User login
Moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: No increased infection risk with long-term dupilumab use
Key clinical point: In patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), continuous long-term dupilumab treatment was not associated with an increased risk for overall systemic/cutaneous infections.
Major finding: At 4 years, the overall infection rate was 71.27 number of patients with ≥1 event per 100 patient-years (nP/100 PY), with most infections being mild to moderate in severity, and only a very small number of infections resulted in treatment discontinuation (0.34 nP/100 PY). The rate of total skin infections decreased from 28.10 to 11.48 nP/100 PY from week 16 to year 4.
Study details: Findings are from the analysis of the LIBERTY AD OLE study including 2677 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received dupilumab, of which 13.1% completed treatment up to week 204.
Disclosures: This research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Three authors declared being employees or holding stock options in Sanofi. The other authors reported ties with several sources, including Regeneron and Sanofi.
Source: Blauvelt A et al. No increased risk of overall infection in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated for up to 4 years with dupilumab. Adv Ther. 2022 (Nov 1). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02322-y
Key clinical point: In patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), continuous long-term dupilumab treatment was not associated with an increased risk for overall systemic/cutaneous infections.
Major finding: At 4 years, the overall infection rate was 71.27 number of patients with ≥1 event per 100 patient-years (nP/100 PY), with most infections being mild to moderate in severity, and only a very small number of infections resulted in treatment discontinuation (0.34 nP/100 PY). The rate of total skin infections decreased from 28.10 to 11.48 nP/100 PY from week 16 to year 4.
Study details: Findings are from the analysis of the LIBERTY AD OLE study including 2677 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received dupilumab, of which 13.1% completed treatment up to week 204.
Disclosures: This research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Three authors declared being employees or holding stock options in Sanofi. The other authors reported ties with several sources, including Regeneron and Sanofi.
Source: Blauvelt A et al. No increased risk of overall infection in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated for up to 4 years with dupilumab. Adv Ther. 2022 (Nov 1). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02322-y
Key clinical point: In patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), continuous long-term dupilumab treatment was not associated with an increased risk for overall systemic/cutaneous infections.
Major finding: At 4 years, the overall infection rate was 71.27 number of patients with ≥1 event per 100 patient-years (nP/100 PY), with most infections being mild to moderate in severity, and only a very small number of infections resulted in treatment discontinuation (0.34 nP/100 PY). The rate of total skin infections decreased from 28.10 to 11.48 nP/100 PY from week 16 to year 4.
Study details: Findings are from the analysis of the LIBERTY AD OLE study including 2677 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received dupilumab, of which 13.1% completed treatment up to week 204.
Disclosures: This research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Three authors declared being employees or holding stock options in Sanofi. The other authors reported ties with several sources, including Regeneron and Sanofi.
Source: Blauvelt A et al. No increased risk of overall infection in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated for up to 4 years with dupilumab. Adv Ther. 2022 (Nov 1). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02322-y
Exposure to wildfire air pollution increases atopic dermatitis risk in older adults
Key clinical point: Air pollution due to a wildfire increased the rate of clinic visits for atopic dermatitis (AD), especially at a 0-week lag, in adults aged ≥65 years.
Major finding: In adults aged ≥65 years, the adjusted rate of clinic visits for AD during a week with a wildfire was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1-1.9) times the rate during weeks without wildfire and every 1-unit increase in the mean weekly smoke plume density score increased the rate of clinic visits for AD by 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6) times.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of outpatient dermatology visits for AD (5529 visits) and itch (1319 visits).
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. Dr. Grimes declared receiving grants from the University of California, San Francisco.
Source: Fadadu RP et al. Association of exposure to wildfire air pollution with exacerbations of atopic dermatitis and itch among older adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2238594 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38594
Key clinical point: Air pollution due to a wildfire increased the rate of clinic visits for atopic dermatitis (AD), especially at a 0-week lag, in adults aged ≥65 years.
Major finding: In adults aged ≥65 years, the adjusted rate of clinic visits for AD during a week with a wildfire was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1-1.9) times the rate during weeks without wildfire and every 1-unit increase in the mean weekly smoke plume density score increased the rate of clinic visits for AD by 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6) times.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of outpatient dermatology visits for AD (5529 visits) and itch (1319 visits).
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. Dr. Grimes declared receiving grants from the University of California, San Francisco.
Source: Fadadu RP et al. Association of exposure to wildfire air pollution with exacerbations of atopic dermatitis and itch among older adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2238594 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38594
Key clinical point: Air pollution due to a wildfire increased the rate of clinic visits for atopic dermatitis (AD), especially at a 0-week lag, in adults aged ≥65 years.
Major finding: In adults aged ≥65 years, the adjusted rate of clinic visits for AD during a week with a wildfire was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1-1.9) times the rate during weeks without wildfire and every 1-unit increase in the mean weekly smoke plume density score increased the rate of clinic visits for AD by 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6) times.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of outpatient dermatology visits for AD (5529 visits) and itch (1319 visits).
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. Dr. Grimes declared receiving grants from the University of California, San Francisco.
Source: Fadadu RP et al. Association of exposure to wildfire air pollution with exacerbations of atopic dermatitis and itch among older adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2238594 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38594
Atopic dermatitis: Dupilumab serum levels not associated with treatment response or adverse effects
Key clinical point: In patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), serum dupilumab levels at week 16 were not associated with treatment response or adverse effects due to dupilumab during the first year of treatment.
Major finding: Serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks were not associated with the prediction of treatment response at 52 weeks (≥90% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index; odds ratio [OR] 0.96; P = .34) or adverse events during the first year of treatment (OR 1.01; P = .83).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective clinical cohort study including 295 patients with AD who started dupilumab and had treatment week 16 serum samples available.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and other sources. The authors declared receiving consulting fees, speaking fees, investigator fees, or research funding from several sources.
Source: Spekhorst LS et al. Association of serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks with treatment response and adverse effects in patients with atopic dermatitis: A prospective clinical cohort study from the BioDay registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2022 (Nov 2). Doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4639
Key clinical point: In patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), serum dupilumab levels at week 16 were not associated with treatment response or adverse effects due to dupilumab during the first year of treatment.
Major finding: Serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks were not associated with the prediction of treatment response at 52 weeks (≥90% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index; odds ratio [OR] 0.96; P = .34) or adverse events during the first year of treatment (OR 1.01; P = .83).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective clinical cohort study including 295 patients with AD who started dupilumab and had treatment week 16 serum samples available.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and other sources. The authors declared receiving consulting fees, speaking fees, investigator fees, or research funding from several sources.
Source: Spekhorst LS et al. Association of serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks with treatment response and adverse effects in patients with atopic dermatitis: A prospective clinical cohort study from the BioDay registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2022 (Nov 2). Doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4639
Key clinical point: In patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), serum dupilumab levels at week 16 were not associated with treatment response or adverse effects due to dupilumab during the first year of treatment.
Major finding: Serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks were not associated with the prediction of treatment response at 52 weeks (≥90% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index; odds ratio [OR] 0.96; P = .34) or adverse events during the first year of treatment (OR 1.01; P = .83).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective clinical cohort study including 295 patients with AD who started dupilumab and had treatment week 16 serum samples available.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and other sources. The authors declared receiving consulting fees, speaking fees, investigator fees, or research funding from several sources.
Source: Spekhorst LS et al. Association of serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks with treatment response and adverse effects in patients with atopic dermatitis: A prospective clinical cohort study from the BioDay registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2022 (Nov 2). Doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4639
More weight loss with surgery than new obesity meds: meta-analysis
SAN DIEGO – but glycemic control was similar after either treatment.
However, researchers have yet to directly compare bariatric surgery with new dual and even triple agonists that are in development.
The review by Shohinee Sarma, MD, MPH, and Patricia Palcu, MD, from the University of Toronto, was published in Obesity. Dr. Sarma also presented the findings virtually at the Obesity journal symposium at ObesityWeek® 2022.
Eric Ravussin, PhD, outgoing editor-in-chief of Obesity, explained to in an interview that this is one of five articles the editors chose from about 20 papers submitted for consideration for the symposium, and it was selected because it is a first review and meta-analysis of this direct comparison.
It showed that in “a straight head-to-head comparison, weight loss is larger by about 20 kg (44 lb) with bariatric surgery versus a GLP-1 agonist, but the improvement in glycemia (carbohydrate metabolism) was similar,” said Dr. Ravussin, from Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Study limitations, which the authors also acknowledge, include that this was a small review of small studies: There were only six studies and 322 patients.
Moreover, the data are from 2007 to 2017, and newer weight-loss drugs are more potent.
Most studies in the review compared bariatric surgery with liraglutide, Dr. Ravussin noted, whereas, “we have now better GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide,” as well as drugs that are combinations of a GLP-1 agonist with another agonist or agonists.
“Tirzepatide, for example, which is a combination of a GLP-1 agonist and a [glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist], is showing results that are very close to weight loss with bariatric surgery,” he observed.
There are quite a few other drugs in development, too, he continued, which are going to approach the weight loss obtained with bariatric surgery.
Novo Nordisk is coming out with a combination of an amylin analog (cagrilintide) and a GLP-1 agonist (semaglutide), he noted. “There are others coming in with GLP-1 and glucagon [dual agonists], and there is even a ... combo called triple G, which is a glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP [agonist].”
We now need a head-to-head comparison between bariatric surgery versus a combination drug like tirzepatide in a large population, he said.
“This is an exciting period,” Dr. Ravussin summarized, “because, 10 years ago, nobody thought that [results with] pharmacotherapy can approach bariatric surgery. Now we have other drugs that are still in development that are going to approach really close bariatric surgery.”
In an email to this news organization, Dr. Sarma noted that “due to the potent weight loss and glycemic benefits of GLP-1 agonists, patients who wish to avoid the risks of bariatric surgery may wish to discuss the option of medical therapy with their health professionals.”
“For next steps,” she said, “we need long-term studies comparing the weight-lowering, glycemic, and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists in comparison to bariatric surgery for better counseling in obesity treatment.”
Three RCTs, three observational studies
The researchers searched the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies up to April 21, 2021, which directly compared absolute weight loss with a GLP-1 agonist – liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and albiglutide (which are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or Health Canada) – versus any type of bariatric surgery including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion.
The studies included patients aged 18 and older with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2.
Secondary outcomes included change in BMI, and for patients with type 2 diabetes, change in A1c.
The researchers identified three RCTs and three observational studies, with diverse drugs and diverse types of bariatric surgery, which enrolled 13 to 134 patients, with follow-up from 6 months to 10 years.
During follow-up, the overall mean weight loss was 22.7 kg greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 25.1 kg greater in the two non-RCTs with these data (Capristo et al. and Cotugno et al.).
The overall mean decrease in BMI was 8.2 kg/m2 greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 10.6 kg/m2 greater in the three non-RCTs with these data.
The overall mean decrease in A1c was 1.28% lower in the three RCTs with these data, and it was 0.9% lower in the one non-RCT with these data.
“In adults with obesity, bariatric surgery still confers the highest reductions in weight and BMI but confers similar effects in glycemic control when compared with GLP-1 agonists,” the researchers summarize.
Dr. Sarma received funding from the Clinical Investigator Program. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – but glycemic control was similar after either treatment.
However, researchers have yet to directly compare bariatric surgery with new dual and even triple agonists that are in development.
The review by Shohinee Sarma, MD, MPH, and Patricia Palcu, MD, from the University of Toronto, was published in Obesity. Dr. Sarma also presented the findings virtually at the Obesity journal symposium at ObesityWeek® 2022.
Eric Ravussin, PhD, outgoing editor-in-chief of Obesity, explained to in an interview that this is one of five articles the editors chose from about 20 papers submitted for consideration for the symposium, and it was selected because it is a first review and meta-analysis of this direct comparison.
It showed that in “a straight head-to-head comparison, weight loss is larger by about 20 kg (44 lb) with bariatric surgery versus a GLP-1 agonist, but the improvement in glycemia (carbohydrate metabolism) was similar,” said Dr. Ravussin, from Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Study limitations, which the authors also acknowledge, include that this was a small review of small studies: There were only six studies and 322 patients.
Moreover, the data are from 2007 to 2017, and newer weight-loss drugs are more potent.
Most studies in the review compared bariatric surgery with liraglutide, Dr. Ravussin noted, whereas, “we have now better GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide,” as well as drugs that are combinations of a GLP-1 agonist with another agonist or agonists.
“Tirzepatide, for example, which is a combination of a GLP-1 agonist and a [glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist], is showing results that are very close to weight loss with bariatric surgery,” he observed.
There are quite a few other drugs in development, too, he continued, which are going to approach the weight loss obtained with bariatric surgery.
Novo Nordisk is coming out with a combination of an amylin analog (cagrilintide) and a GLP-1 agonist (semaglutide), he noted. “There are others coming in with GLP-1 and glucagon [dual agonists], and there is even a ... combo called triple G, which is a glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP [agonist].”
We now need a head-to-head comparison between bariatric surgery versus a combination drug like tirzepatide in a large population, he said.
“This is an exciting period,” Dr. Ravussin summarized, “because, 10 years ago, nobody thought that [results with] pharmacotherapy can approach bariatric surgery. Now we have other drugs that are still in development that are going to approach really close bariatric surgery.”
In an email to this news organization, Dr. Sarma noted that “due to the potent weight loss and glycemic benefits of GLP-1 agonists, patients who wish to avoid the risks of bariatric surgery may wish to discuss the option of medical therapy with their health professionals.”
“For next steps,” she said, “we need long-term studies comparing the weight-lowering, glycemic, and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists in comparison to bariatric surgery for better counseling in obesity treatment.”
Three RCTs, three observational studies
The researchers searched the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies up to April 21, 2021, which directly compared absolute weight loss with a GLP-1 agonist – liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and albiglutide (which are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or Health Canada) – versus any type of bariatric surgery including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion.
The studies included patients aged 18 and older with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2.
Secondary outcomes included change in BMI, and for patients with type 2 diabetes, change in A1c.
The researchers identified three RCTs and three observational studies, with diverse drugs and diverse types of bariatric surgery, which enrolled 13 to 134 patients, with follow-up from 6 months to 10 years.
During follow-up, the overall mean weight loss was 22.7 kg greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 25.1 kg greater in the two non-RCTs with these data (Capristo et al. and Cotugno et al.).
The overall mean decrease in BMI was 8.2 kg/m2 greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 10.6 kg/m2 greater in the three non-RCTs with these data.
The overall mean decrease in A1c was 1.28% lower in the three RCTs with these data, and it was 0.9% lower in the one non-RCT with these data.
“In adults with obesity, bariatric surgery still confers the highest reductions in weight and BMI but confers similar effects in glycemic control when compared with GLP-1 agonists,” the researchers summarize.
Dr. Sarma received funding from the Clinical Investigator Program. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – but glycemic control was similar after either treatment.
However, researchers have yet to directly compare bariatric surgery with new dual and even triple agonists that are in development.
The review by Shohinee Sarma, MD, MPH, and Patricia Palcu, MD, from the University of Toronto, was published in Obesity. Dr. Sarma also presented the findings virtually at the Obesity journal symposium at ObesityWeek® 2022.
Eric Ravussin, PhD, outgoing editor-in-chief of Obesity, explained to in an interview that this is one of five articles the editors chose from about 20 papers submitted for consideration for the symposium, and it was selected because it is a first review and meta-analysis of this direct comparison.
It showed that in “a straight head-to-head comparison, weight loss is larger by about 20 kg (44 lb) with bariatric surgery versus a GLP-1 agonist, but the improvement in glycemia (carbohydrate metabolism) was similar,” said Dr. Ravussin, from Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Study limitations, which the authors also acknowledge, include that this was a small review of small studies: There were only six studies and 322 patients.
Moreover, the data are from 2007 to 2017, and newer weight-loss drugs are more potent.
Most studies in the review compared bariatric surgery with liraglutide, Dr. Ravussin noted, whereas, “we have now better GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide,” as well as drugs that are combinations of a GLP-1 agonist with another agonist or agonists.
“Tirzepatide, for example, which is a combination of a GLP-1 agonist and a [glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist], is showing results that are very close to weight loss with bariatric surgery,” he observed.
There are quite a few other drugs in development, too, he continued, which are going to approach the weight loss obtained with bariatric surgery.
Novo Nordisk is coming out with a combination of an amylin analog (cagrilintide) and a GLP-1 agonist (semaglutide), he noted. “There are others coming in with GLP-1 and glucagon [dual agonists], and there is even a ... combo called triple G, which is a glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP [agonist].”
We now need a head-to-head comparison between bariatric surgery versus a combination drug like tirzepatide in a large population, he said.
“This is an exciting period,” Dr. Ravussin summarized, “because, 10 years ago, nobody thought that [results with] pharmacotherapy can approach bariatric surgery. Now we have other drugs that are still in development that are going to approach really close bariatric surgery.”
In an email to this news organization, Dr. Sarma noted that “due to the potent weight loss and glycemic benefits of GLP-1 agonists, patients who wish to avoid the risks of bariatric surgery may wish to discuss the option of medical therapy with their health professionals.”
“For next steps,” she said, “we need long-term studies comparing the weight-lowering, glycemic, and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists in comparison to bariatric surgery for better counseling in obesity treatment.”
Three RCTs, three observational studies
The researchers searched the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies up to April 21, 2021, which directly compared absolute weight loss with a GLP-1 agonist – liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and albiglutide (which are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or Health Canada) – versus any type of bariatric surgery including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion.
The studies included patients aged 18 and older with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2.
Secondary outcomes included change in BMI, and for patients with type 2 diabetes, change in A1c.
The researchers identified three RCTs and three observational studies, with diverse drugs and diverse types of bariatric surgery, which enrolled 13 to 134 patients, with follow-up from 6 months to 10 years.
During follow-up, the overall mean weight loss was 22.7 kg greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 25.1 kg greater in the two non-RCTs with these data (Capristo et al. and Cotugno et al.).
The overall mean decrease in BMI was 8.2 kg/m2 greater in the bariatric surgery groups than in the GLP-1 agonist groups in the two RCTs with these data (Migrone et al. and Schauer et al.), and it was 10.6 kg/m2 greater in the three non-RCTs with these data.
The overall mean decrease in A1c was 1.28% lower in the three RCTs with these data, and it was 0.9% lower in the one non-RCT with these data.
“In adults with obesity, bariatric surgery still confers the highest reductions in weight and BMI but confers similar effects in glycemic control when compared with GLP-1 agonists,” the researchers summarize.
