User login
Expected spike in acute flaccid myelitis did not occur in 2020
suggested researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
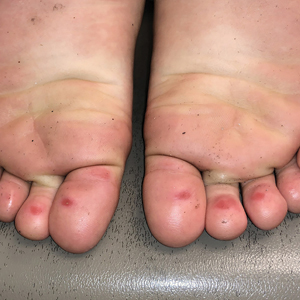
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is an uncommon but serious complication of some viral infections, including West Nile virus and nonpolio enteroviruses. It is “characterized by sudden onset of limb weakness and lesions in the gray matter of the spinal cord,” they said, and more than 90% of cases occur in young children.
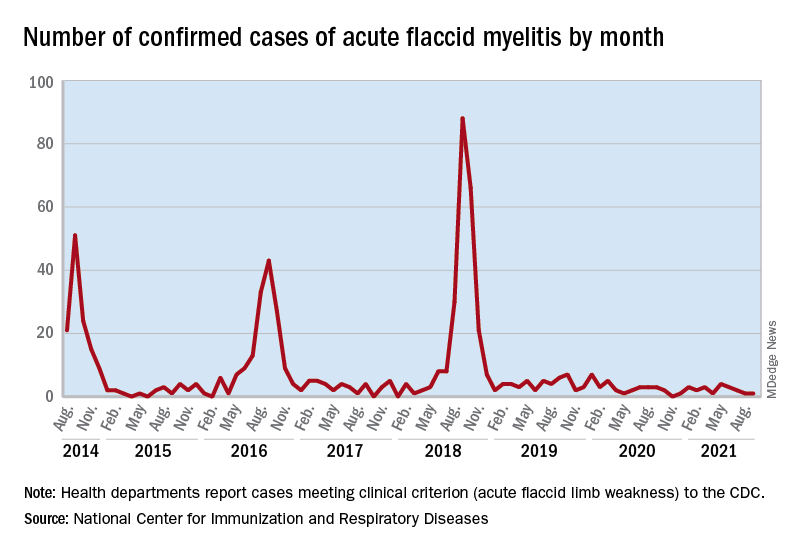
Cases of AFM, which can lead to respiratory insufficiency and permanent paralysis, spiked during the late summer and early fall in 2014, 2016, and 2018 and were expected to do so again in 2020, Sarah Kidd, MD, and associates at the division of viral diseases at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Monthly peaks in those previous years – each occurring in September – reached 51 cases in 2014, 43 cases in 2016, and 88 cases in 2018, but in 2020 there was only 1 case reported in September, with a high of 4 coming in May, CDC data show. The total number of cases for 2020 (32) was, in fact, lower than in 2019, when 47 were reported.
The investigators’ main objective was to see if there were any differences between the 2018 and 2019-2020 cases. Reports from state health departments to the CDC showed that, in 2019-2020, “patients were older; more likely to have lower limb involvement; and less likely to have upper limb involvement, prodromal illness, [cerebrospinal fluid] pleocytosis, or specimens that tested positive for EV [enterovirus]-D68” than patients from 2018, Dr. Kidd and associates said.
Mask wearing and reduced in-school attendance may have decreased circulation of EV-D68 – the enterovirus type most often detected in the stool and respiratory specimens of AFM patients – as was seen with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, in 2020. Previous studies have suggested that EV-D68 drives the increases in cases during peak years, the researchers noted.
The absence of such an increase “in 2020 reflects a deviation from the previously observed biennial pattern, and it is unclear when the next increase in AFM should be expected. Clinicians should continue to maintain vigilance and suspect AFM in any child with acute flaccid limb weakness, particularly in the setting of recent febrile or respiratory illness,” they wrote.
suggested researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is an uncommon but serious complication of some viral infections, including West Nile virus and nonpolio enteroviruses. It is “characterized by sudden onset of limb weakness and lesions in the gray matter of the spinal cord,” they said, and more than 90% of cases occur in young children.
Cases of AFM, which can lead to respiratory insufficiency and permanent paralysis, spiked during the late summer and early fall in 2014, 2016, and 2018 and were expected to do so again in 2020, Sarah Kidd, MD, and associates at the division of viral diseases at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Monthly peaks in those previous years – each occurring in September – reached 51 cases in 2014, 43 cases in 2016, and 88 cases in 2018, but in 2020 there was only 1 case reported in September, with a high of 4 coming in May, CDC data show. The total number of cases for 2020 (32) was, in fact, lower than in 2019, when 47 were reported.
The investigators’ main objective was to see if there were any differences between the 2018 and 2019-2020 cases. Reports from state health departments to the CDC showed that, in 2019-2020, “patients were older; more likely to have lower limb involvement; and less likely to have upper limb involvement, prodromal illness, [cerebrospinal fluid] pleocytosis, or specimens that tested positive for EV [enterovirus]-D68” than patients from 2018, Dr. Kidd and associates said.
Mask wearing and reduced in-school attendance may have decreased circulation of EV-D68 – the enterovirus type most often detected in the stool and respiratory specimens of AFM patients – as was seen with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, in 2020. Previous studies have suggested that EV-D68 drives the increases in cases during peak years, the researchers noted.
The absence of such an increase “in 2020 reflects a deviation from the previously observed biennial pattern, and it is unclear when the next increase in AFM should be expected. Clinicians should continue to maintain vigilance and suspect AFM in any child with acute flaccid limb weakness, particularly in the setting of recent febrile or respiratory illness,” they wrote.
suggested researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is an uncommon but serious complication of some viral infections, including West Nile virus and nonpolio enteroviruses. It is “characterized by sudden onset of limb weakness and lesions in the gray matter of the spinal cord,” they said, and more than 90% of cases occur in young children.
Cases of AFM, which can lead to respiratory insufficiency and permanent paralysis, spiked during the late summer and early fall in 2014, 2016, and 2018 and were expected to do so again in 2020, Sarah Kidd, MD, and associates at the division of viral diseases at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Monthly peaks in those previous years – each occurring in September – reached 51 cases in 2014, 43 cases in 2016, and 88 cases in 2018, but in 2020 there was only 1 case reported in September, with a high of 4 coming in May, CDC data show. The total number of cases for 2020 (32) was, in fact, lower than in 2019, when 47 were reported.
The investigators’ main objective was to see if there were any differences between the 2018 and 2019-2020 cases. Reports from state health departments to the CDC showed that, in 2019-2020, “patients were older; more likely to have lower limb involvement; and less likely to have upper limb involvement, prodromal illness, [cerebrospinal fluid] pleocytosis, or specimens that tested positive for EV [enterovirus]-D68” than patients from 2018, Dr. Kidd and associates said.
Mask wearing and reduced in-school attendance may have decreased circulation of EV-D68 – the enterovirus type most often detected in the stool and respiratory specimens of AFM patients – as was seen with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, in 2020. Previous studies have suggested that EV-D68 drives the increases in cases during peak years, the researchers noted.
The absence of such an increase “in 2020 reflects a deviation from the previously observed biennial pattern, and it is unclear when the next increase in AFM should be expected. Clinicians should continue to maintain vigilance and suspect AFM in any child with acute flaccid limb weakness, particularly in the setting of recent febrile or respiratory illness,” they wrote.
FROM MMWR
Does zinc really help treat colds?
A new study published in BMJ Open adds to the evidence that zinc is effective against viral respiratory infections, such as colds.
Jennifer Hunter, PhD, BMed, of Western Sydney University’s NICM Health Research Institute, New South Wales, Australia, and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 28 randomized controlled trials (RCTs). They searched 17 English and Chinese databases to identify the trials and then used the Cochrane rapid review technique for the analysis.
The trials included 5,446 adults who had received zinc in a variety of formulations and routes — oral, sublingual, and nasal spray. The researchers separately analyzed whether zinc prevented or treated respiratory tract infections (RTIs)
Oral or intranasal zinc prevented five RTIs per 100 person-months (95% CI, 1 – 8; numbers needed to treat, 20). There was a 32% lower relative risk (RR) of developing mild to moderate symptoms consistent with a viral RTI.
Use of zinc was also associated with an 87% lower risk of developing moderately severe symptoms (incidence rate ratio, 0.13; 95% CI, 0.04 – 0.38) and a 28% lower risk of developing milder symptoms. The largest reductions in RR were for moderately severe symptoms consistent with an influenza-like illness.
Symptoms resolved 2 days earlier with sublingual or intranasal zinc compared with placebo (95% CI, 0.61 – 3.50; very low-certainty quality of evidence). There were clinically significant reductions in day 3 symptom severity scores (mean difference, -1.20 points; 95% CI, -0.66 to -1.74; low-certainty quality of evidence) but not in overall symptom severity. Participants who used sublingual or topical nasal zinc early in the course of illness were 1.8 times more likely to recover before those who used a placebo.
However, the investigators found no benefit of zinc when patients were inoculated with rhinovirus; there was no reduction in the risk of developing a cold. Asked about this disparity, Dr. Hunter said, “It might well be that when inoculating people to make sure they get infected, you give them a really high dose of the virus. [This] doesn’t really mimic what happens in the real world.”
On the downside of supplemental zinc, there were more side effects among those who used zinc, including nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort, mouth irritation, or soreness from sublingual lozenges (RR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.17 – 1.69; number needed to harm, 7; moderate-certainty quality of evidence). The risk for a serious adverse event, such as loss of smell or copper deficiency, was low. Although not found in these studies, postmarketing studies have found that there is a risk for severe and in some cases permanent loss of smell associated with the use of nasal gels or sprays containing zinc. Three such products were recalled from the market.
The trial could not provide answers about the comparative efficacy of different types of zinc formulations, nor could the investigators recommend specific doses. The trial was not designed to assess zinc for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19.
Asked for independent comment, pediatrician Aamer Imdad, MBBS, assistant professor at the State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, told this news organization, “It’s a very comprehensive review for zinc-related studies in adults” but was challenging because of the “significant clinical heterogeneity in the population.”
Dr. Imdad explained that zinc has “absolutely” been shown to be effective for children with diarrhea. The World Health Organization has recommended it since 2004. “The way it works in diarrhea is that it helps with the regeneration of the epithelium.... It also improves the immunity itself, especially the cell-mediated immunity.” He raised the question of whether it might work similarly in the respiratory tract. Dr. Imdad has a long-standing interest in the use of zinc for pediatric infections. Regarding this study, he concluded, “I think we still need to know the nuts and bolts of this intervention before we can recommend it more specifically.”
Dr. Hunter said, “We don’t have any high-quality studies that have evaluated zinc orally as treatment once you’re actually infected and have symptoms of the cold or influenza, or COVID.”
Asked about zinc’s possible role, Dr. Hunter said, “So I do think it gives us a viable alternative. More people are going, ‘What can I do?’ And you know as well as I do people come to you, and [they say], ‘Well, just give me something. Even if it’s a day or a little bit of symptom relief, anything to make me feel better that isn’t going to hurt me and doesn’t have any major risks.’ So I think in the short term, clinicians and consumers can consider trying it.”
Dr. Hunter was not keen on giving zinc to family members after they develop an RTI: “Consider it. But I don’t think we have enough evidence to say definitely yes.” But she does see a potential role for “people who are at risk of suboptimal zinc absorption, like people who are taking a variety of pharmaceuticals [notably proton pump inhibitors] that block or reduce the absorption of zinc, people with a whole lot of the chronic diseases that we know are associated with an increased risk of worse outcomes from respiratory viral infections, and older adults. Yes, I think [for] those high-risk groups, you could consider using zinc, either in a moderate dose longer term or in a higher dose for very short bursts of, like, 1 to 2 weeks.”
Dr. Hunter concluded, “Up until now, we all commonly thought that zinc’s role was only for people who were zinc deficient, and now we’ve got some signals pointing towards its potential role as an anti-infective and anti-inflammatory agent in people who don’t have zinc deficiency.”
But both Dr. Hunter and Dr. Imdad emphasized that zinc is not a game changer. There is a hint that it produces a small benefit in prevention and may slightly shorten the duration of RTIs. More research is needed.
Dr. Hunter has received payment for providing expert advice about traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine, including nutraceuticals, to industry, government bodies, and nongovernmental organizations and has spoken at workshops, seminars, and conferences for which registration, travel, and/or accommodation has been paid for by the organizers. Dr. Imdad has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study published in BMJ Open adds to the evidence that zinc is effective against viral respiratory infections, such as colds.
Jennifer Hunter, PhD, BMed, of Western Sydney University’s NICM Health Research Institute, New South Wales, Australia, and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 28 randomized controlled trials (RCTs). They searched 17 English and Chinese databases to identify the trials and then used the Cochrane rapid review technique for the analysis.
The trials included 5,446 adults who had received zinc in a variety of formulations and routes — oral, sublingual, and nasal spray. The researchers separately analyzed whether zinc prevented or treated respiratory tract infections (RTIs)
Oral or intranasal zinc prevented five RTIs per 100 person-months (95% CI, 1 – 8; numbers needed to treat, 20). There was a 32% lower relative risk (RR) of developing mild to moderate symptoms consistent with a viral RTI.
Use of zinc was also associated with an 87% lower risk of developing moderately severe symptoms (incidence rate ratio, 0.13; 95% CI, 0.04 – 0.38) and a 28% lower risk of developing milder symptoms. The largest reductions in RR were for moderately severe symptoms consistent with an influenza-like illness.
Symptoms resolved 2 days earlier with sublingual or intranasal zinc compared with placebo (95% CI, 0.61 – 3.50; very low-certainty quality of evidence). There were clinically significant reductions in day 3 symptom severity scores (mean difference, -1.20 points; 95% CI, -0.66 to -1.74; low-certainty quality of evidence) but not in overall symptom severity. Participants who used sublingual or topical nasal zinc early in the course of illness were 1.8 times more likely to recover before those who used a placebo.
However, the investigators found no benefit of zinc when patients were inoculated with rhinovirus; there was no reduction in the risk of developing a cold. Asked about this disparity, Dr. Hunter said, “It might well be that when inoculating people to make sure they get infected, you give them a really high dose of the virus. [This] doesn’t really mimic what happens in the real world.”
On the downside of supplemental zinc, there were more side effects among those who used zinc, including nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort, mouth irritation, or soreness from sublingual lozenges (RR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.17 – 1.69; number needed to harm, 7; moderate-certainty quality of evidence). The risk for a serious adverse event, such as loss of smell or copper deficiency, was low. Although not found in these studies, postmarketing studies have found that there is a risk for severe and in some cases permanent loss of smell associated with the use of nasal gels or sprays containing zinc. Three such products were recalled from the market.
The trial could not provide answers about the comparative efficacy of different types of zinc formulations, nor could the investigators recommend specific doses. The trial was not designed to assess zinc for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19.
Asked for independent comment, pediatrician Aamer Imdad, MBBS, assistant professor at the State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, told this news organization, “It’s a very comprehensive review for zinc-related studies in adults” but was challenging because of the “significant clinical heterogeneity in the population.”
Dr. Imdad explained that zinc has “absolutely” been shown to be effective for children with diarrhea. The World Health Organization has recommended it since 2004. “The way it works in diarrhea is that it helps with the regeneration of the epithelium.... It also improves the immunity itself, especially the cell-mediated immunity.” He raised the question of whether it might work similarly in the respiratory tract. Dr. Imdad has a long-standing interest in the use of zinc for pediatric infections. Regarding this study, he concluded, “I think we still need to know the nuts and bolts of this intervention before we can recommend it more specifically.”
Dr. Hunter said, “We don’t have any high-quality studies that have evaluated zinc orally as treatment once you’re actually infected and have symptoms of the cold or influenza, or COVID.”
Asked about zinc’s possible role, Dr. Hunter said, “So I do think it gives us a viable alternative. More people are going, ‘What can I do?’ And you know as well as I do people come to you, and [they say], ‘Well, just give me something. Even if it’s a day or a little bit of symptom relief, anything to make me feel better that isn’t going to hurt me and doesn’t have any major risks.’ So I think in the short term, clinicians and consumers can consider trying it.”
Dr. Hunter was not keen on giving zinc to family members after they develop an RTI: “Consider it. But I don’t think we have enough evidence to say definitely yes.” But she does see a potential role for “people who are at risk of suboptimal zinc absorption, like people who are taking a variety of pharmaceuticals [notably proton pump inhibitors] that block or reduce the absorption of zinc, people with a whole lot of the chronic diseases that we know are associated with an increased risk of worse outcomes from respiratory viral infections, and older adults. Yes, I think [for] those high-risk groups, you could consider using zinc, either in a moderate dose longer term or in a higher dose for very short bursts of, like, 1 to 2 weeks.”
Dr. Hunter concluded, “Up until now, we all commonly thought that zinc’s role was only for people who were zinc deficient, and now we’ve got some signals pointing towards its potential role as an anti-infective and anti-inflammatory agent in people who don’t have zinc deficiency.”
But both Dr. Hunter and Dr. Imdad emphasized that zinc is not a game changer. There is a hint that it produces a small benefit in prevention and may slightly shorten the duration of RTIs. More research is needed.
Dr. Hunter has received payment for providing expert advice about traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine, including nutraceuticals, to industry, government bodies, and nongovernmental organizations and has spoken at workshops, seminars, and conferences for which registration, travel, and/or accommodation has been paid for by the organizers. Dr. Imdad has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study published in BMJ Open adds to the evidence that zinc is effective against viral respiratory infections, such as colds.
Jennifer Hunter, PhD, BMed, of Western Sydney University’s NICM Health Research Institute, New South Wales, Australia, and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 28 randomized controlled trials (RCTs). They searched 17 English and Chinese databases to identify the trials and then used the Cochrane rapid review technique for the analysis.
The trials included 5,446 adults who had received zinc in a variety of formulations and routes — oral, sublingual, and nasal spray. The researchers separately analyzed whether zinc prevented or treated respiratory tract infections (RTIs)
Oral or intranasal zinc prevented five RTIs per 100 person-months (95% CI, 1 – 8; numbers needed to treat, 20). There was a 32% lower relative risk (RR) of developing mild to moderate symptoms consistent with a viral RTI.
Use of zinc was also associated with an 87% lower risk of developing moderately severe symptoms (incidence rate ratio, 0.13; 95% CI, 0.04 – 0.38) and a 28% lower risk of developing milder symptoms. The largest reductions in RR were for moderately severe symptoms consistent with an influenza-like illness.
Symptoms resolved 2 days earlier with sublingual or intranasal zinc compared with placebo (95% CI, 0.61 – 3.50; very low-certainty quality of evidence). There were clinically significant reductions in day 3 symptom severity scores (mean difference, -1.20 points; 95% CI, -0.66 to -1.74; low-certainty quality of evidence) but not in overall symptom severity. Participants who used sublingual or topical nasal zinc early in the course of illness were 1.8 times more likely to recover before those who used a placebo.
However, the investigators found no benefit of zinc when patients were inoculated with rhinovirus; there was no reduction in the risk of developing a cold. Asked about this disparity, Dr. Hunter said, “It might well be that when inoculating people to make sure they get infected, you give them a really high dose of the virus. [This] doesn’t really mimic what happens in the real world.”
On the downside of supplemental zinc, there were more side effects among those who used zinc, including nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort, mouth irritation, or soreness from sublingual lozenges (RR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.17 – 1.69; number needed to harm, 7; moderate-certainty quality of evidence). The risk for a serious adverse event, such as loss of smell or copper deficiency, was low. Although not found in these studies, postmarketing studies have found that there is a risk for severe and in some cases permanent loss of smell associated with the use of nasal gels or sprays containing zinc. Three such products were recalled from the market.
The trial could not provide answers about the comparative efficacy of different types of zinc formulations, nor could the investigators recommend specific doses. The trial was not designed to assess zinc for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19.
Asked for independent comment, pediatrician Aamer Imdad, MBBS, assistant professor at the State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, told this news organization, “It’s a very comprehensive review for zinc-related studies in adults” but was challenging because of the “significant clinical heterogeneity in the population.”
Dr. Imdad explained that zinc has “absolutely” been shown to be effective for children with diarrhea. The World Health Organization has recommended it since 2004. “The way it works in diarrhea is that it helps with the regeneration of the epithelium.... It also improves the immunity itself, especially the cell-mediated immunity.” He raised the question of whether it might work similarly in the respiratory tract. Dr. Imdad has a long-standing interest in the use of zinc for pediatric infections. Regarding this study, he concluded, “I think we still need to know the nuts and bolts of this intervention before we can recommend it more specifically.”
Dr. Hunter said, “We don’t have any high-quality studies that have evaluated zinc orally as treatment once you’re actually infected and have symptoms of the cold or influenza, or COVID.”
Asked about zinc’s possible role, Dr. Hunter said, “So I do think it gives us a viable alternative. More people are going, ‘What can I do?’ And you know as well as I do people come to you, and [they say], ‘Well, just give me something. Even if it’s a day or a little bit of symptom relief, anything to make me feel better that isn’t going to hurt me and doesn’t have any major risks.’ So I think in the short term, clinicians and consumers can consider trying it.”
Dr. Hunter was not keen on giving zinc to family members after they develop an RTI: “Consider it. But I don’t think we have enough evidence to say definitely yes.” But she does see a potential role for “people who are at risk of suboptimal zinc absorption, like people who are taking a variety of pharmaceuticals [notably proton pump inhibitors] that block or reduce the absorption of zinc, people with a whole lot of the chronic diseases that we know are associated with an increased risk of worse outcomes from respiratory viral infections, and older adults. Yes, I think [for] those high-risk groups, you could consider using zinc, either in a moderate dose longer term or in a higher dose for very short bursts of, like, 1 to 2 weeks.”
Dr. Hunter concluded, “Up until now, we all commonly thought that zinc’s role was only for people who were zinc deficient, and now we’ve got some signals pointing towards its potential role as an anti-infective and anti-inflammatory agent in people who don’t have zinc deficiency.”
But both Dr. Hunter and Dr. Imdad emphasized that zinc is not a game changer. There is a hint that it produces a small benefit in prevention and may slightly shorten the duration of RTIs. More research is needed.
Dr. Hunter has received payment for providing expert advice about traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine, including nutraceuticals, to industry, government bodies, and nongovernmental organizations and has spoken at workshops, seminars, and conferences for which registration, travel, and/or accommodation has been paid for by the organizers. Dr. Imdad has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMJ OPEN
Maraviroc, metformin fail to control NAFLD in people with HIV
The MAVMET study, the first randomized controlled trial of – and in some cases, prolonged use actually increased liver fat.
And that means clinicians like Yvonne Gilleece, MB BCh, who was not involved in the study but does run a liver clinic in England for people living with HIV, are returning to the one intervention proven to work. “As yet, the only thing that is proven to have a very positive effect that is published is weight loss,” said Dr. Gilleece, who runs the clinic at Brighton and Sussex University Hospital. “You don’t put someone on these particular drugs, particularly this combination, easily. MAVMET has really demonstrated that, actually, it’s not effective, and it’s not particularly beneficial to patients.”
The MAVMET trial data was presented at the 18th European AIDS Conference,
There was good reason to think maraviroc might work. A 2018 study in the journal Hepatology found that one of maraviroc’s molecular cousins, cenicriviroc, significantly reduced fibrosis in people with NAFLD. Dr. Gilleece is co-investigator of another study of maraviroc in NAFLD, the HEPMARC trial, which is wrapping up now. In addition to those studies, there are other potential treatments in ongoing trials, including semaglutide, which is being studied in the United States under the study name SLIM LIVER.
MAVMET enrolled 90 people living with HIV from six clinical sites in London who were 35 or older and who had at least one marker for NAFLD, such as abnormal liver lab results. But 70% qualified via imaging- and/or biopsy-confirmed NAFLD. Almost all participants (93%) were men and 81% were White. The trial excluded people who were pregnant or breastfeeding. The median age was 52, and the participants met the criteria for overweight but not obesity, with a median BMI of 28.
In other words, participants generally had fatty livers without the inflammation that characterizes the more aggressive nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Clinicians can’t yet differentiate between those who will continue to have asymptomatic fatty liver and those who will progress to NASH and potentially need a liver transplant.
All people living with HIV in the trial had undetectable viral loads and were on HIV treatment. Nearly 1 in 5 (19%) were using a treatment regimen containing tenofovir alafenamide (TAF), which has been associated with weight gain. Nearly half were on integrase strand inhibitors.
Investigators divided the participants up into four groups: 24 people stayed on their HIV treatment and added nothing else; 23 people took maraviroc only; 21 took metformin only; and the final group took both maraviroc and metformin. Across groups, liver fat at baseline was 8.9%, and 78% had mild hepatic steatosis.
After taking the medications for 48 weeks, participants returned to clinic to be scanned via MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), which has been found to successfully measure liver fat. However, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, 20 of the 83 people who returned to the clinic came later than 48 weeks after the trial began.
When investigators looked at the results, they didn’t see what they hypothesized, said Sarah Pett, professor of infectious diseases at University College, London: The scatter plot graph of change in weight looked, well, scattershot: People who didn’t take any additional treatment sometimes lost more liver fat than those on treatment. In fact, the mean liver fat percentage rose by 2.2% in the maraviroc group, 1.3% in the metformin group, and 0.8% in the combination group. The control group saw an increase of 1.4% – meaning that there was no difference between the change in fat between those on treatment and those not.
What’s more, those who had delayed scans – and stayed on their treatment for a median of an additional 16 weeks – saw their liver fat increase even more.
