User login
Assessing the impact of glucocorticoids on COVID-19 mortality
Clinical question: Is early glucocorticoid therapy associated with reduced mortality or need for mechanical ventilation in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Background: Glucocorticoids have been used as adjunctive treatment in some infections with inflammatory responses, but their efficacy in COVID-19 infections had not been entirely clear. The RECOVERY trial found a subset of patients with COVID-19 who may benefit from treatment with glucocorticoids. The ideal role of steroids in this infection, and who the subset of patients might be for whom they would benefit, is so far unclear.
Study design: Retrospective cohort analysis.
Setting: Large academic health center in New York.
Synopsis: Researchers analyzed admissions of COVID-19 positive patients hospitalized between March 11, 2020 and April 13, 2020 who did not die or become mechanically ventilated within the first 48 hours of admission. Patients treated with glucocorticoids within 48 hours of admission were compared with patients who were not treated with glucocorticoids during this time frame. In total, 2,998 patients were examined, of whom 1,806 met inclusion criteria, and 140 (7.7%) were treated with glucocorticoids within 48 hours of admission. These treated patients were more likely to have an underlying pulmonary or rheumatologic comorbidity. Early use of glucocorticoids was not associated with in-hospital mortality or mechanical ventilation in either adjusted or unadjusted models. However, if the initial C-reactive protein (CRP) was >20mg/dL, this was associated with a reduced risk of mortality or mechanical ventilation in unadjusted (odds ratio, 0.23; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.70) and adjusted analyses for clinical characteristics (adjusted OR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.06-0.67). Conversely, treatment in patients with CRP <10mg/dL was associated with significantly increased risk of mortality or ventilation during analysis.
Bottom line: Glucocorticoids can benefit patients with significantly elevated CRP but may be harmful to those with lower CRPs.
Citation: Keller MJ et al. Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on mortality or mechanical ventilation in patients with COVID-19. J Hosp Med. 2020;8;489-493. Published online first. 2020 Jul 22. doi:10.12788/jhm.3497.
Dr. Halpern is a med-peds hospitalist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Clinical question: Is early glucocorticoid therapy associated with reduced mortality or need for mechanical ventilation in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Background: Glucocorticoids have been used as adjunctive treatment in some infections with inflammatory responses, but their efficacy in COVID-19 infections had not been entirely clear. The RECOVERY trial found a subset of patients with COVID-19 who may benefit from treatment with glucocorticoids. The ideal role of steroids in this infection, and who the subset of patients might be for whom they would benefit, is so far unclear.
Study design: Retrospective cohort analysis.
Setting: Large academic health center in New York.
Synopsis: Researchers analyzed admissions of COVID-19 positive patients hospitalized between March 11, 2020 and April 13, 2020 who did not die or become mechanically ventilated within the first 48 hours of admission. Patients treated with glucocorticoids within 48 hours of admission were compared with patients who were not treated with glucocorticoids during this time frame. In total, 2,998 patients were examined, of whom 1,806 met inclusion criteria, and 140 (7.7%) were treated with glucocorticoids within 48 hours of admission. These treated patients were more likely to have an underlying pulmonary or rheumatologic comorbidity. Early use of glucocorticoids was not associated with in-hospital mortality or mechanical ventilation in either adjusted or unadjusted models. However, if the initial C-reactive protein (CRP) was >20mg/dL, this was associated with a reduced risk of mortality or mechanical ventilation in unadjusted (odds ratio, 0.23; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.70) and adjusted analyses for clinical characteristics (adjusted OR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.06-0.67). Conversely, treatment in patients with CRP <10mg/dL was associated with significantly increased risk of mortality or ventilation during analysis.
Bottom line: Glucocorticoids can benefit patients with significantly elevated CRP but may be harmful to those with lower CRPs.
Citation: Keller MJ et al. Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on mortality or mechanical ventilation in patients with COVID-19. J Hosp Med. 2020;8;489-493. Published online first. 2020 Jul 22. doi:10.12788/jhm.3497.
Dr. Halpern is a med-peds hospitalist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Clinical question: Is early glucocorticoid therapy associated with reduced mortality or need for mechanical ventilation in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Background: Glucocorticoids have been used as adjunctive treatment in some infections with inflammatory responses, but their efficacy in COVID-19 infections had not been entirely clear. The RECOVERY trial found a subset of patients with COVID-19 who may benefit from treatment with glucocorticoids. The ideal role of steroids in this infection, and who the subset of patients might be for whom they would benefit, is so far unclear.
Study design: Retrospective cohort analysis.
Setting: Large academic health center in New York.
Synopsis: Researchers analyzed admissions of COVID-19 positive patients hospitalized between March 11, 2020 and April 13, 2020 who did not die or become mechanically ventilated within the first 48 hours of admission. Patients treated with glucocorticoids within 48 hours of admission were compared with patients who were not treated with glucocorticoids during this time frame. In total, 2,998 patients were examined, of whom 1,806 met inclusion criteria, and 140 (7.7%) were treated with glucocorticoids within 48 hours of admission. These treated patients were more likely to have an underlying pulmonary or rheumatologic comorbidity. Early use of glucocorticoids was not associated with in-hospital mortality or mechanical ventilation in either adjusted or unadjusted models. However, if the initial C-reactive protein (CRP) was >20mg/dL, this was associated with a reduced risk of mortality or mechanical ventilation in unadjusted (odds ratio, 0.23; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.70) and adjusted analyses for clinical characteristics (adjusted OR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.06-0.67). Conversely, treatment in patients with CRP <10mg/dL was associated with significantly increased risk of mortality or ventilation during analysis.
Bottom line: Glucocorticoids can benefit patients with significantly elevated CRP but may be harmful to those with lower CRPs.
Citation: Keller MJ et al. Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on mortality or mechanical ventilation in patients with COVID-19. J Hosp Med. 2020;8;489-493. Published online first. 2020 Jul 22. doi:10.12788/jhm.3497.
Dr. Halpern is a med-peds hospitalist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF HOSPITAL MEDICINE
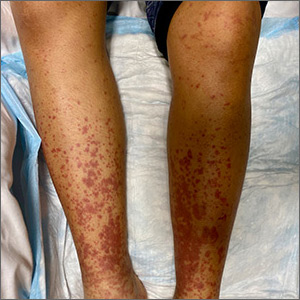
Painful, lower extremity rash
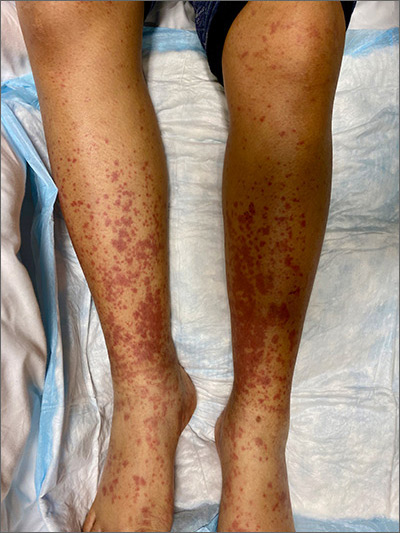
This woman’s palpable purpura with edema in her lower extremities was consistent with cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV).
LCV is characterized by the circulation of immune complexes that promote activation of complement, leading to endothelial injury and palpable purpura. Pain, arthralgia, cutaneous ulceration, and constitutional symptoms may be observed. About 50% of LCV cases are idiopathic. Identified causes include infection (including syphilis infection), drugs, malignancy, and connective tissue disease.
Systemic involvement must be ruled out in any patient with cutaneous LCV. The work-up is based on the individual patient assessment and may include a complete blood count with differential, complete metabolic panel, inflammatory markers, urinalysis, hepatitis panel, anti-nuclear antibody, rheumatoid factor, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, cryoglobulins, serum protein electrophoresis, and serum complement. A cutaneous punch biopsy for both hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and direct immunofluorescence (DIF) confirms the diagnosis of LCV.
For uncomplicated LCV cases without systemic involvement, treatment is generally supportive. Any identified underlying cause should be addressed. Analgesics may be considered for pain. Systemic therapy is indicated for patients with cutaneous ulceration, systemic vasculitis, or recurrent cases; this therapy may include colchicine, dapsone, corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil, and methotrexate.
In this patient’s case, a punch biopsy of the left lower extremity showed findings consistent with cutaneous LCV. She denied a history of intravenous drug use or initiation of new medications. Labs were notable for an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, c-reactive protein, and elevated creatinine.
Incidentally, she was found to be 32-weeks pregnant, went into pre-term labor while admitted, and delivered her baby without complication.
She had a reactive treponemal antibody, with rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:128, which confirmed a diagnosis of syphilis. She was treated with 1 dose of intra-muscular penicillin G while an inpatient. Her arthralgias improved during her hospitalization without initiation of steroids or other immunomodulatory therapy. Outpatient follow-up was expected to consist of completion of 3 total doses of IM penicillin, as well as renal studies, given her elevated creatinine.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle R. Fermin, MD, and text courtesy of Cyrelle R. Fermin, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306.

This woman’s palpable purpura with edema in her lower extremities was consistent with cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV).
LCV is characterized by the circulation of immune complexes that promote activation of complement, leading to endothelial injury and palpable purpura. Pain, arthralgia, cutaneous ulceration, and constitutional symptoms may be observed. About 50% of LCV cases are idiopathic. Identified causes include infection (including syphilis infection), drugs, malignancy, and connective tissue disease.
Systemic involvement must be ruled out in any patient with cutaneous LCV. The work-up is based on the individual patient assessment and may include a complete blood count with differential, complete metabolic panel, inflammatory markers, urinalysis, hepatitis panel, anti-nuclear antibody, rheumatoid factor, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, cryoglobulins, serum protein electrophoresis, and serum complement. A cutaneous punch biopsy for both hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and direct immunofluorescence (DIF) confirms the diagnosis of LCV.
For uncomplicated LCV cases without systemic involvement, treatment is generally supportive. Any identified underlying cause should be addressed. Analgesics may be considered for pain. Systemic therapy is indicated for patients with cutaneous ulceration, systemic vasculitis, or recurrent cases; this therapy may include colchicine, dapsone, corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil, and methotrexate.
In this patient’s case, a punch biopsy of the left lower extremity showed findings consistent with cutaneous LCV. She denied a history of intravenous drug use or initiation of new medications. Labs were notable for an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, c-reactive protein, and elevated creatinine.
Incidentally, she was found to be 32-weeks pregnant, went into pre-term labor while admitted, and delivered her baby without complication.
She had a reactive treponemal antibody, with rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:128, which confirmed a diagnosis of syphilis. She was treated with 1 dose of intra-muscular penicillin G while an inpatient. Her arthralgias improved during her hospitalization without initiation of steroids or other immunomodulatory therapy. Outpatient follow-up was expected to consist of completion of 3 total doses of IM penicillin, as well as renal studies, given her elevated creatinine.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle R. Fermin, MD, and text courtesy of Cyrelle R. Fermin, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

This woman’s palpable purpura with edema in her lower extremities was consistent with cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV).
LCV is characterized by the circulation of immune complexes that promote activation of complement, leading to endothelial injury and palpable purpura. Pain, arthralgia, cutaneous ulceration, and constitutional symptoms may be observed. About 50% of LCV cases are idiopathic. Identified causes include infection (including syphilis infection), drugs, malignancy, and connective tissue disease.
Systemic involvement must be ruled out in any patient with cutaneous LCV. The work-up is based on the individual patient assessment and may include a complete blood count with differential, complete metabolic panel, inflammatory markers, urinalysis, hepatitis panel, anti-nuclear antibody, rheumatoid factor, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, cryoglobulins, serum protein electrophoresis, and serum complement. A cutaneous punch biopsy for both hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and direct immunofluorescence (DIF) confirms the diagnosis of LCV.
For uncomplicated LCV cases without systemic involvement, treatment is generally supportive. Any identified underlying cause should be addressed. Analgesics may be considered for pain. Systemic therapy is indicated for patients with cutaneous ulceration, systemic vasculitis, or recurrent cases; this therapy may include colchicine, dapsone, corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil, and methotrexate.
In this patient’s case, a punch biopsy of the left lower extremity showed findings consistent with cutaneous LCV. She denied a history of intravenous drug use or initiation of new medications. Labs were notable for an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, c-reactive protein, and elevated creatinine.
Incidentally, she was found to be 32-weeks pregnant, went into pre-term labor while admitted, and delivered her baby without complication.
She had a reactive treponemal antibody, with rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:128, which confirmed a diagnosis of syphilis. She was treated with 1 dose of intra-muscular penicillin G while an inpatient. Her arthralgias improved during her hospitalization without initiation of steroids or other immunomodulatory therapy. Outpatient follow-up was expected to consist of completion of 3 total doses of IM penicillin, as well as renal studies, given her elevated creatinine.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle R. Fermin, MD, and text courtesy of Cyrelle R. Fermin, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306.
Goeser MR, Laniosz V, Wetter DA. A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:299-306.
Biden chooses California Attorney General Xavier Becerra to head HHS
If confirmed by the US Senate, Becerra will face the challenge of overseeing the federal agency charged with protecting the health of all Americans in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the time of the announcement, nearly 15 million Americans had tested positive for COVID-19 and more than 280,000 had died.
Becerra served 12 terms in Congress, representing the Los Angeles area. Although his public health experience is limited, he served on the Congressional Ways and Means Committee overseeing health-related issues. Becerra is known as an advocate for the health and well-being of women in particular.
The American College of Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, American Academy of Family Physicians, and the American Psychiatric Association wrote a letter to Biden on December 3 urging him to select leaders with medical and healthcare expertise, in particular physicians.
“We believe that your administration and the country would be well-served by the appointment of qualified physicians to serve in key positions critical to advancing the health of our nation,” they wrote. “Therefore, our organizations, which represent more than 400,000 front-line physicians practicing in the United States, write to request that you identify and appoint physicians to healthcare leadership positions within your administration.”
Recent advocacy
Becerra has worked with Republican attorneys general to lobby HHS to increase access to remdesivir to treat people with COVID-19.
As attorney general, Becerra filed more than 100 lawsuits against the Trump administration. In November, he also represented more than 20 states in arguments supporting the Affordable Care Act before the Supreme Court.
On December 4, Becerra joined with attorneys general from 23 states and the District of Columbia opposing a proposed rule from the outgoing Trump administration. The rule would deregulate HHS and “sunset”many agency provisions before Trump leaves office next month.
Becerra will be the first Latino appointed as HHS secretary, which furthers Biden’s goal to create a diverse cabinet. Becerra has been attorney general of California since 2017, replacing Vice President-elect Kamala Harris when she became senator.
Biden’s choice of Becerra was unexpected, according to The New York Times, and he was not the only candidate. Speculation was that Biden initially considered Vivek Murthy, MD, later chosen as the next US surgeon general, as well New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham and Rhode Island Gov. Gina Raimondo.
A huge undertaking
As HHS secretary, Becerra would oversee a wide range of federal agencies, including the US Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
The fiscal year 2021 budget proposed for HHS includes $94.5 billion in discretionary budget authority and $1.3 trillion in mandatory funding. Overall, HHS controls nearly one quarter of all federal expenditures and provides more grant money than all other federal agencies combined.
Becerra, 62, grew up in Sacramento, California. He was the first in his family to graduate from college. He received his undergraduate and law degrees from Stanford University.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If confirmed by the US Senate, Becerra will face the challenge of overseeing the federal agency charged with protecting the health of all Americans in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the time of the announcement, nearly 15 million Americans had tested positive for COVID-19 and more than 280,000 had died.
Becerra served 12 terms in Congress, representing the Los Angeles area. Although his public health experience is limited, he served on the Congressional Ways and Means Committee overseeing health-related issues. Becerra is known as an advocate for the health and well-being of women in particular.
The American College of Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, American Academy of Family Physicians, and the American Psychiatric Association wrote a letter to Biden on December 3 urging him to select leaders with medical and healthcare expertise, in particular physicians.
“We believe that your administration and the country would be well-served by the appointment of qualified physicians to serve in key positions critical to advancing the health of our nation,” they wrote. “Therefore, our organizations, which represent more than 400,000 front-line physicians practicing in the United States, write to request that you identify and appoint physicians to healthcare leadership positions within your administration.”
Recent advocacy
Becerra has worked with Republican attorneys general to lobby HHS to increase access to remdesivir to treat people with COVID-19.
As attorney general, Becerra filed more than 100 lawsuits against the Trump administration. In November, he also represented more than 20 states in arguments supporting the Affordable Care Act before the Supreme Court.
On December 4, Becerra joined with attorneys general from 23 states and the District of Columbia opposing a proposed rule from the outgoing Trump administration. The rule would deregulate HHS and “sunset”many agency provisions before Trump leaves office next month.
Becerra will be the first Latino appointed as HHS secretary, which furthers Biden’s goal to create a diverse cabinet. Becerra has been attorney general of California since 2017, replacing Vice President-elect Kamala Harris when she became senator.
Biden’s choice of Becerra was unexpected, according to The New York Times, and he was not the only candidate. Speculation was that Biden initially considered Vivek Murthy, MD, later chosen as the next US surgeon general, as well New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham and Rhode Island Gov. Gina Raimondo.
A huge undertaking
As HHS secretary, Becerra would oversee a wide range of federal agencies, including the US Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
The fiscal year 2021 budget proposed for HHS includes $94.5 billion in discretionary budget authority and $1.3 trillion in mandatory funding. Overall, HHS controls nearly one quarter of all federal expenditures and provides more grant money than all other federal agencies combined.
Becerra, 62, grew up in Sacramento, California. He was the first in his family to graduate from college. He received his undergraduate and law degrees from Stanford University.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If confirmed by the US Senate, Becerra will face the challenge of overseeing the federal agency charged with protecting the health of all Americans in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the time of the announcement, nearly 15 million Americans had tested positive for COVID-19 and more than 280,000 had died.
Becerra served 12 terms in Congress, representing the Los Angeles area. Although his public health experience is limited, he served on the Congressional Ways and Means Committee overseeing health-related issues. Becerra is known as an advocate for the health and well-being of women in particular.
The American College of Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, American Academy of Family Physicians, and the American Psychiatric Association wrote a letter to Biden on December 3 urging him to select leaders with medical and healthcare expertise, in particular physicians.
“We believe that your administration and the country would be well-served by the appointment of qualified physicians to serve in key positions critical to advancing the health of our nation,” they wrote. “Therefore, our organizations, which represent more than 400,000 front-line physicians practicing in the United States, write to request that you identify and appoint physicians to healthcare leadership positions within your administration.”
Recent advocacy
Becerra has worked with Republican attorneys general to lobby HHS to increase access to remdesivir to treat people with COVID-19.
As attorney general, Becerra filed more than 100 lawsuits against the Trump administration. In November, he also represented more than 20 states in arguments supporting the Affordable Care Act before the Supreme Court.
On December 4, Becerra joined with attorneys general from 23 states and the District of Columbia opposing a proposed rule from the outgoing Trump administration. The rule would deregulate HHS and “sunset”many agency provisions before Trump leaves office next month.
Becerra will be the first Latino appointed as HHS secretary, which furthers Biden’s goal to create a diverse cabinet. Becerra has been attorney general of California since 2017, replacing Vice President-elect Kamala Harris when she became senator.
Biden’s choice of Becerra was unexpected, according to The New York Times, and he was not the only candidate. Speculation was that Biden initially considered Vivek Murthy, MD, later chosen as the next US surgeon general, as well New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham and Rhode Island Gov. Gina Raimondo.
A huge undertaking
As HHS secretary, Becerra would oversee a wide range of federal agencies, including the US Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
The fiscal year 2021 budget proposed for HHS includes $94.5 billion in discretionary budget authority and $1.3 trillion in mandatory funding. Overall, HHS controls nearly one quarter of all federal expenditures and provides more grant money than all other federal agencies combined.
Becerra, 62, grew up in Sacramento, California. He was the first in his family to graduate from college. He received his undergraduate and law degrees from Stanford University.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
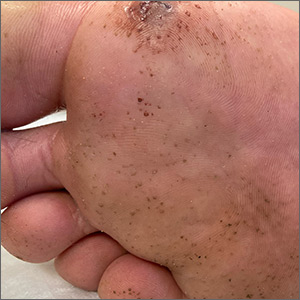
“Polka-dotted” feet
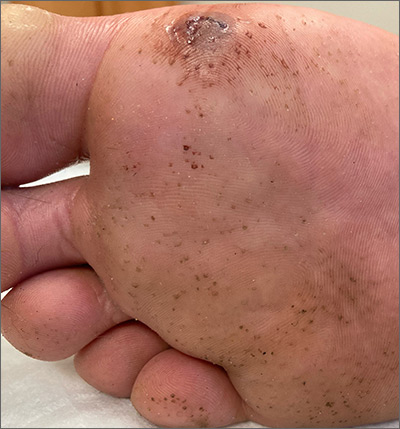
This man has pitted keratolysis (PK), characterized by multiple small pits on the soles of the feet. PK is often associated with hyperhidrosis and significant odor. The lesions usually have a punched-out appearance and are flesh-colored. The dark color of these lesions was due to the patient’s footwear.
PK is caused by bacterial overgrowth in the stratum corneum. Corynebacterium is the most common bacterial culprit, but Kytococcus, Actinomyces, and Dermatophilus have also been implicated. The bacterial infection is thought to be secondary to hyperhidrosis or as a result of hygiene, footwear, or other conditions that retain moisture and promote maceration of the soles of the feet. Therefore, treatment includes a 2-pronged approach: Resolve the bacterial infection and reduce excess moisture. Effective antibacterials include topical clindamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, and benzoyl peroxide. Oral antibiotics are not often required.
Hyperhidrosis can be treated with prescription strength 20% aluminum chloride antiperspirant applied to the feet in a tapering schedule, first daily and then 2 or 3 times weekly. Aluminum chloride is frequently not covered by insurance companies, but over-the-counter (OTC) 12% formulations (Certain DRI) usually suffice. Additionally, changing socks and using moisture-wicking shoes or socks are helpful measures to keep feet dry.
One study treated PK with topical erythromycin 3% gel twice daily, without the use of aluminum chloride antiperspirants, and found that the hyperhidrosis greatly improved. The authors theorized that the gram-positive bacterial infection upregulated eccrine sweat glands causing hyperhidrosis as a secondary, rather than the primary, cause of PK.
This patient was prescribed topical erythromycin gel twice daily for the soles of his feet. For his hyperhidrosis, he was advised to purchase OTC aluminum chloride antiperspirants to apply to his feet daily for the first week and to then decrease to 2 or 3 times per week. He was counseled to take an extra pair of socks for changing midway through his workday and to return for reevaluation if his skin did not improve.
Image courtesy of Sarah Friedberg, MD, and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, and Sarah Friedberg, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Pranteda G, Carlesimo M, Pranteda G, et al. Pitted keratolysis, erythromycin, and hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Ther. 2014;27:101-104.

This man has pitted keratolysis (PK), characterized by multiple small pits on the soles of the feet. PK is often associated with hyperhidrosis and significant odor. The lesions usually have a punched-out appearance and are flesh-colored. The dark color of these lesions was due to the patient’s footwear.
PK is caused by bacterial overgrowth in the stratum corneum. Corynebacterium is the most common bacterial culprit, but Kytococcus, Actinomyces, and Dermatophilus have also been implicated. The bacterial infection is thought to be secondary to hyperhidrosis or as a result of hygiene, footwear, or other conditions that retain moisture and promote maceration of the soles of the feet. Therefore, treatment includes a 2-pronged approach: Resolve the bacterial infection and reduce excess moisture. Effective antibacterials include topical clindamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, and benzoyl peroxide. Oral antibiotics are not often required.
Hyperhidrosis can be treated with prescription strength 20% aluminum chloride antiperspirant applied to the feet in a tapering schedule, first daily and then 2 or 3 times weekly. Aluminum chloride is frequently not covered by insurance companies, but over-the-counter (OTC) 12% formulations (Certain DRI) usually suffice. Additionally, changing socks and using moisture-wicking shoes or socks are helpful measures to keep feet dry.
One study treated PK with topical erythromycin 3% gel twice daily, without the use of aluminum chloride antiperspirants, and found that the hyperhidrosis greatly improved. The authors theorized that the gram-positive bacterial infection upregulated eccrine sweat glands causing hyperhidrosis as a secondary, rather than the primary, cause of PK.
This patient was prescribed topical erythromycin gel twice daily for the soles of his feet. For his hyperhidrosis, he was advised to purchase OTC aluminum chloride antiperspirants to apply to his feet daily for the first week and to then decrease to 2 or 3 times per week. He was counseled to take an extra pair of socks for changing midway through his workday and to return for reevaluation if his skin did not improve.
Image courtesy of Sarah Friedberg, MD, and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, and Sarah Friedberg, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

This man has pitted keratolysis (PK), characterized by multiple small pits on the soles of the feet. PK is often associated with hyperhidrosis and significant odor. The lesions usually have a punched-out appearance and are flesh-colored. The dark color of these lesions was due to the patient’s footwear.
PK is caused by bacterial overgrowth in the stratum corneum. Corynebacterium is the most common bacterial culprit, but Kytococcus, Actinomyces, and Dermatophilus have also been implicated. The bacterial infection is thought to be secondary to hyperhidrosis or as a result of hygiene, footwear, or other conditions that retain moisture and promote maceration of the soles of the feet. Therefore, treatment includes a 2-pronged approach: Resolve the bacterial infection and reduce excess moisture. Effective antibacterials include topical clindamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, and benzoyl peroxide. Oral antibiotics are not often required.
Hyperhidrosis can be treated with prescription strength 20% aluminum chloride antiperspirant applied to the feet in a tapering schedule, first daily and then 2 or 3 times weekly. Aluminum chloride is frequently not covered by insurance companies, but over-the-counter (OTC) 12% formulations (Certain DRI) usually suffice. Additionally, changing socks and using moisture-wicking shoes or socks are helpful measures to keep feet dry.
One study treated PK with topical erythromycin 3% gel twice daily, without the use of aluminum chloride antiperspirants, and found that the hyperhidrosis greatly improved. The authors theorized that the gram-positive bacterial infection upregulated eccrine sweat glands causing hyperhidrosis as a secondary, rather than the primary, cause of PK.
This patient was prescribed topical erythromycin gel twice daily for the soles of his feet. For his hyperhidrosis, he was advised to purchase OTC aluminum chloride antiperspirants to apply to his feet daily for the first week and to then decrease to 2 or 3 times per week. He was counseled to take an extra pair of socks for changing midway through his workday and to return for reevaluation if his skin did not improve.
Image courtesy of Sarah Friedberg, MD, and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, and Sarah Friedberg, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Pranteda G, Carlesimo M, Pranteda G, et al. Pitted keratolysis, erythromycin, and hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Ther. 2014;27:101-104.
Pranteda G, Carlesimo M, Pranteda G, et al. Pitted keratolysis, erythromycin, and hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Ther. 2014;27:101-104.
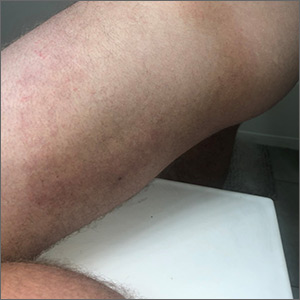
Large circular thigh rash
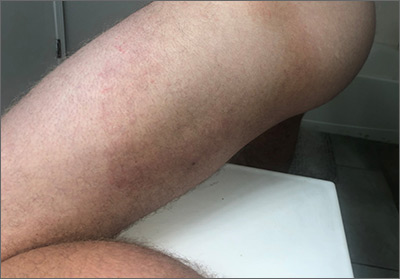
This patient had the deep form of erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC). As the name implies, it manifests as an expanding, red circular pattern that often clears in the middle. There is usually a ring of scale that trails behind the advancing border. However, in the deep form, it may be more subtle than the pronounced scale of the superficial form. Pruritus is a very common symptom associated with this condition.
EAC is a hypersensitivity reaction, which can be in response to several stimuli including underlying malignancy, medications, fungal and dermatophyte infections, inflammatory conditions, and pregnancy. A careful history and physical exam can be helpful in determining if a work-up for malignancy is warranted.
Since many medications including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, and biologicals can cause this condition, a history of which medications were started within the previous several months may be helpful.
When EAC is due to an underlying malignancy, it is called paraneoplastic erythema annulare centrifugum. It can be secondary to solid tumors or lymphoproliferative disorders.
More than 50% percent of the cases are idiopathic, and no underlying condition is identified. The skin findings may last for weeks—and even years.
If an underlying cause is found, treatment is directed at that condition, and the skin findings usually improve with resolution of the instigating condition. If no specific cause is found, the itching can be managed with systemic antihistamines or topical steroids. Some case studies have reported success with the use of systemic antibiotics, including erythromycin. Improvement with antibiotics may be due to treatment of an occult underlying bacterial process or owing to the anti-inflammatory effects of many antibiotics.
Since the patient in this case had onychomycosis of his toenails, and fungal and dermatophyte infections are a common trigger, he was placed on a 12-week course of oral terbinafine 250 mg/d. The plan was to biopsy the rash if it didn’t resolve. At 3 weeks, the rash had resolved, and the patient was asymptomatic.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
McDaniel B, Cook C. Erythema annulare centrifugum. In: Abai B, Abu-Ghosh A, Acharya AB, et al, eds. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL; 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482494/. Accessed December 2, 2020.

This patient had the deep form of erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC). As the name implies, it manifests as an expanding, red circular pattern that often clears in the middle. There is usually a ring of scale that trails behind the advancing border. However, in the deep form, it may be more subtle than the pronounced scale of the superficial form. Pruritus is a very common symptom associated with this condition.
EAC is a hypersensitivity reaction, which can be in response to several stimuli including underlying malignancy, medications, fungal and dermatophyte infections, inflammatory conditions, and pregnancy. A careful history and physical exam can be helpful in determining if a work-up for malignancy is warranted.
Since many medications including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, and biologicals can cause this condition, a history of which medications were started within the previous several months may be helpful.
When EAC is due to an underlying malignancy, it is called paraneoplastic erythema annulare centrifugum. It can be secondary to solid tumors or lymphoproliferative disorders.
More than 50% percent of the cases are idiopathic, and no underlying condition is identified. The skin findings may last for weeks—and even years.
If an underlying cause is found, treatment is directed at that condition, and the skin findings usually improve with resolution of the instigating condition. If no specific cause is found, the itching can be managed with systemic antihistamines or topical steroids. Some case studies have reported success with the use of systemic antibiotics, including erythromycin. Improvement with antibiotics may be due to treatment of an occult underlying bacterial process or owing to the anti-inflammatory effects of many antibiotics.
Since the patient in this case had onychomycosis of his toenails, and fungal and dermatophyte infections are a common trigger, he was placed on a 12-week course of oral terbinafine 250 mg/d. The plan was to biopsy the rash if it didn’t resolve. At 3 weeks, the rash had resolved, and the patient was asymptomatic.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

This patient had the deep form of erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC). As the name implies, it manifests as an expanding, red circular pattern that often clears in the middle. There is usually a ring of scale that trails behind the advancing border. However, in the deep form, it may be more subtle than the pronounced scale of the superficial form. Pruritus is a very common symptom associated with this condition.
EAC is a hypersensitivity reaction, which can be in response to several stimuli including underlying malignancy, medications, fungal and dermatophyte infections, inflammatory conditions, and pregnancy. A careful history and physical exam can be helpful in determining if a work-up for malignancy is warranted.
Since many medications including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, and biologicals can cause this condition, a history of which medications were started within the previous several months may be helpful.
When EAC is due to an underlying malignancy, it is called paraneoplastic erythema annulare centrifugum. It can be secondary to solid tumors or lymphoproliferative disorders.
More than 50% percent of the cases are idiopathic, and no underlying condition is identified. The skin findings may last for weeks—and even years.
If an underlying cause is found, treatment is directed at that condition, and the skin findings usually improve with resolution of the instigating condition. If no specific cause is found, the itching can be managed with systemic antihistamines or topical steroids. Some case studies have reported success with the use of systemic antibiotics, including erythromycin. Improvement with antibiotics may be due to treatment of an occult underlying bacterial process or owing to the anti-inflammatory effects of many antibiotics.
Since the patient in this case had onychomycosis of his toenails, and fungal and dermatophyte infections are a common trigger, he was placed on a 12-week course of oral terbinafine 250 mg/d. The plan was to biopsy the rash if it didn’t resolve. At 3 weeks, the rash had resolved, and the patient was asymptomatic.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
McDaniel B, Cook C. Erythema annulare centrifugum. In: Abai B, Abu-Ghosh A, Acharya AB, et al, eds. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL; 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482494/. Accessed December 2, 2020.
McDaniel B, Cook C. Erythema annulare centrifugum. In: Abai B, Abu-Ghosh A, Acharya AB, et al, eds. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL; 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482494/. Accessed December 2, 2020.
Duvelisib response rate encouraging in phase 2 PRIMO trial of patients with r/r PTCL
Duvelisib is demonstrating encouraging activity and manageable toxicities among patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) in a phase 2 trial, an investigator said.
The overall response rate in the dose-optimization phase of the PRIMO trial was more than 60% among patients receiving 75 mg of duvelisib twice daily, with a median duration of response exceeding 12 months, said investigator Barbara Pro, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the ongoing dose-expansion phase, in which patients start on 75 mg twice daily and then transition to a lower dose, the ORR is over 50%, including complete responses (CRs) in about one-third of patients, Dr. Pro reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Most previously approved treatments for relapsed/refractory PTCL are associated with ORRs of less than 30%, low rates of CR, and median progression-free survival of less than 4 months, Dr. Pro said in her presentation.
There have been no unexpected toxicities in the dose-expansion phase, and the adverse event profile is consistent with what has been observed previously for this oral phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, according to Dr. Pro.
Based on results to date, Dr. Pro said she and coinvestigators are hopeful that duvelisib will have a place in the treatment armamentarium for relapsed/refractory PTCL in the future.
“This is one of the most effective agents in T-cell lymphoma, and hopefully will be approved and available for treatment soon,” she said in remarks following her presentation of PRIMO study data.
“The next question would be how to try to move this agent up front,” she added. “We’ll have to try to see what could be the possible combinations and evaluate the possible overlapping toxicity with alternative treatments.”
The PRIMO trial provides “very exciting numbers” that include roughly half of relapsed/refractory PTCL patients are responding to the oral therapy, said Andrei R. Shustov, MD, professor of medicine in the division of hematology at the University of Washington, Seattle.
Perhaps more importantly, at least half of those responses have been CRs, Dr. Shustov noted in an interview: “We haven’t seen this yet in T-cell lymphomas, short of brentuximab vedotin targeting CD30,” he said, referring to the 2018 Food and Drug Administration approval of brentuximab vedotin for previously untreated CD30-expressing PTCL.
If duvelisib is approved, it would be the first oral agent with an indication for relapsed/refractory PTCL, which could have important implications for patient quality of life, Dr. Shustov added.
“The fact that you can take a pill at home, and don’t have to be in clinic once a week, or have the port device, or be infused every week would be an incredible change in quality of life,” he said, “and this is really amplified in the older population where quality of life is so important.”
Duvelisib was FDA approved in 2018, at a dose of 25 mg orally twice daily, for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma, following at least two previous treatments.
In relapsed/refractory PTCL, results of a phase 1 study previously published in Blood showed that duvelisib demonstrated an ORR of 50%, or 8 out of 16 patients treated with 25 or 75 mg twice daily continuously.
The phase 2 study described by Dr. Pro at this year’s ASH meeting included 33 patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL treated with duvelisib 25 mg or 75 mg twice daily as part of a dose-optimization phase, and 25 patients treated in an expansion phase at 75 mg twice daily for two 28-day cycles, followed by treatment at 25 mg twice daily.
Starting at the higher dose of 75 mg twice daily is intended to achieve rapid tumor control, while switching to the lower 25-mg twice-daily dose is to maintain long-term control of the disease while mitigating potential for later toxicities, according to the published abstract for the PRIMO trial.
Results of the dose-optimization phase included an ORR by independent review committee of 62% for patients treated at the 75-mg twice-daily dose, and 40% for those treated at 25 mg twice daily. The median duration of response in the 75-mg twice-daily group was 12.2 months, which Dr. Pro said was significantly higher than what was observed for the lower dose.
In the ongoing dose-expansion phase, the ORR by investigator was 52% (13 of 25 patients), with a CR rate of 36% (9 of 25 patients). The reported data show that with a median duration of follow-up of 3.78 months, the median duration of response thus far is 4.1 months.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were increases in ALT and AST, seen in 24% and 20% of patients, respectively. The most common grade 3 or greater hematologic toxicity was decreased lymphocyte count, seen in 16%.
Three serious treatment-emergent adverse events thought to be related to duvelisib occurred in two patients, including grade 5 pneumonitis in one patient, and skin lesion plus posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in the other patient, according to Dr. Pro. Serious treatment-emergent adverse events leading to duvelisib discontinuation included increased ALT/AST in 2 patients and pneumonitis in one patient.
Grade 1-2 adverse events reported at ASH included hypertension, nausea, anemia, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation and pyrexia, among others.
Enrollment in the dose-expansion phase of PRIMO is ongoing and should be complete in February, according to Dr. Pro.
Support for the study came from Verastem Oncology and Secura Bio. Dr. Pro reported research funding from Verastem Oncology, Takeda, and other pharmaceutical companies and honoraria from Takeda and Seattle Genetics.
SOURCE: Pro B et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 44.
Duvelisib is demonstrating encouraging activity and manageable toxicities among patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) in a phase 2 trial, an investigator said.
The overall response rate in the dose-optimization phase of the PRIMO trial was more than 60% among patients receiving 75 mg of duvelisib twice daily, with a median duration of response exceeding 12 months, said investigator Barbara Pro, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the ongoing dose-expansion phase, in which patients start on 75 mg twice daily and then transition to a lower dose, the ORR is over 50%, including complete responses (CRs) in about one-third of patients, Dr. Pro reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Most previously approved treatments for relapsed/refractory PTCL are associated with ORRs of less than 30%, low rates of CR, and median progression-free survival of less than 4 months, Dr. Pro said in her presentation.
There have been no unexpected toxicities in the dose-expansion phase, and the adverse event profile is consistent with what has been observed previously for this oral phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, according to Dr. Pro.
Based on results to date, Dr. Pro said she and coinvestigators are hopeful that duvelisib will have a place in the treatment armamentarium for relapsed/refractory PTCL in the future.
“This is one of the most effective agents in T-cell lymphoma, and hopefully will be approved and available for treatment soon,” she said in remarks following her presentation of PRIMO study data.
“The next question would be how to try to move this agent up front,” she added. “We’ll have to try to see what could be the possible combinations and evaluate the possible overlapping toxicity with alternative treatments.”
The PRIMO trial provides “very exciting numbers” that include roughly half of relapsed/refractory PTCL patients are responding to the oral therapy, said Andrei R. Shustov, MD, professor of medicine in the division of hematology at the University of Washington, Seattle.
Perhaps more importantly, at least half of those responses have been CRs, Dr. Shustov noted in an interview: “We haven’t seen this yet in T-cell lymphomas, short of brentuximab vedotin targeting CD30,” he said, referring to the 2018 Food and Drug Administration approval of brentuximab vedotin for previously untreated CD30-expressing PTCL.
If duvelisib is approved, it would be the first oral agent with an indication for relapsed/refractory PTCL, which could have important implications for patient quality of life, Dr. Shustov added.
“The fact that you can take a pill at home, and don’t have to be in clinic once a week, or have the port device, or be infused every week would be an incredible change in quality of life,” he said, “and this is really amplified in the older population where quality of life is so important.”
Duvelisib was FDA approved in 2018, at a dose of 25 mg orally twice daily, for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma, following at least two previous treatments.
In relapsed/refractory PTCL, results of a phase 1 study previously published in Blood showed that duvelisib demonstrated an ORR of 50%, or 8 out of 16 patients treated with 25 or 75 mg twice daily continuously.
The phase 2 study described by Dr. Pro at this year’s ASH meeting included 33 patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL treated with duvelisib 25 mg or 75 mg twice daily as part of a dose-optimization phase, and 25 patients treated in an expansion phase at 75 mg twice daily for two 28-day cycles, followed by treatment at 25 mg twice daily.
Starting at the higher dose of 75 mg twice daily is intended to achieve rapid tumor control, while switching to the lower 25-mg twice-daily dose is to maintain long-term control of the disease while mitigating potential for later toxicities, according to the published abstract for the PRIMO trial.
Results of the dose-optimization phase included an ORR by independent review committee of 62% for patients treated at the 75-mg twice-daily dose, and 40% for those treated at 25 mg twice daily. The median duration of response in the 75-mg twice-daily group was 12.2 months, which Dr. Pro said was significantly higher than what was observed for the lower dose.
In the ongoing dose-expansion phase, the ORR by investigator was 52% (13 of 25 patients), with a CR rate of 36% (9 of 25 patients). The reported data show that with a median duration of follow-up of 3.78 months, the median duration of response thus far is 4.1 months.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were increases in ALT and AST, seen in 24% and 20% of patients, respectively. The most common grade 3 or greater hematologic toxicity was decreased lymphocyte count, seen in 16%.
Three serious treatment-emergent adverse events thought to be related to duvelisib occurred in two patients, including grade 5 pneumonitis in one patient, and skin lesion plus posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in the other patient, according to Dr. Pro. Serious treatment-emergent adverse events leading to duvelisib discontinuation included increased ALT/AST in 2 patients and pneumonitis in one patient.
Grade 1-2 adverse events reported at ASH included hypertension, nausea, anemia, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation and pyrexia, among others.
Enrollment in the dose-expansion phase of PRIMO is ongoing and should be complete in February, according to Dr. Pro.
Support for the study came from Verastem Oncology and Secura Bio. Dr. Pro reported research funding from Verastem Oncology, Takeda, and other pharmaceutical companies and honoraria from Takeda and Seattle Genetics.
SOURCE: Pro B et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 44.
Duvelisib is demonstrating encouraging activity and manageable toxicities among patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) in a phase 2 trial, an investigator said.
The overall response rate in the dose-optimization phase of the PRIMO trial was more than 60% among patients receiving 75 mg of duvelisib twice daily, with a median duration of response exceeding 12 months, said investigator Barbara Pro, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the ongoing dose-expansion phase, in which patients start on 75 mg twice daily and then transition to a lower dose, the ORR is over 50%, including complete responses (CRs) in about one-third of patients, Dr. Pro reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Most previously approved treatments for relapsed/refractory PTCL are associated with ORRs of less than 30%, low rates of CR, and median progression-free survival of less than 4 months, Dr. Pro said in her presentation.
There have been no unexpected toxicities in the dose-expansion phase, and the adverse event profile is consistent with what has been observed previously for this oral phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, according to Dr. Pro.
Based on results to date, Dr. Pro said she and coinvestigators are hopeful that duvelisib will have a place in the treatment armamentarium for relapsed/refractory PTCL in the future.
“This is one of the most effective agents in T-cell lymphoma, and hopefully will be approved and available for treatment soon,” she said in remarks following her presentation of PRIMO study data.
“The next question would be how to try to move this agent up front,” she added. “We’ll have to try to see what could be the possible combinations and evaluate the possible overlapping toxicity with alternative treatments.”
The PRIMO trial provides “very exciting numbers” that include roughly half of relapsed/refractory PTCL patients are responding to the oral therapy, said Andrei R. Shustov, MD, professor of medicine in the division of hematology at the University of Washington, Seattle.
Perhaps more importantly, at least half of those responses have been CRs, Dr. Shustov noted in an interview: “We haven’t seen this yet in T-cell lymphomas, short of brentuximab vedotin targeting CD30,” he said, referring to the 2018 Food and Drug Administration approval of brentuximab vedotin for previously untreated CD30-expressing PTCL.
If duvelisib is approved, it would be the first oral agent with an indication for relapsed/refractory PTCL, which could have important implications for patient quality of life, Dr. Shustov added.
“The fact that you can take a pill at home, and don’t have to be in clinic once a week, or have the port device, or be infused every week would be an incredible change in quality of life,” he said, “and this is really amplified in the older population where quality of life is so important.”
Duvelisib was FDA approved in 2018, at a dose of 25 mg orally twice daily, for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma, following at least two previous treatments.
In relapsed/refractory PTCL, results of a phase 1 study previously published in Blood showed that duvelisib demonstrated an ORR of 50%, or 8 out of 16 patients treated with 25 or 75 mg twice daily continuously.
The phase 2 study described by Dr. Pro at this year’s ASH meeting included 33 patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL treated with duvelisib 25 mg or 75 mg twice daily as part of a dose-optimization phase, and 25 patients treated in an expansion phase at 75 mg twice daily for two 28-day cycles, followed by treatment at 25 mg twice daily.
Starting at the higher dose of 75 mg twice daily is intended to achieve rapid tumor control, while switching to the lower 25-mg twice-daily dose is to maintain long-term control of the disease while mitigating potential for later toxicities, according to the published abstract for the PRIMO trial.
Results of the dose-optimization phase included an ORR by independent review committee of 62% for patients treated at the 75-mg twice-daily dose, and 40% for those treated at 25 mg twice daily. The median duration of response in the 75-mg twice-daily group was 12.2 months, which Dr. Pro said was significantly higher than what was observed for the lower dose.
In the ongoing dose-expansion phase, the ORR by investigator was 52% (13 of 25 patients), with a CR rate of 36% (9 of 25 patients). The reported data show that with a median duration of follow-up of 3.78 months, the median duration of response thus far is 4.1 months.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were increases in ALT and AST, seen in 24% and 20% of patients, respectively. The most common grade 3 or greater hematologic toxicity was decreased lymphocyte count, seen in 16%.
Three serious treatment-emergent adverse events thought to be related to duvelisib occurred in two patients, including grade 5 pneumonitis in one patient, and skin lesion plus posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in the other patient, according to Dr. Pro. Serious treatment-emergent adverse events leading to duvelisib discontinuation included increased ALT/AST in 2 patients and pneumonitis in one patient.
Grade 1-2 adverse events reported at ASH included hypertension, nausea, anemia, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation and pyrexia, among others.
Enrollment in the dose-expansion phase of PRIMO is ongoing and should be complete in February, according to Dr. Pro.
Support for the study came from Verastem Oncology and Secura Bio. Dr. Pro reported research funding from Verastem Oncology, Takeda, and other pharmaceutical companies and honoraria from Takeda and Seattle Genetics.
SOURCE: Pro B et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 44.
FROM ASH 2020
HHS, Surgeon General urge action on maternal health
The U.S. Surgeon General and Department of Health & Human Services are calling on health care professionals, hospitals, employers, insurers, women, and the nation to work together to reduce maternal morbidity and mortality – and the disparities that make the risks higher for women of color.
The maternal mortality rate in the United States is the highest among developed countries of the world and continues to rise. In 2018, for every 100,000 live births, approximately 17 women died while pregnant or within 42 days of the end of pregnancy from causes related to pregnancy or delivery – that’s a substantial increase from 7 deaths per 100,000 live births in 1987, according to the surgeon general’s new call to action.
“Our mothers had much lower rates of dying related to pregnancy, compared to women today,” Dorothy Fink, MD, HHS deputy assistant secretary for women’s health, said at a briefing held Dec. 3 to mark the call to action.
Cardiovascular conditions were the most common cause of pregnancy-related deaths between 2011 and 2015, accounting for more than one in three of the deaths. HHS’s related action plan sets a target of achieving blood pressure control in 80% of women of reproductive age with hypertension by 2025.
The plan also seeks to reduce the maternal mortality rate by 50% and decrease low-risk cesarean deliveries by 25% within 5 years.
Surgeon General Jerome Adams, MD, said at the briefing. “This is not just unacceptable, it is just something that we need to understand is not inevitable,” he said, adding that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has determined that two thirds of the deaths are preventable.
Dr. Adams also noted that it was important to address maternal health now, especially with COVID-19 raging. “Without attention and action, maternal health could actually worsen because of this pandemic,” he said.
“We cannot discuss maternal health, much less improve it, unless we acknowledge women of color are at a much greater risk of harm related to childbirth,” Dr. Adams said. “Black women are two to three times more likely to die of pregnancy-related causes compared to many other racial and ethnic groups.” The disparity increases with age, according to the CDC.
Studies have shown that education does not eliminate those disparities. Black women with a college degree are twice as likely to die as White or Asian American women who did not finish high school, Dr. Adams said.
He held up a photo of a colleague, Shalone Irving, who he said was a PhD-educated epidemiologist who “died not long ago from pregnancy-related complications.”
Income is also not a factor, said Dr. Adams, noting that pop singer Beyonce had a near-death experience with preeclampsia. He also noted that Serena Williams, a top athlete, also struggled with pregnancy complications.
Recommendations not all funded
The HHS action plan is not explicitly funded, although Dr. Fink and Dr. Adams said that President Donald J. Trump’s fiscal 2021 budget includes some specific requests for improving maternal health. It will be up to Congress to grant the requests.
The budget seeks $80 million for the Health Resources and Services Administration to improve access to and quality of care. It also includes money to expand Medicaid coverage for 1 year after birth for women with substance use disorders. The American Medical Association in 2019 adopted a policy urging Medicaid coverage to be expanded to include all women for a year after childbirth. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has also encouraged this extension.
“We are encouraged that the HHS action plan includes support for policies to close coverage and care gaps for all postpartum women after pregnancy-related Medicaid coverage expires,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in an interview.
The HHS could act immediately by approving Medicaid waivers to extend such coverage, Dr. Phipps said.
The budget also requests $24 million to expand maternal mortality review programs to every state, said Dr. Fink. Currently, 43 states and the District of Columbia, have such committees, which are charged with reviewing deaths of women within a year of pregnancy or birth.
The HHS will also join with the March of Dimes to address the disparities in Black women by implementing evidence-based best practices to improve quality in hospital settings.
It is not the first time the Trump administration has taken aim at reducing maternal morbidity and mortality. In 2018, the president signed the Preventing Maternal Deaths Act, which authorized the CDC to award $50 million over 5 years so that every state could form maternal mortality review committees.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Surgeon General and Department of Health & Human Services are calling on health care professionals, hospitals, employers, insurers, women, and the nation to work together to reduce maternal morbidity and mortality – and the disparities that make the risks higher for women of color.
The maternal mortality rate in the United States is the highest among developed countries of the world and continues to rise. In 2018, for every 100,000 live births, approximately 17 women died while pregnant or within 42 days of the end of pregnancy from causes related to pregnancy or delivery – that’s a substantial increase from 7 deaths per 100,000 live births in 1987, according to the surgeon general’s new call to action.
“Our mothers had much lower rates of dying related to pregnancy, compared to women today,” Dorothy Fink, MD, HHS deputy assistant secretary for women’s health, said at a briefing held Dec. 3 to mark the call to action.
Cardiovascular conditions were the most common cause of pregnancy-related deaths between 2011 and 2015, accounting for more than one in three of the deaths. HHS’s related action plan sets a target of achieving blood pressure control in 80% of women of reproductive age with hypertension by 2025.
The plan also seeks to reduce the maternal mortality rate by 50% and decrease low-risk cesarean deliveries by 25% within 5 years.
Surgeon General Jerome Adams, MD, said at the briefing. “This is not just unacceptable, it is just something that we need to understand is not inevitable,” he said, adding that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has determined that two thirds of the deaths are preventable.
Dr. Adams also noted that it was important to address maternal health now, especially with COVID-19 raging. “Without attention and action, maternal health could actually worsen because of this pandemic,” he said.
“We cannot discuss maternal health, much less improve it, unless we acknowledge women of color are at a much greater risk of harm related to childbirth,” Dr. Adams said. “Black women are two to three times more likely to die of pregnancy-related causes compared to many other racial and ethnic groups.” The disparity increases with age, according to the CDC.
Studies have shown that education does not eliminate those disparities. Black women with a college degree are twice as likely to die as White or Asian American women who did not finish high school, Dr. Adams said.
He held up a photo of a colleague, Shalone Irving, who he said was a PhD-educated epidemiologist who “died not long ago from pregnancy-related complications.”
Income is also not a factor, said Dr. Adams, noting that pop singer Beyonce had a near-death experience with preeclampsia. He also noted that Serena Williams, a top athlete, also struggled with pregnancy complications.
Recommendations not all funded
The HHS action plan is not explicitly funded, although Dr. Fink and Dr. Adams said that President Donald J. Trump’s fiscal 2021 budget includes some specific requests for improving maternal health. It will be up to Congress to grant the requests.
The budget seeks $80 million for the Health Resources and Services Administration to improve access to and quality of care. It also includes money to expand Medicaid coverage for 1 year after birth for women with substance use disorders. The American Medical Association in 2019 adopted a policy urging Medicaid coverage to be expanded to include all women for a year after childbirth. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has also encouraged this extension.
“We are encouraged that the HHS action plan includes support for policies to close coverage and care gaps for all postpartum women after pregnancy-related Medicaid coverage expires,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in an interview.
The HHS could act immediately by approving Medicaid waivers to extend such coverage, Dr. Phipps said.
The budget also requests $24 million to expand maternal mortality review programs to every state, said Dr. Fink. Currently, 43 states and the District of Columbia, have such committees, which are charged with reviewing deaths of women within a year of pregnancy or birth.
The HHS will also join with the March of Dimes to address the disparities in Black women by implementing evidence-based best practices to improve quality in hospital settings.
It is not the first time the Trump administration has taken aim at reducing maternal morbidity and mortality. In 2018, the president signed the Preventing Maternal Deaths Act, which authorized the CDC to award $50 million over 5 years so that every state could form maternal mortality review committees.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Surgeon General and Department of Health & Human Services are calling on health care professionals, hospitals, employers, insurers, women, and the nation to work together to reduce maternal morbidity and mortality – and the disparities that make the risks higher for women of color.
The maternal mortality rate in the United States is the highest among developed countries of the world and continues to rise. In 2018, for every 100,000 live births, approximately 17 women died while pregnant or within 42 days of the end of pregnancy from causes related to pregnancy or delivery – that’s a substantial increase from 7 deaths per 100,000 live births in 1987, according to the surgeon general’s new call to action.
“Our mothers had much lower rates of dying related to pregnancy, compared to women today,” Dorothy Fink, MD, HHS deputy assistant secretary for women’s health, said at a briefing held Dec. 3 to mark the call to action.
Cardiovascular conditions were the most common cause of pregnancy-related deaths between 2011 and 2015, accounting for more than one in three of the deaths. HHS’s related action plan sets a target of achieving blood pressure control in 80% of women of reproductive age with hypertension by 2025.
The plan also seeks to reduce the maternal mortality rate by 50% and decrease low-risk cesarean deliveries by 25% within 5 years.
Surgeon General Jerome Adams, MD, said at the briefing. “This is not just unacceptable, it is just something that we need to understand is not inevitable,” he said, adding that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has determined that two thirds of the deaths are preventable.
Dr. Adams also noted that it was important to address maternal health now, especially with COVID-19 raging. “Without attention and action, maternal health could actually worsen because of this pandemic,” he said.
“We cannot discuss maternal health, much less improve it, unless we acknowledge women of color are at a much greater risk of harm related to childbirth,” Dr. Adams said. “Black women are two to three times more likely to die of pregnancy-related causes compared to many other racial and ethnic groups.” The disparity increases with age, according to the CDC.
Studies have shown that education does not eliminate those disparities. Black women with a college degree are twice as likely to die as White or Asian American women who did not finish high school, Dr. Adams said.
He held up a photo of a colleague, Shalone Irving, who he said was a PhD-educated epidemiologist who “died not long ago from pregnancy-related complications.”
Income is also not a factor, said Dr. Adams, noting that pop singer Beyonce had a near-death experience with preeclampsia. He also noted that Serena Williams, a top athlete, also struggled with pregnancy complications.
Recommendations not all funded
The HHS action plan is not explicitly funded, although Dr. Fink and Dr. Adams said that President Donald J. Trump’s fiscal 2021 budget includes some specific requests for improving maternal health. It will be up to Congress to grant the requests.
The budget seeks $80 million for the Health Resources and Services Administration to improve access to and quality of care. It also includes money to expand Medicaid coverage for 1 year after birth for women with substance use disorders. The American Medical Association in 2019 adopted a policy urging Medicaid coverage to be expanded to include all women for a year after childbirth. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has also encouraged this extension.
“We are encouraged that the HHS action plan includes support for policies to close coverage and care gaps for all postpartum women after pregnancy-related Medicaid coverage expires,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in an interview.
The HHS could act immediately by approving Medicaid waivers to extend such coverage, Dr. Phipps said.
The budget also requests $24 million to expand maternal mortality review programs to every state, said Dr. Fink. Currently, 43 states and the District of Columbia, have such committees, which are charged with reviewing deaths of women within a year of pregnancy or birth.
The HHS will also join with the March of Dimes to address the disparities in Black women by implementing evidence-based best practices to improve quality in hospital settings.
It is not the first time the Trump administration has taken aim at reducing maternal morbidity and mortality. In 2018, the president signed the Preventing Maternal Deaths Act, which authorized the CDC to award $50 million over 5 years so that every state could form maternal mortality review committees.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BE: Surveillance endoscopy frequency improving but still overdone
A new analysis of a U.S. national database suggests that surveillance endoscopies are being initiated unnecessarily in patients without a diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus, and sooner than the recommended interval in patients with nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. The study, published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, found some improvements, suggesting that 2016 recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology and the American Board of Internal Medicine have had some impact in reducing unnecessary surveillance, but more work may need to be done. The guidelines recommend surveillance of nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus every 3-5 years, and no biopsy for normal or irregular Z-line (<1 cm of variability).
“There was a notable change in practice after the 2016 ACG guidelines,” said Ziad Gellad, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., in an interview. He noted that fewer providers were recommending 1-2-year surveillance intervals for nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus and an increase in those who recommended a 3-year interval.
But the study also found frequent biopsies of irregular Z-line. Whether that’s a clear signal of overuse of biopsy is unclear, since the researchers couldn’t determine if other macroscopic or endoscopically visible abnormalities may have been present and driven a decision. “We can’t assume that there wasn’t any other abnormality in the esophagus that deserved to be biopsied,” said Dr. Gellad, who was not involved in the study.
The authors, led by Sachin Wani, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, analyzed data from the GI Quality Improvement Consortium Registry on 135,704 endoscopies in 114,894 patients, performed between January 2013 and December 2019. Analyzed data included procedure indication, demographics, endoscopy and histology findings, and recommendations for further endoscopy.
Just over 61% of subjects were men, and 91.0% were White. The mean age at time of endoscopy was 61.7 years. 50.2% of procedures produced a pathology-confirmed diagnosis of intestinal metaplasia (IM). Of these, 5.9% were indefinite for dysplasia or low-grade dysplasia (LGD), and 1.5% were high-grade dysplasia (HGD).
In 81.4% of cases with IM and a normal Z-line, the endoscopist recommended surveillance endoscopy. In 44.2%, the repeat was recommended in 3 years. 26.1% were recommended for surveillance in 1-2 years. Surveillance was recommended in 80.7% of cases with IM and an irregular Z-line; 51.5% in 3 years and 19.5% in 1-2 years. Almost 20% of subjects with normal Z-line and no IM were recommended for surveillance endoscopy, most often in 3 years (8.6%). 24% of those with irregular Z-line and no IM were recommended for surveillance endoscopy (15.8% in 3 years). Overall, between 2016 and 2019, compared with 2013-2015, the researchers found an increase in the frequency of recommendation of 3-year intervals, and a decrease in recommendation of 1-2-year intervals.
Among patients with columnar-lined esophagus and confirmed Barrett’s esophagus, 53.4% of the 1- to 3-cm group and 41.8% of the >3-cm group were recommended surveillance endoscopy at 3 years. 21.9% of the 1- to 3-cm group and 30.3% of the >3-cm group were recommended for surveillance endoscopy sooner than 3 years.
“It confirms overuse of upper endoscopy in the management of Barrett’s. However, there is also a nagging question in my mind about what to do about an irregular Z-line,” said Dr. Gellad. He noted that 33.8% of individuals with irregular Z-line had IM, while 3.8% had LGD and 0.7% had HGD. Those patients would have been missed if biopsies had not been taken, which would have been consistent with the new guidelines. However, he noted that pathology findings were not reviewed by an expert pathologist. “Does this data suggest because you find HGD in irregular Z-line, should we now in fact biopsy irregular Z-line? That’s one of the interesting pieces of this,” said Dr. Gellad.
He also believes that there is much more to be learned about what drives the decisions and timing surrounding surveillance endoscopy. “I think that’s an area that’s ripe for research,” said Dr. Gellad.
The study was funded by the University of Colorado department of medicine. The article authors have consulted for various companies. Dr. Gellad has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wani S et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 11. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000960.
A new analysis of a U.S. national database suggests that surveillance endoscopies are being initiated unnecessarily in patients without a diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus, and sooner than the recommended interval in patients with nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. The study, published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, found some improvements, suggesting that 2016 recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology and the American Board of Internal Medicine have had some impact in reducing unnecessary surveillance, but more work may need to be done. The guidelines recommend surveillance of nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus every 3-5 years, and no biopsy for normal or irregular Z-line (<1 cm of variability).
“There was a notable change in practice after the 2016 ACG guidelines,” said Ziad Gellad, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., in an interview. He noted that fewer providers were recommending 1-2-year surveillance intervals for nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus and an increase in those who recommended a 3-year interval.
But the study also found frequent biopsies of irregular Z-line. Whether that’s a clear signal of overuse of biopsy is unclear, since the researchers couldn’t determine if other macroscopic or endoscopically visible abnormalities may have been present and driven a decision. “We can’t assume that there wasn’t any other abnormality in the esophagus that deserved to be biopsied,” said Dr. Gellad, who was not involved in the study.
The authors, led by Sachin Wani, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, analyzed data from the GI Quality Improvement Consortium Registry on 135,704 endoscopies in 114,894 patients, performed between January 2013 and December 2019. Analyzed data included procedure indication, demographics, endoscopy and histology findings, and recommendations for further endoscopy.
Just over 61% of subjects were men, and 91.0% were White. The mean age at time of endoscopy was 61.7 years. 50.2% of procedures produced a pathology-confirmed diagnosis of intestinal metaplasia (IM). Of these, 5.9% were indefinite for dysplasia or low-grade dysplasia (LGD), and 1.5% were high-grade dysplasia (HGD).
In 81.4% of cases with IM and a normal Z-line, the endoscopist recommended surveillance endoscopy. In 44.2%, the repeat was recommended in 3 years. 26.1% were recommended for surveillance in 1-2 years. Surveillance was recommended in 80.7% of cases with IM and an irregular Z-line; 51.5% in 3 years and 19.5% in 1-2 years. Almost 20% of subjects with normal Z-line and no IM were recommended for surveillance endoscopy, most often in 3 years (8.6%). 24% of those with irregular Z-line and no IM were recommended for surveillance endoscopy (15.8% in 3 years). Overall, between 2016 and 2019, compared with 2013-2015, the researchers found an increase in the frequency of recommendation of 3-year intervals, and a decrease in recommendation of 1-2-year intervals.
Among patients with columnar-lined esophagus and confirmed Barrett’s esophagus, 53.4% of the 1- to 3-cm group and 41.8% of the >3-cm group were recommended surveillance endoscopy at 3 years. 21.9% of the 1- to 3-cm group and 30.3% of the >3-cm group were recommended for surveillance endoscopy sooner than 3 years.
“It confirms overuse of upper endoscopy in the management of Barrett’s. However, there is also a nagging question in my mind about what to do about an irregular Z-line,” said Dr. Gellad. He noted that 33.8% of individuals with irregular Z-line had IM, while 3.8% had LGD and 0.7% had HGD. Those patients would have been missed if biopsies had not been taken, which would have been consistent with the new guidelines. However, he noted that pathology findings were not reviewed by an expert pathologist. “Does this data suggest because you find HGD in irregular Z-line, should we now in fact biopsy irregular Z-line? That’s one of the interesting pieces of this,” said Dr. Gellad.
He also believes that there is much more to be learned about what drives the decisions and timing surrounding surveillance endoscopy. “I think that’s an area that’s ripe for research,” said Dr. Gellad.
The study was funded by the University of Colorado department of medicine. The article authors have consulted for various companies. Dr. Gellad has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wani S et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 11. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000960.
A new analysis of a U.S. national database suggests that surveillance endoscopies are being initiated unnecessarily in patients without a diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus, and sooner than the recommended interval in patients with nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. The study, published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, found some improvements, suggesting that 2016 recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology and the American Board of Internal Medicine have had some impact in reducing unnecessary surveillance, but more work may need to be done. The guidelines recommend surveillance of nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus every 3-5 years, and no biopsy for normal or irregular Z-line (<1 cm of variability).
“There was a notable change in practice after the 2016 ACG guidelines,” said Ziad Gellad, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., in an interview. He noted that fewer providers were recommending 1-2-year surveillance intervals for nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus and an increase in those who recommended a 3-year interval.
But the study also found frequent biopsies of irregular Z-line. Whether that’s a clear signal of overuse of biopsy is unclear, since the researchers couldn’t determine if other macroscopic or endoscopically visible abnormalities may have been present and driven a decision. “We can’t assume that there wasn’t any other abnormality in the esophagus that deserved to be biopsied,” said Dr. Gellad, who was not involved in the study.
The authors, led by Sachin Wani, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, analyzed data from the GI Quality Improvement Consortium Registry on 135,704 endoscopies in 114,894 patients, performed between January 2013 and December 2019. Analyzed data included procedure indication, demographics, endoscopy and histology findings, and recommendations for further endoscopy.
Just over 61% of subjects were men, and 91.0% were White. The mean age at time of endoscopy was 61.7 years. 50.2% of procedures produced a pathology-confirmed diagnosis of intestinal metaplasia (IM). Of these, 5.9% were indefinite for dysplasia or low-grade dysplasia (LGD), and 1.5% were high-grade dysplasia (HGD).
In 81.4% of cases with IM and a normal Z-line, the endoscopist recommended surveillance endoscopy. In 44.2%, the repeat was recommended in 3 years. 26.1% were recommended for surveillance in 1-2 years. Surveillance was recommended in 80.7% of cases with IM and an irregular Z-line; 51.5% in 3 years and 19.5% in 1-2 years. Almost 20% of subjects with normal Z-line and no IM were recommended for surveillance endoscopy, most often in 3 years (8.6%). 24% of those with irregular Z-line and no IM were recommended for surveillance endoscopy (15.8% in 3 years). Overall, between 2016 and 2019, compared with 2013-2015, the researchers found an increase in the frequency of recommendation of 3-year intervals, and a decrease in recommendation of 1-2-year intervals.
Among patients with columnar-lined esophagus and confirmed Barrett’s esophagus, 53.4% of the 1- to 3-cm group and 41.8% of the >3-cm group were recommended surveillance endoscopy at 3 years. 21.9% of the 1- to 3-cm group and 30.3% of the >3-cm group were recommended for surveillance endoscopy sooner than 3 years.
“It confirms overuse of upper endoscopy in the management of Barrett’s. However, there is also a nagging question in my mind about what to do about an irregular Z-line,” said Dr. Gellad. He noted that 33.8% of individuals with irregular Z-line had IM, while 3.8% had LGD and 0.7% had HGD. Those patients would have been missed if biopsies had not been taken, which would have been consistent with the new guidelines. However, he noted that pathology findings were not reviewed by an expert pathologist. “Does this data suggest because you find HGD in irregular Z-line, should we now in fact biopsy irregular Z-line? That’s one of the interesting pieces of this,” said Dr. Gellad.
He also believes that there is much more to be learned about what drives the decisions and timing surrounding surveillance endoscopy. “I think that’s an area that’s ripe for research,” said Dr. Gellad.
The study was funded by the University of Colorado department of medicine. The article authors have consulted for various companies. Dr. Gellad has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wani S et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 11. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000960.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
Cost is the main hurdle to broad use of caplacizumab for TTP
As hematologists debated the role of the anti–von Willebrand factor agent caplacizumab for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), an investigator on the phase 3 trial that led to its approval had a message.
,” said hematologist Spero Cataland, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Ohio State University in Columbus.
If cost is going to be a factor, and it “has to be in our world these days, it’s more of a discussion,” he said during his presentation at the 2020 Update in Nonneoplastic Hematology virtual conference.
The HERCULES trial Dr. Cataland helped conduct found a median time to platelet count normalization of 2.69 days when caplacizumab was started during plasma exchange versus 2.88 days for placebo; 12% of patients had a TTP recurrence while they continued caplacizumab for 30 days past their last exchange and were followed for an additional 28 days versus 38% randomized to placebo. Caplacizumab subjects needed an average of 5.8 days of plasma exchange versus 9.4 days in the placebo arm (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):335-46).
Based on the results, the Food and Drug Administration approved the agent for acquired TTP in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressives in Feb. 2019 for 30 days beyond the last plasma exchange, with up to 28 additional days if ADAMTS13 activity remains suppressed. Labeling notes a risk of severe bleeding.
“The data on refractory disease and mortality aren’t quite there yet, but there’s a suggestion [caplacizumab] might impact that as well,” Dr. Cataland said. In its recent TTP guidelines, the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis gave the agent only a conditional recommendation, in part because it’s backed up only by HERCULES and a phase 2 trial.
Also, the group noted that in the phase 2 study caplacizumab patients had a clinically and statistically significant increase in the number of relapses at 12 months: 31% versus 8% placebo. “Caplacizumab may leave patients prone to experience a later recurrence owing to the unresolved ADAMTS13 deficiency and inhibitors,” Dr. Cataland said.
“We do see some early recurrence” when caplacizumab is stopped, suggesting that when the agent’s “protective effect is removed, the risk is still there,” said Dr. Cataland, who was also an author on the ISTH guidelines, as well as the phase 2 trial.
It raises the question of how long patients should be kept on caplacizumab. There are few data on the issue, “but the consensus has been to stop caplacizumab when two consecutive ADAMTS13 measurements show 20% or greater activity,” or perhaps with one reading above 20% in a patient trending in the right direction. “With a bleeding complication, you might stop it sooner,” he said.
Dr. Cataland anticipates TTP management will eventually move away from plasma exchange to more directed therapies, including caplacizumab and perhaps recombinant ADAMTS13, which is in development.
There have been a few reports of TTP patients who refuse plasma exchange on religious grounds being successfully treated with caplacizumab. Dr. Cataland also noted a patient of his with relapsing TTP who didn’t want to be admitted yet again for plasma exchange and steroids at the start of a new episode.
“We managed her with caplacizumab and rituximab, and in a couple weeks she had recovered her ADAMTS13 activity and was able to stop the caplacizumab.” She was a motivated, knowledgeable person, “someone I trusted, so I was comfortable with the approach. I think that may be where we are headed in the future, hopefully,” he said.
Dr. Cataland disclosed research funding and consulting fees from Alexion, caplacizumab’s maker, Sanofi Genzyme, and Takeda,. The conference was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
As hematologists debated the role of the anti–von Willebrand factor agent caplacizumab for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), an investigator on the phase 3 trial that led to its approval had a message.
,” said hematologist Spero Cataland, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Ohio State University in Columbus.
If cost is going to be a factor, and it “has to be in our world these days, it’s more of a discussion,” he said during his presentation at the 2020 Update in Nonneoplastic Hematology virtual conference.
The HERCULES trial Dr. Cataland helped conduct found a median time to platelet count normalization of 2.69 days when caplacizumab was started during plasma exchange versus 2.88 days for placebo; 12% of patients had a TTP recurrence while they continued caplacizumab for 30 days past their last exchange and were followed for an additional 28 days versus 38% randomized to placebo. Caplacizumab subjects needed an average of 5.8 days of plasma exchange versus 9.4 days in the placebo arm (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):335-46).
Based on the results, the Food and Drug Administration approved the agent for acquired TTP in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressives in Feb. 2019 for 30 days beyond the last plasma exchange, with up to 28 additional days if ADAMTS13 activity remains suppressed. Labeling notes a risk of severe bleeding.
“The data on refractory disease and mortality aren’t quite there yet, but there’s a suggestion [caplacizumab] might impact that as well,” Dr. Cataland said. In its recent TTP guidelines, the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis gave the agent only a conditional recommendation, in part because it’s backed up only by HERCULES and a phase 2 trial.
Also, the group noted that in the phase 2 study caplacizumab patients had a clinically and statistically significant increase in the number of relapses at 12 months: 31% versus 8% placebo. “Caplacizumab may leave patients prone to experience a later recurrence owing to the unresolved ADAMTS13 deficiency and inhibitors,” Dr. Cataland said.
“We do see some early recurrence” when caplacizumab is stopped, suggesting that when the agent’s “protective effect is removed, the risk is still there,” said Dr. Cataland, who was also an author on the ISTH guidelines, as well as the phase 2 trial.
It raises the question of how long patients should be kept on caplacizumab. There are few data on the issue, “but the consensus has been to stop caplacizumab when two consecutive ADAMTS13 measurements show 20% or greater activity,” or perhaps with one reading above 20% in a patient trending in the right direction. “With a bleeding complication, you might stop it sooner,” he said.
Dr. Cataland anticipates TTP management will eventually move away from plasma exchange to more directed therapies, including caplacizumab and perhaps recombinant ADAMTS13, which is in development.
There have been a few reports of TTP patients who refuse plasma exchange on religious grounds being successfully treated with caplacizumab. Dr. Cataland also noted a patient of his with relapsing TTP who didn’t want to be admitted yet again for plasma exchange and steroids at the start of a new episode.
“We managed her with caplacizumab and rituximab, and in a couple weeks she had recovered her ADAMTS13 activity and was able to stop the caplacizumab.” She was a motivated, knowledgeable person, “someone I trusted, so I was comfortable with the approach. I think that may be where we are headed in the future, hopefully,” he said.
Dr. Cataland disclosed research funding and consulting fees from Alexion, caplacizumab’s maker, Sanofi Genzyme, and Takeda,. The conference was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
As hematologists debated the role of the anti–von Willebrand factor agent caplacizumab for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), an investigator on the phase 3 trial that led to its approval had a message.
,” said hematologist Spero Cataland, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Ohio State University in Columbus.
If cost is going to be a factor, and it “has to be in our world these days, it’s more of a discussion,” he said during his presentation at the 2020 Update in Nonneoplastic Hematology virtual conference.
The HERCULES trial Dr. Cataland helped conduct found a median time to platelet count normalization of 2.69 days when caplacizumab was started during plasma exchange versus 2.88 days for placebo; 12% of patients had a TTP recurrence while they continued caplacizumab for 30 days past their last exchange and were followed for an additional 28 days versus 38% randomized to placebo. Caplacizumab subjects needed an average of 5.8 days of plasma exchange versus 9.4 days in the placebo arm (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):335-46).
Based on the results, the Food and Drug Administration approved the agent for acquired TTP in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressives in Feb. 2019 for 30 days beyond the last plasma exchange, with up to 28 additional days if ADAMTS13 activity remains suppressed. Labeling notes a risk of severe bleeding.
“The data on refractory disease and mortality aren’t quite there yet, but there’s a suggestion [caplacizumab] might impact that as well,” Dr. Cataland said. In its recent TTP guidelines, the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis gave the agent only a conditional recommendation, in part because it’s backed up only by HERCULES and a phase 2 trial.
Also, the group noted that in the phase 2 study caplacizumab patients had a clinically and statistically significant increase in the number of relapses at 12 months: 31% versus 8% placebo. “Caplacizumab may leave patients prone to experience a later recurrence owing to the unresolved ADAMTS13 deficiency and inhibitors,” Dr. Cataland said.
“We do see some early recurrence” when caplacizumab is stopped, suggesting that when the agent’s “protective effect is removed, the risk is still there,” said Dr. Cataland, who was also an author on the ISTH guidelines, as well as the phase 2 trial.
It raises the question of how long patients should be kept on caplacizumab. There are few data on the issue, “but the consensus has been to stop caplacizumab when two consecutive ADAMTS13 measurements show 20% or greater activity,” or perhaps with one reading above 20% in a patient trending in the right direction. “With a bleeding complication, you might stop it sooner,” he said.
Dr. Cataland anticipates TTP management will eventually move away from plasma exchange to more directed therapies, including caplacizumab and perhaps recombinant ADAMTS13, which is in development.
There have been a few reports of TTP patients who refuse plasma exchange on religious grounds being successfully treated with caplacizumab. Dr. Cataland also noted a patient of his with relapsing TTP who didn’t want to be admitted yet again for plasma exchange and steroids at the start of a new episode.
“We managed her with caplacizumab and rituximab, and in a couple weeks she had recovered her ADAMTS13 activity and was able to stop the caplacizumab.” She was a motivated, knowledgeable person, “someone I trusted, so I was comfortable with the approach. I think that may be where we are headed in the future, hopefully,” he said.
Dr. Cataland disclosed research funding and consulting fees from Alexion, caplacizumab’s maker, Sanofi Genzyme, and Takeda,. The conference was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM 2020 UNNH
NHS England starts pilot trial of blood test for many cancers
“Early detection, particularly for hard-to-treat conditions like ovarian and pancreatic cancer, has the potential to save many lives,” said NHS Chief Executive Sir Simon Stevens in a statement.
The pilot trial will use the Galleri blood test, developed by Grail. Sir Stevens described the blood test as “promising” and said it could “be a game changer in cancer care, helping thousands more people to get successful treatment.”
However, some clinicians have expressed concerns over the potential for false-positive results with the test.
Results of a study of the Galleri blood test, published earlier this year, showed that the test detected 50 types of cancer with a specificity of 99.3% and a false positive rate of 0.7%.
It also correctly identified the originating tissue in 90% of cases. However, the sensitivity was lower, at 67%, for the 12 most common cancers, as reported at the time.
The senior author of that study, Michael Seiden, MD, PhD, president of the U.S. Oncology Network, The Woodlands, Tex., noted that it was not a screening study: the test had been used in patients with cancer and in healthy volunteers. He said the test “is intended to be complementary to, and not replace, existing guideline-recommended screening tests and might provide new avenues of investigation for cancers that don’t currently have screening tests.”
The Galleri test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the arrangement of methyl groups on circulating cell-free DNA in a blood sample.
Several other blood tests for cancer are under development, including the CancerSEEK test, which has been reported to be able to identify eight common cancers. It measures circulating tumor DNA from 16 genes and eight protein biomarkers and then uses machine learning to analyze the data.
Improving early detection rates
The pilot trial of the blood test is due to start in mid-2021 and will involve 165,000 people.
The trial will include 140,000 individuals aged 50-79 years who were identified through their health records and who have no cancer symptoms. They will undergo blood tests annually for 3 years and will be referred for investigation if a test result is positive.
A second group will include 25,000 people with potential cancer symptoms. These patients will be offered the blood test to speed up their diagnosis after referral to a hospital via the normal channels.
The results of the pilot are expected in 2023. If successful, the test will be rolled out to 1 million individuals from 2024 to 2025.
The pilot trial is part of the NHS Long Term Plan, which aims to increase early detection of cancer. At present, around half of cancers in England are diagnosed in stage I or II; the NHS aims to increase this to 75% by 2028.
“The NHS has set itself an ambitious target,” commented Peter Johnson, MD, PhD, national clinical director for cancer at NHS England and Improvement.
“Tests like this may help us get there far faster, and I am excited to see how this cutting-edge technology will work out as we test it in clinics across the NHS,” he added.
Lord David Prior, chair of NHS England, noted that almost 200,000 people die from cancer in the United Kingdom every year and that “many of these people are diagnosed too late for treatment to be effective.
“This collaboration between the NHS and Grail offers the chance for a wide range of cancers to be diagnosed much earlier and could fundamentally change the outlook for people with cancer,” he said.
However, some clinicians raised potential concerns.
Stephen Duffy, PhD, Center for Cancer Prevention, Queen Mary University of London, described the pilot as “very exciting,” but cautioned: “We will need to find out just how early the test detects cancers and whether it can it be used in a way which minimizes anxiety from false positives.”
Yong-Jie Lu, MD, PhD, also at Queen Mary University of London, said: “It is not clear how early it aims to catch cancer. For a cancer screen test, it needs very high specificity (>99%), otherwise it may end up in a similar situation as the PSA [prostate-specific antigen] test for prostate cancer, or even worse.”
Mangesh Thorat, MD, Cancer Prevention Trials Unit, King’s College London, warned: “It is likely that for every testing round ... there will be about 1,000 false-positive results, and the test may not be able to pinpoint the location of cancer in 3%-4% of those with a true positive result, necessitating a range of imaging and other investigations in these participants.”
No funding for the study has been declared. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Early detection, particularly for hard-to-treat conditions like ovarian and pancreatic cancer, has the potential to save many lives,” said NHS Chief Executive Sir Simon Stevens in a statement.
The pilot trial will use the Galleri blood test, developed by Grail. Sir Stevens described the blood test as “promising” and said it could “be a game changer in cancer care, helping thousands more people to get successful treatment.”
However, some clinicians have expressed concerns over the potential for false-positive results with the test.
Results of a study of the Galleri blood test, published earlier this year, showed that the test detected 50 types of cancer with a specificity of 99.3% and a false positive rate of 0.7%.
It also correctly identified the originating tissue in 90% of cases. However, the sensitivity was lower, at 67%, for the 12 most common cancers, as reported at the time.
The senior author of that study, Michael Seiden, MD, PhD, president of the U.S. Oncology Network, The Woodlands, Tex., noted that it was not a screening study: the test had been used in patients with cancer and in healthy volunteers. He said the test “is intended to be complementary to, and not replace, existing guideline-recommended screening tests and might provide new avenues of investigation for cancers that don’t currently have screening tests.”
The Galleri test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the arrangement of methyl groups on circulating cell-free DNA in a blood sample.
Several other blood tests for cancer are under development, including the CancerSEEK test, which has been reported to be able to identify eight common cancers. It measures circulating tumor DNA from 16 genes and eight protein biomarkers and then uses machine learning to analyze the data.
Improving early detection rates
The pilot trial of the blood test is due to start in mid-2021 and will involve 165,000 people.
The trial will include 140,000 individuals aged 50-79 years who were identified through their health records and who have no cancer symptoms. They will undergo blood tests annually for 3 years and will be referred for investigation if a test result is positive.
A second group will include 25,000 people with potential cancer symptoms. These patients will be offered the blood test to speed up their diagnosis after referral to a hospital via the normal channels.
The results of the pilot are expected in 2023. If successful, the test will be rolled out to 1 million individuals from 2024 to 2025.
The pilot trial is part of the NHS Long Term Plan, which aims to increase early detection of cancer. At present, around half of cancers in England are diagnosed in stage I or II; the NHS aims to increase this to 75% by 2028.
“The NHS has set itself an ambitious target,” commented Peter Johnson, MD, PhD, national clinical director for cancer at NHS England and Improvement.
“Tests like this may help us get there far faster, and I am excited to see how this cutting-edge technology will work out as we test it in clinics across the NHS,” he added.
Lord David Prior, chair of NHS England, noted that almost 200,000 people die from cancer in the United Kingdom every year and that “many of these people are diagnosed too late for treatment to be effective.
“This collaboration between the NHS and Grail offers the chance for a wide range of cancers to be diagnosed much earlier and could fundamentally change the outlook for people with cancer,” he said.
However, some clinicians raised potential concerns.
Stephen Duffy, PhD, Center for Cancer Prevention, Queen Mary University of London, described the pilot as “very exciting,” but cautioned: “We will need to find out just how early the test detects cancers and whether it can it be used in a way which minimizes anxiety from false positives.”
Yong-Jie Lu, MD, PhD, also at Queen Mary University of London, said: “It is not clear how early it aims to catch cancer. For a cancer screen test, it needs very high specificity (>99%), otherwise it may end up in a similar situation as the PSA [prostate-specific antigen] test for prostate cancer, or even worse.”
Mangesh Thorat, MD, Cancer Prevention Trials Unit, King’s College London, warned: “It is likely that for every testing round ... there will be about 1,000 false-positive results, and the test may not be able to pinpoint the location of cancer in 3%-4% of those with a true positive result, necessitating a range of imaging and other investigations in these participants.”
No funding for the study has been declared. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Early detection, particularly for hard-to-treat conditions like ovarian and pancreatic cancer, has the potential to save many lives,” said NHS Chief Executive Sir Simon Stevens in a statement.
The pilot trial will use the Galleri blood test, developed by Grail. Sir Stevens described the blood test as “promising” and said it could “be a game changer in cancer care, helping thousands more people to get successful treatment.”
However, some clinicians have expressed concerns over the potential for false-positive results with the test.
Results of a study of the Galleri blood test, published earlier this year, showed that the test detected 50 types of cancer with a specificity of 99.3% and a false positive rate of 0.7%.
It also correctly identified the originating tissue in 90% of cases. However, the sensitivity was lower, at 67%, for the 12 most common cancers, as reported at the time.
The senior author of that study, Michael Seiden, MD, PhD, president of the U.S. Oncology Network, The Woodlands, Tex., noted that it was not a screening study: the test had been used in patients with cancer and in healthy volunteers. He said the test “is intended to be complementary to, and not replace, existing guideline-recommended screening tests and might provide new avenues of investigation for cancers that don’t currently have screening tests.”
The Galleri test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the arrangement of methyl groups on circulating cell-free DNA in a blood sample.
Several other blood tests for cancer are under development, including the CancerSEEK test, which has been reported to be able to identify eight common cancers. It measures circulating tumor DNA from 16 genes and eight protein biomarkers and then uses machine learning to analyze the data.
Improving early detection rates
The pilot trial of the blood test is due to start in mid-2021 and will involve 165,000 people.
The trial will include 140,000 individuals aged 50-79 years who were identified through their health records and who have no cancer symptoms. They will undergo blood tests annually for 3 years and will be referred for investigation if a test result is positive.
A second group will include 25,000 people with potential cancer symptoms. These patients will be offered the blood test to speed up their diagnosis after referral to a hospital via the normal channels.
The results of the pilot are expected in 2023. If successful, the test will be rolled out to 1 million individuals from 2024 to 2025.
The pilot trial is part of the NHS Long Term Plan, which aims to increase early detection of cancer. At present, around half of cancers in England are diagnosed in stage I or II; the NHS aims to increase this to 75% by 2028.
“The NHS has set itself an ambitious target,” commented Peter Johnson, MD, PhD, national clinical director for cancer at NHS England and Improvement.
“Tests like this may help us get there far faster, and I am excited to see how this cutting-edge technology will work out as we test it in clinics across the NHS,” he added.
Lord David Prior, chair of NHS England, noted that almost 200,000 people die from cancer in the United Kingdom every year and that “many of these people are diagnosed too late for treatment to be effective.
“This collaboration between the NHS and Grail offers the chance for a wide range of cancers to be diagnosed much earlier and could fundamentally change the outlook for people with cancer,” he said.
However, some clinicians raised potential concerns.
Stephen Duffy, PhD, Center for Cancer Prevention, Queen Mary University of London, described the pilot as “very exciting,” but cautioned: “We will need to find out just how early the test detects cancers and whether it can it be used in a way which minimizes anxiety from false positives.”
Yong-Jie Lu, MD, PhD, also at Queen Mary University of London, said: “It is not clear how early it aims to catch cancer. For a cancer screen test, it needs very high specificity (>99%), otherwise it may end up in a similar situation as the PSA [prostate-specific antigen] test for prostate cancer, or even worse.”
Mangesh Thorat, MD, Cancer Prevention Trials Unit, King’s College London, warned: “It is likely that for every testing round ... there will be about 1,000 false-positive results, and the test may not be able to pinpoint the location of cancer in 3%-4% of those with a true positive result, necessitating a range of imaging and other investigations in these participants.”
No funding for the study has been declared. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.