Dr. Sarma received funding from the Clinical Investigator Program. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT OBESITYWEEK®
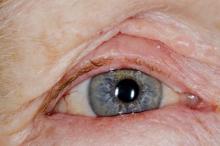
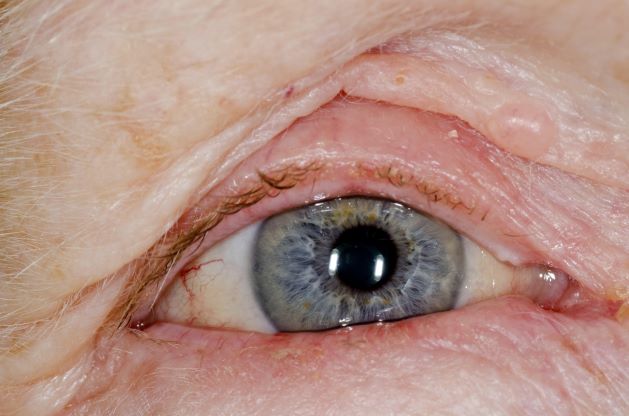
Red swollen eyelids
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 71-year-old woman was referred for an ophthalmologic examination by her dermatologist. The patient reports recent onset of red, swollen eyelids; ocular itching; and a burning sensation. Prior medical history includes severe atopic dermatitis, type 2 diabetes, and osteoarthritis. Current medications include metformin 1000 mg/d, celecoxib 200 mg/d, and clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream twice daily. The patient began receiving subcutaneous dupilumab 300 mg/once every 2 weeks about 6 weeks earlier.
New ACR vaccination guideline: Take your best shot
PHILADELPHIA – The new American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Vaccinations in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (RMDs) emphasizes that both adult and pediatric patients should receive recommended vaccinations whenever possible.
But the guideline, currently in press, also offers recommendations about whether and when to withhold vaccines from patients with RMDs, such as avoiding the use of live attenuated virus vaccines in patients who are on immunosuppressive drug regimens, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic DMARDs, or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
The new consensus guideline was formulated with the understanding that patients with RMDs are at increased risk for vaccine-preventable infections and more serious complications from infections, compared with the general population.
However, the guideline also acknowledges that the immunogenicity and safety of vaccines may differ among patients with RMDs, and that, depending on the patient age and disease state, individuals may benefit from modified vaccine indications, schedules, or modified medication schedules, said guideline panel member Anne Bass, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery and a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who presented the guideline with other panel members in a session outlining the recommendations at the annual meeting of the ACR.
“In addition, vaccination recommendations – since much of it relates to medications – really applies across diseases, and so the ACR felt that, rather than having vaccine recommendations tacked onto the end of treatment guidelines for each individual disease, that the topic should be discussed or tackled as a whole,” she said.
The guideline does not cover vaccinations in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because this class of agents has minimal or no impact on antibody responses to vaccines. The guideline also does not address vaccinations against COVID-19 infections since the rapidly changing formulations would make the recommendations obsolete before they were even published, and because the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides up-to-date guidance on COVID-19 vaccinations in patients with compromised immunity, she said.
Guiding principles
The overarching principles of the guideline are to give indicated vaccines to patients with RMD whenever possible and that any decision to hold medications before or after vaccination consider the dosage used, RMD disease activity, and the patient’s risk for vaccine-preventable infection.
The guideline also states that “shared decision-making with patients is a key component of any vaccination strategy.”
Panel member Clifton O. Bingham III, MD, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, outlined expanded indications for vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infections, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Influenza
The guideline conditionally recommends that patients with RMD aged 65 years and older and adults older than age 18 years who are on immunosuppressive medications should receive either high-dose or adjuvanted influenza vaccination rather than regular-dose vaccines.
“It’s recognized that the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccinations may be unavailable for patients when they’re seen in your practice,” Dr. Bingham said,” and we came out with two additional statements within the guidelines that said that any flu vaccine is recommended over no flu vaccinations, because we do know that responses are elicited, and a flu vaccination today is preferred over a flu vaccination delay.”
Pneumococcal vaccination
The panelists strongly recommended that patients with RMD younger than age 65 years who are on immunosuppressive medication receive pneumococcal vaccinations.
The ACR guideline is in sync with those issued by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Dr. Bingham said. He urged audience members to visit a CDC-ACIP web page for more information on who should receive pneumococcal vaccination and when.
Recombinant varicella zoster
The recommendations strongly support that patients aged 18 years and over who are on immunosuppressive therapies should receive the recombinant VZV vaccine (Shingrix).
HPV
A less robust, conditional recommendation is for patients with RMDs who are between the ages of 26 and 45 years and on immunosuppressive medications to receive the HPV vaccine (if they have not already received the vaccine).
Non-live attenuated vaccines
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, summarized the recommendations for managing immunosuppressive therapies in patients scheduled to receive vaccinations using killed or nonactive antigens.
“In influenza season, don’t pass up the opportunity to vaccinate,” he said, adding, “if you can wait on rituximab dosing, do it, and if you can’t, go ahead and vaccinate.”
The guidelines also recommend a 2-week methotrexate hold at the time of influenza vaccination; other DMARD dosing changes are likely not necessary at the time of vaccination, “but this is an area of fervent study, and I think in a year or two we’ll have more experimental hold data with regard to other DMARDs,” Dr. Winthrop said.
For other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, recommendations are similar to those for influenza, except with more flexible timing because these vaccinations are not seasonal. When and how to hold methotrexate is still up in the air, he said.
Additionally, it’s recommended that vaccinations be delayed in patients on high-dose prednisone until the drug is tapered to below 20 mg per day, and ideally to less than 10 mg per day, he said.
Live-attenuated vaccines
The guideline conditionally recommends deferring live-attenuated vaccines in patients on immunosuppressive drugs. It also recommends holding these medications “for an appropriate period before” vaccination and for 4 weeks afterward.
“Although the evidence around conventional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors is reassuring in terms of their safety at the time of live attenuated vaccines, as you can see the number of studies is quite small, and so the voting panel conditionally recommend against administering live-attenuated virus vaccines to patients who are on conventional synthetics, biologic, or targeted DMARDs,” Dr. Bass said.
In utero exposures
Most women with RMD who have recently given birth will consult their general pediatricians rather than rheumatologists for infant vaccinations, but pediatricians may not be aware of the affect that in utero exposures to biologic DMARDs can have on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in infants, Dr, Bass said.
“It’s important that you, as a provider, give your recommendations regarding infant rotavirus vaccination after in utero exposure to the pregnant rheumatic disease patient prior to delivery, and let that patient know that this is something that they should share with their pediatrician to be,” she advised audience members.
Getting the message out
In an interview, session moderator and guidelines panelist Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of the center for adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University in New York, noted that rheumatologists don’t usually have the full schedule of pediatric vaccinations in stock and often leave the decisions about what to give – and when – to general practitioners.
“Pediatric rheumatologists sometimes will give patients flu vaccinations because they’re a high-risk population of patients, and we want to make sure that they’re getting it in a timely manner,” she said.
In addition, because pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are not indicated in the general pediatric population, children on biologic DMARDs who have completed their standard series of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV13 or PVC15) are recommended to get a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Dr. Imundo said.
She also noted that communication between pediatric rheumatologists and general practitioners about vaccine recommendations can be challenging.
“It’s a huge issue, figuring out how we’re going to communicate all of this information to our pediatric colleagues,” she said. “With individual patients, we may sometimes remind doctors, especially with our younger patients who haven’t gotten their live vaccines, that they really shouldn’t get live vaccines until they’re off medication or until we arrange holding medication for some period of time.”
She said that ACR vaccine committee members are working with infectious disease specialists and guideline developers for the American Academy of Pediatrics to ensure guidelines include the most important vaccination recommendations for pediatric patients with RMDs.
The development process for the guidelines was supported by the ACR. Dr. Bass reported no relevant disclosures, Dr. Bingham disclosed consulting activities, grant/research support, and royalties from various corporate entities. Dr. Winthrop disclosed consulting activities for and research funding from various companies. Dr. Imundo reported no relevant financial relationships.
PHILADELPHIA – The new American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Vaccinations in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (RMDs) emphasizes that both adult and pediatric patients should receive recommended vaccinations whenever possible.
But the guideline, currently in press, also offers recommendations about whether and when to withhold vaccines from patients with RMDs, such as avoiding the use of live attenuated virus vaccines in patients who are on immunosuppressive drug regimens, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic DMARDs, or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
The new consensus guideline was formulated with the understanding that patients with RMDs are at increased risk for vaccine-preventable infections and more serious complications from infections, compared with the general population.
However, the guideline also acknowledges that the immunogenicity and safety of vaccines may differ among patients with RMDs, and that, depending on the patient age and disease state, individuals may benefit from modified vaccine indications, schedules, or modified medication schedules, said guideline panel member Anne Bass, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery and a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who presented the guideline with other panel members in a session outlining the recommendations at the annual meeting of the ACR.
“In addition, vaccination recommendations – since much of it relates to medications – really applies across diseases, and so the ACR felt that, rather than having vaccine recommendations tacked onto the end of treatment guidelines for each individual disease, that the topic should be discussed or tackled as a whole,” she said.
The guideline does not cover vaccinations in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because this class of agents has minimal or no impact on antibody responses to vaccines. The guideline also does not address vaccinations against COVID-19 infections since the rapidly changing formulations would make the recommendations obsolete before they were even published, and because the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides up-to-date guidance on COVID-19 vaccinations in patients with compromised immunity, she said.
Guiding principles
The overarching principles of the guideline are to give indicated vaccines to patients with RMD whenever possible and that any decision to hold medications before or after vaccination consider the dosage used, RMD disease activity, and the patient’s risk for vaccine-preventable infection.
The guideline also states that “shared decision-making with patients is a key component of any vaccination strategy.”
Panel member Clifton O. Bingham III, MD, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, outlined expanded indications for vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infections, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Influenza
The guideline conditionally recommends that patients with RMD aged 65 years and older and adults older than age 18 years who are on immunosuppressive medications should receive either high-dose or adjuvanted influenza vaccination rather than regular-dose vaccines.
“It’s recognized that the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccinations may be unavailable for patients when they’re seen in your practice,” Dr. Bingham said,” and we came out with two additional statements within the guidelines that said that any flu vaccine is recommended over no flu vaccinations, because we do know that responses are elicited, and a flu vaccination today is preferred over a flu vaccination delay.”
Pneumococcal vaccination
The panelists strongly recommended that patients with RMD younger than age 65 years who are on immunosuppressive medication receive pneumococcal vaccinations.
The ACR guideline is in sync with those issued by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Dr. Bingham said. He urged audience members to visit a CDC-ACIP web page for more information on who should receive pneumococcal vaccination and when.
Recombinant varicella zoster
The recommendations strongly support that patients aged 18 years and over who are on immunosuppressive therapies should receive the recombinant VZV vaccine (Shingrix).
HPV
A less robust, conditional recommendation is for patients with RMDs who are between the ages of 26 and 45 years and on immunosuppressive medications to receive the HPV vaccine (if they have not already received the vaccine).
Non-live attenuated vaccines
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, summarized the recommendations for managing immunosuppressive therapies in patients scheduled to receive vaccinations using killed or nonactive antigens.
“In influenza season, don’t pass up the opportunity to vaccinate,” he said, adding, “if you can wait on rituximab dosing, do it, and if you can’t, go ahead and vaccinate.”
The guidelines also recommend a 2-week methotrexate hold at the time of influenza vaccination; other DMARD dosing changes are likely not necessary at the time of vaccination, “but this is an area of fervent study, and I think in a year or two we’ll have more experimental hold data with regard to other DMARDs,” Dr. Winthrop said.
For other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, recommendations are similar to those for influenza, except with more flexible timing because these vaccinations are not seasonal. When and how to hold methotrexate is still up in the air, he said.
Additionally, it’s recommended that vaccinations be delayed in patients on high-dose prednisone until the drug is tapered to below 20 mg per day, and ideally to less than 10 mg per day, he said.
Live-attenuated vaccines
The guideline conditionally recommends deferring live-attenuated vaccines in patients on immunosuppressive drugs. It also recommends holding these medications “for an appropriate period before” vaccination and for 4 weeks afterward.
“Although the evidence around conventional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors is reassuring in terms of their safety at the time of live attenuated vaccines, as you can see the number of studies is quite small, and so the voting panel conditionally recommend against administering live-attenuated virus vaccines to patients who are on conventional synthetics, biologic, or targeted DMARDs,” Dr. Bass said.
In utero exposures
Most women with RMD who have recently given birth will consult their general pediatricians rather than rheumatologists for infant vaccinations, but pediatricians may not be aware of the affect that in utero exposures to biologic DMARDs can have on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in infants, Dr, Bass said.
“It’s important that you, as a provider, give your recommendations regarding infant rotavirus vaccination after in utero exposure to the pregnant rheumatic disease patient prior to delivery, and let that patient know that this is something that they should share with their pediatrician to be,” she advised audience members.
Getting the message out
In an interview, session moderator and guidelines panelist Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of the center for adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University in New York, noted that rheumatologists don’t usually have the full schedule of pediatric vaccinations in stock and often leave the decisions about what to give – and when – to general practitioners.
“Pediatric rheumatologists sometimes will give patients flu vaccinations because they’re a high-risk population of patients, and we want to make sure that they’re getting it in a timely manner,” she said.
In addition, because pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are not indicated in the general pediatric population, children on biologic DMARDs who have completed their standard series of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV13 or PVC15) are recommended to get a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Dr. Imundo said.
She also noted that communication between pediatric rheumatologists and general practitioners about vaccine recommendations can be challenging.
“It’s a huge issue, figuring out how we’re going to communicate all of this information to our pediatric colleagues,” she said. “With individual patients, we may sometimes remind doctors, especially with our younger patients who haven’t gotten their live vaccines, that they really shouldn’t get live vaccines until they’re off medication or until we arrange holding medication for some period of time.”
She said that ACR vaccine committee members are working with infectious disease specialists and guideline developers for the American Academy of Pediatrics to ensure guidelines include the most important vaccination recommendations for pediatric patients with RMDs.
The development process for the guidelines was supported by the ACR. Dr. Bass reported no relevant disclosures, Dr. Bingham disclosed consulting activities, grant/research support, and royalties from various corporate entities. Dr. Winthrop disclosed consulting activities for and research funding from various companies. Dr. Imundo reported no relevant financial relationships.
PHILADELPHIA – The new American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Vaccinations in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (RMDs) emphasizes that both adult and pediatric patients should receive recommended vaccinations whenever possible.
But the guideline, currently in press, also offers recommendations about whether and when to withhold vaccines from patients with RMDs, such as avoiding the use of live attenuated virus vaccines in patients who are on immunosuppressive drug regimens, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic DMARDs, or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
The new consensus guideline was formulated with the understanding that patients with RMDs are at increased risk for vaccine-preventable infections and more serious complications from infections, compared with the general population.
However, the guideline also acknowledges that the immunogenicity and safety of vaccines may differ among patients with RMDs, and that, depending on the patient age and disease state, individuals may benefit from modified vaccine indications, schedules, or modified medication schedules, said guideline panel member Anne Bass, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery and a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who presented the guideline with other panel members in a session outlining the recommendations at the annual meeting of the ACR.
“In addition, vaccination recommendations – since much of it relates to medications – really applies across diseases, and so the ACR felt that, rather than having vaccine recommendations tacked onto the end of treatment guidelines for each individual disease, that the topic should be discussed or tackled as a whole,” she said.
The guideline does not cover vaccinations in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because this class of agents has minimal or no impact on antibody responses to vaccines. The guideline also does not address vaccinations against COVID-19 infections since the rapidly changing formulations would make the recommendations obsolete before they were even published, and because the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides up-to-date guidance on COVID-19 vaccinations in patients with compromised immunity, she said.
Guiding principles
The overarching principles of the guideline are to give indicated vaccines to patients with RMD whenever possible and that any decision to hold medications before or after vaccination consider the dosage used, RMD disease activity, and the patient’s risk for vaccine-preventable infection.
The guideline also states that “shared decision-making with patients is a key component of any vaccination strategy.”
Panel member Clifton O. Bingham III, MD, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, outlined expanded indications for vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infections, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Influenza
The guideline conditionally recommends that patients with RMD aged 65 years and older and adults older than age 18 years who are on immunosuppressive medications should receive either high-dose or adjuvanted influenza vaccination rather than regular-dose vaccines.
“It’s recognized that the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccinations may be unavailable for patients when they’re seen in your practice,” Dr. Bingham said,” and we came out with two additional statements within the guidelines that said that any flu vaccine is recommended over no flu vaccinations, because we do know that responses are elicited, and a flu vaccination today is preferred over a flu vaccination delay.”
Pneumococcal vaccination
The panelists strongly recommended that patients with RMD younger than age 65 years who are on immunosuppressive medication receive pneumococcal vaccinations.
The ACR guideline is in sync with those issued by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Dr. Bingham said. He urged audience members to visit a CDC-ACIP web page for more information on who should receive pneumococcal vaccination and when.
Recombinant varicella zoster
The recommendations strongly support that patients aged 18 years and over who are on immunosuppressive therapies should receive the recombinant VZV vaccine (Shingrix).
HPV
A less robust, conditional recommendation is for patients with RMDs who are between the ages of 26 and 45 years and on immunosuppressive medications to receive the HPV vaccine (if they have not already received the vaccine).
Non-live attenuated vaccines
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, summarized the recommendations for managing immunosuppressive therapies in patients scheduled to receive vaccinations using killed or nonactive antigens.
“In influenza season, don’t pass up the opportunity to vaccinate,” he said, adding, “if you can wait on rituximab dosing, do it, and if you can’t, go ahead and vaccinate.”
The guidelines also recommend a 2-week methotrexate hold at the time of influenza vaccination; other DMARD dosing changes are likely not necessary at the time of vaccination, “but this is an area of fervent study, and I think in a year or two we’ll have more experimental hold data with regard to other DMARDs,” Dr. Winthrop said.
For other nonlive attenuated vaccinations, recommendations are similar to those for influenza, except with more flexible timing because these vaccinations are not seasonal. When and how to hold methotrexate is still up in the air, he said.
Additionally, it’s recommended that vaccinations be delayed in patients on high-dose prednisone until the drug is tapered to below 20 mg per day, and ideally to less than 10 mg per day, he said.
Live-attenuated vaccines
The guideline conditionally recommends deferring live-attenuated vaccines in patients on immunosuppressive drugs. It also recommends holding these medications “for an appropriate period before” vaccination and for 4 weeks afterward.
“Although the evidence around conventional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors is reassuring in terms of their safety at the time of live attenuated vaccines, as you can see the number of studies is quite small, and so the voting panel conditionally recommend against administering live-attenuated virus vaccines to patients who are on conventional synthetics, biologic, or targeted DMARDs,” Dr. Bass said.
In utero exposures
Most women with RMD who have recently given birth will consult their general pediatricians rather than rheumatologists for infant vaccinations, but pediatricians may not be aware of the affect that in utero exposures to biologic DMARDs can have on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in infants, Dr, Bass said.
“It’s important that you, as a provider, give your recommendations regarding infant rotavirus vaccination after in utero exposure to the pregnant rheumatic disease patient prior to delivery, and let that patient know that this is something that they should share with their pediatrician to be,” she advised audience members.
Getting the message out
In an interview, session moderator and guidelines panelist Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of the center for adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University in New York, noted that rheumatologists don’t usually have the full schedule of pediatric vaccinations in stock and often leave the decisions about what to give – and when – to general practitioners.
“Pediatric rheumatologists sometimes will give patients flu vaccinations because they’re a high-risk population of patients, and we want to make sure that they’re getting it in a timely manner,” she said.
In addition, because pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines are not indicated in the general pediatric population, children on biologic DMARDs who have completed their standard series of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV13 or PVC15) are recommended to get a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Dr. Imundo said.
She also noted that communication between pediatric rheumatologists and general practitioners about vaccine recommendations can be challenging.
“It’s a huge issue, figuring out how we’re going to communicate all of this information to our pediatric colleagues,” she said. “With individual patients, we may sometimes remind doctors, especially with our younger patients who haven’t gotten their live vaccines, that they really shouldn’t get live vaccines until they’re off medication or until we arrange holding medication for some period of time.”
She said that ACR vaccine committee members are working with infectious disease specialists and guideline developers for the American Academy of Pediatrics to ensure guidelines include the most important vaccination recommendations for pediatric patients with RMDs.
The development process for the guidelines was supported by the ACR. Dr. Bass reported no relevant disclosures, Dr. Bingham disclosed consulting activities, grant/research support, and royalties from various corporate entities. Dr. Winthrop disclosed consulting activities for and research funding from various companies. Dr. Imundo reported no relevant financial relationships.
AT ACR 2022
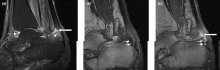
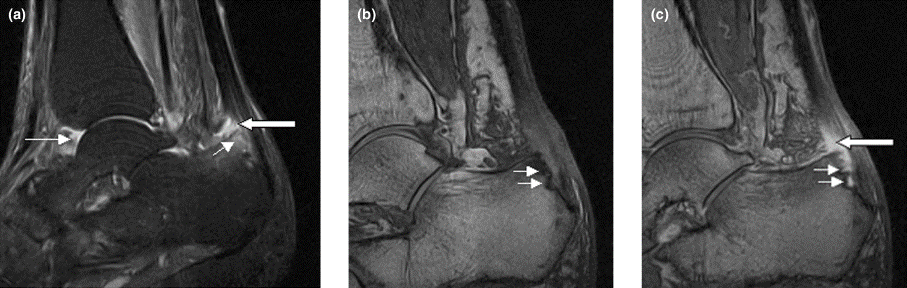
Right ankle pain and swelling
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of psoriatic enthesitis.
Enthesitis is a hallmark manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis are estimated to be affected by PsA, which belongs to the spondyloarthritis (SpA) family of inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
An enthesis is an attachment site of ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules to bone and is a key inflammatory target in SpA. It is a complex structure that dissipates biomechanical stress to preserve homeostasis. Entheses are anatomically and functionally integrated with bursa, fibrocartilage, and synovium in a synovial entheseal complex; biomechanical stress in this area may trigger inflammation. Enthesitis is an early manifestation of PsA that has been associated with radiographic peripheral/axial joint damage and severe disease, as well as reduced quality of life.
Enthesitis can be difficult to diagnose in clinical practice. Symptoms include tenderness, soreness, and pain at entheses on palpation, often without overt clinical evidence of inflammation. In contrast, dactylitis, another hallmark manifestation of PsA, can be recognized by swelling of an entire digit that is different from adjacent digits. Fibromyalgia frequently coexists with enthesitis, and it can be difficult to distinguish the two given the anatomic overlap between the tender points of fibromyalgia and many entheseal sites. Long-lasting morning stiffness and a sustained response to a course of steroids is more suggestive of enthesitis, whereas a higher number of somatoform symptoms is more suggestive of fibromyalgia.
Enthesitis is included in the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) as a hallmark of PsA. While it can be diagnosed clinically, imaging studies may be required, particularly in patients in whom symptoms may be difficult to discern. Evidence of enthesitis by conventional radiography includes bone cortex irregularities, erosions, entheseal soft tissue calcifications, and new bone formation; however, entheseal bone changes detected with conventional radiography appear relatively late in the disease process. Ultrasound is highly sensitive for assessing inflammation and can detect various features of enthesitis, such as increased thickness of tendon insertion, hypoechogenicity, erosions, enthesophytes, and subclinical enthesitis in people with PsA. MRI has the advantage of identifying perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema. Fat-suppressed MRI with or without gadolinium enhancement is a highly sensitive method for visualizing active enthesitis and can identify perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema.
Delayed treatment of PsA can result in irreversible joint damage and reduced quality of life; thus, patients with psoriasis should be closely monitored for early signs of its development, such as enthesitis. A thorough evaluation of the key clinical features of PsA (psoriasis, arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and spondylitis), including evaluation of severity of each feature and impact on physical function and quality of life, is encouraged at each clinical encounter. Because patients may not understand the link between psoriasis and joint pain, specific probing questions can be helpful. Screening questionnaires to detect early signs and symptoms of PsA are available, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST), Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) questionnaire, and Toronto Psoriatic Arthritis Screening (ToPAS) questionnaire. These and many others may be used to help dermatologists detect early signs and symptoms of PsA. Although these questionnaires all have limitations in sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PsA, their use can still improve early diagnosis.
The treatment of PsA focuses on achieving the least amount of disease activity and inflammation possible; optimizing functional status, quality of life, and well-being; and preventing structural damage. Treatment decisions are based on the specific domains affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections are first-line treatments for enthesitis. Early use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF) (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, infliximab, and golimumab) is recommended. Alternative biologic disease-modifying agents are indicated when these TNF inhibitors provide an inadequate response. They include ustekinumab (dual interleukin [IL]-12 and IL-23 inhibitor), secukinumab (IL-17A inhibitor), and apremilast (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) and may be considered for patients with predominantly entheseal manifestations of PsA or dactylitis. Biological disease-modifying agents approved for PsA that have shown efficacy for enthesitis include ixekizumab (which targets IL-17A), abatacept (a T-cell inhibitor), guselkumab (monoclonal antibody), and ustekinumab (monoclonal antibody). Tofacitinib and upadacitinib, both oral Janus kinase inhibitors, may also be considered.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of psoriatic enthesitis.
Enthesitis is a hallmark manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis are estimated to be affected by PsA, which belongs to the spondyloarthritis (SpA) family of inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
An enthesis is an attachment site of ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules to bone and is a key inflammatory target in SpA. It is a complex structure that dissipates biomechanical stress to preserve homeostasis. Entheses are anatomically and functionally integrated with bursa, fibrocartilage, and synovium in a synovial entheseal complex; biomechanical stress in this area may trigger inflammation. Enthesitis is an early manifestation of PsA that has been associated with radiographic peripheral/axial joint damage and severe disease, as well as reduced quality of life.
Enthesitis can be difficult to diagnose in clinical practice. Symptoms include tenderness, soreness, and pain at entheses on palpation, often without overt clinical evidence of inflammation. In contrast, dactylitis, another hallmark manifestation of PsA, can be recognized by swelling of an entire digit that is different from adjacent digits. Fibromyalgia frequently coexists with enthesitis, and it can be difficult to distinguish the two given the anatomic overlap between the tender points of fibromyalgia and many entheseal sites. Long-lasting morning stiffness and a sustained response to a course of steroids is more suggestive of enthesitis, whereas a higher number of somatoform symptoms is more suggestive of fibromyalgia.
Enthesitis is included in the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) as a hallmark of PsA. While it can be diagnosed clinically, imaging studies may be required, particularly in patients in whom symptoms may be difficult to discern. Evidence of enthesitis by conventional radiography includes bone cortex irregularities, erosions, entheseal soft tissue calcifications, and new bone formation; however, entheseal bone changes detected with conventional radiography appear relatively late in the disease process. Ultrasound is highly sensitive for assessing inflammation and can detect various features of enthesitis, such as increased thickness of tendon insertion, hypoechogenicity, erosions, enthesophytes, and subclinical enthesitis in people with PsA. MRI has the advantage of identifying perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema. Fat-suppressed MRI with or without gadolinium enhancement is a highly sensitive method for visualizing active enthesitis and can identify perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema.
Delayed treatment of PsA can result in irreversible joint damage and reduced quality of life; thus, patients with psoriasis should be closely monitored for early signs of its development, such as enthesitis. A thorough evaluation of the key clinical features of PsA (psoriasis, arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and spondylitis), including evaluation of severity of each feature and impact on physical function and quality of life, is encouraged at each clinical encounter. Because patients may not understand the link between psoriasis and joint pain, specific probing questions can be helpful. Screening questionnaires to detect early signs and symptoms of PsA are available, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST), Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) questionnaire, and Toronto Psoriatic Arthritis Screening (ToPAS) questionnaire. These and many others may be used to help dermatologists detect early signs and symptoms of PsA. Although these questionnaires all have limitations in sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PsA, their use can still improve early diagnosis.
The treatment of PsA focuses on achieving the least amount of disease activity and inflammation possible; optimizing functional status, quality of life, and well-being; and preventing structural damage. Treatment decisions are based on the specific domains affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections are first-line treatments for enthesitis. Early use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF) (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, infliximab, and golimumab) is recommended. Alternative biologic disease-modifying agents are indicated when these TNF inhibitors provide an inadequate response. They include ustekinumab (dual interleukin [IL]-12 and IL-23 inhibitor), secukinumab (IL-17A inhibitor), and apremilast (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) and may be considered for patients with predominantly entheseal manifestations of PsA or dactylitis. Biological disease-modifying agents approved for PsA that have shown efficacy for enthesitis include ixekizumab (which targets IL-17A), abatacept (a T-cell inhibitor), guselkumab (monoclonal antibody), and ustekinumab (monoclonal antibody). Tofacitinib and upadacitinib, both oral Janus kinase inhibitors, may also be considered.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of psoriatic enthesitis.
Enthesitis is a hallmark manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis are estimated to be affected by PsA, which belongs to the spondyloarthritis (SpA) family of inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
An enthesis is an attachment site of ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules to bone and is a key inflammatory target in SpA. It is a complex structure that dissipates biomechanical stress to preserve homeostasis. Entheses are anatomically and functionally integrated with bursa, fibrocartilage, and synovium in a synovial entheseal complex; biomechanical stress in this area may trigger inflammation. Enthesitis is an early manifestation of PsA that has been associated with radiographic peripheral/axial joint damage and severe disease, as well as reduced quality of life.
Enthesitis can be difficult to diagnose in clinical practice. Symptoms include tenderness, soreness, and pain at entheses on palpation, often without overt clinical evidence of inflammation. In contrast, dactylitis, another hallmark manifestation of PsA, can be recognized by swelling of an entire digit that is different from adjacent digits. Fibromyalgia frequently coexists with enthesitis, and it can be difficult to distinguish the two given the anatomic overlap between the tender points of fibromyalgia and many entheseal sites. Long-lasting morning stiffness and a sustained response to a course of steroids is more suggestive of enthesitis, whereas a higher number of somatoform symptoms is more suggestive of fibromyalgia.
Enthesitis is included in the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) as a hallmark of PsA. While it can be diagnosed clinically, imaging studies may be required, particularly in patients in whom symptoms may be difficult to discern. Evidence of enthesitis by conventional radiography includes bone cortex irregularities, erosions, entheseal soft tissue calcifications, and new bone formation; however, entheseal bone changes detected with conventional radiography appear relatively late in the disease process. Ultrasound is highly sensitive for assessing inflammation and can detect various features of enthesitis, such as increased thickness of tendon insertion, hypoechogenicity, erosions, enthesophytes, and subclinical enthesitis in people with PsA. MRI has the advantage of identifying perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema. Fat-suppressed MRI with or without gadolinium enhancement is a highly sensitive method for visualizing active enthesitis and can identify perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema.
Delayed treatment of PsA can result in irreversible joint damage and reduced quality of life; thus, patients with psoriasis should be closely monitored for early signs of its development, such as enthesitis. A thorough evaluation of the key clinical features of PsA (psoriasis, arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and spondylitis), including evaluation of severity of each feature and impact on physical function and quality of life, is encouraged at each clinical encounter. Because patients may not understand the link between psoriasis and joint pain, specific probing questions can be helpful. Screening questionnaires to detect early signs and symptoms of PsA are available, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST), Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) questionnaire, and Toronto Psoriatic Arthritis Screening (ToPAS) questionnaire. These and many others may be used to help dermatologists detect early signs and symptoms of PsA. Although these questionnaires all have limitations in sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PsA, their use can still improve early diagnosis.
The treatment of PsA focuses on achieving the least amount of disease activity and inflammation possible; optimizing functional status, quality of life, and well-being; and preventing structural damage. Treatment decisions are based on the specific domains affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections are first-line treatments for enthesitis. Early use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF) (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, infliximab, and golimumab) is recommended. Alternative biologic disease-modifying agents are indicated when these TNF inhibitors provide an inadequate response. They include ustekinumab (dual interleukin [IL]-12 and IL-23 inhibitor), secukinumab (IL-17A inhibitor), and apremilast (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) and may be considered for patients with predominantly entheseal manifestations of PsA or dactylitis. Biological disease-modifying agents approved for PsA that have shown efficacy for enthesitis include ixekizumab (which targets IL-17A), abatacept (a T-cell inhibitor), guselkumab (monoclonal antibody), and ustekinumab (monoclonal antibody). Tofacitinib and upadacitinib, both oral Janus kinase inhibitors, may also be considered.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 42-year-old woman with a 20-year history of plaque psoriasis presents with complaints of a 3-month history of pain, tenderness, and swelling in her right ankle and foot, of unknown origin. Physical examination reveals active psoriasis, with a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 6.7 and psoriatic nail dystrophy, including onycholysis, pitting, and hyperkeratosis. Tenderness and swelling are noted at the back of the heel. The patient denies any other complaints. Laboratory tests are normal, including negative rheumatoid factor and antinuclear factor. MRI reveals soft tissue and bone marrow edema below the Achilles insertion.
Personalized breast screening a step closer to reality
say researchers.
“Several breast cancer risk prediction models have been created, but we believe this is one of the first models designed to guide breast screening strategies over a person’s lifetime using real data from a screening program,” said study author Javier Louro, PhD, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain.
“Our model might be considered a key for designing personalized screening aimed at reducing the harms and increasing the benefits of mammographic screening,” he said in a statement.
Someone with a low risk “might be offered screening with standard mammography every 3 or 4 years instead of 2 years,” Dr. Louro explained.
“Someone with medium risk might be offered screening with advanced 3D mammography every 3 years, while those at a high risk might be offered a new screening test with mammography or MRI every year.”
However, he cautioned that “all of these strategies are still theoretical and should be studied with regard to their effectiveness.”
Dr. Louro was talking about the new model at the 13th European Breast Cancer Conference.
Details of the new prediction model
To develop the new model, Louro and colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 57,411 women who underwent mammography in four counties in Norway between 2007 and 2019 as part of the BreastScreen Norway program, and followed them up to 2022.
The team gathered data on age, breast density, family history of breast cancer, body mass index, age at menarche, alcohol habit, exercise, pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy, and benign breast disease, and compared women with and those without a breast cancer diagnosis.
All of these 10 variables used were found to significantly explain part of the variability in the breast cancer risk.
Overall, the 4-year breast cancer risk predicted by the resulting model varied across the participants, from 0.22% to 7.43%, at a median of 1.10%.
Bootstrap resampling analysis revealed that the model overestimated the risk for breast cancer, at an expected-to-observed ratio of 1.10.
The largest effect on risk was from breast density on mammography. Women with dense breasts were at much higher risk: the adjusted hazard ratio was 1.71 for women with Volpara Density Grade 4 vs Grade 2 and was 1.37 when compared with Grade 3.
Exercise had a large impact on breast cancer risk, the researchers found. Women who exercised for 4 or more hours per week had an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.65 for breast cancer risk compared with women who never exercised. Although this effect of exercise reducing the risk for breast cancer is now widely known, it is not usually included in models that predict breast cancer risk, the team pointed out.
The team concluded that their prediction model could be used to personalize breast screening for women according to their risk assessment, although they acknowledge that more work is needed. This work is based on one screening program in one country, and similar studies in different settings are needed.
Reacting to the findings, Laura Biganzoli, MD, co-chair of the European Breast Cancer Conference and director of the Breast Centre at Santo Stefano Hospital, Prato, Italy, commented, “We know that breast screening programs are beneficial, but we also know that some people will experience potential harms caused by false-positives or overdiagnosis.”
“This research shows how we might be able to identify people with a high risk of breast cancer, but equally how we could identify those with a low risk. So it’s an important step toward personalized screening,” Dr. Biganzoli said.
This study was supported by a grant from Instituto de Salud Carlos III FEDER (grant PI/00047). No relevant financial relationships declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
say researchers.
“Several breast cancer risk prediction models have been created, but we believe this is one of the first models designed to guide breast screening strategies over a person’s lifetime using real data from a screening program,” said study author Javier Louro, PhD, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain.
“Our model might be considered a key for designing personalized screening aimed at reducing the harms and increasing the benefits of mammographic screening,” he said in a statement.
Someone with a low risk “might be offered screening with standard mammography every 3 or 4 years instead of 2 years,” Dr. Louro explained.
“Someone with medium risk might be offered screening with advanced 3D mammography every 3 years, while those at a high risk might be offered a new screening test with mammography or MRI every year.”
However, he cautioned that “all of these strategies are still theoretical and should be studied with regard to their effectiveness.”
Dr. Louro was talking about the new model at the 13th European Breast Cancer Conference.
Details of the new prediction model
To develop the new model, Louro and colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 57,411 women who underwent mammography in four counties in Norway between 2007 and 2019 as part of the BreastScreen Norway program, and followed them up to 2022.
The team gathered data on age, breast density, family history of breast cancer, body mass index, age at menarche, alcohol habit, exercise, pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy, and benign breast disease, and compared women with and those without a breast cancer diagnosis.
All of these 10 variables used were found to significantly explain part of the variability in the breast cancer risk.
Overall, the 4-year breast cancer risk predicted by the resulting model varied across the participants, from 0.22% to 7.43%, at a median of 1.10%.
Bootstrap resampling analysis revealed that the model overestimated the risk for breast cancer, at an expected-to-observed ratio of 1.10.
The largest effect on risk was from breast density on mammography. Women with dense breasts were at much higher risk: the adjusted hazard ratio was 1.71 for women with Volpara Density Grade 4 vs Grade 2 and was 1.37 when compared with Grade 3.
