User login
Bullous Pemphigoid Masquerading as a Prosthesis Allergy
To the Editor:
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune bullous dermatosis characterized by tense subepidermal blisters. It primarily affects older individuals who typically report pruritus in the affected area. Subepidermal blisters are caused by a humoral and cellular autoimmune attack directed against 2 BP antigens—BP180 and BP230—which are 2 critical components of the hemidesmosome whose primary function is to anchor the epidermis to the underlying dermis. Although tense bullae typically prompt immediate consideration of BP in the differential diagnosis, early disease often is characterized by urticarial plaques that require a high degree of suspicion to make the appropriate diagnosis. Locus minoris resistentiae is a term used to describe the phenomenon of skin disease occurring at the point of least resistance.1
A 79-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus, peptic ulcer disease, and hypertension was referred to the dermatology clinic due to concern for allergic contact dermatitis limited to the area of and adjacent to a well-healed surgical wound. History and examination revealed that the patient had sustained a left femoral neck fracture 10 months prior to presentation that required closed reduction and surgical pinning. The surgical site healed well postoperatively; however, 7 months after surgery, she began to develop edema and erythema within and immediately adjacent to the surgical scar. She subsequently developed areas of superficial erosion within the erythema and was evaluated by her surgeon who was concerned for suture granuloma. Superficial wound debridement of the area was performed without improvement. Approximately 9 months after surgery, the patient developed bullae along the old surgical site, which raised concern for an allergic reaction to the implanted screws. Orthopedics elected to remove the hardware but also sent intraoperative tissue for pathologic examination, which revealed subepidermal bullae containing eosinophils and neutrophils, most consistent with a bullous drug eruption. During the ensuing weeks after hardware removal, the plaque spread along the old surgical wound, and several bullous lesions began to appear. The patient’s primary care physician became concerned for allergic contact dermatitis, possibly to the surgical scrub employed during hardware removal. He prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% and referred the patient to dermatology.
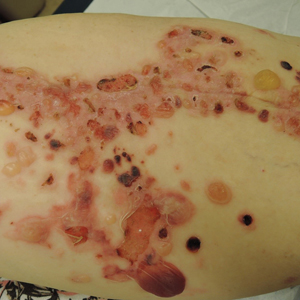
Upon presentation to dermatology, the patient noted stinging pain and intense pruritus of the affected area. Examination revealed a pink edematous plaque distributed along a well-healed surgical wound (Figure). Numerous fluid-filled tense bullae were superimposed on this plaque as well as areas of superficial erosion with serum crust. An expanded examination revealed similar smaller lesions on the upper arms, inner thighs, and lateral breasts. A 4-mm punch biopsy of lesional and perilesional skin was sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence, which demonstrated a subepidermal bullous dermatosis with a predominance of neutrophilic inflammation as well as a band of linear IgG deposition at the dermal-epidermal junction. The patient was diagnosed with BP exhibiting a locus minoris resistentiae phenomenon within the surgical site. She was started on prednisone 1 mg/kg daily and doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and demonstrated rapid improvement.

Although the tense bullae seen in well-developed BP are fairly characteristic, the prodromal phase of this disease can present with urticarial plaques that are nonspecific. This progression is well described, but our case demonstrates the difficulty of considering BP when a patient presents with an urticarial plaque. As lesions progress to the bullous phase, they may be inappropriately diagnosed as allergic contact dermatitis, an error that may lead to unnecessary interventions (eg, removal of an implicated prosthesis). This case is a reminder that not all cutaneous eruptions in and around postsurgical scars are allergic in nature.
This case also depicts BP appearing in the locus minoris resistentiae, a well-healed surgical wound in our patient. Although many diseases have been shown to exhibit this type of isomorphic response, this phenomenon may pose diagnostic and management conundrums. Locus minoris resistentiae has been reported in many different diseases, both cutaneous and otherwise, but there likely are distinct disease- and case-specific mechanisms via which this occurs. Local phenomena reported to trigger BP include contact dermatitis, vaccination, radiation therapy, phototherapy, infection, and surgery.2 We suspect that the mechanism of locus minoris resistentiae in our patient was disruption of the architecture of the dermal-epidermal basement membrane zone due to surgical trauma. Disruption of this architecture may have resulted in exposure of previously occult antigens, recognition by T cells, T-cell stimulation of autoantibody production by B cells, binding of autoantibodies to BP180, complement deposition, recruitment of inflammatory cells, release of proteinases, and degradation of BP180 and extracellular matrix proteins.2
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Russo T, et al. Locus minoris resistentiae: an old but still valid way of thinking in medicine. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:553-556.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Brancaccio G, et al. Bullous pemphigoid: etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing factors: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:391-399.
To the Editor:
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune bullous dermatosis characterized by tense subepidermal blisters. It primarily affects older individuals who typically report pruritus in the affected area. Subepidermal blisters are caused by a humoral and cellular autoimmune attack directed against 2 BP antigens—BP180 and BP230—which are 2 critical components of the hemidesmosome whose primary function is to anchor the epidermis to the underlying dermis. Although tense bullae typically prompt immediate consideration of BP in the differential diagnosis, early disease often is characterized by urticarial plaques that require a high degree of suspicion to make the appropriate diagnosis. Locus minoris resistentiae is a term used to describe the phenomenon of skin disease occurring at the point of least resistance.1
A 79-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus, peptic ulcer disease, and hypertension was referred to the dermatology clinic due to concern for allergic contact dermatitis limited to the area of and adjacent to a well-healed surgical wound. History and examination revealed that the patient had sustained a left femoral neck fracture 10 months prior to presentation that required closed reduction and surgical pinning. The surgical site healed well postoperatively; however, 7 months after surgery, she began to develop edema and erythema within and immediately adjacent to the surgical scar. She subsequently developed areas of superficial erosion within the erythema and was evaluated by her surgeon who was concerned for suture granuloma. Superficial wound debridement of the area was performed without improvement. Approximately 9 months after surgery, the patient developed bullae along the old surgical site, which raised concern for an allergic reaction to the implanted screws. Orthopedics elected to remove the hardware but also sent intraoperative tissue for pathologic examination, which revealed subepidermal bullae containing eosinophils and neutrophils, most consistent with a bullous drug eruption. During the ensuing weeks after hardware removal, the plaque spread along the old surgical wound, and several bullous lesions began to appear. The patient’s primary care physician became concerned for allergic contact dermatitis, possibly to the surgical scrub employed during hardware removal. He prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% and referred the patient to dermatology.
Upon presentation to dermatology, the patient noted stinging pain and intense pruritus of the affected area. Examination revealed a pink edematous plaque distributed along a well-healed surgical wound (Figure). Numerous fluid-filled tense bullae were superimposed on this plaque as well as areas of superficial erosion with serum crust. An expanded examination revealed similar smaller lesions on the upper arms, inner thighs, and lateral breasts. A 4-mm punch biopsy of lesional and perilesional skin was sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence, which demonstrated a subepidermal bullous dermatosis with a predominance of neutrophilic inflammation as well as a band of linear IgG deposition at the dermal-epidermal junction. The patient was diagnosed with BP exhibiting a locus minoris resistentiae phenomenon within the surgical site. She was started on prednisone 1 mg/kg daily and doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and demonstrated rapid improvement.

Although the tense bullae seen in well-developed BP are fairly characteristic, the prodromal phase of this disease can present with urticarial plaques that are nonspecific. This progression is well described, but our case demonstrates the difficulty of considering BP when a patient presents with an urticarial plaque. As lesions progress to the bullous phase, they may be inappropriately diagnosed as allergic contact dermatitis, an error that may lead to unnecessary interventions (eg, removal of an implicated prosthesis). This case is a reminder that not all cutaneous eruptions in and around postsurgical scars are allergic in nature.
This case also depicts BP appearing in the locus minoris resistentiae, a well-healed surgical wound in our patient. Although many diseases have been shown to exhibit this type of isomorphic response, this phenomenon may pose diagnostic and management conundrums. Locus minoris resistentiae has been reported in many different diseases, both cutaneous and otherwise, but there likely are distinct disease- and case-specific mechanisms via which this occurs. Local phenomena reported to trigger BP include contact dermatitis, vaccination, radiation therapy, phototherapy, infection, and surgery.2 We suspect that the mechanism of locus minoris resistentiae in our patient was disruption of the architecture of the dermal-epidermal basement membrane zone due to surgical trauma. Disruption of this architecture may have resulted in exposure of previously occult antigens, recognition by T cells, T-cell stimulation of autoantibody production by B cells, binding of autoantibodies to BP180, complement deposition, recruitment of inflammatory cells, release of proteinases, and degradation of BP180 and extracellular matrix proteins.2
To the Editor:
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune bullous dermatosis characterized by tense subepidermal blisters. It primarily affects older individuals who typically report pruritus in the affected area. Subepidermal blisters are caused by a humoral and cellular autoimmune attack directed against 2 BP antigens—BP180 and BP230—which are 2 critical components of the hemidesmosome whose primary function is to anchor the epidermis to the underlying dermis. Although tense bullae typically prompt immediate consideration of BP in the differential diagnosis, early disease often is characterized by urticarial plaques that require a high degree of suspicion to make the appropriate diagnosis. Locus minoris resistentiae is a term used to describe the phenomenon of skin disease occurring at the point of least resistance.1
A 79-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus, peptic ulcer disease, and hypertension was referred to the dermatology clinic due to concern for allergic contact dermatitis limited to the area of and adjacent to a well-healed surgical wound. History and examination revealed that the patient had sustained a left femoral neck fracture 10 months prior to presentation that required closed reduction and surgical pinning. The surgical site healed well postoperatively; however, 7 months after surgery, she began to develop edema and erythema within and immediately adjacent to the surgical scar. She subsequently developed areas of superficial erosion within the erythema and was evaluated by her surgeon who was concerned for suture granuloma. Superficial wound debridement of the area was performed without improvement. Approximately 9 months after surgery, the patient developed bullae along the old surgical site, which raised concern for an allergic reaction to the implanted screws. Orthopedics elected to remove the hardware but also sent intraoperative tissue for pathologic examination, which revealed subepidermal bullae containing eosinophils and neutrophils, most consistent with a bullous drug eruption. During the ensuing weeks after hardware removal, the plaque spread along the old surgical wound, and several bullous lesions began to appear. The patient’s primary care physician became concerned for allergic contact dermatitis, possibly to the surgical scrub employed during hardware removal. He prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% and referred the patient to dermatology.
Upon presentation to dermatology, the patient noted stinging pain and intense pruritus of the affected area. Examination revealed a pink edematous plaque distributed along a well-healed surgical wound (Figure). Numerous fluid-filled tense bullae were superimposed on this plaque as well as areas of superficial erosion with serum crust. An expanded examination revealed similar smaller lesions on the upper arms, inner thighs, and lateral breasts. A 4-mm punch biopsy of lesional and perilesional skin was sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence, which demonstrated a subepidermal bullous dermatosis with a predominance of neutrophilic inflammation as well as a band of linear IgG deposition at the dermal-epidermal junction. The patient was diagnosed with BP exhibiting a locus minoris resistentiae phenomenon within the surgical site. She was started on prednisone 1 mg/kg daily and doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and demonstrated rapid improvement.

Although the tense bullae seen in well-developed BP are fairly characteristic, the prodromal phase of this disease can present with urticarial plaques that are nonspecific. This progression is well described, but our case demonstrates the difficulty of considering BP when a patient presents with an urticarial plaque. As lesions progress to the bullous phase, they may be inappropriately diagnosed as allergic contact dermatitis, an error that may lead to unnecessary interventions (eg, removal of an implicated prosthesis). This case is a reminder that not all cutaneous eruptions in and around postsurgical scars are allergic in nature.
This case also depicts BP appearing in the locus minoris resistentiae, a well-healed surgical wound in our patient. Although many diseases have been shown to exhibit this type of isomorphic response, this phenomenon may pose diagnostic and management conundrums. Locus minoris resistentiae has been reported in many different diseases, both cutaneous and otherwise, but there likely are distinct disease- and case-specific mechanisms via which this occurs. Local phenomena reported to trigger BP include contact dermatitis, vaccination, radiation therapy, phototherapy, infection, and surgery.2 We suspect that the mechanism of locus minoris resistentiae in our patient was disruption of the architecture of the dermal-epidermal basement membrane zone due to surgical trauma. Disruption of this architecture may have resulted in exposure of previously occult antigens, recognition by T cells, T-cell stimulation of autoantibody production by B cells, binding of autoantibodies to BP180, complement deposition, recruitment of inflammatory cells, release of proteinases, and degradation of BP180 and extracellular matrix proteins.2
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Russo T, et al. Locus minoris resistentiae: an old but still valid way of thinking in medicine. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:553-556.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Brancaccio G, et al. Bullous pemphigoid: etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing factors: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:391-399.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Russo T, et al. Locus minoris resistentiae: an old but still valid way of thinking in medicine. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:553-556.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Brancaccio G, et al. Bullous pemphigoid: etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing factors: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:391-399.
Practice Points
- Bullous pemphigoid frequently presents with urticarial plaques without classic tense blisters in the early phase of disease.
- The phenomenon of locus minoris resistentiae can lead to the presentation of bullous pemphigoid in locations traumatized by surgery.
- Bullous pemphigoid can present as urticarial plaques at surgery sites mimicking allergic contact dermatitis or reaction to surgical sutures or hardware.
Type 2 diabetes remission can happen naturally in 1 in 20
Roughly 5% of adults with type 2 diabetes achieve remission of their disease, often unbeknownst to the patient and without aggressive weight-loss interventions, according to a new analysis of data from more than 160,000 people in a national diabetes registry in Scotland.
“One of our key new findings is that a reasonably large proportion of people [with type 2 diabetes] were able to achieve remission in routine care, without undergoing bariatric surgery and prior to the introduction of very-low-calorie interventions in routine care,” said Mireille Captieux, MBChB, lead author of the report, in an interview.
The findings “support previous reports that weight loss is associated with type 2 diabetes remission,” said Dr. Captieux, a diabetes researcher at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
In her analysis, two of the strongest correlates of remission related to weight loss.
First, a history of bariatric surgery, which included a scant 488 people (0.3% of the study cohort), was associated with a 13-fold increase in the rate of remission, compared with those who did not undergo bariatric surgery. Second, weight loss of 15 kg (33 lb) or more at the time of remission detection in 2019, in comparison with their weight at initial diabetes diagnosis, was linked with a greater than fourfold increase in the rate of remission, compared with those who did not have this amount of weight loss.
But “even losing a small amount of weight increased the chances of remission,” highlights Dr. Captieux. “This finding offers a counterbalance to the pessimistic assumption that almost all people find it very difficult to lose weight.”
Hopeful message, but which people achieve diabetes remission?
“What’s encouraging here is that you have people who probably did not do anything radical, and yet they went into remission. The next step is to find out who these people are and what they did to go into remission,” commented Julia Lawton, PhD, a professor of health and social science at the University of Edinburgh whose research focuses on how patients with diabetes manage their disorder.
“If we can understand who the patients are who can achieve remission without taking extreme measures, it could help people in the health professions get beyond their presumptions about who is, or is not, a good candidate for achieving diabetes remission,” said Dr. Lawton, who was not involved with the study.
The message from this study is “very hopeful,” Dr. Lawton said in an interview. “How can we make this opportunity [for diabetes remission] available to more people? What can we learn from these patients that we could then apply to other patients?”
Dr. Captieux agrees. Given her findings, an important next step is to find out more about the population in remission to better understand “their perspectives on the challenges and benefits of supporting weight loss.
“Obesity is a complex issue, and therefore weight loss interventions that target individual actions and behaviors are much more likely to be effective if they are accompanied by multiple interventions at different levels,” Dr. Captieux said.
In addition, “more evidence is needed to assess the sustainability of diabetes remission and the effect of different durations of remission for a clinically relevant definition.”
Duration, definition of diabetes remission
Dr. Captieux noted that the new international consensus definition of type 2 diabetes remission – which specifies a minimum 3-month duration of glycemic control to qualify as remission – means that people with diabetes “may frequently oscillate” between remission and active disease.
This makes it important to better define the effect of duration of diabetes remission regarding various diabetes complications.
Another issue raised by the new findings is the importance of distinguishing people who lose weight because of a healthier diet and increased activity from those who lose weight because of chronic illness or frailty that’s followed by long-term adverse outcomes.
If these two populations are not distinguished in an observational cohort study – such as the one run by Dr. Captieux and her associates – then the people with chronic illness might appear to have worse outcomes following diabetes remission.
Dr. Captieux and her coauthors used data collected in the Scottish Care Information–Diabetes registry, which includes almost all people diagnosed with diabetes in Scotland. They focused on people with diabetes who had first been diagnosed with diabetes during 2004-2018, who were at least 30 years old at the time of their initial diagnosis, and who had received care in the national health system during 2019.
This yielded a study cohort of 162,316 people, of whom 7,710 (4.8%) were identified by the researchers as being in remission in 2019.
Patients in remission were defined as those whose hemoglobin A1c level was less than 6.5% at their index reading in 2019 and whose A1c level could be documented as being lower than 6.5% for at least 1 year prior to the 2019 measurement.
In a primary logistic regression analysis, the authors identified five variables that were significantly linked with remission: age of at least 65 years (the association was even stronger for age older than 75 years), a lower A1c level at the time of initial diabetes diagnosis, weight loss, prior bariatric surgery, and no prior treatment with a glucose-lowering therapy.
The strongest association was with having had no prior treatment with a glucose-lowering therapy in 2019. People who met this criterion were nearly 15 times more likely to be in remission in 2019, compared with those who had received at least one of these agents.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Captieux and Dr. Lawton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Roughly 5% of adults with type 2 diabetes achieve remission of their disease, often unbeknownst to the patient and without aggressive weight-loss interventions, according to a new analysis of data from more than 160,000 people in a national diabetes registry in Scotland.
“One of our key new findings is that a reasonably large proportion of people [with type 2 diabetes] were able to achieve remission in routine care, without undergoing bariatric surgery and prior to the introduction of very-low-calorie interventions in routine care,” said Mireille Captieux, MBChB, lead author of the report, in an interview.
The findings “support previous reports that weight loss is associated with type 2 diabetes remission,” said Dr. Captieux, a diabetes researcher at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
In her analysis, two of the strongest correlates of remission related to weight loss.
First, a history of bariatric surgery, which included a scant 488 people (0.3% of the study cohort), was associated with a 13-fold increase in the rate of remission, compared with those who did not undergo bariatric surgery. Second, weight loss of 15 kg (33 lb) or more at the time of remission detection in 2019, in comparison with their weight at initial diabetes diagnosis, was linked with a greater than fourfold increase in the rate of remission, compared with those who did not have this amount of weight loss.
But “even losing a small amount of weight increased the chances of remission,” highlights Dr. Captieux. “This finding offers a counterbalance to the pessimistic assumption that almost all people find it very difficult to lose weight.”
Hopeful message, but which people achieve diabetes remission?
“What’s encouraging here is that you have people who probably did not do anything radical, and yet they went into remission. The next step is to find out who these people are and what they did to go into remission,” commented Julia Lawton, PhD, a professor of health and social science at the University of Edinburgh whose research focuses on how patients with diabetes manage their disorder.
“If we can understand who the patients are who can achieve remission without taking extreme measures, it could help people in the health professions get beyond their presumptions about who is, or is not, a good candidate for achieving diabetes remission,” said Dr. Lawton, who was not involved with the study.
The message from this study is “very hopeful,” Dr. Lawton said in an interview. “How can we make this opportunity [for diabetes remission] available to more people? What can we learn from these patients that we could then apply to other patients?”
Dr. Captieux agrees. Given her findings, an important next step is to find out more about the population in remission to better understand “their perspectives on the challenges and benefits of supporting weight loss.
“Obesity is a complex issue, and therefore weight loss interventions that target individual actions and behaviors are much more likely to be effective if they are accompanied by multiple interventions at different levels,” Dr. Captieux said.
In addition, “more evidence is needed to assess the sustainability of diabetes remission and the effect of different durations of remission for a clinically relevant definition.”
Duration, definition of diabetes remission
Dr. Captieux noted that the new international consensus definition of type 2 diabetes remission – which specifies a minimum 3-month duration of glycemic control to qualify as remission – means that people with diabetes “may frequently oscillate” between remission and active disease.
This makes it important to better define the effect of duration of diabetes remission regarding various diabetes complications.
Another issue raised by the new findings is the importance of distinguishing people who lose weight because of a healthier diet and increased activity from those who lose weight because of chronic illness or frailty that’s followed by long-term adverse outcomes.
If these two populations are not distinguished in an observational cohort study – such as the one run by Dr. Captieux and her associates – then the people with chronic illness might appear to have worse outcomes following diabetes remission.
Dr. Captieux and her coauthors used data collected in the Scottish Care Information–Diabetes registry, which includes almost all people diagnosed with diabetes in Scotland. They focused on people with diabetes who had first been diagnosed with diabetes during 2004-2018, who were at least 30 years old at the time of their initial diagnosis, and who had received care in the national health system during 2019.
This yielded a study cohort of 162,316 people, of whom 7,710 (4.8%) were identified by the researchers as being in remission in 2019.
Patients in remission were defined as those whose hemoglobin A1c level was less than 6.5% at their index reading in 2019 and whose A1c level could be documented as being lower than 6.5% for at least 1 year prior to the 2019 measurement.
In a primary logistic regression analysis, the authors identified five variables that were significantly linked with remission: age of at least 65 years (the association was even stronger for age older than 75 years), a lower A1c level at the time of initial diabetes diagnosis, weight loss, prior bariatric surgery, and no prior treatment with a glucose-lowering therapy.
The strongest association was with having had no prior treatment with a glucose-lowering therapy in 2019. People who met this criterion were nearly 15 times more likely to be in remission in 2019, compared with those who had received at least one of these agents.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Captieux and Dr. Lawton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Roughly 5% of adults with type 2 diabetes achieve remission of their disease, often unbeknownst to the patient and without aggressive weight-loss interventions, according to a new analysis of data from more than 160,000 people in a national diabetes registry in Scotland.
“One of our key new findings is that a reasonably large proportion of people [with type 2 diabetes] were able to achieve remission in routine care, without undergoing bariatric surgery and prior to the introduction of very-low-calorie interventions in routine care,” said Mireille Captieux, MBChB, lead author of the report, in an interview.
The findings “support previous reports that weight loss is associated with type 2 diabetes remission,” said Dr. Captieux, a diabetes researcher at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland).
In her analysis, two of the strongest correlates of remission related to weight loss.
First, a history of bariatric surgery, which included a scant 488 people (0.3% of the study cohort), was associated with a 13-fold increase in the rate of remission, compared with those who did not undergo bariatric surgery. Second, weight loss of 15 kg (33 lb) or more at the time of remission detection in 2019, in comparison with their weight at initial diabetes diagnosis, was linked with a greater than fourfold increase in the rate of remission, compared with those who did not have this amount of weight loss.
But “even losing a small amount of weight increased the chances of remission,” highlights Dr. Captieux. “This finding offers a counterbalance to the pessimistic assumption that almost all people find it very difficult to lose weight.”
Hopeful message, but which people achieve diabetes remission?
“What’s encouraging here is that you have people who probably did not do anything radical, and yet they went into remission. The next step is to find out who these people are and what they did to go into remission,” commented Julia Lawton, PhD, a professor of health and social science at the University of Edinburgh whose research focuses on how patients with diabetes manage their disorder.
“If we can understand who the patients are who can achieve remission without taking extreme measures, it could help people in the health professions get beyond their presumptions about who is, or is not, a good candidate for achieving diabetes remission,” said Dr. Lawton, who was not involved with the study.
The message from this study is “very hopeful,” Dr. Lawton said in an interview. “How can we make this opportunity [for diabetes remission] available to more people? What can we learn from these patients that we could then apply to other patients?”
Dr. Captieux agrees. Given her findings, an important next step is to find out more about the population in remission to better understand “their perspectives on the challenges and benefits of supporting weight loss.
“Obesity is a complex issue, and therefore weight loss interventions that target individual actions and behaviors are much more likely to be effective if they are accompanied by multiple interventions at different levels,” Dr. Captieux said.
In addition, “more evidence is needed to assess the sustainability of diabetes remission and the effect of different durations of remission for a clinically relevant definition.”
Duration, definition of diabetes remission
Dr. Captieux noted that the new international consensus definition of type 2 diabetes remission – which specifies a minimum 3-month duration of glycemic control to qualify as remission – means that people with diabetes “may frequently oscillate” between remission and active disease.
This makes it important to better define the effect of duration of diabetes remission regarding various diabetes complications.
Another issue raised by the new findings is the importance of distinguishing people who lose weight because of a healthier diet and increased activity from those who lose weight because of chronic illness or frailty that’s followed by long-term adverse outcomes.
If these two populations are not distinguished in an observational cohort study – such as the one run by Dr. Captieux and her associates – then the people with chronic illness might appear to have worse outcomes following diabetes remission.
Dr. Captieux and her coauthors used data collected in the Scottish Care Information–Diabetes registry, which includes almost all people diagnosed with diabetes in Scotland. They focused on people with diabetes who had first been diagnosed with diabetes during 2004-2018, who were at least 30 years old at the time of their initial diagnosis, and who had received care in the national health system during 2019.
This yielded a study cohort of 162,316 people, of whom 7,710 (4.8%) were identified by the researchers as being in remission in 2019.
Patients in remission were defined as those whose hemoglobin A1c level was less than 6.5% at their index reading in 2019 and whose A1c level could be documented as being lower than 6.5% for at least 1 year prior to the 2019 measurement.
In a primary logistic regression analysis, the authors identified five variables that were significantly linked with remission: age of at least 65 years (the association was even stronger for age older than 75 years), a lower A1c level at the time of initial diabetes diagnosis, weight loss, prior bariatric surgery, and no prior treatment with a glucose-lowering therapy.
The strongest association was with having had no prior treatment with a glucose-lowering therapy in 2019. People who met this criterion were nearly 15 times more likely to be in remission in 2019, compared with those who had received at least one of these agents.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Captieux and Dr. Lawton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Secukinumab beat placebo for sustained remission of giant cell arteritis after steroid taper
Patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) remained in remission longer when they took secukinumab (Cosentyx) during a 6-month–long taper of glucocorticoids, a monoclonal antibody drug that inhibits interleukin-17A, compared with placebo, according to phase 2 trial results presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The mainstay of GCA treatment is glucocorticoids, although IL-6 inhibition with tocilizumab (Actemra) has recently become another option, Jens Thiel, MD, vice director of the Clinic for Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at University Hospital Freiburg (Germany), told attendees.
“Secukinumab has shown significant improvements in the signs and symptoms of IL-17A-driven medical conditions such as psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and it has a very favorable long-term safety profile,” Dr. Thiel said. “There is experimental and preclinical data that points toward the role of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis, and therefore IL-17A inhibition, blocking vascular inflammation, is potentially a new therapeutic target for GCA.”
Christopher R. Palma, MD, ScM, assistant professor in the division of allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), said in an interview that the trial’s preliminary findings were exciting because they suggest that IL-17A is likely to be an effective strategy for treating GCA. ”This aligns with known pathophysiology of GCA, where IL-17A is an important part of pathology of disease,” Dr. Palma said.
In the randomized, controlled, double-blind trial, researchers enrolled 52 patients, all at least 50 years old, who had never taken a biologic for GCA. Most of the participants (80.8%) had new-onset GCA, diagnosed within the previous 6 weeks, and 19.2% had relapsing GCA. The participants received either 300 mg of secukinumab or placebo every week for 5 weeks, and then every 4 weeks for 48 total weeks. At baseline, all participants also began a 26-week taper of prednisolone from a dose of 25-60 mg/day at baseline to 0 at week 27. The primary endpoint was the proportion of participants in sustained remission through week 28.
Among the 27 participants taking secukinumab and the 25 taking placebo, 37 completed the study treatment (71%). At week 28, those still in remission included 70.1% of participants taking secukinumab and 20.3% of those taking placebo (odds ratio [OR], 9.3). Through week 52, the proportion of participants in remission included 59.3% of the secukinumab group and 8% of the placebo group.
Determination of flare was based on signs and symptoms along with a C-reactive protein level of more than 10 mg/L or an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Dr. Thiel did not provide more details on these parameters or on how flares were determined, but reported that participants taking secukinumab did not reach a median time to first flare, compared to a median 197 days in the placebo group.
All the participants taking secukinumab and 96% of those taking placebo experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, with serious adverse events occurring in 22.2% of those taking secukinumab and 44% of those taking placebo. Two patients in each group discontinued the treatment because of adverse events, and one participant in each group died from causes determined to be unrelated to the treatment.
The trial’s effect size was large, but Dr. Palma noted that the study’s generalizability is limited by prednisolone tapering in the placebo arm because that’s not reflective of most clinical practice for treatment of GCA.
“We would be unlikely to mimic this trial design as we know rates of disease flare and recurrence are high without long-term therapy of some kind,” Dr. Palma said. ”The real challenge will be in assessing relative benefit and risk among many possible therapies and how IL-17A–directed therapies fit in. Obviously, a head-to-head trial design would help answer many of these questions.”
Dr. Palma said it’s too early to recommend widespread off-label use of secukinumab for GCA, but he would encourage his patients with GCA to consider participating in a phase 3 trial of the drug.
Novartis, which markets secukinumab, funded the research. Dr. Thiel has received speaking and/or advising fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis. His coauthors had disclosures for a wide range of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Palma has received research funding from AbbVie, Incyte, and Regeneron.
Patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) remained in remission longer when they took secukinumab (Cosentyx) during a 6-month–long taper of glucocorticoids, a monoclonal antibody drug that inhibits interleukin-17A, compared with placebo, according to phase 2 trial results presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The mainstay of GCA treatment is glucocorticoids, although IL-6 inhibition with tocilizumab (Actemra) has recently become another option, Jens Thiel, MD, vice director of the Clinic for Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at University Hospital Freiburg (Germany), told attendees.
“Secukinumab has shown significant improvements in the signs and symptoms of IL-17A-driven medical conditions such as psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and it has a very favorable long-term safety profile,” Dr. Thiel said. “There is experimental and preclinical data that points toward the role of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis, and therefore IL-17A inhibition, blocking vascular inflammation, is potentially a new therapeutic target for GCA.”
Christopher R. Palma, MD, ScM, assistant professor in the division of allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), said in an interview that the trial’s preliminary findings were exciting because they suggest that IL-17A is likely to be an effective strategy for treating GCA. ”This aligns with known pathophysiology of GCA, where IL-17A is an important part of pathology of disease,” Dr. Palma said.
In the randomized, controlled, double-blind trial, researchers enrolled 52 patients, all at least 50 years old, who had never taken a biologic for GCA. Most of the participants (80.8%) had new-onset GCA, diagnosed within the previous 6 weeks, and 19.2% had relapsing GCA. The participants received either 300 mg of secukinumab or placebo every week for 5 weeks, and then every 4 weeks for 48 total weeks. At baseline, all participants also began a 26-week taper of prednisolone from a dose of 25-60 mg/day at baseline to 0 at week 27. The primary endpoint was the proportion of participants in sustained remission through week 28.
Among the 27 participants taking secukinumab and the 25 taking placebo, 37 completed the study treatment (71%). At week 28, those still in remission included 70.1% of participants taking secukinumab and 20.3% of those taking placebo (odds ratio [OR], 9.3). Through week 52, the proportion of participants in remission included 59.3% of the secukinumab group and 8% of the placebo group.
Determination of flare was based on signs and symptoms along with a C-reactive protein level of more than 10 mg/L or an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Dr. Thiel did not provide more details on these parameters or on how flares were determined, but reported that participants taking secukinumab did not reach a median time to first flare, compared to a median 197 days in the placebo group.
All the participants taking secukinumab and 96% of those taking placebo experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, with serious adverse events occurring in 22.2% of those taking secukinumab and 44% of those taking placebo. Two patients in each group discontinued the treatment because of adverse events, and one participant in each group died from causes determined to be unrelated to the treatment.
The trial’s effect size was large, but Dr. Palma noted that the study’s generalizability is limited by prednisolone tapering in the placebo arm because that’s not reflective of most clinical practice for treatment of GCA.
“We would be unlikely to mimic this trial design as we know rates of disease flare and recurrence are high without long-term therapy of some kind,” Dr. Palma said. ”The real challenge will be in assessing relative benefit and risk among many possible therapies and how IL-17A–directed therapies fit in. Obviously, a head-to-head trial design would help answer many of these questions.”
Dr. Palma said it’s too early to recommend widespread off-label use of secukinumab for GCA, but he would encourage his patients with GCA to consider participating in a phase 3 trial of the drug.
Novartis, which markets secukinumab, funded the research. Dr. Thiel has received speaking and/or advising fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis. His coauthors had disclosures for a wide range of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Palma has received research funding from AbbVie, Incyte, and Regeneron.
Patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) remained in remission longer when they took secukinumab (Cosentyx) during a 6-month–long taper of glucocorticoids, a monoclonal antibody drug that inhibits interleukin-17A, compared with placebo, according to phase 2 trial results presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The mainstay of GCA treatment is glucocorticoids, although IL-6 inhibition with tocilizumab (Actemra) has recently become another option, Jens Thiel, MD, vice director of the Clinic for Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at University Hospital Freiburg (Germany), told attendees.
“Secukinumab has shown significant improvements in the signs and symptoms of IL-17A-driven medical conditions such as psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and it has a very favorable long-term safety profile,” Dr. Thiel said. “There is experimental and preclinical data that points toward the role of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis, and therefore IL-17A inhibition, blocking vascular inflammation, is potentially a new therapeutic target for GCA.”
Christopher R. Palma, MD, ScM, assistant professor in the division of allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), said in an interview that the trial’s preliminary findings were exciting because they suggest that IL-17A is likely to be an effective strategy for treating GCA. ”This aligns with known pathophysiology of GCA, where IL-17A is an important part of pathology of disease,” Dr. Palma said.
In the randomized, controlled, double-blind trial, researchers enrolled 52 patients, all at least 50 years old, who had never taken a biologic for GCA. Most of the participants (80.8%) had new-onset GCA, diagnosed within the previous 6 weeks, and 19.2% had relapsing GCA. The participants received either 300 mg of secukinumab or placebo every week for 5 weeks, and then every 4 weeks for 48 total weeks. At baseline, all participants also began a 26-week taper of prednisolone from a dose of 25-60 mg/day at baseline to 0 at week 27. The primary endpoint was the proportion of participants in sustained remission through week 28.
Among the 27 participants taking secukinumab and the 25 taking placebo, 37 completed the study treatment (71%). At week 28, those still in remission included 70.1% of participants taking secukinumab and 20.3% of those taking placebo (odds ratio [OR], 9.3). Through week 52, the proportion of participants in remission included 59.3% of the secukinumab group and 8% of the placebo group.
Determination of flare was based on signs and symptoms along with a C-reactive protein level of more than 10 mg/L or an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Dr. Thiel did not provide more details on these parameters or on how flares were determined, but reported that participants taking secukinumab did not reach a median time to first flare, compared to a median 197 days in the placebo group.
All the participants taking secukinumab and 96% of those taking placebo experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, with serious adverse events occurring in 22.2% of those taking secukinumab and 44% of those taking placebo. Two patients in each group discontinued the treatment because of adverse events, and one participant in each group died from causes determined to be unrelated to the treatment.
The trial’s effect size was large, but Dr. Palma noted that the study’s generalizability is limited by prednisolone tapering in the placebo arm because that’s not reflective of most clinical practice for treatment of GCA.
“We would be unlikely to mimic this trial design as we know rates of disease flare and recurrence are high without long-term therapy of some kind,” Dr. Palma said. ”The real challenge will be in assessing relative benefit and risk among many possible therapies and how IL-17A–directed therapies fit in. Obviously, a head-to-head trial design would help answer many of these questions.”
Dr. Palma said it’s too early to recommend widespread off-label use of secukinumab for GCA, but he would encourage his patients with GCA to consider participating in a phase 3 trial of the drug.
Novartis, which markets secukinumab, funded the research. Dr. Thiel has received speaking and/or advising fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis. His coauthors had disclosures for a wide range of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Palma has received research funding from AbbVie, Incyte, and Regeneron.
FROM ACR 2021
COVID surge in Europe: A preview of what’s ahead for the U.S.?
Health experts are warning the United States could be headed for another COVID-19 surge just as we enter the holiday season, following a massive new wave of infections in Europe – a troubling pattern seen throughout the pandemic.
Eighteen months into the global health crisis that has killed 5.1 million people worldwide including more than 767,000 Americans, Europe has become the epicenter of the global health crisis once again.
And some infectious disease specialists say the United States may be next.
“It’s déjà vu, yet again,” says Eric Topol, M.D., founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute. In a new analysis published in The Guardian, the professor of molecular medicine argues that it’s “wishful thinking” for U.S. authorities to believe the nation is “immune” to what’s happening in Europe.
Dr. Topol is also editor-in-chief of Medscape, MDedge’s sister site for medical professionals.
Three times over the past 18 months coronavirus surges in the United States followed similar spikes in Europe, where COVID-19 deaths grew by 10% this month.
Dr. Topol argues another wave may be in store for the states, as European countries implement new lockdowns. COVID-19 spikes are hitting some regions of the continent hard, including areas with high vaccination rates and strict control measures.
Eastern Europe and Russia, where vaccination rates are low, have experienced the worst of it. But even western countries, such as Germany, Austria and the United Kingdom, are reporting some of the highest daily infection figures in the world today.
Countries are responding in increasingly drastic ways.
In Russia, President Vladimir Putin ordered tens of thousands of workers to stay home earlier this month.
In the Dutch city of Utrecht, traditional Christmas celebrations have been canceled as the country is headed for a partial lockdown.
Austria announced a 20-day lockdown beginning Nov. 22 and on Nov. 19 leaders there announced that all 9 million residents will be required to be vaccinated by February. Leaders there are telling unvaccinated individuals to stay at home and out of restaurants, cafes, and other shops in hard-hit regions of the country.
And in Germany, where daily new-infection rates now stand at 50,000, officials have introduced stricter mask mandates and made proof of vaccination or past infection mandatory for entry to many venues. Berlin is also eyeing proposals to shut down the city’s traditional Christmas markets while authorities in Cologne have already called off holiday celebrations, after the ceremonial head of festivities tested positive for COVID-19. Bavaria canceled its popular Christmas markets and will order lockdowns in particularly vulnerable districts, while unvaccinated people will face serious restrictions on where they can go.
Former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, says what’s happening across the European continent is troubling.
But he also believes it’s possible the United States may be better prepared to head off a similar surge this time around, with increased testing, vaccination and new therapies such as monoclonal antibodies, and antiviral therapeutics.
“Germany’s challenges are [a] caution to [the] world, the COVID pandemic isn’t over globally, won’t be for long time,” he says. “But [the] U.S. is further along than many other countries, in part because we already suffered more spread, in part because we’re making progress on vaccines, therapeutics, testing.”
Other experts agree the United States may not be as vulnerable to another wave of COVID-19 in coming weeks but have stopped short of suggesting we’re out of the woods.
“I don’t think that what we’re seeing in Europe necessarily means that we’re in for a huge surge of serious illness and death the way that we saw last year here in the states,” says David Dowdy, MD, PhD, an associate professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and a general internist with Baltimore Medical Services.
“But I think anyone who says that they can predict the course of the pandemic for the next few months or few years has been proven wrong in the past and will probably be proven wrong in the future,” Dr. Dowdy says. “None of us knows the future of this pandemic, but I do think that we are in for an increase of cases, not necessarily of deaths and serious illness.”
Looking back, and forward
What’s happening in Europe today mirrors past COVID-19 spikes that presaged big upticks in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the United States.
When the pandemic first hit Europe in March 2020, then-President Donald Trump downplayed the threat of the virus despite the warnings of his own advisors and independent public health experts who said COVID-19 could have dire impacts without an aggressive federal action plan.
By late spring the United States had become the epicenter of the pandemic, when case totals eclipsed those of other countries and New York City became a hot zone, according to data compiled by the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Over the summer, spread of the disease slowed in New York, after tough control measures were instituted, but steadily increased in other states.
Then, later in the year, the Alpha variant of the virus took hold in the United Kingdom and the United States was again unprepared. By winter, the number of cases accelerated in every state in a major second surge that kept millions of Americans from traveling and gathering for the winter holidays.
With the rollout of COVID vaccines last December, cases in the United States – and in many parts of the world – began to fall. Some experts even suggested we’d turned a corner on the pandemic.
But then, last spring and summer, the Delta variant popped up in India and spread to the United Kingdom in a third major wave of COVID. Once again, the United States was unprepared, with 4 in 10 Americans refusing the vaccine and even some vaccinated individuals succumbing to breakthrough Delta infections.
The resulting Delta surge swept the country, preventing many businesses and schools from fully reopening and stressing hospitals in some areas of the country – particularly southern states – with new influxes of COVID-19 patients.
Now, Europe is facing another rise in COVID, with about 350 cases per 100,000 people and many countries hitting new record highs.
What’s driving the European resurgence?
So, what’s behind the new COVID-19 wave in Europe and what might it mean for the United States?
Shaun Truelove, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and faculty member of the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, says experts are examining several likely factors:
Waning immunity from the vaccines. Data from Johns Hopkins shows infections rising in nations with lower vaccination rates.
The impact of the Delta variant, which is three times more transmissible than the original virus and can even sicken some vaccinated individuals.
The spread of COVID-19 among teens and children; the easing of precautions (such as masking and social distancing); differences in the types of vaccines used in European nations and the United States.
“These are all possibilities,” says Dr. Truelove. “There are so many factors and so it’s difficult to pinpoint exactly what’s driving it and what effect each of those things might be having.”
As a result, it’s difficult to predict and prepare for what might lie ahead for the United States, he says.
“There’s a ton of uncertainty and we’re trying to understand what’s going to happen here over the next 6 months,” he says.
Even so, Dr. Truelove adds that what’s happening overseas might not be “super predictive” of a new wave of COVID in the United States.
For one thing, he says, the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, the two mRNA vaccines used predominantly in the United States, are far more effective – 94-95% – than the Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID shot (63%) widely administered across Europe.
Secondly, European countries have imposed much stronger and stricter control measures throughout the pandemic than the United States. That might actually be driving the new surges because fewer unvaccinated people have been exposed to the virus, which means they have lower “natural immunity” from prior COVID infection.
Dr. Truelove explains: “Stronger and stricter control measures … have the consequence of leaving a lot more susceptible individuals in the population, [because] the stronger the controls, the fewer people get infected. And so, you have more individuals remaining in the population who are more susceptible and at risk of getting infected in the future.”
By contrast, he notes, a “large chunk” of the United States has not put strict lockdowns in place.
“So, what we’ve seen over the past couple months with the Delta wave is that in a lot of those states with lower vaccination coverage and lower controls this virus has really burned through a lot of the susceptible population. As a result, we’re seeing the curves coming down and what really looks like a lot of the built-up immunity in these states, especially southern states.”
But whether these differences will be enough for the United States to dodge another COVID-19 bullet this winter is uncertain.
“I don’t want to say that the [Europe] surge is NOT a predictor of what might come in the U.S., because I think that it very well could be,” Dr. Truelove says. “And so, people need to be aware of that, and be cautious and be sure get their vaccines and everything else.
“But I’m hopeful that because of some of the differences that maybe we’ll have a little bit of a different situation.”
The takeaway: How best to prepare?
Dr. Dowdy agrees that Europe’s current troubles might not necessarily mean a major new winter surge in the United States.
But he also points out that cases are beginning to head up again in New England, the Midwest, and other regions of the country that are just experiencing the first chill of winter.
“After reaching a low point about 3 weeks ago, cases due to COVID-19 have started to rise again in the United States,” he says. “Cases were falling consistently until mid-October, but over the last 3 weeks, cases have started to rise again in most states.
“Cases in Eastern and Central Europe have more than doubled during that time, meaning that the possibility of a winter surge here is very real.”
Even so, Dr. Dowdy believes the rising rates of vaccination could limit the number of Americans who will be hospitalized with severe disease or die this winter.
Still, he warns against being too optimistic, as Americans travel and get together for the winter holidays.
None of us knows the future of this pandemic, but I do think that we are in for an increase of cases, not necessarily of deaths and serious illness, Dr. Dowdy says.”
The upshot?
“People need to realize that it’s not quite over,” Dr. Truelove says. “We still have a substantial amount of infection in our country. We’re still above 200 cases per million [and] 500,000 incident cases per week or so. That’s a lot of death and a lot of hospitalizations. So, we still have to be concerned and do our best to reduce transmission … by wearing masks, getting vaccinated, getting a booster shot, and getting your children vaccinated.”
Johns Hopkins social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, MPH, adds that while COVID vaccines have been a “game changer” in the pandemic, more than a third of Americans have yet to receive one.
“That’s really what we need to be messaging around -- that people can still get COVID, there can still be breakthrough infections,” says Dr. Limaye, a health communications scholar. “But the great news is if you have been vaccinated, you are very much less likely, I think it’s 12 times, to be hospitalized or have severe COVID compared to those that are un-vaccinated.”
Dr. Topol agrees, adding: “Now is the time for the U.S. to heed the European signal for the first time, to pull out all the stops. Promote primary vaccination and boosters like there’s no tomorrow. Aggressively counter the pervasive misinformation and disinformation. Accelerate and expand the vaccine mandates ...
“Instead of succumbing to yet another major rise in cases and their sequelae, this is a chance for America to finally rise to the occasion, showing an ability to lead and execute.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Health experts are warning the United States could be headed for another COVID-19 surge just as we enter the holiday season, following a massive new wave of infections in Europe – a troubling pattern seen throughout the pandemic.
Eighteen months into the global health crisis that has killed 5.1 million people worldwide including more than 767,000 Americans, Europe has become the epicenter of the global health crisis once again.
And some infectious disease specialists say the United States may be next.
“It’s déjà vu, yet again,” says Eric Topol, M.D., founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute. In a new analysis published in The Guardian, the professor of molecular medicine argues that it’s “wishful thinking” for U.S. authorities to believe the nation is “immune” to what’s happening in Europe.
Dr. Topol is also editor-in-chief of Medscape, MDedge’s sister site for medical professionals.
Three times over the past 18 months coronavirus surges in the United States followed similar spikes in Europe, where COVID-19 deaths grew by 10% this month.
Dr. Topol argues another wave may be in store for the states, as European countries implement new lockdowns. COVID-19 spikes are hitting some regions of the continent hard, including areas with high vaccination rates and strict control measures.
Eastern Europe and Russia, where vaccination rates are low, have experienced the worst of it. But even western countries, such as Germany, Austria and the United Kingdom, are reporting some of the highest daily infection figures in the world today.
Countries are responding in increasingly drastic ways.
In Russia, President Vladimir Putin ordered tens of thousands of workers to stay home earlier this month.
In the Dutch city of Utrecht, traditional Christmas celebrations have been canceled as the country is headed for a partial lockdown.
Austria announced a 20-day lockdown beginning Nov. 22 and on Nov. 19 leaders there announced that all 9 million residents will be required to be vaccinated by February. Leaders there are telling unvaccinated individuals to stay at home and out of restaurants, cafes, and other shops in hard-hit regions of the country.
And in Germany, where daily new-infection rates now stand at 50,000, officials have introduced stricter mask mandates and made proof of vaccination or past infection mandatory for entry to many venues. Berlin is also eyeing proposals to shut down the city’s traditional Christmas markets while authorities in Cologne have already called off holiday celebrations, after the ceremonial head of festivities tested positive for COVID-19. Bavaria canceled its popular Christmas markets and will order lockdowns in particularly vulnerable districts, while unvaccinated people will face serious restrictions on where they can go.
Former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, says what’s happening across the European continent is troubling.
But he also believes it’s possible the United States may be better prepared to head off a similar surge this time around, with increased testing, vaccination and new therapies such as monoclonal antibodies, and antiviral therapeutics.
“Germany’s challenges are [a] caution to [the] world, the COVID pandemic isn’t over globally, won’t be for long time,” he says. “But [the] U.S. is further along than many other countries, in part because we already suffered more spread, in part because we’re making progress on vaccines, therapeutics, testing.”
Other experts agree the United States may not be as vulnerable to another wave of COVID-19 in coming weeks but have stopped short of suggesting we’re out of the woods.
“I don’t think that what we’re seeing in Europe necessarily means that we’re in for a huge surge of serious illness and death the way that we saw last year here in the states,” says David Dowdy, MD, PhD, an associate professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and a general internist with Baltimore Medical Services.
“But I think anyone who says that they can predict the course of the pandemic for the next few months or few years has been proven wrong in the past and will probably be proven wrong in the future,” Dr. Dowdy says. “None of us knows the future of this pandemic, but I do think that we are in for an increase of cases, not necessarily of deaths and serious illness.”
Looking back, and forward
What’s happening in Europe today mirrors past COVID-19 spikes that presaged big upticks in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the United States.
When the pandemic first hit Europe in March 2020, then-President Donald Trump downplayed the threat of the virus despite the warnings of his own advisors and independent public health experts who said COVID-19 could have dire impacts without an aggressive federal action plan.
By late spring the United States had become the epicenter of the pandemic, when case totals eclipsed those of other countries and New York City became a hot zone, according to data compiled by the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Over the summer, spread of the disease slowed in New York, after tough control measures were instituted, but steadily increased in other states.
Then, later in the year, the Alpha variant of the virus took hold in the United Kingdom and the United States was again unprepared. By winter, the number of cases accelerated in every state in a major second surge that kept millions of Americans from traveling and gathering for the winter holidays.
With the rollout of COVID vaccines last December, cases in the United States – and in many parts of the world – began to fall. Some experts even suggested we’d turned a corner on the pandemic.
But then, last spring and summer, the Delta variant popped up in India and spread to the United Kingdom in a third major wave of COVID. Once again, the United States was unprepared, with 4 in 10 Americans refusing the vaccine and even some vaccinated individuals succumbing to breakthrough Delta infections.
The resulting Delta surge swept the country, preventing many businesses and schools from fully reopening and stressing hospitals in some areas of the country – particularly southern states – with new influxes of COVID-19 patients.
Now, Europe is facing another rise in COVID, with about 350 cases per 100,000 people and many countries hitting new record highs.
What’s driving the European resurgence?
So, what’s behind the new COVID-19 wave in Europe and what might it mean for the United States?
Shaun Truelove, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and faculty member of the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, says experts are examining several likely factors:
Waning immunity from the vaccines. Data from Johns Hopkins shows infections rising in nations with lower vaccination rates.
The impact of the Delta variant, which is three times more transmissible than the original virus and can even sicken some vaccinated individuals.
The spread of COVID-19 among teens and children; the easing of precautions (such as masking and social distancing); differences in the types of vaccines used in European nations and the United States.
“These are all possibilities,” says Dr. Truelove. “There are so many factors and so it’s difficult to pinpoint exactly what’s driving it and what effect each of those things might be having.”
As a result, it’s difficult to predict and prepare for what might lie ahead for the United States, he says.
“There’s a ton of uncertainty and we’re trying to understand what’s going to happen here over the next 6 months,” he says.
Even so, Dr. Truelove adds that what’s happening overseas might not be “super predictive” of a new wave of COVID in the United States.
For one thing, he says, the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, the two mRNA vaccines used predominantly in the United States, are far more effective – 94-95% – than the Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID shot (63%) widely administered across Europe.
Secondly, European countries have imposed much stronger and stricter control measures throughout the pandemic than the United States. That might actually be driving the new surges because fewer unvaccinated people have been exposed to the virus, which means they have lower “natural immunity” from prior COVID infection.
Dr. Truelove explains: “Stronger and stricter control measures … have the consequence of leaving a lot more susceptible individuals in the population, [because] the stronger the controls, the fewer people get infected. And so, you have more individuals remaining in the population who are more susceptible and at risk of getting infected in the future.”
By contrast, he notes, a “large chunk” of the United States has not put strict lockdowns in place.
“So, what we’ve seen over the past couple months with the Delta wave is that in a lot of those states with lower vaccination coverage and lower controls this virus has really burned through a lot of the susceptible population. As a result, we’re seeing the curves coming down and what really looks like a lot of the built-up immunity in these states, especially southern states.”
But whether these differences will be enough for the United States to dodge another COVID-19 bullet this winter is uncertain.
“I don’t want to say that the [Europe] surge is NOT a predictor of what might come in the U.S., because I think that it very well could be,” Dr. Truelove says. “And so, people need to be aware of that, and be cautious and be sure get their vaccines and everything else.
“But I’m hopeful that because of some of the differences that maybe we’ll have a little bit of a different situation.”
The takeaway: How best to prepare?
Dr. Dowdy agrees that Europe’s current troubles might not necessarily mean a major new winter surge in the United States.
But he also points out that cases are beginning to head up again in New England, the Midwest, and other regions of the country that are just experiencing the first chill of winter.
“After reaching a low point about 3 weeks ago, cases due to COVID-19 have started to rise again in the United States,” he says. “Cases were falling consistently until mid-October, but over the last 3 weeks, cases have started to rise again in most states.
“Cases in Eastern and Central Europe have more than doubled during that time, meaning that the possibility of a winter surge here is very real.”
Even so, Dr. Dowdy believes the rising rates of vaccination could limit the number of Americans who will be hospitalized with severe disease or die this winter.
Still, he warns against being too optimistic, as Americans travel and get together for the winter holidays.
None of us knows the future of this pandemic, but I do think that we are in for an increase of cases, not necessarily of deaths and serious illness, Dr. Dowdy says.”
The upshot?
“People need to realize that it’s not quite over,” Dr. Truelove says. “We still have a substantial amount of infection in our country. We’re still above 200 cases per million [and] 500,000 incident cases per week or so. That’s a lot of death and a lot of hospitalizations. So, we still have to be concerned and do our best to reduce transmission … by wearing masks, getting vaccinated, getting a booster shot, and getting your children vaccinated.”
Johns Hopkins social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, MPH, adds that while COVID vaccines have been a “game changer” in the pandemic, more than a third of Americans have yet to receive one.
“That’s really what we need to be messaging around -- that people can still get COVID, there can still be breakthrough infections,” says Dr. Limaye, a health communications scholar. “But the great news is if you have been vaccinated, you are very much less likely, I think it’s 12 times, to be hospitalized or have severe COVID compared to those that are un-vaccinated.”
Dr. Topol agrees, adding: “Now is the time for the U.S. to heed the European signal for the first time, to pull out all the stops. Promote primary vaccination and boosters like there’s no tomorrow. Aggressively counter the pervasive misinformation and disinformation. Accelerate and expand the vaccine mandates ...
“Instead of succumbing to yet another major rise in cases and their sequelae, this is a chance for America to finally rise to the occasion, showing an ability to lead and execute.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Health experts are warning the United States could be headed for another COVID-19 surge just as we enter the holiday season, following a massive new wave of infections in Europe – a troubling pattern seen throughout the pandemic.
Eighteen months into the global health crisis that has killed 5.1 million people worldwide including more than 767,000 Americans, Europe has become the epicenter of the global health crisis once again.
And some infectious disease specialists say the United States may be next.
“It’s déjà vu, yet again,” says Eric Topol, M.D., founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute. In a new analysis published in The Guardian, the professor of molecular medicine argues that it’s “wishful thinking” for U.S. authorities to believe the nation is “immune” to what’s happening in Europe.
Dr. Topol is also editor-in-chief of Medscape, MDedge’s sister site for medical professionals.
Three times over the past 18 months coronavirus surges in the United States followed similar spikes in Europe, where COVID-19 deaths grew by 10% this month.
Dr. Topol argues another wave may be in store for the states, as European countries implement new lockdowns. COVID-19 spikes are hitting some regions of the continent hard, including areas with high vaccination rates and strict control measures.
Eastern Europe and Russia, where vaccination rates are low, have experienced the worst of it. But even western countries, such as Germany, Austria and the United Kingdom, are reporting some of the highest daily infection figures in the world today.
Countries are responding in increasingly drastic ways.
In Russia, President Vladimir Putin ordered tens of thousands of workers to stay home earlier this month.
In the Dutch city of Utrecht, traditional Christmas celebrations have been canceled as the country is headed for a partial lockdown.
Austria announced a 20-day lockdown beginning Nov. 22 and on Nov. 19 leaders there announced that all 9 million residents will be required to be vaccinated by February. Leaders there are telling unvaccinated individuals to stay at home and out of restaurants, cafes, and other shops in hard-hit regions of the country.
And in Germany, where daily new-infection rates now stand at 50,000, officials have introduced stricter mask mandates and made proof of vaccination or past infection mandatory for entry to many venues. Berlin is also eyeing proposals to shut down the city’s traditional Christmas markets while authorities in Cologne have already called off holiday celebrations, after the ceremonial head of festivities tested positive for COVID-19. Bavaria canceled its popular Christmas markets and will order lockdowns in particularly vulnerable districts, while unvaccinated people will face serious restrictions on where they can go.
Former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, says what’s happening across the European continent is troubling.
But he also believes it’s possible the United States may be better prepared to head off a similar surge this time around, with increased testing, vaccination and new therapies such as monoclonal antibodies, and antiviral therapeutics.
“Germany’s challenges are [a] caution to [the] world, the COVID pandemic isn’t over globally, won’t be for long time,” he says. “But [the] U.S. is further along than many other countries, in part because we already suffered more spread, in part because we’re making progress on vaccines, therapeutics, testing.”
Other experts agree the United States may not be as vulnerable to another wave of COVID-19 in coming weeks but have stopped short of suggesting we’re out of the woods.
“I don’t think that what we’re seeing in Europe necessarily means that we’re in for a huge surge of serious illness and death the way that we saw last year here in the states,” says David Dowdy, MD, PhD, an associate professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and a general internist with Baltimore Medical Services.
“But I think anyone who says that they can predict the course of the pandemic for the next few months or few years has been proven wrong in the past and will probably be proven wrong in the future,” Dr. Dowdy says. “None of us knows the future of this pandemic, but I do think that we are in for an increase of cases, not necessarily of deaths and serious illness.”
Looking back, and forward
What’s happening in Europe today mirrors past COVID-19 spikes that presaged big upticks in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the United States.
When the pandemic first hit Europe in March 2020, then-President Donald Trump downplayed the threat of the virus despite the warnings of his own advisors and independent public health experts who said COVID-19 could have dire impacts without an aggressive federal action plan.
By late spring the United States had become the epicenter of the pandemic, when case totals eclipsed those of other countries and New York City became a hot zone, according to data compiled by the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Over the summer, spread of the disease slowed in New York, after tough control measures were instituted, but steadily increased in other states.
Then, later in the year, the Alpha variant of the virus took hold in the United Kingdom and the United States was again unprepared. By winter, the number of cases accelerated in every state in a major second surge that kept millions of Americans from traveling and gathering for the winter holidays.
With the rollout of COVID vaccines last December, cases in the United States – and in many parts of the world – began to fall. Some experts even suggested we’d turned a corner on the pandemic.
But then, last spring and summer, the Delta variant popped up in India and spread to the United Kingdom in a third major wave of COVID. Once again, the United States was unprepared, with 4 in 10 Americans refusing the vaccine and even some vaccinated individuals succumbing to breakthrough Delta infections.
The resulting Delta surge swept the country, preventing many businesses and schools from fully reopening and stressing hospitals in some areas of the country – particularly southern states – with new influxes of COVID-19 patients.
Now, Europe is facing another rise in COVID, with about 350 cases per 100,000 people and many countries hitting new record highs.
What’s driving the European resurgence?
So, what’s behind the new COVID-19 wave in Europe and what might it mean for the United States?
Shaun Truelove, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and faculty member of the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, says experts are examining several likely factors:
Waning immunity from the vaccines. Data from Johns Hopkins shows infections rising in nations with lower vaccination rates.
The impact of the Delta variant, which is three times more transmissible than the original virus and can even sicken some vaccinated individuals.
The spread of COVID-19 among teens and children; the easing of precautions (such as masking and social distancing); differences in the types of vaccines used in European nations and the United States.
“These are all possibilities,” says Dr. Truelove. “There are so many factors and so it’s difficult to pinpoint exactly what’s driving it and what effect each of those things might be having.”
As a result, it’s difficult to predict and prepare for what might lie ahead for the United States, he says.
“There’s a ton of uncertainty and we’re trying to understand what’s going to happen here over the next 6 months,” he says.
Even so, Dr. Truelove adds that what’s happening overseas might not be “super predictive” of a new wave of COVID in the United States.
For one thing, he says, the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, the two mRNA vaccines used predominantly in the United States, are far more effective – 94-95% – than the Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID shot (63%) widely administered across Europe.
Secondly, European countries have imposed much stronger and stricter control measures throughout the pandemic than the United States. That might actually be driving the new surges because fewer unvaccinated people have been exposed to the virus, which means they have lower “natural immunity” from prior COVID infection.
Dr. Truelove explains: “Stronger and stricter control measures … have the consequence of leaving a lot more susceptible individuals in the population, [because] the stronger the controls, the fewer people get infected. And so, you have more individuals remaining in the population who are more susceptible and at risk of getting infected in the future.”
By contrast, he notes, a “large chunk” of the United States has not put strict lockdowns in place.
“So, what we’ve seen over the past couple months with the Delta wave is that in a lot of those states with lower vaccination coverage and lower controls this virus has really burned through a lot of the susceptible population. As a result, we’re seeing the curves coming down and what really looks like a lot of the built-up immunity in these states, especially southern states.”
But whether these differences will be enough for the United States to dodge another COVID-19 bullet this winter is uncertain.
“I don’t want to say that the [Europe] surge is NOT a predictor of what might come in the U.S., because I think that it very well could be,” Dr. Truelove says. “And so, people need to be aware of that, and be cautious and be sure get their vaccines and everything else.
“But I’m hopeful that because of some of the differences that maybe we’ll have a little bit of a different situation.”
The takeaway: How best to prepare?
Dr. Dowdy agrees that Europe’s current troubles might not necessarily mean a major new winter surge in the United States.
But he also points out that cases are beginning to head up again in New England, the Midwest, and other regions of the country that are just experiencing the first chill of winter.
“After reaching a low point about 3 weeks ago, cases due to COVID-19 have started to rise again in the United States,” he says. “Cases were falling consistently until mid-October, but over the last 3 weeks, cases have started to rise again in most states.
“Cases in Eastern and Central Europe have more than doubled during that time, meaning that the possibility of a winter surge here is very real.”
Even so, Dr. Dowdy believes the rising rates of vaccination could limit the number of Americans who will be hospitalized with severe disease or die this winter.
Still, he warns against being too optimistic, as Americans travel and get together for the winter holidays.
None of us knows the future of this pandemic, but I do think that we are in for an increase of cases, not necessarily of deaths and serious illness, Dr. Dowdy says.”
The upshot?
“People need to realize that it’s not quite over,” Dr. Truelove says. “We still have a substantial amount of infection in our country. We’re still above 200 cases per million [and] 500,000 incident cases per week or so. That’s a lot of death and a lot of hospitalizations. So, we still have to be concerned and do our best to reduce transmission … by wearing masks, getting vaccinated, getting a booster shot, and getting your children vaccinated.”
Johns Hopkins social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, MPH, adds that while COVID vaccines have been a “game changer” in the pandemic, more than a third of Americans have yet to receive one.
“That’s really what we need to be messaging around -- that people can still get COVID, there can still be breakthrough infections,” says Dr. Limaye, a health communications scholar. “But the great news is if you have been vaccinated, you are very much less likely, I think it’s 12 times, to be hospitalized or have severe COVID compared to those that are un-vaccinated.”
Dr. Topol agrees, adding: “Now is the time for the U.S. to heed the European signal for the first time, to pull out all the stops. Promote primary vaccination and boosters like there’s no tomorrow. Aggressively counter the pervasive misinformation and disinformation. Accelerate and expand the vaccine mandates ...
“Instead of succumbing to yet another major rise in cases and their sequelae, this is a chance for America to finally rise to the occasion, showing an ability to lead and execute.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
HIV services are bouncing back from COVID-19 disruptions, data suggest, but recovery is ‘precarious’
Over the past 2 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous disruptions in health care, including in global HIV/AIDS services. But new data presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (ANAC) 2021 Annual Meeting suggest that practitioners quickly adapted to challenges posed by the pandemic, and care and prevention services around the world have begun to return to prepandemic levels.
These rebounding numbers “show how resilient the HIV system can be,” Jennifer Kates, PhD, senior vice president and director of global health and HIV policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), said in an interview. She presented the data during her ANAC plenary talk on Nov. 11. Dr. Kates noted that continued recovery relies on improving global access to and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines. “If we do not have control of COVID, we are going to see endless cycles of impact,” she said during her talk.
COVID-19 and HIV services
Although there was concern that the pandemic could disrupt access to antiretrovirals, the Global Fund previously reported a nearly 9% increase in people receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) from 2019 to 2020. HIV prevention and testing did take a hit: There was a 22% decrease in testing for HIV and an 11% decline in the number of people receiving HIV prevention services over that period.
New data from the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) showed similar trends. Consistent with the Global Fund’s findings, a KFF analysis of PEPFAR data found that the number of people receiving ART grew in 2020, climbing from 16.0 million in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020 to 17.4 million by the end of the year. The most recent data from PEPFAR suggest that the number had climbed to 18.4 million by September 2021.
However, there was a 24% decrease in the number of newly enrolled individuals receiving ART from Q2 to Q3 in 2020. It dipped from 669,436 to 509,509. There was a similar decrease in the number of people being tested for HIV, dropping 25% from an estimated 16,700 to 12,500 from Q2 to Q3. But by the end of the year, both measurements had rebounded: New enrollments in ART grew 31%, and HIV testing grew nearly 41% compared to Q3.
The DREAMS (Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe) program, which is focused on adolescent girls and young women, saw a dip in preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and other preventive services in Q4 2020, but numbers surpassed prepandemic levels by June 2021.
PEPFAR helped speed recovery, Dr. Kates said, by providing guidance on COVID-19 protocols to the field and implementing innovations, such as accelerated 3- and 6-month medication dispensing, virtual platforms, and decentralized drug delivery. In addition, the U.S. Congress allocated $3.8 billion in emergency funding in fiscal year 2021 to help mitigate the effects of COVID-19 on HIV and AIDS care.
Longer-term outcomes still unclear
Although these numbers are encouraging, some of the effects of COVID-19 on the HIV epidemic are still unknown – in particular, whether these documented dips in preventive services will translate to an increase in new infections. This will not be clear until a year or 2 from now, Dr. Kates noted. Increased use of ART as well as an increase in some behaviors associated with the pandemic, such as decreased social contact, are factors that mitigate an increase in the rate of infections, she said, but “how that all is going to play out we don’t know for sure.”
Other conference attendees expressed anxiety about the possibility of an increase in the rate of infections. “I’m waiting for the other shoe to drop, as it were,” Barb Cardell, training and technical assistance director at Positive Women’s Network–USA, in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview. The Positive Women’s Network is a national organization of women living with HIV. “Starting late in 2019, we have been cautioning public health officials in states and federally that there will likely be an uptick in HIV diagnosis as we return to whatever ‘normal’ looks like these days,” Ms. Cardell noted, adding, “We have all heard stories of folks that had an exposure and weren’t able to access PrEP during the pandemic and hence seroconverted.”
Kara McGee, associate clinical professor at Duke University School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., shared similar sentiments. “Many people at risk of acquiring HIV had trouble accessing testing and prevention prior to the pandemic, and service interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic have only worsened access – especially in rural areas,” she told this news organization.
Need for equitable vaccine access
For HIV services to continue to rebound, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be made a priority globally, Dr. Kates said. But data suggest lower-income countries are being left behind. In high-income countries, 65% of the population has been fully vaccinated, compared to 2% of people in the lowest-income countries. A KFF analysis projected that at the current rates of vaccination, these disparities will widen over time. COVID-19 testing rates in lower-income countries also lag. In high-income countries, 740 tests per 100,000 individuals are conducted daily; in low-income countries, that rate is 13 daily tests per 100,000 people. Until we can achieve more equitable access globally, the documented recovery of HIV is “precarious,” Dr. Kates said.
Ms. McGee agreed with Dr. Kates and was surprised by the extent of global inequities in the COVID-19 response. She said these issues should be a focus for the HIV health care community moving forward. “I think there are lot of us who have worked in the HIV field for many years – both domestically and internationally – who did not fully grasp the global disparities and need to consider how we can advocate for more equal access and distribution,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past 2 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous disruptions in health care, including in global HIV/AIDS services. But new data presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (ANAC) 2021 Annual Meeting suggest that practitioners quickly adapted to challenges posed by the pandemic, and care and prevention services around the world have begun to return to prepandemic levels.
These rebounding numbers “show how resilient the HIV system can be,” Jennifer Kates, PhD, senior vice president and director of global health and HIV policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), said in an interview. She presented the data during her ANAC plenary talk on Nov. 11. Dr. Kates noted that continued recovery relies on improving global access to and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines. “If we do not have control of COVID, we are going to see endless cycles of impact,” she said during her talk.
COVID-19 and HIV services
Although there was concern that the pandemic could disrupt access to antiretrovirals, the Global Fund previously reported a nearly 9% increase in people receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) from 2019 to 2020. HIV prevention and testing did take a hit: There was a 22% decrease in testing for HIV and an 11% decline in the number of people receiving HIV prevention services over that period.
New data from the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) showed similar trends. Consistent with the Global Fund’s findings, a KFF analysis of PEPFAR data found that the number of people receiving ART grew in 2020, climbing from 16.0 million in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020 to 17.4 million by the end of the year. The most recent data from PEPFAR suggest that the number had climbed to 18.4 million by September 2021.
However, there was a 24% decrease in the number of newly enrolled individuals receiving ART from Q2 to Q3 in 2020. It dipped from 669,436 to 509,509. There was a similar decrease in the number of people being tested for HIV, dropping 25% from an estimated 16,700 to 12,500 from Q2 to Q3. But by the end of the year, both measurements had rebounded: New enrollments in ART grew 31%, and HIV testing grew nearly 41% compared to Q3.
The DREAMS (Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe) program, which is focused on adolescent girls and young women, saw a dip in preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and other preventive services in Q4 2020, but numbers surpassed prepandemic levels by June 2021.
PEPFAR helped speed recovery, Dr. Kates said, by providing guidance on COVID-19 protocols to the field and implementing innovations, such as accelerated 3- and 6-month medication dispensing, virtual platforms, and decentralized drug delivery. In addition, the U.S. Congress allocated $3.8 billion in emergency funding in fiscal year 2021 to help mitigate the effects of COVID-19 on HIV and AIDS care.
Longer-term outcomes still unclear
Although these numbers are encouraging, some of the effects of COVID-19 on the HIV epidemic are still unknown – in particular, whether these documented dips in preventive services will translate to an increase in new infections. This will not be clear until a year or 2 from now, Dr. Kates noted. Increased use of ART as well as an increase in some behaviors associated with the pandemic, such as decreased social contact, are factors that mitigate an increase in the rate of infections, she said, but “how that all is going to play out we don’t know for sure.”
Other conference attendees expressed anxiety about the possibility of an increase in the rate of infections. “I’m waiting for the other shoe to drop, as it were,” Barb Cardell, training and technical assistance director at Positive Women’s Network–USA, in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview. The Positive Women’s Network is a national organization of women living with HIV. “Starting late in 2019, we have been cautioning public health officials in states and federally that there will likely be an uptick in HIV diagnosis as we return to whatever ‘normal’ looks like these days,” Ms. Cardell noted, adding, “We have all heard stories of folks that had an exposure and weren’t able to access PrEP during the pandemic and hence seroconverted.”
Kara McGee, associate clinical professor at Duke University School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., shared similar sentiments. “Many people at risk of acquiring HIV had trouble accessing testing and prevention prior to the pandemic, and service interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic have only worsened access – especially in rural areas,” she told this news organization.
Need for equitable vaccine access
For HIV services to continue to rebound, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be made a priority globally, Dr. Kates said. But data suggest lower-income countries are being left behind. In high-income countries, 65% of the population has been fully vaccinated, compared to 2% of people in the lowest-income countries. A KFF analysis projected that at the current rates of vaccination, these disparities will widen over time. COVID-19 testing rates in lower-income countries also lag. In high-income countries, 740 tests per 100,000 individuals are conducted daily; in low-income countries, that rate is 13 daily tests per 100,000 people. Until we can achieve more equitable access globally, the documented recovery of HIV is “precarious,” Dr. Kates said.
Ms. McGee agreed with Dr. Kates and was surprised by the extent of global inequities in the COVID-19 response. She said these issues should be a focus for the HIV health care community moving forward. “I think there are lot of us who have worked in the HIV field for many years – both domestically and internationally – who did not fully grasp the global disparities and need to consider how we can advocate for more equal access and distribution,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past 2 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous disruptions in health care, including in global HIV/AIDS services. But new data presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (ANAC) 2021 Annual Meeting suggest that practitioners quickly adapted to challenges posed by the pandemic, and care and prevention services around the world have begun to return to prepandemic levels.
These rebounding numbers “show how resilient the HIV system can be,” Jennifer Kates, PhD, senior vice president and director of global health and HIV policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), said in an interview. She presented the data during her ANAC plenary talk on Nov. 11. Dr. Kates noted that continued recovery relies on improving global access to and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines. “If we do not have control of COVID, we are going to see endless cycles of impact,” she said during her talk.
COVID-19 and HIV services
Although there was concern that the pandemic could disrupt access to antiretrovirals, the Global Fund previously reported a nearly 9% increase in people receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) from 2019 to 2020. HIV prevention and testing did take a hit: There was a 22% decrease in testing for HIV and an 11% decline in the number of people receiving HIV prevention services over that period.
New data from the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) showed similar trends. Consistent with the Global Fund’s findings, a KFF analysis of PEPFAR data found that the number of people receiving ART grew in 2020, climbing from 16.0 million in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020 to 17.4 million by the end of the year. The most recent data from PEPFAR suggest that the number had climbed to 18.4 million by September 2021.
However, there was a 24% decrease in the number of newly enrolled individuals receiving ART from Q2 to Q3 in 2020. It dipped from 669,436 to 509,509. There was a similar decrease in the number of people being tested for HIV, dropping 25% from an estimated 16,700 to 12,500 from Q2 to Q3. But by the end of the year, both measurements had rebounded: New enrollments in ART grew 31%, and HIV testing grew nearly 41% compared to Q3.
The DREAMS (Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe) program, which is focused on adolescent girls and young women, saw a dip in preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and other preventive services in Q4 2020, but numbers surpassed prepandemic levels by June 2021.
PEPFAR helped speed recovery, Dr. Kates said, by providing guidance on COVID-19 protocols to the field and implementing innovations, such as accelerated 3- and 6-month medication dispensing, virtual platforms, and decentralized drug delivery. In addition, the U.S. Congress allocated $3.8 billion in emergency funding in fiscal year 2021 to help mitigate the effects of COVID-19 on HIV and AIDS care.
Longer-term outcomes still unclear
Although these numbers are encouraging, some of the effects of COVID-19 on the HIV epidemic are still unknown – in particular, whether these documented dips in preventive services will translate to an increase in new infections. This will not be clear until a year or 2 from now, Dr. Kates noted. Increased use of ART as well as an increase in some behaviors associated with the pandemic, such as decreased social contact, are factors that mitigate an increase in the rate of infections, she said, but “how that all is going to play out we don’t know for sure.”
Other conference attendees expressed anxiety about the possibility of an increase in the rate of infections. “I’m waiting for the other shoe to drop, as it were,” Barb Cardell, training and technical assistance director at Positive Women’s Network–USA, in Oakland, Calif., said in an interview. The Positive Women’s Network is a national organization of women living with HIV. “Starting late in 2019, we have been cautioning public health officials in states and federally that there will likely be an uptick in HIV diagnosis as we return to whatever ‘normal’ looks like these days,” Ms. Cardell noted, adding, “We have all heard stories of folks that had an exposure and weren’t able to access PrEP during the pandemic and hence seroconverted.”
Kara McGee, associate clinical professor at Duke University School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., shared similar sentiments. “Many people at risk of acquiring HIV had trouble accessing testing and prevention prior to the pandemic, and service interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic have only worsened access – especially in rural areas,” she told this news organization.
Need for equitable vaccine access
For HIV services to continue to rebound, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be made a priority globally, Dr. Kates said. But data suggest lower-income countries are being left behind. In high-income countries, 65% of the population has been fully vaccinated, compared to 2% of people in the lowest-income countries. A KFF analysis projected that at the current rates of vaccination, these disparities will widen over time. COVID-19 testing rates in lower-income countries also lag. In high-income countries, 740 tests per 100,000 individuals are conducted daily; in low-income countries, that rate is 13 daily tests per 100,000 people. Until we can achieve more equitable access globally, the documented recovery of HIV is “precarious,” Dr. Kates said.
Ms. McGee agreed with Dr. Kates and was surprised by the extent of global inequities in the COVID-19 response. She said these issues should be a focus for the HIV health care community moving forward. “I think there are lot of us who have worked in the HIV field for many years – both domestically and internationally – who did not fully grasp the global disparities and need to consider how we can advocate for more equal access and distribution,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sociocultural stigmas provide barriers to sexual health in gay and bisexual Hispanic men
Religion and masculine ideology remain significant social cultural barriers to sexual health in Hispanic gay or bisexual men, according to new qualitative research presented at the 2021 Association of Nurses in AIDS Care conference. The pilot study also found that these men learned more sexual health information from friends and social networks than from their health care professionals.
“There’s still so much we do not know about cultural factors and the different levels of influence that shape sexual health promotion beliefs among Latinos, but moreover in Latino same-gender–loving men,” lead author Lisvel Matos, MSN, FNP-C, WHNP-BC, a PhD candidate at Duke University’s School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. Ms. Matos prefers the term same-gender–loving men (SGLM) over men who have sex with men, as the latter term is more clinical and can be stigmatizing.
In Ms. Matos’ 10 years of working in nursing, she noticed that this lack of understanding about sexual health in Hispanic SGLM impeded culturally relevant interventions in this population. “When we don’t have the evidence to show what’s effective for these populations,” she said, “then we’re kind of working blind.”
To get a better sense of social cultural barriers that influence sexual health, Ms. Matos and colleagues conducted 60- to 75-minute interviews with Hispanic SGLM through the secure web conferencing app WebEx from October 2020 to October 2021. The study used the World Health Organization’s definition of sexual health: “a state of physical, emotional, mental and social well-being in relation to sexuality; it is not merely the absence of disease, dysfunction or infirmity.” The pilot study included 15 individuals, 8 of whom were born outside of the United States. The mean age of participants was 31.4 years, and 47% reported being single and sexually active. 93% of participants said they were aware of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and 47% reported using PrEP.
Ms. Matos identified three common themes in barriers to sexual health in these men: sexual silence, religion, and machismo, a term meaning aggressive masculine pride and patriarchal ideas of manhood. “Because of social constructs, because of what it meant to be a man, [sexual health] was a very difficult subject in adolescence,” said one participant in a quote included on the poster. “I definitely believe in Christianity, and I think that has affected my sexual preference,” said another quoted individual. “It came into that Catholic guilt where you always feel bad.”
More than half of the study participants reported not having access to health care at one time in their life, because of lack of insurance or other factors such as feeling uncomfortable or even dehumanized by health care professionals. Most men said they learned about sexual health, including PrEP, from dating apps like Grindr or friend-based social media platforms rather than in care settings. Ms. Matos, who presented the study at the conference, received the Student Poster Research Award for her work.
The findings are “a good reminder for providers” that these barriers, which have been identified for decades, are still major impediments to sexual health in Hispanic SGLM, both individually and at the clinic level, Dalmacio Dennis Flores, PhD, ACRN, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia, said in an interview. He was not involved with the work. “We need to be in a space to normalize their attractions, behaviors, and identities and then help them to be more confident about it,” he noted.
Self-confidence as well as trust in sexual partners and health providers were factors that helped these men overcome this negative messaging and sociocultural stigmas, Ms. Matos found.
“The fact that [the researchers] have individual level data about the experiences of this group of men can inform how we develop clinic-level structures that can, for example, promote trust with the provider,” added Kamila Alexander, PhD, MPH, RN, an assistant professor and associate director of PhD and postdoctoral programs at Johns Hopkins University’s School of Nursing, Baltimore.
Dr. Alexander, who was not involved with the research, added that the small study is a good starting point to better inform culturally relevant care for populations marginalized by society, like Hispanic SGLM, and to challenge ingrained stereotypes around religion, masculinity, and sexuality. The researchers “highlighted these intersectional stigmas that have a lot to do with structural factors,” she said, “and those things are really ripe for intervention.”
Ms. Matos, Dr. Flores, and Dr. Alexander disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Religion and masculine ideology remain significant social cultural barriers to sexual health in Hispanic gay or bisexual men, according to new qualitative research presented at the 2021 Association of Nurses in AIDS Care conference. The pilot study also found that these men learned more sexual health information from friends and social networks than from their health care professionals.
“There’s still so much we do not know about cultural factors and the different levels of influence that shape sexual health promotion beliefs among Latinos, but moreover in Latino same-gender–loving men,” lead author Lisvel Matos, MSN, FNP-C, WHNP-BC, a PhD candidate at Duke University’s School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. Ms. Matos prefers the term same-gender–loving men (SGLM) over men who have sex with men, as the latter term is more clinical and can be stigmatizing.
In Ms. Matos’ 10 years of working in nursing, she noticed that this lack of understanding about sexual health in Hispanic SGLM impeded culturally relevant interventions in this population. “When we don’t have the evidence to show what’s effective for these populations,” she said, “then we’re kind of working blind.”
To get a better sense of social cultural barriers that influence sexual health, Ms. Matos and colleagues conducted 60- to 75-minute interviews with Hispanic SGLM through the secure web conferencing app WebEx from October 2020 to October 2021. The study used the World Health Organization’s definition of sexual health: “a state of physical, emotional, mental and social well-being in relation to sexuality; it is not merely the absence of disease, dysfunction or infirmity.” The pilot study included 15 individuals, 8 of whom were born outside of the United States. The mean age of participants was 31.4 years, and 47% reported being single and sexually active. 93% of participants said they were aware of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and 47% reported using PrEP.
Ms. Matos identified three common themes in barriers to sexual health in these men: sexual silence, religion, and machismo, a term meaning aggressive masculine pride and patriarchal ideas of manhood. “Because of social constructs, because of what it meant to be a man, [sexual health] was a very difficult subject in adolescence,” said one participant in a quote included on the poster. “I definitely believe in Christianity, and I think that has affected my sexual preference,” said another quoted individual. “It came into that Catholic guilt where you always feel bad.”
More than half of the study participants reported not having access to health care at one time in their life, because of lack of insurance or other factors such as feeling uncomfortable or even dehumanized by health care professionals. Most men said they learned about sexual health, including PrEP, from dating apps like Grindr or friend-based social media platforms rather than in care settings. Ms. Matos, who presented the study at the conference, received the Student Poster Research Award for her work.
The findings are “a good reminder for providers” that these barriers, which have been identified for decades, are still major impediments to sexual health in Hispanic SGLM, both individually and at the clinic level, Dalmacio Dennis Flores, PhD, ACRN, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia, said in an interview. He was not involved with the work. “We need to be in a space to normalize their attractions, behaviors, and identities and then help them to be more confident about it,” he noted.
Self-confidence as well as trust in sexual partners and health providers were factors that helped these men overcome this negative messaging and sociocultural stigmas, Ms. Matos found.
“The fact that [the researchers] have individual level data about the experiences of this group of men can inform how we develop clinic-level structures that can, for example, promote trust with the provider,” added Kamila Alexander, PhD, MPH, RN, an assistant professor and associate director of PhD and postdoctoral programs at Johns Hopkins University’s School of Nursing, Baltimore.
Dr. Alexander, who was not involved with the research, added that the small study is a good starting point to better inform culturally relevant care for populations marginalized by society, like Hispanic SGLM, and to challenge ingrained stereotypes around religion, masculinity, and sexuality. The researchers “highlighted these intersectional stigmas that have a lot to do with structural factors,” she said, “and those things are really ripe for intervention.”
Ms. Matos, Dr. Flores, and Dr. Alexander disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Religion and masculine ideology remain significant social cultural barriers to sexual health in Hispanic gay or bisexual men, according to new qualitative research presented at the 2021 Association of Nurses in AIDS Care conference. The pilot study also found that these men learned more sexual health information from friends and social networks than from their health care professionals.
“There’s still so much we do not know about cultural factors and the different levels of influence that shape sexual health promotion beliefs among Latinos, but moreover in Latino same-gender–loving men,” lead author Lisvel Matos, MSN, FNP-C, WHNP-BC, a PhD candidate at Duke University’s School of Nursing, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. Ms. Matos prefers the term same-gender–loving men (SGLM) over men who have sex with men, as the latter term is more clinical and can be stigmatizing.
In Ms. Matos’ 10 years of working in nursing, she noticed that this lack of understanding about sexual health in Hispanic SGLM impeded culturally relevant interventions in this population. “When we don’t have the evidence to show what’s effective for these populations,” she said, “then we’re kind of working blind.”
To get a better sense of social cultural barriers that influence sexual health, Ms. Matos and colleagues conducted 60- to 75-minute interviews with Hispanic SGLM through the secure web conferencing app WebEx from October 2020 to October 2021. The study used the World Health Organization’s definition of sexual health: “a state of physical, emotional, mental and social well-being in relation to sexuality; it is not merely the absence of disease, dysfunction or infirmity.” The pilot study included 15 individuals, 8 of whom were born outside of the United States. The mean age of participants was 31.4 years, and 47% reported being single and sexually active. 93% of participants said they were aware of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and 47% reported using PrEP.
Ms. Matos identified three common themes in barriers to sexual health in these men: sexual silence, religion, and machismo, a term meaning aggressive masculine pride and patriarchal ideas of manhood. “Because of social constructs, because of what it meant to be a man, [sexual health] was a very difficult subject in adolescence,” said one participant in a quote included on the poster. “I definitely believe in Christianity, and I think that has affected my sexual preference,” said another quoted individual. “It came into that Catholic guilt where you always feel bad.”
More than half of the study participants reported not having access to health care at one time in their life, because of lack of insurance or other factors such as feeling uncomfortable or even dehumanized by health care professionals. Most men said they learned about sexual health, including PrEP, from dating apps like Grindr or friend-based social media platforms rather than in care settings. Ms. Matos, who presented the study at the conference, received the Student Poster Research Award for her work.
The findings are “a good reminder for providers” that these barriers, which have been identified for decades, are still major impediments to sexual health in Hispanic SGLM, both individually and at the clinic level, Dalmacio Dennis Flores, PhD, ACRN, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia, said in an interview. He was not involved with the work. “We need to be in a space to normalize their attractions, behaviors, and identities and then help them to be more confident about it,” he noted.
Self-confidence as well as trust in sexual partners and health providers were factors that helped these men overcome this negative messaging and sociocultural stigmas, Ms. Matos found.
“The fact that [the researchers] have individual level data about the experiences of this group of men can inform how we develop clinic-level structures that can, for example, promote trust with the provider,” added Kamila Alexander, PhD, MPH, RN, an assistant professor and associate director of PhD and postdoctoral programs at Johns Hopkins University’s School of Nursing, Baltimore.
Dr. Alexander, who was not involved with the research, added that the small study is a good starting point to better inform culturally relevant care for populations marginalized by society, like Hispanic SGLM, and to challenge ingrained stereotypes around religion, masculinity, and sexuality. The researchers “highlighted these intersectional stigmas that have a lot to do with structural factors,” she said, “and those things are really ripe for intervention.”
Ms. Matos, Dr. Flores, and Dr. Alexander disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANAC 2021
Is ERCP indicated in gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis?
Background: The timing and need for ERCP in the setting of gallstone pancreatitis without acute cholangitis has been debated widely. Guidelines recommend urgent ERCP for patients with gallstone pancreatitis with concurrent cholangitis, severe cholestasis, or a visualized stone in the duct, but it is unclear if ERCP benefits those with gallstone pancreatitis without those clear indicators.
Study design: Prospective randomized controlled superiority trial.
Setting: 26 hospitals in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: Of patients with severe gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis, 232 were randomized 1:1 to undergo urgent ERCP with biliary sphincterotomy (less than 24 hours after presentation) or conservative therapy (analgesia, intravenous fluids, with selective ERCP for cholangitis or persistent cholestasis). The primary endpoint was a composite score of mortality or major complications within 6 months of randomization. There was no difference in the primary endpoint, which occurred in 38% of the urgent-ERCP group and 44% of the conservative-therapy group (P = .37). In a subgroup of patients with cholestasis suggestive of biliary obstruction, the primary endpoint occurred in 32% of the urgent-ERCP group and 42% in the conservative group (P = .18). Similar rates of adverse events were observed between both groups. Limitations included difficulty in diagnosis of cholangitis, moderate positive predictive value of scoring tools to isolate those with severe pancreatitis, and lack of endoscopic ultrasound to determine the presence of ductal stones or sludge.
Bottom line: Conservative management was equal to ERCP with sphincterotomy in patients with severe gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis, and ERCP may be best reserved for patients with persistent cholestasis or later-developed cholangitis.
Citation: Schepers NJ et al. Urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment in predicted severe acute gallstone pancreatitis (APEC): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;396:167-76. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30539-0.
Dr. Reddy is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and instructor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, both in Chicago.
Background: The timing and need for ERCP in the setting of gallstone pancreatitis without acute cholangitis has been debated widely. Guidelines recommend urgent ERCP for patients with gallstone pancreatitis with concurrent cholangitis, severe cholestasis, or a visualized stone in the duct, but it is unclear if ERCP benefits those with gallstone pancreatitis without those clear indicators.
Study design: Prospective randomized controlled superiority trial.
Setting: 26 hospitals in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: Of patients with severe gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis, 232 were randomized 1:1 to undergo urgent ERCP with biliary sphincterotomy (less than 24 hours after presentation) or conservative therapy (analgesia, intravenous fluids, with selective ERCP for cholangitis or persistent cholestasis). The primary endpoint was a composite score of mortality or major complications within 6 months of randomization. There was no difference in the primary endpoint, which occurred in 38% of the urgent-ERCP group and 44% of the conservative-therapy group (P = .37). In a subgroup of patients with cholestasis suggestive of biliary obstruction, the primary endpoint occurred in 32% of the urgent-ERCP group and 42% in the conservative group (P = .18). Similar rates of adverse events were observed between both groups. Limitations included difficulty in diagnosis of cholangitis, moderate positive predictive value of scoring tools to isolate those with severe pancreatitis, and lack of endoscopic ultrasound to determine the presence of ductal stones or sludge.
Bottom line: Conservative management was equal to ERCP with sphincterotomy in patients with severe gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis, and ERCP may be best reserved for patients with persistent cholestasis or later-developed cholangitis.
Citation: Schepers NJ et al. Urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment in predicted severe acute gallstone pancreatitis (APEC): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;396:167-76. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30539-0.
Dr. Reddy is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and instructor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, both in Chicago.
Background: The timing and need for ERCP in the setting of gallstone pancreatitis without acute cholangitis has been debated widely. Guidelines recommend urgent ERCP for patients with gallstone pancreatitis with concurrent cholangitis, severe cholestasis, or a visualized stone in the duct, but it is unclear if ERCP benefits those with gallstone pancreatitis without those clear indicators.
Study design: Prospective randomized controlled superiority trial.
Setting: 26 hospitals in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: Of patients with severe gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis, 232 were randomized 1:1 to undergo urgent ERCP with biliary sphincterotomy (less than 24 hours after presentation) or conservative therapy (analgesia, intravenous fluids, with selective ERCP for cholangitis or persistent cholestasis). The primary endpoint was a composite score of mortality or major complications within 6 months of randomization. There was no difference in the primary endpoint, which occurred in 38% of the urgent-ERCP group and 44% of the conservative-therapy group (P = .37). In a subgroup of patients with cholestasis suggestive of biliary obstruction, the primary endpoint occurred in 32% of the urgent-ERCP group and 42% in the conservative group (P = .18). Similar rates of adverse events were observed between both groups. Limitations included difficulty in diagnosis of cholangitis, moderate positive predictive value of scoring tools to isolate those with severe pancreatitis, and lack of endoscopic ultrasound to determine the presence of ductal stones or sludge.
Bottom line: Conservative management was equal to ERCP with sphincterotomy in patients with severe gallstone pancreatitis without cholangitis, and ERCP may be best reserved for patients with persistent cholestasis or later-developed cholangitis.
Citation: Schepers NJ et al. Urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment in predicted severe acute gallstone pancreatitis (APEC): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;396:167-76. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30539-0.
Dr. Reddy is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and instructor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, both in Chicago.
In pill or food form, healthy fatty acids reduce liver fat
For patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) who supplement their diets with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), liver and metabolic parameters improve, results of a systematic review and meta-analysis suggest.
Data from randomized clinical trials show that, for participants with NAFLD who used PUFA supplements with or without additional dietary interventions, hepatic steatosis and lobular inflammation decreased, and in one study, fibrosis decreased. There were also improvements in liver enzyme levels, said Saleh Alqahtani, MBChB, associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Since there’s no effective medical therapy for NAFLD, weight loss through lifestyle modifications becomes the most important focused intervention for patients with NAFLD,” he said. “However, the majority of patients fail to achieve or to maintain weight loss for long-term therapy. Therefore, dietary intervention or supplementation might help reduce the prevalence of NAFLD and decrease the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH] and liver cirrhosis.
“More clinical trials are warranted to determine the long-term efficacy of the Mediterranean diet and polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation among adult patients with NAFLD,” he added.
RCTs and case-control studies
It’s well documented that consumption of PUFAs, found in fatty fish and in canola, grapeseed, corn, and soybean oils, as well as monounsaturated fatty acids, found in olive oil and peanut oil, can contribute to improvement of NALFD, Dr. Alqahtani said.
In contrast, foods high in saturated fatty acids, such as butter, as well as trans fats and cholesterol can contribute to NAFLD progression, he said.
In their studies of intrahepatic triglyceride content, Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues found that fatty acids in the liver come from three major sources: dietary fatty acids, which account for about 15% of liver fat, tissue lipolysis, and de novo hepatic lipogenesis.
Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the relationship between diet and NAFLD have focused on marine-based (n-3) PUFAs, but “the data regarding the evidence of unsaturated fatty acids through supplements or monounsaturated fatty acids through dietary supplementation are lacking,” he said.
To summarize the effects of dietary or supplemental fatty acids on liver and metabolic parameters in adults with NAFLD, Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis, concentrating on studies that included specifics about interventions and outcomes.
They identified a total of 18 randomized controlled trials and 4 case-control studies that met their criteria. The studies were published from 2008 to 2020.
Regarding the effects of interventions on the components of NASH, they found that, in 1 or more of 12 randomized trials of PUFA supplementation with or without dietary interventions, there were associations with decreased hepatic steatosis, lobular inflammation, and fibrosis and declines in ALT and AST levels.
In three trials of dietary-only interventions, there were decreases in hepatic steatosis and ALT and/or AST levels. In two studies of the effects of healthy cooking oils only, hepatic steatosis decreased, but there was no effect on ALT or AST levels.
All three interventions were associated with improvements in fasting glucose levels and insulin metabolism, as well as decreases in total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol and increases in HDL cholesterol.
Better understanding of dietary composition
“We’ve known for a while that dietary composition may impact NAFLD and NASH,” said Manal F. Abdelmalek, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., who commented on the study.
“What [Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues] have shown is that supplementation with healthy fatty acids improves fatty liver. This really does extend our knowledge of what we understand about dietary composition, particularly the recommendations that support higher fish consumption and a Mediterranean-style diet,” she said.
“It’s not just about the fat but the type of fat that’s consumed, and drilling down to the particulars of dietary composition beyond calories alone,” she added.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. Dr. Alqahtani and Dr. Abdelmalek have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) who supplement their diets with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), liver and metabolic parameters improve, results of a systematic review and meta-analysis suggest.
Data from randomized clinical trials show that, for participants with NAFLD who used PUFA supplements with or without additional dietary interventions, hepatic steatosis and lobular inflammation decreased, and in one study, fibrosis decreased. There were also improvements in liver enzyme levels, said Saleh Alqahtani, MBChB, associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Since there’s no effective medical therapy for NAFLD, weight loss through lifestyle modifications becomes the most important focused intervention for patients with NAFLD,” he said. “However, the majority of patients fail to achieve or to maintain weight loss for long-term therapy. Therefore, dietary intervention or supplementation might help reduce the prevalence of NAFLD and decrease the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH] and liver cirrhosis.
“More clinical trials are warranted to determine the long-term efficacy of the Mediterranean diet and polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation among adult patients with NAFLD,” he added.
RCTs and case-control studies
It’s well documented that consumption of PUFAs, found in fatty fish and in canola, grapeseed, corn, and soybean oils, as well as monounsaturated fatty acids, found in olive oil and peanut oil, can contribute to improvement of NALFD, Dr. Alqahtani said.
In contrast, foods high in saturated fatty acids, such as butter, as well as trans fats and cholesterol can contribute to NAFLD progression, he said.
In their studies of intrahepatic triglyceride content, Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues found that fatty acids in the liver come from three major sources: dietary fatty acids, which account for about 15% of liver fat, tissue lipolysis, and de novo hepatic lipogenesis.
Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the relationship between diet and NAFLD have focused on marine-based (n-3) PUFAs, but “the data regarding the evidence of unsaturated fatty acids through supplements or monounsaturated fatty acids through dietary supplementation are lacking,” he said.
To summarize the effects of dietary or supplemental fatty acids on liver and metabolic parameters in adults with NAFLD, Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis, concentrating on studies that included specifics about interventions and outcomes.
They identified a total of 18 randomized controlled trials and 4 case-control studies that met their criteria. The studies were published from 2008 to 2020.
Regarding the effects of interventions on the components of NASH, they found that, in 1 or more of 12 randomized trials of PUFA supplementation with or without dietary interventions, there were associations with decreased hepatic steatosis, lobular inflammation, and fibrosis and declines in ALT and AST levels.
In three trials of dietary-only interventions, there were decreases in hepatic steatosis and ALT and/or AST levels. In two studies of the effects of healthy cooking oils only, hepatic steatosis decreased, but there was no effect on ALT or AST levels.
All three interventions were associated with improvements in fasting glucose levels and insulin metabolism, as well as decreases in total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol and increases in HDL cholesterol.
Better understanding of dietary composition
“We’ve known for a while that dietary composition may impact NAFLD and NASH,” said Manal F. Abdelmalek, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., who commented on the study.
“What [Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues] have shown is that supplementation with healthy fatty acids improves fatty liver. This really does extend our knowledge of what we understand about dietary composition, particularly the recommendations that support higher fish consumption and a Mediterranean-style diet,” she said.
“It’s not just about the fat but the type of fat that’s consumed, and drilling down to the particulars of dietary composition beyond calories alone,” she added.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. Dr. Alqahtani and Dr. Abdelmalek have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) who supplement their diets with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), liver and metabolic parameters improve, results of a systematic review and meta-analysis suggest.
Data from randomized clinical trials show that, for participants with NAFLD who used PUFA supplements with or without additional dietary interventions, hepatic steatosis and lobular inflammation decreased, and in one study, fibrosis decreased. There were also improvements in liver enzyme levels, said Saleh Alqahtani, MBChB, associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Since there’s no effective medical therapy for NAFLD, weight loss through lifestyle modifications becomes the most important focused intervention for patients with NAFLD,” he said. “However, the majority of patients fail to achieve or to maintain weight loss for long-term therapy. Therefore, dietary intervention or supplementation might help reduce the prevalence of NAFLD and decrease the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH] and liver cirrhosis.
“More clinical trials are warranted to determine the long-term efficacy of the Mediterranean diet and polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation among adult patients with NAFLD,” he added.
RCTs and case-control studies
It’s well documented that consumption of PUFAs, found in fatty fish and in canola, grapeseed, corn, and soybean oils, as well as monounsaturated fatty acids, found in olive oil and peanut oil, can contribute to improvement of NALFD, Dr. Alqahtani said.
In contrast, foods high in saturated fatty acids, such as butter, as well as trans fats and cholesterol can contribute to NAFLD progression, he said.
In their studies of intrahepatic triglyceride content, Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues found that fatty acids in the liver come from three major sources: dietary fatty acids, which account for about 15% of liver fat, tissue lipolysis, and de novo hepatic lipogenesis.
Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the relationship between diet and NAFLD have focused on marine-based (n-3) PUFAs, but “the data regarding the evidence of unsaturated fatty acids through supplements or monounsaturated fatty acids through dietary supplementation are lacking,” he said.
To summarize the effects of dietary or supplemental fatty acids on liver and metabolic parameters in adults with NAFLD, Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis, concentrating on studies that included specifics about interventions and outcomes.
They identified a total of 18 randomized controlled trials and 4 case-control studies that met their criteria. The studies were published from 2008 to 2020.
Regarding the effects of interventions on the components of NASH, they found that, in 1 or more of 12 randomized trials of PUFA supplementation with or without dietary interventions, there were associations with decreased hepatic steatosis, lobular inflammation, and fibrosis and declines in ALT and AST levels.
In three trials of dietary-only interventions, there were decreases in hepatic steatosis and ALT and/or AST levels. In two studies of the effects of healthy cooking oils only, hepatic steatosis decreased, but there was no effect on ALT or AST levels.
All three interventions were associated with improvements in fasting glucose levels and insulin metabolism, as well as decreases in total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol and increases in HDL cholesterol.
Better understanding of dietary composition
“We’ve known for a while that dietary composition may impact NAFLD and NASH,” said Manal F. Abdelmalek, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., who commented on the study.
“What [Dr. Alqahtani and colleagues] have shown is that supplementation with healthy fatty acids improves fatty liver. This really does extend our knowledge of what we understand about dietary composition, particularly the recommendations that support higher fish consumption and a Mediterranean-style diet,” she said.
“It’s not just about the fat but the type of fat that’s consumed, and drilling down to the particulars of dietary composition beyond calories alone,” she added.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. Dr. Alqahtani and Dr. Abdelmalek have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2021
Immunotherapies for children with r/r ALL face off
It’s possible to compare apples and oranges – both are fruits, after all; likewise, in the absence of head-to-head trials, it’s possible to make an indirect comparison of two immunotherapy strategies for treating relapsed or refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (r/r ALL): chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), and immunotherapy with the bi-specific T-cell engager (BiTE) blinatumomab (Blincyto).
Michael Verneris, MD, of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Center in Aurora, and associates carried out the first such indirect, patient-level comparison of these two immunotherapies.
“The large differences in CR and OS outcomes across multiple differing assessments suggest that our findings describe a true treatment impact. Although the current analysis is retrospective and limited by cross-study comparison, these findings support the growing body of clinical trial and real-world evidence demonstrating that tisagenlecleucel is an important treatment option for children and young adults with r/r ALL,” they wrote in an article published in Blood Advances.
However, as two pediatric leukemia experts uninvolved in the study noted, the comparison may be of limited use because the two immunotherapy agents can have different indications and applications, depending on the clinical situation.
Trial data compared
Dr. Verneris and colleagues looked at patient-level data from two clinical trials: the phase 2 single-arm ELIANA trial evaluating tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell lineage ALL (79 patients), and the efficacy phase of the MT103-205 trial assessing blinatumomab in a similar population (70 patients).
To account for differences between the studies, the investigators used five different statistical approaches, including propensity score weighting and adjustment for prognostic factors.
Regardless of the analytical method they used, results showed that patients treated with tisagenlecleucel were significantly more likely to have complete remissions than were patients treated with blinatumomab, with odds ratios favoring the CAR T-cell construct ranging from 6.71 to 9.76.
Similarly, treatment with tisagenlecleucel was associated with lower risk for death, with hazard ratios ranging from 68% to 74%.
The authors acknowledged that some prognostic variables such as bone marrow blast count, remission duration, and performance status were not recorded in the patient level data from the blinatumomab trial and therefore they could not be used in the analyses. They also conceded that selection bias could account for some of the differences in outcomes between the trials.
Patient characteristics drive choice
The comparison of the two agents “is something we as treating physicians often think about, because we are faced with a choice often of tisagenlecleucel or blinatumomab when we have a relapsed/refractory patient, ” Melinda Pauly, MD, medical director of oncology at the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, said in an interview.
Dr. Pauly, who was not involved in the study, said that the choice of therapy is based primarily on patient characteristics and the specific clinical situation.
“For patients who have prior toxicity with bone marrow transplant or don’t have a good donor option for bone marrow transplant, those are certainly patients that we are looking for a therapy that would be more sustained, and that would definitely be the tisagenlecleucel,” she said.
CAR T-cell therapy may not be an immediate option for patients for whom time is critical, however, due to the requirements of apheresis for T-cell harvesting, cell transduction, expansion, and infusion, and for such patients who have disease refractory to chemotherapy, blinatumomab may be an option.
Blinatumomab may also serve as a bridge to transplant, she said.
Dr. Pauly, who has a special interest in the care of infants with ALL, noted that apheresis can be difficult to accomplish in very young patients and may not yield T-cells sufficient for CAR T therapy, and for these patients blinatumomab may be the better option.
Howard Weinstein, MD, unit chief of the division of pediatric hematology/oncology at Mass General Hospital for Children in Boston, noted that “there are all kinds of statistical methodologies to try to balance the two populations in the studies, and they did as best as you can at balancing the risk factors, such as the number of patients with relapses after prior bone marrow transplants.”
“But there are so many genetic subtypes of acute lymphoblastic leukemia that have differing prognoses, it’s hard to do this kind of retrospective analysis when it’s not a randomized head-to-head trial,” he said in an interview.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, maker of tisagenlecleucel, sponsored the study. Dr. Verneris disclosed serving on advisory boards for Novartis, and five of the study coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Pauly and Dr. Weinstein reported having no conflicts of interest.
It’s possible to compare apples and oranges – both are fruits, after all; likewise, in the absence of head-to-head trials, it’s possible to make an indirect comparison of two immunotherapy strategies for treating relapsed or refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (r/r ALL): chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), and immunotherapy with the bi-specific T-cell engager (BiTE) blinatumomab (Blincyto).
Michael Verneris, MD, of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Center in Aurora, and associates carried out the first such indirect, patient-level comparison of these two immunotherapies.
“The large differences in CR and OS outcomes across multiple differing assessments suggest that our findings describe a true treatment impact. Although the current analysis is retrospective and limited by cross-study comparison, these findings support the growing body of clinical trial and real-world evidence demonstrating that tisagenlecleucel is an important treatment option for children and young adults with r/r ALL,” they wrote in an article published in Blood Advances.
However, as two pediatric leukemia experts uninvolved in the study noted, the comparison may be of limited use because the two immunotherapy agents can have different indications and applications, depending on the clinical situation.
Trial data compared
Dr. Verneris and colleagues looked at patient-level data from two clinical trials: the phase 2 single-arm ELIANA trial evaluating tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell lineage ALL (79 patients), and the efficacy phase of the MT103-205 trial assessing blinatumomab in a similar population (70 patients).
To account for differences between the studies, the investigators used five different statistical approaches, including propensity score weighting and adjustment for prognostic factors.
Regardless of the analytical method they used, results showed that patients treated with tisagenlecleucel were significantly more likely to have complete remissions than were patients treated with blinatumomab, with odds ratios favoring the CAR T-cell construct ranging from 6.71 to 9.76.
Similarly, treatment with tisagenlecleucel was associated with lower risk for death, with hazard ratios ranging from 68% to 74%.
The authors acknowledged that some prognostic variables such as bone marrow blast count, remission duration, and performance status were not recorded in the patient level data from the blinatumomab trial and therefore they could not be used in the analyses. They also conceded that selection bias could account for some of the differences in outcomes between the trials.
Patient characteristics drive choice
The comparison of the two agents “is something we as treating physicians often think about, because we are faced with a choice often of tisagenlecleucel or blinatumomab when we have a relapsed/refractory patient, ” Melinda Pauly, MD, medical director of oncology at the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, said in an interview.
Dr. Pauly, who was not involved in the study, said that the choice of therapy is based primarily on patient characteristics and the specific clinical situation.
“For patients who have prior toxicity with bone marrow transplant or don’t have a good donor option for bone marrow transplant, those are certainly patients that we are looking for a therapy that would be more sustained, and that would definitely be the tisagenlecleucel,” she said.
CAR T-cell therapy may not be an immediate option for patients for whom time is critical, however, due to the requirements of apheresis for T-cell harvesting, cell transduction, expansion, and infusion, and for such patients who have disease refractory to chemotherapy, blinatumomab may be an option.
Blinatumomab may also serve as a bridge to transplant, she said.
Dr. Pauly, who has a special interest in the care of infants with ALL, noted that apheresis can be difficult to accomplish in very young patients and may not yield T-cells sufficient for CAR T therapy, and for these patients blinatumomab may be the better option.
Howard Weinstein, MD, unit chief of the division of pediatric hematology/oncology at Mass General Hospital for Children in Boston, noted that “there are all kinds of statistical methodologies to try to balance the two populations in the studies, and they did as best as you can at balancing the risk factors, such as the number of patients with relapses after prior bone marrow transplants.”
“But there are so many genetic subtypes of acute lymphoblastic leukemia that have differing prognoses, it’s hard to do this kind of retrospective analysis when it’s not a randomized head-to-head trial,” he said in an interview.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, maker of tisagenlecleucel, sponsored the study. Dr. Verneris disclosed serving on advisory boards for Novartis, and five of the study coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Pauly and Dr. Weinstein reported having no conflicts of interest.
It’s possible to compare apples and oranges – both are fruits, after all; likewise, in the absence of head-to-head trials, it’s possible to make an indirect comparison of two immunotherapy strategies for treating relapsed or refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (r/r ALL): chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), and immunotherapy with the bi-specific T-cell engager (BiTE) blinatumomab (Blincyto).
Michael Verneris, MD, of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Center in Aurora, and associates carried out the first such indirect, patient-level comparison of these two immunotherapies.
“The large differences in CR and OS outcomes across multiple differing assessments suggest that our findings describe a true treatment impact. Although the current analysis is retrospective and limited by cross-study comparison, these findings support the growing body of clinical trial and real-world evidence demonstrating that tisagenlecleucel is an important treatment option for children and young adults with r/r ALL,” they wrote in an article published in Blood Advances.
However, as two pediatric leukemia experts uninvolved in the study noted, the comparison may be of limited use because the two immunotherapy agents can have different indications and applications, depending on the clinical situation.
Trial data compared
Dr. Verneris and colleagues looked at patient-level data from two clinical trials: the phase 2 single-arm ELIANA trial evaluating tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell lineage ALL (79 patients), and the efficacy phase of the MT103-205 trial assessing blinatumomab in a similar population (70 patients).
To account for differences between the studies, the investigators used five different statistical approaches, including propensity score weighting and adjustment for prognostic factors.
Regardless of the analytical method they used, results showed that patients treated with tisagenlecleucel were significantly more likely to have complete remissions than were patients treated with blinatumomab, with odds ratios favoring the CAR T-cell construct ranging from 6.71 to 9.76.
Similarly, treatment with tisagenlecleucel was associated with lower risk for death, with hazard ratios ranging from 68% to 74%.
The authors acknowledged that some prognostic variables such as bone marrow blast count, remission duration, and performance status were not recorded in the patient level data from the blinatumomab trial and therefore they could not be used in the analyses. They also conceded that selection bias could account for some of the differences in outcomes between the trials.
Patient characteristics drive choice
The comparison of the two agents “is something we as treating physicians often think about, because we are faced with a choice often of tisagenlecleucel or blinatumomab when we have a relapsed/refractory patient, ” Melinda Pauly, MD, medical director of oncology at the Aflac Cancer and Blood Disorders Center of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, said in an interview.
Dr. Pauly, who was not involved in the study, said that the choice of therapy is based primarily on patient characteristics and the specific clinical situation.
“For patients who have prior toxicity with bone marrow transplant or don’t have a good donor option for bone marrow transplant, those are certainly patients that we are looking for a therapy that would be more sustained, and that would definitely be the tisagenlecleucel,” she said.
CAR T-cell therapy may not be an immediate option for patients for whom time is critical, however, due to the requirements of apheresis for T-cell harvesting, cell transduction, expansion, and infusion, and for such patients who have disease refractory to chemotherapy, blinatumomab may be an option.
Blinatumomab may also serve as a bridge to transplant, she said.
Dr. Pauly, who has a special interest in the care of infants with ALL, noted that apheresis can be difficult to accomplish in very young patients and may not yield T-cells sufficient for CAR T therapy, and for these patients blinatumomab may be the better option.
Howard Weinstein, MD, unit chief of the division of pediatric hematology/oncology at Mass General Hospital for Children in Boston, noted that “there are all kinds of statistical methodologies to try to balance the two populations in the studies, and they did as best as you can at balancing the risk factors, such as the number of patients with relapses after prior bone marrow transplants.”
“But there are so many genetic subtypes of acute lymphoblastic leukemia that have differing prognoses, it’s hard to do this kind of retrospective analysis when it’s not a randomized head-to-head trial,” he said in an interview.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, maker of tisagenlecleucel, sponsored the study. Dr. Verneris disclosed serving on advisory boards for Novartis, and five of the study coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Pauly and Dr. Weinstein reported having no conflicts of interest.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Topical options for acne patients continue to expand
yet they are likely underused in today’s clinical practice.
A study of prescribing practices from 2012 to 2014 indicated that dermatologists prescribed retinoids for just 58.8% of acne cases, while nondermatologists prescribed them for only 32.4% of cases. “If the guidelines are telling us that we should use topical retinoids for almost all of our acne patients, why are we using them for half of the patients?” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, asked during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “We have a lot of options today for topical retinoids,” she added, noting that, in the past few years, trifarotene cream 0.005% and new formulations of tazarotene lotion (0.045%) and tretinoin lotion (0.05%) have become available.
According to Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, tazarotene has been considered the most efficacious topical retinoid but is generally the least well tolerated, while adapalene has often been considered to be one of the better-tolerated topical retinoids. “This is a broad generalization,” she said. “One should also take into account the concentration and formulation of the retinoid. Cutaneous adverse events increase in severity as the concentration increases regardless of the vehicle.” There are no studies comparing trifarotene with other topical retinoids, she added.
In two phase 2, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies (PERFECT 1 and PERFECT 2), researchers randomized more than 2,400 patients with moderate facial or truncal acne to receive trifarotene cream or a vehicle for 12 weeks. The mean percent change from baseline in facial inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated group was –54.4% and –66.2% in PERFECT 1, and PERFECT 2, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in facial noninflammatory lesions was –49.7% and –57.7%, respectively.
In addition, the mean percent change from baseline in truncal inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated groups was –57.4% and –65.4%, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in truncal noninflammatory lesions was –49.1% and –55.2%, respectively.
The choice of vehicle may affect absorption of topical retinoids, and some formulations may increase skin hydration and decrease transepidermal water loss, “which is a good thing,” Dr. Graber said. “Also, vehicles aim to slow drug delivery over time while also making sure that the drug penetrates into the pilosebaceous unit.”
One recent advance is the honeycomb-like polymeric emulsion technology found in tretinoin 0.05% lotion and tazarotene 0.045% lotion. These formulations contain droplets of the tretinoin and tazarotene embedded in a honeycomb matrix with hydrating agents. “I think this is exciting and could enhance our patient compliance and tolerability,” she said. Another unique feature about these two products, especially the tretinoin product, is the very small particle size with this new formulation. “It’s small enough that it can penetrate down into the pilosebaceous unit,” which is different than with older formulations, in which the tretinoin “largely just sat on the surface of the skin and didn’t penetrate into the pilosebaceous unit.” In addition, she said, “there’s only 9% degradation of the tretinoin in UV light, compared to 72% degradation of standard tretinoin 0.025% gel, and with the new tretinoin formulation, there’s no degradation when used with benzoyl peroxide.”
Another new topical retinoid to consider is a fixed-dose combination of encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and encapsulated tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the treatment of acne in adults and children aged 9 years and older. “Typically, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin cannot be mixed in the same tube to stability issues,” she said. “Here, each product is individually encapsulated in a silica shell so that they can be applied together.”
The approval was supported by positive results from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter studies (NCT03761784 and NCT03761810), in which Twyneo demonstrated efficacy and a favorable tolerability profile in patients aged 9 years and older with facial acne.
Another topical treatment option, dapsone, is now FDA approved for ages 9 and up, expanded from its initial indication for ages 12 and up. The new indication is based on a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study in which acne patients aged 9-11 years applied dapsone 7.5% gel once daily to the face and acne-affected areas on the upper chest, upper back, and shoulders for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, facial acne was clear or almost clear in about 47% of patients. “Inflammatory, noninflammatory, and total lesions decreased from baseline, but there was a greater reduction in noninflammatory lesions, so if you have a very young patient with acne, now you can consider dapsone gel,” Dr. Graber said.
In August 2020, clascoterone cream became the first topical androgen receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years of age and older. It is a drug believed to address sebum and inflammation directly in the sebaceous gland and is structurally similar to dihydrotestosterone and spironolactone.
“This is a completely new drug category in acne,” she said. “Unlike all oral antiandrogen therapies, clascoterone cream can be used in both males and females with acne. It’s the first acne drug to have a new mechanism of action in almost 40 years, since isotretinoin was approved in 1982.”
In vitro, she continued, clascoterone competes with dihydrotestosterone for binding to the androgen receptor, inhibiting downstream signaling and leading to inhibited sebum production, reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Two phase 3 studies that led to its approval involved 1,440 patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-58 years. The cream was applied twice a day for 12 weeks and treatment adherence was approximately 90%. The researchers found that clascoterone cream was significantly more effective than vehicle cream at achieving Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), the definition of treatment success in the study, and reducing noninflammatory lesion and inflammatory lesion counts at week 12. “There were no safety issues noted during these studies, and clascoterone cream was well tolerated,” Dr. Graber said.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Commentary by Lawrence W. Eichenfield, MD
Acne vulgaris remains an issue of tremendous importance to preteens, teens, and young adults, with approximately 85% of individuals aged 12-24 being affected. Expanding options for topical treatments may help bring effective disease control. Dr. Graber pointed out that historically, pediatricians and other primary care practitioners utilize topical retinoids less often for acne care as compared with dermatologists or guidelines recommendations (either the AAP’s or AAD’s). There are now expanded options, including over-the-counter retinoids (adapalene 0.1% gel), generic and trade brand topical tretinoin products, prescription adapalene medications, older and recently approved tazarotene products, and a newer type of topical retinoid, trifarotene. Novel formulations and emulsion technology, as well as retinoid developed in combination products, give more options in patients down to 9 years of age. A novel topical anti-androgen, clascoterone, is in its own category, as the first topical “hormonal agent,” allowing hormonal therapy to be used for males as well as females (aged 12 years and up). A recent review in JAMA (2021 Nov 23;326[20]:2055-67) incorporates many of these newer medications into management suggestions, emphasizing that first-line therapies are topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or combinations of topicals, whereas in more severe disease, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline, hormonal therapies such as combination oral conceptive agents or spironolactone, or isotretinoin are most effective.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
yet they are likely underused in today’s clinical practice.
A study of prescribing practices from 2012 to 2014 indicated that dermatologists prescribed retinoids for just 58.8% of acne cases, while nondermatologists prescribed them for only 32.4% of cases. “If the guidelines are telling us that we should use topical retinoids for almost all of our acne patients, why are we using them for half of the patients?” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, asked during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “We have a lot of options today for topical retinoids,” she added, noting that, in the past few years, trifarotene cream 0.005% and new formulations of tazarotene lotion (0.045%) and tretinoin lotion (0.05%) have become available.
According to Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, tazarotene has been considered the most efficacious topical retinoid but is generally the least well tolerated, while adapalene has often been considered to be one of the better-tolerated topical retinoids. “This is a broad generalization,” she said. “One should also take into account the concentration and formulation of the retinoid. Cutaneous adverse events increase in severity as the concentration increases regardless of the vehicle.” There are no studies comparing trifarotene with other topical retinoids, she added.
In two phase 2, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies (PERFECT 1 and PERFECT 2), researchers randomized more than 2,400 patients with moderate facial or truncal acne to receive trifarotene cream or a vehicle for 12 weeks. The mean percent change from baseline in facial inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated group was –54.4% and –66.2% in PERFECT 1, and PERFECT 2, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in facial noninflammatory lesions was –49.7% and –57.7%, respectively.
In addition, the mean percent change from baseline in truncal inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated groups was –57.4% and –65.4%, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in truncal noninflammatory lesions was –49.1% and –55.2%, respectively.
The choice of vehicle may affect absorption of topical retinoids, and some formulations may increase skin hydration and decrease transepidermal water loss, “which is a good thing,” Dr. Graber said. “Also, vehicles aim to slow drug delivery over time while also making sure that the drug penetrates into the pilosebaceous unit.”
One recent advance is the honeycomb-like polymeric emulsion technology found in tretinoin 0.05% lotion and tazarotene 0.045% lotion. These formulations contain droplets of the tretinoin and tazarotene embedded in a honeycomb matrix with hydrating agents. “I think this is exciting and could enhance our patient compliance and tolerability,” she said. Another unique feature about these two products, especially the tretinoin product, is the very small particle size with this new formulation. “It’s small enough that it can penetrate down into the pilosebaceous unit,” which is different than with older formulations, in which the tretinoin “largely just sat on the surface of the skin and didn’t penetrate into the pilosebaceous unit.” In addition, she said, “there’s only 9% degradation of the tretinoin in UV light, compared to 72% degradation of standard tretinoin 0.025% gel, and with the new tretinoin formulation, there’s no degradation when used with benzoyl peroxide.”
Another new topical retinoid to consider is a fixed-dose combination of encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and encapsulated tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the treatment of acne in adults and children aged 9 years and older. “Typically, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin cannot be mixed in the same tube to stability issues,” she said. “Here, each product is individually encapsulated in a silica shell so that they can be applied together.”
The approval was supported by positive results from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter studies (NCT03761784 and NCT03761810), in which Twyneo demonstrated efficacy and a favorable tolerability profile in patients aged 9 years and older with facial acne.
Another topical treatment option, dapsone, is now FDA approved for ages 9 and up, expanded from its initial indication for ages 12 and up. The new indication is based on a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study in which acne patients aged 9-11 years applied dapsone 7.5% gel once daily to the face and acne-affected areas on the upper chest, upper back, and shoulders for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, facial acne was clear or almost clear in about 47% of patients. “Inflammatory, noninflammatory, and total lesions decreased from baseline, but there was a greater reduction in noninflammatory lesions, so if you have a very young patient with acne, now you can consider dapsone gel,” Dr. Graber said.
In August 2020, clascoterone cream became the first topical androgen receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years of age and older. It is a drug believed to address sebum and inflammation directly in the sebaceous gland and is structurally similar to dihydrotestosterone and spironolactone.
“This is a completely new drug category in acne,” she said. “Unlike all oral antiandrogen therapies, clascoterone cream can be used in both males and females with acne. It’s the first acne drug to have a new mechanism of action in almost 40 years, since isotretinoin was approved in 1982.”
In vitro, she continued, clascoterone competes with dihydrotestosterone for binding to the androgen receptor, inhibiting downstream signaling and leading to inhibited sebum production, reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Two phase 3 studies that led to its approval involved 1,440 patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-58 years. The cream was applied twice a day for 12 weeks and treatment adherence was approximately 90%. The researchers found that clascoterone cream was significantly more effective than vehicle cream at achieving Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), the definition of treatment success in the study, and reducing noninflammatory lesion and inflammatory lesion counts at week 12. “There were no safety issues noted during these studies, and clascoterone cream was well tolerated,” Dr. Graber said.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Commentary by Lawrence W. Eichenfield, MD
Acne vulgaris remains an issue of tremendous importance to preteens, teens, and young adults, with approximately 85% of individuals aged 12-24 being affected. Expanding options for topical treatments may help bring effective disease control. Dr. Graber pointed out that historically, pediatricians and other primary care practitioners utilize topical retinoids less often for acne care as compared with dermatologists or guidelines recommendations (either the AAP’s or AAD’s). There are now expanded options, including over-the-counter retinoids (adapalene 0.1% gel), generic and trade brand topical tretinoin products, prescription adapalene medications, older and recently approved tazarotene products, and a newer type of topical retinoid, trifarotene. Novel formulations and emulsion technology, as well as retinoid developed in combination products, give more options in patients down to 9 years of age. A novel topical anti-androgen, clascoterone, is in its own category, as the first topical “hormonal agent,” allowing hormonal therapy to be used for males as well as females (aged 12 years and up). A recent review in JAMA (2021 Nov 23;326[20]:2055-67) incorporates many of these newer medications into management suggestions, emphasizing that first-line therapies are topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or combinations of topicals, whereas in more severe disease, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline, hormonal therapies such as combination oral conceptive agents or spironolactone, or isotretinoin are most effective.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
yet they are likely underused in today’s clinical practice.
A study of prescribing practices from 2012 to 2014 indicated that dermatologists prescribed retinoids for just 58.8% of acne cases, while nondermatologists prescribed them for only 32.4% of cases. “If the guidelines are telling us that we should use topical retinoids for almost all of our acne patients, why are we using them for half of the patients?” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, asked during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “We have a lot of options today for topical retinoids,” she added, noting that, in the past few years, trifarotene cream 0.005% and new formulations of tazarotene lotion (0.045%) and tretinoin lotion (0.05%) have become available.
According to Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, tazarotene has been considered the most efficacious topical retinoid but is generally the least well tolerated, while adapalene has often been considered to be one of the better-tolerated topical retinoids. “This is a broad generalization,” she said. “One should also take into account the concentration and formulation of the retinoid. Cutaneous adverse events increase in severity as the concentration increases regardless of the vehicle.” There are no studies comparing trifarotene with other topical retinoids, she added.
In two phase 2, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies (PERFECT 1 and PERFECT 2), researchers randomized more than 2,400 patients with moderate facial or truncal acne to receive trifarotene cream or a vehicle for 12 weeks. The mean percent change from baseline in facial inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated group was –54.4% and –66.2% in PERFECT 1, and PERFECT 2, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in facial noninflammatory lesions was –49.7% and –57.7%, respectively.
In addition, the mean percent change from baseline in truncal inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated groups was –57.4% and –65.4%, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in truncal noninflammatory lesions was –49.1% and –55.2%, respectively.
The choice of vehicle may affect absorption of topical retinoids, and some formulations may increase skin hydration and decrease transepidermal water loss, “which is a good thing,” Dr. Graber said. “Also, vehicles aim to slow drug delivery over time while also making sure that the drug penetrates into the pilosebaceous unit.”
One recent advance is the honeycomb-like polymeric emulsion technology found in tretinoin 0.05% lotion and tazarotene 0.045% lotion. These formulations contain droplets of the tretinoin and tazarotene embedded in a honeycomb matrix with hydrating agents. “I think this is exciting and could enhance our patient compliance and tolerability,” she said. Another unique feature about these two products, especially the tretinoin product, is the very small particle size with this new formulation. “It’s small enough that it can penetrate down into the pilosebaceous unit,” which is different than with older formulations, in which the tretinoin “largely just sat on the surface of the skin and didn’t penetrate into the pilosebaceous unit.” In addition, she said, “there’s only 9% degradation of the tretinoin in UV light, compared to 72% degradation of standard tretinoin 0.025% gel, and with the new tretinoin formulation, there’s no degradation when used with benzoyl peroxide.”
Another new topical retinoid to consider is a fixed-dose combination of encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and encapsulated tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the treatment of acne in adults and children aged 9 years and older. “Typically, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin cannot be mixed in the same tube to stability issues,” she said. “Here, each product is individually encapsulated in a silica shell so that they can be applied together.”
The approval was supported by positive results from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter studies (NCT03761784 and NCT03761810), in which Twyneo demonstrated efficacy and a favorable tolerability profile in patients aged 9 years and older with facial acne.
Another topical treatment option, dapsone, is now FDA approved for ages 9 and up, expanded from its initial indication for ages 12 and up. The new indication is based on a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study in which acne patients aged 9-11 years applied dapsone 7.5% gel once daily to the face and acne-affected areas on the upper chest, upper back, and shoulders for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, facial acne was clear or almost clear in about 47% of patients. “Inflammatory, noninflammatory, and total lesions decreased from baseline, but there was a greater reduction in noninflammatory lesions, so if you have a very young patient with acne, now you can consider dapsone gel,” Dr. Graber said.
In August 2020, clascoterone cream became the first topical androgen receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years of age and older. It is a drug believed to address sebum and inflammation directly in the sebaceous gland and is structurally similar to dihydrotestosterone and spironolactone.
“This is a completely new drug category in acne,” she said. “Unlike all oral antiandrogen therapies, clascoterone cream can be used in both males and females with acne. It’s the first acne drug to have a new mechanism of action in almost 40 years, since isotretinoin was approved in 1982.”
In vitro, she continued, clascoterone competes with dihydrotestosterone for binding to the androgen receptor, inhibiting downstream signaling and leading to inhibited sebum production, reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Two phase 3 studies that led to its approval involved 1,440 patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-58 years. The cream was applied twice a day for 12 weeks and treatment adherence was approximately 90%. The researchers found that clascoterone cream was significantly more effective than vehicle cream at achieving Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), the definition of treatment success in the study, and reducing noninflammatory lesion and inflammatory lesion counts at week 12. “There were no safety issues noted during these studies, and clascoterone cream was well tolerated,” Dr. Graber said.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Commentary by Lawrence W. Eichenfield, MD
Acne vulgaris remains an issue of tremendous importance to preteens, teens, and young adults, with approximately 85% of individuals aged 12-24 being affected. Expanding options for topical treatments may help bring effective disease control. Dr. Graber pointed out that historically, pediatricians and other primary care practitioners utilize topical retinoids less often for acne care as compared with dermatologists or guidelines recommendations (either the AAP’s or AAD’s). There are now expanded options, including over-the-counter retinoids (adapalene 0.1% gel), generic and trade brand topical tretinoin products, prescription adapalene medications, older and recently approved tazarotene products, and a newer type of topical retinoid, trifarotene. Novel formulations and emulsion technology, as well as retinoid developed in combination products, give more options in patients down to 9 years of age. A novel topical anti-androgen, clascoterone, is in its own category, as the first topical “hormonal agent,” allowing hormonal therapy to be used for males as well as females (aged 12 years and up). A recent review in JAMA (2021 Nov 23;326[20]:2055-67) incorporates many of these newer medications into management suggestions, emphasizing that first-line therapies are topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or combinations of topicals, whereas in more severe disease, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline, hormonal therapies such as combination oral conceptive agents or spironolactone, or isotretinoin are most effective.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
FROM THE MEDSCAPELIVE LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR