User login
GI involvement may signal risk for MIS-C after COVID
While evaluating an adolescent who had endured a several-day history of vomiting and diarrhea, I mentioned the likelihood of a viral causation, including SARS-CoV-2 infection. His well-informed mother responded, “He has no respiratory symptoms. Does COVID cause GI disease?”
Indeed, not only is the gastrointestinal tract a potential portal of entry of the virus but it may well be the site of mediation of both local and remote injury and thus a harbinger of more severe clinical phenotypes.
As we learn more about the clinical spectrum of COVID, it is becoming increasingly clear that certain features of GI tract involvement may allow us to establish a timeline of the clinical course and perhaps predict the outcome.
The GI tract’s involvement isn’t surprising
The ways in which the GI tract serves as a target organ of SARS-CoV-2 have been postulated in the literature. In part, this is related to the presence of abundant receptors for SARS-CoV-2 cell binding and internalization. The virus uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors to enter various cells. These receptors are highly expressed on not only lung cells but also enterocytes. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptors allows GI involvement, leading to microscopic mucosal inflammation, increased permeability, and altered intestinal absorption.
The clinical GI manifestations of this include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be the earliest, or sole, symptoms of COVID-19, often noted before the onset of fever or respiratory symptoms. In fact, John Ong, MBBS, and colleagues, in a discussion about patients with primary GI SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms, use the term “GI-COVID.”
Clinical course of GI manifestations
After SARS-CoV-2 exposure, adults most commonly present with respiratory symptoms, with GI symptoms reported in 10%-15% of cases. However, the overall incidence of GI involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection varies according to age, with children more likely than adults to manifest intestinal symptoms.
There are also differences in incidence reported when comparing hospitalized with nonhospitalized individuals. In early reports from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 11%-43% of hospitalized adult patients manifested GI symptoms. Of note, the presence of GI symptoms was associated with more severe disease and thus predictive of outcomes in those admitted to hospitals.
In a multicenter study that assessed pediatric inpatients with COVID-19, GI manifestations were present in 57% of patients and were the first manifestation in 14%. Adjusted by confounding factors, those with GI symptoms had a higher risk for pediatric intensive care unit admission. Patients admitted to the PICU also had higher serum C-reactive protein and aspartate aminotransferase values.
Emerging data on MIS-C
In previously healthy children and adolescents, the severe, life-threatening complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) may present 2-6 weeks after acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. MIS-C appears to be an immune activation syndrome and is presumed to be the delayed immunologic sequelae of mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response manifests as hyperinflammation in conjunction with a peak in antibody production a few weeks later.
One report of 186 children with MIS-C in the United States noted that the involved organ system included the GI tract in 92%, followed by cardiovascular in 80%, hematologic in 76%, mucocutaneous in 74%, and respiratory in 70%. Affected children were hospitalized for a median of 7 days, with 80% requiring intensive care, 20% receiving mechanical ventilation, and 48% receiving vasoactive support; 2% died. In a similar study of patients hospitalized in New York, 88% had GI symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea). A retrospective chart review of patients with MIS-C found that the majority had GI symptoms with any portion of the GI tract potentially involved, but ileal and colonic inflammation predominated.
Elizabeth Whittaker, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of children in eight hospitals in England who met criteria for MIS-C that were temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. At presentation, all of the patients manifested fever and nonspecific GI symptoms, including vomiting (45%), abdominal pain (53%), and diarrhea (52%). During hospitalization, 50% developed shock with evidence of myocardial dysfunction.
Ermias D. Belay, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of a large cohort of patients with MIS-C that were reported to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of 1,733 patients identified, GI symptoms were reported in 53%-67%. Over half developed hypotension or shock and were admitted for intensive care. Younger children more frequently presented with abdominal pain in contrast with adolescents, who more frequently manifest respiratory symptoms.
In a multicenter retrospective study of Italian children with COVID-19 that was conducted from the onset of the pandemic to early 2021, GI symptoms were noted in 38%. These manifestations were mild and self-limiting, comparable to other viral intestinal infections. However, a subset of children (9.5%) had severe GI manifestations of MIS-C, defined as a medical and/or radiologic diagnosis of acute abdomen, appendicitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, abdominal fluid collection, or diffuse adenomesenteritis requiring surgical consultation. Overall, 42% of this group underwent surgery. The authors noted that the clinical presentation of abdominal pain, lymphopenia, and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels were associated with a 9- to 30-fold increased probability of these severe sequelae. In addition, the severity of the GI manifestations was correlated with age (5-10 years: overall response, 8.33; >10 years: OR, 6.37). Again, the presence of GI symptoms was a harbinger of hospitalization and PICU admission.
Given that GI symptoms are a common presentation of MIS-C, its diagnosis may be delayed as clinicians first consider other GI/viral infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or Kawasaki disease. Prompt identification of GI involvement and awareness of the potential outcomes may guide the management and improve the outcome.
These studies provide a clear picture of the differential presenting features of COVID-19 and MIS-C. Although there may be other environmental/genetic factors that govern the incidence, impact, and manifestations, COVID’s status as an ongoing pandemic gives these observations worldwide relevance. This is evident in a recent report documenting pronounced GI symptoms in African children with COVID-19.
It should be noted, however, that the published data cited here reflect the impact of the initial variants of SARS-CoV-2. The GI binding, effects, and aftermath of infection with the Delta and Omicron variants is not yet known.
Cause and effect, or simply coincidental?
Some insight into MIS-C pathogenesis was provided by Lael M. Yonker, MD, and colleagues in their analysis of biospecimens from 100 children: 19 with MIS-C, 26 with acute COVID-19, and 55 controls. They demonstrated that in children with MIS-C the prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the GI tract led to the release of zonulin, a biomarker of intestinal permeability, with subsequent trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 antigens into the bloodstream, leading to hyperinflammation. They were then able to decrease plasma SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen levels and inflammatory markers, with resulting clinical improvement after administration of larazotide, a zonulin antagonist.
These observations regarding the potential mechanism and triggers of MIS-C may offer biomarkers for early detection and/or strategies for prevention and treatment of MIS-C.
Bottom line
The GI tract is the target of an immune-mediated inflammatory response that is triggered by SARS-CoV-2, with MIS-C being the major manifestation of the resultant high degree of inflammation. These observations will allow an increased awareness of nonrespiratory symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection by clinicians working in emergency departments and primary care settings.
Clues that may enhance the ability of pediatric clinicians to recognize the potential for severe GI involvement include the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers. Their presence should raise suspicion of MIS-C and lead to early evaluation.
Of note, COVID-19 mRNA vaccination is associated with a lower incidence of MIS-C in adolescents. This underscores the importance of COVID vaccination for all eligible children. Yet, we clearly have our work cut out for us. Of 107 children with MIS-C who were hospitalized in France, 31% were adolescents eligible for vaccination; however, none had been fully vaccinated. At the end of 2021, CDC data noted that less than 1% of vaccine-eligible children (12-17 years) were fully vaccinated.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is now authorized for receipt by children aged 5-11 years, the age group that is at highest risk for MIS-C. However, despite the approval of vaccines for these younger children, there is limited access in some parts of the United States at a time of rising incidence.
We look forward to broad availability of pediatric vaccination strategies. In addition, with the intense focus on safe and effective therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we hope to soon have strategies to prevent and/or treat the life-threatening manifestations and long-term consequences of MIS-C. For example, the recently reported central role of the gut microbiota in immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection offer the possibility that “microbiota modulation” may both reduce GI injury and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Dr. Balistreri has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
William F. Balistreri, MD, is the Dorothy M.M. Kersten Professor of Pediatrics; director emeritus, Pediatric Liver Care Center; medical director emeritus, liver transplantation; and professor, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. He has served as director of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s for 25 years and frequently covers gastroenterology, liver, and nutrition-related topics for this news organization. Dr Balistreri is currently editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pediatrics, having previously served as editor-in-chief of several journals and textbooks. He also became the first pediatrician to act as president of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. In his spare time, he coaches youth lacrosse.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While evaluating an adolescent who had endured a several-day history of vomiting and diarrhea, I mentioned the likelihood of a viral causation, including SARS-CoV-2 infection. His well-informed mother responded, “He has no respiratory symptoms. Does COVID cause GI disease?”
Indeed, not only is the gastrointestinal tract a potential portal of entry of the virus but it may well be the site of mediation of both local and remote injury and thus a harbinger of more severe clinical phenotypes.
As we learn more about the clinical spectrum of COVID, it is becoming increasingly clear that certain features of GI tract involvement may allow us to establish a timeline of the clinical course and perhaps predict the outcome.
The GI tract’s involvement isn’t surprising
The ways in which the GI tract serves as a target organ of SARS-CoV-2 have been postulated in the literature. In part, this is related to the presence of abundant receptors for SARS-CoV-2 cell binding and internalization. The virus uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors to enter various cells. These receptors are highly expressed on not only lung cells but also enterocytes. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptors allows GI involvement, leading to microscopic mucosal inflammation, increased permeability, and altered intestinal absorption.
The clinical GI manifestations of this include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be the earliest, or sole, symptoms of COVID-19, often noted before the onset of fever or respiratory symptoms. In fact, John Ong, MBBS, and colleagues, in a discussion about patients with primary GI SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms, use the term “GI-COVID.”
Clinical course of GI manifestations
After SARS-CoV-2 exposure, adults most commonly present with respiratory symptoms, with GI symptoms reported in 10%-15% of cases. However, the overall incidence of GI involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection varies according to age, with children more likely than adults to manifest intestinal symptoms.
There are also differences in incidence reported when comparing hospitalized with nonhospitalized individuals. In early reports from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 11%-43% of hospitalized adult patients manifested GI symptoms. Of note, the presence of GI symptoms was associated with more severe disease and thus predictive of outcomes in those admitted to hospitals.
In a multicenter study that assessed pediatric inpatients with COVID-19, GI manifestations were present in 57% of patients and were the first manifestation in 14%. Adjusted by confounding factors, those with GI symptoms had a higher risk for pediatric intensive care unit admission. Patients admitted to the PICU also had higher serum C-reactive protein and aspartate aminotransferase values.
Emerging data on MIS-C
In previously healthy children and adolescents, the severe, life-threatening complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) may present 2-6 weeks after acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. MIS-C appears to be an immune activation syndrome and is presumed to be the delayed immunologic sequelae of mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response manifests as hyperinflammation in conjunction with a peak in antibody production a few weeks later.
One report of 186 children with MIS-C in the United States noted that the involved organ system included the GI tract in 92%, followed by cardiovascular in 80%, hematologic in 76%, mucocutaneous in 74%, and respiratory in 70%. Affected children were hospitalized for a median of 7 days, with 80% requiring intensive care, 20% receiving mechanical ventilation, and 48% receiving vasoactive support; 2% died. In a similar study of patients hospitalized in New York, 88% had GI symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea). A retrospective chart review of patients with MIS-C found that the majority had GI symptoms with any portion of the GI tract potentially involved, but ileal and colonic inflammation predominated.
Elizabeth Whittaker, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of children in eight hospitals in England who met criteria for MIS-C that were temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. At presentation, all of the patients manifested fever and nonspecific GI symptoms, including vomiting (45%), abdominal pain (53%), and diarrhea (52%). During hospitalization, 50% developed shock with evidence of myocardial dysfunction.
Ermias D. Belay, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of a large cohort of patients with MIS-C that were reported to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of 1,733 patients identified, GI symptoms were reported in 53%-67%. Over half developed hypotension or shock and were admitted for intensive care. Younger children more frequently presented with abdominal pain in contrast with adolescents, who more frequently manifest respiratory symptoms.
In a multicenter retrospective study of Italian children with COVID-19 that was conducted from the onset of the pandemic to early 2021, GI symptoms were noted in 38%. These manifestations were mild and self-limiting, comparable to other viral intestinal infections. However, a subset of children (9.5%) had severe GI manifestations of MIS-C, defined as a medical and/or radiologic diagnosis of acute abdomen, appendicitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, abdominal fluid collection, or diffuse adenomesenteritis requiring surgical consultation. Overall, 42% of this group underwent surgery. The authors noted that the clinical presentation of abdominal pain, lymphopenia, and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels were associated with a 9- to 30-fold increased probability of these severe sequelae. In addition, the severity of the GI manifestations was correlated with age (5-10 years: overall response, 8.33; >10 years: OR, 6.37). Again, the presence of GI symptoms was a harbinger of hospitalization and PICU admission.
Given that GI symptoms are a common presentation of MIS-C, its diagnosis may be delayed as clinicians first consider other GI/viral infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or Kawasaki disease. Prompt identification of GI involvement and awareness of the potential outcomes may guide the management and improve the outcome.
These studies provide a clear picture of the differential presenting features of COVID-19 and MIS-C. Although there may be other environmental/genetic factors that govern the incidence, impact, and manifestations, COVID’s status as an ongoing pandemic gives these observations worldwide relevance. This is evident in a recent report documenting pronounced GI symptoms in African children with COVID-19.
It should be noted, however, that the published data cited here reflect the impact of the initial variants of SARS-CoV-2. The GI binding, effects, and aftermath of infection with the Delta and Omicron variants is not yet known.
Cause and effect, or simply coincidental?
Some insight into MIS-C pathogenesis was provided by Lael M. Yonker, MD, and colleagues in their analysis of biospecimens from 100 children: 19 with MIS-C, 26 with acute COVID-19, and 55 controls. They demonstrated that in children with MIS-C the prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the GI tract led to the release of zonulin, a biomarker of intestinal permeability, with subsequent trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 antigens into the bloodstream, leading to hyperinflammation. They were then able to decrease plasma SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen levels and inflammatory markers, with resulting clinical improvement after administration of larazotide, a zonulin antagonist.
These observations regarding the potential mechanism and triggers of MIS-C may offer biomarkers for early detection and/or strategies for prevention and treatment of MIS-C.
Bottom line
The GI tract is the target of an immune-mediated inflammatory response that is triggered by SARS-CoV-2, with MIS-C being the major manifestation of the resultant high degree of inflammation. These observations will allow an increased awareness of nonrespiratory symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection by clinicians working in emergency departments and primary care settings.
Clues that may enhance the ability of pediatric clinicians to recognize the potential for severe GI involvement include the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers. Their presence should raise suspicion of MIS-C and lead to early evaluation.
Of note, COVID-19 mRNA vaccination is associated with a lower incidence of MIS-C in adolescents. This underscores the importance of COVID vaccination for all eligible children. Yet, we clearly have our work cut out for us. Of 107 children with MIS-C who were hospitalized in France, 31% were adolescents eligible for vaccination; however, none had been fully vaccinated. At the end of 2021, CDC data noted that less than 1% of vaccine-eligible children (12-17 years) were fully vaccinated.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is now authorized for receipt by children aged 5-11 years, the age group that is at highest risk for MIS-C. However, despite the approval of vaccines for these younger children, there is limited access in some parts of the United States at a time of rising incidence.
We look forward to broad availability of pediatric vaccination strategies. In addition, with the intense focus on safe and effective therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we hope to soon have strategies to prevent and/or treat the life-threatening manifestations and long-term consequences of MIS-C. For example, the recently reported central role of the gut microbiota in immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection offer the possibility that “microbiota modulation” may both reduce GI injury and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Dr. Balistreri has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
William F. Balistreri, MD, is the Dorothy M.M. Kersten Professor of Pediatrics; director emeritus, Pediatric Liver Care Center; medical director emeritus, liver transplantation; and professor, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. He has served as director of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s for 25 years and frequently covers gastroenterology, liver, and nutrition-related topics for this news organization. Dr Balistreri is currently editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pediatrics, having previously served as editor-in-chief of several journals and textbooks. He also became the first pediatrician to act as president of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. In his spare time, he coaches youth lacrosse.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While evaluating an adolescent who had endured a several-day history of vomiting and diarrhea, I mentioned the likelihood of a viral causation, including SARS-CoV-2 infection. His well-informed mother responded, “He has no respiratory symptoms. Does COVID cause GI disease?”
Indeed, not only is the gastrointestinal tract a potential portal of entry of the virus but it may well be the site of mediation of both local and remote injury and thus a harbinger of more severe clinical phenotypes.
As we learn more about the clinical spectrum of COVID, it is becoming increasingly clear that certain features of GI tract involvement may allow us to establish a timeline of the clinical course and perhaps predict the outcome.
The GI tract’s involvement isn’t surprising
The ways in which the GI tract serves as a target organ of SARS-CoV-2 have been postulated in the literature. In part, this is related to the presence of abundant receptors for SARS-CoV-2 cell binding and internalization. The virus uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors to enter various cells. These receptors are highly expressed on not only lung cells but also enterocytes. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptors allows GI involvement, leading to microscopic mucosal inflammation, increased permeability, and altered intestinal absorption.
The clinical GI manifestations of this include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be the earliest, or sole, symptoms of COVID-19, often noted before the onset of fever or respiratory symptoms. In fact, John Ong, MBBS, and colleagues, in a discussion about patients with primary GI SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms, use the term “GI-COVID.”
Clinical course of GI manifestations
After SARS-CoV-2 exposure, adults most commonly present with respiratory symptoms, with GI symptoms reported in 10%-15% of cases. However, the overall incidence of GI involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection varies according to age, with children more likely than adults to manifest intestinal symptoms.
There are also differences in incidence reported when comparing hospitalized with nonhospitalized individuals. In early reports from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 11%-43% of hospitalized adult patients manifested GI symptoms. Of note, the presence of GI symptoms was associated with more severe disease and thus predictive of outcomes in those admitted to hospitals.
In a multicenter study that assessed pediatric inpatients with COVID-19, GI manifestations were present in 57% of patients and were the first manifestation in 14%. Adjusted by confounding factors, those with GI symptoms had a higher risk for pediatric intensive care unit admission. Patients admitted to the PICU also had higher serum C-reactive protein and aspartate aminotransferase values.
Emerging data on MIS-C
In previously healthy children and adolescents, the severe, life-threatening complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) may present 2-6 weeks after acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. MIS-C appears to be an immune activation syndrome and is presumed to be the delayed immunologic sequelae of mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response manifests as hyperinflammation in conjunction with a peak in antibody production a few weeks later.
One report of 186 children with MIS-C in the United States noted that the involved organ system included the GI tract in 92%, followed by cardiovascular in 80%, hematologic in 76%, mucocutaneous in 74%, and respiratory in 70%. Affected children were hospitalized for a median of 7 days, with 80% requiring intensive care, 20% receiving mechanical ventilation, and 48% receiving vasoactive support; 2% died. In a similar study of patients hospitalized in New York, 88% had GI symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea). A retrospective chart review of patients with MIS-C found that the majority had GI symptoms with any portion of the GI tract potentially involved, but ileal and colonic inflammation predominated.
Elizabeth Whittaker, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of children in eight hospitals in England who met criteria for MIS-C that were temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. At presentation, all of the patients manifested fever and nonspecific GI symptoms, including vomiting (45%), abdominal pain (53%), and diarrhea (52%). During hospitalization, 50% developed shock with evidence of myocardial dysfunction.
Ermias D. Belay, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of a large cohort of patients with MIS-C that were reported to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of 1,733 patients identified, GI symptoms were reported in 53%-67%. Over half developed hypotension or shock and were admitted for intensive care. Younger children more frequently presented with abdominal pain in contrast with adolescents, who more frequently manifest respiratory symptoms.
In a multicenter retrospective study of Italian children with COVID-19 that was conducted from the onset of the pandemic to early 2021, GI symptoms were noted in 38%. These manifestations were mild and self-limiting, comparable to other viral intestinal infections. However, a subset of children (9.5%) had severe GI manifestations of MIS-C, defined as a medical and/or radiologic diagnosis of acute abdomen, appendicitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, abdominal fluid collection, or diffuse adenomesenteritis requiring surgical consultation. Overall, 42% of this group underwent surgery. The authors noted that the clinical presentation of abdominal pain, lymphopenia, and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels were associated with a 9- to 30-fold increased probability of these severe sequelae. In addition, the severity of the GI manifestations was correlated with age (5-10 years: overall response, 8.33; >10 years: OR, 6.37). Again, the presence of GI symptoms was a harbinger of hospitalization and PICU admission.
Given that GI symptoms are a common presentation of MIS-C, its diagnosis may be delayed as clinicians first consider other GI/viral infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or Kawasaki disease. Prompt identification of GI involvement and awareness of the potential outcomes may guide the management and improve the outcome.
These studies provide a clear picture of the differential presenting features of COVID-19 and MIS-C. Although there may be other environmental/genetic factors that govern the incidence, impact, and manifestations, COVID’s status as an ongoing pandemic gives these observations worldwide relevance. This is evident in a recent report documenting pronounced GI symptoms in African children with COVID-19.
It should be noted, however, that the published data cited here reflect the impact of the initial variants of SARS-CoV-2. The GI binding, effects, and aftermath of infection with the Delta and Omicron variants is not yet known.
Cause and effect, or simply coincidental?
Some insight into MIS-C pathogenesis was provided by Lael M. Yonker, MD, and colleagues in their analysis of biospecimens from 100 children: 19 with MIS-C, 26 with acute COVID-19, and 55 controls. They demonstrated that in children with MIS-C the prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the GI tract led to the release of zonulin, a biomarker of intestinal permeability, with subsequent trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 antigens into the bloodstream, leading to hyperinflammation. They were then able to decrease plasma SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen levels and inflammatory markers, with resulting clinical improvement after administration of larazotide, a zonulin antagonist.
These observations regarding the potential mechanism and triggers of MIS-C may offer biomarkers for early detection and/or strategies for prevention and treatment of MIS-C.
Bottom line
The GI tract is the target of an immune-mediated inflammatory response that is triggered by SARS-CoV-2, with MIS-C being the major manifestation of the resultant high degree of inflammation. These observations will allow an increased awareness of nonrespiratory symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection by clinicians working in emergency departments and primary care settings.
Clues that may enhance the ability of pediatric clinicians to recognize the potential for severe GI involvement include the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers. Their presence should raise suspicion of MIS-C and lead to early evaluation.
Of note, COVID-19 mRNA vaccination is associated with a lower incidence of MIS-C in adolescents. This underscores the importance of COVID vaccination for all eligible children. Yet, we clearly have our work cut out for us. Of 107 children with MIS-C who were hospitalized in France, 31% were adolescents eligible for vaccination; however, none had been fully vaccinated. At the end of 2021, CDC data noted that less than 1% of vaccine-eligible children (12-17 years) were fully vaccinated.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is now authorized for receipt by children aged 5-11 years, the age group that is at highest risk for MIS-C. However, despite the approval of vaccines for these younger children, there is limited access in some parts of the United States at a time of rising incidence.
We look forward to broad availability of pediatric vaccination strategies. In addition, with the intense focus on safe and effective therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we hope to soon have strategies to prevent and/or treat the life-threatening manifestations and long-term consequences of MIS-C. For example, the recently reported central role of the gut microbiota in immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection offer the possibility that “microbiota modulation” may both reduce GI injury and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Dr. Balistreri has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
William F. Balistreri, MD, is the Dorothy M.M. Kersten Professor of Pediatrics; director emeritus, Pediatric Liver Care Center; medical director emeritus, liver transplantation; and professor, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. He has served as director of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s for 25 years and frequently covers gastroenterology, liver, and nutrition-related topics for this news organization. Dr Balistreri is currently editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pediatrics, having previously served as editor-in-chief of several journals and textbooks. He also became the first pediatrician to act as president of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. In his spare time, he coaches youth lacrosse.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New cases down to pre-Omicron level
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the fifth consecutive week, but the rate of decline slowed considerably, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The national count of new cases has now fallen for five straight weeks since peaking Jan. 14-20, and this week’s figure is the lowest since the pre-Omicron days of mid-November, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.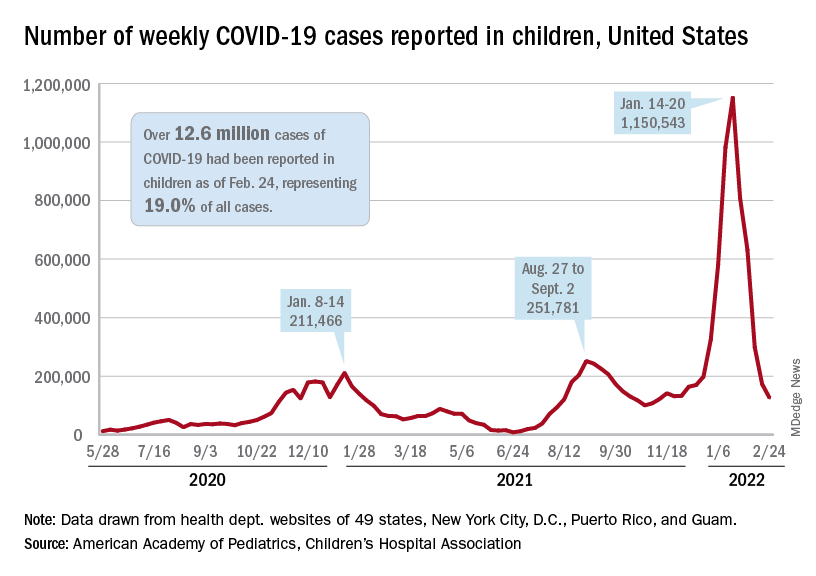
Over 12.6 million pediatric cases have been reported by those jurisdictions since the start of the pandemic, representing 19.0% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
The highest cumulative rate among the states, 27.5%, can be found in Vermont, followed by New Hampshire (26.7%) and Alaska (26.6%). Alabama’s 12.1% is lower than any other jurisdiction, but the state stopped reporting during the summer of 2021, just as the Delta surge was beginning. The next two lowest states, Florida (12.8%) and Utah (13.9%), both define children as those aged 0-14 years, so the state with the lowest rate and no qualifiers is Idaho at 14.3%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The downward trend in new cases is reflected in other national measures. The daily rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.32 per 100,000 population on Feb. 26, which is a drop of 75% since admissions peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 on Jan. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The most recent 7-day average (Feb. 20-26) for child admissions with confirmed COVID-19 was 237 per day, compared with 914 per day during the peak week of Jan. 10-16. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits by age group, are down even more. The 7-day average was 1.2% on Feb. 25 for children aged 0-11 years, compared with a peak of 13.9% in mid-January, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The current rates for older children are even lower.
The decline of the Omicron surge over the last few weeks is allowing states to end mask mandates in schools around the country. The governors of California, Oregon, and Washington just announced that their states will be lifting their mask requirements on March 11, and New York State will end its mandate on March 2, while New York City is scheduled to go mask-free as of March 7, according to District Administration.
Those types of government moves, however, do not seem to be entirely supported by the public. In a survey conducted Feb. 9-21 by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 43% of the 1,502 respondents said that all students and staff should be required to wear masks in schools, while 40% said that there should be no mask requirements at all.
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the fifth consecutive week, but the rate of decline slowed considerably, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The national count of new cases has now fallen for five straight weeks since peaking Jan. 14-20, and this week’s figure is the lowest since the pre-Omicron days of mid-November, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Over 12.6 million pediatric cases have been reported by those jurisdictions since the start of the pandemic, representing 19.0% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
The highest cumulative rate among the states, 27.5%, can be found in Vermont, followed by New Hampshire (26.7%) and Alaska (26.6%). Alabama’s 12.1% is lower than any other jurisdiction, but the state stopped reporting during the summer of 2021, just as the Delta surge was beginning. The next two lowest states, Florida (12.8%) and Utah (13.9%), both define children as those aged 0-14 years, so the state with the lowest rate and no qualifiers is Idaho at 14.3%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The downward trend in new cases is reflected in other national measures. The daily rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.32 per 100,000 population on Feb. 26, which is a drop of 75% since admissions peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 on Jan. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The most recent 7-day average (Feb. 20-26) for child admissions with confirmed COVID-19 was 237 per day, compared with 914 per day during the peak week of Jan. 10-16. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits by age group, are down even more. The 7-day average was 1.2% on Feb. 25 for children aged 0-11 years, compared with a peak of 13.9% in mid-January, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The current rates for older children are even lower.
The decline of the Omicron surge over the last few weeks is allowing states to end mask mandates in schools around the country. The governors of California, Oregon, and Washington just announced that their states will be lifting their mask requirements on March 11, and New York State will end its mandate on March 2, while New York City is scheduled to go mask-free as of March 7, according to District Administration.
Those types of government moves, however, do not seem to be entirely supported by the public. In a survey conducted Feb. 9-21 by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 43% of the 1,502 respondents said that all students and staff should be required to wear masks in schools, while 40% said that there should be no mask requirements at all.
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the fifth consecutive week, but the rate of decline slowed considerably, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The national count of new cases has now fallen for five straight weeks since peaking Jan. 14-20, and this week’s figure is the lowest since the pre-Omicron days of mid-November, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Over 12.6 million pediatric cases have been reported by those jurisdictions since the start of the pandemic, representing 19.0% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
The highest cumulative rate among the states, 27.5%, can be found in Vermont, followed by New Hampshire (26.7%) and Alaska (26.6%). Alabama’s 12.1% is lower than any other jurisdiction, but the state stopped reporting during the summer of 2021, just as the Delta surge was beginning. The next two lowest states, Florida (12.8%) and Utah (13.9%), both define children as those aged 0-14 years, so the state with the lowest rate and no qualifiers is Idaho at 14.3%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The downward trend in new cases is reflected in other national measures. The daily rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.32 per 100,000 population on Feb. 26, which is a drop of 75% since admissions peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 on Jan. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The most recent 7-day average (Feb. 20-26) for child admissions with confirmed COVID-19 was 237 per day, compared with 914 per day during the peak week of Jan. 10-16. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits by age group, are down even more. The 7-day average was 1.2% on Feb. 25 for children aged 0-11 years, compared with a peak of 13.9% in mid-January, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The current rates for older children are even lower.
The decline of the Omicron surge over the last few weeks is allowing states to end mask mandates in schools around the country. The governors of California, Oregon, and Washington just announced that their states will be lifting their mask requirements on March 11, and New York State will end its mandate on March 2, while New York City is scheduled to go mask-free as of March 7, according to District Administration.
Those types of government moves, however, do not seem to be entirely supported by the public. In a survey conducted Feb. 9-21 by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 43% of the 1,502 respondents said that all students and staff should be required to wear masks in schools, while 40% said that there should be no mask requirements at all.
Columbia names interim chair of psychiatry after Twitter controversy
Helen Blair Simpson, MD, PhD, will take over for Jeffrey Lieberman, MD, who was suspended over a tweet he sent that was widely condemned as both racist and sexist.
She will also serve as interim director of the New York State Psychiatric Institute and interim psychiatrist-in-chief at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, the email stated.
All appointments were effective on Feb. 28.
Latest response
Dr. Simpson, who joined the faculty at Columbia in 1999, previously served as a professor and vice chair of research for the psychiatry department, director of Columbia’s Center for Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, and director of psychiatry research at the New York State Psychiatric Institute. Dr. Simpson is associate editor of JAMA Psychiatry and is president-elect of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
Her research has been continuously funded by the National Institute of Mental Health since 1999, and she has advised both the World Health Organization and the American Psychiatric Association on the diagnosis and treatment of OCD.
Dr. Simpson has a bachelor’s degree in biology from Yale University and completed an MD-PhD program at The Rockefeller University and Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. She did her residency in psychiatry at New York–Presbyterian.
The announcement is Columbia’s latest response to the furor that erupted on social media following Dr. Lieberman’s tweet about Sudanese model Nyakim Gatwech, in which he wrote, “Whether a work of art or a freak of nature she’s a beautiful sight to behold.”
Twitter reacted immediately and negatively to the tweet, which even Dr. Lieberman later acknowledged was “racist and sexist” in an email apology he sent Feb. 22 to faculty and staff in the department of psychiatry.
As reported by this news organization, Columbia suspended Dr. Lieberman from his chair position on Feb. 23 and permanently removed him from the post of psychiatrist-in-chief at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Lieberman also resigned as executive director of the New York State Psychiatric Institute.
The email announcing Simpson’s appointment was signed by Katrina Armstrong, MD, incoming CEO, Columbia University Irving Medical Center and dean of the Faculties of Health Sciences and the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons; Anil K. Rustgi, MD, interim executive vice president and dean of the Faculties of Health Sciences and Medicine; Steven J. Corwin, MD; president and CEO, New York–Presbyterian; and Ann Marie Sullivan, MD, commissioner of the New York State Office of Mental Health.
This is a developing story.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helen Blair Simpson, MD, PhD, will take over for Jeffrey Lieberman, MD, who was suspended over a tweet he sent that was widely condemned as both racist and sexist.
She will also serve as interim director of the New York State Psychiatric Institute and interim psychiatrist-in-chief at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, the email stated.
All appointments were effective on Feb. 28.
Latest response
Dr. Simpson, who joined the faculty at Columbia in 1999, previously served as a professor and vice chair of research for the psychiatry department, director of Columbia’s Center for Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, and director of psychiatry research at the New York State Psychiatric Institute. Dr. Simpson is associate editor of JAMA Psychiatry and is president-elect of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
Her research has been continuously funded by the National Institute of Mental Health since 1999, and she has advised both the World Health Organization and the American Psychiatric Association on the diagnosis and treatment of OCD.
Dr. Simpson has a bachelor’s degree in biology from Yale University and completed an MD-PhD program at The Rockefeller University and Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. She did her residency in psychiatry at New York–Presbyterian.
The announcement is Columbia’s latest response to the furor that erupted on social media following Dr. Lieberman’s tweet about Sudanese model Nyakim Gatwech, in which he wrote, “Whether a work of art or a freak of nature she’s a beautiful sight to behold.”
Twitter reacted immediately and negatively to the tweet, which even Dr. Lieberman later acknowledged was “racist and sexist” in an email apology he sent Feb. 22 to faculty and staff in the department of psychiatry.
As reported by this news organization, Columbia suspended Dr. Lieberman from his chair position on Feb. 23 and permanently removed him from the post of psychiatrist-in-chief at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Lieberman also resigned as executive director of the New York State Psychiatric Institute.
The email announcing Simpson’s appointment was signed by Katrina Armstrong, MD, incoming CEO, Columbia University Irving Medical Center and dean of the Faculties of Health Sciences and the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons; Anil K. Rustgi, MD, interim executive vice president and dean of the Faculties of Health Sciences and Medicine; Steven J. Corwin, MD; president and CEO, New York–Presbyterian; and Ann Marie Sullivan, MD, commissioner of the New York State Office of Mental Health.
This is a developing story.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helen Blair Simpson, MD, PhD, will take over for Jeffrey Lieberman, MD, who was suspended over a tweet he sent that was widely condemned as both racist and sexist.
She will also serve as interim director of the New York State Psychiatric Institute and interim psychiatrist-in-chief at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, the email stated.
All appointments were effective on Feb. 28.
Latest response
Dr. Simpson, who joined the faculty at Columbia in 1999, previously served as a professor and vice chair of research for the psychiatry department, director of Columbia’s Center for Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, and director of psychiatry research at the New York State Psychiatric Institute. Dr. Simpson is associate editor of JAMA Psychiatry and is president-elect of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
Her research has been continuously funded by the National Institute of Mental Health since 1999, and she has advised both the World Health Organization and the American Psychiatric Association on the diagnosis and treatment of OCD.
Dr. Simpson has a bachelor’s degree in biology from Yale University and completed an MD-PhD program at The Rockefeller University and Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. She did her residency in psychiatry at New York–Presbyterian.
The announcement is Columbia’s latest response to the furor that erupted on social media following Dr. Lieberman’s tweet about Sudanese model Nyakim Gatwech, in which he wrote, “Whether a work of art or a freak of nature she’s a beautiful sight to behold.”
Twitter reacted immediately and negatively to the tweet, which even Dr. Lieberman later acknowledged was “racist and sexist” in an email apology he sent Feb. 22 to faculty and staff in the department of psychiatry.
As reported by this news organization, Columbia suspended Dr. Lieberman from his chair position on Feb. 23 and permanently removed him from the post of psychiatrist-in-chief at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Lieberman also resigned as executive director of the New York State Psychiatric Institute.
The email announcing Simpson’s appointment was signed by Katrina Armstrong, MD, incoming CEO, Columbia University Irving Medical Center and dean of the Faculties of Health Sciences and the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons; Anil K. Rustgi, MD, interim executive vice president and dean of the Faculties of Health Sciences and Medicine; Steven J. Corwin, MD; president and CEO, New York–Presbyterian; and Ann Marie Sullivan, MD, commissioner of the New York State Office of Mental Health.
This is a developing story.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immediate postpartum IUD insertion increases expulsion risk
Expulsion of intrauterine devices was significantly more likely when the devices were inserted within the first 3 days after delivery compared with later insertions, based on data from more than 300,000 women.
Intrauterine devices are effective contraception, and current guidelines support immediate postpartum IUD insertion as a safe, effective, and convenient option, Mary Anne Armstrong, MA, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland, and colleagues wrote. Although IUD expulsion rates are low overall, data from previous studies suggest that timing of insertion may affect expulsion rates, and that breastfeeding may play a role.
In the Association of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX-IUD) cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the electronic health records at four sites; the study population included women aged 50 years and younger who underwent IUD insertion between 2001 and 2018.
The women were grouped by postpartum status and timing of IUD placement: 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 weeks, 6-14 weeks, 14-52 weeks, and nonpostpartum (defined as more than 52 weeks or no evidence of delivery).
The researchers also compared expulsion rates in postpartum women who were and were not breastfeeding at the time of IUD insertion based on clinical records, diagnostic codes, or questionnaires at well-baby visits.
The total study population included 326,658 women with a mean age of 32.0 years; 42% were non-Hispanic White, 17.2% were Hispanic other, 13.0% were Hispanic White, 11.9% were Asian or Pacific Islander, 8.7% were non-Hispanic Black, and 0.2% were Hispanic Black. Approximately 80% of the IUDs were levonorgestrel releasing.
A total of 8,943 expulsions were reported, for an overall expulsion rate of 13.94 per 1,000 person-years.
The adjusted hazard ratios for IUD expulsion were 5.34, 1.22, 1.06, and 1.43 for women with insertion times, respectively, of 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 or fewer weeks, 6-14 weeks, and 14-52 weeks. Women with nonpostpartum IUD insertion served as the referent.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of IUD expulsion was highest with placement between 0 and 3 days post partum and lowest with placement at 6-14 weeks postpartum (10.73% and 3.18%, respectively).
“Within the group with IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum, the highest expulsion rates were discovered within 12 weeks of insertion, with the highest incidence rate occurring at week 6 (844 per 1,000 person-years), a time women are commonly seen post delivery,” the researchers noted.
In a subcohort of 94,817 women with known breastfeeding status, the 5-year cumulative incidence of expulsion was 3.49% for breastfeeding women and 4.57% for nonbreastfeeding women, with an adjusted HR of 0.71 for breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding.
“While women who accept immediate postpartum IUD placement report high satisfaction rates, information on women’s preferences and satisfaction associated with different timing of postpartum placement would also be helpful to understand the benefit-risk profile,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “The fact that most expulsions in the immediate postpartum group occurred early presents an opportunity to mitigate risk of unrecognized expulsion and unintended pregnancy via counseling on signs of expulsion and follow-up examination.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of exposures and the primary outcome of expulsion, especially since some postpartum women may be lactating whether or not they are breastfeeding, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the combination of complete and partial expulsions, and the dating of IUD expulsion based on when it came to medical attention, which was not necessarily when it occurred. More data are needed on the potential association between lactational amenorrhea and lower expulsion risk among postpartum women who are breastfeeding.
However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, the use of linked mother-infant records to identify exposures, and the use electronic health records to identify outcomes, and the data can inform patient counseling for postpartum IUDs, the researchers concluded.
Study reflects findings from Europe
“The FDA mandated this study in response to a European study, EURAS-IUD1, a European prospective observational study that enrolled 61,448 participants between 2006 and 2012,” Ms. Armstrong said in an interview. In the European study “women breastfeeding at the time of device insertion or with the device inserted at 36 weeks’ postpartum or less had higher risk of uterine perforation. The FDA wanted to know if the risks were similar in the United States population”
The APEX-IUD study was designed to reflect current United States clinical practice. “The aims of APEX-IUD are to evaluate risk of IUD-related uterine perforation and device expulsion among women who are breastfeeding or within 12 months postpartum at insertion. The perforation outcome is addressed in a separate paper,” Ms. Armstrong noted.
“We were not surprised by the findings; they aligned with previous findings and confirm the overall safety of intrauterine devices,” said Ms. Armstrong. “Data from this study provides IUD expulsion risk estimates that can be used to inform clinical practice and preinsertion counseling. IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum might decrease the risk of unintended pregnancy and provide more convenience and efficiency for new mothers. This has proven to be especially important during the pandemic. The higher risk of expulsion at 0-3 days post partum must be balanced with the low IUD-related uterine perforation risk to provide a comprehensive picture that aids in clinical decision-making.
“Potential barriers to postpartum IUD placement include lack of provision of education on the range of contraceptive options available during prenatal care and failure or inability of hospital inpatient units to stock the intrauterine devices for use when needed,” said Ms. Armstrong.
Looking ahead, “future research could evaluate risk factors for partial versus complete expulsions, the association of preinsertion counseling with recognition of potential expulsions and corresponding IUD failure rates, and whether ultrasound verification of IUD position in the uterus after insertion is associated with expulsion risk,” she said.
Identifying risk factors informs patient counseling
“The current study examines breastfeeding at time of IUD insertion as a risk factor for expulsion,” Iris Krishna, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “There is biologic plausibility that breastfeeding may be a risk factor of IUD expulsion. Breastfeeding stimulates secretion of oxytocin, a hormone which plays a key role in the contraction of the uterus during labor and uterine involution postpartum. It also plays a key role in the contraction of milk ducts to allow for milk letdown. Because of its dual role some mothers may occasionally report uterine cramping with breastfeeding. Prior studies have suggested that breastfeeding may be associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation with postpartum IUD placement, but how breastfeeding may contribute to risk of IUD expulsion has not been studied extensively.”
The current data are consistent with previous studies suggesting the highest risk of IUD expulsion is with placement in the immediate postpartum period (0-3 days). “In a subcohort analysis by breastfeeding status, the risk of IUD expulsion was lower for women who were breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding;” however, “these findings may be due to amenorrhea that can also be seen with breastfeeding,” Dr. Krishna said. “Menstrual bleeding is an independent risk factor for IUD expulsion and not having menstrual bleeding while breastfeeding may lower risk of expulsion.
“Patients should be counseled on the benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement, the risk of IUD expulsion, and alternative contraception options to be able to make an informed decision about the right contraception for them,” Dr. Krishna emphasized. “Clinicians can reassure patients that the uterine cramping they may feel while breastfeeding does not appear to increase the risk of IUD expulsion and that the amenorrhea that may result from breastfeeding also may lower the risk of IUD expulsion.”
The study was supported by Bayer through support to RTI Health Solutions, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Kaiser Permanente Washington, and the Regenstrief Institute. Ms. Armstrong and several coauthors disclosed support from Bayer during the study. Dr. Krishna had no relevant disclosures.
Expulsion of intrauterine devices was significantly more likely when the devices were inserted within the first 3 days after delivery compared with later insertions, based on data from more than 300,000 women.
Intrauterine devices are effective contraception, and current guidelines support immediate postpartum IUD insertion as a safe, effective, and convenient option, Mary Anne Armstrong, MA, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland, and colleagues wrote. Although IUD expulsion rates are low overall, data from previous studies suggest that timing of insertion may affect expulsion rates, and that breastfeeding may play a role.
In the Association of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX-IUD) cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the electronic health records at four sites; the study population included women aged 50 years and younger who underwent IUD insertion between 2001 and 2018.
The women were grouped by postpartum status and timing of IUD placement: 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 weeks, 6-14 weeks, 14-52 weeks, and nonpostpartum (defined as more than 52 weeks or no evidence of delivery).
The researchers also compared expulsion rates in postpartum women who were and were not breastfeeding at the time of IUD insertion based on clinical records, diagnostic codes, or questionnaires at well-baby visits.
The total study population included 326,658 women with a mean age of 32.0 years; 42% were non-Hispanic White, 17.2% were Hispanic other, 13.0% were Hispanic White, 11.9% were Asian or Pacific Islander, 8.7% were non-Hispanic Black, and 0.2% were Hispanic Black. Approximately 80% of the IUDs were levonorgestrel releasing.
A total of 8,943 expulsions were reported, for an overall expulsion rate of 13.94 per 1,000 person-years.
The adjusted hazard ratios for IUD expulsion were 5.34, 1.22, 1.06, and 1.43 for women with insertion times, respectively, of 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 or fewer weeks, 6-14 weeks, and 14-52 weeks. Women with nonpostpartum IUD insertion served as the referent.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of IUD expulsion was highest with placement between 0 and 3 days post partum and lowest with placement at 6-14 weeks postpartum (10.73% and 3.18%, respectively).
“Within the group with IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum, the highest expulsion rates were discovered within 12 weeks of insertion, with the highest incidence rate occurring at week 6 (844 per 1,000 person-years), a time women are commonly seen post delivery,” the researchers noted.
In a subcohort of 94,817 women with known breastfeeding status, the 5-year cumulative incidence of expulsion was 3.49% for breastfeeding women and 4.57% for nonbreastfeeding women, with an adjusted HR of 0.71 for breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding.
“While women who accept immediate postpartum IUD placement report high satisfaction rates, information on women’s preferences and satisfaction associated with different timing of postpartum placement would also be helpful to understand the benefit-risk profile,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “The fact that most expulsions in the immediate postpartum group occurred early presents an opportunity to mitigate risk of unrecognized expulsion and unintended pregnancy via counseling on signs of expulsion and follow-up examination.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of exposures and the primary outcome of expulsion, especially since some postpartum women may be lactating whether or not they are breastfeeding, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the combination of complete and partial expulsions, and the dating of IUD expulsion based on when it came to medical attention, which was not necessarily when it occurred. More data are needed on the potential association between lactational amenorrhea and lower expulsion risk among postpartum women who are breastfeeding.
However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, the use of linked mother-infant records to identify exposures, and the use electronic health records to identify outcomes, and the data can inform patient counseling for postpartum IUDs, the researchers concluded.
Study reflects findings from Europe
“The FDA mandated this study in response to a European study, EURAS-IUD1, a European prospective observational study that enrolled 61,448 participants between 2006 and 2012,” Ms. Armstrong said in an interview. In the European study “women breastfeeding at the time of device insertion or with the device inserted at 36 weeks’ postpartum or less had higher risk of uterine perforation. The FDA wanted to know if the risks were similar in the United States population”
The APEX-IUD study was designed to reflect current United States clinical practice. “The aims of APEX-IUD are to evaluate risk of IUD-related uterine perforation and device expulsion among women who are breastfeeding or within 12 months postpartum at insertion. The perforation outcome is addressed in a separate paper,” Ms. Armstrong noted.
“We were not surprised by the findings; they aligned with previous findings and confirm the overall safety of intrauterine devices,” said Ms. Armstrong. “Data from this study provides IUD expulsion risk estimates that can be used to inform clinical practice and preinsertion counseling. IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum might decrease the risk of unintended pregnancy and provide more convenience and efficiency for new mothers. This has proven to be especially important during the pandemic. The higher risk of expulsion at 0-3 days post partum must be balanced with the low IUD-related uterine perforation risk to provide a comprehensive picture that aids in clinical decision-making.
