.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Stelvio for Life Foundation, the Dutch Cancer Society, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, pharma&, Eisai Co., Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Gelderblom declared no conflicts of interest, and Dr. Gyawali declared no conflicts of interest related to his comment.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, published online in Clinical Cancer Research, highlighted the potential benefits of broadening eligibility criteria for clinical trials.
“It is well known that results in an ‘ideal’ population do not always translate to the real-world population,” senior author Hans Gelderblom, MD, chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, said in a press release. “Eligibility criteria are often too strict, and educated exemptions by experienced investigators can help individual patients, especially in a last-resort trial.”
Although experts have expressed interest in improving trial inclusivity, it’s unclear how doing so might impact treatment safety and efficacy.
In the Drug Rediscovery Protocol (DRUP), Dr. Gelderblom and colleagues examined the impact of broadening trial eligibility on patient outcomes. DRUP is an ongoing Dutch national, multicenter, pan-cancer, nonrandomized clinical trial in which patients are treated off-label with approved molecularly targeted or immunotherapies.
In the trial, 1019 patients with treatment-refractory disease were matched to one of the available study drugs based on their tumor molecular profile and enrolled in parallel cohorts. Cohorts were defined by tumor type, molecular profile, and study drug.
Among these patients, 82 patients — 8% of the cohort — were granted waivers to participate. Most waivers (45%) were granted as exceptions to general- or drug-related eligibility criteria, often because of out-of-range lab results. Other categories included treatment and testing exceptions, as well as out-of-window testing.
The researchers then compared safety and efficacy outcomes between the 82 participants granted waivers and the 937 who did not receive waivers.
Overall, Dr. Gelderblom’s team found that the rate of serious adverse events was similar between patients who received a waiver and those who did not: 39% vs 41%, respectively.
A relationship between waivers and serious adverse events was deemed “unlikely” for 86% of patients and “possible” for 14%. In two cases concerning a direct relationship, for instance, patients who received waivers for decreased hemoglobin levels developed anemia.
The rate of clinical benefit — defined as an objective response or stable disease for at least 16 weeks — was similar between the groups. Overall, 40% of patients who received a waiver (33 of 82) had a clinical benefit vs 33% of patients without a waiver (P = .43). Median overall survival for patients that received a waiver was also similar — 11 months in the waiver group and 8 months in the nonwaiver group (hazard ratio, 0.87; P = .33).
“Safety and clinical benefit were preserved in patients for whom a waiver was granted,” the authors concluded.
The study had several limitations. The diversity of cancer types, treatments, and reasons for protocol exemptions precluded subgroup analyses. In addition, because the decision to grant waivers depended in large part on the likelihood of clinical benefit, “it is possible that patients who received waivers were positively selected for clinical benefit compared with the general study population,” the authors wrote.
So, “although the clinical benefit rate of the patient group for whom a waiver was granted appears to be slightly higher, this difference might be explained by the selection process of the central study team, in which each waiver request was carefully considered, weighing the risks and potential benefits for the patient in question,” the authors explained.
Overall, “these findings advocate for a broader and more inclusive design when establishing novel trials, paving the way for a more effective and tailored application of cancer therapies in patients with advanced or refractory disease,” Dr. Gelderblom said.
Commenting on the study, Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, said that “relaxing eligibility criteria is important, and I support this. Trials should include patients that are more representative of the real-world, so that results are generalizable.”
However, “the paper overemphasized efficacy,” said Dr. Gyawali, from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. The sample size of waiver-granted patients was small, plus “the clinical benefit rate is not a marker of efficacy.
“The response rate is somewhat better, but for a heterogeneous study with multiple targets and drugs, it is difficult to say much about treatment effects here,” Dr. Gyawali added. Overall, “we shouldn’t read too much into treatment benefits based on these numbers.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Stelvio for Life Foundation, the Dutch Cancer Society, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, pharma&, Eisai Co., Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Gelderblom declared no conflicts of interest, and Dr. Gyawali declared no conflicts of interest related to his comment.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Weight Loss Drugs Cut Cancer Risk in Diabetes Patients
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Urticaria Linked to Higher Cancer Risk, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.