In an interview, Dr. Pett called the results “disappointing.” “The numbers are quite small, but we still didn’t expect this,” she said. “It’s not explained by lockdown weight gain, although we still have to look in detail at how alcohol consumption could have contributed.”
There were also some limits to what the design of this particular trial could tell the researchers. For instance, nearly half of the participants in the maraviroc group, a third of the people in the metformin group, and 36% of those in the combination group had hepatic steatosis grades of 0, meaning that their livers were healthy. And MRI-PDFF becomes less reliable at that level.
“One of the regrets is that perhaps we should have done FibroScan [ultrasound], as well,” Dr. Pett said. The consequence is that the study may have undercounted the fat level by using MRI-PFDD.
“This suggests that the surrogate markers of NAFLD used in MAVMET were not very sensitive to those with a higher percentage of fat,” Dr. Pett said during her presentation. “We were really trying to be pragmatic and not require an MRI at screening.”
Whatever the case, she said that the failure of this particular treatment just highlights the growing need to look more seriously, and more collaboratively, at fat and liver health in people living with HIV.
“We need to really focus on setting up large cohorts of people living with HIV to look in a rigorous way at weight gain, changes in waist circumference, ectopic fat, capture fatty liver disease index scores, and cardiovascular risk, to acquire some longitudinal data,” she said. “And [we need to] join with our fellow researchers in overweight and obesity medicine and hepatology to make sure that people living with HIV are included in new treatments for NASH, as several large RCTs have excluded [people living with HIV].”
From Dr. Gilleece’s perspective, it also just speaks to how far the field has to go in identifying those with asymptomatic fatty livers from those who will progress to fibrosis and potentially need liver transplants.
“MAVMET shows the difficulty in managing NAFLD,” she said. “It seems quite an innocuous disease, because for the majority of people it’s not going to cause a problem in their lifetime. But the reality is, for some it will, and we don’t really know how to treat it.”
Dr. Gilleece has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pett reported receiving funding for trials from Gilead Sciences and Janssen-Cilag. ViiV Healthcare funded the MAVMET trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The MAVMET study, the first randomized controlled trial of – and in some cases, prolonged use actually increased liver fat.
And that means clinicians like Yvonne Gilleece, MB BCh, who was not involved in the study but does run a liver clinic in England for people living with HIV, are returning to the one intervention proven to work. “As yet, the only thing that is proven to have a very positive effect that is published is weight loss,” said Dr. Gilleece, who runs the clinic at Brighton and Sussex University Hospital. “You don’t put someone on these particular drugs, particularly this combination, easily. MAVMET has really demonstrated that, actually, it’s not effective, and it’s not particularly beneficial to patients.”
The MAVMET trial data was presented at the 18th European AIDS Conference,
There was good reason to think maraviroc might work. A 2018 study in the journal Hepatology found that one of maraviroc’s molecular cousins, cenicriviroc, significantly reduced fibrosis in people with NAFLD. Dr. Gilleece is co-investigator of another study of maraviroc in NAFLD, the HEPMARC trial, which is wrapping up now. In addition to those studies, there are other potential treatments in ongoing trials, including semaglutide, which is being studied in the United States under the study name SLIM LIVER.
MAVMET enrolled 90 people living with HIV from six clinical sites in London who were 35 or older and who had at least one marker for NAFLD, such as abnormal liver lab results. But 70% qualified via imaging- and/or biopsy-confirmed NAFLD. Almost all participants (93%) were men and 81% were White. The trial excluded people who were pregnant or breastfeeding. The median age was 52, and the participants met the criteria for overweight but not obesity, with a median BMI of 28.
In other words, participants generally had fatty livers without the inflammation that characterizes the more aggressive nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Clinicians can’t yet differentiate between those who will continue to have asymptomatic fatty liver and those who will progress to NASH and potentially need a liver transplant.
All people living with HIV in the trial had undetectable viral loads and were on HIV treatment. Nearly 1 in 5 (19%) were using a treatment regimen containing tenofovir alafenamide (TAF), which has been associated with weight gain. Nearly half were on integrase strand inhibitors.
Investigators divided the participants up into four groups: 24 people stayed on their HIV treatment and added nothing else; 23 people took maraviroc only; 21 took metformin only; and the final group took both maraviroc and metformin. Across groups, liver fat at baseline was 8.9%, and 78% had mild hepatic steatosis.
After taking the medications for 48 weeks, participants returned to clinic to be scanned via MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), which has been found to successfully measure liver fat. However, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, 20 of the 83 people who returned to the clinic came later than 48 weeks after the trial began.
When investigators looked at the results, they didn’t see what they hypothesized, said Sarah Pett, professor of infectious diseases at University College, London: The scatter plot graph of change in weight looked, well, scattershot: People who didn’t take any additional treatment sometimes lost more liver fat than those on treatment. In fact, the mean liver fat percentage rose by 2.2% in the maraviroc group, 1.3% in the metformin group, and 0.8% in the combination group. The control group saw an increase of 1.4% – meaning that there was no difference between the change in fat between those on treatment and those not.
What’s more, those who had delayed scans – and stayed on their treatment for a median of an additional 16 weeks – saw their liver fat increase even more.
In an interview, Dr. Pett called the results “disappointing.” “The numbers are quite small, but we still didn’t expect this,” she said. “It’s not explained by lockdown weight gain, although we still have to look in detail at how alcohol consumption could have contributed.”
There were also some limits to what the design of this particular trial could tell the researchers. For instance, nearly half of the participants in the maraviroc group, a third of the people in the metformin group, and 36% of those in the combination group had hepatic steatosis grades of 0, meaning that their livers were healthy. And MRI-PDFF becomes less reliable at that level.
“One of the regrets is that perhaps we should have done FibroScan [ultrasound], as well,” Dr. Pett said. The consequence is that the study may have undercounted the fat level by using MRI-PFDD.
“This suggests that the surrogate markers of NAFLD used in MAVMET were not very sensitive to those with a higher percentage of fat,” Dr. Pett said during her presentation. “We were really trying to be pragmatic and not require an MRI at screening.”
Whatever the case, she said that the failure of this particular treatment just highlights the growing need to look more seriously, and more collaboratively, at fat and liver health in people living with HIV.
“We need to really focus on setting up large cohorts of people living with HIV to look in a rigorous way at weight gain, changes in waist circumference, ectopic fat, capture fatty liver disease index scores, and cardiovascular risk, to acquire some longitudinal data,” she said. “And [we need to] join with our fellow researchers in overweight and obesity medicine and hepatology to make sure that people living with HIV are included in new treatments for NASH, as several large RCTs have excluded [people living with HIV].”
From Dr. Gilleece’s perspective, it also just speaks to how far the field has to go in identifying those with asymptomatic fatty livers from those who will progress to fibrosis and potentially need liver transplants.
“MAVMET shows the difficulty in managing NAFLD,” she said. “It seems quite an innocuous disease, because for the majority of people it’s not going to cause a problem in their lifetime. But the reality is, for some it will, and we don’t really know how to treat it.”
Dr. Gilleece has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pett reported receiving funding for trials from Gilead Sciences and Janssen-Cilag. ViiV Healthcare funded the MAVMET trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The MAVMET study, the first randomized controlled trial of – and in some cases, prolonged use actually increased liver fat.
And that means clinicians like Yvonne Gilleece, MB BCh, who was not involved in the study but does run a liver clinic in England for people living with HIV, are returning to the one intervention proven to work. “As yet, the only thing that is proven to have a very positive effect that is published is weight loss,” said Dr. Gilleece, who runs the clinic at Brighton and Sussex University Hospital. “You don’t put someone on these particular drugs, particularly this combination, easily. MAVMET has really demonstrated that, actually, it’s not effective, and it’s not particularly beneficial to patients.”
The MAVMET trial data was presented at the 18th European AIDS Conference,
There was good reason to think maraviroc might work. A 2018 study in the journal Hepatology found that one of maraviroc’s molecular cousins, cenicriviroc, significantly reduced fibrosis in people with NAFLD. Dr. Gilleece is co-investigator of another study of maraviroc in NAFLD, the HEPMARC trial, which is wrapping up now. In addition to those studies, there are other potential treatments in ongoing trials, including semaglutide, which is being studied in the United States under the study name SLIM LIVER.
MAVMET enrolled 90 people living with HIV from six clinical sites in London who were 35 or older and who had at least one marker for NAFLD, such as abnormal liver lab results. But 70% qualified via imaging- and/or biopsy-confirmed NAFLD. Almost all participants (93%) were men and 81% were White. The trial excluded people who were pregnant or breastfeeding. The median age was 52, and the participants met the criteria for overweight but not obesity, with a median BMI of 28.
In other words, participants generally had fatty livers without the inflammation that characterizes the more aggressive nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Clinicians can’t yet differentiate between those who will continue to have asymptomatic fatty liver and those who will progress to NASH and potentially need a liver transplant.
All people living with HIV in the trial had undetectable viral loads and were on HIV treatment. Nearly 1 in 5 (19%) were using a treatment regimen containing tenofovir alafenamide (TAF), which has been associated with weight gain. Nearly half were on integrase strand inhibitors.
Investigators divided the participants up into four groups: 24 people stayed on their HIV treatment and added nothing else; 23 people took maraviroc only; 21 took metformin only; and the final group took both maraviroc and metformin. Across groups, liver fat at baseline was 8.9%, and 78% had mild hepatic steatosis.
After taking the medications for 48 weeks, participants returned to clinic to be scanned via MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), which has been found to successfully measure liver fat. However, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, 20 of the 83 people who returned to the clinic came later than 48 weeks after the trial began.
When investigators looked at the results, they didn’t see what they hypothesized, said Sarah Pett, professor of infectious diseases at University College, London: The scatter plot graph of change in weight looked, well, scattershot: People who didn’t take any additional treatment sometimes lost more liver fat than those on treatment. In fact, the mean liver fat percentage rose by 2.2% in the maraviroc group, 1.3% in the metformin group, and 0.8% in the combination group. The control group saw an increase of 1.4% – meaning that there was no difference between the change in fat between those on treatment and those not.
What’s more, those who had delayed scans – and stayed on their treatment for a median of an additional 16 weeks – saw their liver fat increase even more.
In an interview, Dr. Pett called the results “disappointing.” “The numbers are quite small, but we still didn’t expect this,” she said. “It’s not explained by lockdown weight gain, although we still have to look in detail at how alcohol consumption could have contributed.”
There were also some limits to what the design of this particular trial could tell the researchers. For instance, nearly half of the participants in the maraviroc group, a third of the people in the metformin group, and 36% of those in the combination group had hepatic steatosis grades of 0, meaning that their livers were healthy. And MRI-PDFF becomes less reliable at that level.
“One of the regrets is that perhaps we should have done FibroScan [ultrasound], as well,” Dr. Pett said. The consequence is that the study may have undercounted the fat level by using MRI-PFDD.
“This suggests that the surrogate markers of NAFLD used in MAVMET were not very sensitive to those with a higher percentage of fat,” Dr. Pett said during her presentation. “We were really trying to be pragmatic and not require an MRI at screening.”
Whatever the case, she said that the failure of this particular treatment just highlights the growing need to look more seriously, and more collaboratively, at fat and liver health in people living with HIV.
“We need to really focus on setting up large cohorts of people living with HIV to look in a rigorous way at weight gain, changes in waist circumference, ectopic fat, capture fatty liver disease index scores, and cardiovascular risk, to acquire some longitudinal data,” she said. “And [we need to] join with our fellow researchers in overweight and obesity medicine and hepatology to make sure that people living with HIV are included in new treatments for NASH, as several large RCTs have excluded [people living with HIV].”
From Dr. Gilleece’s perspective, it also just speaks to how far the field has to go in identifying those with asymptomatic fatty livers from those who will progress to fibrosis and potentially need liver transplants.
“MAVMET shows the difficulty in managing NAFLD,” she said. “It seems quite an innocuous disease, because for the majority of people it’s not going to cause a problem in their lifetime. But the reality is, for some it will, and we don’t really know how to treat it.”
Dr. Gilleece has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pett reported receiving funding for trials from Gilead Sciences and Janssen-Cilag. ViiV Healthcare funded the MAVMET trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ACIP recommends universal HBV vaccination for adults under 60, expands recommendations for vaccines against orthopoxviruses and Ebola
The group also voted to expand recommendations for vaccinating people at risk for occupational exposure to Ebola and to recommend Jynneos, a smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, for at-risk populations.
The recommendations were approved Nov. 3.
Previously, ACIP recommended HBV vaccination for unvaccinated adults at increased risk for infection because of sexual exposure, percutaneous or mucosal exposure to blood, hepatitis C infection, chronic liver disease, end-stage renal disease, HIV infection, and travel to areas with high to intermediate levels of HBV infection. But experts agreed a new strategy was needed, as previously falling rates of HBV have plateaued. “The past decade has illustrated that risk-based screening has got us as far as it can take us,” Mark Weng, MD, a lieutenant commander in the U.S. Public Health Service and lead of the ACIP Hepatitis Vaccine Working Group, said during the meeting.
There are 1.9 million people living with chronic HBV in the United States, with over 20,000 new acute infections every year. Rates are highest among those in their 40s and 50s, Dr. Weng noted.
The group debated whether to apply the universal recommendation to all ages, but in a close vote (eight yes, seven no), ACIP included an age cutoff of 59. The majority argued that adults 60 and older are at lower risk for infection and vaccination efforts targeting younger adults would be more effective. Those 60 and older would continue to follow the risk-based guidelines, but anyone, regardless of age, can receive the vaccine if they wish to be protected, the group added.
The CDC director as well as several professional societies need to approve the recommendation before it becomes public policy.
ACIP also voted to recommend the following:
- Adding updated recommendations to the 2022 immunization schedules for children, adolescents, and adults, including dengue vaccination for children aged 9-16 years in endemic areas and in adults over 65 and those aged 19-64 with certain chronic conditions.
- The use of Jynneos, a smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, as an alternative to ACAM2000 for those at risk for occupational exposure.
- Pre-exposure vaccination of health care personnel involved in the transport and treatment of suspected Ebola patients at special treatment centers, or lab and support staff working with or handling specimens that may contain the Ebola virus.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The group also voted to expand recommendations for vaccinating people at risk for occupational exposure to Ebola and to recommend Jynneos, a smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, for at-risk populations.
The recommendations were approved Nov. 3.
Previously, ACIP recommended HBV vaccination for unvaccinated adults at increased risk for infection because of sexual exposure, percutaneous or mucosal exposure to blood, hepatitis C infection, chronic liver disease, end-stage renal disease, HIV infection, and travel to areas with high to intermediate levels of HBV infection. But experts agreed a new strategy was needed, as previously falling rates of HBV have plateaued. “The past decade has illustrated that risk-based screening has got us as far as it can take us,” Mark Weng, MD, a lieutenant commander in the U.S. Public Health Service and lead of the ACIP Hepatitis Vaccine Working Group, said during the meeting.
There are 1.9 million people living with chronic HBV in the United States, with over 20,000 new acute infections every year. Rates are highest among those in their 40s and 50s, Dr. Weng noted.
The group debated whether to apply the universal recommendation to all ages, but in a close vote (eight yes, seven no), ACIP included an age cutoff of 59. The majority argued that adults 60 and older are at lower risk for infection and vaccination efforts targeting younger adults would be more effective. Those 60 and older would continue to follow the risk-based guidelines, but anyone, regardless of age, can receive the vaccine if they wish to be protected, the group added.
The CDC director as well as several professional societies need to approve the recommendation before it becomes public policy.
ACIP also voted to recommend the following:
- Adding updated recommendations to the 2022 immunization schedules for children, adolescents, and adults, including dengue vaccination for children aged 9-16 years in endemic areas and in adults over 65 and those aged 19-64 with certain chronic conditions.
- The use of Jynneos, a smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, as an alternative to ACAM2000 for those at risk for occupational exposure.
- Pre-exposure vaccination of health care personnel involved in the transport and treatment of suspected Ebola patients at special treatment centers, or lab and support staff working with or handling specimens that may contain the Ebola virus.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The group also voted to expand recommendations for vaccinating people at risk for occupational exposure to Ebola and to recommend Jynneos, a smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, for at-risk populations.
The recommendations were approved Nov. 3.
Previously, ACIP recommended HBV vaccination for unvaccinated adults at increased risk for infection because of sexual exposure, percutaneous or mucosal exposure to blood, hepatitis C infection, chronic liver disease, end-stage renal disease, HIV infection, and travel to areas with high to intermediate levels of HBV infection. But experts agreed a new strategy was needed, as previously falling rates of HBV have plateaued. “The past decade has illustrated that risk-based screening has got us as far as it can take us,” Mark Weng, MD, a lieutenant commander in the U.S. Public Health Service and lead of the ACIP Hepatitis Vaccine Working Group, said during the meeting.
There are 1.9 million people living with chronic HBV in the United States, with over 20,000 new acute infections every year. Rates are highest among those in their 40s and 50s, Dr. Weng noted.
The group debated whether to apply the universal recommendation to all ages, but in a close vote (eight yes, seven no), ACIP included an age cutoff of 59. The majority argued that adults 60 and older are at lower risk for infection and vaccination efforts targeting younger adults would be more effective. Those 60 and older would continue to follow the risk-based guidelines, but anyone, regardless of age, can receive the vaccine if they wish to be protected, the group added.
The CDC director as well as several professional societies need to approve the recommendation before it becomes public policy.
ACIP also voted to recommend the following:
- Adding updated recommendations to the 2022 immunization schedules for children, adolescents, and adults, including dengue vaccination for children aged 9-16 years in endemic areas and in adults over 65 and those aged 19-64 with certain chronic conditions.
- The use of Jynneos, a smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, as an alternative to ACAM2000 for those at risk for occupational exposure.
- Pre-exposure vaccination of health care personnel involved in the transport and treatment of suspected Ebola patients at special treatment centers, or lab and support staff working with or handling specimens that may contain the Ebola virus.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HIV prescription mandate controversy reaches the Supreme Court
A firestorm of controversy over access to HIV medications and protection against discriminatory insurance practices has been making its way through U.S. district courts for the past 3 years, pitting HIV patients against pharmacy benefits managers and, ostensibly, the healthcare industry itself.
.
At odds are whether or not mandatory mail-order requirements for specialty medications violate specific provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, both of which prohibit discrimination by programs that receive federal funds.
An amicus brief submitted on October 29 by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation (CHLPI) of Harvard Law School on behalf of five John Does and a number of medical practitioners and practitioner organizations underscores the degree to which advances in HIV treatment, viral suppression, and care linkage — not to mention the national mandate to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030 — might ultimately be affected.
“We decided to file the brief at the Supreme Court level because we wanted to make sure that the perspectives of people living with HIV, their providers, and advocates were in the record,” Maryanne Tomazic, a clinical instructor at CHLPI, toldthis news organization.
“It’s important for the court to consider why robust access to prescription drug coverage and pharmacy services are so important for people living with HIV, and why it’s not appropriate to compromise access to antiretroviral therapy,” she explained.
A bitter pill, regardless of who swallows it
CVS Pharmacy Inc. v. Doe focuses on a legal concept known as “disparate impact discrimination,” which refers to a policy that appears neutral but unintentionally discriminates against a protected class of people (eg, on the basis of sex, age, or ethnicity).
The Supreme Court’s decision in the case will address a central question: did CVS Pharmacy, Caremark, and Caremark Specialty Pharmacy (“CVS”) discriminate against the respondents by requiring that they obtain specialty medications (including those for HIV) by mail order or drop shipment for pickup, or, alternatively, pay out-of-network prices for these medications at non-CVS pharmacies?
The decision will also address whether the ACA’s inclusion of clause 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, which prohibits protected class discrimination, allows patients to challenge terms and conditions of their healthcare plans, a decision that has broad and far-reaching implications for insurers’ abilities to set plan restrictions and pricing.
A spokesperson for CVS declined to comment when contacted by this news organization but provided a link to an April 9, 2021 SCOTUS blog post about the filing. In its court filing, CVS contended that the program applies to all specialty medications (not just HIV) and simply reflects the cost/complexity of specialty medications.
Not everyone agrees that cost is the most important issue at play. Indeed, a critical take-away for practitioners is how mandated mail-order pharmacy programs can disrupt coordination of care.
“In the traditional model, the physician is talking to the pharmacists [or] talking with the patient, and you have kind of triangular communication model that helps not only the patient stay engaged in care but [also] allows the healthcare provider team to adjust the medication quickly without delay,” said Ms. Tomazic.
The John Doe statements in the original case highlight these concerns. They focus on how mandatory mail orders restrict highly personable relationships with local specialty pharmacists who are familiar with their patients’ medical histories as well as their medication dosing and adjustments and who regularly communicate with the complete care team on the patients’ behalf.
“JOHN DOE THREE and others depend on these types of long standing relationships with local pharmacists to maximize the benefits of HIV/AIDS medications and treat the complex and ever-changing needs of the HIV/AIDS patients,” wrote attorneys in the 2018 class action filing.
Other issues raised by the suit involve the following: privacy with respect to medication pickup; specialty care customer representatives’ lack of understanding and knowledge of HIV medications; incomplete prescription fills; late medication deliveries; exposure of medications to the elements; work and employment interruptions; and restrictions on early fills and reorders, which increase the risk for missed doses and potentially serious health problems, including interruptions in viral suppression and resistance.
Discrimination issues also raised
CHLPI’s amicus joins several others in support of the unique needs of persons with HIV, especially in Black and Hispanic/Latino communities, which are disproportionately affected by HIV.
A press release distributed by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Legal Defense and Educational Fund (LDF) reinforces the idea that not only are Black people more likely to have a disability other groups, owing to the country’s legacy of racial inequality, but also that they are likely to encounter unique forms of discrimination and specific barriers to full participation in society, further underscoring the need for disparate impact liability to address unfair policies and practices.
“Inequity in access to resources, including healthcare, further amplifies the instance and persistence of disabilities among Black people,” LDF attorneys wrote in the brief.
“We saw with COVID-19 that [mail-order prescription] programs can serve in a supportive role in access to care,” said Ms. Tomazic. “But we don’t want those programs to be mandated, and we don’t want to forget about communities where these kinds of programs are simply not a viable option,” she said.
Oral arguments in the case begin on December 7. A decision is expected some months later.
No relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A firestorm of controversy over access to HIV medications and protection against discriminatory insurance practices has been making its way through U.S. district courts for the past 3 years, pitting HIV patients against pharmacy benefits managers and, ostensibly, the healthcare industry itself.
.
At odds are whether or not mandatory mail-order requirements for specialty medications violate specific provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, both of which prohibit discrimination by programs that receive federal funds.
An amicus brief submitted on October 29 by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation (CHLPI) of Harvard Law School on behalf of five John Does and a number of medical practitioners and practitioner organizations underscores the degree to which advances in HIV treatment, viral suppression, and care linkage — not to mention the national mandate to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030 — might ultimately be affected.
“We decided to file the brief at the Supreme Court level because we wanted to make sure that the perspectives of people living with HIV, their providers, and advocates were in the record,” Maryanne Tomazic, a clinical instructor at CHLPI, toldthis news organization.
“It’s important for the court to consider why robust access to prescription drug coverage and pharmacy services are so important for people living with HIV, and why it’s not appropriate to compromise access to antiretroviral therapy,” she explained.
A bitter pill, regardless of who swallows it
CVS Pharmacy Inc. v. Doe focuses on a legal concept known as “disparate impact discrimination,” which refers to a policy that appears neutral but unintentionally discriminates against a protected class of people (eg, on the basis of sex, age, or ethnicity).
The Supreme Court’s decision in the case will address a central question: did CVS Pharmacy, Caremark, and Caremark Specialty Pharmacy (“CVS”) discriminate against the respondents by requiring that they obtain specialty medications (including those for HIV) by mail order or drop shipment for pickup, or, alternatively, pay out-of-network prices for these medications at non-CVS pharmacies?
The decision will also address whether the ACA’s inclusion of clause 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, which prohibits protected class discrimination, allows patients to challenge terms and conditions of their healthcare plans, a decision that has broad and far-reaching implications for insurers’ abilities to set plan restrictions and pricing.
A spokesperson for CVS declined to comment when contacted by this news organization but provided a link to an April 9, 2021 SCOTUS blog post about the filing. In its court filing, CVS contended that the program applies to all specialty medications (not just HIV) and simply reflects the cost/complexity of specialty medications.
Not everyone agrees that cost is the most important issue at play. Indeed, a critical take-away for practitioners is how mandated mail-order pharmacy programs can disrupt coordination of care.
“In the traditional model, the physician is talking to the pharmacists [or] talking with the patient, and you have kind of triangular communication model that helps not only the patient stay engaged in care but [also] allows the healthcare provider team to adjust the medication quickly without delay,” said Ms. Tomazic.
The John Doe statements in the original case highlight these concerns. They focus on how mandatory mail orders restrict highly personable relationships with local specialty pharmacists who are familiar with their patients’ medical histories as well as their medication dosing and adjustments and who regularly communicate with the complete care team on the patients’ behalf.
“JOHN DOE THREE and others depend on these types of long standing relationships with local pharmacists to maximize the benefits of HIV/AIDS medications and treat the complex and ever-changing needs of the HIV/AIDS patients,” wrote attorneys in the 2018 class action filing.
Other issues raised by the suit involve the following: privacy with respect to medication pickup; specialty care customer representatives’ lack of understanding and knowledge of HIV medications; incomplete prescription fills; late medication deliveries; exposure of medications to the elements; work and employment interruptions; and restrictions on early fills and reorders, which increase the risk for missed doses and potentially serious health problems, including interruptions in viral suppression and resistance.
Discrimination issues also raised
CHLPI’s amicus joins several others in support of the unique needs of persons with HIV, especially in Black and Hispanic/Latino communities, which are disproportionately affected by HIV.
A press release distributed by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Legal Defense and Educational Fund (LDF) reinforces the idea that not only are Black people more likely to have a disability other groups, owing to the country’s legacy of racial inequality, but also that they are likely to encounter unique forms of discrimination and specific barriers to full participation in society, further underscoring the need for disparate impact liability to address unfair policies and practices.
“Inequity in access to resources, including healthcare, further amplifies the instance and persistence of disabilities among Black people,” LDF attorneys wrote in the brief.
“We saw with COVID-19 that [mail-order prescription] programs can serve in a supportive role in access to care,” said Ms. Tomazic. “But we don’t want those programs to be mandated, and we don’t want to forget about communities where these kinds of programs are simply not a viable option,” she said.
Oral arguments in the case begin on December 7. A decision is expected some months later.
No relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A firestorm of controversy over access to HIV medications and protection against discriminatory insurance practices has been making its way through U.S. district courts for the past 3 years, pitting HIV patients against pharmacy benefits managers and, ostensibly, the healthcare industry itself.
.
At odds are whether or not mandatory mail-order requirements for specialty medications violate specific provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, both of which prohibit discrimination by programs that receive federal funds.
An amicus brief submitted on October 29 by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation (CHLPI) of Harvard Law School on behalf of five John Does and a number of medical practitioners and practitioner organizations underscores the degree to which advances in HIV treatment, viral suppression, and care linkage — not to mention the national mandate to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030 — might ultimately be affected.
“We decided to file the brief at the Supreme Court level because we wanted to make sure that the perspectives of people living with HIV, their providers, and advocates were in the record,” Maryanne Tomazic, a clinical instructor at CHLPI, toldthis news organization.
“It’s important for the court to consider why robust access to prescription drug coverage and pharmacy services are so important for people living with HIV, and why it’s not appropriate to compromise access to antiretroviral therapy,” she explained.
A bitter pill, regardless of who swallows it
CVS Pharmacy Inc. v. Doe focuses on a legal concept known as “disparate impact discrimination,” which refers to a policy that appears neutral but unintentionally discriminates against a protected class of people (eg, on the basis of sex, age, or ethnicity).
The Supreme Court’s decision in the case will address a central question: did CVS Pharmacy, Caremark, and Caremark Specialty Pharmacy (“CVS”) discriminate against the respondents by requiring that they obtain specialty medications (including those for HIV) by mail order or drop shipment for pickup, or, alternatively, pay out-of-network prices for these medications at non-CVS pharmacies?
The decision will also address whether the ACA’s inclusion of clause 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, which prohibits protected class discrimination, allows patients to challenge terms and conditions of their healthcare plans, a decision that has broad and far-reaching implications for insurers’ abilities to set plan restrictions and pricing.
A spokesperson for CVS declined to comment when contacted by this news organization but provided a link to an April 9, 2021 SCOTUS blog post about the filing. In its court filing, CVS contended that the program applies to all specialty medications (not just HIV) and simply reflects the cost/complexity of specialty medications.
Not everyone agrees that cost is the most important issue at play. Indeed, a critical take-away for practitioners is how mandated mail-order pharmacy programs can disrupt coordination of care.
“In the traditional model, the physician is talking to the pharmacists [or] talking with the patient, and you have kind of triangular communication model that helps not only the patient stay engaged in care but [also] allows the healthcare provider team to adjust the medication quickly without delay,” said Ms. Tomazic.
The John Doe statements in the original case highlight these concerns. They focus on how mandatory mail orders restrict highly personable relationships with local specialty pharmacists who are familiar with their patients’ medical histories as well as their medication dosing and adjustments and who regularly communicate with the complete care team on the patients’ behalf.
“JOHN DOE THREE and others depend on these types of long standing relationships with local pharmacists to maximize the benefits of HIV/AIDS medications and treat the complex and ever-changing needs of the HIV/AIDS patients,” wrote attorneys in the 2018 class action filing.
Other issues raised by the suit involve the following: privacy with respect to medication pickup; specialty care customer representatives’ lack of understanding and knowledge of HIV medications; incomplete prescription fills; late medication deliveries; exposure of medications to the elements; work and employment interruptions; and restrictions on early fills and reorders, which increase the risk for missed doses and potentially serious health problems, including interruptions in viral suppression and resistance.
Discrimination issues also raised
CHLPI’s amicus joins several others in support of the unique needs of persons with HIV, especially in Black and Hispanic/Latino communities, which are disproportionately affected by HIV.
A press release distributed by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Legal Defense and Educational Fund (LDF) reinforces the idea that not only are Black people more likely to have a disability other groups, owing to the country’s legacy of racial inequality, but also that they are likely to encounter unique forms of discrimination and specific barriers to full participation in society, further underscoring the need for disparate impact liability to address unfair policies and practices.
“Inequity in access to resources, including healthcare, further amplifies the instance and persistence of disabilities among Black people,” LDF attorneys wrote in the brief.
“We saw with COVID-19 that [mail-order prescription] programs can serve in a supportive role in access to care,” said Ms. Tomazic. “But we don’t want those programs to be mandated, and we don’t want to forget about communities where these kinds of programs are simply not a viable option,” she said.
Oral arguments in the case begin on December 7. A decision is expected some months later.
No relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 has brought more complex, longer office visits
Evidence of this came from the latest Primary Care Collaborative (PCC) survey, which found that primary care clinicians are seeing more complex patients requiring longer appointments in the wake of COVID-19.
The PCC with the Larry A. Green Center regularly surveys primary care clinicians. This round of questions came August 14-17 and included 1,263 respondents from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories.
More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents said their patients are more complex and nearly the same percentage said appointments are taking more time.
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the PCC, said in an interview that 55% of respondents reported that clinicians are struggling to keep up with pent-up demand after patients have delayed or canceled care. Sixty-five percent in the survey said they had seen a rise in children’s mental health issues, and 58% said they were unsure how to help their patients with long COVID.
In addition, primary care clinicians are having repeated conversations with patients on why they should get a vaccine and which one.
“I think that’s adding to the complexity. There is a lot going on here with patient trust,” Ms. Greiner said.
‘We’re going to be playing catch-up’
Jacqueline Fincher, MD, an internist in Thompson, Ga., said in an interview that appointments have gotten longer and more complex in the wake of the pandemic – “no question.”
The immediate past president of the American College of Physicians is seeing patients with chronic disease that has gone untreated for sometimes a year or more, she said.
“Their blood pressure was not under good control, they were under more stress, their sugars were up and weren’t being followed as closely for conditions such as congestive heart failure,” she said.
Dr. Fincher, who works in a rural practice 40 miles from Augusta, Ga., with her physician husband and two other physicians, said patients are ready to come back in, “but I don’t have enough slots for them.”
She said she prioritizes what to help patients with first and schedules the next tier for the next appointment, but added, “honestly, over the next 2 years we’re going to be playing catch-up.”
At the same time, the CDC has estimated that 45% of U.S. adults are at increased risk for complications from COVID-19 because of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, hypertension, or cancer. Rates ranged from 19.8% for people 18-29 years old to 80.7% for people over 80 years of age.
Long COVID could overwhelm existing health care capacity
Primary care physicians are also having to diagnose sometimes “invisible” symptoms after people have recovered from acute COVID-19 infection. Diagnosing takes intent listening to patients who describe symptoms that tests can’t confirm.
As this news organization has previously reported, half of COVID-19 survivors report postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) lasting longer than 6 months.
“These long-term PASC effects occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries,” the authors wrote.
Anxiety, depression ‘have gone off the charts’
Danielle Loeb, MD, MPH, associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver, who studies complexity in primary care, said in the wake of COVID-19, more patients have developed “new, serious anxiety.”
“That got extremely exacerbated during the pandemic. Anxiety and depression have gone off the charts,” said Dr. Loeb, who prefers the pronoun “they.”
Dr. Loeb cares for a large number of transgender patients. As offices reopen, some patients are having trouble reintegrating into the workplace and resuming social contacts. The primary care doctor says appointments can get longer because of the need to complete tasks, such as filling out forms for Family Medical Leave Act for those not yet ready to return to work.
COVID-19–related fears are keeping many patients from coming into the office, Dr. Loeb said, either from fear of exposure or because they have mental health issues that keep them from feeling safe leaving the house.
“That really affects my ability to care for them,” they said.
Loss of employment in the pandemic or fear of job loss and subsequent changing of insurance has complicated primary care in terms of treatment and administrative tasks, according to Dr. Loeb.
To help treat patients with acute mental health issues and manage other patients, Dr. Loeb’s practice has brought in a social worker and a therapist.
Team-based care is key in the survival of primary care practices, though providing that is difficult in the smaller clinics because of the critical mass of patients needed to make it viable, they said.
“It’s the only answer. It’s the only way you don’t drown,” Dr. Loeb added. “I’m not drowning, and I credit that to my clinic having the help to support the mental health piece of things.”
Rethinking workflow
Tricia McGinnis, MPP, MPH, executive vice president of the nonprofit Center for Health Care Strategies (CHCS) says complexity has forced rethinking workflow.
“A lot of the trends we’re seeing in primary care were there pre-COVID, but COVID has exacerbated those trends,” she said in an interview.
“The good news ... is that it was already becoming clear that primary care needed to provide basic mental health services and integrate with behavioral health. It had also become clear that effective primary care needed to address social issues that keep patients from accessing health care,” she said.
Expanding care teams, as Dr. Loeb mentioned, is a key strategy, according to Ms. McGinnis. Potential teams would include the clinical staff, but also social workers and community health workers – people who come from the community primary care is serving who can help build trust with patients and connect the patient to the primary care team.
“There’s a lot that needs to happen that the clinician doesn’t need to do,” she said.
Telehealth can be a big factor in coordinating the team, Ms. McGinnis added.
“It’s thinking less about who’s doing the work, but more about the work that needs to be done to keep people healthy. Then let’s think about the type of workers best suited to perform those tasks,” she said.
As for reimbursing more complex care, population-based, up-front capitated payments linked to high-quality care and better outcomes will need to replace fee-for-service models, according to Ms. McGinnis.
That will provide reliable incomes for primary care offices, but also flexibility in how each patient with different levels of complexity is managed, she said.
Ms. Greiner, Dr. Fincher, Dr. Loeb, and Ms. McGinnis have no relevant financial relationships.
Evidence of this came from the latest Primary Care Collaborative (PCC) survey, which found that primary care clinicians are seeing more complex patients requiring longer appointments in the wake of COVID-19.
The PCC with the Larry A. Green Center regularly surveys primary care clinicians. This round of questions came August 14-17 and included 1,263 respondents from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories.
More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents said their patients are more complex and nearly the same percentage said appointments are taking more time.
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the PCC, said in an interview that 55% of respondents reported that clinicians are struggling to keep up with pent-up demand after patients have delayed or canceled care. Sixty-five percent in the survey said they had seen a rise in children’s mental health issues, and 58% said they were unsure how to help their patients with long COVID.
In addition, primary care clinicians are having repeated conversations with patients on why they should get a vaccine and which one.
“I think that’s adding to the complexity. There is a lot going on here with patient trust,” Ms. Greiner said.
‘We’re going to be playing catch-up’
Jacqueline Fincher, MD, an internist in Thompson, Ga., said in an interview that appointments have gotten longer and more complex in the wake of the pandemic – “no question.”
The immediate past president of the American College of Physicians is seeing patients with chronic disease that has gone untreated for sometimes a year or more, she said.
“Their blood pressure was not under good control, they were under more stress, their sugars were up and weren’t being followed as closely for conditions such as congestive heart failure,” she said.
Dr. Fincher, who works in a rural practice 40 miles from Augusta, Ga., with her physician husband and two other physicians, said patients are ready to come back in, “but I don’t have enough slots for them.”
She said she prioritizes what to help patients with first and schedules the next tier for the next appointment, but added, “honestly, over the next 2 years we’re going to be playing catch-up.”
At the same time, the CDC has estimated that 45% of U.S. adults are at increased risk for complications from COVID-19 because of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, hypertension, or cancer. Rates ranged from 19.8% for people 18-29 years old to 80.7% for people over 80 years of age.
Long COVID could overwhelm existing health care capacity
Primary care physicians are also having to diagnose sometimes “invisible” symptoms after people have recovered from acute COVID-19 infection. Diagnosing takes intent listening to patients who describe symptoms that tests can’t confirm.
As this news organization has previously reported, half of COVID-19 survivors report postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) lasting longer than 6 months.
“These long-term PASC effects occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries,” the authors wrote.
Anxiety, depression ‘have gone off the charts’
Danielle Loeb, MD, MPH, associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver, who studies complexity in primary care, said in the wake of COVID-19, more patients have developed “new, serious anxiety.”
“That got extremely exacerbated during the pandemic. Anxiety and depression have gone off the charts,” said Dr. Loeb, who prefers the pronoun “they.”
Dr. Loeb cares for a large number of transgender patients. As offices reopen, some patients are having trouble reintegrating into the workplace and resuming social contacts. The primary care doctor says appointments can get longer because of the need to complete tasks, such as filling out forms for Family Medical Leave Act for those not yet ready to return to work.
COVID-19–related fears are keeping many patients from coming into the office, Dr. Loeb said, either from fear of exposure or because they have mental health issues that keep them from feeling safe leaving the house.
“That really affects my ability to care for them,” they said.
Loss of employment in the pandemic or fear of job loss and subsequent changing of insurance has complicated primary care in terms of treatment and administrative tasks, according to Dr. Loeb.
To help treat patients with acute mental health issues and manage other patients, Dr. Loeb’s practice has brought in a social worker and a therapist.
Team-based care is key in the survival of primary care practices, though providing that is difficult in the smaller clinics because of the critical mass of patients needed to make it viable, they said.
“It’s the only answer. It’s the only way you don’t drown,” Dr. Loeb added. “I’m not drowning, and I credit that to my clinic having the help to support the mental health piece of things.”
Rethinking workflow
Tricia McGinnis, MPP, MPH, executive vice president of the nonprofit Center for Health Care Strategies (CHCS) says complexity has forced rethinking workflow.
“A lot of the trends we’re seeing in primary care were there pre-COVID, but COVID has exacerbated those trends,” she said in an interview.
“The good news ... is that it was already becoming clear that primary care needed to provide basic mental health services and integrate with behavioral health. It had also become clear that effective primary care needed to address social issues that keep patients from accessing health care,” she said.
Expanding care teams, as Dr. Loeb mentioned, is a key strategy, according to Ms. McGinnis. Potential teams would include the clinical staff, but also social workers and community health workers – people who come from the community primary care is serving who can help build trust with patients and connect the patient to the primary care team.
“There’s a lot that needs to happen that the clinician doesn’t need to do,” she said.
Telehealth can be a big factor in coordinating the team, Ms. McGinnis added.
“It’s thinking less about who’s doing the work, but more about the work that needs to be done to keep people healthy. Then let’s think about the type of workers best suited to perform those tasks,” she said.
As for reimbursing more complex care, population-based, up-front capitated payments linked to high-quality care and better outcomes will need to replace fee-for-service models, according to Ms. McGinnis.
That will provide reliable incomes for primary care offices, but also flexibility in how each patient with different levels of complexity is managed, she said.
Ms. Greiner, Dr. Fincher, Dr. Loeb, and Ms. McGinnis have no relevant financial relationships.
Evidence of this came from the latest Primary Care Collaborative (PCC) survey, which found that primary care clinicians are seeing more complex patients requiring longer appointments in the wake of COVID-19.
The PCC with the Larry A. Green Center regularly surveys primary care clinicians. This round of questions came August 14-17 and included 1,263 respondents from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories.
More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents said their patients are more complex and nearly the same percentage said appointments are taking more time.
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the PCC, said in an interview that 55% of respondents reported that clinicians are struggling to keep up with pent-up demand after patients have delayed or canceled care. Sixty-five percent in the survey said they had seen a rise in children’s mental health issues, and 58% said they were unsure how to help their patients with long COVID.
In addition, primary care clinicians are having repeated conversations with patients on why they should get a vaccine and which one.
“I think that’s adding to the complexity. There is a lot going on here with patient trust,” Ms. Greiner said.
‘We’re going to be playing catch-up’
Jacqueline Fincher, MD, an internist in Thompson, Ga., said in an interview that appointments have gotten longer and more complex in the wake of the pandemic – “no question.”
The immediate past president of the American College of Physicians is seeing patients with chronic disease that has gone untreated for sometimes a year or more, she said.
“Their blood pressure was not under good control, they were under more stress, their sugars were up and weren’t being followed as closely for conditions such as congestive heart failure,” she said.
Dr. Fincher, who works in a rural practice 40 miles from Augusta, Ga., with her physician husband and two other physicians, said patients are ready to come back in, “but I don’t have enough slots for them.”
She said she prioritizes what to help patients with first and schedules the next tier for the next appointment, but added, “honestly, over the next 2 years we’re going to be playing catch-up.”
At the same time, the CDC has estimated that 45% of U.S. adults are at increased risk for complications from COVID-19 because of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, hypertension, or cancer. Rates ranged from 19.8% for people 18-29 years old to 80.7% for people over 80 years of age.
Long COVID could overwhelm existing health care capacity
Primary care physicians are also having to diagnose sometimes “invisible” symptoms after people have recovered from acute COVID-19 infection. Diagnosing takes intent listening to patients who describe symptoms that tests can’t confirm.
As this news organization has previously reported, half of COVID-19 survivors report postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) lasting longer than 6 months.
“These long-term PASC effects occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries,” the authors wrote.
Anxiety, depression ‘have gone off the charts’
Danielle Loeb, MD, MPH, associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver, who studies complexity in primary care, said in the wake of COVID-19, more patients have developed “new, serious anxiety.”
“That got extremely exacerbated during the pandemic. Anxiety and depression have gone off the charts,” said Dr. Loeb, who prefers the pronoun “they.”
Dr. Loeb cares for a large number of transgender patients. As offices reopen, some patients are having trouble reintegrating into the workplace and resuming social contacts. The primary care doctor says appointments can get longer because of the need to complete tasks, such as filling out forms for Family Medical Leave Act for those not yet ready to return to work.
COVID-19–related fears are keeping many patients from coming into the office, Dr. Loeb said, either from fear of exposure or because they have mental health issues that keep them from feeling safe leaving the house.
“That really affects my ability to care for them,” they said.
Loss of employment in the pandemic or fear of job loss and subsequent changing of insurance has complicated primary care in terms of treatment and administrative tasks, according to Dr. Loeb.
To help treat patients with acute mental health issues and manage other patients, Dr. Loeb’s practice has brought in a social worker and a therapist.
Team-based care is key in the survival of primary care practices, though providing that is difficult in the smaller clinics because of the critical mass of patients needed to make it viable, they said.
“It’s the only answer. It’s the only way you don’t drown,” Dr. Loeb added. “I’m not drowning, and I credit that to my clinic having the help to support the mental health piece of things.”
Rethinking workflow
Tricia McGinnis, MPP, MPH, executive vice president of the nonprofit Center for Health Care Strategies (CHCS) says complexity has forced rethinking workflow.
“A lot of the trends we’re seeing in primary care were there pre-COVID, but COVID has exacerbated those trends,” she said in an interview.
“The good news ... is that it was already becoming clear that primary care needed to provide basic mental health services and integrate with behavioral health. It had also become clear that effective primary care needed to address social issues that keep patients from accessing health care,” she said.
Expanding care teams, as Dr. Loeb mentioned, is a key strategy, according to Ms. McGinnis. Potential teams would include the clinical staff, but also social workers and community health workers – people who come from the community primary care is serving who can help build trust with patients and connect the patient to the primary care team.
“There’s a lot that needs to happen that the clinician doesn’t need to do,” she said.
Telehealth can be a big factor in coordinating the team, Ms. McGinnis added.
“It’s thinking less about who’s doing the work, but more about the work that needs to be done to keep people healthy. Then let’s think about the type of workers best suited to perform those tasks,” she said.
As for reimbursing more complex care, population-based, up-front capitated payments linked to high-quality care and better outcomes will need to replace fee-for-service models, according to Ms. McGinnis.
That will provide reliable incomes for primary care offices, but also flexibility in how each patient with different levels of complexity is managed, she said.
Ms. Greiner, Dr. Fincher, Dr. Loeb, and Ms. McGinnis have no relevant financial relationships.
‘Residents’ Viewpoint’ revisited
We are currently republishing an installment of this column as part of our continuing celebration of Family Practice News’s 50th anniversary.
Bruce A. Bagley, MD, wrote the first batch of these columns, when he was chief resident in family medicine at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Syracuse, N.Y. Joseph E. Scherger, MD, was the second writer for Family Practice News’s monthly “Residents’ Viewpoint.” At the time Dr. Scherger became a columnist, he was a 26-year-old, 2nd-year family practice resident at the Family Medical Center, University Hospital, University of Washington, Seattle.
Dr. Scherger’s first column was published on Feb. 5, 1977. We are republishing his “Residents’ Viewpoint” from June 15, 1977 (see below) and a new column by Victoria Persampiere, DO, who is currently a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine program at Abington Jefferson Health. (See “My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021” after Dr. Scherger’s column.).
We hope you will enjoy comparing and contrasting the experiences of a resident practicing family medicine today to those of a resident practicing family medicine nearly 4½ decades ago.To learn about Dr. Scherger’s current practice and long career, you can read his profile on the cover of the September 2021 issue of Family Practice News or on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine in our “Family Practice News 50th Anniversary” section.
Art of medicine or deception?
Originally published in Family Practice News on June 15, 1977.
In medical school I learned the science of medicine. There I diligently studied the basic sciences and gained a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology of disease. In the clinical years I learned to apply this knowledge to a wide variety of interesting patients who came to the academic center.
Yet, when I started my family practice residency, I lacked the ability to care for patients. Though I could take a thorough history, perform a complete physical examination, and diagnose and treat specific illnesses, I had little idea how to satisfy patients by meeting their needs.
The art of medicine is the nonscientific part of a successful doctor-patient interaction. For a doctor-patient interaction to be successful, not only must the illness be appropriately addressed, but both patient and physician must be satisfied.
In the university environment, the art of medicine often gets inadequate attention. Indeed, most academic physicians think that only scientific medicine exists and that patients should be satisfied with a sophisticated approach to their problems. Some patients are satisfied, but many are disgruntled. It is not unusual for a patient, after a $1,000 work-up, to go to a family physician or chiropractor for satisfaction.
I was eager to discover the art of medicine at its finest during my rotation away from the university in a rural community. During these 2 months I looked for the pearls of wisdom that allowed community physicians to be so successful. I found that a very explicit technique was used by some physicians to achieve not only satisfaction but adoration from their patients. Unfortunately, this technique is dishonest.
Early in my community experience I was impressed by how often patients told me a doctor had saved them. I heard such statements as “Dr. X saved my leg,” or “Dr. X saved my life.” I know that it does occur, but not as often as I was hearing it.
Investigating these statements I found such stories as, “One day l twisted my ankle very badly, and it became quite swollen. My doctor told me 1 could lose my leg from this but that he would take x-rays, put my leg in an Ace bandage, and give me crutches. In 3 days I was well. I am so thankful he saved my leg.”
And, “One day I had a temperature of 104. All of my muscles ached, my head hurt, and I had a terrible sore throat and cough. My doctor told me l could die from this, but he gave me a medicine and made me stay home. I was sick for about 2 weeks, but I got better. He saved my life.”
Is the art of medicine the art of deception? This horrifying thought actually came to me after hearing several such stories, but I learned that most of the physicians involved in such stories were not well respected by their colleagues.
I learned many honest techniques for successfully caring for patients. The several family physicians with whom I worked, all clinical instructors associated with my residency, were impeccably honest and taught me to combine compassion and efficiency.
Despite learning many positive techniques and having good role models, I left the community experience somewhat saddened by the lack of integrity that can exist in the profession. I was naive in believing that all the nonscientific aspects of medicine that made patients happy must be good.
By experiencing deception, I learned why quackery continues to flourish despite the widespread availability of honest medical care. Most significantly, I learned the importance of a sometimes frustrating humility; my patients with sprained ankles and influenza will not believe I saved their lives.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19 era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome, which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today; you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician. ■
Dr. Persampiere is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at [email protected] or via [email protected].
We are currently republishing an installment of this column as part of our continuing celebration of Family Practice News’s 50th anniversary.
Bruce A. Bagley, MD, wrote the first batch of these columns, when he was chief resident in family medicine at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Syracuse, N.Y. Joseph E. Scherger, MD, was the second writer for Family Practice News’s monthly “Residents’ Viewpoint.” At the time Dr. Scherger became a columnist, he was a 26-year-old, 2nd-year family practice resident at the Family Medical Center, University Hospital, University of Washington, Seattle.
Dr. Scherger’s first column was published on Feb. 5, 1977. We are republishing his “Residents’ Viewpoint” from June 15, 1977 (see below) and a new column by Victoria Persampiere, DO, who is currently a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine program at Abington Jefferson Health. (See “My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021” after Dr. Scherger’s column.).
We hope you will enjoy comparing and contrasting the experiences of a resident practicing family medicine today to those of a resident practicing family medicine nearly 4½ decades ago.To learn about Dr. Scherger’s current practice and long career, you can read his profile on the cover of the September 2021 issue of Family Practice News or on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine in our “Family Practice News 50th Anniversary” section.
Art of medicine or deception?
Originally published in Family Practice News on June 15, 1977.
In medical school I learned the science of medicine. There I diligently studied the basic sciences and gained a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology of disease. In the clinical years I learned to apply this knowledge to a wide variety of interesting patients who came to the academic center.
Yet, when I started my family practice residency, I lacked the ability to care for patients. Though I could take a thorough history, perform a complete physical examination, and diagnose and treat specific illnesses, I had little idea how to satisfy patients by meeting their needs.
The art of medicine is the nonscientific part of a successful doctor-patient interaction. For a doctor-patient interaction to be successful, not only must the illness be appropriately addressed, but both patient and physician must be satisfied.
In the university environment, the art of medicine often gets inadequate attention. Indeed, most academic physicians think that only scientific medicine exists and that patients should be satisfied with a sophisticated approach to their problems. Some patients are satisfied, but many are disgruntled. It is not unusual for a patient, after a $1,000 work-up, to go to a family physician or chiropractor for satisfaction.
I was eager to discover the art of medicine at its finest during my rotation away from the university in a rural community. During these 2 months I looked for the pearls of wisdom that allowed community physicians to be so successful. I found that a very explicit technique was used by some physicians to achieve not only satisfaction but adoration from their patients. Unfortunately, this technique is dishonest.
Early in my community experience I was impressed by how often patients told me a doctor had saved them. I heard such statements as “Dr. X saved my leg,” or “Dr. X saved my life.” I know that it does occur, but not as often as I was hearing it.
Investigating these statements I found such stories as, “One day l twisted my ankle very badly, and it became quite swollen. My doctor told me 1 could lose my leg from this but that he would take x-rays, put my leg in an Ace bandage, and give me crutches. In 3 days I was well. I am so thankful he saved my leg.”
And, “One day I had a temperature of 104. All of my muscles ached, my head hurt, and I had a terrible sore throat and cough. My doctor told me l could die from this, but he gave me a medicine and made me stay home. I was sick for about 2 weeks, but I got better. He saved my life.”
Is the art of medicine the art of deception? This horrifying thought actually came to me after hearing several such stories, but I learned that most of the physicians involved in such stories were not well respected by their colleagues.
I learned many honest techniques for successfully caring for patients. The several family physicians with whom I worked, all clinical instructors associated with my residency, were impeccably honest and taught me to combine compassion and efficiency.
Despite learning many positive techniques and having good role models, I left the community experience somewhat saddened by the lack of integrity that can exist in the profession. I was naive in believing that all the nonscientific aspects of medicine that made patients happy must be good.
By experiencing deception, I learned why quackery continues to flourish despite the widespread availability of honest medical care. Most significantly, I learned the importance of a sometimes frustrating humility; my patients with sprained ankles and influenza will not believe I saved their lives.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19 era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome, which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today; you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician. ■
Dr. Persampiere is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at [email protected] or via [email protected].
We are currently republishing an installment of this column as part of our continuing celebration of Family Practice News’s 50th anniversary.
Bruce A. Bagley, MD, wrote the first batch of these columns, when he was chief resident in family medicine at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Syracuse, N.Y. Joseph E. Scherger, MD, was the second writer for Family Practice News’s monthly “Residents’ Viewpoint.” At the time Dr. Scherger became a columnist, he was a 26-year-old, 2nd-year family practice resident at the Family Medical Center, University Hospital, University of Washington, Seattle.
Dr. Scherger’s first column was published on Feb. 5, 1977. We are republishing his “Residents’ Viewpoint” from June 15, 1977 (see below) and a new column by Victoria Persampiere, DO, who is currently a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine program at Abington Jefferson Health. (See “My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021” after Dr. Scherger’s column.).
We hope you will enjoy comparing and contrasting the experiences of a resident practicing family medicine today to those of a resident practicing family medicine nearly 4½ decades ago.To learn about Dr. Scherger’s current practice and long career, you can read his profile on the cover of the September 2021 issue of Family Practice News or on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine in our “Family Practice News 50th Anniversary” section.
Art of medicine or deception?
Originally published in Family Practice News on June 15, 1977.
In medical school I learned the science of medicine. There I diligently studied the basic sciences and gained a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology of disease. In the clinical years I learned to apply this knowledge to a wide variety of interesting patients who came to the academic center.
Yet, when I started my family practice residency, I lacked the ability to care for patients. Though I could take a thorough history, perform a complete physical examination, and diagnose and treat specific illnesses, I had little idea how to satisfy patients by meeting their needs.
The art of medicine is the nonscientific part of a successful doctor-patient interaction. For a doctor-patient interaction to be successful, not only must the illness be appropriately addressed, but both patient and physician must be satisfied.
In the university environment, the art of medicine often gets inadequate attention. Indeed, most academic physicians think that only scientific medicine exists and that patients should be satisfied with a sophisticated approach to their problems. Some patients are satisfied, but many are disgruntled. It is not unusual for a patient, after a $1,000 work-up, to go to a family physician or chiropractor for satisfaction.
I was eager to discover the art of medicine at its finest during my rotation away from the university in a rural community. During these 2 months I looked for the pearls of wisdom that allowed community physicians to be so successful. I found that a very explicit technique was used by some physicians to achieve not only satisfaction but adoration from their patients. Unfortunately, this technique is dishonest.
Early in my community experience I was impressed by how often patients told me a doctor had saved them. I heard such statements as “Dr. X saved my leg,” or “Dr. X saved my life.” I know that it does occur, but not as often as I was hearing it.
Investigating these statements I found such stories as, “One day l twisted my ankle very badly, and it became quite swollen. My doctor told me 1 could lose my leg from this but that he would take x-rays, put my leg in an Ace bandage, and give me crutches. In 3 days I was well. I am so thankful he saved my leg.”
And, “One day I had a temperature of 104. All of my muscles ached, my head hurt, and I had a terrible sore throat and cough. My doctor told me l could die from this, but he gave me a medicine and made me stay home. I was sick for about 2 weeks, but I got better. He saved my life.”
Is the art of medicine the art of deception? This horrifying thought actually came to me after hearing several such stories, but I learned that most of the physicians involved in such stories were not well respected by their colleagues.
I learned many honest techniques for successfully caring for patients. The several family physicians with whom I worked, all clinical instructors associated with my residency, were impeccably honest and taught me to combine compassion and efficiency.
Despite learning many positive techniques and having good role models, I left the community experience somewhat saddened by the lack of integrity that can exist in the profession. I was naive in believing that all the nonscientific aspects of medicine that made patients happy must be good.
By experiencing deception, I learned why quackery continues to flourish despite the widespread availability of honest medical care. Most significantly, I learned the importance of a sometimes frustrating humility; my patients with sprained ankles and influenza will not believe I saved their lives.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19 era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome, which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today; you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician. ■
Dr. Persampiere is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at [email protected] or via [email protected].
Not COVID Toes: Pool Palms and Feet in Pediatric Patients
Practice Gap
Frictional, symmetric, asymptomatic, erythematous macules of the hands and feet can be mistaken for perniolike lesions associated with COVID-19, commonly known as COVID toes. However, in a low-risk setting without other associated symptoms or concerning findings on examination, consider and inquire about frequent use of a swimming pool. This activity can lead to localized pressure- and friction-induced erythema on palmar and plantar surfaces, called “pool palms and feet,” expanding on the already-named lesion “pool palms”—an entity that is distinct from COVID toes.
Technique for Diagnosis
We evaluated 4 patients in the outpatient setting who presented with localized, patterned, erythematous lesions of the hands or feet, or both, during the COVID-19 pandemic. The parents of our patients were concerned that the rash represented “COVID fingers and toes,” which are perniolike lesions seen in patients with suspected or confirmed current or prior COVID-19.1
Pernio, also known as chilblains, is a superficial inflammatory vascular response, usually in the setting of exposure to cold.2 This phenomenon usually appears as erythematous or violaceous macules and papules on acral skin, particularly on the dorsum and sides of the fingers and toes, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in more severe cases. Initially, it is pruritic and painful at times.
With COVID toes, there often is a delayed presentation of perniolike lesions after the onset of other COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, and sore throat.2,3 It has been described more often in younger patients and those with milder disease. However, because our patients had no known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or other associated symptoms, our suspicion was low.
The 4 patients we evaluated—aged 4 to 12 years and in their usual good health—had blanchable erythema of the palmar fingers, palmar eminences of both hands, and plantar surfaces of both feet (Figure). There was no swelling or tenderness, and the lesions had no violaceous coloration, vesiculation, or ulceration. There was no associated pruritus or pain. One patient reported rough texture and mild peeling of the hands.
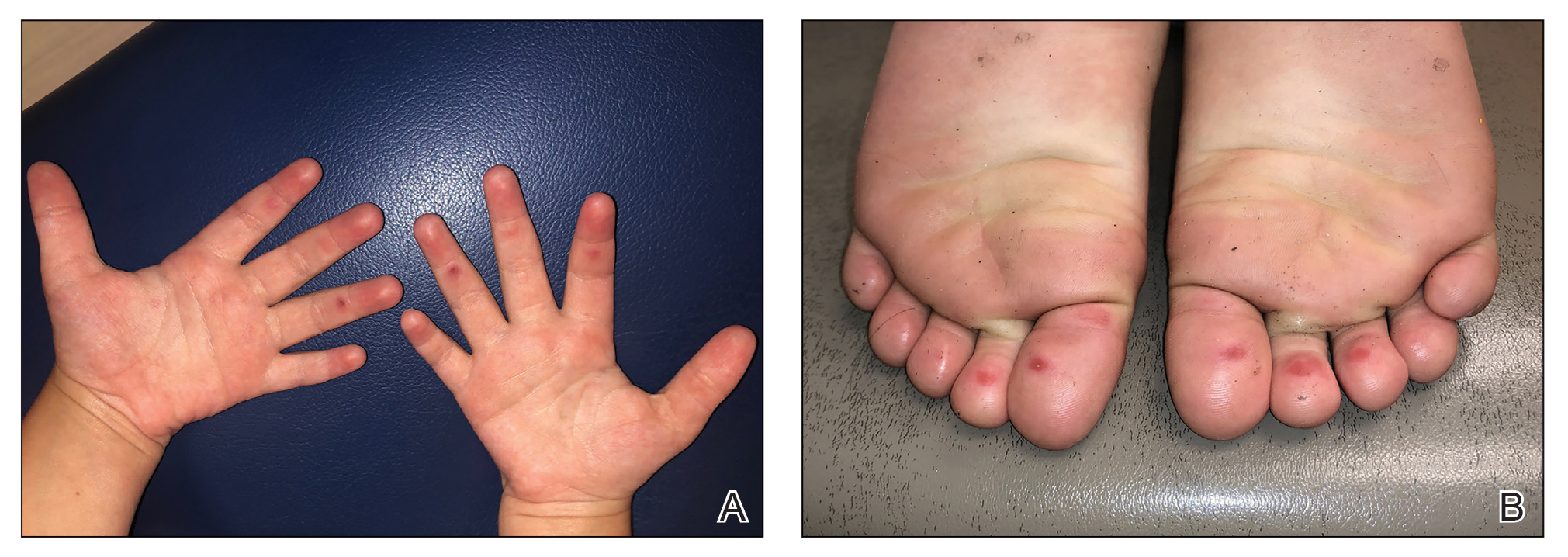
Upon further inquiry, the patients reported a history of extended time spent in home swimming pools, including holding on to the edge of the pool, due to limitation of activities because of COVID restrictions. One parent noted that the pool that caused the rash had a rough nonslip surface, whereas other pools that the children used, which had a smoother surface, caused no problems.
The morphology of symmetric blanching erythema in areas of pressure and friction, in the absence of a notable medical history, signs, or symptoms, was consistent with a diagnosis of pool palms, which has been described in the medical literature.4-9 Pool palms can affect the palms and soles, which are subject to substantial friction, especially when a person is getting in and out of the pool. There is a general consensus that pool palms is a frictional dermatitis affecting children because the greater fragility of their skin is exacerbated by immersion in water.4-9
Pool palms and feet is benign. Only supportive care, with cessation of swimming and application of emollients, is necessary.
Apart from COVID-19, other conditions to consider in a patient with erythematous lesions of the palms and soles include eczematous dermatitis; neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis; and, if lesions are vesicular, hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Juvenile plantar dermatosis, which is thought to be due to moisture with occlusion in shoes, also might be considered but is distinguished by more scales and fissures that can be painful.
Location of the lesions is a critical variable. The patients we evaluated had lesions primarily on palmar and plantar surfaces where contact with pool surfaces was greatest, such as at bony prominences, which supported a diagnosis of frictional dermatitis, such as pool palms and feet. A thorough history and physical examination are helpful in determining the diagnosis.
Practical Implications
It is important to consider and recognize this localized pressure phenomenon of pool palms and feet, thus obviating an unnecessary workup or therapeutic interventions. Specifically, a finding of erythematous asymptomatic macules, with or without scaling, on bony prominences of the palms and soles is more consistent with pool palms and feet.
Pernio and COVID toes both present as erythematous to violaceous papules and macules, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in severe cases, often on the dorsum and sides of fingers and toes; typically the conditions are pruritic and painful at times.
Explaining the diagnosis of pool palms and feet and sharing one’s experience with similar cases might help alleviate parental fear and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- de Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Sulimovic L, et al; SNDV (French National Union of Dermatologists–Venereologists). Chilblains is a common cutaneous finding during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective nationwide study from France. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.161
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al; American Academy of Dermatology Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19. Pernio-like skin lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series of 318 patients from 8 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:486-492. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.109
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: an international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1118-1129. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016
- Blauvelt A, Duarte AM, Schachner LA. Pool palms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:111. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80819-5
- Wong L-C, Rogers M. Pool palms. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:95. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00347.x
- Novoa A, Klear S. Pool palms. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:41. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2015-309633
- Morgado-Carasco D, Feola H, Vargas-Mora P. Pool palms. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2020;10:e2020009. doi:10.5826/dpc.1001a09
- Cutrone M, Valerio E, Grimalt R. Pool palms: a case report. Dermatol Case Rep. 2019;4:1000154.
- Martína JM, Ricart JM. Erythematous–violaceous lesions on the palms. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:507-508.
Practice Gap
Frictional, symmetric, asymptomatic, erythematous macules of the hands and feet can be mistaken for perniolike lesions associated with COVID-19, commonly known as COVID toes. However, in a low-risk setting without other associated symptoms or concerning findings on examination, consider and inquire about frequent use of a swimming pool. This activity can lead to localized pressure- and friction-induced erythema on palmar and plantar surfaces, called “pool palms and feet,” expanding on the already-named lesion “pool palms”—an entity that is distinct from COVID toes.
Technique for Diagnosis
We evaluated 4 patients in the outpatient setting who presented with localized, patterned, erythematous lesions of the hands or feet, or both, during the COVID-19 pandemic. The parents of our patients were concerned that the rash represented “COVID fingers and toes,” which are perniolike lesions seen in patients with suspected or confirmed current or prior COVID-19.1
Pernio, also known as chilblains, is a superficial inflammatory vascular response, usually in the setting of exposure to cold.2 This phenomenon usually appears as erythematous or violaceous macules and papules on acral skin, particularly on the dorsum and sides of the fingers and toes, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in more severe cases. Initially, it is pruritic and painful at times.
With COVID toes, there often is a delayed presentation of perniolike lesions after the onset of other COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, and sore throat.2,3 It has been described more often in younger patients and those with milder disease. However, because our patients had no known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or other associated symptoms, our suspicion was low.
The 4 patients we evaluated—aged 4 to 12 years and in their usual good health—had blanchable erythema of the palmar fingers, palmar eminences of both hands, and plantar surfaces of both feet (Figure). There was no swelling or tenderness, and the lesions had no violaceous coloration, vesiculation, or ulceration. There was no associated pruritus or pain. One patient reported rough texture and mild peeling of the hands.

Upon further inquiry, the patients reported a history of extended time spent in home swimming pools, including holding on to the edge of the pool, due to limitation of activities because of COVID restrictions. One parent noted that the pool that caused the rash had a rough nonslip surface, whereas other pools that the children used, which had a smoother surface, caused no problems.
The morphology of symmetric blanching erythema in areas of pressure and friction, in the absence of a notable medical history, signs, or symptoms, was consistent with a diagnosis of pool palms, which has been described in the medical literature.4-9 Pool palms can affect the palms and soles, which are subject to substantial friction, especially when a person is getting in and out of the pool. There is a general consensus that pool palms is a frictional dermatitis affecting children because the greater fragility of their skin is exacerbated by immersion in water.4-9
Pool palms and feet is benign. Only supportive care, with cessation of swimming and application of emollients, is necessary.
Apart from COVID-19, other conditions to consider in a patient with erythematous lesions of the palms and soles include eczematous dermatitis; neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis; and, if lesions are vesicular, hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Juvenile plantar dermatosis, which is thought to be due to moisture with occlusion in shoes, also might be considered but is distinguished by more scales and fissures that can be painful.
Location of the lesions is a critical variable. The patients we evaluated had lesions primarily on palmar and plantar surfaces where contact with pool surfaces was greatest, such as at bony prominences, which supported a diagnosis of frictional dermatitis, such as pool palms and feet. A thorough history and physical examination are helpful in determining the diagnosis.
Practical Implications
It is important to consider and recognize this localized pressure phenomenon of pool palms and feet, thus obviating an unnecessary workup or therapeutic interventions. Specifically, a finding of erythematous asymptomatic macules, with or without scaling, on bony prominences of the palms and soles is more consistent with pool palms and feet.
Pernio and COVID toes both present as erythematous to violaceous papules and macules, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in severe cases, often on the dorsum and sides of fingers and toes; typically the conditions are pruritic and painful at times.
Explaining the diagnosis of pool palms and feet and sharing one’s experience with similar cases might help alleviate parental fear and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Practice Gap
Frictional, symmetric, asymptomatic, erythematous macules of the hands and feet can be mistaken for perniolike lesions associated with COVID-19, commonly known as COVID toes. However, in a low-risk setting without other associated symptoms or concerning findings on examination, consider and inquire about frequent use of a swimming pool. This activity can lead to localized pressure- and friction-induced erythema on palmar and plantar surfaces, called “pool palms and feet,” expanding on the already-named lesion “pool palms”—an entity that is distinct from COVID toes.
Technique for Diagnosis
We evaluated 4 patients in the outpatient setting who presented with localized, patterned, erythematous lesions of the hands or feet, or both, during the COVID-19 pandemic. The parents of our patients were concerned that the rash represented “COVID fingers and toes,” which are perniolike lesions seen in patients with suspected or confirmed current or prior COVID-19.1
Pernio, also known as chilblains, is a superficial inflammatory vascular response, usually in the setting of exposure to cold.2 This phenomenon usually appears as erythematous or violaceous macules and papules on acral skin, particularly on the dorsum and sides of the fingers and toes, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in more severe cases. Initially, it is pruritic and painful at times.
With COVID toes, there often is a delayed presentation of perniolike lesions after the onset of other COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, and sore throat.2,3 It has been described more often in younger patients and those with milder disease. However, because our patients had no known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or other associated symptoms, our suspicion was low.
The 4 patients we evaluated—aged 4 to 12 years and in their usual good health—had blanchable erythema of the palmar fingers, palmar eminences of both hands, and plantar surfaces of both feet (Figure). There was no swelling or tenderness, and the lesions had no violaceous coloration, vesiculation, or ulceration. There was no associated pruritus or pain. One patient reported rough texture and mild peeling of the hands.

Upon further inquiry, the patients reported a history of extended time spent in home swimming pools, including holding on to the edge of the pool, due to limitation of activities because of COVID restrictions. One parent noted that the pool that caused the rash had a rough nonslip surface, whereas other pools that the children used, which had a smoother surface, caused no problems.
The morphology of symmetric blanching erythema in areas of pressure and friction, in the absence of a notable medical history, signs, or symptoms, was consistent with a diagnosis of pool palms, which has been described in the medical literature.4-9 Pool palms can affect the palms and soles, which are subject to substantial friction, especially when a person is getting in and out of the pool. There is a general consensus that pool palms is a frictional dermatitis affecting children because the greater fragility of their skin is exacerbated by immersion in water.4-9
Pool palms and feet is benign. Only supportive care, with cessation of swimming and application of emollients, is necessary.
Apart from COVID-19, other conditions to consider in a patient with erythematous lesions of the palms and soles include eczematous dermatitis; neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis; and, if lesions are vesicular, hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Juvenile plantar dermatosis, which is thought to be due to moisture with occlusion in shoes, also might be considered but is distinguished by more scales and fissures that can be painful.
Location of the lesions is a critical variable. The patients we evaluated had lesions primarily on palmar and plantar surfaces where contact with pool surfaces was greatest, such as at bony prominences, which supported a diagnosis of frictional dermatitis, such as pool palms and feet. A thorough history and physical examination are helpful in determining the diagnosis.
Practical Implications
It is important to consider and recognize this localized pressure phenomenon of pool palms and feet, thus obviating an unnecessary workup or therapeutic interventions. Specifically, a finding of erythematous asymptomatic macules, with or without scaling, on bony prominences of the palms and soles is more consistent with pool palms and feet.
Pernio and COVID toes both present as erythematous to violaceous papules and macules, with edema, vesiculation, and ulceration in severe cases, often on the dorsum and sides of fingers and toes; typically the conditions are pruritic and painful at times.
Explaining the diagnosis of pool palms and feet and sharing one’s experience with similar cases might help alleviate parental fear and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- de Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Sulimovic L, et al; SNDV (French National Union of Dermatologists–Venereologists). Chilblains is a common cutaneous finding during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective nationwide study from France. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.161
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al; American Academy of Dermatology Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19. Pernio-like skin lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series of 318 patients from 8 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:486-492. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.109
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: an international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1118-1129. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016
- Blauvelt A, Duarte AM, Schachner LA. Pool palms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:111. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80819-5
- Wong L-C, Rogers M. Pool palms. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:95. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00347.x
- Novoa A, Klear S. Pool palms. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:41. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2015-309633
- Morgado-Carasco D, Feola H, Vargas-Mora P. Pool palms. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2020;10:e2020009. doi:10.5826/dpc.1001a09
- Cutrone M, Valerio E, Grimalt R. Pool palms: a case report. Dermatol Case Rep. 2019;4:1000154.
- Martína JM, Ricart JM. Erythematous–violaceous lesions on the palms. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:507-508.
- de Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Sulimovic L, et al; SNDV (French National Union of Dermatologists–Venereologists). Chilblains is a common cutaneous finding during the COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective nationwide study from France. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:667-670. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.161
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al; American Academy of Dermatology Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19. Pernio-like skin lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series of 318 patients from 8 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:486-492. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.109
- Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: an international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1118-1129. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016
- Blauvelt A, Duarte AM, Schachner LA. Pool palms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:111. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80819-5
- Wong L-C, Rogers M. Pool palms. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:95. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00347.x
- Novoa A, Klear S. Pool palms. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:41. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2015-309633
- Morgado-Carasco D, Feola H, Vargas-Mora P. Pool palms. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2020;10:e2020009. doi:10.5826/dpc.1001a09
- Cutrone M, Valerio E, Grimalt R. Pool palms: a case report. Dermatol Case Rep. 2019;4:1000154.
- Martína JM, Ricart JM. Erythematous–violaceous lesions on the palms. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:507-508.
My patient is having an affair and has an STI. I’m treating both partners. What would you do?
A psychiatrist was treating a couple individually, one of whom was HIV-positive. During a session, the infected partner revealed he was having sex with other men outside the relationship and not using safe sex practices.
“He was being treated for major depression and anxiety at the time,” explained the anonymous psychiatrist. “I strongly encouraged him to tell his partner, but he was scared of doing so. He stated that they had not been using safe sex practices between the two of them, but he was willing to start at that point.”
At a session with the HIV-negative partner, the psychiatrist inquired about the couple’s current sex practices. The HIV-negative partner reported no changes and said the two continued to have sex without condoms, said the psychiatrist, who shared the experience in Medscape’s Ethics 2020 Survey open-ended questions.
“My dilemma now was whether or not to inform him about his partner’s ‘extracurricular sex behavior,’ the psychiatrist said. “Since he was now at greater risk of contracting HIV, I felt compelled to do something to intervene.”
What would you do in this situation?
according to responses from the Ethics 2020 Report. When asked to share their toughest ethical dilemma, one internist for example, wrote, “I have couples as patients, and it is very challenging if they reveal infidelity or separate/divorce; I cannot reveal info to the spouse, but it makes me very uncomfortable caring for both.” Similarly, an obstetrician-gynecologist wrote about her experience counseling patients who reveal extramarital affairs.
“Women confide deeply with their gynecologist, and although I was not successful in rescuing 100% of them, the majority accepted my counseling and saved their marriages,” the anonymous ob/gyn wrote. “In every case in which my patient was willing to resume her marital relationship, I always ensured that she advised her spouse of the infidelity, and the couple was referred to a qualified provider for marriage counseling.”
When a sexually transmitted infection (STI) comes into play however, physicians describe a deeper level of internal conflict. A family physician wrote her top ethical dilemma was “Cheating spouses and STIs: how do you get the other spouse treated?” An ob-gyn stated that, “disclosure of STI status in couples when this may indicate infidelity,” was a frequent ethical issue in her specialty. Commenters on Medscape’s recent story, “The Secret I’ll Take to my Grave: Doc Reveals,” also raised the uncomfortable topic. One physician recalled a deaf female patient who requested in writing not to test for syphilis and not to discuss the issue with her husband. “Patient knew that she had syphilis, but she did not want her husband to know,” the physician wrote.
It’s not uncommon for physicians to encounter such scenarios when treating long-term couples, especially in the digital era, said Shannon Dowler, MD, chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid and a family physician at the Buncombe County STI Clinic.
“This is definitely something I think we see more of in our age of ‘hookup apps’ and easier access to casual sexual connections than we did before,” said Dr. Dowler, who serves on the CDC Advisory Committee on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and STD Prevention and Treatment.
The topic is particularly timely because of the pandemic’s impact on STI testing and the expected rise in sexually transmitted infection rates over the next year, Dr. Dowler notes.
“People weren’t necessarily coming in for routine screening or testing during the pandemic because they didn’t want to take a chance on being exposed to COVID,” she said. “But also, the reagent used for testing for certain types of transmitted infections was in short supply because they use that same reagent for the COVID test. We had shortages of STI testing in many parts of the country. I expect what we’re going to see over the next year are a lot of diagnoses that were missed during the pandemic and a lot of asymptomatic spread.”
What do the experts suggest?
Caring for spouses or two partners when an STI is discovered can be challenging for physicians, particularly in small towns where many people know each other, said Kenneth Goodman, PhD, founder and director of the Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy at the University of Miami.
“This can be a real challenge for family physicians and others in a small town,” he said. “If you discover one partner is positive for a sexually transmitted infection and the other is negative, then you’ve got a challenge to manage. The way to do that is to start with moral persuasion, namely you tell your patient, ‘You really need to disclose this. Because when he or she gets it, chances are, you’re going to be the prime suspect.’ “
Dr. Dowler, who practices in an STI clinic, said she once diagnosed a sexually transmitted infection in a patient who was married to one of Dowler’s coworkers. The patient would not allow the partner to be notified, she said. In this case, Dr. Dowler practiced expedited partner therapy (EPT), the clinical practice of treating sex partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by giving the patient prescriptions or medications to take to the partner without having first examined the partner. The practice is legal to some extent in all states, Dr. Dowler said, but some states have different rules about how the practice can be utilized.
Physicians are obligated to report communicable diseases to their local health department, Dr. Goodman said. The health department would then do contract tracing and be responsible for conveying the STI diagnosis to any relevant parties. Even so, Dr. Goodman said physicians have a moral obligation to strongly encourage patients to divulge the infection to their partner.
“Doctors should work on being persuasive to change behavior,” he said. “Tell your patients to do the right thing and follow up with them. You should tell patients they have a responsibility to disclose a sexually transmitted infection to any of their partners and a responsibility not to have unprotected sex. Doctors can be very powerful advocates for that.”
Dr. Dowler said if she is treating two partners, and one is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, she generally asks the patient for their consent to disclose the diagnosis to the partner. She ensures a witness, usually a nurse, is present when she asks. If consent is refused, Dr. Dowler guides her treatment to be as protective as possible, she said. A helpful resource for patients is Tellyourpartner.org, a website that sends an anonymous text or email about infection exposure and provides guidance on treatment locations and options.
Of course, if the sexually transmitted infection is HIV, another set of rules apply. As of 2021, 35 states have laws that criminalize HIV exposure. Laws vary, but many hold patients criminally liable if they knowingly expose another party to HIV. Many states and some cities also have ‘partner notification’ laws that require health providers to disclose an HIV diagnosis to the patient’s sex partners or to report the names of sex partners to the health department, if known.
However, case law on a physician’s duty to warn is mixed, and doctors’ responsibility for STI reporting and partner notification is determined by individual states. Making matters more complex is the fact that some states have recently changed their HIV control requirements, Dr. Dowler said. In North Carolina for example, patients living with HIV who have been virally suppressed for 6 months and who are adherent to medications, are no longer in violation of the control measure if they do not disclose their HIV diagnosis to sex partners or if they don’t wear a condom.
“This means physicians would not have to report a virally suppressed, adequately treated HIV-positive patient who is having unprotected sex or take measures to inform any known sex partners of the diagnosis,” she said. “The landscape is constantly changing so physicians have to be vigilant about their state public health statutes. It’s a tricky area. It takes an already complicated topic and makes it just a little more complicated.”
Consider drafting a policy
It’s a good idea to have a policy in place at your practice that addresses such ethical dilemmas before they occur, says Michael Heitt, PsyD, a clinical psychologist on the faculty of Loyola University Maryland in Baltimore, and a member of the Maryland Psychological Association’s Ethics Committee. Dr. Heitt developed a model of ethical reasoning called CLEAR Lenses, which stands for Clinical, Legal, Ethical, Administrative, and Risk management. The approach encourages clinicians to identify often competing factors in the decision-making process before choosing a course of action to take.
In the situation of an unfaithful spouse who contracted an STI for example, the physician should consider clinical issues such as the medical likelihood the unaware partner has the STI, and legal issues such as maintaining the confidentiality of all patient information and possible mandated reporting of STI data, Dr. Heitt said. The lenses overlap since confidentiality is also a key ethical issue, and other ethical issues involve the balance of helping the unaware spouse and not harming the infected spouse, he explained. Administrative issues might include how medical records are maintained and whether the physician documents information about patients’ family members in the medical record, while risk management elements may include informed consent, documentation, and consultation.
“So, if the physician has a policy about how such matters are dealt with, and patients are informed about this when they come to the practice, this can guide the physician much more easily through this sticky situation,” Dr. Heitt said. “Documentation of the decision-making process in the medical record demonstrates the physician’s thought process should it ever be challenged in the future, and consultation with peers (while disguising the identity of the patients, of course) sets a foundation of what a ‘reasonable standard’ might be in such situations.”
There is also the conflict-avoidant approach, Dr. Heitt said, in which the physician could perform “routine” STI testing if the unaware spouse was due for an appointment soon.
“But of course, this is far from avoiding any conflict; it just kicks the can down the road as there will surely be conflict — and plenty of confusion — if the wife tests positive for an STI,” he said. “In most situations, it is usually best to be brave, do the hard work upfront, and deal with the tough situation then, rather than trying to avoid the probable inevitable difficult conversation.”
As for the psychiatrist who was treating the cheating HIV-positive partner, the physician ultimately convinced both patients to come in for a couple’s session. The doctor allowed for a 2-hour timeframe to encourage discussion of any conflicts and unresolved issues, the psychiatrist said. After several more couple’s sessions, it was apparent the HIV-positive partner wanted out of the relationship, according to the psychiatrist’s account. The physician referred them to a couples’ therapist for ongoing treatment.
“During that same session, the HIV positive partner disclosed his recent behaviors and, as a result, they decided not to have further sexual contact until they could explore this further in therapy,” the psychiatrist wrote. “At last communication the couple decided to end the relationship, and the HIV negative partner remained negative.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A psychiatrist was treating a couple individually, one of whom was HIV-positive. During a session, the infected partner revealed he was having sex with other men outside the relationship and not using safe sex practices.
“He was being treated for major depression and anxiety at the time,” explained the anonymous psychiatrist. “I strongly encouraged him to tell his partner, but he was scared of doing so. He stated that they had not been using safe sex practices between the two of them, but he was willing to start at that point.”
At a session with the HIV-negative partner, the psychiatrist inquired about the couple’s current sex practices. The HIV-negative partner reported no changes and said the two continued to have sex without condoms, said the psychiatrist, who shared the experience in Medscape’s Ethics 2020 Survey open-ended questions.
“My dilemma now was whether or not to inform him about his partner’s ‘extracurricular sex behavior,’ the psychiatrist said. “Since he was now at greater risk of contracting HIV, I felt compelled to do something to intervene.”
What would you do in this situation?
according to responses from the Ethics 2020 Report. When asked to share their toughest ethical dilemma, one internist for example, wrote, “I have couples as patients, and it is very challenging if they reveal infidelity or separate/divorce; I cannot reveal info to the spouse, but it makes me very uncomfortable caring for both.” Similarly, an obstetrician-gynecologist wrote about her experience counseling patients who reveal extramarital affairs.
“Women confide deeply with their gynecologist, and although I was not successful in rescuing 100% of them, the majority accepted my counseling and saved their marriages,” the anonymous ob/gyn wrote. “In every case in which my patient was willing to resume her marital relationship, I always ensured that she advised her spouse of the infidelity, and the couple was referred to a qualified provider for marriage counseling.”
When a sexually transmitted infection (STI) comes into play however, physicians describe a deeper level of internal conflict. A family physician wrote her top ethical dilemma was “Cheating spouses and STIs: how do you get the other spouse treated?” An ob-gyn stated that, “disclosure of STI status in couples when this may indicate infidelity,” was a frequent ethical issue in her specialty. Commenters on Medscape’s recent story, “The Secret I’ll Take to my Grave: Doc Reveals,” also raised the uncomfortable topic. One physician recalled a deaf female patient who requested in writing not to test for syphilis and not to discuss the issue with her husband. “Patient knew that she had syphilis, but she did not want her husband to know,” the physician wrote.
It’s not uncommon for physicians to encounter such scenarios when treating long-term couples, especially in the digital era, said Shannon Dowler, MD, chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid and a family physician at the Buncombe County STI Clinic.
“This is definitely something I think we see more of in our age of ‘hookup apps’ and easier access to casual sexual connections than we did before,” said Dr. Dowler, who serves on the CDC Advisory Committee on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and STD Prevention and Treatment.
The topic is particularly timely because of the pandemic’s impact on STI testing and the expected rise in sexually transmitted infection rates over the next year, Dr. Dowler notes.
“People weren’t necessarily coming in for routine screening or testing during the pandemic because they didn’t want to take a chance on being exposed to COVID,” she said. “But also, the reagent used for testing for certain types of transmitted infections was in short supply because they use that same reagent for the COVID test. We had shortages of STI testing in many parts of the country. I expect what we’re going to see over the next year are a lot of diagnoses that were missed during the pandemic and a lot of asymptomatic spread.”
What do the experts suggest?
Caring for spouses or two partners when an STI is discovered can be challenging for physicians, particularly in small towns where many people know each other, said Kenneth Goodman, PhD, founder and director of the Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy at the University of Miami.
“This can be a real challenge for family physicians and others in a small town,” he said. “If you discover one partner is positive for a sexually transmitted infection and the other is negative, then you’ve got a challenge to manage. The way to do that is to start with moral persuasion, namely you tell your patient, ‘You really need to disclose this. Because when he or she gets it, chances are, you’re going to be the prime suspect.’ “
Dr. Dowler, who practices in an STI clinic, said she once diagnosed a sexually transmitted infection in a patient who was married to one of Dowler’s coworkers. The patient would not allow the partner to be notified, she said. In this case, Dr. Dowler practiced expedited partner therapy (EPT), the clinical practice of treating sex partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by giving the patient prescriptions or medications to take to the partner without having first examined the partner. The practice is legal to some extent in all states, Dr. Dowler said, but some states have different rules about how the practice can be utilized.
Physicians are obligated to report communicable diseases to their local health department, Dr. Goodman said. The health department would then do contract tracing and be responsible for conveying the STI diagnosis to any relevant parties. Even so, Dr. Goodman said physicians have a moral obligation to strongly encourage patients to divulge the infection to their partner.
“Doctors should work on being persuasive to change behavior,” he said. “Tell your patients to do the right thing and follow up with them. You should tell patients they have a responsibility to disclose a sexually transmitted infection to any of their partners and a responsibility not to have unprotected sex. Doctors can be very powerful advocates for that.”
Dr. Dowler said if she is treating two partners, and one is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, she generally asks the patient for their consent to disclose the diagnosis to the partner. She ensures a witness, usually a nurse, is present when she asks. If consent is refused, Dr. Dowler guides her treatment to be as protective as possible, she said. A helpful resource for patients is Tellyourpartner.org, a website that sends an anonymous text or email about infection exposure and provides guidance on treatment locations and options.
Of course, if the sexually transmitted infection is HIV, another set of rules apply. As of 2021, 35 states have laws that criminalize HIV exposure. Laws vary, but many hold patients criminally liable if they knowingly expose another party to HIV. Many states and some cities also have ‘partner notification’ laws that require health providers to disclose an HIV diagnosis to the patient’s sex partners or to report the names of sex partners to the health department, if known.
However, case law on a physician’s duty to warn is mixed, and doctors’ responsibility for STI reporting and partner notification is determined by individual states. Making matters more complex is the fact that some states have recently changed their HIV control requirements, Dr. Dowler said. In North Carolina for example, patients living with HIV who have been virally suppressed for 6 months and who are adherent to medications, are no longer in violation of the control measure if they do not disclose their HIV diagnosis to sex partners or if they don’t wear a condom.
“This means physicians would not have to report a virally suppressed, adequately treated HIV-positive patient who is having unprotected sex or take measures to inform any known sex partners of the diagnosis,” she said. “The landscape is constantly changing so physicians have to be vigilant about their state public health statutes. It’s a tricky area. It takes an already complicated topic and makes it just a little more complicated.”
Consider drafting a policy
It’s a good idea to have a policy in place at your practice that addresses such ethical dilemmas before they occur, says Michael Heitt, PsyD, a clinical psychologist on the faculty of Loyola University Maryland in Baltimore, and a member of the Maryland Psychological Association’s Ethics Committee. Dr. Heitt developed a model of ethical reasoning called CLEAR Lenses, which stands for Clinical, Legal, Ethical, Administrative, and Risk management. The approach encourages clinicians to identify often competing factors in the decision-making process before choosing a course of action to take.
In the situation of an unfaithful spouse who contracted an STI for example, the physician should consider clinical issues such as the medical likelihood the unaware partner has the STI, and legal issues such as maintaining the confidentiality of all patient information and possible mandated reporting of STI data, Dr. Heitt said. The lenses overlap since confidentiality is also a key ethical issue, and other ethical issues involve the balance of helping the unaware spouse and not harming the infected spouse, he explained. Administrative issues might include how medical records are maintained and whether the physician documents information about patients’ family members in the medical record, while risk management elements may include informed consent, documentation, and consultation.
“So, if the physician has a policy about how such matters are dealt with, and patients are informed about this when they come to the practice, this can guide the physician much more easily through this sticky situation,” Dr. Heitt said. “Documentation of the decision-making process in the medical record demonstrates the physician’s thought process should it ever be challenged in the future, and consultation with peers (while disguising the identity of the patients, of course) sets a foundation of what a ‘reasonable standard’ might be in such situations.”
There is also the conflict-avoidant approach, Dr. Heitt said, in which the physician could perform “routine” STI testing if the unaware spouse was due for an appointment soon.
“But of course, this is far from avoiding any conflict; it just kicks the can down the road as there will surely be conflict — and plenty of confusion — if the wife tests positive for an STI,” he said. “In most situations, it is usually best to be brave, do the hard work upfront, and deal with the tough situation then, rather than trying to avoid the probable inevitable difficult conversation.”
As for the psychiatrist who was treating the cheating HIV-positive partner, the physician ultimately convinced both patients to come in for a couple’s session. The doctor allowed for a 2-hour timeframe to encourage discussion of any conflicts and unresolved issues, the psychiatrist said. After several more couple’s sessions, it was apparent the HIV-positive partner wanted out of the relationship, according to the psychiatrist’s account. The physician referred them to a couples’ therapist for ongoing treatment.
“During that same session, the HIV positive partner disclosed his recent behaviors and, as a result, they decided not to have further sexual contact until they could explore this further in therapy,” the psychiatrist wrote. “At last communication the couple decided to end the relationship, and the HIV negative partner remained negative.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A psychiatrist was treating a couple individually, one of whom was HIV-positive. During a session, the infected partner revealed he was having sex with other men outside the relationship and not using safe sex practices.
“He was being treated for major depression and anxiety at the time,” explained the anonymous psychiatrist. “I strongly encouraged him to tell his partner, but he was scared of doing so. He stated that they had not been using safe sex practices between the two of them, but he was willing to start at that point.”
At a session with the HIV-negative partner, the psychiatrist inquired about the couple’s current sex practices. The HIV-negative partner reported no changes and said the two continued to have sex without condoms, said the psychiatrist, who shared the experience in Medscape’s Ethics 2020 Survey open-ended questions.
“My dilemma now was whether or not to inform him about his partner’s ‘extracurricular sex behavior,’ the psychiatrist said. “Since he was now at greater risk of contracting HIV, I felt compelled to do something to intervene.”
What would you do in this situation?
according to responses from the Ethics 2020 Report. When asked to share their toughest ethical dilemma, one internist for example, wrote, “I have couples as patients, and it is very challenging if they reveal infidelity or separate/divorce; I cannot reveal info to the spouse, but it makes me very uncomfortable caring for both.” Similarly, an obstetrician-gynecologist wrote about her experience counseling patients who reveal extramarital affairs.
“Women confide deeply with their gynecologist, and although I was not successful in rescuing 100% of them, the majority accepted my counseling and saved their marriages,” the anonymous ob/gyn wrote. “In every case in which my patient was willing to resume her marital relationship, I always ensured that she advised her spouse of the infidelity, and the couple was referred to a qualified provider for marriage counseling.”
When a sexually transmitted infection (STI) comes into play however, physicians describe a deeper level of internal conflict. A family physician wrote her top ethical dilemma was “Cheating spouses and STIs: how do you get the other spouse treated?” An ob-gyn stated that, “disclosure of STI status in couples when this may indicate infidelity,” was a frequent ethical issue in her specialty. Commenters on Medscape’s recent story, “The Secret I’ll Take to my Grave: Doc Reveals,” also raised the uncomfortable topic. One physician recalled a deaf female patient who requested in writing not to test for syphilis and not to discuss the issue with her husband. “Patient knew that she had syphilis, but she did not want her husband to know,” the physician wrote.
It’s not uncommon for physicians to encounter such scenarios when treating long-term couples, especially in the digital era, said Shannon Dowler, MD, chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid and a family physician at the Buncombe County STI Clinic.
“This is definitely something I think we see more of in our age of ‘hookup apps’ and easier access to casual sexual connections than we did before,” said Dr. Dowler, who serves on the CDC Advisory Committee on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and STD Prevention and Treatment.
The topic is particularly timely because of the pandemic’s impact on STI testing and the expected rise in sexually transmitted infection rates over the next year, Dr. Dowler notes.
“People weren’t necessarily coming in for routine screening or testing during the pandemic because they didn’t want to take a chance on being exposed to COVID,” she said. “But also, the reagent used for testing for certain types of transmitted infections was in short supply because they use that same reagent for the COVID test. We had shortages of STI testing in many parts of the country. I expect what we’re going to see over the next year are a lot of diagnoses that were missed during the pandemic and a lot of asymptomatic spread.”
What do the experts suggest?
Caring for spouses or two partners when an STI is discovered can be challenging for physicians, particularly in small towns where many people know each other, said Kenneth Goodman, PhD, founder and director of the Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy at the University of Miami.
“This can be a real challenge for family physicians and others in a small town,” he said. “If you discover one partner is positive for a sexually transmitted infection and the other is negative, then you’ve got a challenge to manage. The way to do that is to start with moral persuasion, namely you tell your patient, ‘You really need to disclose this. Because when he or she gets it, chances are, you’re going to be the prime suspect.’ “
Dr. Dowler, who practices in an STI clinic, said she once diagnosed a sexually transmitted infection in a patient who was married to one of Dowler’s coworkers. The patient would not allow the partner to be notified, she said. In this case, Dr. Dowler practiced expedited partner therapy (EPT), the clinical practice of treating sex partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by giving the patient prescriptions or medications to take to the partner without having first examined the partner. The practice is legal to some extent in all states, Dr. Dowler said, but some states have different rules about how the practice can be utilized.
Physicians are obligated to report communicable diseases to their local health department, Dr. Goodman said. The health department would then do contract tracing and be responsible for conveying the STI diagnosis to any relevant parties. Even so, Dr. Goodman said physicians have a moral obligation to strongly encourage patients to divulge the infection to their partner.
“Doctors should work on being persuasive to change behavior,” he said. “Tell your patients to do the right thing and follow up with them. You should tell patients they have a responsibility to disclose a sexually transmitted infection to any of their partners and a responsibility not to have unprotected sex. Doctors can be very powerful advocates for that.”
Dr. Dowler said if she is treating two partners, and one is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, she generally asks the patient for their consent to disclose the diagnosis to the partner. She ensures a witness, usually a nurse, is present when she asks. If consent is refused, Dr. Dowler guides her treatment to be as protective as possible, she said. A helpful resource for patients is Tellyourpartner.org, a website that sends an anonymous text or email about infection exposure and provides guidance on treatment locations and options.
Of course, if the sexually transmitted infection is HIV, another set of rules apply. As of 2021, 35 states have laws that criminalize HIV exposure. Laws vary, but many hold patients criminally liable if they knowingly expose another party to HIV. Many states and some cities also have ‘partner notification’ laws that require health providers to disclose an HIV diagnosis to the patient’s sex partners or to report the names of sex partners to the health department, if known.
However, case law on a physician’s duty to warn is mixed, and doctors’ responsibility for STI reporting and partner notification is determined by individual states. Making matters more complex is the fact that some states have recently changed their HIV control requirements, Dr. Dowler said. In North Carolina for example, patients living with HIV who have been virally suppressed for 6 months and who are adherent to medications, are no longer in violation of the control measure if they do not disclose their HIV diagnosis to sex partners or if they don’t wear a condom.
“This means physicians would not have to report a virally suppressed, adequately treated HIV-positive patient who is having unprotected sex or take measures to inform any known sex partners of the diagnosis,” she said. “The landscape is constantly changing so physicians have to be vigilant about their state public health statutes. It’s a tricky area. It takes an already complicated topic and makes it just a little more complicated.”
Consider drafting a policy
It’s a good idea to have a policy in place at your practice that addresses such ethical dilemmas before they occur, says Michael Heitt, PsyD, a clinical psychologist on the faculty of Loyola University Maryland in Baltimore, and a member of the Maryland Psychological Association’s Ethics Committee. Dr. Heitt developed a model of ethical reasoning called CLEAR Lenses, which stands for Clinical, Legal, Ethical, Administrative, and Risk management. The approach encourages clinicians to identify often competing factors in the decision-making process before choosing a course of action to take.
In the situation of an unfaithful spouse who contracted an STI for example, the physician should consider clinical issues such as the medical likelihood the unaware partner has the STI, and legal issues such as maintaining the confidentiality of all patient information and possible mandated reporting of STI data, Dr. Heitt said. The lenses overlap since confidentiality is also a key ethical issue, and other ethical issues involve the balance of helping the unaware spouse and not harming the infected spouse, he explained. Administrative issues might include how medical records are maintained and whether the physician documents information about patients’ family members in the medical record, while risk management elements may include informed consent, documentation, and consultation.
“So, if the physician has a policy about how such matters are dealt with, and patients are informed about this when they come to the practice, this can guide the physician much more easily through this sticky situation,” Dr. Heitt said. “Documentation of the decision-making process in the medical record demonstrates the physician’s thought process should it ever be challenged in the future, and consultation with peers (while disguising the identity of the patients, of course) sets a foundation of what a ‘reasonable standard’ might be in such situations.”
There is also the conflict-avoidant approach, Dr. Heitt said, in which the physician could perform “routine” STI testing if the unaware spouse was due for an appointment soon.
“But of course, this is far from avoiding any conflict; it just kicks the can down the road as there will surely be conflict — and plenty of confusion — if the wife tests positive for an STI,” he said. “In most situations, it is usually best to be brave, do the hard work upfront, and deal with the tough situation then, rather than trying to avoid the probable inevitable difficult conversation.”
As for the psychiatrist who was treating the cheating HIV-positive partner, the physician ultimately convinced both patients to come in for a couple’s session. The doctor allowed for a 2-hour timeframe to encourage discussion of any conflicts and unresolved issues, the psychiatrist said. After several more couple’s sessions, it was apparent the HIV-positive partner wanted out of the relationship, according to the psychiatrist’s account. The physician referred them to a couples’ therapist for ongoing treatment.
“During that same session, the HIV positive partner disclosed his recent behaviors and, as a result, they decided not to have further sexual contact until they could explore this further in therapy,” the psychiatrist wrote. “At last communication the couple decided to end the relationship, and the HIV negative partner remained negative.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Babies are dying of syphilis. It’s 100% preventable.
This story was originally published on ProPublica and was co-published with NPR.
When Mai Yang is looking for a patient, she travels light. She dresses deliberately — not too formal, so she won’t be mistaken for a police officer; not too casual, so people will look past her tiny 4-foot-10 stature and youthful face and trust her with sensitive health information. Always, she wears closed-toed shoes, “just in case I need to run.”
Yang carries a stack of cards issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show what happens when the Treponema pallidum bacteria invades a patient’s body. There’s a photo of an angry red sore on a penis. There’s one of a tongue, marred by mucus-lined lesions. And there’s one of a newborn baby, its belly, torso and thighs dotted in a rash, its mouth open, as if caught midcry.
