User login
Longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis often overlooked, expert says
In the opinion of Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, the longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis (AD) is an important yet overlooked clinical domain of the disease.
“We know that AD is associated with fluctuating severity, disease flares, long-term persistence, and periods of quiescence, but its longitudinal course is not routinely incorporated into guidelines or clinical trials,” Dr. Chovatiya, assistant professor in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “Understanding the long-term course may improve our ability to phenotype, prognosticate, and personalize our care.”
The classic view of AD is that it starts in early childhood, follows a waxing and waning course for a few years, and burns out by adulthood. “I think we all know that this is generally false,” he said. “This was largely based on anecdotal clinical experience and large cross-sectional studies, not ones that consider the heterogeneity of AD.”
Results from a large-scale, prospective study of 7,157 children enrolled in the Pediatric Eczema Elective Registry (PEER), suggests that AD commonly persists beyond adulthood. PEER was a phase IV postmarketing safety study of children aged 12-17 with moderate to severe AD who were exposed to topical pimecrolimus and who were surveyed every 6 months (JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150[6]:593-600). The researchers found that more persistent disease was associated with self-reported disease activity, many environmental exposures, White race, history of AD, and an annual household income of less than $50,000. By age 20, 50% reported at least one 6-month symptom- and medication-free period. “The important takeaway was that at every age, greater than 80% reported active AD as defined by symptoms or medication use, meaning that persistence was extremely high – much higher than what was originally thought,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “If you take a look at the literature before this study, many were retrospective analyses, and persistence was estimated to be in the 40%-60% range.”
International prospective studies have provided a more conservative estimate of persistence. For example, the German Multicenter Allergy Study followed 1,314 from birth through age 7 (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113[5]:925-31). Of these, 22% had AD within the first 2 years of life. Of these, 43% were in remission by age 3, while 38% had intermittent AD, and 19% had symptoms every year of the study. “Studies of other birth cohorts in the world came out suggesting that the rates of AD persistence ranges in the single digits to the teens,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
To reconcile these heterogeneous estimates of AD persistence, researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 45 studies that included 110,651 subjects from 15 countries and spanned 434,992 patient-years (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:681-7.e11). They found that 80% of childhood AD had at least one observed period of disease clearance by 8 years of age. “Most importantly, less than 5% of childhood AD was persistent 20 years after diagnosis,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “However, interestingly, increased persistence was associated with later onset AD, more years of persistence, and more patient/caregiver-assessed disease.” He pointed out inherent limitations to all studies of AD persistence, including nonuniform methods of data collection, differing cohorts, different ways of diagnosing AD, different disease severity scales, and the fact that most don’t assess flares or recurrence beyond the initial period of disease clearance. “This can lead to a potential underestimation of longer-term persistence,” he said.
Childhood AD features unique predictors of persistence that may define AD trajectories. For example, in several existing studies, more persistent disease was associated with higher baseline severity, earlier-onset AD, personal history of atopy, family history of AD, AD genetic risk score (heritability, including common Filaggrin mutations), urban environment, non-White race, Hispanic ethnicity, female sex, lower household income, and overall poorer health status.
Dr. Chovatiya said. “I think that AD classification can take a lesson from asthma. When we think about how our allergy colleagues think about asthma, it is commonly classified as intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent. Those that have intermittent disease get reactive treatment, while those with persistent disease get proactive treatment. Similarly, AD could be classified as mild intermittent, mild persistent, moderate to severe intermittent and moderate to severe persistent.”
He concluded his presentation by recommending that the fluctuating course of AD be better captured in clinical trials. “Current randomized, controlled trials use validated measures of AD signs and symptoms as inclusion criteria and measures of efficacy,” he said. “Static assessments may confound treatment effects, and assessment of prespecified time points are somewhat arbitrary in the context of disease subsets.” He proposes studies that examine aggregate measures of long-term disease control, such as number of itch-free days, weeks with clear skin, and flares experienced. “Long-term control assessment in RCTs should include signs, symptoms, health-related quality of life, and a patient global domain over time to better understand how AD is doing in the long run,” he said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
In the opinion of Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, the longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis (AD) is an important yet overlooked clinical domain of the disease.
“We know that AD is associated with fluctuating severity, disease flares, long-term persistence, and periods of quiescence, but its longitudinal course is not routinely incorporated into guidelines or clinical trials,” Dr. Chovatiya, assistant professor in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “Understanding the long-term course may improve our ability to phenotype, prognosticate, and personalize our care.”
The classic view of AD is that it starts in early childhood, follows a waxing and waning course for a few years, and burns out by adulthood. “I think we all know that this is generally false,” he said. “This was largely based on anecdotal clinical experience and large cross-sectional studies, not ones that consider the heterogeneity of AD.”
Results from a large-scale, prospective study of 7,157 children enrolled in the Pediatric Eczema Elective Registry (PEER), suggests that AD commonly persists beyond adulthood. PEER was a phase IV postmarketing safety study of children aged 12-17 with moderate to severe AD who were exposed to topical pimecrolimus and who were surveyed every 6 months (JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150[6]:593-600). The researchers found that more persistent disease was associated with self-reported disease activity, many environmental exposures, White race, history of AD, and an annual household income of less than $50,000. By age 20, 50% reported at least one 6-month symptom- and medication-free period. “The important takeaway was that at every age, greater than 80% reported active AD as defined by symptoms or medication use, meaning that persistence was extremely high – much higher than what was originally thought,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “If you take a look at the literature before this study, many were retrospective analyses, and persistence was estimated to be in the 40%-60% range.”
International prospective studies have provided a more conservative estimate of persistence. For example, the German Multicenter Allergy Study followed 1,314 from birth through age 7 (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113[5]:925-31). Of these, 22% had AD within the first 2 years of life. Of these, 43% were in remission by age 3, while 38% had intermittent AD, and 19% had symptoms every year of the study. “Studies of other birth cohorts in the world came out suggesting that the rates of AD persistence ranges in the single digits to the teens,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
To reconcile these heterogeneous estimates of AD persistence, researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 45 studies that included 110,651 subjects from 15 countries and spanned 434,992 patient-years (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:681-7.e11). They found that 80% of childhood AD had at least one observed period of disease clearance by 8 years of age. “Most importantly, less than 5% of childhood AD was persistent 20 years after diagnosis,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “However, interestingly, increased persistence was associated with later onset AD, more years of persistence, and more patient/caregiver-assessed disease.” He pointed out inherent limitations to all studies of AD persistence, including nonuniform methods of data collection, differing cohorts, different ways of diagnosing AD, different disease severity scales, and the fact that most don’t assess flares or recurrence beyond the initial period of disease clearance. “This can lead to a potential underestimation of longer-term persistence,” he said.
Childhood AD features unique predictors of persistence that may define AD trajectories. For example, in several existing studies, more persistent disease was associated with higher baseline severity, earlier-onset AD, personal history of atopy, family history of AD, AD genetic risk score (heritability, including common Filaggrin mutations), urban environment, non-White race, Hispanic ethnicity, female sex, lower household income, and overall poorer health status.
Dr. Chovatiya said. “I think that AD classification can take a lesson from asthma. When we think about how our allergy colleagues think about asthma, it is commonly classified as intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent. Those that have intermittent disease get reactive treatment, while those with persistent disease get proactive treatment. Similarly, AD could be classified as mild intermittent, mild persistent, moderate to severe intermittent and moderate to severe persistent.”
He concluded his presentation by recommending that the fluctuating course of AD be better captured in clinical trials. “Current randomized, controlled trials use validated measures of AD signs and symptoms as inclusion criteria and measures of efficacy,” he said. “Static assessments may confound treatment effects, and assessment of prespecified time points are somewhat arbitrary in the context of disease subsets.” He proposes studies that examine aggregate measures of long-term disease control, such as number of itch-free days, weeks with clear skin, and flares experienced. “Long-term control assessment in RCTs should include signs, symptoms, health-related quality of life, and a patient global domain over time to better understand how AD is doing in the long run,” he said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
In the opinion of Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, the longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis (AD) is an important yet overlooked clinical domain of the disease.
“We know that AD is associated with fluctuating severity, disease flares, long-term persistence, and periods of quiescence, but its longitudinal course is not routinely incorporated into guidelines or clinical trials,” Dr. Chovatiya, assistant professor in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “Understanding the long-term course may improve our ability to phenotype, prognosticate, and personalize our care.”
The classic view of AD is that it starts in early childhood, follows a waxing and waning course for a few years, and burns out by adulthood. “I think we all know that this is generally false,” he said. “This was largely based on anecdotal clinical experience and large cross-sectional studies, not ones that consider the heterogeneity of AD.”
Results from a large-scale, prospective study of 7,157 children enrolled in the Pediatric Eczema Elective Registry (PEER), suggests that AD commonly persists beyond adulthood. PEER was a phase IV postmarketing safety study of children aged 12-17 with moderate to severe AD who were exposed to topical pimecrolimus and who were surveyed every 6 months (JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150[6]:593-600). The researchers found that more persistent disease was associated with self-reported disease activity, many environmental exposures, White race, history of AD, and an annual household income of less than $50,000. By age 20, 50% reported at least one 6-month symptom- and medication-free period. “The important takeaway was that at every age, greater than 80% reported active AD as defined by symptoms or medication use, meaning that persistence was extremely high – much higher than what was originally thought,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “If you take a look at the literature before this study, many were retrospective analyses, and persistence was estimated to be in the 40%-60% range.”
International prospective studies have provided a more conservative estimate of persistence. For example, the German Multicenter Allergy Study followed 1,314 from birth through age 7 (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113[5]:925-31). Of these, 22% had AD within the first 2 years of life. Of these, 43% were in remission by age 3, while 38% had intermittent AD, and 19% had symptoms every year of the study. “Studies of other birth cohorts in the world came out suggesting that the rates of AD persistence ranges in the single digits to the teens,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
To reconcile these heterogeneous estimates of AD persistence, researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 45 studies that included 110,651 subjects from 15 countries and spanned 434,992 patient-years (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:681-7.e11). They found that 80% of childhood AD had at least one observed period of disease clearance by 8 years of age. “Most importantly, less than 5% of childhood AD was persistent 20 years after diagnosis,” Dr. Chovatiya said. “However, interestingly, increased persistence was associated with later onset AD, more years of persistence, and more patient/caregiver-assessed disease.” He pointed out inherent limitations to all studies of AD persistence, including nonuniform methods of data collection, differing cohorts, different ways of diagnosing AD, different disease severity scales, and the fact that most don’t assess flares or recurrence beyond the initial period of disease clearance. “This can lead to a potential underestimation of longer-term persistence,” he said.
Childhood AD features unique predictors of persistence that may define AD trajectories. For example, in several existing studies, more persistent disease was associated with higher baseline severity, earlier-onset AD, personal history of atopy, family history of AD, AD genetic risk score (heritability, including common Filaggrin mutations), urban environment, non-White race, Hispanic ethnicity, female sex, lower household income, and overall poorer health status.
Dr. Chovatiya said. “I think that AD classification can take a lesson from asthma. When we think about how our allergy colleagues think about asthma, it is commonly classified as intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent. Those that have intermittent disease get reactive treatment, while those with persistent disease get proactive treatment. Similarly, AD could be classified as mild intermittent, mild persistent, moderate to severe intermittent and moderate to severe persistent.”
