User login
TB treatment can be shortened for most children: study
The World Health Organization is expected to recommend truncating treatment of children with mild tuberculosis by 2 months – from 6 months to 4 – after a randomized trial found similar outcomes with the shorter regimen.
An international team of investigators found the abbreviated course of antibiotics was no less effective or safe than conventional treatment and saved an average of $17.34 per child – money that could be used to mitigate the toll of TB, which is estimated to sicken 1.1 million children worldwide each year.
The findings come as deaths from TB are rising as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has hindered efforts to find and treat patients. In 2020, according to the WHO, an estimated 1.5 million people died from TB, the first year-over-year increase in such deaths since 2005.
Nearly a quarter of children with TB die, primarily because they go undiagnosed, according to the researchers, who published the study in the New England Journal of Medicine. Shorter treatment “translates into very large cost savings that could be used to improve screening and diagnosis to address the current case detection gap,” first author Anna Turkova, MD, of University College London, told this news organization.
The standard TB regimen is based on trials in adults with severe respiratory disease. However, about two-thirds of children have nonsevere infections.
For the study, Dr. Turkova and colleagues assigned 1,204 children with TB in four countries – Uganda, Zambia, South Africa, and India – to either a 4- or 6-month regimen with first-line medications rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Participants were aged 2 months to 15 years and had symptomatic nonsevere lung or lymph node infections with a negative test on a sputum smear microscopy. Eleven percent also had HIV.
After 18 months, 16 participants in the group that received the shortened treatment and 18 in the standard treatment group had experienced an unfavorable outcome – defined as treatment failure, recurrence of TB, loss to follow-up, or death (adjusted difference, -0.4 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, -2.2 to 1.5).
Similar numbers – 47 in the 4-month group and 48 in the 6-month group – experienced severe or life-threatening adverse events, most commonly chest infections, such as pneumonia, and liver problems, during treatment or up to 30 days after the last dose.
New guidelines coming soon
The WHO plans to issue new guidelines and a handbook for TB management in children and adolescents on March 24, World Tuberculosis Day, a spokesman for the agency told Medscape.
Anna Mandalakas, MD, PhD, director of the Global Tuberculosis Program at Baylor College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Houston, said the shorter regimen should enable more children to successfully complete TB treatment.
“It can be challenging to convince young children to take medications on a regular basis for 6 months,” Dr. Mandalakas, a member of a WHO guidelines development group that reviewed the study, told this news organization. “Despite best intentions, parents often become fatigued and give up the medicine battle.”
Leo Martinez, PhD, an epidemiologist at Boston University School of Public Health who studies pediatric TB, noted that study’s cost-effectiveness analysis applies only to health care costs. Families often suffer financially through lost wages, transportation to health care facilities, and lost employment, fueling a cycle of poverty and disease in low-income countries, he said.
A WHO statement noted that long treatment regimens can add toxicity and risk of drug interactions for children with HIV.
Separate efforts have been underway to hasten TB treatment in different groups of patients. A study published in NEJM showed that 4 months of the potent antibiotic rifapentine, along with another antibiotic, moxifloxacin, was non-inferior to the standard 6-month regimen in patients aged 12 and older. According to the editorial accompanying that study, the research illustrated the potential for shorter treatment courses that would be cheaper and less cumbersome, although that particular combination poses hurdles such as adherence issues and potential bacterial resistance.
Experts agreed that improved diagnostic procedures are critical to significantly reducing TB pediatric deaths – an issue that Dr. Turkova said will be addressed in WHO’s forthcoming handbook.
Because no gold-standard test exists for TB, and symptoms often overlap with other infections, widespread screening of children in households where adults have been diagnosed with TB has been found to improve detection of the disease. “Training of health care workers, easy-to-implement diagnostic algorithms, and widely accessible training materials on chest radiography in childhood TB should also improve case finding and treatment initiation,” she said.
The trial was supported by U.K. government and charitable research funders. Dr. Turkova and Dr. Martinez reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Mandalakas reported honoraria from WHO to support the preparation of diagnostics and treatment chapters in the operational handbook, for providing lectures for Medscape, and for serving on a data safety monitoring board for Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The World Health Organization is expected to recommend truncating treatment of children with mild tuberculosis by 2 months – from 6 months to 4 – after a randomized trial found similar outcomes with the shorter regimen.
An international team of investigators found the abbreviated course of antibiotics was no less effective or safe than conventional treatment and saved an average of $17.34 per child – money that could be used to mitigate the toll of TB, which is estimated to sicken 1.1 million children worldwide each year.
The findings come as deaths from TB are rising as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has hindered efforts to find and treat patients. In 2020, according to the WHO, an estimated 1.5 million people died from TB, the first year-over-year increase in such deaths since 2005.
Nearly a quarter of children with TB die, primarily because they go undiagnosed, according to the researchers, who published the study in the New England Journal of Medicine. Shorter treatment “translates into very large cost savings that could be used to improve screening and diagnosis to address the current case detection gap,” first author Anna Turkova, MD, of University College London, told this news organization.
The standard TB regimen is based on trials in adults with severe respiratory disease. However, about two-thirds of children have nonsevere infections.
For the study, Dr. Turkova and colleagues assigned 1,204 children with TB in four countries – Uganda, Zambia, South Africa, and India – to either a 4- or 6-month regimen with first-line medications rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Participants were aged 2 months to 15 years and had symptomatic nonsevere lung or lymph node infections with a negative test on a sputum smear microscopy. Eleven percent also had HIV.
After 18 months, 16 participants in the group that received the shortened treatment and 18 in the standard treatment group had experienced an unfavorable outcome – defined as treatment failure, recurrence of TB, loss to follow-up, or death (adjusted difference, -0.4 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, -2.2 to 1.5).
Similar numbers – 47 in the 4-month group and 48 in the 6-month group – experienced severe or life-threatening adverse events, most commonly chest infections, such as pneumonia, and liver problems, during treatment or up to 30 days after the last dose.
New guidelines coming soon
The WHO plans to issue new guidelines and a handbook for TB management in children and adolescents on March 24, World Tuberculosis Day, a spokesman for the agency told Medscape.
Anna Mandalakas, MD, PhD, director of the Global Tuberculosis Program at Baylor College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Houston, said the shorter regimen should enable more children to successfully complete TB treatment.
“It can be challenging to convince young children to take medications on a regular basis for 6 months,” Dr. Mandalakas, a member of a WHO guidelines development group that reviewed the study, told this news organization. “Despite best intentions, parents often become fatigued and give up the medicine battle.”
Leo Martinez, PhD, an epidemiologist at Boston University School of Public Health who studies pediatric TB, noted that study’s cost-effectiveness analysis applies only to health care costs. Families often suffer financially through lost wages, transportation to health care facilities, and lost employment, fueling a cycle of poverty and disease in low-income countries, he said.
A WHO statement noted that long treatment regimens can add toxicity and risk of drug interactions for children with HIV.
Separate efforts have been underway to hasten TB treatment in different groups of patients. A study published in NEJM showed that 4 months of the potent antibiotic rifapentine, along with another antibiotic, moxifloxacin, was non-inferior to the standard 6-month regimen in patients aged 12 and older. According to the editorial accompanying that study, the research illustrated the potential for shorter treatment courses that would be cheaper and less cumbersome, although that particular combination poses hurdles such as adherence issues and potential bacterial resistance.
Experts agreed that improved diagnostic procedures are critical to significantly reducing TB pediatric deaths – an issue that Dr. Turkova said will be addressed in WHO’s forthcoming handbook.
Because no gold-standard test exists for TB, and symptoms often overlap with other infections, widespread screening of children in households where adults have been diagnosed with TB has been found to improve detection of the disease. “Training of health care workers, easy-to-implement diagnostic algorithms, and widely accessible training materials on chest radiography in childhood TB should also improve case finding and treatment initiation,” she said.
The trial was supported by U.K. government and charitable research funders. Dr. Turkova and Dr. Martinez reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Mandalakas reported honoraria from WHO to support the preparation of diagnostics and treatment chapters in the operational handbook, for providing lectures for Medscape, and for serving on a data safety monitoring board for Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The World Health Organization is expected to recommend truncating treatment of children with mild tuberculosis by 2 months – from 6 months to 4 – after a randomized trial found similar outcomes with the shorter regimen.
An international team of investigators found the abbreviated course of antibiotics was no less effective or safe than conventional treatment and saved an average of $17.34 per child – money that could be used to mitigate the toll of TB, which is estimated to sicken 1.1 million children worldwide each year.
The findings come as deaths from TB are rising as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has hindered efforts to find and treat patients. In 2020, according to the WHO, an estimated 1.5 million people died from TB, the first year-over-year increase in such deaths since 2005.
Nearly a quarter of children with TB die, primarily because they go undiagnosed, according to the researchers, who published the study in the New England Journal of Medicine. Shorter treatment “translates into very large cost savings that could be used to improve screening and diagnosis to address the current case detection gap,” first author Anna Turkova, MD, of University College London, told this news organization.
The standard TB regimen is based on trials in adults with severe respiratory disease. However, about two-thirds of children have nonsevere infections.
For the study, Dr. Turkova and colleagues assigned 1,204 children with TB in four countries – Uganda, Zambia, South Africa, and India – to either a 4- or 6-month regimen with first-line medications rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Participants were aged 2 months to 15 years and had symptomatic nonsevere lung or lymph node infections with a negative test on a sputum smear microscopy. Eleven percent also had HIV.
After 18 months, 16 participants in the group that received the shortened treatment and 18 in the standard treatment group had experienced an unfavorable outcome – defined as treatment failure, recurrence of TB, loss to follow-up, or death (adjusted difference, -0.4 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, -2.2 to 1.5).
Similar numbers – 47 in the 4-month group and 48 in the 6-month group – experienced severe or life-threatening adverse events, most commonly chest infections, such as pneumonia, and liver problems, during treatment or up to 30 days after the last dose.
New guidelines coming soon
The WHO plans to issue new guidelines and a handbook for TB management in children and adolescents on March 24, World Tuberculosis Day, a spokesman for the agency told Medscape.
Anna Mandalakas, MD, PhD, director of the Global Tuberculosis Program at Baylor College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Houston, said the shorter regimen should enable more children to successfully complete TB treatment.
“It can be challenging to convince young children to take medications on a regular basis for 6 months,” Dr. Mandalakas, a member of a WHO guidelines development group that reviewed the study, told this news organization. “Despite best intentions, parents often become fatigued and give up the medicine battle.”
Leo Martinez, PhD, an epidemiologist at Boston University School of Public Health who studies pediatric TB, noted that study’s cost-effectiveness analysis applies only to health care costs. Families often suffer financially through lost wages, transportation to health care facilities, and lost employment, fueling a cycle of poverty and disease in low-income countries, he said.
A WHO statement noted that long treatment regimens can add toxicity and risk of drug interactions for children with HIV.
Separate efforts have been underway to hasten TB treatment in different groups of patients. A study published in NEJM showed that 4 months of the potent antibiotic rifapentine, along with another antibiotic, moxifloxacin, was non-inferior to the standard 6-month regimen in patients aged 12 and older. According to the editorial accompanying that study, the research illustrated the potential for shorter treatment courses that would be cheaper and less cumbersome, although that particular combination poses hurdles such as adherence issues and potential bacterial resistance.
Experts agreed that improved diagnostic procedures are critical to significantly reducing TB pediatric deaths – an issue that Dr. Turkova said will be addressed in WHO’s forthcoming handbook.
Because no gold-standard test exists for TB, and symptoms often overlap with other infections, widespread screening of children in households where adults have been diagnosed with TB has been found to improve detection of the disease. “Training of health care workers, easy-to-implement diagnostic algorithms, and widely accessible training materials on chest radiography in childhood TB should also improve case finding and treatment initiation,” she said.
The trial was supported by U.K. government and charitable research funders. Dr. Turkova and Dr. Martinez reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Mandalakas reported honoraria from WHO to support the preparation of diagnostics and treatment chapters in the operational handbook, for providing lectures for Medscape, and for serving on a data safety monitoring board for Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Schizophrenia and HIV: missed opportunities for care
“People don’t think about schizophrenia when they think about HIV,” Christina Mangurian, MD, professor of clinical psychiatry and vice chair for diversity and health equity at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), told this news organization.
The problem is complicated. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health, roughly 6% of people with serious mental illness are living with HIV, a rate that is about 10 times higher than the general U.S. population (0.4%). However, findings from a study by Dr. Mangurian and her team, published online in the journal AIDS, demonstrated that half of Medicaid patients with schizophrenia and HIV admitted to inpatient units in New York State were not coded as such upon discharge.
These data raise the question: , lack of social support, and under-recognition by practitioners that a problem even exists?
Lost in the care continuum
Dr. Mangurian and her research team examined documentation of pre-existing HIV/AIDS diagnoses and absence of ICD-9-CM HIV/AIDS coding at psychiatric discharge among 14,602 adults (aged 18-64 years) admitted to hospital inpatient units in New York State between Jan. 1, 2012, and Dec. 31, 2013. HIV diagnoses were defined as recent (within 30 days of admission) or distant (within 30-366 days of admission), and first admission was used as the index in people with multiple hospitalizations.
People living with HIV comprised 5.1% (741) of the overall dataset; 34% were diagnosed with schizophrenia and 27.9% with bipolar disorders. Overall, 54.5% were male and 50.7% were non-Hispanic Black. Furthermore, 58.3% were discharged without HIV/AIDS ICD-9 coding, reinforcing the likelihood that they were lost in the care continuum.
Dr. Mangurian explained that this break in the chain of care upon discharge can have an important impact on efforts to break the cycle of HIV transmission.
“There’s data that people with serious mental illnesses like schizophrenia are less likely to have sex, but when they do they’re more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors, including sex for money [and] unprotected sex with partners who use injection drugs or who have HIV,” she said.
Although the majority of patients – both with and without prior HIV diagnoses – were older, adjusted models demonstrated that people aged 18-24 years had more than twice the odds of having their HIV/AIDS undocumented at discharge, compared with older adults aged 55-64 years (adjusted odds ratio, 2.37; P = .038), as were those aged 25-34 years (aOR, 2.17; P = .003). Individuals with more distant HIV diagnoses had three times the odds for an undocumented HIV/AIDS discharge, compared with more recent diagnoses (aOR, 3.25; P < .001).
Additional factors contributing to the lack of ICD-9 discharge coding included shorter lengths of stay (0-3 days vs. 15-30 days; aOR, 0.03; P = .01) and fewer HIV claims for HIV/AIDS services before hospitalization (1-2 vs. 3-9; aOR, 0.34; P < .01). Hospitals serving medium or high levels of Medicaid patients were also less likely to document HIV/AIDS before discharge (medium aOR, 1.69, P = .01; high aOR, 1.71, P = .03).
The study is not without limitations. For example, the 10-year-old dataset might not entirely reflect more recent structural or systemic changes for improving HIV detection on inpatient psychiatric units. Moreover, there was no comparator group without psychiatric inpatient admission.
Still, “[if these patients] didn’t have a discharge diagnosis, then it’s possible that they were not managed for their HIV, or their HIV was not addressed while they were in the hospital,” Sarah Andrews, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and AIDS psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, explained.
Dr. Andrews, who was not involved in the study, noted that this omission is significant. “A psychiatric admission or medical admission in general is a great opportunity to further manage and treat comorbidities. When we have a patient who comes in with HIV and they haven’t been on an antiviral prior to admission, we try to get infectious disease to give us recommendations of what to start, what labs to draw, to help them re-establish care,” she said.
Severe mental health an HIV disparity
Despite the burden of HIV among patient populations with serious mental health issues and data suggesting that these populations are over-represented among new HIV infections, the study findings point to an important missed opportunity for meeting several key outcomes on the HIV/AIDS care continuum, especially linkage to and retention in care.
The challenge is multifactorial.
In an earlier publication appearing in April 2021 in The Lancet HIV, Dr. Mangurian and colleagues explore a concept known as the “purview paradox,” which refers to a practitioner’s belief about who should be responsible for offering patients a particular intervention.
Structural and systemic issues also abound, as psychiatry records are often kept separate from the rest of the medical system due to insurer billing issues. “The true integration of all psychiatric and medical care has to happen to make sure that all of our patients receive the care that they deserve,” explained Dr. Mangurian.
Dr. Andrews agrees. “HIV care, as well as psychiatry, case management, pharmacy ... putting them together really helps decrease the risk of falling through the cracks and being able to refer appropriately for mental health,” she said.
Aside from changing practitioner attitudes and awareness and changing systems to include the wrap-around care model, current guidelines also need to reflect the role that patients with HIV and psychiatric comorbidities play in HIV transmission. Dr. Andrews and Dr. Mangurian agree: Routine screening in psychiatric inpatient units might be a good start.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Mangurian has reported grant funding from Genentech Charitable Foundation. Dr. Andrews has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“People don’t think about schizophrenia when they think about HIV,” Christina Mangurian, MD, professor of clinical psychiatry and vice chair for diversity and health equity at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), told this news organization.
The problem is complicated. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health, roughly 6% of people with serious mental illness are living with HIV, a rate that is about 10 times higher than the general U.S. population (0.4%). However, findings from a study by Dr. Mangurian and her team, published online in the journal AIDS, demonstrated that half of Medicaid patients with schizophrenia and HIV admitted to inpatient units in New York State were not coded as such upon discharge.
These data raise the question: , lack of social support, and under-recognition by practitioners that a problem even exists?
Lost in the care continuum
Dr. Mangurian and her research team examined documentation of pre-existing HIV/AIDS diagnoses and absence of ICD-9-CM HIV/AIDS coding at psychiatric discharge among 14,602 adults (aged 18-64 years) admitted to hospital inpatient units in New York State between Jan. 1, 2012, and Dec. 31, 2013. HIV diagnoses were defined as recent (within 30 days of admission) or distant (within 30-366 days of admission), and first admission was used as the index in people with multiple hospitalizations.
People living with HIV comprised 5.1% (741) of the overall dataset; 34% were diagnosed with schizophrenia and 27.9% with bipolar disorders. Overall, 54.5% were male and 50.7% were non-Hispanic Black. Furthermore, 58.3% were discharged without HIV/AIDS ICD-9 coding, reinforcing the likelihood that they were lost in the care continuum.
Dr. Mangurian explained that this break in the chain of care upon discharge can have an important impact on efforts to break the cycle of HIV transmission.
“There’s data that people with serious mental illnesses like schizophrenia are less likely to have sex, but when they do they’re more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors, including sex for money [and] unprotected sex with partners who use injection drugs or who have HIV,” she said.
Although the majority of patients – both with and without prior HIV diagnoses – were older, adjusted models demonstrated that people aged 18-24 years had more than twice the odds of having their HIV/AIDS undocumented at discharge, compared with older adults aged 55-64 years (adjusted odds ratio, 2.37; P = .038), as were those aged 25-34 years (aOR, 2.17; P = .003). Individuals with more distant HIV diagnoses had three times the odds for an undocumented HIV/AIDS discharge, compared with more recent diagnoses (aOR, 3.25; P < .001).
Additional factors contributing to the lack of ICD-9 discharge coding included shorter lengths of stay (0-3 days vs. 15-30 days; aOR, 0.03; P = .01) and fewer HIV claims for HIV/AIDS services before hospitalization (1-2 vs. 3-9; aOR, 0.34; P < .01). Hospitals serving medium or high levels of Medicaid patients were also less likely to document HIV/AIDS before discharge (medium aOR, 1.69, P = .01; high aOR, 1.71, P = .03).
The study is not without limitations. For example, the 10-year-old dataset might not entirely reflect more recent structural or systemic changes for improving HIV detection on inpatient psychiatric units. Moreover, there was no comparator group without psychiatric inpatient admission.
Still, “[if these patients] didn’t have a discharge diagnosis, then it’s possible that they were not managed for their HIV, or their HIV was not addressed while they were in the hospital,” Sarah Andrews, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and AIDS psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, explained.
Dr. Andrews, who was not involved in the study, noted that this omission is significant. “A psychiatric admission or medical admission in general is a great opportunity to further manage and treat comorbidities. When we have a patient who comes in with HIV and they haven’t been on an antiviral prior to admission, we try to get infectious disease to give us recommendations of what to start, what labs to draw, to help them re-establish care,” she said.
Severe mental health an HIV disparity
Despite the burden of HIV among patient populations with serious mental health issues and data suggesting that these populations are over-represented among new HIV infections, the study findings point to an important missed opportunity for meeting several key outcomes on the HIV/AIDS care continuum, especially linkage to and retention in care.
The challenge is multifactorial.
In an earlier publication appearing in April 2021 in The Lancet HIV, Dr. Mangurian and colleagues explore a concept known as the “purview paradox,” which refers to a practitioner’s belief about who should be responsible for offering patients a particular intervention.
Structural and systemic issues also abound, as psychiatry records are often kept separate from the rest of the medical system due to insurer billing issues. “The true integration of all psychiatric and medical care has to happen to make sure that all of our patients receive the care that they deserve,” explained Dr. Mangurian.
Dr. Andrews agrees. “HIV care, as well as psychiatry, case management, pharmacy ... putting them together really helps decrease the risk of falling through the cracks and being able to refer appropriately for mental health,” she said.
Aside from changing practitioner attitudes and awareness and changing systems to include the wrap-around care model, current guidelines also need to reflect the role that patients with HIV and psychiatric comorbidities play in HIV transmission. Dr. Andrews and Dr. Mangurian agree: Routine screening in psychiatric inpatient units might be a good start.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Mangurian has reported grant funding from Genentech Charitable Foundation. Dr. Andrews has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“People don’t think about schizophrenia when they think about HIV,” Christina Mangurian, MD, professor of clinical psychiatry and vice chair for diversity and health equity at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), told this news organization.
The problem is complicated. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health, roughly 6% of people with serious mental illness are living with HIV, a rate that is about 10 times higher than the general U.S. population (0.4%). However, findings from a study by Dr. Mangurian and her team, published online in the journal AIDS, demonstrated that half of Medicaid patients with schizophrenia and HIV admitted to inpatient units in New York State were not coded as such upon discharge.
These data raise the question: , lack of social support, and under-recognition by practitioners that a problem even exists?
Lost in the care continuum
Dr. Mangurian and her research team examined documentation of pre-existing HIV/AIDS diagnoses and absence of ICD-9-CM HIV/AIDS coding at psychiatric discharge among 14,602 adults (aged 18-64 years) admitted to hospital inpatient units in New York State between Jan. 1, 2012, and Dec. 31, 2013. HIV diagnoses were defined as recent (within 30 days of admission) or distant (within 30-366 days of admission), and first admission was used as the index in people with multiple hospitalizations.
People living with HIV comprised 5.1% (741) of the overall dataset; 34% were diagnosed with schizophrenia and 27.9% with bipolar disorders. Overall, 54.5% were male and 50.7% were non-Hispanic Black. Furthermore, 58.3% were discharged without HIV/AIDS ICD-9 coding, reinforcing the likelihood that they were lost in the care continuum.
Dr. Mangurian explained that this break in the chain of care upon discharge can have an important impact on efforts to break the cycle of HIV transmission.
“There’s data that people with serious mental illnesses like schizophrenia are less likely to have sex, but when they do they’re more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors, including sex for money [and] unprotected sex with partners who use injection drugs or who have HIV,” she said.
Although the majority of patients – both with and without prior HIV diagnoses – were older, adjusted models demonstrated that people aged 18-24 years had more than twice the odds of having their HIV/AIDS undocumented at discharge, compared with older adults aged 55-64 years (adjusted odds ratio, 2.37; P = .038), as were those aged 25-34 years (aOR, 2.17; P = .003). Individuals with more distant HIV diagnoses had three times the odds for an undocumented HIV/AIDS discharge, compared with more recent diagnoses (aOR, 3.25; P < .001).
Additional factors contributing to the lack of ICD-9 discharge coding included shorter lengths of stay (0-3 days vs. 15-30 days; aOR, 0.03; P = .01) and fewer HIV claims for HIV/AIDS services before hospitalization (1-2 vs. 3-9; aOR, 0.34; P < .01). Hospitals serving medium or high levels of Medicaid patients were also less likely to document HIV/AIDS before discharge (medium aOR, 1.69, P = .01; high aOR, 1.71, P = .03).
The study is not without limitations. For example, the 10-year-old dataset might not entirely reflect more recent structural or systemic changes for improving HIV detection on inpatient psychiatric units. Moreover, there was no comparator group without psychiatric inpatient admission.
Still, “[if these patients] didn’t have a discharge diagnosis, then it’s possible that they were not managed for their HIV, or their HIV was not addressed while they were in the hospital,” Sarah Andrews, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and AIDS psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, explained.
Dr. Andrews, who was not involved in the study, noted that this omission is significant. “A psychiatric admission or medical admission in general is a great opportunity to further manage and treat comorbidities. When we have a patient who comes in with HIV and they haven’t been on an antiviral prior to admission, we try to get infectious disease to give us recommendations of what to start, what labs to draw, to help them re-establish care,” she said.
Severe mental health an HIV disparity
Despite the burden of HIV among patient populations with serious mental health issues and data suggesting that these populations are over-represented among new HIV infections, the study findings point to an important missed opportunity for meeting several key outcomes on the HIV/AIDS care continuum, especially linkage to and retention in care.
The challenge is multifactorial.
In an earlier publication appearing in April 2021 in The Lancet HIV, Dr. Mangurian and colleagues explore a concept known as the “purview paradox,” which refers to a practitioner’s belief about who should be responsible for offering patients a particular intervention.
Structural and systemic issues also abound, as psychiatry records are often kept separate from the rest of the medical system due to insurer billing issues. “The true integration of all psychiatric and medical care has to happen to make sure that all of our patients receive the care that they deserve,” explained Dr. Mangurian.
Dr. Andrews agrees. “HIV care, as well as psychiatry, case management, pharmacy ... putting them together really helps decrease the risk of falling through the cracks and being able to refer appropriately for mental health,” she said.
Aside from changing practitioner attitudes and awareness and changing systems to include the wrap-around care model, current guidelines also need to reflect the role that patients with HIV and psychiatric comorbidities play in HIV transmission. Dr. Andrews and Dr. Mangurian agree: Routine screening in psychiatric inpatient units might be a good start.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Mangurian has reported grant funding from Genentech Charitable Foundation. Dr. Andrews has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Decline in new cases reaches 7th week
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children have fallen to their lowest level since the beginning of the Delta surge in July of 2021, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. Over those 7 weeks, new cases dropped over 96% from the 1.15 million reported for Jan. 14-20, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health departments.
The last time that the weekly count was below 42,000 was July 16-22, 2021, when almost 39,000 cases were reported in the midst of the Delta upsurge. That was shortly after cases had reached their lowest point, 8,447, since the early stages of the pandemic in 2020, the AAP/CHA data show.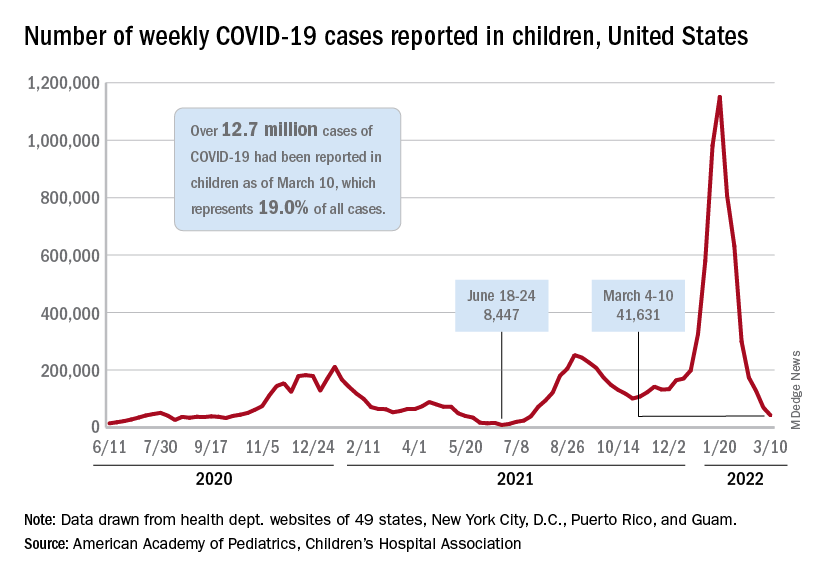
The cumulative number of pediatric cases is now up to 12.7 million, while the overall proportion of cases occurring in children held steady at 19.0% for the 4th week in a row, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, using an age range of 0-18 versus the states’ variety of ages, puts total cases at 11.7 million and deaths at 1,656 as of March 14.
Data from the CDC’s COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network show that hospitalizations with laboratory-confirmed infection were down by 50% in children aged 0-4 years, by 63% among 5- to 11-year-olds, and by 58% in those aged 12-17 years for the week of Feb. 27 to March 5, compared with the week before.
The pace of vaccination continues to follow a similar trend, as the declines seen through February have continued into March. Cumulatively, 33.7% of children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose, and 26.8% are fully vaccinated, with corresponding numbers of 68.0% and 58.0% for children aged 12-17, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
State-level data show that children aged 5-11 in Vermont, with a rate of 65%, are the most likely to have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, while just 15% of 5- to 11-year-olds in Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi have gotten their first dose. Among children aged 12-17, that rate ranges from 40% in Wyoming to 94% in Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island, the AAP said in a separate report based on CDC data.
In a recent report involving 1,364 children aged 5-15 years, two doses of the COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of infection from the Omicron variant by 31% in children aged 5-11 years and by 59% among children aged 12-15 years, said Ashley L. Fowlkes, ScD, of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, and associates (MMWR 2022 Mar 11;71).
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children have fallen to their lowest level since the beginning of the Delta surge in July of 2021, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. Over those 7 weeks, new cases dropped over 96% from the 1.15 million reported for Jan. 14-20, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health departments.
The last time that the weekly count was below 42,000 was July 16-22, 2021, when almost 39,000 cases were reported in the midst of the Delta upsurge. That was shortly after cases had reached their lowest point, 8,447, since the early stages of the pandemic in 2020, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of pediatric cases is now up to 12.7 million, while the overall proportion of cases occurring in children held steady at 19.0% for the 4th week in a row, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, using an age range of 0-18 versus the states’ variety of ages, puts total cases at 11.7 million and deaths at 1,656 as of March 14.
Data from the CDC’s COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network show that hospitalizations with laboratory-confirmed infection were down by 50% in children aged 0-4 years, by 63% among 5- to 11-year-olds, and by 58% in those aged 12-17 years for the week of Feb. 27 to March 5, compared with the week before.
The pace of vaccination continues to follow a similar trend, as the declines seen through February have continued into March. Cumulatively, 33.7% of children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose, and 26.8% are fully vaccinated, with corresponding numbers of 68.0% and 58.0% for children aged 12-17, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
State-level data show that children aged 5-11 in Vermont, with a rate of 65%, are the most likely to have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, while just 15% of 5- to 11-year-olds in Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi have gotten their first dose. Among children aged 12-17, that rate ranges from 40% in Wyoming to 94% in Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island, the AAP said in a separate report based on CDC data.
In a recent report involving 1,364 children aged 5-15 years, two doses of the COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of infection from the Omicron variant by 31% in children aged 5-11 years and by 59% among children aged 12-15 years, said Ashley L. Fowlkes, ScD, of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, and associates (MMWR 2022 Mar 11;71).
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children have fallen to their lowest level since the beginning of the Delta surge in July of 2021, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. Over those 7 weeks, new cases dropped over 96% from the 1.15 million reported for Jan. 14-20, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health departments.
The last time that the weekly count was below 42,000 was July 16-22, 2021, when almost 39,000 cases were reported in the midst of the Delta upsurge. That was shortly after cases had reached their lowest point, 8,447, since the early stages of the pandemic in 2020, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of pediatric cases is now up to 12.7 million, while the overall proportion of cases occurring in children held steady at 19.0% for the 4th week in a row, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, using an age range of 0-18 versus the states’ variety of ages, puts total cases at 11.7 million and deaths at 1,656 as of March 14.
Data from the CDC’s COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network show that hospitalizations with laboratory-confirmed infection were down by 50% in children aged 0-4 years, by 63% among 5- to 11-year-olds, and by 58% in those aged 12-17 years for the week of Feb. 27 to March 5, compared with the week before.
The pace of vaccination continues to follow a similar trend, as the declines seen through February have continued into March. Cumulatively, 33.7% of children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose, and 26.8% are fully vaccinated, with corresponding numbers of 68.0% and 58.0% for children aged 12-17, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
State-level data show that children aged 5-11 in Vermont, with a rate of 65%, are the most likely to have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, while just 15% of 5- to 11-year-olds in Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi have gotten their first dose. Among children aged 12-17, that rate ranges from 40% in Wyoming to 94% in Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island, the AAP said in a separate report based on CDC data.
In a recent report involving 1,364 children aged 5-15 years, two doses of the COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of infection from the Omicron variant by 31% in children aged 5-11 years and by 59% among children aged 12-15 years, said Ashley L. Fowlkes, ScD, of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, and associates (MMWR 2022 Mar 11;71).
MSM have higher CD4 counts at HIV diagnosis than heterosexuals
according to an analysis of more than 300,000 people living with HIV globally.
“It was quite a startling finding for us, because it’s now telling everybody, ‘Look, if you have MSM [men who have sex with men] coming into your clinic, expect CD4 counts at diagnosis to be higher than if the person got the infection as a heterosexual,’” Narendra Dixit, PhD, senior fellow at the Indian Institute of Science’s Centre for Biosystems Science and Engineering, Bangalore, India, said in an interview.
And that means, he said, that the pattern may appear in local clinics.
“If they find that there are differences in the CD4 counts between heterosexuals and MSMs, they should not be surprised anymore,” he said.
Dr. Dixit proposed that the reason for this may be that the viruses transmitted among heterosexuals are more virulent, but the study didn’t provide evidence of that.
Immune health at HIV diagnosis
In this study, which was published online March 10 in PLOS Pathogens, Dr. Dixit and colleague Anathu James, PhD, a data scientist and an epidemiologist at the Indian Institute of Science, culled data from 337,119 people captured in studies in the United Kingdom, the United States, Europe, Australia, and China. For all participants, CD4 counts were drawn at the time of diagnosis and before starting HIV treatment. Dr. Dixit and Dr. James then divided the studies by HIV transmission group – gay and bisexual men versus heterosexuals – and then averaged CD4 counts in each study.
Then they created a mathematical model to estimate how quickly each group might progress to an AIDS-defining illness, given those initial CD4 counts.
What they found was that the mean CD4 count was consistently higher in the gay and bisexual males than in the heterosexuals, no matter where they lived. For instance, mean CD4 counts at diagnosis were a mean of 437 cells/mm3 among gay and bisexual men in one European cohort, compared to a mean of 307 among heterosexuals. In the U.S. data, the mean CD4 count for gay and bisexual men was 390, compared to 314 among heterosexuals. In China, the same held true: Gay men had a mean CD4 count of 368 cells/mm3; heterosexuals had a mean CD4 count of 270.
This remained true when they only looked at people between the ages of 13 and 29 years in the United States or whether they were younger than 40 in Europe and Australia. In Europe and Australia, though, heterosexual women younger than 40 had higher CD4 counts than either straight or gay men. But this difference did not reach statistical significance, and gay men had higher CD4 counts overall when the investigators didn’t segregate the data by age group.
“We were stunned,” Dr. Dixit told this news organization. “People never thought there could be a difference in the CD4 counts just because the mode of transmission is different – or, in this case, because the risk groups are different.”
There was no difference, though, in viral load at diagnosis.
In their mathematical model on progression to AIDS, the investigators estimated that these lower CD4 counts at diagnosis would lead to a progression to AIDS that was 19% higher for straight people than for gay and bisexual men. What this implies for practice is less clear. Right now, Dr. Dixit hopes the data will be used to conduct molecular analysis of HIV strains in heterosexuals and gay and bisexual men to see if the HIV circulating in straight communities is different – and perhaps more virulent – than the HIV circulating among gay and bisexual men. Previous research has suggested that CD4 counts can be used as a proxy for virulence.
Dr. Dixit’s mathematical model follows recent news of a highly virulent strain of HIV that’s been present in the Netherlands for decades. “More virulent” in that case meant that it was more highly transmissible and led to higher viral loads and a quicker decline of the immune CD4 cells. So when news of Dr. Dixit’s study went out, it was accompanied by a press release stating as fact that “HIV-1 infections are more virulent when transmitted through penile-vaginal intercourse.” The study’s title states that HIV is “more virulent” in heterosexuals.
But this study doesn’t actually show that, said virology researcher Timothy Henrich, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, in an interview. In the Netherlands study, investigators took the additional step of analyzing HIV genomes. But this was not done in the recent PLOS Pathogens study.
“This was essentially a large meta-analysis of multiple large cohorts across many different countries,” said Dr. Henrich, who was not involved in the study. “There was no in-depth sequence analysis to say, ‘Oh yeah, this is because of a difference in the viruses that are being transmitted.’ If I were reviewing this paper, I probably would have said, ‘This is an interesting observation, but please don’t go overboard in your conclusions.’”
The study made Dr. Henrich want to know more. For instance, what method did each study use to determine CD4 counts? Did they control for the length of time since acquisition? Dr. Henrich said that if they didn’t differentiate between acute infection and chronic infection, he wasn’t sure what conclusions could be drawn from the data. Dr. Dixit told this news organization that they used the plateau level – the point after acute infection when CD4 counts settle into a consistent level. But it’s unclear how far from HIV acquisition each of the people in these studies was.
What Dr. Henrich does know, he said, is that big data are going to continue to change how we think about and investigate HIV transmission and virulence and what it could mean for clinical practice. The National Institutes of Health, for instance, will soon require all researchers receiving their funding to make their raw data publicly available soon after publication.
“We’re going to see a lot more of these large studies going forward,” he said. And if molecular analyses bear out Dr. Dixit’s conclusion – which he called “a big if” – “maybe we could use this study as a way” to do this work in the future.
The study was funded by DBT Network and the Wellcome Trust India Alliance Senior Fellowship. Dr. Dixit has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Henrich is conducting studies funded in whole or in part by Merck and Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to an analysis of more than 300,000 people living with HIV globally.
“It was quite a startling finding for us, because it’s now telling everybody, ‘Look, if you have MSM [men who have sex with men] coming into your clinic, expect CD4 counts at diagnosis to be higher than if the person got the infection as a heterosexual,’” Narendra Dixit, PhD, senior fellow at the Indian Institute of Science’s Centre for Biosystems Science and Engineering, Bangalore, India, said in an interview.
And that means, he said, that the pattern may appear in local clinics.
“If they find that there are differences in the CD4 counts between heterosexuals and MSMs, they should not be surprised anymore,” he said.
Dr. Dixit proposed that the reason for this may be that the viruses transmitted among heterosexuals are more virulent, but the study didn’t provide evidence of that.
Immune health at HIV diagnosis
In this study, which was published online March 10 in PLOS Pathogens, Dr. Dixit and colleague Anathu James, PhD, a data scientist and an epidemiologist at the Indian Institute of Science, culled data from 337,119 people captured in studies in the United Kingdom, the United States, Europe, Australia, and China. For all participants, CD4 counts were drawn at the time of diagnosis and before starting HIV treatment. Dr. Dixit and Dr. James then divided the studies by HIV transmission group – gay and bisexual men versus heterosexuals – and then averaged CD4 counts in each study.
Then they created a mathematical model to estimate how quickly each group might progress to an AIDS-defining illness, given those initial CD4 counts.
What they found was that the mean CD4 count was consistently higher in the gay and bisexual males than in the heterosexuals, no matter where they lived. For instance, mean CD4 counts at diagnosis were a mean of 437 cells/mm3 among gay and bisexual men in one European cohort, compared to a mean of 307 among heterosexuals. In the U.S. data, the mean CD4 count for gay and bisexual men was 390, compared to 314 among heterosexuals. In China, the same held true: Gay men had a mean CD4 count of 368 cells/mm3; heterosexuals had a mean CD4 count of 270.
This remained true when they only looked at people between the ages of 13 and 29 years in the United States or whether they were younger than 40 in Europe and Australia. In Europe and Australia, though, heterosexual women younger than 40 had higher CD4 counts than either straight or gay men. But this difference did not reach statistical significance, and gay men had higher CD4 counts overall when the investigators didn’t segregate the data by age group.
“We were stunned,” Dr. Dixit told this news organization. “People never thought there could be a difference in the CD4 counts just because the mode of transmission is different – or, in this case, because the risk groups are different.”
There was no difference, though, in viral load at diagnosis.
In their mathematical model on progression to AIDS, the investigators estimated that these lower CD4 counts at diagnosis would lead to a progression to AIDS that was 19% higher for straight people than for gay and bisexual men. What this implies for practice is less clear. Right now, Dr. Dixit hopes the data will be used to conduct molecular analysis of HIV strains in heterosexuals and gay and bisexual men to see if the HIV circulating in straight communities is different – and perhaps more virulent – than the HIV circulating among gay and bisexual men. Previous research has suggested that CD4 counts can be used as a proxy for virulence.
Dr. Dixit’s mathematical model follows recent news of a highly virulent strain of HIV that’s been present in the Netherlands for decades. “More virulent” in that case meant that it was more highly transmissible and led to higher viral loads and a quicker decline of the immune CD4 cells. So when news of Dr. Dixit’s study went out, it was accompanied by a press release stating as fact that “HIV-1 infections are more virulent when transmitted through penile-vaginal intercourse.” The study’s title states that HIV is “more virulent” in heterosexuals.
But this study doesn’t actually show that, said virology researcher Timothy Henrich, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, in an interview. In the Netherlands study, investigators took the additional step of analyzing HIV genomes. But this was not done in the recent PLOS Pathogens study.
“This was essentially a large meta-analysis of multiple large cohorts across many different countries,” said Dr. Henrich, who was not involved in the study. “There was no in-depth sequence analysis to say, ‘Oh yeah, this is because of a difference in the viruses that are being transmitted.’ If I were reviewing this paper, I probably would have said, ‘This is an interesting observation, but please don’t go overboard in your conclusions.’”
The study made Dr. Henrich want to know more. For instance, what method did each study use to determine CD4 counts? Did they control for the length of time since acquisition? Dr. Henrich said that if they didn’t differentiate between acute infection and chronic infection, he wasn’t sure what conclusions could be drawn from the data. Dr. Dixit told this news organization that they used the plateau level – the point after acute infection when CD4 counts settle into a consistent level. But it’s unclear how far from HIV acquisition each of the people in these studies was.
What Dr. Henrich does know, he said, is that big data are going to continue to change how we think about and investigate HIV transmission and virulence and what it could mean for clinical practice. The National Institutes of Health, for instance, will soon require all researchers receiving their funding to make their raw data publicly available soon after publication.
“We’re going to see a lot more of these large studies going forward,” he said. And if molecular analyses bear out Dr. Dixit’s conclusion – which he called “a big if” – “maybe we could use this study as a way” to do this work in the future.
The study was funded by DBT Network and the Wellcome Trust India Alliance Senior Fellowship. Dr. Dixit has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Henrich is conducting studies funded in whole or in part by Merck and Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to an analysis of more than 300,000 people living with HIV globally.
“It was quite a startling finding for us, because it’s now telling everybody, ‘Look, if you have MSM [men who have sex with men] coming into your clinic, expect CD4 counts at diagnosis to be higher than if the person got the infection as a heterosexual,’” Narendra Dixit, PhD, senior fellow at the Indian Institute of Science’s Centre for Biosystems Science and Engineering, Bangalore, India, said in an interview.
And that means, he said, that the pattern may appear in local clinics.
“If they find that there are differences in the CD4 counts between heterosexuals and MSMs, they should not be surprised anymore,” he said.
Dr. Dixit proposed that the reason for this may be that the viruses transmitted among heterosexuals are more virulent, but the study didn’t provide evidence of that.
Immune health at HIV diagnosis
In this study, which was published online March 10 in PLOS Pathogens, Dr. Dixit and colleague Anathu James, PhD, a data scientist and an epidemiologist at the Indian Institute of Science, culled data from 337,119 people captured in studies in the United Kingdom, the United States, Europe, Australia, and China. For all participants, CD4 counts were drawn at the time of diagnosis and before starting HIV treatment. Dr. Dixit and Dr. James then divided the studies by HIV transmission group – gay and bisexual men versus heterosexuals – and then averaged CD4 counts in each study.
Then they created a mathematical model to estimate how quickly each group might progress to an AIDS-defining illness, given those initial CD4 counts.
What they found was that the mean CD4 count was consistently higher in the gay and bisexual males than in the heterosexuals, no matter where they lived. For instance, mean CD4 counts at diagnosis were a mean of 437 cells/mm3 among gay and bisexual men in one European cohort, compared to a mean of 307 among heterosexuals. In the U.S. data, the mean CD4 count for gay and bisexual men was 390, compared to 314 among heterosexuals. In China, the same held true: Gay men had a mean CD4 count of 368 cells/mm3; heterosexuals had a mean CD4 count of 270.
This remained true when they only looked at people between the ages of 13 and 29 years in the United States or whether they were younger than 40 in Europe and Australia. In Europe and Australia, though, heterosexual women younger than 40 had higher CD4 counts than either straight or gay men. But this difference did not reach statistical significance, and gay men had higher CD4 counts overall when the investigators didn’t segregate the data by age group.
“We were stunned,” Dr. Dixit told this news organization. “People never thought there could be a difference in the CD4 counts just because the mode of transmission is different – or, in this case, because the risk groups are different.”
There was no difference, though, in viral load at diagnosis.
In their mathematical model on progression to AIDS, the investigators estimated that these lower CD4 counts at diagnosis would lead to a progression to AIDS that was 19% higher for straight people than for gay and bisexual men. What this implies for practice is less clear. Right now, Dr. Dixit hopes the data will be used to conduct molecular analysis of HIV strains in heterosexuals and gay and bisexual men to see if the HIV circulating in straight communities is different – and perhaps more virulent – than the HIV circulating among gay and bisexual men. Previous research has suggested that CD4 counts can be used as a proxy for virulence.
Dr. Dixit’s mathematical model follows recent news of a highly virulent strain of HIV that’s been present in the Netherlands for decades. “More virulent” in that case meant that it was more highly transmissible and led to higher viral loads and a quicker decline of the immune CD4 cells. So when news of Dr. Dixit’s study went out, it was accompanied by a press release stating as fact that “HIV-1 infections are more virulent when transmitted through penile-vaginal intercourse.” The study’s title states that HIV is “more virulent” in heterosexuals.
But this study doesn’t actually show that, said virology researcher Timothy Henrich, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, in an interview. In the Netherlands study, investigators took the additional step of analyzing HIV genomes. But this was not done in the recent PLOS Pathogens study.
“This was essentially a large meta-analysis of multiple large cohorts across many different countries,” said Dr. Henrich, who was not involved in the study. “There was no in-depth sequence analysis to say, ‘Oh yeah, this is because of a difference in the viruses that are being transmitted.’ If I were reviewing this paper, I probably would have said, ‘This is an interesting observation, but please don’t go overboard in your conclusions.’”
The study made Dr. Henrich want to know more. For instance, what method did each study use to determine CD4 counts? Did they control for the length of time since acquisition? Dr. Henrich said that if they didn’t differentiate between acute infection and chronic infection, he wasn’t sure what conclusions could be drawn from the data. Dr. Dixit told this news organization that they used the plateau level – the point after acute infection when CD4 counts settle into a consistent level. But it’s unclear how far from HIV acquisition each of the people in these studies was.
What Dr. Henrich does know, he said, is that big data are going to continue to change how we think about and investigate HIV transmission and virulence and what it could mean for clinical practice. The National Institutes of Health, for instance, will soon require all researchers receiving their funding to make their raw data publicly available soon after publication.
“We’re going to see a lot more of these large studies going forward,” he said. And if molecular analyses bear out Dr. Dixit’s conclusion – which he called “a big if” – “maybe we could use this study as a way” to do this work in the future.
The study was funded by DBT Network and the Wellcome Trust India Alliance Senior Fellowship. Dr. Dixit has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Henrich is conducting studies funded in whole or in part by Merck and Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PLOS PATHOGENS
Antiseptic as good as antibiotics for preventing recurrent UTI
The antiseptic methenamine hippurate (MH) is known to sterilize urine and has been suggested to be of use in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), but firm evidence has so far been lacking. Now researchers led by clinicians and scientists from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England, have provided the ALTAR trial (Alternative to Prophylactic Antibiotics for the Treatment of Recurrent UTIs in Women).
Daily low-dose antibiotics as recommended by current guidelines for prophylactic treatment of recurrent UTI have been linked to antibiotic resistance. Using MH as an alternative could play an important role in helping to tackle the global problem of increasing antibiotic resistance, the team said.
Study details
They recruited 240 women aged 18 or over with recurrent UTIs requiring prophylactic treatment from eight secondary care urology and urogynecology centers in the United Kingdom from June 2016 to June 2018. Women were randomized to receive MH or daily low-dose antibiotics for 12 months, with follow up for a further 6 months beyond that.
Before trial entry the women had experienced an average of more than six UTI episodes per year. During the 12-month treatment period, in the modified intention-to-treat population, there were 90 symptomatic, antibiotic-treated UTI episodes reported over 101 person-years of follow-up in the antibiotic group, and 141 episodes over 102 person-years in the MH group.
This yielded a UTI rate of 0.89 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic group, compared with 1.38 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.49 episodes per person-year. In the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period, the UTI incidence rate was 1.19 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic prophylaxis group versus 1.72 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.53.
Before the trial, a patient and public involvement group had predefined the noninferiority margin as one episode of UTI per person-year. The small difference between the two groups was less than this, confirming noninferiority of MH to antibiotic prophylaxis in this setting. This finding was consistent across the modified intention-to-treat, strict intention-to-treat, per protocol, and modified per protocol (post hoc) analyses.
Thus the ALTAR results showed that MH was no worse than antibiotics at preventing UTIs, and MH was also associated with reduced antibiotic consumption.
The vast majority of participants were over 90% adherent with the allocated treatment. Patient satisfaction was generally high and rates of adverse events and adverse reactions generally low, and both were comparable between treatment groups. Adverse reactions were reported by 34/142 (24%) in the antibiotic group and 35/127 (28%) in the MH group, and most reactions were mild. In the antibiotic group there were two serious adverse reactions (severe abdominal pain and raised alanine transaminase), whereas six participants in the MH group reported an episode of febrile UTI and four were admitted to hospital because of UTI.
Substantial global health care problem
At least 50% and up to 80% of all women have at least one acute UTI in their lifetime, most often uncomplicated acute cystitis. About a quarter of them go on to suffer recurrent infection, defined as three or more repeat infections in the past year, or two infections in the preceding 6 months. Frequent recurrences thus represent “a substantial global health care problem,” the authors say.
Guidelines from the United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States acknowledge the need for preventive strategies and strongly recommend the use of daily, low-dose antibiotics as standard prophylactic treatment. However, the United Kingdom’s antimicrobial resistance strategy recommends a “strong focus on infection prevention,” and aims to reduce antimicrobial use in humans by 15% before 2024.
“To achieve that, exploration of nonantibiotic preventive treatments in common conditions such as UTI is essential,” the team said.
MH is one such nonantibiotic treatment. It is bactericidal and works by denaturing bacterial proteins and nucleic acids. Although previous Cochrane systematic reviews had concluded that it could be effective for preventing UTI, further large trials were needed.
“This trial adds to the evidence base for the use of MH for prophylactic treatment in adult women with recurrent UTI. Although the MH group had a 55% higher rate of UTI episodes than the antibiotics group, the absolute difference was just 0.49 UTI episodes per year, which has limited clinical consequence,” the team concluded.
Results could ‘support a change in practice’
In older patients, particularly, the risks of long-term antibiotic prophylaxis might outweigh the benefits, and the authors said that their results “could support a change in practice in terms of preventive treatments for recurrent UTI and provide patients and clinicians with a credible alternative to daily antibiotics, giving them the confidence to pursue strategies that avoid long-term antibiotic use.”
They acknowledged limitations of the study, including that treatment allocation was not masked, crossover between arms was allowed, and differences in antibiotics prescribed may have affected the results. In addition, data regarding long-term safety of MH are scarce.
However, they said that the trial accurately represented the broad range of women with recurrent UTI, and that its results “might encourage patients and clinicians to consider MH as a first line treatment for UTI prevention in women.”
In a linked editorial, scientists from the Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare at Bond University in Queensland, Australia, commented: “Although the results need cautious interpretation, they align with others, and this new research increases the confidence with which MH can be offered as an option to women needing prophylaxis against recurrent urinary tract infection.”
References
Harding C et al. Alternative to prophylactic antibiotics for the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: multicentre, open label, randomised, noninferiority trial. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:e068229.
Hoffmann TC et al. Methenamine hippurate for recurrent urinary tract infections. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:o533.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
The antiseptic methenamine hippurate (MH) is known to sterilize urine and has been suggested to be of use in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), but firm evidence has so far been lacking. Now researchers led by clinicians and scientists from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England, have provided the ALTAR trial (Alternative to Prophylactic Antibiotics for the Treatment of Recurrent UTIs in Women).
Daily low-dose antibiotics as recommended by current guidelines for prophylactic treatment of recurrent UTI have been linked to antibiotic resistance. Using MH as an alternative could play an important role in helping to tackle the global problem of increasing antibiotic resistance, the team said.
Study details
They recruited 240 women aged 18 or over with recurrent UTIs requiring prophylactic treatment from eight secondary care urology and urogynecology centers in the United Kingdom from June 2016 to June 2018. Women were randomized to receive MH or daily low-dose antibiotics for 12 months, with follow up for a further 6 months beyond that.
Before trial entry the women had experienced an average of more than six UTI episodes per year. During the 12-month treatment period, in the modified intention-to-treat population, there were 90 symptomatic, antibiotic-treated UTI episodes reported over 101 person-years of follow-up in the antibiotic group, and 141 episodes over 102 person-years in the MH group.
This yielded a UTI rate of 0.89 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic group, compared with 1.38 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.49 episodes per person-year. In the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period, the UTI incidence rate was 1.19 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic prophylaxis group versus 1.72 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.53.
Before the trial, a patient and public involvement group had predefined the noninferiority margin as one episode of UTI per person-year. The small difference between the two groups was less than this, confirming noninferiority of MH to antibiotic prophylaxis in this setting. This finding was consistent across the modified intention-to-treat, strict intention-to-treat, per protocol, and modified per protocol (post hoc) analyses.
Thus the ALTAR results showed that MH was no worse than antibiotics at preventing UTIs, and MH was also associated with reduced antibiotic consumption.
The vast majority of participants were over 90% adherent with the allocated treatment. Patient satisfaction was generally high and rates of adverse events and adverse reactions generally low, and both were comparable between treatment groups. Adverse reactions were reported by 34/142 (24%) in the antibiotic group and 35/127 (28%) in the MH group, and most reactions were mild. In the antibiotic group there were two serious adverse reactions (severe abdominal pain and raised alanine transaminase), whereas six participants in the MH group reported an episode of febrile UTI and four were admitted to hospital because of UTI.
Substantial global health care problem
At least 50% and up to 80% of all women have at least one acute UTI in their lifetime, most often uncomplicated acute cystitis. About a quarter of them go on to suffer recurrent infection, defined as three or more repeat infections in the past year, or two infections in the preceding 6 months. Frequent recurrences thus represent “a substantial global health care problem,” the authors say.
Guidelines from the United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States acknowledge the need for preventive strategies and strongly recommend the use of daily, low-dose antibiotics as standard prophylactic treatment. However, the United Kingdom’s antimicrobial resistance strategy recommends a “strong focus on infection prevention,” and aims to reduce antimicrobial use in humans by 15% before 2024.
“To achieve that, exploration of nonantibiotic preventive treatments in common conditions such as UTI is essential,” the team said.
MH is one such nonantibiotic treatment. It is bactericidal and works by denaturing bacterial proteins and nucleic acids. Although previous Cochrane systematic reviews had concluded that it could be effective for preventing UTI, further large trials were needed.
“This trial adds to the evidence base for the use of MH for prophylactic treatment in adult women with recurrent UTI. Although the MH group had a 55% higher rate of UTI episodes than the antibiotics group, the absolute difference was just 0.49 UTI episodes per year, which has limited clinical consequence,” the team concluded.
Results could ‘support a change in practice’
In older patients, particularly, the risks of long-term antibiotic prophylaxis might outweigh the benefits, and the authors said that their results “could support a change in practice in terms of preventive treatments for recurrent UTI and provide patients and clinicians with a credible alternative to daily antibiotics, giving them the confidence to pursue strategies that avoid long-term antibiotic use.”
They acknowledged limitations of the study, including that treatment allocation was not masked, crossover between arms was allowed, and differences in antibiotics prescribed may have affected the results. In addition, data regarding long-term safety of MH are scarce.
However, they said that the trial accurately represented the broad range of women with recurrent UTI, and that its results “might encourage patients and clinicians to consider MH as a first line treatment for UTI prevention in women.”
In a linked editorial, scientists from the Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare at Bond University in Queensland, Australia, commented: “Although the results need cautious interpretation, they align with others, and this new research increases the confidence with which MH can be offered as an option to women needing prophylaxis against recurrent urinary tract infection.”
References
Harding C et al. Alternative to prophylactic antibiotics for the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: multicentre, open label, randomised, noninferiority trial. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:e068229.
Hoffmann TC et al. Methenamine hippurate for recurrent urinary tract infections. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:o533.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
The antiseptic methenamine hippurate (MH) is known to sterilize urine and has been suggested to be of use in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), but firm evidence has so far been lacking. Now researchers led by clinicians and scientists from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England, have provided the ALTAR trial (Alternative to Prophylactic Antibiotics for the Treatment of Recurrent UTIs in Women).
Daily low-dose antibiotics as recommended by current guidelines for prophylactic treatment of recurrent UTI have been linked to antibiotic resistance. Using MH as an alternative could play an important role in helping to tackle the global problem of increasing antibiotic resistance, the team said.
Study details
They recruited 240 women aged 18 or over with recurrent UTIs requiring prophylactic treatment from eight secondary care urology and urogynecology centers in the United Kingdom from June 2016 to June 2018. Women were randomized to receive MH or daily low-dose antibiotics for 12 months, with follow up for a further 6 months beyond that.
Before trial entry the women had experienced an average of more than six UTI episodes per year. During the 12-month treatment period, in the modified intention-to-treat population, there were 90 symptomatic, antibiotic-treated UTI episodes reported over 101 person-years of follow-up in the antibiotic group, and 141 episodes over 102 person-years in the MH group.
This yielded a UTI rate of 0.89 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic group, compared with 1.38 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.49 episodes per person-year. In the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period, the UTI incidence rate was 1.19 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic prophylaxis group versus 1.72 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.53.
Before the trial, a patient and public involvement group had predefined the noninferiority margin as one episode of UTI per person-year. The small difference between the two groups was less than this, confirming noninferiority of MH to antibiotic prophylaxis in this setting. This finding was consistent across the modified intention-to-treat, strict intention-to-treat, per protocol, and modified per protocol (post hoc) analyses.
Thus the ALTAR results showed that MH was no worse than antibiotics at preventing UTIs, and MH was also associated with reduced antibiotic consumption.
The vast majority of participants were over 90% adherent with the allocated treatment. Patient satisfaction was generally high and rates of adverse events and adverse reactions generally low, and both were comparable between treatment groups. Adverse reactions were reported by 34/142 (24%) in the antibiotic group and 35/127 (28%) in the MH group, and most reactions were mild. In the antibiotic group there were two serious adverse reactions (severe abdominal pain and raised alanine transaminase), whereas six participants in the MH group reported an episode of febrile UTI and four were admitted to hospital because of UTI.
Substantial global health care problem
At least 50% and up to 80% of all women have at least one acute UTI in their lifetime, most often uncomplicated acute cystitis. About a quarter of them go on to suffer recurrent infection, defined as three or more repeat infections in the past year, or two infections in the preceding 6 months. Frequent recurrences thus represent “a substantial global health care problem,” the authors say.
Guidelines from the United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States acknowledge the need for preventive strategies and strongly recommend the use of daily, low-dose antibiotics as standard prophylactic treatment. However, the United Kingdom’s antimicrobial resistance strategy recommends a “strong focus on infection prevention,” and aims to reduce antimicrobial use in humans by 15% before 2024.
“To achieve that, exploration of nonantibiotic preventive treatments in common conditions such as UTI is essential,” the team said.
MH is one such nonantibiotic treatment. It is bactericidal and works by denaturing bacterial proteins and nucleic acids. Although previous Cochrane systematic reviews had concluded that it could be effective for preventing UTI, further large trials were needed.
“This trial adds to the evidence base for the use of MH for prophylactic treatment in adult women with recurrent UTI. Although the MH group had a 55% higher rate of UTI episodes than the antibiotics group, the absolute difference was just 0.49 UTI episodes per year, which has limited clinical consequence,” the team concluded.
Results could ‘support a change in practice’
In older patients, particularly, the risks of long-term antibiotic prophylaxis might outweigh the benefits, and the authors said that their results “could support a change in practice in terms of preventive treatments for recurrent UTI and provide patients and clinicians with a credible alternative to daily antibiotics, giving them the confidence to pursue strategies that avoid long-term antibiotic use.”
They acknowledged limitations of the study, including that treatment allocation was not masked, crossover between arms was allowed, and differences in antibiotics prescribed may have affected the results. In addition, data regarding long-term safety of MH are scarce.
However, they said that the trial accurately represented the broad range of women with recurrent UTI, and that its results “might encourage patients and clinicians to consider MH as a first line treatment for UTI prevention in women.”
In a linked editorial, scientists from the Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare at Bond University in Queensland, Australia, commented: “Although the results need cautious interpretation, they align with others, and this new research increases the confidence with which MH can be offered as an option to women needing prophylaxis against recurrent urinary tract infection.”
References
Harding C et al. Alternative to prophylactic antibiotics for the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: multicentre, open label, randomised, noninferiority trial. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:e068229.
Hoffmann TC et al. Methenamine hippurate for recurrent urinary tract infections. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:o533.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
COVID-19 often more severe with congenital heart defects
Adults with a congenital heart defect (CHD) are at increased risk for serious illness and death when hospitalized with COVID-19, making vaccination and other preventive measures even important in this population, say researchers with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We found that hospitalized patients with heart defects are up to twice as likely to have critical outcomes of COVID-19 illness (admission to the intensive care unit, use of a ventilator to help with breathing, or death) compared to hospitalized COVID-19 patients without heart defects,” Karrie Downing, MPH, epidemiologist, with the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, said in an interview.
“Additionally, we learned that people with hearts defects who were older or who also had other conditions like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity were the most likely to have critical COVID-19 illness, but children and adults with heart defects without these other conditions were still at increased risk,” Ms. Downing said.
The message for health care providers is clear: “Encourage your patients with heart defects to get vaccinated and discuss with your patients the need for other preventive measures to avoid infection that may progress to severe COVID-19 illness,” Ms. Downing added.
The study was published online March 7, 2022, in Circulation.
The researchers analyzed data on 235,638 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021, including 421 (0.2%) with CHD. Most CHD patients were older than 30 years (73%) and 61% were men, with 55% non-Hispanic white, 19% Hispanic and 16% non-Hispanic Black.
Overall, 68% of CHD patients had at least one comorbidity, as did 59% of patients without CHD.
Rates of ICU admission were higher in the CHD group (54% vs. 43%), as were rates of invasive mechanical ventilation (24% vs. 15%) and in-hospital death (11% vs. 7%).
After accounting for patient characteristics, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death were more prevalent among COVID-19 patients with rather than without CHD, with adjusted prevalence ratios of 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0, respectively.
When stratified by high-risk characteristics, prevalence estimates for ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death remained higher among patients with COVID-19 and CHD across nearly all strata, including younger age groups and those without heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity, the researchers reported.
Ms. Downing said more work is needed to identify why the clinical course of COVID-19 disease results in admission to the ICU, the need for a ventilator, or death for some hospitalized patients with CHD and not for others.
“There could be a number of social, environmental, economic, medical, and genetic factors playing a role. But staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and following preventive measures for COVID-19 are effective ways to reduce the risk of severe illness from COVID-19,” Ms. Downing said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adults with a congenital heart defect (CHD) are at increased risk for serious illness and death when hospitalized with COVID-19, making vaccination and other preventive measures even important in this population, say researchers with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We found that hospitalized patients with heart defects are up to twice as likely to have critical outcomes of COVID-19 illness (admission to the intensive care unit, use of a ventilator to help with breathing, or death) compared to hospitalized COVID-19 patients without heart defects,” Karrie Downing, MPH, epidemiologist, with the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, said in an interview.
“Additionally, we learned that people with hearts defects who were older or who also had other conditions like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity were the most likely to have critical COVID-19 illness, but children and adults with heart defects without these other conditions were still at increased risk,” Ms. Downing said.
The message for health care providers is clear: “Encourage your patients with heart defects to get vaccinated and discuss with your patients the need for other preventive measures to avoid infection that may progress to severe COVID-19 illness,” Ms. Downing added.
The study was published online March 7, 2022, in Circulation.
The researchers analyzed data on 235,638 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021, including 421 (0.2%) with CHD. Most CHD patients were older than 30 years (73%) and 61% were men, with 55% non-Hispanic white, 19% Hispanic and 16% non-Hispanic Black.
Overall, 68% of CHD patients had at least one comorbidity, as did 59% of patients without CHD.
Rates of ICU admission were higher in the CHD group (54% vs. 43%), as were rates of invasive mechanical ventilation (24% vs. 15%) and in-hospital death (11% vs. 7%).
After accounting for patient characteristics, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death were more prevalent among COVID-19 patients with rather than without CHD, with adjusted prevalence ratios of 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0, respectively.
When stratified by high-risk characteristics, prevalence estimates for ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death remained higher among patients with COVID-19 and CHD across nearly all strata, including younger age groups and those without heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity, the researchers reported.
Ms. Downing said more work is needed to identify why the clinical course of COVID-19 disease results in admission to the ICU, the need for a ventilator, or death for some hospitalized patients with CHD and not for others.
“There could be a number of social, environmental, economic, medical, and genetic factors playing a role. But staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and following preventive measures for COVID-19 are effective ways to reduce the risk of severe illness from COVID-19,” Ms. Downing said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adults with a congenital heart defect (CHD) are at increased risk for serious illness and death when hospitalized with COVID-19, making vaccination and other preventive measures even important in this population, say researchers with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We found that hospitalized patients with heart defects are up to twice as likely to have critical outcomes of COVID-19 illness (admission to the intensive care unit, use of a ventilator to help with breathing, or death) compared to hospitalized COVID-19 patients without heart defects,” Karrie Downing, MPH, epidemiologist, with the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, said in an interview.
“Additionally, we learned that people with hearts defects who were older or who also had other conditions like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity were the most likely to have critical COVID-19 illness, but children and adults with heart defects without these other conditions were still at increased risk,” Ms. Downing said.
The message for health care providers is clear: “Encourage your patients with heart defects to get vaccinated and discuss with your patients the need for other preventive measures to avoid infection that may progress to severe COVID-19 illness,” Ms. Downing added.
The study was published online March 7, 2022, in Circulation.
The researchers analyzed data on 235,638 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021, including 421 (0.2%) with CHD. Most CHD patients were older than 30 years (73%) and 61% were men, with 55% non-Hispanic white, 19% Hispanic and 16% non-Hispanic Black.
Overall, 68% of CHD patients had at least one comorbidity, as did 59% of patients without CHD.
Rates of ICU admission were higher in the CHD group (54% vs. 43%), as were rates of invasive mechanical ventilation (24% vs. 15%) and in-hospital death (11% vs. 7%).
After accounting for patient characteristics, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death were more prevalent among COVID-19 patients with rather than without CHD, with adjusted prevalence ratios of 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0, respectively.
When stratified by high-risk characteristics, prevalence estimates for ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death remained higher among patients with COVID-19 and CHD across nearly all strata, including younger age groups and those without heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity, the researchers reported.
Ms. Downing said more work is needed to identify why the clinical course of COVID-19 disease results in admission to the ICU, the need for a ventilator, or death for some hospitalized patients with CHD and not for others.
“There could be a number of social, environmental, economic, medical, and genetic factors playing a role. But staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and following preventive measures for COVID-19 are effective ways to reduce the risk of severe illness from COVID-19,” Ms. Downing said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
COVID-19 vax effectiveness quantified in immunosuppressed patients
People taking immunosuppressive drugs benefit significantly from SARS-CoV-2 vaccines approved in the United States to prevent and reduce the severity of COVID-19, according to the first study to quantify the vaccines’ real-world effectiveness in this population.
Researchers’ analysis of the electronic medical records of more than 150,000 people in the University of Michigan’s health care system showed that even after becoming fully vaccinated, immunosuppressed individuals remain at higher risk for COVID-19 than are vaccinated people in the wider population who aren’t receiving immunosuppressive therapy. However, they still derive benefit from vaccination, particularly when bolstered with a booster dose.
The study, published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, also claims to be the first to show that the Moderna (mRNA-1273) vaccine is as effective as the Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine for people taking immunosuppressants.
“Booster doses are effective and important for individuals on immunosuppressants,” corresponding author Lili Zhao, PhD, a research associate professor in biostatistics at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “Previous studies focused mostly on the Pfizer vaccine, whereas our study is the first that also investigates the Moderna vaccine in a large, immunosuppressed population.”
The epidemiologic study included 154,519 fully vaccinated and unvaccinated adults in the Michigan Medicine electronic health record database. Participants were considered fully vaccinated if they were within 2 weeks of having received a second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines or the single-dose Johnson & Johnson (Ad26.COV2.S) vaccine. The study population included 5,536 immunosuppressed patients; of those, 4,283 were fully vaccinated, and 1,253 were unvaccinated.
The researchers focused on data collected from Jan. 1 to Dec. 7, 2021, so the study doesn’t cover the Omicron variant. “The conclusions for immunosuppressed individuals are likely to remain the same during the Omicron period,” Dr. Zhao said. “We are currently investigating this.” Johnson & Johnson paused production of its vaccine in February.
The researchers found that, among unvaccinated individuals, the immunosuppressed group had about a 40% higher risk of infection than did the immunocompetent patients (hazard ratio, 1.398; 95% confidence interval, 1.068-1.829; P = .0075) but a similar risk of COVID-19 hospitalization (HR, 0.951; 95% CI, 0.435-2.080; P = .9984). For the fully vaccinated, the gap was significantly wider: Immunosuppressed patients had more than double the risk of infection (HR, 2.173; 95% CI, 1.690-2.794; P < .0001) and almost five times the risk of hospitalization (HR, 4.861; 95% CI, 2.238-10.56; P < .0001), compared with immunocompetent patients.
However, among immunosuppressed individuals, the vaccinations significantly lowered risks, compared with not being vaccinated. There was a statistically significant 45% lower risk of infection (HR, 0.550; 95% CI, 0.387-0.781; P = .001) and similarly lower risk of hospitalization that did not reach statistical significance (HR, 0.534; 95% CI, 0.196-1.452; P = .3724).
When those immunosuppressed patients received a booster dose, their protection against COVID-19 improved, compared with their immunosuppressed counterparts who didn’t get a booster, with a 58% lower risk of infection after adjustment for age, gender, race, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (adjusted HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.76; P = .0037). The study included nearly 4 months of data after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended a booster dose of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines for immunocompromised individuals in August 2021. Among the immunosuppressed patients, 38.5% had received a booster dose.
There also was no apparent difference in the effectiveness between the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, with adjusted hazard ratios showing 41%-48% lower risk of infection. Too few individuals in the study were vaccinated with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to enable a sufficiently powered calculation of its effectiveness.
Other studies reach similar conclusions
The study findings fall into line with other studies of patient populations on immunosuppressants. A retrospective cohort study of Veterans Affairs patients with inflammatory bowel disease who were taking immunosuppressants, published in Gastroenterology, found that full vaccination with either Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines was about 80% effective. Another retrospective cohort study of data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, reported that full vaccination significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19 breakthrough infection regardless of immune status. Immunosuppressed patients in this study had higher rates of breakthrough infections than immunocompetent patients, but the disparities were in line with what Dr. Zhao and the University of Michigan researchers reported.
A review of 23 studies of COVID-19 vaccinations, published in Lancet Global Health, found that immunocompromised people – 1,722 of whom were included in the studies – had lower rates of producing antibodies after two vaccine doses than did immunocompetent people, ranging from 27% to 92%, depending on the nature of their immunocompromised status, compared with 99% for the immunocompetent.
Strengths and limitations
One strength of the Michigan study is the quality of data, which were drawn from the Michigan Medicine electronic health record, Dr. Zhao said. “So, we know who received the vaccine and who didn’t. We also have access to data on patient health conditions, such as comorbidities, in addition to demographic variables (age, gender, and race), which were controlled in making fair comparisons between immunosuppressants and immunocompetent groups.”
Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of internal medicine and rheumatology at Washington University in St. Louis, who was not involved with the study, credited Dr. Zhao and associates for delivering the first data that specifically quantified COVID-19 risk reduction in a large study population. Although he noted that the large sample size and the design reduced the chances of confounding and were strengths, he said in an interview that “lumping” the patients taking immunosuppressive drugs into one group was a weakness of the study.
“Clearly, there are certain medications (B-cell depleters, mycophenolate, for example) that carry the greatest risk of poor antibody responses post vaccination,” he said. “One would have to guess that the greatest risk of breakthrough infections continues to be in those patients taking these high-risk medications.”
Another possible problem, which the authors acknowledged, is spotty SARS-CoV-2 testing of study participants – “a systemic issue,” Dr. Kim noted.
“The easiest and most durable way to reduce the risk of getting COVID-19 is through vaccination, period,” he said. “Now we have infection-rates data from a real-world study cohort to prove this. Furthermore, boosting clearly provides additional benefit to this population.”
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided funding for the study. Dr. Zhao, Dr. Zhao’s coauthors, and Kim disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People taking immunosuppressive drugs benefit significantly from SARS-CoV-2 vaccines approved in the United States to prevent and reduce the severity of COVID-19, according to the first study to quantify the vaccines’ real-world effectiveness in this population.
Researchers’ analysis of the electronic medical records of more than 150,000 people in the University of Michigan’s health care system showed that even after becoming fully vaccinated, immunosuppressed individuals remain at higher risk for COVID-19 than are vaccinated people in the wider population who aren’t receiving immunosuppressive therapy. However, they still derive benefit from vaccination, particularly when bolstered with a booster dose.
The study, published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, also claims to be the first to show that the Moderna (mRNA-1273) vaccine is as effective as the Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine for people taking immunosuppressants.
“Booster doses are effective and important for individuals on immunosuppressants,” corresponding author Lili Zhao, PhD, a research associate professor in biostatistics at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “Previous studies focused mostly on the Pfizer vaccine, whereas our study is the first that also investigates the Moderna vaccine in a large, immunosuppressed population.”
The epidemiologic study included 154,519 fully vaccinated and unvaccinated adults in the Michigan Medicine electronic health record database. Participants were considered fully vaccinated if they were within 2 weeks of having received a second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines or the single-dose Johnson & Johnson (Ad26.COV2.S) vaccine. The study population included 5,536 immunosuppressed patients; of those, 4,283 were fully vaccinated, and 1,253 were unvaccinated.
The researchers focused on data collected from Jan. 1 to Dec. 7, 2021, so the study doesn’t cover the Omicron variant. “The conclusions for immunosuppressed individuals are likely to remain the same during the Omicron period,” Dr. Zhao said. “We are currently investigating this.” Johnson & Johnson paused production of its vaccine in February.
The researchers found that, among unvaccinated individuals, the immunosuppressed group had about a 40% higher risk of infection than did the immunocompetent patients (hazard ratio, 1.398; 95% confidence interval, 1.068-1.829; P = .0075) but a similar risk of COVID-19 hospitalization (HR, 0.951; 95% CI, 0.435-2.080; P = .9984). For the fully vaccinated, the gap was significantly wider: Immunosuppressed patients had more than double the risk of infection (HR, 2.173; 95% CI, 1.690-2.794; P < .0001) and almost five times the risk of hospitalization (HR, 4.861; 95% CI, 2.238-10.56; P < .0001), compared with immunocompetent patients.
However, among immunosuppressed individuals, the vaccinations significantly lowered risks, compared with not being vaccinated. There was a statistically significant 45% lower risk of infection (HR, 0.550; 95% CI, 0.387-0.781; P = .001) and similarly lower risk of hospitalization that did not reach statistical significance (HR, 0.534; 95% CI, 0.196-1.452; P = .3724).
When those immunosuppressed patients received a booster dose, their protection against COVID-19 improved, compared with their immunosuppressed counterparts who didn’t get a booster, with a 58% lower risk of infection after adjustment for age, gender, race, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (adjusted HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.76; P = .0037). The study included nearly 4 months of data after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended a booster dose of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines for immunocompromised individuals in August 2021. Among the immunosuppressed patients, 38.5% had received a booster dose.
There also was no apparent difference in the effectiveness between the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, with adjusted hazard ratios showing 41%-48% lower risk of infection. Too few individuals in the study were vaccinated with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to enable a sufficiently powered calculation of its effectiveness.
Other studies reach similar conclusions
The study findings fall into line with other studies of patient populations on immunosuppressants. A retrospective cohort study of Veterans Affairs patients with inflammatory bowel disease who were taking immunosuppressants, published in Gastroenterology, found that full vaccination with either Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines was about 80% effective. Another retrospective cohort study of data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, reported that full vaccination significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19 breakthrough infection regardless of immune status. Immunosuppressed patients in this study had higher rates of breakthrough infections than immunocompetent patients, but the disparities were in line with what Dr. Zhao and the University of Michigan researchers reported.
A review of 23 studies of COVID-19 vaccinations, published in Lancet Global Health, found that immunocompromised people – 1,722 of whom were included in the studies – had lower rates of producing antibodies after two vaccine doses than did immunocompetent people, ranging from 27% to 92%, depending on the nature of their immunocompromised status, compared with 99% for the immunocompetent.
Strengths and limitations
One strength of the Michigan study is the quality of data, which were drawn from the Michigan Medicine electronic health record, Dr. Zhao said. “So, we know who received the vaccine and who didn’t. We also have access to data on patient health conditions, such as comorbidities, in addition to demographic variables (age, gender, and race), which were controlled in making fair comparisons between immunosuppressants and immunocompetent groups.”
Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of internal medicine and rheumatology at Washington University in St. Louis, who was not involved with the study, credited Dr. Zhao and associates for delivering the first data that specifically quantified COVID-19 risk reduction in a large study population. Although he noted that the large sample size and the design reduced the chances of confounding and were strengths, he said in an interview that “lumping” the patients taking immunosuppressive drugs into one group was a weakness of the study.
“Clearly, there are certain medications (B-cell depleters, mycophenolate, for example) that carry the greatest risk of poor antibody responses post vaccination,” he said. “One would have to guess that the greatest risk of breakthrough infections continues to be in those patients taking these high-risk medications.”
Another possible problem, which the authors acknowledged, is spotty SARS-CoV-2 testing of study participants – “a systemic issue,” Dr. Kim noted.
“The easiest and most durable way to reduce the risk of getting COVID-19 is through vaccination, period,” he said. “Now we have infection-rates data from a real-world study cohort to prove this. Furthermore, boosting clearly provides additional benefit to this population.”
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided funding for the study. Dr. Zhao, Dr. Zhao’s coauthors, and Kim disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People taking immunosuppressive drugs benefit significantly from SARS-CoV-2 vaccines approved in the United States to prevent and reduce the severity of COVID-19, according to the first study to quantify the vaccines’ real-world effectiveness in this population.
Researchers’ analysis of the electronic medical records of more than 150,000 people in the University of Michigan’s health care system showed that even after becoming fully vaccinated, immunosuppressed individuals remain at higher risk for COVID-19 than are vaccinated people in the wider population who aren’t receiving immunosuppressive therapy. However, they still derive benefit from vaccination, particularly when bolstered with a booster dose.
The study, published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, also claims to be the first to show that the Moderna (mRNA-1273) vaccine is as effective as the Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine for people taking immunosuppressants.
“Booster doses are effective and important for individuals on immunosuppressants,” corresponding author Lili Zhao, PhD, a research associate professor in biostatistics at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “Previous studies focused mostly on the Pfizer vaccine, whereas our study is the first that also investigates the Moderna vaccine in a large, immunosuppressed population.”
The epidemiologic study included 154,519 fully vaccinated and unvaccinated adults in the Michigan Medicine electronic health record database. Participants were considered fully vaccinated if they were within 2 weeks of having received a second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines or the single-dose Johnson & Johnson (Ad26.COV2.S) vaccine. The study population included 5,536 immunosuppressed patients; of those, 4,283 were fully vaccinated, and 1,253 were unvaccinated.
The researchers focused on data collected from Jan. 1 to Dec. 7, 2021, so the study doesn’t cover the Omicron variant. “The conclusions for immunosuppressed individuals are likely to remain the same during the Omicron period,” Dr. Zhao said. “We are currently investigating this.” Johnson & Johnson paused production of its vaccine in February.
The researchers found that, among unvaccinated individuals, the immunosuppressed group had about a 40% higher risk of infection than did the immunocompetent patients (hazard ratio, 1.398; 95% confidence interval, 1.068-1.829; P = .0075) but a similar risk of COVID-19 hospitalization (HR, 0.951; 95% CI, 0.435-2.080; P = .9984). For the fully vaccinated, the gap was significantly wider: Immunosuppressed patients had more than double the risk of infection (HR, 2.173; 95% CI, 1.690-2.794; P < .0001) and almost five times the risk of hospitalization (HR, 4.861; 95% CI, 2.238-10.56; P < .0001), compared with immunocompetent patients.
However, among immunosuppressed individuals, the vaccinations significantly lowered risks, compared with not being vaccinated. There was a statistically significant 45% lower risk of infection (HR, 0.550; 95% CI, 0.387-0.781; P = .001) and similarly lower risk of hospitalization that did not reach statistical significance (HR, 0.534; 95% CI, 0.196-1.452; P = .3724).
When those immunosuppressed patients received a booster dose, their protection against COVID-19 improved, compared with their immunosuppressed counterparts who didn’t get a booster, with a 58% lower risk of infection after adjustment for age, gender, race, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (adjusted HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.24-0.76; P = .0037). The study included nearly 4 months of data after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended a booster dose of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines for immunocompromised individuals in August 2021. Among the immunosuppressed patients, 38.5% had received a booster dose.
There also was no apparent difference in the effectiveness between the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, with adjusted hazard ratios showing 41%-48% lower risk of infection. Too few individuals in the study were vaccinated with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to enable a sufficiently powered calculation of its effectiveness.
Other studies reach similar conclusions
The study findings fall into line with other studies of patient populations on immunosuppressants. A retrospective cohort study of Veterans Affairs patients with inflammatory bowel disease who were taking immunosuppressants, published in Gastroenterology, found that full vaccination with either Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines was about 80% effective. Another retrospective cohort study of data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, reported that full vaccination significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19 breakthrough infection regardless of immune status. Immunosuppressed patients in this study had higher rates of breakthrough infections than immunocompetent patients, but the disparities were in line with what Dr. Zhao and the University of Michigan researchers reported.
A review of 23 studies of COVID-19 vaccinations, published in Lancet Global Health, found that immunocompromised people – 1,722 of whom were included in the studies – had lower rates of producing antibodies after two vaccine doses than did immunocompetent people, ranging from 27% to 92%, depending on the nature of their immunocompromised status, compared with 99% for the immunocompetent.
Strengths and limitations
One strength of the Michigan study is the quality of data, which were drawn from the Michigan Medicine electronic health record, Dr. Zhao said. “So, we know who received the vaccine and who didn’t. We also have access to data on patient health conditions, such as comorbidities, in addition to demographic variables (age, gender, and race), which were controlled in making fair comparisons between immunosuppressants and immunocompetent groups.”
Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of internal medicine and rheumatology at Washington University in St. Louis, who was not involved with the study, credited Dr. Zhao and associates for delivering the first data that specifically quantified COVID-19 risk reduction in a large study population. Although he noted that the large sample size and the design reduced the chances of confounding and were strengths, he said in an interview that “lumping” the patients taking immunosuppressive drugs into one group was a weakness of the study.
“Clearly, there are certain medications (B-cell depleters, mycophenolate, for example) that carry the greatest risk of poor antibody responses post vaccination,” he said. “One would have to guess that the greatest risk of breakthrough infections continues to be in those patients taking these high-risk medications.”
Another possible problem, which the authors acknowledged, is spotty SARS-CoV-2 testing of study participants – “a systemic issue,” Dr. Kim noted.
“The easiest and most durable way to reduce the risk of getting COVID-19 is through vaccination, period,” he said. “Now we have infection-rates data from a real-world study cohort to prove this. Furthermore, boosting clearly provides additional benefit to this population.”
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided funding for the study. Dr. Zhao, Dr. Zhao’s coauthors, and Kim disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Cat ownership in childhood linked ‘conditionally’ to psychosis in adult males
Owning an outdoor cat as a child is associated with an increased risk of psychotic experiences in adulthood – but only in males, new research suggests.
Investigators found
The suspected culprit is not the cat itself but rather exposure to Toxoplasma gondii, a common parasite carried by rodents and sometimes found in cat feces. The study adds to a growing evidence showing exposure to T. gondii may be a risk factor for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
“These are small pieces of evidence but it’s interesting to consider that there might be combinations of risk factors at play,” lead author Vincent Paquin, MD, psychiatry resident at McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview.
“And even if the magnitude of the risk is small at the individual level,” he added, “cats and Toxoplasma gondii are so present in our society that if we add up all these small potential effects then it becomes a potential public health question.”
The study was published online Jan. 30, 2022, in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Inconsistent evidence
T. gondii infects about 30% of the human population and is usually transmitted by cats. Most infections are asymptomatic, but T. gondii can cause toxoplasmosis in humans, which has been linked to increased risk of schizophrenia, suicide attempts, and more recently, mild cognitive impairment.
Although some studies show an association between cat ownership and increased risk of mental illness, the research findings have been inconsistent.
“The evidence has been mixed about the association between cat ownership and psychosis expression, so our approach was to consider whether specific factors or combinations of factors could explain this mixed evidence,” Dr. Paquin said.
For the study, 2206 individuals aged 18-40 years completed the Community Assessment of Psychic Experiences (CAPE-42) and a questionnaire to gather information about cat ownership at any time between birth and age 13 and if the cats lived exclusively indoors (nonhunting) or if they were allowed outside (rodent hunting).
Participants were also asked about the number of residential moves between birth and age 15, date and place of birth, lifetime history of head trauma, and tobacco smoking history.
Rodent-hunting cat ownership was associated with higher risk of psychosis in male participants, compared with owning no cat or a nonhunting cat. When the investigators added head trauma and residential moves to rodent-hunting cat ownership, psychosis risk was elevated in both men and women.
Independent of cat ownership, younger age, moving more than three times as a child, a history of head trauma, and being a smoker were all associated with higher psychosis risk.
The study wasn’t designed to explore potential biological mechanisms to explain the sex differences in psychosis risk seen among rodent-hunting cat owners, but “one possible explanation based on the animal model literature is that the neurobiological effects of parasitic exposure may be greater with male sex,” senior author Suzanne King, PhD, professor of psychiatry at McGill, said in an interview.
The new study is part of a larger, long-term project called EnviroGen, led by Dr. King, examining the environmental and genetic risk factors for schizophrenia.
Need for replication
Commenting on the findings, E. Fuller Torrey, MD, who was among the first researchers to identify a link between cat ownership, T. gondii infection, and schizophrenia, said the study is “an interesting addition to the studies of cat ownership in childhood as a risk factor for psychosis.”
Of the approximately 10 published studies on the topic, about half suggest a link between cat ownership and psychosis later in life, said Dr. Torrey, associate director for research at the Stanley Medical Research Institute in Rockville, Md.
“The Canadian study is interesting in that it is the first study that separates exposure to permanently indoor cats from cats that are allowed to go outdoors, and the results were positive only for outdoor cats,” Dr. Torrey said.
The study has limitations, Dr. Torrey added, including its retrospective design and the use of a self-report questionnaire to assess psychotic experiences in adulthood.
Also commenting on findings, James Kirkbride, PhD, professor of psychiatric and social epidemiology, University College London, noted the same limitations.
Dr. Kirkbride is the lead author of a 2017 study that showed no link between cat ownership and serious mental illness that included nearly 5,000 people born in 1991 or 1992 and followed until age 18. In this study, there was no link between psychosis and cat ownership during pregnancy or at ages 4 or 10 years.
“Researchers have long been fascinated with the idea that cat ownership may affect mental health. This paper may have them chasing their own tail,” Dr. Kirkbride said.
“Evidence of any association is limited to certain subgroups without a strong theoretical basis for why this may be the case,” he added. “The retrospective and cross-sectional nature of the survey also raise the possibility that the results are impacted by differential recall bias, as well as the broader issues of chance and unobserved confounding.”
Dr. King noted that recall bias is a limitation the researchers highlighted in their study, but “considering the exposures are relatively objective and factual, we do not believe the potential for recall bias is substantial.”
“Nonetheless, we strongly believe that replication of our results in prospective, population-representative cohorts will be crucial to making firmer conclusions,” he added.
The study was funded by grants from the Quebec Health Research Fund. The study authors and Dr. Kirkbride disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Owning an outdoor cat as a child is associated with an increased risk of psychotic experiences in adulthood – but only in males, new research suggests.
Investigators found
The suspected culprit is not the cat itself but rather exposure to Toxoplasma gondii, a common parasite carried by rodents and sometimes found in cat feces. The study adds to a growing evidence showing exposure to T. gondii may be a risk factor for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
“These are small pieces of evidence but it’s interesting to consider that there might be combinations of risk factors at play,” lead author Vincent Paquin, MD, psychiatry resident at McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview.
“And even if the magnitude of the risk is small at the individual level,” he added, “cats and Toxoplasma gondii are so present in our society that if we add up all these small potential effects then it becomes a potential public health question.”
The study was published online Jan. 30, 2022, in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Inconsistent evidence
T. gondii infects about 30% of the human population and is usually transmitted by cats. Most infections are asymptomatic, but T. gondii can cause toxoplasmosis in humans, which has been linked to increased risk of schizophrenia, suicide attempts, and more recently, mild cognitive impairment.
Although some studies show an association between cat ownership and increased risk of mental illness, the research findings have been inconsistent.
“The evidence has been mixed about the association between cat ownership and psychosis expression, so our approach was to consider whether specific factors or combinations of factors could explain this mixed evidence,” Dr. Paquin said.
For the study, 2206 individuals aged 18-40 years completed the Community Assessment of Psychic Experiences (CAPE-42) and a questionnaire to gather information about cat ownership at any time between birth and age 13 and if the cats lived exclusively indoors (nonhunting) or if they were allowed outside (rodent hunting).
Participants were also asked about the number of residential moves between birth and age 15, date and place of birth, lifetime history of head trauma, and tobacco smoking history.
Rodent-hunting cat ownership was associated with higher risk of psychosis in male participants, compared with owning no cat or a nonhunting cat. When the investigators added head trauma and residential moves to rodent-hunting cat ownership, psychosis risk was elevated in both men and women.
Independent of cat ownership, younger age, moving more than three times as a child, a history of head trauma, and being a smoker were all associated with higher psychosis risk.
The study wasn’t designed to explore potential biological mechanisms to explain the sex differences in psychosis risk seen among rodent-hunting cat owners, but “one possible explanation based on the animal model literature is that the neurobiological effects of parasitic exposure may be greater with male sex,” senior author Suzanne King, PhD, professor of psychiatry at McGill, said in an interview.
The new study is part of a larger, long-term project called EnviroGen, led by Dr. King, examining the environmental and genetic risk factors for schizophrenia.
Need for replication
Commenting on the findings, E. Fuller Torrey, MD, who was among the first researchers to identify a link between cat ownership, T. gondii infection, and schizophrenia, said the study is “an interesting addition to the studies of cat ownership in childhood as a risk factor for psychosis.”
Of the approximately 10 published studies on the topic, about half suggest a link between cat ownership and psychosis later in life, said Dr. Torrey, associate director for research at the Stanley Medical Research Institute in Rockville, Md.
“The Canadian study is interesting in that it is the first study that separates exposure to permanently indoor cats from cats that are allowed to go outdoors, and the results were positive only for outdoor cats,” Dr. Torrey said.
The study has limitations, Dr. Torrey added, including its retrospective design and the use of a self-report questionnaire to assess psychotic experiences in adulthood.
Also commenting on findings, James Kirkbride, PhD, professor of psychiatric and social epidemiology, University College London, noted the same limitations.
Dr. Kirkbride is the lead author of a 2017 study that showed no link between cat ownership and serious mental illness that included nearly 5,000 people born in 1991 or 1992 and followed until age 18. In this study, there was no link between psychosis and cat ownership during pregnancy or at ages 4 or 10 years.
“Researchers have long been fascinated with the idea that cat ownership may affect mental health. This paper may have them chasing their own tail,” Dr. Kirkbride said.
“Evidence of any association is limited to certain subgroups without a strong theoretical basis for why this may be the case,” he added. “The retrospective and cross-sectional nature of the survey also raise the possibility that the results are impacted by differential recall bias, as well as the broader issues of chance and unobserved confounding.”
Dr. King noted that recall bias is a limitation the researchers highlighted in their study, but “considering the exposures are relatively objective and factual, we do not believe the potential for recall bias is substantial.”
“Nonetheless, we strongly believe that replication of our results in prospective, population-representative cohorts will be crucial to making firmer conclusions,” he added.
The study was funded by grants from the Quebec Health Research Fund. The study authors and Dr. Kirkbride disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Owning an outdoor cat as a child is associated with an increased risk of psychotic experiences in adulthood – but only in males, new research suggests.
Investigators found
The suspected culprit is not the cat itself but rather exposure to Toxoplasma gondii, a common parasite carried by rodents and sometimes found in cat feces. The study adds to a growing evidence showing exposure to T. gondii may be a risk factor for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
“These are small pieces of evidence but it’s interesting to consider that there might be combinations of risk factors at play,” lead author Vincent Paquin, MD, psychiatry resident at McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview.
“And even if the magnitude of the risk is small at the individual level,” he added, “cats and Toxoplasma gondii are so present in our society that if we add up all these small potential effects then it becomes a potential public health question.”
The study was published online Jan. 30, 2022, in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Inconsistent evidence
T. gondii infects about 30% of the human population and is usually transmitted by cats. Most infections are asymptomatic, but T. gondii can cause toxoplasmosis in humans, which has been linked to increased risk of schizophrenia, suicide attempts, and more recently, mild cognitive impairment.
Although some studies show an association between cat ownership and increased risk of mental illness, the research findings have been inconsistent.
“The evidence has been mixed about the association between cat ownership and psychosis expression, so our approach was to consider whether specific factors or combinations of factors could explain this mixed evidence,” Dr. Paquin said.
For the study, 2206 individuals aged 18-40 years completed the Community Assessment of Psychic Experiences (CAPE-42) and a questionnaire to gather information about cat ownership at any time between birth and age 13 and if the cats lived exclusively indoors (nonhunting) or if they were allowed outside (rodent hunting).
Participants were also asked about the number of residential moves between birth and age 15, date and place of birth, lifetime history of head trauma, and tobacco smoking history.
Rodent-hunting cat ownership was associated with higher risk of psychosis in male participants, compared with owning no cat or a nonhunting cat. When the investigators added head trauma and residential moves to rodent-hunting cat ownership, psychosis risk was elevated in both men and women.
Independent of cat ownership, younger age, moving more than three times as a child, a history of head trauma, and being a smoker were all associated with higher psychosis risk.
The study wasn’t designed to explore potential biological mechanisms to explain the sex differences in psychosis risk seen among rodent-hunting cat owners, but “one possible explanation based on the animal model literature is that the neurobiological effects of parasitic exposure may be greater with male sex,” senior author Suzanne King, PhD, professor of psychiatry at McGill, said in an interview.
The new study is part of a larger, long-term project called EnviroGen, led by Dr. King, examining the environmental and genetic risk factors for schizophrenia.
Need for replication
Commenting on the findings, E. Fuller Torrey, MD, who was among the first researchers to identify a link between cat ownership, T. gondii infection, and schizophrenia, said the study is “an interesting addition to the studies of cat ownership in childhood as a risk factor for psychosis.”
Of the approximately 10 published studies on the topic, about half suggest a link between cat ownership and psychosis later in life, said Dr. Torrey, associate director for research at the Stanley Medical Research Institute in Rockville, Md.
“The Canadian study is interesting in that it is the first study that separates exposure to permanently indoor cats from cats that are allowed to go outdoors, and the results were positive only for outdoor cats,” Dr. Torrey said.
The study has limitations, Dr. Torrey added, including its retrospective design and the use of a self-report questionnaire to assess psychotic experiences in adulthood.
Also commenting on findings, James Kirkbride, PhD, professor of psychiatric and social epidemiology, University College London, noted the same limitations.
Dr. Kirkbride is the lead author of a 2017 study that showed no link between cat ownership and serious mental illness that included nearly 5,000 people born in 1991 or 1992 and followed until age 18. In this study, there was no link between psychosis and cat ownership during pregnancy or at ages 4 or 10 years.
“Researchers have long been fascinated with the idea that cat ownership may affect mental health. This paper may have them chasing their own tail,” Dr. Kirkbride said.
“Evidence of any association is limited to certain subgroups without a strong theoretical basis for why this may be the case,” he added. “The retrospective and cross-sectional nature of the survey also raise the possibility that the results are impacted by differential recall bias, as well as the broader issues of chance and unobserved confounding.”
Dr. King noted that recall bias is a limitation the researchers highlighted in their study, but “considering the exposures are relatively objective and factual, we do not believe the potential for recall bias is substantial.”
“Nonetheless, we strongly believe that replication of our results in prospective, population-representative cohorts will be crucial to making firmer conclusions,” he added.
The study was funded by grants from the Quebec Health Research Fund. The study authors and Dr. Kirkbride disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH
C. difficile vaccine: Pfizer’s phase 3 CLOVER trial shows mixed results
, a phase 3 study involving 17,500 adults aged 50 and older that evaluated their candidate vaccine (PF-06425090) against Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) for the prevention of C. diff. infection (CDI).
The bad news is that the trial didn’t meet its efficacy endpoint – the prevention of primary CDI. According to a Pfizer press release, “Vaccine efficacy under the primary endpoint was 31% (96.4%, confidence interval -38.7, 66.6) following the third dose and 28.6% (96.4%, CI -28.4, 61.0) following the second dose. For all CDI cases recorded at 14 days post dose 3, vaccine efficacy was 49%, 47%, and 31% up to 12 months, 24 months, and at final analysis, respectively.”
This news organization requested an interview with a Pfizer spokesperson, but the company declined to comment further.
The good news is that the vaccine did meet its secondary endpoint. There were no cases of CDI requiring medical attention among vaccine recipients; by comparison, there were 11 cases among those who received placebo.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention classifies C. diff with other antimicrobial resistance “threat” organisms, as the two often go hand in hand. Their 2019 report noted that in 2017, 223,900 people in the United States required hospitalization for CDI, and at least 12,800 died. C. diff is the most common cause of health care-associated infection and increasingly occurs outside of acute care hospitals. Age older than 65 is a risk factor for disease. And at least 20% of patients experience recurrence.
The trial enrolled people older than 50 who were at higher risk of CDI because of having received antibiotics within the previous 12 weeks or because they were likely to have contact with health care systems. They received three doses of an investigational vaccine containing detoxified toxins A and B. These are the principal virulence factors produced by C. diff. Doses were given at 0, 1, and 6 months.
This news organization asked C. diff specialist David Aronoff, MD, chair of the department of medicine at Indiana University, for comment. Dr. Aronoff was not involved in the Pfizer clinical trials. He told this news organization via email, “Given the very low number of cases, I am impressed, from the limited data that have been made available, that the vaccine appears to have efficacy of around 50% for reducing CDI and, importantly, might reduce the severity of disease significantly, possibly preventing hospitalizations or worse clinical outcomes. It is unclear if the vaccine reduces the risk of recurrent CDI, but that would be a strong finding if true. I think we need to see these data after being subject to peer review, to better define its potential role in preventing CDI on a larger scale.”
Asked about the numbers needed to treat and cost-effectiveness of treatment, Dr. Aronoff added, “It is not clear how many people would need to receive the vaccine to prevent one hospitalization from CDI, or one death, or one case. Because the study groups had fewer episodes of CDI than anticipated, it watered down the power of this investigation to provide definitive answers regarding its true efficacy.”
Dr. Aronoff concluded, “All things considered, I am a cup half-full type of person on these topline results, since there are indications of reducing disease incidence and severity. We can build on these results.”
Dr. Aronoff had a basic science C. diff research grant from Pfizer in 2018-2019 that was not related to vaccines or therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a phase 3 study involving 17,500 adults aged 50 and older that evaluated their candidate vaccine (PF-06425090) against Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) for the prevention of C. diff. infection (CDI).
The bad news is that the trial didn’t meet its efficacy endpoint – the prevention of primary CDI. According to a Pfizer press release, “Vaccine efficacy under the primary endpoint was 31% (96.4%, confidence interval -38.7, 66.6) following the third dose and 28.6% (96.4%, CI -28.4, 61.0) following the second dose. For all CDI cases recorded at 14 days post dose 3, vaccine efficacy was 49%, 47%, and 31% up to 12 months, 24 months, and at final analysis, respectively.”
This news organization requested an interview with a Pfizer spokesperson, but the company declined to comment further.
The good news is that the vaccine did meet its secondary endpoint. There were no cases of CDI requiring medical attention among vaccine recipients; by comparison, there were 11 cases among those who received placebo.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention classifies C. diff with other antimicrobial resistance “threat” organisms, as the two often go hand in hand. Their 2019 report noted that in 2017, 223,900 people in the United States required hospitalization for CDI, and at least 12,800 died. C. diff is the most common cause of health care-associated infection and increasingly occurs outside of acute care hospitals. Age older than 65 is a risk factor for disease. And at least 20% of patients experience recurrence.
The trial enrolled people older than 50 who were at higher risk of CDI because of having received antibiotics within the previous 12 weeks or because they were likely to have contact with health care systems. They received three doses of an investigational vaccine containing detoxified toxins A and B. These are the principal virulence factors produced by C. diff. Doses were given at 0, 1, and 6 months.
This news organization asked C. diff specialist David Aronoff, MD, chair of the department of medicine at Indiana University, for comment. Dr. Aronoff was not involved in the Pfizer clinical trials. He told this news organization via email, “Given the very low number of cases, I am impressed, from the limited data that have been made available, that the vaccine appears to have efficacy of around 50% for reducing CDI and, importantly, might reduce the severity of disease significantly, possibly preventing hospitalizations or worse clinical outcomes. It is unclear if the vaccine reduces the risk of recurrent CDI, but that would be a strong finding if true. I think we need to see these data after being subject to peer review, to better define its potential role in preventing CDI on a larger scale.”
Asked about the numbers needed to treat and cost-effectiveness of treatment, Dr. Aronoff added, “It is not clear how many people would need to receive the vaccine to prevent one hospitalization from CDI, or one death, or one case. Because the study groups had fewer episodes of CDI than anticipated, it watered down the power of this investigation to provide definitive answers regarding its true efficacy.”
Dr. Aronoff concluded, “All things considered, I am a cup half-full type of person on these topline results, since there are indications of reducing disease incidence and severity. We can build on these results.”
Dr. Aronoff had a basic science C. diff research grant from Pfizer in 2018-2019 that was not related to vaccines or therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a phase 3 study involving 17,500 adults aged 50 and older that evaluated their candidate vaccine (PF-06425090) against Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) for the prevention of C. diff. infection (CDI).
The bad news is that the trial didn’t meet its efficacy endpoint – the prevention of primary CDI. According to a Pfizer press release, “Vaccine efficacy under the primary endpoint was 31% (96.4%, confidence interval -38.7, 66.6) following the third dose and 28.6% (96.4%, CI -28.4, 61.0) following the second dose. For all CDI cases recorded at 14 days post dose 3, vaccine efficacy was 49%, 47%, and 31% up to 12 months, 24 months, and at final analysis, respectively.”
This news organization requested an interview with a Pfizer spokesperson, but the company declined to comment further.
The good news is that the vaccine did meet its secondary endpoint. There were no cases of CDI requiring medical attention among vaccine recipients; by comparison, there were 11 cases among those who received placebo.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention classifies C. diff with other antimicrobial resistance “threat” organisms, as the two often go hand in hand. Their 2019 report noted that in 2017, 223,900 people in the United States required hospitalization for CDI, and at least 12,800 died. C. diff is the most common cause of health care-associated infection and increasingly occurs outside of acute care hospitals. Age older than 65 is a risk factor for disease. And at least 20% of patients experience recurrence.
The trial enrolled people older than 50 who were at higher risk of CDI because of having received antibiotics within the previous 12 weeks or because they were likely to have contact with health care systems. They received three doses of an investigational vaccine containing detoxified toxins A and B. These are the principal virulence factors produced by C. diff. Doses were given at 0, 1, and 6 months.
This news organization asked C. diff specialist David Aronoff, MD, chair of the department of medicine at Indiana University, for comment. Dr. Aronoff was not involved in the Pfizer clinical trials. He told this news organization via email, “Given the very low number of cases, I am impressed, from the limited data that have been made available, that the vaccine appears to have efficacy of around 50% for reducing CDI and, importantly, might reduce the severity of disease significantly, possibly preventing hospitalizations or worse clinical outcomes. It is unclear if the vaccine reduces the risk of recurrent CDI, but that would be a strong finding if true. I think we need to see these data after being subject to peer review, to better define its potential role in preventing CDI on a larger scale.”
Asked about the numbers needed to treat and cost-effectiveness of treatment, Dr. Aronoff added, “It is not clear how many people would need to receive the vaccine to prevent one hospitalization from CDI, or one death, or one case. Because the study groups had fewer episodes of CDI than anticipated, it watered down the power of this investigation to provide definitive answers regarding its true efficacy.”
Dr. Aronoff concluded, “All things considered, I am a cup half-full type of person on these topline results, since there are indications of reducing disease incidence and severity. We can build on these results.”
Dr. Aronoff had a basic science C. diff research grant from Pfizer in 2018-2019 that was not related to vaccines or therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mutation drives persistent Pseudomonas in COPD
Pseudomonas aeruginosa persisted in the airways of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), based on data from 23 patients over a 1-year period.
P. aeruginosa is cultured in as many as 20% of bacterial exacerbations and has been linked to increased morbidity and mortality in patients with COPD, wrote Josefin Eklöf, MD, of the University of Copenhagen and colleagues. However, its patterns and characteristics have not been well studied, and researchers proposed that P. aerunginosa persists in COPD patients in part because of genetic adaptations in the genes related to antibiotic resistance.
In a study published in Clinical Microbiology and Infection, the researchers identified 23 consecutive patients enrolled in an ongoing randomized clinical trial at four sites in Denmark between Jan. 2018 and Jan. 2020. Participants were randomized 1:1 to targeted antipseudomonal antibiotic treatment for 14 days (between visit day 1 and visit day 14) or no antipseudomonal treatment. Sputum samples were collected at baseline on day 1 and on days 14, 30, 60, 90, and 365.
The researchers sequenced isolates from 23 adult patients over 365 days of follow-up. The recurrence of P. aeruginosa occurred in 19 patients (83%) during this period. Ultimately, a total of 153 isolates were analyzed. The researchers found that each patient carried their own unique lineage, with the except of one patient in whom two distinct lineages were identified.
“Independent mutation of the same gene across multiple lineages may be the result of positive selection of adaptive mutations,” Dr. Eklöf and colleagues wrote. They found 38 genes for P. aeruginosa that were mutated in at least two lineages, which suggested adaptive mutations. Some of the more frequently mutated genes were those important to antibiotic resistance and chronic infections, the researchers said. Specifically, mutations occurred in 40 of 140 pathoadaptive genes, compared with 265 of 5,572 other genes (P < .001). In addition, the 24 total lineages carried 4-6 antibiotic resistance genes, and no evidence suggested that lineages acquired or lost these genes during carriage.
Overall, the results indicate that the recurrence of P. aeruginosa was caused by persistence of the same clonal lineage in each patient. “This pattern of persistence was associated with genetic adaptation related to phenotypes considered important for P. aeruginosa infections,” the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small number of samples and isolates per sample, the follow-up of only 1 year, and the inability to account for mutations in the early stage because few patients were naive to P. aeruginosa at the start of the study, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the relatively large and well-defined study population and high rate of sampling compliance, they said.
Overall, “the findings warrant research to improve therapy, including trial data on possible clinical benefits of attempting antibiotic eradication of P. aeruginosa in this vulnerable group of patients,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Independent Research Fund Denmark and the Research committee at Copenhagen University Hospital-Herlev and Gentofte Hospital. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa persisted in the airways of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), based on data from 23 patients over a 1-year period.
P. aeruginosa is cultured in as many as 20% of bacterial exacerbations and has been linked to increased morbidity and mortality in patients with COPD, wrote Josefin Eklöf, MD, of the University of Copenhagen and colleagues. However, its patterns and characteristics have not been well studied, and researchers proposed that P. aerunginosa persists in COPD patients in part because of genetic adaptations in the genes related to antibiotic resistance.
In a study published in Clinical Microbiology and Infection, the researchers identified 23 consecutive patients enrolled in an ongoing randomized clinical trial at four sites in Denmark between Jan. 2018 and Jan. 2020. Participants were randomized 1:1 to targeted antipseudomonal antibiotic treatment for 14 days (between visit day 1 and visit day 14) or no antipseudomonal treatment. Sputum samples were collected at baseline on day 1 and on days 14, 30, 60, 90, and 365.
The researchers sequenced isolates from 23 adult patients over 365 days of follow-up. The recurrence of P. aeruginosa occurred in 19 patients (83%) during this period. Ultimately, a total of 153 isolates were analyzed. The researchers found that each patient carried their own unique lineage, with the except of one patient in whom two distinct lineages were identified.
“Independent mutation of the same gene across multiple lineages may be the result of positive selection of adaptive mutations,” Dr. Eklöf and colleagues wrote. They found 38 genes for P. aeruginosa that were mutated in at least two lineages, which suggested adaptive mutations. Some of the more frequently mutated genes were those important to antibiotic resistance and chronic infections, the researchers said. Specifically, mutations occurred in 40 of 140 pathoadaptive genes, compared with 265 of 5,572 other genes (P < .001). In addition, the 24 total lineages carried 4-6 antibiotic resistance genes, and no evidence suggested that lineages acquired or lost these genes during carriage.
Overall, the results indicate that the recurrence of P. aeruginosa was caused by persistence of the same clonal lineage in each patient. “This pattern of persistence was associated with genetic adaptation related to phenotypes considered important for P. aeruginosa infections,” the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small number of samples and isolates per sample, the follow-up of only 1 year, and the inability to account for mutations in the early stage because few patients were naive to P. aeruginosa at the start of the study, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the relatively large and well-defined study population and high rate of sampling compliance, they said.
Overall, “the findings warrant research to improve therapy, including trial data on possible clinical benefits of attempting antibiotic eradication of P. aeruginosa in this vulnerable group of patients,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Independent Research Fund Denmark and the Research committee at Copenhagen University Hospital-Herlev and Gentofte Hospital. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa persisted in the airways of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), based on data from 23 patients over a 1-year period.
P. aeruginosa is cultured in as many as 20% of bacterial exacerbations and has been linked to increased morbidity and mortality in patients with COPD, wrote Josefin Eklöf, MD, of the University of Copenhagen and colleagues. However, its patterns and characteristics have not been well studied, and researchers proposed that P. aerunginosa persists in COPD patients in part because of genetic adaptations in the genes related to antibiotic resistance.
In a study published in Clinical Microbiology and Infection, the researchers identified 23 consecutive patients enrolled in an ongoing randomized clinical trial at four sites in Denmark between Jan. 2018 and Jan. 2020. Participants were randomized 1:1 to targeted antipseudomonal antibiotic treatment for 14 days (between visit day 1 and visit day 14) or no antipseudomonal treatment. Sputum samples were collected at baseline on day 1 and on days 14, 30, 60, 90, and 365.
The researchers sequenced isolates from 23 adult patients over 365 days of follow-up. The recurrence of P. aeruginosa occurred in 19 patients (83%) during this period. Ultimately, a total of 153 isolates were analyzed. The researchers found that each patient carried their own unique lineage, with the except of one patient in whom two distinct lineages were identified.
“Independent mutation of the same gene across multiple lineages may be the result of positive selection of adaptive mutations,” Dr. Eklöf and colleagues wrote. They found 38 genes for P. aeruginosa that were mutated in at least two lineages, which suggested adaptive mutations. Some of the more frequently mutated genes were those important to antibiotic resistance and chronic infections, the researchers said. Specifically, mutations occurred in 40 of 140 pathoadaptive genes, compared with 265 of 5,572 other genes (P < .001). In addition, the 24 total lineages carried 4-6 antibiotic resistance genes, and no evidence suggested that lineages acquired or lost these genes during carriage.
Overall, the results indicate that the recurrence of P. aeruginosa was caused by persistence of the same clonal lineage in each patient. “This pattern of persistence was associated with genetic adaptation related to phenotypes considered important for P. aeruginosa infections,” the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small number of samples and isolates per sample, the follow-up of only 1 year, and the inability to account for mutations in the early stage because few patients were naive to P. aeruginosa at the start of the study, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the relatively large and well-defined study population and high rate of sampling compliance, they said.
Overall, “the findings warrant research to improve therapy, including trial data on possible clinical benefits of attempting antibiotic eradication of P. aeruginosa in this vulnerable group of patients,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Independent Research Fund Denmark and the Research committee at Copenhagen University Hospital-Herlev and Gentofte Hospital. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND INFECTION