“Potential barriers to postpartum IUD placement include lack of provision of education on the range of contraceptive options available during prenatal care and failure or inability of hospital inpatient units to stock the intrauterine devices for use when needed,” said Ms. Armstrong.
Looking ahead, “future research could evaluate risk factors for partial versus complete expulsions, the association of preinsertion counseling with recognition of potential expulsions and corresponding IUD failure rates, and whether ultrasound verification of IUD position in the uterus after insertion is associated with expulsion risk,” she said.
Identifying risk factors informs patient counseling
“The current study examines breastfeeding at time of IUD insertion as a risk factor for expulsion,” Iris Krishna, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “There is biologic plausibility that breastfeeding may be a risk factor of IUD expulsion. Breastfeeding stimulates secretion of oxytocin, a hormone which plays a key role in the contraction of the uterus during labor and uterine involution postpartum. It also plays a key role in the contraction of milk ducts to allow for milk letdown. Because of its dual role some mothers may occasionally report uterine cramping with breastfeeding. Prior studies have suggested that breastfeeding may be associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation with postpartum IUD placement, but how breastfeeding may contribute to risk of IUD expulsion has not been studied extensively.”
The current data are consistent with previous studies suggesting the highest risk of IUD expulsion is with placement in the immediate postpartum period (0-3 days). “In a subcohort analysis by breastfeeding status, the risk of IUD expulsion was lower for women who were breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding;” however, “these findings may be due to amenorrhea that can also be seen with breastfeeding,” Dr. Krishna said. “Menstrual bleeding is an independent risk factor for IUD expulsion and not having menstrual bleeding while breastfeeding may lower risk of expulsion.
“Patients should be counseled on the benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement, the risk of IUD expulsion, and alternative contraception options to be able to make an informed decision about the right contraception for them,” Dr. Krishna emphasized. “Clinicians can reassure patients that the uterine cramping they may feel while breastfeeding does not appear to increase the risk of IUD expulsion and that the amenorrhea that may result from breastfeeding also may lower the risk of IUD expulsion.”
The study was supported by Bayer through support to RTI Health Solutions, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Kaiser Permanente Washington, and the Regenstrief Institute. Ms. Armstrong and several coauthors disclosed support from Bayer during the study. Dr. Krishna had no relevant disclosures.
Expulsion of intrauterine devices was significantly more likely when the devices were inserted within the first 3 days after delivery compared with later insertions, based on data from more than 300,000 women.
Intrauterine devices are effective contraception, and current guidelines support immediate postpartum IUD insertion as a safe, effective, and convenient option, Mary Anne Armstrong, MA, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland, and colleagues wrote. Although IUD expulsion rates are low overall, data from previous studies suggest that timing of insertion may affect expulsion rates, and that breastfeeding may play a role.
In the Association of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX-IUD) cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the electronic health records at four sites; the study population included women aged 50 years and younger who underwent IUD insertion between 2001 and 2018.
The women were grouped by postpartum status and timing of IUD placement: 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 weeks, 6-14 weeks, 14-52 weeks, and nonpostpartum (defined as more than 52 weeks or no evidence of delivery).
The researchers also compared expulsion rates in postpartum women who were and were not breastfeeding at the time of IUD insertion based on clinical records, diagnostic codes, or questionnaires at well-baby visits.
The total study population included 326,658 women with a mean age of 32.0 years; 42% were non-Hispanic White, 17.2% were Hispanic other, 13.0% were Hispanic White, 11.9% were Asian or Pacific Islander, 8.7% were non-Hispanic Black, and 0.2% were Hispanic Black. Approximately 80% of the IUDs were levonorgestrel releasing.
A total of 8,943 expulsions were reported, for an overall expulsion rate of 13.94 per 1,000 person-years.
The adjusted hazard ratios for IUD expulsion were 5.34, 1.22, 1.06, and 1.43 for women with insertion times, respectively, of 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 or fewer weeks, 6-14 weeks, and 14-52 weeks. Women with nonpostpartum IUD insertion served as the referent.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of IUD expulsion was highest with placement between 0 and 3 days post partum and lowest with placement at 6-14 weeks postpartum (10.73% and 3.18%, respectively).
“Within the group with IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum, the highest expulsion rates were discovered within 12 weeks of insertion, with the highest incidence rate occurring at week 6 (844 per 1,000 person-years), a time women are commonly seen post delivery,” the researchers noted.
In a subcohort of 94,817 women with known breastfeeding status, the 5-year cumulative incidence of expulsion was 3.49% for breastfeeding women and 4.57% for nonbreastfeeding women, with an adjusted HR of 0.71 for breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding.
“While women who accept immediate postpartum IUD placement report high satisfaction rates, information on women’s preferences and satisfaction associated with different timing of postpartum placement would also be helpful to understand the benefit-risk profile,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “The fact that most expulsions in the immediate postpartum group occurred early presents an opportunity to mitigate risk of unrecognized expulsion and unintended pregnancy via counseling on signs of expulsion and follow-up examination.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of exposures and the primary outcome of expulsion, especially since some postpartum women may be lactating whether or not they are breastfeeding, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the combination of complete and partial expulsions, and the dating of IUD expulsion based on when it came to medical attention, which was not necessarily when it occurred. More data are needed on the potential association between lactational amenorrhea and lower expulsion risk among postpartum women who are breastfeeding.
However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, the use of linked mother-infant records to identify exposures, and the use electronic health records to identify outcomes, and the data can inform patient counseling for postpartum IUDs, the researchers concluded.
Study reflects findings from Europe
“The FDA mandated this study in response to a European study, EURAS-IUD1, a European prospective observational study that enrolled 61,448 participants between 2006 and 2012,” Ms. Armstrong said in an interview. In the European study “women breastfeeding at the time of device insertion or with the device inserted at 36 weeks’ postpartum or less had higher risk of uterine perforation. The FDA wanted to know if the risks were similar in the United States population”
The APEX-IUD study was designed to reflect current United States clinical practice. “The aims of APEX-IUD are to evaluate risk of IUD-related uterine perforation and device expulsion among women who are breastfeeding or within 12 months postpartum at insertion. The perforation outcome is addressed in a separate paper,” Ms. Armstrong noted.
“We were not surprised by the findings; they aligned with previous findings and confirm the overall safety of intrauterine devices,” said Ms. Armstrong. “Data from this study provides IUD expulsion risk estimates that can be used to inform clinical practice and preinsertion counseling. IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum might decrease the risk of unintended pregnancy and provide more convenience and efficiency for new mothers. This has proven to be especially important during the pandemic. The higher risk of expulsion at 0-3 days post partum must be balanced with the low IUD-related uterine perforation risk to provide a comprehensive picture that aids in clinical decision-making.
“Potential barriers to postpartum IUD placement include lack of provision of education on the range of contraceptive options available during prenatal care and failure or inability of hospital inpatient units to stock the intrauterine devices for use when needed,” said Ms. Armstrong.
Looking ahead, “future research could evaluate risk factors for partial versus complete expulsions, the association of preinsertion counseling with recognition of potential expulsions and corresponding IUD failure rates, and whether ultrasound verification of IUD position in the uterus after insertion is associated with expulsion risk,” she said.
Identifying risk factors informs patient counseling
“The current study examines breastfeeding at time of IUD insertion as a risk factor for expulsion,” Iris Krishna, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “There is biologic plausibility that breastfeeding may be a risk factor of IUD expulsion. Breastfeeding stimulates secretion of oxytocin, a hormone which plays a key role in the contraction of the uterus during labor and uterine involution postpartum. It also plays a key role in the contraction of milk ducts to allow for milk letdown. Because of its dual role some mothers may occasionally report uterine cramping with breastfeeding. Prior studies have suggested that breastfeeding may be associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation with postpartum IUD placement, but how breastfeeding may contribute to risk of IUD expulsion has not been studied extensively.”
The current data are consistent with previous studies suggesting the highest risk of IUD expulsion is with placement in the immediate postpartum period (0-3 days). “In a subcohort analysis by breastfeeding status, the risk of IUD expulsion was lower for women who were breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding;” however, “these findings may be due to amenorrhea that can also be seen with breastfeeding,” Dr. Krishna said. “Menstrual bleeding is an independent risk factor for IUD expulsion and not having menstrual bleeding while breastfeeding may lower risk of expulsion.
“Patients should be counseled on the benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement, the risk of IUD expulsion, and alternative contraception options to be able to make an informed decision about the right contraception for them,” Dr. Krishna emphasized. “Clinicians can reassure patients that the uterine cramping they may feel while breastfeeding does not appear to increase the risk of IUD expulsion and that the amenorrhea that may result from breastfeeding also may lower the risk of IUD expulsion.”
The study was supported by Bayer through support to RTI Health Solutions, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Kaiser Permanente Washington, and the Regenstrief Institute. Ms. Armstrong and several coauthors disclosed support from Bayer during the study. Dr. Krishna had no relevant disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
FDA approves first drug for myelofibrosis with thrombocytopenia
Pacritinib (Vonjo, CTI BioPharma) is indicated for use in the treatment of adults with intermediate- or high-risk primary or secondary (post–polycythemia vera or post–essential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis with a platelet count below 50 × 109/L.
Pacritinib is a novel oral kinase inhibitor with specificity for activity against Janus associated kinase 2 (JAK2) and IRAK1, without inhibiting JAK1. The recommended dosage is 200 mg orally twice daily.
In the United States, there are approximately 21,000 patients with myelofibrosis, notes the manufacturer. About one-third develop severe thrombocytopenia.
“Myelofibrosis with severe thrombocytopenia, defined as blood platelet counts below 50 × 109/L, has been shown to result in poor survival outcomes coupled with debilitating symptoms. Limited treatment options have rendered this disease as an area of urgent unmet medical need,” said John Mascarenhas, MD, associate professor, medicine, hematology, and medical oncology, Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“I am pleased to see that a new, efficacious, and safe treatment option is now available for these patients,” he said in a company press release.
Dr. Mascarenhas was the lead investigator of the phase 3 PERSIST-2 trial that was the basis for the approval. Results from the trial were published in 2018 in JAMA Oncology and reported in detail at the time by this news organization.
Authors of an accompanying editorial noted the trial was truncated after the FDA imposed a clinical hold on pacritinib in February 2016 after reports from an earlier trial, PERSIST-1, of patient deaths related to cardiac failure and arrest as well as intracranial hemorrhage. The clinical hold was lifted in January 2017 after the manufacturer provided the FDA with more mature data.
Despite the truncation, the PERSIST-2 trial provided sufficient data to obtain accelerated approval for the drug. The study compared pacritinib with best available therapy (BAT).
In the cohort of patients treated with pacritinib 200 mg twice daily, 29% of patients had a reduction in spleen volume of at least 35% compared with 3% of patients receiving BAT, which included ruxolitinib.
The company is now expected to demonstrate clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial and has the PACIFICA trial underway. Results are expected in mid-2025.
The most common adverse reactions (reported by ≥ 20% of patients) were diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, nausea, anemia, and peripheral edema. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥ 3%) were anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonia, cardiac failure, disease progression, pyrexia, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pacritinib (Vonjo, CTI BioPharma) is indicated for use in the treatment of adults with intermediate- or high-risk primary or secondary (post–polycythemia vera or post–essential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis with a platelet count below 50 × 109/L.
Pacritinib is a novel oral kinase inhibitor with specificity for activity against Janus associated kinase 2 (JAK2) and IRAK1, without inhibiting JAK1. The recommended dosage is 200 mg orally twice daily.
In the United States, there are approximately 21,000 patients with myelofibrosis, notes the manufacturer. About one-third develop severe thrombocytopenia.
“Myelofibrosis with severe thrombocytopenia, defined as blood platelet counts below 50 × 109/L, has been shown to result in poor survival outcomes coupled with debilitating symptoms. Limited treatment options have rendered this disease as an area of urgent unmet medical need,” said John Mascarenhas, MD, associate professor, medicine, hematology, and medical oncology, Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“I am pleased to see that a new, efficacious, and safe treatment option is now available for these patients,” he said in a company press release.
Dr. Mascarenhas was the lead investigator of the phase 3 PERSIST-2 trial that was the basis for the approval. Results from the trial were published in 2018 in JAMA Oncology and reported in detail at the time by this news organization.
Authors of an accompanying editorial noted the trial was truncated after the FDA imposed a clinical hold on pacritinib in February 2016 after reports from an earlier trial, PERSIST-1, of patient deaths related to cardiac failure and arrest as well as intracranial hemorrhage. The clinical hold was lifted in January 2017 after the manufacturer provided the FDA with more mature data.
Despite the truncation, the PERSIST-2 trial provided sufficient data to obtain accelerated approval for the drug. The study compared pacritinib with best available therapy (BAT).
In the cohort of patients treated with pacritinib 200 mg twice daily, 29% of patients had a reduction in spleen volume of at least 35% compared with 3% of patients receiving BAT, which included ruxolitinib.
The company is now expected to demonstrate clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial and has the PACIFICA trial underway. Results are expected in mid-2025.
The most common adverse reactions (reported by ≥ 20% of patients) were diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, nausea, anemia, and peripheral edema. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥ 3%) were anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonia, cardiac failure, disease progression, pyrexia, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pacritinib (Vonjo, CTI BioPharma) is indicated for use in the treatment of adults with intermediate- or high-risk primary or secondary (post–polycythemia vera or post–essential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis with a platelet count below 50 × 109/L.
Pacritinib is a novel oral kinase inhibitor with specificity for activity against Janus associated kinase 2 (JAK2) and IRAK1, without inhibiting JAK1. The recommended dosage is 200 mg orally twice daily.
In the United States, there are approximately 21,000 patients with myelofibrosis, notes the manufacturer. About one-third develop severe thrombocytopenia.
“Myelofibrosis with severe thrombocytopenia, defined as blood platelet counts below 50 × 109/L, has been shown to result in poor survival outcomes coupled with debilitating symptoms. Limited treatment options have rendered this disease as an area of urgent unmet medical need,” said John Mascarenhas, MD, associate professor, medicine, hematology, and medical oncology, Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“I am pleased to see that a new, efficacious, and safe treatment option is now available for these patients,” he said in a company press release.
Dr. Mascarenhas was the lead investigator of the phase 3 PERSIST-2 trial that was the basis for the approval. Results from the trial were published in 2018 in JAMA Oncology and reported in detail at the time by this news organization.
Authors of an accompanying editorial noted the trial was truncated after the FDA imposed a clinical hold on pacritinib in February 2016 after reports from an earlier trial, PERSIST-1, of patient deaths related to cardiac failure and arrest as well as intracranial hemorrhage. The clinical hold was lifted in January 2017 after the manufacturer provided the FDA with more mature data.
Despite the truncation, the PERSIST-2 trial provided sufficient data to obtain accelerated approval for the drug. The study compared pacritinib with best available therapy (BAT).
In the cohort of patients treated with pacritinib 200 mg twice daily, 29% of patients had a reduction in spleen volume of at least 35% compared with 3% of patients receiving BAT, which included ruxolitinib.
The company is now expected to demonstrate clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial and has the PACIFICA trial underway. Results are expected in mid-2025.
The most common adverse reactions (reported by ≥ 20% of patients) were diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, nausea, anemia, and peripheral edema. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥ 3%) were anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonia, cardiac failure, disease progression, pyrexia, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elective surgery should be delayed 7 weeks after COVID-19 infection for unvaccinated patients, statement recommends
.
For patients fully vaccinated against COVID-19 with breakthrough infections, there is no consensus on how vaccination affects the time between COVID-19 infection and elective surgery. Clinicians should use their clinical judgment to schedule procedures, said Randall M. Clark, MD, president of the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). “We need all physicians, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and others to base their decision to go ahead with elective surgery on the patient’s symptoms, their need for the procedure, and whether delays could cause other problems with their health,” he said in an interview.
Prior to these updated recommendations, which were published Feb. 22, the ASA and the APSF recommended a 4-week gap between COVID-19 diagnosis and elective surgery for asymptomatic or mild cases, regardless of a patient’s vaccination status.
Extending the wait time from 4 to 7 weeks was based on a multination study conducted in October 2020 following more than 140,000 surgical patients. Patients with previous COVID-19 infection had an increased risk for complications and death in elective surgery for up to 6 weeks following their diagnosis, compared with patients without COVID-19. Additional research in the United States found that patients with a preoperative COVID diagnosis were at higher risk for postoperative complications of respiratory failure for up to 4 weeks after diagnosis and postoperative pneumonia complications for up to 8 weeks after diagnosis.
Because these studies were conducted in unvaccinated populations or those with low vaccination rates, and preliminary data suggest vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections may have a lower risk for complications and death postinfection, “we felt that it was prudent to just make recommendations specific to unvaccinated patients,” Dr. Clark added.
Although this guidance is “very helpful” in that it summarizes the currently available research to give evidence-based recommendations, the 7-week wait time is a “very conservative estimate,” Brent Matthews, MD, surgeon-in-chief of the surgery care division of Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C., told this news organization. At Atrium Health, surgery is scheduled at least 21 days after a patient’s COVID-19 diagnosis, regardless of their vaccination status, Dr. Matthews said.
The studies currently available were conducted earlier in the pandemic, when a different variant was prevalent, Dr. Matthews explained. The Omicron variant is currently the most prevalent COVID-19 variant and is less virulent than earlier strains of the virus. The joint statement does note that there is currently “no robust data” on patients infected with the Delta or Omicron variants of COVID-19, and that “the Omicron variant causes less severe disease and is more likely to reside in the oro- and nasopharynx without infiltration and damage to the lungs.”
Still, the new recommendations are a reminder to re-evaluate the potential complications from surgery for previously infected patients and to consider what comorbidities might make them more vulnerable, Dr. Matthews said. “The real power of the joint statement is to get people to ensure that they make an assessment of every patient that comes in front of them who has had a recent positive COVID test.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
For patients fully vaccinated against COVID-19 with breakthrough infections, there is no consensus on how vaccination affects the time between COVID-19 infection and elective surgery. Clinicians should use their clinical judgment to schedule procedures, said Randall M. Clark, MD, president of the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). “We need all physicians, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and others to base their decision to go ahead with elective surgery on the patient’s symptoms, their need for the procedure, and whether delays could cause other problems with their health,” he said in an interview.
Prior to these updated recommendations, which were published Feb. 22, the ASA and the APSF recommended a 4-week gap between COVID-19 diagnosis and elective surgery for asymptomatic or mild cases, regardless of a patient’s vaccination status.
Extending the wait time from 4 to 7 weeks was based on a multination study conducted in October 2020 following more than 140,000 surgical patients. Patients with previous COVID-19 infection had an increased risk for complications and death in elective surgery for up to 6 weeks following their diagnosis, compared with patients without COVID-19. Additional research in the United States found that patients with a preoperative COVID diagnosis were at higher risk for postoperative complications of respiratory failure for up to 4 weeks after diagnosis and postoperative pneumonia complications for up to 8 weeks after diagnosis.
Because these studies were conducted in unvaccinated populations or those with low vaccination rates, and preliminary data suggest vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections may have a lower risk for complications and death postinfection, “we felt that it was prudent to just make recommendations specific to unvaccinated patients,” Dr. Clark added.
Although this guidance is “very helpful” in that it summarizes the currently available research to give evidence-based recommendations, the 7-week wait time is a “very conservative estimate,” Brent Matthews, MD, surgeon-in-chief of the surgery care division of Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C., told this news organization. At Atrium Health, surgery is scheduled at least 21 days after a patient’s COVID-19 diagnosis, regardless of their vaccination status, Dr. Matthews said.
The studies currently available were conducted earlier in the pandemic, when a different variant was prevalent, Dr. Matthews explained. The Omicron variant is currently the most prevalent COVID-19 variant and is less virulent than earlier strains of the virus. The joint statement does note that there is currently “no robust data” on patients infected with the Delta or Omicron variants of COVID-19, and that “the Omicron variant causes less severe disease and is more likely to reside in the oro- and nasopharynx without infiltration and damage to the lungs.”
Still, the new recommendations are a reminder to re-evaluate the potential complications from surgery for previously infected patients and to consider what comorbidities might make them more vulnerable, Dr. Matthews said. “The real power of the joint statement is to get people to ensure that they make an assessment of every patient that comes in front of them who has had a recent positive COVID test.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
For patients fully vaccinated against COVID-19 with breakthrough infections, there is no consensus on how vaccination affects the time between COVID-19 infection and elective surgery. Clinicians should use their clinical judgment to schedule procedures, said Randall M. Clark, MD, president of the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). “We need all physicians, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and others to base their decision to go ahead with elective surgery on the patient’s symptoms, their need for the procedure, and whether delays could cause other problems with their health,” he said in an interview.
Prior to these updated recommendations, which were published Feb. 22, the ASA and the APSF recommended a 4-week gap between COVID-19 diagnosis and elective surgery for asymptomatic or mild cases, regardless of a patient’s vaccination status.
Extending the wait time from 4 to 7 weeks was based on a multination study conducted in October 2020 following more than 140,000 surgical patients. Patients with previous COVID-19 infection had an increased risk for complications and death in elective surgery for up to 6 weeks following their diagnosis, compared with patients without COVID-19. Additional research in the United States found that patients with a preoperative COVID diagnosis were at higher risk for postoperative complications of respiratory failure for up to 4 weeks after diagnosis and postoperative pneumonia complications for up to 8 weeks after diagnosis.
Because these studies were conducted in unvaccinated populations or those with low vaccination rates, and preliminary data suggest vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections may have a lower risk for complications and death postinfection, “we felt that it was prudent to just make recommendations specific to unvaccinated patients,” Dr. Clark added.
Although this guidance is “very helpful” in that it summarizes the currently available research to give evidence-based recommendations, the 7-week wait time is a “very conservative estimate,” Brent Matthews, MD, surgeon-in-chief of the surgery care division of Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C., told this news organization. At Atrium Health, surgery is scheduled at least 21 days after a patient’s COVID-19 diagnosis, regardless of their vaccination status, Dr. Matthews said.
The studies currently available were conducted earlier in the pandemic, when a different variant was prevalent, Dr. Matthews explained. The Omicron variant is currently the most prevalent COVID-19 variant and is less virulent than earlier strains of the virus. The joint statement does note that there is currently “no robust data” on patients infected with the Delta or Omicron variants of COVID-19, and that “the Omicron variant causes less severe disease and is more likely to reside in the oro- and nasopharynx without infiltration and damage to the lungs.”
Still, the new recommendations are a reminder to re-evaluate the potential complications from surgery for previously infected patients and to consider what comorbidities might make them more vulnerable, Dr. Matthews said. “The real power of the joint statement is to get people to ensure that they make an assessment of every patient that comes in front of them who has had a recent positive COVID test.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lung cancer drug price trends cause alarm, highlight need for reform
The findings underscore the need for price reform, according to the investigators, who analyzed prices for 17 brand-name medications used for treating metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Prices increased during the study period and correlated within each drug class, Aakash Desai, MBBS, and colleagues from the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., found.
“Because numerous new drugs have been approved for the treatment of NSCLC in recent years, we sought to specifically study the price competition among drugs used to treat this cancer subtype,” they explained, noting that for most drug classes price increases outpaced changes in the consumer price index for prescription medications and the inflation rate.
The findings were published Jan. 25, 2022, in JAMA Network Open.
Multiple brand-name medications across several drug classes, including four immune checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, and durvalumab), five epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (gefitinib, afatinib, erlotinib, osimertinib, and dacomitinib), five anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors (crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, and lorlatinib), two BRAF inhibitors (dabrafenib, vemurafenib), and one MEK inhibitor (trametinib) were included in the analysis.
Median Pearson correlation coefficients approached 1.0 for all drug classes, indicating that prices increased despite within-class drug competition. Median values ranged from 0.898 for epidermal growth factor inhibitors to 0.999 for anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors and BRAF and MEK inhibitors, the investigators found.
Median compounded annual growth rates (CAGRs) were 1.81% for immune checkpoint inhibitors, 2.56% for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, 2.46% for anaplastic lymphoma kinase and ROS1 inhibitors, and 3.06% for BRAF and MEK inhibitors.
“With the exception of the immunotherapy class, the median cost CAGR outpaced the annual growth rate of the consumer price index for prescription drugs at 2.10% and, for all classes, the average yearly inflation rate of 1.75% during the same period,” they wrote.
Also of note, only one price decrease occurred among all therapeutic classes studied.
“This was observed for erlotinib between 2019 and 2020, and it corresponded with the introduction of a generic competitor to the market,” the authors said.
The findings are reminiscent of an earlier study that showed a 25% increase in the price of 24 patented injectable anticancer agents in the United States over a period of 8 years after launch.
“These increases in cost were not offset by supplemental U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals, new competitors, or new off-label indications. Thus, price increases over time were not substantially reduced by market competition and increased at similar rates among drugs within the same class,” they wrote, adding that “although one might expect oncology drug prices to decrease over time after market entry, the list price of most anticancer agents increases paradoxically.”
The “lock-step price increases” observed without evidence of price competition in this analysis raise concerns about the affordability of promising oncology drugs, they said, concluding that “academic, industry, and government partnerships should be developed to address the high costs of prescription oncology drugs, which may soon be unaffordable for most patients if the trends discovered in the present study continue.”
Dr. Desai reported having no disclosures.
The findings underscore the need for price reform, according to the investigators, who analyzed prices for 17 brand-name medications used for treating metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Prices increased during the study period and correlated within each drug class, Aakash Desai, MBBS, and colleagues from the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., found.
“Because numerous new drugs have been approved for the treatment of NSCLC in recent years, we sought to specifically study the price competition among drugs used to treat this cancer subtype,” they explained, noting that for most drug classes price increases outpaced changes in the consumer price index for prescription medications and the inflation rate.
The findings were published Jan. 25, 2022, in JAMA Network Open.
Multiple brand-name medications across several drug classes, including four immune checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, and durvalumab), five epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (gefitinib, afatinib, erlotinib, osimertinib, and dacomitinib), five anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors (crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, and lorlatinib), two BRAF inhibitors (dabrafenib, vemurafenib), and one MEK inhibitor (trametinib) were included in the analysis.
Median Pearson correlation coefficients approached 1.0 for all drug classes, indicating that prices increased despite within-class drug competition. Median values ranged from 0.898 for epidermal growth factor inhibitors to 0.999 for anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors and BRAF and MEK inhibitors, the investigators found.
Median compounded annual growth rates (CAGRs) were 1.81% for immune checkpoint inhibitors, 2.56% for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, 2.46% for anaplastic lymphoma kinase and ROS1 inhibitors, and 3.06% for BRAF and MEK inhibitors.
“With the exception of the immunotherapy class, the median cost CAGR outpaced the annual growth rate of the consumer price index for prescription drugs at 2.10% and, for all classes, the average yearly inflation rate of 1.75% during the same period,” they wrote.
Also of note, only one price decrease occurred among all therapeutic classes studied.
“This was observed for erlotinib between 2019 and 2020, and it corresponded with the introduction of a generic competitor to the market,” the authors said.
The findings are reminiscent of an earlier study that showed a 25% increase in the price of 24 patented injectable anticancer agents in the United States over a period of 8 years after launch.
“These increases in cost were not offset by supplemental U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals, new competitors, or new off-label indications. Thus, price increases over time were not substantially reduced by market competition and increased at similar rates among drugs within the same class,” they wrote, adding that “although one might expect oncology drug prices to decrease over time after market entry, the list price of most anticancer agents increases paradoxically.”
The “lock-step price increases” observed without evidence of price competition in this analysis raise concerns about the affordability of promising oncology drugs, they said, concluding that “academic, industry, and government partnerships should be developed to address the high costs of prescription oncology drugs, which may soon be unaffordable for most patients if the trends discovered in the present study continue.”
Dr. Desai reported having no disclosures.
The findings underscore the need for price reform, according to the investigators, who analyzed prices for 17 brand-name medications used for treating metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Prices increased during the study period and correlated within each drug class, Aakash Desai, MBBS, and colleagues from the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., found.
“Because numerous new drugs have been approved for the treatment of NSCLC in recent years, we sought to specifically study the price competition among drugs used to treat this cancer subtype,” they explained, noting that for most drug classes price increases outpaced changes in the consumer price index for prescription medications and the inflation rate.
The findings were published Jan. 25, 2022, in JAMA Network Open.
Multiple brand-name medications across several drug classes, including four immune checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, and durvalumab), five epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (gefitinib, afatinib, erlotinib, osimertinib, and dacomitinib), five anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors (crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, and lorlatinib), two BRAF inhibitors (dabrafenib, vemurafenib), and one MEK inhibitor (trametinib) were included in the analysis.
Median Pearson correlation coefficients approached 1.0 for all drug classes, indicating that prices increased despite within-class drug competition. Median values ranged from 0.898 for epidermal growth factor inhibitors to 0.999 for anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors and BRAF and MEK inhibitors, the investigators found.
Median compounded annual growth rates (CAGRs) were 1.81% for immune checkpoint inhibitors, 2.56% for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, 2.46% for anaplastic lymphoma kinase and ROS1 inhibitors, and 3.06% for BRAF and MEK inhibitors.
“With the exception of the immunotherapy class, the median cost CAGR outpaced the annual growth rate of the consumer price index for prescription drugs at 2.10% and, for all classes, the average yearly inflation rate of 1.75% during the same period,” they wrote.
Also of note, only one price decrease occurred among all therapeutic classes studied.
“This was observed for erlotinib between 2019 and 2020, and it corresponded with the introduction of a generic competitor to the market,” the authors said.
The findings are reminiscent of an earlier study that showed a 25% increase in the price of 24 patented injectable anticancer agents in the United States over a period of 8 years after launch.
“These increases in cost were not offset by supplemental U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals, new competitors, or new off-label indications. Thus, price increases over time were not substantially reduced by market competition and increased at similar rates among drugs within the same class,” they wrote, adding that “although one might expect oncology drug prices to decrease over time after market entry, the list price of most anticancer agents increases paradoxically.”
The “lock-step price increases” observed without evidence of price competition in this analysis raise concerns about the affordability of promising oncology drugs, they said, concluding that “academic, industry, and government partnerships should be developed to address the high costs of prescription oncology drugs, which may soon be unaffordable for most patients if the trends discovered in the present study continue.”
Dr. Desai reported having no disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
How Lp(a) can help improve ASCVD risk assessment
A look back at a pair of large cohort studies suggests a telling relation between two distinct predictors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk and may offer guidance on how to interpret them together.
Elevated levels of lipoprotein(a), or Lp(a), and high coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores were both predictive of ASCVD risk over 10 years, but independent of each other and a host of more traditional cardiovascular risk factors, for example, in the analysis of data from the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) and DHS (Dallas Heart Study) longitudinal cohorts.
Notably, the risk when both Lp(a) and CAC scores were high far exceeded that associated with either marker alone. But when CAC scores were less than 100 Agatston units, predicted ASCVD risk wasn’t influenced by levels of Lp(a). Indeed, a CAC score of 0 predicted the lowest levels of ASCVD risk, even with elevated Lp(a).
That is, the findings suggest, the addition of Lp(a) makes a difference to the risk assessment only when CAC scores are high, at least 100 units, and elevated Lp(a) doesn’t mean increased ASCVD risk in the absence of coronary calcium.
“Our novel findings indicate that elevated Lp(a) drives ASCVD risk independent of the subclinical coronary atherosclerosis burden captured by CAC score,” concluded a report on the analysis, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, with lead author Anurag Mehta, MD, Emory University, Atlanta.
There are no formal recommendations on how to interpret Lp(a) and CAC scores together, but the current findings “provide impetus for measuring Lp(a) in more individuals as part of the shared decision-making process,” the authors contended.
“Really, the calcium score carries the majority of the information in terms of risk, except in the highest CAC score group. That is, if you have a high Lp(a) and a high burden of calcium, your risk is significantly higher than if you just have the high calcium score and the normal Lp(a),” senior author Parag H. Joshi, MD, MHS, said in an interview.
“We thought we would see that the group with higher Lp(a) would have more events over 10 years, even among those who didn’t have coronary calcium,” said Dr. Joshi, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. “But we really don’t see that, at least in a statistically significant way.”
A CAC score of 0 would at least support a more conservative approach in a patient with elevated Lp(a) “who is hesitant to be on a statin or to be more aggressive managing their risk,” Dr. Joshi said.
“This study should be very reassuring for a patient like that,” Ron Blankstein, MD, director of cardiac computed tomography at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If you have a high Lp(a) and you’re concerned, I think this study really supports the role of calcium scoring for further risk assessment,” said Dr. Blankstein, who is not associated with the new report. “We often check Lp(a) in individuals who perhaps have a family history or who come to see us in a preventive cardiology clinic. If it is high and there is concern, a calcium score can be very helpful. If it’s zero, that really means a very low risk of events. And if it’s elevated, I think we’re going to be more concerned about that patient.”
The current analysis suggests “that, when a patient without clinical cardiovascular disease is identified with either CAC ≥100 or Lp(a) >50 mg/dL, the next step in the risk evaluation should be to measure either Lp(a) or CAC, respectively – if not already performed – to identify the patients at highest risk,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, director of vascular medicine at University of California, San Diego, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Both Lp(a) and CAC should be more broadly applied in clinical care settings in patients without prior ASCVD to identify those that most likely will benefit from more aggressive therapy and, in the future, from Lp(a)-lowering therapies,” he wrote.
The analyses were conducted separately on data from 4,512 initially asymptomatic patients in MESA and 2,078 from the DHS cohort, who were followed for ASCVD events an average of 13 years and 11 years, respectively. Such events included coronary heart disease–related death, nonfatal MI, and fatal or nonfatal stroke.
In the MESA cohort – 52% women, 36.8% White, 29.3% Black, 22.2% Hispanic, and 11.7% Chinese – elevated Lp(a) (quintile 5 vs. quintiles 1-4) and CAC scores of 1-99 and above 100 (both compared with 0) were each independently associated with increased risk for ASCVD events. The hazard ratio was 1.29 (P = .02) for elevated Lp(a), 1.68 (P < .01) for a CAC score of 1-99, and 2.66 (P < .01) for a CAC score of at least 100.
The corresponding HRs in the DHS cohort were 1.54 (P = .07) for Lp(a), 3.32 (P < .01) for a CAC score of 1-99, and 5.21 (P < .01) for a CAC score of at least 100.
Of note, the authors wrote, ASCVD risk among MESA participants with a CAC score of 0 was not significantly different in those with normal and elevated Lp(a).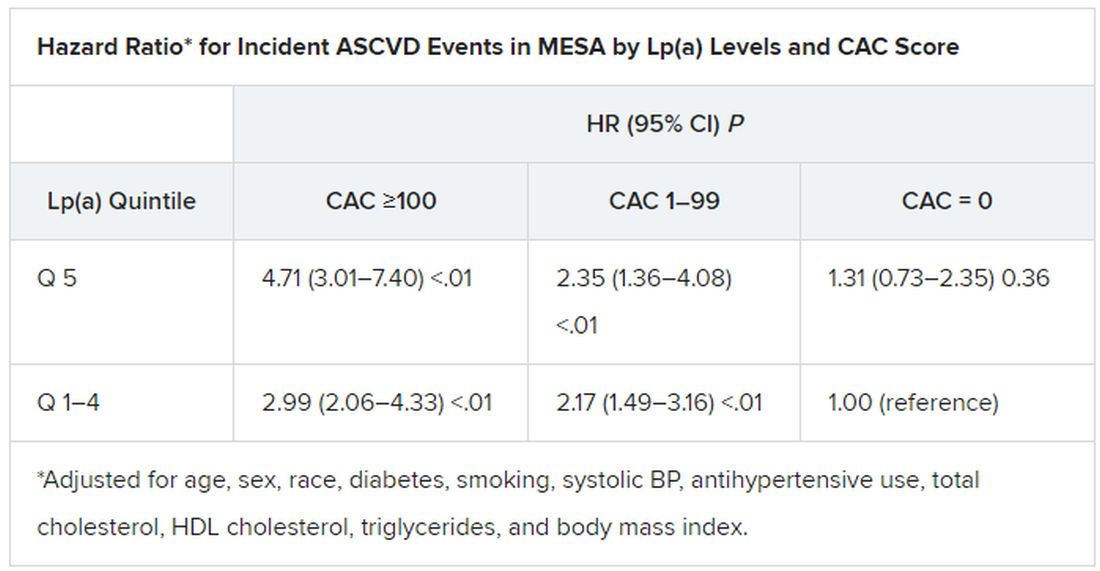
The findings were similar in the corresponding DHS analysis, the authors noted.
When both Lp(a) and CAC scores are considered as dichotomous variables, the highest 10-year ASCVD incidence in MESA was in participants with both elevated Lp(a) (≥50 mg/dL) and a high CAC score (≥100). The lowest risk was seen when Lp(a) was normal (<50 mg/dL) and the CAC score was no more than moderately high (<100).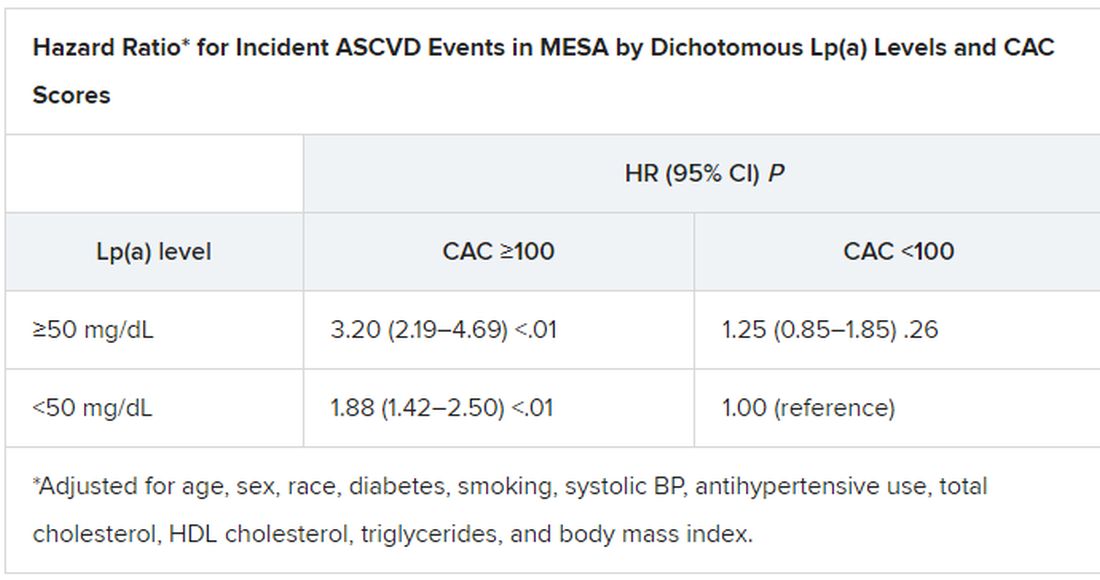
The results in the corresponding DHS analysis, according to the report, again mirrored those from MESA.
“This study has important implications for our patients and also potentially for future clinical trial design,” Dr. Blankstein noted. “A big part of developing a trial in this space is identifying the patients who are at higher risk,” and the current analysis supports CAC scores for identifying the highest-risk patient among those with elevated Lp(a).
Current wisdom is that, for the most part, Lp(a) levels are genetically mediated and are mostly unaffected by interventions such as diet management or exercise. It’s unknown whether reducing elevated Lp(a) levels pharmacologically will cut ASCVD risk, but there are a number of clinical trial programs currently aimed at learning just that. They include the Novartis-sponsored phase 3 HORIZON trial of the antisense agent pelacarsen (TQJ230), with an estimated enrollment of almost 7,700; a randomized, controlled dose-finding study of the small interfering RNA agent olpasiran (AMG890), with 290 patients and funded by Amgen; and an 88-patient phase 1 study of another siRNA agent, SLN360, supported by Silence Therapeutics.
Dr. Mehta reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Joshi has received grant support from Novo Nordisk and consulting income from Bayer and Regeneron; holds equity in G3 Therapeutics; and has served as site investigator for GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. Dr. Blankstein reported serving as a consultant to Amgen, Novartis, and Silence Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A look back at a pair of large cohort studies suggests a telling relation between two distinct predictors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk and may offer guidance on how to interpret them together.
Elevated levels of lipoprotein(a), or Lp(a), and high coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores were both predictive of ASCVD risk over 10 years, but independent of each other and a host of more traditional cardiovascular risk factors, for example, in the analysis of data from the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) and DHS (Dallas Heart Study) longitudinal cohorts.
Notably, the risk when both Lp(a) and CAC scores were high far exceeded that associated with either marker alone. But when CAC scores were less than 100 Agatston units, predicted ASCVD risk wasn’t influenced by levels of Lp(a). Indeed, a CAC score of 0 predicted the lowest levels of ASCVD risk, even with elevated Lp(a).
That is, the findings suggest, the addition of Lp(a) makes a difference to the risk assessment only when CAC scores are high, at least 100 units, and elevated Lp(a) doesn’t mean increased ASCVD risk in the absence of coronary calcium.
“Our novel findings indicate that elevated Lp(a) drives ASCVD risk independent of the subclinical coronary atherosclerosis burden captured by CAC score,” concluded a report on the analysis, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, with lead author Anurag Mehta, MD, Emory University, Atlanta.
There are no formal recommendations on how to interpret Lp(a) and CAC scores together, but the current findings “provide impetus for measuring Lp(a) in more individuals as part of the shared decision-making process,” the authors contended.
“Really, the calcium score carries the majority of the information in terms of risk, except in the highest CAC score group. That is, if you have a high Lp(a) and a high burden of calcium, your risk is significantly higher than if you just have the high calcium score and the normal Lp(a),” senior author Parag H. Joshi, MD, MHS, said in an interview.
“We thought we would see that the group with higher Lp(a) would have more events over 10 years, even among those who didn’t have coronary calcium,” said Dr. Joshi, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. “But we really don’t see that, at least in a statistically significant way.”
A CAC score of 0 would at least support a more conservative approach in a patient with elevated Lp(a) “who is hesitant to be on a statin or to be more aggressive managing their risk,” Dr. Joshi said.
“This study should be very reassuring for a patient like that,” Ron Blankstein, MD, director of cardiac computed tomography at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If you have a high Lp(a) and you’re concerned, I think this study really supports the role of calcium scoring for further risk assessment,” said Dr. Blankstein, who is not associated with the new report. “We often check Lp(a) in individuals who perhaps have a family history or who come to see us in a preventive cardiology clinic. If it is high and there is concern, a calcium score can be very helpful. If it’s zero, that really means a very low risk of events. And if it’s elevated, I think we’re going to be more concerned about that patient.”
The current analysis suggests “that, when a patient without clinical cardiovascular disease is identified with either CAC ≥100 or Lp(a) >50 mg/dL, the next step in the risk evaluation should be to measure either Lp(a) or CAC, respectively – if not already performed – to identify the patients at highest risk,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, director of vascular medicine at University of California, San Diego, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Both Lp(a) and CAC should be more broadly applied in clinical care settings in patients without prior ASCVD to identify those that most likely will benefit from more aggressive therapy and, in the future, from Lp(a)-lowering therapies,” he wrote.
The analyses were conducted separately on data from 4,512 initially asymptomatic patients in MESA and 2,078 from the DHS cohort, who were followed for ASCVD events an average of 13 years and 11 years, respectively. Such events included coronary heart disease–related death, nonfatal MI, and fatal or nonfatal stroke.
In the MESA cohort – 52% women, 36.8% White, 29.3% Black, 22.2% Hispanic, and 11.7% Chinese – elevated Lp(a) (quintile 5 vs. quintiles 1-4) and CAC scores of 1-99 and above 100 (both compared with 0) were each independently associated with increased risk for ASCVD events. The hazard ratio was 1.29 (P = .02) for elevated Lp(a), 1.68 (P < .01) for a CAC score of 1-99, and 2.66 (P < .01) for a CAC score of at least 100.
The corresponding HRs in the DHS cohort were 1.54 (P = .07) for Lp(a), 3.32 (P < .01) for a CAC score of 1-99, and 5.21 (P < .01) for a CAC score of at least 100.
Of note, the authors wrote, ASCVD risk among MESA participants with a CAC score of 0 was not significantly different in those with normal and elevated Lp(a).
The findings were similar in the corresponding DHS analysis, the authors noted.
When both Lp(a) and CAC scores are considered as dichotomous variables, the highest 10-year ASCVD incidence in MESA was in participants with both elevated Lp(a) (≥50 mg/dL) and a high CAC score (≥100). The lowest risk was seen when Lp(a) was normal (<50 mg/dL) and the CAC score was no more than moderately high (<100).
The results in the corresponding DHS analysis, according to the report, again mirrored those from MESA.
“This study has important implications for our patients and also potentially for future clinical trial design,” Dr. Blankstein noted. “A big part of developing a trial in this space is identifying the patients who are at higher risk,” and the current analysis supports CAC scores for identifying the highest-risk patient among those with elevated Lp(a).
Current wisdom is that, for the most part, Lp(a) levels are genetically mediated and are mostly unaffected by interventions such as diet management or exercise. It’s unknown whether reducing elevated Lp(a) levels pharmacologically will cut ASCVD risk, but there are a number of clinical trial programs currently aimed at learning just that. They include the Novartis-sponsored phase 3 HORIZON trial of the antisense agent pelacarsen (TQJ230), with an estimated enrollment of almost 7,700; a randomized, controlled dose-finding study of the small interfering RNA agent olpasiran (AMG890), with 290 patients and funded by Amgen; and an 88-patient phase 1 study of another siRNA agent, SLN360, supported by Silence Therapeutics.
Dr. Mehta reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Joshi has received grant support from Novo Nordisk and consulting income from Bayer and Regeneron; holds equity in G3 Therapeutics; and has served as site investigator for GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. Dr. Blankstein reported serving as a consultant to Amgen, Novartis, and Silence Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A look back at a pair of large cohort studies suggests a telling relation between two distinct predictors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk and may offer guidance on how to interpret them together.
Elevated levels of lipoprotein(a), or Lp(a), and high coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores were both predictive of ASCVD risk over 10 years, but independent of each other and a host of more traditional cardiovascular risk factors, for example, in the analysis of data from the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) and DHS (Dallas Heart Study) longitudinal cohorts.
Notably, the risk when both Lp(a) and CAC scores were high far exceeded that associated with either marker alone. But when CAC scores were less than 100 Agatston units, predicted ASCVD risk wasn’t influenced by levels of Lp(a). Indeed, a CAC score of 0 predicted the lowest levels of ASCVD risk, even with elevated Lp(a).
That is, the findings suggest, the addition of Lp(a) makes a difference to the risk assessment only when CAC scores are high, at least 100 units, and elevated Lp(a) doesn’t mean increased ASCVD risk in the absence of coronary calcium.
“Our novel findings indicate that elevated Lp(a) drives ASCVD risk independent of the subclinical coronary atherosclerosis burden captured by CAC score,” concluded a report on the analysis, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, with lead author Anurag Mehta, MD, Emory University, Atlanta.
There are no formal recommendations on how to interpret Lp(a) and CAC scores together, but the current findings “provide impetus for measuring Lp(a) in more individuals as part of the shared decision-making process,” the authors contended.
“Really, the calcium score carries the majority of the information in terms of risk, except in the highest CAC score group. That is, if you have a high Lp(a) and a high burden of calcium, your risk is significantly higher than if you just have the high calcium score and the normal Lp(a),” senior author Parag H. Joshi, MD, MHS, said in an interview.
“We thought we would see that the group with higher Lp(a) would have more events over 10 years, even among those who didn’t have coronary calcium,” said Dr. Joshi, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. “But we really don’t see that, at least in a statistically significant way.”
A CAC score of 0 would at least support a more conservative approach in a patient with elevated Lp(a) “who is hesitant to be on a statin or to be more aggressive managing their risk,” Dr. Joshi said.
“This study should be very reassuring for a patient like that,” Ron Blankstein, MD, director of cardiac computed tomography at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If you have a high Lp(a) and you’re concerned, I think this study really supports the role of calcium scoring for further risk assessment,” said Dr. Blankstein, who is not associated with the new report. “We often check Lp(a) in individuals who perhaps have a family history or who come to see us in a preventive cardiology clinic. If it is high and there is concern, a calcium score can be very helpful. If it’s zero, that really means a very low risk of events. And if it’s elevated, I think we’re going to be more concerned about that patient.”
The current analysis suggests “that, when a patient without clinical cardiovascular disease is identified with either CAC ≥100 or Lp(a) >50 mg/dL, the next step in the risk evaluation should be to measure either Lp(a) or CAC, respectively – if not already performed – to identify the patients at highest risk,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, director of vascular medicine at University of California, San Diego, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Both Lp(a) and CAC should be more broadly applied in clinical care settings in patients without prior ASCVD to identify those that most likely will benefit from more aggressive therapy and, in the future, from Lp(a)-lowering therapies,” he wrote.
The analyses were conducted separately on data from 4,512 initially asymptomatic patients in MESA and 2,078 from the DHS cohort, who were followed for ASCVD events an average of 13 years and 11 years, respectively. Such events included coronary heart disease–related death, nonfatal MI, and fatal or nonfatal stroke.
In the MESA cohort – 52% women, 36.8% White, 29.3% Black, 22.2% Hispanic, and 11.7% Chinese – elevated Lp(a) (quintile 5 vs. quintiles 1-4) and CAC scores of 1-99 and above 100 (both compared with 0) were each independently associated with increased risk for ASCVD events. The hazard ratio was 1.29 (P = .02) for elevated Lp(a), 1.68 (P < .01) for a CAC score of 1-99, and 2.66 (P < .01) for a CAC score of at least 100.
The corresponding HRs in the DHS cohort were 1.54 (P = .07) for Lp(a), 3.32 (P < .01) for a CAC score of 1-99, and 5.21 (P < .01) for a CAC score of at least 100.
Of note, the authors wrote, ASCVD risk among MESA participants with a CAC score of 0 was not significantly different in those with normal and elevated Lp(a).
The findings were similar in the corresponding DHS analysis, the authors noted.
When both Lp(a) and CAC scores are considered as dichotomous variables, the highest 10-year ASCVD incidence in MESA was in participants with both elevated Lp(a) (≥50 mg/dL) and a high CAC score (≥100). The lowest risk was seen when Lp(a) was normal (<50 mg/dL) and the CAC score was no more than moderately high (<100).
The results in the corresponding DHS analysis, according to the report, again mirrored those from MESA.
“This study has important implications for our patients and also potentially for future clinical trial design,” Dr. Blankstein noted. “A big part of developing a trial in this space is identifying the patients who are at higher risk,” and the current analysis supports CAC scores for identifying the highest-risk patient among those with elevated Lp(a).
Current wisdom is that, for the most part, Lp(a) levels are genetically mediated and are mostly unaffected by interventions such as diet management or exercise. It’s unknown whether reducing elevated Lp(a) levels pharmacologically will cut ASCVD risk, but there are a number of clinical trial programs currently aimed at learning just that. They include the Novartis-sponsored phase 3 HORIZON trial of the antisense agent pelacarsen (TQJ230), with an estimated enrollment of almost 7,700; a randomized, controlled dose-finding study of the small interfering RNA agent olpasiran (AMG890), with 290 patients and funded by Amgen; and an 88-patient phase 1 study of another siRNA agent, SLN360, supported by Silence Therapeutics.
Dr. Mehta reported no relevant relationships. Dr. Joshi has received grant support from Novo Nordisk and consulting income from Bayer and Regeneron; holds equity in G3 Therapeutics; and has served as site investigator for GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. Dr. Blankstein reported serving as a consultant to Amgen, Novartis, and Silence Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Phthalate exposure via maternal and cord blood affects infant outcomes
Exposure to phthalates through maternal blood and cord blood affected outcomes including head circumference and anogenital index for male and female infants, according to data from 65 mother-infant pairs.
Phthalates are recognized endocrine disruptors that have been associated with adverse birth outcomes, but the specific relationship between maternal phthalate exposure and birth outcomes has not been well studied, wrote Hsiao-Lin Hwa, MD, of National Taiwan University, Taipei, and colleagues.
Previous research suggests that trace exposure to hazardous chemicals during the fetal period “may cause fetal metabolic dysfunction and adversely change the morphology of body systems,” they said. In 2011, “the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration found that di‐2‐ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) and DiNP [di‐isononyl phthalate] had been illegally added as emulsifiers to replace palm oil in beverages and food,” they added. The researchers sought to examine the association between infant birth outcomes and phthalate exposure levels in the Taiwanese population after 2011. In a study published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, the researchers recruited 65 pregnant women in Taiwan between 2016 and 2017. Birth length, birth weight, head circumference, anogenital distance (AGD), anoscrotal distance (ASD), and anofourchette distance (AFD) were measured for each newborn at the time of delivery. The average age of the women was 33.6 years, and the rate of low birth weight was 13.7%. The mean measures of birth length, birth weight, head circumference, and chest circumference were 47.6 cm, 3022 g, 32.9 cm, and 30.8 mm, respectively. The mean AFD and ASD were 14.2 mm and 22.3 mm, respectively.
The researchers tested for 12 phthalates in maternal blood and cord blood samples. Of these, the six most frequently detected phthalate metabolites were mono‐ethyl phthalate (MEP), mono‐isobutyl phthalate (MiBP), mono‐n‐butyl phthalate (MnBP), mono‐(2‐ethyl‐5‐oxohexyl)‐phthalate (MEOHP), mono‐(2‐ethyl‐5‐hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP), and mono‐n‐octyl phthalate (MOP); these six were present in 80%–100% of the maternal blood samples.
Overall, the mean levels of MEP, MiBP, MnBP, and MEHP were relatively higher in both maternal and infant blood than other phthalates, the researchers noted. The mean concentrations of metabolites in maternal blood and infant cord blood were 0.03-2.27 ng/mL and 0.01-3.74 ng/mL, respectively.
Among male infants, levels of MMP, MiBP, and MEHP in maternal blood were inversely related to anogenital index (AGI), with P values for regression coefficients ranging from .011 to .033. In addition, the total concentration of MEHP, MEOHP, and MEHHP (designated as Σdi‐2‐ethylhexyl phthalate, ΣDEHP) was inversely related to AGI in males.
Among female infants, however, phthalates in cord blood, rather than maternal blood, were positively related to AGI, including MMP, MibP, MnBP, and MOP, with P values for regression coefficients ranging from .001 to .034.
Cord blood levels of MnBP, MEOHP, MEHP, and ΣDEHP were inversely associated with gestational age-adjusted head circumference in all infants, with beta coefficients of –0.15, –0.12, –0.01, and –0.01, respectively (P < .05 for all).
“The detection rates of MEHHP, MEOHP, and MEHP in the cord blood were lower than those in the maternal blood, particularly those of MEHHP and MEOHP, which were approximately 25% lower,” which may be caused by slow placental transfer, the researchers wrote in their discussion section. “The high detection rate of phthalate metabolites indicated that our subjects may continue to be exposed to these phthalates even after the 2011 Taiwan DEHP incident,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility for contamination of samples and other environmental confounders, the researchers noted. However, the results support the role of phthalates as endocrine disruptors, and the distinction in effects between males and females “may suggest that phthalate monoesters are potentially estrogenic and antiandrogenic chemicals,” they added.
“Further investigations involving multiple phthalate analyses during pregnancy and measurements throughout childhood are necessary to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
Direct clinical implications remain uncertain
“Phthalates are a group of chemicals that are used to make plastic more durable; they are found in multiple everyday materials, food products, and common household products,” Marissa Platner, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “It is known that we are exposed to phthalates on a routine basis but the long-term effects of this exposure are unclear,” she said.
The current study findings “were not entirely surprising given data from prior animal studies because they do imply that there is some placental transfer of the phthalate metabolites that can cause adverse effects on the developing fetus,” said Dr. Platner. “However, they also demonstrate that the placenta acts as a filter for certain larger molecules to protect the fetus,” she said.
“This study was based on a small sample size, therefore the clinical implications are not clear,” Dr. Platner noted. “However it may be worthwhile after further research to encourage our pregnant patients to try to decrease their exposure to phthalates,” she said.
Dr. Platner identified two areas for additional research to explore the role of phthalate exposure.
“The first would be to assess the level of maternal phthalate exposure throughout the pregnancy instead of just at one point in time, and the second would be to assess how the reproductive system differences at birth translate to long-term outcomes in children, such as early puberty in females or decreased fertility in males,” she said.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan and the Far Eastern Memorial Hospital‐National Taiwan University Hospital. The researchers and Dr. Platner had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Exposure to phthalates through maternal blood and cord blood affected outcomes including head circumference and anogenital index for male and female infants, according to data from 65 mother-infant pairs.
Phthalates are recognized endocrine disruptors that have been associated with adverse birth outcomes, but the specific relationship between maternal phthalate exposure and birth outcomes has not been well studied, wrote Hsiao-Lin Hwa, MD, of National Taiwan University, Taipei, and colleagues.
Previous research suggests that trace exposure to hazardous chemicals during the fetal period “may cause fetal metabolic dysfunction and adversely change the morphology of body systems,” they said. In 2011, “the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration found that di‐2‐ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) and DiNP [di‐isononyl phthalate] had been illegally added as emulsifiers to replace palm oil in beverages and food,” they added. The researchers sought to examine the association between infant birth outcomes and phthalate exposure levels in the Taiwanese population after 2011. In a study published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, the researchers recruited 65 pregnant women in Taiwan between 2016 and 2017. Birth length, birth weight, head circumference, anogenital distance (AGD), anoscrotal distance (ASD), and anofourchette distance (AFD) were measured for each newborn at the time of delivery. The average age of the women was 33.6 years, and the rate of low birth weight was 13.7%. The mean measures of birth length, birth weight, head circumference, and chest circumference were 47.6 cm, 3022 g, 32.9 cm, and 30.8 mm, respectively. The mean AFD and ASD were 14.2 mm and 22.3 mm, respectively.
The researchers tested for 12 phthalates in maternal blood and cord blood samples. Of these, the six most frequently detected phthalate metabolites were mono‐ethyl phthalate (MEP), mono‐isobutyl phthalate (MiBP), mono‐n‐butyl phthalate (MnBP), mono‐(2‐ethyl‐5‐oxohexyl)‐phthalate (MEOHP), mono‐(2‐ethyl‐5‐hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP), and mono‐n‐octyl phthalate (MOP); these six were present in 80%–100% of the maternal blood samples.
Overall, the mean levels of MEP, MiBP, MnBP, and MEHP were relatively higher in both maternal and infant blood than other phthalates, the researchers noted. The mean concentrations of metabolites in maternal blood and infant cord blood were 0.03-2.27 ng/mL and 0.01-3.74 ng/mL, respectively.
Among male infants, levels of MMP, MiBP, and MEHP in maternal blood were inversely related to anogenital index (AGI), with P values for regression coefficients ranging from .011 to .033. In addition, the total concentration of MEHP, MEOHP, and MEHHP (designated as Σdi‐2‐ethylhexyl phthalate, ΣDEHP) was inversely related to AGI in males.
Among female infants, however, phthalates in cord blood, rather than maternal blood, were positively related to AGI, including MMP, MibP, MnBP, and MOP, with P values for regression coefficients ranging from .001 to .034.
Cord blood levels of MnBP, MEOHP, MEHP, and ΣDEHP were inversely associated with gestational age-adjusted head circumference in all infants, with beta coefficients of –0.15, –0.12, –0.01, and –0.01, respectively (P < .05 for all).
“The detection rates of MEHHP, MEOHP, and MEHP in the cord blood were lower than those in the maternal blood, particularly those of MEHHP and MEOHP, which were approximately 25% lower,” which may be caused by slow placental transfer, the researchers wrote in their discussion section. “The high detection rate of phthalate metabolites indicated that our subjects may continue to be exposed to these phthalates even after the 2011 Taiwan DEHP incident,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility for contamination of samples and other environmental confounders, the researchers noted. However, the results support the role of phthalates as endocrine disruptors, and the distinction in effects between males and females “may suggest that phthalate monoesters are potentially estrogenic and antiandrogenic chemicals,” they added.
“Further investigations involving multiple phthalate analyses during pregnancy and measurements throughout childhood are necessary to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
Direct clinical implications remain uncertain
“Phthalates are a group of chemicals that are used to make plastic more durable; they are found in multiple everyday materials, food products, and common household products,” Marissa Platner, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “It is known that we are exposed to phthalates on a routine basis but the long-term effects of this exposure are unclear,” she said.
The current study findings “were not entirely surprising given data from prior animal studies because they do imply that there is some placental transfer of the phthalate metabolites that can cause adverse effects on the developing fetus,” said Dr. Platner. “However, they also demonstrate that the placenta acts as a filter for certain larger molecules to protect the fetus,” she said.
“This study was based on a small sample size, therefore the clinical implications are not clear,” Dr. Platner noted. “However it may be worthwhile after further research to encourage our pregnant patients to try to decrease their exposure to phthalates,” she said.
Dr. Platner identified two areas for additional research to explore the role of phthalate exposure.
“The first would be to assess the level of maternal phthalate exposure throughout the pregnancy instead of just at one point in time, and the second would be to assess how the reproductive system differences at birth translate to long-term outcomes in children, such as early puberty in females or decreased fertility in males,” she said.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan and the Far Eastern Memorial Hospital‐National Taiwan University Hospital. The researchers and Dr. Platner had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Exposure to phthalates through maternal blood and cord blood affected outcomes including head circumference and anogenital index for male and female infants, according to data from 65 mother-infant pairs.
Phthalates are recognized endocrine disruptors that have been associated with adverse birth outcomes, but the specific relationship between maternal phthalate exposure and birth outcomes has not been well studied, wrote Hsiao-Lin Hwa, MD, of National Taiwan University, Taipei, and colleagues.
Previous research suggests that trace exposure to hazardous chemicals during the fetal period “may cause fetal metabolic dysfunction and adversely change the morphology of body systems,” they said. In 2011, “the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration found that di‐2‐ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) and DiNP [di‐isononyl phthalate] had been illegally added as emulsifiers to replace palm oil in beverages and food,” they added. The researchers sought to examine the association between infant birth outcomes and phthalate exposure levels in the Taiwanese population after 2011. In a study published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, the researchers recruited 65 pregnant women in Taiwan between 2016 and 2017. Birth length, birth weight, head circumference, anogenital distance (AGD), anoscrotal distance (ASD), and anofourchette distance (AFD) were measured for each newborn at the time of delivery. The average age of the women was 33.6 years, and the rate of low birth weight was 13.7%. The mean measures of birth length, birth weight, head circumference, and chest circumference were 47.6 cm, 3022 g, 32.9 cm, and 30.8 mm, respectively. The mean AFD and ASD were 14.2 mm and 22.3 mm, respectively.
The researchers tested for 12 phthalates in maternal blood and cord blood samples. Of these, the six most frequently detected phthalate metabolites were mono‐ethyl phthalate (MEP), mono‐isobutyl phthalate (MiBP), mono‐n‐butyl phthalate (MnBP), mono‐(2‐ethyl‐5‐oxohexyl)‐phthalate (MEOHP), mono‐(2‐ethyl‐5‐hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP), and mono‐n‐octyl phthalate (MOP); these six were present in 80%–100% of the maternal blood samples.
Overall, the mean levels of MEP, MiBP, MnBP, and MEHP were relatively higher in both maternal and infant blood than other phthalates, the researchers noted. The mean concentrations of metabolites in maternal blood and infant cord blood were 0.03-2.27 ng/mL and 0.01-3.74 ng/mL, respectively.
Among male infants, levels of MMP, MiBP, and MEHP in maternal blood were inversely related to anogenital index (AGI), with P values for regression coefficients ranging from .011 to .033. In addition, the total concentration of MEHP, MEOHP, and MEHHP (designated as Σdi‐2‐ethylhexyl phthalate, ΣDEHP) was inversely related to AGI in males.
Among female infants, however, phthalates in cord blood, rather than maternal blood, were positively related to AGI, including MMP, MibP, MnBP, and MOP, with P values for regression coefficients ranging from .001 to .034.
Cord blood levels of MnBP, MEOHP, MEHP, and ΣDEHP were inversely associated with gestational age-adjusted head circumference in all infants, with beta coefficients of –0.15, –0.12, –0.01, and –0.01, respectively (P < .05 for all).
“The detection rates of MEHHP, MEOHP, and MEHP in the cord blood were lower than those in the maternal blood, particularly those of MEHHP and MEOHP, which were approximately 25% lower,” which may be caused by slow placental transfer, the researchers wrote in their discussion section. “The high detection rate of phthalate metabolites indicated that our subjects may continue to be exposed to these phthalates even after the 2011 Taiwan DEHP incident,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility for contamination of samples and other environmental confounders, the researchers noted. However, the results support the role of phthalates as endocrine disruptors, and the distinction in effects between males and females “may suggest that phthalate monoesters are potentially estrogenic and antiandrogenic chemicals,” they added.
“Further investigations involving multiple phthalate analyses during pregnancy and measurements throughout childhood are necessary to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
Direct clinical implications remain uncertain
“Phthalates are a group of chemicals that are used to make plastic more durable; they are found in multiple everyday materials, food products, and common household products,” Marissa Platner, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “It is known that we are exposed to phthalates on a routine basis but the long-term effects of this exposure are unclear,” she said.
The current study findings “were not entirely surprising given data from prior animal studies because they do imply that there is some placental transfer of the phthalate metabolites that can cause adverse effects on the developing fetus,” said Dr. Platner. “However, they also demonstrate that the placenta acts as a filter for certain larger molecules to protect the fetus,” she said.
“This study was based on a small sample size, therefore the clinical implications are not clear,” Dr. Platner noted. “However it may be worthwhile after further research to encourage our pregnant patients to try to decrease their exposure to phthalates,” she said.
Dr. Platner identified two areas for additional research to explore the role of phthalate exposure.
“The first would be to assess the level of maternal phthalate exposure throughout the pregnancy instead of just at one point in time, and the second would be to assess how the reproductive system differences at birth translate to long-term outcomes in children, such as early puberty in females or decreased fertility in males,” she said.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan and the Far Eastern Memorial Hospital‐National Taiwan University Hospital. The researchers and Dr. Platner had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY
Eating disorder may be common in celiac disease
A new study examining avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) among patients with celiac disease found that the condition is common but is not associated with any difference in disease control. The findings suggest that some with celiac disease may pursue dietary control too far, but experts warn that ARFID is only recently being recognized in patients with GI diseases, the definition is in flux, and it’s important to not overpathologize patient behavior.
The new study, published in Gastro Hep Advances, comes in the wake of a 2021 cross-sectional study, which found that 53.7% of celiac disease patients met the criteria for ARFID based on the Nine-Item ARFID Screen, and were more likely to have anxiety, depression, and reduced food-related quality of life.
“I think both studies are hypothesizing that there might be greater fear around eating in these patients with celiac, but that the possible outcomes related to their disease may not actually be different,” said Helen Burton Murray, PhD, director of the GI behavioral health program and staff psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who was asked to comment on the study.
She also noted that ARFID may represent a subgroup of celiac patients with more severe disease or worse quality of life, though the two studies can’t definitively prove that. The surveys used are intended for screening rather than diagnosis and have not yet been validated in patients with a gastrointestinal disease like celiac.
Although the symptoms of ARFID have been recognized for many years, it only became an official diagnosis with its inclusion in DSM-5 in 2013. Physicians are becoming increasingly aware of this potential comorbidity, but it can be difficult to diagnose or understand the impact of an eating disorder in a condition like celiac disease, where intense dietary management is the key to controlling it. “There’s concern about overpathologizing patients where dietary management can be a normative strategy, and overpathologizing by diagnosing ARFID. Is diagnosing ARFID going to change the patient’s treatment course and improve outcomes for them?” asked Dr. Burton Murray.
In some cases, the answer may be yes. Patients may be so restrictive in their eating that it impacts physical health or lifestyle. “Hypervigilance or worry around eating could extend to even non–gluten based foods. That may be a marker of where a patient’s eating behaviors are crossing the line into ARFID, if their diet is so limited when it doesn’t need to be, and those limitations might be harming them nutritionally, leading to weight loss or making it difficult to live their life in the way that they would like to,” said Dr. Burton Murray.
Still, the results of these studies shouldn’t be overinterpreted, according to Anne R. Lee, EdD, RDN, LD, associate professor of nutritional medicine at the celiac disease center at Columbia University, New York. “In the world of eating disorders, ARFID is the newest kid on the block, and one that’s in transition,” she said. What differentiates ARFID from other eating disorders is that food behavior is related to things like appetite or picky eating, but not body shape and size. Therefore, it helps to combine the ARFID screen with other eating disorder screening tools, Dr. Lee said.
“We need to differentiate between diagnosing someone with a disordered eating pattern versus helping them navigate their life within a gluten-free diet. We need to help them with developing strategies to maneuver through work lunches and social outings and all of those things so that we don’t overdiagnose,” said Dr. Lee.
In the new study, researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 137 patients with celiac disease at the Center for Human Nutrition at Vanderbilt University Medical Center; 107 were women, and the median age was 37 years. The researchers used questionnaires to evaluate diet, including the ARFID Symptom Checklist.
Seventy-eight participants (57%) had suspected ARFID; 30 had symptoms consistent with clinical ARFID and 48 consistent with subclinical ARFID. There were no differences between patients with and without ARFID with respect to anxiety and depression, length of illness, age, gender, body mass index, bone disease, or micronutrient or vitamin deficiency. Serology studies revealed only one difference: a higher frequency of tissue transglutaminase IgG antibody in the ARFID group (15% vs. 2%; P = .007).
There was a strong correlation between ARFID and the Impact of the Gluten Free Diet questionnaire (IGFDQ), with patients scoring higher on the social and food components more likely to also have ARFID. It was also the only predictor of ARFID in a multivariable analysis, with associations in the food (odds ratio, 1.64; P = .01), emotional (OR, 1.66; P = .05), and social (OR, 1.59; P = .01) sections.
The authors concluded that, although there were some study limitations, including possible patient misunderstanding of the survey questions and lack of knowledge of whether the patients had access to gluten-free foods, AFID is not only common, but it also has a significant impact on patients with celiac disease. The authors also noted that this assessment occurred over a 2-year period, with patients attending clinic only once a year. Follow-up surveys, duodenal biopsies, and bone density assessments could identify more differences over time.
Dr. Burton Murray and Dr. Lee have no relevant financial disclosures.
AGA offers guidance on celiac disease to help patients maintain a gluten free diet in the AGA GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/celiac
A new study examining avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) among patients with celiac disease found that the condition is common but is not associated with any difference in disease control. The findings suggest that some with celiac disease may pursue dietary control too far, but experts warn that ARFID is only recently being recognized in patients with GI diseases, the definition is in flux, and it’s important to not overpathologize patient behavior.
The new study, published in Gastro Hep Advances, comes in the wake of a 2021 cross-sectional study, which found that 53.7% of celiac disease patients met the criteria for ARFID based on the Nine-Item ARFID Screen, and were more likely to have anxiety, depression, and reduced food-related quality of life.
“I think both studies are hypothesizing that there might be greater fear around eating in these patients with celiac, but that the possible outcomes related to their disease may not actually be different,” said Helen Burton Murray, PhD, director of the GI behavioral health program and staff psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who was asked to comment on the study.
She also noted that ARFID may represent a subgroup of celiac patients with more severe disease or worse quality of life, though the two studies can’t definitively prove that. The surveys used are intended for screening rather than diagnosis and have not yet been validated in patients with a gastrointestinal disease like celiac.
Although the symptoms of ARFID have been recognized for many years, it only became an official diagnosis with its inclusion in DSM-5 in 2013. Physicians are becoming increasingly aware of this potential comorbidity, but it can be difficult to diagnose or understand the impact of an eating disorder in a condition like celiac disease, where intense dietary management is the key to controlling it. “There’s concern about overpathologizing patients where dietary management can be a normative strategy, and overpathologizing by diagnosing ARFID. Is diagnosing ARFID going to change the patient’s treatment course and improve outcomes for them?” asked Dr. Burton Murray.
In some cases, the answer may be yes. Patients may be so restrictive in their eating that it impacts physical health or lifestyle. “Hypervigilance or worry around eating could extend to even non–gluten based foods. That may be a marker of where a patient’s eating behaviors are crossing the line into ARFID, if their diet is so limited when it doesn’t need to be, and those limitations might be harming them nutritionally, leading to weight loss or making it difficult to live their life in the way that they would like to,” said Dr. Burton Murray.
Still, the results of these studies shouldn’t be overinterpreted, according to Anne R. Lee, EdD, RDN, LD, associate professor of nutritional medicine at the celiac disease center at Columbia University, New York. “In the world of eating disorders, ARFID is the newest kid on the block, and one that’s in transition,” she said. What differentiates ARFID from other eating disorders is that food behavior is related to things like appetite or picky eating, but not body shape and size. Therefore, it helps to combine the ARFID screen with other eating disorder screening tools, Dr. Lee said.
“We need to differentiate between diagnosing someone with a disordered eating pattern versus helping them navigate their life within a gluten-free diet. We need to help them with developing strategies to maneuver through work lunches and social outings and all of those things so that we don’t overdiagnose,” said Dr. Lee.
In the new study, researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 137 patients with celiac disease at the Center for Human Nutrition at Vanderbilt University Medical Center; 107 were women, and the median age was 37 years. The researchers used questionnaires to evaluate diet, including the ARFID Symptom Checklist.
Seventy-eight participants (57%) had suspected ARFID; 30 had symptoms consistent with clinical ARFID and 48 consistent with subclinical ARFID. There were no differences between patients with and without ARFID with respect to anxiety and depression, length of illness, age, gender, body mass index, bone disease, or micronutrient or vitamin deficiency. Serology studies revealed only one difference: a higher frequency of tissue transglutaminase IgG antibody in the ARFID group (15% vs. 2%; P = .007).
There was a strong correlation between ARFID and the Impact of the Gluten Free Diet questionnaire (IGFDQ), with patients scoring higher on the social and food components more likely to also have ARFID. It was also the only predictor of ARFID in a multivariable analysis, with associations in the food (odds ratio, 1.64; P = .01), emotional (OR, 1.66; P = .05), and social (OR, 1.59; P = .01) sections.
The authors concluded that, although there were some study limitations, including possible patient misunderstanding of the survey questions and lack of knowledge of whether the patients had access to gluten-free foods, AFID is not only common, but it also has a significant impact on patients with celiac disease. The authors also noted that this assessment occurred over a 2-year period, with patients attending clinic only once a year. Follow-up surveys, duodenal biopsies, and bone density assessments could identify more differences over time.
Dr. Burton Murray and Dr. Lee have no relevant financial disclosures.
AGA offers guidance on celiac disease to help patients maintain a gluten free diet in the AGA GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/celiac
A new study examining avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) among patients with celiac disease found that the condition is common but is not associated with any difference in disease control. The findings suggest that some with celiac disease may pursue dietary control too far, but experts warn that ARFID is only recently being recognized in patients with GI diseases, the definition is in flux, and it’s important to not overpathologize patient behavior.
The new study, published in Gastro Hep Advances, comes in the wake of a 2021 cross-sectional study, which found that 53.7% of celiac disease patients met the criteria for ARFID based on the Nine-Item ARFID Screen, and were more likely to have anxiety, depression, and reduced food-related quality of life.
“I think both studies are hypothesizing that there might be greater fear around eating in these patients with celiac, but that the possible outcomes related to their disease may not actually be different,” said Helen Burton Murray, PhD, director of the GI behavioral health program and staff psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who was asked to comment on the study.
She also noted that ARFID may represent a subgroup of celiac patients with more severe disease or worse quality of life, though the two studies can’t definitively prove that. The surveys used are intended for screening rather than diagnosis and have not yet been validated in patients with a gastrointestinal disease like celiac.
Although the symptoms of ARFID have been recognized for many years, it only became an official diagnosis with its inclusion in DSM-5 in 2013. Physicians are becoming increasingly aware of this potential comorbidity, but it can be difficult to diagnose or understand the impact of an eating disorder in a condition like celiac disease, where intense dietary management is the key to controlling it. “There’s concern about overpathologizing patients where dietary management can be a normative strategy, and overpathologizing by diagnosing ARFID. Is diagnosing ARFID going to change the patient’s treatment course and improve outcomes for them?” asked Dr. Burton Murray.
In some cases, the answer may be yes. Patients may be so restrictive in their eating that it impacts physical health or lifestyle. “Hypervigilance or worry around eating could extend to even non–gluten based foods. That may be a marker of where a patient’s eating behaviors are crossing the line into ARFID, if their diet is so limited when it doesn’t need to be, and those limitations might be harming them nutritionally, leading to weight loss or making it difficult to live their life in the way that they would like to,” said Dr. Burton Murray.
Still, the results of these studies shouldn’t be overinterpreted, according to Anne R. Lee, EdD, RDN, LD, associate professor of nutritional medicine at the celiac disease center at Columbia University, New York. “In the world of eating disorders, ARFID is the newest kid on the block, and one that’s in transition,” she said. What differentiates ARFID from other eating disorders is that food behavior is related to things like appetite or picky eating, but not body shape and size. Therefore, it helps to combine the ARFID screen with other eating disorder screening tools, Dr. Lee said.
“We need to differentiate between diagnosing someone with a disordered eating pattern versus helping them navigate their life within a gluten-free diet. We need to help them with developing strategies to maneuver through work lunches and social outings and all of those things so that we don’t overdiagnose,” said Dr. Lee.
In the new study, researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 137 patients with celiac disease at the Center for Human Nutrition at Vanderbilt University Medical Center; 107 were women, and the median age was 37 years. The researchers used questionnaires to evaluate diet, including the ARFID Symptom Checklist.
Seventy-eight participants (57%) had suspected ARFID; 30 had symptoms consistent with clinical ARFID and 48 consistent with subclinical ARFID. There were no differences between patients with and without ARFID with respect to anxiety and depression, length of illness, age, gender, body mass index, bone disease, or micronutrient or vitamin deficiency. Serology studies revealed only one difference: a higher frequency of tissue transglutaminase IgG antibody in the ARFID group (15% vs. 2%; P = .007).
There was a strong correlation between ARFID and the Impact of the Gluten Free Diet questionnaire (IGFDQ), with patients scoring higher on the social and food components more likely to also have ARFID. It was also the only predictor of ARFID in a multivariable analysis, with associations in the food (odds ratio, 1.64; P = .01), emotional (OR, 1.66; P = .05), and social (OR, 1.59; P = .01) sections.
The authors concluded that, although there were some study limitations, including possible patient misunderstanding of the survey questions and lack of knowledge of whether the patients had access to gluten-free foods, AFID is not only common, but it also has a significant impact on patients with celiac disease. The authors also noted that this assessment occurred over a 2-year period, with patients attending clinic only once a year. Follow-up surveys, duodenal biopsies, and bone density assessments could identify more differences over time.
Dr. Burton Murray and Dr. Lee have no relevant financial disclosures.
AGA offers guidance on celiac disease to help patients maintain a gluten free diet in the AGA GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/celiac
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES





