User login
PASDAS beats DAS28 in measuring psoriatic arthritis treat-to-target success
Measuring success with a treat-to-target strategy in psoriatic arthritis patients proved to be more comprehensive with the Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) than it was with the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28), according to findings from a prospective cohort study.
Fewer patients had a low disease activity score according to DAS28, and a higher percentage of patients deemed adequately treated according to DAS28 were found to have residual disease activity, compared with the number of patients so categorized according to PASDAS, researcher Michelle Mulder reported in her presentation of the study at the virtual annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
“PASDAS implementation in a tightly monitored PsA [psoriatic arthritis] cohort suggests relevant residual disease burden, even though DAS28 was measured at every visit previously,” said Ms. Mulder, an MD/PhD student at Sint Maartenskliniek in Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
The presentation was convincing to Philip Helliwell, MD, PhD, who is a professor of clinical rheumatology at Leeds (England) University, and was also one of the developers of PASDAS. “We know it can be used in clinical practice with a certain amount of organization and clinical staff to help you,” he said during another presentation at GRAPPA.
Treat to target is a widely accepted therapeutic strategy. It’s particularly common in rheumatoid arthritis, but increasing evidence suggests that it improves patient outcomes in psoriatic arthritis. DAS28 is frequently used in treat-to-target approaches in rheumatoid arthritis, and often gets applied to psoriatic arthritis since rheumatologists are already comfortable with it, according to Ms. Mulder. “However, DAS28 has shown some limitations when used in psoriatic arthritis. For example, its joint count is limited to only 28 joints, and it does not take all PsA domains into account,” she said.
DAS28 was previously used at Sint Maartenskliniek in combination with psoriatic arthritis–specific assessment recommendations, but the institution opted in 2019 to switch to PASDAS, which was developed by GRAPPA and the European League Against Rheumatism. “To better adhere to international PsA guidelines, we chose to implement PASDAS in our cohort with the assumption that it might improve patient care,” Ms. Mulder said.
With DAS28, clinicians measured the C-reactive protein (CRP) and Patient Global Visual Analog Scale (VAS) domains and were advised to examine 28 joints for tender and swollen joint count domains. Under the PASDAS guidance, clinicians examined 68 joints for tenderness, 66 joints for swelling, CRP, Patient Global VAS, Physician Global VAS, Leeds Enthesitis Index, dactylitis, and the 12-item Short Form Physical Composite Scale. They also examined the skin, nails, and axial disease.
To examine the effects of the switch from DAS28 to PASDAS, the researchers compared outcomes in 855 patients before and after the change during March to December 2019. The mean age of patients was 55 years, and 46% were female. The mean disease duration was 10 years, and the mean PASDAS score was 3.1. A total of 96% of participants were negative for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide. Overall, 30% had arthritis, 9% had axial disease, 3% had dactylitis, 21% had enthesitis, 51% had skin disease, and 42% had nail disease.
About three-quarters (77.4%) of patients reached the threshold of low disease activity (LDA) according to the DAS28 measure, while 53.1% did so using the PASDAS. High disease activity occurred in 7.8% of patients according to DAS28, compared with 2.7% as measured by PASDAS. Patients who reached only the DAS28 LDA target but not the PASDAS target, compared with patients who reached the LDA target in both measures, had significantly worse counts for swelling in 66 joints (0.7 vs. 0.2; P < .001) and tenderness in 68 joints (2.1 vs. 0.7; P < .001), as well as worse scores for enthesitis (0.5 vs. 0.1; P < .001), dactylitis (4% vs. 1%; P = .005), patient global VAS (44.0 vs. 14.4; P < .001), Health Assessment Questionnaire (0.8 vs. 0.4; P < .001) and Patient Acceptable Symptom State (unacceptable score in 17% vs. 3%; P < .001).
Ms. Mulder acknowledged that PASDAS imposes a significant burden on clinicians, and noted that Sint Maartenskliniek created patient infrastructure to handle the load. “It’s very important that you set up your clinic in a specific way. When the patient comes in, we draw blood immediately and we ask them to fill in the questionnaires, and then they go to a specialized nurse who measures all the different components of the PASDAS. It took a lot of time to train the specialized nurses and to implement the PASDAS score in our electronic health records. After we did those things, it was quite easy because we have this whole setup. It takes time and it is difficult, but it is definitely possible to do it,” Ms. Mulder said during a live Q&A following her prerecorded presentation.
The study received no funding. Ms. Mulder had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Helliwell has financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Celgen, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
SOURCE: Mulder M et al. GRAPPA 2020 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Measuring success with a treat-to-target strategy in psoriatic arthritis patients proved to be more comprehensive with the Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) than it was with the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28), according to findings from a prospective cohort study.
Fewer patients had a low disease activity score according to DAS28, and a higher percentage of patients deemed adequately treated according to DAS28 were found to have residual disease activity, compared with the number of patients so categorized according to PASDAS, researcher Michelle Mulder reported in her presentation of the study at the virtual annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
“PASDAS implementation in a tightly monitored PsA [psoriatic arthritis] cohort suggests relevant residual disease burden, even though DAS28 was measured at every visit previously,” said Ms. Mulder, an MD/PhD student at Sint Maartenskliniek in Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
The presentation was convincing to Philip Helliwell, MD, PhD, who is a professor of clinical rheumatology at Leeds (England) University, and was also one of the developers of PASDAS. “We know it can be used in clinical practice with a certain amount of organization and clinical staff to help you,” he said during another presentation at GRAPPA.
Treat to target is a widely accepted therapeutic strategy. It’s particularly common in rheumatoid arthritis, but increasing evidence suggests that it improves patient outcomes in psoriatic arthritis. DAS28 is frequently used in treat-to-target approaches in rheumatoid arthritis, and often gets applied to psoriatic arthritis since rheumatologists are already comfortable with it, according to Ms. Mulder. “However, DAS28 has shown some limitations when used in psoriatic arthritis. For example, its joint count is limited to only 28 joints, and it does not take all PsA domains into account,” she said.
DAS28 was previously used at Sint Maartenskliniek in combination with psoriatic arthritis–specific assessment recommendations, but the institution opted in 2019 to switch to PASDAS, which was developed by GRAPPA and the European League Against Rheumatism. “To better adhere to international PsA guidelines, we chose to implement PASDAS in our cohort with the assumption that it might improve patient care,” Ms. Mulder said.
With DAS28, clinicians measured the C-reactive protein (CRP) and Patient Global Visual Analog Scale (VAS) domains and were advised to examine 28 joints for tender and swollen joint count domains. Under the PASDAS guidance, clinicians examined 68 joints for tenderness, 66 joints for swelling, CRP, Patient Global VAS, Physician Global VAS, Leeds Enthesitis Index, dactylitis, and the 12-item Short Form Physical Composite Scale. They also examined the skin, nails, and axial disease.
To examine the effects of the switch from DAS28 to PASDAS, the researchers compared outcomes in 855 patients before and after the change during March to December 2019. The mean age of patients was 55 years, and 46% were female. The mean disease duration was 10 years, and the mean PASDAS score was 3.1. A total of 96% of participants were negative for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide. Overall, 30% had arthritis, 9% had axial disease, 3% had dactylitis, 21% had enthesitis, 51% had skin disease, and 42% had nail disease.
About three-quarters (77.4%) of patients reached the threshold of low disease activity (LDA) according to the DAS28 measure, while 53.1% did so using the PASDAS. High disease activity occurred in 7.8% of patients according to DAS28, compared with 2.7% as measured by PASDAS. Patients who reached only the DAS28 LDA target but not the PASDAS target, compared with patients who reached the LDA target in both measures, had significantly worse counts for swelling in 66 joints (0.7 vs. 0.2; P < .001) and tenderness in 68 joints (2.1 vs. 0.7; P < .001), as well as worse scores for enthesitis (0.5 vs. 0.1; P < .001), dactylitis (4% vs. 1%; P = .005), patient global VAS (44.0 vs. 14.4; P < .001), Health Assessment Questionnaire (0.8 vs. 0.4; P < .001) and Patient Acceptable Symptom State (unacceptable score in 17% vs. 3%; P < .001).
Ms. Mulder acknowledged that PASDAS imposes a significant burden on clinicians, and noted that Sint Maartenskliniek created patient infrastructure to handle the load. “It’s very important that you set up your clinic in a specific way. When the patient comes in, we draw blood immediately and we ask them to fill in the questionnaires, and then they go to a specialized nurse who measures all the different components of the PASDAS. It took a lot of time to train the specialized nurses and to implement the PASDAS score in our electronic health records. After we did those things, it was quite easy because we have this whole setup. It takes time and it is difficult, but it is definitely possible to do it,” Ms. Mulder said during a live Q&A following her prerecorded presentation.
The study received no funding. Ms. Mulder had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Helliwell has financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Celgen, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
SOURCE: Mulder M et al. GRAPPA 2020 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Measuring success with a treat-to-target strategy in psoriatic arthritis patients proved to be more comprehensive with the Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) than it was with the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28), according to findings from a prospective cohort study.
Fewer patients had a low disease activity score according to DAS28, and a higher percentage of patients deemed adequately treated according to DAS28 were found to have residual disease activity, compared with the number of patients so categorized according to PASDAS, researcher Michelle Mulder reported in her presentation of the study at the virtual annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
“PASDAS implementation in a tightly monitored PsA [psoriatic arthritis] cohort suggests relevant residual disease burden, even though DAS28 was measured at every visit previously,” said Ms. Mulder, an MD/PhD student at Sint Maartenskliniek in Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
The presentation was convincing to Philip Helliwell, MD, PhD, who is a professor of clinical rheumatology at Leeds (England) University, and was also one of the developers of PASDAS. “We know it can be used in clinical practice with a certain amount of organization and clinical staff to help you,” he said during another presentation at GRAPPA.
Treat to target is a widely accepted therapeutic strategy. It’s particularly common in rheumatoid arthritis, but increasing evidence suggests that it improves patient outcomes in psoriatic arthritis. DAS28 is frequently used in treat-to-target approaches in rheumatoid arthritis, and often gets applied to psoriatic arthritis since rheumatologists are already comfortable with it, according to Ms. Mulder. “However, DAS28 has shown some limitations when used in psoriatic arthritis. For example, its joint count is limited to only 28 joints, and it does not take all PsA domains into account,” she said.
DAS28 was previously used at Sint Maartenskliniek in combination with psoriatic arthritis–specific assessment recommendations, but the institution opted in 2019 to switch to PASDAS, which was developed by GRAPPA and the European League Against Rheumatism. “To better adhere to international PsA guidelines, we chose to implement PASDAS in our cohort with the assumption that it might improve patient care,” Ms. Mulder said.
With DAS28, clinicians measured the C-reactive protein (CRP) and Patient Global Visual Analog Scale (VAS) domains and were advised to examine 28 joints for tender and swollen joint count domains. Under the PASDAS guidance, clinicians examined 68 joints for tenderness, 66 joints for swelling, CRP, Patient Global VAS, Physician Global VAS, Leeds Enthesitis Index, dactylitis, and the 12-item Short Form Physical Composite Scale. They also examined the skin, nails, and axial disease.
To examine the effects of the switch from DAS28 to PASDAS, the researchers compared outcomes in 855 patients before and after the change during March to December 2019. The mean age of patients was 55 years, and 46% were female. The mean disease duration was 10 years, and the mean PASDAS score was 3.1. A total of 96% of participants were negative for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide. Overall, 30% had arthritis, 9% had axial disease, 3% had dactylitis, 21% had enthesitis, 51% had skin disease, and 42% had nail disease.
About three-quarters (77.4%) of patients reached the threshold of low disease activity (LDA) according to the DAS28 measure, while 53.1% did so using the PASDAS. High disease activity occurred in 7.8% of patients according to DAS28, compared with 2.7% as measured by PASDAS. Patients who reached only the DAS28 LDA target but not the PASDAS target, compared with patients who reached the LDA target in both measures, had significantly worse counts for swelling in 66 joints (0.7 vs. 0.2; P < .001) and tenderness in 68 joints (2.1 vs. 0.7; P < .001), as well as worse scores for enthesitis (0.5 vs. 0.1; P < .001), dactylitis (4% vs. 1%; P = .005), patient global VAS (44.0 vs. 14.4; P < .001), Health Assessment Questionnaire (0.8 vs. 0.4; P < .001) and Patient Acceptable Symptom State (unacceptable score in 17% vs. 3%; P < .001).
Ms. Mulder acknowledged that PASDAS imposes a significant burden on clinicians, and noted that Sint Maartenskliniek created patient infrastructure to handle the load. “It’s very important that you set up your clinic in a specific way. When the patient comes in, we draw blood immediately and we ask them to fill in the questionnaires, and then they go to a specialized nurse who measures all the different components of the PASDAS. It took a lot of time to train the specialized nurses and to implement the PASDAS score in our electronic health records. After we did those things, it was quite easy because we have this whole setup. It takes time and it is difficult, but it is definitely possible to do it,” Ms. Mulder said during a live Q&A following her prerecorded presentation.
The study received no funding. Ms. Mulder had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Helliwell has financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Celgen, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
SOURCE: Mulder M et al. GRAPPA 2020 Virtual Annual Meeting.
FROM GRAPPA 2020 VIRTUAL ANNUAL MEETING
COVID-19 symptoms can linger for months
Clinicians and researchers have focused on the acute phase of COVID-19 infection, but it’s increasingly clear that some recovered patients discharged from acute care need continued monitoring for long-lasting effects, a study has found.
In a research letter published online July 9 in JAMA, Angelo Carfi, MD, and colleagues from the Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post–Acute Care Study Group in Rome, report that
Postdischarge assessments of patients who met criteria for SARS-CoV-2 negativity, including a reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction test, were conducted from April 21 to May 29. Among the results:
- Only 12.6% of the 143 patients were completely free of any COVID-19 symptom
- About 32% of patients had one or two symptoms and 55% had three or more
- None had fever or other signs and symptoms of acute illness
- About 53% of patients still had fatigue, 43.4% had dyspnea, 27.3% had joint pain, and had 21.7% chest pain
- About 44% reported worsened quality of life on the EuroQol visual analog scale.
The sample cohort, assessed in a COVID-19 patient service recently established at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli had a mean age of 56.5 years and 37% were women. The mean length of hospital stay was 13.5 days. During their hospitalization, 72.7% of patients showed evidence of interstitial pneumonia. Noninvasive ventilation was given to 14.7% of patients and 4.9% received invasive ventilation.
The reality of lingering symptoms has led Dr. Carfi’s clinic to schedule a final “wrap-up visit” for patients after full assessment. “On that occasion the doctor prescribes anything necessary to correct the anomalies found during the full evaluation,” Dr. Carfi, a geriatrician at the Gemelli clinic, said in an interview. “These usually include vitamin supplementation and, in selected cases, a new drug prescription such as a blood thinner if necessary.”
Patients can also enroll in a training program in which breathing status is monitored.
In North America, doctors are also addressing the reality that the road to recovery can be a long and upward one, with persistent symptoms worse than those seen with acute influenza infection. “We see patients who were first diagnosed in March or April and still have symptoms in July,” said Zijian Chen, MD, an endocrinologist and medical director of Mount Sinai Health System’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York.
“Persistent symptoms are much worse for COVID patients than flu patients. Even flu patients who spent time in the intensive care unit recover fully, and we can optimize their breathing before discharge,” Dr. Chen said in an interview.
As in the Italian study, Dr. Chen sees patients with COVID-19 who have ongoing shortness of breath, some requiring supplemental oxygen, or with persistent chest pain on exertion, blood clotting problems, poor concentration, gastrointestinal distress, and reduced muscle strength and impaired grasping power. He doesn’t rule out permanent lung damage in some. “Even asymptomatic individuals already show lung scarring on imaging,” he said.
The Mount Sinai program provides specialized interdisciplinary management that may include CT scans, endoscopy, and drugs such as respiratory medications or anticoagulants. It also offers training to combat the fatigue and deconditioning caused by the infection, symptoms that are not medically treatable but impact quality of life.
“These patients do get better, but I expect they may still have symptoms requiring monitoring after a year,” Dr. Chen said.
The study received no specific funding. Dr. Carfi and colleagues have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Chen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians and researchers have focused on the acute phase of COVID-19 infection, but it’s increasingly clear that some recovered patients discharged from acute care need continued monitoring for long-lasting effects, a study has found.
In a research letter published online July 9 in JAMA, Angelo Carfi, MD, and colleagues from the Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post–Acute Care Study Group in Rome, report that
Postdischarge assessments of patients who met criteria for SARS-CoV-2 negativity, including a reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction test, were conducted from April 21 to May 29. Among the results:
- Only 12.6% of the 143 patients were completely free of any COVID-19 symptom
- About 32% of patients had one or two symptoms and 55% had three or more
- None had fever or other signs and symptoms of acute illness
- About 53% of patients still had fatigue, 43.4% had dyspnea, 27.3% had joint pain, and had 21.7% chest pain
- About 44% reported worsened quality of life on the EuroQol visual analog scale.
The sample cohort, assessed in a COVID-19 patient service recently established at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli had a mean age of 56.5 years and 37% were women. The mean length of hospital stay was 13.5 days. During their hospitalization, 72.7% of patients showed evidence of interstitial pneumonia. Noninvasive ventilation was given to 14.7% of patients and 4.9% received invasive ventilation.
The reality of lingering symptoms has led Dr. Carfi’s clinic to schedule a final “wrap-up visit” for patients after full assessment. “On that occasion the doctor prescribes anything necessary to correct the anomalies found during the full evaluation,” Dr. Carfi, a geriatrician at the Gemelli clinic, said in an interview. “These usually include vitamin supplementation and, in selected cases, a new drug prescription such as a blood thinner if necessary.”
Patients can also enroll in a training program in which breathing status is monitored.
In North America, doctors are also addressing the reality that the road to recovery can be a long and upward one, with persistent symptoms worse than those seen with acute influenza infection. “We see patients who were first diagnosed in March or April and still have symptoms in July,” said Zijian Chen, MD, an endocrinologist and medical director of Mount Sinai Health System’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York.
“Persistent symptoms are much worse for COVID patients than flu patients. Even flu patients who spent time in the intensive care unit recover fully, and we can optimize their breathing before discharge,” Dr. Chen said in an interview.
As in the Italian study, Dr. Chen sees patients with COVID-19 who have ongoing shortness of breath, some requiring supplemental oxygen, or with persistent chest pain on exertion, blood clotting problems, poor concentration, gastrointestinal distress, and reduced muscle strength and impaired grasping power. He doesn’t rule out permanent lung damage in some. “Even asymptomatic individuals already show lung scarring on imaging,” he said.
The Mount Sinai program provides specialized interdisciplinary management that may include CT scans, endoscopy, and drugs such as respiratory medications or anticoagulants. It also offers training to combat the fatigue and deconditioning caused by the infection, symptoms that are not medically treatable but impact quality of life.
“These patients do get better, but I expect they may still have symptoms requiring monitoring after a year,” Dr. Chen said.
The study received no specific funding. Dr. Carfi and colleagues have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Chen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians and researchers have focused on the acute phase of COVID-19 infection, but it’s increasingly clear that some recovered patients discharged from acute care need continued monitoring for long-lasting effects, a study has found.
In a research letter published online July 9 in JAMA, Angelo Carfi, MD, and colleagues from the Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post–Acute Care Study Group in Rome, report that
Postdischarge assessments of patients who met criteria for SARS-CoV-2 negativity, including a reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction test, were conducted from April 21 to May 29. Among the results:
- Only 12.6% of the 143 patients were completely free of any COVID-19 symptom
- About 32% of patients had one or two symptoms and 55% had three or more
- None had fever or other signs and symptoms of acute illness
- About 53% of patients still had fatigue, 43.4% had dyspnea, 27.3% had joint pain, and had 21.7% chest pain
- About 44% reported worsened quality of life on the EuroQol visual analog scale.
The sample cohort, assessed in a COVID-19 patient service recently established at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli had a mean age of 56.5 years and 37% were women. The mean length of hospital stay was 13.5 days. During their hospitalization, 72.7% of patients showed evidence of interstitial pneumonia. Noninvasive ventilation was given to 14.7% of patients and 4.9% received invasive ventilation.
The reality of lingering symptoms has led Dr. Carfi’s clinic to schedule a final “wrap-up visit” for patients after full assessment. “On that occasion the doctor prescribes anything necessary to correct the anomalies found during the full evaluation,” Dr. Carfi, a geriatrician at the Gemelli clinic, said in an interview. “These usually include vitamin supplementation and, in selected cases, a new drug prescription such as a blood thinner if necessary.”
Patients can also enroll in a training program in which breathing status is monitored.
In North America, doctors are also addressing the reality that the road to recovery can be a long and upward one, with persistent symptoms worse than those seen with acute influenza infection. “We see patients who were first diagnosed in March or April and still have symptoms in July,” said Zijian Chen, MD, an endocrinologist and medical director of Mount Sinai Health System’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York.
“Persistent symptoms are much worse for COVID patients than flu patients. Even flu patients who spent time in the intensive care unit recover fully, and we can optimize their breathing before discharge,” Dr. Chen said in an interview.
As in the Italian study, Dr. Chen sees patients with COVID-19 who have ongoing shortness of breath, some requiring supplemental oxygen, or with persistent chest pain on exertion, blood clotting problems, poor concentration, gastrointestinal distress, and reduced muscle strength and impaired grasping power. He doesn’t rule out permanent lung damage in some. “Even asymptomatic individuals already show lung scarring on imaging,” he said.
The Mount Sinai program provides specialized interdisciplinary management that may include CT scans, endoscopy, and drugs such as respiratory medications or anticoagulants. It also offers training to combat the fatigue and deconditioning caused by the infection, symptoms that are not medically treatable but impact quality of life.
“These patients do get better, but I expect they may still have symptoms requiring monitoring after a year,” Dr. Chen said.
The study received no specific funding. Dr. Carfi and colleagues have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Chen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
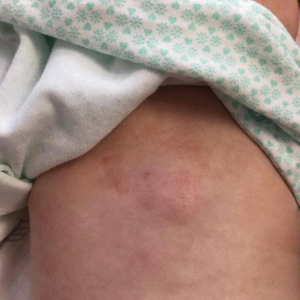
Biopsies of ascending, descending colon alone detected microscopic colitis
All patients with microscopic colitis who had biopsies of both the ascending and descending colon had positive slide review for at least one of the two sites, according to the findings of a single-center retrospective study.
“Microscopic colitis can be detected with 100% sensitivity by analyzing biopsy specimens from the ascending and descending colon. We propose a Western protocol (taking two biopsy specimens each from the ascending colon and the descending colon) in the evaluation of patients for microscopic colitis,” wrote Boris Virine, MD, of London (Ont.) Health Sciences Centre, Western University, together with his associates in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
That is half the minimum number of samples recommended by current guidelines, the researchers noted. “The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends two or more biopsy specimens from the right, transverse, left, and sigmoid colons; however, these recommendations were based on expert opinion rather than scientific evidence, and these guidelines have not been validated,” they wrote.
Microscopic colitis includes lymphocytic and collagenous subtypes, neither of which is grossly apparent on colonoscopy. “Endoscopists therefore often collect multiple random colonic biopsies, potentially oversampling, increasing times of colonoscopy and slide review,” Dr. Virine and his associates wrote.
To better pinpoint optimal biopsy sites and specimen numbers, they studied 101 patients consecutively diagnosed with biopsy-confirmed microscopic colitis at London Health Sciences Centre from 2017 through 2018. Patients with other colonic diseases were excluded from the study. Dr. Virine assessed all individual biopsy fragments, and another pathologist performed a second review of complex cases.
A total of 52 patients had biopsy-confirmed collagenous colitis – that is, normal crypt architecture, increased mononuclear inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and a thickened subepithelial collagen band. Forty-two patients had lymphocytic colitis, defined as normal crypt architecture, increased mononuclear inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and increased intraepithelial lymphocytosis. Seven patients had both disease subtypes.
For each patient, an average of nine (standard deviation, 4.9) biopsies had been collected. The most commonly sampled site was the ascending colon (biopsied in 47% of patients in whom at least one sample was labeled by site), followed by the descending colon (40%), rectum (21%), transverse colon (20%), sigmoid colon (15%), cecum (8%), and splenic and hepatic flexures (2% each). Diagnostic sensitivity was highest for the ascending colon (97%), transverse colon (96%), and sigmoid colon (91%) and lowest for the splenic flexure (75%), hepatic flexure (78%), and rectum (82%). The diagnostic sensitivity of the descending colon was 85%. However, all 39 patients with biopsies of both the ascending and descending colon had at least one biopsy that was positive for microscopic colitis (sensitivity, 100%).
“Based on the results of our study, collecting biopsy specimens from both the ascending and descending colons has the same overall sensitivity as following the guidelines,” the researchers concluded. “Because no single site in the colon was diffusely positive for microscopic colitis in 100% of cases, the possibility remains that collecting biopsy specimens from two sites could offer comparable sensitivity with biopsy specimens from each segment of the colon.”
No funding sources were reported. Dr. Virine and the senior author reported having no conflicts of interest. One coauthor disclosed ties to AbbVie, Allergan, Ferring, Janssen, Lupin Pendopharm, Pfizer, Shire, and Takeda.
SOURCE: Virine B et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Feb 25. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.02.036.
Microscopic colitis is a common cause of watery diarrhea. This debilitating disease is easy to treat, but the diagnosis can be challenging. Without lesions to target, guidelines recommend colonoscopy with at least two biopsies from the right, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon (total: eight-plus biopsies). With little evidence to guide this recommendation, this time-consuming protocol was proposed to minimize the risk of false-negative results.
A more efficient and less invasive procedure is better for patients as sedation time and sampling the colon are associated with risks. In the future, a prospective, colonoscopy-based study in patients with diarrhea will allow us to confirm the optimal number and location of biopsies needed to establish a diagnosis of microscopic colitis. This work will be important to inform diagnostic guidelines and change practice.
Anne F. Peery, MD, MSCR, is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill. She has no conflicts of interest.
Microscopic colitis is a common cause of watery diarrhea. This debilitating disease is easy to treat, but the diagnosis can be challenging. Without lesions to target, guidelines recommend colonoscopy with at least two biopsies from the right, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon (total: eight-plus biopsies). With little evidence to guide this recommendation, this time-consuming protocol was proposed to minimize the risk of false-negative results.
A more efficient and less invasive procedure is better for patients as sedation time and sampling the colon are associated with risks. In the future, a prospective, colonoscopy-based study in patients with diarrhea will allow us to confirm the optimal number and location of biopsies needed to establish a diagnosis of microscopic colitis. This work will be important to inform diagnostic guidelines and change practice.
Anne F. Peery, MD, MSCR, is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill. She has no conflicts of interest.
Microscopic colitis is a common cause of watery diarrhea. This debilitating disease is easy to treat, but the diagnosis can be challenging. Without lesions to target, guidelines recommend colonoscopy with at least two biopsies from the right, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon (total: eight-plus biopsies). With little evidence to guide this recommendation, this time-consuming protocol was proposed to minimize the risk of false-negative results.
A more efficient and less invasive procedure is better for patients as sedation time and sampling the colon are associated with risks. In the future, a prospective, colonoscopy-based study in patients with diarrhea will allow us to confirm the optimal number and location of biopsies needed to establish a diagnosis of microscopic colitis. This work will be important to inform diagnostic guidelines and change practice.
Anne F. Peery, MD, MSCR, is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill. She has no conflicts of interest.
All patients with microscopic colitis who had biopsies of both the ascending and descending colon had positive slide review for at least one of the two sites, according to the findings of a single-center retrospective study.
“Microscopic colitis can be detected with 100% sensitivity by analyzing biopsy specimens from the ascending and descending colon. We propose a Western protocol (taking two biopsy specimens each from the ascending colon and the descending colon) in the evaluation of patients for microscopic colitis,” wrote Boris Virine, MD, of London (Ont.) Health Sciences Centre, Western University, together with his associates in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
That is half the minimum number of samples recommended by current guidelines, the researchers noted. “The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends two or more biopsy specimens from the right, transverse, left, and sigmoid colons; however, these recommendations were based on expert opinion rather than scientific evidence, and these guidelines have not been validated,” they wrote.
Microscopic colitis includes lymphocytic and collagenous subtypes, neither of which is grossly apparent on colonoscopy. “Endoscopists therefore often collect multiple random colonic biopsies, potentially oversampling, increasing times of colonoscopy and slide review,” Dr. Virine and his associates wrote.
To better pinpoint optimal biopsy sites and specimen numbers, they studied 101 patients consecutively diagnosed with biopsy-confirmed microscopic colitis at London Health Sciences Centre from 2017 through 2018. Patients with other colonic diseases were excluded from the study. Dr. Virine assessed all individual biopsy fragments, and another pathologist performed a second review of complex cases.
A total of 52 patients had biopsy-confirmed collagenous colitis – that is, normal crypt architecture, increased mononuclear inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and a thickened subepithelial collagen band. Forty-two patients had lymphocytic colitis, defined as normal crypt architecture, increased mononuclear inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and increased intraepithelial lymphocytosis. Seven patients had both disease subtypes.
For each patient, an average of nine (standard deviation, 4.9) biopsies had been collected. The most commonly sampled site was the ascending colon (biopsied in 47% of patients in whom at least one sample was labeled by site), followed by the descending colon (40%), rectum (21%), transverse colon (20%), sigmoid colon (15%), cecum (8%), and splenic and hepatic flexures (2% each). Diagnostic sensitivity was highest for the ascending colon (97%), transverse colon (96%), and sigmoid colon (91%) and lowest for the splenic flexure (75%), hepatic flexure (78%), and rectum (82%). The diagnostic sensitivity of the descending colon was 85%. However, all 39 patients with biopsies of both the ascending and descending colon had at least one biopsy that was positive for microscopic colitis (sensitivity, 100%).
“Based on the results of our study, collecting biopsy specimens from both the ascending and descending colons has the same overall sensitivity as following the guidelines,” the researchers concluded. “Because no single site in the colon was diffusely positive for microscopic colitis in 100% of cases, the possibility remains that collecting biopsy specimens from two sites could offer comparable sensitivity with biopsy specimens from each segment of the colon.”
No funding sources were reported. Dr. Virine and the senior author reported having no conflicts of interest. One coauthor disclosed ties to AbbVie, Allergan, Ferring, Janssen, Lupin Pendopharm, Pfizer, Shire, and Takeda.
SOURCE: Virine B et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Feb 25. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.02.036.
All patients with microscopic colitis who had biopsies of both the ascending and descending colon had positive slide review for at least one of the two sites, according to the findings of a single-center retrospective study.
“Microscopic colitis can be detected with 100% sensitivity by analyzing biopsy specimens from the ascending and descending colon. We propose a Western protocol (taking two biopsy specimens each from the ascending colon and the descending colon) in the evaluation of patients for microscopic colitis,” wrote Boris Virine, MD, of London (Ont.) Health Sciences Centre, Western University, together with his associates in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
That is half the minimum number of samples recommended by current guidelines, the researchers noted. “The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends two or more biopsy specimens from the right, transverse, left, and sigmoid colons; however, these recommendations were based on expert opinion rather than scientific evidence, and these guidelines have not been validated,” they wrote.
Microscopic colitis includes lymphocytic and collagenous subtypes, neither of which is grossly apparent on colonoscopy. “Endoscopists therefore often collect multiple random colonic biopsies, potentially oversampling, increasing times of colonoscopy and slide review,” Dr. Virine and his associates wrote.
To better pinpoint optimal biopsy sites and specimen numbers, they studied 101 patients consecutively diagnosed with biopsy-confirmed microscopic colitis at London Health Sciences Centre from 2017 through 2018. Patients with other colonic diseases were excluded from the study. Dr. Virine assessed all individual biopsy fragments, and another pathologist performed a second review of complex cases.
A total of 52 patients had biopsy-confirmed collagenous colitis – that is, normal crypt architecture, increased mononuclear inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and a thickened subepithelial collagen band. Forty-two patients had lymphocytic colitis, defined as normal crypt architecture, increased mononuclear inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and increased intraepithelial lymphocytosis. Seven patients had both disease subtypes.
For each patient, an average of nine (standard deviation, 4.9) biopsies had been collected. The most commonly sampled site was the ascending colon (biopsied in 47% of patients in whom at least one sample was labeled by site), followed by the descending colon (40%), rectum (21%), transverse colon (20%), sigmoid colon (15%), cecum (8%), and splenic and hepatic flexures (2% each). Diagnostic sensitivity was highest for the ascending colon (97%), transverse colon (96%), and sigmoid colon (91%) and lowest for the splenic flexure (75%), hepatic flexure (78%), and rectum (82%). The diagnostic sensitivity of the descending colon was 85%. However, all 39 patients with biopsies of both the ascending and descending colon had at least one biopsy that was positive for microscopic colitis (sensitivity, 100%).
“Based on the results of our study, collecting biopsy specimens from both the ascending and descending colons has the same overall sensitivity as following the guidelines,” the researchers concluded. “Because no single site in the colon was diffusely positive for microscopic colitis in 100% of cases, the possibility remains that collecting biopsy specimens from two sites could offer comparable sensitivity with biopsy specimens from each segment of the colon.”
No funding sources were reported. Dr. Virine and the senior author reported having no conflicts of interest. One coauthor disclosed ties to AbbVie, Allergan, Ferring, Janssen, Lupin Pendopharm, Pfizer, Shire, and Takeda.
SOURCE: Virine B et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Feb 25. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.02.036.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Blood biomarker detects concussion, shows severity, predicts recovery
(TBI), new research indicates.
“Blood NfL may be used to aid in the diagnosis of patients with concussion or mild TBI [and] to identify individuals at increased risk of developing persistent postconcussive symptoms following TBI,” said lead author Pashtun Shahim, MD, PhD, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Md.
“This study is the first to do a detailed assessment of serum NfL chain and advanced brain imaging in multiple cohorts, brain injury severities, and time points after injury. The cohorts included professional athletes and nonathletes, and over time up to 5 years after TBI,” Dr. Shahim added.
The study was published online July 8 in Neurology.
Rapid indicator of neuronal damage
The researchers studied two cohorts of patients with head injuries. In the first, they determined serum and CSF NfL chain levels in professional Swedish ice hockey players (median age, 27 years), including 45 with acute concussion, 31 with repetitive concussions and persistent post-concussive symptoms (PCS), 28 who contributed samples during preseason with no recent concussion, and 14 healthy nonathletes.
CSF and serum NfL concentrations were closely correlated (r = 0.71; P < .0001). Serum NfL distinguished players with persistent PCS due to repetitive concussions from preseason concussion-free players, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.97. Higher CSF and serum NfL levels were associated with a higher number of concussions and severity of PCS after 1 year.
The second cohort involved 230 clinic-based adults (mean age, 43 years), including 162 with TBI and 68 healthy controls. In this cohort, patients with TBI had increased serum NfL concentrations compared with controls for up to 5 years, and these concentrations were able to distinguish between mild, moderate, and severe TBI. Serum NfL also correlated with measures of functional outcome, MRI brain atrophy, and diffusion tensor imaging estimates of traumatic axonal injury.
“Our findings suggest that NfL concentrations in serum offer rapid and accessible means of assessing and predicting neuronal damage in patients with TBI,” the investigators wrote.
What’s needed going forward, said Dr. Shahim, is “validation in larger cohorts for determining what levels of NfL in blood may be associated with a specific type of TBI, and what the levels are in healthy individuals of different ages.”
Not ready for prime time
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher Filley, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, noted that NfL “may prove useful in identifying TBI patients at risk for prolonged symptoms and in enabling more focused treatment for these individuals.”
“These reports are richly laden with acute and longitudinal data that not only support the use of NfL as a convenient diagnostic test for TBI, but plausibly correlate with the neuropathology of TBI that is thought to play a major role in immediate and lasting cognitive disability,” he wrote.
Although the origin of TBI-induced cognitive decline is not entirely explained by traumatic axonal injury, “NfL appears to have much promise as a blood test that relates directly to the ubiquitous white matter damage of TBI, revealing a great deal about not only whether a TBI occurred, but also the extent of injury sustained, and how this injury may affect patient outcome for years thereafter,” Dr. Filley wrote.
However, he cautioned more research is needed before the blood test can be routinely applied to TBI diagnosis in clinical practice. “Among the hurdles still ahead are the standardization of measurement techniques across analytical platforms, and the determination of precise cutoffs between normal and abnormal values in different ages groups and at varying levels of TBI severity,” Dr. Filley noted.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the Center for Neuroscience and Regenerative Medicine at the Uniformed Services University, and the Swedish Research Council. Dr. Shahim and Dr. Filley have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(TBI), new research indicates.
“Blood NfL may be used to aid in the diagnosis of patients with concussion or mild TBI [and] to identify individuals at increased risk of developing persistent postconcussive symptoms following TBI,” said lead author Pashtun Shahim, MD, PhD, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Md.
“This study is the first to do a detailed assessment of serum NfL chain and advanced brain imaging in multiple cohorts, brain injury severities, and time points after injury. The cohorts included professional athletes and nonathletes, and over time up to 5 years after TBI,” Dr. Shahim added.
The study was published online July 8 in Neurology.
Rapid indicator of neuronal damage
The researchers studied two cohorts of patients with head injuries. In the first, they determined serum and CSF NfL chain levels in professional Swedish ice hockey players (median age, 27 years), including 45 with acute concussion, 31 with repetitive concussions and persistent post-concussive symptoms (PCS), 28 who contributed samples during preseason with no recent concussion, and 14 healthy nonathletes.
CSF and serum NfL concentrations were closely correlated (r = 0.71; P < .0001). Serum NfL distinguished players with persistent PCS due to repetitive concussions from preseason concussion-free players, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.97. Higher CSF and serum NfL levels were associated with a higher number of concussions and severity of PCS after 1 year.
The second cohort involved 230 clinic-based adults (mean age, 43 years), including 162 with TBI and 68 healthy controls. In this cohort, patients with TBI had increased serum NfL concentrations compared with controls for up to 5 years, and these concentrations were able to distinguish between mild, moderate, and severe TBI. Serum NfL also correlated with measures of functional outcome, MRI brain atrophy, and diffusion tensor imaging estimates of traumatic axonal injury.
“Our findings suggest that NfL concentrations in serum offer rapid and accessible means of assessing and predicting neuronal damage in patients with TBI,” the investigators wrote.
What’s needed going forward, said Dr. Shahim, is “validation in larger cohorts for determining what levels of NfL in blood may be associated with a specific type of TBI, and what the levels are in healthy individuals of different ages.”
Not ready for prime time
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher Filley, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, noted that NfL “may prove useful in identifying TBI patients at risk for prolonged symptoms and in enabling more focused treatment for these individuals.”
“These reports are richly laden with acute and longitudinal data that not only support the use of NfL as a convenient diagnostic test for TBI, but plausibly correlate with the neuropathology of TBI that is thought to play a major role in immediate and lasting cognitive disability,” he wrote.
Although the origin of TBI-induced cognitive decline is not entirely explained by traumatic axonal injury, “NfL appears to have much promise as a blood test that relates directly to the ubiquitous white matter damage of TBI, revealing a great deal about not only whether a TBI occurred, but also the extent of injury sustained, and how this injury may affect patient outcome for years thereafter,” Dr. Filley wrote.
However, he cautioned more research is needed before the blood test can be routinely applied to TBI diagnosis in clinical practice. “Among the hurdles still ahead are the standardization of measurement techniques across analytical platforms, and the determination of precise cutoffs between normal and abnormal values in different ages groups and at varying levels of TBI severity,” Dr. Filley noted.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the Center for Neuroscience and Regenerative Medicine at the Uniformed Services University, and the Swedish Research Council. Dr. Shahim and Dr. Filley have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(TBI), new research indicates.
“Blood NfL may be used to aid in the diagnosis of patients with concussion or mild TBI [and] to identify individuals at increased risk of developing persistent postconcussive symptoms following TBI,” said lead author Pashtun Shahim, MD, PhD, National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Md.
“This study is the first to do a detailed assessment of serum NfL chain and advanced brain imaging in multiple cohorts, brain injury severities, and time points after injury. The cohorts included professional athletes and nonathletes, and over time up to 5 years after TBI,” Dr. Shahim added.
The study was published online July 8 in Neurology.
Rapid indicator of neuronal damage
The researchers studied two cohorts of patients with head injuries. In the first, they determined serum and CSF NfL chain levels in professional Swedish ice hockey players (median age, 27 years), including 45 with acute concussion, 31 with repetitive concussions and persistent post-concussive symptoms (PCS), 28 who contributed samples during preseason with no recent concussion, and 14 healthy nonathletes.
CSF and serum NfL concentrations were closely correlated (r = 0.71; P < .0001). Serum NfL distinguished players with persistent PCS due to repetitive concussions from preseason concussion-free players, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.97. Higher CSF and serum NfL levels were associated with a higher number of concussions and severity of PCS after 1 year.
The second cohort involved 230 clinic-based adults (mean age, 43 years), including 162 with TBI and 68 healthy controls. In this cohort, patients with TBI had increased serum NfL concentrations compared with controls for up to 5 years, and these concentrations were able to distinguish between mild, moderate, and severe TBI. Serum NfL also correlated with measures of functional outcome, MRI brain atrophy, and diffusion tensor imaging estimates of traumatic axonal injury.
“Our findings suggest that NfL concentrations in serum offer rapid and accessible means of assessing and predicting neuronal damage in patients with TBI,” the investigators wrote.
What’s needed going forward, said Dr. Shahim, is “validation in larger cohorts for determining what levels of NfL in blood may be associated with a specific type of TBI, and what the levels are in healthy individuals of different ages.”
Not ready for prime time
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher Filley, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, noted that NfL “may prove useful in identifying TBI patients at risk for prolonged symptoms and in enabling more focused treatment for these individuals.”
“These reports are richly laden with acute and longitudinal data that not only support the use of NfL as a convenient diagnostic test for TBI, but plausibly correlate with the neuropathology of TBI that is thought to play a major role in immediate and lasting cognitive disability,” he wrote.
Although the origin of TBI-induced cognitive decline is not entirely explained by traumatic axonal injury, “NfL appears to have much promise as a blood test that relates directly to the ubiquitous white matter damage of TBI, revealing a great deal about not only whether a TBI occurred, but also the extent of injury sustained, and how this injury may affect patient outcome for years thereafter,” Dr. Filley wrote.
However, he cautioned more research is needed before the blood test can be routinely applied to TBI diagnosis in clinical practice. “Among the hurdles still ahead are the standardization of measurement techniques across analytical platforms, and the determination of precise cutoffs between normal and abnormal values in different ages groups and at varying levels of TBI severity,” Dr. Filley noted.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the Center for Neuroscience and Regenerative Medicine at the Uniformed Services University, and the Swedish Research Council. Dr. Shahim and Dr. Filley have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Good for profits, good for patients: A new form of medical visits
Ten patients smiled and waved out on the computer monitor, as Jacob Mirsky, MD, greeted each one, asked them to introduce themselves, and inquired as to how each was doing with their stress reduction tactics.
The attendees of the online session had been patients at in-person group visits at the Massachusetts General Hospital Revere HealthCare Center. But those in-person group sessions, known as shared medical appointments (SMAs), were shut down when COVID-19 arrived.
“Our group patients have been missing the sessions,” said Dr. Mirsky, a general internist who codirects the center’s group visit program. The online sessions, called virtual SMAs (V-SMAs), work well with COVID-19 social distancing.
In the group sessions, Dr. Mirsky reads a standardized message that addresses privacy concerns during the session. For the next 60-90 minutes, “we ask them to talk about what has gone well for them and what they are struggling with,” he said. “Then I answer their questions using materials in a PowerPoint to address key points, such as reducing salt for high blood pressure or interpreting blood sugar levels for diabetes.
“I try to end group sessions with one area of focus,” Dr. Mirsky said. “In the stress reduction group, this could be meditation. In the diabetes group, it could be a discussion on weight loss.” Then the program’s health coach goes over some key concepts on behavior change and invites participants to contact her after the session.
“The nice thing is that these virtual sessions are fully reimbursable by all of our insurers in Massachusetts,” Dr. Mirsky said. Through evaluation and management (E/M) codes, each patient in a group visit is paid the same as a patient in an individual visit with the same level of complexity.
Dr. Mirsky writes a note in the chart about each patient who was in the group session. “This includes information about the specific patient, such as the history and physical, and information about the group meeting,” he said. In the next few months, the center plans to put its other group sessions online – on blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and insomnia.
Attracting doctors who hadn’t done groups before
said Marianne Sumego, MD, director of the Cleveland Clinic’s SMA program, which began 21 years ago.
In this era of COVID-19, group visits have either switched to V-SMAs or halted. However, the COVID-19 crisis has given group visits a second wind. Some doctors who never used SMAs before are now trying out this new mode of patient engagement,
Many of the 100 doctors using SMAs at the Cleveland Clinic have switched over to V-SMAs for now, and the new mode is also attracting colleagues who are new to SMAs, she said.
“When doctors started using telemedicine, virtual group visits started making sense to them,” Dr. Sumego said. “This is a time of a great deal of experimentation in practice design.”
Indeed, V-SMAs have eliminated some problems that had discouraged doctors from trying SMAs, said Amy Wheeler, MD, a general internist who founded the Revere SMA program and codirects it with Dr. Mirsky.
V-SMAs eliminate the need for a large space to hold sessions and reduce the number of staff needed to run sessions, Dr. Wheeler said. “Virtual group visits can actually be easier to use than in-person group visits.”
Dr. Sumego believes small practices in particular will take up V-SMAs because they are easier to run than regular SMAs. “Necessity drives change,” she said. “Across the country everyone is looking at the virtual group model.”
Group visits can help your bottom line
Medicare and many private payers cover group visits. In most cases, they tend to pay the same rate as for an individual office visit. As with telehealth, Medicare and many other payers are temporarily reimbursing for virtual visits at the same rate as for real visits.
Not all payers have a stated policy about covering SMAs, and physicians have to ask. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, for example, has not published any coding rules on SMAs. But in response to a query by the American Academy of Family Physicians, CMS said it would allow use of CPT codes for E/M services for individual patients.
Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina is one of the few payers with a clearly stated policy on its website. Like Medicare, the insurer accepts E/M codes, and it requires that patients’ attendance must be voluntary; they must be established patients; and the visit must be specific to a disease or condition, although several conditions are allowed.
Dr. Mirsky said his group uses the same E/M level – 99213 – for all of his SMA patients. “Since a regular primary care visit is usually billed at a level 3 or 4, depending on how many topics are covered, we chose level 3 for groups, because the group session deals with just one topic.”
One challenge for billing for SMAs is that most health insurers require patients to provide a copay for each visit, which can discourage patients in groups that meet frequently, says Wayne Dysinger, MD, founder of Lifestyle Medical Solutions, a two-physician primary care practice in Riverside, Calif.
But Dr. Dysinger, who has been using SMAs for 5 years, usually doesn’t have to worry about copays because much of his work is capitated and doesn’t require a copay.
Also, some of Dr. Dysinger’s SMA patients are in direct primary care, in which the patients pay an $18 monthly membership fee. Other practices may charge a flat out-of-pocket fee.
How group visits operate
SMAs are based on the observation that patients with the same condition generally ask their doctor the same questions, and rather than repeat the answers each time, why not provide them to a group?
Dr. Wheeler said trying to be more efficient with her time was the primary reason she became interested in SMAs a dozen years ago. “I was trying to squeeze the advice patients needed into a normal patient visit, and it wasn’t working. When I tried to tell them everything they needed to know, I’d run behind for the rest of my day’s visits.”
She found she was continually repeating the same conversation with patients, but these talks weren’t detailed enough to be effective. “When my weight loss patients came back for the next appointment, they had not made the recommended changes in lifestyle. I started to realize how complicated weight loss was.” So Dr. Wheeler founded the SMA program at the Revere Center.
Doctors enjoy the patient interaction
Some doctors who use SMAs talk about how connected they feel with their patients. “For me, the group sessions are the most gratifying part of the week,” Dr. Dysinger says. “I like to see the patients interacting with me and with each other, and watch their health behavior change over time.”
“These groups have a great deal of energy,” he said. “They have a kind of vulnerability that is very raw, very human. People make commitments to meet goals. Will they meet them or not?”
Dr. Dysinger’s enthusiasm has been echoed by other doctors. In a study of older patients, physicians who used SMAs were more satisfied with care than physicians who relied on standard one-to-one interactions. In another study, the researchers surmised that, in SMAs, doctors learn from their patients how they can better meet their needs.
Dr. Dysinger thinks SMAs are widely applicable in primary care. He estimates that 80%-85% of appointments at a primary care practice involve chronic diseases, and this type of patient is a good fit for group visits. SMAs typically treat patients with diabetes, asthma, arthritis, and obesity.
Dr. Sumego said SMAs are used for specialty care at Cleveland Clinic, such as to help patients before and after bariatric surgery. SMAs have also been used to treat patients with ulcerative colitis, multiple sclerosis, cancer, HIV, menopause, insomnia, and stress, according to one report.
Dr. Dysinger, who runs a small practice, organizes his group sessions somewhat differently. He doesn’t organize his groups around conditions like diabetes, but instead his groups focus on four “pillars” of lifestyle medicine: nourishment, movement, resilience (involving sleep and stress), and connectedness.
Why patients like group visits
Feeling part of a whole is a major draw for many patients. “Patients seem to like committing to something bigger than just themselves,” Dr. Wheeler said. “They enjoy the sense of community that groups have, the joy of supporting one another.”
“It’s feeling that you’re not alone,” Dr. Mirsky said. “When a patient struggling with diabetes hears how hard it is for another patient, it validates their experience and gives them someone to connect with. There is a positive peer pressure.”
Many programs, including Dr. Wheeler’s and Dr. Mirsky’s in Boston, allow patients to drop in and out of sessions, rather than attending one course all the way through. But even under this format, Dr. Wheeler said that patients often tend to stick together. “At the end of a session, one patient asks another: ‘Which session do you want to go to next?’ ” she said.
Patients also learn from each other in SMAs. Patients exchange experiences and share advice they may not have had the chance to get during an individual visit.
The group dynamic can make it easier for some patients to reveal sensitive information, said Dr. Dysinger. “In these groups, people feel free to talk about their bowel movements, or about having to deal with the influence of a parent on their lives,” Dr. Dysinger said. “The sessions can have the feel of an [Alcoholics Anonymous] meeting, but they’re firmly grounded in medicine.”
Potential downsides of virtual group visits
SMAs and VSMAs may not work for every practice. Some small practices may not have enough patients to organize a group visit around a particular condition – even a common one like diabetes. In a presentation before the Society of General Internal Medicine, a physician from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, warned that it may be difficult for a practice to fill diabetes group visits every year.
Additionally, some patients don’t want to talk about personal matters in a group. “They may not want to reveal certain things about themselves,” Dr. Mirsky said. “So I tell the group that if there is anything that anyone wants to talk about in private, I’m available.”
Another drawback of SMAs is that more experienced patients may have to slog through information they already know, which is a particular problem when patients can drop in and out of sessions. Dr. Mirsky noted that “what often ends up happening is that the experienced participant helps the newcomer.”
Finally, confidentially is a big concern in a group session. “In a one-on-one visit, you can go into details about the patient’s health, and even bring up an entry in the chart,” Dr. Wheeler said. “But in a group visit, you can’t raise any personal details about a patient unless the patient brings it up first.”
SMA patients sign confidentiality agreements in which they agree not to talk about other patients outside the session. Ensuring confidentiality becomes more complicated in virtual group visits, because someone located in the room near a participant could overhear the conversation. For this reason, patients in V-SMAs are advised to use headphones or, at a minimum, close the door to the room they are in.
To address privacy concerns, Zoom encrypts its data, but some privacy breeches have been reported, and a U.S. senator has been looking into Zoom’s privacy vulnerabilities.
Transferring groups to virtual groups
It took the COVID-19 crisis for most doctors to take up virtual SMAs. Dr. Sumego said that the Cleveland Clinic started virtual SMAs more than a year ago, but most other groups operating SMAs were apparently not providing them virtually before COVID-19 started.
Dr. Dysinger said he tried virtual SMAs in 2017 but dropped them because the technology – using Zoom – was challenging at the time, and his staff and most patients were resistant. “Only three to five people were attending the virtual sessions, and the meetings took place in the evening, which was hard on the staff.”
“When COVID-19 first appeared, our initial response was to try to keep the in-person group and add social distancing to it, but that wasn’t workable, so very quickly we shifted to Zoom meetings,” Dr. Dysinger said. “We had experience with Zoom already, and the Zoom technology had improved and was easier to use. COVID-19 forced it all forward.”
Are V-SMAs effective? While there have been many studies showing the effectiveness of in-person SMAs, there have been very few on V-SMAs. One 2018 study of obesity patients found that those attending in-person SMAs lost somewhat more weight than those in V-SMAs.
As with telemedicine, some patients have trouble with the technology of V-SMAs. Dr. Dysinger said 5%-10% of his SMA patients don’t make the switch over to V-SMAs – mainly because of problems in adapting to the technology – but the rest are happy. “We’re averaging 10 people per meeting, and as many as 20.”
Getting comfortable with group visits
Dealing with group visits takes a very different mindset than what doctors normally have, Dr. Wheeler said. “It took me 6-8 months to feel comfortable enough with group sessions to do them myself,” she recalled. “This was a very different way to practice, compared to the one-on-one care I was trained to give patients. Others may find the transition easier, though.
“Doctors are used to being in control of the patient visit, but the exchange in a group visit is more fluid,” Dr. Wheeler said. “Patients offer their own opinions, and this sends the discussion off on a tangent that is often quite useful. As doctors, we have to learn when to let these tangents continue, and know when the discussion might have to be brought back to the theme at hand. Often it’s better not to intercede.”
Do doctors need training to conduct SMAs? Patients in group visits reported worse communication with physicians than those in individual visits, according to a 2014 study. The authors surmised that the doctors needed to learn how to talk to groups and suggested that they get some training.
The potential staying power of V-SMAs post COVID?
Once the COVID-19 crisis is over, Medicare is scheduled to no longer provide the same level of reimbursement for virtual sessions as for real sessions. Dr. Mirsky anticipates a great deal of resistance to this change from thousands of physicians and patients who have become comfortable with telehealth, including virtual SMAs.
Dr. Dysinger thinks V-SMAs will continue. “When COVID-19 clears and we can go back to in-person groups, we expect to keep some virtual groups. People have already come to accept and value virtual groups.”
Dr. Wheeler sees virtual groups playing an essential role post COVID-19, when practices have to get back up to speed. “Virtual group visits could make it easier to deal with a large backlog of patients who couldn’t be seen up until now,” she said. “And virtual groups will be the only way to see patients who are still reluctant to meet in a group.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Ten patients smiled and waved out on the computer monitor, as Jacob Mirsky, MD, greeted each one, asked them to introduce themselves, and inquired as to how each was doing with their stress reduction tactics.
The attendees of the online session had been patients at in-person group visits at the Massachusetts General Hospital Revere HealthCare Center. But those in-person group sessions, known as shared medical appointments (SMAs), were shut down when COVID-19 arrived.
“Our group patients have been missing the sessions,” said Dr. Mirsky, a general internist who codirects the center’s group visit program. The online sessions, called virtual SMAs (V-SMAs), work well with COVID-19 social distancing.
In the group sessions, Dr. Mirsky reads a standardized message that addresses privacy concerns during the session. For the next 60-90 minutes, “we ask them to talk about what has gone well for them and what they are struggling with,” he said. “Then I answer their questions using materials in a PowerPoint to address key points, such as reducing salt for high blood pressure or interpreting blood sugar levels for diabetes.
“I try to end group sessions with one area of focus,” Dr. Mirsky said. “In the stress reduction group, this could be meditation. In the diabetes group, it could be a discussion on weight loss.” Then the program’s health coach goes over some key concepts on behavior change and invites participants to contact her after the session.
“The nice thing is that these virtual sessions are fully reimbursable by all of our insurers in Massachusetts,” Dr. Mirsky said. Through evaluation and management (E/M) codes, each patient in a group visit is paid the same as a patient in an individual visit with the same level of complexity.
Dr. Mirsky writes a note in the chart about each patient who was in the group session. “This includes information about the specific patient, such as the history and physical, and information about the group meeting,” he said. In the next few months, the center plans to put its other group sessions online – on blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and insomnia.
Attracting doctors who hadn’t done groups before
said Marianne Sumego, MD, director of the Cleveland Clinic’s SMA program, which began 21 years ago.
In this era of COVID-19, group visits have either switched to V-SMAs or halted. However, the COVID-19 crisis has given group visits a second wind. Some doctors who never used SMAs before are now trying out this new mode of patient engagement,
Many of the 100 doctors using SMAs at the Cleveland Clinic have switched over to V-SMAs for now, and the new mode is also attracting colleagues who are new to SMAs, she said.
“When doctors started using telemedicine, virtual group visits started making sense to them,” Dr. Sumego said. “This is a time of a great deal of experimentation in practice design.”
Indeed, V-SMAs have eliminated some problems that had discouraged doctors from trying SMAs, said Amy Wheeler, MD, a general internist who founded the Revere SMA program and codirects it with Dr. Mirsky.
V-SMAs eliminate the need for a large space to hold sessions and reduce the number of staff needed to run sessions, Dr. Wheeler said. “Virtual group visits can actually be easier to use than in-person group visits.”
Dr. Sumego believes small practices in particular will take up V-SMAs because they are easier to run than regular SMAs. “Necessity drives change,” she said. “Across the country everyone is looking at the virtual group model.”
Group visits can help your bottom line
Medicare and many private payers cover group visits. In most cases, they tend to pay the same rate as for an individual office visit. As with telehealth, Medicare and many other payers are temporarily reimbursing for virtual visits at the same rate as for real visits.
Not all payers have a stated policy about covering SMAs, and physicians have to ask. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, for example, has not published any coding rules on SMAs. But in response to a query by the American Academy of Family Physicians, CMS said it would allow use of CPT codes for E/M services for individual patients.
Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina is one of the few payers with a clearly stated policy on its website. Like Medicare, the insurer accepts E/M codes, and it requires that patients’ attendance must be voluntary; they must be established patients; and the visit must be specific to a disease or condition, although several conditions are allowed.
Dr. Mirsky said his group uses the same E/M level – 99213 – for all of his SMA patients. “Since a regular primary care visit is usually billed at a level 3 or 4, depending on how many topics are covered, we chose level 3 for groups, because the group session deals with just one topic.”
One challenge for billing for SMAs is that most health insurers require patients to provide a copay for each visit, which can discourage patients in groups that meet frequently, says Wayne Dysinger, MD, founder of Lifestyle Medical Solutions, a two-physician primary care practice in Riverside, Calif.
But Dr. Dysinger, who has been using SMAs for 5 years, usually doesn’t have to worry about copays because much of his work is capitated and doesn’t require a copay.
Also, some of Dr. Dysinger’s SMA patients are in direct primary care, in which the patients pay an $18 monthly membership fee. Other practices may charge a flat out-of-pocket fee.
How group visits operate
SMAs are based on the observation that patients with the same condition generally ask their doctor the same questions, and rather than repeat the answers each time, why not provide them to a group?
Dr. Wheeler said trying to be more efficient with her time was the primary reason she became interested in SMAs a dozen years ago. “I was trying to squeeze the advice patients needed into a normal patient visit, and it wasn’t working. When I tried to tell them everything they needed to know, I’d run behind for the rest of my day’s visits.”
She found she was continually repeating the same conversation with patients, but these talks weren’t detailed enough to be effective. “When my weight loss patients came back for the next appointment, they had not made the recommended changes in lifestyle. I started to realize how complicated weight loss was.” So Dr. Wheeler founded the SMA program at the Revere Center.
Doctors enjoy the patient interaction
Some doctors who use SMAs talk about how connected they feel with their patients. “For me, the group sessions are the most gratifying part of the week,” Dr. Dysinger says. “I like to see the patients interacting with me and with each other, and watch their health behavior change over time.”
“These groups have a great deal of energy,” he said. “They have a kind of vulnerability that is very raw, very human. People make commitments to meet goals. Will they meet them or not?”
Dr. Dysinger’s enthusiasm has been echoed by other doctors. In a study of older patients, physicians who used SMAs were more satisfied with care than physicians who relied on standard one-to-one interactions. In another study, the researchers surmised that, in SMAs, doctors learn from their patients how they can better meet their needs.
Dr. Dysinger thinks SMAs are widely applicable in primary care. He estimates that 80%-85% of appointments at a primary care practice involve chronic diseases, and this type of patient is a good fit for group visits. SMAs typically treat patients with diabetes, asthma, arthritis, and obesity.
Dr. Sumego said SMAs are used for specialty care at Cleveland Clinic, such as to help patients before and after bariatric surgery. SMAs have also been used to treat patients with ulcerative colitis, multiple sclerosis, cancer, HIV, menopause, insomnia, and stress, according to one report.
Dr. Dysinger, who runs a small practice, organizes his group sessions somewhat differently. He doesn’t organize his groups around conditions like diabetes, but instead his groups focus on four “pillars” of lifestyle medicine: nourishment, movement, resilience (involving sleep and stress), and connectedness.
Why patients like group visits
Feeling part of a whole is a major draw for many patients. “Patients seem to like committing to something bigger than just themselves,” Dr. Wheeler said. “They enjoy the sense of community that groups have, the joy of supporting one another.”
“It’s feeling that you’re not alone,” Dr. Mirsky said. “When a patient struggling with diabetes hears how hard it is for another patient, it validates their experience and gives them someone to connect with. There is a positive peer pressure.”
Many programs, including Dr. Wheeler’s and Dr. Mirsky’s in Boston, allow patients to drop in and out of sessions, rather than attending one course all the way through. But even under this format, Dr. Wheeler said that patients often tend to stick together. “At the end of a session, one patient asks another: ‘Which session do you want to go to next?’ ” she said.
Patients also learn from each other in SMAs. Patients exchange experiences and share advice they may not have had the chance to get during an individual visit.
The group dynamic can make it easier for some patients to reveal sensitive information, said Dr. Dysinger. “In these groups, people feel free to talk about their bowel movements, or about having to deal with the influence of a parent on their lives,” Dr. Dysinger said. “The sessions can have the feel of an [Alcoholics Anonymous] meeting, but they’re firmly grounded in medicine.”
Potential downsides of virtual group visits
SMAs and VSMAs may not work for every practice. Some small practices may not have enough patients to organize a group visit around a particular condition – even a common one like diabetes. In a presentation before the Society of General Internal Medicine, a physician from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, warned that it may be difficult for a practice to fill diabetes group visits every year.
Additionally, some patients don’t want to talk about personal matters in a group. “They may not want to reveal certain things about themselves,” Dr. Mirsky said. “So I tell the group that if there is anything that anyone wants to talk about in private, I’m available.”
Another drawback of SMAs is that more experienced patients may have to slog through information they already know, which is a particular problem when patients can drop in and out of sessions. Dr. Mirsky noted that “what often ends up happening is that the experienced participant helps the newcomer.”
Finally, confidentially is a big concern in a group session. “In a one-on-one visit, you can go into details about the patient’s health, and even bring up an entry in the chart,” Dr. Wheeler said. “But in a group visit, you can’t raise any personal details about a patient unless the patient brings it up first.”
SMA patients sign confidentiality agreements in which they agree not to talk about other patients outside the session. Ensuring confidentiality becomes more complicated in virtual group visits, because someone located in the room near a participant could overhear the conversation. For this reason, patients in V-SMAs are advised to use headphones or, at a minimum, close the door to the room they are in.
To address privacy concerns, Zoom encrypts its data, but some privacy breeches have been reported, and a U.S. senator has been looking into Zoom’s privacy vulnerabilities.
Transferring groups to virtual groups
It took the COVID-19 crisis for most doctors to take up virtual SMAs. Dr. Sumego said that the Cleveland Clinic started virtual SMAs more than a year ago, but most other groups operating SMAs were apparently not providing them virtually before COVID-19 started.
Dr. Dysinger said he tried virtual SMAs in 2017 but dropped them because the technology – using Zoom – was challenging at the time, and his staff and most patients were resistant. “Only three to five people were attending the virtual sessions, and the meetings took place in the evening, which was hard on the staff.”
“When COVID-19 first appeared, our initial response was to try to keep the in-person group and add social distancing to it, but that wasn’t workable, so very quickly we shifted to Zoom meetings,” Dr. Dysinger said. “We had experience with Zoom already, and the Zoom technology had improved and was easier to use. COVID-19 forced it all forward.”
Are V-SMAs effective? While there have been many studies showing the effectiveness of in-person SMAs, there have been very few on V-SMAs. One 2018 study of obesity patients found that those attending in-person SMAs lost somewhat more weight than those in V-SMAs.
As with telemedicine, some patients have trouble with the technology of V-SMAs. Dr. Dysinger said 5%-10% of his SMA patients don’t make the switch over to V-SMAs – mainly because of problems in adapting to the technology – but the rest are happy. “We’re averaging 10 people per meeting, and as many as 20.”
Getting comfortable with group visits
Dealing with group visits takes a very different mindset than what doctors normally have, Dr. Wheeler said. “It took me 6-8 months to feel comfortable enough with group sessions to do them myself,” she recalled. “This was a very different way to practice, compared to the one-on-one care I was trained to give patients. Others may find the transition easier, though.
“Doctors are used to being in control of the patient visit, but the exchange in a group visit is more fluid,” Dr. Wheeler said. “Patients offer their own opinions, and this sends the discussion off on a tangent that is often quite useful. As doctors, we have to learn when to let these tangents continue, and know when the discussion might have to be brought back to the theme at hand. Often it’s better not to intercede.”
Do doctors need training to conduct SMAs? Patients in group visits reported worse communication with physicians than those in individual visits, according to a 2014 study. The authors surmised that the doctors needed to learn how to talk to groups and suggested that they get some training.
The potential staying power of V-SMAs post COVID?
Once the COVID-19 crisis is over, Medicare is scheduled to no longer provide the same level of reimbursement for virtual sessions as for real sessions. Dr. Mirsky anticipates a great deal of resistance to this change from thousands of physicians and patients who have become comfortable with telehealth, including virtual SMAs.
Dr. Dysinger thinks V-SMAs will continue. “When COVID-19 clears and we can go back to in-person groups, we expect to keep some virtual groups. People have already come to accept and value virtual groups.”
Dr. Wheeler sees virtual groups playing an essential role post COVID-19, when practices have to get back up to speed. “Virtual group visits could make it easier to deal with a large backlog of patients who couldn’t be seen up until now,” she said. “And virtual groups will be the only way to see patients who are still reluctant to meet in a group.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Ten patients smiled and waved out on the computer monitor, as Jacob Mirsky, MD, greeted each one, asked them to introduce themselves, and inquired as to how each was doing with their stress reduction tactics.
The attendees of the online session had been patients at in-person group visits at the Massachusetts General Hospital Revere HealthCare Center. But those in-person group sessions, known as shared medical appointments (SMAs), were shut down when COVID-19 arrived.
“Our group patients have been missing the sessions,” said Dr. Mirsky, a general internist who codirects the center’s group visit program. The online sessions, called virtual SMAs (V-SMAs), work well with COVID-19 social distancing.
In the group sessions, Dr. Mirsky reads a standardized message that addresses privacy concerns during the session. For the next 60-90 minutes, “we ask them to talk about what has gone well for them and what they are struggling with,” he said. “Then I answer their questions using materials in a PowerPoint to address key points, such as reducing salt for high blood pressure or interpreting blood sugar levels for diabetes.
“I try to end group sessions with one area of focus,” Dr. Mirsky said. “In the stress reduction group, this could be meditation. In the diabetes group, it could be a discussion on weight loss.” Then the program’s health coach goes over some key concepts on behavior change and invites participants to contact her after the session.
“The nice thing is that these virtual sessions are fully reimbursable by all of our insurers in Massachusetts,” Dr. Mirsky said. Through evaluation and management (E/M) codes, each patient in a group visit is paid the same as a patient in an individual visit with the same level of complexity.
Dr. Mirsky writes a note in the chart about each patient who was in the group session. “This includes information about the specific patient, such as the history and physical, and information about the group meeting,” he said. In the next few months, the center plans to put its other group sessions online – on blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and insomnia.
Attracting doctors who hadn’t done groups before
said Marianne Sumego, MD, director of the Cleveland Clinic’s SMA program, which began 21 years ago.
In this era of COVID-19, group visits have either switched to V-SMAs or halted. However, the COVID-19 crisis has given group visits a second wind. Some doctors who never used SMAs before are now trying out this new mode of patient engagement,
Many of the 100 doctors using SMAs at the Cleveland Clinic have switched over to V-SMAs for now, and the new mode is also attracting colleagues who are new to SMAs, she said.
“When doctors started using telemedicine, virtual group visits started making sense to them,” Dr. Sumego said. “This is a time of a great deal of experimentation in practice design.”
Indeed, V-SMAs have eliminated some problems that had discouraged doctors from trying SMAs, said Amy Wheeler, MD, a general internist who founded the Revere SMA program and codirects it with Dr. Mirsky.
V-SMAs eliminate the need for a large space to hold sessions and reduce the number of staff needed to run sessions, Dr. Wheeler said. “Virtual group visits can actually be easier to use than in-person group visits.”
Dr. Sumego believes small practices in particular will take up V-SMAs because they are easier to run than regular SMAs. “Necessity drives change,” she said. “Across the country everyone is looking at the virtual group model.”
Group visits can help your bottom line
Medicare and many private payers cover group visits. In most cases, they tend to pay the same rate as for an individual office visit. As with telehealth, Medicare and many other payers are temporarily reimbursing for virtual visits at the same rate as for real visits.
Not all payers have a stated policy about covering SMAs, and physicians have to ask. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, for example, has not published any coding rules on SMAs. But in response to a query by the American Academy of Family Physicians, CMS said it would allow use of CPT codes for E/M services for individual patients.
Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina is one of the few payers with a clearly stated policy on its website. Like Medicare, the insurer accepts E/M codes, and it requires that patients’ attendance must be voluntary; they must be established patients; and the visit must be specific to a disease or condition, although several conditions are allowed.
Dr. Mirsky said his group uses the same E/M level – 99213 – for all of his SMA patients. “Since a regular primary care visit is usually billed at a level 3 or 4, depending on how many topics are covered, we chose level 3 for groups, because the group session deals with just one topic.”
One challenge for billing for SMAs is that most health insurers require patients to provide a copay for each visit, which can discourage patients in groups that meet frequently, says Wayne Dysinger, MD, founder of Lifestyle Medical Solutions, a two-physician primary care practice in Riverside, Calif.
But Dr. Dysinger, who has been using SMAs for 5 years, usually doesn’t have to worry about copays because much of his work is capitated and doesn’t require a copay.
Also, some of Dr. Dysinger’s SMA patients are in direct primary care, in which the patients pay an $18 monthly membership fee. Other practices may charge a flat out-of-pocket fee.
How group visits operate
SMAs are based on the observation that patients with the same condition generally ask their doctor the same questions, and rather than repeat the answers each time, why not provide them to a group?
Dr. Wheeler said trying to be more efficient with her time was the primary reason she became interested in SMAs a dozen years ago. “I was trying to squeeze the advice patients needed into a normal patient visit, and it wasn’t working. When I tried to tell them everything they needed to know, I’d run behind for the rest of my day’s visits.”
She found she was continually repeating the same conversation with patients, but these talks weren’t detailed enough to be effective. “When my weight loss patients came back for the next appointment, they had not made the recommended changes in lifestyle. I started to realize how complicated weight loss was.” So Dr. Wheeler founded the SMA program at the Revere Center.
Doctors enjoy the patient interaction
Some doctors who use SMAs talk about how connected they feel with their patients. “For me, the group sessions are the most gratifying part of the week,” Dr. Dysinger says. “I like to see the patients interacting with me and with each other, and watch their health behavior change over time.”
“These groups have a great deal of energy,” he said. “They have a kind of vulnerability that is very raw, very human. People make commitments to meet goals. Will they meet them or not?”
Dr. Dysinger’s enthusiasm has been echoed by other doctors. In a study of older patients, physicians who used SMAs were more satisfied with care than physicians who relied on standard one-to-one interactions. In another study, the researchers surmised that, in SMAs, doctors learn from their patients how they can better meet their needs.
Dr. Dysinger thinks SMAs are widely applicable in primary care. He estimates that 80%-85% of appointments at a primary care practice involve chronic diseases, and this type of patient is a good fit for group visits. SMAs typically treat patients with diabetes, asthma, arthritis, and obesity.
Dr. Sumego said SMAs are used for specialty care at Cleveland Clinic, such as to help patients before and after bariatric surgery. SMAs have also been used to treat patients with ulcerative colitis, multiple sclerosis, cancer, HIV, menopause, insomnia, and stress, according to one report.
Dr. Dysinger, who runs a small practice, organizes his group sessions somewhat differently. He doesn’t organize his groups around conditions like diabetes, but instead his groups focus on four “pillars” of lifestyle medicine: nourishment, movement, resilience (involving sleep and stress), and connectedness.
Why patients like group visits
Feeling part of a whole is a major draw for many patients. “Patients seem to like committing to something bigger than just themselves,” Dr. Wheeler said. “They enjoy the sense of community that groups have, the joy of supporting one another.”
“It’s feeling that you’re not alone,” Dr. Mirsky said. “When a patient struggling with diabetes hears how hard it is for another patient, it validates their experience and gives them someone to connect with. There is a positive peer pressure.”
Many programs, including Dr. Wheeler’s and Dr. Mirsky’s in Boston, allow patients to drop in and out of sessions, rather than attending one course all the way through. But even under this format, Dr. Wheeler said that patients often tend to stick together. “At the end of a session, one patient asks another: ‘Which session do you want to go to next?’ ” she said.
Patients also learn from each other in SMAs. Patients exchange experiences and share advice they may not have had the chance to get during an individual visit.
The group dynamic can make it easier for some patients to reveal sensitive information, said Dr. Dysinger. “In these groups, people feel free to talk about their bowel movements, or about having to deal with the influence of a parent on their lives,” Dr. Dysinger said. “The sessions can have the feel of an [Alcoholics Anonymous] meeting, but they’re firmly grounded in medicine.”
Potential downsides of virtual group visits
SMAs and VSMAs may not work for every practice. Some small practices may not have enough patients to organize a group visit around a particular condition – even a common one like diabetes. In a presentation before the Society of General Internal Medicine, a physician from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, warned that it may be difficult for a practice to fill diabetes group visits every year.
Additionally, some patients don’t want to talk about personal matters in a group. “They may not want to reveal certain things about themselves,” Dr. Mirsky said. “So I tell the group that if there is anything that anyone wants to talk about in private, I’m available.”
Another drawback of SMAs is that more experienced patients may have to slog through information they already know, which is a particular problem when patients can drop in and out of sessions. Dr. Mirsky noted that “what often ends up happening is that the experienced participant helps the newcomer.”
Finally, confidentially is a big concern in a group session. “In a one-on-one visit, you can go into details about the patient’s health, and even bring up an entry in the chart,” Dr. Wheeler said. “But in a group visit, you can’t raise any personal details about a patient unless the patient brings it up first.”
SMA patients sign confidentiality agreements in which they agree not to talk about other patients outside the session. Ensuring confidentiality becomes more complicated in virtual group visits, because someone located in the room near a participant could overhear the conversation. For this reason, patients in V-SMAs are advised to use headphones or, at a minimum, close the door to the room they are in.
To address privacy concerns, Zoom encrypts its data, but some privacy breeches have been reported, and a U.S. senator has been looking into Zoom’s privacy vulnerabilities.
Transferring groups to virtual groups
It took the COVID-19 crisis for most doctors to take up virtual SMAs. Dr. Sumego said that the Cleveland Clinic started virtual SMAs more than a year ago, but most other groups operating SMAs were apparently not providing them virtually before COVID-19 started.
Dr. Dysinger said he tried virtual SMAs in 2017 but dropped them because the technology – using Zoom – was challenging at the time, and his staff and most patients were resistant. “Only three to five people were attending the virtual sessions, and the meetings took place in the evening, which was hard on the staff.”
“When COVID-19 first appeared, our initial response was to try to keep the in-person group and add social distancing to it, but that wasn’t workable, so very quickly we shifted to Zoom meetings,” Dr. Dysinger said. “We had experience with Zoom already, and the Zoom technology had improved and was easier to use. COVID-19 forced it all forward.”
Are V-SMAs effective? While there have been many studies showing the effectiveness of in-person SMAs, there have been very few on V-SMAs. One 2018 study of obesity patients found that those attending in-person SMAs lost somewhat more weight than those in V-SMAs.
As with telemedicine, some patients have trouble with the technology of V-SMAs. Dr. Dysinger said 5%-10% of his SMA patients don’t make the switch over to V-SMAs – mainly because of problems in adapting to the technology – but the rest are happy. “We’re averaging 10 people per meeting, and as many as 20.”
Getting comfortable with group visits
Dealing with group visits takes a very different mindset than what doctors normally have, Dr. Wheeler said. “It took me 6-8 months to feel comfortable enough with group sessions to do them myself,” she recalled. “This was a very different way to practice, compared to the one-on-one care I was trained to give patients. Others may find the transition easier, though.
“Doctors are used to being in control of the patient visit, but the exchange in a group visit is more fluid,” Dr. Wheeler said. “Patients offer their own opinions, and this sends the discussion off on a tangent that is often quite useful. As doctors, we have to learn when to let these tangents continue, and know when the discussion might have to be brought back to the theme at hand. Often it’s better not to intercede.”
Do doctors need training to conduct SMAs? Patients in group visits reported worse communication with physicians than those in individual visits, according to a 2014 study. The authors surmised that the doctors needed to learn how to talk to groups and suggested that they get some training.
The potential staying power of V-SMAs post COVID?
Once the COVID-19 crisis is over, Medicare is scheduled to no longer provide the same level of reimbursement for virtual sessions as for real sessions. Dr. Mirsky anticipates a great deal of resistance to this change from thousands of physicians and patients who have become comfortable with telehealth, including virtual SMAs.
Dr. Dysinger thinks V-SMAs will continue. “When COVID-19 clears and we can go back to in-person groups, we expect to keep some virtual groups. People have already come to accept and value virtual groups.”
Dr. Wheeler sees virtual groups playing an essential role post COVID-19, when practices have to get back up to speed. “Virtual group visits could make it easier to deal with a large backlog of patients who couldn’t be seen up until now,” she said. “And virtual groups will be the only way to see patients who are still reluctant to meet in a group.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Older adults often underestimate ability to prevent falls
but did identify important ways for clinicians to help, including screening all older patients for fall risk and deprescribing certain medications when possible.
The study was conducted by Shalender Bhasin, MD, MBBS, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston and colleagues on behalf of the Strategies to Reduce Injuries and Develop Confidence in Elders (STRIDE) trial investigators and was published online July 8 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients are often unaware of their increased risk until they have fallen for the first time, and they often underestimate how many of their risk factors can be improved, Dr. Bhasin said in an interview.
“Fall injuries are a very important cause of injury-related deaths among older adults, and these are preventable. Yet they are so difficult; for 30 years the rates of fall injuries have not declined,” he said.
Using a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial, the researchers studied the clinical effectiveness of a “patient-centered intervention that combined elements of practice redesign (reconfiguration of workflow to improve quality of care) and an evidence-based, multifactorial, individually tailored intervention implemented by specially trained nurses in primary care settings,” the authors explained.
Participants in the intervention group worked with trained nurses (fall care managers) to identify their risk factors and determine which risks they wanted to modify. Participants in the control group received their typical care and a pamphlet with information on falls and were encouraged to talk with their primary care physicians (who received the results on risk factor screening) about fall prevention. Those in the intervention group also received the pamphlet.
Fall care managers evaluated patients’ home environments and in some cases visited the patient’s home, Dr. Bhasin said.
The researchers enrolled community-dwelling adults aged 70 years or older who were at higher risk for fall injuries from 86 primary care practices across 10 U.S. health care systems. Half of the practices were randomly assigned to provide the intervention to their patients; the other half of the practices provided enhanced usual care.
The researchers defined patients with increased risk for fall injuries as those who had suffered a fall-related injury at least twice during the previous year or those whose difficulties with balance or walking made them fearful of falling. Serious fall injuries were defined as falls that cause a fracture (other than a thoracic or lumbar vertebral fracture), joint dislocation, a cut needing closure, or falls that resulted in hospital admission for a “head injury, sprain or strain, bruising or swelling, or other serious injury,” they explained.
Demographic and baseline characteristics were similar for both groups of patients (mean age, 80 years; 62.0% women); 38.9% had experienced a fall-related injury during the previous year, and 35.1% had suffered at least two falls during the previous year.
The researchers hypothesized that serious fall injuries would be 20% lower in the intervention group, compared with the control group, but that was not the case.
The findings showed no significant difference between the intervention group (4.9 events per 100 person-years of follow-up) and the control group (5.3 events per 100 person-years of follow-up) for the rate of first adjudicated serious fall injury (hazard ratio, 0.92; P = .25). Results were similar in a practice-level analysis and a sensitivity analysis adjusted for participant-level covariates.
However, there was a difference in rates of first participant-reported fall injury, which was a secondary endpoint, at 25.6 events per 100 person-years of follow-up among participants in the intervention group versus 28.6 events among those in the control group (HR, 0.90; P = .004).
There were no significant differences between the groups for rates of all adjudicated serious fall injuries and all patient-reported fall injuries. Bone fractures and injuries resulting in hospitalization were the most frequent types of adjudicated serious fall injuries.
Rates of serious adverse events resulting in hospitalization were similar for the intervention group and the control group (32.8 and 33.3 hospitalizations per 100 person-years of follow-up, respectively), as well as rates of death (3.3 deaths per 100 person-years of follow-up in both groups).
Simple steps can help
“The most important thing clinicians can do is a quick screen for fall injury risk,” Dr. Bhasin said in an interview. The screening tool he uses consists of three questions and can be completed in less than a minute. Clinicians should share that information with patients, he continued.
“Just recognizing that they are at risk for falls, patients are much more motivated to take action,” Dr. Bhasin added.
The top three risk factors identified among trial participants were trouble with strength, gait, or balance; osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency; and impaired vision. “The use of certain medications, postural hypotension, problems with feet or footwear, and home safety hazards were less commonly identified, and the use of certain medications was the least commonly prioritized,” the authors wrote.
It is vital that clinicians help patients implement changes, Dr. Bhasin said. He noted that many patients encounter barriers that prevent them from taking action, including transportation or insurance problems and lack of access to exercise programs in the community.
Deprescribing medications such as sleep medications and benzodiazepines is also a key piece of the puzzle, he added. “They’re pretty huge risks, and yet it is so hard to get people off these medications.”
Future research will focus on how to improve the intervention’s effectiveness and also will test the strategy among those with cognitive impairments who have even higher risk for fall injuries, Dr. Bhasin said.
Falls remain common
A report published online July 9 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report underscores the prevalence of fall-related injuries: In 2018, more than one quarter (27.5%) of adults 65 years or older said they had fallen at least once during the previous year (35.6 million falls), and 10.2% said they had experienced a fall-related injury (8.4 million fall-related injuries). The percentage of adults who reported a fall increased during 2012-2016, then decreased during 2016-2018.
Briana Moreland, MPH, from Synergy America and the Division of Injury Prevention at National Center for Injury Prevention and Control of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and colleagues wrote that older adults and health care providers can work together to reduce fall risk.
“CDC created the Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries (STEADI) initiative, which offers tools and resources for health care providers to screen their older patients for fall risk, assess modifiable fall risk factors, and to intervene with evidence-based fall prevention interventions (https://www.cdc.gov/steadi). These include medication management, vision screening, home modifications, referral to physical therapists who can address problems with gait, strength, and balance, and referral to effective community-based fall prevention programs,” Ms. Moreland and colleagues explain.
Dr. Bhasin has received grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) during the conduct of the study. He has received grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from AbbVie; grants from Transition Therapeutics, Alivegen, and Metro International Biotechnology; and personal fees from OPKO outside the submitted work. A coauthor received grants from the NIA and PCORI during the conduct of the study and is co-owner of Lynx Health, and another Peduzzi received grants and other compensation from NIA-PCORI during the conduct of the study. Two other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The remaining authors report a variety of relevant financial relationships; a complete list is available on the journal’s website. The authors of the article in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
but did identify important ways for clinicians to help, including screening all older patients for fall risk and deprescribing certain medications when possible.
The study was conducted by Shalender Bhasin, MD, MBBS, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston and colleagues on behalf of the Strategies to Reduce Injuries and Develop Confidence in Elders (STRIDE) trial investigators and was published online July 8 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients are often unaware of their increased risk until they have fallen for the first time, and they often underestimate how many of their risk factors can be improved, Dr. Bhasin said in an interview.
“Fall injuries are a very important cause of injury-related deaths among older adults, and these are preventable. Yet they are so difficult; for 30 years the rates of fall injuries have not declined,” he said.
Using a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial, the researchers studied the clinical effectiveness of a “patient-centered intervention that combined elements of practice redesign (reconfiguration of workflow to improve quality of care) and an evidence-based, multifactorial, individually tailored intervention implemented by specially trained nurses in primary care settings,” the authors explained.
Participants in the intervention group worked with trained nurses (fall care managers) to identify their risk factors and determine which risks they wanted to modify. Participants in the control group received their typical care and a pamphlet with information on falls and were encouraged to talk with their primary care physicians (who received the results on risk factor screening) about fall prevention. Those in the intervention group also received the pamphlet.
Fall care managers evaluated patients’ home environments and in some cases visited the patient’s home, Dr. Bhasin said.
The researchers enrolled community-dwelling adults aged 70 years or older who were at higher risk for fall injuries from 86 primary care practices across 10 U.S. health care systems. Half of the practices were randomly assigned to provide the intervention to their patients; the other half of the practices provided enhanced usual care.
