User login
TRAIN-2: Anthracyclines added toxicity, with no increased efficacy, in HER2+ breast cancer
Anthracyclines add toxicity with no evidence of improved survival in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receiving a neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen plus dual HER2 blockade, results of a phase 3 trial have suggested.
Event-free survival (EFS) estimates at 3 years were 93% for patients receiving anthracycline-containing chemotherapy plus trastuzumab/pertuzumab and 94% for those receiving an anthracycline-free regimen, according to long-term follow-up results of TRAIN-2, a randomized, phase 3 trial.
There was also “no evidence” that higher-risk patients would benefit from anthracyclines, said investigator Anna Van der Voort of the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam.
“Today, anthracyclines are often used, especially in patients with higher risk of recurrence,” said Ms. Van der Voort in her presentation, which was part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program.
“Importantly, anthracyclines increased the risk of febrile neutropenia, cardiac toxicity, and chemotherapy-associated leukemia, and therefore, a neoadjuvant anthracycline-free regimen with dual HER2 blockade should be considered in all stage II and III HER2-positive breast cancer patients,” she suggested.
With these new results, there are now “great safety data and very promising efficacy data” from two comparative studies favoring nonanthracycline regimens plus HER2 blockade over an anthracycline approach, even in patients with disease thought to be at high risk of recurrence, said Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of California Los Angeles Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The other comparative study, BCIRG-006, demonstrated that docetaxel and carboplatin plus trastuzumab (TCH) had similar efficacy, fewer acute toxicities, and less cardiotoxicity and leukemia than did doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC-T).
In a follow-up analysis focused on patients with four or more positive lymph nodes, disease-free survival was similar for the nonanthracycline and anthracycline regimens, Dr. Hurvitz noted.
“I would challenge us to think carefully about the standard use of anthracyclines when we have so many targeted therapies available for our patients with HER2-positive disease now,” Dr. Hurvitz said in her commentary on TRAIN-2 that was also part of the virtual ASCO proceedings.
The TRAIN-2 trial included 438 patients in the Netherlands with previously untreated stage II to III HER2-positive breast cancer. Patients randomized to the anthracycline-containing arm received 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide in three 3-week cycles followed by paclitaxel and carboplatin in six 3-week cycles.
Patients in the anthracycline-free arm received paclitaxel and carboplatin for nine 3-week cycles. Both groups also received trastuzumab and pertuzumab concurrent with chemotherapy.
The pathological complete response (pCR) rate was high with and without anthracyclines, Ms. Van der Voort said, referring to primary results of TRAIN-2 previously published in Lancet Oncology.
In that report, pCR was seen in 67% of patients in the anthracycline group, and 68% in the nonanthracycline group (P = .95), a finding that was consistent regardless of tumor size, nodal status, or hormone receptor status, said Ms. Van der Voort. She added that significantly more febrile neutropenia and hypokalemia were seen in the anthracycline group.
At virtual ASCO, Ms. Van der Voort presented results of the EFS analysis. At the time of analysis, there were 21 events among 219 patients in the nonanthracycline group (10%) and 23 events among 219 patients in the anthracycline group (11%). The corresponding 3-year EFS estimates were 93.5% and 92.7%, with a hazard ratio that favored the nonanthracycline group, though the difference between arms was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-1.63).
“The results were independent of hormone receptor status, age, tumor size, nodal status, and grade, so we found no evidence that high-risk patients require anthracyclines,” said Ms. Van der Voort. Of note, results divided by nodal status suggested similar or better outcomes in the absence of anthracyclines, even in the highest-risk group, she added.
Estimated 3-year overall survival rates were likewise similar between groups, at 98.2% and 97.7% in the nonanthracycline and anthracycline arms, respectively.
Declines in left ventricular ejection fraction were more frequent in the anthracycline group (36% vs. 22% for the nonanthracycline group; P = .0016), and about one-third of patients did not recover that decline. New malignancies were found in 5% of the anthracycline group and 2% of the nonanthracycline group.
The TRAIN-2 study was sponsored by the Netherlands Cancer Institute and Roche. Ms. Van der Voort said she had no relationships to disclose. Dr. Hurwitz reported institutional research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies including Genentech/Roche.
SOURCE: Van der Voort A et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 501.
Anthracyclines add toxicity with no evidence of improved survival in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receiving a neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen plus dual HER2 blockade, results of a phase 3 trial have suggested.
Event-free survival (EFS) estimates at 3 years were 93% for patients receiving anthracycline-containing chemotherapy plus trastuzumab/pertuzumab and 94% for those receiving an anthracycline-free regimen, according to long-term follow-up results of TRAIN-2, a randomized, phase 3 trial.
There was also “no evidence” that higher-risk patients would benefit from anthracyclines, said investigator Anna Van der Voort of the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam.
“Today, anthracyclines are often used, especially in patients with higher risk of recurrence,” said Ms. Van der Voort in her presentation, which was part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program.
“Importantly, anthracyclines increased the risk of febrile neutropenia, cardiac toxicity, and chemotherapy-associated leukemia, and therefore, a neoadjuvant anthracycline-free regimen with dual HER2 blockade should be considered in all stage II and III HER2-positive breast cancer patients,” she suggested.
With these new results, there are now “great safety data and very promising efficacy data” from two comparative studies favoring nonanthracycline regimens plus HER2 blockade over an anthracycline approach, even in patients with disease thought to be at high risk of recurrence, said Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of California Los Angeles Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The other comparative study, BCIRG-006, demonstrated that docetaxel and carboplatin plus trastuzumab (TCH) had similar efficacy, fewer acute toxicities, and less cardiotoxicity and leukemia than did doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC-T).
In a follow-up analysis focused on patients with four or more positive lymph nodes, disease-free survival was similar for the nonanthracycline and anthracycline regimens, Dr. Hurvitz noted.
“I would challenge us to think carefully about the standard use of anthracyclines when we have so many targeted therapies available for our patients with HER2-positive disease now,” Dr. Hurvitz said in her commentary on TRAIN-2 that was also part of the virtual ASCO proceedings.
The TRAIN-2 trial included 438 patients in the Netherlands with previously untreated stage II to III HER2-positive breast cancer. Patients randomized to the anthracycline-containing arm received 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide in three 3-week cycles followed by paclitaxel and carboplatin in six 3-week cycles.
Patients in the anthracycline-free arm received paclitaxel and carboplatin for nine 3-week cycles. Both groups also received trastuzumab and pertuzumab concurrent with chemotherapy.
The pathological complete response (pCR) rate was high with and without anthracyclines, Ms. Van der Voort said, referring to primary results of TRAIN-2 previously published in Lancet Oncology.
In that report, pCR was seen in 67% of patients in the anthracycline group, and 68% in the nonanthracycline group (P = .95), a finding that was consistent regardless of tumor size, nodal status, or hormone receptor status, said Ms. Van der Voort. She added that significantly more febrile neutropenia and hypokalemia were seen in the anthracycline group.
At virtual ASCO, Ms. Van der Voort presented results of the EFS analysis. At the time of analysis, there were 21 events among 219 patients in the nonanthracycline group (10%) and 23 events among 219 patients in the anthracycline group (11%). The corresponding 3-year EFS estimates were 93.5% and 92.7%, with a hazard ratio that favored the nonanthracycline group, though the difference between arms was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-1.63).
“The results were independent of hormone receptor status, age, tumor size, nodal status, and grade, so we found no evidence that high-risk patients require anthracyclines,” said Ms. Van der Voort. Of note, results divided by nodal status suggested similar or better outcomes in the absence of anthracyclines, even in the highest-risk group, she added.
Estimated 3-year overall survival rates were likewise similar between groups, at 98.2% and 97.7% in the nonanthracycline and anthracycline arms, respectively.
Declines in left ventricular ejection fraction were more frequent in the anthracycline group (36% vs. 22% for the nonanthracycline group; P = .0016), and about one-third of patients did not recover that decline. New malignancies were found in 5% of the anthracycline group and 2% of the nonanthracycline group.
The TRAIN-2 study was sponsored by the Netherlands Cancer Institute and Roche. Ms. Van der Voort said she had no relationships to disclose. Dr. Hurwitz reported institutional research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies including Genentech/Roche.
SOURCE: Van der Voort A et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 501.
Anthracyclines add toxicity with no evidence of improved survival in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receiving a neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen plus dual HER2 blockade, results of a phase 3 trial have suggested.
Event-free survival (EFS) estimates at 3 years were 93% for patients receiving anthracycline-containing chemotherapy plus trastuzumab/pertuzumab and 94% for those receiving an anthracycline-free regimen, according to long-term follow-up results of TRAIN-2, a randomized, phase 3 trial.
There was also “no evidence” that higher-risk patients would benefit from anthracyclines, said investigator Anna Van der Voort of the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam.
“Today, anthracyclines are often used, especially in patients with higher risk of recurrence,” said Ms. Van der Voort in her presentation, which was part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program.
“Importantly, anthracyclines increased the risk of febrile neutropenia, cardiac toxicity, and chemotherapy-associated leukemia, and therefore, a neoadjuvant anthracycline-free regimen with dual HER2 blockade should be considered in all stage II and III HER2-positive breast cancer patients,” she suggested.
With these new results, there are now “great safety data and very promising efficacy data” from two comparative studies favoring nonanthracycline regimens plus HER2 blockade over an anthracycline approach, even in patients with disease thought to be at high risk of recurrence, said Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of California Los Angeles Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The other comparative study, BCIRG-006, demonstrated that docetaxel and carboplatin plus trastuzumab (TCH) had similar efficacy, fewer acute toxicities, and less cardiotoxicity and leukemia than did doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC-T).
In a follow-up analysis focused on patients with four or more positive lymph nodes, disease-free survival was similar for the nonanthracycline and anthracycline regimens, Dr. Hurvitz noted.
“I would challenge us to think carefully about the standard use of anthracyclines when we have so many targeted therapies available for our patients with HER2-positive disease now,” Dr. Hurvitz said in her commentary on TRAIN-2 that was also part of the virtual ASCO proceedings.
The TRAIN-2 trial included 438 patients in the Netherlands with previously untreated stage II to III HER2-positive breast cancer. Patients randomized to the anthracycline-containing arm received 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide in three 3-week cycles followed by paclitaxel and carboplatin in six 3-week cycles.
Patients in the anthracycline-free arm received paclitaxel and carboplatin for nine 3-week cycles. Both groups also received trastuzumab and pertuzumab concurrent with chemotherapy.
The pathological complete response (pCR) rate was high with and without anthracyclines, Ms. Van der Voort said, referring to primary results of TRAIN-2 previously published in Lancet Oncology.
In that report, pCR was seen in 67% of patients in the anthracycline group, and 68% in the nonanthracycline group (P = .95), a finding that was consistent regardless of tumor size, nodal status, or hormone receptor status, said Ms. Van der Voort. She added that significantly more febrile neutropenia and hypokalemia were seen in the anthracycline group.
At virtual ASCO, Ms. Van der Voort presented results of the EFS analysis. At the time of analysis, there were 21 events among 219 patients in the nonanthracycline group (10%) and 23 events among 219 patients in the anthracycline group (11%). The corresponding 3-year EFS estimates were 93.5% and 92.7%, with a hazard ratio that favored the nonanthracycline group, though the difference between arms was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-1.63).
“The results were independent of hormone receptor status, age, tumor size, nodal status, and grade, so we found no evidence that high-risk patients require anthracyclines,” said Ms. Van der Voort. Of note, results divided by nodal status suggested similar or better outcomes in the absence of anthracyclines, even in the highest-risk group, she added.
Estimated 3-year overall survival rates were likewise similar between groups, at 98.2% and 97.7% in the nonanthracycline and anthracycline arms, respectively.
Declines in left ventricular ejection fraction were more frequent in the anthracycline group (36% vs. 22% for the nonanthracycline group; P = .0016), and about one-third of patients did not recover that decline. New malignancies were found in 5% of the anthracycline group and 2% of the nonanthracycline group.
The TRAIN-2 study was sponsored by the Netherlands Cancer Institute and Roche. Ms. Van der Voort said she had no relationships to disclose. Dr. Hurwitz reported institutional research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies including Genentech/Roche.
SOURCE: Van der Voort A et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 501.
FROM ASCO 2020
Capecitabine maintenance improved DFS, not OS, in TNBC patients
according to results of a phase 3 trial.
Patients who received metronomic capecitabine maintenance had significantly higher rates of 5-year DFS and distant DFS, but not OS, when compared with patients who did not receive capecitabine, reported Xi Wang, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, who presented the findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“TNBC has the worst outcomes among all subtypes of breast cancer,” Dr. Wang said. “Effective strategies to reduce risk of relapse are a critical clinical need.”
He went on to describe capecitabine as a “potential ideal drug for metronomic administration,” particularly among patients with high risk of distant metastasis.
With that in mind, Dr. Wang and colleagues tested metronomic capecitabine maintenance in the phase 3 SYSUCC-001 trial. The trial included 434 patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. They had undergone standard therapy, which included surgery, neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Patients were randomized to receive capecitabine at 650 mg/m2 twice daily for 1 year (n = 221) or undergo observation (n = 213). The primary endpoint was DFS, while secondary endpoints included safety, distant DFS, and OS.
According to Dr. Wang, the two patient groups were “well balanced,” with similar baseline characteristics. Most patients underwent adjuvant chemotherapy (93%), had histological grade 3 tumors (71%-74%), had a Ki-67 index of at least 30% (73%-80%), had negative lymph node status (61%-62%), had a tumor size of 2.1-5 cm (55%-58%), and/or pathologic stage II disease (54%-55%).
Survival and safety
At a median follow-up of 56.5 months, the median 5-year DFS rate was 83% in the capecitabine group, compared with 73% in the observation group (P = .027). Similarly, capecitabine use correlated with a significantly better rate of distant DFS (85% vs. 76%; P = .016).
Although the capecitabine group demonstrated a slight trend toward improved OS at 5 years, this finding was not statistically significant (86% vs. 81%; P = .203).
Capecitabine was generally well tolerated, with 91% of patients completing 1 year of therapy, and 75% completing therapy at the full dose.
Almost half of patients in the capecitabine group experienced hand-foot syndrome (45%), and one in four developed leukopenia (24%). Less common adverse events included hyperbilirubinemia (13%), gastrointestinal pain (7%), and elevated serum transaminases (5%). No unexpected serious adverse events occurred.
Effects on practice
Amy Tiersten, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, suggested these findings may lead to broader use of capecitabine among patients with TNBC.
“[This is a] very exciting study showing an impressive disease-free survival benefit in the adjuvant setting for capecitabine in patients with early stage TNBC,” Dr. Tiersten said. “Presently, we only have positive data for capecitabine in patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy, but this current study now suggests that this benefit could extend to all comers.”
Dr. Tiersten advised that the medical community stay tuned, since longer-term data may provide a clearer picture of survival benefit.
“It will be interesting to see if there is an impact on overall survival with further follow-up,” she said.
According to invited discussant Naamit Kurshan Gerber, MD, of New York University, the results support previous findings from the CREATE-X trial, along with meta-analyses that have shown a “preferential benefit” of capecitabine when used to treat TNBC, compared with estrogen receptor–positive disease.
Still, Dr. Gerber noted that, for most patients, the findings from the SYSUCC-001 trial are unlikely to influence clinical decision-making since most patients with TNBC receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by treatment based on pathologic response. However, she also suggested that, after peer review, the findings could influence treatment for a select few.
“For the small population of patients who receive adjuvant chemotherapy for higher-stage TNBC and who would have met eligibility criteria, this approach may be considered,” Dr. Gerber said.
The study was funded by the Sun Yat-sen University Clinical Research 5010 Program. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gerber reported a relationship with OncLive. Dr. Tiersten reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang X et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 507.
according to results of a phase 3 trial.
Patients who received metronomic capecitabine maintenance had significantly higher rates of 5-year DFS and distant DFS, but not OS, when compared with patients who did not receive capecitabine, reported Xi Wang, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, who presented the findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“TNBC has the worst outcomes among all subtypes of breast cancer,” Dr. Wang said. “Effective strategies to reduce risk of relapse are a critical clinical need.”
He went on to describe capecitabine as a “potential ideal drug for metronomic administration,” particularly among patients with high risk of distant metastasis.
With that in mind, Dr. Wang and colleagues tested metronomic capecitabine maintenance in the phase 3 SYSUCC-001 trial. The trial included 434 patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. They had undergone standard therapy, which included surgery, neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Patients were randomized to receive capecitabine at 650 mg/m2 twice daily for 1 year (n = 221) or undergo observation (n = 213). The primary endpoint was DFS, while secondary endpoints included safety, distant DFS, and OS.
According to Dr. Wang, the two patient groups were “well balanced,” with similar baseline characteristics. Most patients underwent adjuvant chemotherapy (93%), had histological grade 3 tumors (71%-74%), had a Ki-67 index of at least 30% (73%-80%), had negative lymph node status (61%-62%), had a tumor size of 2.1-5 cm (55%-58%), and/or pathologic stage II disease (54%-55%).
Survival and safety
At a median follow-up of 56.5 months, the median 5-year DFS rate was 83% in the capecitabine group, compared with 73% in the observation group (P = .027). Similarly, capecitabine use correlated with a significantly better rate of distant DFS (85% vs. 76%; P = .016).
Although the capecitabine group demonstrated a slight trend toward improved OS at 5 years, this finding was not statistically significant (86% vs. 81%; P = .203).
Capecitabine was generally well tolerated, with 91% of patients completing 1 year of therapy, and 75% completing therapy at the full dose.
Almost half of patients in the capecitabine group experienced hand-foot syndrome (45%), and one in four developed leukopenia (24%). Less common adverse events included hyperbilirubinemia (13%), gastrointestinal pain (7%), and elevated serum transaminases (5%). No unexpected serious adverse events occurred.
Effects on practice
Amy Tiersten, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, suggested these findings may lead to broader use of capecitabine among patients with TNBC.
“[This is a] very exciting study showing an impressive disease-free survival benefit in the adjuvant setting for capecitabine in patients with early stage TNBC,” Dr. Tiersten said. “Presently, we only have positive data for capecitabine in patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy, but this current study now suggests that this benefit could extend to all comers.”
Dr. Tiersten advised that the medical community stay tuned, since longer-term data may provide a clearer picture of survival benefit.
“It will be interesting to see if there is an impact on overall survival with further follow-up,” she said.
According to invited discussant Naamit Kurshan Gerber, MD, of New York University, the results support previous findings from the CREATE-X trial, along with meta-analyses that have shown a “preferential benefit” of capecitabine when used to treat TNBC, compared with estrogen receptor–positive disease.
Still, Dr. Gerber noted that, for most patients, the findings from the SYSUCC-001 trial are unlikely to influence clinical decision-making since most patients with TNBC receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by treatment based on pathologic response. However, she also suggested that, after peer review, the findings could influence treatment for a select few.
“For the small population of patients who receive adjuvant chemotherapy for higher-stage TNBC and who would have met eligibility criteria, this approach may be considered,” Dr. Gerber said.
The study was funded by the Sun Yat-sen University Clinical Research 5010 Program. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gerber reported a relationship with OncLive. Dr. Tiersten reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang X et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 507.
according to results of a phase 3 trial.
Patients who received metronomic capecitabine maintenance had significantly higher rates of 5-year DFS and distant DFS, but not OS, when compared with patients who did not receive capecitabine, reported Xi Wang, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, who presented the findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“TNBC has the worst outcomes among all subtypes of breast cancer,” Dr. Wang said. “Effective strategies to reduce risk of relapse are a critical clinical need.”
He went on to describe capecitabine as a “potential ideal drug for metronomic administration,” particularly among patients with high risk of distant metastasis.
With that in mind, Dr. Wang and colleagues tested metronomic capecitabine maintenance in the phase 3 SYSUCC-001 trial. The trial included 434 patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. They had undergone standard therapy, which included surgery, neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Patients were randomized to receive capecitabine at 650 mg/m2 twice daily for 1 year (n = 221) or undergo observation (n = 213). The primary endpoint was DFS, while secondary endpoints included safety, distant DFS, and OS.
According to Dr. Wang, the two patient groups were “well balanced,” with similar baseline characteristics. Most patients underwent adjuvant chemotherapy (93%), had histological grade 3 tumors (71%-74%), had a Ki-67 index of at least 30% (73%-80%), had negative lymph node status (61%-62%), had a tumor size of 2.1-5 cm (55%-58%), and/or pathologic stage II disease (54%-55%).
Survival and safety
At a median follow-up of 56.5 months, the median 5-year DFS rate was 83% in the capecitabine group, compared with 73% in the observation group (P = .027). Similarly, capecitabine use correlated with a significantly better rate of distant DFS (85% vs. 76%; P = .016).
Although the capecitabine group demonstrated a slight trend toward improved OS at 5 years, this finding was not statistically significant (86% vs. 81%; P = .203).
Capecitabine was generally well tolerated, with 91% of patients completing 1 year of therapy, and 75% completing therapy at the full dose.
Almost half of patients in the capecitabine group experienced hand-foot syndrome (45%), and one in four developed leukopenia (24%). Less common adverse events included hyperbilirubinemia (13%), gastrointestinal pain (7%), and elevated serum transaminases (5%). No unexpected serious adverse events occurred.
Effects on practice
Amy Tiersten, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, suggested these findings may lead to broader use of capecitabine among patients with TNBC.
“[This is a] very exciting study showing an impressive disease-free survival benefit in the adjuvant setting for capecitabine in patients with early stage TNBC,” Dr. Tiersten said. “Presently, we only have positive data for capecitabine in patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy, but this current study now suggests that this benefit could extend to all comers.”
Dr. Tiersten advised that the medical community stay tuned, since longer-term data may provide a clearer picture of survival benefit.
“It will be interesting to see if there is an impact on overall survival with further follow-up,” she said.
According to invited discussant Naamit Kurshan Gerber, MD, of New York University, the results support previous findings from the CREATE-X trial, along with meta-analyses that have shown a “preferential benefit” of capecitabine when used to treat TNBC, compared with estrogen receptor–positive disease.
Still, Dr. Gerber noted that, for most patients, the findings from the SYSUCC-001 trial are unlikely to influence clinical decision-making since most patients with TNBC receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by treatment based on pathologic response. However, she also suggested that, after peer review, the findings could influence treatment for a select few.
“For the small population of patients who receive adjuvant chemotherapy for higher-stage TNBC and who would have met eligibility criteria, this approach may be considered,” Dr. Gerber said.
The study was funded by the Sun Yat-sen University Clinical Research 5010 Program. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gerber reported a relationship with OncLive. Dr. Tiersten reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang X et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 507.
FROM ASCO 2020
PPI added to chemo improves breast tumor response rate
The proton pump inhibitor (PPI) omeprazole may be a useful addition to treatment for triple-negative breast cancer, as it boosted the expected rate of tumor disappearance among women with early-stage disease, according to the results of a phase 2 trial.
The trial results are presented online at the 2020 virtual annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The rationale behind the approach includes the fact that PPIs inhibit fatty acid synthase (FASN), an enzyme overexpressed in 70% of newly diagnosed triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) and associated with poor prognosis.
In the study, omeprazole, a generic drug for gastroesophageal reflux, was added to standard chemotherapy. Both were given to 42 women as neoadjuvant treatment in the weeks before breast surgery at five US centers in the single-arm study.
The pathologic complete response (pCR) rate was 71% in the study population, which is higher than the typical 40% seen in patients treated with standard AC-T (adriamycin and cyclophosphamide plus a taxane), said lead author Sagar D. Sardesai, MBBS, a medical oncologist at Ohio State Comprehensive Cancer Center in Columbus.
“It’s exciting,” said Dr. Sardesai in an interview. “Overall, triple-negative patients who achieve a pCR have a very good outcome.”
That complete disappearance of the tumor is a surrogate for overall survival in TNBC, and patients who achieve it have a greatly reduced risk of recurrence or death, he explained.
Natalie Berger, MD, medical oncologist, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, said the study’s pCR rates were “much higher” than expected and “intriguing and hypothesis generating.”
But Dr. Berger, who was not involved in the study, wanted to see more data.
“Having a non-chemotherapeutic agent to offer our patients with TNBC that improves pCR rates without added toxicity would be an exciting finding, but we need a larger randomized study,” she said in an email.
The researchers, who include high-profile breast cancer specialist Kathy Miller, MD, of Indiana University, are seeking a National Cancer Institute or Department of Defense grant to mount a 100-plus patient randomized trial.
Potential Drug Target for Some Years
Dr. Sardesai explained that FASN, which is an enzyme, helps generate fatty acids that are a key to cancer cell survival. FASN is primarily found in hormone-dominated tissue such as those of the endometrium, prostate, and breast.
PPIs “selectively inhibit FASN activity and induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines with minimal effect on non-malignant cells,” wrote the study authors in their meeting abstract.
The only other known agent known to inhibit FASN is the weight loss drug orlistat, which is poorly absorbed by the body and unlikely to impact cancer cells, Dr. Sardesai said.
FASN has been a potential drug target in TNBC for 10 to 15 years, but the first clinical evidence of efficacy in solid tumors was only seen in the last 5 years, he commented.
In 2015, Chinese investigators reported that the PPI esomeprazole in combination with chemotherapy produced a 5-month improvement in progression-free survival (vs. chemo alone) among a subset of 15 TNBC patients in a randomized trial of 94 patients with a variety of breast cancer types.
No Added Toxicity, But Some Unexpected Findings
The study was conducted in patients with early-stage, operable TNBC (with and without baseline FASN expression) and no prior PPI use within 12 months.
All patients started daily high-dose omeprazole 4 to 7 days prior to start of AC-T neoadjuvant chemotherapy (the addition of carboplatin was allowed per physician discretion) and continued until surgery.
The primary endpoint was pCR, defined as no residual invasive disease in breast or axilla, in patients with baseline FASN expression (FASN+). The pCR rate was 71.4% in the 28 FASN+ patients and 71.8% in all 42 enrolled patients. The researchers had targeted a pCR rate of 60% in the FASN+ patients. Also, among the subset of 15 patients who received carboplatin with AC-T, the pCR was 73%.
These two findings both have limitations, commented Dr. Berger. She pointed out that it is “unexplained” as to why the pCR rates were similar among the FASN+ patients and the total population (including 14 FASN– patients); the pCR rate would be expected to be lower in the total population, she suggested.
Further, it was also unexplained as to why there were similar pCR rates with or without carboplatin; other research has demonstrated improved pCR rates in patients receiving additional carboplatin (compared to AC-T alone) but at the cost of increased toxicity, she said.
Dr. Sardesai said that omeprazole was well tolerated with no known grade 3 or 4 toxicities and that the chemotherapy toxicity was similar to prior studies of AC-T. PPIs have side effects if taken for longer than a year, including a higher risk of infections, osteoporosis, and low magnesium, he also commented.
“Omeprazole can be safely administered in doses that inhibit FASN. The addition of high-dose omeprazole to neoadjuvant AC-T yields a promising pCR rate without adding toxicity,” the authors concluded in their abstract.
Dr. Sardesai also highlighted the fact that using a PPI for breast cancer is an example of drug repurposing. The approach offers a way of rapid drug development because PPIs have complete safety and pharmacokinetics data available, he said. “If we can prove the efficacy, the treatment can move forward quickly and be available in clinical practice much sooner than with traditional drug development.”
The study was funded by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Sardesai disclosed financial ties to Novartis and Immunomedics. Other study authors have ties to industry. Dr. Berger disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The proton pump inhibitor (PPI) omeprazole may be a useful addition to treatment for triple-negative breast cancer, as it boosted the expected rate of tumor disappearance among women with early-stage disease, according to the results of a phase 2 trial.
The trial results are presented online at the 2020 virtual annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The rationale behind the approach includes the fact that PPIs inhibit fatty acid synthase (FASN), an enzyme overexpressed in 70% of newly diagnosed triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) and associated with poor prognosis.
In the study, omeprazole, a generic drug for gastroesophageal reflux, was added to standard chemotherapy. Both were given to 42 women as neoadjuvant treatment in the weeks before breast surgery at five US centers in the single-arm study.
The pathologic complete response (pCR) rate was 71% in the study population, which is higher than the typical 40% seen in patients treated with standard AC-T (adriamycin and cyclophosphamide plus a taxane), said lead author Sagar D. Sardesai, MBBS, a medical oncologist at Ohio State Comprehensive Cancer Center in Columbus.
“It’s exciting,” said Dr. Sardesai in an interview. “Overall, triple-negative patients who achieve a pCR have a very good outcome.”
That complete disappearance of the tumor is a surrogate for overall survival in TNBC, and patients who achieve it have a greatly reduced risk of recurrence or death, he explained.
Natalie Berger, MD, medical oncologist, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, said the study’s pCR rates were “much higher” than expected and “intriguing and hypothesis generating.”
But Dr. Berger, who was not involved in the study, wanted to see more data.
“Having a non-chemotherapeutic agent to offer our patients with TNBC that improves pCR rates without added toxicity would be an exciting finding, but we need a larger randomized study,” she said in an email.
The researchers, who include high-profile breast cancer specialist Kathy Miller, MD, of Indiana University, are seeking a National Cancer Institute or Department of Defense grant to mount a 100-plus patient randomized trial.
Potential Drug Target for Some Years
Dr. Sardesai explained that FASN, which is an enzyme, helps generate fatty acids that are a key to cancer cell survival. FASN is primarily found in hormone-dominated tissue such as those of the endometrium, prostate, and breast.
PPIs “selectively inhibit FASN activity and induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines with minimal effect on non-malignant cells,” wrote the study authors in their meeting abstract.
The only other known agent known to inhibit FASN is the weight loss drug orlistat, which is poorly absorbed by the body and unlikely to impact cancer cells, Dr. Sardesai said.
FASN has been a potential drug target in TNBC for 10 to 15 years, but the first clinical evidence of efficacy in solid tumors was only seen in the last 5 years, he commented.
In 2015, Chinese investigators reported that the PPI esomeprazole in combination with chemotherapy produced a 5-month improvement in progression-free survival (vs. chemo alone) among a subset of 15 TNBC patients in a randomized trial of 94 patients with a variety of breast cancer types.
No Added Toxicity, But Some Unexpected Findings
The study was conducted in patients with early-stage, operable TNBC (with and without baseline FASN expression) and no prior PPI use within 12 months.
All patients started daily high-dose omeprazole 4 to 7 days prior to start of AC-T neoadjuvant chemotherapy (the addition of carboplatin was allowed per physician discretion) and continued until surgery.
The primary endpoint was pCR, defined as no residual invasive disease in breast or axilla, in patients with baseline FASN expression (FASN+). The pCR rate was 71.4% in the 28 FASN+ patients and 71.8% in all 42 enrolled patients. The researchers had targeted a pCR rate of 60% in the FASN+ patients. Also, among the subset of 15 patients who received carboplatin with AC-T, the pCR was 73%.
These two findings both have limitations, commented Dr. Berger. She pointed out that it is “unexplained” as to why the pCR rates were similar among the FASN+ patients and the total population (including 14 FASN– patients); the pCR rate would be expected to be lower in the total population, she suggested.
Further, it was also unexplained as to why there were similar pCR rates with or without carboplatin; other research has demonstrated improved pCR rates in patients receiving additional carboplatin (compared to AC-T alone) but at the cost of increased toxicity, she said.
Dr. Sardesai said that omeprazole was well tolerated with no known grade 3 or 4 toxicities and that the chemotherapy toxicity was similar to prior studies of AC-T. PPIs have side effects if taken for longer than a year, including a higher risk of infections, osteoporosis, and low magnesium, he also commented.
“Omeprazole can be safely administered in doses that inhibit FASN. The addition of high-dose omeprazole to neoadjuvant AC-T yields a promising pCR rate without adding toxicity,” the authors concluded in their abstract.
Dr. Sardesai also highlighted the fact that using a PPI for breast cancer is an example of drug repurposing. The approach offers a way of rapid drug development because PPIs have complete safety and pharmacokinetics data available, he said. “If we can prove the efficacy, the treatment can move forward quickly and be available in clinical practice much sooner than with traditional drug development.”
The study was funded by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Sardesai disclosed financial ties to Novartis and Immunomedics. Other study authors have ties to industry. Dr. Berger disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The proton pump inhibitor (PPI) omeprazole may be a useful addition to treatment for triple-negative breast cancer, as it boosted the expected rate of tumor disappearance among women with early-stage disease, according to the results of a phase 2 trial.
The trial results are presented online at the 2020 virtual annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The rationale behind the approach includes the fact that PPIs inhibit fatty acid synthase (FASN), an enzyme overexpressed in 70% of newly diagnosed triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) and associated with poor prognosis.
In the study, omeprazole, a generic drug for gastroesophageal reflux, was added to standard chemotherapy. Both were given to 42 women as neoadjuvant treatment in the weeks before breast surgery at five US centers in the single-arm study.
The pathologic complete response (pCR) rate was 71% in the study population, which is higher than the typical 40% seen in patients treated with standard AC-T (adriamycin and cyclophosphamide plus a taxane), said lead author Sagar D. Sardesai, MBBS, a medical oncologist at Ohio State Comprehensive Cancer Center in Columbus.
“It’s exciting,” said Dr. Sardesai in an interview. “Overall, triple-negative patients who achieve a pCR have a very good outcome.”
That complete disappearance of the tumor is a surrogate for overall survival in TNBC, and patients who achieve it have a greatly reduced risk of recurrence or death, he explained.
Natalie Berger, MD, medical oncologist, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, said the study’s pCR rates were “much higher” than expected and “intriguing and hypothesis generating.”
But Dr. Berger, who was not involved in the study, wanted to see more data.
“Having a non-chemotherapeutic agent to offer our patients with TNBC that improves pCR rates without added toxicity would be an exciting finding, but we need a larger randomized study,” she said in an email.
The researchers, who include high-profile breast cancer specialist Kathy Miller, MD, of Indiana University, are seeking a National Cancer Institute or Department of Defense grant to mount a 100-plus patient randomized trial.
Potential Drug Target for Some Years
Dr. Sardesai explained that FASN, which is an enzyme, helps generate fatty acids that are a key to cancer cell survival. FASN is primarily found in hormone-dominated tissue such as those of the endometrium, prostate, and breast.
PPIs “selectively inhibit FASN activity and induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines with minimal effect on non-malignant cells,” wrote the study authors in their meeting abstract.
The only other known agent known to inhibit FASN is the weight loss drug orlistat, which is poorly absorbed by the body and unlikely to impact cancer cells, Dr. Sardesai said.
FASN has been a potential drug target in TNBC for 10 to 15 years, but the first clinical evidence of efficacy in solid tumors was only seen in the last 5 years, he commented.
In 2015, Chinese investigators reported that the PPI esomeprazole in combination with chemotherapy produced a 5-month improvement in progression-free survival (vs. chemo alone) among a subset of 15 TNBC patients in a randomized trial of 94 patients with a variety of breast cancer types.
No Added Toxicity, But Some Unexpected Findings
The study was conducted in patients with early-stage, operable TNBC (with and without baseline FASN expression) and no prior PPI use within 12 months.
All patients started daily high-dose omeprazole 4 to 7 days prior to start of AC-T neoadjuvant chemotherapy (the addition of carboplatin was allowed per physician discretion) and continued until surgery.
The primary endpoint was pCR, defined as no residual invasive disease in breast or axilla, in patients with baseline FASN expression (FASN+). The pCR rate was 71.4% in the 28 FASN+ patients and 71.8% in all 42 enrolled patients. The researchers had targeted a pCR rate of 60% in the FASN+ patients. Also, among the subset of 15 patients who received carboplatin with AC-T, the pCR was 73%.
These two findings both have limitations, commented Dr. Berger. She pointed out that it is “unexplained” as to why the pCR rates were similar among the FASN+ patients and the total population (including 14 FASN– patients); the pCR rate would be expected to be lower in the total population, she suggested.
Further, it was also unexplained as to why there were similar pCR rates with or without carboplatin; other research has demonstrated improved pCR rates in patients receiving additional carboplatin (compared to AC-T alone) but at the cost of increased toxicity, she said.
Dr. Sardesai said that omeprazole was well tolerated with no known grade 3 or 4 toxicities and that the chemotherapy toxicity was similar to prior studies of AC-T. PPIs have side effects if taken for longer than a year, including a higher risk of infections, osteoporosis, and low magnesium, he also commented.
“Omeprazole can be safely administered in doses that inhibit FASN. The addition of high-dose omeprazole to neoadjuvant AC-T yields a promising pCR rate without adding toxicity,” the authors concluded in their abstract.
Dr. Sardesai also highlighted the fact that using a PPI for breast cancer is an example of drug repurposing. The approach offers a way of rapid drug development because PPIs have complete safety and pharmacokinetics data available, he said. “If we can prove the efficacy, the treatment can move forward quickly and be available in clinical practice much sooner than with traditional drug development.”
The study was funded by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. Dr. Sardesai disclosed financial ties to Novartis and Immunomedics. Other study authors have ties to industry. Dr. Berger disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2020
First-line nivolumab plus platinum/etoposide effective in extensive-stage SCLC
While nivolumab plus doublet chemotherapy was effective in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) in a recent randomized trial, the results might not be sufficient to change current clinical practice, in which two first-line chemo-immunotherapies are already approved and recommended, sources said.
Nivolumab added to platinum/etoposide doublet chemotherapy was well tolerated and significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to chemotherapy alone, according to results of ECOG-ACRIN EA5161, a randomized, phase 2 trial including 160 patients with ES-SCLC.
Risks of progression and death were reduced by 32% and 27%, respectively, when the immune checkpoint inhibitor was given along with chemotherapy, according to data presented by investigator Ticiana A. Leal, MD, of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center in Madison.
“Our study, EA5161, confirms the efficacy of nivolumab in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer,” Dr. Leal said in a presentation she gave as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Nivolumab did demonstrate a clear PFS advantage in EA5161, but “more surprisingly for a small trial” it also showed a clear OS advantage, said Taofeek K. Owonikoko, MD, PhD, in a commentary on the study.
“While the study as currently reported is insufficient to change practice, it does however provide very strong data to make the combination of nivolumab and platinum doublet acceptable as a platform for future clinical trials,” he said in the commentary, which was also included in the virtual ASCO proceedings.
Going forward, it would be difficult to justify another nondefinitive randomized phase 2 chemo-immunotherapy trial, especially if there are no “immediate plans” for a confirmatory phase 3 trial, added Dr. Owonikoko, who is director of thoracic oncology at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University in Atlanta.
Nivolumab wasn’t the only immune checkpoint with new first-line data in ES-SCLC at ASCO. In the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 KEYNOTE-604 trial, pembrolizumab added to etoposide and platinum significantly prolonged PFS and showed a trend toward improved OS. However, the significance threshold for OS was missed, according to the report.
While these pembrolizumab data are also insufficient to change today’s practice standards, results for both the pembrolizumab- and nivolumab-containing regimens are nevertheless compelling to support their use as a platform for new treatment strategies, according to Dr. Owonikoko.
With these new ASCO data, there are now randomized data confirming a benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitor–based regimens in ES-SCLC, according to Lauren A. Byers, MD, from the department of thoracic/head and neck medical oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors that are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for first-line treatment of ES-SCLC include atezolizumab (in combination with carboplatin and etoposide) and durvalumab (in combination with either carboplatin or cisplatin plus etoposide). In current National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, both are described as “preferred” regimens for primary or adjuvant therapy.
“A lot of times in oncology we have trials with similar drugs, and you get somewhat different answers in terms of the outcome of the trials, so we’re kind of trying to tease them apart,” Dr. Byers said in an interview.
“I think in this situation, we’ve got four studies, and they essentially are extremely similar in terms of the result, which just gives us even more confidence that there is benefit, at least for a subset of patients.”
The EA5161 study was developed to evaluate the role of nivolumab in ES-SCLC, Dr. Leal said in her virtual ASCO presentation.
Of the 160 patients enrolled and randomized, 145 were eligible and treated, including 75 in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm and 70 in the chemotherapy arm. Participants were evenly split between performance status 0 and 1, and little more than half of patients were women, and a median of five treatment cycles were delivered in each arm.
Median PFS, the primary end point of the trial, was 5.5 months for nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus 4.7 months for chemotherapy alone for all eligible and treated patients (hazard ratio, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-1.00; P = .047). In the intent-to-treat population, median PFS was 5.5 and 4.6 months in the respective arms (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.46-0.91; P = .012).
Median overall survival was 11.3 months and 9.3 months for the nivolumab plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy-only arms, respectively, for all eligible and treated patients (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.49-1.1), and in the intent-to-treat population, median OS was 11.3 and 8.5 months for the respective arms (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.98; P = .038).
The overall response rate was 52% for nivolumab plus chemotherapy and 47% for chemotherapy alone, with a median duration of response of 5.6 and 3.3 months, respectively, Dr. Leal reported.
Treatment was generally well tolerated in both arms, according to the investigator, with no safety signals observed. Toxicities resulting in death occurred in nine patients in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm and seven in the chemotherapy-only arm. “Most of the events were related to progression of disease,” Dr. Leal said.
While nivolumab and pembrolizumab’s use in the first-line setting may be uncertain, it is currently approved for metastatic SCLC that has progressed following platinum-based chemotherapy and at least one more line of therapy, according to the drug’s package insert.
The EA5161 study was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Leal provided disclosures related to AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeyondSpring, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, InvisionFirst Lung, Merck, Mirati, Novocure, and Takeda.
Dr. Owonikoko provided disclosures related to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Celgene, Lilly, Sandoz, AbbVie, Eisai, and Takeda, among others. Dr. Byers reported disclosures related to Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, GenMab, PharmaMar, and Sierra Oncology, Tolero, Alethia, Merck, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Leal TA et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 9000.
While nivolumab plus doublet chemotherapy was effective in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) in a recent randomized trial, the results might not be sufficient to change current clinical practice, in which two first-line chemo-immunotherapies are already approved and recommended, sources said.
Nivolumab added to platinum/etoposide doublet chemotherapy was well tolerated and significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to chemotherapy alone, according to results of ECOG-ACRIN EA5161, a randomized, phase 2 trial including 160 patients with ES-SCLC.
Risks of progression and death were reduced by 32% and 27%, respectively, when the immune checkpoint inhibitor was given along with chemotherapy, according to data presented by investigator Ticiana A. Leal, MD, of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center in Madison.
“Our study, EA5161, confirms the efficacy of nivolumab in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer,” Dr. Leal said in a presentation she gave as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Nivolumab did demonstrate a clear PFS advantage in EA5161, but “more surprisingly for a small trial” it also showed a clear OS advantage, said Taofeek K. Owonikoko, MD, PhD, in a commentary on the study.
“While the study as currently reported is insufficient to change practice, it does however provide very strong data to make the combination of nivolumab and platinum doublet acceptable as a platform for future clinical trials,” he said in the commentary, which was also included in the virtual ASCO proceedings.
Going forward, it would be difficult to justify another nondefinitive randomized phase 2 chemo-immunotherapy trial, especially if there are no “immediate plans” for a confirmatory phase 3 trial, added Dr. Owonikoko, who is director of thoracic oncology at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University in Atlanta.
Nivolumab wasn’t the only immune checkpoint with new first-line data in ES-SCLC at ASCO. In the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 KEYNOTE-604 trial, pembrolizumab added to etoposide and platinum significantly prolonged PFS and showed a trend toward improved OS. However, the significance threshold for OS was missed, according to the report.
While these pembrolizumab data are also insufficient to change today’s practice standards, results for both the pembrolizumab- and nivolumab-containing regimens are nevertheless compelling to support their use as a platform for new treatment strategies, according to Dr. Owonikoko.
With these new ASCO data, there are now randomized data confirming a benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitor–based regimens in ES-SCLC, according to Lauren A. Byers, MD, from the department of thoracic/head and neck medical oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors that are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for first-line treatment of ES-SCLC include atezolizumab (in combination with carboplatin and etoposide) and durvalumab (in combination with either carboplatin or cisplatin plus etoposide). In current National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, both are described as “preferred” regimens for primary or adjuvant therapy.
“A lot of times in oncology we have trials with similar drugs, and you get somewhat different answers in terms of the outcome of the trials, so we’re kind of trying to tease them apart,” Dr. Byers said in an interview.
“I think in this situation, we’ve got four studies, and they essentially are extremely similar in terms of the result, which just gives us even more confidence that there is benefit, at least for a subset of patients.”
The EA5161 study was developed to evaluate the role of nivolumab in ES-SCLC, Dr. Leal said in her virtual ASCO presentation.
Of the 160 patients enrolled and randomized, 145 were eligible and treated, including 75 in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm and 70 in the chemotherapy arm. Participants were evenly split between performance status 0 and 1, and little more than half of patients were women, and a median of five treatment cycles were delivered in each arm.
Median PFS, the primary end point of the trial, was 5.5 months for nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus 4.7 months for chemotherapy alone for all eligible and treated patients (hazard ratio, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-1.00; P = .047). In the intent-to-treat population, median PFS was 5.5 and 4.6 months in the respective arms (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.46-0.91; P = .012).
Median overall survival was 11.3 months and 9.3 months for the nivolumab plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy-only arms, respectively, for all eligible and treated patients (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.49-1.1), and in the intent-to-treat population, median OS was 11.3 and 8.5 months for the respective arms (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.98; P = .038).
The overall response rate was 52% for nivolumab plus chemotherapy and 47% for chemotherapy alone, with a median duration of response of 5.6 and 3.3 months, respectively, Dr. Leal reported.
Treatment was generally well tolerated in both arms, according to the investigator, with no safety signals observed. Toxicities resulting in death occurred in nine patients in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm and seven in the chemotherapy-only arm. “Most of the events were related to progression of disease,” Dr. Leal said.
While nivolumab and pembrolizumab’s use in the first-line setting may be uncertain, it is currently approved for metastatic SCLC that has progressed following platinum-based chemotherapy and at least one more line of therapy, according to the drug’s package insert.
The EA5161 study was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Leal provided disclosures related to AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeyondSpring, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, InvisionFirst Lung, Merck, Mirati, Novocure, and Takeda.
Dr. Owonikoko provided disclosures related to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Celgene, Lilly, Sandoz, AbbVie, Eisai, and Takeda, among others. Dr. Byers reported disclosures related to Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, GenMab, PharmaMar, and Sierra Oncology, Tolero, Alethia, Merck, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Leal TA et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 9000.
While nivolumab plus doublet chemotherapy was effective in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) in a recent randomized trial, the results might not be sufficient to change current clinical practice, in which two first-line chemo-immunotherapies are already approved and recommended, sources said.
Nivolumab added to platinum/etoposide doublet chemotherapy was well tolerated and significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to chemotherapy alone, according to results of ECOG-ACRIN EA5161, a randomized, phase 2 trial including 160 patients with ES-SCLC.
Risks of progression and death were reduced by 32% and 27%, respectively, when the immune checkpoint inhibitor was given along with chemotherapy, according to data presented by investigator Ticiana A. Leal, MD, of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center in Madison.
“Our study, EA5161, confirms the efficacy of nivolumab in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer,” Dr. Leal said in a presentation she gave as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Nivolumab did demonstrate a clear PFS advantage in EA5161, but “more surprisingly for a small trial” it also showed a clear OS advantage, said Taofeek K. Owonikoko, MD, PhD, in a commentary on the study.
“While the study as currently reported is insufficient to change practice, it does however provide very strong data to make the combination of nivolumab and platinum doublet acceptable as a platform for future clinical trials,” he said in the commentary, which was also included in the virtual ASCO proceedings.
Going forward, it would be difficult to justify another nondefinitive randomized phase 2 chemo-immunotherapy trial, especially if there are no “immediate plans” for a confirmatory phase 3 trial, added Dr. Owonikoko, who is director of thoracic oncology at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University in Atlanta.
Nivolumab wasn’t the only immune checkpoint with new first-line data in ES-SCLC at ASCO. In the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 KEYNOTE-604 trial, pembrolizumab added to etoposide and platinum significantly prolonged PFS and showed a trend toward improved OS. However, the significance threshold for OS was missed, according to the report.
While these pembrolizumab data are also insufficient to change today’s practice standards, results for both the pembrolizumab- and nivolumab-containing regimens are nevertheless compelling to support their use as a platform for new treatment strategies, according to Dr. Owonikoko.
With these new ASCO data, there are now randomized data confirming a benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitor–based regimens in ES-SCLC, according to Lauren A. Byers, MD, from the department of thoracic/head and neck medical oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors that are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for first-line treatment of ES-SCLC include atezolizumab (in combination with carboplatin and etoposide) and durvalumab (in combination with either carboplatin or cisplatin plus etoposide). In current National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, both are described as “preferred” regimens for primary or adjuvant therapy.
“A lot of times in oncology we have trials with similar drugs, and you get somewhat different answers in terms of the outcome of the trials, so we’re kind of trying to tease them apart,” Dr. Byers said in an interview.
“I think in this situation, we’ve got four studies, and they essentially are extremely similar in terms of the result, which just gives us even more confidence that there is benefit, at least for a subset of patients.”
The EA5161 study was developed to evaluate the role of nivolumab in ES-SCLC, Dr. Leal said in her virtual ASCO presentation.
Of the 160 patients enrolled and randomized, 145 were eligible and treated, including 75 in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm and 70 in the chemotherapy arm. Participants were evenly split between performance status 0 and 1, and little more than half of patients were women, and a median of five treatment cycles were delivered in each arm.
Median PFS, the primary end point of the trial, was 5.5 months for nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus 4.7 months for chemotherapy alone for all eligible and treated patients (hazard ratio, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-1.00; P = .047). In the intent-to-treat population, median PFS was 5.5 and 4.6 months in the respective arms (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.46-0.91; P = .012).
Median overall survival was 11.3 months and 9.3 months for the nivolumab plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy-only arms, respectively, for all eligible and treated patients (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.49-1.1), and in the intent-to-treat population, median OS was 11.3 and 8.5 months for the respective arms (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.98; P = .038).
The overall response rate was 52% for nivolumab plus chemotherapy and 47% for chemotherapy alone, with a median duration of response of 5.6 and 3.3 months, respectively, Dr. Leal reported.
Treatment was generally well tolerated in both arms, according to the investigator, with no safety signals observed. Toxicities resulting in death occurred in nine patients in the nivolumab plus chemotherapy arm and seven in the chemotherapy-only arm. “Most of the events were related to progression of disease,” Dr. Leal said.
While nivolumab and pembrolizumab’s use in the first-line setting may be uncertain, it is currently approved for metastatic SCLC that has progressed following platinum-based chemotherapy and at least one more line of therapy, according to the drug’s package insert.
The EA5161 study was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Leal provided disclosures related to AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeyondSpring, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, InvisionFirst Lung, Merck, Mirati, Novocure, and Takeda.
Dr. Owonikoko provided disclosures related to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Celgene, Lilly, Sandoz, AbbVie, Eisai, and Takeda, among others. Dr. Byers reported disclosures related to Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, GenMab, PharmaMar, and Sierra Oncology, Tolero, Alethia, Merck, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Leal TA et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 9000.
FROM ASCO 2020
Despite guidelines, controversy remains over corticosteroids in COVID-19
Three main reasons have been put forth for using corticosteroids in critically ill patients with COVID-19, but only one – the hope of preventing lung fibrosis in patients with unresolved acute respiratory distress syndrome – is reasonable to employ now outside of formal randomized trials, Peter Pickkers, MD, PhD, asserted at a webinar on COVID-19 sponsored by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine.
The most commonly invoked rationale for giving steroids in patients with severe COVID-19 is to modulate the destructive inflammatory immune response that occurs with advancing disease. Another justification cited for giving steroids is to treat suspected adrenal insufficiency in those with refractory shock. Of note, both practices are endorsed in the recent Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines on management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 (Intensive Care Med. 2020 May;46[5]:854-87).
But those recommendations – numbers 22 and 42 out of a total of 50 recommendations included in the guidelines – should never have been made, according to Dr. Pickkers, professor of experimental intensive care medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
Dueling guidelines
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines, which were developed by a panel comprising 36 experts in 12 countries, are quite frank in conceding that the guidance in favor of corticosteroids are weak recommendations based on low-quality evidence.
The guidelines recommend against using corticosteroids to try to modulate the immune system in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), but do recommend steroids in those with COVID-19 and ARDS. However, the guidelines also note that, because of the very low quality of the evidence, some experts on the panel preferred not to issue a pro-steroids recommendation at all until higher-quality evidence becomes available. Dr. Pickkers said he believes that the minority view should have prevailed. Moreover, current COVID-19 guidance from the World Health Organization is at odds with the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendations; the WHO advises against corticosteroids unless the treatment is indicated for a reason other than immunomodulation, he noted.
The evidence in favor of steroids in an effort to blunt the immune response in COVID patients with ARDS is based largely upon a single small, retrospective, non–peer-reviewed report that 5-7 days of treatment with 1-2 mg/kg per day of methylprednisolone was associated with shortened fever duration and need for supplemental oxygen.
The evidence against steroids for immunomodulation comes mainly from earlier studies of the SARS and MERS novel coronaviruses. For example, in a multicenter study of 309 patients with the MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) virus, those who received corticosteroids received no benefit and experienced delayed viral clearance (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Mar 15;197[6]:757-67).
“The thing is, virtually all COVID-19 patients in the ICU fulfill the criteria for ARDS, so following the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines would have far-reaching consequences,” Dr. Pickkers said.
Those consequences include a theoretic potential for serious harm arising from dampening the immune response at a point in the course of COVID-19 when the virus is still present, which could result in slowed viral clearance and prolonged viral shedding. Moreover so far no one has been able to identify a sweet spot in the disease course where the viral load has waned and the immune response is sufficiently early that intervention with corticosteroids might have an optimal benefit/risk ratio, he continued.
“My opinion is that at this moment there is no benefit at all for corticosteroids for immunomodulation in patients with COVID-19,” Dr. Pickkers said. “My personal recommendation, in contrast to the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendation, is not to use this therapy outside of a study.”
He added that randomized, controlled trials of corticosteroid therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19 are ongoing in Europe and the United States, including the large RECOVERY study of dexamethasone in the United Kingdom.
As for the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendation to use corticosteroids to treat refractory shock in COVID-19, Dr. Pickkers dismissed this guidance as largely irrelevant. That’s because few patients with COVID-19 who need mechanical ventilation have refractory shock as evidenced by the need for a high infusion rate of norepinephrine. Anyway, he noted, that Surviving Sepsis recommendation is based upon extrapolation from evidence of benefit in bacterial septic shock patients, which he deemed to be of questionable relevance to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Attacking the fibroproliferative phase of ARDS
First off, Dr. Pickkers conceded, there is no evidence that treatment with corticosteroids to prevent lung fibrosis in COVID-19 patients with nonresolving ARDS is an effective strategy; the pandemic is simply too new at this point for the appropriate studies to have been done. But this much is known: Postmortem pathologic studies show fibroplastic proliferation is present in the lungs of COVID-19 patients, as in those who die of ARDS of other causes. Also, COVID-19 patients typically aren’t admitted to the ICU until day 11 or 12 after developing their first symptoms, so by the time they display indications that their ARDS is not resolving, the virus has typically left the scene; thus, there is little risk at that point that corticosteroids will promote viral proliferation. Additionally, studies in critically ill patients with nonresolving ARDS of other causes show clinically meaningful benefits for corticosteroid therapy.
Dr. Pickkers cited as “must reading” an analysis of five randomized trials of corticosteroid therapy in a total of 518 patients with acute lung injury ARDS of non–COVID-19 origin. The analysis by investigators at the University of Tennessee, Memphis, concluded that treatment resulted in clinically meaningful reductions in duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU length of stay. Moreover, in the 400 patients whose steroid therapy commenced before day 14 of ARDS, there was a statistically significant 22% reduction in risk of death, compared with patients in whom corticosteroids were started later (Intensive Care Med. 2008 Jan;34[1]:61-9).
Session cochair Jan De Waele, MD, PhD, struck a cautious note, remarking, “It’s my perception that we’re using the evidence that we’ve gathered in other conditions and are now trying to apply it in COVID-19. But quality data on patients with COVID-19 itself is pretty scare, and it’s really hard to say whether this disease behaves similarly to bacterial septic shock or to other viral infections.”
“We need more information about the use of corticosteroids in COVID-19, although I think a lot of people are using it at this moment,” added Dr. De Waele, a surgical intensivist at Ghent (Belgium) University.
That being said, he asked Dr. Pickkers when he considers using corticosteroids to prevent pulmonary fibrosis.
Dr. Pickkers said that when he notices that a COVID-19 patient’s lung compliance is worsening, that stiff lung is a clue that fibrosis is occurring and is having clinical consequences. “We also measure blood procollagen, a not very sensitive but moderately specific marker of fibroproliferation. If we see an increase in this biomarker and the lung mechanics are changing, then we do treat these patients with corticosteroids,” Dr. Pickkers replied.
He and his colleagues try to start steroids before day 14 of ARDS, and they continue treatment for longer than 7 days in order to prevent a rebound inflammatory response upon treatment discontinuation. They also avoid using neuromuscular agents and engage in meticulous infection surveillance in order to minimize potential complications of corticosteroid therapy in the ICU.
Dr. Pickkers reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
Three main reasons have been put forth for using corticosteroids in critically ill patients with COVID-19, but only one – the hope of preventing lung fibrosis in patients with unresolved acute respiratory distress syndrome – is reasonable to employ now outside of formal randomized trials, Peter Pickkers, MD, PhD, asserted at a webinar on COVID-19 sponsored by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine.
The most commonly invoked rationale for giving steroids in patients with severe COVID-19 is to modulate the destructive inflammatory immune response that occurs with advancing disease. Another justification cited for giving steroids is to treat suspected adrenal insufficiency in those with refractory shock. Of note, both practices are endorsed in the recent Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines on management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 (Intensive Care Med. 2020 May;46[5]:854-87).
But those recommendations – numbers 22 and 42 out of a total of 50 recommendations included in the guidelines – should never have been made, according to Dr. Pickkers, professor of experimental intensive care medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
Dueling guidelines
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines, which were developed by a panel comprising 36 experts in 12 countries, are quite frank in conceding that the guidance in favor of corticosteroids are weak recommendations based on low-quality evidence.
The guidelines recommend against using corticosteroids to try to modulate the immune system in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), but do recommend steroids in those with COVID-19 and ARDS. However, the guidelines also note that, because of the very low quality of the evidence, some experts on the panel preferred not to issue a pro-steroids recommendation at all until higher-quality evidence becomes available. Dr. Pickkers said he believes that the minority view should have prevailed. Moreover, current COVID-19 guidance from the World Health Organization is at odds with the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendations; the WHO advises against corticosteroids unless the treatment is indicated for a reason other than immunomodulation, he noted.
The evidence in favor of steroids in an effort to blunt the immune response in COVID patients with ARDS is based largely upon a single small, retrospective, non–peer-reviewed report that 5-7 days of treatment with 1-2 mg/kg per day of methylprednisolone was associated with shortened fever duration and need for supplemental oxygen.
The evidence against steroids for immunomodulation comes mainly from earlier studies of the SARS and MERS novel coronaviruses. For example, in a multicenter study of 309 patients with the MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) virus, those who received corticosteroids received no benefit and experienced delayed viral clearance (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Mar 15;197[6]:757-67).
“The thing is, virtually all COVID-19 patients in the ICU fulfill the criteria for ARDS, so following the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines would have far-reaching consequences,” Dr. Pickkers said.
Those consequences include a theoretic potential for serious harm arising from dampening the immune response at a point in the course of COVID-19 when the virus is still present, which could result in slowed viral clearance and prolonged viral shedding. Moreover so far no one has been able to identify a sweet spot in the disease course where the viral load has waned and the immune response is sufficiently early that intervention with corticosteroids might have an optimal benefit/risk ratio, he continued.
“My opinion is that at this moment there is no benefit at all for corticosteroids for immunomodulation in patients with COVID-19,” Dr. Pickkers said. “My personal recommendation, in contrast to the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendation, is not to use this therapy outside of a study.”
He added that randomized, controlled trials of corticosteroid therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19 are ongoing in Europe and the United States, including the large RECOVERY study of dexamethasone in the United Kingdom.
As for the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendation to use corticosteroids to treat refractory shock in COVID-19, Dr. Pickkers dismissed this guidance as largely irrelevant. That’s because few patients with COVID-19 who need mechanical ventilation have refractory shock as evidenced by the need for a high infusion rate of norepinephrine. Anyway, he noted, that Surviving Sepsis recommendation is based upon extrapolation from evidence of benefit in bacterial septic shock patients, which he deemed to be of questionable relevance to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Attacking the fibroproliferative phase of ARDS
First off, Dr. Pickkers conceded, there is no evidence that treatment with corticosteroids to prevent lung fibrosis in COVID-19 patients with nonresolving ARDS is an effective strategy; the pandemic is simply too new at this point for the appropriate studies to have been done. But this much is known: Postmortem pathologic studies show fibroplastic proliferation is present in the lungs of COVID-19 patients, as in those who die of ARDS of other causes. Also, COVID-19 patients typically aren’t admitted to the ICU until day 11 or 12 after developing their first symptoms, so by the time they display indications that their ARDS is not resolving, the virus has typically left the scene; thus, there is little risk at that point that corticosteroids will promote viral proliferation. Additionally, studies in critically ill patients with nonresolving ARDS of other causes show clinically meaningful benefits for corticosteroid therapy.
Dr. Pickkers cited as “must reading” an analysis of five randomized trials of corticosteroid therapy in a total of 518 patients with acute lung injury ARDS of non–COVID-19 origin. The analysis by investigators at the University of Tennessee, Memphis, concluded that treatment resulted in clinically meaningful reductions in duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU length of stay. Moreover, in the 400 patients whose steroid therapy commenced before day 14 of ARDS, there was a statistically significant 22% reduction in risk of death, compared with patients in whom corticosteroids were started later (Intensive Care Med. 2008 Jan;34[1]:61-9).
Session cochair Jan De Waele, MD, PhD, struck a cautious note, remarking, “It’s my perception that we’re using the evidence that we’ve gathered in other conditions and are now trying to apply it in COVID-19. But quality data on patients with COVID-19 itself is pretty scare, and it’s really hard to say whether this disease behaves similarly to bacterial septic shock or to other viral infections.”
“We need more information about the use of corticosteroids in COVID-19, although I think a lot of people are using it at this moment,” added Dr. De Waele, a surgical intensivist at Ghent (Belgium) University.
That being said, he asked Dr. Pickkers when he considers using corticosteroids to prevent pulmonary fibrosis.
Dr. Pickkers said that when he notices that a COVID-19 patient’s lung compliance is worsening, that stiff lung is a clue that fibrosis is occurring and is having clinical consequences. “We also measure blood procollagen, a not very sensitive but moderately specific marker of fibroproliferation. If we see an increase in this biomarker and the lung mechanics are changing, then we do treat these patients with corticosteroids,” Dr. Pickkers replied.
He and his colleagues try to start steroids before day 14 of ARDS, and they continue treatment for longer than 7 days in order to prevent a rebound inflammatory response upon treatment discontinuation. They also avoid using neuromuscular agents and engage in meticulous infection surveillance in order to minimize potential complications of corticosteroid therapy in the ICU.
Dr. Pickkers reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
Three main reasons have been put forth for using corticosteroids in critically ill patients with COVID-19, but only one – the hope of preventing lung fibrosis in patients with unresolved acute respiratory distress syndrome – is reasonable to employ now outside of formal randomized trials, Peter Pickkers, MD, PhD, asserted at a webinar on COVID-19 sponsored by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine.
The most commonly invoked rationale for giving steroids in patients with severe COVID-19 is to modulate the destructive inflammatory immune response that occurs with advancing disease. Another justification cited for giving steroids is to treat suspected adrenal insufficiency in those with refractory shock. Of note, both practices are endorsed in the recent Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines on management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 (Intensive Care Med. 2020 May;46[5]:854-87).
But those recommendations – numbers 22 and 42 out of a total of 50 recommendations included in the guidelines – should never have been made, according to Dr. Pickkers, professor of experimental intensive care medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
Dueling guidelines
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines, which were developed by a panel comprising 36 experts in 12 countries, are quite frank in conceding that the guidance in favor of corticosteroids are weak recommendations based on low-quality evidence.
The guidelines recommend against using corticosteroids to try to modulate the immune system in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), but do recommend steroids in those with COVID-19 and ARDS. However, the guidelines also note that, because of the very low quality of the evidence, some experts on the panel preferred not to issue a pro-steroids recommendation at all until higher-quality evidence becomes available. Dr. Pickkers said he believes that the minority view should have prevailed. Moreover, current COVID-19 guidance from the World Health Organization is at odds with the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendations; the WHO advises against corticosteroids unless the treatment is indicated for a reason other than immunomodulation, he noted.
The evidence in favor of steroids in an effort to blunt the immune response in COVID patients with ARDS is based largely upon a single small, retrospective, non–peer-reviewed report that 5-7 days of treatment with 1-2 mg/kg per day of methylprednisolone was associated with shortened fever duration and need for supplemental oxygen.
The evidence against steroids for immunomodulation comes mainly from earlier studies of the SARS and MERS novel coronaviruses. For example, in a multicenter study of 309 patients with the MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) virus, those who received corticosteroids received no benefit and experienced delayed viral clearance (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Mar 15;197[6]:757-67).
“The thing is, virtually all COVID-19 patients in the ICU fulfill the criteria for ARDS, so following the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines would have far-reaching consequences,” Dr. Pickkers said.
Those consequences include a theoretic potential for serious harm arising from dampening the immune response at a point in the course of COVID-19 when the virus is still present, which could result in slowed viral clearance and prolonged viral shedding. Moreover so far no one has been able to identify a sweet spot in the disease course where the viral load has waned and the immune response is sufficiently early that intervention with corticosteroids might have an optimal benefit/risk ratio, he continued.
“My opinion is that at this moment there is no benefit at all for corticosteroids for immunomodulation in patients with COVID-19,” Dr. Pickkers said. “My personal recommendation, in contrast to the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendation, is not to use this therapy outside of a study.”
He added that randomized, controlled trials of corticosteroid therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19 are ongoing in Europe and the United States, including the large RECOVERY study of dexamethasone in the United Kingdom.
As for the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendation to use corticosteroids to treat refractory shock in COVID-19, Dr. Pickkers dismissed this guidance as largely irrelevant. That’s because few patients with COVID-19 who need mechanical ventilation have refractory shock as evidenced by the need for a high infusion rate of norepinephrine. Anyway, he noted, that Surviving Sepsis recommendation is based upon extrapolation from evidence of benefit in bacterial septic shock patients, which he deemed to be of questionable relevance to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Attacking the fibroproliferative phase of ARDS
First off, Dr. Pickkers conceded, there is no evidence that treatment with corticosteroids to prevent lung fibrosis in COVID-19 patients with nonresolving ARDS is an effective strategy; the pandemic is simply too new at this point for the appropriate studies to have been done. But this much is known: Postmortem pathologic studies show fibroplastic proliferation is present in the lungs of COVID-19 patients, as in those who die of ARDS of other causes. Also, COVID-19 patients typically aren’t admitted to the ICU until day 11 or 12 after developing their first symptoms, so by the time they display indications that their ARDS is not resolving, the virus has typically left the scene; thus, there is little risk at that point that corticosteroids will promote viral proliferation. Additionally, studies in critically ill patients with nonresolving ARDS of other causes show clinically meaningful benefits for corticosteroid therapy.
Dr. Pickkers cited as “must reading” an analysis of five randomized trials of corticosteroid therapy in a total of 518 patients with acute lung injury ARDS of non–COVID-19 origin. The analysis by investigators at the University of Tennessee, Memphis, concluded that treatment resulted in clinically meaningful reductions in duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU length of stay. Moreover, in the 400 patients whose steroid therapy commenced before day 14 of ARDS, there was a statistically significant 22% reduction in risk of death, compared with patients in whom corticosteroids were started later (Intensive Care Med. 2008 Jan;34[1]:61-9).
Session cochair Jan De Waele, MD, PhD, struck a cautious note, remarking, “It’s my perception that we’re using the evidence that we’ve gathered in other conditions and are now trying to apply it in COVID-19. But quality data on patients with COVID-19 itself is pretty scare, and it’s really hard to say whether this disease behaves similarly to bacterial septic shock or to other viral infections.”
“We need more information about the use of corticosteroids in COVID-19, although I think a lot of people are using it at this moment,” added Dr. De Waele, a surgical intensivist at Ghent (Belgium) University.
That being said, he asked Dr. Pickkers when he considers using corticosteroids to prevent pulmonary fibrosis.
Dr. Pickkers said that when he notices that a COVID-19 patient’s lung compliance is worsening, that stiff lung is a clue that fibrosis is occurring and is having clinical consequences. “We also measure blood procollagen, a not very sensitive but moderately specific marker of fibroproliferation. If we see an increase in this biomarker and the lung mechanics are changing, then we do treat these patients with corticosteroids,” Dr. Pickkers replied.
He and his colleagues try to start steroids before day 14 of ARDS, and they continue treatment for longer than 7 days in order to prevent a rebound inflammatory response upon treatment discontinuation. They also avoid using neuromuscular agents and engage in meticulous infection surveillance in order to minimize potential complications of corticosteroid therapy in the ICU.
Dr. Pickkers reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
What is your diagnosis? - June 2020
Phlegmonous gastritis
The patient was treated with intravenous antibiotics (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 6.6 g/d) and a proton pump inhibitor (esomeprazole 80 mg/d). Within a few days, her clinical status improved and abdominal ultrasound examination documented regression of the gastric wall thickening. Laboratory screening for predisposing factors such as diabetes mellitus, infection with human immunodeficiency virus, or immunoglobulin deficiency were negative and there was no clinical evidence of Crohn’s disease. Antibiotic treatment was stopped after 2 weeks. Six months later, follow-up gastroscopy was performed confirming complete resolution of the inflammatory changes in the stomach.
Phlegmonous gastritis is a rare but potentially life-threatening bacterial infection of the gastric wall. Since its first description in 1862, about 500 cases have been reported worldwide. Whereas the original reports dating back to the preantibiotic area suggest very high mortality rates in the range of 90%, phlegmonous gastritis still represents a life-threatening condition.1,2 In about one-half of the cases, acquired immunodeficiency states such as diabetes mellitus, human immunodeficiency virus, or alcoholism are identified as predisposing factors. In addition, gastric biopsies may herald the development of phlegmonous gastritis. Streptococcus spp. account for the majority of the cases, which can be isolated in about 70% of patients.1 Other organisms such as Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli Haemophilus influenzae, and Proteus or Clostridium spp. have been described as pathogens associated with this uncommon condition. Affected patients typically present with nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomitus, hematemesis, or diarrhea. In light of the devastating natural course of phlegmonous gastritis, timely preemptive administration of broad spectrum antibiotic along with a high index of suspicion are paramount. A computed tomography scan and transabdominal ultrasound examination are useful as initial tests, whereas endoscopic ultrasound examination typically demonstrates a diffusely thickened, hypoechogenic submucosal wall layer that is not commonly found in patients with other submucosal lesions, such as carcinoid or leiomyoma. The diagnosis can be confirmed by endoscopic forceps biopsy provided that sufficient submucosal tissue is included.1 Surgery should only be considered for cases refractory to conservative treatment.
References
1. Kim G, Ward J, Henessey B, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:168-74.
2. Starr A, Wilson J. Phlegmonous gastritis. Ann Surg. 1957;145:88-93.
Phlegmonous gastritis
The patient was treated with intravenous antibiotics (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 6.6 g/d) and a proton pump inhibitor (esomeprazole 80 mg/d). Within a few days, her clinical status improved and abdominal ultrasound examination documented regression of the gastric wall thickening. Laboratory screening for predisposing factors such as diabetes mellitus, infection with human immunodeficiency virus, or immunoglobulin deficiency were negative and there was no clinical evidence of Crohn’s disease. Antibiotic treatment was stopped after 2 weeks. Six months later, follow-up gastroscopy was performed confirming complete resolution of the inflammatory changes in the stomach.
Phlegmonous gastritis is a rare but potentially life-threatening bacterial infection of the gastric wall. Since its first description in 1862, about 500 cases have been reported worldwide. Whereas the original reports dating back to the preantibiotic area suggest very high mortality rates in the range of 90%, phlegmonous gastritis still represents a life-threatening condition.1,2 In about one-half of the cases, acquired immunodeficiency states such as diabetes mellitus, human immunodeficiency virus, or alcoholism are identified as predisposing factors. In addition, gastric biopsies may herald the development of phlegmonous gastritis. Streptococcus spp. account for the majority of the cases, which can be isolated in about 70% of patients.1 Other organisms such as Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli Haemophilus influenzae, and Proteus or Clostridium spp. have been described as pathogens associated with this uncommon condition. Affected patients typically present with nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomitus, hematemesis, or diarrhea. In light of the devastating natural course of phlegmonous gastritis, timely preemptive administration of broad spectrum antibiotic along with a high index of suspicion are paramount. A computed tomography scan and transabdominal ultrasound examination are useful as initial tests, whereas endoscopic ultrasound examination typically demonstrates a diffusely thickened, hypoechogenic submucosal wall layer that is not commonly found in patients with other submucosal lesions, such as carcinoid or leiomyoma. The diagnosis can be confirmed by endoscopic forceps biopsy provided that sufficient submucosal tissue is included.1 Surgery should only be considered for cases refractory to conservative treatment.
References
1. Kim G, Ward J, Henessey B, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:168-74.
2. Starr A, Wilson J. Phlegmonous gastritis. Ann Surg. 1957;145:88-93.
Phlegmonous gastritis
The patient was treated with intravenous antibiotics (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 6.6 g/d) and a proton pump inhibitor (esomeprazole 80 mg/d). Within a few days, her clinical status improved and abdominal ultrasound examination documented regression of the gastric wall thickening. Laboratory screening for predisposing factors such as diabetes mellitus, infection with human immunodeficiency virus, or immunoglobulin deficiency were negative and there was no clinical evidence of Crohn’s disease. Antibiotic treatment was stopped after 2 weeks. Six months later, follow-up gastroscopy was performed confirming complete resolution of the inflammatory changes in the stomach.
Phlegmonous gastritis is a rare but potentially life-threatening bacterial infection of the gastric wall. Since its first description in 1862, about 500 cases have been reported worldwide. Whereas the original reports dating back to the preantibiotic area suggest very high mortality rates in the range of 90%, phlegmonous gastritis still represents a life-threatening condition.1,2 In about one-half of the cases, acquired immunodeficiency states such as diabetes mellitus, human immunodeficiency virus, or alcoholism are identified as predisposing factors. In addition, gastric biopsies may herald the development of phlegmonous gastritis. Streptococcus spp. account for the majority of the cases, which can be isolated in about 70% of patients.1 Other organisms such as Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli Haemophilus influenzae, and Proteus or Clostridium spp. have been described as pathogens associated with this uncommon condition. Affected patients typically present with nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomitus, hematemesis, or diarrhea. In light of the devastating natural course of phlegmonous gastritis, timely preemptive administration of broad spectrum antibiotic along with a high index of suspicion are paramount. A computed tomography scan and transabdominal ultrasound examination are useful as initial tests, whereas endoscopic ultrasound examination typically demonstrates a diffusely thickened, hypoechogenic submucosal wall layer that is not commonly found in patients with other submucosal lesions, such as carcinoid or leiomyoma. The diagnosis can be confirmed by endoscopic forceps biopsy provided that sufficient submucosal tissue is included.1 Surgery should only be considered for cases refractory to conservative treatment.
References
1. Kim G, Ward J, Henessey B, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:168-74.
2. Starr A, Wilson J. Phlegmonous gastritis. Ann Surg. 1957;145:88-93.
A previously healthy 41-year-old woman presented with upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever for 4 days. On admission, the patient was febrile (40.1°C); her blood pressure, heart rate, and peripheral oxygen saturation were normal. Laboratory findings were notable for a C-reactive protein of 190 mg/L (reference range, less than 5 mg/L) along with a white cell count of 21,600/mm3 (reference range, 4,500-10,500/mm3). Liver enzymes, pancreatic lipase, and bilirubin were within normal limits. A computed tomography scan of the abdomen revealed wall thickening of the gastric antrum (Figure A).

Gastroscopy showed a heavily distorted gastric antrum with a fistula (Figure B, C). Consecutively, endoscopic ultrasound examination was performed, confirming circumferential thickening of the antral wall up to 20 mm with inhomogeneous hypoechogenic areas within the submucosa (Figure D). Deep endoscopic forceps biopsies were obtained. Histopathologic examination revealed extensive infiltration of the mucosa and submucosa by neutrophils (Figure E, F) and microbial cultures were positive for Streptococcus spp. (S. pyogenes, viridans group streptococci) and Rothia mucilaginosa.
Today’s top news highlights: Cancer makes COVID-19 more dangerous, treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding, and more
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Active cancer ups death risk for patients with COVID-19
New data show that patients with COVID-19 and progressing cancer had a significantly higher risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients who were in remission or had no evidence of cancer. Interestingly, one of the independent risk factor for death in patients with COVID-19 and cancer was treatment with hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin. This finding, however, was of “uncertain validity due to a high risk of residual confounding; for example, patients receiving this combination were more likely to have severe disease or more likely to be hospitalized,” said Jeremy L. Warner, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville. Read more.
Two new studies indicate that social distancing successfully flattened the curve on COVID-19 hospitalizations. One study, published in JAMA, showed significantly lower numbers of observed cases versus worst-case projections in four states: Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In a separate study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention. Read more.
FDA approves treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a medication for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. The medication, marketed as Oriahnn, is an estrogen and progestin combination product that consists of elagolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate capsules packaged together for oral use. The most common side effects of the drug included hot flushes, headache, fatigue, and irregular vaginal bleeding. The drug’s label includes a boxed warning about a risk of strokes and blood clots, especially in women at increased risk for these events. Read more.
Lessons from a drive-through COVID testing center
Chris Notte, MD, and Neil Skolnik, MD, were part of a team of clinicians charged with launching a drive-through COVID-19 testing center. Their task was to get the operation up and running in 2 days. It took them 3 days. While the launch was a success, the experience taught them some lessons about the limits of medical technology and the importance of personal protective equipment. “Prior to the coronavirus pandemic, I had never considered surgical masks, face shields, and nasal swabs to be critical components of medical technology. My opinion quickly changed after opening our drive-through COVID-19 site,” they wrote. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Active cancer ups death risk for patients with COVID-19
New data show that patients with COVID-19 and progressing cancer had a significantly higher risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients who were in remission or had no evidence of cancer. Interestingly, one of the independent risk factor for death in patients with COVID-19 and cancer was treatment with hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin. This finding, however, was of “uncertain validity due to a high risk of residual confounding; for example, patients receiving this combination were more likely to have severe disease or more likely to be hospitalized,” said Jeremy L. Warner, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville. Read more.
Two new studies indicate that social distancing successfully flattened the curve on COVID-19 hospitalizations. One study, published in JAMA, showed significantly lower numbers of observed cases versus worst-case projections in four states: Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In a separate study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention. Read more.
FDA approves treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a medication for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. The medication, marketed as Oriahnn, is an estrogen and progestin combination product that consists of elagolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate capsules packaged together for oral use. The most common side effects of the drug included hot flushes, headache, fatigue, and irregular vaginal bleeding. The drug’s label includes a boxed warning about a risk of strokes and blood clots, especially in women at increased risk for these events. Read more.
Lessons from a drive-through COVID testing center
Chris Notte, MD, and Neil Skolnik, MD, were part of a team of clinicians charged with launching a drive-through COVID-19 testing center. Their task was to get the operation up and running in 2 days. It took them 3 days. While the launch was a success, the experience taught them some lessons about the limits of medical technology and the importance of personal protective equipment. “Prior to the coronavirus pandemic, I had never considered surgical masks, face shields, and nasal swabs to be critical components of medical technology. My opinion quickly changed after opening our drive-through COVID-19 site,” they wrote. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Active cancer ups death risk for patients with COVID-19
New data show that patients with COVID-19 and progressing cancer had a significantly higher risk of 30-day mortality, compared with COVID-19–positive cancer patients who were in remission or had no evidence of cancer. Interestingly, one of the independent risk factor for death in patients with COVID-19 and cancer was treatment with hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin. This finding, however, was of “uncertain validity due to a high risk of residual confounding; for example, patients receiving this combination were more likely to have severe disease or more likely to be hospitalized,” said Jeremy L. Warner, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville. Read more.
Two new studies indicate that social distancing successfully flattened the curve on COVID-19 hospitalizations. One study, published in JAMA, showed significantly lower numbers of observed cases versus worst-case projections in four states: Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In a separate study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention. Read more.
FDA approves treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a medication for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. The medication, marketed as Oriahnn, is an estrogen and progestin combination product that consists of elagolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate capsules packaged together for oral use. The most common side effects of the drug included hot flushes, headache, fatigue, and irregular vaginal bleeding. The drug’s label includes a boxed warning about a risk of strokes and blood clots, especially in women at increased risk for these events. Read more.
Lessons from a drive-through COVID testing center
Chris Notte, MD, and Neil Skolnik, MD, were part of a team of clinicians charged with launching a drive-through COVID-19 testing center. Their task was to get the operation up and running in 2 days. It took them 3 days. While the launch was a success, the experience taught them some lessons about the limits of medical technology and the importance of personal protective equipment. “Prior to the coronavirus pandemic, I had never considered surgical masks, face shields, and nasal swabs to be critical components of medical technology. My opinion quickly changed after opening our drive-through COVID-19 site,” they wrote. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Upfront pembrolizumab doubles PFS in MSI-H/dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer
The median PFS was 16.5 months for patients who received pembrolizumab and 8.2 months for those who received investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (one of six regimens).
“In the past, no medical treatment has shown such difference in terms of improvement of PFS in metastatic colorectal cancer,” said study investigator Thierry André, MD, of Hôpital Saint Antoine in Paris.
“Today, this study demonstrates that the majority of the 5% of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer selected by MSI-high status benefited greatly from anti–PD-1 [programmed death-1] pembrolizumab, compared with standard of care,” he added.
Dr. André discussed the study in a press briefing prior to his presentation of the data as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“I think this is setting a new standard of care,” said Michael J. Overman, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Dr. Overman, the invited discussant, commented on the KEYNOTE-177 study in an interview prior to the presentation.
Dr. Overman noted that, although the overall response rate was higher with pembrolizumab, the rate of progressive disease was higher in the pembrolizumab arm than in the chemotherapy arm. Progressive disease was the best response in 29.4% of patients on pembrolizumab and 12.3% of patients on chemotherapy.
“The only area where I think the question on pembrolizumab is still open would be in the group of patients where we’re saying ‘I care about the near future – this patient has so many symptoms and so much disease burden that I care what happens in the short term,’” Dr. Overman said. He added that, for this subgroup of patients, chemotherapy or pembrolizumab in combination with another immunotherapy, such as ipilimumab, might be more appropriate.
KEYNOTE-177 details
Investigators enrolled 307 patients with confirmed, untreated MSI-H/dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer and good performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0 or 1).
Patients were randomized to pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (n = 153) or to the investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (n = 154). Chemotherapy regimens were modified FOLFOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab, or FOLFIRI (leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab.
Patients assigned to the chemotherapy arm were allowed to cross over to pembrolizumab for up to 35 cycles if they had disease progression confirmed by central review.
PFS is a coprimary endpoint with overall survival. The trial was deemed to be successful if either of the coprimary endpoints was met. Overall survival results are not yet available.
The median PFS was 16.5 months with pembrolizumab and 8.2 months with chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.60; P = .0002). The 12-month PFS rates were 55% and 37%, respectively. The 24-month PFS rates were 48% and 19%, respectively.
Overall response rates were 43.8% with pembrolizumab, consisting of 11.1% complete responses and 32.7% partial responses. The overall response rate with chemotherapy was 33.1%, consisting of 3.9% complete responses and 29.2% partial responses.
In all, 20.9% of patients on pembrolizumab and 42.2% of those on chemotherapy had stable disease. Rates of progressive disease were 29.4% and 12.3%, respectively.
The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm and was 10.6 months in the chemotherapy arm. At 2 years, 83% of patients treated with pembrolizumab and 35% treated with chemotherapy had ongoing responses.
Grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events occurred in 22% of patients on pembrolizumab and 66% on chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse events and infusion reactions were more common with pembrolizumab than with chemotherapy (31% and 13%, respectively). Adverse events that were common with chemotherapy included gastrointestinal events, fatigue, neutropenia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. André disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including MSD Oncology. Dr. Overman disclosed consulting activities with various companies, not including Merck.
SOURCE: André T et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA4.
The median PFS was 16.5 months for patients who received pembrolizumab and 8.2 months for those who received investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (one of six regimens).
“In the past, no medical treatment has shown such difference in terms of improvement of PFS in metastatic colorectal cancer,” said study investigator Thierry André, MD, of Hôpital Saint Antoine in Paris.
“Today, this study demonstrates that the majority of the 5% of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer selected by MSI-high status benefited greatly from anti–PD-1 [programmed death-1] pembrolizumab, compared with standard of care,” he added.
Dr. André discussed the study in a press briefing prior to his presentation of the data as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“I think this is setting a new standard of care,” said Michael J. Overman, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Dr. Overman, the invited discussant, commented on the KEYNOTE-177 study in an interview prior to the presentation.
Dr. Overman noted that, although the overall response rate was higher with pembrolizumab, the rate of progressive disease was higher in the pembrolizumab arm than in the chemotherapy arm. Progressive disease was the best response in 29.4% of patients on pembrolizumab and 12.3% of patients on chemotherapy.
“The only area where I think the question on pembrolizumab is still open would be in the group of patients where we’re saying ‘I care about the near future – this patient has so many symptoms and so much disease burden that I care what happens in the short term,’” Dr. Overman said. He added that, for this subgroup of patients, chemotherapy or pembrolizumab in combination with another immunotherapy, such as ipilimumab, might be more appropriate.
KEYNOTE-177 details
Investigators enrolled 307 patients with confirmed, untreated MSI-H/dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer and good performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0 or 1).
Patients were randomized to pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (n = 153) or to the investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (n = 154). Chemotherapy regimens were modified FOLFOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab, or FOLFIRI (leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab.
Patients assigned to the chemotherapy arm were allowed to cross over to pembrolizumab for up to 35 cycles if they had disease progression confirmed by central review.
PFS is a coprimary endpoint with overall survival. The trial was deemed to be successful if either of the coprimary endpoints was met. Overall survival results are not yet available.
The median PFS was 16.5 months with pembrolizumab and 8.2 months with chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.60; P = .0002). The 12-month PFS rates were 55% and 37%, respectively. The 24-month PFS rates were 48% and 19%, respectively.
Overall response rates were 43.8% with pembrolizumab, consisting of 11.1% complete responses and 32.7% partial responses. The overall response rate with chemotherapy was 33.1%, consisting of 3.9% complete responses and 29.2% partial responses.
In all, 20.9% of patients on pembrolizumab and 42.2% of those on chemotherapy had stable disease. Rates of progressive disease were 29.4% and 12.3%, respectively.
The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm and was 10.6 months in the chemotherapy arm. At 2 years, 83% of patients treated with pembrolizumab and 35% treated with chemotherapy had ongoing responses.
Grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events occurred in 22% of patients on pembrolizumab and 66% on chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse events and infusion reactions were more common with pembrolizumab than with chemotherapy (31% and 13%, respectively). Adverse events that were common with chemotherapy included gastrointestinal events, fatigue, neutropenia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. André disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including MSD Oncology. Dr. Overman disclosed consulting activities with various companies, not including Merck.
SOURCE: André T et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA4.
The median PFS was 16.5 months for patients who received pembrolizumab and 8.2 months for those who received investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (one of six regimens).
“In the past, no medical treatment has shown such difference in terms of improvement of PFS in metastatic colorectal cancer,” said study investigator Thierry André, MD, of Hôpital Saint Antoine in Paris.
“Today, this study demonstrates that the majority of the 5% of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer selected by MSI-high status benefited greatly from anti–PD-1 [programmed death-1] pembrolizumab, compared with standard of care,” he added.
Dr. André discussed the study in a press briefing prior to his presentation of the data as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“I think this is setting a new standard of care,” said Michael J. Overman, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Dr. Overman, the invited discussant, commented on the KEYNOTE-177 study in an interview prior to the presentation.
Dr. Overman noted that, although the overall response rate was higher with pembrolizumab, the rate of progressive disease was higher in the pembrolizumab arm than in the chemotherapy arm. Progressive disease was the best response in 29.4% of patients on pembrolizumab and 12.3% of patients on chemotherapy.
“The only area where I think the question on pembrolizumab is still open would be in the group of patients where we’re saying ‘I care about the near future – this patient has so many symptoms and so much disease burden that I care what happens in the short term,’” Dr. Overman said. He added that, for this subgroup of patients, chemotherapy or pembrolizumab in combination with another immunotherapy, such as ipilimumab, might be more appropriate.
KEYNOTE-177 details
Investigators enrolled 307 patients with confirmed, untreated MSI-H/dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer and good performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0 or 1).
Patients were randomized to pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (n = 153) or to the investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (n = 154). Chemotherapy regimens were modified FOLFOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab, or FOLFIRI (leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab.
Patients assigned to the chemotherapy arm were allowed to cross over to pembrolizumab for up to 35 cycles if they had disease progression confirmed by central review.
PFS is a coprimary endpoint with overall survival. The trial was deemed to be successful if either of the coprimary endpoints was met. Overall survival results are not yet available.
The median PFS was 16.5 months with pembrolizumab and 8.2 months with chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.60; P = .0002). The 12-month PFS rates were 55% and 37%, respectively. The 24-month PFS rates were 48% and 19%, respectively.
Overall response rates were 43.8% with pembrolizumab, consisting of 11.1% complete responses and 32.7% partial responses. The overall response rate with chemotherapy was 33.1%, consisting of 3.9% complete responses and 29.2% partial responses.
In all, 20.9% of patients on pembrolizumab and 42.2% of those on chemotherapy had stable disease. Rates of progressive disease were 29.4% and 12.3%, respectively.
The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm and was 10.6 months in the chemotherapy arm. At 2 years, 83% of patients treated with pembrolizumab and 35% treated with chemotherapy had ongoing responses.
Grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events occurred in 22% of patients on pembrolizumab and 66% on chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse events and infusion reactions were more common with pembrolizumab than with chemotherapy (31% and 13%, respectively). Adverse events that were common with chemotherapy included gastrointestinal events, fatigue, neutropenia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. André disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including MSD Oncology. Dr. Overman disclosed consulting activities with various companies, not including Merck.
SOURCE: André T et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract LBA4.
FROM ASCO 2020
Pembrolizumab plus chemo shows benefits for PD-L1–rich triple-negative breast cancer
Adding pembrolizumab to standard chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, but only if their tumors were enriched with comparatively high levels of the target programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), results of the KEYNOTE 355 trial showed.
Among 843 patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) randomized to receive either investigator’s choice of chemotherapy plus pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or placebo, patients whose tumors had a PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) of 10 or higher had a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 9.7 months when treated with pembrolizumab and chemotherapy, compared with 5.6 months among patients treated with chemotherapy and placebo, reported Javier Cortes, MD, PhD, from the Vall d´Hebron Institute of Oncology in Madrid and Barcelona.
However, among patients with CPS between 1 and 10, there was no significant difference in PFS between the treatment arms, he said in a presentation made as a part of the 2020 American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“The inclusion of taxanes and a known taxane/platinum–based regimen permits assessment of the clinical benefit of pembro in combination with several routinely used chemo partners. A trend toward improved efficacy with PD-L1 enrichment was observed in patients treated with pembro plus chemo. The improvement in progression-free survival with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab was observed across patient subgroups,” said Dr. Cortes.
In the KEYNOTE-522 study, adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting increased the likelihood that women with stage III or early node-positive TNBC would have a pathologic complete response and sustained clinical benefit.
KEYNOTE-355 examined whether pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy could provide additional benefit over chemotherapy alone in patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC.
Patients with previously untreated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who had at least 6 months between definite surgery or last dose of adjuvant chemotherapy (whichever came last) and first disease recurrence were stratified by study chemotherapy received, tumor PD-L1 expression at baseline, and prior treatment with the same class of chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant setting.
The patients were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy based on the investigator’s choice of nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, or carboplatin-gemcitabine (562 patients) or to chemotherapy alone (281).
Pembrolizumab and placebo were administered in a double-blind fashion for up to 35 doses. Chemotherapy was given at the investigator’s discretion according to local guidelines. This trial was not powered or designed to compare differential efficacy of the various chemotherapy regimens, Dr. Cortes noted.
The trial had dual primary endpoints of PFS in patients with PD-L1–positive tumors (CPS > 10 and > 1) and in the intention-to-treat population, and overall survival both in PD-L1-positive patients and the ITT population. Overall survival results will be reported at a later date.
As noted before, the primary endpoint was met in the population of patients with CPS higher than 10, with median PFS of 9.7 among those receiving pembrolizumab versus 5.6 months among those receiving placebo, and an estimated 1 year PFS of 39.1% versus 23% for controls, translating into a hazard ratio for progression on pembrolizumab of 0.65 (P = .0012).
In the patients with CPS higher than 1, however, the median PFS was 7.6 months with pembrolizumab compared with 5.6 months with placebo, translating into a hazard ratio of 0.74. However, the results did not meet the prespecified boundary for significance. Because of this, the statistical significance in the ITT population was not tested.
“In patients with PD-L1 CPS 10 or higher tumors, the benefit of pembro/chemo on progression-free survival was generally consistent across most predefined subgroups, including eight geographic regions, ECOG performance status, on-study chemo, and prior treatment with the same class of chemo,” Dr. Cortes said.
Treatment-related adverse events occurred in 96.3% of the patients on pembrolizumab and 95% of patients on placebo. Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 68.1% versus 66.9%, respectively. Two patients in the pembrolizumab arm died from a treatment-related event. There were no treatment-related deaths in the placebo arm.
The most common events were those typically associated with chemotherapy, including anemia, neutropenia, nausea, alopecia, fatigue, decreased neutrophil counts, and elevated liver transaminases. Immune-mediated adverse events of any grade occurred in 25.6% of patients in the pembrolizumab arm versus 6% of controls; none of these events were fatal.
“What is clear in this study is that again we’re seeing efficacy of pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy increases with increases in CPS,” according to the invited discussant Catherine M. Kelly, MB, BCh, from University College Dublin and Mater Misericordiae University Hospital in Dublin.
“The results from today’s KEYNOTE-355 appear consistent in terms of progression-free survival. However, it is ‘watch this space’ until we get overall survival data before we can make any further comparisons,” she added.
Questions that still need to be answered include which is the best test for measuring PD-L1, whether patients with CPS of 1 or more but less than 10 benefit from the treatment, which of the available chemotherapy regimens is the best partner for pembrolizumab, how to treat patients who don’t respond to the combination, and what are the implications for PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in late-stage disease if they are approved in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting, Dr. Kelly said.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Cortes disclosed honoraria from, a consulting/advisory role for, and institutional research funding from Merck and others. Dr. Kelly disclosed honoraria from MSD Oncology and others, and travel expenses from Pfizer and Roche.
SOURCE: Cortes J et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 1000.
Adding pembrolizumab to standard chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, but only if their tumors were enriched with comparatively high levels of the target programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), results of the KEYNOTE 355 trial showed.
Among 843 patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) randomized to receive either investigator’s choice of chemotherapy plus pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or placebo, patients whose tumors had a PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) of 10 or higher had a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 9.7 months when treated with pembrolizumab and chemotherapy, compared with 5.6 months among patients treated with chemotherapy and placebo, reported Javier Cortes, MD, PhD, from the Vall d´Hebron Institute of Oncology in Madrid and Barcelona.
However, among patients with CPS between 1 and 10, there was no significant difference in PFS between the treatment arms, he said in a presentation made as a part of the 2020 American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“The inclusion of taxanes and a known taxane/platinum–based regimen permits assessment of the clinical benefit of pembro in combination with several routinely used chemo partners. A trend toward improved efficacy with PD-L1 enrichment was observed in patients treated with pembro plus chemo. The improvement in progression-free survival with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab was observed across patient subgroups,” said Dr. Cortes.
In the KEYNOTE-522 study, adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting increased the likelihood that women with stage III or early node-positive TNBC would have a pathologic complete response and sustained clinical benefit.
KEYNOTE-355 examined whether pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy could provide additional benefit over chemotherapy alone in patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC.
Patients with previously untreated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who had at least 6 months between definite surgery or last dose of adjuvant chemotherapy (whichever came last) and first disease recurrence were stratified by study chemotherapy received, tumor PD-L1 expression at baseline, and prior treatment with the same class of chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant setting.
The patients were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy based on the investigator’s choice of nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, or carboplatin-gemcitabine (562 patients) or to chemotherapy alone (281).
Pembrolizumab and placebo were administered in a double-blind fashion for up to 35 doses. Chemotherapy was given at the investigator’s discretion according to local guidelines. This trial was not powered or designed to compare differential efficacy of the various chemotherapy regimens, Dr. Cortes noted.
The trial had dual primary endpoints of PFS in patients with PD-L1–positive tumors (CPS > 10 and > 1) and in the intention-to-treat population, and overall survival both in PD-L1-positive patients and the ITT population. Overall survival results will be reported at a later date.
As noted before, the primary endpoint was met in the population of patients with CPS higher than 10, with median PFS of 9.7 among those receiving pembrolizumab versus 5.6 months among those receiving placebo, and an estimated 1 year PFS of 39.1% versus 23% for controls, translating into a hazard ratio for progression on pembrolizumab of 0.65 (P = .0012).
In the patients with CPS higher than 1, however, the median PFS was 7.6 months with pembrolizumab compared with 5.6 months with placebo, translating into a hazard ratio of 0.74. However, the results did not meet the prespecified boundary for significance. Because of this, the statistical significance in the ITT population was not tested.
“In patients with PD-L1 CPS 10 or higher tumors, the benefit of pembro/chemo on progression-free survival was generally consistent across most predefined subgroups, including eight geographic regions, ECOG performance status, on-study chemo, and prior treatment with the same class of chemo,” Dr. Cortes said.
Treatment-related adverse events occurred in 96.3% of the patients on pembrolizumab and 95% of patients on placebo. Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 68.1% versus 66.9%, respectively. Two patients in the pembrolizumab arm died from a treatment-related event. There were no treatment-related deaths in the placebo arm.
The most common events were those typically associated with chemotherapy, including anemia, neutropenia, nausea, alopecia, fatigue, decreased neutrophil counts, and elevated liver transaminases. Immune-mediated adverse events of any grade occurred in 25.6% of patients in the pembrolizumab arm versus 6% of controls; none of these events were fatal.
“What is clear in this study is that again we’re seeing efficacy of pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy increases with increases in CPS,” according to the invited discussant Catherine M. Kelly, MB, BCh, from University College Dublin and Mater Misericordiae University Hospital in Dublin.
“The results from today’s KEYNOTE-355 appear consistent in terms of progression-free survival. However, it is ‘watch this space’ until we get overall survival data before we can make any further comparisons,” she added.
Questions that still need to be answered include which is the best test for measuring PD-L1, whether patients with CPS of 1 or more but less than 10 benefit from the treatment, which of the available chemotherapy regimens is the best partner for pembrolizumab, how to treat patients who don’t respond to the combination, and what are the implications for PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in late-stage disease if they are approved in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting, Dr. Kelly said.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Cortes disclosed honoraria from, a consulting/advisory role for, and institutional research funding from Merck and others. Dr. Kelly disclosed honoraria from MSD Oncology and others, and travel expenses from Pfizer and Roche.
SOURCE: Cortes J et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 1000.
Adding pembrolizumab to standard chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, but only if their tumors were enriched with comparatively high levels of the target programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), results of the KEYNOTE 355 trial showed.
Among 843 patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) randomized to receive either investigator’s choice of chemotherapy plus pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or placebo, patients whose tumors had a PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) of 10 or higher had a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 9.7 months when treated with pembrolizumab and chemotherapy, compared with 5.6 months among patients treated with chemotherapy and placebo, reported Javier Cortes, MD, PhD, from the Vall d´Hebron Institute of Oncology in Madrid and Barcelona.
However, among patients with CPS between 1 and 10, there was no significant difference in PFS between the treatment arms, he said in a presentation made as a part of the 2020 American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“The inclusion of taxanes and a known taxane/platinum–based regimen permits assessment of the clinical benefit of pembro in combination with several routinely used chemo partners. A trend toward improved efficacy with PD-L1 enrichment was observed in patients treated with pembro plus chemo. The improvement in progression-free survival with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab was observed across patient subgroups,” said Dr. Cortes.
In the KEYNOTE-522 study, adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting increased the likelihood that women with stage III or early node-positive TNBC would have a pathologic complete response and sustained clinical benefit.
KEYNOTE-355 examined whether pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy could provide additional benefit over chemotherapy alone in patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC.
Patients with previously untreated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who had at least 6 months between definite surgery or last dose of adjuvant chemotherapy (whichever came last) and first disease recurrence were stratified by study chemotherapy received, tumor PD-L1 expression at baseline, and prior treatment with the same class of chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant setting.
The patients were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy based on the investigator’s choice of nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, or carboplatin-gemcitabine (562 patients) or to chemotherapy alone (281).
Pembrolizumab and placebo were administered in a double-blind fashion for up to 35 doses. Chemotherapy was given at the investigator’s discretion according to local guidelines. This trial was not powered or designed to compare differential efficacy of the various chemotherapy regimens, Dr. Cortes noted.
The trial had dual primary endpoints of PFS in patients with PD-L1–positive tumors (CPS > 10 and > 1) and in the intention-to-treat population, and overall survival both in PD-L1-positive patients and the ITT population. Overall survival results will be reported at a later date.
As noted before, the primary endpoint was met in the population of patients with CPS higher than 10, with median PFS of 9.7 among those receiving pembrolizumab versus 5.6 months among those receiving placebo, and an estimated 1 year PFS of 39.1% versus 23% for controls, translating into a hazard ratio for progression on pembrolizumab of 0.65 (P = .0012).
In the patients with CPS higher than 1, however, the median PFS was 7.6 months with pembrolizumab compared with 5.6 months with placebo, translating into a hazard ratio of 0.74. However, the results did not meet the prespecified boundary for significance. Because of this, the statistical significance in the ITT population was not tested.
“In patients with PD-L1 CPS 10 or higher tumors, the benefit of pembro/chemo on progression-free survival was generally consistent across most predefined subgroups, including eight geographic regions, ECOG performance status, on-study chemo, and prior treatment with the same class of chemo,” Dr. Cortes said.
Treatment-related adverse events occurred in 96.3% of the patients on pembrolizumab and 95% of patients on placebo. Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 68.1% versus 66.9%, respectively. Two patients in the pembrolizumab arm died from a treatment-related event. There were no treatment-related deaths in the placebo arm.
The most common events were those typically associated with chemotherapy, including anemia, neutropenia, nausea, alopecia, fatigue, decreased neutrophil counts, and elevated liver transaminases. Immune-mediated adverse events of any grade occurred in 25.6% of patients in the pembrolizumab arm versus 6% of controls; none of these events were fatal.
“What is clear in this study is that again we’re seeing efficacy of pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy increases with increases in CPS,” according to the invited discussant Catherine M. Kelly, MB, BCh, from University College Dublin and Mater Misericordiae University Hospital in Dublin.
“The results from today’s KEYNOTE-355 appear consistent in terms of progression-free survival. However, it is ‘watch this space’ until we get overall survival data before we can make any further comparisons,” she added.
Questions that still need to be answered include which is the best test for measuring PD-L1, whether patients with CPS of 1 or more but less than 10 benefit from the treatment, which of the available chemotherapy regimens is the best partner for pembrolizumab, how to treat patients who don’t respond to the combination, and what are the implications for PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in late-stage disease if they are approved in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting, Dr. Kelly said.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Cortes disclosed honoraria from, a consulting/advisory role for, and institutional research funding from Merck and others. Dr. Kelly disclosed honoraria from MSD Oncology and others, and travel expenses from Pfizer and Roche.
SOURCE: Cortes J et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 1000.
FROM ASCO 2020
COVID-19 effect: Prescription fills mostly down for leading drugs
Prescription fills for hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine spiked right after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency in March, but use of the drugs still remains well above 2019 levels, based on data from more than 58,000 U.S. pharmacies.
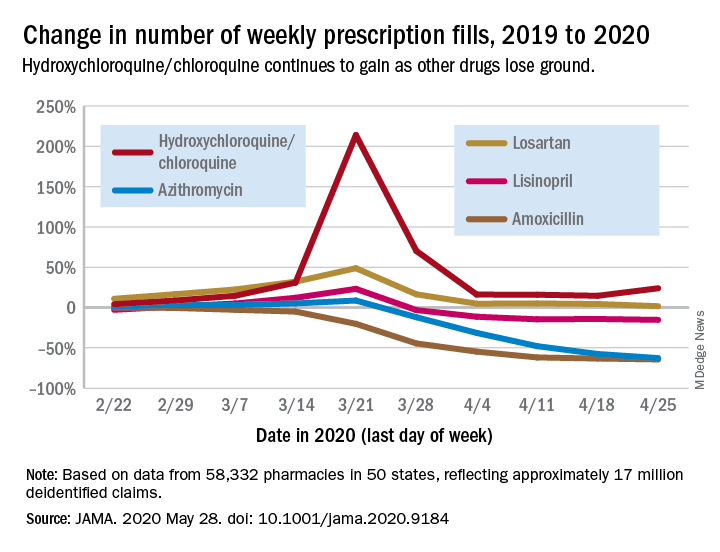
Hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine are also doing better than any of the prescription drugs in the top 10 based on total claims in 2019, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and associates reported May 28 in a research letter in JAMA.
Prescription fills for hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine have been above 2019 levels every week since the national emergency was declared on March 13, with the high occurring during the week of March 15-21, when fills were 214% higher than the corresponding week in 2019. The lowest level in that time came during the week of April 12-18, with growth of 14.6% over 2019, the investigators said.
The drugs occupying the top 10 – amlodipine, amoxicillin, atorvastatin, gabapentin, hydrocodone-acetaminophen, levothyroxine, lisinopril, losartan, omeprazole, and sertraline – have not done as well. Losartan, the only one that hasn’t lost ground in any week since March 13, rose by almost 49% during March 15-21, but was down to a 1.7% rise by the end of the study period, they reported.
Meanwhile, the other drug touted as a treatment for COVID-19, azithromycin, has fallen farther than most of the top 10. By April 19-25, the last week of the study period, fills for the antibiotic were down 62.7%, compared with last year, the analysis showed. Only amoxicillin had dropped more (64.4%).
“The modest decline for most common long-term therapies after peak could represent reduced contact with prescribing clinicians, restricted access to pharmacies, pharmacist rationing, loss of insurance from unemployment, or replete supplies from early stockpiling,” Dr. Vaduganathan and associates wrote.
The investigators “used all-payer U.S. pharmacy data from 58,332 chain, independent, and mail-order pharmacies across 14,421 zip codes in 50 states, reflecting approximately 17 million deidentified claims,” to estimate national prescription fills, they explained.
SOURCE: Vaduganathan M et al. JAMA 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9184.
Prescription fills for hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine spiked right after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency in March, but use of the drugs still remains well above 2019 levels, based on data from more than 58,000 U.S. pharmacies.

Hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine are also doing better than any of the prescription drugs in the top 10 based on total claims in 2019, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and associates reported May 28 in a research letter in JAMA.
Prescription fills for hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine have been above 2019 levels every week since the national emergency was declared on March 13, with the high occurring during the week of March 15-21, when fills were 214% higher than the corresponding week in 2019. The lowest level in that time came during the week of April 12-18, with growth of 14.6% over 2019, the investigators said.
The drugs occupying the top 10 – amlodipine, amoxicillin, atorvastatin, gabapentin, hydrocodone-acetaminophen, levothyroxine, lisinopril, losartan, omeprazole, and sertraline – have not done as well. Losartan, the only one that hasn’t lost ground in any week since March 13, rose by almost 49% during March 15-21, but was down to a 1.7% rise by the end of the study period, they reported.
Meanwhile, the other drug touted as a treatment for COVID-19, azithromycin, has fallen farther than most of the top 10. By April 19-25, the last week of the study period, fills for the antibiotic were down 62.7%, compared with last year, the analysis showed. Only amoxicillin had dropped more (64.4%).
“The modest decline for most common long-term therapies after peak could represent reduced contact with prescribing clinicians, restricted access to pharmacies, pharmacist rationing, loss of insurance from unemployment, or replete supplies from early stockpiling,” Dr. Vaduganathan and associates wrote.
The investigators “used all-payer U.S. pharmacy data from 58,332 chain, independent, and mail-order pharmacies across 14,421 zip codes in 50 states, reflecting approximately 17 million deidentified claims,” to estimate national prescription fills, they explained.
SOURCE: Vaduganathan M et al. JAMA 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9184.
Prescription fills for hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine spiked right after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency in March, but use of the drugs still remains well above 2019 levels, based on data from more than 58,000 U.S. pharmacies.

Hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine are also doing better than any of the prescription drugs in the top 10 based on total claims in 2019, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and associates reported May 28 in a research letter in JAMA.
Prescription fills for hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine have been above 2019 levels every week since the national emergency was declared on March 13, with the high occurring during the week of March 15-21, when fills were 214% higher than the corresponding week in 2019. The lowest level in that time came during the week of April 12-18, with growth of 14.6% over 2019, the investigators said.
The drugs occupying the top 10 – amlodipine, amoxicillin, atorvastatin, gabapentin, hydrocodone-acetaminophen, levothyroxine, lisinopril, losartan, omeprazole, and sertraline – have not done as well. Losartan, the only one that hasn’t lost ground in any week since March 13, rose by almost 49% during March 15-21, but was down to a 1.7% rise by the end of the study period, they reported.
Meanwhile, the other drug touted as a treatment for COVID-19, azithromycin, has fallen farther than most of the top 10. By April 19-25, the last week of the study period, fills for the antibiotic were down 62.7%, compared with last year, the analysis showed. Only amoxicillin had dropped more (64.4%).
“The modest decline for most common long-term therapies after peak could represent reduced contact with prescribing clinicians, restricted access to pharmacies, pharmacist rationing, loss of insurance from unemployment, or replete supplies from early stockpiling,” Dr. Vaduganathan and associates wrote.
The investigators “used all-payer U.S. pharmacy data from 58,332 chain, independent, and mail-order pharmacies across 14,421 zip codes in 50 states, reflecting approximately 17 million deidentified claims,” to estimate national prescription fills, they explained.
SOURCE: Vaduganathan M et al. JAMA 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9184.
FROM JAMA