He concluded his presentation by recommending that the fluctuating course of AD be better captured in clinical trials. “Current randomized, controlled trials use validated measures of AD signs and symptoms as inclusion criteria and measures of efficacy,” he said. “Static assessments may confound treatment effects, and assessment of prespecified time points are somewhat arbitrary in the context of disease subsets.” He proposes studies that examine aggregate measures of long-term disease control, such as number of itch-free days, weeks with clear skin, and flares experienced. “Long-term control assessment in RCTs should include signs, symptoms, health-related quality of life, and a patient global domain over time to better understand how AD is doing in the long run,” he said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
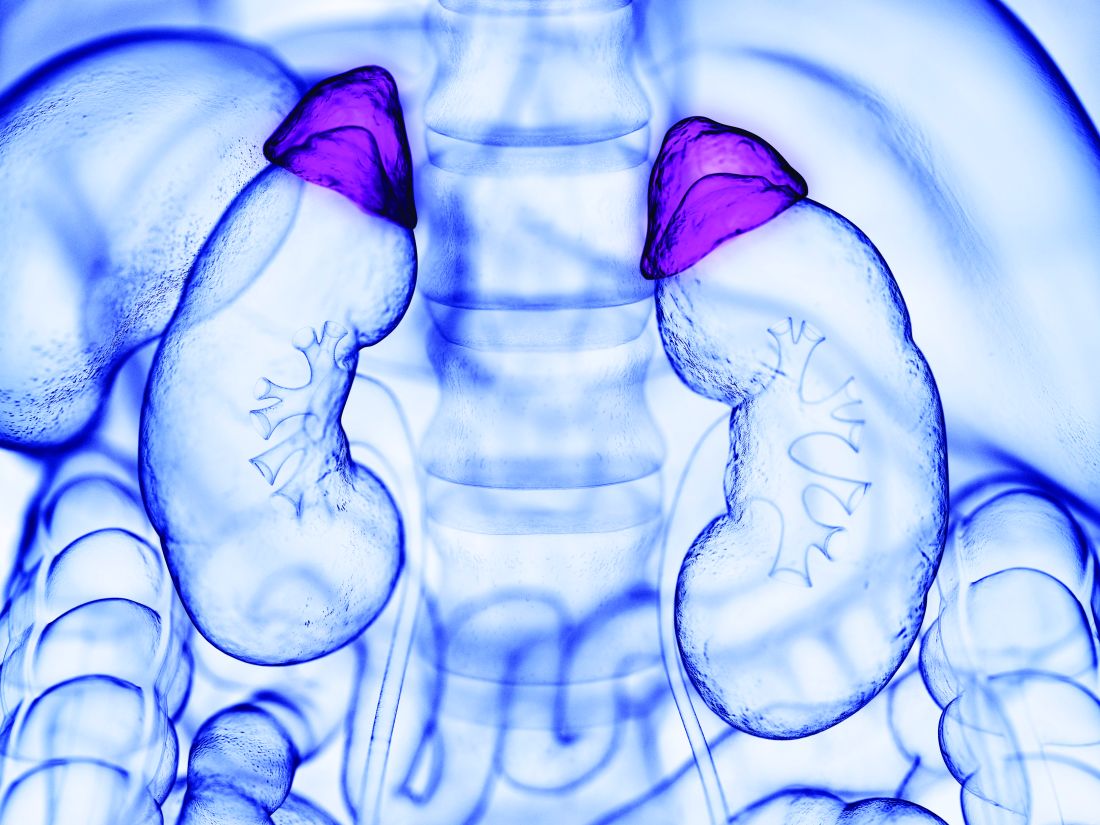
Benign adrenal tumors linked to hypertension, type 2 diabetes
In more than 15% of people with benign adrenal tumors, the growths produce clinically relevant levels of serum cortisol that are significantly linked with an increased prevalence of hypertension and, in 5% of those with Cushing syndrome (CS), an increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes, based on data from more than 1,300 people with benign adrenal tumors, the largest reported prospective study of the disorder.
The study results showed that mild autonomous cortisol secretion (MACS) from benign adrenal tumors “is very frequent and is an important risk condition for high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, especially in older women,” said Alessandro Prete, MD, lead author of the study which was published online Jan. 3, 2022, in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“The impact of MACS on high blood pressure and risk for type 2 diabetes has been underestimated until now,” said Dr. Prete, an endocrinologist at the University of Birmingham (England), in a written statement.
Results from previous studies “suggested that MACS is associated with poor health. Our study is the largest to establish conclusively the extent of the risk and severity of high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes in patients with MACS,” said Wiebke Arlt, MD, DSc, senior author and director of the Institute of Metabolism & Systems Research at the University of Birmingham.
All patients found to have a benign adrenal tumor should undergo testing for MACS and have their blood pressure and glucose levels measured regularly, Dr. Arlt advised in the statement released by the University of Birmingham.
MACS more common than previously thought
The new findings show that MACS “is more common and may have a more negative impact on health than previously thought, including increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes,” commented Lucy Chambers, PhD, head of research communications at Diabetes UK. “The findings suggest that screening for MACS could help identify people – particularly women, in whom the condition was found to be more common – who may benefit from support to reduce their risk of type 2 diabetes.”
The study included 1,305 people with newly diagnosed, benign adrenal tumors greater than 1 cm, a subset of patients prospectively enrolled in a study with the primary purpose of validating a novel way to diagnose adrenocortical carcinomas. Patients underwent treatment in 2011-2016 at any of 14 tertiary centers in 11 countries.
Researchers used a MACS definition of failure to suppress morning serum cortisol concentration to less than 50 nmol/L after treatment with 1 mg oral dexamethasone at 11 p.m. the previous evening in those with no clinical features of CS.
Roughly half of patients (n = 649) showed normal cortisol suppression with dexamethasone, identifying them as having nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, and about 35% showed possible MACS based on having moderate levels of excess cortisol.
Nearly 11% (n = 140) showed definitive MACS with more robust cortisol levels, and 5% (n = 65) received a diagnosis of clinically overt CS despite selection criteria meant to exclude people with clinical signs of CS.
There was a clear relationship between patient sex and severity of autonomous cortisol production. Among those with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, 64% were women, which rose to 74% women in those with definitive MACS and 86% women among those with CS. The median age of participants was 60 years old.
Increasing cortisol levels linked with cardiometabolic disease
Analysis of the prevalence of hypertension and type 2 diabetes after adjustment for age, sex, and body mass index showed that, compared with people with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, those with definitive MACS had a significant 15% higher rate of hypertension and those with overt CS had a 37% higher rate.
Higher levels of excess cortisol were also directly linked with an increased need for treatment with three or more antihypertensive agents to control blood pressure. Those with definitive MACS had a significant 31% higher rate of being on three or more drugs, and those with overt CS had a greater than twofold higher rate.
People with overt CS also had a significant 62% higher rate of type 2 diabetes, compared with those with a nonfunctioning tumor, but in those with definitive MACS the association was not significant. However, people with definitive MACS or overt CS who had type 2 diabetes and also had significantly increased rates of requiring insulin treatment.
The findings show that “people with definitive MACS carry an increased cardiometabolic burden similar to that seen in CS even if they do not display typical features of clinically overt cortisol excess,” the authors wrote in the report.
Even among those with apparently nonfunctioning tumors, each 10 nmol/L rise in cortisol level during a dexamethasone-suppression test was associated with a higher cardiometabolic disease burden. This observation suggests that current diagnostic cutoffs for the suppression test may miss some people with clinically relevant autonomous cortisol secretion, the report said. The study findings also suggest that people with benign adrenal tumors show a progressive continuum of excess cortisol with clinical consequences that increase as levels increase.
Determine the consequences of cortisol secretion
“These data clearly support the European Society of Endocrinology guideline recommendations that clinicians should determine precisely the cardiometabolic consequences of mild cortisol secretion in patients with adrenal lesions,” André Lacroix, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
But Dr. Lacroix included some caveats. He noted the “potential pitfalls in relying on a single total serum cortisol value after the 1-mg dexamethasone test.” He also wondered whether the analysis used optimal cortisol values to distinguish patient subgroups.
Plus, “even in patients with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors the prevalence of diabetes and hypertension is higher than in the general population, raising concerns about the cardiometabolic consequences of barely detectable cortisol excess,” wrote Dr. Lacroix, an endocrinologist at the CHUM Research Center and professor of medicine at the University of Montreal.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Prete, Dr. Chambers, and Dr. Lacroix have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Arlt is listed as an inventor on a patent on the use of steroid profiling as a biomarker tool for the differential diagnosis of adrenal tumors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In more than 15% of people with benign adrenal tumors, the growths produce clinically relevant levels of serum cortisol that are significantly linked with an increased prevalence of hypertension and, in 5% of those with Cushing syndrome (CS), an increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes, based on data from more than 1,300 people with benign adrenal tumors, the largest reported prospective study of the disorder.
The study results showed that mild autonomous cortisol secretion (MACS) from benign adrenal tumors “is very frequent and is an important risk condition for high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, especially in older women,” said Alessandro Prete, MD, lead author of the study which was published online Jan. 3, 2022, in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“The impact of MACS on high blood pressure and risk for type 2 diabetes has been underestimated until now,” said Dr. Prete, an endocrinologist at the University of Birmingham (England), in a written statement.
Results from previous studies “suggested that MACS is associated with poor health. Our study is the largest to establish conclusively the extent of the risk and severity of high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes in patients with MACS,” said Wiebke Arlt, MD, DSc, senior author and director of the Institute of Metabolism & Systems Research at the University of Birmingham.
All patients found to have a benign adrenal tumor should undergo testing for MACS and have their blood pressure and glucose levels measured regularly, Dr. Arlt advised in the statement released by the University of Birmingham.
MACS more common than previously thought
The new findings show that MACS “is more common and may have a more negative impact on health than previously thought, including increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes,” commented Lucy Chambers, PhD, head of research communications at Diabetes UK. “The findings suggest that screening for MACS could help identify people – particularly women, in whom the condition was found to be more common – who may benefit from support to reduce their risk of type 2 diabetes.”
The study included 1,305 people with newly diagnosed, benign adrenal tumors greater than 1 cm, a subset of patients prospectively enrolled in a study with the primary purpose of validating a novel way to diagnose adrenocortical carcinomas. Patients underwent treatment in 2011-2016 at any of 14 tertiary centers in 11 countries.
Researchers used a MACS definition of failure to suppress morning serum cortisol concentration to less than 50 nmol/L after treatment with 1 mg oral dexamethasone at 11 p.m. the previous evening in those with no clinical features of CS.
Roughly half of patients (n = 649) showed normal cortisol suppression with dexamethasone, identifying them as having nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, and about 35% showed possible MACS based on having moderate levels of excess cortisol.
Nearly 11% (n = 140) showed definitive MACS with more robust cortisol levels, and 5% (n = 65) received a diagnosis of clinically overt CS despite selection criteria meant to exclude people with clinical signs of CS.
There was a clear relationship between patient sex and severity of autonomous cortisol production. Among those with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, 64% were women, which rose to 74% women in those with definitive MACS and 86% women among those with CS. The median age of participants was 60 years old.
Increasing cortisol levels linked with cardiometabolic disease
Analysis of the prevalence of hypertension and type 2 diabetes after adjustment for age, sex, and body mass index showed that, compared with people with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, those with definitive MACS had a significant 15% higher rate of hypertension and those with overt CS had a 37% higher rate.
Higher levels of excess cortisol were also directly linked with an increased need for treatment with three or more antihypertensive agents to control blood pressure. Those with definitive MACS had a significant 31% higher rate of being on three or more drugs, and those with overt CS had a greater than twofold higher rate.
People with overt CS also had a significant 62% higher rate of type 2 diabetes, compared with those with a nonfunctioning tumor, but in those with definitive MACS the association was not significant. However, people with definitive MACS or overt CS who had type 2 diabetes and also had significantly increased rates of requiring insulin treatment.
The findings show that “people with definitive MACS carry an increased cardiometabolic burden similar to that seen in CS even if they do not display typical features of clinically overt cortisol excess,” the authors wrote in the report.
Even among those with apparently nonfunctioning tumors, each 10 nmol/L rise in cortisol level during a dexamethasone-suppression test was associated with a higher cardiometabolic disease burden. This observation suggests that current diagnostic cutoffs for the suppression test may miss some people with clinically relevant autonomous cortisol secretion, the report said. The study findings also suggest that people with benign adrenal tumors show a progressive continuum of excess cortisol with clinical consequences that increase as levels increase.
Determine the consequences of cortisol secretion
“These data clearly support the European Society of Endocrinology guideline recommendations that clinicians should determine precisely the cardiometabolic consequences of mild cortisol secretion in patients with adrenal lesions,” André Lacroix, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
But Dr. Lacroix included some caveats. He noted the “potential pitfalls in relying on a single total serum cortisol value after the 1-mg dexamethasone test.” He also wondered whether the analysis used optimal cortisol values to distinguish patient subgroups.
Plus, “even in patients with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors the prevalence of diabetes and hypertension is higher than in the general population, raising concerns about the cardiometabolic consequences of barely detectable cortisol excess,” wrote Dr. Lacroix, an endocrinologist at the CHUM Research Center and professor of medicine at the University of Montreal.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Prete, Dr. Chambers, and Dr. Lacroix have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Arlt is listed as an inventor on a patent on the use of steroid profiling as a biomarker tool for the differential diagnosis of adrenal tumors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In more than 15% of people with benign adrenal tumors, the growths produce clinically relevant levels of serum cortisol that are significantly linked with an increased prevalence of hypertension and, in 5% of those with Cushing syndrome (CS), an increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes, based on data from more than 1,300 people with benign adrenal tumors, the largest reported prospective study of the disorder.
The study results showed that mild autonomous cortisol secretion (MACS) from benign adrenal tumors “is very frequent and is an important risk condition for high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, especially in older women,” said Alessandro Prete, MD, lead author of the study which was published online Jan. 3, 2022, in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“The impact of MACS on high blood pressure and risk for type 2 diabetes has been underestimated until now,” said Dr. Prete, an endocrinologist at the University of Birmingham (England), in a written statement.
Results from previous studies “suggested that MACS is associated with poor health. Our study is the largest to establish conclusively the extent of the risk and severity of high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes in patients with MACS,” said Wiebke Arlt, MD, DSc, senior author and director of the Institute of Metabolism & Systems Research at the University of Birmingham.
All patients found to have a benign adrenal tumor should undergo testing for MACS and have their blood pressure and glucose levels measured regularly, Dr. Arlt advised in the statement released by the University of Birmingham.
MACS more common than previously thought
The new findings show that MACS “is more common and may have a more negative impact on health than previously thought, including increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes,” commented Lucy Chambers, PhD, head of research communications at Diabetes UK. “The findings suggest that screening for MACS could help identify people – particularly women, in whom the condition was found to be more common – who may benefit from support to reduce their risk of type 2 diabetes.”
The study included 1,305 people with newly diagnosed, benign adrenal tumors greater than 1 cm, a subset of patients prospectively enrolled in a study with the primary purpose of validating a novel way to diagnose adrenocortical carcinomas. Patients underwent treatment in 2011-2016 at any of 14 tertiary centers in 11 countries.
Researchers used a MACS definition of failure to suppress morning serum cortisol concentration to less than 50 nmol/L after treatment with 1 mg oral dexamethasone at 11 p.m. the previous evening in those with no clinical features of CS.
Roughly half of patients (n = 649) showed normal cortisol suppression with dexamethasone, identifying them as having nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, and about 35% showed possible MACS based on having moderate levels of excess cortisol.
Nearly 11% (n = 140) showed definitive MACS with more robust cortisol levels, and 5% (n = 65) received a diagnosis of clinically overt CS despite selection criteria meant to exclude people with clinical signs of CS.
There was a clear relationship between patient sex and severity of autonomous cortisol production. Among those with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, 64% were women, which rose to 74% women in those with definitive MACS and 86% women among those with CS. The median age of participants was 60 years old.
Increasing cortisol levels linked with cardiometabolic disease
Analysis of the prevalence of hypertension and type 2 diabetes after adjustment for age, sex, and body mass index showed that, compared with people with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors, those with definitive MACS had a significant 15% higher rate of hypertension and those with overt CS had a 37% higher rate.
Higher levels of excess cortisol were also directly linked with an increased need for treatment with three or more antihypertensive agents to control blood pressure. Those with definitive MACS had a significant 31% higher rate of being on three or more drugs, and those with overt CS had a greater than twofold higher rate.
People with overt CS also had a significant 62% higher rate of type 2 diabetes, compared with those with a nonfunctioning tumor, but in those with definitive MACS the association was not significant. However, people with definitive MACS or overt CS who had type 2 diabetes and also had significantly increased rates of requiring insulin treatment.
The findings show that “people with definitive MACS carry an increased cardiometabolic burden similar to that seen in CS even if they do not display typical features of clinically overt cortisol excess,” the authors wrote in the report.
Even among those with apparently nonfunctioning tumors, each 10 nmol/L rise in cortisol level during a dexamethasone-suppression test was associated with a higher cardiometabolic disease burden. This observation suggests that current diagnostic cutoffs for the suppression test may miss some people with clinically relevant autonomous cortisol secretion, the report said. The study findings also suggest that people with benign adrenal tumors show a progressive continuum of excess cortisol with clinical consequences that increase as levels increase.
Determine the consequences of cortisol secretion
“These data clearly support the European Society of Endocrinology guideline recommendations that clinicians should determine precisely the cardiometabolic consequences of mild cortisol secretion in patients with adrenal lesions,” André Lacroix, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
But Dr. Lacroix included some caveats. He noted the “potential pitfalls in relying on a single total serum cortisol value after the 1-mg dexamethasone test.” He also wondered whether the analysis used optimal cortisol values to distinguish patient subgroups.
Plus, “even in patients with nonfunctioning adrenal tumors the prevalence of diabetes and hypertension is higher than in the general population, raising concerns about the cardiometabolic consequences of barely detectable cortisol excess,” wrote Dr. Lacroix, an endocrinologist at the CHUM Research Center and professor of medicine at the University of Montreal.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Prete, Dr. Chambers, and Dr. Lacroix have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Arlt is listed as an inventor on a patent on the use of steroid profiling as a biomarker tool for the differential diagnosis of adrenal tumors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
CDC panel recommends Pfizer COVID-19 boosters for ages 12-15
The CDC had already said 16- and 17-year-olds “may” receive a Pfizer booster but the new recommendation adds the 12- to 15-year-old group and strengthens the “may” to “should” for 16- and 17-year-olds.
The committee voted 13-1 to recommend the booster for ages 12-17. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must still approve the recommendation for it to take effect.
The vote comes after the FDA on Jan. 3 authorized the Pfizer vaccine booster dose for 12- to 15-year-olds.
The FDA action updated the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, and the agency also shortened the recommended time between a second dose and the booster to 5 months or more (from 6 months). A third primary series dose is also now authorized for certain immunocompromised children between 5 and 11 years old. Full details are available in an FDA news release.
The CDC on Jan. 4 also backed the shortened time frame and a third primary series dose for some immunocompromised children 5-11 years old. But the CDC delayed a decision on a booster for 12- to 15-year-olds until it heard from its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Jan. 5.
The decision came as school districts nationwide are wrestling with decisions of whether to keep schools open or revert to a virtual format as cases surge, and as pediatric COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations reach new highs.
The only dissenting vote came from Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
She said after the vote, “I am just fine with kids getting a booster. This is not me against all boosters. I just really want the U.S. to move forward with all kids.”
Dr. Talbot said earlier in the comment period, “If we divert our public health from the unvaccinated to the vaccinated, we are not going to make a big impact. Boosters are incredibly important but they won’t solve this problem of the crowded hospitals.”
She said vaccinating the unvaccinated must be the priority.
“If you are a parent out there who has not yet vaccinated your child because you have questions, please, please talk to a health care provider,” she said.
Among the 13 supporters of the recommendation was Oliver Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of Watts HealthCare Corporation in Los Angeles.
Dr. Brooks said extending the population for boosters is another tool in the toolbox.
“If it’s a hammer, we should hit that nail hard,” he said.
Sara Oliver, MD, ACIP’s lead for the COVID-19 work group, presented the case behind the recommendation.
She noted the soaring Omicron cases.
“As of Jan. 3, the 7-day average had reached an all-time high of nearly 500,000 cases,” Dr. Oliver noted.
Since this summer, she said, adolescents have had a higher rate of incidence than that of adults.
“The majority of COVID cases continue to occur among the unvaccinated,” she said, “with unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds having a 7-times-higher risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds. Unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds have around 11 times higher risk of hospitalization than vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds.
“Vaccine effectiveness in adolescents 12-15 years old remains high,” Dr. Oliver said, but evidence shows there may be “some waning over time.”
Discussion of risk centered on myocarditis.
Dr. Oliver said myocarditis rates reported after the Pfizer vaccine in Israel across all populations as of Dec. 15 show that “the rates of myocarditis after a third dose are lower than what is seen after the second dose.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC had already said 16- and 17-year-olds “may” receive a Pfizer booster but the new recommendation adds the 12- to 15-year-old group and strengthens the “may” to “should” for 16- and 17-year-olds.
The committee voted 13-1 to recommend the booster for ages 12-17. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must still approve the recommendation for it to take effect.
The vote comes after the FDA on Jan. 3 authorized the Pfizer vaccine booster dose for 12- to 15-year-olds.
The FDA action updated the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, and the agency also shortened the recommended time between a second dose and the booster to 5 months or more (from 6 months). A third primary series dose is also now authorized for certain immunocompromised children between 5 and 11 years old. Full details are available in an FDA news release.
The CDC on Jan. 4 also backed the shortened time frame and a third primary series dose for some immunocompromised children 5-11 years old. But the CDC delayed a decision on a booster for 12- to 15-year-olds until it heard from its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Jan. 5.
The decision came as school districts nationwide are wrestling with decisions of whether to keep schools open or revert to a virtual format as cases surge, and as pediatric COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations reach new highs.
The only dissenting vote came from Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
She said after the vote, “I am just fine with kids getting a booster. This is not me against all boosters. I just really want the U.S. to move forward with all kids.”
Dr. Talbot said earlier in the comment period, “If we divert our public health from the unvaccinated to the vaccinated, we are not going to make a big impact. Boosters are incredibly important but they won’t solve this problem of the crowded hospitals.”
She said vaccinating the unvaccinated must be the priority.
“If you are a parent out there who has not yet vaccinated your child because you have questions, please, please talk to a health care provider,” she said.
Among the 13 supporters of the recommendation was Oliver Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of Watts HealthCare Corporation in Los Angeles.
Dr. Brooks said extending the population for boosters is another tool in the toolbox.
“If it’s a hammer, we should hit that nail hard,” he said.
Sara Oliver, MD, ACIP’s lead for the COVID-19 work group, presented the case behind the recommendation.
She noted the soaring Omicron cases.
“As of Jan. 3, the 7-day average had reached an all-time high of nearly 500,000 cases,” Dr. Oliver noted.
Since this summer, she said, adolescents have had a higher rate of incidence than that of adults.
“The majority of COVID cases continue to occur among the unvaccinated,” she said, “with unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds having a 7-times-higher risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds. Unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds have around 11 times higher risk of hospitalization than vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds.
“Vaccine effectiveness in adolescents 12-15 years old remains high,” Dr. Oliver said, but evidence shows there may be “some waning over time.”
Discussion of risk centered on myocarditis.
Dr. Oliver said myocarditis rates reported after the Pfizer vaccine in Israel across all populations as of Dec. 15 show that “the rates of myocarditis after a third dose are lower than what is seen after the second dose.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC had already said 16- and 17-year-olds “may” receive a Pfizer booster but the new recommendation adds the 12- to 15-year-old group and strengthens the “may” to “should” for 16- and 17-year-olds.
The committee voted 13-1 to recommend the booster for ages 12-17. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must still approve the recommendation for it to take effect.
The vote comes after the FDA on Jan. 3 authorized the Pfizer vaccine booster dose for 12- to 15-year-olds.
The FDA action updated the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, and the agency also shortened the recommended time between a second dose and the booster to 5 months or more (from 6 months). A third primary series dose is also now authorized for certain immunocompromised children between 5 and 11 years old. Full details are available in an FDA news release.
The CDC on Jan. 4 also backed the shortened time frame and a third primary series dose for some immunocompromised children 5-11 years old. But the CDC delayed a decision on a booster for 12- to 15-year-olds until it heard from its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on Jan. 5.
The decision came as school districts nationwide are wrestling with decisions of whether to keep schools open or revert to a virtual format as cases surge, and as pediatric COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations reach new highs.
The only dissenting vote came from Helen Keipp Talbot, MD, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
She said after the vote, “I am just fine with kids getting a booster. This is not me against all boosters. I just really want the U.S. to move forward with all kids.”
Dr. Talbot said earlier in the comment period, “If we divert our public health from the unvaccinated to the vaccinated, we are not going to make a big impact. Boosters are incredibly important but they won’t solve this problem of the crowded hospitals.”
She said vaccinating the unvaccinated must be the priority.
“If you are a parent out there who has not yet vaccinated your child because you have questions, please, please talk to a health care provider,” she said.
Among the 13 supporters of the recommendation was Oliver Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of Watts HealthCare Corporation in Los Angeles.
Dr. Brooks said extending the population for boosters is another tool in the toolbox.
“If it’s a hammer, we should hit that nail hard,” he said.
Sara Oliver, MD, ACIP’s lead for the COVID-19 work group, presented the case behind the recommendation.
She noted the soaring Omicron cases.
“As of Jan. 3, the 7-day average had reached an all-time high of nearly 500,000 cases,” Dr. Oliver noted.
Since this summer, she said, adolescents have had a higher rate of incidence than that of adults.
“The majority of COVID cases continue to occur among the unvaccinated,” she said, “with unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds having a 7-times-higher risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds. Unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds have around 11 times higher risk of hospitalization than vaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds.
“Vaccine effectiveness in adolescents 12-15 years old remains high,” Dr. Oliver said, but evidence shows there may be “some waning over time.”
Discussion of risk centered on myocarditis.
Dr. Oliver said myocarditis rates reported after the Pfizer vaccine in Israel across all populations as of Dec. 15 show that “the rates of myocarditis after a third dose are lower than what is seen after the second dose.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Who needs self-driving cars when we’ve got goldfish?
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
Experts disappointed by NICE’s decision to reject prostate cancer drug
In draft guidance, NICE rejected olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca) as a treatment option for hormone-relapsed metastatic prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 mutations.
The list price of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, at 37,491 pounds for an average cost of treatment, meant it was not cost effective to recommend for routine NHS use, the medicines regulator said.
The Institute of Cancer Research said the decision by NICE put patients in England and Wales at a disadvantage to those in Scotland where the regulator had approved olaparib for men with the same condition under a patient access scheme.
Kristian Helin, ICR chief executive, said: “I urge NICE and the manufacturer to come back to the table and try to find agreement on a way to make olaparib available at an agreeable price.”
Encouraging clinical evidence
Results from the PROfound trial, published in 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine, suggested that progression-free survival for patients with prostate cancers who had faulty BRCA2, BRCA1, or ATM genes was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in a control group who received either enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Median survival in the Olaparib cohort was 7.4 months, compared with 3.6 months in the control group.
Retreatment with abiraterone or enzalutamide is not considered effective for men with this type of prostate cancer, and is not standard care in the NHS, NICE said.
Current treatment for metastatic hormone-relapsed prostate cancer is chemotherapy with docetaxel, cabazitaxel, or radium-223 dichloride.
NICE acknowledged that while an indirect comparison suggested that in men previously treated with docetaxel, olaparib increased survival, compared with cabazitaxel, there were no evidence directly comparing them.
Consultation period
Gillian Leng, CBE, NICE chief executive, said: “We know how important it is for people with this type of prostate cancer to have more treatment options that can help them live longer and enable them to maintain or improve their quality of life, as well as delay chemotherapy and its associated side effects.
“We’re therefore disappointed not to be able to recommend olaparib for use in this way. However, the company’s own economic model demonstrated that the drug does not offer enough benefit to justify the price it is asking.
“We’ll continue working with the company to try and address the issues highlighted by the committee.”
Johann De Bono, professor of experimental cancer medicine at the ICR, who leads the PROfound trial, said: “Olaparib is a precision drug that can extend life for men with some mutations in their tumors while sparing them the side effects of chemotherapy.
“I was delighted when olaparib was approved for NHS patients in Scotland earlier this year – and it’s disappointing that this decision means their counterparts in England and Wales will miss out on such a valuable new treatment option. It’s an example of the barriers that exist to making innovative drugs available at prices that the NHS can afford and is going to result in postcode prescribing across the U.K.”
The list price of olaparib is 2,317.50 pounds for a pack of 56 tablets covering 14 days of treatment. A confidential discount has been agreed by the manufacturer to make olaparib available to the NHS.
It is estimated that around 100 men would be eligible for treatment with olaparib if it was to be approved by NICE.
Consultation on the draft guidance closes on Jan. 31.
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.com.
In draft guidance, NICE rejected olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca) as a treatment option for hormone-relapsed metastatic prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 mutations.
The list price of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, at 37,491 pounds for an average cost of treatment, meant it was not cost effective to recommend for routine NHS use, the medicines regulator said.
The Institute of Cancer Research said the decision by NICE put patients in England and Wales at a disadvantage to those in Scotland where the regulator had approved olaparib for men with the same condition under a patient access scheme.
Kristian Helin, ICR chief executive, said: “I urge NICE and the manufacturer to come back to the table and try to find agreement on a way to make olaparib available at an agreeable price.”
Encouraging clinical evidence
Results from the PROfound trial, published in 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine, suggested that progression-free survival for patients with prostate cancers who had faulty BRCA2, BRCA1, or ATM genes was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in a control group who received either enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Median survival in the Olaparib cohort was 7.4 months, compared with 3.6 months in the control group.
Retreatment with abiraterone or enzalutamide is not considered effective for men with this type of prostate cancer, and is not standard care in the NHS, NICE said.
Current treatment for metastatic hormone-relapsed prostate cancer is chemotherapy with docetaxel, cabazitaxel, or radium-223 dichloride.
NICE acknowledged that while an indirect comparison suggested that in men previously treated with docetaxel, olaparib increased survival, compared with cabazitaxel, there were no evidence directly comparing them.
Consultation period
Gillian Leng, CBE, NICE chief executive, said: “We know how important it is for people with this type of prostate cancer to have more treatment options that can help them live longer and enable them to maintain or improve their quality of life, as well as delay chemotherapy and its associated side effects.
“We’re therefore disappointed not to be able to recommend olaparib for use in this way. However, the company’s own economic model demonstrated that the drug does not offer enough benefit to justify the price it is asking.
“We’ll continue working with the company to try and address the issues highlighted by the committee.”
Johann De Bono, professor of experimental cancer medicine at the ICR, who leads the PROfound trial, said: “Olaparib is a precision drug that can extend life for men with some mutations in their tumors while sparing them the side effects of chemotherapy.
“I was delighted when olaparib was approved for NHS patients in Scotland earlier this year – and it’s disappointing that this decision means their counterparts in England and Wales will miss out on such a valuable new treatment option. It’s an example of the barriers that exist to making innovative drugs available at prices that the NHS can afford and is going to result in postcode prescribing across the U.K.”
The list price of olaparib is 2,317.50 pounds for a pack of 56 tablets covering 14 days of treatment. A confidential discount has been agreed by the manufacturer to make olaparib available to the NHS.
It is estimated that around 100 men would be eligible for treatment with olaparib if it was to be approved by NICE.
Consultation on the draft guidance closes on Jan. 31.
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.com.
In draft guidance, NICE rejected olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca) as a treatment option for hormone-relapsed metastatic prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 mutations.
The list price of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, at 37,491 pounds for an average cost of treatment, meant it was not cost effective to recommend for routine NHS use, the medicines regulator said.
The Institute of Cancer Research said the decision by NICE put patients in England and Wales at a disadvantage to those in Scotland where the regulator had approved olaparib for men with the same condition under a patient access scheme.
Kristian Helin, ICR chief executive, said: “I urge NICE and the manufacturer to come back to the table and try to find agreement on a way to make olaparib available at an agreeable price.”
Encouraging clinical evidence
Results from the PROfound trial, published in 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine, suggested that progression-free survival for patients with prostate cancers who had faulty BRCA2, BRCA1, or ATM genes was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in a control group who received either enzalutamide or abiraterone.
Median survival in the Olaparib cohort was 7.4 months, compared with 3.6 months in the control group.
Retreatment with abiraterone or enzalutamide is not considered effective for men with this type of prostate cancer, and is not standard care in the NHS, NICE said.
Current treatment for metastatic hormone-relapsed prostate cancer is chemotherapy with docetaxel, cabazitaxel, or radium-223 dichloride.
NICE acknowledged that while an indirect comparison suggested that in men previously treated with docetaxel, olaparib increased survival, compared with cabazitaxel, there were no evidence directly comparing them.
Consultation period
Gillian Leng, CBE, NICE chief executive, said: “We know how important it is for people with this type of prostate cancer to have more treatment options that can help them live longer and enable them to maintain or improve their quality of life, as well as delay chemotherapy and its associated side effects.
“We’re therefore disappointed not to be able to recommend olaparib for use in this way. However, the company’s own economic model demonstrated that the drug does not offer enough benefit to justify the price it is asking.
“We’ll continue working with the company to try and address the issues highlighted by the committee.”
Johann De Bono, professor of experimental cancer medicine at the ICR, who leads the PROfound trial, said: “Olaparib is a precision drug that can extend life for men with some mutations in their tumors while sparing them the side effects of chemotherapy.
“I was delighted when olaparib was approved for NHS patients in Scotland earlier this year – and it’s disappointing that this decision means their counterparts in England and Wales will miss out on such a valuable new treatment option. It’s an example of the barriers that exist to making innovative drugs available at prices that the NHS can afford and is going to result in postcode prescribing across the U.K.”
The list price of olaparib is 2,317.50 pounds for a pack of 56 tablets covering 14 days of treatment. A confidential discount has been agreed by the manufacturer to make olaparib available to the NHS.
It is estimated that around 100 men would be eligible for treatment with olaparib if it was to be approved by NICE.
Consultation on the draft guidance closes on Jan. 31.
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.com.
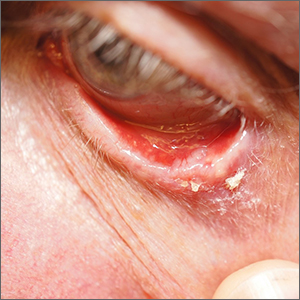
Growth on eyelid
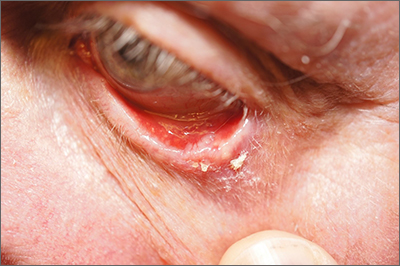
A shave biopsy (performed carefully to avoid caustic hemostatic agents irritating the conjunctiva) confirmed the diagnosis of a micronodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
BCC is a common tumor occurring on the eyelids and in the periocular region. Any new growing papule on the eyelids, history of focal bleeding, irritation, or focal loss of eyelashes should cause suspicion for BCC. Patients are often unaware of any symptoms when lesions begin, highlighting the importance of close inspection of the eyelids when skin or eye exams are performed. The differential diagnosis includes benign lesions such as hidrocystomas and nevi, as well as malignancies, including sebaceous carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.1
Factors that come into play when exploring eyelid BCC treatment options include tumor removal, eyelid function, and appearance. The potential morbidity associated with tumor spread in the periorbital region highlights the importance of early detection of eyelid cancers. Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a first choice for tumor removal of an eyelid BCC and offers a high cure rate with minimal tissue removal.
Removal of an eyelid BCC may be a multidisciplinary endeavor with MMS achieving a clear margin, and Ophthalmology or Oculoplastics following with repair and closure soon after. Patients who can’t tolerate surgery should consider vismodegib, a targeted chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
The patient in this case opted for a single staged excision and repair with Oculoplastics and has had no recurrence. He subsequently underwent a revision procedure to improve ectropion.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Shi Y, Jia R, Fan X. Ocular basal cell carcinoma: a brief literature review of clinical diagnosis and treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2483-2489. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S130371

A shave biopsy (performed carefully to avoid caustic hemostatic agents irritating the conjunctiva) confirmed the diagnosis of a micronodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
BCC is a common tumor occurring on the eyelids and in the periocular region. Any new growing papule on the eyelids, history of focal bleeding, irritation, or focal loss of eyelashes should cause suspicion for BCC. Patients are often unaware of any symptoms when lesions begin, highlighting the importance of close inspection of the eyelids when skin or eye exams are performed. The differential diagnosis includes benign lesions such as hidrocystomas and nevi, as well as malignancies, including sebaceous carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.1
Factors that come into play when exploring eyelid BCC treatment options include tumor removal, eyelid function, and appearance. The potential morbidity associated with tumor spread in the periorbital region highlights the importance of early detection of eyelid cancers. Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a first choice for tumor removal of an eyelid BCC and offers a high cure rate with minimal tissue removal.
Removal of an eyelid BCC may be a multidisciplinary endeavor with MMS achieving a clear margin, and Ophthalmology or Oculoplastics following with repair and closure soon after. Patients who can’t tolerate surgery should consider vismodegib, a targeted chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
The patient in this case opted for a single staged excision and repair with Oculoplastics and has had no recurrence. He subsequently underwent a revision procedure to improve ectropion.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

A shave biopsy (performed carefully to avoid caustic hemostatic agents irritating the conjunctiva) confirmed the diagnosis of a micronodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
BCC is a common tumor occurring on the eyelids and in the periocular region. Any new growing papule on the eyelids, history of focal bleeding, irritation, or focal loss of eyelashes should cause suspicion for BCC. Patients are often unaware of any symptoms when lesions begin, highlighting the importance of close inspection of the eyelids when skin or eye exams are performed. The differential diagnosis includes benign lesions such as hidrocystomas and nevi, as well as malignancies, including sebaceous carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.1
Factors that come into play when exploring eyelid BCC treatment options include tumor removal, eyelid function, and appearance. The potential morbidity associated with tumor spread in the periorbital region highlights the importance of early detection of eyelid cancers. Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a first choice for tumor removal of an eyelid BCC and offers a high cure rate with minimal tissue removal.
Removal of an eyelid BCC may be a multidisciplinary endeavor with MMS achieving a clear margin, and Ophthalmology or Oculoplastics following with repair and closure soon after. Patients who can’t tolerate surgery should consider vismodegib, a targeted chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
The patient in this case opted for a single staged excision and repair with Oculoplastics and has had no recurrence. He subsequently underwent a revision procedure to improve ectropion.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Shi Y, Jia R, Fan X. Ocular basal cell carcinoma: a brief literature review of clinical diagnosis and treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2483-2489. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S130371
1. Shi Y, Jia R, Fan X. Ocular basal cell carcinoma: a brief literature review of clinical diagnosis and treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2483-2489. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S130371
Psychiatry and semantics
I am a psychiatrist, which means I am a mental health professional, which means I work with people with mental illness. Sometimes people with mental health conditions who suffer from mental illness need to take a day off work – also called a mental health day – because they are too symptomatic to work, and sometimes people who don’t have a mental illness need to take a day off work, also called a mental health day, because they are feeling stressed.
Sometimes professional athletes don’t do things they agreed to do in their contracts because they realize that doing these things is very upsetting and will be detrimental to their mental health, or maybe they have a mental illness and doing these things will worsen their mental health condition, which is, in fact, a mental illness. Other times people with mental health conditions need to have pets travel with them because this mitigates the symptoms of their mental illness or perhaps it’s just good for their mental health. And finally, some people suffer from mental illnesses, or sometimes from learning problems, which are severe enough that a person with these conditions has a disability and needs special accommodations to function optimally in educational or occupational settings, or needs public financial support because their difficulties disable them to the point that they can’t work at all.
Is your head spinning yet? who we serve, and differentiating the fact that what someone with a psychiatric disorder needs to do to function or to alleviate emotional suffering may be entirely different from the things that everyone needs to do, regardless of whether they have a psychiatric disorder, to feel their emotional best.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness tells us that one in five Americans are suffering from a mental illness, while the Epidemiologic Catchment Area Program revealed that half of people will meet criteria for a mental illness at some point in their lives. We hear about “the mentally ill” constantly in the news – often in relation to mass shooters or homelessness – yet even psychiatrists might be pressed to define who exactly the “mentally ill” are. And how many of us could not somehow, at some time, find ourselves in 1 of the 157 disorders that DSM-5 lists – down from 365 disorders in the DSM-IV-TR?
Differentiating mental health from mental illness is just the beginning of our semantic confusion. As psychiatrists we treat major depression, and yet the illness “depression,” a syndromic constellation of symptoms, includes the key symptom of sadness. People often say they are “depressed” when they mean they are sad or demoralized, and yet, if their sadness persists in the absence of other symptoms, they may well want, or feel they “should” have medications, even in the absence of a disorder. And maybe those medications help them feel better, so that the presence or absence of a verified illness doesn’t really matter. But if the medications cause adverse reactions, then psychiatry might have done a better job by that person’s sadness. Melancholia, or perhaps any designation than “depression,” with its multiple meanings, might better serve our patients and our profession. This is only one example, as the number of people who tell me they have obsessive-compulsive disorder – or more often announce, “I’m OCD!” because they are well organized in a productive way is remarkable. And while I have treated only a few people who meet the criteria for narcissistic personality disorder, from general conversation it would seem that they are at every dinner table and by every water cooler.
Does it matter? A diagnostic lexicon can be so helpful when it guides treatment, provides a heterogeneous group of patients for research studies, and allows for an understanding of the etiology, course, and prognosis of a given condition. When someone is so depressed that they can’t get out of bed, or is so disorganized that they can’t perform their job and might cause a disturbance in their workplace, it is good to instruct them to take time off work and send them back well with a doctor’s note. But this is different from the person who doesn’t want to face a difficult situation, who simply doesn’t like their job or their boss, or who wants their pet declared an emotional support animal to avoid the fee the airlines charge to bring an animal on board if one does not have a psychiatric diagnosis. Sometimes these lines are blurry – if someone does not want to do something because it makes them anxious, does it matter how deep the pit in their stomach is, or if they are having full-blown panic attacks? When do we agree that their distress is reason to allow them to avoid responsibilities without repercussions versus a violation of their obligations and an infringement on others?
Diagnoses offer solace to some patients: There is a name for their suffering, available treatment, and often others with the same condition to look to for guidance and community. For others, a psychiatric diagnosis is a source of shame, a label they see as damaging to their character and sometimes to their careers – including in medicine – where we have been particularly unsympathetic to those who announce a psychiatric history.
In some cultures, the label itself decreases someone’s attractiveness as a potential marriage partner. We would all like to see the stigma of mental illness vanish, but we have a long way to go.
Psychiatric diagnoses move over time and with our politics and culture. This is good; we don’t hold on to what we learn to be untrue. But they may well add to issues of inequity. Those who can afford to pay for expensive educational assessments can request educational accommodations, including untimed standardized tests. This advantage may not be available to those without the resources to pay for these evaluations, and one might wonder why all comers can’t take untimed tests so as not to favor the privileged. Psychiatry has long been accused of diagnosing people of color with poor prognosis illnesses and women with conditions that imply emotional weakness.
While our diagnoses have clinical utility, it is unfortunate that they have come to be about reimbursement. A diagnosis needs to be assigned for insurers to pay for care, and so we create diagnostic categories to allow for treatment. Is this reasonable? Do we need to say that someone who is suffering after the death of a loved one has a mental illness in order to allow them to seek relief from their suffering? It leads us to believe that all suffering is about pathology, that we should expect pain-free emotional lives. Perhaps we need a diagnostic category of psychic pain, not otherwise specified, to allow for treatment for those who simply ache.
Mental illness is about interventions to alleviate the suffering of those with disorders. Mental health is about interventions that may benefit everyone, whether they suffer from a mental illness or not. Sleep, nutrition, exercise, sunlight, nature, entertainment and escape, yoga, meditation, vacations in beautiful places with loving people – these are things that potentially help us all whether we do or do not have an illness. With so much confusion about what it is we do, and about who “should” get help, who can get help, who might want help, and where they should go to seek help, perhaps it would be better if our lingo were more precise.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). The has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry ad behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore. She has no disclosures.
I am a psychiatrist, which means I am a mental health professional, which means I work with people with mental illness. Sometimes people with mental health conditions who suffer from mental illness need to take a day off work – also called a mental health day – because they are too symptomatic to work, and sometimes people who don’t have a mental illness need to take a day off work, also called a mental health day, because they are feeling stressed.
Sometimes professional athletes don’t do things they agreed to do in their contracts because they realize that doing these things is very upsetting and will be detrimental to their mental health, or maybe they have a mental illness and doing these things will worsen their mental health condition, which is, in fact, a mental illness. Other times people with mental health conditions need to have pets travel with them because this mitigates the symptoms of their mental illness or perhaps it’s just good for their mental health. And finally, some people suffer from mental illnesses, or sometimes from learning problems, which are severe enough that a person with these conditions has a disability and needs special accommodations to function optimally in educational or occupational settings, or needs public financial support because their difficulties disable them to the point that they can’t work at all.
Is your head spinning yet? who we serve, and differentiating the fact that what someone with a psychiatric disorder needs to do to function or to alleviate emotional suffering may be entirely different from the things that everyone needs to do, regardless of whether they have a psychiatric disorder, to feel their emotional best.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness tells us that one in five Americans are suffering from a mental illness, while the Epidemiologic Catchment Area Program revealed that half of people will meet criteria for a mental illness at some point in their lives. We hear about “the mentally ill” constantly in the news – often in relation to mass shooters or homelessness – yet even psychiatrists might be pressed to define who exactly the “mentally ill” are. And how many of us could not somehow, at some time, find ourselves in 1 of the 157 disorders that DSM-5 lists – down from 365 disorders in the DSM-IV-TR?
Differentiating mental health from mental illness is just the beginning of our semantic confusion. As psychiatrists we treat major depression, and yet the illness “depression,” a syndromic constellation of symptoms, includes the key symptom of sadness. People often say they are “depressed” when they mean they are sad or demoralized, and yet, if their sadness persists in the absence of other symptoms, they may well want, or feel they “should” have medications, even in the absence of a disorder. And maybe those medications help them feel better, so that the presence or absence of a verified illness doesn’t really matter. But if the medications cause adverse reactions, then psychiatry might have done a better job by that person’s sadness. Melancholia, or perhaps any designation than “depression,” with its multiple meanings, might better serve our patients and our profession. This is only one example, as the number of people who tell me they have obsessive-compulsive disorder – or more often announce, “I’m OCD!” because they are well organized in a productive way is remarkable. And while I have treated only a few people who meet the criteria for narcissistic personality disorder, from general conversation it would seem that they are at every dinner table and by every water cooler.
Does it matter? A diagnostic lexicon can be so helpful when it guides treatment, provides a heterogeneous group of patients for research studies, and allows for an understanding of the etiology, course, and prognosis of a given condition. When someone is so depressed that they can’t get out of bed, or is so disorganized that they can’t perform their job and might cause a disturbance in their workplace, it is good to instruct them to take time off work and send them back well with a doctor’s note. But this is different from the person who doesn’t want to face a difficult situation, who simply doesn’t like their job or their boss, or who wants their pet declared an emotional support animal to avoid the fee the airlines charge to bring an animal on board if one does not have a psychiatric diagnosis. Sometimes these lines are blurry – if someone does not want to do something because it makes them anxious, does it matter how deep the pit in their stomach is, or if they are having full-blown panic attacks? When do we agree that their distress is reason to allow them to avoid responsibilities without repercussions versus a violation of their obligations and an infringement on others?
Diagnoses offer solace to some patients: There is a name for their suffering, available treatment, and often others with the same condition to look to for guidance and community. For others, a psychiatric diagnosis is a source of shame, a label they see as damaging to their character and sometimes to their careers – including in medicine – where we have been particularly unsympathetic to those who announce a psychiatric history.
In some cultures, the label itself decreases someone’s attractiveness as a potential marriage partner. We would all like to see the stigma of mental illness vanish, but we have a long way to go.
Psychiatric diagnoses move over time and with our politics and culture. This is good; we don’t hold on to what we learn to be untrue. But they may well add to issues of inequity. Those who can afford to pay for expensive educational assessments can request educational accommodations, including untimed standardized tests. This advantage may not be available to those without the resources to pay for these evaluations, and one might wonder why all comers can’t take untimed tests so as not to favor the privileged. Psychiatry has long been accused of diagnosing people of color with poor prognosis illnesses and women with conditions that imply emotional weakness.
While our diagnoses have clinical utility, it is unfortunate that they have come to be about reimbursement. A diagnosis needs to be assigned for insurers to pay for care, and so we create diagnostic categories to allow for treatment. Is this reasonable? Do we need to say that someone who is suffering after the death of a loved one has a mental illness in order to allow them to seek relief from their suffering? It leads us to believe that all suffering is about pathology, that we should expect pain-free emotional lives. Perhaps we need a diagnostic category of psychic pain, not otherwise specified, to allow for treatment for those who simply ache.
Mental illness is about interventions to alleviate the suffering of those with disorders. Mental health is about interventions that may benefit everyone, whether they suffer from a mental illness or not. Sleep, nutrition, exercise, sunlight, nature, entertainment and escape, yoga, meditation, vacations in beautiful places with loving people – these are things that potentially help us all whether we do or do not have an illness. With so much confusion about what it is we do, and about who “should” get help, who can get help, who might want help, and where they should go to seek help, perhaps it would be better if our lingo were more precise.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). The has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry ad behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore. She has no disclosures.
I am a psychiatrist, which means I am a mental health professional, which means I work with people with mental illness. Sometimes people with mental health conditions who suffer from mental illness need to take a day off work – also called a mental health day – because they are too symptomatic to work, and sometimes people who don’t have a mental illness need to take a day off work, also called a mental health day, because they are feeling stressed.
Sometimes professional athletes don’t do things they agreed to do in their contracts because they realize that doing these things is very upsetting and will be detrimental to their mental health, or maybe they have a mental illness and doing these things will worsen their mental health condition, which is, in fact, a mental illness. Other times people with mental health conditions need to have pets travel with them because this mitigates the symptoms of their mental illness or perhaps it’s just good for their mental health. And finally, some people suffer from mental illnesses, or sometimes from learning problems, which are severe enough that a person with these conditions has a disability and needs special accommodations to function optimally in educational or occupational settings, or needs public financial support because their difficulties disable them to the point that they can’t work at all.
Is your head spinning yet? who we serve, and differentiating the fact that what someone with a psychiatric disorder needs to do to function or to alleviate emotional suffering may be entirely different from the things that everyone needs to do, regardless of whether they have a psychiatric disorder, to feel their emotional best.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness tells us that one in five Americans are suffering from a mental illness, while the Epidemiologic Catchment Area Program revealed that half of people will meet criteria for a mental illness at some point in their lives. We hear about “the mentally ill” constantly in the news – often in relation to mass shooters or homelessness – yet even psychiatrists might be pressed to define who exactly the “mentally ill” are. And how many of us could not somehow, at some time, find ourselves in 1 of the 157 disorders that DSM-5 lists – down from 365 disorders in the DSM-IV-TR?
Differentiating mental health from mental illness is just the beginning of our semantic confusion. As psychiatrists we treat major depression, and yet the illness “depression,” a syndromic constellation of symptoms, includes the key symptom of sadness. People often say they are “depressed” when they mean they are sad or demoralized, and yet, if their sadness persists in the absence of other symptoms, they may well want, or feel they “should” have medications, even in the absence of a disorder. And maybe those medications help them feel better, so that the presence or absence of a verified illness doesn’t really matter. But if the medications cause adverse reactions, then psychiatry might have done a better job by that person’s sadness. Melancholia, or perhaps any designation than “depression,” with its multiple meanings, might better serve our patients and our profession. This is only one example, as the number of people who tell me they have obsessive-compulsive disorder – or more often announce, “I’m OCD!” because they are well organized in a productive way is remarkable. And while I have treated only a few people who meet the criteria for narcissistic personality disorder, from general conversation it would seem that they are at every dinner table and by every water cooler.
Does it matter? A diagnostic lexicon can be so helpful when it guides treatment, provides a heterogeneous group of patients for research studies, and allows for an understanding of the etiology, course, and prognosis of a given condition. When someone is so depressed that they can’t get out of bed, or is so disorganized that they can’t perform their job and might cause a disturbance in their workplace, it is good to instruct them to take time off work and send them back well with a doctor’s note. But this is different from the person who doesn’t want to face a difficult situation, who simply doesn’t like their job or their boss, or who wants their pet declared an emotional support animal to avoid the fee the airlines charge to bring an animal on board if one does not have a psychiatric diagnosis. Sometimes these lines are blurry – if someone does not want to do something because it makes them anxious, does it matter how deep the pit in their stomach is, or if they are having full-blown panic attacks? When do we agree that their distress is reason to allow them to avoid responsibilities without repercussions versus a violation of their obligations and an infringement on others?
Diagnoses offer solace to some patients: There is a name for their suffering, available treatment, and often others with the same condition to look to for guidance and community. For others, a psychiatric diagnosis is a source of shame, a label they see as damaging to their character and sometimes to their careers – including in medicine – where we have been particularly unsympathetic to those who announce a psychiatric history.
In some cultures, the label itself decreases someone’s attractiveness as a potential marriage partner. We would all like to see the stigma of mental illness vanish, but we have a long way to go.
Psychiatric diagnoses move over time and with our politics and culture. This is good; we don’t hold on to what we learn to be untrue. But they may well add to issues of inequity. Those who can afford to pay for expensive educational assessments can request educational accommodations, including untimed standardized tests. This advantage may not be available to those without the resources to pay for these evaluations, and one might wonder why all comers can’t take untimed tests so as not to favor the privileged. Psychiatry has long been accused of diagnosing people of color with poor prognosis illnesses and women with conditions that imply emotional weakness.
While our diagnoses have clinical utility, it is unfortunate that they have come to be about reimbursement. A diagnosis needs to be assigned for insurers to pay for care, and so we create diagnostic categories to allow for treatment. Is this reasonable? Do we need to say that someone who is suffering after the death of a loved one has a mental illness in order to allow them to seek relief from their suffering? It leads us to believe that all suffering is about pathology, that we should expect pain-free emotional lives. Perhaps we need a diagnostic category of psychic pain, not otherwise specified, to allow for treatment for those who simply ache.
Mental illness is about interventions to alleviate the suffering of those with disorders. Mental health is about interventions that may benefit everyone, whether they suffer from a mental illness or not. Sleep, nutrition, exercise, sunlight, nature, entertainment and escape, yoga, meditation, vacations in beautiful places with loving people – these are things that potentially help us all whether we do or do not have an illness. With so much confusion about what it is we do, and about who “should” get help, who can get help, who might want help, and where they should go to seek help, perhaps it would be better if our lingo were more precise.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). The has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry ad behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore. She has no disclosures.
Duloxetine added to usual care doesn’t improve hip, knee OA pain
A small, open-label, randomized trial of patients with chronic pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis in the Netherlands shows that adding duloxetine to usual care doesn’t significantly improve clinical outcomes.
The results, published on Jan. 6 in Arthritis & Rheumatology, also showed duloxetine did not affect outcomes for a subgroup of patients who had symptoms of centrally sensitized pain, according to Jacoline J. van den Driest, MD, of the department of general practice at Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
The researchers acknowledged their findings contrast with other studies that showed a “small to moderate effect of duloxetine” for patients with chronic pain from hip and knee OA. There was also a higher rate of discontinuation of duloxetine around 3 months in the current trial, compared with previous studies, the authors said, which they attributed to the fact that clinicians were asked to discontinue treatment at 3 months if patients saw no effect or increased side effects.
“This difference in outcome can be due to the fact that we studied the effectiveness of duloxetine in primary care, while the other studies examined the efficacy in placebo-controlled trials in secondary care,” the researchers wrote. Patients in the current trial were also older, had more comorbidities, and had been living with OA symptoms “for a longer time” than patients in other trials, they explained.
“It is known that, in these more ‘real-life’ primary care populations and in effectiveness studies, smaller effects are found than in highly controlled efficacy trials,” they noted.
Dr. van den Driest and colleagues evaluated 132 patients with hip or knee OA between January 2016 and February 2019 who were cluster randomized at 66 general practitioner practice sites to receive duloxetine (30 mg/day in the first week, 60 mg/day in the second week and beyond) in addition to usual care that consisted of analgesics, physiotherapy, patient education, diet, and lifestyle advice. Patients were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old, met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hip or knee OA, and experienced chronic pain for “most days” over 3 months that was not improved through use of NSAIDs or acetaminophen or were unable to use NSAIDs because of contraindications or adverse effects. They were excluded if taking duloxetine was contraindicated for them, if they were taking an antidepressant or neuropathic pain medication, and if they had rheumatoid arthritis or were scheduled for total hip or total knee replacement.
The researchers assessed patients’ Western Ontario McMaster Universities (WOMAC) Osteoarthritis Index pain scores at 3 months, compared with baseline, as a primary outcome, with secondary outcomes of WOMAC pain and function at 1 year, and cost-effectiveness as measured by the EQ-5D-5L. A modified painDETECT questionnaire was also used at baseline to identify a subset of patients with presence of centralized pain, which was defined as a score >12.
At 12 months, 80.3% of patients in both groups completed follow-up. Patient characteristics differed in duloxetine and usual-care groups, with the duloxetine group being younger (63.2 years vs. 65.4 years) and having fewer women (59.1% vs. 75.8%). The duloxetine group also had a lower percentage of patients with knee OA (77.3% vs. 86.4%) and a lower percentage of patients with two or more comorbidities (15.2% vs. 33.2%).
Duloxetine led to a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months, compared with usual care (adjusted difference, –0.58; 95% confidence interval, –1.80 to 0.63), and at 12 months (adjusted difference, –0.26; 95% CI, –1.86 to 1.34). Among a subgroup of patients with central sensitization symptoms, there was a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months (adjusted difference, –0.32; 95% CI, –2.32 to 1.67) and 12 months (adjusted difference, 1.02; 95% CI, –1.22 to 3.27).
Duloxetine also did not significantly improve WOMAC-measured function at 3 months (adjusted difference, –2.10; 95% CI, –6.39 to 2.20) or 12 months (adjusted difference, –1.79; 95% CI, –7.22 to 3.64).
For other secondary outcomes of quality of life, patient satisfaction, and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT)-Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) responder criteria, Dr. van den Driest and colleagues noted that “none of the differences between the two groups were clinically relevant or statistically significant.”
Some patients may likely still benefit from duloxetine
Commenting on the results, Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania and Philadelphia VA Medical Center, said the study by van den Driest and colleagues is pragmatic and demonstrates the “ ‘real-world’ benefits of trying duloxetine” – one of the study’s strengths.
“As we would probably expect, the benefits are small, and somewhat smaller in this setting than what was observed in more standard clinical trials evaluating this question,” he said, noting that the study is limited by a small sample size and loss to follow-up, as well as its open-label design and the fact that most patients stopped treatment during follow-up.
Dr. Baker also explained that while patients on average did not have a meaningful effect after taking duloxetine, “that doesn’t mean that the therapy didn’t have a meaningful effect for some people.”
“In fact, though most people didn’t receive a meaningful benefit in this study, some did,” he said. “[A]ccording to these data, treating 8 people would be expected to result in 1 person achieving an [OMERACT-OARSI] response. That’s pretty good for a disease with few things that work.”
Future study of duloxetine should focus on who is most likely to benefit from treatment “since while most probably don’t benefit a lot, some probably do,” he said.
Dr. Baker also called attention to the questions surrounding use of antidepressants. “Use of antidepressants has been questioned by some, since the average clinical benefit is low, even for conditions like depression,” he explained. “However, some would argue that even small benefits may be important since there are few things that do work very well, and because a multimodal approach that provides multiple small benefits to patients can add up to a meaningful benefit.”
This study was funded by The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. One author reported receiving grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, the European Union, FOREUM, and the Dutch Arthritis Association, as well as personal fees from OARSI and Pfizer. The other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
* This story was updated 1/6/22.
A small, open-label, randomized trial of patients with chronic pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis in the Netherlands shows that adding duloxetine to usual care doesn’t significantly improve clinical outcomes.
The results, published on Jan. 6 in Arthritis & Rheumatology, also showed duloxetine did not affect outcomes for a subgroup of patients who had symptoms of centrally sensitized pain, according to Jacoline J. van den Driest, MD, of the department of general practice at Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
The researchers acknowledged their findings contrast with other studies that showed a “small to moderate effect of duloxetine” for patients with chronic pain from hip and knee OA. There was also a higher rate of discontinuation of duloxetine around 3 months in the current trial, compared with previous studies, the authors said, which they attributed to the fact that clinicians were asked to discontinue treatment at 3 months if patients saw no effect or increased side effects.
“This difference in outcome can be due to the fact that we studied the effectiveness of duloxetine in primary care, while the other studies examined the efficacy in placebo-controlled trials in secondary care,” the researchers wrote. Patients in the current trial were also older, had more comorbidities, and had been living with OA symptoms “for a longer time” than patients in other trials, they explained.
“It is known that, in these more ‘real-life’ primary care populations and in effectiveness studies, smaller effects are found than in highly controlled efficacy trials,” they noted.
Dr. van den Driest and colleagues evaluated 132 patients with hip or knee OA between January 2016 and February 2019 who were cluster randomized at 66 general practitioner practice sites to receive duloxetine (30 mg/day in the first week, 60 mg/day in the second week and beyond) in addition to usual care that consisted of analgesics, physiotherapy, patient education, diet, and lifestyle advice. Patients were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old, met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hip or knee OA, and experienced chronic pain for “most days” over 3 months that was not improved through use of NSAIDs or acetaminophen or were unable to use NSAIDs because of contraindications or adverse effects. They were excluded if taking duloxetine was contraindicated for them, if they were taking an antidepressant or neuropathic pain medication, and if they had rheumatoid arthritis or were scheduled for total hip or total knee replacement.
The researchers assessed patients’ Western Ontario McMaster Universities (WOMAC) Osteoarthritis Index pain scores at 3 months, compared with baseline, as a primary outcome, with secondary outcomes of WOMAC pain and function at 1 year, and cost-effectiveness as measured by the EQ-5D-5L. A modified painDETECT questionnaire was also used at baseline to identify a subset of patients with presence of centralized pain, which was defined as a score >12.
At 12 months, 80.3% of patients in both groups completed follow-up. Patient characteristics differed in duloxetine and usual-care groups, with the duloxetine group being younger (63.2 years vs. 65.4 years) and having fewer women (59.1% vs. 75.8%). The duloxetine group also had a lower percentage of patients with knee OA (77.3% vs. 86.4%) and a lower percentage of patients with two or more comorbidities (15.2% vs. 33.2%).
Duloxetine led to a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months, compared with usual care (adjusted difference, –0.58; 95% confidence interval, –1.80 to 0.63), and at 12 months (adjusted difference, –0.26; 95% CI, –1.86 to 1.34). Among a subgroup of patients with central sensitization symptoms, there was a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months (adjusted difference, –0.32; 95% CI, –2.32 to 1.67) and 12 months (adjusted difference, 1.02; 95% CI, –1.22 to 3.27).
Duloxetine also did not significantly improve WOMAC-measured function at 3 months (adjusted difference, –2.10; 95% CI, –6.39 to 2.20) or 12 months (adjusted difference, –1.79; 95% CI, –7.22 to 3.64).
For other secondary outcomes of quality of life, patient satisfaction, and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT)-Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) responder criteria, Dr. van den Driest and colleagues noted that “none of the differences between the two groups were clinically relevant or statistically significant.”
Some patients may likely still benefit from duloxetine
Commenting on the results, Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania and Philadelphia VA Medical Center, said the study by van den Driest and colleagues is pragmatic and demonstrates the “ ‘real-world’ benefits of trying duloxetine” – one of the study’s strengths.
“As we would probably expect, the benefits are small, and somewhat smaller in this setting than what was observed in more standard clinical trials evaluating this question,” he said, noting that the study is limited by a small sample size and loss to follow-up, as well as its open-label design and the fact that most patients stopped treatment during follow-up.
Dr. Baker also explained that while patients on average did not have a meaningful effect after taking duloxetine, “that doesn’t mean that the therapy didn’t have a meaningful effect for some people.”
“In fact, though most people didn’t receive a meaningful benefit in this study, some did,” he said. “[A]ccording to these data, treating 8 people would be expected to result in 1 person achieving an [OMERACT-OARSI] response. That’s pretty good for a disease with few things that work.”
Future study of duloxetine should focus on who is most likely to benefit from treatment “since while most probably don’t benefit a lot, some probably do,” he said.
Dr. Baker also called attention to the questions surrounding use of antidepressants. “Use of antidepressants has been questioned by some, since the average clinical benefit is low, even for conditions like depression,” he explained. “However, some would argue that even small benefits may be important since there are few things that do work very well, and because a multimodal approach that provides multiple small benefits to patients can add up to a meaningful benefit.”
This study was funded by The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. One author reported receiving grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, the European Union, FOREUM, and the Dutch Arthritis Association, as well as personal fees from OARSI and Pfizer. The other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
* This story was updated 1/6/22.
A small, open-label, randomized trial of patients with chronic pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis in the Netherlands shows that adding duloxetine to usual care doesn’t significantly improve clinical outcomes.
The results, published on Jan. 6 in Arthritis & Rheumatology, also showed duloxetine did not affect outcomes for a subgroup of patients who had symptoms of centrally sensitized pain, according to Jacoline J. van den Driest, MD, of the department of general practice at Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
The researchers acknowledged their findings contrast with other studies that showed a “small to moderate effect of duloxetine” for patients with chronic pain from hip and knee OA. There was also a higher rate of discontinuation of duloxetine around 3 months in the current trial, compared with previous studies, the authors said, which they attributed to the fact that clinicians were asked to discontinue treatment at 3 months if patients saw no effect or increased side effects.
“This difference in outcome can be due to the fact that we studied the effectiveness of duloxetine in primary care, while the other studies examined the efficacy in placebo-controlled trials in secondary care,” the researchers wrote. Patients in the current trial were also older, had more comorbidities, and had been living with OA symptoms “for a longer time” than patients in other trials, they explained.
“It is known that, in these more ‘real-life’ primary care populations and in effectiveness studies, smaller effects are found than in highly controlled efficacy trials,” they noted.
Dr. van den Driest and colleagues evaluated 132 patients with hip or knee OA between January 2016 and February 2019 who were cluster randomized at 66 general practitioner practice sites to receive duloxetine (30 mg/day in the first week, 60 mg/day in the second week and beyond) in addition to usual care that consisted of analgesics, physiotherapy, patient education, diet, and lifestyle advice. Patients were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old, met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hip or knee OA, and experienced chronic pain for “most days” over 3 months that was not improved through use of NSAIDs or acetaminophen or were unable to use NSAIDs because of contraindications or adverse effects. They were excluded if taking duloxetine was contraindicated for them, if they were taking an antidepressant or neuropathic pain medication, and if they had rheumatoid arthritis or were scheduled for total hip or total knee replacement.
The researchers assessed patients’ Western Ontario McMaster Universities (WOMAC) Osteoarthritis Index pain scores at 3 months, compared with baseline, as a primary outcome, with secondary outcomes of WOMAC pain and function at 1 year, and cost-effectiveness as measured by the EQ-5D-5L. A modified painDETECT questionnaire was also used at baseline to identify a subset of patients with presence of centralized pain, which was defined as a score >12.
At 12 months, 80.3% of patients in both groups completed follow-up. Patient characteristics differed in duloxetine and usual-care groups, with the duloxetine group being younger (63.2 years vs. 65.4 years) and having fewer women (59.1% vs. 75.8%). The duloxetine group also had a lower percentage of patients with knee OA (77.3% vs. 86.4%) and a lower percentage of patients with two or more comorbidities (15.2% vs. 33.2%).
Duloxetine led to a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months, compared with usual care (adjusted difference, –0.58; 95% confidence interval, –1.80 to 0.63), and at 12 months (adjusted difference, –0.26; 95% CI, –1.86 to 1.34). Among a subgroup of patients with central sensitization symptoms, there was a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months (adjusted difference, –0.32; 95% CI, –2.32 to 1.67) and 12 months (adjusted difference, 1.02; 95% CI, –1.22 to 3.27).
Duloxetine also did not significantly improve WOMAC-measured function at 3 months (adjusted difference, –2.10; 95% CI, –6.39 to 2.20) or 12 months (adjusted difference, –1.79; 95% CI, –7.22 to 3.64).
For other secondary outcomes of quality of life, patient satisfaction, and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT)-Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) responder criteria, Dr. van den Driest and colleagues noted that “none of the differences between the two groups were clinically relevant or statistically significant.”
Some patients may likely still benefit from duloxetine
Commenting on the results, Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania and Philadelphia VA Medical Center, said the study by van den Driest and colleagues is pragmatic and demonstrates the “ ‘real-world’ benefits of trying duloxetine” – one of the study’s strengths.
“As we would probably expect, the benefits are small, and somewhat smaller in this setting than what was observed in more standard clinical trials evaluating this question,” he said, noting that the study is limited by a small sample size and loss to follow-up, as well as its open-label design and the fact that most patients stopped treatment during follow-up.
Dr. Baker also explained that while patients on average did not have a meaningful effect after taking duloxetine, “that doesn’t mean that the therapy didn’t have a meaningful effect for some people.”
“In fact, though most people didn’t receive a meaningful benefit in this study, some did,” he said. “[A]ccording to these data, treating 8 people would be expected to result in 1 person achieving an [OMERACT-OARSI] response. That’s pretty good for a disease with few things that work.”
Future study of duloxetine should focus on who is most likely to benefit from treatment “since while most probably don’t benefit a lot, some probably do,” he said.
Dr. Baker also called attention to the questions surrounding use of antidepressants. “Use of antidepressants has been questioned by some, since the average clinical benefit is low, even for conditions like depression,” he explained. “However, some would argue that even small benefits may be important since there are few things that do work very well, and because a multimodal approach that provides multiple small benefits to patients can add up to a meaningful benefit.”
This study was funded by The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. One author reported receiving grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, the European Union, FOREUM, and the Dutch Arthritis Association, as well as personal fees from OARSI and Pfizer. The other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
* This story was updated 1/6/22.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Updates From ASH 2021
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, highlights findings from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studies presented at the 2021 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
Dr Brown begins with several studies in the front-line setting. The CLL13 trial compared three venetoclax CD20 antibody regimens in young, fit patients. Most notably, obinutuzumab plus venetoclax demonstrated superiority over chemoimmunotherapy.
Next, Dr Brown shares results from the FLAIR trial, in which oral ibrutinib plus intravenous rituximab showed superior progression-free survival over oral fludarabine, oral cyclophosphamide, and intravenous rituximab (FCR).
She also discusses long-term results from a study of ibrutinib plus FCR in younger patients. The rate of undetectable minimal residual disease was sustained and the rate of complete remission increased compared with the initial analysis.
Dr Brown also reports that in the SEQUOIA trial, zanubrutinib demonstrated superiority in progression-free survival, even in high-risk subgroups.
In the relapsed/refractory setting, Dr Brown looks at the BRUIN study, in which pirtobrutinib demonstrated promising efficacy in patients who were previously treated with Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors, as well as promising early data on the novel covalent inhibitor MK-1026.
Dr Brown concludes with a review of two studies of humoral and T-cell responses to COVID-19 vaccines in patients with CLL, which both underscored the importance of vaccinations, boosters, and follow-up doses in this group.
--
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, Worthington and Margaret Collette Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Institute Physician, Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Brigham & Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Acerta/AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Catapult; Genentech/Roche; Hutchmed; Janssen; MEI Pharma
Received research grant from: Gilead; Loxo/Lilly; TG Therapeutics; Verastem/SecuraBio
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, highlights findings from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studies presented at the 2021 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
Dr Brown begins with several studies in the front-line setting. The CLL13 trial compared three venetoclax CD20 antibody regimens in young, fit patients. Most notably, obinutuzumab plus venetoclax demonstrated superiority over chemoimmunotherapy.
Next, Dr Brown shares results from the FLAIR trial, in which oral ibrutinib plus intravenous rituximab showed superior progression-free survival over oral fludarabine, oral cyclophosphamide, and intravenous rituximab (FCR).
She also discusses long-term results from a study of ibrutinib plus FCR in younger patients. The rate of undetectable minimal residual disease was sustained and the rate of complete remission increased compared with the initial analysis.
Dr Brown also reports that in the SEQUOIA trial, zanubrutinib demonstrated superiority in progression-free survival, even in high-risk subgroups.
In the relapsed/refractory setting, Dr Brown looks at the BRUIN study, in which pirtobrutinib demonstrated promising efficacy in patients who were previously treated with Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors, as well as promising early data on the novel covalent inhibitor MK-1026.
Dr Brown concludes with a review of two studies of humoral and T-cell responses to COVID-19 vaccines in patients with CLL, which both underscored the importance of vaccinations, boosters, and follow-up doses in this group.
--
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, Worthington and Margaret Collette Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Institute Physician, Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Brigham & Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Acerta/AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Catapult; Genentech/Roche; Hutchmed; Janssen; MEI Pharma
Received research grant from: Gilead; Loxo/Lilly; TG Therapeutics; Verastem/SecuraBio
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, highlights findings from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studies presented at the 2021 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
Dr Brown begins with several studies in the front-line setting. The CLL13 trial compared three venetoclax CD20 antibody regimens in young, fit patients. Most notably, obinutuzumab plus venetoclax demonstrated superiority over chemoimmunotherapy.
Next, Dr Brown shares results from the FLAIR trial, in which oral ibrutinib plus intravenous rituximab showed superior progression-free survival over oral fludarabine, oral cyclophosphamide, and intravenous rituximab (FCR).
She also discusses long-term results from a study of ibrutinib plus FCR in younger patients. The rate of undetectable minimal residual disease was sustained and the rate of complete remission increased compared with the initial analysis.
Dr Brown also reports that in the SEQUOIA trial, zanubrutinib demonstrated superiority in progression-free survival, even in high-risk subgroups.
In the relapsed/refractory setting, Dr Brown looks at the BRUIN study, in which pirtobrutinib demonstrated promising efficacy in patients who were previously treated with Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors, as well as promising early data on the novel covalent inhibitor MK-1026.
Dr Brown concludes with a review of two studies of humoral and T-cell responses to COVID-19 vaccines in patients with CLL, which both underscored the importance of vaccinations, boosters, and follow-up doses in this group.
--
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, Worthington and Margaret Collette Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Institute Physician, Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Brigham & Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
Jennifer Brown, MD, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Acerta/AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Catapult; Genentech/Roche; Hutchmed; Janssen; MEI Pharma
Received research grant from: Gilead; Loxo/Lilly; TG Therapeutics; Verastem/SecuraBio

Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Updates From ASH 2021
Brad Kahl, MD, shares results from non-Hodgkin lymphoma clinical trials that were presented at the 2021 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
Dr Kahl looks first at a frontline study examining a new combination therapy. The POLARIX study compared polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (Pola-R-CHP) with standard of care in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Pola-R-CHP demonstrated significant improvement in progression-free survival.
In relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Dr Kahl highlights several studies in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. He starts with a primary analysis of the ZUMA-7 trial, in which axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) demonstrated improved survival compared with standard of care in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
Next, he reports on the TRANSFORM study, which compared lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) with standard of care in the second-line setting for patients with high-risk relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Liso-cel demonstrated favorable outcomes, with improved event-free survival and no new safety concerns.
The third CAR T-cell study he discusses is an updated analysis from ZUMA-5 that shows longer-term data for axi-cel in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma or marginal zone lymphoma. Consistent with the primary analysis, this study demonstrated positive survival and safety outcomes in both groups.
Finally, Dr Kahl examines a phase 1/2 study of mosunetuzumab monotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have received at least two lines of therapy. The study demonstrated improved response rates and favorable safety results.
--
Brad Kahl, MD, Professor of Medicine, Department of Medical Oncology; Director, Lymphoma Program, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Brad Kahl, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; ADC Therapeutics; AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Celgene: Epizyme; Genentech; Pharmacyclics; Roche; TG Therapeutics
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Genentech; AbbVie; Janssen
Brad Kahl, MD, shares results from non-Hodgkin lymphoma clinical trials that were presented at the 2021 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
Dr Kahl looks first at a frontline study examining a new combination therapy. The POLARIX study compared polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (Pola-R-CHP) with standard of care in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Pola-R-CHP demonstrated significant improvement in progression-free survival.
In relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Dr Kahl highlights several studies in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. He starts with a primary analysis of the ZUMA-7 trial, in which axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) demonstrated improved survival compared with standard of care in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
Next, he reports on the TRANSFORM study, which compared lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) with standard of care in the second-line setting for patients with high-risk relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Liso-cel demonstrated favorable outcomes, with improved event-free survival and no new safety concerns.
The third CAR T-cell study he discusses is an updated analysis from ZUMA-5 that shows longer-term data for axi-cel in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma or marginal zone lymphoma. Consistent with the primary analysis, this study demonstrated positive survival and safety outcomes in both groups.
Finally, Dr Kahl examines a phase 1/2 study of mosunetuzumab monotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have received at least two lines of therapy. The study demonstrated improved response rates and favorable safety results.
--
Brad Kahl, MD, Professor of Medicine, Department of Medical Oncology; Director, Lymphoma Program, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Brad Kahl, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; ADC Therapeutics; AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Celgene: Epizyme; Genentech; Pharmacyclics; Roche; TG Therapeutics
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Genentech; AbbVie; Janssen
Brad Kahl, MD, shares results from non-Hodgkin lymphoma clinical trials that were presented at the 2021 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting.
Dr Kahl looks first at a frontline study examining a new combination therapy. The POLARIX study compared polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (Pola-R-CHP) with standard of care in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Pola-R-CHP demonstrated significant improvement in progression-free survival.
In relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Dr Kahl highlights several studies in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. He starts with a primary analysis of the ZUMA-7 trial, in which axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) demonstrated improved survival compared with standard of care in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
Next, he reports on the TRANSFORM study, which compared lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) with standard of care in the second-line setting for patients with high-risk relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Liso-cel demonstrated favorable outcomes, with improved event-free survival and no new safety concerns.
The third CAR T-cell study he discusses is an updated analysis from ZUMA-5 that shows longer-term data for axi-cel in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma or marginal zone lymphoma. Consistent with the primary analysis, this study demonstrated positive survival and safety outcomes in both groups.
Finally, Dr Kahl examines a phase 1/2 study of mosunetuzumab monotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma who have received at least two lines of therapy. The study demonstrated improved response rates and favorable safety results.
--
Brad Kahl, MD, Professor of Medicine, Department of Medical Oncology; Director, Lymphoma Program, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Brad Kahl, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; ADC Therapeutics; AstraZeneca; BeiGene; Celgene: Epizyme; Genentech; Pharmacyclics; Roche; TG Therapeutics
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Genentech; AbbVie; Janssen