It was because of the prospect of one such baby that Yang found herself walking through a homeless encampment on a blazing July day in Huron, Calif., an hour’s drive southwest of her office at the Fresno County Department of Public Health. She was looking for a pregnant woman named Angelica, whose visit to a community clinic had triggered a report to the health department’s sexually transmitted disease program. Angelica had tested positive for syphilis. If she was not treated, her baby could end up like the one in the picture or worse — there was a 40% chance the baby would die.
Ms. Yang knew, though, that if she helped Angelica get treated with three weekly shots of penicillin at least 30 days before she gave birth, it was likely that the infection would be wiped out and her baby would be born without any symptoms at all. Every case of congenital syphilis, when a baby is born with the disease, is avoidable. Each is considered a “sentinel event,” a warning that the public health system is failing.
The alarms are now clamoring. In the United States, more than 129,800 syphilis cases were recorded in 2019, double the case count of five years prior. In the same time period, cases of congenital syphilis quadrupled: 1,870 babies were born with the disease; 128 died. Case counts from 2020 are still being finalized, but the CDC has said that reported cases of congenital syphilis have already exceeded the prior year. Black, Hispanic, and Native American babies are disproportionately at risk.
There was a time, not too long ago, when CDC officials thought they could eliminate the centuries-old scourge from the United States, for adults and babies. But the effort lost steam and cases soon crept up again. Syphilis is not an outlier. The United States goes through what former CDC director Dr. Tom Frieden calls “a deadly cycle of panic and neglect” in which emergencies propel officials to scramble and throw money at a problem — whether that’s Ebola, Zika, or COVID-19. Then, as fear ebbs, so does the attention and motivation to finish the task.
The last fraction of cases can be the hardest to solve, whether that’s eradicating a bug or getting vaccines into arms, yet too often, that’s exactly when political attention gets diverted to the next alarm. The result: The hardest to reach and most vulnerable populations are the ones left suffering, after everyone else looks away.
Ms. Yang first received Angelica’s lab report on June 17. The address listed was a P.O. box, and the phone number belonged to her sister, who said Angelica was living in Huron. That was a piece of luck: Huron is tiny; the city spans just 1.6 square miles. On her first visit, a worker at the Alamo Motel said she knew Angelica and directed Ms. Yang to a nearby homeless encampment. Angelica wasn’t there, so Ms. Yang returned a second time, bringing one of the health department nurses who could serve as an interpreter.
They made their way to the barren patch of land behind Huron Valley Foods, the local grocery store, where people took shelter in makeshift lean-tos composed of cardboard boxes, scrap wood ,and scavenged furniture, draped with sheets that served as ceilings and curtains. Yang stopped outside one of the structures, calling a greeting.
“Hi, I’m from the health department, I’m looking for Angelica.”
The nurse echoed her in Spanish.
Angelica emerged, squinting in the sunlight. Ms. Yang couldn’t tell if she was visibly pregnant yet, as her body was obscured by an oversized shirt. The two women were about the same age: Ms. Yang 26 and Angelica 27. Ms. Yang led her away from the tent, so they could speak privately. Angelica seemed reticent, surprised by the sudden appearance of the two health officers. “You’re not in trouble,” Ms. Yang said, before revealing the results of her blood test.
Angelica had never heard of syphilis.
“Have you been to prenatal care?”
Angelica shook her head. The local clinic had referred her to an obstetrician in Hanford, a 30-minute drive away. She had no car. She also mentioned that she didn’t intend to raise her baby; her two oldest children lived with her mother, and this one likely would, too.
Ms. Yang pulled out the CDC cards, showing them to Angelica and asking if she had experienced any of the symptoms illustrated. No, Angelica said, her lips pursed with disgust.
“Right now you still feel healthy, but this bacteria is still in your body,” Ms. Yang pressed. “You need to get the infection treated to prevent further health complications to yourself and your baby.”
The community clinic was just across the street. “Can we walk you over to the clinic and make sure you get seen so we can get this taken care of?”
Angelica demurred. She said she hadn’t showered for a week and wanted to wash up first. She said she’d go later.
Ms. Yang tried once more to extract a promise: “What time do you think you’ll go?”
“Today, for sure.”
Syphilis is called The Great Imitator: It can look like any number of diseases. In its first stage, the only evidence of infection is a painless sore at the bacteria’s point of entry. Weeks later, as the bacteria multiplies, skin rashes bloom on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet. Other traits of this stage include fever, headaches, muscle aches, sore throat, and fatigue. These symptoms eventually disappear and the patient progresses into the latent phase, which betrays no external signs. But if left untreated, after a decade or more, syphilis will reemerge in up to 30% of patients, capable of wreaking horror on a wide range of organ systems. Dr. Marion Sims, president of the American Medical Association in 1876, called it a “terrible scourge, which begins with lamb-like mildness and ends with lion-like rage that ruthlessly destroys everything in its way.”
The corkscrew-shaped bacteria can infiltrate the nervous system at any stage of the infection. Ms. Yang is haunted by her memory of interviewing a young man whose dementia was so severe that he didn’t know why he was in the hospital or how old he was. And regardless of symptoms or stage, the bacteria can penetrate the placenta to infect a fetus. Even in these cases the infection is unpredictable: Many babies are born with normal physical features, but others can have deformed bones or damaged brains, and they can struggle to hear, see, or breathe.
From its earliest days, syphilis has been shrouded in stigma. The first recorded outbreak was in the late 15th century, when Charles VIII led the French army to invade Naples. Italian physicians described French soldiers covered with pustules, dying from a sexually transmitted disease. As the affliction spread, Italians called it the French Disease. The French blamed the Neopolitans. It was also called the German, Polish, or Spanish disease, depending on which neighbor one wanted to blame. Even its name bears the taint of divine judgement: It comes from a 16th-century poem that tells of a shepherd, Syphilus, who offended the god Apollo and was punished with a hideous disease.
By 1937 in America, when former Surgeon General Thomas Parran wrote the book “Shadow on the Land,” he estimated some 680,000 people were under treatment for syphilis; about 60,000 babies were being born annually with congenital syphilis. There was no cure, and the stigma was so strong that public health officials feared even properly documenting cases.
Thanks to Dr. Parran’s ardent advocacy, Congress in 1938 passed the National Venereal Disease Control Act, which created grants for states to set up clinics and support testing and treatment. Other than a short-lived funding effort during World War I, this was the first coordinated federal push to respond to the disease.
Around the same time, the Public Health Service launched an effort to record the natural history of syphilis. Situated in Tuskegee, Ala., the infamous study recruited 600 black men. By the early 1940s, penicillin became widely available and was found to be a reliable cure, but the treatment was withheld from the study participants. Outrage over the ethical violations would cast a stain across syphilis research for decades to come and fuel generations of mistrust in the medical system among Black Americans that continues to this day.
With the introduction of penicillin, cases began to plummet. Twice, the CDC has announced efforts to wipe out the disease — once in the 1960s and again in 1999.
In the latest effort, the CDC announced that the United States had “a unique opportunity to eliminate syphilis within its borders,” thanks to historically low rates, with 80% of counties reporting zero cases. The concentration of cases in the South “identifies communities in which there is a fundamental failure of public health capacity,” the agency noted, adding that elimination — which it defined as fewer than 1,000 cases a year — would “decrease one of our most glaring racial disparities in health.”
Two years after the campaign began, cases started climbing, first among gay men and later, heterosexuals. Cases in women started accelerating in 2013, followed shortly by increasing numbers of babies born with syphilis.The reasons for failure are complex; people relaxed safer sex practices after the advent of potent HIV combination therapies, increased methamphetamine use drove riskier behavior and an explosion of online dating made it hard to track and test sexual partners, according to Dr. Ina Park, medical director of the California Prevention Training Center at the University of California San Francisco.
But federal and state public health efforts were hamstrung from the get-go. In 1999, the CDC said it would need about $35 million to $39 million in new federal funds annually for at least five years to eliminate syphilis. The agency got less than half of what it asked for, according to Jo Valentine, former program coordinator of the CDC’s Syphilis Elimination Effort. As cases rose, the CDC modified its goals in 2006 from 0.4 primary and secondary syphilis cases per 100,000 in population to 2.2 cases per 100,000. By 2013, as elimination seemed less and less viable, the CDC changed its focus to ending congenital syphilis only.
Since then, funding has remained anemic. From 2015 to 2020, the CDC’s budget for preventing sexually transmitted infections grew by 2.2%. Taking inflation into account, that’s a 7.4% reduction in purchasing power. In the same period, cases of syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia — the three STDs that have federally funded control programs — increased by nearly 30%.
“We have a long history of nearly eradicating something, then changing our attention, and seeing a resurgence in numbers,” said David Harvey, executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors. “We have more congenital syphilis cases today in America than we ever had pediatric AIDS at the height of the AIDS epidemic. It’s heartbreaking.”
Adriane Casalotti, chief of government and public affairs at the National Association of County and City Health Officials, warns that the United States should not be surprised to see case counts continue to climb. “The bugs don’t go away,” she said. “They’re just waiting for the next opportunity, when you’re not paying attention.”
Ms. Yang waited until the end of the day, then called the clinic to see if Angelica had gone for her shot. She had not. Ms. Yang would have to block off another half day to visit Huron again, but she had three dozen other cases to deal with.
States in the South and West have seen the highest syphilis rates in recent years. In 2017, 64 babies in Fresno County were born with syphilis at a rate of 440 babies per 100,000 live births — about 19 times the national rate. While the county had managed to lower case counts in the two years that followed, the pandemic threatened to unravel that progress, forcing STD staffers to do COVID-19 contact tracing, pausing field visits to find infected people, and scaring patients from seeking care. Ms. Yang’s colleague handled three cases of stillbirth in 2020; in each, the woman was never diagnosed with syphilis because she feared catching the coronavirus and skipped prenatal care.
Ms. Yang, whose caseload peaked at 70 during a COVID-19 surge, knew she would not be able handle them all as thoroughly as she’d like to. “When I was being mentored by another investigator, he said: ‘You’re not a superhero. You can’t save everybody,’” she said. She prioritizes men who have sex with men, because there’s a higher prevalence of syphilis in that population, and pregnant people, because of the horrific consequences for babies.
The job of a disease intervention specialist isn’t for everyone: It means meeting patients whenever and wherever they are available — in the mop closet of a bus station, in a quiet parking lot — to inform them about the disease, to extract names of sex partners and to encourage treatment. Patients are often reluctant to talk. They can get belligerent, upset that “the government” has their personal information or shattered at the thought that a partner is likely cheating on them. Salaries typically start in the low $40,000s.
Jena Adams, Ms. Yang’s supervisor, has eight investigators working on HIV and syphilis. In the middle of 2020, she lost two and replaced them only recently. “It’s been exhausting,” Ms. Adams said. She has only one specialist who is trained to take blood samples in the field, crucial for guaranteeing that the partners of those who test positive for syphilis also get tested. Ms. Adams wants to get phlebotomy training for the rest of her staff, but it’s $2,000 per person. The department also doesn’t have anyone who can administer penicillin injections in the field; that would have been key when Ms. Yang met Angelica. For a while, a nurse who worked in the tuberculosis program would ride along to give penicillin shots on a volunteer basis. Then he, too, left the health department.
Much of the resources in public health trickle down from the CDC, which distributes money to states, which then parcel it out to counties. The CDC gets its budget from Congress, which tells the agency, by line item, exactly how much money it can spend to fight a disease or virus, in an uncommonly specific manner not seen in many other agencies. The decisions are often politically driven and can be detached from actual health needs.
When the House and Senate appropriations committees meet to decide how much the CDC will get for each line item, they are barraged by lobbyists for individual disease interests. Stephanie Arnold Pang, senior director of policy and government relations at the National Coalition of STD Directors, can pick out the groups by sight: breast cancer wears pink, Alzheimer’s goes in purple, multiple sclerosis comes in orange, HIV in red. STD prevention advocates, like herself, don a green ribbon, but they’re far outnumbered.
And unlike diseases that might already be familiar to lawmakers, or have patient and family spokespeople who can tell their own powerful stories, syphilis doesn’t have many willing poster children. “Congressmen don’t wake up one day and say, ‘Oh hey, there’s congenital syphilis in my jurisdiction.’ You have to raise awareness,” Arnold Pang said. It can be hard jockeying for a meeting. “Some offices might say, ‘I don’t have time for you because we’ve just seen HIV.’ ... Sometimes, it feels like you’re talking into a void.”
The consequences of the political nature of public health funding have become more obvious during the coronavirus pandemic. The 2014 Ebola epidemic was seen as a “global wakeup call” that the world wasn’t prepared for a major pandemic, yet in 2018, the CDC scaled back its epidemic prevention work as money ran out. “If you’ve got to choose between Alzheimer’s research and stopping an outbreak that may not happen? Stopping an outbreak that might not happen doesn’t do well,” said Dr. Frieden, the former CDC director. “The CDC needs to have more money and more flexible money. Otherwise, we’re going to be in this situation long term.”
In May 2021, President Joe Biden’s administration announced it would set aside $7.4 billion over the next five years to hire and train public health workers, including $1.1 billion for more disease intervention specialists like Ms. Yang. Public health officials are thrilled to have the chance to expand their workforce, but some worry the time horizon may be too short. “We’ve seen this movie before, right?” Dr. Frieden said. “Everyone gets concerned when there’s an outbreak, and when that outbreak stops, the headlines stop, and an economic downturn happens, the budget gets cut.”
Fresno’s STD clinic was shuttered in 2010 amid the Great Recession. Many others have vanished since the passage of the Affordable Care Act. Health leaders thought “by magically beefing up the primary care system, that we would do a better job of catching STIs and treating them,” said Mr. Harvey, the executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors. That hasn’t worked out; people want access to anonymous services, and primary care doctors often don’t have STDs top of mind. The coalition is lobbying Congress for funding to support STD clinical services, proposing a three-year demonstration project funded at $600 million.
It’s one of Ms. Adams’ dreams to see Fresno’s STD clinic restored as it was. “You could come in for an HIV test and get other STDs checked,” she said. “And if a patient is positive, you can give a first injection on the spot.”
On Aug. 12, Ms. Yang set out for Huron again, speeding past groves of almond trees and fields of grapes in the department’s white Chevy Cruze. She brought along a colleague, Jorge Sevilla, who had recently transferred to the STD program from COVID-19 contact tracing. Ms. Yang was anxious to find Angelica again. “She’s probably in her second trimester now,” she said.
They found her outside of a pale yellow house a few blocks from the homeless encampment; the owner was letting her stay in a shed tucked in the corner of the dirt yard. This time, it was evident that she was pregnant. Ms. Yang noted that Angelica was wearing a wig; hair loss is a symptom of syphilis.
“Do you remember me?” Ms. Yang asked.
Angelica nodded. She didn’t seem surprised to see Ms. Yang again. (I came along, and Mr. Sevilla explained who I was and that I was writing about syphilis and the people affected by it. Angelica signed a release for me to report about her case, and she said she had no problem with me writing about her or even using her full name. ProPublica chose to only print her first name.)
“How are you doing? How’s the baby?”
“Bien.”
“So the last time we talked, we were going to have you go to United Healthcare Center to get treatment. Have you gone since?”
Angelica shook her head.
“We brought some gift cards...” Mr. Sevilla started in Spanish. The department uses them as incentives for completing injections. But Angelica was already shaking her head. The nearest Walmart was the next town over.
Ms. Yang turned to her partner. “Tell her: So the reason why we’re coming out here again is because we really need her to go in for treatment. ... We really are concerned for the baby’s health especially since she’s had the infection for quite a while.”
Angelica listened while Mr. Sevilla interpreted, her eyes on the ground. Then she looked up. “Orita?” she asked. Right now?
“I’ll walk with you,” Ms. Yang offered. Angelica shook her head. “She said she wants to shower first before she goes over there,” Mr. Sevilla said.
Ms. Yang made a face. “She said that to me last time.” Ms. Yang offered to wait, but Angelica didn’t want the health officers to linger by the house. She said she would meet them by the clinic in 15 minutes.
Ms. Yang was reluctant to let her go but again had no other option. She and Mr. Sevilla drove to the clinic, then stood on the corner of the parking lot, staring down the road.
Talk to the pediatricians, obstetricians, and families on the front lines of the congenital syphilis surge and it becomes clear why Ms. Yang and others are trying so desperately to prevent cases. Dr. J. B. Cantey, associate professor in pediatrics at UT Health San Antonio, remembers a baby girl born at 25 weeks gestation who weighed a pound and a half. Syphilis had spread through her bones and lungs. She spent five months in the neonatal intensive care unit, breathing through a ventilator, and was still eating through a tube when she was discharged.
Then, there are the miscarriages, the stillbirths and the inconsolable parents. Dr. Irene Stafford, an associate professor and maternal-fetal medicine specialist at UT Health in Houston, cannot forget a patient who came in at 36 weeks for a routine checkup, pregnant with her first child. Dr. Stafford realized that there was no heartbeat. “She could see on my face that something was really wrong,” Dr. Stafford recalled. She had to let the patient know that syphilis had killed her baby. “She was hysterical, just bawling,” Dr. Stafford said. “I’ve seen people’s families ripped apart and I’ve seen beautiful babies die.” Fewer than 10% of patients who experience a stillbirth are tested for syphilis, suggesting that cases are underdiagnosed.
A Texas grandmother named Solidad Odunuga offers a glimpse into what the future could hold for Angelica’s mother, who may wind up raising her baby.
In February of last year, Ms. Odunuga got a call from the Lyndon B. Johnson Hospital in Houston. A nurse told her that her daughter was about to give birth and that child protective services had been called. Ms. Odunuga had lost contact with her daughter, who struggled with homelessness and substance abuse. She arrived in time to see her grandson delivered, premature at 30 weeks old, weighing 2.7 pounds. He tested positive for syphilis.
When a child protective worker asked Ms. Odunuga to take custody of the infant, she felt a wave of dread. “I was in denial,” she recalled. “I did not plan to be a mom again.” The baby’s medical problems were daunting: “Global developmental delays ... concerns for visual impairments ... high risk of cerebral palsy,” read a note from the doctor at the time.
Still, Ms. Odunuga visited her grandson every day for three months, driving to the NICU from her job at the University of Houston. “I’d put him in my shirt to keep him warm and hold him there.” She fell in love. She named him Emmanuel.
Once Emmanuel was discharged, Ms. Odunuga realized she had no choice but to quit her job. While Medicaid covered the costs of Emmanuel’s treatment, it was on her to care for him. From infancy, Emmanuel’s life has been a whirlwind of constant therapy. Today, at 20 months old, Odunuga brings him to physical, occupational, speech, and developmental therapy, each a different appointment on a different day of the week.
Emmanuel has thrived beyond what his doctors predicted, toddling so fast that Ms. Odunuga can’t look away for a minute and beaming as he waves his favorite toy phone. Yet he still suffers from gagging issues, which means Ms. Odunuga can’t feed him any solid foods. Liquid gets into his lungs when he aspirates; it has led to pneumonia three times. Emmanuel has a special stroller that helps keep his head in a position that won’t aggravate his persistent reflux, but Odunuga said she still has to pull over on the side of the road sometimes when she hears him projectile vomiting from the backseat.
The days are endless. Once she puts Emmanuel to bed, Ms. Odunuga starts planning the next day’s appointments. “I’ve had to cry alone, scream out alone,” she said. “Sometimes I wake up and think, Is this real? And then I hear him in the next room.”
Putting aside the challenge of eliminating syphilis entirely, everyone agrees it’s both doable and necessary to prevent newborn cases. “There was a crisis in perinatal HIV almost 30 years ago and people stood up and said this is not OK — it’s not acceptable for babies to be born in that condition. ... [We] brought it down from 1,700 babies born each year with perinatal HIV to less than 40 per year today,” said Virginia Bowen, an epidemiologist at the CDC. “Now here we are with a slightly different condition. We can also stand up and say, ‘This is not acceptable.’” Belarus, Bermuda, Cuba, Malaysia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka are among countries recognized by the World Health Organization for eliminating congenital syphilis.
Success starts with filling gaps across the health care system.
For almost a century, public health experts have advocated for testing pregnant patients more than once for syphilis in order to catch the infection. But policies nationwide still don’t reflect this best practice. Six states have no prenatal screening requirement at all. Even in states that require three tests, public health officials say that many physicians aren’t aware of the requirements. Dr. Stafford, the maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Houston, says she’s tired of hearing her own peers in medicine tell her, “Oh, syphilis is a problem?”
It costs public health departments less than 25 cents a dose to buy penicillin, but for a private practice, it’s more than $1,000, according to Dr. Park of the University of California San Francisco. “There’s no incentive for a private physician to stock a dose that could expire before it’s used, so they often don’t have it. So a woman comes in, they say, ‘We’ll send you to the emergency department or health department to get it,’ then [the patients] don’t show up.”
A vaccine would be invaluable for preventing spread among people at high risk for reinfection. But there is none. Scientists only recently figured out how to grow the bacteria in the lab, prompting grants from the National Institutes of Health to fund research into a vaccine. Dr. Justin Radolf, a researcher at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine, said he hopes his team will have a vaccine candidate by the end of its five-year grant. But it’ll likely take years more to find a manufacturer and run human trials.
Public health agencies also need to recognize that many of the hurdles to getting pregnant people treated involve access to care, economic stability, safe housing and transportation. In Fresno, Ms. Adams has been working on ways her department can collaborate with mental health services. Recently, one of her disease intervention specialists managed to get a pregnant woman treated with penicillin shots and, at the patient’s request, connected her with an addiction treatment center.
Gaining a patient’s cooperation means seeing them as complex humans instead of just a case to solve. “There may be past traumas with the health care system,” said Cynthia Deverson, project manager of the Houston Fetal Infant Morbidity Review. “There’s the fear of being discovered if she’s doing something illegal to survive. ... She may need to be in a certain place at a certain time so she can get something to eat, or maybe it’s the only time of the day that’s safe for her to sleep. They’re not going to tell you that. Yes, they understand there’s a problem, but it’s not an immediate threat, maybe they don’t feel bad yet, so obviously this is not urgent. ...
“What helps to gain trust is consistency,” she said. “Literally, it’s seeing that [disease specialist] constantly, daily. ... The woman can see that you’re not going to harm her, you’re saying, ‘I’m here at this time if you need me.’”
Ms. Yang stood outside the clinic, waiting for Angelica to show up, baking in the 90-degree heat. Her feelings ranged from irritation — Why didn’t she just go? I’d have more energy for other cases — to an appreciation for the parts of Angelica’s story that she didn’t know — She’s in survival mode. I need to be more patient.
Fifteen minutes ticked by, then 20.
“OK,” Ms. Yang announced. “We’re going back.”
She asked Sevilla if he would be OK if they drove Angelica to the clinic; they technically weren’t supposed to because of coronavirus precautions, but Ms. Yang wasn’t sure she could convince Angelica to walk. Mr. Sevilla gave her the thumbs up.
When they pulled up, they saw Angelica sitting in the backyard, chatting with a friend. She now wore a fresh T-shirt and had shoes on her feet. Angelica sat silently in the back seat as Ms. Yang drove to the clinic. A few minutes later, they pulled up to the parking lot.
Finally, Ms. Yang thought. We got her here.
The clinic was packed with people waiting for COVID-19 tests and vaccinations. A worker there had previously told Ms. Yang that a walk-in would be fine, but a receptionist now said they were too busy to treat Angelica. She would have to return.
Ms. Yang felt a surge of frustration, sensing that her hard-fought opportunity was slipping away. She tried to talk to the nurse supervisor, but he wasn’t available. She tried to leave the gift cards at the office to reward Angelica if she came, but the receptionist said she couldn’t hold them. While Ms. Yang negotiated, Mr. Sevilla sat with Angelica in the car, waiting.
Finally, Ms. Yang accepted this was yet another thing she couldn’t control.
She drove Angelica back to the yellow house. As they arrived, she tried once more to impress on her just how important it was to get treated, asking Mr. Sevilla to interpret. “We don’t want it to get any more serious, because she can go blind, she could go deaf, she could lose her baby.”
Angelica already had the door halfway open.
“So on a scale from one to 10, how important is this to get treated?” Ms. Yang asked.
“Ten,” Angelica said. Ms. Yang reminded her of the appointment that afternoon. Then Angelica stepped out and returned to the dusty yard.
Ms. Yang lingered for a moment, watching Angelica go. Then she turned the car back onto the highway and set off toward Fresno, knowing, already, that she’d be back.
Postscript: A reporter visited Huron twice more in the months that followed, including once independently to try to interview Angelica, but she wasn’t in town. Ms. Yang has visited Huron twice more as well — six times in total thus far. In October, a couple of men at the yellow house said Angelica was still in town, still pregnant. Ms. Yang and Mr. Sevilla spent an hour driving around, talking to residents, hoping to catch Angelica. But she was nowhere to be found.
ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
This story was originally published on ProPublica and was co-published with NPR.
When Mai Yang is looking for a patient, she travels light. She dresses deliberately — not too formal, so she won’t be mistaken for a police officer; not too casual, so people will look past her tiny 4-foot-10 stature and youthful face and trust her with sensitive health information. Always, she wears closed-toed shoes, “just in case I need to run.”
Yang carries a stack of cards issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show what happens when the Treponema pallidum bacteria invades a patient’s body. There’s a photo of an angry red sore on a penis. There’s one of a tongue, marred by mucus-lined lesions. And there’s one of a newborn baby, its belly, torso and thighs dotted in a rash, its mouth open, as if caught midcry.
It was because of the prospect of one such baby that Yang found herself walking through a homeless encampment on a blazing July day in Huron, Calif., an hour’s drive southwest of her office at the Fresno County Department of Public Health. She was looking for a pregnant woman named Angelica, whose visit to a community clinic had triggered a report to the health department’s sexually transmitted disease program. Angelica had tested positive for syphilis. If she was not treated, her baby could end up like the one in the picture or worse — there was a 40% chance the baby would die.
Ms. Yang knew, though, that if she helped Angelica get treated with three weekly shots of penicillin at least 30 days before she gave birth, it was likely that the infection would be wiped out and her baby would be born without any symptoms at all. Every case of congenital syphilis, when a baby is born with the disease, is avoidable. Each is considered a “sentinel event,” a warning that the public health system is failing.
The alarms are now clamoring. In the United States, more than 129,800 syphilis cases were recorded in 2019, double the case count of five years prior. In the same time period, cases of congenital syphilis quadrupled: 1,870 babies were born with the disease; 128 died. Case counts from 2020 are still being finalized, but the CDC has said that reported cases of congenital syphilis have already exceeded the prior year. Black, Hispanic, and Native American babies are disproportionately at risk.
There was a time, not too long ago, when CDC officials thought they could eliminate the centuries-old scourge from the United States, for adults and babies. But the effort lost steam and cases soon crept up again. Syphilis is not an outlier. The United States goes through what former CDC director Dr. Tom Frieden calls “a deadly cycle of panic and neglect” in which emergencies propel officials to scramble and throw money at a problem — whether that’s Ebola, Zika, or COVID-19. Then, as fear ebbs, so does the attention and motivation to finish the task.
The last fraction of cases can be the hardest to solve, whether that’s eradicating a bug or getting vaccines into arms, yet too often, that’s exactly when political attention gets diverted to the next alarm. The result: The hardest to reach and most vulnerable populations are the ones left suffering, after everyone else looks away.
Ms. Yang first received Angelica’s lab report on June 17. The address listed was a P.O. box, and the phone number belonged to her sister, who said Angelica was living in Huron. That was a piece of luck: Huron is tiny; the city spans just 1.6 square miles. On her first visit, a worker at the Alamo Motel said she knew Angelica and directed Ms. Yang to a nearby homeless encampment. Angelica wasn’t there, so Ms. Yang returned a second time, bringing one of the health department nurses who could serve as an interpreter.
They made their way to the barren patch of land behind Huron Valley Foods, the local grocery store, where people took shelter in makeshift lean-tos composed of cardboard boxes, scrap wood ,and scavenged furniture, draped with sheets that served as ceilings and curtains. Yang stopped outside one of the structures, calling a greeting.
“Hi, I’m from the health department, I’m looking for Angelica.”
The nurse echoed her in Spanish.
Angelica emerged, squinting in the sunlight. Ms. Yang couldn’t tell if she was visibly pregnant yet, as her body was obscured by an oversized shirt. The two women were about the same age: Ms. Yang 26 and Angelica 27. Ms. Yang led her away from the tent, so they could speak privately. Angelica seemed reticent, surprised by the sudden appearance of the two health officers. “You’re not in trouble,” Ms. Yang said, before revealing the results of her blood test.
Angelica had never heard of syphilis.
“Have you been to prenatal care?”
Angelica shook her head. The local clinic had referred her to an obstetrician in Hanford, a 30-minute drive away. She had no car. She also mentioned that she didn’t intend to raise her baby; her two oldest children lived with her mother, and this one likely would, too.
Ms. Yang pulled out the CDC cards, showing them to Angelica and asking if she had experienced any of the symptoms illustrated. No, Angelica said, her lips pursed with disgust.
“Right now you still feel healthy, but this bacteria is still in your body,” Ms. Yang pressed. “You need to get the infection treated to prevent further health complications to yourself and your baby.”
The community clinic was just across the street. “Can we walk you over to the clinic and make sure you get seen so we can get this taken care of?”
Angelica demurred. She said she hadn’t showered for a week and wanted to wash up first. She said she’d go later.
Ms. Yang tried once more to extract a promise: “What time do you think you’ll go?”
“Today, for sure.”
Syphilis is called The Great Imitator: It can look like any number of diseases. In its first stage, the only evidence of infection is a painless sore at the bacteria’s point of entry. Weeks later, as the bacteria multiplies, skin rashes bloom on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet. Other traits of this stage include fever, headaches, muscle aches, sore throat, and fatigue. These symptoms eventually disappear and the patient progresses into the latent phase, which betrays no external signs. But if left untreated, after a decade or more, syphilis will reemerge in up to 30% of patients, capable of wreaking horror on a wide range of organ systems. Dr. Marion Sims, president of the American Medical Association in 1876, called it a “terrible scourge, which begins with lamb-like mildness and ends with lion-like rage that ruthlessly destroys everything in its way.”
The corkscrew-shaped bacteria can infiltrate the nervous system at any stage of the infection. Ms. Yang is haunted by her memory of interviewing a young man whose dementia was so severe that he didn’t know why he was in the hospital or how old he was. And regardless of symptoms or stage, the bacteria can penetrate the placenta to infect a fetus. Even in these cases the infection is unpredictable: Many babies are born with normal physical features, but others can have deformed bones or damaged brains, and they can struggle to hear, see, or breathe.
From its earliest days, syphilis has been shrouded in stigma. The first recorded outbreak was in the late 15th century, when Charles VIII led the French army to invade Naples. Italian physicians described French soldiers covered with pustules, dying from a sexually transmitted disease. As the affliction spread, Italians called it the French Disease. The French blamed the Neopolitans. It was also called the German, Polish, or Spanish disease, depending on which neighbor one wanted to blame. Even its name bears the taint of divine judgement: It comes from a 16th-century poem that tells of a shepherd, Syphilus, who offended the god Apollo and was punished with a hideous disease.
By 1937 in America, when former Surgeon General Thomas Parran wrote the book “Shadow on the Land,” he estimated some 680,000 people were under treatment for syphilis; about 60,000 babies were being born annually with congenital syphilis. There was no cure, and the stigma was so strong that public health officials feared even properly documenting cases.
Thanks to Dr. Parran’s ardent advocacy, Congress in 1938 passed the National Venereal Disease Control Act, which created grants for states to set up clinics and support testing and treatment. Other than a short-lived funding effort during World War I, this was the first coordinated federal push to respond to the disease.
Around the same time, the Public Health Service launched an effort to record the natural history of syphilis. Situated in Tuskegee, Ala., the infamous study recruited 600 black men. By the early 1940s, penicillin became widely available and was found to be a reliable cure, but the treatment was withheld from the study participants. Outrage over the ethical violations would cast a stain across syphilis research for decades to come and fuel generations of mistrust in the medical system among Black Americans that continues to this day.
With the introduction of penicillin, cases began to plummet. Twice, the CDC has announced efforts to wipe out the disease — once in the 1960s and again in 1999.
In the latest effort, the CDC announced that the United States had “a unique opportunity to eliminate syphilis within its borders,” thanks to historically low rates, with 80% of counties reporting zero cases. The concentration of cases in the South “identifies communities in which there is a fundamental failure of public health capacity,” the agency noted, adding that elimination — which it defined as fewer than 1,000 cases a year — would “decrease one of our most glaring racial disparities in health.”
Two years after the campaign began, cases started climbing, first among gay men and later, heterosexuals. Cases in women started accelerating in 2013, followed shortly by increasing numbers of babies born with syphilis.The reasons for failure are complex; people relaxed safer sex practices after the advent of potent HIV combination therapies, increased methamphetamine use drove riskier behavior and an explosion of online dating made it hard to track and test sexual partners, according to Dr. Ina Park, medical director of the California Prevention Training Center at the University of California San Francisco.
But federal and state public health efforts were hamstrung from the get-go. In 1999, the CDC said it would need about $35 million to $39 million in new federal funds annually for at least five years to eliminate syphilis. The agency got less than half of what it asked for, according to Jo Valentine, former program coordinator of the CDC’s Syphilis Elimination Effort. As cases rose, the CDC modified its goals in 2006 from 0.4 primary and secondary syphilis cases per 100,000 in population to 2.2 cases per 100,000. By 2013, as elimination seemed less and less viable, the CDC changed its focus to ending congenital syphilis only.
Since then, funding has remained anemic. From 2015 to 2020, the CDC’s budget for preventing sexually transmitted infections grew by 2.2%. Taking inflation into account, that’s a 7.4% reduction in purchasing power. In the same period, cases of syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia — the three STDs that have federally funded control programs — increased by nearly 30%.
“We have a long history of nearly eradicating something, then changing our attention, and seeing a resurgence in numbers,” said David Harvey, executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors. “We have more congenital syphilis cases today in America than we ever had pediatric AIDS at the height of the AIDS epidemic. It’s heartbreaking.”
Adriane Casalotti, chief of government and public affairs at the National Association of County and City Health Officials, warns that the United States should not be surprised to see case counts continue to climb. “The bugs don’t go away,” she said. “They’re just waiting for the next opportunity, when you’re not paying attention.”
Ms. Yang waited until the end of the day, then called the clinic to see if Angelica had gone for her shot. She had not. Ms. Yang would have to block off another half day to visit Huron again, but she had three dozen other cases to deal with.
States in the South and West have seen the highest syphilis rates in recent years. In 2017, 64 babies in Fresno County were born with syphilis at a rate of 440 babies per 100,000 live births — about 19 times the national rate. While the county had managed to lower case counts in the two years that followed, the pandemic threatened to unravel that progress, forcing STD staffers to do COVID-19 contact tracing, pausing field visits to find infected people, and scaring patients from seeking care. Ms. Yang’s colleague handled three cases of stillbirth in 2020; in each, the woman was never diagnosed with syphilis because she feared catching the coronavirus and skipped prenatal care.
Ms. Yang, whose caseload peaked at 70 during a COVID-19 surge, knew she would not be able handle them all as thoroughly as she’d like to. “When I was being mentored by another investigator, he said: ‘You’re not a superhero. You can’t save everybody,’” she said. She prioritizes men who have sex with men, because there’s a higher prevalence of syphilis in that population, and pregnant people, because of the horrific consequences for babies.
The job of a disease intervention specialist isn’t for everyone: It means meeting patients whenever and wherever they are available — in the mop closet of a bus station, in a quiet parking lot — to inform them about the disease, to extract names of sex partners and to encourage treatment. Patients are often reluctant to talk. They can get belligerent, upset that “the government” has their personal information or shattered at the thought that a partner is likely cheating on them. Salaries typically start in the low $40,000s.
Jena Adams, Ms. Yang’s supervisor, has eight investigators working on HIV and syphilis. In the middle of 2020, she lost two and replaced them only recently. “It’s been exhausting,” Ms. Adams said. She has only one specialist who is trained to take blood samples in the field, crucial for guaranteeing that the partners of those who test positive for syphilis also get tested. Ms. Adams wants to get phlebotomy training for the rest of her staff, but it’s $2,000 per person. The department also doesn’t have anyone who can administer penicillin injections in the field; that would have been key when Ms. Yang met Angelica. For a while, a nurse who worked in the tuberculosis program would ride along to give penicillin shots on a volunteer basis. Then he, too, left the health department.
Much of the resources in public health trickle down from the CDC, which distributes money to states, which then parcel it out to counties. The CDC gets its budget from Congress, which tells the agency, by line item, exactly how much money it can spend to fight a disease or virus, in an uncommonly specific manner not seen in many other agencies. The decisions are often politically driven and can be detached from actual health needs.
When the House and Senate appropriations committees meet to decide how much the CDC will get for each line item, they are barraged by lobbyists for individual disease interests. Stephanie Arnold Pang, senior director of policy and government relations at the National Coalition of STD Directors, can pick out the groups by sight: breast cancer wears pink, Alzheimer’s goes in purple, multiple sclerosis comes in orange, HIV in red. STD prevention advocates, like herself, don a green ribbon, but they’re far outnumbered.
And unlike diseases that might already be familiar to lawmakers, or have patient and family spokespeople who can tell their own powerful stories, syphilis doesn’t have many willing poster children. “Congressmen don’t wake up one day and say, ‘Oh hey, there’s congenital syphilis in my jurisdiction.’ You have to raise awareness,” Arnold Pang said. It can be hard jockeying for a meeting. “Some offices might say, ‘I don’t have time for you because we’ve just seen HIV.’ ... Sometimes, it feels like you’re talking into a void.”
The consequences of the political nature of public health funding have become more obvious during the coronavirus pandemic. The 2014 Ebola epidemic was seen as a “global wakeup call” that the world wasn’t prepared for a major pandemic, yet in 2018, the CDC scaled back its epidemic prevention work as money ran out. “If you’ve got to choose between Alzheimer’s research and stopping an outbreak that may not happen? Stopping an outbreak that might not happen doesn’t do well,” said Dr. Frieden, the former CDC director. “The CDC needs to have more money and more flexible money. Otherwise, we’re going to be in this situation long term.”
In May 2021, President Joe Biden’s administration announced it would set aside $7.4 billion over the next five years to hire and train public health workers, including $1.1 billion for more disease intervention specialists like Ms. Yang. Public health officials are thrilled to have the chance to expand their workforce, but some worry the time horizon may be too short. “We’ve seen this movie before, right?” Dr. Frieden said. “Everyone gets concerned when there’s an outbreak, and when that outbreak stops, the headlines stop, and an economic downturn happens, the budget gets cut.”
Fresno’s STD clinic was shuttered in 2010 amid the Great Recession. Many others have vanished since the passage of the Affordable Care Act. Health leaders thought “by magically beefing up the primary care system, that we would do a better job of catching STIs and treating them,” said Mr. Harvey, the executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors. That hasn’t worked out; people want access to anonymous services, and primary care doctors often don’t have STDs top of mind. The coalition is lobbying Congress for funding to support STD clinical services, proposing a three-year demonstration project funded at $600 million.
It’s one of Ms. Adams’ dreams to see Fresno’s STD clinic restored as it was. “You could come in for an HIV test and get other STDs checked,” she said. “And if a patient is positive, you can give a first injection on the spot.”
On Aug. 12, Ms. Yang set out for Huron again, speeding past groves of almond trees and fields of grapes in the department’s white Chevy Cruze. She brought along a colleague, Jorge Sevilla, who had recently transferred to the STD program from COVID-19 contact tracing. Ms. Yang was anxious to find Angelica again. “She’s probably in her second trimester now,” she said.
They found her outside of a pale yellow house a few blocks from the homeless encampment; the owner was letting her stay in a shed tucked in the corner of the dirt yard. This time, it was evident that she was pregnant. Ms. Yang noted that Angelica was wearing a wig; hair loss is a symptom of syphilis.
“Do you remember me?” Ms. Yang asked.
Angelica nodded. She didn’t seem surprised to see Ms. Yang again. (I came along, and Mr. Sevilla explained who I was and that I was writing about syphilis and the people affected by it. Angelica signed a release for me to report about her case, and she said she had no problem with me writing about her or even using her full name. ProPublica chose to only print her first name.)
“How are you doing? How’s the baby?”
“Bien.”
“So the last time we talked, we were going to have you go to United Healthcare Center to get treatment. Have you gone since?”
Angelica shook her head.
“We brought some gift cards...” Mr. Sevilla started in Spanish. The department uses them as incentives for completing injections. But Angelica was already shaking her head. The nearest Walmart was the next town over.
Ms. Yang turned to her partner. “Tell her: So the reason why we’re coming out here again is because we really need her to go in for treatment. ... We really are concerned for the baby’s health especially since she’s had the infection for quite a while.”
Angelica listened while Mr. Sevilla interpreted, her eyes on the ground. Then she looked up. “Orita?” she asked. Right now?
“I’ll walk with you,” Ms. Yang offered. Angelica shook her head. “She said she wants to shower first before she goes over there,” Mr. Sevilla said.
Ms. Yang made a face. “She said that to me last time.” Ms. Yang offered to wait, but Angelica didn’t want the health officers to linger by the house. She said she would meet them by the clinic in 15 minutes.
Ms. Yang was reluctant to let her go but again had no other option. She and Mr. Sevilla drove to the clinic, then stood on the corner of the parking lot, staring down the road.
Talk to the pediatricians, obstetricians, and families on the front lines of the congenital syphilis surge and it becomes clear why Ms. Yang and others are trying so desperately to prevent cases. Dr. J. B. Cantey, associate professor in pediatrics at UT Health San Antonio, remembers a baby girl born at 25 weeks gestation who weighed a pound and a half. Syphilis had spread through her bones and lungs. She spent five months in the neonatal intensive care unit, breathing through a ventilator, and was still eating through a tube when she was discharged.
Then, there are the miscarriages, the stillbirths and the inconsolable parents. Dr. Irene Stafford, an associate professor and maternal-fetal medicine specialist at UT Health in Houston, cannot forget a patient who came in at 36 weeks for a routine checkup, pregnant with her first child. Dr. Stafford realized that there was no heartbeat. “She could see on my face that something was really wrong,” Dr. Stafford recalled. She had to let the patient know that syphilis had killed her baby. “She was hysterical, just bawling,” Dr. Stafford said. “I’ve seen people’s families ripped apart and I’ve seen beautiful babies die.” Fewer than 10% of patients who experience a stillbirth are tested for syphilis, suggesting that cases are underdiagnosed.
A Texas grandmother named Solidad Odunuga offers a glimpse into what the future could hold for Angelica’s mother, who may wind up raising her baby.
In February of last year, Ms. Odunuga got a call from the Lyndon B. Johnson Hospital in Houston. A nurse told her that her daughter was about to give birth and that child protective services had been called. Ms. Odunuga had lost contact with her daughter, who struggled with homelessness and substance abuse. She arrived in time to see her grandson delivered, premature at 30 weeks old, weighing 2.7 pounds. He tested positive for syphilis.
When a child protective worker asked Ms. Odunuga to take custody of the infant, she felt a wave of dread. “I was in denial,” she recalled. “I did not plan to be a mom again.” The baby’s medical problems were daunting: “Global developmental delays ... concerns for visual impairments ... high risk of cerebral palsy,” read a note from the doctor at the time.
Still, Ms. Odunuga visited her grandson every day for three months, driving to the NICU from her job at the University of Houston. “I’d put him in my shirt to keep him warm and hold him there.” She fell in love. She named him Emmanuel.
Once Emmanuel was discharged, Ms. Odunuga realized she had no choice but to quit her job. While Medicaid covered the costs of Emmanuel’s treatment, it was on her to care for him. From infancy, Emmanuel’s life has been a whirlwind of constant therapy. Today, at 20 months old, Odunuga brings him to physical, occupational, speech, and developmental therapy, each a different appointment on a different day of the week.
Emmanuel has thrived beyond what his doctors predicted, toddling so fast that Ms. Odunuga can’t look away for a minute and beaming as he waves his favorite toy phone. Yet he still suffers from gagging issues, which means Ms. Odunuga can’t feed him any solid foods. Liquid gets into his lungs when he aspirates; it has led to pneumonia three times. Emmanuel has a special stroller that helps keep his head in a position that won’t aggravate his persistent reflux, but Odunuga said she still has to pull over on the side of the road sometimes when she hears him projectile vomiting from the backseat.
The days are endless. Once she puts Emmanuel to bed, Ms. Odunuga starts planning the next day’s appointments. “I’ve had to cry alone, scream out alone,” she said. “Sometimes I wake up and think, Is this real? And then I hear him in the next room.”
Putting aside the challenge of eliminating syphilis entirely, everyone agrees it’s both doable and necessary to prevent newborn cases. “There was a crisis in perinatal HIV almost 30 years ago and people stood up and said this is not OK — it’s not acceptable for babies to be born in that condition. ... [We] brought it down from 1,700 babies born each year with perinatal HIV to less than 40 per year today,” said Virginia Bowen, an epidemiologist at the CDC. “Now here we are with a slightly different condition. We can also stand up and say, ‘This is not acceptable.’” Belarus, Bermuda, Cuba, Malaysia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka are among countries recognized by the World Health Organization for eliminating congenital syphilis.
Success starts with filling gaps across the health care system.
For almost a century, public health experts have advocated for testing pregnant patients more than once for syphilis in order to catch the infection. But policies nationwide still don’t reflect this best practice. Six states have no prenatal screening requirement at all. Even in states that require three tests, public health officials say that many physicians aren’t aware of the requirements. Dr. Stafford, the maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Houston, says she’s tired of hearing her own peers in medicine tell her, “Oh, syphilis is a problem?”
It costs public health departments less than 25 cents a dose to buy penicillin, but for a private practice, it’s more than $1,000, according to Dr. Park of the University of California San Francisco. “There’s no incentive for a private physician to stock a dose that could expire before it’s used, so they often don’t have it. So a woman comes in, they say, ‘We’ll send you to the emergency department or health department to get it,’ then [the patients] don’t show up.”
A vaccine would be invaluable for preventing spread among people at high risk for reinfection. But there is none. Scientists only recently figured out how to grow the bacteria in the lab, prompting grants from the National Institutes of Health to fund research into a vaccine. Dr. Justin Radolf, a researcher at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine, said he hopes his team will have a vaccine candidate by the end of its five-year grant. But it’ll likely take years more to find a manufacturer and run human trials.
Public health agencies also need to recognize that many of the hurdles to getting pregnant people treated involve access to care, economic stability, safe housing and transportation. In Fresno, Ms. Adams has been working on ways her department can collaborate with mental health services. Recently, one of her disease intervention specialists managed to get a pregnant woman treated with penicillin shots and, at the patient’s request, connected her with an addiction treatment center.
Gaining a patient’s cooperation means seeing them as complex humans instead of just a case to solve. “There may be past traumas with the health care system,” said Cynthia Deverson, project manager of the Houston Fetal Infant Morbidity Review. “There’s the fear of being discovered if she’s doing something illegal to survive. ... She may need to be in a certain place at a certain time so she can get something to eat, or maybe it’s the only time of the day that’s safe for her to sleep. They’re not going to tell you that. Yes, they understand there’s a problem, but it’s not an immediate threat, maybe they don’t feel bad yet, so obviously this is not urgent. ...
“What helps to gain trust is consistency,” she said. “Literally, it’s seeing that [disease specialist] constantly, daily. ... The woman can see that you’re not going to harm her, you’re saying, ‘I’m here at this time if you need me.’”
Ms. Yang stood outside the clinic, waiting for Angelica to show up, baking in the 90-degree heat. Her feelings ranged from irritation — Why didn’t she just go? I’d have more energy for other cases — to an appreciation for the parts of Angelica’s story that she didn’t know — She’s in survival mode. I need to be more patient.
Fifteen minutes ticked by, then 20.
“OK,” Ms. Yang announced. “We’re going back.”
She asked Sevilla if he would be OK if they drove Angelica to the clinic; they technically weren’t supposed to because of coronavirus precautions, but Ms. Yang wasn’t sure she could convince Angelica to walk. Mr. Sevilla gave her the thumbs up.
When they pulled up, they saw Angelica sitting in the backyard, chatting with a friend. She now wore a fresh T-shirt and had shoes on her feet. Angelica sat silently in the back seat as Ms. Yang drove to the clinic. A few minutes later, they pulled up to the parking lot.
Finally, Ms. Yang thought. We got her here.
The clinic was packed with people waiting for COVID-19 tests and vaccinations. A worker there had previously told Ms. Yang that a walk-in would be fine, but a receptionist now said they were too busy to treat Angelica. She would have to return.
Ms. Yang felt a surge of frustration, sensing that her hard-fought opportunity was slipping away. She tried to talk to the nurse supervisor, but he wasn’t available. She tried to leave the gift cards at the office to reward Angelica if she came, but the receptionist said she couldn’t hold them. While Ms. Yang negotiated, Mr. Sevilla sat with Angelica in the car, waiting.
Finally, Ms. Yang accepted this was yet another thing she couldn’t control.
She drove Angelica back to the yellow house. As they arrived, she tried once more to impress on her just how important it was to get treated, asking Mr. Sevilla to interpret. “We don’t want it to get any more serious, because she can go blind, she could go deaf, she could lose her baby.”
Angelica already had the door halfway open.
“So on a scale from one to 10, how important is this to get treated?” Ms. Yang asked.
“Ten,” Angelica said. Ms. Yang reminded her of the appointment that afternoon. Then Angelica stepped out and returned to the dusty yard.
Ms. Yang lingered for a moment, watching Angelica go. Then she turned the car back onto the highway and set off toward Fresno, knowing, already, that she’d be back.
Postscript: A reporter visited Huron twice more in the months that followed, including once independently to try to interview Angelica, but she wasn’t in town. Ms. Yang has visited Huron twice more as well — six times in total thus far. In October, a couple of men at the yellow house said Angelica was still in town, still pregnant. Ms. Yang and Mr. Sevilla spent an hour driving around, talking to residents, hoping to catch Angelica. But she was nowhere to be found.
ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
This story was originally published on ProPublica and was co-published with NPR.
When Mai Yang is looking for a patient, she travels light. She dresses deliberately — not too formal, so she won’t be mistaken for a police officer; not too casual, so people will look past her tiny 4-foot-10 stature and youthful face and trust her with sensitive health information. Always, she wears closed-toed shoes, “just in case I need to run.”
Yang carries a stack of cards issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show what happens when the Treponema pallidum bacteria invades a patient’s body. There’s a photo of an angry red sore on a penis. There’s one of a tongue, marred by mucus-lined lesions. And there’s one of a newborn baby, its belly, torso and thighs dotted in a rash, its mouth open, as if caught midcry.
It was because of the prospect of one such baby that Yang found herself walking through a homeless encampment on a blazing July day in Huron, Calif., an hour’s drive southwest of her office at the Fresno County Department of Public Health. She was looking for a pregnant woman named Angelica, whose visit to a community clinic had triggered a report to the health department’s sexually transmitted disease program. Angelica had tested positive for syphilis. If she was not treated, her baby could end up like the one in the picture or worse — there was a 40% chance the baby would die.
Ms. Yang knew, though, that if she helped Angelica get treated with three weekly shots of penicillin at least 30 days before she gave birth, it was likely that the infection would be wiped out and her baby would be born without any symptoms at all. Every case of congenital syphilis, when a baby is born with the disease, is avoidable. Each is considered a “sentinel event,” a warning that the public health system is failing.
The alarms are now clamoring. In the United States, more than 129,800 syphilis cases were recorded in 2019, double the case count of five years prior. In the same time period, cases of congenital syphilis quadrupled: 1,870 babies were born with the disease; 128 died. Case counts from 2020 are still being finalized, but the CDC has said that reported cases of congenital syphilis have already exceeded the prior year. Black, Hispanic, and Native American babies are disproportionately at risk.
There was a time, not too long ago, when CDC officials thought they could eliminate the centuries-old scourge from the United States, for adults and babies. But the effort lost steam and cases soon crept up again. Syphilis is not an outlier. The United States goes through what former CDC director Dr. Tom Frieden calls “a deadly cycle of panic and neglect” in which emergencies propel officials to scramble and throw money at a problem — whether that’s Ebola, Zika, or COVID-19. Then, as fear ebbs, so does the attention and motivation to finish the task.
The last fraction of cases can be the hardest to solve, whether that’s eradicating a bug or getting vaccines into arms, yet too often, that’s exactly when political attention gets diverted to the next alarm. The result: The hardest to reach and most vulnerable populations are the ones left suffering, after everyone else looks away.
Ms. Yang first received Angelica’s lab report on June 17. The address listed was a P.O. box, and the phone number belonged to her sister, who said Angelica was living in Huron. That was a piece of luck: Huron is tiny; the city spans just 1.6 square miles. On her first visit, a worker at the Alamo Motel said she knew Angelica and directed Ms. Yang to a nearby homeless encampment. Angelica wasn’t there, so Ms. Yang returned a second time, bringing one of the health department nurses who could serve as an interpreter.
They made their way to the barren patch of land behind Huron Valley Foods, the local grocery store, where people took shelter in makeshift lean-tos composed of cardboard boxes, scrap wood ,and scavenged furniture, draped with sheets that served as ceilings and curtains. Yang stopped outside one of the structures, calling a greeting.
“Hi, I’m from the health department, I’m looking for Angelica.”
The nurse echoed her in Spanish.
Angelica emerged, squinting in the sunlight. Ms. Yang couldn’t tell if she was visibly pregnant yet, as her body was obscured by an oversized shirt. The two women were about the same age: Ms. Yang 26 and Angelica 27. Ms. Yang led her away from the tent, so they could speak privately. Angelica seemed reticent, surprised by the sudden appearance of the two health officers. “You’re not in trouble,” Ms. Yang said, before revealing the results of her blood test.
Angelica had never heard of syphilis.
“Have you been to prenatal care?”
Angelica shook her head. The local clinic had referred her to an obstetrician in Hanford, a 30-minute drive away. She had no car. She also mentioned that she didn’t intend to raise her baby; her two oldest children lived with her mother, and this one likely would, too.
Ms. Yang pulled out the CDC cards, showing them to Angelica and asking if she had experienced any of the symptoms illustrated. No, Angelica said, her lips pursed with disgust.
“Right now you still feel healthy, but this bacteria is still in your body,” Ms. Yang pressed. “You need to get the infection treated to prevent further health complications to yourself and your baby.”
The community clinic was just across the street. “Can we walk you over to the clinic and make sure you get seen so we can get this taken care of?”
Angelica demurred. She said she hadn’t showered for a week and wanted to wash up first. She said she’d go later.
Ms. Yang tried once more to extract a promise: “What time do you think you’ll go?”
“Today, for sure.”
Syphilis is called The Great Imitator: It can look like any number of diseases. In its first stage, the only evidence of infection is a painless sore at the bacteria’s point of entry. Weeks later, as the bacteria multiplies, skin rashes bloom on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet. Other traits of this stage include fever, headaches, muscle aches, sore throat, and fatigue. These symptoms eventually disappear and the patient progresses into the latent phase, which betrays no external signs. But if left untreated, after a decade or more, syphilis will reemerge in up to 30% of patients, capable of wreaking horror on a wide range of organ systems. Dr. Marion Sims, president of the American Medical Association in 1876, called it a “terrible scourge, which begins with lamb-like mildness and ends with lion-like rage that ruthlessly destroys everything in its way.”
The corkscrew-shaped bacteria can infiltrate the nervous system at any stage of the infection. Ms. Yang is haunted by her memory of interviewing a young man whose dementia was so severe that he didn’t know why he was in the hospital or how old he was. And regardless of symptoms or stage, the bacteria can penetrate the placenta to infect a fetus. Even in these cases the infection is unpredictable: Many babies are born with normal physical features, but others can have deformed bones or damaged brains, and they can struggle to hear, see, or breathe.
From its earliest days, syphilis has been shrouded in stigma. The first recorded outbreak was in the late 15th century, when Charles VIII led the French army to invade Naples. Italian physicians described French soldiers covered with pustules, dying from a sexually transmitted disease. As the affliction spread, Italians called it the French Disease. The French blamed the Neopolitans. It was also called the German, Polish, or Spanish disease, depending on which neighbor one wanted to blame. Even its name bears the taint of divine judgement: It comes from a 16th-century poem that tells of a shepherd, Syphilus, who offended the god Apollo and was punished with a hideous disease.
By 1937 in America, when former Surgeon General Thomas Parran wrote the book “Shadow on the Land,” he estimated some 680,000 people were under treatment for syphilis; about 60,000 babies were being born annually with congenital syphilis. There was no cure, and the stigma was so strong that public health officials feared even properly documenting cases.
Thanks to Dr. Parran’s ardent advocacy, Congress in 1938 passed the National Venereal Disease Control Act, which created grants for states to set up clinics and support testing and treatment. Other than a short-lived funding effort during World War I, this was the first coordinated federal push to respond to the disease.
Around the same time, the Public Health Service launched an effort to record the natural history of syphilis. Situated in Tuskegee, Ala., the infamous study recruited 600 black men. By the early 1940s, penicillin became widely available and was found to be a reliable cure, but the treatment was withheld from the study participants. Outrage over the ethical violations would cast a stain across syphilis research for decades to come and fuel generations of mistrust in the medical system among Black Americans that continues to this day.
With the introduction of penicillin, cases began to plummet. Twice, the CDC has announced efforts to wipe out the disease — once in the 1960s and again in 1999.
In the latest effort, the CDC announced that the United States had “a unique opportunity to eliminate syphilis within its borders,” thanks to historically low rates, with 80% of counties reporting zero cases. The concentration of cases in the South “identifies communities in which there is a fundamental failure of public health capacity,” the agency noted, adding that elimination — which it defined as fewer than 1,000 cases a year — would “decrease one of our most glaring racial disparities in health.”
Two years after the campaign began, cases started climbing, first among gay men and later, heterosexuals. Cases in women started accelerating in 2013, followed shortly by increasing numbers of babies born with syphilis.The reasons for failure are complex; people relaxed safer sex practices after the advent of potent HIV combination therapies, increased methamphetamine use drove riskier behavior and an explosion of online dating made it hard to track and test sexual partners, according to Dr. Ina Park, medical director of the California Prevention Training Center at the University of California San Francisco.
But federal and state public health efforts were hamstrung from the get-go. In 1999, the CDC said it would need about $35 million to $39 million in new federal funds annually for at least five years to eliminate syphilis. The agency got less than half of what it asked for, according to Jo Valentine, former program coordinator of the CDC’s Syphilis Elimination Effort. As cases rose, the CDC modified its goals in 2006 from 0.4 primary and secondary syphilis cases per 100,000 in population to 2.2 cases per 100,000. By 2013, as elimination seemed less and less viable, the CDC changed its focus to ending congenital syphilis only.
Since then, funding has remained anemic. From 2015 to 2020, the CDC’s budget for preventing sexually transmitted infections grew by 2.2%. Taking inflation into account, that’s a 7.4% reduction in purchasing power. In the same period, cases of syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia — the three STDs that have federally funded control programs — increased by nearly 30%.
“We have a long history of nearly eradicating something, then changing our attention, and seeing a resurgence in numbers,” said David Harvey, executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors. “We have more congenital syphilis cases today in America than we ever had pediatric AIDS at the height of the AIDS epidemic. It’s heartbreaking.”
Adriane Casalotti, chief of government and public affairs at the National Association of County and City Health Officials, warns that the United States should not be surprised to see case counts continue to climb. “The bugs don’t go away,” she said. “They’re just waiting for the next opportunity, when you’re not paying attention.”
Ms. Yang waited until the end of the day, then called the clinic to see if Angelica had gone for her shot. She had not. Ms. Yang would have to block off another half day to visit Huron again, but she had three dozen other cases to deal with.
States in the South and West have seen the highest syphilis rates in recent years. In 2017, 64 babies in Fresno County were born with syphilis at a rate of 440 babies per 100,000 live births — about 19 times the national rate. While the county had managed to lower case counts in the two years that followed, the pandemic threatened to unravel that progress, forcing STD staffers to do COVID-19 contact tracing, pausing field visits to find infected people, and scaring patients from seeking care. Ms. Yang’s colleague handled three cases of stillbirth in 2020; in each, the woman was never diagnosed with syphilis because she feared catching the coronavirus and skipped prenatal care.
Ms. Yang, whose caseload peaked at 70 during a COVID-19 surge, knew she would not be able handle them all as thoroughly as she’d like to. “When I was being mentored by another investigator, he said: ‘You’re not a superhero. You can’t save everybody,’” she said. She prioritizes men who have sex with men, because there’s a higher prevalence of syphilis in that population, and pregnant people, because of the horrific consequences for babies.
The job of a disease intervention specialist isn’t for everyone: It means meeting patients whenever and wherever they are available — in the mop closet of a bus station, in a quiet parking lot — to inform them about the disease, to extract names of sex partners and to encourage treatment. Patients are often reluctant to talk. They can get belligerent, upset that “the government” has their personal information or shattered at the thought that a partner is likely cheating on them. Salaries typically start in the low $40,000s.
Jena Adams, Ms. Yang’s supervisor, has eight investigators working on HIV and syphilis. In the middle of 2020, she lost two and replaced them only recently. “It’s been exhausting,” Ms. Adams said. She has only one specialist who is trained to take blood samples in the field, crucial for guaranteeing that the partners of those who test positive for syphilis also get tested. Ms. Adams wants to get phlebotomy training for the rest of her staff, but it’s $2,000 per person. The department also doesn’t have anyone who can administer penicillin injections in the field; that would have been key when Ms. Yang met Angelica. For a while, a nurse who worked in the tuberculosis program would ride along to give penicillin shots on a volunteer basis. Then he, too, left the health department.
Much of the resources in public health trickle down from the CDC, which distributes money to states, which then parcel it out to counties. The CDC gets its budget from Congress, which tells the agency, by line item, exactly how much money it can spend to fight a disease or virus, in an uncommonly specific manner not seen in many other agencies. The decisions are often politically driven and can be detached from actual health needs.
When the House and Senate appropriations committees meet to decide how much the CDC will get for each line item, they are barraged by lobbyists for individual disease interests. Stephanie Arnold Pang, senior director of policy and government relations at the National Coalition of STD Directors, can pick out the groups by sight: breast cancer wears pink, Alzheimer’s goes in purple, multiple sclerosis comes in orange, HIV in red. STD prevention advocates, like herself, don a green ribbon, but they’re far outnumbered.
And unlike diseases that might already be familiar to lawmakers, or have patient and family spokespeople who can tell their own powerful stories, syphilis doesn’t have many willing poster children. “Congressmen don’t wake up one day and say, ‘Oh hey, there’s congenital syphilis in my jurisdiction.’ You have to raise awareness,” Arnold Pang said. It can be hard jockeying for a meeting. “Some offices might say, ‘I don’t have time for you because we’ve just seen HIV.’ ... Sometimes, it feels like you’re talking into a void.”
The consequences of the political nature of public health funding have become more obvious during the coronavirus pandemic. The 2014 Ebola epidemic was seen as a “global wakeup call” that the world wasn’t prepared for a major pandemic, yet in 2018, the CDC scaled back its epidemic prevention work as money ran out. “If you’ve got to choose between Alzheimer’s research and stopping an outbreak that may not happen? Stopping an outbreak that might not happen doesn’t do well,” said Dr. Frieden, the former CDC director. “The CDC needs to have more money and more flexible money. Otherwise, we’re going to be in this situation long term.”
In May 2021, President Joe Biden’s administration announced it would set aside $7.4 billion over the next five years to hire and train public health workers, including $1.1 billion for more disease intervention specialists like Ms. Yang. Public health officials are thrilled to have the chance to expand their workforce, but some worry the time horizon may be too short. “We’ve seen this movie before, right?” Dr. Frieden said. “Everyone gets concerned when there’s an outbreak, and when that outbreak stops, the headlines stop, and an economic downturn happens, the budget gets cut.”
Fresno’s STD clinic was shuttered in 2010 amid the Great Recession. Many others have vanished since the passage of the Affordable Care Act. Health leaders thought “by magically beefing up the primary care system, that we would do a better job of catching STIs and treating them,” said Mr. Harvey, the executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors. That hasn’t worked out; people want access to anonymous services, and primary care doctors often don’t have STDs top of mind. The coalition is lobbying Congress for funding to support STD clinical services, proposing a three-year demonstration project funded at $600 million.
It’s one of Ms. Adams’ dreams to see Fresno’s STD clinic restored as it was. “You could come in for an HIV test and get other STDs checked,” she said. “And if a patient is positive, you can give a first injection on the spot.”
On Aug. 12, Ms. Yang set out for Huron again, speeding past groves of almond trees and fields of grapes in the department’s white Chevy Cruze. She brought along a colleague, Jorge Sevilla, who had recently transferred to the STD program from COVID-19 contact tracing. Ms. Yang was anxious to find Angelica again. “She’s probably in her second trimester now,” she said.
They found her outside of a pale yellow house a few blocks from the homeless encampment; the owner was letting her stay in a shed tucked in the corner of the dirt yard. This time, it was evident that she was pregnant. Ms. Yang noted that Angelica was wearing a wig; hair loss is a symptom of syphilis.
“Do you remember me?” Ms. Yang asked.
Angelica nodded. She didn’t seem surprised to see Ms. Yang again. (I came along, and Mr. Sevilla explained who I was and that I was writing about syphilis and the people affected by it. Angelica signed a release for me to report about her case, and she said she had no problem with me writing about her or even using her full name. ProPublica chose to only print her first name.)
“How are you doing? How’s the baby?”
“Bien.”
“So the last time we talked, we were going to have you go to United Healthcare Center to get treatment. Have you gone since?”
Angelica shook her head.
“We brought some gift cards...” Mr. Sevilla started in Spanish. The department uses them as incentives for completing injections. But Angelica was already shaking her head. The nearest Walmart was the next town over.
Ms. Yang turned to her partner. “Tell her: So the reason why we’re coming out here again is because we really need her to go in for treatment. ... We really are concerned for the baby’s health especially since she’s had the infection for quite a while.”
Angelica listened while Mr. Sevilla interpreted, her eyes on the ground. Then she looked up. “Orita?” she asked. Right now?
“I’ll walk with you,” Ms. Yang offered. Angelica shook her head. “She said she wants to shower first before she goes over there,” Mr. Sevilla said.
Ms. Yang made a face. “She said that to me last time.” Ms. Yang offered to wait, but Angelica didn’t want the health officers to linger by the house. She said she would meet them by the clinic in 15 minutes.
Ms. Yang was reluctant to let her go but again had no other option. She and Mr. Sevilla drove to the clinic, then stood on the corner of the parking lot, staring down the road.
Talk to the pediatricians, obstetricians, and families on the front lines of the congenital syphilis surge and it becomes clear why Ms. Yang and others are trying so desperately to prevent cases. Dr. J. B. Cantey, associate professor in pediatrics at UT Health San Antonio, remembers a baby girl born at 25 weeks gestation who weighed a pound and a half. Syphilis had spread through her bones and lungs. She spent five months in the neonatal intensive care unit, breathing through a ventilator, and was still eating through a tube when she was discharged.
Then, there are the miscarriages, the stillbirths and the inconsolable parents. Dr. Irene Stafford, an associate professor and maternal-fetal medicine specialist at UT Health in Houston, cannot forget a patient who came in at 36 weeks for a routine checkup, pregnant with her first child. Dr. Stafford realized that there was no heartbeat. “She could see on my face that something was really wrong,” Dr. Stafford recalled. She had to let the patient know that syphilis had killed her baby. “She was hysterical, just bawling,” Dr. Stafford said. “I’ve seen people’s families ripped apart and I’ve seen beautiful babies die.” Fewer than 10% of patients who experience a stillbirth are tested for syphilis, suggesting that cases are underdiagnosed.
A Texas grandmother named Solidad Odunuga offers a glimpse into what the future could hold for Angelica’s mother, who may wind up raising her baby.
In February of last year, Ms. Odunuga got a call from the Lyndon B. Johnson Hospital in Houston. A nurse told her that her daughter was about to give birth and that child protective services had been called. Ms. Odunuga had lost contact with her daughter, who struggled with homelessness and substance abuse. She arrived in time to see her grandson delivered, premature at 30 weeks old, weighing 2.7 pounds. He tested positive for syphilis.
When a child protective worker asked Ms. Odunuga to take custody of the infant, she felt a wave of dread. “I was in denial,” she recalled. “I did not plan to be a mom again.” The baby’s medical problems were daunting: “Global developmental delays ... concerns for visual impairments ... high risk of cerebral palsy,” read a note from the doctor at the time.
Still, Ms. Odunuga visited her grandson every day for three months, driving to the NICU from her job at the University of Houston. “I’d put him in my shirt to keep him warm and hold him there.” She fell in love. She named him Emmanuel.
Once Emmanuel was discharged, Ms. Odunuga realized she had no choice but to quit her job. While Medicaid covered the costs of Emmanuel’s treatment, it was on her to care for him. From infancy, Emmanuel’s life has been a whirlwind of constant therapy. Today, at 20 months old, Odunuga brings him to physical, occupational, speech, and developmental therapy, each a different appointment on a different day of the week.
Emmanuel has thrived beyond what his doctors predicted, toddling so fast that Ms. Odunuga can’t look away for a minute and beaming as he waves his favorite toy phone. Yet he still suffers from gagging issues, which means Ms. Odunuga can’t feed him any solid foods. Liquid gets into his lungs when he aspirates; it has led to pneumonia three times. Emmanuel has a special stroller that helps keep his head in a position that won’t aggravate his persistent reflux, but Odunuga said she still has to pull over on the side of the road sometimes when she hears him projectile vomiting from the backseat.
The days are endless. Once she puts Emmanuel to bed, Ms. Odunuga starts planning the next day’s appointments. “I’ve had to cry alone, scream out alone,” she said. “Sometimes I wake up and think, Is this real? And then I hear him in the next room.”
Putting aside the challenge of eliminating syphilis entirely, everyone agrees it’s both doable and necessary to prevent newborn cases. “There was a crisis in perinatal HIV almost 30 years ago and people stood up and said this is not OK — it’s not acceptable for babies to be born in that condition. ... [We] brought it down from 1,700 babies born each year with perinatal HIV to less than 40 per year today,” said Virginia Bowen, an epidemiologist at the CDC. “Now here we are with a slightly different condition. We can also stand up and say, ‘This is not acceptable.’” Belarus, Bermuda, Cuba, Malaysia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka are among countries recognized by the World Health Organization for eliminating congenital syphilis.
Success starts with filling gaps across the health care system.
For almost a century, public health experts have advocated for testing pregnant patients more than once for syphilis in order to catch the infection. But policies nationwide still don’t reflect this best practice. Six states have no prenatal screening requirement at all. Even in states that require three tests, public health officials say that many physicians aren’t aware of the requirements. Dr. Stafford, the maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Houston, says she’s tired of hearing her own peers in medicine tell her, “Oh, syphilis is a problem?”
It costs public health departments less than 25 cents a dose to buy penicillin, but for a private practice, it’s more than $1,000, according to Dr. Park of the University of California San Francisco. “There’s no incentive for a private physician to stock a dose that could expire before it’s used, so they often don’t have it. So a woman comes in, they say, ‘We’ll send you to the emergency department or health department to get it,’ then [the patients] don’t show up.”
A vaccine would be invaluable for preventing spread among people at high risk for reinfection. But there is none. Scientists only recently figured out how to grow the bacteria in the lab, prompting grants from the National Institutes of Health to fund research into a vaccine. Dr. Justin Radolf, a researcher at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine, said he hopes his team will have a vaccine candidate by the end of its five-year grant. But it’ll likely take years more to find a manufacturer and run human trials.
Public health agencies also need to recognize that many of the hurdles to getting pregnant people treated involve access to care, economic stability, safe housing and transportation. In Fresno, Ms. Adams has been working on ways her department can collaborate with mental health services. Recently, one of her disease intervention specialists managed to get a pregnant woman treated with penicillin shots and, at the patient’s request, connected her with an addiction treatment center.
Gaining a patient’s cooperation means seeing them as complex humans instead of just a case to solve. “There may be past traumas with the health care system,” said Cynthia Deverson, project manager of the Houston Fetal Infant Morbidity Review. “There’s the fear of being discovered if she’s doing something illegal to survive. ... She may need to be in a certain place at a certain time so she can get something to eat, or maybe it’s the only time of the day that’s safe for her to sleep. They’re not going to tell you that. Yes, they understand there’s a problem, but it’s not an immediate threat, maybe they don’t feel bad yet, so obviously this is not urgent. ...
“What helps to gain trust is consistency,” she said. “Literally, it’s seeing that [disease specialist] constantly, daily. ... The woman can see that you’re not going to harm her, you’re saying, ‘I’m here at this time if you need me.’”
Ms. Yang stood outside the clinic, waiting for Angelica to show up, baking in the 90-degree heat. Her feelings ranged from irritation — Why didn’t she just go? I’d have more energy for other cases — to an appreciation for the parts of Angelica’s story that she didn’t know — She’s in survival mode. I need to be more patient.
Fifteen minutes ticked by, then 20.
“OK,” Ms. Yang announced. “We’re going back.”
She asked Sevilla if he would be OK if they drove Angelica to the clinic; they technically weren’t supposed to because of coronavirus precautions, but Ms. Yang wasn’t sure she could convince Angelica to walk. Mr. Sevilla gave her the thumbs up.
When they pulled up, they saw Angelica sitting in the backyard, chatting with a friend. She now wore a fresh T-shirt and had shoes on her feet. Angelica sat silently in the back seat as Ms. Yang drove to the clinic. A few minutes later, they pulled up to the parking lot.
Finally, Ms. Yang thought. We got her here.
The clinic was packed with people waiting for COVID-19 tests and vaccinations. A worker there had previously told Ms. Yang that a walk-in would be fine, but a receptionist now said they were too busy to treat Angelica. She would have to return.
Ms. Yang felt a surge of frustration, sensing that her hard-fought opportunity was slipping away. She tried to talk to the nurse supervisor, but he wasn’t available. She tried to leave the gift cards at the office to reward Angelica if she came, but the receptionist said she couldn’t hold them. While Ms. Yang negotiated, Mr. Sevilla sat with Angelica in the car, waiting.
Finally, Ms. Yang accepted this was yet another thing she couldn’t control.
She drove Angelica back to the yellow house. As they arrived, she tried once more to impress on her just how important it was to get treated, asking Mr. Sevilla to interpret. “We don’t want it to get any more serious, because she can go blind, she could go deaf, she could lose her baby.”
Angelica already had the door halfway open.
“So on a scale from one to 10, how important is this to get treated?” Ms. Yang asked.
“Ten,” Angelica said. Ms. Yang reminded her of the appointment that afternoon. Then Angelica stepped out and returned to the dusty yard.
Ms. Yang lingered for a moment, watching Angelica go. Then she turned the car back onto the highway and set off toward Fresno, knowing, already, that she’d be back.
Postscript: A reporter visited Huron twice more in the months that followed, including once independently to try to interview Angelica, but she wasn’t in town. Ms. Yang has visited Huron twice more as well — six times in total thus far. In October, a couple of men at the yellow house said Angelica was still in town, still pregnant. Ms. Yang and Mr. Sevilla spent an hour driving around, talking to residents, hoping to catch Angelica. But she was nowhere to be found.
ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.