User login
Hand outcomes similar with distal or proximal radial cardiac cath
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
FROM SCAI 2022
FDA clears Abbott Freestyle Libre 3 glucose sensor
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared Abbot’s Freestyle Libre 3 system for use by people aged 4 years and older with diabetes.
The new system was cleared for use for both iOS- and Android-compatible mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose readings in contrast to the “intermittently scanned” capability of prior Libre versions. The Libre 3 allows for optional alarms and notifications of urgent low or high glucose levels, as well as remote monitoring by health care professionals or the patient’s family members and/or friends.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 was granted a CE Mark in Europe in October 2020.
Smaller, thinner, and better integration
According to Abbott, the Libre 3 is the first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to show a mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of less than 8% compared with a gold-standard glucose measure. The average Libre 3 MARD is 7.9%, compared with 9.3% for the Libre 2. The Libre 3 is also the “smallest and thinnest” CGM, roughly the size of two stacked U.S. pennies, worn on the upper arm.
And, the company said, the Libre 3 has a Bluetooth integration of up to 33 feet, a range 50% further than other CGMs.
This version follows the FreeStyle Libre 2, approved in June 2020, and its compatible iPhone app, approved in August 2021.
The Libre 3 will be priced the same as the Libre 2, at about one-third the cost of other CGM systems. However, it is not currently eligible for Medicare reimbursement. Medicaid eligibility may vary by state.
“I applaud Abbott for making their CGM system the most affordable and addressing disparities in care so patients living with diabetes can avoid complications and optimize their quality of life,” Eugene E. Wright Jr., MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an Abbott statement.
“I have seen real-world evidence that diabetes technologies like CGMs have helped my patients safely achieve improved glycemic control,” he said.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor will be available at participating pharmacies later this year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared Abbot’s Freestyle Libre 3 system for use by people aged 4 years and older with diabetes.
The new system was cleared for use for both iOS- and Android-compatible mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose readings in contrast to the “intermittently scanned” capability of prior Libre versions. The Libre 3 allows for optional alarms and notifications of urgent low or high glucose levels, as well as remote monitoring by health care professionals or the patient’s family members and/or friends.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 was granted a CE Mark in Europe in October 2020.
Smaller, thinner, and better integration
According to Abbott, the Libre 3 is the first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to show a mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of less than 8% compared with a gold-standard glucose measure. The average Libre 3 MARD is 7.9%, compared with 9.3% for the Libre 2. The Libre 3 is also the “smallest and thinnest” CGM, roughly the size of two stacked U.S. pennies, worn on the upper arm.
And, the company said, the Libre 3 has a Bluetooth integration of up to 33 feet, a range 50% further than other CGMs.
This version follows the FreeStyle Libre 2, approved in June 2020, and its compatible iPhone app, approved in August 2021.
The Libre 3 will be priced the same as the Libre 2, at about one-third the cost of other CGM systems. However, it is not currently eligible for Medicare reimbursement. Medicaid eligibility may vary by state.
“I applaud Abbott for making their CGM system the most affordable and addressing disparities in care so patients living with diabetes can avoid complications and optimize their quality of life,” Eugene E. Wright Jr., MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an Abbott statement.
“I have seen real-world evidence that diabetes technologies like CGMs have helped my patients safely achieve improved glycemic control,” he said.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor will be available at participating pharmacies later this year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared Abbot’s Freestyle Libre 3 system for use by people aged 4 years and older with diabetes.
The new system was cleared for use for both iOS- and Android-compatible mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose readings in contrast to the “intermittently scanned” capability of prior Libre versions. The Libre 3 allows for optional alarms and notifications of urgent low or high glucose levels, as well as remote monitoring by health care professionals or the patient’s family members and/or friends.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 was granted a CE Mark in Europe in October 2020.
Smaller, thinner, and better integration
According to Abbott, the Libre 3 is the first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to show a mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of less than 8% compared with a gold-standard glucose measure. The average Libre 3 MARD is 7.9%, compared with 9.3% for the Libre 2. The Libre 3 is also the “smallest and thinnest” CGM, roughly the size of two stacked U.S. pennies, worn on the upper arm.
And, the company said, the Libre 3 has a Bluetooth integration of up to 33 feet, a range 50% further than other CGMs.
This version follows the FreeStyle Libre 2, approved in June 2020, and its compatible iPhone app, approved in August 2021.
The Libre 3 will be priced the same as the Libre 2, at about one-third the cost of other CGM systems. However, it is not currently eligible for Medicare reimbursement. Medicaid eligibility may vary by state.
“I applaud Abbott for making their CGM system the most affordable and addressing disparities in care so patients living with diabetes can avoid complications and optimize their quality of life,” Eugene E. Wright Jr., MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an Abbott statement.
“I have seen real-world evidence that diabetes technologies like CGMs have helped my patients safely achieve improved glycemic control,” he said.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor will be available at participating pharmacies later this year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paraphilic disorders and sexual criminality
Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
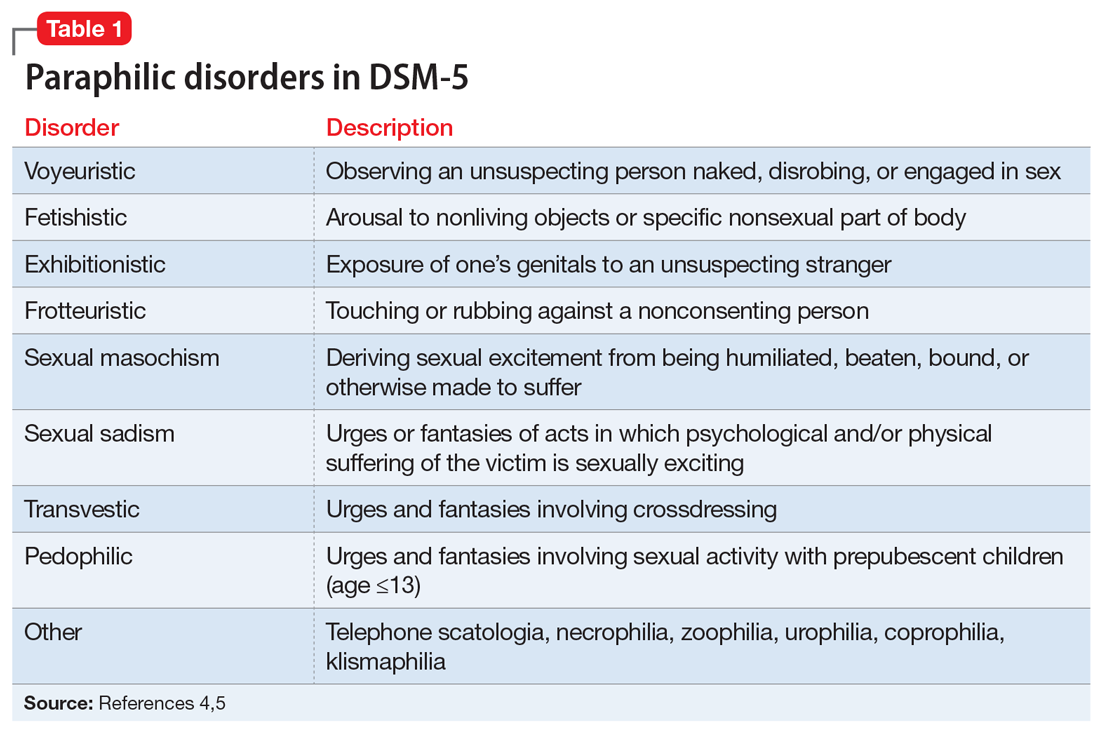
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5
Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...
Paraphilic disorders are more common in men than in women; the 2 most prevalent are voyeuristic disorder and frotteuristic disorder.6 The incidence of paraphilias in the general outpatient setting varies by disorder. Approximately 45% of individuals with pedophilic disorder seek treatment, whereas only 1% of individuals with zoophilia seek treatment.6 The incidence of paraphilic acts also varies drastically; individuals with exhibitionistic disorder engaged in an average of 50 acts vs only 3 for individuals with sexual sadism.6 Not all individuals with paraphilic disorders commit crimes. Approximately 58% of sexual offenders meet the criteria for a paraphilic disorder, but antisocial personality disorder is a far more common diagnosis.7
Sexual psychopath statutes: Phase 1
In 1937, Michigan became the first state to enact sexual psychopath statutes, allowing for indeterminate sentencing and the civil commitment/treatment of sex offenders with repeated convictions. By the 1970s, more than 30 states had enacted similar statutes. It was not until 1967, in Specht v Patterson,8 that the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment Due Process Clause was violated when Francis Eddie Specht faced life in prison following his conviction for indecent liberties under the Colorado Sex Offenders Act.
Specht was convicted in 1959 for indecent liberties after pleading guilty to enticing a child younger than age 16 into an office and engaging in sexual activities with them. At the time of Specht’s conviction, the crime of indecent liberties carried a punishment of 10 years. However, Specht was sentenced under the Sexual Offenders Act, which allowed for an indeterminate sentence of 1 day to life in prison. The Supreme Court noted that Specht was denied the right to be present with counsel, to confront the evidence against him, to cross-examine witnesses, and to offer his own evidence, which was a violation of his constitutionally guaranteed Fourteenth Amendment right to Procedural Due Process. The decision led most states to repeal early sexual psychopath statutes.8
Sexually violent predator laws: Phase 2
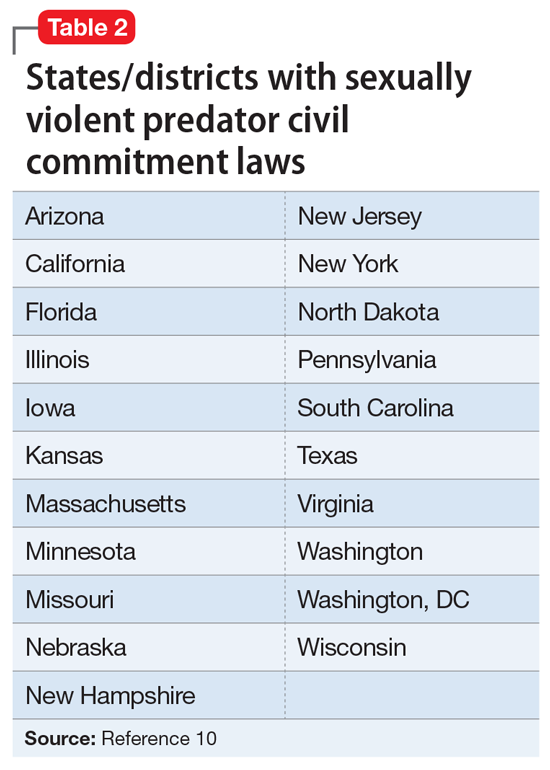
After early sexual psychopath statutes were repealed, many states pushed to update sex offender laws in response to the Earl Shriner case.9 In 1989, Shriner was released from prison after serving a 10-year sentence for sexually assaulting 2 teenage girls. At the time, he did not meet the criteria for civil commitment in the state of Washington. On the day he was released, Shriner cut off a young boy’s penis and left him to die. Washington subsequently became the first of many states to enact sexually violent predator (SVP) laws. Table 210 shows states and districts that have SVP civil commitment laws.
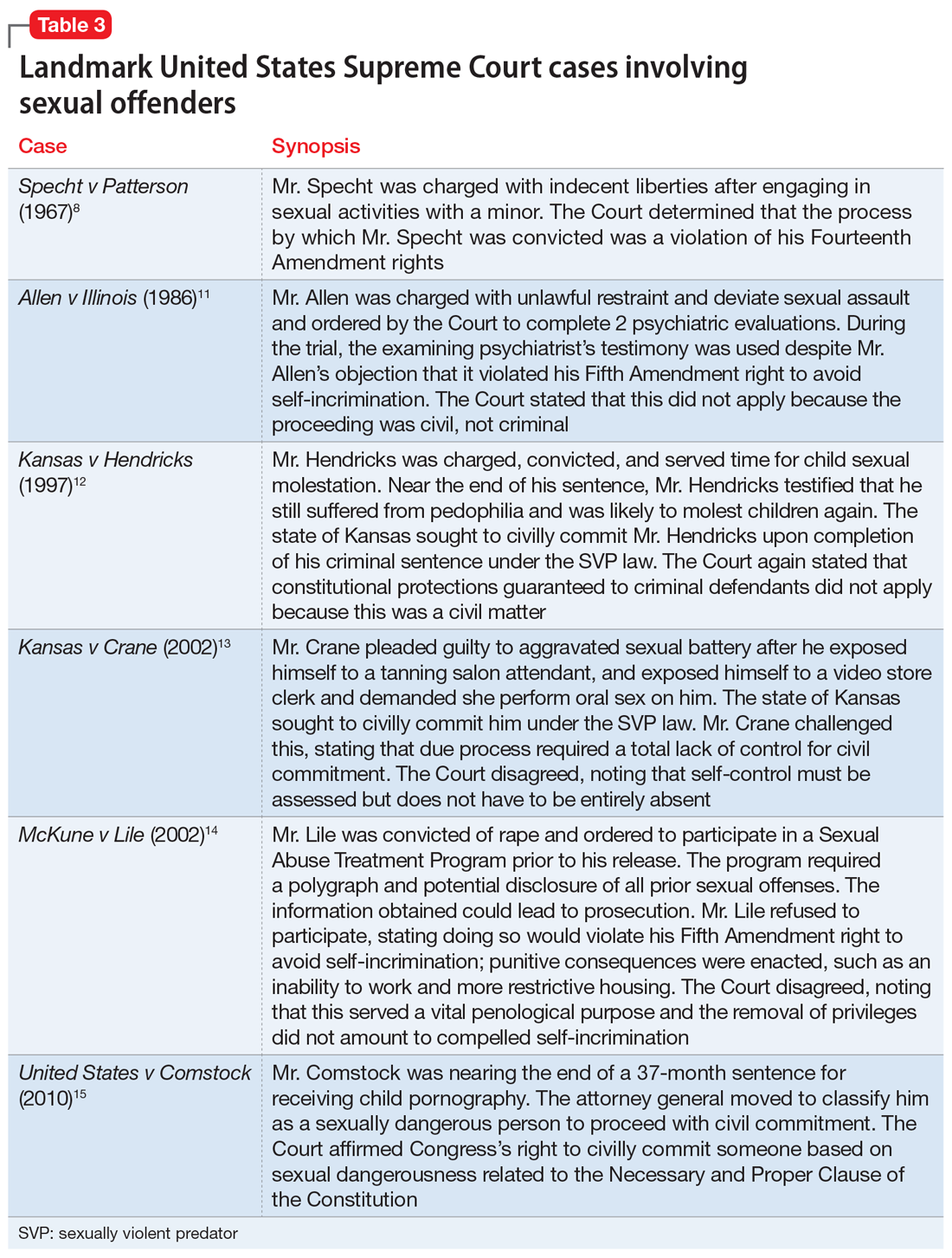
A series of United States Supreme Court cases solidified current sexual offender civil commitment laws (Table 38,11-15).
Continue to: Allen v Illinois
Allen v Illinois (1986).11 The Court ruled that forcing an individual to participate in a psychiatric evaluation prior to a sexually dangerous person’s commitment hearing did not violate the individual’s Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination because the purpose of the evaluation was to provide treatment, not punishment.
Kansas v Hendricks (1997).12 The Court upheld that the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act was constitutional and noted that the use of the broad term “mental abnormality” (in lieu of the more specific term “mental illness”) does not violate an individual’s Fourteenth Amendment right to substantive due process. Additionally, the Court opined that the constitutional ban on double jeopardy and ex post facto lawmaking does not apply because the procedures are civil, not criminal.
Kansas v Crane (2002).13 The Court upheld the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act, stating that mental illness and dangerousness are essential elements to meet the criteria for civil commitment. The Court added that proof of partial (not total) “volitional impairment” is all that is required to meet the threshold of sexual dangerousness.
McKune v Lile (2002).14 The Court ruled that a policy requiring participation in polygraph testing, which would lead to the disclosure of sexual crimes (even those that have not been prosecuted), does not violate an individual’s Fifth Amendment rights because it serves a vital penological purpose.
Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 200616; United States v Comstock (2010).15 This act and subsequent case reinforced the federal government’s right to civilly commit sexually dangerous persons approaching the end of their prison sentences.
Continue to: What is requiried for civil commitment?
What is required for civil commitment?
SVP laws require 4 conditions to be met for the civil commitment of sexual offenders (Table 417). In criteria 1, “charges” is a key word, because this allows individuals found Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity or Incompetent to Stand Trial to be civilly committed. Criteria 2 defines “mental abnormality” as a “congenital or acquired condition affecting the emotional or volitional capacity which predisposes the person to commit criminal sexual acts in a degree constituting such person a menace to the health and safety of others.”18 This is a broad definition, and allows individuals with personality disorders to be civilly committed (although most sexual offenders are committed for having a paraphilic disorder). To determine risk, various actuarial instruments are used to assess for sexually violent recidivism, including (but not limited to) the Static-99R, Sexual Violence Risk-20, and the Sex Offender Risk Appraisal Guide.19
Although the percentages vary, sex offenders rarely are civilly committed following their criminal sentence. In California, approximately 1.5% of sex offenders are civilly committed.17 The standard of proof for civil commitment varies by state between “clear and convincing evidence” and “beyond a reasonable doubt.” As sex offenders approach the end of their sentence, sexually violent offenders are identified to the general population and referred for a psychiatric evaluation. If the individual meets the 4 criteria for commitment (Table 417), their case is sent to the prosecuting attorney’s office. If accepted, the court holds a probable cause hearing, followed by a full trial.
Pornography and sex offenders
Pornography has long been considered a risk factor for sexual offending, and the role of pornography in influencing sexual behavior has drawn recent interest in research towards predicting future offenses. However, a 2019 systematic review by Mellor et al20 on the relationship between pornography and sexual offending suggested that early exposure to pornography is not a risk factor for sexual offending, nor is the risk of offending increased shortly after pornography exposure. Additionally, pornography use did not predict recidivism in low-risk sexual offenders, but did in high-risk offenders.
The use of child pornography presents a set of new risk factors. Prohibited by federal and state law, child pornography is defined under Section 2256 of Title 18, United States Code, as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (someone <age 18). Visual depictions include photographs, videos, digital or computer-generated images indistinguishable from an actual minor, and images created to depict a minor. The law does not require an image of a child engaging in sexual activity for the image to be characterized as child pornography. Offenders are also commonly charged with the distribution of child pornography. A conviction of child pornography possession carries a 15- to 30-year sentence, and distribution carries a 5- to 20-year sentence.21 The individual must also file for the sex offender registry, which may restrict their employment and place of residency.
It is unclear what percentage of individuals charged with child pornography have a history of prior sexual offenses. Numerous studies suggest there is a low risk of online offenders without prior offenses becoming contact offenders. Characteristics of online-only offenders include being White, a single male, age 20 to 30, well-educated, and employed, and having antisocial traits and a history of sexual deviancy.22 Contact offenders tend to be married with easy access to children, unemployed, uneducated, and to have a history of mental illness or criminal offenses.22
Continue to: Recidivism and treatment
Recidivism and treatment
The recidivism rate among sexual offenders averages 13.7% at 3- to 6-year follow-up,although rates vary by type of sexual offense.23 Individuals who committed rape have the highest rate of recidivism, while those who engaged in incest have the lowest. Three key points about sexual offender recidivism are:
- it declines over time and with increased age.
- sexual offenders are more like to commit a nonsexual offense than a sexual offense.
- sexual offenders who have undergone treatment are 26.3% less likely to reoffend.23
Although there is no standard of treatment, current interventions include external control, reduction of sexual drive, treatment of comorbid conditions, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and dynamic psychotherapy. External control relies on an outside entity that affects the individual’s behavior. For sexually deviant behaviors, simply making the act illegal or involving the law may inhibit many individuals from acting on a thought. Additional external control may include pharmacotherapy, which ranges from nonhormonal options such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to hormonal options. Therapy tends to focus on social skills training, sex education, cognitive restructuring, and identifying triggers, as well as victim empathy. The best indicators for successful treatment include an absence of comorbidities, increased age, and adult interpersonal relationships.24
Treatment choice may be predicated on the severity of the paraphilia. Psychotherapy alone is recommended for individuals able to maintain functioning if it does not affect their conventional sexual activity. Common treatment for low-risk individuals is psychotherapy and an SSRI. As risk increases, so does treatment with pharmacologic agents. Beyond SSRIs, moderate offenders may be treated with an SSRI and a low-dose antiandrogen. This is escalated in high-risk violent offenders to long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs and synthetic steroidal analogs.25
An evolving class of disorders
With the evolution and accessibility of pornography, uncommon sexual practices have become more common, gaining notoriety and increased social acceptance. As a result, mental health professionals may be tasked with evaluating patients for possible paraphilic disorders. A common misconception is that individuals with sexually deviant thoughts, sexual offenders, and patients with paraphilic disorders are all the same. However, more commonly, sexual offenders do not have a paraphilic disorder. In the case of SVPs, outside of imprisonment, civil commitment remains a consideration for possible treatment. To meet the threshold of civil commitment, a sexual offender must have a “mental abnormality,” which is most commonly a paraphilic disorder. The treatment of paraphilic disorders remains a difficult task and includes a mixture of psychotherapy and medication options.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. J begins weekly CBT to gain control of his voyeuristic fantasies without impacting his conventional sexual activity and desire. He responds well to treatment, and after 18 months, begins a typical sexual relationship with a woman. Although his voyeuristic thoughts remain, the urge to act on the thoughts decreases as Mr. J develops coping mechanisms. He does not require pharmacologic treatment.
Bottom Line
Individuals with paraphilic disorders are too often portrayed as sexual deviants or criminals. Psychiatrists must review each case with careful consideration of individual risk factors, such as the patient’s sexual history, to evaluate potential treatment options while determining if they pose a threat to the public.
Related Resources
- Sorrentino R, Abramowitz J. Minor-attracted persons: a neglected population. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(7):21-27. doi:10.12788/cp.0149
- Berlin FS. Paraphilic disorders: a better understanding. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):22-26,28.
1. Federoff JP. The paraphilias. In: Gelder MG, Andreasen NC, López-Ibor JJ Jr, Geddes JR, eds. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2012:832-842.
2. Grubin D. Medical models and interventions in sexual deviance. In: Laws R, O’Donohue WT, eds. Sexual Deviance: Theory, Assessment and Treatment. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 2008:594-610.
3. Guidry LL, Saleh FM. Clinical considerations of paraphilic sex offenders with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2004;11(1-2):21-34.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
5. Balon R. Paraphilic disorders. In: Roberts LW, Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:749-770.
6. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Paraphilic disorders. Kaplan and Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry. 11th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2015:593-599.
7. First MB, Halon RL. Use of DSM paraphilia diagnosis in sexually violent predator commitment cases. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2008;36(4):443-454.
8. Specht v Patterson, 386 US 605 (1967).
9. Ra EP. The civil confinement of sexual predators: a delicate balance. J Civ Rts Econ Dev. 2007;22(1):335-372.
10. Felthous AR, Ko J. Sexually violent predator law in the United States. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2018;28(4):159-173.
11. Allen v Illinois, 478 US 364 (1986).
12. Kansas v Hendricks, 521 US 346 (1997).
13. Kansas v Crane, 534 US 407 (2002).
14. McKune v Lile, 536 US 24 (2002).
15. United States v Comstock, 560 US 126 (2010).
16. Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 2006, HR 4472, 109th Cong (2006). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/4472
17. Tucker DE, Brakel SJ. Sexually violent predator laws. In: Rosner R, Scott C, eds. Principles and Practice of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. CRC Press; 2017:823-831.
18. Wash. Rev. Code. Ann. §71.09.020(8)
19. Bradford J, de Amorim Levin GV, Booth BD, et al. Forensic assessment of sex offenders. In: Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2017:382-397.
20. Mellor E, Duff S. The use of pornography and the relationship between pornography exposure and sexual offending in males: a systematic review. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;46:116-126.
21. Failure To Register, 18 USC § 2250 (2012). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap109B-sec2250
22. Hirschtritt ME, Tucker D, Binder RL. Risk assessment of online child sexual exploitation offenders. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2019;47(2):155-164.
23. Blasko BL. Overview of sexual offender typologies, recidivism, and treatment. In: Jeglic EL, Calkins C, eds. Sexual Violence: Evidence Based Policy and Prevention. Springer; 2016:11-29.
24. Thibaut F, Cosyns P, Fedoroff JP, et al; WFSBP Task Force on Paraphilias. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) 2020 guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of paraphilic disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(6):412-490.
25. Holoyda B. Paraphilias: from diagnosis to treatment. Psychiatric Times. 2019;36(12).
Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5

Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...
Paraphilic disorders are more common in men than in women; the 2 most prevalent are voyeuristic disorder and frotteuristic disorder.6 The incidence of paraphilias in the general outpatient setting varies by disorder. Approximately 45% of individuals with pedophilic disorder seek treatment, whereas only 1% of individuals with zoophilia seek treatment.6 The incidence of paraphilic acts also varies drastically; individuals with exhibitionistic disorder engaged in an average of 50 acts vs only 3 for individuals with sexual sadism.6 Not all individuals with paraphilic disorders commit crimes. Approximately 58% of sexual offenders meet the criteria for a paraphilic disorder, but antisocial personality disorder is a far more common diagnosis.7
Sexual psychopath statutes: Phase 1
In 1937, Michigan became the first state to enact sexual psychopath statutes, allowing for indeterminate sentencing and the civil commitment/treatment of sex offenders with repeated convictions. By the 1970s, more than 30 states had enacted similar statutes. It was not until 1967, in Specht v Patterson,8 that the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment Due Process Clause was violated when Francis Eddie Specht faced life in prison following his conviction for indecent liberties under the Colorado Sex Offenders Act.
Specht was convicted in 1959 for indecent liberties after pleading guilty to enticing a child younger than age 16 into an office and engaging in sexual activities with them. At the time of Specht’s conviction, the crime of indecent liberties carried a punishment of 10 years. However, Specht was sentenced under the Sexual Offenders Act, which allowed for an indeterminate sentence of 1 day to life in prison. The Supreme Court noted that Specht was denied the right to be present with counsel, to confront the evidence against him, to cross-examine witnesses, and to offer his own evidence, which was a violation of his constitutionally guaranteed Fourteenth Amendment right to Procedural Due Process. The decision led most states to repeal early sexual psychopath statutes.8
Sexually violent predator laws: Phase 2
After early sexual psychopath statutes were repealed, many states pushed to update sex offender laws in response to the Earl Shriner case.9 In 1989, Shriner was released from prison after serving a 10-year sentence for sexually assaulting 2 teenage girls. At the time, he did not meet the criteria for civil commitment in the state of Washington. On the day he was released, Shriner cut off a young boy’s penis and left him to die. Washington subsequently became the first of many states to enact sexually violent predator (SVP) laws. Table 210 shows states and districts that have SVP civil commitment laws.

A series of United States Supreme Court cases solidified current sexual offender civil commitment laws (Table 38,11-15).

Continue to: Allen v Illinois
Allen v Illinois (1986).11 The Court ruled that forcing an individual to participate in a psychiatric evaluation prior to a sexually dangerous person’s commitment hearing did not violate the individual’s Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination because the purpose of the evaluation was to provide treatment, not punishment.
Kansas v Hendricks (1997).12 The Court upheld that the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act was constitutional and noted that the use of the broad term “mental abnormality” (in lieu of the more specific term “mental illness”) does not violate an individual’s Fourteenth Amendment right to substantive due process. Additionally, the Court opined that the constitutional ban on double jeopardy and ex post facto lawmaking does not apply because the procedures are civil, not criminal.
Kansas v Crane (2002).13 The Court upheld the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act, stating that mental illness and dangerousness are essential elements to meet the criteria for civil commitment. The Court added that proof of partial (not total) “volitional impairment” is all that is required to meet the threshold of sexual dangerousness.
McKune v Lile (2002).14 The Court ruled that a policy requiring participation in polygraph testing, which would lead to the disclosure of sexual crimes (even those that have not been prosecuted), does not violate an individual’s Fifth Amendment rights because it serves a vital penological purpose.
Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 200616; United States v Comstock (2010).15 This act and subsequent case reinforced the federal government’s right to civilly commit sexually dangerous persons approaching the end of their prison sentences.
Continue to: What is requiried for civil commitment?
What is required for civil commitment?
SVP laws require 4 conditions to be met for the civil commitment of sexual offenders (Table 417). In criteria 1, “charges” is a key word, because this allows individuals found Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity or Incompetent to Stand Trial to be civilly committed. Criteria 2 defines “mental abnormality” as a “congenital or acquired condition affecting the emotional or volitional capacity which predisposes the person to commit criminal sexual acts in a degree constituting such person a menace to the health and safety of others.”18 This is a broad definition, and allows individuals with personality disorders to be civilly committed (although most sexual offenders are committed for having a paraphilic disorder). To determine risk, various actuarial instruments are used to assess for sexually violent recidivism, including (but not limited to) the Static-99R, Sexual Violence Risk-20, and the Sex Offender Risk Appraisal Guide.19
Although the percentages vary, sex offenders rarely are civilly committed following their criminal sentence. In California, approximately 1.5% of sex offenders are civilly committed.17 The standard of proof for civil commitment varies by state between “clear and convincing evidence” and “beyond a reasonable doubt.” As sex offenders approach the end of their sentence, sexually violent offenders are identified to the general population and referred for a psychiatric evaluation. If the individual meets the 4 criteria for commitment (Table 417), their case is sent to the prosecuting attorney’s office. If accepted, the court holds a probable cause hearing, followed by a full trial.
Pornography and sex offenders
Pornography has long been considered a risk factor for sexual offending, and the role of pornography in influencing sexual behavior has drawn recent interest in research towards predicting future offenses. However, a 2019 systematic review by Mellor et al20 on the relationship between pornography and sexual offending suggested that early exposure to pornography is not a risk factor for sexual offending, nor is the risk of offending increased shortly after pornography exposure. Additionally, pornography use did not predict recidivism in low-risk sexual offenders, but did in high-risk offenders.
The use of child pornography presents a set of new risk factors. Prohibited by federal and state law, child pornography is defined under Section 2256 of Title 18, United States Code, as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (someone <age 18). Visual depictions include photographs, videos, digital or computer-generated images indistinguishable from an actual minor, and images created to depict a minor. The law does not require an image of a child engaging in sexual activity for the image to be characterized as child pornography. Offenders are also commonly charged with the distribution of child pornography. A conviction of child pornography possession carries a 15- to 30-year sentence, and distribution carries a 5- to 20-year sentence.21 The individual must also file for the sex offender registry, which may restrict their employment and place of residency.
It is unclear what percentage of individuals charged with child pornography have a history of prior sexual offenses. Numerous studies suggest there is a low risk of online offenders without prior offenses becoming contact offenders. Characteristics of online-only offenders include being White, a single male, age 20 to 30, well-educated, and employed, and having antisocial traits and a history of sexual deviancy.22 Contact offenders tend to be married with easy access to children, unemployed, uneducated, and to have a history of mental illness or criminal offenses.22
Continue to: Recidivism and treatment
Recidivism and treatment
The recidivism rate among sexual offenders averages 13.7% at 3- to 6-year follow-up,although rates vary by type of sexual offense.23 Individuals who committed rape have the highest rate of recidivism, while those who engaged in incest have the lowest. Three key points about sexual offender recidivism are:
- it declines over time and with increased age.
- sexual offenders are more like to commit a nonsexual offense than a sexual offense.
- sexual offenders who have undergone treatment are 26.3% less likely to reoffend.23
Although there is no standard of treatment, current interventions include external control, reduction of sexual drive, treatment of comorbid conditions, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and dynamic psychotherapy. External control relies on an outside entity that affects the individual’s behavior. For sexually deviant behaviors, simply making the act illegal or involving the law may inhibit many individuals from acting on a thought. Additional external control may include pharmacotherapy, which ranges from nonhormonal options such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to hormonal options. Therapy tends to focus on social skills training, sex education, cognitive restructuring, and identifying triggers, as well as victim empathy. The best indicators for successful treatment include an absence of comorbidities, increased age, and adult interpersonal relationships.24
Treatment choice may be predicated on the severity of the paraphilia. Psychotherapy alone is recommended for individuals able to maintain functioning if it does not affect their conventional sexual activity. Common treatment for low-risk individuals is psychotherapy and an SSRI. As risk increases, so does treatment with pharmacologic agents. Beyond SSRIs, moderate offenders may be treated with an SSRI and a low-dose antiandrogen. This is escalated in high-risk violent offenders to long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs and synthetic steroidal analogs.25
An evolving class of disorders
With the evolution and accessibility of pornography, uncommon sexual practices have become more common, gaining notoriety and increased social acceptance. As a result, mental health professionals may be tasked with evaluating patients for possible paraphilic disorders. A common misconception is that individuals with sexually deviant thoughts, sexual offenders, and patients with paraphilic disorders are all the same. However, more commonly, sexual offenders do not have a paraphilic disorder. In the case of SVPs, outside of imprisonment, civil commitment remains a consideration for possible treatment. To meet the threshold of civil commitment, a sexual offender must have a “mental abnormality,” which is most commonly a paraphilic disorder. The treatment of paraphilic disorders remains a difficult task and includes a mixture of psychotherapy and medication options.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. J begins weekly CBT to gain control of his voyeuristic fantasies without impacting his conventional sexual activity and desire. He responds well to treatment, and after 18 months, begins a typical sexual relationship with a woman. Although his voyeuristic thoughts remain, the urge to act on the thoughts decreases as Mr. J develops coping mechanisms. He does not require pharmacologic treatment.
Bottom Line
Individuals with paraphilic disorders are too often portrayed as sexual deviants or criminals. Psychiatrists must review each case with careful consideration of individual risk factors, such as the patient’s sexual history, to evaluate potential treatment options while determining if they pose a threat to the public.
Related Resources
- Sorrentino R, Abramowitz J. Minor-attracted persons: a neglected population. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(7):21-27. doi:10.12788/cp.0149
- Berlin FS. Paraphilic disorders: a better understanding. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):22-26,28.
Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5

Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...
Paraphilic disorders are more common in men than in women; the 2 most prevalent are voyeuristic disorder and frotteuristic disorder.6 The incidence of paraphilias in the general outpatient setting varies by disorder. Approximately 45% of individuals with pedophilic disorder seek treatment, whereas only 1% of individuals with zoophilia seek treatment.6 The incidence of paraphilic acts also varies drastically; individuals with exhibitionistic disorder engaged in an average of 50 acts vs only 3 for individuals with sexual sadism.6 Not all individuals with paraphilic disorders commit crimes. Approximately 58% of sexual offenders meet the criteria for a paraphilic disorder, but antisocial personality disorder is a far more common diagnosis.7
Sexual psychopath statutes: Phase 1
In 1937, Michigan became the first state to enact sexual psychopath statutes, allowing for indeterminate sentencing and the civil commitment/treatment of sex offenders with repeated convictions. By the 1970s, more than 30 states had enacted similar statutes. It was not until 1967, in Specht v Patterson,8 that the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment Due Process Clause was violated when Francis Eddie Specht faced life in prison following his conviction for indecent liberties under the Colorado Sex Offenders Act.
Specht was convicted in 1959 for indecent liberties after pleading guilty to enticing a child younger than age 16 into an office and engaging in sexual activities with them. At the time of Specht’s conviction, the crime of indecent liberties carried a punishment of 10 years. However, Specht was sentenced under the Sexual Offenders Act, which allowed for an indeterminate sentence of 1 day to life in prison. The Supreme Court noted that Specht was denied the right to be present with counsel, to confront the evidence against him, to cross-examine witnesses, and to offer his own evidence, which was a violation of his constitutionally guaranteed Fourteenth Amendment right to Procedural Due Process. The decision led most states to repeal early sexual psychopath statutes.8
Sexually violent predator laws: Phase 2
After early sexual psychopath statutes were repealed, many states pushed to update sex offender laws in response to the Earl Shriner case.9 In 1989, Shriner was released from prison after serving a 10-year sentence for sexually assaulting 2 teenage girls. At the time, he did not meet the criteria for civil commitment in the state of Washington. On the day he was released, Shriner cut off a young boy’s penis and left him to die. Washington subsequently became the first of many states to enact sexually violent predator (SVP) laws. Table 210 shows states and districts that have SVP civil commitment laws.

A series of United States Supreme Court cases solidified current sexual offender civil commitment laws (Table 38,11-15).

Continue to: Allen v Illinois
Allen v Illinois (1986).11 The Court ruled that forcing an individual to participate in a psychiatric evaluation prior to a sexually dangerous person’s commitment hearing did not violate the individual’s Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination because the purpose of the evaluation was to provide treatment, not punishment.
Kansas v Hendricks (1997).12 The Court upheld that the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act was constitutional and noted that the use of the broad term “mental abnormality” (in lieu of the more specific term “mental illness”) does not violate an individual’s Fourteenth Amendment right to substantive due process. Additionally, the Court opined that the constitutional ban on double jeopardy and ex post facto lawmaking does not apply because the procedures are civil, not criminal.
Kansas v Crane (2002).13 The Court upheld the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act, stating that mental illness and dangerousness are essential elements to meet the criteria for civil commitment. The Court added that proof of partial (not total) “volitional impairment” is all that is required to meet the threshold of sexual dangerousness.
McKune v Lile (2002).14 The Court ruled that a policy requiring participation in polygraph testing, which would lead to the disclosure of sexual crimes (even those that have not been prosecuted), does not violate an individual’s Fifth Amendment rights because it serves a vital penological purpose.
Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 200616; United States v Comstock (2010).15 This act and subsequent case reinforced the federal government’s right to civilly commit sexually dangerous persons approaching the end of their prison sentences.
Continue to: What is requiried for civil commitment?
What is required for civil commitment?
SVP laws require 4 conditions to be met for the civil commitment of sexual offenders (Table 417). In criteria 1, “charges” is a key word, because this allows individuals found Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity or Incompetent to Stand Trial to be civilly committed. Criteria 2 defines “mental abnormality” as a “congenital or acquired condition affecting the emotional or volitional capacity which predisposes the person to commit criminal sexual acts in a degree constituting such person a menace to the health and safety of others.”18 This is a broad definition, and allows individuals with personality disorders to be civilly committed (although most sexual offenders are committed for having a paraphilic disorder). To determine risk, various actuarial instruments are used to assess for sexually violent recidivism, including (but not limited to) the Static-99R, Sexual Violence Risk-20, and the Sex Offender Risk Appraisal Guide.19
Although the percentages vary, sex offenders rarely are civilly committed following their criminal sentence. In California, approximately 1.5% of sex offenders are civilly committed.17 The standard of proof for civil commitment varies by state between “clear and convincing evidence” and “beyond a reasonable doubt.” As sex offenders approach the end of their sentence, sexually violent offenders are identified to the general population and referred for a psychiatric evaluation. If the individual meets the 4 criteria for commitment (Table 417), their case is sent to the prosecuting attorney’s office. If accepted, the court holds a probable cause hearing, followed by a full trial.
Pornography and sex offenders
Pornography has long been considered a risk factor for sexual offending, and the role of pornography in influencing sexual behavior has drawn recent interest in research towards predicting future offenses. However, a 2019 systematic review by Mellor et al20 on the relationship between pornography and sexual offending suggested that early exposure to pornography is not a risk factor for sexual offending, nor is the risk of offending increased shortly after pornography exposure. Additionally, pornography use did not predict recidivism in low-risk sexual offenders, but did in high-risk offenders.
The use of child pornography presents a set of new risk factors. Prohibited by federal and state law, child pornography is defined under Section 2256 of Title 18, United States Code, as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (someone <age 18). Visual depictions include photographs, videos, digital or computer-generated images indistinguishable from an actual minor, and images created to depict a minor. The law does not require an image of a child engaging in sexual activity for the image to be characterized as child pornography. Offenders are also commonly charged with the distribution of child pornography. A conviction of child pornography possession carries a 15- to 30-year sentence, and distribution carries a 5- to 20-year sentence.21 The individual must also file for the sex offender registry, which may restrict their employment and place of residency.
It is unclear what percentage of individuals charged with child pornography have a history of prior sexual offenses. Numerous studies suggest there is a low risk of online offenders without prior offenses becoming contact offenders. Characteristics of online-only offenders include being White, a single male, age 20 to 30, well-educated, and employed, and having antisocial traits and a history of sexual deviancy.22 Contact offenders tend to be married with easy access to children, unemployed, uneducated, and to have a history of mental illness or criminal offenses.22
Continue to: Recidivism and treatment
Recidivism and treatment
The recidivism rate among sexual offenders averages 13.7% at 3- to 6-year follow-up,although rates vary by type of sexual offense.23 Individuals who committed rape have the highest rate of recidivism, while those who engaged in incest have the lowest. Three key points about sexual offender recidivism are:
- it declines over time and with increased age.
- sexual offenders are more like to commit a nonsexual offense than a sexual offense.
- sexual offenders who have undergone treatment are 26.3% less likely to reoffend.23
Although there is no standard of treatment, current interventions include external control, reduction of sexual drive, treatment of comorbid conditions, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and dynamic psychotherapy. External control relies on an outside entity that affects the individual’s behavior. For sexually deviant behaviors, simply making the act illegal or involving the law may inhibit many individuals from acting on a thought. Additional external control may include pharmacotherapy, which ranges from nonhormonal options such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to hormonal options. Therapy tends to focus on social skills training, sex education, cognitive restructuring, and identifying triggers, as well as victim empathy. The best indicators for successful treatment include an absence of comorbidities, increased age, and adult interpersonal relationships.24
Treatment choice may be predicated on the severity of the paraphilia. Psychotherapy alone is recommended for individuals able to maintain functioning if it does not affect their conventional sexual activity. Common treatment for low-risk individuals is psychotherapy and an SSRI. As risk increases, so does treatment with pharmacologic agents. Beyond SSRIs, moderate offenders may be treated with an SSRI and a low-dose antiandrogen. This is escalated in high-risk violent offenders to long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs and synthetic steroidal analogs.25
An evolving class of disorders
With the evolution and accessibility of pornography, uncommon sexual practices have become more common, gaining notoriety and increased social acceptance. As a result, mental health professionals may be tasked with evaluating patients for possible paraphilic disorders. A common misconception is that individuals with sexually deviant thoughts, sexual offenders, and patients with paraphilic disorders are all the same. However, more commonly, sexual offenders do not have a paraphilic disorder. In the case of SVPs, outside of imprisonment, civil commitment remains a consideration for possible treatment. To meet the threshold of civil commitment, a sexual offender must have a “mental abnormality,” which is most commonly a paraphilic disorder. The treatment of paraphilic disorders remains a difficult task and includes a mixture of psychotherapy and medication options.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. J begins weekly CBT to gain control of his voyeuristic fantasies without impacting his conventional sexual activity and desire. He responds well to treatment, and after 18 months, begins a typical sexual relationship with a woman. Although his voyeuristic thoughts remain, the urge to act on the thoughts decreases as Mr. J develops coping mechanisms. He does not require pharmacologic treatment.
Bottom Line
Individuals with paraphilic disorders are too often portrayed as sexual deviants or criminals. Psychiatrists must review each case with careful consideration of individual risk factors, such as the patient’s sexual history, to evaluate potential treatment options while determining if they pose a threat to the public.
Related Resources
- Sorrentino R, Abramowitz J. Minor-attracted persons: a neglected population. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(7):21-27. doi:10.12788/cp.0149
- Berlin FS. Paraphilic disorders: a better understanding. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):22-26,28.
1. Federoff JP. The paraphilias. In: Gelder MG, Andreasen NC, López-Ibor JJ Jr, Geddes JR, eds. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2012:832-842.
2. Grubin D. Medical models and interventions in sexual deviance. In: Laws R, O’Donohue WT, eds. Sexual Deviance: Theory, Assessment and Treatment. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 2008:594-610.
3. Guidry LL, Saleh FM. Clinical considerations of paraphilic sex offenders with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2004;11(1-2):21-34.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
5. Balon R. Paraphilic disorders. In: Roberts LW, Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:749-770.
6. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Paraphilic disorders. Kaplan and Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry. 11th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2015:593-599.
7. First MB, Halon RL. Use of DSM paraphilia diagnosis in sexually violent predator commitment cases. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2008;36(4):443-454.
8. Specht v Patterson, 386 US 605 (1967).
9. Ra EP. The civil confinement of sexual predators: a delicate balance. J Civ Rts Econ Dev. 2007;22(1):335-372.
10. Felthous AR, Ko J. Sexually violent predator law in the United States. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2018;28(4):159-173.
11. Allen v Illinois, 478 US 364 (1986).
12. Kansas v Hendricks, 521 US 346 (1997).
13. Kansas v Crane, 534 US 407 (2002).
14. McKune v Lile, 536 US 24 (2002).
15. United States v Comstock, 560 US 126 (2010).
16. Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 2006, HR 4472, 109th Cong (2006). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/4472
17. Tucker DE, Brakel SJ. Sexually violent predator laws. In: Rosner R, Scott C, eds. Principles and Practice of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. CRC Press; 2017:823-831.
18. Wash. Rev. Code. Ann. §71.09.020(8)
19. Bradford J, de Amorim Levin GV, Booth BD, et al. Forensic assessment of sex offenders. In: Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2017:382-397.
20. Mellor E, Duff S. The use of pornography and the relationship between pornography exposure and sexual offending in males: a systematic review. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;46:116-126.
21. Failure To Register, 18 USC § 2250 (2012). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap109B-sec2250
22. Hirschtritt ME, Tucker D, Binder RL. Risk assessment of online child sexual exploitation offenders. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2019;47(2):155-164.
23. Blasko BL. Overview of sexual offender typologies, recidivism, and treatment. In: Jeglic EL, Calkins C, eds. Sexual Violence: Evidence Based Policy and Prevention. Springer; 2016:11-29.
24. Thibaut F, Cosyns P, Fedoroff JP, et al; WFSBP Task Force on Paraphilias. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) 2020 guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of paraphilic disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(6):412-490.
25. Holoyda B. Paraphilias: from diagnosis to treatment. Psychiatric Times. 2019;36(12).
1. Federoff JP. The paraphilias. In: Gelder MG, Andreasen NC, López-Ibor JJ Jr, Geddes JR, eds. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2012:832-842.
2. Grubin D. Medical models and interventions in sexual deviance. In: Laws R, O’Donohue WT, eds. Sexual Deviance: Theory, Assessment and Treatment. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 2008:594-610.
3. Guidry LL, Saleh FM. Clinical considerations of paraphilic sex offenders with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2004;11(1-2):21-34.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
5. Balon R. Paraphilic disorders. In: Roberts LW, Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:749-770.
6. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Paraphilic disorders. Kaplan and Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry. 11th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2015:593-599.
7. First MB, Halon RL. Use of DSM paraphilia diagnosis in sexually violent predator commitment cases. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2008;36(4):443-454.
8. Specht v Patterson, 386 US 605 (1967).
9. Ra EP. The civil confinement of sexual predators: a delicate balance. J Civ Rts Econ Dev. 2007;22(1):335-372.
10. Felthous AR, Ko J. Sexually violent predator law in the United States. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2018;28(4):159-173.
11. Allen v Illinois, 478 US 364 (1986).
12. Kansas v Hendricks, 521 US 346 (1997).
13. Kansas v Crane, 534 US 407 (2002).
14. McKune v Lile, 536 US 24 (2002).
15. United States v Comstock, 560 US 126 (2010).
16. Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 2006, HR 4472, 109th Cong (2006). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/4472
17. Tucker DE, Brakel SJ. Sexually violent predator laws. In: Rosner R, Scott C, eds. Principles and Practice of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. CRC Press; 2017:823-831.
18. Wash. Rev. Code. Ann. §71.09.020(8)
19. Bradford J, de Amorim Levin GV, Booth BD, et al. Forensic assessment of sex offenders. In: Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2017:382-397.
20. Mellor E, Duff S. The use of pornography and the relationship between pornography exposure and sexual offending in males: a systematic review. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;46:116-126.
21. Failure To Register, 18 USC § 2250 (2012). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap109B-sec2250
22. Hirschtritt ME, Tucker D, Binder RL. Risk assessment of online child sexual exploitation offenders. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2019;47(2):155-164.
23. Blasko BL. Overview of sexual offender typologies, recidivism, and treatment. In: Jeglic EL, Calkins C, eds. Sexual Violence: Evidence Based Policy and Prevention. Springer; 2016:11-29.
24. Thibaut F, Cosyns P, Fedoroff JP, et al; WFSBP Task Force on Paraphilias. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) 2020 guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of paraphilic disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(6):412-490.
25. Holoyda B. Paraphilias: from diagnosis to treatment. Psychiatric Times. 2019;36(12).
Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: A hypothesis (Part 2)
There is a need to connect mental and physical symptoms in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. Obviously, we are not yet equipped to clearly recognize which neurotransmitters cause which symptoms. The science of defining the underlying mechanisms is lagging behind the clinical needs. However, in this article, we present a few hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms in order to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. Our descriptions do not reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by these neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known (or suspected). Additional research is needed to confirm or disprove the hypotheses we present.
In Part 1 (

Endorphin excess (Table 11-16)
Ms. R is a frustrated chronic pain patient who bitterly complains that despite having seen more than 20 physicians, she does not have an answer to what causes her “all over” pain and headache.4,5,11 She does not believe that all her laboratory test are normal, and insists that “something is missing.” She aches all over but says she can actually tolerate more pain than others and experiences only a little discomfort during an electromyogram or dental interventions. Though Ms. R is not very susceptible to acute pain,4,5,9,16 pain all over without an identifiable cause is part of her life.4,5,11 She says that listening to music and social interactions help decrease her pain.4,5,10 Ms. R states that opioid medications do not help her pain, though she has a history of opioid overuse and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.6,11,16

Ms. R tends to overdo pleasureful activities to achieve satisfaction.2 She says exercise is particularly satisfying, to the point that she experiences euphoria and a loss of time.9 She is angry that her neurologist suggested she see a psychiatrist. Her depression bothers her more than her anxiety.2,5,7
Ms. R clearly has a self-image problem, alternating between high and low self-esteem. She has a low appetite1,12,14-16 and sleeps excessively.2,4,7,9,10 Her mother privately tells you that Ms. R has a history of childhood sexual abuse and lagged in life due to a lack of motivation. Ms. R used to self-mutilate “to feel normal.”12 Her primary care physician chronically addresses Ms. R’s poorly explained cholestasis and pruritus8 as well as dysregulation of blood pressure and heart rate, both of which tend to be low.12,13,16
Impression. Ms. R shows multiple symptoms associated with endorphin excess. A trial of an opioid antagonist may be reasonable. Dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression and also may be used for this patient. Using a low starting dose and a slow titration of such medications would be beneficial due to frequent intolerance issues, especially nausea. Gamma aminobutyric acid-ergic medications modulate the opioid system and may be considered. A serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) or mirtazapine may help patients such as Ms. R to control mood and pain through norepinephrine’s influence on endorphins.
Endorphin deficiency (Table 11,16-24)
Mr. J complains of low back pain, diffuse body pain, depression, and moodiness.19,20,24 He is sluggish and plagued by psychomotor retardation.24 All his life, a heightened perception of pain has caused him problems,19,20 but has not stopped him from engaging in self-mutilation
Continue to: Mr. J responds to treatment...
Mr. J responds to treatment with opioids16,20 but comments that his mood, and not necessarily his pain, improves when he takes these medications.20 He tends to overuse his pain medications, and had run into trouble with his previous pain management physician. Nitrous oxide is remarkably effective during dental procedures.19 Acupuncture helps to control his pain and mood.17 Exercise is also rewarding.18
Mr. J has difficulty achieving orgasm, a decreased sexual drive, and emotional sensitivity.24 He is impulsive.19,20,24 His baseline mood is low-grade; anxiety bothers him more than depression.23,24 Mr. J is thin, has a poor appetite,1,16 and sleeps poorly.24 His primary care physician struggles to help Mr. J to control dysregulation of his heart rate, blood pressure,21 and urinary retention,16,22 as well as episodes of hypoglycemia.1,16 He reluctantly admits to abusing alcohol, but explains that it helps with his mood and pain better than his prescribed medications.18,23
Impression. Mr. J exhibits multiple symptoms associated with endorphin deficiency. Short-term use of opioids is warranted, but he should avoid long-term opioid use, and he and his physician should work together to establish strict control of their intake. Buprenorphine would be the opioid of choice for such a patient. Psychiatric treatment, including for alcohol use disorder, should be a mandatory part of his treatment regimen. Behavioral therapy with a focus on finding healthy ways to achieve gratification would be effective. Alternative treatments such as acupuncture may be of value.
Norepinephrine excess (Table 216,25-30)
Mr. G comes to the office irritable and angry28,30 because no one can help him with his intractable headaches.
Comment. Norepinephrine and dopamine functions are connected through common neuronal and glial uptake mechanisms. This is a foundation of norepinephrine excess symptoms crossing over with symptoms of dopamine deficiency.
Continue to: Impression
Impression. Mr. G shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine excess. It is important to avoid caffeine intake in patients with clinical signs of excessive norepinephrine. Beta-blockers and alpha-2 agonists work well in patients such as Mr. G. Benzodiazepines indirectly decrease norepinephrine activity, but need to be used carefully due to the potential for misuse and addiction. In particular, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam must be avoided due to the induction of CNS instability with rapidly changing medication blood levels. Chlordiazepoxide may be a good choice for a patient such as Mr. G because it has the fewest adverse effects and the lowest abuse potential compared with other benzodiazepines. Avoid SNRIs in such a patient. Using mood-stabilizing antipsychotic medications may be especially warranted in treating Mr. G’s depression and pain.
Norepinephrine deficiency (Table 216,26,31-39)
Two years ago, Ms. A was diagnosed with chronic fatigue31 and fibromyalgia. She also had been diagnosed with depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). She presents with concerns of “brain fog,” no energy, low sex drive, and daytime sleepiness.33,35 Allodynia is widespread.16,36,37 Ms. A suffers from bulimia; she eats once a day but is still overweight.26 She has orthostatic hypotension in addition to baseline low blood pressure and bradycardia.16,38,39 Her pupils are almost pinpoint, even when she does not take opioid medications.
Comment. As mentioned earlier, because of the norepinephrine/dopamine relationship, symptoms of excess dopamine overlap with symptoms of norepinephrine deficiency.
Impression. Ms. A shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine deficiency. The use of noradrenergic antidepressants (such as SNRIs and mirtazapine)26 and stimulants may be warranted. Physical exercise, participating in social activities, massage, acupuncture, and family support may help with Ms. A’s pain as well as her depression, as might vasopressors.
In Part 3, we will address gamma aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of endorphins and norepinephrine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Arbuck DM, Salmerón JM, Mueller R. Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: a hypothesis (Part 1). Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):30-36. doi:10.12788/cp.0242
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
1. Applyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-1760.
2. Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;6(3):104-111.
3. Dabo F, Nyberg F, Qin Zhou, et al. Plasma levels of beta-endorphin during pregnancy and use of labor analgesia. Reprod Sci. 2010;17(8):742-747.
4. Dunbar RI, Kaskatis K, MacDonald I, et al. Performance of music elevates pain threshold and positive affect: implications for the evolutionary function of music. Evol Psychol. 2012;10(4):688-702.
5. Dunbar RIM, Baron R, Frangou A, et al. Social laughter is correlated with an elevated pain threshold. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1731):1161-1167.
6. Grisel JE, Bartels JL, Allen SA, et al. Influence of beta-Endorphin on anxious behavior in mice: interaction with EtOH. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;200(1):105-115.
7. Zorrilla EP, DeRubeis RJ, Redei E. High self-esteem, hardiness, and affective stability are associated with higher basal pituitary-adrenal hormone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20(6):591-601.
8. Li X, Zhu J, Tao Y, et al. Elevated endogenous opioids in obstructive jaundice: the possible skin mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2018;116:119-121.
9. Hicks SD, Jacob P, Perez O, et al. The transcriptional signature of a runner’s high. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):970-978.
10. Dunbar RIM. The anatomy of friendship. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(1):32-51.
11. Stephan BC, Parsa FD. Avoiding opioids and their harmful side effects in the postoperative patient: exogenous opioids, endogenous endorphins, wellness, mood, and their relation to postoperative pain. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2016;75(3):63-70.
12. Cuthbert BN, Holaday JW, Meyerhoff J, et al. Intravenous beta-endorphin: behavioral and physiological effects in conscious monkeys. Peptides. 1989;10(4):729-734.
13. Levin ER, Mills S, Weber MA. Endogenous opioids and opiate antagonists modulate the blood pressure of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Peptides. 1986;(6):977-981.
14. Davis JM, Lowy MT, Yim GK, et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and food intake in rats. Peptides. 1983;4(1):79-83.
15. Leibowitz SF, Hor L. Endorphinergic and alpha-noradrenergic systems in the paraventricular nucleus: effects on eating behavior. Peptides. 1982;3(3): 421-428.
16. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:587-588.
17. Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
18. Harte JL, Eifert GH, Smith R. The effects of running and meditation on beta-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone and cortisol in plasma, and on mood. Biol Psychol. 1995;40(3):251-265.
19. Petrizzo R, Mohr J, Mantione K, et al. The role of endogenous morphine and nitric oxide in pain management. Pract Pain Manag. 2014;14(9).
20. Sprouse-Blum AS, Smith G, Sugai D, et al. Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J. 2010;69(3):70-100.
21. Dontsov AV. The influence of deficit of endogenous neuropeptides on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2017;95(2):127-131. In Russian.
22. Dray A, Metsch R, Davis TP. Endorphins and the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Peptides. 1984;5(3):645-647.
23. Zalewska-Kaszubska J, Czarnecka E. Deficit in beta-endorphin peptide and tendency to alcohol abuse. Peptides. 2005;26(4):701-705.
24. McLay RN, Pan W, Kastin AJ. Effects of peptides on animal and human behavior: a review of studies published in the first twenty years of the journal Peptides. Peptides. 2001;22(12):2181-2255.
25. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st ed. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:424-428.
26. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
27. Winklewski PJ, Radkowski M, Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, et al. Stress response, brain noradrenergic system and cognition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;980:67-74.
28. McCall JG, Al-Hasani R, Siuda ER, et al. Engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron. 2015;87(3):605-620.
29. Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, Wolf J, Szarmach A, et al. Central sympathetic nervous system reinforcement in obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;39:143-154.
30. Yamamoto K, Shinba T, Yoshii M. Psychiatric symptoms of noradrenergic dysfunction: a pathophysiological view. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;201(68):1-20.
31. Stone EA, Lin Y, Sarfraz Y, et al. The role of the central noradrenergic system in behavioral inhibition. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):193-208.
32. Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C. Effect of the alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist mirtazapine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine system in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:861-871.
33. De Carvalho D, Patrone LG, Taxini CL, et al. Neurochemical and electrical modulation of the locus coeruleus: contribution to CO2 drive to breathe. Front Physiol. 2014;5(288):1-13.
34. Markianos M, Evangelopoulos ME, Koutsis G, et al. Evidence for involvement of central noradrenergic activity in crying proneness. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;23:403-408.
35. Cao S, Fisher DW, Yu T, et al. The link between chronic pain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;(16):204-215.
36. Caraci F, Merlo S, Drago F, et al. Rescue of noradrenergic system as a novel pharmacological strategy in the treatment of chronic pain: focus on microglia activation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;(10):1024.
37. Hayashida KI, Obata H. Strategies to treat chronic pain and strengthen impaired descending noradrenergic inhibitory system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):822.
38. Kur’yanova EV, Tryasuchev AV, Stupin VO, et al. Effect of atropine on adrenergic responsiveness of erythrocyte and heart rhythm variability in outbred rats with stimulation of the central neurotransmitter systems. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165(5):165(5):597-601.
39. Peterson AC, Li CR. Noradrenergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an overview of imaging studies. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;(10):127.
There is a need to connect mental and physical symptoms in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. Obviously, we are not yet equipped to clearly recognize which neurotransmitters cause which symptoms. The science of defining the underlying mechanisms is lagging behind the clinical needs. However, in this article, we present a few hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms in order to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. Our descriptions do not reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by these neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known (or suspected). Additional research is needed to confirm or disprove the hypotheses we present.
In Part 1 (

Endorphin excess (Table 11-16)
Ms. R is a frustrated chronic pain patient who bitterly complains that despite having seen more than 20 physicians, she does not have an answer to what causes her “all over” pain and headache.4,5,11 She does not believe that all her laboratory test are normal, and insists that “something is missing.” She aches all over but says she can actually tolerate more pain than others and experiences only a little discomfort during an electromyogram or dental interventions. Though Ms. R is not very susceptible to acute pain,4,5,9,16 pain all over without an identifiable cause is part of her life.4,5,11 She says that listening to music and social interactions help decrease her pain.4,5,10 Ms. R states that opioid medications do not help her pain, though she has a history of opioid overuse and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.6,11,16

Ms. R tends to overdo pleasureful activities to achieve satisfaction.2 She says exercise is particularly satisfying, to the point that she experiences euphoria and a loss of time.9 She is angry that her neurologist suggested she see a psychiatrist. Her depression bothers her more than her anxiety.2,5,7
Ms. R clearly has a self-image problem, alternating between high and low self-esteem. She has a low appetite1,12,14-16 and sleeps excessively.2,4,7,9,10 Her mother privately tells you that Ms. R has a history of childhood sexual abuse and lagged in life due to a lack of motivation. Ms. R used to self-mutilate “to feel normal.”12 Her primary care physician chronically addresses Ms. R’s poorly explained cholestasis and pruritus8 as well as dysregulation of blood pressure and heart rate, both of which tend to be low.12,13,16
Impression. Ms. R shows multiple symptoms associated with endorphin excess. A trial of an opioid antagonist may be reasonable. Dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression and also may be used for this patient. Using a low starting dose and a slow titration of such medications would be beneficial due to frequent intolerance issues, especially nausea. Gamma aminobutyric acid-ergic medications modulate the opioid system and may be considered. A serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) or mirtazapine may help patients such as Ms. R to control mood and pain through norepinephrine’s influence on endorphins.
Endorphin deficiency (Table 11,16-24)
Mr. J complains of low back pain, diffuse body pain, depression, and moodiness.19,20,24 He is sluggish and plagued by psychomotor retardation.24 All his life, a heightened perception of pain has caused him problems,19,20 but has not stopped him from engaging in self-mutilation
Continue to: Mr. J responds to treatment...
Mr. J responds to treatment with opioids16,20 but comments that his mood, and not necessarily his pain, improves when he takes these medications.20 He tends to overuse his pain medications, and had run into trouble with his previous pain management physician. Nitrous oxide is remarkably effective during dental procedures.19 Acupuncture helps to control his pain and mood.17 Exercise is also rewarding.18
Mr. J has difficulty achieving orgasm, a decreased sexual drive, and emotional sensitivity.24 He is impulsive.19,20,24 His baseline mood is low-grade; anxiety bothers him more than depression.23,24 Mr. J is thin, has a poor appetite,1,16 and sleeps poorly.24 His primary care physician struggles to help Mr. J to control dysregulation of his heart rate, blood pressure,21 and urinary retention,16,22 as well as episodes of hypoglycemia.1,16 He reluctantly admits to abusing alcohol, but explains that it helps with his mood and pain better than his prescribed medications.18,23
Impression. Mr. J exhibits multiple symptoms associated with endorphin deficiency. Short-term use of opioids is warranted, but he should avoid long-term opioid use, and he and his physician should work together to establish strict control of their intake. Buprenorphine would be the opioid of choice for such a patient. Psychiatric treatment, including for alcohol use disorder, should be a mandatory part of his treatment regimen. Behavioral therapy with a focus on finding healthy ways to achieve gratification would be effective. Alternative treatments such as acupuncture may be of value.
Norepinephrine excess (Table 216,25-30)
Mr. G comes to the office irritable and angry28,30 because no one can help him with his intractable headaches.
Comment. Norepinephrine and dopamine functions are connected through common neuronal and glial uptake mechanisms. This is a foundation of norepinephrine excess symptoms crossing over with symptoms of dopamine deficiency.
Continue to: Impression
Impression. Mr. G shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine excess. It is important to avoid caffeine intake in patients with clinical signs of excessive norepinephrine. Beta-blockers and alpha-2 agonists work well in patients such as Mr. G. Benzodiazepines indirectly decrease norepinephrine activity, but need to be used carefully due to the potential for misuse and addiction. In particular, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam must be avoided due to the induction of CNS instability with rapidly changing medication blood levels. Chlordiazepoxide may be a good choice for a patient such as Mr. G because it has the fewest adverse effects and the lowest abuse potential compared with other benzodiazepines. Avoid SNRIs in such a patient. Using mood-stabilizing antipsychotic medications may be especially warranted in treating Mr. G’s depression and pain.
Norepinephrine deficiency (Table 216,26,31-39)
Two years ago, Ms. A was diagnosed with chronic fatigue31 and fibromyalgia. She also had been diagnosed with depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). She presents with concerns of “brain fog,” no energy, low sex drive, and daytime sleepiness.33,35 Allodynia is widespread.16,36,37 Ms. A suffers from bulimia; she eats once a day but is still overweight.26 She has orthostatic hypotension in addition to baseline low blood pressure and bradycardia.16,38,39 Her pupils are almost pinpoint, even when she does not take opioid medications.
Comment. As mentioned earlier, because of the norepinephrine/dopamine relationship, symptoms of excess dopamine overlap with symptoms of norepinephrine deficiency.
Impression. Ms. A shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine deficiency. The use of noradrenergic antidepressants (such as SNRIs and mirtazapine)26 and stimulants may be warranted. Physical exercise, participating in social activities, massage, acupuncture, and family support may help with Ms. A’s pain as well as her depression, as might vasopressors.
In Part 3, we will address gamma aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of endorphins and norepinephrine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Arbuck DM, Salmerón JM, Mueller R. Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: a hypothesis (Part 1). Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):30-36. doi:10.12788/cp.0242
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
There is a need to connect mental and physical symptoms in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. Obviously, we are not yet equipped to clearly recognize which neurotransmitters cause which symptoms. The science of defining the underlying mechanisms is lagging behind the clinical needs. However, in this article, we present a few hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms in order to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. Our descriptions do not reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by these neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known (or suspected). Additional research is needed to confirm or disprove the hypotheses we present.
In Part 1 (

Endorphin excess (Table 11-16)
Ms. R is a frustrated chronic pain patient who bitterly complains that despite having seen more than 20 physicians, she does not have an answer to what causes her “all over” pain and headache.4,5,11 She does not believe that all her laboratory test are normal, and insists that “something is missing.” She aches all over but says she can actually tolerate more pain than others and experiences only a little discomfort during an electromyogram or dental interventions. Though Ms. R is not very susceptible to acute pain,4,5,9,16 pain all over without an identifiable cause is part of her life.4,5,11 She says that listening to music and social interactions help decrease her pain.4,5,10 Ms. R states that opioid medications do not help her pain, though she has a history of opioid overuse and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.6,11,16

Ms. R tends to overdo pleasureful activities to achieve satisfaction.2 She says exercise is particularly satisfying, to the point that she experiences euphoria and a loss of time.9 She is angry that her neurologist suggested she see a psychiatrist. Her depression bothers her more than her anxiety.2,5,7
Ms. R clearly has a self-image problem, alternating between high and low self-esteem. She has a low appetite1,12,14-16 and sleeps excessively.2,4,7,9,10 Her mother privately tells you that Ms. R has a history of childhood sexual abuse and lagged in life due to a lack of motivation. Ms. R used to self-mutilate “to feel normal.”12 Her primary care physician chronically addresses Ms. R’s poorly explained cholestasis and pruritus8 as well as dysregulation of blood pressure and heart rate, both of which tend to be low.12,13,16
Impression. Ms. R shows multiple symptoms associated with endorphin excess. A trial of an opioid antagonist may be reasonable. Dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression and also may be used for this patient. Using a low starting dose and a slow titration of such medications would be beneficial due to frequent intolerance issues, especially nausea. Gamma aminobutyric acid-ergic medications modulate the opioid system and may be considered. A serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) or mirtazapine may help patients such as Ms. R to control mood and pain through norepinephrine’s influence on endorphins.
Endorphin deficiency (Table 11,16-24)
Mr. J complains of low back pain, diffuse body pain, depression, and moodiness.19,20,24 He is sluggish and plagued by psychomotor retardation.24 All his life, a heightened perception of pain has caused him problems,19,20 but has not stopped him from engaging in self-mutilation
Continue to: Mr. J responds to treatment...
Mr. J responds to treatment with opioids16,20 but comments that his mood, and not necessarily his pain, improves when he takes these medications.20 He tends to overuse his pain medications, and had run into trouble with his previous pain management physician. Nitrous oxide is remarkably effective during dental procedures.19 Acupuncture helps to control his pain and mood.17 Exercise is also rewarding.18
Mr. J has difficulty achieving orgasm, a decreased sexual drive, and emotional sensitivity.24 He is impulsive.19,20,24 His baseline mood is low-grade; anxiety bothers him more than depression.23,24 Mr. J is thin, has a poor appetite,1,16 and sleeps poorly.24 His primary care physician struggles to help Mr. J to control dysregulation of his heart rate, blood pressure,21 and urinary retention,16,22 as well as episodes of hypoglycemia.1,16 He reluctantly admits to abusing alcohol, but explains that it helps with his mood and pain better than his prescribed medications.18,23
Impression. Mr. J exhibits multiple symptoms associated with endorphin deficiency. Short-term use of opioids is warranted, but he should avoid long-term opioid use, and he and his physician should work together to establish strict control of their intake. Buprenorphine would be the opioid of choice for such a patient. Psychiatric treatment, including for alcohol use disorder, should be a mandatory part of his treatment regimen. Behavioral therapy with a focus on finding healthy ways to achieve gratification would be effective. Alternative treatments such as acupuncture may be of value.
Norepinephrine excess (Table 216,25-30)
Mr. G comes to the office irritable and angry28,30 because no one can help him with his intractable headaches.
Comment. Norepinephrine and dopamine functions are connected through common neuronal and glial uptake mechanisms. This is a foundation of norepinephrine excess symptoms crossing over with symptoms of dopamine deficiency.
Continue to: Impression
Impression. Mr. G shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine excess. It is important to avoid caffeine intake in patients with clinical signs of excessive norepinephrine. Beta-blockers and alpha-2 agonists work well in patients such as Mr. G. Benzodiazepines indirectly decrease norepinephrine activity, but need to be used carefully due to the potential for misuse and addiction. In particular, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam must be avoided due to the induction of CNS instability with rapidly changing medication blood levels. Chlordiazepoxide may be a good choice for a patient such as Mr. G because it has the fewest adverse effects and the lowest abuse potential compared with other benzodiazepines. Avoid SNRIs in such a patient. Using mood-stabilizing antipsychotic medications may be especially warranted in treating Mr. G’s depression and pain.
Norepinephrine deficiency (Table 216,26,31-39)
Two years ago, Ms. A was diagnosed with chronic fatigue31 and fibromyalgia. She also had been diagnosed with depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). She presents with concerns of “brain fog,” no energy, low sex drive, and daytime sleepiness.33,35 Allodynia is widespread.16,36,37 Ms. A suffers from bulimia; she eats once a day but is still overweight.26 She has orthostatic hypotension in addition to baseline low blood pressure and bradycardia.16,38,39 Her pupils are almost pinpoint, even when she does not take opioid medications.
Comment. As mentioned earlier, because of the norepinephrine/dopamine relationship, symptoms of excess dopamine overlap with symptoms of norepinephrine deficiency.
Impression. Ms. A shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine deficiency. The use of noradrenergic antidepressants (such as SNRIs and mirtazapine)26 and stimulants may be warranted. Physical exercise, participating in social activities, massage, acupuncture, and family support may help with Ms. A’s pain as well as her depression, as might vasopressors.
In Part 3, we will address gamma aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of endorphins and norepinephrine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Arbuck DM, Salmerón JM, Mueller R. Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: a hypothesis (Part 1). Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):30-36. doi:10.12788/cp.0242
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
1. Applyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-1760.
2. Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;6(3):104-111.
3. Dabo F, Nyberg F, Qin Zhou, et al. Plasma levels of beta-endorphin during pregnancy and use of labor analgesia. Reprod Sci. 2010;17(8):742-747.
4. Dunbar RI, Kaskatis K, MacDonald I, et al. Performance of music elevates pain threshold and positive affect: implications for the evolutionary function of music. Evol Psychol. 2012;10(4):688-702.
5. Dunbar RIM, Baron R, Frangou A, et al. Social laughter is correlated with an elevated pain threshold. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1731):1161-1167.
6. Grisel JE, Bartels JL, Allen SA, et al. Influence of beta-Endorphin on anxious behavior in mice: interaction with EtOH. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;200(1):105-115.
7. Zorrilla EP, DeRubeis RJ, Redei E. High self-esteem, hardiness, and affective stability are associated with higher basal pituitary-adrenal hormone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20(6):591-601.
8. Li X, Zhu J, Tao Y, et al. Elevated endogenous opioids in obstructive jaundice: the possible skin mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2018;116:119-121.
9. Hicks SD, Jacob P, Perez O, et al. The transcriptional signature of a runner’s high. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):970-978.
10. Dunbar RIM. The anatomy of friendship. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(1):32-51.
11. Stephan BC, Parsa FD. Avoiding opioids and their harmful side effects in the postoperative patient: exogenous opioids, endogenous endorphins, wellness, mood, and their relation to postoperative pain. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2016;75(3):63-70.
12. Cuthbert BN, Holaday JW, Meyerhoff J, et al. Intravenous beta-endorphin: behavioral and physiological effects in conscious monkeys. Peptides. 1989;10(4):729-734.
13. Levin ER, Mills S, Weber MA. Endogenous opioids and opiate antagonists modulate the blood pressure of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Peptides. 1986;(6):977-981.
14. Davis JM, Lowy MT, Yim GK, et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and food intake in rats. Peptides. 1983;4(1):79-83.
15. Leibowitz SF, Hor L. Endorphinergic and alpha-noradrenergic systems in the paraventricular nucleus: effects on eating behavior. Peptides. 1982;3(3): 421-428.
16. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:587-588.
17. Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
18. Harte JL, Eifert GH, Smith R. The effects of running and meditation on beta-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone and cortisol in plasma, and on mood. Biol Psychol. 1995;40(3):251-265.
19. Petrizzo R, Mohr J, Mantione K, et al. The role of endogenous morphine and nitric oxide in pain management. Pract Pain Manag. 2014;14(9).
20. Sprouse-Blum AS, Smith G, Sugai D, et al. Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J. 2010;69(3):70-100.
21. Dontsov AV. The influence of deficit of endogenous neuropeptides on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2017;95(2):127-131. In Russian.
22. Dray A, Metsch R, Davis TP. Endorphins and the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Peptides. 1984;5(3):645-647.
23. Zalewska-Kaszubska J, Czarnecka E. Deficit in beta-endorphin peptide and tendency to alcohol abuse. Peptides. 2005;26(4):701-705.
24. McLay RN, Pan W, Kastin AJ. Effects of peptides on animal and human behavior: a review of studies published in the first twenty years of the journal Peptides. Peptides. 2001;22(12):2181-2255.
25. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st ed. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:424-428.
26. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
27. Winklewski PJ, Radkowski M, Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, et al. Stress response, brain noradrenergic system and cognition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;980:67-74.
28. McCall JG, Al-Hasani R, Siuda ER, et al. Engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron. 2015;87(3):605-620.
29. Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, Wolf J, Szarmach A, et al. Central sympathetic nervous system reinforcement in obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;39:143-154.
30. Yamamoto K, Shinba T, Yoshii M. Psychiatric symptoms of noradrenergic dysfunction: a pathophysiological view. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;201(68):1-20.
31. Stone EA, Lin Y, Sarfraz Y, et al. The role of the central noradrenergic system in behavioral inhibition. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):193-208.
32. Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C. Effect of the alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist mirtazapine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine system in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:861-871.
33. De Carvalho D, Patrone LG, Taxini CL, et al. Neurochemical and electrical modulation of the locus coeruleus: contribution to CO2 drive to breathe. Front Physiol. 2014;5(288):1-13.
34. Markianos M, Evangelopoulos ME, Koutsis G, et al. Evidence for involvement of central noradrenergic activity in crying proneness. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;23:403-408.
35. Cao S, Fisher DW, Yu T, et al. The link between chronic pain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;(16):204-215.
36. Caraci F, Merlo S, Drago F, et al. Rescue of noradrenergic system as a novel pharmacological strategy in the treatment of chronic pain: focus on microglia activation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;(10):1024.
37. Hayashida KI, Obata H. Strategies to treat chronic pain and strengthen impaired descending noradrenergic inhibitory system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):822.
38. Kur’yanova EV, Tryasuchev AV, Stupin VO, et al. Effect of atropine on adrenergic responsiveness of erythrocyte and heart rhythm variability in outbred rats with stimulation of the central neurotransmitter systems. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165(5):165(5):597-601.
39. Peterson AC, Li CR. Noradrenergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an overview of imaging studies. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;(10):127.
1. Applyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-1760.
2. Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;6(3):104-111.
3. Dabo F, Nyberg F, Qin Zhou, et al. Plasma levels of beta-endorphin during pregnancy and use of labor analgesia. Reprod Sci. 2010;17(8):742-747.
4. Dunbar RI, Kaskatis K, MacDonald I, et al. Performance of music elevates pain threshold and positive affect: implications for the evolutionary function of music. Evol Psychol. 2012;10(4):688-702.
5. Dunbar RIM, Baron R, Frangou A, et al. Social laughter is correlated with an elevated pain threshold. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1731):1161-1167.
6. Grisel JE, Bartels JL, Allen SA, et al. Influence of beta-Endorphin on anxious behavior in mice: interaction with EtOH. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;200(1):105-115.
7. Zorrilla EP, DeRubeis RJ, Redei E. High self-esteem, hardiness, and affective stability are associated with higher basal pituitary-adrenal hormone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20(6):591-601.
8. Li X, Zhu J, Tao Y, et al. Elevated endogenous opioids in obstructive jaundice: the possible skin mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2018;116:119-121.
9. Hicks SD, Jacob P, Perez O, et al. The transcriptional signature of a runner’s high. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):970-978.
10. Dunbar RIM. The anatomy of friendship. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(1):32-51.
11. Stephan BC, Parsa FD. Avoiding opioids and their harmful side effects in the postoperative patient: exogenous opioids, endogenous endorphins, wellness, mood, and their relation to postoperative pain. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2016;75(3):63-70.
12. Cuthbert BN, Holaday JW, Meyerhoff J, et al. Intravenous beta-endorphin: behavioral and physiological effects in conscious monkeys. Peptides. 1989;10(4):729-734.
13. Levin ER, Mills S, Weber MA. Endogenous opioids and opiate antagonists modulate the blood pressure of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Peptides. 1986;(6):977-981.
14. Davis JM, Lowy MT, Yim GK, et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and food intake in rats. Peptides. 1983;4(1):79-83.
15. Leibowitz SF, Hor L. Endorphinergic and alpha-noradrenergic systems in the paraventricular nucleus: effects on eating behavior. Peptides. 1982;3(3): 421-428.
16. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:587-588.
17. Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
18. Harte JL, Eifert GH, Smith R. The effects of running and meditation on beta-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone and cortisol in plasma, and on mood. Biol Psychol. 1995;40(3):251-265.
19. Petrizzo R, Mohr J, Mantione K, et al. The role of endogenous morphine and nitric oxide in pain management. Pract Pain Manag. 2014;14(9).
20. Sprouse-Blum AS, Smith G, Sugai D, et al. Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J. 2010;69(3):70-100.
21. Dontsov AV. The influence of deficit of endogenous neuropeptides on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2017;95(2):127-131. In Russian.
22. Dray A, Metsch R, Davis TP. Endorphins and the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Peptides. 1984;5(3):645-647.
23. Zalewska-Kaszubska J, Czarnecka E. Deficit in beta-endorphin peptide and tendency to alcohol abuse. Peptides. 2005;26(4):701-705.
24. McLay RN, Pan W, Kastin AJ. Effects of peptides on animal and human behavior: a review of studies published in the first twenty years of the journal Peptides. Peptides. 2001;22(12):2181-2255.
25. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st ed. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:424-428.
26. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
27. Winklewski PJ, Radkowski M, Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, et al. Stress response, brain noradrenergic system and cognition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;980:67-74.
28. McCall JG, Al-Hasani R, Siuda ER, et al. Engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron. 2015;87(3):605-620.
29. Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, Wolf J, Szarmach A, et al. Central sympathetic nervous system reinforcement in obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;39:143-154.
30. Yamamoto K, Shinba T, Yoshii M. Psychiatric symptoms of noradrenergic dysfunction: a pathophysiological view. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;201(68):1-20.
31. Stone EA, Lin Y, Sarfraz Y, et al. The role of the central noradrenergic system in behavioral inhibition. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):193-208.
32. Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C. Effect of the alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist mirtazapine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine system in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:861-871.
33. De Carvalho D, Patrone LG, Taxini CL, et al. Neurochemical and electrical modulation of the locus coeruleus: contribution to CO2 drive to breathe. Front Physiol. 2014;5(288):1-13.
34. Markianos M, Evangelopoulos ME, Koutsis G, et al. Evidence for involvement of central noradrenergic activity in crying proneness. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;23:403-408.
35. Cao S, Fisher DW, Yu T, et al. The link between chronic pain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;(16):204-215.
36. Caraci F, Merlo S, Drago F, et al. Rescue of noradrenergic system as a novel pharmacological strategy in the treatment of chronic pain: focus on microglia activation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;(10):1024.
37. Hayashida KI, Obata H. Strategies to treat chronic pain and strengthen impaired descending noradrenergic inhibitory system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):822.
38. Kur’yanova EV, Tryasuchev AV, Stupin VO, et al. Effect of atropine on adrenergic responsiveness of erythrocyte and heart rhythm variability in outbred rats with stimulation of the central neurotransmitter systems. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165(5):165(5):597-601.
39. Peterson AC, Li CR. Noradrenergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an overview of imaging studies. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;(10):127.
A PSYCHIATRIC MANIFESTO: Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime
Having witnessed the devastating impact of stigma on patients with mental illness throughout my psychiatric career, I am fed up and disgusted with this malevolent scourge.
I regard the stigma that engulfs neuropsychiatric disorders as a malignancy that mutilates patients’ souls and hastens their mortality.
Stigma is hate speech
How would you feel if you had a serious medical illness, a disabling brain disorder such as schizophrenia, depression, or anxiety, and people refer to you with pejorative and insulting terms such as crazy, deranged, lunatic, unhinged, nutty, insane, wacky, berserk, cuckoo, bonkers, flaky, screwball, or unglued? This is hate speech generated by stigma against people with mental illness. Individuals with heart disease, cancer, or diabetes never get called such disgraceful and stigmatizing terms that shame, stain, besmirch, and scar them, which happens daily to persons with psychiatric brain disorders.
The damage and harm of the discriminatory stigma on our patients is multifaceted. It is painful, detrimental, pernicious, and deleterious. It is corrosive to their spirits, crippling to their self-image, and subversive to their self-confidence. Hate speech is not simply words, but a menacing weapon that assaults the core humanity of medically ill psychiatric patients.
Although hate speech is punishable by law, there are rarely any legal actions against those who hurl hate speech at psychiatric patients every day. Society has institutionalized the stigma of mental illness and takes it in stride instead of recognizing it as an illegal, harmful act.
Long before the stresses of the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of the population had been shown to experience a diagnosable psychiatric disorder over the course of their life.1 Thus, tens of millions of people are burdened by stigma and the hate speech associated with it. This is directly related to massive ignorance about mental illness being the result of a neurobiological condition due to either genetic or intrauterine adverse events that disrupt brain development. Delusions and hallucinations are symptoms of a malfunctioning brain, depression is not a sign of personal weakness, anxiety is the most prevalent mental disorder in the world, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not odd behavior but the result of dysfunction of neural circuits. Correcting public misperceptions about psychiatric brain disorders can mitigate stigma, but it has yet to happen.
Stigma is a hate crime
Stigma can accelerate physical death and premature mortality. Many studies have confirmed that persons with schizophrenia do not receive basic primary care treatments for the life-shortening medical conditions that often afflict them, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.2 Stigma is responsible for a significant disparity of medical3-5 and intensive care6 among individuals with mental illness compared to the general population. It’s no wonder most psychiatric disorders are associated with accelerated mortality.7 A recent study during the pandemic by Balasuriya et al8 reported that patients with depression had poor access to care. Stigma interferes with or delays necessary medical care, leading to clinical deterioration and unnecessary, preventable death. Stigma shortens life and is a hate crime.
Continue to: The extremely high suicide rates...
The extremely high suicide rates among individuals with serious mental illness, who live under the oppressiveness of stigma, is another example of how stigma is a hate crime that can cause patients with psychiatric disorders to give up and end their lives. Zaheer et al9 found that young patients with schizophrenia had an astronomical suicide rate compared to the general population (1 in 52 in individuals with schizophrenia, compared to 12 in 100,000 in the general population, roughly a 200-fold increase!). This is clearly a consequence of stigma and discrimination,10 which leads to demoralization, shame, loneliness, distress, and hopelessness. Stigma can be fatal, and that makes it a hate crime.
Stigma also limits vocational opportunities for individuals with mental illness. They are either not hired, or quickly fired. Even highly educated professionals such as physicians, nurses, lawyers, or teachers can lose their jobs if they divulge a history of a psychiatric disorder or alcohol or substance abuse, regardless of whether they are receiving treatment and are medically in remission. Even highly qualified politicians have been deemed “ineligible” for higher office if they disclose a history of psychiatric treatment. Stigma is loaded with outrageous discrimination that deprives our patients of “the pursuit of happiness,” a fundamental constitutional right.
Stigma surrounding the mental health professions
Stigma also engulfs mental health professionals, simply because they deal with psychiatric patients every day. In a classic article titled “The Enigma of Stigma,”11 Dr. Paul Fink, past president of the American Psychiatric Association (1988-1989), described how psychiatrists are perceived as “different” from other physicians by the public and by the media. He said psychiatrists are tarred by the same brush as their patients as “undesirables” in society. And movies such as Psycho and One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest reinforce the stigma against both psychiatric patients and the psychiatrists and nurses who treat them. The health care system that carves out “behavioral health” from the umbrella of “medical care” further accentuates the stigma by portraying the “separateness” of psychiatry, a genuine medical specialty, from its fellow medical disciplines. This becomes fodder for the antipsychiatry movement at every turn and can even lead to questioning the existence of mental illness, as Thomas Szasz12 did by declaring that mental illness is a myth and describing psychiatry as “the science of lies.” No other medical specialty endures abuse and insults like psychiatry, and that’s a direct result of stigma.
Extinguishing stigma is a societal imperative
So what can be done to squelch stigma and defeat it once and for all, so that psychiatric patients can be treated with dignity and compassion, like people with cancer, heart attacks, diabetes, or brain tumors? The pandemic, terrible as it has been for the entire world, did have the silver lining of raising awareness about the ubiquity of psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, across all ages, genders, educational and religious backgrounds, and socioeconomic classes. But there should also be a robust legal battle against the damaging effects of stigma. There are laws to sanction and penalize hate speech and hate crimes that must be implemented when stigma is documented. There are also parity laws, but they have no teeth and have not ameliorated the insurance discrepancies and economic burden of psychiatric disorders. A bold step would be to reclassify serious psychiatric brain disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, OCD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, generalized anxiety disorder/panic attacks, and borderline personality disorder) as neurologic disorders, which would automatically give patients with these disorders broad access to medical care, which happened when autism was reclassified as a neurologic disorder. Finally, a much more intensive public education must be disseminated about the neurobiological etiologies, brain structure, and function in psychiatric disorders, and the psychiatric symptoms associated with all neurologic disorders. Regrettably, empathy can be difficult to teach.
Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime. It must be permanently eliminated by effective laws and by erasing the widespread ignorance about the medical and neurologic roots of mental disorders, and by emphasizing the fact that they are as treatable as other general medical conditions.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Nasrallah HA, Meyer JM, Goff DC, et al. Low rates of treatment for hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes in schizophrenia: data from the CATIE schizophrenia trial sample at baseline. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):15-22.
3. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Use of medical services by veterans with mental disorders. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):451-458.
4. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Mental disorders and access to medical care in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(12):1775-1777.
5. Druss BG, Bradford WD, Rosenheck RA, et al. Quality of medical care and excess mortality in older patients with mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(6):565-572.
6. Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283(4):506-511.
7. Nasrallah HA. Transformative advances are unfolding in psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(9):10-12.
8. Balasuriya L, Quinton JK, Canavan ME, et al. The association between history of depression and access to care among Medicare beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(12):3778-3785.
9. Zaheer J, Olfson M, Mallia E, et al. Predictors of suicide at time of diagnosis in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a 20-year total population study in Ontario, Canada. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:382-388.
10. Brohan E, Thornicroft G, Rüsch N, et al. Measuring discrimination experienced by people with a mental illness: replication of the short-form DISCUS in six world regions. Psychol Med. 2022:1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000630
11. Fink P. The enigma of stigma and its relation to psychiatric education. Psychiatric Annals. 1983;13(9):669-690.
12. Szasz T. The Myth of Mental Illness. Harper Collins; 1960.
Having witnessed the devastating impact of stigma on patients with mental illness throughout my psychiatric career, I am fed up and disgusted with this malevolent scourge.
I regard the stigma that engulfs neuropsychiatric disorders as a malignancy that mutilates patients’ souls and hastens their mortality.
Stigma is hate speech
How would you feel if you had a serious medical illness, a disabling brain disorder such as schizophrenia, depression, or anxiety, and people refer to you with pejorative and insulting terms such as crazy, deranged, lunatic, unhinged, nutty, insane, wacky, berserk, cuckoo, bonkers, flaky, screwball, or unglued? This is hate speech generated by stigma against people with mental illness. Individuals with heart disease, cancer, or diabetes never get called such disgraceful and stigmatizing terms that shame, stain, besmirch, and scar them, which happens daily to persons with psychiatric brain disorders.
The damage and harm of the discriminatory stigma on our patients is multifaceted. It is painful, detrimental, pernicious, and deleterious. It is corrosive to their spirits, crippling to their self-image, and subversive to their self-confidence. Hate speech is not simply words, but a menacing weapon that assaults the core humanity of medically ill psychiatric patients.
Although hate speech is punishable by law, there are rarely any legal actions against those who hurl hate speech at psychiatric patients every day. Society has institutionalized the stigma of mental illness and takes it in stride instead of recognizing it as an illegal, harmful act.
Long before the stresses of the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of the population had been shown to experience a diagnosable psychiatric disorder over the course of their life.1 Thus, tens of millions of people are burdened by stigma and the hate speech associated with it. This is directly related to massive ignorance about mental illness being the result of a neurobiological condition due to either genetic or intrauterine adverse events that disrupt brain development. Delusions and hallucinations are symptoms of a malfunctioning brain, depression is not a sign of personal weakness, anxiety is the most prevalent mental disorder in the world, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not odd behavior but the result of dysfunction of neural circuits. Correcting public misperceptions about psychiatric brain disorders can mitigate stigma, but it has yet to happen.
Stigma is a hate crime
Stigma can accelerate physical death and premature mortality. Many studies have confirmed that persons with schizophrenia do not receive basic primary care treatments for the life-shortening medical conditions that often afflict them, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.2 Stigma is responsible for a significant disparity of medical3-5 and intensive care6 among individuals with mental illness compared to the general population. It’s no wonder most psychiatric disorders are associated with accelerated mortality.7 A recent study during the pandemic by Balasuriya et al8 reported that patients with depression had poor access to care. Stigma interferes with or delays necessary medical care, leading to clinical deterioration and unnecessary, preventable death. Stigma shortens life and is a hate crime.
Continue to: The extremely high suicide rates...
The extremely high suicide rates among individuals with serious mental illness, who live under the oppressiveness of stigma, is another example of how stigma is a hate crime that can cause patients with psychiatric disorders to give up and end their lives. Zaheer et al9 found that young patients with schizophrenia had an astronomical suicide rate compared to the general population (1 in 52 in individuals with schizophrenia, compared to 12 in 100,000 in the general population, roughly a 200-fold increase!). This is clearly a consequence of stigma and discrimination,10 which leads to demoralization, shame, loneliness, distress, and hopelessness. Stigma can be fatal, and that makes it a hate crime.
Stigma also limits vocational opportunities for individuals with mental illness. They are either not hired, or quickly fired. Even highly educated professionals such as physicians, nurses, lawyers, or teachers can lose their jobs if they divulge a history of a psychiatric disorder or alcohol or substance abuse, regardless of whether they are receiving treatment and are medically in remission. Even highly qualified politicians have been deemed “ineligible” for higher office if they disclose a history of psychiatric treatment. Stigma is loaded with outrageous discrimination that deprives our patients of “the pursuit of happiness,” a fundamental constitutional right.
Stigma surrounding the mental health professions
Stigma also engulfs mental health professionals, simply because they deal with psychiatric patients every day. In a classic article titled “The Enigma of Stigma,”11 Dr. Paul Fink, past president of the American Psychiatric Association (1988-1989), described how psychiatrists are perceived as “different” from other physicians by the public and by the media. He said psychiatrists are tarred by the same brush as their patients as “undesirables” in society. And movies such as Psycho and One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest reinforce the stigma against both psychiatric patients and the psychiatrists and nurses who treat them. The health care system that carves out “behavioral health” from the umbrella of “medical care” further accentuates the stigma by portraying the “separateness” of psychiatry, a genuine medical specialty, from its fellow medical disciplines. This becomes fodder for the antipsychiatry movement at every turn and can even lead to questioning the existence of mental illness, as Thomas Szasz12 did by declaring that mental illness is a myth and describing psychiatry as “the science of lies.” No other medical specialty endures abuse and insults like psychiatry, and that’s a direct result of stigma.
Extinguishing stigma is a societal imperative
So what can be done to squelch stigma and defeat it once and for all, so that psychiatric patients can be treated with dignity and compassion, like people with cancer, heart attacks, diabetes, or brain tumors? The pandemic, terrible as it has been for the entire world, did have the silver lining of raising awareness about the ubiquity of psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, across all ages, genders, educational and religious backgrounds, and socioeconomic classes. But there should also be a robust legal battle against the damaging effects of stigma. There are laws to sanction and penalize hate speech and hate crimes that must be implemented when stigma is documented. There are also parity laws, but they have no teeth and have not ameliorated the insurance discrepancies and economic burden of psychiatric disorders. A bold step would be to reclassify serious psychiatric brain disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, OCD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, generalized anxiety disorder/panic attacks, and borderline personality disorder) as neurologic disorders, which would automatically give patients with these disorders broad access to medical care, which happened when autism was reclassified as a neurologic disorder. Finally, a much more intensive public education must be disseminated about the neurobiological etiologies, brain structure, and function in psychiatric disorders, and the psychiatric symptoms associated with all neurologic disorders. Regrettably, empathy can be difficult to teach.
Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime. It must be permanently eliminated by effective laws and by erasing the widespread ignorance about the medical and neurologic roots of mental disorders, and by emphasizing the fact that they are as treatable as other general medical conditions.
Having witnessed the devastating impact of stigma on patients with mental illness throughout my psychiatric career, I am fed up and disgusted with this malevolent scourge.
I regard the stigma that engulfs neuropsychiatric disorders as a malignancy that mutilates patients’ souls and hastens their mortality.
Stigma is hate speech
How would you feel if you had a serious medical illness, a disabling brain disorder such as schizophrenia, depression, or anxiety, and people refer to you with pejorative and insulting terms such as crazy, deranged, lunatic, unhinged, nutty, insane, wacky, berserk, cuckoo, bonkers, flaky, screwball, or unglued? This is hate speech generated by stigma against people with mental illness. Individuals with heart disease, cancer, or diabetes never get called such disgraceful and stigmatizing terms that shame, stain, besmirch, and scar them, which happens daily to persons with psychiatric brain disorders.
The damage and harm of the discriminatory stigma on our patients is multifaceted. It is painful, detrimental, pernicious, and deleterious. It is corrosive to their spirits, crippling to their self-image, and subversive to their self-confidence. Hate speech is not simply words, but a menacing weapon that assaults the core humanity of medically ill psychiatric patients.
Although hate speech is punishable by law, there are rarely any legal actions against those who hurl hate speech at psychiatric patients every day. Society has institutionalized the stigma of mental illness and takes it in stride instead of recognizing it as an illegal, harmful act.
Long before the stresses of the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of the population had been shown to experience a diagnosable psychiatric disorder over the course of their life.1 Thus, tens of millions of people are burdened by stigma and the hate speech associated with it. This is directly related to massive ignorance about mental illness being the result of a neurobiological condition due to either genetic or intrauterine adverse events that disrupt brain development. Delusions and hallucinations are symptoms of a malfunctioning brain, depression is not a sign of personal weakness, anxiety is the most prevalent mental disorder in the world, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not odd behavior but the result of dysfunction of neural circuits. Correcting public misperceptions about psychiatric brain disorders can mitigate stigma, but it has yet to happen.
Stigma is a hate crime
Stigma can accelerate physical death and premature mortality. Many studies have confirmed that persons with schizophrenia do not receive basic primary care treatments for the life-shortening medical conditions that often afflict them, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.2 Stigma is responsible for a significant disparity of medical3-5 and intensive care6 among individuals with mental illness compared to the general population. It’s no wonder most psychiatric disorders are associated with accelerated mortality.7 A recent study during the pandemic by Balasuriya et al8 reported that patients with depression had poor access to care. Stigma interferes with or delays necessary medical care, leading to clinical deterioration and unnecessary, preventable death. Stigma shortens life and is a hate crime.
Continue to: The extremely high suicide rates...
The extremely high suicide rates among individuals with serious mental illness, who live under the oppressiveness of stigma, is another example of how stigma is a hate crime that can cause patients with psychiatric disorders to give up and end their lives. Zaheer et al9 found that young patients with schizophrenia had an astronomical suicide rate compared to the general population (1 in 52 in individuals with schizophrenia, compared to 12 in 100,000 in the general population, roughly a 200-fold increase!). This is clearly a consequence of stigma and discrimination,10 which leads to demoralization, shame, loneliness, distress, and hopelessness. Stigma can be fatal, and that makes it a hate crime.
Stigma also limits vocational opportunities for individuals with mental illness. They are either not hired, or quickly fired. Even highly educated professionals such as physicians, nurses, lawyers, or teachers can lose their jobs if they divulge a history of a psychiatric disorder or alcohol or substance abuse, regardless of whether they are receiving treatment and are medically in remission. Even highly qualified politicians have been deemed “ineligible” for higher office if they disclose a history of psychiatric treatment. Stigma is loaded with outrageous discrimination that deprives our patients of “the pursuit of happiness,” a fundamental constitutional right.
Stigma surrounding the mental health professions
Stigma also engulfs mental health professionals, simply because they deal with psychiatric patients every day. In a classic article titled “The Enigma of Stigma,”11 Dr. Paul Fink, past president of the American Psychiatric Association (1988-1989), described how psychiatrists are perceived as “different” from other physicians by the public and by the media. He said psychiatrists are tarred by the same brush as their patients as “undesirables” in society. And movies such as Psycho and One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest reinforce the stigma against both psychiatric patients and the psychiatrists and nurses who treat them. The health care system that carves out “behavioral health” from the umbrella of “medical care” further accentuates the stigma by portraying the “separateness” of psychiatry, a genuine medical specialty, from its fellow medical disciplines. This becomes fodder for the antipsychiatry movement at every turn and can even lead to questioning the existence of mental illness, as Thomas Szasz12 did by declaring that mental illness is a myth and describing psychiatry as “the science of lies.” No other medical specialty endures abuse and insults like psychiatry, and that’s a direct result of stigma.
Extinguishing stigma is a societal imperative
So what can be done to squelch stigma and defeat it once and for all, so that psychiatric patients can be treated with dignity and compassion, like people with cancer, heart attacks, diabetes, or brain tumors? The pandemic, terrible as it has been for the entire world, did have the silver lining of raising awareness about the ubiquity of psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, across all ages, genders, educational and religious backgrounds, and socioeconomic classes. But there should also be a robust legal battle against the damaging effects of stigma. There are laws to sanction and penalize hate speech and hate crimes that must be implemented when stigma is documented. There are also parity laws, but they have no teeth and have not ameliorated the insurance discrepancies and economic burden of psychiatric disorders. A bold step would be to reclassify serious psychiatric brain disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, OCD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, generalized anxiety disorder/panic attacks, and borderline personality disorder) as neurologic disorders, which would automatically give patients with these disorders broad access to medical care, which happened when autism was reclassified as a neurologic disorder. Finally, a much more intensive public education must be disseminated about the neurobiological etiologies, brain structure, and function in psychiatric disorders, and the psychiatric symptoms associated with all neurologic disorders. Regrettably, empathy can be difficult to teach.
Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime. It must be permanently eliminated by effective laws and by erasing the widespread ignorance about the medical and neurologic roots of mental disorders, and by emphasizing the fact that they are as treatable as other general medical conditions.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Nasrallah HA, Meyer JM, Goff DC, et al. Low rates of treatment for hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes in schizophrenia: data from the CATIE schizophrenia trial sample at baseline. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):15-22.
3. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Use of medical services by veterans with mental disorders. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):451-458.
4. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Mental disorders and access to medical care in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(12):1775-1777.
5. Druss BG, Bradford WD, Rosenheck RA, et al. Quality of medical care and excess mortality in older patients with mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(6):565-572.
6. Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283(4):506-511.
7. Nasrallah HA. Transformative advances are unfolding in psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(9):10-12.
8. Balasuriya L, Quinton JK, Canavan ME, et al. The association between history of depression and access to care among Medicare beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(12):3778-3785.
9. Zaheer J, Olfson M, Mallia E, et al. Predictors of suicide at time of diagnosis in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a 20-year total population study in Ontario, Canada. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:382-388.
10. Brohan E, Thornicroft G, Rüsch N, et al. Measuring discrimination experienced by people with a mental illness: replication of the short-form DISCUS in six world regions. Psychol Med. 2022:1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000630
11. Fink P. The enigma of stigma and its relation to psychiatric education. Psychiatric Annals. 1983;13(9):669-690.
12. Szasz T. The Myth of Mental Illness. Harper Collins; 1960.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Nasrallah HA, Meyer JM, Goff DC, et al. Low rates of treatment for hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes in schizophrenia: data from the CATIE schizophrenia trial sample at baseline. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):15-22.
3. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Use of medical services by veterans with mental disorders. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):451-458.
4. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Mental disorders and access to medical care in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(12):1775-1777.
5. Druss BG, Bradford WD, Rosenheck RA, et al. Quality of medical care and excess mortality in older patients with mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(6):565-572.
6. Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283(4):506-511.
7. Nasrallah HA. Transformative advances are unfolding in psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(9):10-12.
8. Balasuriya L, Quinton JK, Canavan ME, et al. The association between history of depression and access to care among Medicare beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(12):3778-3785.
9. Zaheer J, Olfson M, Mallia E, et al. Predictors of suicide at time of diagnosis in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a 20-year total population study in Ontario, Canada. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:382-388.
10. Brohan E, Thornicroft G, Rüsch N, et al. Measuring discrimination experienced by people with a mental illness: replication of the short-form DISCUS in six world regions. Psychol Med. 2022:1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000630
11. Fink P. The enigma of stigma and its relation to psychiatric education. Psychiatric Annals. 1983;13(9):669-690.
12. Szasz T. The Myth of Mental Illness. Harper Collins; 1960.
The brain’s Twitter system: Neuronal extracellular vesicles
Twitter, a microblogging and social networking service, has become a “go-to’” for conversations, updates, breaking news, and sharing the more mundane aspects of our lives. Tweets, which were lengthened from 140 to 280 characters in 2017, rapidly communicate and disseminate information to a wide audience. Generally, tweets are visible to everyone, though users can mute and block other users from viewing their tweets. Spikes in tweets and tweeting frequency reflect hyper-current events: the last minutes of the Super Bowl, certification of an election, or a new movie release. In fact, social scientists have analyzed tweet frequencies to examine the impact of local and national events. However, few are aware that like celebrities, politicians, influencers, and ordinary citizens, the human brain also tweets.
In this article, we describe the components of the brain’s “Twitter” system, how it works, and how it might someday be used to improve the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders.
Brain tweets
The brain’s Twitter system involves extracellular vesicles (EVs), tiny (<1 µm) membrane-bound vesicles that are released from neurons, glia, and other neuronal cells (Table). These EVs cross the blood-brain barrier and facilitate cell-to-cell communication within and among tissues (Figure 1).
First described in the 1980s,1 EVs are secreted by a diverse array of cells: mast cells reticulocytes, epithelial cells, immune cells, neurons, glia, and oligodendrocytes. Like tweets, EVs rapidly disseminate packets of information throughout the brain and body and direct the molecular activity of recipient cells in both health and disease. These “brain tweets” contain short, circumscribed messages, and the characters are the EV cargos: RNAs, proteins, lipids, and metabolites. Like a Twitter feed, EVs cast a wide communication net across the body, much of which finds its way to the blood. As neuroscientists, we can follow these tweets by isolating tissue-derived EVs in plasma and examining their surface molecules and cargo. By following this Twitter feed, we can tap into important molecular communications and identify “trending” (evolving) pathological processes, and perhaps use the brain Twitter feed to improve diagnosis and treatments. We can pinpoint, in the blood, signals from CNS processes, down to the level of identifying EV cargos from specific brain cell types.
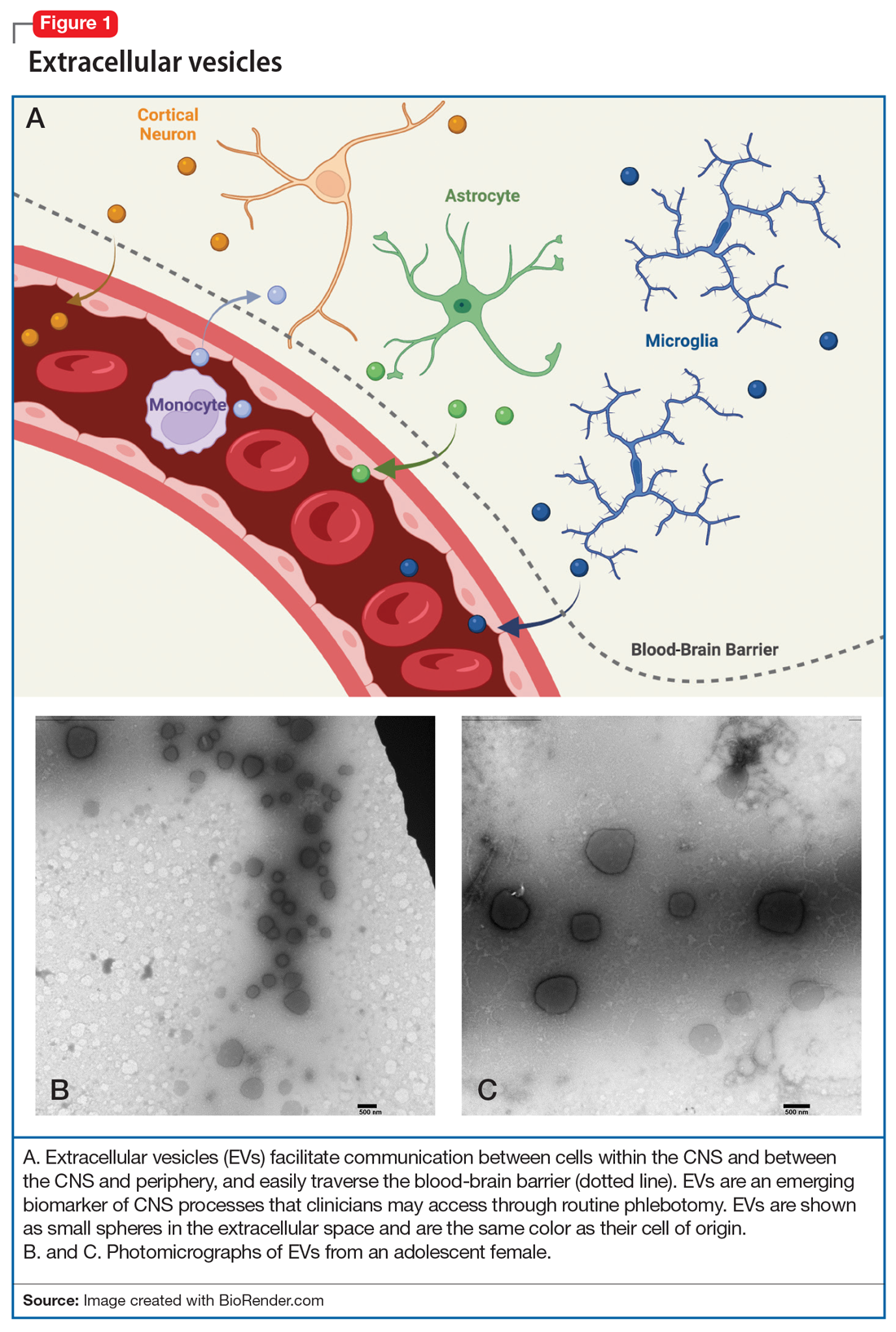
Within the CNS, EVs are secreted by neurons, where they may modulate synaptic plasticity and transfer molecular cargo among neurons. EVs also facilitate communication between neurons and glia, maintain homeostasis, trigger neuroprotective processes, and even regulate synaptic transmission.2
What’s in a brain tweet?
To discuss what’s in a brain tweet, we must first understand how a brain tweet is composed. EVs are pinched off from membranes of intercellular structures (eg, golgi or endoplasmic reticulum) or pinched off directly from cell membranes, where upon release they become EVs. There is a complex cellular machinery that transports what ultimately becomes an EV to the cell membrane.3 EVs contain unique mixtures of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (eg, microRNA [miRNA], mRNA, and noncoding RNA).4 To date, nearly 10,000 proteins, 11,000 lipids, 3,500 mRNAs, and 3,000 miRNAs have been identified as cargos in extracellular vesicles (Figure 1). Similar to how the release of EVs is dependent on complex intracellular machinery, the packing of these contents into what will become the EV involves a parallel set of complex machinery that is largely directed by endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins.5 Of interest, when viruses attack cells, they hijack this EV packaging system to package and release new viruses. EVs vary in size, shape, and density; this variation is related to the cell origin, among other things. EVs also differ in their membrane lipid composition and in terms of transmembrane proteins as well as the proteins that facilitate EV binding to target cells (Figure 2).6 Ultimately, these exosomes are taken up by the recipient cells.
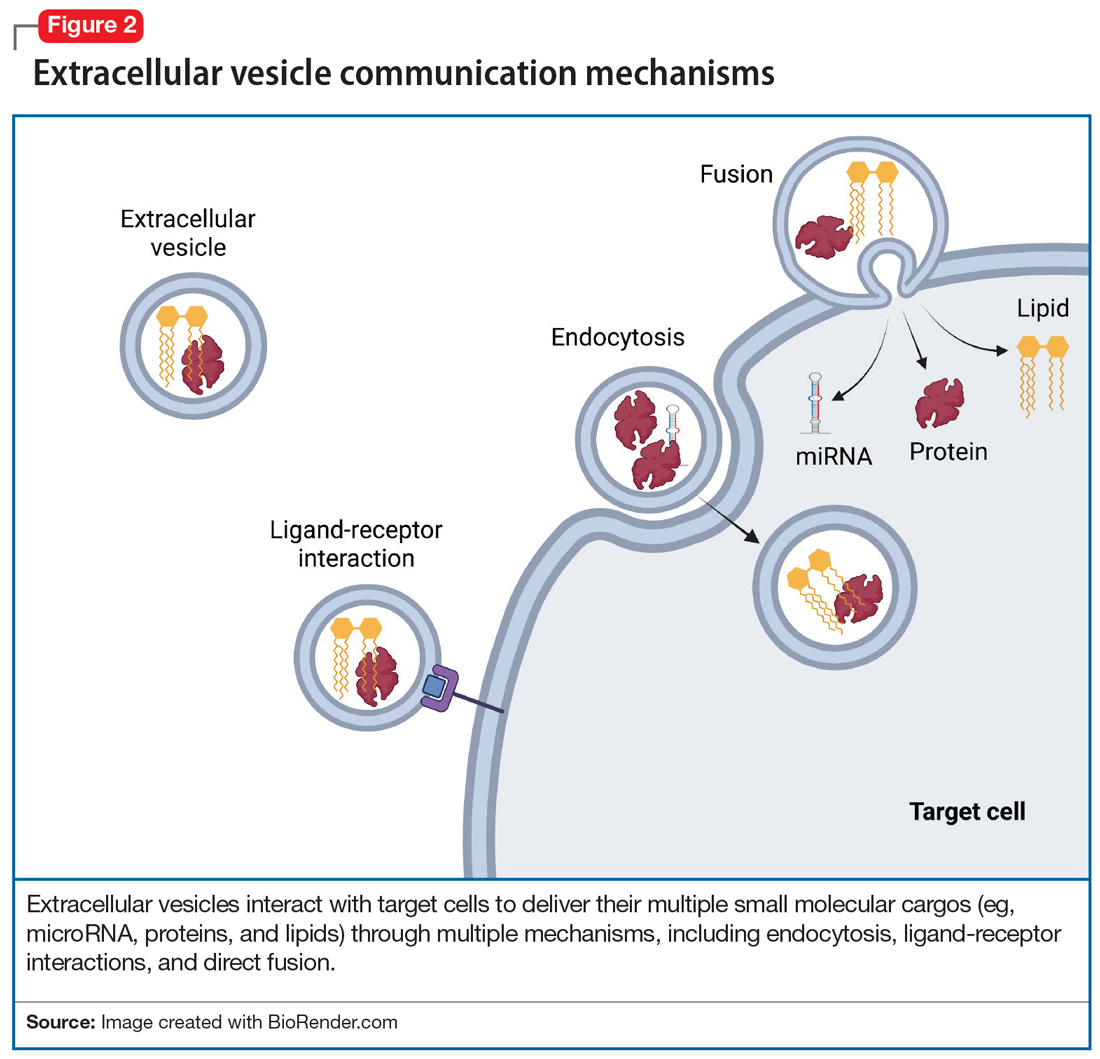
EV-facilitated neuron-to-neuron tweets have been implicated in neuronal growth and differentiation.7 EV-driven communication between cells also can decrease dendrite growth and can trigger microglia to prune synapses.8 EVs from glial cells may promote neuronal integrity, directly boost presynaptic glutamate release,9 or even, through miRNAs, change the expression of glutamate receptors.10 EVs from astrocytes transport proteins that enable neuronal repair, while EVs from microglia regulate neuronal homeostasis. EV cargos—lipids, proteins, and miRNAs—from neurons modify signal transduction and protein expression in recipient cells. Taken together, data suggest that EVs facilitate anterograde and retrograde transfer of signals across synapses,7,11 a putative mechanism for driving synaptic plasticity,12 which is a process implicated in the therapeutic efficacy of psychotropic medications and psychotherapies.
Continue to: #Targets and #neuron
#Targets and #neuron
Adding a hashtag to a tweet links it to other tweets, just as membrane features of EVs direct how EVs link to target cells. When these EVs bind to target cells, they fuse and release their cargo into the target cell (Figure 2). These directed cargo—whether mRNA, proteins, or other molecules—can direct the recipient cell to modify its firing rate (in the case of neurons), alter transmitter release, and increase or decrease expression of various genes. The targeting process is complex, and our understanding of this process is evolving. Briefly, integrin, lipid composition, glycans (eg, polysaccharides), and tetraspanin components of EVs influence their affinity for specific target cells.13 Recently, we have been able to read these hashtags and isolate cell-specific, neuron-derived EVs. Immunoadsorption techniques that leverage antibodies against L1 cell adhesion molecule protein (L1CAM(+)), primarily expressed in neurons, can identify neuronally-derived EVs (Figure 3). The specific EVs contain cargos of neuronal origin and provide a “window” into molecular processes in the brain by way of the blood (or other peripheral fluids). In following the neuronal tweets, we can follow molecular measures of important brain molecules in biofluids outside the CNS, including saliva and potentially urine (Figure 1B and 1C). In following these specific neuronal Twitter feeds, we can gain critical insights into specific brain processes.
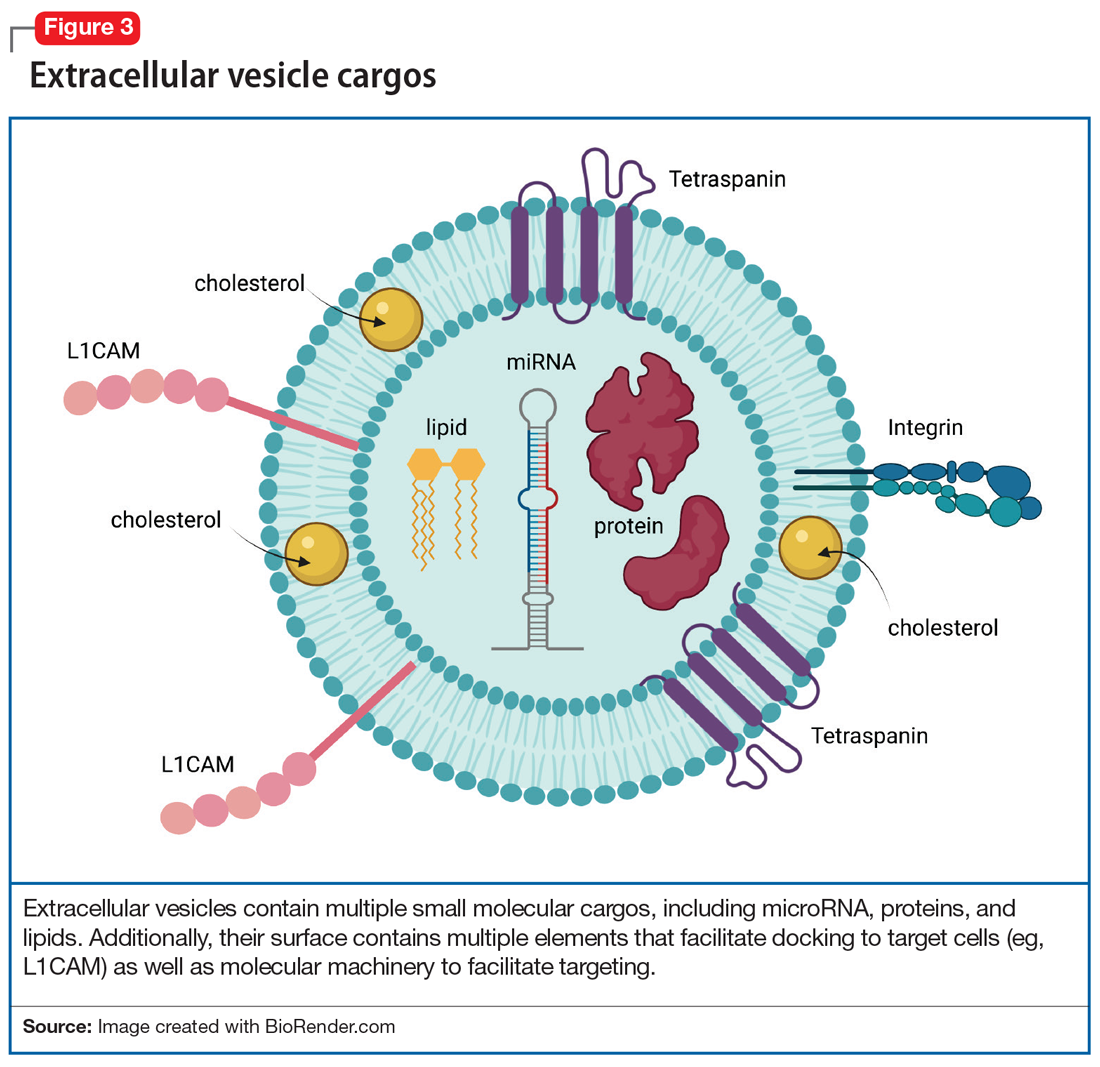
EVs in psychiatric disorders
EVs are implicated in neuroinflammation,14 neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and epigenetic regulation—all processes that are involved in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Postmortem research suggests that EVs in the brain carry proinflammatory molecules from microglia, as well as secretions of regulatory miRNA that are responsible for synaptic plasticity and dendritic growth in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and addiction. In addition, second-generation antipsychotics change the composition of EV cargos in the brain, altering their RNA, protein, and lipid content, often reflecting profound changes in gene expression in various cells in the CNS. In our lab, we have identified several molecules in plasma EVs, both lipids and miRNA, that can potentially predict the response to treatment of pediatric anxiety with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as well as opiate addiction.15
Further, given our increasing understanding of the way in which EV cargo reflects neuronal physiology as well as the potential pathophysiologic states of cells (including neurons), studying EVs’ molecular content can identify molecular messages—in blood—that are derived from the neurons in the brain. Having the tools to examine molecular brain regulators or other markers of disease progression (eg, beta amyloid) or brain health (eg, brain-derived neurotrophic factor) may advance our understanding and treatment of psychiatric disorders and create opportunities for precision medicine driven by biological rather than ethnologic and phenomenological markers. Whereas in the not-too-distant past molecular processes in the brain were only accessible through invasive measures—such as brain biopsy or through a lumbar puncture—studying CNS-derived EVs in blood offers us an opportunity to gain access to brain molecular signatures with relative ease. Often, these molecular signatures predate clinical changes by years or months, allowing us the prospects of potentially identifying and treating CNS disorders early on, possibly even before the onset of symptoms.
Therapeutic use of the Twitter feed
EV may be used to alter brain receptor structures in a targeted way to facilitate treatment of various psychiatric disorders. One example is a proof-of-concept study in mice in which administration of artificially manufactured EVs led to a decrease of opioid receptor mu.16 This was done by constructing EVs that carry neuron-specific rabies viral glycoprotein (RVG) peptide on the membrane surface to deliver mu opioid receptor small interfering RNA into the brain. This resulted in downregulation of mu opioid receptor and a decrease in morphine relapse.16
Additional ways in which EVs can be used therapeutically is via targeted drug delivery CNS methods. EVs may represent the next generation of treatment by allowing not only medication transport into the CNS,17 but also by facilitating directed CNS transport. What if we could use a molecular hashtag to send a dopaminergic agent to the substantia nigra of a patient with Parkinson disease but avoid sending that same treatment to the limbic cortex, where it might produce perceptual disturbances or hallucinations? In the future, EVs may help clinicians access the CNS, which is traditionally restricted by the blood brain barrier, and make it easier to achieve CNS concentrations of medications13 while decreasing medication exposure in other parts of the body. The therapeutic potential of EVs for medication delivery and regenerative medicine is awe-inspiring. Several studies have modified EVs to improve their therapeutic properties and to target delivery to specific cells13 by leveraging EV surface markers.18
Future directions for EVs
A better understanding of neuron-derived EVs may eventually help us abandon nosology-based diagnostic criteria and adopt molecular-based diagnostic approaches in psychiatry. It may allow us to consider a molecular synaptic etiology of psychiatric disorders, and diagnose patients based on synaptic pathology utilizing “neuron-derived EV liquid biopsies.” Such a shift would align psychiatry with other medical fields in which diagnosis and treatment are often based on biopsies and blood tests. Because proteins in EVs often exist in their native states, intact with their posttranslational modifications, they provide a window into testing their actual in vivo functioning. EVs have an immense potential to revolutionize psychiatric diagnosis, facilitate precision treatment, predict response, and discover much-needed novel therapeutics.
Bottom Line
Much like a tweet, extracellular vesicles (EVs) encode short messages that are transmit ted efficiently throughout the CNS and body. They may represent a reservoir for CNS-specific biomarkers that can be is olated from plasma to guide psychiatric diagnosis and treatment. EVs represent a new frontier in the molecular study of psychiatric illness.
Related Resources
Vesiclepedia. www.microvesicles.org/
1. Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329-339. doi:10.1083/jcb.97.2.329
2. Huo L, Du X, Li X, et al. The emerging role of neural cell-derived exosomes in intercellular communication in health and neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:738442. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021
3. Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138
4. Keerthikumar S, Chisanga D, Ariyaratne D, et al. ExoCarta: a web-based compendium of exosomal cargo. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(4):688-692. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.019
5. Babst M. A protein’s final ESCRT. Traffic. 2005;6(1):2-9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00246.x
6. Anakor E, Le Gall L, Dumonceaux J, et al. Exosomes in ageing and motor neurone disease: biogenesis, uptake mechanisms, modifications in disease and uses in the development of biomarkers and therapeutics. Cells. 2021;10(11)29-30. doi:10.3390/cells10112930
7. Chivet M, Javalet C, Hemming F, et al. Exosomes as a novel way of interneuronal communication. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(1):241-244. doi:10.1042/BST20120266
8. Liu HY, Huang CM, Hung YF, et al. The microRNAs Let7c and miR21 are recognized by neuronal Toll-like receptor 7 to restrict dendritic growth of neurons. Exp Neurol. 2015;269:202-212. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.04.011
9. Antonucci F, Turola E, Riganti L, et al. Microvesicles released from microglia stimulate synaptic activity via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism. EMBO J. 2012;31(5):1231-1240. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.489
10. Goncalves MB, Malmqvist T, Clarke E, et al. Neuronal RARβ signaling modulates PTEN activity directly in neurons and via exosome transfer in astrocytes to prevent glial scar formation and induce spinal cord regeneration. J Neurosci. 2015;35(47):15731-15745. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1339-15.2015
11. Korkut C, Li Y, Koles K, et al. Regulation of postsynaptic retrograde signaling by presynaptic exosome release. Neuron. 2013;77(6):1039-1046. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.01.013
12. Chivet M, Javalet C, Laulagnier K, et al. Exosomes secreted by cortical neurons upon glutamatergic synapse activation specifically interact with neurons. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(1):24722. doi:10.3402/jev.v3
13. Dickens AM, Tovar-Y-Romo LB, Yoo SW, et al. Astrocyte-shed extracellular vesicles regulate the peripheral leukocyte response to inflammatory brain lesions. Sci Signal. 2017;10(473). doi:10.1126/scisignal.aai7696
14. Strawn J, Levine A. Treatment response biomarkers in anxiety disorders: from neuroimaging to neuronally-derived extracellular vesicles and beyond. Biomark Neuropsychiatry. 2020;3:100024.
15. Liu Y, Li D, Liu Z, et al. Targeted exosome-mediated delivery of opioid receptor Mu siRNA for the treatment of morphine relapse. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17543. doi:10.1038/srep17543
16. Shahjin F, Chand S, Yelamanchili S V. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery vehicles to the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020;15(3):443-458. doi:10.1007/s11481-019-09875-w
17. Murphy DE, de Jong OG, Brouwer M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(3):1-12. doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0223-5
18. Meng W, He C, Hao Y, et al. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):585-598. doi:10.1080/10717544.2020.1748758
Twitter, a microblogging and social networking service, has become a “go-to’” for conversations, updates, breaking news, and sharing the more mundane aspects of our lives. Tweets, which were lengthened from 140 to 280 characters in 2017, rapidly communicate and disseminate information to a wide audience. Generally, tweets are visible to everyone, though users can mute and block other users from viewing their tweets. Spikes in tweets and tweeting frequency reflect hyper-current events: the last minutes of the Super Bowl, certification of an election, or a new movie release. In fact, social scientists have analyzed tweet frequencies to examine the impact of local and national events. However, few are aware that like celebrities, politicians, influencers, and ordinary citizens, the human brain also tweets.
In this article, we describe the components of the brain’s “Twitter” system, how it works, and how it might someday be used to improve the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders.
Brain tweets
The brain’s Twitter system involves extracellular vesicles (EVs), tiny (<1 µm) membrane-bound vesicles that are released from neurons, glia, and other neuronal cells (Table). These EVs cross the blood-brain barrier and facilitate cell-to-cell communication within and among tissues (Figure 1).
First described in the 1980s,1 EVs are secreted by a diverse array of cells: mast cells reticulocytes, epithelial cells, immune cells, neurons, glia, and oligodendrocytes. Like tweets, EVs rapidly disseminate packets of information throughout the brain and body and direct the molecular activity of recipient cells in both health and disease. These “brain tweets” contain short, circumscribed messages, and the characters are the EV cargos: RNAs, proteins, lipids, and metabolites. Like a Twitter feed, EVs cast a wide communication net across the body, much of which finds its way to the blood. As neuroscientists, we can follow these tweets by isolating tissue-derived EVs in plasma and examining their surface molecules and cargo. By following this Twitter feed, we can tap into important molecular communications and identify “trending” (evolving) pathological processes, and perhaps use the brain Twitter feed to improve diagnosis and treatments. We can pinpoint, in the blood, signals from CNS processes, down to the level of identifying EV cargos from specific brain cell types.

