User login
Calendar
For more information about upcoming events and award deadlines, please visit http://agau.gastro.org and http://www.gastro.org/research-funding.
UPCOMING EVENTS
Aug. 13-14, Sept. 16-17, and Oct. 7-8, 2020
2-Day, In-Depth Coding and Billing Seminar
Become a certified GI coder with a 2-day, in-depth training course provided by McVey Associates.
Baltimore, Md. (Aug. 13-14); Atlanta, Ga. (Sept. 16-17); Las Vegas, Nev. (Oct. 7-8)
Aug. 15-16, 2020
2020 Principles of GI for the NP and PA
Because of COVID-19, the American Gastroenterological Association has transitioned the 2020 Principles of GI for the NP and PA course from a live meeting to a virtual course. The virtual course will provide you with team-based expert guidance on managing GI patients through case-based learning from faculty who are seasoned physicians and advanced practice providers. Register at https://bit.ly/38oeK4C.
AWARD DEADLINES
AGA-Pilot Research Award
This award provides $30,000 for 1 year to recipients at any career stage researching new directions in gastroenterology- or hepatology-related areas.
Application deadline: Sept. 2, 2020
AGA-Medtronic Pilot Research Award in Technology Innovation
This award provides $30,000 for 1 year to independent investigators at any career stage to support the research and development of novel devices or technologies that will potentially impact the diagnosis or treatment of digestive disease.
Application deadline: Sept. 2, 2020
AGA–Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in Celiac Disease
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in celiac disease research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA Research Scholar Award (RSA)
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in digestive disease research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA–Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA–Moti L. & Kamla Rustgi International Travel Awards
This $750 travel award provides support to early career (i.e., 35 years or younger at the time of Digestive Disease Week® [DDW]) basic, translational, or clinical investigators residing outside North America to offset travel and related expenses to attend DDW.
Application deadline: Feb. 24, 2021
AGA Student Abstract Award
This $500 travel award supports recipients who are graduate students, medical students, or medical residents (residents up to postgraduate year 3) giving abstract-based oral or poster presentations at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). The top-scoring abstract will be designated the Student Abstract of the Year and receive a $1,000 award.
Application deadline: Feb 26, 2021
AGA Fellow Abstract Award
This $500 travel award supports recipients who are MD, PhD, or equivalent fellows giving abstract-based oral or poster presentations at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). The top-scoring abstract will be designated the Fellow Abstract of the Year and receive a $1,000 award.
Application deadline: Feb. 24, 2021
For more information about upcoming events and award deadlines, please visit http://agau.gastro.org and http://www.gastro.org/research-funding.
UPCOMING EVENTS
Aug. 13-14, Sept. 16-17, and Oct. 7-8, 2020
2-Day, In-Depth Coding and Billing Seminar
Become a certified GI coder with a 2-day, in-depth training course provided by McVey Associates.
Baltimore, Md. (Aug. 13-14); Atlanta, Ga. (Sept. 16-17); Las Vegas, Nev. (Oct. 7-8)
Aug. 15-16, 2020
2020 Principles of GI for the NP and PA
Because of COVID-19, the American Gastroenterological Association has transitioned the 2020 Principles of GI for the NP and PA course from a live meeting to a virtual course. The virtual course will provide you with team-based expert guidance on managing GI patients through case-based learning from faculty who are seasoned physicians and advanced practice providers. Register at https://bit.ly/38oeK4C.
AWARD DEADLINES
AGA-Pilot Research Award
This award provides $30,000 for 1 year to recipients at any career stage researching new directions in gastroenterology- or hepatology-related areas.
Application deadline: Sept. 2, 2020
AGA-Medtronic Pilot Research Award in Technology Innovation
This award provides $30,000 for 1 year to independent investigators at any career stage to support the research and development of novel devices or technologies that will potentially impact the diagnosis or treatment of digestive disease.
Application deadline: Sept. 2, 2020
AGA–Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in Celiac Disease
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in celiac disease research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA Research Scholar Award (RSA)
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in digestive disease research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA–Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA–Moti L. & Kamla Rustgi International Travel Awards
This $750 travel award provides support to early career (i.e., 35 years or younger at the time of Digestive Disease Week® [DDW]) basic, translational, or clinical investigators residing outside North America to offset travel and related expenses to attend DDW.
Application deadline: Feb. 24, 2021
AGA Student Abstract Award
This $500 travel award supports recipients who are graduate students, medical students, or medical residents (residents up to postgraduate year 3) giving abstract-based oral or poster presentations at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). The top-scoring abstract will be designated the Student Abstract of the Year and receive a $1,000 award.
Application deadline: Feb 26, 2021
AGA Fellow Abstract Award
This $500 travel award supports recipients who are MD, PhD, or equivalent fellows giving abstract-based oral or poster presentations at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). The top-scoring abstract will be designated the Fellow Abstract of the Year and receive a $1,000 award.
Application deadline: Feb. 24, 2021
For more information about upcoming events and award deadlines, please visit http://agau.gastro.org and http://www.gastro.org/research-funding.
UPCOMING EVENTS
Aug. 13-14, Sept. 16-17, and Oct. 7-8, 2020
2-Day, In-Depth Coding and Billing Seminar
Become a certified GI coder with a 2-day, in-depth training course provided by McVey Associates.
Baltimore, Md. (Aug. 13-14); Atlanta, Ga. (Sept. 16-17); Las Vegas, Nev. (Oct. 7-8)
Aug. 15-16, 2020
2020 Principles of GI for the NP and PA
Because of COVID-19, the American Gastroenterological Association has transitioned the 2020 Principles of GI for the NP and PA course from a live meeting to a virtual course. The virtual course will provide you with team-based expert guidance on managing GI patients through case-based learning from faculty who are seasoned physicians and advanced practice providers. Register at https://bit.ly/38oeK4C.
AWARD DEADLINES
AGA-Pilot Research Award
This award provides $30,000 for 1 year to recipients at any career stage researching new directions in gastroenterology- or hepatology-related areas.
Application deadline: Sept. 2, 2020
AGA-Medtronic Pilot Research Award in Technology Innovation
This award provides $30,000 for 1 year to independent investigators at any career stage to support the research and development of novel devices or technologies that will potentially impact the diagnosis or treatment of digestive disease.
Application deadline: Sept. 2, 2020
AGA–Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in Celiac Disease
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in celiac disease research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA Research Scholar Award (RSA)
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in digestive disease research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA–Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
This award provides $100,000 per year for 3 years (totaling $300,000) to early-career faculty (i.e., investigator, instructor, research associate, or equivalent) working toward an independent career in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) research.
Application deadline: Nov. 9, 2020
AGA–Moti L. & Kamla Rustgi International Travel Awards
This $750 travel award provides support to early career (i.e., 35 years or younger at the time of Digestive Disease Week® [DDW]) basic, translational, or clinical investigators residing outside North America to offset travel and related expenses to attend DDW.
Application deadline: Feb. 24, 2021
AGA Student Abstract Award
This $500 travel award supports recipients who are graduate students, medical students, or medical residents (residents up to postgraduate year 3) giving abstract-based oral or poster presentations at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). The top-scoring abstract will be designated the Student Abstract of the Year and receive a $1,000 award.
Application deadline: Feb 26, 2021
AGA Fellow Abstract Award
This $500 travel award supports recipients who are MD, PhD, or equivalent fellows giving abstract-based oral or poster presentations at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW). The top-scoring abstract will be designated the Fellow Abstract of the Year and receive a $1,000 award.
Application deadline: Feb. 24, 2021
Hypercalcemia Is of Uncertain Significance in Patients With Advanced Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate
Hypercalcemia is found when the corrected serum calcium level is > 10.5 mg/dL.1 Its symptoms are not specific and may include polyuria, dehydration, polydipsia, anorexia, nausea and/or vomiting, constipation, and other central nervous system manifestations, including confusion, delirium, cognitive impairment, muscle weakness, psychotic symptoms, and even coma.1,2
Hypercalcemia has varied etiologies; however, malignancy-induced hypercalcemia is one of the most common causes. In the US, the most common causes of malignancy-induced hypercalcemia are primary tumors of the lung or breast, multiple myeloma (MM), squamous cell carcinoma of the head or neck, renal cancer, and ovarian cancer.1
Men with prostate cancer and bone metastasis have relatively worse prognosis than do patient with no metastasis.3 In a recent meta-analysis of patients with bone-involved castration-resistant prostate cancer, the median survival was 21 months.3
Hypercalcemia is a rare manifestation of prostate cancer. In a retrospective study conducted between 2009 and 2013 using the Oncology Services Comprehensive Electronic Records (OSCER) warehouse of electronic health records (EHR), the rates of malignancy-induced hypercalcemia were the lowest among patients with prostate cancer, ranging from 1.4 to 2.1%.1
We present this case to discuss different pathophysiologic mechanisms leading to hypercalcemia in a patient with prostate cancer with bone metastasis and to study the role of humoral and growth factors in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Case Presentation
An African American man aged 69 years presented to the emergency department (ED) with generalized weakness, fatigue, and lower extremities muscle weakness. He reported a 40-lb weight loss over the past 3 months, intermittent lower back pain, and a 50 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination suggested clinical signs of dehydration.
Laboratory test results indicated hypercalcemia, macrocytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia: calcium 15.8 mg/dL, serum albumin 4.1 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 139 μ/L, blood urea nitrogen 55 mg/dL, creatinine 3.4 mg/dL (baseline 1.4-1.5 mg/dL), hemoglobin 8 g/dL, mean corpuscular volume 99.6 fL, and platelets 100,000/μL. The patient was admitted for hypercalcemia. His intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) was suppressed at 16 pg/mL, phosphorous was 3.8 mg/dL, parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) was < 0.74 pmol/L, vitamin D (25 hydroxy cholecalciferol) was mildly decreased at 17.2 ng/mL, and 1,25 dihydroxy cholecalciferol (calcitriol) was < 5.0 (normal range 20-79.3 pg/mL).
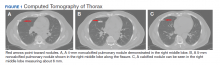
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest and abdomen was taken due to the patient’s heavy smoking history, an incidentally detected right lung base nodule on chest X-ray, and hypercalcemia. The CT scan showed multiple right middle lobe lung nodules with and without calcifications and calcified right hilar lymph nodes (Figure 1).
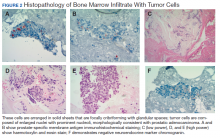
To evaluate the pancytopenia, a bone marrow biopsy was done, which showed that 80 to 90% of the marrow space was replaced by fibrosis and metastatic malignancy. Trilinear hematopoiesis was not seen (Figure 2). The tumor cells were positive for prostate- specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and negative for cytokeratin 7 and 20 (CK7 and CK20).4 The former is a membrane protein expressed on prostate tissues, including cancer; the latter is a form of protein used to identify adenocarcinoma of unknown primary origin (CK7 usually found in primary/ metastatic lung adenocarcinoma and CK20 usually in primary and some metastatic diseases of colon adenocarcinoma).5 A prostatic specific antigen (PSA) test was markedly elevated: 335.94 ng/mL (1.46 ng/mL on a previous 2011 test).
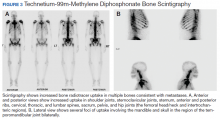
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate was diagnosed without a prostate biopsy. To determine the extent of bone metastases, a technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate (MDP) bone scintigraphy demonstrated a superscan with intense foci of increased radiotracer uptake involving the bilateral shoulders, sternoclavicular joints, and sternum with heterogeneous uptake involving bilateral anterior and posterior ribs; cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines; sacrum, pelvis, and bilateral hips, including the femoral head/neck and intertrochanteric regions. Also noted were several foci of radiotracer uptake involving the mandible and bilateral skull in the region of the temporomandibular joints (Figure 3).
The patient was initially treated with IV isotonic saline, followed by calcitonin and then pamidronate after kidney function improved. His calcium level responded to the therapy, and a plan was made by medical oncology to start androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) prior to discharge.
He was initially treated with bicalutamide, while a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide) was added 1 week later. Bicalutamide was then discontinued and a combined androgen blockade consisting of leuprolide, ketoconazole, and hydrocortisone was started. This therapy resulted in remission, and PSA declined to 1.73 ng/ mL 3 months later. At that time the patient enrolled in a clinical trial with leuprolide and bicalutamide combined therapy. About 6 months after his diagnosis, patient’s cancer progressed and became hormone refractory disease. At that time, bicalutamide was discontinued, and his therapy was switched to combined leuprolide and enzalutamide. After 6 months of therapy with enzalutamide, the patient’s cancer progressed again. He was later treated with docetaxel chemotherapy but died 16 months after diagnosis.
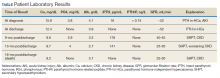
showed improvement of hypercalcemia at the time of discharge, but 9 months later and toward the time of expiration, our patient developed secondary hyperparathyroidism, with calcium maintained in the normal range, while iPTH was significantly elevated, a finding likely explained by a decline in kidney function and a fall in glomerular filtration rate (Table).
Discussion
Hypercalcemia in the setting of prostate cancer is a rare complication with an uncertain pathophysiology.6 Several mechanisms have been proposed for hypercalcemia of malignancy, these comprise humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy mediated by increased PTHrP; local osteolytic hypercalcemia with secretion of other humoral factors; excess extrarenal activation of vitamin D (1,25[OH]2D); PTH secretion, ectopic or primary; and multiple concurrent etiologies.7
PTHrP is the predominant mediator for hypercalcemia of malignancy and is estimated to account for 80% of hypercalcemia in patients with cancer. This protein shares a substantial sequence homology with PTH; in fact, 8 of the first 13 amino acids at the N-terminal portion of PTH were identical.8 PTHrP has multiple isoforms (PTHrP 141, PTHrP 139, and PTHrP 173). Like PTH, it enhances renal tubular reabsorption of calcium while increasing urinary phosphorus excretion.7 The result is both hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia. However, unlike PTH, PTHrP does not increase 1,25(OH)2D and thus does not increase intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. PTHrP acts on osteoblasts, leading to enhanced synthesis of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL).7
In one study, PTHrP was detected immunohistochemically in prostate cancer cells. Iwamura and colleagues used 33 radical prostatectomy specimens from patients with clinically localized carcinoma of the prostate.9 None of these patients demonstrated hypercalcemia prior to the surgery. Using a mouse monoclonal antibody to an amino acid fragment, all cases demonstrated some degree of immunoreactivity throughout the cytoplasm of the tumor cells, but immunostaining was absent from inflammatory and stromal cells.9Furthermore, the intensity of the staining appeared to directly correlate with increasing tumor grade.9
Another study by Iwamura and colleagues suggested that PTHrP may play a significant role in the growth of prostate cancer by acting locally in an autocrine fashion.10 In this study, all prostate cancer cell lines from different sources expressed PTHrP immunoreactivity as well as evidence of DNA synthesis, the latter being measured by thymidine incorporation assay. Moreover, when these cells were incubated with various concentrations of mouse monoclonal antibody directed to PTHrP fragment, PTHrP-induced DNA synthesis was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner and almost completely neutralized at a specific concentration. Interestingly, the study demonstrated that cancer cell line derived from bone metastatic lesions secreted significantly greater amounts of PTHrP than did the cell line derived from the metastasis in the brain or in the lymph node. These findings suggest that PTHrP production may confer some advantage on the ability of prostate cancer cells to grow in bone.10
Ando and colleagues reported that neuroendocrine dedifferentiated prostate cancer can develop as a result of long-term ADT even after several years of therapy and has the potential to worsen and develop severe hypercalcemia.8 Neuron-specific enolase was used as the specific marker for the neuroendocrine cell, which suggested that the prostate cancer cell derived from the neuroendocrine cell might synthesize PTHrP and be responsible for the observed hypercalcemia.8
Other mechanisms cited for hypercalcemia of malignancy include other humoral factors associated with increased remodeling and comprise interleukin 1, 3, 6 (IL-1, IL-3, IL-6); tumor necrosis factor α; transforming growth factor A and B observed in metastatic bone lesions in breast cancer; lymphotoxin; E series prostaglandins; and macrophage inflammatory protein 1α seen in MM.
Local osteolytic hypercalcemia accounts for about 20% of cases and is usually associated with extensive bone metastases. It is most commonly seen in MM and metastatic breast cancer and less commonly in leukemia. The proposed mechanism is thought to be because of the release of local cytokines from the tumor, resulting in excess osteoclast activation and enhanced bone resorption often through RANK/RANKL interaction.
Extrarenal production of 1,25(OH)2D by the tumor accounts for about 1% of cases of hypercalcemia in malignancy. 1,25(OH)2D causes increased intestinal absorption of calcium and enhances osteolytic bone resorption, resulting in increased serum calcium. This mechanism is most commonly seen with Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and had been reported in ovarian dysgerminoma.7
In our patient, bone imaging showed osteoblastic lesions, a finding that likely contrasts the local osteolytic bone destruction theory. PTHrP was not significantly elevated in the serum, and PTH levels ruled out any form of primary hyperparathyroidism. In addition, histopathology showed no evidence of mosaicism or neuroendocrine dedifferentiation.
Findings in aggregate tell us that an exact pathophysiologic mechanism leading to hypercalcemia in prostate cancer is still unclear and may involve an interplay between growth factors and possible osteolytic materials, yet it must be studied thoroughly.
Conclusions
Hypercalcemia in pure metastatic adenocarcinoma of prostate is a rare finding and is of uncertain significance. Some studies suggested a search for unusual histopathologies, including neuroendocrine cancer and neuroendocrine dedifferentiation.8,11 However, in adenocarcinoma alone, it has an uncertain pathophysiology that needs to be further studied. Studies needed to investigate the role of PTHrP as a growth factor for both prostate cancer cells and development of hypercalcemia and possibly target-directed monoclonal antibody therapies may need to be extensively researched.
1. Gastanaga VM, Schwartzberg LS, Jain RK, et al. Prevalence of hypercalcemia among cancer patients in the United States. Cancer Med. 2016;5(8):2091‐2100. doi:10.1002/cam4.749
2. Grill V, Martin TJ. Hypercalcemia of malignancy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000;1(4):253‐263. doi:10.1023/a:1026597816193
3. Halabi S, Kelly WK, Ma H, et al. Meta-analysis evaluating the impact of site of metastasis on overall survival in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(14):1652‐1659. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.65.7270
4. Chang SS. Overview of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Rev Urol. 2004;6(suppl 10):S13‐S18.
5. Kummar S, Fogarasi M, Canova A, Mota A, Ciesielski T. Cytokeratin 7 and 20 staining for the diagnosis of lung and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;86(12):1884‐1887. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600326
6. Avashia JH, Walsh TD, Thomas AJ Jr, Kaye M, Licata A. Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate with hypercalcemia [published correction appears in Cleve Clin J Med. 1991;58(3):284]. Cleve Clin J Med. 1990;57(7):636‐638. doi:10.3949/ccjm.57.7.636.
7. Goldner W. Cancer-related hypercalcemia. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12(5):426‐432. doi:10.1200/JOP.2016.011155.
8. Ando T, Watanabe K, Mizusawa T, Katagiri A. Hypercalcemia due to parathyroid hormone-related peptide secreted by neuroendocrine dedifferentiated prostate cancer. Urol Case Rep. 2018;22:67‐69. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.11.001
9. Iwamura M, di Sant’Agnese PA, Wu G, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of parathyroid hormonerelated protein in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53(8):1724‐1726.
10. Iwamura M, Abrahamsson PA, Foss KA, Wu G, Cockett AT, Deftos LJ. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: a potential autocrine growth regulator in human prostate cancer cell lines. Urology. 1994;43(5):675‐679. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(94)90183-x
11. Smith DC, Tucker JA, Trump DL. Hypercalcemia and neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate: a report of three cases and a review of the literature. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10(3):499‐505. doi:10.1200/JCO.1992.10.3.499.
Hypercalcemia is found when the corrected serum calcium level is > 10.5 mg/dL.1 Its symptoms are not specific and may include polyuria, dehydration, polydipsia, anorexia, nausea and/or vomiting, constipation, and other central nervous system manifestations, including confusion, delirium, cognitive impairment, muscle weakness, psychotic symptoms, and even coma.1,2
Hypercalcemia has varied etiologies; however, malignancy-induced hypercalcemia is one of the most common causes. In the US, the most common causes of malignancy-induced hypercalcemia are primary tumors of the lung or breast, multiple myeloma (MM), squamous cell carcinoma of the head or neck, renal cancer, and ovarian cancer.1
Men with prostate cancer and bone metastasis have relatively worse prognosis than do patient with no metastasis.3 In a recent meta-analysis of patients with bone-involved castration-resistant prostate cancer, the median survival was 21 months.3
Hypercalcemia is a rare manifestation of prostate cancer. In a retrospective study conducted between 2009 and 2013 using the Oncology Services Comprehensive Electronic Records (OSCER) warehouse of electronic health records (EHR), the rates of malignancy-induced hypercalcemia were the lowest among patients with prostate cancer, ranging from 1.4 to 2.1%.1
We present this case to discuss different pathophysiologic mechanisms leading to hypercalcemia in a patient with prostate cancer with bone metastasis and to study the role of humoral and growth factors in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Case Presentation
An African American man aged 69 years presented to the emergency department (ED) with generalized weakness, fatigue, and lower extremities muscle weakness. He reported a 40-lb weight loss over the past 3 months, intermittent lower back pain, and a 50 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination suggested clinical signs of dehydration.
Laboratory test results indicated hypercalcemia, macrocytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia: calcium 15.8 mg/dL, serum albumin 4.1 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 139 μ/L, blood urea nitrogen 55 mg/dL, creatinine 3.4 mg/dL (baseline 1.4-1.5 mg/dL), hemoglobin 8 g/dL, mean corpuscular volume 99.6 fL, and platelets 100,000/μL. The patient was admitted for hypercalcemia. His intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) was suppressed at 16 pg/mL, phosphorous was 3.8 mg/dL, parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) was < 0.74 pmol/L, vitamin D (25 hydroxy cholecalciferol) was mildly decreased at 17.2 ng/mL, and 1,25 dihydroxy cholecalciferol (calcitriol) was < 5.0 (normal range 20-79.3 pg/mL).
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest and abdomen was taken due to the patient’s heavy smoking history, an incidentally detected right lung base nodule on chest X-ray, and hypercalcemia. The CT scan showed multiple right middle lobe lung nodules with and without calcifications and calcified right hilar lymph nodes (Figure 1).
To evaluate the pancytopenia, a bone marrow biopsy was done, which showed that 80 to 90% of the marrow space was replaced by fibrosis and metastatic malignancy. Trilinear hematopoiesis was not seen (Figure 2). The tumor cells were positive for prostate- specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and negative for cytokeratin 7 and 20 (CK7 and CK20).4 The former is a membrane protein expressed on prostate tissues, including cancer; the latter is a form of protein used to identify adenocarcinoma of unknown primary origin (CK7 usually found in primary/ metastatic lung adenocarcinoma and CK20 usually in primary and some metastatic diseases of colon adenocarcinoma).5 A prostatic specific antigen (PSA) test was markedly elevated: 335.94 ng/mL (1.46 ng/mL on a previous 2011 test).
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate was diagnosed without a prostate biopsy. To determine the extent of bone metastases, a technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate (MDP) bone scintigraphy demonstrated a superscan with intense foci of increased radiotracer uptake involving the bilateral shoulders, sternoclavicular joints, and sternum with heterogeneous uptake involving bilateral anterior and posterior ribs; cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines; sacrum, pelvis, and bilateral hips, including the femoral head/neck and intertrochanteric regions. Also noted were several foci of radiotracer uptake involving the mandible and bilateral skull in the region of the temporomandibular joints (Figure 3).
The patient was initially treated with IV isotonic saline, followed by calcitonin and then pamidronate after kidney function improved. His calcium level responded to the therapy, and a plan was made by medical oncology to start androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) prior to discharge.
He was initially treated with bicalutamide, while a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide) was added 1 week later. Bicalutamide was then discontinued and a combined androgen blockade consisting of leuprolide, ketoconazole, and hydrocortisone was started. This therapy resulted in remission, and PSA declined to 1.73 ng/ mL 3 months later. At that time the patient enrolled in a clinical trial with leuprolide and bicalutamide combined therapy. About 6 months after his diagnosis, patient’s cancer progressed and became hormone refractory disease. At that time, bicalutamide was discontinued, and his therapy was switched to combined leuprolide and enzalutamide. After 6 months of therapy with enzalutamide, the patient’s cancer progressed again. He was later treated with docetaxel chemotherapy but died 16 months after diagnosis.
showed improvement of hypercalcemia at the time of discharge, but 9 months later and toward the time of expiration, our patient developed secondary hyperparathyroidism, with calcium maintained in the normal range, while iPTH was significantly elevated, a finding likely explained by a decline in kidney function and a fall in glomerular filtration rate (Table).
Discussion
Hypercalcemia in the setting of prostate cancer is a rare complication with an uncertain pathophysiology.6 Several mechanisms have been proposed for hypercalcemia of malignancy, these comprise humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy mediated by increased PTHrP; local osteolytic hypercalcemia with secretion of other humoral factors; excess extrarenal activation of vitamin D (1,25[OH]2D); PTH secretion, ectopic or primary; and multiple concurrent etiologies.7
PTHrP is the predominant mediator for hypercalcemia of malignancy and is estimated to account for 80% of hypercalcemia in patients with cancer. This protein shares a substantial sequence homology with PTH; in fact, 8 of the first 13 amino acids at the N-terminal portion of PTH were identical.8 PTHrP has multiple isoforms (PTHrP 141, PTHrP 139, and PTHrP 173). Like PTH, it enhances renal tubular reabsorption of calcium while increasing urinary phosphorus excretion.7 The result is both hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia. However, unlike PTH, PTHrP does not increase 1,25(OH)2D and thus does not increase intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. PTHrP acts on osteoblasts, leading to enhanced synthesis of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL).7
In one study, PTHrP was detected immunohistochemically in prostate cancer cells. Iwamura and colleagues used 33 radical prostatectomy specimens from patients with clinically localized carcinoma of the prostate.9 None of these patients demonstrated hypercalcemia prior to the surgery. Using a mouse monoclonal antibody to an amino acid fragment, all cases demonstrated some degree of immunoreactivity throughout the cytoplasm of the tumor cells, but immunostaining was absent from inflammatory and stromal cells.9Furthermore, the intensity of the staining appeared to directly correlate with increasing tumor grade.9
Another study by Iwamura and colleagues suggested that PTHrP may play a significant role in the growth of prostate cancer by acting locally in an autocrine fashion.10 In this study, all prostate cancer cell lines from different sources expressed PTHrP immunoreactivity as well as evidence of DNA synthesis, the latter being measured by thymidine incorporation assay. Moreover, when these cells were incubated with various concentrations of mouse monoclonal antibody directed to PTHrP fragment, PTHrP-induced DNA synthesis was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner and almost completely neutralized at a specific concentration. Interestingly, the study demonstrated that cancer cell line derived from bone metastatic lesions secreted significantly greater amounts of PTHrP than did the cell line derived from the metastasis in the brain or in the lymph node. These findings suggest that PTHrP production may confer some advantage on the ability of prostate cancer cells to grow in bone.10
Ando and colleagues reported that neuroendocrine dedifferentiated prostate cancer can develop as a result of long-term ADT even after several years of therapy and has the potential to worsen and develop severe hypercalcemia.8 Neuron-specific enolase was used as the specific marker for the neuroendocrine cell, which suggested that the prostate cancer cell derived from the neuroendocrine cell might synthesize PTHrP and be responsible for the observed hypercalcemia.8
Other mechanisms cited for hypercalcemia of malignancy include other humoral factors associated with increased remodeling and comprise interleukin 1, 3, 6 (IL-1, IL-3, IL-6); tumor necrosis factor α; transforming growth factor A and B observed in metastatic bone lesions in breast cancer; lymphotoxin; E series prostaglandins; and macrophage inflammatory protein 1α seen in MM.
Local osteolytic hypercalcemia accounts for about 20% of cases and is usually associated with extensive bone metastases. It is most commonly seen in MM and metastatic breast cancer and less commonly in leukemia. The proposed mechanism is thought to be because of the release of local cytokines from the tumor, resulting in excess osteoclast activation and enhanced bone resorption often through RANK/RANKL interaction.
Extrarenal production of 1,25(OH)2D by the tumor accounts for about 1% of cases of hypercalcemia in malignancy. 1,25(OH)2D causes increased intestinal absorption of calcium and enhances osteolytic bone resorption, resulting in increased serum calcium. This mechanism is most commonly seen with Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and had been reported in ovarian dysgerminoma.7
In our patient, bone imaging showed osteoblastic lesions, a finding that likely contrasts the local osteolytic bone destruction theory. PTHrP was not significantly elevated in the serum, and PTH levels ruled out any form of primary hyperparathyroidism. In addition, histopathology showed no evidence of mosaicism or neuroendocrine dedifferentiation.
Findings in aggregate tell us that an exact pathophysiologic mechanism leading to hypercalcemia in prostate cancer is still unclear and may involve an interplay between growth factors and possible osteolytic materials, yet it must be studied thoroughly.
Conclusions
Hypercalcemia in pure metastatic adenocarcinoma of prostate is a rare finding and is of uncertain significance. Some studies suggested a search for unusual histopathologies, including neuroendocrine cancer and neuroendocrine dedifferentiation.8,11 However, in adenocarcinoma alone, it has an uncertain pathophysiology that needs to be further studied. Studies needed to investigate the role of PTHrP as a growth factor for both prostate cancer cells and development of hypercalcemia and possibly target-directed monoclonal antibody therapies may need to be extensively researched.
Hypercalcemia is found when the corrected serum calcium level is > 10.5 mg/dL.1 Its symptoms are not specific and may include polyuria, dehydration, polydipsia, anorexia, nausea and/or vomiting, constipation, and other central nervous system manifestations, including confusion, delirium, cognitive impairment, muscle weakness, psychotic symptoms, and even coma.1,2
Hypercalcemia has varied etiologies; however, malignancy-induced hypercalcemia is one of the most common causes. In the US, the most common causes of malignancy-induced hypercalcemia are primary tumors of the lung or breast, multiple myeloma (MM), squamous cell carcinoma of the head or neck, renal cancer, and ovarian cancer.1
Men with prostate cancer and bone metastasis have relatively worse prognosis than do patient with no metastasis.3 In a recent meta-analysis of patients with bone-involved castration-resistant prostate cancer, the median survival was 21 months.3
Hypercalcemia is a rare manifestation of prostate cancer. In a retrospective study conducted between 2009 and 2013 using the Oncology Services Comprehensive Electronic Records (OSCER) warehouse of electronic health records (EHR), the rates of malignancy-induced hypercalcemia were the lowest among patients with prostate cancer, ranging from 1.4 to 2.1%.1
We present this case to discuss different pathophysiologic mechanisms leading to hypercalcemia in a patient with prostate cancer with bone metastasis and to study the role of humoral and growth factors in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Case Presentation
An African American man aged 69 years presented to the emergency department (ED) with generalized weakness, fatigue, and lower extremities muscle weakness. He reported a 40-lb weight loss over the past 3 months, intermittent lower back pain, and a 50 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination suggested clinical signs of dehydration.
Laboratory test results indicated hypercalcemia, macrocytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia: calcium 15.8 mg/dL, serum albumin 4.1 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 139 μ/L, blood urea nitrogen 55 mg/dL, creatinine 3.4 mg/dL (baseline 1.4-1.5 mg/dL), hemoglobin 8 g/dL, mean corpuscular volume 99.6 fL, and platelets 100,000/μL. The patient was admitted for hypercalcemia. His intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) was suppressed at 16 pg/mL, phosphorous was 3.8 mg/dL, parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) was < 0.74 pmol/L, vitamin D (25 hydroxy cholecalciferol) was mildly decreased at 17.2 ng/mL, and 1,25 dihydroxy cholecalciferol (calcitriol) was < 5.0 (normal range 20-79.3 pg/mL).
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest and abdomen was taken due to the patient’s heavy smoking history, an incidentally detected right lung base nodule on chest X-ray, and hypercalcemia. The CT scan showed multiple right middle lobe lung nodules with and without calcifications and calcified right hilar lymph nodes (Figure 1).
To evaluate the pancytopenia, a bone marrow biopsy was done, which showed that 80 to 90% of the marrow space was replaced by fibrosis and metastatic malignancy. Trilinear hematopoiesis was not seen (Figure 2). The tumor cells were positive for prostate- specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and negative for cytokeratin 7 and 20 (CK7 and CK20).4 The former is a membrane protein expressed on prostate tissues, including cancer; the latter is a form of protein used to identify adenocarcinoma of unknown primary origin (CK7 usually found in primary/ metastatic lung adenocarcinoma and CK20 usually in primary and some metastatic diseases of colon adenocarcinoma).5 A prostatic specific antigen (PSA) test was markedly elevated: 335.94 ng/mL (1.46 ng/mL on a previous 2011 test).
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate was diagnosed without a prostate biopsy. To determine the extent of bone metastases, a technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate (MDP) bone scintigraphy demonstrated a superscan with intense foci of increased radiotracer uptake involving the bilateral shoulders, sternoclavicular joints, and sternum with heterogeneous uptake involving bilateral anterior and posterior ribs; cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines; sacrum, pelvis, and bilateral hips, including the femoral head/neck and intertrochanteric regions. Also noted were several foci of radiotracer uptake involving the mandible and bilateral skull in the region of the temporomandibular joints (Figure 3).
The patient was initially treated with IV isotonic saline, followed by calcitonin and then pamidronate after kidney function improved. His calcium level responded to the therapy, and a plan was made by medical oncology to start androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) prior to discharge.
He was initially treated with bicalutamide, while a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide) was added 1 week later. Bicalutamide was then discontinued and a combined androgen blockade consisting of leuprolide, ketoconazole, and hydrocortisone was started. This therapy resulted in remission, and PSA declined to 1.73 ng/ mL 3 months later. At that time the patient enrolled in a clinical trial with leuprolide and bicalutamide combined therapy. About 6 months after his diagnosis, patient’s cancer progressed and became hormone refractory disease. At that time, bicalutamide was discontinued, and his therapy was switched to combined leuprolide and enzalutamide. After 6 months of therapy with enzalutamide, the patient’s cancer progressed again. He was later treated with docetaxel chemotherapy but died 16 months after diagnosis.
showed improvement of hypercalcemia at the time of discharge, but 9 months later and toward the time of expiration, our patient developed secondary hyperparathyroidism, with calcium maintained in the normal range, while iPTH was significantly elevated, a finding likely explained by a decline in kidney function and a fall in glomerular filtration rate (Table).
Discussion
Hypercalcemia in the setting of prostate cancer is a rare complication with an uncertain pathophysiology.6 Several mechanisms have been proposed for hypercalcemia of malignancy, these comprise humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy mediated by increased PTHrP; local osteolytic hypercalcemia with secretion of other humoral factors; excess extrarenal activation of vitamin D (1,25[OH]2D); PTH secretion, ectopic or primary; and multiple concurrent etiologies.7
PTHrP is the predominant mediator for hypercalcemia of malignancy and is estimated to account for 80% of hypercalcemia in patients with cancer. This protein shares a substantial sequence homology with PTH; in fact, 8 of the first 13 amino acids at the N-terminal portion of PTH were identical.8 PTHrP has multiple isoforms (PTHrP 141, PTHrP 139, and PTHrP 173). Like PTH, it enhances renal tubular reabsorption of calcium while increasing urinary phosphorus excretion.7 The result is both hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia. However, unlike PTH, PTHrP does not increase 1,25(OH)2D and thus does not increase intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. PTHrP acts on osteoblasts, leading to enhanced synthesis of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL).7
In one study, PTHrP was detected immunohistochemically in prostate cancer cells. Iwamura and colleagues used 33 radical prostatectomy specimens from patients with clinically localized carcinoma of the prostate.9 None of these patients demonstrated hypercalcemia prior to the surgery. Using a mouse monoclonal antibody to an amino acid fragment, all cases demonstrated some degree of immunoreactivity throughout the cytoplasm of the tumor cells, but immunostaining was absent from inflammatory and stromal cells.9Furthermore, the intensity of the staining appeared to directly correlate with increasing tumor grade.9
Another study by Iwamura and colleagues suggested that PTHrP may play a significant role in the growth of prostate cancer by acting locally in an autocrine fashion.10 In this study, all prostate cancer cell lines from different sources expressed PTHrP immunoreactivity as well as evidence of DNA synthesis, the latter being measured by thymidine incorporation assay. Moreover, when these cells were incubated with various concentrations of mouse monoclonal antibody directed to PTHrP fragment, PTHrP-induced DNA synthesis was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner and almost completely neutralized at a specific concentration. Interestingly, the study demonstrated that cancer cell line derived from bone metastatic lesions secreted significantly greater amounts of PTHrP than did the cell line derived from the metastasis in the brain or in the lymph node. These findings suggest that PTHrP production may confer some advantage on the ability of prostate cancer cells to grow in bone.10
Ando and colleagues reported that neuroendocrine dedifferentiated prostate cancer can develop as a result of long-term ADT even after several years of therapy and has the potential to worsen and develop severe hypercalcemia.8 Neuron-specific enolase was used as the specific marker for the neuroendocrine cell, which suggested that the prostate cancer cell derived from the neuroendocrine cell might synthesize PTHrP and be responsible for the observed hypercalcemia.8
Other mechanisms cited for hypercalcemia of malignancy include other humoral factors associated with increased remodeling and comprise interleukin 1, 3, 6 (IL-1, IL-3, IL-6); tumor necrosis factor α; transforming growth factor A and B observed in metastatic bone lesions in breast cancer; lymphotoxin; E series prostaglandins; and macrophage inflammatory protein 1α seen in MM.
Local osteolytic hypercalcemia accounts for about 20% of cases and is usually associated with extensive bone metastases. It is most commonly seen in MM and metastatic breast cancer and less commonly in leukemia. The proposed mechanism is thought to be because of the release of local cytokines from the tumor, resulting in excess osteoclast activation and enhanced bone resorption often through RANK/RANKL interaction.
Extrarenal production of 1,25(OH)2D by the tumor accounts for about 1% of cases of hypercalcemia in malignancy. 1,25(OH)2D causes increased intestinal absorption of calcium and enhances osteolytic bone resorption, resulting in increased serum calcium. This mechanism is most commonly seen with Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and had been reported in ovarian dysgerminoma.7
In our patient, bone imaging showed osteoblastic lesions, a finding that likely contrasts the local osteolytic bone destruction theory. PTHrP was not significantly elevated in the serum, and PTH levels ruled out any form of primary hyperparathyroidism. In addition, histopathology showed no evidence of mosaicism or neuroendocrine dedifferentiation.
Findings in aggregate tell us that an exact pathophysiologic mechanism leading to hypercalcemia in prostate cancer is still unclear and may involve an interplay between growth factors and possible osteolytic materials, yet it must be studied thoroughly.
Conclusions
Hypercalcemia in pure metastatic adenocarcinoma of prostate is a rare finding and is of uncertain significance. Some studies suggested a search for unusual histopathologies, including neuroendocrine cancer and neuroendocrine dedifferentiation.8,11 However, in adenocarcinoma alone, it has an uncertain pathophysiology that needs to be further studied. Studies needed to investigate the role of PTHrP as a growth factor for both prostate cancer cells and development of hypercalcemia and possibly target-directed monoclonal antibody therapies may need to be extensively researched.
1. Gastanaga VM, Schwartzberg LS, Jain RK, et al. Prevalence of hypercalcemia among cancer patients in the United States. Cancer Med. 2016;5(8):2091‐2100. doi:10.1002/cam4.749
2. Grill V, Martin TJ. Hypercalcemia of malignancy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000;1(4):253‐263. doi:10.1023/a:1026597816193
3. Halabi S, Kelly WK, Ma H, et al. Meta-analysis evaluating the impact of site of metastasis on overall survival in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(14):1652‐1659. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.65.7270
4. Chang SS. Overview of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Rev Urol. 2004;6(suppl 10):S13‐S18.
5. Kummar S, Fogarasi M, Canova A, Mota A, Ciesielski T. Cytokeratin 7 and 20 staining for the diagnosis of lung and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;86(12):1884‐1887. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600326
6. Avashia JH, Walsh TD, Thomas AJ Jr, Kaye M, Licata A. Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate with hypercalcemia [published correction appears in Cleve Clin J Med. 1991;58(3):284]. Cleve Clin J Med. 1990;57(7):636‐638. doi:10.3949/ccjm.57.7.636.
7. Goldner W. Cancer-related hypercalcemia. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12(5):426‐432. doi:10.1200/JOP.2016.011155.
8. Ando T, Watanabe K, Mizusawa T, Katagiri A. Hypercalcemia due to parathyroid hormone-related peptide secreted by neuroendocrine dedifferentiated prostate cancer. Urol Case Rep. 2018;22:67‐69. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.11.001
9. Iwamura M, di Sant’Agnese PA, Wu G, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of parathyroid hormonerelated protein in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53(8):1724‐1726.
10. Iwamura M, Abrahamsson PA, Foss KA, Wu G, Cockett AT, Deftos LJ. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: a potential autocrine growth regulator in human prostate cancer cell lines. Urology. 1994;43(5):675‐679. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(94)90183-x
11. Smith DC, Tucker JA, Trump DL. Hypercalcemia and neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate: a report of three cases and a review of the literature. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10(3):499‐505. doi:10.1200/JCO.1992.10.3.499.
1. Gastanaga VM, Schwartzberg LS, Jain RK, et al. Prevalence of hypercalcemia among cancer patients in the United States. Cancer Med. 2016;5(8):2091‐2100. doi:10.1002/cam4.749
2. Grill V, Martin TJ. Hypercalcemia of malignancy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000;1(4):253‐263. doi:10.1023/a:1026597816193
3. Halabi S, Kelly WK, Ma H, et al. Meta-analysis evaluating the impact of site of metastasis on overall survival in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(14):1652‐1659. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.65.7270
4. Chang SS. Overview of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Rev Urol. 2004;6(suppl 10):S13‐S18.
5. Kummar S, Fogarasi M, Canova A, Mota A, Ciesielski T. Cytokeratin 7 and 20 staining for the diagnosis of lung and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;86(12):1884‐1887. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600326
6. Avashia JH, Walsh TD, Thomas AJ Jr, Kaye M, Licata A. Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate with hypercalcemia [published correction appears in Cleve Clin J Med. 1991;58(3):284]. Cleve Clin J Med. 1990;57(7):636‐638. doi:10.3949/ccjm.57.7.636.
7. Goldner W. Cancer-related hypercalcemia. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12(5):426‐432. doi:10.1200/JOP.2016.011155.
8. Ando T, Watanabe K, Mizusawa T, Katagiri A. Hypercalcemia due to parathyroid hormone-related peptide secreted by neuroendocrine dedifferentiated prostate cancer. Urol Case Rep. 2018;22:67‐69. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.11.001
9. Iwamura M, di Sant’Agnese PA, Wu G, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of parathyroid hormonerelated protein in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53(8):1724‐1726.
10. Iwamura M, Abrahamsson PA, Foss KA, Wu G, Cockett AT, Deftos LJ. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: a potential autocrine growth regulator in human prostate cancer cell lines. Urology. 1994;43(5):675‐679. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(94)90183-x
11. Smith DC, Tucker JA, Trump DL. Hypercalcemia and neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate: a report of three cases and a review of the literature. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10(3):499‐505. doi:10.1200/JCO.1992.10.3.499.
Combination probiotic formulations might improve outcomes in preterm infants
For preterm, low-birth-weight infants, probiotic formulations containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains appear to be superior to single-strain probiotics and to other multiple-strain formulations for reducing the risk of all-cause mortality, according to the findings of a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.
The results of a prior Cochrane review indicated that probiotics can help prevent severe necrotizing enterocolitis and all-cause mortality in preterm infants, but the most effective formulations remained unclear. Therefore, Rebecca L. Morgan, PhD, MPH, and her associates searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Citation Index Expanded, CINAHL, Scopus, Cochrane CENTRAL, BIOSIS Previews, and Google Scholar through Jan. 1, 2019, to identify studies of single-strain and multistrain probiotic formulations in preterm, low-birth-weight neonates. A total of 63 studies involving 15,712 infants met inclusion criteria. “We used a frequentist approach for network meta-analysis and [a] GRADE approach to assess certainty of evidence,” they noted.
“High-certainty” evidence indicated that combination therapy with one or more Lactobacillus species and one or more Bifidobacterium species significantly reduced all-cause mortality, compared with placebo (odds ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.80), wrote Dr. Morgan, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, and her coinvestigators. This was the only intervention to have moderate- or high-quality evidence for a reduction in mortality, the researchers wrote in Gastroenterology.
They added that, among the probiotic formulations with moderate- or high-quality evidence for efficacy, compared with placebo, those containing at least one species of Lactobacillus and at least one species of Bifidobacterium, and the single-strain probiotics containing Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis, Lactobacillus reuteri, or Lactobacillus rhamnosus significantly reduced the risk of severe necrotizing enterocolitis (Bell stage II or higher), with statistically significant odds ratios of 0.35, 0.31, 0.55, and 0.44, respectively.
Three formulations were associated with “low-” or “very low-certainty” evidence for a reduction in risk for severe necrotizing enterocolitis, compared with placebo: Bacillus plus Enterococcus species, Lactobacillus plus Bifidobacterium plus Enterococcus species and Bifidobacterium plus Streptococcus salivarius subspecies thermophilus. Estimated odds ratios were 0.23 (risk difference, –4.9%), 0.28 (RD, –4.9%), and 0.38 (RD, –3.9%), respectively.
“The combinations of Bacillus species and Enterococcus species, and one or more Bifidobacterium species and S. salivarius subspecies thermophilus, might produce the largest reduction in necrotizing enterocolitis development,” the investigators wrote. “Further trials are needed.”
Compared with placebo, no probiotic formulation significantly improved the third primary outcome in the meta-analysis, culture-confirmed sepsis. However, several formulations were associated with moderate- or high-quality evidence for efficacy on secondary outcome measures. Compared with placebo, combinations of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium and Saccharomyces boulardii were associated with a significant decrease in the number of days to reach full feeding (mean reduction, 3.3 days; 95% CI, 5.9-0.7 days). Compared with placebo, single-strain therapy with B. animalis subspecies lactis or Lactobacillus reuteri was associated with a shorter duration of hospitalization, with mean reductions of 13.0 days (95% CI, 22.7-3.3 days) and 7.9 days (95% CI, 11.6-4.2 days), respectively.
“Multicenter and large randomized controlled trials should be prioritized to distinguish between the efficacy of single- and multiple-strain probiotics among preterm infants,” Dr. Morgan and her associates concluded. Such studies would further clarify the safety of probiotic formulations in this “fragile population,” they wrote. “Although the primary concern of live microbe administration, intestinal barrier translocation leading to sepsis, is decreased by several probiotic formulations, sound clinical judgement should be exercised.”
Partial support was provided by Mitacs Canada, in partnership with Nestlé Canada. The funder was not involved in designing or conducting the study or writing the manuscript. Dr. Morgan reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to AbbVie, Ferring, Janssen, and Takeda.
SOURCE: Morgan RL et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.096.
The demonstration of decreased risks of both death and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in randomized placebo-controlled trials of probiotic microbes in very preterm babies is the most compelling case for administration of probiotics to date. Questions remain, including the optimal probiotic microbe(s) and dose for this population. The ideal studies would compare commercially available probiotic products and doses to each other (rather than to placebo). In the absence of these ideal studies, a network meta-analysis is a valuable tool to compare and rank multiple treatments. One of the drawbacks of a network meta-analysis is the assumption that all interventions have similar effects in all populations (an assumption that is challenging given the marked differences in the incidence of NEC between hospitals and populations).
The study conclusion that the combination of at least one Lactobacillus strain and at least one Bifidobacterium strain is most effective in preventing both death and NEC in very preterm infants is consistent with a previous network meta-analysis and with recent recommendations of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition and the American Gastroenterological Association.
Mark A. Underwood, MD, MAS, is a professor of pediatrics and chief of the division of neonatology in the department of pediatrics at the University of California, Davis. He has received honoraria from Abbott and conducted a clinical trial of probiotics that was funded by Evolve Biosystems.
The demonstration of decreased risks of both death and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in randomized placebo-controlled trials of probiotic microbes in very preterm babies is the most compelling case for administration of probiotics to date. Questions remain, including the optimal probiotic microbe(s) and dose for this population. The ideal studies would compare commercially available probiotic products and doses to each other (rather than to placebo). In the absence of these ideal studies, a network meta-analysis is a valuable tool to compare and rank multiple treatments. One of the drawbacks of a network meta-analysis is the assumption that all interventions have similar effects in all populations (an assumption that is challenging given the marked differences in the incidence of NEC between hospitals and populations).
The study conclusion that the combination of at least one Lactobacillus strain and at least one Bifidobacterium strain is most effective in preventing both death and NEC in very preterm infants is consistent with a previous network meta-analysis and with recent recommendations of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition and the American Gastroenterological Association.
Mark A. Underwood, MD, MAS, is a professor of pediatrics and chief of the division of neonatology in the department of pediatrics at the University of California, Davis. He has received honoraria from Abbott and conducted a clinical trial of probiotics that was funded by Evolve Biosystems.
The demonstration of decreased risks of both death and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in randomized placebo-controlled trials of probiotic microbes in very preterm babies is the most compelling case for administration of probiotics to date. Questions remain, including the optimal probiotic microbe(s) and dose for this population. The ideal studies would compare commercially available probiotic products and doses to each other (rather than to placebo). In the absence of these ideal studies, a network meta-analysis is a valuable tool to compare and rank multiple treatments. One of the drawbacks of a network meta-analysis is the assumption that all interventions have similar effects in all populations (an assumption that is challenging given the marked differences in the incidence of NEC between hospitals and populations).
The study conclusion that the combination of at least one Lactobacillus strain and at least one Bifidobacterium strain is most effective in preventing both death and NEC in very preterm infants is consistent with a previous network meta-analysis and with recent recommendations of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition and the American Gastroenterological Association.
Mark A. Underwood, MD, MAS, is a professor of pediatrics and chief of the division of neonatology in the department of pediatrics at the University of California, Davis. He has received honoraria from Abbott and conducted a clinical trial of probiotics that was funded by Evolve Biosystems.
For preterm, low-birth-weight infants, probiotic formulations containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains appear to be superior to single-strain probiotics and to other multiple-strain formulations for reducing the risk of all-cause mortality, according to the findings of a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.
The results of a prior Cochrane review indicated that probiotics can help prevent severe necrotizing enterocolitis and all-cause mortality in preterm infants, but the most effective formulations remained unclear. Therefore, Rebecca L. Morgan, PhD, MPH, and her associates searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Citation Index Expanded, CINAHL, Scopus, Cochrane CENTRAL, BIOSIS Previews, and Google Scholar through Jan. 1, 2019, to identify studies of single-strain and multistrain probiotic formulations in preterm, low-birth-weight neonates. A total of 63 studies involving 15,712 infants met inclusion criteria. “We used a frequentist approach for network meta-analysis and [a] GRADE approach to assess certainty of evidence,” they noted.
“High-certainty” evidence indicated that combination therapy with one or more Lactobacillus species and one or more Bifidobacterium species significantly reduced all-cause mortality, compared with placebo (odds ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.80), wrote Dr. Morgan, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, and her coinvestigators. This was the only intervention to have moderate- or high-quality evidence for a reduction in mortality, the researchers wrote in Gastroenterology.
They added that, among the probiotic formulations with moderate- or high-quality evidence for efficacy, compared with placebo, those containing at least one species of Lactobacillus and at least one species of Bifidobacterium, and the single-strain probiotics containing Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis, Lactobacillus reuteri, or Lactobacillus rhamnosus significantly reduced the risk of severe necrotizing enterocolitis (Bell stage II or higher), with statistically significant odds ratios of 0.35, 0.31, 0.55, and 0.44, respectively.
Three formulations were associated with “low-” or “very low-certainty” evidence for a reduction in risk for severe necrotizing enterocolitis, compared with placebo: Bacillus plus Enterococcus species, Lactobacillus plus Bifidobacterium plus Enterococcus species and Bifidobacterium plus Streptococcus salivarius subspecies thermophilus. Estimated odds ratios were 0.23 (risk difference, –4.9%), 0.28 (RD, –4.9%), and 0.38 (RD, –3.9%), respectively.
“The combinations of Bacillus species and Enterococcus species, and one or more Bifidobacterium species and S. salivarius subspecies thermophilus, might produce the largest reduction in necrotizing enterocolitis development,” the investigators wrote. “Further trials are needed.”
Compared with placebo, no probiotic formulation significantly improved the third primary outcome in the meta-analysis, culture-confirmed sepsis. However, several formulations were associated with moderate- or high-quality evidence for efficacy on secondary outcome measures. Compared with placebo, combinations of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium and Saccharomyces boulardii were associated with a significant decrease in the number of days to reach full feeding (mean reduction, 3.3 days; 95% CI, 5.9-0.7 days). Compared with placebo, single-strain therapy with B. animalis subspecies lactis or Lactobacillus reuteri was associated with a shorter duration of hospitalization, with mean reductions of 13.0 days (95% CI, 22.7-3.3 days) and 7.9 days (95% CI, 11.6-4.2 days), respectively.
“Multicenter and large randomized controlled trials should be prioritized to distinguish between the efficacy of single- and multiple-strain probiotics among preterm infants,” Dr. Morgan and her associates concluded. Such studies would further clarify the safety of probiotic formulations in this “fragile population,” they wrote. “Although the primary concern of live microbe administration, intestinal barrier translocation leading to sepsis, is decreased by several probiotic formulations, sound clinical judgement should be exercised.”
Partial support was provided by Mitacs Canada, in partnership with Nestlé Canada. The funder was not involved in designing or conducting the study or writing the manuscript. Dr. Morgan reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to AbbVie, Ferring, Janssen, and Takeda.
SOURCE: Morgan RL et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.096.
For preterm, low-birth-weight infants, probiotic formulations containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains appear to be superior to single-strain probiotics and to other multiple-strain formulations for reducing the risk of all-cause mortality, according to the findings of a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.
The results of a prior Cochrane review indicated that probiotics can help prevent severe necrotizing enterocolitis and all-cause mortality in preterm infants, but the most effective formulations remained unclear. Therefore, Rebecca L. Morgan, PhD, MPH, and her associates searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Citation Index Expanded, CINAHL, Scopus, Cochrane CENTRAL, BIOSIS Previews, and Google Scholar through Jan. 1, 2019, to identify studies of single-strain and multistrain probiotic formulations in preterm, low-birth-weight neonates. A total of 63 studies involving 15,712 infants met inclusion criteria. “We used a frequentist approach for network meta-analysis and [a] GRADE approach to assess certainty of evidence,” they noted.
“High-certainty” evidence indicated that combination therapy with one or more Lactobacillus species and one or more Bifidobacterium species significantly reduced all-cause mortality, compared with placebo (odds ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.80), wrote Dr. Morgan, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, and her coinvestigators. This was the only intervention to have moderate- or high-quality evidence for a reduction in mortality, the researchers wrote in Gastroenterology.
They added that, among the probiotic formulations with moderate- or high-quality evidence for efficacy, compared with placebo, those containing at least one species of Lactobacillus and at least one species of Bifidobacterium, and the single-strain probiotics containing Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis, Lactobacillus reuteri, or Lactobacillus rhamnosus significantly reduced the risk of severe necrotizing enterocolitis (Bell stage II or higher), with statistically significant odds ratios of 0.35, 0.31, 0.55, and 0.44, respectively.
Three formulations were associated with “low-” or “very low-certainty” evidence for a reduction in risk for severe necrotizing enterocolitis, compared with placebo: Bacillus plus Enterococcus species, Lactobacillus plus Bifidobacterium plus Enterococcus species and Bifidobacterium plus Streptococcus salivarius subspecies thermophilus. Estimated odds ratios were 0.23 (risk difference, –4.9%), 0.28 (RD, –4.9%), and 0.38 (RD, –3.9%), respectively.
“The combinations of Bacillus species and Enterococcus species, and one or more Bifidobacterium species and S. salivarius subspecies thermophilus, might produce the largest reduction in necrotizing enterocolitis development,” the investigators wrote. “Further trials are needed.”
Compared with placebo, no probiotic formulation significantly improved the third primary outcome in the meta-analysis, culture-confirmed sepsis. However, several formulations were associated with moderate- or high-quality evidence for efficacy on secondary outcome measures. Compared with placebo, combinations of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium and Saccharomyces boulardii were associated with a significant decrease in the number of days to reach full feeding (mean reduction, 3.3 days; 95% CI, 5.9-0.7 days). Compared with placebo, single-strain therapy with B. animalis subspecies lactis or Lactobacillus reuteri was associated with a shorter duration of hospitalization, with mean reductions of 13.0 days (95% CI, 22.7-3.3 days) and 7.9 days (95% CI, 11.6-4.2 days), respectively.
“Multicenter and large randomized controlled trials should be prioritized to distinguish between the efficacy of single- and multiple-strain probiotics among preterm infants,” Dr. Morgan and her associates concluded. Such studies would further clarify the safety of probiotic formulations in this “fragile population,” they wrote. “Although the primary concern of live microbe administration, intestinal barrier translocation leading to sepsis, is decreased by several probiotic formulations, sound clinical judgement should be exercised.”
Partial support was provided by Mitacs Canada, in partnership with Nestlé Canada. The funder was not involved in designing or conducting the study or writing the manuscript. Dr. Morgan reported having no relevant conflicts of interest. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to AbbVie, Ferring, Janssen, and Takeda.
SOURCE: Morgan RL et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.096.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Delayed diagnoses seen in children during COVID-19
There were also nine deaths where delayed presentation was considered a contributing factor, resulting mainly from sepsis and malignancy.
By comparison, over the same 2-week period of the survey there were three child deaths from COVID-19 directly, according to senior study author Shamez Ladhani, MRCPCH, PhD, chair of the British Paediatric Surveillance Unit (BPSU), Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, London.
“The unintended consequences of COVID are far greater, in children, than the disease itself. The way we are trying to prevent this is causing more harm than the disease,” he lamented.
One-third of senior U.K. pediatric specialists who responded to the survey reported dealing with so-called emergency delayed presentations in children who they would normally have expected to present much earlier.
After diabetes, the most commonly reported delayed diagnoses were sepsis and child protection issues. Cancer also featured prominently.
“We’ve found that there is great concern that children are not accessing healthcare as they should during lockdown and after,” Dr. Ladhani stressed. “Our emergency departments saw a 50% reduction during the peak, and now it is still 40% less than expected. The problem is improving but it remains.”
The survey findings were recently published online in Archives of Disease in Childhood, by first author Richard M. Lynn, MSc, of the Institute of Child Health, department of epidemiology and public health, University College London Research, and colleagues.
New diabetes cases presented very late during lockdown
Over the 2-week reporting period in mid-April 2020, type 1 diabetes was the most frequently reported delayed diagnosis, with 44 cases overall, 23 of which involved diabetic ketoacidosis.
“If you talk to the diabetes specialists, they tell us that generally, most cases of new diabetes arrive late because it has very nonspecific symptoms,” Dr. Ladhani explained.
However, he added, “pediatricians on the frontline know what to expect with diabetes. Those children who would have come in late prior to the pandemic are now arriving very late. Those consultants surveyed were not junior doctors but consultant pediatricians with many years of experience.”
In a recent article looking at pediatric delayed presentations, one patient with diabetes entered intensive care, and the BPSU report recorded one death possibly associated with diabetes, Dr. Ladhani pointed out.
“Pediatricians are worried that children are coming in late. We need to raise awareness that parents need to access healthcare and this message needs to go out now,” he said. “We can’t wait until a second wave. It has to be now because A&E [accident and emergency] attendance is still 40% [lower than] ... expected.”
BPSU survey covers over 90% of pediatricians in U.K. and Ireland
After numerous anecdotal reports of delayed presentations in the United Kingdom and abroad, the snapshot survey was conducted as part of routine monthly reports where pediatricians are asked to document any cases of rare conditions seen.
“We had heard stories of delayed presentations, but we wanted to know was this a real problem or just anecdotal?” Dr. Ladhani said.
The regular BPSU survey covers over 90% of U.K.- and Ireland-based pediatric consultants (numbering 4,075). On the back of this established communication, the BPSU decided to gauge the extent of delayed presentations during the peak weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Over the next 7 days, 2,433 pediatricians, representing 60% of BPSU participants, responded.
“This response rate in 7 days highlights the importance given to the survey by pediatricians ... and the widespread professional concern about delayed presentations,” the authors wrote.
Participants were asked whether they had seen any children during the previous 14 days who, in their opinion, presented later than they would have expected prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s no one definition for this but these senior clinicians know when something is unusual,” said Dr. Ladhani.
ED attendances were compared with figures for the same period last year. Overall, a total of 32% of 752 pediatricians working in EDs and pediatric assessment units reported witnessing delayed presentations, with 57 (8%) reporting at least three patients with delayed presentation.
“It was clear that those doctors on the frontline were seeing a lot of delayed presentations. Also, neonatologists reported women arriving late for labor, and community physicians said they just weren’t witnessing child protection cases anymore,” added Dr. Ladhani.
Other issues included early discharges following births because of COVID-19 concerns, before feeding had been established, prompting return visits because of feeding problems and dehydration.
The top five delayed diagnoses were diabetes (n = 44), sepsis (n = 21), child protection (n = 14), malignancy (n = 8), and appendicitis (n = 6). There were 10 delayed perinatal presentations.
Of the nine deaths, for which delayed presentation was considered to play a role, three were caused by sepsis, three were caused by new malignancy diagnoses, one was caused by new diagnosis of metabolic disease, and two did not have the cause reported.
The delays in presentation are likely to have been influenced by the U.K. government’s message to “stay at home” during the strict lockdown period, which perhaps was sometimes interpreted too literally, Dr. Ladhani suggested. “It was the right message socially, but not medically.”
Russell Viner, MB, PhD, president of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, said in a statement: “The impact for children is what we call ‘collateral damage’, including long absences from school and delays or interruptions to vital services. We know that parents adhered very strongly to the ‘stay at home’ [message] and we need to say clearly that this doesn’t apply if your child is very sick. Should we experience a second wave or regional outbreaks, it is vital that we get the message out to parents that we want to see unwell children at the earliest possible stage.”
Dr. Ladhani reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
There were also nine deaths where delayed presentation was considered a contributing factor, resulting mainly from sepsis and malignancy.
By comparison, over the same 2-week period of the survey there were three child deaths from COVID-19 directly, according to senior study author Shamez Ladhani, MRCPCH, PhD, chair of the British Paediatric Surveillance Unit (BPSU), Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, London.
“The unintended consequences of COVID are far greater, in children, than the disease itself. The way we are trying to prevent this is causing more harm than the disease,” he lamented.
One-third of senior U.K. pediatric specialists who responded to the survey reported dealing with so-called emergency delayed presentations in children who they would normally have expected to present much earlier.
After diabetes, the most commonly reported delayed diagnoses were sepsis and child protection issues. Cancer also featured prominently.
“We’ve found that there is great concern that children are not accessing healthcare as they should during lockdown and after,” Dr. Ladhani stressed. “Our emergency departments saw a 50% reduction during the peak, and now it is still 40% less than expected. The problem is improving but it remains.”
The survey findings were recently published online in Archives of Disease in Childhood, by first author Richard M. Lynn, MSc, of the Institute of Child Health, department of epidemiology and public health, University College London Research, and colleagues.
New diabetes cases presented very late during lockdown
Over the 2-week reporting period in mid-April 2020, type 1 diabetes was the most frequently reported delayed diagnosis, with 44 cases overall, 23 of which involved diabetic ketoacidosis.
“If you talk to the diabetes specialists, they tell us that generally, most cases of new diabetes arrive late because it has very nonspecific symptoms,” Dr. Ladhani explained.
However, he added, “pediatricians on the frontline know what to expect with diabetes. Those children who would have come in late prior to the pandemic are now arriving very late. Those consultants surveyed were not junior doctors but consultant pediatricians with many years of experience.”
In a recent article looking at pediatric delayed presentations, one patient with diabetes entered intensive care, and the BPSU report recorded one death possibly associated with diabetes, Dr. Ladhani pointed out.
“Pediatricians are worried that children are coming in late. We need to raise awareness that parents need to access healthcare and this message needs to go out now,” he said. “We can’t wait until a second wave. It has to be now because A&E [accident and emergency] attendance is still 40% [lower than] ... expected.”
BPSU survey covers over 90% of pediatricians in U.K. and Ireland
After numerous anecdotal reports of delayed presentations in the United Kingdom and abroad, the snapshot survey was conducted as part of routine monthly reports where pediatricians are asked to document any cases of rare conditions seen.
“We had heard stories of delayed presentations, but we wanted to know was this a real problem or just anecdotal?” Dr. Ladhani said.
The regular BPSU survey covers over 90% of U.K.- and Ireland-based pediatric consultants (numbering 4,075). On the back of this established communication, the BPSU decided to gauge the extent of delayed presentations during the peak weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Over the next 7 days, 2,433 pediatricians, representing 60% of BPSU participants, responded.
“This response rate in 7 days highlights the importance given to the survey by pediatricians ... and the widespread professional concern about delayed presentations,” the authors wrote.
Participants were asked whether they had seen any children during the previous 14 days who, in their opinion, presented later than they would have expected prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s no one definition for this but these senior clinicians know when something is unusual,” said Dr. Ladhani.
ED attendances were compared with figures for the same period last year. Overall, a total of 32% of 752 pediatricians working in EDs and pediatric assessment units reported witnessing delayed presentations, with 57 (8%) reporting at least three patients with delayed presentation.
“It was clear that those doctors on the frontline were seeing a lot of delayed presentations. Also, neonatologists reported women arriving late for labor, and community physicians said they just weren’t witnessing child protection cases anymore,” added Dr. Ladhani.
Other issues included early discharges following births because of COVID-19 concerns, before feeding had been established, prompting return visits because of feeding problems and dehydration.
The top five delayed diagnoses were diabetes (n = 44), sepsis (n = 21), child protection (n = 14), malignancy (n = 8), and appendicitis (n = 6). There were 10 delayed perinatal presentations.
Of the nine deaths, for which delayed presentation was considered to play a role, three were caused by sepsis, three were caused by new malignancy diagnoses, one was caused by new diagnosis of metabolic disease, and two did not have the cause reported.
The delays in presentation are likely to have been influenced by the U.K. government’s message to “stay at home” during the strict lockdown period, which perhaps was sometimes interpreted too literally, Dr. Ladhani suggested. “It was the right message socially, but not medically.”
Russell Viner, MB, PhD, president of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, said in a statement: “The impact for children is what we call ‘collateral damage’, including long absences from school and delays or interruptions to vital services. We know that parents adhered very strongly to the ‘stay at home’ [message] and we need to say clearly that this doesn’t apply if your child is very sick. Should we experience a second wave or regional outbreaks, it is vital that we get the message out to parents that we want to see unwell children at the earliest possible stage.”
Dr. Ladhani reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
There were also nine deaths where delayed presentation was considered a contributing factor, resulting mainly from sepsis and malignancy.
By comparison, over the same 2-week period of the survey there were three child deaths from COVID-19 directly, according to senior study author Shamez Ladhani, MRCPCH, PhD, chair of the British Paediatric Surveillance Unit (BPSU), Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, London.
“The unintended consequences of COVID are far greater, in children, than the disease itself. The way we are trying to prevent this is causing more harm than the disease,” he lamented.
One-third of senior U.K. pediatric specialists who responded to the survey reported dealing with so-called emergency delayed presentations in children who they would normally have expected to present much earlier.
After diabetes, the most commonly reported delayed diagnoses were sepsis and child protection issues. Cancer also featured prominently.
“We’ve found that there is great concern that children are not accessing healthcare as they should during lockdown and after,” Dr. Ladhani stressed. “Our emergency departments saw a 50% reduction during the peak, and now it is still 40% less than expected. The problem is improving but it remains.”
The survey findings were recently published online in Archives of Disease in Childhood, by first author Richard M. Lynn, MSc, of the Institute of Child Health, department of epidemiology and public health, University College London Research, and colleagues.
New diabetes cases presented very late during lockdown
Over the 2-week reporting period in mid-April 2020, type 1 diabetes was the most frequently reported delayed diagnosis, with 44 cases overall, 23 of which involved diabetic ketoacidosis.
“If you talk to the diabetes specialists, they tell us that generally, most cases of new diabetes arrive late because it has very nonspecific symptoms,” Dr. Ladhani explained.
However, he added, “pediatricians on the frontline know what to expect with diabetes. Those children who would have come in late prior to the pandemic are now arriving very late. Those consultants surveyed were not junior doctors but consultant pediatricians with many years of experience.”
In a recent article looking at pediatric delayed presentations, one patient with diabetes entered intensive care, and the BPSU report recorded one death possibly associated with diabetes, Dr. Ladhani pointed out.
“Pediatricians are worried that children are coming in late. We need to raise awareness that parents need to access healthcare and this message needs to go out now,” he said. “We can’t wait until a second wave. It has to be now because A&E [accident and emergency] attendance is still 40% [lower than] ... expected.”
BPSU survey covers over 90% of pediatricians in U.K. and Ireland
After numerous anecdotal reports of delayed presentations in the United Kingdom and abroad, the snapshot survey was conducted as part of routine monthly reports where pediatricians are asked to document any cases of rare conditions seen.
“We had heard stories of delayed presentations, but we wanted to know was this a real problem or just anecdotal?” Dr. Ladhani said.
The regular BPSU survey covers over 90% of U.K.- and Ireland-based pediatric consultants (numbering 4,075). On the back of this established communication, the BPSU decided to gauge the extent of delayed presentations during the peak weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Over the next 7 days, 2,433 pediatricians, representing 60% of BPSU participants, responded.
“This response rate in 7 days highlights the importance given to the survey by pediatricians ... and the widespread professional concern about delayed presentations,” the authors wrote.
Participants were asked whether they had seen any children during the previous 14 days who, in their opinion, presented later than they would have expected prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s no one definition for this but these senior clinicians know when something is unusual,” said Dr. Ladhani.
ED attendances were compared with figures for the same period last year. Overall, a total of 32% of 752 pediatricians working in EDs and pediatric assessment units reported witnessing delayed presentations, with 57 (8%) reporting at least three patients with delayed presentation.
“It was clear that those doctors on the frontline were seeing a lot of delayed presentations. Also, neonatologists reported women arriving late for labor, and community physicians said they just weren’t witnessing child protection cases anymore,” added Dr. Ladhani.
Other issues included early discharges following births because of COVID-19 concerns, before feeding had been established, prompting return visits because of feeding problems and dehydration.
The top five delayed diagnoses were diabetes (n = 44), sepsis (n = 21), child protection (n = 14), malignancy (n = 8), and appendicitis (n = 6). There were 10 delayed perinatal presentations.
Of the nine deaths, for which delayed presentation was considered to play a role, three were caused by sepsis, three were caused by new malignancy diagnoses, one was caused by new diagnosis of metabolic disease, and two did not have the cause reported.
The delays in presentation are likely to have been influenced by the U.K. government’s message to “stay at home” during the strict lockdown period, which perhaps was sometimes interpreted too literally, Dr. Ladhani suggested. “It was the right message socially, but not medically.”
Russell Viner, MB, PhD, president of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, said in a statement: “The impact for children is what we call ‘collateral damage’, including long absences from school and delays or interruptions to vital services. We know that parents adhered very strongly to the ‘stay at home’ [message] and we need to say clearly that this doesn’t apply if your child is very sick. Should we experience a second wave or regional outbreaks, it is vital that we get the message out to parents that we want to see unwell children at the earliest possible stage.”
Dr. Ladhani reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary prevention statins cut mortality even in the very elderly: VHA study
Patients in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) system 75 years or older, free of cardiovascular (CV) disease and prescribed statins for the first time, had a one-fourth lower risk for death and a 20% lower risk for CV death over an average 7 years than that of comparable patients not prescribed the drugs in an observational study.
Ariela R. Orkaby, MD, MPH, lead author on the study, published in the July 7 issue of JAMA, said in an interview.
The very elderly are frequently undertreated, particularly in primary prevention, as many physicians consider it unnecessary for them to initiate or continue preventive measures, said Dr. Orkaby, of VA Boston Healthcare System and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“From available data, we don’t really expect statins to start providing benefit in primary prevention until they’ve been taken for about 2 to 5 years. So for people who have very limited life expectancy, it may not be a great idea to add to their pill burden or increase the possibility that they might decline functionally,” Dr. Orkaby said.
“But what we saw in this study is that there is benefit to prescribing statins even in elderly patients, even within 2 years” of follow-up.
Despite being among the most studied drugs in the world, statins are understudied in older people. Fewer than 2% of the 186,854 participants in 28 statin trials were aged 75 years or older, wrote Dr. Orkaby and associates.
Most of what is known about initiating statin therapy in the 75-and-older age group comes from underpowered subgroup analyses and a few observational studies, Steven J. Nicholls, MBBS, PhD, Monash University, Melbourne, and Adam J. Nelson, MBBS, PhD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., wrote in an accompanying editorial. As a result, the evidence is conflicting, with some reports suggesting marked benefit and others possible harm.
The current findings, they wrote, “provide additional support for treatment guidelines that have increasingly advocated for more widespread use of statin therapy for ASCVD prevention in older individuals.”
Of the 326,981 people in the analysis, 57,178 (17.5%) were new statin users or initiated a statin during the study period, usually simvastatin. Their mean age was about 81 years, and 97.3% of the patients were men, 90% were white, and 72% were former smokers.
Using propensity scoring, the authors compared statin users with the other remaining patients who had the same likelihood of being prescribed a statin based on clinical characteristics but did not receive a prescription for a statin.
Michael W. Rich, MD, Washington University, St. Louis, who was not involved in the study but has previously worked with Dr. Orkaby, praised the analysis.
“It’s one of the best studies I’ve seen addressing this particular issue. It’s a large sample size, the analysis was very well done, and I think that it comes to a pretty unequivocal conclusion that, at least in this population, those individuals who were started on statins for the first time, and having no known prior ASCVD, clearly had a lower all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality, as well as a lower risk of composite cardiovascular events,” he said in an interview.
But the data have limitations, he added. The findings are still observational and could be confounded by unknown variables, and the select population – mostly white, male veterans – is known to be at somewhat higher risk for events than the general population.
Perhaps even more impressive than the risk reductions seen at a mean 6.8 years of follow-up, Dr. Rich said, are the sensitivity analyses at 2, 4, and 6 years that showed the benefit manifesting early.
The researchers saw a 32% reduction in all-cause mortality risk (P < .05) at 2 years, 21% at 4 years, and 13% at 6 years (P < .05 for all). Risk reductions for CV death followed a similar pattern, they wrote.
Dr. Rich said that the trial, although not a “slam dunk,” has persuaded him to shift from being very conservative about prescribing statins to elderly patients to being much more willing to consider it.
“This doesn’t mean that I will be running to routinely prescribe my 90-plus patients a statin, nor should we should be starting statins in everyone over 75, not even in all male former smokers over 75 – the type of people in this study – but I do think that it provides a stronger basis for talking to these patients about the possibility of starting a statin.”
There are two ongoing trials that may provide greater clarity, the authors observed. The STAREE trial has enrolled adults 70 years and older in Australia and includes serial evaluation of cognitive scores. Also, PREVENTABLE will examine the role of statins for prevention of dementia and disability-free survival in adults 75 years and older.
However, neither trial may fully resolve the question of primary prevention statin use in the elderly, they wrote. “While these trials are necessary to broaden the evidence base for older adults, it is unlikely that any trial will enroll large numbers of individuals at very advanced ages, black individuals, and those with dementia, as were included in this study.”
Dr. Orkaby had no disclosures; potential conflicts for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Rich reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Nicholls disclosed receiving research support from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Anthera, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Cerenis, The Medicines Company, Resverlogix, InfraReDx, Roche, Sanofi-Regeneron, and LipoScience; and receiving consulting fees or honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Anthera, Omthera, Merck, Takeda, Resverlogix, Sanofi-Regeneron, CSL Behring, Esperion, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Nelson had no disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) system 75 years or older, free of cardiovascular (CV) disease and prescribed statins for the first time, had a one-fourth lower risk for death and a 20% lower risk for CV death over an average 7 years than that of comparable patients not prescribed the drugs in an observational study.
Ariela R. Orkaby, MD, MPH, lead author on the study, published in the July 7 issue of JAMA, said in an interview.
The very elderly are frequently undertreated, particularly in primary prevention, as many physicians consider it unnecessary for them to initiate or continue preventive measures, said Dr. Orkaby, of VA Boston Healthcare System and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“From available data, we don’t really expect statins to start providing benefit in primary prevention until they’ve been taken for about 2 to 5 years. So for people who have very limited life expectancy, it may not be a great idea to add to their pill burden or increase the possibility that they might decline functionally,” Dr. Orkaby said.
“But what we saw in this study is that there is benefit to prescribing statins even in elderly patients, even within 2 years” of follow-up.
Despite being among the most studied drugs in the world, statins are understudied in older people. Fewer than 2% of the 186,854 participants in 28 statin trials were aged 75 years or older, wrote Dr. Orkaby and associates.
Most of what is known about initiating statin therapy in the 75-and-older age group comes from underpowered subgroup analyses and a few observational studies, Steven J. Nicholls, MBBS, PhD, Monash University, Melbourne, and Adam J. Nelson, MBBS, PhD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., wrote in an accompanying editorial. As a result, the evidence is conflicting, with some reports suggesting marked benefit and others possible harm.
The current findings, they wrote, “provide additional support for treatment guidelines that have increasingly advocated for more widespread use of statin therapy for ASCVD prevention in older individuals.”
Of the 326,981 people in the analysis, 57,178 (17.5%) were new statin users or initiated a statin during the study period, usually simvastatin. Their mean age was about 81 years, and 97.3% of the patients were men, 90% were white, and 72% were former smokers.
Using propensity scoring, the authors compared statin users with the other remaining patients who had the same likelihood of being prescribed a statin based on clinical characteristics but did not receive a prescription for a statin.
Michael W. Rich, MD, Washington University, St. Louis, who was not involved in the study but has previously worked with Dr. Orkaby, praised the analysis.
“It’s one of the best studies I’ve seen addressing this particular issue. It’s a large sample size, the analysis was very well done, and I think that it comes to a pretty unequivocal conclusion that, at least in this population, those individuals who were started on statins for the first time, and having no known prior ASCVD, clearly had a lower all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality, as well as a lower risk of composite cardiovascular events,” he said in an interview.
But the data have limitations, he added. The findings are still observational and could be confounded by unknown variables, and the select population – mostly white, male veterans – is known to be at somewhat higher risk for events than the general population.
Perhaps even more impressive than the risk reductions seen at a mean 6.8 years of follow-up, Dr. Rich said, are the sensitivity analyses at 2, 4, and 6 years that showed the benefit manifesting early.
The researchers saw a 32% reduction in all-cause mortality risk (P < .05) at 2 years, 21% at 4 years, and 13% at 6 years (P < .05 for all). Risk reductions for CV death followed a similar pattern, they wrote.
Dr. Rich said that the trial, although not a “slam dunk,” has persuaded him to shift from being very conservative about prescribing statins to elderly patients to being much more willing to consider it.
“This doesn’t mean that I will be running to routinely prescribe my 90-plus patients a statin, nor should we should be starting statins in everyone over 75, not even in all male former smokers over 75 – the type of people in this study – but I do think that it provides a stronger basis for talking to these patients about the possibility of starting a statin.”
There are two ongoing trials that may provide greater clarity, the authors observed. The STAREE trial has enrolled adults 70 years and older in Australia and includes serial evaluation of cognitive scores. Also, PREVENTABLE will examine the role of statins for prevention of dementia and disability-free survival in adults 75 years and older.
However, neither trial may fully resolve the question of primary prevention statin use in the elderly, they wrote. “While these trials are necessary to broaden the evidence base for older adults, it is unlikely that any trial will enroll large numbers of individuals at very advanced ages, black individuals, and those with dementia, as were included in this study.”
Dr. Orkaby had no disclosures; potential conflicts for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Rich reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Nicholls disclosed receiving research support from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Anthera, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Cerenis, The Medicines Company, Resverlogix, InfraReDx, Roche, Sanofi-Regeneron, and LipoScience; and receiving consulting fees or honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Anthera, Omthera, Merck, Takeda, Resverlogix, Sanofi-Regeneron, CSL Behring, Esperion, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Nelson had no disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) system 75 years or older, free of cardiovascular (CV) disease and prescribed statins for the first time, had a one-fourth lower risk for death and a 20% lower risk for CV death over an average 7 years than that of comparable patients not prescribed the drugs in an observational study.
Ariela R. Orkaby, MD, MPH, lead author on the study, published in the July 7 issue of JAMA, said in an interview.
The very elderly are frequently undertreated, particularly in primary prevention, as many physicians consider it unnecessary for them to initiate or continue preventive measures, said Dr. Orkaby, of VA Boston Healthcare System and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“From available data, we don’t really expect statins to start providing benefit in primary prevention until they’ve been taken for about 2 to 5 years. So for people who have very limited life expectancy, it may not be a great idea to add to their pill burden or increase the possibility that they might decline functionally,” Dr. Orkaby said.
“But what we saw in this study is that there is benefit to prescribing statins even in elderly patients, even within 2 years” of follow-up.
Despite being among the most studied drugs in the world, statins are understudied in older people. Fewer than 2% of the 186,854 participants in 28 statin trials were aged 75 years or older, wrote Dr. Orkaby and associates.
Most of what is known about initiating statin therapy in the 75-and-older age group comes from underpowered subgroup analyses and a few observational studies, Steven J. Nicholls, MBBS, PhD, Monash University, Melbourne, and Adam J. Nelson, MBBS, PhD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., wrote in an accompanying editorial. As a result, the evidence is conflicting, with some reports suggesting marked benefit and others possible harm.
The current findings, they wrote, “provide additional support for treatment guidelines that have increasingly advocated for more widespread use of statin therapy for ASCVD prevention in older individuals.”
Of the 326,981 people in the analysis, 57,178 (17.5%) were new statin users or initiated a statin during the study period, usually simvastatin. Their mean age was about 81 years, and 97.3% of the patients were men, 90% were white, and 72% were former smokers.
Using propensity scoring, the authors compared statin users with the other remaining patients who had the same likelihood of being prescribed a statin based on clinical characteristics but did not receive a prescription for a statin.
Michael W. Rich, MD, Washington University, St. Louis, who was not involved in the study but has previously worked with Dr. Orkaby, praised the analysis.
“It’s one of the best studies I’ve seen addressing this particular issue. It’s a large sample size, the analysis was very well done, and I think that it comes to a pretty unequivocal conclusion that, at least in this population, those individuals who were started on statins for the first time, and having no known prior ASCVD, clearly had a lower all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality, as well as a lower risk of composite cardiovascular events,” he said in an interview.
But the data have limitations, he added. The findings are still observational and could be confounded by unknown variables, and the select population – mostly white, male veterans – is known to be at somewhat higher risk for events than the general population.
Perhaps even more impressive than the risk reductions seen at a mean 6.8 years of follow-up, Dr. Rich said, are the sensitivity analyses at 2, 4, and 6 years that showed the benefit manifesting early.
The researchers saw a 32% reduction in all-cause mortality risk (P < .05) at 2 years, 21% at 4 years, and 13% at 6 years (P < .05 for all). Risk reductions for CV death followed a similar pattern, they wrote.
Dr. Rich said that the trial, although not a “slam dunk,” has persuaded him to shift from being very conservative about prescribing statins to elderly patients to being much more willing to consider it.
“This doesn’t mean that I will be running to routinely prescribe my 90-plus patients a statin, nor should we should be starting statins in everyone over 75, not even in all male former smokers over 75 – the type of people in this study – but I do think that it provides a stronger basis for talking to these patients about the possibility of starting a statin.”
There are two ongoing trials that may provide greater clarity, the authors observed. The STAREE trial has enrolled adults 70 years and older in Australia and includes serial evaluation of cognitive scores. Also, PREVENTABLE will examine the role of statins for prevention of dementia and disability-free survival in adults 75 years and older.
However, neither trial may fully resolve the question of primary prevention statin use in the elderly, they wrote. “While these trials are necessary to broaden the evidence base for older adults, it is unlikely that any trial will enroll large numbers of individuals at very advanced ages, black individuals, and those with dementia, as were included in this study.”
Dr. Orkaby had no disclosures; potential conflicts for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Rich reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Nicholls disclosed receiving research support from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Anthera, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Cerenis, The Medicines Company, Resverlogix, InfraReDx, Roche, Sanofi-Regeneron, and LipoScience; and receiving consulting fees or honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Anthera, Omthera, Merck, Takeda, Resverlogix, Sanofi-Regeneron, CSL Behring, Esperion, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Nelson had no disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Risky business: Longer-course prophylactic perioperative antimicrobials
Background: National guidelines recommend that surgical prophylactic antimicrobials be initiated within 1 hour prior to incision and discontinued 24 hours postoperatively. However, the risks and benefits of longer duration of antimicrobials are uncertain.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Synopsis: After stratification by type of surgery and adjustment for covariates, antibiotic prophylaxis greater than 24 hours was not associated with lower SSI risk.
However, the odds of postoperative AKI increased with each additional day of prophylaxis (adjusted odds ratios, 1.82; 95% confidence interval,1.54-2.16 and aOR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.27-2.53) with longer than 72 hours prophylaxis for cardiac and noncardiac surgery, respectively). Similarly, C. difficile infections increased with each additional day beyond 24 hours (aOR, 3.65; 95% CI, 2.40-5.55 with more than 72 hours of use).
Bottom line: Each day of perioperative antimicrobial prophylaxis beyond 24 hours increases the risk for postoperative AKI or C. difficile infection without reducing the risk of surgical site infection.
Citation: Branch-Elliman W et al. Association of duration and type of surgical prophylaxis with antimicrobial-associated adverse events. JAMA Surg. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0569.
Dr. Miller is a hospitalist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Background: National guidelines recommend that surgical prophylactic antimicrobials be initiated within 1 hour prior to incision and discontinued 24 hours postoperatively. However, the risks and benefits of longer duration of antimicrobials are uncertain.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Synopsis: After stratification by type of surgery and adjustment for covariates, antibiotic prophylaxis greater than 24 hours was not associated with lower SSI risk.
However, the odds of postoperative AKI increased with each additional day of prophylaxis (adjusted odds ratios, 1.82; 95% confidence interval,1.54-2.16 and aOR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.27-2.53) with longer than 72 hours prophylaxis for cardiac and noncardiac surgery, respectively). Similarly, C. difficile infections increased with each additional day beyond 24 hours (aOR, 3.65; 95% CI, 2.40-5.55 with more than 72 hours of use).
Bottom line: Each day of perioperative antimicrobial prophylaxis beyond 24 hours increases the risk for postoperative AKI or C. difficile infection without reducing the risk of surgical site infection.
Citation: Branch-Elliman W et al. Association of duration and type of surgical prophylaxis with antimicrobial-associated adverse events. JAMA Surg. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0569.
Dr. Miller is a hospitalist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Background: National guidelines recommend that surgical prophylactic antimicrobials be initiated within 1 hour prior to incision and discontinued 24 hours postoperatively. However, the risks and benefits of longer duration of antimicrobials are uncertain.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Synopsis: After stratification by type of surgery and adjustment for covariates, antibiotic prophylaxis greater than 24 hours was not associated with lower SSI risk.
However, the odds of postoperative AKI increased with each additional day of prophylaxis (adjusted odds ratios, 1.82; 95% confidence interval,1.54-2.16 and aOR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.27-2.53) with longer than 72 hours prophylaxis for cardiac and noncardiac surgery, respectively). Similarly, C. difficile infections increased with each additional day beyond 24 hours (aOR, 3.65; 95% CI, 2.40-5.55 with more than 72 hours of use).
Bottom line: Each day of perioperative antimicrobial prophylaxis beyond 24 hours increases the risk for postoperative AKI or C. difficile infection without reducing the risk of surgical site infection.
Citation: Branch-Elliman W et al. Association of duration and type of surgical prophylaxis with antimicrobial-associated adverse events. JAMA Surg. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0569.
Dr. Miller is a hospitalist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Steroids linked to increased hypertension in RA
Although the adverse effects of systemic glucocorticoids (GCs) are well known, their association with hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been unclear. Now, a large population-based study shows that the drugs are linked to a 17% overall increased risk for incident hypertension among patients with RA.
Further, when the researchers stratified participants by dose category, they found that doses higher than 7.5 mg were significantly associated with hypertension. Cumulative dosage was not tied to any clear pattern of risk.
The authors, led by Ruth E. Costello, a researcher at the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis in the Centre for Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Manchester (England) concluded that patients who are taking these drugs for the treatment of RA should be monitored for high blood pressure, which is an important but modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, and treated appropriately.
The results of Ms. Costello and colleagues’ study were published June 27 in Rheumatology.
“While fractures associated with these steroid drugs are well studied, hypertension is a side effect that seems to have been less well studied, and yet it is an important cardiovascular risk factor that can be managed,” Ms. Costello said in an interview.
To better understand the possible association, Ms. Costello and colleagues identified 17,760 patients who were newly diagnosed with RA between 1992 and 2019 and were included in the Clinical Practice Research Datalink, which represents about 7% of the U.K. population. None of the patients had hypertension at initial RA diagnosis. Slightly more than two-thirds were women (68.1%), and the mean age was 56.3 years.
Of those patients, 7,421 (41.8%) were prescribed GCs during postdiagnosis follow-up. Most patients (73%) were followed for at least 2 years.
Patients who used GCs were slightly older than never-users (mean age, 57.7 vs. 55.3 years), were predominantly women, had a history of smoking, and had more comorbidities.
The overall incidence rate (IR) of hypertension was 64.1 per 1,000 person-years (95% confidence interval, 62.5-65.7). There were 6,243 cases of incident hypertension over 97,547 person-years of follow-up.
Among those exposed to GCs, 1,321 patients developed hypertension, for an IR of 87.6 per 1,000 person-years. Among unexposed participants, the IR for hypertension was 59.7 per 1,000 person-years. In Cox proportional hazards modeling, GC use was associated with a 17% increased risk for hypertension (hazard ratio, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.10-1.24).
The researchers noted that 40% of GC users with hypertension were not prescribed an antihypertensive agent at any point during the study. “Whilst some may have been offered lifestyle advice, left untreated this has important implications in terms of addressing modifiable risk factors in an RA population already at increased risk of CV disease,” they wrote.
They noted that cardiovascular disease is a major driver of the elevated mortality risk seen among adults with RA compared with the general population and that recent treatment recommendations address management of cardiovascular risks in these patients.
“There are several routes by which GCs may promote cardiovascular disease, including hypertension, metabolic changes, diabetes, and weight gain. We don’t currently know the extent to which each of these individual mechanisms may be increasing cardiovascular disease,” said Ms. Costello.
“Glucocorticoids increase fluid retention and promote obesity and hypertension,” said Rajat S. Bhatt, MD, a rheumatologist at Prime Rheumatology and Memorial Hermann Katy Hospital in Richmond, Texas, who sees hypertension in GC users in his clinical practice. “So patients need to be monitored for these risk factors,” he said in an interview.
Although hypertension may be a significant factor in the increase in cardiovascular disease in the RA population, Dr. Bhatt said the major driver is likely the intrinsic inflammatory state caused by the disease itself. As to why the GC-hypertension connection has flown under the radar in RA, he added, “That specific link has been difficult to tease out since RA patients are often on multiple medications.”
In regard to the role of dosage, Dr. Bhatt said that hypertension risk increases with higher GC doses, as the U.K. study indicates, and usually subsides when patients stop using GCs.
“Whether the observed dose association is causal or influenced by the underlying disease severity, our results suggest we should be vigilant in patients on all doses of GC, especially higher doses,” Ms. Costello added.
In regard to using drugs that are less cardiotoxic than GCs, Dr. Bhatt said that there are clinical scenarios in which GC therapy is the best choice, so just switching to nonsteroidal drugs is no panacea. “All RA drugs have adverse side effects, and anyway, the goal of rheumatology treatment is always to get patients off corticosteroids as soon as possible,” he said.
Ms. Costello and colleagues noted that their results are consonant with earlier research, including a single-center, cross-sectional study in which less than 6 months’ use of prednisolone at a median dose of 7.5 mg was associated with hypertension. In a German registry study, among patients who received doses of less than 7.5 mg for less than 6 months, there were higher rates of self-reported elevations in blood pressure.
The findings are at odds, however, with a recent matched-cohort study, which also used data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. That study found no association between GC use and hypertension.
GCs have come under increasing scrutiny in regard to several diseases. A study published July 7 found that even short-term courses of a few days’ duration entail risks for serious adverse events.
Ms. Costello’s group says that an estimate of GC-related incident hypertension in RA should allow more informed treatment decisions and that their findings highlight the ongoing need to monitor for and address this risk.
The study was supported by the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis and by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Coauthor William G. Dixon, PhD, has received consultancy fees from Google and Bayer unrelated to this study. Dr. Bhatt has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Costello RE et al. Rheumatology. 2020 June 27. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa209.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Although the adverse effects of systemic glucocorticoids (GCs) are well known, their association with hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been unclear. Now, a large population-based study shows that the drugs are linked to a 17% overall increased risk for incident hypertension among patients with RA.
Further, when the researchers stratified participants by dose category, they found that doses higher than 7.5 mg were significantly associated with hypertension. Cumulative dosage was not tied to any clear pattern of risk.
The authors, led by Ruth E. Costello, a researcher at the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis in the Centre for Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Manchester (England) concluded that patients who are taking these drugs for the treatment of RA should be monitored for high blood pressure, which is an important but modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, and treated appropriately.
The results of Ms. Costello and colleagues’ study were published June 27 in Rheumatology.
“While fractures associated with these steroid drugs are well studied, hypertension is a side effect that seems to have been less well studied, and yet it is an important cardiovascular risk factor that can be managed,” Ms. Costello said in an interview.
To better understand the possible association, Ms. Costello and colleagues identified 17,760 patients who were newly diagnosed with RA between 1992 and 2019 and were included in the Clinical Practice Research Datalink, which represents about 7% of the U.K. population. None of the patients had hypertension at initial RA diagnosis. Slightly more than two-thirds were women (68.1%), and the mean age was 56.3 years.
Of those patients, 7,421 (41.8%) were prescribed GCs during postdiagnosis follow-up. Most patients (73%) were followed for at least 2 years.
Patients who used GCs were slightly older than never-users (mean age, 57.7 vs. 55.3 years), were predominantly women, had a history of smoking, and had more comorbidities.
The overall incidence rate (IR) of hypertension was 64.1 per 1,000 person-years (95% confidence interval, 62.5-65.7). There were 6,243 cases of incident hypertension over 97,547 person-years of follow-up.
Among those exposed to GCs, 1,321 patients developed hypertension, for an IR of 87.6 per 1,000 person-years. Among unexposed participants, the IR for hypertension was 59.7 per 1,000 person-years. In Cox proportional hazards modeling, GC use was associated with a 17% increased risk for hypertension (hazard ratio, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.10-1.24).
The researchers noted that 40% of GC users with hypertension were not prescribed an antihypertensive agent at any point during the study. “Whilst some may have been offered lifestyle advice, left untreated this has important implications in terms of addressing modifiable risk factors in an RA population already at increased risk of CV disease,” they wrote.
They noted that cardiovascular disease is a major driver of the elevated mortality risk seen among adults with RA compared with the general population and that recent treatment recommendations address management of cardiovascular risks in these patients.
“There are several routes by which GCs may promote cardiovascular disease, including hypertension, metabolic changes, diabetes, and weight gain. We don’t currently know the extent to which each of these individual mechanisms may be increasing cardiovascular disease,” said Ms. Costello.
“Glucocorticoids increase fluid retention and promote obesity and hypertension,” said Rajat S. Bhatt, MD, a rheumatologist at Prime Rheumatology and Memorial Hermann Katy Hospital in Richmond, Texas, who sees hypertension in GC users in his clinical practice. “So patients need to be monitored for these risk factors,” he said in an interview.
Although hypertension may be a significant factor in the increase in cardiovascular disease in the RA population, Dr. Bhatt said the major driver is likely the intrinsic inflammatory state caused by the disease itself. As to why the GC-hypertension connection has flown under the radar in RA, he added, “That specific link has been difficult to tease out since RA patients are often on multiple medications.”
In regard to the role of dosage, Dr. Bhatt said that hypertension risk increases with higher GC doses, as the U.K. study indicates, and usually subsides when patients stop using GCs.
“Whether the observed dose association is causal or influenced by the underlying disease severity, our results suggest we should be vigilant in patients on all doses of GC, especially higher doses,” Ms. Costello added.
In regard to using drugs that are less cardiotoxic than GCs, Dr. Bhatt said that there are clinical scenarios in which GC therapy is the best choice, so just switching to nonsteroidal drugs is no panacea. “All RA drugs have adverse side effects, and anyway, the goal of rheumatology treatment is always to get patients off corticosteroids as soon as possible,” he said.
Ms. Costello and colleagues noted that their results are consonant with earlier research, including a single-center, cross-sectional study in which less than 6 months’ use of prednisolone at a median dose of 7.5 mg was associated with hypertension. In a German registry study, among patients who received doses of less than 7.5 mg for less than 6 months, there were higher rates of self-reported elevations in blood pressure.
The findings are at odds, however, with a recent matched-cohort study, which also used data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. That study found no association between GC use and hypertension.
GCs have come under increasing scrutiny in regard to several diseases. A study published July 7 found that even short-term courses of a few days’ duration entail risks for serious adverse events.
Ms. Costello’s group says that an estimate of GC-related incident hypertension in RA should allow more informed treatment decisions and that their findings highlight the ongoing need to monitor for and address this risk.
The study was supported by the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis and by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Coauthor William G. Dixon, PhD, has received consultancy fees from Google and Bayer unrelated to this study. Dr. Bhatt has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Costello RE et al. Rheumatology. 2020 June 27. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa209.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Although the adverse effects of systemic glucocorticoids (GCs) are well known, their association with hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been unclear. Now, a large population-based study shows that the drugs are linked to a 17% overall increased risk for incident hypertension among patients with RA.
Further, when the researchers stratified participants by dose category, they found that doses higher than 7.5 mg were significantly associated with hypertension. Cumulative dosage was not tied to any clear pattern of risk.
The authors, led by Ruth E. Costello, a researcher at the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis in the Centre for Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Manchester (England) concluded that patients who are taking these drugs for the treatment of RA should be monitored for high blood pressure, which is an important but modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, and treated appropriately.
The results of Ms. Costello and colleagues’ study were published June 27 in Rheumatology.
“While fractures associated with these steroid drugs are well studied, hypertension is a side effect that seems to have been less well studied, and yet it is an important cardiovascular risk factor that can be managed,” Ms. Costello said in an interview.
To better understand the possible association, Ms. Costello and colleagues identified 17,760 patients who were newly diagnosed with RA between 1992 and 2019 and were included in the Clinical Practice Research Datalink, which represents about 7% of the U.K. population. None of the patients had hypertension at initial RA diagnosis. Slightly more than two-thirds were women (68.1%), and the mean age was 56.3 years.
Of those patients, 7,421 (41.8%) were prescribed GCs during postdiagnosis follow-up. Most patients (73%) were followed for at least 2 years.
Patients who used GCs were slightly older than never-users (mean age, 57.7 vs. 55.3 years), were predominantly women, had a history of smoking, and had more comorbidities.
The overall incidence rate (IR) of hypertension was 64.1 per 1,000 person-years (95% confidence interval, 62.5-65.7). There were 6,243 cases of incident hypertension over 97,547 person-years of follow-up.
Among those exposed to GCs, 1,321 patients developed hypertension, for an IR of 87.6 per 1,000 person-years. Among unexposed participants, the IR for hypertension was 59.7 per 1,000 person-years. In Cox proportional hazards modeling, GC use was associated with a 17% increased risk for hypertension (hazard ratio, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.10-1.24).
The researchers noted that 40% of GC users with hypertension were not prescribed an antihypertensive agent at any point during the study. “Whilst some may have been offered lifestyle advice, left untreated this has important implications in terms of addressing modifiable risk factors in an RA population already at increased risk of CV disease,” they wrote.
They noted that cardiovascular disease is a major driver of the elevated mortality risk seen among adults with RA compared with the general population and that recent treatment recommendations address management of cardiovascular risks in these patients.
“There are several routes by which GCs may promote cardiovascular disease, including hypertension, metabolic changes, diabetes, and weight gain. We don’t currently know the extent to which each of these individual mechanisms may be increasing cardiovascular disease,” said Ms. Costello.
“Glucocorticoids increase fluid retention and promote obesity and hypertension,” said Rajat S. Bhatt, MD, a rheumatologist at Prime Rheumatology and Memorial Hermann Katy Hospital in Richmond, Texas, who sees hypertension in GC users in his clinical practice. “So patients need to be monitored for these risk factors,” he said in an interview.
Although hypertension may be a significant factor in the increase in cardiovascular disease in the RA population, Dr. Bhatt said the major driver is likely the intrinsic inflammatory state caused by the disease itself. As to why the GC-hypertension connection has flown under the radar in RA, he added, “That specific link has been difficult to tease out since RA patients are often on multiple medications.”
In regard to the role of dosage, Dr. Bhatt said that hypertension risk increases with higher GC doses, as the U.K. study indicates, and usually subsides when patients stop using GCs.
“Whether the observed dose association is causal or influenced by the underlying disease severity, our results suggest we should be vigilant in patients on all doses of GC, especially higher doses,” Ms. Costello added.
In regard to using drugs that are less cardiotoxic than GCs, Dr. Bhatt said that there are clinical scenarios in which GC therapy is the best choice, so just switching to nonsteroidal drugs is no panacea. “All RA drugs have adverse side effects, and anyway, the goal of rheumatology treatment is always to get patients off corticosteroids as soon as possible,” he said.
Ms. Costello and colleagues noted that their results are consonant with earlier research, including a single-center, cross-sectional study in which less than 6 months’ use of prednisolone at a median dose of 7.5 mg was associated with hypertension. In a German registry study, among patients who received doses of less than 7.5 mg for less than 6 months, there were higher rates of self-reported elevations in blood pressure.
The findings are at odds, however, with a recent matched-cohort study, which also used data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. That study found no association between GC use and hypertension.
GCs have come under increasing scrutiny in regard to several diseases. A study published July 7 found that even short-term courses of a few days’ duration entail risks for serious adverse events.
Ms. Costello’s group says that an estimate of GC-related incident hypertension in RA should allow more informed treatment decisions and that their findings highlight the ongoing need to monitor for and address this risk.
The study was supported by the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis and by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Coauthor William G. Dixon, PhD, has received consultancy fees from Google and Bayer unrelated to this study. Dr. Bhatt has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Costello RE et al. Rheumatology. 2020 June 27. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa209.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
USPSTF: Earlier lung cancer screening can double eligibility
The new proposals include lowering the age at which screening starts from 55 to 50 years, and to reduce the smoking history from 30 to 20 pack-years.
The draft recommendation from the United States Preventive Service Task Force (USPSTF) is available for public comment until August 3.
The task force recommends that adults age 50 to 80 who have a 20 pack-year or greater smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the last 15 years undergo annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose CT,
“In my opinion, the proposed criteria by USPSTF represent a huge step in the right direction,” Lecia Sequist, MD, director of innovation at the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“If these are adopted and implemented, we could see the benefit of screening (measured as reduction in lung cancer mortality) go from 9.8% with current parameters up to 13% with the broader parameters,” she said. “In addition, the new criteria should reduce racial disparities in screening eligibility.”
The recommendation also earned high marks from the American Lung Association.
The USPSTF has continued its ‘B’ recommendation – allowing for coverage of the screening with no cost for many under the Affordable Care Act – and is now proposing to expand the eligibility criteria “so that even more Americans at higher risk for lung cancer can be screened,” the ALA commented.
Start screening at 50
Lowering the minimum age of screening to 50 would likely mean that more Black individuals and women would be eligible for screening, the recommendation authors contend. The current screening age of 55 is currently recommended under guidelines issued by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, and National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
“African Americans have a higher risk of lung cancer, compared with whites, and this risk difference is more apparent at lower levels of smoking intensity,” they write.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, lung cancer screening in an urban, largely black cohort yielded roughly double the rates of positive screens and detected lung cancers compared with results from the National Lung Screening Trial, which enrolled mostly White individuals.
In addition, although lung cancer risk is greater for men than women who smoke, and women generally accumulate fewer pack-years than men, there is evidence to suggest that women who smoke may develop lung cancer earlier and with lower levels of exposure.
Therefore, “a strategy of screening persons ages 50 to 80 years who have at least a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years (A-50-80-20-15) would lead to a relative increase in the percentage of persons eligible for screening by 81% in men and by 96% in women,” the proposed recommendation states.
What’s the harm?
One of the major concerns about low-dose CT screening for lung cancer is the relatively high rate of false-positive results reported in two large scale clinical trials, the recommendation authors acknowledged.
For example, in the NLST, which was the basis for an earlier USPSTF recommendation (for annual screening of adults 55 to 80 years of age who have a 30 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit in the previous 15 years), the false-positive rates were 26.3% at baseline, 27.2% at year 1, and 15.9% at year 2.
Similarly, in the NELSON trial, results of which were published earlier this year, false-positive rates for men were 19.8% at baseline, 7.1% at year 1, 9% at year 3, and 3.9% at year 5.5 of screening, they noted.
“Yes, false-positive results are one of the things we need to think carefully about when embarking on lung screening,” Dr. Sequist told Medscape Medical News. “The potential harm of a false-positive (unnecessary scans, biopsies or even surgery) can be minimized by having a multidisciplinary team with experience working up lung nodules see patients who have a positive screening test. In fact, the American College of Radiology recommends that all lung screening programs be paired with such a team.”
Mass General has a pulmonary nodule clinic to evaluate screen-detected lung nodules, with the goal of minimizing unnecessary procedures, she noted.
Asked about the potential harm from radiation exposure, Sequist said that exposure from low-dose CT screening is fairly minimal, comparable to that from solar radiation at sea level over a 6-month period, or about the level from three cross-country airplane trips.
“While it is not zero radiation, there is very little concern that this low level of radiation would cause a cancer or damage one’s lungs,” she said.
Albert Rizzo, MD, chief medical officer of the ALA, said that the potential harms of unnecessary interventions are outweighed by the benefits of detecting lung cancer at an early stage.
“I think what has been learned over the last 5 years is that the original recommendations that were put out really allowed the overall rate of positivity well within what’s seen with mammography, for example, and the number of patients who have needlessly gone on to procedures remains very low, and the morbidity of those procedures remains low as well,” Dr. Rizzo told Medscape Medical News.
Not enough takers
Despite the clear benefits of low-dose CT screening, however, US screening rates for high-risk individuals are still very low, ranging from 12.3% in Massachusetts to a low of 0.5% in Nevada, according to a 2019 research report on the state of lung cancer from the ALA.
“For screening to be most effective, more of the high-risk population should be screened. Currently, screening rates are very low among those at high risk. This may be because of a lack of access or low awareness and knowledge among patients and providers. As rates vary tremendously between states, it is clear that more can be done to increase screening rates,” the report stated.
“I think that there are some mixed messages sent out into the population as to whether or not an individual patient should be screened,” Dr. Rizzo said.
He noted that some physicians may be reluctant to take on the nuanced risk–benefit discussion required, or may not have the time during a brief patient visit.
“It really boils down to that discussion between the physician and the patient who falls under these risk categories, to say, ‘Look, this is what these studies have found, and you fall under a category where if we find a cancer early, it’s very likely you’re going to be saved,’ as compared for waiting for it to present by itself,” he said.
Dr. Sequist and Dr. Rizzo have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new proposals include lowering the age at which screening starts from 55 to 50 years, and to reduce the smoking history from 30 to 20 pack-years.
The draft recommendation from the United States Preventive Service Task Force (USPSTF) is available for public comment until August 3.
The task force recommends that adults age 50 to 80 who have a 20 pack-year or greater smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the last 15 years undergo annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose CT,
“In my opinion, the proposed criteria by USPSTF represent a huge step in the right direction,” Lecia Sequist, MD, director of innovation at the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“If these are adopted and implemented, we could see the benefit of screening (measured as reduction in lung cancer mortality) go from 9.8% with current parameters up to 13% with the broader parameters,” she said. “In addition, the new criteria should reduce racial disparities in screening eligibility.”
The recommendation also earned high marks from the American Lung Association.
The USPSTF has continued its ‘B’ recommendation – allowing for coverage of the screening with no cost for many under the Affordable Care Act – and is now proposing to expand the eligibility criteria “so that even more Americans at higher risk for lung cancer can be screened,” the ALA commented.
Start screening at 50
Lowering the minimum age of screening to 50 would likely mean that more Black individuals and women would be eligible for screening, the recommendation authors contend. The current screening age of 55 is currently recommended under guidelines issued by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, and National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
“African Americans have a higher risk of lung cancer, compared with whites, and this risk difference is more apparent at lower levels of smoking intensity,” they write.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, lung cancer screening in an urban, largely black cohort yielded roughly double the rates of positive screens and detected lung cancers compared with results from the National Lung Screening Trial, which enrolled mostly White individuals.
In addition, although lung cancer risk is greater for men than women who smoke, and women generally accumulate fewer pack-years than men, there is evidence to suggest that women who smoke may develop lung cancer earlier and with lower levels of exposure.
Therefore, “a strategy of screening persons ages 50 to 80 years who have at least a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years (A-50-80-20-15) would lead to a relative increase in the percentage of persons eligible for screening by 81% in men and by 96% in women,” the proposed recommendation states.
What’s the harm?
One of the major concerns about low-dose CT screening for lung cancer is the relatively high rate of false-positive results reported in two large scale clinical trials, the recommendation authors acknowledged.
For example, in the NLST, which was the basis for an earlier USPSTF recommendation (for annual screening of adults 55 to 80 years of age who have a 30 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit in the previous 15 years), the false-positive rates were 26.3% at baseline, 27.2% at year 1, and 15.9% at year 2.
Similarly, in the NELSON trial, results of which were published earlier this year, false-positive rates for men were 19.8% at baseline, 7.1% at year 1, 9% at year 3, and 3.9% at year 5.5 of screening, they noted.
“Yes, false-positive results are one of the things we need to think carefully about when embarking on lung screening,” Dr. Sequist told Medscape Medical News. “The potential harm of a false-positive (unnecessary scans, biopsies or even surgery) can be minimized by having a multidisciplinary team with experience working up lung nodules see patients who have a positive screening test. In fact, the American College of Radiology recommends that all lung screening programs be paired with such a team.”
Mass General has a pulmonary nodule clinic to evaluate screen-detected lung nodules, with the goal of minimizing unnecessary procedures, she noted.
Asked about the potential harm from radiation exposure, Sequist said that exposure from low-dose CT screening is fairly minimal, comparable to that from solar radiation at sea level over a 6-month period, or about the level from three cross-country airplane trips.
“While it is not zero radiation, there is very little concern that this low level of radiation would cause a cancer or damage one’s lungs,” she said.
Albert Rizzo, MD, chief medical officer of the ALA, said that the potential harms of unnecessary interventions are outweighed by the benefits of detecting lung cancer at an early stage.
“I think what has been learned over the last 5 years is that the original recommendations that were put out really allowed the overall rate of positivity well within what’s seen with mammography, for example, and the number of patients who have needlessly gone on to procedures remains very low, and the morbidity of those procedures remains low as well,” Dr. Rizzo told Medscape Medical News.
Not enough takers
Despite the clear benefits of low-dose CT screening, however, US screening rates for high-risk individuals are still very low, ranging from 12.3% in Massachusetts to a low of 0.5% in Nevada, according to a 2019 research report on the state of lung cancer from the ALA.
“For screening to be most effective, more of the high-risk population should be screened. Currently, screening rates are very low among those at high risk. This may be because of a lack of access or low awareness and knowledge among patients and providers. As rates vary tremendously between states, it is clear that more can be done to increase screening rates,” the report stated.
“I think that there are some mixed messages sent out into the population as to whether or not an individual patient should be screened,” Dr. Rizzo said.
He noted that some physicians may be reluctant to take on the nuanced risk–benefit discussion required, or may not have the time during a brief patient visit.
“It really boils down to that discussion between the physician and the patient who falls under these risk categories, to say, ‘Look, this is what these studies have found, and you fall under a category where if we find a cancer early, it’s very likely you’re going to be saved,’ as compared for waiting for it to present by itself,” he said.
Dr. Sequist and Dr. Rizzo have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new proposals include lowering the age at which screening starts from 55 to 50 years, and to reduce the smoking history from 30 to 20 pack-years.
The draft recommendation from the United States Preventive Service Task Force (USPSTF) is available for public comment until August 3.
The task force recommends that adults age 50 to 80 who have a 20 pack-year or greater smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the last 15 years undergo annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose CT,
“In my opinion, the proposed criteria by USPSTF represent a huge step in the right direction,” Lecia Sequist, MD, director of innovation at the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“If these are adopted and implemented, we could see the benefit of screening (measured as reduction in lung cancer mortality) go from 9.8% with current parameters up to 13% with the broader parameters,” she said. “In addition, the new criteria should reduce racial disparities in screening eligibility.”
The recommendation also earned high marks from the American Lung Association.
The USPSTF has continued its ‘B’ recommendation – allowing for coverage of the screening with no cost for many under the Affordable Care Act – and is now proposing to expand the eligibility criteria “so that even more Americans at higher risk for lung cancer can be screened,” the ALA commented.
Start screening at 50
Lowering the minimum age of screening to 50 would likely mean that more Black individuals and women would be eligible for screening, the recommendation authors contend. The current screening age of 55 is currently recommended under guidelines issued by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, and National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
“African Americans have a higher risk of lung cancer, compared with whites, and this risk difference is more apparent at lower levels of smoking intensity,” they write.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, lung cancer screening in an urban, largely black cohort yielded roughly double the rates of positive screens and detected lung cancers compared with results from the National Lung Screening Trial, which enrolled mostly White individuals.
In addition, although lung cancer risk is greater for men than women who smoke, and women generally accumulate fewer pack-years than men, there is evidence to suggest that women who smoke may develop lung cancer earlier and with lower levels of exposure.
Therefore, “a strategy of screening persons ages 50 to 80 years who have at least a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years (A-50-80-20-15) would lead to a relative increase in the percentage of persons eligible for screening by 81% in men and by 96% in women,” the proposed recommendation states.
What’s the harm?
One of the major concerns about low-dose CT screening for lung cancer is the relatively high rate of false-positive results reported in two large scale clinical trials, the recommendation authors acknowledged.
For example, in the NLST, which was the basis for an earlier USPSTF recommendation (for annual screening of adults 55 to 80 years of age who have a 30 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit in the previous 15 years), the false-positive rates were 26.3% at baseline, 27.2% at year 1, and 15.9% at year 2.
Similarly, in the NELSON trial, results of which were published earlier this year, false-positive rates for men were 19.8% at baseline, 7.1% at year 1, 9% at year 3, and 3.9% at year 5.5 of screening, they noted.
“Yes, false-positive results are one of the things we need to think carefully about when embarking on lung screening,” Dr. Sequist told Medscape Medical News. “The potential harm of a false-positive (unnecessary scans, biopsies or even surgery) can be minimized by having a multidisciplinary team with experience working up lung nodules see patients who have a positive screening test. In fact, the American College of Radiology recommends that all lung screening programs be paired with such a team.”
Mass General has a pulmonary nodule clinic to evaluate screen-detected lung nodules, with the goal of minimizing unnecessary procedures, she noted.
Asked about the potential harm from radiation exposure, Sequist said that exposure from low-dose CT screening is fairly minimal, comparable to that from solar radiation at sea level over a 6-month period, or about the level from three cross-country airplane trips.
“While it is not zero radiation, there is very little concern that this low level of radiation would cause a cancer or damage one’s lungs,” she said.
Albert Rizzo, MD, chief medical officer of the ALA, said that the potential harms of unnecessary interventions are outweighed by the benefits of detecting lung cancer at an early stage.
“I think what has been learned over the last 5 years is that the original recommendations that were put out really allowed the overall rate of positivity well within what’s seen with mammography, for example, and the number of patients who have needlessly gone on to procedures remains very low, and the morbidity of those procedures remains low as well,” Dr. Rizzo told Medscape Medical News.
Not enough takers
Despite the clear benefits of low-dose CT screening, however, US screening rates for high-risk individuals are still very low, ranging from 12.3% in Massachusetts to a low of 0.5% in Nevada, according to a 2019 research report on the state of lung cancer from the ALA.
“For screening to be most effective, more of the high-risk population should be screened. Currently, screening rates are very low among those at high risk. This may be because of a lack of access or low awareness and knowledge among patients and providers. As rates vary tremendously between states, it is clear that more can be done to increase screening rates,” the report stated.
“I think that there are some mixed messages sent out into the population as to whether or not an individual patient should be screened,” Dr. Rizzo said.
He noted that some physicians may be reluctant to take on the nuanced risk–benefit discussion required, or may not have the time during a brief patient visit.
“It really boils down to that discussion between the physician and the patient who falls under these risk categories, to say, ‘Look, this is what these studies have found, and you fall under a category where if we find a cancer early, it’s very likely you’re going to be saved,’ as compared for waiting for it to present by itself,” he said.
Dr. Sequist and Dr. Rizzo have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medication-assisted treatment in corrections: A life-saving intervention
Opioid overdose deaths in the United States have more than tripled in recent years, from 6.1 deaths per 100,000 individuals in 1999 to 20.7 per 100,000 individuals in 2018.1 Although the availability of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) has expanded over the past decade, this lifesaving treatment remains largely inaccessible to some of the most vulnerable members of our communities: opioid users facing reentry after incarceration.
Just as abstinence in the community brings a loss of tolerance to opioids, individuals who are incarcerated lose tolerance as well. Clinicians who treat patients with opioid use disorders (OUD) are accustomed to warning patients about the risk of returning to prior levels of use too quickly. Harm reduction strategies include using slowly, using with friends, and having naloxone on hand to prevent unintended overdose.
The risks of opioid use are magnified for those facing reentry; incarceration contributes to a loss of employment, social supports, and connection to care. Those changes can create an exceptionally stressful reentry period – one that places individuals at an acutely high risk of relapse and overdose. Within the first 2 years of release, an individual with a history of incarceration has a risk of death 3.5 times higher than that of someone in the general population. Within the first 2 weeks, those recently incarcerated are 129 times more likely to overdose on opioids and 12.7 times more likely to die than members of the general population.2
Treatment with MAT dramatically reduces deaths during this crucial period. In England, large national studies have shown a similar 75% decrease in all-cause mortality within the first 4 weeks of release among individuals with OUD.4 In California, the counties with the highest overdose death rates are consistently those with fewer opioid treatment programs, which suggests that access to treatment is necessary to prolong the lives of those suffering from OUD.5 In-custody overdose deaths are quite rare, and access to MAT during incarceration has decreased in-custody deaths by 74%.6
Decreased opioid overdose deaths is not the only outcome of MAT. Pharmacotherapy for OUD also has been shown to increase treatment retention,7 reduce reincarceration,8 prevent communicable infections,9 and decrease use of other illicit substances.10 The provision of MAT also has been shown to be cost effective.11
Despite those benefits, as of 2017, only 30 out of 5,100 jails and prisons in the United States provided treatment with methadone or buprenorphine.12 When individuals on maintenance therapy are incarcerated, most correctional facilities force them to taper and discontinue those medications. This practice can cause distressing withdrawal symptoms and actively increase the risk of death for these individuals.
Concerns related to the provision of MAT, and specifically buprenorphine, in the correctional health setting often are related to diversion. Although safe administration of opioid full and partial agonists is a priority, recent literature has suggested that buprenorphine is not a medication frequently used for euphoric properties. In fact, the literature suggests that individuals using illicit buprenorphine primarily do so to treat withdrawal symptoms and that illicit use diminishes with access to formal treatment.13,14
Another concern is that pharmacotherapy for OUD should not be used without adjunctive psychotherapies and social supports. While dual pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy is ideal, the American Society for Addiction Medicine 2020 National Practice Guidelines for the treatment of OUD state: “a patient’s decision to decline psychosocial treatment or the absence of available psychosocial treatment should not preclude or delay pharmacotherapy, with appropriate medication management.”15 Just as some patients wish to engage in mutual help or psychotherapeutic modalities only, some patients wish to engage only in psychopharmacologic interventions. Declaring one modality of treatment better, or worse, or more worthwhile is not borne out by the literature and often places clinicians’ preferences over the preferences of patients.
Individuals who suffer from substance use disorders are at high risk of incarceration, relapse, and overdose death. These patients also suffer from stigmatization from peers and health care workers alike, making the process of engaging in care incredibly burdensome. Because of the disease of addiction, many of our patients cannot envision a healthy future: a future with the potential for intimate relationships, meaningful community engagement, and a rich inner life. The provision of MAT is lifesaving and improves the chances of a successful reentry – an intuitive first step in a long, but worthwhile, journey.
References
1. Hedegaard H et al; National Center for Health Statistics. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999–2018. NCHS Data Brief, 2020 Jan, No. 356.
2. Binswanger IA et al. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:157-65.
3. Green TC et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75(4):405-7.
4. Marsden J et al. Addiction. 2017;112(8):1408-18.
5. Joshi V and Urada D. State Targeted Response to the Opioid Crisis: California Strategic Plan. 2017 Aug 30.
6. Larney S et al. BMJ Open. 2014. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004666.
7. Rich JD et al. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):350-9.
8. Deck D et al. J Addict Dis. 2009. 28(2):89-102.
9. MacArthur GJ et al. BMJ. 2012. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e5945.
10. Tsui J et al. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019. 109:80-5.
11. Gisev N et al. Addiction. 2015 Dec;110(12):1975-84.
12. National Mental Health and Substance Use Policy Laboratory. “Use of Medication-Assisted Treatment for Opioid Use Disorder in Criminal Justice Settings.” HHS Publication No. PEP19-MATUSECJS. Rockville, Md.: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2019.
13. Bazazi AR et al. J Addict Med. 2011;5(3):175-80.
14. Schuman-Olivier Z. et al. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010 Jul;39(1):41-50.
15. Crotty K et al. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2)99-112.
Dr. Barnes is chief resident at San Mateo County Behavioral Health and Recovery Services in California. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lenane is resident* at San Mateo County Behavioral Health and Recovery Services. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The opinions shared in this article represent the viewpoints of the authors and are not necessarily representative of the viewpoints or policies of their academic program or employer.
*This article was updated 7/9/2020.
Opioid overdose deaths in the United States have more than tripled in recent years, from 6.1 deaths per 100,000 individuals in 1999 to 20.7 per 100,000 individuals in 2018.1 Although the availability of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) has expanded over the past decade, this lifesaving treatment remains largely inaccessible to some of the most vulnerable members of our communities: opioid users facing reentry after incarceration.
Just as abstinence in the community brings a loss of tolerance to opioids, individuals who are incarcerated lose tolerance as well. Clinicians who treat patients with opioid use disorders (OUD) are accustomed to warning patients about the risk of returning to prior levels of use too quickly. Harm reduction strategies include using slowly, using with friends, and having naloxone on hand to prevent unintended overdose.
The risks of opioid use are magnified for those facing reentry; incarceration contributes to a loss of employment, social supports, and connection to care. Those changes can create an exceptionally stressful reentry period – one that places individuals at an acutely high risk of relapse and overdose. Within the first 2 years of release, an individual with a history of incarceration has a risk of death 3.5 times higher than that of someone in the general population. Within the first 2 weeks, those recently incarcerated are 129 times more likely to overdose on opioids and 12.7 times more likely to die than members of the general population.2
Treatment with MAT dramatically reduces deaths during this crucial period. In England, large national studies have shown a similar 75% decrease in all-cause mortality within the first 4 weeks of release among individuals with OUD.4 In California, the counties with the highest overdose death rates are consistently those with fewer opioid treatment programs, which suggests that access to treatment is necessary to prolong the lives of those suffering from OUD.5 In-custody overdose deaths are quite rare, and access to MAT during incarceration has decreased in-custody deaths by 74%.6
Decreased opioid overdose deaths is not the only outcome of MAT. Pharmacotherapy for OUD also has been shown to increase treatment retention,7 reduce reincarceration,8 prevent communicable infections,9 and decrease use of other illicit substances.10 The provision of MAT also has been shown to be cost effective.11
Despite those benefits, as of 2017, only 30 out of 5,100 jails and prisons in the United States provided treatment with methadone or buprenorphine.12 When individuals on maintenance therapy are incarcerated, most correctional facilities force them to taper and discontinue those medications. This practice can cause distressing withdrawal symptoms and actively increase the risk of death for these individuals.
Concerns related to the provision of MAT, and specifically buprenorphine, in the correctional health setting often are related to diversion. Although safe administration of opioid full and partial agonists is a priority, recent literature has suggested that buprenorphine is not a medication frequently used for euphoric properties. In fact, the literature suggests that individuals using illicit buprenorphine primarily do so to treat withdrawal symptoms and that illicit use diminishes with access to formal treatment.13,14
Another concern is that pharmacotherapy for OUD should not be used without adjunctive psychotherapies and social supports. While dual pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy is ideal, the American Society for Addiction Medicine 2020 National Practice Guidelines for the treatment of OUD state: “a patient’s decision to decline psychosocial treatment or the absence of available psychosocial treatment should not preclude or delay pharmacotherapy, with appropriate medication management.”15 Just as some patients wish to engage in mutual help or psychotherapeutic modalities only, some patients wish to engage only in psychopharmacologic interventions. Declaring one modality of treatment better, or worse, or more worthwhile is not borne out by the literature and often places clinicians’ preferences over the preferences of patients.
Individuals who suffer from substance use disorders are at high risk of incarceration, relapse, and overdose death. These patients also suffer from stigmatization from peers and health care workers alike, making the process of engaging in care incredibly burdensome. Because of the disease of addiction, many of our patients cannot envision a healthy future: a future with the potential for intimate relationships, meaningful community engagement, and a rich inner life. The provision of MAT is lifesaving and improves the chances of a successful reentry – an intuitive first step in a long, but worthwhile, journey.
References
1. Hedegaard H et al; National Center for Health Statistics. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999–2018. NCHS Data Brief, 2020 Jan, No. 356.
2. Binswanger IA et al. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:157-65.
3. Green TC et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75(4):405-7.
4. Marsden J et al. Addiction. 2017;112(8):1408-18.
5. Joshi V and Urada D. State Targeted Response to the Opioid Crisis: California Strategic Plan. 2017 Aug 30.
6. Larney S et al. BMJ Open. 2014. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004666.
7. Rich JD et al. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):350-9.
8. Deck D et al. J Addict Dis. 2009. 28(2):89-102.
9. MacArthur GJ et al. BMJ. 2012. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e5945.
10. Tsui J et al. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019. 109:80-5.
11. Gisev N et al. Addiction. 2015 Dec;110(12):1975-84.
12. National Mental Health and Substance Use Policy Laboratory. “Use of Medication-Assisted Treatment for Opioid Use Disorder in Criminal Justice Settings.” HHS Publication No. PEP19-MATUSECJS. Rockville, Md.: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2019.
13. Bazazi AR et al. J Addict Med. 2011;5(3):175-80.
14. Schuman-Olivier Z. et al. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010 Jul;39(1):41-50.
15. Crotty K et al. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2)99-112.
Dr. Barnes is chief resident at San Mateo County Behavioral Health and Recovery Services in California. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lenane is resident* at San Mateo County Behavioral Health and Recovery Services. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The opinions shared in this article represent the viewpoints of the authors and are not necessarily representative of the viewpoints or policies of their academic program or employer.
*This article was updated 7/9/2020.
Opioid overdose deaths in the United States have more than tripled in recent years, from 6.1 deaths per 100,000 individuals in 1999 to 20.7 per 100,000 individuals in 2018.1 Although the availability of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) has expanded over the past decade, this lifesaving treatment remains largely inaccessible to some of the most vulnerable members of our communities: opioid users facing reentry after incarceration.
Just as abstinence in the community brings a loss of tolerance to opioids, individuals who are incarcerated lose tolerance as well. Clinicians who treat patients with opioid use disorders (OUD) are accustomed to warning patients about the risk of returning to prior levels of use too quickly. Harm reduction strategies include using slowly, using with friends, and having naloxone on hand to prevent unintended overdose.
The risks of opioid use are magnified for those facing reentry; incarceration contributes to a loss of employment, social supports, and connection to care. Those changes can create an exceptionally stressful reentry period – one that places individuals at an acutely high risk of relapse and overdose. Within the first 2 years of release, an individual with a history of incarceration has a risk of death 3.5 times higher than that of someone in the general population. Within the first 2 weeks, those recently incarcerated are 129 times more likely to overdose on opioids and 12.7 times more likely to die than members of the general population.2
Treatment with MAT dramatically reduces deaths during this crucial period. In England, large national studies have shown a similar 75% decrease in all-cause mortality within the first 4 weeks of release among individuals with OUD.4 In California, the counties with the highest overdose death rates are consistently those with fewer opioid treatment programs, which suggests that access to treatment is necessary to prolong the lives of those suffering from OUD.5 In-custody overdose deaths are quite rare, and access to MAT during incarceration has decreased in-custody deaths by 74%.6
Decreased opioid overdose deaths is not the only outcome of MAT. Pharmacotherapy for OUD also has been shown to increase treatment retention,7 reduce reincarceration,8 prevent communicable infections,9 and decrease use of other illicit substances.10 The provision of MAT also has been shown to be cost effective.11
Despite those benefits, as of 2017, only 30 out of 5,100 jails and prisons in the United States provided treatment with methadone or buprenorphine.12 When individuals on maintenance therapy are incarcerated, most correctional facilities force them to taper and discontinue those medications. This practice can cause distressing withdrawal symptoms and actively increase the risk of death for these individuals.
Concerns related to the provision of MAT, and specifically buprenorphine, in the correctional health setting often are related to diversion. Although safe administration of opioid full and partial agonists is a priority, recent literature has suggested that buprenorphine is not a medication frequently used for euphoric properties. In fact, the literature suggests that individuals using illicit buprenorphine primarily do so to treat withdrawal symptoms and that illicit use diminishes with access to formal treatment.13,14
Another concern is that pharmacotherapy for OUD should not be used without adjunctive psychotherapies and social supports. While dual pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy is ideal, the American Society for Addiction Medicine 2020 National Practice Guidelines for the treatment of OUD state: “a patient’s decision to decline psychosocial treatment or the absence of available psychosocial treatment should not preclude or delay pharmacotherapy, with appropriate medication management.”15 Just as some patients wish to engage in mutual help or psychotherapeutic modalities only, some patients wish to engage only in psychopharmacologic interventions. Declaring one modality of treatment better, or worse, or more worthwhile is not borne out by the literature and often places clinicians’ preferences over the preferences of patients.
Individuals who suffer from substance use disorders are at high risk of incarceration, relapse, and overdose death. These patients also suffer from stigmatization from peers and health care workers alike, making the process of engaging in care incredibly burdensome. Because of the disease of addiction, many of our patients cannot envision a healthy future: a future with the potential for intimate relationships, meaningful community engagement, and a rich inner life. The provision of MAT is lifesaving and improves the chances of a successful reentry – an intuitive first step in a long, but worthwhile, journey.
References
1. Hedegaard H et al; National Center for Health Statistics. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999–2018. NCHS Data Brief, 2020 Jan, No. 356.
2. Binswanger IA et al. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:157-65.
3. Green TC et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75(4):405-7.
4. Marsden J et al. Addiction. 2017;112(8):1408-18.
5. Joshi V and Urada D. State Targeted Response to the Opioid Crisis: California Strategic Plan. 2017 Aug 30.
6. Larney S et al. BMJ Open. 2014. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004666.
7. Rich JD et al. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):350-9.
8. Deck D et al. J Addict Dis. 2009. 28(2):89-102.
9. MacArthur GJ et al. BMJ. 2012. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e5945.
10. Tsui J et al. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019. 109:80-5.
11. Gisev N et al. Addiction. 2015 Dec;110(12):1975-84.
12. National Mental Health and Substance Use Policy Laboratory. “Use of Medication-Assisted Treatment for Opioid Use Disorder in Criminal Justice Settings.” HHS Publication No. PEP19-MATUSECJS. Rockville, Md.: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2019.
13. Bazazi AR et al. J Addict Med. 2011;5(3):175-80.
14. Schuman-Olivier Z. et al. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010 Jul;39(1):41-50.
15. Crotty K et al. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2)99-112.
Dr. Barnes is chief resident at San Mateo County Behavioral Health and Recovery Services in California. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lenane is resident* at San Mateo County Behavioral Health and Recovery Services. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The opinions shared in this article represent the viewpoints of the authors and are not necessarily representative of the viewpoints or policies of their academic program or employer.
*This article was updated 7/9/2020.
Transitioning regimen may prolong proteasome inhibitor–based therapy for MM
Transitioning from parenteral bortezomib-based induction to all-oral ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone therapy increased proteasome inhibitor (PI)–based treatment adherence and duration, according to early results from a clinical trial designed to include patients representing the real-world U.S. multiple myeloma population.
The US MM-6 study was designed to evaluate a novel in-class therapy (iCT) transitioning approach from intravenous to oral treatment in the community-based setting with the aims of increasing PI-based treatment duration and adherence, maintaining health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and improving outcomes in a representative, real-world, community population of multiple myeloma patients, according to Sudhir Manda, MD, of Arizona Oncology/U.S. Oncology Research, Tucson, and colleagues.
Dr. Manda and colleagues reported on the early results of the US MM-6 trial (NCT03173092), which is a community-based, real-world, open-label, single-arm, phase 4 study of adult multiple myeloma patients who do not meet transplant-eligibility criteria, or for whom transplant would be delayed for 2 years or more, and who are receiving first-line bortezomib-based induction. All patients in the study had no evidence of progressive disease after three treatment cycles.
By the data cutoff for the reported analysis, 84 patients had been treated. The patients had a median age of 73 years; 49% were men; 15% black/African American; 10% Hispanic/Latino. A total of 62% of the patients remain on therapy, with a mean duration of total PI therapy of 10.1 months and of ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (ixazomib-Rd) of 7.3 months.
The overall response rate was 62% (complete response, 4%; very good partial response, 25%; partial response, 33%) after bortezomib-based induction and 70% (complete response, 26%; very good partial response, 29%; partial response, 15%) after induction to all-oral ixazomib-Rd.
“The use of this novel iCT approach from parenteral bortezomib-based to oral ixazomib-based therapy facilitates long-term PI-based treatment that is well tolerated in real-world, nontransplant [newly diagnosed multiple myeloma] patients,” according to Dr. Manda and colleagues. In addition, “preliminary findings indicate that the iCT approach results in promising efficacy and high medication adherence, with no adverse impact on patients’ HRQoL or treatment satisfaction.”
The study was sponsored by Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Four of the authors are employees of Millennium Pharmaceuticals and several authors disclosed relationships with various pharmaceutical companies, including Millennium Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Manda S et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Jun 30. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.024.
Transitioning from parenteral bortezomib-based induction to all-oral ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone therapy increased proteasome inhibitor (PI)–based treatment adherence and duration, according to early results from a clinical trial designed to include patients representing the real-world U.S. multiple myeloma population.
The US MM-6 study was designed to evaluate a novel in-class therapy (iCT) transitioning approach from intravenous to oral treatment in the community-based setting with the aims of increasing PI-based treatment duration and adherence, maintaining health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and improving outcomes in a representative, real-world, community population of multiple myeloma patients, according to Sudhir Manda, MD, of Arizona Oncology/U.S. Oncology Research, Tucson, and colleagues.
Dr. Manda and colleagues reported on the early results of the US MM-6 trial (NCT03173092), which is a community-based, real-world, open-label, single-arm, phase 4 study of adult multiple myeloma patients who do not meet transplant-eligibility criteria, or for whom transplant would be delayed for 2 years or more, and who are receiving first-line bortezomib-based induction. All patients in the study had no evidence of progressive disease after three treatment cycles.
By the data cutoff for the reported analysis, 84 patients had been treated. The patients had a median age of 73 years; 49% were men; 15% black/African American; 10% Hispanic/Latino. A total of 62% of the patients remain on therapy, with a mean duration of total PI therapy of 10.1 months and of ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (ixazomib-Rd) of 7.3 months.
The overall response rate was 62% (complete response, 4%; very good partial response, 25%; partial response, 33%) after bortezomib-based induction and 70% (complete response, 26%; very good partial response, 29%; partial response, 15%) after induction to all-oral ixazomib-Rd.
“The use of this novel iCT approach from parenteral bortezomib-based to oral ixazomib-based therapy facilitates long-term PI-based treatment that is well tolerated in real-world, nontransplant [newly diagnosed multiple myeloma] patients,” according to Dr. Manda and colleagues. In addition, “preliminary findings indicate that the iCT approach results in promising efficacy and high medication adherence, with no adverse impact on patients’ HRQoL or treatment satisfaction.”
The study was sponsored by Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Four of the authors are employees of Millennium Pharmaceuticals and several authors disclosed relationships with various pharmaceutical companies, including Millennium Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Manda S et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Jun 30. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.024.
Transitioning from parenteral bortezomib-based induction to all-oral ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone therapy increased proteasome inhibitor (PI)–based treatment adherence and duration, according to early results from a clinical trial designed to include patients representing the real-world U.S. multiple myeloma population.
The US MM-6 study was designed to evaluate a novel in-class therapy (iCT) transitioning approach from intravenous to oral treatment in the community-based setting with the aims of increasing PI-based treatment duration and adherence, maintaining health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and improving outcomes in a representative, real-world, community population of multiple myeloma patients, according to Sudhir Manda, MD, of Arizona Oncology/U.S. Oncology Research, Tucson, and colleagues.
Dr. Manda and colleagues reported on the early results of the US MM-6 trial (NCT03173092), which is a community-based, real-world, open-label, single-arm, phase 4 study of adult multiple myeloma patients who do not meet transplant-eligibility criteria, or for whom transplant would be delayed for 2 years or more, and who are receiving first-line bortezomib-based induction. All patients in the study had no evidence of progressive disease after three treatment cycles.
By the data cutoff for the reported analysis, 84 patients had been treated. The patients had a median age of 73 years; 49% were men; 15% black/African American; 10% Hispanic/Latino. A total of 62% of the patients remain on therapy, with a mean duration of total PI therapy of 10.1 months and of ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (ixazomib-Rd) of 7.3 months.
The overall response rate was 62% (complete response, 4%; very good partial response, 25%; partial response, 33%) after bortezomib-based induction and 70% (complete response, 26%; very good partial response, 29%; partial response, 15%) after induction to all-oral ixazomib-Rd.
“The use of this novel iCT approach from parenteral bortezomib-based to oral ixazomib-based therapy facilitates long-term PI-based treatment that is well tolerated in real-world, nontransplant [newly diagnosed multiple myeloma] patients,” according to Dr. Manda and colleagues. In addition, “preliminary findings indicate that the iCT approach results in promising efficacy and high medication adherence, with no adverse impact on patients’ HRQoL or treatment satisfaction.”
The study was sponsored by Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Four of the authors are employees of Millennium Pharmaceuticals and several authors disclosed relationships with various pharmaceutical companies, including Millennium Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Manda S et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Jun 30. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.024.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA AND LEUKEMIA