Exercise had a large impact on breast cancer risk, the researchers found. Women who exercised for 4 or more hours per week had an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.65 for breast cancer risk compared with women who never exercised. Although this effect of exercise reducing the risk for breast cancer is now widely known, it is not usually included in models that predict breast cancer risk, the team pointed out.
The team concluded that their prediction model could be used to personalize breast screening for women according to their risk assessment, although they acknowledge that more work is needed. This work is based on one screening program in one country, and similar studies in different settings are needed.
Reacting to the findings, Laura Biganzoli, MD, co-chair of the European Breast Cancer Conference and director of the Breast Centre at Santo Stefano Hospital, Prato, Italy, commented, “We know that breast screening programs are beneficial, but we also know that some people will experience potential harms caused by false-positives or overdiagnosis.”
“This research shows how we might be able to identify people with a high risk of breast cancer, but equally how we could identify those with a low risk. So it’s an important step toward personalized screening,” Dr. Biganzoli said.
This study was supported by a grant from Instituto de Salud Carlos III FEDER (grant PI/00047). No relevant financial relationships declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
say researchers.
“Several breast cancer risk prediction models have been created, but we believe this is one of the first models designed to guide breast screening strategies over a person’s lifetime using real data from a screening program,” said study author Javier Louro, PhD, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain.
“Our model might be considered a key for designing personalized screening aimed at reducing the harms and increasing the benefits of mammographic screening,” he said in a statement.
Someone with a low risk “might be offered screening with standard mammography every 3 or 4 years instead of 2 years,” Dr. Louro explained.
“Someone with medium risk might be offered screening with advanced 3D mammography every 3 years, while those at a high risk might be offered a new screening test with mammography or MRI every year.”
However, he cautioned that “all of these strategies are still theoretical and should be studied with regard to their effectiveness.”
Dr. Louro was talking about the new model at the 13th European Breast Cancer Conference.
Details of the new prediction model
To develop the new model, Louro and colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 57,411 women who underwent mammography in four counties in Norway between 2007 and 2019 as part of the BreastScreen Norway program, and followed them up to 2022.
The team gathered data on age, breast density, family history of breast cancer, body mass index, age at menarche, alcohol habit, exercise, pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy, and benign breast disease, and compared women with and those without a breast cancer diagnosis.
All of these 10 variables used were found to significantly explain part of the variability in the breast cancer risk.
Overall, the 4-year breast cancer risk predicted by the resulting model varied across the participants, from 0.22% to 7.43%, at a median of 1.10%.
Bootstrap resampling analysis revealed that the model overestimated the risk for breast cancer, at an expected-to-observed ratio of 1.10.
The largest effect on risk was from breast density on mammography. Women with dense breasts were at much higher risk: the adjusted hazard ratio was 1.71 for women with Volpara Density Grade 4 vs Grade 2 and was 1.37 when compared with Grade 3.
Exercise had a large impact on breast cancer risk, the researchers found. Women who exercised for 4 or more hours per week had an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.65 for breast cancer risk compared with women who never exercised. Although this effect of exercise reducing the risk for breast cancer is now widely known, it is not usually included in models that predict breast cancer risk, the team pointed out.
The team concluded that their prediction model could be used to personalize breast screening for women according to their risk assessment, although they acknowledge that more work is needed. This work is based on one screening program in one country, and similar studies in different settings are needed.
Reacting to the findings, Laura Biganzoli, MD, co-chair of the European Breast Cancer Conference and director of the Breast Centre at Santo Stefano Hospital, Prato, Italy, commented, “We know that breast screening programs are beneficial, but we also know that some people will experience potential harms caused by false-positives or overdiagnosis.”
“This research shows how we might be able to identify people with a high risk of breast cancer, but equally how we could identify those with a low risk. So it’s an important step toward personalized screening,” Dr. Biganzoli said.
This study was supported by a grant from Instituto de Salud Carlos III FEDER (grant PI/00047). No relevant financial relationships declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EBCC-13
Decline in ambulatory function
Based on this patient's history and presentation, the likely diagnosis is primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). PPMS represents around 10% of MS cases and tends to develop about a decade later than relapsing MS. Unlike other forms of MS, this phenotype progresses steadily instead of in an episodic fashion like relapsing forms of MS. Most patients with PPMS present with gait difficulty because lesions often develop on the spinal cord. While relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is much more common among women than men, men with MS are more likely to have the progressive form.
Although this patient's MRI ultimately points to multiple sclerosis, his functional deficits may initially suggest other conditions in the differential diagnosis. Brainstem gliomas typically manifest in unsteady gait, weakness, double vision, difficulty swallowing, dysarthria, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Transverse myelitis often presents with rapid-onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Musculoskeletal and neurologic symptoms are common in Lyme disease. B12 deficiency can present with worsening weakness and a sensory ataxia that can present as balance difficulties, but it would not cause focal lesions on the MRI, nor would it present with bladder symptoms. In addition, the patient's steady decline in function rules out RRMS.
PPMS is diagnosed with confirmation of gradual change in functional ability (often ambulation) over time without remission or relapse. These criteria include 1 full year of worsening neurologic function without asymptomatic periods as well as two of these signs of disease: brain lesion, two or more spinal cord lesions, and oligoclonal bands or elevated Immunoglobulin G index. These timing-specific criteria can delay diagnosis, as seen here.
Ocrelizumab is the only FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy (DMT) proven to alter disease progression in ambulatory patients with PPMS. American Academy of Neurology guidelines recommend ocrelizumab for patients with PPMS who are likely to benefit from this therapy. While it is thought that DMTs are more effective at targeting inflammation in RRMS than nerve degeneration in PPMS, these agents may show benefit for patients with active PPMS (relapse and/or evidence of new MRI activity) rather than inactive disease. A recent PPMS study concluded that among patients with relapse or disease activity, DMTs were associated with a significant reduction of long-term disability risk. Together with immunomodulatory therapy, rehabilitation can help manage symptoms.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on this patient's history and presentation, the likely diagnosis is primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). PPMS represents around 10% of MS cases and tends to develop about a decade later than relapsing MS. Unlike other forms of MS, this phenotype progresses steadily instead of in an episodic fashion like relapsing forms of MS. Most patients with PPMS present with gait difficulty because lesions often develop on the spinal cord. While relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is much more common among women than men, men with MS are more likely to have the progressive form.
Although this patient's MRI ultimately points to multiple sclerosis, his functional deficits may initially suggest other conditions in the differential diagnosis. Brainstem gliomas typically manifest in unsteady gait, weakness, double vision, difficulty swallowing, dysarthria, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Transverse myelitis often presents with rapid-onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Musculoskeletal and neurologic symptoms are common in Lyme disease. B12 deficiency can present with worsening weakness and a sensory ataxia that can present as balance difficulties, but it would not cause focal lesions on the MRI, nor would it present with bladder symptoms. In addition, the patient's steady decline in function rules out RRMS.
PPMS is diagnosed with confirmation of gradual change in functional ability (often ambulation) over time without remission or relapse. These criteria include 1 full year of worsening neurologic function without asymptomatic periods as well as two of these signs of disease: brain lesion, two or more spinal cord lesions, and oligoclonal bands or elevated Immunoglobulin G index. These timing-specific criteria can delay diagnosis, as seen here.
Ocrelizumab is the only FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy (DMT) proven to alter disease progression in ambulatory patients with PPMS. American Academy of Neurology guidelines recommend ocrelizumab for patients with PPMS who are likely to benefit from this therapy. While it is thought that DMTs are more effective at targeting inflammation in RRMS than nerve degeneration in PPMS, these agents may show benefit for patients with active PPMS (relapse and/or evidence of new MRI activity) rather than inactive disease. A recent PPMS study concluded that among patients with relapse or disease activity, DMTs were associated with a significant reduction of long-term disability risk. Together with immunomodulatory therapy, rehabilitation can help manage symptoms.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on this patient's history and presentation, the likely diagnosis is primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). PPMS represents around 10% of MS cases and tends to develop about a decade later than relapsing MS. Unlike other forms of MS, this phenotype progresses steadily instead of in an episodic fashion like relapsing forms of MS. Most patients with PPMS present with gait difficulty because lesions often develop on the spinal cord. While relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is much more common among women than men, men with MS are more likely to have the progressive form.
Although this patient's MRI ultimately points to multiple sclerosis, his functional deficits may initially suggest other conditions in the differential diagnosis. Brainstem gliomas typically manifest in unsteady gait, weakness, double vision, difficulty swallowing, dysarthria, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Transverse myelitis often presents with rapid-onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Musculoskeletal and neurologic symptoms are common in Lyme disease. B12 deficiency can present with worsening weakness and a sensory ataxia that can present as balance difficulties, but it would not cause focal lesions on the MRI, nor would it present with bladder symptoms. In addition, the patient's steady decline in function rules out RRMS.
PPMS is diagnosed with confirmation of gradual change in functional ability (often ambulation) over time without remission or relapse. These criteria include 1 full year of worsening neurologic function without asymptomatic periods as well as two of these signs of disease: brain lesion, two or more spinal cord lesions, and oligoclonal bands or elevated Immunoglobulin G index. These timing-specific criteria can delay diagnosis, as seen here.
Ocrelizumab is the only FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy (DMT) proven to alter disease progression in ambulatory patients with PPMS. American Academy of Neurology guidelines recommend ocrelizumab for patients with PPMS who are likely to benefit from this therapy. While it is thought that DMTs are more effective at targeting inflammation in RRMS than nerve degeneration in PPMS, these agents may show benefit for patients with active PPMS (relapse and/or evidence of new MRI activity) rather than inactive disease. A recent PPMS study concluded that among patients with relapse or disease activity, DMTs were associated with a significant reduction of long-term disability risk. Together with immunomodulatory therapy, rehabilitation can help manage symptoms.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 59-year-old man presents with worsening decline in ambulatory function and worsening bladder function. He reports "difficulty getting around" for the past year and a half, which he theorized might be because of arthritis, aging, or many years of biking. He presented to his primary care physician 2 months ago and was referred to rheumatology. His height is 5 ft 11 in and his weight is 166 lb (BMI 23.1). The patient subsequently reported a decreased attention span to the rheumatologist. He has no other significant medical or surgical history, though his brother has psoriatic arthritis. MRI shows multiple brain lesions without gadolinium enhancement and multiple spinal cord lesions.
Screen time may help concussion recovery
research shows.
Now a study suggests that getting back on TikTok and Snapchat may help, too.
After surveying 700 patients ages 8-16 following an injury, researchers for the Pediatric Emergency Research Canada A-CAP study team found that
A “moderate” amount was between 2 and 7 hours per day on various screens. “That includes their phones, computers, and televisions,” says lead author Molly Cairncross, PhD, of Simon Fraser University, Vancouver.
People in the study who reported either less or more screen time than that in the 7-10 days after injury also reported more symptoms, such as headaches and fatigue, during the first month. After that month, all the participants reported similar symptoms, regardless of their early screen use – suggesting that screen time makes little difference long term in pediatric concussion recovery.
The findings differ from a 2021 study by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Boston, that found screen time slowed recovery. Why the clashing results? “I think what it comes down to are differences in study design,” says Dr. Cairncross. While the earlier study measured screen use in the first 48 hours, and recovery over 10 days, “we focused on screen time use over the first 7-10 days, and tracked recovery over 6 months,” she says.
“Taken together, the studies suggest a need to find balance – not too little and not too much time on screens for kids and teens following a concussion,” Dr. Cairncross says.
Ultimately, the findings support moderation rather than blanket restrictions on screen time as the best way to manage pediatric concussion, especially after the first 48 hours.
“It’s actually unsurprising,” says Sarah Brittain, MS, a speech-language pathologist and founder of Colorado Brain Recovery in Wheat Ridge, who was not involved in the study. “An early return to both cognitive and physical activity in a controlled fashion is really important. Sitting in a dark room and resting is not the answer and has been disproven in the literature.”
Old advice involved lying in a quiet, dark room for days, but recent evidence reveals that such “cocoon therapy” may actually prolong symptoms.
“With time, we have found this can negatively impact quality of life and depression scores, especially in teenagers,” says Katherine Labiner, MD, a child neurologist at Pediatrix Child Neurology Consultants of Austin, Tex., who was not involved in the study.
So, how might screens help? Dr. Labiner, Ms. Brittain, and Dr. Cairncross all point to the importance of connection – not the Internet kind, but the social kind. Children and teens use smartphones and computers to stay connected with peers, so banning screen time could have a negative impact on mental health by leading to loneliness, separation, and lack of social support.
“Depression can prolong the course of recovery,” says Ms. Brittain.
It’s worth noting that screen time could trigger visual symptoms in some patients, she says. “If someone feels worse within 2 minutes of being on a screen, that’s a good indicator that screens aren’t working for them,” Ms. Brittain says. “If being on a screen makes them dizzy or wiped out, or the words on the screen look like they’re moving when they’re not, that means it’s time to back off.”
She advises parents to watch for behavior changes like increased crankiness, impatience, and/or fatigue, which could mean that the child has returned to screen time – or any activity – too soon and should scale back until symptoms subside.
“The most important thing to stress with concussion is full recovery before complete return to activity,” Dr. Labiner says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
research shows.
Now a study suggests that getting back on TikTok and Snapchat may help, too.
After surveying 700 patients ages 8-16 following an injury, researchers for the Pediatric Emergency Research Canada A-CAP study team found that
A “moderate” amount was between 2 and 7 hours per day on various screens. “That includes their phones, computers, and televisions,” says lead author Molly Cairncross, PhD, of Simon Fraser University, Vancouver.
People in the study who reported either less or more screen time than that in the 7-10 days after injury also reported more symptoms, such as headaches and fatigue, during the first month. After that month, all the participants reported similar symptoms, regardless of their early screen use – suggesting that screen time makes little difference long term in pediatric concussion recovery.
The findings differ from a 2021 study by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Boston, that found screen time slowed recovery. Why the clashing results? “I think what it comes down to are differences in study design,” says Dr. Cairncross. While the earlier study measured screen use in the first 48 hours, and recovery over 10 days, “we focused on screen time use over the first 7-10 days, and tracked recovery over 6 months,” she says.
“Taken together, the studies suggest a need to find balance – not too little and not too much time on screens for kids and teens following a concussion,” Dr. Cairncross says.
Ultimately, the findings support moderation rather than blanket restrictions on screen time as the best way to manage pediatric concussion, especially after the first 48 hours.
“It’s actually unsurprising,” says Sarah Brittain, MS, a speech-language pathologist and founder of Colorado Brain Recovery in Wheat Ridge, who was not involved in the study. “An early return to both cognitive and physical activity in a controlled fashion is really important. Sitting in a dark room and resting is not the answer and has been disproven in the literature.”
Old advice involved lying in a quiet, dark room for days, but recent evidence reveals that such “cocoon therapy” may actually prolong symptoms.
“With time, we have found this can negatively impact quality of life and depression scores, especially in teenagers,” says Katherine Labiner, MD, a child neurologist at Pediatrix Child Neurology Consultants of Austin, Tex., who was not involved in the study.
So, how might screens help? Dr. Labiner, Ms. Brittain, and Dr. Cairncross all point to the importance of connection – not the Internet kind, but the social kind. Children and teens use smartphones and computers to stay connected with peers, so banning screen time could have a negative impact on mental health by leading to loneliness, separation, and lack of social support.
“Depression can prolong the course of recovery,” says Ms. Brittain.
It’s worth noting that screen time could trigger visual symptoms in some patients, she says. “If someone feels worse within 2 minutes of being on a screen, that’s a good indicator that screens aren’t working for them,” Ms. Brittain says. “If being on a screen makes them dizzy or wiped out, or the words on the screen look like they’re moving when they’re not, that means it’s time to back off.”
She advises parents to watch for behavior changes like increased crankiness, impatience, and/or fatigue, which could mean that the child has returned to screen time – or any activity – too soon and should scale back until symptoms subside.
“The most important thing to stress with concussion is full recovery before complete return to activity,” Dr. Labiner says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
research shows.
Now a study suggests that getting back on TikTok and Snapchat may help, too.
After surveying 700 patients ages 8-16 following an injury, researchers for the Pediatric Emergency Research Canada A-CAP study team found that
A “moderate” amount was between 2 and 7 hours per day on various screens. “That includes their phones, computers, and televisions,” says lead author Molly Cairncross, PhD, of Simon Fraser University, Vancouver.
People in the study who reported either less or more screen time than that in the 7-10 days after injury also reported more symptoms, such as headaches and fatigue, during the first month. After that month, all the participants reported similar symptoms, regardless of their early screen use – suggesting that screen time makes little difference long term in pediatric concussion recovery.
The findings differ from a 2021 study by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Boston, that found screen time slowed recovery. Why the clashing results? “I think what it comes down to are differences in study design,” says Dr. Cairncross. While the earlier study measured screen use in the first 48 hours, and recovery over 10 days, “we focused on screen time use over the first 7-10 days, and tracked recovery over 6 months,” she says.
“Taken together, the studies suggest a need to find balance – not too little and not too much time on screens for kids and teens following a concussion,” Dr. Cairncross says.
Ultimately, the findings support moderation rather than blanket restrictions on screen time as the best way to manage pediatric concussion, especially after the first 48 hours.
“It’s actually unsurprising,” says Sarah Brittain, MS, a speech-language pathologist and founder of Colorado Brain Recovery in Wheat Ridge, who was not involved in the study. “An early return to both cognitive and physical activity in a controlled fashion is really important. Sitting in a dark room and resting is not the answer and has been disproven in the literature.”
Old advice involved lying in a quiet, dark room for days, but recent evidence reveals that such “cocoon therapy” may actually prolong symptoms.
“With time, we have found this can negatively impact quality of life and depression scores, especially in teenagers,” says Katherine Labiner, MD, a child neurologist at Pediatrix Child Neurology Consultants of Austin, Tex., who was not involved in the study.
So, how might screens help? Dr. Labiner, Ms. Brittain, and Dr. Cairncross all point to the importance of connection – not the Internet kind, but the social kind. Children and teens use smartphones and computers to stay connected with peers, so banning screen time could have a negative impact on mental health by leading to loneliness, separation, and lack of social support.
“Depression can prolong the course of recovery,” says Ms. Brittain.
It’s worth noting that screen time could trigger visual symptoms in some patients, she says. “If someone feels worse within 2 minutes of being on a screen, that’s a good indicator that screens aren’t working for them,” Ms. Brittain says. “If being on a screen makes them dizzy or wiped out, or the words on the screen look like they’re moving when they’re not, that means it’s time to back off.”
She advises parents to watch for behavior changes like increased crankiness, impatience, and/or fatigue, which could mean that the child has returned to screen time – or any activity – too soon and should scale back until symptoms subside.
“The most important thing to stress with concussion is full recovery before complete return to activity,” Dr. Labiner says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS