User login
Do No Harm: What Smoldering Myeloma Teaches Us
My approach to treating SMM takes into account what its history can teach us about 1) how advancements in imaging and diagnostic reclassifications can revise the entire natural history of a disease, and 2) how evidence generated by even the best of studies may have an expiration date.
Much of what we know about SMM today dates to a pivotal study by Robert A. Kyle, MD, and colleagues, published in 2007. That inspirational team of investigators followed people diagnosed with SMM from 1970 to 1995 and established the first natural history of the condition. Their monumental effort and the data and conclusions it generated (eg,10% risk annually of SMM becoming MM for the first 5 years) are still cited today in references, papers, and slide sets.
Despite the seminal importance of this work, from today’s perspective the 2007 study might just as well have been describing a different disease. Back then people were diagnosed with SMM if their blood work detected a monoclonal protein and a follow-up bone marrow biopsy found at least 10% plasma cells (or a monoclonal protein exceeding 3g/dL). If there were no signs of end-organ damage (ie, no anemia or kidney problems) and an x-ray showed no fractures or lesions in the bones, the diagnosis was determined to be SMM.
What’s different in 2024? First and foremost: advanced, highly sensitive imaging techniques. MRIs can pick up small lytic lesions (and even the precursor to lytic lesions) that would not appear on an x-ray. In fact, relying solely on x-rays risks missing half of the lytic lesions.
Therefore, using the same criteria, many people who in the past were diagnosed with SMM would today be diagnosed with MM. Furthermore, in 2014 a diagnostic change reclassified people’s diagnosis from the highest risk category of SMM to the category of active MM.
Due to these scientific advances and classification changes, I believe that the natural history of SMM is unknown. Risk stratification models for SMM derived from data sets of people who had not undergone rigorous advanced imaging likely are skewed by data from people who had MM. In addition, current risk stratification models have very poor concordance with each other. I routinely see people whose 2-year risk according to different models varies by more than 30%-40%.
All this information tells us that SMM today is more indolent than the SMM of the past. Paradoxically, however, our therapies keep getting more and more aggressive, exposing this vulnerable group of people to intense treatment regimens that they may not require. Therapies tested on people diagnosed with SMM include an aggressive three-drug regimen, autologous stem cell transplant, and 2 years of additional therapy, as well as, more recently CAR T-cell therapy which so far has at least a 4%-5% treatment-related mortality risk in people with myeloma and a strong signal for secondary cancer risk. Other trials are testing bispecific therapies such as talquetamab, a drug which in my experience causes horrendous skin toxicity, profound weight loss, and one’s nails to fall off.
Doctors routinely keep showing slides from Kyle’s pivotal work to describe the natural history of SMM and to justify the need for treatment, and trials continue to use outdated progression prediction models. In my opinion, as people with MM keep living longer and treatments for MM keep getting better, the threshold for intervening with asymptomatic, healthy people with SMM should be getting higher, not lower.
I strongly believe that the current landscape of SMM treatment exemplifies good intentions leading to bad outcomes. A routine blood test in a completely healthy person that finds elevated total protein in the blood could culminate in well-intentioned but aggressive therapies that can lead to many serious side effects. (I repeat: Secondary cancers and deaths from infections have all occurred in SMM trials.)
With no control arm, we simply don’t know how well these people might have fared without any therapy. For all we know, treatment may have shortened their lives due to complications up to and including death — all because of a blood test often conducted for reasons that have no evidentiary basis.
For example, plasma cell diseases are not linked to low bone density or auto-immune diseases, yet these labs are sent routinely as part of a workup for those conditions, leading to increasing anxiety and costs.
So, what is my approach? When treating people with SMM, I hold nuanced discussions of this data to help prioritize and reach informed decisions. After our honest conversation about the limitations of SMM models, older data, and the limitations of prospective data studying pharmacological treatment, almost no one signs up for treatment.
I want these people to stay safe, and I’m proud to be a part of a trial (SPOTLIGHT, NCT06212323) that aims to show prospectively that these people can be watched off treatment with monitoring via advanced imaging modalities.
In conclusion: SMM teaches us how, even in the absence of pharmacological interventions, the natural history of a disease can change over time, simply via better imaging techniques and changes in diagnostic classifications. Unfortunately, SMM also illustrates how good intentions can lead to harm.
Dr. Mohyuddin is assistant professor in the multiple myeloma program at the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
My approach to treating SMM takes into account what its history can teach us about 1) how advancements in imaging and diagnostic reclassifications can revise the entire natural history of a disease, and 2) how evidence generated by even the best of studies may have an expiration date.
Much of what we know about SMM today dates to a pivotal study by Robert A. Kyle, MD, and colleagues, published in 2007. That inspirational team of investigators followed people diagnosed with SMM from 1970 to 1995 and established the first natural history of the condition. Their monumental effort and the data and conclusions it generated (eg,10% risk annually of SMM becoming MM for the first 5 years) are still cited today in references, papers, and slide sets.
Despite the seminal importance of this work, from today’s perspective the 2007 study might just as well have been describing a different disease. Back then people were diagnosed with SMM if their blood work detected a monoclonal protein and a follow-up bone marrow biopsy found at least 10% plasma cells (or a monoclonal protein exceeding 3g/dL). If there were no signs of end-organ damage (ie, no anemia or kidney problems) and an x-ray showed no fractures or lesions in the bones, the diagnosis was determined to be SMM.
What’s different in 2024? First and foremost: advanced, highly sensitive imaging techniques. MRIs can pick up small lytic lesions (and even the precursor to lytic lesions) that would not appear on an x-ray. In fact, relying solely on x-rays risks missing half of the lytic lesions.
Therefore, using the same criteria, many people who in the past were diagnosed with SMM would today be diagnosed with MM. Furthermore, in 2014 a diagnostic change reclassified people’s diagnosis from the highest risk category of SMM to the category of active MM.
Due to these scientific advances and classification changes, I believe that the natural history of SMM is unknown. Risk stratification models for SMM derived from data sets of people who had not undergone rigorous advanced imaging likely are skewed by data from people who had MM. In addition, current risk stratification models have very poor concordance with each other. I routinely see people whose 2-year risk according to different models varies by more than 30%-40%.
All this information tells us that SMM today is more indolent than the SMM of the past. Paradoxically, however, our therapies keep getting more and more aggressive, exposing this vulnerable group of people to intense treatment regimens that they may not require. Therapies tested on people diagnosed with SMM include an aggressive three-drug regimen, autologous stem cell transplant, and 2 years of additional therapy, as well as, more recently CAR T-cell therapy which so far has at least a 4%-5% treatment-related mortality risk in people with myeloma and a strong signal for secondary cancer risk. Other trials are testing bispecific therapies such as talquetamab, a drug which in my experience causes horrendous skin toxicity, profound weight loss, and one’s nails to fall off.
Doctors routinely keep showing slides from Kyle’s pivotal work to describe the natural history of SMM and to justify the need for treatment, and trials continue to use outdated progression prediction models. In my opinion, as people with MM keep living longer and treatments for MM keep getting better, the threshold for intervening with asymptomatic, healthy people with SMM should be getting higher, not lower.
I strongly believe that the current landscape of SMM treatment exemplifies good intentions leading to bad outcomes. A routine blood test in a completely healthy person that finds elevated total protein in the blood could culminate in well-intentioned but aggressive therapies that can lead to many serious side effects. (I repeat: Secondary cancers and deaths from infections have all occurred in SMM trials.)
With no control arm, we simply don’t know how well these people might have fared without any therapy. For all we know, treatment may have shortened their lives due to complications up to and including death — all because of a blood test often conducted for reasons that have no evidentiary basis.
For example, plasma cell diseases are not linked to low bone density or auto-immune diseases, yet these labs are sent routinely as part of a workup for those conditions, leading to increasing anxiety and costs.
So, what is my approach? When treating people with SMM, I hold nuanced discussions of this data to help prioritize and reach informed decisions. After our honest conversation about the limitations of SMM models, older data, and the limitations of prospective data studying pharmacological treatment, almost no one signs up for treatment.
I want these people to stay safe, and I’m proud to be a part of a trial (SPOTLIGHT, NCT06212323) that aims to show prospectively that these people can be watched off treatment with monitoring via advanced imaging modalities.
In conclusion: SMM teaches us how, even in the absence of pharmacological interventions, the natural history of a disease can change over time, simply via better imaging techniques and changes in diagnostic classifications. Unfortunately, SMM also illustrates how good intentions can lead to harm.
Dr. Mohyuddin is assistant professor in the multiple myeloma program at the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
My approach to treating SMM takes into account what its history can teach us about 1) how advancements in imaging and diagnostic reclassifications can revise the entire natural history of a disease, and 2) how evidence generated by even the best of studies may have an expiration date.
Much of what we know about SMM today dates to a pivotal study by Robert A. Kyle, MD, and colleagues, published in 2007. That inspirational team of investigators followed people diagnosed with SMM from 1970 to 1995 and established the first natural history of the condition. Their monumental effort and the data and conclusions it generated (eg,10% risk annually of SMM becoming MM for the first 5 years) are still cited today in references, papers, and slide sets.
Despite the seminal importance of this work, from today’s perspective the 2007 study might just as well have been describing a different disease. Back then people were diagnosed with SMM if their blood work detected a monoclonal protein and a follow-up bone marrow biopsy found at least 10% plasma cells (or a monoclonal protein exceeding 3g/dL). If there were no signs of end-organ damage (ie, no anemia or kidney problems) and an x-ray showed no fractures or lesions in the bones, the diagnosis was determined to be SMM.
What’s different in 2024? First and foremost: advanced, highly sensitive imaging techniques. MRIs can pick up small lytic lesions (and even the precursor to lytic lesions) that would not appear on an x-ray. In fact, relying solely on x-rays risks missing half of the lytic lesions.
Therefore, using the same criteria, many people who in the past were diagnosed with SMM would today be diagnosed with MM. Furthermore, in 2014 a diagnostic change reclassified people’s diagnosis from the highest risk category of SMM to the category of active MM.
Due to these scientific advances and classification changes, I believe that the natural history of SMM is unknown. Risk stratification models for SMM derived from data sets of people who had not undergone rigorous advanced imaging likely are skewed by data from people who had MM. In addition, current risk stratification models have very poor concordance with each other. I routinely see people whose 2-year risk according to different models varies by more than 30%-40%.
All this information tells us that SMM today is more indolent than the SMM of the past. Paradoxically, however, our therapies keep getting more and more aggressive, exposing this vulnerable group of people to intense treatment regimens that they may not require. Therapies tested on people diagnosed with SMM include an aggressive three-drug regimen, autologous stem cell transplant, and 2 years of additional therapy, as well as, more recently CAR T-cell therapy which so far has at least a 4%-5% treatment-related mortality risk in people with myeloma and a strong signal for secondary cancer risk. Other trials are testing bispecific therapies such as talquetamab, a drug which in my experience causes horrendous skin toxicity, profound weight loss, and one’s nails to fall off.
Doctors routinely keep showing slides from Kyle’s pivotal work to describe the natural history of SMM and to justify the need for treatment, and trials continue to use outdated progression prediction models. In my opinion, as people with MM keep living longer and treatments for MM keep getting better, the threshold for intervening with asymptomatic, healthy people with SMM should be getting higher, not lower.
I strongly believe that the current landscape of SMM treatment exemplifies good intentions leading to bad outcomes. A routine blood test in a completely healthy person that finds elevated total protein in the blood could culminate in well-intentioned but aggressive therapies that can lead to many serious side effects. (I repeat: Secondary cancers and deaths from infections have all occurred in SMM trials.)
With no control arm, we simply don’t know how well these people might have fared without any therapy. For all we know, treatment may have shortened their lives due to complications up to and including death — all because of a blood test often conducted for reasons that have no evidentiary basis.
For example, plasma cell diseases are not linked to low bone density or auto-immune diseases, yet these labs are sent routinely as part of a workup for those conditions, leading to increasing anxiety and costs.
So, what is my approach? When treating people with SMM, I hold nuanced discussions of this data to help prioritize and reach informed decisions. After our honest conversation about the limitations of SMM models, older data, and the limitations of prospective data studying pharmacological treatment, almost no one signs up for treatment.
I want these people to stay safe, and I’m proud to be a part of a trial (SPOTLIGHT, NCT06212323) that aims to show prospectively that these people can be watched off treatment with monitoring via advanced imaging modalities.
In conclusion: SMM teaches us how, even in the absence of pharmacological interventions, the natural history of a disease can change over time, simply via better imaging techniques and changes in diagnostic classifications. Unfortunately, SMM also illustrates how good intentions can lead to harm.
Dr. Mohyuddin is assistant professor in the multiple myeloma program at the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
Managing Obesity Can Lead to Sarcopenia: A ‘Hidden’ Problem
ASUNCIÓN, PARAGUAY — Sarcopenic obesity, which is characterized by excess adiposity and muscle loss, is an “underestimated and underdiagnosed” condition, said the panelists at a session of the XV Latin American Obesity Congress (FLASO 2024) and II Paraguayan Congress of Obesity. The condition often affects older adults but can also occur at any age as a result of unhealthy habits or intensive or repeated weight loss efforts.
“The drugs currently used for managing obesity promote significant weight loss, but by losing fat, muscle is also lost,” said Fabiola Romero Gómez, MD, a professor of medicine at the National University of Asunción and president of the Paraguayan Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. “We must handle [these drugs] with extreme care. When we employ a strategy that achieves this significant weight loss, we must ensure that the patient receives a good protein intake and engages in resistance exercises, because otherwise, the cure may be worse than the disease.”
Some patients develop sarcopenic obesity after using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, undergoing bariatric surgery, or pursuing restrictive diets, Dr. Romero said in an interview. The condition is more common when there are long-standing cycles of weight loss and subsequent gain, “which accounts for the majority of our patients,” she said.
“An important, largely ignored aspect of weight loss, whether through pharmacological or lifestyle intervention, is that a portion of the weight loss comprises lean muscle,” according to a recent editorial in Nature Medicine. “Weight regain, however, is almost entirely fat. People with chronic obesity often lose and regain weight in repeated cycles, each of which results in body-composition changes (even if they experience some net weight loss). This cycling puts people unable to sustain weight loss at risk of being metabolically less healthy than they were before the initial weight loss was achieved — in effect, at risk of developing sarcopenic obesity.”
A ‘Hidden’ Problem
,” said Dr. Romero.
According to the 2022 consensus of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, clinical signs or factors suggesting sarcopenic obesity include age over 70 years, diagnosis of a chronic disease, repeated falls or weakness, and nutritional events such as recent weight loss or rapid gain, long-standing restrictive diets, and bariatric surgery.
The European guidelines also propose screening in individuals at risk to check for an increased body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference and suspicion parameters of sarcopenia. In this group of patients, the diagnosis should be made based on the analysis of alterations in muscle-skeletal functional parameters, such as grip or pinch strength or the 30-second chair stand test, followed by a determination of body mass alteration using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or electrical bioimpedance.
Electrical bioimpedance is Dr. Romero’s preferred method. It is an economical, simple, and easily transportable test that calculates lean muscle mass, fat mass, and body water based on electrical conductivity, she said. Experts have pointed out that bioimpedance scales “will revolutionize the way we measure obesity,” she added.
In an as-yet-unpublished study that received an honorable mention at the 3rd Paraguayan Congress of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism last year, Dr. Romero and colleagues studied 126 patients (median age, 45 years) with obesity defined by percentage of fat mass determined by bioimpedance. When their BMI was analyzed, 11.1% were “normal” weight, and 35.7% were “overweight.” Even waist circumference measurement suggested that about 15% of participants were without obesity. Moreover, almost one in four participants presented with sarcopenia, “implying a decrease in quality of life and physical disability in the future if not investigated, diagnosed, and treated correctly,” said Dr. Romero.
Prevention and Recommendations
Exercise and nutrition are two key components in the prevention and management of sarcopenic obesity. Physicians prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists “must also counsel patients about incorporating aerobic exercise and resistance training as part of the treatment plan, as well as ensuring they eat a high-protein diet,” Yoon Ji Ahn, MD, and Vibha Singhal, MD, MPH, of the Weight Management Center of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, wrote in a commentary published by this news organization.
Paraguayan nutritionist Patricia López Soto, a diabetes educator with postgraduate degrees in obesity, diabetes, and bariatric surgery from Favaloro University in Buenos Aires, shared with this news organization the following general recommendations to prevent sarcopenic obesity in patients undergoing weight loss treatment:
- Follow a healthy and balanced Mediterranean or DASH-style diet.
- Increase protein intake at the three to four main meals to a minimum of 1.4-1.5 g/kg/day.
- Try to make the protein intake mostly of high biological value: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, seafood, cheese, skim milk, and yogurt.
- Ensure protein intake at each meal of between 25 g and 30 g to increase protein synthesis. For example, a 150 g portion of meat or chicken provides 30 g of protein.
- If the protein intake is not achieved through food, a supplement measure like isolated and hydrolyzed whey protein is a good option.
- Engage in strength or resistance training (weightlifting) three to four times per week and 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise every day.
- To improve adherence, treatment should be carried out with a multidisciplinary team that includes a physician, nutritionist, and physical trainer, with frequent check-ups and body composition studies by bioimpedance.
Dr. Romero and Ms. López declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ASUNCIÓN, PARAGUAY — Sarcopenic obesity, which is characterized by excess adiposity and muscle loss, is an “underestimated and underdiagnosed” condition, said the panelists at a session of the XV Latin American Obesity Congress (FLASO 2024) and II Paraguayan Congress of Obesity. The condition often affects older adults but can also occur at any age as a result of unhealthy habits or intensive or repeated weight loss efforts.
“The drugs currently used for managing obesity promote significant weight loss, but by losing fat, muscle is also lost,” said Fabiola Romero Gómez, MD, a professor of medicine at the National University of Asunción and president of the Paraguayan Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. “We must handle [these drugs] with extreme care. When we employ a strategy that achieves this significant weight loss, we must ensure that the patient receives a good protein intake and engages in resistance exercises, because otherwise, the cure may be worse than the disease.”
Some patients develop sarcopenic obesity after using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, undergoing bariatric surgery, or pursuing restrictive diets, Dr. Romero said in an interview. The condition is more common when there are long-standing cycles of weight loss and subsequent gain, “which accounts for the majority of our patients,” she said.
“An important, largely ignored aspect of weight loss, whether through pharmacological or lifestyle intervention, is that a portion of the weight loss comprises lean muscle,” according to a recent editorial in Nature Medicine. “Weight regain, however, is almost entirely fat. People with chronic obesity often lose and regain weight in repeated cycles, each of which results in body-composition changes (even if they experience some net weight loss). This cycling puts people unable to sustain weight loss at risk of being metabolically less healthy than they were before the initial weight loss was achieved — in effect, at risk of developing sarcopenic obesity.”
A ‘Hidden’ Problem
,” said Dr. Romero.
According to the 2022 consensus of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, clinical signs or factors suggesting sarcopenic obesity include age over 70 years, diagnosis of a chronic disease, repeated falls or weakness, and nutritional events such as recent weight loss or rapid gain, long-standing restrictive diets, and bariatric surgery.
The European guidelines also propose screening in individuals at risk to check for an increased body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference and suspicion parameters of sarcopenia. In this group of patients, the diagnosis should be made based on the analysis of alterations in muscle-skeletal functional parameters, such as grip or pinch strength or the 30-second chair stand test, followed by a determination of body mass alteration using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or electrical bioimpedance.
Electrical bioimpedance is Dr. Romero’s preferred method. It is an economical, simple, and easily transportable test that calculates lean muscle mass, fat mass, and body water based on electrical conductivity, she said. Experts have pointed out that bioimpedance scales “will revolutionize the way we measure obesity,” she added.
In an as-yet-unpublished study that received an honorable mention at the 3rd Paraguayan Congress of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism last year, Dr. Romero and colleagues studied 126 patients (median age, 45 years) with obesity defined by percentage of fat mass determined by bioimpedance. When their BMI was analyzed, 11.1% were “normal” weight, and 35.7% were “overweight.” Even waist circumference measurement suggested that about 15% of participants were without obesity. Moreover, almost one in four participants presented with sarcopenia, “implying a decrease in quality of life and physical disability in the future if not investigated, diagnosed, and treated correctly,” said Dr. Romero.
Prevention and Recommendations
Exercise and nutrition are two key components in the prevention and management of sarcopenic obesity. Physicians prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists “must also counsel patients about incorporating aerobic exercise and resistance training as part of the treatment plan, as well as ensuring they eat a high-protein diet,” Yoon Ji Ahn, MD, and Vibha Singhal, MD, MPH, of the Weight Management Center of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, wrote in a commentary published by this news organization.
Paraguayan nutritionist Patricia López Soto, a diabetes educator with postgraduate degrees in obesity, diabetes, and bariatric surgery from Favaloro University in Buenos Aires, shared with this news organization the following general recommendations to prevent sarcopenic obesity in patients undergoing weight loss treatment:
- Follow a healthy and balanced Mediterranean or DASH-style diet.
- Increase protein intake at the three to four main meals to a minimum of 1.4-1.5 g/kg/day.
- Try to make the protein intake mostly of high biological value: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, seafood, cheese, skim milk, and yogurt.
- Ensure protein intake at each meal of between 25 g and 30 g to increase protein synthesis. For example, a 150 g portion of meat or chicken provides 30 g of protein.
- If the protein intake is not achieved through food, a supplement measure like isolated and hydrolyzed whey protein is a good option.
- Engage in strength or resistance training (weightlifting) three to four times per week and 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise every day.
- To improve adherence, treatment should be carried out with a multidisciplinary team that includes a physician, nutritionist, and physical trainer, with frequent check-ups and body composition studies by bioimpedance.
Dr. Romero and Ms. López declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ASUNCIÓN, PARAGUAY — Sarcopenic obesity, which is characterized by excess adiposity and muscle loss, is an “underestimated and underdiagnosed” condition, said the panelists at a session of the XV Latin American Obesity Congress (FLASO 2024) and II Paraguayan Congress of Obesity. The condition often affects older adults but can also occur at any age as a result of unhealthy habits or intensive or repeated weight loss efforts.
“The drugs currently used for managing obesity promote significant weight loss, but by losing fat, muscle is also lost,” said Fabiola Romero Gómez, MD, a professor of medicine at the National University of Asunción and president of the Paraguayan Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. “We must handle [these drugs] with extreme care. When we employ a strategy that achieves this significant weight loss, we must ensure that the patient receives a good protein intake and engages in resistance exercises, because otherwise, the cure may be worse than the disease.”
Some patients develop sarcopenic obesity after using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, undergoing bariatric surgery, or pursuing restrictive diets, Dr. Romero said in an interview. The condition is more common when there are long-standing cycles of weight loss and subsequent gain, “which accounts for the majority of our patients,” she said.
“An important, largely ignored aspect of weight loss, whether through pharmacological or lifestyle intervention, is that a portion of the weight loss comprises lean muscle,” according to a recent editorial in Nature Medicine. “Weight regain, however, is almost entirely fat. People with chronic obesity often lose and regain weight in repeated cycles, each of which results in body-composition changes (even if they experience some net weight loss). This cycling puts people unable to sustain weight loss at risk of being metabolically less healthy than they were before the initial weight loss was achieved — in effect, at risk of developing sarcopenic obesity.”
A ‘Hidden’ Problem
,” said Dr. Romero.
According to the 2022 consensus of the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism and the European Association for the Study of Obesity, clinical signs or factors suggesting sarcopenic obesity include age over 70 years, diagnosis of a chronic disease, repeated falls or weakness, and nutritional events such as recent weight loss or rapid gain, long-standing restrictive diets, and bariatric surgery.
The European guidelines also propose screening in individuals at risk to check for an increased body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference and suspicion parameters of sarcopenia. In this group of patients, the diagnosis should be made based on the analysis of alterations in muscle-skeletal functional parameters, such as grip or pinch strength or the 30-second chair stand test, followed by a determination of body mass alteration using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or electrical bioimpedance.
Electrical bioimpedance is Dr. Romero’s preferred method. It is an economical, simple, and easily transportable test that calculates lean muscle mass, fat mass, and body water based on electrical conductivity, she said. Experts have pointed out that bioimpedance scales “will revolutionize the way we measure obesity,” she added.
In an as-yet-unpublished study that received an honorable mention at the 3rd Paraguayan Congress of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism last year, Dr. Romero and colleagues studied 126 patients (median age, 45 years) with obesity defined by percentage of fat mass determined by bioimpedance. When their BMI was analyzed, 11.1% were “normal” weight, and 35.7% were “overweight.” Even waist circumference measurement suggested that about 15% of participants were without obesity. Moreover, almost one in four participants presented with sarcopenia, “implying a decrease in quality of life and physical disability in the future if not investigated, diagnosed, and treated correctly,” said Dr. Romero.
Prevention and Recommendations
Exercise and nutrition are two key components in the prevention and management of sarcopenic obesity. Physicians prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists “must also counsel patients about incorporating aerobic exercise and resistance training as part of the treatment plan, as well as ensuring they eat a high-protein diet,” Yoon Ji Ahn, MD, and Vibha Singhal, MD, MPH, of the Weight Management Center of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, wrote in a commentary published by this news organization.
Paraguayan nutritionist Patricia López Soto, a diabetes educator with postgraduate degrees in obesity, diabetes, and bariatric surgery from Favaloro University in Buenos Aires, shared with this news organization the following general recommendations to prevent sarcopenic obesity in patients undergoing weight loss treatment:
- Follow a healthy and balanced Mediterranean or DASH-style diet.
- Increase protein intake at the three to four main meals to a minimum of 1.4-1.5 g/kg/day.
- Try to make the protein intake mostly of high biological value: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, seafood, cheese, skim milk, and yogurt.
- Ensure protein intake at each meal of between 25 g and 30 g to increase protein synthesis. For example, a 150 g portion of meat or chicken provides 30 g of protein.
- If the protein intake is not achieved through food, a supplement measure like isolated and hydrolyzed whey protein is a good option.
- Engage in strength or resistance training (weightlifting) three to four times per week and 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise every day.
- To improve adherence, treatment should be carried out with a multidisciplinary team that includes a physician, nutritionist, and physical trainer, with frequent check-ups and body composition studies by bioimpedance.
Dr. Romero and Ms. López declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pancreatic Fat Is the Main Driver for Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreatic Diseases
TOPLINE:
Excessive intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) leading to fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was prevalent in almost 18% of participants in a large population-based cohort, and both IPFD and FP were associated with an increased risk for diabetes, acute pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study conducted from July 2014 to January 2023 investigated the prevalence of FP and the link between IPFD and pancreatic diseases in 42,599 participants (median age, 65 years; 46.6% men) from the UK Biobank who underwent abdominal Dixon MRI.
- IPFD levels were measured using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet.
- The outcomes assessed in this study were diseases of the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas, including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and other pancreatic conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of FP was 17.86%.
- Elevation in IPFD levels by one quintile increased the risk for the development of acute pancreatitis by 51.3% (P = .001), pancreatic cancer by 36.5% (P = .017), diabetes by 22.1% (P < .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 22.7% (P < .001).
- FP increased the risk for acute pancreatitis by 298.2% (P < .001), pancreatic cancer by 97.6% (P = .034), diabetes by 33.7% (P = .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 44.1% (P < .001).
- An increasing trend in the prevalence of FP with advancing age was observed in both men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Xiaowu Dong, MD, of the Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors acknowledged that most of the enrolled participants were White and older than 45 years. A low response rate to recruitment invitations in the UK Biobank database may have introduced self-selection bias. The median follow-up duration of 4.61 years was short and may be insufficient to fully capture the impact of IPFD. Additionally, the use of the average fat fraction for the entire pancreas may have led to spatial variations being ignored.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratory, The Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, Yangzhou key research and development plan, and Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects-Municipal Key Laboratory Construction. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Excessive intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) leading to fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was prevalent in almost 18% of participants in a large population-based cohort, and both IPFD and FP were associated with an increased risk for diabetes, acute pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study conducted from July 2014 to January 2023 investigated the prevalence of FP and the link between IPFD and pancreatic diseases in 42,599 participants (median age, 65 years; 46.6% men) from the UK Biobank who underwent abdominal Dixon MRI.
- IPFD levels were measured using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet.
- The outcomes assessed in this study were diseases of the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas, including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and other pancreatic conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of FP was 17.86%.
- Elevation in IPFD levels by one quintile increased the risk for the development of acute pancreatitis by 51.3% (P = .001), pancreatic cancer by 36.5% (P = .017), diabetes by 22.1% (P < .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 22.7% (P < .001).
- FP increased the risk for acute pancreatitis by 298.2% (P < .001), pancreatic cancer by 97.6% (P = .034), diabetes by 33.7% (P = .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 44.1% (P < .001).
- An increasing trend in the prevalence of FP with advancing age was observed in both men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Xiaowu Dong, MD, of the Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors acknowledged that most of the enrolled participants were White and older than 45 years. A low response rate to recruitment invitations in the UK Biobank database may have introduced self-selection bias. The median follow-up duration of 4.61 years was short and may be insufficient to fully capture the impact of IPFD. Additionally, the use of the average fat fraction for the entire pancreas may have led to spatial variations being ignored.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratory, The Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, Yangzhou key research and development plan, and Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects-Municipal Key Laboratory Construction. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Excessive intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) leading to fatty change of the pancreas (FP) was prevalent in almost 18% of participants in a large population-based cohort, and both IPFD and FP were associated with an increased risk for diabetes, acute pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study conducted from July 2014 to January 2023 investigated the prevalence of FP and the link between IPFD and pancreatic diseases in 42,599 participants (median age, 65 years; 46.6% men) from the UK Biobank who underwent abdominal Dixon MRI.
- IPFD levels were measured using MRI and a deep learning-based framework called nnUNet.
- The outcomes assessed in this study were diseases of the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas, including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and other pancreatic conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of FP was 17.86%.
- Elevation in IPFD levels by one quintile increased the risk for the development of acute pancreatitis by 51.3% (P = .001), pancreatic cancer by 36.5% (P = .017), diabetes by 22.1% (P < .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 22.7% (P < .001).
- FP increased the risk for acute pancreatitis by 298.2% (P < .001), pancreatic cancer by 97.6% (P = .034), diabetes by 33.7% (P = .001), and all pancreatic diseases by 44.1% (P < .001).
- An increasing trend in the prevalence of FP with advancing age was observed in both men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“FP is a common pancreatic disorder. Fat in the pancreas is an independent risk factor for diseases of both the exocrine pancreas and endocrine pancreas,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Xiaowu Dong, MD, of the Pancreatic Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Yangzhou Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors acknowledged that most of the enrolled participants were White and older than 45 years. A low response rate to recruitment invitations in the UK Biobank database may have introduced self-selection bias. The median follow-up duration of 4.61 years was short and may be insufficient to fully capture the impact of IPFD. Additionally, the use of the average fat fraction for the entire pancreas may have led to spatial variations being ignored.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou Municipal Key Laboratory, The Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission, Yangzhou key research and development plan, and Suzhou Innovation Platform Construction Projects-Municipal Key Laboratory Construction. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Plus HIV Ups Risk for CVD but Not Liver Disease
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) co-occurring with HIV infection does not appear to increase the risk for cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with MASLD alone. However, the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) is significantly increased among patients with MASLD and HIV, a large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- MASLD is highly prevalent in people living with HIV, but the impact of HIV on liver and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes in people with MASLD remains unclear.
