User login
Can Vitamin D Prevent Acute Respiratory Infections?

Ms. M, a generally healthy 55-year-old woman, was diagnosed recently with severe vitamin D deficiency (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] level of 8 ng/mL). She presents with her second episode of acute viral bronchitis in the past 6 months. She has no history of significant smoking or exposure or history of asthma and does not take respiratory medications. Standard treatment for her level of vitamin D deficiency is 50,000 IU/wk in bolus dosing—but is that your best option for the patient?
ARTIs include nonspecific upper respiratory illnesses, otitis media, sinusitis (~70% viral), pharyngitis, acute bronchitis (also ~70% viral), influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and pneumonia.1,2 In the United States, ARTIs strain the health care system and are the most common reason for ambulatory care visits, accounting for almost 120 million (about 10% of all) visits per year.3 In addition, ARTIs account for almost 50% of antibiotic prescriptions for adults and almost 75% of antibiotic prescriptions for children—many of which are unnecessary.2,4
While patient and parent education, antibiotic stewardship programs, and demand management may reduce inappropriate antibiotic use and the overall burden of ARTIs on the health care system, prevention of infections is a powerful tool within the overall approach to managing ARTIs.
STUDY SUMMARY
Vitamin D is protective in smaller doses
This 2017 systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 trials (N = 10,933) evaluated vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of ARTIs in the primary care setting. Individual participant data were reevaluated to reduce risk for bias. The Cochrane risk-for-bias tool was used to address threats to validity.
The study included institutional review board–approved, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D3 or D2 supplementation of any duration and in any language. The incidence of ARTI was a prespecified efficacy outcome. Duration of the included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) ranged from 7 weeks to 1.5 years.
Outcomes. The primary outcome was an incidence of at least 1 ARTI. Secondary outcomes included incidence of upper and lower ARTIs; incidence of adverse reactions to vitamin D; incidence of emergency department visits or hospital admission or both for ARTI; use of antimicrobials for ARTI; absence from work or school due to ARTI; and mortality (ARTI-related and all-cause).
Findings. Daily or weekly vitamin D supplementation (in doses ranging from < 20 to ≥ 50 µg/d) reduced the risk for ARTI (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.88; number needed to treat [NNT], 33). In subgroup analysis, daily or weekly vitamin D was protective (AOR, 0.81), but bolus dosing (≥ 30,000 IU) was not (AOR, 0.97).
In 2-step analysis, patients benefited if they had baseline circulating 25(OH)D concentrations < 10 ng/mL (AOR, 0.30; NNT, 4); had baseline circulating 25(OH)D levels of 10 to 28 ng/mL (AOR, 0.75; NNT, 15); were ages 1.1 to 15.9 (AOR, 0.59); were ages 16 to 65 (AOR, 0.79); or had a BMI < 25 (AOR, 0.82).
Higher D levels are a different story. Vitamin D supplementation in people with circulating levels of 25(OH)D ≥ 30 ng/mL did not appear to provide benefit (AOR, 0.96). Supplementation in this population did not influence any of the secondary outcomes, including risk for all-cause serious adverse events (AOR, 0.98).
WHAT’S NEW
A more accurate snapshot
Previous studies of vitamin D and respiratory tract infections were mostly observational in nature. Those that were RCTs used variable doses of vitamin D, had variable baseline 25(OH)D levels, and employed various methods to monitor ARTI symptoms/incidence.5-8 This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with supplementation using vitamin D3 or D2 that used individual participant-level data, which gives a more accurate estimate of outcomes when compared with traditional meta-analyses.
CAVEATS
Only the most deficient benefit?
Vitamin D supplementation was safe and protected against ARTIs overall, but the greatest effect was noted in those who were most severely vitamin D deficient (those with circulating 25(OH)D levels < 10 ng/mL [NNT, 4] and those with circulating 25(OH)D levels 10-28 ng/mL [NNT, 15]). There was no demonstrable effect once circulating 25(OH)D levels reached 30 ng/mL.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Breaking tradition
The study found that both daily and weekly doses of vitamin D were effective in reducing the incidence of ARTIs. However, the doses studied were much lower than those commonly used (10,000 to 50,000 IU bolus), which were ineffective in reducing ARTIs in this meta-analysis. Changing from bolus dosing may prove challenging, a
In addition, the authors of the study suggest that one way to provide this level of vitamin D is through food fortification. But this method is often complicated by emotional and/or political issues that could thwart implementation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2019. The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
Reprinted with permission from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network and The Journal of Family Practice (2019;68[4]:230-231).
1. Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2017;356:i6583.
2. Renati S, Linder JA. Necessity of office visits for acute respiratory infections in primary care. Fam Pract. 2016,33:312-317.
3. CDC National Center for Health Statistics. National Health Care Surveys. www.cdc.gov/nchs/dhcs.htm. Accessed September 5, 2019.
4. Grijalva CG, Nuorti JP, Griffin MR. Antibiotic prescription rates for acute respiratory tract infections in US ambulatory settings. JAMA. 2009;302:758-766.
5. Rees JR, Hendricks K, Barry EL, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation and upper respiratory tract infections in a randomized, controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1384-1392.
6. Murdoch DR, Slow S, Chambers ST, et al. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on upper respiratory tract infections in healthy adults: the VIDARIS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308:1333-1339.
7. Laaksi I, Ruohola J-P, Mattila V, et al. Vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of acute respiratory tract infection: a randomized, double-blinded trial among young Finnish men. Infect Dis. 2010;202:809-814.
8. Bergman P, Norlin A-C, Hansen S, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation in patients with frequent respiratory tract infections: a randomised and double-blind intervention study. BMJ Open. 2012;2:e001663.

Ms. M, a generally healthy 55-year-old woman, was diagnosed recently with severe vitamin D deficiency (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] level of 8 ng/mL). She presents with her second episode of acute viral bronchitis in the past 6 months. She has no history of significant smoking or exposure or history of asthma and does not take respiratory medications. Standard treatment for her level of vitamin D deficiency is 50,000 IU/wk in bolus dosing—but is that your best option for the patient?
ARTIs include nonspecific upper respiratory illnesses, otitis media, sinusitis (~70% viral), pharyngitis, acute bronchitis (also ~70% viral), influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and pneumonia.1,2 In the United States, ARTIs strain the health care system and are the most common reason for ambulatory care visits, accounting for almost 120 million (about 10% of all) visits per year.3 In addition, ARTIs account for almost 50% of antibiotic prescriptions for adults and almost 75% of antibiotic prescriptions for children—many of which are unnecessary.2,4
While patient and parent education, antibiotic stewardship programs, and demand management may reduce inappropriate antibiotic use and the overall burden of ARTIs on the health care system, prevention of infections is a powerful tool within the overall approach to managing ARTIs.
STUDY SUMMARY
Vitamin D is protective in smaller doses
This 2017 systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 trials (N = 10,933) evaluated vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of ARTIs in the primary care setting. Individual participant data were reevaluated to reduce risk for bias. The Cochrane risk-for-bias tool was used to address threats to validity.
The study included institutional review board–approved, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D3 or D2 supplementation of any duration and in any language. The incidence of ARTI was a prespecified efficacy outcome. Duration of the included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) ranged from 7 weeks to 1.5 years.
Outcomes. The primary outcome was an incidence of at least 1 ARTI. Secondary outcomes included incidence of upper and lower ARTIs; incidence of adverse reactions to vitamin D; incidence of emergency department visits or hospital admission or both for ARTI; use of antimicrobials for ARTI; absence from work or school due to ARTI; and mortality (ARTI-related and all-cause).
Findings. Daily or weekly vitamin D supplementation (in doses ranging from < 20 to ≥ 50 µg/d) reduced the risk for ARTI (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.88; number needed to treat [NNT], 33). In subgroup analysis, daily or weekly vitamin D was protective (AOR, 0.81), but bolus dosing (≥ 30,000 IU) was not (AOR, 0.97).
In 2-step analysis, patients benefited if they had baseline circulating 25(OH)D concentrations < 10 ng/mL (AOR, 0.30; NNT, 4); had baseline circulating 25(OH)D levels of 10 to 28 ng/mL (AOR, 0.75; NNT, 15); were ages 1.1 to 15.9 (AOR, 0.59); were ages 16 to 65 (AOR, 0.79); or had a BMI < 25 (AOR, 0.82).
Higher D levels are a different story. Vitamin D supplementation in people with circulating levels of 25(OH)D ≥ 30 ng/mL did not appear to provide benefit (AOR, 0.96). Supplementation in this population did not influence any of the secondary outcomes, including risk for all-cause serious adverse events (AOR, 0.98).
WHAT’S NEW
A more accurate snapshot
Previous studies of vitamin D and respiratory tract infections were mostly observational in nature. Those that were RCTs used variable doses of vitamin D, had variable baseline 25(OH)D levels, and employed various methods to monitor ARTI symptoms/incidence.5-8 This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with supplementation using vitamin D3 or D2 that used individual participant-level data, which gives a more accurate estimate of outcomes when compared with traditional meta-analyses.
CAVEATS
Only the most deficient benefit?
Vitamin D supplementation was safe and protected against ARTIs overall, but the greatest effect was noted in those who were most severely vitamin D deficient (those with circulating 25(OH)D levels < 10 ng/mL [NNT, 4] and those with circulating 25(OH)D levels 10-28 ng/mL [NNT, 15]). There was no demonstrable effect once circulating 25(OH)D levels reached 30 ng/mL.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Breaking tradition
The study found that both daily and weekly doses of vitamin D were effective in reducing the incidence of ARTIs. However, the doses studied were much lower than those commonly used (10,000 to 50,000 IU bolus), which were ineffective in reducing ARTIs in this meta-analysis. Changing from bolus dosing may prove challenging, a
In addition, the authors of the study suggest that one way to provide this level of vitamin D is through food fortification. But this method is often complicated by emotional and/or political issues that could thwart implementation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2019. The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
Reprinted with permission from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network and The Journal of Family Practice (2019;68[4]:230-231).

Ms. M, a generally healthy 55-year-old woman, was diagnosed recently with severe vitamin D deficiency (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] level of 8 ng/mL). She presents with her second episode of acute viral bronchitis in the past 6 months. She has no history of significant smoking or exposure or history of asthma and does not take respiratory medications. Standard treatment for her level of vitamin D deficiency is 50,000 IU/wk in bolus dosing—but is that your best option for the patient?
ARTIs include nonspecific upper respiratory illnesses, otitis media, sinusitis (~70% viral), pharyngitis, acute bronchitis (also ~70% viral), influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and pneumonia.1,2 In the United States, ARTIs strain the health care system and are the most common reason for ambulatory care visits, accounting for almost 120 million (about 10% of all) visits per year.3 In addition, ARTIs account for almost 50% of antibiotic prescriptions for adults and almost 75% of antibiotic prescriptions for children—many of which are unnecessary.2,4
While patient and parent education, antibiotic stewardship programs, and demand management may reduce inappropriate antibiotic use and the overall burden of ARTIs on the health care system, prevention of infections is a powerful tool within the overall approach to managing ARTIs.
STUDY SUMMARY
Vitamin D is protective in smaller doses
This 2017 systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 trials (N = 10,933) evaluated vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of ARTIs in the primary care setting. Individual participant data were reevaluated to reduce risk for bias. The Cochrane risk-for-bias tool was used to address threats to validity.
The study included institutional review board–approved, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D3 or D2 supplementation of any duration and in any language. The incidence of ARTI was a prespecified efficacy outcome. Duration of the included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) ranged from 7 weeks to 1.5 years.
Outcomes. The primary outcome was an incidence of at least 1 ARTI. Secondary outcomes included incidence of upper and lower ARTIs; incidence of adverse reactions to vitamin D; incidence of emergency department visits or hospital admission or both for ARTI; use of antimicrobials for ARTI; absence from work or school due to ARTI; and mortality (ARTI-related and all-cause).
Findings. Daily or weekly vitamin D supplementation (in doses ranging from < 20 to ≥ 50 µg/d) reduced the risk for ARTI (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.88; number needed to treat [NNT], 33). In subgroup analysis, daily or weekly vitamin D was protective (AOR, 0.81), but bolus dosing (≥ 30,000 IU) was not (AOR, 0.97).
In 2-step analysis, patients benefited if they had baseline circulating 25(OH)D concentrations < 10 ng/mL (AOR, 0.30; NNT, 4); had baseline circulating 25(OH)D levels of 10 to 28 ng/mL (AOR, 0.75; NNT, 15); were ages 1.1 to 15.9 (AOR, 0.59); were ages 16 to 65 (AOR, 0.79); or had a BMI < 25 (AOR, 0.82).
Higher D levels are a different story. Vitamin D supplementation in people with circulating levels of 25(OH)D ≥ 30 ng/mL did not appear to provide benefit (AOR, 0.96). Supplementation in this population did not influence any of the secondary outcomes, including risk for all-cause serious adverse events (AOR, 0.98).
WHAT’S NEW
A more accurate snapshot
Previous studies of vitamin D and respiratory tract infections were mostly observational in nature. Those that were RCTs used variable doses of vitamin D, had variable baseline 25(OH)D levels, and employed various methods to monitor ARTI symptoms/incidence.5-8 This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with supplementation using vitamin D3 or D2 that used individual participant-level data, which gives a more accurate estimate of outcomes when compared with traditional meta-analyses.
CAVEATS
Only the most deficient benefit?
Vitamin D supplementation was safe and protected against ARTIs overall, but the greatest effect was noted in those who were most severely vitamin D deficient (those with circulating 25(OH)D levels < 10 ng/mL [NNT, 4] and those with circulating 25(OH)D levels 10-28 ng/mL [NNT, 15]). There was no demonstrable effect once circulating 25(OH)D levels reached 30 ng/mL.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Breaking tradition
The study found that both daily and weekly doses of vitamin D were effective in reducing the incidence of ARTIs. However, the doses studied were much lower than those commonly used (10,000 to 50,000 IU bolus), which were ineffective in reducing ARTIs in this meta-analysis. Changing from bolus dosing may prove challenging, a
In addition, the authors of the study suggest that one way to provide this level of vitamin D is through food fortification. But this method is often complicated by emotional and/or political issues that could thwart implementation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2019. The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
Reprinted with permission from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network and The Journal of Family Practice (2019;68[4]:230-231).
1. Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2017;356:i6583.
2. Renati S, Linder JA. Necessity of office visits for acute respiratory infections in primary care. Fam Pract. 2016,33:312-317.
3. CDC National Center for Health Statistics. National Health Care Surveys. www.cdc.gov/nchs/dhcs.htm. Accessed September 5, 2019.
4. Grijalva CG, Nuorti JP, Griffin MR. Antibiotic prescription rates for acute respiratory tract infections in US ambulatory settings. JAMA. 2009;302:758-766.
5. Rees JR, Hendricks K, Barry EL, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation and upper respiratory tract infections in a randomized, controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1384-1392.
6. Murdoch DR, Slow S, Chambers ST, et al. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on upper respiratory tract infections in healthy adults: the VIDARIS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308:1333-1339.
7. Laaksi I, Ruohola J-P, Mattila V, et al. Vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of acute respiratory tract infection: a randomized, double-blinded trial among young Finnish men. Infect Dis. 2010;202:809-814.
8. Bergman P, Norlin A-C, Hansen S, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation in patients with frequent respiratory tract infections: a randomised and double-blind intervention study. BMJ Open. 2012;2:e001663.
1. Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2017;356:i6583.
2. Renati S, Linder JA. Necessity of office visits for acute respiratory infections in primary care. Fam Pract. 2016,33:312-317.
3. CDC National Center for Health Statistics. National Health Care Surveys. www.cdc.gov/nchs/dhcs.htm. Accessed September 5, 2019.
4. Grijalva CG, Nuorti JP, Griffin MR. Antibiotic prescription rates for acute respiratory tract infections in US ambulatory settings. JAMA. 2009;302:758-766.
5. Rees JR, Hendricks K, Barry EL, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation and upper respiratory tract infections in a randomized, controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1384-1392.
6. Murdoch DR, Slow S, Chambers ST, et al. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on upper respiratory tract infections in healthy adults: the VIDARIS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308:1333-1339.
7. Laaksi I, Ruohola J-P, Mattila V, et al. Vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of acute respiratory tract infection: a randomized, double-blinded trial among young Finnish men. Infect Dis. 2010;202:809-814.
8. Bergman P, Norlin A-C, Hansen S, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation in patients with frequent respiratory tract infections: a randomised and double-blind intervention study. BMJ Open. 2012;2:e001663.
Oral drug for postpartum depression aces phase 3 trial
COPENHAGEN – A first-in-class, once-daily, orally administered neuroactive steroid known for now as SAGE-217 aced all of its primary and secondary outcomes for the treatment of postpartum depression in the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ROBIN study, Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD, said at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“I think this changes the paradigm in the treatment of postpartum depression,” declared Dr. Vieta, professor of psychiatry and head of the bipolar disorders program at the University of Barcelona.
Like brexanolone (Zulresso), an intravenous formulation of allopregnanolone approved by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2019 as the first-ever drug specifically targeting postpartum depression, SAGE-217 is a positive allosteric modifier of synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA-A receptors. That differentiates the two drugs from benzodiazepines, which target only synaptic receptors. Both brexanolone and SAGE-217 are drugs developed by Sage Therapeutics. But SAGE-217, an investigational agent, is vastly more convenient to use than brexanolone since, as an oral drug, it doesn’t require hospitalization for intravenous administration.
Dr. Vieta ticked off five reasons why he considers SAGE-217 a game changer in the treatment of postpartum depression: “It’s an amazingly effective compound, with an effect size that’s bigger than we usually see with antidepressants. It has an early onset of action, similar to what we see with glutaminergic agents, although with an opposite mechanism: enhancing GABA rather than opposing glutamate. It has excellent tolerability, similar to placebo. It’s made to be used orally, a major advantage over other drugs that are available or close to becoming available, which have to be given IV. And last but not least, a patient will get it for only 2 weeks. The treatment can be stopped after 2 weeks, and there is long-term improvement.”