Within the CNS, EVs are secreted by neurons, where they may modulate synaptic plasticity and transfer molecular cargo among neurons. EVs also facilitate communication between neurons and glia, maintain homeostasis, trigger neuroprotective processes, and even regulate synaptic transmission.2
What’s in a brain tweet?
To discuss what’s in a brain tweet, we must first understand how a brain tweet is composed. EVs are pinched off from membranes of intercellular structures (eg, golgi or endoplasmic reticulum) or pinched off directly from cell membranes, where upon release they become EVs. There is a complex cellular machinery that transports what ultimately becomes an EV to the cell membrane.3 EVs contain unique mixtures of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (eg, microRNA [miRNA], mRNA, and noncoding RNA).4 To date, nearly 10,000 proteins, 11,000 lipids, 3,500 mRNAs, and 3,000 miRNAs have been identified as cargos in extracellular vesicles (Figure 1). Similar to how the release of EVs is dependent on complex intracellular machinery, the packing of these contents into what will become the EV involves a parallel set of complex machinery that is largely directed by endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins.5 Of interest, when viruses attack cells, they hijack this EV packaging system to package and release new viruses. EVs vary in size, shape, and density; this variation is related to the cell origin, among other things. EVs also differ in their membrane lipid composition and in terms of transmembrane proteins as well as the proteins that facilitate EV binding to target cells (Figure 2).6 Ultimately, these exosomes are taken up by the recipient cells.

EV-facilitated neuron-to-neuron tweets have been implicated in neuronal growth and differentiation.7 EV-driven communication between cells also can decrease dendrite growth and can trigger microglia to prune synapses.8 EVs from glial cells may promote neuronal integrity, directly boost presynaptic glutamate release,9 or even, through miRNAs, change the expression of glutamate receptors.10 EVs from astrocytes transport proteins that enable neuronal repair, while EVs from microglia regulate neuronal homeostasis. EV cargos—lipids, proteins, and miRNAs—from neurons modify signal transduction and protein expression in recipient cells. Taken together, data suggest that EVs facilitate anterograde and retrograde transfer of signals across synapses,7,11 a putative mechanism for driving synaptic plasticity,12 which is a process implicated in the therapeutic efficacy of psychotropic medications and psychotherapies.
Continue to: #Targets and #neuron
#Targets and #neuron
Adding a hashtag to a tweet links it to other tweets, just as membrane features of EVs direct how EVs link to target cells. When these EVs bind to target cells, they fuse and release their cargo into the target cell (Figure 2). These directed cargo—whether mRNA, proteins, or other molecules—can direct the recipient cell to modify its firing rate (in the case of neurons), alter transmitter release, and increase or decrease expression of various genes. The targeting process is complex, and our understanding of this process is evolving. Briefly, integrin, lipid composition, glycans (eg, polysaccharides), and tetraspanin components of EVs influence their affinity for specific target cells.13 Recently, we have been able to read these hashtags and isolate cell-specific, neuron-derived EVs. Immunoadsorption techniques that leverage antibodies against L1 cell adhesion molecule protein (L1CAM(+)), primarily expressed in neurons, can identify neuronally-derived EVs (Figure 3). The specific EVs contain cargos of neuronal origin and provide a “window” into molecular processes in the brain by way of the blood (or other peripheral fluids). In following the neuronal tweets, we can follow molecular measures of important brain molecules in biofluids outside the CNS, including saliva and potentially urine (Figure 1B and 1C). In following these specific neuronal Twitter feeds, we can gain critical insights into specific brain processes.