The researchers defined patients with increased risk for fall injuries as those who had suffered a fall-related injury at least twice during the previous year or those whose difficulties with balance or walking made them fearful of falling. Serious fall injuries were defined as falls that cause a fracture (other than a thoracic or lumbar vertebral fracture), joint dislocation, a cut needing closure, or falls that resulted in hospital admission for a “head injury, sprain or strain, bruising or swelling, or other serious injury,” they explained.
Demographic and baseline characteristics were similar for both groups of patients (mean age, 80 years; 62.0% women); 38.9% had experienced a fall-related injury during the previous year, and 35.1% had suffered at least two falls during the previous year.
The researchers hypothesized that serious fall injuries would be 20% lower in the intervention group, compared with the control group, but that was not the case.
The findings showed no significant difference between the intervention group (4.9 events per 100 person-years of follow-up) and the control group (5.3 events per 100 person-years of follow-up) for the rate of first adjudicated serious fall injury (hazard ratio, 0.92; P = .25). Results were similar in a practice-level analysis and a sensitivity analysis adjusted for participant-level covariates.
However, there was a difference in rates of first participant-reported fall injury, which was a secondary endpoint, at 25.6 events per 100 person-years of follow-up among participants in the intervention group versus 28.6 events among those in the control group (HR, 0.90; P = .004).
There were no significant differences between the groups for rates of all adjudicated serious fall injuries and all patient-reported fall injuries. Bone fractures and injuries resulting in hospitalization were the most frequent types of adjudicated serious fall injuries.
Rates of serious adverse events resulting in hospitalization were similar for the intervention group and the control group (32.8 and 33.3 hospitalizations per 100 person-years of follow-up, respectively), as well as rates of death (3.3 deaths per 100 person-years of follow-up in both groups).
Simple steps can help
“The most important thing clinicians can do is a quick screen for fall injury risk,” Dr. Bhasin said in an interview. The screening tool he uses consists of three questions and can be completed in less than a minute. Clinicians should share that information with patients, he continued.
“Just recognizing that they are at risk for falls, patients are much more motivated to take action,” Dr. Bhasin added.
The top three risk factors identified among trial participants were trouble with strength, gait, or balance; osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency; and impaired vision. “The use of certain medications, postural hypotension, problems with feet or footwear, and home safety hazards were less commonly identified, and the use of certain medications was the least commonly prioritized,” the authors wrote.
It is vital that clinicians help patients implement changes, Dr. Bhasin said. He noted that many patients encounter barriers that prevent them from taking action, including transportation or insurance problems and lack of access to exercise programs in the community.
Deprescribing medications such as sleep medications and benzodiazepines is also a key piece of the puzzle, he added. “They’re pretty huge risks, and yet it is so hard to get people off these medications.”
Future research will focus on how to improve the intervention’s effectiveness and also will test the strategy among those with cognitive impairments who have even higher risk for fall injuries, Dr. Bhasin said.
Falls remain common
A report published online July 9 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report underscores the prevalence of fall-related injuries: In 2018, more than one quarter (27.5%) of adults 65 years or older said they had fallen at least once during the previous year (35.6 million falls), and 10.2% said they had experienced a fall-related injury (8.4 million fall-related injuries). The percentage of adults who reported a fall increased during 2012-2016, then decreased during 2016-2018.
Briana Moreland, MPH, from Synergy America and the Division of Injury Prevention at National Center for Injury Prevention and Control of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and colleagues wrote that older adults and health care providers can work together to reduce fall risk.
“CDC created the Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries (STEADI) initiative, which offers tools and resources for health care providers to screen their older patients for fall risk, assess modifiable fall risk factors, and to intervene with evidence-based fall prevention interventions (https://www.cdc.gov/steadi). These include medication management, vision screening, home modifications, referral to physical therapists who can address problems with gait, strength, and balance, and referral to effective community-based fall prevention programs,” Ms. Moreland and colleagues explain.
Dr. Bhasin has received grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) during the conduct of the study. He has received grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from AbbVie; grants from Transition Therapeutics, Alivegen, and Metro International Biotechnology; and personal fees from OPKO outside the submitted work. A coauthor received grants from the NIA and PCORI during the conduct of the study and is co-owner of Lynx Health, and another Peduzzi received grants and other compensation from NIA-PCORI during the conduct of the study. Two other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The remaining authors report a variety of relevant financial relationships; a complete list is available on the journal’s website. The authors of the article in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
but did identify important ways for clinicians to help, including screening all older patients for fall risk and deprescribing certain medications when possible.
The study was conducted by Shalender Bhasin, MD, MBBS, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston and colleagues on behalf of the Strategies to Reduce Injuries and Develop Confidence in Elders (STRIDE) trial investigators and was published online July 8 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients are often unaware of their increased risk until they have fallen for the first time, and they often underestimate how many of their risk factors can be improved, Dr. Bhasin said in an interview.
“Fall injuries are a very important cause of injury-related deaths among older adults, and these are preventable. Yet they are so difficult; for 30 years the rates of fall injuries have not declined,” he said.
Using a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial, the researchers studied the clinical effectiveness of a “patient-centered intervention that combined elements of practice redesign (reconfiguration of workflow to improve quality of care) and an evidence-based, multifactorial, individually tailored intervention implemented by specially trained nurses in primary care settings,” the authors explained.
Participants in the intervention group worked with trained nurses (fall care managers) to identify their risk factors and determine which risks they wanted to modify. Participants in the control group received their typical care and a pamphlet with information on falls and were encouraged to talk with their primary care physicians (who received the results on risk factor screening) about fall prevention. Those in the intervention group also received the pamphlet.
Fall care managers evaluated patients’ home environments and in some cases visited the patient’s home, Dr. Bhasin said.
The researchers enrolled community-dwelling adults aged 70 years or older who were at higher risk for fall injuries from 86 primary care practices across 10 U.S. health care systems. Half of the practices were randomly assigned to provide the intervention to their patients; the other half of the practices provided enhanced usual care.
The researchers defined patients with increased risk for fall injuries as those who had suffered a fall-related injury at least twice during the previous year or those whose difficulties with balance or walking made them fearful of falling. Serious fall injuries were defined as falls that cause a fracture (other than a thoracic or lumbar vertebral fracture), joint dislocation, a cut needing closure, or falls that resulted in hospital admission for a “head injury, sprain or strain, bruising or swelling, or other serious injury,” they explained.
Demographic and baseline characteristics were similar for both groups of patients (mean age, 80 years; 62.0% women); 38.9% had experienced a fall-related injury during the previous year, and 35.1% had suffered at least two falls during the previous year.
The researchers hypothesized that serious fall injuries would be 20% lower in the intervention group, compared with the control group, but that was not the case.
The findings showed no significant difference between the intervention group (4.9 events per 100 person-years of follow-up) and the control group (5.3 events per 100 person-years of follow-up) for the rate of first adjudicated serious fall injury (hazard ratio, 0.92; P = .25). Results were similar in a practice-level analysis and a sensitivity analysis adjusted for participant-level covariates.
However, there was a difference in rates of first participant-reported fall injury, which was a secondary endpoint, at 25.6 events per 100 person-years of follow-up among participants in the intervention group versus 28.6 events among those in the control group (HR, 0.90; P = .004).
There were no significant differences between the groups for rates of all adjudicated serious fall injuries and all patient-reported fall injuries. Bone fractures and injuries resulting in hospitalization were the most frequent types of adjudicated serious fall injuries.
Rates of serious adverse events resulting in hospitalization were similar for the intervention group and the control group (32.8 and 33.3 hospitalizations per 100 person-years of follow-up, respectively), as well as rates of death (3.3 deaths per 100 person-years of follow-up in both groups).
Simple steps can help
“The most important thing clinicians can do is a quick screen for fall injury risk,” Dr. Bhasin said in an interview. The screening tool he uses consists of three questions and can be completed in less than a minute. Clinicians should share that information with patients, he continued.
“Just recognizing that they are at risk for falls, patients are much more motivated to take action,” Dr. Bhasin added.
The top three risk factors identified among trial participants were trouble with strength, gait, or balance; osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency; and impaired vision. “The use of certain medications, postural hypotension, problems with feet or footwear, and home safety hazards were less commonly identified, and the use of certain medications was the least commonly prioritized,” the authors wrote.
It is vital that clinicians help patients implement changes, Dr. Bhasin said. He noted that many patients encounter barriers that prevent them from taking action, including transportation or insurance problems and lack of access to exercise programs in the community.
Deprescribing medications such as sleep medications and benzodiazepines is also a key piece of the puzzle, he added. “They’re pretty huge risks, and yet it is so hard to get people off these medications.”
Future research will focus on how to improve the intervention’s effectiveness and also will test the strategy among those with cognitive impairments who have even higher risk for fall injuries, Dr. Bhasin said.
Falls remain common
A report published online July 9 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report underscores the prevalence of fall-related injuries: In 2018, more than one quarter (27.5%) of adults 65 years or older said they had fallen at least once during the previous year (35.6 million falls), and 10.2% said they had experienced a fall-related injury (8.4 million fall-related injuries). The percentage of adults who reported a fall increased during 2012-2016, then decreased during 2016-2018.
Briana Moreland, MPH, from Synergy America and the Division of Injury Prevention at National Center for Injury Prevention and Control of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and colleagues wrote that older adults and health care providers can work together to reduce fall risk.
“CDC created the Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries (STEADI) initiative, which offers tools and resources for health care providers to screen their older patients for fall risk, assess modifiable fall risk factors, and to intervene with evidence-based fall prevention interventions (https://www.cdc.gov/steadi). These include medication management, vision screening, home modifications, referral to physical therapists who can address problems with gait, strength, and balance, and referral to effective community-based fall prevention programs,” Ms. Moreland and colleagues explain.
Dr. Bhasin has received grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) during the conduct of the study. He has received grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from AbbVie; grants from Transition Therapeutics, Alivegen, and Metro International Biotechnology; and personal fees from OPKO outside the submitted work. A coauthor received grants from the NIA and PCORI during the conduct of the study and is co-owner of Lynx Health, and another Peduzzi received grants and other compensation from NIA-PCORI during the conduct of the study. Two other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The remaining authors report a variety of relevant financial relationships; a complete list is available on the journal’s website. The authors of the article in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Erythematous Plaque on the Back of a Newborn
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is a benign and self-limited condition that commonly occurs in term to postterm infants.1 However, it is an important diagnosis to recognize, as the potential exists for co-occurring metabolic derangements, most commonly hypercalcemia.1-4 Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is characterized by a panniculitis, most often on the back, shoulders, face, and buttocks. Lesions commonly present as erythematous nodules and plaques with overlying induration and can appear from birth to up to the first 6 weeks of life; calcification can be present in long-standing cases.2 Biopsy is diagnostic, showing a normal epidermis and dermis with a diffuse lobular panniculitis (Figure, A). Fat degeneration, radial crystal formation, and interstitial histiocytes also can be seen (Figure, B).
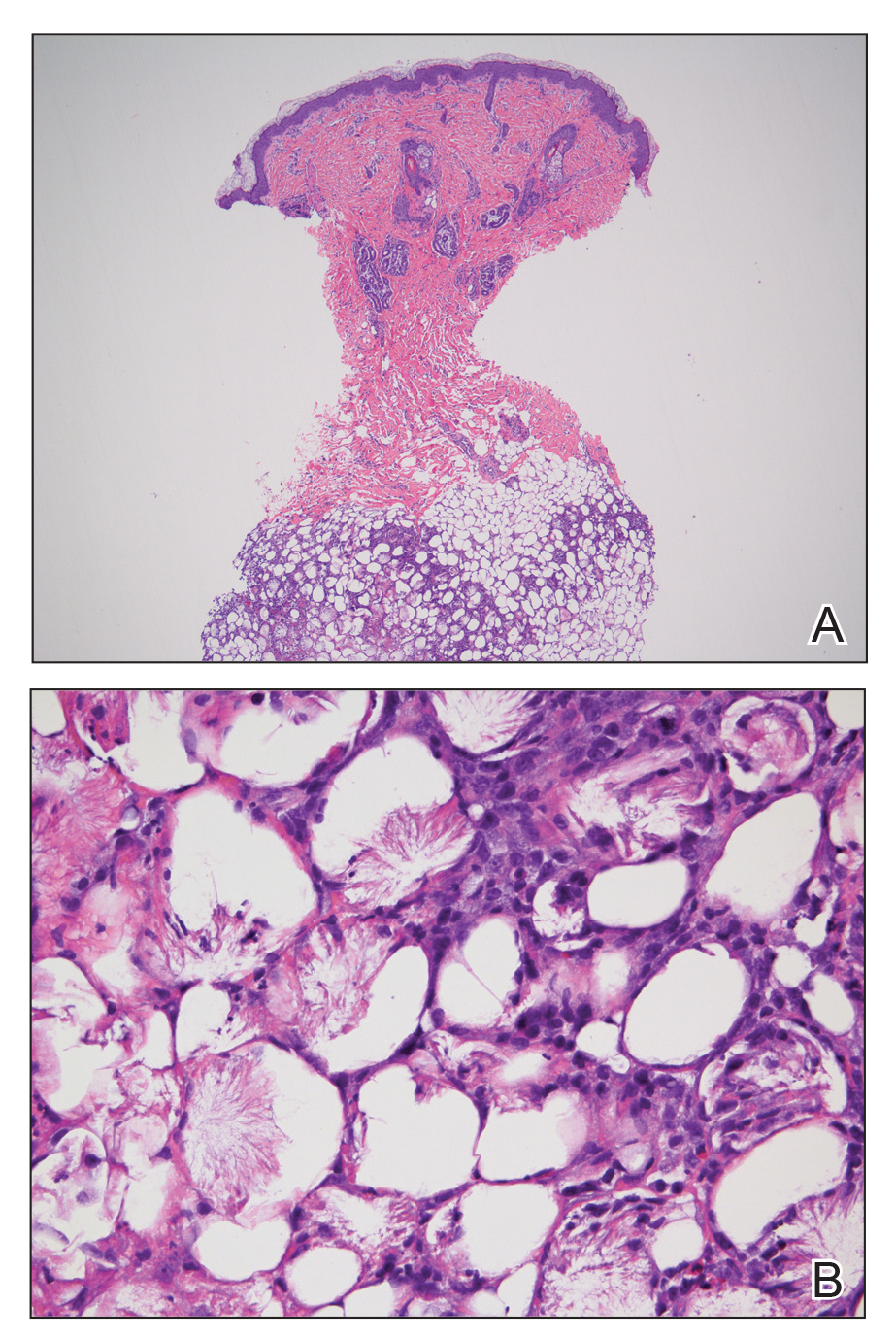
Patients with suspected subcutaneous fat necrosis should have their calcium levels checked, as up to 25% of patients may have coexisting hypercalcemia, which can contribute to morbidity and mortality.2 The hypercalcemia can occur with the onset of the lesions; however, it may be seen after they resolve completely.3 Thus, it is recommended that calcium levels be monitored for at least 1 month after lesions resolve. The exact etiology of subcutaneous fat necrosis is unknown, but it has been associated with perinatal stress and neonatal and maternal risk factors such as umbilical cord prolapse, meconium aspiration, neonatal sepsis, preeclampsia, and Rh incompatibility.1 The prognosis generally is excellent, with no treatment necessary for the skin lesions, as they resolve within a few months without subsequent sequelae or scarring.1,2 Patients with hypercalcemia should be treated appropriately with measures such as hydration and restriction of vitamin D; severe cases can be treated with bisphosphonates or loop diuretics.4
Cutis marmorata presents symmetrically on the trunk and may affect the upper and lower extremities as a reticulated erythema, often in response to cold temperature. Lesions are transient and resolve with warming. The isolated location of the skin lesions on the back, consistent course, and induration is unlikely to be seen in cutis marmorata. Infantile hemangiomas present several weeks to months after birth, and they undergo a rapid growth phase and subsequent slower involution phase. Furthermore, infantile hemangiomas have a rubbery feel and typically are not hard plaques, as seen in our patient.5 Patients with bacterial cellulitis often have systemic symptoms such as fever or chills, and the lesion generally is an ill-defined area of erythema and edema that can enlarge and become fluctuant.6 Sclerema neonatorum is a rare condition characterized by diffuse thickening of the skin that occurs in premature infants.7 These patients often are severely ill, as opposed to our asymptomatic full-term patient.
- Rubin G, Spagnut G, Morandi F, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3:1017-1020.
- de Campos Luciano Gomes MP, Porro AM, Simões da Silva Enokihara MM, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn: clinical manifestations in two cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 suppl 1):154-157.
- Karochristou K, Siahanidou T, Kakourou-Tsivitanidou T, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis associated with severe hypocalcemia in a neonate. J Perinatol. 2005;26:64-66.
- Salas IV, Miralbell AR, Peinado CM, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn and hypercalcemia: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:AB149.
- Darrow DH, Greene AK, Mancini AJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of infantile hemangioma. Pediatrics. 2015;136:E1060-E1104.
- Linder KA, Malani PN. Cellulitis. JAMA. 2017;317:2142.
- Jardine D, Atherton DJ, Trompeter RS. Sclerema neonaturm and subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn in the same infant. Eur J Pediatr. 1990;150:125-126.
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is a benign and self-limited condition that commonly occurs in term to postterm infants.1 However, it is an important diagnosis to recognize, as the potential exists for co-occurring metabolic derangements, most commonly hypercalcemia.1-4 Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is characterized by a panniculitis, most often on the back, shoulders, face, and buttocks. Lesions commonly present as erythematous nodules and plaques with overlying induration and can appear from birth to up to the first 6 weeks of life; calcification can be present in long-standing cases.2 Biopsy is diagnostic, showing a normal epidermis and dermis with a diffuse lobular panniculitis (Figure, A). Fat degeneration, radial crystal formation, and interstitial histiocytes also can be seen (Figure, B).

Patients with suspected subcutaneous fat necrosis should have their calcium levels checked, as up to 25% of patients may have coexisting hypercalcemia, which can contribute to morbidity and mortality.2 The hypercalcemia can occur with the onset of the lesions; however, it may be seen after they resolve completely.3 Thus, it is recommended that calcium levels be monitored for at least 1 month after lesions resolve. The exact etiology of subcutaneous fat necrosis is unknown, but it has been associated with perinatal stress and neonatal and maternal risk factors such as umbilical cord prolapse, meconium aspiration, neonatal sepsis, preeclampsia, and Rh incompatibility.1 The prognosis generally is excellent, with no treatment necessary for the skin lesions, as they resolve within a few months without subsequent sequelae or scarring.1,2 Patients with hypercalcemia should be treated appropriately with measures such as hydration and restriction of vitamin D; severe cases can be treated with bisphosphonates or loop diuretics.4
Cutis marmorata presents symmetrically on the trunk and may affect the upper and lower extremities as a reticulated erythema, often in response to cold temperature. Lesions are transient and resolve with warming. The isolated location of the skin lesions on the back, consistent course, and induration is unlikely to be seen in cutis marmorata. Infantile hemangiomas present several weeks to months after birth, and they undergo a rapid growth phase and subsequent slower involution phase. Furthermore, infantile hemangiomas have a rubbery feel and typically are not hard plaques, as seen in our patient.5 Patients with bacterial cellulitis often have systemic symptoms such as fever or chills, and the lesion generally is an ill-defined area of erythema and edema that can enlarge and become fluctuant.6 Sclerema neonatorum is a rare condition characterized by diffuse thickening of the skin that occurs in premature infants.7 These patients often are severely ill, as opposed to our asymptomatic full-term patient.
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is a benign and self-limited condition that commonly occurs in term to postterm infants.1 However, it is an important diagnosis to recognize, as the potential exists for co-occurring metabolic derangements, most commonly hypercalcemia.1-4 Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is characterized by a panniculitis, most often on the back, shoulders, face, and buttocks. Lesions commonly present as erythematous nodules and plaques with overlying induration and can appear from birth to up to the first 6 weeks of life; calcification can be present in long-standing cases.2 Biopsy is diagnostic, showing a normal epidermis and dermis with a diffuse lobular panniculitis (Figure, A). Fat degeneration, radial crystal formation, and interstitial histiocytes also can be seen (Figure, B).

Patients with suspected subcutaneous fat necrosis should have their calcium levels checked, as up to 25% of patients may have coexisting hypercalcemia, which can contribute to morbidity and mortality.2 The hypercalcemia can occur with the onset of the lesions; however, it may be seen after they resolve completely.3 Thus, it is recommended that calcium levels be monitored for at least 1 month after lesions resolve. The exact etiology of subcutaneous fat necrosis is unknown, but it has been associated with perinatal stress and neonatal and maternal risk factors such as umbilical cord prolapse, meconium aspiration, neonatal sepsis, preeclampsia, and Rh incompatibility.1 The prognosis generally is excellent, with no treatment necessary for the skin lesions, as they resolve within a few months without subsequent sequelae or scarring.1,2 Patients with hypercalcemia should be treated appropriately with measures such as hydration and restriction of vitamin D; severe cases can be treated with bisphosphonates or loop diuretics.4
Cutis marmorata presents symmetrically on the trunk and may affect the upper and lower extremities as a reticulated erythema, often in response to cold temperature. Lesions are transient and resolve with warming. The isolated location of the skin lesions on the back, consistent course, and induration is unlikely to be seen in cutis marmorata. Infantile hemangiomas present several weeks to months after birth, and they undergo a rapid growth phase and subsequent slower involution phase. Furthermore, infantile hemangiomas have a rubbery feel and typically are not hard plaques, as seen in our patient.5 Patients with bacterial cellulitis often have systemic symptoms such as fever or chills, and the lesion generally is an ill-defined area of erythema and edema that can enlarge and become fluctuant.6 Sclerema neonatorum is a rare condition characterized by diffuse thickening of the skin that occurs in premature infants.7 These patients often are severely ill, as opposed to our asymptomatic full-term patient.
- Rubin G, Spagnut G, Morandi F, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3:1017-1020.
- de Campos Luciano Gomes MP, Porro AM, Simões da Silva Enokihara MM, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn: clinical manifestations in two cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 suppl 1):154-157.
- Karochristou K, Siahanidou T, Kakourou-Tsivitanidou T, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis associated with severe hypocalcemia in a neonate. J Perinatol. 2005;26:64-66.
- Salas IV, Miralbell AR, Peinado CM, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn and hypercalcemia: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:AB149.
- Darrow DH, Greene AK, Mancini AJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of infantile hemangioma. Pediatrics. 2015;136:E1060-E1104.
- Linder KA, Malani PN. Cellulitis. JAMA. 2017;317:2142.
- Jardine D, Atherton DJ, Trompeter RS. Sclerema neonaturm and subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn in the same infant. Eur J Pediatr. 1990;150:125-126.
- Rubin G, Spagnut G, Morandi F, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3:1017-1020.
- de Campos Luciano Gomes MP, Porro AM, Simões da Silva Enokihara MM, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn: clinical manifestations in two cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 suppl 1):154-157.
- Karochristou K, Siahanidou T, Kakourou-Tsivitanidou T, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis associated with severe hypocalcemia in a neonate. J Perinatol. 2005;26:64-66.
- Salas IV, Miralbell AR, Peinado CM, et al. Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn and hypercalcemia: a case report. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:AB149.
- Darrow DH, Greene AK, Mancini AJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of infantile hemangioma. Pediatrics. 2015;136:E1060-E1104.
- Linder KA, Malani PN. Cellulitis. JAMA. 2017;317:2142.
- Jardine D, Atherton DJ, Trompeter RS. Sclerema neonaturm and subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn in the same infant. Eur J Pediatr. 1990;150:125-126.
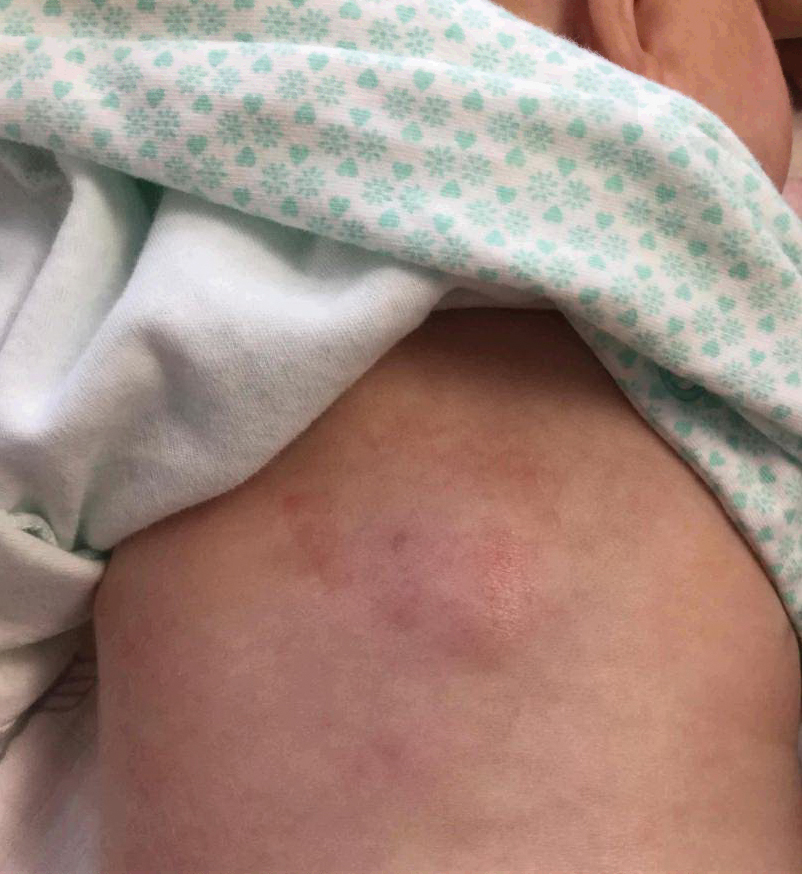
An 8-day-old female infant presented with a mass on the lower back that had been present since birth. The patient was well appearing, alert, and active. Physical examination revealed a 6×5-cm, erythematous, ill-defined, indurated plaque on the lower thoracic back. There was no associated family history of similar findings. According to the mother, the patient was feeding well with no recent fever, irritability, or lethargy. The patient was born via elective induction of labor at term due to maternal intrauterine infection from chorioamnionitis. The birth was complicated by shoulder dystocia with an Erb palsy, and she was hospitalized for 5 days after delivery for management of hypotension and ABO isoimmunization and to rule out sepsis; blood cultures were negative for neonatal infection.
Caution urged for antidepressant use in bipolar depression
Although patients with bipolar disorder commonly experience depressive symptoms, clinicians should be very cautious about treating them with antidepressants, especially as monotherapy, experts asserted in a recent debate on the topic as part of the European Psychiatric Association (EPA) 2020 Congress.
At the Congress, which was virtual this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic, psychiatric experts said that clinicians should also screen patients for mixed symptoms that are better treated with mood stabilizers. These same experts also raised concerns over long-term antidepressant use, recommending continued use only in patients who relapse after stopping antidepressants.
Isabella Pacchiarotti, MD, PhD, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Salud Mental, Barcelona, Spain, argued against the use of antidepressants in treating bipolar disorder; Guy Goodwin, PhD, however, took the “pro” stance.
Goodwin, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Oxford in the UK, admitted that there is a “paucity of data” on the role of antidepressants in bipolar disorder.
Nevertheless, there are “circumstances that one really has to treat with antidepressants simply because other things have been tried and have not worked,” he told conference attendees.
Challenging, Controversial Topic
The debate was chaired by Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD, chair of the Department of Psychiatry and Psychology at the University of Barcelona Hospital Clinic, Spain.
Vieta said the question over whether antidepressants should be used in the depressive phase of bipolar illness is “perhaps the most challenging ... especially in the area of bipolar disorder.”
At the beginning of the presentation, Vieta asked the audience for their opinion in order to have a “baseline” for the debate: among 164 respondents, 73% were in favor of using antidepressants in bipolar depression.
“Clearly there is a majority, so Isabella [Dr Pacchiarotti] is going to have a hard time improving these numbers,” Vieta noted.
Up first, Pacchiarotti began by noting that this topic remains “an area of big controversy.” However, the real question “should not be the pros and cons of antidepressants but more when and how to use them.»
Of the three phases of bipolar disorder, acute depression «poses the greatest difficulties,» she added.
This is because of the relative paucity of studies in the area, the often heated debates on the specific role of antidepressants, the discrepancy in conclusions between meta-analyses, and the currently approved therapeutic options being associated with “not very high response rates,” Pacchiarotti said.
The diagnostic criteria for unipolar and bipolar depression are “basically the same,” she noted. However, it’s important to be able to distinguish between the two conditions, as up to one fifth of patients with unipolar depression suffer from undiagnosed bipolar disorder, she explained.
Moreover, several studies have identified key symptoms in bipolar depression, such as hyperphagia and hypersomnia, increased anxiety, and psychotic and psychomotor symptoms.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, a task force report was released in 2013 by the International Society for Bipolar Disorder (ISBD) on antidepressant use in bipolar disorders. Pacchiarotti and Goodwin were among the report’s authors, which concluded that available evidence on this issue is methodologically weak.
This is largely because of a lack of placebo-controlled studies in this patient population (bipolar depression, alongside suicidal ideation, is often an exclusion criteria in clinical antidepressant trials).
Many guidelines consequently do not consider antidepressants to be a first-line option as monotherapy in bipolar depression, although some name the drugs as second- or third-line options.
In 2013, the ISBD recommended that antidepressant monotherapy should be “avoided” in bipolar I disorder; and in bipolar I and II depression, the treatment should be accompanied by at least two concomitant core manic symptoms.
“What Has Changed?”
Antidepressants should be used “only if there is a history of a positive response,” whereas maintenance therapy should be considered if a patient relapses into a depressive episode after stopping the drugs, the report notes.
Pacchiarotti noted that since the recommendations were published nothing has changed, noting that antidepressant efficacy in bipolar depression “remains unproven.”
The issue is not whether antidepressants are effective in bipolar depression but rather are there subpopulations where these medications are helpful or harmful, she added.
The key to understanding the heterogeneity of responses to antidepressants, she said, is the concept of a bipolar spectrum and a dimensional approach to distinguishing between bipolar disorder and unipolar depression.
In addition, the definition of a mixed episode in the DSM-IV-TR differs from that of an episode with mixed characteristics in the DSM-5, which Pacchiarotti said offers a better understanding of the phenomenon while seemingly disposing with the idea of mixed depression.
Based on previous research, there is some suggestion that a depressive state exists between major depressive disorder and bipolar I disorder with mixed features, and hypomania state between bipolar II and I disorder, also with mixed features.
Pacchiarotti said the role of antidepressants in the treatment of bipolar depression remains “controversial” and there is a need for both short- and long-term studies of their use in both bipolar I and bipolar II disorder with real-world inclusion criteria.
The concept of a bipolar spectrum needs to be considered a more “dimensional approach” to depression, with mixed features seen as a “transversal” contraindication for antidepressant use, she concluded.
In Favor — With Caveats
Taking the opposite position and arguing in favor of antidepressant use, albeit cautiously, Goodwin said previous work has shown that stable patients with bipolar disorder experience depression of variable severity about 50% of the time.
The truth is that patients do not have a depressive episode for extended periods but instead have depressive symptoms, he said. “So how we manage and treat depression really matters.”
In an analysis, Goodwin and his colleagues estimated that the cost of bipolar disorder is approximately £12,600 ($16,000) per patient per year, of which only 30.6% is attributable to healthcare costs and 68.1% to indirect costs. This means the impact on the patient is also felt by society.
He agreed with Pacchiarotti’s assertion of a bipolar spectrum and the need for a dimensional approach.
“All the patients along the spectrum have the symptoms of depression and they differ in the extent to which they show symptoms of mania, which will include irritability,” he added.
Goodwin argued that there is no evidence to suggest that the depression experienced at one end of the scale is any different from that at the other. However, safety issues around antidepressant use “really relate to the additional symptoms you see with increasing evidence of bipolarity.”
In addition, the whole discussion is confounded by comorbidity, “with symptoms that sometimes coalesce into our concept of borderline personality disorder” or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, he said.
Goodwin said there is “very little doubt” that antidepressants have an effect vs placebo. “The argument is over whether the effect is large and whether we should regard it as clinically significant.”
He noted that previous studies have shown a range of effect sizes with antidepressants, but the “massive” confidence intervals mean that “one is free to believe pretty much what one likes.”
The only antidepressant medication that is statistically significantly different from placebo is fluoxetine combined with olanzapine. However, that conclusion is based on “little data,” said Goodwin.
In terms of long-term management, there is “extremely little” randomized data for maintenance treatment with antidepressants in bipolar disorder. “So this does not support” long-term use, he added.
Still, although choice of antidepressant remains a guess, there is “just about support” for using them, Goodwin noted.
He urged clinicians not to dismiss antidepressant use, but to use them only where there is a clinical need and for as little time as possible. Patients with bipolar disorder should continue to take antidepressants if they relapse after they come off these medications.
However, all of that sits “in contrast” to how they’re currently used in clinical practice, Goodwin said.
Caution Urged
After the debate, the audience was asked to vote again. This time, The remaining 12% voted against the practice.
Summarizing the discussion, Vieta said that “we should be cautious” when using antidepressants in bipolar depression. However, “we should be able to use them when necessary,” he added.
Although their use as monotherapy is not best practice, especially in bipolar I disorder, there may be a subset of bipolar II patients in whom monotherapy “might still be acceptable; but I don’t think it’s a good idea,” Vieta said.
He added that clinicians should very carefully screen for mixed symptoms, which call for the prescription of other drugs, such as olanzapine and fluoxetine.
“The other important message is that we have to be even more cautious in the long term with the use of antidepressants, and we should be able to use them when there is a comorbidity” that calls for their use, Vieta concluded.
Pacchiarotti reported having received speaker fees and educational grants from Adamed, AstraZeneca, Janssen-Cilag, and Lundbeck. Goodwin reported having received honoraria from Angellini, Medscape, Pfizer, Servier, Shire, and Sun; having shares in P1vital Products; past employment as medical director of P1vital Products; and advisory board membership for Compass Pathways, Minerva, MSD, Novartis, Lundbeck, Sage, Servier, and Shire. Vieta has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although patients with bipolar disorder commonly experience depressive symptoms, clinicians should be very cautious about treating them with antidepressants, especially as monotherapy, experts asserted in a recent debate on the topic as part of the European Psychiatric Association (EPA) 2020 Congress.
At the Congress, which was virtual this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic, psychiatric experts said that clinicians should also screen patients for mixed symptoms that are better treated with mood stabilizers. These same experts also raised concerns over long-term antidepressant use, recommending continued use only in patients who relapse after stopping antidepressants.
Isabella Pacchiarotti, MD, PhD, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Salud Mental, Barcelona, Spain, argued against the use of antidepressants in treating bipolar disorder; Guy Goodwin, PhD, however, took the “pro” stance.
Goodwin, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Oxford in the UK, admitted that there is a “paucity of data” on the role of antidepressants in bipolar disorder.
Nevertheless, there are “circumstances that one really has to treat with antidepressants simply because other things have been tried and have not worked,” he told conference attendees.
Challenging, Controversial Topic
The debate was chaired by Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD, chair of the Department of Psychiatry and Psychology at the University of Barcelona Hospital Clinic, Spain.
Vieta said the question over whether antidepressants should be used in the depressive phase of bipolar illness is “perhaps the most challenging ... especially in the area of bipolar disorder.”
At the beginning of the presentation, Vieta asked the audience for their opinion in order to have a “baseline” for the debate: among 164 respondents, 73% were in favor of using antidepressants in bipolar depression.
“Clearly there is a majority, so Isabella [Dr Pacchiarotti] is going to have a hard time improving these numbers,” Vieta noted.
Up first, Pacchiarotti began by noting that this topic remains “an area of big controversy.” However, the real question “should not be the pros and cons of antidepressants but more when and how to use them.»
Of the three phases of bipolar disorder, acute depression «poses the greatest difficulties,» she added.
This is because of the relative paucity of studies in the area, the often heated debates on the specific role of antidepressants, the discrepancy in conclusions between meta-analyses, and the currently approved therapeutic options being associated with “not very high response rates,” Pacchiarotti said.
The diagnostic criteria for unipolar and bipolar depression are “basically the same,” she noted. However, it’s important to be able to distinguish between the two conditions, as up to one fifth of patients with unipolar depression suffer from undiagnosed bipolar disorder, she explained.
Moreover, several studies have identified key symptoms in bipolar depression, such as hyperphagia and hypersomnia, increased anxiety, and psychotic and psychomotor symptoms.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, a task force report was released in 2013 by the International Society for Bipolar Disorder (ISBD) on antidepressant use in bipolar disorders. Pacchiarotti and Goodwin were among the report’s authors, which concluded that available evidence on this issue is methodologically weak.
This is largely because of a lack of placebo-controlled studies in this patient population (bipolar depression, alongside suicidal ideation, is often an exclusion criteria in clinical antidepressant trials).
Many guidelines consequently do not consider antidepressants to be a first-line option as monotherapy in bipolar depression, although some name the drugs as second- or third-line options.
In 2013, the ISBD recommended that antidepressant monotherapy should be “avoided” in bipolar I disorder; and in bipolar I and II depression, the treatment should be accompanied by at least two concomitant core manic symptoms.
“What Has Changed?”
Antidepressants should be used “only if there is a history of a positive response,” whereas maintenance therapy should be considered if a patient relapses into a depressive episode after stopping the drugs, the report notes.
Pacchiarotti noted that since the recommendations were published nothing has changed, noting that antidepressant efficacy in bipolar depression “remains unproven.”
The issue is not whether antidepressants are effective in bipolar depression but rather are there subpopulations where these medications are helpful or harmful, she added.
The key to understanding the heterogeneity of responses to antidepressants, she said, is the concept of a bipolar spectrum and a dimensional approach to distinguishing between bipolar disorder and unipolar depression.
In addition, the definition of a mixed episode in the DSM-IV-TR differs from that of an episode with mixed characteristics in the DSM-5, which Pacchiarotti said offers a better understanding of the phenomenon while seemingly disposing with the idea of mixed depression.
Based on previous research, there is some suggestion that a depressive state exists between major depressive disorder and bipolar I disorder with mixed features, and hypomania state between bipolar II and I disorder, also with mixed features.
Pacchiarotti said the role of antidepressants in the treatment of bipolar depression remains “controversial” and there is a need for both short- and long-term studies of their use in both bipolar I and bipolar II disorder with real-world inclusion criteria.
The concept of a bipolar spectrum needs to be considered a more “dimensional approach” to depression, with mixed features seen as a “transversal” contraindication for antidepressant use, she concluded.
In Favor — With Caveats
Taking the opposite position and arguing in favor of antidepressant use, albeit cautiously, Goodwin said previous work has shown that stable patients with bipolar disorder experience depression of variable severity about 50% of the time.
The truth is that patients do not have a depressive episode for extended periods but instead have depressive symptoms, he said. “So how we manage and treat depression really matters.”
In an analysis, Goodwin and his colleagues estimated that the cost of bipolar disorder is approximately £12,600 ($16,000) per patient per year, of which only 30.6% is attributable to healthcare costs and 68.1% to indirect costs. This means the impact on the patient is also felt by society.
He agreed with Pacchiarotti’s assertion of a bipolar spectrum and the need for a dimensional approach.
“All the patients along the spectrum have the symptoms of depression and they differ in the extent to which they show symptoms of mania, which will include irritability,” he added.
Goodwin argued that there is no evidence to suggest that the depression experienced at one end of the scale is any different from that at the other. However, safety issues around antidepressant use “really relate to the additional symptoms you see with increasing evidence of bipolarity.”
In addition, the whole discussion is confounded by comorbidity, “with symptoms that sometimes coalesce into our concept of borderline personality disorder” or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, he said.
Goodwin said there is “very little doubt” that antidepressants have an effect vs placebo. “The argument is over whether the effect is large and whether we should regard it as clinically significant.”
He noted that previous studies have shown a range of effect sizes with antidepressants, but the “massive” confidence intervals mean that “one is free to believe pretty much what one likes.”
The only antidepressant medication that is statistically significantly different from placebo is fluoxetine combined with olanzapine. However, that conclusion is based on “little data,” said Goodwin.
In terms of long-term management, there is “extremely little” randomized data for maintenance treatment with antidepressants in bipolar disorder. “So this does not support” long-term use, he added.
Still, although choice of antidepressant remains a guess, there is “just about support” for using them, Goodwin noted.
He urged clinicians not to dismiss antidepressant use, but to use them only where there is a clinical need and for as little time as possible. Patients with bipolar disorder should continue to take antidepressants if they relapse after they come off these medications.
However, all of that sits “in contrast” to how they’re currently used in clinical practice, Goodwin said.
Caution Urged
After the debate, the audience was asked to vote again. This time, The remaining 12% voted against the practice.
Summarizing the discussion, Vieta said that “we should be cautious” when using antidepressants in bipolar depression. However, “we should be able to use them when necessary,” he added.
Although their use as monotherapy is not best practice, especially in bipolar I disorder, there may be a subset of bipolar II patients in whom monotherapy “might still be acceptable; but I don’t think it’s a good idea,” Vieta said.
He added that clinicians should very carefully screen for mixed symptoms, which call for the prescription of other drugs, such as olanzapine and fluoxetine.
“The other important message is that we have to be even more cautious in the long term with the use of antidepressants, and we should be able to use them when there is a comorbidity” that calls for their use, Vieta concluded.
Pacchiarotti reported having received speaker fees and educational grants from Adamed, AstraZeneca, Janssen-Cilag, and Lundbeck. Goodwin reported having received honoraria from Angellini, Medscape, Pfizer, Servier, Shire, and Sun; having shares in P1vital Products; past employment as medical director of P1vital Products; and advisory board membership for Compass Pathways, Minerva, MSD, Novartis, Lundbeck, Sage, Servier, and Shire. Vieta has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although patients with bipolar disorder commonly experience depressive symptoms, clinicians should be very cautious about treating them with antidepressants, especially as monotherapy, experts asserted in a recent debate on the topic as part of the European Psychiatric Association (EPA) 2020 Congress.
At the Congress, which was virtual this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic, psychiatric experts said that clinicians should also screen patients for mixed symptoms that are better treated with mood stabilizers. These same experts also raised concerns over long-term antidepressant use, recommending continued use only in patients who relapse after stopping antidepressants.
Isabella Pacchiarotti, MD, PhD, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Salud Mental, Barcelona, Spain, argued against the use of antidepressants in treating bipolar disorder; Guy Goodwin, PhD, however, took the “pro” stance.
Goodwin, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Oxford in the UK, admitted that there is a “paucity of data” on the role of antidepressants in bipolar disorder.
Nevertheless, there are “circumstances that one really has to treat with antidepressants simply because other things have been tried and have not worked,” he told conference attendees.
Challenging, Controversial Topic
The debate was chaired by Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD, chair of the Department of Psychiatry and Psychology at the University of Barcelona Hospital Clinic, Spain.
Vieta said the question over whether antidepressants should be used in the depressive phase of bipolar illness is “perhaps the most challenging ... especially in the area of bipolar disorder.”
At the beginning of the presentation, Vieta asked the audience for their opinion in order to have a “baseline” for the debate: among 164 respondents, 73% were in favor of using antidepressants in bipolar depression.
“Clearly there is a majority, so Isabella [Dr Pacchiarotti] is going to have a hard time improving these numbers,” Vieta noted.
Up first, Pacchiarotti began by noting that this topic remains “an area of big controversy.” However, the real question “should not be the pros and cons of antidepressants but more when and how to use them.»
Of the three phases of bipolar disorder, acute depression «poses the greatest difficulties,» she added.
This is because of the relative paucity of studies in the area, the often heated debates on the specific role of antidepressants, the discrepancy in conclusions between meta-analyses, and the currently approved therapeutic options being associated with “not very high response rates,” Pacchiarotti said.
The diagnostic criteria for unipolar and bipolar depression are “basically the same,” she noted. However, it’s important to be able to distinguish between the two conditions, as up to one fifth of patients with unipolar depression suffer from undiagnosed bipolar disorder, she explained.
Moreover, several studies have identified key symptoms in bipolar depression, such as hyperphagia and hypersomnia, increased anxiety, and psychotic and psychomotor symptoms.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, a task force report was released in 2013 by the International Society for Bipolar Disorder (ISBD) on antidepressant use in bipolar disorders. Pacchiarotti and Goodwin were among the report’s authors, which concluded that available evidence on this issue is methodologically weak.
This is largely because of a lack of placebo-controlled studies in this patient population (bipolar depression, alongside suicidal ideation, is often an exclusion criteria in clinical antidepressant trials).
Many guidelines consequently do not consider antidepressants to be a first-line option as monotherapy in bipolar depression, although some name the drugs as second- or third-line options.
In 2013, the ISBD recommended that antidepressant monotherapy should be “avoided” in bipolar I disorder; and in bipolar I and II depression, the treatment should be accompanied by at least two concomitant core manic symptoms.
“What Has Changed?”
Antidepressants should be used “only if there is a history of a positive response,” whereas maintenance therapy should be considered if a patient relapses into a depressive episode after stopping the drugs, the report notes.
Pacchiarotti noted that since the recommendations were published nothing has changed, noting that antidepressant efficacy in bipolar depression “remains unproven.”
The issue is not whether antidepressants are effective in bipolar depression but rather are there subpopulations where these medications are helpful or harmful, she added.
The key to understanding the heterogeneity of responses to antidepressants, she said, is the concept of a bipolar spectrum and a dimensional approach to distinguishing between bipolar disorder and unipolar depression.
In addition, the definition of a mixed episode in the DSM-IV-TR differs from that of an episode with mixed characteristics in the DSM-5, which Pacchiarotti said offers a better understanding of the phenomenon while seemingly disposing with the idea of mixed depression.
Based on previous research, there is some suggestion that a depressive state exists between major depressive disorder and bipolar I disorder with mixed features, and hypomania state between bipolar II and I disorder, also with mixed features.
Pacchiarotti said the role of antidepressants in the treatment of bipolar depression remains “controversial” and there is a need for both short- and long-term studies of their use in both bipolar I and bipolar II disorder with real-world inclusion criteria.
The concept of a bipolar spectrum needs to be considered a more “dimensional approach” to depression, with mixed features seen as a “transversal” contraindication for antidepressant use, she concluded.
In Favor — With Caveats
Taking the opposite position and arguing in favor of antidepressant use, albeit cautiously, Goodwin said previous work has shown that stable patients with bipolar disorder experience depression of variable severity about 50% of the time.
The truth is that patients do not have a depressive episode for extended periods but instead have depressive symptoms, he said. “So how we manage and treat depression really matters.”
In an analysis, Goodwin and his colleagues estimated that the cost of bipolar disorder is approximately £12,600 ($16,000) per patient per year, of which only 30.6% is attributable to healthcare costs and 68.1% to indirect costs. This means the impact on the patient is also felt by society.
He agreed with Pacchiarotti’s assertion of a bipolar spectrum and the need for a dimensional approach.
“All the patients along the spectrum have the symptoms of depression and they differ in the extent to which they show symptoms of mania, which will include irritability,” he added.
Goodwin argued that there is no evidence to suggest that the depression experienced at one end of the scale is any different from that at the other. However, safety issues around antidepressant use “really relate to the additional symptoms you see with increasing evidence of bipolarity.”
In addition, the whole discussion is confounded by comorbidity, “with symptoms that sometimes coalesce into our concept of borderline personality disorder” or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, he said.
Goodwin said there is “very little doubt” that antidepressants have an effect vs placebo. “The argument is over whether the effect is large and whether we should regard it as clinically significant.”
He noted that previous studies have shown a range of effect sizes with antidepressants, but the “massive” confidence intervals mean that “one is free to believe pretty much what one likes.”
The only antidepressant medication that is statistically significantly different from placebo is fluoxetine combined with olanzapine. However, that conclusion is based on “little data,” said Goodwin.
In terms of long-term management, there is “extremely little” randomized data for maintenance treatment with antidepressants in bipolar disorder. “So this does not support” long-term use, he added.
Still, although choice of antidepressant remains a guess, there is “just about support” for using them, Goodwin noted.
He urged clinicians not to dismiss antidepressant use, but to use them only where there is a clinical need and for as little time as possible. Patients with bipolar disorder should continue to take antidepressants if they relapse after they come off these medications.
However, all of that sits “in contrast” to how they’re currently used in clinical practice, Goodwin said.
Caution Urged
After the debate, the audience was asked to vote again. This time, The remaining 12% voted against the practice.
Summarizing the discussion, Vieta said that “we should be cautious” when using antidepressants in bipolar depression. However, “we should be able to use them when necessary,” he added.
Although their use as monotherapy is not best practice, especially in bipolar I disorder, there may be a subset of bipolar II patients in whom monotherapy “might still be acceptable; but I don’t think it’s a good idea,” Vieta said.
He added that clinicians should very carefully screen for mixed symptoms, which call for the prescription of other drugs, such as olanzapine and fluoxetine.
“The other important message is that we have to be even more cautious in the long term with the use of antidepressants, and we should be able to use them when there is a comorbidity” that calls for their use, Vieta concluded.
Pacchiarotti reported having received speaker fees and educational grants from Adamed, AstraZeneca, Janssen-Cilag, and Lundbeck. Goodwin reported having received honoraria from Angellini, Medscape, Pfizer, Servier, Shire, and Sun; having shares in P1vital Products; past employment as medical director of P1vital Products; and advisory board membership for Compass Pathways, Minerva, MSD, Novartis, Lundbeck, Sage, Servier, and Shire. Vieta has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s been surreal
Hopefully 2020 will be the strangest year in modern memory, but who knows?
Things continue to be surreal at my office. I haven’t seen my staff since mid-March, even though I’m in touch with them all day long. Fortunately we live in an age where many things can be handled from home.
At the office I’d started to see an increase in patients, but that has dropped off again as the infection rate in Arizona has soared out of control. I’m not complaining about patients staying home; many neurology patients are frail or on immune-suppressing agents, and should not be out and about.
Normally I’m a stickler for stable patients coming in once a year for refills, but in 2020 I’m letting that slide. Sumatriptan, levetiracetam, and nortriptyline are better filled for 90 days to minimize potential COVID-19 contacts on all parts – including mine.
Originally I thought that some degree of normalcy would be back by August, but clearly that won’t be the case. Arizona, and many other states, continue to get worse as political ambitions trounce sound science.
A year ago I routinely fielded calls asking whether various supplements would fend off Alzheimer’s disease as the manufacturers claimed (NO! THEY DON’T!). Today similar calls come in asking about stuff marketed to prevent and cure COVID-19 (same answer).
I have no idea when this will improve. My kids are scheduled to move back into their dorms in about a month, but realistically I don’t see that safely happening. Classrooms, with the reduced capacity needed and cost of frequent cleanings, seem impractical, compared with Zoom.
The college football season is almost certainly going to be canceled. The NFL maybe. Basketball and baseball are playing out reduced seasons in sterilized bubbles. Sports, next to holidays and school, are the cyclical touchstones our society is measured by. Their disruption reflects the strangeness of the year as a whole.
As always during the Phoenix summer, I’m hiding in an air-conditioned office, waiting for patients to come in. It’s quieter without my secretary and her energetic 4-year-old daughter. But I’m still here. It’s strange with the unfamiliar silence, but the routine of coming to work each day, even on a reduced schedule, brings a sense of normalcy. There may not be as many patients, but those who need me come in, and as long as I’m able to, I’ll be here to help them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Hopefully 2020 will be the strangest year in modern memory, but who knows?
Things continue to be surreal at my office. I haven’t seen my staff since mid-March, even though I’m in touch with them all day long. Fortunately we live in an age where many things can be handled from home.
At the office I’d started to see an increase in patients, but that has dropped off again as the infection rate in Arizona has soared out of control. I’m not complaining about patients staying home; many neurology patients are frail or on immune-suppressing agents, and should not be out and about.
Normally I’m a stickler for stable patients coming in once a year for refills, but in 2020 I’m letting that slide. Sumatriptan, levetiracetam, and nortriptyline are better filled for 90 days to minimize potential COVID-19 contacts on all parts – including mine.
Originally I thought that some degree of normalcy would be back by August, but clearly that won’t be the case. Arizona, and many other states, continue to get worse as political ambitions trounce sound science.
A year ago I routinely fielded calls asking whether various supplements would fend off Alzheimer’s disease as the manufacturers claimed (NO! THEY DON’T!). Today similar calls come in asking about stuff marketed to prevent and cure COVID-19 (same answer).
I have no idea when this will improve. My kids are scheduled to move back into their dorms in about a month, but realistically I don’t see that safely happening. Classrooms, with the reduced capacity needed and cost of frequent cleanings, seem impractical, compared with Zoom.
The college football season is almost certainly going to be canceled. The NFL maybe. Basketball and baseball are playing out reduced seasons in sterilized bubbles. Sports, next to holidays and school, are the cyclical touchstones our society is measured by. Their disruption reflects the strangeness of the year as a whole.
As always during the Phoenix summer, I’m hiding in an air-conditioned office, waiting for patients to come in. It’s quieter without my secretary and her energetic 4-year-old daughter. But I’m still here. It’s strange with the unfamiliar silence, but the routine of coming to work each day, even on a reduced schedule, brings a sense of normalcy. There may not be as many patients, but those who need me come in, and as long as I’m able to, I’ll be here to help them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Hopefully 2020 will be the strangest year in modern memory, but who knows?
Things continue to be surreal at my office. I haven’t seen my staff since mid-March, even though I’m in touch with them all day long. Fortunately we live in an age where many things can be handled from home.
At the office I’d started to see an increase in patients, but that has dropped off again as the infection rate in Arizona has soared out of control. I’m not complaining about patients staying home; many neurology patients are frail or on immune-suppressing agents, and should not be out and about.
Normally I’m a stickler for stable patients coming in once a year for refills, but in 2020 I’m letting that slide. Sumatriptan, levetiracetam, and nortriptyline are better filled for 90 days to minimize potential COVID-19 contacts on all parts – including mine.
Originally I thought that some degree of normalcy would be back by August, but clearly that won’t be the case. Arizona, and many other states, continue to get worse as political ambitions trounce sound science.
A year ago I routinely fielded calls asking whether various supplements would fend off Alzheimer’s disease as the manufacturers claimed (NO! THEY DON’T!). Today similar calls come in asking about stuff marketed to prevent and cure COVID-19 (same answer).
I have no idea when this will improve. My kids are scheduled to move back into their dorms in about a month, but realistically I don’t see that safely happening. Classrooms, with the reduced capacity needed and cost of frequent cleanings, seem impractical, compared with Zoom.
The college football season is almost certainly going to be canceled. The NFL maybe. Basketball and baseball are playing out reduced seasons in sterilized bubbles. Sports, next to holidays and school, are the cyclical touchstones our society is measured by. Their disruption reflects the strangeness of the year as a whole.
As always during the Phoenix summer, I’m hiding in an air-conditioned office, waiting for patients to come in. It’s quieter without my secretary and her energetic 4-year-old daughter. But I’m still here. It’s strange with the unfamiliar silence, but the routine of coming to work each day, even on a reduced schedule, brings a sense of normalcy. There may not be as many patients, but those who need me come in, and as long as I’m able to, I’ll be here to help them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
New hope for ALS
. Both studies investigated potential benefits of suppressing the toxic activity in cells of a mutant gene (SOD1) that encodes superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) in patients with ALS.
One study investigated the antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) tofersen (Biogen); the other study examined viral vector–mediated gene suppression.
The studies’ promising results signal “the beginning of a new precision medicine–based approach towards treating ALS,” said Orla Hardiman, BSc, MB, BCh, BAO, MD, a consultant neurologist and professor of neurology at Trinity College and Beaumont Hospital in Dublin, Ireland. Dr. Hardiman co-authored an editorial that accompanied the two studies, which were published July 9 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Genetic culprits
ALS is a disorder of progressive degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons. It typically leads to death from ventilatory failure within 5 years of symptom onset.
Genetic factors are responsible for about half the risk variance of ALS. In populations of European origin, variants in SOD1 account for an estimated 13% to 20% of familial ALS, although this rate varies around the world. Although SOD1 is not the most common variant in ALS, it is the one that researchers are most familiar with and has been studied in an animal model.
In the first study, investigators evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the ASO tofersen in adults with ALS.
An ASO is a small piece of nucleic acid that enters neurons in the spinal cord and brain, explained co-investigator Toby A. Ferguson, MD, PhD, vice president and head of the neuromuscular development unit at Biogen.
ASO binds to the SOD1 gene and knocks down the SOD1 protein, which is the “toxic engine [that] drives the disease, kills neurons, and causes patients to have loss of function and eventually to die,” said Dr. Ferguson. “The ASO turns off the motor that produces that toxic protein,” he added.
Animal studies have shown that ASOs that target SOD1 messenger RNA transcripts prolong survival, improve motor performance, and reduce SOD1 protein concentrations.
The new phase 1/2 double-blind study included 50 adults at 18 sites in the United States, Canada, and four European countries. All had muscle weakness attributed to ALS and a documented SOD1 mutation. Participants were randomly assigned to receive one of four doses of tofersen—20, 40, 60, or 100 mg—or placebo. Treatment was administered via a lumbar intrathecal bolus injection. The study included a screening period followed by a 12-week intervention period and a 12-week follow-up.
Adverse events
A primary outcome was the incidence of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs. Results showed that all participants reported one or more AEs. The most common AEs were headache, pain at the injection site, post–lumbar puncture syndrome, and falls. Three deaths occurred, one in the placebo group, one in the 20-mg dose group, and one in the 60-mg dose group. There were no serious AEs in the 100-mg group.
Although the investigators found an increase in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein and white cell counts, there was no clear association between these observations and higher doses of tofersen or longer duration of exposure.
“We don’t know the implications of this, and it’s something we need to keep an eye on as we move these studies forward,” Dr. Ferguson said.
None of the AEs or CSF abnormalities led to trial discontinuation.
A secondary outcome was change in SOD1 protein concentration in CSF at day 85. The study showed that SOD1 concentrations decreased by 36% among the participants who received tofersen 100 mg and by lesser amounts in the patients who received lower doses. Concentrations in the placebo group were reduced by 3%.
The 36% reduction in the highest dose group is likely meaningful and “foundational to the concept of what this molecule can do,” Dr. Ferguson said.
“If the number one cause of SOD1 ALS is accumulation of toxic SOD1 protein, then the demonstration that we can reduce SOD1 protein in the CSF ... is saying that’s the first step on the way to showing the molecule is doing what it should do,” he added.
Emerging tool
In patients with ALS, neurofilament concentrations typically increase as the disease progresses. However, this study documented a reduction in these CSF concentrations. “One interpretation of that could be that there is less neurodegeneration or neuro injury” in patients treated with tofersen, Dr. Ferguson said.
He noted that neurofilament is “an emerging tool” for understanding neurodegeneration. It could also “be another sort of biochemical signal that the molecule is doing something important,” he added.
However, he noted that neurofilament concentration is still an exploratory marker.
Exploratory analyses suggested a possible slowing of functional loss, as measured by the ALS Functional Rating Scale–Revised (ALSFRS-R) score and the handheld dynamometry megascore. The latter assesses strength in 16 muscle groups in the arms and legs. The investigators noted that no conclusions can be drawn from these outcomes.
A post hoc analysis showed that among patients with SOD1 mutations associated with a fast-progressing disease course, the slope of clinical decline might have been gentler, and there was a greater decrease in CSF neurofilament concentration compared among those whose disease followed a slower course.
This suggests that “if you pick the right target,” even patients with severe disease can be treated, Dr. Ferguson said.
He acknowledged that in a relatively short study such as this one, it may be easier to see benefits in patients whose disease is progressing rapidly. However, he’s convinced that the treatment “would work for all SOD1 ALS patients, not just fast patients.”
Dr. Ferguson said the study investigators are encouraged by the new data, which “really suggest that we may be developing a meaningful treatment for SOD1 ALS.” However, “it’s still early” in terms of rolling out this therapy for patients with ALS, he said.
The safety and efficacy of tofersen are currently being evaluated in a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Limitations of the current study were the small number of participants, the short duration of treatment and follow-up, the exploratory nature of efficacy outcomes, and the post hoc methods for defining the fast-progressing subgroup.
Although an advantage of tofersen is that it can enter the nucleus of the cell, perhaps boosting effectiveness, a drawback might be that patients need several treatments administered via lumbar puncture. Following three initial doses, the drug is given every month.
An alternative approach might be a viral vector approach.
“Stunning” finding
In the second study, investigators assessed the safety of a single intrathecal infusion of a viral vector therapy designed to target SOD1 in two patients with familial ALS. The two patients were a 22-year-old man whose mother had died of ALS at age 45 and a 56-year-old man who had a family history of ALS.
The aim of the viral vector therapy is to continually suppress mutant gene activity, said study co-investigator Robert H. Brown, Jr, MD, professor of neurology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester.
“The virus essentially drops off a piece of DNA, and that DNA keeps making the agent that suppresses the gene,” Dr. Brown said.
He noted that the first patient had a mutation that causes a rapidly developing, “horribly devastating” disease.
Initially, the patient’s right leg, in which movement had been worsening over several weeks, “seemed to get stronger and remain strong for quite a long time. I’ve never seen that in this kind of mutation,” said Dr. Brown.
The patient died of ALS. At autopsy, there was evidence of suppression of SOD1 in the spinal cord. There was some preservation of motor neurons on the right side of the spinal cord, which Dr. Brown called a “stunning” finding.
“We have never seen preservation of motor neurons in an autopsy of a patient with this kind of mutation before,” he said.
Prior to the patient’s death, there were some initial signs of a decrease of SOD1 in CSF. However, the patient developed an inflammatory response in the lining of the CSF known as meningoradiculitis.
“In that setting, the SOD1 level went back up, so we could not say that we produced a significant lasting decrease,” Dr. Brown said.
One and done
Because meningoradiculitis occurred in the first patient, immunosuppressive drugs were administered to the second patient.
The functional status and vital capacity of the second patient were relatively stable during a 60-week period, a course that could be typical of the slow disease progression in patients with this SOD1 genotype.
As with the first patient, this man did not experience a substantial change in SOD1 protein levels in CSF, and he did not show clinical improvement.
The main advantage of a viral gene therapy is that it could be a one-time treatment; ideally, it could be used to replace a single missing gene in conditions such as cystic fibrosis. “The hope is that the virus will drop off the gene modulator or the gene itself of interest, depending on the disease, and that the gene will be there more or less indefinitely,” said Dr. Brown. “So the cliché is, ‘one and done’—if all goes well.”
This small study illustrates that gene therapy safely “turns off genes and that the extent of suppression of genes can be significant,” said Dr. Brown.
Most SOD1 mutations could be treated with this microRNA viral vector, he added. More than 180 such mutations have been identified in ALS.
Additional studies are now needed to determine the results of this method in a larger number of patients who have ALS with SOD1 mutations, the investigators wrote.
Within reach
Both studies are encouraging in that they show that a precision-medicine approach to ALS associated with single mutated genes “may be within reach,” said Dr. Hardiman.
She noted that gene therapies have been used successfully in other motor neuron conditions. For example, an ASO and a viral vector have “very significant efficacy” in a form of spinal muscular atrophy that occurs in infants. “So the underlying proof of principle is already there.”
The reduction in SOD1 levels among the highest-dose tofersen group in the first study indicates “target engagement,” Dr. Hardiman said.
In that study, the documented decreased protein in the CSF appeared to be dose related, as was the effect for neurofilaments, which is biomarker evidence of neuronal damage, she noted.
In the second study, the pathologic evidence from the first patient also suggests “evidence of target engagement,” Dr. Hardiman said.
However, she added, “We don’t know very much about the outcome of the second case other than immunosuppression seemed to be beneficial.”
New hope
Both studies have caveats, said Dr. Hardiman. For example, it is unclear whether the treatments would be beneficial for every variant in SOD1.
“These are very expensive therapies, and we will need to have some level of certainty in order to be able to determine whether this should be a treatment for a patient or not,” said Dr. Hardiman.
She also noted that the studies were not powered to provide evidence of efficacy and that they raise questions about the accuracy of the ALSFRS-R.
One issue is that the respiratory part of that scale is “very insensitive”; another is that the scale doesn’t capture nonmotor elements, such as cognition and behavior, she said.
Utilizing a combination of the ALSFRS-R slope and survival would “probably be more beneficial,” Dr. Hardiman said.
Understanding how to alter the genetic influence in a disorder is important to be able to identify successful treatments, Dr. Hardiman added. For example, the discovery of the BRCA gene led oncologists to develop a precision medicine approach to the treatment of breast cancer.
In regard to ALS, by starting with subgroups that have specific genomic features, “investigators are providing new hope for patients at genetic risk for this devastating fatal disease,” said Dr. Hardiman.
The first study was funded by Biogen. The second study was funded by a fellowship grant from the Alzheimer’s Association, a Jack Satter Foundation Award, the ALS Association, the Angel Fund for ALS Research, ALS Finding a Cure, ALS-One, Project ALS, the Massachusetts General Hospital, the Max Rosenfeld and Cellucci Funds for ALS Research, and several senior members of Bain Capital. Dr. Ferguson is employed by and holds stock in Biogen. Dr. Brown receives grant support from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. He is also co-founder of Apic Bio. Dr. Hardiman is the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degenerations, has consulted for Cytokinetics, Mitsubishi, and Wave, and holds research grants from Novartis and Merck. During the past 2 years, she has also been a principal investigator on ALS clinical trials sponsored by Orion and Cytokinetics and is currently on the data and safety monitoring board of Accelsior.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
. Both studies investigated potential benefits of suppressing the toxic activity in cells of a mutant gene (SOD1) that encodes superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) in patients with ALS.
One study investigated the antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) tofersen (Biogen); the other study examined viral vector–mediated gene suppression.
The studies’ promising results signal “the beginning of a new precision medicine–based approach towards treating ALS,” said Orla Hardiman, BSc, MB, BCh, BAO, MD, a consultant neurologist and professor of neurology at Trinity College and Beaumont Hospital in Dublin, Ireland. Dr. Hardiman co-authored an editorial that accompanied the two studies, which were published July 9 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Genetic culprits
ALS is a disorder of progressive degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons. It typically leads to death from ventilatory failure within 5 years of symptom onset.
Genetic factors are responsible for about half the risk variance of ALS. In populations of European origin, variants in SOD1 account for an estimated 13% to 20% of familial ALS, although this rate varies around the world. Although SOD1 is not the most common variant in ALS, it is the one that researchers are most familiar with and has been studied in an animal model.
In the first study, investigators evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the ASO tofersen in adults with ALS.
An ASO is a small piece of nucleic acid that enters neurons in the spinal cord and brain, explained co-investigator Toby A. Ferguson, MD, PhD, vice president and head of the neuromuscular development unit at Biogen.
ASO binds to the SOD1 gene and knocks down the SOD1 protein, which is the “toxic engine [that] drives the disease, kills neurons, and causes patients to have loss of function and eventually to die,” said Dr. Ferguson. “The ASO turns off the motor that produces that toxic protein,” he added.
Animal studies have shown that ASOs that target SOD1 messenger RNA transcripts prolong survival, improve motor performance, and reduce SOD1 protein concentrations.
The new phase 1/2 double-blind study included 50 adults at 18 sites in the United States, Canada, and four European countries. All had muscle weakness attributed to ALS and a documented SOD1 mutation. Participants were randomly assigned to receive one of four doses of tofersen—20, 40, 60, or 100 mg—or placebo. Treatment was administered via a lumbar intrathecal bolus injection. The study included a screening period followed by a 12-week intervention period and a 12-week follow-up.
Adverse events
A primary outcome was the incidence of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs. Results showed that all participants reported one or more AEs. The most common AEs were headache, pain at the injection site, post–lumbar puncture syndrome, and falls. Three deaths occurred, one in the placebo group, one in the 20-mg dose group, and one in the 60-mg dose group. There were no serious AEs in the 100-mg group.
Although the investigators found an increase in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein and white cell counts, there was no clear association between these observations and higher doses of tofersen or longer duration of exposure.
“We don’t know the implications of this, and it’s something we need to keep an eye on as we move these studies forward,” Dr. Ferguson said.
None of the AEs or CSF abnormalities led to trial discontinuation.
A secondary outcome was change in SOD1 protein concentration in CSF at day 85. The study showed that SOD1 concentrations decreased by 36% among the participants who received tofersen 100 mg and by lesser amounts in the patients who received lower doses. Concentrations in the placebo group were reduced by 3%.
The 36% reduction in the highest dose group is likely meaningful and “foundational to the concept of what this molecule can do,” Dr. Ferguson said.
“If the number one cause of SOD1 ALS is accumulation of toxic SOD1 protein, then the demonstration that we can reduce SOD1 protein in the CSF ... is saying that’s the first step on the way to showing the molecule is doing what it should do,” he added.
Emerging tool
In patients with ALS, neurofilament concentrations typically increase as the disease progresses. However, this study documented a reduction in these CSF concentrations. “One interpretation of that could be that there is less neurodegeneration or neuro injury” in patients treated with tofersen, Dr. Ferguson said.
He noted that neurofilament is “an emerging tool” for understanding neurodegeneration. It could also “be another sort of biochemical signal that the molecule is doing something important,” he added.
However, he noted that neurofilament concentration is still an exploratory marker.
Exploratory analyses suggested a possible slowing of functional loss, as measured by the ALS Functional Rating Scale–Revised (ALSFRS-R) score and the handheld dynamometry megascore. The latter assesses strength in 16 muscle groups in the arms and legs. The investigators noted that no conclusions can be drawn from these outcomes.
A post hoc analysis showed that among patients with SOD1 mutations associated with a fast-progressing disease course, the slope of clinical decline might have been gentler, and there was a greater decrease in CSF neurofilament concentration compared among those whose disease followed a slower course.
This suggests that “if you pick the right target,” even patients with severe disease can be treated, Dr. Ferguson said.
He acknowledged that in a relatively short study such as this one, it may be easier to see benefits in patients whose disease is progressing rapidly. However, he’s convinced that the treatment “would work for all SOD1 ALS patients, not just fast patients.”
Dr. Ferguson said the study investigators are encouraged by the new data, which “really suggest that we may be developing a meaningful treatment for SOD1 ALS.” However, “it’s still early” in terms of rolling out this therapy for patients with ALS, he said.
The safety and efficacy of tofersen are currently being evaluated in a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Limitations of the current study were the small number of participants, the short duration of treatment and follow-up, the exploratory nature of efficacy outcomes, and the post hoc methods for defining the fast-progressing subgroup.
Although an advantage of tofersen is that it can enter the nucleus of the cell, perhaps boosting effectiveness, a drawback might be that patients need several treatments administered via lumbar puncture. Following three initial doses, the drug is given every month.
An alternative approach might be a viral vector approach.
“Stunning” finding
In the second study, investigators assessed the safety of a single intrathecal infusion of a viral vector therapy designed to target SOD1 in two patients with familial ALS. The two patients were a 22-year-old man whose mother had died of ALS at age 45 and a 56-year-old man who had a family history of ALS.
The aim of the viral vector therapy is to continually suppress mutant gene activity, said study co-investigator Robert H. Brown, Jr, MD, professor of neurology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester.
“The virus essentially drops off a piece of DNA, and that DNA keeps making the agent that suppresses the gene,” Dr. Brown said.
He noted that the first patient had a mutation that causes a rapidly developing, “horribly devastating” disease.
Initially, the patient’s right leg, in which movement had been worsening over several weeks, “seemed to get stronger and remain strong for quite a long time. I’ve never seen that in this kind of mutation,” said Dr. Brown.
The patient died of ALS. At autopsy, there was evidence of suppression of SOD1 in the spinal cord. There was some preservation of motor neurons on the right side of the spinal cord, which Dr. Brown called a “stunning” finding.
“We have never seen preservation of motor neurons in an autopsy of a patient with this kind of mutation before,” he said.
Prior to the patient’s death, there were some initial signs of a decrease of SOD1 in CSF. However, the patient developed an inflammatory response in the lining of the CSF known as meningoradiculitis.
“In that setting, the SOD1 level went back up, so we could not say that we produced a significant lasting decrease,” Dr. Brown said.
One and done
Because meningoradiculitis occurred in the first patient, immunosuppressive drugs were administered to the second patient.
The functional status and vital capacity of the second patient were relatively stable during a 60-week period, a course that could be typical of the slow disease progression in patients with this SOD1 genotype.
As with the first patient, this man did not experience a substantial change in SOD1 protein levels in CSF, and he did not show clinical improvement.
The main advantage of a viral gene therapy is that it could be a one-time treatment; ideally, it could be used to replace a single missing gene in conditions such as cystic fibrosis. “The hope is that the virus will drop off the gene modulator or the gene itself of interest, depending on the disease, and that the gene will be there more or less indefinitely,” said Dr. Brown. “So the cliché is, ‘one and done’—if all goes well.”
This small study illustrates that gene therapy safely “turns off genes and that the extent of suppression of genes can be significant,” said Dr. Brown.
Most SOD1 mutations could be treated with this microRNA viral vector, he added. More than 180 such mutations have been identified in ALS.
Additional studies are now needed to determine the results of this method in a larger number of patients who have ALS with SOD1 mutations, the investigators wrote.
Within reach
Both studies are encouraging in that they show that a precision-medicine approach to ALS associated with single mutated genes “may be within reach,” said Dr. Hardiman.
She noted that gene therapies have been used successfully in other motor neuron conditions. For example, an ASO and a viral vector have “very significant efficacy” in a form of spinal muscular atrophy that occurs in infants. “So the underlying proof of principle is already there.”
The reduction in SOD1 levels among the highest-dose tofersen group in the first study indicates “target engagement,” Dr. Hardiman said.
In that study, the documented decreased protein in the CSF appeared to be dose related, as was the effect for neurofilaments, which is biomarker evidence of neuronal damage, she noted.
In the second study, the pathologic evidence from the first patient also suggests “evidence of target engagement,” Dr. Hardiman said.
However, she added, “We don’t know very much about the outcome of the second case other than immunosuppression seemed to be beneficial.”
New hope
Both studies have caveats, said Dr. Hardiman. For example, it is unclear whether the treatments would be beneficial for every variant in SOD1.
“These are very expensive therapies, and we will need to have some level of certainty in order to be able to determine whether this should be a treatment for a patient or not,” said Dr. Hardiman.
She also noted that the studies were not powered to provide evidence of efficacy and that they raise questions about the accuracy of the ALSFRS-R.
One issue is that the respiratory part of that scale is “very insensitive”; another is that the scale doesn’t capture nonmotor elements, such as cognition and behavior, she said.
Utilizing a combination of the ALSFRS-R slope and survival would “probably be more beneficial,” Dr. Hardiman said.
Understanding how to alter the genetic influence in a disorder is important to be able to identify successful treatments, Dr. Hardiman added. For example, the discovery of the BRCA gene led oncologists to develop a precision medicine approach to the treatment of breast cancer.
In regard to ALS, by starting with subgroups that have specific genomic features, “investigators are providing new hope for patients at genetic risk for this devastating fatal disease,” said Dr. Hardiman.
The first study was funded by Biogen. The second study was funded by a fellowship grant from the Alzheimer’s Association, a Jack Satter Foundation Award, the ALS Association, the Angel Fund for ALS Research, ALS Finding a Cure, ALS-One, Project ALS, the Massachusetts General Hospital, the Max Rosenfeld and Cellucci Funds for ALS Research, and several senior members of Bain Capital. Dr. Ferguson is employed by and holds stock in Biogen. Dr. Brown receives grant support from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. He is also co-founder of Apic Bio. Dr. Hardiman is the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degenerations, has consulted for Cytokinetics, Mitsubishi, and Wave, and holds research grants from Novartis and Merck. During the past 2 years, she has also been a principal investigator on ALS clinical trials sponsored by Orion and Cytokinetics and is currently on the data and safety monitoring board of Accelsior.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
. Both studies investigated potential benefits of suppressing the toxic activity in cells of a mutant gene (SOD1) that encodes superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) in patients with ALS.
One study investigated the antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) tofersen (Biogen); the other study examined viral vector–mediated gene suppression.
The studies’ promising results signal “the beginning of a new precision medicine–based approach towards treating ALS,” said Orla Hardiman, BSc, MB, BCh, BAO, MD, a consultant neurologist and professor of neurology at Trinity College and Beaumont Hospital in Dublin, Ireland. Dr. Hardiman co-authored an editorial that accompanied the two studies, which were published July 9 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Genetic culprits
ALS is a disorder of progressive degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons. It typically leads to death from ventilatory failure within 5 years of symptom onset.
Genetic factors are responsible for about half the risk variance of ALS. In populations of European origin, variants in SOD1 account for an estimated 13% to 20% of familial ALS, although this rate varies around the world. Although SOD1 is not the most common variant in ALS, it is the one that researchers are most familiar with and has been studied in an animal model.
In the first study, investigators evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the ASO tofersen in adults with ALS.
An ASO is a small piece of nucleic acid that enters neurons in the spinal cord and brain, explained co-investigator Toby A. Ferguson, MD, PhD, vice president and head of the neuromuscular development unit at Biogen.
ASO binds to the SOD1 gene and knocks down the SOD1 protein, which is the “toxic engine [that] drives the disease, kills neurons, and causes patients to have loss of function and eventually to die,” said Dr. Ferguson. “The ASO turns off the motor that produces that toxic protein,” he added.
Animal studies have shown that ASOs that target SOD1 messenger RNA transcripts prolong survival, improve motor performance, and reduce SOD1 protein concentrations.
The new phase 1/2 double-blind study included 50 adults at 18 sites in the United States, Canada, and four European countries. All had muscle weakness attributed to ALS and a documented SOD1 mutation. Participants were randomly assigned to receive one of four doses of tofersen—20, 40, 60, or 100 mg—or placebo. Treatment was administered via a lumbar intrathecal bolus injection. The study included a screening period followed by a 12-week intervention period and a 12-week follow-up.
Adverse events
A primary outcome was the incidence of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs. Results showed that all participants reported one or more AEs. The most common AEs were headache, pain at the injection site, post–lumbar puncture syndrome, and falls. Three deaths occurred, one in the placebo group, one in the 20-mg dose group, and one in the 60-mg dose group. There were no serious AEs in the 100-mg group.
Although the investigators found an increase in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein and white cell counts, there was no clear association between these observations and higher doses of tofersen or longer duration of exposure.
“We don’t know the implications of this, and it’s something we need to keep an eye on as we move these studies forward,” Dr. Ferguson said.
None of the AEs or CSF abnormalities led to trial discontinuation.
A secondary outcome was change in SOD1 protein concentration in CSF at day 85. The study showed that SOD1 concentrations decreased by 36% among the participants who received tofersen 100 mg and by lesser amounts in the patients who received lower doses. Concentrations in the placebo group were reduced by 3%.
The 36% reduction in the highest dose group is likely meaningful and “foundational to the concept of what this molecule can do,” Dr. Ferguson said.
“If the number one cause of SOD1 ALS is accumulation of toxic SOD1 protein, then the demonstration that we can reduce SOD1 protein in the CSF ... is saying that’s the first step on the way to showing the molecule is doing what it should do,” he added.
Emerging tool
In patients with ALS, neurofilament concentrations typically increase as the disease progresses. However, this study documented a reduction in these CSF concentrations. “One interpretation of that could be that there is less neurodegeneration or neuro injury” in patients treated with tofersen, Dr. Ferguson said.
He noted that neurofilament is “an emerging tool” for understanding neurodegeneration. It could also “be another sort of biochemical signal that the molecule is doing something important,” he added.
However, he noted that neurofilament concentration is still an exploratory marker.
Exploratory analyses suggested a possible slowing of functional loss, as measured by the ALS Functional Rating Scale–Revised (ALSFRS-R) score and the handheld dynamometry megascore. The latter assesses strength in 16 muscle groups in the arms and legs. The investigators noted that no conclusions can be drawn from these outcomes.
A post hoc analysis showed that among patients with SOD1 mutations associated with a fast-progressing disease course, the slope of clinical decline might have been gentler, and there was a greater decrease in CSF neurofilament concentration compared among those whose disease followed a slower course.
This suggests that “if you pick the right target,” even patients with severe disease can be treated, Dr. Ferguson said.
He acknowledged that in a relatively short study such as this one, it may be easier to see benefits in patients whose disease is progressing rapidly. However, he’s convinced that the treatment “would work for all SOD1 ALS patients, not just fast patients.”
Dr. Ferguson said the study investigators are encouraged by the new data, which “really suggest that we may be developing a meaningful treatment for SOD1 ALS.” However, “it’s still early” in terms of rolling out this therapy for patients with ALS, he said.
The safety and efficacy of tofersen are currently being evaluated in a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Limitations of the current study were the small number of participants, the short duration of treatment and follow-up, the exploratory nature of efficacy outcomes, and the post hoc methods for defining the fast-progressing subgroup.
Although an advantage of tofersen is that it can enter the nucleus of the cell, perhaps boosting effectiveness, a drawback might be that patients need several treatments administered via lumbar puncture. Following three initial doses, the drug is given every month.
An alternative approach might be a viral vector approach.
“Stunning” finding
In the second study, investigators assessed the safety of a single intrathecal infusion of a viral vector therapy designed to target SOD1 in two patients with familial ALS. The two patients were a 22-year-old man whose mother had died of ALS at age 45 and a 56-year-old man who had a family history of ALS.
The aim of the viral vector therapy is to continually suppress mutant gene activity, said study co-investigator Robert H. Brown, Jr, MD, professor of neurology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester.
“The virus essentially drops off a piece of DNA, and that DNA keeps making the agent that suppresses the gene,” Dr. Brown said.
He noted that the first patient had a mutation that causes a rapidly developing, “horribly devastating” disease.
Initially, the patient’s right leg, in which movement had been worsening over several weeks, “seemed to get stronger and remain strong for quite a long time. I’ve never seen that in this kind of mutation,” said Dr. Brown.
The patient died of ALS. At autopsy, there was evidence of suppression of SOD1 in the spinal cord. There was some preservation of motor neurons on the right side of the spinal cord, which Dr. Brown called a “stunning” finding.
“We have never seen preservation of motor neurons in an autopsy of a patient with this kind of mutation before,” he said.
Prior to the patient’s death, there were some initial signs of a decrease of SOD1 in CSF. However, the patient developed an inflammatory response in the lining of the CSF known as meningoradiculitis.
“In that setting, the SOD1 level went back up, so we could not say that we produced a significant lasting decrease,” Dr. Brown said.
One and done
Because meningoradiculitis occurred in the first patient, immunosuppressive drugs were administered to the second patient.
The functional status and vital capacity of the second patient were relatively stable during a 60-week period, a course that could be typical of the slow disease progression in patients with this SOD1 genotype.
As with the first patient, this man did not experience a substantial change in SOD1 protein levels in CSF, and he did not show clinical improvement.
The main advantage of a viral gene therapy is that it could be a one-time treatment; ideally, it could be used to replace a single missing gene in conditions such as cystic fibrosis. “The hope is that the virus will drop off the gene modulator or the gene itself of interest, depending on the disease, and that the gene will be there more or less indefinitely,” said Dr. Brown. “So the cliché is, ‘one and done’—if all goes well.”
This small study illustrates that gene therapy safely “turns off genes and that the extent of suppression of genes can be significant,” said Dr. Brown.
Most SOD1 mutations could be treated with this microRNA viral vector, he added. More than 180 such mutations have been identified in ALS.
Additional studies are now needed to determine the results of this method in a larger number of patients who have ALS with SOD1 mutations, the investigators wrote.
Within reach
Both studies are encouraging in that they show that a precision-medicine approach to ALS associated with single mutated genes “may be within reach,” said Dr. Hardiman.
She noted that gene therapies have been used successfully in other motor neuron conditions. For example, an ASO and a viral vector have “very significant efficacy” in a form of spinal muscular atrophy that occurs in infants. “So the underlying proof of principle is already there.”
The reduction in SOD1 levels among the highest-dose tofersen group in the first study indicates “target engagement,” Dr. Hardiman said.
In that study, the documented decreased protein in the CSF appeared to be dose related, as was the effect for neurofilaments, which is biomarker evidence of neuronal damage, she noted.
In the second study, the pathologic evidence from the first patient also suggests “evidence of target engagement,” Dr. Hardiman said.
However, she added, “We don’t know very much about the outcome of the second case other than immunosuppression seemed to be beneficial.”
New hope
Both studies have caveats, said Dr. Hardiman. For example, it is unclear whether the treatments would be beneficial for every variant in SOD1.
“These are very expensive therapies, and we will need to have some level of certainty in order to be able to determine whether this should be a treatment for a patient or not,” said Dr. Hardiman.
She also noted that the studies were not powered to provide evidence of efficacy and that they raise questions about the accuracy of the ALSFRS-R.
One issue is that the respiratory part of that scale is “very insensitive”; another is that the scale doesn’t capture nonmotor elements, such as cognition and behavior, she said.
Utilizing a combination of the ALSFRS-R slope and survival would “probably be more beneficial,” Dr. Hardiman said.
Understanding how to alter the genetic influence in a disorder is important to be able to identify successful treatments, Dr. Hardiman added. For example, the discovery of the BRCA gene led oncologists to develop a precision medicine approach to the treatment of breast cancer.
In regard to ALS, by starting with subgroups that have specific genomic features, “investigators are providing new hope for patients at genetic risk for this devastating fatal disease,” said Dr. Hardiman.
The first study was funded by Biogen. The second study was funded by a fellowship grant from the Alzheimer’s Association, a Jack Satter Foundation Award, the ALS Association, the Angel Fund for ALS Research, ALS Finding a Cure, ALS-One, Project ALS, the Massachusetts General Hospital, the Max Rosenfeld and Cellucci Funds for ALS Research, and several senior members of Bain Capital. Dr. Ferguson is employed by and holds stock in Biogen. Dr. Brown receives grant support from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. He is also co-founder of Apic Bio. Dr. Hardiman is the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degenerations, has consulted for Cytokinetics, Mitsubishi, and Wave, and holds research grants from Novartis and Merck. During the past 2 years, she has also been a principal investigator on ALS clinical trials sponsored by Orion and Cytokinetics and is currently on the data and safety monitoring board of Accelsior.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE