User login
New CDC guidance for health care personnel exposed to HCV
The new guidance was developed in part as a result of an increase in the incidence of acute HCV infection in the United States, which increases the risk for occupational exposure among HCP. “[I]n certain health care settings, HCP might be exposed to source patients with early HCV infection before those patients develop serologic evidence of infection or symptoms indicative of viral hepatitis,” wrote the authors of the report, published online July 24 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The guidelines, which no longer recommend waiting for spontaneous resolution upon initial diagnosis, include recommendations and algorithms for baseline and follow-up testing, appropriate test type, and recommendations for clinical management. The recommendations were developed on the basis of a current literature review, expert opinion from subject matter experts, and recent guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Baseline testing ASAP
Baseline testing of the source patient and the HCP should be performed as soon as possible, preferably within 48 hours of exposure. The source patient should be tested for HCV RNA using a nucleic acid test. Alternatively, screening anti-HCV serology can be performed in patients at low risk for HCV and a nucleic acid test performed if serology is positive.
Baseline testing for the HCP should include anti-HCV testing and, if positive, HCV RNA testing is recommended. HCPs who test positive for HCV RNA at baseline are considered to have a preexisting HCV infection and should be referred for treatment.
Follow-up testing
For HCPs with exposure to blood or body fluids from a patient who is anti-HCV positive but HCV RNA negative, follow-up testing is not required.
If the source patient is HCV RNA positive, or if status of the source patient is unknown, the authors recommend that exposed HCPs have HCV RNA follow-up testing at 3-6 weeks post exposure, in addition to baseline testing. A final anti-HCV test is recommended at 4-6 months post exposure as there can be potential periods of aviremia during acute HCV infection.
Exposed HCPs who develop signs of illness indicative of HCV infection at any time should be tested for HCV RNA.
HCPs with positive HCV RNA test results should be referred for care and curative antiviral therapy.
Postexposure prophylaxis is not recommended
Recent data have shown that the risk for HCV infection from percutaneous exposure is 0.2% and from mucocutaneous exposure is 0%. On the basis of this information, the CDC guidelines no longer recommend routine postexposure prophylaxis for HCPs with occupational exposure to HCV. Rather, curative antiviral regimens should be reserved for instances of documented HCV transmission.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guidance was developed in part as a result of an increase in the incidence of acute HCV infection in the United States, which increases the risk for occupational exposure among HCP. “[I]n certain health care settings, HCP might be exposed to source patients with early HCV infection before those patients develop serologic evidence of infection or symptoms indicative of viral hepatitis,” wrote the authors of the report, published online July 24 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The guidelines, which no longer recommend waiting for spontaneous resolution upon initial diagnosis, include recommendations and algorithms for baseline and follow-up testing, appropriate test type, and recommendations for clinical management. The recommendations were developed on the basis of a current literature review, expert opinion from subject matter experts, and recent guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Baseline testing ASAP
Baseline testing of the source patient and the HCP should be performed as soon as possible, preferably within 48 hours of exposure. The source patient should be tested for HCV RNA using a nucleic acid test. Alternatively, screening anti-HCV serology can be performed in patients at low risk for HCV and a nucleic acid test performed if serology is positive.
Baseline testing for the HCP should include anti-HCV testing and, if positive, HCV RNA testing is recommended. HCPs who test positive for HCV RNA at baseline are considered to have a preexisting HCV infection and should be referred for treatment.
Follow-up testing
For HCPs with exposure to blood or body fluids from a patient who is anti-HCV positive but HCV RNA negative, follow-up testing is not required.
If the source patient is HCV RNA positive, or if status of the source patient is unknown, the authors recommend that exposed HCPs have HCV RNA follow-up testing at 3-6 weeks post exposure, in addition to baseline testing. A final anti-HCV test is recommended at 4-6 months post exposure as there can be potential periods of aviremia during acute HCV infection.
Exposed HCPs who develop signs of illness indicative of HCV infection at any time should be tested for HCV RNA.
HCPs with positive HCV RNA test results should be referred for care and curative antiviral therapy.
Postexposure prophylaxis is not recommended
Recent data have shown that the risk for HCV infection from percutaneous exposure is 0.2% and from mucocutaneous exposure is 0%. On the basis of this information, the CDC guidelines no longer recommend routine postexposure prophylaxis for HCPs with occupational exposure to HCV. Rather, curative antiviral regimens should be reserved for instances of documented HCV transmission.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guidance was developed in part as a result of an increase in the incidence of acute HCV infection in the United States, which increases the risk for occupational exposure among HCP. “[I]n certain health care settings, HCP might be exposed to source patients with early HCV infection before those patients develop serologic evidence of infection or symptoms indicative of viral hepatitis,” wrote the authors of the report, published online July 24 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The guidelines, which no longer recommend waiting for spontaneous resolution upon initial diagnosis, include recommendations and algorithms for baseline and follow-up testing, appropriate test type, and recommendations for clinical management. The recommendations were developed on the basis of a current literature review, expert opinion from subject matter experts, and recent guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Baseline testing ASAP
Baseline testing of the source patient and the HCP should be performed as soon as possible, preferably within 48 hours of exposure. The source patient should be tested for HCV RNA using a nucleic acid test. Alternatively, screening anti-HCV serology can be performed in patients at low risk for HCV and a nucleic acid test performed if serology is positive.
Baseline testing for the HCP should include anti-HCV testing and, if positive, HCV RNA testing is recommended. HCPs who test positive for HCV RNA at baseline are considered to have a preexisting HCV infection and should be referred for treatment.
Follow-up testing
For HCPs with exposure to blood or body fluids from a patient who is anti-HCV positive but HCV RNA negative, follow-up testing is not required.
If the source patient is HCV RNA positive, or if status of the source patient is unknown, the authors recommend that exposed HCPs have HCV RNA follow-up testing at 3-6 weeks post exposure, in addition to baseline testing. A final anti-HCV test is recommended at 4-6 months post exposure as there can be potential periods of aviremia during acute HCV infection.
Exposed HCPs who develop signs of illness indicative of HCV infection at any time should be tested for HCV RNA.
HCPs with positive HCV RNA test results should be referred for care and curative antiviral therapy.
Postexposure prophylaxis is not recommended
Recent data have shown that the risk for HCV infection from percutaneous exposure is 0.2% and from mucocutaneous exposure is 0%. On the basis of this information, the CDC guidelines no longer recommend routine postexposure prophylaxis for HCPs with occupational exposure to HCV. Rather, curative antiviral regimens should be reserved for instances of documented HCV transmission.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lenalidomide may be an answer for refractory cutaneous lupus
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) is present in 25% of patients with systemic lupus at the time of diagnosis, but it can also occur in up to 85% of cases at some point in their disease course, Eveline Y. Wu, MD, said during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
“CLE can also occur without any systemic disease,” said Dr. Wu, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “It’s been shown that the risk of developing systemic lupus differs according to the type of skin involvement, meaning that cutaneous lupus can be classified into acute, subacute, chronic, and intermittent forms.”
Malar rash is the prototypical acute cutaneous lesion and is associated with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and anti–double stranded DNA antibody positivity, while discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common chronic lesion. “A small percentage of patients with discoid lupus can develop systemic lupus, particularly when the lesions are more disseminated,” said Dr. Wu, who specializes in pediatric rheumatology as well as allergy and immunology.
In the American College of Rheumatology’s 1997 classification system, mucocutaneous manifestations constitute 4 out of the 11 criteria that clinicians use to make a diagnosis of SLE: malar rash, discoid-lupus rash, photosensitivity, and oral or nasal mucocutaneous ulcerations. Dr. Wu recommends performing an oral exam on suspect cases, “because the oral ulcers that we see in systemic lupus tend to be painless, so oftentimes patients don’t realize they have them.”
Five other organ-specific manifestations of SLE include nonerosive arthritis, nephritis, encephalopathy, pleuritis or pericarditis, and cytopenia. The two other criteria are positive immunoserology and a positive antinuclear antibody test. “If you have any individuals present with one of these [mucocutaneous manifestations criteria], you want to think about getting a CBC to look for cytopenia or a urinalysis to look for evidence of nephritis, and potentially some additional blood studies, depending on your level of suspicion for systemic lupus,” Dr. Wu said.
Other rarer CLE manifestations include lupus pernio or chilblains, lupus panniculitis, livedo reticularis, bullous LE, urticarial vasculitis, neutrophilic dermatoses, and alopecia.
Common treatments for cutaneous manifestations associated pediatric SLE include hydroxychloroquine, low dose corticosteroids, topical steroids, methotrexate, and leflunomide. Other options for increasing severity of systemic disease include lenalidomide/thalidomide, azathioprine, calcineurin inhibitors, belimumab (Benlysta), high-dose corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), rituximab (Rituxan), and cyclophosphamide. Cutaneous manifestations of pediatric SLE can often be refractory to treatments.
In 2017, Dr. Wu and associates published a retrospective chart review of 10 adolescents who received lenalidomide for refractory CLE. One of the subjects was a 21-year-old male with a significant malar rash despite being on hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine, and prednisone 40 mg daily. “One month after being on lenalidomide he had a pretty impressive response,” Dr. Wu said. “It’s not quite clear how lenalidomide works in cutaneous lupus. Currently it’s only approved for use in myelodysplastic syndromes, multiple myeloma, as well as certain lymphomas. It’s thought to modulate different parts of the immune system, which collectively result in the cytotoxicity against tumor cells.”
Lenalidomide is supplied in capsule sizes ranging from 2.5 mg to 25 mg and is given once daily. “For a smaller child, I would think about starting 5 mg once a day,” Dr. Wu said. “For an adult-sized adolescent, you could start at 10 mg once a day and then titrate up based on response. Side effects that you need to worry about are cytopenia and GI symptoms. The venous and arterial thromboembolism risk has been seen in patients with multiple myeloma, and it is unclear if this risk is applicable to all indications.” Use of the medication requires enrollment into a safety monitoring program.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) is present in 25% of patients with systemic lupus at the time of diagnosis, but it can also occur in up to 85% of cases at some point in their disease course, Eveline Y. Wu, MD, said during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
“CLE can also occur without any systemic disease,” said Dr. Wu, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “It’s been shown that the risk of developing systemic lupus differs according to the type of skin involvement, meaning that cutaneous lupus can be classified into acute, subacute, chronic, and intermittent forms.”
Malar rash is the prototypical acute cutaneous lesion and is associated with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and anti–double stranded DNA antibody positivity, while discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common chronic lesion. “A small percentage of patients with discoid lupus can develop systemic lupus, particularly when the lesions are more disseminated,” said Dr. Wu, who specializes in pediatric rheumatology as well as allergy and immunology.
In the American College of Rheumatology’s 1997 classification system, mucocutaneous manifestations constitute 4 out of the 11 criteria that clinicians use to make a diagnosis of SLE: malar rash, discoid-lupus rash, photosensitivity, and oral or nasal mucocutaneous ulcerations. Dr. Wu recommends performing an oral exam on suspect cases, “because the oral ulcers that we see in systemic lupus tend to be painless, so oftentimes patients don’t realize they have them.”
Five other organ-specific manifestations of SLE include nonerosive arthritis, nephritis, encephalopathy, pleuritis or pericarditis, and cytopenia. The two other criteria are positive immunoserology and a positive antinuclear antibody test. “If you have any individuals present with one of these [mucocutaneous manifestations criteria], you want to think about getting a CBC to look for cytopenia or a urinalysis to look for evidence of nephritis, and potentially some additional blood studies, depending on your level of suspicion for systemic lupus,” Dr. Wu said.
Other rarer CLE manifestations include lupus pernio or chilblains, lupus panniculitis, livedo reticularis, bullous LE, urticarial vasculitis, neutrophilic dermatoses, and alopecia.
Common treatments for cutaneous manifestations associated pediatric SLE include hydroxychloroquine, low dose corticosteroids, topical steroids, methotrexate, and leflunomide. Other options for increasing severity of systemic disease include lenalidomide/thalidomide, azathioprine, calcineurin inhibitors, belimumab (Benlysta), high-dose corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), rituximab (Rituxan), and cyclophosphamide. Cutaneous manifestations of pediatric SLE can often be refractory to treatments.
In 2017, Dr. Wu and associates published a retrospective chart review of 10 adolescents who received lenalidomide for refractory CLE. One of the subjects was a 21-year-old male with a significant malar rash despite being on hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine, and prednisone 40 mg daily. “One month after being on lenalidomide he had a pretty impressive response,” Dr. Wu said. “It’s not quite clear how lenalidomide works in cutaneous lupus. Currently it’s only approved for use in myelodysplastic syndromes, multiple myeloma, as well as certain lymphomas. It’s thought to modulate different parts of the immune system, which collectively result in the cytotoxicity against tumor cells.”
Lenalidomide is supplied in capsule sizes ranging from 2.5 mg to 25 mg and is given once daily. “For a smaller child, I would think about starting 5 mg once a day,” Dr. Wu said. “For an adult-sized adolescent, you could start at 10 mg once a day and then titrate up based on response. Side effects that you need to worry about are cytopenia and GI symptoms. The venous and arterial thromboembolism risk has been seen in patients with multiple myeloma, and it is unclear if this risk is applicable to all indications.” Use of the medication requires enrollment into a safety monitoring program.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) is present in 25% of patients with systemic lupus at the time of diagnosis, but it can also occur in up to 85% of cases at some point in their disease course, Eveline Y. Wu, MD, said during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
“CLE can also occur without any systemic disease,” said Dr. Wu, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “It’s been shown that the risk of developing systemic lupus differs according to the type of skin involvement, meaning that cutaneous lupus can be classified into acute, subacute, chronic, and intermittent forms.”
Malar rash is the prototypical acute cutaneous lesion and is associated with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and anti–double stranded DNA antibody positivity, while discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common chronic lesion. “A small percentage of patients with discoid lupus can develop systemic lupus, particularly when the lesions are more disseminated,” said Dr. Wu, who specializes in pediatric rheumatology as well as allergy and immunology.
In the American College of Rheumatology’s 1997 classification system, mucocutaneous manifestations constitute 4 out of the 11 criteria that clinicians use to make a diagnosis of SLE: malar rash, discoid-lupus rash, photosensitivity, and oral or nasal mucocutaneous ulcerations. Dr. Wu recommends performing an oral exam on suspect cases, “because the oral ulcers that we see in systemic lupus tend to be painless, so oftentimes patients don’t realize they have them.”
Five other organ-specific manifestations of SLE include nonerosive arthritis, nephritis, encephalopathy, pleuritis or pericarditis, and cytopenia. The two other criteria are positive immunoserology and a positive antinuclear antibody test. “If you have any individuals present with one of these [mucocutaneous manifestations criteria], you want to think about getting a CBC to look for cytopenia or a urinalysis to look for evidence of nephritis, and potentially some additional blood studies, depending on your level of suspicion for systemic lupus,” Dr. Wu said.
Other rarer CLE manifestations include lupus pernio or chilblains, lupus panniculitis, livedo reticularis, bullous LE, urticarial vasculitis, neutrophilic dermatoses, and alopecia.
Common treatments for cutaneous manifestations associated pediatric SLE include hydroxychloroquine, low dose corticosteroids, topical steroids, methotrexate, and leflunomide. Other options for increasing severity of systemic disease include lenalidomide/thalidomide, azathioprine, calcineurin inhibitors, belimumab (Benlysta), high-dose corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), rituximab (Rituxan), and cyclophosphamide. Cutaneous manifestations of pediatric SLE can often be refractory to treatments.
In 2017, Dr. Wu and associates published a retrospective chart review of 10 adolescents who received lenalidomide for refractory CLE. One of the subjects was a 21-year-old male with a significant malar rash despite being on hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine, and prednisone 40 mg daily. “One month after being on lenalidomide he had a pretty impressive response,” Dr. Wu said. “It’s not quite clear how lenalidomide works in cutaneous lupus. Currently it’s only approved for use in myelodysplastic syndromes, multiple myeloma, as well as certain lymphomas. It’s thought to modulate different parts of the immune system, which collectively result in the cytotoxicity against tumor cells.”
Lenalidomide is supplied in capsule sizes ranging from 2.5 mg to 25 mg and is given once daily. “For a smaller child, I would think about starting 5 mg once a day,” Dr. Wu said. “For an adult-sized adolescent, you could start at 10 mg once a day and then titrate up based on response. Side effects that you need to worry about are cytopenia and GI symptoms. The venous and arterial thromboembolism risk has been seen in patients with multiple myeloma, and it is unclear if this risk is applicable to all indications.” Use of the medication requires enrollment into a safety monitoring program.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM SPD 2020
Marked improvements seen for women in dermatology since the 1970s
Wilma F. Bergfeld, MD, one of only five women in her medical school class of 1964 and the third female in her dermatology residency program, had recently been appointed as a junior clinical dermatologist and head of dermatopathology at the Cleveland Clinic when she was told by a superior that she would not be promoted or invited to serve on any committee or decision-making group.
“I was told I should go home at night and take care of my husband and two children,” she recalled of that moment in the 1970s. The comment made her feel “outraged,” and it drove her, calmly and steadily, to work harder and to “challenge the system.”
Dr. Bergfeld not only was elected to the Cleveland Clinic’s board of governors and board of trustees and served as president of the Clinic’s staff in 1990, she also became the first woman president of the American Academy of Dermatology (1992) and led numerous other dermatologic organizations. Much earlier on, in 1973, to help fulfill her vision of “women helping women,” she had also founded the Women’s Dermatologic Society (WDS). Three years earlier, in 1970, 6.9% of the approximately 4,000 dermatologists in the United States were women, according to the American Medical Association.
Today, when she goes to work as the long-time director of the Clinic’s dermatopathology fellowship and professor of dermatology and pathology at the Cleveland Clinic Educational Foundation, she sees a transformed staff and, more broadly, a national physician workforce in which women made up almost 50% of active dermatologists in 2017 and almost 60% of dermatology residents in 2018, according to data from the American Association of Medical Colleges.
It’s a different and better world, she and other women dermatologists said, but one in which women must continue to mentor other women and continue to challenge the system. Achieving work-life balance, fairer compensation, and a greater proportion of women in the higher ranks of academia are all on their work list.
Women’s impact on the specialty
Dr. Bergfeld and Molly Hinshaw, MD, the current president of the WDS, said they believe women are drawn to dermatology for its visual nature, the growth in diagnostic tests and therapies, and the opportunity to diagnose early and prevent progression of disease in patients of all ages. “It’s a small but mighty specialty,” said Dr. Hinshaw, associate professor of dermatology and section chief of dermatopathology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
It’s also a versatile specialty with a variety of subspecialties and niches to pursue – and women have been stepping in to fill unmet needs, Dr. Hinshaw said. “Women dermatologists are directing vulvar specialty clinics across the country, for example. There aren’t that many, but they’re filling an important niche. We have one at [our university] and it is packed.”
Women have also been drawn to the in-demand subspecialty of pediatric dermatology, she noted. They now make up more than two-thirds of all pediatric dermatologists, and many in practice have trained the old-fashioned way, completing two residencies. “That’s [involved] self-selection into an additional year of years training and a commitment to caring for special populations that, quite honestly, takes more time,” said Dr. Hinshaw, who, as part of her dermatology practice, runs a nail clinic at UW Health in Madison.
Amy S. Paller, MD, who chairs the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, where she is professor of dermatology and pediatrics and directs the Skin Biology & Diseases Resource-Based Center, is one of these women. She took a long and determined journey into the subspecialty, encountering bias and discouragement while actively seeking out mentors who helped her advance.
While in medical school at Stanford (Calif.) University in the late 1970s in a class “very progressively” made up of about one-third women, Dr. Paller met Alvin Jacobs, MD, who, in 1975, had founded the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “There wasn’t much pediatric dermatology in the world at the time, and it was Al who helped [me realize] that it combined my love of genetic research with my [desire] to work with children,” she recalled.
Per Dr. Jacob’s advice, she went to Northwestern to train in both pediatrics and dermatology under Nancy Esterly, MD, who “is considered by many to be the mother of pediatric dermatology.” And knowing that she wanted to do research, Dr. Paller also worked with Ruth Freinkel, MD, who “was the strongest bench researcher” at Northwestern. (Dr. Freinkel had been one of the first female dermatology residents at Harvard and was the first full-time faculty member in dermatology at Northwestern).
After completing postdoctoral research at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Dr. Paller returned to Chicago and assumed Dr. Esterly’s position as chief of dermatology at the Children’s National Hospital of Chicago. It was there that “someone in a leadership position questioned me about how I could possibly be a scientist, a strong clinician, and a good mother to my three children – and suggested that I drop research,” Dr. Paller recalled.
“I think this person was trying to be helpful to me, but I was shocked,” she said. Just as Dr. Bergfeld had done, Dr. Paller channeled her frustration into new pursuits.
“It made me go home and think, how could I strengthen myself? What else could I do?” she said. “Soon after, with a highly supportive husband, I did a ‘pseudosabbatical,’ basically spending every ounce of spare time I had working with one of the premier female scientists in the country, Elaine Fuchs, and learning molecular biology” in her lab at the University of Chicago.
“I think we’ve all had discrimination along the way. Sometimes there’s implicit bias and sometimes there’s overt bias,” said Dr. Paller, who in 2004 led the society which her mentor Dr. Jacobs had founded several decades earlier. “I just jumped right in, and that’s enabled me to find good role models.”
Across dermatology broadly, the often holistic nature of the specialty – of the ability to peer into the body and its internal health – is another quality that women have been drawn to and advanced, Dr. Hinshaw said. “One of the reasons why I chose dermatology is because it’s a window to total patient health. Patients often see their dermatologists as physicians who help them identify next steps in their health care, who can help them address issues related to their overall health and well-being, including their mental health.”
In a WDS membership survey conducted in 2018, most respondents reported that they frequently or occasionally detect and diagnose systemic/internal diseases and conditions in their female patients, and that they consult and collaborate with different kinds of physicians (Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018 Nov 15;4[4]:189-92).
And in a March 2019 “Dialogues in Dermatology” podcast episode on the history and advancement of women in dermatology produced by the American Academy of Dermatology, Pearl Grimes, MD, a clinical professor of dermatology of the University of California, Los Angeles, and then-president of the WDS, described why “total women’s health” had become an additional focus for the society.
“We’re already gatekeepers” in many respects, Dr. Grimes said. “In addition to my addressing specific skin issues, my patients query me on hormone issues, on nutrition, on stress-related issues….and on [what other physicians they should see].”
Phoebe Rich, MD, who owns a small all-woman practice and a research center in Portland, Oregon, said that, in general, many women also communicate and practice in a way that facilitates holistic care. “These qualities aren’t exclusive to women, but women are very caring. We take time and are interested in [patients’] lives in general, not just their disease.”
Disparities in academia
Dermatology departments in academic medicine have burgeoned in size in the past 50 years, and women are well represented overall. In 2018, women comprised 51.2% of dermatology department faculty – up from 10.8% in 1970 – a current proportion that ranks fifth among specialties for the proportion of female faculty, according to a cross-sectional study of faculty diversity trends using data from the AAMC faculty roster (JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jan 8;156[3]:280-7).
The AAMC data show the share of women dermatology faculty declining at each subsequent rank, however – a finding that suggests that women are not promoted as quickly or to the same levels of leadership as men, the report’s authors noted. (Dermatology isn’t alone: The AAMC issued a call to action on gender equity in medicine this year, citing this inverse association.)
Another recently published study of gender trends in academic dermatology – this one looking at a smaller sample of data from 15 institutions – similarly found that women dermatologists made up a majority of faculty (53.6%) and were well represented as assistant professors (60.7%) but underrepresented as full professors (17%).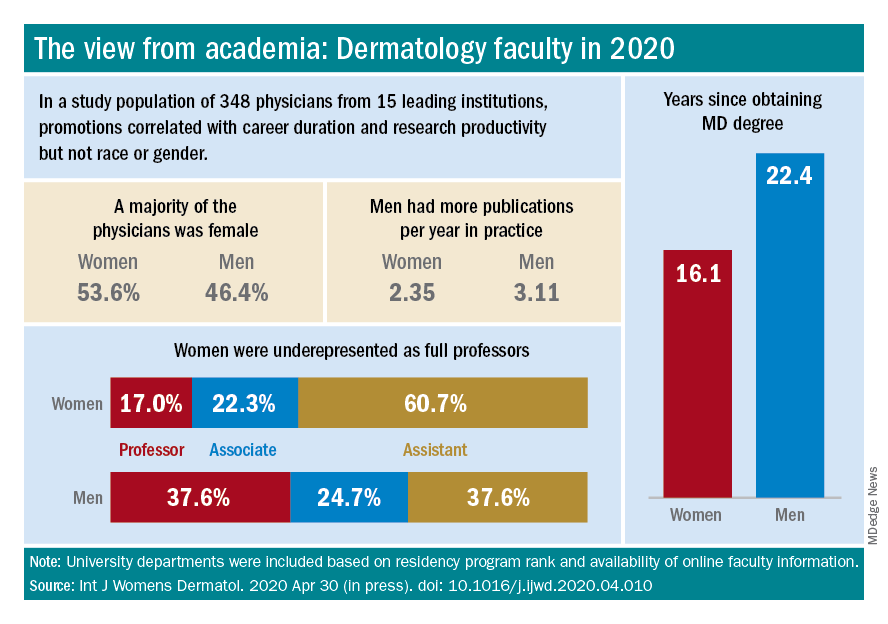
This study differed from the larger AAMC study, however, in that it controlled for “achievement indicators” – career duration, publications per year, and National Institutes of Health research funding – and found that gender alone was not associated with higher rank. Instead, promotions were correlated most significantly with NIH research funding and also with career duration and publications per year.
“If research achievement is to be used as a benchmark for academic promotion, increased efforts are needed to support the research activities of women,” the authors wrote, adding that recognition should be given to other factors as well.
Dr. Paller and Dr. Hinshaw both described the situation as complex and multifaceted. Some research on promotion in academia in general – but not all – has suggested that women do need to publish more than men in order to be promoted. But “the promotion process also has within it the ability to use judgment [about] the impact and merits of work,” said Dr. Hinshaw. “Not all publications [and levels of authorship] may be considered equal, for instance.”
Dr. Hinshaw said she is also concerned by data showing that women still perform the majority of household duties, “even in households in which both partners work outside the home equivalently.” As long as this is the case, women may be “inherently disadvantaged” in their ability to have adequate research time and to advance.
From where she sits, Dr. Paller sees several factors at play: “The pipeline, achievement during the pipeline, and decision-making about advancement” on the part of women themselves. Having served on search committees for top leadership in specialties in which women are well represented, she said, “I’ve seen fewer women who’ve come forward and been interested in rising into a chair or a dean position.”
And “having talked to so many women,” Dr. Paller added, “I think there’s a phenomenon where it’s harder for women to accept positions [that require] a significant change.”
Women “are nurturers, which makes them extremely good [leaders] and chairs, but it also makes it harder to make life changes that affect the people they love,” she said, noting that becoming a department chair or a dean often involves moving. “I also think that women in general are happier and committed to what they’re [currently] doing.”
Dr. Paller is optimistic that, with the support of department chairs and continued attention to role modeling and mentoring, the portrait of women in academic dermatology will continue to improve. Currently, 34 chairs of dermatology departments are female, she noted. “That number was 11 less 15 years ago.”
In the meantime, researchers are increasingly documenting trends in women’s editorships of journals as well as leadership and speaking opportunities at professional conferences.
The authors of one study published this year, for instance, reviewed the editorial boards of dermatology journals and found that women occupied 18% of editor in chief roles, 36% of deputy editor positions, and 22% of overall editorial board roles (Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Sep 12;6[1]:20-4). Other research shows women comprising 43% of all authorships across 23 dermatologic journals from 2008 to May 2017, 50.2% of first authorships, and 33.1% of last authorships (BMJ Open. 2018 Apr 13;8[4]:e020089).
Both in academic medicine and in practice, a gender pay gap still affects women physicians across the board. Medscape’s 2020 dermatologist compensation report shows male dermatologists earning about 12% more than their female peers (average, $435,000 vs. $387,000, respectively), while the average number of hours per week spent seeing patients is similar (36.2 vs. 35.6 hours, respectively).
And in its 2020 statement on gender equity, the AAMC said that women in academic medicine are offered less in starting salary, negotiated pay, and other forms of compensation than men “despite equal effort, rank, training, and experience.”
It’s complicated to tease apart all the factors that may be involved – but important to keep challenging the system, said Dr. Bergfeld, who was a long-time board adviser for Dermatology News. “I was underpaid,” she noted, and “this was only rectified in the last 10 years.”
Work-life balance
In the AAD podcast on women in dermatology, Dr. Grimes said that achieving a healthy and balanced work life remains one of the greatest challenges for women dermatologists – and it may be even greater than in the past given the growing numbers of group practices. “When women enter the realm of group practice, they have less flexibility in controlling their time and their own schedules.”
If Anna Hare, MD, is any indication, younger dermatologists may buck this trend. The daughter of Dr. Rich in Portland, Dr. Hare joined her mother’s dermatology practice and research center knowing that she’d have “the respect and flexibility for deciding how I want to practice.”
Younger dermatologists, she said, place “more of an emphasis on work-life balance and quality of life.”
Fortunately, said Dr. Bergfeld, women have advanced enough in the ranks of dermatology that, in networking, in mentorship, and in workplace settings, attention can be paid more fully to discussions about work-life management – “how to manage your life when you’re working with family and kids and parents.”
In the 1970s, at the Cleveland Clinic, “there were only five women on staff and we were fighting for [basic] rights,” she said. “We wanted equality – we were [perceived as] little worker bees….We needed to climb as the men did to positions of leadership and address the problems of women.”
In pursuing their goals and making further progress, women dermatologists today should be “steady and calm,” she advised. Formally acquiring leadership skills and communication skills is a timeless need. And when there are biases or conflicts, “you cannot have righteous indignation, you cannot have revenge. You have to calm yourself and move forward.”
Wilma F. Bergfeld, MD, one of only five women in her medical school class of 1964 and the third female in her dermatology residency program, had recently been appointed as a junior clinical dermatologist and head of dermatopathology at the Cleveland Clinic when she was told by a superior that she would not be promoted or invited to serve on any committee or decision-making group.
“I was told I should go home at night and take care of my husband and two children,” she recalled of that moment in the 1970s. The comment made her feel “outraged,” and it drove her, calmly and steadily, to work harder and to “challenge the system.”
Dr. Bergfeld not only was elected to the Cleveland Clinic’s board of governors and board of trustees and served as president of the Clinic’s staff in 1990, she also became the first woman president of the American Academy of Dermatology (1992) and led numerous other dermatologic organizations. Much earlier on, in 1973, to help fulfill her vision of “women helping women,” she had also founded the Women’s Dermatologic Society (WDS). Three years earlier, in 1970, 6.9% of the approximately 4,000 dermatologists in the United States were women, according to the American Medical Association.
Today, when she goes to work as the long-time director of the Clinic’s dermatopathology fellowship and professor of dermatology and pathology at the Cleveland Clinic Educational Foundation, she sees a transformed staff and, more broadly, a national physician workforce in which women made up almost 50% of active dermatologists in 2017 and almost 60% of dermatology residents in 2018, according to data from the American Association of Medical Colleges.
It’s a different and better world, she and other women dermatologists said, but one in which women must continue to mentor other women and continue to challenge the system. Achieving work-life balance, fairer compensation, and a greater proportion of women in the higher ranks of academia are all on their work list.
Women’s impact on the specialty
Dr. Bergfeld and Molly Hinshaw, MD, the current president of the WDS, said they believe women are drawn to dermatology for its visual nature, the growth in diagnostic tests and therapies, and the opportunity to diagnose early and prevent progression of disease in patients of all ages. “It’s a small but mighty specialty,” said Dr. Hinshaw, associate professor of dermatology and section chief of dermatopathology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
It’s also a versatile specialty with a variety of subspecialties and niches to pursue – and women have been stepping in to fill unmet needs, Dr. Hinshaw said. “Women dermatologists are directing vulvar specialty clinics across the country, for example. There aren’t that many, but they’re filling an important niche. We have one at [our university] and it is packed.”
Women have also been drawn to the in-demand subspecialty of pediatric dermatology, she noted. They now make up more than two-thirds of all pediatric dermatologists, and many in practice have trained the old-fashioned way, completing two residencies. “That’s [involved] self-selection into an additional year of years training and a commitment to caring for special populations that, quite honestly, takes more time,” said Dr. Hinshaw, who, as part of her dermatology practice, runs a nail clinic at UW Health in Madison.
Amy S. Paller, MD, who chairs the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, where she is professor of dermatology and pediatrics and directs the Skin Biology & Diseases Resource-Based Center, is one of these women. She took a long and determined journey into the subspecialty, encountering bias and discouragement while actively seeking out mentors who helped her advance.
While in medical school at Stanford (Calif.) University in the late 1970s in a class “very progressively” made up of about one-third women, Dr. Paller met Alvin Jacobs, MD, who, in 1975, had founded the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “There wasn’t much pediatric dermatology in the world at the time, and it was Al who helped [me realize] that it combined my love of genetic research with my [desire] to work with children,” she recalled.
Per Dr. Jacob’s advice, she went to Northwestern to train in both pediatrics and dermatology under Nancy Esterly, MD, who “is considered by many to be the mother of pediatric dermatology.” And knowing that she wanted to do research, Dr. Paller also worked with Ruth Freinkel, MD, who “was the strongest bench researcher” at Northwestern. (Dr. Freinkel had been one of the first female dermatology residents at Harvard and was the first full-time faculty member in dermatology at Northwestern).
After completing postdoctoral research at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Dr. Paller returned to Chicago and assumed Dr. Esterly’s position as chief of dermatology at the Children’s National Hospital of Chicago. It was there that “someone in a leadership position questioned me about how I could possibly be a scientist, a strong clinician, and a good mother to my three children – and suggested that I drop research,” Dr. Paller recalled.
“I think this person was trying to be helpful to me, but I was shocked,” she said. Just as Dr. Bergfeld had done, Dr. Paller channeled her frustration into new pursuits.
“It made me go home and think, how could I strengthen myself? What else could I do?” she said. “Soon after, with a highly supportive husband, I did a ‘pseudosabbatical,’ basically spending every ounce of spare time I had working with one of the premier female scientists in the country, Elaine Fuchs, and learning molecular biology” in her lab at the University of Chicago.
“I think we’ve all had discrimination along the way. Sometimes there’s implicit bias and sometimes there’s overt bias,” said Dr. Paller, who in 2004 led the society which her mentor Dr. Jacobs had founded several decades earlier. “I just jumped right in, and that’s enabled me to find good role models.”
Across dermatology broadly, the often holistic nature of the specialty – of the ability to peer into the body and its internal health – is another quality that women have been drawn to and advanced, Dr. Hinshaw said. “One of the reasons why I chose dermatology is because it’s a window to total patient health. Patients often see their dermatologists as physicians who help them identify next steps in their health care, who can help them address issues related to their overall health and well-being, including their mental health.”
In a WDS membership survey conducted in 2018, most respondents reported that they frequently or occasionally detect and diagnose systemic/internal diseases and conditions in their female patients, and that they consult and collaborate with different kinds of physicians (Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018 Nov 15;4[4]:189-92).
And in a March 2019 “Dialogues in Dermatology” podcast episode on the history and advancement of women in dermatology produced by the American Academy of Dermatology, Pearl Grimes, MD, a clinical professor of dermatology of the University of California, Los Angeles, and then-president of the WDS, described why “total women’s health” had become an additional focus for the society.
“We’re already gatekeepers” in many respects, Dr. Grimes said. “In addition to my addressing specific skin issues, my patients query me on hormone issues, on nutrition, on stress-related issues….and on [what other physicians they should see].”
Phoebe Rich, MD, who owns a small all-woman practice and a research center in Portland, Oregon, said that, in general, many women also communicate and practice in a way that facilitates holistic care. “These qualities aren’t exclusive to women, but women are very caring. We take time and are interested in [patients’] lives in general, not just their disease.”
Disparities in academia
Dermatology departments in academic medicine have burgeoned in size in the past 50 years, and women are well represented overall. In 2018, women comprised 51.2% of dermatology department faculty – up from 10.8% in 1970 – a current proportion that ranks fifth among specialties for the proportion of female faculty, according to a cross-sectional study of faculty diversity trends using data from the AAMC faculty roster (JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jan 8;156[3]:280-7).
The AAMC data show the share of women dermatology faculty declining at each subsequent rank, however – a finding that suggests that women are not promoted as quickly or to the same levels of leadership as men, the report’s authors noted. (Dermatology isn’t alone: The AAMC issued a call to action on gender equity in medicine this year, citing this inverse association.)
Another recently published study of gender trends in academic dermatology – this one looking at a smaller sample of data from 15 institutions – similarly found that women dermatologists made up a majority of faculty (53.6%) and were well represented as assistant professors (60.7%) but underrepresented as full professors (17%).
This study differed from the larger AAMC study, however, in that it controlled for “achievement indicators” – career duration, publications per year, and National Institutes of Health research funding – and found that gender alone was not associated with higher rank. Instead, promotions were correlated most significantly with NIH research funding and also with career duration and publications per year.
“If research achievement is to be used as a benchmark for academic promotion, increased efforts are needed to support the research activities of women,” the authors wrote, adding that recognition should be given to other factors as well.
Dr. Paller and Dr. Hinshaw both described the situation as complex and multifaceted. Some research on promotion in academia in general – but not all – has suggested that women do need to publish more than men in order to be promoted. But “the promotion process also has within it the ability to use judgment [about] the impact and merits of work,” said Dr. Hinshaw. “Not all publications [and levels of authorship] may be considered equal, for instance.”
Dr. Hinshaw said she is also concerned by data showing that women still perform the majority of household duties, “even in households in which both partners work outside the home equivalently.” As long as this is the case, women may be “inherently disadvantaged” in their ability to have adequate research time and to advance.
From where she sits, Dr. Paller sees several factors at play: “The pipeline, achievement during the pipeline, and decision-making about advancement” on the part of women themselves. Having served on search committees for top leadership in specialties in which women are well represented, she said, “I’ve seen fewer women who’ve come forward and been interested in rising into a chair or a dean position.”
And “having talked to so many women,” Dr. Paller added, “I think there’s a phenomenon where it’s harder for women to accept positions [that require] a significant change.”
Women “are nurturers, which makes them extremely good [leaders] and chairs, but it also makes it harder to make life changes that affect the people they love,” she said, noting that becoming a department chair or a dean often involves moving. “I also think that women in general are happier and committed to what they’re [currently] doing.”
Dr. Paller is optimistic that, with the support of department chairs and continued attention to role modeling and mentoring, the portrait of women in academic dermatology will continue to improve. Currently, 34 chairs of dermatology departments are female, she noted. “That number was 11 less 15 years ago.”
In the meantime, researchers are increasingly documenting trends in women’s editorships of journals as well as leadership and speaking opportunities at professional conferences.
The authors of one study published this year, for instance, reviewed the editorial boards of dermatology journals and found that women occupied 18% of editor in chief roles, 36% of deputy editor positions, and 22% of overall editorial board roles (Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Sep 12;6[1]:20-4). Other research shows women comprising 43% of all authorships across 23 dermatologic journals from 2008 to May 2017, 50.2% of first authorships, and 33.1% of last authorships (BMJ Open. 2018 Apr 13;8[4]:e020089).
Both in academic medicine and in practice, a gender pay gap still affects women physicians across the board. Medscape’s 2020 dermatologist compensation report shows male dermatologists earning about 12% more than their female peers (average, $435,000 vs. $387,000, respectively), while the average number of hours per week spent seeing patients is similar (36.2 vs. 35.6 hours, respectively).
And in its 2020 statement on gender equity, the AAMC said that women in academic medicine are offered less in starting salary, negotiated pay, and other forms of compensation than men “despite equal effort, rank, training, and experience.”
It’s complicated to tease apart all the factors that may be involved – but important to keep challenging the system, said Dr. Bergfeld, who was a long-time board adviser for Dermatology News. “I was underpaid,” she noted, and “this was only rectified in the last 10 years.”
Work-life balance
In the AAD podcast on women in dermatology, Dr. Grimes said that achieving a healthy and balanced work life remains one of the greatest challenges for women dermatologists – and it may be even greater than in the past given the growing numbers of group practices. “When women enter the realm of group practice, they have less flexibility in controlling their time and their own schedules.”
If Anna Hare, MD, is any indication, younger dermatologists may buck this trend. The daughter of Dr. Rich in Portland, Dr. Hare joined her mother’s dermatology practice and research center knowing that she’d have “the respect and flexibility for deciding how I want to practice.”
Younger dermatologists, she said, place “more of an emphasis on work-life balance and quality of life.”
Fortunately, said Dr. Bergfeld, women have advanced enough in the ranks of dermatology that, in networking, in mentorship, and in workplace settings, attention can be paid more fully to discussions about work-life management – “how to manage your life when you’re working with family and kids and parents.”
In the 1970s, at the Cleveland Clinic, “there were only five women on staff and we were fighting for [basic] rights,” she said. “We wanted equality – we were [perceived as] little worker bees….We needed to climb as the men did to positions of leadership and address the problems of women.”
In pursuing their goals and making further progress, women dermatologists today should be “steady and calm,” she advised. Formally acquiring leadership skills and communication skills is a timeless need. And when there are biases or conflicts, “you cannot have righteous indignation, you cannot have revenge. You have to calm yourself and move forward.”
Wilma F. Bergfeld, MD, one of only five women in her medical school class of 1964 and the third female in her dermatology residency program, had recently been appointed as a junior clinical dermatologist and head of dermatopathology at the Cleveland Clinic when she was told by a superior that she would not be promoted or invited to serve on any committee or decision-making group.
“I was told I should go home at night and take care of my husband and two children,” she recalled of that moment in the 1970s. The comment made her feel “outraged,” and it drove her, calmly and steadily, to work harder and to “challenge the system.”
Dr. Bergfeld not only was elected to the Cleveland Clinic’s board of governors and board of trustees and served as president of the Clinic’s staff in 1990, she also became the first woman president of the American Academy of Dermatology (1992) and led numerous other dermatologic organizations. Much earlier on, in 1973, to help fulfill her vision of “women helping women,” she had also founded the Women’s Dermatologic Society (WDS). Three years earlier, in 1970, 6.9% of the approximately 4,000 dermatologists in the United States were women, according to the American Medical Association.
Today, when she goes to work as the long-time director of the Clinic’s dermatopathology fellowship and professor of dermatology and pathology at the Cleveland Clinic Educational Foundation, she sees a transformed staff and, more broadly, a national physician workforce in which women made up almost 50% of active dermatologists in 2017 and almost 60% of dermatology residents in 2018, according to data from the American Association of Medical Colleges.
It’s a different and better world, she and other women dermatologists said, but one in which women must continue to mentor other women and continue to challenge the system. Achieving work-life balance, fairer compensation, and a greater proportion of women in the higher ranks of academia are all on their work list.
Women’s impact on the specialty
Dr. Bergfeld and Molly Hinshaw, MD, the current president of the WDS, said they believe women are drawn to dermatology for its visual nature, the growth in diagnostic tests and therapies, and the opportunity to diagnose early and prevent progression of disease in patients of all ages. “It’s a small but mighty specialty,” said Dr. Hinshaw, associate professor of dermatology and section chief of dermatopathology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
It’s also a versatile specialty with a variety of subspecialties and niches to pursue – and women have been stepping in to fill unmet needs, Dr. Hinshaw said. “Women dermatologists are directing vulvar specialty clinics across the country, for example. There aren’t that many, but they’re filling an important niche. We have one at [our university] and it is packed.”
Women have also been drawn to the in-demand subspecialty of pediatric dermatology, she noted. They now make up more than two-thirds of all pediatric dermatologists, and many in practice have trained the old-fashioned way, completing two residencies. “That’s [involved] self-selection into an additional year of years training and a commitment to caring for special populations that, quite honestly, takes more time,” said Dr. Hinshaw, who, as part of her dermatology practice, runs a nail clinic at UW Health in Madison.
Amy S. Paller, MD, who chairs the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, where she is professor of dermatology and pediatrics and directs the Skin Biology & Diseases Resource-Based Center, is one of these women. She took a long and determined journey into the subspecialty, encountering bias and discouragement while actively seeking out mentors who helped her advance.
While in medical school at Stanford (Calif.) University in the late 1970s in a class “very progressively” made up of about one-third women, Dr. Paller met Alvin Jacobs, MD, who, in 1975, had founded the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “There wasn’t much pediatric dermatology in the world at the time, and it was Al who helped [me realize] that it combined my love of genetic research with my [desire] to work with children,” she recalled.
Per Dr. Jacob’s advice, she went to Northwestern to train in both pediatrics and dermatology under Nancy Esterly, MD, who “is considered by many to be the mother of pediatric dermatology.” And knowing that she wanted to do research, Dr. Paller also worked with Ruth Freinkel, MD, who “was the strongest bench researcher” at Northwestern. (Dr. Freinkel had been one of the first female dermatology residents at Harvard and was the first full-time faculty member in dermatology at Northwestern).
After completing postdoctoral research at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Dr. Paller returned to Chicago and assumed Dr. Esterly’s position as chief of dermatology at the Children’s National Hospital of Chicago. It was there that “someone in a leadership position questioned me about how I could possibly be a scientist, a strong clinician, and a good mother to my three children – and suggested that I drop research,” Dr. Paller recalled.
“I think this person was trying to be helpful to me, but I was shocked,” she said. Just as Dr. Bergfeld had done, Dr. Paller channeled her frustration into new pursuits.
“It made me go home and think, how could I strengthen myself? What else could I do?” she said. “Soon after, with a highly supportive husband, I did a ‘pseudosabbatical,’ basically spending every ounce of spare time I had working with one of the premier female scientists in the country, Elaine Fuchs, and learning molecular biology” in her lab at the University of Chicago.
“I think we’ve all had discrimination along the way. Sometimes there’s implicit bias and sometimes there’s overt bias,” said Dr. Paller, who in 2004 led the society which her mentor Dr. Jacobs had founded several decades earlier. “I just jumped right in, and that’s enabled me to find good role models.”
Across dermatology broadly, the often holistic nature of the specialty – of the ability to peer into the body and its internal health – is another quality that women have been drawn to and advanced, Dr. Hinshaw said. “One of the reasons why I chose dermatology is because it’s a window to total patient health. Patients often see their dermatologists as physicians who help them identify next steps in their health care, who can help them address issues related to their overall health and well-being, including their mental health.”
In a WDS membership survey conducted in 2018, most respondents reported that they frequently or occasionally detect and diagnose systemic/internal diseases and conditions in their female patients, and that they consult and collaborate with different kinds of physicians (Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018 Nov 15;4[4]:189-92).
And in a March 2019 “Dialogues in Dermatology” podcast episode on the history and advancement of women in dermatology produced by the American Academy of Dermatology, Pearl Grimes, MD, a clinical professor of dermatology of the University of California, Los Angeles, and then-president of the WDS, described why “total women’s health” had become an additional focus for the society.
“We’re already gatekeepers” in many respects, Dr. Grimes said. “In addition to my addressing specific skin issues, my patients query me on hormone issues, on nutrition, on stress-related issues….and on [what other physicians they should see].”
Phoebe Rich, MD, who owns a small all-woman practice and a research center in Portland, Oregon, said that, in general, many women also communicate and practice in a way that facilitates holistic care. “These qualities aren’t exclusive to women, but women are very caring. We take time and are interested in [patients’] lives in general, not just their disease.”
Disparities in academia
Dermatology departments in academic medicine have burgeoned in size in the past 50 years, and women are well represented overall. In 2018, women comprised 51.2% of dermatology department faculty – up from 10.8% in 1970 – a current proportion that ranks fifth among specialties for the proportion of female faculty, according to a cross-sectional study of faculty diversity trends using data from the AAMC faculty roster (JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jan 8;156[3]:280-7).
The AAMC data show the share of women dermatology faculty declining at each subsequent rank, however – a finding that suggests that women are not promoted as quickly or to the same levels of leadership as men, the report’s authors noted. (Dermatology isn’t alone: The AAMC issued a call to action on gender equity in medicine this year, citing this inverse association.)
Another recently published study of gender trends in academic dermatology – this one looking at a smaller sample of data from 15 institutions – similarly found that women dermatologists made up a majority of faculty (53.6%) and were well represented as assistant professors (60.7%) but underrepresented as full professors (17%).
This study differed from the larger AAMC study, however, in that it controlled for “achievement indicators” – career duration, publications per year, and National Institutes of Health research funding – and found that gender alone was not associated with higher rank. Instead, promotions were correlated most significantly with NIH research funding and also with career duration and publications per year.
“If research achievement is to be used as a benchmark for academic promotion, increased efforts are needed to support the research activities of women,” the authors wrote, adding that recognition should be given to other factors as well.
Dr. Paller and Dr. Hinshaw both described the situation as complex and multifaceted. Some research on promotion in academia in general – but not all – has suggested that women do need to publish more than men in order to be promoted. But “the promotion process also has within it the ability to use judgment [about] the impact and merits of work,” said Dr. Hinshaw. “Not all publications [and levels of authorship] may be considered equal, for instance.”
Dr. Hinshaw said she is also concerned by data showing that women still perform the majority of household duties, “even in households in which both partners work outside the home equivalently.” As long as this is the case, women may be “inherently disadvantaged” in their ability to have adequate research time and to advance.
From where she sits, Dr. Paller sees several factors at play: “The pipeline, achievement during the pipeline, and decision-making about advancement” on the part of women themselves. Having served on search committees for top leadership in specialties in which women are well represented, she said, “I’ve seen fewer women who’ve come forward and been interested in rising into a chair or a dean position.”
And “having talked to so many women,” Dr. Paller added, “I think there’s a phenomenon where it’s harder for women to accept positions [that require] a significant change.”
Women “are nurturers, which makes them extremely good [leaders] and chairs, but it also makes it harder to make life changes that affect the people they love,” she said, noting that becoming a department chair or a dean often involves moving. “I also think that women in general are happier and committed to what they’re [currently] doing.”
Dr. Paller is optimistic that, with the support of department chairs and continued attention to role modeling and mentoring, the portrait of women in academic dermatology will continue to improve. Currently, 34 chairs of dermatology departments are female, she noted. “That number was 11 less 15 years ago.”
In the meantime, researchers are increasingly documenting trends in women’s editorships of journals as well as leadership and speaking opportunities at professional conferences.
The authors of one study published this year, for instance, reviewed the editorial boards of dermatology journals and found that women occupied 18% of editor in chief roles, 36% of deputy editor positions, and 22% of overall editorial board roles (Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Sep 12;6[1]:20-4). Other research shows women comprising 43% of all authorships across 23 dermatologic journals from 2008 to May 2017, 50.2% of first authorships, and 33.1% of last authorships (BMJ Open. 2018 Apr 13;8[4]:e020089).
Both in academic medicine and in practice, a gender pay gap still affects women physicians across the board. Medscape’s 2020 dermatologist compensation report shows male dermatologists earning about 12% more than their female peers (average, $435,000 vs. $387,000, respectively), while the average number of hours per week spent seeing patients is similar (36.2 vs. 35.6 hours, respectively).
And in its 2020 statement on gender equity, the AAMC said that women in academic medicine are offered less in starting salary, negotiated pay, and other forms of compensation than men “despite equal effort, rank, training, and experience.”
It’s complicated to tease apart all the factors that may be involved – but important to keep challenging the system, said Dr. Bergfeld, who was a long-time board adviser for Dermatology News. “I was underpaid,” she noted, and “this was only rectified in the last 10 years.”
Work-life balance
In the AAD podcast on women in dermatology, Dr. Grimes said that achieving a healthy and balanced work life remains one of the greatest challenges for women dermatologists – and it may be even greater than in the past given the growing numbers of group practices. “When women enter the realm of group practice, they have less flexibility in controlling their time and their own schedules.”
If Anna Hare, MD, is any indication, younger dermatologists may buck this trend. The daughter of Dr. Rich in Portland, Dr. Hare joined her mother’s dermatology practice and research center knowing that she’d have “the respect and flexibility for deciding how I want to practice.”
Younger dermatologists, she said, place “more of an emphasis on work-life balance and quality of life.”
Fortunately, said Dr. Bergfeld, women have advanced enough in the ranks of dermatology that, in networking, in mentorship, and in workplace settings, attention can be paid more fully to discussions about work-life management – “how to manage your life when you’re working with family and kids and parents.”
In the 1970s, at the Cleveland Clinic, “there were only five women on staff and we were fighting for [basic] rights,” she said. “We wanted equality – we were [perceived as] little worker bees….We needed to climb as the men did to positions of leadership and address the problems of women.”
In pursuing their goals and making further progress, women dermatologists today should be “steady and calm,” she advised. Formally acquiring leadership skills and communication skills is a timeless need. And when there are biases or conflicts, “you cannot have righteous indignation, you cannot have revenge. You have to calm yourself and move forward.”
Rapid drop of antibodies seen in those with mild COVID-19
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is the presence of enanthem a clue for COVID-19?
Larger studies should explore and confirm this association, the study’s authors and other experts suggested.
Dermatologists are already aware of the connection between enanthem and viral etiology. “As seen with other viral infections, we wondered if COVID-19 could produce enanthem in addition to skin rash exanthem,” one of the study author’s, Juan Jiménez-Cauhe, MD, a dermatologist with Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, said in an interview. He and his colleagues summarized their findings in a research letter in JAMA Dermatology.
They examined the oral cavity of 21 COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care hospital who also had a skin rash from March 30 to April 8. They classified enanthems into four categories: petechial, macular, macular with petechiae, or erythematovesicular. Six of the patients presented with oral lesions, all of them located in the palate; in one patient, the enanthem was macular, it was petechial in two patients and was macular with petechiae in three patients. The six patients ranged between the ages of 40 and 69 years; four were women.
Petechial or vesicular patterns are often associated with viral infections. In this particular study, the investigators did not observe vesicular lesions.
On average, mucocutaneous lesions appeared about 12 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. “Interestingly, this latency was shorter in patients with petechial enanthem, compared with those with a macular lesion with petechiae appearance,” the authors wrote.
This shorter time might suggest an association for SARS-CoV-2, said Dr. Jiménez-Cauhe. Strong cough may have also caused petechial lesions on the palate, but it’s unlikely, as they appeared close in time to COVID-19 symptoms. It’s also unlikely that any drugs caused the lesions, as drug rashes can take 2-3 weeks to appear.
This fits in line with other evidence of broader skin manifestations appearing at the same time or after COVID-19, Esther Freeman, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Freeman, director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, is the principal investigator of the COVID-19 Dermatology Registry, a collaboration of the American Academy of Dermatology and International League of Dermatological Societies.
The study’s small cohort made it difficult to establish a solid association between the oral lesions and SARS-CoV-2. “However, the presence of enanthem in a patient with a skin rash is a useful finding that suggests a viral etiology rather than a drug reaction. This is particularly useful in COVID-19 patients, who were receiving many drugs as part of the treatment,” Dr. Jimenez-Cauhe said. Future studies should assess whether the presence of enanthem and exanthem lead physicians to consider SARS-CoV-2 as possible agents, ruling out infection with a blood or nasopharyngeal test.
This study adds to the growing body of knowledge on cutaneous and mucocutaneous findings associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Jules Lipoff, MD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “One challenge in evaluating these findings is that these findings are nonspecific, and medication reactions can often cause similar rashes, such as morbilliform eruptions that can be associated with both viruses and medications.”
Enanthems, as the study authors noted, are more specific to viral infections and are less commonly associated with medication reactions. “So, even though this is a small case series with significant limitations, it does add more evidence that COVID-19 is directly responsible for findings in the skin and mucous membranes,” said Dr. Lipoff.
Dr. Freeman noted that the study may also encourage clinicians to look in a patient’s mouth when assessing for SARS-CoV-2. Additional research should examine these data in a larger population.
Several studies by Dr. Freeman, Dr. Lipoff, and others strongly suggest that SARS-CoV-2 has a spectrum of associated dermatologic manifestations. One evaluated perniolike skin lesions (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug; 83[2]:486-92). The other was a case series from the COVID-19 registry that examined 716 cases of new-onset dermatologic symptoms in patients from 31 countries with confirmed/suspected SARS-CoV-2 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul 2;S0190-9622[20]32126-5.).
The authors of the report had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jimenez-Cauhe J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2550.
Larger studies should explore and confirm this association, the study’s authors and other experts suggested.
Dermatologists are already aware of the connection between enanthem and viral etiology. “As seen with other viral infections, we wondered if COVID-19 could produce enanthem in addition to skin rash exanthem,” one of the study author’s, Juan Jiménez-Cauhe, MD, a dermatologist with Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, said in an interview. He and his colleagues summarized their findings in a research letter in JAMA Dermatology.
They examined the oral cavity of 21 COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care hospital who also had a skin rash from March 30 to April 8. They classified enanthems into four categories: petechial, macular, macular with petechiae, or erythematovesicular. Six of the patients presented with oral lesions, all of them located in the palate; in one patient, the enanthem was macular, it was petechial in two patients and was macular with petechiae in three patients. The six patients ranged between the ages of 40 and 69 years; four were women.
Petechial or vesicular patterns are often associated with viral infections. In this particular study, the investigators did not observe vesicular lesions.
On average, mucocutaneous lesions appeared about 12 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. “Interestingly, this latency was shorter in patients with petechial enanthem, compared with those with a macular lesion with petechiae appearance,” the authors wrote.
This shorter time might suggest an association for SARS-CoV-2, said Dr. Jiménez-Cauhe. Strong cough may have also caused petechial lesions on the palate, but it’s unlikely, as they appeared close in time to COVID-19 symptoms. It’s also unlikely that any drugs caused the lesions, as drug rashes can take 2-3 weeks to appear.
This fits in line with other evidence of broader skin manifestations appearing at the same time or after COVID-19, Esther Freeman, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Freeman, director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, is the principal investigator of the COVID-19 Dermatology Registry, a collaboration of the American Academy of Dermatology and International League of Dermatological Societies.
The study’s small cohort made it difficult to establish a solid association between the oral lesions and SARS-CoV-2. “However, the presence of enanthem in a patient with a skin rash is a useful finding that suggests a viral etiology rather than a drug reaction. This is particularly useful in COVID-19 patients, who were receiving many drugs as part of the treatment,” Dr. Jimenez-Cauhe said. Future studies should assess whether the presence of enanthem and exanthem lead physicians to consider SARS-CoV-2 as possible agents, ruling out infection with a blood or nasopharyngeal test.
This study adds to the growing body of knowledge on cutaneous and mucocutaneous findings associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Jules Lipoff, MD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “One challenge in evaluating these findings is that these findings are nonspecific, and medication reactions can often cause similar rashes, such as morbilliform eruptions that can be associated with both viruses and medications.”
Enanthems, as the study authors noted, are more specific to viral infections and are less commonly associated with medication reactions. “So, even though this is a small case series with significant limitations, it does add more evidence that COVID-19 is directly responsible for findings in the skin and mucous membranes,” said Dr. Lipoff.
Dr. Freeman noted that the study may also encourage clinicians to look in a patient’s mouth when assessing for SARS-CoV-2. Additional research should examine these data in a larger population.
Several studies by Dr. Freeman, Dr. Lipoff, and others strongly suggest that SARS-CoV-2 has a spectrum of associated dermatologic manifestations. One evaluated perniolike skin lesions (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug; 83[2]:486-92). The other was a case series from the COVID-19 registry that examined 716 cases of new-onset dermatologic symptoms in patients from 31 countries with confirmed/suspected SARS-CoV-2 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul 2;S0190-9622[20]32126-5.).
The authors of the report had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jimenez-Cauhe J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2550.
Larger studies should explore and confirm this association, the study’s authors and other experts suggested.
Dermatologists are already aware of the connection between enanthem and viral etiology. “As seen with other viral infections, we wondered if COVID-19 could produce enanthem in addition to skin rash exanthem,” one of the study author’s, Juan Jiménez-Cauhe, MD, a dermatologist with Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, said in an interview. He and his colleagues summarized their findings in a research letter in JAMA Dermatology.
They examined the oral cavity of 21 COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care hospital who also had a skin rash from March 30 to April 8. They classified enanthems into four categories: petechial, macular, macular with petechiae, or erythematovesicular. Six of the patients presented with oral lesions, all of them located in the palate; in one patient, the enanthem was macular, it was petechial in two patients and was macular with petechiae in three patients. The six patients ranged between the ages of 40 and 69 years; four were women.
Petechial or vesicular patterns are often associated with viral infections. In this particular study, the investigators did not observe vesicular lesions.
On average, mucocutaneous lesions appeared about 12 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. “Interestingly, this latency was shorter in patients with petechial enanthem, compared with those with a macular lesion with petechiae appearance,” the authors wrote.
This shorter time might suggest an association for SARS-CoV-2, said Dr. Jiménez-Cauhe. Strong cough may have also caused petechial lesions on the palate, but it’s unlikely, as they appeared close in time to COVID-19 symptoms. It’s also unlikely that any drugs caused the lesions, as drug rashes can take 2-3 weeks to appear.
This fits in line with other evidence of broader skin manifestations appearing at the same time or after COVID-19, Esther Freeman, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Freeman, director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, is the principal investigator of the COVID-19 Dermatology Registry, a collaboration of the American Academy of Dermatology and International League of Dermatological Societies.
The study’s small cohort made it difficult to establish a solid association between the oral lesions and SARS-CoV-2. “However, the presence of enanthem in a patient with a skin rash is a useful finding that suggests a viral etiology rather than a drug reaction. This is particularly useful in COVID-19 patients, who were receiving many drugs as part of the treatment,” Dr. Jimenez-Cauhe said. Future studies should assess whether the presence of enanthem and exanthem lead physicians to consider SARS-CoV-2 as possible agents, ruling out infection with a blood or nasopharyngeal test.
This study adds to the growing body of knowledge on cutaneous and mucocutaneous findings associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Jules Lipoff, MD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “One challenge in evaluating these findings is that these findings are nonspecific, and medication reactions can often cause similar rashes, such as morbilliform eruptions that can be associated with both viruses and medications.”
Enanthems, as the study authors noted, are more specific to viral infections and are less commonly associated with medication reactions. “So, even though this is a small case series with significant limitations, it does add more evidence that COVID-19 is directly responsible for findings in the skin and mucous membranes,” said Dr. Lipoff.
Dr. Freeman noted that the study may also encourage clinicians to look in a patient’s mouth when assessing for SARS-CoV-2. Additional research should examine these data in a larger population.
Several studies by Dr. Freeman, Dr. Lipoff, and others strongly suggest that SARS-CoV-2 has a spectrum of associated dermatologic manifestations. One evaluated perniolike skin lesions (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug; 83[2]:486-92). The other was a case series from the COVID-19 registry that examined 716 cases of new-onset dermatologic symptoms in patients from 31 countries with confirmed/suspected SARS-CoV-2 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul 2;S0190-9622[20]32126-5.).
The authors of the report had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jimenez-Cauhe J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2550.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
New developments in pustular psoriasis
It has various dermatologic and rheumatologic manifestations and sometimes overlaps with plaque psoriasis. Pustular palmoplantar psoriasis (PPP) affects the palmar and plantar areas of the skin, while generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) can affect large areas of skin and tends to be more severe, even life threatening. PPP can accompany psoriatic arthritis or can be a side effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy, or a non–drug-induced component of rheumatologic syndromes, according to Kristina Callis Duffin, MD, an associate professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“Each phenotype could be considered an orphan disease, and the response to therapy is often unpredictable,” Dr. Duffin said during a session on pustular psoriasis at the virtual annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
But there is some positive news. A study in 2011 of several people with GPP opened the door to better understanding the pathophysiology of pustular psoriasis. Researchers identified a causal autosomal mutation in the IL36RN gene, which encodes an antagonist to the interleukin-36 receptor (Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Sep 9;89[3]:432-7). “As a result of this paper and others, drug development in this space has recently accelerated,” Dr. Duffin said.
In fact, she added,“it’s my opinion that pustular psoriasis is now where plaque psoriasis was 20 years ago, when accelerated drug development was driving a better understanding of the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease and its comorbidities, and also driving outcome measure development.”
In another presentation at the meeting, Hervé Bachelez, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and immunologist at the University of Paris and Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris, discussed recent advances in drug development for pustular psoriasis. He noted other recent findings of genetic variants related to the disease, including AP1S3, CARD14, and SERPINA3.
For GPP, he said, the current algorithm for management is based on weak evidence for treatments like acitretin, cyclosporine, methotrexate, and infliximab. The story is similar for other biologics, with evidence in the form of case series; open-label studies; controlled, prospective studies; or retrospective analyses. Most of the evidence has been amassed for TNF inhibitors. A retrospective study of all TNF inhibitors suggested they may be effective as induction and maintenance therapy, he noted.
Among IL-17A inhibitors, a prospective study of 12 patients in Japan found secukinumab showed efficacy against GPP, as did studies of ixekizumab and brodalumab. A small phase 3 study in Japan demonstrated efficacy for the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab in patients with erythrodermic psoriasis and GPP (J Dermatol. 2018 May;45[5]:529-39).
The limited data are a reflection in part of the difficulty in studying GPP, since its flares tend to be more self-remitting than with psoriasis vulgaris or PPP.
There are two monoclonal antibodies against the IL-36 receptor currently being developed. A proof-of-concept study of one of them, spesolimab, showed promise against GPP, with five of seven patients reaching “clear” or “almost clear” scores on the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment within a week after infusion and in all seven by the fourth week (N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar 7;380[10]:981-3).
With respect to PPP, the strongest evidence for conventional therapies comes from two randomized, controlled trials of cyclosporine, with response rates of 48% and 89%, compared with 19% and 21%, respectively, in the placebo groups, although the primary endpoint was poorly designed, according to Dr. Bachelez. Retinoids like etretinate and acitretin, combined with psoralen and UVA, also have some supporting evidence regarding efficacy.
Among biologics, secukinumab did not fare well in a phase 3 study of patients with PPP. A subset of patients may benefit from it, but there are no biomarkers available to identify them, Dr. Bachelez said. A phase 2 study of guselkumab in Japan told a similar story, with only weak signs of efficacy. While there are many more ongoing clinical trials evaluating treatments for PPP, which is encouraging, PPP seems to be more challenging at this stage to tackle than GPP, Dr. Bachelez added. “The genetically inherited IL-36 antagonist abnormalities are clearly driving the advances regarding the pathogenesis of the disease, mainly for GPP rather than PPP.”
Part of the efforts to develop therapies for pustular psoriasis relies on the development of new outcome measures, or adaptation of existing ones. “We have a need to adapt or develop new investigator-reported measures, we need to adapt or develop new patient-reported outcomes,” Dr. Duffin said.
Many existing measures use inconsistent language and anchoring definitions, and some may be proprietary, she added. “The language varies by sponsor and is sometimes tweaked or modified by the agencies. Often synonyms are being used … it raises questions, does it change the validity of the instrument?”
Dr. Duffin called for the research community to use the pause in clinical research during the COVID-19 pandemic to reassess the research agenda, develop consensus on performing and training for GPP and PPP assessments, develop patient-reported outcomes, and strengthen connections to industry.
Dr. Duffin and Dr. Bachelez have consulted, served on the advisory board, been a speaker for, and/or received research support from a wide range of pharmaceutical companies, including those that manufacture and develop psoriasis treatments.
It has various dermatologic and rheumatologic manifestations and sometimes overlaps with plaque psoriasis. Pustular palmoplantar psoriasis (PPP) affects the palmar and plantar areas of the skin, while generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) can affect large areas of skin and tends to be more severe, even life threatening. PPP can accompany psoriatic arthritis or can be a side effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy, or a non–drug-induced component of rheumatologic syndromes, according to Kristina Callis Duffin, MD, an associate professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“Each phenotype could be considered an orphan disease, and the response to therapy is often unpredictable,” Dr. Duffin said during a session on pustular psoriasis at the virtual annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
But there is some positive news. A study in 2011 of several people with GPP opened the door to better understanding the pathophysiology of pustular psoriasis. Researchers identified a causal autosomal mutation in the IL36RN gene, which encodes an antagonist to the interleukin-36 receptor (Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Sep 9;89[3]:432-7). “As a result of this paper and others, drug development in this space has recently accelerated,” Dr. Duffin said.
In fact, she added,“it’s my opinion that pustular psoriasis is now where plaque psoriasis was 20 years ago, when accelerated drug development was driving a better understanding of the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease and its comorbidities, and also driving outcome measure development.”
In another presentation at the meeting, Hervé Bachelez, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and immunologist at the University of Paris and Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris, discussed recent advances in drug development for pustular psoriasis. He noted other recent findings of genetic variants related to the disease, including AP1S3, CARD14, and SERPINA3.
For GPP, he said, the current algorithm for management is based on weak evidence for treatments like acitretin, cyclosporine, methotrexate, and infliximab. The story is similar for other biologics, with evidence in the form of case series; open-label studies; controlled, prospective studies; or retrospective analyses. Most of the evidence has been amassed for TNF inhibitors. A retrospective study of all TNF inhibitors suggested they may be effective as induction and maintenance therapy, he noted.
Among IL-17A inhibitors, a prospective study of 12 patients in Japan found secukinumab showed efficacy against GPP, as did studies of ixekizumab and brodalumab. A small phase 3 study in Japan demonstrated efficacy for the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab in patients with erythrodermic psoriasis and GPP (J Dermatol. 2018 May;45[5]:529-39).
The limited data are a reflection in part of the difficulty in studying GPP, since its flares tend to be more self-remitting than with psoriasis vulgaris or PPP.
There are two monoclonal antibodies against the IL-36 receptor currently being developed. A proof-of-concept study of one of them, spesolimab, showed promise against GPP, with five of seven patients reaching “clear” or “almost clear” scores on the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment within a week after infusion and in all seven by the fourth week (N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar 7;380[10]:981-3).
With respect to PPP, the strongest evidence for conventional therapies comes from two randomized, controlled trials of cyclosporine, with response rates of 48% and 89%, compared with 19% and 21%, respectively, in the placebo groups, although the primary endpoint was poorly designed, according to Dr. Bachelez. Retinoids like etretinate and acitretin, combined with psoralen and UVA, also have some supporting evidence regarding efficacy.
Among biologics, secukinumab did not fare well in a phase 3 study of patients with PPP. A subset of patients may benefit from it, but there are no biomarkers available to identify them, Dr. Bachelez said. A phase 2 study of guselkumab in Japan told a similar story, with only weak signs of efficacy. While there are many more ongoing clinical trials evaluating treatments for PPP, which is encouraging, PPP seems to be more challenging at this stage to tackle than GPP, Dr. Bachelez added. “The genetically inherited IL-36 antagonist abnormalities are clearly driving the advances regarding the pathogenesis of the disease, mainly for GPP rather than PPP.”
Part of the efforts to develop therapies for pustular psoriasis relies on the development of new outcome measures, or adaptation of existing ones. “We have a need to adapt or develop new investigator-reported measures, we need to adapt or develop new patient-reported outcomes,” Dr. Duffin said.
Many existing measures use inconsistent language and anchoring definitions, and some may be proprietary, she added. “The language varies by sponsor and is sometimes tweaked or modified by the agencies. Often synonyms are being used … it raises questions, does it change the validity of the instrument?”
Dr. Duffin called for the research community to use the pause in clinical research during the COVID-19 pandemic to reassess the research agenda, develop consensus on performing and training for GPP and PPP assessments, develop patient-reported outcomes, and strengthen connections to industry.
Dr. Duffin and Dr. Bachelez have consulted, served on the advisory board, been a speaker for, and/or received research support from a wide range of pharmaceutical companies, including those that manufacture and develop psoriasis treatments.
It has various dermatologic and rheumatologic manifestations and sometimes overlaps with plaque psoriasis. Pustular palmoplantar psoriasis (PPP) affects the palmar and plantar areas of the skin, while generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) can affect large areas of skin and tends to be more severe, even life threatening. PPP can accompany psoriatic arthritis or can be a side effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy, or a non–drug-induced component of rheumatologic syndromes, according to Kristina Callis Duffin, MD, an associate professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“Each phenotype could be considered an orphan disease, and the response to therapy is often unpredictable,” Dr. Duffin said during a session on pustular psoriasis at the virtual annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
But there is some positive news. A study in 2011 of several people with GPP opened the door to better understanding the pathophysiology of pustular psoriasis. Researchers identified a causal autosomal mutation in the IL36RN gene, which encodes an antagonist to the interleukin-36 receptor (Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Sep 9;89[3]:432-7). “As a result of this paper and others, drug development in this space has recently accelerated,” Dr. Duffin said.
In fact, she added,“it’s my opinion that pustular psoriasis is now where plaque psoriasis was 20 years ago, when accelerated drug development was driving a better understanding of the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease and its comorbidities, and also driving outcome measure development.”
In another presentation at the meeting, Hervé Bachelez, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and immunologist at the University of Paris and Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris, discussed recent advances in drug development for pustular psoriasis. He noted other recent findings of genetic variants related to the disease, including AP1S3, CARD14, and SERPINA3.
For GPP, he said, the current algorithm for management is based on weak evidence for treatments like acitretin, cyclosporine, methotrexate, and infliximab. The story is similar for other biologics, with evidence in the form of case series; open-label studies; controlled, prospective studies; or retrospective analyses. Most of the evidence has been amassed for TNF inhibitors. A retrospective study of all TNF inhibitors suggested they may be effective as induction and maintenance therapy, he noted.
Among IL-17A inhibitors, a prospective study of 12 patients in Japan found secukinumab showed efficacy against GPP, as did studies of ixekizumab and brodalumab. A small phase 3 study in Japan demonstrated efficacy for the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab in patients with erythrodermic psoriasis and GPP (J Dermatol. 2018 May;45[5]:529-39).
The limited data are a reflection in part of the difficulty in studying GPP, since its flares tend to be more self-remitting than with psoriasis vulgaris or PPP.
There are two monoclonal antibodies against the IL-36 receptor currently being developed. A proof-of-concept study of one of them, spesolimab, showed promise against GPP, with five of seven patients reaching “clear” or “almost clear” scores on the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment within a week after infusion and in all seven by the fourth week (N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar 7;380[10]:981-3).
With respect to PPP, the strongest evidence for conventional therapies comes from two randomized, controlled trials of cyclosporine, with response rates of 48% and 89%, compared with 19% and 21%, respectively, in the placebo groups, although the primary endpoint was poorly designed, according to Dr. Bachelez. Retinoids like etretinate and acitretin, combined with psoralen and UVA, also have some supporting evidence regarding efficacy.
Among biologics, secukinumab did not fare well in a phase 3 study of patients with PPP. A subset of patients may benefit from it, but there are no biomarkers available to identify them, Dr. Bachelez said. A phase 2 study of guselkumab in Japan told a similar story, with only weak signs of efficacy. While there are many more ongoing clinical trials evaluating treatments for PPP, which is encouraging, PPP seems to be more challenging at this stage to tackle than GPP, Dr. Bachelez added. “The genetically inherited IL-36 antagonist abnormalities are clearly driving the advances regarding the pathogenesis of the disease, mainly for GPP rather than PPP.”
Part of the efforts to develop therapies for pustular psoriasis relies on the development of new outcome measures, or adaptation of existing ones. “We have a need to adapt or develop new investigator-reported measures, we need to adapt or develop new patient-reported outcomes,” Dr. Duffin said.
Many existing measures use inconsistent language and anchoring definitions, and some may be proprietary, she added. “The language varies by sponsor and is sometimes tweaked or modified by the agencies. Often synonyms are being used … it raises questions, does it change the validity of the instrument?”
Dr. Duffin called for the research community to use the pause in clinical research during the COVID-19 pandemic to reassess the research agenda, develop consensus on performing and training for GPP and PPP assessments, develop patient-reported outcomes, and strengthen connections to industry.
Dr. Duffin and Dr. Bachelez have consulted, served on the advisory board, been a speaker for, and/or received research support from a wide range of pharmaceutical companies, including those that manufacture and develop psoriasis treatments.
FROM THE GRAPPA 2020 VIRTUAL ANNUAL MEETING
Levonorgestrel IUDs offer safe, effective care for disabled adolescents
for menstrual management and contraception, based on data from a retrospective study of 159 patients.
“Desire for menstrual management or suppression is common in young women with special needs, including complex medical conditions and physical, intellectual, and developmental disabilities,” and many of these patients require estrogen-free options because of comorbidities, medication interactions, or decreased mobility, wrote Beth I. Schwartz, MD, and colleagues at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz currently is of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers identified 159 nulliparous patients aged 22 years and younger with physical, intellectual, or developmental disabilities who received levonorgestrel IUDs at a tertiary care children’s hospital between July 1, 2004, and June 30, 2014.
A total of 185 levonorgestrel IUDs were placed. The patients ranged in age from 9 to 22 years with a mean age of 16 years; 4% had ever been sexually active.
Overall, the IUD continuation rate was 95% after 1 year and 73% after 5 years. Most of the IUDs (96%) were inserted in the operating room.
Device malposition and expulsion accounted for a 5% rate of complications. Of the five expulsions, four were completely expelled from the uterus, and a fifth was partial and identified on ultrasound. No cases of pelvic inflammatory disease, pregnancy, or uterine perforation were reported, and the amenorrhea rate was approximately 60%.
Unique concerns regarding the use of IUDs in the disabled population include the appropriateness of IUDs as a first strategy for menstrual management or contraception, as well as potential distress related to bleeding and cramping that patients might find hard to articulate, the researchers said. However, the high continuation rate and low reports of side effects in the study suggests that the devices were well tolerated, and the data show that complications were minimal and manageable, they said.
The study findings were limited primarily by the retrospective design, “which involved loss of patients to follow-up, missing data, and reliance on adequate documentation,” Dr. Schwartz and associates noted. However, the study is the largest to date on levonorgestrel IUD use in young people with disabilities, and provides needed data on the safety and benefits of IUDs for menstrual management and contraception in this population, they said. Prospective studies are needed to assess continuation, outcomes, and long-term satisfaction with IUDs.
“However, these data are promising and should be used to allow more accurate counseling of adolescents with special needs and their families,” and it should be considered as an option for them, Dr. Schwartz and colleagues concluded.
“Clinicians should recognize that adolescents with disabilities have a range of decision-making capacities,” Cynthia Robbins, MD, and Mary A. Ott, MD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Adolescents with disabilities may be left out of reproductive health discussions even if they are able, and the decisions are made by parents and caregivers.
For adolescents with mild disability, a shared decision-making approach is appropriate, in which providers and adolescents discuss reproductive health, with parent involvement as needed; “the adolescent is supported by the provider to express their preferences,” the editorialists wrote.
For those with more significant disability, they advised supported decision-making, in which the adolescent identifies a parent, family member, or caregiver as a trusted adult. “This supportive adult helps the adolescent communicate their goals and understand the decision and assists the provider in communication with the adolescent,” they said. For adolescents with a profound disability, the risks of placement and use of IUDs “should be thought of in a similar manner as other procedures that are routinely done to improve quality of life.”
“As clinicians, it is up to us to highlight these adolescents’ abilities to exercise their rights to sexual and reproductive health,” Dr. Robbins and Dr. Ott conclude.
The study was supported by a Bayer Healthcare Investigator-Initiated Research grant for women’s health to Dr. Schwartz and coauthor Lesley L. Breech, MD. The researchers had no other financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Ott disclosed providing expert consultation to Bayer, and that her spouse is employed Eli Lilly. Dr. Robbins had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose. They received no external funding for their editorial.
SOURCE: Schwartz BI et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0016. Robbins C and Ott MA. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-006296.
for menstrual management and contraception, based on data from a retrospective study of 159 patients.
“Desire for menstrual management or suppression is common in young women with special needs, including complex medical conditions and physical, intellectual, and developmental disabilities,” and many of these patients require estrogen-free options because of comorbidities, medication interactions, or decreased mobility, wrote Beth I. Schwartz, MD, and colleagues at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz currently is of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers identified 159 nulliparous patients aged 22 years and younger with physical, intellectual, or developmental disabilities who received levonorgestrel IUDs at a tertiary care children’s hospital between July 1, 2004, and June 30, 2014.
A total of 185 levonorgestrel IUDs were placed. The patients ranged in age from 9 to 22 years with a mean age of 16 years; 4% had ever been sexually active.
Overall, the IUD continuation rate was 95% after 1 year and 73% after 5 years. Most of the IUDs (96%) were inserted in the operating room.
Device malposition and expulsion accounted for a 5% rate of complications. Of the five expulsions, four were completely expelled from the uterus, and a fifth was partial and identified on ultrasound. No cases of pelvic inflammatory disease, pregnancy, or uterine perforation were reported, and the amenorrhea rate was approximately 60%.
Unique concerns regarding the use of IUDs in the disabled population include the appropriateness of IUDs as a first strategy for menstrual management or contraception, as well as potential distress related to bleeding and cramping that patients might find hard to articulate, the researchers said. However, the high continuation rate and low reports of side effects in the study suggests that the devices were well tolerated, and the data show that complications were minimal and manageable, they said.
The study findings were limited primarily by the retrospective design, “which involved loss of patients to follow-up, missing data, and reliance on adequate documentation,” Dr. Schwartz and associates noted. However, the study is the largest to date on levonorgestrel IUD use in young people with disabilities, and provides needed data on the safety and benefits of IUDs for menstrual management and contraception in this population, they said. Prospective studies are needed to assess continuation, outcomes, and long-term satisfaction with IUDs.
“However, these data are promising and should be used to allow more accurate counseling of adolescents with special needs and their families,” and it should be considered as an option for them, Dr. Schwartz and colleagues concluded.
“Clinicians should recognize that adolescents with disabilities have a range of decision-making capacities,” Cynthia Robbins, MD, and Mary A. Ott, MD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Adolescents with disabilities may be left out of reproductive health discussions even if they are able, and the decisions are made by parents and caregivers.
For adolescents with mild disability, a shared decision-making approach is appropriate, in which providers and adolescents discuss reproductive health, with parent involvement as needed; “the adolescent is supported by the provider to express their preferences,” the editorialists wrote.
For those with more significant disability, they advised supported decision-making, in which the adolescent identifies a parent, family member, or caregiver as a trusted adult. “This supportive adult helps the adolescent communicate their goals and understand the decision and assists the provider in communication with the adolescent,” they said. For adolescents with a profound disability, the risks of placement and use of IUDs “should be thought of in a similar manner as other procedures that are routinely done to improve quality of life.”
“As clinicians, it is up to us to highlight these adolescents’ abilities to exercise their rights to sexual and reproductive health,” Dr. Robbins and Dr. Ott conclude.
The study was supported by a Bayer Healthcare Investigator-Initiated Research grant for women’s health to Dr. Schwartz and coauthor Lesley L. Breech, MD. The researchers had no other financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Ott disclosed providing expert consultation to Bayer, and that her spouse is employed Eli Lilly. Dr. Robbins had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose. They received no external funding for their editorial.
SOURCE: Schwartz BI et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0016. Robbins C and Ott MA. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-006296.
for menstrual management and contraception, based on data from a retrospective study of 159 patients.
“Desire for menstrual management or suppression is common in young women with special needs, including complex medical conditions and physical, intellectual, and developmental disabilities,” and many of these patients require estrogen-free options because of comorbidities, medication interactions, or decreased mobility, wrote Beth I. Schwartz, MD, and colleagues at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz currently is of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers identified 159 nulliparous patients aged 22 years and younger with physical, intellectual, or developmental disabilities who received levonorgestrel IUDs at a tertiary care children’s hospital between July 1, 2004, and June 30, 2014.
A total of 185 levonorgestrel IUDs were placed. The patients ranged in age from 9 to 22 years with a mean age of 16 years; 4% had ever been sexually active.
Overall, the IUD continuation rate was 95% after 1 year and 73% after 5 years. Most of the IUDs (96%) were inserted in the operating room.
Device malposition and expulsion accounted for a 5% rate of complications. Of the five expulsions, four were completely expelled from the uterus, and a fifth was partial and identified on ultrasound. No cases of pelvic inflammatory disease, pregnancy, or uterine perforation were reported, and the amenorrhea rate was approximately 60%.
Unique concerns regarding the use of IUDs in the disabled population include the appropriateness of IUDs as a first strategy for menstrual management or contraception, as well as potential distress related to bleeding and cramping that patients might find hard to articulate, the researchers said. However, the high continuation rate and low reports of side effects in the study suggests that the devices were well tolerated, and the data show that complications were minimal and manageable, they said.
The study findings were limited primarily by the retrospective design, “which involved loss of patients to follow-up, missing data, and reliance on adequate documentation,” Dr. Schwartz and associates noted. However, the study is the largest to date on levonorgestrel IUD use in young people with disabilities, and provides needed data on the safety and benefits of IUDs for menstrual management and contraception in this population, they said. Prospective studies are needed to assess continuation, outcomes, and long-term satisfaction with IUDs.
“However, these data are promising and should be used to allow more accurate counseling of adolescents with special needs and their families,” and it should be considered as an option for them, Dr. Schwartz and colleagues concluded.
“Clinicians should recognize that adolescents with disabilities have a range of decision-making capacities,” Cynthia Robbins, MD, and Mary A. Ott, MD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Adolescents with disabilities may be left out of reproductive health discussions even if they are able, and the decisions are made by parents and caregivers.
For adolescents with mild disability, a shared decision-making approach is appropriate, in which providers and adolescents discuss reproductive health, with parent involvement as needed; “the adolescent is supported by the provider to express their preferences,” the editorialists wrote.
For those with more significant disability, they advised supported decision-making, in which the adolescent identifies a parent, family member, or caregiver as a trusted adult. “This supportive adult helps the adolescent communicate their goals and understand the decision and assists the provider in communication with the adolescent,” they said. For adolescents with a profound disability, the risks of placement and use of IUDs “should be thought of in a similar manner as other procedures that are routinely done to improve quality of life.”
“As clinicians, it is up to us to highlight these adolescents’ abilities to exercise their rights to sexual and reproductive health,” Dr. Robbins and Dr. Ott conclude.
The study was supported by a Bayer Healthcare Investigator-Initiated Research grant for women’s health to Dr. Schwartz and coauthor Lesley L. Breech, MD. The researchers had no other financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Ott disclosed providing expert consultation to Bayer, and that her spouse is employed Eli Lilly. Dr. Robbins had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose. They received no external funding for their editorial.
SOURCE: Schwartz BI et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0016. Robbins C and Ott MA. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-006296.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Patch testing in children: An evolving science
“Time needs to be allocated for a patch test consultation, placement, removal, and reading,” she said at the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “You will need more time in the day that you’re reading the patch test for patient education. However, your staff will need more time on the front end of the patch test process for application. Also, if they are customizing patch tests, they’ll need time to make the patch tests along with access to a refrigerator and plenty of counter space.”
Other factors to consider are the site of service, your payer mix, and if you need to complete prior authorizations for patch testing.
Dr. Martin, associate professor of dermatology and child health at the University of Missouri–Columbia, said that the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) crosses her mind when she sees a patient with new dermatitis, especially in an older child; if the dermatitis is patterned or regional; if there’s exacerbation of an underlying, previously stable skin disease; or if it’s a pattern known to be associated with systemic contact dermatitis. “In fact, 13%-25% of healthy, asymptomatic kids have allergen sensitization,” she said. “If you take that a step further and look at kids who are suspected of having allergic contact dermatitis, 25%-96% have allergen sensitization. Still, that doesn’t mean that those tests are relevant to the dermatitis that’s going on. If you take kids who are referred to tertiary centers for patch testing, about half will have relevant patch test results.”
Pediatric ACD differs from adult ACD in three ways, Dr. Martin said. First, children have a different clinical morphology and distribution on presentation, compared with adults. “In adults, the most common clinical presentation is hand dermatitis, while kids more often present with a scattered generalized morphology of dermatitis,” she said. “This occurs in about one-third of children with ACD. Their patterns of allergen exposure are also different. For the most part, adults are in control of their own environments and what is placed on their skin, whereas kids are not. When thinking about what you might need to patch test a child to if you’re considering ACD, it’s important to think about not only what the parent or caregiver puts directly on the child’s skin but also any connubial or consort allergen exposure – the most common ones coming from the caregivers themselves, such as fragrance or hair dyes that are transferred to a young child.”
The third factor that differs between pediatric and adult ACD is the allergen source. Dr. Martin noted that children and adults use different personal care products, wear different types of clothing, and spend different amounts of time in play versus work. “Children have many more hobbies in general that are unfortunately lost as many of us age,” she said. That means “thinking through the child’s entire day and how the seasons differ for them, such as what sports they’re in and what protective equipment may be involved with where their dermatitis is, or what musical instruments they play.”
Applying the T.R.U.E. patch test panel or a customized patch test panel to young children poses certain challenges, considering their limited body surface area and propensity to squirm. Dr. Martin often employs distraction techniques when placing patches on young patients, including the use of bubbles, music, movies, and games. “The goal is always to get as much of the patches on the back or the flanks as possible,” she said. “If you need additional space you can use the upper outer arms, the abdomen, or the anterior lateral thighs. Another thing to consider is how to set up your week for pediatric patch testing. There’s a standardized process for adults where we place the patches on day 0, read them on day 2, with removal of the patches at that time, and then perform a delayed read between day 4-7.”
The process is similar for postpubescent children, despite the lack of clear guidelines in the medical literature. “There is much controversy and different practices between different pediatric patch test centers,” Dr. Martin said. “There is more consensus between the older kids and the prepubescent group ages 6-12. Most clinicians will still do a similar placement on day 0 with removal and initial read on day 2, with a delayed read on day 4-7. However, some groups will remove patches at 24 hours, especially in those with atopic dermatitis (AD) or a generalized dermatitis, to reduce irritant reactions. Others will also use half-strength concentrations of allergens.”
The most controversy lies with children younger than 6 years, she said. For those aged 3-6 years, who do not have AD, most practices use a standardized pediatric tray with a 24- to 48-hour contact time. However, patch testing can be “very challenging” for children who are under 3 years of age, and children with AD who are under 6 years, “so there needs to be a very high degree of suspicion for ACD and very careful selection of the allergens and contact time that is used in those particular cases,” she noted.
The most common allergens in children are nickel, fragrance mix I, cobalt, balsam of Peru, neomycin, and bacitracin, which largely match the common allergens seen in adults. However, allergens more common in children, compared with adults, include gold, propylene glycol, 2-Bromo-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol, and cocamidopropyl betaine. “If the child presents with a regional dermatitis or a patterned dermatitis, sometimes you can hone in on your suspected allergens and only test for a few,” Dr. Martin said. “In a child with eyelid dermatitis, you’re going to worry more about cocamidopropyl betaine in their shampoos and cleansers. Also, a metal allergen could be transferred from their hands from toys or coins, specifically nickel and cobalt. They also may have different sports gear such as goggles that may be affecting their eyelid dermatitis, which you would not necessarily see in an adult.”
Periorificial contact dermatitis can also differ in presentation between children and adults. “In kids, think about musical instruments, flavored lip balms, gum, and pacifiers,” she said. “For ACD on the buttocks and posterior thighs, think about toilet seat allergens, especially those in the potty training ages, and the nickel bolts on school chairs.”
In 2018, Dr. Martin and her colleagues on the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup published a pediatric baseline patch test series as a way to expand on the T.R.U.E. test (Dermatitis. 2018;29[4]:206-12). “It’s nice to have this panel available as a baseline screening tool when you’re unsure of possible triggers of the dermatitis but you still have high suspicion of allergic dermatitis,” Dr. Martin said. “This also is helpful for patients who present with generalized dermatitis. It’s still not perfect. We are collecting prospective data to fine-tune this baseline series.”
She reported having no financial disclosures.
“Time needs to be allocated for a patch test consultation, placement, removal, and reading,” she said at the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “You will need more time in the day that you’re reading the patch test for patient education. However, your staff will need more time on the front end of the patch test process for application. Also, if they are customizing patch tests, they’ll need time to make the patch tests along with access to a refrigerator and plenty of counter space.”
Other factors to consider are the site of service, your payer mix, and if you need to complete prior authorizations for patch testing.
Dr. Martin, associate professor of dermatology and child health at the University of Missouri–Columbia, said that the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) crosses her mind when she sees a patient with new dermatitis, especially in an older child; if the dermatitis is patterned or regional; if there’s exacerbation of an underlying, previously stable skin disease; or if it’s a pattern known to be associated with systemic contact dermatitis. “In fact, 13%-25% of healthy, asymptomatic kids have allergen sensitization,” she said. “If you take that a step further and look at kids who are suspected of having allergic contact dermatitis, 25%-96% have allergen sensitization. Still, that doesn’t mean that those tests are relevant to the dermatitis that’s going on. If you take kids who are referred to tertiary centers for patch testing, about half will have relevant patch test results.”
Pediatric ACD differs from adult ACD in three ways, Dr. Martin said. First, children have a different clinical morphology and distribution on presentation, compared with adults. “In adults, the most common clinical presentation is hand dermatitis, while kids more often present with a scattered generalized morphology of dermatitis,” she said. “This occurs in about one-third of children with ACD. Their patterns of allergen exposure are also different. For the most part, adults are in control of their own environments and what is placed on their skin, whereas kids are not. When thinking about what you might need to patch test a child to if you’re considering ACD, it’s important to think about not only what the parent or caregiver puts directly on the child’s skin but also any connubial or consort allergen exposure – the most common ones coming from the caregivers themselves, such as fragrance or hair dyes that are transferred to a young child.”
The third factor that differs between pediatric and adult ACD is the allergen source. Dr. Martin noted that children and adults use different personal care products, wear different types of clothing, and spend different amounts of time in play versus work. “Children have many more hobbies in general that are unfortunately lost as many of us age,” she said. That means “thinking through the child’s entire day and how the seasons differ for them, such as what sports they’re in and what protective equipment may be involved with where their dermatitis is, or what musical instruments they play.”
Applying the T.R.U.E. patch test panel or a customized patch test panel to young children poses certain challenges, considering their limited body surface area and propensity to squirm. Dr. Martin often employs distraction techniques when placing patches on young patients, including the use of bubbles, music, movies, and games. “The goal is always to get as much of the patches on the back or the flanks as possible,” she said. “If you need additional space you can use the upper outer arms, the abdomen, or the anterior lateral thighs. Another thing to consider is how to set up your week for pediatric patch testing. There’s a standardized process for adults where we place the patches on day 0, read them on day 2, with removal of the patches at that time, and then perform a delayed read between day 4-7.”
The process is similar for postpubescent children, despite the lack of clear guidelines in the medical literature. “There is much controversy and different practices between different pediatric patch test centers,” Dr. Martin said. “There is more consensus between the older kids and the prepubescent group ages 6-12. Most clinicians will still do a similar placement on day 0 with removal and initial read on day 2, with a delayed read on day 4-7. However, some groups will remove patches at 24 hours, especially in those with atopic dermatitis (AD) or a generalized dermatitis, to reduce irritant reactions. Others will also use half-strength concentrations of allergens.”
The most controversy lies with children younger than 6 years, she said. For those aged 3-6 years, who do not have AD, most practices use a standardized pediatric tray with a 24- to 48-hour contact time. However, patch testing can be “very challenging” for children who are under 3 years of age, and children with AD who are under 6 years, “so there needs to be a very high degree of suspicion for ACD and very careful selection of the allergens and contact time that is used in those particular cases,” she noted.
The most common allergens in children are nickel, fragrance mix I, cobalt, balsam of Peru, neomycin, and bacitracin, which largely match the common allergens seen in adults. However, allergens more common in children, compared with adults, include gold, propylene glycol, 2-Bromo-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol, and cocamidopropyl betaine. “If the child presents with a regional dermatitis or a patterned dermatitis, sometimes you can hone in on your suspected allergens and only test for a few,” Dr. Martin said. “In a child with eyelid dermatitis, you’re going to worry more about cocamidopropyl betaine in their shampoos and cleansers. Also, a metal allergen could be transferred from their hands from toys or coins, specifically nickel and cobalt. They also may have different sports gear such as goggles that may be affecting their eyelid dermatitis, which you would not necessarily see in an adult.”
Periorificial contact dermatitis can also differ in presentation between children and adults. “In kids, think about musical instruments, flavored lip balms, gum, and pacifiers,” she said. “For ACD on the buttocks and posterior thighs, think about toilet seat allergens, especially those in the potty training ages, and the nickel bolts on school chairs.”
In 2018, Dr. Martin and her colleagues on the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup published a pediatric baseline patch test series as a way to expand on the T.R.U.E. test (Dermatitis. 2018;29[4]:206-12). “It’s nice to have this panel available as a baseline screening tool when you’re unsure of possible triggers of the dermatitis but you still have high suspicion of allergic dermatitis,” Dr. Martin said. “This also is helpful for patients who present with generalized dermatitis. It’s still not perfect. We are collecting prospective data to fine-tune this baseline series.”
She reported having no financial disclosures.
“Time needs to be allocated for a patch test consultation, placement, removal, and reading,” she said at the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “You will need more time in the day that you’re reading the patch test for patient education. However, your staff will need more time on the front end of the patch test process for application. Also, if they are customizing patch tests, they’ll need time to make the patch tests along with access to a refrigerator and plenty of counter space.”
Other factors to consider are the site of service, your payer mix, and if you need to complete prior authorizations for patch testing.
Dr. Martin, associate professor of dermatology and child health at the University of Missouri–Columbia, said that the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) crosses her mind when she sees a patient with new dermatitis, especially in an older child; if the dermatitis is patterned or regional; if there’s exacerbation of an underlying, previously stable skin disease; or if it’s a pattern known to be associated with systemic contact dermatitis. “In fact, 13%-25% of healthy, asymptomatic kids have allergen sensitization,” she said. “If you take that a step further and look at kids who are suspected of having allergic contact dermatitis, 25%-96% have allergen sensitization. Still, that doesn’t mean that those tests are relevant to the dermatitis that’s going on. If you take kids who are referred to tertiary centers for patch testing, about half will have relevant patch test results.”
Pediatric ACD differs from adult ACD in three ways, Dr. Martin said. First, children have a different clinical morphology and distribution on presentation, compared with adults. “In adults, the most common clinical presentation is hand dermatitis, while kids more often present with a scattered generalized morphology of dermatitis,” she said. “This occurs in about one-third of children with ACD. Their patterns of allergen exposure are also different. For the most part, adults are in control of their own environments and what is placed on their skin, whereas kids are not. When thinking about what you might need to patch test a child to if you’re considering ACD, it’s important to think about not only what the parent or caregiver puts directly on the child’s skin but also any connubial or consort allergen exposure – the most common ones coming from the caregivers themselves, such as fragrance or hair dyes that are transferred to a young child.”
The third factor that differs between pediatric and adult ACD is the allergen source. Dr. Martin noted that children and adults use different personal care products, wear different types of clothing, and spend different amounts of time in play versus work. “Children have many more hobbies in general that are unfortunately lost as many of us age,” she said. That means “thinking through the child’s entire day and how the seasons differ for them, such as what sports they’re in and what protective equipment may be involved with where their dermatitis is, or what musical instruments they play.”
Applying the T.R.U.E. patch test panel or a customized patch test panel to young children poses certain challenges, considering their limited body surface area and propensity to squirm. Dr. Martin often employs distraction techniques when placing patches on young patients, including the use of bubbles, music, movies, and games. “The goal is always to get as much of the patches on the back or the flanks as possible,” she said. “If you need additional space you can use the upper outer arms, the abdomen, or the anterior lateral thighs. Another thing to consider is how to set up your week for pediatric patch testing. There’s a standardized process for adults where we place the patches on day 0, read them on day 2, with removal of the patches at that time, and then perform a delayed read between day 4-7.”
The process is similar for postpubescent children, despite the lack of clear guidelines in the medical literature. “There is much controversy and different practices between different pediatric patch test centers,” Dr. Martin said. “There is more consensus between the older kids and the prepubescent group ages 6-12. Most clinicians will still do a similar placement on day 0 with removal and initial read on day 2, with a delayed read on day 4-7. However, some groups will remove patches at 24 hours, especially in those with atopic dermatitis (AD) or a generalized dermatitis, to reduce irritant reactions. Others will also use half-strength concentrations of allergens.”
The most controversy lies with children younger than 6 years, she said. For those aged 3-6 years, who do not have AD, most practices use a standardized pediatric tray with a 24- to 48-hour contact time. However, patch testing can be “very challenging” for children who are under 3 years of age, and children with AD who are under 6 years, “so there needs to be a very high degree of suspicion for ACD and very careful selection of the allergens and contact time that is used in those particular cases,” she noted.
The most common allergens in children are nickel, fragrance mix I, cobalt, balsam of Peru, neomycin, and bacitracin, which largely match the common allergens seen in adults. However, allergens more common in children, compared with adults, include gold, propylene glycol, 2-Bromo-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol, and cocamidopropyl betaine. “If the child presents with a regional dermatitis or a patterned dermatitis, sometimes you can hone in on your suspected allergens and only test for a few,” Dr. Martin said. “In a child with eyelid dermatitis, you’re going to worry more about cocamidopropyl betaine in their shampoos and cleansers. Also, a metal allergen could be transferred from their hands from toys or coins, specifically nickel and cobalt. They also may have different sports gear such as goggles that may be affecting their eyelid dermatitis, which you would not necessarily see in an adult.”
Periorificial contact dermatitis can also differ in presentation between children and adults. “In kids, think about musical instruments, flavored lip balms, gum, and pacifiers,” she said. “For ACD on the buttocks and posterior thighs, think about toilet seat allergens, especially those in the potty training ages, and the nickel bolts on school chairs.”
In 2018, Dr. Martin and her colleagues on the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup published a pediatric baseline patch test series as a way to expand on the T.R.U.E. test (Dermatitis. 2018;29[4]:206-12). “It’s nice to have this panel available as a baseline screening tool when you’re unsure of possible triggers of the dermatitis but you still have high suspicion of allergic dermatitis,” Dr. Martin said. “This also is helpful for patients who present with generalized dermatitis. It’s still not perfect. We are collecting prospective data to fine-tune this baseline series.”
She reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM SPD 2020
Atretic Cephalocele With Hypertrichosis
To the Editor:
A 2-week-old female infant presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a 4.0×4.5-cm pink-red patch with a 1-cm central nodule and an overlying tuft of hair on the midline occipital region (Figure). The patient was born at 39 weeks’ gestation to nonconsanguineous parents via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery and had an unremarkable prenatal course with no complications since birth. The red patch and tuft of hair were noted at birth, and the parents reported that the redness varied somewhat in size throughout the day and from day to day. An initial neurologic workup revealed no gross neurologic abnormalities. A head ultrasound revealed a soft-tissue hypervascular nodule that appeared separate from bony structures but showed evidence of a necklike extension from the nodule to the underlying soft tissues. The ultrasound could not definitively rule out intracranial extension; gross brain structures appeared normal. The initial differential diagnosis consisted of a congenital hemangioma (either a rapidly involuting or noninvoluting subtype), meningioma, or cephalocele.
Consultation with the pediatric neurosurgery service was sought, and magnetic resonance imaging of the head was performed, which demonstrated a cystic lesion within the subcutaneous soft tissue in the midline posterior scalp approximately 2 cm above the torcula. There also was a thin stalk extending from the cyst and going through an osseous defect within the occipital bone and attaching to the falx cerebri. There was no evidence of any venous communication with the cerebral sinus tracts or intraparenchymal extension. No intracranial abnormalities were noted. Given the radiographic evidence, a presumptive diagnosis of an atretic cephalocele was made with the plan for surgical repair.
The patient was re-evaluated at 3 and 4 months of age; there were no changes in the size or appearance of the lesion, and she continued to meet all developmental milestones. At 9 months of age the patient underwent uncomplicated neurosurgery to repair the cephalocele. Histopathologic examination of the resected lesion was consistent with an atretic cephalocele and showed positive staining for epithelial membrane antigen, which further confirmed a meningothelial origin; no glial elements were identified. The postoperative course was uncomplicated, and the patient was healing well at a follow-up examination 2 weeks after the procedure.
This case highlights the importance of an extensive workup when a patient presents with a midline lesion and hypertrichosis. The patient’s red patch, excluding the hair tuft, was reminiscent of a vascular malformation or hemangioma precursor lesion given the hypervascularity, the history of the lesion being present since birth, the lack of neurologic symptomatology, and the history of meeting all developmental milestones. The differential diagnosis for this patient was extensive, as many neurologic conditions present with cutaneous findings. Having central nervous system (CNS) and cutaneous comorbidities coincide underscores their common neuroectodermal origin during embryogenesis.1,2
Atretic cephalocele is a rare diagnosis, with the prevalence of cephaloceles estimated to be 0.8 to 3.0 per 10,000 births.3 It typically occurs in either the parietal or occipital scalp as a skin nodule with a hair tuft or alopecic lesion with or without a hair collar. A cephalocele is defined as a skin-covered protrusion of intracranial contents through a bony defect. Central nervous system tissue, meninges, or cerebrospinal fluid can protrude outside the skull with this condition. An atretic cephalocele refers to a cephalocele that arrested in development and represents approximately 40% to 50% of all cephaloceles.4 Various hypotheses have explained the development of atretic cephaloceles: it represents a neural crest remnant, regression of a meningocele in utero, injury of multipotential mesenchymal cells, and either failure of the neural tube to close or reopening of the neural tube after closure.4-6 There is evidence of developmental defects in skin appendages including sweat and sebaceous glands, arrector pili muscles, and hair follicles in and around the skin overlying the cephalocele, suggesting that there is a developmental abnormality of not only the CNS but also the cutaneous tissue.5 Typical radiographic findings include a cystic lesion with underlying defect in the skull. A vertical positioning of the straight sinus also has been demonstrated to be a consistent finding that can aid in diagnosis.4
Imaging is of utmost importance when a patient presents with a tuft of hair on the scalp to rule out intracranial extension and associated abnormalities such as gray matter heterotopia, hypogenesis of the corpus callosum, hydrocephalus, and Dandy-Walker and Walker-Warburg syndromes, which have all been associated with atretic cephaloceles.4,7 The impact of location of the intracranial abnormality on prognosis has been contested, with some reporting a better prognosis with occipital cephalocele vs parietal cephalocele while others have found the opposite to be true.6,7
Cutaneous abnormalities presenting with hypertrichosis (ie, hair tuft, hair collar) and/or capillary malformations increase the likelihood of a cranial dysraphism, especially when these findings present together and occur in and around the midline. Clinical examination cannot rule out an underlying connection to the CNS; these findings require appropriate radiographic imaging assessment prior to any procedural intervention.
- Drolet BA, Clowry L, McTigue K, et al. The hair collar sign: marker for cranial dysraphism. Pediatrics. 1995;96(2, pt 1):309-313.
- Sewell MJ, Chiu YE, Drolet BA. Neural tube dysraphism: review of cutaneous markers and imaging. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:161-170.
- Carvalho DR, Giuliani LR, Simão GN, et al. Autosomal dominant atretic cephalocele with phenotype variability: report of a Brazilian family with six affected in four generation. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140:1458-1462.
- Bick DS, Brockland JJ, Scott AR. A scalp lesion with intracranial extension. atretic cephalocele. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;141:289-290.
- Fukuyama M, Tanese K, Yasuda F, et al. Two cases of atretic cephalocele, and histological evaluation of skin appendages in the surrounding skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:48-52.
- Martinez-Lage JF, Sola J, Casas C, et al. Atretic cephalocele: the tip of the iceberg. J Neurosurg. 1992;77:230-235.
- Yakota A, Kajiwara H, Kohchi M, et al. Parietal cephalocele: clinical importance of its atretic form and associated malformation. J Neurosurg. 1988;69:545-551.
To the Editor:
A 2-week-old female infant presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a 4.0×4.5-cm pink-red patch with a 1-cm central nodule and an overlying tuft of hair on the midline occipital region (Figure). The patient was born at 39 weeks’ gestation to nonconsanguineous parents via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery and had an unremarkable prenatal course with no complications since birth. The red patch and tuft of hair were noted at birth, and the parents reported that the redness varied somewhat in size throughout the day and from day to day. An initial neurologic workup revealed no gross neurologic abnormalities. A head ultrasound revealed a soft-tissue hypervascular nodule that appeared separate from bony structures but showed evidence of a necklike extension from the nodule to the underlying soft tissues. The ultrasound could not definitively rule out intracranial extension; gross brain structures appeared normal. The initial differential diagnosis consisted of a congenital hemangioma (either a rapidly involuting or noninvoluting subtype), meningioma, or cephalocele.

Consultation with the pediatric neurosurgery service was sought, and magnetic resonance imaging of the head was performed, which demonstrated a cystic lesion within the subcutaneous soft tissue in the midline posterior scalp approximately 2 cm above the torcula. There also was a thin stalk extending from the cyst and going through an osseous defect within the occipital bone and attaching to the falx cerebri. There was no evidence of any venous communication with the cerebral sinus tracts or intraparenchymal extension. No intracranial abnormalities were noted. Given the radiographic evidence, a presumptive diagnosis of an atretic cephalocele was made with the plan for surgical repair.
The patient was re-evaluated at 3 and 4 months of age; there were no changes in the size or appearance of the lesion, and she continued to meet all developmental milestones. At 9 months of age the patient underwent uncomplicated neurosurgery to repair the cephalocele. Histopathologic examination of the resected lesion was consistent with an atretic cephalocele and showed positive staining for epithelial membrane antigen, which further confirmed a meningothelial origin; no glial elements were identified. The postoperative course was uncomplicated, and the patient was healing well at a follow-up examination 2 weeks after the procedure.
This case highlights the importance of an extensive workup when a patient presents with a midline lesion and hypertrichosis. The patient’s red patch, excluding the hair tuft, was reminiscent of a vascular malformation or hemangioma precursor lesion given the hypervascularity, the history of the lesion being present since birth, the lack of neurologic symptomatology, and the history of meeting all developmental milestones. The differential diagnosis for this patient was extensive, as many neurologic conditions present with cutaneous findings. Having central nervous system (CNS) and cutaneous comorbidities coincide underscores their common neuroectodermal origin during embryogenesis.1,2
Atretic cephalocele is a rare diagnosis, with the prevalence of cephaloceles estimated to be 0.8 to 3.0 per 10,000 births.3 It typically occurs in either the parietal or occipital scalp as a skin nodule with a hair tuft or alopecic lesion with or without a hair collar. A cephalocele is defined as a skin-covered protrusion of intracranial contents through a bony defect. Central nervous system tissue, meninges, or cerebrospinal fluid can protrude outside the skull with this condition. An atretic cephalocele refers to a cephalocele that arrested in development and represents approximately 40% to 50% of all cephaloceles.4 Various hypotheses have explained the development of atretic cephaloceles: it represents a neural crest remnant, regression of a meningocele in utero, injury of multipotential mesenchymal cells, and either failure of the neural tube to close or reopening of the neural tube after closure.4-6 There is evidence of developmental defects in skin appendages including sweat and sebaceous glands, arrector pili muscles, and hair follicles in and around the skin overlying the cephalocele, suggesting that there is a developmental abnormality of not only the CNS but also the cutaneous tissue.5 Typical radiographic findings include a cystic lesion with underlying defect in the skull. A vertical positioning of the straight sinus also has been demonstrated to be a consistent finding that can aid in diagnosis.4
Imaging is of utmost importance when a patient presents with a tuft of hair on the scalp to rule out intracranial extension and associated abnormalities such as gray matter heterotopia, hypogenesis of the corpus callosum, hydrocephalus, and Dandy-Walker and Walker-Warburg syndromes, which have all been associated with atretic cephaloceles.4,7 The impact of location of the intracranial abnormality on prognosis has been contested, with some reporting a better prognosis with occipital cephalocele vs parietal cephalocele while others have found the opposite to be true.6,7
Cutaneous abnormalities presenting with hypertrichosis (ie, hair tuft, hair collar) and/or capillary malformations increase the likelihood of a cranial dysraphism, especially when these findings present together and occur in and around the midline. Clinical examination cannot rule out an underlying connection to the CNS; these findings require appropriate radiographic imaging assessment prior to any procedural intervention.
To the Editor:
A 2-week-old female infant presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a 4.0×4.5-cm pink-red patch with a 1-cm central nodule and an overlying tuft of hair on the midline occipital region (Figure). The patient was born at 39 weeks’ gestation to nonconsanguineous parents via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery and had an unremarkable prenatal course with no complications since birth. The red patch and tuft of hair were noted at birth, and the parents reported that the redness varied somewhat in size throughout the day and from day to day. An initial neurologic workup revealed no gross neurologic abnormalities. A head ultrasound revealed a soft-tissue hypervascular nodule that appeared separate from bony structures but showed evidence of a necklike extension from the nodule to the underlying soft tissues. The ultrasound could not definitively rule out intracranial extension; gross brain structures appeared normal. The initial differential diagnosis consisted of a congenital hemangioma (either a rapidly involuting or noninvoluting subtype), meningioma, or cephalocele.

Consultation with the pediatric neurosurgery service was sought, and magnetic resonance imaging of the head was performed, which demonstrated a cystic lesion within the subcutaneous soft tissue in the midline posterior scalp approximately 2 cm above the torcula. There also was a thin stalk extending from the cyst and going through an osseous defect within the occipital bone and attaching to the falx cerebri. There was no evidence of any venous communication with the cerebral sinus tracts or intraparenchymal extension. No intracranial abnormalities were noted. Given the radiographic evidence, a presumptive diagnosis of an atretic cephalocele was made with the plan for surgical repair.
The patient was re-evaluated at 3 and 4 months of age; there were no changes in the size or appearance of the lesion, and she continued to meet all developmental milestones. At 9 months of age the patient underwent uncomplicated neurosurgery to repair the cephalocele. Histopathologic examination of the resected lesion was consistent with an atretic cephalocele and showed positive staining for epithelial membrane antigen, which further confirmed a meningothelial origin; no glial elements were identified. The postoperative course was uncomplicated, and the patient was healing well at a follow-up examination 2 weeks after the procedure.
This case highlights the importance of an extensive workup when a patient presents with a midline lesion and hypertrichosis. The patient’s red patch, excluding the hair tuft, was reminiscent of a vascular malformation or hemangioma precursor lesion given the hypervascularity, the history of the lesion being present since birth, the lack of neurologic symptomatology, and the history of meeting all developmental milestones. The differential diagnosis for this patient was extensive, as many neurologic conditions present with cutaneous findings. Having central nervous system (CNS) and cutaneous comorbidities coincide underscores their common neuroectodermal origin during embryogenesis.1,2
Atretic cephalocele is a rare diagnosis, with the prevalence of cephaloceles estimated to be 0.8 to 3.0 per 10,000 births.3 It typically occurs in either the parietal or occipital scalp as a skin nodule with a hair tuft or alopecic lesion with or without a hair collar. A cephalocele is defined as a skin-covered protrusion of intracranial contents through a bony defect. Central nervous system tissue, meninges, or cerebrospinal fluid can protrude outside the skull with this condition. An atretic cephalocele refers to a cephalocele that arrested in development and represents approximately 40% to 50% of all cephaloceles.4 Various hypotheses have explained the development of atretic cephaloceles: it represents a neural crest remnant, regression of a meningocele in utero, injury of multipotential mesenchymal cells, and either failure of the neural tube to close or reopening of the neural tube after closure.4-6 There is evidence of developmental defects in skin appendages including sweat and sebaceous glands, arrector pili muscles, and hair follicles in and around the skin overlying the cephalocele, suggesting that there is a developmental abnormality of not only the CNS but also the cutaneous tissue.5 Typical radiographic findings include a cystic lesion with underlying defect in the skull. A vertical positioning of the straight sinus also has been demonstrated to be a consistent finding that can aid in diagnosis.4
Imaging is of utmost importance when a patient presents with a tuft of hair on the scalp to rule out intracranial extension and associated abnormalities such as gray matter heterotopia, hypogenesis of the corpus callosum, hydrocephalus, and Dandy-Walker and Walker-Warburg syndromes, which have all been associated with atretic cephaloceles.4,7 The impact of location of the intracranial abnormality on prognosis has been contested, with some reporting a better prognosis with occipital cephalocele vs parietal cephalocele while others have found the opposite to be true.6,7
Cutaneous abnormalities presenting with hypertrichosis (ie, hair tuft, hair collar) and/or capillary malformations increase the likelihood of a cranial dysraphism, especially when these findings present together and occur in and around the midline. Clinical examination cannot rule out an underlying connection to the CNS; these findings require appropriate radiographic imaging assessment prior to any procedural intervention.
- Drolet BA, Clowry L, McTigue K, et al. The hair collar sign: marker for cranial dysraphism. Pediatrics. 1995;96(2, pt 1):309-313.
- Sewell MJ, Chiu YE, Drolet BA. Neural tube dysraphism: review of cutaneous markers and imaging. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:161-170.
- Carvalho DR, Giuliani LR, Simão GN, et al. Autosomal dominant atretic cephalocele with phenotype variability: report of a Brazilian family with six affected in four generation. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140:1458-1462.
- Bick DS, Brockland JJ, Scott AR. A scalp lesion with intracranial extension. atretic cephalocele. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;141:289-290.
- Fukuyama M, Tanese K, Yasuda F, et al. Two cases of atretic cephalocele, and histological evaluation of skin appendages in the surrounding skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:48-52.
- Martinez-Lage JF, Sola J, Casas C, et al. Atretic cephalocele: the tip of the iceberg. J Neurosurg. 1992;77:230-235.
- Yakota A, Kajiwara H, Kohchi M, et al. Parietal cephalocele: clinical importance of its atretic form and associated malformation. J Neurosurg. 1988;69:545-551.
- Drolet BA, Clowry L, McTigue K, et al. The hair collar sign: marker for cranial dysraphism. Pediatrics. 1995;96(2, pt 1):309-313.
- Sewell MJ, Chiu YE, Drolet BA. Neural tube dysraphism: review of cutaneous markers and imaging. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:161-170.
- Carvalho DR, Giuliani LR, Simão GN, et al. Autosomal dominant atretic cephalocele with phenotype variability: report of a Brazilian family with six affected in four generation. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140:1458-1462.
- Bick DS, Brockland JJ, Scott AR. A scalp lesion with intracranial extension. atretic cephalocele. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;141:289-290.
- Fukuyama M, Tanese K, Yasuda F, et al. Two cases of atretic cephalocele, and histological evaluation of skin appendages in the surrounding skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:48-52.
- Martinez-Lage JF, Sola J, Casas C, et al. Atretic cephalocele: the tip of the iceberg. J Neurosurg. 1992;77:230-235.
- Yakota A, Kajiwara H, Kohchi M, et al. Parietal cephalocele: clinical importance of its atretic form and associated malformation. J Neurosurg. 1988;69:545-551.
Practice Points
- Atretic cephalocele is a rare diagnosis occurring on the scalp as a nodule with an overlying hair tuft or alopecia with or without a hair collar.
- Imaging is of utmost importance when presented with a tuft of hair on the midline to rule out intracranial extension and associated abnormalities.
Non–COVID-19 VA Hospital Admissions Drop During the Pandemic
Anecdotal reports have suggested that people have been less likely to go to the hospital for emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings from a study by 2 physicians at Mount Sinai in New York now provide support for that: Between March 11 and April 21, 2020, 42% fewer patients were admitted to US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) inpatient facilities when compared with the preceding 6 weeks.
The researchers analyzed data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and examined at trends during the first 16 weeks of 2019 and 2020 for 6 common emergency conditions: stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), appendicitis, and pneumonia. Strikingly, the number of patients admitted dropped from 77,624 in weeks 5 to 10 of 2020 to 45,155 in weeks 11 to 16.
The number of patients admitted for stroke declined by 52%; myocardial infarction, 40%; COPD, 48%; heart failure, 49%; and appendicitis, 57%. By contrast, the number of patients admitted overall and for each condition did not decline during the same weeks in 2019. Admissions for pneumonia dropped during weeks 11 to 16 by 14% in 2019 and 28% in 2020. When patients who tested positive for COVID-19 were excluded, however, pneumonia admissions decreased by 46%. Of patients who were admitted during weeks 11 to 16 of 2020, 2,458 had tested positive for COVID-19 during weeks 5 to 10.
The authers contend that the marked drop in admissions is unlikely to be attributable to a reduction in disease incidence. Rather, they theorize that many patients may be avoiding hospitals out of fear of becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2. These data “should raise serious concerns,” the authors say, about the well-being and health outcomes of the patients who aren’t getting the emergency or inpatient care they need.
Anecdotal reports have suggested that people have been less likely to go to the hospital for emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings from a study by 2 physicians at Mount Sinai in New York now provide support for that: Between March 11 and April 21, 2020, 42% fewer patients were admitted to US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) inpatient facilities when compared with the preceding 6 weeks.
The researchers analyzed data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and examined at trends during the first 16 weeks of 2019 and 2020 for 6 common emergency conditions: stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), appendicitis, and pneumonia. Strikingly, the number of patients admitted dropped from 77,624 in weeks 5 to 10 of 2020 to 45,155 in weeks 11 to 16.
The number of patients admitted for stroke declined by 52%; myocardial infarction, 40%; COPD, 48%; heart failure, 49%; and appendicitis, 57%. By contrast, the number of patients admitted overall and for each condition did not decline during the same weeks in 2019. Admissions for pneumonia dropped during weeks 11 to 16 by 14% in 2019 and 28% in 2020. When patients who tested positive for COVID-19 were excluded, however, pneumonia admissions decreased by 46%. Of patients who were admitted during weeks 11 to 16 of 2020, 2,458 had tested positive for COVID-19 during weeks 5 to 10.
The authers contend that the marked drop in admissions is unlikely to be attributable to a reduction in disease incidence. Rather, they theorize that many patients may be avoiding hospitals out of fear of becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2. These data “should raise serious concerns,” the authors say, about the well-being and health outcomes of the patients who aren’t getting the emergency or inpatient care they need.
Anecdotal reports have suggested that people have been less likely to go to the hospital for emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings from a study by 2 physicians at Mount Sinai in New York now provide support for that: Between March 11 and April 21, 2020, 42% fewer patients were admitted to US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) inpatient facilities when compared with the preceding 6 weeks.
The researchers analyzed data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and examined at trends during the first 16 weeks of 2019 and 2020 for 6 common emergency conditions: stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), appendicitis, and pneumonia. Strikingly, the number of patients admitted dropped from 77,624 in weeks 5 to 10 of 2020 to 45,155 in weeks 11 to 16.
The number of patients admitted for stroke declined by 52%; myocardial infarction, 40%; COPD, 48%; heart failure, 49%; and appendicitis, 57%. By contrast, the number of patients admitted overall and for each condition did not decline during the same weeks in 2019. Admissions for pneumonia dropped during weeks 11 to 16 by 14% in 2019 and 28% in 2020. When patients who tested positive for COVID-19 were excluded, however, pneumonia admissions decreased by 46%. Of patients who were admitted during weeks 11 to 16 of 2020, 2,458 had tested positive for COVID-19 during weeks 5 to 10.
The authers contend that the marked drop in admissions is unlikely to be attributable to a reduction in disease incidence. Rather, they theorize that many patients may be avoiding hospitals out of fear of becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2. These data “should raise serious concerns,” the authors say, about the well-being and health outcomes of the patients who aren’t getting the emergency or inpatient care they need.