User login
‘Decapitated’ boy saved by surgery team
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE: I am joined today by Dr. Ohad Einav. He’s a staff surgeon in orthopedics at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem. He’s with me to talk about an absolutely incredible surgical case, something that is terrifying to most non–orthopedic surgeons and I imagine is fairly scary for spine surgeons like him as well. But what we don’t have is information about how this works from a medical perspective. So, first of all, Dr. Einav, thank you for taking time to speak with me today.
Ohad Einav, MD: Thank you for having me.
Dr. Wilson: Can you tell us about Suleiman Hassan and what happened to him before he came into your care?
Dr. Einav: Hassan is a 12-year-old child who was riding his bicycle on the West Bank, about 40 minutes from here. Unfortunately, he was involved in a motor vehicle accident and he suffered injuries to his abdomen and cervical spine. He was transported to our service by helicopter from the scene of the accident.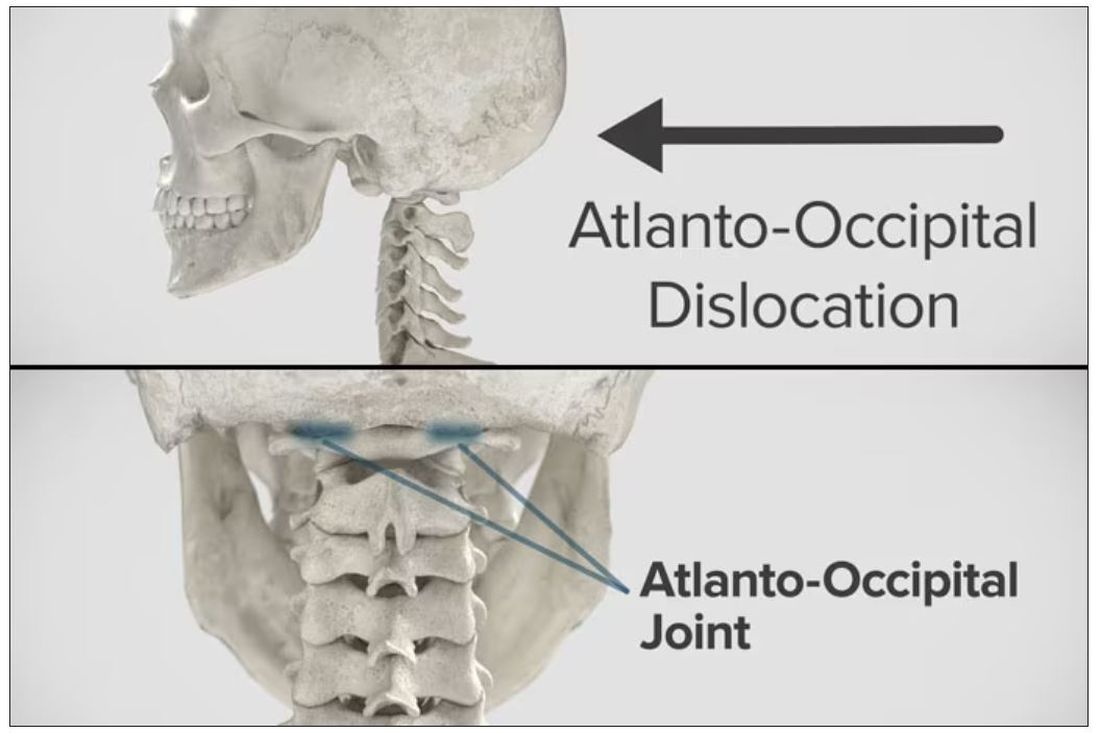
Dr. Wilson: “Injury to the cervical spine” might be something of an understatement. He had what’s called atlanto-occipital dislocation, colloquially often referred to as internal decapitation. Can you tell us what that means? It sounds terrifying.
Dr. Einav: It’s an injury to the ligaments between the occiput and the upper cervical spine, with or without bony fracture. The atlanto-occipital joint is formed by the superior articular facet of the atlas and the occipital condyle, stabilized by an articular capsule between the head and neck, and is supported by various ligaments around it that stabilize the joint and allow joint movements, including flexion, extension, and some rotation in the lower levels.
Dr. Wilson: This joint has several degrees of freedom, which means it needs a lot of support. With this type of injury, where essentially you have severing of the ligaments, is it usually survivable? How dangerous is this?
Dr. Einav: The mortality rate is 50%-60%, depending on the primary impact, the injury, transportation later on, and then the surgery and surgical management.
Dr. Wilson: Tell us a bit about this patient’s status when he came to your medical center. I assume he was in bad shape.
Dr. Einav: Hassan arrived at our medical center with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15. He was fully conscious. He was hemodynamically stable except for a bad laceration on his abdomen. He had a Philadelphia collar around his neck. He was transported by chopper because the paramedics suspected that he had a cervical spine injury and decided to bring him to a Level 1 trauma center.
He was monitored and we treated him according to the ATLS [advanced trauma life support] protocol. He didn’t have any gross sensory deficits, but he was a little confused about the whole situation and the accident. Therefore, we could do a general examination but we couldn’t rely on that regarding any sensory deficit that he may or may not have. We decided as a team that it would be better to slow down and control the situation. We decided not to operate on him immediately. We basically stabilized him and made sure that he didn’t have any traumatic internal organ damage. Later on we took him to the OR and performed surgery.
Dr. Wilson: It’s amazing that he had intact motor function, considering the extent of his injury. The spinal cord was spared somewhat during the injury. There must have been a moment when you realized that this kid, who was conscious and could move all four extremities, had a very severe neck injury. Was that due to a CT scan or physical exam? And what was your feeling when you saw that he had atlanto-occipital dislocation?
Dr. Einav: As a surgeon, you have a gut feeling in regard to the general examination of the patient. But I never rely on gut feelings. On the CT, I understood exactly what he had, what we needed to do, and the time frame.
Dr. Wilson: You’ve done these types of surgeries before, right? Obviously, no one has done a lot of them because this isn’t very common. But you knew what to do. Did you have a plan? Where does your experience come into play in a situation like this?
Dr. Einav: I graduated from the spine program of Toronto University, where I did a fellowship in trauma of the spine and complex spine surgery. I had very good teachers, and during my fellowship I treated a few cases in older patients that were similar but not the same. Therefore, I knew exactly what needed to be done.
Dr. Wilson: For those of us who aren’t surgeons, take us into the OR with you. This is obviously an incredibly delicate procedure. You are high up in the spinal cord at the base of the brain. The slightest mistake could have devastating consequences. What are the key elements of this procedure? What can go wrong here? What is the number-one thing you have to look out for when you’re trying to fix an internal decapitation?
Dr. Einav: The key element in surgeries of the cervical spine – trauma and complex spine surgery – is planning. I never go to the OR without knowing what I’m going to do. I have a few plans – plan A, plan B, plan C – in case something fails. So, I definitely know what the next step will be. I always think about the surgery a few hours before, if I have time to prepare.
The second thing that is very important is teamwork. The team needs to be coordinated. Everybody needs to know what their job is. With these types of injuries, it’s not the time for rookies. If you are new, please stand back and let the more experienced people do that job. I’m talking about surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists – everyone.
Another important thing in planning is choosing the right hardware. For example, in this case we had a problem because most of the hardware is designed for adults, and we had to improvise because there isn’t a lot of hardware on the market for the pediatric population. The adult plates and screws are too big, so we had to improvise.
Dr. Wilson: Tell us more about that. How do you improvise spinal hardware for a 12-year-old?
Dr. Einav: In this case, I chose to use hardware from one of the companies that works with us.
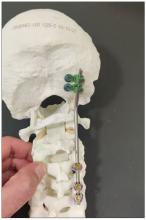
You can see in this model the area of the injury, and the area that we worked on. To perform the surgery, I had to use some plates and rods from a different company. This company’s (NuVasive) hardware has a small attachment to the skull, which was helpful for affixing the skull to the cervical spine, instead of using a big plate that would sit at the base of the skull and would not be very good for him. Most of the hardware is made for adults and not for kids.
Dr. Wilson: Will that hardware preserve the motor function of his neck? Will he be able to turn his head and extend and flex it?
Dr. Einav: The injury leads to instability and destruction of both articulations between the head and neck. Therefore, those articulations won’t be able to function the same way in the future. There is a decrease of something like 50% of the flexion and extension of Hassan’s cervical spine. Therefore, I decided that in this case there would be no chance of saving Hassan’s motor function unless we performed a fusion between the head and the neck, and therefore I decided that this would be the best procedure with the best survival rate. So, in the future, he will have some diminished flexion, extension, and rotation of his head.
Dr. Wilson: How long did his surgery take?
Dr. Einav: To be honest, I don’t remember. But I can tell you that it took us time. It was very challenging to coordinate with everyone. The most problematic part of the surgery to perform is what we call “flip-over.”
The anesthesiologist intubated the patient when he was supine, and later on, we flipped him prone to operate on the spine. This maneuver can actually lead to injury by itself, and injury at this level is fatal. So, we took our time and got Hassan into the OR. The anesthesiologist did a great job with the GlideScope – inserting the endotracheal tube. Later on, we neuromonitored him. Basically, we connected Hassan’s peripheral nerves to a computer and monitored his motor function. Gently we flipped him over, and after that we saw a little change in his motor function, so we had to modify his position so we could preserve his motor function. We then started the procedure, which took a few hours. I don’t know exactly how many.
Dr. Wilson: That just speaks to how delicate this is for everything from the intubation, where typically you’re manipulating the head, to the repositioning. Clearly this requires a lot of teamwork.
What happened after the operation? How is he doing?
Dr. Einav: After the operation, Hassan had a great recovery. He’s doing well. He doesn’t have any motor or sensory deficits. He’s able to ambulate without any aid. He had no signs of infection, which can happen after a car accident, neither from his abdominal wound nor from the occipital cervical surgery. He feels well. We saw him in the clinic. We removed his collar. We monitored him at the clinic. He looked amazing.
Dr. Wilson: That’s incredible. Are there long-term risks for him that you need to be looking out for?
Dr. Einav: Yes, and that’s the reason that we are monitoring him post surgery. While he was in the hospital, we monitored his motor and sensory functions, as well as his wound healing. Later on, in the clinic, for a few weeks after surgery we monitored for any failure of the hardware and bone graft. We check for healing of the bone graft and bone substitutes we put in to heal those bones.
Dr. Wilson: He will grow, right? He’s only 12, so he still has some years of growth in him. Is he going to need more surgery or any kind of hardware upgrade?
Dr. Einav: I hope not. In my surgeries, I never rely on the hardware for long durations. If I decide to do, for example, fusion, I rely on the hardware for a certain amount of time. And then I plan that the biology will do the work. If I plan for fusion, I put bone grafts in the preferred area for a fusion. Then if the hardware fails, I wouldn’t need to take out the hardware, and there would be no change in the condition of the patient.
Dr. Wilson: What an incredible story. It’s clear that you and your team kept your cool despite a very high-acuity situation with a ton of risk. What a tremendous outcome that this boy is not only alive but fully functional. So, congratulations to you and your team. That was very strong work.
Dr. Einav: Thank you very much. I would like to thank our team. We have to remember that the surgeon is not standing alone in the war. Hassan’s story is a success story of a very big group of people from various backgrounds and religions. They work day and night to help people and save lives. To the paramedics, the physiologists, the traumatologists, the pediatricians, the nurses, the physiotherapists, and obviously the surgeons, a big thank you. His story is our success story.
Dr. Wilson: It’s inspiring to see so many people come together to do what we all are here for, which is to fight against suffering, disease, and death. Thank you for keeping up that fight. And thank you for joining me here.
Dr. Einav: Thank you very much.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE: I am joined today by Dr. Ohad Einav. He’s a staff surgeon in orthopedics at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem. He’s with me to talk about an absolutely incredible surgical case, something that is terrifying to most non–orthopedic surgeons and I imagine is fairly scary for spine surgeons like him as well. But what we don’t have is information about how this works from a medical perspective. So, first of all, Dr. Einav, thank you for taking time to speak with me today.
Ohad Einav, MD: Thank you for having me.
Dr. Wilson: Can you tell us about Suleiman Hassan and what happened to him before he came into your care?
Dr. Einav: Hassan is a 12-year-old child who was riding his bicycle on the West Bank, about 40 minutes from here. Unfortunately, he was involved in a motor vehicle accident and he suffered injuries to his abdomen and cervical spine. He was transported to our service by helicopter from the scene of the accident.
Dr. Wilson: “Injury to the cervical spine” might be something of an understatement. He had what’s called atlanto-occipital dislocation, colloquially often referred to as internal decapitation. Can you tell us what that means? It sounds terrifying.
Dr. Einav: It’s an injury to the ligaments between the occiput and the upper cervical spine, with or without bony fracture. The atlanto-occipital joint is formed by the superior articular facet of the atlas and the occipital condyle, stabilized by an articular capsule between the head and neck, and is supported by various ligaments around it that stabilize the joint and allow joint movements, including flexion, extension, and some rotation in the lower levels.
Dr. Wilson: This joint has several degrees of freedom, which means it needs a lot of support. With this type of injury, where essentially you have severing of the ligaments, is it usually survivable? How dangerous is this?
Dr. Einav: The mortality rate is 50%-60%, depending on the primary impact, the injury, transportation later on, and then the surgery and surgical management.
Dr. Wilson: Tell us a bit about this patient’s status when he came to your medical center. I assume he was in bad shape.
Dr. Einav: Hassan arrived at our medical center with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15. He was fully conscious. He was hemodynamically stable except for a bad laceration on his abdomen. He had a Philadelphia collar around his neck. He was transported by chopper because the paramedics suspected that he had a cervical spine injury and decided to bring him to a Level 1 trauma center.
He was monitored and we treated him according to the ATLS [advanced trauma life support] protocol. He didn’t have any gross sensory deficits, but he was a little confused about the whole situation and the accident. Therefore, we could do a general examination but we couldn’t rely on that regarding any sensory deficit that he may or may not have. We decided as a team that it would be better to slow down and control the situation. We decided not to operate on him immediately. We basically stabilized him and made sure that he didn’t have any traumatic internal organ damage. Later on we took him to the OR and performed surgery.
Dr. Wilson: It’s amazing that he had intact motor function, considering the extent of his injury. The spinal cord was spared somewhat during the injury. There must have been a moment when you realized that this kid, who was conscious and could move all four extremities, had a very severe neck injury. Was that due to a CT scan or physical exam? And what was your feeling when you saw that he had atlanto-occipital dislocation?
Dr. Einav: As a surgeon, you have a gut feeling in regard to the general examination of the patient. But I never rely on gut feelings. On the CT, I understood exactly what he had, what we needed to do, and the time frame.
Dr. Wilson: You’ve done these types of surgeries before, right? Obviously, no one has done a lot of them because this isn’t very common. But you knew what to do. Did you have a plan? Where does your experience come into play in a situation like this?
Dr. Einav: I graduated from the spine program of Toronto University, where I did a fellowship in trauma of the spine and complex spine surgery. I had very good teachers, and during my fellowship I treated a few cases in older patients that were similar but not the same. Therefore, I knew exactly what needed to be done.
Dr. Wilson: For those of us who aren’t surgeons, take us into the OR with you. This is obviously an incredibly delicate procedure. You are high up in the spinal cord at the base of the brain. The slightest mistake could have devastating consequences. What are the key elements of this procedure? What can go wrong here? What is the number-one thing you have to look out for when you’re trying to fix an internal decapitation?
Dr. Einav: The key element in surgeries of the cervical spine – trauma and complex spine surgery – is planning. I never go to the OR without knowing what I’m going to do. I have a few plans – plan A, plan B, plan C – in case something fails. So, I definitely know what the next step will be. I always think about the surgery a few hours before, if I have time to prepare.
The second thing that is very important is teamwork. The team needs to be coordinated. Everybody needs to know what their job is. With these types of injuries, it’s not the time for rookies. If you are new, please stand back and let the more experienced people do that job. I’m talking about surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists – everyone.
Another important thing in planning is choosing the right hardware. For example, in this case we had a problem because most of the hardware is designed for adults, and we had to improvise because there isn’t a lot of hardware on the market for the pediatric population. The adult plates and screws are too big, so we had to improvise.
Dr. Wilson: Tell us more about that. How do you improvise spinal hardware for a 12-year-old?
Dr. Einav: In this case, I chose to use hardware from one of the companies that works with us.
You can see in this model the area of the injury, and the area that we worked on. To perform the surgery, I had to use some plates and rods from a different company. This company’s (NuVasive) hardware has a small attachment to the skull, which was helpful for affixing the skull to the cervical spine, instead of using a big plate that would sit at the base of the skull and would not be very good for him. Most of the hardware is made for adults and not for kids.
Dr. Wilson: Will that hardware preserve the motor function of his neck? Will he be able to turn his head and extend and flex it?
Dr. Einav: The injury leads to instability and destruction of both articulations between the head and neck. Therefore, those articulations won’t be able to function the same way in the future. There is a decrease of something like 50% of the flexion and extension of Hassan’s cervical spine. Therefore, I decided that in this case there would be no chance of saving Hassan’s motor function unless we performed a fusion between the head and the neck, and therefore I decided that this would be the best procedure with the best survival rate. So, in the future, he will have some diminished flexion, extension, and rotation of his head.
Dr. Wilson: How long did his surgery take?
Dr. Einav: To be honest, I don’t remember. But I can tell you that it took us time. It was very challenging to coordinate with everyone. The most problematic part of the surgery to perform is what we call “flip-over.”
The anesthesiologist intubated the patient when he was supine, and later on, we flipped him prone to operate on the spine. This maneuver can actually lead to injury by itself, and injury at this level is fatal. So, we took our time and got Hassan into the OR. The anesthesiologist did a great job with the GlideScope – inserting the endotracheal tube. Later on, we neuromonitored him. Basically, we connected Hassan’s peripheral nerves to a computer and monitored his motor function. Gently we flipped him over, and after that we saw a little change in his motor function, so we had to modify his position so we could preserve his motor function. We then started the procedure, which took a few hours. I don’t know exactly how many.
Dr. Wilson: That just speaks to how delicate this is for everything from the intubation, where typically you’re manipulating the head, to the repositioning. Clearly this requires a lot of teamwork.
What happened after the operation? How is he doing?
Dr. Einav: After the operation, Hassan had a great recovery. He’s doing well. He doesn’t have any motor or sensory deficits. He’s able to ambulate without any aid. He had no signs of infection, which can happen after a car accident, neither from his abdominal wound nor from the occipital cervical surgery. He feels well. We saw him in the clinic. We removed his collar. We monitored him at the clinic. He looked amazing.
Dr. Wilson: That’s incredible. Are there long-term risks for him that you need to be looking out for?
Dr. Einav: Yes, and that’s the reason that we are monitoring him post surgery. While he was in the hospital, we monitored his motor and sensory functions, as well as his wound healing. Later on, in the clinic, for a few weeks after surgery we monitored for any failure of the hardware and bone graft. We check for healing of the bone graft and bone substitutes we put in to heal those bones.
Dr. Wilson: He will grow, right? He’s only 12, so he still has some years of growth in him. Is he going to need more surgery or any kind of hardware upgrade?
Dr. Einav: I hope not. In my surgeries, I never rely on the hardware for long durations. If I decide to do, for example, fusion, I rely on the hardware for a certain amount of time. And then I plan that the biology will do the work. If I plan for fusion, I put bone grafts in the preferred area for a fusion. Then if the hardware fails, I wouldn’t need to take out the hardware, and there would be no change in the condition of the patient.
Dr. Wilson: What an incredible story. It’s clear that you and your team kept your cool despite a very high-acuity situation with a ton of risk. What a tremendous outcome that this boy is not only alive but fully functional. So, congratulations to you and your team. That was very strong work.
Dr. Einav: Thank you very much. I would like to thank our team. We have to remember that the surgeon is not standing alone in the war. Hassan’s story is a success story of a very big group of people from various backgrounds and religions. They work day and night to help people and save lives. To the paramedics, the physiologists, the traumatologists, the pediatricians, the nurses, the physiotherapists, and obviously the surgeons, a big thank you. His story is our success story.
Dr. Wilson: It’s inspiring to see so many people come together to do what we all are here for, which is to fight against suffering, disease, and death. Thank you for keeping up that fight. And thank you for joining me here.
Dr. Einav: Thank you very much.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE: I am joined today by Dr. Ohad Einav. He’s a staff surgeon in orthopedics at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem. He’s with me to talk about an absolutely incredible surgical case, something that is terrifying to most non–orthopedic surgeons and I imagine is fairly scary for spine surgeons like him as well. But what we don’t have is information about how this works from a medical perspective. So, first of all, Dr. Einav, thank you for taking time to speak with me today.
Ohad Einav, MD: Thank you for having me.
Dr. Wilson: Can you tell us about Suleiman Hassan and what happened to him before he came into your care?
Dr. Einav: Hassan is a 12-year-old child who was riding his bicycle on the West Bank, about 40 minutes from here. Unfortunately, he was involved in a motor vehicle accident and he suffered injuries to his abdomen and cervical spine. He was transported to our service by helicopter from the scene of the accident.
Dr. Wilson: “Injury to the cervical spine” might be something of an understatement. He had what’s called atlanto-occipital dislocation, colloquially often referred to as internal decapitation. Can you tell us what that means? It sounds terrifying.
Dr. Einav: It’s an injury to the ligaments between the occiput and the upper cervical spine, with or without bony fracture. The atlanto-occipital joint is formed by the superior articular facet of the atlas and the occipital condyle, stabilized by an articular capsule between the head and neck, and is supported by various ligaments around it that stabilize the joint and allow joint movements, including flexion, extension, and some rotation in the lower levels.
Dr. Wilson: This joint has several degrees of freedom, which means it needs a lot of support. With this type of injury, where essentially you have severing of the ligaments, is it usually survivable? How dangerous is this?
Dr. Einav: The mortality rate is 50%-60%, depending on the primary impact, the injury, transportation later on, and then the surgery and surgical management.
Dr. Wilson: Tell us a bit about this patient’s status when he came to your medical center. I assume he was in bad shape.
Dr. Einav: Hassan arrived at our medical center with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15. He was fully conscious. He was hemodynamically stable except for a bad laceration on his abdomen. He had a Philadelphia collar around his neck. He was transported by chopper because the paramedics suspected that he had a cervical spine injury and decided to bring him to a Level 1 trauma center.
He was monitored and we treated him according to the ATLS [advanced trauma life support] protocol. He didn’t have any gross sensory deficits, but he was a little confused about the whole situation and the accident. Therefore, we could do a general examination but we couldn’t rely on that regarding any sensory deficit that he may or may not have. We decided as a team that it would be better to slow down and control the situation. We decided not to operate on him immediately. We basically stabilized him and made sure that he didn’t have any traumatic internal organ damage. Later on we took him to the OR and performed surgery.
Dr. Wilson: It’s amazing that he had intact motor function, considering the extent of his injury. The spinal cord was spared somewhat during the injury. There must have been a moment when you realized that this kid, who was conscious and could move all four extremities, had a very severe neck injury. Was that due to a CT scan or physical exam? And what was your feeling when you saw that he had atlanto-occipital dislocation?
Dr. Einav: As a surgeon, you have a gut feeling in regard to the general examination of the patient. But I never rely on gut feelings. On the CT, I understood exactly what he had, what we needed to do, and the time frame.
Dr. Wilson: You’ve done these types of surgeries before, right? Obviously, no one has done a lot of them because this isn’t very common. But you knew what to do. Did you have a plan? Where does your experience come into play in a situation like this?
Dr. Einav: I graduated from the spine program of Toronto University, where I did a fellowship in trauma of the spine and complex spine surgery. I had very good teachers, and during my fellowship I treated a few cases in older patients that were similar but not the same. Therefore, I knew exactly what needed to be done.
Dr. Wilson: For those of us who aren’t surgeons, take us into the OR with you. This is obviously an incredibly delicate procedure. You are high up in the spinal cord at the base of the brain. The slightest mistake could have devastating consequences. What are the key elements of this procedure? What can go wrong here? What is the number-one thing you have to look out for when you’re trying to fix an internal decapitation?
Dr. Einav: The key element in surgeries of the cervical spine – trauma and complex spine surgery – is planning. I never go to the OR without knowing what I’m going to do. I have a few plans – plan A, plan B, plan C – in case something fails. So, I definitely know what the next step will be. I always think about the surgery a few hours before, if I have time to prepare.
The second thing that is very important is teamwork. The team needs to be coordinated. Everybody needs to know what their job is. With these types of injuries, it’s not the time for rookies. If you are new, please stand back and let the more experienced people do that job. I’m talking about surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists – everyone.
Another important thing in planning is choosing the right hardware. For example, in this case we had a problem because most of the hardware is designed for adults, and we had to improvise because there isn’t a lot of hardware on the market for the pediatric population. The adult plates and screws are too big, so we had to improvise.
Dr. Wilson: Tell us more about that. How do you improvise spinal hardware for a 12-year-old?
Dr. Einav: In this case, I chose to use hardware from one of the companies that works with us.
You can see in this model the area of the injury, and the area that we worked on. To perform the surgery, I had to use some plates and rods from a different company. This company’s (NuVasive) hardware has a small attachment to the skull, which was helpful for affixing the skull to the cervical spine, instead of using a big plate that would sit at the base of the skull and would not be very good for him. Most of the hardware is made for adults and not for kids.
Dr. Wilson: Will that hardware preserve the motor function of his neck? Will he be able to turn his head and extend and flex it?
Dr. Einav: The injury leads to instability and destruction of both articulations between the head and neck. Therefore, those articulations won’t be able to function the same way in the future. There is a decrease of something like 50% of the flexion and extension of Hassan’s cervical spine. Therefore, I decided that in this case there would be no chance of saving Hassan’s motor function unless we performed a fusion between the head and the neck, and therefore I decided that this would be the best procedure with the best survival rate. So, in the future, he will have some diminished flexion, extension, and rotation of his head.
Dr. Wilson: How long did his surgery take?
Dr. Einav: To be honest, I don’t remember. But I can tell you that it took us time. It was very challenging to coordinate with everyone. The most problematic part of the surgery to perform is what we call “flip-over.”
The anesthesiologist intubated the patient when he was supine, and later on, we flipped him prone to operate on the spine. This maneuver can actually lead to injury by itself, and injury at this level is fatal. So, we took our time and got Hassan into the OR. The anesthesiologist did a great job with the GlideScope – inserting the endotracheal tube. Later on, we neuromonitored him. Basically, we connected Hassan’s peripheral nerves to a computer and monitored his motor function. Gently we flipped him over, and after that we saw a little change in his motor function, so we had to modify his position so we could preserve his motor function. We then started the procedure, which took a few hours. I don’t know exactly how many.
Dr. Wilson: That just speaks to how delicate this is for everything from the intubation, where typically you’re manipulating the head, to the repositioning. Clearly this requires a lot of teamwork.
What happened after the operation? How is he doing?
Dr. Einav: After the operation, Hassan had a great recovery. He’s doing well. He doesn’t have any motor or sensory deficits. He’s able to ambulate without any aid. He had no signs of infection, which can happen after a car accident, neither from his abdominal wound nor from the occipital cervical surgery. He feels well. We saw him in the clinic. We removed his collar. We monitored him at the clinic. He looked amazing.
Dr. Wilson: That’s incredible. Are there long-term risks for him that you need to be looking out for?
Dr. Einav: Yes, and that’s the reason that we are monitoring him post surgery. While he was in the hospital, we monitored his motor and sensory functions, as well as his wound healing. Later on, in the clinic, for a few weeks after surgery we monitored for any failure of the hardware and bone graft. We check for healing of the bone graft and bone substitutes we put in to heal those bones.
Dr. Wilson: He will grow, right? He’s only 12, so he still has some years of growth in him. Is he going to need more surgery or any kind of hardware upgrade?
Dr. Einav: I hope not. In my surgeries, I never rely on the hardware for long durations. If I decide to do, for example, fusion, I rely on the hardware for a certain amount of time. And then I plan that the biology will do the work. If I plan for fusion, I put bone grafts in the preferred area for a fusion. Then if the hardware fails, I wouldn’t need to take out the hardware, and there would be no change in the condition of the patient.
Dr. Wilson: What an incredible story. It’s clear that you and your team kept your cool despite a very high-acuity situation with a ton of risk. What a tremendous outcome that this boy is not only alive but fully functional. So, congratulations to you and your team. That was very strong work.
Dr. Einav: Thank you very much. I would like to thank our team. We have to remember that the surgeon is not standing alone in the war. Hassan’s story is a success story of a very big group of people from various backgrounds and religions. They work day and night to help people and save lives. To the paramedics, the physiologists, the traumatologists, the pediatricians, the nurses, the physiotherapists, and obviously the surgeons, a big thank you. His story is our success story.
Dr. Wilson: It’s inspiring to see so many people come together to do what we all are here for, which is to fight against suffering, disease, and death. Thank you for keeping up that fight. And thank you for joining me here.
Dr. Einav: Thank you very much.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Targeted warnings
I was probably about 9 or 10 and I am assuming it was early winter when my mother took me aside and said in her usual quiet tone, “Willy, don’t ever stick your tongue on a metal pipe when it is cold outside.”
Putting my tongue on a frozen pipe was something that had never occurred to me even in my wildest preadolescent dreams. My mother’s caution only served to pique my interest and provide me with one more tempting scenario to consider.
Recently, a prank has gone viral on TikTok that shows an adult, usually the parent, cracking (not smashing) an egg on the child’s head and then emptying the egg contents into a bowl. Unlike the tongue-pipe disaster, it is hard to imagine how this stunt can be dangerous as long as the child is old enough to be walking around. But, at least one pediatrician has warned that there is a risk to the child from contracting salmonella.
There may be a few young children who are frightened by having an egg cracked on their head, but I can’t imagine that it would leave any lasting emotional scars. Given the minuscule theoretical risk of infection and the fact that the videos have accumulated more than 670 million views, this is another example of when we “experts” should keep a low profile and let the virus fade into Internet oblivion.
There is, however, a difference between harmless foolishness and stupidity, and one wonders when and in what manner we pediatricians should become involved. For example, in a recent study published in the journal Pediatrics, the investigators searched through a national emergency department database and found that
There were two peaks of distribution, one at less than 1 year of age and another at age 4. The older children were more often injured playing on furniture, most often bunk beds. The younger children were more likely to have been injured by being lifted or tossed in the air. No deaths were reported.
Is this a phenomenon that demands a response by pediatricians? Do we have time to ask every family if they have a ceiling fan? Should we be handing out brochures to every family? To whom should we target our message? This is a situation that seems to sort easily into two categories. One that involves stupidity and a second that is ignorance that may respond to education.
Tossing young children in the air is fun for the tosser and the child. I am sure there are a few children every year who slip out of the grasp of an adult and are injured. I have never seen a child brought in with this history. But it must happen. The result is likely to trigger a very tricky child protective investigation. But tossing a child underneath a ceiling fan is just plain stupid. I’m not sure our intervention is going to prevent it from happening. Bunk beds and ceiling fans are a different story. Posters in our offices and warnings and labels at the point of purchase of both fans and bunk beds makes some sense.
And while we are sticking labels on furniture, we should take a hard look at couches. Researchers have recently found that the accumulation of sedentary time in childhood can lead to early evidence of heart damage, which may portend heart disease in adulthood. Instead of those tags under the cushions, we need a big blaze orange sticker in prominent view that warns of the danger of becoming a couch potato.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I was probably about 9 or 10 and I am assuming it was early winter when my mother took me aside and said in her usual quiet tone, “Willy, don’t ever stick your tongue on a metal pipe when it is cold outside.”
Putting my tongue on a frozen pipe was something that had never occurred to me even in my wildest preadolescent dreams. My mother’s caution only served to pique my interest and provide me with one more tempting scenario to consider.
Recently, a prank has gone viral on TikTok that shows an adult, usually the parent, cracking (not smashing) an egg on the child’s head and then emptying the egg contents into a bowl. Unlike the tongue-pipe disaster, it is hard to imagine how this stunt can be dangerous as long as the child is old enough to be walking around. But, at least one pediatrician has warned that there is a risk to the child from contracting salmonella.
There may be a few young children who are frightened by having an egg cracked on their head, but I can’t imagine that it would leave any lasting emotional scars. Given the minuscule theoretical risk of infection and the fact that the videos have accumulated more than 670 million views, this is another example of when we “experts” should keep a low profile and let the virus fade into Internet oblivion.
There is, however, a difference between harmless foolishness and stupidity, and one wonders when and in what manner we pediatricians should become involved. For example, in a recent study published in the journal Pediatrics, the investigators searched through a national emergency department database and found that
There were two peaks of distribution, one at less than 1 year of age and another at age 4. The older children were more often injured playing on furniture, most often bunk beds. The younger children were more likely to have been injured by being lifted or tossed in the air. No deaths were reported.
Is this a phenomenon that demands a response by pediatricians? Do we have time to ask every family if they have a ceiling fan? Should we be handing out brochures to every family? To whom should we target our message? This is a situation that seems to sort easily into two categories. One that involves stupidity and a second that is ignorance that may respond to education.
Tossing young children in the air is fun for the tosser and the child. I am sure there are a few children every year who slip out of the grasp of an adult and are injured. I have never seen a child brought in with this history. But it must happen. The result is likely to trigger a very tricky child protective investigation. But tossing a child underneath a ceiling fan is just plain stupid. I’m not sure our intervention is going to prevent it from happening. Bunk beds and ceiling fans are a different story. Posters in our offices and warnings and labels at the point of purchase of both fans and bunk beds makes some sense.
And while we are sticking labels on furniture, we should take a hard look at couches. Researchers have recently found that the accumulation of sedentary time in childhood can lead to early evidence of heart damage, which may portend heart disease in adulthood. Instead of those tags under the cushions, we need a big blaze orange sticker in prominent view that warns of the danger of becoming a couch potato.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I was probably about 9 or 10 and I am assuming it was early winter when my mother took me aside and said in her usual quiet tone, “Willy, don’t ever stick your tongue on a metal pipe when it is cold outside.”
Putting my tongue on a frozen pipe was something that had never occurred to me even in my wildest preadolescent dreams. My mother’s caution only served to pique my interest and provide me with one more tempting scenario to consider.
Recently, a prank has gone viral on TikTok that shows an adult, usually the parent, cracking (not smashing) an egg on the child’s head and then emptying the egg contents into a bowl. Unlike the tongue-pipe disaster, it is hard to imagine how this stunt can be dangerous as long as the child is old enough to be walking around. But, at least one pediatrician has warned that there is a risk to the child from contracting salmonella.
There may be a few young children who are frightened by having an egg cracked on their head, but I can’t imagine that it would leave any lasting emotional scars. Given the minuscule theoretical risk of infection and the fact that the videos have accumulated more than 670 million views, this is another example of when we “experts” should keep a low profile and let the virus fade into Internet oblivion.
There is, however, a difference between harmless foolishness and stupidity, and one wonders when and in what manner we pediatricians should become involved. For example, in a recent study published in the journal Pediatrics, the investigators searched through a national emergency department database and found that
There were two peaks of distribution, one at less than 1 year of age and another at age 4. The older children were more often injured playing on furniture, most often bunk beds. The younger children were more likely to have been injured by being lifted or tossed in the air. No deaths were reported.
Is this a phenomenon that demands a response by pediatricians? Do we have time to ask every family if they have a ceiling fan? Should we be handing out brochures to every family? To whom should we target our message? This is a situation that seems to sort easily into two categories. One that involves stupidity and a second that is ignorance that may respond to education.
Tossing young children in the air is fun for the tosser and the child. I am sure there are a few children every year who slip out of the grasp of an adult and are injured. I have never seen a child brought in with this history. But it must happen. The result is likely to trigger a very tricky child protective investigation. But tossing a child underneath a ceiling fan is just plain stupid. I’m not sure our intervention is going to prevent it from happening. Bunk beds and ceiling fans are a different story. Posters in our offices and warnings and labels at the point of purchase of both fans and bunk beds makes some sense.
And while we are sticking labels on furniture, we should take a hard look at couches. Researchers have recently found that the accumulation of sedentary time in childhood can lead to early evidence of heart damage, which may portend heart disease in adulthood. Instead of those tags under the cushions, we need a big blaze orange sticker in prominent view that warns of the danger of becoming a couch potato.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Five ways to avert a malpractice lawsuit with better EHR techniques
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-dose aspirin cuts type 2 diabetes risk in over-65s
The data come from a secondary analysis of ASPREE, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of healthy adults aged 65 years or older, showing that 100 mg of aspirin taken daily for about 5 years did not provide a cardiovascular benefit but did significantly raise the risk for bleeding.
This new analysis shows that individuals taking aspirin had a 15% lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes and that the medication slowed the rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose, compared with placebo, during follow-up.
However, lead author Sophia Zoungas, MBBS, PhD, head of the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, said: “Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack. ... Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
Nonetheless, she said in an interview, “at this time, our findings are exploratory but ignite the debate of the important role that anti-inflammatory approaches may play in preventing diabetes. Further work is currently underway to understand which subpopulations may be better targeted and to understand the balance of risk versus benefit.”
The results are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, taking place Oct. 2-6 in Hamburg, Germany.
New findings not robust enough to change current practice
Asked to comment, Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, said: “Given the post hoc secondary nature of the analysis, the findings should be considered hypothesis generating and not definitive… At this time, based on prospective randomized studies, the risks of aspirin outweigh the benefits for aspirin in older adults.”
Among those studies was an ASPREE substudy showing failure of low-dose aspirin to reduce fracture risk while increasing the risk for serious falls, and two other trials, ARRIVE and ASCEND, also showing that harms of aspirin outweigh the benefits in people with cardiovascular risk but not diabetes, and in those with diabetes, respectively, said Dr. Mukherjee, professor and chair of the department of internal medicine at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso.
And, Mukherjee noted, in 2019 the American College of Cardiology updated its practice guidelines to say that low-dose aspirin should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in adults over age 70. In 2021, the American Diabetes Association seconded that recommendation.
Asked whether these newest findings might change current practice for any higher-risk subgroup, such as people with prediabetes, Dr. Mukherjee replied: “Unless there is a prospective randomized trial that validates these findings in those with prediabetes, the findings should not change practice. There are also no data [showing] that another antiplatelet agent would be indicated or would be beneficial. Instead, I would recommend lifestyle changes including regular exercise and a healthy diet to minimize risk of diabetes.”
The 16,209 ASPREE participants were community dwelling and did not have diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or dementia at baseline. They were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 100 mg/d of enteric-coated aspirin or placebo. Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, the proportions developing type 2 diabetes were 5.7% with aspirin versus 6.6% with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.85; P = .01).
The annual rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose over the follow-up period was slowed by 0.006 mmol/L with aspirin, compared with placebo, also a significant difference (P = .004).
According to Dr. Zoungas, “the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
The ASPREE trial was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Monash University, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Zoungas and Dr. Mukherjee have no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data come from a secondary analysis of ASPREE, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of healthy adults aged 65 years or older, showing that 100 mg of aspirin taken daily for about 5 years did not provide a cardiovascular benefit but did significantly raise the risk for bleeding.
This new analysis shows that individuals taking aspirin had a 15% lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes and that the medication slowed the rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose, compared with placebo, during follow-up.
However, lead author Sophia Zoungas, MBBS, PhD, head of the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, said: “Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack. ... Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
Nonetheless, she said in an interview, “at this time, our findings are exploratory but ignite the debate of the important role that anti-inflammatory approaches may play in preventing diabetes. Further work is currently underway to understand which subpopulations may be better targeted and to understand the balance of risk versus benefit.”
The results are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, taking place Oct. 2-6 in Hamburg, Germany.
New findings not robust enough to change current practice
Asked to comment, Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, said: “Given the post hoc secondary nature of the analysis, the findings should be considered hypothesis generating and not definitive… At this time, based on prospective randomized studies, the risks of aspirin outweigh the benefits for aspirin in older adults.”
Among those studies was an ASPREE substudy showing failure of low-dose aspirin to reduce fracture risk while increasing the risk for serious falls, and two other trials, ARRIVE and ASCEND, also showing that harms of aspirin outweigh the benefits in people with cardiovascular risk but not diabetes, and in those with diabetes, respectively, said Dr. Mukherjee, professor and chair of the department of internal medicine at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso.
And, Mukherjee noted, in 2019 the American College of Cardiology updated its practice guidelines to say that low-dose aspirin should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in adults over age 70. In 2021, the American Diabetes Association seconded that recommendation.
Asked whether these newest findings might change current practice for any higher-risk subgroup, such as people with prediabetes, Dr. Mukherjee replied: “Unless there is a prospective randomized trial that validates these findings in those with prediabetes, the findings should not change practice. There are also no data [showing] that another antiplatelet agent would be indicated or would be beneficial. Instead, I would recommend lifestyle changes including regular exercise and a healthy diet to minimize risk of diabetes.”
The 16,209 ASPREE participants were community dwelling and did not have diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or dementia at baseline. They were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 100 mg/d of enteric-coated aspirin or placebo. Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, the proportions developing type 2 diabetes were 5.7% with aspirin versus 6.6% with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.85; P = .01).
The annual rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose over the follow-up period was slowed by 0.006 mmol/L with aspirin, compared with placebo, also a significant difference (P = .004).
According to Dr. Zoungas, “the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
The ASPREE trial was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Monash University, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Zoungas and Dr. Mukherjee have no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data come from a secondary analysis of ASPREE, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of healthy adults aged 65 years or older, showing that 100 mg of aspirin taken daily for about 5 years did not provide a cardiovascular benefit but did significantly raise the risk for bleeding.
This new analysis shows that individuals taking aspirin had a 15% lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes and that the medication slowed the rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose, compared with placebo, during follow-up.
However, lead author Sophia Zoungas, MBBS, PhD, head of the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, said: “Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack. ... Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
Nonetheless, she said in an interview, “at this time, our findings are exploratory but ignite the debate of the important role that anti-inflammatory approaches may play in preventing diabetes. Further work is currently underway to understand which subpopulations may be better targeted and to understand the balance of risk versus benefit.”
The results are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, taking place Oct. 2-6 in Hamburg, Germany.
New findings not robust enough to change current practice
Asked to comment, Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, said: “Given the post hoc secondary nature of the analysis, the findings should be considered hypothesis generating and not definitive… At this time, based on prospective randomized studies, the risks of aspirin outweigh the benefits for aspirin in older adults.”
Among those studies was an ASPREE substudy showing failure of low-dose aspirin to reduce fracture risk while increasing the risk for serious falls, and two other trials, ARRIVE and ASCEND, also showing that harms of aspirin outweigh the benefits in people with cardiovascular risk but not diabetes, and in those with diabetes, respectively, said Dr. Mukherjee, professor and chair of the department of internal medicine at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso.
And, Mukherjee noted, in 2019 the American College of Cardiology updated its practice guidelines to say that low-dose aspirin should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in adults over age 70. In 2021, the American Diabetes Association seconded that recommendation.
Asked whether these newest findings might change current practice for any higher-risk subgroup, such as people with prediabetes, Dr. Mukherjee replied: “Unless there is a prospective randomized trial that validates these findings in those with prediabetes, the findings should not change practice. There are also no data [showing] that another antiplatelet agent would be indicated or would be beneficial. Instead, I would recommend lifestyle changes including regular exercise and a healthy diet to minimize risk of diabetes.”
The 16,209 ASPREE participants were community dwelling and did not have diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or dementia at baseline. They were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 100 mg/d of enteric-coated aspirin or placebo. Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, the proportions developing type 2 diabetes were 5.7% with aspirin versus 6.6% with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.85; P = .01).
The annual rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose over the follow-up period was slowed by 0.006 mmol/L with aspirin, compared with placebo, also a significant difference (P = .004).
According to Dr. Zoungas, “the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
The ASPREE trial was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Monash University, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Zoungas and Dr. Mukherjee have no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2023
Pruritic Papules in the Perianal and Gluteal Cleft Regions
The Diagnosis: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
The shave biopsy revealed suprabasal clefts associated with acantholytic and dyskeratotic cells as well as overlying hyperkeratosis. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) was negative. Based on the combined clinical and histological findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD), a rare disease that clinically presents as small whitishgreyish papules with the potential to coalesce into larger plaques.1,2 The condition predominantly manifests without symptoms, though pruritus and burning have been reported in affected sites. Most cases of PAD have been reported in older adults rather than in children or adolescents; it is more prevalent in women than in men. Lesions generally are localized to the penis, vulva, scrotum, inguinal folds, and perianal region.3 More specific terms have been used to describe this presentation such as papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital region and papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the genital-crural region. Histologic findings of PAD include epidermal acantholysis and dyskeratosis with hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis (quiz image).
The histologic differential diagnosis of PAD is broad due to its overlapping features with other diseases such as pemphigus vulgaris, Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), Darier disease, and Grover disease. The acantholytic pathophysiology of these conditions involves dysfunction in cell adhesion markers. The correct diagnosis can be made by considering both the clinical location of involvement and histopathologic clues.
Pemphigus is a family of disorders involving mucocutaneous blistering of an autoimmune nature (Figure 1). Pemphigus vulgaris is the most prevalent variant of the pemphigus family, with symptomatically painful involvement of mucosal and cutaneous tissue. Autoantibodies to desmoglein 3 alone or both desmoglein 1 and 3 are present. Pemphigus vulgaris displays positive DIF findings with intercellular IgG and C3.
Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) is an autosomal-dominant disease that shares the acantholytic feature that is common in this class of diseases and caused by a defect in cell-cell adhesion as well as a loss of function in the ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1. Blistering lesions typically appear in the neck, axillary, inguinal, or genital regions, and they can develop into crusted, exudate-filled lesions. No autoimmunity has been associated with this disease, unlike other diseases in the pemphigus family, and mutations in the ATP2C1 gene have been linked with dysregulation of cell-cell adhesion, particularly in cadherins and calcium-dependent cell adhesion processes. Histologically, HHD will show diffuse keratinocyte acantholysis with suprabasal clefting (Figure 2).4 Dyskeratosis is mild, if present at all, and dyskeratotic keratinocytes show a well-defined nucleus with cytoplasmic preservation. In contrast to HHD, PAD typically shows more dyskeratosis.
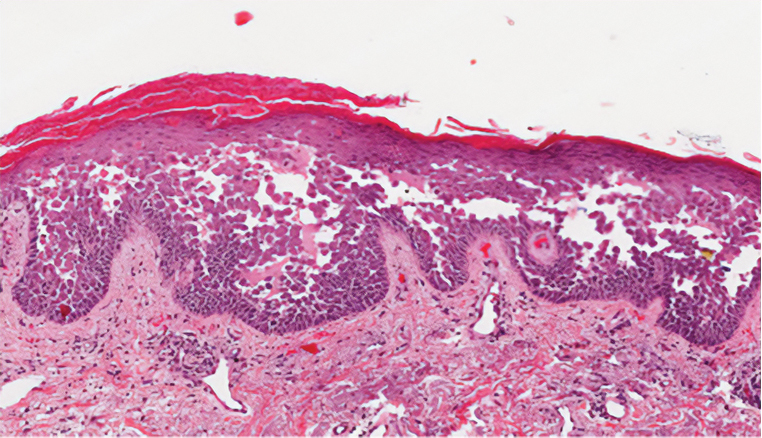
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) is an autosomal-dominant condition that normally presents with seborrheic eruptions in intertriginous areas, usually with onset during adolescence. Darier disease is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ATP2A2 gene found on chromosome 12q23-24.1 that encodes for the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium ATPase2 (SERCA2) enzymes involved in calcium-dependent transport of the endoplasmic reticulum within the cell. Due to calcium dysregulation, desmosomes are unable to carry out their function in cell-cell adhesion, resulting in keratinocyte acantholysis. Histopathology of Darier disease is identical to HHD but displays more dyskeratosis than HHD (Figure 3), possibly due to the endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores that are affected in Darier disease compared to the Golgi apparatus calcium stores that are implicated in HHD.5 The lowered endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores in Darier-White disease are associated with more pronounced dyskeratosis, which is seen histologically as corps ronds. Suprabasal hyperkeratosis also is found in Darier disease. The histopathologic findings of Darier disease and PAD can be identical, but the clinical presentations are distinct, with Darier disease typically manifesting as seborrheic eruptions appearing in adolescence and PAD presenting as small white papules in the anogenital or crural regions.
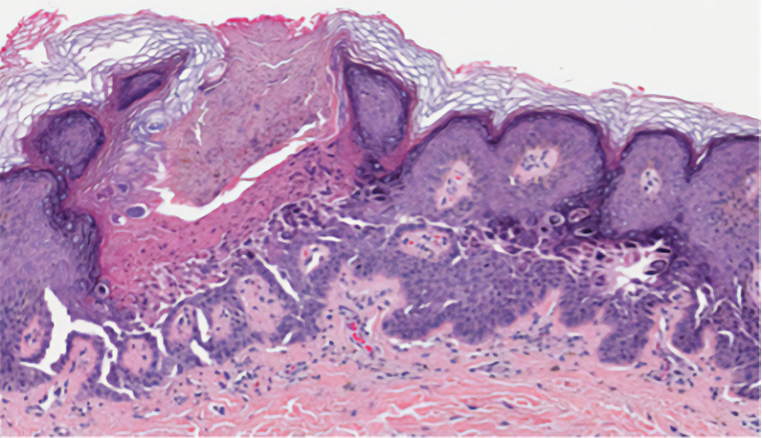
Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) has an idiopathic pathophysiology. It clinically manifests with eruptions of erythematous, pruritic, truncal papules on the chest or back. Grover disease has a predilection for White men older than 50 years, and symptoms may be exacerbated in heat and diaphoretic conditions. Histologically, Grover disease may show acantholytic features seen in pemphigus vulgaris, HHD, and Darier disease; the pattern can only follow a specific disease or consist of a combination of all disease features (Figure 4). The acantholytic pattern of Grover disease was found to be similar to pemphigus vulgaris, Darier disease, pemphigus foliaceus, and HHD 47%, 18%, 9%, and 8% of the time, respectively. In 9% of cases, Grover disease will exhibit a mixed histopathology in which its acantholytic pattern will consist of a combination of features seen in the pemphigus family of diseases.6 Biopsy results showing mixed histologic patterns or a combination of different acantholytic features are suggestive of Grover disease over PAD. Moreover, the clinical distribution helps to differentiate Grover disease from PAD.
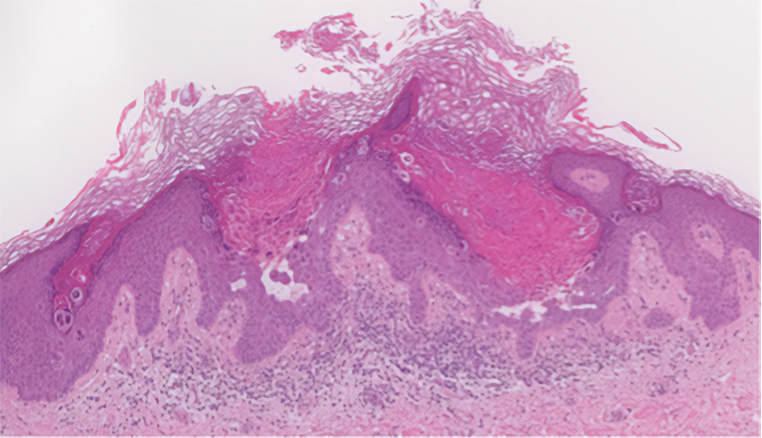
Because the histologic characteristics of these diseases overlap, certain nuances in clinical correlations and histology allow for distinction. In our patient, the diagnosis was most consistent with PAD based on the clinical manifestation of the disease and the biopsy results. Considering solely the clinical location of the lesions, Grover disease was a less likely diagnosis because our patient’s lesions were observed in the perianal region, not the truncal region as typically seen in Grover disease. Taking into account the DIF assay results in our patient, the pemphigus family of diseases also moved lower on the differential diagnosis. Finally, because the biopsy showed more dyskeratosis than would be present in HHD and also was inconsistent with the location and onset that would be expected to be seen in Darier disease, PAD was the most probable diagnosis. Interestingly, studies have shown mosaic mutations in ATP2A2 and ATP2C1 as possible causes of PAD, suggesting that this may be an allelic variant of Darier disease and HHD.7-9 No genetic testing was performed in our patient.
- Dowd ML, Ansell LH, Husain S, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the genitocrural area: a rare unilateral asymptomatic intertrigo. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:132-134. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.11.003
- Konstantinou MP, Krasagakis K. Benign familial pemphigus (Hailey Hailey disease). StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585136/
- Montis-Palos MC, Acebo-Mariñas E, Catón-Santarén B, et al. Papular acantholytic dermatosis in the genito-crural region: a localized form of Darier disease or Hailey-Hailey disease? Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2013;104:170-172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adengl.2012.02.008
- Verma SB. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis localized to the perineal and perianal area in a young male. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:393-395.
- Schmieder SJ, Rosario-Collazo JA. Keratosis follicularis. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/books/NBK519557/
- Weaver J, Bergfeld WF. Grover disease (transient acantholytic dermatosis). Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:1490-1494.
- Knopp EA, Saraceni C, Moss J, et al. Somatic ATP2A2 mutation in a case of papular acantholytic dyskeratosis: mosaic Darier disease [published online August 12, 2015]. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:853-857. doi:10.1111/cup.12551
- Lipoff JB, Mudgil AV, Young S, et al. Acantholytic dermatosis of the crural folds with ATP2C1 mutation is a possible variant of Hailey-Hailey Disease. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:151.
- Vodo D, Malchin N, Furman M, et al. Identification of a recurrent mutation in ATP2C1 demonstrates that papular acantholytic dyskeratosis and Hailey-Hailey disease are allelic disorders. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1001-1002.
The Diagnosis: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
The shave biopsy revealed suprabasal clefts associated with acantholytic and dyskeratotic cells as well as overlying hyperkeratosis. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) was negative. Based on the combined clinical and histological findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD), a rare disease that clinically presents as small whitishgreyish papules with the potential to coalesce into larger plaques.1,2 The condition predominantly manifests without symptoms, though pruritus and burning have been reported in affected sites. Most cases of PAD have been reported in older adults rather than in children or adolescents; it is more prevalent in women than in men. Lesions generally are localized to the penis, vulva, scrotum, inguinal folds, and perianal region.3 More specific terms have been used to describe this presentation such as papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital region and papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the genital-crural region. Histologic findings of PAD include epidermal acantholysis and dyskeratosis with hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis (quiz image).
The histologic differential diagnosis of PAD is broad due to its overlapping features with other diseases such as pemphigus vulgaris, Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), Darier disease, and Grover disease. The acantholytic pathophysiology of these conditions involves dysfunction in cell adhesion markers. The correct diagnosis can be made by considering both the clinical location of involvement and histopathologic clues.
Pemphigus is a family of disorders involving mucocutaneous blistering of an autoimmune nature (Figure 1). Pemphigus vulgaris is the most prevalent variant of the pemphigus family, with symptomatically painful involvement of mucosal and cutaneous tissue. Autoantibodies to desmoglein 3 alone or both desmoglein 1 and 3 are present. Pemphigus vulgaris displays positive DIF findings with intercellular IgG and C3.

Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) is an autosomal-dominant disease that shares the acantholytic feature that is common in this class of diseases and caused by a defect in cell-cell adhesion as well as a loss of function in the ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1. Blistering lesions typically appear in the neck, axillary, inguinal, or genital regions, and they can develop into crusted, exudate-filled lesions. No autoimmunity has been associated with this disease, unlike other diseases in the pemphigus family, and mutations in the ATP2C1 gene have been linked with dysregulation of cell-cell adhesion, particularly in cadherins and calcium-dependent cell adhesion processes. Histologically, HHD will show diffuse keratinocyte acantholysis with suprabasal clefting (Figure 2).4 Dyskeratosis is mild, if present at all, and dyskeratotic keratinocytes show a well-defined nucleus with cytoplasmic preservation. In contrast to HHD, PAD typically shows more dyskeratosis.

Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) is an autosomal-dominant condition that normally presents with seborrheic eruptions in intertriginous areas, usually with onset during adolescence. Darier disease is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ATP2A2 gene found on chromosome 12q23-24.1 that encodes for the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium ATPase2 (SERCA2) enzymes involved in calcium-dependent transport of the endoplasmic reticulum within the cell. Due to calcium dysregulation, desmosomes are unable to carry out their function in cell-cell adhesion, resulting in keratinocyte acantholysis. Histopathology of Darier disease is identical to HHD but displays more dyskeratosis than HHD (Figure 3), possibly due to the endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores that are affected in Darier disease compared to the Golgi apparatus calcium stores that are implicated in HHD.5 The lowered endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores in Darier-White disease are associated with more pronounced dyskeratosis, which is seen histologically as corps ronds. Suprabasal hyperkeratosis also is found in Darier disease. The histopathologic findings of Darier disease and PAD can be identical, but the clinical presentations are distinct, with Darier disease typically manifesting as seborrheic eruptions appearing in adolescence and PAD presenting as small white papules in the anogenital or crural regions.

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) has an idiopathic pathophysiology. It clinically manifests with eruptions of erythematous, pruritic, truncal papules on the chest or back. Grover disease has a predilection for White men older than 50 years, and symptoms may be exacerbated in heat and diaphoretic conditions. Histologically, Grover disease may show acantholytic features seen in pemphigus vulgaris, HHD, and Darier disease; the pattern can only follow a specific disease or consist of a combination of all disease features (Figure 4). The acantholytic pattern of Grover disease was found to be similar to pemphigus vulgaris, Darier disease, pemphigus foliaceus, and HHD 47%, 18%, 9%, and 8% of the time, respectively. In 9% of cases, Grover disease will exhibit a mixed histopathology in which its acantholytic pattern will consist of a combination of features seen in the pemphigus family of diseases.6 Biopsy results showing mixed histologic patterns or a combination of different acantholytic features are suggestive of Grover disease over PAD. Moreover, the clinical distribution helps to differentiate Grover disease from PAD.

Because the histologic characteristics of these diseases overlap, certain nuances in clinical correlations and histology allow for distinction. In our patient, the diagnosis was most consistent with PAD based on the clinical manifestation of the disease and the biopsy results. Considering solely the clinical location of the lesions, Grover disease was a less likely diagnosis because our patient’s lesions were observed in the perianal region, not the truncal region as typically seen in Grover disease. Taking into account the DIF assay results in our patient, the pemphigus family of diseases also moved lower on the differential diagnosis. Finally, because the biopsy showed more dyskeratosis than would be present in HHD and also was inconsistent with the location and onset that would be expected to be seen in Darier disease, PAD was the most probable diagnosis. Interestingly, studies have shown mosaic mutations in ATP2A2 and ATP2C1 as possible causes of PAD, suggesting that this may be an allelic variant of Darier disease and HHD.7-9 No genetic testing was performed in our patient.
The Diagnosis: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
The shave biopsy revealed suprabasal clefts associated with acantholytic and dyskeratotic cells as well as overlying hyperkeratosis. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) was negative. Based on the combined clinical and histological findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD), a rare disease that clinically presents as small whitishgreyish papules with the potential to coalesce into larger plaques.1,2 The condition predominantly manifests without symptoms, though pruritus and burning have been reported in affected sites. Most cases of PAD have been reported in older adults rather than in children or adolescents; it is more prevalent in women than in men. Lesions generally are localized to the penis, vulva, scrotum, inguinal folds, and perianal region.3 More specific terms have been used to describe this presentation such as papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital region and papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the genital-crural region. Histologic findings of PAD include epidermal acantholysis and dyskeratosis with hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis (quiz image).
The histologic differential diagnosis of PAD is broad due to its overlapping features with other diseases such as pemphigus vulgaris, Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), Darier disease, and Grover disease. The acantholytic pathophysiology of these conditions involves dysfunction in cell adhesion markers. The correct diagnosis can be made by considering both the clinical location of involvement and histopathologic clues.
Pemphigus is a family of disorders involving mucocutaneous blistering of an autoimmune nature (Figure 1). Pemphigus vulgaris is the most prevalent variant of the pemphigus family, with symptomatically painful involvement of mucosal and cutaneous tissue. Autoantibodies to desmoglein 3 alone or both desmoglein 1 and 3 are present. Pemphigus vulgaris displays positive DIF findings with intercellular IgG and C3.

Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) is an autosomal-dominant disease that shares the acantholytic feature that is common in this class of diseases and caused by a defect in cell-cell adhesion as well as a loss of function in the ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1. Blistering lesions typically appear in the neck, axillary, inguinal, or genital regions, and they can develop into crusted, exudate-filled lesions. No autoimmunity has been associated with this disease, unlike other diseases in the pemphigus family, and mutations in the ATP2C1 gene have been linked with dysregulation of cell-cell adhesion, particularly in cadherins and calcium-dependent cell adhesion processes. Histologically, HHD will show diffuse keratinocyte acantholysis with suprabasal clefting (Figure 2).4 Dyskeratosis is mild, if present at all, and dyskeratotic keratinocytes show a well-defined nucleus with cytoplasmic preservation. In contrast to HHD, PAD typically shows more dyskeratosis.

Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) is an autosomal-dominant condition that normally presents with seborrheic eruptions in intertriginous areas, usually with onset during adolescence. Darier disease is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ATP2A2 gene found on chromosome 12q23-24.1 that encodes for the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium ATPase2 (SERCA2) enzymes involved in calcium-dependent transport of the endoplasmic reticulum within the cell. Due to calcium dysregulation, desmosomes are unable to carry out their function in cell-cell adhesion, resulting in keratinocyte acantholysis. Histopathology of Darier disease is identical to HHD but displays more dyskeratosis than HHD (Figure 3), possibly due to the endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores that are affected in Darier disease compared to the Golgi apparatus calcium stores that are implicated in HHD.5 The lowered endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores in Darier-White disease are associated with more pronounced dyskeratosis, which is seen histologically as corps ronds. Suprabasal hyperkeratosis also is found in Darier disease. The histopathologic findings of Darier disease and PAD can be identical, but the clinical presentations are distinct, with Darier disease typically manifesting as seborrheic eruptions appearing in adolescence and PAD presenting as small white papules in the anogenital or crural regions.

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) has an idiopathic pathophysiology. It clinically manifests with eruptions of erythematous, pruritic, truncal papules on the chest or back. Grover disease has a predilection for White men older than 50 years, and symptoms may be exacerbated in heat and diaphoretic conditions. Histologically, Grover disease may show acantholytic features seen in pemphigus vulgaris, HHD, and Darier disease; the pattern can only follow a specific disease or consist of a combination of all disease features (Figure 4). The acantholytic pattern of Grover disease was found to be similar to pemphigus vulgaris, Darier disease, pemphigus foliaceus, and HHD 47%, 18%, 9%, and 8% of the time, respectively. In 9% of cases, Grover disease will exhibit a mixed histopathology in which its acantholytic pattern will consist of a combination of features seen in the pemphigus family of diseases.6 Biopsy results showing mixed histologic patterns or a combination of different acantholytic features are suggestive of Grover disease over PAD. Moreover, the clinical distribution helps to differentiate Grover disease from PAD.

Because the histologic characteristics of these diseases overlap, certain nuances in clinical correlations and histology allow for distinction. In our patient, the diagnosis was most consistent with PAD based on the clinical manifestation of the disease and the biopsy results. Considering solely the clinical location of the lesions, Grover disease was a less likely diagnosis because our patient’s lesions were observed in the perianal region, not the truncal region as typically seen in Grover disease. Taking into account the DIF assay results in our patient, the pemphigus family of diseases also moved lower on the differential diagnosis. Finally, because the biopsy showed more dyskeratosis than would be present in HHD and also was inconsistent with the location and onset that would be expected to be seen in Darier disease, PAD was the most probable diagnosis. Interestingly, studies have shown mosaic mutations in ATP2A2 and ATP2C1 as possible causes of PAD, suggesting that this may be an allelic variant of Darier disease and HHD.7-9 No genetic testing was performed in our patient.
- Dowd ML, Ansell LH, Husain S, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the genitocrural area: a rare unilateral asymptomatic intertrigo. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:132-134. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.11.003
- Konstantinou MP, Krasagakis K. Benign familial pemphigus (Hailey Hailey disease). StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585136/
- Montis-Palos MC, Acebo-Mariñas E, Catón-Santarén B, et al. Papular acantholytic dermatosis in the genito-crural region: a localized form of Darier disease or Hailey-Hailey disease? Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2013;104:170-172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adengl.2012.02.008
- Verma SB. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis localized to the perineal and perianal area in a young male. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:393-395.
- Schmieder SJ, Rosario-Collazo JA. Keratosis follicularis. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/books/NBK519557/
- Weaver J, Bergfeld WF. Grover disease (transient acantholytic dermatosis). Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:1490-1494.
- Knopp EA, Saraceni C, Moss J, et al. Somatic ATP2A2 mutation in a case of papular acantholytic dyskeratosis: mosaic Darier disease [published online August 12, 2015]. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:853-857. doi:10.1111/cup.12551
- Lipoff JB, Mudgil AV, Young S, et al. Acantholytic dermatosis of the crural folds with ATP2C1 mutation is a possible variant of Hailey-Hailey Disease. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:151.
- Vodo D, Malchin N, Furman M, et al. Identification of a recurrent mutation in ATP2C1 demonstrates that papular acantholytic dyskeratosis and Hailey-Hailey disease are allelic disorders. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1001-1002.
- Dowd ML, Ansell LH, Husain S, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the genitocrural area: a rare unilateral asymptomatic intertrigo. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:132-134. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.11.003
- Konstantinou MP, Krasagakis K. Benign familial pemphigus (Hailey Hailey disease). StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585136/
- Montis-Palos MC, Acebo-Mariñas E, Catón-Santarén B, et al. Papular acantholytic dermatosis in the genito-crural region: a localized form of Darier disease or Hailey-Hailey disease? Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2013;104:170-172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adengl.2012.02.008
- Verma SB. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis localized to the perineal and perianal area in a young male. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:393-395.
- Schmieder SJ, Rosario-Collazo JA. Keratosis follicularis. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/books/NBK519557/
- Weaver J, Bergfeld WF. Grover disease (transient acantholytic dermatosis). Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:1490-1494.
- Knopp EA, Saraceni C, Moss J, et al. Somatic ATP2A2 mutation in a case of papular acantholytic dyskeratosis: mosaic Darier disease [published online August 12, 2015]. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:853-857. doi:10.1111/cup.12551
- Lipoff JB, Mudgil AV, Young S, et al. Acantholytic dermatosis of the crural folds with ATP2C1 mutation is a possible variant of Hailey-Hailey Disease. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:151.
- Vodo D, Malchin N, Furman M, et al. Identification of a recurrent mutation in ATP2C1 demonstrates that papular acantholytic dyskeratosis and Hailey-Hailey disease are allelic disorders. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1001-1002.
A 66-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with pruritus of the gluteal cleft and perianal region of several months’ duration. He had been prescribed permethrin by an outside physician, as well as oral acyclovir, triamcinolone-nystatin combination ointment, and topical zinc oxide prescribed by dermatology, without improvement. Physical examination showed several papules and erosions (<1 mm) in the perianal and gluteal cleft regions (inset). Hyperpigmented macules also were noted in the inguinal folds. A shave biopsy of a lesion from the perianal region was performed.
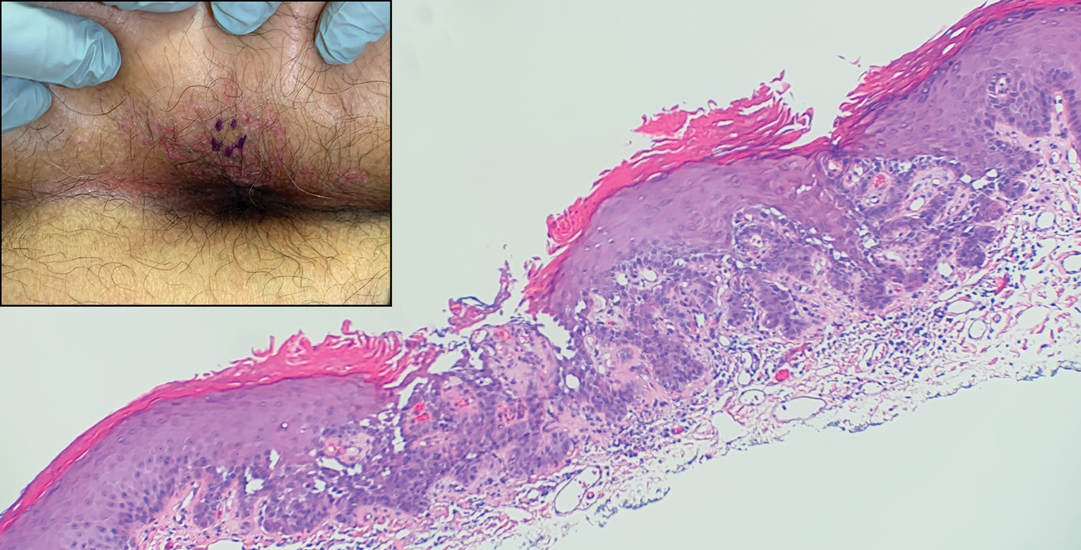
Results From the First Annual Association of Professors of Dermatology Program Directors Survey
Educational organizations across several specialties, including internal medicine and obstetrics and gynecology, have formal surveys1; however, the field of dermatology has been without one. This study aimed to establish a formal survey for dermatology program directors (PDs) and clinician-educators. Because the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) and American Board of Dermatology surveys do not capture all metrics relevant to dermatology residency educators, an annual survey for our specialty may be helpful to compare dermatology-specific data among programs. Responses could provide context and perspective to faculty and residents who respond to the ACGME annual survey, as our Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) survey asks more in-depth questions, such as how often didactics occur and who leads them. Resident commute time and faculty demographics and training also are covered. Current ad hoc surveys disseminated through listserves of various medical associations contain overlapping questions and reflect relatively low response rates; dermatology PDs may benefit from a survey with a high response rate to which they can contribute future questions and topics that reflect recent trends and current needs in graduate medical education. As future surveys are administered, the results can be captured in a centralized database accessible by dermatology PDs.
Methods
A survey of PDs from 141 ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs was conducted by the Residency Program Director Steering Committee of the APD from November 2022 to January 2023 using a prevalidated questionnaire. Personalized survey links were created and sent individually to each PD’s email listed in the ACGME accreditation data system. All survey responses were captured anonymously, with a number assigned to keep de-identified responses separate and organized. The survey consisted of 137 survey questions addressing topics that included program characteristics, PD demographics, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on clinical rotation and educational conferences, available resident resources, quality improvement, clinical and didactic instruction, research content, diversity and inclusion, wellness, professionalism, evaluation systems, and graduate outcomes.
Data were collected using Qualtrics survey tools. After removing duplicate and incomplete surveys, data were analyzed using Qualtrics reports and Microsoft Excel for data plotting, averages, and range calculations.
Results
One hundred forty-one personalized survey links were created and sent individually to each program’s filed email obtained from the APD listserv. Fifty-three responses were recorded after removing duplicate or incomplete surveys (38% [53/141] response rate). As of May 2023, there were 144 ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs due to 3 newly accredited programs in 2022-2023 academic year, which were not included in our survey population.
Program Characteristics—Forty-four respondents (83%) were from a university-based program. Fifty respondents (94%) were from programs that were ACGME accredited prior to 2020, while 3 programs (6%) were American Osteopathic Association accredited prior to singular accreditation. Seventy-one percent (38/53) of respondents had 1 or more associate PDs.
PD Demographics—Eighty-seven percent (45/52) of PDs who responded to the survey graduated from a US allopathic medical school (MD), 10% (5/52) graduated from a US osteopathic medical school (DO), and 4% (2/52) graduated from an international medical school. Seventy-four percent (35/47) of respondents were White, 17% (8/47) were Asian, and 2% (1/47) were Black or African American; this data was not provided for 4 respondents. Forty-eight percent (23/48) of PDs identified as cisgender man, 48% (23/48) identified as cisgender woman, and 4% (2/48) preferred not to answer. Eighty-one percent (38/47) of PDs identified as heterosexual or straight, 15% (7/47) identified as gay or lesbian, and 4% (2/47) preferred not to answer.
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Residency Training—Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, 88% (45/51) of respondents incorporated telemedicine into the resident clinical rotation schedule. Moving forward, 75% (38/51) of respondents indicated that their programs plan to continue to incorporate telemedicine into the rotation schedule. Based on 50 responses, the average of educational conferences that became virtual at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic was 87%; based on 46 responses, the percentage of educational conferences that will remain virtual moving forward is 46%, while 90% (46/51) of respondents indicated that their programs plan to use virtual conferences in some capacity moving forward. Seventy-three percent (37/51) of respondents indicated that they plan to use virtual interviews as part of residency recruitment moving forward.
Available Resources—Twenty-four percent (11/46) of respondents indicated that residents in their program do not get protected time or time off for CORE examinations. Seventy-five percent (33/44) of PDs said their program provides funding for residents to participate in board review courses. The chief residents at 63% (31/49) of programs receive additional compensation, and 69% (34/49) provide additional administrative time to chief residents. Seventy-one percent (24/34) of PDs reported their programs have scribes for attendings, and 12% (4/34) have scribes for residents. Support staff help residents with callbacks and in-basket messages according to 76% (35/46) of respondents. The majority (98% [45/46]) of PDs indicated that residents follow-up on results and messages from patients seen in resident clinics, and 43% (20/46) of programs have residents follow-up with patients seen in faculty clinics. Only 15% (7/46) of PDs responded they have schedules with residents dedicated to handle these tasks. According to respondents, 33% (17/52) have residents who are required to travel more than 25 miles to distant clinical sites. Of them, 35% (6/17) provide accommodations.
Quality Improvement—Seventy-one percent (35/49) of respondents indicated their department has a quality improvement/patient safety team or committee, and 94% (33/35) of these teams include residents. A lecture series on quality improvement and patient safety is offered at 67% (33/49) of the respondents’ programs, while morbidity and mortality conferences are offered in 73% (36/49).
Clinical Instruction—Our survey asked PDs how many months each residency year spends on a certain rotational service. Based on 46 respondents, the average number of months dedicated to medical dermatology is 7, 5, and 6 months for postgraduate year (PGY) 2, PGY3, and PGY4, respectively. The average number of months spent in other subspecialties is provided in the Table. On average, PGY2 residents spend 8 half-days per week seeing patients in clinic, while PGY3 and PGY4 residents see patients for 7 half-days. The median and mean number of patients staffed by a single attending per hour in teaching clinics are 6 and 5.88, respectively. Respondents indicated that residents participate in the following specialty clinics: pediatric dermatology (96% [44/46]), laser/cosmetic (87% [40/44]), high-risk skin cancer (ie, immunosuppressed/transplant patient)(65% [30/44]), pigmented lesion/melanoma (52% [24/44]), connective tissue disease (52% [24/44]), teledermatology (50% [23/44]), free clinic for homeless and/or indigent populations (48% [22/44]), contact dermatitis (43% [20/44]), skin of color (43% [20/44]), oncodermatology (41% [19/44]), and bullous disease (33% [15/44]).
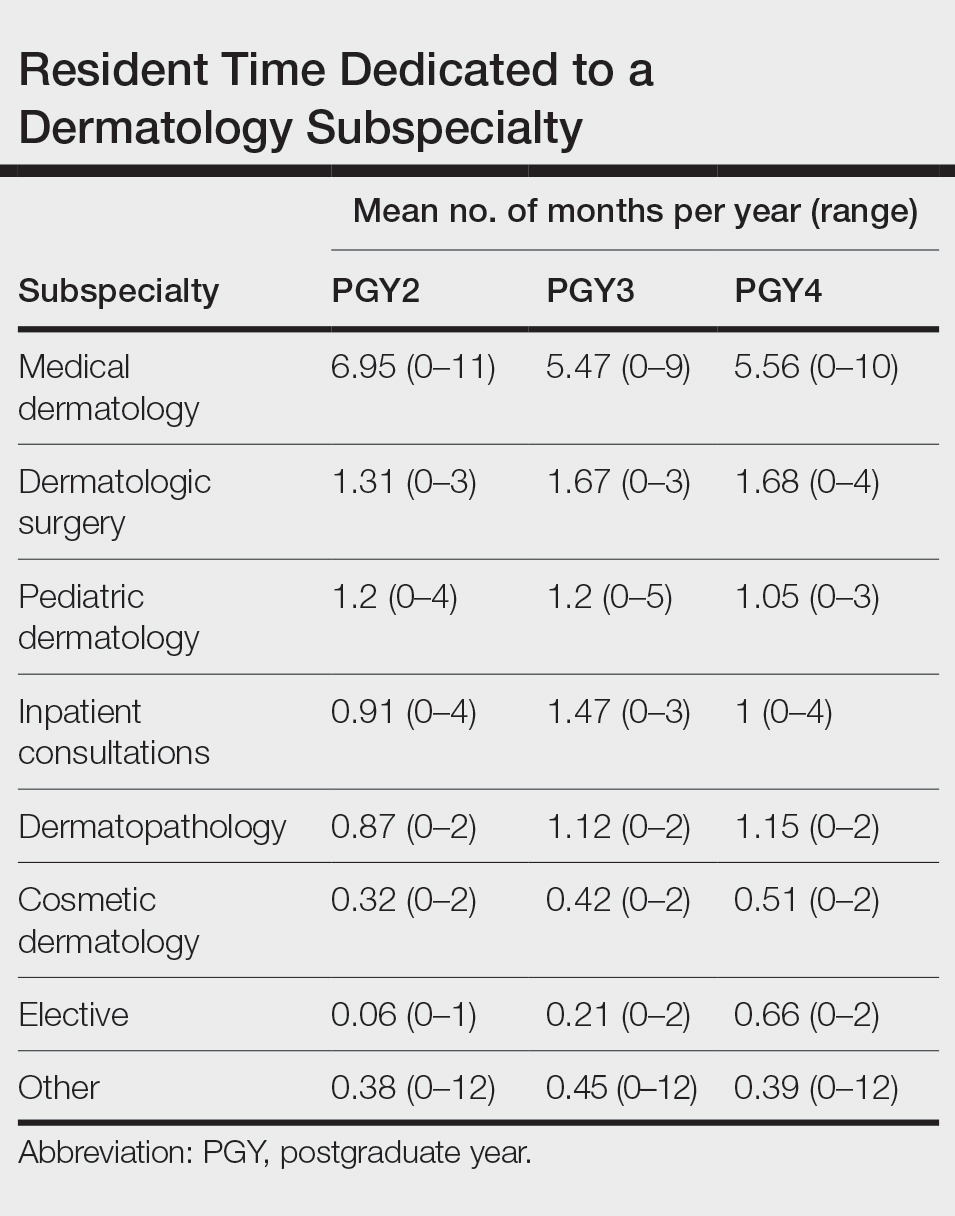
Additionally, in 87% (40/46) of programs, residents participate in a dedicated inpatient consultation service. Most respondents (98% [45/46]) responded that they utilize in-person consultations with a teledermatology supplement. Fifteen percent (7/46) utilize virtual teledermatology (live video-based consultations), and 57% (26/46) utilize asynchronous teledermatology (picture-based consultations). All respondents (n=46) indicated that 0% to 25% of patient encounters involving residents are teledermatology visits. Thirty-three percent (6/18) of programs have a global health special training track, 56% (10/18) have a Specialty Training and Advanced Research/Physician-Scientist Research Training track, 28% (5/18) have a diversity training track, and 50% (9/18) have a clinician educator training track.
Didactic Instruction—Five programs have a full day per week dedicated to didactics, while 36 programs have at least one half-day per week for didactics. On average, didactics in 57% (26/46) of programs are led by faculty alone, while 43% (20/46) are led at least in part by residents or fellows.
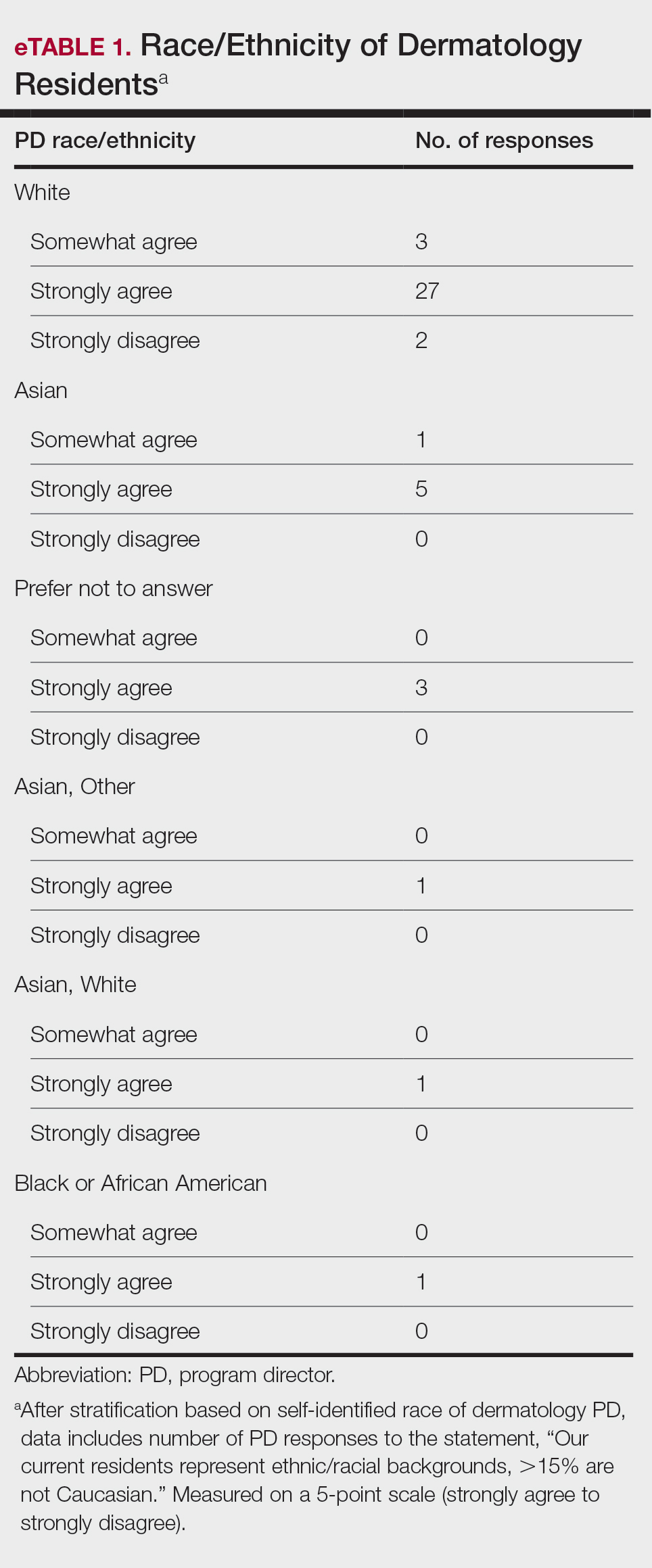
Research Content—Fifty percent (23/46) of programs have a specific research requirement for residents beyond general ACGME requirements, and 35% (16/46) require residents to participate in a longitudinal research project over the course of residency. There is a dedicated research coordinator for resident support at 63% (29/46) of programs. Dedicated biostatistics research support is available for resident projects at 42% (19/45) of programs. Additionally, at 42% (19/45) of programs, there is a dedicated faculty member for oversight of resident research.
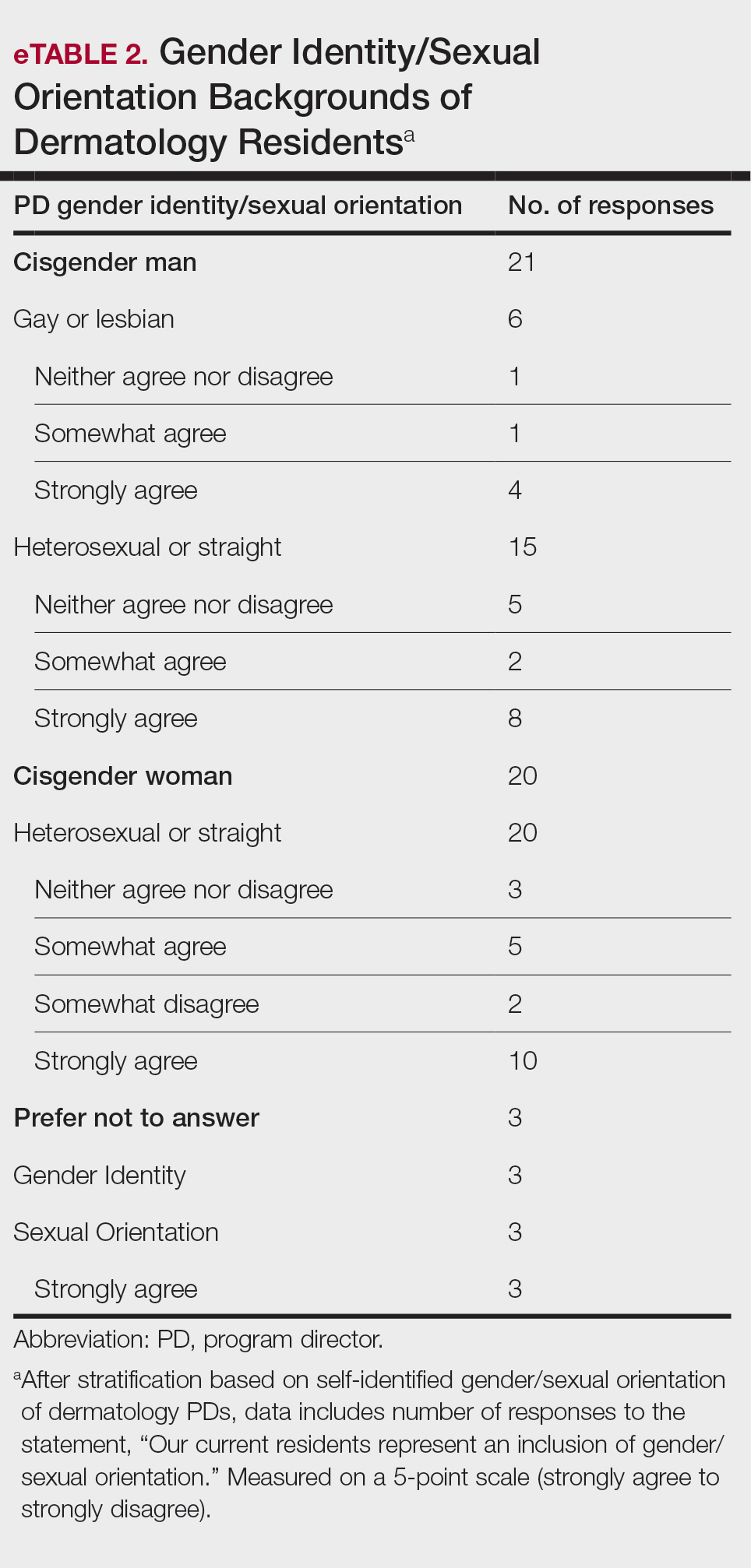
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion—Seventy-three percent (29/40) of programs have special diversity, equity, and inclusion programs or meetings specific to residency, 60% (24/40) have residency initiatives, and 55% (22/40) have a residency diversity committee. Eighty-six percent (42/49) of respondents strongly agreed that their current residents represent diverse ethnic and racial backgrounds (ie, >15% are not White). eTable 1 shows PD responses to this statement, which were stratified based on self-identified race. eTable 2 shows PD responses to the statement, “Our current residents represent an inclusion of gender/sexual orientation,” which were stratified based on self-identified gender identity/sexual orientation. Lastly, eTable 3 highlights the percentage of residents with an MD and DO degree, stratified based on PD degree.
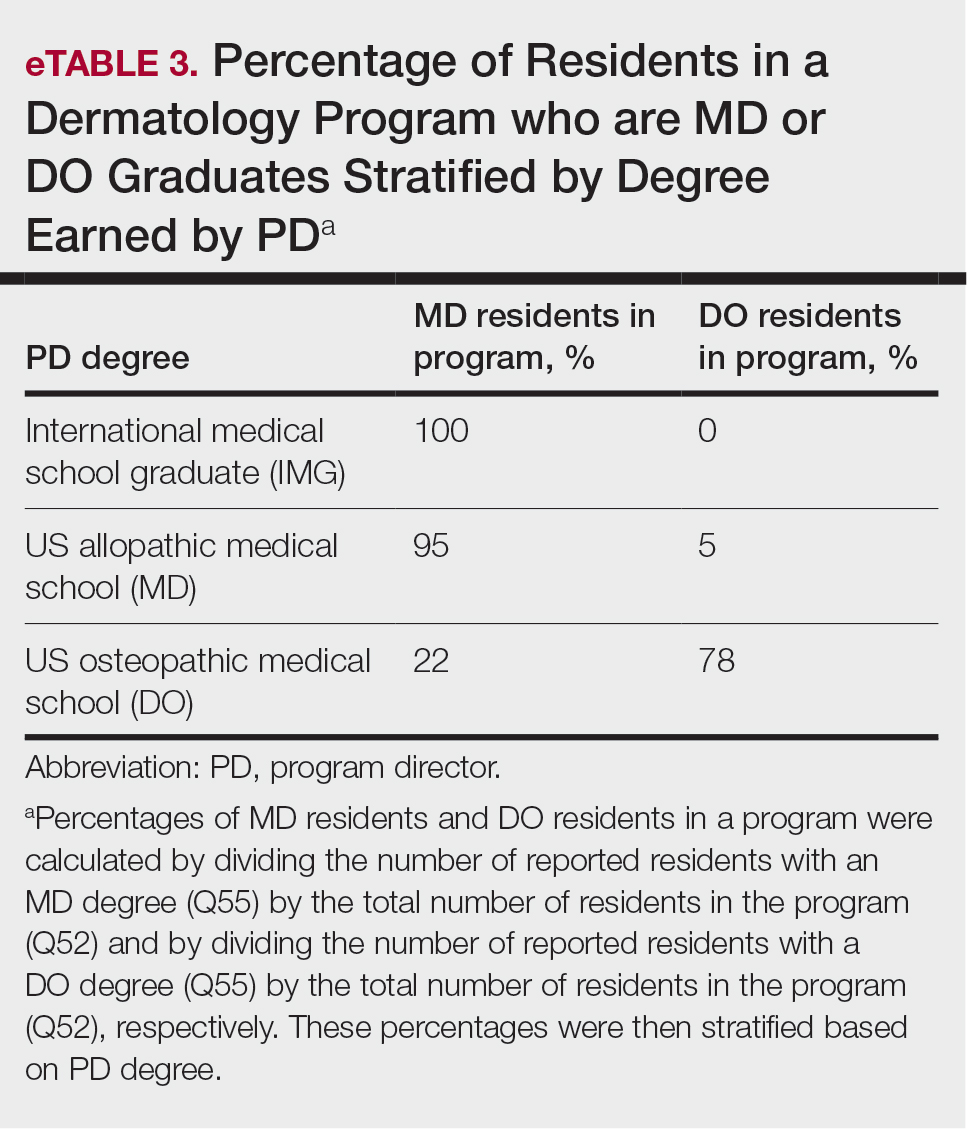
Wellness—Forty-eight percent (20/42) of respondents indicated they are under stress and do not always have as much energy as before becoming a PD but do not feel burned out. Thirty-one percent (13/42) indicated they have 1 or more symptoms of burnout, such as emotional exhaustion. Eighty-six percent (36/42) are satisfied with their jobs overall (43% agree and 43% strongly agree [18/42 each]).
Evaluation System—Seventy-five percent (33/44) of programs deliver evaluations of residents by faculty online, 86% (38/44) of programs have PDs discuss evaluations in-person, and 20% (9/44) of programs have faculty evaluators discuss evaluations in-person. Seventy-seven percent (34/44) of programs have formal faculty-resident mentor-mentee programs. Clinical competency committee chair positions are filled by PDs, assistant PDs, or core faculty members 47%, 38%, and 16% of the time, respectively.
Graduation Outcomes of PGY4 Residents—About 28% (55/199) of graduating residents applied to a fellowship position, with the majority (15% [29/55]) matching into Mohs micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology (MSDO) fellowships. Approximately 5% (9/199) and 4% (7/199) of graduates matched into dermatopathology and pediatric dermatology, respectively. The remaining 5% (10/199) of graduating residents applied to a fellowship but did not match. The majority (45% [91/199]) of residency graduates entered private practice after graduation. Approximately 21% (42/199) of graduating residents chose an academic practice with 17% (33/199), 2% (4/199), and 2% (3/199) of those positions being full-time, part-time, and adjunct, respectively.
Comment
The first annual APD survey is a novel data source and provides opportunities for areas of discussion and investigation. Evaluating the similarities and differences among dermatology residency programs across the United States can strengthen individual programs through collaboration and provide areas of cohesion among programs.
Diversity of PDs—An important area of discussion is diversity and PD demographics. Although DO students make up 1 in 4 US graduating medical students, they are not interviewed or ranked as often as MD students.2 Diversity in PD race and ethnicity may be worthy of investigation in future studies, as match rates and recruitment of diverse medical school applicants may be impacted by these demographics.
Continued Use of Telemedicine in Training—Since 2020, the benefits of virtual residency recruitment have been debated among PDs across all medical specialties. Points in favor of virtual interviews include cost savings for programs and especially for applicants, as well as time efficiency, reduced burden of travel, and reduced carbon footprint. A problem posed by virtual interviews is that candidates are unable to fully learn institutional cultures and social environments of the programs.3 Likewise, telehealth was an important means of clinical teaching for residents during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, with benefits that included cost-effectiveness and reduction of disparities in access to dermatologic care.4 Seventy-five percent (38/51) of PDs indicated that their program plans to include telemedicine in resident clinical rotation moving forward.
Resources Available—Our survey showed that resources available for residents, delivery of lectures and program time allocated to didactics, protected academic or study time for residents, and allocation of program time for CORE examinations are highly variable across programs. This could inspire future studies to be done to determine the differences in success of the resident on CORE examinations and in digesting material.
Postgraduate Career Plans and Fellowship Matches—Residents of programs that have a home MSDO fellowship are more likely to successfully match into a MSDO fellowship.5 Based on this survey, approximately 28% of graduating residents applied to a fellowship position, with 15%, 5%, and 3% matching into desired MSDO, dermatopathology, and pediatric dermatology fellowships, respectively. Additional studies are needed to determine advantages and disadvantages that lead to residents reaching their career goals.
Limitations—Limitations of this study include a small sample size that may not adequately represent all ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs and selection bias toward respondents who are more likely to participate in survey-based research.
Conclusion
The APD plans to continue to administer this survey on an annual basis, with updates to the content and questions based on input from PDs. This survey will continue to provide valuable information to drive collaboration among residency programs and optimize the learning experience for residents. Our hope is that the response rate will increase in coming years, allowing us to draw more generalizable conclusions. Nonetheless, the survey data allow individual dermatology residency programs to compare their specific characteristics to other programs.
- Maciejko L, Cope A, Mara K, et al. A national survey of obstetrics and gynecology emergency training and deficits in office emergency preparation [A53]. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:16S. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000826548.05758.26
- Lavertue SM, Terry R. A comparison of surgical subspecialty match rates in 2022 in the United States. Cureus. 2023;15:E37178. doi:10.7759/cureus.37178
- Domingo A, Rdesinski RE, Stenson A, et al. Virtual residency interviews: applicant perceptions regarding virtual interview effectiveness, advantages, and barriers. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14:224-228. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-21-00675.1
- Rustad AM, Lio PA. Pandemic pressure: teledermatology and health care disparities. J Patient Exp. 2021;8:2374373521996982. doi:10.1177/2374373521996982
- Rickstrew J, Rajpara A, Hocker TLH. Dermatology residency program influences chance of successful surgery fellowship match. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1040-1042. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002859
Educational organizations across several specialties, including internal medicine and obstetrics and gynecology, have formal surveys1; however, the field of dermatology has been without one. This study aimed to establish a formal survey for dermatology program directors (PDs) and clinician-educators. Because the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) and American Board of Dermatology surveys do not capture all metrics relevant to dermatology residency educators, an annual survey for our specialty may be helpful to compare dermatology-specific data among programs. Responses could provide context and perspective to faculty and residents who respond to the ACGME annual survey, as our Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) survey asks more in-depth questions, such as how often didactics occur and who leads them. Resident commute time and faculty demographics and training also are covered. Current ad hoc surveys disseminated through listserves of various medical associations contain overlapping questions and reflect relatively low response rates; dermatology PDs may benefit from a survey with a high response rate to which they can contribute future questions and topics that reflect recent trends and current needs in graduate medical education. As future surveys are administered, the results can be captured in a centralized database accessible by dermatology PDs.
Methods
A survey of PDs from 141 ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs was conducted by the Residency Program Director Steering Committee of the APD from November 2022 to January 2023 using a prevalidated questionnaire. Personalized survey links were created and sent individually to each PD’s email listed in the ACGME accreditation data system. All survey responses were captured anonymously, with a number assigned to keep de-identified responses separate and organized. The survey consisted of 137 survey questions addressing topics that included program characteristics, PD demographics, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on clinical rotation and educational conferences, available resident resources, quality improvement, clinical and didactic instruction, research content, diversity and inclusion, wellness, professionalism, evaluation systems, and graduate outcomes.
Data were collected using Qualtrics survey tools. After removing duplicate and incomplete surveys, data were analyzed using Qualtrics reports and Microsoft Excel for data plotting, averages, and range calculations.
Results
One hundred forty-one personalized survey links were created and sent individually to each program’s filed email obtained from the APD listserv. Fifty-three responses were recorded after removing duplicate or incomplete surveys (38% [53/141] response rate). As of May 2023, there were 144 ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs due to 3 newly accredited programs in 2022-2023 academic year, which were not included in our survey population.
Program Characteristics—Forty-four respondents (83%) were from a university-based program. Fifty respondents (94%) were from programs that were ACGME accredited prior to 2020, while 3 programs (6%) were American Osteopathic Association accredited prior to singular accreditation. Seventy-one percent (38/53) of respondents had 1 or more associate PDs.
PD Demographics—Eighty-seven percent (45/52) of PDs who responded to the survey graduated from a US allopathic medical school (MD), 10% (5/52) graduated from a US osteopathic medical school (DO), and 4% (2/52) graduated from an international medical school. Seventy-four percent (35/47) of respondents were White, 17% (8/47) were Asian, and 2% (1/47) were Black or African American; this data was not provided for 4 respondents. Forty-eight percent (23/48) of PDs identified as cisgender man, 48% (23/48) identified as cisgender woman, and 4% (2/48) preferred not to answer. Eighty-one percent (38/47) of PDs identified as heterosexual or straight, 15% (7/47) identified as gay or lesbian, and 4% (2/47) preferred not to answer.
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Residency Training—Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, 88% (45/51) of respondents incorporated telemedicine into the resident clinical rotation schedule. Moving forward, 75% (38/51) of respondents indicated that their programs plan to continue to incorporate telemedicine into the rotation schedule. Based on 50 responses, the average of educational conferences that became virtual at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic was 87%; based on 46 responses, the percentage of educational conferences that will remain virtual moving forward is 46%, while 90% (46/51) of respondents indicated that their programs plan to use virtual conferences in some capacity moving forward. Seventy-three percent (37/51) of respondents indicated that they plan to use virtual interviews as part of residency recruitment moving forward.
Available Resources—Twenty-four percent (11/46) of respondents indicated that residents in their program do not get protected time or time off for CORE examinations. Seventy-five percent (33/44) of PDs said their program provides funding for residents to participate in board review courses. The chief residents at 63% (31/49) of programs receive additional compensation, and 69% (34/49) provide additional administrative time to chief residents. Seventy-one percent (24/34) of PDs reported their programs have scribes for attendings, and 12% (4/34) have scribes for residents. Support staff help residents with callbacks and in-basket messages according to 76% (35/46) of respondents. The majority (98% [45/46]) of PDs indicated that residents follow-up on results and messages from patients seen in resident clinics, and 43% (20/46) of programs have residents follow-up with patients seen in faculty clinics. Only 15% (7/46) of PDs responded they have schedules with residents dedicated to handle these tasks. According to respondents, 33% (17/52) have residents who are required to travel more than 25 miles to distant clinical sites. Of them, 35% (6/17) provide accommodations.
Quality Improvement—Seventy-one percent (35/49) of respondents indicated their department has a quality improvement/patient safety team or committee, and 94% (33/35) of these teams include residents. A lecture series on quality improvement and patient safety is offered at 67% (33/49) of the respondents’ programs, while morbidity and mortality conferences are offered in 73% (36/49).
Clinical Instruction—Our survey asked PDs how many months each residency year spends on a certain rotational service. Based on 46 respondents, the average number of months dedicated to medical dermatology is 7, 5, and 6 months for postgraduate year (PGY) 2, PGY3, and PGY4, respectively. The average number of months spent in other subspecialties is provided in the Table. On average, PGY2 residents spend 8 half-days per week seeing patients in clinic, while PGY3 and PGY4 residents see patients for 7 half-days. The median and mean number of patients staffed by a single attending per hour in teaching clinics are 6 and 5.88, respectively. Respondents indicated that residents participate in the following specialty clinics: pediatric dermatology (96% [44/46]), laser/cosmetic (87% [40/44]), high-risk skin cancer (ie, immunosuppressed/transplant patient)(65% [30/44]), pigmented lesion/melanoma (52% [24/44]), connective tissue disease (52% [24/44]), teledermatology (50% [23/44]), free clinic for homeless and/or indigent populations (48% [22/44]), contact dermatitis (43% [20/44]), skin of color (43% [20/44]), oncodermatology (41% [19/44]), and bullous disease (33% [15/44]).

Additionally, in 87% (40/46) of programs, residents participate in a dedicated inpatient consultation service. Most respondents (98% [45/46]) responded that they utilize in-person consultations with a teledermatology supplement. Fifteen percent (7/46) utilize virtual teledermatology (live video-based consultations), and 57% (26/46) utilize asynchronous teledermatology (picture-based consultations). All respondents (n=46) indicated that 0% to 25% of patient encounters involving residents are teledermatology visits. Thirty-three percent (6/18) of programs have a global health special training track, 56% (10/18) have a Specialty Training and Advanced Research/Physician-Scientist Research Training track, 28% (5/18) have a diversity training track, and 50% (9/18) have a clinician educator training track.
Didactic Instruction—Five programs have a full day per week dedicated to didactics, while 36 programs have at least one half-day per week for didactics. On average, didactics in 57% (26/46) of programs are led by faculty alone, while 43% (20/46) are led at least in part by residents or fellows.

Research Content—Fifty percent (23/46) of programs have a specific research requirement for residents beyond general ACGME requirements, and 35% (16/46) require residents to participate in a longitudinal research project over the course of residency. There is a dedicated research coordinator for resident support at 63% (29/46) of programs. Dedicated biostatistics research support is available for resident projects at 42% (19/45) of programs. Additionally, at 42% (19/45) of programs, there is a dedicated faculty member for oversight of resident research.

Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion—Seventy-three percent (29/40) of programs have special diversity, equity, and inclusion programs or meetings specific to residency, 60% (24/40) have residency initiatives, and 55% (22/40) have a residency diversity committee. Eighty-six percent (42/49) of respondents strongly agreed that their current residents represent diverse ethnic and racial backgrounds (ie, >15% are not White). eTable 1 shows PD responses to this statement, which were stratified based on self-identified race. eTable 2 shows PD responses to the statement, “Our current residents represent an inclusion of gender/sexual orientation,” which were stratified based on self-identified gender identity/sexual orientation. Lastly, eTable 3 highlights the percentage of residents with an MD and DO degree, stratified based on PD degree.

Wellness—Forty-eight percent (20/42) of respondents indicated they are under stress and do not always have as much energy as before becoming a PD but do not feel burned out. Thirty-one percent (13/42) indicated they have 1 or more symptoms of burnout, such as emotional exhaustion. Eighty-six percent (36/42) are satisfied with their jobs overall (43% agree and 43% strongly agree [18/42 each]).
Evaluation System—Seventy-five percent (33/44) of programs deliver evaluations of residents by faculty online, 86% (38/44) of programs have PDs discuss evaluations in-person, and 20% (9/44) of programs have faculty evaluators discuss evaluations in-person. Seventy-seven percent (34/44) of programs have formal faculty-resident mentor-mentee programs. Clinical competency committee chair positions are filled by PDs, assistant PDs, or core faculty members 47%, 38%, and 16% of the time, respectively.
Graduation Outcomes of PGY4 Residents—About 28% (55/199) of graduating residents applied to a fellowship position, with the majority (15% [29/55]) matching into Mohs micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology (MSDO) fellowships. Approximately 5% (9/199) and 4% (7/199) of graduates matched into dermatopathology and pediatric dermatology, respectively. The remaining 5% (10/199) of graduating residents applied to a fellowship but did not match. The majority (45% [91/199]) of residency graduates entered private practice after graduation. Approximately 21% (42/199) of graduating residents chose an academic practice with 17% (33/199), 2% (4/199), and 2% (3/199) of those positions being full-time, part-time, and adjunct, respectively.
Comment
The first annual APD survey is a novel data source and provides opportunities for areas of discussion and investigation. Evaluating the similarities and differences among dermatology residency programs across the United States can strengthen individual programs through collaboration and provide areas of cohesion among programs.
Diversity of PDs—An important area of discussion is diversity and PD demographics. Although DO students make up 1 in 4 US graduating medical students, they are not interviewed or ranked as often as MD students.2 Diversity in PD race and ethnicity may be worthy of investigation in future studies, as match rates and recruitment of diverse medical school applicants may be impacted by these demographics.
Continued Use of Telemedicine in Training—Since 2020, the benefits of virtual residency recruitment have been debated among PDs across all medical specialties. Points in favor of virtual interviews include cost savings for programs and especially for applicants, as well as time efficiency, reduced burden of travel, and reduced carbon footprint. A problem posed by virtual interviews is that candidates are unable to fully learn institutional cultures and social environments of the programs.3 Likewise, telehealth was an important means of clinical teaching for residents during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, with benefits that included cost-effectiveness and reduction of disparities in access to dermatologic care.4 Seventy-five percent (38/51) of PDs indicated that their program plans to include telemedicine in resident clinical rotation moving forward.
Resources Available—Our survey showed that resources available for residents, delivery of lectures and program time allocated to didactics, protected academic or study time for residents, and allocation of program time for CORE examinations are highly variable across programs. This could inspire future studies to be done to determine the differences in success of the resident on CORE examinations and in digesting material.
Postgraduate Career Plans and Fellowship Matches—Residents of programs that have a home MSDO fellowship are more likely to successfully match into a MSDO fellowship.5 Based on this survey, approximately 28% of graduating residents applied to a fellowship position, with 15%, 5%, and 3% matching into desired MSDO, dermatopathology, and pediatric dermatology fellowships, respectively. Additional studies are needed to determine advantages and disadvantages that lead to residents reaching their career goals.
Limitations—Limitations of this study include a small sample size that may not adequately represent all ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs and selection bias toward respondents who are more likely to participate in survey-based research.
Conclusion
The APD plans to continue to administer this survey on an annual basis, with updates to the content and questions based on input from PDs. This survey will continue to provide valuable information to drive collaboration among residency programs and optimize the learning experience for residents. Our hope is that the response rate will increase in coming years, allowing us to draw more generalizable conclusions. Nonetheless, the survey data allow individual dermatology residency programs to compare their specific characteristics to other programs.
Educational organizations across several specialties, including internal medicine and obstetrics and gynecology, have formal surveys1; however, the field of dermatology has been without one. This study aimed to establish a formal survey for dermatology program directors (PDs) and clinician-educators. Because the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) and American Board of Dermatology surveys do not capture all metrics relevant to dermatology residency educators, an annual survey for our specialty may be helpful to compare dermatology-specific data among programs. Responses could provide context and perspective to faculty and residents who respond to the ACGME annual survey, as our Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) survey asks more in-depth questions, such as how often didactics occur and who leads them. Resident commute time and faculty demographics and training also are covered. Current ad hoc surveys disseminated through listserves of various medical associations contain overlapping questions and reflect relatively low response rates; dermatology PDs may benefit from a survey with a high response rate to which they can contribute future questions and topics that reflect recent trends and current needs in graduate medical education. As future surveys are administered, the results can be captured in a centralized database accessible by dermatology PDs.
Methods
A survey of PDs from 141 ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs was conducted by the Residency Program Director Steering Committee of the APD from November 2022 to January 2023 using a prevalidated questionnaire. Personalized survey links were created and sent individually to each PD’s email listed in the ACGME accreditation data system. All survey responses were captured anonymously, with a number assigned to keep de-identified responses separate and organized. The survey consisted of 137 survey questions addressing topics that included program characteristics, PD demographics, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on clinical rotation and educational conferences, available resident resources, quality improvement, clinical and didactic instruction, research content, diversity and inclusion, wellness, professionalism, evaluation systems, and graduate outcomes.
Data were collected using Qualtrics survey tools. After removing duplicate and incomplete surveys, data were analyzed using Qualtrics reports and Microsoft Excel for data plotting, averages, and range calculations.
Results
One hundred forty-one personalized survey links were created and sent individually to each program’s filed email obtained from the APD listserv. Fifty-three responses were recorded after removing duplicate or incomplete surveys (38% [53/141] response rate). As of May 2023, there were 144 ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs due to 3 newly accredited programs in 2022-2023 academic year, which were not included in our survey population.
Program Characteristics—Forty-four respondents (83%) were from a university-based program. Fifty respondents (94%) were from programs that were ACGME accredited prior to 2020, while 3 programs (6%) were American Osteopathic Association accredited prior to singular accreditation. Seventy-one percent (38/53) of respondents had 1 or more associate PDs.
PD Demographics—Eighty-seven percent (45/52) of PDs who responded to the survey graduated from a US allopathic medical school (MD), 10% (5/52) graduated from a US osteopathic medical school (DO), and 4% (2/52) graduated from an international medical school. Seventy-four percent (35/47) of respondents were White, 17% (8/47) were Asian, and 2% (1/47) were Black or African American; this data was not provided for 4 respondents. Forty-eight percent (23/48) of PDs identified as cisgender man, 48% (23/48) identified as cisgender woman, and 4% (2/48) preferred not to answer. Eighty-one percent (38/47) of PDs identified as heterosexual or straight, 15% (7/47) identified as gay or lesbian, and 4% (2/47) preferred not to answer.
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Residency Training—Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, 88% (45/51) of respondents incorporated telemedicine into the resident clinical rotation schedule. Moving forward, 75% (38/51) of respondents indicated that their programs plan to continue to incorporate telemedicine into the rotation schedule. Based on 50 responses, the average of educational conferences that became virtual at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic was 87%; based on 46 responses, the percentage of educational conferences that will remain virtual moving forward is 46%, while 90% (46/51) of respondents indicated that their programs plan to use virtual conferences in some capacity moving forward. Seventy-three percent (37/51) of respondents indicated that they plan to use virtual interviews as part of residency recruitment moving forward.
Available Resources—Twenty-four percent (11/46) of respondents indicated that residents in their program do not get protected time or time off for CORE examinations. Seventy-five percent (33/44) of PDs said their program provides funding for residents to participate in board review courses. The chief residents at 63% (31/49) of programs receive additional compensation, and 69% (34/49) provide additional administrative time to chief residents. Seventy-one percent (24/34) of PDs reported their programs have scribes for attendings, and 12% (4/34) have scribes for residents. Support staff help residents with callbacks and in-basket messages according to 76% (35/46) of respondents. The majority (98% [45/46]) of PDs indicated that residents follow-up on results and messages from patients seen in resident clinics, and 43% (20/46) of programs have residents follow-up with patients seen in faculty clinics. Only 15% (7/46) of PDs responded they have schedules with residents dedicated to handle these tasks. According to respondents, 33% (17/52) have residents who are required to travel more than 25 miles to distant clinical sites. Of them, 35% (6/17) provide accommodations.
Quality Improvement—Seventy-one percent (35/49) of respondents indicated their department has a quality improvement/patient safety team or committee, and 94% (33/35) of these teams include residents. A lecture series on quality improvement and patient safety is offered at 67% (33/49) of the respondents’ programs, while morbidity and mortality conferences are offered in 73% (36/49).
Clinical Instruction—Our survey asked PDs how many months each residency year spends on a certain rotational service. Based on 46 respondents, the average number of months dedicated to medical dermatology is 7, 5, and 6 months for postgraduate year (PGY) 2, PGY3, and PGY4, respectively. The average number of months spent in other subspecialties is provided in the Table. On average, PGY2 residents spend 8 half-days per week seeing patients in clinic, while PGY3 and PGY4 residents see patients for 7 half-days. The median and mean number of patients staffed by a single attending per hour in teaching clinics are 6 and 5.88, respectively. Respondents indicated that residents participate in the following specialty clinics: pediatric dermatology (96% [44/46]), laser/cosmetic (87% [40/44]), high-risk skin cancer (ie, immunosuppressed/transplant patient)(65% [30/44]), pigmented lesion/melanoma (52% [24/44]), connective tissue disease (52% [24/44]), teledermatology (50% [23/44]), free clinic for homeless and/or indigent populations (48% [22/44]), contact dermatitis (43% [20/44]), skin of color (43% [20/44]), oncodermatology (41% [19/44]), and bullous disease (33% [15/44]).

Additionally, in 87% (40/46) of programs, residents participate in a dedicated inpatient consultation service. Most respondents (98% [45/46]) responded that they utilize in-person consultations with a teledermatology supplement. Fifteen percent (7/46) utilize virtual teledermatology (live video-based consultations), and 57% (26/46) utilize asynchronous teledermatology (picture-based consultations). All respondents (n=46) indicated that 0% to 25% of patient encounters involving residents are teledermatology visits. Thirty-three percent (6/18) of programs have a global health special training track, 56% (10/18) have a Specialty Training and Advanced Research/Physician-Scientist Research Training track, 28% (5/18) have a diversity training track, and 50% (9/18) have a clinician educator training track.
Didactic Instruction—Five programs have a full day per week dedicated to didactics, while 36 programs have at least one half-day per week for didactics. On average, didactics in 57% (26/46) of programs are led by faculty alone, while 43% (20/46) are led at least in part by residents or fellows.

Research Content—Fifty percent (23/46) of programs have a specific research requirement for residents beyond general ACGME requirements, and 35% (16/46) require residents to participate in a longitudinal research project over the course of residency. There is a dedicated research coordinator for resident support at 63% (29/46) of programs. Dedicated biostatistics research support is available for resident projects at 42% (19/45) of programs. Additionally, at 42% (19/45) of programs, there is a dedicated faculty member for oversight of resident research.

Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion—Seventy-three percent (29/40) of programs have special diversity, equity, and inclusion programs or meetings specific to residency, 60% (24/40) have residency initiatives, and 55% (22/40) have a residency diversity committee. Eighty-six percent (42/49) of respondents strongly agreed that their current residents represent diverse ethnic and racial backgrounds (ie, >15% are not White). eTable 1 shows PD responses to this statement, which were stratified based on self-identified race. eTable 2 shows PD responses to the statement, “Our current residents represent an inclusion of gender/sexual orientation,” which were stratified based on self-identified gender identity/sexual orientation. Lastly, eTable 3 highlights the percentage of residents with an MD and DO degree, stratified based on PD degree.

Wellness—Forty-eight percent (20/42) of respondents indicated they are under stress and do not always have as much energy as before becoming a PD but do not feel burned out. Thirty-one percent (13/42) indicated they have 1 or more symptoms of burnout, such as emotional exhaustion. Eighty-six percent (36/42) are satisfied with their jobs overall (43% agree and 43% strongly agree [18/42 each]).
Evaluation System—Seventy-five percent (33/44) of programs deliver evaluations of residents by faculty online, 86% (38/44) of programs have PDs discuss evaluations in-person, and 20% (9/44) of programs have faculty evaluators discuss evaluations in-person. Seventy-seven percent (34/44) of programs have formal faculty-resident mentor-mentee programs. Clinical competency committee chair positions are filled by PDs, assistant PDs, or core faculty members 47%, 38%, and 16% of the time, respectively.
Graduation Outcomes of PGY4 Residents—About 28% (55/199) of graduating residents applied to a fellowship position, with the majority (15% [29/55]) matching into Mohs micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology (MSDO) fellowships. Approximately 5% (9/199) and 4% (7/199) of graduates matched into dermatopathology and pediatric dermatology, respectively. The remaining 5% (10/199) of graduating residents applied to a fellowship but did not match. The majority (45% [91/199]) of residency graduates entered private practice after graduation. Approximately 21% (42/199) of graduating residents chose an academic practice with 17% (33/199), 2% (4/199), and 2% (3/199) of those positions being full-time, part-time, and adjunct, respectively.
Comment
The first annual APD survey is a novel data source and provides opportunities for areas of discussion and investigation. Evaluating the similarities and differences among dermatology residency programs across the United States can strengthen individual programs through collaboration and provide areas of cohesion among programs.
Diversity of PDs—An important area of discussion is diversity and PD demographics. Although DO students make up 1 in 4 US graduating medical students, they are not interviewed or ranked as often as MD students.2 Diversity in PD race and ethnicity may be worthy of investigation in future studies, as match rates and recruitment of diverse medical school applicants may be impacted by these demographics.
Continued Use of Telemedicine in Training—Since 2020, the benefits of virtual residency recruitment have been debated among PDs across all medical specialties. Points in favor of virtual interviews include cost savings for programs and especially for applicants, as well as time efficiency, reduced burden of travel, and reduced carbon footprint. A problem posed by virtual interviews is that candidates are unable to fully learn institutional cultures and social environments of the programs.3 Likewise, telehealth was an important means of clinical teaching for residents during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, with benefits that included cost-effectiveness and reduction of disparities in access to dermatologic care.4 Seventy-five percent (38/51) of PDs indicated that their program plans to include telemedicine in resident clinical rotation moving forward.
Resources Available—Our survey showed that resources available for residents, delivery of lectures and program time allocated to didactics, protected academic or study time for residents, and allocation of program time for CORE examinations are highly variable across programs. This could inspire future studies to be done to determine the differences in success of the resident on CORE examinations and in digesting material.
Postgraduate Career Plans and Fellowship Matches—Residents of programs that have a home MSDO fellowship are more likely to successfully match into a MSDO fellowship.5 Based on this survey, approximately 28% of graduating residents applied to a fellowship position, with 15%, 5%, and 3% matching into desired MSDO, dermatopathology, and pediatric dermatology fellowships, respectively. Additional studies are needed to determine advantages and disadvantages that lead to residents reaching their career goals.
Limitations—Limitations of this study include a small sample size that may not adequately represent all ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs and selection bias toward respondents who are more likely to participate in survey-based research.
Conclusion
The APD plans to continue to administer this survey on an annual basis, with updates to the content and questions based on input from PDs. This survey will continue to provide valuable information to drive collaboration among residency programs and optimize the learning experience for residents. Our hope is that the response rate will increase in coming years, allowing us to draw more generalizable conclusions. Nonetheless, the survey data allow individual dermatology residency programs to compare their specific characteristics to other programs.
- Maciejko L, Cope A, Mara K, et al. A national survey of obstetrics and gynecology emergency training and deficits in office emergency preparation [A53]. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:16S. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000826548.05758.26
- Lavertue SM, Terry R. A comparison of surgical subspecialty match rates in 2022 in the United States. Cureus. 2023;15:E37178. doi:10.7759/cureus.37178
- Domingo A, Rdesinski RE, Stenson A, et al. Virtual residency interviews: applicant perceptions regarding virtual interview effectiveness, advantages, and barriers. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14:224-228. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-21-00675.1
- Rustad AM, Lio PA. Pandemic pressure: teledermatology and health care disparities. J Patient Exp. 2021;8:2374373521996982. doi:10.1177/2374373521996982
- Rickstrew J, Rajpara A, Hocker TLH. Dermatology residency program influences chance of successful surgery fellowship match. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1040-1042. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002859
- Maciejko L, Cope A, Mara K, et al. A national survey of obstetrics and gynecology emergency training and deficits in office emergency preparation [A53]. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:16S. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000826548.05758.26
- Lavertue SM, Terry R. A comparison of surgical subspecialty match rates in 2022 in the United States. Cureus. 2023;15:E37178. doi:10.7759/cureus.37178
- Domingo A, Rdesinski RE, Stenson A, et al. Virtual residency interviews: applicant perceptions regarding virtual interview effectiveness, advantages, and barriers. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14:224-228. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-21-00675.1
- Rustad AM, Lio PA. Pandemic pressure: teledermatology and health care disparities. J Patient Exp. 2021;8:2374373521996982. doi:10.1177/2374373521996982
- Rickstrew J, Rajpara A, Hocker TLH. Dermatology residency program influences chance of successful surgery fellowship match. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1040-1042. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002859
Practice Points
- The first annual Association of Professors of Dermatology program directors survey allows faculty to compare their programs to other dermatology residency programs across the United States.
- The results should inspire opportunities for growth, improvement, and collaboration among dermatology residency programs.
Going into solo practice? An expert shares tips
SAN DIEGO – When the Boston-based cosmetic dermatology practice that employed Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, MS, was sold to a private equity firm a few years ago, she found herself at a crossroads: Stay and work for a large corporation, or open a solo practice?
She opted to start her own practice in Boston, “because I didn’t want to work for a large corporation, and I want to provide the best care for my patients in a more intimate manner,” Dr. DiGiorgio, a board-certified laser and cosmetic dermatologist, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
The decision also tested her mettle. “I spoke to several colleagues and friends, and I was terrified,” she said. “I was like: ‘I don’t even know where to start.’ ”
On the heels of opening a new office in a matter of weeks, she offered the following tips and questions to consider when launching a solo dermatology practice:
Select a location. “That’s your first decision,” she said. “Where in the city are you going to open? Are you going to a new city, or are you moving back home? Don’t be afraid to start from scratch, and don’t be afraid to start a [solo] practice if you already have a patient base.”
Will you lease or purchase your space? After she secured a bank loan, Dr. DiGiorgio chose to lease the space for her new practice, “because you can kind of see where things go, get all the kinks out and figure out how to build things in a space that you don’t own. Then, when you’re ready and you have grown, you can invest more into your practice.”
Will you accept insurance? She built her practice around the direct specialty care model, which emphasizes the patient-physician relationship and removes third-party payors. “It’s not a concierge practice, but it’s a transparent, reasonable fee schedule for medical dermatology,” she explained. “I’ve done 100% cosmetics for about 5 years now, [but] I do medical dermatology for a fee. On my website I have a full price list on how much a full skin check is, [and] how much biopsies are. It’s completely transparent. Patients can submit to their insurance for reimbursement, but we don’t guarantee that they’re going to be reimbursed.”
Where will your patients come from? Will you advertise? Do you have physicians in the area who will refer to you if you’re a board-certified dermatologist? She emphasized the importance of “learning how to present yourself” on a website dedicated to your own practice. “Instagram, Facebook, and social media are great, but you don’t own those pages,” noted Dr. DiGiorgio, who served as the program cochair of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery and was recently elected to serve on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatology Surgery. “You don’t own one of those pictures that are posted on your social media page. They can disappear in a second. If that happens, how are people going to find you?”
Are you going to hire more physicians in the future? That will influence the size of the new office and the floor plan.
Lawyer up. Hiring a health care attorney can “help you navigate transitioning from whatever position you’re in to opening up your own practice, as well as setting up the regulatory paperwork necessary for your new practice. You’ll also need a real estate attorney to help once you have selected a place, to help you navigate through that process,” she said, such as figuring out if the elevator in the building meets the Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements.
Create a mission statement. That way, “you know why you’re doing this, and it stays with you as you’re getting through the hard roadblocks.”
Find an architect, contractor, or designer. “If you’re building out a space from scratch, you’re going to need an architect,” she said. “Along with that architect will come a full-on contracting firm. I ended up hiring everyone individually, because I’m trying to spend as little money as possible.” She also hired a designer to help select furnishings and create the office atmosphere.
Secure a building permit ASAP. “It’s almost better to have the city permit before you sign the lease, because the permits can take a year, and you don’t want to pay rent on an empty space for a year if you don’t have a permit or if there are other hoops to go through,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
Find an agent to help you set up medical malpractice insurance, liability insurance, and worker’s compensation insurance. “Make sure you read all the paperwork, because it can be very intricate,” she said.
Find an accountant. That person can help set up a bookkeeping process.
What equipment and devices will you need? That depends largely on the patient population a physician serves. Dr. DiGiorgio noted that eligible small businesses may take a tax credit of up to $5,000 per year for accommodations made to comply with the ADA. “That’s a nice feature, so that you can purchase ADA compliant items like a larger exam chair and custom reception areas.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – When the Boston-based cosmetic dermatology practice that employed Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, MS, was sold to a private equity firm a few years ago, she found herself at a crossroads: Stay and work for a large corporation, or open a solo practice?
She opted to start her own practice in Boston, “because I didn’t want to work for a large corporation, and I want to provide the best care for my patients in a more intimate manner,” Dr. DiGiorgio, a board-certified laser and cosmetic dermatologist, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
The decision also tested her mettle. “I spoke to several colleagues and friends, and I was terrified,” she said. “I was like: ‘I don’t even know where to start.’ ”
On the heels of opening a new office in a matter of weeks, she offered the following tips and questions to consider when launching a solo dermatology practice:
Select a location. “That’s your first decision,” she said. “Where in the city are you going to open? Are you going to a new city, or are you moving back home? Don’t be afraid to start from scratch, and don’t be afraid to start a [solo] practice if you already have a patient base.”
Will you lease or purchase your space? After she secured a bank loan, Dr. DiGiorgio chose to lease the space for her new practice, “because you can kind of see where things go, get all the kinks out and figure out how to build things in a space that you don’t own. Then, when you’re ready and you have grown, you can invest more into your practice.”
Will you accept insurance? She built her practice around the direct specialty care model, which emphasizes the patient-physician relationship and removes third-party payors. “It’s not a concierge practice, but it’s a transparent, reasonable fee schedule for medical dermatology,” she explained. “I’ve done 100% cosmetics for about 5 years now, [but] I do medical dermatology for a fee. On my website I have a full price list on how much a full skin check is, [and] how much biopsies are. It’s completely transparent. Patients can submit to their insurance for reimbursement, but we don’t guarantee that they’re going to be reimbursed.”
Where will your patients come from? Will you advertise? Do you have physicians in the area who will refer to you if you’re a board-certified dermatologist? She emphasized the importance of “learning how to present yourself” on a website dedicated to your own practice. “Instagram, Facebook, and social media are great, but you don’t own those pages,” noted Dr. DiGiorgio, who served as the program cochair of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery and was recently elected to serve on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatology Surgery. “You don’t own one of those pictures that are posted on your social media page. They can disappear in a second. If that happens, how are people going to find you?”
Are you going to hire more physicians in the future? That will influence the size of the new office and the floor plan.
Lawyer up. Hiring a health care attorney can “help you navigate transitioning from whatever position you’re in to opening up your own practice, as well as setting up the regulatory paperwork necessary for your new practice. You’ll also need a real estate attorney to help once you have selected a place, to help you navigate through that process,” she said, such as figuring out if the elevator in the building meets the Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements.
Create a mission statement. That way, “you know why you’re doing this, and it stays with you as you’re getting through the hard roadblocks.”
Find an architect, contractor, or designer. “If you’re building out a space from scratch, you’re going to need an architect,” she said. “Along with that architect will come a full-on contracting firm. I ended up hiring everyone individually, because I’m trying to spend as little money as possible.” She also hired a designer to help select furnishings and create the office atmosphere.
Secure a building permit ASAP. “It’s almost better to have the city permit before you sign the lease, because the permits can take a year, and you don’t want to pay rent on an empty space for a year if you don’t have a permit or if there are other hoops to go through,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
Find an agent to help you set up medical malpractice insurance, liability insurance, and worker’s compensation insurance. “Make sure you read all the paperwork, because it can be very intricate,” she said.
Find an accountant. That person can help set up a bookkeeping process.
What equipment and devices will you need? That depends largely on the patient population a physician serves. Dr. DiGiorgio noted that eligible small businesses may take a tax credit of up to $5,000 per year for accommodations made to comply with the ADA. “That’s a nice feature, so that you can purchase ADA compliant items like a larger exam chair and custom reception areas.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – When the Boston-based cosmetic dermatology practice that employed Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, MS, was sold to a private equity firm a few years ago, she found herself at a crossroads: Stay and work for a large corporation, or open a solo practice?
She opted to start her own practice in Boston, “because I didn’t want to work for a large corporation, and I want to provide the best care for my patients in a more intimate manner,” Dr. DiGiorgio, a board-certified laser and cosmetic dermatologist, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
The decision also tested her mettle. “I spoke to several colleagues and friends, and I was terrified,” she said. “I was like: ‘I don’t even know where to start.’ ”
On the heels of opening a new office in a matter of weeks, she offered the following tips and questions to consider when launching a solo dermatology practice:
Select a location. “That’s your first decision,” she said. “Where in the city are you going to open? Are you going to a new city, or are you moving back home? Don’t be afraid to start from scratch, and don’t be afraid to start a [solo] practice if you already have a patient base.”
Will you lease or purchase your space? After she secured a bank loan, Dr. DiGiorgio chose to lease the space for her new practice, “because you can kind of see where things go, get all the kinks out and figure out how to build things in a space that you don’t own. Then, when you’re ready and you have grown, you can invest more into your practice.”
Will you accept insurance? She built her practice around the direct specialty care model, which emphasizes the patient-physician relationship and removes third-party payors. “It’s not a concierge practice, but it’s a transparent, reasonable fee schedule for medical dermatology,” she explained. “I’ve done 100% cosmetics for about 5 years now, [but] I do medical dermatology for a fee. On my website I have a full price list on how much a full skin check is, [and] how much biopsies are. It’s completely transparent. Patients can submit to their insurance for reimbursement, but we don’t guarantee that they’re going to be reimbursed.”
Where will your patients come from? Will you advertise? Do you have physicians in the area who will refer to you if you’re a board-certified dermatologist? She emphasized the importance of “learning how to present yourself” on a website dedicated to your own practice. “Instagram, Facebook, and social media are great, but you don’t own those pages,” noted Dr. DiGiorgio, who served as the program cochair of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery and was recently elected to serve on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatology Surgery. “You don’t own one of those pictures that are posted on your social media page. They can disappear in a second. If that happens, how are people going to find you?”
Are you going to hire more physicians in the future? That will influence the size of the new office and the floor plan.
Lawyer up. Hiring a health care attorney can “help you navigate transitioning from whatever position you’re in to opening up your own practice, as well as setting up the regulatory paperwork necessary for your new practice. You’ll also need a real estate attorney to help once you have selected a place, to help you navigate through that process,” she said, such as figuring out if the elevator in the building meets the Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements.
Create a mission statement. That way, “you know why you’re doing this, and it stays with you as you’re getting through the hard roadblocks.”
Find an architect, contractor, or designer. “If you’re building out a space from scratch, you’re going to need an architect,” she said. “Along with that architect will come a full-on contracting firm. I ended up hiring everyone individually, because I’m trying to spend as little money as possible.” She also hired a designer to help select furnishings and create the office atmosphere.
Secure a building permit ASAP. “It’s almost better to have the city permit before you sign the lease, because the permits can take a year, and you don’t want to pay rent on an empty space for a year if you don’t have a permit or if there are other hoops to go through,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
Find an agent to help you set up medical malpractice insurance, liability insurance, and worker’s compensation insurance. “Make sure you read all the paperwork, because it can be very intricate,” she said.
Find an accountant. That person can help set up a bookkeeping process.
What equipment and devices will you need? That depends largely on the patient population a physician serves. Dr. DiGiorgio noted that eligible small businesses may take a tax credit of up to $5,000 per year for accommodations made to comply with the ADA. “That’s a nice feature, so that you can purchase ADA compliant items like a larger exam chair and custom reception areas.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT MOAS 2023
Optimizing Biomarker Testing in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
Over the past decade, a revolution in the treatment of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been sparked by the ongoing discovery of targetable oncogenic driver mutations. Because of the growing number of targeted therapies, comprehensive biomarker testing is essential in this patient population to determine the best individualized treatment.
Dr Thomas Stinchcombe, of Duke Cancer Institute in Durham, North Carolina, discusses the latest standards for identifying the pathology of NSCLC patients as well as the accepted sequence of treatments informed by the presence or absence of mutations. He also reports on new immunotherapy research for this patient population.
Molecular testing of tumor tissue is the standard of care for genotyping, but gathering and processing the results takes time. Dr Stinchcombe points out that liquid biopsies complement tissue testing by using a patient's blood to identify circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the plasma, helping to determine pathologic diagnosis more quickly.
--
Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Duke Cancer Institute, Durham, North Carolina
Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Consulting or Advisory Role: Janssen Oncology; Genentech/Roche; Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca; Takeda; Eisai/H3 Biomedicine; G1 Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences; AstraZeneca; Coherus BioSciences
Member of the data and safety monitoring board for: GlaxoSmithKline; Genentech/Roche
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Seagen; Mirati Therapeutics; Genentech/Roche
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Janssen Oncology; Genentech/Roche; Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca; Takeda; Eisai/H3 Biomedicine; G1 Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences; AstraZeneca; Coherus BioSciences; GlaxoSmithKline
Over the past decade, a revolution in the treatment of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been sparked by the ongoing discovery of targetable oncogenic driver mutations. Because of the growing number of targeted therapies, comprehensive biomarker testing is essential in this patient population to determine the best individualized treatment.
Dr Thomas Stinchcombe, of Duke Cancer Institute in Durham, North Carolina, discusses the latest standards for identifying the pathology of NSCLC patients as well as the accepted sequence of treatments informed by the presence or absence of mutations. He also reports on new immunotherapy research for this patient population.
Molecular testing of tumor tissue is the standard of care for genotyping, but gathering and processing the results takes time. Dr Stinchcombe points out that liquid biopsies complement tissue testing by using a patient's blood to identify circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the plasma, helping to determine pathologic diagnosis more quickly.
--
Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Duke Cancer Institute, Durham, North Carolina
Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Consulting or Advisory Role: Janssen Oncology; Genentech/Roche; Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca; Takeda; Eisai/H3 Biomedicine; G1 Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences; AstraZeneca; Coherus BioSciences
Member of the data and safety monitoring board for: GlaxoSmithKline; Genentech/Roche
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Seagen; Mirati Therapeutics; Genentech/Roche
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Janssen Oncology; Genentech/Roche; Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca; Takeda; Eisai/H3 Biomedicine; G1 Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences; AstraZeneca; Coherus BioSciences; GlaxoSmithKline
Over the past decade, a revolution in the treatment of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been sparked by the ongoing discovery of targetable oncogenic driver mutations. Because of the growing number of targeted therapies, comprehensive biomarker testing is essential in this patient population to determine the best individualized treatment.
Dr Thomas Stinchcombe, of Duke Cancer Institute in Durham, North Carolina, discusses the latest standards for identifying the pathology of NSCLC patients as well as the accepted sequence of treatments informed by the presence or absence of mutations. He also reports on new immunotherapy research for this patient population.
Molecular testing of tumor tissue is the standard of care for genotyping, but gathering and processing the results takes time. Dr Stinchcombe points out that liquid biopsies complement tissue testing by using a patient's blood to identify circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the plasma, helping to determine pathologic diagnosis more quickly.
--
Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Duke Cancer Institute, Durham, North Carolina
Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Consulting or Advisory Role: Janssen Oncology; Genentech/Roche; Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca; Takeda; Eisai/H3 Biomedicine; G1 Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences; AstraZeneca; Coherus BioSciences
Member of the data and safety monitoring board for: GlaxoSmithKline; Genentech/Roche
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Seagen; Mirati Therapeutics; Genentech/Roche
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Janssen Oncology; Genentech/Roche; Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca; Takeda; Eisai/H3 Biomedicine; G1 Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences; AstraZeneca; Coherus BioSciences; GlaxoSmithKline

Effect of COVID-19 Vaccination on Disease Severity in Patients With Stable Plaque Psoriasis: A Cross-sectional Study
To the Editor:
COVID-19 infection has resulted in 6.9 million deaths worldwide. India has the third highest mortality from COVID-19 infection after the United States and Brazil.1 Vaccination plays a crucial role in containing COVID-19 infection and reducing its severity. At present, 11 vaccines have been approved by the World Health Organization. India started its vaccination program on January 16, 2021, with approval for use of Covaxin (Bharat Biotech) and Covishield (Oxford/AstraZeneca formulation)(Serum Institute of India). More than 2 billion doses have been administered since then.2,3
Patients with psoriasis are prone to develop a severe form of COVID-19 due to comorbidities and the intake of immunosuppressive drugs.4 These patients often are hesitant to receive the vaccine without an expert opinion. COVID-19 vaccines are considered to increase tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and IFN-γ production by CD4+ T cells. Tumor necrosis factor α is a key proinflammatory cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccines induce elevation of IL-6 and helper T cells (TH17), which can induce a flare of psoriasis in a subset of patients.5The International Psoriasis Council recommends that patients with psoriasis receive one of the vaccines approved to prevent COVID-19 infection as soon as possible.6 Reports of new-onset psoriasis and flare of psoriasis after the use of COVID-19 vaccines, such as those manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca, have been published from different parts of the world.7 India used locally developed whole virion inactivated BBV152 (Covaxin) and nonreplicating viral vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Covishield) in its vaccination program and exported them to other developing countries. There is a dearth of data on the safety of these vaccines in patients with psoriasis, which needs to be assessed. Later, Covaxin, ZyCoV-D (DNA plasmid vaccine; Cadila Healthcare), and CorbeVax (protein subunit vaccine; Biological E) were approved for usage in children.8 We conducted a cross-sectional study using the direct interview method.
Patients with psoriasis who attended the outpatient department of the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (Chandigarh, India) from April 2022 to June 2022 were invited to participate in the study after written informed consent was received. Patients 18 years and older with chronic plaque psoriasis who had received a COVID-19 vaccine dose in the last 90 days were enrolled. Data on demographics, comorbidities, treatment received for psoriasis, vaccination concerns, history of COVID-19 infection, type of vaccine received with doses, adverse effects, and psoriasis flare after receiving the vaccine (considered up to 2 weeks from the date of vaccination) were collected. Ordinal logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with a psoriasis flare following vaccination. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 202 patients with chronic plaque psoriasis who received either Covaxin or Covishield were enrolled during the study period. The mean age (SD) was 40.3 (13.1) years, and 149 (73.8%) patients were male. One hundred thirty-five (66.8%) patients completed 2 doses of the vaccine. eTable 1 provides the clinicodemographic details of the patients. Eighty-three (41.1%) patients had a fear of psoriasis flare after vaccination. Seventy-two (35.6%) patients received the vaccine after clearance from their treating physician/dermatologist. One hundred sixty-four (81.2%) patients received the Covishield vaccine, and 38 (18.8%) patients received Covaxin. Eighty-three (41.1%) patients reported flulike symptoms, such as fever, myalgia, or body pain, within the first week of vaccination. Sixty-one (30.2%) patients reported a psoriasis flare after vaccination in the form of new lesions or worsening of pre-existing lesions. Of these patients, 51 reported a flare after receiving the first dose of vaccine, 8 patients reported a flare after receiving the second dose of vaccine, and 2 patients reported a flare after receiving both doses of vaccine. The mean (SD) flare onset was 8.1 (3.4) days after the vaccination. Eighteen patients considered the flare to be severe. Seventeen (8.4%) patients reported a positive history of COVID-19 infection before vaccination. None of the patients reported breakthrough COVID-19 infection or pustular aggravation of psoriasis following the vaccination.
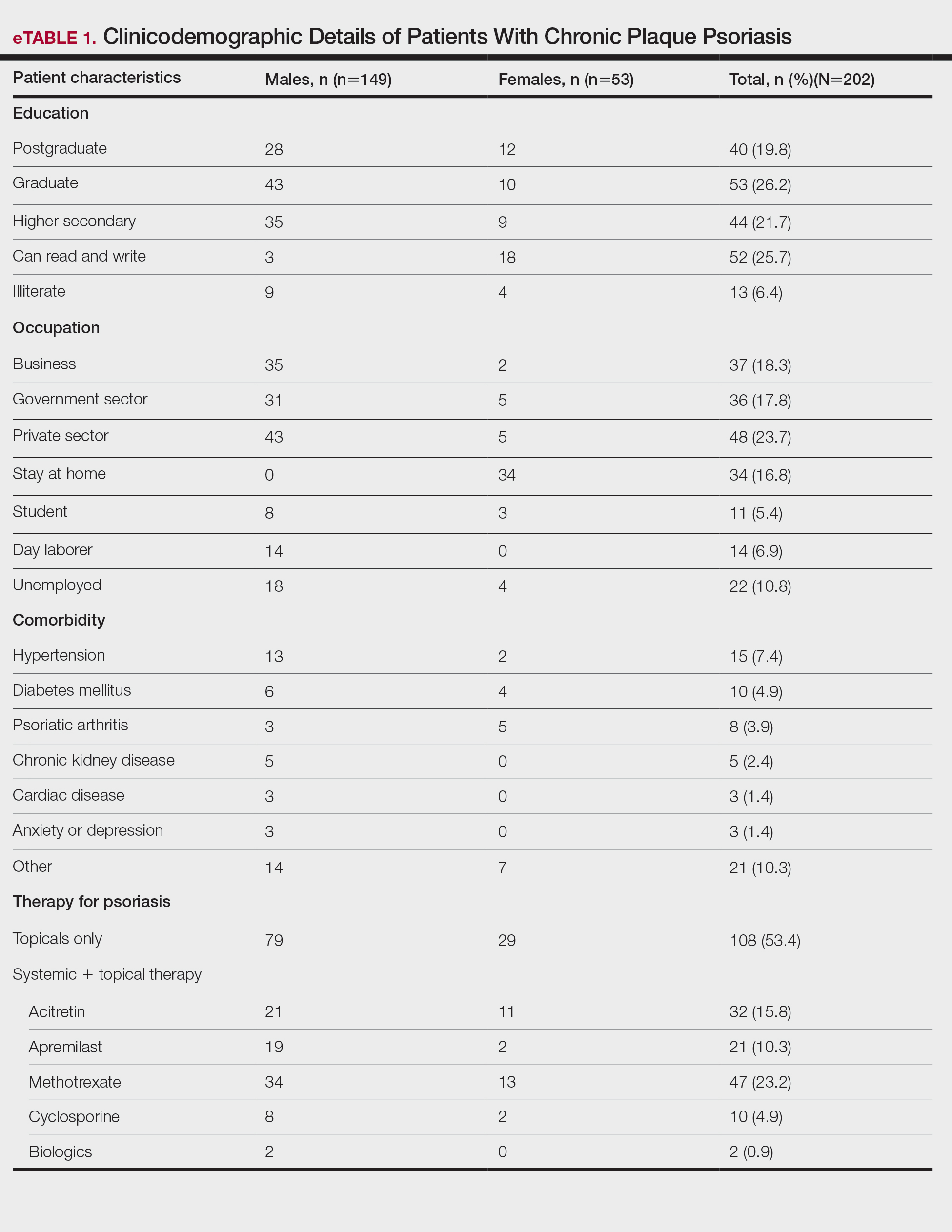
The self-reported psoriasis flare after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine was significantly higher in patients who experienced immediate adverse effects (P=.005), which included fever, myalgia, joint pain, and injection-site reaction. The reported postvaccination psoriasis flare was not significantly associated with patient sex, history of COVID-19 infection, type of vaccine received, comorbidities, or therapy for psoriasis (eTable 2).

Nearly 30% of our patients reported a postvaccination psoriasis flare, which was more common after the first vaccine dose. Sotiriou et al7 reported 14 cases of psoriasis flare in patients after receiving Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines. These patients experienced an exacerbation of disease soon after the second dose of vaccine (mean [SD], 10.36 [7.71] days), and 21% of the 713 enrolled patients wanted to forego the immunization due to concern of a postvaccination psoriasis flare.7 In another report, 14 (27%) patients developed a psoriasis flare after COVID-19 vaccination; the mean (SD) flare onset was 9.3 (4.3) days after vaccination.9
Data on the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine in patients using immunosuppressive drugs are limited. We did not find a significant association between the psoriasis flare and use of immunosuppressive drugs or type of vaccine received. Huang and Tsai9 observed similar results, with no association between psoriasis flare and use of immunosuppressive drugs or biologics, while Damiani et al10 demonstrated a protective role of biologics in preventing vaccine-induced psoriasis flare.
Similar to another study from India,11 the immediate adverse effects due to immunization with Covaxin and Covishield were mild in our study and resolved within a week. The incidence of psoriasis flare was significantly higher in patients who reported adverse effects (P=.005). Activation of immune response after vaccination leads to the release of proinflammatory and pyrogenic cytokines (ie, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α), which may explain the higher incidence of psoriasis flare in patients experiencing adverse effects to vaccination.12
Our study showed approximately 30% of patients developed a psoriasis flare after COVID-19 vaccination, with no patients experiencing any vaccine-related serious adverse events, which suggests that Covaxin and Covishield are safe for patients with psoriasis in India. Limitations of our study include potential inaccuracy of the patient’s self-assessment of symptoms and disease flare, recall bias that may lead to errors in estimating patient-reported outcomes, the flare of psoriasis potentially being a part of disease fluctuation, and flare being enhanced by the psychological stress of vaccination.
Considering a high risk for severe COVID-19 infection in patients with psoriasis with comorbidities and those using immunosuppressive drugs, Covaxin and Covishield can be safely recommended in India. However, caution needs to be exercised when vaccinating patients with an unstable disease or severe psoriasis.
- COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic: weekly trends. Worldometer. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- National COVID-19 vaccination programme meets its goals by overcoming R&D and logistical challenges, says economic survey 2022-23. Government of India Press Information Bureau website. Published January 31, 2023. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1894907
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. CoWIN. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.cowin.gov.in/
- Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, et al. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021;397:1301-1315.
- Wu D, Yang XO. TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: anemerging target of JAK2 inhibitor fedratinib. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020;53:368-370.
- International Psoriasis Council. Revised IPC statement on COVID-19. Published December 19, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://psoriasiscouncil.org/covid-19/revised-statement-covid-19/
- Sotiriou E, Tsentemeidou A, Bakirtzi K, et al. Psoriasis exacerbation after COVID-19 vaccination: a report of 14 cases from a single centre. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:E857-E859.
- Kaul R. India clears 2 vaccines for kids under 12 years. Hindustan Times. Published April 27, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-clears-2-vaccines-for-kids-under-12-years-101650998027336.html
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination: report from a single center. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:812010.
- Damiani G, Allocco F, Young Dermatologists Italian Network, et al. COVID-19 vaccination and patients with psoriasis under biologics: real-life evidence on safety and effectiveness from Italian vaccinated healthcare workers. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;460:1106-1108.
- Joshi RK, Muralidharan CG, Gulati DS, et al. Higher incidence of reported adverse events following immunisation (AEFI) after first dose of COVID-19 vaccine among previously infected health care workers. Med J Armed Forces India. 2021;77(suppl 2):S505-S507.
- Hervé C, Laupèze B, Del Giudice G, et al. The how’s and what’s of vaccine reactogenicity. NPJ Vaccines. 2019;4:39.
To the Editor:
COVID-19 infection has resulted in 6.9 million deaths worldwide. India has the third highest mortality from COVID-19 infection after the United States and Brazil.1 Vaccination plays a crucial role in containing COVID-19 infection and reducing its severity. At present, 11 vaccines have been approved by the World Health Organization. India started its vaccination program on January 16, 2021, with approval for use of Covaxin (Bharat Biotech) and Covishield (Oxford/AstraZeneca formulation)(Serum Institute of India). More than 2 billion doses have been administered since then.2,3
Patients with psoriasis are prone to develop a severe form of COVID-19 due to comorbidities and the intake of immunosuppressive drugs.4 These patients often are hesitant to receive the vaccine without an expert opinion. COVID-19 vaccines are considered to increase tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and IFN-γ production by CD4+ T cells. Tumor necrosis factor α is a key proinflammatory cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccines induce elevation of IL-6 and helper T cells (TH17), which can induce a flare of psoriasis in a subset of patients.5The International Psoriasis Council recommends that patients with psoriasis receive one of the vaccines approved to prevent COVID-19 infection as soon as possible.6 Reports of new-onset psoriasis and flare of psoriasis after the use of COVID-19 vaccines, such as those manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca, have been published from different parts of the world.7 India used locally developed whole virion inactivated BBV152 (Covaxin) and nonreplicating viral vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Covishield) in its vaccination program and exported them to other developing countries. There is a dearth of data on the safety of these vaccines in patients with psoriasis, which needs to be assessed. Later, Covaxin, ZyCoV-D (DNA plasmid vaccine; Cadila Healthcare), and CorbeVax (protein subunit vaccine; Biological E) were approved for usage in children.8 We conducted a cross-sectional study using the direct interview method.
Patients with psoriasis who attended the outpatient department of the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (Chandigarh, India) from April 2022 to June 2022 were invited to participate in the study after written informed consent was received. Patients 18 years and older with chronic plaque psoriasis who had received a COVID-19 vaccine dose in the last 90 days were enrolled. Data on demographics, comorbidities, treatment received for psoriasis, vaccination concerns, history of COVID-19 infection, type of vaccine received with doses, adverse effects, and psoriasis flare after receiving the vaccine (considered up to 2 weeks from the date of vaccination) were collected. Ordinal logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with a psoriasis flare following vaccination. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 202 patients with chronic plaque psoriasis who received either Covaxin or Covishield were enrolled during the study period. The mean age (SD) was 40.3 (13.1) years, and 149 (73.8%) patients were male. One hundred thirty-five (66.8%) patients completed 2 doses of the vaccine. eTable 1 provides the clinicodemographic details of the patients. Eighty-three (41.1%) patients had a fear of psoriasis flare after vaccination. Seventy-two (35.6%) patients received the vaccine after clearance from their treating physician/dermatologist. One hundred sixty-four (81.2%) patients received the Covishield vaccine, and 38 (18.8%) patients received Covaxin. Eighty-three (41.1%) patients reported flulike symptoms, such as fever, myalgia, or body pain, within the first week of vaccination. Sixty-one (30.2%) patients reported a psoriasis flare after vaccination in the form of new lesions or worsening of pre-existing lesions. Of these patients, 51 reported a flare after receiving the first dose of vaccine, 8 patients reported a flare after receiving the second dose of vaccine, and 2 patients reported a flare after receiving both doses of vaccine. The mean (SD) flare onset was 8.1 (3.4) days after the vaccination. Eighteen patients considered the flare to be severe. Seventeen (8.4%) patients reported a positive history of COVID-19 infection before vaccination. None of the patients reported breakthrough COVID-19 infection or pustular aggravation of psoriasis following the vaccination.

The self-reported psoriasis flare after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine was significantly higher in patients who experienced immediate adverse effects (P=.005), which included fever, myalgia, joint pain, and injection-site reaction. The reported postvaccination psoriasis flare was not significantly associated with patient sex, history of COVID-19 infection, type of vaccine received, comorbidities, or therapy for psoriasis (eTable 2).

Nearly 30% of our patients reported a postvaccination psoriasis flare, which was more common after the first vaccine dose. Sotiriou et al7 reported 14 cases of psoriasis flare in patients after receiving Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines. These patients experienced an exacerbation of disease soon after the second dose of vaccine (mean [SD], 10.36 [7.71] days), and 21% of the 713 enrolled patients wanted to forego the immunization due to concern of a postvaccination psoriasis flare.7 In another report, 14 (27%) patients developed a psoriasis flare after COVID-19 vaccination; the mean (SD) flare onset was 9.3 (4.3) days after vaccination.9
Data on the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine in patients using immunosuppressive drugs are limited. We did not find a significant association between the psoriasis flare and use of immunosuppressive drugs or type of vaccine received. Huang and Tsai9 observed similar results, with no association between psoriasis flare and use of immunosuppressive drugs or biologics, while Damiani et al10 demonstrated a protective role of biologics in preventing vaccine-induced psoriasis flare.
Similar to another study from India,11 the immediate adverse effects due to immunization with Covaxin and Covishield were mild in our study and resolved within a week. The incidence of psoriasis flare was significantly higher in patients who reported adverse effects (P=.005). Activation of immune response after vaccination leads to the release of proinflammatory and pyrogenic cytokines (ie, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α), which may explain the higher incidence of psoriasis flare in patients experiencing adverse effects to vaccination.12
Our study showed approximately 30% of patients developed a psoriasis flare after COVID-19 vaccination, with no patients experiencing any vaccine-related serious adverse events, which suggests that Covaxin and Covishield are safe for patients with psoriasis in India. Limitations of our study include potential inaccuracy of the patient’s self-assessment of symptoms and disease flare, recall bias that may lead to errors in estimating patient-reported outcomes, the flare of psoriasis potentially being a part of disease fluctuation, and flare being enhanced by the psychological stress of vaccination.
Considering a high risk for severe COVID-19 infection in patients with psoriasis with comorbidities and those using immunosuppressive drugs, Covaxin and Covishield can be safely recommended in India. However, caution needs to be exercised when vaccinating patients with an unstable disease or severe psoriasis.
To the Editor:
COVID-19 infection has resulted in 6.9 million deaths worldwide. India has the third highest mortality from COVID-19 infection after the United States and Brazil.1 Vaccination plays a crucial role in containing COVID-19 infection and reducing its severity. At present, 11 vaccines have been approved by the World Health Organization. India started its vaccination program on January 16, 2021, with approval for use of Covaxin (Bharat Biotech) and Covishield (Oxford/AstraZeneca formulation)(Serum Institute of India). More than 2 billion doses have been administered since then.2,3
Patients with psoriasis are prone to develop a severe form of COVID-19 due to comorbidities and the intake of immunosuppressive drugs.4 These patients often are hesitant to receive the vaccine without an expert opinion. COVID-19 vaccines are considered to increase tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and IFN-γ production by CD4+ T cells. Tumor necrosis factor α is a key proinflammatory cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccines induce elevation of IL-6 and helper T cells (TH17), which can induce a flare of psoriasis in a subset of patients.5The International Psoriasis Council recommends that patients with psoriasis receive one of the vaccines approved to prevent COVID-19 infection as soon as possible.6 Reports of new-onset psoriasis and flare of psoriasis after the use of COVID-19 vaccines, such as those manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca, have been published from different parts of the world.7 India used locally developed whole virion inactivated BBV152 (Covaxin) and nonreplicating viral vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Covishield) in its vaccination program and exported them to other developing countries. There is a dearth of data on the safety of these vaccines in patients with psoriasis, which needs to be assessed. Later, Covaxin, ZyCoV-D (DNA plasmid vaccine; Cadila Healthcare), and CorbeVax (protein subunit vaccine; Biological E) were approved for usage in children.8 We conducted a cross-sectional study using the direct interview method.
Patients with psoriasis who attended the outpatient department of the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (Chandigarh, India) from April 2022 to June 2022 were invited to participate in the study after written informed consent was received. Patients 18 years and older with chronic plaque psoriasis who had received a COVID-19 vaccine dose in the last 90 days were enrolled. Data on demographics, comorbidities, treatment received for psoriasis, vaccination concerns, history of COVID-19 infection, type of vaccine received with doses, adverse effects, and psoriasis flare after receiving the vaccine (considered up to 2 weeks from the date of vaccination) were collected. Ordinal logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with a psoriasis flare following vaccination. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 202 patients with chronic plaque psoriasis who received either Covaxin or Covishield were enrolled during the study period. The mean age (SD) was 40.3 (13.1) years, and 149 (73.8%) patients were male. One hundred thirty-five (66.8%) patients completed 2 doses of the vaccine. eTable 1 provides the clinicodemographic details of the patients. Eighty-three (41.1%) patients had a fear of psoriasis flare after vaccination. Seventy-two (35.6%) patients received the vaccine after clearance from their treating physician/dermatologist. One hundred sixty-four (81.2%) patients received the Covishield vaccine, and 38 (18.8%) patients received Covaxin. Eighty-three (41.1%) patients reported flulike symptoms, such as fever, myalgia, or body pain, within the first week of vaccination. Sixty-one (30.2%) patients reported a psoriasis flare after vaccination in the form of new lesions or worsening of pre-existing lesions. Of these patients, 51 reported a flare after receiving the first dose of vaccine, 8 patients reported a flare after receiving the second dose of vaccine, and 2 patients reported a flare after receiving both doses of vaccine. The mean (SD) flare onset was 8.1 (3.4) days after the vaccination. Eighteen patients considered the flare to be severe. Seventeen (8.4%) patients reported a positive history of COVID-19 infection before vaccination. None of the patients reported breakthrough COVID-19 infection or pustular aggravation of psoriasis following the vaccination.

The self-reported psoriasis flare after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine was significantly higher in patients who experienced immediate adverse effects (P=.005), which included fever, myalgia, joint pain, and injection-site reaction. The reported postvaccination psoriasis flare was not significantly associated with patient sex, history of COVID-19 infection, type of vaccine received, comorbidities, or therapy for psoriasis (eTable 2).

Nearly 30% of our patients reported a postvaccination psoriasis flare, which was more common after the first vaccine dose. Sotiriou et al7 reported 14 cases of psoriasis flare in patients after receiving Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines. These patients experienced an exacerbation of disease soon after the second dose of vaccine (mean [SD], 10.36 [7.71] days), and 21% of the 713 enrolled patients wanted to forego the immunization due to concern of a postvaccination psoriasis flare.7 In another report, 14 (27%) patients developed a psoriasis flare after COVID-19 vaccination; the mean (SD) flare onset was 9.3 (4.3) days after vaccination.9
Data on the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine in patients using immunosuppressive drugs are limited. We did not find a significant association between the psoriasis flare and use of immunosuppressive drugs or type of vaccine received. Huang and Tsai9 observed similar results, with no association between psoriasis flare and use of immunosuppressive drugs or biologics, while Damiani et al10 demonstrated a protective role of biologics in preventing vaccine-induced psoriasis flare.
Similar to another study from India,11 the immediate adverse effects due to immunization with Covaxin and Covishield were mild in our study and resolved within a week. The incidence of psoriasis flare was significantly higher in patients who reported adverse effects (P=.005). Activation of immune response after vaccination leads to the release of proinflammatory and pyrogenic cytokines (ie, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α), which may explain the higher incidence of psoriasis flare in patients experiencing adverse effects to vaccination.12
Our study showed approximately 30% of patients developed a psoriasis flare after COVID-19 vaccination, with no patients experiencing any vaccine-related serious adverse events, which suggests that Covaxin and Covishield are safe for patients with psoriasis in India. Limitations of our study include potential inaccuracy of the patient’s self-assessment of symptoms and disease flare, recall bias that may lead to errors in estimating patient-reported outcomes, the flare of psoriasis potentially being a part of disease fluctuation, and flare being enhanced by the psychological stress of vaccination.
Considering a high risk for severe COVID-19 infection in patients with psoriasis with comorbidities and those using immunosuppressive drugs, Covaxin and Covishield can be safely recommended in India. However, caution needs to be exercised when vaccinating patients with an unstable disease or severe psoriasis.
- COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic: weekly trends. Worldometer. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- National COVID-19 vaccination programme meets its goals by overcoming R&D and logistical challenges, says economic survey 2022-23. Government of India Press Information Bureau website. Published January 31, 2023. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1894907
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. CoWIN. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.cowin.gov.in/
- Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, et al. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021;397:1301-1315.
- Wu D, Yang XO. TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: anemerging target of JAK2 inhibitor fedratinib. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020;53:368-370.
- International Psoriasis Council. Revised IPC statement on COVID-19. Published December 19, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://psoriasiscouncil.org/covid-19/revised-statement-covid-19/
- Sotiriou E, Tsentemeidou A, Bakirtzi K, et al. Psoriasis exacerbation after COVID-19 vaccination: a report of 14 cases from a single centre. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:E857-E859.
- Kaul R. India clears 2 vaccines for kids under 12 years. Hindustan Times. Published April 27, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-clears-2-vaccines-for-kids-under-12-years-101650998027336.html
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination: report from a single center. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:812010.
- Damiani G, Allocco F, Young Dermatologists Italian Network, et al. COVID-19 vaccination and patients with psoriasis under biologics: real-life evidence on safety and effectiveness from Italian vaccinated healthcare workers. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;460:1106-1108.
- Joshi RK, Muralidharan CG, Gulati DS, et al. Higher incidence of reported adverse events following immunisation (AEFI) after first dose of COVID-19 vaccine among previously infected health care workers. Med J Armed Forces India. 2021;77(suppl 2):S505-S507.
- Hervé C, Laupèze B, Del Giudice G, et al. The how’s and what’s of vaccine reactogenicity. NPJ Vaccines. 2019;4:39.
- COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic: weekly trends. Worldometer. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- National COVID-19 vaccination programme meets its goals by overcoming R&D and logistical challenges, says economic survey 2022-23. Government of India Press Information Bureau website. Published January 31, 2023. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1894907
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. CoWIN. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.cowin.gov.in/
- Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, et al. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021;397:1301-1315.
- Wu D, Yang XO. TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: anemerging target of JAK2 inhibitor fedratinib. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020;53:368-370.
- International Psoriasis Council. Revised IPC statement on COVID-19. Published December 19, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://psoriasiscouncil.org/covid-19/revised-statement-covid-19/
- Sotiriou E, Tsentemeidou A, Bakirtzi K, et al. Psoriasis exacerbation after COVID-19 vaccination: a report of 14 cases from a single centre. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:E857-E859.
- Kaul R. India clears 2 vaccines for kids under 12 years. Hindustan Times. Published April 27, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2023. https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-clears-2-vaccines-for-kids-under-12-years-101650998027336.html
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. Exacerbation of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccination: report from a single center. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:812010.
- Damiani G, Allocco F, Young Dermatologists Italian Network, et al. COVID-19 vaccination and patients with psoriasis under biologics: real-life evidence on safety and effectiveness from Italian vaccinated healthcare workers. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;460:1106-1108.
- Joshi RK, Muralidharan CG, Gulati DS, et al. Higher incidence of reported adverse events following immunisation (AEFI) after first dose of COVID-19 vaccine among previously infected health care workers. Med J Armed Forces India. 2021;77(suppl 2):S505-S507.
- Hervé C, Laupèze B, Del Giudice G, et al. The how’s and what’s of vaccine reactogenicity. NPJ Vaccines. 2019;4:39.
Practice Points
- Vaccines are known to induce a psoriasis flare.
- Given the high risk for severe COVID infection in individuals with psoriasis who have comorbidities, vaccination with Covaxin and Covishield can be safely recommended in India for this population.
What’s Eating You? Tropical Rat Mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti)
The tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) belongs to the family Macronyssidae. Theses mites are commonly mistaken for red bird mites or Nordic bird mites because they belong to the same family and have similar characteristics.1 Although O bacoti is called the tropical rat mite, it also can be found in moderate climates.2,3
Characteristics
The life cycle of a tropical rat mite lasts 11 to 13 days and includes 5 stages: egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph, and adult.1,2 The length of the mite (0.3–0.7 mm) varies with the stage of development.1 Adults can reach 0.75 to 1.40 mm, with females larger than males and possibly visible with the naked eye.1,2
Two or 3 days after a blood meal, the female mite lays approximately 100 eggs in its nest but not on the surface of a host. The eggs hatch into larvae after 1 to 4 days and go on to complete their life cyle.1 During developmental stages, mites occupy their hosts for blood meals. Mites search for their hosts at night and prefer wild or pet rodents for blood meals but are not host specific and can be found on many mammals including birds, cats, racoons, and squirrels.4
Although tropical rat mites prefer rodent hosts, they can infest humans when their preferred host is unavailable. In the United States, the first case of human dermatitis due to a tropical rate mite occurred in 1923. In Europe, rat mite dermatitis was first reported in a human in 1931, possibly due to contamination of sailing vessels.4
Infestation and Transmission
Tropical rat mites prefer wild and pet rodents as hosts because the mites are able to feed on their blood over long periods.4 During the day, the mite spends most of its time hiding in dark dry spaces; it is most active during the night, traveling to find a host for meals.3-5 If a preferred host is not present, the mite may choose to infest a human.5
Human infestation occurs most often upon close bodily contact with an infected animal or pet rodent that was sold without parasites having been eliminated.3-5 Mites are able to survive without a host for as long as 6 months; they may travel after a meal.1,2 Therefore, individuals who do not have a pet rodent can be infested if an infected wild rodent has infested their living space.1,3-5
Clinical Presentation of Infestation
Patients infested with tropical rat mites present with pruritic cutaneous lesions, most often on unclothed parts of the body that are easily exposed to mites; lesions rarely occur on the scalp.5 People of any age or gender can be infested. Rat mite bites can present as single or grouped, pruritic, erythematous papules ranging in size from 4 to 10 mm in diameter.5-7 Excoriations may be present due to excessive scratching. Although rare, vesicles or nodules have been reported.5,7
Diagnosis of the underlying cause of the cutaneous manifestations often is difficult because mites are not visible during the day, as they are less active then.2 Lesions often are misdiagnosed as an allergic response, a bacterial infection, or various forms of dermatitis.1 A parasitic cause often is not considered unless the physician or patient detects a mite or many trials of therapies fail to provide relief.1,3-5 Eliciting a thorough history may disclose that the patient has had close contact with rodents or lives in a community center, shelter, or shared space. If any of the patient’s close contacts have a similar presentation, infestation with mites should be considered.
Treatment and Prevention
Patients should be educated about treatment options and measures that need to be taken to prevent reinfection. It has been reported that tropical rat mites can survive without a blood meal for as long as 6 months; therefore, meticulous inspection and decontamination of all living spaces is required.1,4 Once identified, physicians may prescribe an antiparasitic such as permethrin or pyriproxyfen to prevent further infestation and eliminate mites on the host.5 Lindane and benzyl benzoate previously were reported to be effective but should be prescribed only in correctly diagnosed cases due to the potential adverse effects of both therapies.4,7-10 For effective treatment, physicians should thoroughly review the proper application of topical treatments with patients. Topical creams should be massaged into the skin from the head to the soles of the feet, covering all creases of the skin and between the fingers and toes. Antiparasitic creams should be left on the skin for 8 to 14 hours, and all members of the household should be examined and treated, if necessary, by a physician. A thorough bath removes tropical rat mites, but preventive measures should be taken to prevent reinfestation.4 Antihistamines or glucocorticoids also can be used as symptomatic treatment.6,8
Avoiding Reinfestation—Preventive measures should be taken to prevent reinfestation, including evaluation by an exterminator for any wild rodents to remove nests and treat the living space with an acaricide.5 Insecticides administered by exterminators, including malathion, methyl carbamate, and lindane, also have been reported to be effective for preventing reinfestation.5,7-9 A veterinarian should be consulted if the patient owns any pets to ensure proper identification of any potential tropical rat mites and treatments that may be necessary for any household pets.1
Case Report
A 68-year-old man presented to the dermatology outpatient clinic with diffuse pruritus of the skin and scalp. He reported no other symptoms and had never had a total-body skin examination. His primary care physician recently prescribed a dose pack of methylprednisolone 4-mg tablets, which relieved the symptoms except for a mild scalp itch. His wife did not experience itching, and he denied noticing mites or fleas on his pet dog. Physical examination did not reveal any contributory findings, such as erythema or rash. Ketoconazole shampoo 2% and fluocinolone solution 0.01% were prescribed for scalp pruritus; however, he could not afford those medications and therefore did not take them.
Two weeks later, the patient presented with diffuse itching that involved the scalp, trunk, and extremities. He denied groin pruritus. He reported that the itching was worse at night. His wife continued to be asymptomatic. The patient reported that his health screening was up-to-date, and he had no interval health changes. A complete blood cell count, thyroid studies, and a comprehensive metabolic panel performed recently were within reference range. He denied recent travel or taking new medications. Physical examination revealed a somewhat linear distribution of erythematous urticarial papules on the right side of the abdomen. Red dermatographic excoriations were noted on the back. No burrows were visualized. He was given intramuscular triamcinolone 60 mg and was advised to have his house evaluated for bed bugs and his pet dog evaluated by a veterinarian for mites. During the triamcinolone injection, the medical assistant observed a 1- to 2-mm red insect, which fell into his clothing and could not be further evaluated.
After 1 month, the patient had no improvement of the pruritus; instead, it became worse. During this time, his wife developed intermittent urticarial-like eruptions. He was taking oral diphenhydramine nightly and applying triamcinolone cream 0.5% that he had at home from an earlier skin problem as needed. Physical examination findings correlated with worsening symptoms. He had multiple erythematous urticarial papules—many of which were excoriated—across the chest, abdomen, buttocks, and back. The arms had multiple excoriations. The urticarial papules coalesced in the anterior axillary folds, yet no burrows were visualized. In the left anterior axillary fold adjacent to one of the urticarial papules, a 1-mm mobile mite was identified on dermoscopy. Further evaluation by microscopy showed morphologic characteristics of a tropical rat mite (Figure). The patient admitted that his house had a mouse infestation that he was struggling to eliminate. Permethrin cream 5% was prescribed. Because the patient could not afford the prescription, he was advised to use the triamcinolone cream 0.5%and oral diphenhydramine that he had at home nightly for symptomatic relief. He was advised to hire an exterminator to eradicate the mouse and mite infestation to prevent reinfestation.
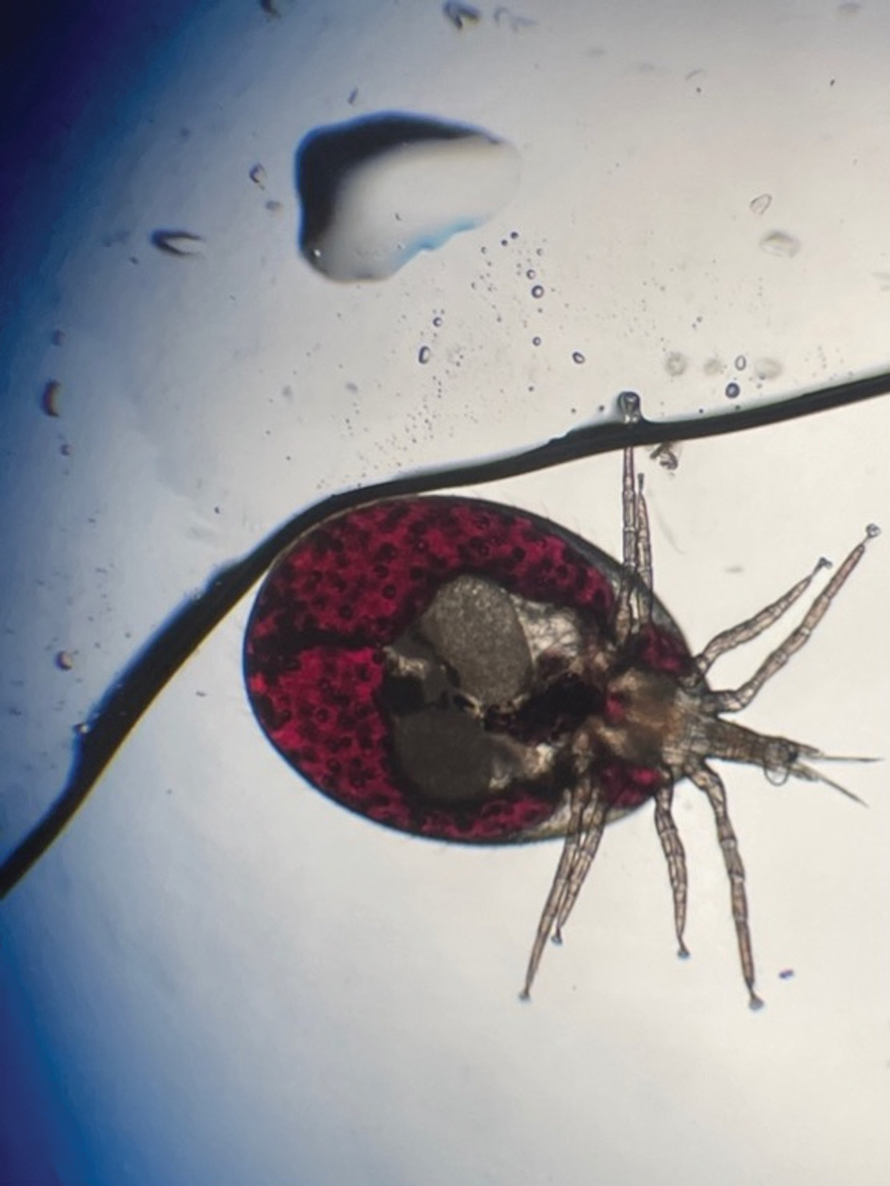

Identification of Rate Mite Dermatitis
The characteristics of tropical rat mite dermatitis can be confused with many other conditions, such as infection. Even when a mite is identified, it can be difficult to classify it as a tropical rat mite. To confirm the diagnosis of tropical rat mite dermatitis, the parasite needs to be identified. Skin scrapings can be collected from pruritic lesions and examined microscopically in the hope of revealing the rat mites. The recommendation is to collect skin scrapings from the dorsal aspect of the hands or from the neck.5 Patients may report finding mites in their living space or on their bedding or clothing.
Although the tropical rat mite was reported as a vector for endemic typhus between humans, no other cases of transmission between humans have been reported since.11,12 Studies reporting non–human subject research and case reports have shown that O bacoti is a vector for Rickettsia akari, Coxiella burnetii, Francisella tularensis, Yersinia pestis, Eastern equine encephalitis virus (Alphavirus), Enterovirus (Picornaviridae), Langat virus (Flavivirus), and Hantaan orthohantavirus.5,11-17 However, no cases of these infectious diseases being transmitted naturally have been reported.5
Confirmation of O bacoti as a vector for human pathogens is difficult because it relies on identification of the mite in the clinic.5 The epidemiologic importance of the mite in transmitting infectious disease is unknown; reports of human cases of mite infestation are rare. We present this information to increase awareness and help dermatologists and other health care providers identify O bacoti.
- Beck W, Fölster-Holst R. Tropical rat mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti)—serious ectoparasites. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2009;7:667-670. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2009.07140.x
- Baumstark J, Beck W, Hofmann H. Outbreak of tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) dermatitis in a home for disabled persons. Dermatology. 2007;215:66-68. doi:10.1159/000102037
- Beck W. Occurrence of a house-infesting tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) on murides and human beings. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2008;6:245-249. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2008.01.002
- Beck W. Tropical rat mites as newly emerging disease pathogens in rodents and man. Trav Med Infect Dis. 2007;5:403. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2007.09.016
- Engel PM, Welzel J, Maass M, et al. Tropical rat mite dermatitis: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:1465-1469. doi:10.1086/515016
- Hetherington GW, Holder WR, Smith EB. Rat mite dermatitis. JAMA. 1971;215:1499-1500.
- Fox JG. Outbreak of tropical rat mite dermatitis in laboratory personnel. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:676-678. doi:10.1001/archderm.1982.01650210056019
- Fishman HC. Rat mite dermatitis. Cutis. 1988;42:414-416.
- Ram SM, Satija KC, Kaushik RK. Ornithonyssus bacoti infestation in laboratory personnel and veterinary students. Int J Zoonoses. 1986;13:138-140.
- Brown S, Becher J, Brady W. Treatment of ectoparasitic infections: review of the English-language literature, 1982-1992. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20(suppl 1):S104-S109. doi:10.1093/clinids/20.supplement_1.s104
- Reeves WK, Loftis AD, Szumlas DE, et al. Rickettsial pathogens in the tropical rat mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Egyptian rats (Rattus spp.). Exp Appl Acarol. 2007;41:101-107. doi:10.1007/s10493-006-9040-3
- Philip CB, Hughes LE. The tropical rat mite; Liponyssus bacoti, as an experimental vector of rickettsialpox. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1948;28:697-705. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1948.s1-28.697
- Zemskaia AA, Pchelkina AA. Experimental infection of ticks Dermanyssus gallinae Redi Bdellonyssus bacoti Hirst with Q fever. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1955;101:391-392.
- Hopla CE. Experimental transmission of tularemia by the tropical rat mite. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1951;31:768-783. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.768
- Clark GM, Lutz AE, Fadnessl. Observations on the ability of Haemogamasus liponyssoides Ewing and Ornithonyssus bacoti (Hirst) (Acarina, Gamasina) to retain eastern equine encephalitis virus: preliminary report. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966;15:107-112. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.107
- Schwab M, Allen R, Sulkin SE. The tropical rat mite (Liponyssus bacoti) as an experimental vector of Coxsackie virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1952;1:982-986. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1952.1.982
- Durden LA, Turell MJ. Inefficient mechanical transmission of Langat (tick-borne encephalitis virus complex) virus by blood-feeding mites (Acari) to laboratory mice. J Med Entomol. 1993;30:639-641. doi:10.1093/jmedent/30.3.639
The tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) belongs to the family Macronyssidae. Theses mites are commonly mistaken for red bird mites or Nordic bird mites because they belong to the same family and have similar characteristics.1 Although O bacoti is called the tropical rat mite, it also can be found in moderate climates.2,3
Characteristics
The life cycle of a tropical rat mite lasts 11 to 13 days and includes 5 stages: egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph, and adult.1,2 The length of the mite (0.3–0.7 mm) varies with the stage of development.1 Adults can reach 0.75 to 1.40 mm, with females larger than males and possibly visible with the naked eye.1,2
Two or 3 days after a blood meal, the female mite lays approximately 100 eggs in its nest but not on the surface of a host. The eggs hatch into larvae after 1 to 4 days and go on to complete their life cyle.1 During developmental stages, mites occupy their hosts for blood meals. Mites search for their hosts at night and prefer wild or pet rodents for blood meals but are not host specific and can be found on many mammals including birds, cats, racoons, and squirrels.4
Although tropical rat mites prefer rodent hosts, they can infest humans when their preferred host is unavailable. In the United States, the first case of human dermatitis due to a tropical rate mite occurred in 1923. In Europe, rat mite dermatitis was first reported in a human in 1931, possibly due to contamination of sailing vessels.4
Infestation and Transmission
Tropical rat mites prefer wild and pet rodents as hosts because the mites are able to feed on their blood over long periods.4 During the day, the mite spends most of its time hiding in dark dry spaces; it is most active during the night, traveling to find a host for meals.3-5 If a preferred host is not present, the mite may choose to infest a human.5
Human infestation occurs most often upon close bodily contact with an infected animal or pet rodent that was sold without parasites having been eliminated.3-5 Mites are able to survive without a host for as long as 6 months; they may travel after a meal.1,2 Therefore, individuals who do not have a pet rodent can be infested if an infected wild rodent has infested their living space.1,3-5
Clinical Presentation of Infestation
Patients infested with tropical rat mites present with pruritic cutaneous lesions, most often on unclothed parts of the body that are easily exposed to mites; lesions rarely occur on the scalp.5 People of any age or gender can be infested. Rat mite bites can present as single or grouped, pruritic, erythematous papules ranging in size from 4 to 10 mm in diameter.5-7 Excoriations may be present due to excessive scratching. Although rare, vesicles or nodules have been reported.5,7
Diagnosis of the underlying cause of the cutaneous manifestations often is difficult because mites are not visible during the day, as they are less active then.2 Lesions often are misdiagnosed as an allergic response, a bacterial infection, or various forms of dermatitis.1 A parasitic cause often is not considered unless the physician or patient detects a mite or many trials of therapies fail to provide relief.1,3-5 Eliciting a thorough history may disclose that the patient has had close contact with rodents or lives in a community center, shelter, or shared space. If any of the patient’s close contacts have a similar presentation, infestation with mites should be considered.
Treatment and Prevention
Patients should be educated about treatment options and measures that need to be taken to prevent reinfection. It has been reported that tropical rat mites can survive without a blood meal for as long as 6 months; therefore, meticulous inspection and decontamination of all living spaces is required.1,4 Once identified, physicians may prescribe an antiparasitic such as permethrin or pyriproxyfen to prevent further infestation and eliminate mites on the host.5 Lindane and benzyl benzoate previously were reported to be effective but should be prescribed only in correctly diagnosed cases due to the potential adverse effects of both therapies.4,7-10 For effective treatment, physicians should thoroughly review the proper application of topical treatments with patients. Topical creams should be massaged into the skin from the head to the soles of the feet, covering all creases of the skin and between the fingers and toes. Antiparasitic creams should be left on the skin for 8 to 14 hours, and all members of the household should be examined and treated, if necessary, by a physician. A thorough bath removes tropical rat mites, but preventive measures should be taken to prevent reinfestation.4 Antihistamines or glucocorticoids also can be used as symptomatic treatment.6,8
Avoiding Reinfestation—Preventive measures should be taken to prevent reinfestation, including evaluation by an exterminator for any wild rodents to remove nests and treat the living space with an acaricide.5 Insecticides administered by exterminators, including malathion, methyl carbamate, and lindane, also have been reported to be effective for preventing reinfestation.5,7-9 A veterinarian should be consulted if the patient owns any pets to ensure proper identification of any potential tropical rat mites and treatments that may be necessary for any household pets.1
Case Report
A 68-year-old man presented to the dermatology outpatient clinic with diffuse pruritus of the skin and scalp. He reported no other symptoms and had never had a total-body skin examination. His primary care physician recently prescribed a dose pack of methylprednisolone 4-mg tablets, which relieved the symptoms except for a mild scalp itch. His wife did not experience itching, and he denied noticing mites or fleas on his pet dog. Physical examination did not reveal any contributory findings, such as erythema or rash. Ketoconazole shampoo 2% and fluocinolone solution 0.01% were prescribed for scalp pruritus; however, he could not afford those medications and therefore did not take them.
Two weeks later, the patient presented with diffuse itching that involved the scalp, trunk, and extremities. He denied groin pruritus. He reported that the itching was worse at night. His wife continued to be asymptomatic. The patient reported that his health screening was up-to-date, and he had no interval health changes. A complete blood cell count, thyroid studies, and a comprehensive metabolic panel performed recently were within reference range. He denied recent travel or taking new medications. Physical examination revealed a somewhat linear distribution of erythematous urticarial papules on the right side of the abdomen. Red dermatographic excoriations were noted on the back. No burrows were visualized. He was given intramuscular triamcinolone 60 mg and was advised to have his house evaluated for bed bugs and his pet dog evaluated by a veterinarian for mites. During the triamcinolone injection, the medical assistant observed a 1- to 2-mm red insect, which fell into his clothing and could not be further evaluated.
After 1 month, the patient had no improvement of the pruritus; instead, it became worse. During this time, his wife developed intermittent urticarial-like eruptions. He was taking oral diphenhydramine nightly and applying triamcinolone cream 0.5% that he had at home from an earlier skin problem as needed. Physical examination findings correlated with worsening symptoms. He had multiple erythematous urticarial papules—many of which were excoriated—across the chest, abdomen, buttocks, and back. The arms had multiple excoriations. The urticarial papules coalesced in the anterior axillary folds, yet no burrows were visualized. In the left anterior axillary fold adjacent to one of the urticarial papules, a 1-mm mobile mite was identified on dermoscopy. Further evaluation by microscopy showed morphologic characteristics of a tropical rat mite (Figure). The patient admitted that his house had a mouse infestation that he was struggling to eliminate. Permethrin cream 5% was prescribed. Because the patient could not afford the prescription, he was advised to use the triamcinolone cream 0.5%and oral diphenhydramine that he had at home nightly for symptomatic relief. He was advised to hire an exterminator to eradicate the mouse and mite infestation to prevent reinfestation.

Identification of Rate Mite Dermatitis
The characteristics of tropical rat mite dermatitis can be confused with many other conditions, such as infection. Even when a mite is identified, it can be difficult to classify it as a tropical rat mite. To confirm the diagnosis of tropical rat mite dermatitis, the parasite needs to be identified. Skin scrapings can be collected from pruritic lesions and examined microscopically in the hope of revealing the rat mites. The recommendation is to collect skin scrapings from the dorsal aspect of the hands or from the neck.5 Patients may report finding mites in their living space or on their bedding or clothing.
Although the tropical rat mite was reported as a vector for endemic typhus between humans, no other cases of transmission between humans have been reported since.11,12 Studies reporting non–human subject research and case reports have shown that O bacoti is a vector for Rickettsia akari, Coxiella burnetii, Francisella tularensis, Yersinia pestis, Eastern equine encephalitis virus (Alphavirus), Enterovirus (Picornaviridae), Langat virus (Flavivirus), and Hantaan orthohantavirus.5,11-17 However, no cases of these infectious diseases being transmitted naturally have been reported.5
Confirmation of O bacoti as a vector for human pathogens is difficult because it relies on identification of the mite in the clinic.5 The epidemiologic importance of the mite in transmitting infectious disease is unknown; reports of human cases of mite infestation are rare. We present this information to increase awareness and help dermatologists and other health care providers identify O bacoti.
The tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) belongs to the family Macronyssidae. Theses mites are commonly mistaken for red bird mites or Nordic bird mites because they belong to the same family and have similar characteristics.1 Although O bacoti is called the tropical rat mite, it also can be found in moderate climates.2,3
Characteristics
The life cycle of a tropical rat mite lasts 11 to 13 days and includes 5 stages: egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph, and adult.1,2 The length of the mite (0.3–0.7 mm) varies with the stage of development.1 Adults can reach 0.75 to 1.40 mm, with females larger than males and possibly visible with the naked eye.1,2
Two or 3 days after a blood meal, the female mite lays approximately 100 eggs in its nest but not on the surface of a host. The eggs hatch into larvae after 1 to 4 days and go on to complete their life cyle.1 During developmental stages, mites occupy their hosts for blood meals. Mites search for their hosts at night and prefer wild or pet rodents for blood meals but are not host specific and can be found on many mammals including birds, cats, racoons, and squirrels.4
Although tropical rat mites prefer rodent hosts, they can infest humans when their preferred host is unavailable. In the United States, the first case of human dermatitis due to a tropical rate mite occurred in 1923. In Europe, rat mite dermatitis was first reported in a human in 1931, possibly due to contamination of sailing vessels.4
Infestation and Transmission
Tropical rat mites prefer wild and pet rodents as hosts because the mites are able to feed on their blood over long periods.4 During the day, the mite spends most of its time hiding in dark dry spaces; it is most active during the night, traveling to find a host for meals.3-5 If a preferred host is not present, the mite may choose to infest a human.5
Human infestation occurs most often upon close bodily contact with an infected animal or pet rodent that was sold without parasites having been eliminated.3-5 Mites are able to survive without a host for as long as 6 months; they may travel after a meal.1,2 Therefore, individuals who do not have a pet rodent can be infested if an infected wild rodent has infested their living space.1,3-5
Clinical Presentation of Infestation
Patients infested with tropical rat mites present with pruritic cutaneous lesions, most often on unclothed parts of the body that are easily exposed to mites; lesions rarely occur on the scalp.5 People of any age or gender can be infested. Rat mite bites can present as single or grouped, pruritic, erythematous papules ranging in size from 4 to 10 mm in diameter.5-7 Excoriations may be present due to excessive scratching. Although rare, vesicles or nodules have been reported.5,7
Diagnosis of the underlying cause of the cutaneous manifestations often is difficult because mites are not visible during the day, as they are less active then.2 Lesions often are misdiagnosed as an allergic response, a bacterial infection, or various forms of dermatitis.1 A parasitic cause often is not considered unless the physician or patient detects a mite or many trials of therapies fail to provide relief.1,3-5 Eliciting a thorough history may disclose that the patient has had close contact with rodents or lives in a community center, shelter, or shared space. If any of the patient’s close contacts have a similar presentation, infestation with mites should be considered.
Treatment and Prevention
Patients should be educated about treatment options and measures that need to be taken to prevent reinfection. It has been reported that tropical rat mites can survive without a blood meal for as long as 6 months; therefore, meticulous inspection and decontamination of all living spaces is required.1,4 Once identified, physicians may prescribe an antiparasitic such as permethrin or pyriproxyfen to prevent further infestation and eliminate mites on the host.5 Lindane and benzyl benzoate previously were reported to be effective but should be prescribed only in correctly diagnosed cases due to the potential adverse effects of both therapies.4,7-10 For effective treatment, physicians should thoroughly review the proper application of topical treatments with patients. Topical creams should be massaged into the skin from the head to the soles of the feet, covering all creases of the skin and between the fingers and toes. Antiparasitic creams should be left on the skin for 8 to 14 hours, and all members of the household should be examined and treated, if necessary, by a physician. A thorough bath removes tropical rat mites, but preventive measures should be taken to prevent reinfestation.4 Antihistamines or glucocorticoids also can be used as symptomatic treatment.6,8
Avoiding Reinfestation—Preventive measures should be taken to prevent reinfestation, including evaluation by an exterminator for any wild rodents to remove nests and treat the living space with an acaricide.5 Insecticides administered by exterminators, including malathion, methyl carbamate, and lindane, also have been reported to be effective for preventing reinfestation.5,7-9 A veterinarian should be consulted if the patient owns any pets to ensure proper identification of any potential tropical rat mites and treatments that may be necessary for any household pets.1
Case Report
A 68-year-old man presented to the dermatology outpatient clinic with diffuse pruritus of the skin and scalp. He reported no other symptoms and had never had a total-body skin examination. His primary care physician recently prescribed a dose pack of methylprednisolone 4-mg tablets, which relieved the symptoms except for a mild scalp itch. His wife did not experience itching, and he denied noticing mites or fleas on his pet dog. Physical examination did not reveal any contributory findings, such as erythema or rash. Ketoconazole shampoo 2% and fluocinolone solution 0.01% were prescribed for scalp pruritus; however, he could not afford those medications and therefore did not take them.
Two weeks later, the patient presented with diffuse itching that involved the scalp, trunk, and extremities. He denied groin pruritus. He reported that the itching was worse at night. His wife continued to be asymptomatic. The patient reported that his health screening was up-to-date, and he had no interval health changes. A complete blood cell count, thyroid studies, and a comprehensive metabolic panel performed recently were within reference range. He denied recent travel or taking new medications. Physical examination revealed a somewhat linear distribution of erythematous urticarial papules on the right side of the abdomen. Red dermatographic excoriations were noted on the back. No burrows were visualized. He was given intramuscular triamcinolone 60 mg and was advised to have his house evaluated for bed bugs and his pet dog evaluated by a veterinarian for mites. During the triamcinolone injection, the medical assistant observed a 1- to 2-mm red insect, which fell into his clothing and could not be further evaluated.
After 1 month, the patient had no improvement of the pruritus; instead, it became worse. During this time, his wife developed intermittent urticarial-like eruptions. He was taking oral diphenhydramine nightly and applying triamcinolone cream 0.5% that he had at home from an earlier skin problem as needed. Physical examination findings correlated with worsening symptoms. He had multiple erythematous urticarial papules—many of which were excoriated—across the chest, abdomen, buttocks, and back. The arms had multiple excoriations. The urticarial papules coalesced in the anterior axillary folds, yet no burrows were visualized. In the left anterior axillary fold adjacent to one of the urticarial papules, a 1-mm mobile mite was identified on dermoscopy. Further evaluation by microscopy showed morphologic characteristics of a tropical rat mite (Figure). The patient admitted that his house had a mouse infestation that he was struggling to eliminate. Permethrin cream 5% was prescribed. Because the patient could not afford the prescription, he was advised to use the triamcinolone cream 0.5%and oral diphenhydramine that he had at home nightly for symptomatic relief. He was advised to hire an exterminator to eradicate the mouse and mite infestation to prevent reinfestation.

Identification of Rate Mite Dermatitis
The characteristics of tropical rat mite dermatitis can be confused with many other conditions, such as infection. Even when a mite is identified, it can be difficult to classify it as a tropical rat mite. To confirm the diagnosis of tropical rat mite dermatitis, the parasite needs to be identified. Skin scrapings can be collected from pruritic lesions and examined microscopically in the hope of revealing the rat mites. The recommendation is to collect skin scrapings from the dorsal aspect of the hands or from the neck.5 Patients may report finding mites in their living space or on their bedding or clothing.
Although the tropical rat mite was reported as a vector for endemic typhus between humans, no other cases of transmission between humans have been reported since.11,12 Studies reporting non–human subject research and case reports have shown that O bacoti is a vector for Rickettsia akari, Coxiella burnetii, Francisella tularensis, Yersinia pestis, Eastern equine encephalitis virus (Alphavirus), Enterovirus (Picornaviridae), Langat virus (Flavivirus), and Hantaan orthohantavirus.5,11-17 However, no cases of these infectious diseases being transmitted naturally have been reported.5
Confirmation of O bacoti as a vector for human pathogens is difficult because it relies on identification of the mite in the clinic.5 The epidemiologic importance of the mite in transmitting infectious disease is unknown; reports of human cases of mite infestation are rare. We present this information to increase awareness and help dermatologists and other health care providers identify O bacoti.
- Beck W, Fölster-Holst R. Tropical rat mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti)—serious ectoparasites. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2009;7:667-670. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2009.07140.x
- Baumstark J, Beck W, Hofmann H. Outbreak of tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) dermatitis in a home for disabled persons. Dermatology. 2007;215:66-68. doi:10.1159/000102037
- Beck W. Occurrence of a house-infesting tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) on murides and human beings. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2008;6:245-249. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2008.01.002
- Beck W. Tropical rat mites as newly emerging disease pathogens in rodents and man. Trav Med Infect Dis. 2007;5:403. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2007.09.016
- Engel PM, Welzel J, Maass M, et al. Tropical rat mite dermatitis: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:1465-1469. doi:10.1086/515016
- Hetherington GW, Holder WR, Smith EB. Rat mite dermatitis. JAMA. 1971;215:1499-1500.
- Fox JG. Outbreak of tropical rat mite dermatitis in laboratory personnel. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:676-678. doi:10.1001/archderm.1982.01650210056019
- Fishman HC. Rat mite dermatitis. Cutis. 1988;42:414-416.
- Ram SM, Satija KC, Kaushik RK. Ornithonyssus bacoti infestation in laboratory personnel and veterinary students. Int J Zoonoses. 1986;13:138-140.
- Brown S, Becher J, Brady W. Treatment of ectoparasitic infections: review of the English-language literature, 1982-1992. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20(suppl 1):S104-S109. doi:10.1093/clinids/20.supplement_1.s104
- Reeves WK, Loftis AD, Szumlas DE, et al. Rickettsial pathogens in the tropical rat mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Egyptian rats (Rattus spp.). Exp Appl Acarol. 2007;41:101-107. doi:10.1007/s10493-006-9040-3
- Philip CB, Hughes LE. The tropical rat mite; Liponyssus bacoti, as an experimental vector of rickettsialpox. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1948;28:697-705. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1948.s1-28.697
- Zemskaia AA, Pchelkina AA. Experimental infection of ticks Dermanyssus gallinae Redi Bdellonyssus bacoti Hirst with Q fever. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1955;101:391-392.
- Hopla CE. Experimental transmission of tularemia by the tropical rat mite. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1951;31:768-783. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.768
- Clark GM, Lutz AE, Fadnessl. Observations on the ability of Haemogamasus liponyssoides Ewing and Ornithonyssus bacoti (Hirst) (Acarina, Gamasina) to retain eastern equine encephalitis virus: preliminary report. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966;15:107-112. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.107
- Schwab M, Allen R, Sulkin SE. The tropical rat mite (Liponyssus bacoti) as an experimental vector of Coxsackie virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1952;1:982-986. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1952.1.982
- Durden LA, Turell MJ. Inefficient mechanical transmission of Langat (tick-borne encephalitis virus complex) virus by blood-feeding mites (Acari) to laboratory mice. J Med Entomol. 1993;30:639-641. doi:10.1093/jmedent/30.3.639
- Beck W, Fölster-Holst R. Tropical rat mites (Ornithonyssus bacoti)—serious ectoparasites. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2009;7:667-670. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2009.07140.x
- Baumstark J, Beck W, Hofmann H. Outbreak of tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) dermatitis in a home for disabled persons. Dermatology. 2007;215:66-68. doi:10.1159/000102037
- Beck W. Occurrence of a house-infesting tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) on murides and human beings. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2008;6:245-249. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2008.01.002
- Beck W. Tropical rat mites as newly emerging disease pathogens in rodents and man. Trav Med Infect Dis. 2007;5:403. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2007.09.016
- Engel PM, Welzel J, Maass M, et al. Tropical rat mite dermatitis: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:1465-1469. doi:10.1086/515016
- Hetherington GW, Holder WR, Smith EB. Rat mite dermatitis. JAMA. 1971;215:1499-1500.
- Fox JG. Outbreak of tropical rat mite dermatitis in laboratory personnel. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:676-678. doi:10.1001/archderm.1982.01650210056019
- Fishman HC. Rat mite dermatitis. Cutis. 1988;42:414-416.
- Ram SM, Satija KC, Kaushik RK. Ornithonyssus bacoti infestation in laboratory personnel and veterinary students. Int J Zoonoses. 1986;13:138-140.
- Brown S, Becher J, Brady W. Treatment of ectoparasitic infections: review of the English-language literature, 1982-1992. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20(suppl 1):S104-S109. doi:10.1093/clinids/20.supplement_1.s104
- Reeves WK, Loftis AD, Szumlas DE, et al. Rickettsial pathogens in the tropical rat mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Egyptian rats (Rattus spp.). Exp Appl Acarol. 2007;41:101-107. doi:10.1007/s10493-006-9040-3
- Philip CB, Hughes LE. The tropical rat mite; Liponyssus bacoti, as an experimental vector of rickettsialpox. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1948;28:697-705. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1948.s1-28.697
- Zemskaia AA, Pchelkina AA. Experimental infection of ticks Dermanyssus gallinae Redi Bdellonyssus bacoti Hirst with Q fever. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1955;101:391-392.
- Hopla CE. Experimental transmission of tularemia by the tropical rat mite. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1951;31:768-783. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.768
- Clark GM, Lutz AE, Fadnessl. Observations on the ability of Haemogamasus liponyssoides Ewing and Ornithonyssus bacoti (Hirst) (Acarina, Gamasina) to retain eastern equine encephalitis virus: preliminary report. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966;15:107-112. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.107
- Schwab M, Allen R, Sulkin SE. The tropical rat mite (Liponyssus bacoti) as an experimental vector of Coxsackie virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1952;1:982-986. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1952.1.982
- Durden LA, Turell MJ. Inefficient mechanical transmission of Langat (tick-borne encephalitis virus complex) virus by blood-feeding mites (Acari) to laboratory mice. J Med Entomol. 1993;30:639-641. doi:10.1093/jmedent/30.3.639
Practice Points
- The tropical rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) can infest humans who make bodily contact with a rodent, reside in living spaces infested with rodents, or own any pets.
- Patients infested with rat mites may present with pruritic, erythematous, cutaneous lesions with secondary excoriations that can be mistaken for an infection or dermatitis.
- The recommended treatment of rate mite infestation includes antiparasitic medications such as permethrin or pyriproxyfen. Preventive measures include proper disinfestation of living spaces.