- To investigate, researchers created a propensity score-matched cohort of veterans with noncirrhotic MASLD, with and without HIV (920 patients in each group).
- They evaluated the incidence of cirrhosis, HCC, and MACE, as well as overall survival, among the two groups. They also assessed these outcomes in MASLD patients with HIV on the basis of whether they were on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 10.4 years in the MASLD with HIV group and 11.8 years in the MASLD-only group, the overall incidence of cirrhosis and HCC was similar in MASLD with vs without HIV (cirrhosis: 0.97 vs 1.06 per 100 person-years, P = .54; HCC: 0.26 vs 0.17 per 100,000 person-years, P = .23), regardless of ART use.
- In contrast, the incidence of MACE was significantly higher in MASLD with vs without HIV (5.18 vs 4.48 per 100 person-years, P = .03). The incidence also was higher in patients with MASLD and HIV who were not on ART compared with those on ART (5.83 vs 4.7 per 100 person-years, P = .07).
- Compared with MASLD without HIV, the overall 5-year survival was significantly lower in MASLD with HIV (91.3% vs 85.7%). In MASLD with HIV, receipt of ART was associated with a significantly higher 5-year survival than no ART (87.4% vs 81.6%).
IN PRACTICE:
“Ensuring timely and appropriate initiation of HIV treatment is critical in patients with MASLD who have concurrent HIV infection, as well as optimizing metabolic comorbidities that may also contribute to increased risks of CVD and increased mortality,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Robert J. Wong, MD, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California, was published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study cohort consisted predominantly of older men, which may limit generalizability to women and younger populations. Metabolic comorbidities are more common in veterans compared with the general population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the CVD risk findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by an investigator-initiated research grant from Theratechnologies. Wong has received funding for his institution from Gilead Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Durect Corporation and has served as a consultant for Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
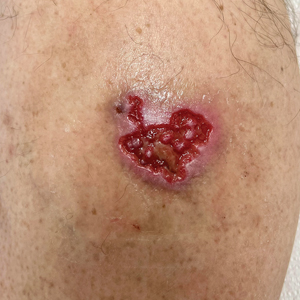
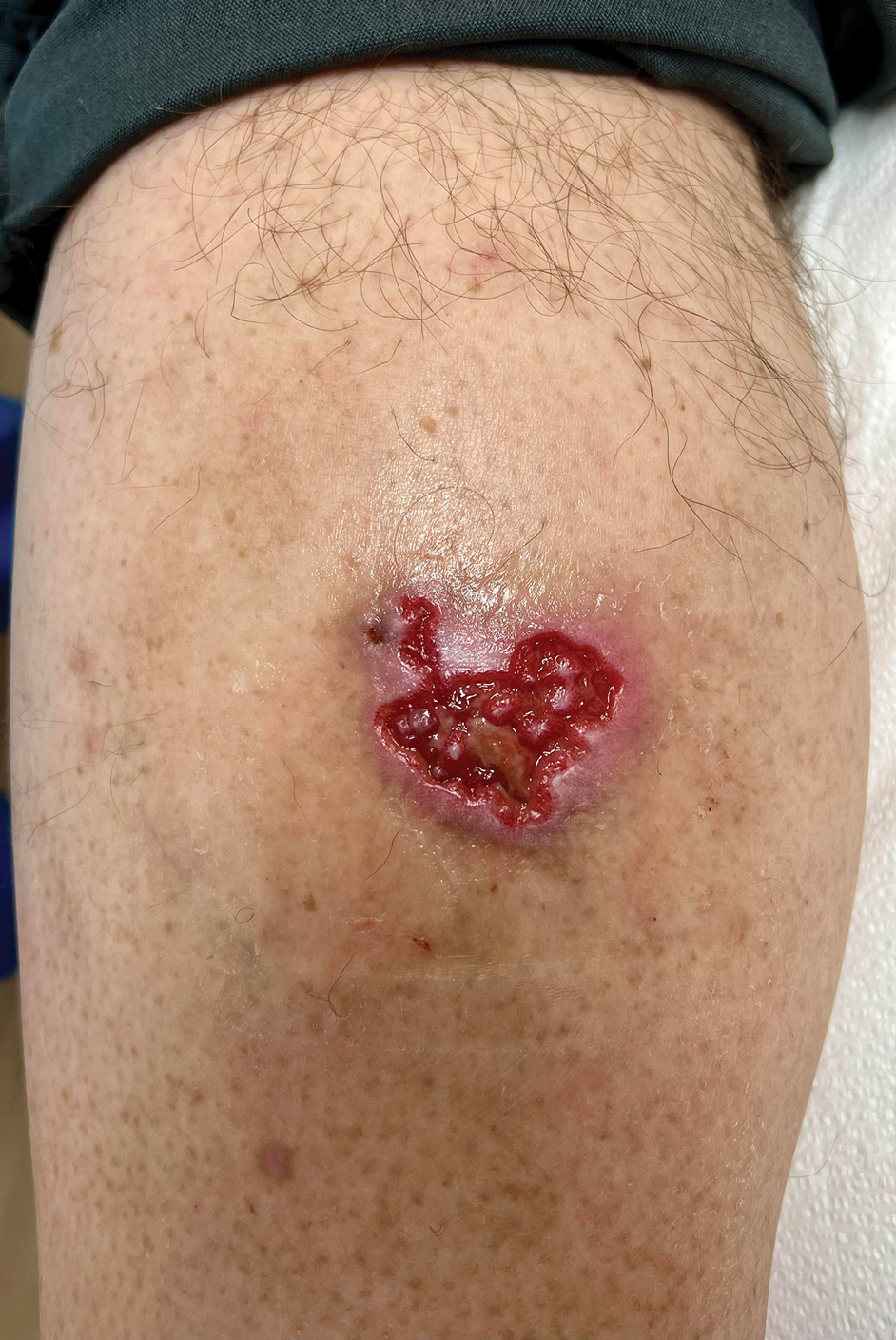
Chronic Cribriform Ulcerated Plaque on the Left Calf
The Diagnosis: Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Histopathology of the lesion showed a large basaloid lobule with focal epidermal attachment, peripheral nuclear palisading with cleft formation between the tumor and surrounding stroma, fibromyxoid stroma and mild pleomorphism, and variable mitotic activity and apoptosis (Figure). Based on the clinical presentation and histopathology, the patient was diagnosed with nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). He underwent a wide local excision of the affected area that was repaired with a splitthickness skin graft.
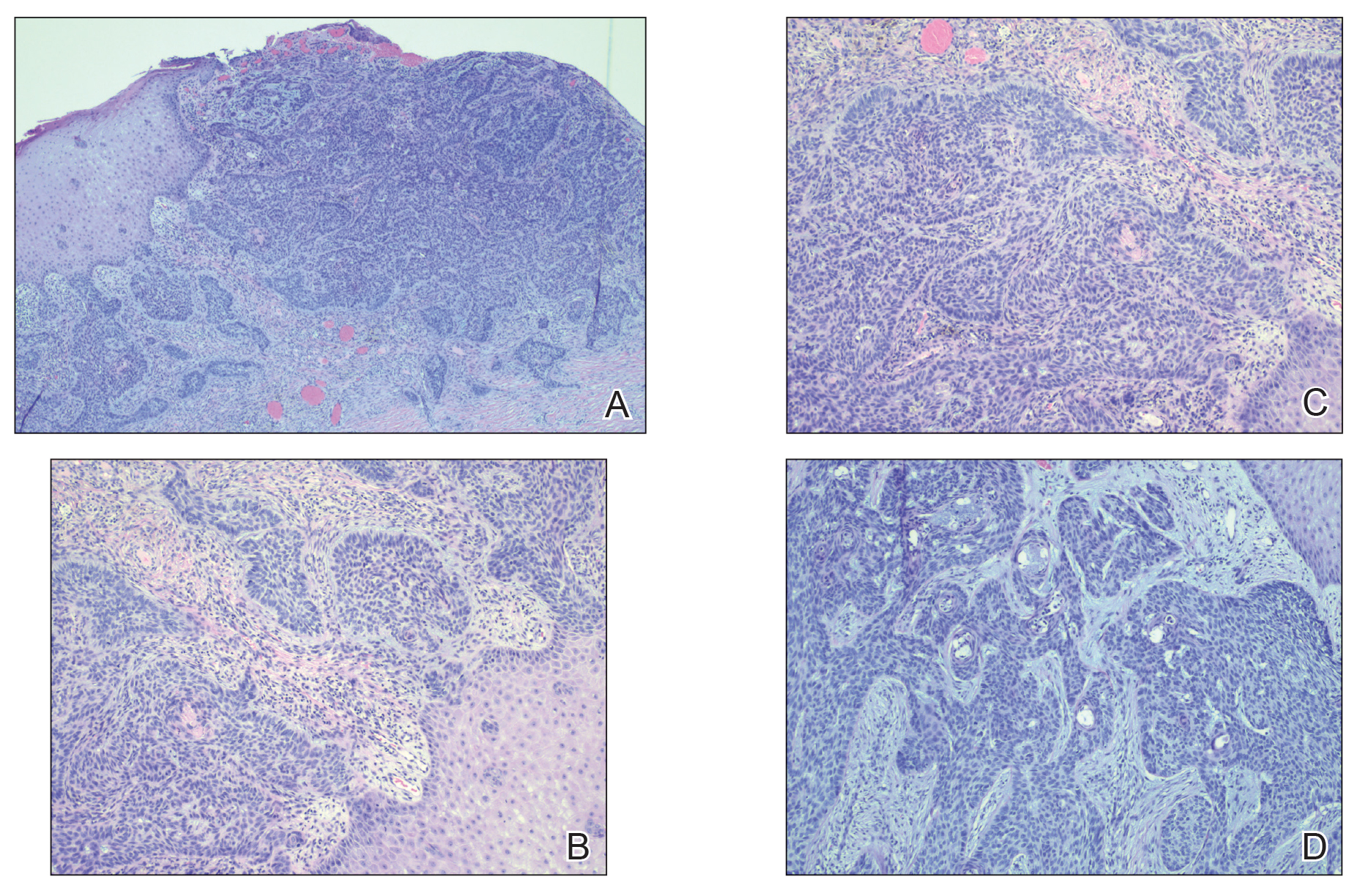
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer worldwide and typically occurs due to years of UV radiation damage on sun-exposed skin, which accounts for a higher frequency of BCC occurring in patients residing in geographic locations with greater UV exposure (eg, higher and lower latitudes). In addition to cumulative UV dose, the duration of the exposure as well as its intensity also play a role in the development of BCC, particularly in early childhood and adolescence. Nevertheless, UV exposure is not the only risk factor, as 20% of BCCs arise in skin that is not exposed to the sun. Other risk factors include exposure to ionizing radiation and arsenic, immunosuppression, and genetic predisposition.1 Although these malignancies typically do not metastasize, growth can lead to local tissue destruction and major disfigurement if not treated in a timely fashion.2
In our patient, the differential diagnosis included pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) given the clinical appearance of the cribriform base and violaceous undermined rim of the ulcer. Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare neutrophilic disorder that often results in ulcers that have been associated with various systemic autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease. There are 4 main subtypes of PG: the classic ulcerative type (our patient); the pustular type, which most often is seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; the bullous type, which can be seen in patients with an associated lymphoproliferative disorder; and the vegetative type. It frequently is thought of as both a clinical and histologic diagnosis of exclusion due to the nonspecific histopathologic features; most lesions demonstrate an infiltrate of neutrophils in the dermis. A biopsy was crucial in our patient, considering that diagnosis and treatment would have been further delayed had the patient been empirically treated with oral and topical steroids for presumed PG, which is precisely why PG is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is imperative for clinicians to rule out other pathologies, such as infection or malignancy, as demonstrated in our patient. The progressive onset and slow evolution of the lesion over years along with a lack of pain were more suggestive of BCC rather than PG. However, there is a report in the literature of PG mimicking BCC with both clinical and dermoscopic findings.3
Venous or stasis ulcers are painless, and although they rarely occur on the calf, they typically are seen lower on the leg such as on the medial ankles. Our patient endorsed occasional swelling of the affected leg and presented with edema, but overlying stasis change and other signs of venous insufficiency were absent.
Buruli ulcer is a painless chronic debilitating cutaneous disease resulting in indolent necrotizing skin as well as subcutaneous and bone lesions. It is caused by the environmental organism Mycobacterium ulcerans and typically is reported in Africa, Central/South America, the Western Pacific Region, and Australia.4 Histopathology usually demonstrates necrosis of subcutaneous tissue and dermal collagen accompanied by inflammation and acidfast bacilli highlighted by Ziehl-Neelsen stain.5 Smears of the lesions as well as culture and polymerase chain reaction for acid-fast bacilli also can be performed. Our patient reported no recent travel to any endemic areas and had no other risk factors or exposures to the pathogen responsible for this condition.
Traumatic ulcer also was included in the differential diagnosis, but the patient denied preceding trauma to the area, and the contralateral foot prosthesis did not rub on or impact the affected leg.
Basal cell carcinoma typically is treated surgically, but choice of treatment can depend on the subtype, size, tumor site, and/or patient preference.1 Other treatment modalities include electrodesiccation and curettage, cryosurgical destruction, photodynamic therapy, radiation, topical therapies, and systemic medications. Radiotherapy can be considered as a primary treatment option for BCC if surgery is contraindicated or declined by the patient, but it also is useful as an adjuvant therapy when there is perineural invasion of the tumor or positive margins. Hedgehog pathway inhibitors such as vismodegib currently are indicated for patients who are not candidates for surgery or radiation as well as for those with metastatic or locally advanced, recurrent BCC. There is no single treatment method ideal for every lesion or patient. Specific populations such as the elderly, the immunosuppressed, or those with poor baseline functional status may warrant a nonsurgical approach. The clinician must take into consideration all factors while at the same time thinking about how to best accomplish the goals of recurrencefree tumor removal, correction of any underlying functional impairment from the tumor, and maintenance of cosmesis.1
- McDaniel B, Badri T, Steele RB. Basal cell carcinoma. In: StatPearls. StatPearls; 2022.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Rosina P, Papagrigoraki A, Colato C. A case of superficial granulomatous pyoderma mimicking a basal cell carcinoma. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2014;22:48-51.
- Yotsu RR, Suzuki K, Simmonds RE, et al. Buruli ulcer: a review of the current knowledge. Curr Trop Med Rep. 2018;5:247-256.
- Guarner J, Bartlett J, Whitney EA, et al. Histopathologic features of Mycobacterium ulcerans infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:651-656.
The Diagnosis: Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Histopathology of the lesion showed a large basaloid lobule with focal epidermal attachment, peripheral nuclear palisading with cleft formation between the tumor and surrounding stroma, fibromyxoid stroma and mild pleomorphism, and variable mitotic activity and apoptosis (Figure). Based on the clinical presentation and histopathology, the patient was diagnosed with nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). He underwent a wide local excision of the affected area that was repaired with a splitthickness skin graft.

Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer worldwide and typically occurs due to years of UV radiation damage on sun-exposed skin, which accounts for a higher frequency of BCC occurring in patients residing in geographic locations with greater UV exposure (eg, higher and lower latitudes). In addition to cumulative UV dose, the duration of the exposure as well as its intensity also play a role in the development of BCC, particularly in early childhood and adolescence. Nevertheless, UV exposure is not the only risk factor, as 20% of BCCs arise in skin that is not exposed to the sun. Other risk factors include exposure to ionizing radiation and arsenic, immunosuppression, and genetic predisposition.1 Although these malignancies typically do not metastasize, growth can lead to local tissue destruction and major disfigurement if not treated in a timely fashion.2
In our patient, the differential diagnosis included pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) given the clinical appearance of the cribriform base and violaceous undermined rim of the ulcer. Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare neutrophilic disorder that often results in ulcers that have been associated with various systemic autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease. There are 4 main subtypes of PG: the classic ulcerative type (our patient); the pustular type, which most often is seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; the bullous type, which can be seen in patients with an associated lymphoproliferative disorder; and the vegetative type. It frequently is thought of as both a clinical and histologic diagnosis of exclusion due to the nonspecific histopathologic features; most lesions demonstrate an infiltrate of neutrophils in the dermis. A biopsy was crucial in our patient, considering that diagnosis and treatment would have been further delayed had the patient been empirically treated with oral and topical steroids for presumed PG, which is precisely why PG is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is imperative for clinicians to rule out other pathologies, such as infection or malignancy, as demonstrated in our patient. The progressive onset and slow evolution of the lesion over years along with a lack of pain were more suggestive of BCC rather than PG. However, there is a report in the literature of PG mimicking BCC with both clinical and dermoscopic findings.3
Venous or stasis ulcers are painless, and although they rarely occur on the calf, they typically are seen lower on the leg such as on the medial ankles. Our patient endorsed occasional swelling of the affected leg and presented with edema, but overlying stasis change and other signs of venous insufficiency were absent.
Buruli ulcer is a painless chronic debilitating cutaneous disease resulting in indolent necrotizing skin as well as subcutaneous and bone lesions. It is caused by the environmental organism Mycobacterium ulcerans and typically is reported in Africa, Central/South America, the Western Pacific Region, and Australia.4 Histopathology usually demonstrates necrosis of subcutaneous tissue and dermal collagen accompanied by inflammation and acidfast bacilli highlighted by Ziehl-Neelsen stain.5 Smears of the lesions as well as culture and polymerase chain reaction for acid-fast bacilli also can be performed. Our patient reported no recent travel to any endemic areas and had no other risk factors or exposures to the pathogen responsible for this condition.
Traumatic ulcer also was included in the differential diagnosis, but the patient denied preceding trauma to the area, and the contralateral foot prosthesis did not rub on or impact the affected leg.
Basal cell carcinoma typically is treated surgically, but choice of treatment can depend on the subtype, size, tumor site, and/or patient preference.1 Other treatment modalities include electrodesiccation and curettage, cryosurgical destruction, photodynamic therapy, radiation, topical therapies, and systemic medications. Radiotherapy can be considered as a primary treatment option for BCC if surgery is contraindicated or declined by the patient, but it also is useful as an adjuvant therapy when there is perineural invasion of the tumor or positive margins. Hedgehog pathway inhibitors such as vismodegib currently are indicated for patients who are not candidates for surgery or radiation as well as for those with metastatic or locally advanced, recurrent BCC. There is no single treatment method ideal for every lesion or patient. Specific populations such as the elderly, the immunosuppressed, or those with poor baseline functional status may warrant a nonsurgical approach. The clinician must take into consideration all factors while at the same time thinking about how to best accomplish the goals of recurrencefree tumor removal, correction of any underlying functional impairment from the tumor, and maintenance of cosmesis.1
The Diagnosis: Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Histopathology of the lesion showed a large basaloid lobule with focal epidermal attachment, peripheral nuclear palisading with cleft formation between the tumor and surrounding stroma, fibromyxoid stroma and mild pleomorphism, and variable mitotic activity and apoptosis (Figure). Based on the clinical presentation and histopathology, the patient was diagnosed with nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). He underwent a wide local excision of the affected area that was repaired with a splitthickness skin graft.

Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer worldwide and typically occurs due to years of UV radiation damage on sun-exposed skin, which accounts for a higher frequency of BCC occurring in patients residing in geographic locations with greater UV exposure (eg, higher and lower latitudes). In addition to cumulative UV dose, the duration of the exposure as well as its intensity also play a role in the development of BCC, particularly in early childhood and adolescence. Nevertheless, UV exposure is not the only risk factor, as 20% of BCCs arise in skin that is not exposed to the sun. Other risk factors include exposure to ionizing radiation and arsenic, immunosuppression, and genetic predisposition.1 Although these malignancies typically do not metastasize, growth can lead to local tissue destruction and major disfigurement if not treated in a timely fashion.2
In our patient, the differential diagnosis included pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) given the clinical appearance of the cribriform base and violaceous undermined rim of the ulcer. Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare neutrophilic disorder that often results in ulcers that have been associated with various systemic autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease. There are 4 main subtypes of PG: the classic ulcerative type (our patient); the pustular type, which most often is seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; the bullous type, which can be seen in patients with an associated lymphoproliferative disorder; and the vegetative type. It frequently is thought of as both a clinical and histologic diagnosis of exclusion due to the nonspecific histopathologic features; most lesions demonstrate an infiltrate of neutrophils in the dermis. A biopsy was crucial in our patient, considering that diagnosis and treatment would have been further delayed had the patient been empirically treated with oral and topical steroids for presumed PG, which is precisely why PG is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is imperative for clinicians to rule out other pathologies, such as infection or malignancy, as demonstrated in our patient. The progressive onset and slow evolution of the lesion over years along with a lack of pain were more suggestive of BCC rather than PG. However, there is a report in the literature of PG mimicking BCC with both clinical and dermoscopic findings.3
Venous or stasis ulcers are painless, and although they rarely occur on the calf, they typically are seen lower on the leg such as on the medial ankles. Our patient endorsed occasional swelling of the affected leg and presented with edema, but overlying stasis change and other signs of venous insufficiency were absent.
Buruli ulcer is a painless chronic debilitating cutaneous disease resulting in indolent necrotizing skin as well as subcutaneous and bone lesions. It is caused by the environmental organism Mycobacterium ulcerans and typically is reported in Africa, Central/South America, the Western Pacific Region, and Australia.4 Histopathology usually demonstrates necrosis of subcutaneous tissue and dermal collagen accompanied by inflammation and acidfast bacilli highlighted by Ziehl-Neelsen stain.5 Smears of the lesions as well as culture and polymerase chain reaction for acid-fast bacilli also can be performed. Our patient reported no recent travel to any endemic areas and had no other risk factors or exposures to the pathogen responsible for this condition.
Traumatic ulcer also was included in the differential diagnosis, but the patient denied preceding trauma to the area, and the contralateral foot prosthesis did not rub on or impact the affected leg.
Basal cell carcinoma typically is treated surgically, but choice of treatment can depend on the subtype, size, tumor site, and/or patient preference.1 Other treatment modalities include electrodesiccation and curettage, cryosurgical destruction, photodynamic therapy, radiation, topical therapies, and systemic medications. Radiotherapy can be considered as a primary treatment option for BCC if surgery is contraindicated or declined by the patient, but it also is useful as an adjuvant therapy when there is perineural invasion of the tumor or positive margins. Hedgehog pathway inhibitors such as vismodegib currently are indicated for patients who are not candidates for surgery or radiation as well as for those with metastatic or locally advanced, recurrent BCC. There is no single treatment method ideal for every lesion or patient. Specific populations such as the elderly, the immunosuppressed, or those with poor baseline functional status may warrant a nonsurgical approach. The clinician must take into consideration all factors while at the same time thinking about how to best accomplish the goals of recurrencefree tumor removal, correction of any underlying functional impairment from the tumor, and maintenance of cosmesis.1
- McDaniel B, Badri T, Steele RB. Basal cell carcinoma. In: StatPearls. StatPearls; 2022.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Rosina P, Papagrigoraki A, Colato C. A case of superficial granulomatous pyoderma mimicking a basal cell carcinoma. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2014;22:48-51.
- Yotsu RR, Suzuki K, Simmonds RE, et al. Buruli ulcer: a review of the current knowledge. Curr Trop Med Rep. 2018;5:247-256.
- Guarner J, Bartlett J, Whitney EA, et al. Histopathologic features of Mycobacterium ulcerans infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:651-656.
- McDaniel B, Badri T, Steele RB. Basal cell carcinoma. In: StatPearls. StatPearls; 2022.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Rosina P, Papagrigoraki A, Colato C. A case of superficial granulomatous pyoderma mimicking a basal cell carcinoma. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2014;22:48-51.
- Yotsu RR, Suzuki K, Simmonds RE, et al. Buruli ulcer: a review of the current knowledge. Curr Trop Med Rep. 2018;5:247-256.
- Guarner J, Bartlett J, Whitney EA, et al. Histopathologic features of Mycobacterium ulcerans infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:651-656.
A 61-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a painless nonhealing wound on the left calf of 4 years’ duration. The patient had a history of amputation of the right foot as an infant, for which he wore an orthopedic prosthesis. He also had chronic lymphedema of the left leg, hyperlipidemia, and osteoarthritis of the right hip. There was no history of gastrointestinal tract issues. The lesion initially was small, then grew and began to ulcerate and bleed. His presentation to dermatology was delayed due to office closures during the COVID-19 pandemic. Physical examination revealed a 5-cm, erythematous, cribriform ulcer with a violaceous undermined rim. A punch biopsy was performed on the edge of the ulcer.
Could Aspirin Help Treat Breast Cancer?
These data are more robust than the efficacy signals from previous studies, meaning healthcare providers should not recommend aspirin as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, reported lead author Wendy Y. Chen, MD, of Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues.
What Data Support Aspirin for Treating Breast Cancer?
“Multiple observational studies have reported a decreased risk of death among survivors of breast cancer who were regular aspirin users,” the investigators wrote in JAMA. “Even more compelling were data from randomized trials of aspirin for cardiovascular disease.”
This possible benefit was reported with mechanistic support, as aspirin’s anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet properties could theoretically control tumor growth, they added. Furthermore, aspirin impacts several cancer pathways currently targeted by agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
“Collectively, evidence from laboratory and epidemiologic studies and randomized trials strongly suggested a role for aspirin to improve breast cancer outcomes, leading to [this new study, Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (Alliance) A011502,] which, to our knowledge, is the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial of aspirin to report results among survivors of breast cancer,” Dr. Chen and colleagues wrote.
What Were The Key Findings From The A011502 Trial?
The A011502 trial enrolled 3,020 patients aged 18-70 years with ERBB2-negative breast cancer who had received standard therapy via routine clinical care. Eligibility required that chemotherapy and local therapy were complete, but ongoing endocrine therapy was allowed.
Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive aspirin 300 mg per day or matching placebo for 5 years. The primary outcome was invasive disease-free survival, and the key secondary outcome was overall survival.
After a median follow-up of almost 3 years, at the first interim analysis, the study was suspended early due to statistical futility. By that timepoint, 253 invasive disease-free survival events occurred, of which 141 occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 112 in the placebo group, providing a hazard ratio of 1.27 (95% CI, 0.99-1.63) that was not statistically significant (P = .06). No statistically significant difference in overall survival was observed (hazard ratio, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.82-1.72). Safety profiles were similar across groups.
How Will This Study Change Practice?
In an accompanying editorial, Jeanne S. Mandelblatt, MD, of Georgetown Lombardi Institute for Cancer and Aging Research, Washington, and colleagues, praised the trial for its comprehensive approach, but they predicted that the negative result could spell friction for health care providers.
“[C]linicians may find it challenging to communicate with their patients about the negative result in the Alliance trial, because prior lay press articles, observational studies, and meta-analyses of cardiovascular trials suggested that aspirin may decrease breast cancer recurrence,” they wrote.
Dr. Mandelblatt and colleagues went on to explore broader implications beyond breast cancer, including considerations for communication of negative results in other medical specialties, discussions between clinicians and patients regarding aspirin use for non–breast cancer purposes, and questions about the timing of aspirin use and the role of age and biological aging.
How Might the Findings From the A011502 Trial Impact Future Research?
Finally, and “most critically,” the editorialists raised concerns about health equity, noting the limited diversity in trial participants and the potential exclusion of subgroups that might benefit from aspirin use, particularly those more likely to experience accelerated biological aging and disparities in cancer risk and outcomes due to systemic racism or adverse social determinants of health.
They concluded by emphasizing the need to consider the intersectionality of aging, cancer, and disparities in designing future trials to advance health equity.
This study was funded by the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program and the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The research was also supported in part by Bayer, which provided the study drug. The investigators disclosed relationships with Novartis, Seagen, Orum Clinical, and others. The editorialists disclosed relationships with Cantex Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer.
These data are more robust than the efficacy signals from previous studies, meaning healthcare providers should not recommend aspirin as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, reported lead author Wendy Y. Chen, MD, of Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues.
What Data Support Aspirin for Treating Breast Cancer?
“Multiple observational studies have reported a decreased risk of death among survivors of breast cancer who were regular aspirin users,” the investigators wrote in JAMA. “Even more compelling were data from randomized trials of aspirin for cardiovascular disease.”
This possible benefit was reported with mechanistic support, as aspirin’s anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet properties could theoretically control tumor growth, they added. Furthermore, aspirin impacts several cancer pathways currently targeted by agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
“Collectively, evidence from laboratory and epidemiologic studies and randomized trials strongly suggested a role for aspirin to improve breast cancer outcomes, leading to [this new study, Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (Alliance) A011502,] which, to our knowledge, is the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial of aspirin to report results among survivors of breast cancer,” Dr. Chen and colleagues wrote.
What Were The Key Findings From The A011502 Trial?
The A011502 trial enrolled 3,020 patients aged 18-70 years with ERBB2-negative breast cancer who had received standard therapy via routine clinical care. Eligibility required that chemotherapy and local therapy were complete, but ongoing endocrine therapy was allowed.
Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive aspirin 300 mg per day or matching placebo for 5 years. The primary outcome was invasive disease-free survival, and the key secondary outcome was overall survival.
After a median follow-up of almost 3 years, at the first interim analysis, the study was suspended early due to statistical futility. By that timepoint, 253 invasive disease-free survival events occurred, of which 141 occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 112 in the placebo group, providing a hazard ratio of 1.27 (95% CI, 0.99-1.63) that was not statistically significant (P = .06). No statistically significant difference in overall survival was observed (hazard ratio, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.82-1.72). Safety profiles were similar across groups.
How Will This Study Change Practice?
In an accompanying editorial, Jeanne S. Mandelblatt, MD, of Georgetown Lombardi Institute for Cancer and Aging Research, Washington, and colleagues, praised the trial for its comprehensive approach, but they predicted that the negative result could spell friction for health care providers.
“[C]linicians may find it challenging to communicate with their patients about the negative result in the Alliance trial, because prior lay press articles, observational studies, and meta-analyses of cardiovascular trials suggested that aspirin may decrease breast cancer recurrence,” they wrote.
Dr. Mandelblatt and colleagues went on to explore broader implications beyond breast cancer, including considerations for communication of negative results in other medical specialties, discussions between clinicians and patients regarding aspirin use for non–breast cancer purposes, and questions about the timing of aspirin use and the role of age and biological aging.
How Might the Findings From the A011502 Trial Impact Future Research?
Finally, and “most critically,” the editorialists raised concerns about health equity, noting the limited diversity in trial participants and the potential exclusion of subgroups that might benefit from aspirin use, particularly those more likely to experience accelerated biological aging and disparities in cancer risk and outcomes due to systemic racism or adverse social determinants of health.
They concluded by emphasizing the need to consider the intersectionality of aging, cancer, and disparities in designing future trials to advance health equity.
This study was funded by the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program and the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The research was also supported in part by Bayer, which provided the study drug. The investigators disclosed relationships with Novartis, Seagen, Orum Clinical, and others. The editorialists disclosed relationships with Cantex Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer.
These data are more robust than the efficacy signals from previous studies, meaning healthcare providers should not recommend aspirin as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, reported lead author Wendy Y. Chen, MD, of Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues.
What Data Support Aspirin for Treating Breast Cancer?
“Multiple observational studies have reported a decreased risk of death among survivors of breast cancer who were regular aspirin users,” the investigators wrote in JAMA. “Even more compelling were data from randomized trials of aspirin for cardiovascular disease.”
This possible benefit was reported with mechanistic support, as aspirin’s anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet properties could theoretically control tumor growth, they added. Furthermore, aspirin impacts several cancer pathways currently targeted by agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
“Collectively, evidence from laboratory and epidemiologic studies and randomized trials strongly suggested a role for aspirin to improve breast cancer outcomes, leading to [this new study, Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (Alliance) A011502,] which, to our knowledge, is the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial of aspirin to report results among survivors of breast cancer,” Dr. Chen and colleagues wrote.
What Were The Key Findings From The A011502 Trial?
The A011502 trial enrolled 3,020 patients aged 18-70 years with ERBB2-negative breast cancer who had received standard therapy via routine clinical care. Eligibility required that chemotherapy and local therapy were complete, but ongoing endocrine therapy was allowed.
Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive aspirin 300 mg per day or matching placebo for 5 years. The primary outcome was invasive disease-free survival, and the key secondary outcome was overall survival.
After a median follow-up of almost 3 years, at the first interim analysis, the study was suspended early due to statistical futility. By that timepoint, 253 invasive disease-free survival events occurred, of which 141 occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 112 in the placebo group, providing a hazard ratio of 1.27 (95% CI, 0.99-1.63) that was not statistically significant (P = .06). No statistically significant difference in overall survival was observed (hazard ratio, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.82-1.72). Safety profiles were similar across groups.
How Will This Study Change Practice?
In an accompanying editorial, Jeanne S. Mandelblatt, MD, of Georgetown Lombardi Institute for Cancer and Aging Research, Washington, and colleagues, praised the trial for its comprehensive approach, but they predicted that the negative result could spell friction for health care providers.
“[C]linicians may find it challenging to communicate with their patients about the negative result in the Alliance trial, because prior lay press articles, observational studies, and meta-analyses of cardiovascular trials suggested that aspirin may decrease breast cancer recurrence,” they wrote.
Dr. Mandelblatt and colleagues went on to explore broader implications beyond breast cancer, including considerations for communication of negative results in other medical specialties, discussions between clinicians and patients regarding aspirin use for non–breast cancer purposes, and questions about the timing of aspirin use and the role of age and biological aging.
How Might the Findings From the A011502 Trial Impact Future Research?
Finally, and “most critically,” the editorialists raised concerns about health equity, noting the limited diversity in trial participants and the potential exclusion of subgroups that might benefit from aspirin use, particularly those more likely to experience accelerated biological aging and disparities in cancer risk and outcomes due to systemic racism or adverse social determinants of health.
They concluded by emphasizing the need to consider the intersectionality of aging, cancer, and disparities in designing future trials to advance health equity.
This study was funded by the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program and the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The research was also supported in part by Bayer, which provided the study drug. The investigators disclosed relationships with Novartis, Seagen, Orum Clinical, and others. The editorialists disclosed relationships with Cantex Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer.
FROM JAMA
Optimized Hospital Care for Gout Improves Uptake of Urate-Lowering Therapy
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND — Optimizing how people experiencing a gout flare are managed in hospital and then followed-up afterwards can substantially increase the uptake of guideline-recommended urate-lowering therapy (ULT), researchers reported at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR).
In a prospective study, 92% of 97 people admitted to hospital for gout flares were using ULT within 6 months of discharge after a multifaceted intervention was introduced. By comparison, 49% of 94 people admitted for gout flares before the introduction of the intervention were taking ULT within the same postdischarge time frame.
Moreover, a higher proportion of individuals had urate blood tests done at least once within the 6-month postdischarge period after the intervention’s introduction (58% vs 32%) and fewer (9% vs 15%) needed repeated hospital treatment.
“Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis affecting one in 30 adults in the United Kingdom, yet it’s one of the most poorly managed,” study investigator Mark D. Russell, MB, BChir, pointed out during a poster presentation.
“There are very effective treatments,” added Dr. Russell, a rheumatology registrar and postdoctoral research fellow at King’s College London in London, England. “Urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol, which when taken at the correct dose, in the long term, effectively cures patients of their symptoms and prevents complications.”
Dr. Russell said in an interview that there was still work to be done as the rate of people achieving urate levels below the recommended threshold of 360 micromol/L (6 mg/dL) within 6 months was still low, at 27%, even it if was still better than the 11% seen before the intervention was introduced.
Improving the In- and Post-Hospital Pathway
“We developed and implemented an in-hospital management pathway which encouraged urate-lowering therapy initiation prior to discharge, followed by a post-discharge nurse-led review,” Dr. Russell explained.
The in-hospital pathway was based upon BSR, European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, and American College of Rheumatology guidelines and involved diagnosing and managing the gout flare appropriately. This may have been via early joint aspiration, medication, or both, as directed by the rheumatology team. Affected individuals also received education and were directed where to obtain further information on the use of ULT. Outpatient follow-up was considered if an individual had severe or tophaceous gout, recurrent episodes, or contraindications or intolerances to ULT. Otherwise, a rheumatology nurse telephoned the individual 2 weeks later to review symptoms and discuss next steps.
The researchers recorded improvements in in-hospital outcomes. The frequency of in-hospital serum urate level measurements rose from 66% in the 12-month preimplementation period to 93% in the 12-month period after the intervention’s introduction. Almost two thirds (62%) of patients were discharged on ULT compared with 18% preimplementation. And gout-specific recommendations were given 86% of the time compared with 59% before the intervention.
Related Work on Gout Incidence
Separately, Dr. Russell also presented data from a nationwide, population-level cohort study that used data from OpenSAFELY, the secure data analytics platform used by the National Health Service in England.
“We did an analysis previously using the CPRD [Clinical Research Practice Datalink], which is another good primary care database, showing that only a third of people with gout in the UK get urate-lowering drugs, when really it should be the vast majority,” he said in the interview.
“And then we wanted to look at, on top of that, what was the impact of the [COVID-19] pandemic,” Russell added. Specifically, the aim was to look at how the pandemic had affected the incidence, management, and prevalence of gout.
Between March 2015 and February 2023, 246,695 new cases of gout were identified among 17.9 million adults, seen in primary and secondary care.
COVID-19 Pandemic Affected Cases
“The number of new cases of gout dropped by about one third in the first year of the pandemic,” Dr. Russell said. Incidence declined from 1.78 to 1.23 per 1000 adults. “Whether that was through people not feeling comfortable going to their GP [general practitioner] or not being able to get an appointment, we don’t know.”
While there was a subsequent increase in new cases of gout since this time, the rates still haven’t reached what they were before the pandemic. This implies that there could be a substantial number of people who may be undiagnosed because of the pandemic, Dr. Russell suggested.
Moreover, he reported that in 2022-2023, the prevalence of gout was 3.21%, up slightly from the 3.07% recorded 7 years earlier in 2015-2016.
ULT Treatment Rates Low
“If you did see a GP, however, so as long as you saw someone, the treatment wasn’t any worse,” Dr. Russell said. Just under 30% of people with incident gout for whom follow-up data were available had initiated ULT within 6 months of their diagnosis. And, of these new starters, around a quarter had a serum urate level below a target of 360 micromol/L.
“This doesn’t detract from the fact that this is pretty low. Despite guidelines, we’re still not getting the majority of people on these very effective urate-lowering drugs,” Dr. Russell said.
There is perhaps too much reliance on modifying diet and lifestyle, he added, which are important for many reasons but will not do much to lower blood urate levels.
As a final word, Dr. Russell said, “It’s not just a case of preventing a bit of joint pain. People get lots of complications when they’re undertreated — erosive joint damage, work disability, impaired quality of life — and yet we’ve got very cheap, well-tolerated drugs.”
The work was independently funded. Dr. Russell acknowledged grant or research support from Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, and UCB and receipt of honoraria from AbbVie, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, and Menarini.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND — Optimizing how people experiencing a gout flare are managed in hospital and then followed-up afterwards can substantially increase the uptake of guideline-recommended urate-lowering therapy (ULT), researchers reported at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR).
In a prospective study, 92% of 97 people admitted to hospital for gout flares were using ULT within 6 months of discharge after a multifaceted intervention was introduced. By comparison, 49% of 94 people admitted for gout flares before the introduction of the intervention were taking ULT within the same postdischarge time frame.
Moreover, a higher proportion of individuals had urate blood tests done at least once within the 6-month postdischarge period after the intervention’s introduction (58% vs 32%) and fewer (9% vs 15%) needed repeated hospital treatment.
“Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis affecting one in 30 adults in the United Kingdom, yet it’s one of the most poorly managed,” study investigator Mark D. Russell, MB, BChir, pointed out during a poster presentation.
“There are very effective treatments,” added Dr. Russell, a rheumatology registrar and postdoctoral research fellow at King’s College London in London, England. “Urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol, which when taken at the correct dose, in the long term, effectively cures patients of their symptoms and prevents complications.”
Dr. Russell said in an interview that there was still work to be done as the rate of people achieving urate levels below the recommended threshold of 360 micromol/L (6 mg/dL) within 6 months was still low, at 27%, even it if was still better than the 11% seen before the intervention was introduced.
Improving the In- and Post-Hospital Pathway
“We developed and implemented an in-hospital management pathway which encouraged urate-lowering therapy initiation prior to discharge, followed by a post-discharge nurse-led review,” Dr. Russell explained.
The in-hospital pathway was based upon BSR, European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, and American College of Rheumatology guidelines and involved diagnosing and managing the gout flare appropriately. This may have been via early joint aspiration, medication, or both, as directed by the rheumatology team. Affected individuals also received education and were directed where to obtain further information on the use of ULT. Outpatient follow-up was considered if an individual had severe or tophaceous gout, recurrent episodes, or contraindications or intolerances to ULT. Otherwise, a rheumatology nurse telephoned the individual 2 weeks later to review symptoms and discuss next steps.
The researchers recorded improvements in in-hospital outcomes. The frequency of in-hospital serum urate level measurements rose from 66% in the 12-month preimplementation period to 93% in the 12-month period after the intervention’s introduction. Almost two thirds (62%) of patients were discharged on ULT compared with 18% preimplementation. And gout-specific recommendations were given 86% of the time compared with 59% before the intervention.
Related Work on Gout Incidence
Separately, Dr. Russell also presented data from a nationwide, population-level cohort study that used data from OpenSAFELY, the secure data analytics platform used by the National Health Service in England.
“We did an analysis previously using the CPRD [Clinical Research Practice Datalink], which is another good primary care database, showing that only a third of people with gout in the UK get urate-lowering drugs, when really it should be the vast majority,” he said in the interview.
“And then we wanted to look at, on top of that, what was the impact of the [COVID-19] pandemic,” Russell added. Specifically, the aim was to look at how the pandemic had affected the incidence, management, and prevalence of gout.
Between March 2015 and February 2023, 246,695 new cases of gout were identified among 17.9 million adults, seen in primary and secondary care.
COVID-19 Pandemic Affected Cases
“The number of new cases of gout dropped by about one third in the first year of the pandemic,” Dr. Russell said. Incidence declined from 1.78 to 1.23 per 1000 adults. “Whether that was through people not feeling comfortable going to their GP [general practitioner] or not being able to get an appointment, we don’t know.”
While there was a subsequent increase in new cases of gout since this time, the rates still haven’t reached what they were before the pandemic. This implies that there could be a substantial number of people who may be undiagnosed because of the pandemic, Dr. Russell suggested.
Moreover, he reported that in 2022-2023, the prevalence of gout was 3.21%, up slightly from the 3.07% recorded 7 years earlier in 2015-2016.
ULT Treatment Rates Low
“If you did see a GP, however, so as long as you saw someone, the treatment wasn’t any worse,” Dr. Russell said. Just under 30% of people with incident gout for whom follow-up data were available had initiated ULT within 6 months of their diagnosis. And, of these new starters, around a quarter had a serum urate level below a target of 360 micromol/L.
“This doesn’t detract from the fact that this is pretty low. Despite guidelines, we’re still not getting the majority of people on these very effective urate-lowering drugs,” Dr. Russell said.
There is perhaps too much reliance on modifying diet and lifestyle, he added, which are important for many reasons but will not do much to lower blood urate levels.
As a final word, Dr. Russell said, “It’s not just a case of preventing a bit of joint pain. People get lots of complications when they’re undertreated — erosive joint damage, work disability, impaired quality of life — and yet we’ve got very cheap, well-tolerated drugs.”
The work was independently funded. Dr. Russell acknowledged grant or research support from Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, and UCB and receipt of honoraria from AbbVie, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, and Menarini.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND — Optimizing how people experiencing a gout flare are managed in hospital and then followed-up afterwards can substantially increase the uptake of guideline-recommended urate-lowering therapy (ULT), researchers reported at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR).
In a prospective study, 92% of 97 people admitted to hospital for gout flares were using ULT within 6 months of discharge after a multifaceted intervention was introduced. By comparison, 49% of 94 people admitted for gout flares before the introduction of the intervention were taking ULT within the same postdischarge time frame.
Moreover, a higher proportion of individuals had urate blood tests done at least once within the 6-month postdischarge period after the intervention’s introduction (58% vs 32%) and fewer (9% vs 15%) needed repeated hospital treatment.
“Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis affecting one in 30 adults in the United Kingdom, yet it’s one of the most poorly managed,” study investigator Mark D. Russell, MB, BChir, pointed out during a poster presentation.
“There are very effective treatments,” added Dr. Russell, a rheumatology registrar and postdoctoral research fellow at King’s College London in London, England. “Urate-lowering therapies such as allopurinol, which when taken at the correct dose, in the long term, effectively cures patients of their symptoms and prevents complications.”
Dr. Russell said in an interview that there was still work to be done as the rate of people achieving urate levels below the recommended threshold of 360 micromol/L (6 mg/dL) within 6 months was still low, at 27%, even it if was still better than the 11% seen before the intervention was introduced.
Improving the In- and Post-Hospital Pathway
“We developed and implemented an in-hospital management pathway which encouraged urate-lowering therapy initiation prior to discharge, followed by a post-discharge nurse-led review,” Dr. Russell explained.
The in-hospital pathway was based upon BSR, European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, and American College of Rheumatology guidelines and involved diagnosing and managing the gout flare appropriately. This may have been via early joint aspiration, medication, or both, as directed by the rheumatology team. Affected individuals also received education and were directed where to obtain further information on the use of ULT. Outpatient follow-up was considered if an individual had severe or tophaceous gout, recurrent episodes, or contraindications or intolerances to ULT. Otherwise, a rheumatology nurse telephoned the individual 2 weeks later to review symptoms and discuss next steps.
The researchers recorded improvements in in-hospital outcomes. The frequency of in-hospital serum urate level measurements rose from 66% in the 12-month preimplementation period to 93% in the 12-month period after the intervention’s introduction. Almost two thirds (62%) of patients were discharged on ULT compared with 18% preimplementation. And gout-specific recommendations were given 86% of the time compared with 59% before the intervention.
Related Work on Gout Incidence
Separately, Dr. Russell also presented data from a nationwide, population-level cohort study that used data from OpenSAFELY, the secure data analytics platform used by the National Health Service in England.
“We did an analysis previously using the CPRD [Clinical Research Practice Datalink], which is another good primary care database, showing that only a third of people with gout in the UK get urate-lowering drugs, when really it should be the vast majority,” he said in the interview.
“And then we wanted to look at, on top of that, what was the impact of the [COVID-19] pandemic,” Russell added. Specifically, the aim was to look at how the pandemic had affected the incidence, management, and prevalence of gout.
Between March 2015 and February 2023, 246,695 new cases of gout were identified among 17.9 million adults, seen in primary and secondary care.
COVID-19 Pandemic Affected Cases
“The number of new cases of gout dropped by about one third in the first year of the pandemic,” Dr. Russell said. Incidence declined from 1.78 to 1.23 per 1000 adults. “Whether that was through people not feeling comfortable going to their GP [general practitioner] or not being able to get an appointment, we don’t know.”
While there was a subsequent increase in new cases of gout since this time, the rates still haven’t reached what they were before the pandemic. This implies that there could be a substantial number of people who may be undiagnosed because of the pandemic, Dr. Russell suggested.
Moreover, he reported that in 2022-2023, the prevalence of gout was 3.21%, up slightly from the 3.07% recorded 7 years earlier in 2015-2016.
ULT Treatment Rates Low
“If you did see a GP, however, so as long as you saw someone, the treatment wasn’t any worse,” Dr. Russell said. Just under 30% of people with incident gout for whom follow-up data were available had initiated ULT within 6 months of their diagnosis. And, of these new starters, around a quarter had a serum urate level below a target of 360 micromol/L.
“This doesn’t detract from the fact that this is pretty low. Despite guidelines, we’re still not getting the majority of people on these very effective urate-lowering drugs,” Dr. Russell said.
There is perhaps too much reliance on modifying diet and lifestyle, he added, which are important for many reasons but will not do much to lower blood urate levels.
As a final word, Dr. Russell said, “It’s not just a case of preventing a bit of joint pain. People get lots of complications when they’re undertreated — erosive joint damage, work disability, impaired quality of life — and yet we’ve got very cheap, well-tolerated drugs.”
The work was independently funded. Dr. Russell acknowledged grant or research support from Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, and UCB and receipt of honoraria from AbbVie, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, and Menarini.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BSR 2024
Blood Biomarkers Predict Knee Osteoarthritis Years in Advance
A small number of blood biomarkers can identify patients who will develop knee osteoarthritis (OA) up to 8 years before signs of the disease are detectable via X-ray, according to new research.
The study “provides more evidence for a pre-radiographic phase of disease,” wrote Virginia Byers Dr. Kraus, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine, pathology, and orthopedic surgery at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, and colleagues. The results also “provide valuable information for understanding the molecular events of early disease that could inform strategies to develop disease-modifying drugs for preclinical OA,” they continued.
In the study, published in Science Advances, researchers analyzed blood samples from a population-based, longitudinal study of women in London that assessed participants annually for osteoporosis and OA. They selected individuals at low risk for radiographic knee OA, who did not have traditional risk factors for knee OA such as a history of major knee injury, knee surgery, or OA of the hand or opposite knee.
The researchers analyzed serum of 100 women who went on to develop radiographic knee OA and 100 controls who were matched by age and body mass index (BMI). Participants were, on average, aged 54 years with a BMI of 26 and all were White. They analyzed serum peptides via mass spectrometry and used machine learning to select which out of the 115 identified peptides were most predictive of OA.
Ultimately, the team zeroed in on six peptides, corresponding to six proteins, that could most accurately distinguish women who went on to develop radiographic signs of OA from controls (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, 0.77) up to 8 years before x-rays detected these changes.
“The value of our study is a panel that, in the absence of clinical factors indicative of high-risk knee OA, has the potential to discriminate individuals at risk for incident radiographic knee OA from those not at risk,” the authors wrote.
In earlier work, a similar group of biomarkers could accurately diagnose knee OA as well as predict the progression of the disease. More than half (58%) of biomarkers that predicted incident OA also predicted OA progression.
“Even for the ones that didn’t overlap with OA progression, they all pointed to the same sort of disease process, which is an unresolved acute phase response type of biological process,” Dr. Kraus told this news organization.
Commenting on the study, Andrew Grose, MD, an orthopedic trauma surgeon at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City, noted that the methods and conclusions seemed sound but cautioned that the study only looked for radiographic evidence of OA, and not symptomatic OA.
“Clinically relevant OA is correlated with what you see on an x-ray, but the x-ray is definitely not the whole story,” he said in an interview with this news organization.
To be clinically relevant, patients must also have symptoms, such as pain and stiffness, and interfere with daily life. But what shows up on an x-ray is not necessarily indicative of what patients are experiencing, he said. Solely focusing on radiographic findings could lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of OA, he said.
The study population was also small, and only included White women, he added, so further validation is necessary. Dr. Kraus and colleagues also acknowledged these limitations.
“Further validation will be needed in independent and larger cohorts, preferability prospectively collected and including male participants and the combination of incident radiographic and symptomatic OA,” they wrote. They noted that while this current study included only women, the biomarkers were not associated with sex in previous studies that used larger and mixed-sex cohorts.
“If they did more studies showing that this [test] was able to predict clinically relevant OA, then I think you could have a meaningful conversation with a patient in a primary care doctor’s office,” Dr. Grose added. “Until that time, just the fact that it predicts an x-ray finding is a little bit of a red herring.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kraus is an inventor on a patent related to OA progression biomarkers. Dr. Grose had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A small number of blood biomarkers can identify patients who will develop knee osteoarthritis (OA) up to 8 years before signs of the disease are detectable via X-ray, according to new research.
The study “provides more evidence for a pre-radiographic phase of disease,” wrote Virginia Byers Dr. Kraus, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine, pathology, and orthopedic surgery at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, and colleagues. The results also “provide valuable information for understanding the molecular events of early disease that could inform strategies to develop disease-modifying drugs for preclinical OA,” they continued.
In the study, published in Science Advances, researchers analyzed blood samples from a population-based, longitudinal study of women in London that assessed participants annually for osteoporosis and OA. They selected individuals at low risk for radiographic knee OA, who did not have traditional risk factors for knee OA such as a history of major knee injury, knee surgery, or OA of the hand or opposite knee.
The researchers analyzed serum of 100 women who went on to develop radiographic knee OA and 100 controls who were matched by age and body mass index (BMI). Participants were, on average, aged 54 years with a BMI of 26 and all were White. They analyzed serum peptides via mass spectrometry and used machine learning to select which out of the 115 identified peptides were most predictive of OA.
Ultimately, the team zeroed in on six peptides, corresponding to six proteins, that could most accurately distinguish women who went on to develop radiographic signs of OA from controls (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, 0.77) up to 8 years before x-rays detected these changes.
“The value of our study is a panel that, in the absence of clinical factors indicative of high-risk knee OA, has the potential to discriminate individuals at risk for incident radiographic knee OA from those not at risk,” the authors wrote.
In earlier work, a similar group of biomarkers could accurately diagnose knee OA as well as predict the progression of the disease. More than half (58%) of biomarkers that predicted incident OA also predicted OA progression.
“Even for the ones that didn’t overlap with OA progression, they all pointed to the same sort of disease process, which is an unresolved acute phase response type of biological process,” Dr. Kraus told this news organization.
Commenting on the study, Andrew Grose, MD, an orthopedic trauma surgeon at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City, noted that the methods and conclusions seemed sound but cautioned that the study only looked for radiographic evidence of OA, and not symptomatic OA.
“Clinically relevant OA is correlated with what you see on an x-ray, but the x-ray is definitely not the whole story,” he said in an interview with this news organization.
To be clinically relevant, patients must also have symptoms, such as pain and stiffness, and interfere with daily life. But what shows up on an x-ray is not necessarily indicative of what patients are experiencing, he said. Solely focusing on radiographic findings could lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of OA, he said.
The study population was also small, and only included White women, he added, so further validation is necessary. Dr. Kraus and colleagues also acknowledged these limitations.
“Further validation will be needed in independent and larger cohorts, preferability prospectively collected and including male participants and the combination of incident radiographic and symptomatic OA,” they wrote. They noted that while this current study included only women, the biomarkers were not associated with sex in previous studies that used larger and mixed-sex cohorts.
“If they did more studies showing that this [test] was able to predict clinically relevant OA, then I think you could have a meaningful conversation with a patient in a primary care doctor’s office,” Dr. Grose added. “Until that time, just the fact that it predicts an x-ray finding is a little bit of a red herring.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kraus is an inventor on a patent related to OA progression biomarkers. Dr. Grose had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A small number of blood biomarkers can identify patients who will develop knee osteoarthritis (OA) up to 8 years before signs of the disease are detectable via X-ray, according to new research.
The study “provides more evidence for a pre-radiographic phase of disease,” wrote Virginia Byers Dr. Kraus, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine, pathology, and orthopedic surgery at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, and colleagues. The results also “provide valuable information for understanding the molecular events of early disease that could inform strategies to develop disease-modifying drugs for preclinical OA,” they continued.
In the study, published in Science Advances, researchers analyzed blood samples from a population-based, longitudinal study of women in London that assessed participants annually for osteoporosis and OA. They selected individuals at low risk for radiographic knee OA, who did not have traditional risk factors for knee OA such as a history of major knee injury, knee surgery, or OA of the hand or opposite knee.
The researchers analyzed serum of 100 women who went on to develop radiographic knee OA and 100 controls who were matched by age and body mass index (BMI). Participants were, on average, aged 54 years with a BMI of 26 and all were White. They analyzed serum peptides via mass spectrometry and used machine learning to select which out of the 115 identified peptides were most predictive of OA.
Ultimately, the team zeroed in on six peptides, corresponding to six proteins, that could most accurately distinguish women who went on to develop radiographic signs of OA from controls (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, 0.77) up to 8 years before x-rays detected these changes.
“The value of our study is a panel that, in the absence of clinical factors indicative of high-risk knee OA, has the potential to discriminate individuals at risk for incident radiographic knee OA from those not at risk,” the authors wrote.
In earlier work, a similar group of biomarkers could accurately diagnose knee OA as well as predict the progression of the disease. More than half (58%) of biomarkers that predicted incident OA also predicted OA progression.
“Even for the ones that didn’t overlap with OA progression, they all pointed to the same sort of disease process, which is an unresolved acute phase response type of biological process,” Dr. Kraus told this news organization.
Commenting on the study, Andrew Grose, MD, an orthopedic trauma surgeon at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City, noted that the methods and conclusions seemed sound but cautioned that the study only looked for radiographic evidence of OA, and not symptomatic OA.
“Clinically relevant OA is correlated with what you see on an x-ray, but the x-ray is definitely not the whole story,” he said in an interview with this news organization.
To be clinically relevant, patients must also have symptoms, such as pain and stiffness, and interfere with daily life. But what shows up on an x-ray is not necessarily indicative of what patients are experiencing, he said. Solely focusing on radiographic findings could lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of OA, he said.
The study population was also small, and only included White women, he added, so further validation is necessary. Dr. Kraus and colleagues also acknowledged these limitations.
“Further validation will be needed in independent and larger cohorts, preferability prospectively collected and including male participants and the combination of incident radiographic and symptomatic OA,” they wrote. They noted that while this current study included only women, the biomarkers were not associated with sex in previous studies that used larger and mixed-sex cohorts.
“If they did more studies showing that this [test] was able to predict clinically relevant OA, then I think you could have a meaningful conversation with a patient in a primary care doctor’s office,” Dr. Grose added. “Until that time, just the fact that it predicts an x-ray finding is a little bit of a red herring.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kraus is an inventor on a patent related to OA progression biomarkers. Dr. Grose had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
Avian Flu Threat Still Low and Vaccine Measures Are Ready
After cow-to-cow transmission of avian influenza A subtype H5N1 in US dairy herds led to a cow-to-human transmission in Texas, the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials convened a panel of experts for a scientific symposium on Thursday to talk about the public health implications.
From the sequencing data, “we can expect and anticipate that [the candidate vaccine viruses] will provide good protection,” she explained.
Establishing candidate vaccine viruses “are the precursor to moving into large-scale vaccine production,” Dr. Dugan explained. Should that be needed, the candidate viruses can be used by manufacturers to produce new vaccines.
The CDC is also actively partnering with commercial diagnostic developers and testing companies in case there is a need to scale-up testing, Dr. Dugan said.
The only current human case in the United States was reported on April 1 and confirmed by the CDC within 24 hours, reported Sonja Olsen, PhD, associate director for preparedness and response of the Influenza Division at the CDC.
The person had direct exposure to cattle and reported eye redness, consistent with conjunctivitis, as the only symptom. The person received treatment and has recovered, and there were no reports of illness among the person’s household contacts, Dr. Olsen said.
Person With the Virus Has Recovered
The only other detection of the virus in a human in the United States was in 2022 and it was associated with infected poultry exposure. That person also had mild illness and recovered, Dr. Olsen explained.
Since 1997, when the first case of human infection was reported globally, “there have been 909 [human cases] reported from 23 countries,” Dr. Olsen said. “About half [52%] of the human cases have resulted in death.” Only a small number of human cases have been reported since 2015, but since 2022, more than two dozen human cases have been reported to the World Health Organization.
Experience with the virus in the United States has been about a year behind that in Europe, said Rosemary Sifford, DVM, chief veterinary officer at the US Department of Agriculture. In the United States, the first detection — in January 2022 — was in wild birds; this was followed the next month by the first detection in a commercial poultry flock.
In March of this year, the United States had its first detection in cattle, specifically dairy cattle. But testing has shown that “it remains very much an avian virus. It’s not becoming a bovine virus,” Dr. Sifford reported.
Detected in Cattle
Earlier this week, in an effort to minimize the risk of disease spread, the USDA issued a federal order that requires the reporting of positive influenza tests in livestock and mandatory testing for influenza of dairy cattle before interstate movement.
“As of today, there are affected herds in 33 farms across eight states,” reported Dr. Olsen.
Tests are ongoing to determine how the virus is traveling, but “what we can say is that there’s a high viral load in the milk in the cattle, and it appears that the transmission is happening mostly within the lactating herds,” Dr. Sifford reported. It is unclear whether that is happening during the milking of the cows or whether contaminated milk from a cow with a high viral load is transmitting the virus to other cattle.
“We are strongly encouraging producers to limit the movement of cattle, particularly lactating cattle, as much as possible,” she says.
Milk Is Likely the Source of Transmission
“We haven’t seen anything that would change our assessment that the commercial milk supply is safe,” says Donald Prater, DVM, acting director of the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition at the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In the federal and state milk safety system, he explained, nearly 99% of the commercial milk supply comes from farms that participate in the Grade A program and follow the Pasteurized Milk Ordinance, which outlines pasteurization requirements.
Because detection of the virus in dairy cattle is new, there are many questions to be answered in research, he reported. Among them:
- What level of virus might be leaving the farms from shedding by apparently healthy cows?
- Does any live virus survive the pasteurization process?
- Do different methods of pasteurization and dairy production have different effects on the viability of H5N1?
- Are effects different in various forms of dairy products, such as cheese and cream?
A critical question regarding the potential risk to humans is how much milk would have to be consumed for the virus to become an established infection. That information is essential to determine “what type of pasteurization criteria” are needed to provide “acceptable public health outcomes,” Dr. Prater said.
The CDC is currently using the flu surveillance system to monitor for H5N1 activity in people. The systems show no current indicators of unusual influenza activity in people.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
After cow-to-cow transmission of avian influenza A subtype H5N1 in US dairy herds led to a cow-to-human transmission in Texas, the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials convened a panel of experts for a scientific symposium on Thursday to talk about the public health implications.
From the sequencing data, “we can expect and anticipate that [the candidate vaccine viruses] will provide good protection,” she explained.
Establishing candidate vaccine viruses “are the precursor to moving into large-scale vaccine production,” Dr. Dugan explained. Should that be needed, the candidate viruses can be used by manufacturers to produce new vaccines.
The CDC is also actively partnering with commercial diagnostic developers and testing companies in case there is a need to scale-up testing, Dr. Dugan said.
The only current human case in the United States was reported on April 1 and confirmed by the CDC within 24 hours, reported Sonja Olsen, PhD, associate director for preparedness and response of the Influenza Division at the CDC.
The person had direct exposure to cattle and reported eye redness, consistent with conjunctivitis, as the only symptom. The person received treatment and has recovered, and there were no reports of illness among the person’s household contacts, Dr. Olsen said.
Person With the Virus Has Recovered
The only other detection of the virus in a human in the United States was in 2022 and it was associated with infected poultry exposure. That person also had mild illness and recovered, Dr. Olsen explained.
Since 1997, when the first case of human infection was reported globally, “there have been 909 [human cases] reported from 23 countries,” Dr. Olsen said. “About half [52%] of the human cases have resulted in death.” Only a small number of human cases have been reported since 2015, but since 2022, more than two dozen human cases have been reported to the World Health Organization.
Experience with the virus in the United States has been about a year behind that in Europe, said Rosemary Sifford, DVM, chief veterinary officer at the US Department of Agriculture. In the United States, the first detection — in January 2022 — was in wild birds; this was followed the next month by the first detection in a commercial poultry flock.
In March of this year, the United States had its first detection in cattle, specifically dairy cattle. But testing has shown that “it remains very much an avian virus. It’s not becoming a bovine virus,” Dr. Sifford reported.
Detected in Cattle
Earlier this week, in an effort to minimize the risk of disease spread, the USDA issued a federal order that requires the reporting of positive influenza tests in livestock and mandatory testing for influenza of dairy cattle before interstate movement.
“As of today, there are affected herds in 33 farms across eight states,” reported Dr. Olsen.
Tests are ongoing to determine how the virus is traveling, but “what we can say is that there’s a high viral load in the milk in the cattle, and it appears that the transmission is happening mostly within the lactating herds,” Dr. Sifford reported. It is unclear whether that is happening during the milking of the cows or whether contaminated milk from a cow with a high viral load is transmitting the virus to other cattle.
“We are strongly encouraging producers to limit the movement of cattle, particularly lactating cattle, as much as possible,” she says.
Milk Is Likely the Source of Transmission
“We haven’t seen anything that would change our assessment that the commercial milk supply is safe,” says Donald Prater, DVM, acting director of the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition at the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In the federal and state milk safety system, he explained, nearly 99% of the commercial milk supply comes from farms that participate in the Grade A program and follow the Pasteurized Milk Ordinance, which outlines pasteurization requirements.
Because detection of the virus in dairy cattle is new, there are many questions to be answered in research, he reported. Among them:
- What level of virus might be leaving the farms from shedding by apparently healthy cows?
- Does any live virus survive the pasteurization process?
- Do different methods of pasteurization and dairy production have different effects on the viability of H5N1?
- Are effects different in various forms of dairy products, such as cheese and cream?
A critical question regarding the potential risk to humans is how much milk would have to be consumed for the virus to become an established infection. That information is essential to determine “what type of pasteurization criteria” are needed to provide “acceptable public health outcomes,” Dr. Prater said.
The CDC is currently using the flu surveillance system to monitor for H5N1 activity in people. The systems show no current indicators of unusual influenza activity in people.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
After cow-to-cow transmission of avian influenza A subtype H5N1 in US dairy herds led to a cow-to-human transmission in Texas, the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials convened a panel of experts for a scientific symposium on Thursday to talk about the public health implications.
From the sequencing data, “we can expect and anticipate that [the candidate vaccine viruses] will provide good protection,” she explained.
Establishing candidate vaccine viruses “are the precursor to moving into large-scale vaccine production,” Dr. Dugan explained. Should that be needed, the candidate viruses can be used by manufacturers to produce new vaccines.
The CDC is also actively partnering with commercial diagnostic developers and testing companies in case there is a need to scale-up testing, Dr. Dugan said.
The only current human case in the United States was reported on April 1 and confirmed by the CDC within 24 hours, reported Sonja Olsen, PhD, associate director for preparedness and response of the Influenza Division at the CDC.
The person had direct exposure to cattle and reported eye redness, consistent with conjunctivitis, as the only symptom. The person received treatment and has recovered, and there were no reports of illness among the person’s household contacts, Dr. Olsen said.
Person With the Virus Has Recovered
The only other detection of the virus in a human in the United States was in 2022 and it was associated with infected poultry exposure. That person also had mild illness and recovered, Dr. Olsen explained.
Since 1997, when the first case of human infection was reported globally, “there have been 909 [human cases] reported from 23 countries,” Dr. Olsen said. “About half [52%] of the human cases have resulted in death.” Only a small number of human cases have been reported since 2015, but since 2022, more than two dozen human cases have been reported to the World Health Organization.
Experience with the virus in the United States has been about a year behind that in Europe, said Rosemary Sifford, DVM, chief veterinary officer at the US Department of Agriculture. In the United States, the first detection — in January 2022 — was in wild birds; this was followed the next month by the first detection in a commercial poultry flock.
In March of this year, the United States had its first detection in cattle, specifically dairy cattle. But testing has shown that “it remains very much an avian virus. It’s not becoming a bovine virus,” Dr. Sifford reported.
Detected in Cattle
Earlier this week, in an effort to minimize the risk of disease spread, the USDA issued a federal order that requires the reporting of positive influenza tests in livestock and mandatory testing for influenza of dairy cattle before interstate movement.
“As of today, there are affected herds in 33 farms across eight states,” reported Dr. Olsen.
Tests are ongoing to determine how the virus is traveling, but “what we can say is that there’s a high viral load in the milk in the cattle, and it appears that the transmission is happening mostly within the lactating herds,” Dr. Sifford reported. It is unclear whether that is happening during the milking of the cows or whether contaminated milk from a cow with a high viral load is transmitting the virus to other cattle.
“We are strongly encouraging producers to limit the movement of cattle, particularly lactating cattle, as much as possible,” she says.
Milk Is Likely the Source of Transmission
“We haven’t seen anything that would change our assessment that the commercial milk supply is safe,” says Donald Prater, DVM, acting director of the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition at the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In the federal and state milk safety system, he explained, nearly 99% of the commercial milk supply comes from farms that participate in the Grade A program and follow the Pasteurized Milk Ordinance, which outlines pasteurization requirements.
Because detection of the virus in dairy cattle is new, there are many questions to be answered in research, he reported. Among them:
- What level of virus might be leaving the farms from shedding by apparently healthy cows?
- Does any live virus survive the pasteurization process?
- Do different methods of pasteurization and dairy production have different effects on the viability of H5N1?
- Are effects different in various forms of dairy products, such as cheese and cream?
A critical question regarding the potential risk to humans is how much milk would have to be consumed for the virus to become an established infection. That information is essential to determine “what type of pasteurization criteria” are needed to provide “acceptable public health outcomes,” Dr. Prater said.
The CDC is currently using the flu surveillance system to monitor for H5N1 activity in people. The systems show no current indicators of unusual influenza activity in people.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Working Hard or Work Addiction — Have You Crossed the Line?
When child psychiatrist Javeed Sukhera, MD, PhD, was a few years into his career, he found himself doing it all. “I was in a leadership role academically at the medical school, I had a leadership role at the hospital, and I was seeing as many patients as I could. I could work all day every day.”
“It still wouldn’t have been enough,” he said.
Whenever there was a shift available, Dr. Sukhera would take it. His job was stressful, but as a new physician with a young family, he saw this obsession with work as necessary. “I began to cope with the stress from work by doing extra work and feeling like I needed to be everywhere. It was like I became a hamster on a spinning wheel. I was just running, running, running.”
Things shifted for Dr. Sukhera when he realized that while he was emotionally available for the children who were his patients, at home, his own children weren’t getting the best of him. “There was a specific moment when I thought my son was afraid of me,” he said. “I just stopped and realized that there was something happening that I needed to break. I needed to make a change.”
Dr. Sukhera, now chair of psychiatry at the Institute of Living and chief of the Department of Psychiatry at Hartford Hospital, Hartford, Connecticut, believes what he experienced was a steep fall into work addiction.
What Does Work Addiction Look Like for Doctors?
Behavioral addictions are fairly new in the addiction space. When gambling disorder, the first and only behavioral addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was added in 2013, it was seen as a “breakthrough addiction,” said Mark D. Griffiths, PhD, a leading behavioral addiction researcher and a distinguished professor at Nottingham Trent University.
Because there is not enough evidence yet to classify work addiction as a formal diagnosis, there is no clear consensus on how to define it. To further complicate things, the terms “workaholism” and “work addiction” can be used interchangeably, and some experts say the two are not the same, though they can overlap.
That said, a 2018 review of literature from several countries found that work addiction “fits very well into recently postulated criteria for conceptualization of a behavioral addiction.
“If you accept that gambling can be genuinely addictive, then there’s no reason to think that something like work, exercise, or video game playing couldn’t be an addiction as well,” said Dr. Griffiths.
“The neurobiology of addiction is that we get drawn to something that gives us a dopamine hit,” Dr. Sukhera added. “But to do that all day, every day, has consequences. It drains our emotional reserves, and it can greatly impact our relationships.”
On top of that, work addiction has been linked with poor sleep, poor cardiovascular health, high blood pressure, burnout, the development of autoimmune disorders, and other health issues.
Physicians are particularly susceptible. Doctors, after all, are expected to work long hours and put their patients’ needs first, even at the expense of their own health and well-being.
“Workaholism is not just socially acceptable in medicine,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s baked into the system and built into the structures. The healthcare system has largely functioned on the emotional labor of health workers, whose tendency to show up and work harder can, at times, in certain organizations, be exploited.”
Dr. Griffiths agreed that with the limited amount of data available, work addiction does appear to exist at higher rates in medicine than in other fields. As early as the 1970s, medical literature describes work as a “socially acceptable” addiction among doctors. A 2014 study published in Occupational Medicine reported that of 445 physicians who took part in the research, nearly half exhibited some level of work addiction with 13% “highly work addicted.”
Of course, working hard or even meeting unreasonable demands from work is not the same as work addiction, as Dr. Griffiths clarified in a 2023 editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety. The difference, as with other behavioral addictions, is when people obsess about work and use it to cope with stress. It can be easier to stay distracted and busy to gain a sense of control rather than learning to deal with complex emotions.
A 2021 study that Dr. Sukhera conducted with resident physicians found that working harder was one of the main ways they dealt with stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. “This idea that we deal with the stress of being burnt out by doing more and more of what burns us out is fairly ubiquitous at all stages of medical professionals’ careers,” he said.
Financial incentives also can fuel work addiction, said Dr. Sukhera. In residency, there are some safeguards around overwork and duty hours. When you become an attending, those limits no longer exist. As a young physician, Dr. Sukhera had student debt to pay off and a family to support. When he found opportunities to earn more by working more, his answer was always “yes.”
Pressure to produce medical research also can pose issues. Some physicians can become addicted to publishing studies, fearing that they might lose their professional status or position if they stop. It’s a cycle that can force a doctor to not only work long hours doing their job but also practically take on a second one.
How Physicians Can Recognize Work Addiction in Themselves
Work addiction can look and feel different for every person, said Malissa Clark, PhD, associate professor at the University of Georgia and author of the recent book Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business—and How to Fix It.
Dr. Clark noted that people who are highly engaged in their work tend to be driven by intrinsic motivation: “You work because you love it.” With work addiction, “you work because you feel like you ought to be working all the time.”
Of course, it’s not always so cut and dried; you can experience both forms of motivation and not necessarily become addicted to work. But if you are solely driven by the feeling that you ought to be working all the time, that can be a red flag.
Dr. Griffiths said that while many people may have problematic work habits or work too much, true work addicts must meet six criteria that apply to all addictions:
1. Salience: Work is the single most important thing in your life, to the point of neglecting everything else. Even if you’re on vacation, your mind might be flooded with work thoughts.
2. Mood modification: You use work to modify your mood, either to get a “high” or to cope with stress.
3. Tolerance: Over time, you’ve gone from working 8 or 10 hours a day to 12 hours a day, to a point where you’re working all the time.
4. Withdrawal: On a physiological level, you will have symptoms such as anxiety, nausea, or headaches when unable to work.
5. Conflict: You feel conflicted with yourself (you know you’re working too much) or with others (partners, friends, and children) about work, but you can’t stop.
6. Relapse: If you manage to cut down your hours but can’t resist overworking 1 day, you wind up right back where you were.
When It’s Time to Address Work Addiction
The lack of a formal diagnosis for work addiction makes getting treatment difficult. But there are ways to seek help. Unlike the drug and alcohol literature, abstinence is not the goal. “The therapeutic goal is getting a behavior under control and looking for the triggers of why you’re compulsively working,” said Dr. Griffiths.
Practice self-compassion
Dr. Sukhera eventually realized that his work addiction stemmed from the fear of being somehow excluded or unworthy. He actively corrected much of this through self-compassion and self-kindness, which helped him set boundaries. “Self-compassion is the root of everything,” he said. “Reminding ourselves that we’re doing our best is an important ingredient in breaking the cycle.”
Slowly expose yourself to relaxation
Many workaholics find rest very difficult. “When I conducted interviews with people [who considered themselves workaholics], a very common thing I heard was, ‘I have a very hard time being idle,’ ” said Dr. Clark. If rest feels hard, Dr. Sukhera suggests practicing relaxation for 2 minutes to start. Even small periods of downtime can challenge the belief that you must be constantly productive.
Reframe your to-do list
For work addicts, to-do lists can seem like they must be finished, which prolongs work hours. Instead, use to-do lists to help prioritize what is urgent, identify what can wait, and delegate out tasks to others, Dr. Clark recommends.
Pick up a mastery experience
Research from professor Sabine Sonnentag, Dr. rer. nat., at the University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany, suggests that mastery experiences — leisure activities that require thought and focus like learning a new language or taking a woodworking class — can help you actively disengage from work.
Try cognitive behavioral therapy
Widely used for other forms of addiction, cognitive behavioral therapy centers around recognizing emotions, challenging thought patterns, and changing behaviors. However, Dr. Clark admits the research on its impact on work addiction, in particular, is “pretty nascent.”
Shift your mindset
It seems logical to think that detaching from your feelings will allow you to “do more,” but experts say that idea is both untrue and dangerous. “The safest hospitals are the hospitals where people are attuned to their humanness,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s normal to overwork in medicine, and if you’re challenging a norm, you really have to be thoughtful about how you frame that for yourself.”
Most importantly: Seek support
Today, there is increased awareness about work addiction and more resources for physicians who are struggling, including programs such as Workaholics Anonymous or Physicians Anonymous and workplace wellness initiatives. But try not to overwhelm yourself with choosing whom to talk to or what specific resource to utilize, Dr. Sukhera advised. “Just talk to someone about it. You don’t have to carry this on your own.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When child psychiatrist Javeed Sukhera, MD, PhD, was a few years into his career, he found himself doing it all. “I was in a leadership role academically at the medical school, I had a leadership role at the hospital, and I was seeing as many patients as I could. I could work all day every day.”
“It still wouldn’t have been enough,” he said.
Whenever there was a shift available, Dr. Sukhera would take it. His job was stressful, but as a new physician with a young family, he saw this obsession with work as necessary. “I began to cope with the stress from work by doing extra work and feeling like I needed to be everywhere. It was like I became a hamster on a spinning wheel. I was just running, running, running.”
Things shifted for Dr. Sukhera when he realized that while he was emotionally available for the children who were his patients, at home, his own children weren’t getting the best of him. “There was a specific moment when I thought my son was afraid of me,” he said. “I just stopped and realized that there was something happening that I needed to break. I needed to make a change.”
Dr. Sukhera, now chair of psychiatry at the Institute of Living and chief of the Department of Psychiatry at Hartford Hospital, Hartford, Connecticut, believes what he experienced was a steep fall into work addiction.
What Does Work Addiction Look Like for Doctors?
Behavioral addictions are fairly new in the addiction space. When gambling disorder, the first and only behavioral addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was added in 2013, it was seen as a “breakthrough addiction,” said Mark D. Griffiths, PhD, a leading behavioral addiction researcher and a distinguished professor at Nottingham Trent University.
Because there is not enough evidence yet to classify work addiction as a formal diagnosis, there is no clear consensus on how to define it. To further complicate things, the terms “workaholism” and “work addiction” can be used interchangeably, and some experts say the two are not the same, though they can overlap.
That said, a 2018 review of literature from several countries found that work addiction “fits very well into recently postulated criteria for conceptualization of a behavioral addiction.
“If you accept that gambling can be genuinely addictive, then there’s no reason to think that something like work, exercise, or video game playing couldn’t be an addiction as well,” said Dr. Griffiths.
“The neurobiology of addiction is that we get drawn to something that gives us a dopamine hit,” Dr. Sukhera added. “But to do that all day, every day, has consequences. It drains our emotional reserves, and it can greatly impact our relationships.”
On top of that, work addiction has been linked with poor sleep, poor cardiovascular health, high blood pressure, burnout, the development of autoimmune disorders, and other health issues.
Physicians are particularly susceptible. Doctors, after all, are expected to work long hours and put their patients’ needs first, even at the expense of their own health and well-being.
“Workaholism is not just socially acceptable in medicine,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s baked into the system and built into the structures. The healthcare system has largely functioned on the emotional labor of health workers, whose tendency to show up and work harder can, at times, in certain organizations, be exploited.”
Dr. Griffiths agreed that with the limited amount of data available, work addiction does appear to exist at higher rates in medicine than in other fields. As early as the 1970s, medical literature describes work as a “socially acceptable” addiction among doctors. A 2014 study published in Occupational Medicine reported that of 445 physicians who took part in the research, nearly half exhibited some level of work addiction with 13% “highly work addicted.”
Of course, working hard or even meeting unreasonable demands from work is not the same as work addiction, as Dr. Griffiths clarified in a 2023 editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety. The difference, as with other behavioral addictions, is when people obsess about work and use it to cope with stress. It can be easier to stay distracted and busy to gain a sense of control rather than learning to deal with complex emotions.
A 2021 study that Dr. Sukhera conducted with resident physicians found that working harder was one of the main ways they dealt with stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. “This idea that we deal with the stress of being burnt out by doing more and more of what burns us out is fairly ubiquitous at all stages of medical professionals’ careers,” he said.
Financial incentives also can fuel work addiction, said Dr. Sukhera. In residency, there are some safeguards around overwork and duty hours. When you become an attending, those limits no longer exist. As a young physician, Dr. Sukhera had student debt to pay off and a family to support. When he found opportunities to earn more by working more, his answer was always “yes.”
Pressure to produce medical research also can pose issues. Some physicians can become addicted to publishing studies, fearing that they might lose their professional status or position if they stop. It’s a cycle that can force a doctor to not only work long hours doing their job but also practically take on a second one.
How Physicians Can Recognize Work Addiction in Themselves
Work addiction can look and feel different for every person, said Malissa Clark, PhD, associate professor at the University of Georgia and author of the recent book Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business—and How to Fix It.
Dr. Clark noted that people who are highly engaged in their work tend to be driven by intrinsic motivation: “You work because you love it.” With work addiction, “you work because you feel like you ought to be working all the time.”
Of course, it’s not always so cut and dried; you can experience both forms of motivation and not necessarily become addicted to work. But if you are solely driven by the feeling that you ought to be working all the time, that can be a red flag.
Dr. Griffiths said that while many people may have problematic work habits or work too much, true work addicts must meet six criteria that apply to all addictions:
1. Salience: Work is the single most important thing in your life, to the point of neglecting everything else. Even if you’re on vacation, your mind might be flooded with work thoughts.
2. Mood modification: You use work to modify your mood, either to get a “high” or to cope with stress.
3. Tolerance: Over time, you’ve gone from working 8 or 10 hours a day to 12 hours a day, to a point where you’re working all the time.
4. Withdrawal: On a physiological level, you will have symptoms such as anxiety, nausea, or headaches when unable to work.
5. Conflict: You feel conflicted with yourself (you know you’re working too much) or with others (partners, friends, and children) about work, but you can’t stop.
6. Relapse: If you manage to cut down your hours but can’t resist overworking 1 day, you wind up right back where you were.
When It’s Time to Address Work Addiction
The lack of a formal diagnosis for work addiction makes getting treatment difficult. But there are ways to seek help. Unlike the drug and alcohol literature, abstinence is not the goal. “The therapeutic goal is getting a behavior under control and looking for the triggers of why you’re compulsively working,” said Dr. Griffiths.
Practice self-compassion
Dr. Sukhera eventually realized that his work addiction stemmed from the fear of being somehow excluded or unworthy. He actively corrected much of this through self-compassion and self-kindness, which helped him set boundaries. “Self-compassion is the root of everything,” he said. “Reminding ourselves that we’re doing our best is an important ingredient in breaking the cycle.”
Slowly expose yourself to relaxation
Many workaholics find rest very difficult. “When I conducted interviews with people [who considered themselves workaholics], a very common thing I heard was, ‘I have a very hard time being idle,’ ” said Dr. Clark. If rest feels hard, Dr. Sukhera suggests practicing relaxation for 2 minutes to start. Even small periods of downtime can challenge the belief that you must be constantly productive.
Reframe your to-do list
For work addicts, to-do lists can seem like they must be finished, which prolongs work hours. Instead, use to-do lists to help prioritize what is urgent, identify what can wait, and delegate out tasks to others, Dr. Clark recommends.
Pick up a mastery experience
Research from professor Sabine Sonnentag, Dr. rer. nat., at the University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany, suggests that mastery experiences — leisure activities that require thought and focus like learning a new language or taking a woodworking class — can help you actively disengage from work.
Try cognitive behavioral therapy
Widely used for other forms of addiction, cognitive behavioral therapy centers around recognizing emotions, challenging thought patterns, and changing behaviors. However, Dr. Clark admits the research on its impact on work addiction, in particular, is “pretty nascent.”
Shift your mindset
It seems logical to think that detaching from your feelings will allow you to “do more,” but experts say that idea is both untrue and dangerous. “The safest hospitals are the hospitals where people are attuned to their humanness,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s normal to overwork in medicine, and if you’re challenging a norm, you really have to be thoughtful about how you frame that for yourself.”
Most importantly: Seek support
Today, there is increased awareness about work addiction and more resources for physicians who are struggling, including programs such as Workaholics Anonymous or Physicians Anonymous and workplace wellness initiatives. But try not to overwhelm yourself with choosing whom to talk to or what specific resource to utilize, Dr. Sukhera advised. “Just talk to someone about it. You don’t have to carry this on your own.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When child psychiatrist Javeed Sukhera, MD, PhD, was a few years into his career, he found himself doing it all. “I was in a leadership role academically at the medical school, I had a leadership role at the hospital, and I was seeing as many patients as I could. I could work all day every day.”
“It still wouldn’t have been enough,” he said.
Whenever there was a shift available, Dr. Sukhera would take it. His job was stressful, but as a new physician with a young family, he saw this obsession with work as necessary. “I began to cope with the stress from work by doing extra work and feeling like I needed to be everywhere. It was like I became a hamster on a spinning wheel. I was just running, running, running.”
Things shifted for Dr. Sukhera when he realized that while he was emotionally available for the children who were his patients, at home, his own children weren’t getting the best of him. “There was a specific moment when I thought my son was afraid of me,” he said. “I just stopped and realized that there was something happening that I needed to break. I needed to make a change.”
Dr. Sukhera, now chair of psychiatry at the Institute of Living and chief of the Department of Psychiatry at Hartford Hospital, Hartford, Connecticut, believes what he experienced was a steep fall into work addiction.
What Does Work Addiction Look Like for Doctors?
Behavioral addictions are fairly new in the addiction space. When gambling disorder, the first and only behavioral addiction in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was added in 2013, it was seen as a “breakthrough addiction,” said Mark D. Griffiths, PhD, a leading behavioral addiction researcher and a distinguished professor at Nottingham Trent University.
Because there is not enough evidence yet to classify work addiction as a formal diagnosis, there is no clear consensus on how to define it. To further complicate things, the terms “workaholism” and “work addiction” can be used interchangeably, and some experts say the two are not the same, though they can overlap.
That said, a 2018 review of literature from several countries found that work addiction “fits very well into recently postulated criteria for conceptualization of a behavioral addiction.
“If you accept that gambling can be genuinely addictive, then there’s no reason to think that something like work, exercise, or video game playing couldn’t be an addiction as well,” said Dr. Griffiths.
“The neurobiology of addiction is that we get drawn to something that gives us a dopamine hit,” Dr. Sukhera added. “But to do that all day, every day, has consequences. It drains our emotional reserves, and it can greatly impact our relationships.”
On top of that, work addiction has been linked with poor sleep, poor cardiovascular health, high blood pressure, burnout, the development of autoimmune disorders, and other health issues.
Physicians are particularly susceptible. Doctors, after all, are expected to work long hours and put their patients’ needs first, even at the expense of their own health and well-being.
“Workaholism is not just socially acceptable in medicine,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s baked into the system and built into the structures. The healthcare system has largely functioned on the emotional labor of health workers, whose tendency to show up and work harder can, at times, in certain organizations, be exploited.”
Dr. Griffiths agreed that with the limited amount of data available, work addiction does appear to exist at higher rates in medicine than in other fields. As early as the 1970s, medical literature describes work as a “socially acceptable” addiction among doctors. A 2014 study published in Occupational Medicine reported that of 445 physicians who took part in the research, nearly half exhibited some level of work addiction with 13% “highly work addicted.”
Of course, working hard or even meeting unreasonable demands from work is not the same as work addiction, as Dr. Griffiths clarified in a 2023 editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety. The difference, as with other behavioral addictions, is when people obsess about work and use it to cope with stress. It can be easier to stay distracted and busy to gain a sense of control rather than learning to deal with complex emotions.
A 2021 study that Dr. Sukhera conducted with resident physicians found that working harder was one of the main ways they dealt with stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. “This idea that we deal with the stress of being burnt out by doing more and more of what burns us out is fairly ubiquitous at all stages of medical professionals’ careers,” he said.
Financial incentives also can fuel work addiction, said Dr. Sukhera. In residency, there are some safeguards around overwork and duty hours. When you become an attending, those limits no longer exist. As a young physician, Dr. Sukhera had student debt to pay off and a family to support. When he found opportunities to earn more by working more, his answer was always “yes.”
Pressure to produce medical research also can pose issues. Some physicians can become addicted to publishing studies, fearing that they might lose their professional status or position if they stop. It’s a cycle that can force a doctor to not only work long hours doing their job but also practically take on a second one.
How Physicians Can Recognize Work Addiction in Themselves
Work addiction can look and feel different for every person, said Malissa Clark, PhD, associate professor at the University of Georgia and author of the recent book Never Not Working: Why the Always-On Culture Is Bad for Business—and How to Fix It.
Dr. Clark noted that people who are highly engaged in their work tend to be driven by intrinsic motivation: “You work because you love it.” With work addiction, “you work because you feel like you ought to be working all the time.”
Of course, it’s not always so cut and dried; you can experience both forms of motivation and not necessarily become addicted to work. But if you are solely driven by the feeling that you ought to be working all the time, that can be a red flag.
Dr. Griffiths said that while many people may have problematic work habits or work too much, true work addicts must meet six criteria that apply to all addictions:
1. Salience: Work is the single most important thing in your life, to the point of neglecting everything else. Even if you’re on vacation, your mind might be flooded with work thoughts.
2. Mood modification: You use work to modify your mood, either to get a “high” or to cope with stress.
3. Tolerance: Over time, you’ve gone from working 8 or 10 hours a day to 12 hours a day, to a point where you’re working all the time.
4. Withdrawal: On a physiological level, you will have symptoms such as anxiety, nausea, or headaches when unable to work.
5. Conflict: You feel conflicted with yourself (you know you’re working too much) or with others (partners, friends, and children) about work, but you can’t stop.
6. Relapse: If you manage to cut down your hours but can’t resist overworking 1 day, you wind up right back where you were.
When It’s Time to Address Work Addiction
The lack of a formal diagnosis for work addiction makes getting treatment difficult. But there are ways to seek help. Unlike the drug and alcohol literature, abstinence is not the goal. “The therapeutic goal is getting a behavior under control and looking for the triggers of why you’re compulsively working,” said Dr. Griffiths.
Practice self-compassion
Dr. Sukhera eventually realized that his work addiction stemmed from the fear of being somehow excluded or unworthy. He actively corrected much of this through self-compassion and self-kindness, which helped him set boundaries. “Self-compassion is the root of everything,” he said. “Reminding ourselves that we’re doing our best is an important ingredient in breaking the cycle.”
Slowly expose yourself to relaxation
Many workaholics find rest very difficult. “When I conducted interviews with people [who considered themselves workaholics], a very common thing I heard was, ‘I have a very hard time being idle,’ ” said Dr. Clark. If rest feels hard, Dr. Sukhera suggests practicing relaxation for 2 minutes to start. Even small periods of downtime can challenge the belief that you must be constantly productive.
Reframe your to-do list
For work addicts, to-do lists can seem like they must be finished, which prolongs work hours. Instead, use to-do lists to help prioritize what is urgent, identify what can wait, and delegate out tasks to others, Dr. Clark recommends.
Pick up a mastery experience
Research from professor Sabine Sonnentag, Dr. rer. nat., at the University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany, suggests that mastery experiences — leisure activities that require thought and focus like learning a new language or taking a woodworking class — can help you actively disengage from work.
Try cognitive behavioral therapy
Widely used for other forms of addiction, cognitive behavioral therapy centers around recognizing emotions, challenging thought patterns, and changing behaviors. However, Dr. Clark admits the research on its impact on work addiction, in particular, is “pretty nascent.”
Shift your mindset
It seems logical to think that detaching from your feelings will allow you to “do more,” but experts say that idea is both untrue and dangerous. “The safest hospitals are the hospitals where people are attuned to their humanness,” said Dr. Sukhera. “It’s normal to overwork in medicine, and if you’re challenging a norm, you really have to be thoughtful about how you frame that for yourself.”
Most importantly: Seek support
Today, there is increased awareness about work addiction and more resources for physicians who are struggling, including programs such as Workaholics Anonymous or Physicians Anonymous and workplace wellness initiatives. But try not to overwhelm yourself with choosing whom to talk to or what specific resource to utilize, Dr. Sukhera advised. “Just talk to someone about it. You don’t have to carry this on your own.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.