User login
What makes a urinary tract infection complicated?
Consider anatomical and severity risk factors
Case
A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with acute dysuria, fever, and flank pain. She had a urinary tract infection (UTI) 3 months prior treated with nitrofurantoin. Temperature is 102° F, heart rate 112 beats per minute, and the remainder of vital signs are normal. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine microscopy shows 70 WBCs per high power field and bacteria. Is this urinary tract infection complicated?
Background
The urinary tract is divided into the upper tract, which includes the kidneys and ureters, and the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and prostate. Infection of the lower urinary tract is referred to as cystitis while infection of the upper urinary tract is pyelonephritis. A UTI is the colonization of pathogen(s) within the urinary system that causes an inflammatory response resulting in symptoms and requiring treatment. UTIs occur when there is reduced urine flow, an increase in colonization risk, and when there are factors that facilitate ascent such as catheterization or incontinence.
There are an estimated 150 million cases of UTIs worldwide per year, accounting for $6 billion in health care expenditures.1 In the inpatient setting, about 40% of nosocomial infections are associated with urinary catheters. This equates to about 1 million catheter-associated UTIs per year in the United States, and up to 40% of hospital gram-negative bacteremia per year are caused by UTIs.1
UTIs are often classified as either uncomplicated or complicated infections, which can influence the depth of management. UTIs have a wide spectrum of symptoms and can manifest anywhere from mild dysuria treated successfully with outpatient antibiotics to florid sepsis. Uncomplicated simple cystitis is often treated as an outpatient with oral nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.2 Complicated UTIs are treated with broader antimicrobial coverage, and depending on severity, could require intravenous antibiotics. Many factors affect how a UTI manifests and determining whether an infection is “uncomplicated” or “complicated” is an important first step in guiding management. Unfortunately, there are differing classifications of “complicated” UTIs, making it a complicated issue itself. We outline two common approaches.
Anatomic approach
A commonly recognized definition is from the American Urological Association, which states that complicated UTIs are symptomatic cases associated with the presence of “underlying, predisposing conditions and not necessarily clinical severity, invasiveness, or complications.”3 These factors include structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities or urinary instrumentation (see Table 1). These predisposing conditions can increase microbial colonization and decrease therapy efficacy, thus increasing the frequency of infection and relapse.
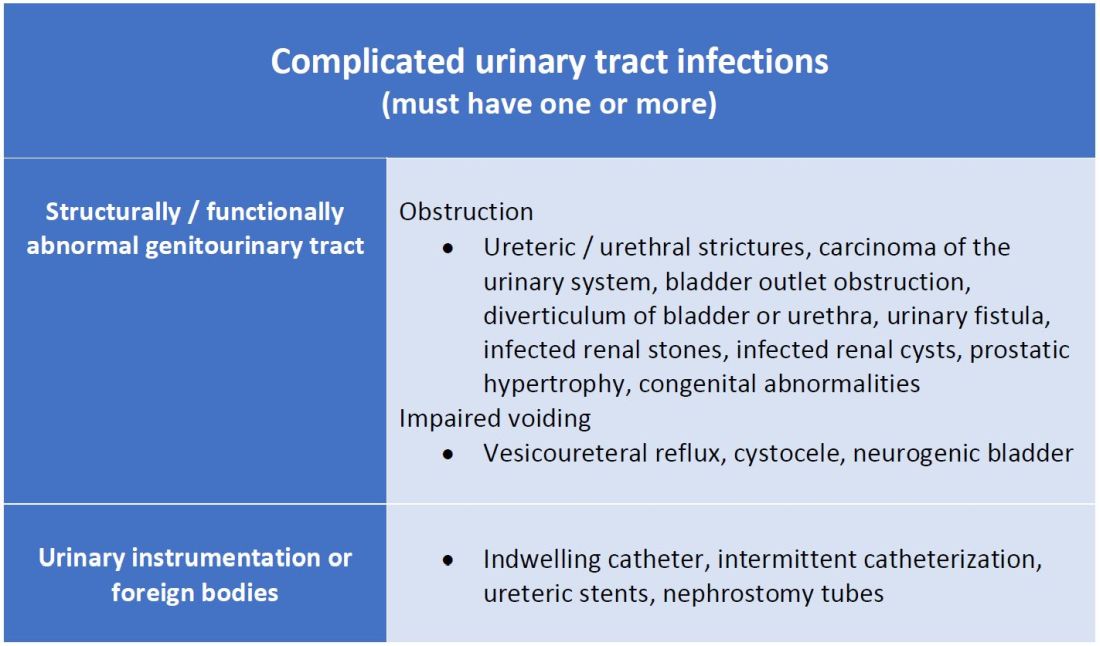
This population of patients is at high risk of infections with more resistant bacteria such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli since they often lack the natural genitourinary barriers to infection. In addition, these patients more often undergo multiple antibiotic courses for their frequent infections, which also contributes to their risk of ESBL infections. Genitourinary abnormalities interfere with normal voiding, resulting in impaired flushing of bacteria. For instance, obstruction inhibits complete urinary drainage and increases the persistence of bacteria in biofilms, especially if there are stones or indwelling devices present. Biofilms usually contain a high concentration of organisms including Proteus mirabilis, Morgenella morganii, and Providencia spp.4 Keep in mind that, if there is an obstruction, the urinalysis might be without pyuria or bacteriuria.
Instrumentation increases infection risks through the direct introduction of bacteria into the genitourinary tract. Despite the efforts in maintaining sterility in urinary catheter placement, catheters provide a nidus for infection. Catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is defined by the Infectious Disease Society of America as UTIs that occur in patients with an indwelling catheter or who had a catheter removed for less than 48 hours who develop urinary symptoms and cultures positive for uropathogenic bacteria.4 Studies show that in general, patients with indwelling catheters will develop bacteriuria over time, with 10%-25% eventually developing symptoms.
Severity approach
There are other schools of thought that categorize uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs based on the severity of presentation (see Table 2). An uncomplicated UTI would be classified as symptoms and signs of simple cystitis limited to dysuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic pain. Using a symptom severity approach, systemic findings such as fever, chills, emesis, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, or other findings of sepsis would be classified as a complicated UTI. These systemic findings would suggest an extension of infection beyond the bladder.
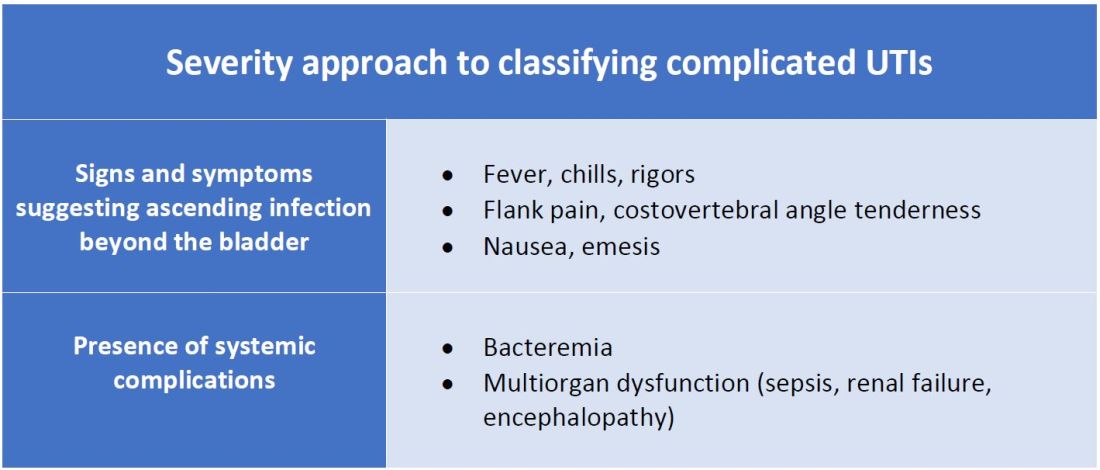
The argument for a symptomatic-based approach of classification is that the severity of symptoms should dictate the degree of management. Not all UTIs in the anatomic approach are severe. In fact, populations that are considered at risk for complicated UTIs by the AUA guidelines in Table 1 often have mild symptomatic cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the colonization of organisms in the urinary tract without active infection. For instance, bacteriuria is present in almost 100% of people with chronic indwelling catheters, 30%-40% of neurogenic bladder requiring intermittent catheterization, and 50% of elderly nursing home residents.4 Not all bacteriuria triggers enough of an inflammatory response to cause symptoms that require treatment.
Ultimate clinical judgment
Although there are multiple different society recommendations in distinguishing uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs, considering both anatomical and severity risk factors can better aid in clinical decision-making rather than abiding by one classification method alone.
Uncomplicated UTIs from the AUA guidelines can cause severe infections that might require longer courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. On the other hand, people with anatomic abnormalities can present with mild symptoms that can be treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for a standard time course. Recognizing the severity of the infection and using clinical judgment aids in antibiotic stewardship.
Although the existence of algorithmic approaches can help guide clinical judgment, accounting for the spectrum of host and bacterial factors should ultimately determine the complexity of the disease and management.3 Using clinical suspicion to determine when a UTI should be treated as a complicated infection can ensure effective treatment and decrease the likelihood of sepsis, renal scarring, or end-stage disease.5
Back to the case
The case presents an elderly woman with diabetes presenting with sepsis from a UTI. Because of a normal urinary tract and no prior instrumentation, by the AUA definition, she would be classified as an uncomplicated UTI; however, we would classify her as a complicated UTI based on the severity of her presentation. She has a fever, tachycardia, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness that are evidence of infection extending beyond the bladder. She has sepsis warranting inpatient management. Prior urine culture results could aid in determining empiric treatment while waiting for new cultures. In her case, an intravenous antibiotic with broad gram-negative coverage such as ceftriaxone would be appropriate.
Bottom line
There are multiple interpretations of complicated UTIs including both an anatomical and severity approach. Clinical judgment regarding infection severity should determine the depth of management.
Dr. Vu is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Dr. Gray is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky and the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
References
1. Folk CS. AUA Core Curriculum: Urinary Tract Infection (Adult). 2021 Mar 1. https://university.auanet.org/core_topic.cfm?coreid=92.
2. Gupta K et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 1;52(5):e103-20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257.
3. Johnson JR. Definition of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 February 15;64(4):529. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw751.
4. Nicolle LE, AMMI Canada Guidelines Committee. Complicated urinary tract infection in adults. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005;16(6):349-60. doi: 10.1155/2005/385768.
5. Melekos MD and Naber KG. Complicated urinary tract infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;15(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(00)00168-0.
Key points
- The anatomical approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the presence of underlying, predisposing conditions such as structurally or functionally abnormal genitourinary tract or urinary instrumentation or foreign bodies.
- The severity approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the severity of presentation including the presence of systemic manifestations.
- Both approaches should consider populations that are at risk for recurrent or multidrug-resistant infections and infections that can lead to high morbidity.
- Either approach can be used as a guide, but neither should replace clinical suspicion and judgment in determining the depth of treatment.
Additional reading
Choe HS et al. Summary of the UAA‐AAUS guidelines for urinary tract infections. Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):175-85. doi:10.1111/iju.13493.
Nicolle LE et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;40(5):643-54. doi: 10.1086/427507.
Wagenlehner FME et al. Epidemiology, definition and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17:586-600. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0362-4.
Wallace DW et al. Urinalysis: A simple test with complicated interpretation. J Urgent Care Med. 2020 July-Aug;14(10):11-4.
Quiz
A 68-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with acute fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has associated nausea, malaise, and fatigue. She takes metformin and denies recent antibiotic use. Her temperature is 102.8° F, heart rate 118 beats per minute, blood pressure 118/71 mm Hg, and her respiratory rate is 24 breaths per minute. She is ill-appearing and has mild suprapubic tenderness. White blood cell count is 18 k/mcL. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and bacteria. Urine microscopy has 120 white blood cells per high power field. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Azithromycin
B. Ceftriaxone
C. Cefepime and vancomycin
D. Nitrofurantoin
The answer is B. The patient presents with sepsis secondary to a urinary tract infection. Using the anatomic approach this would be classified as uncomplicated. Using the severity approach, this would be classified as a complicated urinary tract infection. With fever, chills, and signs of sepsis, it’s likely her infection extends beyond the bladder. Given the severity of her presentation, we’d favor treating her as a complicated urinary tract infection with intravenous ceftriaxone. There is no suggestion of resistance or additional MRSA risk factors requiring intravenous vancomycin or cefepime. Nitrofurantoin, although a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis, would not be appropriate if there is suspicion infection extends beyond the bladder. Azithromycin is a first-line option for chlamydia trachomatis, but not a urinary tract infection.
Consider anatomical and severity risk factors
Consider anatomical and severity risk factors
Case
A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with acute dysuria, fever, and flank pain. She had a urinary tract infection (UTI) 3 months prior treated with nitrofurantoin. Temperature is 102° F, heart rate 112 beats per minute, and the remainder of vital signs are normal. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine microscopy shows 70 WBCs per high power field and bacteria. Is this urinary tract infection complicated?
Background
The urinary tract is divided into the upper tract, which includes the kidneys and ureters, and the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and prostate. Infection of the lower urinary tract is referred to as cystitis while infection of the upper urinary tract is pyelonephritis. A UTI is the colonization of pathogen(s) within the urinary system that causes an inflammatory response resulting in symptoms and requiring treatment. UTIs occur when there is reduced urine flow, an increase in colonization risk, and when there are factors that facilitate ascent such as catheterization or incontinence.
There are an estimated 150 million cases of UTIs worldwide per year, accounting for $6 billion in health care expenditures.1 In the inpatient setting, about 40% of nosocomial infections are associated with urinary catheters. This equates to about 1 million catheter-associated UTIs per year in the United States, and up to 40% of hospital gram-negative bacteremia per year are caused by UTIs.1
UTIs are often classified as either uncomplicated or complicated infections, which can influence the depth of management. UTIs have a wide spectrum of symptoms and can manifest anywhere from mild dysuria treated successfully with outpatient antibiotics to florid sepsis. Uncomplicated simple cystitis is often treated as an outpatient with oral nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.2 Complicated UTIs are treated with broader antimicrobial coverage, and depending on severity, could require intravenous antibiotics. Many factors affect how a UTI manifests and determining whether an infection is “uncomplicated” or “complicated” is an important first step in guiding management. Unfortunately, there are differing classifications of “complicated” UTIs, making it a complicated issue itself. We outline two common approaches.
Anatomic approach
A commonly recognized definition is from the American Urological Association, which states that complicated UTIs are symptomatic cases associated with the presence of “underlying, predisposing conditions and not necessarily clinical severity, invasiveness, or complications.”3 These factors include structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities or urinary instrumentation (see Table 1). These predisposing conditions can increase microbial colonization and decrease therapy efficacy, thus increasing the frequency of infection and relapse.

This population of patients is at high risk of infections with more resistant bacteria such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli since they often lack the natural genitourinary barriers to infection. In addition, these patients more often undergo multiple antibiotic courses for their frequent infections, which also contributes to their risk of ESBL infections. Genitourinary abnormalities interfere with normal voiding, resulting in impaired flushing of bacteria. For instance, obstruction inhibits complete urinary drainage and increases the persistence of bacteria in biofilms, especially if there are stones or indwelling devices present. Biofilms usually contain a high concentration of organisms including Proteus mirabilis, Morgenella morganii, and Providencia spp.4 Keep in mind that, if there is an obstruction, the urinalysis might be without pyuria or bacteriuria.
Instrumentation increases infection risks through the direct introduction of bacteria into the genitourinary tract. Despite the efforts in maintaining sterility in urinary catheter placement, catheters provide a nidus for infection. Catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is defined by the Infectious Disease Society of America as UTIs that occur in patients with an indwelling catheter or who had a catheter removed for less than 48 hours who develop urinary symptoms and cultures positive for uropathogenic bacteria.4 Studies show that in general, patients with indwelling catheters will develop bacteriuria over time, with 10%-25% eventually developing symptoms.
Severity approach
There are other schools of thought that categorize uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs based on the severity of presentation (see Table 2). An uncomplicated UTI would be classified as symptoms and signs of simple cystitis limited to dysuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic pain. Using a symptom severity approach, systemic findings such as fever, chills, emesis, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, or other findings of sepsis would be classified as a complicated UTI. These systemic findings would suggest an extension of infection beyond the bladder.

The argument for a symptomatic-based approach of classification is that the severity of symptoms should dictate the degree of management. Not all UTIs in the anatomic approach are severe. In fact, populations that are considered at risk for complicated UTIs by the AUA guidelines in Table 1 often have mild symptomatic cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the colonization of organisms in the urinary tract without active infection. For instance, bacteriuria is present in almost 100% of people with chronic indwelling catheters, 30%-40% of neurogenic bladder requiring intermittent catheterization, and 50% of elderly nursing home residents.4 Not all bacteriuria triggers enough of an inflammatory response to cause symptoms that require treatment.
Ultimate clinical judgment
Although there are multiple different society recommendations in distinguishing uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs, considering both anatomical and severity risk factors can better aid in clinical decision-making rather than abiding by one classification method alone.
Uncomplicated UTIs from the AUA guidelines can cause severe infections that might require longer courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. On the other hand, people with anatomic abnormalities can present with mild symptoms that can be treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for a standard time course. Recognizing the severity of the infection and using clinical judgment aids in antibiotic stewardship.
Although the existence of algorithmic approaches can help guide clinical judgment, accounting for the spectrum of host and bacterial factors should ultimately determine the complexity of the disease and management.3 Using clinical suspicion to determine when a UTI should be treated as a complicated infection can ensure effective treatment and decrease the likelihood of sepsis, renal scarring, or end-stage disease.5
Back to the case
The case presents an elderly woman with diabetes presenting with sepsis from a UTI. Because of a normal urinary tract and no prior instrumentation, by the AUA definition, she would be classified as an uncomplicated UTI; however, we would classify her as a complicated UTI based on the severity of her presentation. She has a fever, tachycardia, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness that are evidence of infection extending beyond the bladder. She has sepsis warranting inpatient management. Prior urine culture results could aid in determining empiric treatment while waiting for new cultures. In her case, an intravenous antibiotic with broad gram-negative coverage such as ceftriaxone would be appropriate.
Bottom line
There are multiple interpretations of complicated UTIs including both an anatomical and severity approach. Clinical judgment regarding infection severity should determine the depth of management.
Dr. Vu is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Dr. Gray is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky and the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
References
1. Folk CS. AUA Core Curriculum: Urinary Tract Infection (Adult). 2021 Mar 1. https://university.auanet.org/core_topic.cfm?coreid=92.
2. Gupta K et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 1;52(5):e103-20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257.
3. Johnson JR. Definition of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 February 15;64(4):529. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw751.
4. Nicolle LE, AMMI Canada Guidelines Committee. Complicated urinary tract infection in adults. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005;16(6):349-60. doi: 10.1155/2005/385768.
5. Melekos MD and Naber KG. Complicated urinary tract infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;15(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(00)00168-0.
Key points
- The anatomical approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the presence of underlying, predisposing conditions such as structurally or functionally abnormal genitourinary tract or urinary instrumentation or foreign bodies.
- The severity approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the severity of presentation including the presence of systemic manifestations.
- Both approaches should consider populations that are at risk for recurrent or multidrug-resistant infections and infections that can lead to high morbidity.
- Either approach can be used as a guide, but neither should replace clinical suspicion and judgment in determining the depth of treatment.
Additional reading
Choe HS et al. Summary of the UAA‐AAUS guidelines for urinary tract infections. Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):175-85. doi:10.1111/iju.13493.
Nicolle LE et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;40(5):643-54. doi: 10.1086/427507.
Wagenlehner FME et al. Epidemiology, definition and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17:586-600. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0362-4.
Wallace DW et al. Urinalysis: A simple test with complicated interpretation. J Urgent Care Med. 2020 July-Aug;14(10):11-4.
Quiz
A 68-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with acute fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has associated nausea, malaise, and fatigue. She takes metformin and denies recent antibiotic use. Her temperature is 102.8° F, heart rate 118 beats per minute, blood pressure 118/71 mm Hg, and her respiratory rate is 24 breaths per minute. She is ill-appearing and has mild suprapubic tenderness. White blood cell count is 18 k/mcL. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and bacteria. Urine microscopy has 120 white blood cells per high power field. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Azithromycin
B. Ceftriaxone
C. Cefepime and vancomycin
D. Nitrofurantoin
The answer is B. The patient presents with sepsis secondary to a urinary tract infection. Using the anatomic approach this would be classified as uncomplicated. Using the severity approach, this would be classified as a complicated urinary tract infection. With fever, chills, and signs of sepsis, it’s likely her infection extends beyond the bladder. Given the severity of her presentation, we’d favor treating her as a complicated urinary tract infection with intravenous ceftriaxone. There is no suggestion of resistance or additional MRSA risk factors requiring intravenous vancomycin or cefepime. Nitrofurantoin, although a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis, would not be appropriate if there is suspicion infection extends beyond the bladder. Azithromycin is a first-line option for chlamydia trachomatis, but not a urinary tract infection.
Case
A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with acute dysuria, fever, and flank pain. She had a urinary tract infection (UTI) 3 months prior treated with nitrofurantoin. Temperature is 102° F, heart rate 112 beats per minute, and the remainder of vital signs are normal. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine microscopy shows 70 WBCs per high power field and bacteria. Is this urinary tract infection complicated?
Background
The urinary tract is divided into the upper tract, which includes the kidneys and ureters, and the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and prostate. Infection of the lower urinary tract is referred to as cystitis while infection of the upper urinary tract is pyelonephritis. A UTI is the colonization of pathogen(s) within the urinary system that causes an inflammatory response resulting in symptoms and requiring treatment. UTIs occur when there is reduced urine flow, an increase in colonization risk, and when there are factors that facilitate ascent such as catheterization or incontinence.
There are an estimated 150 million cases of UTIs worldwide per year, accounting for $6 billion in health care expenditures.1 In the inpatient setting, about 40% of nosocomial infections are associated with urinary catheters. This equates to about 1 million catheter-associated UTIs per year in the United States, and up to 40% of hospital gram-negative bacteremia per year are caused by UTIs.1
UTIs are often classified as either uncomplicated or complicated infections, which can influence the depth of management. UTIs have a wide spectrum of symptoms and can manifest anywhere from mild dysuria treated successfully with outpatient antibiotics to florid sepsis. Uncomplicated simple cystitis is often treated as an outpatient with oral nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.2 Complicated UTIs are treated with broader antimicrobial coverage, and depending on severity, could require intravenous antibiotics. Many factors affect how a UTI manifests and determining whether an infection is “uncomplicated” or “complicated” is an important first step in guiding management. Unfortunately, there are differing classifications of “complicated” UTIs, making it a complicated issue itself. We outline two common approaches.
Anatomic approach
A commonly recognized definition is from the American Urological Association, which states that complicated UTIs are symptomatic cases associated with the presence of “underlying, predisposing conditions and not necessarily clinical severity, invasiveness, or complications.”3 These factors include structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities or urinary instrumentation (see Table 1). These predisposing conditions can increase microbial colonization and decrease therapy efficacy, thus increasing the frequency of infection and relapse.

This population of patients is at high risk of infections with more resistant bacteria such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli since they often lack the natural genitourinary barriers to infection. In addition, these patients more often undergo multiple antibiotic courses for their frequent infections, which also contributes to their risk of ESBL infections. Genitourinary abnormalities interfere with normal voiding, resulting in impaired flushing of bacteria. For instance, obstruction inhibits complete urinary drainage and increases the persistence of bacteria in biofilms, especially if there are stones or indwelling devices present. Biofilms usually contain a high concentration of organisms including Proteus mirabilis, Morgenella morganii, and Providencia spp.4 Keep in mind that, if there is an obstruction, the urinalysis might be without pyuria or bacteriuria.
Instrumentation increases infection risks through the direct introduction of bacteria into the genitourinary tract. Despite the efforts in maintaining sterility in urinary catheter placement, catheters provide a nidus for infection. Catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is defined by the Infectious Disease Society of America as UTIs that occur in patients with an indwelling catheter or who had a catheter removed for less than 48 hours who develop urinary symptoms and cultures positive for uropathogenic bacteria.4 Studies show that in general, patients with indwelling catheters will develop bacteriuria over time, with 10%-25% eventually developing symptoms.
Severity approach
There are other schools of thought that categorize uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs based on the severity of presentation (see Table 2). An uncomplicated UTI would be classified as symptoms and signs of simple cystitis limited to dysuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic pain. Using a symptom severity approach, systemic findings such as fever, chills, emesis, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, or other findings of sepsis would be classified as a complicated UTI. These systemic findings would suggest an extension of infection beyond the bladder.

The argument for a symptomatic-based approach of classification is that the severity of symptoms should dictate the degree of management. Not all UTIs in the anatomic approach are severe. In fact, populations that are considered at risk for complicated UTIs by the AUA guidelines in Table 1 often have mild symptomatic cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the colonization of organisms in the urinary tract without active infection. For instance, bacteriuria is present in almost 100% of people with chronic indwelling catheters, 30%-40% of neurogenic bladder requiring intermittent catheterization, and 50% of elderly nursing home residents.4 Not all bacteriuria triggers enough of an inflammatory response to cause symptoms that require treatment.
Ultimate clinical judgment
Although there are multiple different society recommendations in distinguishing uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs, considering both anatomical and severity risk factors can better aid in clinical decision-making rather than abiding by one classification method alone.
Uncomplicated UTIs from the AUA guidelines can cause severe infections that might require longer courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. On the other hand, people with anatomic abnormalities can present with mild symptoms that can be treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for a standard time course. Recognizing the severity of the infection and using clinical judgment aids in antibiotic stewardship.
Although the existence of algorithmic approaches can help guide clinical judgment, accounting for the spectrum of host and bacterial factors should ultimately determine the complexity of the disease and management.3 Using clinical suspicion to determine when a UTI should be treated as a complicated infection can ensure effective treatment and decrease the likelihood of sepsis, renal scarring, or end-stage disease.5
Back to the case
The case presents an elderly woman with diabetes presenting with sepsis from a UTI. Because of a normal urinary tract and no prior instrumentation, by the AUA definition, she would be classified as an uncomplicated UTI; however, we would classify her as a complicated UTI based on the severity of her presentation. She has a fever, tachycardia, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness that are evidence of infection extending beyond the bladder. She has sepsis warranting inpatient management. Prior urine culture results could aid in determining empiric treatment while waiting for new cultures. In her case, an intravenous antibiotic with broad gram-negative coverage such as ceftriaxone would be appropriate.
Bottom line
There are multiple interpretations of complicated UTIs including both an anatomical and severity approach. Clinical judgment regarding infection severity should determine the depth of management.
Dr. Vu is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Dr. Gray is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky and the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
References
1. Folk CS. AUA Core Curriculum: Urinary Tract Infection (Adult). 2021 Mar 1. https://university.auanet.org/core_topic.cfm?coreid=92.
2. Gupta K et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 1;52(5):e103-20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257.
3. Johnson JR. Definition of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 February 15;64(4):529. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw751.
4. Nicolle LE, AMMI Canada Guidelines Committee. Complicated urinary tract infection in adults. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005;16(6):349-60. doi: 10.1155/2005/385768.
5. Melekos MD and Naber KG. Complicated urinary tract infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;15(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(00)00168-0.
Key points
- The anatomical approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the presence of underlying, predisposing conditions such as structurally or functionally abnormal genitourinary tract or urinary instrumentation or foreign bodies.
- The severity approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the severity of presentation including the presence of systemic manifestations.
- Both approaches should consider populations that are at risk for recurrent or multidrug-resistant infections and infections that can lead to high morbidity.
- Either approach can be used as a guide, but neither should replace clinical suspicion and judgment in determining the depth of treatment.
Additional reading
Choe HS et al. Summary of the UAA‐AAUS guidelines for urinary tract infections. Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):175-85. doi:10.1111/iju.13493.
Nicolle LE et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;40(5):643-54. doi: 10.1086/427507.
Wagenlehner FME et al. Epidemiology, definition and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17:586-600. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0362-4.
Wallace DW et al. Urinalysis: A simple test with complicated interpretation. J Urgent Care Med. 2020 July-Aug;14(10):11-4.
Quiz
A 68-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with acute fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has associated nausea, malaise, and fatigue. She takes metformin and denies recent antibiotic use. Her temperature is 102.8° F, heart rate 118 beats per minute, blood pressure 118/71 mm Hg, and her respiratory rate is 24 breaths per minute. She is ill-appearing and has mild suprapubic tenderness. White blood cell count is 18 k/mcL. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and bacteria. Urine microscopy has 120 white blood cells per high power field. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Azithromycin
B. Ceftriaxone
C. Cefepime and vancomycin
D. Nitrofurantoin
The answer is B. The patient presents with sepsis secondary to a urinary tract infection. Using the anatomic approach this would be classified as uncomplicated. Using the severity approach, this would be classified as a complicated urinary tract infection. With fever, chills, and signs of sepsis, it’s likely her infection extends beyond the bladder. Given the severity of her presentation, we’d favor treating her as a complicated urinary tract infection with intravenous ceftriaxone. There is no suggestion of resistance or additional MRSA risk factors requiring intravenous vancomycin or cefepime. Nitrofurantoin, although a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis, would not be appropriate if there is suspicion infection extends beyond the bladder. Azithromycin is a first-line option for chlamydia trachomatis, but not a urinary tract infection.
Schools, pediatricians look to make up lost ground on non–COVID-19 vaccinations
WESTMINSTER, COLO. – Melissa Blatzer was determined to get her three children caught up on their routine immunizations on a recent Saturday morning at a walk-in clinic in this Denver suburb. It had been about a year since the kids’ last shots, a delay Ms. Blatzer chalked up to the pandemic.
Two-year-old Lincoln Blatzer, in his fleece dinosaur pajamas, waited anxiously in line for his hepatitis A vaccine. His siblings, 14-year-old Nyla Kusumah and 11-year-old Nevan Kusumah, were there for their TDAP, HPV and meningococcal vaccines, plus a COVID-19 shot for Nyla.
“You don’t have to make an appointment and you can take all three at once,” said Ms. Blatzer, who lives several miles away in Commerce City. That convenience outweighed the difficulty of getting everyone up early on a weekend.
Child health experts hope community clinics like this – along with the return to in-person classes, more well-child visits, and the rollout of COVID shots for younger children – can help boost routine childhood immunizations, which dropped during the pandemic. Despite a rebound, immunization rates are still lower than in 2019, and disparities in rates between racial and economic groups, particularly for Black children, have been exacerbated.
“We’re still not back to where we need to be,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, a pediatric infectious disease doctor at Children’s Hospital Colorado and a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Routine immunizations protect children against 16 infectious diseases, including measles, diphtheria and chickenpox, and inhibit transmission to the community.
The rollout of COVID shots for younger kids is an opportunity to catch up on routine vaccinations, said Dr. O’Leary, adding that children can receive these vaccines together. Primary care practices, where many children are likely to receive the COVID shots, usually have other childhood vaccines on hand.
“It’s really important that parents and health care providers work together so that all children are up to date on these recommended vaccines,” said Malini DeSilva, MD, an internist and pediatrician at HealthPartners in the Minneapolis–St. Paul area. “Not only for the child’s health but for our community’s health.”
People were reluctant to come out for routine immunizations at the height of the pandemic, said Karen Miller, an immunization nurse manager for the Denver area’s Tri-County Health Department, which ran the Westminster clinic. National and global data confirm what Ms. Miller saw on the ground.
Global vaccine coverage in children fell from 2019 to 2020, according to a recent study by scientists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Health Organization, and UNICEF. Reasons included reduced access, lack of transportation, worries about COVID exposure and supply chain interruptions, the study said.
Third doses of the DTP vaccine and of the polio vaccine decreased from 86% of all eligible children in 2019 to 83% in 2020, according to the study. Worldwide, 22.7 million children had not had their third dose of DTP in 2020, compared with 19 million in 2019. Three doses are far more effective than one or two at protecting children and communities.
In the United States, researchers who studied 2019 and 2020 data on routine vaccinations in California, Colorado, Minnesota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin found substantial disruptions in vaccination rates during the pandemic that continued into September 2020. For example, the percentage of 7-month-old babies who were up to date on vaccinations decreased from 81% in September 2019 to 74% a year later.
The proportion of Black children up to date on immunizations in almost all age groups was lower than that of children in other racial and ethnic groups. This was most pronounced in those turning 18 months old: Only 41% of Black children that age were caught up on vaccinations in September 2020, compared with 57% of all children at 18 months, said Dr. DeSilva, who led that study.
A CDC study of data from the National Immunization Surveys found that race and ethnicity, poverty, and lack of insurance created the greatest disparities in vaccination rates, and the authors noted that extra efforts are needed to counter the pandemic’s disruptions.
In addition to the problems caused by COVID, Ms. Miller said, competing life priorities like work and school impede families from keeping up with shots. Weekend vaccination clinics can help working parents get their children caught up on routine immunizations while they get a flu or COVID shot. Ms. Miller and O’Leary also said reminders via phone, text or email can boost immunizations.
“Vaccines are so effective that I think it’s easy for families to put immunizations on the back burner because we don’t often hear about these diseases,” she said.
It’s a long and nasty list that includes hepatitis A and B, measles, mumps, whooping cough, polio, rubella, rotavirus, pneumococcus, tetanus, diphtheria, human papillomavirus, and meningococcal disease, among others. Even small drops in vaccination coverage can lead to outbreaks. And measles is the perfect example that worries experts, particularly as international travel opens up.
“Measles is among the most contagious diseases known to humankind, meaning that we have to keep very high vaccination coverage to keep it from spreading,” said Dr. O’Leary.
In 2019, 22 measles outbreaks occurred in 17 states in mostly unvaccinated children and adults. Dr. O’Leary said outbreaks in New York City were contained because surrounding areas had high vaccination coverage. But an outbreak in an undervaccinated community still could spread beyond its borders.
In some states a significant number of parents were opposed to routine childhood vaccines even before the pandemic for religious or personal reasons, posing another challenge for health professionals. For example, 87% of Colorado kindergartners were vaccinated against measles, mumps, and rubella during the 2018-19 school year, one of the nation’s lowest rates.
Those rates bumped up to 91% in 2019-20 but are still below the CDC’s target of 95%.
Dr. O’Leary said he does not see the same level of hesitancy for routine immunizations as for COVID. “There has always been vaccine hesitancy and vaccine refusers. But we’ve maintained vaccination rates north of 90% for all routine childhood vaccines for a long time now,” he said.
Dr. DeSilva said the “ripple effects” of missed vaccinations earlier in the pandemic continued into 2021. As children returned to in-person learning this fall, schools may have been the first place families heard about missed vaccinations. Individual states set vaccination requirements, and allowable exemptions, for entry at schools and child care facilities. In 2020, Colorado passed a school entry immunization law that tightened allowable exemptions.
“Schools, where vaccination requirements are generally enforced, are stretched thin for a variety of reasons, including COVID,” said Dr. O’Leary, adding that managing vaccine requirements may be more difficult for some, but not all, schools.
Anayeli Dominguez, 13, was at the Westminster clinic for a Tdap vaccine because her middle school had noticed she was not up to date.
“School nurses play an important role in helping identify students in need of immunizations, and also by connecting families to resources both within the district and in the larger community,” said Denver Public Schools spokesperson Will Jones.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
WESTMINSTER, COLO. – Melissa Blatzer was determined to get her three children caught up on their routine immunizations on a recent Saturday morning at a walk-in clinic in this Denver suburb. It had been about a year since the kids’ last shots, a delay Ms. Blatzer chalked up to the pandemic.
Two-year-old Lincoln Blatzer, in his fleece dinosaur pajamas, waited anxiously in line for his hepatitis A vaccine. His siblings, 14-year-old Nyla Kusumah and 11-year-old Nevan Kusumah, were there for their TDAP, HPV and meningococcal vaccines, plus a COVID-19 shot for Nyla.
“You don’t have to make an appointment and you can take all three at once,” said Ms. Blatzer, who lives several miles away in Commerce City. That convenience outweighed the difficulty of getting everyone up early on a weekend.
Child health experts hope community clinics like this – along with the return to in-person classes, more well-child visits, and the rollout of COVID shots for younger children – can help boost routine childhood immunizations, which dropped during the pandemic. Despite a rebound, immunization rates are still lower than in 2019, and disparities in rates between racial and economic groups, particularly for Black children, have been exacerbated.
“We’re still not back to where we need to be,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, a pediatric infectious disease doctor at Children’s Hospital Colorado and a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Routine immunizations protect children against 16 infectious diseases, including measles, diphtheria and chickenpox, and inhibit transmission to the community.
The rollout of COVID shots for younger kids is an opportunity to catch up on routine vaccinations, said Dr. O’Leary, adding that children can receive these vaccines together. Primary care practices, where many children are likely to receive the COVID shots, usually have other childhood vaccines on hand.
“It’s really important that parents and health care providers work together so that all children are up to date on these recommended vaccines,” said Malini DeSilva, MD, an internist and pediatrician at HealthPartners in the Minneapolis–St. Paul area. “Not only for the child’s health but for our community’s health.”
People were reluctant to come out for routine immunizations at the height of the pandemic, said Karen Miller, an immunization nurse manager for the Denver area’s Tri-County Health Department, which ran the Westminster clinic. National and global data confirm what Ms. Miller saw on the ground.
Global vaccine coverage in children fell from 2019 to 2020, according to a recent study by scientists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Health Organization, and UNICEF. Reasons included reduced access, lack of transportation, worries about COVID exposure and supply chain interruptions, the study said.
Third doses of the DTP vaccine and of the polio vaccine decreased from 86% of all eligible children in 2019 to 83% in 2020, according to the study. Worldwide, 22.7 million children had not had their third dose of DTP in 2020, compared with 19 million in 2019. Three doses are far more effective than one or two at protecting children and communities.
In the United States, researchers who studied 2019 and 2020 data on routine vaccinations in California, Colorado, Minnesota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin found substantial disruptions in vaccination rates during the pandemic that continued into September 2020. For example, the percentage of 7-month-old babies who were up to date on vaccinations decreased from 81% in September 2019 to 74% a year later.
The proportion of Black children up to date on immunizations in almost all age groups was lower than that of children in other racial and ethnic groups. This was most pronounced in those turning 18 months old: Only 41% of Black children that age were caught up on vaccinations in September 2020, compared with 57% of all children at 18 months, said Dr. DeSilva, who led that study.
A CDC study of data from the National Immunization Surveys found that race and ethnicity, poverty, and lack of insurance created the greatest disparities in vaccination rates, and the authors noted that extra efforts are needed to counter the pandemic’s disruptions.
In addition to the problems caused by COVID, Ms. Miller said, competing life priorities like work and school impede families from keeping up with shots. Weekend vaccination clinics can help working parents get their children caught up on routine immunizations while they get a flu or COVID shot. Ms. Miller and O’Leary also said reminders via phone, text or email can boost immunizations.
“Vaccines are so effective that I think it’s easy for families to put immunizations on the back burner because we don’t often hear about these diseases,” she said.
It’s a long and nasty list that includes hepatitis A and B, measles, mumps, whooping cough, polio, rubella, rotavirus, pneumococcus, tetanus, diphtheria, human papillomavirus, and meningococcal disease, among others. Even small drops in vaccination coverage can lead to outbreaks. And measles is the perfect example that worries experts, particularly as international travel opens up.
“Measles is among the most contagious diseases known to humankind, meaning that we have to keep very high vaccination coverage to keep it from spreading,” said Dr. O’Leary.
In 2019, 22 measles outbreaks occurred in 17 states in mostly unvaccinated children and adults. Dr. O’Leary said outbreaks in New York City were contained because surrounding areas had high vaccination coverage. But an outbreak in an undervaccinated community still could spread beyond its borders.
In some states a significant number of parents were opposed to routine childhood vaccines even before the pandemic for religious or personal reasons, posing another challenge for health professionals. For example, 87% of Colorado kindergartners were vaccinated against measles, mumps, and rubella during the 2018-19 school year, one of the nation’s lowest rates.
Those rates bumped up to 91% in 2019-20 but are still below the CDC’s target of 95%.
Dr. O’Leary said he does not see the same level of hesitancy for routine immunizations as for COVID. “There has always been vaccine hesitancy and vaccine refusers. But we’ve maintained vaccination rates north of 90% for all routine childhood vaccines for a long time now,” he said.
Dr. DeSilva said the “ripple effects” of missed vaccinations earlier in the pandemic continued into 2021. As children returned to in-person learning this fall, schools may have been the first place families heard about missed vaccinations. Individual states set vaccination requirements, and allowable exemptions, for entry at schools and child care facilities. In 2020, Colorado passed a school entry immunization law that tightened allowable exemptions.
“Schools, where vaccination requirements are generally enforced, are stretched thin for a variety of reasons, including COVID,” said Dr. O’Leary, adding that managing vaccine requirements may be more difficult for some, but not all, schools.
Anayeli Dominguez, 13, was at the Westminster clinic for a Tdap vaccine because her middle school had noticed she was not up to date.
“School nurses play an important role in helping identify students in need of immunizations, and also by connecting families to resources both within the district and in the larger community,” said Denver Public Schools spokesperson Will Jones.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
WESTMINSTER, COLO. – Melissa Blatzer was determined to get her three children caught up on their routine immunizations on a recent Saturday morning at a walk-in clinic in this Denver suburb. It had been about a year since the kids’ last shots, a delay Ms. Blatzer chalked up to the pandemic.
Two-year-old Lincoln Blatzer, in his fleece dinosaur pajamas, waited anxiously in line for his hepatitis A vaccine. His siblings, 14-year-old Nyla Kusumah and 11-year-old Nevan Kusumah, were there for their TDAP, HPV and meningococcal vaccines, plus a COVID-19 shot for Nyla.
“You don’t have to make an appointment and you can take all three at once,” said Ms. Blatzer, who lives several miles away in Commerce City. That convenience outweighed the difficulty of getting everyone up early on a weekend.
Child health experts hope community clinics like this – along with the return to in-person classes, more well-child visits, and the rollout of COVID shots for younger children – can help boost routine childhood immunizations, which dropped during the pandemic. Despite a rebound, immunization rates are still lower than in 2019, and disparities in rates between racial and economic groups, particularly for Black children, have been exacerbated.
“We’re still not back to where we need to be,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, a pediatric infectious disease doctor at Children’s Hospital Colorado and a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Routine immunizations protect children against 16 infectious diseases, including measles, diphtheria and chickenpox, and inhibit transmission to the community.
The rollout of COVID shots for younger kids is an opportunity to catch up on routine vaccinations, said Dr. O’Leary, adding that children can receive these vaccines together. Primary care practices, where many children are likely to receive the COVID shots, usually have other childhood vaccines on hand.
“It’s really important that parents and health care providers work together so that all children are up to date on these recommended vaccines,” said Malini DeSilva, MD, an internist and pediatrician at HealthPartners in the Minneapolis–St. Paul area. “Not only for the child’s health but for our community’s health.”
People were reluctant to come out for routine immunizations at the height of the pandemic, said Karen Miller, an immunization nurse manager for the Denver area’s Tri-County Health Department, which ran the Westminster clinic. National and global data confirm what Ms. Miller saw on the ground.
Global vaccine coverage in children fell from 2019 to 2020, according to a recent study by scientists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Health Organization, and UNICEF. Reasons included reduced access, lack of transportation, worries about COVID exposure and supply chain interruptions, the study said.
Third doses of the DTP vaccine and of the polio vaccine decreased from 86% of all eligible children in 2019 to 83% in 2020, according to the study. Worldwide, 22.7 million children had not had their third dose of DTP in 2020, compared with 19 million in 2019. Three doses are far more effective than one or two at protecting children and communities.
In the United States, researchers who studied 2019 and 2020 data on routine vaccinations in California, Colorado, Minnesota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin found substantial disruptions in vaccination rates during the pandemic that continued into September 2020. For example, the percentage of 7-month-old babies who were up to date on vaccinations decreased from 81% in September 2019 to 74% a year later.
The proportion of Black children up to date on immunizations in almost all age groups was lower than that of children in other racial and ethnic groups. This was most pronounced in those turning 18 months old: Only 41% of Black children that age were caught up on vaccinations in September 2020, compared with 57% of all children at 18 months, said Dr. DeSilva, who led that study.
A CDC study of data from the National Immunization Surveys found that race and ethnicity, poverty, and lack of insurance created the greatest disparities in vaccination rates, and the authors noted that extra efforts are needed to counter the pandemic’s disruptions.
In addition to the problems caused by COVID, Ms. Miller said, competing life priorities like work and school impede families from keeping up with shots. Weekend vaccination clinics can help working parents get their children caught up on routine immunizations while they get a flu or COVID shot. Ms. Miller and O’Leary also said reminders via phone, text or email can boost immunizations.
“Vaccines are so effective that I think it’s easy for families to put immunizations on the back burner because we don’t often hear about these diseases,” she said.
It’s a long and nasty list that includes hepatitis A and B, measles, mumps, whooping cough, polio, rubella, rotavirus, pneumococcus, tetanus, diphtheria, human papillomavirus, and meningococcal disease, among others. Even small drops in vaccination coverage can lead to outbreaks. And measles is the perfect example that worries experts, particularly as international travel opens up.
“Measles is among the most contagious diseases known to humankind, meaning that we have to keep very high vaccination coverage to keep it from spreading,” said Dr. O’Leary.
In 2019, 22 measles outbreaks occurred in 17 states in mostly unvaccinated children and adults. Dr. O’Leary said outbreaks in New York City were contained because surrounding areas had high vaccination coverage. But an outbreak in an undervaccinated community still could spread beyond its borders.
In some states a significant number of parents were opposed to routine childhood vaccines even before the pandemic for religious or personal reasons, posing another challenge for health professionals. For example, 87% of Colorado kindergartners were vaccinated against measles, mumps, and rubella during the 2018-19 school year, one of the nation’s lowest rates.
Those rates bumped up to 91% in 2019-20 but are still below the CDC’s target of 95%.
Dr. O’Leary said he does not see the same level of hesitancy for routine immunizations as for COVID. “There has always been vaccine hesitancy and vaccine refusers. But we’ve maintained vaccination rates north of 90% for all routine childhood vaccines for a long time now,” he said.
Dr. DeSilva said the “ripple effects” of missed vaccinations earlier in the pandemic continued into 2021. As children returned to in-person learning this fall, schools may have been the first place families heard about missed vaccinations. Individual states set vaccination requirements, and allowable exemptions, for entry at schools and child care facilities. In 2020, Colorado passed a school entry immunization law that tightened allowable exemptions.
“Schools, where vaccination requirements are generally enforced, are stretched thin for a variety of reasons, including COVID,” said Dr. O’Leary, adding that managing vaccine requirements may be more difficult for some, but not all, schools.
Anayeli Dominguez, 13, was at the Westminster clinic for a Tdap vaccine because her middle school had noticed she was not up to date.
“School nurses play an important role in helping identify students in need of immunizations, and also by connecting families to resources both within the district and in the larger community,” said Denver Public Schools spokesperson Will Jones.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
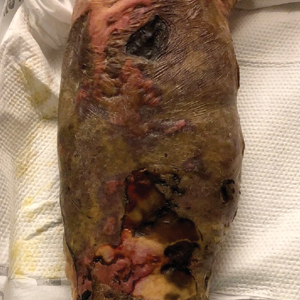
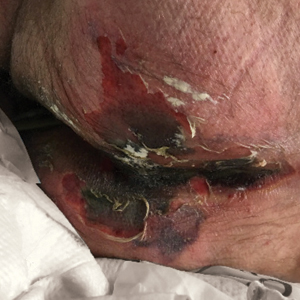
Large Leg Ulcers After Swimming in the Ocean
The Diagnosis: Vibrio vulnificus Infection
At the initial presentation, the differential diagnosis included infectious processes such as bacterial or angioinvasive fungal infections or an inflammatory process such as pyoderma gangrenosum. Blood cultures were found to be positive for pansensitive Vibrio vulnificus. He initially was treated with piperacillin-tazobactam and received surgical debridement of the affected tissues. Pathologic interpretation of the wound tissues revealed a diagnosis of necrotizing softtissue infection and positive Candida albicans growth. He received topical bacitracin on discharge as well as a 7-day course of amoxicillin-clavulanate and fluconazole. He continued to receive debridement procedures and skin grafts, followed by topical mupirocin treatment and silver sulfadiazine. He was seen 6 weeks after discharge with healing wounds and healthy-appearing granulation tissue at the base.
Our patient’s presentation of retiform purpura with stellate necrosis was consistent with a wide range of serious pathologies ranging from medium-vessel vasculitis to thromboembolic phenomena and angioinvasive fungal infections.1 Although Vibrio infection rarely is the first explanation that comes to mind when observing necrotic retiform purpura, the chronic nonhealing injury on the leg combined with the recent history of ocean swimming made V vulnificus stand out as a likely culprit. Although V vulnificus infection traditionally presents with cellulitis, edema, and hemorrhagic bulla,2 necrosis also has been observed.3 Vibrio vulnificus produces multiple virulence factors, and it is believed that these severe cutaneous symptoms are attributable to the production of a specific metalloprotease that enhances vascular permeability, thereby inducing hemorrhage within the vascular basement membrane zone.2
Vibrio vulnificus is an opportunistic bacterial pathogen associated with consumption of contaminated seafood or swimming in ocean waters with open wounds. Infections are rare, with only approximately 100 cases reported annually in the United States.4 However, V vulnificus infections have demonstrated increasing incidence in recent years, especially infections of pre-existing wounds.4,5 Risk factors for their development include age over 40 years and underlying conditions including liver disease, diabetes mellitus, and immune dysfunction.4 Vibrio vulnificus infections also demonstrate a strong male predilection, with almost 90% of infections occurring in males.4 Although the precise etiology of this sex discrepancy remains unknown, estrogen has been suggested to be a protective factor.6 Alternatively, behavioral differences also have been proposed as possible explanations for this discrepancy, with women less likely to consume seafood or go swimming. However, epidemiologic data reveal strong correlations between male sex and liver cirrhosis, a primary risk factor for V vulnificus infections, suggesting that male sex may simply be a confounding variable.7
Infections with V vulnificus are notable for their short incubation periods, with onset of symptoms occurring within 24 hours of exposure, making prompt diagnosis and treatment of high importance.8 Although rare, V vulnificus infections are associated with high mortality rates. From 1988 to 2010, nearly 600 deaths were reported secondary to V vulnificus infections.4 Wound infections carry a 17.6% fatality rate,4 while bloodborne V vulnificus infections exceed 50% fatality.8 Although sepsis secondary to V vulnificus usually is caused by ingestion of raw or undercooked shellfish, primarily oysters,4 our case highlights a rarer instance of both sepsis and localized infection stemming from ocean water exposure.
Vibrio vulnificus is an obligate halophile and therefore is found in marine environments rather than freshwater bodies. However, it rarely is isolated from bodies of water with salinities over 25 parts per thousand, such as the Mediterranean Sea; it usually is found in warmer waters, making it more common in the summer months from May to October.4 Given this proclivity for warmer environments, climate change has contributed to both a greater incidence and global distribution of V vulnificus. 9,10
Treatment of V vulnificus infections centers on antibiotic treatment, with Vibrio species generally demonstrating susceptibility to most antibiotics of human significance.11 However, some Vibrio isolates within the United States have demonstrated antibiotic resistance; 45% of a variety of clinical and environmental samples from South Carolina and Georgia demonstrated resistance to at least 3 antibiotic classes, and 17.3% resisted 8 or more classes of antibiotics.12 These included medications such as doxycycline, tetracycline, aminoglycosides, and cephalosporins—agents that normally are prescribed for V vulnificus infections. Although tetracyclines have long been touted as the preferred treatment of V vulnificus infections, the spread of antibiotic resistance may require greater reliance on alternative regimens such as combinations of cephalosporins and doxycycline or a single fluoroquinolone.13 Although rare, Vibrio infections can have rapidly fatal consequences and should be given serious consideration when evaluating patients with relevant risk factors.
The differential diagnosis included angioinvasive mucormycosis, calciphylaxis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Mucormycosis is a fungal infection caused by Mucorales fungi that most commonly is seen in patients with diabetes mellitus, hematologic malignancies, neutropenia, and immunocompromise.14 Calciphylaxis is a condition involving microvascular occlusion due to diffuse calcium deposition in cutaneous blood vessels. It typically presents as violaceous retiform patches and plaques commonly seen on areas such as the thighs, buttocks, or abdomen and usually is associated with chronic renal failure, hemodialysis, and/or secondary hyperparathyroidism.15 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory condition involving neutrophilic ulceration of the skin that typically presents as ulceration with a classically undermined border. It frequently is considered a diagnosis of exclusion and therefore requires that providers rule out other causes of ulceration prior to diagnosis.16 Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis is a rare drug reaction involving mucosal erosions and cutaneous detachment.17 This diagnosis is less likely given that our patient lacked mucosal involvement and did not have any notable medication exposures prior to symptom onset.
- Wysong A, Venkatesan P. An approach to the patient with retiform purpura. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:151-172. doi:10.1111/j .1529-8019.2011.01392.x
- Miyoshi S-I. Vibrio vulnificus infection and metalloprotease. J Dermatol. 2006;33:589-595. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2006.00139.x
- Patel VJ, Gardner E, Burton CS. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia and leg ulcer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(5 suppl):S144-S145. doi:10.1067 /mjd.2002.107778
- Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:423-430. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13955
- Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food —10 states, 2009. CDC website. Published April 16, 2010. Accessed November 3, 2021. https://www.cdc .gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5914a2.htm
- Merkel SM, Alexander S, Zufall E, et al. Essential role for estrogen in protection against Vibrio vulnificus-induced endotoxic shock. Infect Immun. 2001;69:6119-6122. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.10.6119 -6122.2001
- Scaglione S, Kliethermes S, Cao G, et al. The epidemiology of cirrhosis in the United States: a population-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;49:690-696. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000208
- Jones M, Oliver J. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis [published online December 20, 2020]. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128 /IAI.01046-08
- Paz S, Bisharat N, Paz E, et al. Climate change and the emergence of Vibrio vulnificus disease in Israel. Environ Res. 2007;103:390-396. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2006.07.002
- Martinez-Urtaza J, Bowers JC, Trinanes J, et al. Climate anomalies and the increasing risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus illnesses. Food Res Int. 2010;43:1780-1790. doi:10.1016/j. foodres.2010.04.001
- Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus. In: Thompson FL, Austin B, Swings J, eds. The Biology of Vibrios. ASM Press; 2006:349-366.
- Baker-Austin C, McArthur JV, Lindell AH, et al. Multi-site analysis reveals widespread antibiotic resistance in the marine pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Microb Ecol. 2009;57:151-159. doi:10.1007 /s00248-008-9413-8
- Elmahdi S, DaSilva LV, Parveen S. Antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in various countries: a review. Food Microbiol. 2016;57:128-134. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2016.02.008
- Prasad P, Wong V, Burgin S, et al. Mucormycosis. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/mucormycosis?diagnosisId=51981 &moduleId=101
- Blum A, Song P, Tan B, et al. Calciphylaxis. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/calciphylaxis?diagnosisId=51241&moduleId=101
- Cohen J, Wong V, Burgin S. Pyoderma gangrenosum. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/pyoderma+gangrenosum?diagnosis Id=52242&moduleId=101
- Walls A, Burgin S. Stevens-Johnson syndrome. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/stevens-johnson+syndrome?diagnosisId=52342&moduleId=101
The Diagnosis: Vibrio vulnificus Infection
At the initial presentation, the differential diagnosis included infectious processes such as bacterial or angioinvasive fungal infections or an inflammatory process such as pyoderma gangrenosum. Blood cultures were found to be positive for pansensitive Vibrio vulnificus. He initially was treated with piperacillin-tazobactam and received surgical debridement of the affected tissues. Pathologic interpretation of the wound tissues revealed a diagnosis of necrotizing softtissue infection and positive Candida albicans growth. He received topical bacitracin on discharge as well as a 7-day course of amoxicillin-clavulanate and fluconazole. He continued to receive debridement procedures and skin grafts, followed by topical mupirocin treatment and silver sulfadiazine. He was seen 6 weeks after discharge with healing wounds and healthy-appearing granulation tissue at the base.
Our patient’s presentation of retiform purpura with stellate necrosis was consistent with a wide range of serious pathologies ranging from medium-vessel vasculitis to thromboembolic phenomena and angioinvasive fungal infections.1 Although Vibrio infection rarely is the first explanation that comes to mind when observing necrotic retiform purpura, the chronic nonhealing injury on the leg combined with the recent history of ocean swimming made V vulnificus stand out as a likely culprit. Although V vulnificus infection traditionally presents with cellulitis, edema, and hemorrhagic bulla,2 necrosis also has been observed.3 Vibrio vulnificus produces multiple virulence factors, and it is believed that these severe cutaneous symptoms are attributable to the production of a specific metalloprotease that enhances vascular permeability, thereby inducing hemorrhage within the vascular basement membrane zone.2
Vibrio vulnificus is an opportunistic bacterial pathogen associated with consumption of contaminated seafood or swimming in ocean waters with open wounds. Infections are rare, with only approximately 100 cases reported annually in the United States.4 However, V vulnificus infections have demonstrated increasing incidence in recent years, especially infections of pre-existing wounds.4,5 Risk factors for their development include age over 40 years and underlying conditions including liver disease, diabetes mellitus, and immune dysfunction.4 Vibrio vulnificus infections also demonstrate a strong male predilection, with almost 90% of infections occurring in males.4 Although the precise etiology of this sex discrepancy remains unknown, estrogen has been suggested to be a protective factor.6 Alternatively, behavioral differences also have been proposed as possible explanations for this discrepancy, with women less likely to consume seafood or go swimming. However, epidemiologic data reveal strong correlations between male sex and liver cirrhosis, a primary risk factor for V vulnificus infections, suggesting that male sex may simply be a confounding variable.7
Infections with V vulnificus are notable for their short incubation periods, with onset of symptoms occurring within 24 hours of exposure, making prompt diagnosis and treatment of high importance.8 Although rare, V vulnificus infections are associated with high mortality rates. From 1988 to 2010, nearly 600 deaths were reported secondary to V vulnificus infections.4 Wound infections carry a 17.6% fatality rate,4 while bloodborne V vulnificus infections exceed 50% fatality.8 Although sepsis secondary to V vulnificus usually is caused by ingestion of raw or undercooked shellfish, primarily oysters,4 our case highlights a rarer instance of both sepsis and localized infection stemming from ocean water exposure.
Vibrio vulnificus is an obligate halophile and therefore is found in marine environments rather than freshwater bodies. However, it rarely is isolated from bodies of water with salinities over 25 parts per thousand, such as the Mediterranean Sea; it usually is found in warmer waters, making it more common in the summer months from May to October.4 Given this proclivity for warmer environments, climate change has contributed to both a greater incidence and global distribution of V vulnificus. 9,10
Treatment of V vulnificus infections centers on antibiotic treatment, with Vibrio species generally demonstrating susceptibility to most antibiotics of human significance.11 However, some Vibrio isolates within the United States have demonstrated antibiotic resistance; 45% of a variety of clinical and environmental samples from South Carolina and Georgia demonstrated resistance to at least 3 antibiotic classes, and 17.3% resisted 8 or more classes of antibiotics.12 These included medications such as doxycycline, tetracycline, aminoglycosides, and cephalosporins—agents that normally are prescribed for V vulnificus infections. Although tetracyclines have long been touted as the preferred treatment of V vulnificus infections, the spread of antibiotic resistance may require greater reliance on alternative regimens such as combinations of cephalosporins and doxycycline or a single fluoroquinolone.13 Although rare, Vibrio infections can have rapidly fatal consequences and should be given serious consideration when evaluating patients with relevant risk factors.
The differential diagnosis included angioinvasive mucormycosis, calciphylaxis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Mucormycosis is a fungal infection caused by Mucorales fungi that most commonly is seen in patients with diabetes mellitus, hematologic malignancies, neutropenia, and immunocompromise.14 Calciphylaxis is a condition involving microvascular occlusion due to diffuse calcium deposition in cutaneous blood vessels. It typically presents as violaceous retiform patches and plaques commonly seen on areas such as the thighs, buttocks, or abdomen and usually is associated with chronic renal failure, hemodialysis, and/or secondary hyperparathyroidism.15 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory condition involving neutrophilic ulceration of the skin that typically presents as ulceration with a classically undermined border. It frequently is considered a diagnosis of exclusion and therefore requires that providers rule out other causes of ulceration prior to diagnosis.16 Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis is a rare drug reaction involving mucosal erosions and cutaneous detachment.17 This diagnosis is less likely given that our patient lacked mucosal involvement and did not have any notable medication exposures prior to symptom onset.
The Diagnosis: Vibrio vulnificus Infection
At the initial presentation, the differential diagnosis included infectious processes such as bacterial or angioinvasive fungal infections or an inflammatory process such as pyoderma gangrenosum. Blood cultures were found to be positive for pansensitive Vibrio vulnificus. He initially was treated with piperacillin-tazobactam and received surgical debridement of the affected tissues. Pathologic interpretation of the wound tissues revealed a diagnosis of necrotizing softtissue infection and positive Candida albicans growth. He received topical bacitracin on discharge as well as a 7-day course of amoxicillin-clavulanate and fluconazole. He continued to receive debridement procedures and skin grafts, followed by topical mupirocin treatment and silver sulfadiazine. He was seen 6 weeks after discharge with healing wounds and healthy-appearing granulation tissue at the base.
Our patient’s presentation of retiform purpura with stellate necrosis was consistent with a wide range of serious pathologies ranging from medium-vessel vasculitis to thromboembolic phenomena and angioinvasive fungal infections.1 Although Vibrio infection rarely is the first explanation that comes to mind when observing necrotic retiform purpura, the chronic nonhealing injury on the leg combined with the recent history of ocean swimming made V vulnificus stand out as a likely culprit. Although V vulnificus infection traditionally presents with cellulitis, edema, and hemorrhagic bulla,2 necrosis also has been observed.3 Vibrio vulnificus produces multiple virulence factors, and it is believed that these severe cutaneous symptoms are attributable to the production of a specific metalloprotease that enhances vascular permeability, thereby inducing hemorrhage within the vascular basement membrane zone.2
Vibrio vulnificus is an opportunistic bacterial pathogen associated with consumption of contaminated seafood or swimming in ocean waters with open wounds. Infections are rare, with only approximately 100 cases reported annually in the United States.4 However, V vulnificus infections have demonstrated increasing incidence in recent years, especially infections of pre-existing wounds.4,5 Risk factors for their development include age over 40 years and underlying conditions including liver disease, diabetes mellitus, and immune dysfunction.4 Vibrio vulnificus infections also demonstrate a strong male predilection, with almost 90% of infections occurring in males.4 Although the precise etiology of this sex discrepancy remains unknown, estrogen has been suggested to be a protective factor.6 Alternatively, behavioral differences also have been proposed as possible explanations for this discrepancy, with women less likely to consume seafood or go swimming. However, epidemiologic data reveal strong correlations between male sex and liver cirrhosis, a primary risk factor for V vulnificus infections, suggesting that male sex may simply be a confounding variable.7
Infections with V vulnificus are notable for their short incubation periods, with onset of symptoms occurring within 24 hours of exposure, making prompt diagnosis and treatment of high importance.8 Although rare, V vulnificus infections are associated with high mortality rates. From 1988 to 2010, nearly 600 deaths were reported secondary to V vulnificus infections.4 Wound infections carry a 17.6% fatality rate,4 while bloodborne V vulnificus infections exceed 50% fatality.8 Although sepsis secondary to V vulnificus usually is caused by ingestion of raw or undercooked shellfish, primarily oysters,4 our case highlights a rarer instance of both sepsis and localized infection stemming from ocean water exposure.
Vibrio vulnificus is an obligate halophile and therefore is found in marine environments rather than freshwater bodies. However, it rarely is isolated from bodies of water with salinities over 25 parts per thousand, such as the Mediterranean Sea; it usually is found in warmer waters, making it more common in the summer months from May to October.4 Given this proclivity for warmer environments, climate change has contributed to both a greater incidence and global distribution of V vulnificus. 9,10
Treatment of V vulnificus infections centers on antibiotic treatment, with Vibrio species generally demonstrating susceptibility to most antibiotics of human significance.11 However, some Vibrio isolates within the United States have demonstrated antibiotic resistance; 45% of a variety of clinical and environmental samples from South Carolina and Georgia demonstrated resistance to at least 3 antibiotic classes, and 17.3% resisted 8 or more classes of antibiotics.12 These included medications such as doxycycline, tetracycline, aminoglycosides, and cephalosporins—agents that normally are prescribed for V vulnificus infections. Although tetracyclines have long been touted as the preferred treatment of V vulnificus infections, the spread of antibiotic resistance may require greater reliance on alternative regimens such as combinations of cephalosporins and doxycycline or a single fluoroquinolone.13 Although rare, Vibrio infections can have rapidly fatal consequences and should be given serious consideration when evaluating patients with relevant risk factors.
The differential diagnosis included angioinvasive mucormycosis, calciphylaxis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Mucormycosis is a fungal infection caused by Mucorales fungi that most commonly is seen in patients with diabetes mellitus, hematologic malignancies, neutropenia, and immunocompromise.14 Calciphylaxis is a condition involving microvascular occlusion due to diffuse calcium deposition in cutaneous blood vessels. It typically presents as violaceous retiform patches and plaques commonly seen on areas such as the thighs, buttocks, or abdomen and usually is associated with chronic renal failure, hemodialysis, and/or secondary hyperparathyroidism.15 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory condition involving neutrophilic ulceration of the skin that typically presents as ulceration with a classically undermined border. It frequently is considered a diagnosis of exclusion and therefore requires that providers rule out other causes of ulceration prior to diagnosis.16 Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis is a rare drug reaction involving mucosal erosions and cutaneous detachment.17 This diagnosis is less likely given that our patient lacked mucosal involvement and did not have any notable medication exposures prior to symptom onset.
- Wysong A, Venkatesan P. An approach to the patient with retiform purpura. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:151-172. doi:10.1111/j .1529-8019.2011.01392.x
- Miyoshi S-I. Vibrio vulnificus infection and metalloprotease. J Dermatol. 2006;33:589-595. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2006.00139.x
- Patel VJ, Gardner E, Burton CS. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia and leg ulcer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(5 suppl):S144-S145. doi:10.1067 /mjd.2002.107778
- Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:423-430. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13955
- Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food —10 states, 2009. CDC website. Published April 16, 2010. Accessed November 3, 2021. https://www.cdc .gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5914a2.htm
- Merkel SM, Alexander S, Zufall E, et al. Essential role for estrogen in protection against Vibrio vulnificus-induced endotoxic shock. Infect Immun. 2001;69:6119-6122. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.10.6119 -6122.2001
- Scaglione S, Kliethermes S, Cao G, et al. The epidemiology of cirrhosis in the United States: a population-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;49:690-696. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000208
- Jones M, Oliver J. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis [published online December 20, 2020]. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128 /IAI.01046-08
- Paz S, Bisharat N, Paz E, et al. Climate change and the emergence of Vibrio vulnificus disease in Israel. Environ Res. 2007;103:390-396. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2006.07.002
- Martinez-Urtaza J, Bowers JC, Trinanes J, et al. Climate anomalies and the increasing risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus illnesses. Food Res Int. 2010;43:1780-1790. doi:10.1016/j. foodres.2010.04.001
- Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus. In: Thompson FL, Austin B, Swings J, eds. The Biology of Vibrios. ASM Press; 2006:349-366.
- Baker-Austin C, McArthur JV, Lindell AH, et al. Multi-site analysis reveals widespread antibiotic resistance in the marine pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Microb Ecol. 2009;57:151-159. doi:10.1007 /s00248-008-9413-8
- Elmahdi S, DaSilva LV, Parveen S. Antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in various countries: a review. Food Microbiol. 2016;57:128-134. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2016.02.008
- Prasad P, Wong V, Burgin S, et al. Mucormycosis. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/mucormycosis?diagnosisId=51981 &moduleId=101
- Blum A, Song P, Tan B, et al. Calciphylaxis. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/calciphylaxis?diagnosisId=51241&moduleId=101
- Cohen J, Wong V, Burgin S. Pyoderma gangrenosum. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/pyoderma+gangrenosum?diagnosis Id=52242&moduleId=101
- Walls A, Burgin S. Stevens-Johnson syndrome. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/stevens-johnson+syndrome?diagnosisId=52342&moduleId=101
- Wysong A, Venkatesan P. An approach to the patient with retiform purpura. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:151-172. doi:10.1111/j .1529-8019.2011.01392.x
- Miyoshi S-I. Vibrio vulnificus infection and metalloprotease. J Dermatol. 2006;33:589-595. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2006.00139.x
- Patel VJ, Gardner E, Burton CS. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia and leg ulcer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(5 suppl):S144-S145. doi:10.1067 /mjd.2002.107778
- Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:423-430. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13955
- Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food —10 states, 2009. CDC website. Published April 16, 2010. Accessed November 3, 2021. https://www.cdc .gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5914a2.htm
- Merkel SM, Alexander S, Zufall E, et al. Essential role for estrogen in protection against Vibrio vulnificus-induced endotoxic shock. Infect Immun. 2001;69:6119-6122. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.10.6119 -6122.2001
- Scaglione S, Kliethermes S, Cao G, et al. The epidemiology of cirrhosis in the United States: a population-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;49:690-696. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000208
- Jones M, Oliver J. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis [published online December 20, 2020]. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128 /IAI.01046-08
- Paz S, Bisharat N, Paz E, et al. Climate change and the emergence of Vibrio vulnificus disease in Israel. Environ Res. 2007;103:390-396. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2006.07.002
- Martinez-Urtaza J, Bowers JC, Trinanes J, et al. Climate anomalies and the increasing risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus illnesses. Food Res Int. 2010;43:1780-1790. doi:10.1016/j. foodres.2010.04.001
- Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus. In: Thompson FL, Austin B, Swings J, eds. The Biology of Vibrios. ASM Press; 2006:349-366.
- Baker-Austin C, McArthur JV, Lindell AH, et al. Multi-site analysis reveals widespread antibiotic resistance in the marine pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Microb Ecol. 2009;57:151-159. doi:10.1007 /s00248-008-9413-8
- Elmahdi S, DaSilva LV, Parveen S. Antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in various countries: a review. Food Microbiol. 2016;57:128-134. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2016.02.008
- Prasad P, Wong V, Burgin S, et al. Mucormycosis. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/mucormycosis?diagnosisId=51981 &moduleId=101
- Blum A, Song P, Tan B, et al. Calciphylaxis. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/calciphylaxis?diagnosisId=51241&moduleId=101
- Cohen J, Wong V, Burgin S. Pyoderma gangrenosum. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/pyoderma+gangrenosum?diagnosis Id=52242&moduleId=101
- Walls A, Burgin S. Stevens-Johnson syndrome. VisualDx website. Accessed November 13, 2021. https://www-visualdx-com.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/visualdx/diagnosis/stevens-johnson+syndrome?diagnosisId=52342&moduleId=101
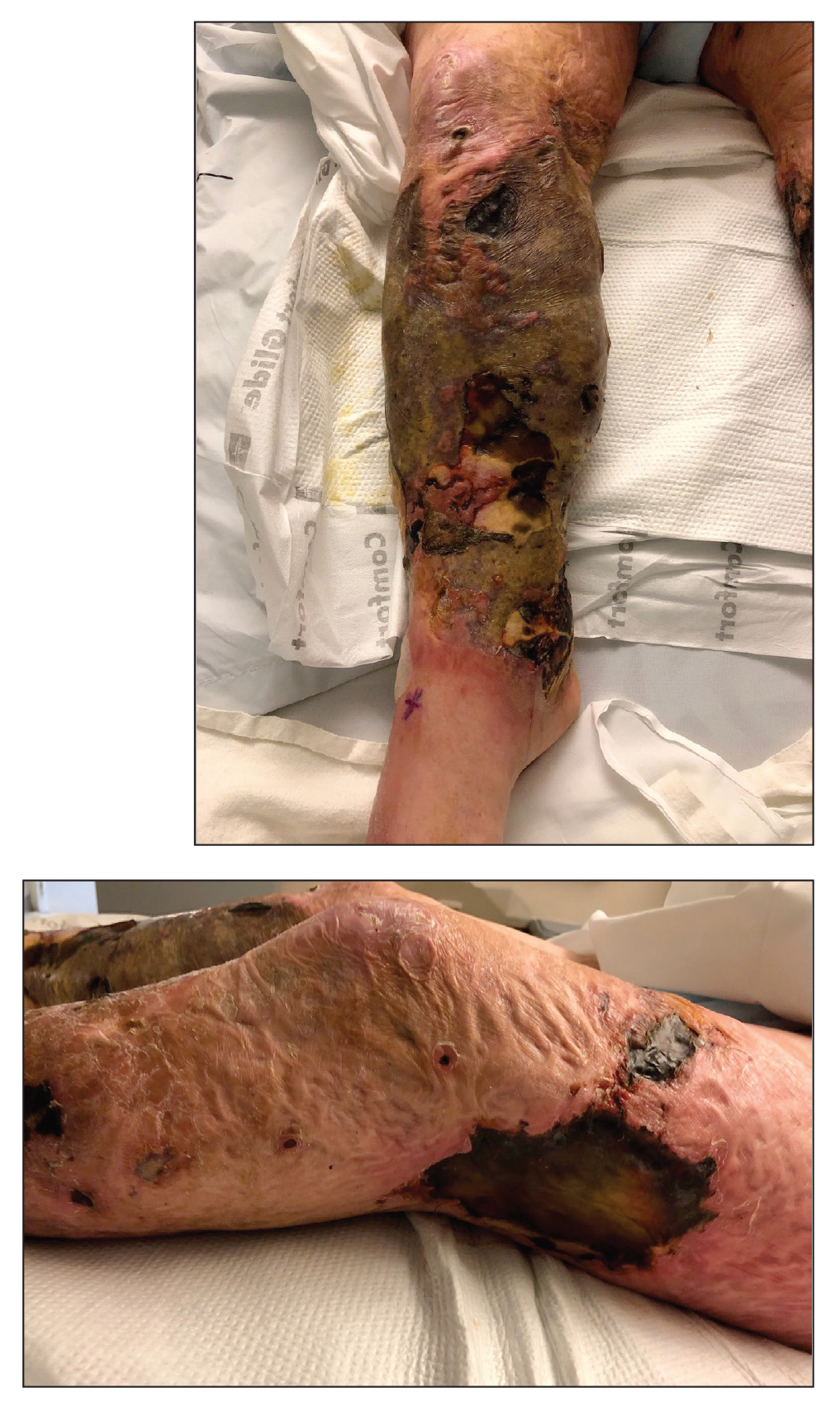
A 48-year-old man presented to the emergency department with pain in both legs after swimming in the ocean surrounding Florida 1 month prior to presentation. His medical history included skin graft treatment of burns during childhood and a chronic lower extremity ulcer that developed after trauma. He received hemodialysis for acute renal failure approximately 1 month prior to the current presentation. At the current presentation he was found to be septic and quickly developed rapidly expanding regions of retiform purpura with stellate necrosis on the legs.
HIV services are bouncing back from COVID-19 disruptions, data suggest, but recovery is ‘precarious’
Over the past 2 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous disruptions in health care, including in global HIV/AIDS services. But new data presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (ANAC) 2021 Annual Meeting suggest that practitioners quickly adapted to challenges posed by the pandemic, and care and prevention services around the world have begun to return to prepandemic levels.
These rebounding numbers “show how resilient the HIV system can be,” Jennifer Kates, PhD, senior vice president and director of global health and HIV policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), said in an interview. She presented the data during her ANAC plenary talk on Nov. 11. Dr. Kates noted that continued recovery relies on improving global access to and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines. “If we do not have control of COVID, we are going to see endless cycles of impact,” she said during her talk.
COVID-19 and HIV services
Although there was concern that the pandemic could disrupt access to antiretrovirals, the Global Fund previously reported a nearly 9% increase in people receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) from 2019 to 2020. HIV prevention and testing did take a hit: There was a 22% decrease in testing for HIV and an 11% decline in the number of people receiving HIV prevention services over that period.
New data from the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) showed similar trends. Consistent with the Global Fund’s findings, a KFF analysis of PEPFAR data found that the number of people receiving ART grew in 2020, climbing from 16.0 million in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020 to 17.4 million by the end of the year. The most recent data from PEPFAR suggest that the number had climbed to 18.4 million by September 2021.
However, there was a 24% decrease in the number of newly enrolled individuals receiving ART from Q2 to Q3 in 2020. It dipped from 669,436 to 509,509. There was a similar decrease in the number of people being tested for HIV, dropping 25% from an estimated 16,700 to 12,500 from Q2 to Q3. But by the end of the year, both measurements had rebounded: New enrollments in ART grew 31%, and HIV testing grew nearly 41% compared to Q3.
The DREAMS (Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe) program, which is focused on adolescent girls and young women, saw a dip in preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and other preventive services in Q4 2020, but numbers surpassed prepandemic levels by June 2021.
PEPFAR helped speed recovery, Dr. Kates said, by providing guidance on COVID-19 protocols to the field and implementing innovations, such as accelerated 3- and 6-month medication dispensing, virtual platforms, and decentralized drug delivery. In addition, the U.S. Congress allocated $3.8 billion in emergency funding in fiscal year 2021 to help mitigate the effects of COVID-19 on HIV and AIDS care.
Longer-term outcomes still unclear
Although these numbers are encouraging, some of the effects of COVID-19 on the HIV epidemic are still unknown – in particular, whether these documented dips in preventive services will translate to an increase in new infections. This will not be clear until a year or 2 from now, Dr. Kates noted. Increased use of ART as well as an increase in some behaviors associated with the pandemic, such as decreased social contact, are factors that mitigate an increase in the rate of infections, she said, but “how that all is going to play out we don’t know for sure.”
Other conference attendees expressed anxiety about the possibility of an increase in the rate of infections. “I’m waiting for the other shoe to drop, as it were,” Barb Cardell, training and technical assistance director at Positive Women’s Network–USA, in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview. The Positive Women’s Network is a national organization of women living with HIV. “Starting late in 2019, we have been cautioning public health officials in states and federally that there will likely be an uptick in HIV diagnosis as we return to whatever ‘normal’ looks like these days,” Ms. Cardell noted, adding, “We have all heard stories of folks that had an exposure and weren’t able to access PrEP during the pandemic and hence seroconverted.”
Kara McGee, associate clinical professor at Duke University School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., shared similar sentiments. “Many people at risk of acquiring HIV had trouble accessing testing and prevention prior to the pandemic, and service interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic have only worsened access – especially in rural areas,” she told this news organization.
Need for equitable vaccine access
For HIV services to continue to rebound, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be made a priority globally, Dr. Kates said. But data suggest lower-income countries are being left behind. In high-income countries, 65% of the population has been fully vaccinated, compared to 2% of people in the lowest-income countries. A KFF analysis projected that at the current rates of vaccination, these disparities will widen over time. COVID-19 testing rates in lower-income countries also lag. In high-income countries, 740 tests per 100,000 individuals are conducted daily; in low-income countries, that rate is 13 daily tests per 100,000 people. Until we can achieve more equitable access globally, the documented recovery of HIV is “precarious,” Dr. Kates said.
Ms. McGee agreed with Dr. Kates and was surprised by the extent of global inequities in the COVID-19 response. She said these issues should be a focus for the HIV health care community moving forward. “I think there are lot of us who have worked in the HIV field for many years – both domestically and internationally – who did not fully grasp the global disparities and need to consider how we can advocate for more equal access and distribution,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past 2 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous disruptions in health care, including in global HIV/AIDS services. But new data presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (ANAC) 2021 Annual Meeting suggest that practitioners quickly adapted to challenges posed by the pandemic, and care and prevention services around the world have begun to return to prepandemic levels.
These rebounding numbers “show how resilient the HIV system can be,” Jennifer Kates, PhD, senior vice president and director of global health and HIV policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), said in an interview. She presented the data during her ANAC plenary talk on Nov. 11. Dr. Kates noted that continued recovery relies on improving global access to and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines. “If we do not have control of COVID, we are going to see endless cycles of impact,” she said during her talk.
COVID-19 and HIV services
Although there was concern that the pandemic could disrupt access to antiretrovirals, the Global Fund previously reported a nearly 9% increase in people receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) from 2019 to 2020. HIV prevention and testing did take a hit: There was a 22% decrease in testing for HIV and an 11% decline in the number of people receiving HIV prevention services over that period.
New data from the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) showed similar trends. Consistent with the Global Fund’s findings, a KFF analysis of PEPFAR data found that the number of people receiving ART grew in 2020, climbing from 16.0 million in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020 to 17.4 million by the end of the year. The most recent data from PEPFAR suggest that the number had climbed to 18.4 million by September 2021.
However, there was a 24% decrease in the number of newly enrolled individuals receiving ART from Q2 to Q3 in 2020. It dipped from 669,436 to 509,509. There was a similar decrease in the number of people being tested for HIV, dropping 25% from an estimated 16,700 to 12,500 from Q2 to Q3. But by the end of the year, both measurements had rebounded: New enrollments in ART grew 31%, and HIV testing grew nearly 41% compared to Q3.
The DREAMS (Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe) program, which is focused on adolescent girls and young women, saw a dip in preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and other preventive services in Q4 2020, but numbers surpassed prepandemic levels by June 2021.
PEPFAR helped speed recovery, Dr. Kates said, by providing guidance on COVID-19 protocols to the field and implementing innovations, such as accelerated 3- and 6-month medication dispensing, virtual platforms, and decentralized drug delivery. In addition, the U.S. Congress allocated $3.8 billion in emergency funding in fiscal year 2021 to help mitigate the effects of COVID-19 on HIV and AIDS care.
Longer-term outcomes still unclear
Although these numbers are encouraging, some of the effects of COVID-19 on the HIV epidemic are still unknown – in particular, whether these documented dips in preventive services will translate to an increase in new infections. This will not be clear until a year or 2 from now, Dr. Kates noted. Increased use of ART as well as an increase in some behaviors associated with the pandemic, such as decreased social contact, are factors that mitigate an increase in the rate of infections, she said, but “how that all is going to play out we don’t know for sure.”
Other conference attendees expressed anxiety about the possibility of an increase in the rate of infections. “I’m waiting for the other shoe to drop, as it were,” Barb Cardell, training and technical assistance director at Positive Women’s Network–USA, in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview. The Positive Women’s Network is a national organization of women living with HIV. “Starting late in 2019, we have been cautioning public health officials in states and federally that there will likely be an uptick in HIV diagnosis as we return to whatever ‘normal’ looks like these days,” Ms. Cardell noted, adding, “We have all heard stories of folks that had an exposure and weren’t able to access PrEP during the pandemic and hence seroconverted.”
Kara McGee, associate clinical professor at Duke University School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., shared similar sentiments. “Many people at risk of acquiring HIV had trouble accessing testing and prevention prior to the pandemic, and service interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic have only worsened access – especially in rural areas,” she told this news organization.
Need for equitable vaccine access
For HIV services to continue to rebound, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be made a priority globally, Dr. Kates said. But data suggest lower-income countries are being left behind. In high-income countries, 65% of the population has been fully vaccinated, compared to 2% of people in the lowest-income countries. A KFF analysis projected that at the current rates of vaccination, these disparities will widen over time. COVID-19 testing rates in lower-income countries also lag. In high-income countries, 740 tests per 100,000 individuals are conducted daily; in low-income countries, that rate is 13 daily tests per 100,000 people. Until we can achieve more equitable access globally, the documented recovery of HIV is “precarious,” Dr. Kates said.
Ms. McGee agreed with Dr. Kates and was surprised by the extent of global inequities in the COVID-19 response. She said these issues should be a focus for the HIV health care community moving forward. “I think there are lot of us who have worked in the HIV field for many years – both domestically and internationally – who did not fully grasp the global disparities and need to consider how we can advocate for more equal access and distribution,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past 2 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous disruptions in health care, including in global HIV/AIDS services. But new data presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (ANAC) 2021 Annual Meeting suggest that practitioners quickly adapted to challenges posed by the pandemic, and care and prevention services around the world have begun to return to prepandemic levels.
These rebounding numbers “show how resilient the HIV system can be,” Jennifer Kates, PhD, senior vice president and director of global health and HIV policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), said in an interview. She presented the data during her ANAC plenary talk on Nov. 11. Dr. Kates noted that continued recovery relies on improving global access to and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines. “If we do not have control of COVID, we are going to see endless cycles of impact,” she said during her talk.
COVID-19 and HIV services
Although there was concern that the pandemic could disrupt access to antiretrovirals, the Global Fund previously reported a nearly 9% increase in people receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) from 2019 to 2020. HIV prevention and testing did take a hit: There was a 22% decrease in testing for HIV and an 11% decline in the number of people receiving HIV prevention services over that period.
New data from the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) showed similar trends. Consistent with the Global Fund’s findings, a KFF analysis of PEPFAR data found that the number of people receiving ART grew in 2020, climbing from 16.0 million in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020 to 17.4 million by the end of the year. The most recent data from PEPFAR suggest that the number had climbed to 18.4 million by September 2021.
However, there was a 24% decrease in the number of newly enrolled individuals receiving ART from Q2 to Q3 in 2020. It dipped from 669,436 to 509,509. There was a similar decrease in the number of people being tested for HIV, dropping 25% from an estimated 16,700 to 12,500 from Q2 to Q3. But by the end of the year, both measurements had rebounded: New enrollments in ART grew 31%, and HIV testing grew nearly 41% compared to Q3.
The DREAMS (Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe) program, which is focused on adolescent girls and young women, saw a dip in preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and other preventive services in Q4 2020, but numbers surpassed prepandemic levels by June 2021.
PEPFAR helped speed recovery, Dr. Kates said, by providing guidance on COVID-19 protocols to the field and implementing innovations, such as accelerated 3- and 6-month medication dispensing, virtual platforms, and decentralized drug delivery. In addition, the U.S. Congress allocated $3.8 billion in emergency funding in fiscal year 2021 to help mitigate the effects of COVID-19 on HIV and AIDS care.
Longer-term outcomes still unclear
Although these numbers are encouraging, some of the effects of COVID-19 on the HIV epidemic are still unknown – in particular, whether these documented dips in preventive services will translate to an increase in new infections. This will not be clear until a year or 2 from now, Dr. Kates noted. Increased use of ART as well as an increase in some behaviors associated with the pandemic, such as decreased social contact, are factors that mitigate an increase in the rate of infections, she said, but “how that all is going to play out we don’t know for sure.”
Other conference attendees expressed anxiety about the possibility of an increase in the rate of infections. “I’m waiting for the other shoe to drop, as it were,” Barb Cardell, training and technical assistance director at Positive Women’s Network–USA, in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview. The Positive Women’s Network is a national organization of women living with HIV. “Starting late in 2019, we have been cautioning public health officials in states and federally that there will likely be an uptick in HIV diagnosis as we return to whatever ‘normal’ looks like these days,” Ms. Cardell noted, adding, “We have all heard stories of folks that had an exposure and weren’t able to access PrEP during the pandemic and hence seroconverted.”
Kara McGee, associate clinical professor at Duke University School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., shared similar sentiments. “Many people at risk of acquiring HIV had trouble accessing testing and prevention prior to the pandemic, and service interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic have only worsened access – especially in rural areas,” she told this news organization.
Need for equitable vaccine access
For HIV services to continue to rebound, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be made a priority globally, Dr. Kates said. But data suggest lower-income countries are being left behind. In high-income countries, 65% of the population has been fully vaccinated, compared to 2% of people in the lowest-income countries. A KFF analysis projected that at the current rates of vaccination, these disparities will widen over time. COVID-19 testing rates in lower-income countries also lag. In high-income countries, 740 tests per 100,000 individuals are conducted daily; in low-income countries, that rate is 13 daily tests per 100,000 people. Until we can achieve more equitable access globally, the documented recovery of HIV is “precarious,” Dr. Kates said.
Ms. McGee agreed with Dr. Kates and was surprised by the extent of global inequities in the COVID-19 response. She said these issues should be a focus for the HIV health care community moving forward. “I think there are lot of us who have worked in the HIV field for many years – both domestically and internationally – who did not fully grasp the global disparities and need to consider how we can advocate for more equal access and distribution,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA authorizes COVID boosters for all U.S. adults
“Authorizing the use of a single booster dose of either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for individuals 18 years of age and older helps to provide continued protection against COVID-19, including the serious consequences that can occur, such as hospitalization and death,” said acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, in an FDA press statement.
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet on Nov. 19 to review the science supporting a more widespread need for booster doses, and is expected to vote on official recommendations for their use in the United States. The CDC director must then sign off on the panel’s recommendations.
“As soon as the FDA reviews those data and provides an authorization, we at CDC will act swiftly,” Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, said at a recent White House briefing.
Several states – including Louisiana, Maine, and Colorado – have already authorized boosters for all adults as cases rise in Europe and across the Western and Northeastern regions of the United States.
FDA officials said they hoped that widening eligibility for boosters would cut down on confusion for people and hopefully speed uptake of the shots.
“Streamlining the eligibility criteria and making booster doses available to all individuals 18 years of age and older will also help to eliminate confusion about who may receive a booster dose and ensure booster doses are available to all who may need one,” said Peter Marks, MD, PhD, who heads the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“Authorizing the use of a single booster dose of either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for individuals 18 years of age and older helps to provide continued protection against COVID-19, including the serious consequences that can occur, such as hospitalization and death,” said acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, in an FDA press statement.
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet on Nov. 19 to review the science supporting a more widespread need for booster doses, and is expected to vote on official recommendations for their use in the United States. The CDC director must then sign off on the panel’s recommendations.
“As soon as the FDA reviews those data and provides an authorization, we at CDC will act swiftly,” Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, said at a recent White House briefing.
Several states – including Louisiana, Maine, and Colorado – have already authorized boosters for all adults as cases rise in Europe and across the Western and Northeastern regions of the United States.
FDA officials said they hoped that widening eligibility for boosters would cut down on confusion for people and hopefully speed uptake of the shots.
“Streamlining the eligibility criteria and making booster doses available to all individuals 18 years of age and older will also help to eliminate confusion about who may receive a booster dose and ensure booster doses are available to all who may need one,” said Peter Marks, MD, PhD, who heads the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“Authorizing the use of a single booster dose of either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for individuals 18 years of age and older helps to provide continued protection against COVID-19, including the serious consequences that can occur, such as hospitalization and death,” said acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, in an FDA press statement.
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet on Nov. 19 to review the science supporting a more widespread need for booster doses, and is expected to vote on official recommendations for their use in the United States. The CDC director must then sign off on the panel’s recommendations.
“As soon as the FDA reviews those data and provides an authorization, we at CDC will act swiftly,” Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, said at a recent White House briefing.
Several states – including Louisiana, Maine, and Colorado – have already authorized boosters for all adults as cases rise in Europe and across the Western and Northeastern regions of the United States.
FDA officials said they hoped that widening eligibility for boosters would cut down on confusion for people and hopefully speed uptake of the shots.
“Streamlining the eligibility criteria and making booster doses available to all individuals 18 years of age and older will also help to eliminate confusion about who may receive a booster dose and ensure booster doses are available to all who may need one,” said Peter Marks, MD, PhD, who heads the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Mask-wearing cuts new COVID-19 cases by 53%, study says
Social distancing and handwashing were also effective at lowering the number of cases, but wearing masks was the most effective tool against the coronavirus.
“Personal and social measures, including handwashing, mask wearing, and physical distancing are effective at reducing the incidence of COVID-19,” the study authors wrote.
The research team, which included public health and infectious disease specialists in Australia, China, and the U.K., evaluated 72 studies of COVID-19 precautions during the pandemic. They later looked at eight studies that focused on handwashing, mask wearing, and physical distancing.
Among six studies that looked at mask wearing, the researchers found a 53% reduction in COVID-19 cases. In the broader analysis with additional studies, wearing a mask reduced coronavirus transmission, cases, and deaths.
In one study across 200 countries, mandatory mask wearing resulted in nearly 46% fewer negative outcomes from COVID-19. In another study in the U.S., coronavirus transmission was reduced 29% in states where masks were mandatory.
But the research team couldn’t analyze the impact of the type of face mask used, the frequency of mask wearing, or the overall compliance with wearing face masks.
Among five studies that looked at physical distancing, the researchers found a 25% reduction in the rate of COVID-19. A study in the U.S. showed a 12% decrease in coronavirus transmission, while another study in Iran reported a reduction in COVID-19 mortality.
Handwashing interventions also suggested a substantial reduction of COVID-19 cases up to 53%, the researchers wrote. But in adjusted models, the results weren’t statistically significant due to the small number of studies included.
Other studies found significant decreases related to other public health measures, such as quarantines, broad lockdowns, border closures, school closures, business closures, and travel restrictions. Still, the research team couldn’t analyze the overall effectiveness of these measures due to the different ways the studies were conducted.
The study lines up with other research conducted so far during the pandemic, the research team wrote, which indicates that wearing masks and physical distancing can reduce transmission, cases, and deaths.
That said, more studies are needed, particularly now that vaccinations are available and contagious coronavirus variants have become prevalent.
“Further research is needed to assess the effectiveness of public health measures after adequate vaccination coverage has been achieved,” they wrote.
“It is likely that further control of the COVID-19 pandemic depends not only on high vaccination coverage and its effectiveness but also on ongoing adherence to effective and sustainable public health measures,” they concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Social distancing and handwashing were also effective at lowering the number of cases, but wearing masks was the most effective tool against the coronavirus.
“Personal and social measures, including handwashing, mask wearing, and physical distancing are effective at reducing the incidence of COVID-19,” the study authors wrote.
The research team, which included public health and infectious disease specialists in Australia, China, and the U.K., evaluated 72 studies of COVID-19 precautions during the pandemic. They later looked at eight studies that focused on handwashing, mask wearing, and physical distancing.
Among six studies that looked at mask wearing, the researchers found a 53% reduction in COVID-19 cases. In the broader analysis with additional studies, wearing a mask reduced coronavirus transmission, cases, and deaths.
In one study across 200 countries, mandatory mask wearing resulted in nearly 46% fewer negative outcomes from COVID-19. In another study in the U.S., coronavirus transmission was reduced 29% in states where masks were mandatory.
But the research team couldn’t analyze the impact of the type of face mask used, the frequency of mask wearing, or the overall compliance with wearing face masks.
Among five studies that looked at physical distancing, the researchers found a 25% reduction in the rate of COVID-19. A study in the U.S. showed a 12% decrease in coronavirus transmission, while another study in Iran reported a reduction in COVID-19 mortality.
Handwashing interventions also suggested a substantial reduction of COVID-19 cases up to 53%, the researchers wrote. But in adjusted models, the results weren’t statistically significant due to the small number of studies included.
Other studies found significant decreases related to other public health measures, such as quarantines, broad lockdowns, border closures, school closures, business closures, and travel restrictions. Still, the research team couldn’t analyze the overall effectiveness of these measures due to the different ways the studies were conducted.
The study lines up with other research conducted so far during the pandemic, the research team wrote, which indicates that wearing masks and physical distancing can reduce transmission, cases, and deaths.
That said, more studies are needed, particularly now that vaccinations are available and contagious coronavirus variants have become prevalent.
“Further research is needed to assess the effectiveness of public health measures after adequate vaccination coverage has been achieved,” they wrote.
“It is likely that further control of the COVID-19 pandemic depends not only on high vaccination coverage and its effectiveness but also on ongoing adherence to effective and sustainable public health measures,” they concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Social distancing and handwashing were also effective at lowering the number of cases, but wearing masks was the most effective tool against the coronavirus.
“Personal and social measures, including handwashing, mask wearing, and physical distancing are effective at reducing the incidence of COVID-19,” the study authors wrote.
The research team, which included public health and infectious disease specialists in Australia, China, and the U.K., evaluated 72 studies of COVID-19 precautions during the pandemic. They later looked at eight studies that focused on handwashing, mask wearing, and physical distancing.
Among six studies that looked at mask wearing, the researchers found a 53% reduction in COVID-19 cases. In the broader analysis with additional studies, wearing a mask reduced coronavirus transmission, cases, and deaths.
In one study across 200 countries, mandatory mask wearing resulted in nearly 46% fewer negative outcomes from COVID-19. In another study in the U.S., coronavirus transmission was reduced 29% in states where masks were mandatory.
But the research team couldn’t analyze the impact of the type of face mask used, the frequency of mask wearing, or the overall compliance with wearing face masks.
Among five studies that looked at physical distancing, the researchers found a 25% reduction in the rate of COVID-19. A study in the U.S. showed a 12% decrease in coronavirus transmission, while another study in Iran reported a reduction in COVID-19 mortality.
Handwashing interventions also suggested a substantial reduction of COVID-19 cases up to 53%, the researchers wrote. But in adjusted models, the results weren’t statistically significant due to the small number of studies included.
Other studies found significant decreases related to other public health measures, such as quarantines, broad lockdowns, border closures, school closures, business closures, and travel restrictions. Still, the research team couldn’t analyze the overall effectiveness of these measures due to the different ways the studies were conducted.
The study lines up with other research conducted so far during the pandemic, the research team wrote, which indicates that wearing masks and physical distancing can reduce transmission, cases, and deaths.
That said, more studies are needed, particularly now that vaccinations are available and contagious coronavirus variants have become prevalent.
“Further research is needed to assess the effectiveness of public health measures after adequate vaccination coverage has been achieved,” they wrote.
“It is likely that further control of the COVID-19 pandemic depends not only on high vaccination coverage and its effectiveness but also on ongoing adherence to effective and sustainable public health measures,” they concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE BMJ
Growing evidence supports repurposing antidepressants to treat COVID-19
Mounting evidence suggests selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) are associated with lower COVID-19 severity.
A large analysis of health records shows patients with COVID-19 taking an SSRI were significantly less likely to die of COVID-19 than a matched control group.
“We can’t tell if the drugs are causing these effects, but the statistical analysis is showing significant association. There’s power in the numbers,” Marina Sirota, PhD, University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in a statement.
The study was published online Nov. 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Data-driven approach
, including 3,401 patients who were prescribed SSRIs.
When compared with matched patients with COVID-19 taking SSRIs, patients taking fluoxetine were 28% less likely to die (relative risk, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.97; adjusted P = .03) and those taking either fluoxetine or fluvoxamine were 26% less likely to die (RR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.55-0.99; adjusted P = .04) versus those not on these medications.
Patients with COVID-19 taking any kind of SSRI were 8% less likely to die than the matched controls (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.85-0.99; adjusted P = .03).
“We observed a statistically significant reduction in mortality of COVID-19 patients who were already taking SSRIs. This is a demonstration of a data-driven approach for identifying new uses for existing drugs,” Dr. Sirota said in an interview.
“Our study simply shows an association between SSRIs and COVID-19 outcomes and doesn’t investigate the mechanism of action of why the drugs might work. Additional clinical trials need to be carried out before these drugs can be used in patients going forward,” she cautioned.
“There is currently an open-label trial investigating fluoxetine to reduce intubation and death after COVID-19. To our knowledge, there are no phase 3 randomized controlled trials taking place or planned,” study investigator Tomiko Oskotsky, MD, with UCSF, told this news organization.
Urgent need
The current results “confirm and expand on prior findings from observational, preclinical, and clinical studies suggesting that certain SSRI antidepressants, including fluoxetine or fluvoxamine, could be beneficial against COVID-19,” Nicolas Hoertel, MD, PhD, MPH, with Paris University and Corentin-Celton Hospital, France, writes in a linked editorial.
Dr. Hoertel notes that the anti-inflammatory properties of SSRIs may underlie their potential action against COVID-19, and other potential mechanisms may include reduction in platelet aggregation, decreased mast cell degranulation, increased melatonin levels, interference with endolysosomal viral trafficking, and antioxidant activities.
“Because most of the world’s population is currently unvaccinated and the COVID-19 pandemic is still active, effective treatments of COVID-19 – especially those that are easy to use, show good tolerability, can be administered orally, and have widespread availability at low cost to allow their use in resource-poor countries – are urgently needed to reduce COVID-19-related mortality and morbidity,” Dr. Hoertel points out.
“In this context, short-term use of fluoxetine or fluvoxamine, if proven effective, should be considered as a potential means of reaching this goal,” he adds.
The study was supported by the Christopher Hess Research Fund and, in part, by UCSF and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sirota has reported serving as a scientific advisor at Aria Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Hoertel has reported being listed as an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, filed by Assistance Publique-Hopitaux de Paris, and receiving consulting fees and nonfinancial support from Lundbeck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mounting evidence suggests selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) are associated with lower COVID-19 severity.
A large analysis of health records shows patients with COVID-19 taking an SSRI were significantly less likely to die of COVID-19 than a matched control group.
“We can’t tell if the drugs are causing these effects, but the statistical analysis is showing significant association. There’s power in the numbers,” Marina Sirota, PhD, University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in a statement.
The study was published online Nov. 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Data-driven approach
, including 3,401 patients who were prescribed SSRIs.
When compared with matched patients with COVID-19 taking SSRIs, patients taking fluoxetine were 28% less likely to die (relative risk, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.97; adjusted P = .03) and those taking either fluoxetine or fluvoxamine were 26% less likely to die (RR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.55-0.99; adjusted P = .04) versus those not on these medications.
Patients with COVID-19 taking any kind of SSRI were 8% less likely to die than the matched controls (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.85-0.99; adjusted P = .03).
“We observed a statistically significant reduction in mortality of COVID-19 patients who were already taking SSRIs. This is a demonstration of a data-driven approach for identifying new uses for existing drugs,” Dr. Sirota said in an interview.
“Our study simply shows an association between SSRIs and COVID-19 outcomes and doesn’t investigate the mechanism of action of why the drugs might work. Additional clinical trials need to be carried out before these drugs can be used in patients going forward,” she cautioned.
“There is currently an open-label trial investigating fluoxetine to reduce intubation and death after COVID-19. To our knowledge, there are no phase 3 randomized controlled trials taking place or planned,” study investigator Tomiko Oskotsky, MD, with UCSF, told this news organization.
Urgent need
The current results “confirm and expand on prior findings from observational, preclinical, and clinical studies suggesting that certain SSRI antidepressants, including fluoxetine or fluvoxamine, could be beneficial against COVID-19,” Nicolas Hoertel, MD, PhD, MPH, with Paris University and Corentin-Celton Hospital, France, writes in a linked editorial.
Dr. Hoertel notes that the anti-inflammatory properties of SSRIs may underlie their potential action against COVID-19, and other potential mechanisms may include reduction in platelet aggregation, decreased mast cell degranulation, increased melatonin levels, interference with endolysosomal viral trafficking, and antioxidant activities.
“Because most of the world’s population is currently unvaccinated and the COVID-19 pandemic is still active, effective treatments of COVID-19 – especially those that are easy to use, show good tolerability, can be administered orally, and have widespread availability at low cost to allow their use in resource-poor countries – are urgently needed to reduce COVID-19-related mortality and morbidity,” Dr. Hoertel points out.
“In this context, short-term use of fluoxetine or fluvoxamine, if proven effective, should be considered as a potential means of reaching this goal,” he adds.
The study was supported by the Christopher Hess Research Fund and, in part, by UCSF and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sirota has reported serving as a scientific advisor at Aria Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Hoertel has reported being listed as an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, filed by Assistance Publique-Hopitaux de Paris, and receiving consulting fees and nonfinancial support from Lundbeck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mounting evidence suggests selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) are associated with lower COVID-19 severity.
A large analysis of health records shows patients with COVID-19 taking an SSRI were significantly less likely to die of COVID-19 than a matched control group.
“We can’t tell if the drugs are causing these effects, but the statistical analysis is showing significant association. There’s power in the numbers,” Marina Sirota, PhD, University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in a statement.
The study was published online Nov. 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Data-driven approach
, including 3,401 patients who were prescribed SSRIs.
When compared with matched patients with COVID-19 taking SSRIs, patients taking fluoxetine were 28% less likely to die (relative risk, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.97; adjusted P = .03) and those taking either fluoxetine or fluvoxamine were 26% less likely to die (RR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.55-0.99; adjusted P = .04) versus those not on these medications.
Patients with COVID-19 taking any kind of SSRI were 8% less likely to die than the matched controls (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.85-0.99; adjusted P = .03).
“We observed a statistically significant reduction in mortality of COVID-19 patients who were already taking SSRIs. This is a demonstration of a data-driven approach for identifying new uses for existing drugs,” Dr. Sirota said in an interview.
“Our study simply shows an association between SSRIs and COVID-19 outcomes and doesn’t investigate the mechanism of action of why the drugs might work. Additional clinical trials need to be carried out before these drugs can be used in patients going forward,” she cautioned.
“There is currently an open-label trial investigating fluoxetine to reduce intubation and death after COVID-19. To our knowledge, there are no phase 3 randomized controlled trials taking place or planned,” study investigator Tomiko Oskotsky, MD, with UCSF, told this news organization.
Urgent need
The current results “confirm and expand on prior findings from observational, preclinical, and clinical studies suggesting that certain SSRI antidepressants, including fluoxetine or fluvoxamine, could be beneficial against COVID-19,” Nicolas Hoertel, MD, PhD, MPH, with Paris University and Corentin-Celton Hospital, France, writes in a linked editorial.
Dr. Hoertel notes that the anti-inflammatory properties of SSRIs may underlie their potential action against COVID-19, and other potential mechanisms may include reduction in platelet aggregation, decreased mast cell degranulation, increased melatonin levels, interference with endolysosomal viral trafficking, and antioxidant activities.
“Because most of the world’s population is currently unvaccinated and the COVID-19 pandemic is still active, effective treatments of COVID-19 – especially those that are easy to use, show good tolerability, can be administered orally, and have widespread availability at low cost to allow their use in resource-poor countries – are urgently needed to reduce COVID-19-related mortality and morbidity,” Dr. Hoertel points out.
“In this context, short-term use of fluoxetine or fluvoxamine, if proven effective, should be considered as a potential means of reaching this goal,” he adds.
The study was supported by the Christopher Hess Research Fund and, in part, by UCSF and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sirota has reported serving as a scientific advisor at Aria Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Hoertel has reported being listed as an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, filed by Assistance Publique-Hopitaux de Paris, and receiving consulting fees and nonfinancial support from Lundbeck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Faster testing possible for secondary ICU infections
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has given added impetus for metagenomic testing using nanopore sequencing to progress from a research tool to routine clinical application. A study led by researchers from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust has shown the potential for clinical metagenomics to become a same-day test for identifying secondary infection in ventilated ICU patients. Getting results in hours rather than days would help to ensure rapid treatment with the correct antibiotic, minimize unnecessary prescriptions, and thus reduce the growing menace of antimicrobial resistance.
‘SARS-CoV-2 has put considerable strain on ICUs’
The researchers point out that the setting of an intensive care unit involves frequent staff-patient contact that imparts a risk of secondary or nosocomial infection. In addition, invasive ventilation may introduce organisms into the lungs and lead to ventilator-acquired pneumonia. This carries a high mortality and is responsible for up to 70% of antimicrobial prescribing, with current guidelines requiring empiric antibiotics pending culture results, which typically takes 2-4 days.
Many of these infection problems worsened during SARS-CoV-2. Expanded critical care capacity raised the risk of nosocomial infections, with attendant increased antimicrobial prescriptions and the threat of antimicrobial resistance. In addition, treatment of COVID-19 patients with steroid therapy potentially exacerbates bacterial or fungal infections.
The researchers, from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London, in collaboration with the Quadram Institute in Norwich, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and Viapath, the U.K.’s largest independent pathology service provider, noted that the pandemic thus reinforced “a need for rapid comprehensive diagnostics to improve antimicrobial stewardship and help prevent emergence and transmission of multi-drug-resistant organisms.”
“As soon as the pandemic started, our scientists realized there would be a benefit to sequencing genomes of all bacteria and fungi causing infection in COVID-19 patients while on ICU,” said Professor Jonathan Edgeworth, who led the research team.
“Within a few weeks we showed it can diagnose secondary infection, target antibiotic treatment, and detect outbreaks much earlier than current technologies – all from a single sample.”
Proof-of-concept study
The team performed a proof-of-concept study of nanopore metagenomics sequencing – a type of DNA sequencing that allows direct rapid unbiased detection of all organisms present in a clinical sample – on 43 surplus respiratory samples from 34 intubated COVID-19 patients with suspected secondary bacterial or fungal pneumonia. Patients were drawn from seven ICUs at St. Thomas’ Hospital, London over a 9-week period between April 11 and June 15 2020, during the first wave of COVID-19.
Their median age was 52, 70% were male, 47% White, and 44% Black or minority ethnicities. Median length of stay was 32 days and mortality 24%. Samples sent for metagenomic analysis and culture included 10 bronchoalveolar lavages, 6 tracheal aspirates, and 27 non-direct bronchoalveolar lavages.
The study, published in Genome Medicine, showed that an 8-hour metagenomics workflow was 92% sensitive (95% CI, 75% to 99%) and 82% specific (95% CI, 57% to 96%) for bacterial identification, based on culture-positive and culture-negative samples, respectively.
The main Gram-negative bacteria identified were Klebsiella spp. (53%), Citrobacter spp. (15%), and E coli (9%). The main Gram-positive bacteria were S aureus (9%), C striatum (24%) and Enterococcus spp. (12%). In addition, C albicans, other Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp. were cultured from 38%, 15%, and 9% of patients, respectively.
In every case, the initial antibiotics prescribed according to prevailing guideline recommendations would have been modified by metagenomic sequencing demonstrating the presence or absence of β-lactam-resistant genes carried by Enterobacterales.
Next day results of sequencing also detected Aspergillus fumigatus in four samples, with results 100% concordant with quantitative PCR for both the four positive and 39 negative samples. It identified two multi-drug–resistant outbreaks, one involving K pneumoniae ST307 affecting four patients and one a C striatum outbreak involving 14 patients across three ICUs.
Thus, a single sample can provide enough genetic sequence data to compare pathogen genomes with a database and accurately identify patients carrying the same strain, enabling early detection of outbreaks. This is the first time this combined benefit of a single test has been demonstrated, the team say.
Gordon Sanghera, CEO of Oxford Nanopore commented that “rapidly characterizing co-infections for precision prescribing is a vital next step for both COVID-19 patients and respiratory disease in general.”
Dr. Andrew Page of the Quadram Institute said: “We have been working on metagenomics technology for the last 7 years. It is great to see it applied to patient care during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
He said in an interview: “The pandemic has accelerated the transition from using sequencing purely in research labs to using it in the clinic to rapidly provide clinicians with information they can use to improve outcomes for patients.”
Potential to inform antimicrobial prescribing and infection control
“Clinical metagenomic testing provides accurate pathogen detection and antibiotic resistance prediction in a same-day laboratory workflow, with assembled genomes available the next day for genomic surveillance,” the researchers say.
The technology “could fundamentally change the multi-disciplinary team approach to managing ICU infections.” It has the potential to improve initial targeted antimicrobial treatment and infection control decisions, as well as help rapidly detect unsuspected outbreaks of multi-drug–resistant pathogens.
Professor Edgeworth told this news organization that since the study, “secondary bacterial and fungal infections have increased, perhaps due to immunomodulatory treatments or just the length of time patients spend on ICU recovering from COVID-19. This makes rapid diagnosis even more important to ensure patients get more targeted antibiotics earlier, rather than relying on generic guidelines.”
The team “are planning to move respiratory metagenomics into pilot service under our Trust’s quality improvement framework,” he revealed. This will enable them to gather data on patient benefits.
“We also need to see how clinicians use these tests to improve antibiotic treatment, to stop antibiotics when not needed or to identify outbreaks earlier, and then how that translates into tangible benefits for individual patients and the wider NHS.”
He predicts that the technique will revolutionize the approach to prevention and treatment of serious infection in ICUs, and it is now planned to offer it as a clinical service for COVID-19 and influenza patients during the coming winter.
In addition, he said: “It can be equally applied to other samples such as tissue fluids and biopsies, including those removed at operation. It therefore has potential to impact on diagnostics for many clinical services, particularly if the progress is maintained at the current pace.”
This article first appeared on Medscape UK/Univadis.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has given added impetus for metagenomic testing using nanopore sequencing to progress from a research tool to routine clinical application. A study led by researchers from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust has shown the potential for clinical metagenomics to become a same-day test for identifying secondary infection in ventilated ICU patients. Getting results in hours rather than days would help to ensure rapid treatment with the correct antibiotic, minimize unnecessary prescriptions, and thus reduce the growing menace of antimicrobial resistance.
‘SARS-CoV-2 has put considerable strain on ICUs’
The researchers point out that the setting of an intensive care unit involves frequent staff-patient contact that imparts a risk of secondary or nosocomial infection. In addition, invasive ventilation may introduce organisms into the lungs and lead to ventilator-acquired pneumonia. This carries a high mortality and is responsible for up to 70% of antimicrobial prescribing, with current guidelines requiring empiric antibiotics pending culture results, which typically takes 2-4 days.
Many of these infection problems worsened during SARS-CoV-2. Expanded critical care capacity raised the risk of nosocomial infections, with attendant increased antimicrobial prescriptions and the threat of antimicrobial resistance. In addition, treatment of COVID-19 patients with steroid therapy potentially exacerbates bacterial or fungal infections.
The researchers, from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London, in collaboration with the Quadram Institute in Norwich, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and Viapath, the U.K.’s largest independent pathology service provider, noted that the pandemic thus reinforced “a need for rapid comprehensive diagnostics to improve antimicrobial stewardship and help prevent emergence and transmission of multi-drug-resistant organisms.”
“As soon as the pandemic started, our scientists realized there would be a benefit to sequencing genomes of all bacteria and fungi causing infection in COVID-19 patients while on ICU,” said Professor Jonathan Edgeworth, who led the research team.
“Within a few weeks we showed it can diagnose secondary infection, target antibiotic treatment, and detect outbreaks much earlier than current technologies – all from a single sample.”
Proof-of-concept study
The team performed a proof-of-concept study of nanopore metagenomics sequencing – a type of DNA sequencing that allows direct rapid unbiased detection of all organisms present in a clinical sample – on 43 surplus respiratory samples from 34 intubated COVID-19 patients with suspected secondary bacterial or fungal pneumonia. Patients were drawn from seven ICUs at St. Thomas’ Hospital, London over a 9-week period between April 11 and June 15 2020, during the first wave of COVID-19.
Their median age was 52, 70% were male, 47% White, and 44% Black or minority ethnicities. Median length of stay was 32 days and mortality 24%. Samples sent for metagenomic analysis and culture included 10 bronchoalveolar lavages, 6 tracheal aspirates, and 27 non-direct bronchoalveolar lavages.
The study, published in Genome Medicine, showed that an 8-hour metagenomics workflow was 92% sensitive (95% CI, 75% to 99%) and 82% specific (95% CI, 57% to 96%) for bacterial identification, based on culture-positive and culture-negative samples, respectively.
The main Gram-negative bacteria identified were Klebsiella spp. (53%), Citrobacter spp. (15%), and E coli (9%). The main Gram-positive bacteria were S aureus (9%), C striatum (24%) and Enterococcus spp. (12%). In addition, C albicans, other Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp. were cultured from 38%, 15%, and 9% of patients, respectively.
In every case, the initial antibiotics prescribed according to prevailing guideline recommendations would have been modified by metagenomic sequencing demonstrating the presence or absence of β-lactam-resistant genes carried by Enterobacterales.
Next day results of sequencing also detected Aspergillus fumigatus in four samples, with results 100% concordant with quantitative PCR for both the four positive and 39 negative samples. It identified two multi-drug–resistant outbreaks, one involving K pneumoniae ST307 affecting four patients and one a C striatum outbreak involving 14 patients across three ICUs.
Thus, a single sample can provide enough genetic sequence data to compare pathogen genomes with a database and accurately identify patients carrying the same strain, enabling early detection of outbreaks. This is the first time this combined benefit of a single test has been demonstrated, the team say.
Gordon Sanghera, CEO of Oxford Nanopore commented that “rapidly characterizing co-infections for precision prescribing is a vital next step for both COVID-19 patients and respiratory disease in general.”
Dr. Andrew Page of the Quadram Institute said: “We have been working on metagenomics technology for the last 7 years. It is great to see it applied to patient care during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
He said in an interview: “The pandemic has accelerated the transition from using sequencing purely in research labs to using it in the clinic to rapidly provide clinicians with information they can use to improve outcomes for patients.”
Potential to inform antimicrobial prescribing and infection control
“Clinical metagenomic testing provides accurate pathogen detection and antibiotic resistance prediction in a same-day laboratory workflow, with assembled genomes available the next day for genomic surveillance,” the researchers say.
The technology “could fundamentally change the multi-disciplinary team approach to managing ICU infections.” It has the potential to improve initial targeted antimicrobial treatment and infection control decisions, as well as help rapidly detect unsuspected outbreaks of multi-drug–resistant pathogens.
Professor Edgeworth told this news organization that since the study, “secondary bacterial and fungal infections have increased, perhaps due to immunomodulatory treatments or just the length of time patients spend on ICU recovering from COVID-19. This makes rapid diagnosis even more important to ensure patients get more targeted antibiotics earlier, rather than relying on generic guidelines.”
The team “are planning to move respiratory metagenomics into pilot service under our Trust’s quality improvement framework,” he revealed. This will enable them to gather data on patient benefits.
“We also need to see how clinicians use these tests to improve antibiotic treatment, to stop antibiotics when not needed or to identify outbreaks earlier, and then how that translates into tangible benefits for individual patients and the wider NHS.”
He predicts that the technique will revolutionize the approach to prevention and treatment of serious infection in ICUs, and it is now planned to offer it as a clinical service for COVID-19 and influenza patients during the coming winter.
In addition, he said: “It can be equally applied to other samples such as tissue fluids and biopsies, including those removed at operation. It therefore has potential to impact on diagnostics for many clinical services, particularly if the progress is maintained at the current pace.”
This article first appeared on Medscape UK/Univadis.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has given added impetus for metagenomic testing using nanopore sequencing to progress from a research tool to routine clinical application. A study led by researchers from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust has shown the potential for clinical metagenomics to become a same-day test for identifying secondary infection in ventilated ICU patients. Getting results in hours rather than days would help to ensure rapid treatment with the correct antibiotic, minimize unnecessary prescriptions, and thus reduce the growing menace of antimicrobial resistance.
‘SARS-CoV-2 has put considerable strain on ICUs’
The researchers point out that the setting of an intensive care unit involves frequent staff-patient contact that imparts a risk of secondary or nosocomial infection. In addition, invasive ventilation may introduce organisms into the lungs and lead to ventilator-acquired pneumonia. This carries a high mortality and is responsible for up to 70% of antimicrobial prescribing, with current guidelines requiring empiric antibiotics pending culture results, which typically takes 2-4 days.
Many of these infection problems worsened during SARS-CoV-2. Expanded critical care capacity raised the risk of nosocomial infections, with attendant increased antimicrobial prescriptions and the threat of antimicrobial resistance. In addition, treatment of COVID-19 patients with steroid therapy potentially exacerbates bacterial or fungal infections.
The researchers, from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London, in collaboration with the Quadram Institute in Norwich, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and Viapath, the U.K.’s largest independent pathology service provider, noted that the pandemic thus reinforced “a need for rapid comprehensive diagnostics to improve antimicrobial stewardship and help prevent emergence and transmission of multi-drug-resistant organisms.”
“As soon as the pandemic started, our scientists realized there would be a benefit to sequencing genomes of all bacteria and fungi causing infection in COVID-19 patients while on ICU,” said Professor Jonathan Edgeworth, who led the research team.
“Within a few weeks we showed it can diagnose secondary infection, target antibiotic treatment, and detect outbreaks much earlier than current technologies – all from a single sample.”
Proof-of-concept study
The team performed a proof-of-concept study of nanopore metagenomics sequencing – a type of DNA sequencing that allows direct rapid unbiased detection of all organisms present in a clinical sample – on 43 surplus respiratory samples from 34 intubated COVID-19 patients with suspected secondary bacterial or fungal pneumonia. Patients were drawn from seven ICUs at St. Thomas’ Hospital, London over a 9-week period between April 11 and June 15 2020, during the first wave of COVID-19.
Their median age was 52, 70% were male, 47% White, and 44% Black or minority ethnicities. Median length of stay was 32 days and mortality 24%. Samples sent for metagenomic analysis and culture included 10 bronchoalveolar lavages, 6 tracheal aspirates, and 27 non-direct bronchoalveolar lavages.
The study, published in Genome Medicine, showed that an 8-hour metagenomics workflow was 92% sensitive (95% CI, 75% to 99%) and 82% specific (95% CI, 57% to 96%) for bacterial identification, based on culture-positive and culture-negative samples, respectively.
The main Gram-negative bacteria identified were Klebsiella spp. (53%), Citrobacter spp. (15%), and E coli (9%). The main Gram-positive bacteria were S aureus (9%), C striatum (24%) and Enterococcus spp. (12%). In addition, C albicans, other Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp. were cultured from 38%, 15%, and 9% of patients, respectively.
In every case, the initial antibiotics prescribed according to prevailing guideline recommendations would have been modified by metagenomic sequencing demonstrating the presence or absence of β-lactam-resistant genes carried by Enterobacterales.
Next day results of sequencing also detected Aspergillus fumigatus in four samples, with results 100% concordant with quantitative PCR for both the four positive and 39 negative samples. It identified two multi-drug–resistant outbreaks, one involving K pneumoniae ST307 affecting four patients and one a C striatum outbreak involving 14 patients across three ICUs.
Thus, a single sample can provide enough genetic sequence data to compare pathogen genomes with a database and accurately identify patients carrying the same strain, enabling early detection of outbreaks. This is the first time this combined benefit of a single test has been demonstrated, the team say.
Gordon Sanghera, CEO of Oxford Nanopore commented that “rapidly characterizing co-infections for precision prescribing is a vital next step for both COVID-19 patients and respiratory disease in general.”
Dr. Andrew Page of the Quadram Institute said: “We have been working on metagenomics technology for the last 7 years. It is great to see it applied to patient care during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
He said in an interview: “The pandemic has accelerated the transition from using sequencing purely in research labs to using it in the clinic to rapidly provide clinicians with information they can use to improve outcomes for patients.”
Potential to inform antimicrobial prescribing and infection control
“Clinical metagenomic testing provides accurate pathogen detection and antibiotic resistance prediction in a same-day laboratory workflow, with assembled genomes available the next day for genomic surveillance,” the researchers say.
The technology “could fundamentally change the multi-disciplinary team approach to managing ICU infections.” It has the potential to improve initial targeted antimicrobial treatment and infection control decisions, as well as help rapidly detect unsuspected outbreaks of multi-drug–resistant pathogens.
Professor Edgeworth told this news organization that since the study, “secondary bacterial and fungal infections have increased, perhaps due to immunomodulatory treatments or just the length of time patients spend on ICU recovering from COVID-19. This makes rapid diagnosis even more important to ensure patients get more targeted antibiotics earlier, rather than relying on generic guidelines.”
The team “are planning to move respiratory metagenomics into pilot service under our Trust’s quality improvement framework,” he revealed. This will enable them to gather data on patient benefits.
“We also need to see how clinicians use these tests to improve antibiotic treatment, to stop antibiotics when not needed or to identify outbreaks earlier, and then how that translates into tangible benefits for individual patients and the wider NHS.”
He predicts that the technique will revolutionize the approach to prevention and treatment of serious infection in ICUs, and it is now planned to offer it as a clinical service for COVID-19 and influenza patients during the coming winter.
In addition, he said: “It can be equally applied to other samples such as tissue fluids and biopsies, including those removed at operation. It therefore has potential to impact on diagnostics for many clinical services, particularly if the progress is maintained at the current pace.”
This article first appeared on Medscape UK/Univadis.
Should you worry about picking up COVID or other infections from public bathrooms?
but some experts disagree with the study’s conclusions. The study was published in Science of the Total Environment.
Sotiris Vardoulakis, PhD, of the Australian National University, Canberra, and colleagues reviewed studies of infections associated with public washrooms.
The researchers used keywords to identify potential articles. After screening study abstracts to ensure that only publicly available washrooms with toilets, sinks, and hand dryers were included, 65 studies remained. The investigators excluded washrooms on public transportation (ships, planes, trains, and buses).
“What most of the studies concluded was that what’s really important is to have good hand hygiene and proper maintenance and ventilation of washrooms,” Dr. Vardoulakis said in an interview. “So if the hand washing and drying is effective in the first place, it’s unlikely that the bathroom air or surfaces will pose an infectious disease transmission risk.”
There has been ongoing debate on whether electric hand dryers or paper towels are better. Some studies focused on hygiene. Others focused on the environmental cost of paper towels. One concern is that air dryers might spread germs further.
One study focused on the idea that the air recirculation from electric dryers may spread infective aerosols. Another study determined that the Airblade filters in some electric dryers clean more than 99% of the bacteria. The first study, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings by Cunrui Huang, MMed, MSPH, and colleagues, concluded that “drying hands thoroughly with single-use, disposable paper towels is the preferred method of hand drying in terms of hand hygiene.” Many people prefer to use paper towels because they can be used as a barrier when opening the washroom door.
Dr. Vardoulakis dismissed the air-versus-paper debate, saying, “If the hand washing and drying is effective in the first place, it’s unlikely that the bathroom air or surfaces will pose an infectious disease transmission risk.”
Although Dr. Vardoulakis’ review did not find that public washrooms pose a risk for infection, other researchers have shown that some settings do pose problems. For example, toilet plumes are thought to have contributed to the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome at the Amoy Gardens housing complex in Hong Kong and nearby buildings by aerosolization of fecal waste. Also, norovirus has long been shown to be transmitted by aerosolized particles in vomitus or stool.
Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, professor and chair, clinical lab science program, Texas State University, San Marcos, expressed concern about this systematic review in an interview with this news organization. “I believe one of the major limitations is that studies which involved restrooms on planes, hotels, camping (those camp kids are nasty), and other similar public-access restrooms MUST be included in this type of review. I also believe they excluded restrooms from low-income/rural areas. WHAT? Their ultimate conclusions seem to be in line with the most current understanding about hand hygiene (including drying without devices that create strong air currents, which may create widespread emission of microbes).”
In an interview, Emanuel Goldman, PhD, professor of microbiology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, focused on the COVID-specific aspects of the review. “The chances are less than 1 in 10,000 of getting COVID from a fomite, and that’s very conservative,” he said. “I think it’s a lot lower than that. The virus is fragile. It dies very quickly outside of a human host.” He emphasized, “virtually no infectious virus has been found on fomites over the last 2 years. ... A big mistake in a lot of papers is they confuse viral RNA with the virus. It’s not the same. Viral RNA is the genetic material of the virus, but it also is the ghost of the virus after the virus is dead, and that’s what people are finding. They’re finding the ghost of the virus.”
Because “studies show that the transfer from a surface to fingers is in the neighborhood of 10% efficiency” and one’s fingers also kill the virus, “transmission through your fingers is not easy,” Dr. Goldman said. “You’ve got to really work at it to deliberately infect yourself” with COVID from a fomite.
Dr. Rohde’s conclusion about Dr. Vardoulakis’s review? “So, the question may be, have there been enough studies, in general, of these other areas to include in a review? Otherwise, can we really generalize from this study? I don’t think so.”
Dr. Goldman is not worried about COVID transmission in public bathrooms. His summation: “I think indoor dining is more risky than anything else right now.”
The study was funded by Dyson Technology. Dr. Vardoulakis is a member of the Dyson scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
but some experts disagree with the study’s conclusions. The study was published in Science of the Total Environment.
Sotiris Vardoulakis, PhD, of the Australian National University, Canberra, and colleagues reviewed studies of infections associated with public washrooms.
The researchers used keywords to identify potential articles. After screening study abstracts to ensure that only publicly available washrooms with toilets, sinks, and hand dryers were included, 65 studies remained. The investigators excluded washrooms on public transportation (ships, planes, trains, and buses).
“What most of the studies concluded was that what’s really important is to have good hand hygiene and proper maintenance and ventilation of washrooms,” Dr. Vardoulakis said in an interview. “So if the hand washing and drying is effective in the first place, it’s unlikely that the bathroom air or surfaces will pose an infectious disease transmission risk.”
There has been ongoing debate on whether electric hand dryers or paper towels are better. Some studies focused on hygiene. Others focused on the environmental cost of paper towels. One concern is that air dryers might spread germs further.
One study focused on the idea that the air recirculation from electric dryers may spread infective aerosols. Another study determined that the Airblade filters in some electric dryers clean more than 99% of the bacteria. The first study, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings by Cunrui Huang, MMed, MSPH, and colleagues, concluded that “drying hands thoroughly with single-use, disposable paper towels is the preferred method of hand drying in terms of hand hygiene.” Many people prefer to use paper towels because they can be used as a barrier when opening the washroom door.
Dr. Vardoulakis dismissed the air-versus-paper debate, saying, “If the hand washing and drying is effective in the first place, it’s unlikely that the bathroom air or surfaces will pose an infectious disease transmission risk.”
Although Dr. Vardoulakis’ review did not find that public washrooms pose a risk for infection, other researchers have shown that some settings do pose problems. For example, toilet plumes are thought to have contributed to the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome at the Amoy Gardens housing complex in Hong Kong and nearby buildings by aerosolization of fecal waste. Also, norovirus has long been shown to be transmitted by aerosolized particles in vomitus or stool.
Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, professor and chair, clinical lab science program, Texas State University, San Marcos, expressed concern about this systematic review in an interview with this news organization. “I believe one of the major limitations is that studies which involved restrooms on planes, hotels, camping (those camp kids are nasty), and other similar public-access restrooms MUST be included in this type of review. I also believe they excluded restrooms from low-income/rural areas. WHAT? Their ultimate conclusions seem to be in line with the most current understanding about hand hygiene (including drying without devices that create strong air currents, which may create widespread emission of microbes).”
In an interview, Emanuel Goldman, PhD, professor of microbiology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, focused on the COVID-specific aspects of the review. “The chances are less than 1 in 10,000 of getting COVID from a fomite, and that’s very conservative,” he said. “I think it’s a lot lower than that. The virus is fragile. It dies very quickly outside of a human host.” He emphasized, “virtually no infectious virus has been found on fomites over the last 2 years. ... A big mistake in a lot of papers is they confuse viral RNA with the virus. It’s not the same. Viral RNA is the genetic material of the virus, but it also is the ghost of the virus after the virus is dead, and that’s what people are finding. They’re finding the ghost of the virus.”
Because “studies show that the transfer from a surface to fingers is in the neighborhood of 10% efficiency” and one’s fingers also kill the virus, “transmission through your fingers is not easy,” Dr. Goldman said. “You’ve got to really work at it to deliberately infect yourself” with COVID from a fomite.
Dr. Rohde’s conclusion about Dr. Vardoulakis’s review? “So, the question may be, have there been enough studies, in general, of these other areas to include in a review? Otherwise, can we really generalize from this study? I don’t think so.”
Dr. Goldman is not worried about COVID transmission in public bathrooms. His summation: “I think indoor dining is more risky than anything else right now.”
The study was funded by Dyson Technology. Dr. Vardoulakis is a member of the Dyson scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
but some experts disagree with the study’s conclusions. The study was published in Science of the Total Environment.
Sotiris Vardoulakis, PhD, of the Australian National University, Canberra, and colleagues reviewed studies of infections associated with public washrooms.
The researchers used keywords to identify potential articles. After screening study abstracts to ensure that only publicly available washrooms with toilets, sinks, and hand dryers were included, 65 studies remained. The investigators excluded washrooms on public transportation (ships, planes, trains, and buses).
“What most of the studies concluded was that what’s really important is to have good hand hygiene and proper maintenance and ventilation of washrooms,” Dr. Vardoulakis said in an interview. “So if the hand washing and drying is effective in the first place, it’s unlikely that the bathroom air or surfaces will pose an infectious disease transmission risk.”
There has been ongoing debate on whether electric hand dryers or paper towels are better. Some studies focused on hygiene. Others focused on the environmental cost of paper towels. One concern is that air dryers might spread germs further.
One study focused on the idea that the air recirculation from electric dryers may spread infective aerosols. Another study determined that the Airblade filters in some electric dryers clean more than 99% of the bacteria. The first study, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings by Cunrui Huang, MMed, MSPH, and colleagues, concluded that “drying hands thoroughly with single-use, disposable paper towels is the preferred method of hand drying in terms of hand hygiene.” Many people prefer to use paper towels because they can be used as a barrier when opening the washroom door.
Dr. Vardoulakis dismissed the air-versus-paper debate, saying, “If the hand washing and drying is effective in the first place, it’s unlikely that the bathroom air or surfaces will pose an infectious disease transmission risk.”
Although Dr. Vardoulakis’ review did not find that public washrooms pose a risk for infection, other researchers have shown that some settings do pose problems. For example, toilet plumes are thought to have contributed to the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome at the Amoy Gardens housing complex in Hong Kong and nearby buildings by aerosolization of fecal waste. Also, norovirus has long been shown to be transmitted by aerosolized particles in vomitus or stool.
Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, professor and chair, clinical lab science program, Texas State University, San Marcos, expressed concern about this systematic review in an interview with this news organization. “I believe one of the major limitations is that studies which involved restrooms on planes, hotels, camping (those camp kids are nasty), and other similar public-access restrooms MUST be included in this type of review. I also believe they excluded restrooms from low-income/rural areas. WHAT? Their ultimate conclusions seem to be in line with the most current understanding about hand hygiene (including drying without devices that create strong air currents, which may create widespread emission of microbes).”
In an interview, Emanuel Goldman, PhD, professor of microbiology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, focused on the COVID-specific aspects of the review. “The chances are less than 1 in 10,000 of getting COVID from a fomite, and that’s very conservative,” he said. “I think it’s a lot lower than that. The virus is fragile. It dies very quickly outside of a human host.” He emphasized, “virtually no infectious virus has been found on fomites over the last 2 years. ... A big mistake in a lot of papers is they confuse viral RNA with the virus. It’s not the same. Viral RNA is the genetic material of the virus, but it also is the ghost of the virus after the virus is dead, and that’s what people are finding. They’re finding the ghost of the virus.”
Because “studies show that the transfer from a surface to fingers is in the neighborhood of 10% efficiency” and one’s fingers also kill the virus, “transmission through your fingers is not easy,” Dr. Goldman said. “You’ve got to really work at it to deliberately infect yourself” with COVID from a fomite.
Dr. Rohde’s conclusion about Dr. Vardoulakis’s review? “So, the question may be, have there been enough studies, in general, of these other areas to include in a review? Otherwise, can we really generalize from this study? I don’t think so.”
Dr. Goldman is not worried about COVID transmission in public bathrooms. His summation: “I think indoor dining is more risky than anything else right now.”
The study was funded by Dyson Technology. Dr. Vardoulakis is a member of the Dyson scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
Retiform Purpura on the Buttocks in 6 Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients
To the Editor:
There is emerging evidence of skin findings in patients with COVID-19, including perniolike changes of the toes as well as urticarial and vesicular eruptions.1 Magro et al2 reported 3 cases of livedoid and purpuric skin eruptions in critically ill COVID-19 patients with evidence of thrombotic vasculopathy on skin biopsy, including a 32-year-old man with striking buttocks retiform purpura. Histopathologic analysis revealed thrombotic vasculopathy and pressure-induced ischemic necrosis. Since that patient was first evaluated (March 2020), we identified 6 more cases of critically ill COVID-19 patients from a single academic hospital in New York City with essentially identical clinical findings. Herein, we report those 6 cases of critically ill and intubated patients with COVID-19 who developed retiform purpura on the buttocks only, approximately 11 to 21 days after onset of COVID-19 symptoms.
We provided consultation for 5 men and 1 woman (age range, 42–78 years) who were critically ill with COVID-19 and developed retiform purpura on the buttocks (Figures 1 and 2). All had an elevated D-dimer concentration: 2 patients, >700 ng/mL; 2 patients, >2000 ng/mL; 2 patients, >6000 ng/mL (reference, 229 ng/mL). Three patients experienced a peak D-dimer concentration on the day retiform purpura was reported.
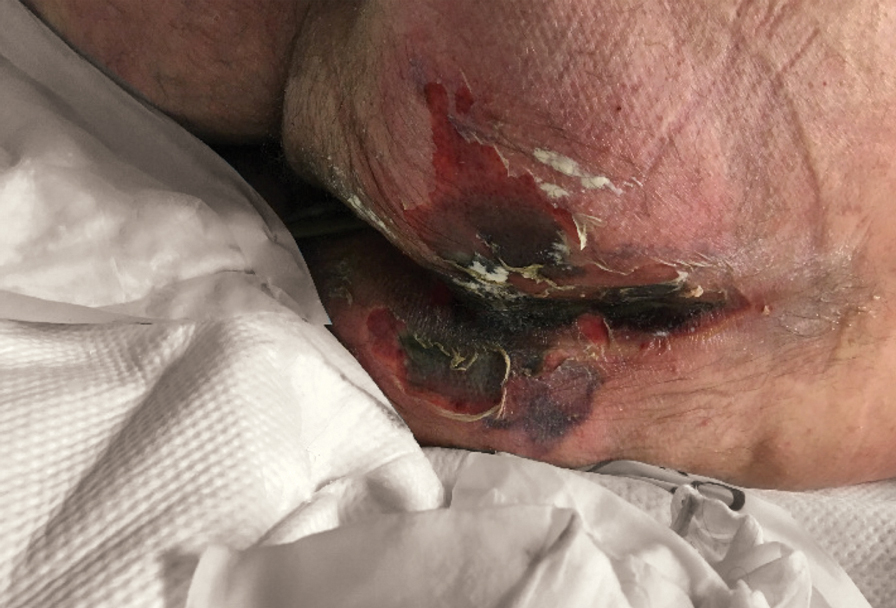
Further evidence of coagulopathy in these patients included 1 patient with a newly diagnosed left popliteal deep vein thrombosis and 1 patient with a known history of protein C deficiency and deep vein thromboses. Five patients were receiving anticoagulation on the day the skin changes were documented; anticoagulation was contraindicated in the sixth patient because of oropharyngeal bleeding. Anticoagulation was continued at the treatment dosage (enoxaparin 80 mg twice daily) in 3 patients, and in 2 patients receiving a prophylactic dose (enoxaparin 40 mg daily), anticoagulation was escalated to treatment dose due to rising D-dimer levels and newly diagnosed retiform purpura. Skin biopsy was deferred for all patients due to positional and ventilatory restrictions. At that point in their care, 3 patients remained admitted on medicine floors, 2 were in the intensive care unit, and 1 had died.
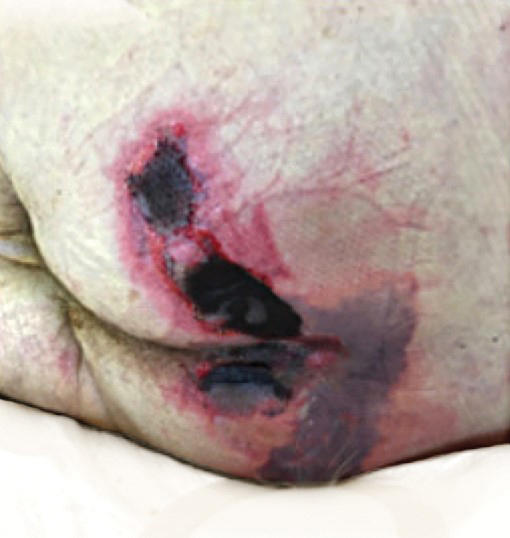
Although the differential diagnosis for retiform purpura is broad and should be fully considered in any patient with this finding, based on the elevated D-dimer concentration, critical illness secondary to COVID-19, and striking similarity to earlier reported case of buttocks retiform purpura with thrombotic vasculopathy and pressure injury noted histopathologically,2 we suspect the buttocks retiform purpura in our 6 cases also represent a combination of cutaneous thrombosis and pressure injury. In addition to acral livedoid eruptions (also reported by Magro and colleagues2), we suspect that this cutaneous manifestation might be associated with a hypercoagulable state in some patients, especially in the setting of a rising D-dimer concentration. One study found that 31% of 184 patients with severe COVID-19 had thrombotic complications,3 a clinical picture that portends a poor prognosis.4
COVID-19 patients presenting with retiform purpura should be fully evaluated based on the broad differential for this morphology. We present 6 cases of buttocks retiform purpura in critically ill COVID-19 patients—all with strikingly similar morphologic findings, an elevated D-dimer concentration, and critical illness due to COVID-19—to alert clinicians to this constellation of findings and propose that this cutaneous manifestation could indicate an associated hypercoaguable state and should prompt a hematology consultation. Additionally, biopsy of this skin finding should be considered, especially if biopsy results might serve to guide management; however, obtaining a biopsy specimen can be technically difficult because of ventilatory requirements.
Given the magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic and the propensity of these patients to experience thrombotic events, recognition of this skin finding in COVID-19 is important and might allow timely intervention.
- Recalcati S. Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: a first perspective. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:e212-e213. doi:10.1111/jdv.16387
- Magro C, Mulvey JJ, Berlin D, et al. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases. Transl Res. 2020;220:1-13. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007
- Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020;191:145-147. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
- Tang N, Li D, Wang X, et al. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:844-847. doi:10.1111/jth.14768
To the Editor:
There is emerging evidence of skin findings in patients with COVID-19, including perniolike changes of the toes as well as urticarial and vesicular eruptions.1 Magro et al2 reported 3 cases of livedoid and purpuric skin eruptions in critically ill COVID-19 patients with evidence of thrombotic vasculopathy on skin biopsy, including a 32-year-old man with striking buttocks retiform purpura. Histopathologic analysis revealed thrombotic vasculopathy and pressure-induced ischemic necrosis. Since that patient was first evaluated (March 2020), we identified 6 more cases of critically ill COVID-19 patients from a single academic hospital in New York City with essentially identical clinical findings. Herein, we report those 6 cases of critically ill and intubated patients with COVID-19 who developed retiform purpura on the buttocks only, approximately 11 to 21 days after onset of COVID-19 symptoms.
We provided consultation for 5 men and 1 woman (age range, 42–78 years) who were critically ill with COVID-19 and developed retiform purpura on the buttocks (Figures 1 and 2). All had an elevated D-dimer concentration: 2 patients, >700 ng/mL; 2 patients, >2000 ng/mL; 2 patients, >6000 ng/mL (reference, 229 ng/mL). Three patients experienced a peak D-dimer concentration on the day retiform purpura was reported.

Further evidence of coagulopathy in these patients included 1 patient with a newly diagnosed left popliteal deep vein thrombosis and 1 patient with a known history of protein C deficiency and deep vein thromboses. Five patients were receiving anticoagulation on the day the skin changes were documented; anticoagulation was contraindicated in the sixth patient because of oropharyngeal bleeding. Anticoagulation was continued at the treatment dosage (enoxaparin 80 mg twice daily) in 3 patients, and in 2 patients receiving a prophylactic dose (enoxaparin 40 mg daily), anticoagulation was escalated to treatment dose due to rising D-dimer levels and newly diagnosed retiform purpura. Skin biopsy was deferred for all patients due to positional and ventilatory restrictions. At that point in their care, 3 patients remained admitted on medicine floors, 2 were in the intensive care unit, and 1 had died.

Although the differential diagnosis for retiform purpura is broad and should be fully considered in any patient with this finding, based on the elevated D-dimer concentration, critical illness secondary to COVID-19, and striking similarity to earlier reported case of buttocks retiform purpura with thrombotic vasculopathy and pressure injury noted histopathologically,2 we suspect the buttocks retiform purpura in our 6 cases also represent a combination of cutaneous thrombosis and pressure injury. In addition to acral livedoid eruptions (also reported by Magro and colleagues2), we suspect that this cutaneous manifestation might be associated with a hypercoagulable state in some patients, especially in the setting of a rising D-dimer concentration. One study found that 31% of 184 patients with severe COVID-19 had thrombotic complications,3 a clinical picture that portends a poor prognosis.4
COVID-19 patients presenting with retiform purpura should be fully evaluated based on the broad differential for this morphology. We present 6 cases of buttocks retiform purpura in critically ill COVID-19 patients—all with strikingly similar morphologic findings, an elevated D-dimer concentration, and critical illness due to COVID-19—to alert clinicians to this constellation of findings and propose that this cutaneous manifestation could indicate an associated hypercoaguable state and should prompt a hematology consultation. Additionally, biopsy of this skin finding should be considered, especially if biopsy results might serve to guide management; however, obtaining a biopsy specimen can be technically difficult because of ventilatory requirements.
Given the magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic and the propensity of these patients to experience thrombotic events, recognition of this skin finding in COVID-19 is important and might allow timely intervention.
To the Editor:
There is emerging evidence of skin findings in patients with COVID-19, including perniolike changes of the toes as well as urticarial and vesicular eruptions.1 Magro et al2 reported 3 cases of livedoid and purpuric skin eruptions in critically ill COVID-19 patients with evidence of thrombotic vasculopathy on skin biopsy, including a 32-year-old man with striking buttocks retiform purpura. Histopathologic analysis revealed thrombotic vasculopathy and pressure-induced ischemic necrosis. Since that patient was first evaluated (March 2020), we identified 6 more cases of critically ill COVID-19 patients from a single academic hospital in New York City with essentially identical clinical findings. Herein, we report those 6 cases of critically ill and intubated patients with COVID-19 who developed retiform purpura on the buttocks only, approximately 11 to 21 days after onset of COVID-19 symptoms.
We provided consultation for 5 men and 1 woman (age range, 42–78 years) who were critically ill with COVID-19 and developed retiform purpura on the buttocks (Figures 1 and 2). All had an elevated D-dimer concentration: 2 patients, >700 ng/mL; 2 patients, >2000 ng/mL; 2 patients, >6000 ng/mL (reference, 229 ng/mL). Three patients experienced a peak D-dimer concentration on the day retiform purpura was reported.

Further evidence of coagulopathy in these patients included 1 patient with a newly diagnosed left popliteal deep vein thrombosis and 1 patient with a known history of protein C deficiency and deep vein thromboses. Five patients were receiving anticoagulation on the day the skin changes were documented; anticoagulation was contraindicated in the sixth patient because of oropharyngeal bleeding. Anticoagulation was continued at the treatment dosage (enoxaparin 80 mg twice daily) in 3 patients, and in 2 patients receiving a prophylactic dose (enoxaparin 40 mg daily), anticoagulation was escalated to treatment dose due to rising D-dimer levels and newly diagnosed retiform purpura. Skin biopsy was deferred for all patients due to positional and ventilatory restrictions. At that point in their care, 3 patients remained admitted on medicine floors, 2 were in the intensive care unit, and 1 had died.

Although the differential diagnosis for retiform purpura is broad and should be fully considered in any patient with this finding, based on the elevated D-dimer concentration, critical illness secondary to COVID-19, and striking similarity to earlier reported case of buttocks retiform purpura with thrombotic vasculopathy and pressure injury noted histopathologically,2 we suspect the buttocks retiform purpura in our 6 cases also represent a combination of cutaneous thrombosis and pressure injury. In addition to acral livedoid eruptions (also reported by Magro and colleagues2), we suspect that this cutaneous manifestation might be associated with a hypercoagulable state in some patients, especially in the setting of a rising D-dimer concentration. One study found that 31% of 184 patients with severe COVID-19 had thrombotic complications,3 a clinical picture that portends a poor prognosis.4
COVID-19 patients presenting with retiform purpura should be fully evaluated based on the broad differential for this morphology. We present 6 cases of buttocks retiform purpura in critically ill COVID-19 patients—all with strikingly similar morphologic findings, an elevated D-dimer concentration, and critical illness due to COVID-19—to alert clinicians to this constellation of findings and propose that this cutaneous manifestation could indicate an associated hypercoaguable state and should prompt a hematology consultation. Additionally, biopsy of this skin finding should be considered, especially if biopsy results might serve to guide management; however, obtaining a biopsy specimen can be technically difficult because of ventilatory requirements.
Given the magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic and the propensity of these patients to experience thrombotic events, recognition of this skin finding in COVID-19 is important and might allow timely intervention.
- Recalcati S. Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: a first perspective. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:e212-e213. doi:10.1111/jdv.16387
- Magro C, Mulvey JJ, Berlin D, et al. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases. Transl Res. 2020;220:1-13. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007
- Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020;191:145-147. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
- Tang N, Li D, Wang X, et al. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:844-847. doi:10.1111/jth.14768
- Recalcati S. Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: a first perspective. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:e212-e213. doi:10.1111/jdv.16387
- Magro C, Mulvey JJ, Berlin D, et al. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases. Transl Res. 2020;220:1-13. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007
- Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020;191:145-147. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
- Tang N, Li D, Wang X, et al. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:844-847. doi:10.1111/jth.14768
Practice Points
- Retiform purpura in a severely ill patient with COVID-19 and a markedly elevated D-dimer concentration might be a cutaneous sign of systemic coagulopathy.
- This constellation of findings should prompt consideration of skin biopsy and hematology consultation.