User login
Helping teens make the switch from pediatrics to gynecology
For many adolescents, the first visit to a gynecologist can be intimidating. The prospect of meeting a new doctor who will ask prying, deeply personal questions about sex and menstruation is scary. And, in all likelihood, a parent, older sibling, or friend has warned them about the notorious pelvic exam.
The exact timing of when adolescent patients should start seeing a gynecologist varies based on when a patient starts puberty. Primary care physicians and pediatricians can help teens transition by referring patients to an adolescent-friendly practice and clearing up some of the misconceptions that surround the first gynecology visit. Gynecologists, on the other side of the referral, can help patients transition by guaranteeing confidentiality and creating a safe space for young patients.
This news organization interviewed three experts in adolescent health about when teens should start having their gynecological needs addressed and how their physicians can help them undergo that transition.
Age-appropriate care
“Most people get very limited information about their reproductive health,” said Anne-Marie E. Amies Oelschlager, MD, a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist at Seattle Children’s, Seattle, and a member of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) clinical consensus committee on gynecology.
Official guidelines from ACOG call for the initial reproductive health visit to take place between the ages of 13 and 15 years. The exact age may vary, however, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
For example, some patients begin menstruating early, at age 9 or 10, said Mary Romano, MD, MPH, a pediatrician and adolescent medicine specialist at Vanderbilt Children’s Hospital, Nashville, Tenn. Pediatricians who are uncomfortable educating young patients about menstruation should refer the patient to a gynecologist or a pediatric gynecologist for whom such discussions are routine.
If a patient does not have a menstrual cycle by age 14 or 15, that also should be addressed by a family physician or gynecologist, Dr. Romano added.
“The importance here is addressing the reproductive health of the teen starting really at the age of 10 or 12, or once puberty starts,” said Patricia S. Huguelet, MD, a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. In those early visits, the physician can provide “anticipatory guidance,” counseling the teen on what is normal in terms of menstruation, sex, and relationships, and addressing what is not, she said.
Ideally, patients who were designated female at birth but now identify as male or nonbinary will meet with a gynecologist early on in the gender affirmation process and a gynecologist will continue to consult as part of the patient’s interdisciplinary care team, added Dr. Romano, who counsels LGBTQ+ youth as part of her practice. A gynecologist may support these patients in myriad ways, including helping those who are considering or using puberty blockers and providing reproductive and health education to patients in a way that is sensitive to the patient’s gender identity.
Patient referrals
Some pediatricians and family practice physicians may be talking with their patients about topics such as menstrual cycles and contraception. But those who are uncomfortable asking adolescent patients about their reproductive and sexual health should refer them to a gynecologist or specialist in adolescent medicine, Dr. Romano advised.
“The biggest benefit I’ve noticed is often [patients] come from a pediatrician or family medicine provider and they often appreciate the opportunity to talk to a doctor they haven’t met before about the more personal questions they may have,” Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Referring adolescents to a specialist who has either trained in adolescent medicine or has experience treating that age group has benefits, Dr. Romano said. Clinicians with that experience understand adolescents are not “mini-adults” but have unique developmental and medical issues. How to counsel and educate them carries unique challenges, she said.
For example, heavy menstrual bleeding is a leading reason a patient – either an adult or an adolescent – presents to a gynecologist, Dr. Huguelet said. But the pathology differs vastly for those two age groups. For patients in their 30s and 40s, polyps and fibroids are common problems associated with heavy bleeding. Those conditions are rare in adolescents, whereas bleeding disorders are common, she said.
Most patients will continue to see their pediatricians and primary care providers for other issues. And in some areas, gynecologists can reinforce advice from pediatricians, such as encouraging patients to get the HPV vaccine, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Common misconceptions
Primary care physicians can also dispel common misconceptions teens – and their parents – have about gynecology. Some parents may believe that certain methods of birth control cause cancer or infertility, have concerns about the HPV vaccine, or think hormonal therapies are harmful, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said. But the biggest misconception involves the infamous pelvic exam.
“Lots of patients assume that every time they go to the gynecologist they are going to have a pelvic exam,” she said. “When I say, ‘We don’t have to do that,’ they are so relieved.”
Guidelines have changed since the parents of today’s teens were going to the gynecologist for the first time. Many patients now do not need an initial Pap smear until age 25, following a recent guideline change by the American Cancer Society. (ACOG is considering adopting the same stance but still recommends screening start at 21.) “Most patients do not need an exam, even when it comes to sexual health and screening [for sexually transmitted infections], that can be done without an exam,” Dr. Huguelet said.
Confidentiality and comfort
On the other side of the referral, gynecologists should follow several best practices to treat adolescent patients. Arguably the most important part of the initial gynecologic visit is to give patients the option of one-on-one time with the physician with no parent in the room. During that time, the physician should make it clear that what they discuss is confidential and will not be shared with their parent or guardian, Dr. Huguelet said. Patients should also have the option of having a friend or another nonparent individual in the room with them during this one-on-one time with the physician, particularly if the patient does not feel comfortable discussing sensitive subjects completely on her own.
Adolescents receive better care, disclose more, and perceive they are getting better care when the process is confidential, Dr. Romano said. Confidentiality does have limits, however, which physicians should also make sure their patients understand, according to the ACOG guidelines for the initial reproductive visit. These limitations can vary by state depending on issues related to mandatory reporting, insurance billing, and legal requirements of patient notifications of specific services such as abortion.
The use of electronic medical records has raised additional challenges when it comes to communicating privately with adolescent patients, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said. In her practice, she tries to ensure the adolescent is the one with the login information for their records. If not, her office will have the patient’s cell number to text or call securely.
“We feel strongly adolescents should be able to access reproductive health care, mental health care, and care for substance abuse disorders without parental notification,” Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Telehealth visits can also be helpful for adolescents coming to gynecology for the first time. And taking the time to establish a rapport with patients at the start of the visit is key, Dr. Huguelet said. By directing questions to the adolescent patient rather than the parent, Dr. Huguelet said, the physician demonstrates that the teen’s treatment needs come first.
ACOG has guidelines on other steps gynecology practices, including those that see both adults and teens, can take to make their offices and visits adolescent-friendly. These steps include asking patients about their preferred names and pronouns at the start of the visit or as part of the initial intake form, training office staff to be comfortable with issues related to adolescent sexuality and gender and sexual diversity among patients, providing a place for teens to wait separately from obstetrics patients, and having age-appropriate literature on hand for adolescents to learn about reproductive health.
After that first reproductive health visit, gynecologists and primary care providers should partner to ensure the whole health of their patients is being addressed, Dr. Huguelet said.
“Collaboration is always going to better serve patients in any area,” said Dr. Romano, “and certainly this area is no different.”
Dr. Amies Oelschlager, Dr. Romano, and Dr. Huguelet have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For many adolescents, the first visit to a gynecologist can be intimidating. The prospect of meeting a new doctor who will ask prying, deeply personal questions about sex and menstruation is scary. And, in all likelihood, a parent, older sibling, or friend has warned them about the notorious pelvic exam.
The exact timing of when adolescent patients should start seeing a gynecologist varies based on when a patient starts puberty. Primary care physicians and pediatricians can help teens transition by referring patients to an adolescent-friendly practice and clearing up some of the misconceptions that surround the first gynecology visit. Gynecologists, on the other side of the referral, can help patients transition by guaranteeing confidentiality and creating a safe space for young patients.
This news organization interviewed three experts in adolescent health about when teens should start having their gynecological needs addressed and how their physicians can help them undergo that transition.
Age-appropriate care
“Most people get very limited information about their reproductive health,” said Anne-Marie E. Amies Oelschlager, MD, a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist at Seattle Children’s, Seattle, and a member of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) clinical consensus committee on gynecology.
Official guidelines from ACOG call for the initial reproductive health visit to take place between the ages of 13 and 15 years. The exact age may vary, however, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
For example, some patients begin menstruating early, at age 9 or 10, said Mary Romano, MD, MPH, a pediatrician and adolescent medicine specialist at Vanderbilt Children’s Hospital, Nashville, Tenn. Pediatricians who are uncomfortable educating young patients about menstruation should refer the patient to a gynecologist or a pediatric gynecologist for whom such discussions are routine.
If a patient does not have a menstrual cycle by age 14 or 15, that also should be addressed by a family physician or gynecologist, Dr. Romano added.
“The importance here is addressing the reproductive health of the teen starting really at the age of 10 or 12, or once puberty starts,” said Patricia S. Huguelet, MD, a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. In those early visits, the physician can provide “anticipatory guidance,” counseling the teen on what is normal in terms of menstruation, sex, and relationships, and addressing what is not, she said.
Ideally, patients who were designated female at birth but now identify as male or nonbinary will meet with a gynecologist early on in the gender affirmation process and a gynecologist will continue to consult as part of the patient’s interdisciplinary care team, added Dr. Romano, who counsels LGBTQ+ youth as part of her practice. A gynecologist may support these patients in myriad ways, including helping those who are considering or using puberty blockers and providing reproductive and health education to patients in a way that is sensitive to the patient’s gender identity.
Patient referrals
Some pediatricians and family practice physicians may be talking with their patients about topics such as menstrual cycles and contraception. But those who are uncomfortable asking adolescent patients about their reproductive and sexual health should refer them to a gynecologist or specialist in adolescent medicine, Dr. Romano advised.
“The biggest benefit I’ve noticed is often [patients] come from a pediatrician or family medicine provider and they often appreciate the opportunity to talk to a doctor they haven’t met before about the more personal questions they may have,” Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Referring adolescents to a specialist who has either trained in adolescent medicine or has experience treating that age group has benefits, Dr. Romano said. Clinicians with that experience understand adolescents are not “mini-adults” but have unique developmental and medical issues. How to counsel and educate them carries unique challenges, she said.
For example, heavy menstrual bleeding is a leading reason a patient – either an adult or an adolescent – presents to a gynecologist, Dr. Huguelet said. But the pathology differs vastly for those two age groups. For patients in their 30s and 40s, polyps and fibroids are common problems associated with heavy bleeding. Those conditions are rare in adolescents, whereas bleeding disorders are common, she said.
Most patients will continue to see their pediatricians and primary care providers for other issues. And in some areas, gynecologists can reinforce advice from pediatricians, such as encouraging patients to get the HPV vaccine, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Common misconceptions
Primary care physicians can also dispel common misconceptions teens – and their parents – have about gynecology. Some parents may believe that certain methods of birth control cause cancer or infertility, have concerns about the HPV vaccine, or think hormonal therapies are harmful, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said. But the biggest misconception involves the infamous pelvic exam.
“Lots of patients assume that every time they go to the gynecologist they are going to have a pelvic exam,” she said. “When I say, ‘We don’t have to do that,’ they are so relieved.”
Guidelines have changed since the parents of today’s teens were going to the gynecologist for the first time. Many patients now do not need an initial Pap smear until age 25, following a recent guideline change by the American Cancer Society. (ACOG is considering adopting the same stance but still recommends screening start at 21.) “Most patients do not need an exam, even when it comes to sexual health and screening [for sexually transmitted infections], that can be done without an exam,” Dr. Huguelet said.
Confidentiality and comfort
On the other side of the referral, gynecologists should follow several best practices to treat adolescent patients. Arguably the most important part of the initial gynecologic visit is to give patients the option of one-on-one time with the physician with no parent in the room. During that time, the physician should make it clear that what they discuss is confidential and will not be shared with their parent or guardian, Dr. Huguelet said. Patients should also have the option of having a friend or another nonparent individual in the room with them during this one-on-one time with the physician, particularly if the patient does not feel comfortable discussing sensitive subjects completely on her own.
Adolescents receive better care, disclose more, and perceive they are getting better care when the process is confidential, Dr. Romano said. Confidentiality does have limits, however, which physicians should also make sure their patients understand, according to the ACOG guidelines for the initial reproductive visit. These limitations can vary by state depending on issues related to mandatory reporting, insurance billing, and legal requirements of patient notifications of specific services such as abortion.
The use of electronic medical records has raised additional challenges when it comes to communicating privately with adolescent patients, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said. In her practice, she tries to ensure the adolescent is the one with the login information for their records. If not, her office will have the patient’s cell number to text or call securely.
“We feel strongly adolescents should be able to access reproductive health care, mental health care, and care for substance abuse disorders without parental notification,” Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Telehealth visits can also be helpful for adolescents coming to gynecology for the first time. And taking the time to establish a rapport with patients at the start of the visit is key, Dr. Huguelet said. By directing questions to the adolescent patient rather than the parent, Dr. Huguelet said, the physician demonstrates that the teen’s treatment needs come first.
ACOG has guidelines on other steps gynecology practices, including those that see both adults and teens, can take to make their offices and visits adolescent-friendly. These steps include asking patients about their preferred names and pronouns at the start of the visit or as part of the initial intake form, training office staff to be comfortable with issues related to adolescent sexuality and gender and sexual diversity among patients, providing a place for teens to wait separately from obstetrics patients, and having age-appropriate literature on hand for adolescents to learn about reproductive health.
After that first reproductive health visit, gynecologists and primary care providers should partner to ensure the whole health of their patients is being addressed, Dr. Huguelet said.
“Collaboration is always going to better serve patients in any area,” said Dr. Romano, “and certainly this area is no different.”
Dr. Amies Oelschlager, Dr. Romano, and Dr. Huguelet have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For many adolescents, the first visit to a gynecologist can be intimidating. The prospect of meeting a new doctor who will ask prying, deeply personal questions about sex and menstruation is scary. And, in all likelihood, a parent, older sibling, or friend has warned them about the notorious pelvic exam.
The exact timing of when adolescent patients should start seeing a gynecologist varies based on when a patient starts puberty. Primary care physicians and pediatricians can help teens transition by referring patients to an adolescent-friendly practice and clearing up some of the misconceptions that surround the first gynecology visit. Gynecologists, on the other side of the referral, can help patients transition by guaranteeing confidentiality and creating a safe space for young patients.
This news organization interviewed three experts in adolescent health about when teens should start having their gynecological needs addressed and how their physicians can help them undergo that transition.
Age-appropriate care
“Most people get very limited information about their reproductive health,” said Anne-Marie E. Amies Oelschlager, MD, a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist at Seattle Children’s, Seattle, and a member of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) clinical consensus committee on gynecology.
Official guidelines from ACOG call for the initial reproductive health visit to take place between the ages of 13 and 15 years. The exact age may vary, however, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
For example, some patients begin menstruating early, at age 9 or 10, said Mary Romano, MD, MPH, a pediatrician and adolescent medicine specialist at Vanderbilt Children’s Hospital, Nashville, Tenn. Pediatricians who are uncomfortable educating young patients about menstruation should refer the patient to a gynecologist or a pediatric gynecologist for whom such discussions are routine.
If a patient does not have a menstrual cycle by age 14 or 15, that also should be addressed by a family physician or gynecologist, Dr. Romano added.
“The importance here is addressing the reproductive health of the teen starting really at the age of 10 or 12, or once puberty starts,” said Patricia S. Huguelet, MD, a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. In those early visits, the physician can provide “anticipatory guidance,” counseling the teen on what is normal in terms of menstruation, sex, and relationships, and addressing what is not, she said.
Ideally, patients who were designated female at birth but now identify as male or nonbinary will meet with a gynecologist early on in the gender affirmation process and a gynecologist will continue to consult as part of the patient’s interdisciplinary care team, added Dr. Romano, who counsels LGBTQ+ youth as part of her practice. A gynecologist may support these patients in myriad ways, including helping those who are considering or using puberty blockers and providing reproductive and health education to patients in a way that is sensitive to the patient’s gender identity.
Patient referrals
Some pediatricians and family practice physicians may be talking with their patients about topics such as menstrual cycles and contraception. But those who are uncomfortable asking adolescent patients about their reproductive and sexual health should refer them to a gynecologist or specialist in adolescent medicine, Dr. Romano advised.
“The biggest benefit I’ve noticed is often [patients] come from a pediatrician or family medicine provider and they often appreciate the opportunity to talk to a doctor they haven’t met before about the more personal questions they may have,” Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Referring adolescents to a specialist who has either trained in adolescent medicine or has experience treating that age group has benefits, Dr. Romano said. Clinicians with that experience understand adolescents are not “mini-adults” but have unique developmental and medical issues. How to counsel and educate them carries unique challenges, she said.
For example, heavy menstrual bleeding is a leading reason a patient – either an adult or an adolescent – presents to a gynecologist, Dr. Huguelet said. But the pathology differs vastly for those two age groups. For patients in their 30s and 40s, polyps and fibroids are common problems associated with heavy bleeding. Those conditions are rare in adolescents, whereas bleeding disorders are common, she said.
Most patients will continue to see their pediatricians and primary care providers for other issues. And in some areas, gynecologists can reinforce advice from pediatricians, such as encouraging patients to get the HPV vaccine, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Common misconceptions
Primary care physicians can also dispel common misconceptions teens – and their parents – have about gynecology. Some parents may believe that certain methods of birth control cause cancer or infertility, have concerns about the HPV vaccine, or think hormonal therapies are harmful, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said. But the biggest misconception involves the infamous pelvic exam.
“Lots of patients assume that every time they go to the gynecologist they are going to have a pelvic exam,” she said. “When I say, ‘We don’t have to do that,’ they are so relieved.”
Guidelines have changed since the parents of today’s teens were going to the gynecologist for the first time. Many patients now do not need an initial Pap smear until age 25, following a recent guideline change by the American Cancer Society. (ACOG is considering adopting the same stance but still recommends screening start at 21.) “Most patients do not need an exam, even when it comes to sexual health and screening [for sexually transmitted infections], that can be done without an exam,” Dr. Huguelet said.
Confidentiality and comfort
On the other side of the referral, gynecologists should follow several best practices to treat adolescent patients. Arguably the most important part of the initial gynecologic visit is to give patients the option of one-on-one time with the physician with no parent in the room. During that time, the physician should make it clear that what they discuss is confidential and will not be shared with their parent or guardian, Dr. Huguelet said. Patients should also have the option of having a friend or another nonparent individual in the room with them during this one-on-one time with the physician, particularly if the patient does not feel comfortable discussing sensitive subjects completely on her own.
Adolescents receive better care, disclose more, and perceive they are getting better care when the process is confidential, Dr. Romano said. Confidentiality does have limits, however, which physicians should also make sure their patients understand, according to the ACOG guidelines for the initial reproductive visit. These limitations can vary by state depending on issues related to mandatory reporting, insurance billing, and legal requirements of patient notifications of specific services such as abortion.
The use of electronic medical records has raised additional challenges when it comes to communicating privately with adolescent patients, Dr. Amies Oelschlager said. In her practice, she tries to ensure the adolescent is the one with the login information for their records. If not, her office will have the patient’s cell number to text or call securely.
“We feel strongly adolescents should be able to access reproductive health care, mental health care, and care for substance abuse disorders without parental notification,” Dr. Amies Oelschlager said.
Telehealth visits can also be helpful for adolescents coming to gynecology for the first time. And taking the time to establish a rapport with patients at the start of the visit is key, Dr. Huguelet said. By directing questions to the adolescent patient rather than the parent, Dr. Huguelet said, the physician demonstrates that the teen’s treatment needs come first.
ACOG has guidelines on other steps gynecology practices, including those that see both adults and teens, can take to make their offices and visits adolescent-friendly. These steps include asking patients about their preferred names and pronouns at the start of the visit or as part of the initial intake form, training office staff to be comfortable with issues related to adolescent sexuality and gender and sexual diversity among patients, providing a place for teens to wait separately from obstetrics patients, and having age-appropriate literature on hand for adolescents to learn about reproductive health.
After that first reproductive health visit, gynecologists and primary care providers should partner to ensure the whole health of their patients is being addressed, Dr. Huguelet said.
“Collaboration is always going to better serve patients in any area,” said Dr. Romano, “and certainly this area is no different.”
Dr. Amies Oelschlager, Dr. Romano, and Dr. Huguelet have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Outstanding’ outcomes: Reduced postop radiation in HPV, oropharynx cancer
Less can sometimes be more.
In the phase 2 trial, 95% of patients with locally advanced oropharynx cancer and HPV remained progression free at 2 years following reduced-dose radiation therapy (50 Gy), compared with 96% of patients receiving standard-dose radiation therapy (60 Gy). Both groups avoided chemotherapy as well.
The results, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, suggest that postoperative radiation therapy at 50 Gy without chemotherapy was safe and effective in this intermediate-risk subset of patients, the authors concluded.
Although it’s hard for one trial to define standard of care, this study “may be an example of a practice-changing phase 2 [trial],” said lead author Robert L. Ferris, MD, PhD, director of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hillman Cancer Center. “We and others have adopted 50 Gy without chemo as our adjuvant treatment for up to 4 positive nodes and 1 mm of extranodal extension.”
Treatment deintensification for patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer is an active area of investigation, but whether undergoing transoral surgery can allow intermediate-risk patients to receive a lower dose of adjuvant therapy remains uncertain.
Recent results from a phase 3 trial, presented during the plenary session at the 2021 annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology, showed that de-escalated adjuvant radiation therapy resulted in robust responses and lower toxicity as compared with standard care radiotherapy in patients with HPV and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
The goal of the current ECON-ACRIN (E3311) trial was to prospectively assess the 2-year progression-free survival of transoral surgery and reduced adjuvant therapy in intermediate-risk patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer.
The phase 2 trial included 359 patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer who underwent surgery and were then assigned to one of four treatment groups based on individual risk factors for recurrence: low-risk patients under observation (arm A); intermediate-risk patients receiving low-dose radiation therapy (50 Gy, arm B) and those receiving standard-dose radiation (60 Gy, arm C) both without chemotherapy; and finally high-risk patients receiving chemotherapy in combination with high-dose radiation (arm D).
Among patients who underwent transoral surgery, 11% were assigned to arm A, 28% and 30% were randomly allocated to arms B and C, respectively, and 31% were assigned to arm D. For those who underwent transoral laser microsurgery, 11% were assigned to arm A, 32% and 24% were randomly allocated to arms B and C, respectively, and 34% were assigned to arm D.
Almost all patients (95%) in arm B remained progression free at 2 years after receiving reduced-dose radiation therapy. This rate of progression-free survival aligned with those observed in the other cohorts: 91% in high-risk patients receiving chemotherapy in combination with standard 66 Gy high-dose radiation, 96% in intermediate-risk patients in the 60 Gy standard-dose radiation arm, and 97% in the low-risk observation arm.
Although progression-free survival did not differ statistically between the arms (P = .90 for B vs. C; P = .30 for B vs. D; P = .30 for C vs. D), the authors urged caution when interpreting the results because the study was not powered to compare arms B and C directly.
Overall, these results show that “we could reduce radiation therapy and eliminate chemotherapy for 70% of patients,” Dr. Ferris said in an interview. Plus, “a small group of the lowest-risk [patients] did well with surgery alone.”
Regarding outcomes for quality of life (functional assessment of cancer therapy–head and neck) and swallowing (MD Anderson Dysphagia Index), patients reported a consistent decline in both during treatment. Patient scores, however, recovered to baseline levels in arms A-C and remained slightly lower after adjuvant therapy in arm D; however, it is unknown whether differences will emerge over a longer-term period.
Bhishamjit S. Chera, MD, an associate professor and radiation oncologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, noted that reduced doses are not the current standard of care but it’s the “direction we’re headed.”
“I have started to use lower doses in selected patients” and other experts are offering it as well, said Dr. Chera, who was not involved in the research.
He also said that patients appear very interested in participating in lower-intensity therapy, judging by how rapidly accrual is for clinical trials of this nature.
However, caution is warranted.
“You have to be careful when you reduce intensity and there are different ways of doing it,” Dr. Chera said. “It’s not ready for community practice, and if it is offered to patients, it needs to be explained carefully with informed consent.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferris has disclosed relationships Novasenta, Merck, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Numab, Macrogenics, Aduro Biotech, Sanofi, Zymeworks, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, and Tesaro. Dr. Chera disclosed stock and other ownership interests in Naveris, and a consulting or advisory role with Naveris. He is a coinventor on a patent application regarding a method for measuring tumor-derived viral nucleic acids in blood samples, which is owned by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and licensed to Naveris.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Less can sometimes be more.
In the phase 2 trial, 95% of patients with locally advanced oropharynx cancer and HPV remained progression free at 2 years following reduced-dose radiation therapy (50 Gy), compared with 96% of patients receiving standard-dose radiation therapy (60 Gy). Both groups avoided chemotherapy as well.
The results, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, suggest that postoperative radiation therapy at 50 Gy without chemotherapy was safe and effective in this intermediate-risk subset of patients, the authors concluded.
Although it’s hard for one trial to define standard of care, this study “may be an example of a practice-changing phase 2 [trial],” said lead author Robert L. Ferris, MD, PhD, director of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hillman Cancer Center. “We and others have adopted 50 Gy without chemo as our adjuvant treatment for up to 4 positive nodes and 1 mm of extranodal extension.”
Treatment deintensification for patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer is an active area of investigation, but whether undergoing transoral surgery can allow intermediate-risk patients to receive a lower dose of adjuvant therapy remains uncertain.
Recent results from a phase 3 trial, presented during the plenary session at the 2021 annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology, showed that de-escalated adjuvant radiation therapy resulted in robust responses and lower toxicity as compared with standard care radiotherapy in patients with HPV and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
The goal of the current ECON-ACRIN (E3311) trial was to prospectively assess the 2-year progression-free survival of transoral surgery and reduced adjuvant therapy in intermediate-risk patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer.
The phase 2 trial included 359 patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer who underwent surgery and were then assigned to one of four treatment groups based on individual risk factors for recurrence: low-risk patients under observation (arm A); intermediate-risk patients receiving low-dose radiation therapy (50 Gy, arm B) and those receiving standard-dose radiation (60 Gy, arm C) both without chemotherapy; and finally high-risk patients receiving chemotherapy in combination with high-dose radiation (arm D).
Among patients who underwent transoral surgery, 11% were assigned to arm A, 28% and 30% were randomly allocated to arms B and C, respectively, and 31% were assigned to arm D. For those who underwent transoral laser microsurgery, 11% were assigned to arm A, 32% and 24% were randomly allocated to arms B and C, respectively, and 34% were assigned to arm D.
Almost all patients (95%) in arm B remained progression free at 2 years after receiving reduced-dose radiation therapy. This rate of progression-free survival aligned with those observed in the other cohorts: 91% in high-risk patients receiving chemotherapy in combination with standard 66 Gy high-dose radiation, 96% in intermediate-risk patients in the 60 Gy standard-dose radiation arm, and 97% in the low-risk observation arm.
Although progression-free survival did not differ statistically between the arms (P = .90 for B vs. C; P = .30 for B vs. D; P = .30 for C vs. D), the authors urged caution when interpreting the results because the study was not powered to compare arms B and C directly.
Overall, these results show that “we could reduce radiation therapy and eliminate chemotherapy for 70% of patients,” Dr. Ferris said in an interview. Plus, “a small group of the lowest-risk [patients] did well with surgery alone.”
Regarding outcomes for quality of life (functional assessment of cancer therapy–head and neck) and swallowing (MD Anderson Dysphagia Index), patients reported a consistent decline in both during treatment. Patient scores, however, recovered to baseline levels in arms A-C and remained slightly lower after adjuvant therapy in arm D; however, it is unknown whether differences will emerge over a longer-term period.
Bhishamjit S. Chera, MD, an associate professor and radiation oncologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, noted that reduced doses are not the current standard of care but it’s the “direction we’re headed.”
“I have started to use lower doses in selected patients” and other experts are offering it as well, said Dr. Chera, who was not involved in the research.
He also said that patients appear very interested in participating in lower-intensity therapy, judging by how rapidly accrual is for clinical trials of this nature.
However, caution is warranted.
“You have to be careful when you reduce intensity and there are different ways of doing it,” Dr. Chera said. “It’s not ready for community practice, and if it is offered to patients, it needs to be explained carefully with informed consent.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferris has disclosed relationships Novasenta, Merck, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Numab, Macrogenics, Aduro Biotech, Sanofi, Zymeworks, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, and Tesaro. Dr. Chera disclosed stock and other ownership interests in Naveris, and a consulting or advisory role with Naveris. He is a coinventor on a patent application regarding a method for measuring tumor-derived viral nucleic acids in blood samples, which is owned by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and licensed to Naveris.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Less can sometimes be more.
In the phase 2 trial, 95% of patients with locally advanced oropharynx cancer and HPV remained progression free at 2 years following reduced-dose radiation therapy (50 Gy), compared with 96% of patients receiving standard-dose radiation therapy (60 Gy). Both groups avoided chemotherapy as well.
The results, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, suggest that postoperative radiation therapy at 50 Gy without chemotherapy was safe and effective in this intermediate-risk subset of patients, the authors concluded.
Although it’s hard for one trial to define standard of care, this study “may be an example of a practice-changing phase 2 [trial],” said lead author Robert L. Ferris, MD, PhD, director of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hillman Cancer Center. “We and others have adopted 50 Gy without chemo as our adjuvant treatment for up to 4 positive nodes and 1 mm of extranodal extension.”
Treatment deintensification for patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer is an active area of investigation, but whether undergoing transoral surgery can allow intermediate-risk patients to receive a lower dose of adjuvant therapy remains uncertain.
Recent results from a phase 3 trial, presented during the plenary session at the 2021 annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology, showed that de-escalated adjuvant radiation therapy resulted in robust responses and lower toxicity as compared with standard care radiotherapy in patients with HPV and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
The goal of the current ECON-ACRIN (E3311) trial was to prospectively assess the 2-year progression-free survival of transoral surgery and reduced adjuvant therapy in intermediate-risk patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer.
The phase 2 trial included 359 patients with HPV and oropharynx cancer who underwent surgery and were then assigned to one of four treatment groups based on individual risk factors for recurrence: low-risk patients under observation (arm A); intermediate-risk patients receiving low-dose radiation therapy (50 Gy, arm B) and those receiving standard-dose radiation (60 Gy, arm C) both without chemotherapy; and finally high-risk patients receiving chemotherapy in combination with high-dose radiation (arm D).
Among patients who underwent transoral surgery, 11% were assigned to arm A, 28% and 30% were randomly allocated to arms B and C, respectively, and 31% were assigned to arm D. For those who underwent transoral laser microsurgery, 11% were assigned to arm A, 32% and 24% were randomly allocated to arms B and C, respectively, and 34% were assigned to arm D.
Almost all patients (95%) in arm B remained progression free at 2 years after receiving reduced-dose radiation therapy. This rate of progression-free survival aligned with those observed in the other cohorts: 91% in high-risk patients receiving chemotherapy in combination with standard 66 Gy high-dose radiation, 96% in intermediate-risk patients in the 60 Gy standard-dose radiation arm, and 97% in the low-risk observation arm.
Although progression-free survival did not differ statistically between the arms (P = .90 for B vs. C; P = .30 for B vs. D; P = .30 for C vs. D), the authors urged caution when interpreting the results because the study was not powered to compare arms B and C directly.
Overall, these results show that “we could reduce radiation therapy and eliminate chemotherapy for 70% of patients,” Dr. Ferris said in an interview. Plus, “a small group of the lowest-risk [patients] did well with surgery alone.”
Regarding outcomes for quality of life (functional assessment of cancer therapy–head and neck) and swallowing (MD Anderson Dysphagia Index), patients reported a consistent decline in both during treatment. Patient scores, however, recovered to baseline levels in arms A-C and remained slightly lower after adjuvant therapy in arm D; however, it is unknown whether differences will emerge over a longer-term period.
Bhishamjit S. Chera, MD, an associate professor and radiation oncologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, noted that reduced doses are not the current standard of care but it’s the “direction we’re headed.”
“I have started to use lower doses in selected patients” and other experts are offering it as well, said Dr. Chera, who was not involved in the research.
He also said that patients appear very interested in participating in lower-intensity therapy, judging by how rapidly accrual is for clinical trials of this nature.
However, caution is warranted.
“You have to be careful when you reduce intensity and there are different ways of doing it,” Dr. Chera said. “It’s not ready for community practice, and if it is offered to patients, it needs to be explained carefully with informed consent.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferris has disclosed relationships Novasenta, Merck, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Numab, Macrogenics, Aduro Biotech, Sanofi, Zymeworks, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, and Tesaro. Dr. Chera disclosed stock and other ownership interests in Naveris, and a consulting or advisory role with Naveris. He is a coinventor on a patent application regarding a method for measuring tumor-derived viral nucleic acids in blood samples, which is owned by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and licensed to Naveris.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Itch-dominant atopic dermatitis often flies under the radar
In the clinical experience of Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH,
That’s because a disconnect often exists between clinician-reported and patient-reported outcome measures, Dr. Silverberg, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. For example, multiple studies showed only weak to moderate correlations between the patient-focused Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) and Average Pruritus NRS compared with clinician-reported outcomes such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), the objective SCORAD, body surface area (BSA), and the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD), with only moderate correlation coefficients ranging from 0.3 to 0.6.
“These findings suggest that clinician-reported outcome measures are poor indicators of the patient experience,” he said. “We need to do a better job capturing patient-reported outcomes to understand how patients are impacted. But there’s something more novel to this because the weak correlations may also suggest that itch and other symptoms follow a different course than the signs of the disease. Just because the lesions flare up doesn’t mean the itch does, and vice versa. Anecdotally, this came up at many patient encounters where the skin looked good, but the patient was miserable with itch.”
To understand how the combination of itch and lesion severity predicts the severity assessment, longitudinal course, burden, and treatment of AD, Dr. Silverberg and colleagues prospectively evaluated 592 adults with AD . They defined four different AD subsets using the verbal rating scale for NRS average itch combined with either the EASI, objective-SCORAD, or vIGA-AD as follows: mild-moderate itch and lesions (MI/ML), mild-moderate itch and severe lesions (MI/SL), severe itch and mild-moderate lesions (SI/ML; the itch dominant subset), and severe itch and lesions (SI/SL). They found that most patients had MI/ML (59.4%-62.3%), followed by SI/ML (21.3%-29.1%), SI/SL (6%-12.9%), and MI/SL (3.8%-6.4%). SI/ML was more common in female and Black patients.
In addition, patients with MI/SL or SI/ML described their AD as being more severe on patient global assessment and had poor quality of life (QOL) scores, while patients with SI/SL were most likely to describe their disease as severe and have poor QOL scores. Patients with SI/ML described their disease as being more severe overall, yet patients with MI/SL or SI/SL were far more likely to be assigned severe PGA scores by clinicians. “The patients who have severe itch and mild lesions consider their disease severe, but the clinician is missing it,” Dr. Silverberg said. “Occasionally they’re picking it up but they’re missing a lot of these severe itch cases when there are milder lesions.”
In other findings, patients who had baseline MI/SL, SI/ML, and SI/SL were associated with similar frequency of AD flares, periods of AD clearance/remission, more itch triggers, and longitudinal courses over time, “which is remarkable,” he said. “It means those that have severe itch, even when they have milder lesions, are going to have unstable, more persistent disease, and have a harder time keeping control of it, and are ultimately going to require systemic therapies.” In fact, most patients with SI/SL (57.8%-66.7%) and MI/SL (53.9%-57.7%) but fewer patients with MI/ML (36.7%-38.4%) and SI/ML (30.8%-32%) initiated systemic, biologic, or phototherapy for their AD during follow-up. “There is a real upshot here clinically, in that patients are just not getting stepped up appropriately to achieve better control of their disease when they have itch-dominant AD,” Dr. Silverberg said.
He described itch-dominant AD as a novel disease phenotype that requires further investigation. “Why is it that some patients are getting such severe itch and milder looking lesions?” he asked. “I don’t think it’s just a matter of poor outcome measures that we have. So, what is it? It’s not entirely clear. Clinically, itch-dominant AD is important as it relates to the issues of diversity and skin of color because in darker skin tones, we cannot easily appreciate erythema. We may totally miss the active lesions. I think that’s a big part of why we see this itch-dominant AD more commonly in Black patients. Therefore, it is so important to ask our patients about their symptoms and to assess the severity of itch. But, even if they have what we think are milder lesions and severe itch, we must recognize they may not be well controlled. They may not be happy. They may have poor quality of life, and they may need to be stepped up appropriately. We need a lot more information to guide the assessment and management of this important subset of patients.”
Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
In the clinical experience of Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH,
That’s because a disconnect often exists between clinician-reported and patient-reported outcome measures, Dr. Silverberg, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. For example, multiple studies showed only weak to moderate correlations between the patient-focused Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) and Average Pruritus NRS compared with clinician-reported outcomes such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), the objective SCORAD, body surface area (BSA), and the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD), with only moderate correlation coefficients ranging from 0.3 to 0.6.
“These findings suggest that clinician-reported outcome measures are poor indicators of the patient experience,” he said. “We need to do a better job capturing patient-reported outcomes to understand how patients are impacted. But there’s something more novel to this because the weak correlations may also suggest that itch and other symptoms follow a different course than the signs of the disease. Just because the lesions flare up doesn’t mean the itch does, and vice versa. Anecdotally, this came up at many patient encounters where the skin looked good, but the patient was miserable with itch.”
To understand how the combination of itch and lesion severity predicts the severity assessment, longitudinal course, burden, and treatment of AD, Dr. Silverberg and colleagues prospectively evaluated 592 adults with AD . They defined four different AD subsets using the verbal rating scale for NRS average itch combined with either the EASI, objective-SCORAD, or vIGA-AD as follows: mild-moderate itch and lesions (MI/ML), mild-moderate itch and severe lesions (MI/SL), severe itch and mild-moderate lesions (SI/ML; the itch dominant subset), and severe itch and lesions (SI/SL). They found that most patients had MI/ML (59.4%-62.3%), followed by SI/ML (21.3%-29.1%), SI/SL (6%-12.9%), and MI/SL (3.8%-6.4%). SI/ML was more common in female and Black patients.
In addition, patients with MI/SL or SI/ML described their AD as being more severe on patient global assessment and had poor quality of life (QOL) scores, while patients with SI/SL were most likely to describe their disease as severe and have poor QOL scores. Patients with SI/ML described their disease as being more severe overall, yet patients with MI/SL or SI/SL were far more likely to be assigned severe PGA scores by clinicians. “The patients who have severe itch and mild lesions consider their disease severe, but the clinician is missing it,” Dr. Silverberg said. “Occasionally they’re picking it up but they’re missing a lot of these severe itch cases when there are milder lesions.”
In other findings, patients who had baseline MI/SL, SI/ML, and SI/SL were associated with similar frequency of AD flares, periods of AD clearance/remission, more itch triggers, and longitudinal courses over time, “which is remarkable,” he said. “It means those that have severe itch, even when they have milder lesions, are going to have unstable, more persistent disease, and have a harder time keeping control of it, and are ultimately going to require systemic therapies.” In fact, most patients with SI/SL (57.8%-66.7%) and MI/SL (53.9%-57.7%) but fewer patients with MI/ML (36.7%-38.4%) and SI/ML (30.8%-32%) initiated systemic, biologic, or phototherapy for their AD during follow-up. “There is a real upshot here clinically, in that patients are just not getting stepped up appropriately to achieve better control of their disease when they have itch-dominant AD,” Dr. Silverberg said.
He described itch-dominant AD as a novel disease phenotype that requires further investigation. “Why is it that some patients are getting such severe itch and milder looking lesions?” he asked. “I don’t think it’s just a matter of poor outcome measures that we have. So, what is it? It’s not entirely clear. Clinically, itch-dominant AD is important as it relates to the issues of diversity and skin of color because in darker skin tones, we cannot easily appreciate erythema. We may totally miss the active lesions. I think that’s a big part of why we see this itch-dominant AD more commonly in Black patients. Therefore, it is so important to ask our patients about their symptoms and to assess the severity of itch. But, even if they have what we think are milder lesions and severe itch, we must recognize they may not be well controlled. They may not be happy. They may have poor quality of life, and they may need to be stepped up appropriately. We need a lot more information to guide the assessment and management of this important subset of patients.”
Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
In the clinical experience of Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH,
That’s because a disconnect often exists between clinician-reported and patient-reported outcome measures, Dr. Silverberg, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. For example, multiple studies showed only weak to moderate correlations between the patient-focused Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) and Average Pruritus NRS compared with clinician-reported outcomes such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), the objective SCORAD, body surface area (BSA), and the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD), with only moderate correlation coefficients ranging from 0.3 to 0.6.
“These findings suggest that clinician-reported outcome measures are poor indicators of the patient experience,” he said. “We need to do a better job capturing patient-reported outcomes to understand how patients are impacted. But there’s something more novel to this because the weak correlations may also suggest that itch and other symptoms follow a different course than the signs of the disease. Just because the lesions flare up doesn’t mean the itch does, and vice versa. Anecdotally, this came up at many patient encounters where the skin looked good, but the patient was miserable with itch.”
To understand how the combination of itch and lesion severity predicts the severity assessment, longitudinal course, burden, and treatment of AD, Dr. Silverberg and colleagues prospectively evaluated 592 adults with AD . They defined four different AD subsets using the verbal rating scale for NRS average itch combined with either the EASI, objective-SCORAD, or vIGA-AD as follows: mild-moderate itch and lesions (MI/ML), mild-moderate itch and severe lesions (MI/SL), severe itch and mild-moderate lesions (SI/ML; the itch dominant subset), and severe itch and lesions (SI/SL). They found that most patients had MI/ML (59.4%-62.3%), followed by SI/ML (21.3%-29.1%), SI/SL (6%-12.9%), and MI/SL (3.8%-6.4%). SI/ML was more common in female and Black patients.
In addition, patients with MI/SL or SI/ML described their AD as being more severe on patient global assessment and had poor quality of life (QOL) scores, while patients with SI/SL were most likely to describe their disease as severe and have poor QOL scores. Patients with SI/ML described their disease as being more severe overall, yet patients with MI/SL or SI/SL were far more likely to be assigned severe PGA scores by clinicians. “The patients who have severe itch and mild lesions consider their disease severe, but the clinician is missing it,” Dr. Silverberg said. “Occasionally they’re picking it up but they’re missing a lot of these severe itch cases when there are milder lesions.”
In other findings, patients who had baseline MI/SL, SI/ML, and SI/SL were associated with similar frequency of AD flares, periods of AD clearance/remission, more itch triggers, and longitudinal courses over time, “which is remarkable,” he said. “It means those that have severe itch, even when they have milder lesions, are going to have unstable, more persistent disease, and have a harder time keeping control of it, and are ultimately going to require systemic therapies.” In fact, most patients with SI/SL (57.8%-66.7%) and MI/SL (53.9%-57.7%) but fewer patients with MI/ML (36.7%-38.4%) and SI/ML (30.8%-32%) initiated systemic, biologic, or phototherapy for their AD during follow-up. “There is a real upshot here clinically, in that patients are just not getting stepped up appropriately to achieve better control of their disease when they have itch-dominant AD,” Dr. Silverberg said.
He described itch-dominant AD as a novel disease phenotype that requires further investigation. “Why is it that some patients are getting such severe itch and milder looking lesions?” he asked. “I don’t think it’s just a matter of poor outcome measures that we have. So, what is it? It’s not entirely clear. Clinically, itch-dominant AD is important as it relates to the issues of diversity and skin of color because in darker skin tones, we cannot easily appreciate erythema. We may totally miss the active lesions. I think that’s a big part of why we see this itch-dominant AD more commonly in Black patients. Therefore, it is so important to ask our patients about their symptoms and to assess the severity of itch. But, even if they have what we think are milder lesions and severe itch, we must recognize they may not be well controlled. They may not be happy. They may have poor quality of life, and they may need to be stepped up appropriately. We need a lot more information to guide the assessment and management of this important subset of patients.”
Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
10 reasons why Omicron could cause big destruction
As a physician first and a mental health clinician second, I hope to provide factual medical information on the Omicron variant to my patients, family members, and friends. I also try to remain curious instead of angry about why some choose not to vaccinate.
The most effective way to encourage people to obtain a vaccination is to use communication free of judgment and criticism, which allows a safe space for the unvaccinated to express their motivations and fears behind their current choice of not vaccinating and explore possible barriers to an alternative option that could lead to vaccination.
As an adult psychiatrist, ADHD specialist, and amateur COVID-19 expert, I’d like to offer 10 reasons why Omicron – which ironically means “small” in Latin, can still cause big destruction. Please share these 10 reasons with your patients.
- If you are not vaccinated, this virus will find you within the next few weeks and likely lead to severe symptoms.
- Long-haul symptoms from COVID-19 infection are still possible even for people who contract a milder case of the Omicron variant.
- The monoclonal antibody and antiviral treatments recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 are limited. For many reasons, now is not the best time to play Russian roulette and intentionally get infected with a “mild” variant.
- There are not enough testing sites or over-the-counter rapid COVID tests available to keep up with the demand, and the latter are cost prohibitive for many people.
- Emergency care during the next few weeks for unforeseen non–COVID-related illnesses, such as a sudden heart attack or stroke, may be affected by the shortage of medical providers because of illness, quarantine, and burnout.
- There will be fewer first responders, including EMTs, police officers, and firefighters, because of COVID quarantines from illness and exposure.
- Although most Americans oppose temporary shutdowns, de facto shutdowns might be necessary because of the absence of healthy, COVID-negative individuals to maintain a functional society.
- Omicron math is deceiving, since the risk of hospitalization with Omicron appears to be far lower than with the Delta variant. However, the higher volume of infections with Omicron will offset the lower severity leading to comparable numbers of hospitalizations.
- Omicron has made it difficult for some schools to reopen after the holiday break, and reopening might become even more difficult as the surge progresses. Many schools already were in desperate need of substitute teachers, bus drivers, and additional staff necessary for COVID safety precautions before the emergence of the Omicron variant.
- And, for a less altruistic reason, as if the nine reasons above weren’t enough – if infections continue, especially among the unvaccinated – where the virus mutates the most – this can lead to a trifecta variant that not only evades the immune system and is highly infectious but causes severe disease in both the unvaccinated as well as the vaccinated.
Because of its extremely high transmissibility, the Omicron variant – layered atop Delta – presents great risk to us as a society. We must do all we can as clinicians to educate our patients so that they can protect themselves and their families.
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
As a physician first and a mental health clinician second, I hope to provide factual medical information on the Omicron variant to my patients, family members, and friends. I also try to remain curious instead of angry about why some choose not to vaccinate.
The most effective way to encourage people to obtain a vaccination is to use communication free of judgment and criticism, which allows a safe space for the unvaccinated to express their motivations and fears behind their current choice of not vaccinating and explore possible barriers to an alternative option that could lead to vaccination.
As an adult psychiatrist, ADHD specialist, and amateur COVID-19 expert, I’d like to offer 10 reasons why Omicron – which ironically means “small” in Latin, can still cause big destruction. Please share these 10 reasons with your patients.
- If you are not vaccinated, this virus will find you within the next few weeks and likely lead to severe symptoms.
- Long-haul symptoms from COVID-19 infection are still possible even for people who contract a milder case of the Omicron variant.
- The monoclonal antibody and antiviral treatments recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 are limited. For many reasons, now is not the best time to play Russian roulette and intentionally get infected with a “mild” variant.
- There are not enough testing sites or over-the-counter rapid COVID tests available to keep up with the demand, and the latter are cost prohibitive for many people.
- Emergency care during the next few weeks for unforeseen non–COVID-related illnesses, such as a sudden heart attack or stroke, may be affected by the shortage of medical providers because of illness, quarantine, and burnout.
- There will be fewer first responders, including EMTs, police officers, and firefighters, because of COVID quarantines from illness and exposure.
- Although most Americans oppose temporary shutdowns, de facto shutdowns might be necessary because of the absence of healthy, COVID-negative individuals to maintain a functional society.
- Omicron math is deceiving, since the risk of hospitalization with Omicron appears to be far lower than with the Delta variant. However, the higher volume of infections with Omicron will offset the lower severity leading to comparable numbers of hospitalizations.
- Omicron has made it difficult for some schools to reopen after the holiday break, and reopening might become even more difficult as the surge progresses. Many schools already were in desperate need of substitute teachers, bus drivers, and additional staff necessary for COVID safety precautions before the emergence of the Omicron variant.
- And, for a less altruistic reason, as if the nine reasons above weren’t enough – if infections continue, especially among the unvaccinated – where the virus mutates the most – this can lead to a trifecta variant that not only evades the immune system and is highly infectious but causes severe disease in both the unvaccinated as well as the vaccinated.
Because of its extremely high transmissibility, the Omicron variant – layered atop Delta – presents great risk to us as a society. We must do all we can as clinicians to educate our patients so that they can protect themselves and their families.
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
As a physician first and a mental health clinician second, I hope to provide factual medical information on the Omicron variant to my patients, family members, and friends. I also try to remain curious instead of angry about why some choose not to vaccinate.
The most effective way to encourage people to obtain a vaccination is to use communication free of judgment and criticism, which allows a safe space for the unvaccinated to express their motivations and fears behind their current choice of not vaccinating and explore possible barriers to an alternative option that could lead to vaccination.
As an adult psychiatrist, ADHD specialist, and amateur COVID-19 expert, I’d like to offer 10 reasons why Omicron – which ironically means “small” in Latin, can still cause big destruction. Please share these 10 reasons with your patients.
- If you are not vaccinated, this virus will find you within the next few weeks and likely lead to severe symptoms.
- Long-haul symptoms from COVID-19 infection are still possible even for people who contract a milder case of the Omicron variant.
- The monoclonal antibody and antiviral treatments recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 are limited. For many reasons, now is not the best time to play Russian roulette and intentionally get infected with a “mild” variant.
- There are not enough testing sites or over-the-counter rapid COVID tests available to keep up with the demand, and the latter are cost prohibitive for many people.
- Emergency care during the next few weeks for unforeseen non–COVID-related illnesses, such as a sudden heart attack or stroke, may be affected by the shortage of medical providers because of illness, quarantine, and burnout.
- There will be fewer first responders, including EMTs, police officers, and firefighters, because of COVID quarantines from illness and exposure.
- Although most Americans oppose temporary shutdowns, de facto shutdowns might be necessary because of the absence of healthy, COVID-negative individuals to maintain a functional society.
- Omicron math is deceiving, since the risk of hospitalization with Omicron appears to be far lower than with the Delta variant. However, the higher volume of infections with Omicron will offset the lower severity leading to comparable numbers of hospitalizations.
- Omicron has made it difficult for some schools to reopen after the holiday break, and reopening might become even more difficult as the surge progresses. Many schools already were in desperate need of substitute teachers, bus drivers, and additional staff necessary for COVID safety precautions before the emergence of the Omicron variant.
- And, for a less altruistic reason, as if the nine reasons above weren’t enough – if infections continue, especially among the unvaccinated – where the virus mutates the most – this can lead to a trifecta variant that not only evades the immune system and is highly infectious but causes severe disease in both the unvaccinated as well as the vaccinated.
Because of its extremely high transmissibility, the Omicron variant – layered atop Delta – presents great risk to us as a society. We must do all we can as clinicians to educate our patients so that they can protect themselves and their families.
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
Lung cancer risk misperceptions impede lifesaving screenings
according to analysis of data from the SUMMIT study recently published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology. Such an approach may be more effective than trying to change risk perceptions.
While 1-year survival among patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer is 88%, it is only 19% for those diagnosed with advanced disease. But only 27% of patients are diagnosed with early-stage disease. Screening high-risk asymptomatic adults using LDCT detects early-stage disease and significantly reduces lung cancer mortality, according to Samantha L. Quaife, PhD, of the Wolfson Institute of Population Health at Queen Mary University of London, and associates.
The effectiveness and equity of LDCT lung cancer screening as a population-level early detection strategy is compromised by low uptake among high-risk groups, the authors wrote.
In the United States, only 2% of eligible smokers have been screened since screening was first recommended in 2013. To provide a scientific evidence base for intervention, an understanding of factors making high-risk groups less likely to participate in LDCT screening is critical, Dr. Quaife and colleagues wrote.
Their longitudinal cohort study evaluating psychological correlates of lung cancer screening uptake included 44,000 ever-smokers (aged 55-77 years) who were invited to mail a self-regulatory questionnaire for lung cancer screening. Eligibility for LDCT lung cancer screening and inclusion in the SUMMIT study were further determined through telephone and in-person Lung Health Check (LHC) appointments. The primary outcome was uptake of the invitation to book an LHC appointment by telephone.
Of those invited, 7,966 (18.1%) returned the questionnaire with 7,730 (45% female; mean age, about 64 years) linked to screening uptake data. About 30% reported being current smokers with high tobacco dependence (60.3% smoking within 30 minutes of waking). The analysis from Dr. Quaife and colleagues looked at psychological correlates of lung cancer screening uptake using a psychometrically validated self-regulatory questionnaire for lung cancer screening (SRQ-LCS) to measure psychological constructs hypothesized to be associated with uptake which included consequences, emotional representation, coherence (lung cancer knowledge), treatment control, personal control, risk perception, perceived stigma, response efficacy of smoking cessation, early diagnosis behavioral response, survival from lung cancer, and treatment intention.
Among those who perceived early diagnosis to be more beneficial as a behavioral response, the positive association with uptake was strongest (adjusted odds ratio, 1.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.33-1.41). Those who perceived greater personal control (aOR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.05-1.11) or believed their risk of lung cancer was high (aOR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10) were also more likely to respond. Other uptake increases were found for those who perceived smoking cessation as an effective means of reducing lung cancer risk or thought the chances of surviving early-stage lung cancer were good or fair (P < .01), and for those who perceived lung cancer as stigmatized (aOR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.14-1.40). Most of these constructs were also perceived more negatively by current than former smokers.
Income, employment, education, social class, and housing conditions were significantly associated with many of the constructs. Greater affluence correlated with perceived personal control and benefit from early diagnosis, but more negative perceptions of the consequences of lung cancer. Also, those from more affluent areas were more likely to perceive lung cancer to be stigmatized and perceive smoking cessation to be less effective in reducing risk. Current daily smokers were less willing to be treated for early-stage disease, more pessimistic about survival, but had the highest-risk perception scores, at odds with their lower participation in lung screening trials. This contradiction, Dr. Quaife and colleagues suggested, may be explained by current smokers also holding more negative perceptions associated with lower uptake, including negative perceptions of lung cancer controllability, early diagnosis and survival, lower willingness to be treated, and belief that smoking cessation is less effective in reducing risk. All of these undermine positive responses to their high perceived risk.
“These findings pinpoint specific psychological targets for intervention,” the authors wrote. Experimental studies investigating the methods and mechanisms through which these perceptions could be changed are needed.
The study was funded by Cancer Research UK Population Research Fellowship (C50664/A24460) awarded to Dr. Quaife. The study investigators declared no support from financial organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years.
according to analysis of data from the SUMMIT study recently published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology. Such an approach may be more effective than trying to change risk perceptions.
While 1-year survival among patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer is 88%, it is only 19% for those diagnosed with advanced disease. But only 27% of patients are diagnosed with early-stage disease. Screening high-risk asymptomatic adults using LDCT detects early-stage disease and significantly reduces lung cancer mortality, according to Samantha L. Quaife, PhD, of the Wolfson Institute of Population Health at Queen Mary University of London, and associates.
The effectiveness and equity of LDCT lung cancer screening as a population-level early detection strategy is compromised by low uptake among high-risk groups, the authors wrote.
In the United States, only 2% of eligible smokers have been screened since screening was first recommended in 2013. To provide a scientific evidence base for intervention, an understanding of factors making high-risk groups less likely to participate in LDCT screening is critical, Dr. Quaife and colleagues wrote.
Their longitudinal cohort study evaluating psychological correlates of lung cancer screening uptake included 44,000 ever-smokers (aged 55-77 years) who were invited to mail a self-regulatory questionnaire for lung cancer screening. Eligibility for LDCT lung cancer screening and inclusion in the SUMMIT study were further determined through telephone and in-person Lung Health Check (LHC) appointments. The primary outcome was uptake of the invitation to book an LHC appointment by telephone.
Of those invited, 7,966 (18.1%) returned the questionnaire with 7,730 (45% female; mean age, about 64 years) linked to screening uptake data. About 30% reported being current smokers with high tobacco dependence (60.3% smoking within 30 minutes of waking). The analysis from Dr. Quaife and colleagues looked at psychological correlates of lung cancer screening uptake using a psychometrically validated self-regulatory questionnaire for lung cancer screening (SRQ-LCS) to measure psychological constructs hypothesized to be associated with uptake which included consequences, emotional representation, coherence (lung cancer knowledge), treatment control, personal control, risk perception, perceived stigma, response efficacy of smoking cessation, early diagnosis behavioral response, survival from lung cancer, and treatment intention.
Among those who perceived early diagnosis to be more beneficial as a behavioral response, the positive association with uptake was strongest (adjusted odds ratio, 1.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.33-1.41). Those who perceived greater personal control (aOR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.05-1.11) or believed their risk of lung cancer was high (aOR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10) were also more likely to respond. Other uptake increases were found for those who perceived smoking cessation as an effective means of reducing lung cancer risk or thought the chances of surviving early-stage lung cancer were good or fair (P < .01), and for those who perceived lung cancer as stigmatized (aOR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.14-1.40). Most of these constructs were also perceived more negatively by current than former smokers.
Income, employment, education, social class, and housing conditions were significantly associated with many of the constructs. Greater affluence correlated with perceived personal control and benefit from early diagnosis, but more negative perceptions of the consequences of lung cancer. Also, those from more affluent areas were more likely to perceive lung cancer to be stigmatized and perceive smoking cessation to be less effective in reducing risk. Current daily smokers were less willing to be treated for early-stage disease, more pessimistic about survival, but had the highest-risk perception scores, at odds with their lower participation in lung screening trials. This contradiction, Dr. Quaife and colleagues suggested, may be explained by current smokers also holding more negative perceptions associated with lower uptake, including negative perceptions of lung cancer controllability, early diagnosis and survival, lower willingness to be treated, and belief that smoking cessation is less effective in reducing risk. All of these undermine positive responses to their high perceived risk.
“These findings pinpoint specific psychological targets for intervention,” the authors wrote. Experimental studies investigating the methods and mechanisms through which these perceptions could be changed are needed.
The study was funded by Cancer Research UK Population Research Fellowship (C50664/A24460) awarded to Dr. Quaife. The study investigators declared no support from financial organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years.
according to analysis of data from the SUMMIT study recently published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology. Such an approach may be more effective than trying to change risk perceptions.
While 1-year survival among patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer is 88%, it is only 19% for those diagnosed with advanced disease. But only 27% of patients are diagnosed with early-stage disease. Screening high-risk asymptomatic adults using LDCT detects early-stage disease and significantly reduces lung cancer mortality, according to Samantha L. Quaife, PhD, of the Wolfson Institute of Population Health at Queen Mary University of London, and associates.
The effectiveness and equity of LDCT lung cancer screening as a population-level early detection strategy is compromised by low uptake among high-risk groups, the authors wrote.
In the United States, only 2% of eligible smokers have been screened since screening was first recommended in 2013. To provide a scientific evidence base for intervention, an understanding of factors making high-risk groups less likely to participate in LDCT screening is critical, Dr. Quaife and colleagues wrote.
Their longitudinal cohort study evaluating psychological correlates of lung cancer screening uptake included 44,000 ever-smokers (aged 55-77 years) who were invited to mail a self-regulatory questionnaire for lung cancer screening. Eligibility for LDCT lung cancer screening and inclusion in the SUMMIT study were further determined through telephone and in-person Lung Health Check (LHC) appointments. The primary outcome was uptake of the invitation to book an LHC appointment by telephone.
Of those invited, 7,966 (18.1%) returned the questionnaire with 7,730 (45% female; mean age, about 64 years) linked to screening uptake data. About 30% reported being current smokers with high tobacco dependence (60.3% smoking within 30 minutes of waking). The analysis from Dr. Quaife and colleagues looked at psychological correlates of lung cancer screening uptake using a psychometrically validated self-regulatory questionnaire for lung cancer screening (SRQ-LCS) to measure psychological constructs hypothesized to be associated with uptake which included consequences, emotional representation, coherence (lung cancer knowledge), treatment control, personal control, risk perception, perceived stigma, response efficacy of smoking cessation, early diagnosis behavioral response, survival from lung cancer, and treatment intention.
Among those who perceived early diagnosis to be more beneficial as a behavioral response, the positive association with uptake was strongest (adjusted odds ratio, 1.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.33-1.41). Those who perceived greater personal control (aOR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.05-1.11) or believed their risk of lung cancer was high (aOR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10) were also more likely to respond. Other uptake increases were found for those who perceived smoking cessation as an effective means of reducing lung cancer risk or thought the chances of surviving early-stage lung cancer were good or fair (P < .01), and for those who perceived lung cancer as stigmatized (aOR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.14-1.40). Most of these constructs were also perceived more negatively by current than former smokers.
Income, employment, education, social class, and housing conditions were significantly associated with many of the constructs. Greater affluence correlated with perceived personal control and benefit from early diagnosis, but more negative perceptions of the consequences of lung cancer. Also, those from more affluent areas were more likely to perceive lung cancer to be stigmatized and perceive smoking cessation to be less effective in reducing risk. Current daily smokers were less willing to be treated for early-stage disease, more pessimistic about survival, but had the highest-risk perception scores, at odds with their lower participation in lung screening trials. This contradiction, Dr. Quaife and colleagues suggested, may be explained by current smokers also holding more negative perceptions associated with lower uptake, including negative perceptions of lung cancer controllability, early diagnosis and survival, lower willingness to be treated, and belief that smoking cessation is less effective in reducing risk. All of these undermine positive responses to their high perceived risk.
“These findings pinpoint specific psychological targets for intervention,” the authors wrote. Experimental studies investigating the methods and mechanisms through which these perceptions could be changed are needed.
The study was funded by Cancer Research UK Population Research Fellowship (C50664/A24460) awarded to Dr. Quaife. The study investigators declared no support from financial organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: RA January 2022
Along with long-standing concerns about immunodeficiency and use of immunosuppressive medication in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are juxtaposed concerns about their additional risk of COVID-19 during the pandemic. Several studies have reported a high risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes in people with rheumatic disease, though few have compared this risk to the general population. This cohort study by Wang et al.1 examines the risk of COVID-19 in people with RA compared to people with OA and the general population based on an electronic medical record database in the UK. The rate of COVID-19 was higher among people with RA than the general population, with a hazard ratio of 1.42 for confirmed COVID-19 cases, while the rate among people with OA was not increased. This finding confirms suspicions, though, due to the study design, it does not lend additional insight into nuances given the lack of information about RA treatment and activity as in prior studies.
Also of concern in the midst of the pandemic is the effect of RA and its treatment on response to vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. The rapid development of mRNA vaccines has been a boon, but research on vaccine response in people with rheumatic disease has suggested that certain medications can impact antibody formation. Iancovici et al.2 examined antibody and B cell responses after vaccination in people with RA being treated with Janus kinase (JAK)-inhibitors or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitors and in healthy volunteers. Though the study is flawed as responses were not assessed at the same timepoint after vaccination in all subjects and limited due to the heterogeneity of treatment and small numbers of subjects, antibody production and other assays were decreased in RA subjects, suggesting reduced humoral immunity. Whether a pause in JAK inhibitor treatment, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology, makes an appreciable difference in these assessments of vaccine response is as yet unknown. Further, given the limited data, it is unclear whether having RA on its own, rather than the treatments involved, was the causative factor. Research is already underway on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response in people with RA and other rheumatic diseases, but studies such as these also imply a relative immunodeficiency due to the diseases and their treatment that could extend to other vaccines or infections.
In addition to impacts on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response, treatment with JAK inhibitors is known to increase risk of herpes zoster (HZ). A post hoc analysis of pooled data from 21 RA and 3 psoriatic arthritis (PsA) tofacitinib trials by Winthrop et al.3 evaluated the number and severity of HZ infections. Interestingly, HZ infections occurred more frequently in participants in the RA clinical trials, with about 11% having an infection compared to 5% in the PsA studies, once again highlighting a potential immunodeficiency particular to people with RA. Most patients had mild to moderate infections, but a small proportion of patients (<5%) had severe infections. Given the possibility of a reduced vaccine response, though unknown, after HZ vaccination in people with RA, consideration should be given not only to vaccination prior to initiation of JAK inhibitor therapy, but to assessment of vaccine efficacy and the ideal dosing schedules in these patients.
References
- Wang Y et al. Increased risk of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a general population-based cohort study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2021(Dec 7).
- Iancovici L et al. Rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with Janus kinase inhibitors show reduced humoral immune responses following BNT162b2 vaccination. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021:keab879 (Nov 25).
- Winthrop KL et al. Clinical management of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis receiving tofacitinib treatment. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 (Dec 6).
Along with long-standing concerns about immunodeficiency and use of immunosuppressive medication in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are juxtaposed concerns about their additional risk of COVID-19 during the pandemic. Several studies have reported a high risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes in people with rheumatic disease, though few have compared this risk to the general population. This cohort study by Wang et al.1 examines the risk of COVID-19 in people with RA compared to people with OA and the general population based on an electronic medical record database in the UK. The rate of COVID-19 was higher among people with RA than the general population, with a hazard ratio of 1.42 for confirmed COVID-19 cases, while the rate among people with OA was not increased. This finding confirms suspicions, though, due to the study design, it does not lend additional insight into nuances given the lack of information about RA treatment and activity as in prior studies.
Also of concern in the midst of the pandemic is the effect of RA and its treatment on response to vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. The rapid development of mRNA vaccines has been a boon, but research on vaccine response in people with rheumatic disease has suggested that certain medications can impact antibody formation. Iancovici et al.2 examined antibody and B cell responses after vaccination in people with RA being treated with Janus kinase (JAK)-inhibitors or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitors and in healthy volunteers. Though the study is flawed as responses were not assessed at the same timepoint after vaccination in all subjects and limited due to the heterogeneity of treatment and small numbers of subjects, antibody production and other assays were decreased in RA subjects, suggesting reduced humoral immunity. Whether a pause in JAK inhibitor treatment, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology, makes an appreciable difference in these assessments of vaccine response is as yet unknown. Further, given the limited data, it is unclear whether having RA on its own, rather than the treatments involved, was the causative factor. Research is already underway on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response in people with RA and other rheumatic diseases, but studies such as these also imply a relative immunodeficiency due to the diseases and their treatment that could extend to other vaccines or infections.
In addition to impacts on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response, treatment with JAK inhibitors is known to increase risk of herpes zoster (HZ). A post hoc analysis of pooled data from 21 RA and 3 psoriatic arthritis (PsA) tofacitinib trials by Winthrop et al.3 evaluated the number and severity of HZ infections. Interestingly, HZ infections occurred more frequently in participants in the RA clinical trials, with about 11% having an infection compared to 5% in the PsA studies, once again highlighting a potential immunodeficiency particular to people with RA. Most patients had mild to moderate infections, but a small proportion of patients (<5%) had severe infections. Given the possibility of a reduced vaccine response, though unknown, after HZ vaccination in people with RA, consideration should be given not only to vaccination prior to initiation of JAK inhibitor therapy, but to assessment of vaccine efficacy and the ideal dosing schedules in these patients.
References
- Wang Y et al. Increased risk of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a general population-based cohort study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2021(Dec 7).
- Iancovici L et al. Rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with Janus kinase inhibitors show reduced humoral immune responses following BNT162b2 vaccination. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021:keab879 (Nov 25).
- Winthrop KL et al. Clinical management of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis receiving tofacitinib treatment. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 (Dec 6).
Along with long-standing concerns about immunodeficiency and use of immunosuppressive medication in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are juxtaposed concerns about their additional risk of COVID-19 during the pandemic. Several studies have reported a high risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes in people with rheumatic disease, though few have compared this risk to the general population. This cohort study by Wang et al.1 examines the risk of COVID-19 in people with RA compared to people with OA and the general population based on an electronic medical record database in the UK. The rate of COVID-19 was higher among people with RA than the general population, with a hazard ratio of 1.42 for confirmed COVID-19 cases, while the rate among people with OA was not increased. This finding confirms suspicions, though, due to the study design, it does not lend additional insight into nuances given the lack of information about RA treatment and activity as in prior studies.
Also of concern in the midst of the pandemic is the effect of RA and its treatment on response to vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. The rapid development of mRNA vaccines has been a boon, but research on vaccine response in people with rheumatic disease has suggested that certain medications can impact antibody formation. Iancovici et al.2 examined antibody and B cell responses after vaccination in people with RA being treated with Janus kinase (JAK)-inhibitors or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitors and in healthy volunteers. Though the study is flawed as responses were not assessed at the same timepoint after vaccination in all subjects and limited due to the heterogeneity of treatment and small numbers of subjects, antibody production and other assays were decreased in RA subjects, suggesting reduced humoral immunity. Whether a pause in JAK inhibitor treatment, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology, makes an appreciable difference in these assessments of vaccine response is as yet unknown. Further, given the limited data, it is unclear whether having RA on its own, rather than the treatments involved, was the causative factor. Research is already underway on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response in people with RA and other rheumatic diseases, but studies such as these also imply a relative immunodeficiency due to the diseases and their treatment that could extend to other vaccines or infections.
In addition to impacts on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response, treatment with JAK inhibitors is known to increase risk of herpes zoster (HZ). A post hoc analysis of pooled data from 21 RA and 3 psoriatic arthritis (PsA) tofacitinib trials by Winthrop et al.3 evaluated the number and severity of HZ infections. Interestingly, HZ infections occurred more frequently in participants in the RA clinical trials, with about 11% having an infection compared to 5% in the PsA studies, once again highlighting a potential immunodeficiency particular to people with RA. Most patients had mild to moderate infections, but a small proportion of patients (<5%) had severe infections. Given the possibility of a reduced vaccine response, though unknown, after HZ vaccination in people with RA, consideration should be given not only to vaccination prior to initiation of JAK inhibitor therapy, but to assessment of vaccine efficacy and the ideal dosing schedules in these patients.
References
- Wang Y et al. Increased risk of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a general population-based cohort study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2021(Dec 7).
- Iancovici L et al. Rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with Janus kinase inhibitors show reduced humoral immune responses following BNT162b2 vaccination. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021:keab879 (Nov 25).
- Winthrop KL et al. Clinical management of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis receiving tofacitinib treatment. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 (Dec 6).
Surgeon General releases child mental health call to action
The nation’s Surgeon General, Vice Admiral Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, recently released an advisory report on the current state of youth mental health and recommendations to improve well-being. This action follows a number of emergency declarations that have been made by professional organizations such as the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and other health care groups to raise awareness about the alarming increase of depression, suicide, anxiety, and other mental health problems in youth.
These reports can be helpful in focusing attention and resources for important public health problems. Many still reference the 1999 report from former Surgeon General David Satcher, MD, PhD, which offered a number of eye-opening statistics regarding the prevalence of mental health conditions and the amount of disability associated with them.
Sadly, the present report indicates that many of these indices have grown worse in the past 20 years. For example, the advisory notes that, even before COVID-19, fully half of female high school students reported persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness (up 40% from 2009). The report then goes on to cite a number of studies documenting even further rises in youth mental health problems associated with the pandemic.
Most of the advisory, however, is devoted to actions that can be taken by different groups, including young people themselves, parents, educators, the government, and even social media and video game companies, to support mental health and well-being. Multiple online resources are provided at the end of each of these sections.
One of the segments is aimed at health care organizations and professionals. While first making a fairly sweeping statement that “our health care system today is not set up optimally to support the mental health and well-being of children and youth,” this part then outlines five broad recommendations that might help improve the fit. These include the following.
- Increase prevention efforts, such as coordination to enrichment programs and referrals for economic and legal supports for families in need.
- Screen routinely for mental health conditions and link those who screen in with appropriate care.
- Identify mental health needs in parents and caregivers such as depression and substance use that can have negative effects on children.
- Increase partnerships between health care groups and community organizations.
- Build multidisciplinary teams that are culturally appropriate and maximally engage children and caretakers in the decision-making process.
The current report is downloadable for free (see reference below) and it is certainly worthwhile for pediatricians to take a look. Dr. Murthy writes, regarding the current state of mental health, that “it would be a tragedy if we beat back one public health crisis only to allow another to grow in its place.”
The report also outlines specific areas where additional research is needed, such as data on racial and sexual minorities and research on innovative and scalable therapies. In addition to the online resources that are provided, the report is backed by over 250 references.
Since its release, the report has generally been well received, and, indeed, there is much to support. The well-known Child Mind Institute in New York tweeted that “this document is a wake-up call for the country and a long-overdue statement of leadership from the federal government.”
Many of the recommendations are admittedly somewhat commons sense, but there are some that are much less so. For example, one recommendation to youth themselves is to serve others – something that may first come across as counterintuitive but can indeed help children and adolescents develop a sense of purpose and self-worth. The call for pediatric health care professionals to screen parents in addition to the patients themselves will likely result in some debate as well. The recommendation to reduce access to lethal means, including the specific naming of firearms, is also a welcome addition. This report also rightly puts a spotlight on the role of societal factors such as racism and poverty in the development of mental health problems and in getting access to quality treatment.
Also worth noting is how much of the advisory examined the role of media in both the problem and the solution. While recognizing that technology, smartphones, and social media are here to stay, a number of suggestions were given to parents, media organizations, journalists, and entertainment companies to reduce the negative impacts these mediums can have. Explicitly recognized in the report is that “there can be tension between what’s best for the technology company and what’s best for the individual user or society.” Also acknowledged was that the link between media of various types and mental health is complex and inconsistent with there being a strong need for additional work in this area when it comes to academic research as well as product development within these companies themselves.
Yet while there is much to like about the advisory, there remain some areas that seem lacking. For example, the text about what causes mental health conditions gets a little dualistic in mentioning biological and environmental factors without much appreciation that these are hardly independent domains. Perhaps more substantially, there was surprisingly little airtime devoted to an enormous issue that underlies so many other challenges related to mental health care – namely an inadequate workforce that gets smaller by the minute. The topic was treated much too superficially with lots of vague calls to “expand” the workforce that lacked substance or detail.
Overall, however, the new Surgeon General’s Advisory is a welcome document that offers updated knowledge of our current challenges and provides practical responses that truly could make a difference. Now all we have to do is put these recommendations into action.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and medical director of Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore. His latest book is “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.” You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
Reference
“Protecting Youth Mental Health – The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory,” U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (2021).
The nation’s Surgeon General, Vice Admiral Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, recently released an advisory report on the current state of youth mental health and recommendations to improve well-being. This action follows a number of emergency declarations that have been made by professional organizations such as the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and other health care groups to raise awareness about the alarming increase of depression, suicide, anxiety, and other mental health problems in youth.
These reports can be helpful in focusing attention and resources for important public health problems. Many still reference the 1999 report from former Surgeon General David Satcher, MD, PhD, which offered a number of eye-opening statistics regarding the prevalence of mental health conditions and the amount of disability associated with them.
Sadly, the present report indicates that many of these indices have grown worse in the past 20 years. For example, the advisory notes that, even before COVID-19, fully half of female high school students reported persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness (up 40% from 2009). The report then goes on to cite a number of studies documenting even further rises in youth mental health problems associated with the pandemic.
Most of the advisory, however, is devoted to actions that can be taken by different groups, including young people themselves, parents, educators, the government, and even social media and video game companies, to support mental health and well-being. Multiple online resources are provided at the end of each of these sections.
One of the segments is aimed at health care organizations and professionals. While first making a fairly sweeping statement that “our health care system today is not set up optimally to support the mental health and well-being of children and youth,” this part then outlines five broad recommendations that might help improve the fit. These include the following.
- Increase prevention efforts, such as coordination to enrichment programs and referrals for economic and legal supports for families in need.
- Screen routinely for mental health conditions and link those who screen in with appropriate care.
- Identify mental health needs in parents and caregivers such as depression and substance use that can have negative effects on children.
- Increase partnerships between health care groups and community organizations.
- Build multidisciplinary teams that are culturally appropriate and maximally engage children and caretakers in the decision-making process.
The current report is downloadable for free (see reference below) and it is certainly worthwhile for pediatricians to take a look. Dr. Murthy writes, regarding the current state of mental health, that “it would be a tragedy if we beat back one public health crisis only to allow another to grow in its place.”
The report also outlines specific areas where additional research is needed, such as data on racial and sexual minorities and research on innovative and scalable therapies. In addition to the online resources that are provided, the report is backed by over 250 references.
Since its release, the report has generally been well received, and, indeed, there is much to support. The well-known Child Mind Institute in New York tweeted that “this document is a wake-up call for the country and a long-overdue statement of leadership from the federal government.”
Many of the recommendations are admittedly somewhat commons sense, but there are some that are much less so. For example, one recommendation to youth themselves is to serve others – something that may first come across as counterintuitive but can indeed help children and adolescents develop a sense of purpose and self-worth. The call for pediatric health care professionals to screen parents in addition to the patients themselves will likely result in some debate as well. The recommendation to reduce access to lethal means, including the specific naming of firearms, is also a welcome addition. This report also rightly puts a spotlight on the role of societal factors such as racism and poverty in the development of mental health problems and in getting access to quality treatment.
Also worth noting is how much of the advisory examined the role of media in both the problem and the solution. While recognizing that technology, smartphones, and social media are here to stay, a number of suggestions were given to parents, media organizations, journalists, and entertainment companies to reduce the negative impacts these mediums can have. Explicitly recognized in the report is that “there can be tension between what’s best for the technology company and what’s best for the individual user or society.” Also acknowledged was that the link between media of various types and mental health is complex and inconsistent with there being a strong need for additional work in this area when it comes to academic research as well as product development within these companies themselves.
Yet while there is much to like about the advisory, there remain some areas that seem lacking. For example, the text about what causes mental health conditions gets a little dualistic in mentioning biological and environmental factors without much appreciation that these are hardly independent domains. Perhaps more substantially, there was surprisingly little airtime devoted to an enormous issue that underlies so many other challenges related to mental health care – namely an inadequate workforce that gets smaller by the minute. The topic was treated much too superficially with lots of vague calls to “expand” the workforce that lacked substance or detail.
Overall, however, the new Surgeon General’s Advisory is a welcome document that offers updated knowledge of our current challenges and provides practical responses that truly could make a difference. Now all we have to do is put these recommendations into action.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and medical director of Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore. His latest book is “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.” You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
Reference
“Protecting Youth Mental Health – The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory,” U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (2021).
The nation’s Surgeon General, Vice Admiral Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, recently released an advisory report on the current state of youth mental health and recommendations to improve well-being. This action follows a number of emergency declarations that have been made by professional organizations such as the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and other health care groups to raise awareness about the alarming increase of depression, suicide, anxiety, and other mental health problems in youth.
These reports can be helpful in focusing attention and resources for important public health problems. Many still reference the 1999 report from former Surgeon General David Satcher, MD, PhD, which offered a number of eye-opening statistics regarding the prevalence of mental health conditions and the amount of disability associated with them.
Sadly, the present report indicates that many of these indices have grown worse in the past 20 years. For example, the advisory notes that, even before COVID-19, fully half of female high school students reported persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness (up 40% from 2009). The report then goes on to cite a number of studies documenting even further rises in youth mental health problems associated with the pandemic.
Most of the advisory, however, is devoted to actions that can be taken by different groups, including young people themselves, parents, educators, the government, and even social media and video game companies, to support mental health and well-being. Multiple online resources are provided at the end of each of these sections.
One of the segments is aimed at health care organizations and professionals. While first making a fairly sweeping statement that “our health care system today is not set up optimally to support the mental health and well-being of children and youth,” this part then outlines five broad recommendations that might help improve the fit. These include the following.
- Increase prevention efforts, such as coordination to enrichment programs and referrals for economic and legal supports for families in need.
- Screen routinely for mental health conditions and link those who screen in with appropriate care.
- Identify mental health needs in parents and caregivers such as depression and substance use that can have negative effects on children.
- Increase partnerships between health care groups and community organizations.
- Build multidisciplinary teams that are culturally appropriate and maximally engage children and caretakers in the decision-making process.
The current report is downloadable for free (see reference below) and it is certainly worthwhile for pediatricians to take a look. Dr. Murthy writes, regarding the current state of mental health, that “it would be a tragedy if we beat back one public health crisis only to allow another to grow in its place.”
The report also outlines specific areas where additional research is needed, such as data on racial and sexual minorities and research on innovative and scalable therapies. In addition to the online resources that are provided, the report is backed by over 250 references.
Since its release, the report has generally been well received, and, indeed, there is much to support. The well-known Child Mind Institute in New York tweeted that “this document is a wake-up call for the country and a long-overdue statement of leadership from the federal government.”
Many of the recommendations are admittedly somewhat commons sense, but there are some that are much less so. For example, one recommendation to youth themselves is to serve others – something that may first come across as counterintuitive but can indeed help children and adolescents develop a sense of purpose and self-worth. The call for pediatric health care professionals to screen parents in addition to the patients themselves will likely result in some debate as well. The recommendation to reduce access to lethal means, including the specific naming of firearms, is also a welcome addition. This report also rightly puts a spotlight on the role of societal factors such as racism and poverty in the development of mental health problems and in getting access to quality treatment.
Also worth noting is how much of the advisory examined the role of media in both the problem and the solution. While recognizing that technology, smartphones, and social media are here to stay, a number of suggestions were given to parents, media organizations, journalists, and entertainment companies to reduce the negative impacts these mediums can have. Explicitly recognized in the report is that “there can be tension between what’s best for the technology company and what’s best for the individual user or society.” Also acknowledged was that the link between media of various types and mental health is complex and inconsistent with there being a strong need for additional work in this area when it comes to academic research as well as product development within these companies themselves.
Yet while there is much to like about the advisory, there remain some areas that seem lacking. For example, the text about what causes mental health conditions gets a little dualistic in mentioning biological and environmental factors without much appreciation that these are hardly independent domains. Perhaps more substantially, there was surprisingly little airtime devoted to an enormous issue that underlies so many other challenges related to mental health care – namely an inadequate workforce that gets smaller by the minute. The topic was treated much too superficially with lots of vague calls to “expand” the workforce that lacked substance or detail.
Overall, however, the new Surgeon General’s Advisory is a welcome document that offers updated knowledge of our current challenges and provides practical responses that truly could make a difference. Now all we have to do is put these recommendations into action.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and medical director of Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore. His latest book is “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.” You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
Reference
“Protecting Youth Mental Health – The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory,” U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (2021).
Surgical principles of vaginal cuff dehiscence repair

Additional videos from SGS are available here, including these recent offerings:
Strategies for safe dissection of cervical fibroids during hysterectomy
Concomitant laparoscopic and vaginal excision of duplicated collecting system

Additional videos from SGS are available here, including these recent offerings:
Strategies for safe dissection of cervical fibroids during hysterectomy
Concomitant laparoscopic and vaginal excision of duplicated collecting system

Additional videos from SGS are available here, including these recent offerings:
Strategies for safe dissection of cervical fibroids during hysterectomy
Concomitant laparoscopic and vaginal excision of duplicated collecting system
Navigating the Evolving Landscape of the Dermatologic Workforce
As of 2018, the mean dermatologist to population ratio in the United States was 1.10 per 100,000 people, highlighting a shortage of dermatologists that is only predicted to increase in coming years.1-4 This undersupply is fueled by both an increasing burden of dermatologic disease and population growth.4 Without readily available access to dermatologic care, many patients are left waiting for weeks to see a dermatologist, depending on geographic region.5-7 It is not simply patients who perceive wait times to be prolonged; approximately half of dermatologists surveyed by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) reported an undersupply of dermatologists in their communities, a finding that strongly correlated with patient wait times.2 Ensuring the dermatologic workforce is sufficient to fulfill patient needs requires innovation of current practice models. To address this unmet demand, many practices have begun incorporating physician extenders, a term that encompasses physicians not board certified in dermatology, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners.7 The evolving landscape of the dermatologic workforce raises questions about future practice models and patient outcomes.
Scope of Practice for Physician Extenders
In practice, the role of physician extenders is highly variable. Legislation involving the scope of practice for physician extenders constantly is changing and varies by state. As of November 2021, 24 states and the District of Columbia permit nurse practitioners “full practice” authority to triage patients, interpret diagnostic tests, and prescribe treatments without physician oversight, including controlled substances.8,9 Even in states with “reduced practice” and “restricted practice” paradigms, which necessitate physician oversight, there remains ambiguity. Across the country, state regulatory bodies differ in statues governing licensing requirements, accessibility of the supervising physician, and ultimately culpability in the case of patient harm. Lack of consensus guidelines that clearly define roles and responsibilities has kindled controversy regarding extent of autonomy and liability for adverse outcomes.10,11
With respect to procedures, the AAD has explicitly recommended that “only active and properly licensed doctors of medicine and osteopathy shall engage in the practice of medicine” but that “under appropriate circumstances, a physician may delegate certain procedures and services to appropriately trained nonphysician office personnel.”12 This statement does not refer to or explicitly list the procedures that are appropriate for delegation to nonphysician personnel, and there is wide variability in how this recommendation is applied in daily practice. As it was originally intended, the AAD’s “Ethics in Medical Practice” position statement indicated that dermatologists must directly oversee physician extenders, a responsibility that is defined as being “present on-site, immediately available and able to respond promptly” to issues arising during the provision of health care services.12
Adverse Events From Cosmetic Procedures
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery has documented a steady growth in the demand for cosmetic, medical, and surgical services,13 a trend that has heralded an increase in the number of procedures performed by physician extenders.14,15 One study contrasted the risk for adverse events following minimally invasive cosmetic procedures performed by physicians or nonphysicians. Of 2116 patients surveyed, 50 adverse events were documented.14 The cohort treated by nonphysicians experienced a higher incidence of laser burns and dyspigmentation, and the use of improper technique was the most frequently implicated cause of developing an adverse event. Approximately 24.6% of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery members reported treating 10 or more complications of cosmetic procedures performed by nonphysicians.14 Beyond laser burns and dyspigmentation, this wide range of complications included inappropriately placed filler product, facial drooping, and scarring. These studies highlight the need for further investigation into the outcomes of procedures performed by physician extenders.
Training of Physician Extenders
Even with medical management, emphasis on proper training of personnel is key and remains a legitimate concern. The training of physician extenders in dermatology differs greatly by location; while some physician extenders operate under meticulous guidance and thus can expand their skill set, other physician extenders shadow dermatologists for an arbitrary amount of time before being thrust into practice.10 It would be a disservice to both patients and nonphysician providers alike to conflate the latter regimen with the 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of rigorous specialized dermatologic training that physicians undergo.
This stark discrepancy between the training of physicians and physician extenders raises difficult questions about the patient’s right to make an informed decision regarding how they receive health care. Indeed, the casually regulated autonomous practice of some nonphysician providers has ignited public shock and ire.11
Reducing Health Care Expenditures
As legislatures deliberate over expanding scope of practice, policies should be based on evidence that prioritizes patient safety. In the appropriate setting, physician extenders can be instrumental to mitigating health care disparities; the use of physician extenders can diminish wait times for patients with routine visits for stable dermatologic disease.16 Moreover, reducing health care expenditures often is cited as a major benefit of increased utilization of physician extenders.14 It stands to reason that compensation of nonphysician providers is less expensive for a practice compared with physicians. Physician extenders participating in the management of stable chronic conditions or mild acute conditions may be cost-efficient in these circumstances; however, evidence suggests that physician extenders may incur greater costs than physicians with respect to the utilization of diagnostic tests or prescribing medications. For example, several studies have documented a substantial difference in the number of biopsies needed per malignant neoplasm by physicians compared to physician extenders.17-19 Particularly in patients younger than 65 years and in patients without history of skin cancer, physician extenders had to perform a greater number of biopsies to diagnose malignant neoplasms vs physicians.18 In addition to increased utilization of diagnostic tests, nonphysician providers more frequently prescribe medications of varying classes.20-22 Whether in outpatient offices, emergency departments, or hospital clinics, physician extenders more frequently prescribe antibiotics, which has concerning implications for antibiotic stewardship.20,21 In states with independent prescription authority, physician extenders are more than 20 times more likely to overprescribeopioids compared to physician extenders in states requiring physician supervision.23 These findings warrant additional investigation into how prescription patterns vary by provider type and how these differences impact patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Improving patient care is inherently a team endeavor, and the contributions of all members of the health care team are critical to success. Engaging physician extenders may help mitigate disparities in dermatologic care, with respect to surveillance of stable chronic conditions or the diagnosis of mild acute diseases. However, the exact scope of practice of physician extenders remains ambiguous, and their training regimens can vary drastically. Therefore, in the interest of patient safety, new patients or medically complex patients (ie, cutaneous lymphomas, nonstable autoimmune connective tissue disease) should be examined and managed by physicians. In either scenario, the patient should be informed of which providers are available and should be integrated into the decision-making process for their care. Through mutual respect, close collaboration, and candid assessments of patient complexity, different parties within the medical team can unite behind the mission to improve patient outcomes and champion equitable access to health care.
- Vaidya T, Zubritsky L, Alikhan A, et al. Socioeconomic and geographic barriers to dermatology care in urban and rural US populations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:406-408.
- Resneck J Jr, Kimball AB. The dermatology workforce shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:50-54.
- American Medical Association. Physician Characteristics and Distribution in the US. American Medical Association; 2002.
- Kimball AB, Resneck JS Jr. The US dermatology workforce: a specialty remains in shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:741-755.
- Tsang MW, Resneck JS Jr. Even patients with changing moles face long dermatology appointment wait-times: a study of simulated patient calls to dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:54-58.
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307.
- Zurfley F Jr, Mostow EN. Association between the use of a physician extender and dermatology appointment wait times in Ohio. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1323-1324.
- Bean M. NP practice authority by state. Becker’s Hospital Review website. Published April 8, 2021. Accessed December 4, 2021. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/nursing/np-practice-authority-by-state.html
- States with full practice authority for nurse practitioners. Maryville University website. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://online.maryville.edu/nursing-degrees/np/resources/states-granting-np-full-practice-authority/
- Slade K, Lazenby M, Grant-Kels JM. Ethics of utilizing nurse practitioners and physician’s assistants in the dermatology setting. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:516-521
- Hafner K, Palmer G. Skin cancers rise, along with questionable treatments. New York Times. November 20, 2017. Accessed December 4, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/11/20/health/dermatology-skin-cancer.html
- American Academy of Dermatology. Policy #P-61.500. the use of non-physician office personnel. Published February 22, 2002. Updated July 31, 2004. http://www.aad.org/Forms/Policies/Uploads/AR/COE%20-%20Ethics%20in%20Medical%20Practice%20Booklet.pdf
- 2016 ASDS Survey on Dermatologic Procedures. American Society for Dermatologic Surgery website. Published May 30, 2017. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://www.asds.net/skin-experts/news-room/press-releases/asds-survey-nearly-105-million-treatments-performed-in-2016
- Rossi AM, Wilson B, Hibler BP, et al. Nonphysician practice of cosmetic dermatology: a patient and physician perspective of outcomes and adverse events. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:588-597.
- Anderson AM, Matsumoto M, Saul MI, et al. Accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis by physician assistants compared with dermatologists in a large health care system. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:569-573.
- O’Brien JC, Chong BF. Reducing outpatient dermatology clinic wait times in a safety net health system in Dallas, Texas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:631-632.
- Aldredge LM, Young MS. Providing guidance for patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis who are candidates for biologic therapy: role of the nurse practitioner and physician assistant. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2016;8:14-26.
- Roblin DW, Howard DH, Becker ER, et al. Use of midlevel practitioners to achieve labor cost savings in the primary care practice of an MCO. Health Serv Res. 2004;39:607-626.
- Nault A, Zhang C, Kim K, et al. Biopsy use in skin cancer diagnosis: comparing dermatology physicians and advanced practice professionals. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:899-902.
- Privalle A, Havighurst T, Kim K, et al. Number of skin biopsies needed per malignancy: comparing the use of skin biopsies among dermatologists and nondermatologist clinicians [published online August 10, 2019]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:110-116.
- Roumie CL, Halasa NB, Edwards KM, et al. Differences in antibiotic prescribing among physicians, residents, and nonphysician clinicians. Am J Med. 2005;118:641-648.
- Sanchez GV, Hersh AL, Shapiro DJ, et al. Outpatient antibiotic prescribing among United States nurse practitioners and physician assistants [published online August 10, 2016]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3:ofw168.
- Lozada MJ, Raji MA, Goodwin JS, et al. Opioid prescribing by primary care providers: a cross-sectional analysis of nurse practitioner, physician assistant, and physician prescribing patterns [published online April 24, 2020]. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:2584-2592.
As of 2018, the mean dermatologist to population ratio in the United States was 1.10 per 100,000 people, highlighting a shortage of dermatologists that is only predicted to increase in coming years.1-4 This undersupply is fueled by both an increasing burden of dermatologic disease and population growth.4 Without readily available access to dermatologic care, many patients are left waiting for weeks to see a dermatologist, depending on geographic region.5-7 It is not simply patients who perceive wait times to be prolonged; approximately half of dermatologists surveyed by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) reported an undersupply of dermatologists in their communities, a finding that strongly correlated with patient wait times.2 Ensuring the dermatologic workforce is sufficient to fulfill patient needs requires innovation of current practice models. To address this unmet demand, many practices have begun incorporating physician extenders, a term that encompasses physicians not board certified in dermatology, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners.7 The evolving landscape of the dermatologic workforce raises questions about future practice models and patient outcomes.
Scope of Practice for Physician Extenders
In practice, the role of physician extenders is highly variable. Legislation involving the scope of practice for physician extenders constantly is changing and varies by state. As of November 2021, 24 states and the District of Columbia permit nurse practitioners “full practice” authority to triage patients, interpret diagnostic tests, and prescribe treatments without physician oversight, including controlled substances.8,9 Even in states with “reduced practice” and “restricted practice” paradigms, which necessitate physician oversight, there remains ambiguity. Across the country, state regulatory bodies differ in statues governing licensing requirements, accessibility of the supervising physician, and ultimately culpability in the case of patient harm. Lack of consensus guidelines that clearly define roles and responsibilities has kindled controversy regarding extent of autonomy and liability for adverse outcomes.10,11
With respect to procedures, the AAD has explicitly recommended that “only active and properly licensed doctors of medicine and osteopathy shall engage in the practice of medicine” but that “under appropriate circumstances, a physician may delegate certain procedures and services to appropriately trained nonphysician office personnel.”12 This statement does not refer to or explicitly list the procedures that are appropriate for delegation to nonphysician personnel, and there is wide variability in how this recommendation is applied in daily practice. As it was originally intended, the AAD’s “Ethics in Medical Practice” position statement indicated that dermatologists must directly oversee physician extenders, a responsibility that is defined as being “present on-site, immediately available and able to respond promptly” to issues arising during the provision of health care services.12
Adverse Events From Cosmetic Procedures
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery has documented a steady growth in the demand for cosmetic, medical, and surgical services,13 a trend that has heralded an increase in the number of procedures performed by physician extenders.14,15 One study contrasted the risk for adverse events following minimally invasive cosmetic procedures performed by physicians or nonphysicians. Of 2116 patients surveyed, 50 adverse events were documented.14 The cohort treated by nonphysicians experienced a higher incidence of laser burns and dyspigmentation, and the use of improper technique was the most frequently implicated cause of developing an adverse event. Approximately 24.6% of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery members reported treating 10 or more complications of cosmetic procedures performed by nonphysicians.14 Beyond laser burns and dyspigmentation, this wide range of complications included inappropriately placed filler product, facial drooping, and scarring. These studies highlight the need for further investigation into the outcomes of procedures performed by physician extenders.
Training of Physician Extenders
Even with medical management, emphasis on proper training of personnel is key and remains a legitimate concern. The training of physician extenders in dermatology differs greatly by location; while some physician extenders operate under meticulous guidance and thus can expand their skill set, other physician extenders shadow dermatologists for an arbitrary amount of time before being thrust into practice.10 It would be a disservice to both patients and nonphysician providers alike to conflate the latter regimen with the 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of rigorous specialized dermatologic training that physicians undergo.
This stark discrepancy between the training of physicians and physician extenders raises difficult questions about the patient’s right to make an informed decision regarding how they receive health care. Indeed, the casually regulated autonomous practice of some nonphysician providers has ignited public shock and ire.11
Reducing Health Care Expenditures
As legislatures deliberate over expanding scope of practice, policies should be based on evidence that prioritizes patient safety. In the appropriate setting, physician extenders can be instrumental to mitigating health care disparities; the use of physician extenders can diminish wait times for patients with routine visits for stable dermatologic disease.16 Moreover, reducing health care expenditures often is cited as a major benefit of increased utilization of physician extenders.14 It stands to reason that compensation of nonphysician providers is less expensive for a practice compared with physicians. Physician extenders participating in the management of stable chronic conditions or mild acute conditions may be cost-efficient in these circumstances; however, evidence suggests that physician extenders may incur greater costs than physicians with respect to the utilization of diagnostic tests or prescribing medications. For example, several studies have documented a substantial difference in the number of biopsies needed per malignant neoplasm by physicians compared to physician extenders.17-19 Particularly in patients younger than 65 years and in patients without history of skin cancer, physician extenders had to perform a greater number of biopsies to diagnose malignant neoplasms vs physicians.18 In addition to increased utilization of diagnostic tests, nonphysician providers more frequently prescribe medications of varying classes.20-22 Whether in outpatient offices, emergency departments, or hospital clinics, physician extenders more frequently prescribe antibiotics, which has concerning implications for antibiotic stewardship.20,21 In states with independent prescription authority, physician extenders are more than 20 times more likely to overprescribeopioids compared to physician extenders in states requiring physician supervision.23 These findings warrant additional investigation into how prescription patterns vary by provider type and how these differences impact patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Improving patient care is inherently a team endeavor, and the contributions of all members of the health care team are critical to success. Engaging physician extenders may help mitigate disparities in dermatologic care, with respect to surveillance of stable chronic conditions or the diagnosis of mild acute diseases. However, the exact scope of practice of physician extenders remains ambiguous, and their training regimens can vary drastically. Therefore, in the interest of patient safety, new patients or medically complex patients (ie, cutaneous lymphomas, nonstable autoimmune connective tissue disease) should be examined and managed by physicians. In either scenario, the patient should be informed of which providers are available and should be integrated into the decision-making process for their care. Through mutual respect, close collaboration, and candid assessments of patient complexity, different parties within the medical team can unite behind the mission to improve patient outcomes and champion equitable access to health care.
As of 2018, the mean dermatologist to population ratio in the United States was 1.10 per 100,000 people, highlighting a shortage of dermatologists that is only predicted to increase in coming years.1-4 This undersupply is fueled by both an increasing burden of dermatologic disease and population growth.4 Without readily available access to dermatologic care, many patients are left waiting for weeks to see a dermatologist, depending on geographic region.5-7 It is not simply patients who perceive wait times to be prolonged; approximately half of dermatologists surveyed by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) reported an undersupply of dermatologists in their communities, a finding that strongly correlated with patient wait times.2 Ensuring the dermatologic workforce is sufficient to fulfill patient needs requires innovation of current practice models. To address this unmet demand, many practices have begun incorporating physician extenders, a term that encompasses physicians not board certified in dermatology, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners.7 The evolving landscape of the dermatologic workforce raises questions about future practice models and patient outcomes.
Scope of Practice for Physician Extenders
In practice, the role of physician extenders is highly variable. Legislation involving the scope of practice for physician extenders constantly is changing and varies by state. As of November 2021, 24 states and the District of Columbia permit nurse practitioners “full practice” authority to triage patients, interpret diagnostic tests, and prescribe treatments without physician oversight, including controlled substances.8,9 Even in states with “reduced practice” and “restricted practice” paradigms, which necessitate physician oversight, there remains ambiguity. Across the country, state regulatory bodies differ in statues governing licensing requirements, accessibility of the supervising physician, and ultimately culpability in the case of patient harm. Lack of consensus guidelines that clearly define roles and responsibilities has kindled controversy regarding extent of autonomy and liability for adverse outcomes.10,11
With respect to procedures, the AAD has explicitly recommended that “only active and properly licensed doctors of medicine and osteopathy shall engage in the practice of medicine” but that “under appropriate circumstances, a physician may delegate certain procedures and services to appropriately trained nonphysician office personnel.”12 This statement does not refer to or explicitly list the procedures that are appropriate for delegation to nonphysician personnel, and there is wide variability in how this recommendation is applied in daily practice. As it was originally intended, the AAD’s “Ethics in Medical Practice” position statement indicated that dermatologists must directly oversee physician extenders, a responsibility that is defined as being “present on-site, immediately available and able to respond promptly” to issues arising during the provision of health care services.12
Adverse Events From Cosmetic Procedures
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery has documented a steady growth in the demand for cosmetic, medical, and surgical services,13 a trend that has heralded an increase in the number of procedures performed by physician extenders.14,15 One study contrasted the risk for adverse events following minimally invasive cosmetic procedures performed by physicians or nonphysicians. Of 2116 patients surveyed, 50 adverse events were documented.14 The cohort treated by nonphysicians experienced a higher incidence of laser burns and dyspigmentation, and the use of improper technique was the most frequently implicated cause of developing an adverse event. Approximately 24.6% of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery members reported treating 10 or more complications of cosmetic procedures performed by nonphysicians.14 Beyond laser burns and dyspigmentation, this wide range of complications included inappropriately placed filler product, facial drooping, and scarring. These studies highlight the need for further investigation into the outcomes of procedures performed by physician extenders.
Training of Physician Extenders
Even with medical management, emphasis on proper training of personnel is key and remains a legitimate concern. The training of physician extenders in dermatology differs greatly by location; while some physician extenders operate under meticulous guidance and thus can expand their skill set, other physician extenders shadow dermatologists for an arbitrary amount of time before being thrust into practice.10 It would be a disservice to both patients and nonphysician providers alike to conflate the latter regimen with the 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of rigorous specialized dermatologic training that physicians undergo.
This stark discrepancy between the training of physicians and physician extenders raises difficult questions about the patient’s right to make an informed decision regarding how they receive health care. Indeed, the casually regulated autonomous practice of some nonphysician providers has ignited public shock and ire.11
Reducing Health Care Expenditures
As legislatures deliberate over expanding scope of practice, policies should be based on evidence that prioritizes patient safety. In the appropriate setting, physician extenders can be instrumental to mitigating health care disparities; the use of physician extenders can diminish wait times for patients with routine visits for stable dermatologic disease.16 Moreover, reducing health care expenditures often is cited as a major benefit of increased utilization of physician extenders.14 It stands to reason that compensation of nonphysician providers is less expensive for a practice compared with physicians. Physician extenders participating in the management of stable chronic conditions or mild acute conditions may be cost-efficient in these circumstances; however, evidence suggests that physician extenders may incur greater costs than physicians with respect to the utilization of diagnostic tests or prescribing medications. For example, several studies have documented a substantial difference in the number of biopsies needed per malignant neoplasm by physicians compared to physician extenders.17-19 Particularly in patients younger than 65 years and in patients without history of skin cancer, physician extenders had to perform a greater number of biopsies to diagnose malignant neoplasms vs physicians.18 In addition to increased utilization of diagnostic tests, nonphysician providers more frequently prescribe medications of varying classes.20-22 Whether in outpatient offices, emergency departments, or hospital clinics, physician extenders more frequently prescribe antibiotics, which has concerning implications for antibiotic stewardship.20,21 In states with independent prescription authority, physician extenders are more than 20 times more likely to overprescribeopioids compared to physician extenders in states requiring physician supervision.23 These findings warrant additional investigation into how prescription patterns vary by provider type and how these differences impact patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Improving patient care is inherently a team endeavor, and the contributions of all members of the health care team are critical to success. Engaging physician extenders may help mitigate disparities in dermatologic care, with respect to surveillance of stable chronic conditions or the diagnosis of mild acute diseases. However, the exact scope of practice of physician extenders remains ambiguous, and their training regimens can vary drastically. Therefore, in the interest of patient safety, new patients or medically complex patients (ie, cutaneous lymphomas, nonstable autoimmune connective tissue disease) should be examined and managed by physicians. In either scenario, the patient should be informed of which providers are available and should be integrated into the decision-making process for their care. Through mutual respect, close collaboration, and candid assessments of patient complexity, different parties within the medical team can unite behind the mission to improve patient outcomes and champion equitable access to health care.
- Vaidya T, Zubritsky L, Alikhan A, et al. Socioeconomic and geographic barriers to dermatology care in urban and rural US populations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:406-408.
- Resneck J Jr, Kimball AB. The dermatology workforce shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:50-54.
- American Medical Association. Physician Characteristics and Distribution in the US. American Medical Association; 2002.
- Kimball AB, Resneck JS Jr. The US dermatology workforce: a specialty remains in shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:741-755.
- Tsang MW, Resneck JS Jr. Even patients with changing moles face long dermatology appointment wait-times: a study of simulated patient calls to dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:54-58.
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307.
- Zurfley F Jr, Mostow EN. Association between the use of a physician extender and dermatology appointment wait times in Ohio. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1323-1324.
- Bean M. NP practice authority by state. Becker’s Hospital Review website. Published April 8, 2021. Accessed December 4, 2021. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/nursing/np-practice-authority-by-state.html
- States with full practice authority for nurse practitioners. Maryville University website. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://online.maryville.edu/nursing-degrees/np/resources/states-granting-np-full-practice-authority/
- Slade K, Lazenby M, Grant-Kels JM. Ethics of utilizing nurse practitioners and physician’s assistants in the dermatology setting. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:516-521
- Hafner K, Palmer G. Skin cancers rise, along with questionable treatments. New York Times. November 20, 2017. Accessed December 4, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/11/20/health/dermatology-skin-cancer.html
- American Academy of Dermatology. Policy #P-61.500. the use of non-physician office personnel. Published February 22, 2002. Updated July 31, 2004. http://www.aad.org/Forms/Policies/Uploads/AR/COE%20-%20Ethics%20in%20Medical%20Practice%20Booklet.pdf
- 2016 ASDS Survey on Dermatologic Procedures. American Society for Dermatologic Surgery website. Published May 30, 2017. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://www.asds.net/skin-experts/news-room/press-releases/asds-survey-nearly-105-million-treatments-performed-in-2016
- Rossi AM, Wilson B, Hibler BP, et al. Nonphysician practice of cosmetic dermatology: a patient and physician perspective of outcomes and adverse events. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:588-597.
- Anderson AM, Matsumoto M, Saul MI, et al. Accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis by physician assistants compared with dermatologists in a large health care system. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:569-573.
- O’Brien JC, Chong BF. Reducing outpatient dermatology clinic wait times in a safety net health system in Dallas, Texas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:631-632.
- Aldredge LM, Young MS. Providing guidance for patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis who are candidates for biologic therapy: role of the nurse practitioner and physician assistant. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2016;8:14-26.
- Roblin DW, Howard DH, Becker ER, et al. Use of midlevel practitioners to achieve labor cost savings in the primary care practice of an MCO. Health Serv Res. 2004;39:607-626.
- Nault A, Zhang C, Kim K, et al. Biopsy use in skin cancer diagnosis: comparing dermatology physicians and advanced practice professionals. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:899-902.
- Privalle A, Havighurst T, Kim K, et al. Number of skin biopsies needed per malignancy: comparing the use of skin biopsies among dermatologists and nondermatologist clinicians [published online August 10, 2019]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:110-116.
- Roumie CL, Halasa NB, Edwards KM, et al. Differences in antibiotic prescribing among physicians, residents, and nonphysician clinicians. Am J Med. 2005;118:641-648.
- Sanchez GV, Hersh AL, Shapiro DJ, et al. Outpatient antibiotic prescribing among United States nurse practitioners and physician assistants [published online August 10, 2016]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3:ofw168.
- Lozada MJ, Raji MA, Goodwin JS, et al. Opioid prescribing by primary care providers: a cross-sectional analysis of nurse practitioner, physician assistant, and physician prescribing patterns [published online April 24, 2020]. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:2584-2592.
- Vaidya T, Zubritsky L, Alikhan A, et al. Socioeconomic and geographic barriers to dermatology care in urban and rural US populations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:406-408.
- Resneck J Jr, Kimball AB. The dermatology workforce shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:50-54.
- American Medical Association. Physician Characteristics and Distribution in the US. American Medical Association; 2002.
- Kimball AB, Resneck JS Jr. The US dermatology workforce: a specialty remains in shortage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:741-755.
- Tsang MW, Resneck JS Jr. Even patients with changing moles face long dermatology appointment wait-times: a study of simulated patient calls to dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:54-58.
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307.
- Zurfley F Jr, Mostow EN. Association between the use of a physician extender and dermatology appointment wait times in Ohio. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1323-1324.
- Bean M. NP practice authority by state. Becker’s Hospital Review website. Published April 8, 2021. Accessed December 4, 2021. https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/nursing/np-practice-authority-by-state.html
- States with full practice authority for nurse practitioners. Maryville University website. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://online.maryville.edu/nursing-degrees/np/resources/states-granting-np-full-practice-authority/
- Slade K, Lazenby M, Grant-Kels JM. Ethics of utilizing nurse practitioners and physician’s assistants in the dermatology setting. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:516-521
- Hafner K, Palmer G. Skin cancers rise, along with questionable treatments. New York Times. November 20, 2017. Accessed December 4, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/11/20/health/dermatology-skin-cancer.html
- American Academy of Dermatology. Policy #P-61.500. the use of non-physician office personnel. Published February 22, 2002. Updated July 31, 2004. http://www.aad.org/Forms/Policies/Uploads/AR/COE%20-%20Ethics%20in%20Medical%20Practice%20Booklet.pdf
- 2016 ASDS Survey on Dermatologic Procedures. American Society for Dermatologic Surgery website. Published May 30, 2017. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://www.asds.net/skin-experts/news-room/press-releases/asds-survey-nearly-105-million-treatments-performed-in-2016
- Rossi AM, Wilson B, Hibler BP, et al. Nonphysician practice of cosmetic dermatology: a patient and physician perspective of outcomes and adverse events. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:588-597.
- Anderson AM, Matsumoto M, Saul MI, et al. Accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis by physician assistants compared with dermatologists in a large health care system. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:569-573.
- O’Brien JC, Chong BF. Reducing outpatient dermatology clinic wait times in a safety net health system in Dallas, Texas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:631-632.
- Aldredge LM, Young MS. Providing guidance for patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis who are candidates for biologic therapy: role of the nurse practitioner and physician assistant. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2016;8:14-26.
- Roblin DW, Howard DH, Becker ER, et al. Use of midlevel practitioners to achieve labor cost savings in the primary care practice of an MCO. Health Serv Res. 2004;39:607-626.
- Nault A, Zhang C, Kim K, et al. Biopsy use in skin cancer diagnosis: comparing dermatology physicians and advanced practice professionals. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:899-902.
- Privalle A, Havighurst T, Kim K, et al. Number of skin biopsies needed per malignancy: comparing the use of skin biopsies among dermatologists and nondermatologist clinicians [published online August 10, 2019]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:110-116.
- Roumie CL, Halasa NB, Edwards KM, et al. Differences in antibiotic prescribing among physicians, residents, and nonphysician clinicians. Am J Med. 2005;118:641-648.
- Sanchez GV, Hersh AL, Shapiro DJ, et al. Outpatient antibiotic prescribing among United States nurse practitioners and physician assistants [published online August 10, 2016]. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3:ofw168.
- Lozada MJ, Raji MA, Goodwin JS, et al. Opioid prescribing by primary care providers: a cross-sectional analysis of nurse practitioner, physician assistant, and physician prescribing patterns [published online April 24, 2020]. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:2584-2592.
Resident Pearl
- Because dermatology residents are immersed in high-volume clinical practice, they offer a unique perspective on current patient needs and daily workflow challenges that can guide the development of health care policies and care models.
Children and COVID: New cases, admissions are higher than ever
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children passed 300,000 for the first time since the pandemic started, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The rate of new COVID-related hospital admissions also reached a new high of 0.74 per 100,000 children as of Dec. 31. The highest rate seen before the current Omicron-fueled surge was 0.47 per 100,000 in early September, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.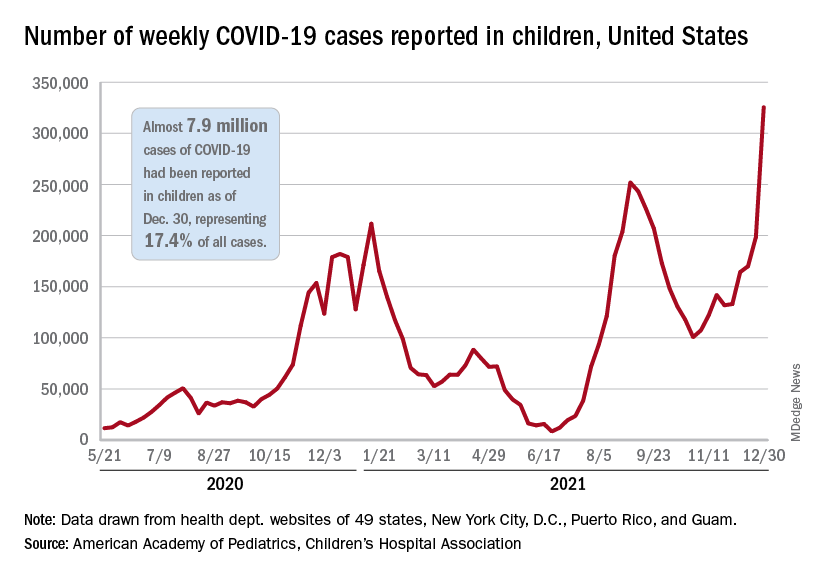
and exceeding the previous week’s count by almost 64%, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
New cases were up in all four regions of the United States, with the Northeast adding the most newly infected children while setting a new high for the fifth consecutive week. The South was just behind for the week but still well off the record it reached in September, the Midwest was third but recorded its busiest week ever, and the West was fourth and nowhere near its previous high, the AAP/CHA report indicated.
The total number of child cases since the pandemic began is almost 7.9 million, they said based on data collected from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. That figure represents 17.4% of all cases reported in the United States, and the cumulative rate of COVID infection is up to almost 10,500 per 100,000 children, meaning that 1 in 10 children have been infected.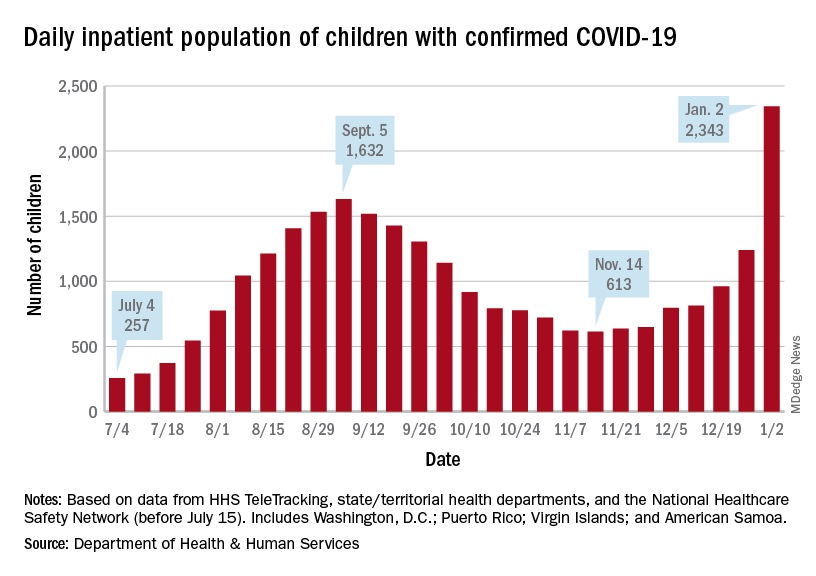
Children are still less likely to be hospitalized than adults, but the gap appears to be closing. On Jan. 2 there were 2,343 children and 87,690 adults in the hospital with confirmed COVID, a ratio of 37 adults for each child, but on Sept. 5, at the height of the previous surge, the ratio of hospitalized adults (93,647) to children (1,632) was 57:1, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
New admissions show a similar pattern: The 0.74 admissions per 100,000 children recorded on Dec. 31 was lower than, for example, adults aged 30-39 years (2.7 per 100,000) or 50-59 years (4.25 per 100,000), but on Sept. 5 the corresponding figures were 0.46 (children), 2.74 (ages 30-39), and 5.03 (aged 50-59), based on the HHS data.
A look at vaccinations
The vaccination response to Omicron, however, has been more subdued and somewhat inconsistent. Vaccine initiation, not surprisingly, was down among eligible children for the week of Dec. 23-29. Before that, both the 5- to 11-year-olds and 12- to 15-year-olds were down for the second week of December and then up a bit (5.6% and 14.3%, respectively) during the third week, while the 16- to 17-year-olds, increased initiation by 63.2%, CDC’s COVID Data Tracker shows.
Less than a quarter (23.5%) of children aged 5-11 received at least one dose of the vaccine in the first 2 months of their eligibility, and only 14.7% are fully vaccinated. Among the older children, coverage looks like this: at least one dose for 61.2% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 67.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds and full vaccination for 51.3% and 57.6%, respectively, the CDC said.
At the state level, Massachusetts and Hawaii have the highest rates for children aged 12-17 years, with 86% having received a least one dose, and Vermont is highest for children aged 5-11 at 56%. The lowest rates can be found in Wyoming (38%) for 12- to 17-year-olds and in Mississippi (6%) for 5- to 11-year-olds, the AAP said in a separate report.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children passed 300,000 for the first time since the pandemic started, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The rate of new COVID-related hospital admissions also reached a new high of 0.74 per 100,000 children as of Dec. 31. The highest rate seen before the current Omicron-fueled surge was 0.47 per 100,000 in early September, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
and exceeding the previous week’s count by almost 64%, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
New cases were up in all four regions of the United States, with the Northeast adding the most newly infected children while setting a new high for the fifth consecutive week. The South was just behind for the week but still well off the record it reached in September, the Midwest was third but recorded its busiest week ever, and the West was fourth and nowhere near its previous high, the AAP/CHA report indicated.
The total number of child cases since the pandemic began is almost 7.9 million, they said based on data collected from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. That figure represents 17.4% of all cases reported in the United States, and the cumulative rate of COVID infection is up to almost 10,500 per 100,000 children, meaning that 1 in 10 children have been infected.
Children are still less likely to be hospitalized than adults, but the gap appears to be closing. On Jan. 2 there were 2,343 children and 87,690 adults in the hospital with confirmed COVID, a ratio of 37 adults for each child, but on Sept. 5, at the height of the previous surge, the ratio of hospitalized adults (93,647) to children (1,632) was 57:1, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
New admissions show a similar pattern: The 0.74 admissions per 100,000 children recorded on Dec. 31 was lower than, for example, adults aged 30-39 years (2.7 per 100,000) or 50-59 years (4.25 per 100,000), but on Sept. 5 the corresponding figures were 0.46 (children), 2.74 (ages 30-39), and 5.03 (aged 50-59), based on the HHS data.
A look at vaccinations
The vaccination response to Omicron, however, has been more subdued and somewhat inconsistent. Vaccine initiation, not surprisingly, was down among eligible children for the week of Dec. 23-29. Before that, both the 5- to 11-year-olds and 12- to 15-year-olds were down for the second week of December and then up a bit (5.6% and 14.3%, respectively) during the third week, while the 16- to 17-year-olds, increased initiation by 63.2%, CDC’s COVID Data Tracker shows.
Less than a quarter (23.5%) of children aged 5-11 received at least one dose of the vaccine in the first 2 months of their eligibility, and only 14.7% are fully vaccinated. Among the older children, coverage looks like this: at least one dose for 61.2% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 67.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds and full vaccination for 51.3% and 57.6%, respectively, the CDC said.
At the state level, Massachusetts and Hawaii have the highest rates for children aged 12-17 years, with 86% having received a least one dose, and Vermont is highest for children aged 5-11 at 56%. The lowest rates can be found in Wyoming (38%) for 12- to 17-year-olds and in Mississippi (6%) for 5- to 11-year-olds, the AAP said in a separate report.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children passed 300,000 for the first time since the pandemic started, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The rate of new COVID-related hospital admissions also reached a new high of 0.74 per 100,000 children as of Dec. 31. The highest rate seen before the current Omicron-fueled surge was 0.47 per 100,000 in early September, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
and exceeding the previous week’s count by almost 64%, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
New cases were up in all four regions of the United States, with the Northeast adding the most newly infected children while setting a new high for the fifth consecutive week. The South was just behind for the week but still well off the record it reached in September, the Midwest was third but recorded its busiest week ever, and the West was fourth and nowhere near its previous high, the AAP/CHA report indicated.
The total number of child cases since the pandemic began is almost 7.9 million, they said based on data collected from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. That figure represents 17.4% of all cases reported in the United States, and the cumulative rate of COVID infection is up to almost 10,500 per 100,000 children, meaning that 1 in 10 children have been infected.
Children are still less likely to be hospitalized than adults, but the gap appears to be closing. On Jan. 2 there were 2,343 children and 87,690 adults in the hospital with confirmed COVID, a ratio of 37 adults for each child, but on Sept. 5, at the height of the previous surge, the ratio of hospitalized adults (93,647) to children (1,632) was 57:1, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
New admissions show a similar pattern: The 0.74 admissions per 100,000 children recorded on Dec. 31 was lower than, for example, adults aged 30-39 years (2.7 per 100,000) or 50-59 years (4.25 per 100,000), but on Sept. 5 the corresponding figures were 0.46 (children), 2.74 (ages 30-39), and 5.03 (aged 50-59), based on the HHS data.
A look at vaccinations
The vaccination response to Omicron, however, has been more subdued and somewhat inconsistent. Vaccine initiation, not surprisingly, was down among eligible children for the week of Dec. 23-29. Before that, both the 5- to 11-year-olds and 12- to 15-year-olds were down for the second week of December and then up a bit (5.6% and 14.3%, respectively) during the third week, while the 16- to 17-year-olds, increased initiation by 63.2%, CDC’s COVID Data Tracker shows.
Less than a quarter (23.5%) of children aged 5-11 received at least one dose of the vaccine in the first 2 months of their eligibility, and only 14.7% are fully vaccinated. Among the older children, coverage looks like this: at least one dose for 61.2% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 67.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds and full vaccination for 51.3% and 57.6%, respectively, the CDC said.
At the state level, Massachusetts and Hawaii have the highest rates for children aged 12-17 years, with 86% having received a least one dose, and Vermont is highest for children aged 5-11 at 56%. The lowest rates can be found in Wyoming (38%) for 12- to 17-year-olds and in Mississippi (6%) for 5- to 11-year-olds, the AAP said in a separate report.