The ROBIN trial included 151 patients with postpartum depression as defined by a baseline Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score of at least 26 who were randomized double-blind to 14 days of SAGE-217 at 30 mg once daily or to placebo. The primary endpoint was the change in HAM-D scores between baseline and day 15. The key finding was that the SAGE-217 group averaged a 17.8-point reduction, significantly greater than the 13.6-point improvement with placebo. This advantage was maintained at assessment on day 45 – a full month after treatment stopped – with a 24.8-point improvement over baseline in the SAGE-217 recipients, compared with a 19-point reduction in controls. The advantage favoring SAGE-217 was significant as early as day 3, the first assessment, at which point the average improvement in HAM-D was 12.5 points, compared with 9.8 points in controls.
Other secondary endpoints included change from baseline to day 15 on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS): a 22.8-point improvement in the SAGE-217 group, significantly greater than the 17.6-point improvement in the placebo arm. The same pattern was evident at day 45, with reductions in MADRS of 24.8 and 19 points, respectively, in the SAGE-217 and placebo groups.
Another key prespecified secondary endpoint was change in scores on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety through day 15. There was a mean 16.6-point drop in the active treatment arm, compared with a 12.7-point improvement with placebo, again a statistically significant and clinically meaningful between-group difference. This is an important endpoint because comorbid anxiety is common in the setting of postpartum depression, the psychiatrist continued.
The SAGE-217 group also demonstrated significantly higher rates of HAM-D response as defined by a 50% or greater reduction in total score at day 15, as well as in HAM-D remission, which entails having a score of 7 or less.
Treatment-emergent adverse events in the SAGE-217 and placebo arms were similar in frequency and type. The most common adverse events associated with SAGE-217 – all occurring in single-digit frequencies – were sleepiness, headache, dizziness, upper respiratory infections, and diarrhea. There was no signal of increased suicidal thoughts or behavior as assessed using the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
SAGE-217 also is the focus of an ongoing pivotal phase 3 trial in patients with major depression. In addition, the drug is under study for bipolar depression, major depressive disorder with comorbid insomnia, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Dr. Vieta reported serving on advisory boards for Sage Therapeutics, the study sponsor, as well as for two dozen other pharmaceutical companies. He receives research funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education, the Stanley Medical Research Institute, and more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
COPENHAGEN – A first-in-class, once-daily, orally administered neuroactive steroid known for now as SAGE-217 aced all of its primary and secondary outcomes for the treatment of postpartum depression in the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ROBIN study, Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD, said at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“I think this changes the paradigm in the treatment of postpartum depression,” declared Dr. Vieta, professor of psychiatry and head of the bipolar disorders program at the University of Barcelona.
Like brexanolone (Zulresso), an intravenous formulation of allopregnanolone approved by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2019 as the first-ever drug specifically targeting postpartum depression, SAGE-217 is a positive allosteric modifier of synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA-A receptors. That differentiates the two drugs from benzodiazepines, which target only synaptic receptors. Both brexanolone and SAGE-217 are drugs developed by Sage Therapeutics. But SAGE-217, an investigational agent, is vastly more convenient to use than brexanolone since, as an oral drug, it doesn’t require hospitalization for intravenous administration.
Dr. Vieta ticked off five reasons why he considers SAGE-217 a game changer in the treatment of postpartum depression: “It’s an amazingly effective compound, with an effect size that’s bigger than we usually see with antidepressants. It has an early onset of action, similar to what we see with glutaminergic agents, although with an opposite mechanism: enhancing GABA rather than opposing glutamate. It has excellent tolerability, similar to placebo. It’s made to be used orally, a major advantage over other drugs that are available or close to becoming available, which have to be given IV. And last but not least, a patient will get it for only 2 weeks. The treatment can be stopped after 2 weeks, and there is long-term improvement.”
The ROBIN trial included 151 patients with postpartum depression as defined by a baseline Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score of at least 26 who were randomized double-blind to 14 days of SAGE-217 at 30 mg once daily or to placebo. The primary endpoint was the change in HAM-D scores between baseline and day 15. The key finding was that the SAGE-217 group averaged a 17.8-point reduction, significantly greater than the 13.6-point improvement with placebo. This advantage was maintained at assessment on day 45 – a full month after treatment stopped – with a 24.8-point improvement over baseline in the SAGE-217 recipients, compared with a 19-point reduction in controls. The advantage favoring SAGE-217 was significant as early as day 3, the first assessment, at which point the average improvement in HAM-D was 12.5 points, compared with 9.8 points in controls.
Other secondary endpoints included change from baseline to day 15 on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS): a 22.8-point improvement in the SAGE-217 group, significantly greater than the 17.6-point improvement in the placebo arm. The same pattern was evident at day 45, with reductions in MADRS of 24.8 and 19 points, respectively, in the SAGE-217 and placebo groups.
Another key prespecified secondary endpoint was change in scores on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety through day 15. There was a mean 16.6-point drop in the active treatment arm, compared with a 12.7-point improvement with placebo, again a statistically significant and clinically meaningful between-group difference. This is an important endpoint because comorbid anxiety is common in the setting of postpartum depression, the psychiatrist continued.
The SAGE-217 group also demonstrated significantly higher rates of HAM-D response as defined by a 50% or greater reduction in total score at day 15, as well as in HAM-D remission, which entails having a score of 7 or less.
Treatment-emergent adverse events in the SAGE-217 and placebo arms were similar in frequency and type. The most common adverse events associated with SAGE-217 – all occurring in single-digit frequencies – were sleepiness, headache, dizziness, upper respiratory infections, and diarrhea. There was no signal of increased suicidal thoughts or behavior as assessed using the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
SAGE-217 also is the focus of an ongoing pivotal phase 3 trial in patients with major depression. In addition, the drug is under study for bipolar depression, major depressive disorder with comorbid insomnia, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Dr. Vieta reported serving on advisory boards for Sage Therapeutics, the study sponsor, as well as for two dozen other pharmaceutical companies. He receives research funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education, the Stanley Medical Research Institute, and more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
COPENHAGEN – A first-in-class, once-daily, orally administered neuroactive steroid known for now as SAGE-217 aced all of its primary and secondary outcomes for the treatment of postpartum depression in the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ROBIN study, Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD, said at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“I think this changes the paradigm in the treatment of postpartum depression,” declared Dr. Vieta, professor of psychiatry and head of the bipolar disorders program at the University of Barcelona.
Like brexanolone (Zulresso), an intravenous formulation of allopregnanolone approved by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2019 as the first-ever drug specifically targeting postpartum depression, SAGE-217 is a positive allosteric modifier of synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA-A receptors. That differentiates the two drugs from benzodiazepines, which target only synaptic receptors. Both brexanolone and SAGE-217 are drugs developed by Sage Therapeutics. But SAGE-217, an investigational agent, is vastly more convenient to use than brexanolone since, as an oral drug, it doesn’t require hospitalization for intravenous administration.
Dr. Vieta ticked off five reasons why he considers SAGE-217 a game changer in the treatment of postpartum depression: “It’s an amazingly effective compound, with an effect size that’s bigger than we usually see with antidepressants. It has an early onset of action, similar to what we see with glutaminergic agents, although with an opposite mechanism: enhancing GABA rather than opposing glutamate. It has excellent tolerability, similar to placebo. It’s made to be used orally, a major advantage over other drugs that are available or close to becoming available, which have to be given IV. And last but not least, a patient will get it for only 2 weeks. The treatment can be stopped after 2 weeks, and there is long-term improvement.”
The ROBIN trial included 151 patients with postpartum depression as defined by a baseline Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score of at least 26 who were randomized double-blind to 14 days of SAGE-217 at 30 mg once daily or to placebo. The primary endpoint was the change in HAM-D scores between baseline and day 15. The key finding was that the SAGE-217 group averaged a 17.8-point reduction, significantly greater than the 13.6-point improvement with placebo. This advantage was maintained at assessment on day 45 – a full month after treatment stopped – with a 24.8-point improvement over baseline in the SAGE-217 recipients, compared with a 19-point reduction in controls. The advantage favoring SAGE-217 was significant as early as day 3, the first assessment, at which point the average improvement in HAM-D was 12.5 points, compared with 9.8 points in controls.
Other secondary endpoints included change from baseline to day 15 on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS): a 22.8-point improvement in the SAGE-217 group, significantly greater than the 17.6-point improvement in the placebo arm. The same pattern was evident at day 45, with reductions in MADRS of 24.8 and 19 points, respectively, in the SAGE-217 and placebo groups.
Another key prespecified secondary endpoint was change in scores on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety through day 15. There was a mean 16.6-point drop in the active treatment arm, compared with a 12.7-point improvement with placebo, again a statistically significant and clinically meaningful between-group difference. This is an important endpoint because comorbid anxiety is common in the setting of postpartum depression, the psychiatrist continued.
The SAGE-217 group also demonstrated significantly higher rates of HAM-D response as defined by a 50% or greater reduction in total score at day 15, as well as in HAM-D remission, which entails having a score of 7 or less.
Treatment-emergent adverse events in the SAGE-217 and placebo arms were similar in frequency and type. The most common adverse events associated with SAGE-217 – all occurring in single-digit frequencies – were sleepiness, headache, dizziness, upper respiratory infections, and diarrhea. There was no signal of increased suicidal thoughts or behavior as assessed using the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
SAGE-217 also is the focus of an ongoing pivotal phase 3 trial in patients with major depression. In addition, the drug is under study for bipolar depression, major depressive disorder with comorbid insomnia, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Dr. Vieta reported serving on advisory boards for Sage Therapeutics, the study sponsor, as well as for two dozen other pharmaceutical companies. He receives research funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education, the Stanley Medical Research Institute, and more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
REPORTING FROM THE ECNP 2019
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Presenting as a Cutaneous Horn
To the Editor:
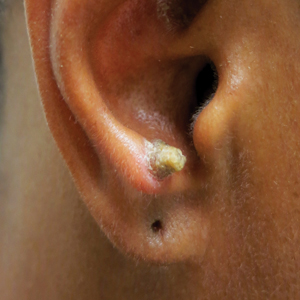
A 53-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a painful growth on the right ear of 2 months’ duration. A complete review of systems was negative except for an isolated episode of shortness of breath prior to presentation that resolved without intervention. During this episode, her primary care physician made a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on a chest radiograph. The patient reported minimal tobacco use, specifically that she had smoked a few cigarettes daily for several years but had quit 6 months prior to the current presentation.
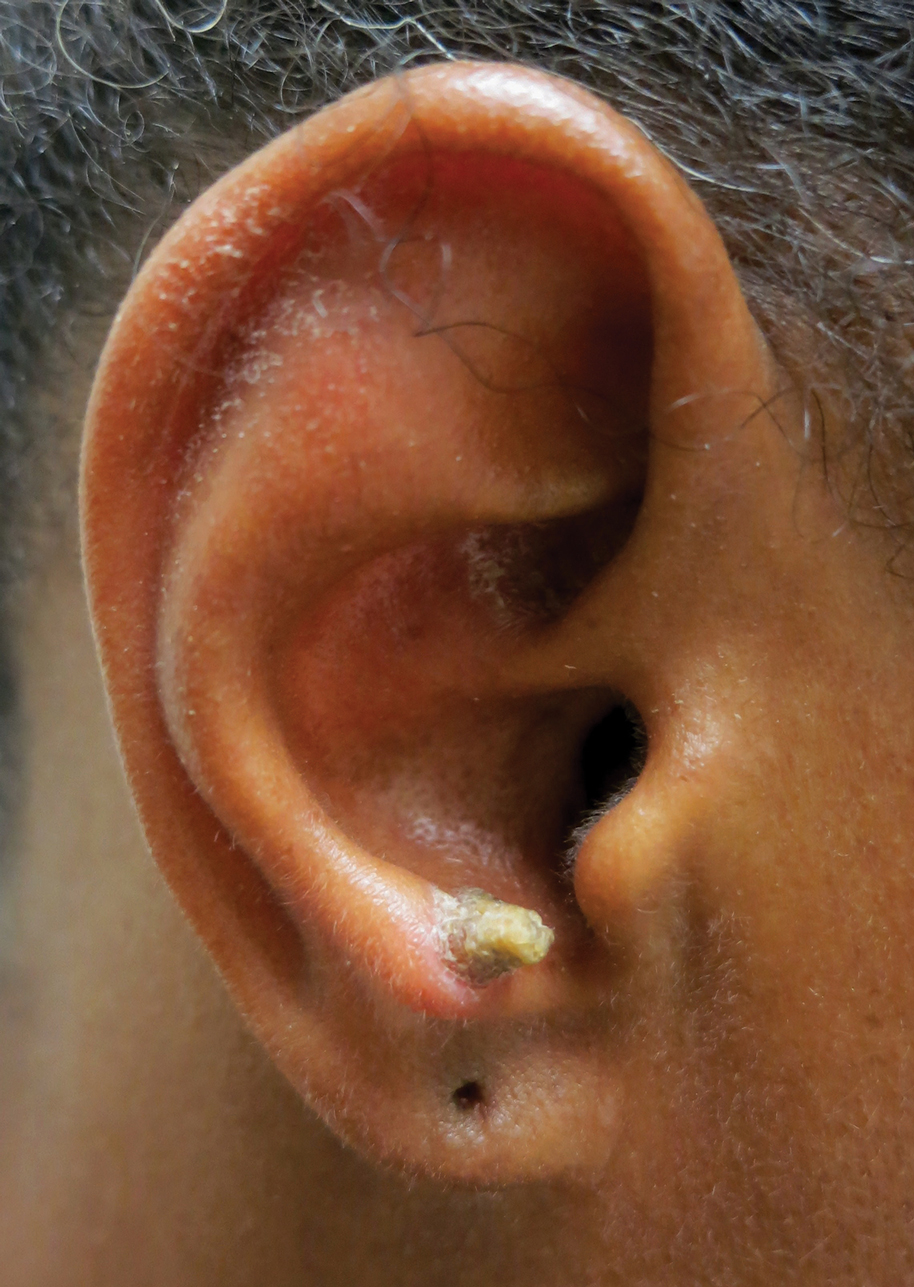
Cutaneous horn is a clinical term used to describe hyperkeratotic horn-shaped growths of highly variable shapes and sizes. Although the pathogenesis and incidence of cutaneous horns remain unknown, these lesions most often are the result of a neoplastic rather than an inflammatory process. The differential diagnosis typically includes entities characterized by marked hyperkeratosis, including hypertrophic actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), seborrheic keratosis, and verruca vulgaris. The base of the horn must be biopsied to determine the underlying etiology, paying careful attention to avoid a superficial biopsy, as it may be nondiagnostic.
Studies analyzing the underlying diagnoses and clinical features of cutaneous horns are limited. In a large retrospective study of 643 cutaneous horns, 61% were benign, 23% were premalignant, and 16% were malignant. In this study, 4 features were associated with premalignant or malignant pathology: (1) older age (mid- 60s to 70s); (2) male sex; (3) location on the nose, pinnae, dorsal hands, scalp, forearms, or face; and (4) a wide base (4.4 mm or larger) and a lower height-to-base ratio than benign lesions.1 Two additional studies of more than 200 horns each showed higher rates of premalignant horns (42% and 38%, respectively) with malignancy found in 7% and 20% of horns, respectively.2,3 One prospective study sought to identify clinical and dermatoscopic features of SCCs underlying cutaneous horns, concluding that SCC diagnosis was more likely if a horn had (1) a height less than the diameter of its base, (2) a lack of terrace morphology (a dermatoscopic feature defined as horizontal parallel layers of keratin), (3) erythema at the base, and (4) the presence of pain.4
Our patient had a cutaneous horn on the pinna that was painful, wider than it was tall, and erythematous at the base, suggesting a malignant process; however, a complete cutaneous physical examination revealed other skin lesions that were concerning for sarcoidosis and raised suspicion that the horn also was a manifestation of the same inflammatory process.
Although unusual, cutaneous sarcoidosis presenting as a cutaneous horn is not unexpected. In a histopathologic study of 62 cases of cutaneous sarcoidosis, 79% (49/62) showed epidermal changes and 13% (8/62) demonstrated hyperkeratosis. Other epidermal changes included parakeratosis (16% [10/62]), acanthosis (10% [6/62]), and epidermal atrophy (57% [35/62]).5 The spectrum of epidermal pathology in cutaneous sarcoidosis is evident in its well-documented verrucous, psoriasiform, and ichthyosiform presentations. For completeness, cutaneous horn is added to the list of clinical morphologies for this “great imitator” of cutaneous diseases.
- Yu RC, Pryce DW, Macfarlane AW, et al. A histopathological study of 643 cutaneous horns. Br J Dermatol. 1991;124:449-452.
- Schosser RH, Hodge SJ, Gaba CR, et al. Cutaneous horns: a histopathologic study. South Med J. 1979;72:1129-1131.
- Mantese SA, Diogo PM, Rocha A, et al. Cutaneous horn: a retrospective histopathological study of 222 cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:157-163.
- Pyne J, Sapkota D, Wong JC. Cutaneous horns: clues to invasive squamous cell carcinoma being present in the horn base. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:3-7.
- Hiroyuki O. Epidermal changes in cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:229-233.
To the Editor:
A 53-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a painful growth on the right ear of 2 months’ duration. A complete review of systems was negative except for an isolated episode of shortness of breath prior to presentation that resolved without intervention. During this episode, her primary care physician made a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on a chest radiograph. The patient reported minimal tobacco use, specifically that she had smoked a few cigarettes daily for several years but had quit 6 months prior to the current presentation.


Cutaneous horn is a clinical term used to describe hyperkeratotic horn-shaped growths of highly variable shapes and sizes. Although the pathogenesis and incidence of cutaneous horns remain unknown, these lesions most often are the result of a neoplastic rather than an inflammatory process. The differential diagnosis typically includes entities characterized by marked hyperkeratosis, including hypertrophic actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), seborrheic keratosis, and verruca vulgaris. The base of the horn must be biopsied to determine the underlying etiology, paying careful attention to avoid a superficial biopsy, as it may be nondiagnostic.
Studies analyzing the underlying diagnoses and clinical features of cutaneous horns are limited. In a large retrospective study of 643 cutaneous horns, 61% were benign, 23% were premalignant, and 16% were malignant. In this study, 4 features were associated with premalignant or malignant pathology: (1) older age (mid- 60s to 70s); (2) male sex; (3) location on the nose, pinnae, dorsal hands, scalp, forearms, or face; and (4) a wide base (4.4 mm or larger) and a lower height-to-base ratio than benign lesions.1 Two additional studies of more than 200 horns each showed higher rates of premalignant horns (42% and 38%, respectively) with malignancy found in 7% and 20% of horns, respectively.2,3 One prospective study sought to identify clinical and dermatoscopic features of SCCs underlying cutaneous horns, concluding that SCC diagnosis was more likely if a horn had (1) a height less than the diameter of its base, (2) a lack of terrace morphology (a dermatoscopic feature defined as horizontal parallel layers of keratin), (3) erythema at the base, and (4) the presence of pain.4
Our patient had a cutaneous horn on the pinna that was painful, wider than it was tall, and erythematous at the base, suggesting a malignant process; however, a complete cutaneous physical examination revealed other skin lesions that were concerning for sarcoidosis and raised suspicion that the horn also was a manifestation of the same inflammatory process.
Although unusual, cutaneous sarcoidosis presenting as a cutaneous horn is not unexpected. In a histopathologic study of 62 cases of cutaneous sarcoidosis, 79% (49/62) showed epidermal changes and 13% (8/62) demonstrated hyperkeratosis. Other epidermal changes included parakeratosis (16% [10/62]), acanthosis (10% [6/62]), and epidermal atrophy (57% [35/62]).5 The spectrum of epidermal pathology in cutaneous sarcoidosis is evident in its well-documented verrucous, psoriasiform, and ichthyosiform presentations. For completeness, cutaneous horn is added to the list of clinical morphologies for this “great imitator” of cutaneous diseases.
To the Editor:
A 53-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a painful growth on the right ear of 2 months’ duration. A complete review of systems was negative except for an isolated episode of shortness of breath prior to presentation that resolved without intervention. During this episode, her primary care physician made a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on a chest radiograph. The patient reported minimal tobacco use, specifically that she had smoked a few cigarettes daily for several years but had quit 6 months prior to the current presentation.


Cutaneous horn is a clinical term used to describe hyperkeratotic horn-shaped growths of highly variable shapes and sizes. Although the pathogenesis and incidence of cutaneous horns remain unknown, these lesions most often are the result of a neoplastic rather than an inflammatory process. The differential diagnosis typically includes entities characterized by marked hyperkeratosis, including hypertrophic actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), seborrheic keratosis, and verruca vulgaris. The base of the horn must be biopsied to determine the underlying etiology, paying careful attention to avoid a superficial biopsy, as it may be nondiagnostic.
Studies analyzing the underlying diagnoses and clinical features of cutaneous horns are limited. In a large retrospective study of 643 cutaneous horns, 61% were benign, 23% were premalignant, and 16% were malignant. In this study, 4 features were associated with premalignant or malignant pathology: (1) older age (mid- 60s to 70s); (2) male sex; (3) location on the nose, pinnae, dorsal hands, scalp, forearms, or face; and (4) a wide base (4.4 mm or larger) and a lower height-to-base ratio than benign lesions.1 Two additional studies of more than 200 horns each showed higher rates of premalignant horns (42% and 38%, respectively) with malignancy found in 7% and 20% of horns, respectively.2,3 One prospective study sought to identify clinical and dermatoscopic features of SCCs underlying cutaneous horns, concluding that SCC diagnosis was more likely if a horn had (1) a height less than the diameter of its base, (2) a lack of terrace morphology (a dermatoscopic feature defined as horizontal parallel layers of keratin), (3) erythema at the base, and (4) the presence of pain.4
Our patient had a cutaneous horn on the pinna that was painful, wider than it was tall, and erythematous at the base, suggesting a malignant process; however, a complete cutaneous physical examination revealed other skin lesions that were concerning for sarcoidosis and raised suspicion that the horn also was a manifestation of the same inflammatory process.
Although unusual, cutaneous sarcoidosis presenting as a cutaneous horn is not unexpected. In a histopathologic study of 62 cases of cutaneous sarcoidosis, 79% (49/62) showed epidermal changes and 13% (8/62) demonstrated hyperkeratosis. Other epidermal changes included parakeratosis (16% [10/62]), acanthosis (10% [6/62]), and epidermal atrophy (57% [35/62]).5 The spectrum of epidermal pathology in cutaneous sarcoidosis is evident in its well-documented verrucous, psoriasiform, and ichthyosiform presentations. For completeness, cutaneous horn is added to the list of clinical morphologies for this “great imitator” of cutaneous diseases.
- Yu RC, Pryce DW, Macfarlane AW, et al. A histopathological study of 643 cutaneous horns. Br J Dermatol. 1991;124:449-452.
- Schosser RH, Hodge SJ, Gaba CR, et al. Cutaneous horns: a histopathologic study. South Med J. 1979;72:1129-1131.
- Mantese SA, Diogo PM, Rocha A, et al. Cutaneous horn: a retrospective histopathological study of 222 cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:157-163.
- Pyne J, Sapkota D, Wong JC. Cutaneous horns: clues to invasive squamous cell carcinoma being present in the horn base. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:3-7.
- Hiroyuki O. Epidermal changes in cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:229-233.
- Yu RC, Pryce DW, Macfarlane AW, et al. A histopathological study of 643 cutaneous horns. Br J Dermatol. 1991;124:449-452.
- Schosser RH, Hodge SJ, Gaba CR, et al. Cutaneous horns: a histopathologic study. South Med J. 1979;72:1129-1131.
- Mantese SA, Diogo PM, Rocha A, et al. Cutaneous horn: a retrospective histopathological study of 222 cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:157-163.
- Pyne J, Sapkota D, Wong JC. Cutaneous horns: clues to invasive squamous cell carcinoma being present in the horn base. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:3-7.
- Hiroyuki O. Epidermal changes in cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:229-233.
Practice Points
- Biopsy of a cutaneous horn should be deep enough to capture the neoplastic or inflammatory process at the base of the lesion.
- Cutaneous sarcoidosis can present with variable morphologies including the epidermal changes of a cutaneous horn.
Did You Know? Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome



Sensory feedback may smooth walking with a prosthetic leg
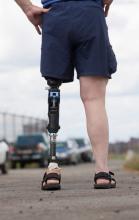
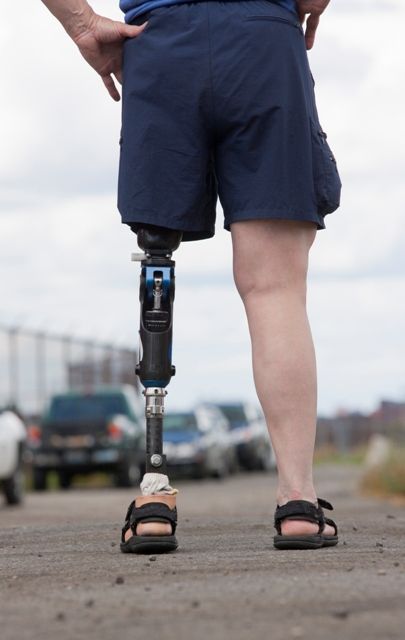
A prosthetic leg that elicits the sensation of knee motion and the feeling of the sole of the foot touching the ground may improve walking performance and reduce phantom limb pain, according to a proof-of-concept study with two patients.
With the bionic leg system, the patients performed better during clinically important tests indoors and outdoors, study author Stanisa Raspopovic, PhD, explained during a press briefing about the research. The findings were published in Nature Medicine.
The results indicate that the use of sensory feedback “could be common practice” in prosthetic devices in the future, he said. Dr. Raspopovic is a researcher at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich and a founder of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Neural prosthetics allow the nervous system and external devices to interact. These brain-machine interfaces may improve quality of life for patients with brain or spinal cord injuries, degenerative disease, or loss of limbs.
“Conventional leg prostheses do not convey sensory information about motion or interaction with the ground to above-knee amputees, thereby reducing confidence and walking speed in the users,” the study authors wrote. Users may also have high levels of mental and physical fatigue, and the lack of physiologic feedback from the extremity to the brain may contribute to the generation of phantom limb pain.
To evaluate whether neural sensory feedback restoration could address these issues, investigators conducted a study with two patients who had undergone transfemoral amputations as a result of traumatic events. The patients were implanted with four intraneural stimulation electrodes in the remaining tibial nerve. The prosthetic leg device included sensors to represent foot touch and pressure and knee joint angle. The sensors transmitted sensory signals to the nervous system through the stimulation electrodes in the tibial nerve.
When the patients walked outdoors over a path traced in the sand, “participants’ speeds were significantly higher when sensory feedback was provided,” the authors wrote. One participant walked 3.56 m/min faster, and the other walked 5.68 m/min faster.
The participants also rated their confidence in the prosthesis on a scale from 0 to 10. For patient 1, self-rated confidence improved from 4.85 to 7.71 with the device. Patient 2 reported a confidence level that climbed from 2.7 to 5.55.
When tested indoors, both patients reached a 0.5 km/hour higher speed on the treadmill when stimulation was provided and both had a lower mean rate of oxygen uptake during the sensory feedback trials, the study authors reported.
Levels of phantom limb pain also decreased significantly after 10-minute stimulation sessions, but not during control sessions.
Longer studies with more patients are required, and fully implantable devices without transcutaneous cables need to be developed, the authors wrote.
Grants from the European Research Council, European Commission, and Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research. Dr. Raspopovic and two coauthors hold shares of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, a start-up company dealing with the commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs.
SOURCE: Petrini FM et al. Nat Med. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0567-3.
A prosthetic leg that elicits the sensation of knee motion and the feeling of the sole of the foot touching the ground may improve walking performance and reduce phantom limb pain, according to a proof-of-concept study with two patients.
With the bionic leg system, the patients performed better during clinically important tests indoors and outdoors, study author Stanisa Raspopovic, PhD, explained during a press briefing about the research. The findings were published in Nature Medicine.
The results indicate that the use of sensory feedback “could be common practice” in prosthetic devices in the future, he said. Dr. Raspopovic is a researcher at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich and a founder of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Neural prosthetics allow the nervous system and external devices to interact. These brain-machine interfaces may improve quality of life for patients with brain or spinal cord injuries, degenerative disease, or loss of limbs.
“Conventional leg prostheses do not convey sensory information about motion or interaction with the ground to above-knee amputees, thereby reducing confidence and walking speed in the users,” the study authors wrote. Users may also have high levels of mental and physical fatigue, and the lack of physiologic feedback from the extremity to the brain may contribute to the generation of phantom limb pain.
To evaluate whether neural sensory feedback restoration could address these issues, investigators conducted a study with two patients who had undergone transfemoral amputations as a result of traumatic events. The patients were implanted with four intraneural stimulation electrodes in the remaining tibial nerve. The prosthetic leg device included sensors to represent foot touch and pressure and knee joint angle. The sensors transmitted sensory signals to the nervous system through the stimulation electrodes in the tibial nerve.
When the patients walked outdoors over a path traced in the sand, “participants’ speeds were significantly higher when sensory feedback was provided,” the authors wrote. One participant walked 3.56 m/min faster, and the other walked 5.68 m/min faster.
The participants also rated their confidence in the prosthesis on a scale from 0 to 10. For patient 1, self-rated confidence improved from 4.85 to 7.71 with the device. Patient 2 reported a confidence level that climbed from 2.7 to 5.55.
When tested indoors, both patients reached a 0.5 km/hour higher speed on the treadmill when stimulation was provided and both had a lower mean rate of oxygen uptake during the sensory feedback trials, the study authors reported.
Levels of phantom limb pain also decreased significantly after 10-minute stimulation sessions, but not during control sessions.
Longer studies with more patients are required, and fully implantable devices without transcutaneous cables need to be developed, the authors wrote.
Grants from the European Research Council, European Commission, and Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research. Dr. Raspopovic and two coauthors hold shares of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, a start-up company dealing with the commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs.
SOURCE: Petrini FM et al. Nat Med. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0567-3.
A prosthetic leg that elicits the sensation of knee motion and the feeling of the sole of the foot touching the ground may improve walking performance and reduce phantom limb pain, according to a proof-of-concept study with two patients.
With the bionic leg system, the patients performed better during clinically important tests indoors and outdoors, study author Stanisa Raspopovic, PhD, explained during a press briefing about the research. The findings were published in Nature Medicine.
The results indicate that the use of sensory feedback “could be common practice” in prosthetic devices in the future, he said. Dr. Raspopovic is a researcher at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich and a founder of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Neural prosthetics allow the nervous system and external devices to interact. These brain-machine interfaces may improve quality of life for patients with brain or spinal cord injuries, degenerative disease, or loss of limbs.
“Conventional leg prostheses do not convey sensory information about motion or interaction with the ground to above-knee amputees, thereby reducing confidence and walking speed in the users,” the study authors wrote. Users may also have high levels of mental and physical fatigue, and the lack of physiologic feedback from the extremity to the brain may contribute to the generation of phantom limb pain.
To evaluate whether neural sensory feedback restoration could address these issues, investigators conducted a study with two patients who had undergone transfemoral amputations as a result of traumatic events. The patients were implanted with four intraneural stimulation electrodes in the remaining tibial nerve. The prosthetic leg device included sensors to represent foot touch and pressure and knee joint angle. The sensors transmitted sensory signals to the nervous system through the stimulation electrodes in the tibial nerve.
When the patients walked outdoors over a path traced in the sand, “participants’ speeds were significantly higher when sensory feedback was provided,” the authors wrote. One participant walked 3.56 m/min faster, and the other walked 5.68 m/min faster.
The participants also rated their confidence in the prosthesis on a scale from 0 to 10. For patient 1, self-rated confidence improved from 4.85 to 7.71 with the device. Patient 2 reported a confidence level that climbed from 2.7 to 5.55.
When tested indoors, both patients reached a 0.5 km/hour higher speed on the treadmill when stimulation was provided and both had a lower mean rate of oxygen uptake during the sensory feedback trials, the study authors reported.
Levels of phantom limb pain also decreased significantly after 10-minute stimulation sessions, but not during control sessions.
Longer studies with more patients are required, and fully implantable devices without transcutaneous cables need to be developed, the authors wrote.
Grants from the European Research Council, European Commission, and Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research. Dr. Raspopovic and two coauthors hold shares of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, a start-up company dealing with the commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs.
SOURCE: Petrini FM et al. Nat Med. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0567-3.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
MYSTIC trial analysis IDs mutations prognostic of mNSCLC outcomes
BARCELONA – Mutations in the tumor suppressor KEAP1 or STK11 genes in patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) in the randomized, phase 3 MYSTIC trial experienced poorer outcomes than did patients without the mutations, according to an exploratory analysis of trial data.
Mutations in ARID1a, however, were associated with improved overall survival (OS) among patients in the trial who were treated with durvalumab + tremelimumab.
Profiling of circulating tumor DNA from 943 evaluable baseline plasma specimens showed median OS of 7.4 vs. 12.9 months among 170 patients with KEAP1 mutations (m) vs. in 773 with KEAP1 wild type (hazard ratio, 1.64), and 6.8 vs. 12.6 months in patients with STK11m vs. 796 with STK11wt (HR, 1.52), Naiyer A. Rizvi, MD, the Price Family Professor of Medicine, director of Thoracic Oncology, and codirector of Cancer Immunotherapy at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, reported at the World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Objective response rates (ORR) in the groups, respectively, were 17.6% vs. 27.7% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, and 16.3% vs. 27.6% for STK11m vs. STK11wt, Dr. Rizvi said at the conference, sponsored by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
This was regardless of MYSTIC trial treatment arm; the open-label, multicenter, global trial compared durvalumab monotherapy or durvalumab plus tremelimumab with platinum-based chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of patients with epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase wild-type, locally-advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
Mutations in the ARID1a gene, however, had no impact on OS (12.6 vs. 11.4 months in 114 vs. 829 patients with ARID1am vs. ARID1awt; HR, 0.94), and ORRs, respectively, were 35.1% vs. 24.6%.
When comparing outcomes by treatment arm, the ORRs with chemotherapy were 15.1% vs. 34% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, 12.2% vs. 33.6% for STK11m vs. STK1wt, and 28.1% vs. 31% for ARID1am vs. ARID1awt.
The ORRs in the durvalumab arm were 16.7% vs. 25.2% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1st, 14.5% vs. 25.7% for STK11m vs. STK11wt and 25.6% vs. 23.4%, respectively, and in the durvalumab + tremelimumab arm they were 20.6% vs. 23.9% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, 21.6% vs. 23.6% for STK11m vs. STK11wt.
“The key finding here is really the ARID1a response,” Dr. Rizvi said, noting the “pretty impressive response rates” of 51.3% with ARID1am vs. 19.4% for ARID1awt.
The relationship between gene alterations and response to anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) therapy with and without anti-CTLA-4 therapy is not well characterized. These findings, which suggest that KEAP1 and STK11 mutations are prognostic for OS in mNSCLC, and that ARID1am may be predictive of OS benefit in patients receiving durvalumab + tremelimumab, provide insights to the potential impact of specific mutations on response to immunotherapy, Dr. Rizvi said.
“STK11 and KEAP1 mutations ... are relatively common mutations – they are actually the third and fourth most common mutations in lung cancer after p53 and KRAS,” he said, adding that they influence outcomes and need to be factored in to analyses of outcomes in lung cancer. “ARID1am patients were about 10% of the population and they did particularly well with durvalumab and tremelimumab, and I think these exploratory analyses can help us think about how we use [tumor mutational burden] and outcomes among cancer patients in future trials.”
The MYSTIC trial was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rizvi disclosed royalties related to intellectual property/patents filed by MSKCC and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
SOURCE: Rizvi N et al. WCLC 2019: Abstract OA04.07.
BARCELONA – Mutations in the tumor suppressor KEAP1 or STK11 genes in patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) in the randomized, phase 3 MYSTIC trial experienced poorer outcomes than did patients without the mutations, according to an exploratory analysis of trial data.
Mutations in ARID1a, however, were associated with improved overall survival (OS) among patients in the trial who were treated with durvalumab + tremelimumab.
Profiling of circulating tumor DNA from 943 evaluable baseline plasma specimens showed median OS of 7.4 vs. 12.9 months among 170 patients with KEAP1 mutations (m) vs. in 773 with KEAP1 wild type (hazard ratio, 1.64), and 6.8 vs. 12.6 months in patients with STK11m vs. 796 with STK11wt (HR, 1.52), Naiyer A. Rizvi, MD, the Price Family Professor of Medicine, director of Thoracic Oncology, and codirector of Cancer Immunotherapy at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, reported at the World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Objective response rates (ORR) in the groups, respectively, were 17.6% vs. 27.7% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, and 16.3% vs. 27.6% for STK11m vs. STK11wt, Dr. Rizvi said at the conference, sponsored by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
This was regardless of MYSTIC trial treatment arm; the open-label, multicenter, global trial compared durvalumab monotherapy or durvalumab plus tremelimumab with platinum-based chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of patients with epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase wild-type, locally-advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
Mutations in the ARID1a gene, however, had no impact on OS (12.6 vs. 11.4 months in 114 vs. 829 patients with ARID1am vs. ARID1awt; HR, 0.94), and ORRs, respectively, were 35.1% vs. 24.6%.
When comparing outcomes by treatment arm, the ORRs with chemotherapy were 15.1% vs. 34% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, 12.2% vs. 33.6% for STK11m vs. STK1wt, and 28.1% vs. 31% for ARID1am vs. ARID1awt.
The ORRs in the durvalumab arm were 16.7% vs. 25.2% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1st, 14.5% vs. 25.7% for STK11m vs. STK11wt and 25.6% vs. 23.4%, respectively, and in the durvalumab + tremelimumab arm they were 20.6% vs. 23.9% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, 21.6% vs. 23.6% for STK11m vs. STK11wt.
“The key finding here is really the ARID1a response,” Dr. Rizvi said, noting the “pretty impressive response rates” of 51.3% with ARID1am vs. 19.4% for ARID1awt.
The relationship between gene alterations and response to anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) therapy with and without anti-CTLA-4 therapy is not well characterized. These findings, which suggest that KEAP1 and STK11 mutations are prognostic for OS in mNSCLC, and that ARID1am may be predictive of OS benefit in patients receiving durvalumab + tremelimumab, provide insights to the potential impact of specific mutations on response to immunotherapy, Dr. Rizvi said.
“STK11 and KEAP1 mutations ... are relatively common mutations – they are actually the third and fourth most common mutations in lung cancer after p53 and KRAS,” he said, adding that they influence outcomes and need to be factored in to analyses of outcomes in lung cancer. “ARID1am patients were about 10% of the population and they did particularly well with durvalumab and tremelimumab, and I think these exploratory analyses can help us think about how we use [tumor mutational burden] and outcomes among cancer patients in future trials.”
The MYSTIC trial was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rizvi disclosed royalties related to intellectual property/patents filed by MSKCC and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
SOURCE: Rizvi N et al. WCLC 2019: Abstract OA04.07.
BARCELONA – Mutations in the tumor suppressor KEAP1 or STK11 genes in patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) in the randomized, phase 3 MYSTIC trial experienced poorer outcomes than did patients without the mutations, according to an exploratory analysis of trial data.
Mutations in ARID1a, however, were associated with improved overall survival (OS) among patients in the trial who were treated with durvalumab + tremelimumab.
Profiling of circulating tumor DNA from 943 evaluable baseline plasma specimens showed median OS of 7.4 vs. 12.9 months among 170 patients with KEAP1 mutations (m) vs. in 773 with KEAP1 wild type (hazard ratio, 1.64), and 6.8 vs. 12.6 months in patients with STK11m vs. 796 with STK11wt (HR, 1.52), Naiyer A. Rizvi, MD, the Price Family Professor of Medicine, director of Thoracic Oncology, and codirector of Cancer Immunotherapy at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, reported at the World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Objective response rates (ORR) in the groups, respectively, were 17.6% vs. 27.7% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, and 16.3% vs. 27.6% for STK11m vs. STK11wt, Dr. Rizvi said at the conference, sponsored by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
This was regardless of MYSTIC trial treatment arm; the open-label, multicenter, global trial compared durvalumab monotherapy or durvalumab plus tremelimumab with platinum-based chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of patients with epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase wild-type, locally-advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
Mutations in the ARID1a gene, however, had no impact on OS (12.6 vs. 11.4 months in 114 vs. 829 patients with ARID1am vs. ARID1awt; HR, 0.94), and ORRs, respectively, were 35.1% vs. 24.6%.
When comparing outcomes by treatment arm, the ORRs with chemotherapy were 15.1% vs. 34% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, 12.2% vs. 33.6% for STK11m vs. STK1wt, and 28.1% vs. 31% for ARID1am vs. ARID1awt.
The ORRs in the durvalumab arm were 16.7% vs. 25.2% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1st, 14.5% vs. 25.7% for STK11m vs. STK11wt and 25.6% vs. 23.4%, respectively, and in the durvalumab + tremelimumab arm they were 20.6% vs. 23.9% for KEAP1m vs. KEAP1wt, 21.6% vs. 23.6% for STK11m vs. STK11wt.
“The key finding here is really the ARID1a response,” Dr. Rizvi said, noting the “pretty impressive response rates” of 51.3% with ARID1am vs. 19.4% for ARID1awt.
The relationship between gene alterations and response to anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) therapy with and without anti-CTLA-4 therapy is not well characterized. These findings, which suggest that KEAP1 and STK11 mutations are prognostic for OS in mNSCLC, and that ARID1am may be predictive of OS benefit in patients receiving durvalumab + tremelimumab, provide insights to the potential impact of specific mutations on response to immunotherapy, Dr. Rizvi said.
“STK11 and KEAP1 mutations ... are relatively common mutations – they are actually the third and fourth most common mutations in lung cancer after p53 and KRAS,” he said, adding that they influence outcomes and need to be factored in to analyses of outcomes in lung cancer. “ARID1am patients were about 10% of the population and they did particularly well with durvalumab and tremelimumab, and I think these exploratory analyses can help us think about how we use [tumor mutational burden] and outcomes among cancer patients in future trials.”
The MYSTIC trial was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rizvi disclosed royalties related to intellectual property/patents filed by MSKCC and Personal Genome Diagnostics.
SOURCE: Rizvi N et al. WCLC 2019: Abstract OA04.07.
REPORTING FROM WCLC 2019
Unusually Early-Onset Plantar Verrucous Carcinoma
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma characterized by a well-differentiated low-grade tumor with a high degree of keratinization. First described by Ackerman1 in 1948, VC presents on the skin or oral and genital mucosae with minimal atypical cytologic findings.1-3 It most commonly is seen in late middle-aged men (85% of cases) and presents as a slow-growing mass, often of more than 10 years’ duration.2,3 Verrucous carcinoma frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, known as oral florid papillomatosis; the anogenital area, known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor; and on the plantar surface, known as epithelioma cuniculatum.2-13
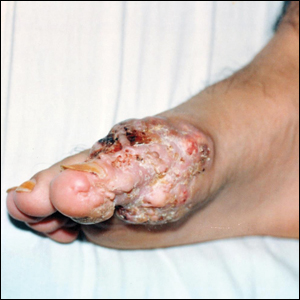
A 19-year-old man presented with an ulcerous lesion on the right big toe of 2 years’ duration. He reported that the lesion had gradually increased in size and was painful when walking. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated lesion on the right big toe with purulent inflammation and necrosis, unclear edges, and border nodules containing a fatty, yellowish, foul-smelling material (Figure 1). Histologic examination of purulent material from deep within the primary lesion revealed gram-negative rods and gram-positive diplococci. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining and culture in Lowenstein-Jensen medium were negative for mycobacteria. Histologic examination and fungal culture were not diagnostic for fungal infection.
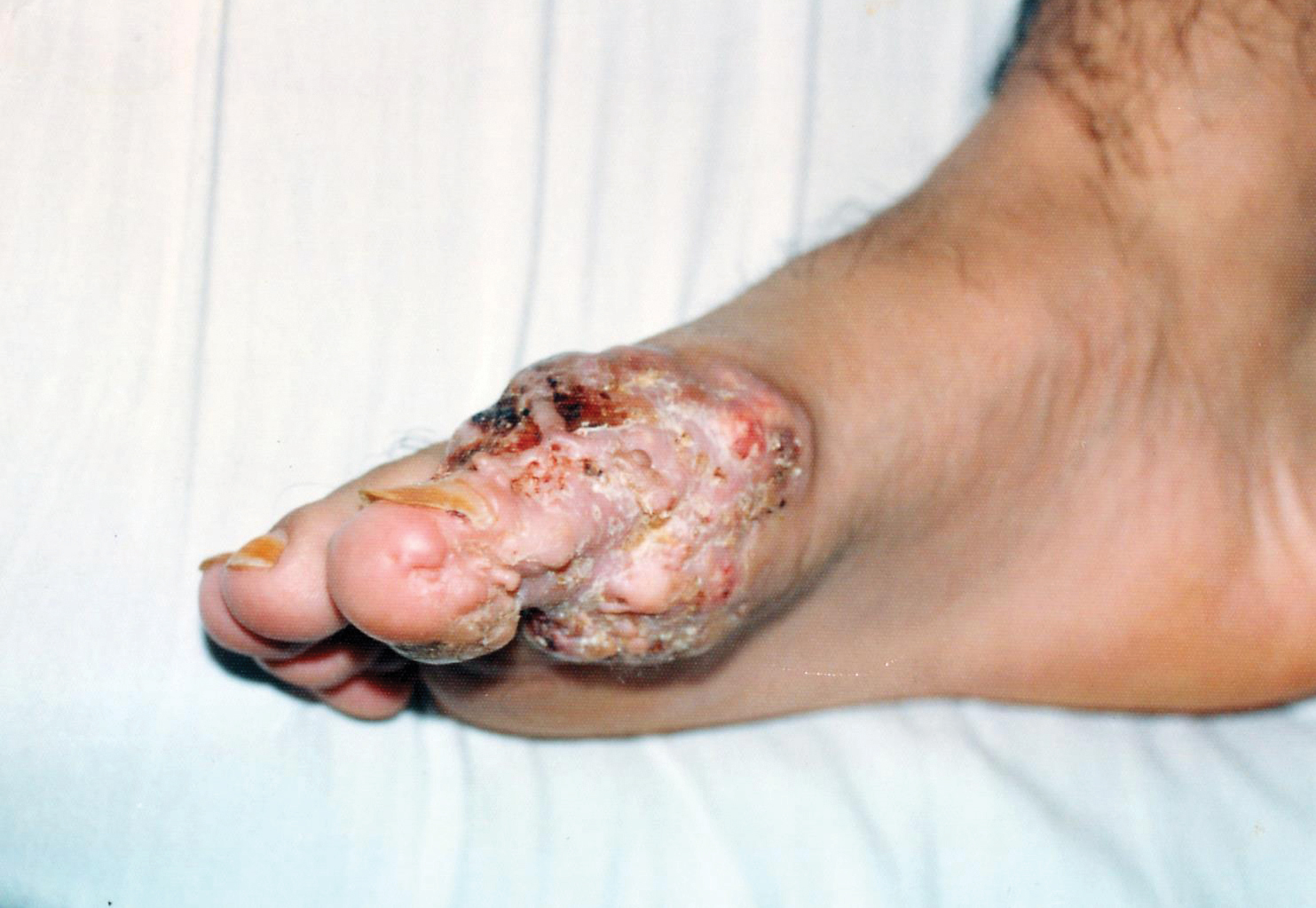
The differential diagnosis included tuberculosis cutis verrucosa, subcutaneous mycoses, swimming pool granuloma, leishmania cutis, chronic pyoderma vegetans, and VC. A punch biopsy of the lesion showed chronic nonspecific inflammation, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A repeat biopsy performed 15 days later also showed a nonspecific inflammation. At the initial presentation, an anti–human immunodeficiency virus test was negative. A purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test was positive and showed a 17-mm induration, and a sputum test was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A chest radiograph was normal. We considered the positive PPD skin test to be clinically insignificant; we did not find an accompanying tuberculosis infection, and the high exposure to atypical tuberculosis in developing countries such as Turkey, which is where the patient resided, often explains a positive PPD test.
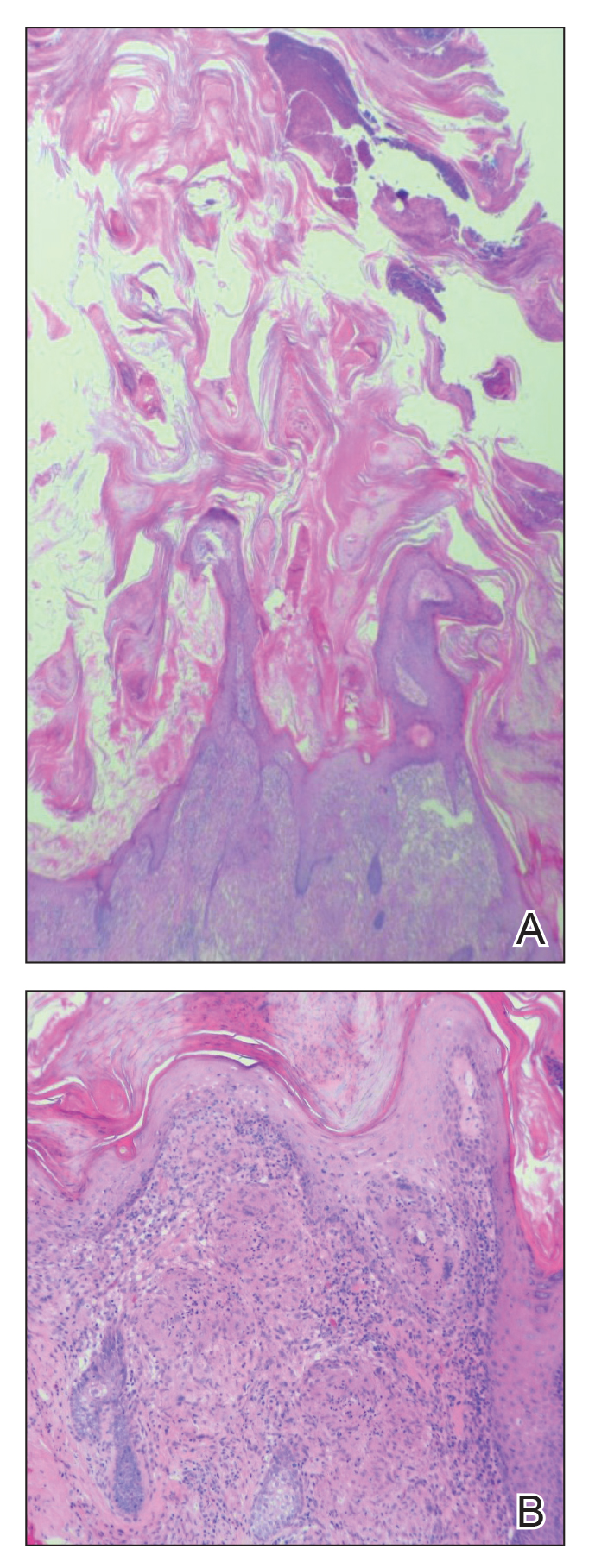
At the initial presentation, radiography of the right big toe revealed porotic signs and cortical irregularity of the distal phalanx. A deep incisional biopsy of the lesion was performed for pathologic and microbiologic analysis. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining was negative, fungal elements could not be observed, and there was no growth in Lowenstein-Jensen medium or Sabouraud dextrose agar. Polymerase chain reaction for human papillomavirus, M tuberculosis, and atypical mycobacterium was negative. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal elements. Histopathologic examination revealed an exophytic as well as endophytic squamous cell proliferation infiltrating deeper layers of the dermis with a desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2). Slight cytologic atypia was noted. A diagnosis of VC was made based on the clinical and histopathologic findings. The patient’s right big toe was amputated by plastic surgery 6 months after the initial presentation.
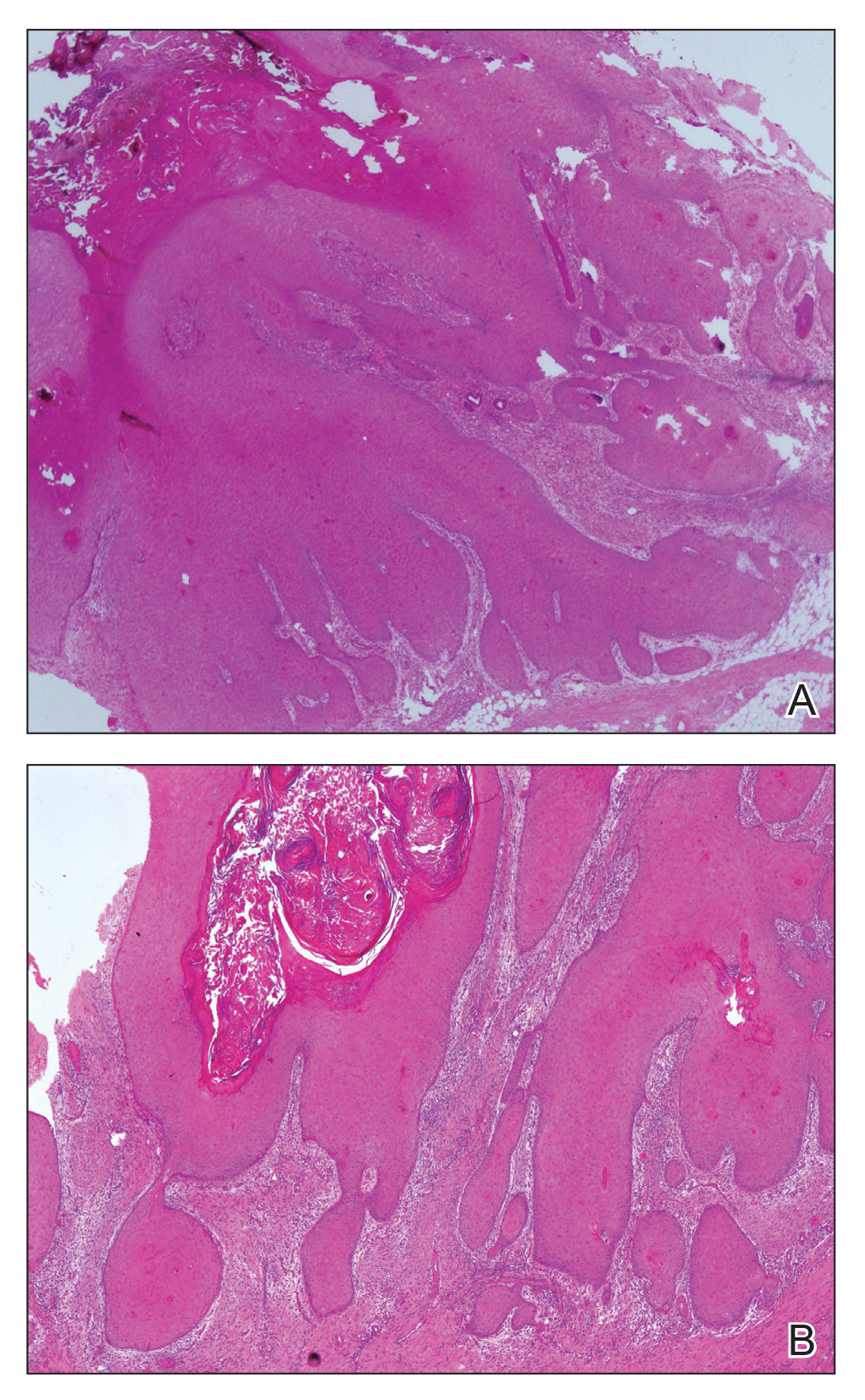
The term epithelioma cuniculatum was first used in 1954 to describe plantar VC. The term cuniculus is Latin for rabbit nest.3 At the distal part of the plantar surface of the foot, VC presents as an exophytic funguslike mass with abundant keratin-filled sinuses.14 When pressure is applied to the lesion, a greasy, yellowish, foul-smelling material with the consistency of toothpaste emerges from the sinuses. The lesion resembles pyoderma vegetans and may present with secondary infections (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, fungal infection) and/or ulcerations. Its appearance resembles an inflammatory lesion more than a neoplasm.6 Sometimes the skin surrounding the lesion may be a yellowish color, giving the impression of a plantar wart.3,4 In most cases, in situ hybridization demonstrates a human papillomavirus genome.2-5,10 Other factors implicated in the etiopathogenesis of VC include chronic inflammation; a cicatrice associated with a condition such as chronic cutaneous tuberculosis, ulcerative leprosy, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, or chronic osteomyelitis4; recurrent trauma3; and/or lichen planus.2,4 In spite of its slow development and benign appearance, VC may cause severe destruction affecting surrounding bony structures and may ultimately require amputation.2,4 In its early stages, VC can be mistaken for a benign tumor or other benign lesion, such as giant seborrheic keratosis, giant keratoacanthoma, eccrine poroma, or verruciform xanthoma, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.5
Histopathologic examination, especially of superficial biopsies, generally reveals squamous cell proliferation demonstrating minimal pleomorphism and cytologic atypia with sparse mitotic figures.4-6 Diagnosis of VC can be challenging if the endophytic proliferation, which characteristically pushes into the dermis and even deeper tissues at the base of the lesion, is not seen. This feature is uncommon in squamous cell carcinomas.3,4,6 Histopathologic detection of koilocytes can lead to difficulty in distinguishing VC from warts.5 The growth of lesions is exophytic in plantar verrucae, whereas in VC it may be either exophytic or endophytic.4 At early stages, it is too difficult to distinguish VC from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia caused by chronic inflammation, as well as from tuberculosis and subcutaneous mycoses.3,6 In these situations, possible responsible microorganisms must be sought out. Amelanotic malignant melanoma and eccrine poroma also should be considered in the differential diagnosis.3,5 If the biopsy specimen is obtained superficially and is fragmented, the diagnosis is more difficult, making deep biopsies essential in suspicious cases.4 Excision is the best treatment, and Mohs micrographic surgery may be required in some cases.2,3,11 It is important to consider that radiotherapy may lead to anaplastic transformation and metastasis.2 Metastasis to lymph nodes is very rare, and the prognosis is excellent when complete excision is performed.2 Recurrence may be observed.4
Our case of plantar VC is notable because of the patient’s young age, which is uncommon, as the typical age for developing VC is late middle age (ie, fifth and sixth decades of life). A long-standing lesion that is therapy resistant and without a detectable microorganism should be investigated for malignancy by repetitive deep biopsy regardless of the patient’s age, as demonstrated in our case.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosal. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- Mc Kee PH, ed. Pathology of the Skin. 2nd ed. London, England: Mosby-Wolfe; 1996.
- Schwartz RA, Stoll HL. Squamous cell carcinoma. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: Mc-Graw Hill; 1999:840-856.
- MacKie RM. Epidermal skin tumours. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Ebling FJG, et al, eds. Textbook of Dermatology. 5th ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific; 1992:1500-1556.
- Yoshtatsu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Van Geertruyden JP, Olemans C, Laporte M, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of the nail bed. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:327-328.
- Sanchez-Yus E, Velasco E, Robledo A. Verrucous carcinoma of the back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5 pt 2):947-950.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Mora RG. Microscopically controlled surgery (Mohs’ chemosurgery) for treatment of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of the foot (epithelioma cuniculatum). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:354-362.
- Kathuria S, Rieker J, Jablokow VR, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum): case report with review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1986;31:71-75.
- Brownstein MH, Shapiro L. Verrucous carcinoma of skin: epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Cancer. 1976;38:1710-1716.
- Ho J, Diven DG, Butler PJ, et al. An ulcerating verrucous plaque on the foot. verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum). Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:547-548, 550-551.
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma characterized by a well-differentiated low-grade tumor with a high degree of keratinization. First described by Ackerman1 in 1948, VC presents on the skin or oral and genital mucosae with minimal atypical cytologic findings.1-3 It most commonly is seen in late middle-aged men (85% of cases) and presents as a slow-growing mass, often of more than 10 years’ duration.2,3 Verrucous carcinoma frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, known as oral florid papillomatosis; the anogenital area, known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor; and on the plantar surface, known as epithelioma cuniculatum.2-13
A 19-year-old man presented with an ulcerous lesion on the right big toe of 2 years’ duration. He reported that the lesion had gradually increased in size and was painful when walking. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated lesion on the right big toe with purulent inflammation and necrosis, unclear edges, and border nodules containing a fatty, yellowish, foul-smelling material (Figure 1). Histologic examination of purulent material from deep within the primary lesion revealed gram-negative rods and gram-positive diplococci. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining and culture in Lowenstein-Jensen medium were negative for mycobacteria. Histologic examination and fungal culture were not diagnostic for fungal infection.

The differential diagnosis included tuberculosis cutis verrucosa, subcutaneous mycoses, swimming pool granuloma, leishmania cutis, chronic pyoderma vegetans, and VC. A punch biopsy of the lesion showed chronic nonspecific inflammation, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A repeat biopsy performed 15 days later also showed a nonspecific inflammation. At the initial presentation, an anti–human immunodeficiency virus test was negative. A purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test was positive and showed a 17-mm induration, and a sputum test was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A chest radiograph was normal. We considered the positive PPD skin test to be clinically insignificant; we did not find an accompanying tuberculosis infection, and the high exposure to atypical tuberculosis in developing countries such as Turkey, which is where the patient resided, often explains a positive PPD test.
At the initial presentation, radiography of the right big toe revealed porotic signs and cortical irregularity of the distal phalanx. A deep incisional biopsy of the lesion was performed for pathologic and microbiologic analysis. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining was negative, fungal elements could not be observed, and there was no growth in Lowenstein-Jensen medium or Sabouraud dextrose agar. Polymerase chain reaction for human papillomavirus, M tuberculosis, and atypical mycobacterium was negative. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal elements. Histopathologic examination revealed an exophytic as well as endophytic squamous cell proliferation infiltrating deeper layers of the dermis with a desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2). Slight cytologic atypia was noted. A diagnosis of VC was made based on the clinical and histopathologic findings. The patient’s right big toe was amputated by plastic surgery 6 months after the initial presentation.

The term epithelioma cuniculatum was first used in 1954 to describe plantar VC. The term cuniculus is Latin for rabbit nest.3 At the distal part of the plantar surface of the foot, VC presents as an exophytic funguslike mass with abundant keratin-filled sinuses.14 When pressure is applied to the lesion, a greasy, yellowish, foul-smelling material with the consistency of toothpaste emerges from the sinuses. The lesion resembles pyoderma vegetans and may present with secondary infections (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, fungal infection) and/or ulcerations. Its appearance resembles an inflammatory lesion more than a neoplasm.6 Sometimes the skin surrounding the lesion may be a yellowish color, giving the impression of a plantar wart.3,4 In most cases, in situ hybridization demonstrates a human papillomavirus genome.2-5,10 Other factors implicated in the etiopathogenesis of VC include chronic inflammation; a cicatrice associated with a condition such as chronic cutaneous tuberculosis, ulcerative leprosy, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, or chronic osteomyelitis4; recurrent trauma3; and/or lichen planus.2,4 In spite of its slow development and benign appearance, VC may cause severe destruction affecting surrounding bony structures and may ultimately require amputation.2,4 In its early stages, VC can be mistaken for a benign tumor or other benign lesion, such as giant seborrheic keratosis, giant keratoacanthoma, eccrine poroma, or verruciform xanthoma, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.5
Histopathologic examination, especially of superficial biopsies, generally reveals squamous cell proliferation demonstrating minimal pleomorphism and cytologic atypia with sparse mitotic figures.4-6 Diagnosis of VC can be challenging if the endophytic proliferation, which characteristically pushes into the dermis and even deeper tissues at the base of the lesion, is not seen. This feature is uncommon in squamous cell carcinomas.3,4,6 Histopathologic detection of koilocytes can lead to difficulty in distinguishing VC from warts.5 The growth of lesions is exophytic in plantar verrucae, whereas in VC it may be either exophytic or endophytic.4 At early stages, it is too difficult to distinguish VC from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia caused by chronic inflammation, as well as from tuberculosis and subcutaneous mycoses.3,6 In these situations, possible responsible microorganisms must be sought out. Amelanotic malignant melanoma and eccrine poroma also should be considered in the differential diagnosis.3,5 If the biopsy specimen is obtained superficially and is fragmented, the diagnosis is more difficult, making deep biopsies essential in suspicious cases.4 Excision is the best treatment, and Mohs micrographic surgery may be required in some cases.2,3,11 It is important to consider that radiotherapy may lead to anaplastic transformation and metastasis.2 Metastasis to lymph nodes is very rare, and the prognosis is excellent when complete excision is performed.2 Recurrence may be observed.4
Our case of plantar VC is notable because of the patient’s young age, which is uncommon, as the typical age for developing VC is late middle age (ie, fifth and sixth decades of life). A long-standing lesion that is therapy resistant and without a detectable microorganism should be investigated for malignancy by repetitive deep biopsy regardless of the patient’s age, as demonstrated in our case.
To the Editor:
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma characterized by a well-differentiated low-grade tumor with a high degree of keratinization. First described by Ackerman1 in 1948, VC presents on the skin or oral and genital mucosae with minimal atypical cytologic findings.1-3 It most commonly is seen in late middle-aged men (85% of cases) and presents as a slow-growing mass, often of more than 10 years’ duration.2,3 Verrucous carcinoma frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, known as oral florid papillomatosis; the anogenital area, known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor; and on the plantar surface, known as epithelioma cuniculatum.2-13
A 19-year-old man presented with an ulcerous lesion on the right big toe of 2 years’ duration. He reported that the lesion had gradually increased in size and was painful when walking. Physical examination revealed an ulcerated lesion on the right big toe with purulent inflammation and necrosis, unclear edges, and border nodules containing a fatty, yellowish, foul-smelling material (Figure 1). Histologic examination of purulent material from deep within the primary lesion revealed gram-negative rods and gram-positive diplococci. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining and culture in Lowenstein-Jensen medium were negative for mycobacteria. Histologic examination and fungal culture were not diagnostic for fungal infection.

The differential diagnosis included tuberculosis cutis verrucosa, subcutaneous mycoses, swimming pool granuloma, leishmania cutis, chronic pyoderma vegetans, and VC. A punch biopsy of the lesion showed chronic nonspecific inflammation, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A repeat biopsy performed 15 days later also showed a nonspecific inflammation. At the initial presentation, an anti–human immunodeficiency virus test was negative. A purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test was positive and showed a 17-mm induration, and a sputum test was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A chest radiograph was normal. We considered the positive PPD skin test to be clinically insignificant; we did not find an accompanying tuberculosis infection, and the high exposure to atypical tuberculosis in developing countries such as Turkey, which is where the patient resided, often explains a positive PPD test.
At the initial presentation, radiography of the right big toe revealed porotic signs and cortical irregularity of the distal phalanx. A deep incisional biopsy of the lesion was performed for pathologic and microbiologic analysis. Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen staining was negative, fungal elements could not be observed, and there was no growth in Lowenstein-Jensen medium or Sabouraud dextrose agar. Polymerase chain reaction for human papillomavirus, M tuberculosis, and atypical mycobacterium was negative. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal elements. Histopathologic examination revealed an exophytic as well as endophytic squamous cell proliferation infiltrating deeper layers of the dermis with a desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2). Slight cytologic atypia was noted. A diagnosis of VC was made based on the clinical and histopathologic findings. The patient’s right big toe was amputated by plastic surgery 6 months after the initial presentation.

The term epithelioma cuniculatum was first used in 1954 to describe plantar VC. The term cuniculus is Latin for rabbit nest.3 At the distal part of the plantar surface of the foot, VC presents as an exophytic funguslike mass with abundant keratin-filled sinuses.14 When pressure is applied to the lesion, a greasy, yellowish, foul-smelling material with the consistency of toothpaste emerges from the sinuses. The lesion resembles pyoderma vegetans and may present with secondary infections (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, fungal infection) and/or ulcerations. Its appearance resembles an inflammatory lesion more than a neoplasm.6 Sometimes the skin surrounding the lesion may be a yellowish color, giving the impression of a plantar wart.3,4 In most cases, in situ hybridization demonstrates a human papillomavirus genome.2-5,10 Other factors implicated in the etiopathogenesis of VC include chronic inflammation; a cicatrice associated with a condition such as chronic cutaneous tuberculosis, ulcerative leprosy, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, or chronic osteomyelitis4; recurrent trauma3; and/or lichen planus.2,4 In spite of its slow development and benign appearance, VC may cause severe destruction affecting surrounding bony structures and may ultimately require amputation.2,4 In its early stages, VC can be mistaken for a benign tumor or other benign lesion, such as giant seborrheic keratosis, giant keratoacanthoma, eccrine poroma, or verruciform xanthoma, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.5
Histopathologic examination, especially of superficial biopsies, generally reveals squamous cell proliferation demonstrating minimal pleomorphism and cytologic atypia with sparse mitotic figures.4-6 Diagnosis of VC can be challenging if the endophytic proliferation, which characteristically pushes into the dermis and even deeper tissues at the base of the lesion, is not seen. This feature is uncommon in squamous cell carcinomas.3,4,6 Histopathologic detection of koilocytes can lead to difficulty in distinguishing VC from warts.5 The growth of lesions is exophytic in plantar verrucae, whereas in VC it may be either exophytic or endophytic.4 At early stages, it is too difficult to distinguish VC from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia caused by chronic inflammation, as well as from tuberculosis and subcutaneous mycoses.3,6 In these situations, possible responsible microorganisms must be sought out. Amelanotic malignant melanoma and eccrine poroma also should be considered in the differential diagnosis.3,5 If the biopsy specimen is obtained superficially and is fragmented, the diagnosis is more difficult, making deep biopsies essential in suspicious cases.4 Excision is the best treatment, and Mohs micrographic surgery may be required in some cases.2,3,11 It is important to consider that radiotherapy may lead to anaplastic transformation and metastasis.2 Metastasis to lymph nodes is very rare, and the prognosis is excellent when complete excision is performed.2 Recurrence may be observed.4
Our case of plantar VC is notable because of the patient’s young age, which is uncommon, as the typical age for developing VC is late middle age (ie, fifth and sixth decades of life). A long-standing lesion that is therapy resistant and without a detectable microorganism should be investigated for malignancy by repetitive deep biopsy regardless of the patient’s age, as demonstrated in our case.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosal. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- Mc Kee PH, ed. Pathology of the Skin. 2nd ed. London, England: Mosby-Wolfe; 1996.
- Schwartz RA, Stoll HL. Squamous cell carcinoma. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: Mc-Graw Hill; 1999:840-856.
- MacKie RM. Epidermal skin tumours. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Ebling FJG, et al, eds. Textbook of Dermatology. 5th ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific; 1992:1500-1556.
- Yoshtatsu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Van Geertruyden JP, Olemans C, Laporte M, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of the nail bed. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:327-328.
- Sanchez-Yus E, Velasco E, Robledo A. Verrucous carcinoma of the back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5 pt 2):947-950.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Mora RG. Microscopically controlled surgery (Mohs’ chemosurgery) for treatment of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of the foot (epithelioma cuniculatum). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:354-362.
- Kathuria S, Rieker J, Jablokow VR, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum): case report with review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1986;31:71-75.
- Brownstein MH, Shapiro L. Verrucous carcinoma of skin: epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Cancer. 1976;38:1710-1716.
- Ho J, Diven DG, Butler PJ, et al. An ulcerating verrucous plaque on the foot. verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum). Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:547-548, 550-551.
- Ackerman LV. Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery. 1948;23:670-678.
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosal. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-21.
- Kao GF, Graham JH, Helwig EB. Carcinoma cuniculatum (verrucous carcinoma of the skin): a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases with ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 1982;49:2395-2403.
- Mc Kee PH, ed. Pathology of the Skin. 2nd ed. London, England: Mosby-Wolfe; 1996.
- Schwartz RA, Stoll HL. Squamous cell carcinoma. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: Mc-Graw Hill; 1999:840-856.
- MacKie RM. Epidermal skin tumours. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Ebling FJG, et al, eds. Textbook of Dermatology. 5th ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific; 1992:1500-1556.
- Yoshtatsu S, Takagi T, Ohata C, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma: report of a case treated with Boyd amputation followed by reconstruction with a free forearm flap. J Dermatol. 2001;28:226-230.
- Van Geertruyden JP, Olemans C, Laporte M, et al. Verrucous carcinoma of the nail bed. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:327-328.
- Sanchez-Yus E, Velasco E, Robledo A. Verrucous carcinoma of the back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5 pt 2):947-950.
- Noel JC, Peny MO, Detremmerie O, et al. Demonstration of human papillomavirus type 2 in a verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Dermatology. 1993;187:58-61.
- Mora RG. Microscopically controlled surgery (Mohs’ chemosurgery) for treatment of verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of the foot (epithelioma cuniculatum). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:354-362.
- Kathuria S, Rieker J, Jablokow VR, et al. Plantar verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum): case report with review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1986;31:71-75.
- Brownstein MH, Shapiro L. Verrucous carcinoma of skin: epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Cancer. 1976;38:1710-1716.
- Ho J, Diven DG, Butler PJ, et al. An ulcerating verrucous plaque on the foot. verrucous carcinoma (epithelioma cuniculatum). Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:547-548, 550-551.
Practice Points
- Verrucous carcinoma (VC) frequently is observed at 3 particular anatomic sites: the oral cavity, the anogenital area, and on the plantar surface.
- Plantar VC is rare, with a male predominance and most patients presenting in the fifth to sixth decades of life.
- Differentiating VS from benign tumors may be difficult, especially if only superficial biopsies are taken. Multiple biopsies and a close clinical correlation are required before a definite diagnosis is possible.
How does diet affect the risk of IBD?
CHICAGO – , according to a lecture delivered at Freston Conference 2019, sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association.
Although the literature is highly consistent, it contains discordant findings, and many questions remain unanswered. “We need more rigorous studies, and particularly more interventions, to truly understand the role diet may play in patients with IBD,” said Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Food can cause symptoms in IBD
Many patients with IBD are convinced that their diet caused their disease. A relevant point for physicians to consider is that these patients are at least as likely as is the general population to have intolerance or sensitivity to food components such as lactose and gluten. In a prospective questionnaire of 400 consecutive patients with IBD in the United Kingdom, 48% expressed the belief that diet could initiate IBD, and 57% said that diet could trigger a flare-up. In addition, 60% of respondents reported worsening of symptoms after eating certain foods, and about two-thirds deprived themselves of their favorite foods to prevent relapses (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22[1]:164-70). A French study found similar results. “Clearly there’s something there,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. Patients’ beliefs about the relationship between food and their symptoms are not simply misconceptions, he added.
A Canadian study published in 2016 found that almost one-third of patients with IBD avoid many food groups. “But there is significant heterogeneity in the foods that are avoided, and sometimes we mistake this heterogeneity for a lack of association between diet and symptoms in IBD,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. A larger number of patients avoid certain foods during periods of active disease, which suggests that food exacerbates their symptoms, he added. The same study showed that patients with IBD have more restrictive diets than do community controls. Patients eat fewer fruits and vegetables and generally consume less iron-rich food and less protein-rich food than healthy controls. GI intolerance, rather than professional advice, is the most common reason that patients with IBD restrict their diets (JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016;40[3]:405-11.).
A cross-sectional survey of 130 patients with IBD and 70 controls yielded similar results. Among patients, GI symptoms that resulted from consuming foods were not related to disease activity, disease location, or prior surgery. Patients with IBD tended to have greater frequency of GI intolerance to foods than did controls (Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32[6]:569-71.).
Diet may cause intestinal inflammation
International research has recorded increases in the consumption of sugar and fat (particularly saturated fat) and concomitant decreases in fiber consumption during the past several decades. The incidence of IBD has increased in parallel with these dietary changes with a remarkably similar trajectory, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. The correlation between dietary changes and IBD incidence “holds true even more strikingly in countries that are now experiencing Westernization,” he added. These countries have undergone more rapid dietary changes, and their IBD incidence has doubled or tripled. The transition to “less traditional diets” appears to promote intestinal inflammation, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
An analysis of data from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC) study found an association between high consumption of sugar and soft drinks, together with low consumption of vegetables, and risk of ulcerative colitis (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22[2]:345-54.). A subsequent analysis of data from two prospective Swedish cohorts, however, found no association between consumption of sugary beverages and risk of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17[1]:123-9.).
Although the data on sugar are mixed, data on the association between other macronutrient groups and risk of IBD are more consistent. When Dr. Ananthakrishnan and colleagues examined data from the Nurses’ Health Study, they found that the highest quintile of dietary fiber intake was associated with a 40% reduction in risk of Crohn’s disease, compared with the lowest quintile. The observed reduction of risk seemed to be greatest for fiber derived from fruits. Fiber from cereals, whole grains, or legumes, however, did not affect risk of Crohn’s disease (Gastroenterology. 2013;145[5]:970-7.).
A separate analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study suggested that high intake of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and low intake of n-6 PUFAs was associated with a 31% reduction in risk of ulcerative colitis and a 15% reduction in the risk of Crohn’s disease. These data were consistent with a previous analysis of EPIC data that found that high intake of n-6 PUFAs was associated with increased risk of ulcerative colitis (Gut. 2009;58[12]:1606-11.). Other analyses indicate that genetic polymorphisms likely modify the association between PUFAs and risk of ulcerative colitis, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. “There may be an additional layer of complexity beyond just measuring your dietary intake.”
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients can modify a patient’s risk of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. When Dr. Ananthakrishnan and colleagues examined the Nurses’ Health Study, they found an inverse association between vitamin D intake and risk of Crohn’s disease (Gastroenterology. 2012;142[3]:482-9.). In a separate study, they found that a zinc intake greater than 16 mg/day was associated with reduced risk of Crohn’s disease (Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44[6]:1995-2005.).
Patients aged older than 40 years and patients of European ancestry tend to be overrepresented in cohort studies, which reduces the generalizability of their conclusions, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. Furthermore, cohort studies have not produced consistent findings regarding the relationship between various dietary components and risk of IBD. Nevertheless, the data suggest that dietary patterns may be associated with incident Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
An influence of diet on IBD risk is plausible
One mechanism through which diet may exercise a causal influence on the risk of IBD is by affecting the microbiome. In 2011, investigators studied 98 healthy volunteers who answered questionnaires about their diet. The researchers also used 16s rDNA sequencing to characterize the population’s stool samples. A diet high in animal protein, amino acids, and saturated fats was associated with large populations of Bacteroides. A diet low in fat and in animal protein, but high in carbohydrates and simple sugars was associated with large populations of Prevotella. When the investigators conducted a controlled-feeding study of 10 patients, microbiome composition changed within 1 day of initiating a high-fat-and-low-fiber or a low-fat-and-high-fiber diet (Science. 2011;334[6052]:105-8.). A more recent study showed that the diversity of the microbiome increased with the adoption of an animal-based diet (Nature. 2014;505[7484]:559-63.).
Diet also may exert a causal influence on IBD risk by altering the intestinal barrier. In an experimental model, 5-mg/mL concentrations of fiber from plantain and broccoli significantly reduced the translocation of Escherichia coli through a human intestinal epithelial barrier (Gut. 2010;59[10]:1331-9.). Increased fiber intake may thus result in reduced intestinal inflammation, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
Observational and experimental evidence thus support an effect of diet on the risk of IBD, and experimental evidence indicates that this effect is biologically plausible. Nevertheless, “there are many missing links,” and further study will clarify the role of diet in IBD incidence, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
AGA offers education for your patients about IBD, including lifestyle and nutrition management, in the AGA GI Patient Center at https://www.gastro.org/practice-guidance/gi-patient-center/topic/inflammatory-bowel-disease-ibd.
CHICAGO – , according to a lecture delivered at Freston Conference 2019, sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association.
Although the literature is highly consistent, it contains discordant findings, and many questions remain unanswered. “We need more rigorous studies, and particularly more interventions, to truly understand the role diet may play in patients with IBD,” said Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Food can cause symptoms in IBD
Many patients with IBD are convinced that their diet caused their disease. A relevant point for physicians to consider is that these patients are at least as likely as is the general population to have intolerance or sensitivity to food components such as lactose and gluten. In a prospective questionnaire of 400 consecutive patients with IBD in the United Kingdom, 48% expressed the belief that diet could initiate IBD, and 57% said that diet could trigger a flare-up. In addition, 60% of respondents reported worsening of symptoms after eating certain foods, and about two-thirds deprived themselves of their favorite foods to prevent relapses (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22[1]:164-70). A French study found similar results. “Clearly there’s something there,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. Patients’ beliefs about the relationship between food and their symptoms are not simply misconceptions, he added.
A Canadian study published in 2016 found that almost one-third of patients with IBD avoid many food groups. “But there is significant heterogeneity in the foods that are avoided, and sometimes we mistake this heterogeneity for a lack of association between diet and symptoms in IBD,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. A larger number of patients avoid certain foods during periods of active disease, which suggests that food exacerbates their symptoms, he added. The same study showed that patients with IBD have more restrictive diets than do community controls. Patients eat fewer fruits and vegetables and generally consume less iron-rich food and less protein-rich food than healthy controls. GI intolerance, rather than professional advice, is the most common reason that patients with IBD restrict their diets (JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016;40[3]:405-11.).
A cross-sectional survey of 130 patients with IBD and 70 controls yielded similar results. Among patients, GI symptoms that resulted from consuming foods were not related to disease activity, disease location, or prior surgery. Patients with IBD tended to have greater frequency of GI intolerance to foods than did controls (Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32[6]:569-71.).
Diet may cause intestinal inflammation
International research has recorded increases in the consumption of sugar and fat (particularly saturated fat) and concomitant decreases in fiber consumption during the past several decades. The incidence of IBD has increased in parallel with these dietary changes with a remarkably similar trajectory, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. The correlation between dietary changes and IBD incidence “holds true even more strikingly in countries that are now experiencing Westernization,” he added. These countries have undergone more rapid dietary changes, and their IBD incidence has doubled or tripled. The transition to “less traditional diets” appears to promote intestinal inflammation, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
An analysis of data from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC) study found an association between high consumption of sugar and soft drinks, together with low consumption of vegetables, and risk of ulcerative colitis (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22[2]:345-54.). A subsequent analysis of data from two prospective Swedish cohorts, however, found no association between consumption of sugary beverages and risk of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17[1]:123-9.).
Although the data on sugar are mixed, data on the association between other macronutrient groups and risk of IBD are more consistent. When Dr. Ananthakrishnan and colleagues examined data from the Nurses’ Health Study, they found that the highest quintile of dietary fiber intake was associated with a 40% reduction in risk of Crohn’s disease, compared with the lowest quintile. The observed reduction of risk seemed to be greatest for fiber derived from fruits. Fiber from cereals, whole grains, or legumes, however, did not affect risk of Crohn’s disease (Gastroenterology. 2013;145[5]:970-7.).
A separate analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study suggested that high intake of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and low intake of n-6 PUFAs was associated with a 31% reduction in risk of ulcerative colitis and a 15% reduction in the risk of Crohn’s disease. These data were consistent with a previous analysis of EPIC data that found that high intake of n-6 PUFAs was associated with increased risk of ulcerative colitis (Gut. 2009;58[12]:1606-11.). Other analyses indicate that genetic polymorphisms likely modify the association between PUFAs and risk of ulcerative colitis, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. “There may be an additional layer of complexity beyond just measuring your dietary intake.”
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients can modify a patient’s risk of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. When Dr. Ananthakrishnan and colleagues examined the Nurses’ Health Study, they found an inverse association between vitamin D intake and risk of Crohn’s disease (Gastroenterology. 2012;142[3]:482-9.). In a separate study, they found that a zinc intake greater than 16 mg/day was associated with reduced risk of Crohn’s disease (Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44[6]:1995-2005.).
Patients aged older than 40 years and patients of European ancestry tend to be overrepresented in cohort studies, which reduces the generalizability of their conclusions, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. Furthermore, cohort studies have not produced consistent findings regarding the relationship between various dietary components and risk of IBD. Nevertheless, the data suggest that dietary patterns may be associated with incident Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
An influence of diet on IBD risk is plausible
One mechanism through which diet may exercise a causal influence on the risk of IBD is by affecting the microbiome. In 2011, investigators studied 98 healthy volunteers who answered questionnaires about their diet. The researchers also used 16s rDNA sequencing to characterize the population’s stool samples. A diet high in animal protein, amino acids, and saturated fats was associated with large populations of Bacteroides. A diet low in fat and in animal protein, but high in carbohydrates and simple sugars was associated with large populations of Prevotella. When the investigators conducted a controlled-feeding study of 10 patients, microbiome composition changed within 1 day of initiating a high-fat-and-low-fiber or a low-fat-and-high-fiber diet (Science. 2011;334[6052]:105-8.). A more recent study showed that the diversity of the microbiome increased with the adoption of an animal-based diet (Nature. 2014;505[7484]:559-63.).
Diet also may exert a causal influence on IBD risk by altering the intestinal barrier. In an experimental model, 5-mg/mL concentrations of fiber from plantain and broccoli significantly reduced the translocation of Escherichia coli through a human intestinal epithelial barrier (Gut. 2010;59[10]:1331-9.). Increased fiber intake may thus result in reduced intestinal inflammation, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
Observational and experimental evidence thus support an effect of diet on the risk of IBD, and experimental evidence indicates that this effect is biologically plausible. Nevertheless, “there are many missing links,” and further study will clarify the role of diet in IBD incidence, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
AGA offers education for your patients about IBD, including lifestyle and nutrition management, in the AGA GI Patient Center at https://www.gastro.org/practice-guidance/gi-patient-center/topic/inflammatory-bowel-disease-ibd.
CHICAGO – , according to a lecture delivered at Freston Conference 2019, sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association.
Although the literature is highly consistent, it contains discordant findings, and many questions remain unanswered. “We need more rigorous studies, and particularly more interventions, to truly understand the role diet may play in patients with IBD,” said Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Food can cause symptoms in IBD
Many patients with IBD are convinced that their diet caused their disease. A relevant point for physicians to consider is that these patients are at least as likely as is the general population to have intolerance or sensitivity to food components such as lactose and gluten. In a prospective questionnaire of 400 consecutive patients with IBD in the United Kingdom, 48% expressed the belief that diet could initiate IBD, and 57% said that diet could trigger a flare-up. In addition, 60% of respondents reported worsening of symptoms after eating certain foods, and about two-thirds deprived themselves of their favorite foods to prevent relapses (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22[1]:164-70). A French study found similar results. “Clearly there’s something there,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. Patients’ beliefs about the relationship between food and their symptoms are not simply misconceptions, he added.
A Canadian study published in 2016 found that almost one-third of patients with IBD avoid many food groups. “But there is significant heterogeneity in the foods that are avoided, and sometimes we mistake this heterogeneity for a lack of association between diet and symptoms in IBD,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. A larger number of patients avoid certain foods during periods of active disease, which suggests that food exacerbates their symptoms, he added. The same study showed that patients with IBD have more restrictive diets than do community controls. Patients eat fewer fruits and vegetables and generally consume less iron-rich food and less protein-rich food than healthy controls. GI intolerance, rather than professional advice, is the most common reason that patients with IBD restrict their diets (JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016;40[3]:405-11.).
A cross-sectional survey of 130 patients with IBD and 70 controls yielded similar results. Among patients, GI symptoms that resulted from consuming foods were not related to disease activity, disease location, or prior surgery. Patients with IBD tended to have greater frequency of GI intolerance to foods than did controls (Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32[6]:569-71.).
Diet may cause intestinal inflammation
International research has recorded increases in the consumption of sugar and fat (particularly saturated fat) and concomitant decreases in fiber consumption during the past several decades. The incidence of IBD has increased in parallel with these dietary changes with a remarkably similar trajectory, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. The correlation between dietary changes and IBD incidence “holds true even more strikingly in countries that are now experiencing Westernization,” he added. These countries have undergone more rapid dietary changes, and their IBD incidence has doubled or tripled. The transition to “less traditional diets” appears to promote intestinal inflammation, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
An analysis of data from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC) study found an association between high consumption of sugar and soft drinks, together with low consumption of vegetables, and risk of ulcerative colitis (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22[2]:345-54.). A subsequent analysis of data from two prospective Swedish cohorts, however, found no association between consumption of sugary beverages and risk of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17[1]:123-9.).
Although the data on sugar are mixed, data on the association between other macronutrient groups and risk of IBD are more consistent. When Dr. Ananthakrishnan and colleagues examined data from the Nurses’ Health Study, they found that the highest quintile of dietary fiber intake was associated with a 40% reduction in risk of Crohn’s disease, compared with the lowest quintile. The observed reduction of risk seemed to be greatest for fiber derived from fruits. Fiber from cereals, whole grains, or legumes, however, did not affect risk of Crohn’s disease (Gastroenterology. 2013;145[5]:970-7.).
A separate analysis of the Nurses’ Health Study suggested that high intake of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and low intake of n-6 PUFAs was associated with a 31% reduction in risk of ulcerative colitis and a 15% reduction in the risk of Crohn’s disease. These data were consistent with a previous analysis of EPIC data that found that high intake of n-6 PUFAs was associated with increased risk of ulcerative colitis (Gut. 2009;58[12]:1606-11.). Other analyses indicate that genetic polymorphisms likely modify the association between PUFAs and risk of ulcerative colitis, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. “There may be an additional layer of complexity beyond just measuring your dietary intake.”
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients can modify a patient’s risk of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. When Dr. Ananthakrishnan and colleagues examined the Nurses’ Health Study, they found an inverse association between vitamin D intake and risk of Crohn’s disease (Gastroenterology. 2012;142[3]:482-9.). In a separate study, they found that a zinc intake greater than 16 mg/day was associated with reduced risk of Crohn’s disease (Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44[6]:1995-2005.).
Patients aged older than 40 years and patients of European ancestry tend to be overrepresented in cohort studies, which reduces the generalizability of their conclusions, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan. Furthermore, cohort studies have not produced consistent findings regarding the relationship between various dietary components and risk of IBD. Nevertheless, the data suggest that dietary patterns may be associated with incident Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
An influence of diet on IBD risk is plausible
One mechanism through which diet may exercise a causal influence on the risk of IBD is by affecting the microbiome. In 2011, investigators studied 98 healthy volunteers who answered questionnaires about their diet. The researchers also used 16s rDNA sequencing to characterize the population’s stool samples. A diet high in animal protein, amino acids, and saturated fats was associated with large populations of Bacteroides. A diet low in fat and in animal protein, but high in carbohydrates and simple sugars was associated with large populations of Prevotella. When the investigators conducted a controlled-feeding study of 10 patients, microbiome composition changed within 1 day of initiating a high-fat-and-low-fiber or a low-fat-and-high-fiber diet (Science. 2011;334[6052]:105-8.). A more recent study showed that the diversity of the microbiome increased with the adoption of an animal-based diet (Nature. 2014;505[7484]:559-63.).
Diet also may exert a causal influence on IBD risk by altering the intestinal barrier. In an experimental model, 5-mg/mL concentrations of fiber from plantain and broccoli significantly reduced the translocation of Escherichia coli through a human intestinal epithelial barrier (Gut. 2010;59[10]:1331-9.). Increased fiber intake may thus result in reduced intestinal inflammation, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
Observational and experimental evidence thus support an effect of diet on the risk of IBD, and experimental evidence indicates that this effect is biologically plausible. Nevertheless, “there are many missing links,” and further study will clarify the role of diet in IBD incidence, said Dr. Ananthakrishnan.
AGA offers education for your patients about IBD, including lifestyle and nutrition management, in the AGA GI Patient Center at https://www.gastro.org/practice-guidance/gi-patient-center/topic/inflammatory-bowel-disease-ibd.
REPORTING FROM FRESTON CONFERENCE 2019
Interview with Andrew Solomon, MD, on diagnosing multiple sclerosis
Andrew Solomon, MD, is a neurologist and Associate Professor in the Department of Neurological Sciences and Division Chief of Multiple Sclerosis at The University of Vermont. We sat down to talk with Dr. Solomon about his experience with multiple sclerosis (MS) misdiagnosis and what can be done to improve MS diagnosis going forward.
How prevalent is the misdiagnosis of MS and what are the effects that it has on patients?
The first thing to clarify is what we mean by MS misdiagnosis. In this case, we’re talking about patients who are incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS. MS is hard to diagnose. Sometimes we take too long to diagnose people who have MS, sometimes we incorrectly diagnose MS in people who don’t have it.
We don’t have very good data in terms of how frequent misdiagnosis is, but we have some. The earliest data we have is from the 1980s. In 1988 there was a study published involving approximately 500 patients who had been diagnosed with MS in life and subsequently died between the 1960s and the 1980s and had a postmortem exam. 6% of those people who had a diagnosis of MS during their lifetime didn’t actually have MS.1
In 2012, we did a survey of 122 MS specialists.2 We asked them if they had encountered patients incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS in the past year, and 95% of them had seen such a patient. This was not the most scientific study because it was just a survey and subject to recall bias. Still, many of these MS providers recalled having seen three to ten such patients in the last year where they strongly felt that a pre-existing MS diagnosis made by another provider was incorrect.
Another study was recently published by Dr. Kaisey.3 She looked at referrals to two academic MS centers on the West Coast, and specifically new patient referrals over 12 months to those two MS centers. She found that out of 241 patients referred to the two MS centers, almost one in five who was referred with a pre-existing diagnosis of MS who came to these MS centers was subsequently found not have MS. This included 17% of patients at Cedars Sinai and 19% at UCLA. That’s an alarmingly high number of patients. And that’s the best data we have right now.
We don’t know how representative that number is of other MS centers and clinical practice nationally, but the bottom line is that misdiagnosis of MS is, unfortunately, fairly common and there’s a lot of risks to patients associated with misdiagnosis, as well as costs to our health care system.
Can you elaborate on the risks to patients?
We published a study where we looked at records from 110 patients who had been incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS. Twenty-three MS specialists from 4 different MS centers participated in this study that was published in Neurology in 2016.4
70% of these patients had been receiving disease modifying therapy for MS, which certainly has risks and side effects associated with it. 24% received disease modifying therapy with a known risk of PML, which is a frequently fatal brain infection associated with these therapies. Approximately 30% of these patients who did not have MS were on disease modifying therapy for in 3 to 9 years and 30% were on disease modifying therapy for 10 years or more.
Dr. Kaisey’s study also supports our findings. She found approximately 110 patient-years of exposure to unnecessary disease modifying therapy in the misdiagnosed patients in her study.3 Patients suffer side effects in addition to unnecessary risk related to these therapies.
It’s also important to emphasize that many of these patients also received inadequate treatment for their correct diagnoses.
How did the 2017 revision to the McDonald criteria address the challenge of MS diagnosis?
The problem of MS misdiagnosis is prominently discussed in the 2017 McDonald criteria.5 Unfortunately, one of the likely causes of misdiagnosis is that many clinicians may not read the full manuscript of the McDonald criteria itself. They instead rely on summary cards or reproductions—condensed versions of how to diagnose MS—which often don’t really provide the full context that would allow physicians to think critically and avoid a misdiagnosis.
MS is still a clinical diagnosis, which means we’re reliant on physician decision-making to confirm a diagnosis of MS. There are multiple steps to it.
First, we must determine if somebody has a syndrome typical for MS and they have objective evidence of a CNS lesion. After that the McDonald criteria can be applied to determine if they meet dissemination in time, dissemination in space, and have no other explanation for this syndrome before making a diagnosis of MS. Each one of those steps is reliant on thoughtful clinical decision-making and may be prone to potential error.
Knowing the ins and outs and the details of each of those steps is important. Reading the diagnostic criteria is probably the first step in becoming skilled at MS diagnosis. It’s important to know the criteria were not developed as a screening tool. The neurologist is essentially the screening tool. The diagnostic criteria can’t be used until a MS-typical syndrome with objective evidence of a CNS lesion is confirmed.
In what way was the previous criteria flawed?
I wouldn’t say any of the MS diagnostic criteria were flawed; they have evolved along with data in our field that has helped us make diagnosis of MS earlier in many patients. When using the criteria, it’s important to understand the types of patients in the cohorts used to validate our diagnostic criteria. They were primarily younger than 50, and usually Caucasian. They had only syndromes typical for MS with objective evidence of CNS damage corroborating these syndromes. Using the criteria more broadly in patients who do not fit this profile can reduce its specificity and lead to misdiagnosis.
For determination of MRI dissemination in time and dissemination space, there are also some misconceptions that frequently lead to misdiagnosis. Knowing which areas are required for dissemination in space in crucial. For example, the optic nerve currently is not an area that can be used to fulfill dissemination in space, which is a mistake people frequently make. Knowing that the terms “juxtacortical” and “periventricular” means touching the ventricle and touching the cortex is very important. This is a mistake that’s often made as well, and many disorders present with MRI lesions near but not touching the cortex or ventricle. Knowing each element of our diagnostic criteria and what those terms specifically mean is important. In the 2017 McDonald criteria there’s an excellent glossary that helps clinicians understand these terms and how to use them appropriately.5
What more needs to be done to prevent MS misdiagnosis?
First, we need to figure out how to better educate clinicians on how to use our diagnostic criteria appropriately.
We recently completed a study that suggests that residents in training, and even MS specialists, have trouble using the diagnostic criteria. This study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Annual meeting but has not been published yet. Education on how to use the diagnostic criteria, and in which patients to use the criteria (and in which patients the criteria do not apply) is important, particularly when new revisions to the diagnostic criteria are published.
We published a paper recently that provided guidance on how to avoid misdiagnosis using the 2017 McDonald criteria, and how to approach patients where the diagnostic criteria didn’t apply.6 Sometimes additional clinical, laboratory, or MRI evaluation and monitoring is required in such patients to either confirm a diagnosis of MS, or determine that a patient does not have MS.
We also desperately need biomarkers that may help us diagnose MS more accurately in patients who have neurological symptoms and an abnormal MRI and are seeing a neurologist for the first time. There’s research going on now to find relevant biomarkers in the form of blood tests, as well as MRI assessments. In particular, ongoing research focused on the MRI finding we have termed the “central vein sign” suggests this approach may be helpful as a MRI-specific biomarker for MS.7,8 We need multicenter studies evaluating this and other biomarkers in patients who come to our clinics for a new evaluation for MS, to confirm that they are accurate. We need more researchers working on how to improve diagnosis of MS.
References:
1. Engell T. A clinico-pathoanatomical study of multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988;78(1):39-44.
2. Solomon AJ, Klein EP, Bourdette D. "Undiagnosing" multiple sclerosis: the challenge of misdiagnosis in MS. Neurology. 2012;78(24):1986-1991.
3. Kaisey M, Solomon AJ, Luu M, Giesser BS, Sicotte NL. Incidence of multiple sclerosis misdiagnosis in referrals to two academic centers. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;30:51-56.
4. Solomon AJ, Bourdette DN, Cross AH, et al. The contemporary spectrum of multiple sclerosis misdiagnosis: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2016;87(13):1393-1399.
5. Thompson AJ, Banwell BL, Barkhof F, et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(2):162-173..
6. Solomon AJ, Naismith RT, Cross AH. Misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis: impact of the 2017 McDonald criteria on clinical practice. Neurology. 2019;92(1):26-33.
7. Sati P, Oh J, Constable RT, et al; NAIMS Cooperative. The central vein sign and its clinical evaluation for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: a consensus statement from the North American Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Cooperative. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(12):714-722.
8. Sinnecker T, Clarke MA, Meier D, et al. Evaluation of the central vein sign as a diagnostic imaging biomarker in multiple sclerosis [published online ahead of print August 19, 2019]. JAMA Neurology. 2019: doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2478.
Andrew Solomon, MD, is a neurologist and Associate Professor in the Department of Neurological Sciences and Division Chief of Multiple Sclerosis at The University of Vermont. We sat down to talk with Dr. Solomon about his experience with multiple sclerosis (MS) misdiagnosis and what can be done to improve MS diagnosis going forward.
How prevalent is the misdiagnosis of MS and what are the effects that it has on patients?
The first thing to clarify is what we mean by MS misdiagnosis. In this case, we’re talking about patients who are incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS. MS is hard to diagnose. Sometimes we take too long to diagnose people who have MS, sometimes we incorrectly diagnose MS in people who don’t have it.
We don’t have very good data in terms of how frequent misdiagnosis is, but we have some. The earliest data we have is from the 1980s. In 1988 there was a study published involving approximately 500 patients who had been diagnosed with MS in life and subsequently died between the 1960s and the 1980s and had a postmortem exam. 6% of those people who had a diagnosis of MS during their lifetime didn’t actually have MS.1
In 2012, we did a survey of 122 MS specialists.2 We asked them if they had encountered patients incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS in the past year, and 95% of them had seen such a patient. This was not the most scientific study because it was just a survey and subject to recall bias. Still, many of these MS providers recalled having seen three to ten such patients in the last year where they strongly felt that a pre-existing MS diagnosis made by another provider was incorrect.
Another study was recently published by Dr. Kaisey.3 She looked at referrals to two academic MS centers on the West Coast, and specifically new patient referrals over 12 months to those two MS centers. She found that out of 241 patients referred to the two MS centers, almost one in five who was referred with a pre-existing diagnosis of MS who came to these MS centers was subsequently found not have MS. This included 17% of patients at Cedars Sinai and 19% at UCLA. That’s an alarmingly high number of patients. And that’s the best data we have right now.
We don’t know how representative that number is of other MS centers and clinical practice nationally, but the bottom line is that misdiagnosis of MS is, unfortunately, fairly common and there’s a lot of risks to patients associated with misdiagnosis, as well as costs to our health care system.
Can you elaborate on the risks to patients?
We published a study where we looked at records from 110 patients who had been incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS. Twenty-three MS specialists from 4 different MS centers participated in this study that was published in Neurology in 2016.4
70% of these patients had been receiving disease modifying therapy for MS, which certainly has risks and side effects associated with it. 24% received disease modifying therapy with a known risk of PML, which is a frequently fatal brain infection associated with these therapies. Approximately 30% of these patients who did not have MS were on disease modifying therapy for in 3 to 9 years and 30% were on disease modifying therapy for 10 years or more.
Dr. Kaisey’s study also supports our findings. She found approximately 110 patient-years of exposure to unnecessary disease modifying therapy in the misdiagnosed patients in her study.3 Patients suffer side effects in addition to unnecessary risk related to these therapies.
It’s also important to emphasize that many of these patients also received inadequate treatment for their correct diagnoses.
How did the 2017 revision to the McDonald criteria address the challenge of MS diagnosis?
The problem of MS misdiagnosis is prominently discussed in the 2017 McDonald criteria.5 Unfortunately, one of the likely causes of misdiagnosis is that many clinicians may not read the full manuscript of the McDonald criteria itself. They instead rely on summary cards or reproductions—condensed versions of how to diagnose MS—which often don’t really provide the full context that would allow physicians to think critically and avoid a misdiagnosis.
MS is still a clinical diagnosis, which means we’re reliant on physician decision-making to confirm a diagnosis of MS. There are multiple steps to it.
First, we must determine if somebody has a syndrome typical for MS and they have objective evidence of a CNS lesion. After that the McDonald criteria can be applied to determine if they meet dissemination in time, dissemination in space, and have no other explanation for this syndrome before making a diagnosis of MS. Each one of those steps is reliant on thoughtful clinical decision-making and may be prone to potential error.
Knowing the ins and outs and the details of each of those steps is important. Reading the diagnostic criteria is probably the first step in becoming skilled at MS diagnosis. It’s important to know the criteria were not developed as a screening tool. The neurologist is essentially the screening tool. The diagnostic criteria can’t be used until a MS-typical syndrome with objective evidence of a CNS lesion is confirmed.
In what way was the previous criteria flawed?
I wouldn’t say any of the MS diagnostic criteria were flawed; they have evolved along with data in our field that has helped us make diagnosis of MS earlier in many patients. When using the criteria, it’s important to understand the types of patients in the cohorts used to validate our diagnostic criteria. They were primarily younger than 50, and usually Caucasian. They had only syndromes typical for MS with objective evidence of CNS damage corroborating these syndromes. Using the criteria more broadly in patients who do not fit this profile can reduce its specificity and lead to misdiagnosis.
For determination of MRI dissemination in time and dissemination space, there are also some misconceptions that frequently lead to misdiagnosis. Knowing which areas are required for dissemination in space in crucial. For example, the optic nerve currently is not an area that can be used to fulfill dissemination in space, which is a mistake people frequently make. Knowing that the terms “juxtacortical” and “periventricular” means touching the ventricle and touching the cortex is very important. This is a mistake that’s often made as well, and many disorders present with MRI lesions near but not touching the cortex or ventricle. Knowing each element of our diagnostic criteria and what those terms specifically mean is important. In the 2017 McDonald criteria there’s an excellent glossary that helps clinicians understand these terms and how to use them appropriately.5
What more needs to be done to prevent MS misdiagnosis?
First, we need to figure out how to better educate clinicians on how to use our diagnostic criteria appropriately.
We recently completed a study that suggests that residents in training, and even MS specialists, have trouble using the diagnostic criteria. This study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Annual meeting but has not been published yet. Education on how to use the diagnostic criteria, and in which patients to use the criteria (and in which patients the criteria do not apply) is important, particularly when new revisions to the diagnostic criteria are published.
We published a paper recently that provided guidance on how to avoid misdiagnosis using the 2017 McDonald criteria, and how to approach patients where the diagnostic criteria didn’t apply.6 Sometimes additional clinical, laboratory, or MRI evaluation and monitoring is required in such patients to either confirm a diagnosis of MS, or determine that a patient does not have MS.
We also desperately need biomarkers that may help us diagnose MS more accurately in patients who have neurological symptoms and an abnormal MRI and are seeing a neurologist for the first time. There’s research going on now to find relevant biomarkers in the form of blood tests, as well as MRI assessments. In particular, ongoing research focused on the MRI finding we have termed the “central vein sign” suggests this approach may be helpful as a MRI-specific biomarker for MS.7,8 We need multicenter studies evaluating this and other biomarkers in patients who come to our clinics for a new evaluation for MS, to confirm that they are accurate. We need more researchers working on how to improve diagnosis of MS.
References:
1. Engell T. A clinico-pathoanatomical study of multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988;78(1):39-44.
2. Solomon AJ, Klein EP, Bourdette D. "Undiagnosing" multiple sclerosis: the challenge of misdiagnosis in MS. Neurology. 2012;78(24):1986-1991.
3. Kaisey M, Solomon AJ, Luu M, Giesser BS, Sicotte NL. Incidence of multiple sclerosis misdiagnosis in referrals to two academic centers. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;30:51-56.
4. Solomon AJ, Bourdette DN, Cross AH, et al. The contemporary spectrum of multiple sclerosis misdiagnosis: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2016;87(13):1393-1399.
5. Thompson AJ, Banwell BL, Barkhof F, et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(2):162-173..
6. Solomon AJ, Naismith RT, Cross AH. Misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis: impact of the 2017 McDonald criteria on clinical practice. Neurology. 2019;92(1):26-33.
7. Sati P, Oh J, Constable RT, et al; NAIMS Cooperative. The central vein sign and its clinical evaluation for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: a consensus statement from the North American Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Cooperative. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(12):714-722.
8. Sinnecker T, Clarke MA, Meier D, et al. Evaluation of the central vein sign as a diagnostic imaging biomarker in multiple sclerosis [published online ahead of print August 19, 2019]. JAMA Neurology. 2019: doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2478.
Andrew Solomon, MD, is a neurologist and Associate Professor in the Department of Neurological Sciences and Division Chief of Multiple Sclerosis at The University of Vermont. We sat down to talk with Dr. Solomon about his experience with multiple sclerosis (MS) misdiagnosis and what can be done to improve MS diagnosis going forward.
How prevalent is the misdiagnosis of MS and what are the effects that it has on patients?
The first thing to clarify is what we mean by MS misdiagnosis. In this case, we’re talking about patients who are incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS. MS is hard to diagnose. Sometimes we take too long to diagnose people who have MS, sometimes we incorrectly diagnose MS in people who don’t have it.
We don’t have very good data in terms of how frequent misdiagnosis is, but we have some. The earliest data we have is from the 1980s. In 1988 there was a study published involving approximately 500 patients who had been diagnosed with MS in life and subsequently died between the 1960s and the 1980s and had a postmortem exam. 6% of those people who had a diagnosis of MS during their lifetime didn’t actually have MS.1
In 2012, we did a survey of 122 MS specialists.2 We asked them if they had encountered patients incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS in the past year, and 95% of them had seen such a patient. This was not the most scientific study because it was just a survey and subject to recall bias. Still, many of these MS providers recalled having seen three to ten such patients in the last year where they strongly felt that a pre-existing MS diagnosis made by another provider was incorrect.
Another study was recently published by Dr. Kaisey.3 She looked at referrals to two academic MS centers on the West Coast, and specifically new patient referrals over 12 months to those two MS centers. She found that out of 241 patients referred to the two MS centers, almost one in five who was referred with a pre-existing diagnosis of MS who came to these MS centers was subsequently found not have MS. This included 17% of patients at Cedars Sinai and 19% at UCLA. That’s an alarmingly high number of patients. And that’s the best data we have right now.
We don’t know how representative that number is of other MS centers and clinical practice nationally, but the bottom line is that misdiagnosis of MS is, unfortunately, fairly common and there’s a lot of risks to patients associated with misdiagnosis, as well as costs to our health care system.
Can you elaborate on the risks to patients?
We published a study where we looked at records from 110 patients who had been incorrectly assigned a diagnosis of MS. Twenty-three MS specialists from 4 different MS centers participated in this study that was published in Neurology in 2016.4
70% of these patients had been receiving disease modifying therapy for MS, which certainly has risks and side effects associated with it. 24% received disease modifying therapy with a known risk of PML, which is a frequently fatal brain infection associated with these therapies. Approximately 30% of these patients who did not have MS were on disease modifying therapy for in 3 to 9 years and 30% were on disease modifying therapy for 10 years or more.
Dr. Kaisey’s study also supports our findings. She found approximately 110 patient-years of exposure to unnecessary disease modifying therapy in the misdiagnosed patients in her study.3 Patients suffer side effects in addition to unnecessary risk related to these therapies.
It’s also important to emphasize that many of these patients also received inadequate treatment for their correct diagnoses.
How did the 2017 revision to the McDonald criteria address the challenge of MS diagnosis?
The problem of MS misdiagnosis is prominently discussed in the 2017 McDonald criteria.5 Unfortunately, one of the likely causes of misdiagnosis is that many clinicians may not read the full manuscript of the McDonald criteria itself. They instead rely on summary cards or reproductions—condensed versions of how to diagnose MS—which often don’t really provide the full context that would allow physicians to think critically and avoid a misdiagnosis.
MS is still a clinical diagnosis, which means we’re reliant on physician decision-making to confirm a diagnosis of MS. There are multiple steps to it.
First, we must determine if somebody has a syndrome typical for MS and they have objective evidence of a CNS lesion. After that the McDonald criteria can be applied to determine if they meet dissemination in time, dissemination in space, and have no other explanation for this syndrome before making a diagnosis of MS. Each one of those steps is reliant on thoughtful clinical decision-making and may be prone to potential error.
Knowing the ins and outs and the details of each of those steps is important. Reading the diagnostic criteria is probably the first step in becoming skilled at MS diagnosis. It’s important to know the criteria were not developed as a screening tool. The neurologist is essentially the screening tool. The diagnostic criteria can’t be used until a MS-typical syndrome with objective evidence of a CNS lesion is confirmed.
In what way was the previous criteria flawed?
I wouldn’t say any of the MS diagnostic criteria were flawed; they have evolved along with data in our field that has helped us make diagnosis of MS earlier in many patients. When using the criteria, it’s important to understand the types of patients in the cohorts used to validate our diagnostic criteria. They were primarily younger than 50, and usually Caucasian. They had only syndromes typical for MS with objective evidence of CNS damage corroborating these syndromes. Using the criteria more broadly in patients who do not fit this profile can reduce its specificity and lead to misdiagnosis.
For determination of MRI dissemination in time and dissemination space, there are also some misconceptions that frequently lead to misdiagnosis. Knowing which areas are required for dissemination in space in crucial. For example, the optic nerve currently is not an area that can be used to fulfill dissemination in space, which is a mistake people frequently make. Knowing that the terms “juxtacortical” and “periventricular” means touching the ventricle and touching the cortex is very important. This is a mistake that’s often made as well, and many disorders present with MRI lesions near but not touching the cortex or ventricle. Knowing each element of our diagnostic criteria and what those terms specifically mean is important. In the 2017 McDonald criteria there’s an excellent glossary that helps clinicians understand these terms and how to use them appropriately.5
What more needs to be done to prevent MS misdiagnosis?
First, we need to figure out how to better educate clinicians on how to use our diagnostic criteria appropriately.
We recently completed a study that suggests that residents in training, and even MS specialists, have trouble using the diagnostic criteria. This study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Annual meeting but has not been published yet. Education on how to use the diagnostic criteria, and in which patients to use the criteria (and in which patients the criteria do not apply) is important, particularly when new revisions to the diagnostic criteria are published.
We published a paper recently that provided guidance on how to avoid misdiagnosis using the 2017 McDonald criteria, and how to approach patients where the diagnostic criteria didn’t apply.6 Sometimes additional clinical, laboratory, or MRI evaluation and monitoring is required in such patients to either confirm a diagnosis of MS, or determine that a patient does not have MS.
We also desperately need biomarkers that may help us diagnose MS more accurately in patients who have neurological symptoms and an abnormal MRI and are seeing a neurologist for the first time. There’s research going on now to find relevant biomarkers in the form of blood tests, as well as MRI assessments. In particular, ongoing research focused on the MRI finding we have termed the “central vein sign” suggests this approach may be helpful as a MRI-specific biomarker for MS.7,8 We need multicenter studies evaluating this and other biomarkers in patients who come to our clinics for a new evaluation for MS, to confirm that they are accurate. We need more researchers working on how to improve diagnosis of MS.
References:
1. Engell T. A clinico-pathoanatomical study of multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988;78(1):39-44.
2. Solomon AJ, Klein EP, Bourdette D. "Undiagnosing" multiple sclerosis: the challenge of misdiagnosis in MS. Neurology. 2012;78(24):1986-1991.
3. Kaisey M, Solomon AJ, Luu M, Giesser BS, Sicotte NL. Incidence of multiple sclerosis misdiagnosis in referrals to two academic centers. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;30:51-56.
4. Solomon AJ, Bourdette DN, Cross AH, et al. The contemporary spectrum of multiple sclerosis misdiagnosis: a multicenter study. Neurology. 2016;87(13):1393-1399.
5. Thompson AJ, Banwell BL, Barkhof F, et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(2):162-173..
6. Solomon AJ, Naismith RT, Cross AH. Misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis: impact of the 2017 McDonald criteria on clinical practice. Neurology. 2019;92(1):26-33.
7. Sati P, Oh J, Constable RT, et al; NAIMS Cooperative. The central vein sign and its clinical evaluation for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: a consensus statement from the North American Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Cooperative. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(12):714-722.
8. Sinnecker T, Clarke MA, Meier D, et al. Evaluation of the central vein sign as a diagnostic imaging biomarker in multiple sclerosis [published online ahead of print August 19, 2019]. JAMA Neurology. 2019: doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2478.
Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation Following Treatment of Hyperkeratosis Lenticularis Perstans With Tazarotene Cream 0.1%
To the Editor:
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (HLP), or Flegel disease, is a rare keratinization disorder characterized by asymptomatic, red-brown, 1- to 5-mm papules with irregular horny scales commonly seen on the dorsal feet and lower legs.1 Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is notorious for being difficult to treat. Various treatment options, including 5-fluorouracil, topical and oral retinoids, vitamin D3 derivatives, psoralen plus UVA therapy, and dermabrasion, have been explored but none have proven to be consistently effective.
A woman in her 50s presented with an asymptomatic eruption on the legs and thighs that had been present for the last 20 years. She had been misdiagnosed by multiple outside providers with atopic dermatitis and was treated with topical steroids without considerable improvement. Upon initial presentation to our clinic , physical examination revealed a woman with Fitzpatrick skin type II with multiple hyperpigmented, red-brown, 2- to 6-mm papules on the extensor surfaces of the lower legs and upper thighs (Figure, A). A 3-mm punch biopsy of a lesion on the right upper thigh revealed hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis with basal layer degeneration and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. The clinical and histopathologic findings were consistent with HLP.
The patient was started on treatment with 5-fluorouracil cream on the right leg and tazarotene cream 0.1% on the left leg to determine which agent would work best. After 9 weeks of treatment, slight improvement was observed on both legs, but the lesions were still erythematous (Figure, B). Treatment was continued, and after 14 weeks complete resolution of the lesions was noted on both legs; however, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) was observed on the left leg, which had been treated with tazarotene (Figure, C). The patient was lost to follow-up prior to treatment of the PIH.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is an acquired excess of pigment due to a prior disease process such as an infection, allergic reaction, trauma, inflammatory disease, or drug reaction. In our patient, this finding was unusual because tazarotene has been shown to be an effective treatment of PIH.2,3
In PIH, there is either abnormal production or distribution of melanin pigment in the epidermis and/or dermis. Several mechanisms for PIH have been suggested. One potential mechanism is disruption of the basal cell layer due to dermal lymphocytic inflammation, causing melanin to be released and trapped by macrophages present in the dermal papillae. Another possible mechanism is epidermal hypermelanosis, in which the release and oxidation of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and leukotrienes alters immune cells and melanocytes, causing an increase in melanin and increased transfer of melanin to keratinocytes in the surrounding epidermis.4
Treatment of PIH can be a difficult and prolonged process, especially when a dermal rather than epidermal melanosis is observed. Topical retinoids, topical hydroquinone, azelaic acid, corticosteroids, tretinoin cream, glycolic acid, and trichloroacetic acid have been shown to be effective in treating epidermal PIH. Tazarotene is a synthetic retinoid that has been proven to be an effective treatment of PIH3; however, in our patient the PIH progressed with treatment. One plausible explanation is that irritation caused by the medication led to further PIH.2,5
It is uncommon for tazarotene to cause PIH. Hyperpigmentation is listed as an adverse effect observed during the postmarketing experience according to one manufacturer6 and the US Food and Drug Administration; however, details about prior incidents of hyperpigmentation have not been reported in the literature. Our case is unique because both treatments showed considerable improvement in HLP, but more PIH was observed on the tazarotene-treated leg.
- Bean SF. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. a clinical, histopathologic, and genetic study. Arch Dermatol. 1969;99:705-709.
- Callender V, St. Surin-Lord S, Davis E, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:87-99.
- McEvoy G. Tazarotene (topical). In: AHFS Drug Information. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc; 2014:84-92.
- Lacz N, Vafaie J, Kihiczak N, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a common but troubling condition. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:362-365.
- Tazorac (tazarotene) cream [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2013.
- Tazorac (tazarotene) gel [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2014.
To the Editor:
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (HLP), or Flegel disease, is a rare keratinization disorder characterized by asymptomatic, red-brown, 1- to 5-mm papules with irregular horny scales commonly seen on the dorsal feet and lower legs.1 Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is notorious for being difficult to treat. Various treatment options, including 5-fluorouracil, topical and oral retinoids, vitamin D3 derivatives, psoralen plus UVA therapy, and dermabrasion, have been explored but none have proven to be consistently effective.
A woman in her 50s presented with an asymptomatic eruption on the legs and thighs that had been present for the last 20 years. She had been misdiagnosed by multiple outside providers with atopic dermatitis and was treated with topical steroids without considerable improvement. Upon initial presentation to our clinic , physical examination revealed a woman with Fitzpatrick skin type II with multiple hyperpigmented, red-brown, 2- to 6-mm papules on the extensor surfaces of the lower legs and upper thighs (Figure, A). A 3-mm punch biopsy of a lesion on the right upper thigh revealed hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis with basal layer degeneration and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. The clinical and histopathologic findings were consistent with HLP.
The patient was started on treatment with 5-fluorouracil cream on the right leg and tazarotene cream 0.1% on the left leg to determine which agent would work best. After 9 weeks of treatment, slight improvement was observed on both legs, but the lesions were still erythematous (Figure, B). Treatment was continued, and after 14 weeks complete resolution of the lesions was noted on both legs; however, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) was observed on the left leg, which had been treated with tazarotene (Figure, C). The patient was lost to follow-up prior to treatment of the PIH.

Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is an acquired excess of pigment due to a prior disease process such as an infection, allergic reaction, trauma, inflammatory disease, or drug reaction. In our patient, this finding was unusual because tazarotene has been shown to be an effective treatment of PIH.2,3
In PIH, there is either abnormal production or distribution of melanin pigment in the epidermis and/or dermis. Several mechanisms for PIH have been suggested. One potential mechanism is disruption of the basal cell layer due to dermal lymphocytic inflammation, causing melanin to be released and trapped by macrophages present in the dermal papillae. Another possible mechanism is epidermal hypermelanosis, in which the release and oxidation of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and leukotrienes alters immune cells and melanocytes, causing an increase in melanin and increased transfer of melanin to keratinocytes in the surrounding epidermis.4
Treatment of PIH can be a difficult and prolonged process, especially when a dermal rather than epidermal melanosis is observed. Topical retinoids, topical hydroquinone, azelaic acid, corticosteroids, tretinoin cream, glycolic acid, and trichloroacetic acid have been shown to be effective in treating epidermal PIH. Tazarotene is a synthetic retinoid that has been proven to be an effective treatment of PIH3; however, in our patient the PIH progressed with treatment. One plausible explanation is that irritation caused by the medication led to further PIH.2,5
It is uncommon for tazarotene to cause PIH. Hyperpigmentation is listed as an adverse effect observed during the postmarketing experience according to one manufacturer6 and the US Food and Drug Administration; however, details about prior incidents of hyperpigmentation have not been reported in the literature. Our case is unique because both treatments showed considerable improvement in HLP, but more PIH was observed on the tazarotene-treated leg.
To the Editor:
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (HLP), or Flegel disease, is a rare keratinization disorder characterized by asymptomatic, red-brown, 1- to 5-mm papules with irregular horny scales commonly seen on the dorsal feet and lower legs.1 Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is notorious for being difficult to treat. Various treatment options, including 5-fluorouracil, topical and oral retinoids, vitamin D3 derivatives, psoralen plus UVA therapy, and dermabrasion, have been explored but none have proven to be consistently effective.
A woman in her 50s presented with an asymptomatic eruption on the legs and thighs that had been present for the last 20 years. She had been misdiagnosed by multiple outside providers with atopic dermatitis and was treated with topical steroids without considerable improvement. Upon initial presentation to our clinic , physical examination revealed a woman with Fitzpatrick skin type II with multiple hyperpigmented, red-brown, 2- to 6-mm papules on the extensor surfaces of the lower legs and upper thighs (Figure, A). A 3-mm punch biopsy of a lesion on the right upper thigh revealed hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis with basal layer degeneration and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. The clinical and histopathologic findings were consistent with HLP.
The patient was started on treatment with 5-fluorouracil cream on the right leg and tazarotene cream 0.1% on the left leg to determine which agent would work best. After 9 weeks of treatment, slight improvement was observed on both legs, but the lesions were still erythematous (Figure, B). Treatment was continued, and after 14 weeks complete resolution of the lesions was noted on both legs; however, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) was observed on the left leg, which had been treated with tazarotene (Figure, C). The patient was lost to follow-up prior to treatment of the PIH.

Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is an acquired excess of pigment due to a prior disease process such as an infection, allergic reaction, trauma, inflammatory disease, or drug reaction. In our patient, this finding was unusual because tazarotene has been shown to be an effective treatment of PIH.2,3
In PIH, there is either abnormal production or distribution of melanin pigment in the epidermis and/or dermis. Several mechanisms for PIH have been suggested. One potential mechanism is disruption of the basal cell layer due to dermal lymphocytic inflammation, causing melanin to be released and trapped by macrophages present in the dermal papillae. Another possible mechanism is epidermal hypermelanosis, in which the release and oxidation of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and leukotrienes alters immune cells and melanocytes, causing an increase in melanin and increased transfer of melanin to keratinocytes in the surrounding epidermis.4
Treatment of PIH can be a difficult and prolonged process, especially when a dermal rather than epidermal melanosis is observed. Topical retinoids, topical hydroquinone, azelaic acid, corticosteroids, tretinoin cream, glycolic acid, and trichloroacetic acid have been shown to be effective in treating epidermal PIH. Tazarotene is a synthetic retinoid that has been proven to be an effective treatment of PIH3; however, in our patient the PIH progressed with treatment. One plausible explanation is that irritation caused by the medication led to further PIH.2,5
It is uncommon for tazarotene to cause PIH. Hyperpigmentation is listed as an adverse effect observed during the postmarketing experience according to one manufacturer6 and the US Food and Drug Administration; however, details about prior incidents of hyperpigmentation have not been reported in the literature. Our case is unique because both treatments showed considerable improvement in HLP, but more PIH was observed on the tazarotene-treated leg.
- Bean SF. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. a clinical, histopathologic, and genetic study. Arch Dermatol. 1969;99:705-709.
- Callender V, St. Surin-Lord S, Davis E, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:87-99.
- McEvoy G. Tazarotene (topical). In: AHFS Drug Information. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc; 2014:84-92.
- Lacz N, Vafaie J, Kihiczak N, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a common but troubling condition. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:362-365.
- Tazorac (tazarotene) cream [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2013.
- Tazorac (tazarotene) gel [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2014.
- Bean SF. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. a clinical, histopathologic, and genetic study. Arch Dermatol. 1969;99:705-709.
- Callender V, St. Surin-Lord S, Davis E, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:87-99.
- McEvoy G. Tazarotene (topical). In: AHFS Drug Information. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc; 2014:84-92.
- Lacz N, Vafaie J, Kihiczak N, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a common but troubling condition. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:362-365.
- Tazorac (tazarotene) cream [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2013.
- Tazorac (tazarotene) gel [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2014.
Practice Points
- Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is a rare keratinization disorder that presents with asymptomatic red-brown papules with irregular horny scales on the lower extremities.
- Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans can be difficult to diagnose and treat. Hematoxylin and eosin staining generally will show hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis with basal layer degeneration and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
- Tazarotene cream 0.1% is a synthetic retinoid sometimes used for treatment of hyperpigmentation, but it also can cause postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.