EVs in psychiatric disorders
EVs are implicated in neuroinflammation,14 neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and epigenetic regulation—all processes that are involved in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Postmortem research suggests that EVs in the brain carry proinflammatory molecules from microglia, as well as secretions of regulatory miRNA that are responsible for synaptic plasticity and dendritic growth in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and addiction. In addition, second-generation antipsychotics change the composition of EV cargos in the brain, altering their RNA, protein, and lipid content, often reflecting profound changes in gene expression in various cells in the CNS. In our lab, we have identified several molecules in plasma EVs, both lipids and miRNA, that can potentially predict the response to treatment of pediatric anxiety with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as well as opiate addiction.15
Further, given our increasing understanding of the way in which EV cargo reflects neuronal physiology as well as the potential pathophysiologic states of cells (including neurons), studying EVs’ molecular content can identify molecular messages—in blood—that are derived from the neurons in the brain. Having the tools to examine molecular brain regulators or other markers of disease progression (eg, beta amyloid) or brain health (eg, brain-derived neurotrophic factor) may advance our understanding and treatment of psychiatric disorders and create opportunities for precision medicine driven by biological rather than ethnologic and phenomenological markers. Whereas in the not-too-distant past molecular processes in the brain were only accessible through invasive measures—such as brain biopsy or through a lumbar puncture—studying CNS-derived EVs in blood offers us an opportunity to gain access to brain molecular signatures with relative ease. Often, these molecular signatures predate clinical changes by years or months, allowing us the prospects of potentially identifying and treating CNS disorders early on, possibly even before the onset of symptoms.
Therapeutic use of the Twitter feed
EV may be used to alter brain receptor structures in a targeted way to facilitate treatment of various psychiatric disorders. One example is a proof-of-concept study in mice in which administration of artificially manufactured EVs led to a decrease of opioid receptor mu.16 This was done by constructing EVs that carry neuron-specific rabies viral glycoprotein (RVG) peptide on the membrane surface to deliver mu opioid receptor small interfering RNA into the brain. This resulted in downregulation of mu opioid receptor and a decrease in morphine relapse.16
Additional ways in which EVs can be used therapeutically is via targeted drug delivery CNS methods. EVs may represent the next generation of treatment by allowing not only medication transport into the CNS,17 but also by facilitating directed CNS transport. What if we could use a molecular hashtag to send a dopaminergic agent to the substantia nigra of a patient with Parkinson disease but avoid sending that same treatment to the limbic cortex, where it might produce perceptual disturbances or hallucinations? In the future, EVs may help clinicians access the CNS, which is traditionally restricted by the blood brain barrier, and make it easier to achieve CNS concentrations of medications13 while decreasing medication exposure in other parts of the body. The therapeutic potential of EVs for medication delivery and regenerative medicine is awe-inspiring. Several studies have modified EVs to improve their therapeutic properties and to target delivery to specific cells13 by leveraging EV surface markers.18
Future directions for EVs
A better understanding of neuron-derived EVs may eventually help us abandon nosology-based diagnostic criteria and adopt molecular-based diagnostic approaches in psychiatry. It may allow us to consider a molecular synaptic etiology of psychiatric disorders, and diagnose patients based on synaptic pathology utilizing “neuron-derived EV liquid biopsies.” Such a shift would align psychiatry with other medical fields in which diagnosis and treatment are often based on biopsies and blood tests. Because proteins in EVs often exist in their native states, intact with their posttranslational modifications, they provide a window into testing their actual in vivo functioning. EVs have an immense potential to revolutionize psychiatric diagnosis, facilitate precision treatment, predict response, and discover much-needed novel therapeutics.
Bottom Line
Much like a tweet, extracellular vesicles (EVs) encode short messages that are transmit ted efficiently throughout the CNS and body. They may represent a reservoir for CNS-specific biomarkers that can be is olated from plasma to guide psychiatric diagnosis and treatment. EVs represent a new frontier in the molecular study of psychiatric illness.
Related Resources
Vesiclepedia. www.microvesicles.org/
Twitter, a microblogging and social networking service, has become a “go-to’” for conversations, updates, breaking news, and sharing the more mundane aspects of our lives. Tweets, which were lengthened from 140 to 280 characters in 2017, rapidly communicate and disseminate information to a wide audience. Generally, tweets are visible to everyone, though users can mute and block other users from viewing their tweets. Spikes in tweets and tweeting frequency reflect hyper-current events: the last minutes of the Super Bowl, certification of an election, or a new movie release. In fact, social scientists have analyzed tweet frequencies to examine the impact of local and national events. However, few are aware that like celebrities, politicians, influencers, and ordinary citizens, the human brain also tweets.
In this article, we describe the components of the brain’s “Twitter” system, how it works, and how it might someday be used to improve the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders.
Brain tweets
The brain’s Twitter system involves extracellular vesicles (EVs), tiny (<1 µm) membrane-bound vesicles that are released from neurons, glia, and other neuronal cells (Table). These EVs cross the blood-brain barrier and facilitate cell-to-cell communication within and among tissues (Figure 1).
First described in the 1980s,1 EVs are secreted by a diverse array of cells: mast cells reticulocytes, epithelial cells, immune cells, neurons, glia, and oligodendrocytes. Like tweets, EVs rapidly disseminate packets of information throughout the brain and body and direct the molecular activity of recipient cells in both health and disease. These “brain tweets” contain short, circumscribed messages, and the characters are the EV cargos: RNAs, proteins, lipids, and metabolites. Like a Twitter feed, EVs cast a wide communication net across the body, much of which finds its way to the blood. As neuroscientists, we can follow these tweets by isolating tissue-derived EVs in plasma and examining their surface molecules and cargo. By following this Twitter feed, we can tap into important molecular communications and identify “trending” (evolving) pathological processes, and perhaps use the brain Twitter feed to improve diagnosis and treatments. We can pinpoint, in the blood, signals from CNS processes, down to the level of identifying EV cargos from specific brain cell types.

Within the CNS, EVs are secreted by neurons, where they may modulate synaptic plasticity and transfer molecular cargo among neurons. EVs also facilitate communication between neurons and glia, maintain homeostasis, trigger neuroprotective processes, and even regulate synaptic transmission.2
What’s in a brain tweet?
To discuss what’s in a brain tweet, we must first understand how a brain tweet is composed. EVs are pinched off from membranes of intercellular structures (eg, golgi or endoplasmic reticulum) or pinched off directly from cell membranes, where upon release they become EVs. There is a complex cellular machinery that transports what ultimately becomes an EV to the cell membrane.3 EVs contain unique mixtures of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (eg, microRNA [miRNA], mRNA, and noncoding RNA).4 To date, nearly 10,000 proteins, 11,000 lipids, 3,500 mRNAs, and 3,000 miRNAs have been identified as cargos in extracellular vesicles (Figure 1). Similar to how the release of EVs is dependent on complex intracellular machinery, the packing of these contents into what will become the EV involves a parallel set of complex machinery that is largely directed by endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins.5 Of interest, when viruses attack cells, they hijack this EV packaging system to package and release new viruses. EVs vary in size, shape, and density; this variation is related to the cell origin, among other things. EVs also differ in their membrane lipid composition and in terms of transmembrane proteins as well as the proteins that facilitate EV binding to target cells (Figure 2).6 Ultimately, these exosomes are taken up by the recipient cells.

EV-facilitated neuron-to-neuron tweets have been implicated in neuronal growth and differentiation.7 EV-driven communication between cells also can decrease dendrite growth and can trigger microglia to prune synapses.8 EVs from glial cells may promote neuronal integrity, directly boost presynaptic glutamate release,9 or even, through miRNAs, change the expression of glutamate receptors.10 EVs from astrocytes transport proteins that enable neuronal repair, while EVs from microglia regulate neuronal homeostasis. EV cargos—lipids, proteins, and miRNAs—from neurons modify signal transduction and protein expression in recipient cells. Taken together, data suggest that EVs facilitate anterograde and retrograde transfer of signals across synapses,7,11 a putative mechanism for driving synaptic plasticity,12 which is a process implicated in the therapeutic efficacy of psychotropic medications and psychotherapies.
Continue to: #Targets and #neuron
#Targets and #neuron
Adding a hashtag to a tweet links it to other tweets, just as membrane features of EVs direct how EVs link to target cells. When these EVs bind to target cells, they fuse and release their cargo into the target cell (Figure 2). These directed cargo—whether mRNA, proteins, or other molecules—can direct the recipient cell to modify its firing rate (in the case of neurons), alter transmitter release, and increase or decrease expression of various genes. The targeting process is complex, and our understanding of this process is evolving. Briefly, integrin, lipid composition, glycans (eg, polysaccharides), and tetraspanin components of EVs influence their affinity for specific target cells.13 Recently, we have been able to read these hashtags and isolate cell-specific, neuron-derived EVs. Immunoadsorption techniques that leverage antibodies against L1 cell adhesion molecule protein (L1CAM(+)), primarily expressed in neurons, can identify neuronally-derived EVs (Figure 3). The specific EVs contain cargos of neuronal origin and provide a “window” into molecular processes in the brain by way of the blood (or other peripheral fluids). In following the neuronal tweets, we can follow molecular measures of important brain molecules in biofluids outside the CNS, including saliva and potentially urine (Figure 1B and 1C). In following these specific neuronal Twitter feeds, we can gain critical insights into specific brain processes.

EVs in psychiatric disorders
EVs are implicated in neuroinflammation,14 neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and epigenetic regulation—all processes that are involved in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Postmortem research suggests that EVs in the brain carry proinflammatory molecules from microglia, as well as secretions of regulatory miRNA that are responsible for synaptic plasticity and dendritic growth in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and addiction. In addition, second-generation antipsychotics change the composition of EV cargos in the brain, altering their RNA, protein, and lipid content, often reflecting profound changes in gene expression in various cells in the CNS. In our lab, we have identified several molecules in plasma EVs, both lipids and miRNA, that can potentially predict the response to treatment of pediatric anxiety with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as well as opiate addiction.15
Further, given our increasing understanding of the way in which EV cargo reflects neuronal physiology as well as the potential pathophysiologic states of cells (including neurons), studying EVs’ molecular content can identify molecular messages—in blood—that are derived from the neurons in the brain. Having the tools to examine molecular brain regulators or other markers of disease progression (eg, beta amyloid) or brain health (eg, brain-derived neurotrophic factor) may advance our understanding and treatment of psychiatric disorders and create opportunities for precision medicine driven by biological rather than ethnologic and phenomenological markers. Whereas in the not-too-distant past molecular processes in the brain were only accessible through invasive measures—such as brain biopsy or through a lumbar puncture—studying CNS-derived EVs in blood offers us an opportunity to gain access to brain molecular signatures with relative ease. Often, these molecular signatures predate clinical changes by years or months, allowing us the prospects of potentially identifying and treating CNS disorders early on, possibly even before the onset of symptoms.
Therapeutic use of the Twitter feed
EV may be used to alter brain receptor structures in a targeted way to facilitate treatment of various psychiatric disorders. One example is a proof-of-concept study in mice in which administration of artificially manufactured EVs led to a decrease of opioid receptor mu.16 This was done by constructing EVs that carry neuron-specific rabies viral glycoprotein (RVG) peptide on the membrane surface to deliver mu opioid receptor small interfering RNA into the brain. This resulted in downregulation of mu opioid receptor and a decrease in morphine relapse.16
Additional ways in which EVs can be used therapeutically is via targeted drug delivery CNS methods. EVs may represent the next generation of treatment by allowing not only medication transport into the CNS,17 but also by facilitating directed CNS transport. What if we could use a molecular hashtag to send a dopaminergic agent to the substantia nigra of a patient with Parkinson disease but avoid sending that same treatment to the limbic cortex, where it might produce perceptual disturbances or hallucinations? In the future, EVs may help clinicians access the CNS, which is traditionally restricted by the blood brain barrier, and make it easier to achieve CNS concentrations of medications13 while decreasing medication exposure in other parts of the body. The therapeutic potential of EVs for medication delivery and regenerative medicine is awe-inspiring. Several studies have modified EVs to improve their therapeutic properties and to target delivery to specific cells13 by leveraging EV surface markers.18
Future directions for EVs
A better understanding of neuron-derived EVs may eventually help us abandon nosology-based diagnostic criteria and adopt molecular-based diagnostic approaches in psychiatry. It may allow us to consider a molecular synaptic etiology of psychiatric disorders, and diagnose patients based on synaptic pathology utilizing “neuron-derived EV liquid biopsies.” Such a shift would align psychiatry with other medical fields in which diagnosis and treatment are often based on biopsies and blood tests. Because proteins in EVs often exist in their native states, intact with their posttranslational modifications, they provide a window into testing their actual in vivo functioning. EVs have an immense potential to revolutionize psychiatric diagnosis, facilitate precision treatment, predict response, and discover much-needed novel therapeutics.
Bottom Line
Much like a tweet, extracellular vesicles (EVs) encode short messages that are transmit ted efficiently throughout the CNS and body. They may represent a reservoir for CNS-specific biomarkers that can be is olated from plasma to guide psychiatric diagnosis and treatment. EVs represent a new frontier in the molecular study of psychiatric illness.
Related Resources
Vesiclepedia. www.microvesicles.org/
1. Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329-339. doi:10.1083/jcb.97.2.329
2. Huo L, Du X, Li X, et al. The emerging role of neural cell-derived exosomes in intercellular communication in health and neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:738442. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021
3. Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138
4. Keerthikumar S, Chisanga D, Ariyaratne D, et al. ExoCarta: a web-based compendium of exosomal cargo. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(4):688-692. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.019
5. Babst M. A protein’s final ESCRT. Traffic. 2005;6(1):2-9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00246.x
6. Anakor E, Le Gall L, Dumonceaux J, et al. Exosomes in ageing and motor neurone disease: biogenesis, uptake mechanisms, modifications in disease and uses in the development of biomarkers and therapeutics. Cells. 2021;10(11)29-30. doi:10.3390/cells10112930
7. Chivet M, Javalet C, Hemming F, et al. Exosomes as a novel way of interneuronal communication. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(1):241-244. doi:10.1042/BST20120266
8. Liu HY, Huang CM, Hung YF, et al. The microRNAs Let7c and miR21 are recognized by neuronal Toll-like receptor 7 to restrict dendritic growth of neurons. Exp Neurol. 2015;269:202-212. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.04.011
9. Antonucci F, Turola E, Riganti L, et al. Microvesicles released from microglia stimulate synaptic activity via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism. EMBO J. 2012;31(5):1231-1240. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.489
10. Goncalves MB, Malmqvist T, Clarke E, et al. Neuronal RARβ signaling modulates PTEN activity directly in neurons and via exosome transfer in astrocytes to prevent glial scar formation and induce spinal cord regeneration. J Neurosci. 2015;35(47):15731-15745. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1339-15.2015
11. Korkut C, Li Y, Koles K, et al. Regulation of postsynaptic retrograde signaling by presynaptic exosome release. Neuron. 2013;77(6):1039-1046. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.01.013
12. Chivet M, Javalet C, Laulagnier K, et al. Exosomes secreted by cortical neurons upon glutamatergic synapse activation specifically interact with neurons. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(1):24722. doi:10.3402/jev.v3
13. Dickens AM, Tovar-Y-Romo LB, Yoo SW, et al. Astrocyte-shed extracellular vesicles regulate the peripheral leukocyte response to inflammatory brain lesions. Sci Signal. 2017;10(473). doi:10.1126/scisignal.aai7696
14. Strawn J, Levine A. Treatment response biomarkers in anxiety disorders: from neuroimaging to neuronally-derived extracellular vesicles and beyond. Biomark Neuropsychiatry. 2020;3:100024.
15. Liu Y, Li D, Liu Z, et al. Targeted exosome-mediated delivery of opioid receptor Mu siRNA for the treatment of morphine relapse. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17543. doi:10.1038/srep17543
16. Shahjin F, Chand S, Yelamanchili S V. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery vehicles to the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020;15(3):443-458. doi:10.1007/s11481-019-09875-w
17. Murphy DE, de Jong OG, Brouwer M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(3):1-12. doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0223-5
18. Meng W, He C, Hao Y, et al. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):585-598. doi:10.1080/10717544.2020.1748758
1. Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329-339. doi:10.1083/jcb.97.2.329
2. Huo L, Du X, Li X, et al. The emerging role of neural cell-derived exosomes in intercellular communication in health and neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:738442. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021
3. Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138
4. Keerthikumar S, Chisanga D, Ariyaratne D, et al. ExoCarta: a web-based compendium of exosomal cargo. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(4):688-692. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.019
5. Babst M. A protein’s final ESCRT. Traffic. 2005;6(1):2-9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00246.x
6. Anakor E, Le Gall L, Dumonceaux J, et al. Exosomes in ageing and motor neurone disease: biogenesis, uptake mechanisms, modifications in disease and uses in the development of biomarkers and therapeutics. Cells. 2021;10(11)29-30. doi:10.3390/cells10112930
7. Chivet M, Javalet C, Hemming F, et al. Exosomes as a novel way of interneuronal communication. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(1):241-244. doi:10.1042/BST20120266
8. Liu HY, Huang CM, Hung YF, et al. The microRNAs Let7c and miR21 are recognized by neuronal Toll-like receptor 7 to restrict dendritic growth of neurons. Exp Neurol. 2015;269:202-212. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.04.011
9. Antonucci F, Turola E, Riganti L, et al. Microvesicles released from microglia stimulate synaptic activity via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism. EMBO J. 2012;31(5):1231-1240. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.489
10. Goncalves MB, Malmqvist T, Clarke E, et al. Neuronal RARβ signaling modulates PTEN activity directly in neurons and via exosome transfer in astrocytes to prevent glial scar formation and induce spinal cord regeneration. J Neurosci. 2015;35(47):15731-15745. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1339-15.2015
11. Korkut C, Li Y, Koles K, et al. Regulation of postsynaptic retrograde signaling by presynaptic exosome release. Neuron. 2013;77(6):1039-1046. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.01.013
12. Chivet M, Javalet C, Laulagnier K, et al. Exosomes secreted by cortical neurons upon glutamatergic synapse activation specifically interact with neurons. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(1):24722. doi:10.3402/jev.v3
13. Dickens AM, Tovar-Y-Romo LB, Yoo SW, et al. Astrocyte-shed extracellular vesicles regulate the peripheral leukocyte response to inflammatory brain lesions. Sci Signal. 2017;10(473). doi:10.1126/scisignal.aai7696
14. Strawn J, Levine A. Treatment response biomarkers in anxiety disorders: from neuroimaging to neuronally-derived extracellular vesicles and beyond. Biomark Neuropsychiatry. 2020;3:100024.
15. Liu Y, Li D, Liu Z, et al. Targeted exosome-mediated delivery of opioid receptor Mu siRNA for the treatment of morphine relapse. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17543. doi:10.1038/srep17543
16. Shahjin F, Chand S, Yelamanchili S V. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery vehicles to the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020;15(3):443-458. doi:10.1007/s11481-019-09875-w
17. Murphy DE, de Jong OG, Brouwer M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(3):1-12. doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0223-5
18. Meng W, He C, Hao Y, et al. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):585-598. doi:10.1080/10717544.2020.1748758
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film for agitation
Approved by the FDA on April 5, 2022, dexmedetomidine sublingual film (Igalmi, manufactured and distributed by BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc., New Haven, CT USA) is indicated in adults for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder (Table).1,2 It is administered sublingually or buccally under the supervision of a health care provider. After administration, patients should have their vital signs and alertness assessed but there is no FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) required for use. A limitation of use is that the safety and effectiveness of dexmedetomidine sublingual film has not been established beyond 24 hours from the first dose.2 There are no contraindications for use.2
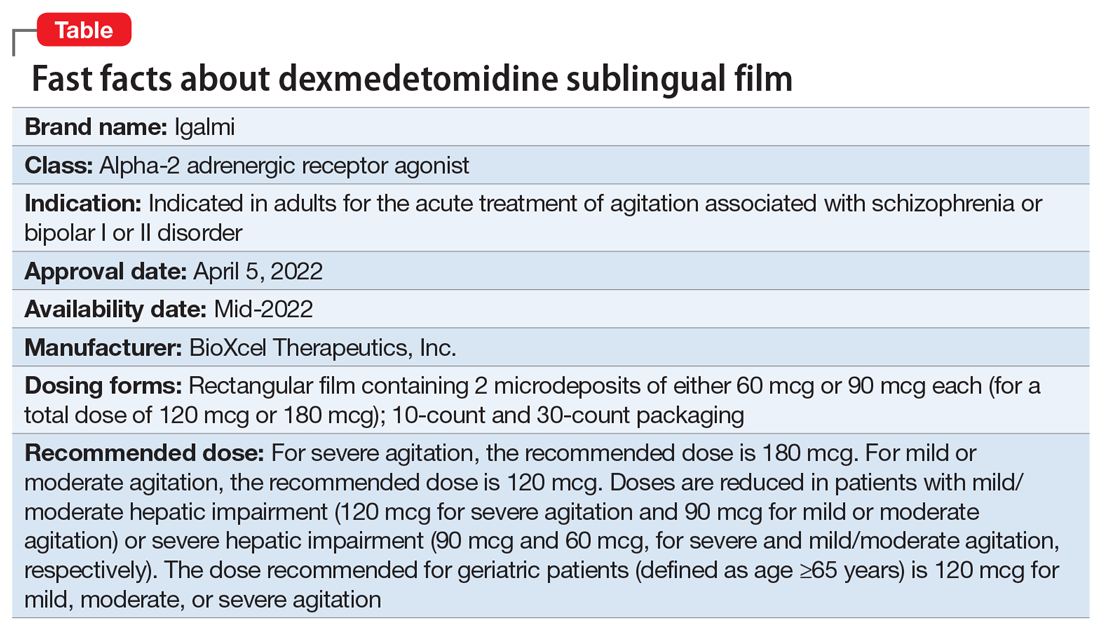
Dexmedetomidine is a well-known efficacious alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist available since 1999 in an IV formulation indicated for sedation of initially intubated and mechanically ventilated patients in an ICU setting, and sedation of nonintubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures.3,4 The reformulation of dexmedetomidine as a sublingual film allows the broader use of this agent in psychiatric settings when managing agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, and thus potentially avoiding the use of IM administration of antipsychotics and/or benzodiazepines. Noninvasive formulations, although requiring cooperation from patients, have the potential to improve overall patient experience, thereby improving future cooperation between patients and health care professionals.5
Dosing
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film is distributed commercially in the following strengths: 180 mcg and 120 mcg. It consists of a lightly mint-flavored, rectangular film containing 2 microdeposits of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride. Dosage strengths of 90 mcg and 60 mcg are available by cutting the 180 mcg or 120 mcg film in half
If agitation persists after the initial dose, up to 2 additional doses (90 mcg if the initial dose was 180 mcg, otherwise 60 mcg if the initial dose was 120, 90, or 60 mcg) may be given at least 2 hours apart. Assessment of vital signs, including orthostatic measurements, is required prior to the administration of any subsequent doses. Due to risk of hypotension, additional doses are not recommended in patients with systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure <60 mm Hg, heart rate <60 beats per minute, or postural decrease in systolic blood pressure ≥20 mm Hg or in diastolic blood pressure ≥10 mm Hg.
Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics
Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist and the mechanism of action in the acute treatment of agitation is thought to be due to activation of presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors.2 Binding affinities (Ki values) are 4 to 6 nM at the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes.2
Dexmedetomidine exhibits concentration-dependent QT prolongation, with mean QTc increases from baseline from 6 msec (120 mcg single dose) to 11 msec (180 mcg plus 2 additional doses of 90 mcg 2 hours apart for a total of 3 doses).2 Placing the observation about QTc prolongation into clinical context, studies of IM administration of ziprasidone 20 mg and 30 mg and haloperidol 7.5 mg and 10 mg resulted in changes of the QTc interval of 4.6 msec and 6.0 msec, respectively, after 1 dose.6 After a second injection, these values were 12.8 msec and 14.7 msec, respectively.6
Clinical pharmacokinetics
The sublingual film formulation is absorbed orally, bypassing first-pass metabolism, and achieving higher dexmedetomidine bioavailability than ingested formulations.7 Exposure is dose-dependent, with dexmedetomidine being quantifiable in plasma after 5 to 20 minutes post dosing, and with a plasma half-life of 2 to 3 hours.2,8 Mean time for the film to dissolve in the mouth was approximately 6 to 8 minutes following sublingual administration, and 18 minutes following buccal administration.2 Absolute bioavailability was approximately 72% and 82% following sublingual and buccal administration, respectively.2 Mean maximal plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine were reached approximately 2 hours after sublingual or buccal administration.2 Compared to drinking water at 2 hours post administration, early water intake (as early as 15 minutes post-dose) had minimal effects on the rate or extent of sublingual absorption but was not assessed after buccal administration.2 The average protein binding was 94% and was constant across the different plasma concentrations evaluated and similar in males and females, but significantly decreased in participants with hepatic impairment compared to healthy individuals.2 In contrast, the pharmacokinetic profile of dexmedetomidine is not significantly different in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/minute compared to those with normal renal function.2 Dexmedetomidine undergoes almost complete biotransformation to inactive metabolites via direct glucuronidation as well as cytochrome P450 (CYP) (primarily CYP2A6)–mediated metabolism.2 There is no evidence of any CYP–mediated drug interactions that are likely to be of clinical relevance.2
Continue to: Efficacy
Efficacy
The efficacy and tolerability of 120 mcg and 180 mcg doses of dexmedetomidine sublingual film was evaluated in 2 similarly designed, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trials in the treatment of acute agitation associated with schizophrenia, schizoaffective, or schizophreniform disorder9 and bipolar I or II disorder.10 These studies included a total of 758 adult patients age range 18 to 71 (mean age approximately 46.5), with about 59% male participants.2 In contrast to other agents approved by the FDA for treatment of agitation associated with bipolar disorder, dexmedetomidine sublingual film was assessed in patients regardless of polarity (manic, mixed features, or depressed).5 The primary efficacy measure for the dexmedetomidine sublingual film studies was the investigator-administered Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component (PANSS-EC), consisting of the following 5 items: excitement, tension, hostility, uncooperativeness, and poor impulse control.11 The items from the PANSS-EC are rated from 1 (not present) to 7 (extremely severe) and thus the total scores range from 5 to 35. For enrollment in the studies, patients had to be judged to be clinically agitated with a total PANSS-EC score ≥14, with at least 1 individual item score ≥4.2
After study medication administration, the PANSS-EC was assessed from 10 minutes through 24 hours, with the primary endpoint being at 2 hours post-dose. Patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder who were treated with dexmedetomidine sublingual film 120 mcg or 180 mcg had superior symptomatic improvements from baseline to 2 hours post-dose compared to placebo, with treatment effects beginning as early as 20 to 30 minutes post-dose (for patients with schizophrenia, dexmedetomidine was statistically significantly superior to placebo beginning at 20 minutes following dosing with the 180 mcg dose and 30 minutes after the 120 mcg dose; for patients with bipolar disorder, differences from placebo were statistically significant beginning at 20 minutes after treatment with both the 120 mcg and 180 mcg doses).2 Evaluation of effect size for dexmedetomidine vs placebo for PANSS-EC response at 2 hours (defined as ≥40% improvement from baseline) resulted in a number needed to treat (NNT) of 3 when combining both studies and both doses,12 comparing favorably with the NNT values observed for IM formulations of aripiprazole, haloperidol, lorazepam, olanzapine, and ziprasidone,13 and inhaled loxapine.14
Overall tolerability and safety
The highlights of the prescribing information contain warnings and precautions regarding hypotension/orthostatic hypotension/bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and somnolence.2 Advice is provided to ensure that patients are alert and not experiencing orthostatic or symptomatic hypotension prior to resuming ambulation, a concern commonly raised when assessing potential treatments for agitation.15 Dexmedetomidine sublingual film should be avoided in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval, a precaution that was evident for the use of ziprasidone16 and where an effect is also noted with haloperidol.6 As per the prescribing information, the most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo) are somnolence, oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia, dizziness, dry mouth, hypotension, and orthostatic hypotension. Rates of adverse reactions of somnolence (including fatigue and sluggishness) with dexmedetomidine 120 mcg or 180 mcg are almost the same (22% and 23%, respectively), and higher than the 6% observed with placebo.2 Other adverse reactions are substantially lower in frequency. These include oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia (6%, 7%, and 1%, for dexmedetomidine 120 mcg, 180 mcg, or placebo, respectively), dizziness (4%, 6%, 1%), hypotension (5%, 5%, 0%), orthostatic hypotension (3%, 5%, <1%), dry mouth (7%, 4%, 1%), nausea (2%, 3%, 2%), bradycardia (2%, 2%, 0%), and abdominal discomfort (0%, 2%, 1%).2
Regarding dose-dependent changes in blood pressure during the studies, 16%, 18%, and 9% of patients treated with 120 mcg, 180 mcg, and placebo, respectively, experienced orthostatic hypotension at 2 hours post dose. However, at 24 hours, none of the patients in the 180-mcg group experienced a systolic blood pressure ≤90 mm Hg with a decrease ≥20 mm Hg, compared with one patient (<1%) in the 120-mcg group and none in the placebo group.2
The prescribing information advises that concomitant use of dexmedetomidine sublingual film with anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, or opioids is likely to lead to enhanced CNS depressant effects, and that the prescriber should consider a reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine or the concomitant anesthetic, sedative, hypnotic, or opioid.2
Summary
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film is an oral medication indicated in adults for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder. The recommended dose depends on severity of agitation, age, and the presence of hepatic impairment. A dose of 180 mcg is recommended for severe agitation and a dose of 120 mcg is recommended for mild or moderate agitation, with doses adjusted lower in the presence of hepatic impairment. There are no contraindications but there are warnings and precautions regarding hypotension/orthostatic hypotension/bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and somnolence. Clinicians should monitor vital signs and alertness after administration to prevent falls and syncope; however, there is no FDA REMS required for use. The clinical trial evidence supporting the use of dexmedetomidine is robust, with evidence of a treatment effect as early as 20 minutes after administration. Noninvasive formulations, although requiring cooperation from patients, have the potential to improve overall patient experience, thereby improving future cooperation between patients and health care professionals.
Bottom Line
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film provides an opportunity to rethink the approach to the management of agitation and avoid the potentially unnecessary use of IM injections. Dexmedetomidine sublingual film acts rapidly and is simple to use.
Related Resources
- Dexmedetomidine sublingual film (Iglami) prescribing information. https://www.igalmihcp.com/igalmi-pi.pdf
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Dexmedetomidine • Igalmi, Precedex
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lorazepam • Ativan
Loxapine inhaled • Adasuve
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. US Food and Drug Administration. NDA 215390 Approval Letter. Accessed April 5, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/215390Orig1s000ltr.pdf
2. Igalmi [package insert]. BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc; 2022.
3. Weerink MAS, Struys MMRF, Hannivoort LN, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(8):893-913. doi:10.1007/s40262-017-0507-7
4. Precedex [package insert]. Hospira, Inc; 2021.
5. Zeller SL, Citrome L. Managing agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in the emergency setting. West J Emerg Med. 2016;17(2):165-172. doi:10.5811/westjem.2015.12.28763
6. Miceli JJ, Tensfeldt TG, Shiovitz T, et al. Effects of high-dose ziprasidone and haloperidol on the QTc interval after intramuscular administration: a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group study in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Clin Ther. 2010;32(3):472-491. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.03.003
7. Yocca F, DeVivo M, Seth S, et al. Dexmedetomidine—highly favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacological features for a CNS therapeutic drug. Poster presented at: 58th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; December 8-11, 2019; Orlando, FL.
8. Adedoyin A, Preskorn S, Lathia CD. Pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine after a single sublingual dose of BXCL501 in patients with agitation associated with schizophrenia. Poster presented at: 23rd Annual Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders; May 13-15, 2021. Virtual. Session 17.
9. Citrome LL, Lauriello J, Risinger R, et al. A novel rapidly effective treatment of agitation for schizophrenia with the oral dissolving film BXCL501. Poster presented at: American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; May 1-3, 2021. Virtual. Accessed November 11, 2021. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Meetings/Annual-Meeting/2021/2021-APA-Annual-Meeting-Poster-Proceedings.pdf
10. Preskorn SH, Zeller S, Citrome L, et al. Effect of sublingual dexmedetomidine vs placebo on acute agitation associated with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327(8):727-736. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0799
11. Montoya A, Valladares A, Lizán L, et al. Validation of the Excited Component of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS-EC) in a naturalistic sample of 278 patients with acute psychosis and agitation in a psychiatric emergency room. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9:18. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-9-18
12. Citrome L, Palko L, Hokett S, et al. Number needed to treat and number needed to harm from two phase 3 studies of BXCL501 for treating acute agitation in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Poster presented at: Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy Nexus 2021; October 18-21, 2021; Denver, CO.
13. Citrome L. Comparison of intramuscular ziprasidone, olanzapine, or aripiprazole for agitation: a quantitative review of efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(12):1876-1885. doi:10.4088/jcp.v68n1207
14. Citrome L. Inhaled loxapine for agitation revisited: focus on effect sizes from 2 Phase III randomised controlled trials in persons with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(3):318-325. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02890.x
15. Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, et al. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry project Beta psychopharmacology workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26-34. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6866
16. Zimbroff DL, Allen MH, Battaglia J, et al. Best clinical practice with ziprasidone IM: update after 2 years of experience. CNS Spectr. 2005;10(9):1-15. doi:10.1017/s1092852900025487
Approved by the FDA on April 5, 2022, dexmedetomidine sublingual film (Igalmi, manufactured and distributed by BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc., New Haven, CT USA) is indicated in adults for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder (Table).1,2 It is administered sublingually or buccally under the supervision of a health care provider. After administration, patients should have their vital signs and alertness assessed but there is no FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) required for use. A limitation of use is that the safety and effectiveness of dexmedetomidine sublingual film has not been established beyond 24 hours from the first dose.2 There are no contraindications for use.2

Dexmedetomidine is a well-known efficacious alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist available since 1999 in an IV formulation indicated for sedation of initially intubated and mechanically ventilated patients in an ICU setting, and sedation of nonintubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures.3,4 The reformulation of dexmedetomidine as a sublingual film allows the broader use of this agent in psychiatric settings when managing agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, and thus potentially avoiding the use of IM administration of antipsychotics and/or benzodiazepines. Noninvasive formulations, although requiring cooperation from patients, have the potential to improve overall patient experience, thereby improving future cooperation between patients and health care professionals.5
Dosing
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film is distributed commercially in the following strengths: 180 mcg and 120 mcg. It consists of a lightly mint-flavored, rectangular film containing 2 microdeposits of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride. Dosage strengths of 90 mcg and 60 mcg are available by cutting the 180 mcg or 120 mcg film in half
If agitation persists after the initial dose, up to 2 additional doses (90 mcg if the initial dose was 180 mcg, otherwise 60 mcg if the initial dose was 120, 90, or 60 mcg) may be given at least 2 hours apart. Assessment of vital signs, including orthostatic measurements, is required prior to the administration of any subsequent doses. Due to risk of hypotension, additional doses are not recommended in patients with systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure <60 mm Hg, heart rate <60 beats per minute, or postural decrease in systolic blood pressure ≥20 mm Hg or in diastolic blood pressure ≥10 mm Hg.
Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics
Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist and the mechanism of action in the acute treatment of agitation is thought to be due to activation of presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors.2 Binding affinities (Ki values) are 4 to 6 nM at the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes.2
Dexmedetomidine exhibits concentration-dependent QT prolongation, with mean QTc increases from baseline from 6 msec (120 mcg single dose) to 11 msec (180 mcg plus 2 additional doses of 90 mcg 2 hours apart for a total of 3 doses).2 Placing the observation about QTc prolongation into clinical context, studies of IM administration of ziprasidone 20 mg and 30 mg and haloperidol 7.5 mg and 10 mg resulted in changes of the QTc interval of 4.6 msec and 6.0 msec, respectively, after 1 dose.6 After a second injection, these values were 12.8 msec and 14.7 msec, respectively.6
Clinical pharmacokinetics
The sublingual film formulation is absorbed orally, bypassing first-pass metabolism, and achieving higher dexmedetomidine bioavailability than ingested formulations.7 Exposure is dose-dependent, with dexmedetomidine being quantifiable in plasma after 5 to 20 minutes post dosing, and with a plasma half-life of 2 to 3 hours.2,8 Mean time for the film to dissolve in the mouth was approximately 6 to 8 minutes following sublingual administration, and 18 minutes following buccal administration.2 Absolute bioavailability was approximately 72% and 82% following sublingual and buccal administration, respectively.2 Mean maximal plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine were reached approximately 2 hours after sublingual or buccal administration.2 Compared to drinking water at 2 hours post administration, early water intake (as early as 15 minutes post-dose) had minimal effects on the rate or extent of sublingual absorption but was not assessed after buccal administration.2 The average protein binding was 94% and was constant across the different plasma concentrations evaluated and similar in males and females, but significantly decreased in participants with hepatic impairment compared to healthy individuals.2 In contrast, the pharmacokinetic profile of dexmedetomidine is not significantly different in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/minute compared to those with normal renal function.2 Dexmedetomidine undergoes almost complete biotransformation to inactive metabolites via direct glucuronidation as well as cytochrome P450 (CYP) (primarily CYP2A6)–mediated metabolism.2 There is no evidence of any CYP–mediated drug interactions that are likely to be of clinical relevance.2
Continue to: Efficacy
Efficacy
The efficacy and tolerability of 120 mcg and 180 mcg doses of dexmedetomidine sublingual film was evaluated in 2 similarly designed, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trials in the treatment of acute agitation associated with schizophrenia, schizoaffective, or schizophreniform disorder9 and bipolar I or II disorder.10 These studies included a total of 758 adult patients age range 18 to 71 (mean age approximately 46.5), with about 59% male participants.2 In contrast to other agents approved by the FDA for treatment of agitation associated with bipolar disorder, dexmedetomidine sublingual film was assessed in patients regardless of polarity (manic, mixed features, or depressed).5 The primary efficacy measure for the dexmedetomidine sublingual film studies was the investigator-administered Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component (PANSS-EC), consisting of the following 5 items: excitement, tension, hostility, uncooperativeness, and poor impulse control.11 The items from the PANSS-EC are rated from 1 (not present) to 7 (extremely severe) and thus the total scores range from 5 to 35. For enrollment in the studies, patients had to be judged to be clinically agitated with a total PANSS-EC score ≥14, with at least 1 individual item score ≥4.2
After study medication administration, the PANSS-EC was assessed from 10 minutes through 24 hours, with the primary endpoint being at 2 hours post-dose. Patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder who were treated with dexmedetomidine sublingual film 120 mcg or 180 mcg had superior symptomatic improvements from baseline to 2 hours post-dose compared to placebo, with treatment effects beginning as early as 20 to 30 minutes post-dose (for patients with schizophrenia, dexmedetomidine was statistically significantly superior to placebo beginning at 20 minutes following dosing with the 180 mcg dose and 30 minutes after the 120 mcg dose; for patients with bipolar disorder, differences from placebo were statistically significant beginning at 20 minutes after treatment with both the 120 mcg and 180 mcg doses).2 Evaluation of effect size for dexmedetomidine vs placebo for PANSS-EC response at 2 hours (defined as ≥40% improvement from baseline) resulted in a number needed to treat (NNT) of 3 when combining both studies and both doses,12 comparing favorably with the NNT values observed for IM formulations of aripiprazole, haloperidol, lorazepam, olanzapine, and ziprasidone,13 and inhaled loxapine.14
Overall tolerability and safety
The highlights of the prescribing information contain warnings and precautions regarding hypotension/orthostatic hypotension/bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and somnolence.2 Advice is provided to ensure that patients are alert and not experiencing orthostatic or symptomatic hypotension prior to resuming ambulation, a concern commonly raised when assessing potential treatments for agitation.15 Dexmedetomidine sublingual film should be avoided in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval, a precaution that was evident for the use of ziprasidone16 and where an effect is also noted with haloperidol.6 As per the prescribing information, the most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo) are somnolence, oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia, dizziness, dry mouth, hypotension, and orthostatic hypotension. Rates of adverse reactions of somnolence (including fatigue and sluggishness) with dexmedetomidine 120 mcg or 180 mcg are almost the same (22% and 23%, respectively), and higher than the 6% observed with placebo.2 Other adverse reactions are substantially lower in frequency. These include oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia (6%, 7%, and 1%, for dexmedetomidine 120 mcg, 180 mcg, or placebo, respectively), dizziness (4%, 6%, 1%), hypotension (5%, 5%, 0%), orthostatic hypotension (3%, 5%, <1%), dry mouth (7%, 4%, 1%), nausea (2%, 3%, 2%), bradycardia (2%, 2%, 0%), and abdominal discomfort (0%, 2%, 1%).2
Regarding dose-dependent changes in blood pressure during the studies, 16%, 18%, and 9% of patients treated with 120 mcg, 180 mcg, and placebo, respectively, experienced orthostatic hypotension at 2 hours post dose. However, at 24 hours, none of the patients in the 180-mcg group experienced a systolic blood pressure ≤90 mm Hg with a decrease ≥20 mm Hg, compared with one patient (<1%) in the 120-mcg group and none in the placebo group.2
The prescribing information advises that concomitant use of dexmedetomidine sublingual film with anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, or opioids is likely to lead to enhanced CNS depressant effects, and that the prescriber should consider a reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine or the concomitant anesthetic, sedative, hypnotic, or opioid.2
Summary
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film is an oral medication indicated in adults for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder. The recommended dose depends on severity of agitation, age, and the presence of hepatic impairment. A dose of 180 mcg is recommended for severe agitation and a dose of 120 mcg is recommended for mild or moderate agitation, with doses adjusted lower in the presence of hepatic impairment. There are no contraindications but there are warnings and precautions regarding hypotension/orthostatic hypotension/bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and somnolence. Clinicians should monitor vital signs and alertness after administration to prevent falls and syncope; however, there is no FDA REMS required for use. The clinical trial evidence supporting the use of dexmedetomidine is robust, with evidence of a treatment effect as early as 20 minutes after administration. Noninvasive formulations, although requiring cooperation from patients, have the potential to improve overall patient experience, thereby improving future cooperation between patients and health care professionals.
Bottom Line
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film provides an opportunity to rethink the approach to the management of agitation and avoid the potentially unnecessary use of IM injections. Dexmedetomidine sublingual film acts rapidly and is simple to use.
Related Resources
- Dexmedetomidine sublingual film (Iglami) prescribing information. https://www.igalmihcp.com/igalmi-pi.pdf
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Dexmedetomidine • Igalmi, Precedex
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lorazepam • Ativan
Loxapine inhaled • Adasuve
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Ziprasidone • Geodon
Approved by the FDA on April 5, 2022, dexmedetomidine sublingual film (Igalmi, manufactured and distributed by BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc., New Haven, CT USA) is indicated in adults for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder (Table).1,2 It is administered sublingually or buccally under the supervision of a health care provider. After administration, patients should have their vital signs and alertness assessed but there is no FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) required for use. A limitation of use is that the safety and effectiveness of dexmedetomidine sublingual film has not been established beyond 24 hours from the first dose.2 There are no contraindications for use.2

Dexmedetomidine is a well-known efficacious alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist available since 1999 in an IV formulation indicated for sedation of initially intubated and mechanically ventilated patients in an ICU setting, and sedation of nonintubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures.3,4 The reformulation of dexmedetomidine as a sublingual film allows the broader use of this agent in psychiatric settings when managing agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, and thus potentially avoiding the use of IM administration of antipsychotics and/or benzodiazepines. Noninvasive formulations, although requiring cooperation from patients, have the potential to improve overall patient experience, thereby improving future cooperation between patients and health care professionals.5
Dosing
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film is distributed commercially in the following strengths: 180 mcg and 120 mcg. It consists of a lightly mint-flavored, rectangular film containing 2 microdeposits of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride. Dosage strengths of 90 mcg and 60 mcg are available by cutting the 180 mcg or 120 mcg film in half
If agitation persists after the initial dose, up to 2 additional doses (90 mcg if the initial dose was 180 mcg, otherwise 60 mcg if the initial dose was 120, 90, or 60 mcg) may be given at least 2 hours apart. Assessment of vital signs, including orthostatic measurements, is required prior to the administration of any subsequent doses. Due to risk of hypotension, additional doses are not recommended in patients with systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure <60 mm Hg, heart rate <60 beats per minute, or postural decrease in systolic blood pressure ≥20 mm Hg or in diastolic blood pressure ≥10 mm Hg.
Mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics
Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist and the mechanism of action in the acute treatment of agitation is thought to be due to activation of presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors.2 Binding affinities (Ki values) are 4 to 6 nM at the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes.2
Dexmedetomidine exhibits concentration-dependent QT prolongation, with mean QTc increases from baseline from 6 msec (120 mcg single dose) to 11 msec (180 mcg plus 2 additional doses of 90 mcg 2 hours apart for a total of 3 doses).2 Placing the observation about QTc prolongation into clinical context, studies of IM administration of ziprasidone 20 mg and 30 mg and haloperidol 7.5 mg and 10 mg resulted in changes of the QTc interval of 4.6 msec and 6.0 msec, respectively, after 1 dose.6 After a second injection, these values were 12.8 msec and 14.7 msec, respectively.6
Clinical pharmacokinetics
The sublingual film formulation is absorbed orally, bypassing first-pass metabolism, and achieving higher dexmedetomidine bioavailability than ingested formulations.7 Exposure is dose-dependent, with dexmedetomidine being quantifiable in plasma after 5 to 20 minutes post dosing, and with a plasma half-life of 2 to 3 hours.2,8 Mean time for the film to dissolve in the mouth was approximately 6 to 8 minutes following sublingual administration, and 18 minutes following buccal administration.2 Absolute bioavailability was approximately 72% and 82% following sublingual and buccal administration, respectively.2 Mean maximal plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine were reached approximately 2 hours after sublingual or buccal administration.2 Compared to drinking water at 2 hours post administration, early water intake (as early as 15 minutes post-dose) had minimal effects on the rate or extent of sublingual absorption but was not assessed after buccal administration.2 The average protein binding was 94% and was constant across the different plasma concentrations evaluated and similar in males and females, but significantly decreased in participants with hepatic impairment compared to healthy individuals.2 In contrast, the pharmacokinetic profile of dexmedetomidine is not significantly different in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/minute compared to those with normal renal function.2 Dexmedetomidine undergoes almost complete biotransformation to inactive metabolites via direct glucuronidation as well as cytochrome P450 (CYP) (primarily CYP2A6)–mediated metabolism.2 There is no evidence of any CYP–mediated drug interactions that are likely to be of clinical relevance.2
Continue to: Efficacy
Efficacy
The efficacy and tolerability of 120 mcg and 180 mcg doses of dexmedetomidine sublingual film was evaluated in 2 similarly designed, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trials in the treatment of acute agitation associated with schizophrenia, schizoaffective, or schizophreniform disorder9 and bipolar I or II disorder.10 These studies included a total of 758 adult patients age range 18 to 71 (mean age approximately 46.5), with about 59% male participants.2 In contrast to other agents approved by the FDA for treatment of agitation associated with bipolar disorder, dexmedetomidine sublingual film was assessed in patients regardless of polarity (manic, mixed features, or depressed).5 The primary efficacy measure for the dexmedetomidine sublingual film studies was the investigator-administered Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component (PANSS-EC), consisting of the following 5 items: excitement, tension, hostility, uncooperativeness, and poor impulse control.11 The items from the PANSS-EC are rated from 1 (not present) to 7 (extremely severe) and thus the total scores range from 5 to 35. For enrollment in the studies, patients had to be judged to be clinically agitated with a total PANSS-EC score ≥14, with at least 1 individual item score ≥4.2
After study medication administration, the PANSS-EC was assessed from 10 minutes through 24 hours, with the primary endpoint being at 2 hours post-dose. Patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder who were treated with dexmedetomidine sublingual film 120 mcg or 180 mcg had superior symptomatic improvements from baseline to 2 hours post-dose compared to placebo, with treatment effects beginning as early as 20 to 30 minutes post-dose (for patients with schizophrenia, dexmedetomidine was statistically significantly superior to placebo beginning at 20 minutes following dosing with the 180 mcg dose and 30 minutes after the 120 mcg dose; for patients with bipolar disorder, differences from placebo were statistically significant beginning at 20 minutes after treatment with both the 120 mcg and 180 mcg doses).2 Evaluation of effect size for dexmedetomidine vs placebo for PANSS-EC response at 2 hours (defined as ≥40% improvement from baseline) resulted in a number needed to treat (NNT) of 3 when combining both studies and both doses,12 comparing favorably with the NNT values observed for IM formulations of aripiprazole, haloperidol, lorazepam, olanzapine, and ziprasidone,13 and inhaled loxapine.14
Overall tolerability and safety
The highlights of the prescribing information contain warnings and precautions regarding hypotension/orthostatic hypotension/bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and somnolence.2 Advice is provided to ensure that patients are alert and not experiencing orthostatic or symptomatic hypotension prior to resuming ambulation, a concern commonly raised when assessing potential treatments for agitation.15 Dexmedetomidine sublingual film should be avoided in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval, a precaution that was evident for the use of ziprasidone16 and where an effect is also noted with haloperidol.6 As per the prescribing information, the most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo) are somnolence, oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia, dizziness, dry mouth, hypotension, and orthostatic hypotension. Rates of adverse reactions of somnolence (including fatigue and sluggishness) with dexmedetomidine 120 mcg or 180 mcg are almost the same (22% and 23%, respectively), and higher than the 6% observed with placebo.2 Other adverse reactions are substantially lower in frequency. These include oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia (6%, 7%, and 1%, for dexmedetomidine 120 mcg, 180 mcg, or placebo, respectively), dizziness (4%, 6%, 1%), hypotension (5%, 5%, 0%), orthostatic hypotension (3%, 5%, <1%), dry mouth (7%, 4%, 1%), nausea (2%, 3%, 2%), bradycardia (2%, 2%, 0%), and abdominal discomfort (0%, 2%, 1%).2
Regarding dose-dependent changes in blood pressure during the studies, 16%, 18%, and 9% of patients treated with 120 mcg, 180 mcg, and placebo, respectively, experienced orthostatic hypotension at 2 hours post dose. However, at 24 hours, none of the patients in the 180-mcg group experienced a systolic blood pressure ≤90 mm Hg with a decrease ≥20 mm Hg, compared with one patient (<1%) in the 120-mcg group and none in the placebo group.2
The prescribing information advises that concomitant use of dexmedetomidine sublingual film with anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, or opioids is likely to lead to enhanced CNS depressant effects, and that the prescriber should consider a reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine or the concomitant anesthetic, sedative, hypnotic, or opioid.2
Summary
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film is an oral medication indicated in adults for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder. The recommended dose depends on severity of agitation, age, and the presence of hepatic impairment. A dose of 180 mcg is recommended for severe agitation and a dose of 120 mcg is recommended for mild or moderate agitation, with doses adjusted lower in the presence of hepatic impairment. There are no contraindications but there are warnings and precautions regarding hypotension/orthostatic hypotension/bradycardia, QT interval prolongation, and somnolence. Clinicians should monitor vital signs and alertness after administration to prevent falls and syncope; however, there is no FDA REMS required for use. The clinical trial evidence supporting the use of dexmedetomidine is robust, with evidence of a treatment effect as early as 20 minutes after administration. Noninvasive formulations, although requiring cooperation from patients, have the potential to improve overall patient experience, thereby improving future cooperation between patients and health care professionals.
Bottom Line
Dexmedetomidine sublingual film provides an opportunity to rethink the approach to the management of agitation and avoid the potentially unnecessary use of IM injections. Dexmedetomidine sublingual film acts rapidly and is simple to use.
Related Resources
- Dexmedetomidine sublingual film (Iglami) prescribing information. https://www.igalmihcp.com/igalmi-pi.pdf
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Dexmedetomidine • Igalmi, Precedex
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lorazepam • Ativan
Loxapine inhaled • Adasuve
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. US Food and Drug Administration. NDA 215390 Approval Letter. Accessed April 5, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/215390Orig1s000ltr.pdf
2. Igalmi [package insert]. BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc; 2022.
3. Weerink MAS, Struys MMRF, Hannivoort LN, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(8):893-913. doi:10.1007/s40262-017-0507-7
4. Precedex [package insert]. Hospira, Inc; 2021.
5. Zeller SL, Citrome L. Managing agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in the emergency setting. West J Emerg Med. 2016;17(2):165-172. doi:10.5811/westjem.2015.12.28763
6. Miceli JJ, Tensfeldt TG, Shiovitz T, et al. Effects of high-dose ziprasidone and haloperidol on the QTc interval after intramuscular administration: a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group study in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Clin Ther. 2010;32(3):472-491. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.03.003
7. Yocca F, DeVivo M, Seth S, et al. Dexmedetomidine—highly favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacological features for a CNS therapeutic drug. Poster presented at: 58th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; December 8-11, 2019; Orlando, FL.
8. Adedoyin A, Preskorn S, Lathia CD. Pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine after a single sublingual dose of BXCL501 in patients with agitation associated with schizophrenia. Poster presented at: 23rd Annual Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders; May 13-15, 2021. Virtual. Session 17.
9. Citrome LL, Lauriello J, Risinger R, et al. A novel rapidly effective treatment of agitation for schizophrenia with the oral dissolving film BXCL501. Poster presented at: American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; May 1-3, 2021. Virtual. Accessed November 11, 2021. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Meetings/Annual-Meeting/2021/2021-APA-Annual-Meeting-Poster-Proceedings.pdf
10. Preskorn SH, Zeller S, Citrome L, et al. Effect of sublingual dexmedetomidine vs placebo on acute agitation associated with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327(8):727-736. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0799
11. Montoya A, Valladares A, Lizán L, et al. Validation of the Excited Component of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS-EC) in a naturalistic sample of 278 patients with acute psychosis and agitation in a psychiatric emergency room. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9:18. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-9-18
12. Citrome L, Palko L, Hokett S, et al. Number needed to treat and number needed to harm from two phase 3 studies of BXCL501 for treating acute agitation in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Poster presented at: Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy Nexus 2021; October 18-21, 2021; Denver, CO.
13. Citrome L. Comparison of intramuscular ziprasidone, olanzapine, or aripiprazole for agitation: a quantitative review of efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(12):1876-1885. doi:10.4088/jcp.v68n1207
14. Citrome L. Inhaled loxapine for agitation revisited: focus on effect sizes from 2 Phase III randomised controlled trials in persons with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(3):318-325. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02890.x
15. Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, et al. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry project Beta psychopharmacology workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26-34. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6866
16. Zimbroff DL, Allen MH, Battaglia J, et al. Best clinical practice with ziprasidone IM: update after 2 years of experience. CNS Spectr. 2005;10(9):1-15. doi:10.1017/s1092852900025487
1. US Food and Drug Administration. NDA 215390 Approval Letter. Accessed April 5, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/215390Orig1s000ltr.pdf
2. Igalmi [package insert]. BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc; 2022.
3. Weerink MAS, Struys MMRF, Hannivoort LN, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(8):893-913. doi:10.1007/s40262-017-0507-7
4. Precedex [package insert]. Hospira, Inc; 2021.
5. Zeller SL, Citrome L. Managing agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in the emergency setting. West J Emerg Med. 2016;17(2):165-172. doi:10.5811/westjem.2015.12.28763
6. Miceli JJ, Tensfeldt TG, Shiovitz T, et al. Effects of high-dose ziprasidone and haloperidol on the QTc interval after intramuscular administration: a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group study in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Clin Ther. 2010;32(3):472-491. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.03.003
7. Yocca F, DeVivo M, Seth S, et al. Dexmedetomidine—highly favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacological features for a CNS therapeutic drug. Poster presented at: 58th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; December 8-11, 2019; Orlando, FL.
8. Adedoyin A, Preskorn S, Lathia CD. Pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine after a single sublingual dose of BXCL501 in patients with agitation associated with schizophrenia. Poster presented at: 23rd Annual Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders; May 13-15, 2021. Virtual. Session 17.
9. Citrome LL, Lauriello J, Risinger R, et al. A novel rapidly effective treatment of agitation for schizophrenia with the oral dissolving film BXCL501. Poster presented at: American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; May 1-3, 2021. Virtual. Accessed November 11, 2021. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Meetings/Annual-Meeting/2021/2021-APA-Annual-Meeting-Poster-Proceedings.pdf
10. Preskorn SH, Zeller S, Citrome L, et al. Effect of sublingual dexmedetomidine vs placebo on acute agitation associated with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327(8):727-736. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0799
11. Montoya A, Valladares A, Lizán L, et al. Validation of the Excited Component of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS-EC) in a naturalistic sample of 278 patients with acute psychosis and agitation in a psychiatric emergency room. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9:18. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-9-18
12. Citrome L, Palko L, Hokett S, et al. Number needed to treat and number needed to harm from two phase 3 studies of BXCL501 for treating acute agitation in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Poster presented at: Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy Nexus 2021; October 18-21, 2021; Denver, CO.
13. Citrome L. Comparison of intramuscular ziprasidone, olanzapine, or aripiprazole for agitation: a quantitative review of efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(12):1876-1885. doi:10.4088/jcp.v68n1207
14. Citrome L. Inhaled loxapine for agitation revisited: focus on effect sizes from 2 Phase III randomised controlled trials in persons with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(3):318-325. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02890.x
15. Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, et al. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry project Beta psychopharmacology workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26-34. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6866
16. Zimbroff DL, Allen MH, Battaglia J, et al. Best clinical practice with ziprasidone IM: update after 2 years of experience. CNS Spectr. 2005;10(9):1-15. doi:10.1017/s1092852900025487
Sublingual buprenorphine plus buprenorphine XR for opioid use disorder
Mr. L, age 31, presents to the emergency department (ED) with somnolence after sustaining an arm laceration at work. While in the ED, Mr. L explains he has opioid use disorder (OUD) and last week received an initial 300 mg injection of extended-release buprenorphine (BUP-XR). Due to ongoing opioid cravings, he took nonprescribed fentanyl and alprazolam before work.
The ED clinicians address Mr. L’s arm injury and transfer him to the hospital’s low-threshold outpatient addiction clinic for further assessment and management. There, he is prescribed sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone (SL-BUP) 8 mg/2 mg daily as needed for 1 week to address ongoing opioid cravings, and is encouraged to return for another visit the following week.
The United States continues to struggle with the overdose crisis, largely fueled by illicitly manufactured opioids such as fentanyl.1 Opioid agonist and partial agonist treatments such as methadone and buprenorphine decrease the risk of death in individuals with OUD by up to 50%.2 While methadone has a history of proven effectiveness for OUD, accessibility is fraught with barriers (eg, patients must attend an opioid treatment program daily to receive a dose, pharmacies are unable to dispense methadone for OUD).
Buprenorphine has been shown to decrease opioid cravings while limiting euphoria due to its partial—as opposed to full—agonist activity.3 Several buprenorphine formulations are available (Table). Buprenorphine presents an opportunity to treat OUD like other chronic illnesses. In accordance with the US Department of Health and Human Services Practice Guideline (2021), any clinician can obtain a waiver to prescribe buprenorphine in any treatment setting, and patients can receive the medication at a pharmacy.4
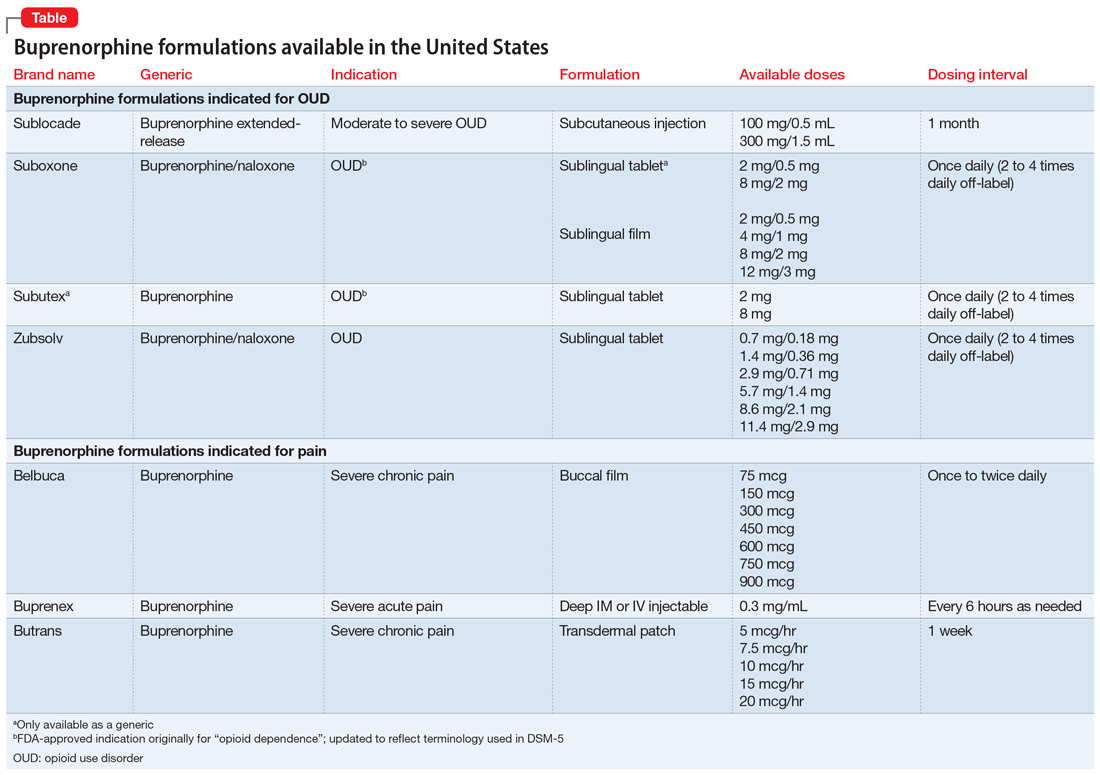
However, many patients have barriers to consistent daily dosing of buprenorphine due to strict clinic/prescriber requirements, transportation difficulties, continued cravings, and other factors. BUP-XR, a buprenorphine injection administered once a month, may address several of these concerns, most notably the potential for better suppression of cravings by delivering a consistent level of buprenorphine over the course of 28 days.5 Since BUP-XR was FDA-approved in 2017, questions remain whether it can adequately quell opioid cravings in early treatment months prior to steady-state concentration.
This article addresses whether clinicians should consider supplemental SL-BUP in addition to BUP-XR during early treatment months and/or prior to steady-state.
Pharmacokinetics of BUP-XR
BUP-XR is administered by subcutaneous injection via an ATRIGEL delivery system (BUP-XR; Albany Molecular Research, Burlington, Massachusetts).6 Upon injection, approximately 7% of the buprenorphine dose dissipates with the solvent, leading to maximum concentration approximately 24 hours post-dose. The remaining dose hardens to create a depot that elutes buprenorphine gradually over 28 days.7
Continue to: Buprenorphine requires...
Buprenorphine requires ≥70% mu-opioid receptor (MOR) occupancy to effectively suppress symptoms of craving and withdrawal in patients with OUD. Buprenorphine serum concentration correlates significantly with MOR occupancy, such that concentrations of 2 to 3 ng/mL are acknowledged as baseline minimums for clinical efficacy.8
BUP-XR is administered in 1 of 2 dosing regimens. In both, 2 separate 300 mg doses are administered 28 days apart during Month 1 and Month 2, followed by maintenance doses of either 300 mg (300/300 mg dosing regimen) or 100 mg (300/100 mg dosing regimen) every 28 days thereafter. Combined Phase II and Phase III data analyzing serum concentrations of BUP-XR across both dosing regimens revealed that, for most patients, there is a noticeable period during Month 1 and Month 2 when serum concentrations fall below 2 ng/mL.7 Steady-state concentrations of both regimens develop after 4 to 6 appropriately timed injections, providing average steady-state serum concentrations in Phase II and Phase III trials of 6.54 ng/mL for the 300/300 mg dosing regimen and 3.00 ng/mL for 300/100 mg dosing regimen.7
Real-world experiences with BUP-XR
The theoretical need for supplementation has been voiced in practice. A case series by Peckham et al9 noted that 55% (n = 22) of patients required SL-BUP supplementation for up to 120 days after the first BUP-XR injection to quell cravings and reduce nonprescribed opioid use.
The RECOVER trial by Ling et al10 demonstrated the importance of the first 2 months of BUP-XR therapy in the overall treatment success for patients with OUD. In this analysis, patients maintained on BUP-XR for 12 months reported a 75% likelihood of abstinence, compared to 24% for patients receiving 0 to 2 months of BUP-XR treatment. Other benefits included improved employment status and reduced depression rates. This trial did not specifically discuss supplemental SL-BUP or subthreshold concentrations of buprenorphine during early months.10
Individualized treatment should be based on OUD symptoms
While BUP-XR was designed to continuously deliver at least 2 ng/mL of buprenorphine, serum concentrations are labile during the first 2 months of treatment. This may result in breakthrough OUD symptoms, particularly withdrawal or opioid cravings. Additionally, due to individual variability, some patients may still experience serum concentrations below 2 ng/mL after Month 2 and until steady-state is achieved between Month 4 and Month 6.7
Continue to: Beyond a theoretical...
Beyond a theoretical need for supplementation with SL-BUP, there is limited information regarding optimal dosing, dosage intervals, or length of supplementation. Therefore, clear guidance is not available at this time, and treatment should be individualized based on subjective and objective OUD symptoms.
What also remains unknown are potential barriers patients may face in receiving 2 concurrent buprenorphine prescriptions. BUP-XR, administered in a health care setting, can be obtained 2 ways. A clinician can directly order the medication from the distributor to be administered via buy-and-bill. An alternate option requires the clinician to send a prescription to an appropriately credentialed pharmacy that will ship patient-specific orders directly to the clinic. Despite this, most SL-BUP prescriptions are billed and dispensed from community pharmacies. At the insurance level, there is risk the prescription claim will be rejected for duplication of therapy, which may require additional collaboration between the prescribing clinician, pharmacist, and insurance representative to ensure patients have access to the medication.
Pending studies and approvals may also provide greater guidance and flexibility in decision-making for patients with OUD. The CoLAB study currently underway in Australia is examining the efficacy and outcomes of an intermediate dose (200 mg) of BUP-XR and will also allow for supplemental SL-BUP doses.11 Additionally, an alternative BUP-XR formulation, Brixadi, currently in use in the European Union as Buvidal, has submitted an application for FDA approval in the United States. The application indicates that Brixadi will be available with a wider range of doses and at both weekly and monthly intervals. Approval has been delayed due to deficiencies in the United States–based third-party production facilities. It is unclear how the FDA and manufacturer plan to proceed.12
Short-term supplementation with SL-BUP during early the months of treatment with BUP-XR should be considered to control OUD symptoms and assist with patient retention. Once steady-state is achieved, trough concentrations of buprenorphine are not expected to drop below 2 ng/mL with continued on-time maintenance doses and thus, supplementation can likely cease.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. L is seen in the low-threshold outpatient clinic 1 week after his ED visit. His arm laceration is healing well, and he is noticeably more alert and engaged. Each morning this week, he awakes with cravings, sweating, and anxiety. These symptoms alleviate after he takes SL-BUP. Mr. L’s clinician gives him a copy of the Subjective Opioid Withdrawal Scale so he can assess his withdrawal symptoms each morning and provide this data at follow-up appointments. Mr. L and his clinician decide to meet weekly until his next injection to continue assessing his current supplemental dose, symptoms, and whether there should be additional adjustments to his treatment plan.
Related Resources
- Cho J, Bhimani J, Patel M, et al. Substance abuse among older adults: a growing problem. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(3):14-20.
- Verma S. Opioid use disorder in adolescents: an overview. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(2):12-14,16-21.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Buprenorphine • Sublocade, Subutex
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone, Zubsolv
Methadone • Methadose
1. Mattson CL, Tanz LJ, Quinn K, et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(6):202-207. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4
2. Ma J, Bao YP, Wang RJ, et al. Effects of medication-assisted treatment on mortality among opioids users: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(12):1868-1883. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0094-5
3. Coe MA, Lofwall MR, Walsh SL. Buprenorphine pharmacology review: update on transmucosal and long-acting formulations. J Addict Med. 2019;13(2):93-103. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000457
4. Becerra X. Practice Guidelines for the Administration of Buprenorphine for Treating Opioid Use Disorder. US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2021:22439-22440. FR Document 2021-08961. Accessed April 5, 2021. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/04/28/2021-08961/practice-guidelines-for-the-administration-of-buprenorphine-for-treating-opioid-use-disorder
5. Haight BR, Learned SM, Laffont CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):778-790. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32259-1
6. Sublocade [package insert]. North Chesterfield, VA: Indivior Inc; 2021.
7. Jones AK, Ngaimisi E, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for the treatment of opioid use disorder: a combined analysis of phase II and phase III trials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021;60(4):527-540. doi:10.1007/s40262-020-00957-0
8. Greenwald MK, Comer SD, Fiellin DA. Buprenorphine maintenance and mu-opioid receptor availability in the treatment of opioid use disorder: implications for clinical use and policy. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;144:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.07.035
9. Peckham AM, Kehoe LG, Gray JR, et al. Real-world outcomes with extended-release buprenorphine (XR-BUP) in a low threshold bridge clinic: a retrospective case series. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;126:108316. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108316
10. Ling W, Nadipelli VR, Aldridge AP, et al. Recovery from opioid use disorder (OUD) after monthly long-acting buprenorphine treatment: 12-month longitudinal outcomes from RECOVER, an observational study. J Addict Med. 2020;14(5):e233-e240. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000647
11. Larance B, Byrne M, Lintzeris N, et al. Open-label, multicentre, single-arm trial of monthly injections of depot buprenorphine in people with opioid dependence: protocol for the CoLAB study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(7):e034389. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-034389
12. Braeburn receives new Complete Response Letter for Brixadi in the US. News release. News Powered by Cision. December 15, 2021. Accessed April 13, 2022. https://news.cision.com/camurus-ab/r/braeburn-receives-new-complete-response-letter-for-brixadi-in-the-us,c3473281
Mr. L, age 31, presents to the emergency department (ED) with somnolence after sustaining an arm laceration at work. While in the ED, Mr. L explains he has opioid use disorder (OUD) and last week received an initial 300 mg injection of extended-release buprenorphine (BUP-XR). Due to ongoing opioid cravings, he took nonprescribed fentanyl and alprazolam before work.
The ED clinicians address Mr. L’s arm injury and transfer him to the hospital’s low-threshold outpatient addiction clinic for further assessment and management. There, he is prescribed sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone (SL-BUP) 8 mg/2 mg daily as needed for 1 week to address ongoing opioid cravings, and is encouraged to return for another visit the following week.
The United States continues to struggle with the overdose crisis, largely fueled by illicitly manufactured opioids such as fentanyl.1 Opioid agonist and partial agonist treatments such as methadone and buprenorphine decrease the risk of death in individuals with OUD by up to 50%.2 While methadone has a history of proven effectiveness for OUD, accessibility is fraught with barriers (eg, patients must attend an opioid treatment program daily to receive a dose, pharmacies are unable to dispense methadone for OUD).
Buprenorphine has been shown to decrease opioid cravings while limiting euphoria due to its partial—as opposed to full—agonist activity.3 Several buprenorphine formulations are available (Table). Buprenorphine presents an opportunity to treat OUD like other chronic illnesses. In accordance with the US Department of Health and Human Services Practice Guideline (2021), any clinician can obtain a waiver to prescribe buprenorphine in any treatment setting, and patients can receive the medication at a pharmacy.4

However, many patients have barriers to consistent daily dosing of buprenorphine due to strict clinic/prescriber requirements, transportation difficulties, continued cravings, and other factors. BUP-XR, a buprenorphine injection administered once a month, may address several of these concerns, most notably the potential for better suppression of cravings by delivering a consistent level of buprenorphine over the course of 28 days.5 Since BUP-XR was FDA-approved in 2017, questions remain whether it can adequately quell opioid cravings in early treatment months prior to steady-state concentration.
This article addresses whether clinicians should consider supplemental SL-BUP in addition to BUP-XR during early treatment months and/or prior to steady-state.
Pharmacokinetics of BUP-XR
BUP-XR is administered by subcutaneous injection via an ATRIGEL delivery system (BUP-XR; Albany Molecular Research, Burlington, Massachusetts).6 Upon injection, approximately 7% of the buprenorphine dose dissipates with the solvent, leading to maximum concentration approximately 24 hours post-dose. The remaining dose hardens to create a depot that elutes buprenorphine gradually over 28 days.7
Continue to: Buprenorphine requires...
Buprenorphine requires ≥70% mu-opioid receptor (MOR) occupancy to effectively suppress symptoms of craving and withdrawal in patients with OUD. Buprenorphine serum concentration correlates significantly with MOR occupancy, such that concentrations of 2 to 3 ng/mL are acknowledged as baseline minimums for clinical efficacy.8
BUP-XR is administered in 1 of 2 dosing regimens. In both, 2 separate 300 mg doses are administered 28 days apart during Month 1 and Month 2, followed by maintenance doses of either 300 mg (300/300 mg dosing regimen) or 100 mg (300/100 mg dosing regimen) every 28 days thereafter. Combined Phase II and Phase III data analyzing serum concentrations of BUP-XR across both dosing regimens revealed that, for most patients, there is a noticeable period during Month 1 and Month 2 when serum concentrations fall below 2 ng/mL.7 Steady-state concentrations of both regimens develop after 4 to 6 appropriately timed injections, providing average steady-state serum concentrations in Phase II and Phase III trials of 6.54 ng/mL for the 300/300 mg dosing regimen and 3.00 ng/mL for 300/100 mg dosing regimen.7
Real-world experiences with BUP-XR
The theoretical need for supplementation has been voiced in practice. A case series by Peckham et al9 noted that 55% (n = 22) of patients required SL-BUP supplementation for up to 120 days after the first BUP-XR injection to quell cravings and reduce nonprescribed opioid use.
The RECOVER trial by Ling et al10 demonstrated the importance of the first 2 months of BUP-XR therapy in the overall treatment success for patients with OUD. In this analysis, patients maintained on BUP-XR for 12 months reported a 75% likelihood of abstinence, compared to 24% for patients receiving 0 to 2 months of BUP-XR treatment. Other benefits included improved employment status and reduced depression rates. This trial did not specifically discuss supplemental SL-BUP or subthreshold concentrations of buprenorphine during early months.10
Individualized treatment should be based on OUD symptoms
While BUP-XR was designed to continuously deliver at least 2 ng/mL of buprenorphine, serum concentrations are labile during the first 2 months of treatment. This may result in breakthrough OUD symptoms, particularly withdrawal or opioid cravings. Additionally, due to individual variability, some patients may still experience serum concentrations below 2 ng/mL after Month 2 and until steady-state is achieved between Month 4 and Month 6.7
Continue to: Beyond a theoretical...
Beyond a theoretical need for supplementation with SL-BUP, there is limited information regarding optimal dosing, dosage intervals, or length of supplementation. Therefore, clear guidance is not available at this time, and treatment should be individualized based on subjective and objective OUD symptoms.
What also remains unknown are potential barriers patients may face in receiving 2 concurrent buprenorphine prescriptions. BUP-XR, administered in a health care setting, can be obtained 2 ways. A clinician can directly order the medication from the distributor to be administered via buy-and-bill. An alternate option requires the clinician to send a prescription to an appropriately credentialed pharmacy that will ship patient-specific orders directly to the clinic. Despite this, most SL-BUP prescriptions are billed and dispensed from community pharmacies. At the insurance level, there is risk the prescription claim will be rejected for duplication of therapy, which may require additional collaboration between the prescribing clinician, pharmacist, and insurance representative to ensure patients have access to the medication.
Pending studies and approvals may also provide greater guidance and flexibility in decision-making for patients with OUD. The CoLAB study currently underway in Australia is examining the efficacy and outcomes of an intermediate dose (200 mg) of BUP-XR and will also allow for supplemental SL-BUP doses.11 Additionally, an alternative BUP-XR formulation, Brixadi, currently in use in the European Union as Buvidal, has submitted an application for FDA approval in the United States. The application indicates that Brixadi will be available with a wider range of doses and at both weekly and monthly intervals. Approval has been delayed due to deficiencies in the United States–based third-party production facilities. It is unclear how the FDA and manufacturer plan to proceed.12
Short-term supplementation with SL-BUP during early the months of treatment with BUP-XR should be considered to control OUD symptoms and assist with patient retention. Once steady-state is achieved, trough concentrations of buprenorphine are not expected to drop below 2 ng/mL with continued on-time maintenance doses and thus, supplementation can likely cease.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. L is seen in the low-threshold outpatient clinic 1 week after his ED visit. His arm laceration is healing well, and he is noticeably more alert and engaged. Each morning this week, he awakes with cravings, sweating, and anxiety. These symptoms alleviate after he takes SL-BUP. Mr. L’s clinician gives him a copy of the Subjective Opioid Withdrawal Scale so he can assess his withdrawal symptoms each morning and provide this data at follow-up appointments. Mr. L and his clinician decide to meet weekly until his next injection to continue assessing his current supplemental dose, symptoms, and whether there should be additional adjustments to his treatment plan.
Related Resources
- Cho J, Bhimani J, Patel M, et al. Substance abuse among older adults: a growing problem. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(3):14-20.
- Verma S. Opioid use disorder in adolescents: an overview. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(2):12-14,16-21.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Buprenorphine • Sublocade, Subutex
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone, Zubsolv
Methadone • Methadose
Mr. L, age 31, presents to the emergency department (ED) with somnolence after sustaining an arm laceration at work. While in the ED, Mr. L explains he has opioid use disorder (OUD) and last week received an initial 300 mg injection of extended-release buprenorphine (BUP-XR). Due to ongoing opioid cravings, he took nonprescribed fentanyl and alprazolam before work.
The ED clinicians address Mr. L’s arm injury and transfer him to the hospital’s low-threshold outpatient addiction clinic for further assessment and management. There, he is prescribed sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone (SL-BUP) 8 mg/2 mg daily as needed for 1 week to address ongoing opioid cravings, and is encouraged to return for another visit the following week.
The United States continues to struggle with the overdose crisis, largely fueled by illicitly manufactured opioids such as fentanyl.1 Opioid agonist and partial agonist treatments such as methadone and buprenorphine decrease the risk of death in individuals with OUD by up to 50%.2 While methadone has a history of proven effectiveness for OUD, accessibility is fraught with barriers (eg, patients must attend an opioid treatment program daily to receive a dose, pharmacies are unable to dispense methadone for OUD).
Buprenorphine has been shown to decrease opioid cravings while limiting euphoria due to its partial—as opposed to full—agonist activity.3 Several buprenorphine formulations are available (Table). Buprenorphine presents an opportunity to treat OUD like other chronic illnesses. In accordance with the US Department of Health and Human Services Practice Guideline (2021), any clinician can obtain a waiver to prescribe buprenorphine in any treatment setting, and patients can receive the medication at a pharmacy.4

However, many patients have barriers to consistent daily dosing of buprenorphine due to strict clinic/prescriber requirements, transportation difficulties, continued cravings, and other factors. BUP-XR, a buprenorphine injection administered once a month, may address several of these concerns, most notably the potential for better suppression of cravings by delivering a consistent level of buprenorphine over the course of 28 days.5 Since BUP-XR was FDA-approved in 2017, questions remain whether it can adequately quell opioid cravings in early treatment months prior to steady-state concentration.
This article addresses whether clinicians should consider supplemental SL-BUP in addition to BUP-XR during early treatment months and/or prior to steady-state.
Pharmacokinetics of BUP-XR
BUP-XR is administered by subcutaneous injection via an ATRIGEL delivery system (BUP-XR; Albany Molecular Research, Burlington, Massachusetts).6 Upon injection, approximately 7% of the buprenorphine dose dissipates with the solvent, leading to maximum concentration approximately 24 hours post-dose. The remaining dose hardens to create a depot that elutes buprenorphine gradually over 28 days.7
Continue to: Buprenorphine requires...
Buprenorphine requires ≥70% mu-opioid receptor (MOR) occupancy to effectively suppress symptoms of craving and withdrawal in patients with OUD. Buprenorphine serum concentration correlates significantly with MOR occupancy, such that concentrations of 2 to 3 ng/mL are acknowledged as baseline minimums for clinical efficacy.8
BUP-XR is administered in 1 of 2 dosing regimens. In both, 2 separate 300 mg doses are administered 28 days apart during Month 1 and Month 2, followed by maintenance doses of either 300 mg (300/300 mg dosing regimen) or 100 mg (300/100 mg dosing regimen) every 28 days thereafter. Combined Phase II and Phase III data analyzing serum concentrations of BUP-XR across both dosing regimens revealed that, for most patients, there is a noticeable period during Month 1 and Month 2 when serum concentrations fall below 2 ng/mL.7 Steady-state concentrations of both regimens develop after 4 to 6 appropriately timed injections, providing average steady-state serum concentrations in Phase II and Phase III trials of 6.54 ng/mL for the 300/300 mg dosing regimen and 3.00 ng/mL for 300/100 mg dosing regimen.7
Real-world experiences with BUP-XR
The theoretical need for supplementation has been voiced in practice. A case series by Peckham et al9 noted that 55% (n = 22) of patients required SL-BUP supplementation for up to 120 days after the first BUP-XR injection to quell cravings and reduce nonprescribed opioid use.
The RECOVER trial by Ling et al10 demonstrated the importance of the first 2 months of BUP-XR therapy in the overall treatment success for patients with OUD. In this analysis, patients maintained on BUP-XR for 12 months reported a 75% likelihood of abstinence, compared to 24% for patients receiving 0 to 2 months of BUP-XR treatment. Other benefits included improved employment status and reduced depression rates. This trial did not specifically discuss supplemental SL-BUP or subthreshold concentrations of buprenorphine during early months.10
Individualized treatment should be based on OUD symptoms
While BUP-XR was designed to continuously deliver at least 2 ng/mL of buprenorphine, serum concentrations are labile during the first 2 months of treatment. This may result in breakthrough OUD symptoms, particularly withdrawal or opioid cravings. Additionally, due to individual variability, some patients may still experience serum concentrations below 2 ng/mL after Month 2 and until steady-state is achieved between Month 4 and Month 6.7
Continue to: Beyond a theoretical...
Beyond a theoretical need for supplementation with SL-BUP, there is limited information regarding optimal dosing, dosage intervals, or length of supplementation. Therefore, clear guidance is not available at this time, and treatment should be individualized based on subjective and objective OUD symptoms.
What also remains unknown are potential barriers patients may face in receiving 2 concurrent buprenorphine prescriptions. BUP-XR, administered in a health care setting, can be obtained 2 ways. A clinician can directly order the medication from the distributor to be administered via buy-and-bill. An alternate option requires the clinician to send a prescription to an appropriately credentialed pharmacy that will ship patient-specific orders directly to the clinic. Despite this, most SL-BUP prescriptions are billed and dispensed from community pharmacies. At the insurance level, there is risk the prescription claim will be rejected for duplication of therapy, which may require additional collaboration between the prescribing clinician, pharmacist, and insurance representative to ensure patients have access to the medication.
Pending studies and approvals may also provide greater guidance and flexibility in decision-making for patients with OUD. The CoLAB study currently underway in Australia is examining the efficacy and outcomes of an intermediate dose (200 mg) of BUP-XR and will also allow for supplemental SL-BUP doses.11 Additionally, an alternative BUP-XR formulation, Brixadi, currently in use in the European Union as Buvidal, has submitted an application for FDA approval in the United States. The application indicates that Brixadi will be available with a wider range of doses and at both weekly and monthly intervals. Approval has been delayed due to deficiencies in the United States–based third-party production facilities. It is unclear how the FDA and manufacturer plan to proceed.12
Short-term supplementation with SL-BUP during early the months of treatment with BUP-XR should be considered to control OUD symptoms and assist with patient retention. Once steady-state is achieved, trough concentrations of buprenorphine are not expected to drop below 2 ng/mL with continued on-time maintenance doses and thus, supplementation can likely cease.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. L is seen in the low-threshold outpatient clinic 1 week after his ED visit. His arm laceration is healing well, and he is noticeably more alert and engaged. Each morning this week, he awakes with cravings, sweating, and anxiety. These symptoms alleviate after he takes SL-BUP. Mr. L’s clinician gives him a copy of the Subjective Opioid Withdrawal Scale so he can assess his withdrawal symptoms each morning and provide this data at follow-up appointments. Mr. L and his clinician decide to meet weekly until his next injection to continue assessing his current supplemental dose, symptoms, and whether there should be additional adjustments to his treatment plan.
Related Resources
- Cho J, Bhimani J, Patel M, et al. Substance abuse among older adults: a growing problem. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(3):14-20.
- Verma S. Opioid use disorder in adolescents: an overview. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(2):12-14,16-21.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Buprenorphine • Sublocade, Subutex
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone, Zubsolv
Methadone • Methadose
1. Mattson CL, Tanz LJ, Quinn K, et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(6):202-207. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4
2. Ma J, Bao YP, Wang RJ, et al. Effects of medication-assisted treatment on mortality among opioids users: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(12):1868-1883. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0094-5
3. Coe MA, Lofwall MR, Walsh SL. Buprenorphine pharmacology review: update on transmucosal and long-acting formulations. J Addict Med. 2019;13(2):93-103. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000457
4. Becerra X. Practice Guidelines for the Administration of Buprenorphine for Treating Opioid Use Disorder. US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2021:22439-22440. FR Document 2021-08961. Accessed April 5, 2021. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/04/28/2021-08961/practice-guidelines-for-the-administration-of-buprenorphine-for-treating-opioid-use-disorder
5. Haight BR, Learned SM, Laffont CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):778-790. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32259-1
6. Sublocade [package insert]. North Chesterfield, VA: Indivior Inc; 2021.
7. Jones AK, Ngaimisi E, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for the treatment of opioid use disorder: a combined analysis of phase II and phase III trials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021;60(4):527-540. doi:10.1007/s40262-020-00957-0
8. Greenwald MK, Comer SD, Fiellin DA. Buprenorphine maintenance and mu-opioid receptor availability in the treatment of opioid use disorder: implications for clinical use and policy. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;144:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.07.035
9. Peckham AM, Kehoe LG, Gray JR, et al. Real-world outcomes with extended-release buprenorphine (XR-BUP) in a low threshold bridge clinic: a retrospective case series. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;126:108316. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108316
10. Ling W, Nadipelli VR, Aldridge AP, et al. Recovery from opioid use disorder (OUD) after monthly long-acting buprenorphine treatment: 12-month longitudinal outcomes from RECOVER, an observational study. J Addict Med. 2020;14(5):e233-e240. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000647
11. Larance B, Byrne M, Lintzeris N, et al. Open-label, multicentre, single-arm trial of monthly injections of depot buprenorphine in people with opioid dependence: protocol for the CoLAB study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(7):e034389. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-034389
12. Braeburn receives new Complete Response Letter for Brixadi in the US. News release. News Powered by Cision. December 15, 2021. Accessed April 13, 2022. https://news.cision.com/camurus-ab/r/braeburn-receives-new-complete-response-letter-for-brixadi-in-the-us,c3473281
1. Mattson CL, Tanz LJ, Quinn K, et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths - United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(6):202-207. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4
2. Ma J, Bao YP, Wang RJ, et al. Effects of medication-assisted treatment on mortality among opioids users: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(12):1868-1883. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0094-5
3. Coe MA, Lofwall MR, Walsh SL. Buprenorphine pharmacology review: update on transmucosal and long-acting formulations. J Addict Med. 2019;13(2):93-103. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000457
4. Becerra X. Practice Guidelines for the Administration of Buprenorphine for Treating Opioid Use Disorder. US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2021:22439-22440. FR Document 2021-08961. Accessed April 5, 2021. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/04/28/2021-08961/practice-guidelines-for-the-administration-of-buprenorphine-for-treating-opioid-use-disorder
5. Haight BR, Learned SM, Laffont CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):778-790. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32259-1
6. Sublocade [package insert]. North Chesterfield, VA: Indivior Inc; 2021.
7. Jones AK, Ngaimisi E, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for the treatment of opioid use disorder: a combined analysis of phase II and phase III trials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021;60(4):527-540. doi:10.1007/s40262-020-00957-0
8. Greenwald MK, Comer SD, Fiellin DA. Buprenorphine maintenance and mu-opioid receptor availability in the treatment of opioid use disorder: implications for clinical use and policy. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;144:1-11. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.07.035
9. Peckham AM, Kehoe LG, Gray JR, et al. Real-world outcomes with extended-release buprenorphine (XR-BUP) in a low threshold bridge clinic: a retrospective case series. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;126:108316. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108316
10. Ling W, Nadipelli VR, Aldridge AP, et al. Recovery from opioid use disorder (OUD) after monthly long-acting buprenorphine treatment: 12-month longitudinal outcomes from RECOVER, an observational study. J Addict Med. 2020;14(5):e233-e240. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000647
11. Larance B, Byrne M, Lintzeris N, et al. Open-label, multicentre, single-arm trial of monthly injections of depot buprenorphine in people with opioid dependence: protocol for the CoLAB study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(7):e034389. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-034389
12. Braeburn receives new Complete Response Letter for Brixadi in the US. News release. News Powered by Cision. December 15, 2021. Accessed April 13, 2022. https://news.cision.com/camurus-ab/r/braeburn-receives-new-complete-response-letter-for-brixadi-in-the-us,c3473281
Should clozapine be discontinued in a patient receiving chemotherapy?
CASE Schizophrenia, leukemia, and chemotherapy
Mr. A, age 30, has schizophrenia but has been stable on clozapine 600 mg/d. He presents to the emergency department with generalized pain that started in his right scapula, arm, elbow, and back. Laboratory tests and a diagnostic examination reveal severe leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and anemia, and clinicians diagnose Mr. A with B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (B-ALL). Upon admission, Mr. A is neutropenic with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of 1,420 µL (reference range 2,500 to 6,000 µL). The hematology team recommends chemotherapy. The treating clinicians also consult the psychiatry team for recommendations on how to best manage Mr. A’s schizophrenia during chemotherapy, including whether clozapine should be discontinued.
HISTORY Stable on clozapine for >10 years
Mr. A was diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 15 after developing paranoia and auditory hallucinations of people talking to him and to each other. He had been hospitalized multiple times for worsened auditory hallucinations and paranoia that led to significant agitation and violence. Previous treatment with multiple antipsychotics, including haloperidol, quetiapine, aripiprazole, olanzapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone, was not successful. Mr. A began clozapine >10 years ago, and his symptoms have been stable since, without any further psychiatric hospitalizations. Mr. A takes clozapine 600 mg/d and divalproex sodium 1,500 mg/d, which he tolerates well and without significant adverse effects. Though he continues to have intermittent auditory hallucinations, they are mild and manageable. Mr. A lives with his mother, who reports he occasionally talks to himself but when he does not take clozapine, the auditory hallucinations worsen and cause him to become paranoid and aggressive. His ANC is monitored monthly and had been normal for several years until he was diagnosed with B-ALL.
[polldaddy:11125941]
The authors’ observations
The decision to continue clozapine during chemotherapy is challenging and should weigh the risk of agranulocytosis against that of psychiatric destabilization. Because clozapine and chemotherapy are both associated with agranulocytosis, there is concern that concurrent treatment could increase this risk in an additive or synergistic manner. To the best of our knowledge, there are currently no controlled studies investigating the interactions between clozapine and chemotherapeutic agents. Evidence on the hematopoietic consequences of concurrent clozapine and chemotherapy treatment has been limited to case reports because the topic does not lend itself well to randomized controlled trials.
A recent systematic review found no adverse outcomes among the 27 published cases in which clozapine was continued during myelosuppressive chemotherapy.1 The most notable finding was an association between clozapine discontinuation and psychiatric decompensation, which was reported in 12 of 13 cases in which clozapine was prophylactically discontinued to minimize the risk of agranulocytosis.
Patient-specific factors must also be considered, such as the likelihood that psychotic symptoms will recur or worsen if clozapine is discontinued, as well as the extent to which symptom recurrence would interfere with cancer treatment. Clinicians should evaluate the feasibility of switching to another antipsychotic by obtaining a thorough history of the patient’s previous antipsychotics, doses, treatment duration, and response. However, many patients are treated with clozapine because their psychotic symptoms did not improve with other treatments. The character and severity of the patient’s psychotic symptoms when untreated or prior to clozapine treatment can provide a clearer understanding of how a recurrence of symptoms may interfere with cancer treatment. To formulate an accurate assessment of risks and benefits, it is necessary to consider both available evidence and patient-specific factors. The significant agitation and paranoia that Mr. A experienced when not taking clozapine was likely to disrupt chemotherapy. Thus, the adverse consequences of discontinuing clozapine were both severe and likely.
TREATMENT Continuing clozapine
After an extensive discussion of risks, benefits, and alternative treatments with the hematology and psychiatry teams, Mr. A and his family decide to continue clozapine with increased ANC monitoring during chemotherapy. Concurrent treatment was pursued with close collaboration among the patient, the patient’s family, and the hematology and pharmacy teams, and in careful consideration of the clozapine risk evaluation and mitigation strategy. Mr. A’s ANC was monitored daily during chemotherapy treatments and weekly in the intervals between treatments.
As expected, chemotherapy resulted in bone marrow suppression and pancytopenia. Mr. A’s ANC steadily decreased during the next 10 days until it reached 0 µL. This was consistent with the predicted ANC nadir between Day 10 and Day 14, after which recovery was expected. However, Mr. A’s ANC remained at 0 µL on Day 15.
[polldaddy:11125947]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Temporary decreases in ANC are expected during chemotherapy, and the timing of onset and recovery is often well characterized. Prior to Day 15, the observed progressive marrow suppression was solely due to chemotherapy. However, because Mr. A’s ANC remained 0 µL longer than anticipated, reevaluation of clozapine’s effects was warranted.
Timing, clinical course, and comprehensive hematologic monitoring can provide important clues as to whether clozapine may be responsible for prolonged neutropenia. Though a prolonged ANC of 0 µL raised concern for clozapine-induced agranulocytosis (CIAG), comprehensive monitoring of hematologic cell lines was reassuring because CIAG selectively targets granulocytic cells (neutrophils).2 In contrast, chemotherapy can affect other cell lineages, including lymphocytes, red blood cells, and platelets, which causes pancytopenia.3 For Mr. A, though the clinical presentation of pancytopenia was significant and concerning, it was inconsistent with CIAG.
Additionally, the patient’s baseline risk of CIAG should be considered. After 18 weeks of clozapine treatment, the risk of CIAG decreases to a level similar to that associated with other antipsychotics.4,5 Therefore, CIAG would be unlikely in a patient treated with clozapine for more than 1 year and who did not have a history of neutropenia, as was the case with Mr. A.
While bone marrow biopsy can help differentiate between the causes of agranulocytosis,6 it is highly invasive and may not be necessary if laboratory evidence is sufficient. However, if a treatment team is strongly considering discontinuing clozapine and there are no suitable alternatives, a biopsy may provide additional clarification.
TREATMENT CAR T-cell therapy and cancer remission
Clozapine is continued with daily monitoring. On Day 19, Mr. A’s ANC increases, reaching 2,600 µL by discharge on Day 40. Mr. A remains psychiatrically stable throughout his hospitalization and does not experience any complications associated with neutropenia, despite its prolonged duration.
Continue to: Unfortunately, multiple cycles of...
Unfortunately, multiple cycles of chemotherapy fail to induce remission. Mr. A is referred for CD19/CD22 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, which helps achieve remission. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) is recommended to maximize the likelihood of sustained remission.7 As with chemotherapy, Mr. A and his family agree with the multidisciplinary treatment recommendation to continue clozapine during both CAR T-cell therapy and HSCT, because the risks associated with psychiatric decompensation were greater than a potential increased risk of agranulocytosis. Clozapine treatment is continued throughout both therapies without issue.
Four months after HSCT, Mr. A is admitted for neutropenic fever and left face cellulitis. Upon admission, his ANC is 30 µL and subsequently decreases to 0 µL. In addition to neutropenia, Mr. A is also anemic and thrombocytopenic. He undergoes a bone marrow biopsy.
[polldaddy:11125950]
The authors’ observations
While no published cases have examined the bone marrow of patients experiencing CIAG, 2 retrospective studies have characterized 2 classes of bone marrow findings associated with drug-induced agranulocytosis resulting from nonchemotherapeutic agents (Table).8,9 Type I marrow appears hypercellular with adequate neutrophil precursors but an arrested neutrophil maturation, with few or no mature forms of neutrophils beyond myelocytes.8,9 Type II demonstrates a severe reduction or complete absence of granulocytic precursors with normal or increased erythropoiesis and megakaryocytes.8,9 These findings have been used to accurately differentiate between chemotherapy and nonchemotherapy drug-induced agranulocytosis,6 resulting in successful identification and discontinuation of the responsible agent.

Mr. A’s bone marrow biopsy showed severe pancytopenia with profound neutropenia and normocytic anemia, without evidence of residual leukemia, inconsistent with Type I or Type II. Findings were suggestive of a myelodysplastic syndrome, consistent with secondary graft failure. Symptoms resolved after treatment with antibiotics, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, epoetin alfa, and thrombopoietin. Mr. A’s ANC remained 0 µL for 22 days before returning to normal (>1,500 µL) by Day 29. He had no secondary complications resulting from neutropenia. As the clinical evidence suggested, Mr. A’s neutropenia was unlikely to be due to clozapine. Clozapine was continued throughout his cancer treatment, and he remained psychiatrically stable.
Clozapine, cancer treatments, and agranulocytosis
This case demonstrates that clozapine can be safely continued during a variety of cancer treatments (ie, chemotherapy, CAR T-cell therapy, HSCT), even with the development of agranulocytosis and prolonged neutropenia. Evidence to guide psychiatric clinicians to evaluate the likelihood that agranulocytosis is clozapine-induced is limited.
Continue to: We offer an algorithm...
We offer an algorithm to assist clinicians faced with this challenging clinical dilemma (Figure). Based on our experience and limited current evidence, we recommend continuing clozapine during cancer treatment unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Presently, no evidence in published literature suggests worsened outcomes in patients treated concurrently with clozapine and cancer therapies.
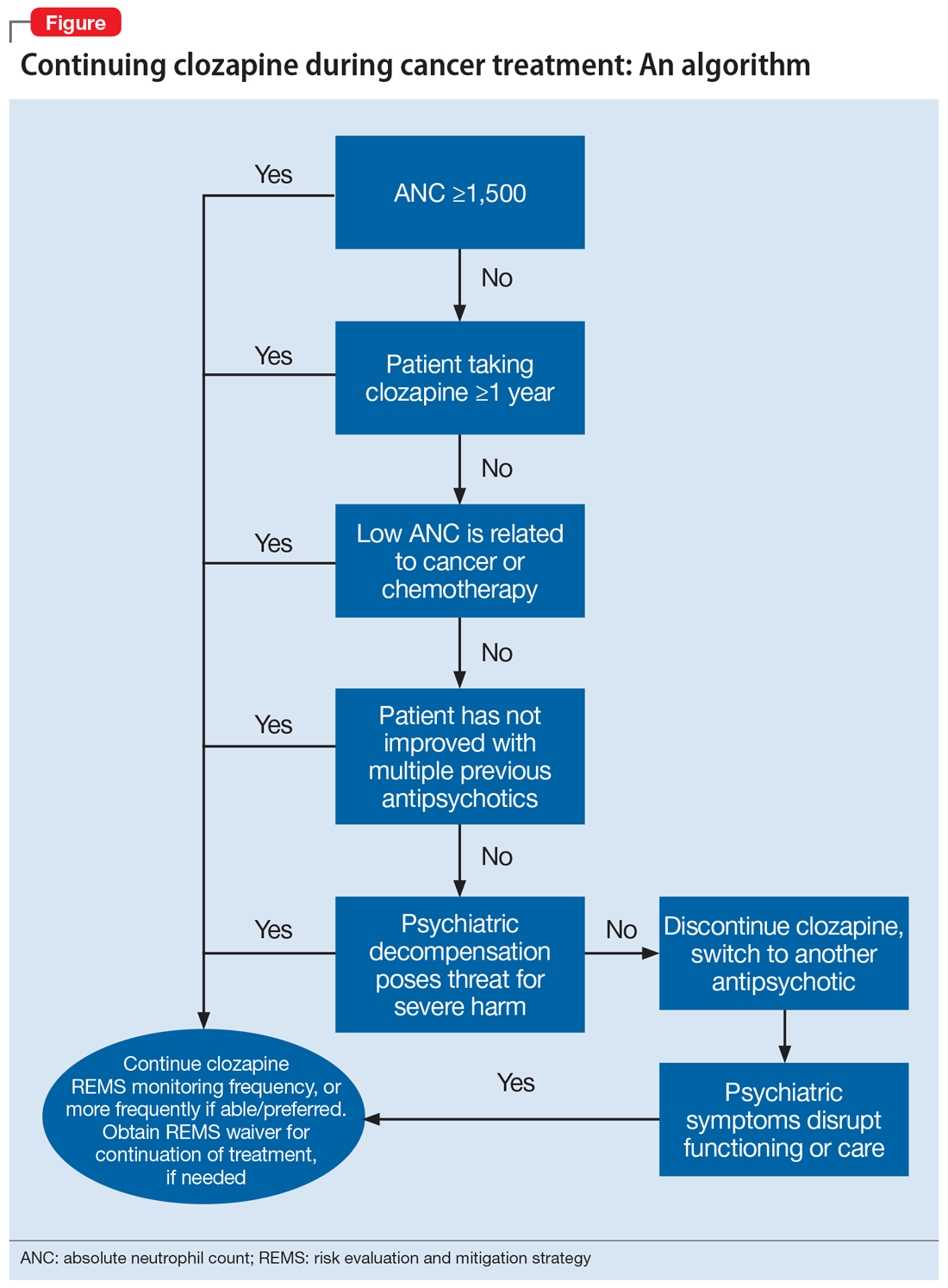
OUTCOME Cancer-free and psychiatrically stable
Mr. A continues clozapine therapy throughout all phases of treatment, without interruption. No adverse effects are determined to be secondary to clozapine. He remains psychiatrically stable throughout treatment, and able to participate and engage in his oncologic therapy. Mr. A is now more than 1 year in remission with no recurrence of graft failure, and his psychiatric symptoms continue to be well controlled with clozapine.
Bottom Line
Clozapine can be safely continued during a variety of cancer treatments (ie, chemotherapy, CAR T-cell therapy, HSCT), even in patients who develop agranulocytosis and prolonged neutropenia. Based on our experience and limited evidence, we offer an algorithm to assist clinicians faced with this challenging clinical dilemma.
Related Resources
- Grainger BT, Arcasoy MO, Kenedi CA. Feasibility of myelosuppressive chemotherapy in psychiatric patients on clozapine: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):277-286. doi:10.1111/ejh.13285
- Daniel JS, Gross T. Managing clozapine-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis. Current Psychiatry. 2016;15(12):51-53.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Clozapine • Clozaril
Divalproex sodium • Depakote
Epoetin alfa • Epogen
Haloperidol • Haldol
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Grainger BT, Arcasoy MO, Kenedi CA. Feasibility of myelosuppressive chemotherapy in psychiatric patients on clozapine: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):277-286.
2. Pick AM, Nystrom KK. Nonchemotherapy drug-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis: could medications be the culprit? J Pharm Pract. 2014:27(5):447-452.
3. Epstein RS, Aapro MS, Basu Roy UK, et al. Patient burden and real-world management of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression: results from an online survey of patients with solid tumors. Adv Ther. 2020;37(8):3606-3618.
4. Alvir JM, Lieberman JA, Safferman AZ, et al. Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. Incidence and risk factors in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(3):162-167.
5. Atkin K, Kendall F, Gould D, et al. Neutropenia and agranulocytosis in patients receiving clozapine in the UK and Ireland. Br J Psychiatry. 1996;169(4):483-488.
6. Azadeh N, Kelemen K, Fonseca R. Amitriptyline-induced agranulocytosis with bone marrow confirmation. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2014;14(5):e183-e185.
7. Liu J, Zhang X, Zhong JF, et al. CAR-T cells and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Immunotherapy. 2017;9(13):1115-1125.
8. Apinantriyo B, Lekhakula A, Rujirojindakul P. Incidence, etiology and bone marrow characteristics of non-chemotherapy-induced agranulocytosis. Hematology. 2011;16(1):50-53.
9. Yang J, Zhong J, Xiao XH, et al. The relationship between bone marrow characteristics and the clinical prognosis of antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis. Endocr J. 2013;60(2):185-189.
CASE Schizophrenia, leukemia, and chemotherapy
Mr. A, age 30, has schizophrenia but has been stable on clozapine 600 mg/d. He presents to the emergency department with generalized pain that started in his right scapula, arm, elbow, and back. Laboratory tests and a diagnostic examination reveal severe leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and anemia, and clinicians diagnose Mr. A with B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (B-ALL). Upon admission, Mr. A is neutropenic with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of 1,420 µL (reference range 2,500 to 6,000 µL). The hematology team recommends chemotherapy. The treating clinicians also consult the psychiatry team for recommendations on how to best manage Mr. A’s schizophrenia during chemotherapy, including whether clozapine should be discontinued.
HISTORY Stable on clozapine for >10 years
Mr. A was diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 15 after developing paranoia and auditory hallucinations of people talking to him and to each other. He had been hospitalized multiple times for worsened auditory hallucinations and paranoia that led to significant agitation and violence. Previous treatment with multiple antipsychotics, including haloperidol, quetiapine, aripiprazole, olanzapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone, was not successful. Mr. A began clozapine >10 years ago, and his symptoms have been stable since, without any further psychiatric hospitalizations. Mr. A takes clozapine 600 mg/d and divalproex sodium 1,500 mg/d, which he tolerates well and without significant adverse effects. Though he continues to have intermittent auditory hallucinations, they are mild and manageable. Mr. A lives with his mother, who reports he occasionally talks to himself but when he does not take clozapine, the auditory hallucinations worsen and cause him to become paranoid and aggressive. His ANC is monitored monthly and had been normal for several years until he was diagnosed with B-ALL.
[polldaddy:11125941]
The authors’ observations
The decision to continue clozapine during chemotherapy is challenging and should weigh the risk of agranulocytosis against that of psychiatric destabilization. Because clozapine and chemotherapy are both associated with agranulocytosis, there is concern that concurrent treatment could increase this risk in an additive or synergistic manner. To the best of our knowledge, there are currently no controlled studies investigating the interactions between clozapine and chemotherapeutic agents. Evidence on the hematopoietic consequences of concurrent clozapine and chemotherapy treatment has been limited to case reports because the topic does not lend itself well to randomized controlled trials.
A recent systematic review found no adverse outcomes among the 27 published cases in which clozapine was continued during myelosuppressive chemotherapy.1 The most notable finding was an association between clozapine discontinuation and psychiatric decompensation, which was reported in 12 of 13 cases in which clozapine was prophylactically discontinued to minimize the risk of agranulocytosis.
Patient-specific factors must also be considered, such as the likelihood that psychotic symptoms will recur or worsen if clozapine is discontinued, as well as the extent to which symptom recurrence would interfere with cancer treatment. Clinicians should evaluate the feasibility of switching to another antipsychotic by obtaining a thorough history of the patient’s previous antipsychotics, doses, treatment duration, and response. However, many patients are treated with clozapine because their psychotic symptoms did not improve with other treatments. The character and severity of the patient’s psychotic symptoms when untreated or prior to clozapine treatment can provide a clearer understanding of how a recurrence of symptoms may interfere with cancer treatment. To formulate an accurate assessment of risks and benefits, it is necessary to consider both available evidence and patient-specific factors. The significant agitation and paranoia that Mr. A experienced when not taking clozapine was likely to disrupt chemotherapy. Thus, the adverse consequences of discontinuing clozapine were both severe and likely.
TREATMENT Continuing clozapine
After an extensive discussion of risks, benefits, and alternative treatments with the hematology and psychiatry teams, Mr. A and his family decide to continue clozapine with increased ANC monitoring during chemotherapy. Concurrent treatment was pursued with close collaboration among the patient, the patient’s family, and the hematology and pharmacy teams, and in careful consideration of the clozapine risk evaluation and mitigation strategy. Mr. A’s ANC was monitored daily during chemotherapy treatments and weekly in the intervals between treatments.
As expected, chemotherapy resulted in bone marrow suppression and pancytopenia. Mr. A’s ANC steadily decreased during the next 10 days until it reached 0 µL. This was consistent with the predicted ANC nadir between Day 10 and Day 14, after which recovery was expected. However, Mr. A’s ANC remained at 0 µL on Day 15.
[polldaddy:11125947]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Temporary decreases in ANC are expected during chemotherapy, and the timing of onset and recovery is often well characterized. Prior to Day 15, the observed progressive marrow suppression was solely due to chemotherapy. However, because Mr. A’s ANC remained 0 µL longer than anticipated, reevaluation of clozapine’s effects was warranted.
Timing, clinical course, and comprehensive hematologic monitoring can provide important clues as to whether clozapine may be responsible for prolonged neutropenia. Though a prolonged ANC of 0 µL raised concern for clozapine-induced agranulocytosis (CIAG), comprehensive monitoring of hematologic cell lines was reassuring because CIAG selectively targets granulocytic cells (neutrophils).2 In contrast, chemotherapy can affect other cell lineages, including lymphocytes, red blood cells, and platelets, which causes pancytopenia.3 For Mr. A, though the clinical presentation of pancytopenia was significant and concerning, it was inconsistent with CIAG.
Additionally, the patient’s baseline risk of CIAG should be considered. After 18 weeks of clozapine treatment, the risk of CIAG decreases to a level similar to that associated with other antipsychotics.4,5 Therefore, CIAG would be unlikely in a patient treated with clozapine for more than 1 year and who did not have a history of neutropenia, as was the case with Mr. A.
While bone marrow biopsy can help differentiate between the causes of agranulocytosis,6 it is highly invasive and may not be necessary if laboratory evidence is sufficient. However, if a treatment team is strongly considering discontinuing clozapine and there are no suitable alternatives, a biopsy may provide additional clarification.
TREATMENT CAR T-cell therapy and cancer remission
Clozapine is continued with daily monitoring. On Day 19, Mr. A’s ANC increases, reaching 2,600 µL by discharge on Day 40. Mr. A remains psychiatrically stable throughout his hospitalization and does not experience any complications associated with neutropenia, despite its prolonged duration.
Continue to: Unfortunately, multiple cycles of...
Unfortunately, multiple cycles of chemotherapy fail to induce remission. Mr. A is referred for CD19/CD22 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, which helps achieve remission. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) is recommended to maximize the likelihood of sustained remission.7 As with chemotherapy, Mr. A and his family agree with the multidisciplinary treatment recommendation to continue clozapine during both CAR T-cell therapy and HSCT, because the risks associated with psychiatric decompensation were greater than a potential increased risk of agranulocytosis. Clozapine treatment is continued throughout both therapies without issue.
Four months after HSCT, Mr. A is admitted for neutropenic fever and left face cellulitis. Upon admission, his ANC is 30 µL and subsequently decreases to 0 µL. In addition to neutropenia, Mr. A is also anemic and thrombocytopenic. He undergoes a bone marrow biopsy.
[polldaddy:11125950]
The authors’ observations
While no published cases have examined the bone marrow of patients experiencing CIAG, 2 retrospective studies have characterized 2 classes of bone marrow findings associated with drug-induced agranulocytosis resulting from nonchemotherapeutic agents (Table).8,9 Type I marrow appears hypercellular with adequate neutrophil precursors but an arrested neutrophil maturation, with few or no mature forms of neutrophils beyond myelocytes.8,9 Type II demonstrates a severe reduction or complete absence of granulocytic precursors with normal or increased erythropoiesis and megakaryocytes.8,9 These findings have been used to accurately differentiate between chemotherapy and nonchemotherapy drug-induced agranulocytosis,6 resulting in successful identification and discontinuation of the responsible agent.

Mr. A’s bone marrow biopsy showed severe pancytopenia with profound neutropenia and normocytic anemia, without evidence of residual leukemia, inconsistent with Type I or Type II. Findings were suggestive of a myelodysplastic syndrome, consistent with secondary graft failure. Symptoms resolved after treatment with antibiotics, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, epoetin alfa, and thrombopoietin. Mr. A’s ANC remained 0 µL for 22 days before returning to normal (>1,500 µL) by Day 29. He had no secondary complications resulting from neutropenia. As the clinical evidence suggested, Mr. A’s neutropenia was unlikely to be due to clozapine. Clozapine was continued throughout his cancer treatment, and he remained psychiatrically stable.
Clozapine, cancer treatments, and agranulocytosis
This case demonstrates that clozapine can be safely continued during a variety of cancer treatments (ie, chemotherapy, CAR T-cell therapy, HSCT), even with the development of agranulocytosis and prolonged neutropenia. Evidence to guide psychiatric clinicians to evaluate the likelihood that agranulocytosis is clozapine-induced is limited.
Continue to: We offer an algorithm...
We offer an algorithm to assist clinicians faced with this challenging clinical dilemma (Figure). Based on our experience and limited current evidence, we recommend continuing clozapine during cancer treatment unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Presently, no evidence in published literature suggests worsened outcomes in patients treated concurrently with clozapine and cancer therapies.

OUTCOME Cancer-free and psychiatrically stable
Mr. A continues clozapine therapy throughout all phases of treatment, without interruption. No adverse effects are determined to be secondary to clozapine. He remains psychiatrically stable throughout treatment, and able to participate and engage in his oncologic therapy. Mr. A is now more than 1 year in remission with no recurrence of graft failure, and his psychiatric symptoms continue to be well controlled with clozapine.
Bottom Line
Clozapine can be safely continued during a variety of cancer treatments (ie, chemotherapy, CAR T-cell therapy, HSCT), even in patients who develop agranulocytosis and prolonged neutropenia. Based on our experience and limited evidence, we offer an algorithm to assist clinicians faced with this challenging clinical dilemma.
Related Resources
- Grainger BT, Arcasoy MO, Kenedi CA. Feasibility of myelosuppressive chemotherapy in psychiatric patients on clozapine: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):277-286. doi:10.1111/ejh.13285
- Daniel JS, Gross T. Managing clozapine-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis. Current Psychiatry. 2016;15(12):51-53.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Clozapine • Clozaril
Divalproex sodium • Depakote
Epoetin alfa • Epogen
Haloperidol • Haldol
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Ziprasidone • Geodon
CASE Schizophrenia, leukemia, and chemotherapy
Mr. A, age 30, has schizophrenia but has been stable on clozapine 600 mg/d. He presents to the emergency department with generalized pain that started in his right scapula, arm, elbow, and back. Laboratory tests and a diagnostic examination reveal severe leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and anemia, and clinicians diagnose Mr. A with B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (B-ALL). Upon admission, Mr. A is neutropenic with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of 1,420 µL (reference range 2,500 to 6,000 µL). The hematology team recommends chemotherapy. The treating clinicians also consult the psychiatry team for recommendations on how to best manage Mr. A’s schizophrenia during chemotherapy, including whether clozapine should be discontinued.
HISTORY Stable on clozapine for >10 years
Mr. A was diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 15 after developing paranoia and auditory hallucinations of people talking to him and to each other. He had been hospitalized multiple times for worsened auditory hallucinations and paranoia that led to significant agitation and violence. Previous treatment with multiple antipsychotics, including haloperidol, quetiapine, aripiprazole, olanzapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone, was not successful. Mr. A began clozapine >10 years ago, and his symptoms have been stable since, without any further psychiatric hospitalizations. Mr. A takes clozapine 600 mg/d and divalproex sodium 1,500 mg/d, which he tolerates well and without significant adverse effects. Though he continues to have intermittent auditory hallucinations, they are mild and manageable. Mr. A lives with his mother, who reports he occasionally talks to himself but when he does not take clozapine, the auditory hallucinations worsen and cause him to become paranoid and aggressive. His ANC is monitored monthly and had been normal for several years until he was diagnosed with B-ALL.
[polldaddy:11125941]
The authors’ observations
The decision to continue clozapine during chemotherapy is challenging and should weigh the risk of agranulocytosis against that of psychiatric destabilization. Because clozapine and chemotherapy are both associated with agranulocytosis, there is concern that concurrent treatment could increase this risk in an additive or synergistic manner. To the best of our knowledge, there are currently no controlled studies investigating the interactions between clozapine and chemotherapeutic agents. Evidence on the hematopoietic consequences of concurrent clozapine and chemotherapy treatment has been limited to case reports because the topic does not lend itself well to randomized controlled trials.
A recent systematic review found no adverse outcomes among the 27 published cases in which clozapine was continued during myelosuppressive chemotherapy.1 The most notable finding was an association between clozapine discontinuation and psychiatric decompensation, which was reported in 12 of 13 cases in which clozapine was prophylactically discontinued to minimize the risk of agranulocytosis.
Patient-specific factors must also be considered, such as the likelihood that psychotic symptoms will recur or worsen if clozapine is discontinued, as well as the extent to which symptom recurrence would interfere with cancer treatment. Clinicians should evaluate the feasibility of switching to another antipsychotic by obtaining a thorough history of the patient’s previous antipsychotics, doses, treatment duration, and response. However, many patients are treated with clozapine because their psychotic symptoms did not improve with other treatments. The character and severity of the patient’s psychotic symptoms when untreated or prior to clozapine treatment can provide a clearer understanding of how a recurrence of symptoms may interfere with cancer treatment. To formulate an accurate assessment of risks and benefits, it is necessary to consider both available evidence and patient-specific factors. The significant agitation and paranoia that Mr. A experienced when not taking clozapine was likely to disrupt chemotherapy. Thus, the adverse consequences of discontinuing clozapine were both severe and likely.
TREATMENT Continuing clozapine
After an extensive discussion of risks, benefits, and alternative treatments with the hematology and psychiatry teams, Mr. A and his family decide to continue clozapine with increased ANC monitoring during chemotherapy. Concurrent treatment was pursued with close collaboration among the patient, the patient’s family, and the hematology and pharmacy teams, and in careful consideration of the clozapine risk evaluation and mitigation strategy. Mr. A’s ANC was monitored daily during chemotherapy treatments and weekly in the intervals between treatments.
As expected, chemotherapy resulted in bone marrow suppression and pancytopenia. Mr. A’s ANC steadily decreased during the next 10 days until it reached 0 µL. This was consistent with the predicted ANC nadir between Day 10 and Day 14, after which recovery was expected. However, Mr. A’s ANC remained at 0 µL on Day 15.
[polldaddy:11125947]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Temporary decreases in ANC are expected during chemotherapy, and the timing of onset and recovery is often well characterized. Prior to Day 15, the observed progressive marrow suppression was solely due to chemotherapy. However, because Mr. A’s ANC remained 0 µL longer than anticipated, reevaluation of clozapine’s effects was warranted.
Timing, clinical course, and comprehensive hematologic monitoring can provide important clues as to whether clozapine may be responsible for prolonged neutropenia. Though a prolonged ANC of 0 µL raised concern for clozapine-induced agranulocytosis (CIAG), comprehensive monitoring of hematologic cell lines was reassuring because CIAG selectively targets granulocytic cells (neutrophils).2 In contrast, chemotherapy can affect other cell lineages, including lymphocytes, red blood cells, and platelets, which causes pancytopenia.3 For Mr. A, though the clinical presentation of pancytopenia was significant and concerning, it was inconsistent with CIAG.
Additionally, the patient’s baseline risk of CIAG should be considered. After 18 weeks of clozapine treatment, the risk of CIAG decreases to a level similar to that associated with other antipsychotics.4,5 Therefore, CIAG would be unlikely in a patient treated with clozapine for more than 1 year and who did not have a history of neutropenia, as was the case with Mr. A.
While bone marrow biopsy can help differentiate between the causes of agranulocytosis,6 it is highly invasive and may not be necessary if laboratory evidence is sufficient. However, if a treatment team is strongly considering discontinuing clozapine and there are no suitable alternatives, a biopsy may provide additional clarification.
TREATMENT CAR T-cell therapy and cancer remission
Clozapine is continued with daily monitoring. On Day 19, Mr. A’s ANC increases, reaching 2,600 µL by discharge on Day 40. Mr. A remains psychiatrically stable throughout his hospitalization and does not experience any complications associated with neutropenia, despite its prolonged duration.
Continue to: Unfortunately, multiple cycles of...
Unfortunately, multiple cycles of chemotherapy fail to induce remission. Mr. A is referred for CD19/CD22 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, which helps achieve remission. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) is recommended to maximize the likelihood of sustained remission.7 As with chemotherapy, Mr. A and his family agree with the multidisciplinary treatment recommendation to continue clozapine during both CAR T-cell therapy and HSCT, because the risks associated with psychiatric decompensation were greater than a potential increased risk of agranulocytosis. Clozapine treatment is continued throughout both therapies without issue.
Four months after HSCT, Mr. A is admitted for neutropenic fever and left face cellulitis. Upon admission, his ANC is 30 µL and subsequently decreases to 0 µL. In addition to neutropenia, Mr. A is also anemic and thrombocytopenic. He undergoes a bone marrow biopsy.
[polldaddy:11125950]
The authors’ observations
While no published cases have examined the bone marrow of patients experiencing CIAG, 2 retrospective studies have characterized 2 classes of bone marrow findings associated with drug-induced agranulocytosis resulting from nonchemotherapeutic agents (Table).8,9 Type I marrow appears hypercellular with adequate neutrophil precursors but an arrested neutrophil maturation, with few or no mature forms of neutrophils beyond myelocytes.8,9 Type II demonstrates a severe reduction or complete absence of granulocytic precursors with normal or increased erythropoiesis and megakaryocytes.8,9 These findings have been used to accurately differentiate between chemotherapy and nonchemotherapy drug-induced agranulocytosis,6 resulting in successful identification and discontinuation of the responsible agent.

Mr. A’s bone marrow biopsy showed severe pancytopenia with profound neutropenia and normocytic anemia, without evidence of residual leukemia, inconsistent with Type I or Type II. Findings were suggestive of a myelodysplastic syndrome, consistent with secondary graft failure. Symptoms resolved after treatment with antibiotics, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, epoetin alfa, and thrombopoietin. Mr. A’s ANC remained 0 µL for 22 days before returning to normal (>1,500 µL) by Day 29. He had no secondary complications resulting from neutropenia. As the clinical evidence suggested, Mr. A’s neutropenia was unlikely to be due to clozapine. Clozapine was continued throughout his cancer treatment, and he remained psychiatrically stable.
Clozapine, cancer treatments, and agranulocytosis
This case demonstrates that clozapine can be safely continued during a variety of cancer treatments (ie, chemotherapy, CAR T-cell therapy, HSCT), even with the development of agranulocytosis and prolonged neutropenia. Evidence to guide psychiatric clinicians to evaluate the likelihood that agranulocytosis is clozapine-induced is limited.
Continue to: We offer an algorithm...
We offer an algorithm to assist clinicians faced with this challenging clinical dilemma (Figure). Based on our experience and limited current evidence, we recommend continuing clozapine during cancer treatment unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Presently, no evidence in published literature suggests worsened outcomes in patients treated concurrently with clozapine and cancer therapies.

OUTCOME Cancer-free and psychiatrically stable
Mr. A continues clozapine therapy throughout all phases of treatment, without interruption. No adverse effects are determined to be secondary to clozapine. He remains psychiatrically stable throughout treatment, and able to participate and engage in his oncologic therapy. Mr. A is now more than 1 year in remission with no recurrence of graft failure, and his psychiatric symptoms continue to be well controlled with clozapine.
Bottom Line
Clozapine can be safely continued during a variety of cancer treatments (ie, chemotherapy, CAR T-cell therapy, HSCT), even in patients who develop agranulocytosis and prolonged neutropenia. Based on our experience and limited evidence, we offer an algorithm to assist clinicians faced with this challenging clinical dilemma.
Related Resources
- Grainger BT, Arcasoy MO, Kenedi CA. Feasibility of myelosuppressive chemotherapy in psychiatric patients on clozapine: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):277-286. doi:10.1111/ejh.13285
- Daniel JS, Gross T. Managing clozapine-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis. Current Psychiatry. 2016;15(12):51-53.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Clozapine • Clozaril
Divalproex sodium • Depakote
Epoetin alfa • Epogen
Haloperidol • Haldol
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Grainger BT, Arcasoy MO, Kenedi CA. Feasibility of myelosuppressive chemotherapy in psychiatric patients on clozapine: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):277-286.
2. Pick AM, Nystrom KK. Nonchemotherapy drug-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis: could medications be the culprit? J Pharm Pract. 2014:27(5):447-452.
3. Epstein RS, Aapro MS, Basu Roy UK, et al. Patient burden and real-world management of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression: results from an online survey of patients with solid tumors. Adv Ther. 2020;37(8):3606-3618.
4. Alvir JM, Lieberman JA, Safferman AZ, et al. Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. Incidence and risk factors in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(3):162-167.
5. Atkin K, Kendall F, Gould D, et al. Neutropenia and agranulocytosis in patients receiving clozapine in the UK and Ireland. Br J Psychiatry. 1996;169(4):483-488.
6. Azadeh N, Kelemen K, Fonseca R. Amitriptyline-induced agranulocytosis with bone marrow confirmation. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2014;14(5):e183-e185.
7. Liu J, Zhang X, Zhong JF, et al. CAR-T cells and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Immunotherapy. 2017;9(13):1115-1125.
8. Apinantriyo B, Lekhakula A, Rujirojindakul P. Incidence, etiology and bone marrow characteristics of non-chemotherapy-induced agranulocytosis. Hematology. 2011;16(1):50-53.
9. Yang J, Zhong J, Xiao XH, et al. The relationship between bone marrow characteristics and the clinical prognosis of antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis. Endocr J. 2013;60(2):185-189.
1. Grainger BT, Arcasoy MO, Kenedi CA. Feasibility of myelosuppressive chemotherapy in psychiatric patients on clozapine: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):277-286.
2. Pick AM, Nystrom KK. Nonchemotherapy drug-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis: could medications be the culprit? J Pharm Pract. 2014:27(5):447-452.
3. Epstein RS, Aapro MS, Basu Roy UK, et al. Patient burden and real-world management of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression: results from an online survey of patients with solid tumors. Adv Ther. 2020;37(8):3606-3618.
4. Alvir JM, Lieberman JA, Safferman AZ, et al. Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. Incidence and risk factors in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(3):162-167.
5. Atkin K, Kendall F, Gould D, et al. Neutropenia and agranulocytosis in patients receiving clozapine in the UK and Ireland. Br J Psychiatry. 1996;169(4):483-488.
6. Azadeh N, Kelemen K, Fonseca R. Amitriptyline-induced agranulocytosis with bone marrow confirmation. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2014;14(5):e183-e185.
7. Liu J, Zhang X, Zhong JF, et al. CAR-T cells and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Immunotherapy. 2017;9(13):1115-1125.
8. Apinantriyo B, Lekhakula A, Rujirojindakul P. Incidence, etiology and bone marrow characteristics of non-chemotherapy-induced agranulocytosis. Hematology. 2011;16(1):50-53.
9. Yang J, Zhong J, Xiao XH, et al. The relationship between bone marrow characteristics and the clinical prognosis of antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis. Endocr J. 2013;60(2):185-189.
BOARDING psychiatric patients in the ED: Key strategies
Boarding of psychiatric patients in the emergency department (ED) has been well documented.1 Numerous researchers have discussed ways to address this public health crisis. In this Pearl, I use the acronym BOARDING to provide key strategies for psychiatric clinicians managing psychiatric patients who are boarding in an ED.
Be vigilant. As a patient’s time waiting in the ED increases, watch for clinical blind spots. New medical problems,2 psychiatric issues, or medication errors3 may unexpectedly arise since the patient was originally stabilized by emergency medicine clinicians.
Orders. Since the patient could be waiting in the ED for 24 hours or longer, consider starting orders (eg, precautions, medications, diet, vital sign checks, labs, etc) as you would for a patient in an inpatient psychiatric unit or a dedicated psychiatric ED.
AWOL. Unlike inpatient psychiatric units, EDs generally are not locked. Extra resources (eg, sitter, safety alarm bracelet) may be needed to help prevent patients from leaving this setting unnoticed, especially those on involuntary psychiatric holds.
Re-evaluate. Ideally, re-evaluate the patient every shift. Does the patient still need an inpatient psychiatric setting? Can the involuntary psychiatric hold be discontinued?
Disposition. Is there a family member or reliable caregiver to whom the patient can be discharged? Can the patient go to a shelter or be stabilized in a short-term residential program, instead of an inpatient psychiatric unit?
Inpatient. If the patient waits 24 hours or longer, begin thinking like an inpatient psychiatric clinician. Are there any interventions you can reasonably begin in the ED that you would otherwise begin on an inpatient psychiatric unit?
Nursing. Work with ED nursing staff to familiarize them with the patient’s specific needs.
Guidelines. With the input of clinical and administrative leadership, establish local hospital-based guidelines for managing psychiatric patients who are boarding in the ED.
1. Nordstrom K, Berlin JS, Nash SS, et al. Boarding of mentally ill patients in emergency departments: American Psychiatric Association Resource Document. West J Emerg Med. 2019;20(5):690-695.
2. Garfinkel E, Rose D, Strouse K, et al. Psychiatric emergency department boarding: from catatonia to cardiac arrest. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(3):543-544.
3. Bakhsh HT, Perona SJ, Shields WA, et al. Medication errors in psychiatric patients boarded in the emergency department. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2014;26(4):191-198.
Boarding of psychiatric patients in the emergency department (ED) has been well documented.1 Numerous researchers have discussed ways to address this public health crisis. In this Pearl, I use the acronym BOARDING to provide key strategies for psychiatric clinicians managing psychiatric patients who are boarding in an ED.
Be vigilant. As a patient’s time waiting in the ED increases, watch for clinical blind spots. New medical problems,2 psychiatric issues, or medication errors3 may unexpectedly arise since the patient was originally stabilized by emergency medicine clinicians.
Orders. Since the patient could be waiting in the ED for 24 hours or longer, consider starting orders (eg, precautions, medications, diet, vital sign checks, labs, etc) as you would for a patient in an inpatient psychiatric unit or a dedicated psychiatric ED.
AWOL. Unlike inpatient psychiatric units, EDs generally are not locked. Extra resources (eg, sitter, safety alarm bracelet) may be needed to help prevent patients from leaving this setting unnoticed, especially those on involuntary psychiatric holds.
Re-evaluate. Ideally, re-evaluate the patient every shift. Does the patient still need an inpatient psychiatric setting? Can the involuntary psychiatric hold be discontinued?
Disposition. Is there a family member or reliable caregiver to whom the patient can be discharged? Can the patient go to a shelter or be stabilized in a short-term residential program, instead of an inpatient psychiatric unit?
Inpatient. If the patient waits 24 hours or longer, begin thinking like an inpatient psychiatric clinician. Are there any interventions you can reasonably begin in the ED that you would otherwise begin on an inpatient psychiatric unit?
Nursing. Work with ED nursing staff to familiarize them with the patient’s specific needs.
Guidelines. With the input of clinical and administrative leadership, establish local hospital-based guidelines for managing psychiatric patients who are boarding in the ED.
Boarding of psychiatric patients in the emergency department (ED) has been well documented.1 Numerous researchers have discussed ways to address this public health crisis. In this Pearl, I use the acronym BOARDING to provide key strategies for psychiatric clinicians managing psychiatric patients who are boarding in an ED.
Be vigilant. As a patient’s time waiting in the ED increases, watch for clinical blind spots. New medical problems,2 psychiatric issues, or medication errors3 may unexpectedly arise since the patient was originally stabilized by emergency medicine clinicians.
Orders. Since the patient could be waiting in the ED for 24 hours or longer, consider starting orders (eg, precautions, medications, diet, vital sign checks, labs, etc) as you would for a patient in an inpatient psychiatric unit or a dedicated psychiatric ED.
AWOL. Unlike inpatient psychiatric units, EDs generally are not locked. Extra resources (eg, sitter, safety alarm bracelet) may be needed to help prevent patients from leaving this setting unnoticed, especially those on involuntary psychiatric holds.
Re-evaluate. Ideally, re-evaluate the patient every shift. Does the patient still need an inpatient psychiatric setting? Can the involuntary psychiatric hold be discontinued?
Disposition. Is there a family member or reliable caregiver to whom the patient can be discharged? Can the patient go to a shelter or be stabilized in a short-term residential program, instead of an inpatient psychiatric unit?
Inpatient. If the patient waits 24 hours or longer, begin thinking like an inpatient psychiatric clinician. Are there any interventions you can reasonably begin in the ED that you would otherwise begin on an inpatient psychiatric unit?
Nursing. Work with ED nursing staff to familiarize them with the patient’s specific needs.
Guidelines. With the input of clinical and administrative leadership, establish local hospital-based guidelines for managing psychiatric patients who are boarding in the ED.
1. Nordstrom K, Berlin JS, Nash SS, et al. Boarding of mentally ill patients in emergency departments: American Psychiatric Association Resource Document. West J Emerg Med. 2019;20(5):690-695.
2. Garfinkel E, Rose D, Strouse K, et al. Psychiatric emergency department boarding: from catatonia to cardiac arrest. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(3):543-544.
3. Bakhsh HT, Perona SJ, Shields WA, et al. Medication errors in psychiatric patients boarded in the emergency department. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2014;26(4):191-198.
1. Nordstrom K, Berlin JS, Nash SS, et al. Boarding of mentally ill patients in emergency departments: American Psychiatric Association Resource Document. West J Emerg Med. 2019;20(5):690-695.
2. Garfinkel E, Rose D, Strouse K, et al. Psychiatric emergency department boarding: from catatonia to cardiac arrest. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(3):543-544.
3. Bakhsh HT, Perona SJ, Shields WA, et al. Medication errors in psychiatric patients boarded in the emergency department. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2014;26(4):191-198.